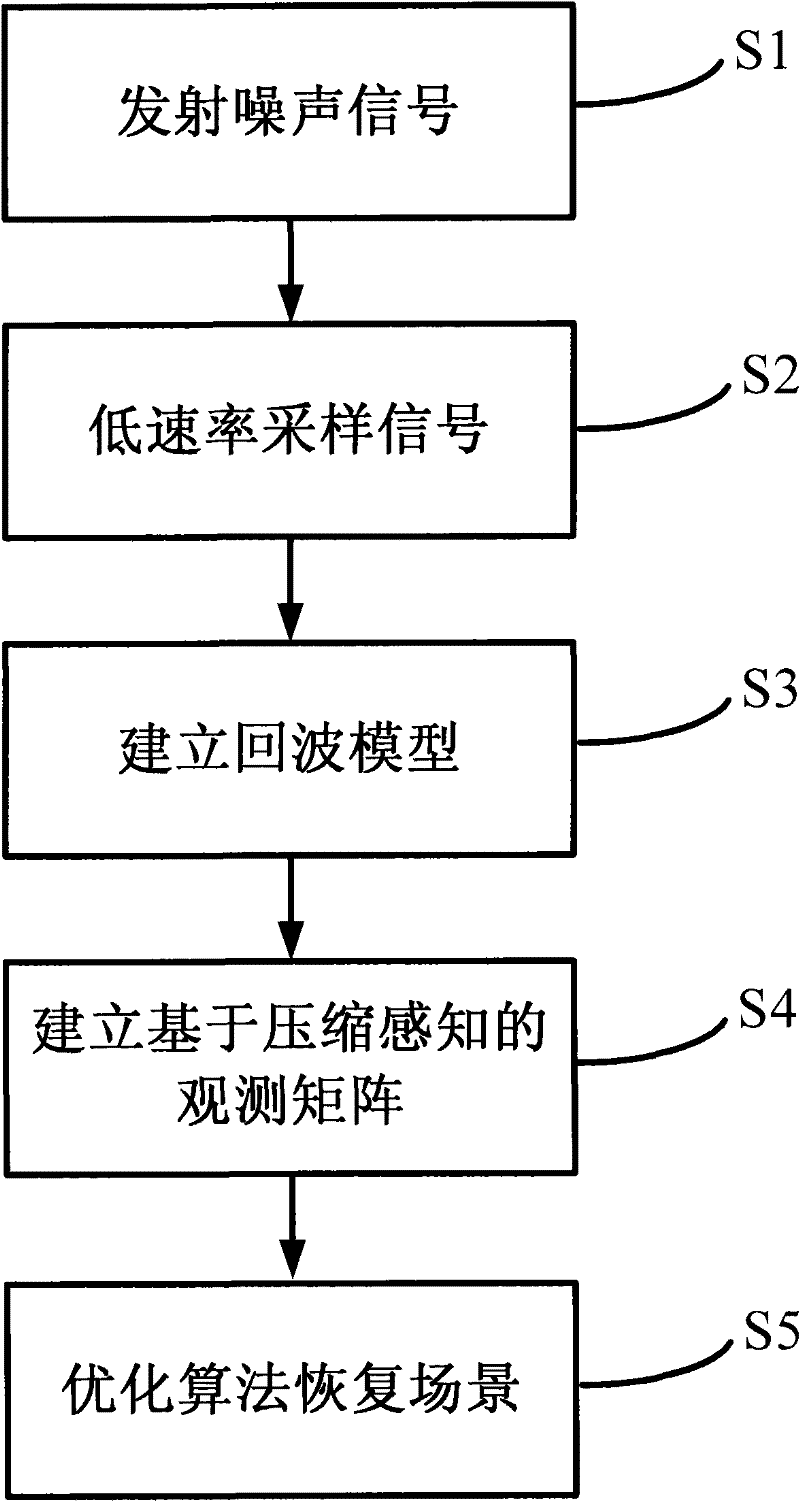
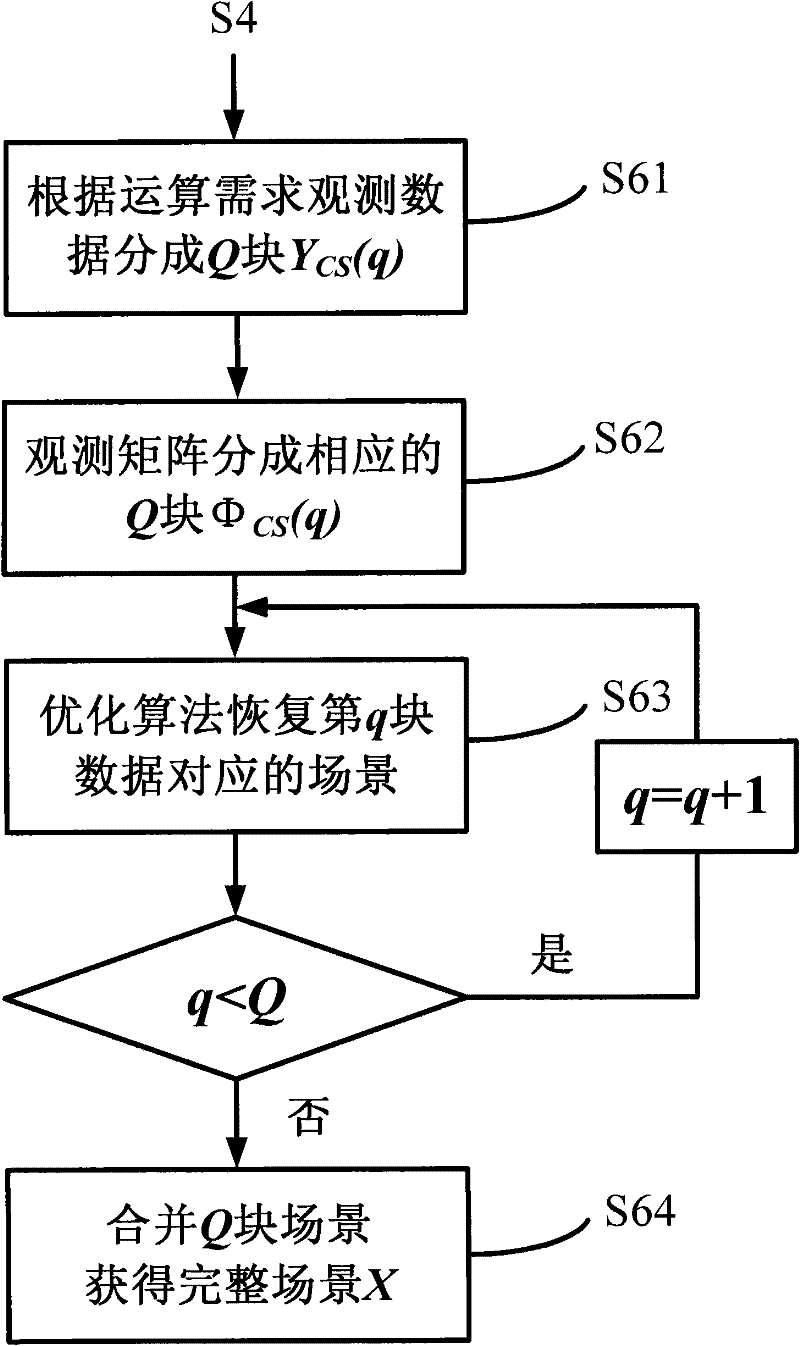
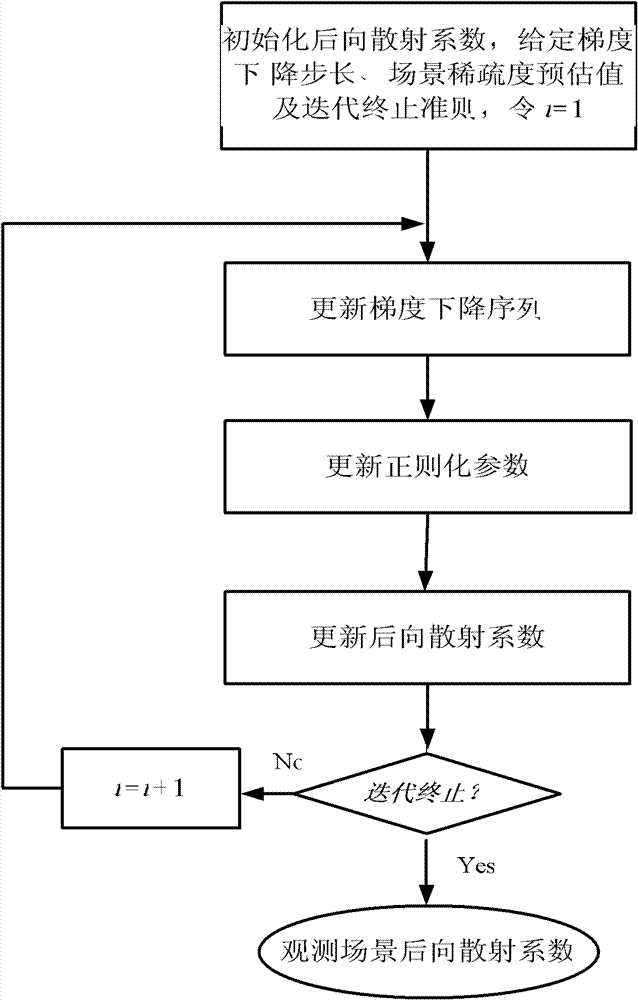
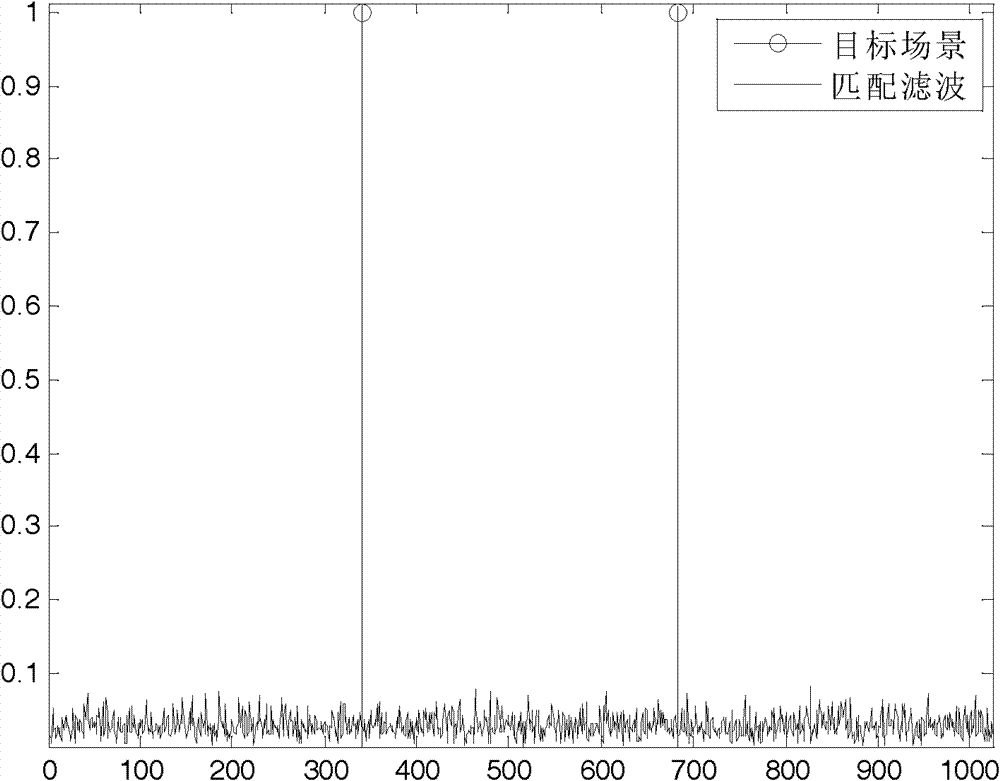
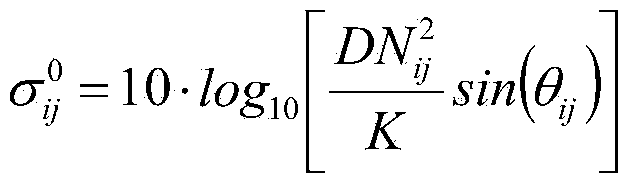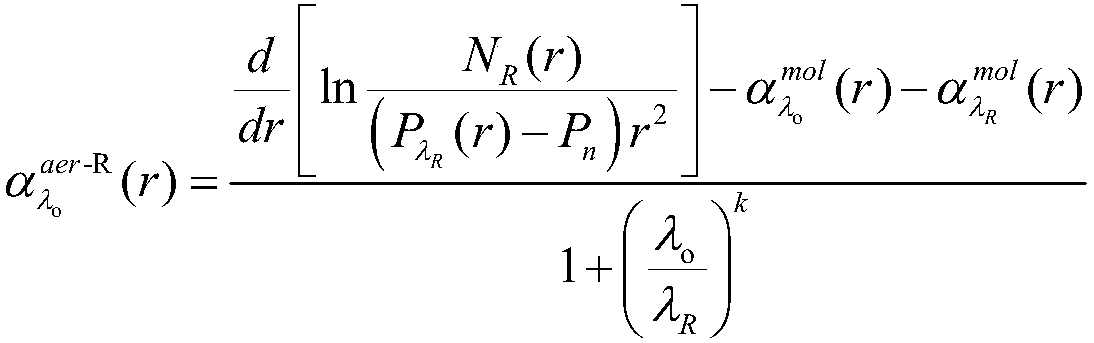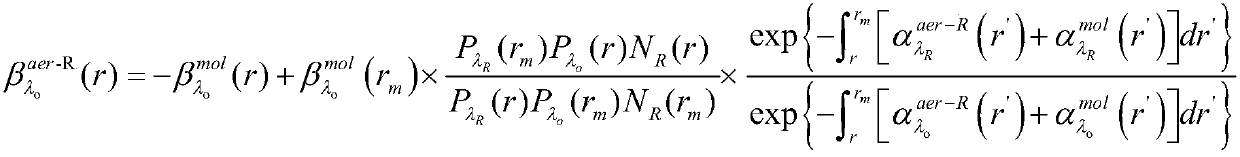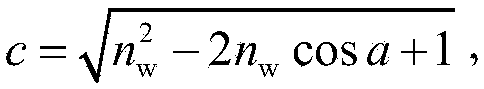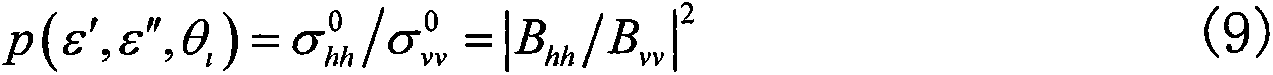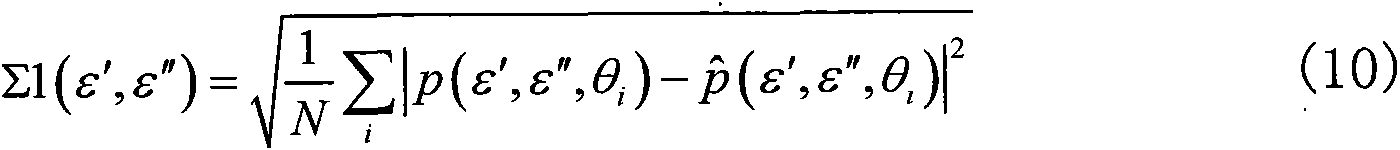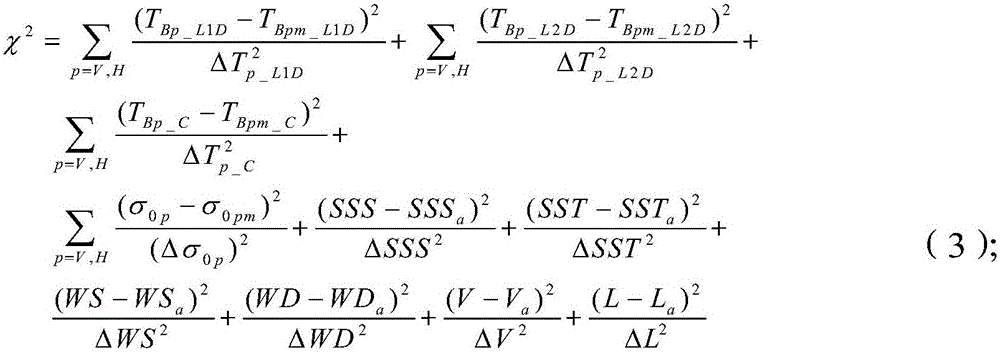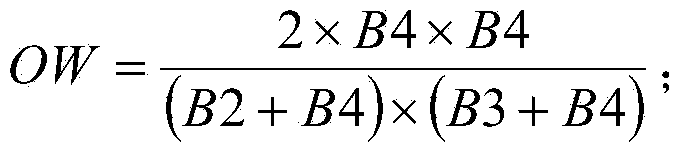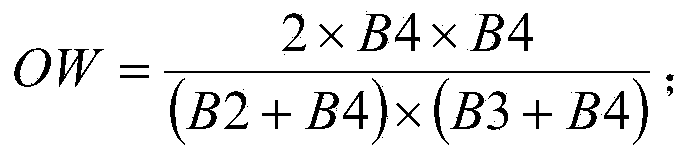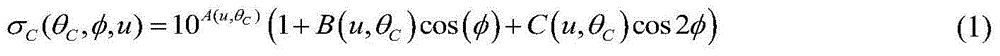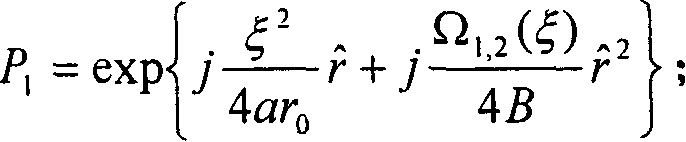Patents
Literature
313 results about "Backscatter coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Backscattering Coefficient (b b) The backscattering, or backward scattering, coefficient, in units of m -1. It indicates the attenuation caused by scattering at angles from 90 to 180 . b b is commonly estimated from measurements of the VSF around a single fixed angle.
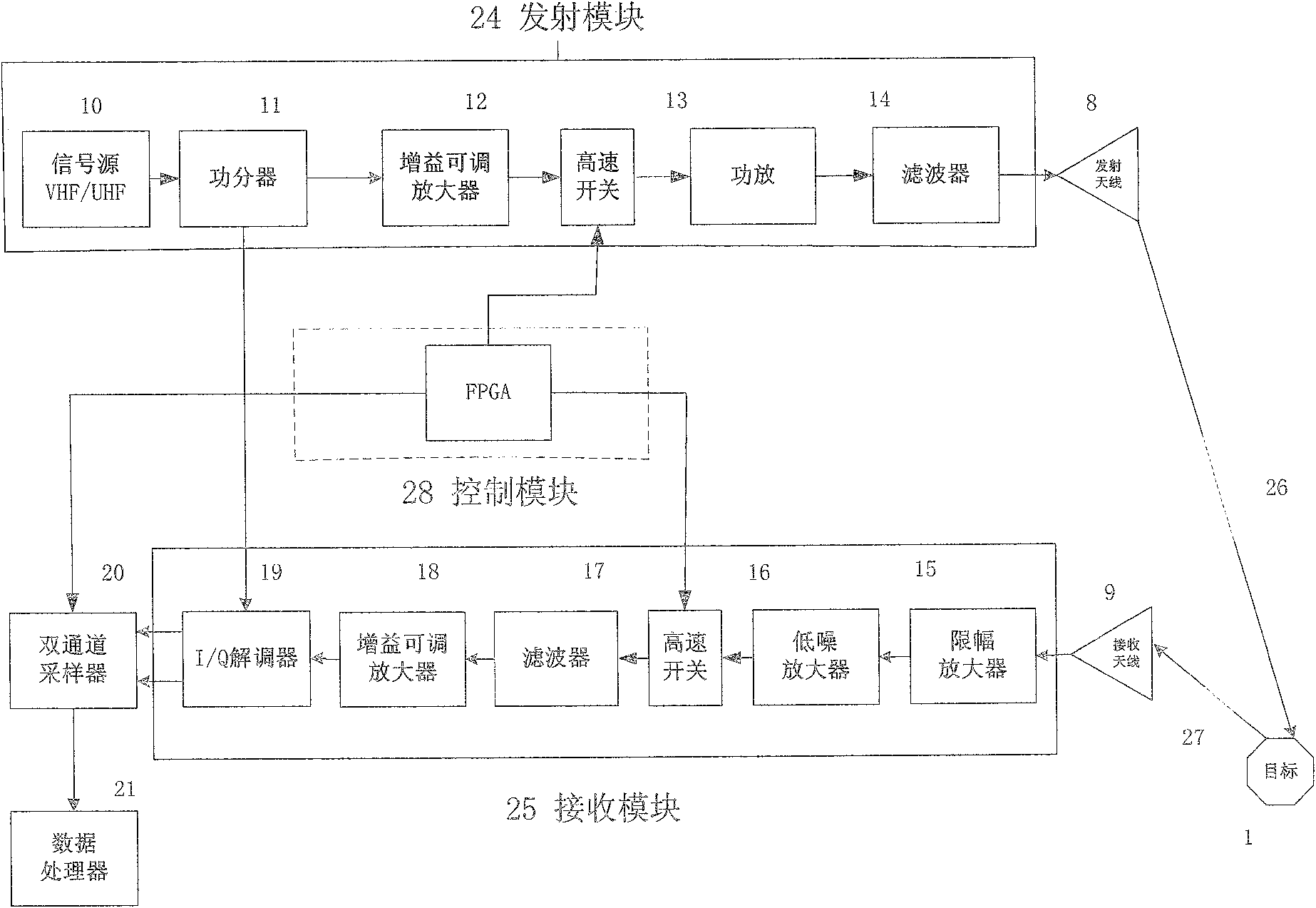
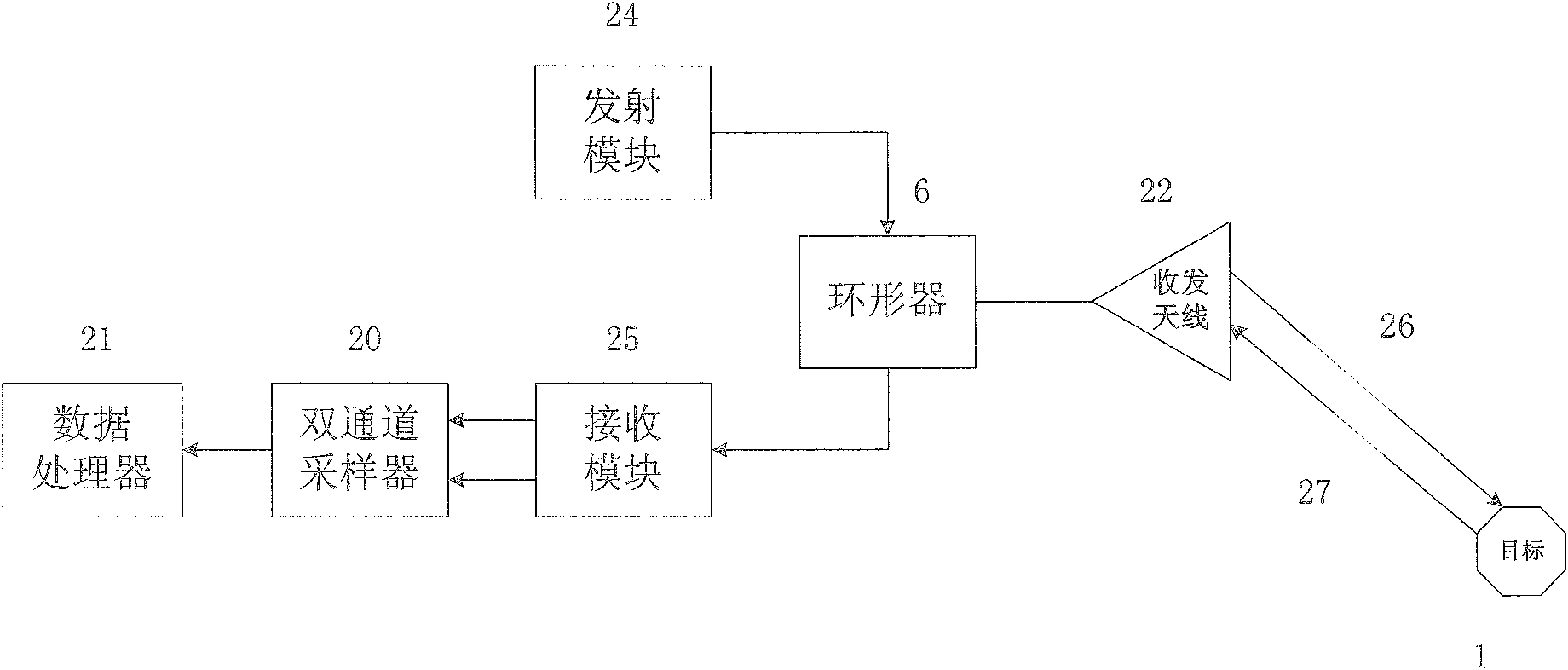
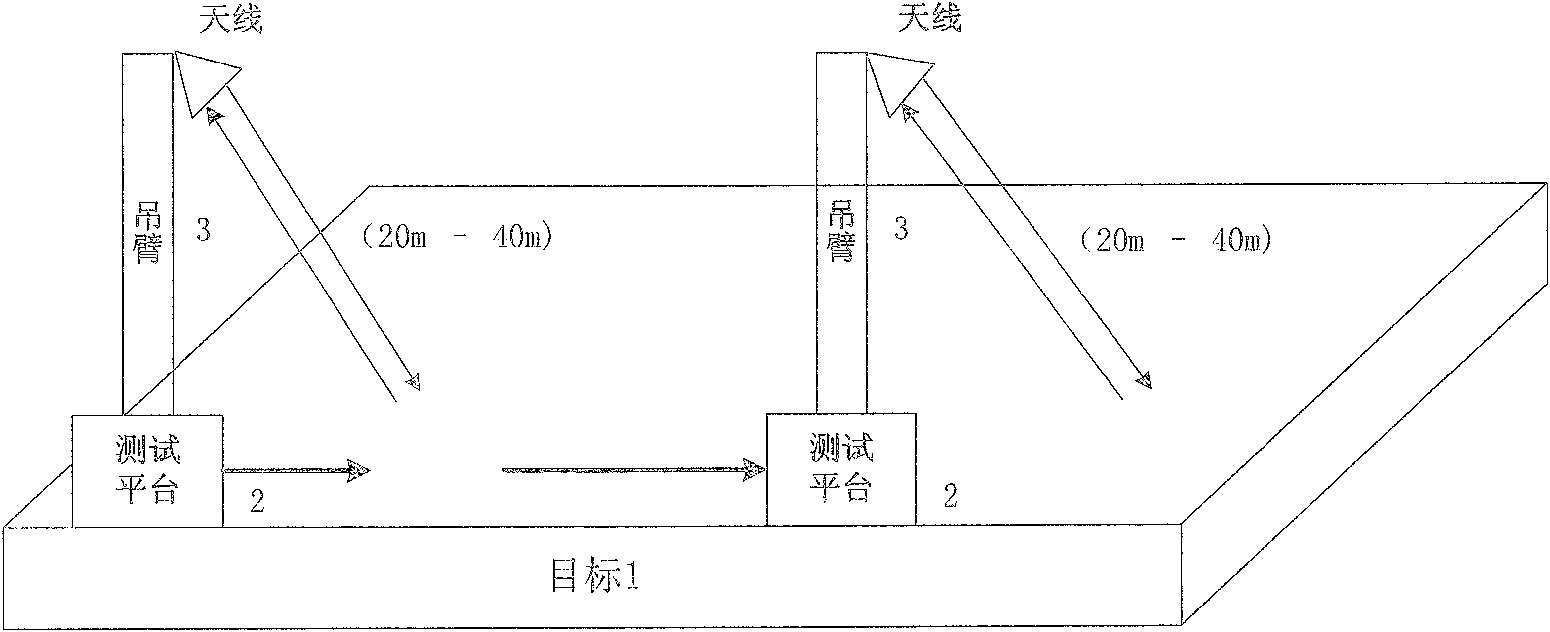
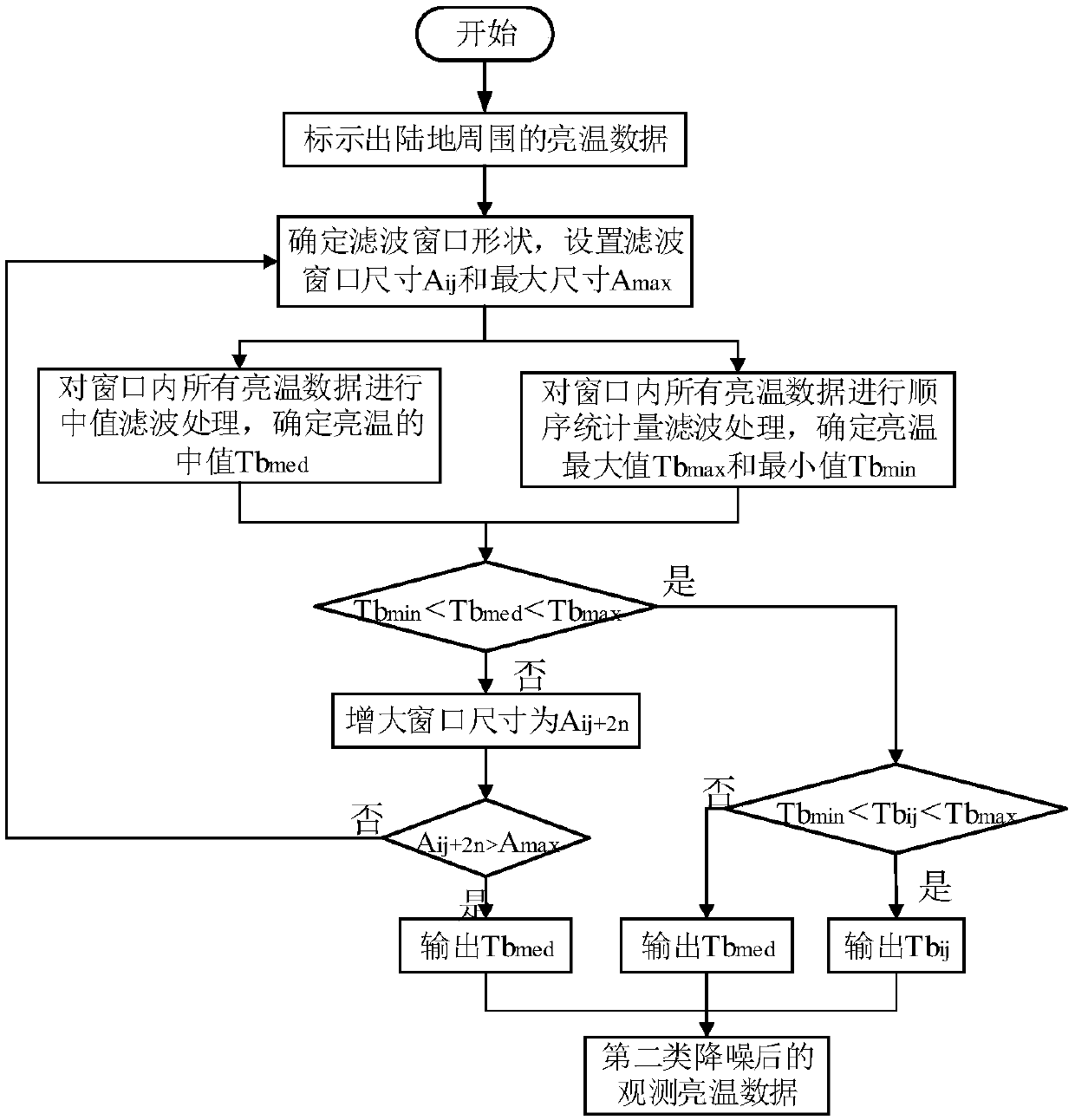
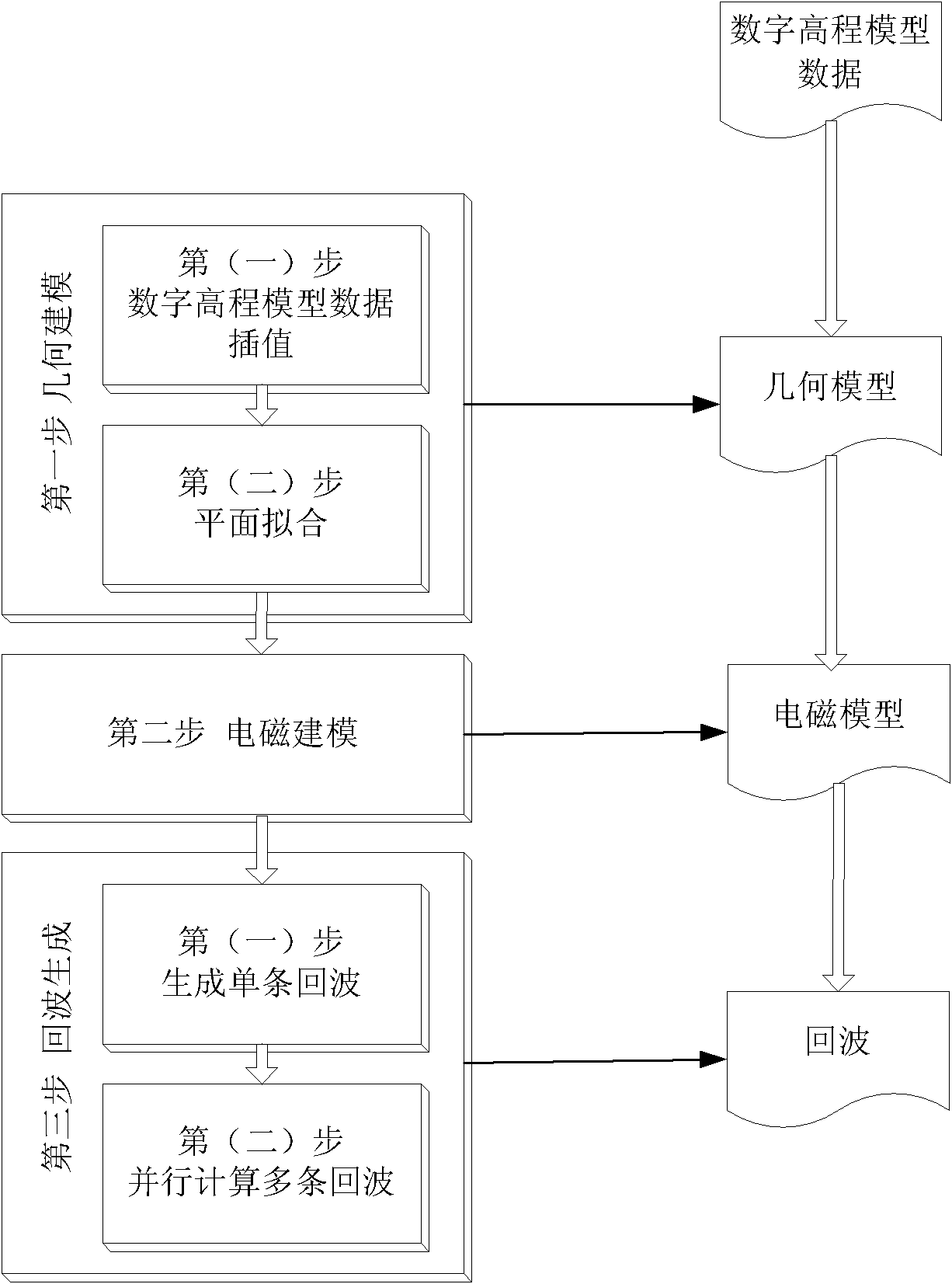
Method and apparatus for detecting deep soil humidity through microwave remote sensing
ActiveCN102735697ALarge-scale spatial and temporal distribution informationDynamic spatio-temporal distribution informationMoisture content investigation using microwavesSoil scienceLow frequency band
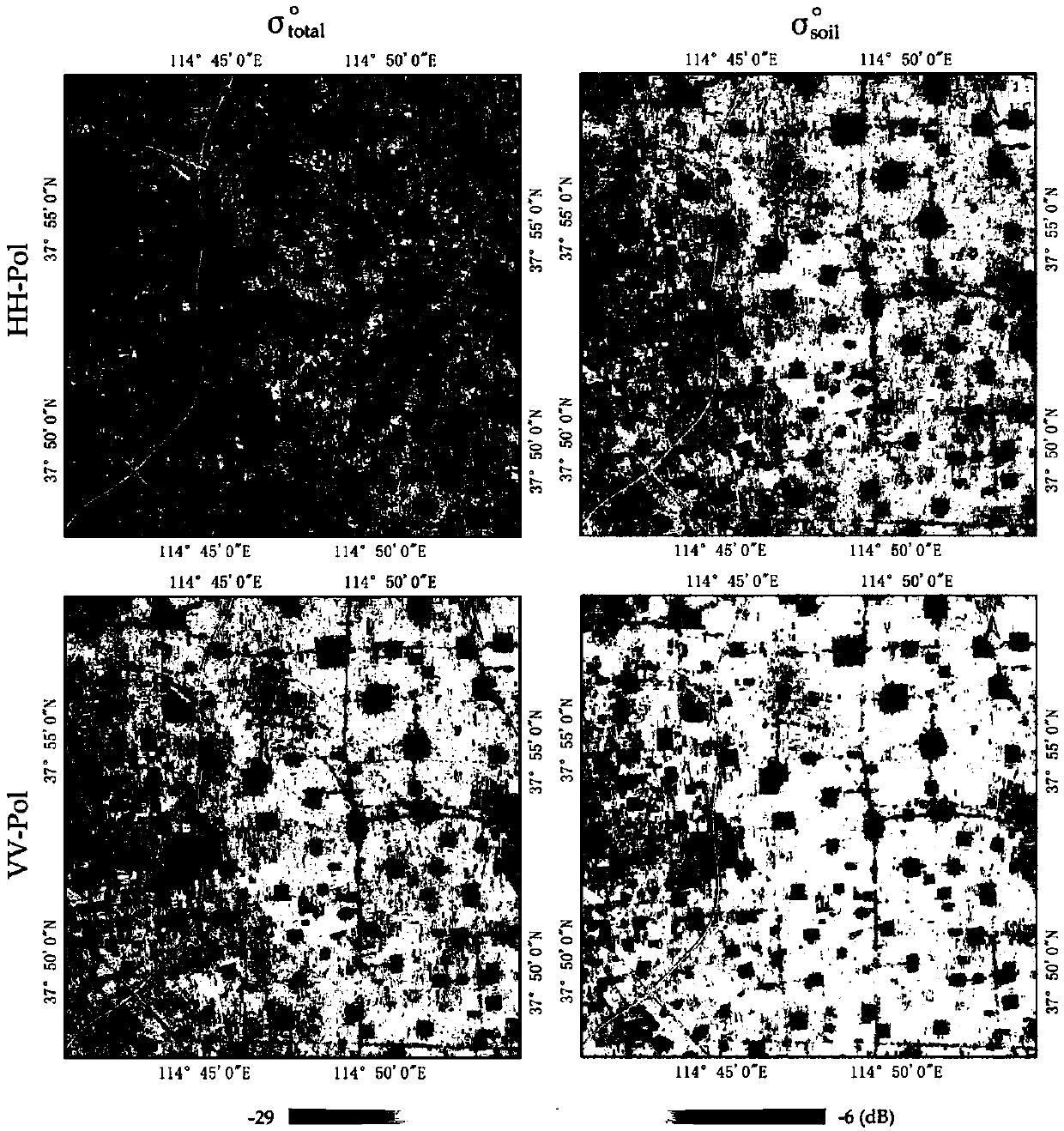
The invention discloses a method and an apparatus for detecting deep soil humidity through microwave remote sensing, and relates to the technology of microwave remote sensing. The method for detecting deep soil humidity through microwave remote sensing is provided by utilizing an object-penetrative property of microwave low-frequency bands and also disclosed is the apparatus for detecting deep soil humidity through microwave remote sensing. Backscattering coefficients of soils are tested. Soil humidity of different depth is obtained through inverting a deep soil scattering model and a soil dielectric model. A three dimensional image of the distribution of soil humidity in a tested area is formed. The working frequency of the apparatus is in the VHF / UHF band. Soil dielectric constants and humidity parameters of different types of soils in a depth of 0.1-10 m can be detected in a contactless and lossless manner.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
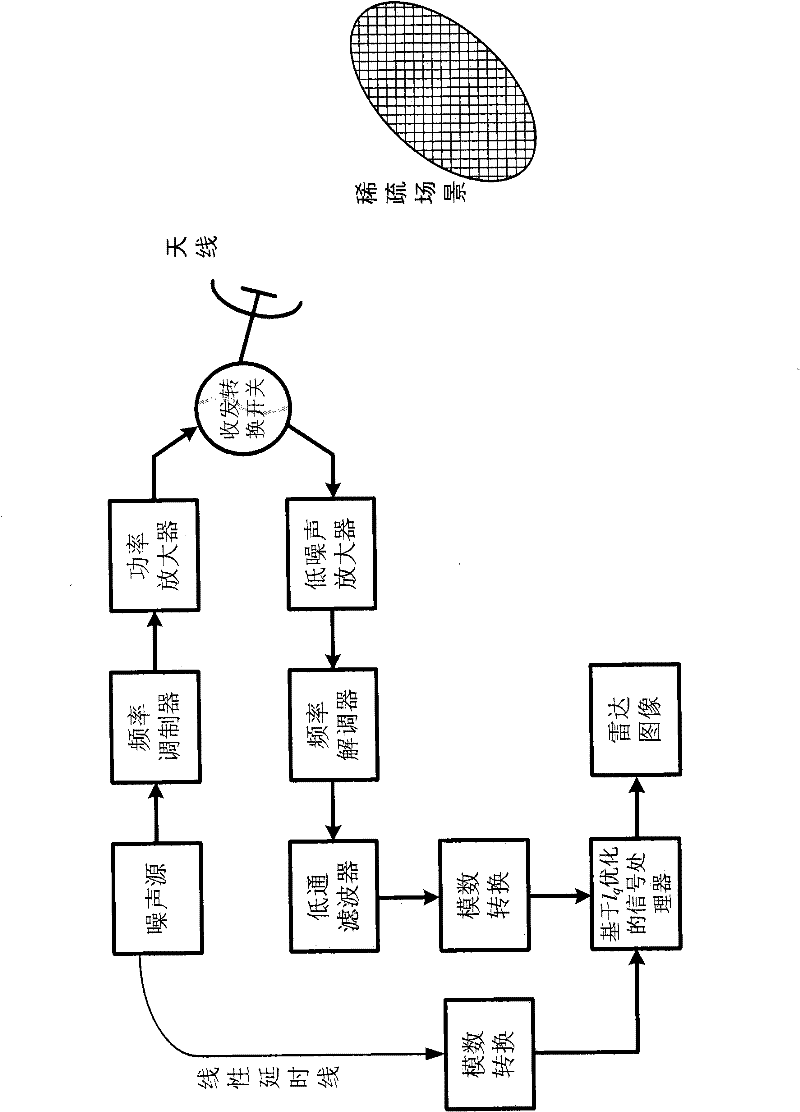
Signal processing method for random noise radar applicable to sparse microwave imaging
ActiveCN102207547AHigh resolutionRecover backscatter coefficientRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPattern recognitionRadar systems
The invention discloses a signal processing method for a random noise radar applicable to sparse microwave imaging, and relates to microwave imaging technologies. For a target scene with sparse characteristics, a transmit signal of a system is band-limited Gaussian random white noise; and observation data with observed quantity less than that required by a nyquist sampling theorem is obtained by a low-speed uniform sampling method during reception. After an observation matrix is set up in combination of a transmit signal form and a data acquisition manner, a backscattering coefficient of a scene target is obtained by optimizing and resolving the compressed sensing of a sparse signal processing theory, and high-resolution target detection and imaging are achieved. In order to improve calculating efficiency, a block signal processing method of the random noise radar applicable to the sparse microwave imaging is adopted; and during block processing, a corresponding block observation matrix is set up in combination with a block form of the data. Compared with the conventional radar system, the invention has the advantages that: a little observation data is needed to achieve the same resolution; and higher resolution can be achieved when the same observation data quantity is adopted.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
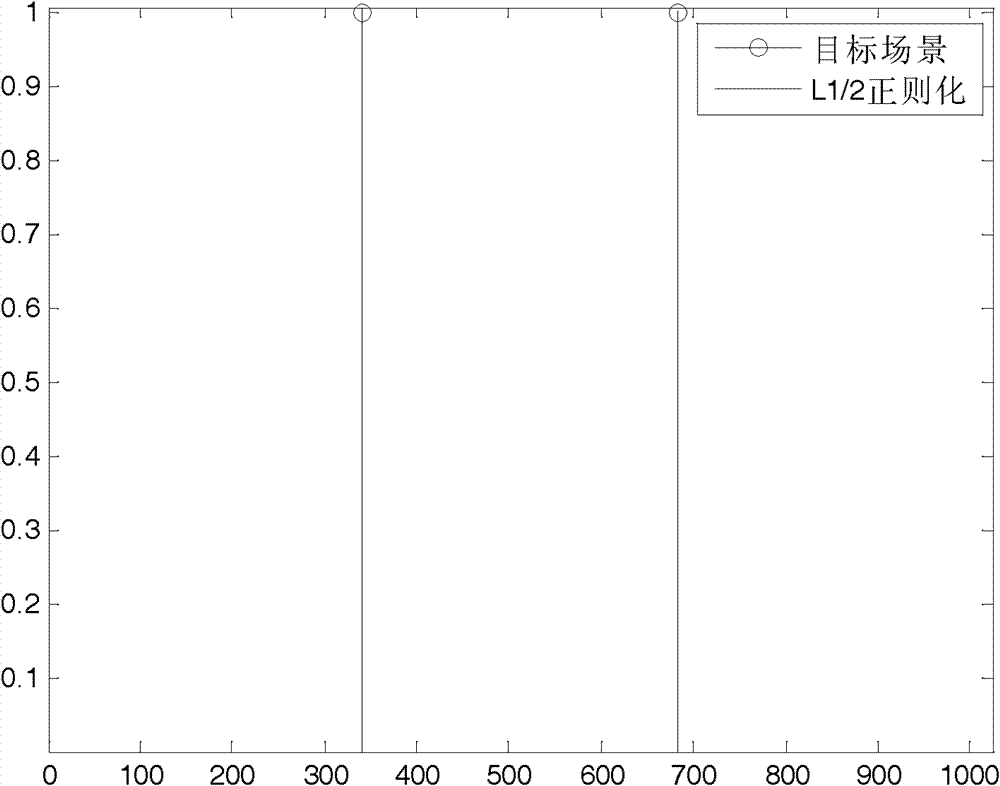
Synthetic aperture radar imaging method based on L<1/2> regularization
ActiveCN102788977AEffective imagingFew samplesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a synthetic aperture radar imaging method based on L<1 / 2> regularization and relates to a radar two-dimension imaging technology. The synthetic aperture radar imaging method includes the steps of a, establishing a synthetic aperture radar imaging model based on the L<1 / 2> regularization according to a synthetic aperture radar observation model; and b, using an iteration half threshold value algorithm to reconstruct an observation scene backscattering coefficient. Compared with traditional synthetic aperture radar imaging methods, the synthetic aperture radar imaging method is capable of reducing a sampling quantity required by the correct reconstruction of an objective scene and achieving effective imaging of synthetic aperture radar data.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
