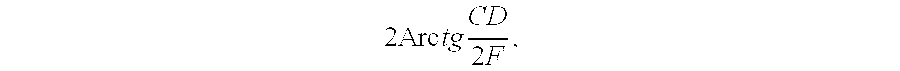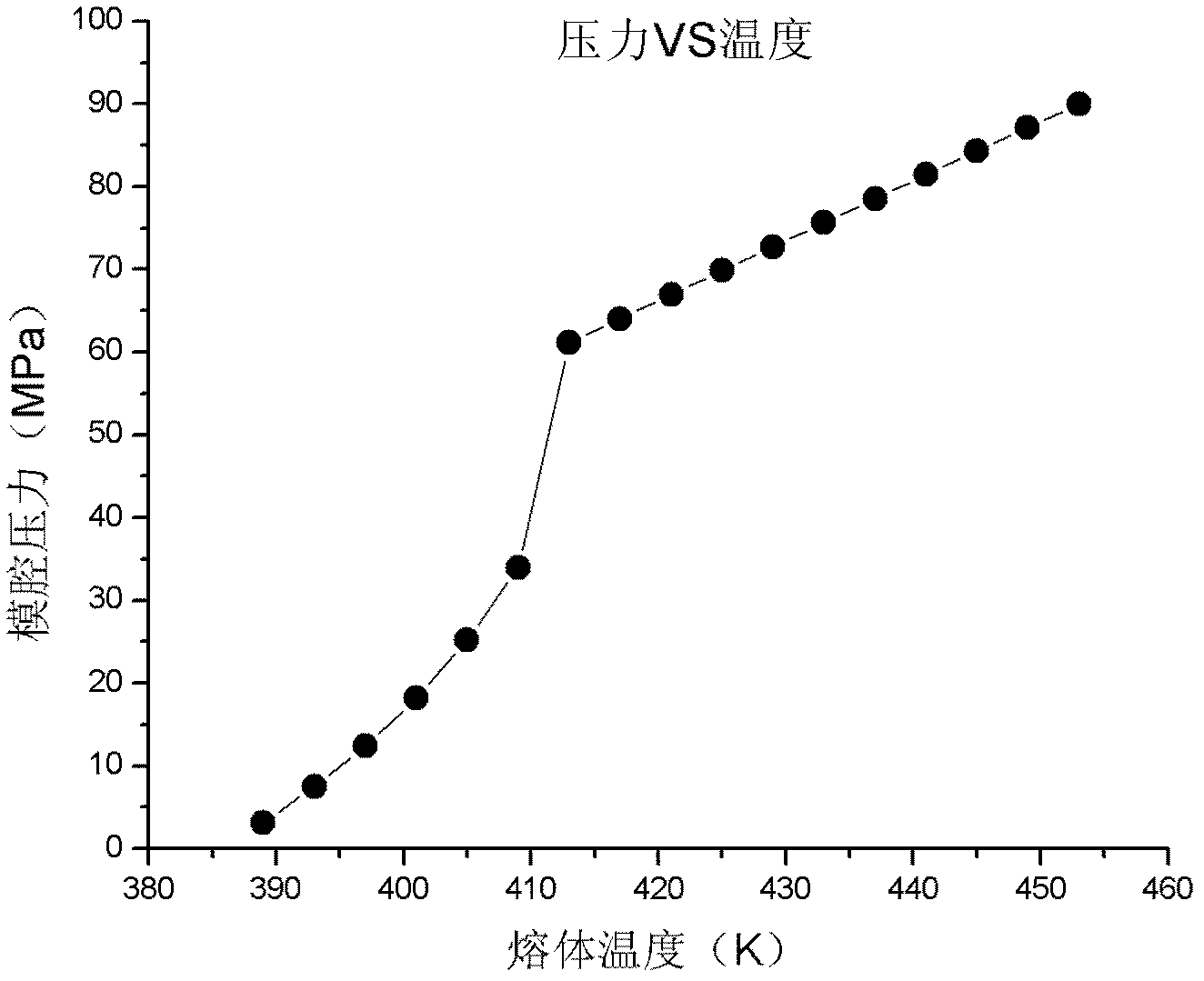Patents
Literature
122 results about "Compression phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
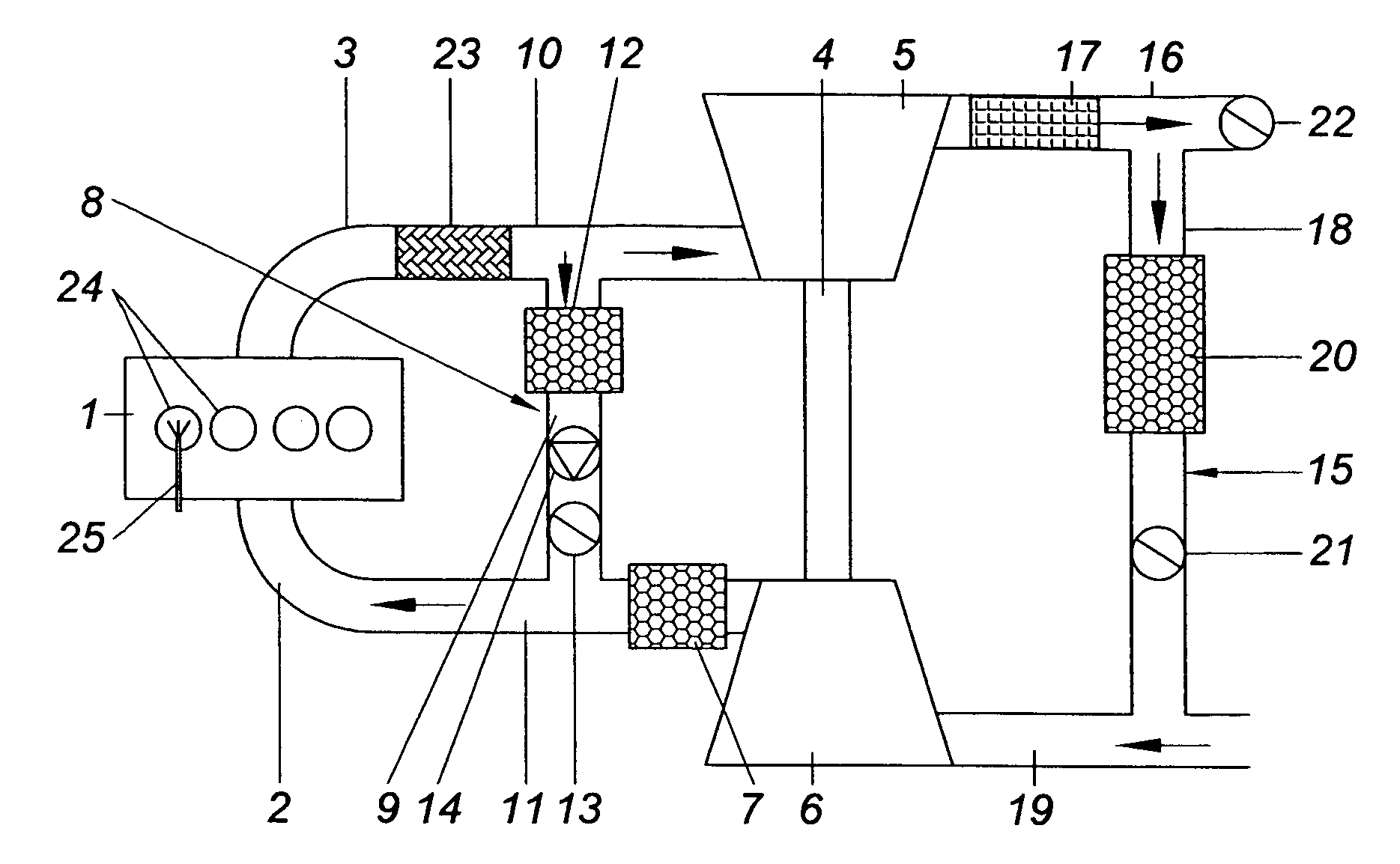
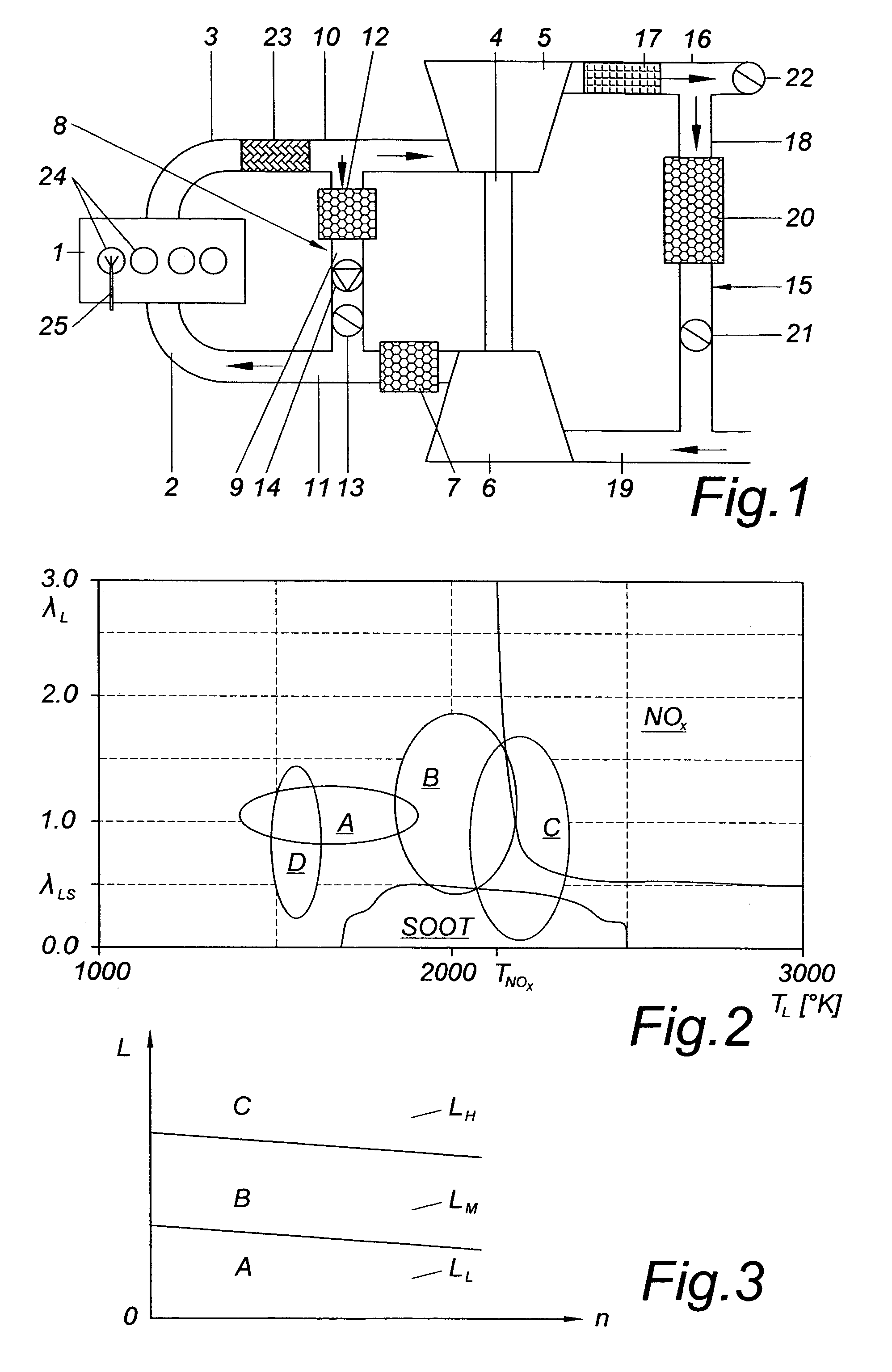
System and method for auto-ignition of gasoline internal combustion engine
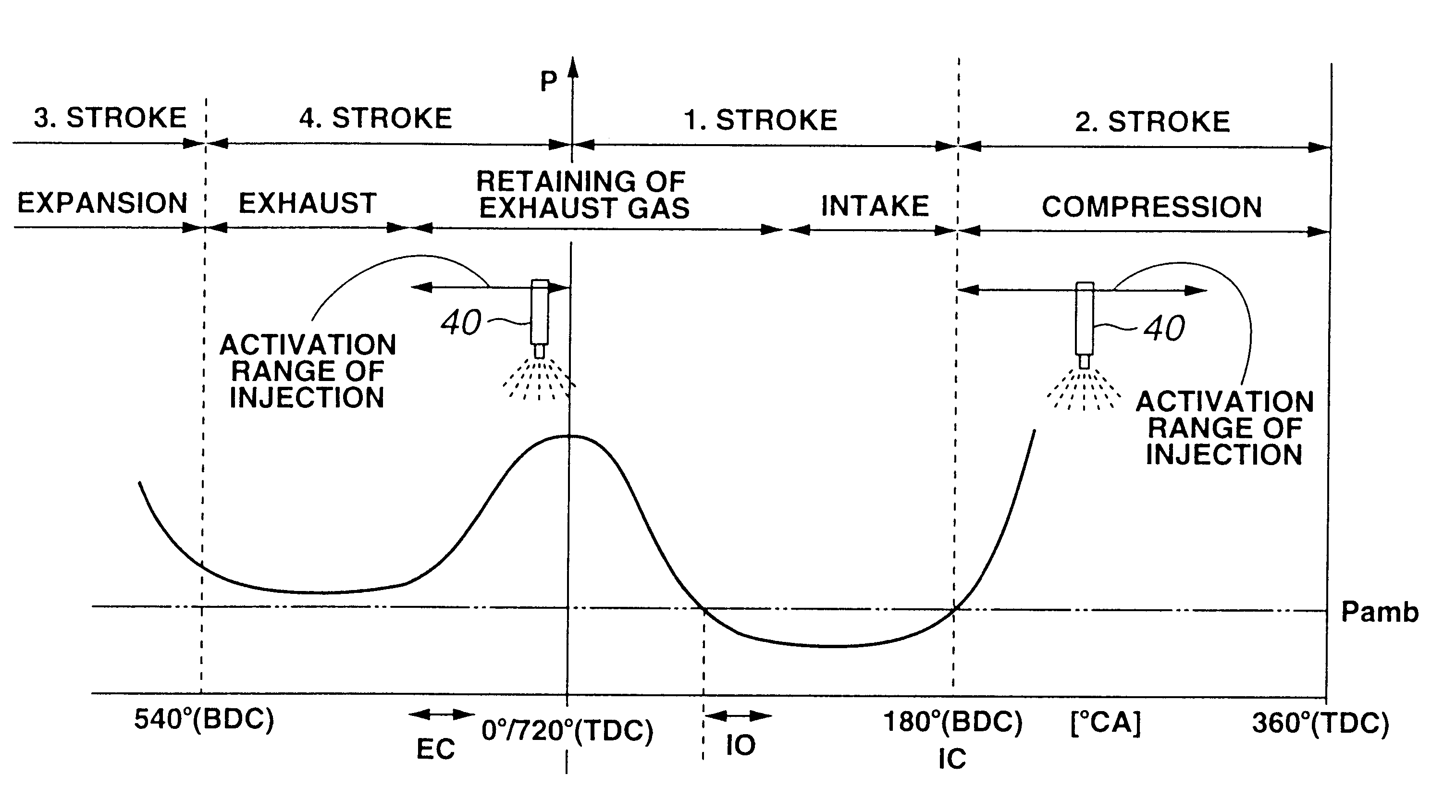
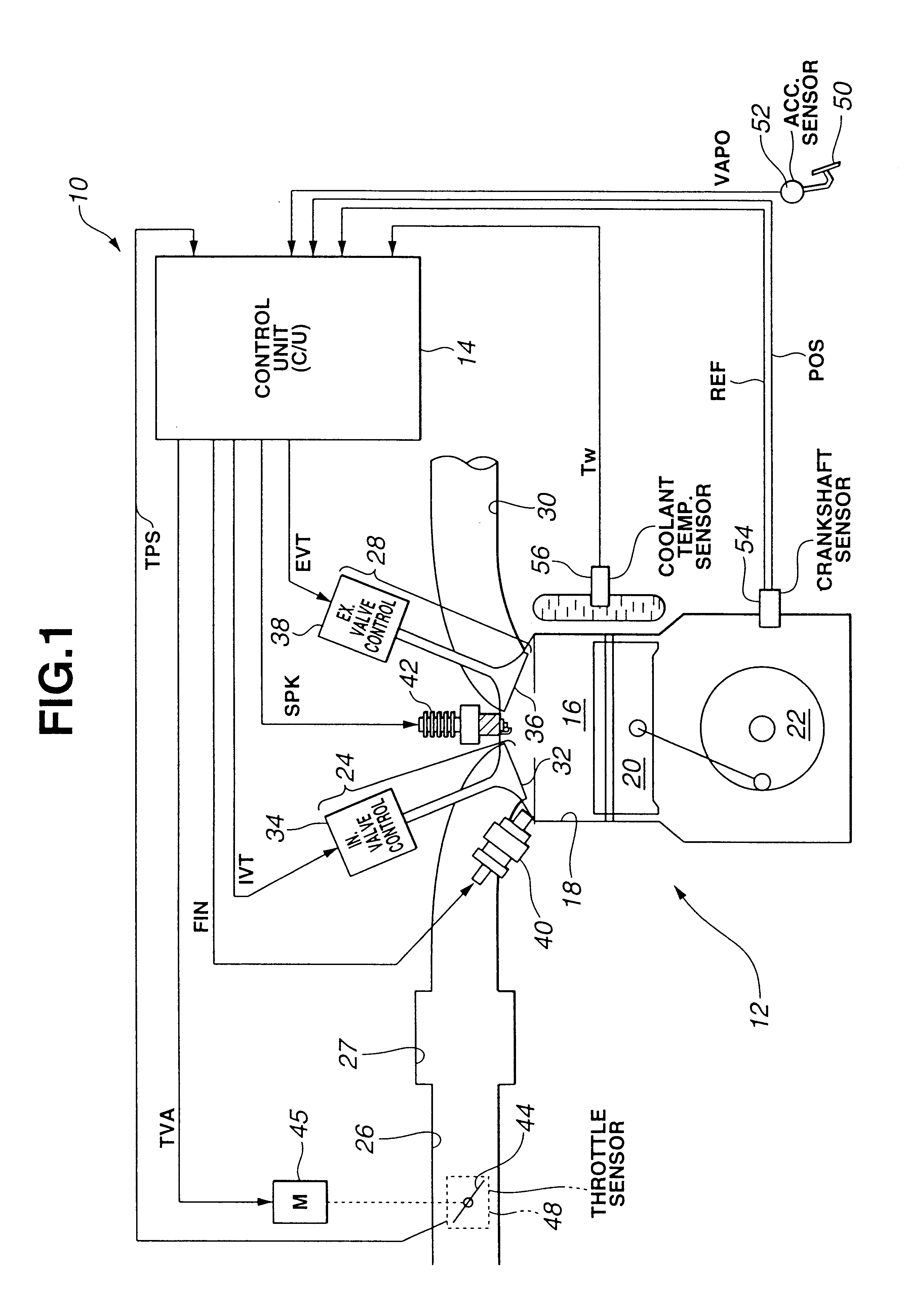
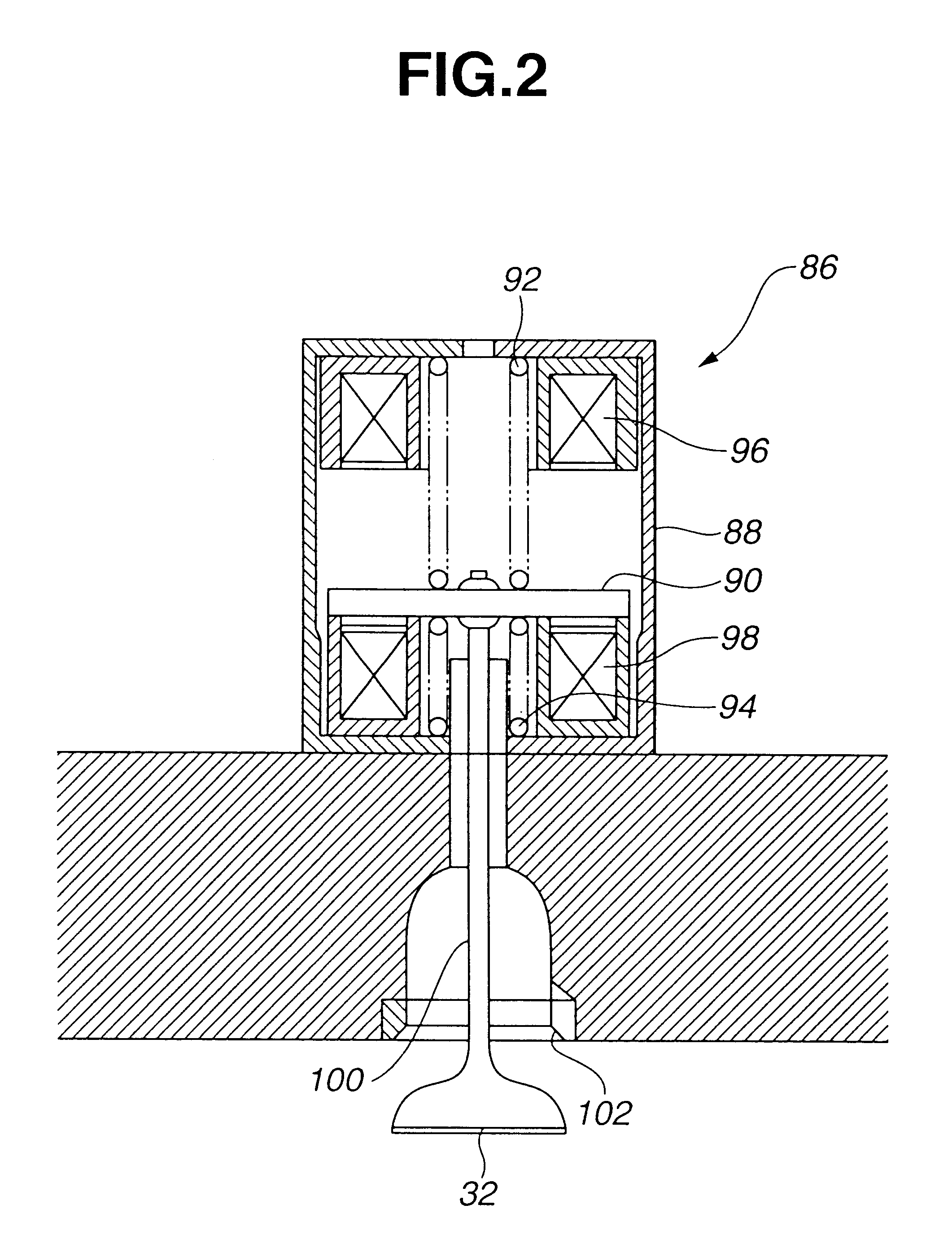
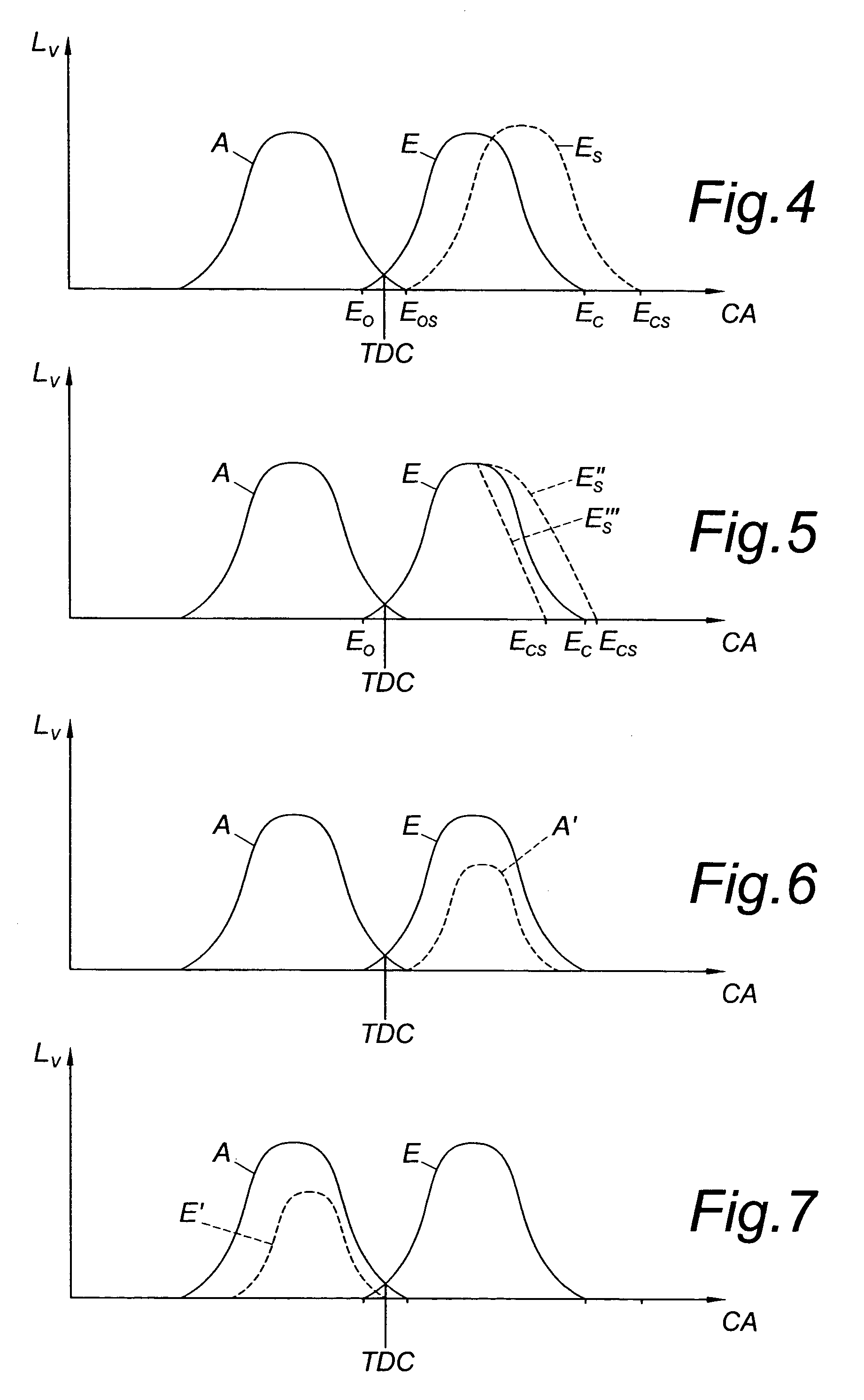
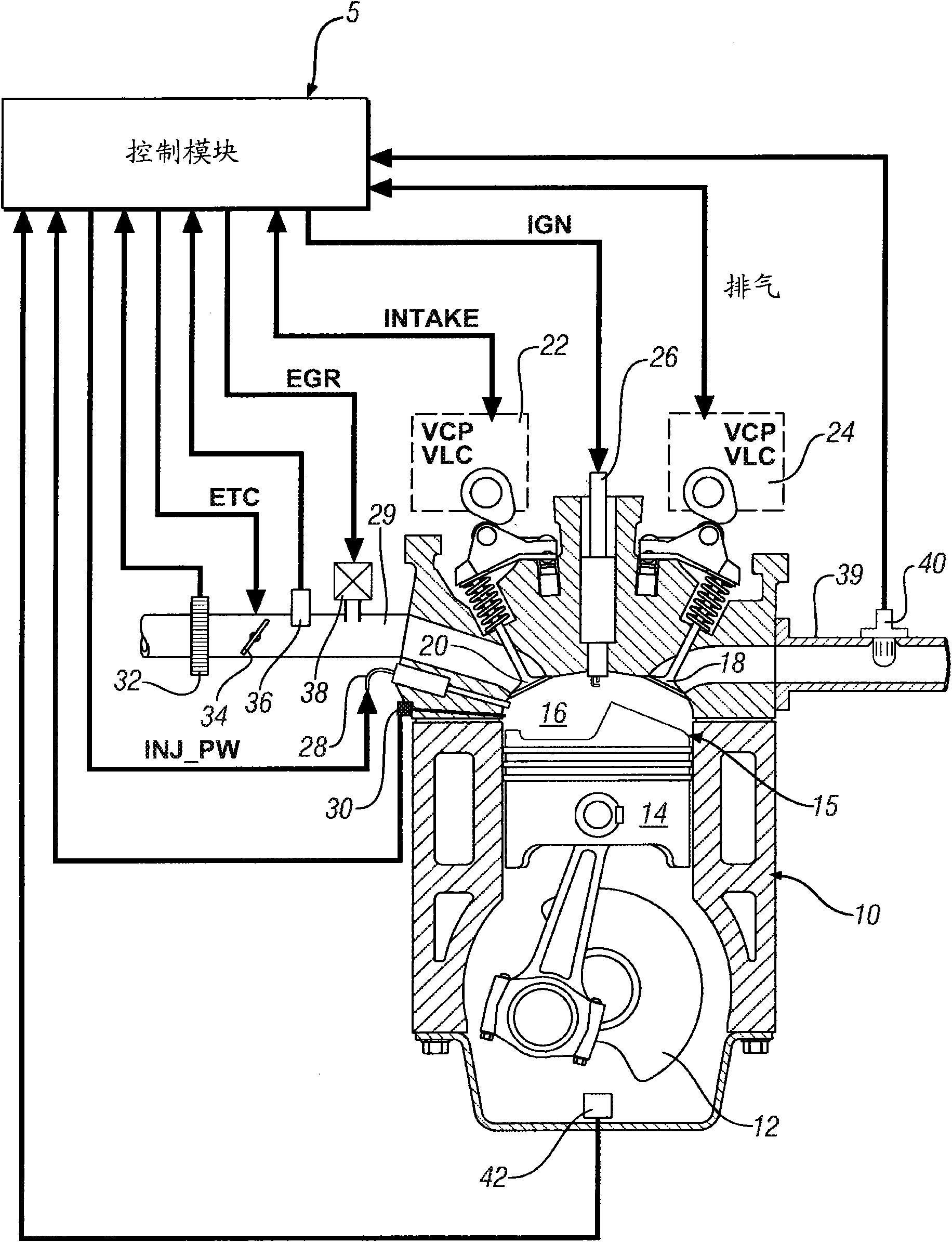
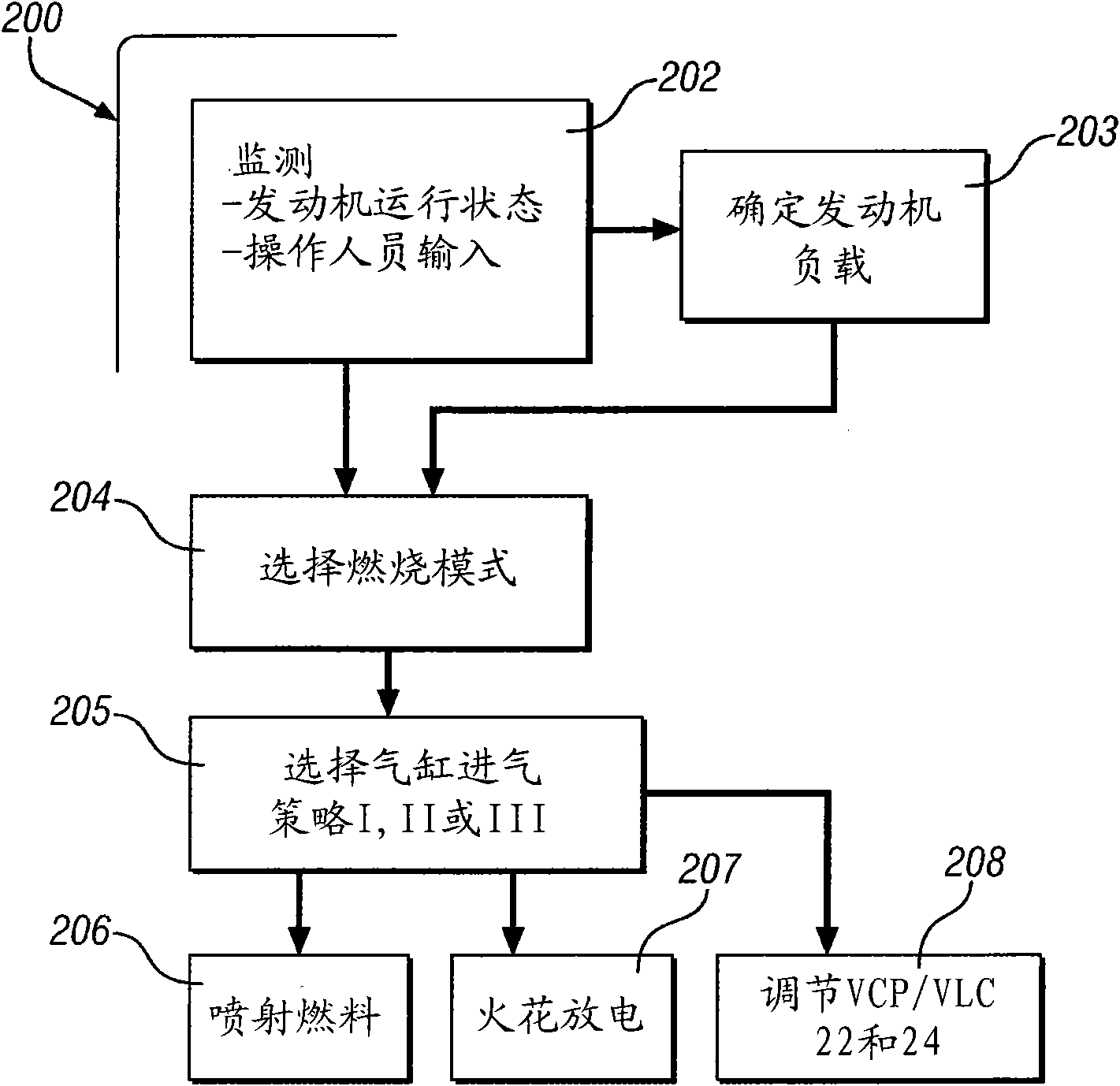
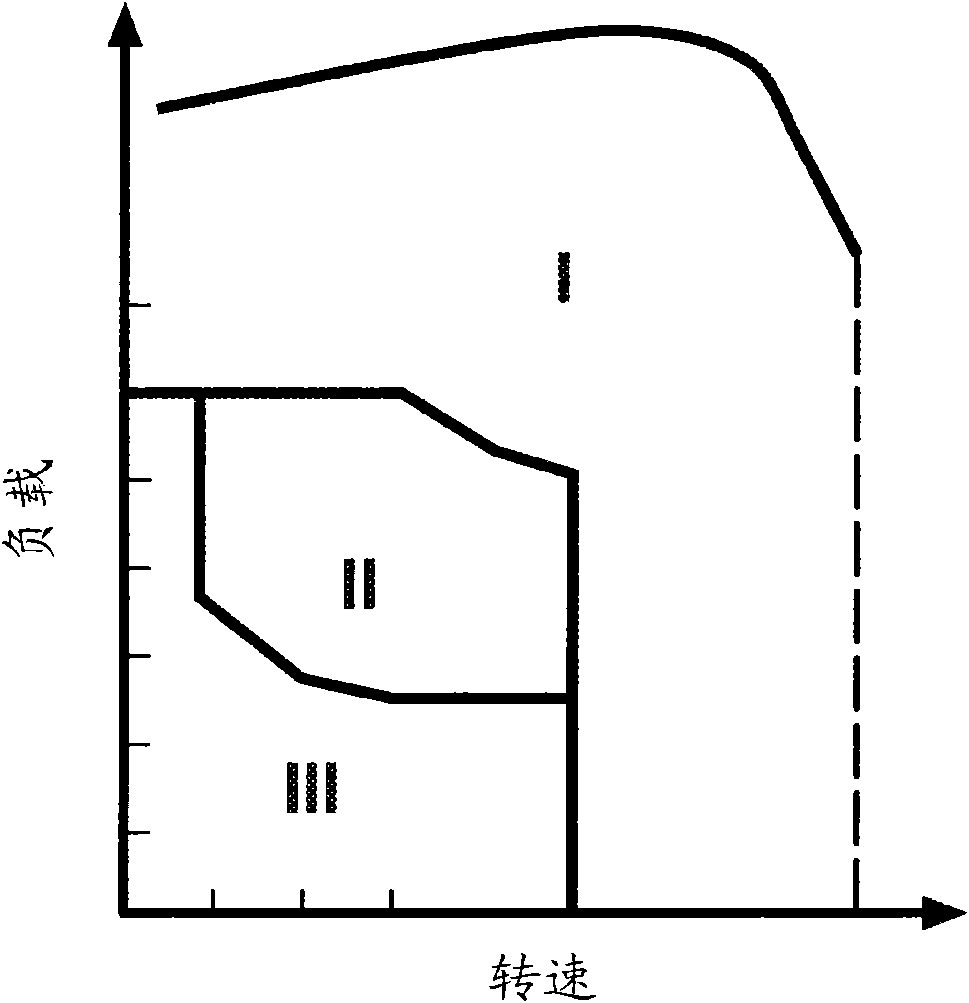
During operation with part load, a gasoline internal combustion engine is operated with a lean air / fuel mixture by auto-ignition. During operation with full load, spark-ignition is used to operate the engine. The internal combustion engine is operated in three auto-ignition combustion modes depending upon magnitude of a predetermined operating parameter. The operating parameter is indicative of the engine load or the engine speed. The three auto-ignition combustion modes are a gasoline reform auto-ignition combustion mode, an auto-ignition stratified charge combustion mode, and an auto-ignition homogeneous charge combustion mode. In the gasoline reform auto-ignition combustion mode that may be selected during operation with low part load, a first fuel injection during an exhaust gas retaining phase produces sufficient amount of active fuel radicals for promotion of auto-ignition of air / fuel mixture produced by a second fuel injection during the subsequent compression phase. In the auto-ignition stratified charge combustion mode that may be selected during operation with intermediate part load, a fuel injection during compression phase supports auto-ignition. In the auto-ignition homogeneous charge combustion mode that may be selected during operation with high part load, a fuel injection during intake phase supports auto-ignition.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Lower extremity compression devices, systems and methods to enhance circulation
InactiveUS20090062701A1Promote blood circulationAdequate vital organ perfusionRespiratorsElectrotherapyPhysical medicine and rehabilitationCompression device
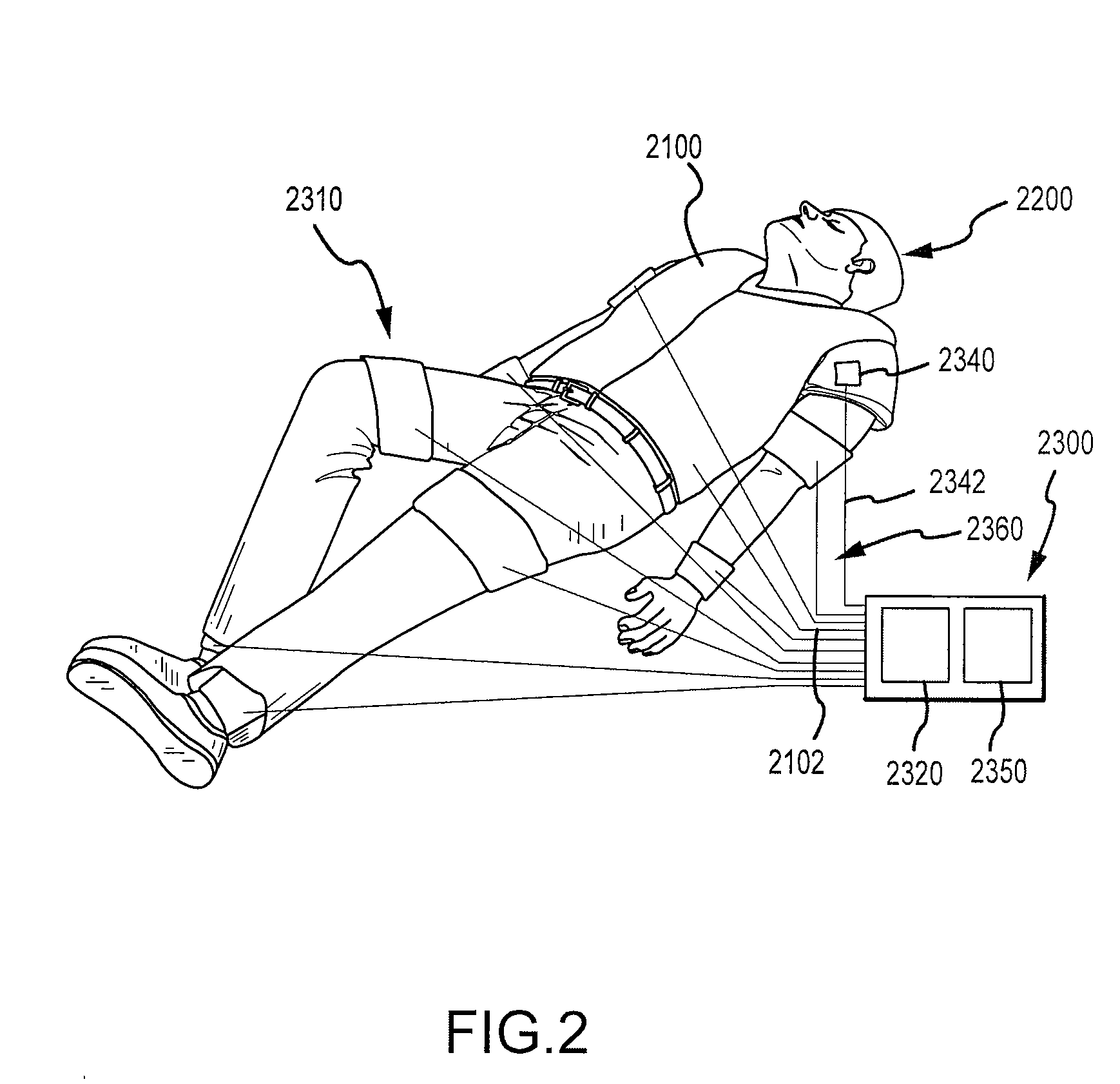
Systems and methods for enhancing circulation are described. In one particular embodiment, the invention provides a method for enhancing circulation. The method comprises attaching at least one compression device to at least a portion of a person's lower extremity. The person's chest is repetitively compressed so that the chest experiences a compression phase and a recoil phase or decompression. Also, the person's lower extremity is compressed using the compression device during at least some of the recoil phases.
