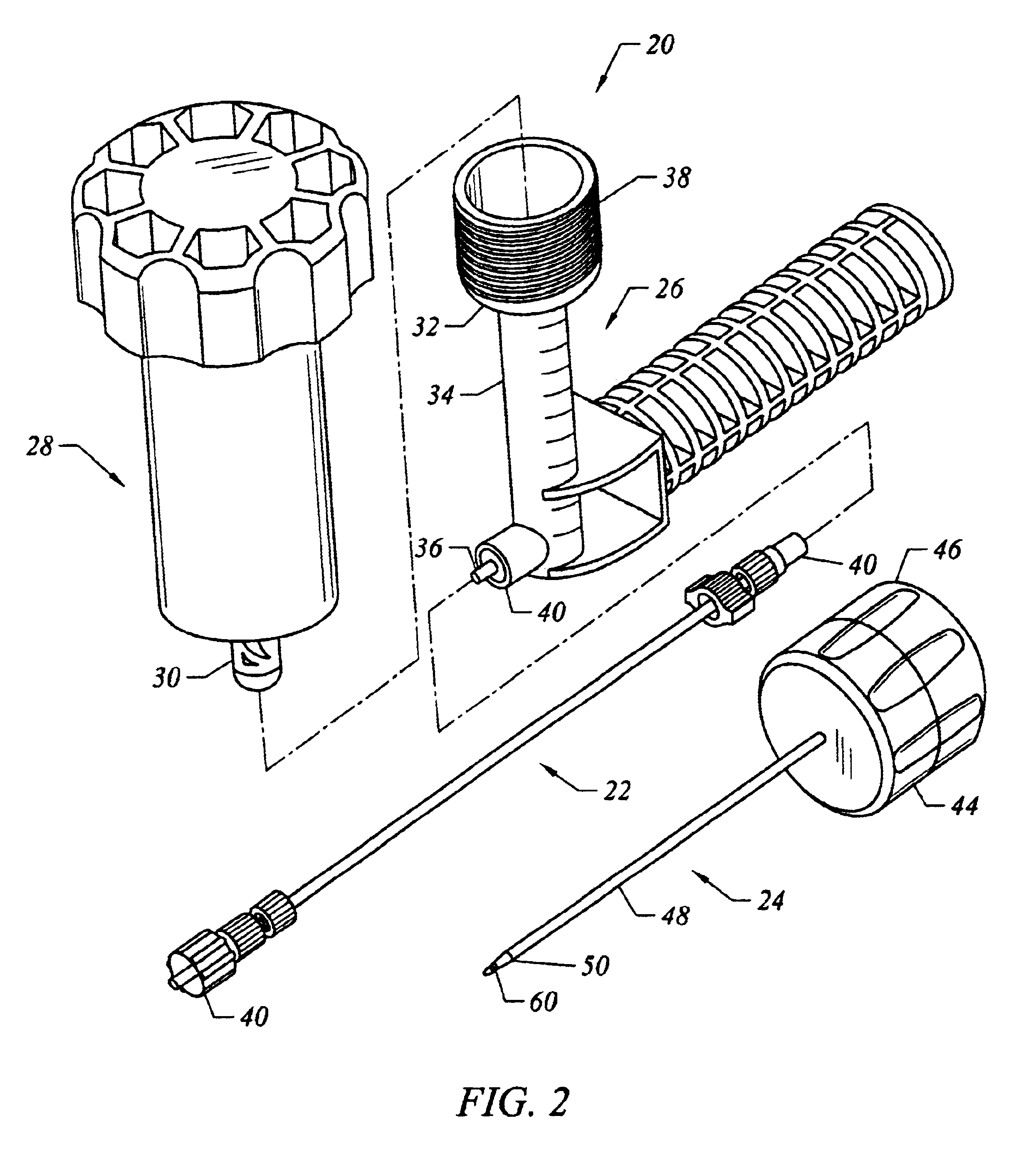
Patents
Literature
756 results about "Cancellous bone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
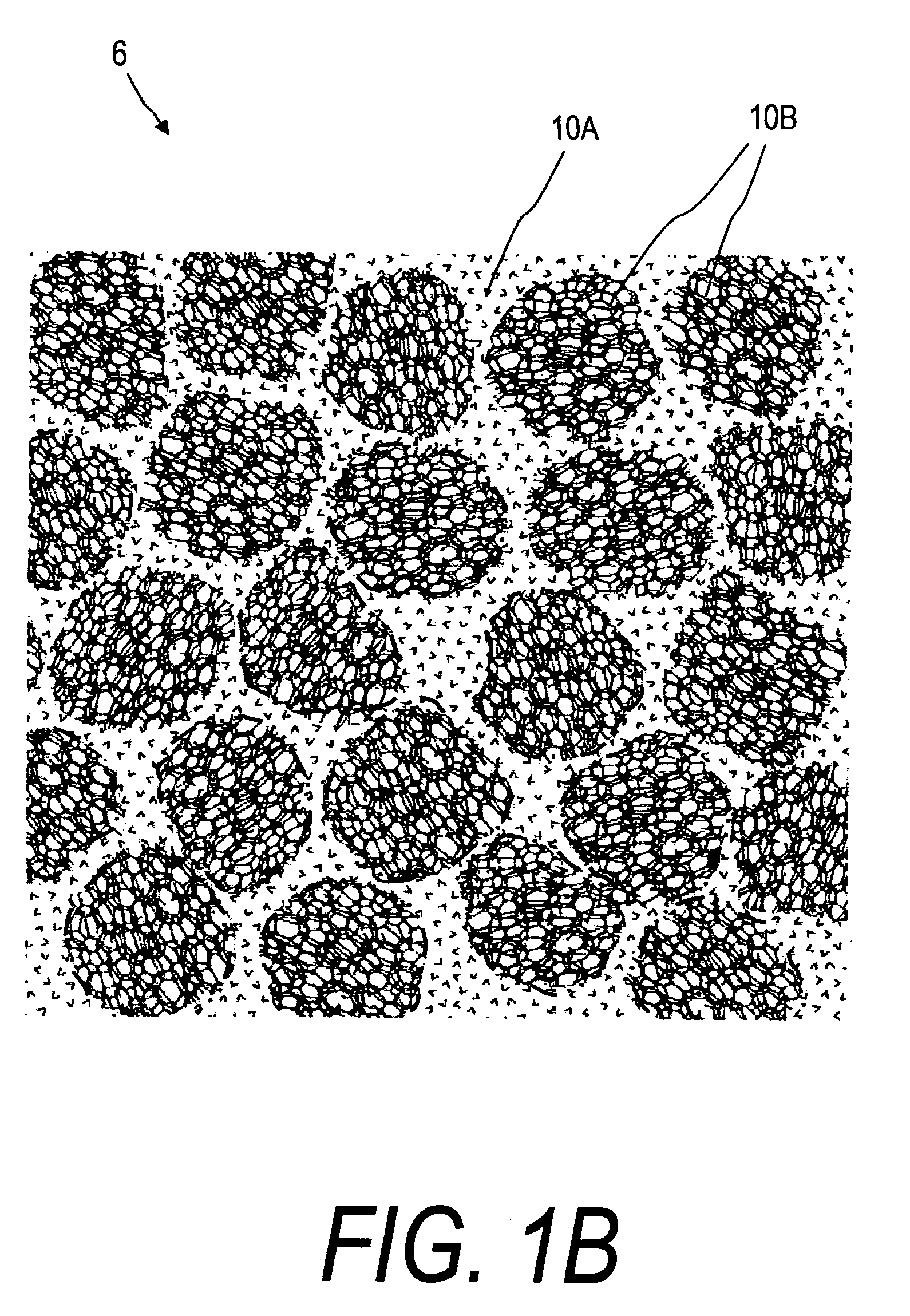
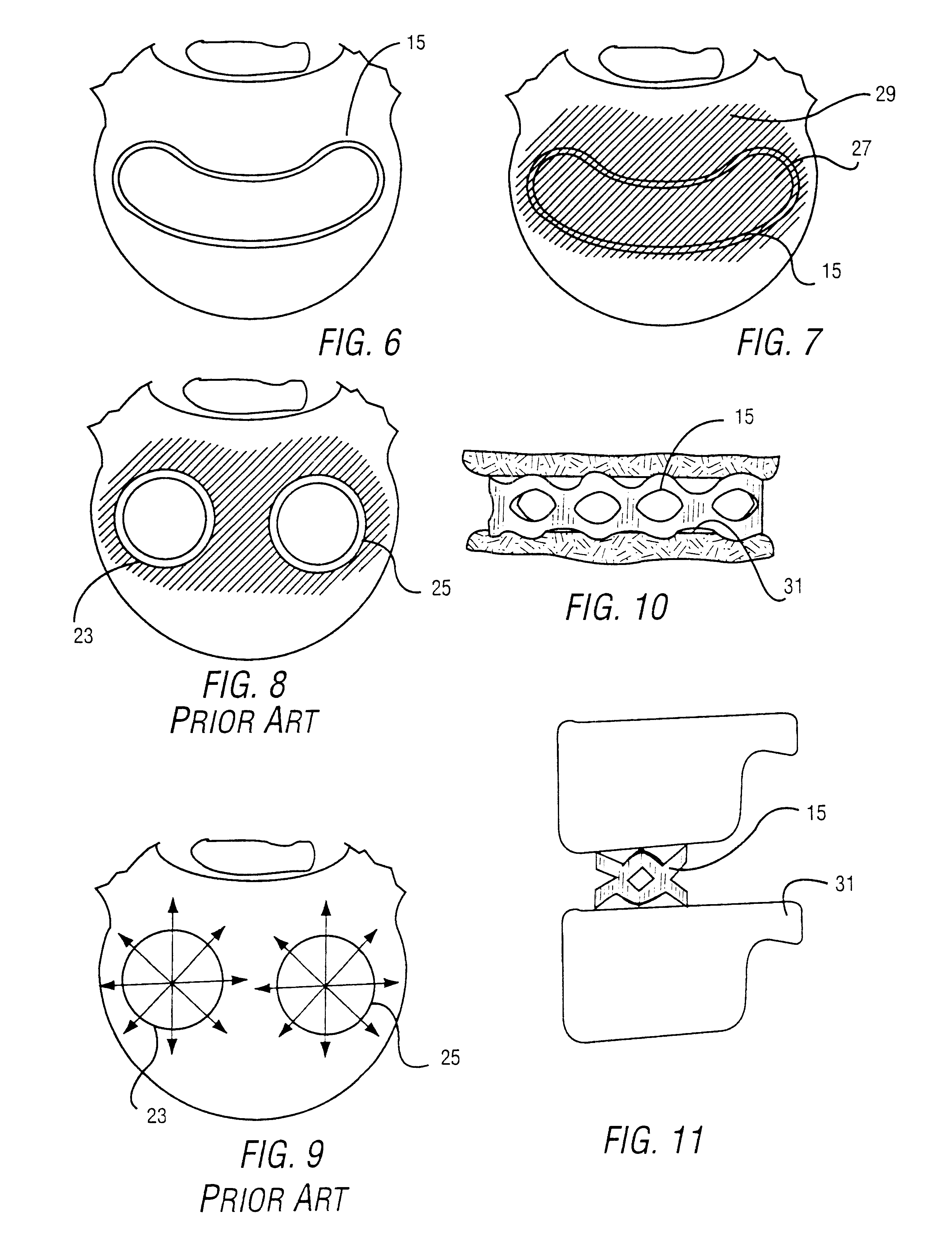
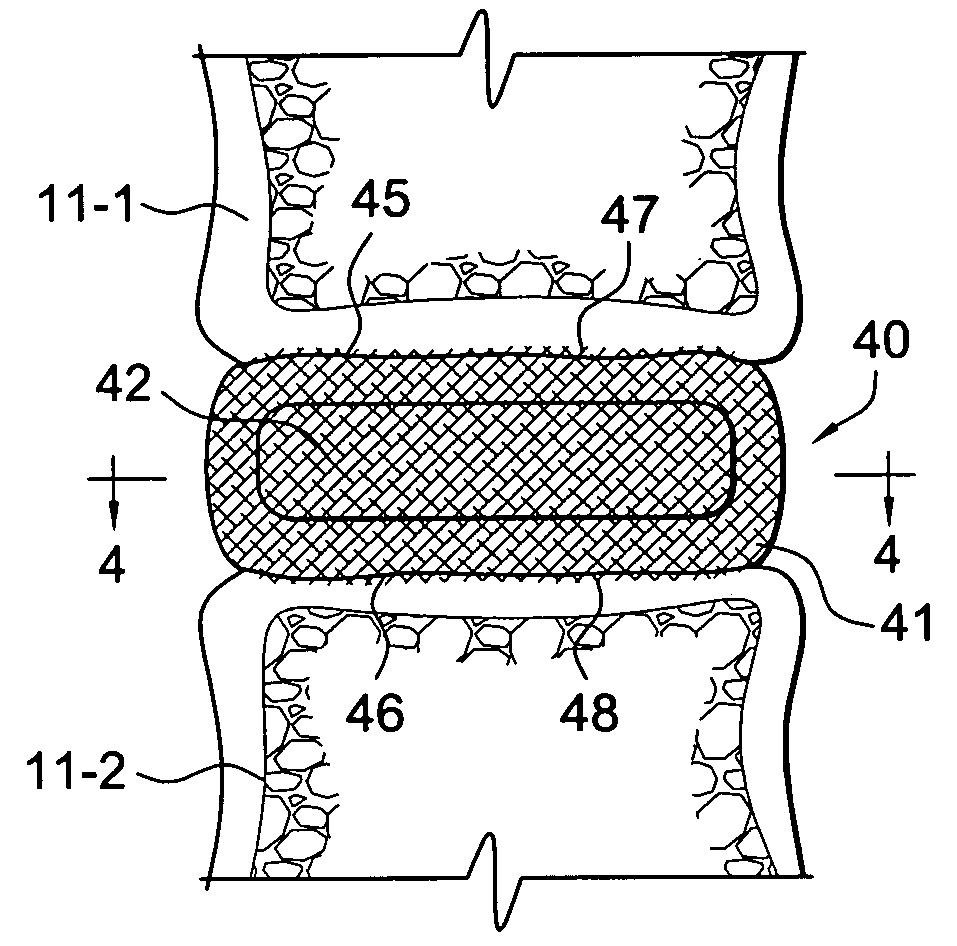
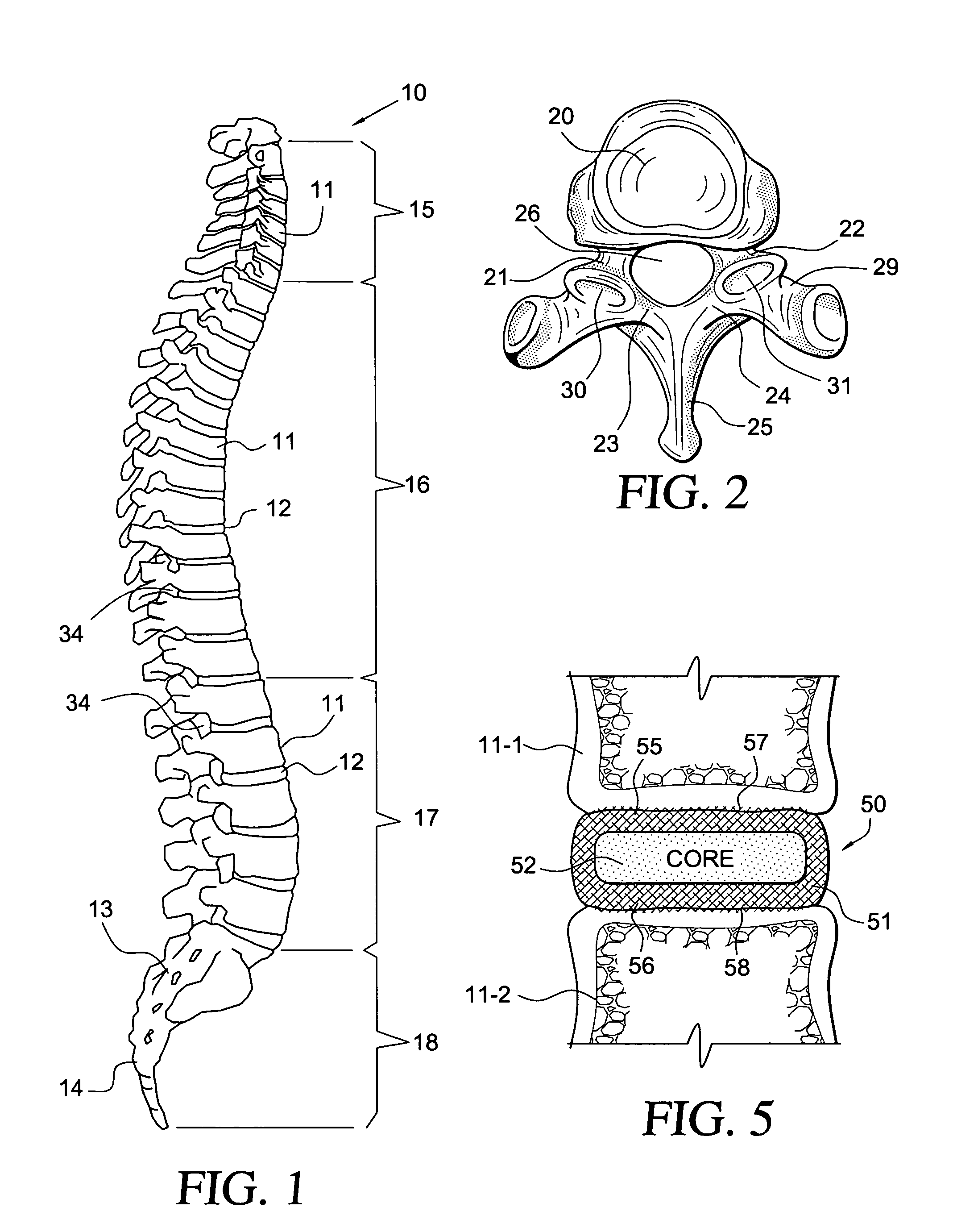
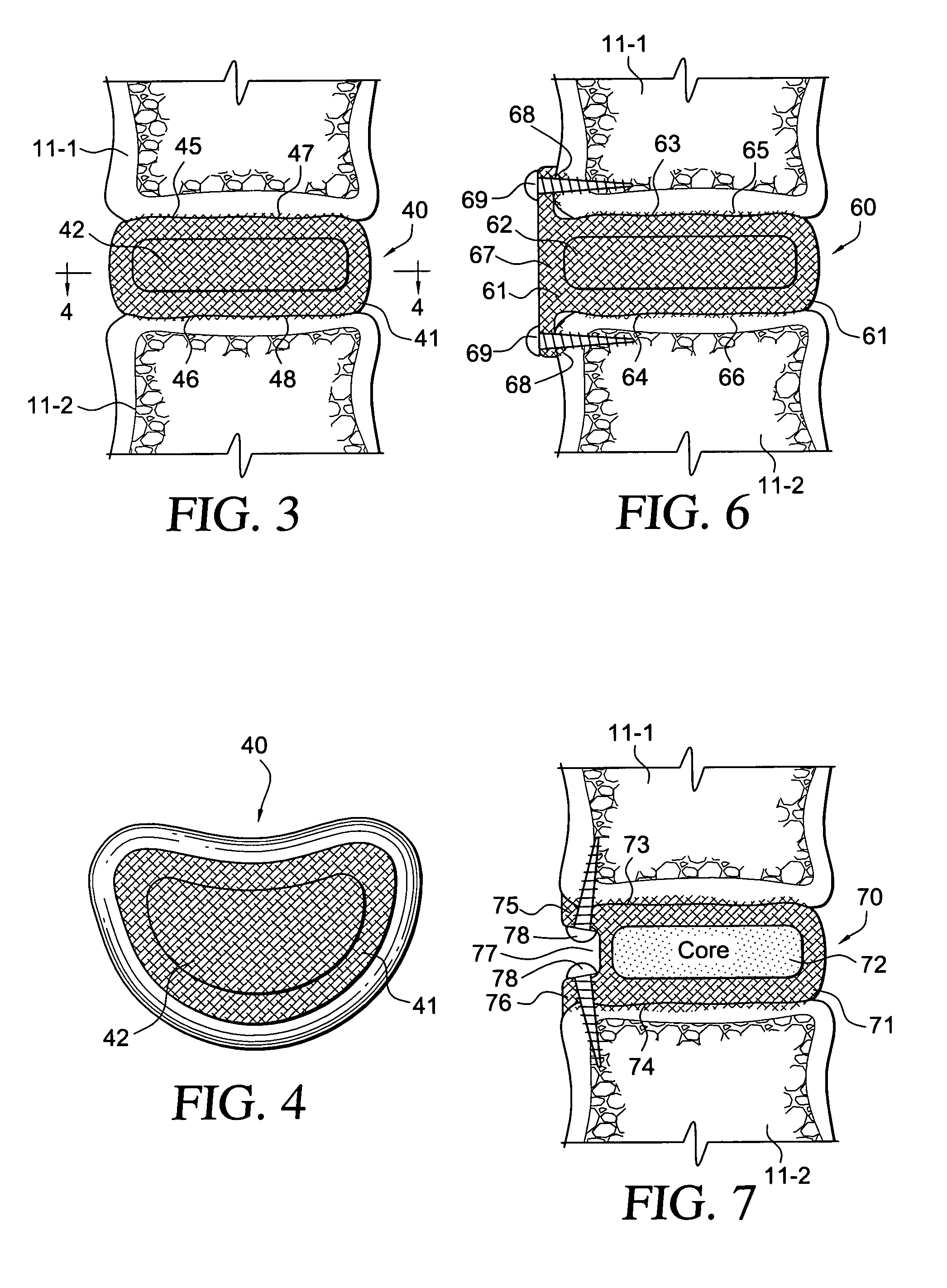
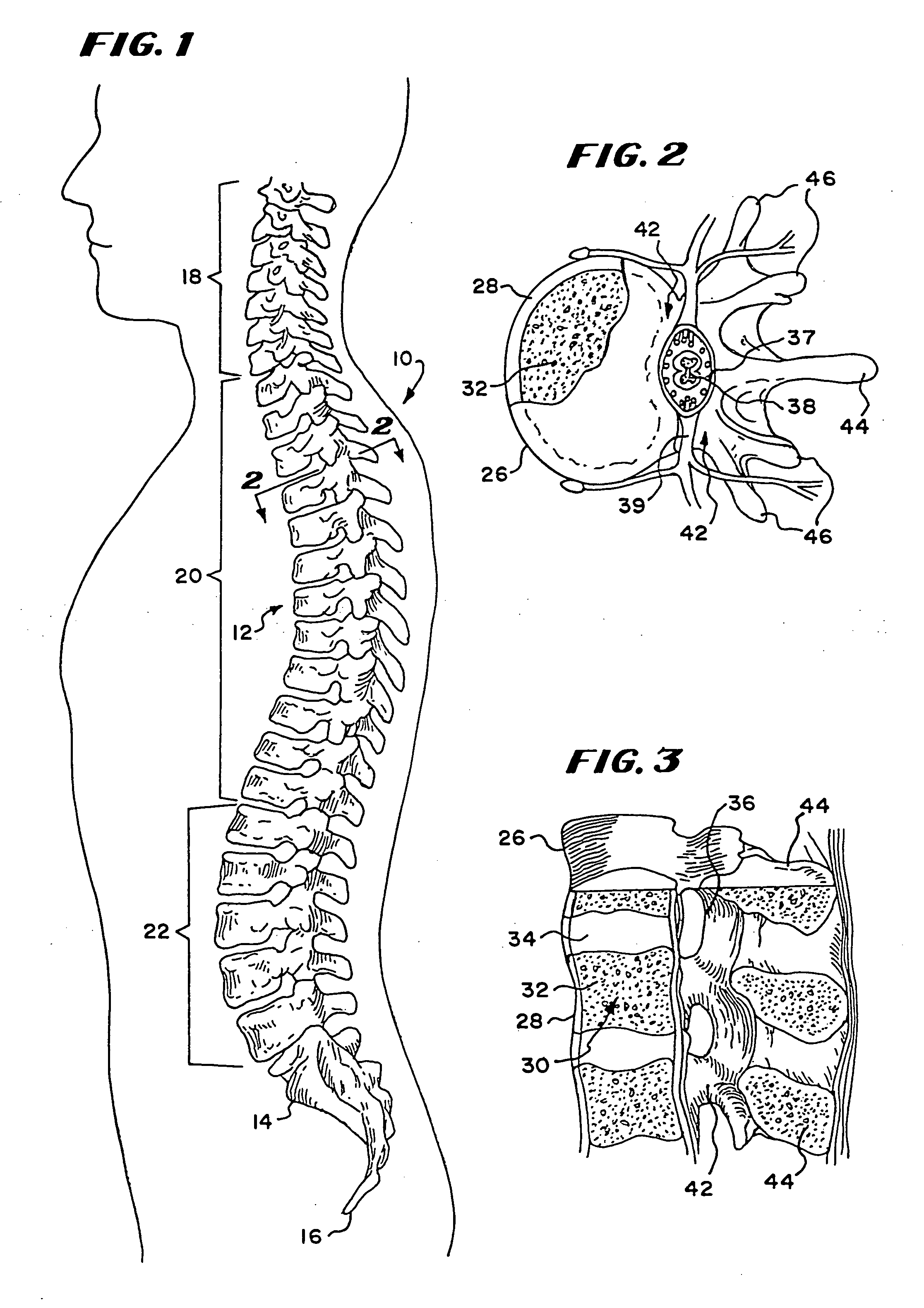
Cancellous bone, synonymous with trabecular bone or spongy bone, is one of two types of osseous tissue that form bones. The other osseous tissue type is cortical bone also called compact bone.
Tissue discrimination and applications in medical procedures
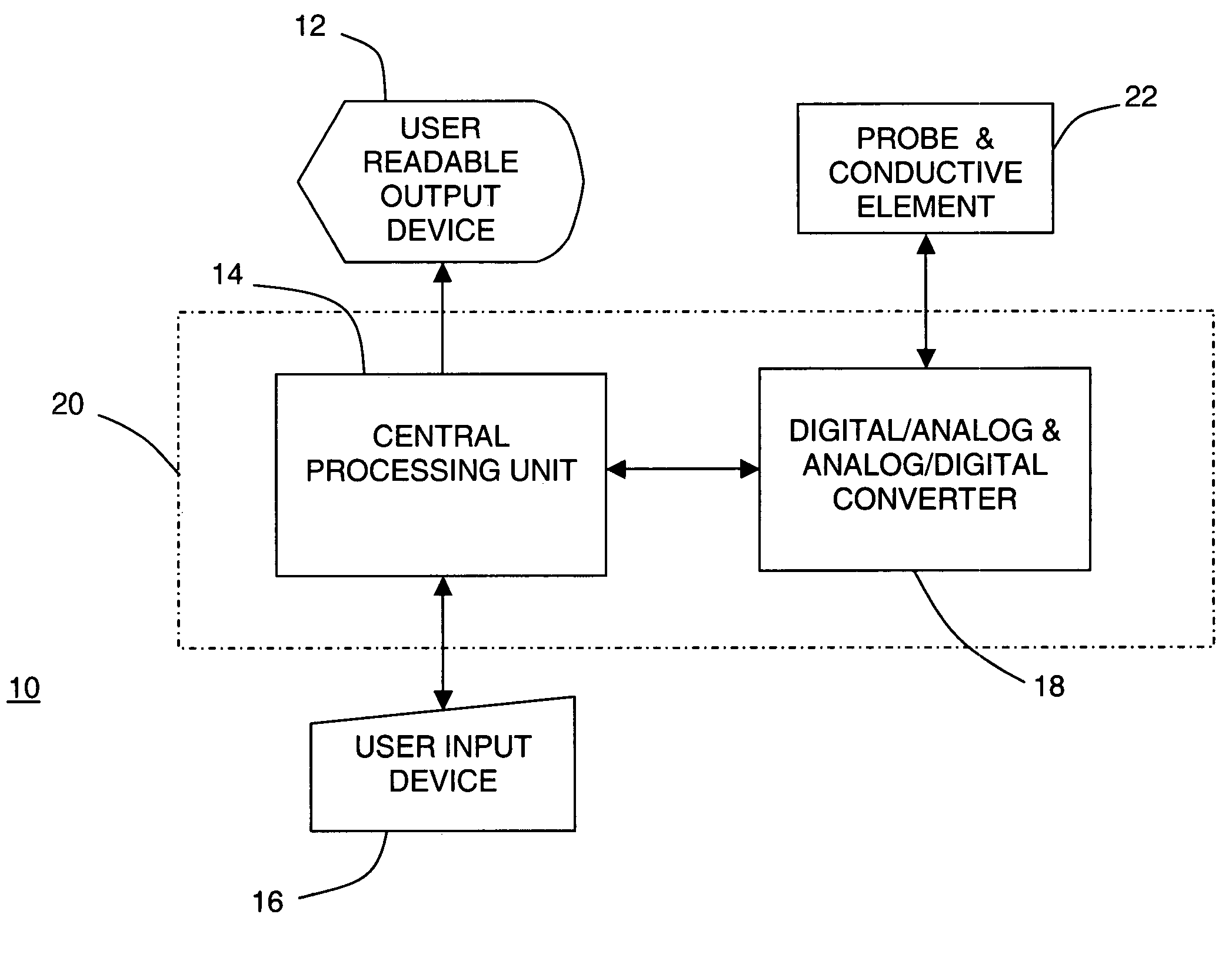
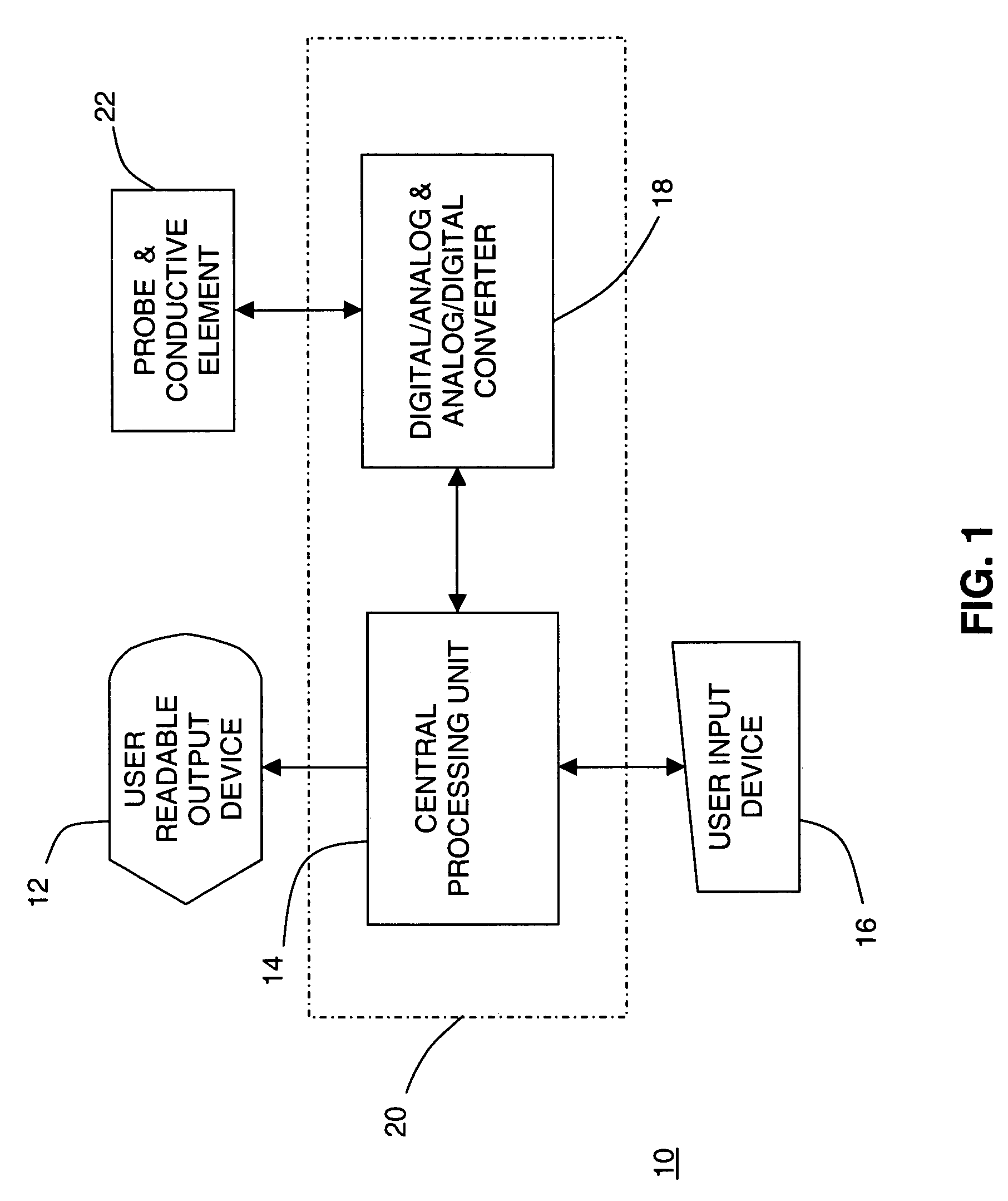
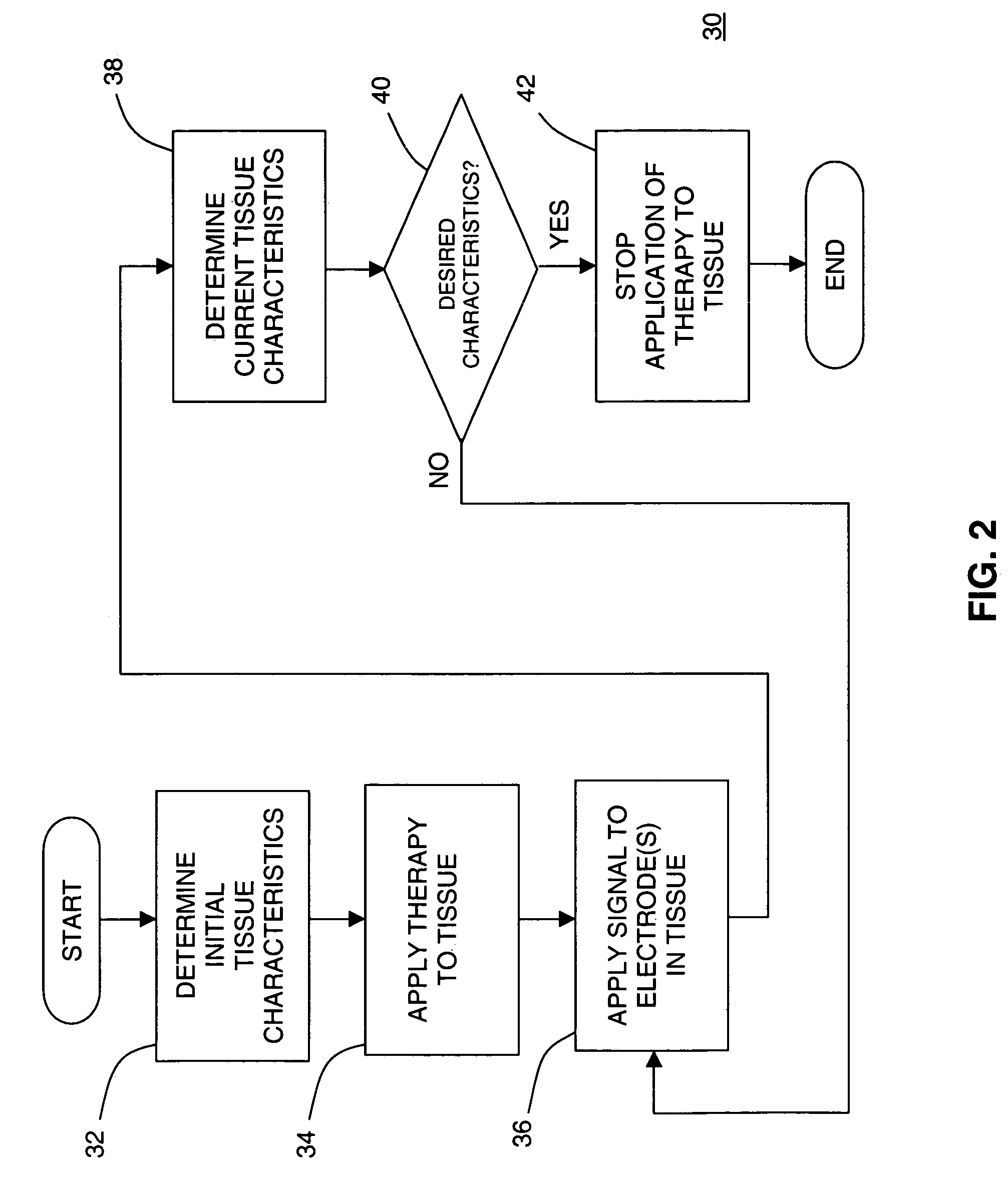
InactiveUS7050848B2Different transmission propertyDifferent capacitanceElectrotherapyInternal osteosythesisTissues typesBone Cortex
A system and method for discriminating tissue types, controlling the level of therapy to tissue, and determining the health or a known tissue by measuring the characteristics an electrical signal applied to conductive element located within or by the tissue. Additionally, the system and method may be used for determining whether the conductive tip of a pedicle probe or pedicle screw is located in one of cortical bone, cancellous bone, and cortical bone near a boundary with soft tissue, whether the conductive tip of a cannula is located adjacent to one of nerve tissue and annulus tissue, and whether the conductive tip of a cathode is located adjacent to one of nerve tissue and prostate gland tissue.