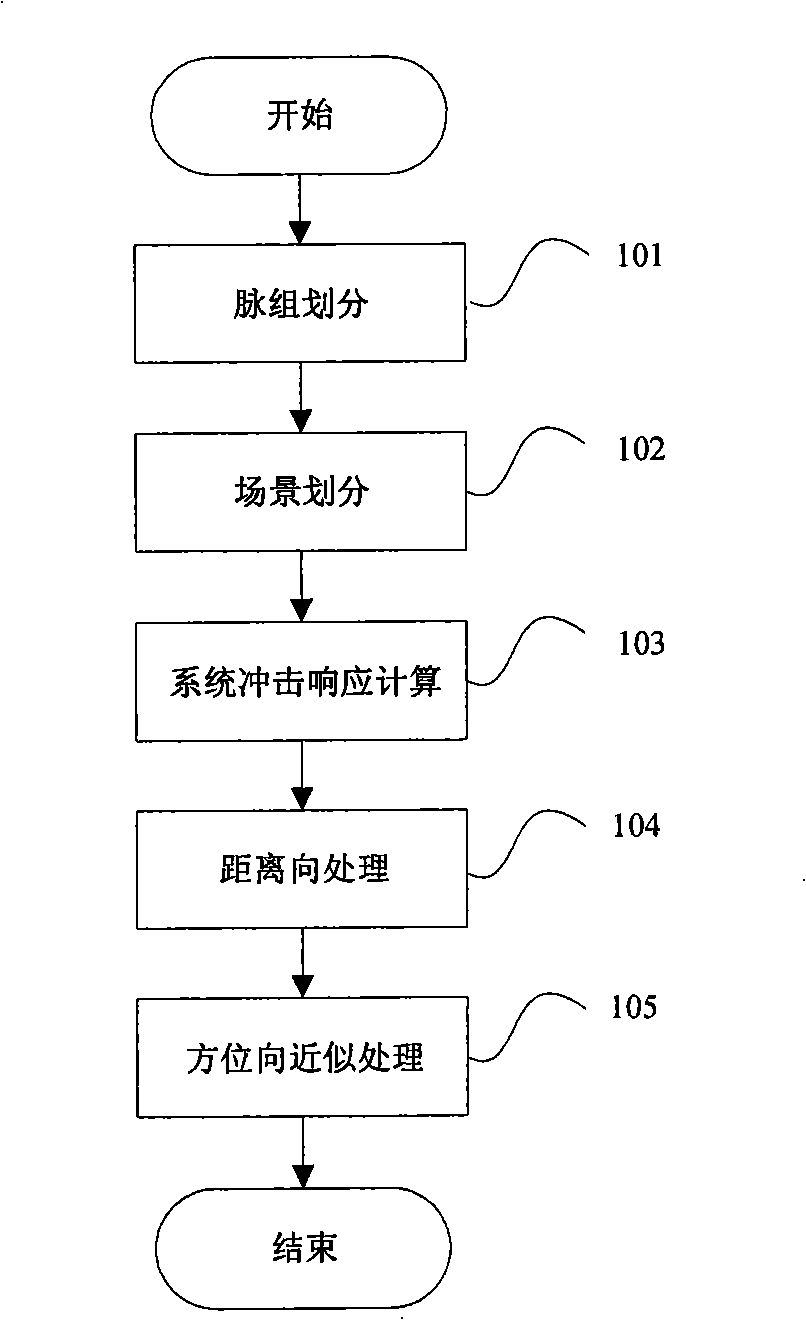
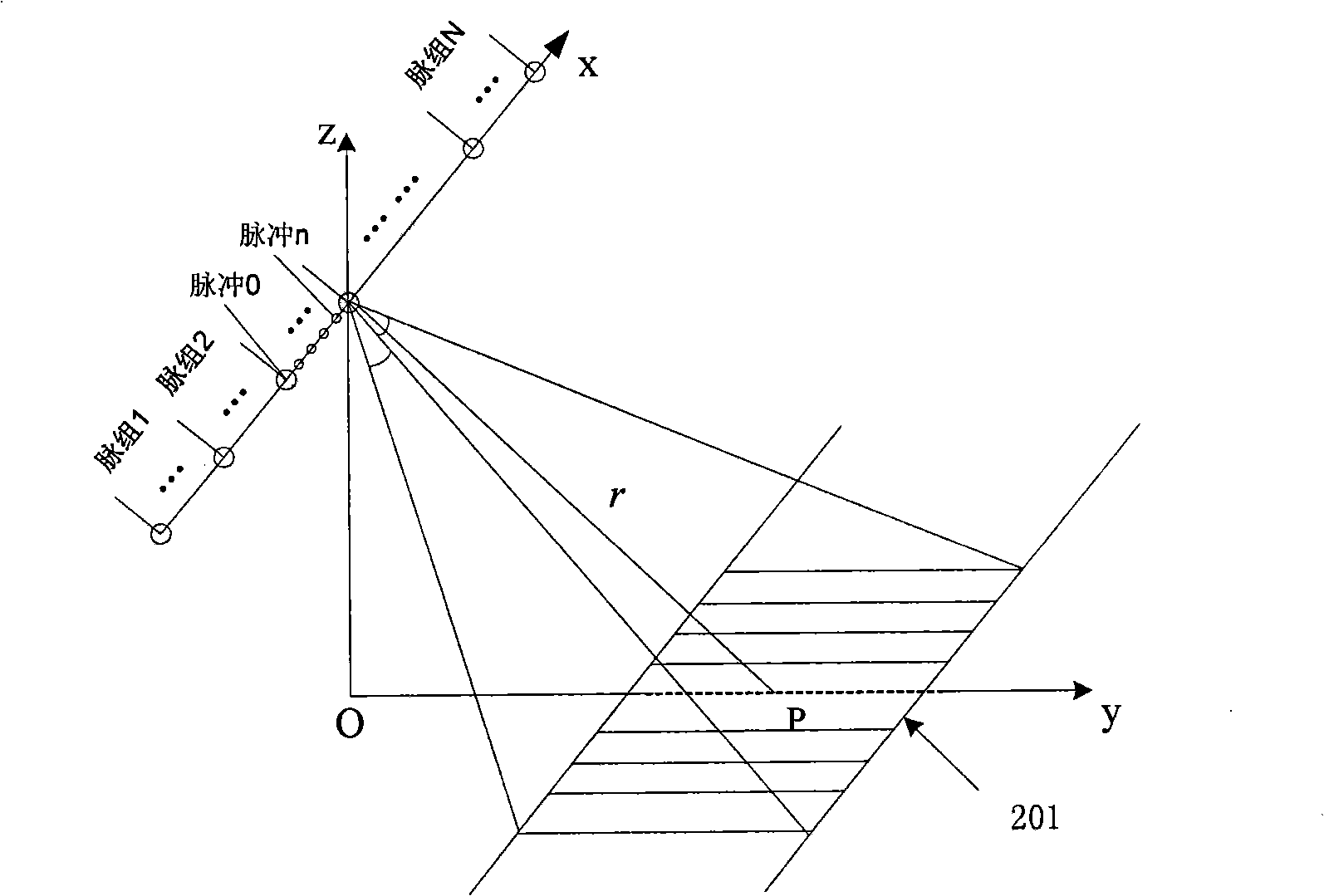
SAR echo rapid simulation method based on sub-aperture and equivalent scatterer
InactiveCN101526614ASmall amount of calculationImprove simulation speedRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarAzimuth direction
The invention relates to a synthetic aperture radar echo rapid simulation method based on sub-aperture and equivalent scatterer, comprising the following steps: 1) pulses corresponding to all track points are divided into a plurality of pulse groups with equal length along the radar flying direction; 2) a scene is divided into a plurality of small rectangular scenes with the same size, and equidistance rings are divided according to the distance between a radar platform and the target scene; 3) in every equidistance annular region of the small rectangular scene, the backscattering coefficient of the equivalent scatterer is calculated, and a pulse response function of the system is obtained; 4) the range direction processing is carried out, and an echo signal of the central pulse of the pulse groups is obtained by the convolution of an emission signal and the pulse response function; 5) azimuth direction processing is carried out, and echo signals of any other pulses in the pulse groups are calculated by the echo signal of the central impulse in the impulse groups. The method of the invention has the advantages of rapid speed and high precision of the frequency domain processing method, introduces the expansion approximate processing of the azimuth direction and effectively improves the simulation velocity.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
GPU-based video SAR echo simulation parallel implementation method
ActiveCN107229051AAchieve parallelismReduce overheadRadio wave reradiation/reflectionVideo memoryRadar systems
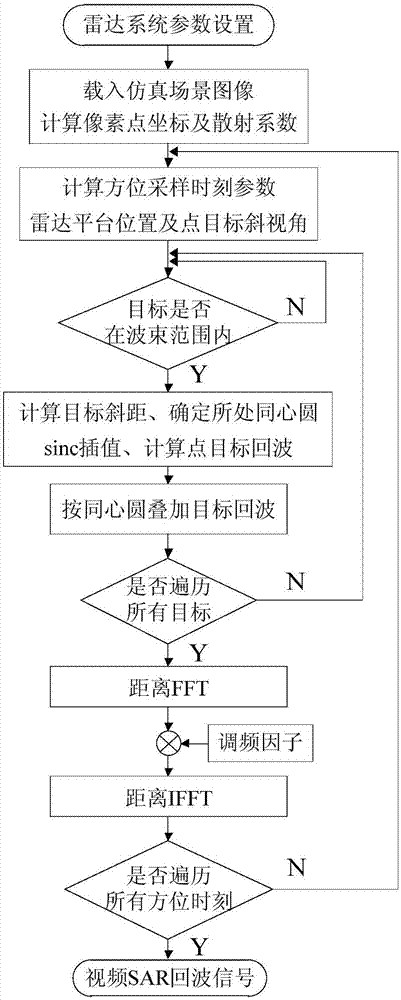
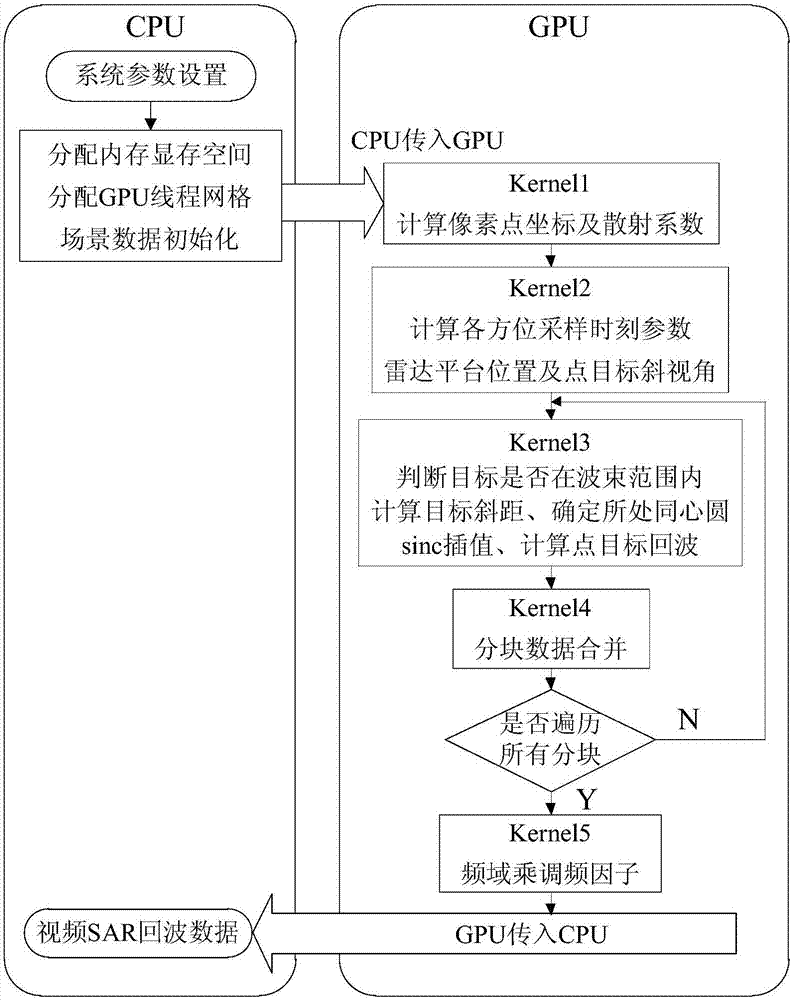
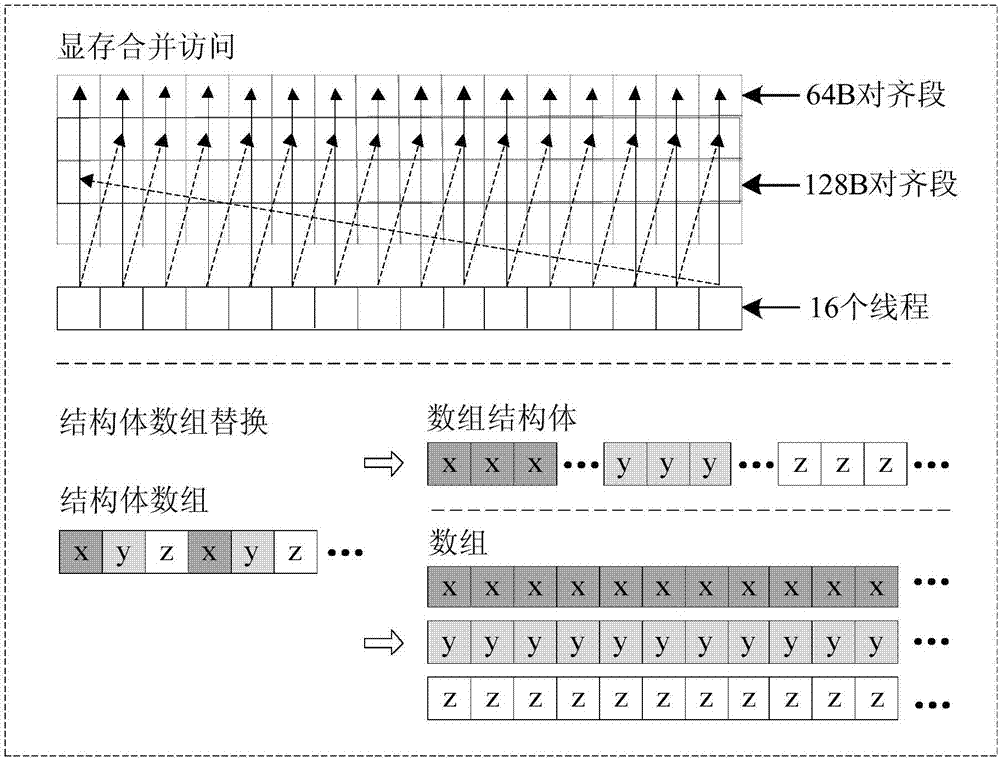
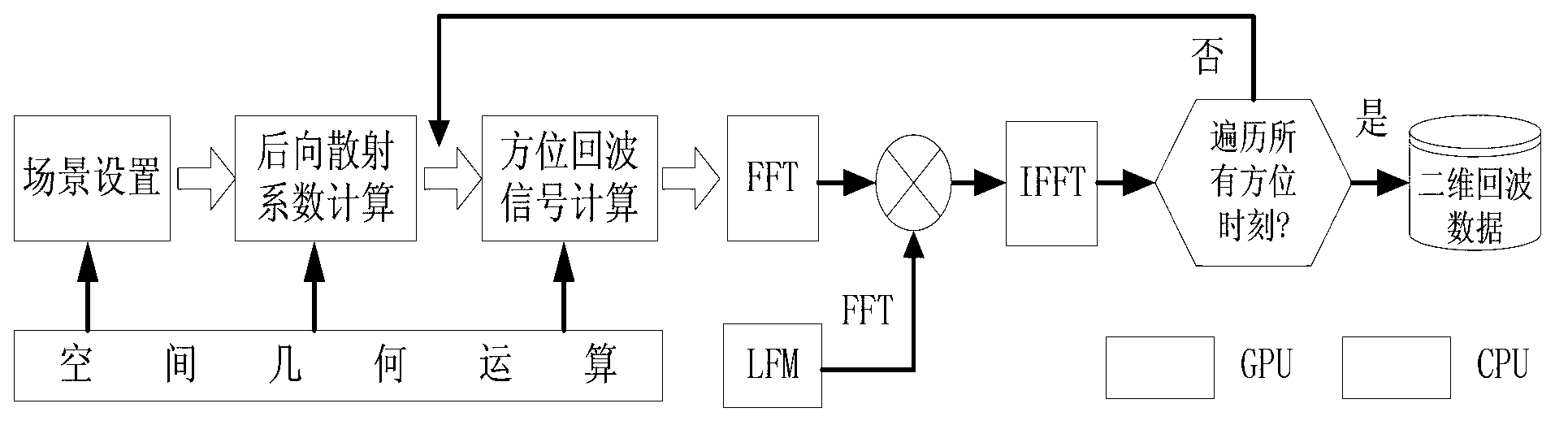
The invention belongs to the field of radar signal processing and discloses a GPU-based video SAR echo simulation parallel implementation method. The method comprises the following steps: copying radar system parameter values from a memory of a CPU to a constant memory of a GPU; transmitting original scene image data in the memory of the CPU to a video memory of the GPU; setting a kernel function and parallelly calculating space coordinates and backscattering coefficients of each point target; setting a kernel function and parallelly calculating space coordinates of a radar platform and instantaneous squint angle between the radar platform and each point target in each azimuth sampling moment; setting a kernel function and carrying out segmentation on all point targets and obtaining echo signals of the point targets in all segmented data; setting a kernel function and obtaining an initial echo signal of the radar at all azimuth moments; and setting a kernel function and obtaining a final echo signal obtained after linear frequency modulation processing as a video SAR echo signal. The method has the advantages of high real-time performance and high efficiency.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
SAR (synthetic aperture radar) echo simulating method based on GPU (graphics processing unit) parallel computing
ActiveCN103176170AIncrease echo simulation speedEasy to addWave based measurement systemsSynthetic aperture sonarInverse synthetic aperture radar
The invention provides an SAR (synthetic aperture radar) echo simulating method based on GPU (graphics processing unit) parallel computing, overcomes defects on influencing SAR echo simulating speed and accuracy, and improves influencing SAR echo simulating speed. The method includes the steps of setting up scene scattering point mesh generation and making sure position relation of double antenna SAR and scene targets; building up backscattering coefficient model, and generating correlated backscattering coefficient pairs according to sight relation of double antenna SAR and ground scene so as to complete backscattering coefficient computing; calculating positioning echo signals in SAR irradiating area; performing convolution to positioning echo signals acquired in step 3 and transmitting signals to acquire current pulsing echo signals; and going through all positioning times to acquire SAR echo data influenced by double antenna in the whole scene.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Peat bog information extracting method based on ENVISAT ASAR, Landsat TM and DEM data
ActiveCN104361338AAutomatic fast and accurate extractionAutomatic Extraction FastScene recognitionLand coverPeat
