Patents
Literature
1722 results about "Vertebral column" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
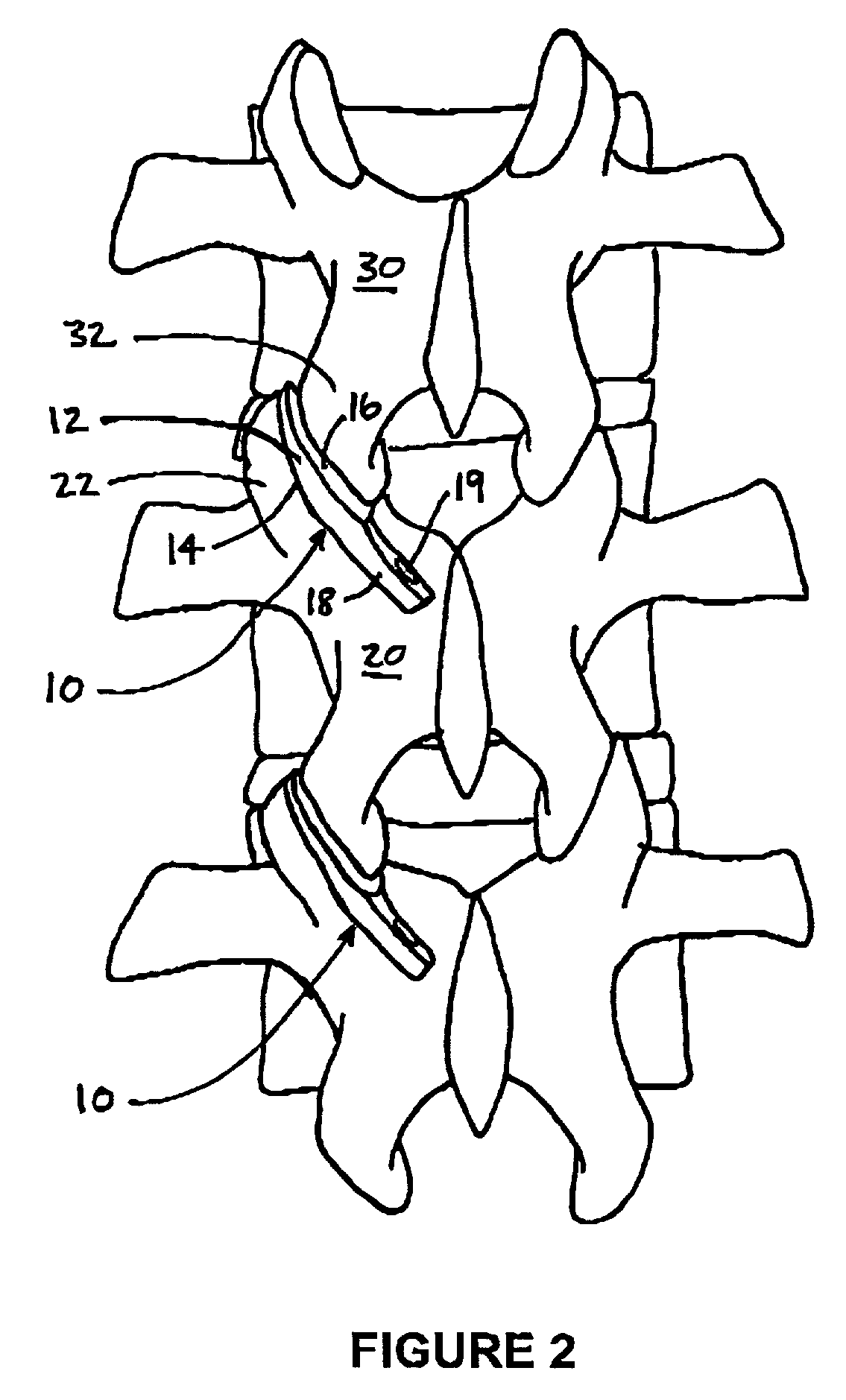
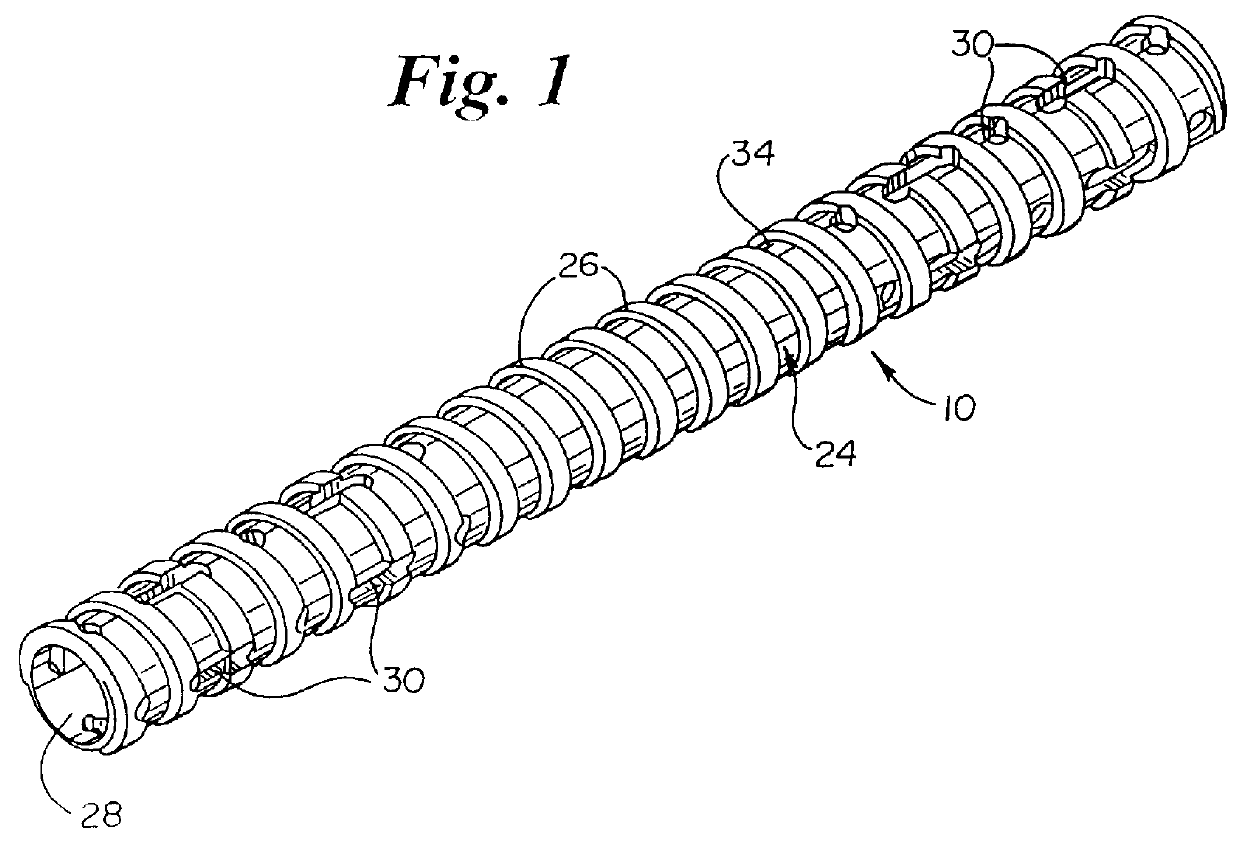
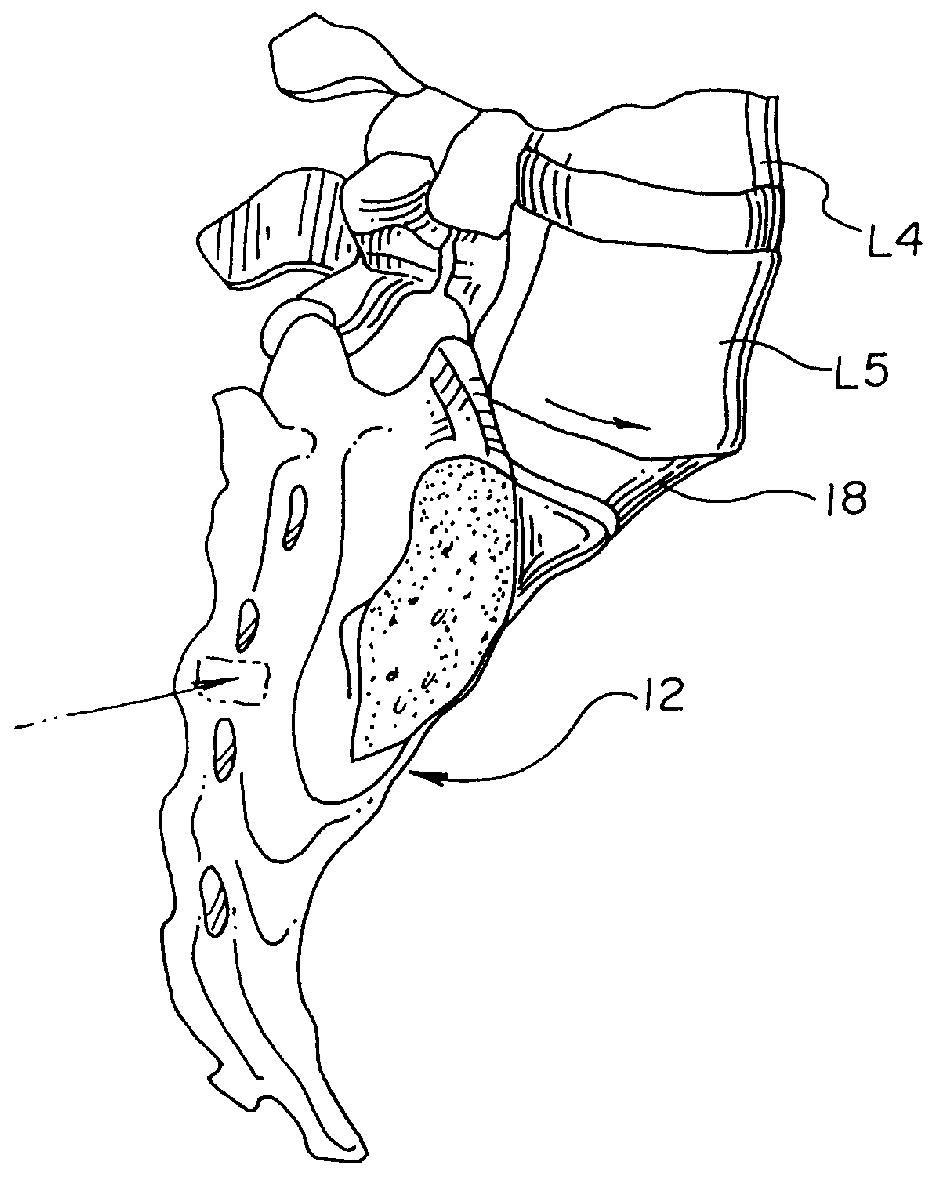
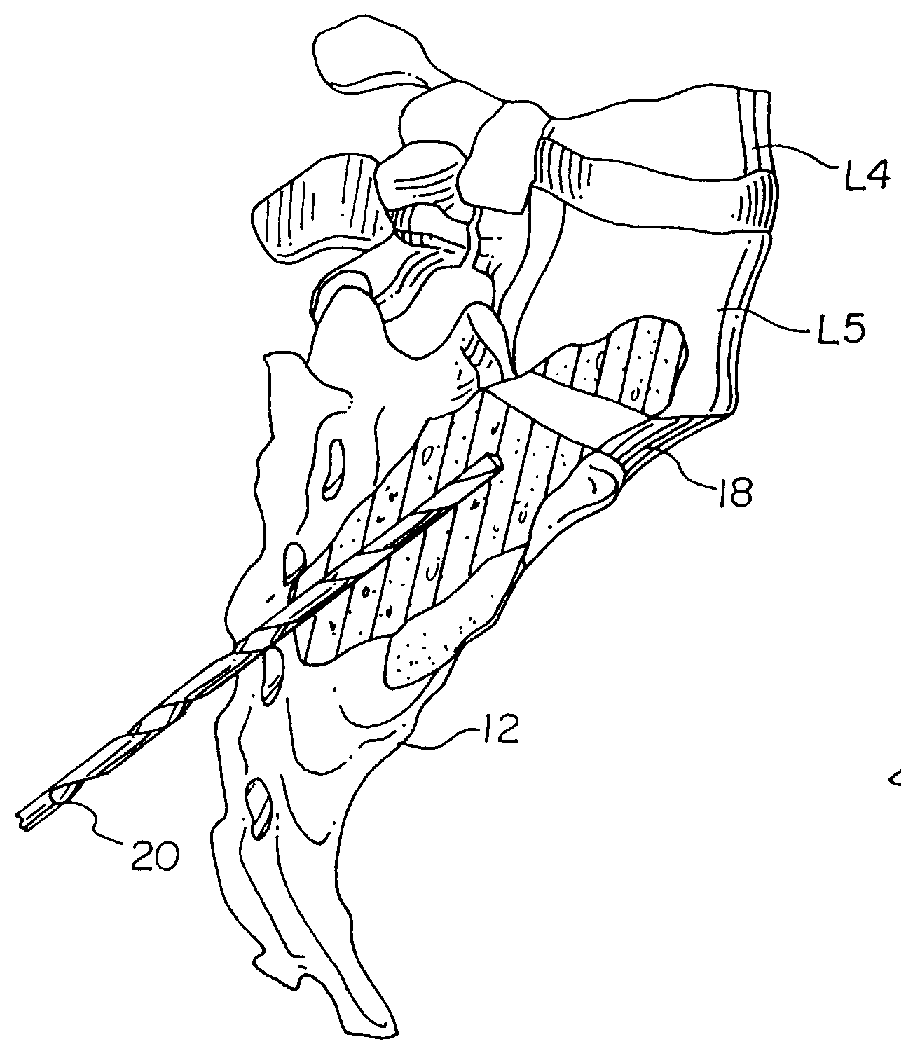
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordates has been replaced by a segmented series of bone: vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs. The vertebral column houses the spinal canal, a cavity that encloses and protects the spinal cord.