Owner:NUVASIVE
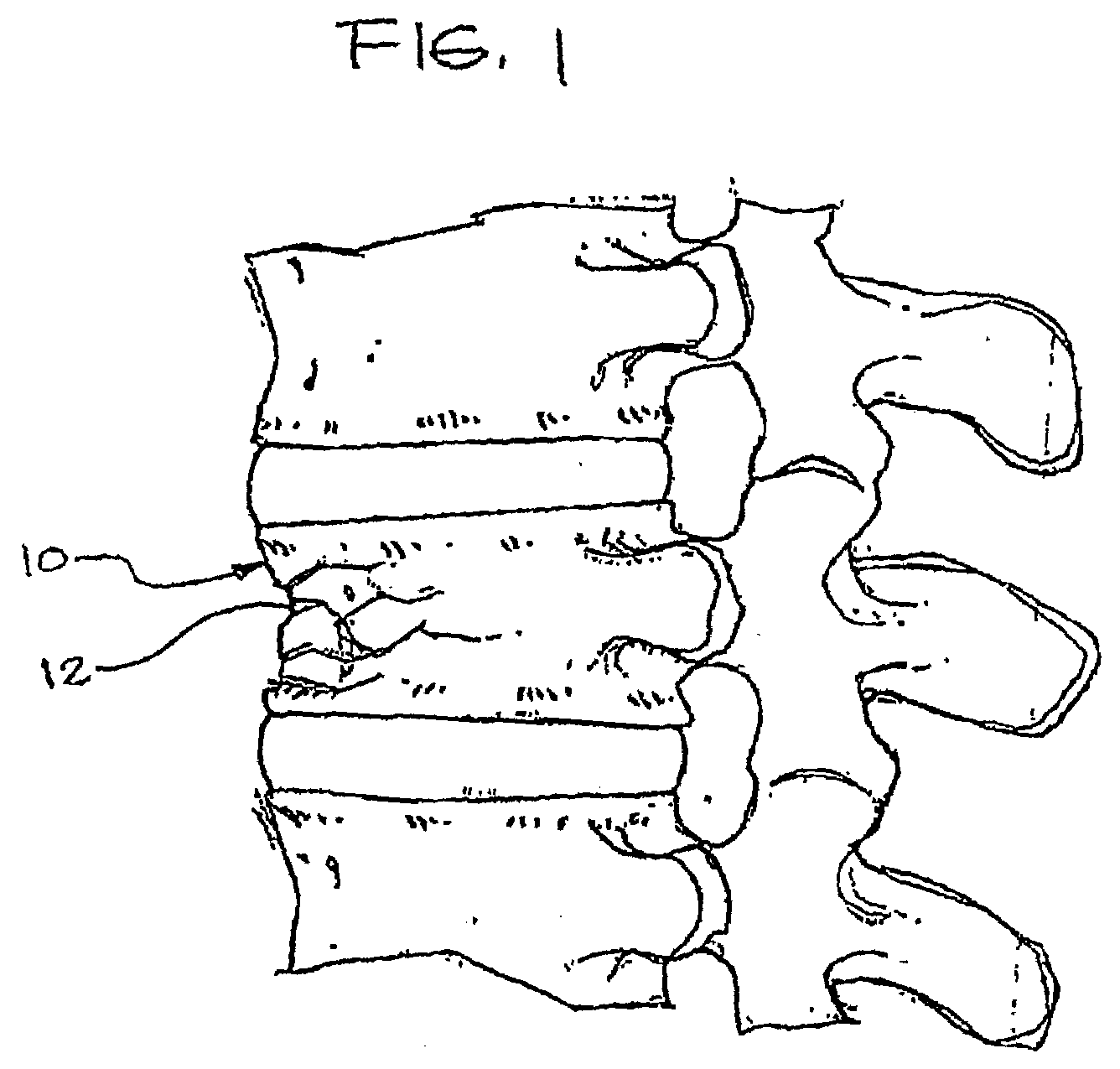
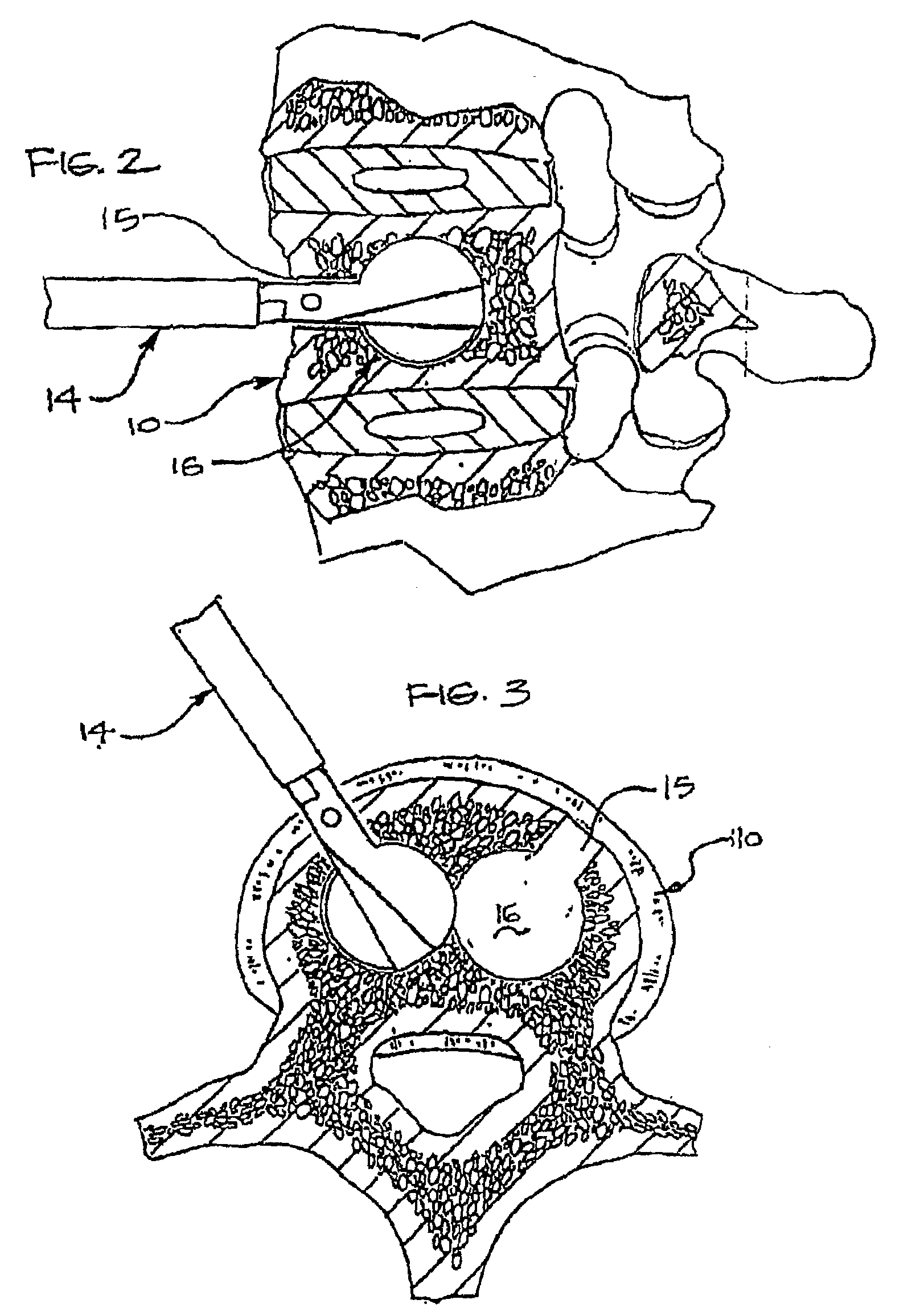
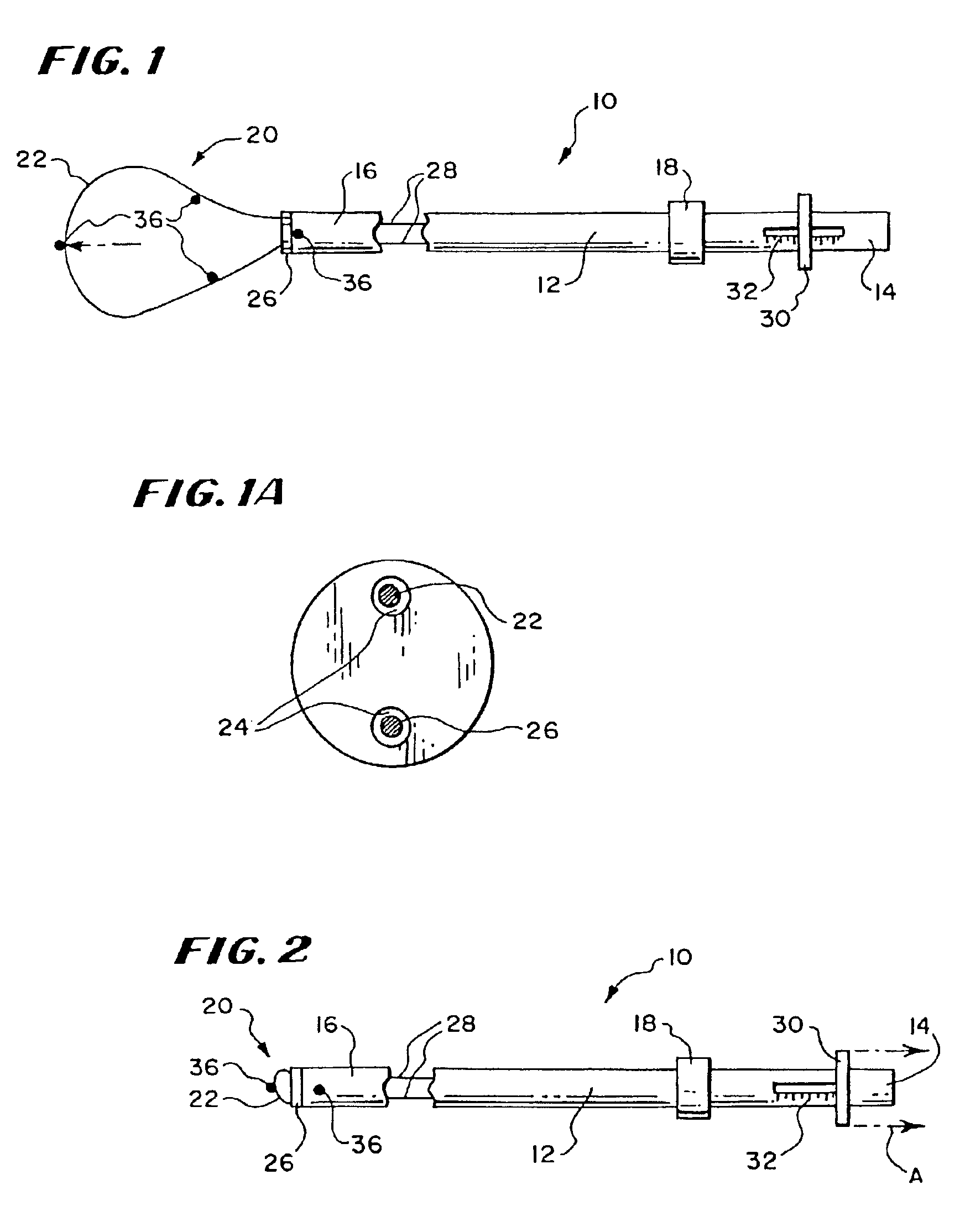
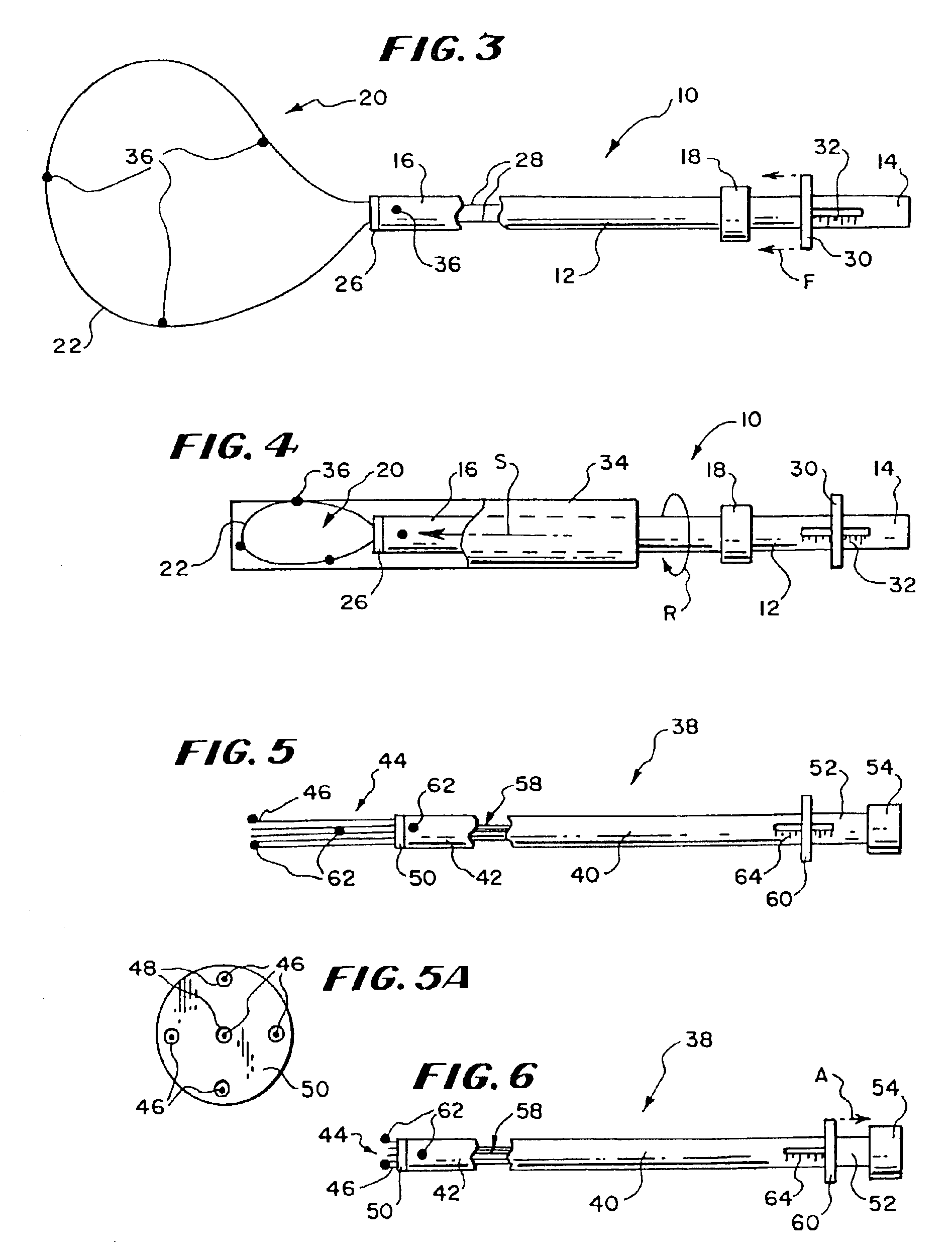
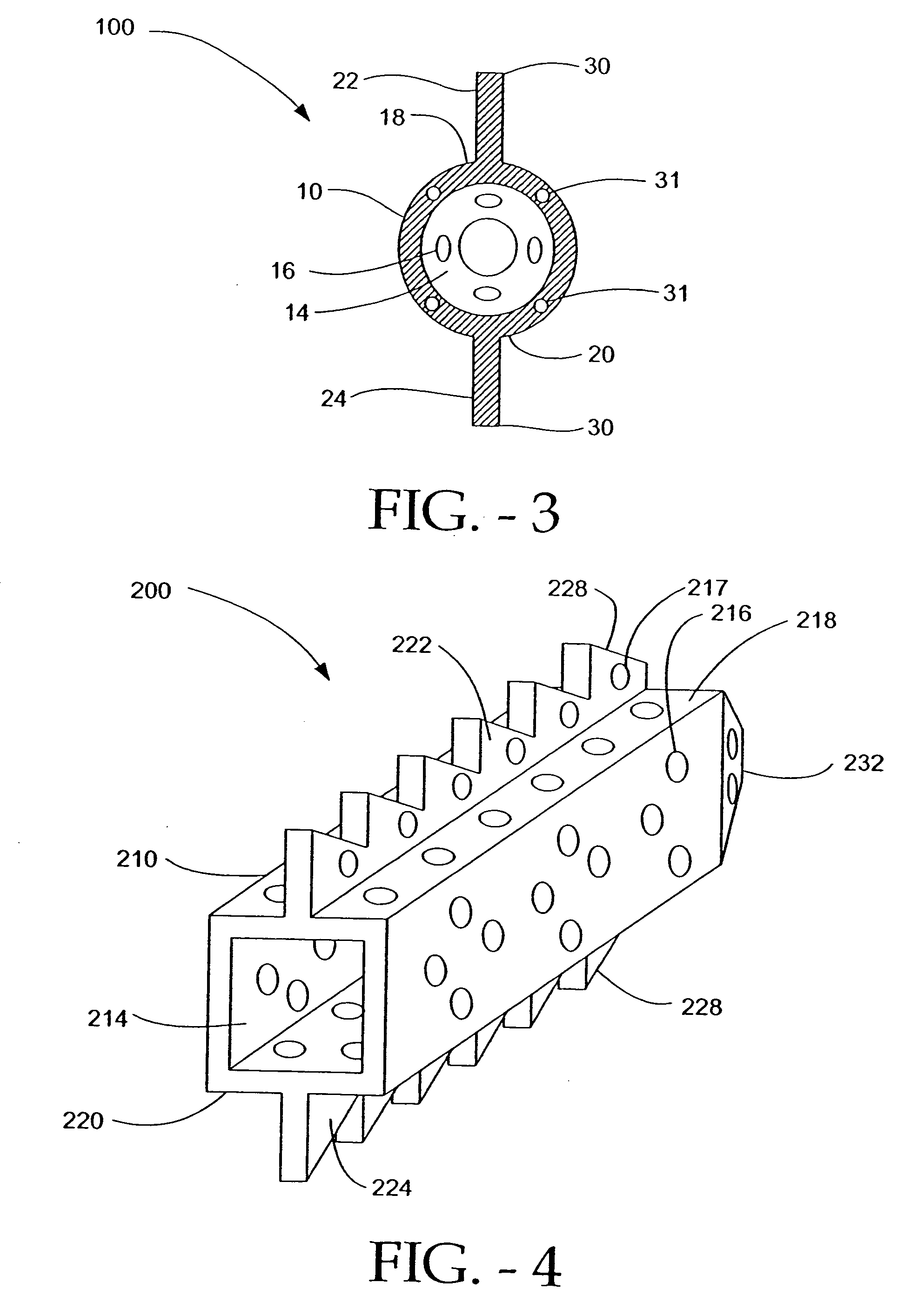
Inflatable device for use in surgical protocol relating to fixation of bone
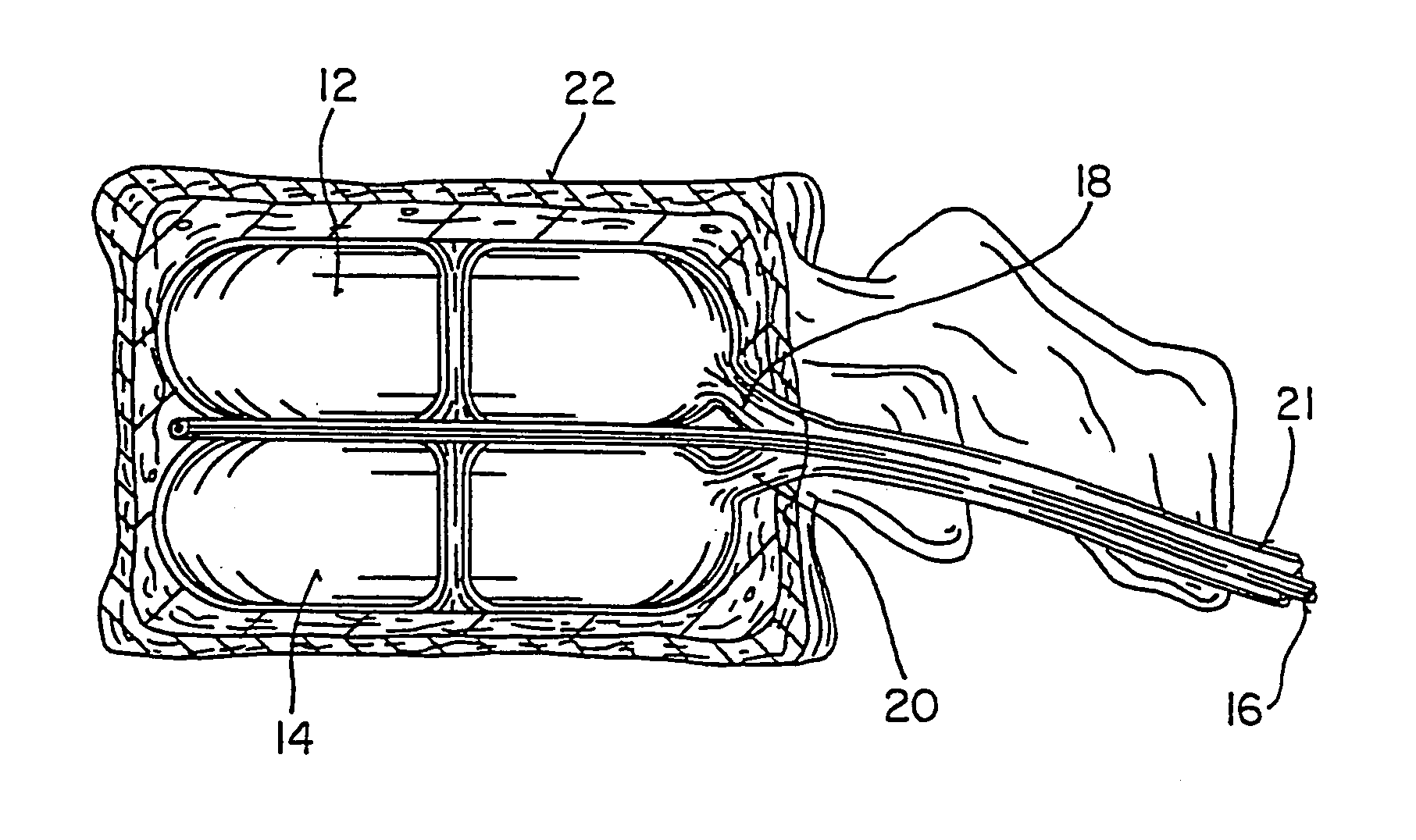
InactiveUS6981981B2Improve clinical outcomesWorsen conditionSurgical furnitureInternal osteosythesisFilling materialsCancellous bone
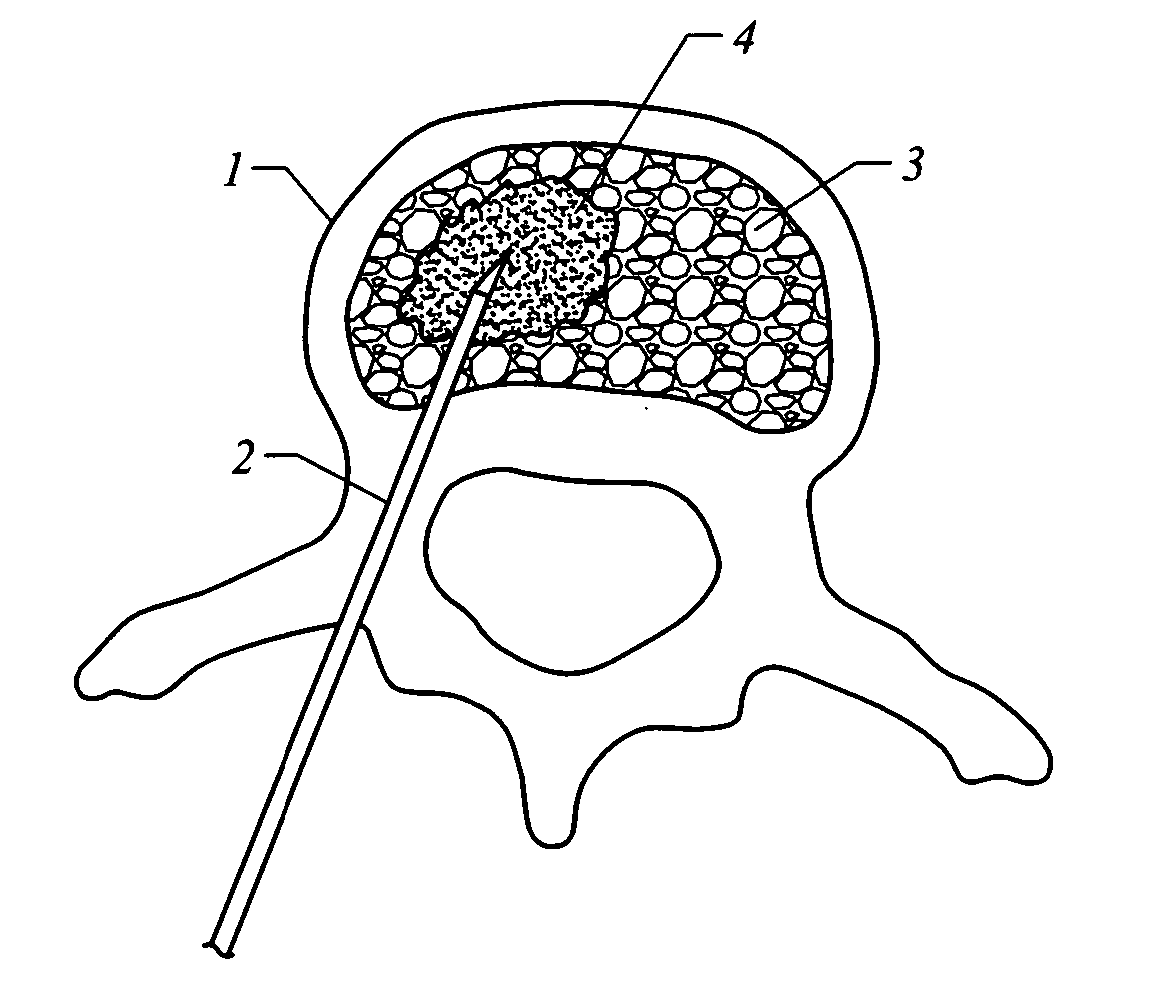
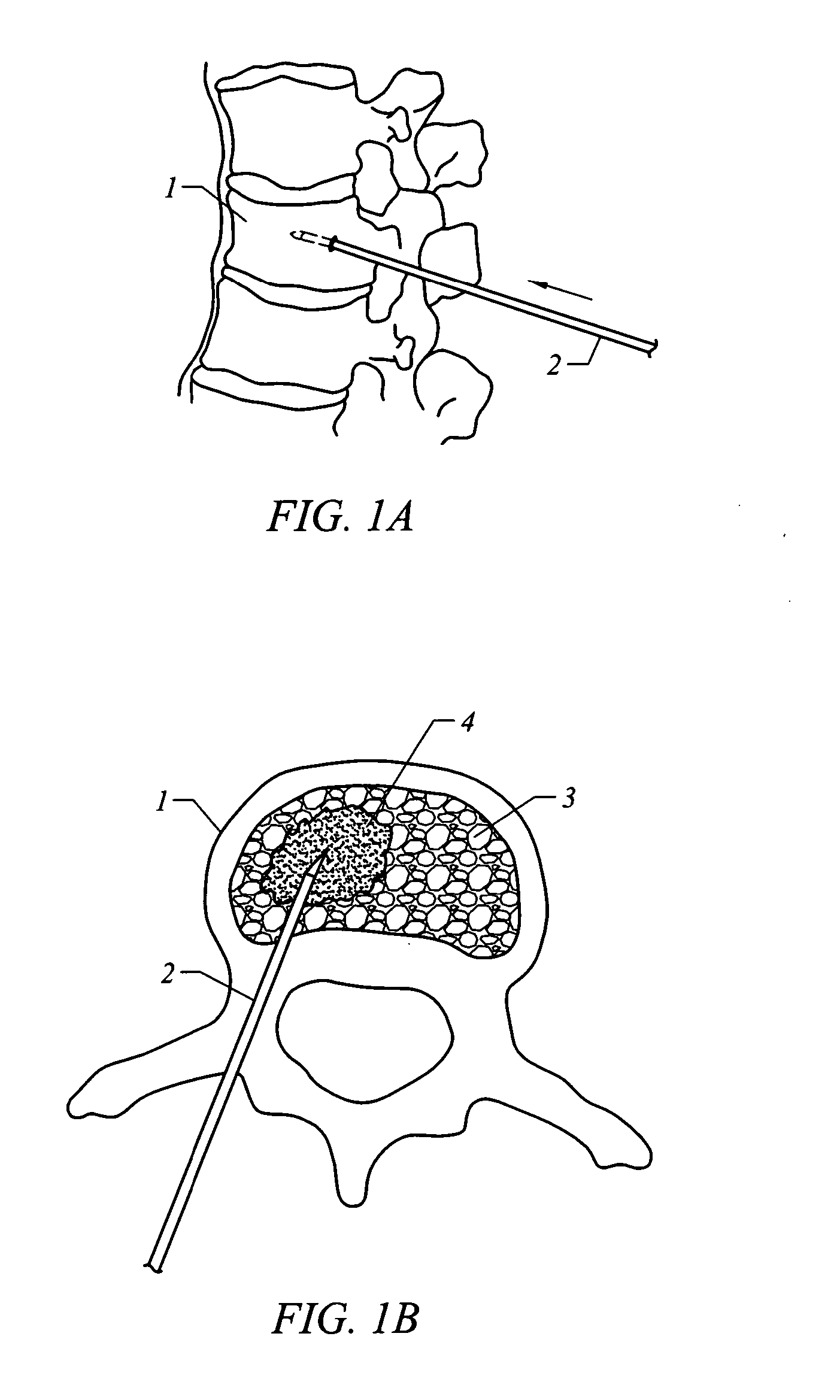
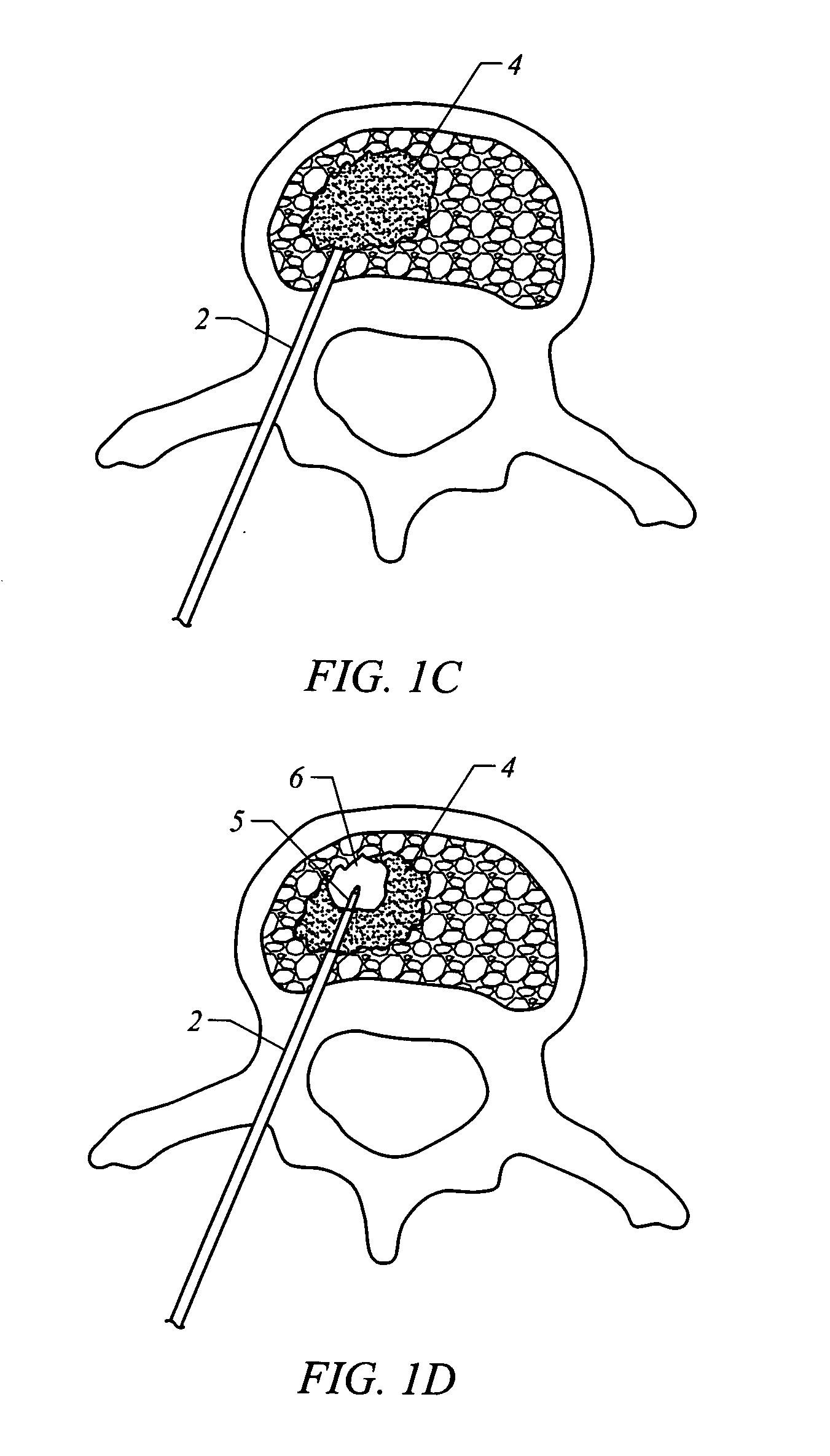
Systems for treating a bone, e.g. a vertebral body, having an interior volume occupied, at least in part, by cancellous bone provide a first tool, a second tool, and a third tool. The first tool establishes a percutaneous access path to bone. The second tool is sized and configured to be introduced through the percutaneous access path to form a void that occupies less than the interior volume. The third tool places within the void through the percutaneous access path a volume of filling material. Related methods for treating a bone, e.g. a vertebral body, having an interior volume occupied, at least in part, by cancellous bone provide establishing a percutaneous access path to bone. A tool is introduced through the percutaneous access path and manipulated to form a void that occupies less than the interior volume. A volume of filling material is then placed within the void through the percutaneous access path.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
Stent systems and methods for spine treatment
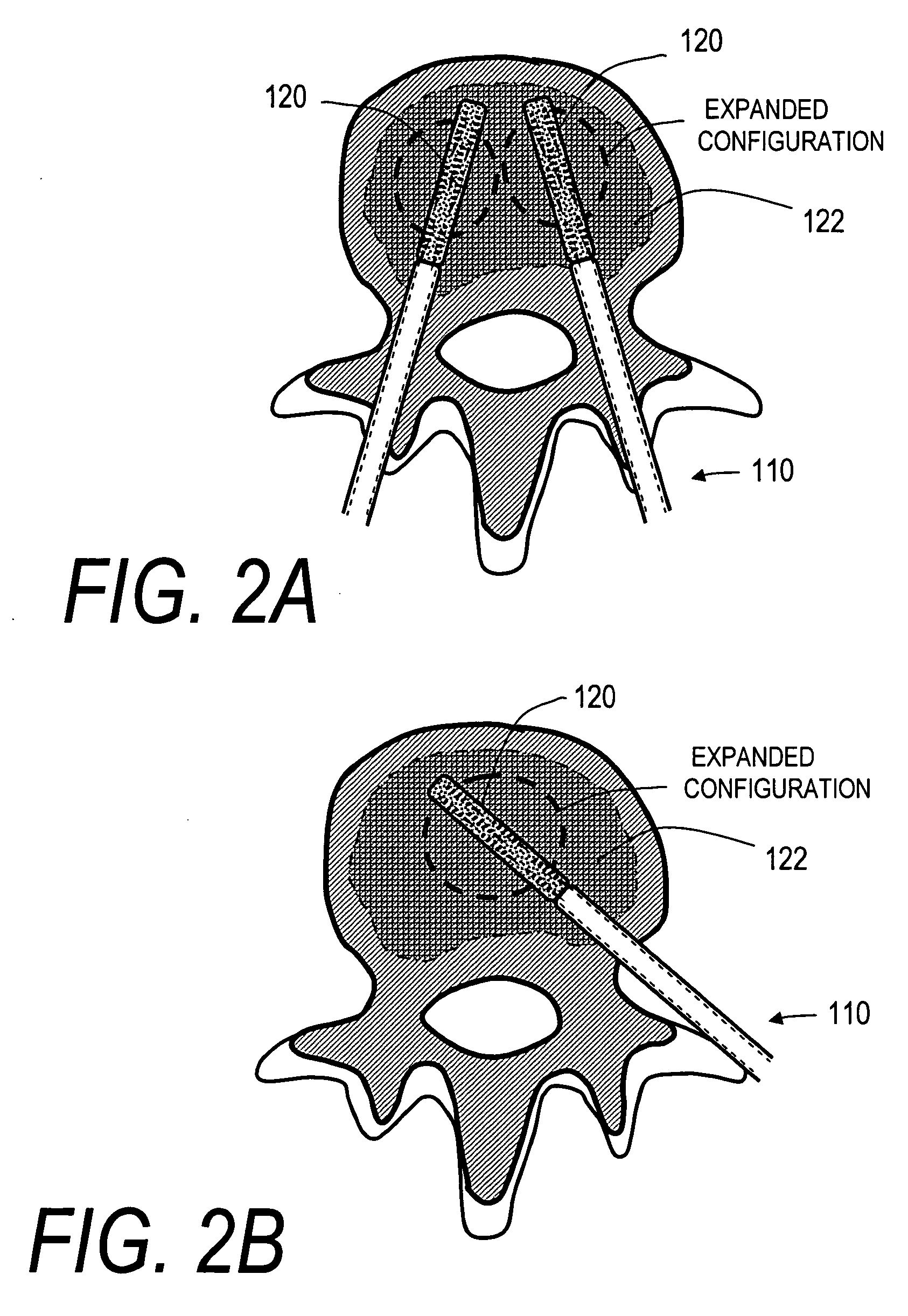
InactiveUS20060100706A1Prevent subsidenceRestore body heightInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsSpinal columnCardiac allograft
Stent systems and methods for expanding and deploying stents in hard tissue such as bone, more particularly within a vertebral body. One exemplary method includes using a stent body that is coupled to a high speed rotational motor with the stent expandable and detachable from an introducer working end. In one embodiment, the stent is a deformable metal body with zig-zag type struts in an expanded configuration that carries diamond cutting particles bonded to the strut surfaces. The “spin” stent is rotated at high rpm's to remove cancellous bone from the deployment site together with irrigation and aspiration at the end of the probe that carries the stent. The stent may be expanded asymmetrically, such as with first and second balloons or by using an interior restraint, to apply vertical