Owner:ADVANCED CIRCULATORY SYST
Vasodilator-enhanced cardiopulmonary resuscitation
InactiveUS20120203147A1Increase blood flowImprove artificial circulationBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsImpedance threshold deviceVascular dilatation
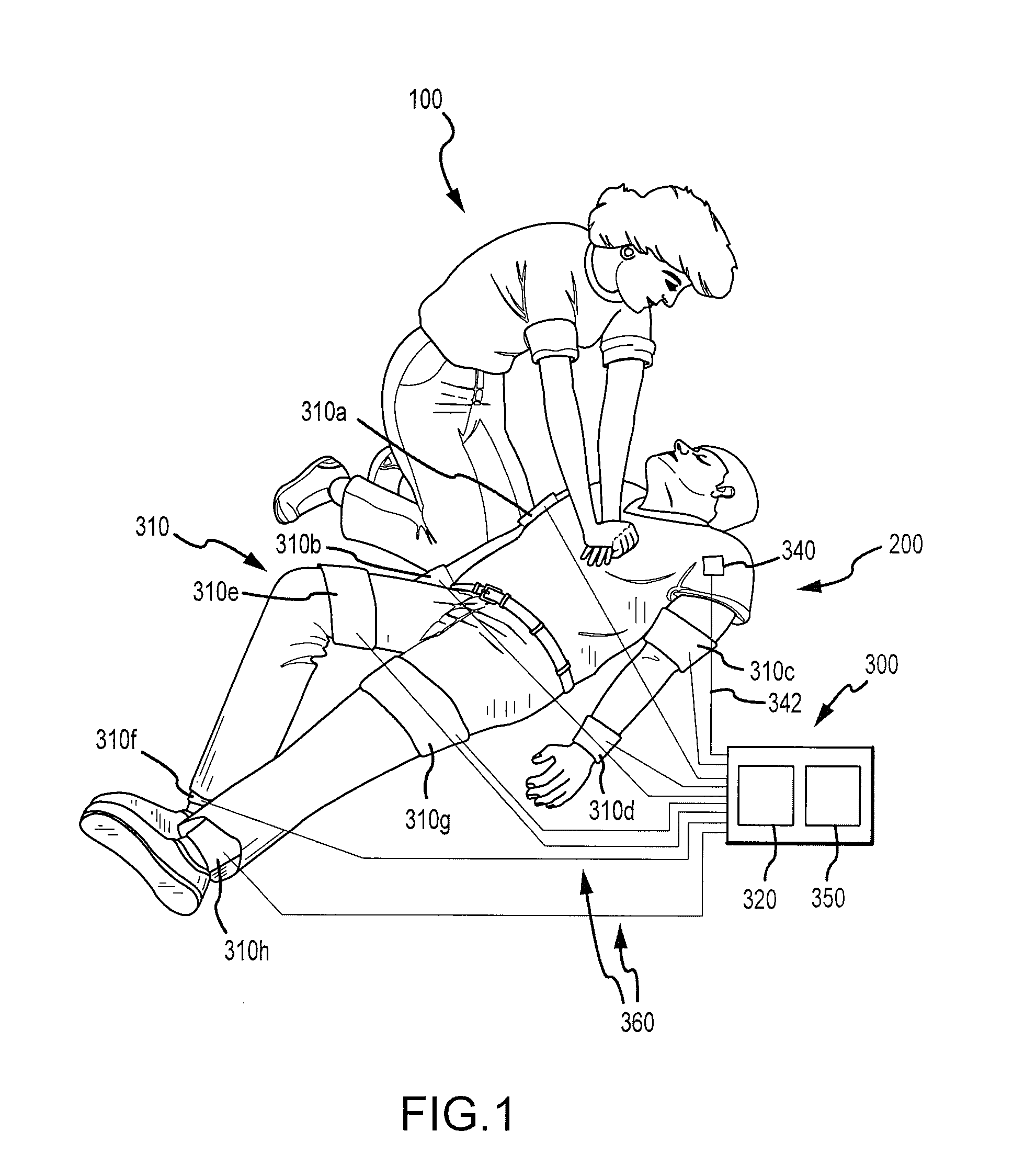
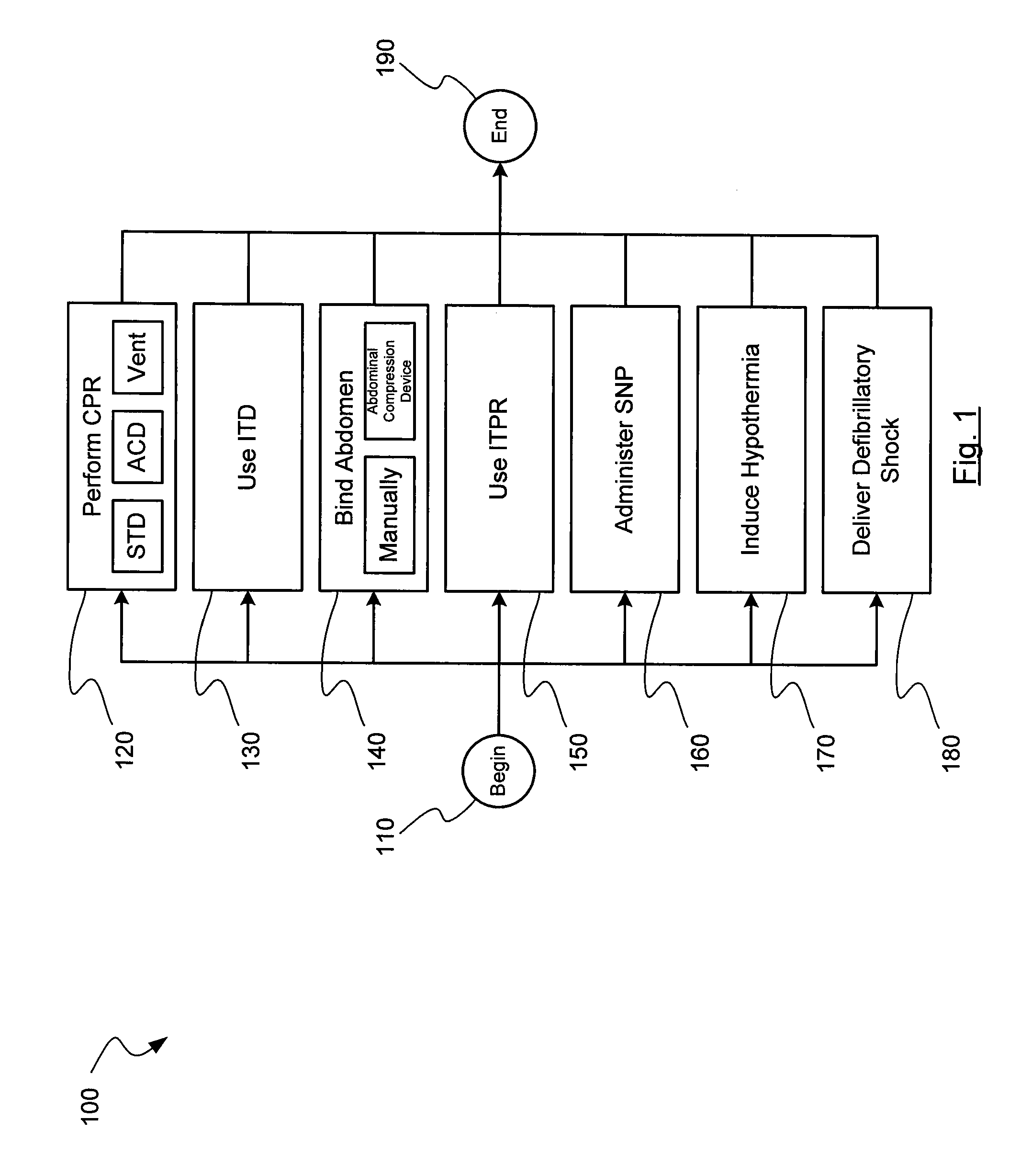
A method for increasing blood flow to vital organs during cardiopulmonary resuscitation of a person experiencing a cardiac arrest may include performing standard or active compression decompression cardiopulmonary resuscitation on a person to create artificial circulation by repetitively compressing the person's chest such that the person's chest is subject to a compression phase and a relaxation or decompression phase. The method may also include administering one or more vasodilator drugs to the person to improve the artificial circulation created by the cardiopulmonary resuscitation. The method may also include binding at least a portion of the person's abdomen, either manually or with an abdominal compression device. Performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation on a person may include ventilating the person with either an impedance threshold device or a intrathoracic pressure regulator.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Vapor Compression System With Condensate Intercooling Between Compression Stages
InactiveUS20080256975A1CompressorCompression machines with non-reversible cycleCompression deviceEngineering
A refrigerant vapor compression system includes a first compression device and a second compression device disposed in a refrigerant circuit in series relationship with respect to refrigerant flow and an intercooler adapted to cool the refrigerant passing from the first compression device to the second compression. An evaporator is provided in the refrigerant circuit wherein the refrigerant accepts heat from a moisture bearing gas such as air. Condensate formed of moisture condensing out of the gas is collected and supplied to the intercooler for cooling the refrigerant flowing from the first compression device to the second compression device.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
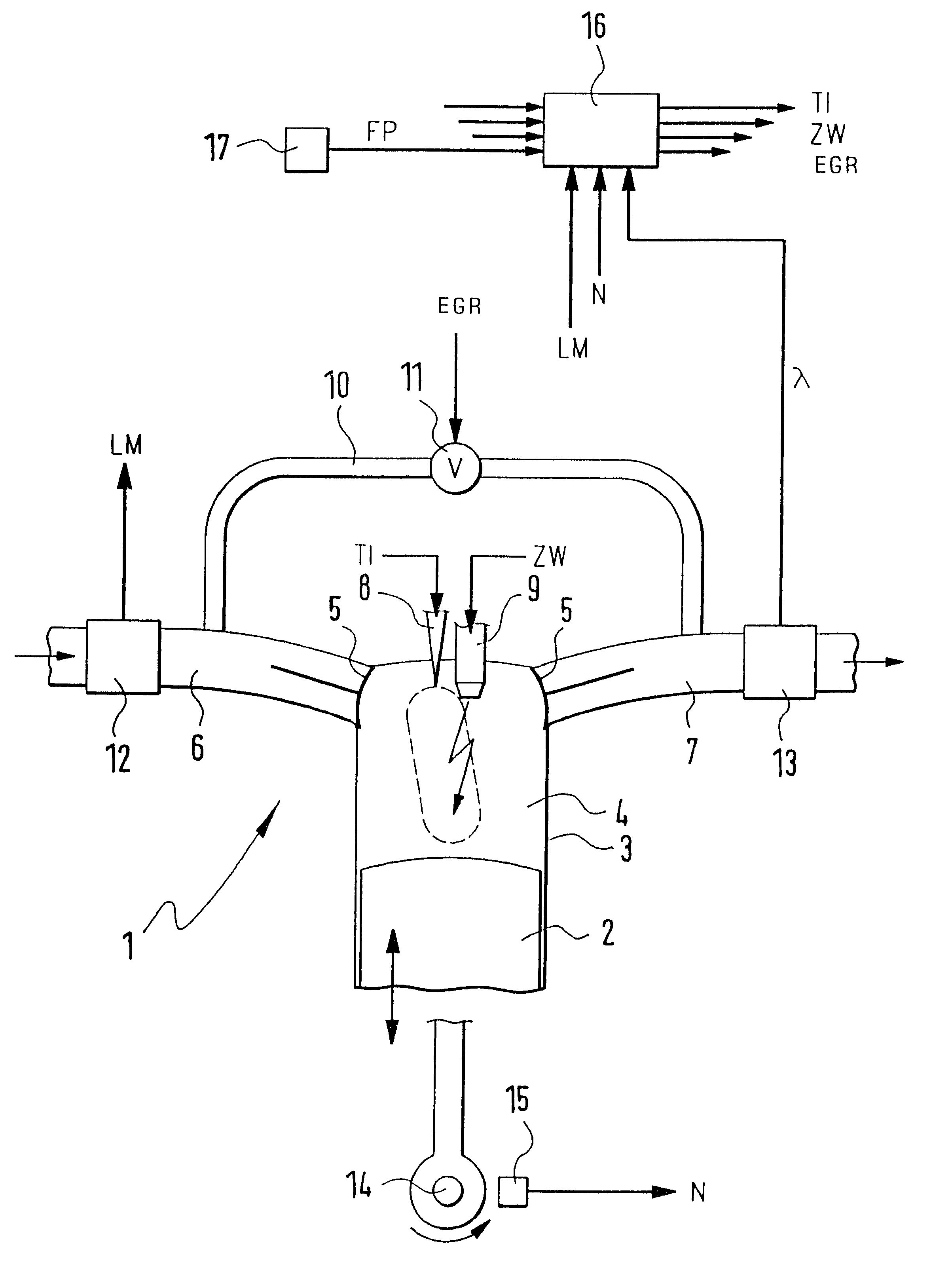
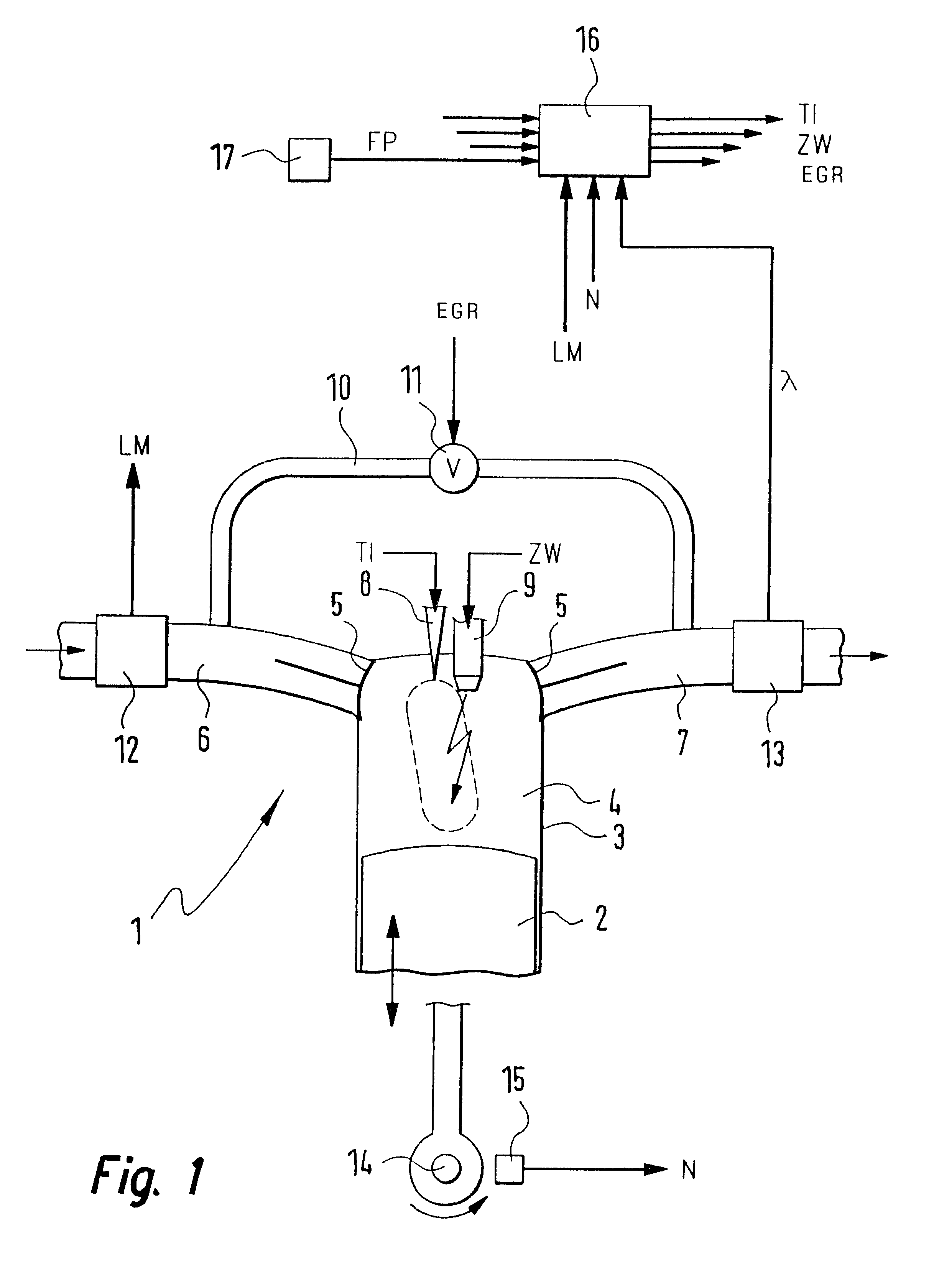
Method for starting an internal combustion engine, in particular on a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6588397B1Large capacityLarge massPower operated startersElectrical controlCombustion chamberOperation mode
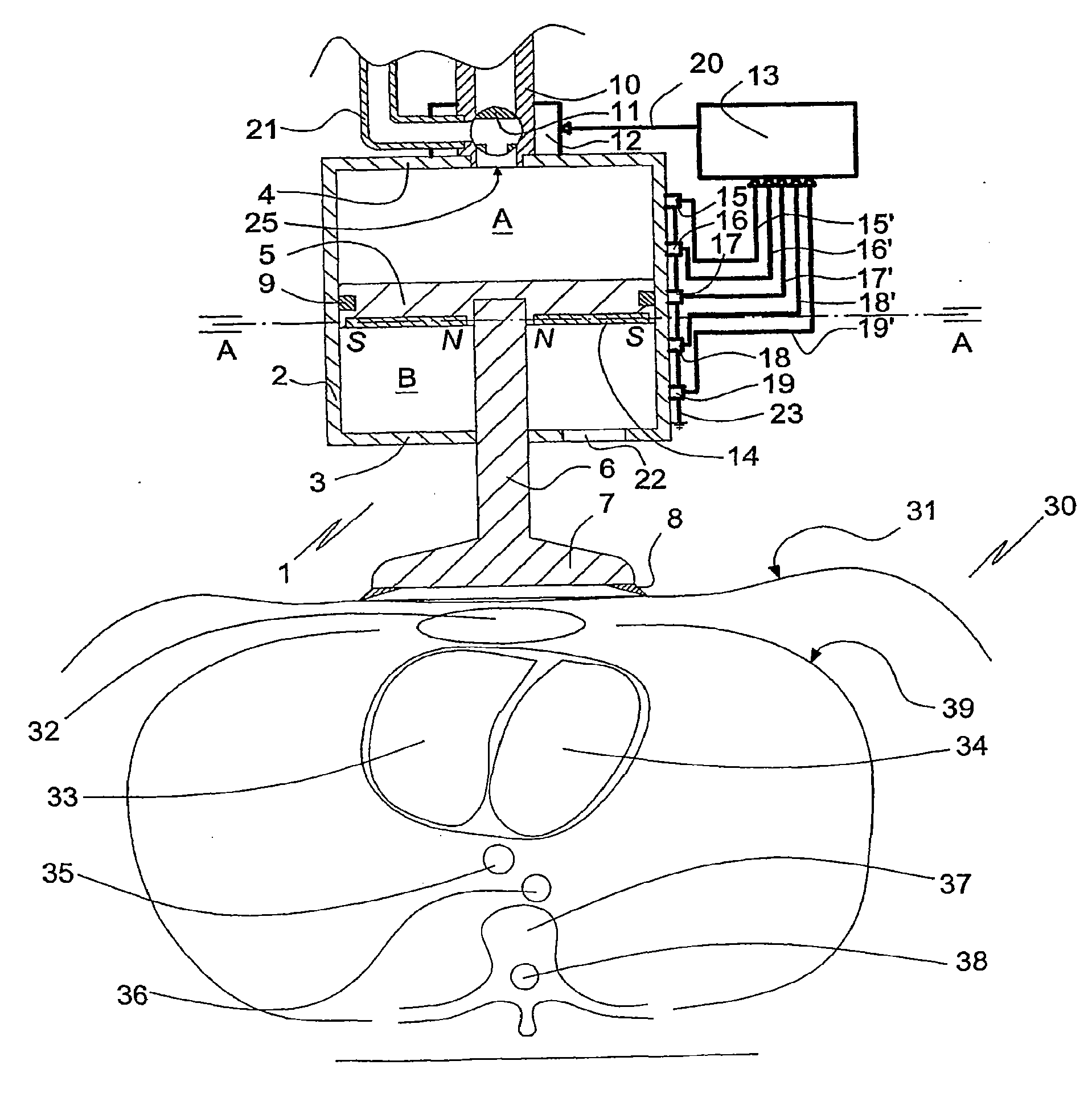
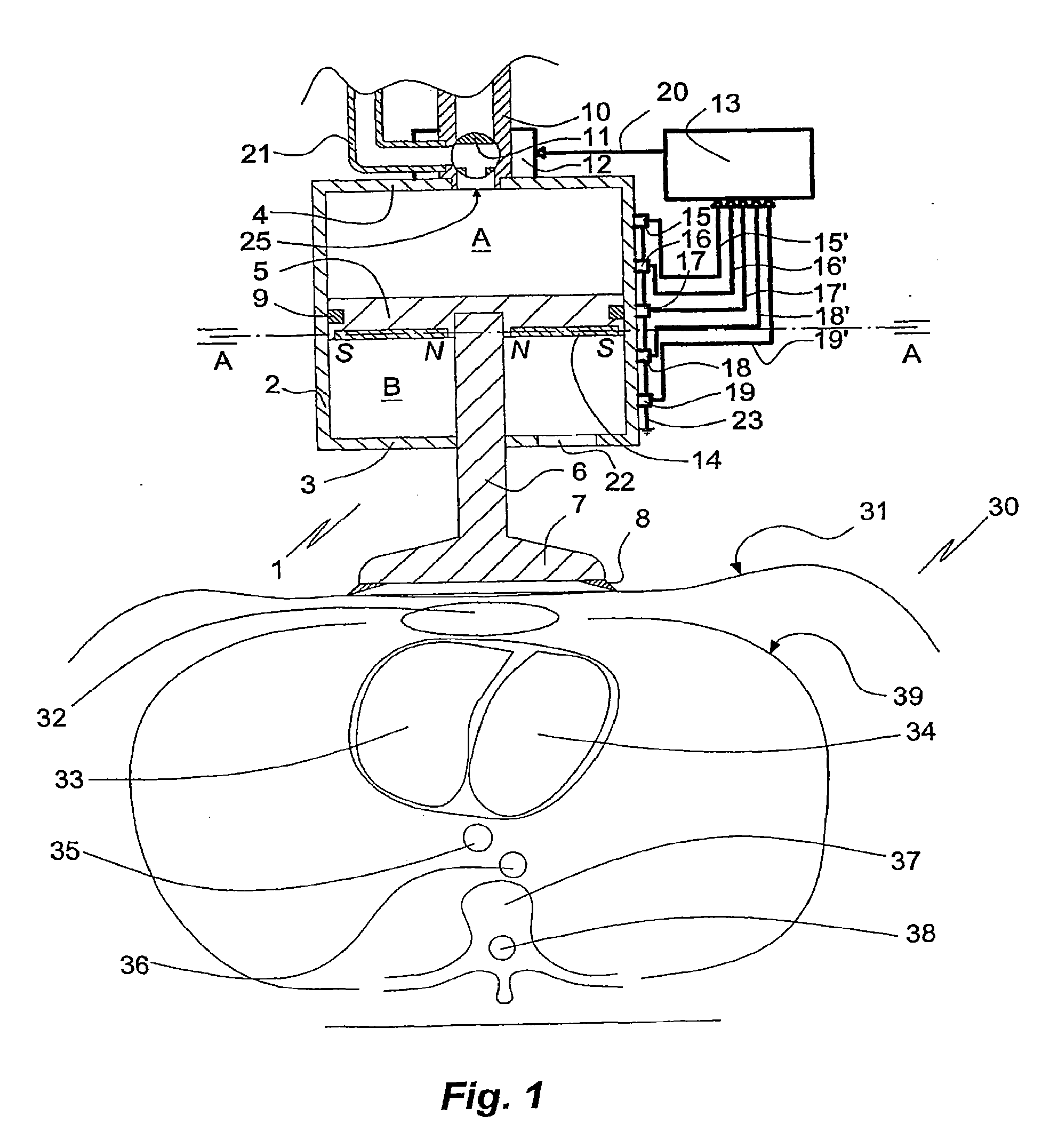
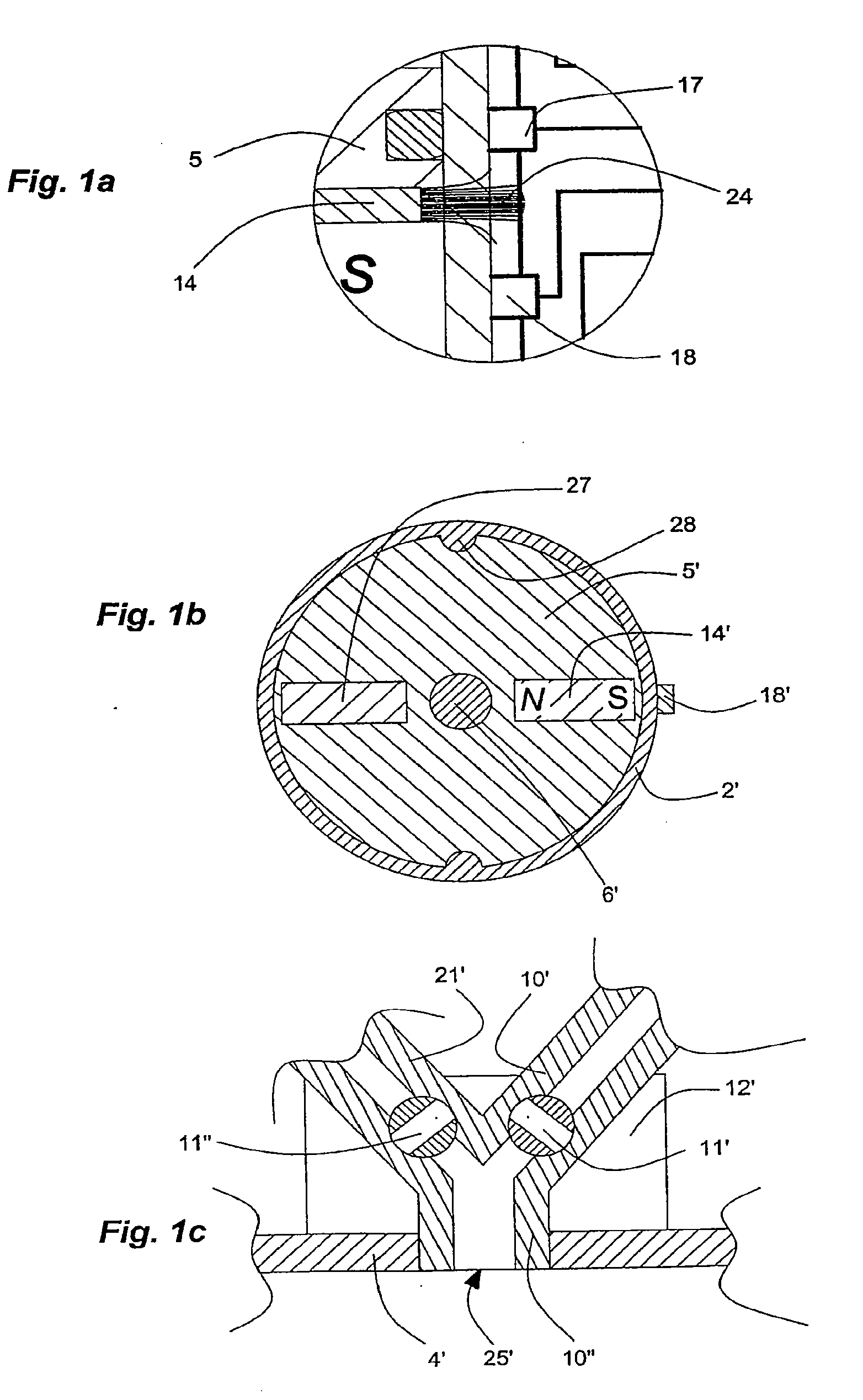
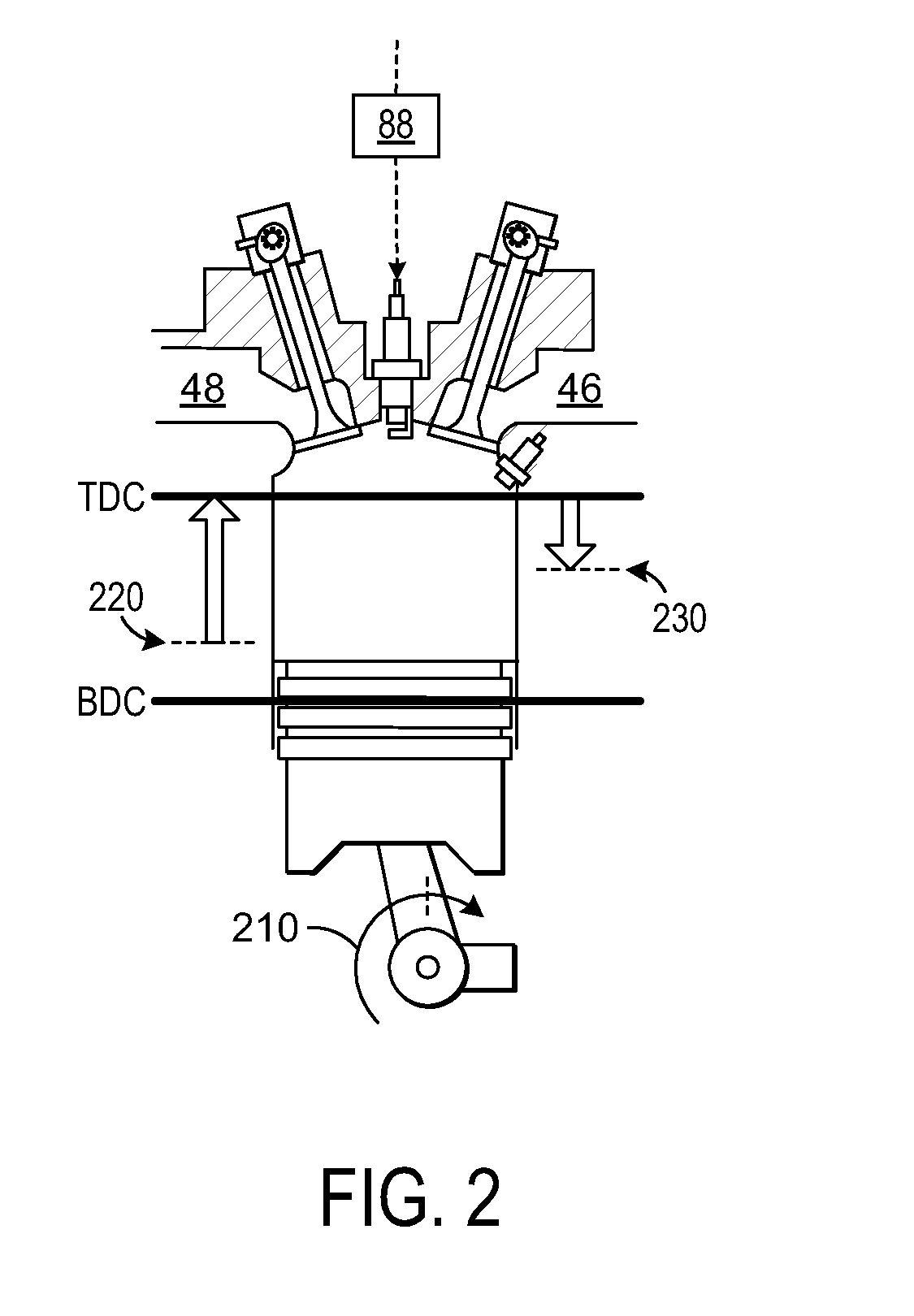
An internal combustion engine, especially an engine for a motor vehicle, is described which is provided with a piston, which is movable in a cylinder and acts on a crankshaft. The piston can run through an intake phase, a compression phase, a work phase and a discharge phase. A control apparatus is provided with which the fuel can be injected directly into a combustion chamber delimited by the cylinder and the piston in a first operating mode during a compression phase or in a second operating mode during an intake phase. The control apparatus is so configured that, for starting the engine at standstill of the crankshaft, fuel can be injected into that cylinder (no. 1) whose piston is disposed in the compression phase and can be ignited (20, 21) so that the crankshaft moves rearwardly (22).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Compression method and air separation