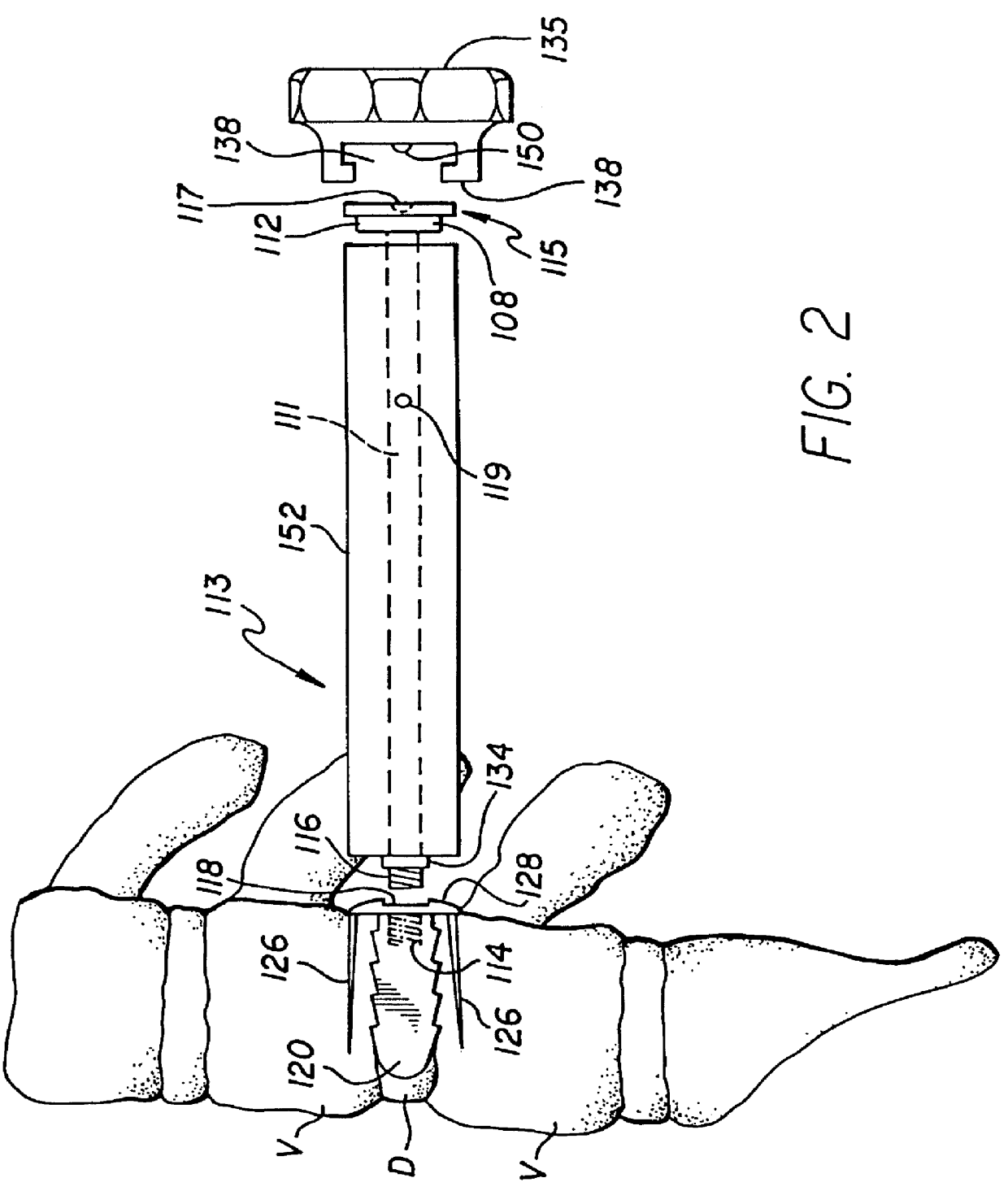
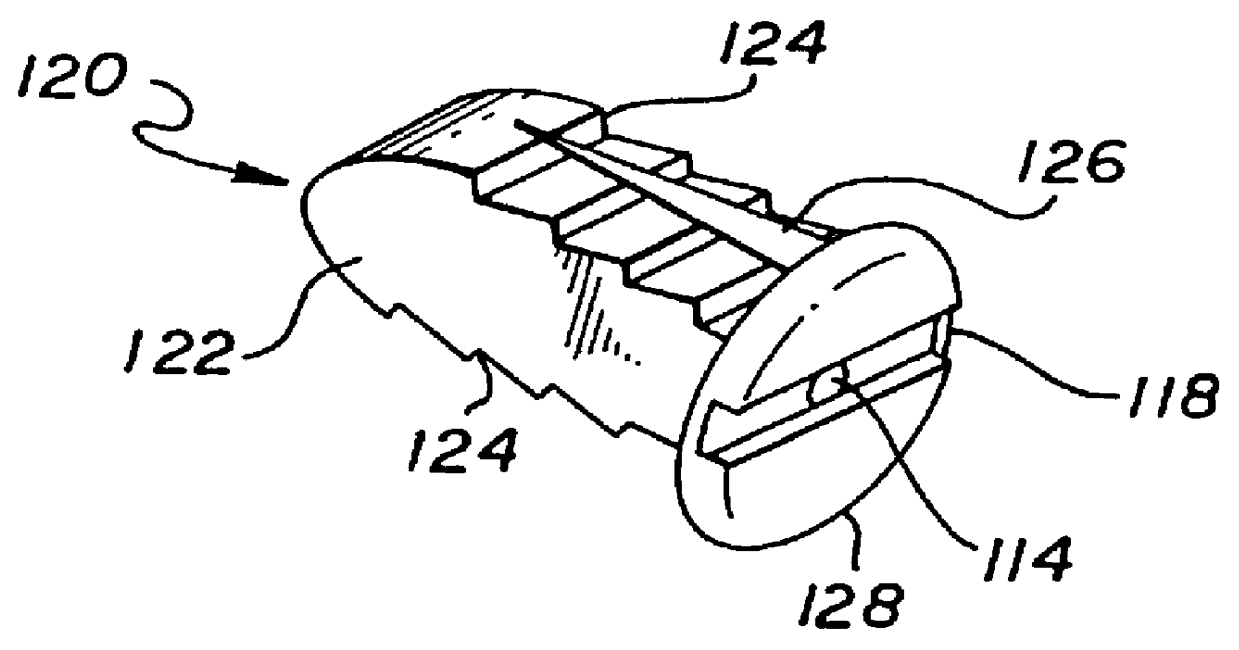
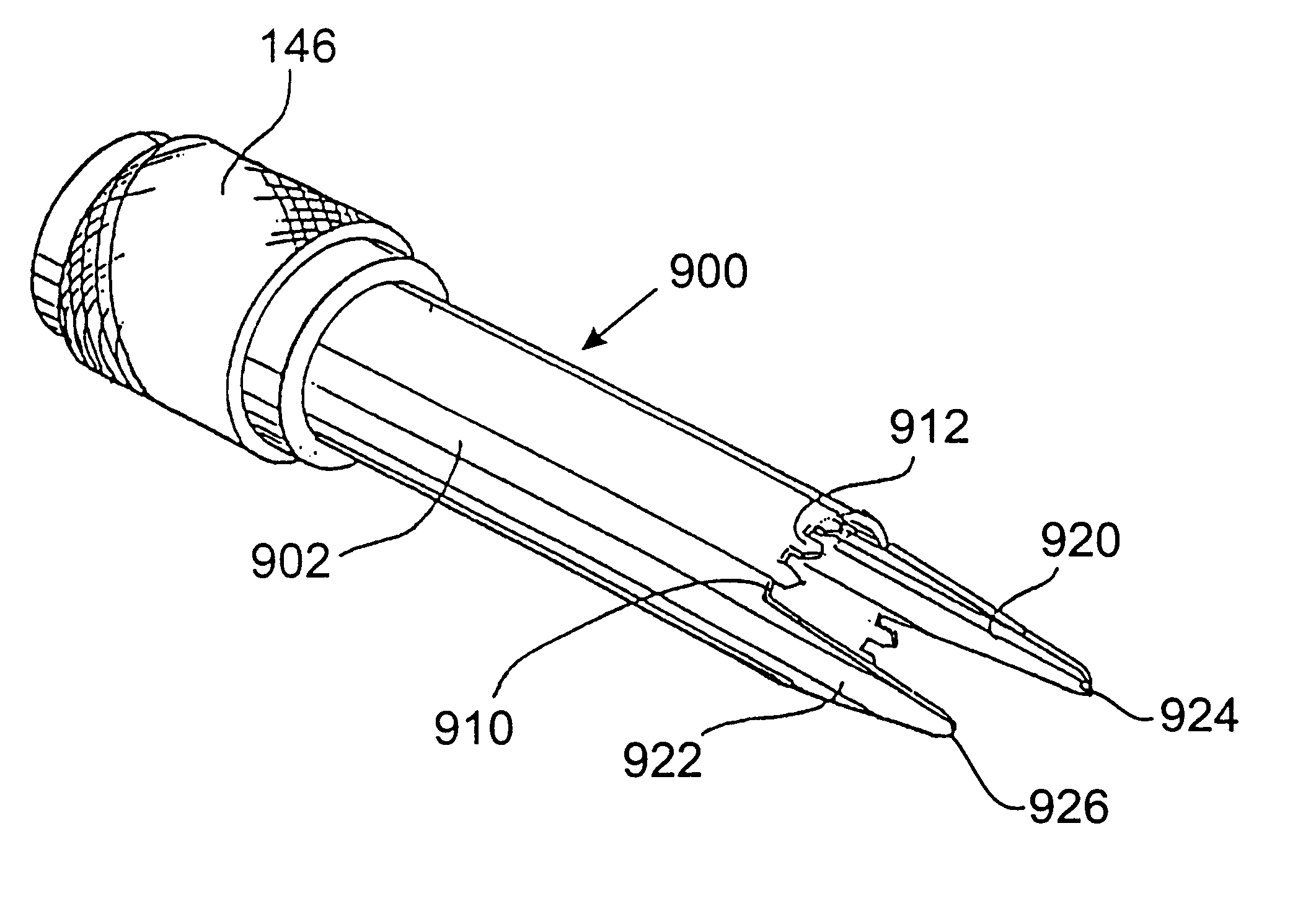
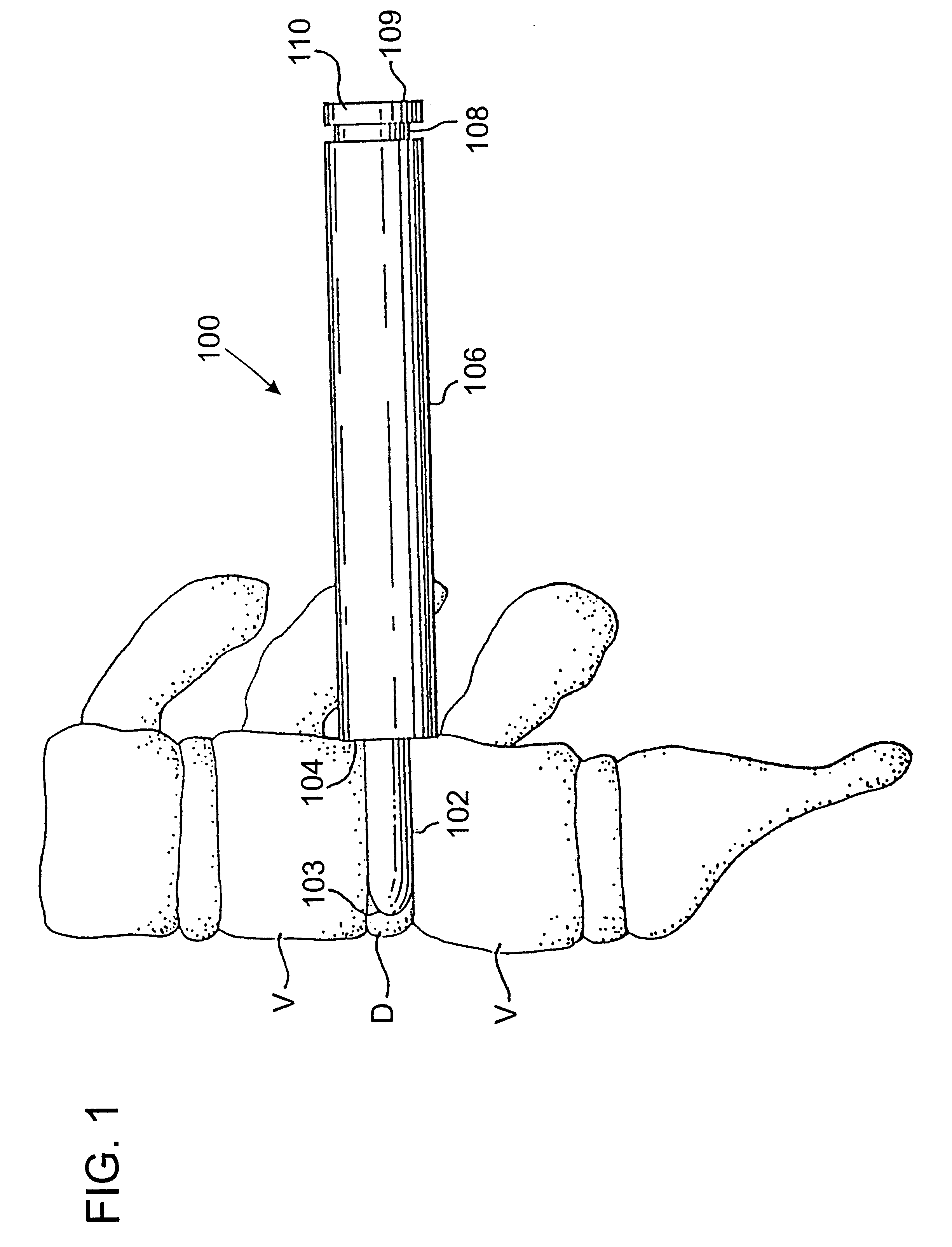
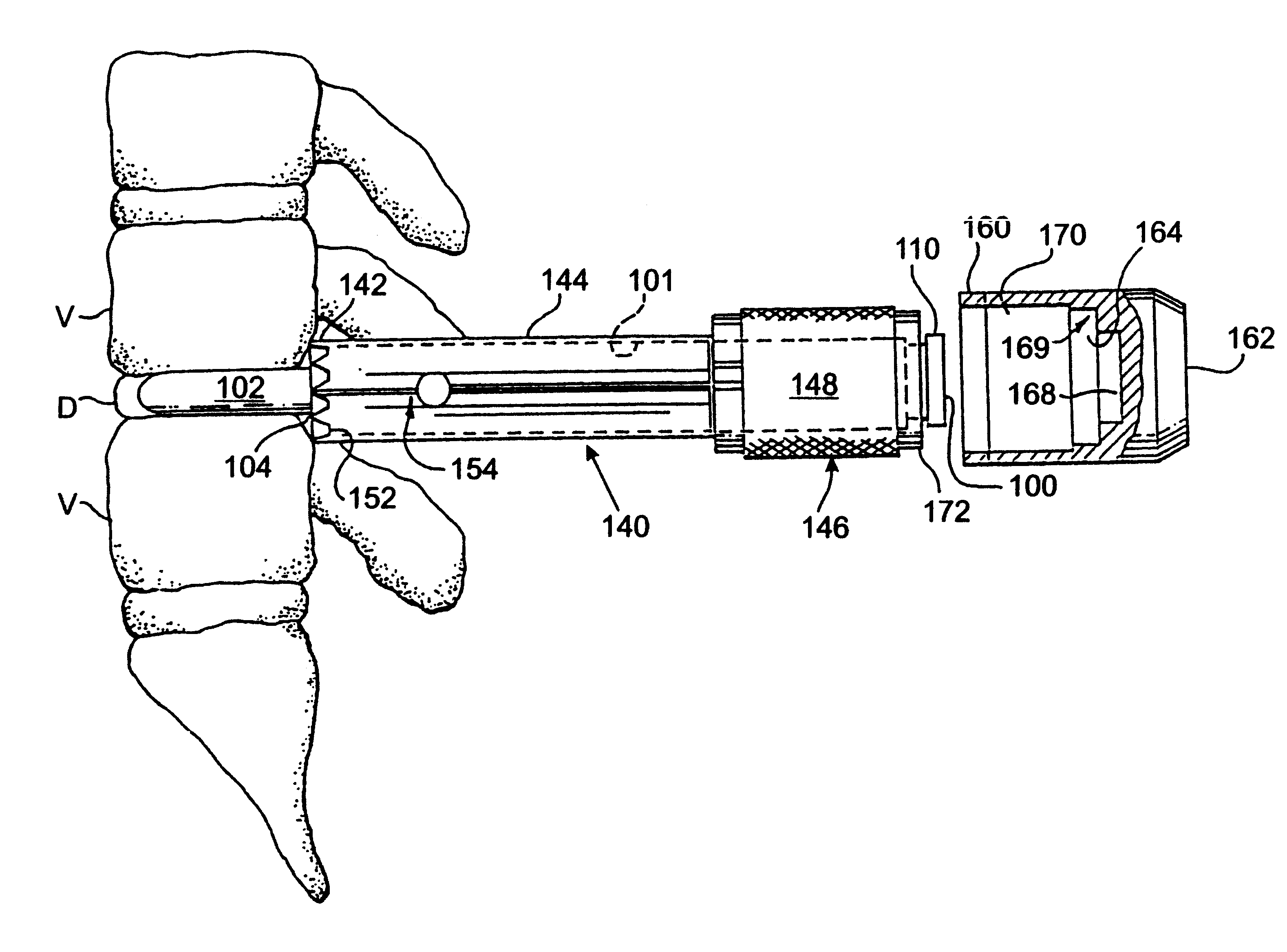
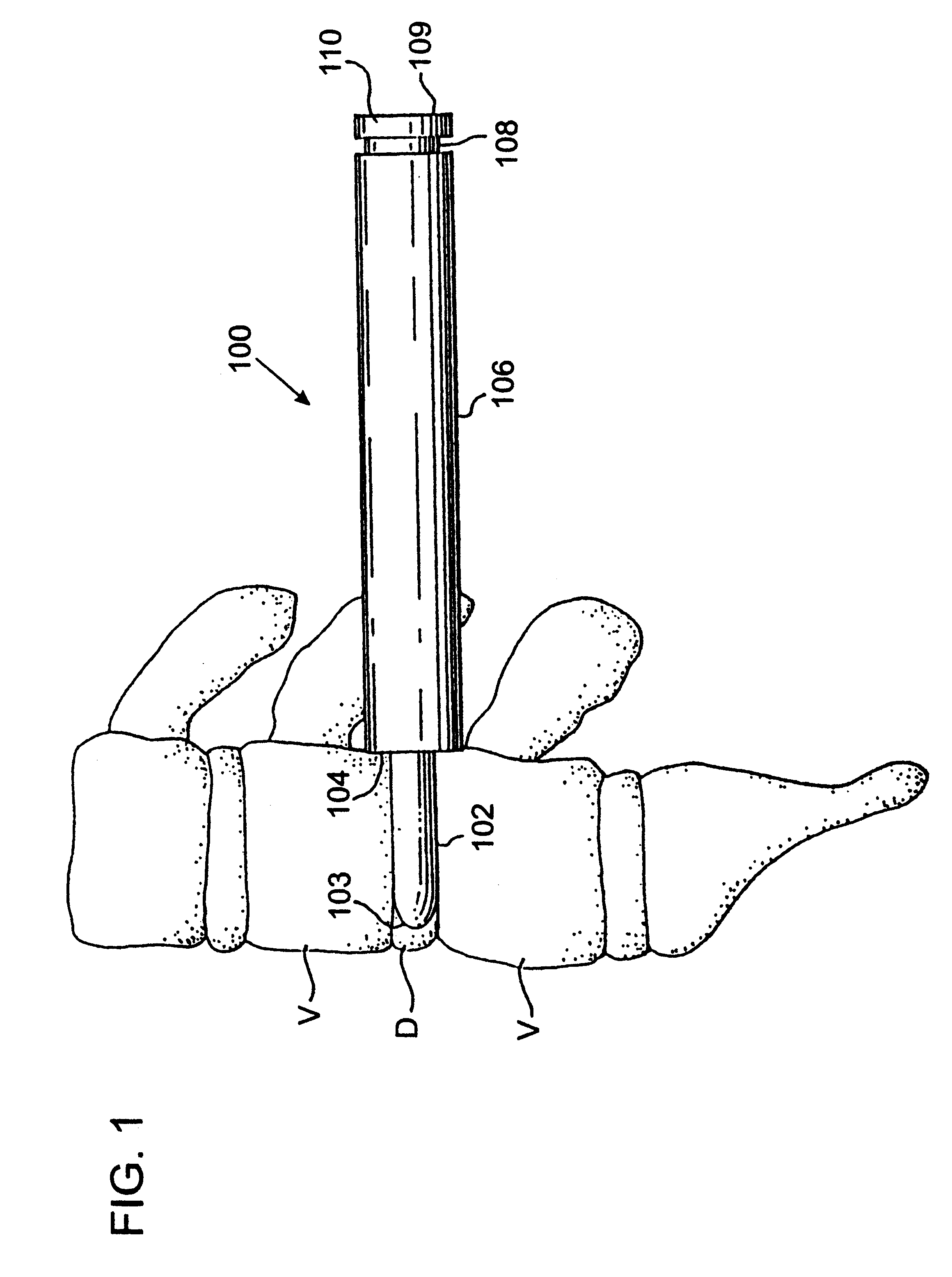
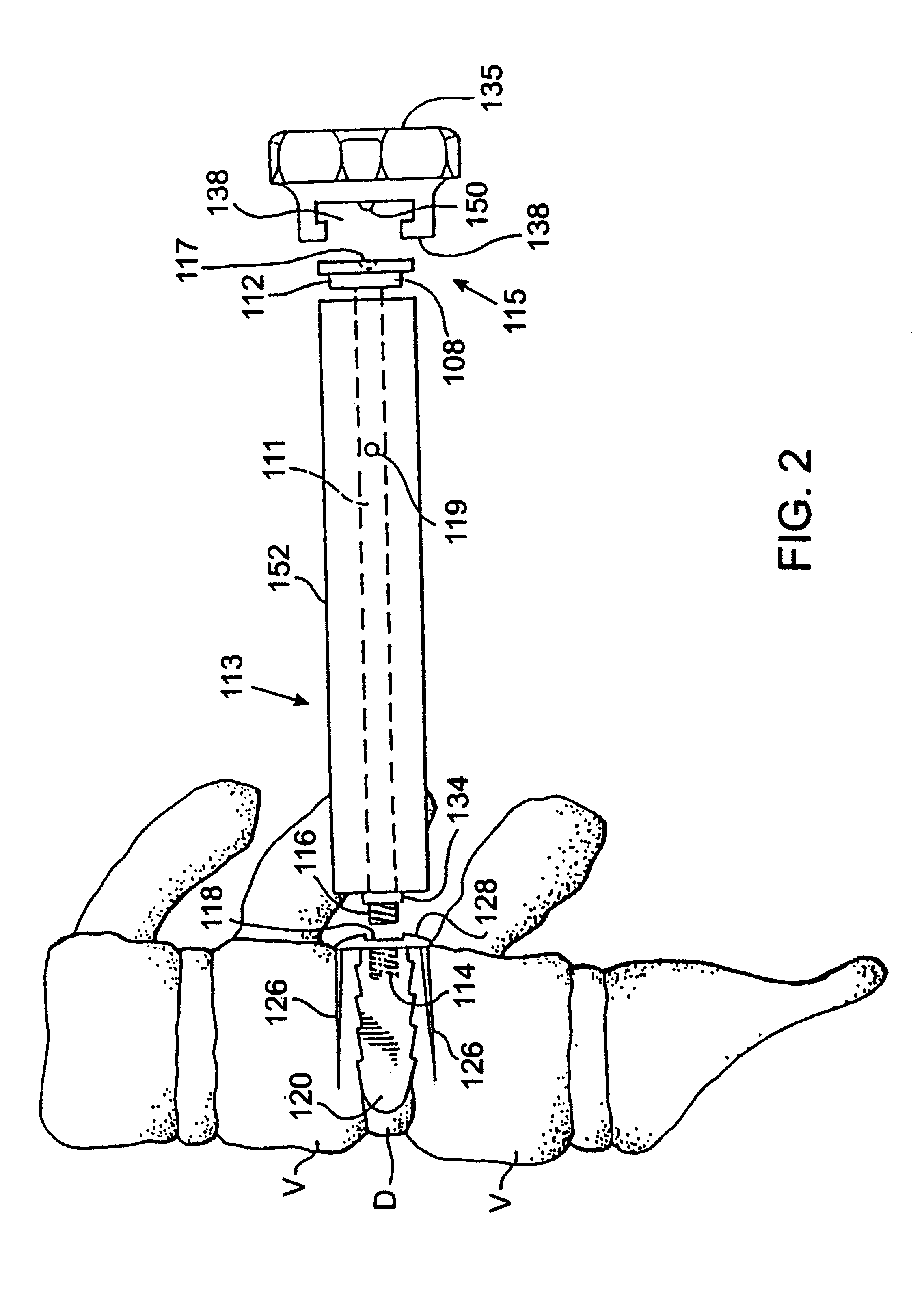
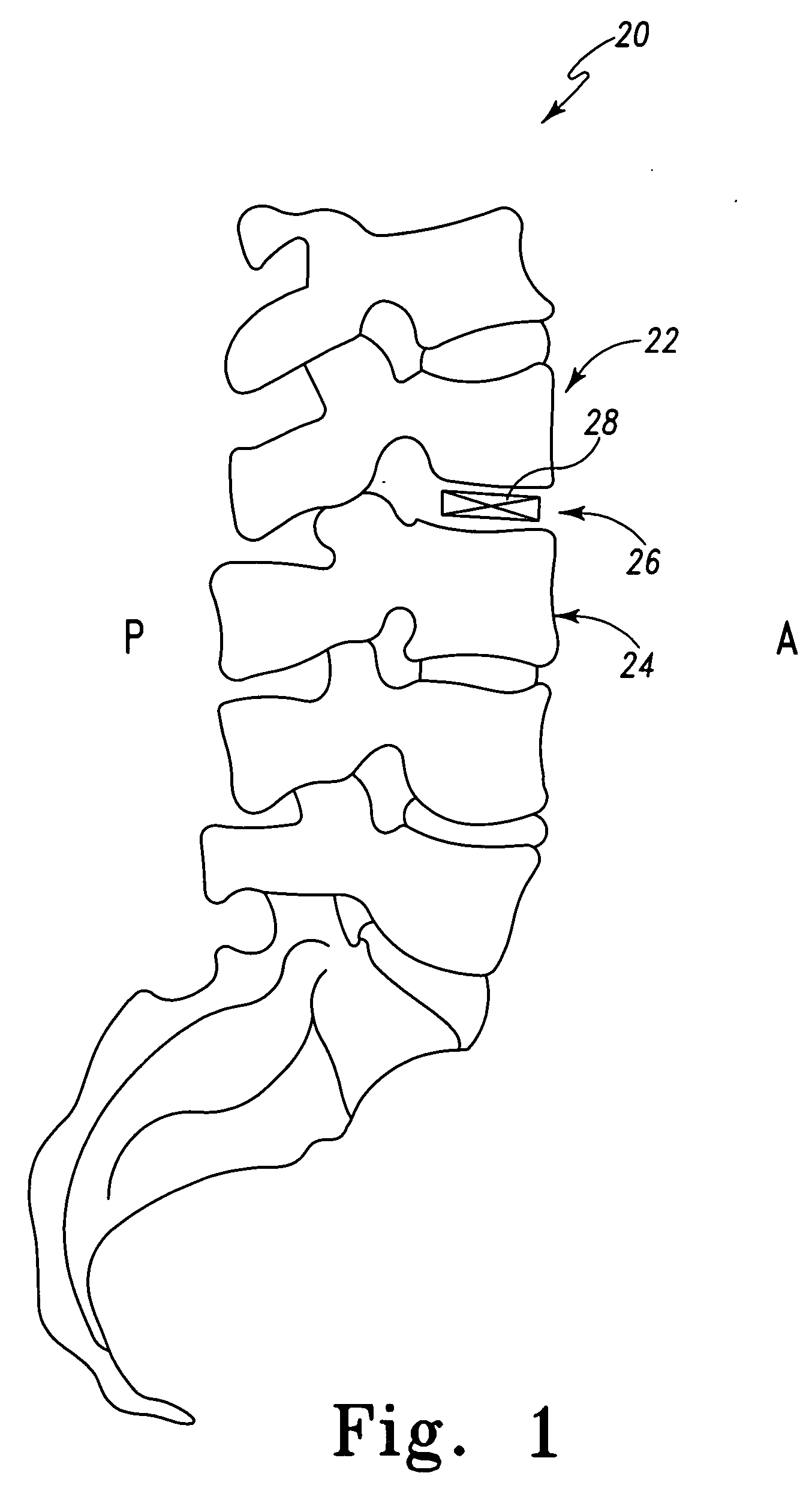
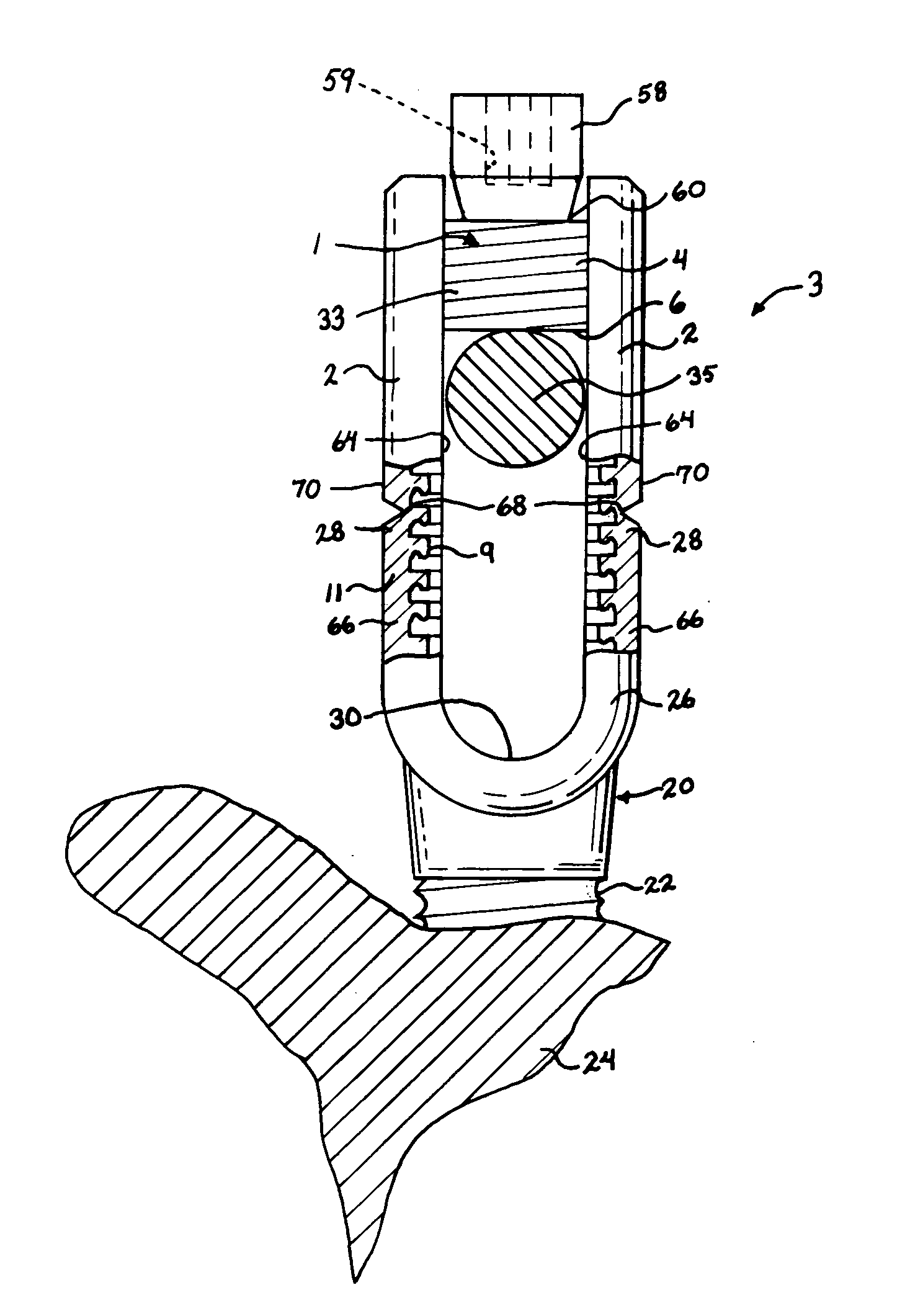
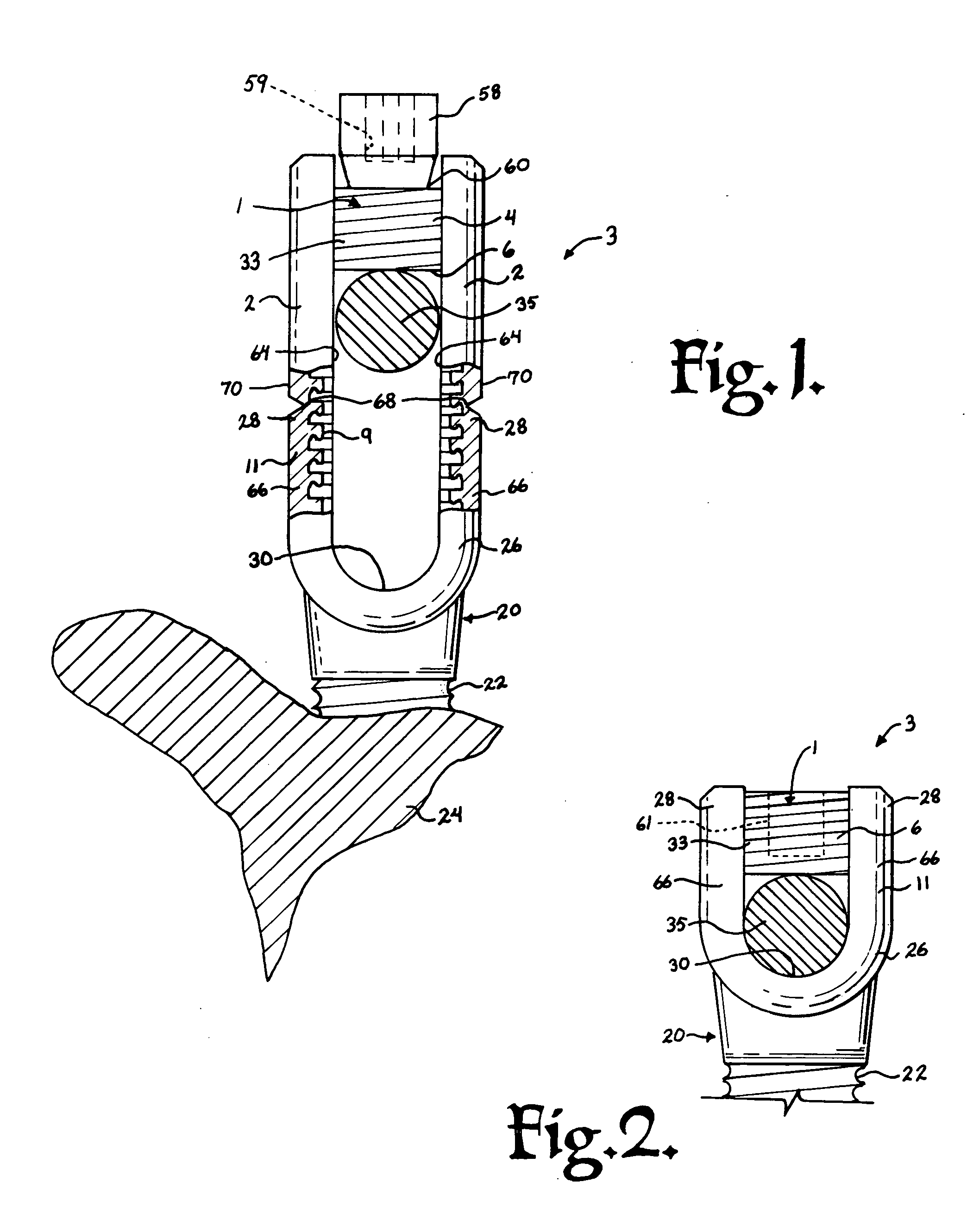
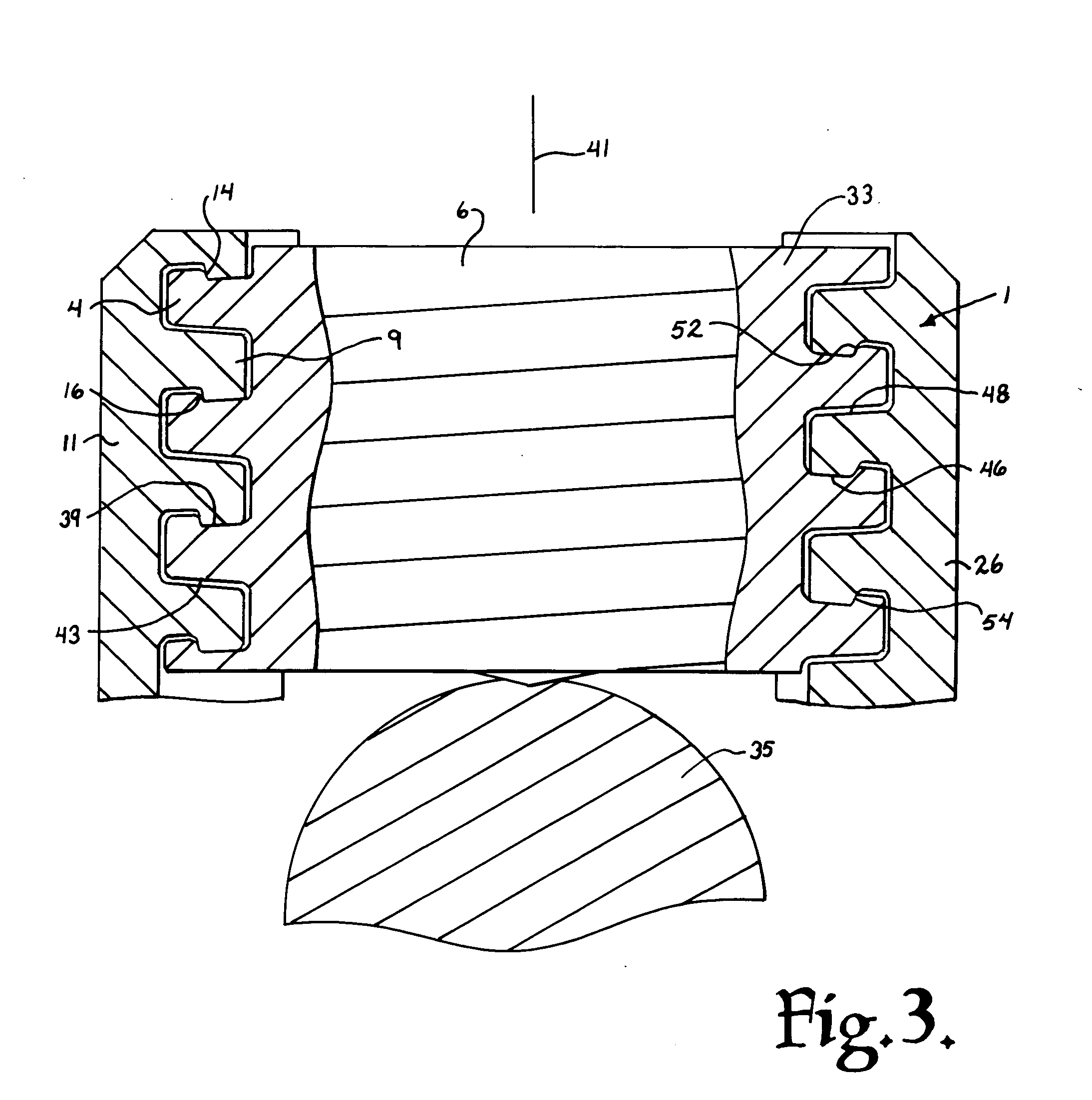
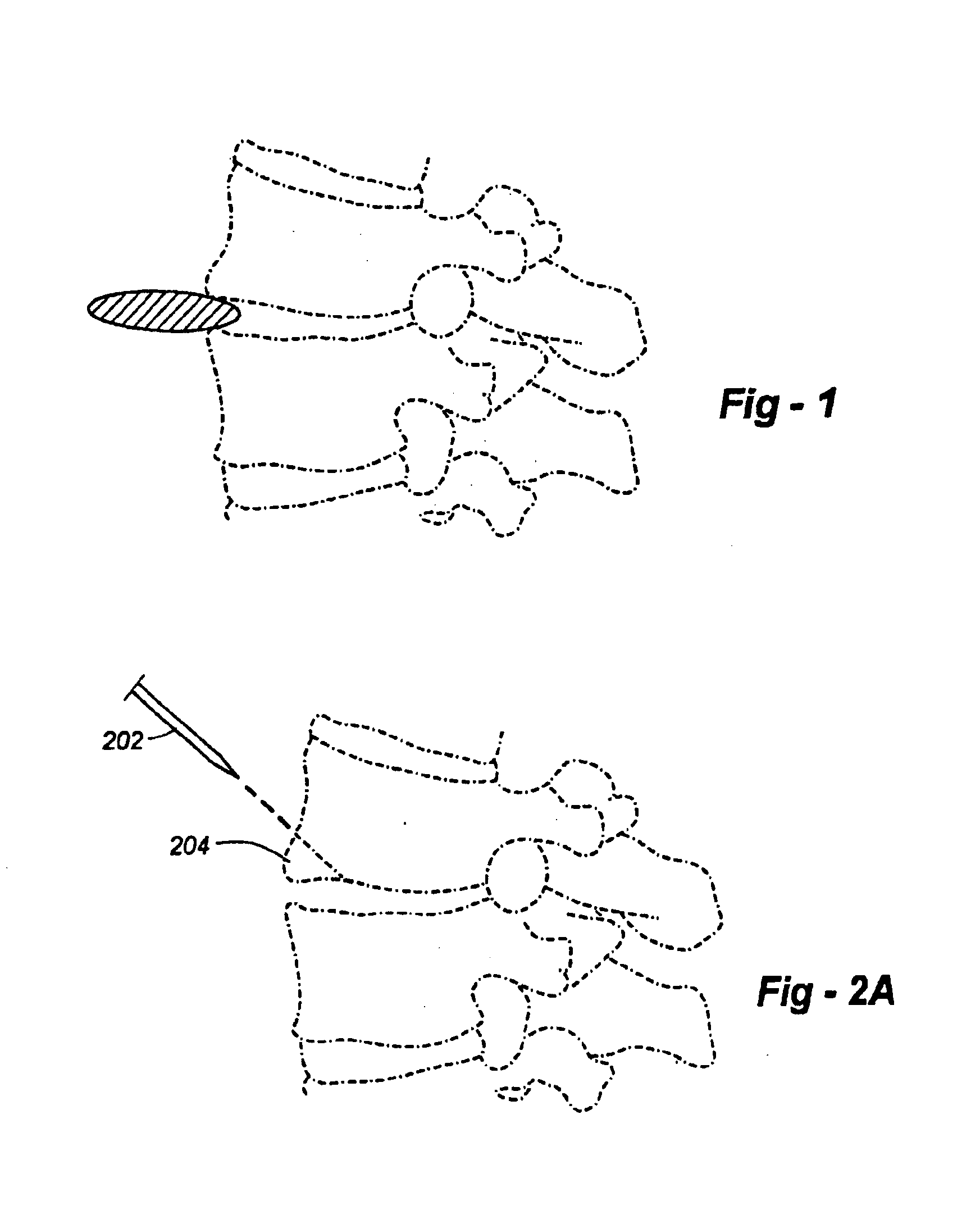
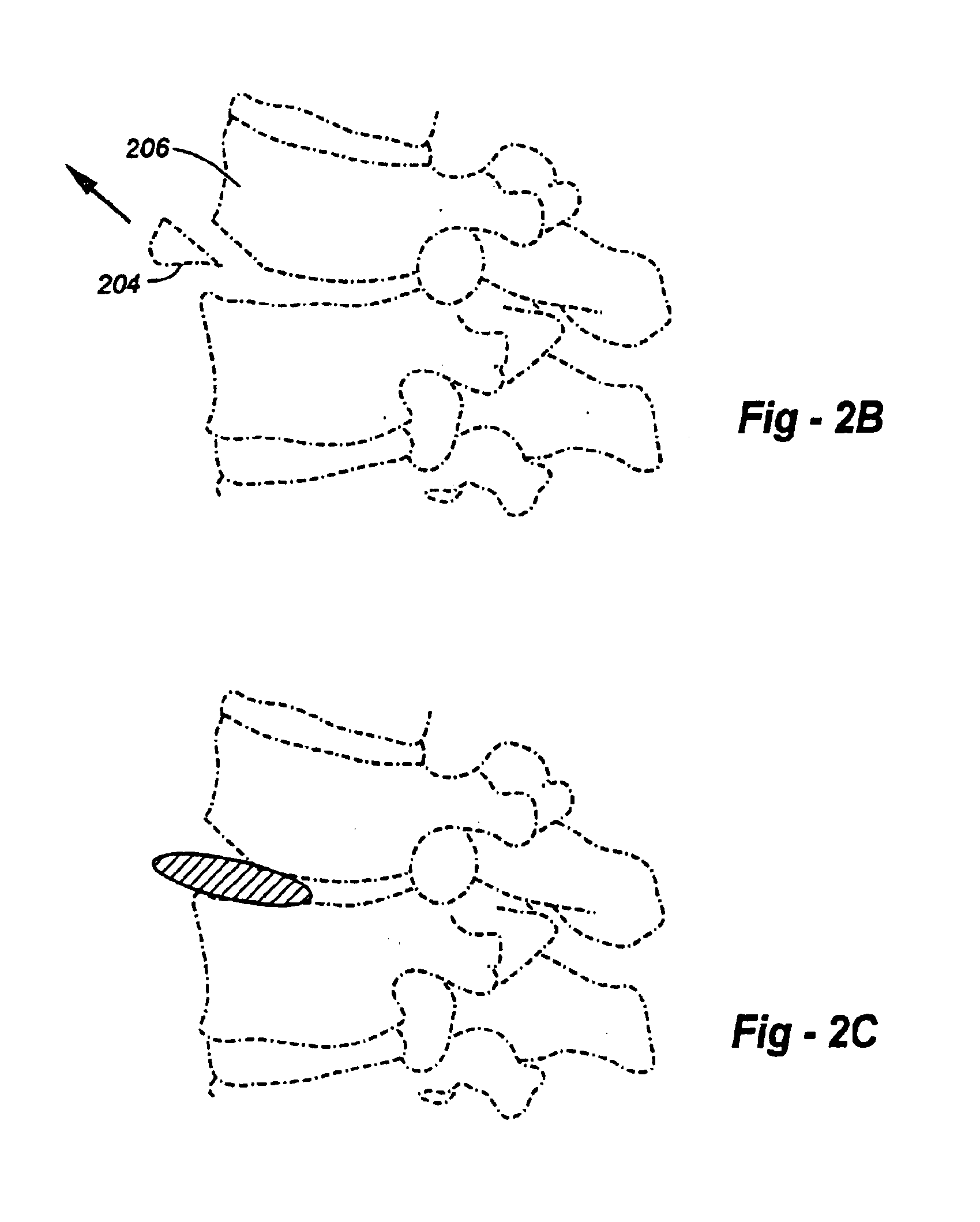
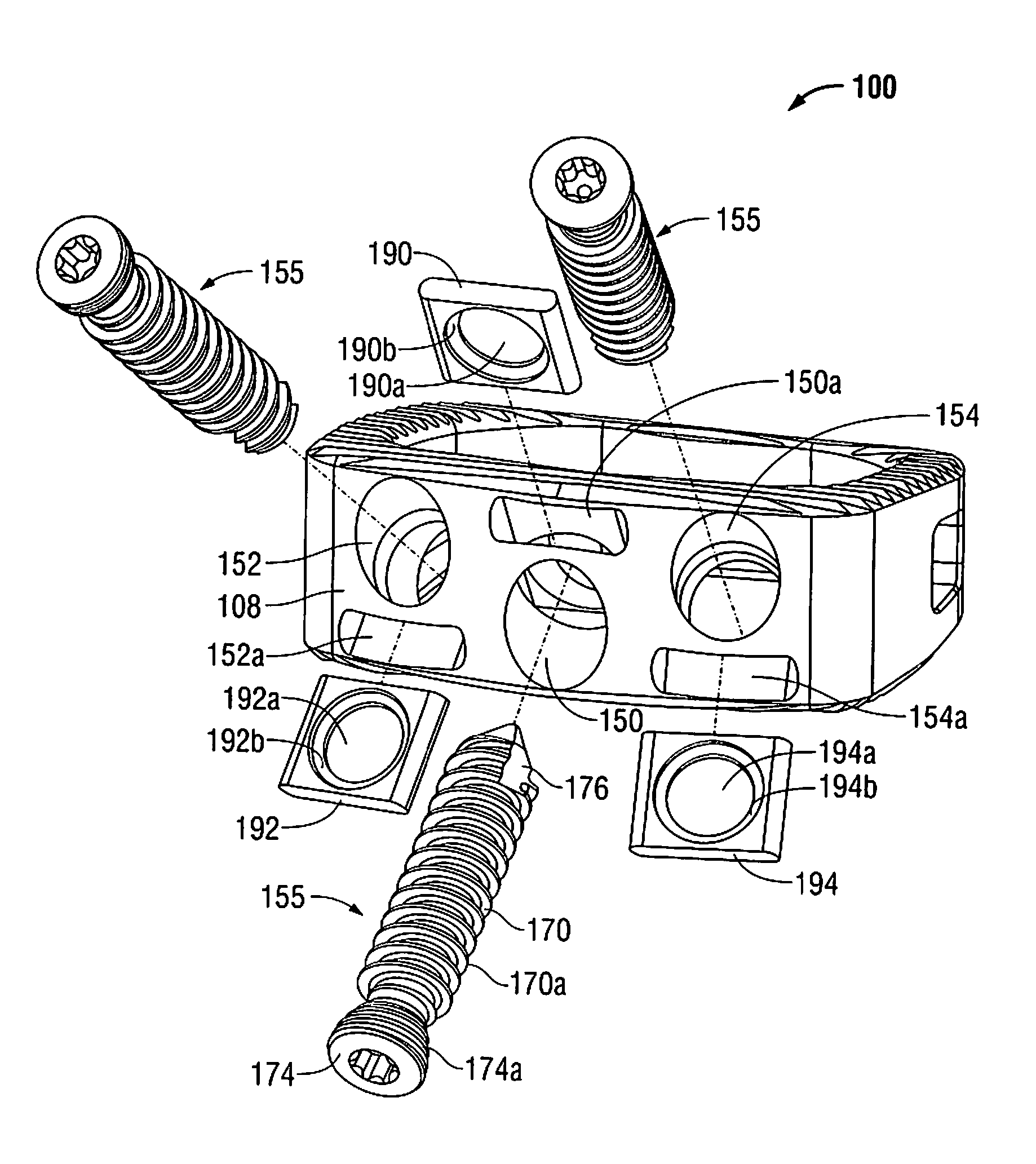
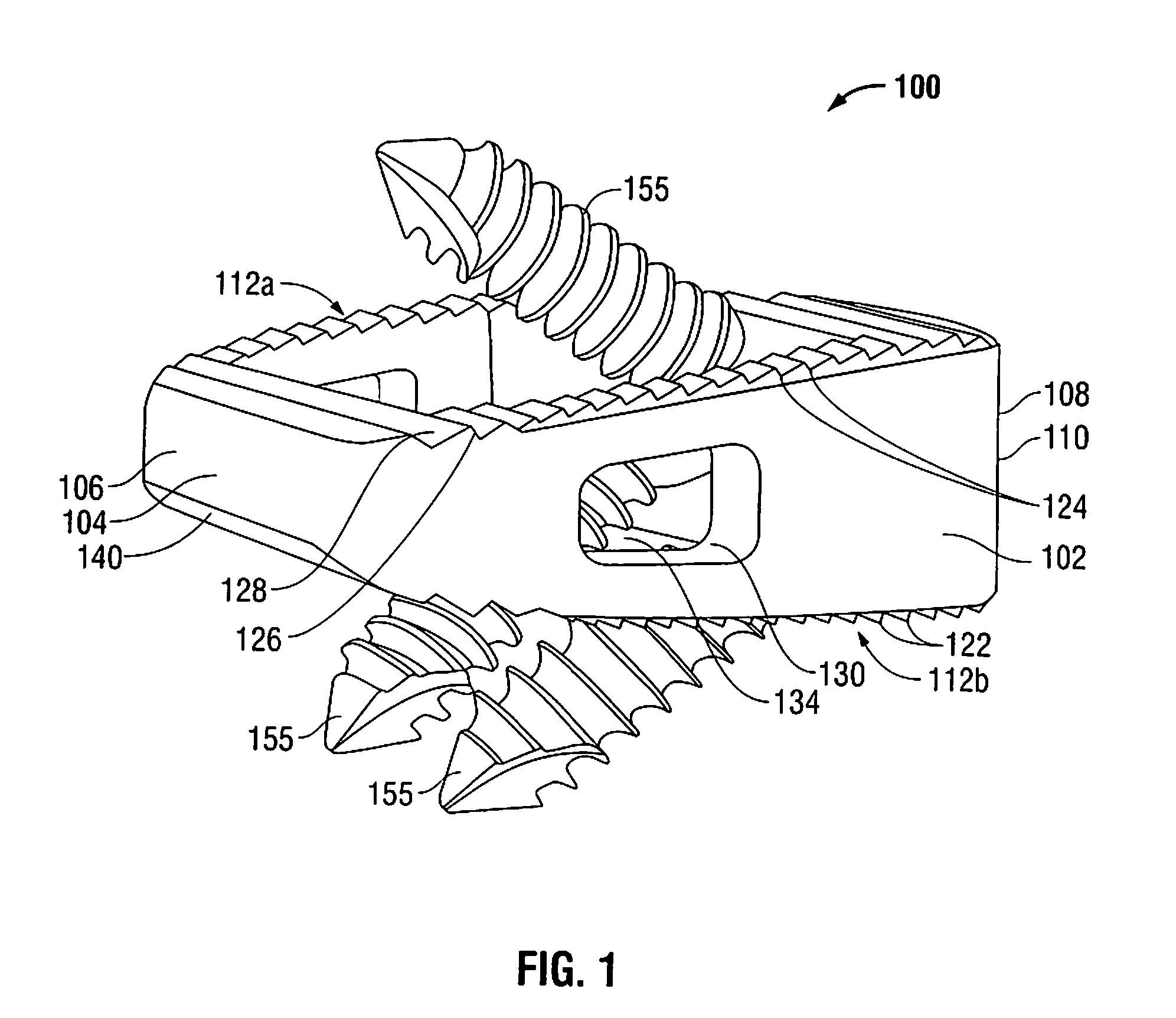
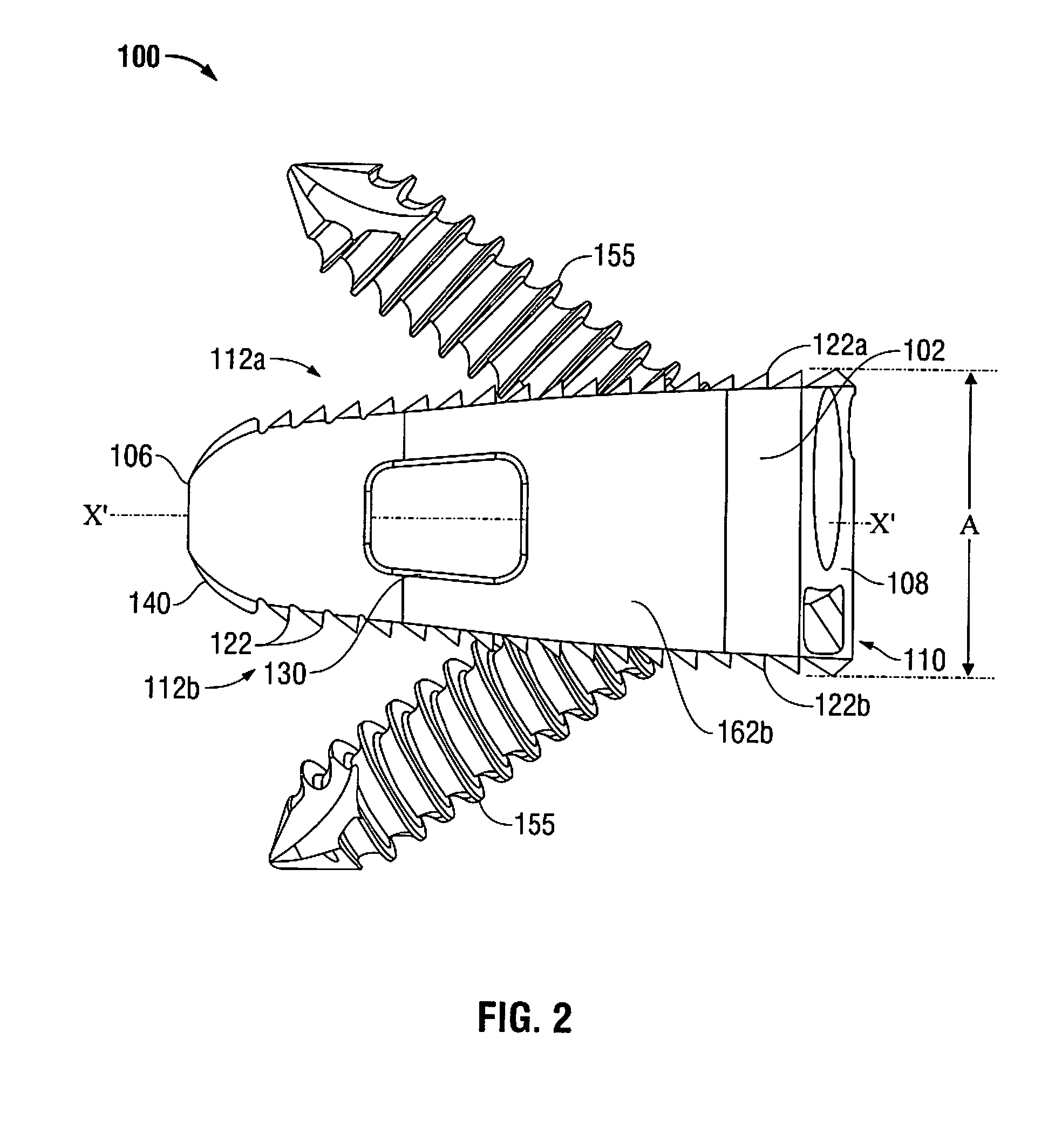