distraction forces to move apart the cortical endplates and support the vertebra in the distracted condition. The cancellous bone about the expanded stent as well as the interior of the stent can be filled with a bone cement, allograft or other bone graft material. In one method of use, the spin stent is designed and adapted for (i) treating a vertebral compression fracture (VCF) or for (ii) reinforcing an osteoporotic vertebral body.
Owner:DFINE INC
Systems and methods for treating fractured or diseased bone using expandable bodies
Systems and methods treat fractured or diseased bone by deploying more than a single therapeutic tool into the bone. In one arrangement, the systems and methods deploy an expandable body in association with a bone cement nozzle into the bone, such that both occupy the bone interior at the same time. In another arrangement, the systems and methods deploy multiple expandable bodies, which occupy the bone interior volume simultaneously. Expansion of the bodies form cavity or cavities in cancellous bone in the interior bone volume.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
Orthopedic surgery access devices
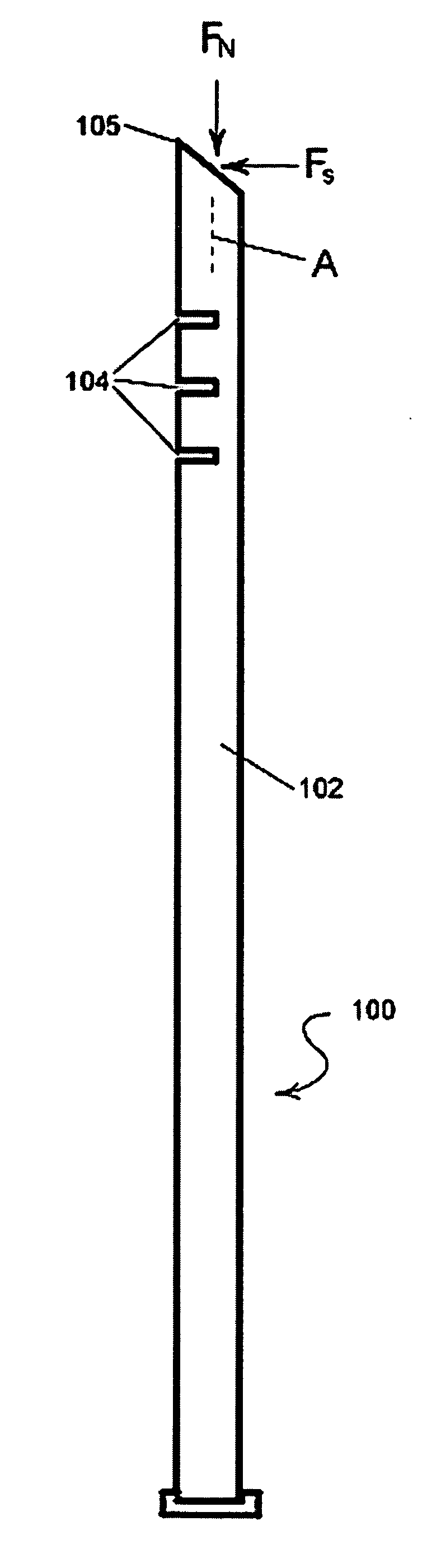
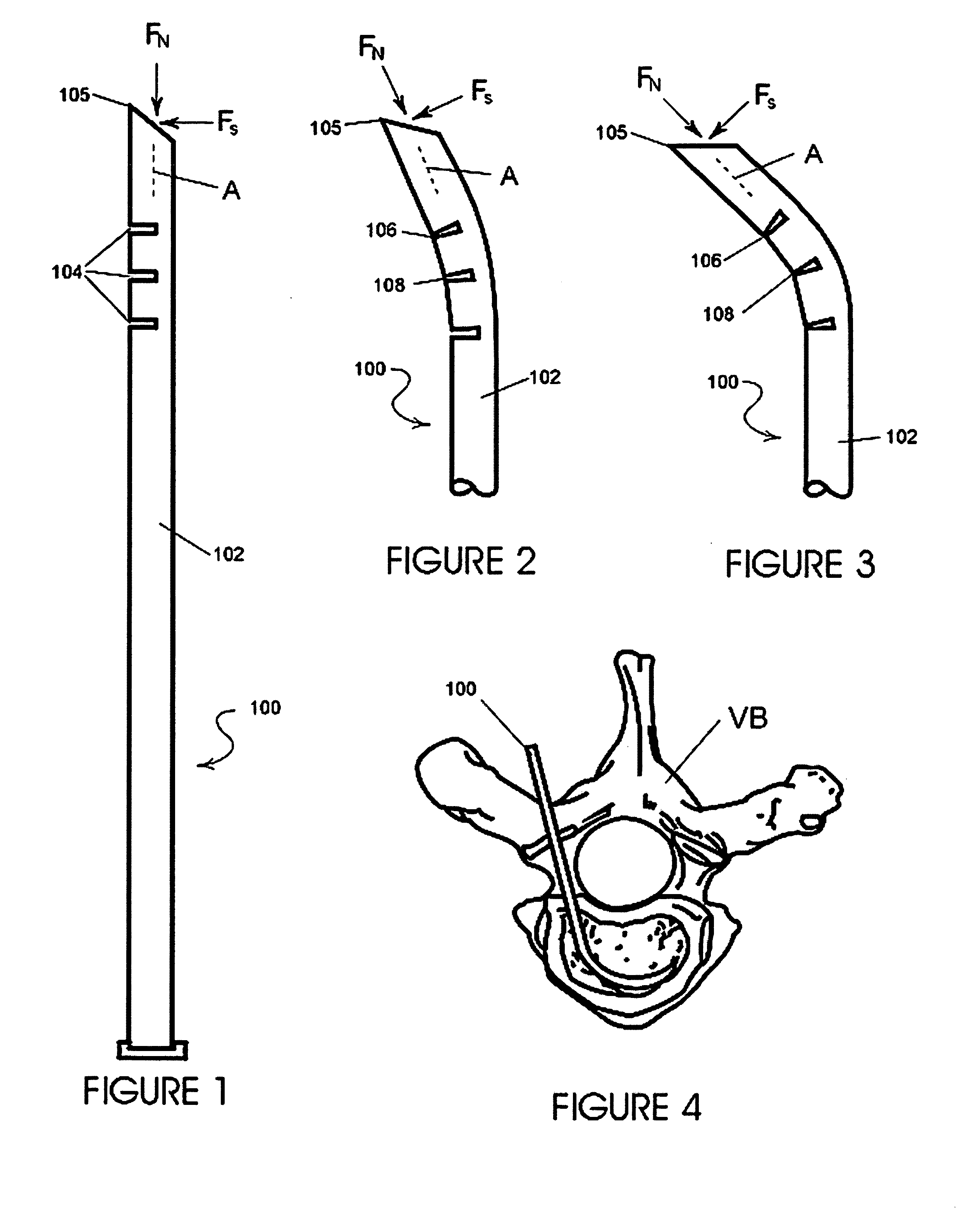
InactiveUS20050216018A1Easy accessLow bending stiffnessCannulasOsteosynthesis devicesCancellous boneBending stiffness
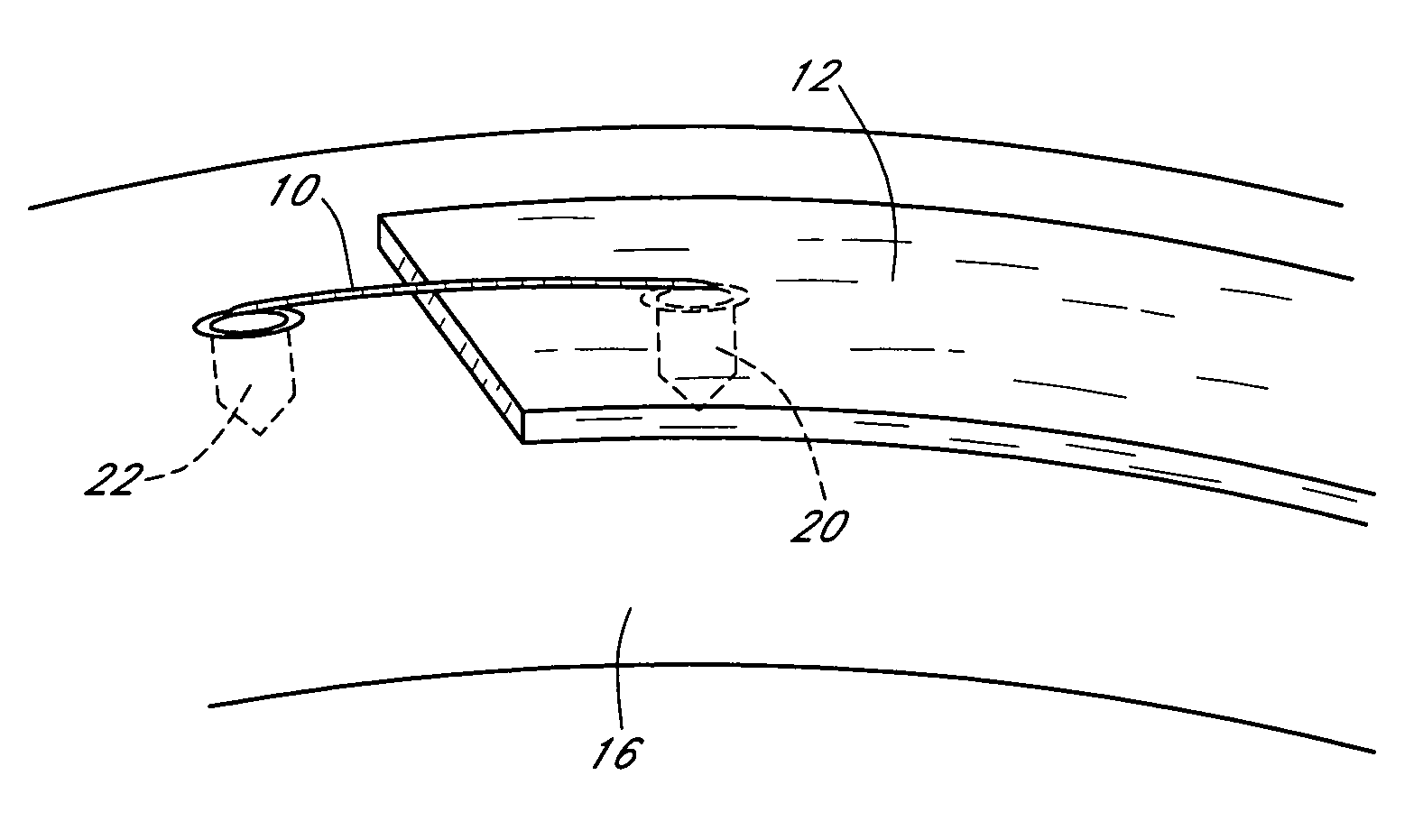
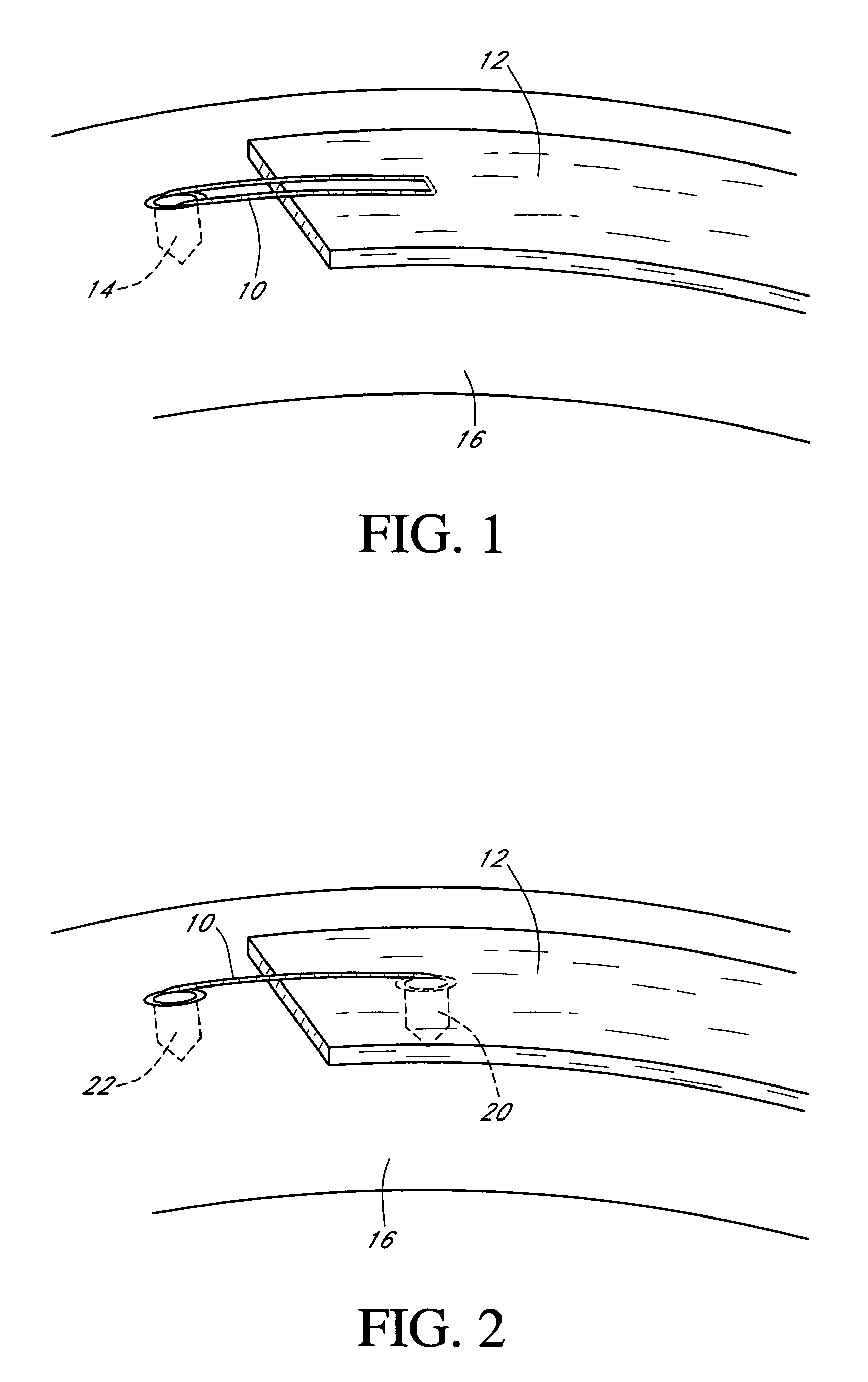
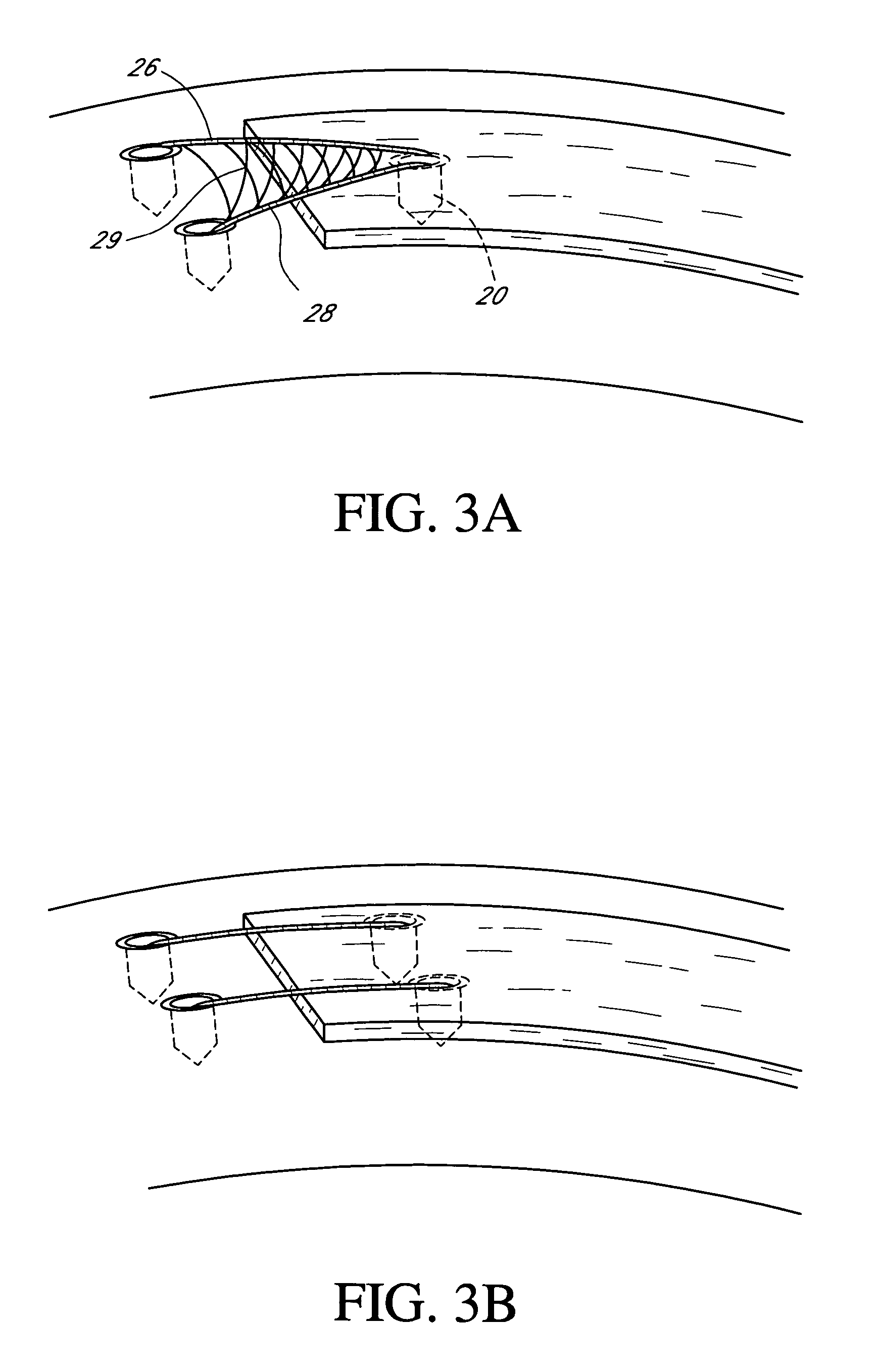
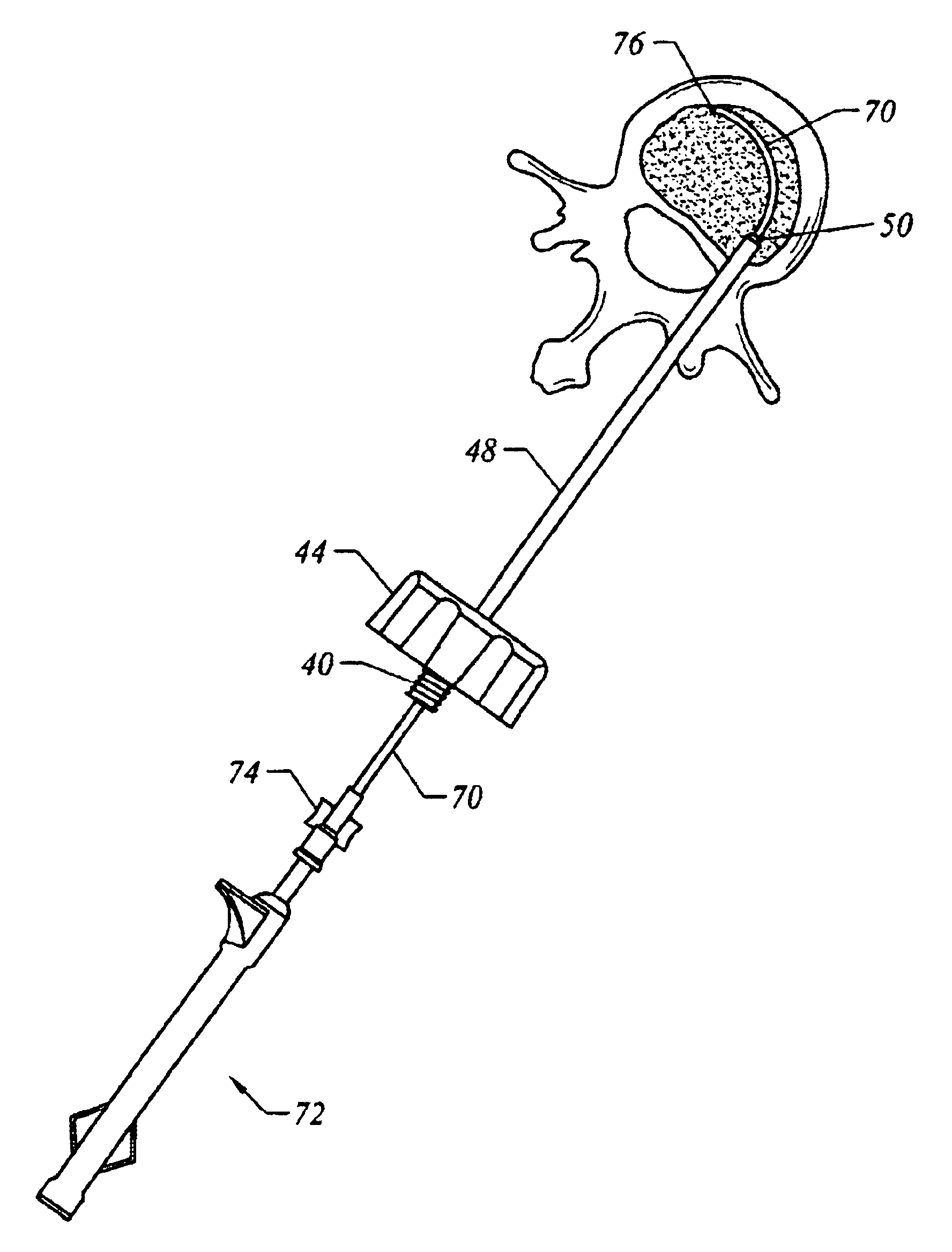
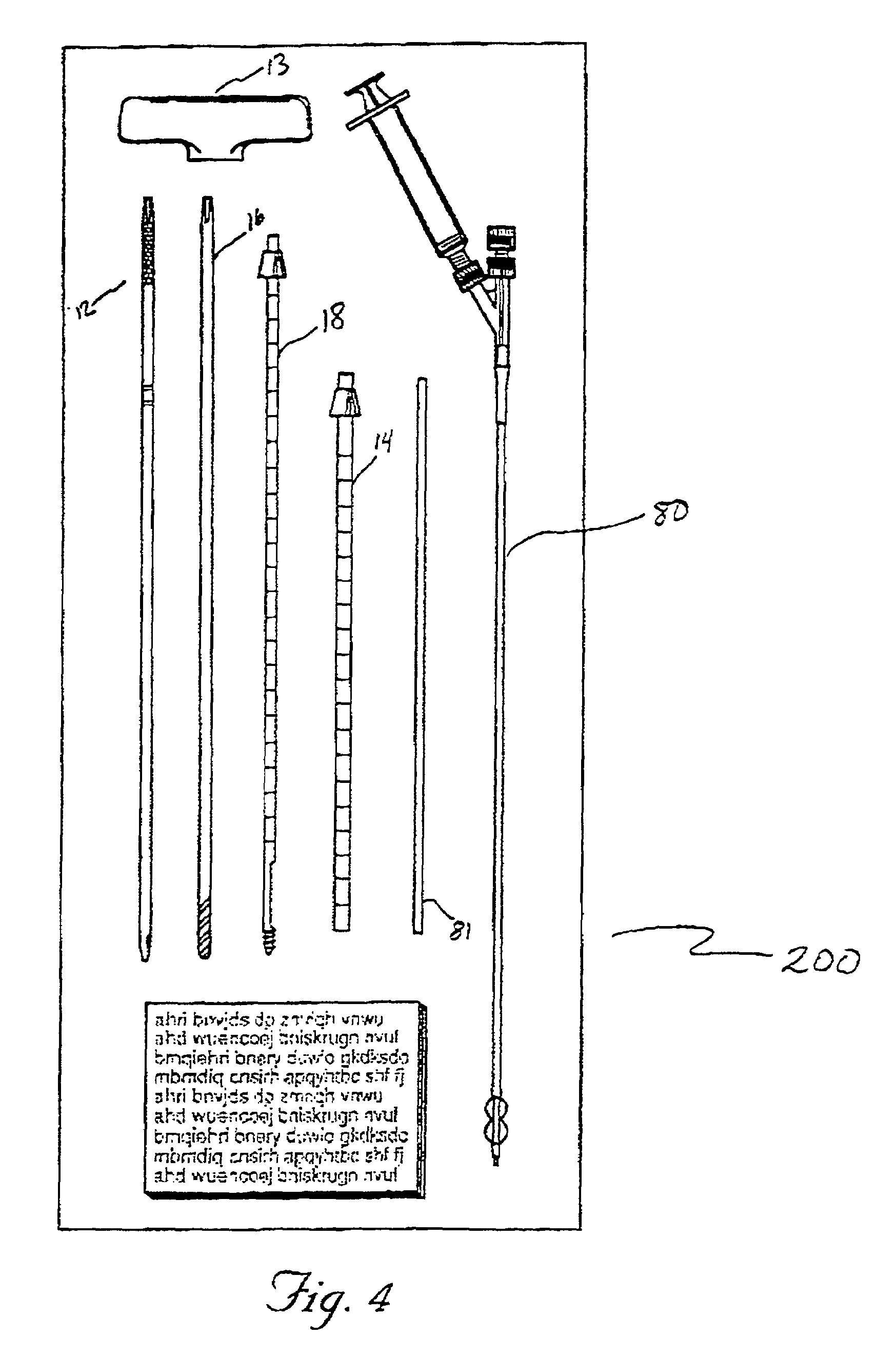
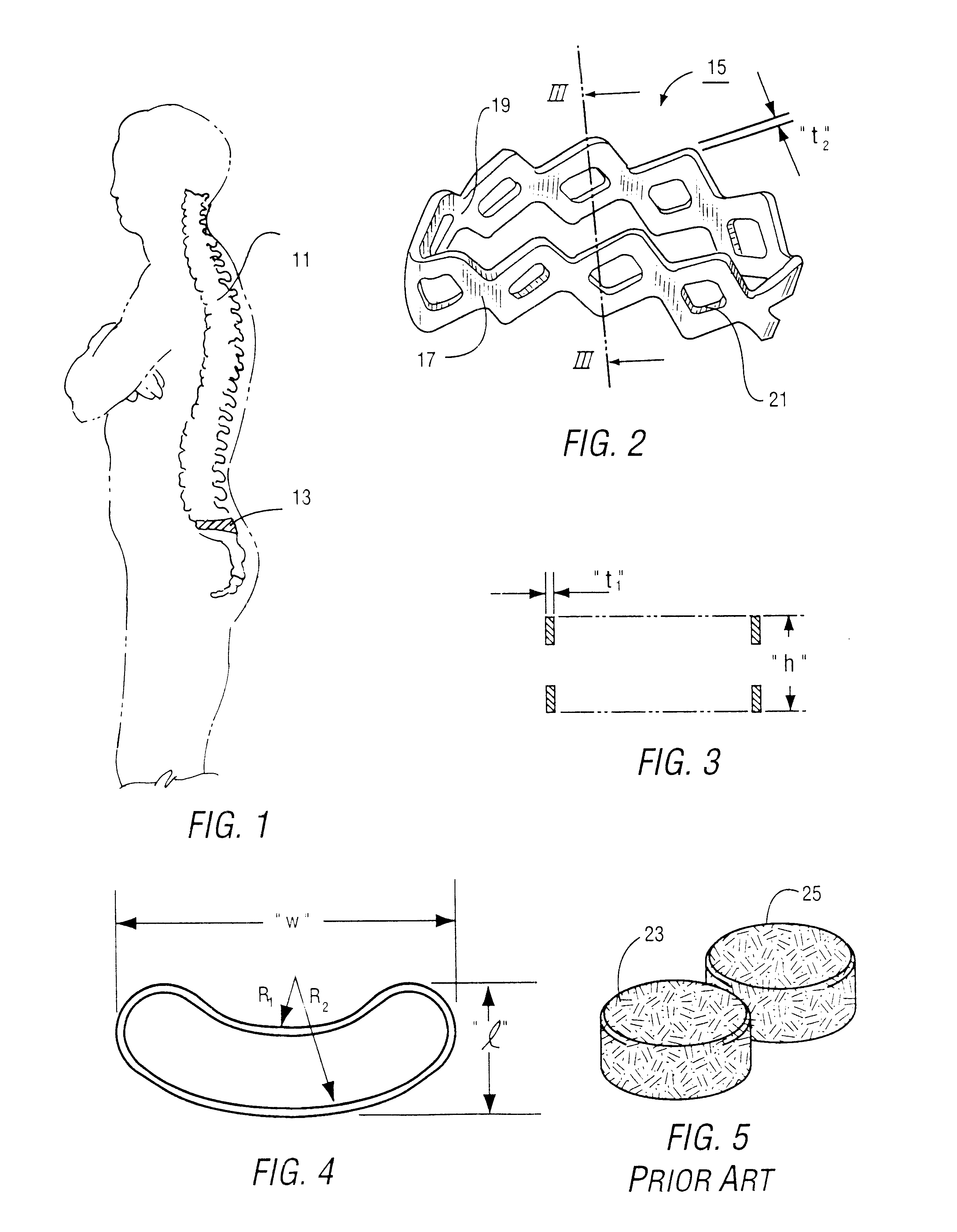
The present invention provides instrumentation that facilitates access to both sides of the vertebral body from a single access point. More particularly, the present invention provides bendable access devices that can be steered so as to traverse the vertebral body from the point of entry into the vertebral body, through the cancellous bone within the vertebral body, and to the contralateral side of the vertebral body. This steerability is provided by forming the access device with a series of slots, grooves, or notches in the side of the access device near the distal end of the access device, which slots, grooves, or notches reduce the bending stiffness of the access device. As a result, the distal end of the access device bends as it is being advanced into the vertebral body.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
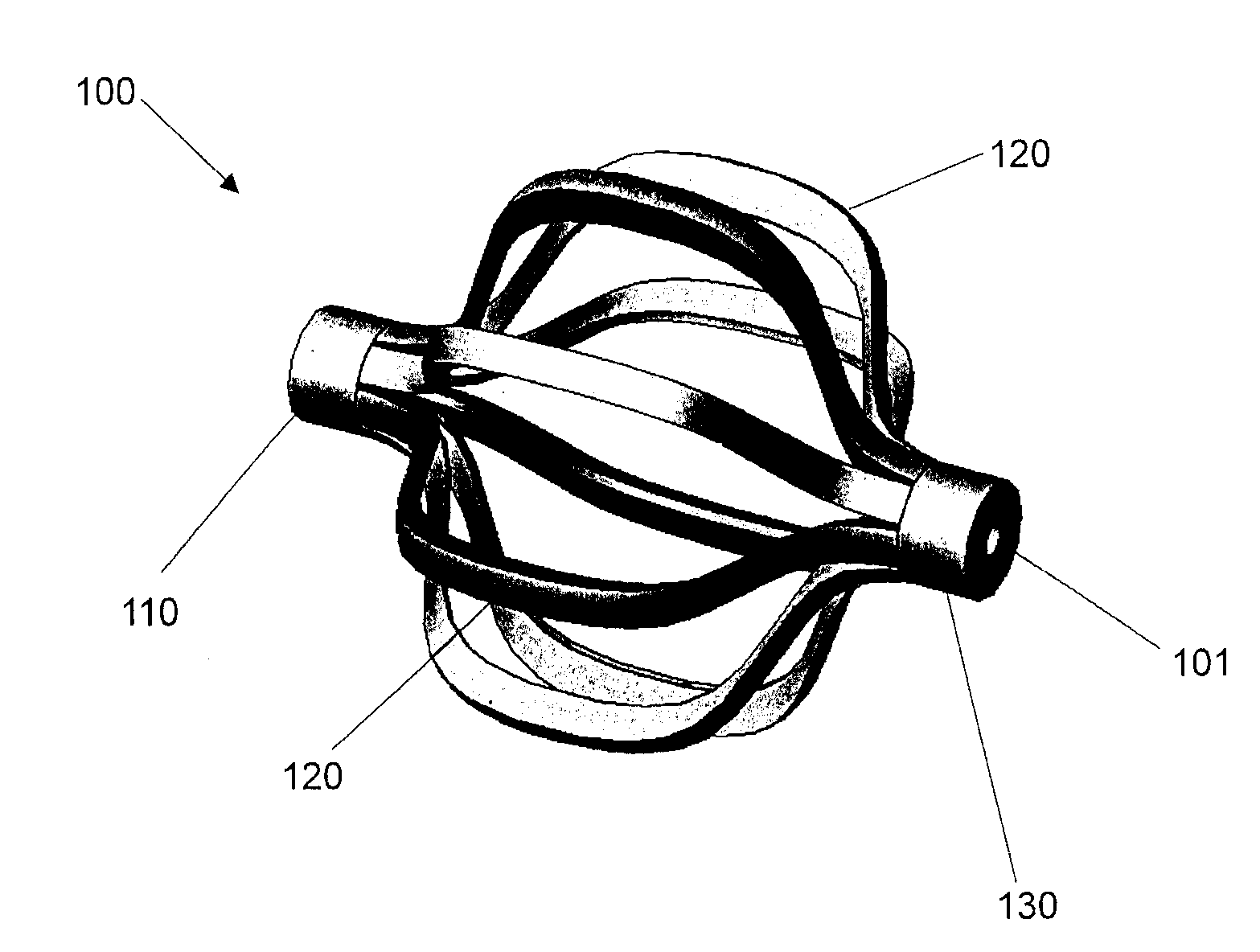
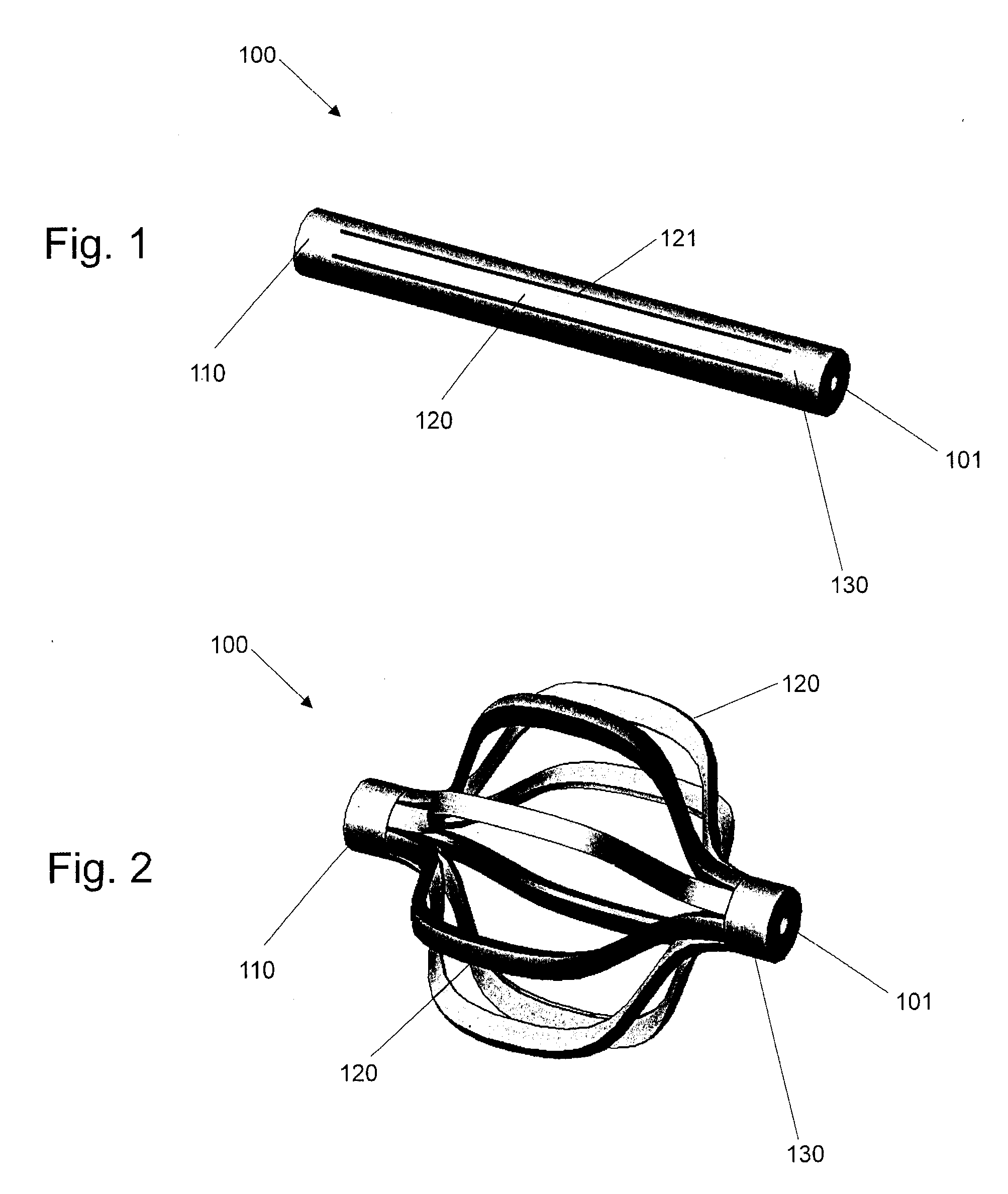
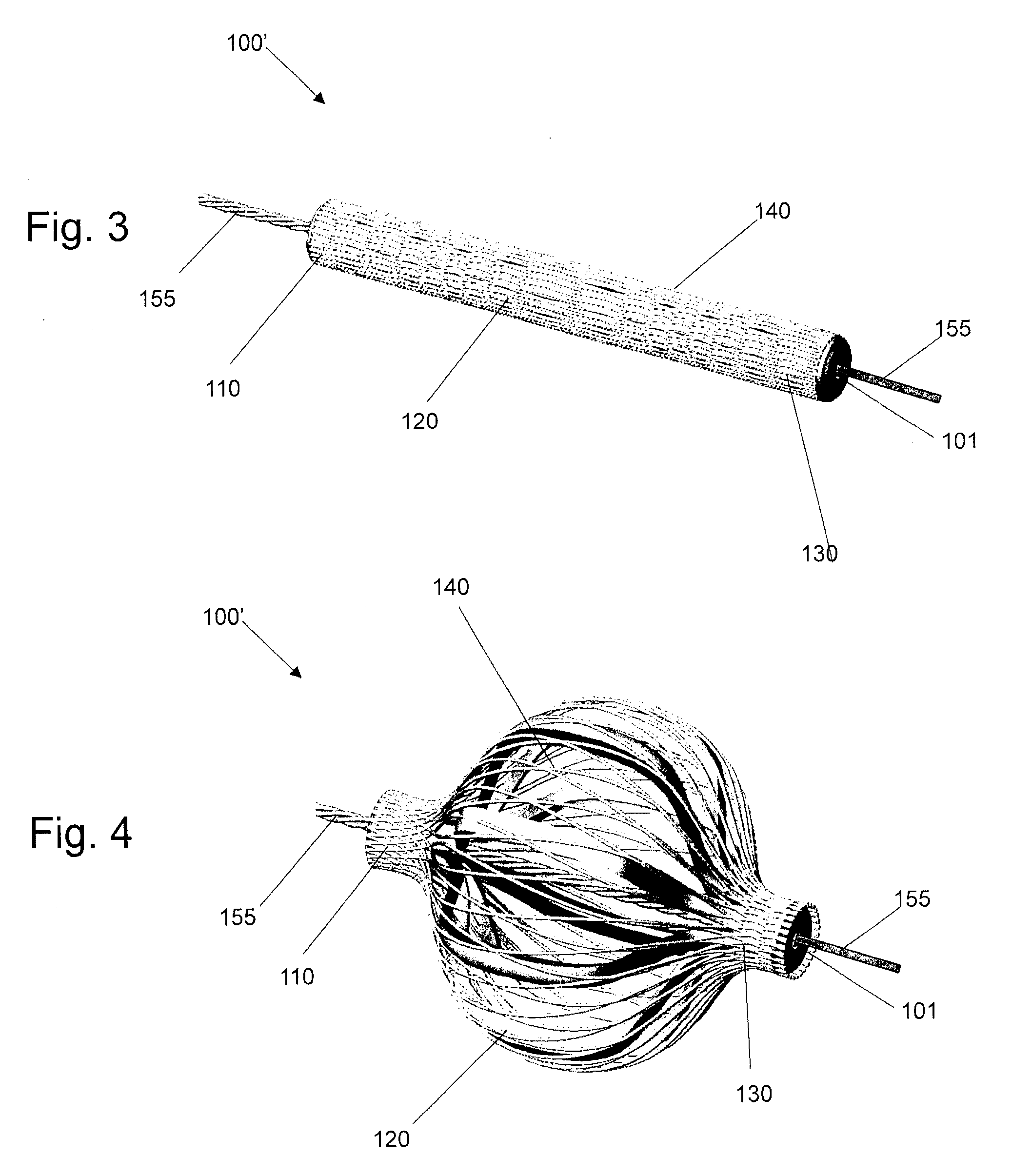