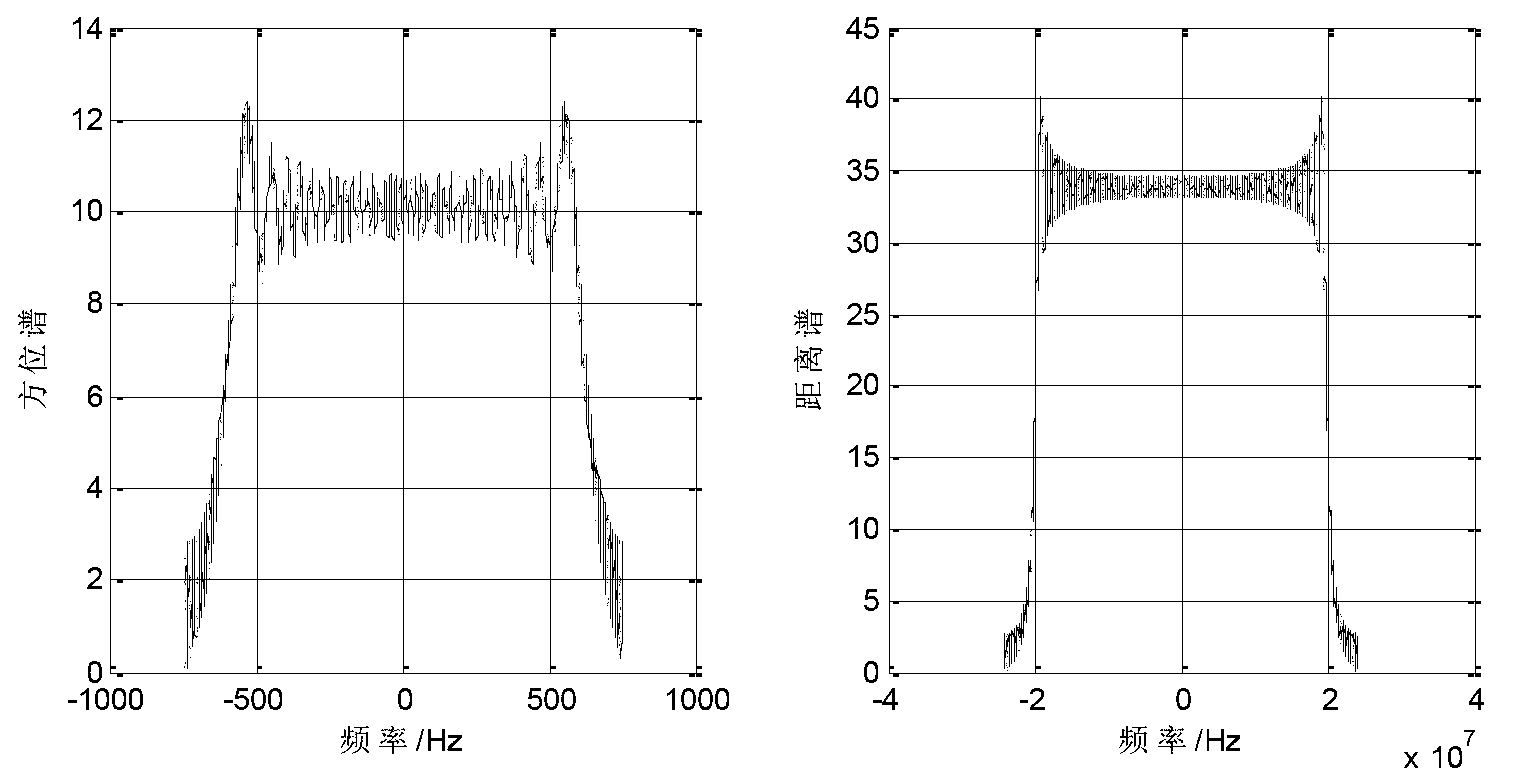
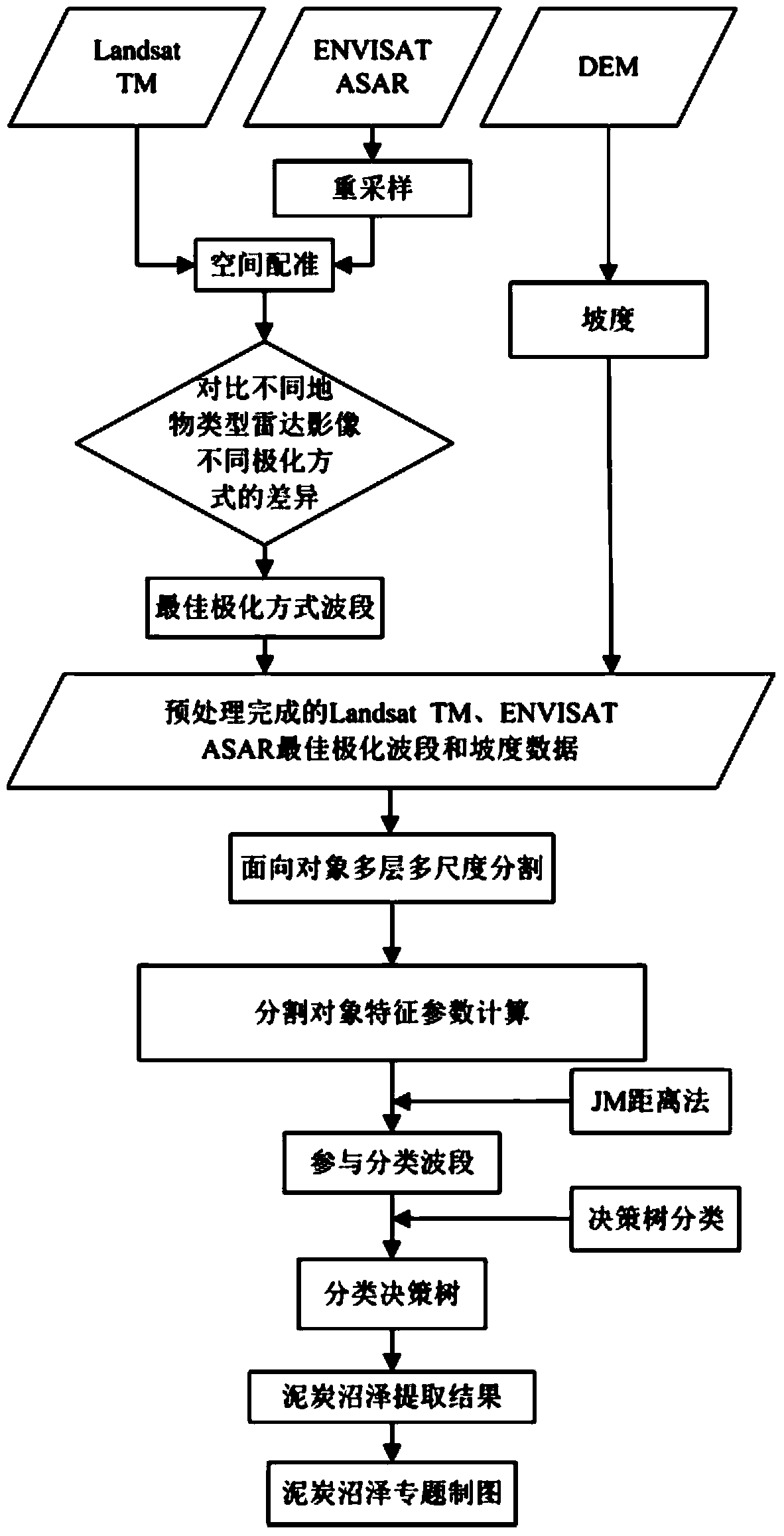
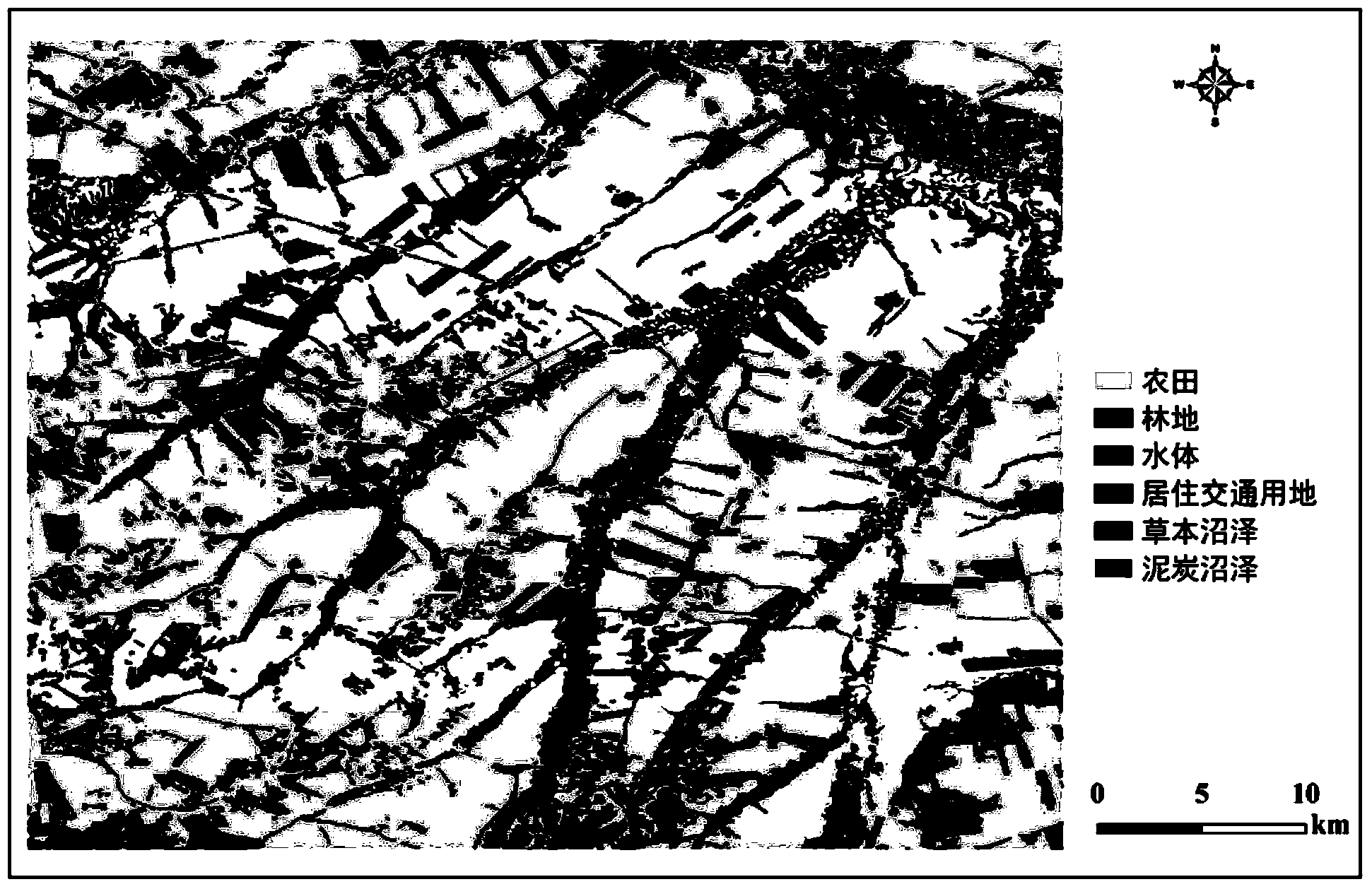
The invention relates to peat bog information extracting methods, in particular to a peat bog information extracting method based on ENVISAT ASAR, Landsat TM and DEM data, and solves the problem that peat bog and other bog types cannot be distinguished by a conventional method. The peat bog information extracting method includes step 1, preprocessing Landsat TM data; step 2, preprocessing ENVISAT ASAR data; step 3, re-sampling the ENVISAT ASAR data; step 4, acquiring an ENVISAT ASAR image; step 5, acquiring gradient data; step 6, extracting back scattering coefficient; step 7, determining optimal polarization mode waveband of the ENVISAT ASAR image; step 8, acquiring a division unit; step 9, extracting feature parameters; step 10, determining optimal classification waveband; step 11, establishing a classification decision-making tree; step 12, generating a soil covering type vector file; step 13, making a peat bog map. The peat bog information extracting method is applied to the field of peat bog information extracting.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
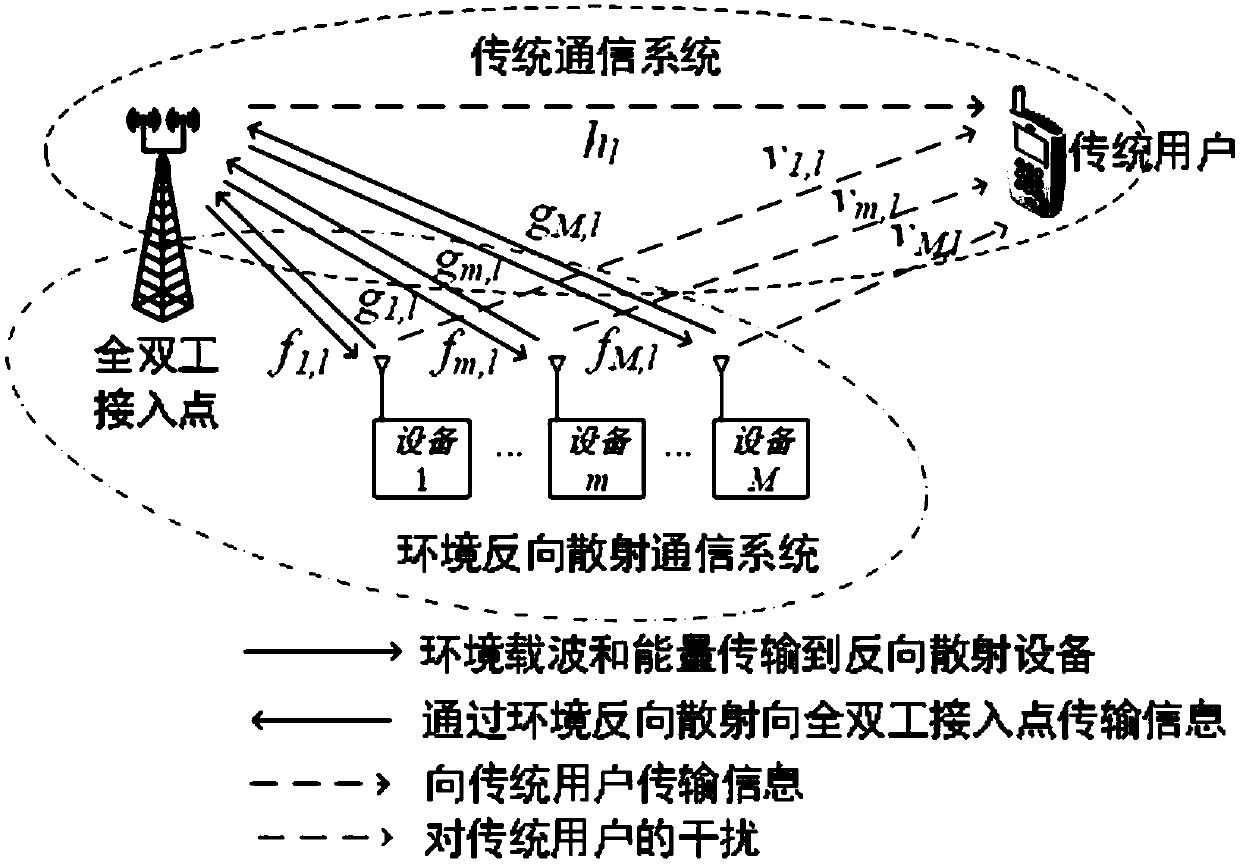
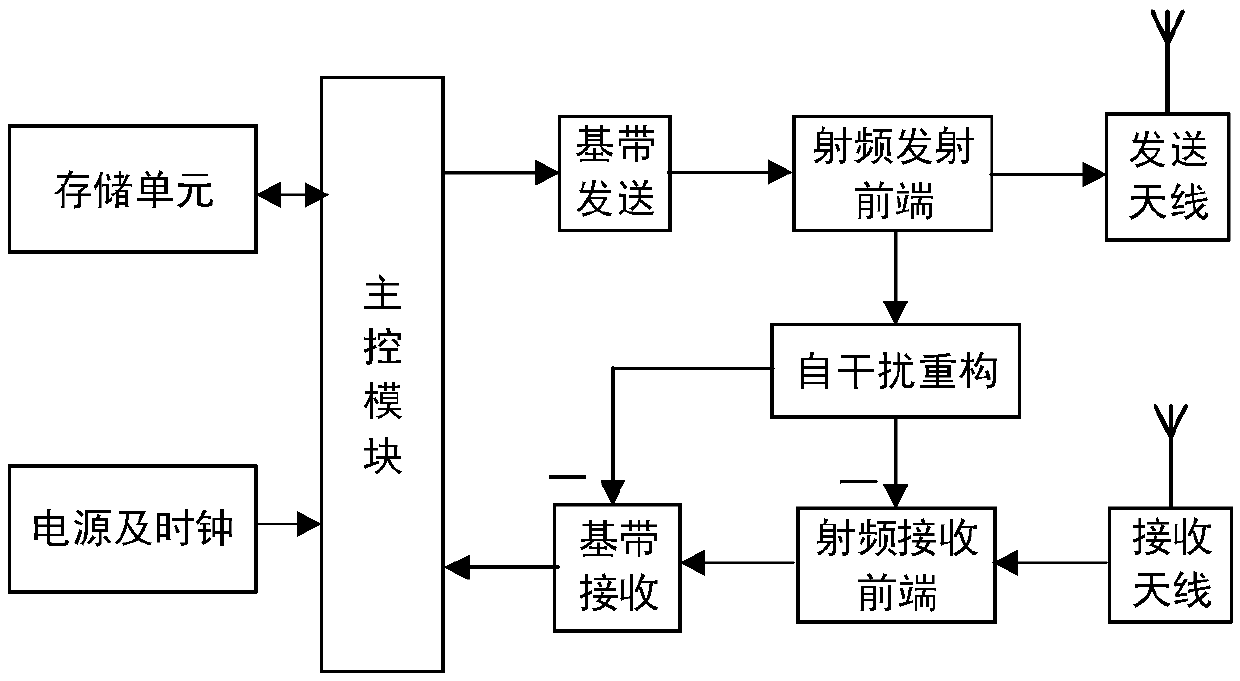
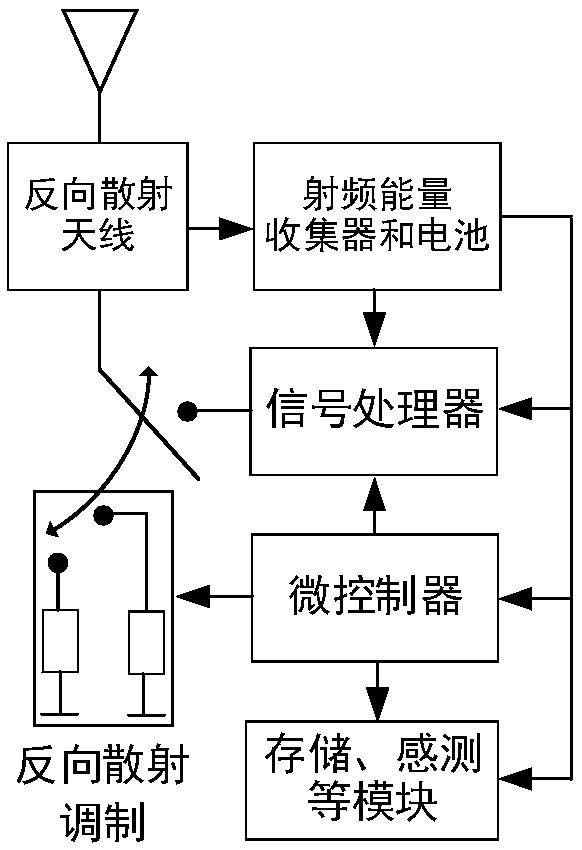
Full-duplex environment backscattering communication system, transmission method and resource allocation method
InactiveCN109547183AReduce complexityImprove throughput performanceBaseband system detailsDuplex signal operationCommunications systemData signal
The invention belongs to the field of communication technology, and relates to a full-duplex environment backscattering communication system, a transmission method and a resource allocation method. According to the system of the invention, a full-duplex-type access point is configured with one or more antennas, and two modes of channel estimation and full-duplex backscattering communication are included; in a channel estimation mode, the access point sends a downlink pilot signal, a plurality of backscattering devices carry out backscattering by respective fixed backscattering coefficients according to a manner of division multiplexing, the access point estimates channels of all the backscattering devices, and a traditional user utilizes the received pilot signal to estimate a downlink channel thereof; and in a full-duplex communication mode, the access point sends a downlink data signal, the traditional user uses the estimated downlink channel to carry out signal receiving detection,the backscattering devices select backscattering coefficients according to information bits for backscattering, and the access point detects signals of the backscattering devices. The system can be used in a variety of low-power-consumption Internet-of-things communication scenes, and has higher practicability.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Polarization SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) terrain radiation correction and geometric correction method based on imaging surface representation
ActiveCN103869296ARemove terrain effectsTerrain radiation correction works wellRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTerrainSynthetic aperture radar
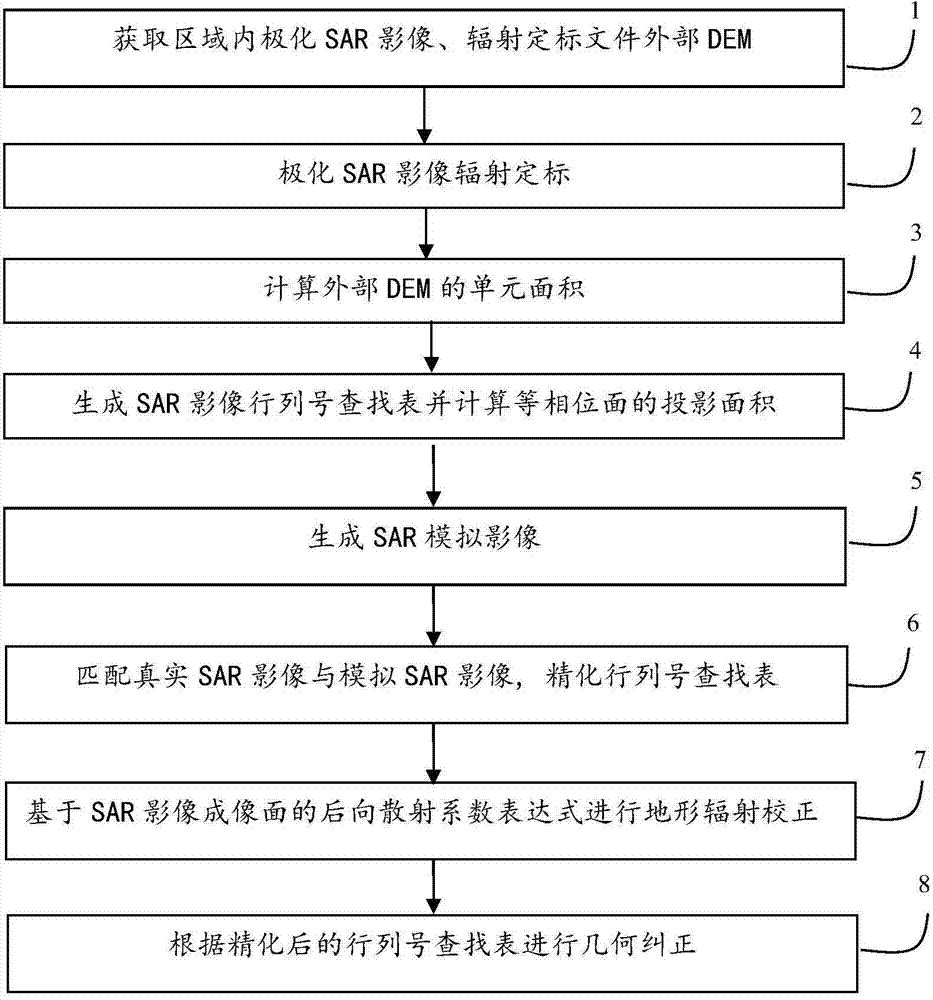
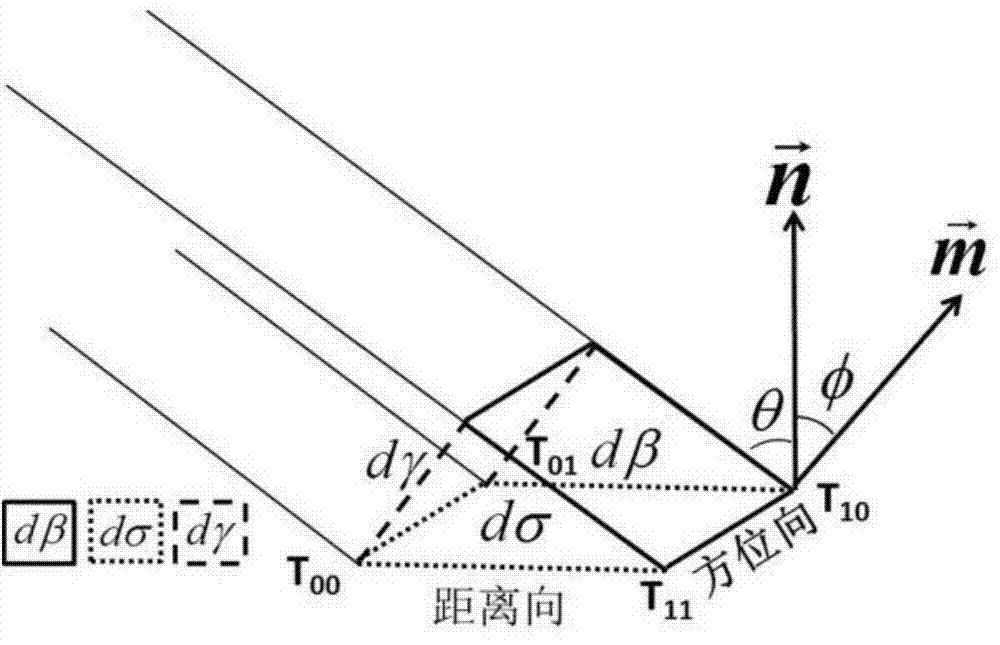
The invention relates to a polarization SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) terrain radiation correction and geometric correction method based on imaging surface representation. According to the method, the radiation value of the imaging surface of an SAR image is taken as the representation of a backscattering coefficient. The method comprises the following steps of 1, obtaining the SAR image and a radiation calibration file external DEM (Dynamic Effect Model) in a region; 2, performing radiation calibration according to a radiation calibration file of the original polarization SAR image; 3, calculating the unit area of the external DEM; 4, generating an SAR image line and column number lookup table according to a distance Doppler SAR positioning model and calculating the projection area of an equiphase surface; 5, generating an SAR simulation image by combining the projection area of the equiphase surface with the line and column number lookup table; 6, matching a real SAR image with the simulation SAR image, building a polynomial correction equation, and refining the line and column number lookup table; 7, carrying out terrain radiation correction on the polarization SAR image according to the backscattering coefficient expression based on the imaging surface of the SAR image; 8, carrying out geometric correction according to the refined line and column number lookup table. According to the scheme provided by the invention, the radiation distortion of the polarization SAR image, caused by terrain can be corrected, and the high-precision geometric positioning and correction of the polarization SAR image are realized.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