InactiveUS20120263605A1Less powerHigh pressure levelSolidificationLiquefactionEngineeringAir separation
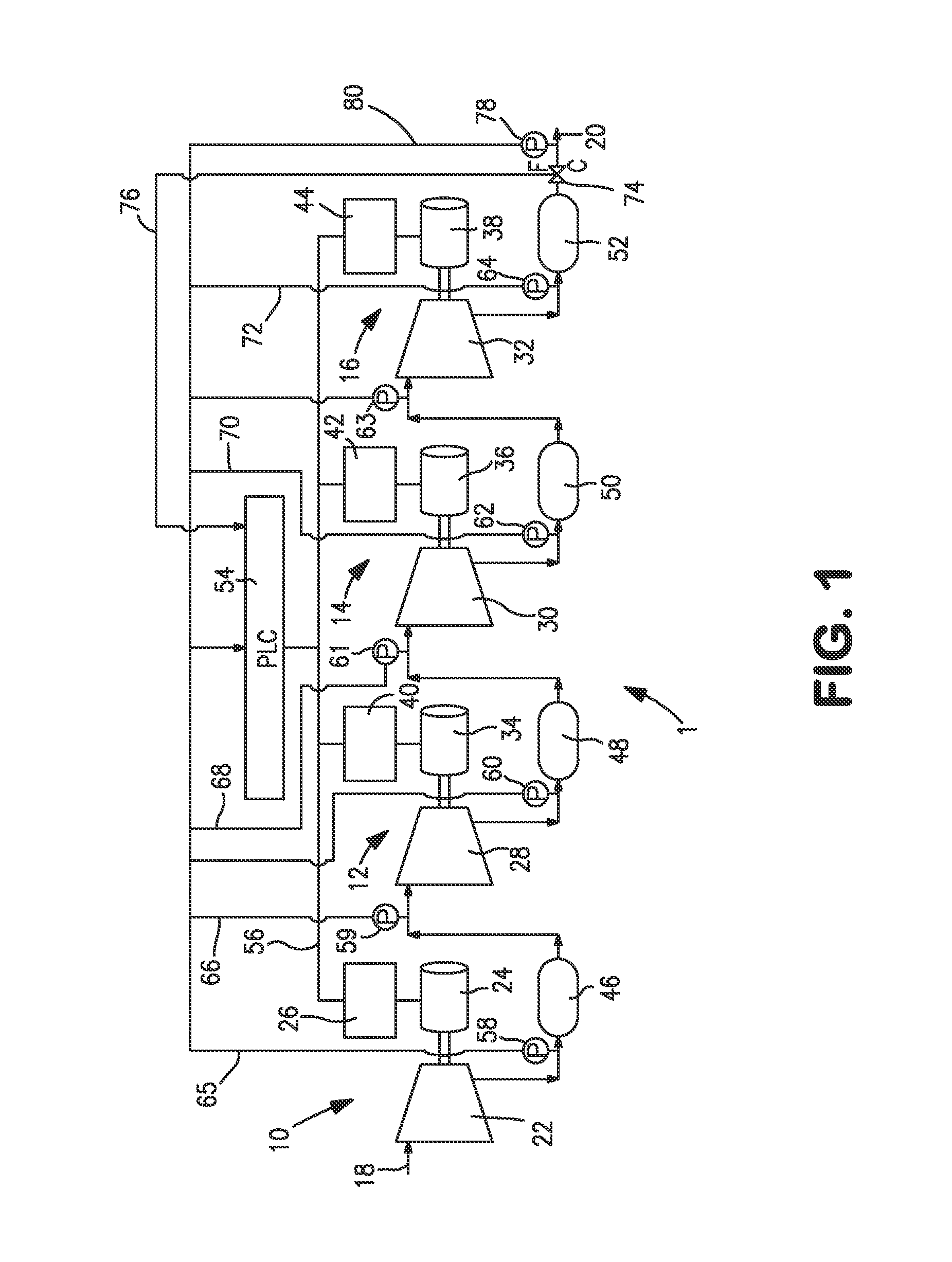
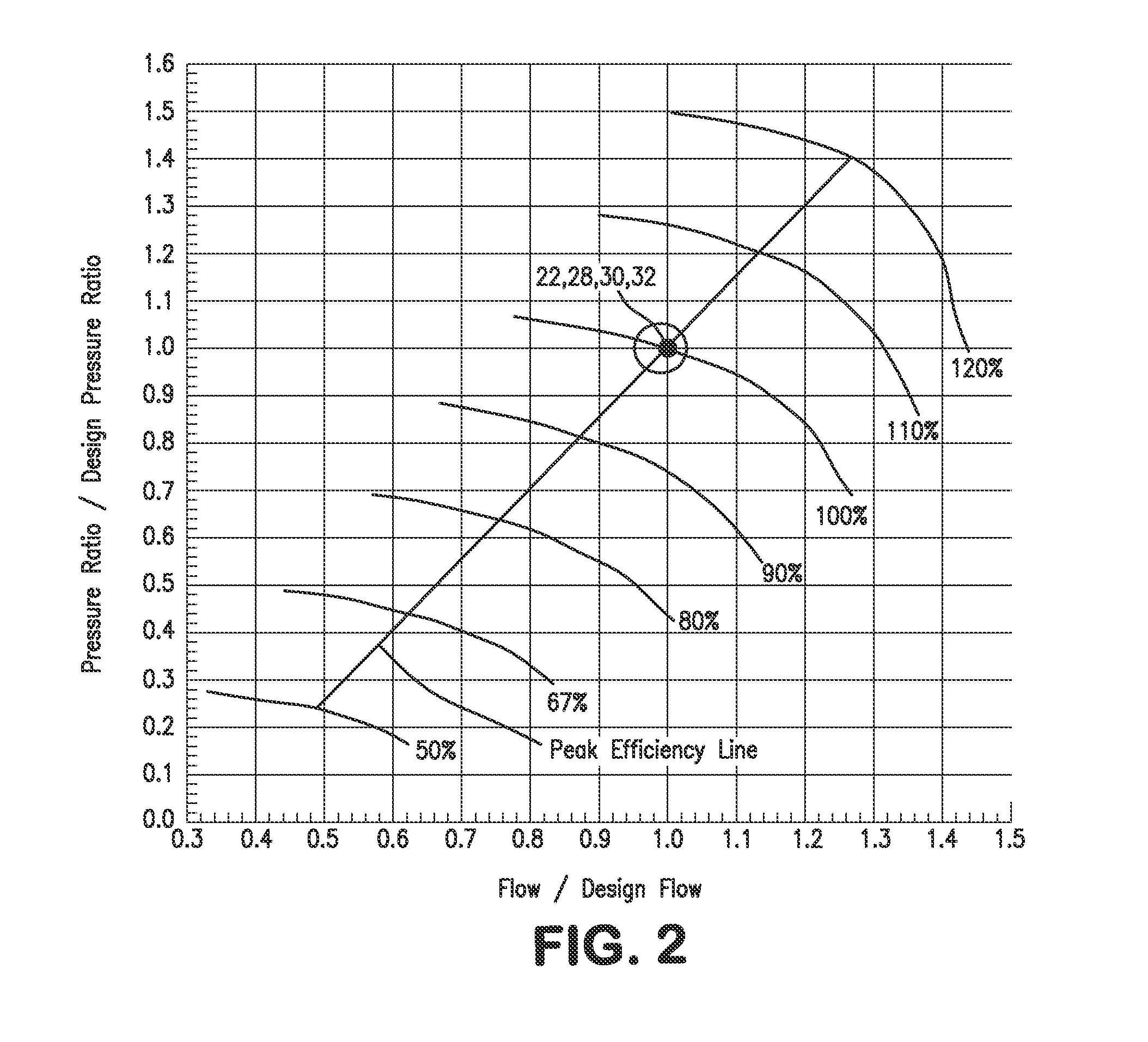
A compression method, a multistage compression system and an air separation method and plant in which a gas is compressed in a series of compression stages to produce a compressed gas and each of the compression stages incorporate a variable speed compressor. In such compression method and system, the compressed air is produced at a pressure that remains stable during both normal operational conditions and during turn down conditions during which the flow rate of the gas is reduced. This reduction is accomplished by reducing the speed of the compressor in an initial compression stage such that the compressor operates at a point along its peak efficiency operating line at which the pressure ratio is directly proportional to the flow rate and such that the lower turn down flow rate is obtained at a reduced pressure which is made up in successive compression stages.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
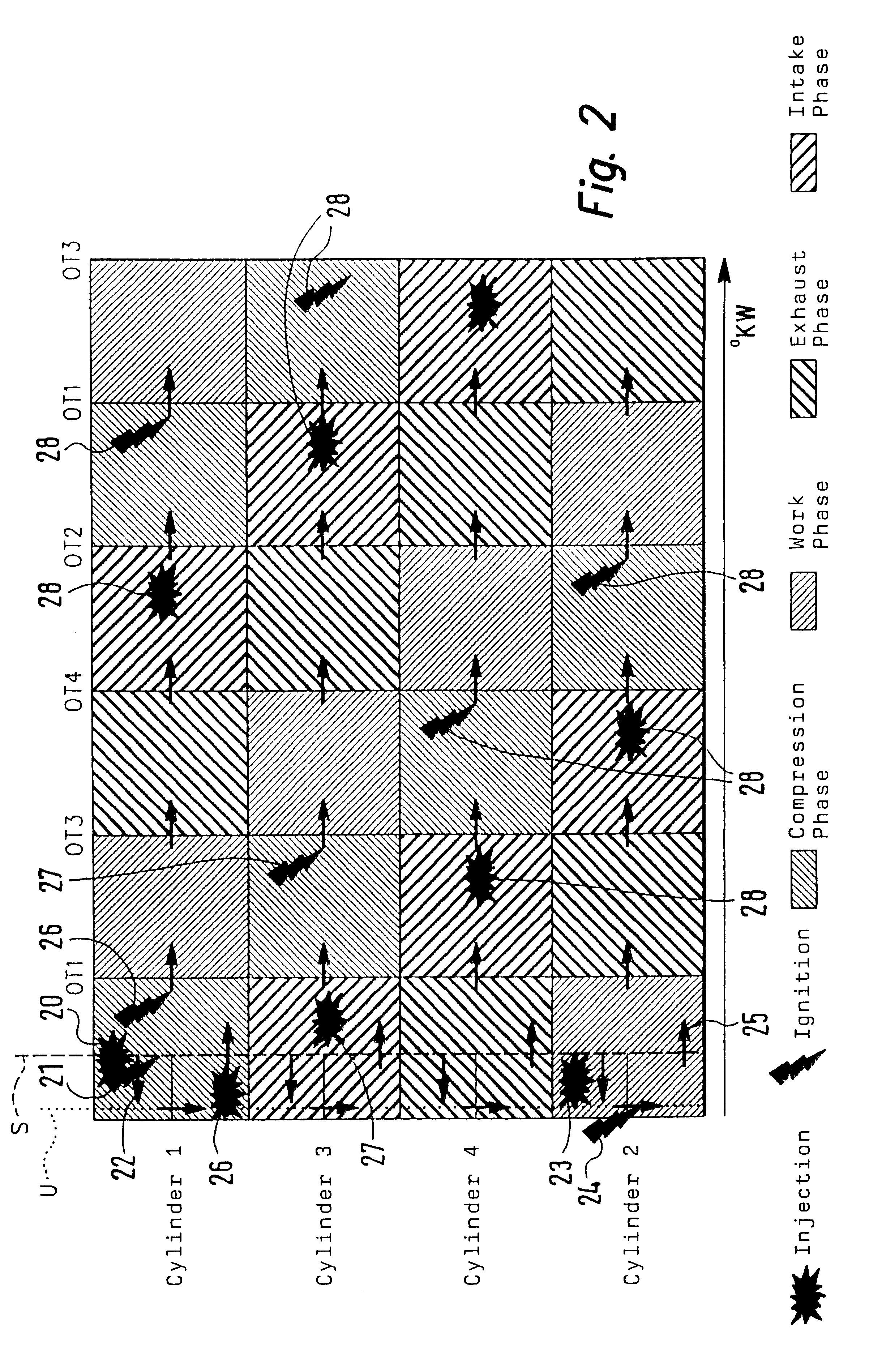
Method and device for controlling the transition between normal operation and overrun fuel cut-off operation of an otto engine operated with direct fuel injection
ActiveUS20060231068A1Delay in buildupTorque reduction is essentially greaterElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMultiple injectionEngineering
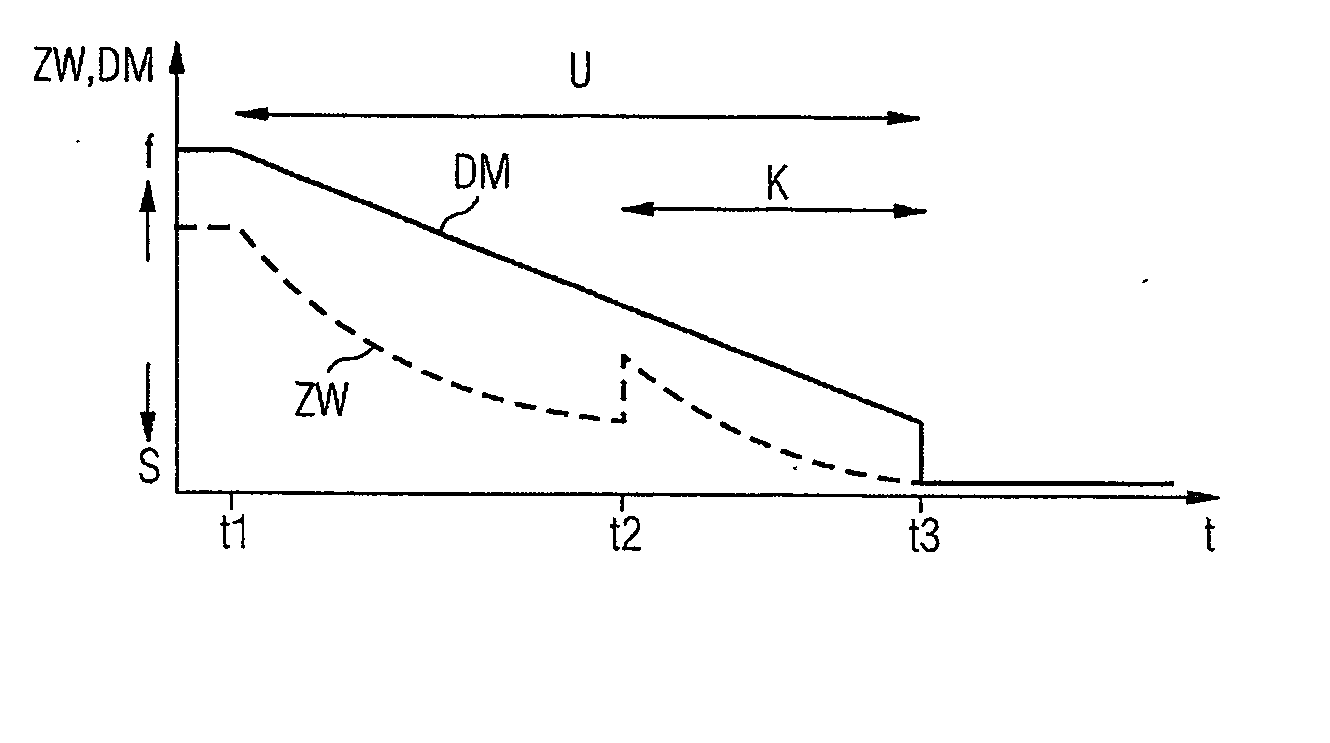
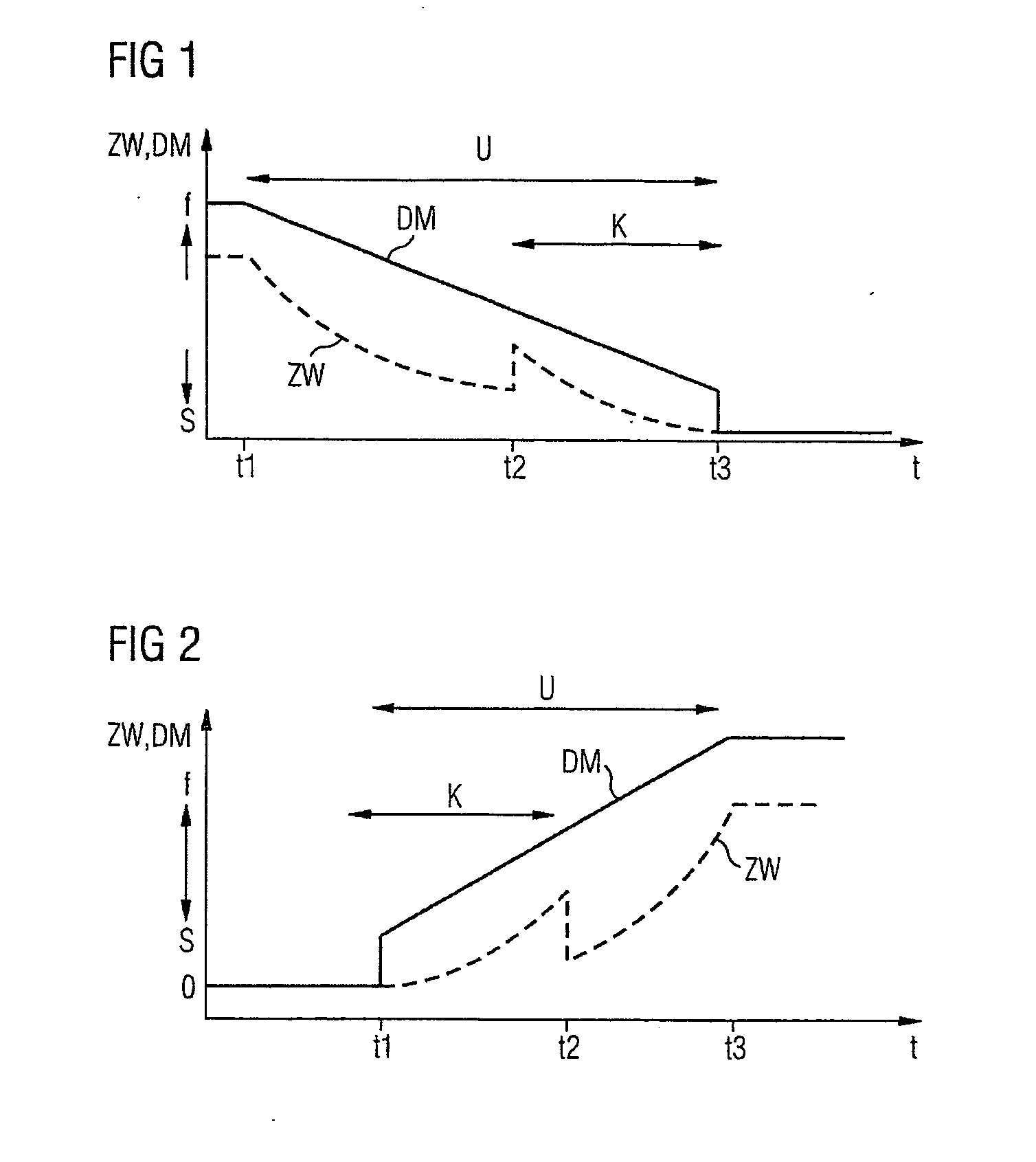
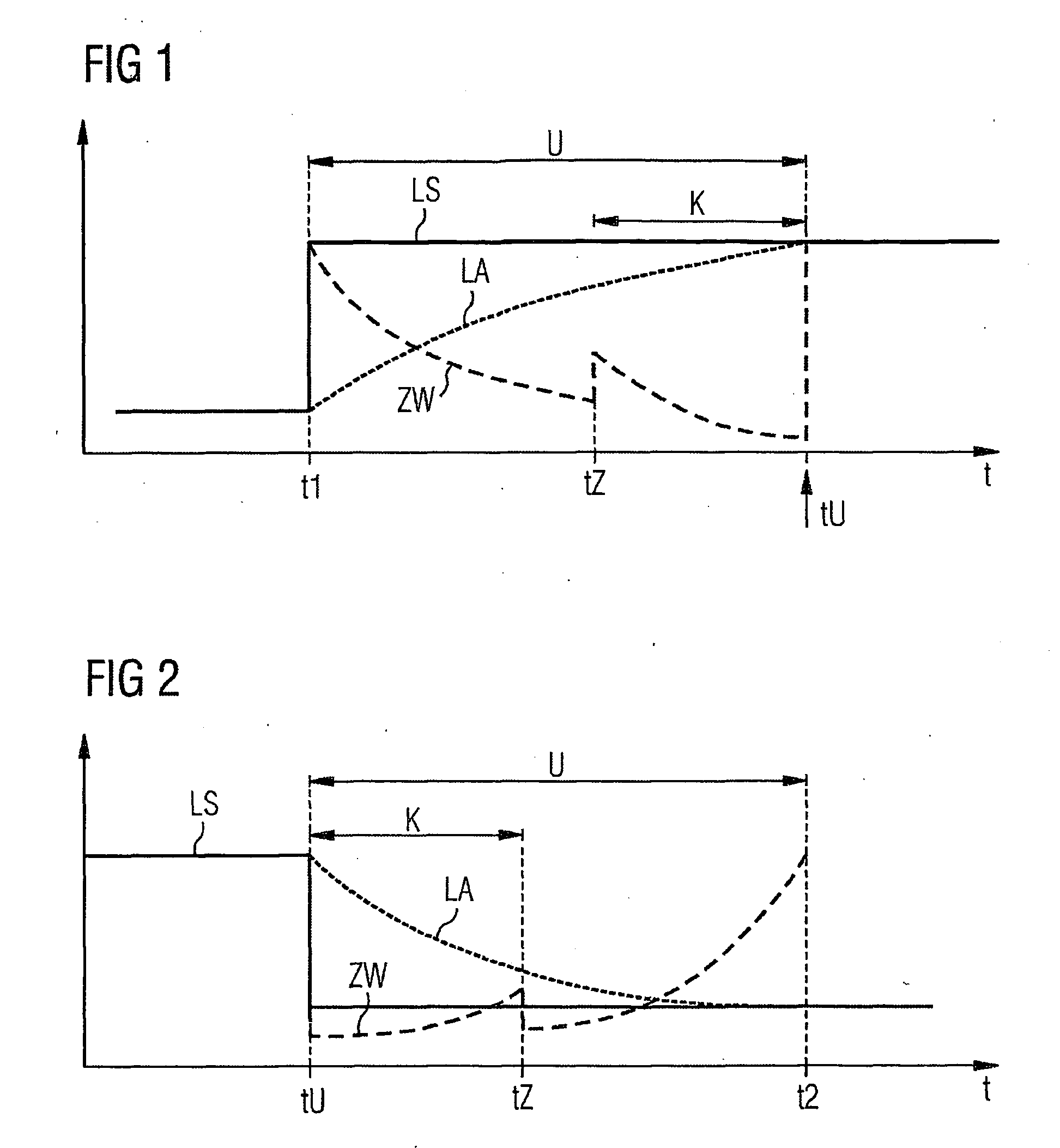
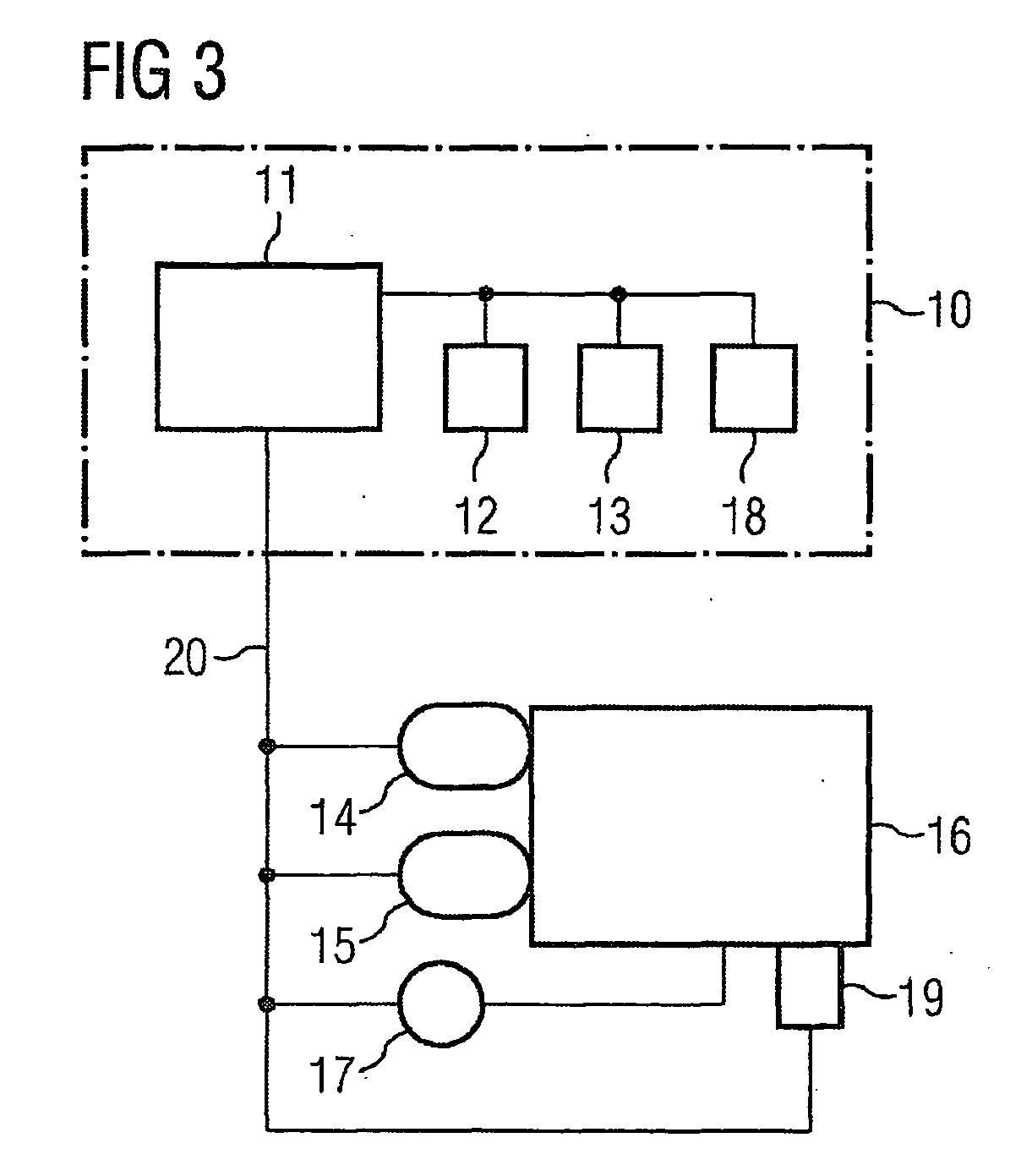
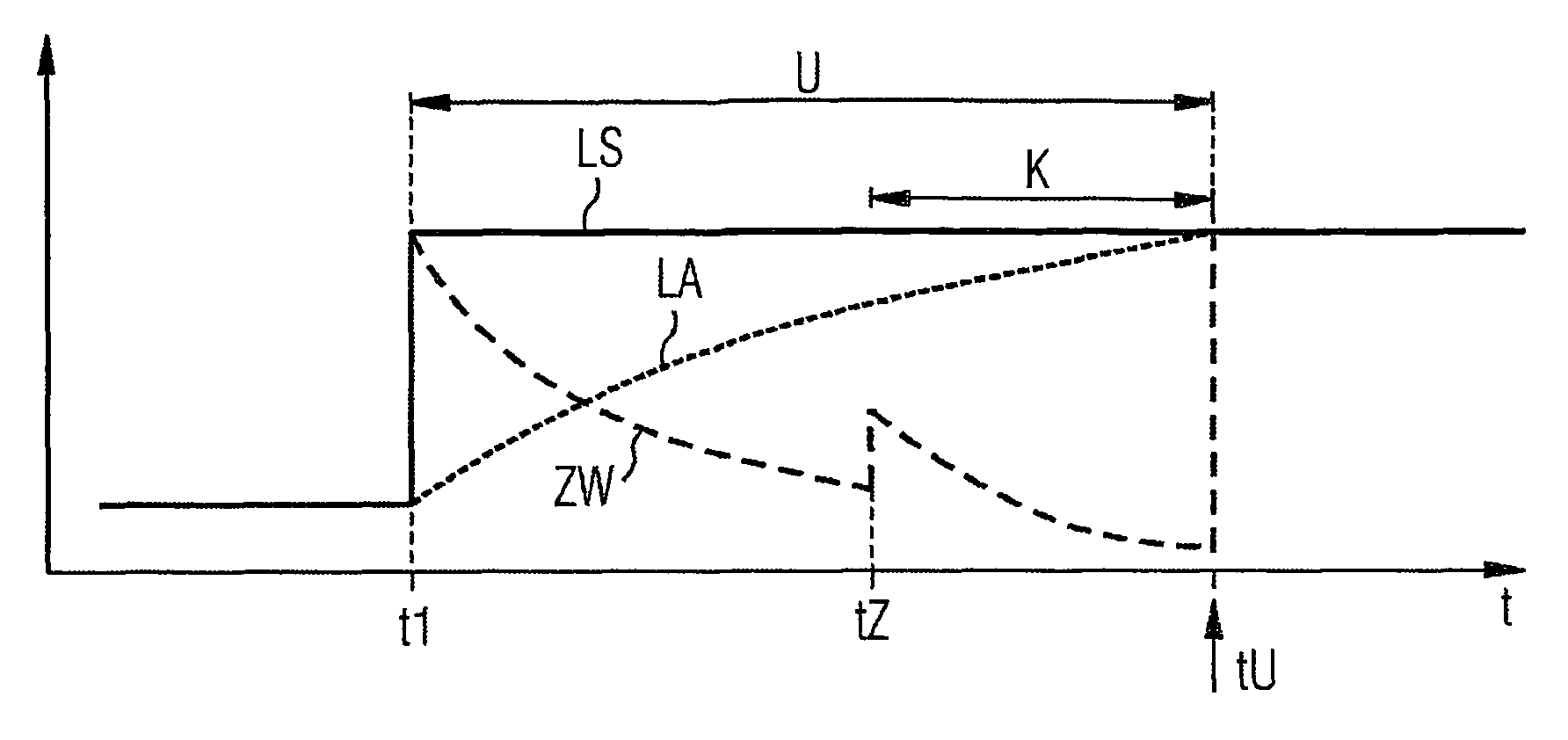
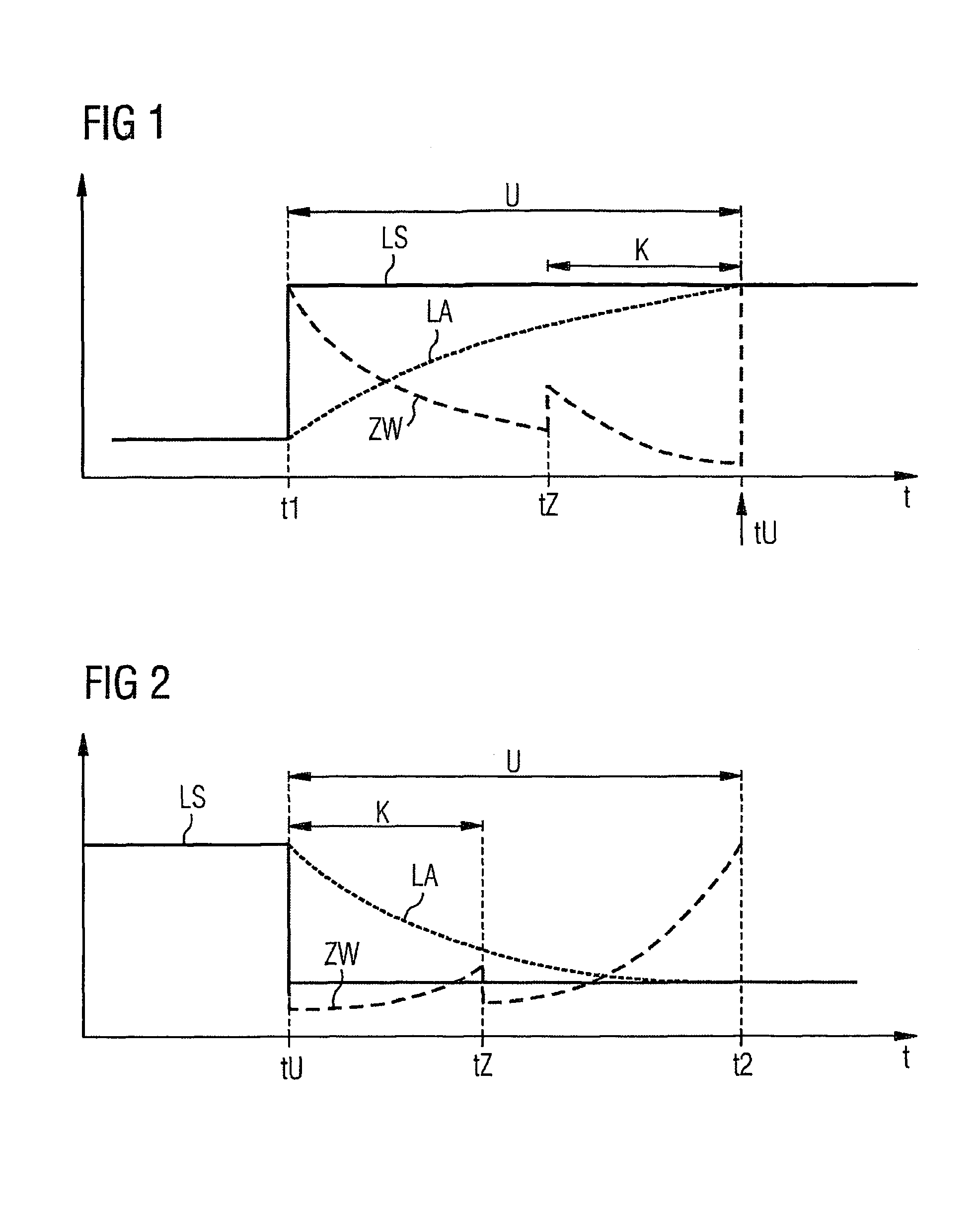
The problem during overrun fuel cut-off operations, i.e. cut-off of fuel injection during trailing throttle conditions of the vehicle, is that the transition entails an undue torque jump, resulting in the smooth operation of the engine and the driving comfort of the passengers of the vehicle being affected. The aim of the invention is to reduce the torque jump. Said aim is achieved by injecting fuel into a cylinder of the Otto engine in a multiple injection process, at least a partial quantity of the fuel that is to be injected being injected during the compression phase, whereby the quantity of air that is taken in advantageously decreases because no internal cooling takes place while the efficiency is advantageously reduced due to the lesser degree of swirling, resulting in lower torque. Overall, torque (DM) is reduced to a significantly greater extent than by merely adjusting the spark angle (ZW) while smooth operation of the Otto engine is not affected.