Expandable porous mesh bag device and methods of use for reduction, filling, fixation, and supporting of bone
ActiveUS7226481B2Less fear of punctureAvoid breakingInternal osteosythesisSurgical needlesSpinal columnDisease area
The invention provides a method of correcting numerous bone abnormalities including bone tumors and cysts, avascular necrosis of the femoral head, tibial plateau fractures and compression fractures of the spine. The abnormality may be corrected by first accessing and boring into the damaged tissue or bone and reaming out the damaged and / or diseased area using any of the presently accepted procedures or the damaged area may be prepared by expanding a bag within the damaged bone to compact cancellous bone. After removal and / or compaction of the damaged tissue the bone must be stabilized.
Owner:SPINEOLOGY
Structures and methods for creating cavities in interior body regions
Tools carry structures that are deployed inside bone and, when manipulated, cut cancellous bone to form a cavity.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
Systems and methods for fixation of bone with an expandable device
InactiveUS20070173939A1Avoid creatingInternal osteosythesisBone implantExpandable cageCancellous bone
Apparatus, systems and methods for providing fixation to an interior body region of a patient are provided. The apparatus includes an expandable cage which is inserted into a body region, such as cancellous bone of a vertebra, in a first geometry, and transitioned to a second geometry. Delivery devices and other tools are included including a material delivery device used to inject an agent into a body region without requiring or creating a void in that region. Methods are also provided for providing fixation to an internal body region.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
System and method for attaching soft tissue to bone
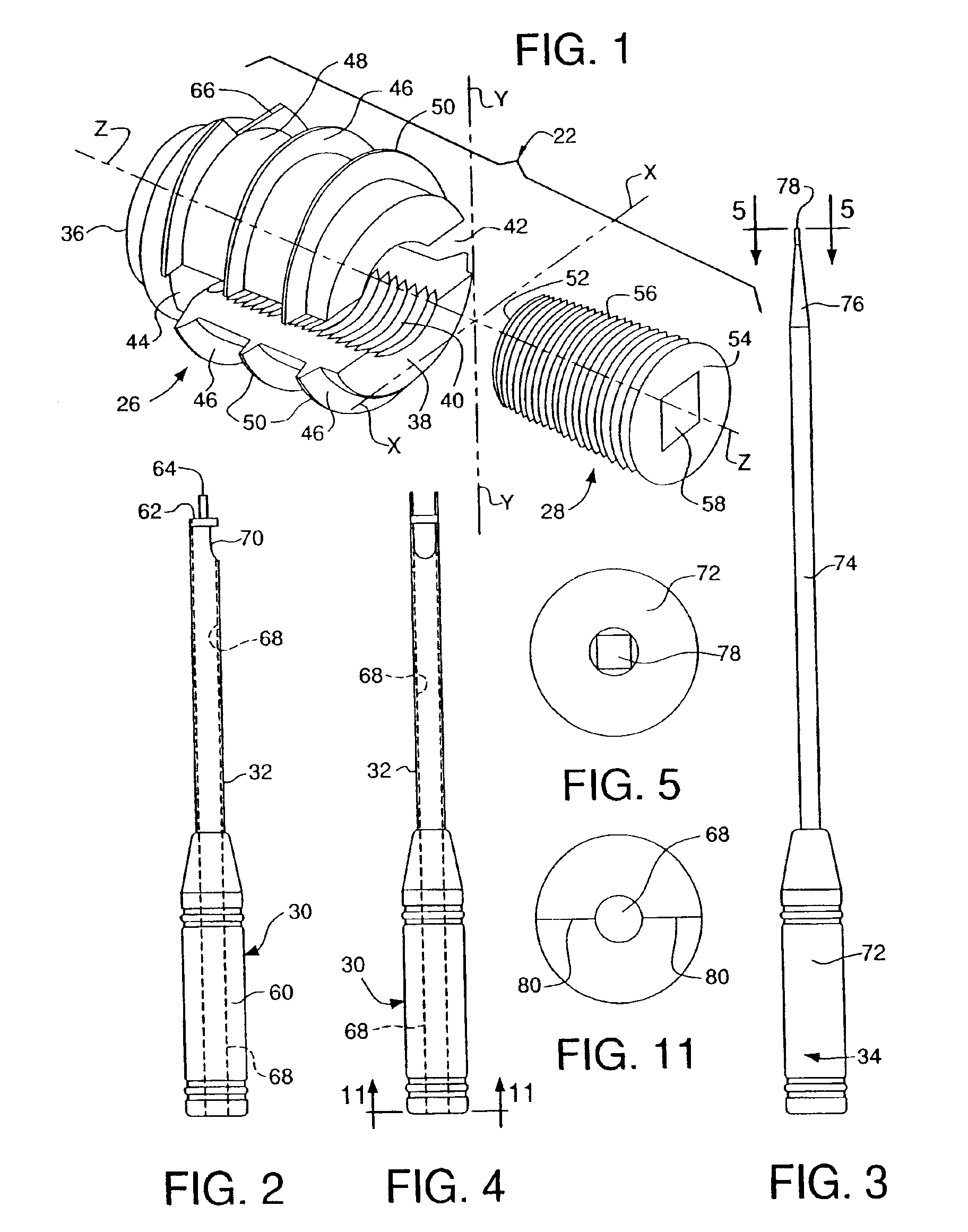
Disclosed herein are methods and devices for securing soft tissue to a rigid material such as bone. A bone anchor is described that comprises a base and a top such that suture material may be compressed between surfaces on the base and top to secure the suture to the anchor. Also described is an inserter that can be used to insert the bone anchor into bone and move the anchor top relative to the anchor base to clamp suture material there between. Also described is a soft-tissue and bone piercing anchor and associated inserter. Methods are described that allow use of the bone anchors to provide multiple lengths of suture material to compress a large area of soft tissue against bone.