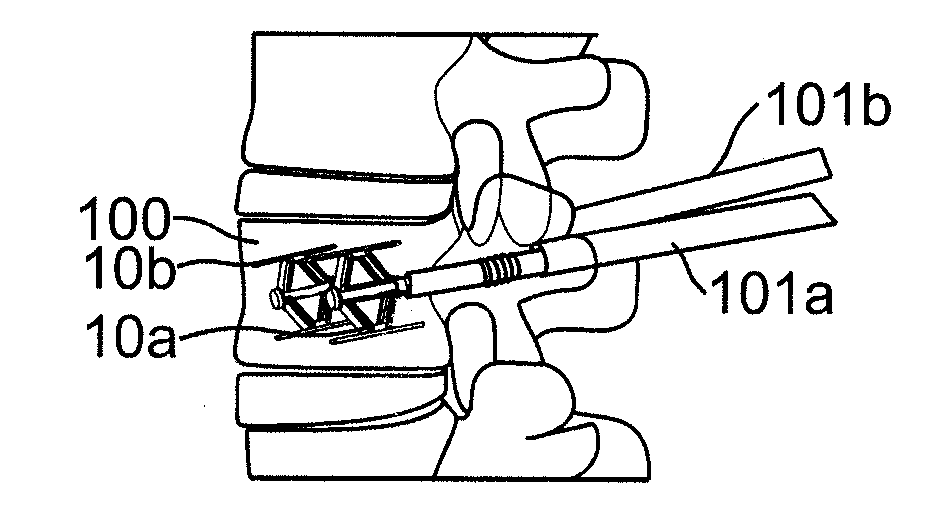
Method of inserting and preloading spinal implants
InactiveUS6080155ARestoring and maintaining normal angular relationshipFaster and safe and more efficaciousInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
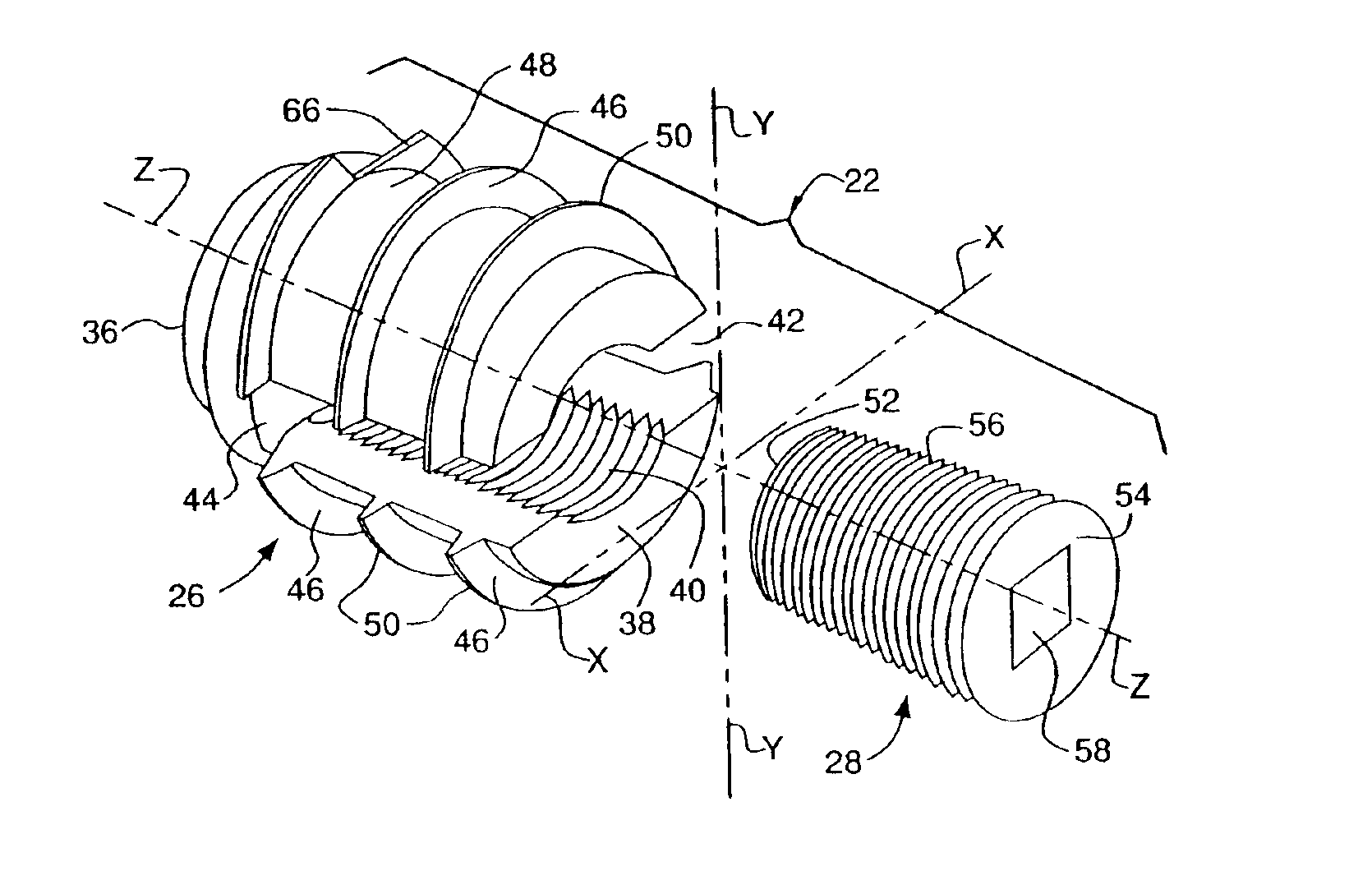
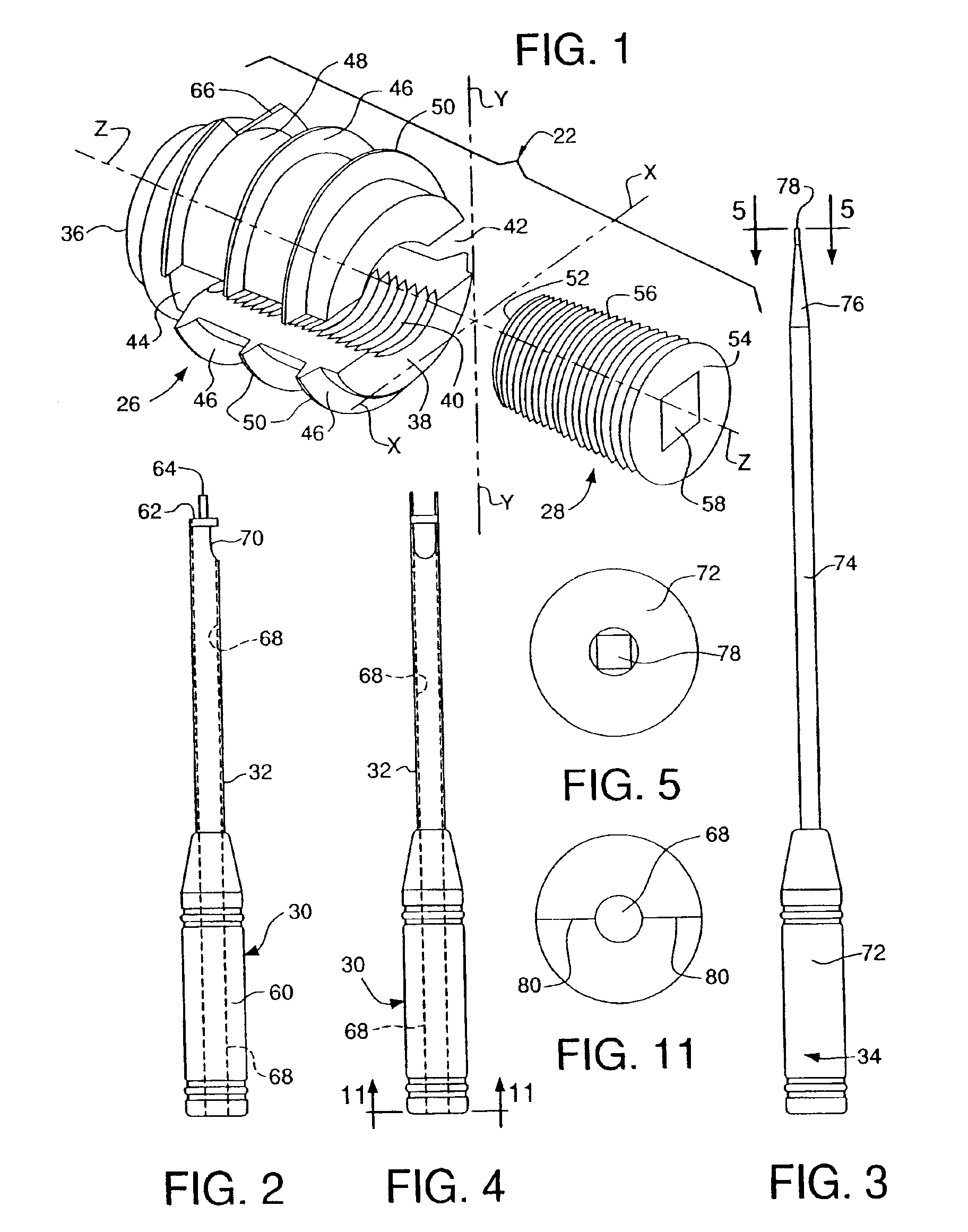
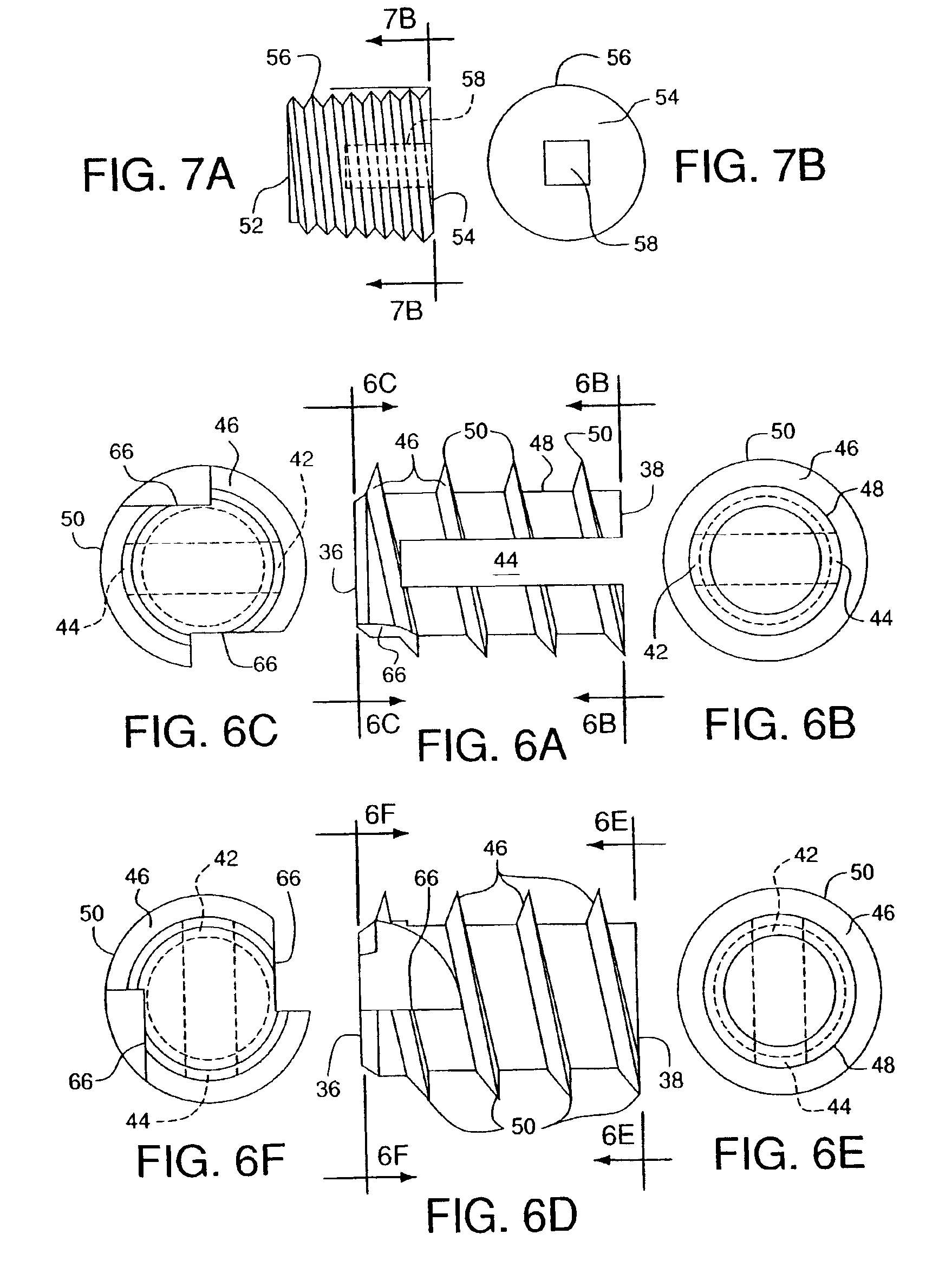
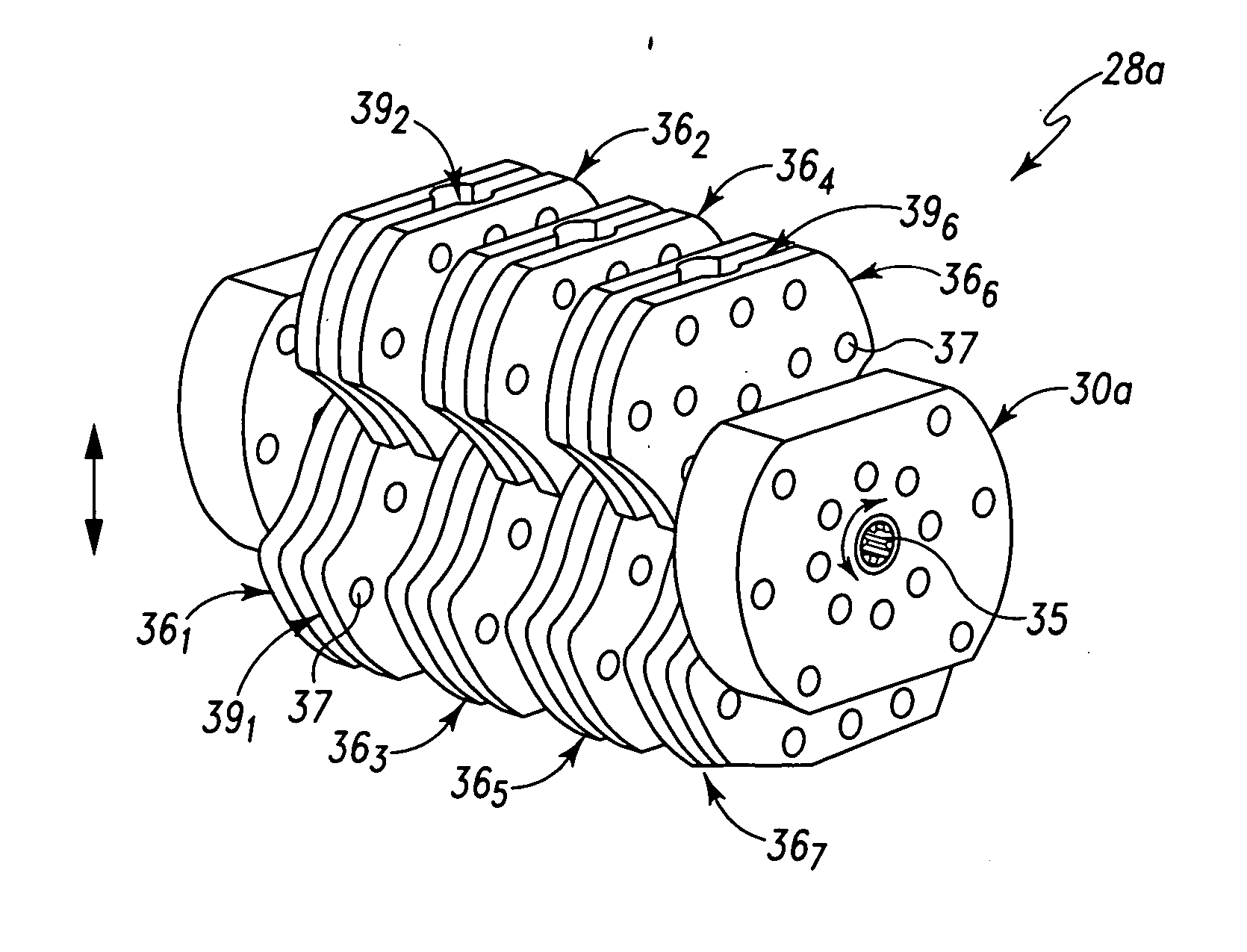
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve. Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted to restore the normal angular relationship of the vertebrae adjacent to that disc space. An extended outer sleeve