Owner:VITESCO TECH GERMANY GMBH
Regulating the Temperature of a Heat Regenerator Used in an Installation for Storing Energy by Adiabatic Compression of Air
InactiveUS20120085087A1Efficient executionMitigate such drawbackFluid couplingsEngine fuctionsEngineeringCompression phase
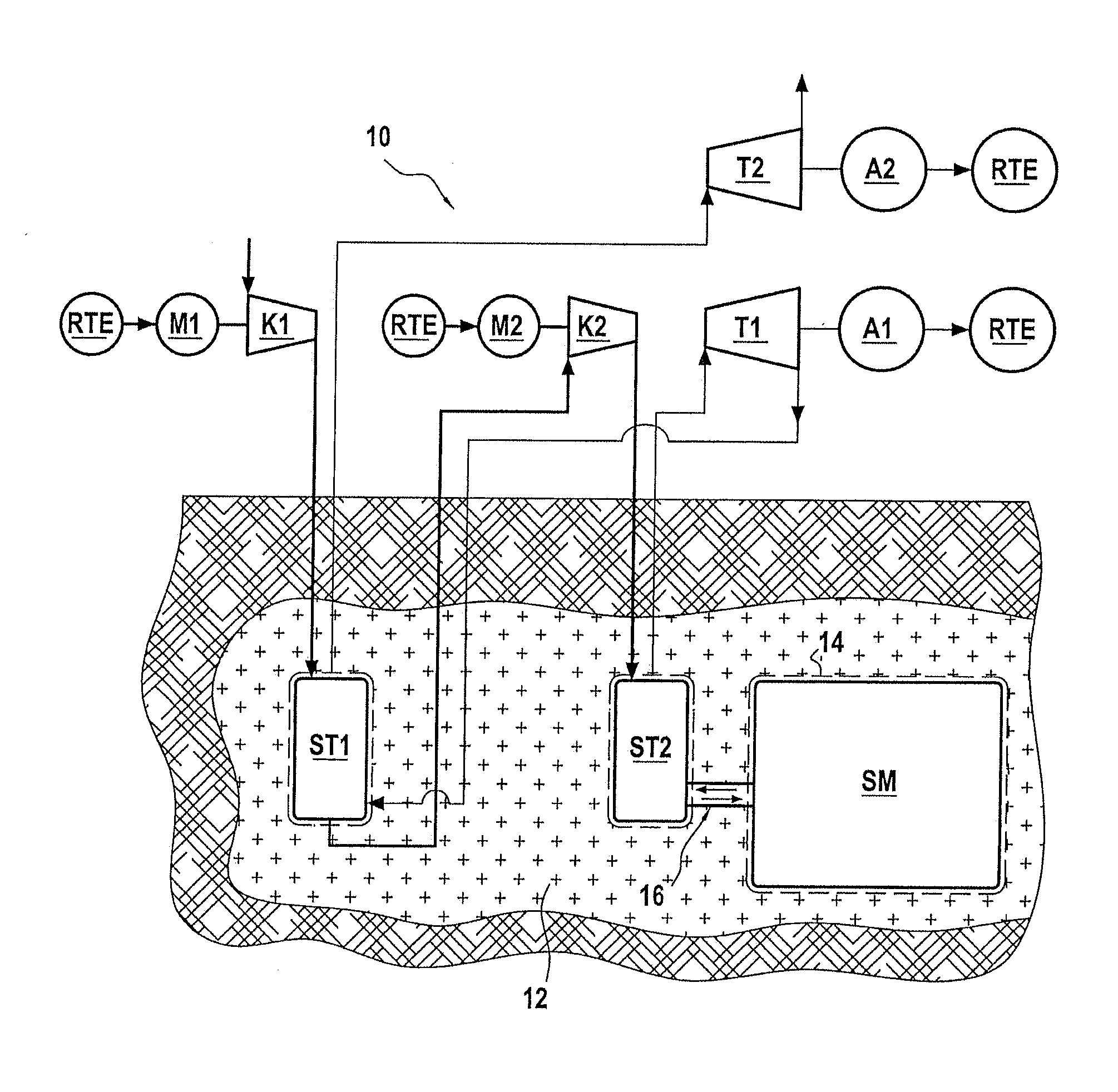
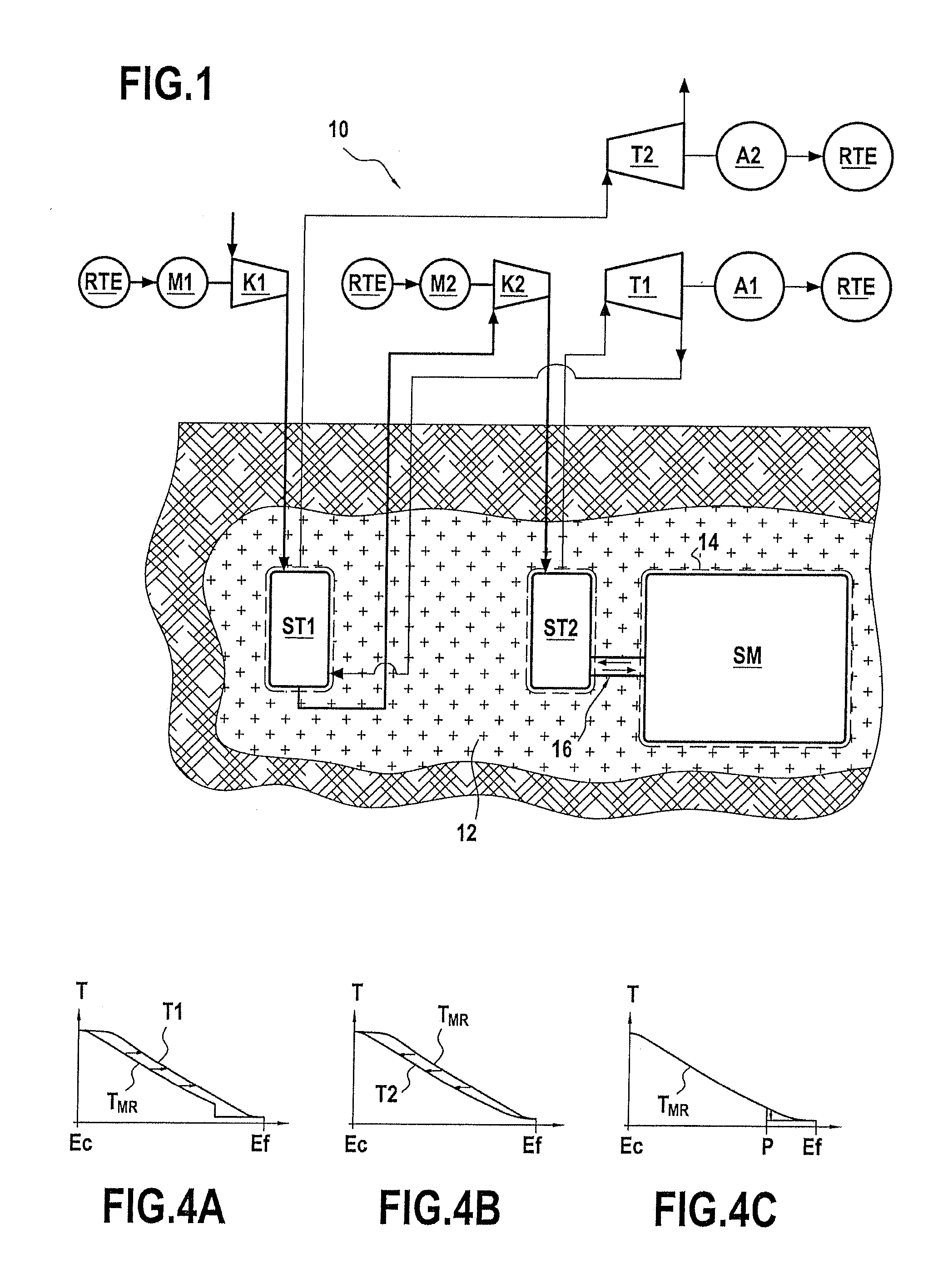
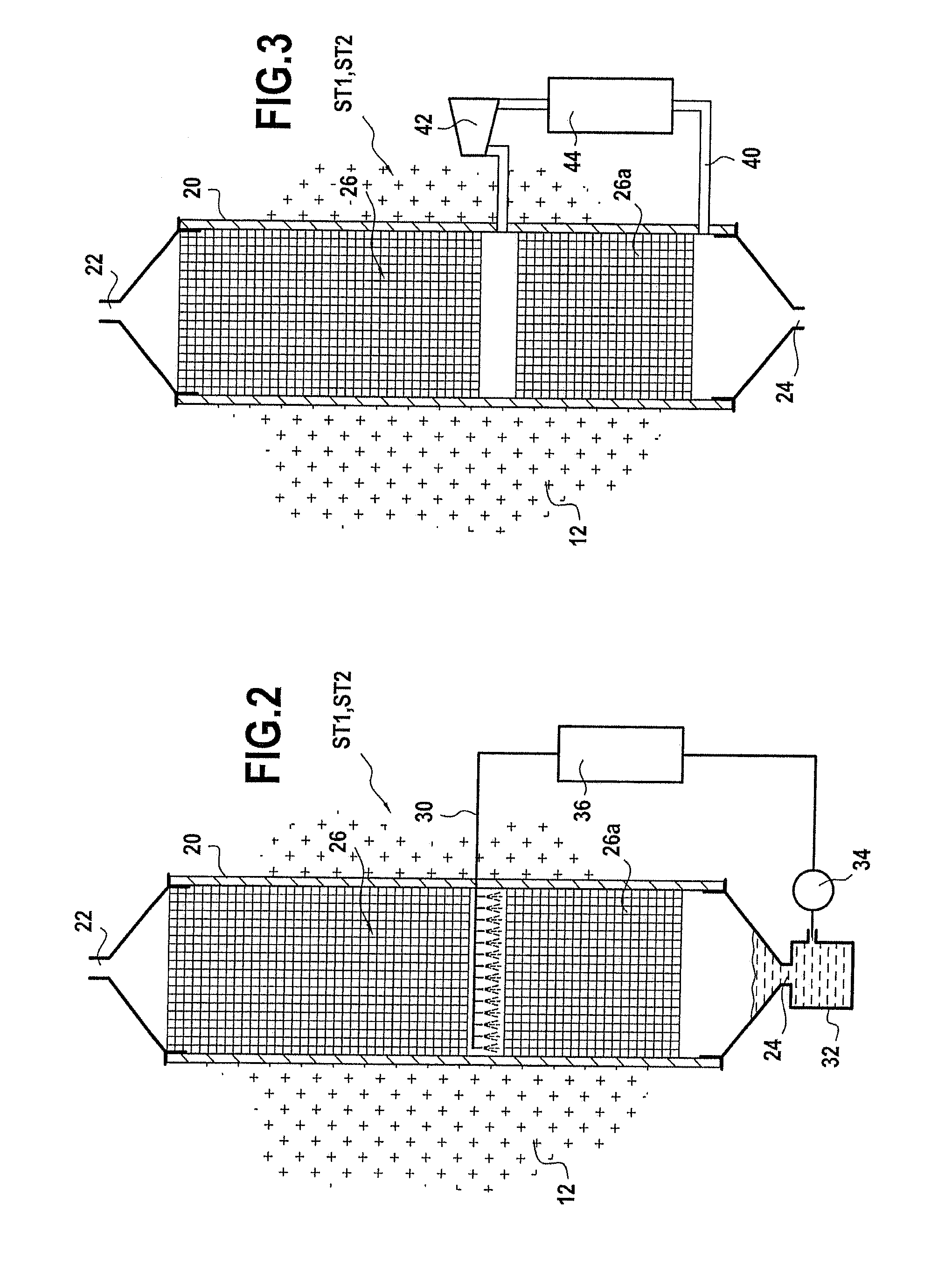
The invention relates to a method of regulating the temperature of a heat regenerator (ST1, ST2) used in an installation (10) for storing energy by adiabatic compression of air. The regenerator is subjected to successive operating cycles, each cycle comprising a compression stage followed by an expansion stage. Between two successive cycles, the method consists in cooling a bottom compartment (26a) of the layer of refractory material (26) of the regenerator that is situated in the proximity of the bottom distribution box (24) in order to bring the air leaving the heat regenerator to a temperature that is compatible with the range of temperatures required during the compression stages. The invention also provides such a heat regenerator.
Owner:GDF SUEZ SA
Regulated dashpot with shock-absorption force controls
ActiveUS7699147B2Adjustable powerRiding comfort will be considerably improvedSpringsResilient suspensionsMobile vehicleDashpot
A regulable dashpot with shock-absorption force controls, especially intended for motor vehicles, with at least one flow-regulating system including one or more shock-absorption components for the compression phase and / or for the decompression phase. The object is to allow the dashpot to shift continuously between the hard and soft phases, whereby the valve-adjustment intervals can be varied at intervals that are not unnecessarily short or even unattainable. At least one valve assembly is accordingly supplied with variable flow impedance by a regulating valve (5 or 6).
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP BILSTEIN
Method and device for controlling the transition in a direct injection internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20070055436A1Reduce torqueLarge step-change in the torque canAnalogue computers for vehiclesValve arrangementsMultiple injectionOperation mode
During the changeover from a first operating mode of a spark-ignition engine with direct fuel injection to a second operating mode, in particular between a homogeneous stoichiometric and homogeneous lean, stratified or HCCI operation with changeovers of the valve stroke or the valve phase, there is the risk of an undesired torque jump, which can lead to a perceptible jolting of the vehicle or to a disturbance in the running of the spark-ignition engine. The invention thus proposes, in particular in the case of an inadmissibly large torque jump, the initiation of a multiple injection of fuel in addition to the conventional compensation by the displacement of the ignition angle. A partial quantity of said fuel is injected during the compression phase to reduce the degree of efficiency, thus reducing the torque produced.
Owner:VITESCO TECH GERMANY GMBH
Method and device for controlling the transition in a direct injection internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7328683B2Reduce torqueLarge step-change in the torque canValve arrangementsElectrical controlMultiple injectionControl theory
During the changeover from a first operating mode of a spark-ignition engine with direct fuel injection to a second operating mode, in particular between a homogeneous stoichiometric and homogeneous lean, stratified or HCCI operation with changeovers of the valve stroke or the valve phase, there is the risk of an undesired torque jump, which can lead to a perceptible jolting of the vehicle or to a disturbance in the running of the spark-ignition engine. The invention thus proposes, in particular in the case of an inadmissibly large torque jump, the initiation of a multiple injection of fuel in addition to the conventional compensation by the displacement of the ignition angle. A partial quantity of said fuel is injected during the compression phase to reduce the degree of efficiency, thus reducing the torque produced.
Owner:VITESCO TECH GERMANY GMBH
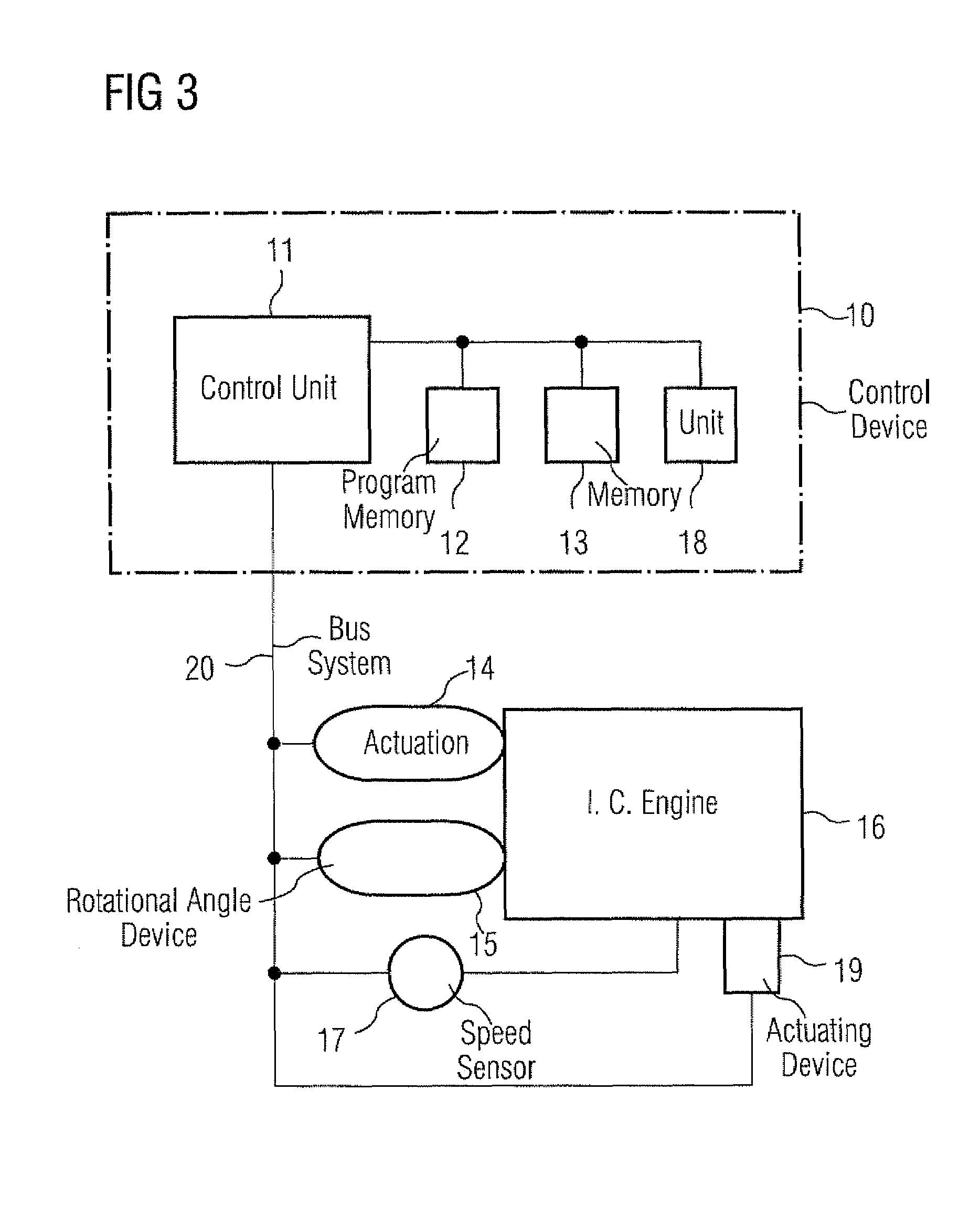
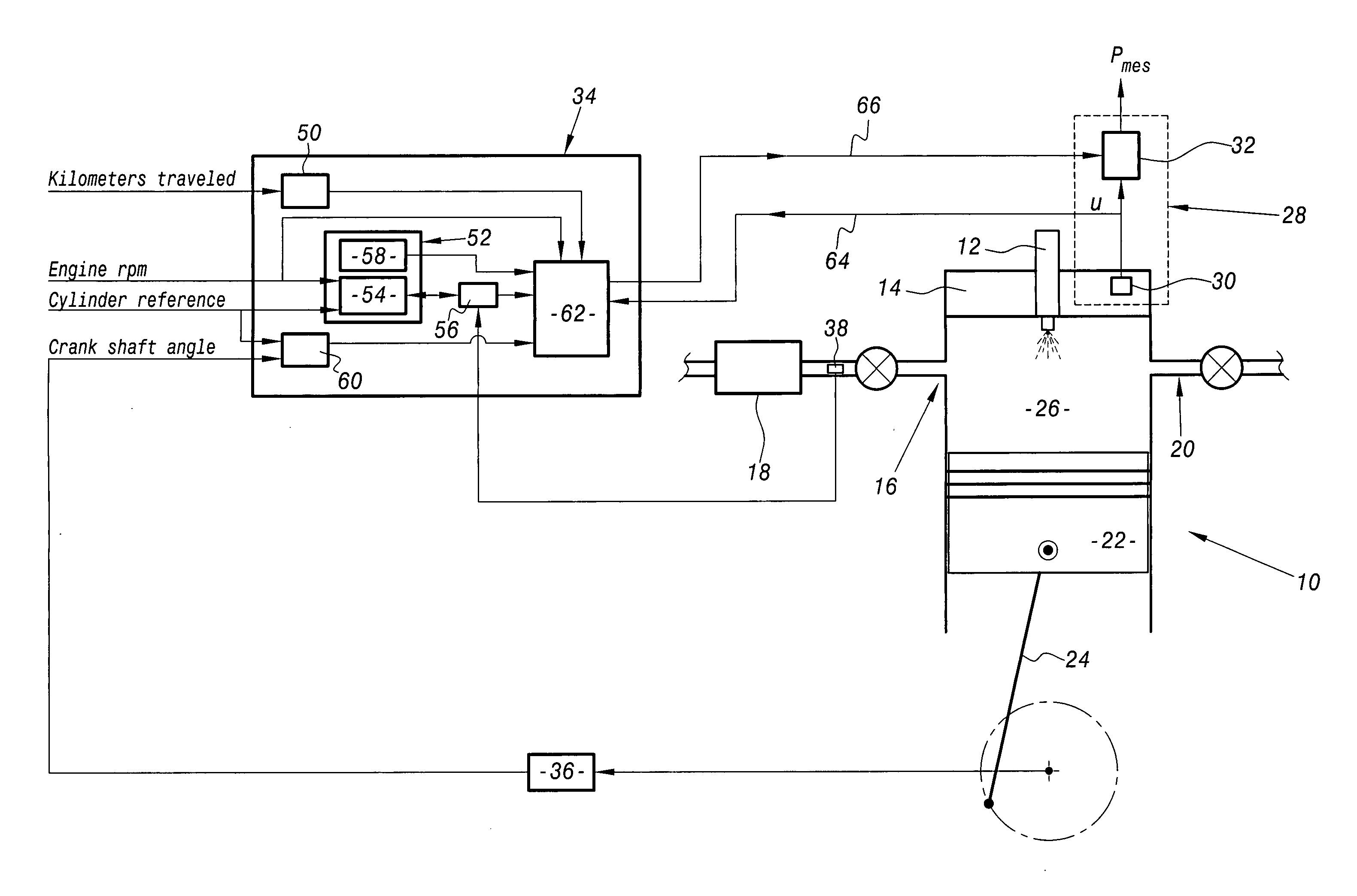
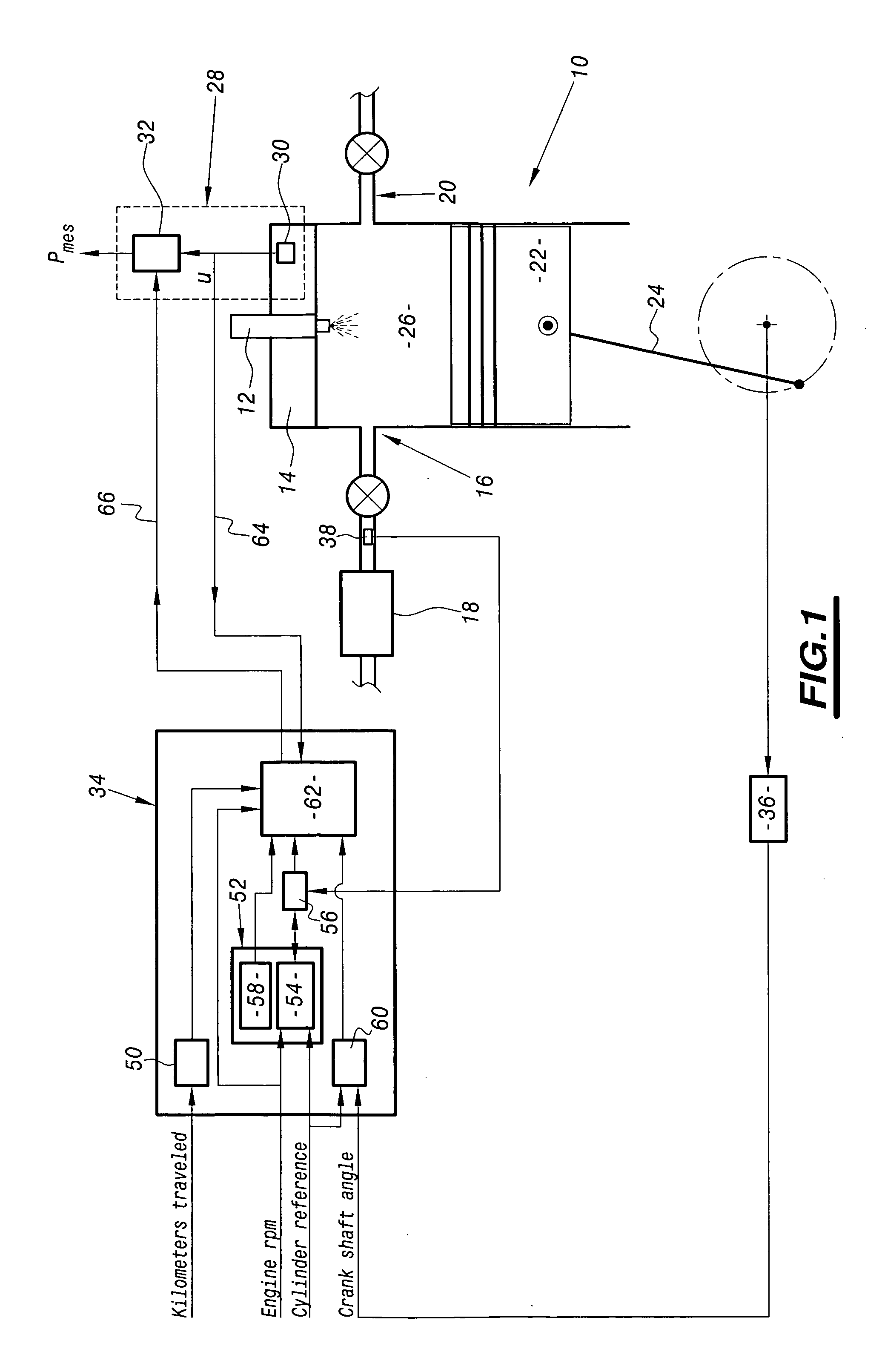