Owner:SCOTT W TATE
Bone access system
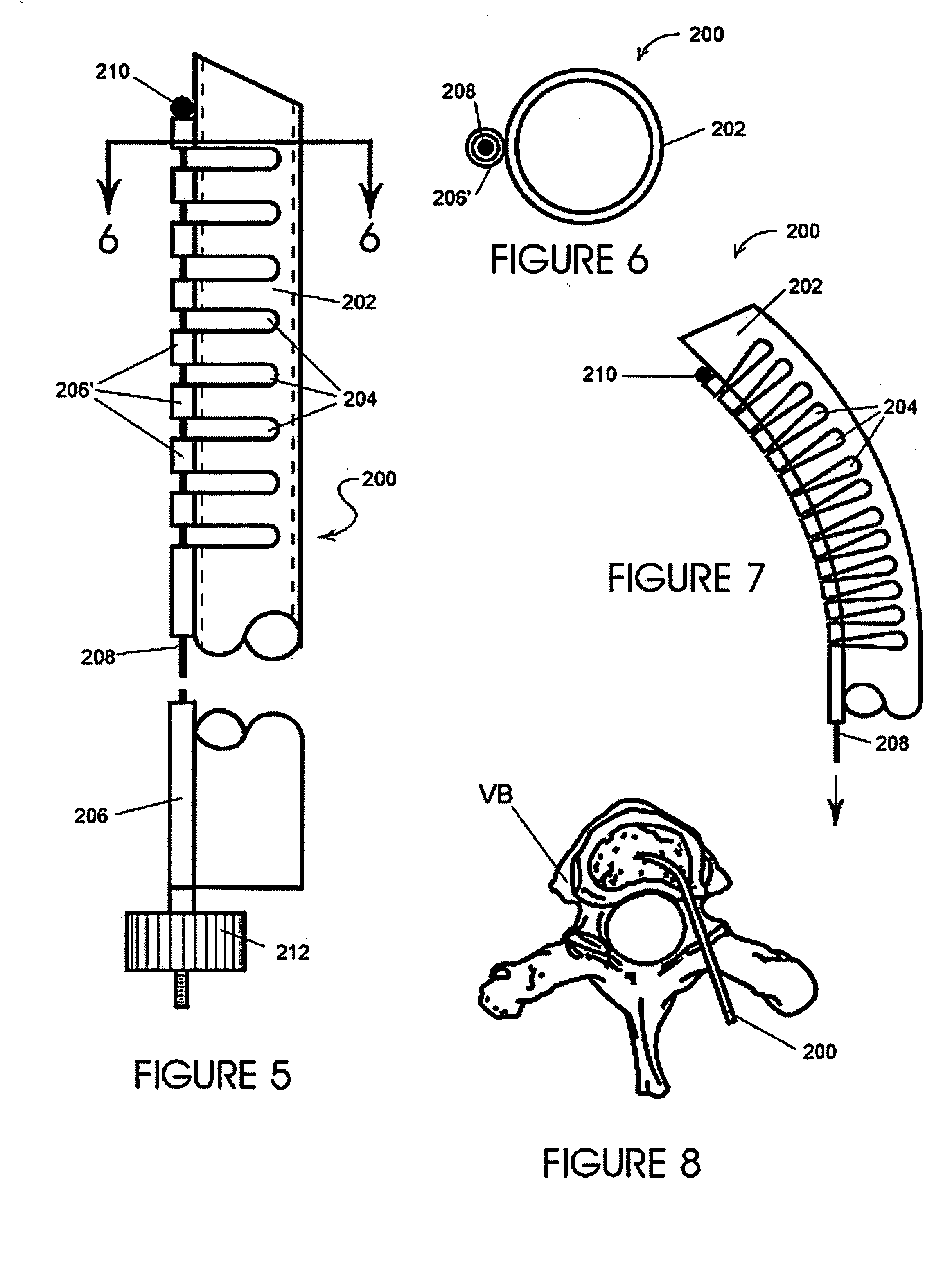
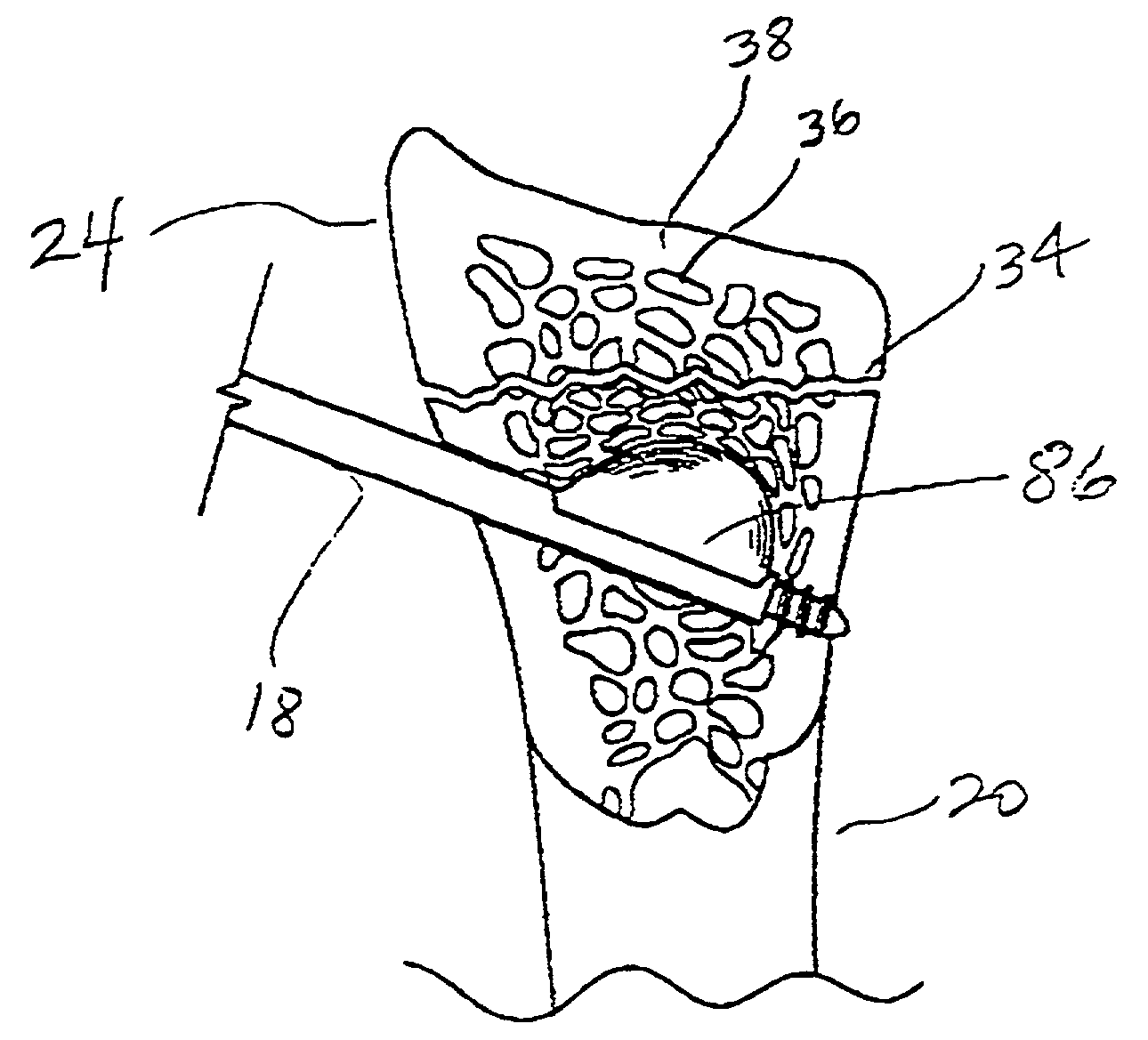
InactiveUS20060064101A1Reduce riskLow stiffnessSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingBone tissueCatheter
Instruments and methodology for nonlinear access to bone tissue sites are described. Embodiments disclosed include a conduit for delivering material or a medical device to a site and a core member that is able to steer the conduit and allow the combination to be advanced thorough cancellous bone. A cannula and stylet may be provided to first advance through hard bone. The core member includes a curved tip that may be straightened by the cannula or an actuator sheath to vary sweep of the curve. An obturator may be included in the system. This instrument may include a flexible portion as well. Each of the obturator and conduit may be provided with any of a variety of active tips. The systems may be used to perform hard tissue site implantation, for example, in connection with a high pressure injection system.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
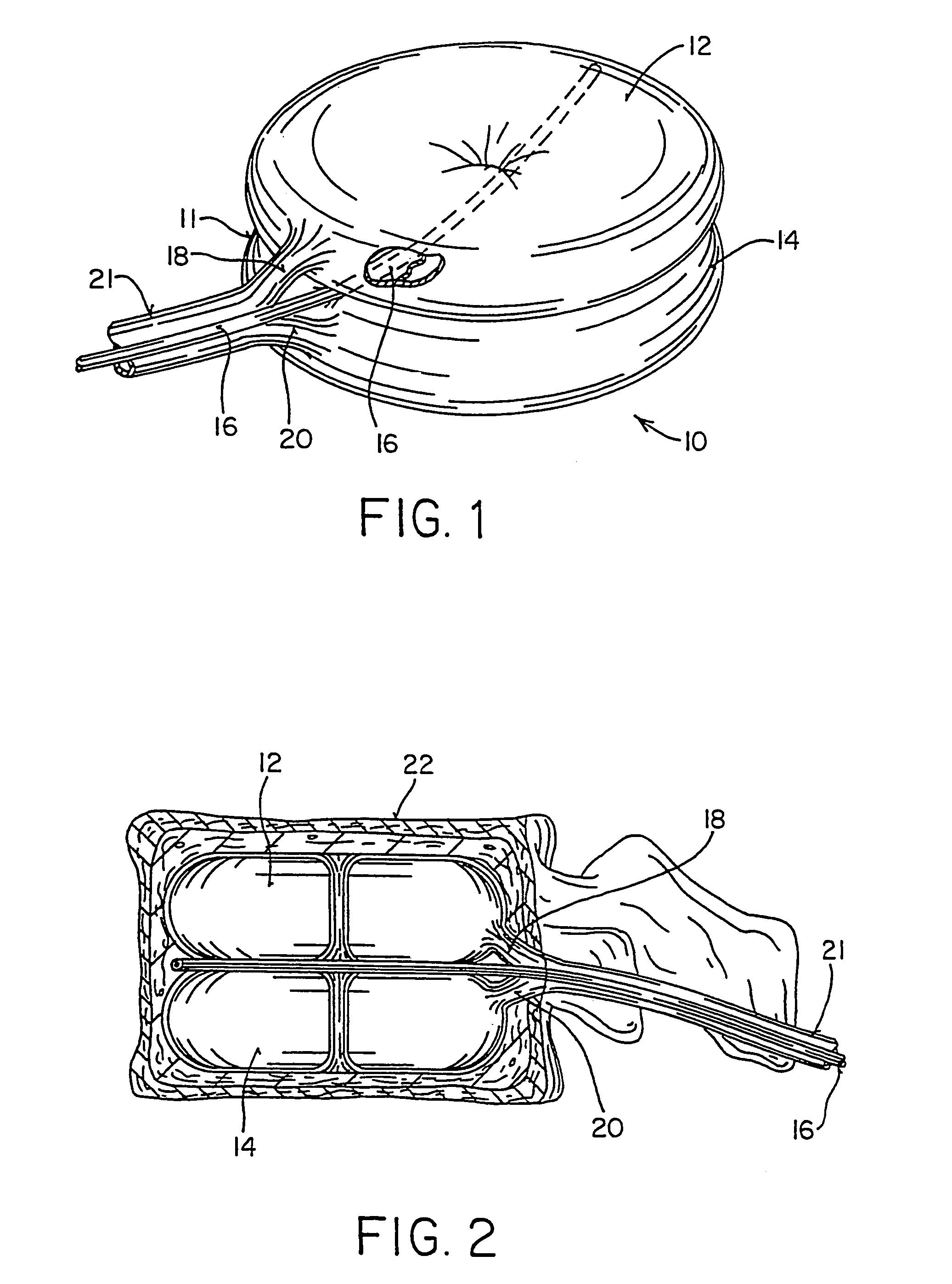
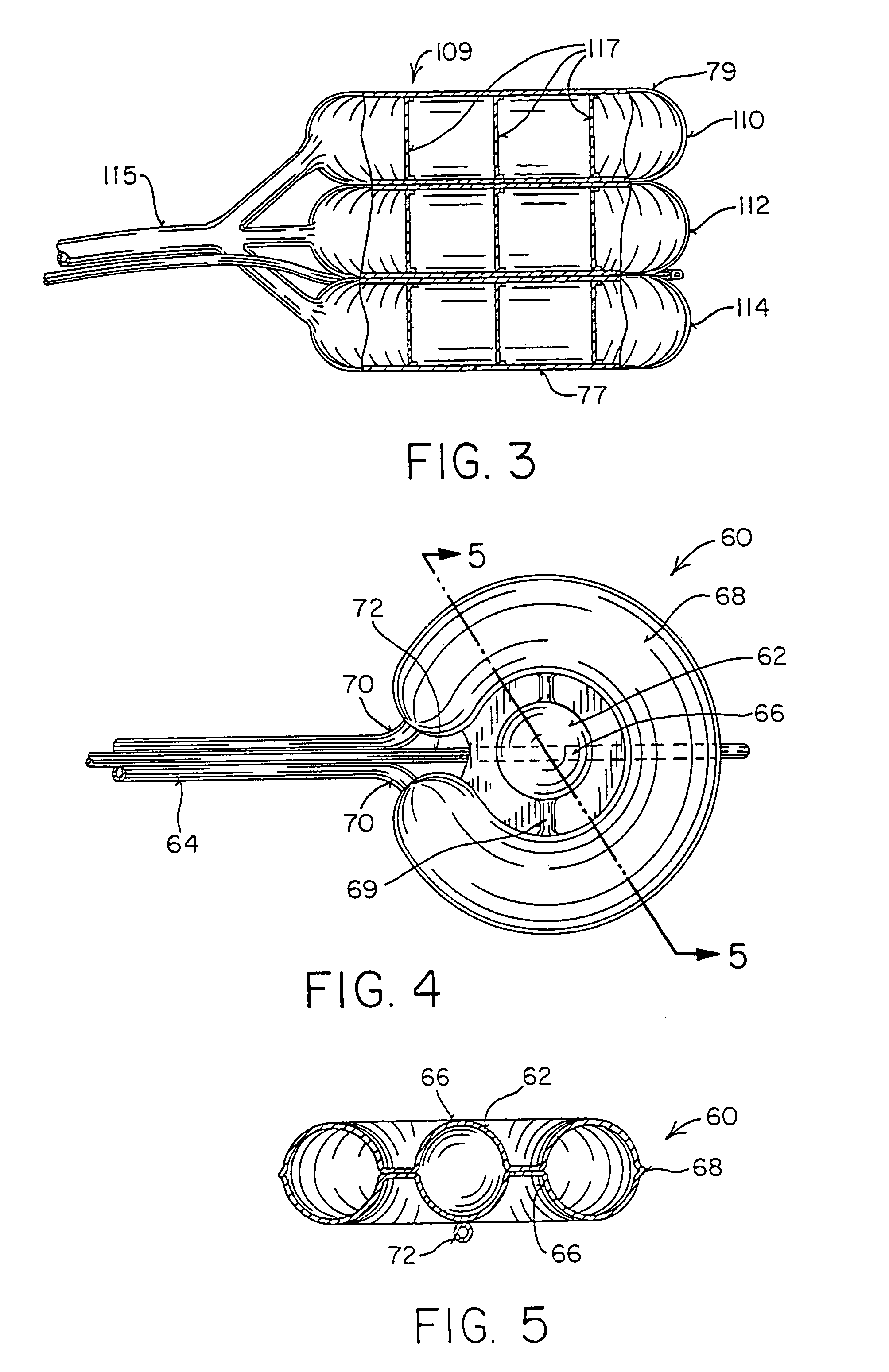
Intervertebral body fusion cage with keels and implantation method
An intervertebral implant has a fusion body with at least one keel that anchors the implant into cancellous bone of at least one vertebral body. A method for implantation includes lateral implantation of the implant.
Owner:KYPHON
Inflatable device for use in surgical protocol relating to fixation of bone
InactiveUS7261720B2Easy to compressEasy to foldSurgical furnitureInternal osteosythesisBone CortexTrabecular bone
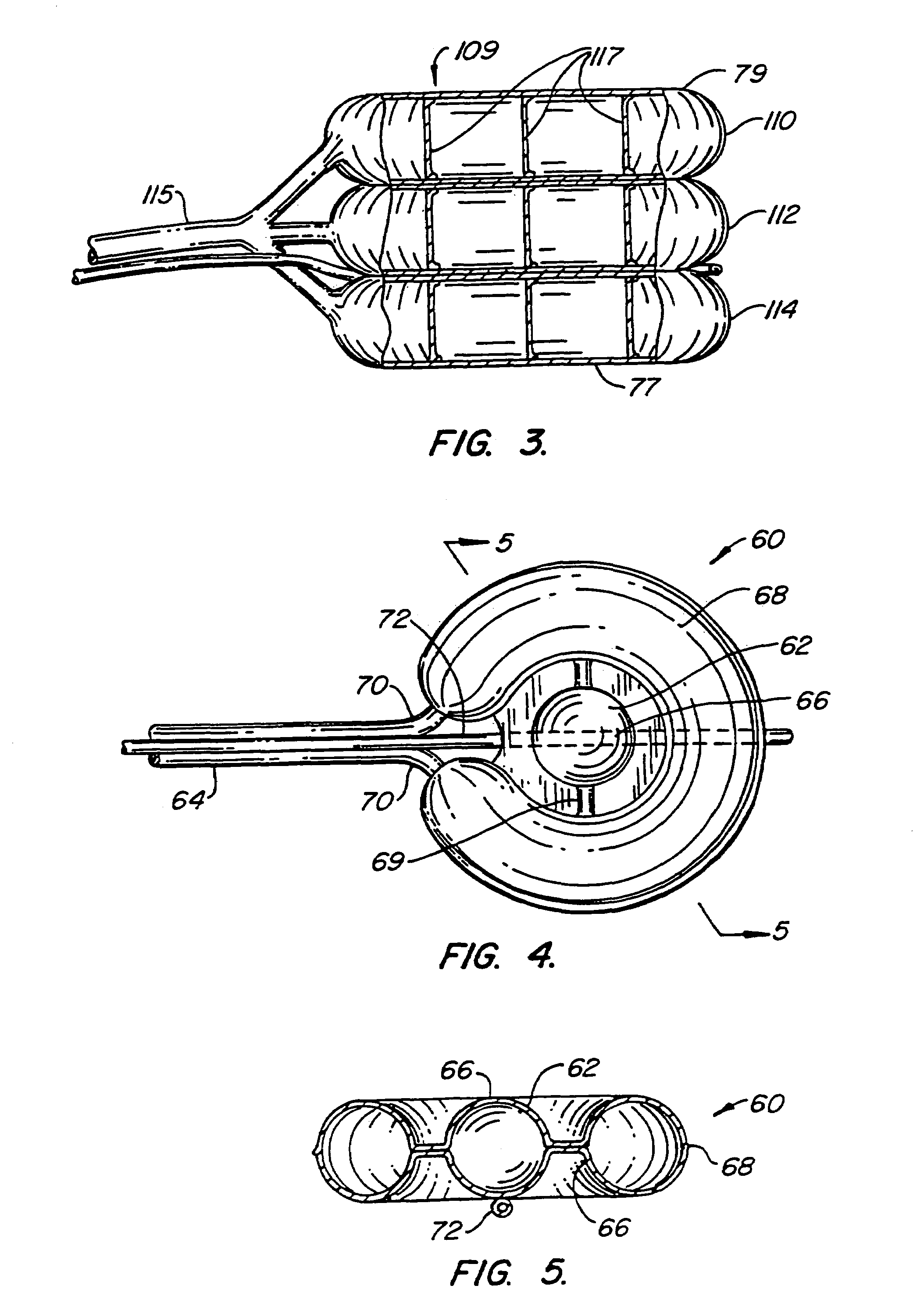
A balloon for use in compressing cancellous bone and marrow (also known as medullary bone or trabecular bone). The balloon comprises an inflatable balloon body for insertion into said bone. The body has a shape and size to compress at least a portion of the cancellous bone to form a cavity in the cancellous bone and / or to restore the original position of the outer cortical bone, if fractured or collapsed. The balloon desirably incorporates restraints which inhibit the balloon from applying excessive pressure to various regions of the cortical bone. The wall or walls of the balloon are such that proper inflation of the balloon body is achieved to provide for optimum compression of the bone marrow. The balloon can be inserted quickly into a bone. The balloon can be made to have a suction catheter. The balloon can be used to form and / or enlarge a cavity or passage in a bone, especially in, but not limited to, vertebral bodies. Various additional embodiments facilitate directionally biasing the inflation of the balloon.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
Bone access system
InactiveUS6875219B2Reduce riskLow stiffnessSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBone tissueCatheter
Instruments and methodology for nonlinear access to bone tissue sites are described. Embodiments disclosed include a conduit for delivering material or a medical device to a site and a core member that is able to steer the conduit and allow the combination to be advanced thorough cancellous bone. A cannula and stylet may be provided to first advance through hard bone. The core member includes a curved tip that may be straightened by the cannula or an actuator sheath to vary sweep of the curve. An obturator may be included in the system. This instrument may include a flexible portion as well. Each of the obturator and conduit may be provided with any of a variety of active tips. The systems may be used to perform hard tissue site implantation, for example, in connection with a high pressure injection system.
Owner:NEUROTHERM
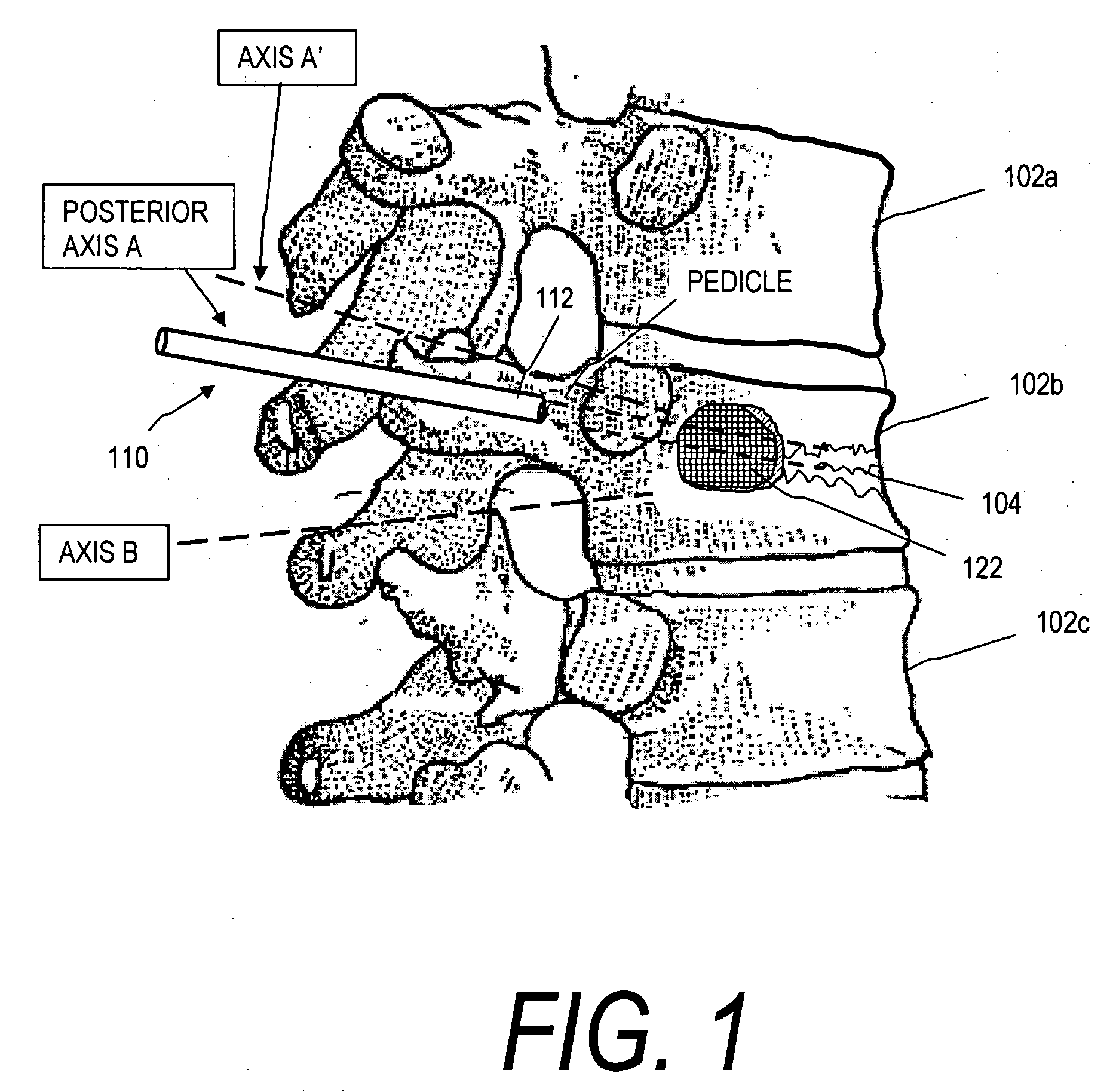
System for stabilizing the vertebral column including deployment instruments and variable expansion inserts therefore
InactiveUS6905512B2Stabilize spineStabilizing the being's vertebral columnJoint implantsSpinal implantsIntervertebral spaceLigament structure
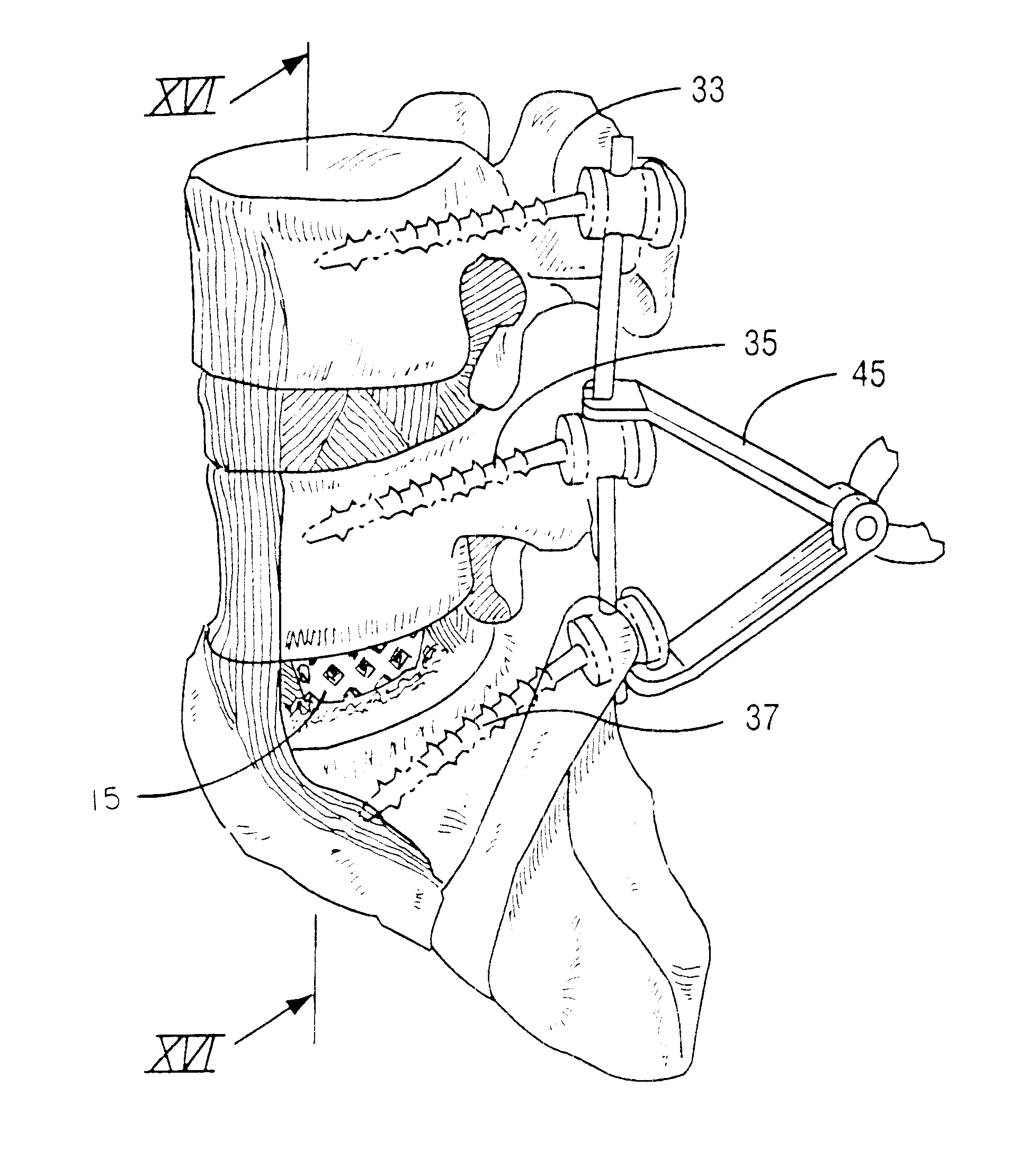
A system is provided for stabilizing adjacent vertebra without excision of bone or resection of ligaments comprising an expansion device and a deployment system which includes a hollow expandable insert and an expansion insert. The expandable insert includes a cylindrical body having a pair of slots having a threaded outer surface. The expandable insert is located with the slots oriented perpendicular to the vertebral column between the vertebrae. The thread cuts into the cortical bone contiguous to the intervertebral space but not substantially into the cancellous bone. The expandable insert is internally threaded. The expansion insert is externally threaded and arranged to be screwed into a bore in the expandable insert by the deployment system, whereupon the slots open to spread the vertebrae apart. The deployment system includes a tool having projecting fingers located within the slots to enable the expandable insert to be screwed into the intervertebral space.