Rapid simulation method of repeat-pass spaceborne natural scene SAR complex image data
ActiveCN105677942AOvercoming slowReduce simulation timeSpecial data processing applicationsSatellite imageImaging Signal
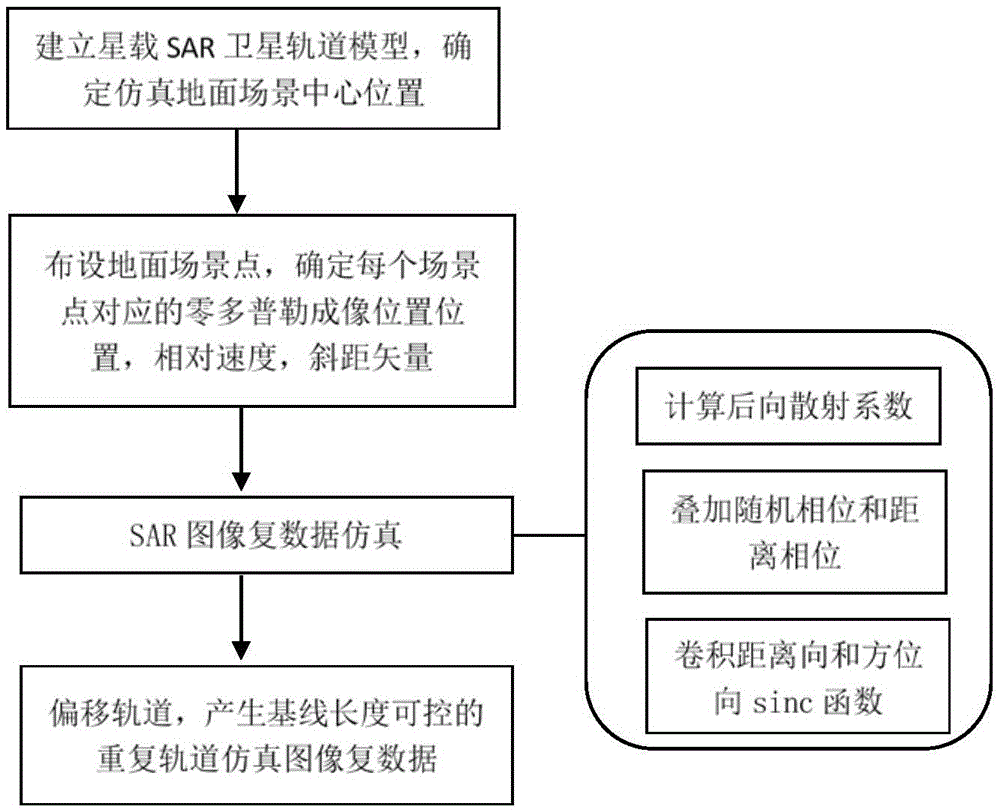
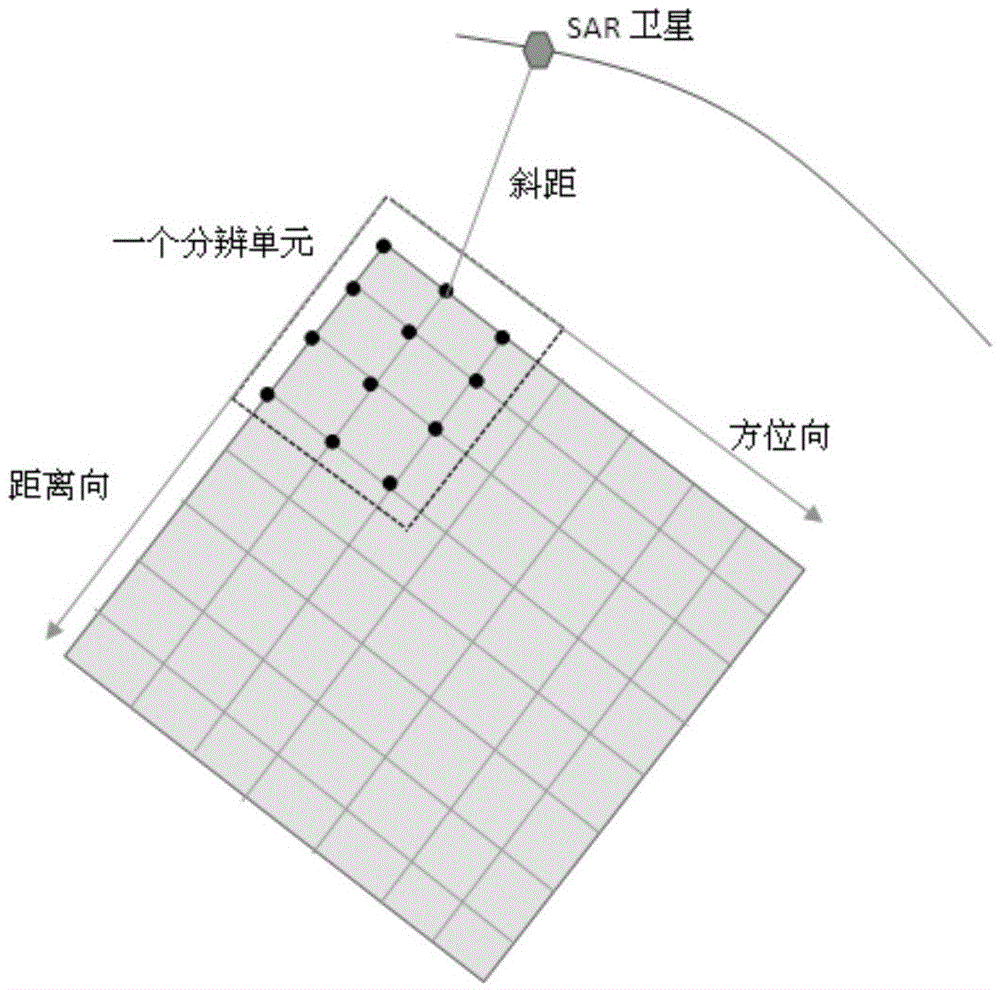
The present invention discloses a rapid simulation method of repeat-pass spaceborne natural scene SAR complex image data. According to the method, an SAR satellite orbit is simulated, the ground scene is simulated according to the spaceborne SAR satellite imaging principle and an SAR satellite single looking complex image signal model, and multi-frame repeat-pass SAR complex image data are directly obtained. Slant-range information is obtained by using a rapid method to iteratively compute a satellite zero doppler imaging position, a backscattering coefficient is calculated by using a simplified scattering model, and a simplified repeat-pass model is provided to generate any multi-frame SAR complex image data with base length controllable. The disadvantage that speed of a traditional echo simulation method is slow is overcome, and prior information can also be provided for interference processing so as to assist in processing or evaluating a processing result.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
OLCI remote sensing monitoring method for shallow lake inherent optical parameters
ActiveCN107589075AEfficient spatio-temporal distributionEfficiently reflect the spatial and temporal distributionColor/spectral properties measurementsRemote sensing reflectanceField tests
The invention provides an OLCI remote sensing monitoring method for shallow lake inherent optical parameters; the method comprises the steps: based on a quasi-analytical algorithm, assuming that 750 nm water body total absorption is equal to pure water absorption, and establishing the relationship of the water body remote sensing reflectance ratio and the total absorption coefficient, and the relationship of the water body remote sensing reflectance ratio and the backscattering coefficient; according to the characteristics of absorption coefficients of all water body components and the relationships of the absorption coefficients with remote sensing reflectance ratio spectra and the backscattering coefficient, further resolving the water body total absorption coefficient into the absorption coefficients of the water body components; combining the water body remote sensing reflectance ratio spectra and the corresponding water body component absorption coefficients measured by Chaohu lake, Taihu lake and Hongze lake field tests, establishing IOP inversion algorithms facing to different lakes with complex water body optical characteristics based on the field actually measured spectra;and extending the IOP inversion algorithm to OLCI image data corrected by 6S atmosphere, and realizing remote sensing monitoring of the water body inherent optical parameter spatial distribution of eutrophic shallow water lakes.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
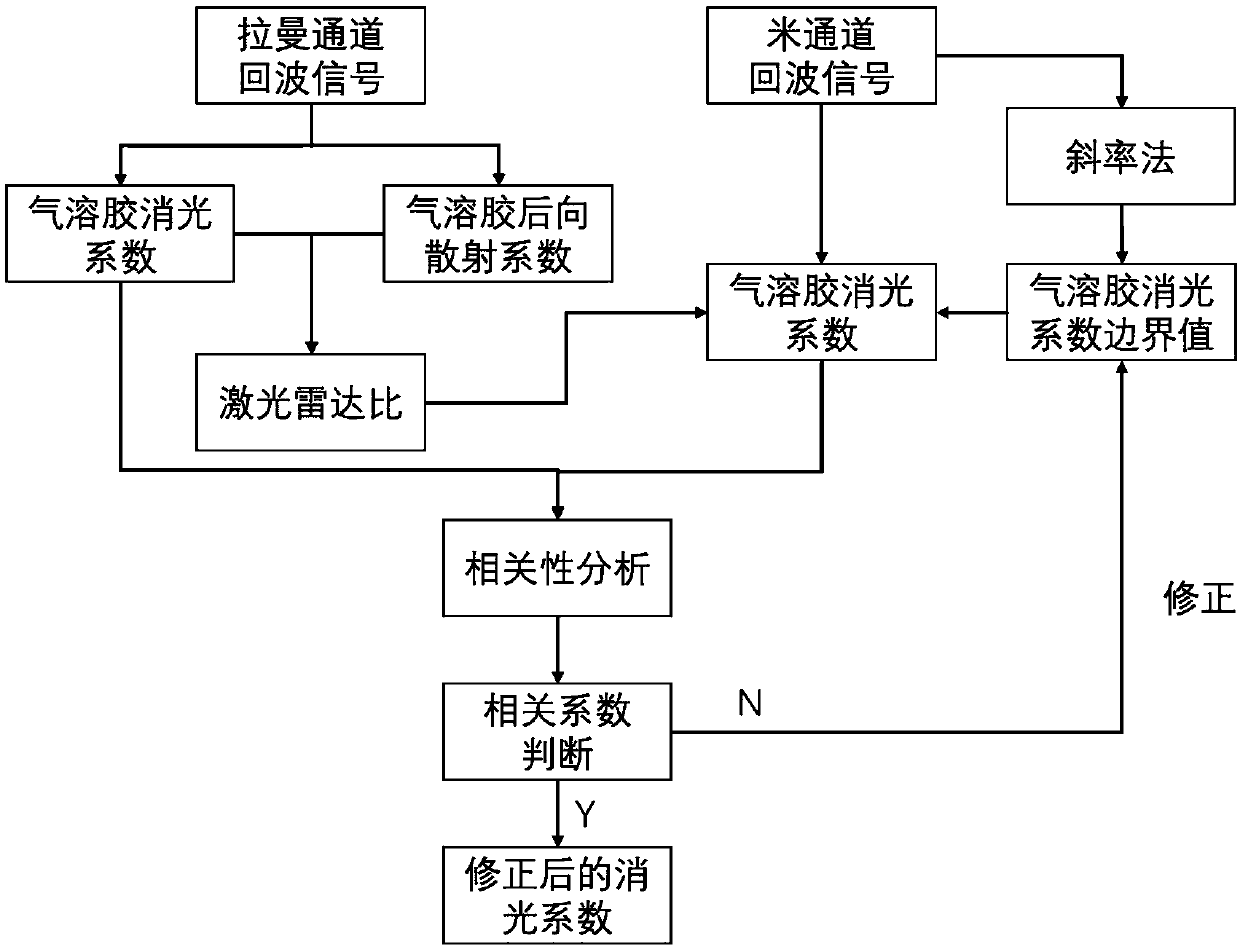
Inversion method of extinction coefficient of aerosol based on Raman-Mie scattering laser radar
ActiveCN109596594ARealize high-precision detectionOvercome limitationsScattering properties measurementsRaman scatteringBoundary valuesExtinction
The invention provides an inversion method for an extinction coefficient of an aerosol based on a Raman-Mie scattering laser radar, comprising the steps of: Step 1: obtaining an echo signal of a Ramanchannel in the Raman-Mie scattering laser radar, and determining an lidar ratio of the aerosol by Ansmann method, that is, obtaining the extinction coefficient and a backscattering coefficient of theaerosol by using Raman method; Step 2: obtaining an echo signal of a Mie channel in the Raman-Mie scattering laser radar, and inverting a distribution profile of the extinction coefficient of the aerosol based on Fernald method; and Step 3: correcting, based on an inversion result of the Raman method in step 1, key parameters required to invert the distribution profile of the extinction coefficient by using the Mie scattering method in step 2, that is, a boundary value of the extinction coefficient of the aerosol, thereby improving the inversion precision of the distribution profile of the extinction coefficient of the Mie scattering channel. According to the inversion method for the extinction coefficient of the aerosol based on the Raman-Mie scattering laser radar provided by the invention, high-precision detection of aerosols is achieved by combining the characteristics of Raman scattering and Mie scattering.