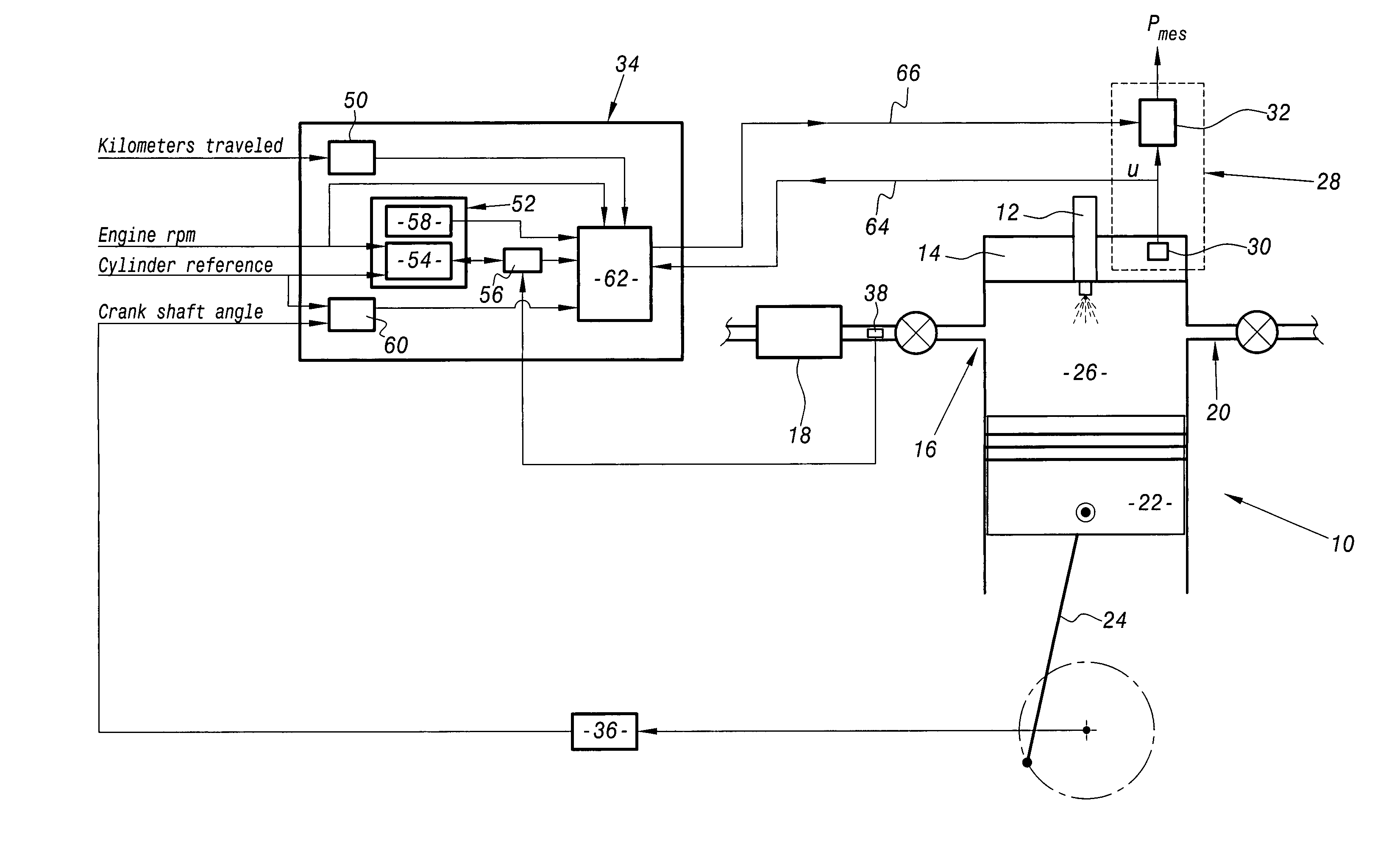
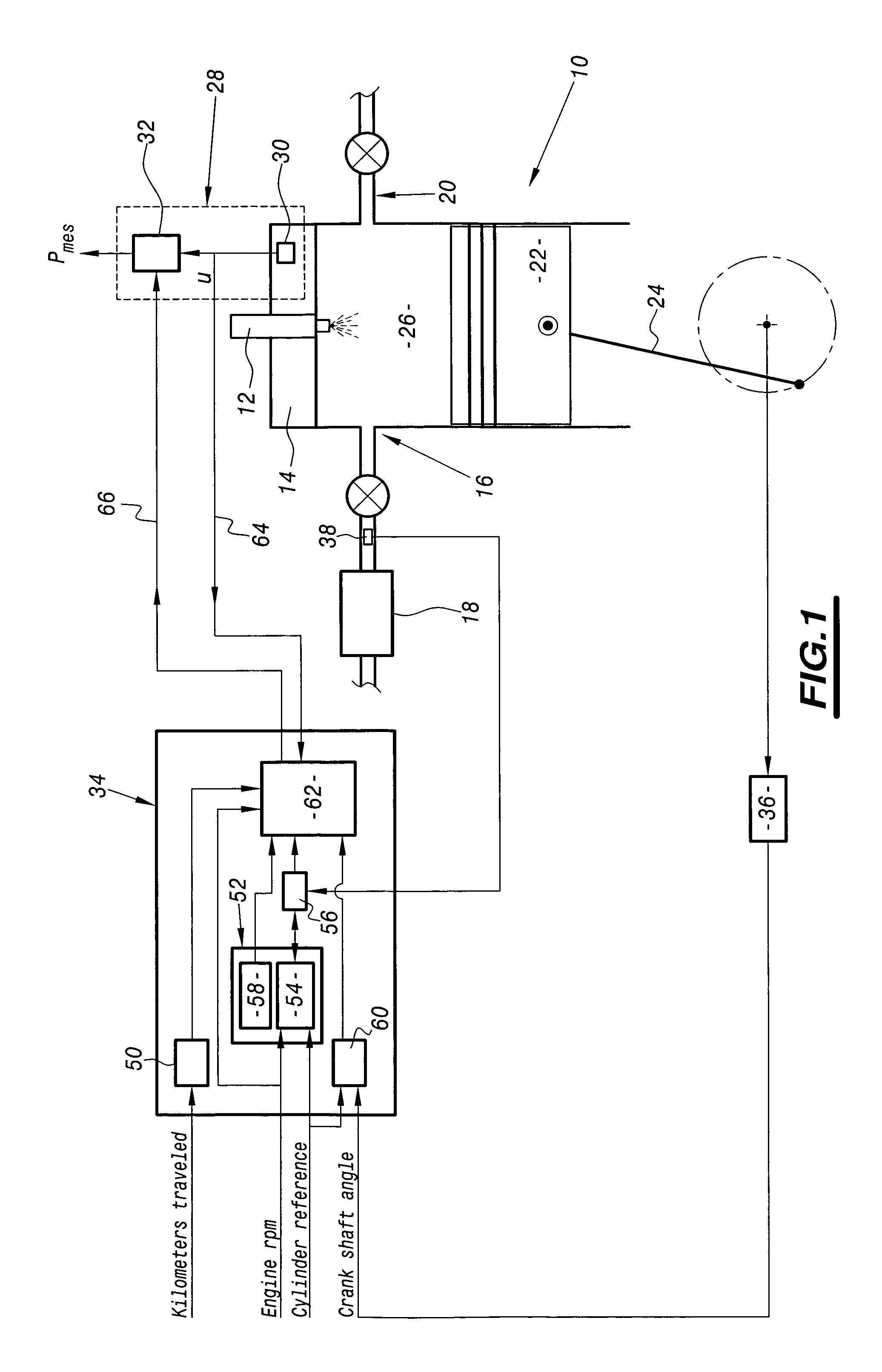
System for calibrating apparatus for acquiring the pressure in a motor vehicle diesel engine cylinder
InactiveUS20050125140A1Analogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlInformation processingAcquisition apparatus
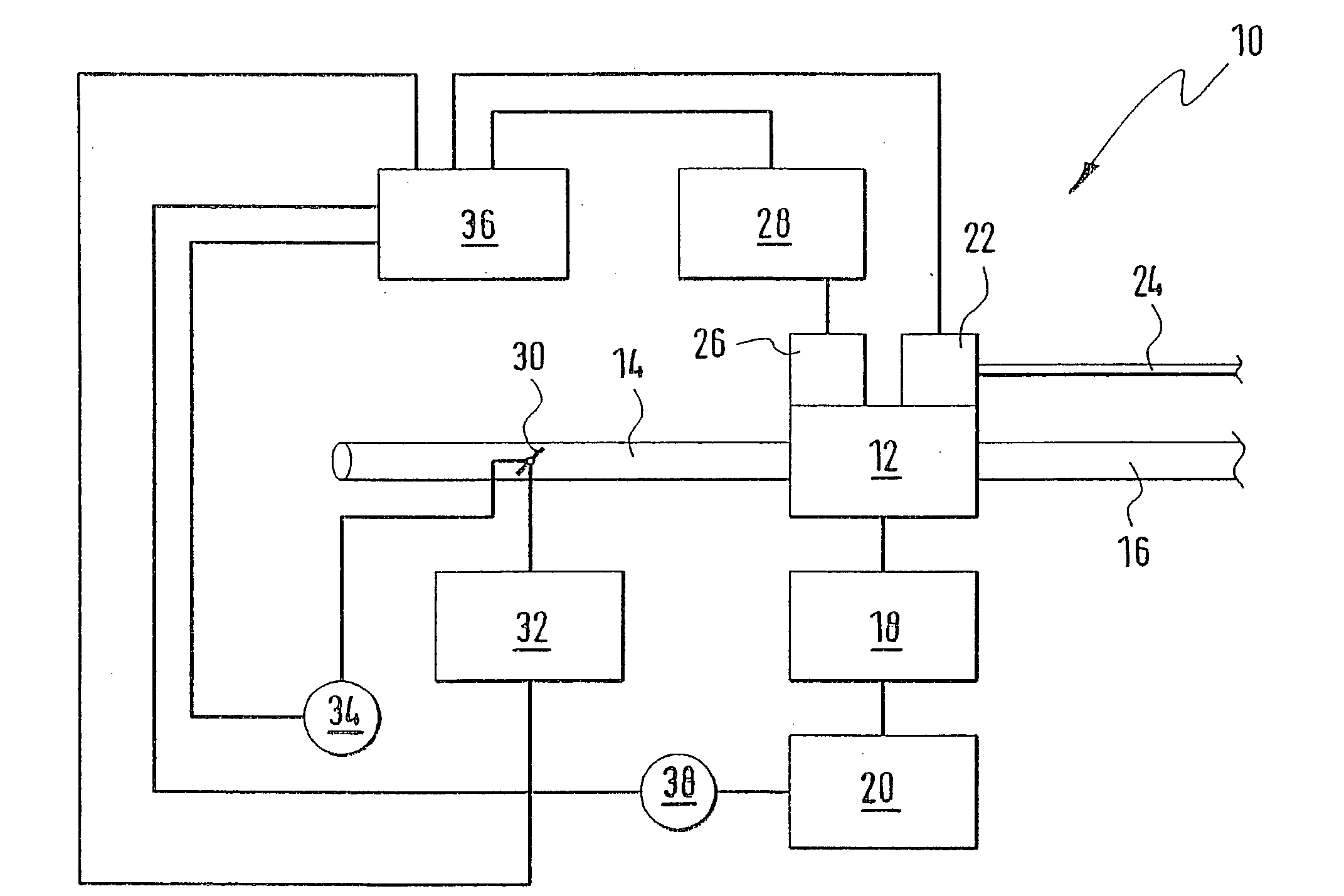
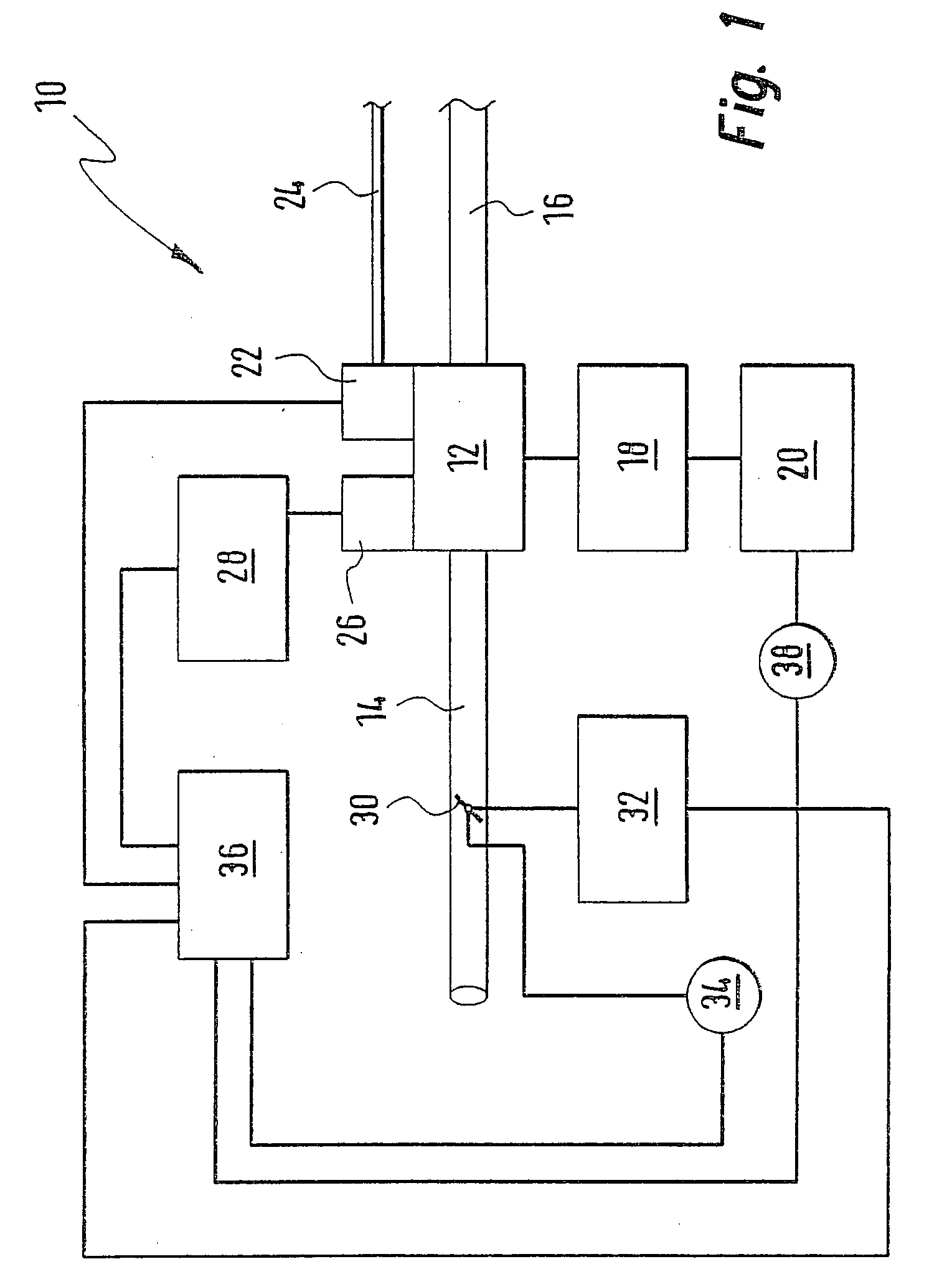
The invention relates to a system for calibrating apparatus (28) for acquiring the pressure in a cylinder (10) of a motor vehicle diesel engine, of the type comprising a cylinder pressure sensor (30) associated with the cylinder and means (32) for conditioning the signal delivered by the sensor (30) as a function of conditioning parameters. The calibration system comprises means (64) for collecting a signal delivered by the cylinder pressure sensor (30), an information processing unit (34) adapted to determine the values of the conditioning parameters as a function of a polytropic thermodynamic model of the evolution of the pressure in the cylinder, a reference pressure of the pure compression phase of the cycle of the cylinder, and the signal delivered by the pressure sensor (30) and collected by the collecting means (64), and means (66) for modifying the values of the conditioning parameters in the acquisition apparatus (28) as a function of the values of the conditioning parameters determined by the information processing unit (34).
Owner:PEZHO SITROEN AUTOMOBILS SA +1
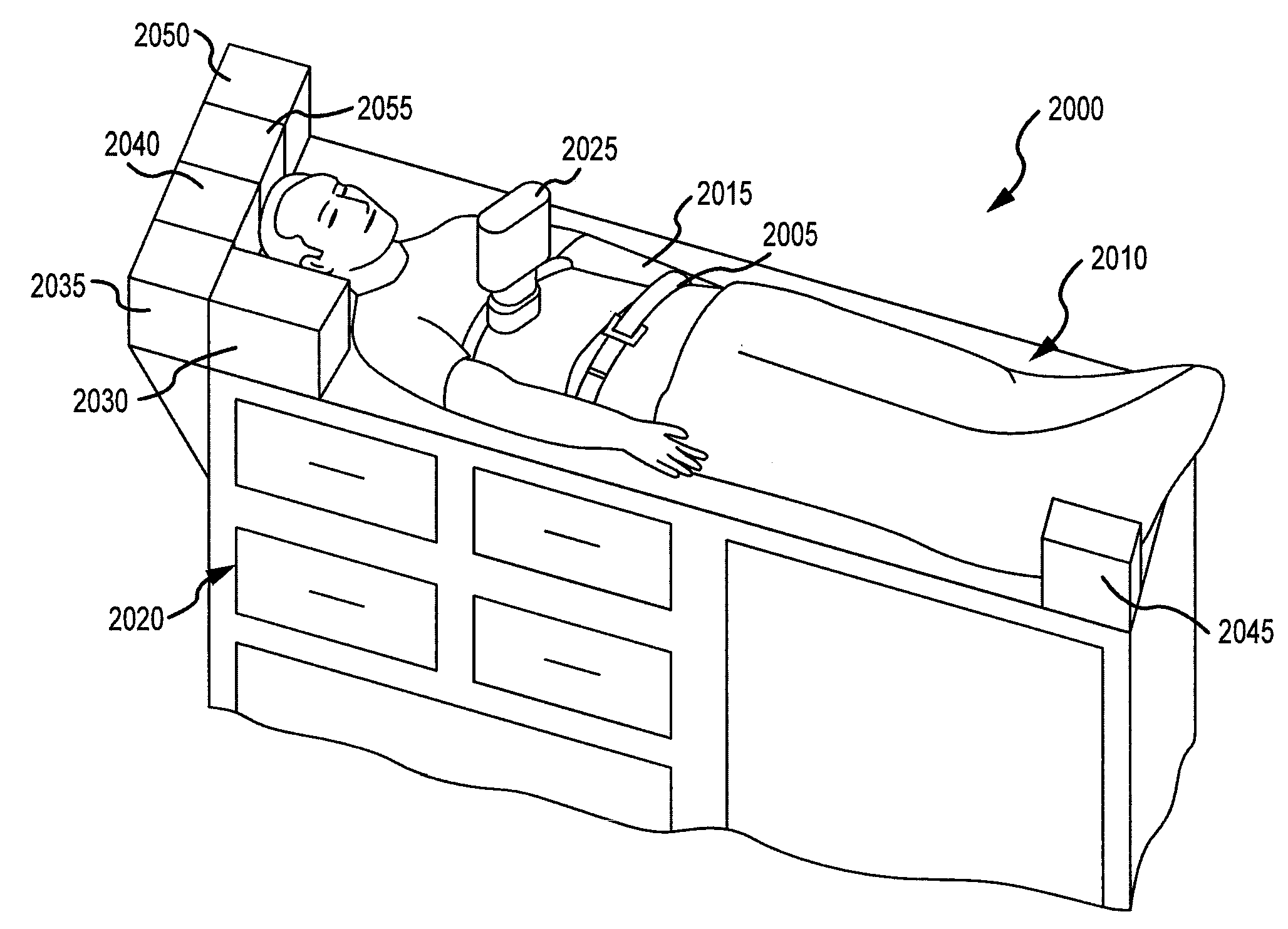
Driving control of a reciprocating cpr apparatus
ActiveUS20120283608A1Reduce consumptionRespiratorsElectrotherapyEngineeringCardio-pulmonary resuscitation
A method of controlling the amount of compressed gas used for driving a reciprocating apparatus for cardio-pulmonary resuscitation (CPR) comprising a valve means for controlling the provision of driving gas comprises operation of the valve means during the compression phase to stop provision of driving gas, which operation is separated in time from the venting of the driving gas from the apparatus at the end of the compression phase. Also disclosed are; a CPR apparatus operated by the method; a method of compression depth sensing.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
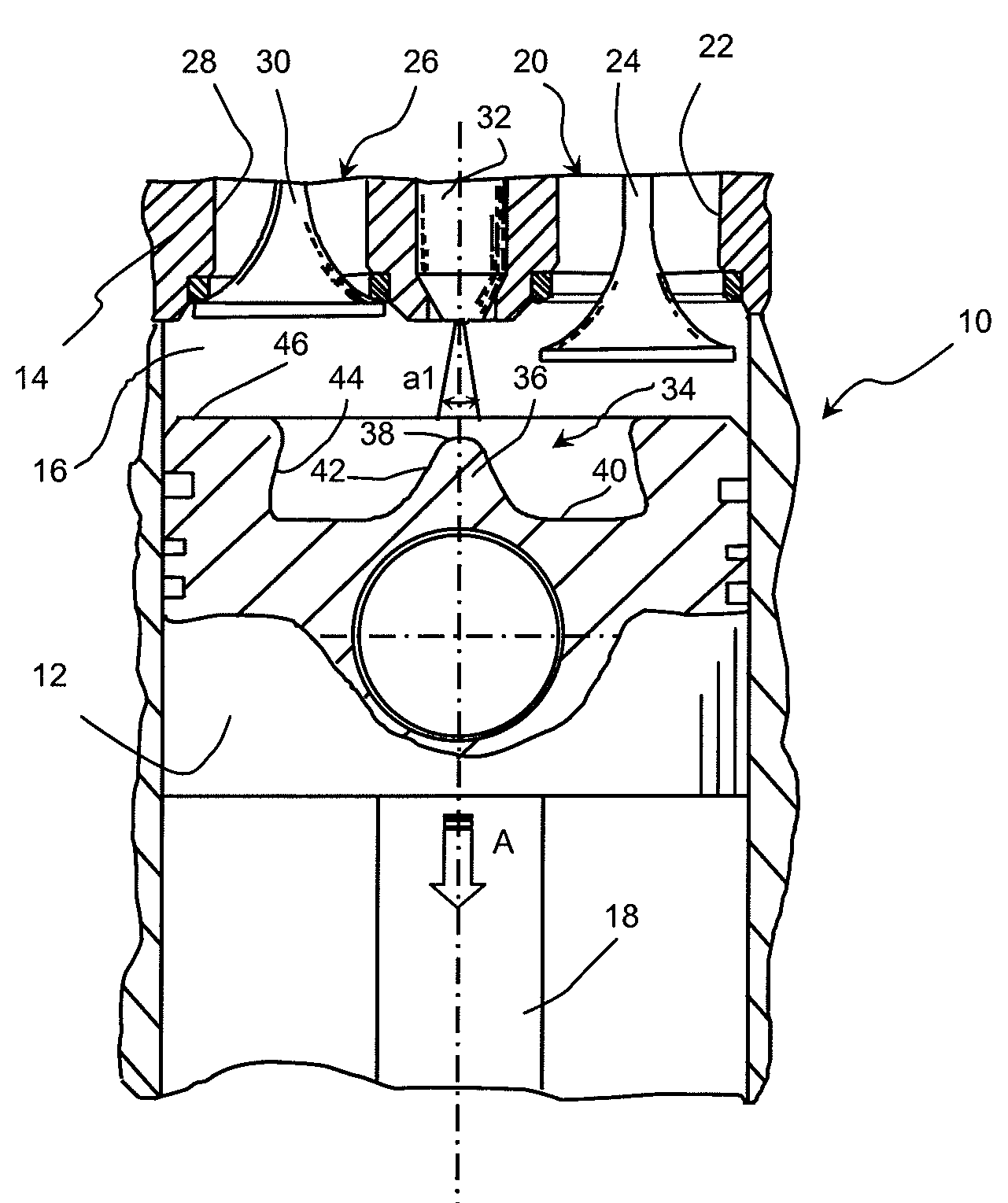
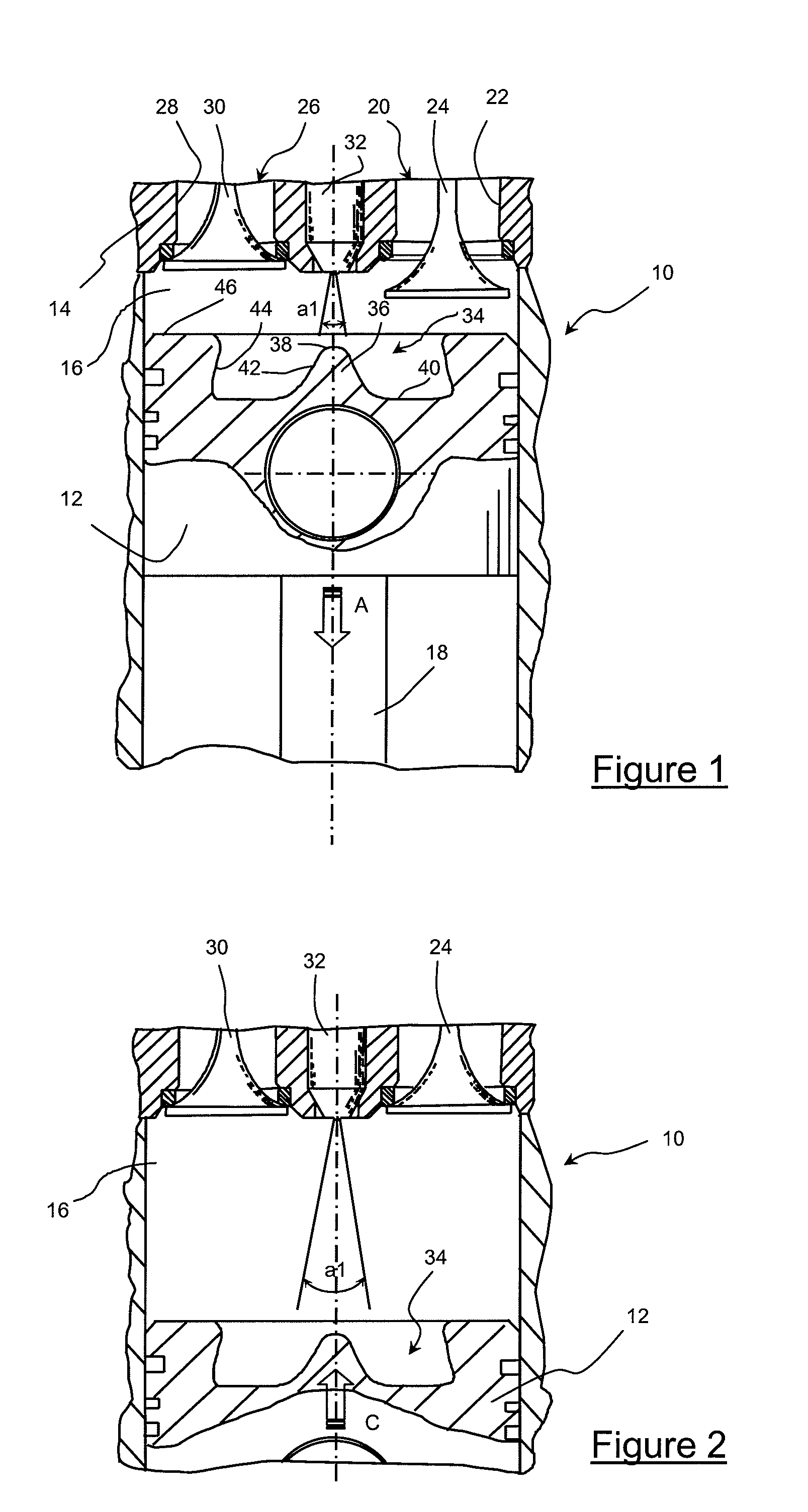
Fuel injection method for internal-combustion engine, notably of direct injection type, comprising a piston provided with a bowl and a teat
InactiveUS20070163535A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberEngineering
The present invention relates to a method of injecting fuel into the combustion chamber (16) of a cylinder of a direct-injection four-stroke internal-combustion engine, notably of diesel type, that can run according to a homogeneous combustion mode and according to a conventional combustion mode. According to the invention, this method consists, for the conventional combustion mode of the engine, in feeding into this chamber a first amount of fuel in the vicinity of the top dead centre of the piston at the beginning of the intake phase and another quantity of fuel in the vicinity of the top dead centre of this piston at the end of the compression phase.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Method for operating a direct injection diesel engine
ActiveUS7207311B2Improve efficiencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesTop dead centerLimit value
A method for operating a direct injection diesel engine which is operated in a first operating region corresponding to low to medium partial load in such a way that fuel combustion takes place at a local temperature below the temperature of NOx formation and with a local air ratio above the limit value for soot formation, and where fuel injection starts in a range of between 50° to 5° crank angle before top dead center of the compression phase and where exhaust gas is recirculated at an exhaust gas recirculation rate of 50% to 70%. In order to achieve high efficiency in each operating region while keeping NOx and particulate emissions low, in a second operating region corresponding to medium partial load, fuel injection is started in a range from approximately 2° crank angle before top dead center to approximately 20° crank angle after top dead center.