Owner:PHOENIX BIOMEDICAL
Systems and methods for reducing fractured bone using a fracture reduction cannula
InactiveUS7153306B2Relieve painRaise the possibilitySurgical furnitureSurgical needlesFracture reductionFilling materials
Systems and methods provide for the fixation of osteoporotic and non-osteoporotic long bones, especially Colles' fractures. A cannula having a circumferential opening is inserted into cancellous bone and directed such that the circumferential opening faces the fracture. The cannula is further adapted to receive an expandable structure, the expandable structure being inserted through the cannula until it is in registration with the circumferential opening. The expandable structure is expanded through the circumferential opening into cancellous bone and toward the fracture. The expansion of the expandable structure through the circumferential opening toward the fracture causes compression of cancellous bone and moves fractured cortical bone, thus creating a cavity proximal to the fracture. The cavity is then filled with a flowable bone filling material and the material allowed to harden.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
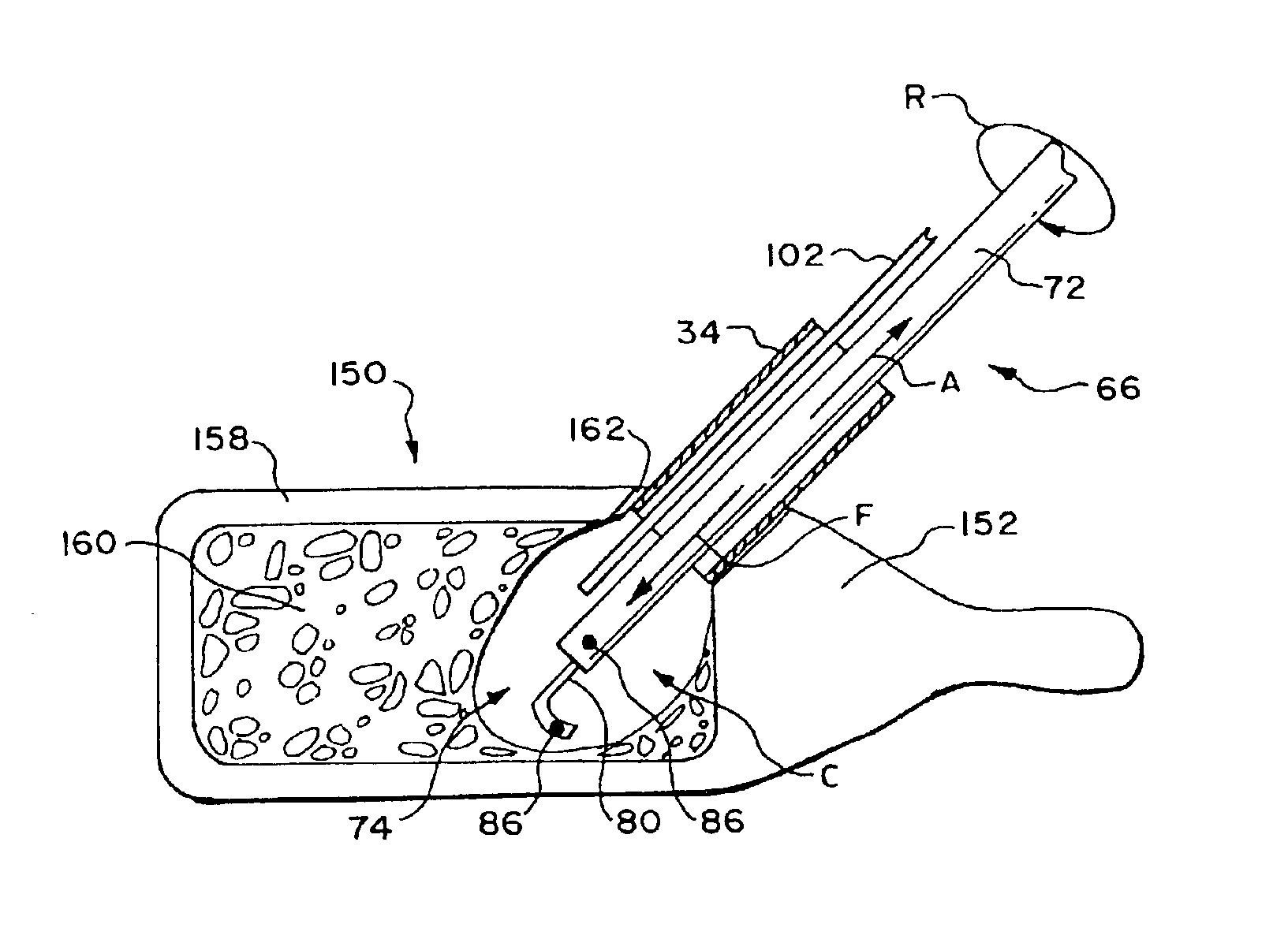
Implantable devices and methods for treating micro-architecture deterioration of bone tissue
InactiveUS20070067034A1Prevent slippagePrevent movementInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsBone tissueImplanted device
An expandable stabilization device is disclosed that is suitable for deployment within cancellous bone, including, for example, within a vertebral body of a spine. The device comprises: an elongate expandable shaft adapted to be positioned within a vertebral body having a first profile and a second profile; wherein the shaft is adapted to cut through cancellous bone within the vertebral body during expansion from the first profile to the second profile; and further wherein the shaft is adapted to abut a surface of cortical bone within the vertebral body without passing therethrough. The invention also includes a method for treating cancellous bone, such as cancellous bone of a vertebral body. The method comprises: delivering an expandable device within the cancellous bone of in an interior of a vertebral body; expanding the delivered device within the cancellous bone of the vertebra body; applying force from a surface of the device to an inner surface of a cancellous bone of the vertebral body sufficient to cut through the cancellous bone; and applying force from a surface of the device to an inner surface of a cortical bone of the vertebral body sufficient to support the vertebral body
Owner:SPINEALIGN MEDICAL
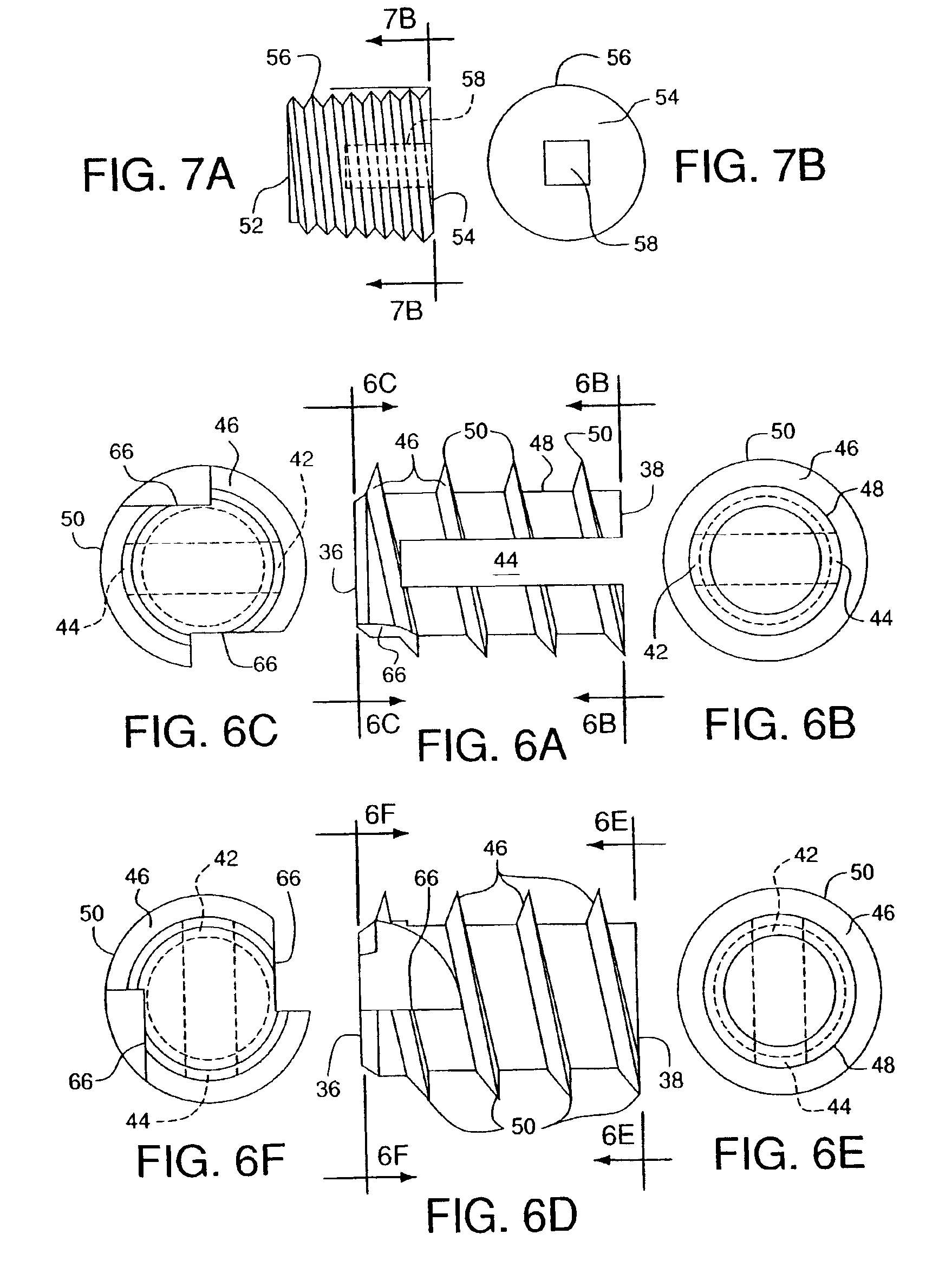
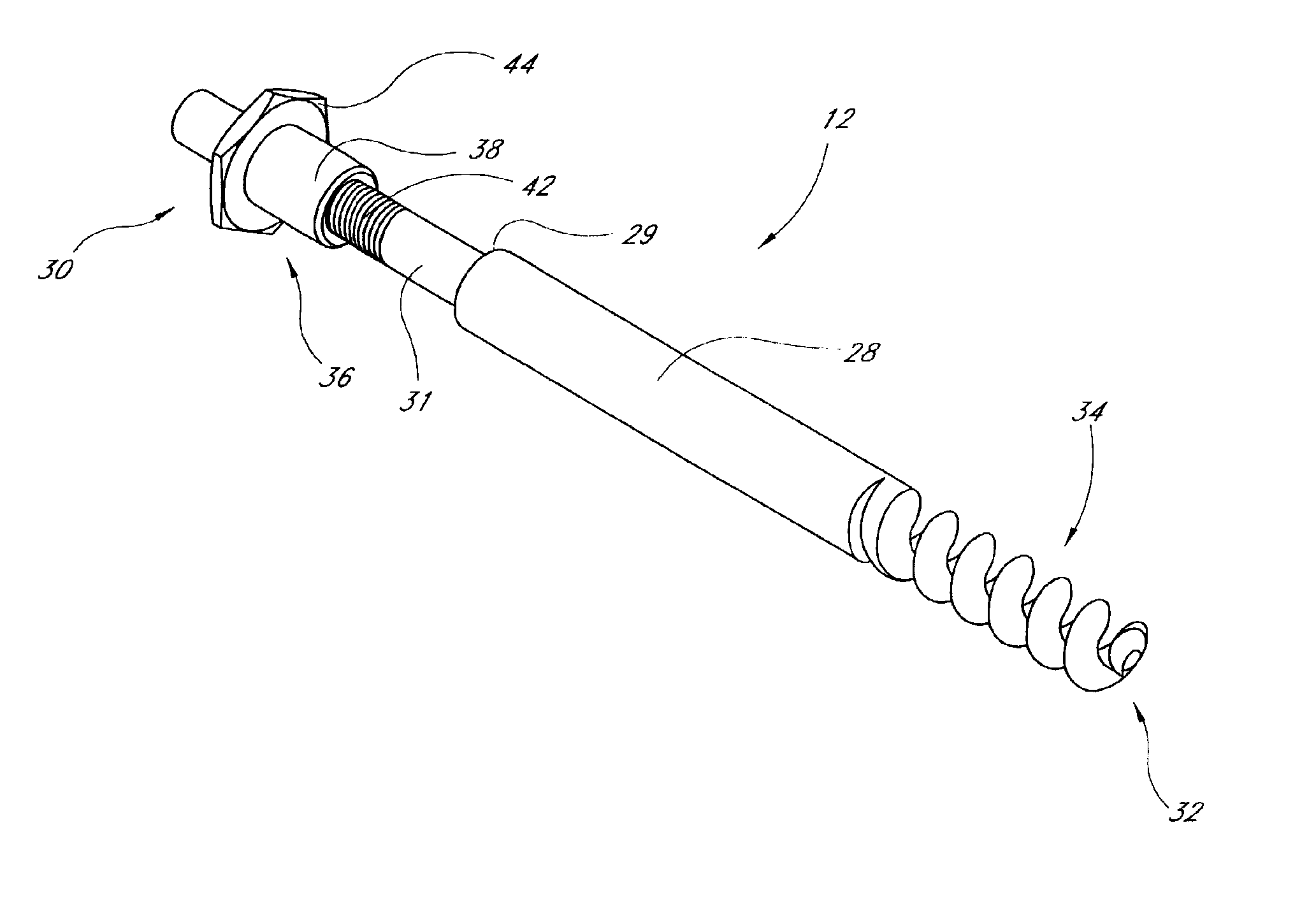
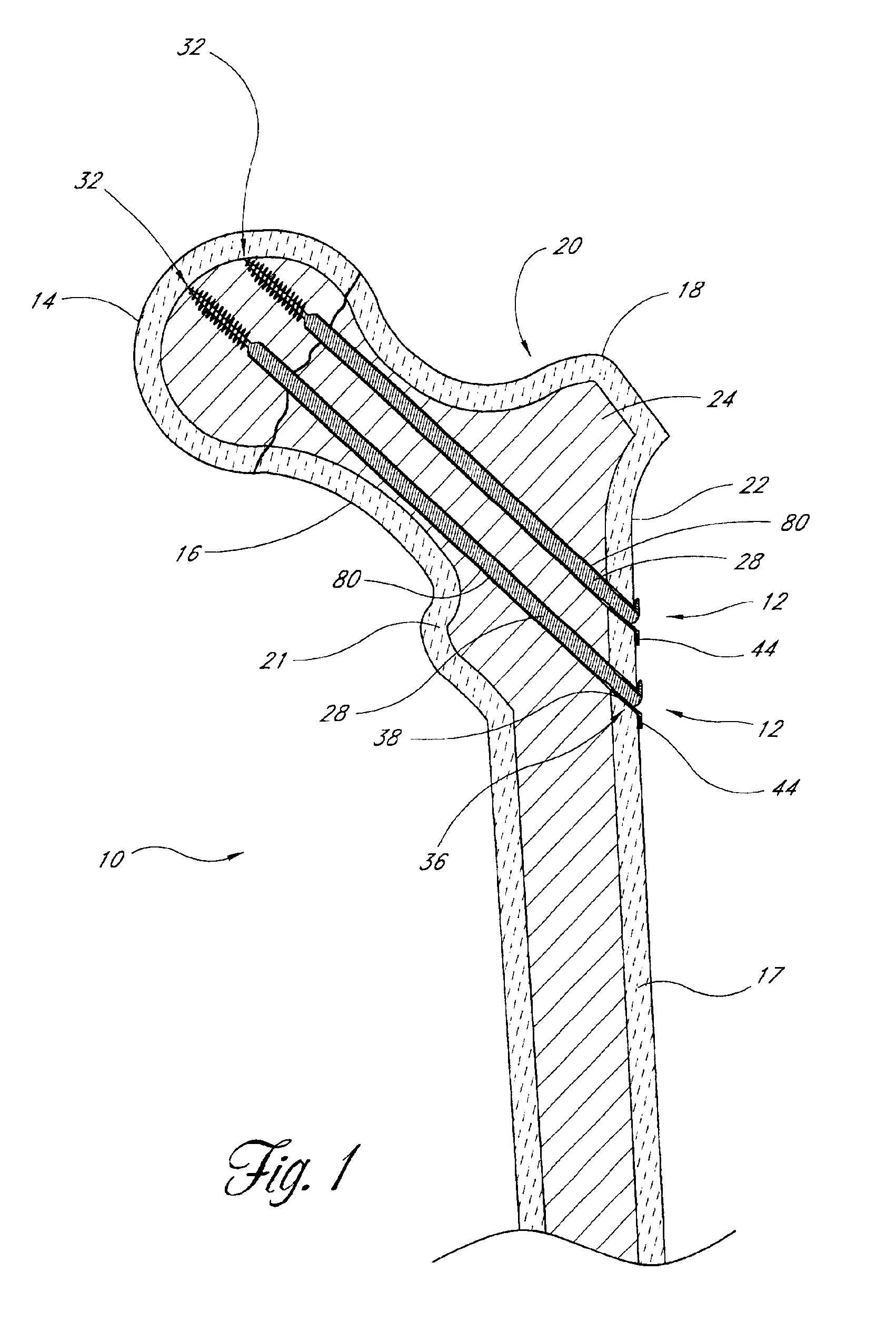
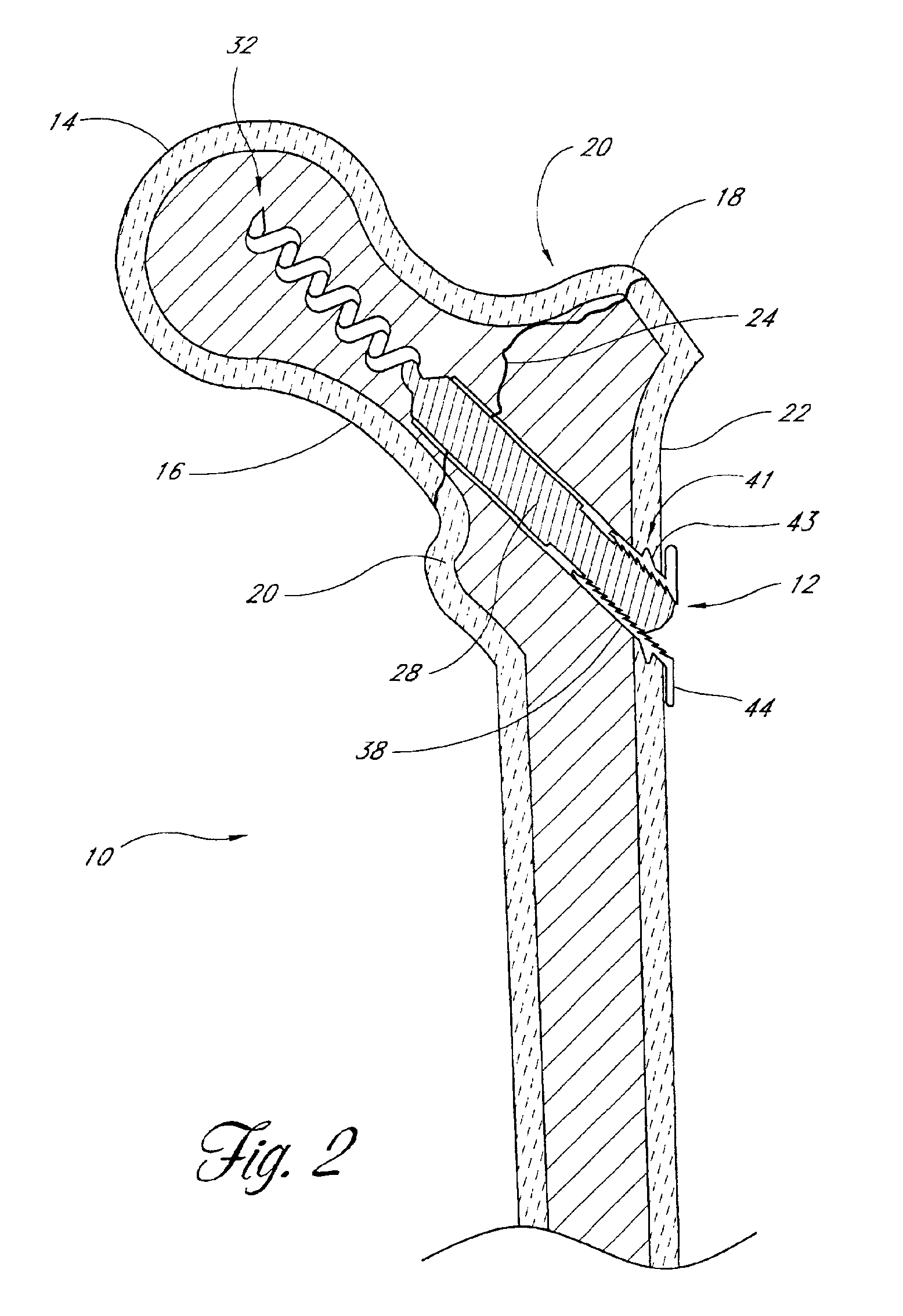
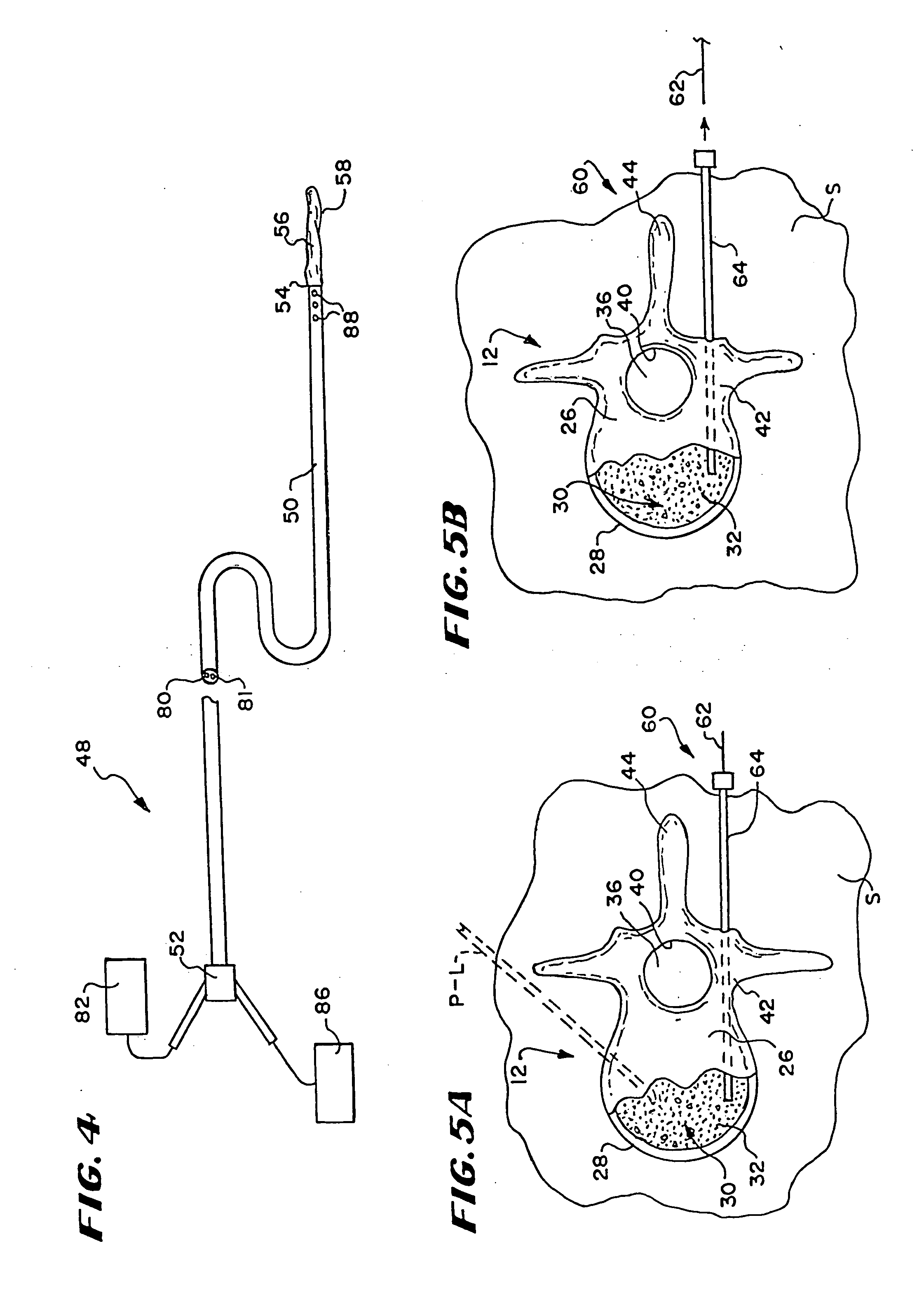
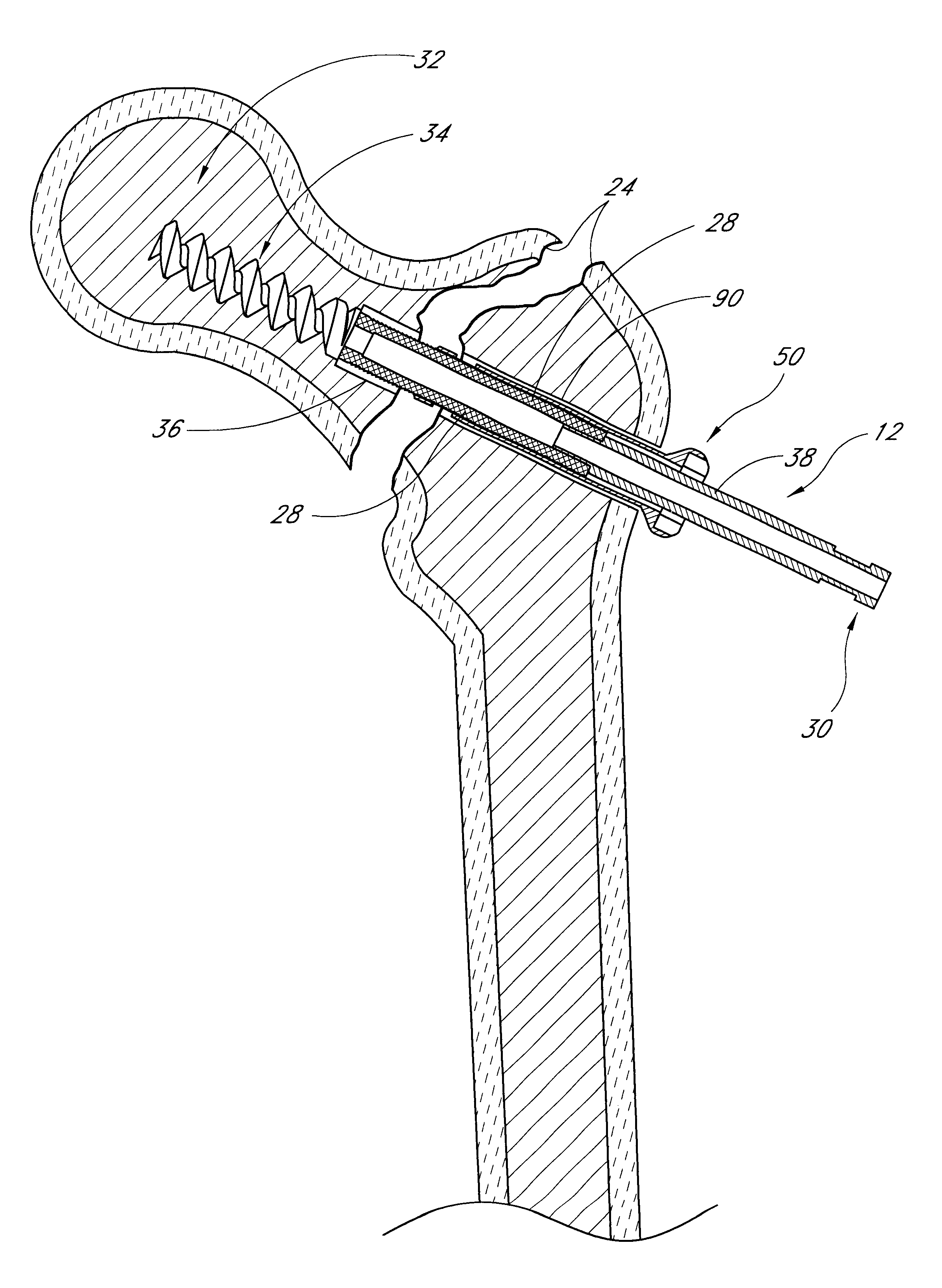
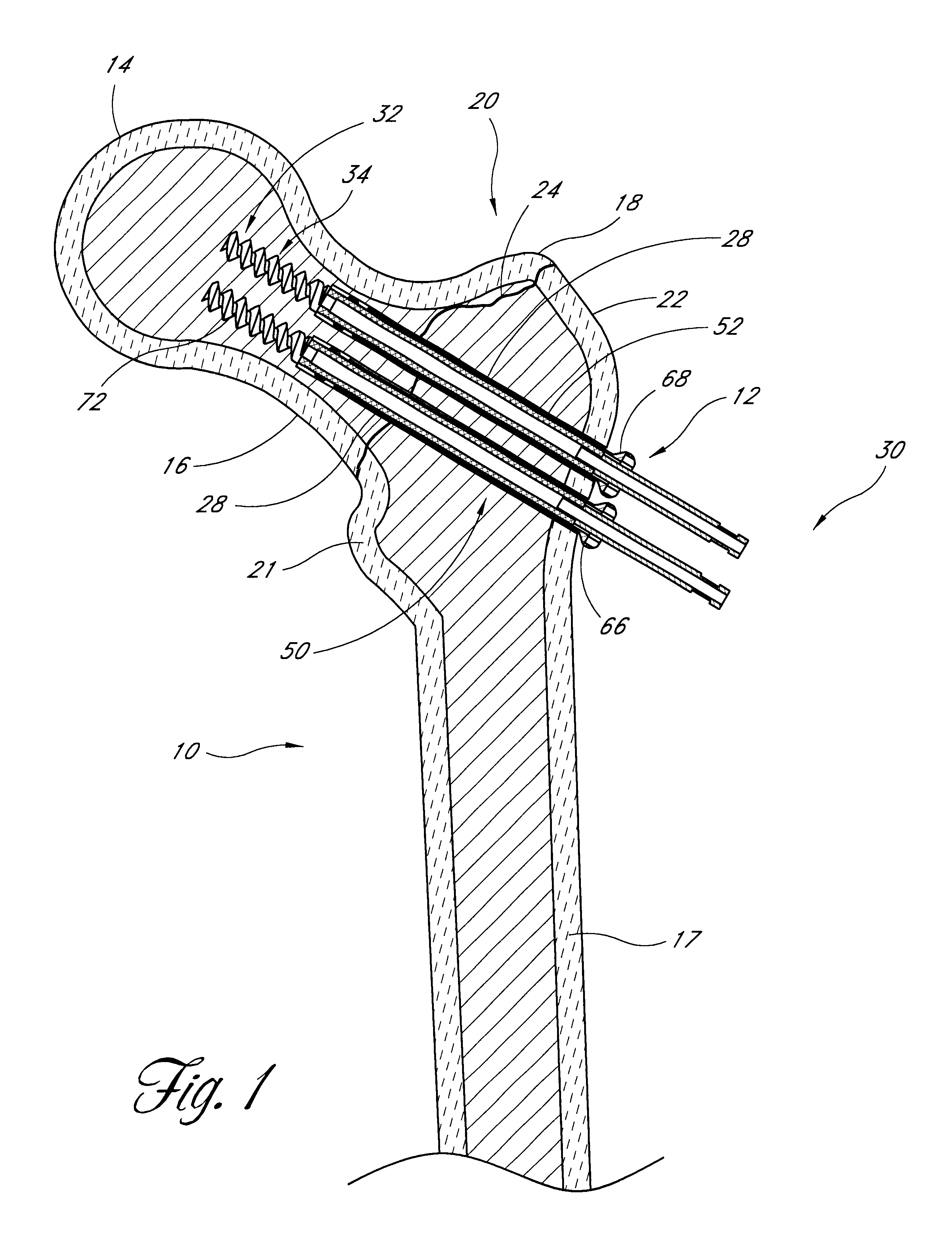
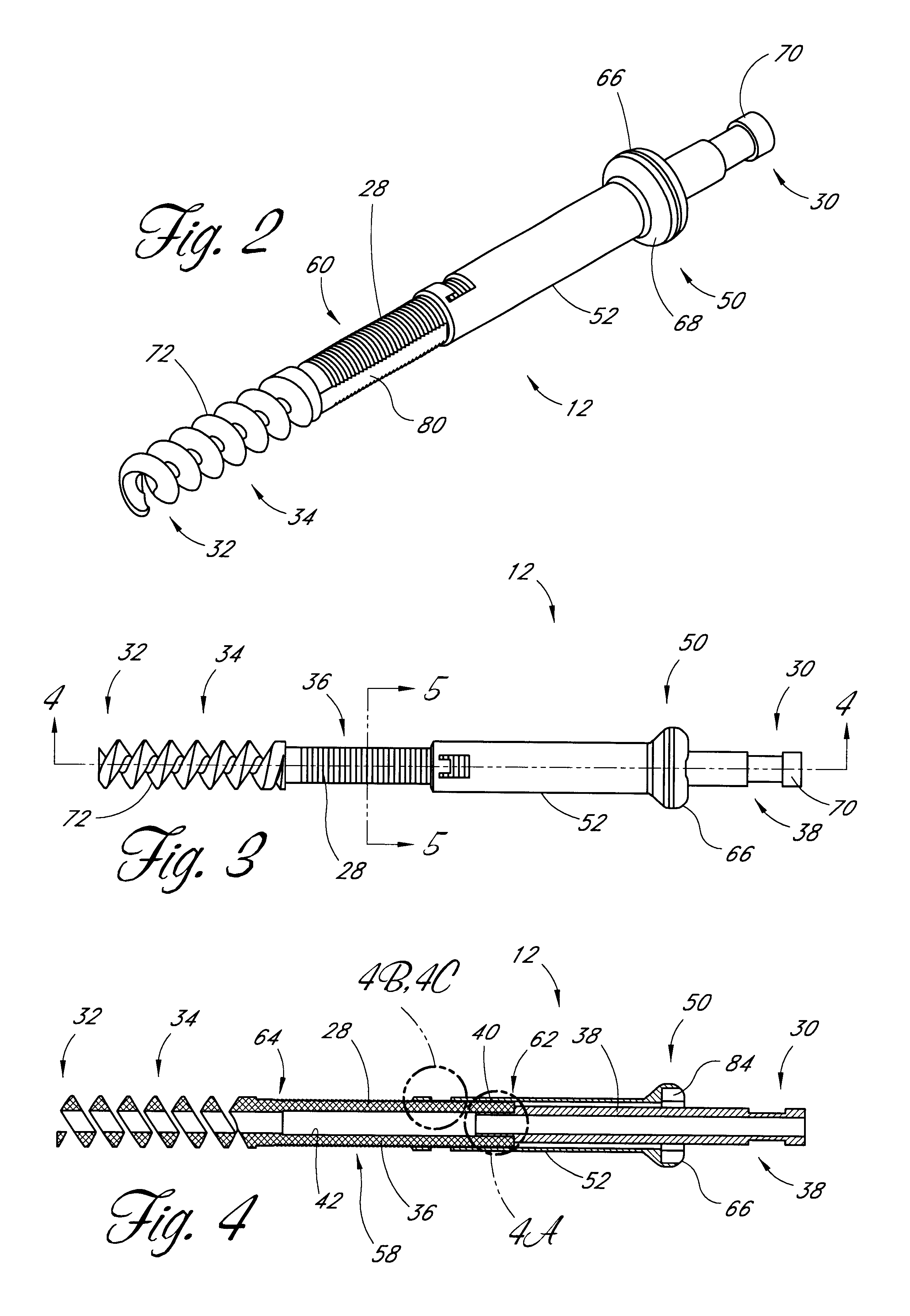
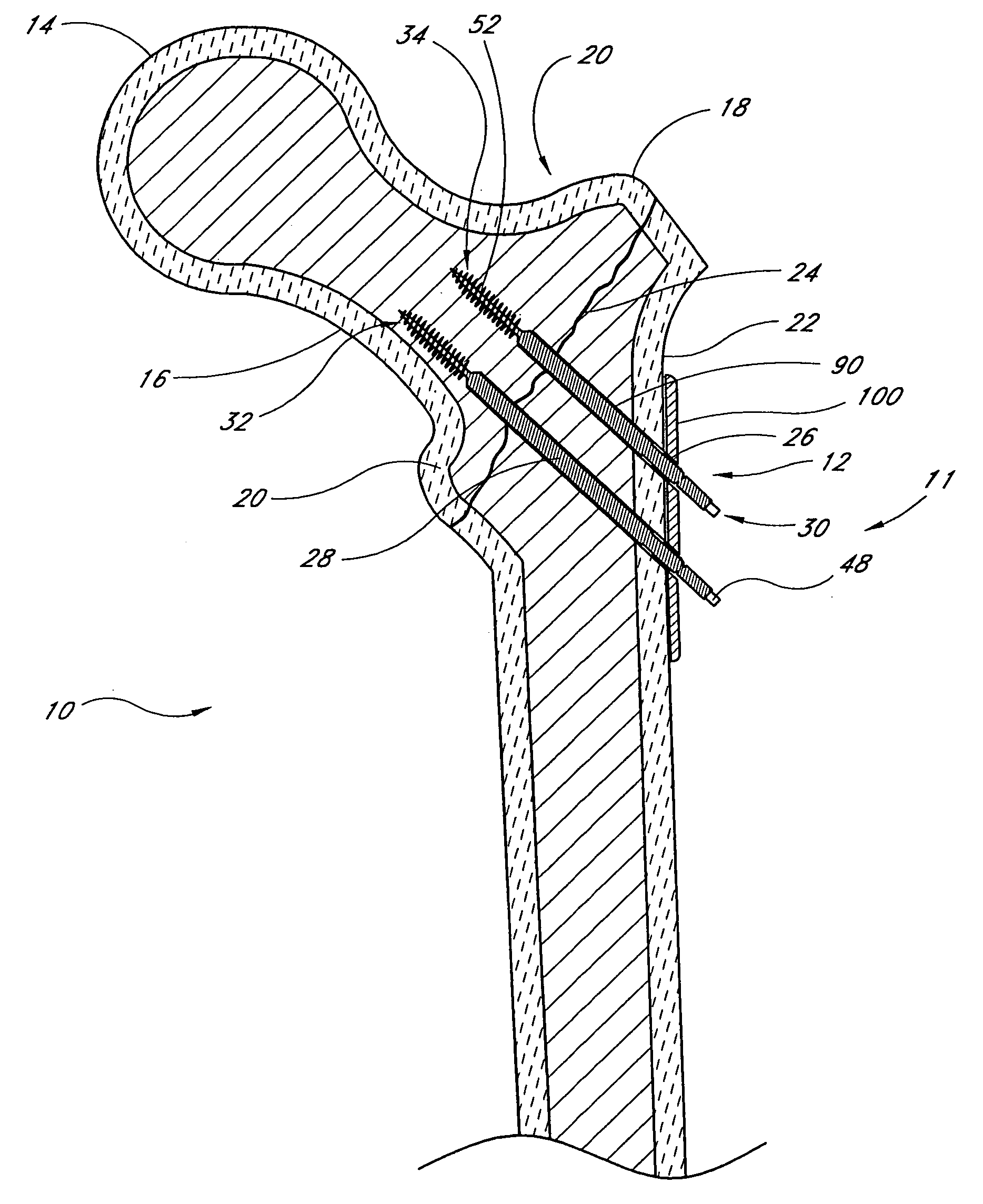
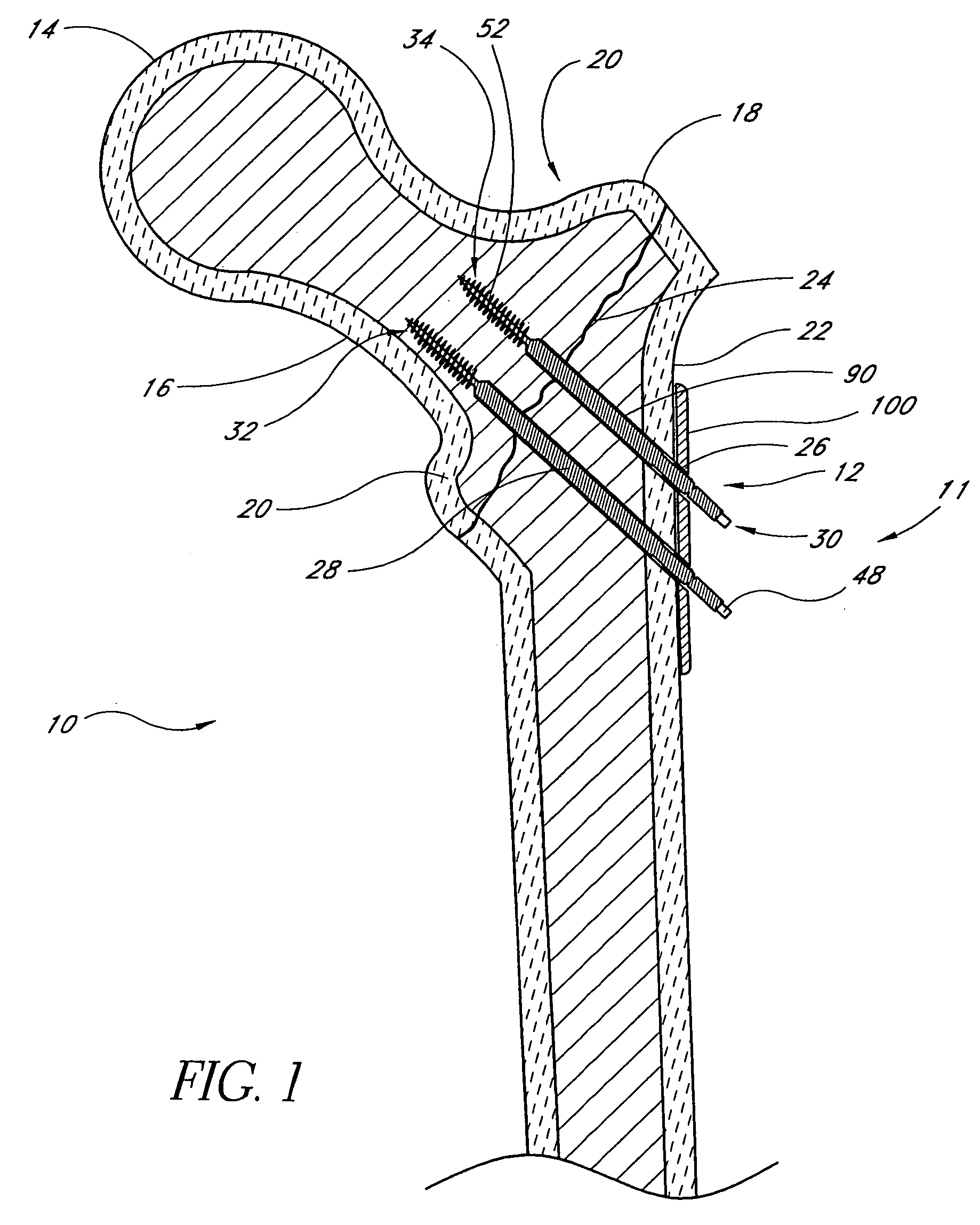
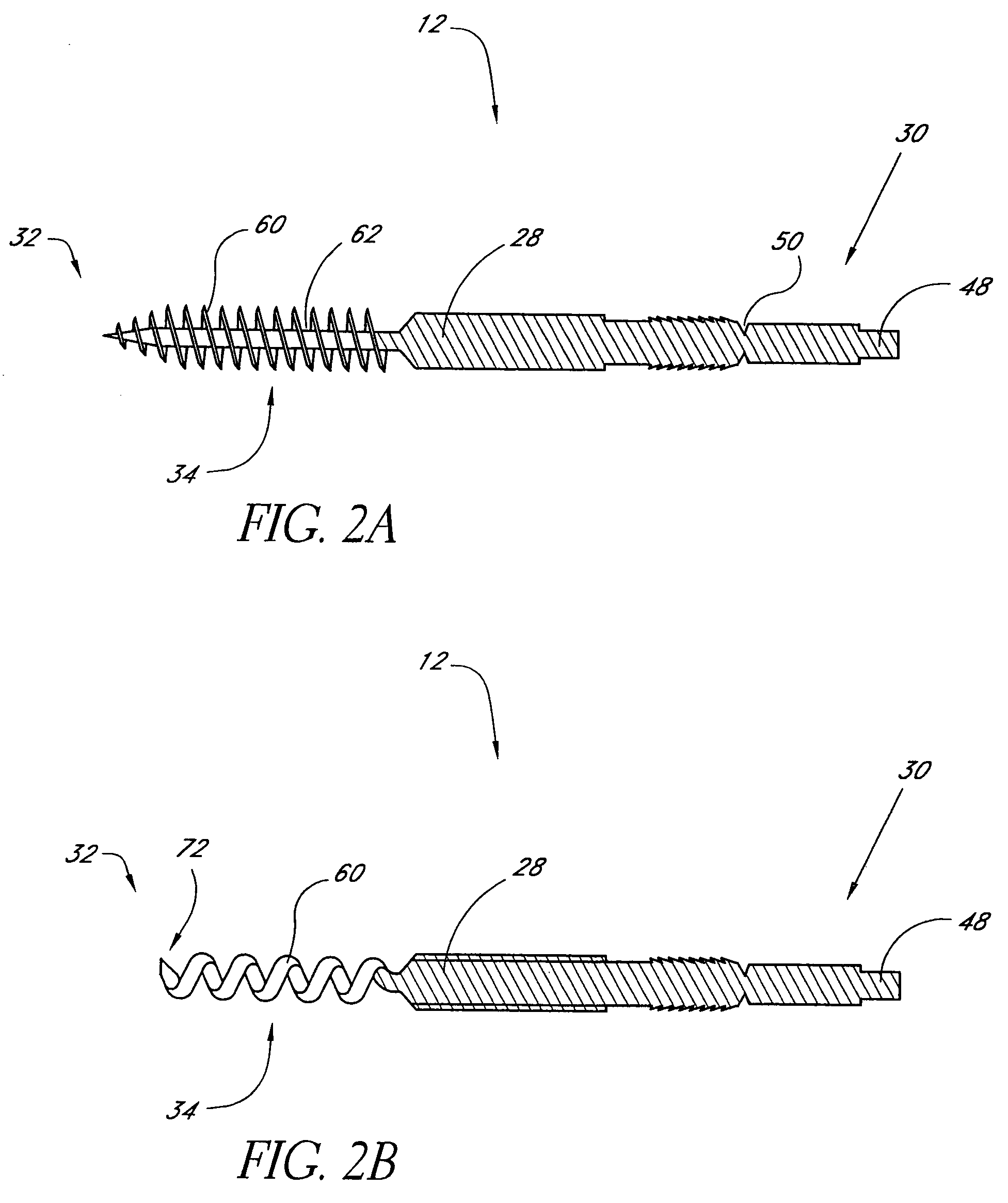
Distal bone anchors for bone fixation with secondary compression
Disclosed is a bone fracture fixation device, such as for reducing and compressing fractures in the proximal femur. The fixation device includes an elongate body with a helical cancellous bone anchor on a distal end. An axially moveable proximal anchor is carried by the proximal end of the fixation device. The device is rotated into position across the fracture or separation between adjacent bones and into the adjacent bone or bone fragment, and the proximal anchor is distally advanced to apply secondary compression and lock the device into place. The device may also be used for soft tissue attachments.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Devices and methods using an expandable body with internal restraint for compressing cancellous bone
Devices and methods compress cancellous bone. In one arrangement, the devices and methods make use of an expandable body that includes an internal restraint coupled to the body. The internal restraint directs expansion of the body. In one arrangement, a method for treating bone inserts the device having the internal restraint inside bone and causes directed expansion of the body in cancellous bone. Cancellous bone is compacted by the directed expansion.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
Intervertebral cage and method of use
InactiveUS6648915B2Restore tensionStable mechanical propertiesInternal osteosythesisBone implantSpinal columnHuman body
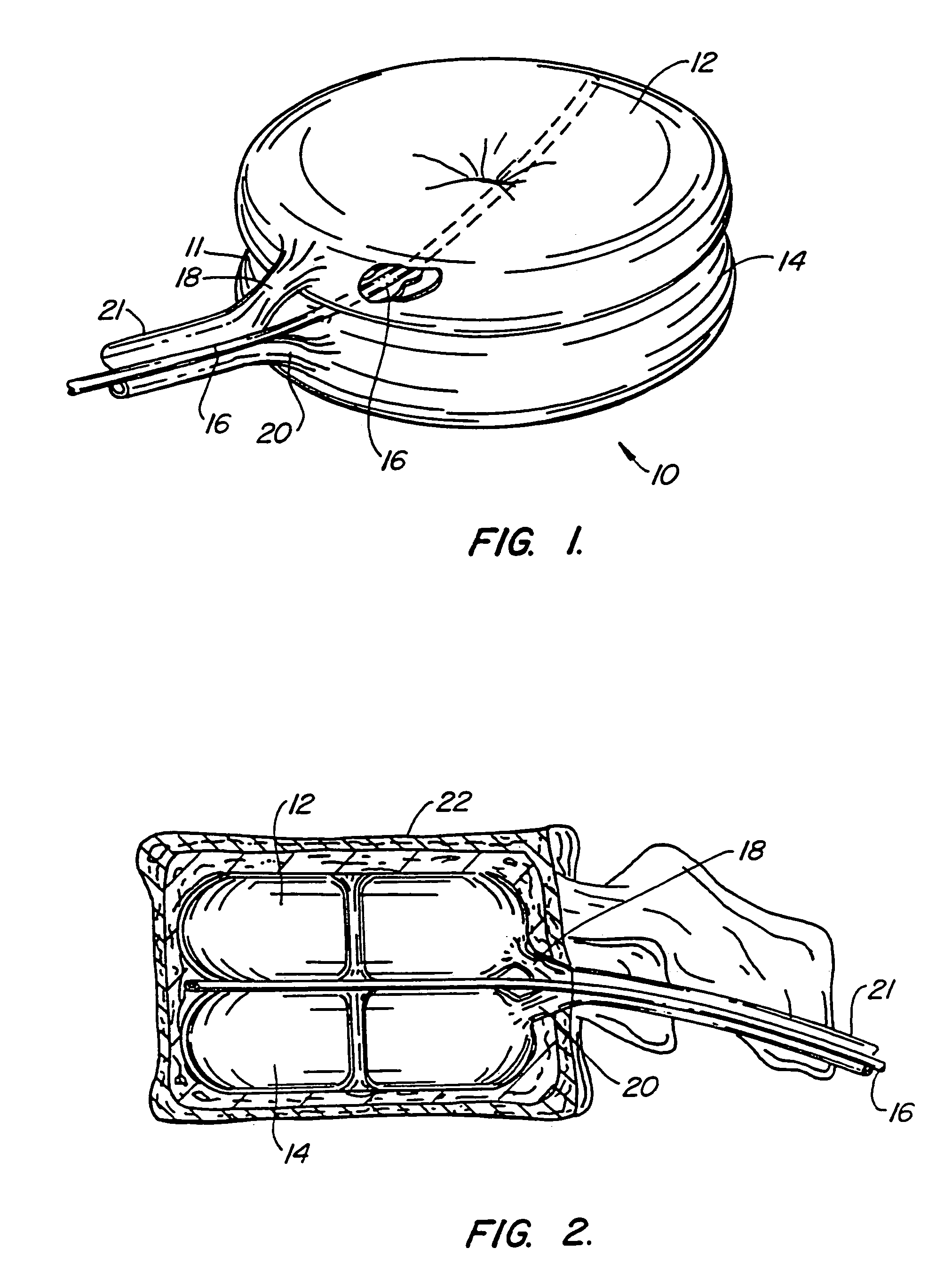
An intervertebral prosthesis for implantation between adjacent vertebrae of the human spine is shown. The prosthesis is formed as a unitary cage body configured and sized to be inserted between adjacent vertebrae in a single step implantation procedure. The cage body is banana shaped as viewed from above, the body having an exterior surface and an interior surface, the interior surface defining an internal recess for receiving cancellous bone material during an implantation procedure. The cage body can be formed as an interlinked mesh.
Owner:DEPUY ACROMED INC
Intervertebral disk replacement
InactiveUS7066960B1Prevent excessive rotation and subluxationDesirable deformabilityInternal osteosythesisBone implantLigament structureEngineering