Owner:江苏光在科技有限公司
Universal aquatic vegetation radiation transmission model
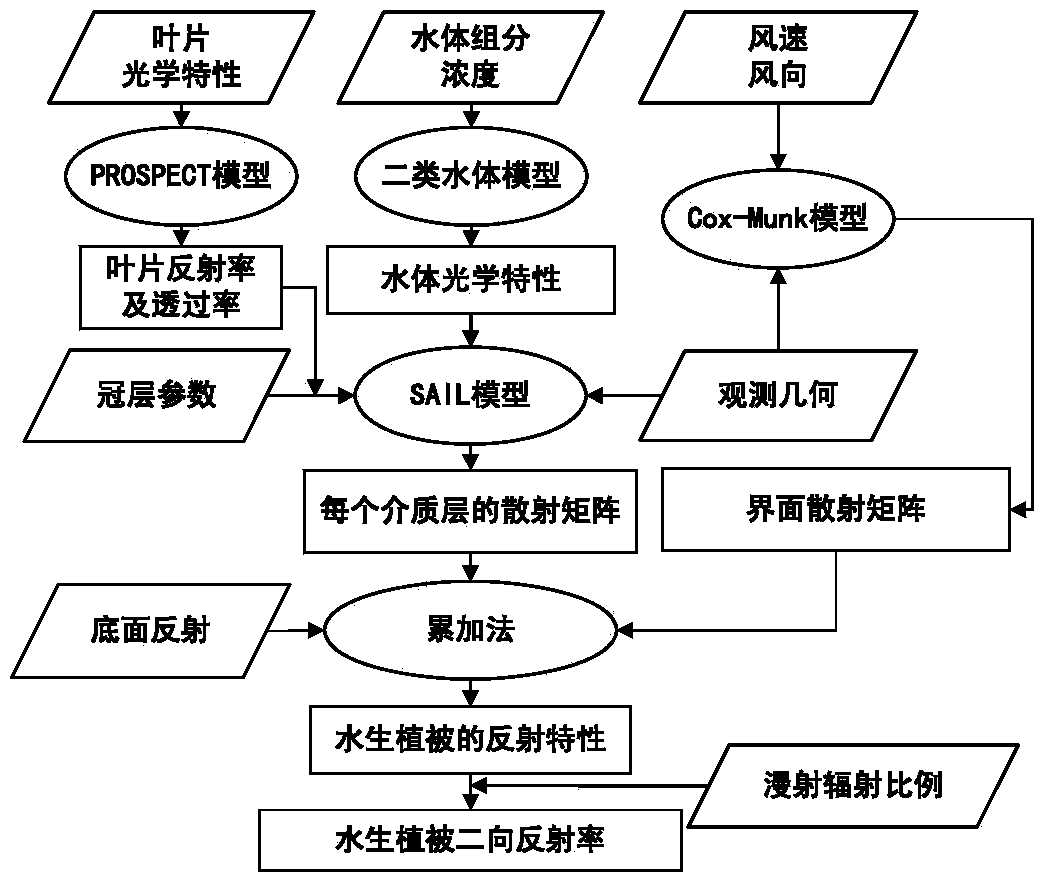
InactiveCN103632040AInnovativePhysical concepts are clearScattering properties measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsExtinctionReflectance spectroscopy
The invention relates to a universal aquatic vegetation radiation transmission model. Building of the model includes the following steps that a whole aquatic vegetation system is divided into a plurality of dielectric layers which are evenly mixed and consistent in horizontal optical properties; vegetation canopy structure parameters, observation geometry and other conditions, and reflectivity and transmittance of a single leaf are input into an SAIL model for calculation extinction and scattering coefficients of a vegetation canopy to radiation, wherein the reflectivity and the transmittance of the single leaf are obtained through calculation of an SPECT model; the water body component concentration is given, absorption and back scattering coefficients of a water body are calculated on the basis of a case 2 water body optical model, and extinction and scattering coefficients of the water body and the vegetation mixed dielectric layers are calculated; according to a Cox-Munk model, scattering matrixes of a wave surface to direct radiation and diffusion radiation are calculated; bidirectional reflectivity of the aquatic vegetation system is calculated according to an adding method. The universal aquatic vegetation radiation transmission model achieves precise description of a reflectance spectrum and directional reflection features of aquatic vegetation, and is the premise and basis of radiation and aquatic vegetation interaction mechanism researches and precise remote sensing inversion of water environment parameters.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
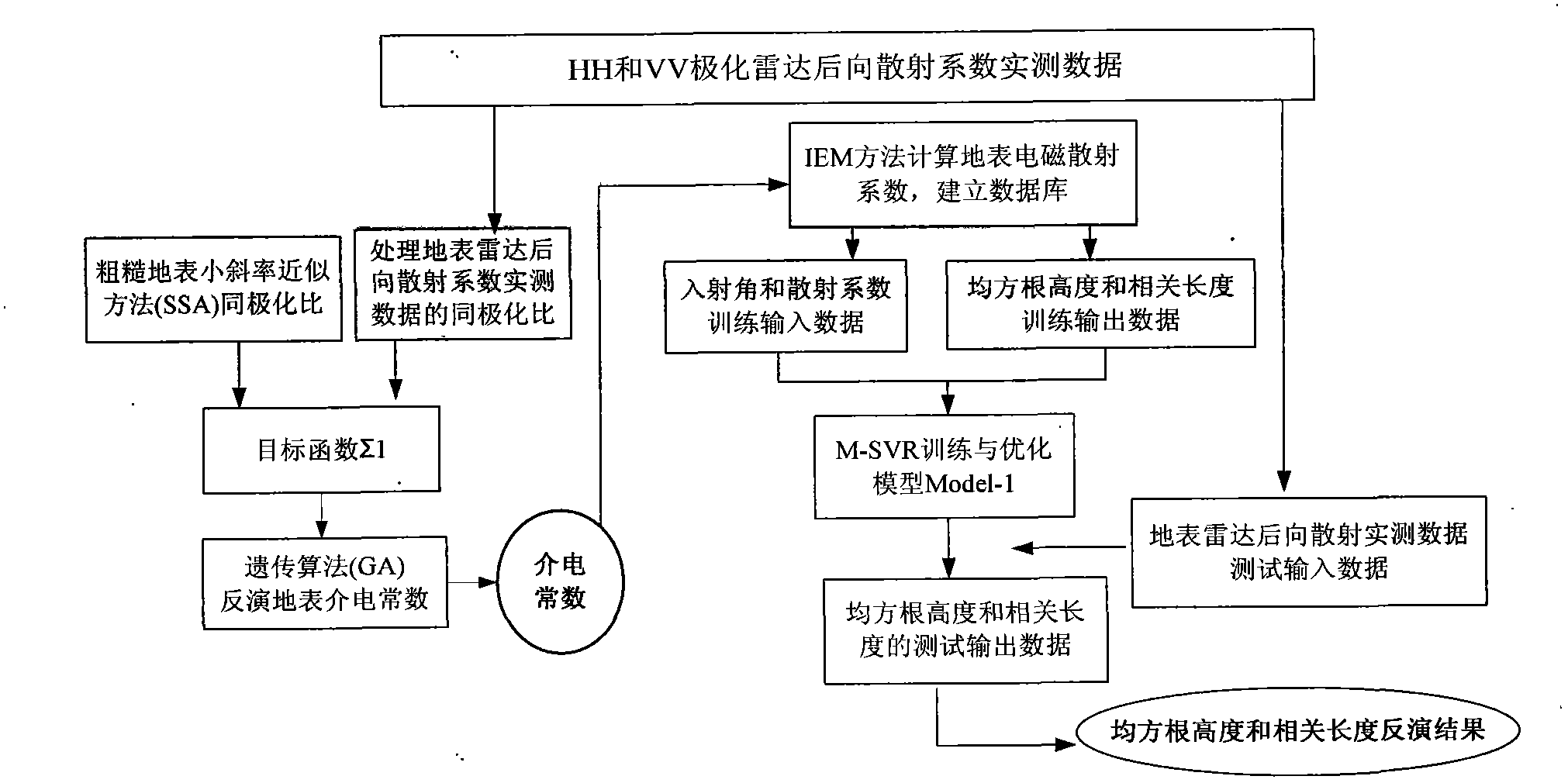
Single-layer earth surface dielectric parameter and roughness parameter fast inversion combined optimization algorithm based on measured radar back scattering data
ActiveCN103617344AEnables real-time forecastingOvercome timeSpecial data processing applicationsSupport vector machineRadar
The invention discloses a combined optimization algorithm of an inheritance multi-output support vector machine. The combined optimization algorithm combines with measured radar back scattering data for fast inversion of single-layer earth surface (root-mean-square height ksigma<1.5, and root-mean-square slope s<0.3) dielectric parameters and roughness parameters. The algorithm includes: using single-layer earth surface HH and VV measured polarizing radar back scattering coefficient data to obtain homo-polarization ratio; using a rough earth surface electromagnetic scattering small slope approximation method to calculate back homo-polarization ratio; combining a genetic algorithm with the small slope approximation homo-polarization ratio and the measured data to invert the earth surface dielectric constant; substituting the inversion result into an electromagnetic scattering integral equation model to generate a data file of back scattering coefficient changing with roughness; combining two kinds of measured polarized radar back scattering data to form a target function, using M-SVR optimization algorithm to invert the earth surface roughness parameters, and evaluating inversion errors and efficiency. By the combined optimization algorithm, real-time prediction of earth surface parameters can be achieved while inversion precision is guaranteed.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
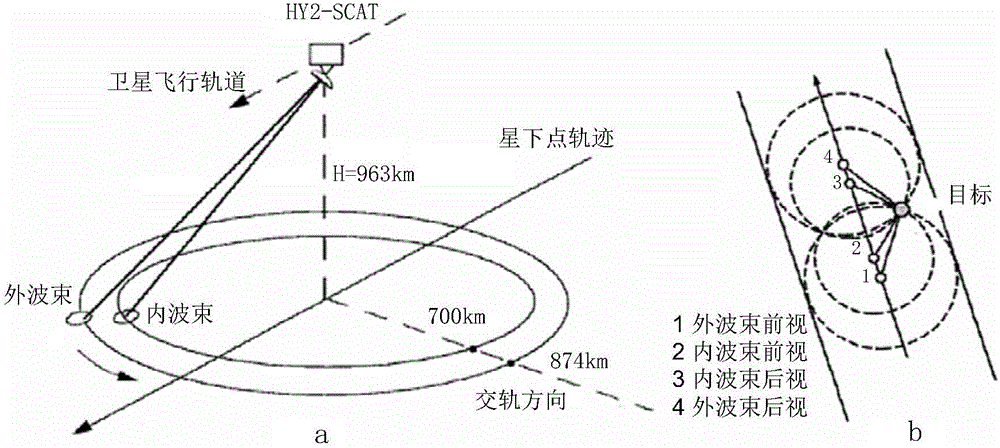
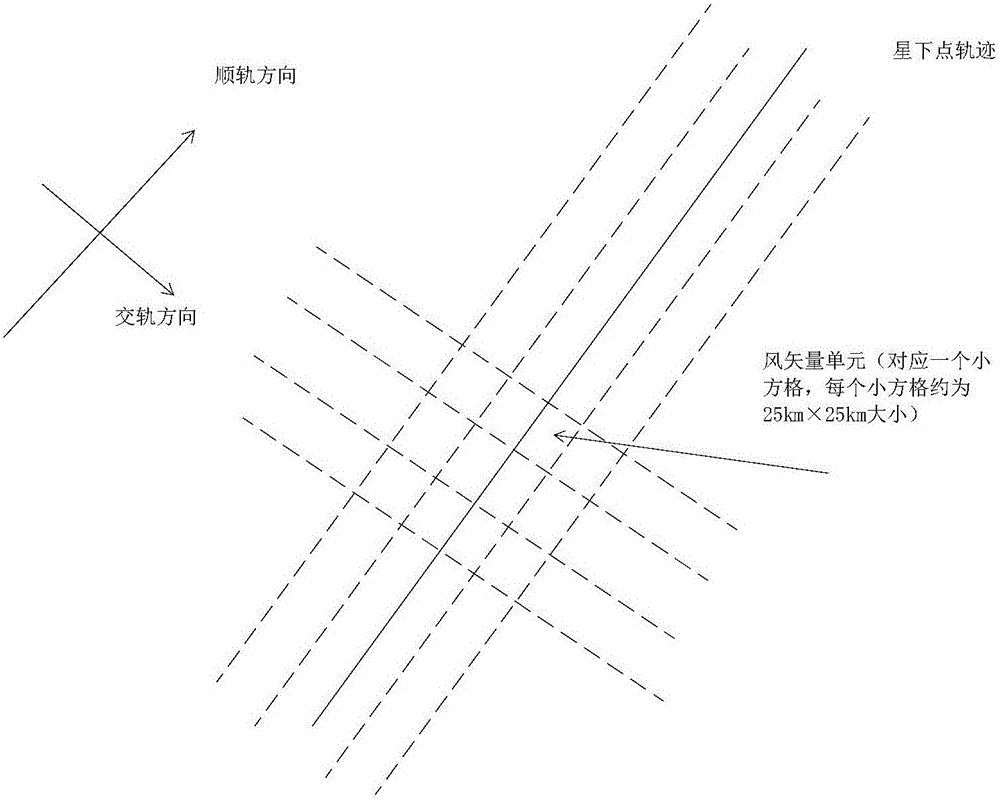
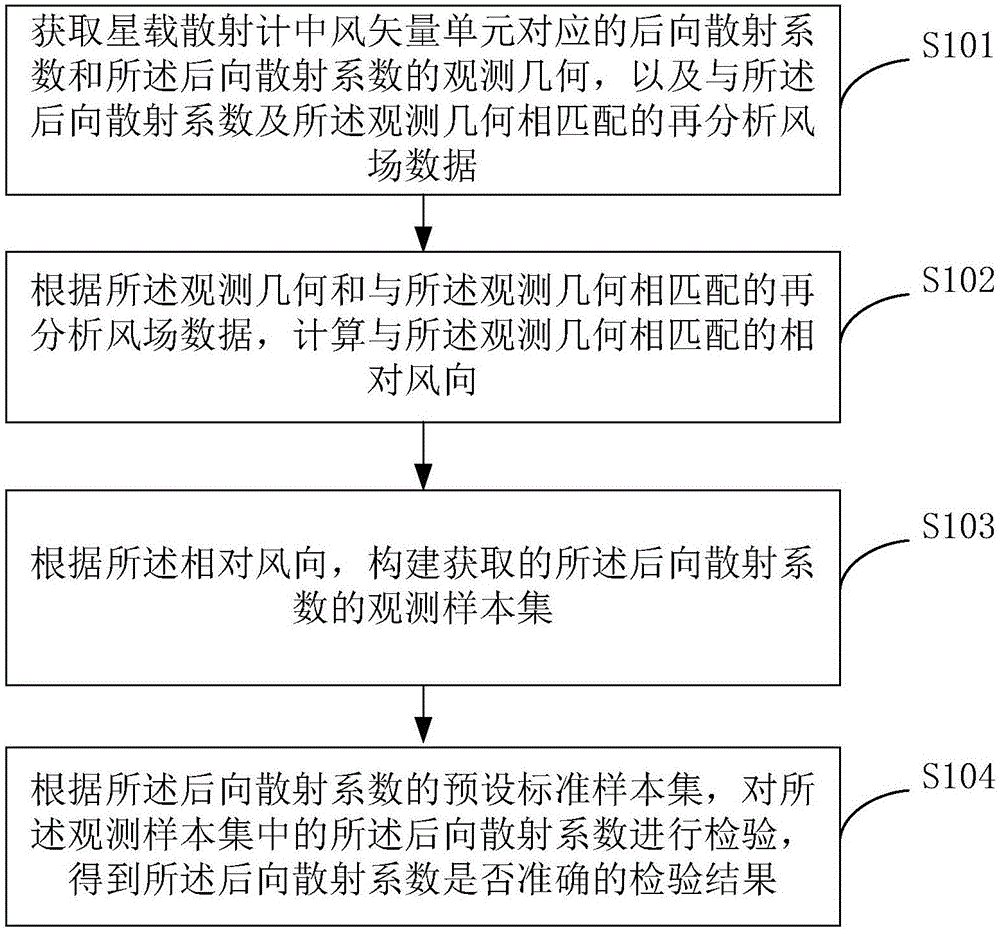
Calibration method and device of back scattering coefficient of space-borne scatterometer
The invention provides a calibration method and device of the back scattering coefficient of a space-borne scatterometer. The calibration method comprises the following steps: obtaining a back scattering coefficient corresponding to a wind vector unit in the space-borne scatterometer, the observation geometry of the back scattering coefficient, and reanalysis wind field data matched with the back scattering coefficient and the observation geometry; according to the observation geometry and the reanalysis wind field data matched with the observation geometry, calculating a relative wind direction matched with the observation geometry; according to the relative wind direction, constructing the observation sample set of the obtained back scattering coefficients; and according to a preset standard sample set, calibrating the observation sample set to obtain a calibration result to show whether the back scattering coefficient measured by the space-borne scatterometer is correct or not. The reanalysis sea surface wind field data is used for developing a quick evaluation method of the back scattering coefficient of the dual-cosine distribution characteristics of the wind direction on the basis of the back scattering coefficient, the quick evaluation of the back scattering coefficient can be realized in short time, evaluation accuracy is high through the reanalysis data, and meanwhile, the evaluation method is high in universality.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE OCEAN APPL SERVICE +1
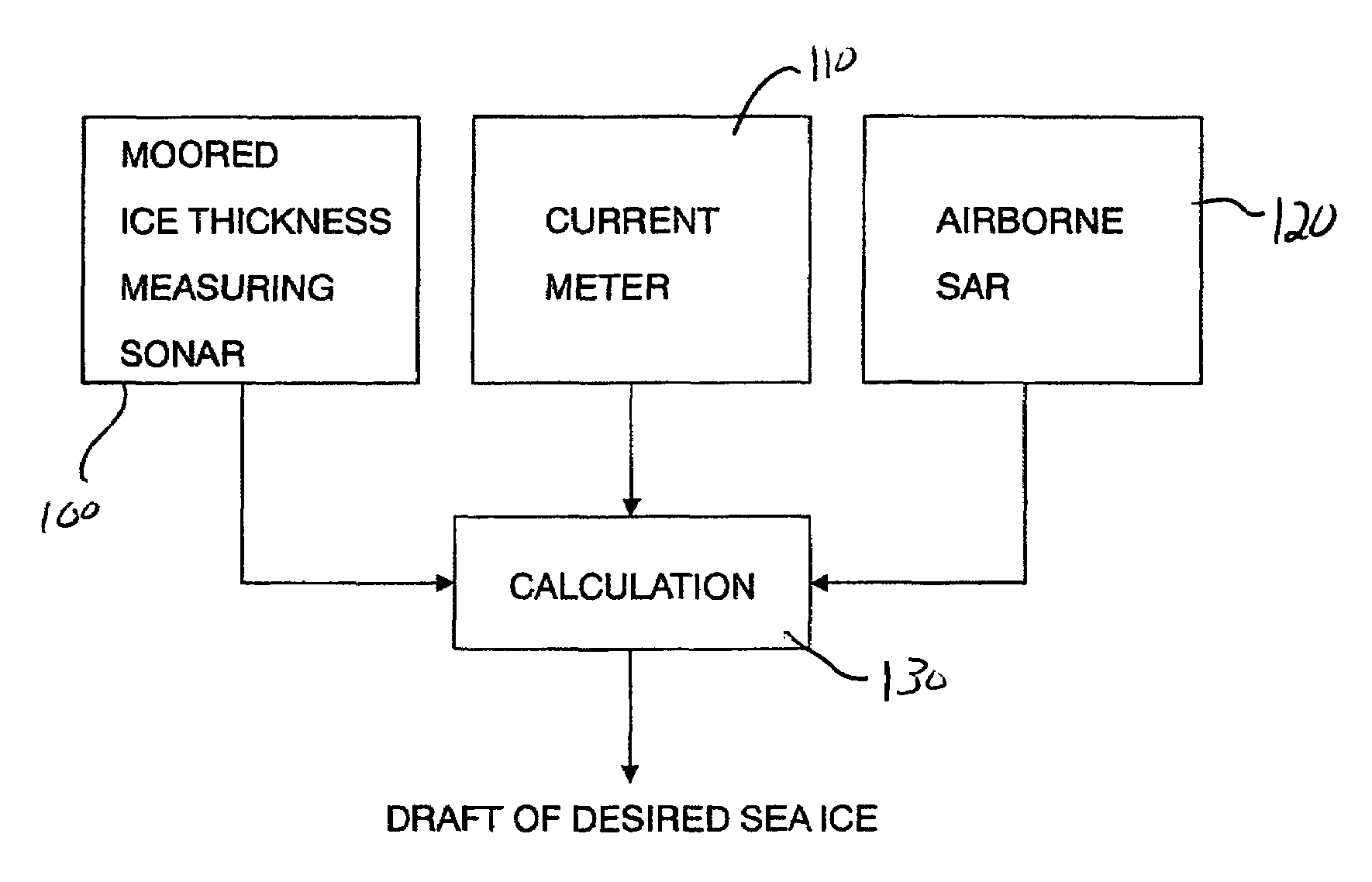
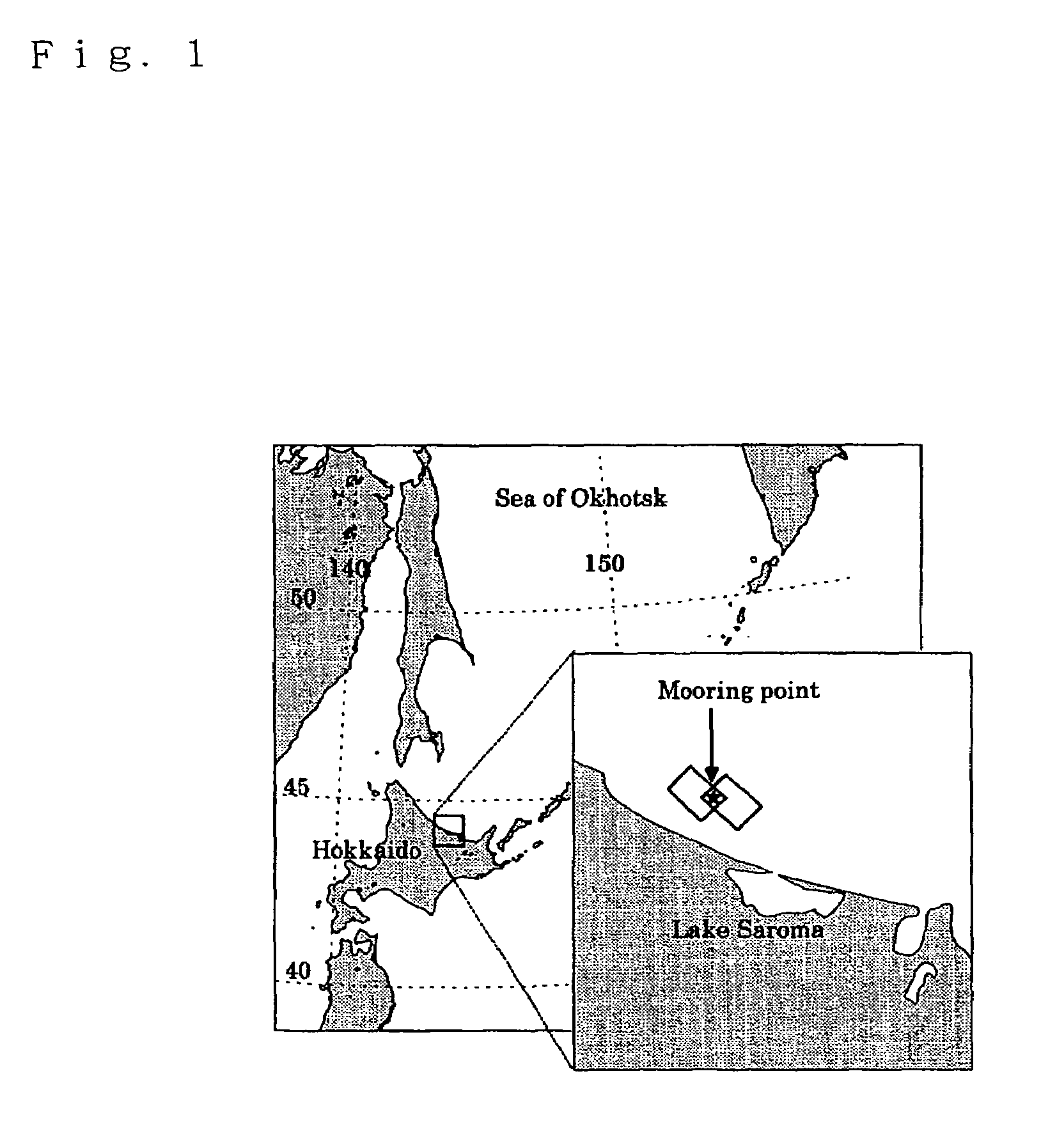
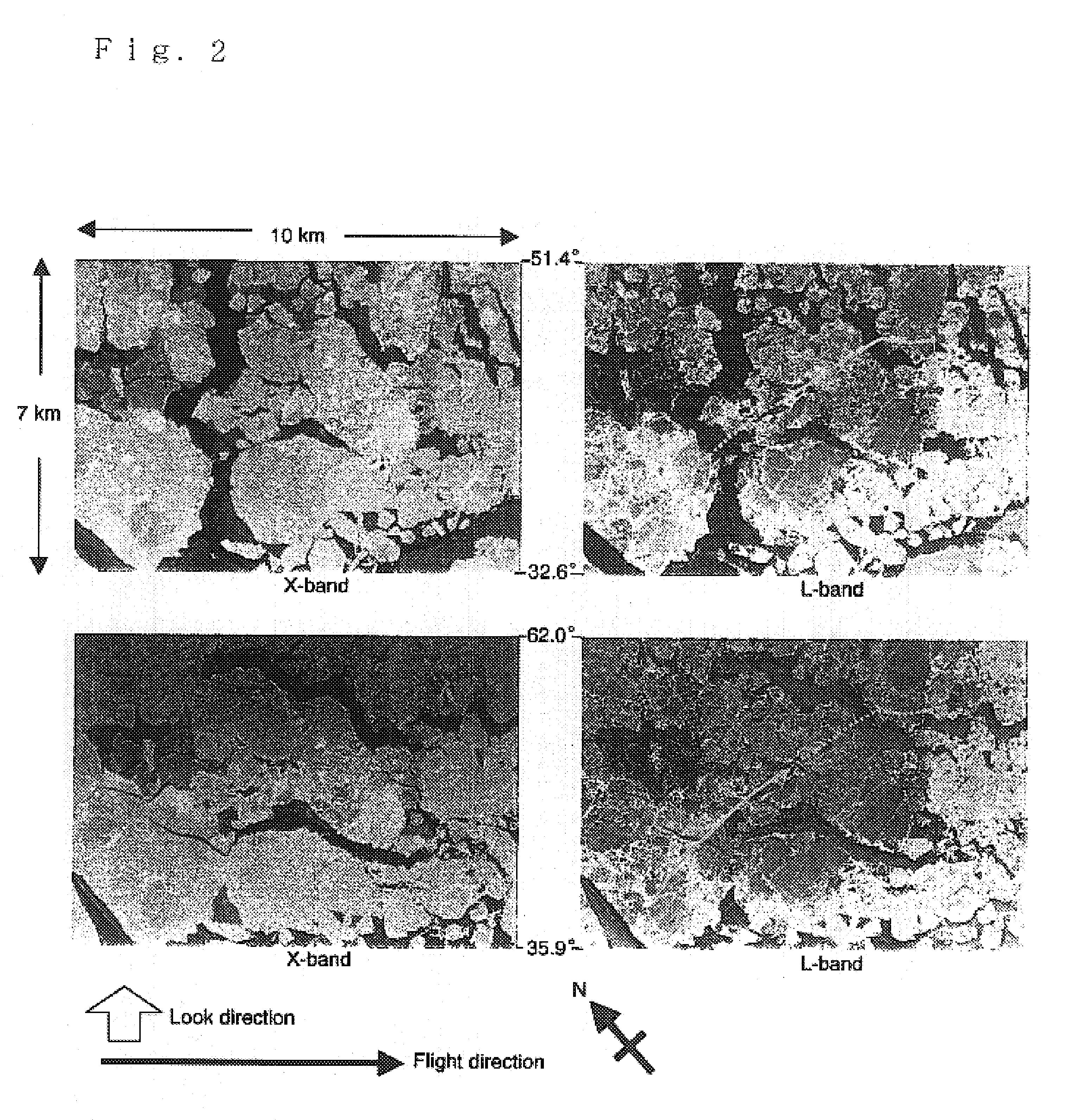
Method of observing sea ice
InactiveUS7095359B2Electric/magnetic detectionSpecial data processing applicationsCurrent meterSonar
An ice thickness / drifting velocity observation of sea ice by using an ice thickness measurement sonar and a current meter moored into the sea and a sea ice observation by a high-resolution airborne SAR are synchronously performed, a correlation between a draft profile of sea ice passing over the sonar and an SAR backscattering coefficient profile is calculated, and an ice draft of desired sea ice is calculated from the relational expression and an SAR backscattering coefficient. As the SAR backscattering coefficient, a backscattering coefficient of L-band HV polarization may be used. A backscattering coefficient of X-band VV polarization is preferably used as the SAR backscattering coefficient to detect thin ice having a thickness of not more than approximately 10 cm.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH +2
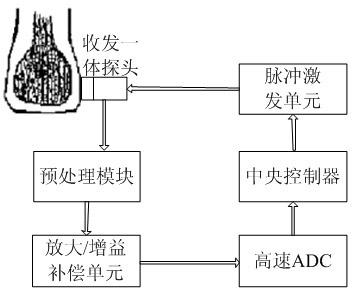
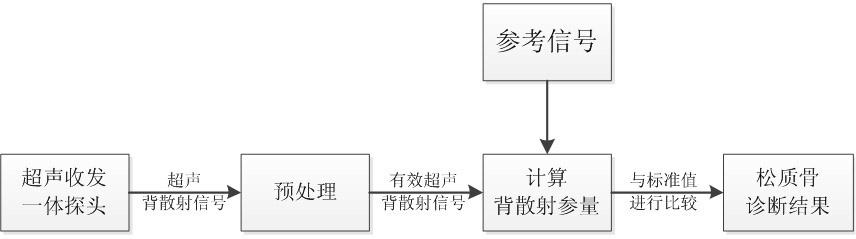
Cancellous bone diagnosis system based on ultrasound backscattering signal parameters
InactiveCN102198009AOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniquesCalcaneusSonification
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical ultrasonography, and particularly relates to a cancellous bone diagnosis system based on ultrasound backscattering signal parameters. The system comprises an ultrasound backscattering signal acquisition module, a pretreatment module, a backscattering parameter calculation module and a cancellous bone state evaluation module. In the invention, an ultrasound transceiver probe is used to acquire ultrasound backscattering signals from the calcaneus of a human body; effective cancellous bone ultrasound backscattering signals are extracted; the calculation module is used to calculate four parameters, i.e. backscattering coefficient, apparent integration backscattering coefficient, spectral centroid shift and mean trabecular bone spacing; and finally, the health state of the cancellous bone is analyzed by comparing the four parameters with standard values stored in an internal standard database in the system. Compared with the traditional ultrasound transmission diagnosis system based on broadband ultrasound attenuation and ultrasound propagation velocity, the diagnosis system provided by the invention can obtain the complete information of the cancellous bone structure, thereby better detecting the health state of the cancellous bone of a human body.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
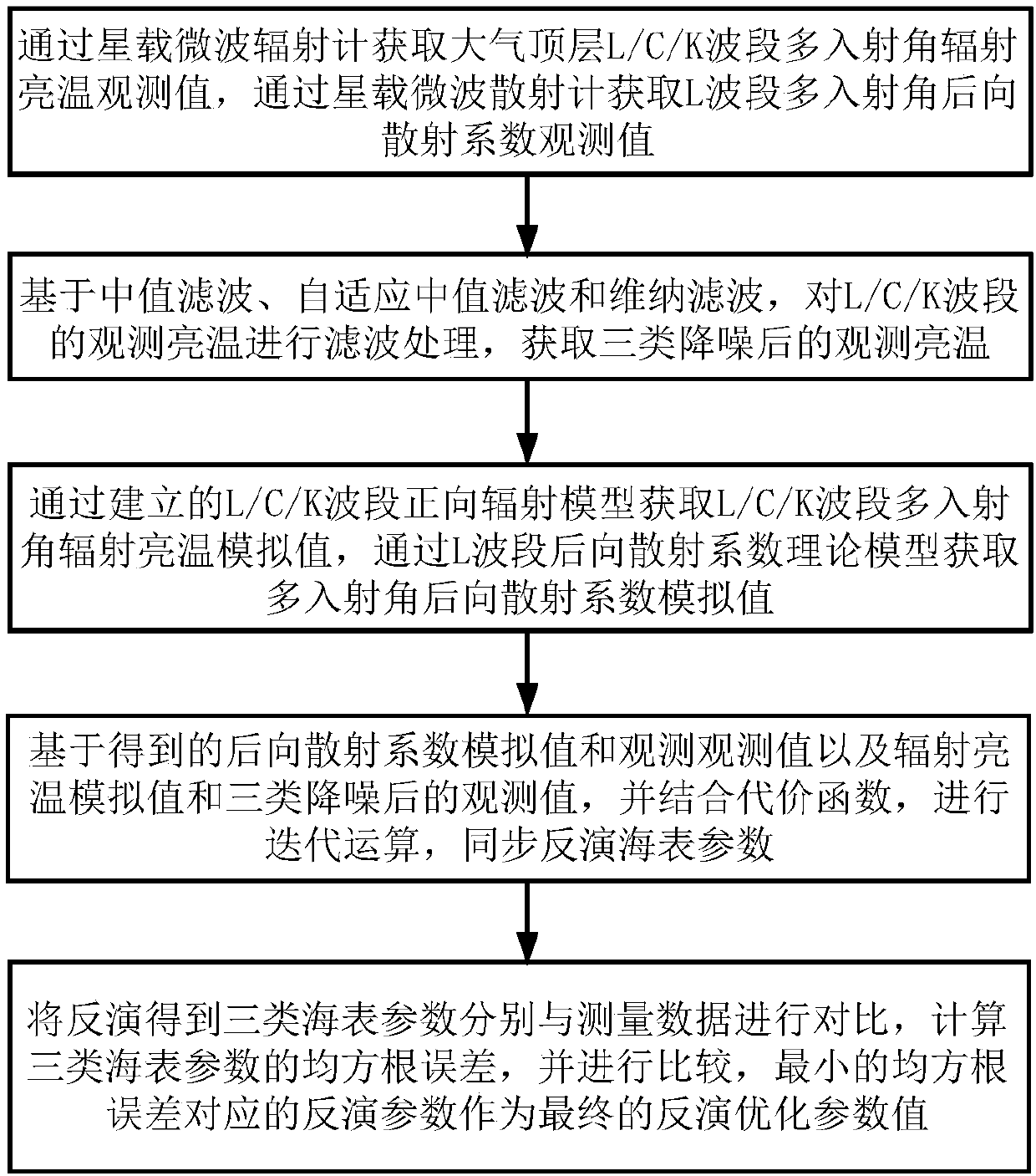
Sea surface parameter synchronous inversion optimization method
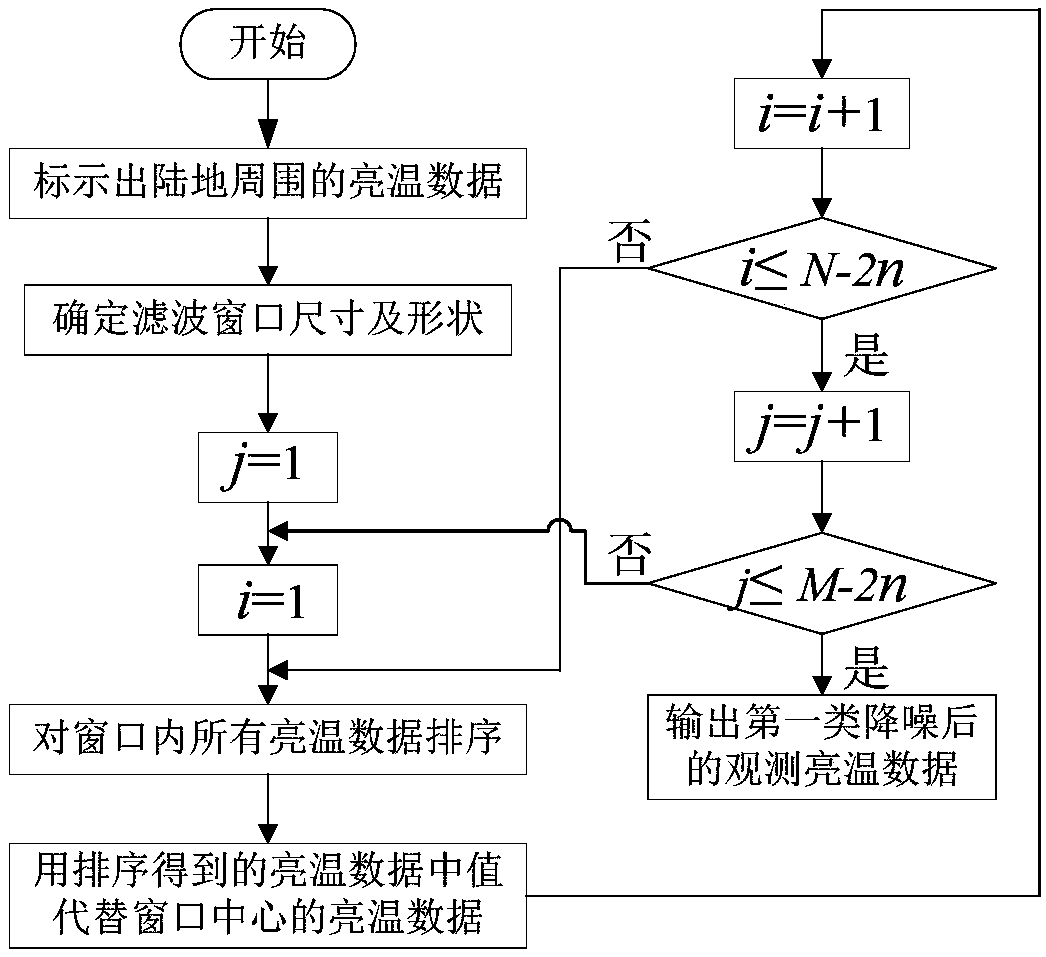
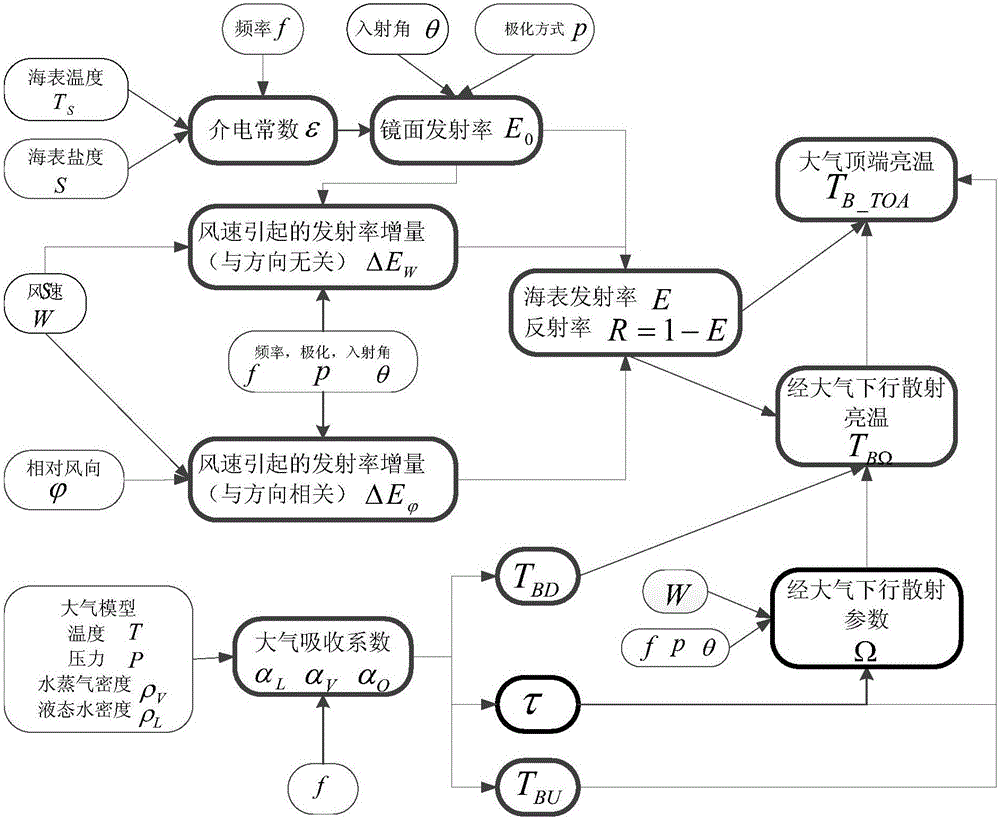
InactiveCN107870043AReduce inversion errorHigh salinityMaterial analysis using microwave meansFluid speed measurementBrightness temperatureAtmospheric sciences
The invention provides a sea surface parameter synchronous inversion optimization method which includes the steps: 1) acquiring multi-incident-angle radiation brightness temperature observation valuesand multi-incident-angle backscattering coefficient observation values; 2) performing median filtering, adaptive median filtering and Wiener filtering on the multi-incident-angle radiation brightnesstemperature observation values to obtain three-type radiation brightness temperature observation values after noise reduction; 3) acquiring multi-incident-angle radiation brightness temperature simulation values by a forward radiation brightness temperature theoretical model, and acquiring multi-incident-angle backscattering coefficient simulation values by a backscattering coefficient theoretical model; 4) substituting the three-type radiation brightness temperature observation values, the radiation brightness temperature simulation values, the backscattering coefficient observation values and the backscattering coefficient simulation values into an L / C / K waveband multi-priced function to synchronously obtain three-type sea surface parameters; 5) comparing the three-type sea surface parameters with float measurement sea surface parameters, calculating inversion root-mean-square errors and selecting sea surface parameter values corresponding to the minimum root-mean-square error as final sea surface parameter values.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
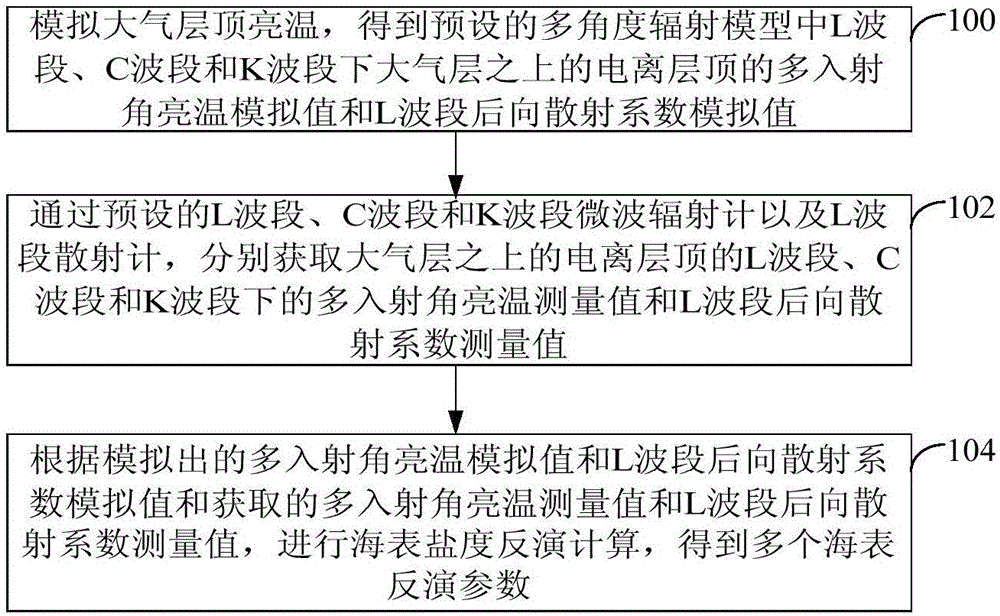
Sea surface salinity retrieval method and device
InactiveCN105760699AImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsBrightness temperatureMicrowave radiometer
The invention provides a sea surface salinity retrieval method and a sea surface salinity retrieval device. The sea surface salinity retrieval method comprises the following steps: simulating atmosphere top brightness temperature so as to acquire a multi-incident angle brightness temperature simulation value of an ionopause above the atmosphere layer at an L wave band, a C wave band and a K wave band of a preset multi-angle radiation model, and a backscatter coefficient simulation value of the L wave band; respectively acquiring a multi-incident angle brightness temperature measuring value of the ionopause above the atmosphere layer at the L wave band, the C wave band and the K wave band, and a backscatter coefficient measuring value of the L wave band; performing sea surface salinity retrieval calculation according to the simulated multi-incident angle brightness temperature simulation value and the backscatter coefficient simulation value of the L wave band, and the acquired multi-incident angle brightness temperature measuring value and the backscatter coefficient measuring value of the L wave band. By adopting the sea surface salinity retrieval method, the accuracy rate of the retrieval calculation result can be improved.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS +1
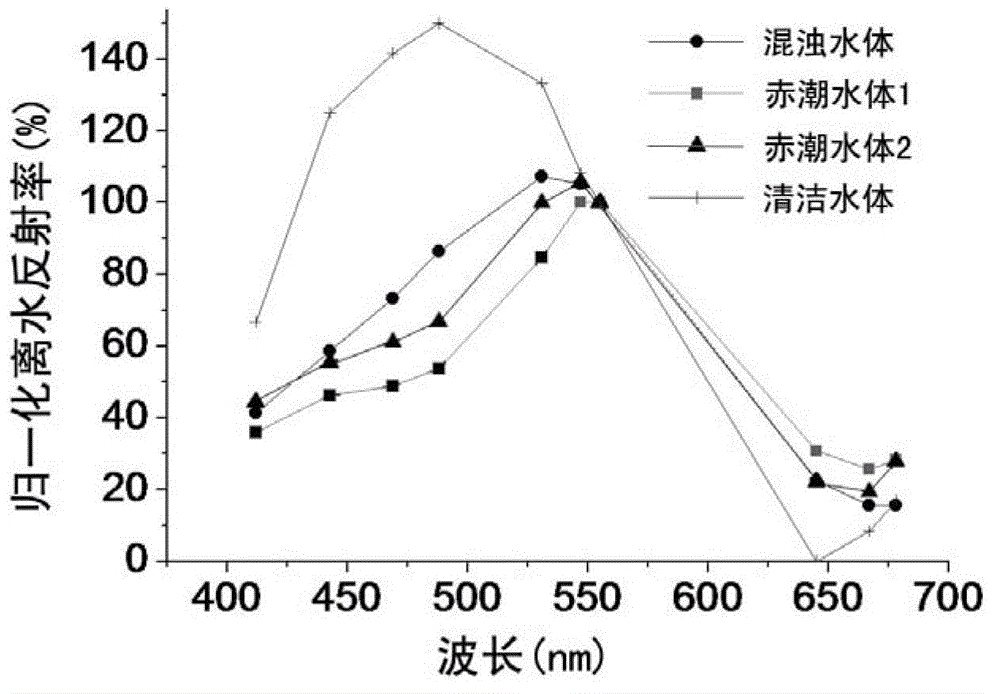
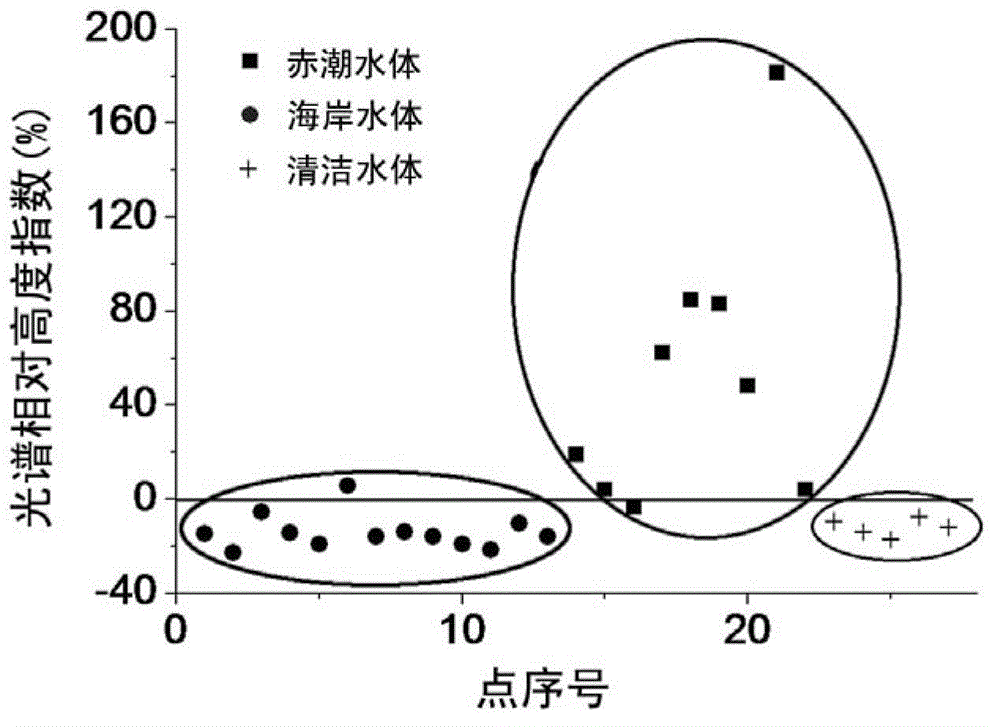
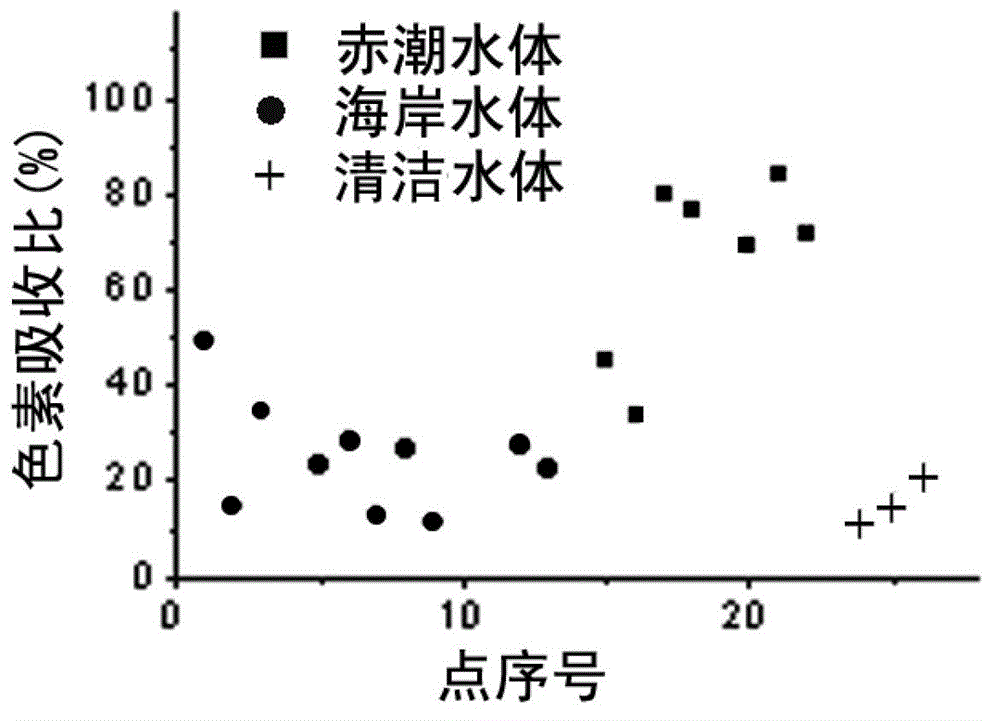
Method for distinguishing marine red tide algaes by using MODIS ocean color remote sensing data
InactiveCN102914505AEffectively eliminate interferenceEasy to distinguishColor/spectral properties measurementsBackscatter coefficientRed tide
The invention discloses a method for distinguishing marine red tide algaes by using MODIS ocean color remote sensing data. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring the data of a MODIS ocean color remote secondary product to calculate the relative height indexes of a spectrum; secondly, using an inverse absorbing coefficient and a backscattering coefficient of the MODIS ocean color remote secondary product to calculate the spectrum ratio, and then using the index methods of the relative height indexes of the spectrum and the fixed optical quantity to identify the red tide water regions; and finally combining the unit logarithmic pigment proportion, the chlorophyll ratio absorbance coefficient and the back scattering ratio to judge the algaes. According to the method, the information difference between the difference wave bands in the ocean color remote sensing data is utilized to simply and legibly judge and provide the red tide suspected regions and the suspected algaes in the marine region.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
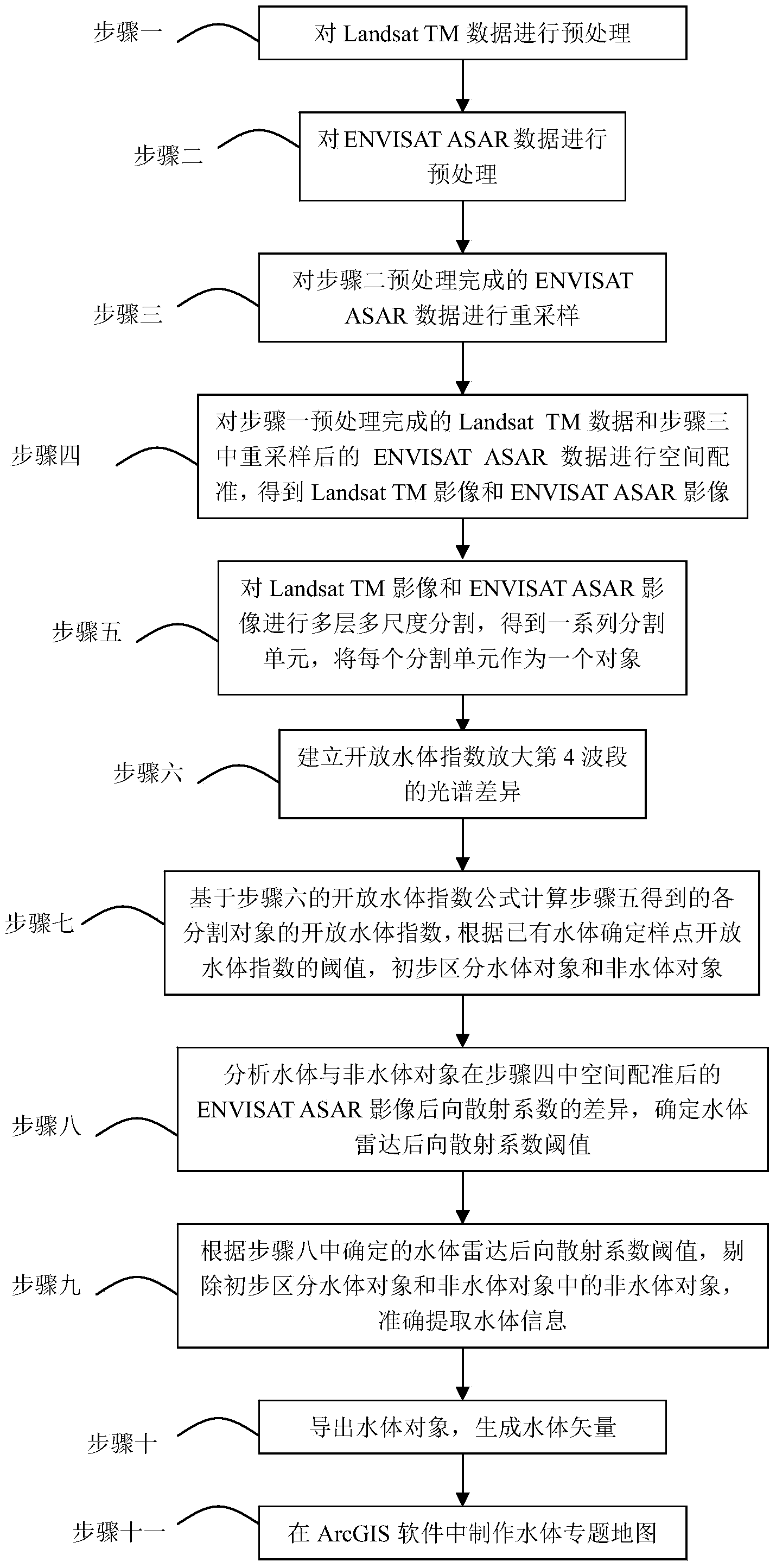
Object-oriented water-body extracting method based on ENVISAT ASAR and Landsat TM remote sensing data
InactiveCN104217426AAutomatic fast and accurate extractionSolve problems such as not having clear geographical significanceImage analysisSpecial data processing applicationsSensing dataOpen water