Owner:AVL LIST GMBH
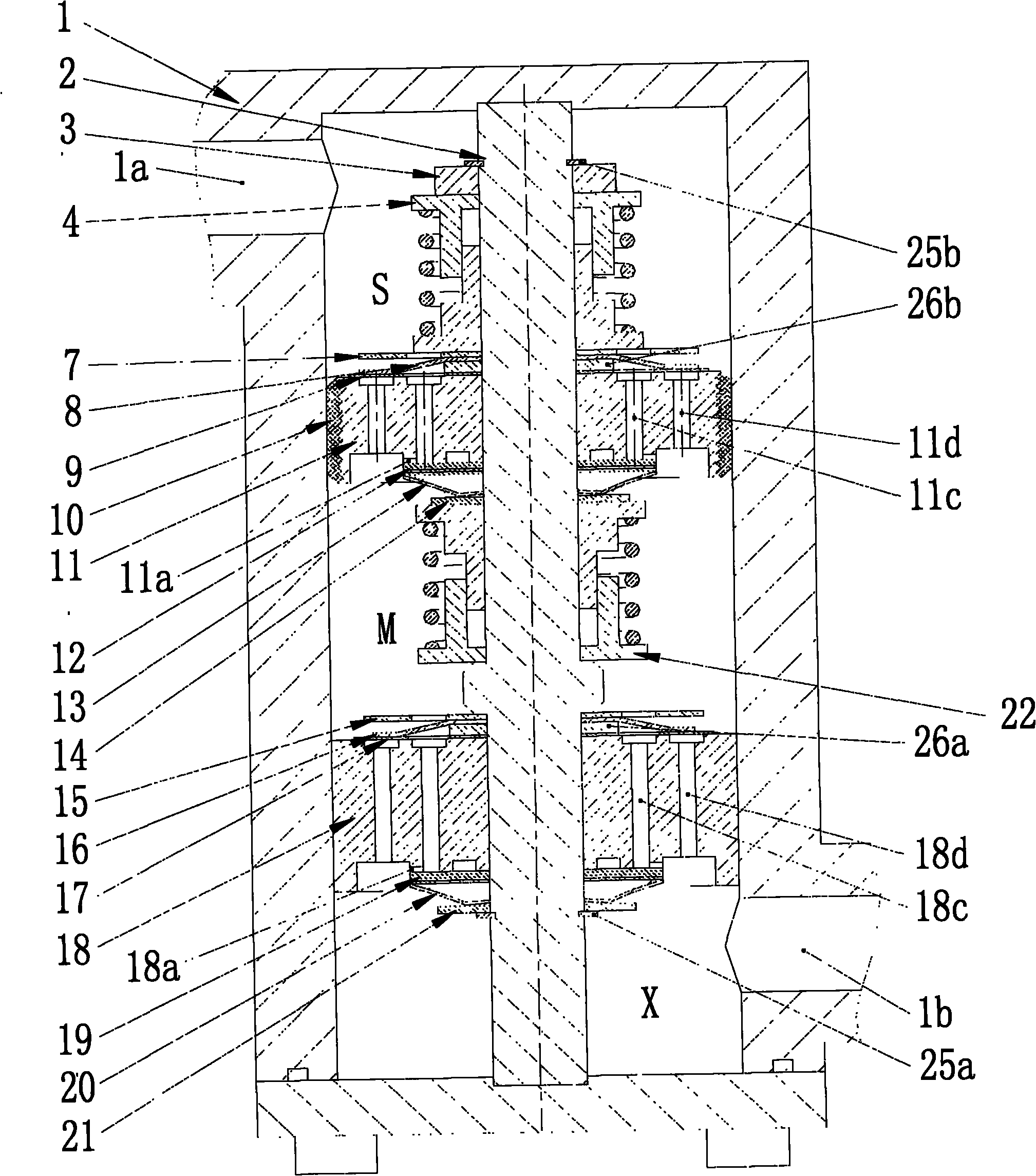
External mechanical induction type adjustable damping valve of oil-gas suspension
InactiveCN101871502AReduce trafficSmall upward motion displacementSpringsResilient suspensionsElectronic control systemControl system
The invention relates to an external mechanical induction type adjustable damping valve of an oil-gas suspension, which comprises an external mechanical induction type adjustable damping valve body, wherein an accumulator interface and an oil cylinder interface of the oil-gas suspension are arranged on the valve body; a mounting pole is arranged in the valve body, and a fixed valve and a floating valve are arranged on the periphery of the mounting pole; the floating valve is arranged between a compression limit spring and an extension limit spring in a suspended way; a fixed valve compression phase damping valve component and a fixed valve extension phase damping valve component are arranged at the two ends of the valve body of the floating valve respectively; a floating valve compression phase damping valve component and a floating valve extension phase damping valve component are arranged at the two ends of the valve body of the floating valve respectively; and a pre-stressing spring is arranged between a valve plate and a limit tray. The external mechanical induction type adjustable damping valve of the oil-gas suspension has the advantages that: the radiation is desirable; the outer diameter of a control valve element is small; the structure is simple; and the damping adjustment can be realized without electronic control system, and the reliability is high.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
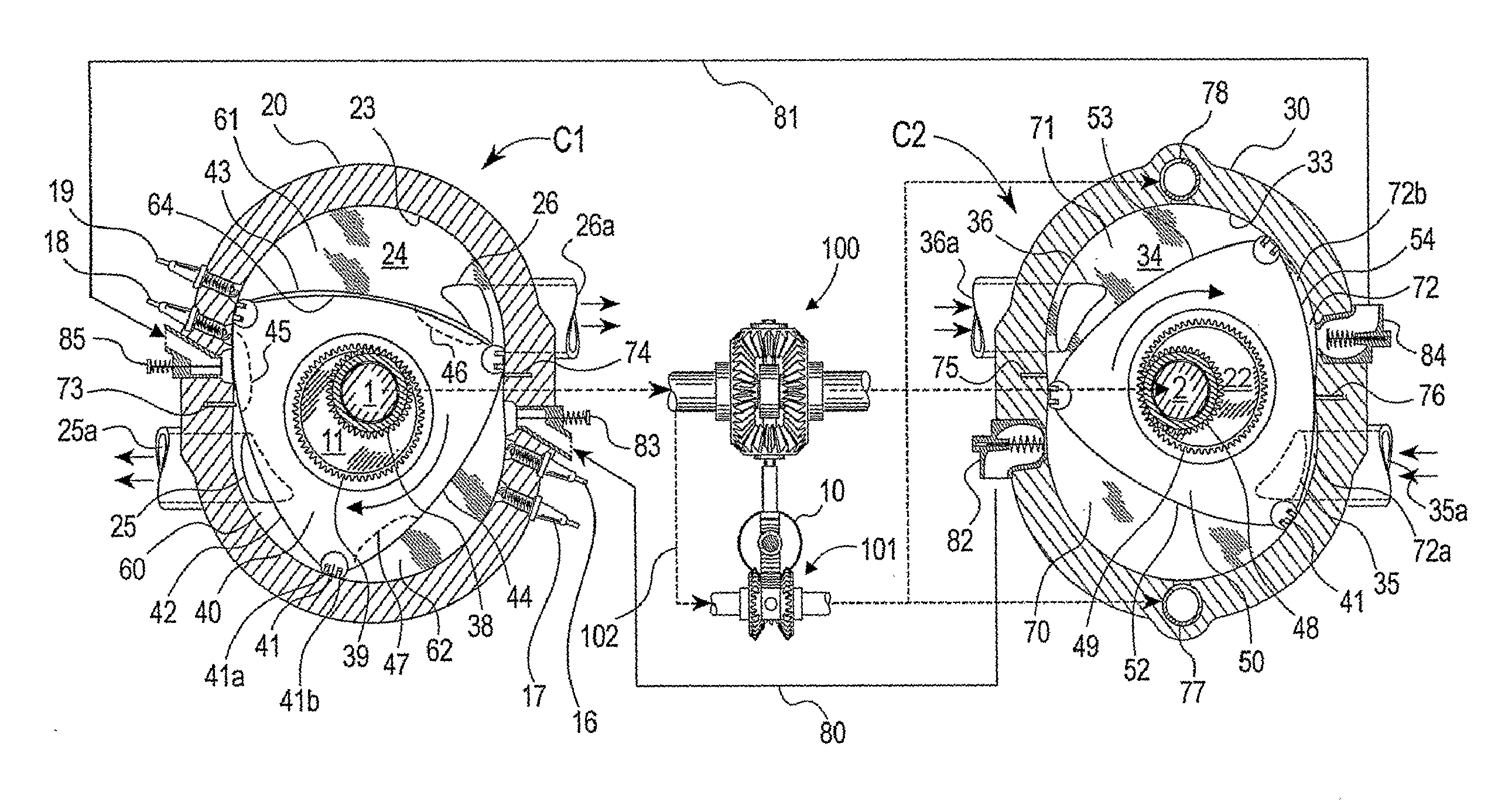
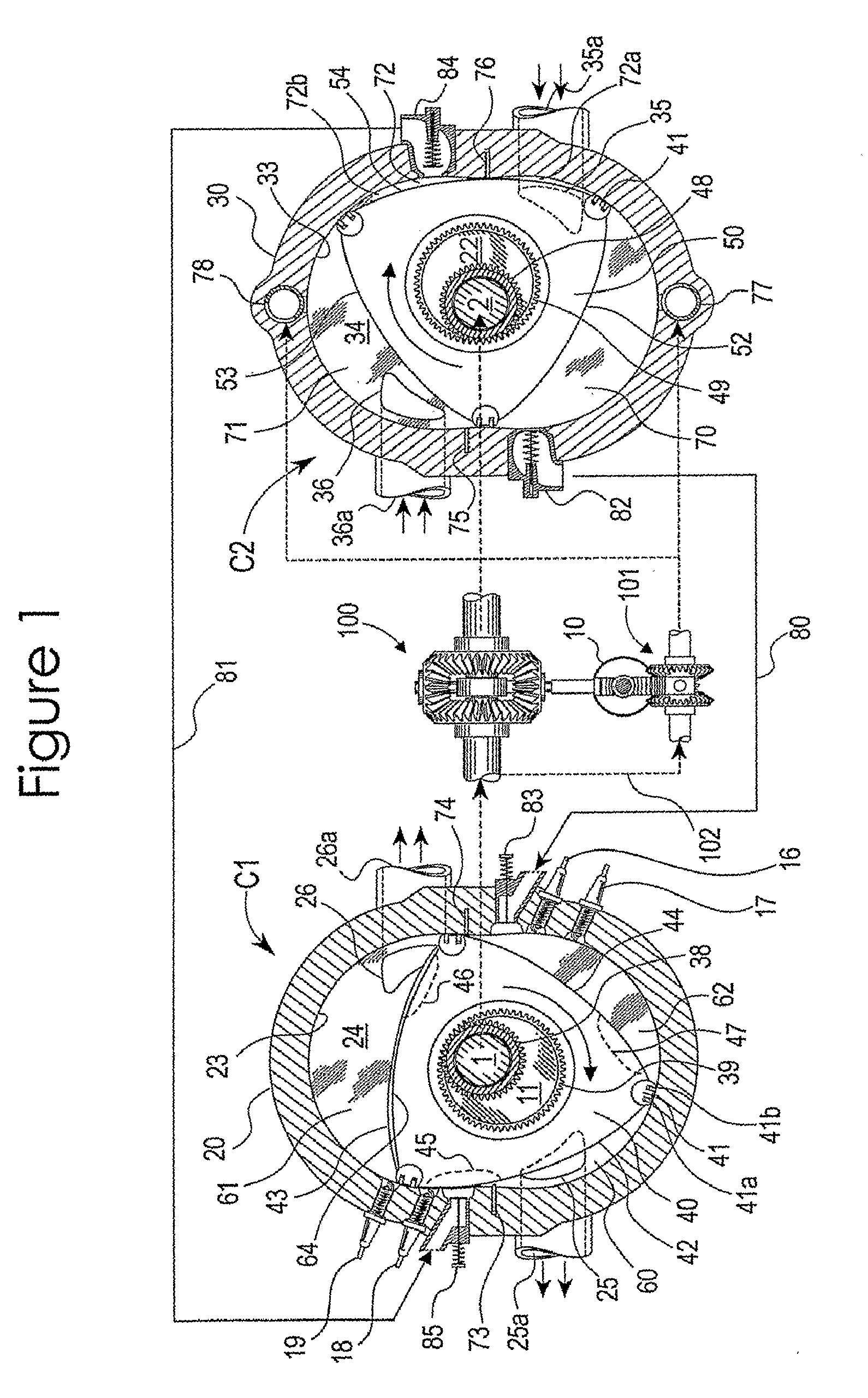
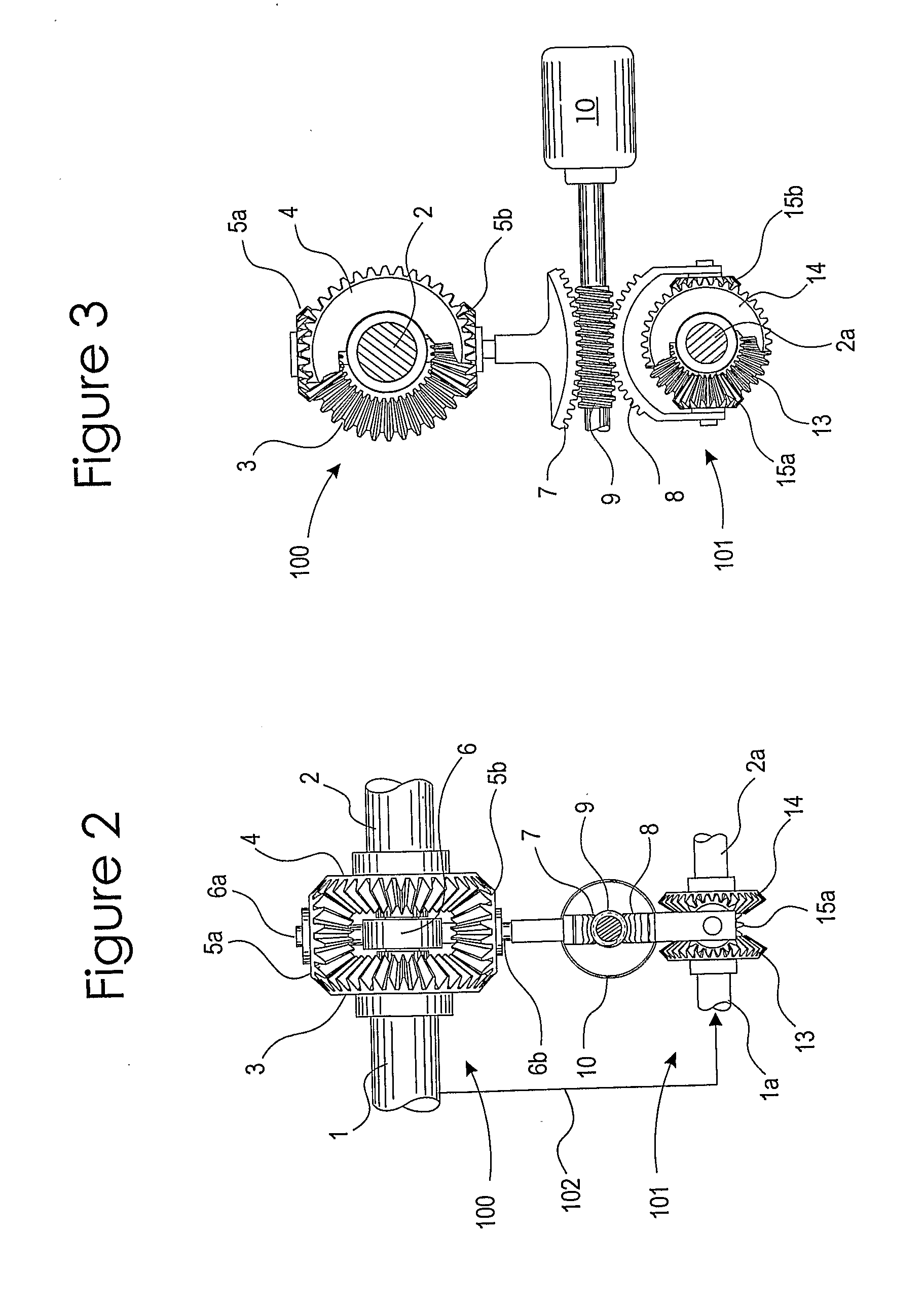
Split Cycle Variable Capacity Rotary Spark Ignition Engine
InactiveUS20100116241A1Improve sealingLess internal stressAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlCombustion chamberMechanical engineering
A split-cycle variable capacity rotary spark ignition engine system having at least a first rotary configuration (C1) including repetitively volume variable working chambers [60, 61, 62] for carrying out the combustion-expansion and exhaust phases and at least a second rotary configuration (C2) including repetitively volume variable working chambers (70, 71, 72) for carrying out the intake and compression phases of a four phase engine cycle. Dividing seal means (73, 74 of C1, 75, 76 of C2) for periodically dividing each of successive working chambers into a volume enlarging leading portion and a volume contracting trailing portion. Discharge valve means for varying compression chamber capacity through discharging fraction of trapped intake gas from compression chambers. A first phase altering arrangement is provided for varying the phase relation between the first rotary configuration (C1) and the second rotary configuration (C2). A second phase altering arrangement varies phase relation between the discharge valve means and corresponding compression chambers. The first rotary configuration (C1) having variable capacity combustion chambers operatively synchronize with the variable capacity compression chambers of the second rotary configuration (C2) so that accomplish nearly full-load-like combustion environment through a substantially wide engine operating range.
Owner:SETH
System for calibrating apparatus for acquiring the pressure in a motor vehicle diesel engine cylinder
InactiveUS7124020B2Internal-combustion engine testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesInformation processingAcquisition apparatus
The invention relates to a system for calibrating apparatus (28) for acquiring the pressure in a cylinder (10) of a motor vehicle diesel engine, of the type comprising a cylinder pressure sensor (30) associated with the cylinder and means (32) for conditioning the signal delivered by the sensor (30) as a function of conditioning parameters. The calibration system comprises means (64) for collecting a signal delivered by the cylinder pressure sensor (30), an information processing unit (34) adapted to determine the values of the conditioning parameters as a function of a polytropic thermodynamic model of the evolution of the pressure in the cylinder, a reference pressure of the pure compression phase of the cycle of the cylinder, and the signal delivered by the pressure sensor (30) and collected by the collecting means (64), and means (66) for modifying the values of the conditioning parameters in the acquisition apparatus (28) as a function of the values of the conditioning parameters determined by the information processing unit (34).
Owner:PEZHO SITROEN AUTOMOBILS SA +1
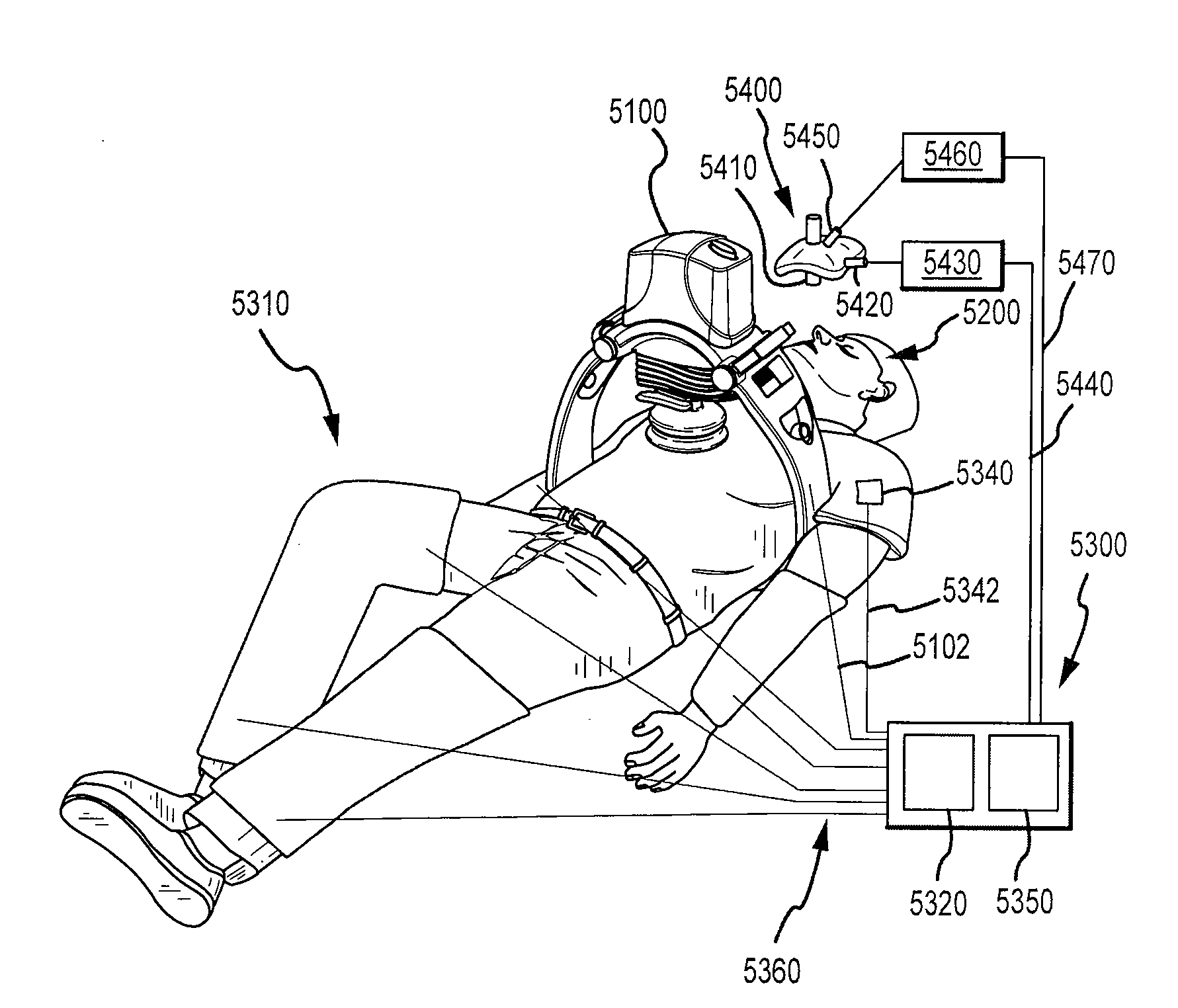
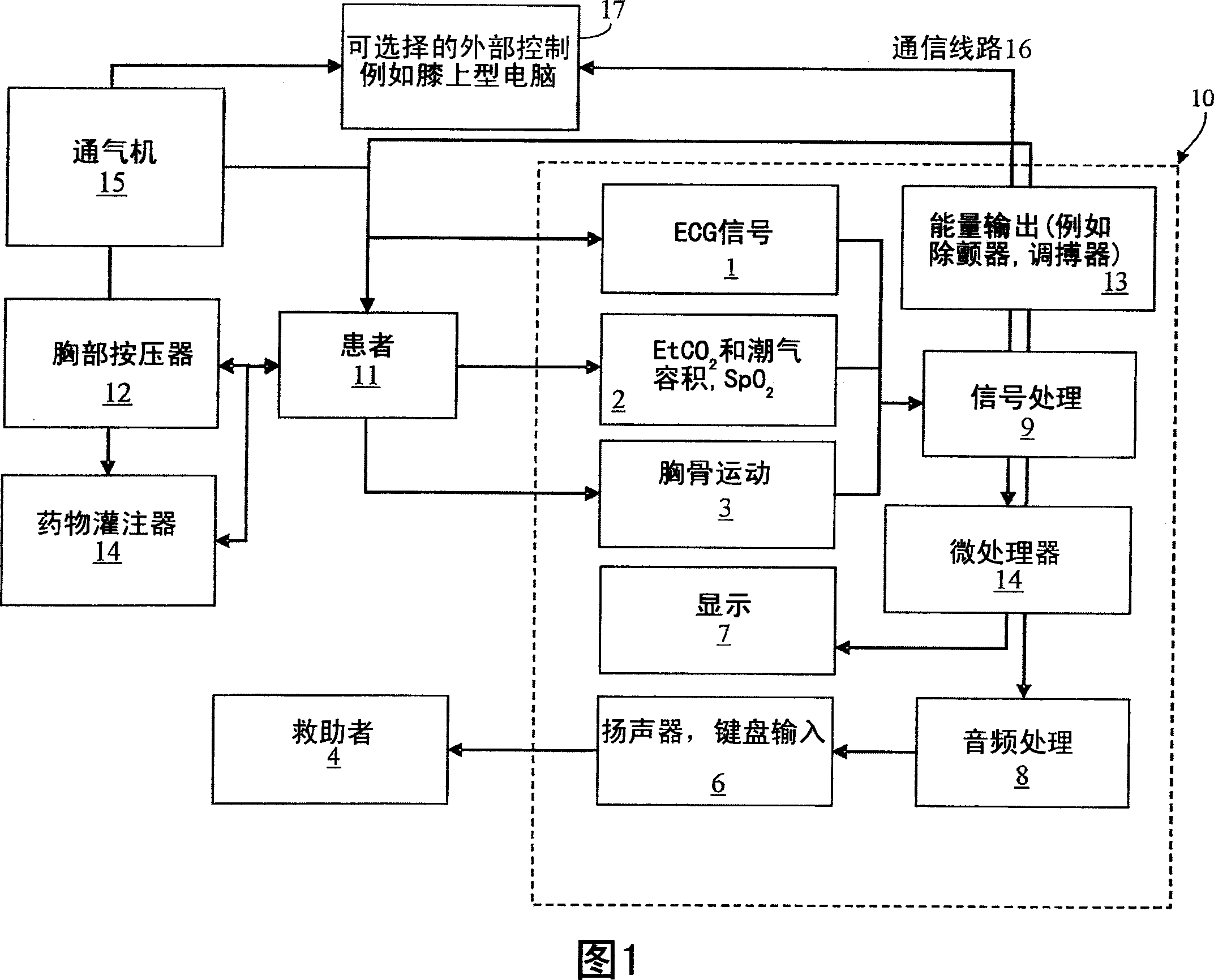
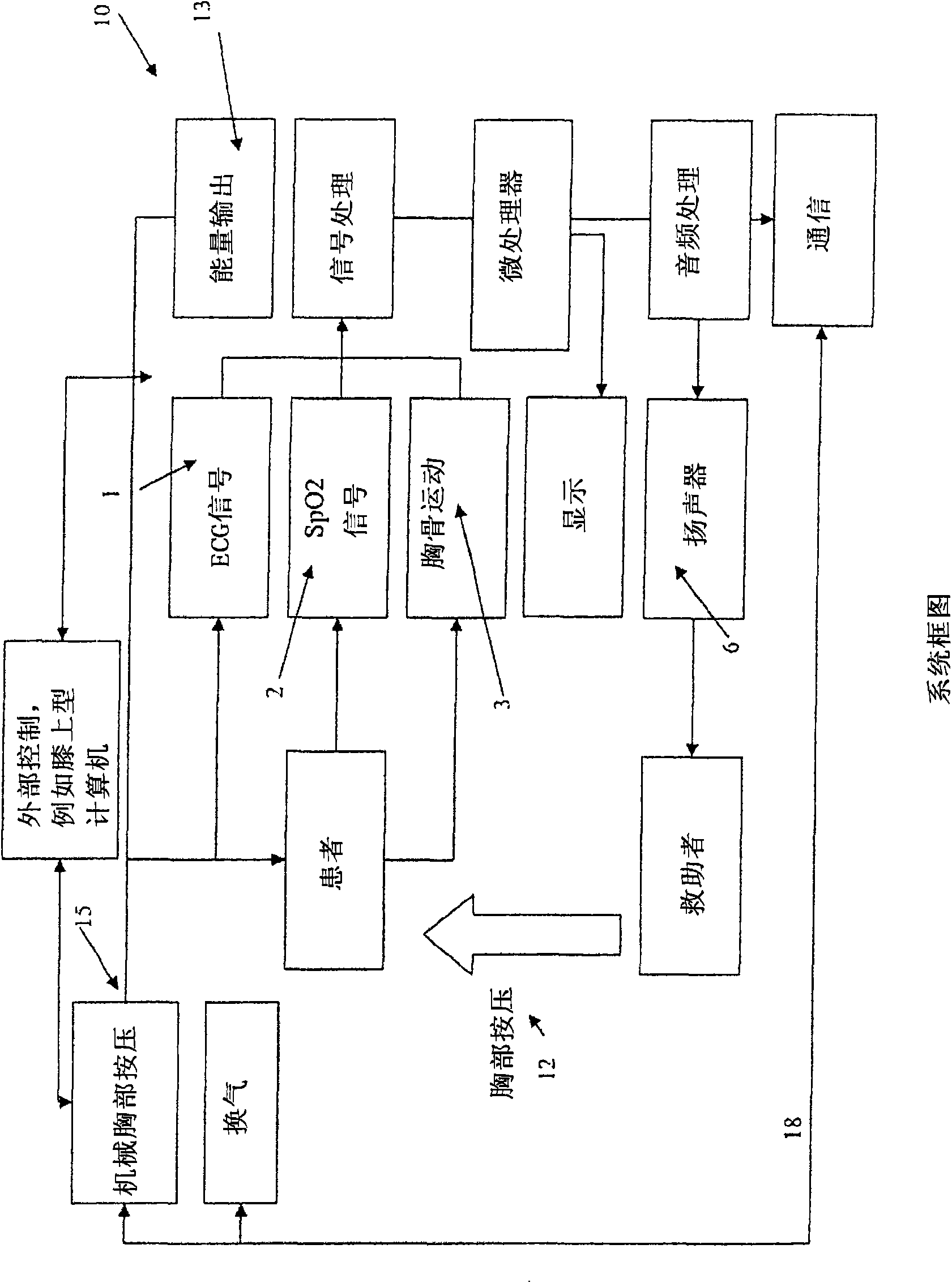
Device for automatically transferring chest compression and ventilation to sufferer
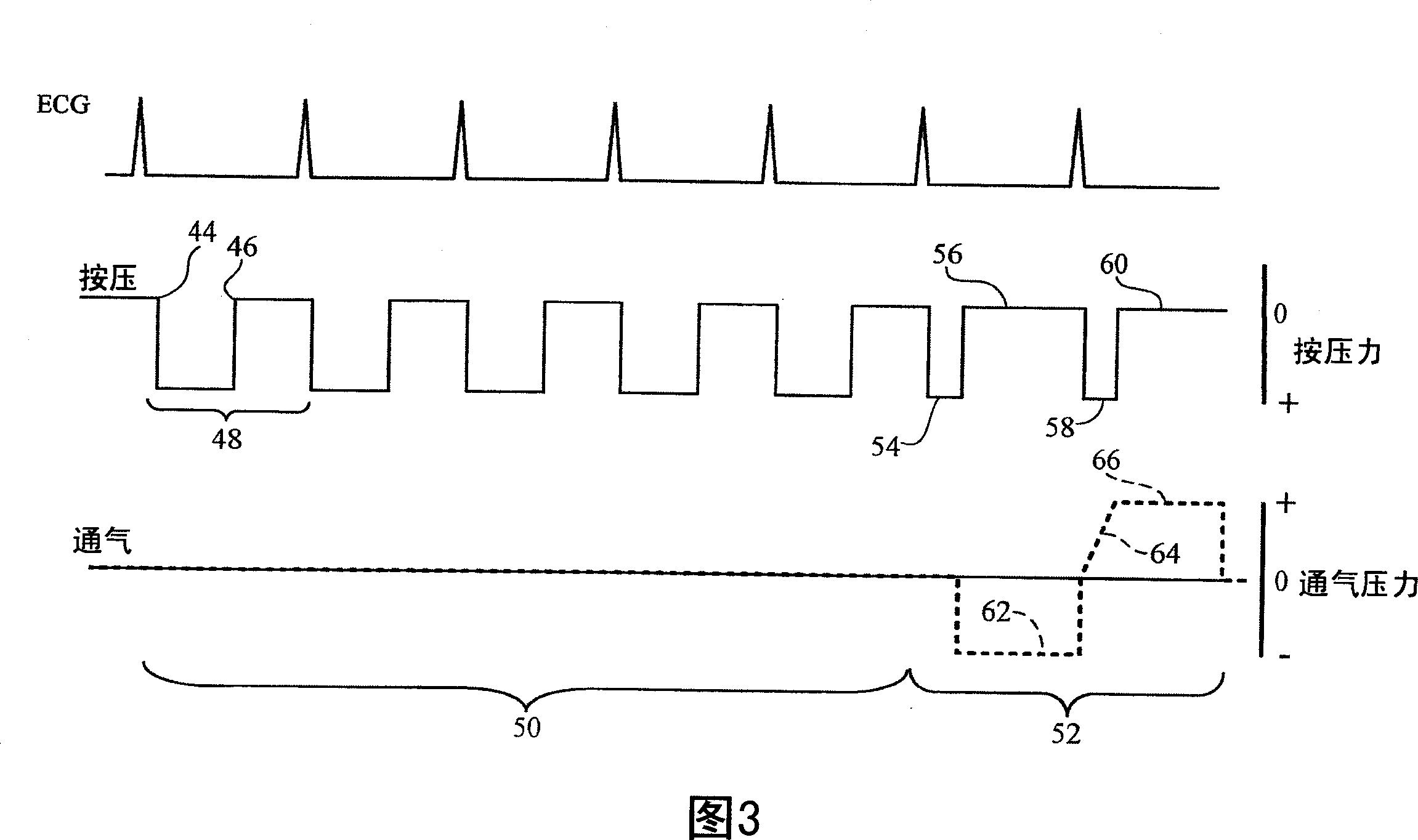
Apparatus for automatic delivery of chest compressions and ventilation to a patient, the apparatus including: a chest compressing device (12) configured to deliver compression phases during which pressure is applied to compress the chest and decompression phases during which approximately zero pressure is applied to the chest; a ventilator (15) configured to deliver positive, negative, or approximately zero pressure to the airway; control circuitry and processor (14), wherein the circuitry and processor are configured to cause the chest compressing device to repeatedly deliver a set containing a plurality of first type flow cycles, each first type flow cycle comprising a first type decompression phase and a first type compression phase, and at least one second type flow cycle interspersed between sets of first type flow cycles, each second type flow cycle comprising a second type decompression phase and a second type compression phase, wherein the second type decompression phase is substantially longer than the first type decompression phase.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
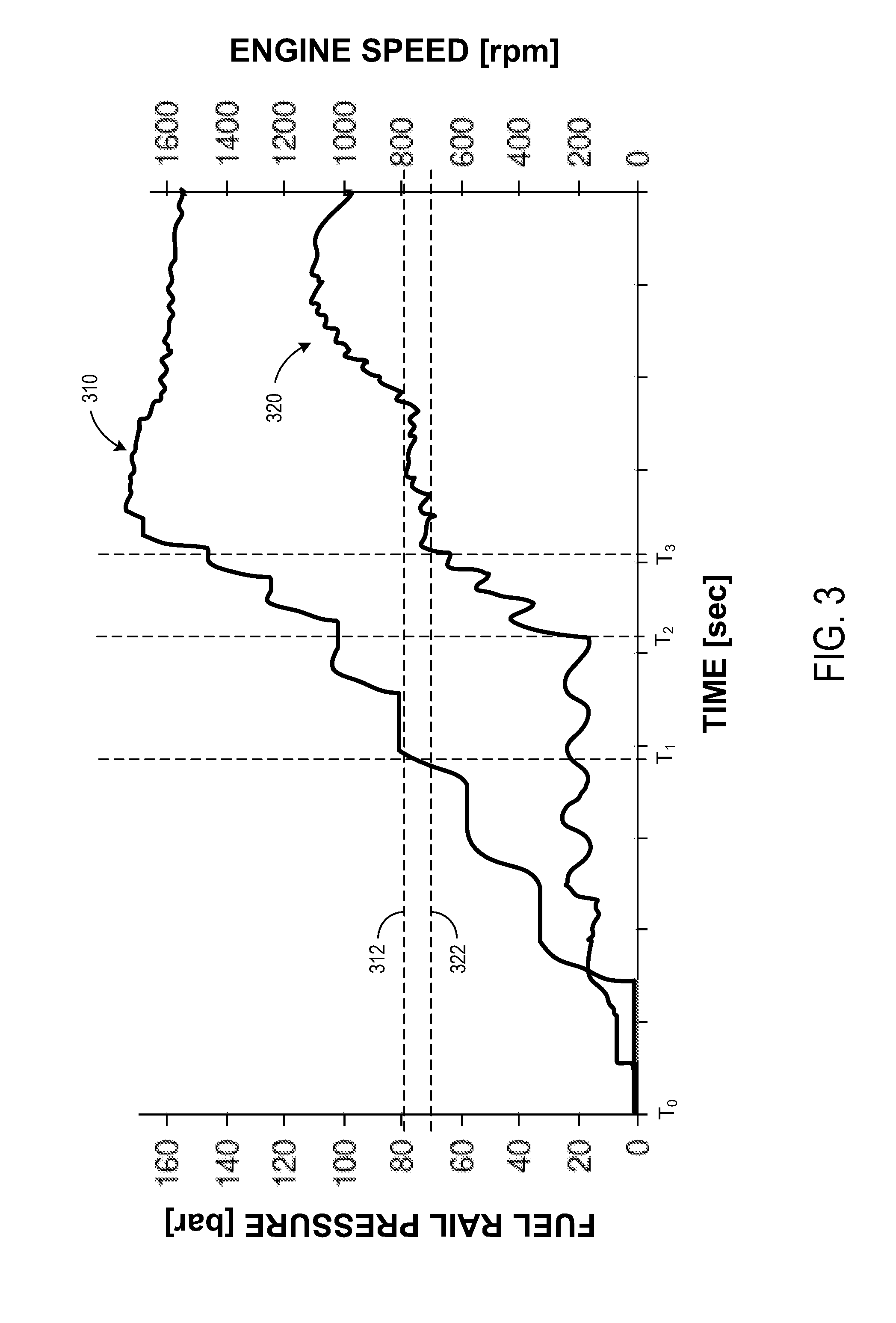
Method and device for operating a pressure reservoir, in particular for common rail injection systems in automobile engineering
ActiveUS20170107931A1Operating reliability can be highHigh operating requirementsElectrical controlMachines/enginesCommon railPump chamber
A method and to a device for operating a pressure reservoir, where during a compression phase in a pump chamber, a pump periodically increases the pressure of a fluid located therein, and by means of a discharge valve controlled by differential pressure fluid under high pressure is allowed to be introduced from the pump chamber into the pressure reservoir. During a decompression phase following a compression phase, fluid from a fluid reservoir is introduced into the pump chamber by means of a controllable intake valve. In order to be able also to operate the pressure reservoir without a high pressure measurement directly in the pressure reservoir, the fluid pressure in the pressure reservoir is ascertained by means of a pressure determination in the pump chamber. The pressure determination takes place indirectly, monitoring of the intake valve in the decompression phase.