An intervertebral disk prosthesis in a preferred embodiment has a matrix of bioincorporable fabric, and a nuclear core centrally mixed into the matrix. The core is formed by impregnating the fabric substrate centrally with a polymer, preferably of liquid form that cures into a viscoelastic solid, in which each component—polymer and fabric—reinforces the other against tearing, shearing and weakening under stress. The core is a hybrid composite adapted for elastic deformation centrally of the matrix, in which the polymer is mixed with the fabric, and is surrounded by the outer bioincorporable fabric margin of the matrix. In another embodiment, the nuclear core is separated from an outer sheath of the bioincorporable fabric by an intermediate ligament encasement that surrounds the purely polymeric core In either embodiment, each edge of the outer fabric that interfaces a vertebral end plate is impregnated with an agent to stimulate osseus incorporation and anchoring. An adjunct anchoring system with penetration of bone of adjacent vertebra may be used to for attachment until and after bioincorporation occurs.
Owner:DICKMAN CURTIS A
Electrosurgical method and apparatus for removing tissue within a bone body
ActiveUS20050119650A1Avoid spreadingSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesActive electrodeCancellous bone
A method for treating a bone body comprises inserting a probe having at least one active electrode into the target tissue and applying a voltage difference between an active electrode and return electrode to ablate the tissue. The method is particularly directed to removing tumors in a bone body and or removing cancellous bone in a bone body. The bone body may be a vertebral body. An apparatus includes a plurality of active electrodes and a distal section including two bends. The bends serve to prevent the active electrodes from impinging upon the shaft of an introducer needle. Also, a kit includes an electrosurgical probe, an electrosurgical generator, an introducer needle, and a fluid connector to connect the introducer needle to a fluid source such that liquid may be supplied to the target site during an application.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Apparatus and method for anchoring sutures
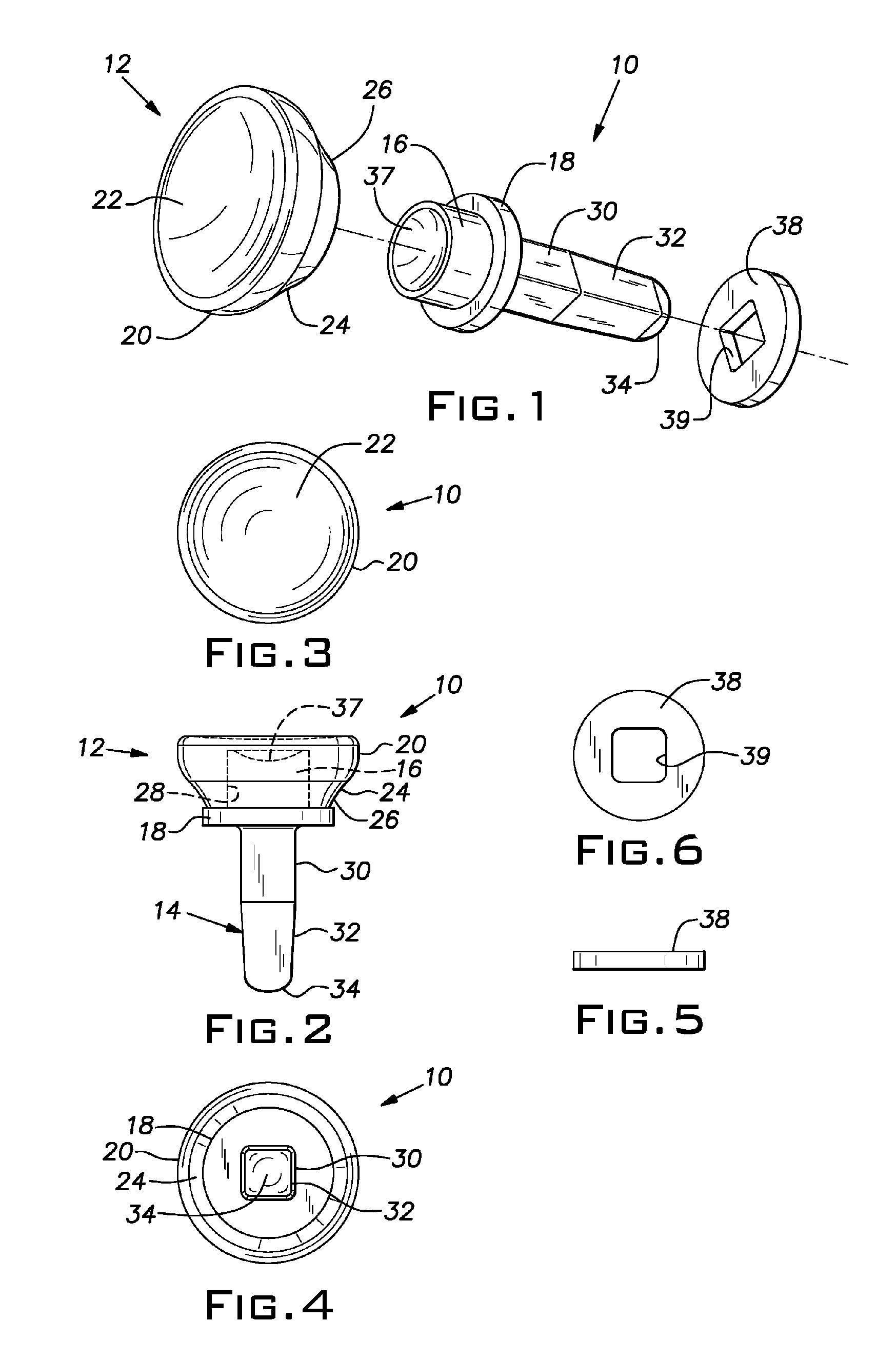
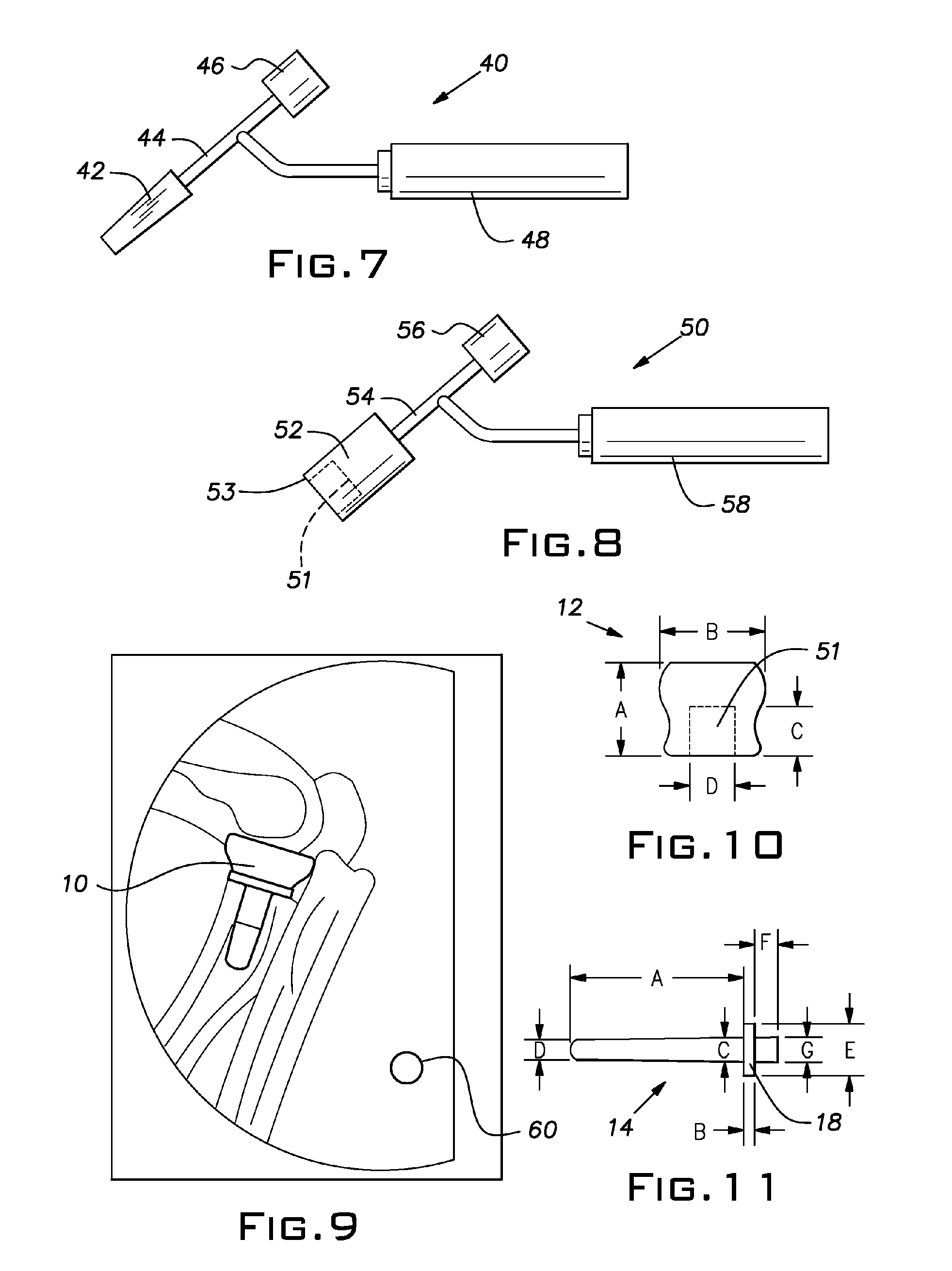
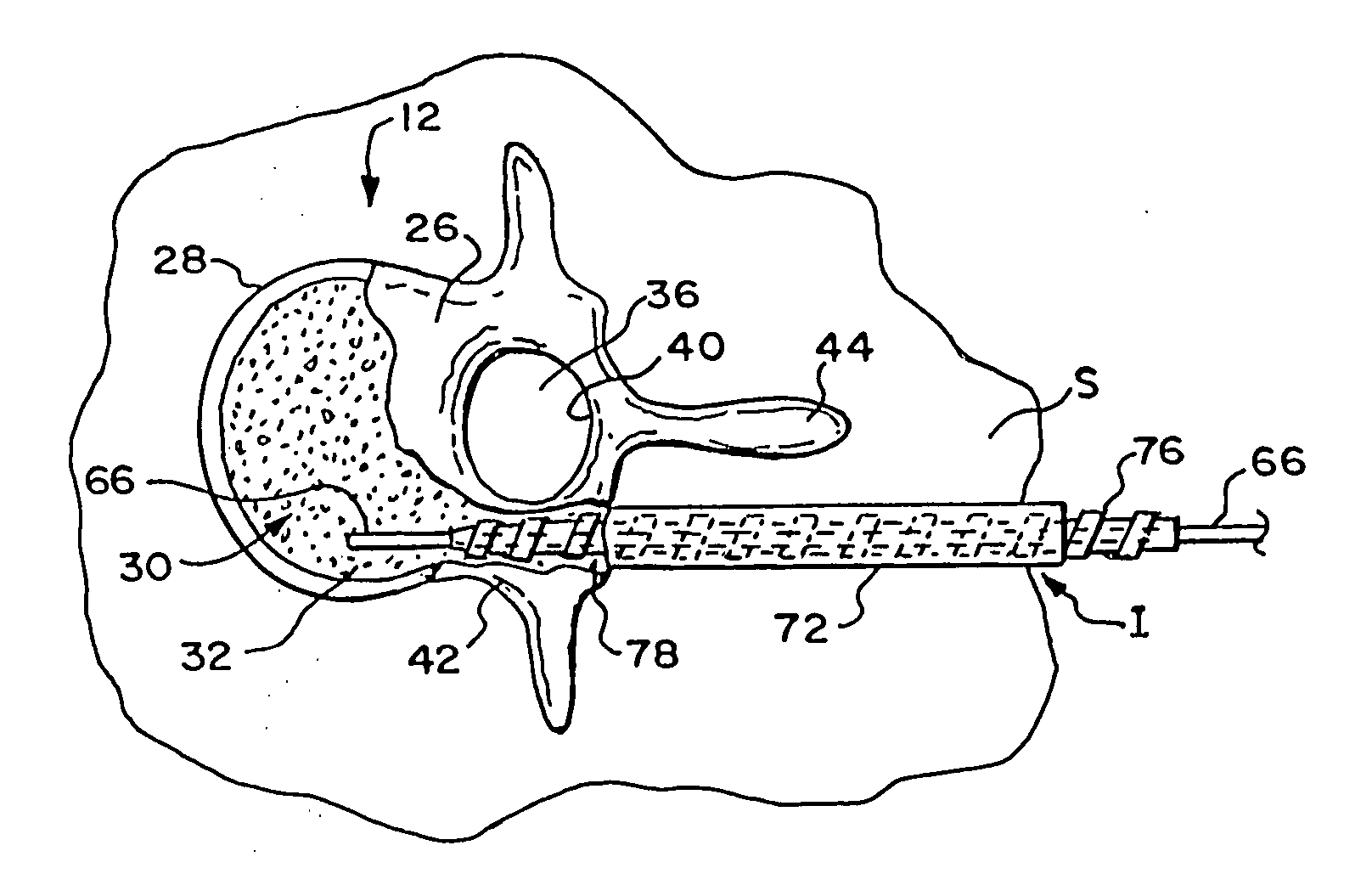
InactiveUS6923823B1Simple and inexpensive to manufactureEasy to insertSuture equipmentsBone implantSuture anchorsCancellous bone
A suture anchor having a conical surface and a bore in which an end of an insertion tool is inserted. The insertion end of the insertion tool is made of material having elastic properties. The bore and base of the suture anchor are angled with respect to the central axis of the suture anchor and preferably are parallel to each other. During insertion, the suture anchor is reoriented to fit into the hole, thereby bending the elastic end of the insertion tool. When the suture anchor is within cancellous bone tissue, the elastic properties of the insertion tool deploys the suture anchor to an orientation in which the suture anchor cannot fit through the bone hole, thereby firmly anchoring the suture anchor in the human bone.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Intervertebral body fusion cage with keels and implantation methods
An intervertebral implant has a fusion body with at least one keel that anchors the implant into cancellous bone of at least one vertebral body. A method for implantation includes lateral implantation of the implant.
Owner:KYPHON
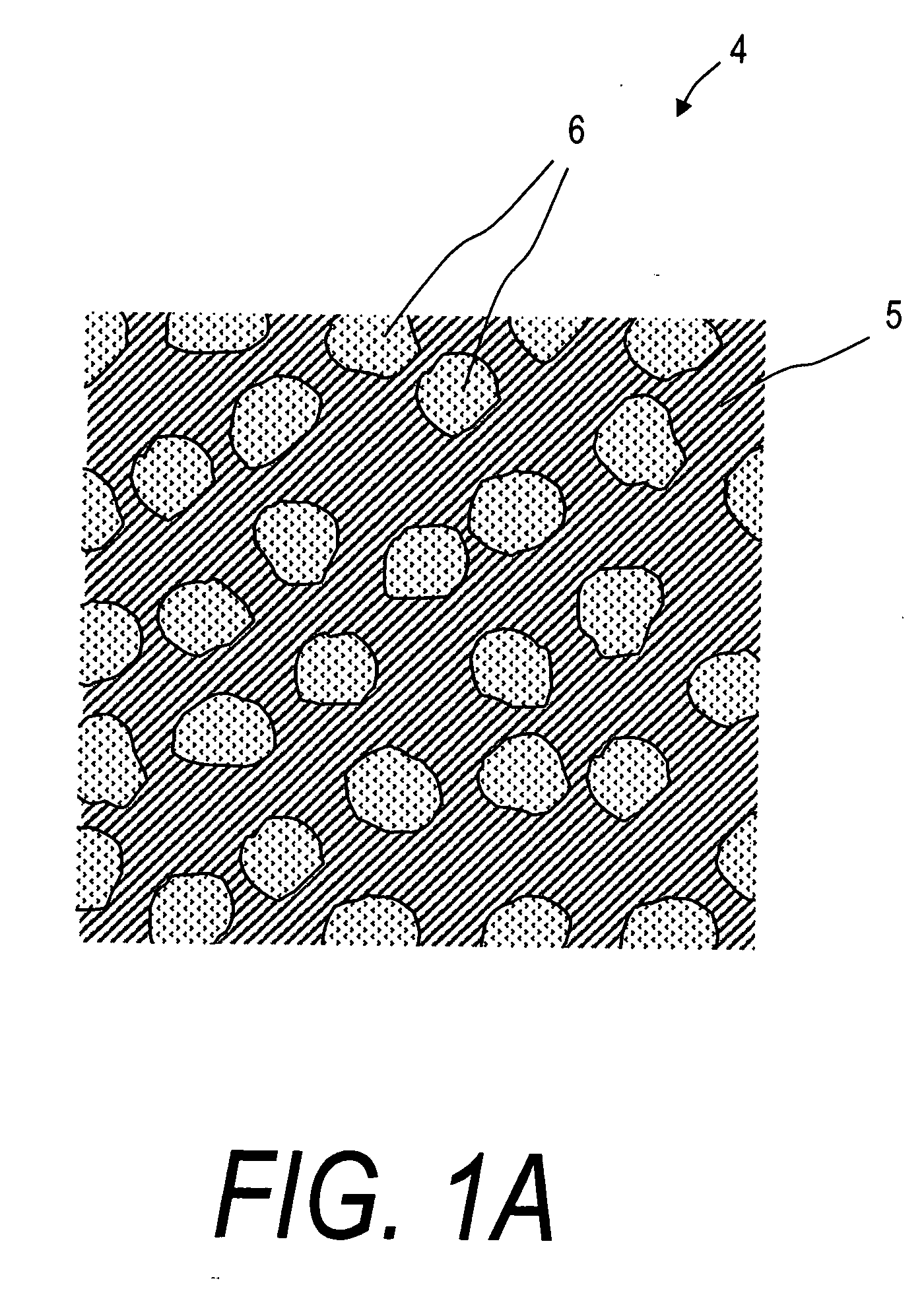
Composites and methods for treating bone
A system and method for treating bone abnormalities including vertebral compression fractures and the like. In one vertebroplasty method, a fill material is injected under high pressures into cancellous bone wherein the fill material includes a flowable bone cement component and an elastomeric polymer component that is carried therein. The elastomer component can further carry microscale or mesoscale reticulated elements. Under suitable injection pressures, the elastomeric component ultimately migrates within the flowable material to alter the apparent viscosity across the plume of fill material to accomplish multiple functions. For example, the differential in apparent viscosity across the fill material creates a broad load-distributing layer within cancellous bone for applying retraction forces to cortical bone endplates. The differential in apparent viscosity also transitions into a flow impermeable layer at the interface of cancellous bone and the flowable material to prevent extravasion of the flowable bone cement component.
Owner:DFINE INC
Small joint orthopedic implants and their manufacture
ActiveUS20060052725A1Simple processLarge inventoryFinger jointsWrist jointsBone CortexCancellous bone
A technique to manufacture small joint orthopedic implants includes the steps of taking standard radiographs of a pathologic joint and the corresponding non-pathologic joint. In order to provide an accurate frame of reference, a specialized marker is placed in the radiographic field. By inspection of the radiographs and by comparison with the marker, the dimensions of the cortical bone and the cancellous bone can be quickly and accurately determined. These dimensions can be used to manufacture a suitable implant and installation tool. Typically, the implant will include a stem from which a post projects. A radially extending collar is located at the intersection between the stem and the post. A mating head is attached to the post. The head closely approximates the size and shape of the natural head being replaced. The stem will be non-round in cross-section to prevent rotation of the stem in the bone. For many applications, the head will not be fixedly attached to the post, but will be rotatable about the longitudinal axis of the post. One or more spacers that fit about the stem also can be provided in order to adjust the distance that the head projects from the bone.