The invention discloses an object-oriented water-body extracting method based on ENVISAT ASAR and Landsat TM remote sensing data, and relates to an object-oriented remote sensing image sorting method based on ENVISAT ASAR and Landsat TM remote sensing image data. The invention aims at overcoming the problems that the existing method for extracting water-body information by remote sensing images is low in extraction precision, complex and difficult to operate. The method comprises the steps of: 1 and 2, preprocessing data; 3, resampling ENVISAT ASAR data; 4, performing space rectification on data; 5, performing multi-level multi-scale segmentation on images; 6, establishing an open water-body index to amplify spectrum difference of a fourth wave band; 7, tentatively distinguishing water-body objects and non-water-body objects; 8, determining a water-body radar backscattering coefficient threshold value; 9, accurately extracting water-body information; 10, leading out the water-body objects, and generating water-body vectors; and 11, making a water-body thematic map.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
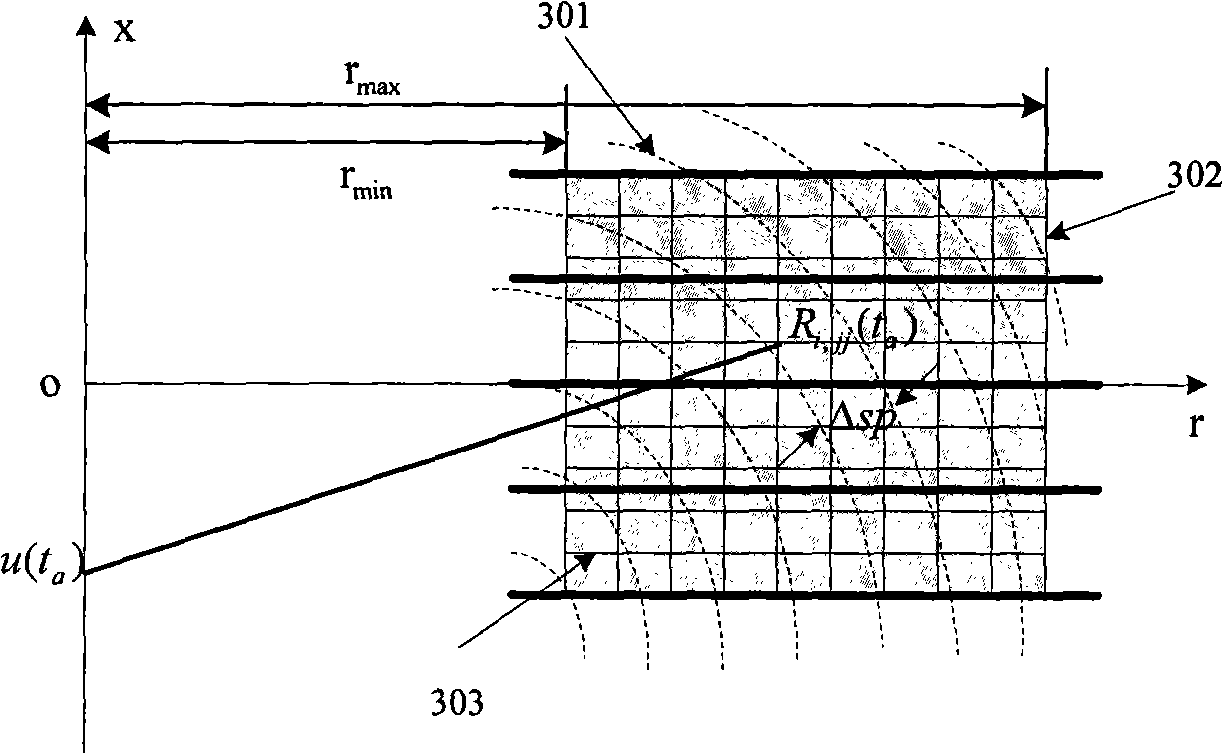
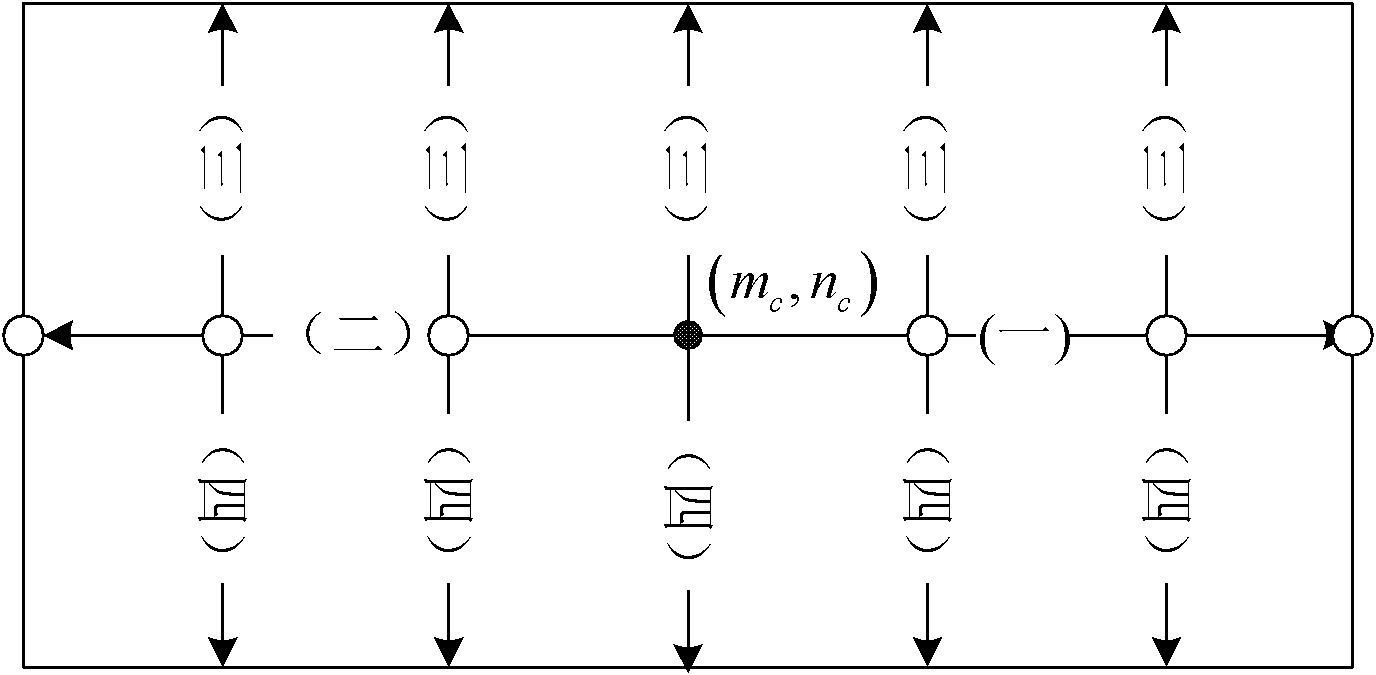
Method for quickly simulating airborne phased array pulse Doppler (PD) radar clutter
ActiveCN103207387AReduce in quantityImprove Simulation EfficiencyWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsSynthetic aperture radar
The invention provides a method for quickly simulating airborne phased array pulse Doppler (PD) radar clutter. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image; dividing the whole clutter scene into rectangular scattering units, and regarding each scattering unit as a point scattering body distributed in the center of the unit; acquiring the initial backscattering coefficient of each scattering unit; dividing the clutter scene into equidistant rings; upsampling a transmitted signal of a PD radar, and performing fast Fourier transform (FFT) on an upsampling result to obtain U(omega); calculating the amplitude A of each scattering unit; calculating the radar backscattering coefficient of each equidistant ring; acquiring an impulse response function of a system, and performing FFT on the function to obtain H(omega); and multiplying U(omega) by H(omega), and performing inverse FFT on a multiplication result to obtain a clutter signal received in a period corresponding to a transmitted pulse. By the method, natural scene clutter is quickly simulated in the airborne PD radar system under the condition of high resolution.
Owner:北京理工雷科电子信息技术有限公司
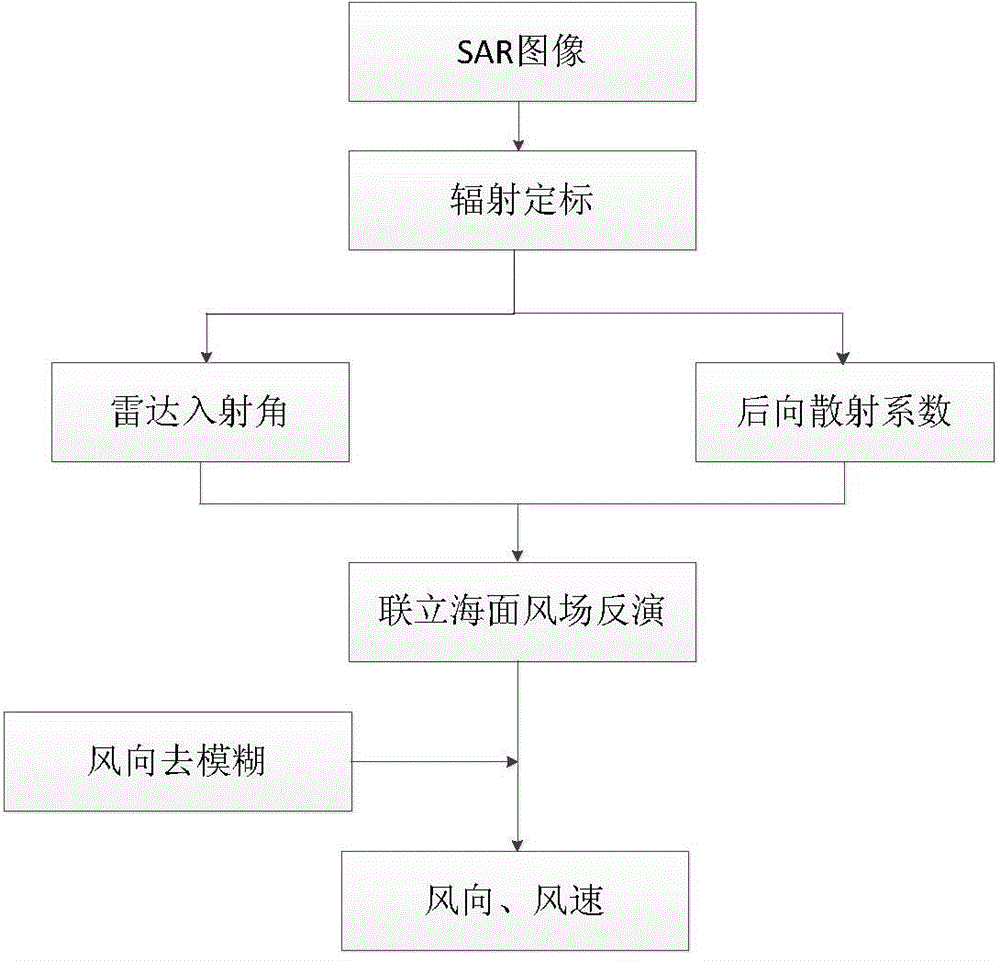
Ocean wind-field retrieval method of double-frequency coplanar synthetic aperture radar (SAR)
The invention discloses an ocean wind-field retrieval method of a double-frequency coplanar synthetic aperture radar (SAR), relates to the technical field of remote sensing, and aims at developing a new ocean wind-field retrieval method according to the ocean detection characteristics of the double-frequency coplanar SAR. The method comprises the steps of performing radiometric calibration for an SAR image to obtain the calibrated SAR image; analyzing calculating backscattering coefficients through L-waveband and C-waveband geophysical model functions; then performing simultaneous restructuring for the L-waveband and C-waveband geophysical model functions to obtain the minimum cost functions; directly solving to obtain the ocean wind speed and wind direction; removing fuzzy wind direction. With the adoption of the method, the problem that the SAR ocean wind-field retrieval method depends on the background field wind direction data and wind stripes can be effectively solved, high-precision ocean wind speed and wind direction can be inverted directly through the back scattering of the radar, and therefore, the support is provided to the service application of the SAR ocean wind-filed detection.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fast Realization method for simulation 3D scene SAR radar echo based on forward method
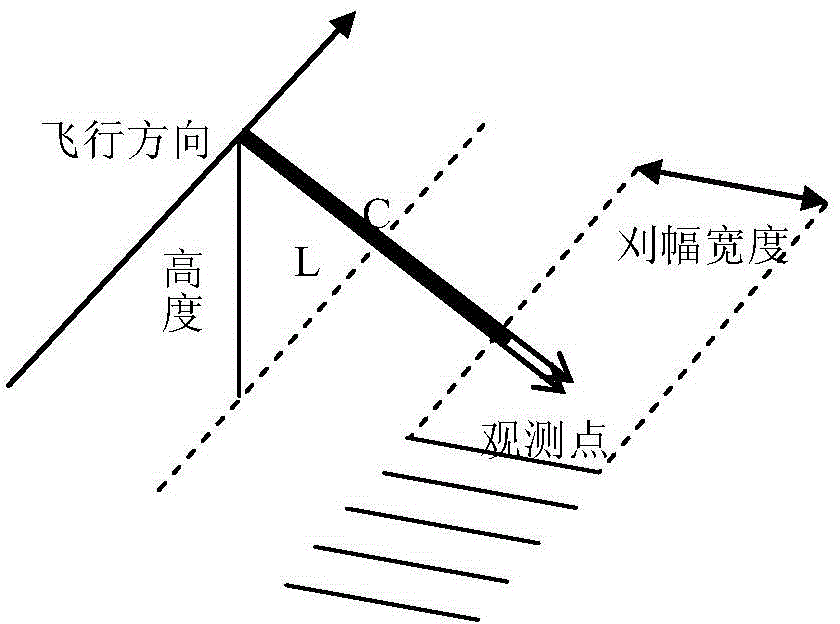
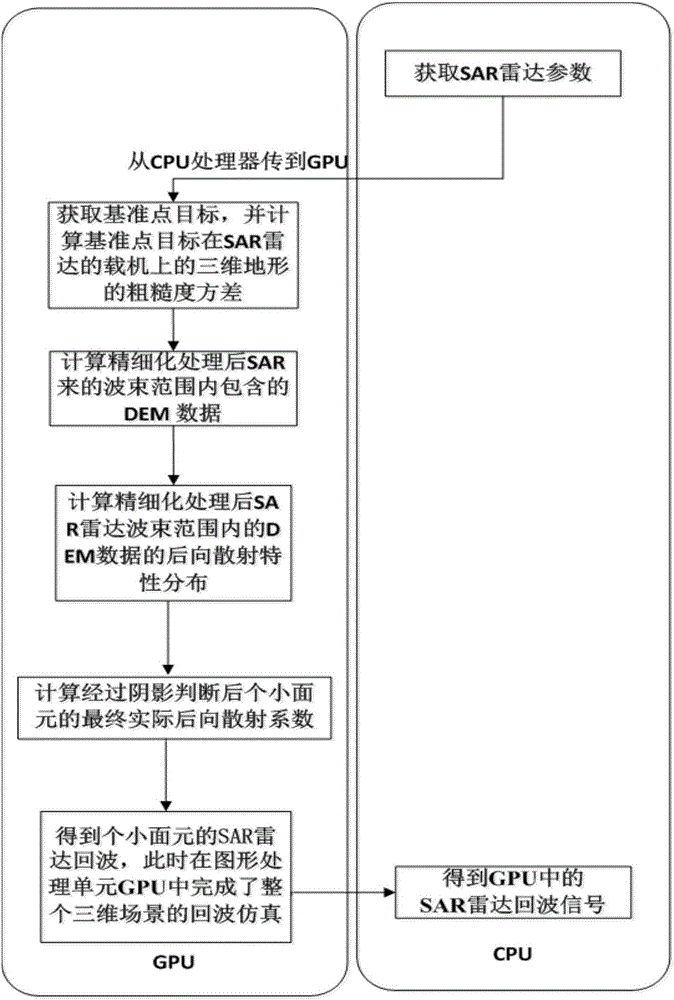
InactiveCN106324571AMeet real-time processing needsGuaranteed Simulation AccuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionProperty distributionMain processing unit
The invention discloses a fast Realization method for simulation 3D scene SAR radar echo based on forward method. The main idea of the fast Realization method comprises the following steps: acquiring digital elevation model (DEM) data within SAR radar beam range, wherein the data comprises K point targets; randomly distributing the K point targets on a 2D ground in the geographic coordinate system, and calculating DEM data within the SAR radar beam range after refinement processing; acquiring back scattering property distribution of the DEM data within the SAR radar beam range after refinement processing; utilizing an improved downward angle comparison method to determine shaded areas of Q small surface elements, calculating final actual back scattering coefficients of the Q small surface elements after shaded area determination, and then calculating SAR radar echo of the Q small surface elements. At this time, the whole 3D scene echo simulation is completed in a graphic processing unit (GPU), and finally an echo signal in the GPU is sent to a CPU processor to be output.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for measuring aerosol parameters by lateral laser radar based on CCD (charge-coupled device) imaging technology
InactiveCN103344611AEasy to measure aerosol parametersAccurate measurement of aerosol parametersScattering properties measurementsOptoelectronicsCcd camera
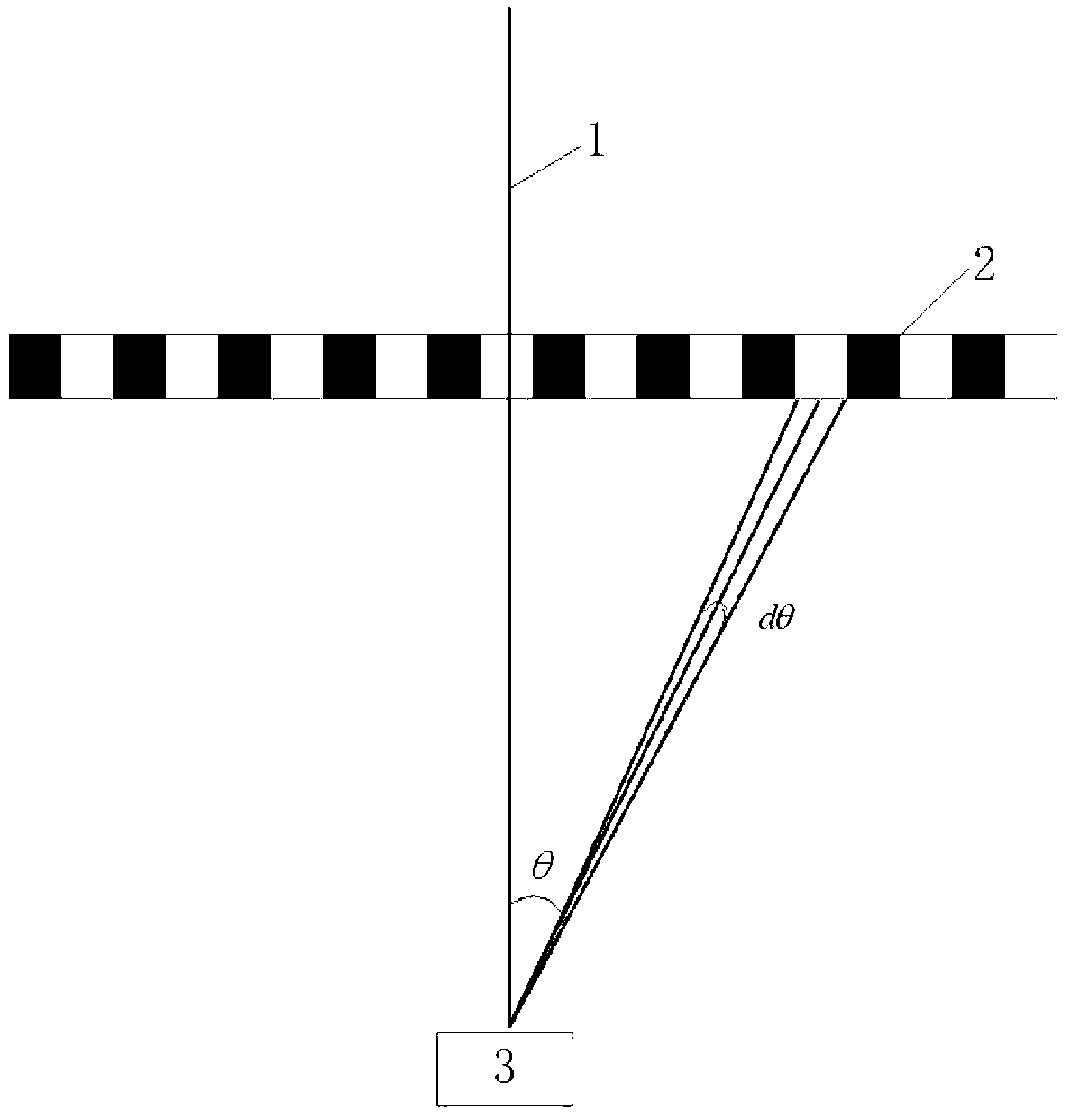
The invention discloses a method for measuring aerosol parameters by a lateral laser radar based on a CCD (charge-coupled device) imaging technology. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, selecting a phase-comparison function value of aerosol to atmospheric molecules of a reference point in a horizontal direction; determining and affirming that a backscatter coefficient value of the aerosol on the reference point is equal to that at each scattering angle; inserting the drift angle (theta) and the angle width (dtheta) with each pixel of a CCD camera, and the vertical distance (D) between the CCD camera (3) and a beam (5) emitted by the laser radar into a lateral laser radar equation shown in the description; taking the adjacent point as a new reference point after solving the phase-comparison function of the aerosol on the adjacent point from the value, gradually solving until a profile of the phase-comparison function of the aerosol is obtained; then affirming that the obtained phase-comparison function value of the aerosol in the horizontal direction is equal to that in the vertical direction, measuring the backscatter coefficient value of the aerosol at one height as the reference point, and obtaining the profile of the backscatter coefficient value of the aerosol by adopting the method. Therefore, the aerosol parameters conforming to the actual condition can be measured.