Owner:VITESCO TECH GERMANY GMBH
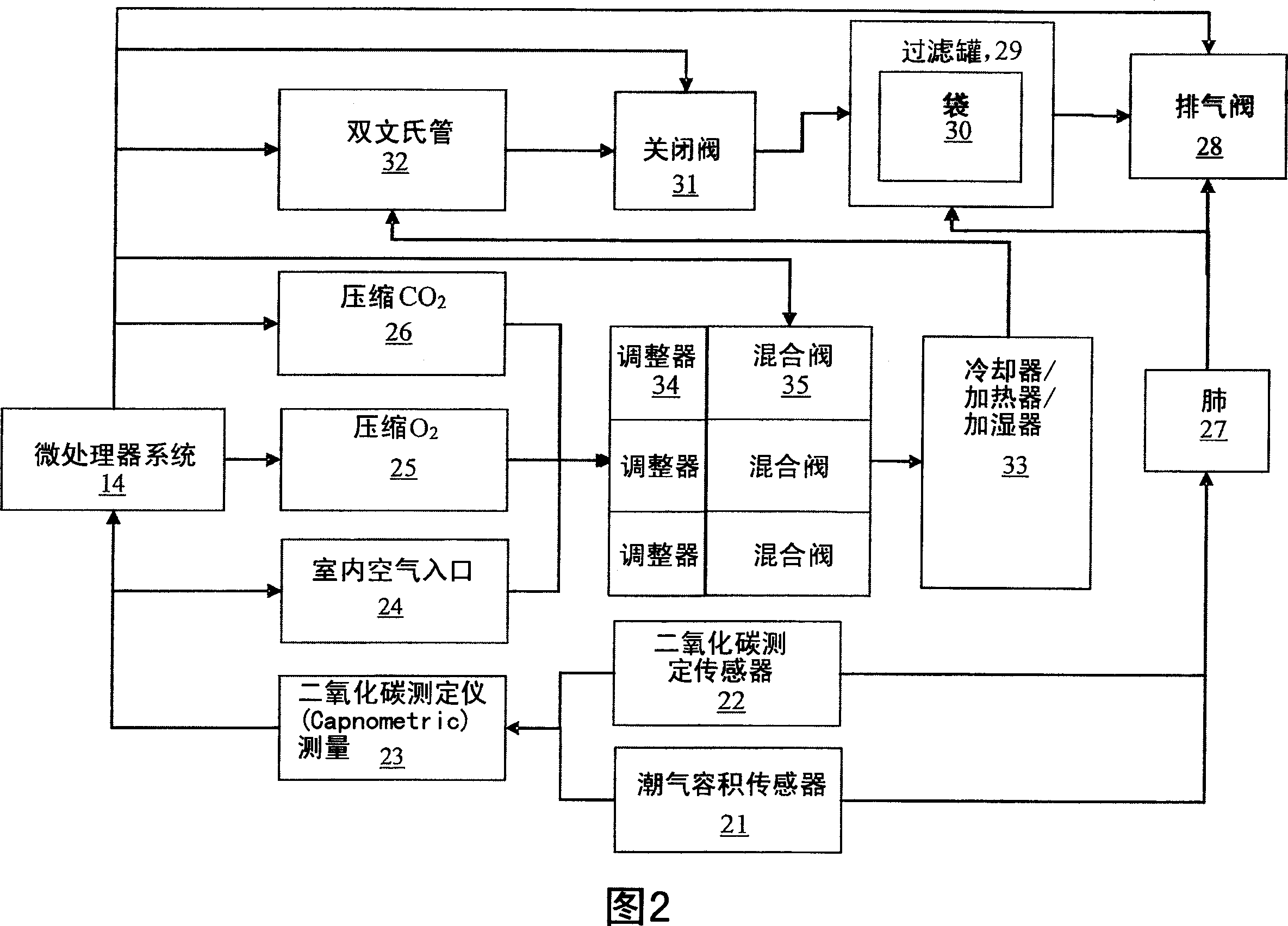
Method and apparatus for a peripheral circulation enhancement system
InactiveUS6921373B1Lower resistanceEasily rammedPneumatic massageDiagnosticsVenous treeVenous structure
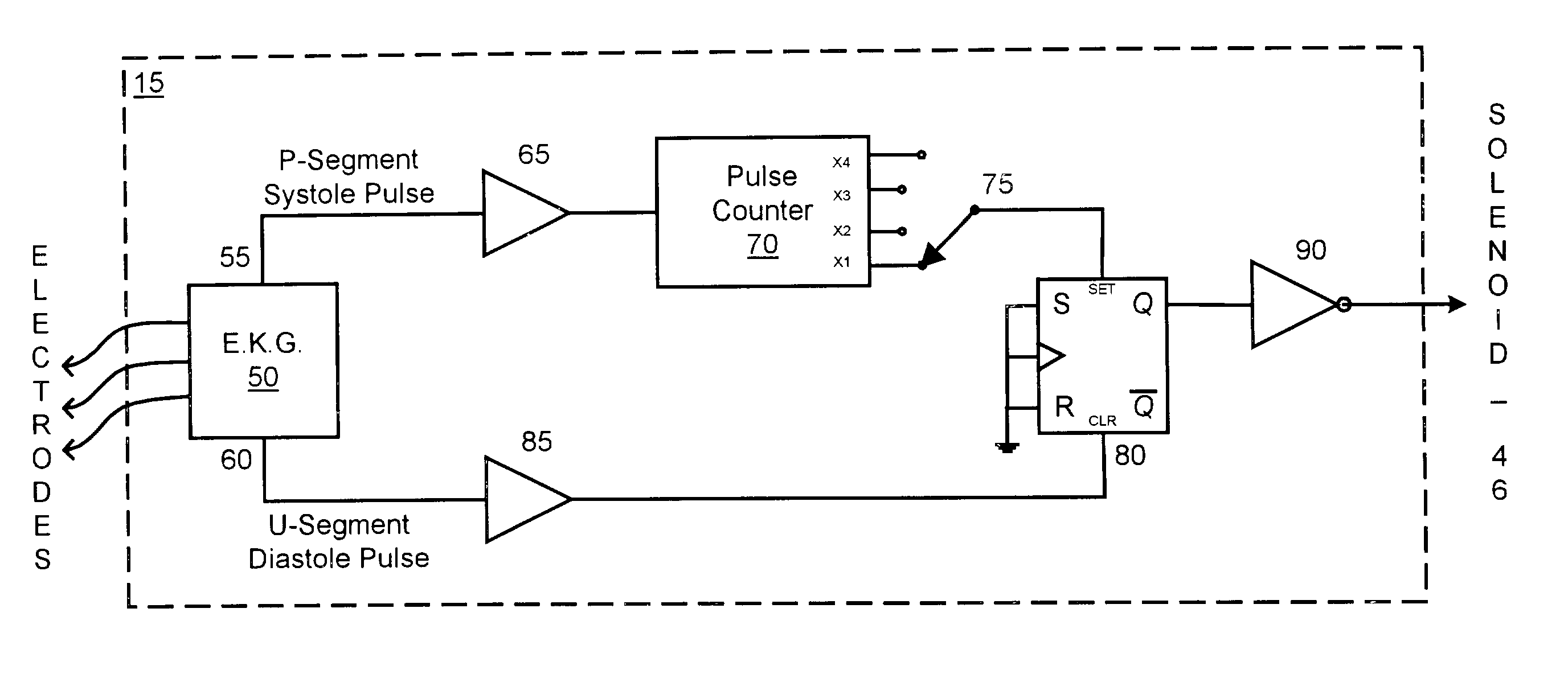
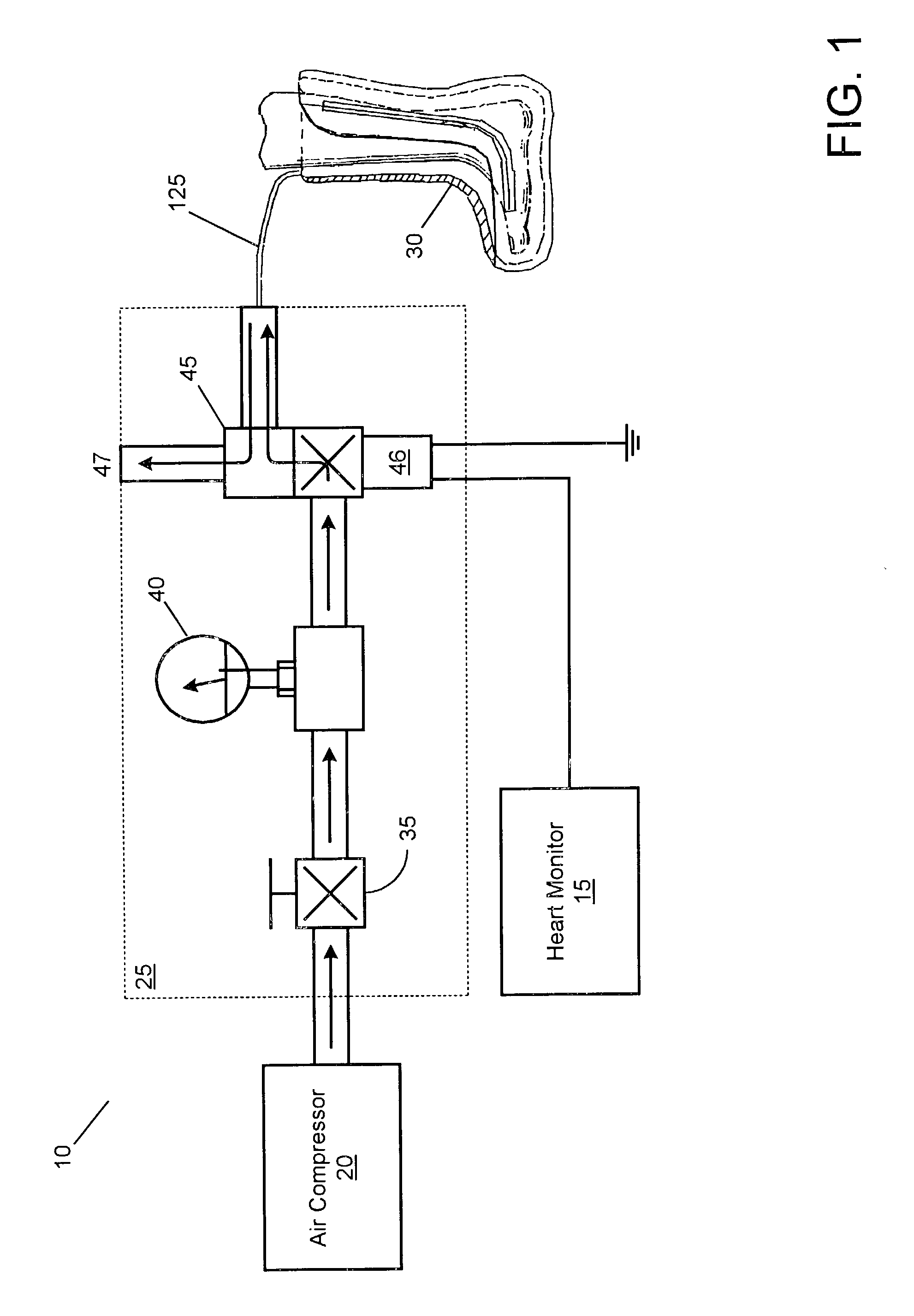
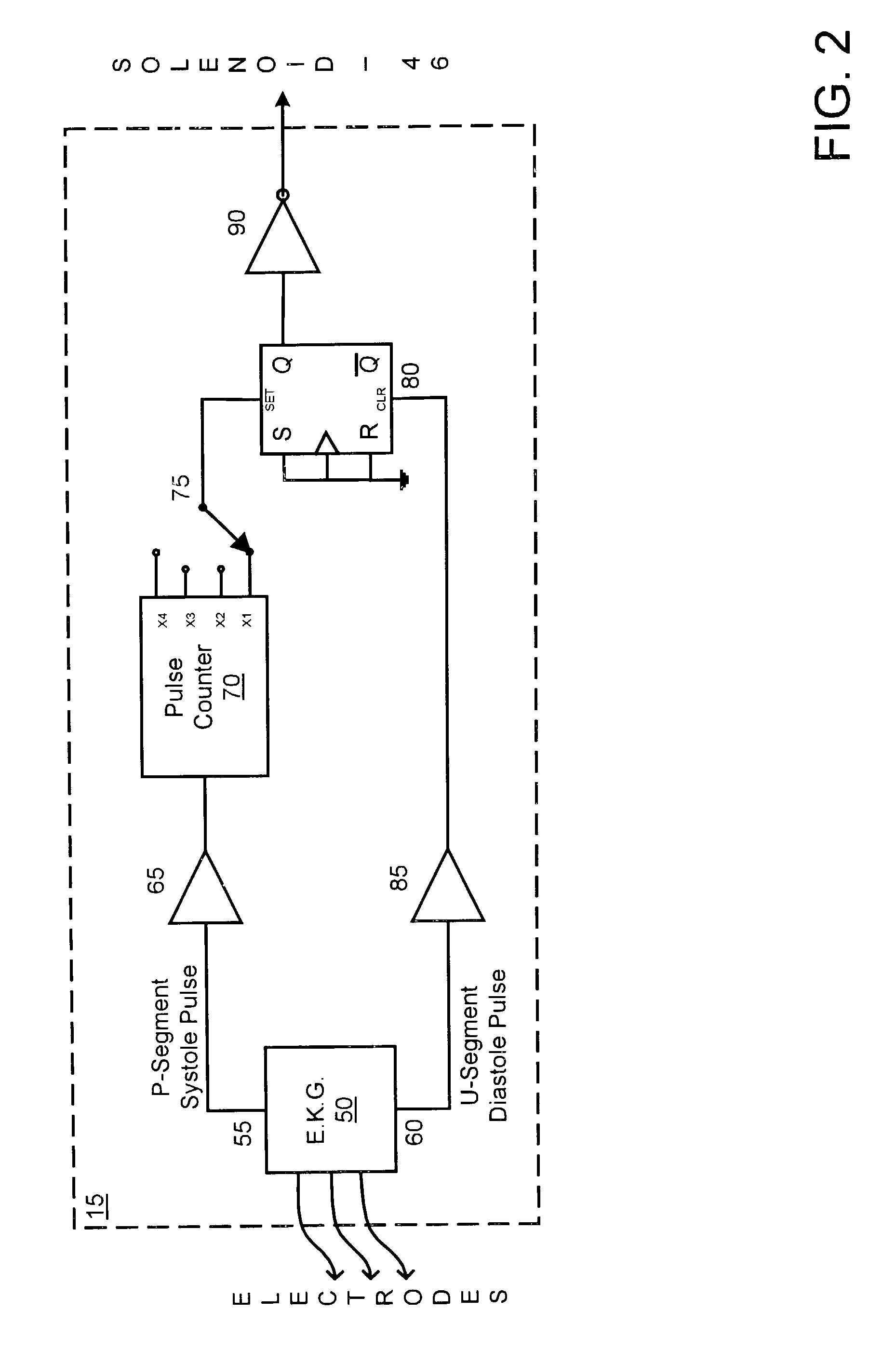
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for enhancing the circulation to an extremity of a patient. During the compression phase, the extremity is compressed, pushing out superficial edema as well as emptying the superficial venous tree. The compression cycle is timed to begin at or slightly after the “P” segment of the heartbeat. Air slowly fills a boot so that it reaches maximum capacity just as the heart reaches the diastolic phase in the heartbeat. Since the heart is at its lowest pressure, there is little resistance from the heart, making it easier for the compression of the extremity to push fluids out into the venous structures carrying them back to the heart. When the heart reaches the next full beat, the extremity is void of some of the fluid, forcing from the heart fresh oxygenated blood into the extremity, thereby promoting circulation through the heart.
Owner:BERNSTEIN MYRON Z
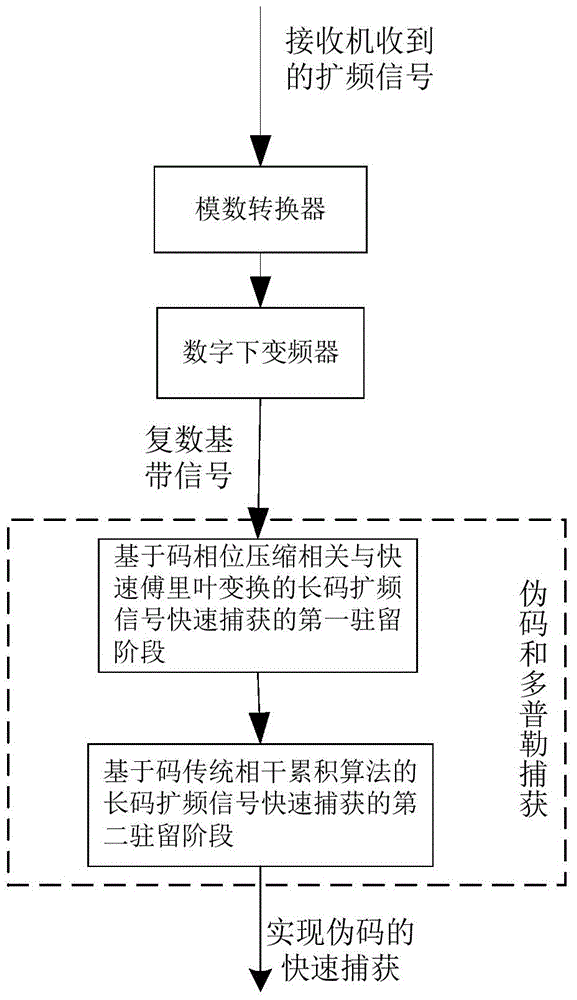
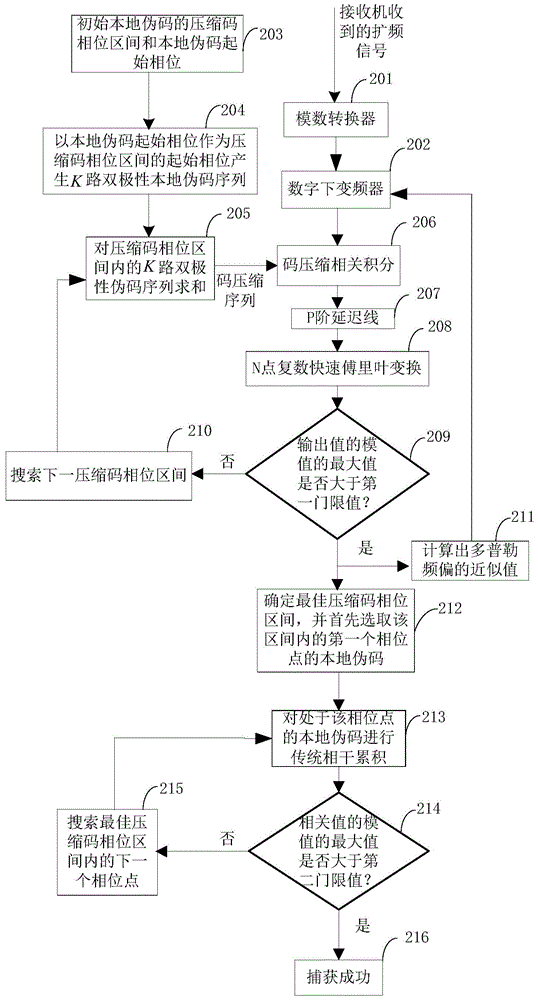
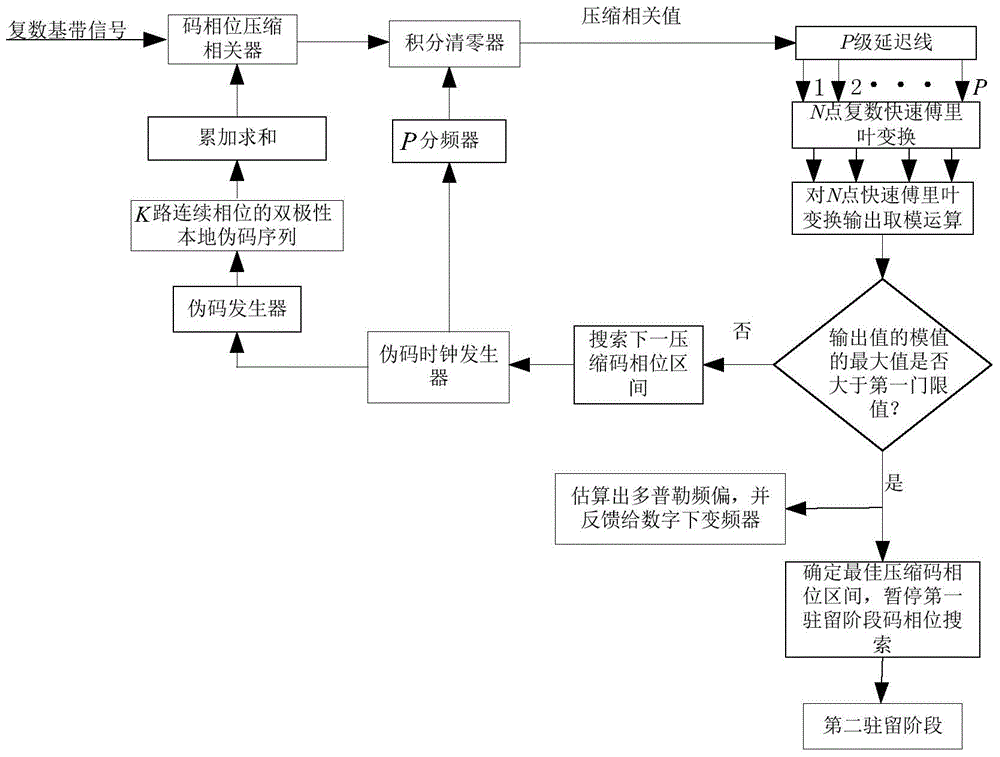
Long-code spread spectrum signal rapid capturing method adaptive to high dynamic environment
InactiveCN105049081AAchieve captureSave resourcesTransmissionFrequency changerDigital down converter
The invention discloses a long-code spread spectrum signal rapid capturing method adaptive to a high dynamic environment. The method comprises the following steps: sampling spread spectrum signals by use of an analog-to-digital converter, and then obtaining complex baseband signals through a digital down converter; then in a first residence phase, realizing time frequency two-dimensional search by use of code phase compression and fast Fourier transform, and determining a substantial pseudo code phase compression interval and a frequency offset estimated value; and in a second residence phase, searching each code phase in a code phase compression phase interval one by one by use of a conventional coherent accumulation algorithm. According to the invention, the method has the following advantages: large-interval search is performed on a time domain by use of a code phase compression correlator and parallel search is carried out on a frequency domain by use of the fast Fourier transform so that large dynamic spread spectrum signals can be rapidly captured; and at the same time, the method is quite low in complexity and can save enormous hardware resources.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
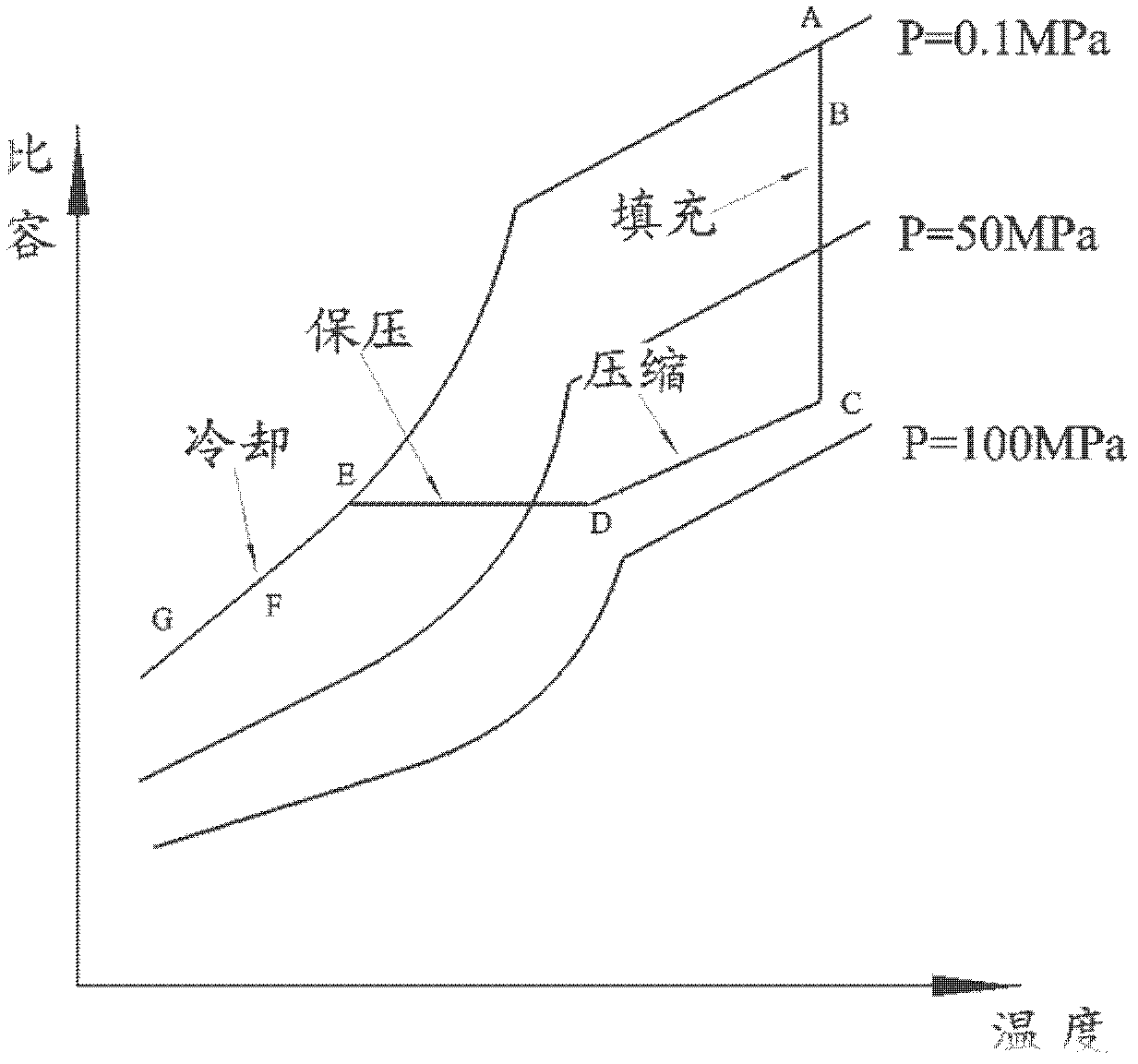
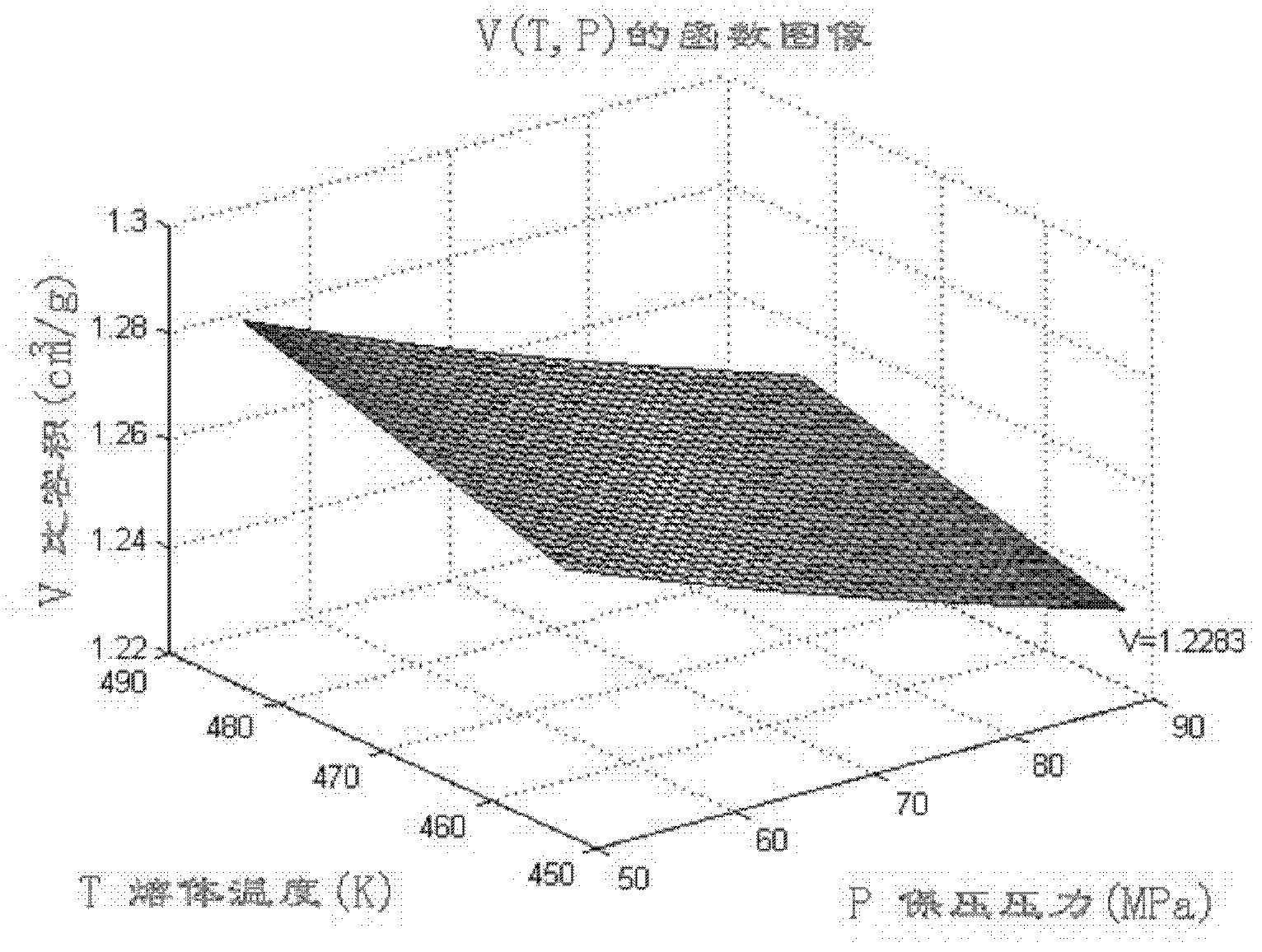
Isometric process control method utilizing PVT (pressure-volume-temperature) relation of polymers
The invention discloses an isometric process control method utilizing PVT (pressure-volume-temperature) relation of polymers. An injection process includes a first step: a PVT curve of an injection molding material is obtained according to the category and the characteristics of the material, an A-B-C-D-E-F process route is obtained from the curve, and an A-B-C section is an injection molding stage; a second step: constant-pressure packing is realized under the maximum packing pressure for a period of time, then isometric packing is carried out, and a C-D section is an isobaric compression stage; a third step: a D-E section is an equal-ratio volume packing stage, a material in a cavity cannot be changed, and cannot backflow or be increased along with reduction of the temperature of the cavity, and packing pressure of melt is obtained by means of calculation by the aid of a Tait equation and physical parameters provided by a PVT database; and a final step: an E-F section is a constant-pressure cooling stage. The constant-pressure packing is realized before the equal-ratio volume packing is realized, the melt is in a flowing state during the constant-pressure packing, accordingly excessively packing alignment is avoided, warpage is low, and quality repeat precision is high.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Full expansion internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20120174881A1Reduce heat lossReduce energy lossInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveTop dead center
A two-stroke, uniflow, full expansion internal combustion (IC) engine having cylinders that include a cylinder wall and a cylinder head having an exhaust port with exhaust valve, a fuel injector, and a spark means in the cylinder head, and a piston mounted in the cylinder for reciprocal stroke movements of compression and power between a top dead center (TDC) position and a bottom dead center (BDC) position. The cylinder has a swirl inlet port passing through the cylinder wall at the bottom of the cylinder that is covered and uncovered in response to the reciprocal movement of the piston. The cylinder is operated through a cycle where the exhaust port is held in an open position for a portion of the compression stroke movement of the piston, to provide a delay in the onset of the compression phase of the cylinder cycle.