Owner:SEITZ JR WILLIAM H +1
Systems and methods for treating fractured or diseased bone using expandable bodies
Systems and methods treat fractured or diseased bone by deploying more than a single therapeutic tool into the bone. In one arrangement, the systems and methods deploy an expandable body in association with a bone cement nozzle into the bone, such that both occupy the bone interior at the same time. In another arrangement, the systems and methods deploy multiple expandable bodies, which occupy the bone interior volume simultaneously. Expansion of the bodies form cavity or cavities in cancellous bone in the interior bone volume.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
Method and apparatus for bone fixation with secondary compression
InactiveUS6890333B2Prevent movementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRight femoral headFemoral neck
Disclosed is a fracture fixation device, for reducing and compressing fractures in a bone. The fixation device includes an elongate body comprising a first portion and a second portion that are detachably coupled to each other. The first portion defines a helical cancellous bone anchor and the second portion defines a distal end. An axially moveable proximal anchor is carried by the proximal end of the fixation device and is rotationally locked to the first portion. The device is rotated into position across the femoral neck and into the femoral head, and the proximal anchor is distally advanced to lock the device into place. The second portion is then detached from the first portion.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Locking plate for bone anchors
InactiveUS7070601B2Simple procedureIncrease resistanceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBone splintersMedicine
Disclosed is a bone fracture fixation system, such as for reducing and compressing fractures in the proximal femur. The fixation system includes a plurality of elongated bodies with a helical cancellous bone anchor on a distal end of each of the bodies. An axially moveable plate with a plurality of openings is carried by the proximal end of the elongated bodies. The elongated bodies are rotated into position across the fracture or separation between adjacent bones and into the adjacent bone or bone fragment, and the plate is distally advanced to apply secondary compression and lock the device into place. The device may also be used for soft tissue attachments.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
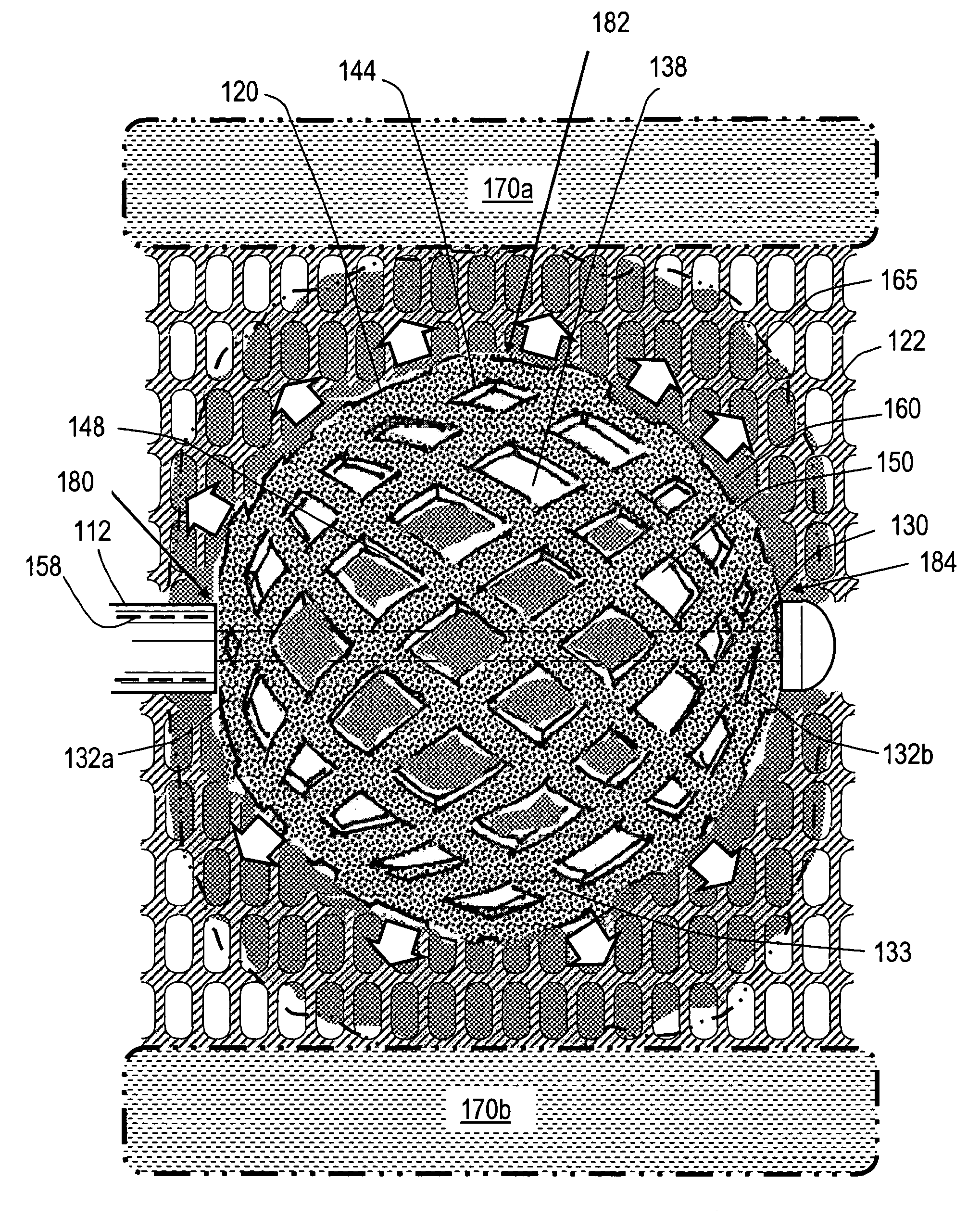
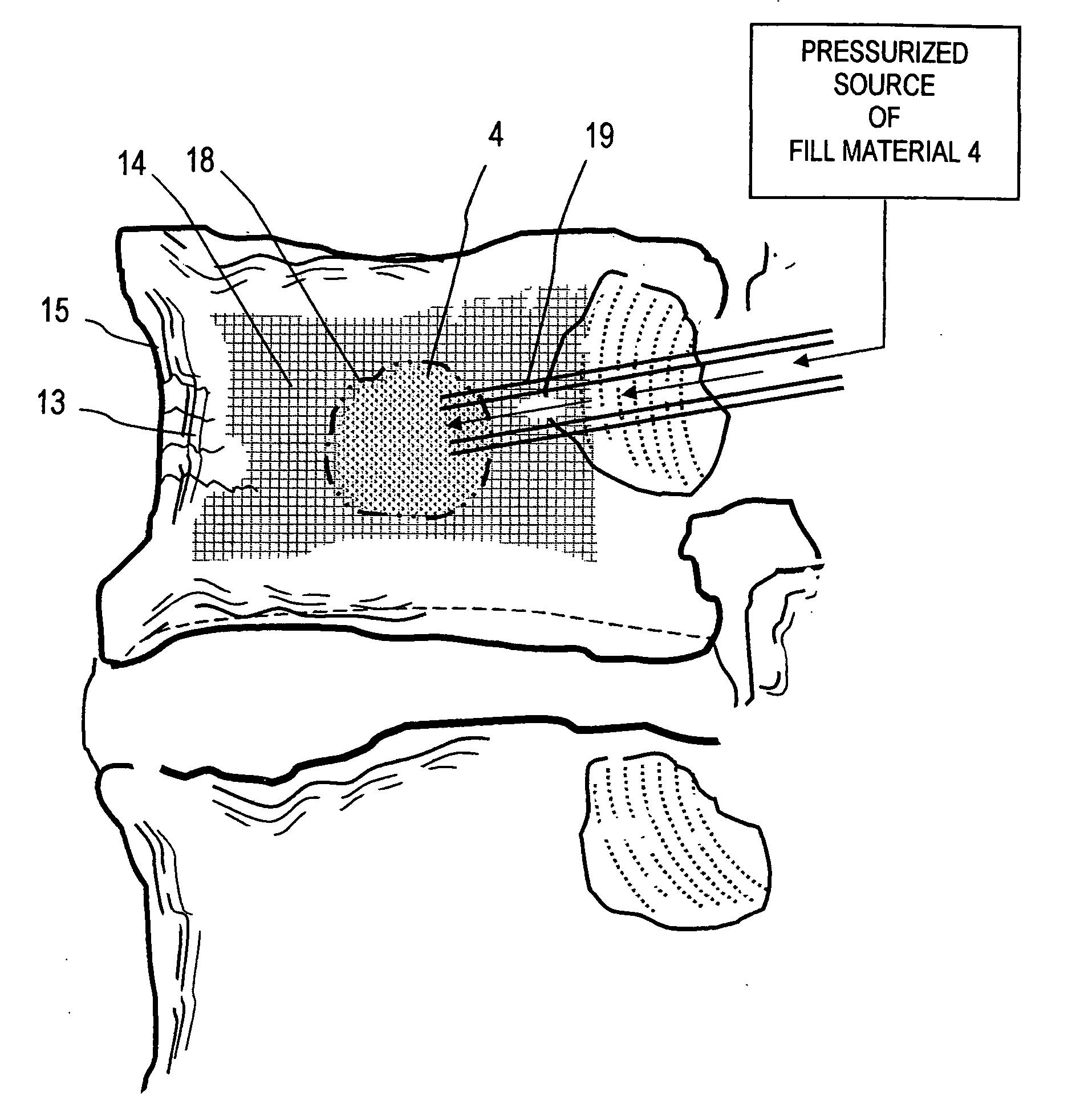
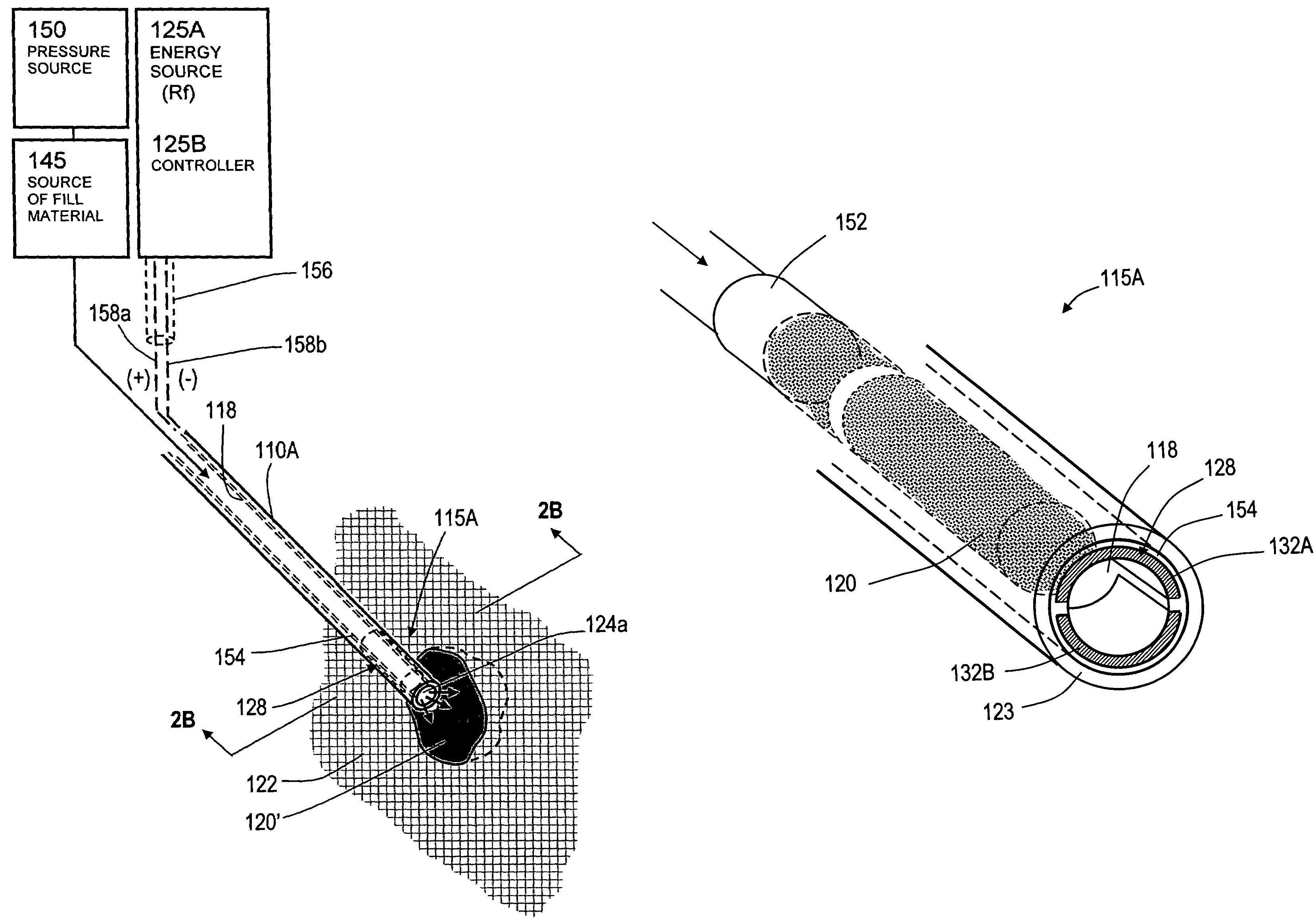
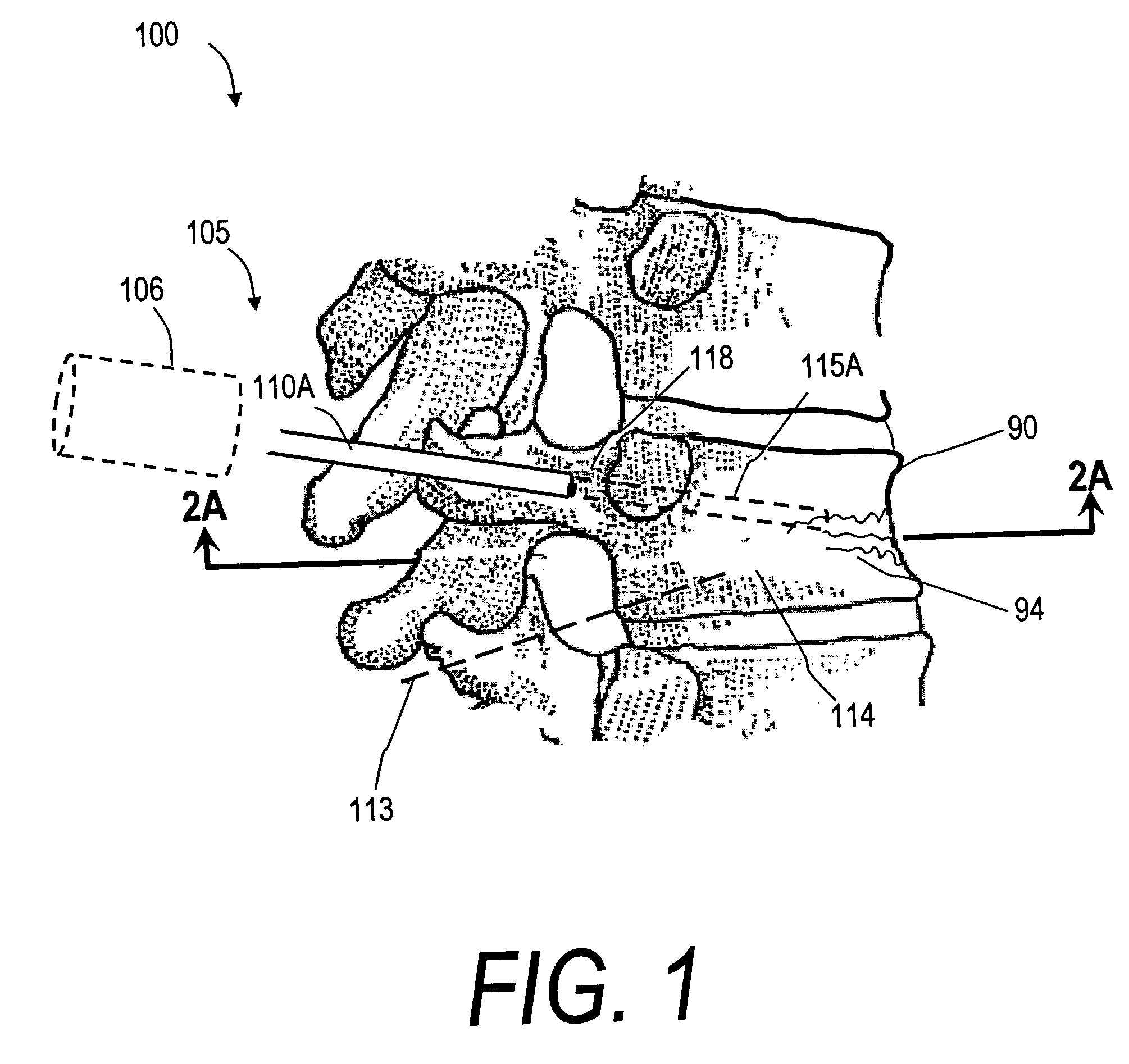
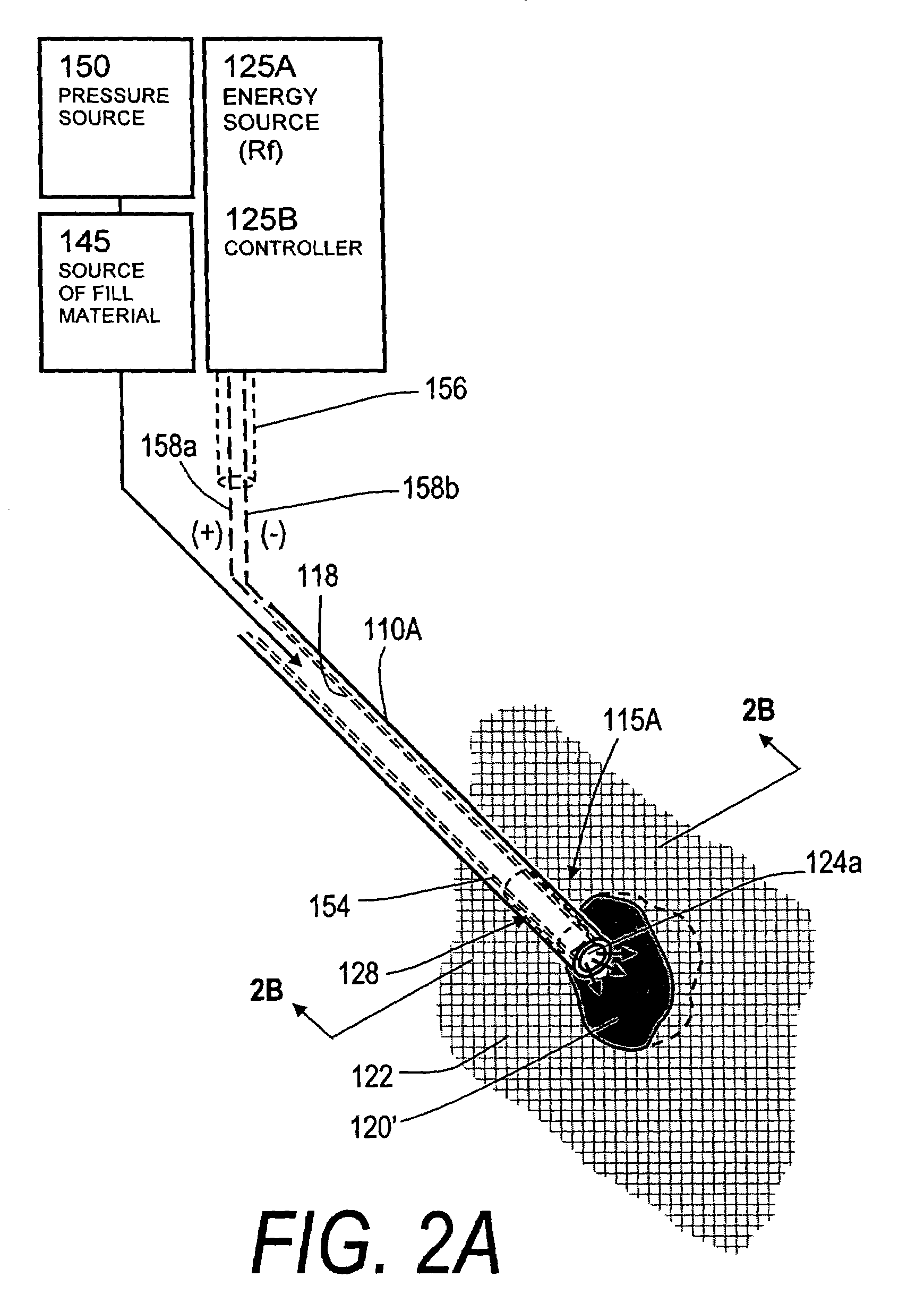
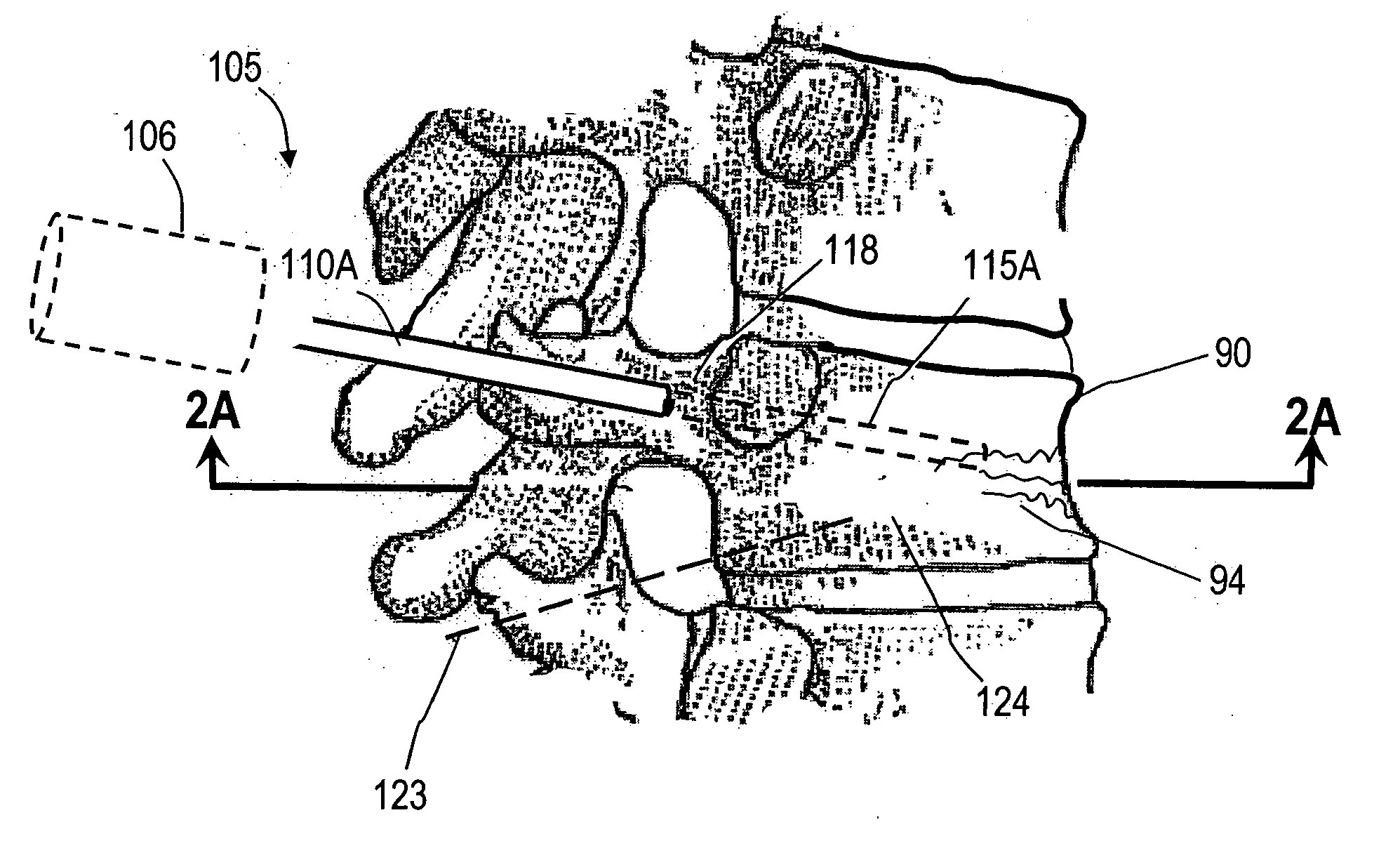
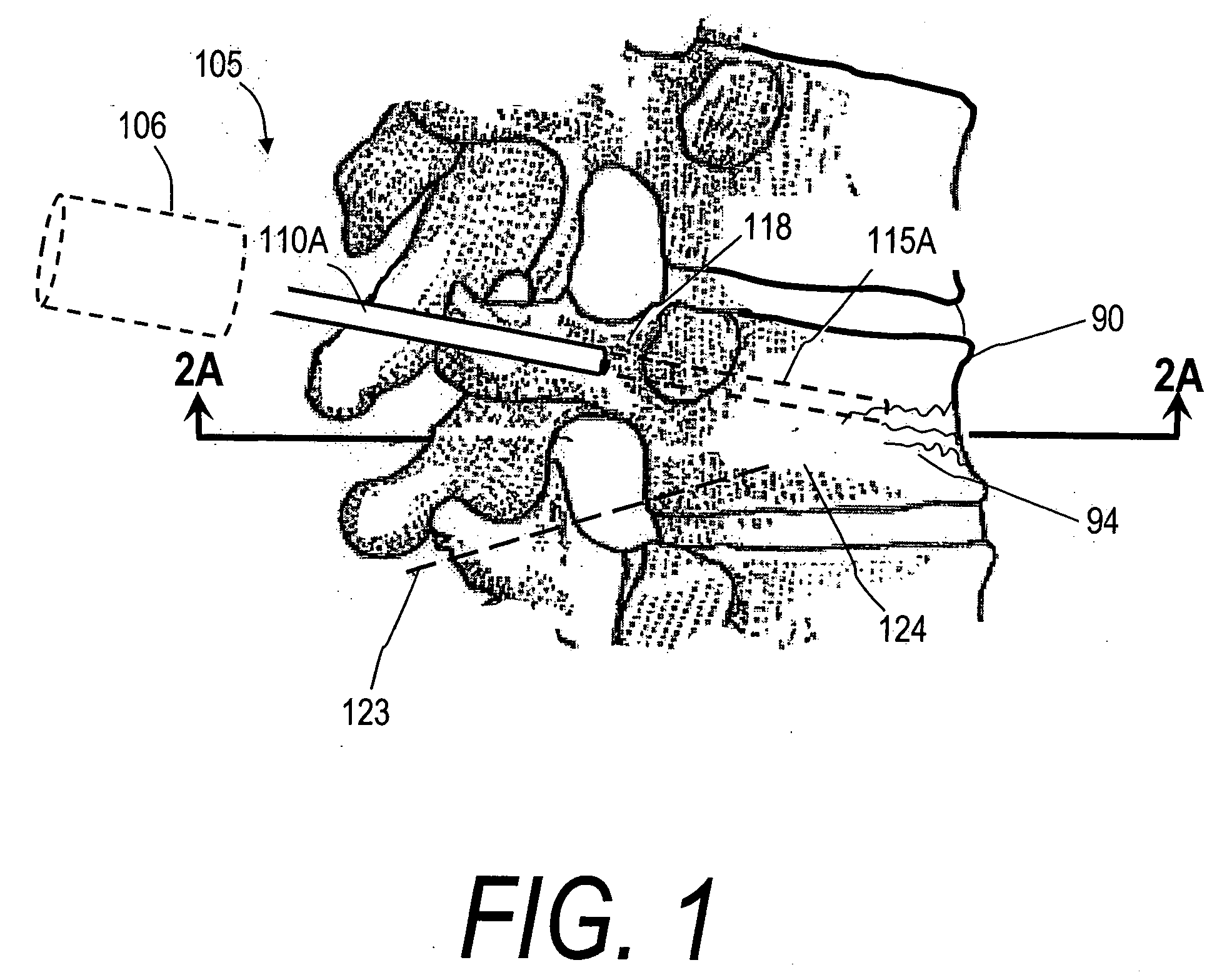
Bone treatment systems and methods
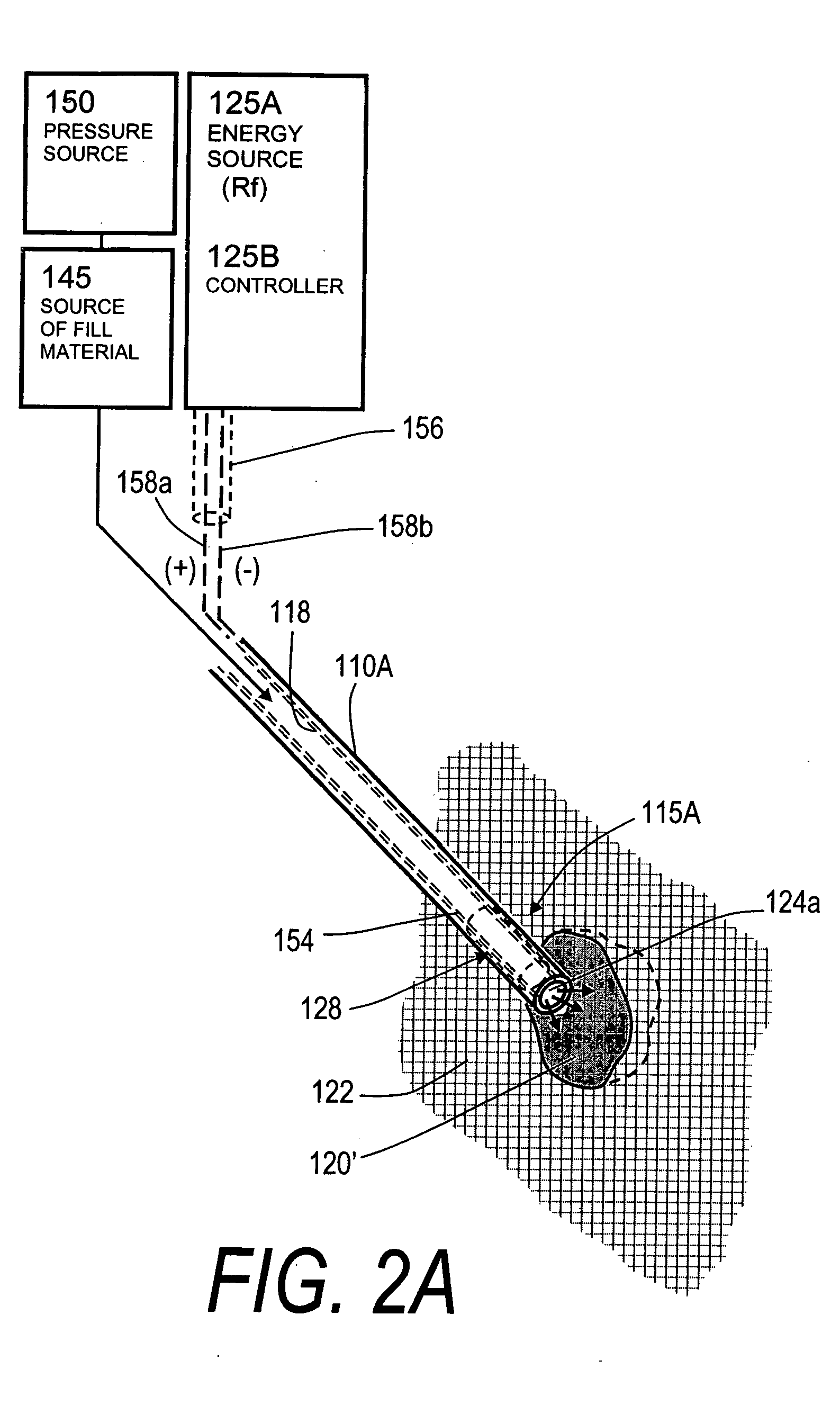
ActiveUS7559932B2Inhibit migrationSpinal implantsFastenersFilling materialsVertebra compression fracture
The present invention relates in certain embodiments to medical devices for treating osteoplasty procedures such as vertebral compression fractures. More particularly, embodiments of the invention relate to instruments and methods for controllably restoring vertebral body height by controlling the geometry of fill material introduced into cancellous bone. An exemplary system utilizes Rf energy in combination a conductive bone fill material for polymerizing the surface of the inflow plume to control the geometry of the fill material and the application of force caused by inflows of fill material. In another embodiment, method of treating bone includes injecting a volume of fill material into a bone and selectively modifying a viscosity of a selected portion of the bone filler to control the direction of flow of the fill material within the bone. A system for treating bone using this method includes an introducer for delivering fill material into the bone and an energy source selectively coupleable to the fill material to alter the viscosity of the fill material as it flows out of the introducer.
Owner:DFINE INC
Bone treatment systems and methods
ActiveUS20060122625A1Inhibit migrationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsHigh accelerationVertebra compression fracture
The present invention relates in certain embodiments to medical devices for treating vertebral compression fractures. More particularly, embodiments of the invention relate to instruments and methods for controllably restoring vertebral body height by controlling the flow of bone cement into the interior of a vertebra and the application of forces causes by the cement flow. An exemplary system utilizes Rf energy in combination a conductive bone cement for selectively polymerizing the inflow plume to increase the viscosity of the cement. In one aspect of the invention, the system utilizes a controller to control bone cement flow parameters to either allow or disallow cement interdigitation into cancellous bone. A method of the invention includes pulsing the flows of bone cement wherein high acceleration of the flow pulses can apply expansion forces across the surface of the cement plume to reduce a vertebral fracture.
Owner:DFINE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com