having extended portions capable of maintaining the vertebrae distracted in their normal angular relationship is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Apparatus for inserting spinal implants
InactiveUS6096038AEliminate separationEfficient removalInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Apparatus for inserting spinal implants
InactiveUS6270498B1Eliminate separationEfficient removalInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve. Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted to restore the normal angular relationship of the vertebrae adjacent to that disc space. An extended outer sleeve having extended portions capable of maintaining the vertebrae distracted in their normal angular relationship is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Methods and apparatus for forming shaped axial bores through spinal vertebrae
InactiveUS6740090B1Easy to understandInternal osteosythesisBone implantSpinal CurvaturesSpinal implant
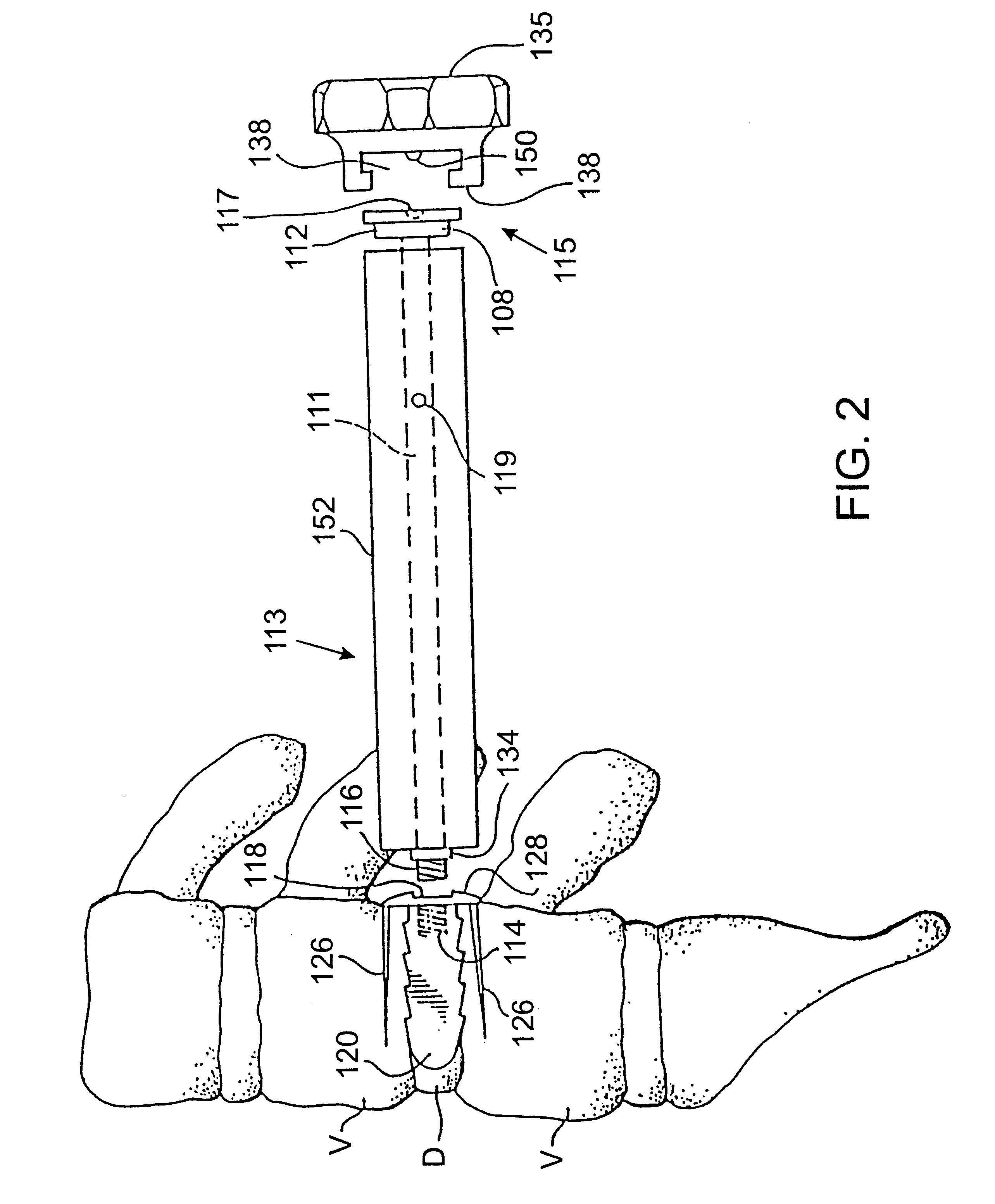
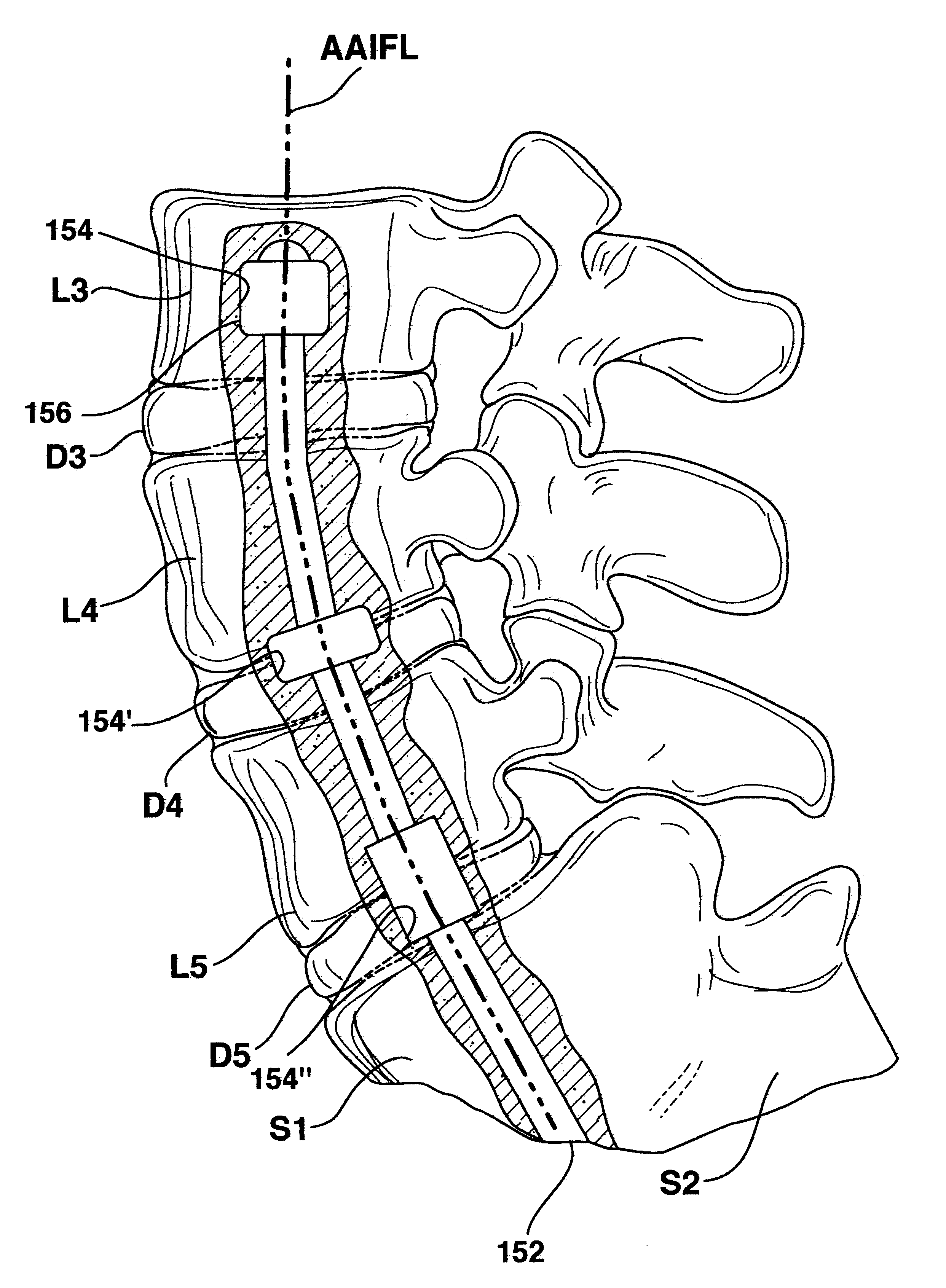
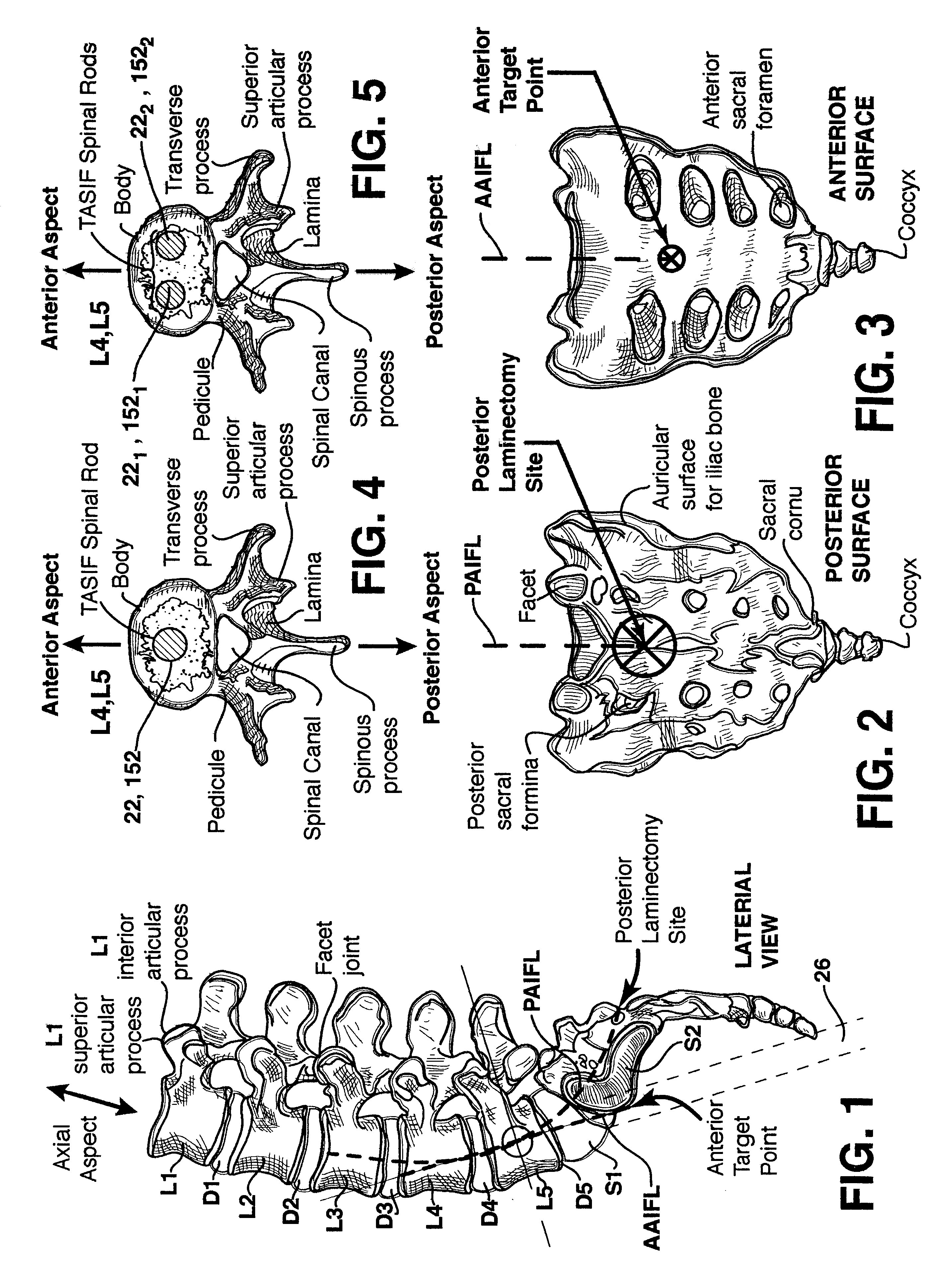
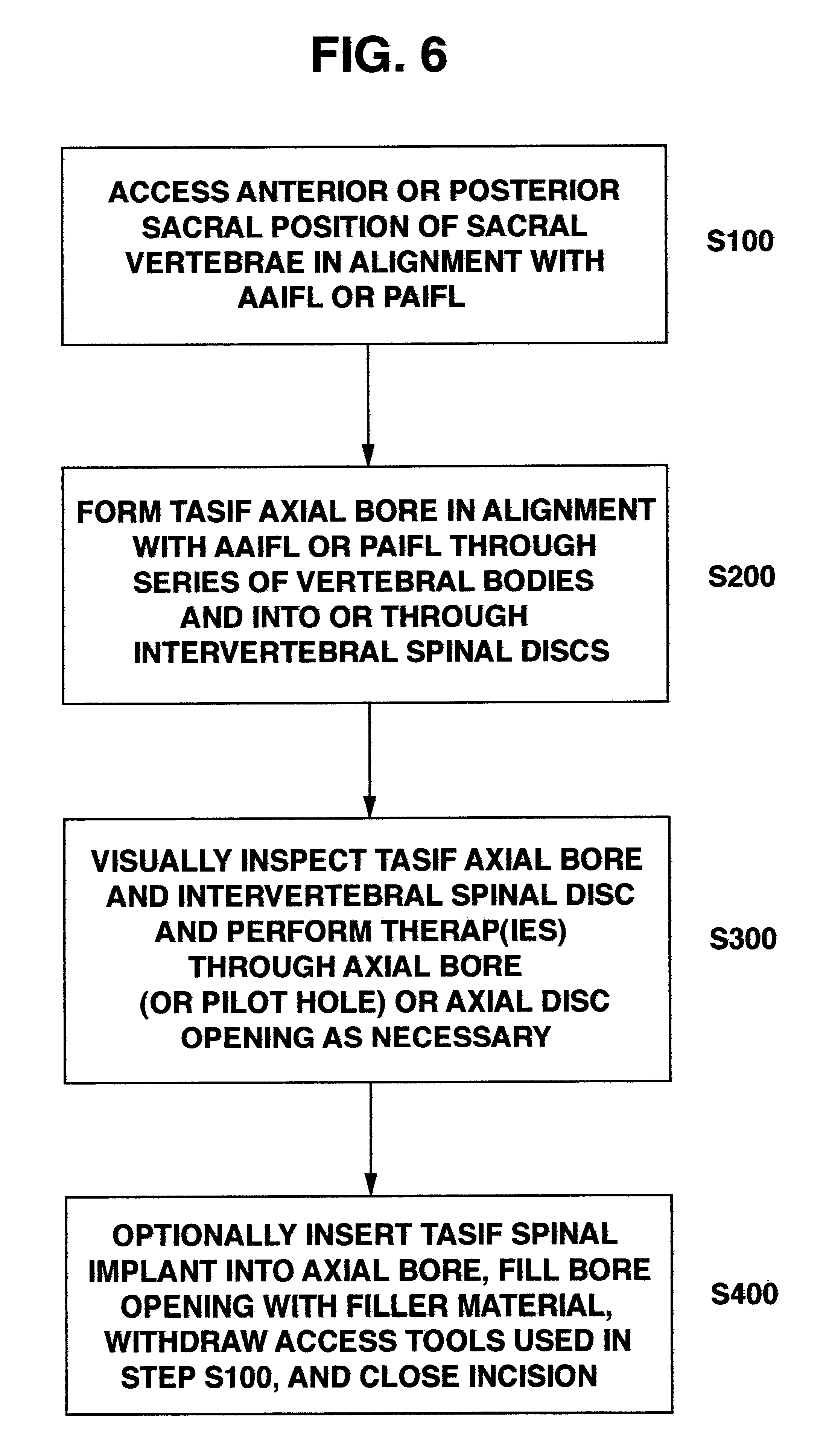
One or more shaped axial bore extending from an accessed posterior or anterior target point are formed in the cephalad direction through vertebral bodies and intervening discs, if present, in general alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) line in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner. An anterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL) or a posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (PAIFL) that extends from the anterior or posterior target point, respectively, in the cephalad direction following the spinal curvature through one or more vertebral body is visualized by radiographic or fluoroscopic equipment. Preferably, curved anterior or posterior TASIF axial bores are formed in axial or parallel or diverging alignment with the visualized AAIFL or PAIFL, respectively, employing bore forming tools that can be manipulated from proximal portions thereof that are located outside the patient's body to adjust the curvature of the anterior or posterior TASIF axial bores as they are formed in the cephalad direction. Further bore enlarging tools are employed to enlarge one or more selected section of the anterior or posterior TASIF axial bore(s), e.g., the cephalad bore end or a disc space, so as to provide a recess therein that can be employed for various purposes, e.g., to provide anchoring surfaces for spinal implants inserted into the anterior or posterior TASIF axial bore(s).