Owner:中国人民解放军陆军军官学院
Method for simulating three-dimensional land scene echoes of interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR)
InactiveCN101876704AGive full play to the advantagesImprove operational efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarGeometric modeling
The invention provides a method for simulating three-dimensional land scene echoes of an interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR), comprising the following steps of: firstly, performing geometric modeling on three-dimensional land scenes and dividing the three-dimensional land scenes into facets which are adjacent to each other; then, performing electromagnetic modeling by using the facets as scatterers and calculating backscattering coefficients of the scatterers; and finally, generating echoes in parallel by calculating a single echo according to a signal model of an InSAR system. The invention has small amount of calculation and can finish calculation within a shorter time under the traditional calculation capability in a parallel calculation mode. Moreover, the invention has high calculation accuracy and can meet requirements of the InSAR for simulation and research.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
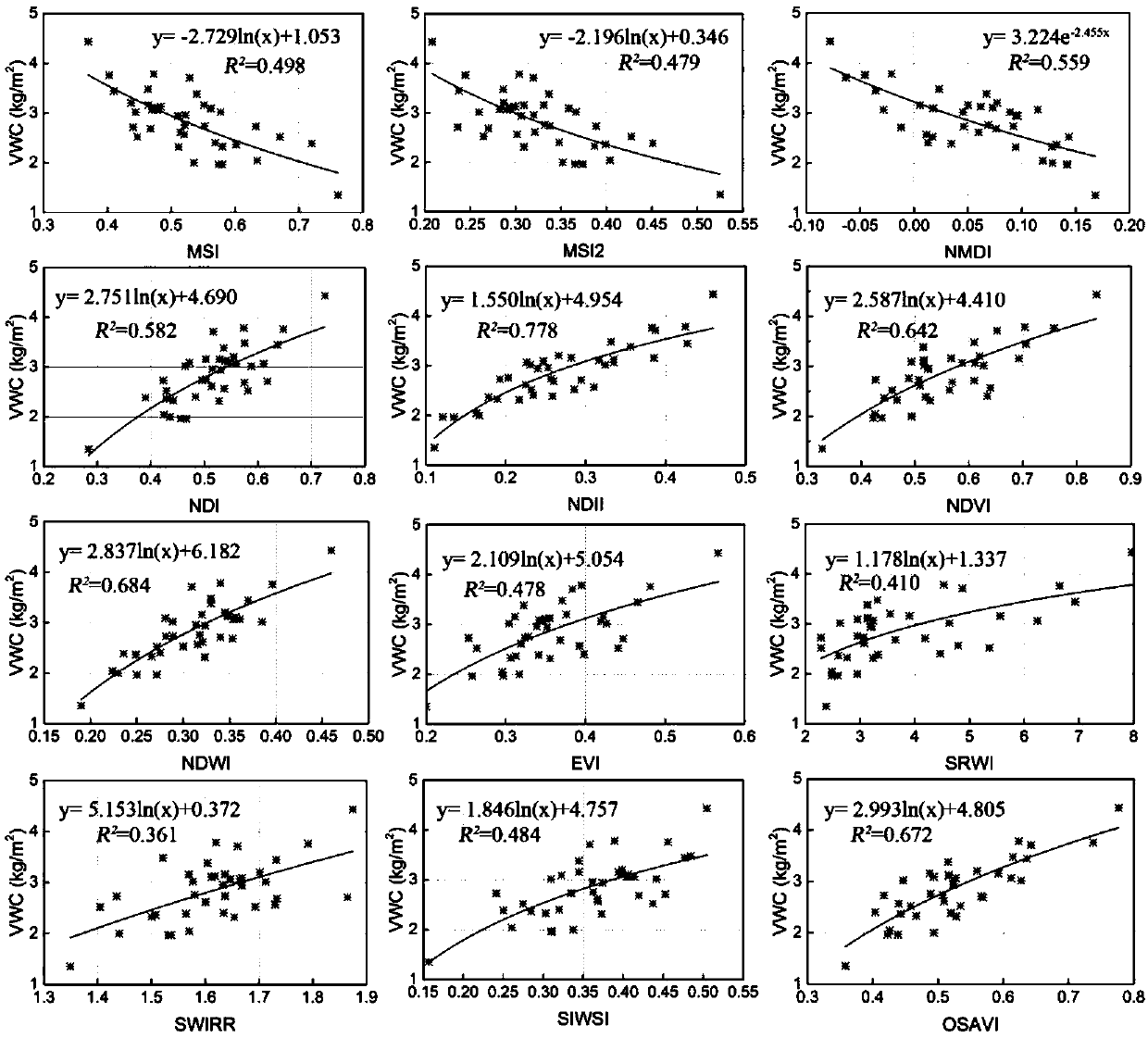
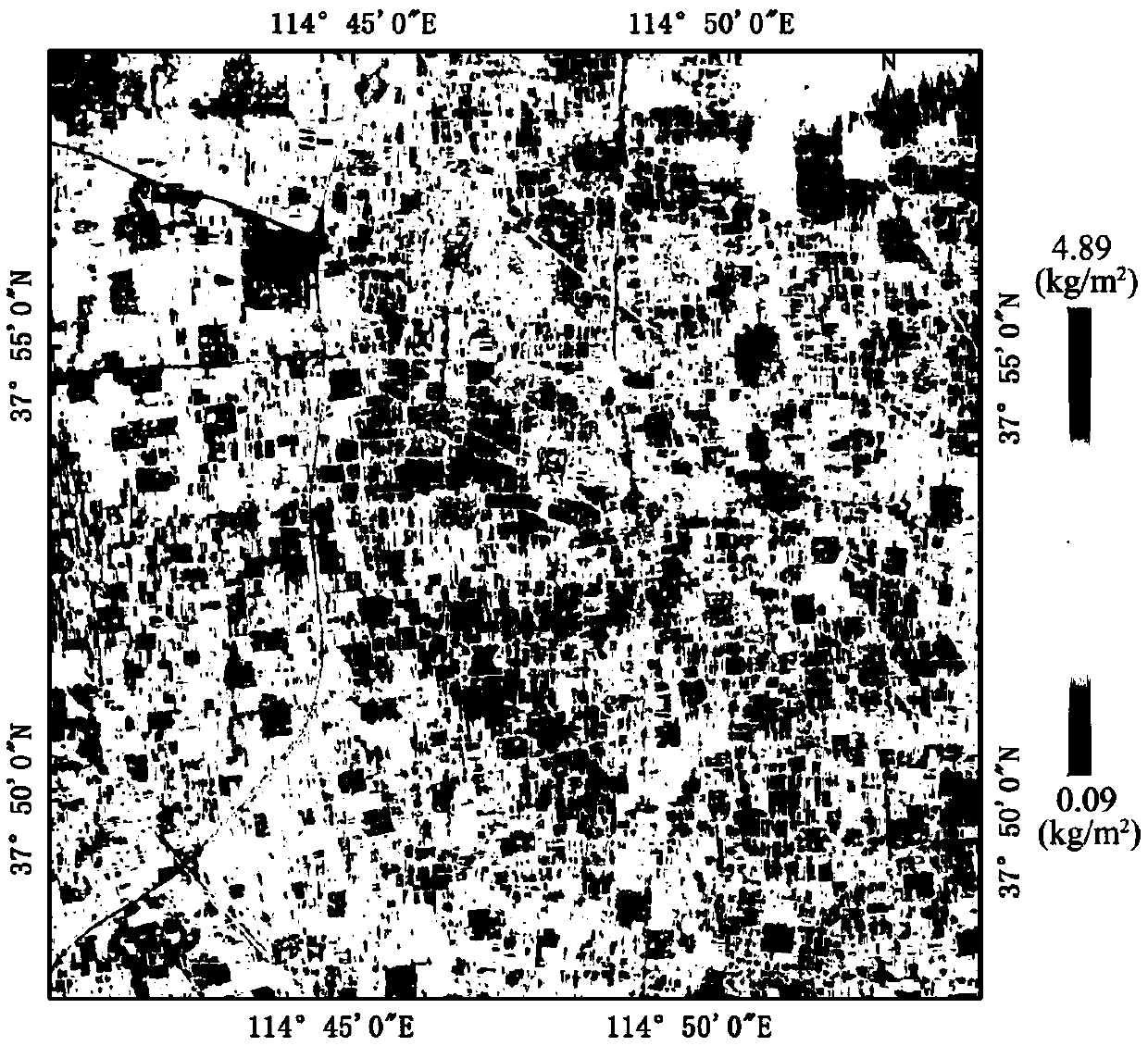
Vegetation coverage area soil moisture inversion method based on Gaofen-3 satellite data
InactiveCN108681652AWave based measurement systemsDesign optimisation/simulationSatellite dataSoil science
Aiming at the first C-band SAR satellite independently developed by China and the problem that the inversion accuracy of soil moisture in the vegetation coverage area is low, the invention discloses avegetation coverage area soil moisture inversion method based on Gaofen-3 satellite data, which can realize the high-precision inversion of soil moisture in the vegetation coverage area. The method comprises the following steps: step 1) the best optical vegetation index suitable for the study area is preferentially selected to realize the vegetation moisture inversion; step 2) a co-polarization backscatter coefficient database is simulated according to the payload characteristics of the Gaofen-3 satellite and in combination with the AI EM model; step 3) the backscatter coefficient of bare soil after correcting the influence of vegetation optical thickness is calculated based on the improved water cloud model; and step 4) based on the newly established cost function Z, the difference of data in HH and VV polarization two channels is minimized simultaneously, and the nearest backscatter coefficient is obtained by matching, and the corresponding soil moisture is taken as the soil moisture of the pixel to realize the soil moisture inversion in the vegetation coverage area.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
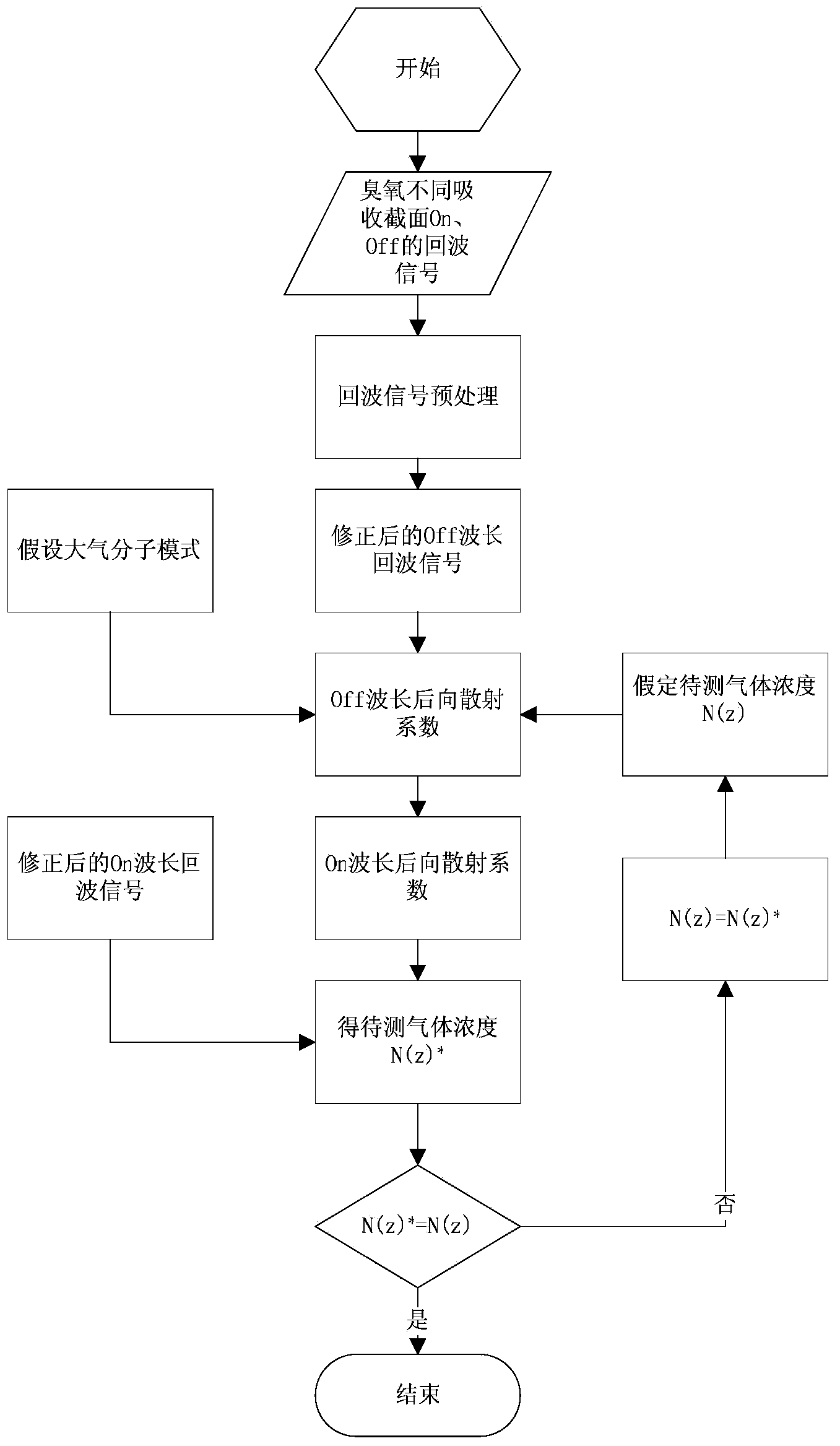
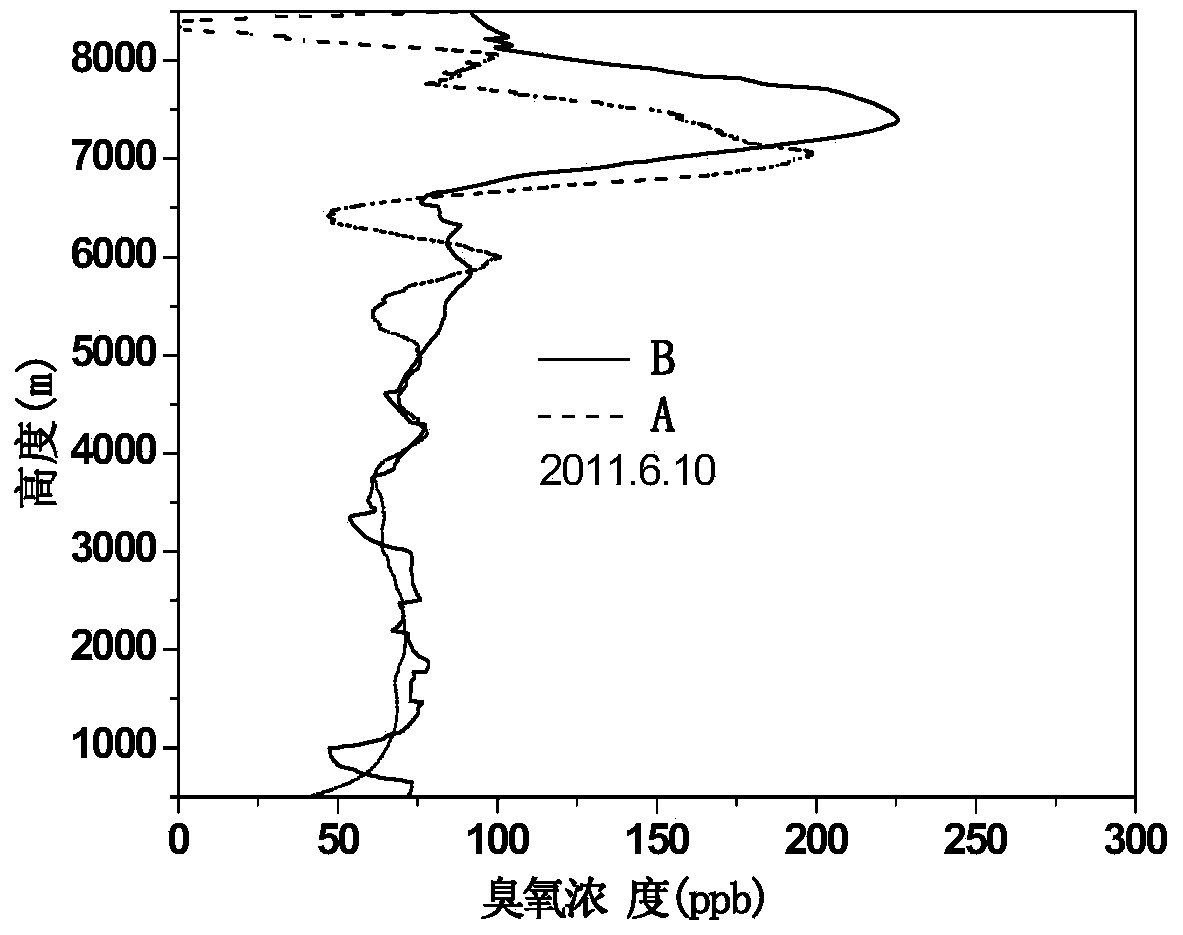
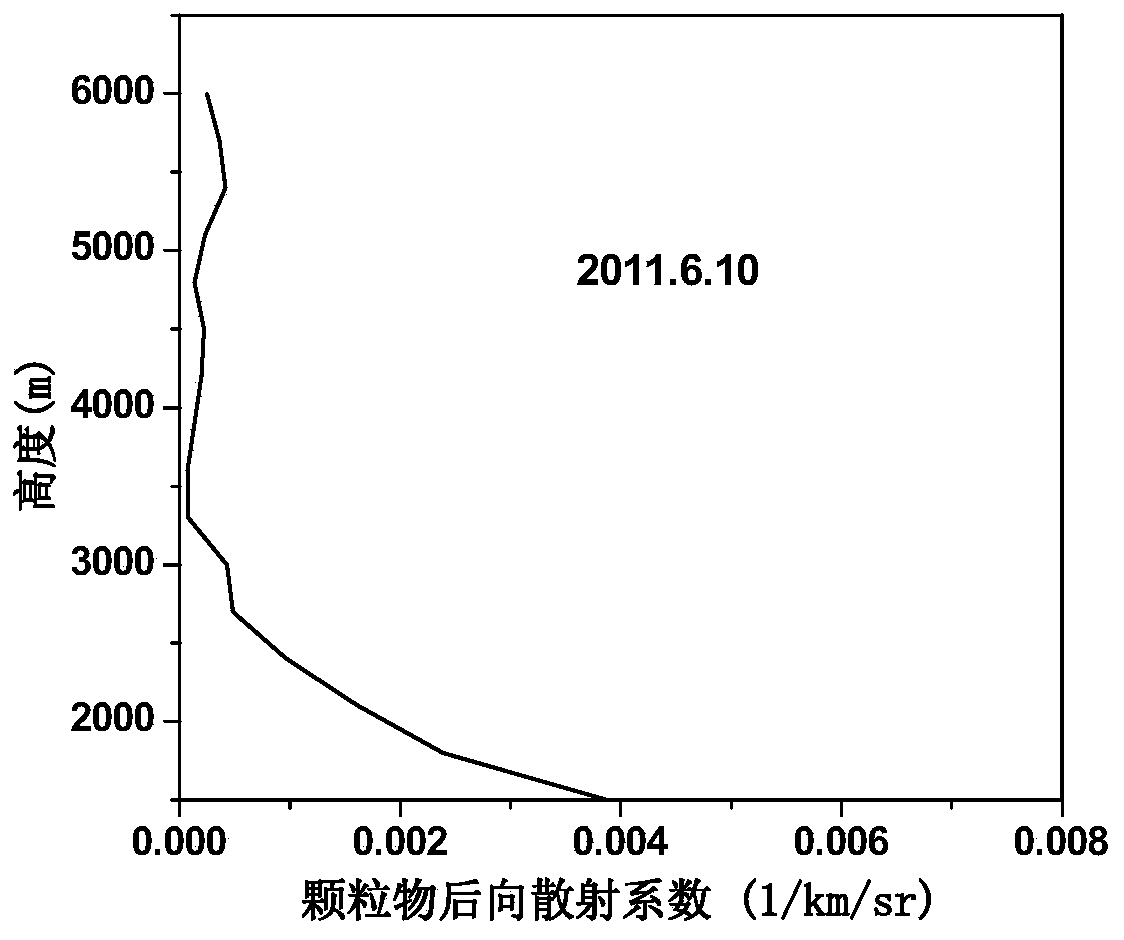
Method for measuring backscattering coefficient of atmospheric particulates and ozone concentration profile simultaneously
ActiveCN103868836AReduce distractionsEasy programmingColor/spectral properties measurementsParticle suspension analysisParticulatesDistance correction
The invention relates to a method for measuring backscattering coefficient of atmospheric particulates and ozone concentration profile simultaneously. A dual-wavelength differential absorption laser radar receives On and Off dual-wavelength backscattering echo signals of different cross sections of ozone simultaneously, and the acquired On and Off dual-wavelength backscattering echo signals are subjected to pretreatments such as background deduction, square distance correction, filtering and the like; the initial ozone concentration value is assumed, the atmospheric molecule mode is a united states standard atmosphere mode, the corrected off wavelength echo signal is utilized to invert the Off wavelength backscattering coefficient, and the On wavelength backscattering coefficient is obtained according to the wavelength conversion relation, and the ozone concentration is inverted in combination with the On wavelength backscattering echo signal; if the difference between the inverted ozone concentration and the initial ozone concentration value is more than a preset value, the above process is carried out in a loop iteration manner until the difference reaches the preset value, and therefore, the backscattering coefficient of atmospheric particulates and ozone concentration can be obtained simultaneously. The method can effectively reduce aerosol interference and improve the zone measurement precision.
Owner:合肥中科环境监测技术国家工程实验室有限公司
Multi-parameter step-by-step sea surface salinity inversion method and device
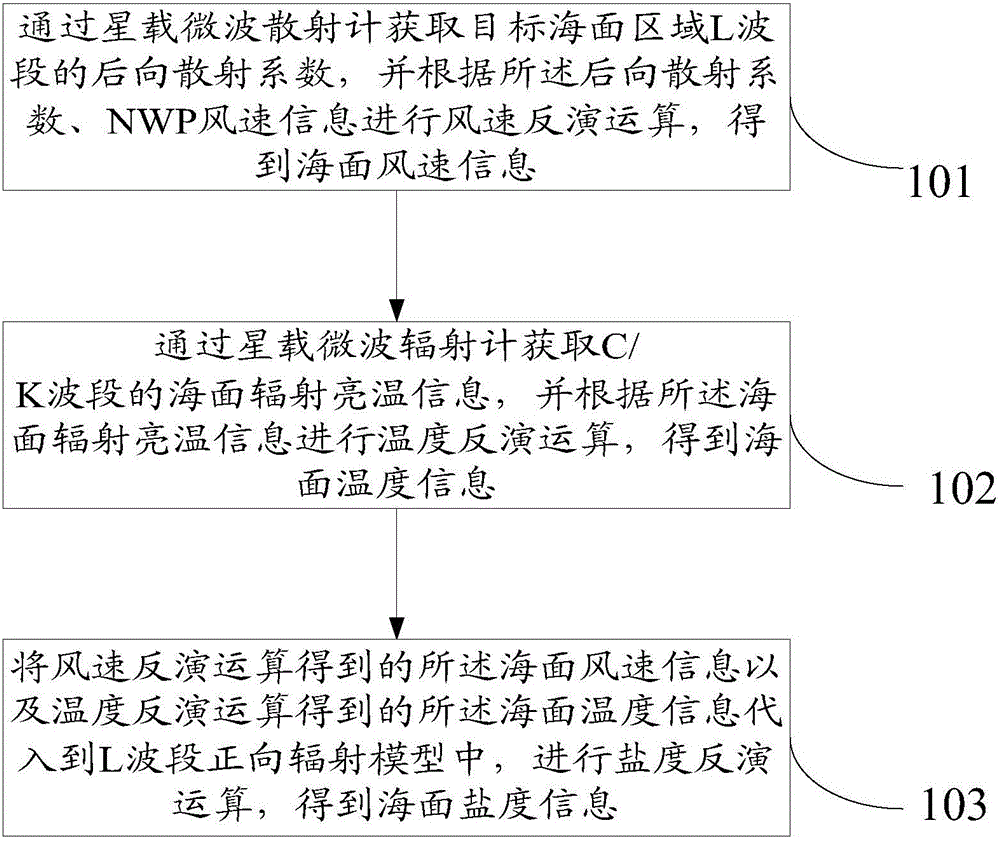
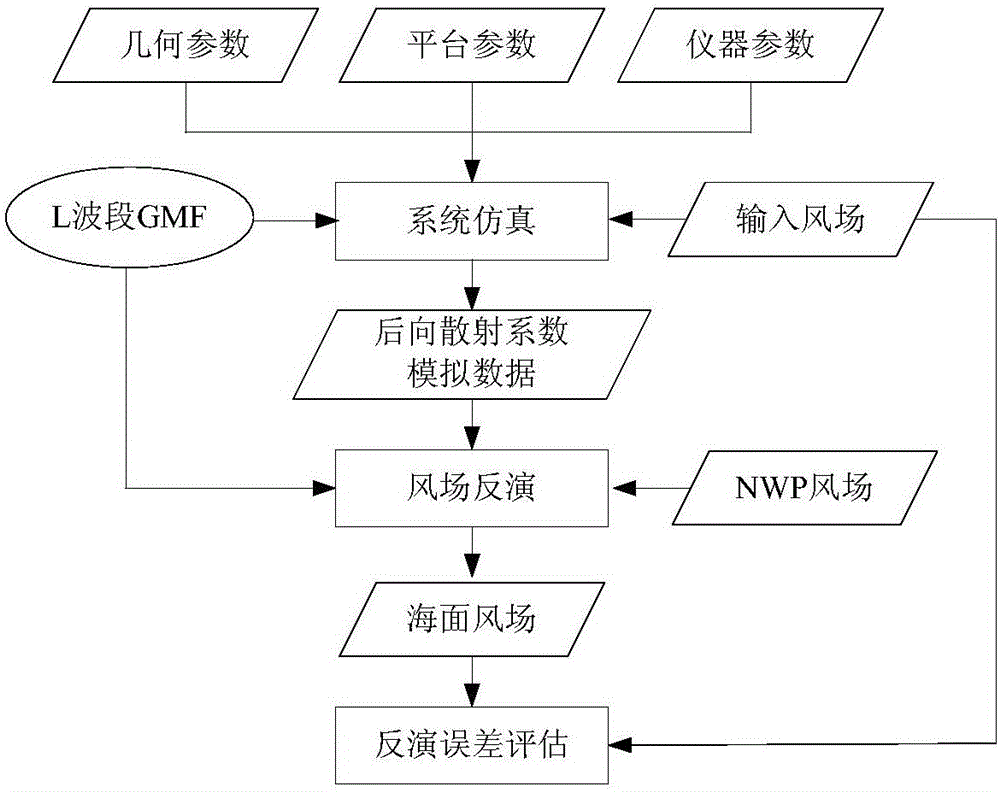
InactiveCN105844090AImprove accuracyReduce mistakesInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical weather predictionScatterometer
The invention relates to the technical field of sea exploration, particularly to a multi-parameter step-by-step sea surface salinity inversion method and device. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the backscattering coefficient of an L waveband of a target sea surface area through a satellite-borne microwave scatterometer, and carrying out wind speed inverse operation according to the backscattering coefficient and NWP (Numerical Weather Prediction) wind speed information to obtain sea surface wind speed information; obtaining the sea surface radiation brightness temperature information of a C / K waveband through the satellite-borne microwave scatterometer, carrying out temperature inversion operation according to the sea surface radiation brightness temperature information to obtain sea surface temperature information; and substituting the sea surface wind speed information and the sea surface temperature information into a forward direction radiation model of the L waveband to carry out salinity inversion operation to obtain sea surface salinity information. The method can utilize load carried by a sea salinity satellite to independently carry out inversion on sea surface wind speed, sea surface temperature and sea surface salinity, dependency on external auxiliary data by sea surface salinity inversion is solved, and the accuracy of a salinity result is finally improved.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE OCEAN APPL SERVICE
Original echo generation method for airborne Interference synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN1808172AShorten the timeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSpace constantInterferometric synthetic aperture radar
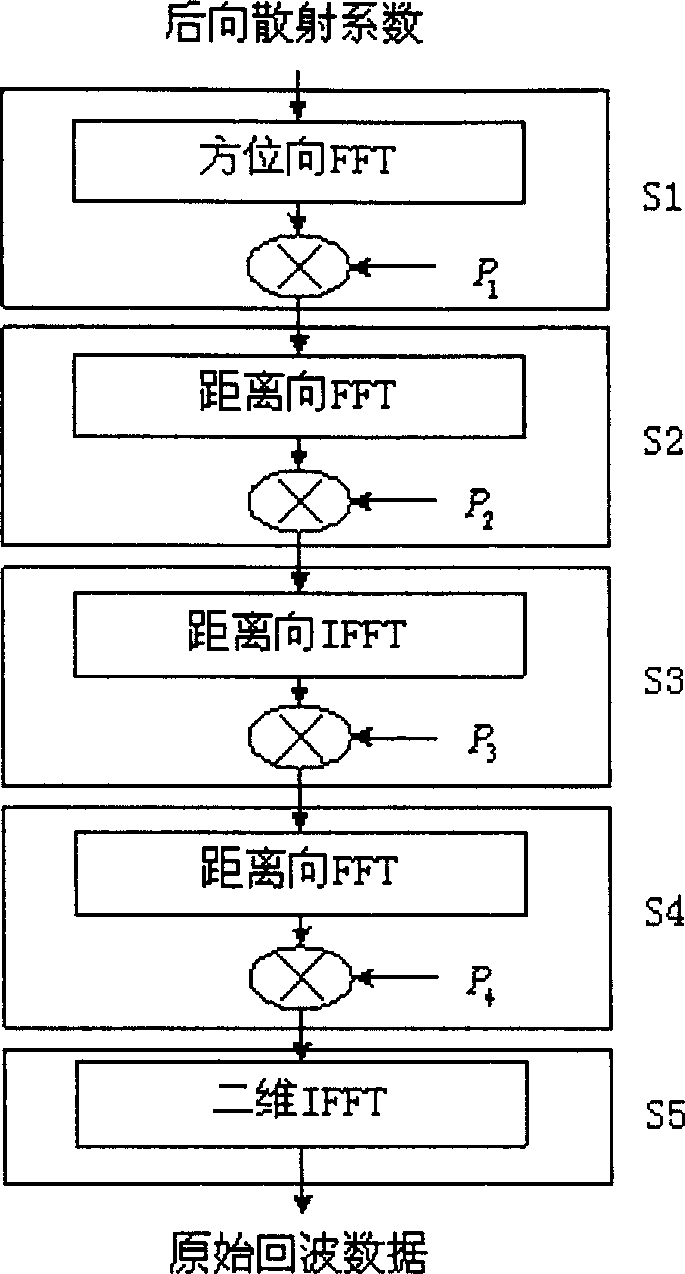
The invention relates to a method for generating a machine carried interference synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) original echo wave. The method comprises: step 1: implementing position method of Fourier transformation (FFT) on equivalent back scattering coefficientª†1ú¼2(xú¼ª†), and then multiplying a phase function with defocus item and reducing and enlarging factor P1ú¢exp{j(ªš2 / alphaª†0ú®ª†ú½j[ª©1,2(ªš) / 4B]ª†2}; stp2: implementing distance FFT on the result form step 1, then multiplying a phase function with reducing and enlarging factor P2ú¢exp{j(1-ª©1,2(ªš)) / ª©1,2(ªš)BªÃ}; step 3: implementing distance inverse FFT on the result from the step 2, then multiplying a phase function with reducing and enlarging factor P3ú¢exp{-Jú¿1 / 4Bú®ª†2}; step 4: implementing distance inverse FFT on the result from the step 3, then multiplying a phase function with space constant exciting response function, distance horizontal shift factor and the reducing and enlarging factor P4ú¢Gú¿ªšú¼ªÃú¼ª†0ú®exp{-jªÃª†s1,2ú½j[ª©1,2(ªš)-1]BªÃ2}; step 5: implementing two dimensional inverse FFT on the result from step 4 and getting the needed original echo wave data h1ú¼2(xíõú¼ríõ).
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com