Owner:TAYLOR PATENT HLDG CO LLC
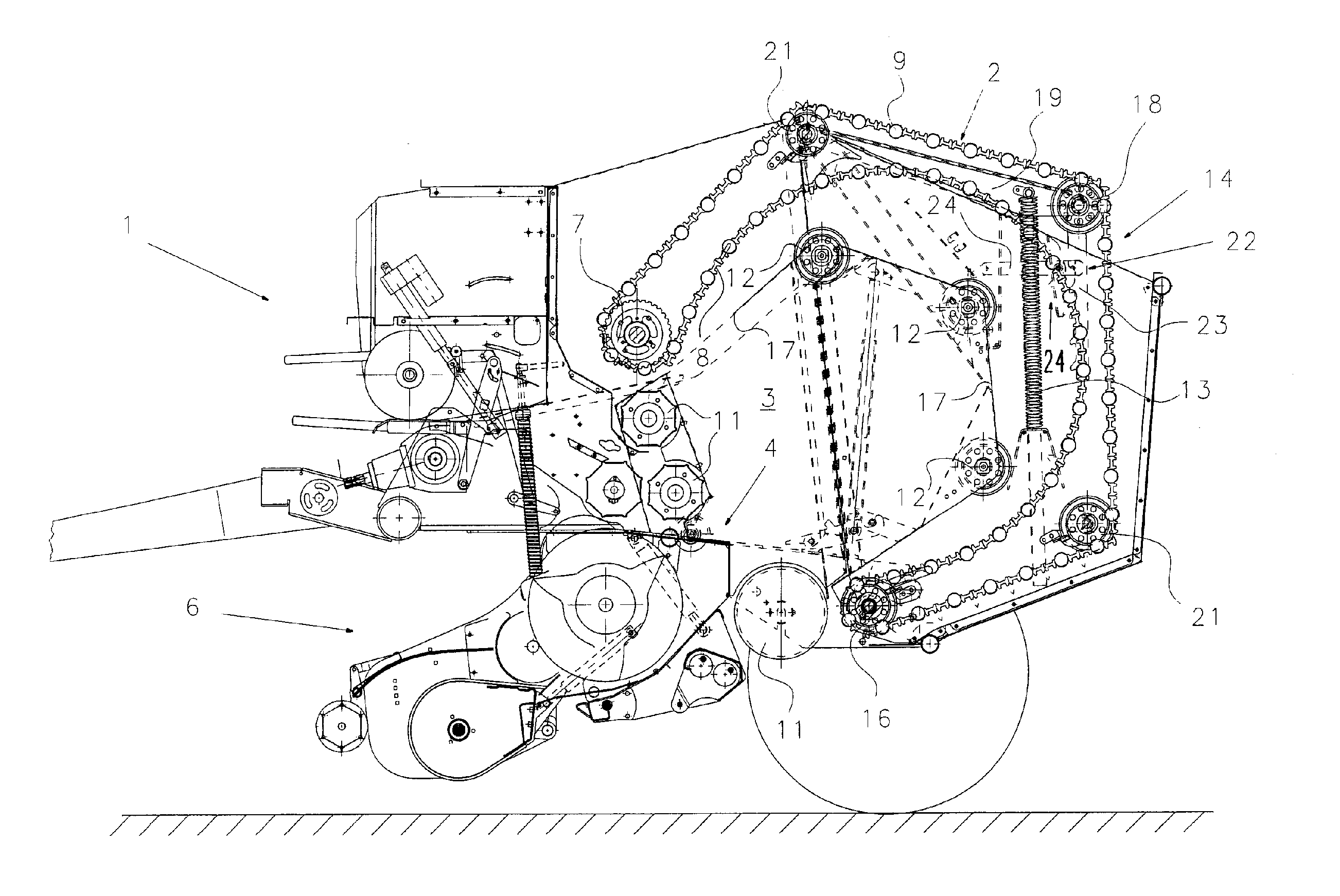
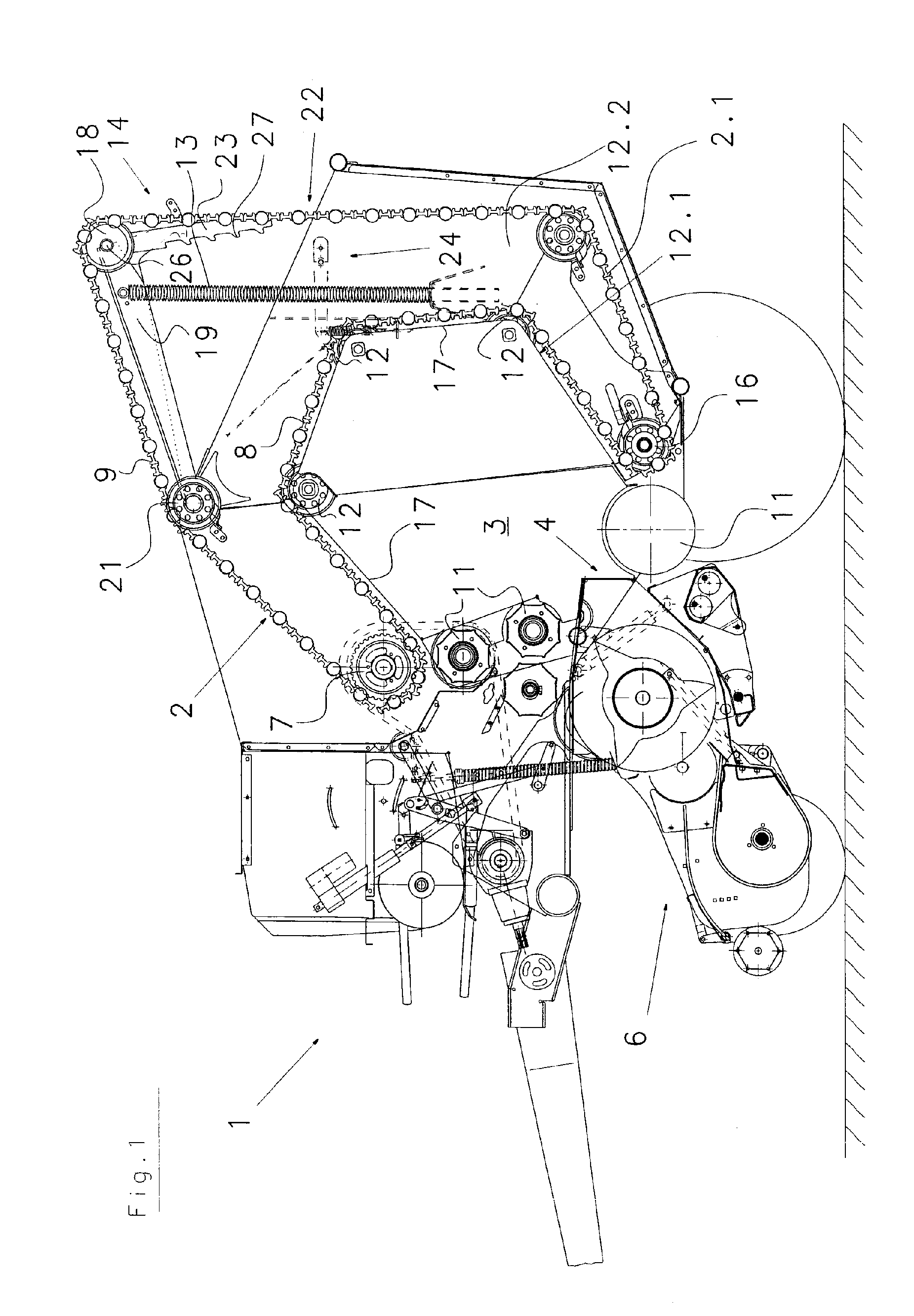
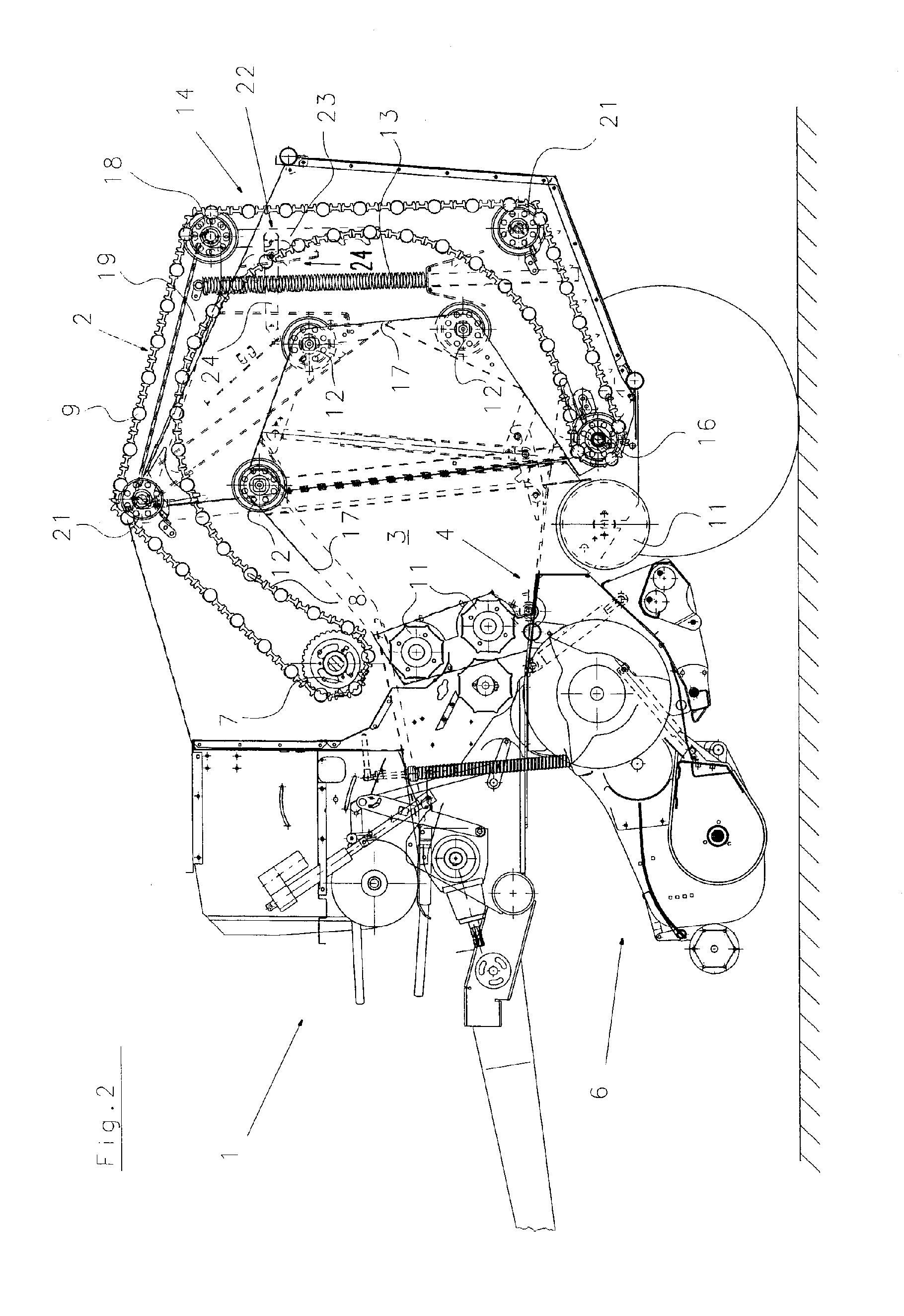
Machine for Collecting and Pressing an Agricultural Harvest
A machine for collecting and pressing a crop to roll-shaped bales has a crop collecting device and a bale-forming device with a winding chamber arranged downstream of the crop collecting device. The bale-forming device is guided about first and second stationary deflection devices. Guides are positioned between the first and second stationary deflection guides. During a first bale-forming phase, the bale-forming device travels along a spatially determined movement path on the guides. During a subsequent bale-forming phase, the bale-forming device is transferred to additional movement paths that are independent of the guides and are determined by the diameter of the bale. The maximum bale diameter is selectable by moveable control devices. After the bale reaches the selected maximum diameter, the bale-forming device initiates a compression phase and exerts a compression force on the bale from the exterior to the interior of the bale.
Owner:MASCHFAB BERNARD KRONE GMBH
Synchronization of defibrillation and chest compressions
A resuscitation system for use by a rescuer for resuscitating a patient having a ventricular arrhythmia, comprising circuitry and processing configured for detection of chest compression / phase timing information indicative of the start of the decompression phase, circuitry and processing configured for delivery of eletromagnetic therapy for the termination of ventricular arrhythmias, wherein the circuitry and processing for the delivery of electromagnetic therapy utilizes the chest compression phase timing information to initiate delivery of the electromagnetic therapy within 300 milliseconds of the start of the decompression phase.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Method for controlling a spark-ignition direct-injection internal combustion engine at low loads
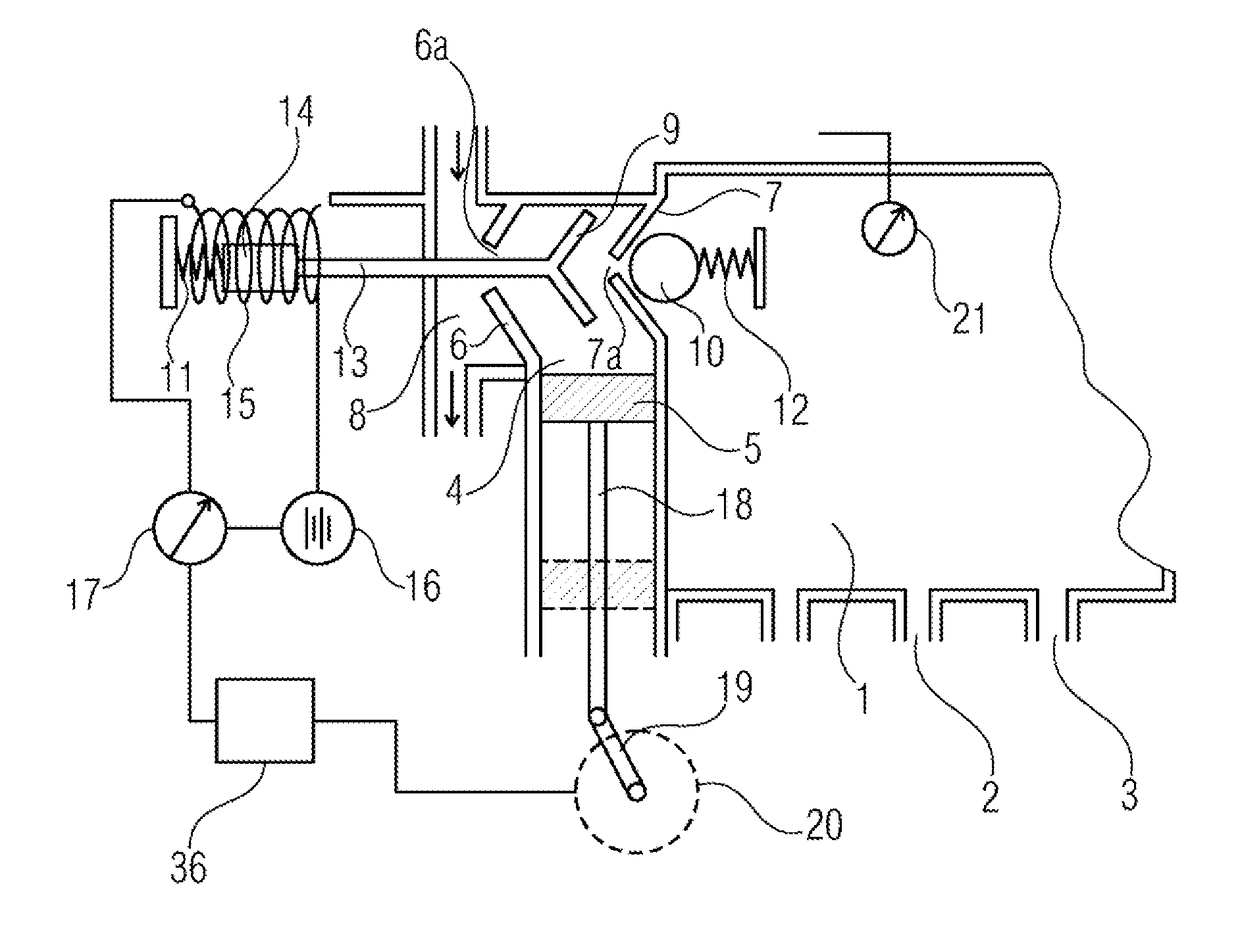
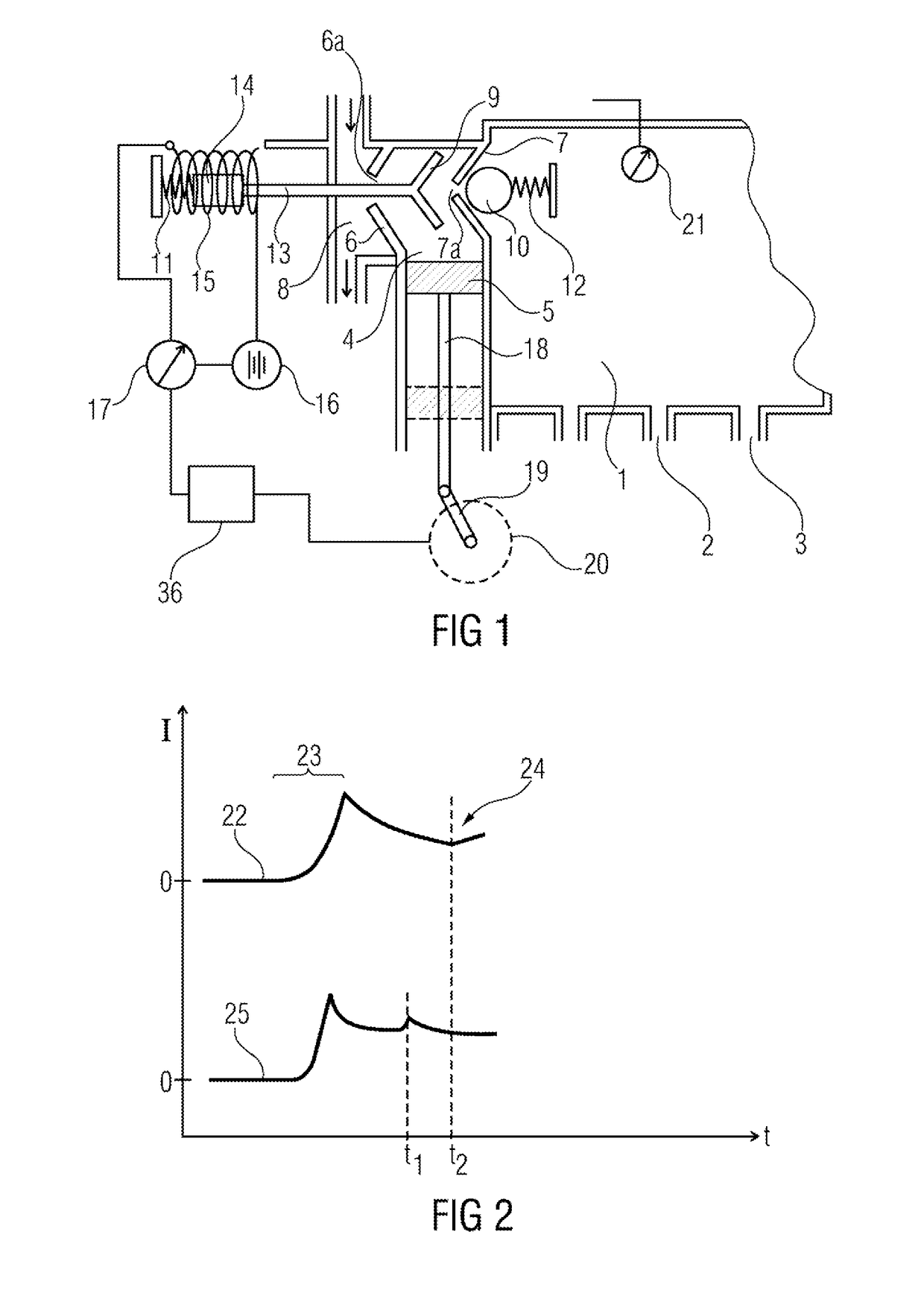
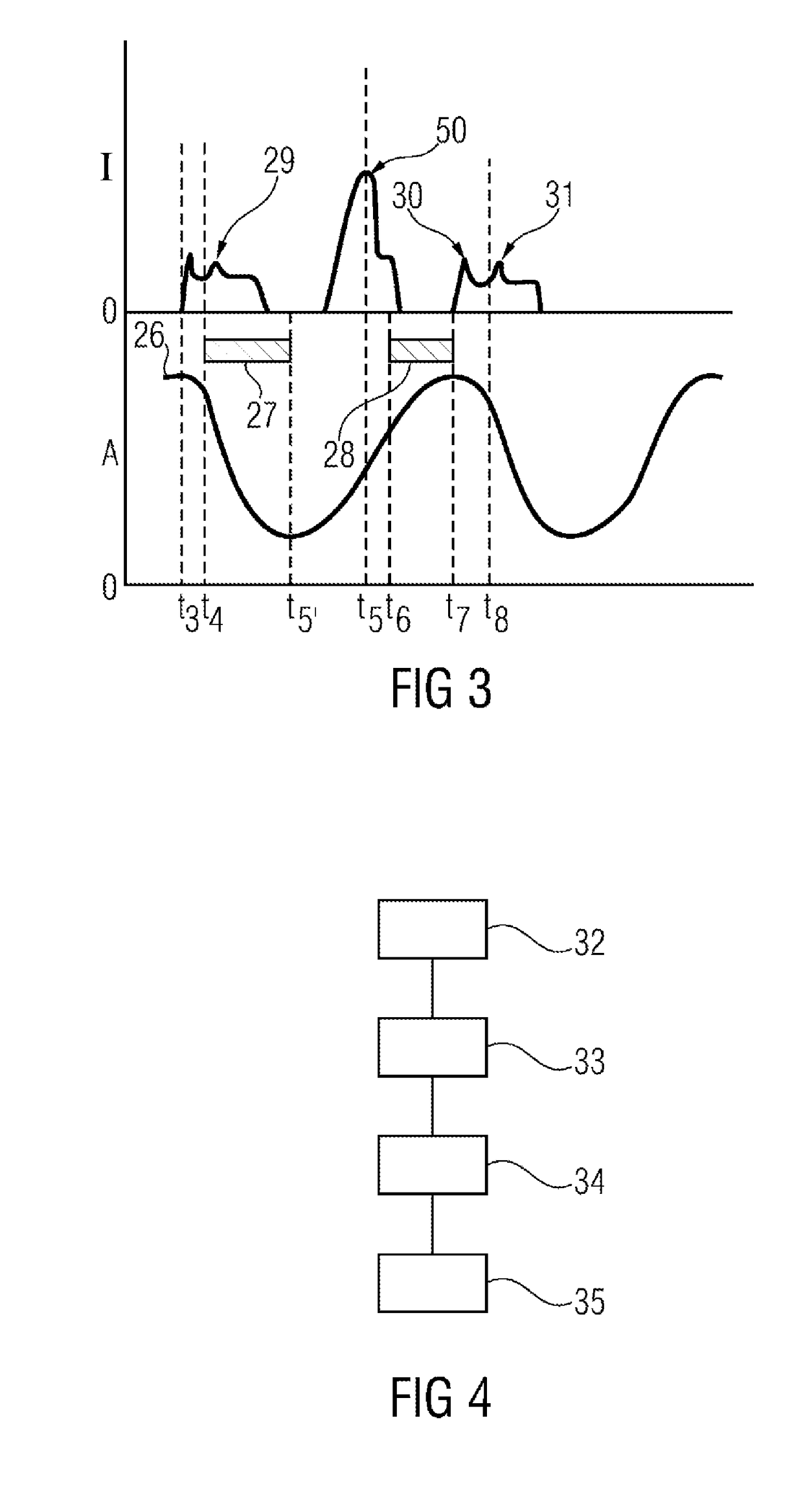
A spark-ignition direct-injection internal combustion engine is controlled at low loads through split fuel injections and spark discharges including one injection and spark during a negative valve overlap period and another injection and spark during a compression phase of the engine cycle.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Methods for reducing raw particulate engine emissions
ActiveUS20140196685A1Fuel consumption is minimizedImprove engine efficiencyElectrical controlCombustion enginesParticulatesExpansion phase
The methods described allow for reducing particulate emissions from a direction injection engine during a starting phase, while also maintaining the engine start phase within a predetermined threshold. In one particular example, the methods comprise adjusting at least one of a fuel release pressure threshold and enrichment factor based on an engine condition; activating a starting device to rotate a crankshaft coupled to an engine cylinder without injecting any fuel; supplying fuel to the cylinder based on the enrichment factor only when a fuel pressure exceeds the fuel release pressure threshold; and stratifying a cylinder charge while adjusting a fuel injection within a compression phase and / or expansion phase of the engine. In this way, an amount of fuel injected may be evaporated in the combustion chamber while preventing a combustion wall wetting, which allows for reduced particulate emissions, particularly at reduced temperatures.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and computer programme for operating an internal combustion engine and an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20040025829A1Low priceLow powerElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberGasoline
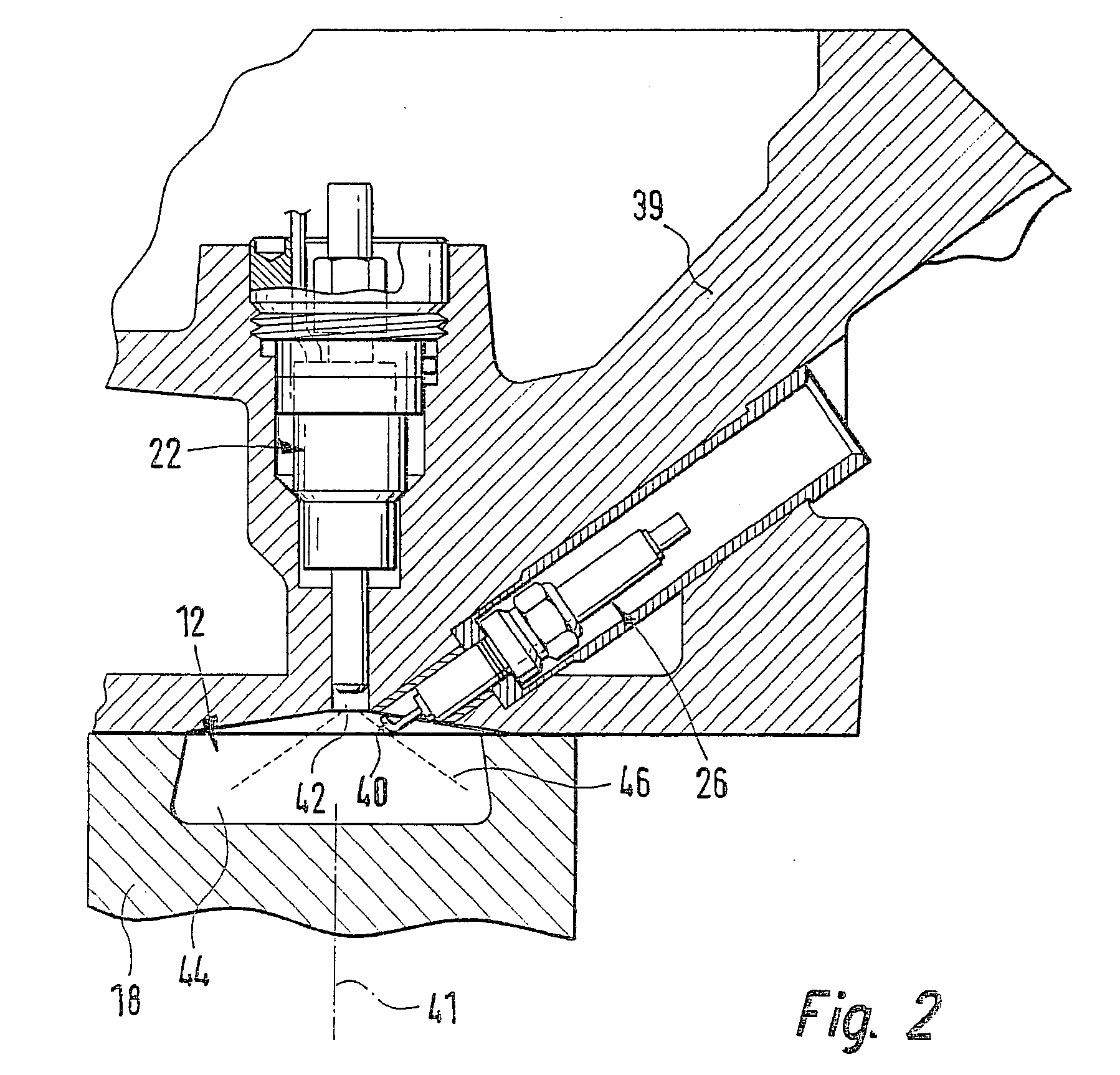
An internal combustion engine (10) is operated with a method wherein fuel is injected directly into a combustion chamber (12). The injection takes place at least from time to time so that, together with a corresponding supply of air into the combustion chamber (12), the air / gasoline mixture is present stratified in the combustion chamber (12). In order to reduce the gasoline consumption in the engine (10) via a higher compression ratio without the danger of knocking, it is suggested that the gasoline be injected exclusively and also at full load during the compression phase of the engine (12) by a multi-hole fuel injection device (22).
Owner:WUERFEL GERNOT
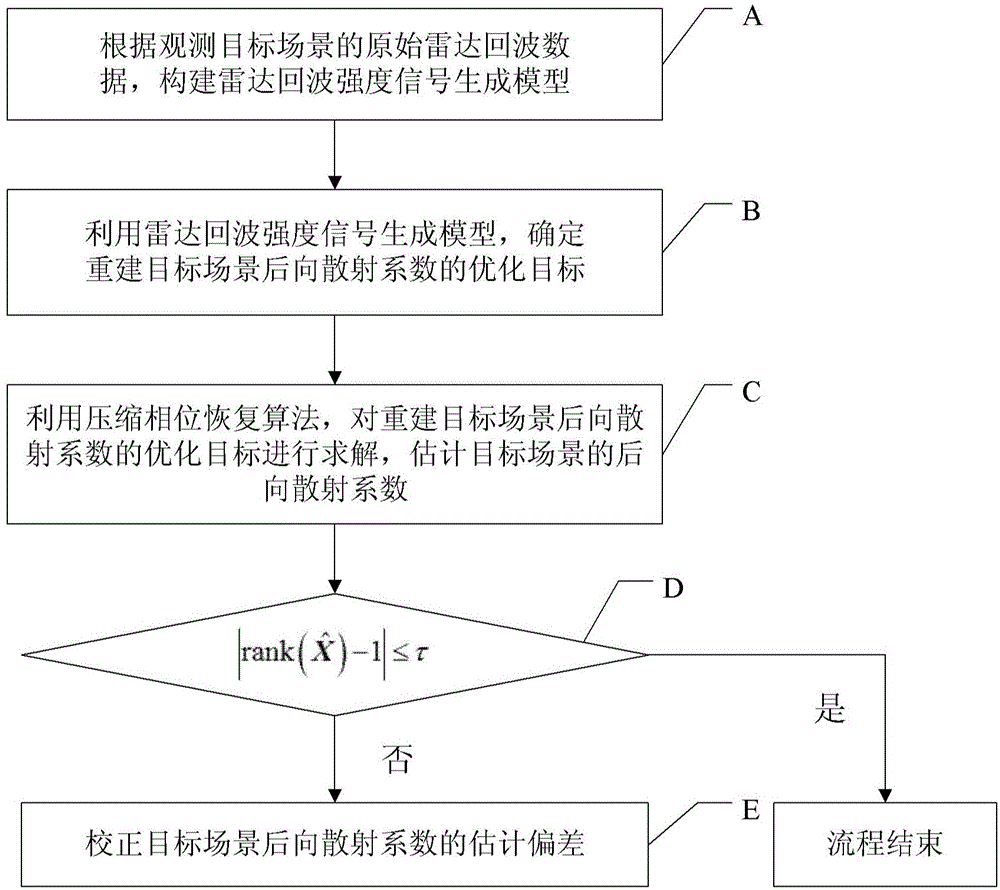
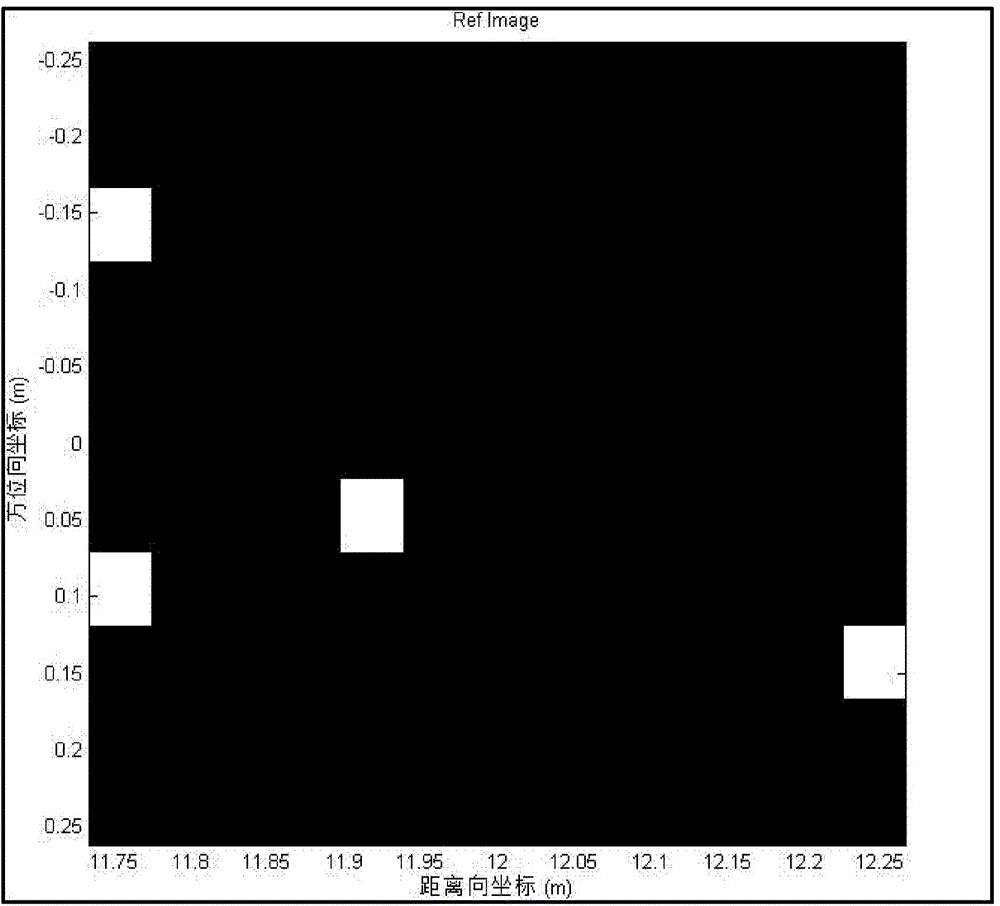
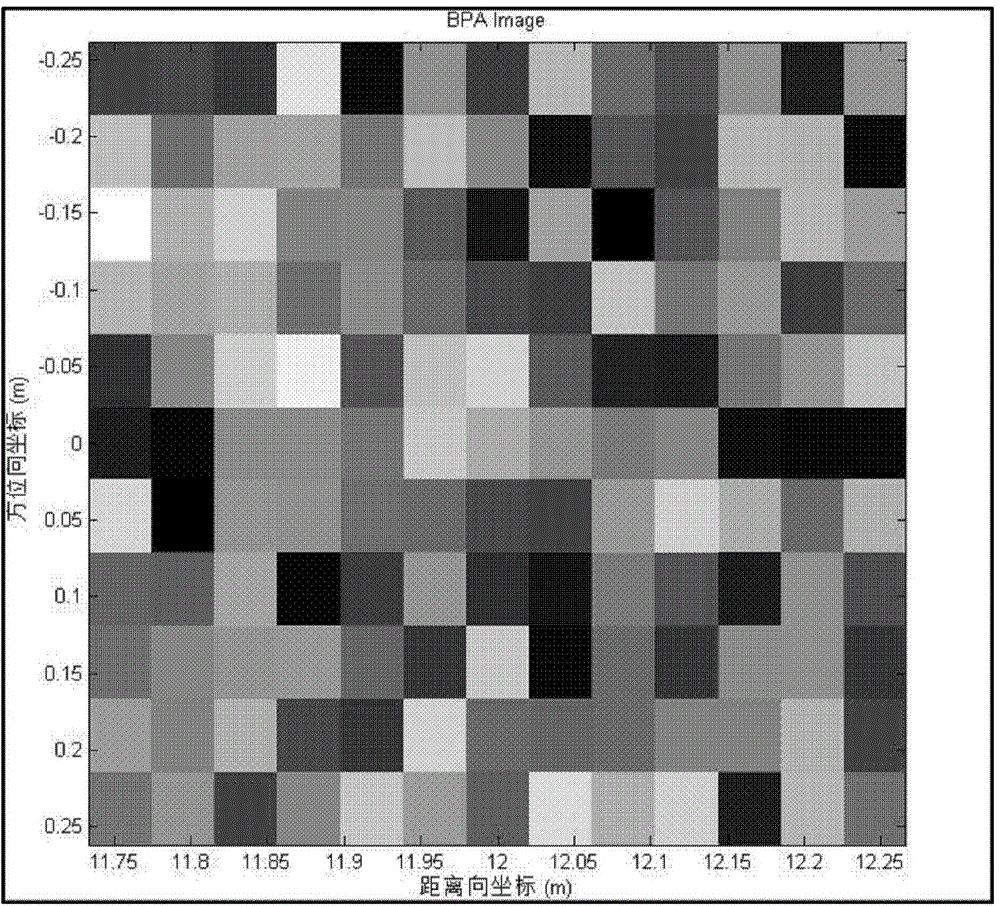
Sparsity microwave imaging method based on compression phase restoring
ActiveCN104459695AAvoid negative effectsEnabling Microwave ImagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarBackscatter coefficient
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com