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
Apparatus for use in inserting spinal implants
InactiveUS6770074B2Eliminate separationEfficient removalBone implantDiagnosticsMedicineIntervertebral space
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve. Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted to restore the normal angular relationship of the vertebrae adjacent to that disc space. An extended outer sleeve having extended portions capable of maintaining the vertebrae distracted in their normal angular relationship is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Method and apparatus for flexible fixation of a spine
InactiveUS20050065516A1Easy constructionSimple designInternal osteosythesisEar treatmentSpinal columnCoupling
A flexible spinal fixation device having a flexible metallic connection unit for non-rigid stabilization of the spinal column. In one embodiment, the fixation device includes at least two securing members configured to be inserted into respective adjacent spinal pedicles, each securing member each including a coupling assembly. The fixation device further includes a flexible metal connection unit configured to be received and secured within the coupling assemblies of each securing member so as to flexibly stabilize the affected area of the spine.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Facet joint replacement
InactiveUS7041136B2Precise and tight press fitExcellent long-term fixation strengthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsProsthesisSacroiliac joint
A prosthesis for the replacement of a diseased or traumatized facet of a mammalian vertebra includes a surface that articulates with another prosthetic facet or a natural facet, a portion that replaces at least a bony portion of the diseased or traumatized spine facet which is to be replaced, and an element to attach the prosthesis to the vertebra in a manner that does not require attachment to or abutment against the posterior arch. A method of installing the prosthesis includes the steps of resecting at least a portion of a facet and attaching the prosthesis in a manner that does not require attachment or abutment against the posterior arch.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Facet arthroplasty devices and methods
InactiveUS20050027361A1Overcome disadvantagesOvercome problemsBone implantJoint implantsDisease causeIntervertebral disk prostheses
A method of treating spine disease including the steps of removing at least a portion of a natural facet joint from a vertebral body; implanting an intervertebral disc prosthesis and replacing the portion of the natural facet joint with a facet joint prosthesis. The removed facet portion may be a cephalad or a caudal facet or both. The replacing step may include the step of attaching the facet joint prosthesis to the vertebral body, such as at or near a pedicle and / or spinous process. The invention also provides spinal prostheses to treat spine disease. The spinal prostheses include an intervertebral disc prosthesis and a facet joint prosthesis having artificial facet joint structure adapted and configured to replace a removed portion of the natural facet joint (cephalad, caudal or both).
Owner:FACET SOLUTIONS
Method and apparatus for flexible fixation of a spine
ActiveUS20050124991A1Easy constructionSimple designInternal osteosythesisCannulasSpinal columnCoupling
A flexible spinal fixation device having a flexible metallic connection unit for non-rigid stabilization of the spinal column. In one embodiment, the fixation device includes at least two securing members configured to be inserted into respective adjacent spinal pedicles, each securing member each including a coupling assembly. The fixation device further includes a flexible metal connection unit configured to be received and secured within the coupling assemblies of each securing member so as to flexibly stabilize the affected area of the spine.
Owner:N SPINE INC
Vertebral facet joint prosthesis and method of fixation
ActiveUS20050177240A1Reduce contactMaintain liquidityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFacet joint prosthesisArticular processes
Devices and methods for altering the spacing and motion at the facet joints of the vertebral column are provided. One embodiment of the invention comprises a prosthesis with surfaces configured to articulate with the facets of the facet joint. A retaining member for anchoring the prosthesis within the facet joint is optionally included. Methods for surgically and less invasively implanting the prosthesis and securing the prosthesis to the articular processes or surrounding soft tissue are also provided.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
Methods for electrosurgical treatment of spinal tissue
InactiveUS20050004634A1Stiffening the interspinous tissue structureStabilizing the vertebral columnEnemata/irrigatorsHeart valvesThermal energySpinal ligaments
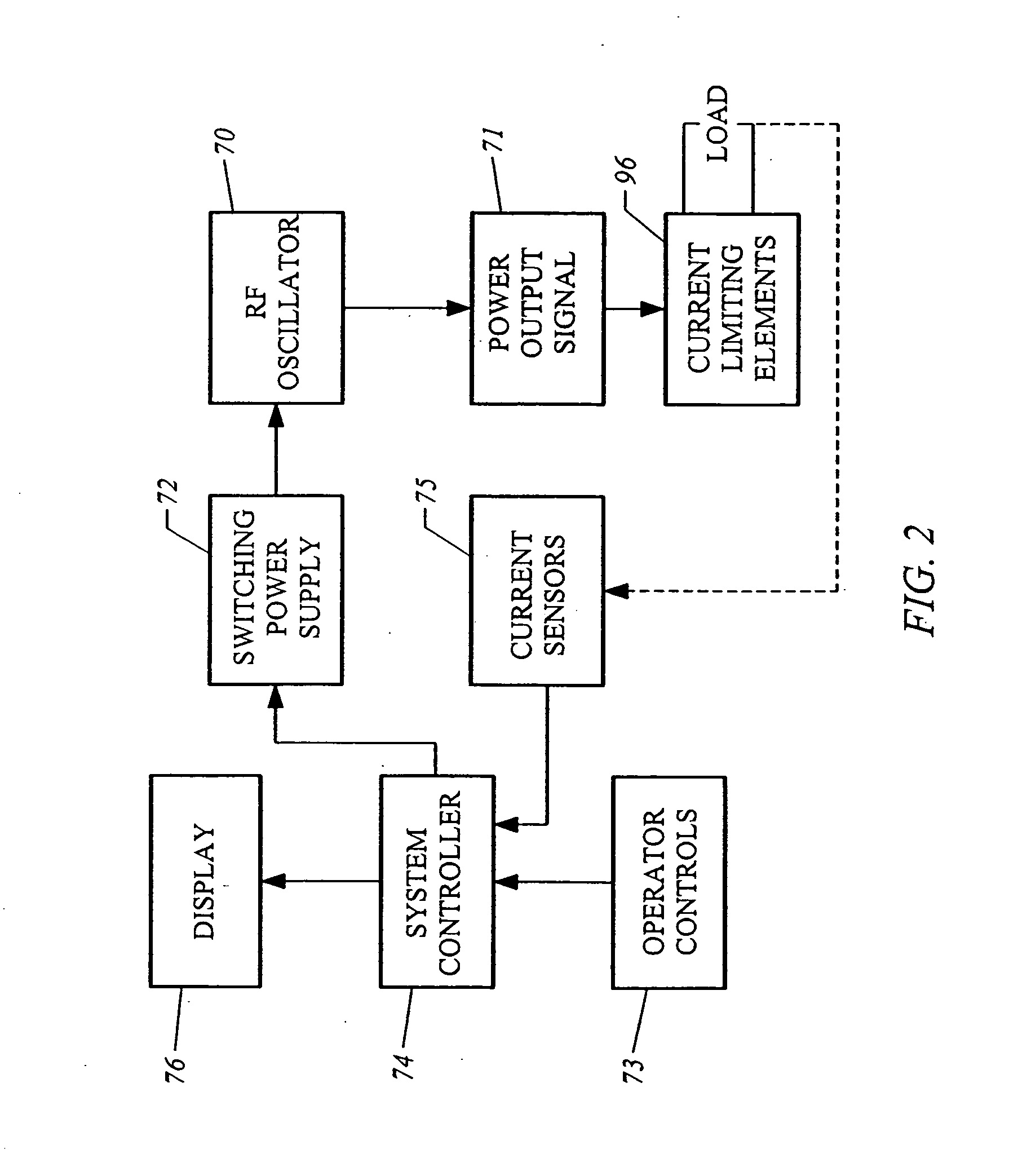
Systems, apparatus, and methods for treating spinal tissue and other body structures in open and endoscopic spine surgery to relieve symptoms, such as neck or back pain. In particular, the present invention provides methods for the controlled heating of various tissues in or around the vertebral column, including various interspinous tissues, such that spinal ligaments and cartilage surrounding the vertebrae and the facet joints are shrunk or tightened to stabilize the vertebral column of a patient. Thermal energy is applied to the target tissue in a subablation mode of an electrosurgical system to cause shrinkage of the tissue, thereby stiffening the interspinous tissue and stabilizing the vertebral column. In an exemplary embodiment, a high frequency RF voltage can be applied between one or more active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to heat a target interspinous tissue to within a temperature range at which irreversible shrinkage of the tissue occurs.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
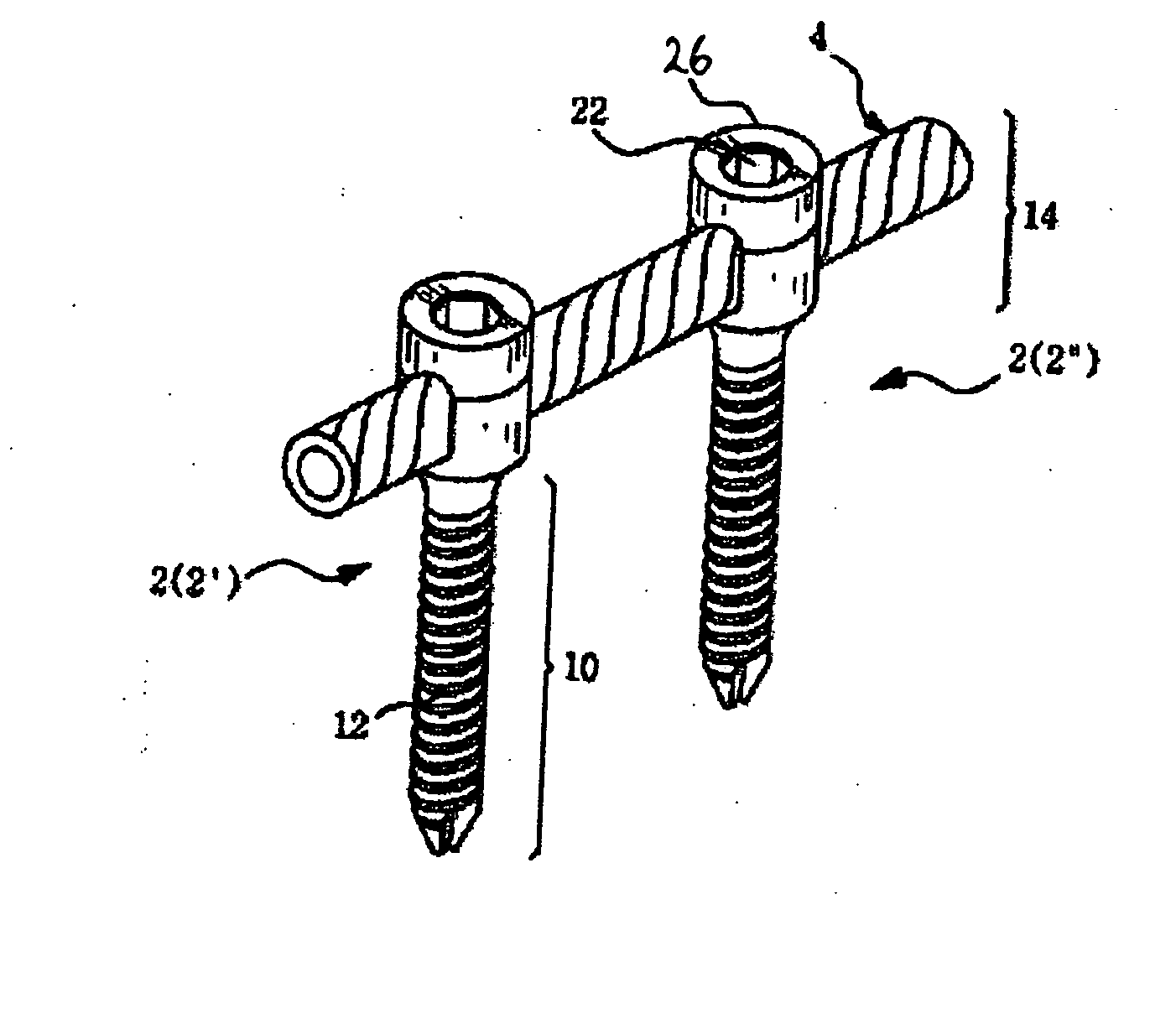
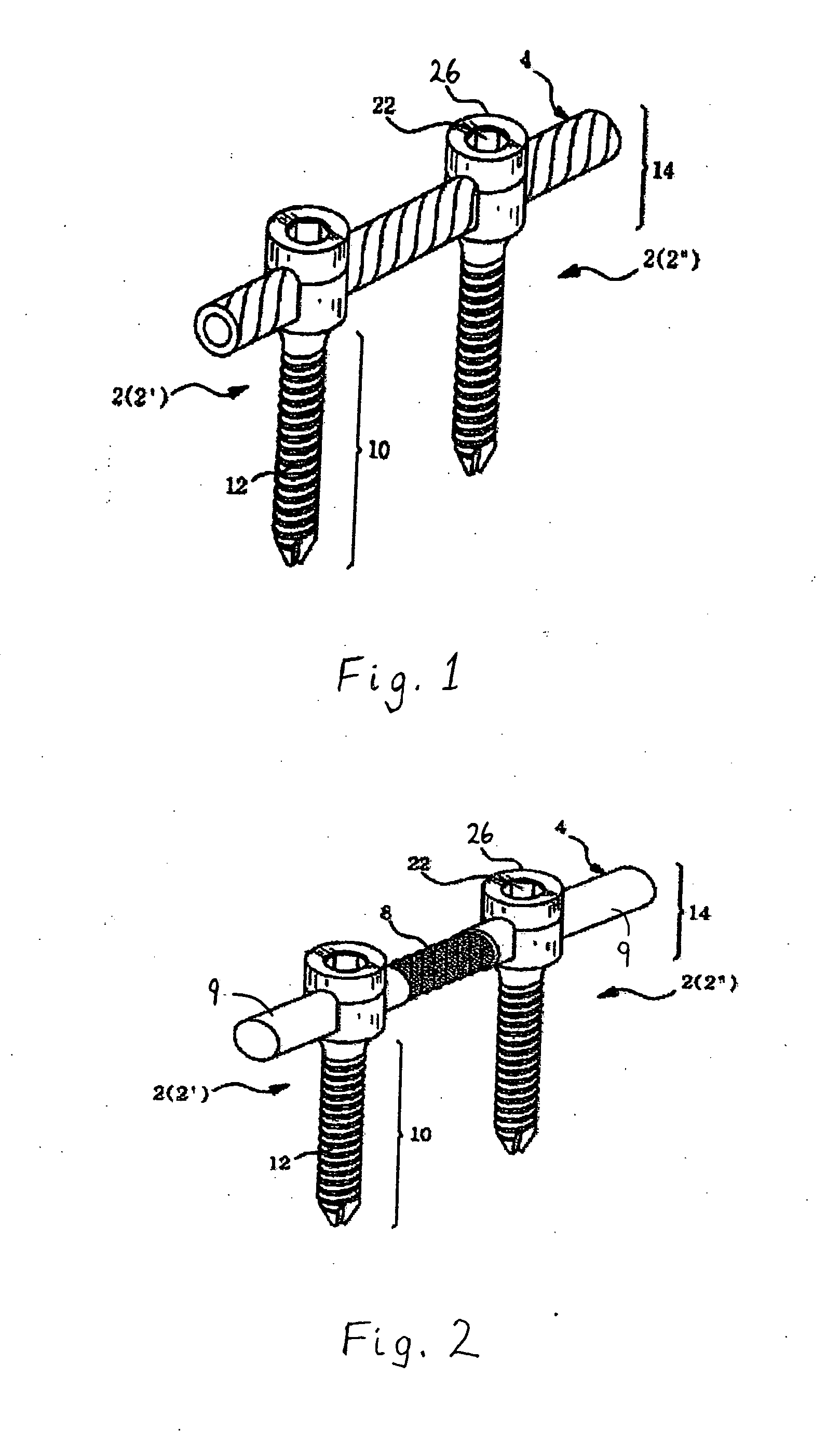
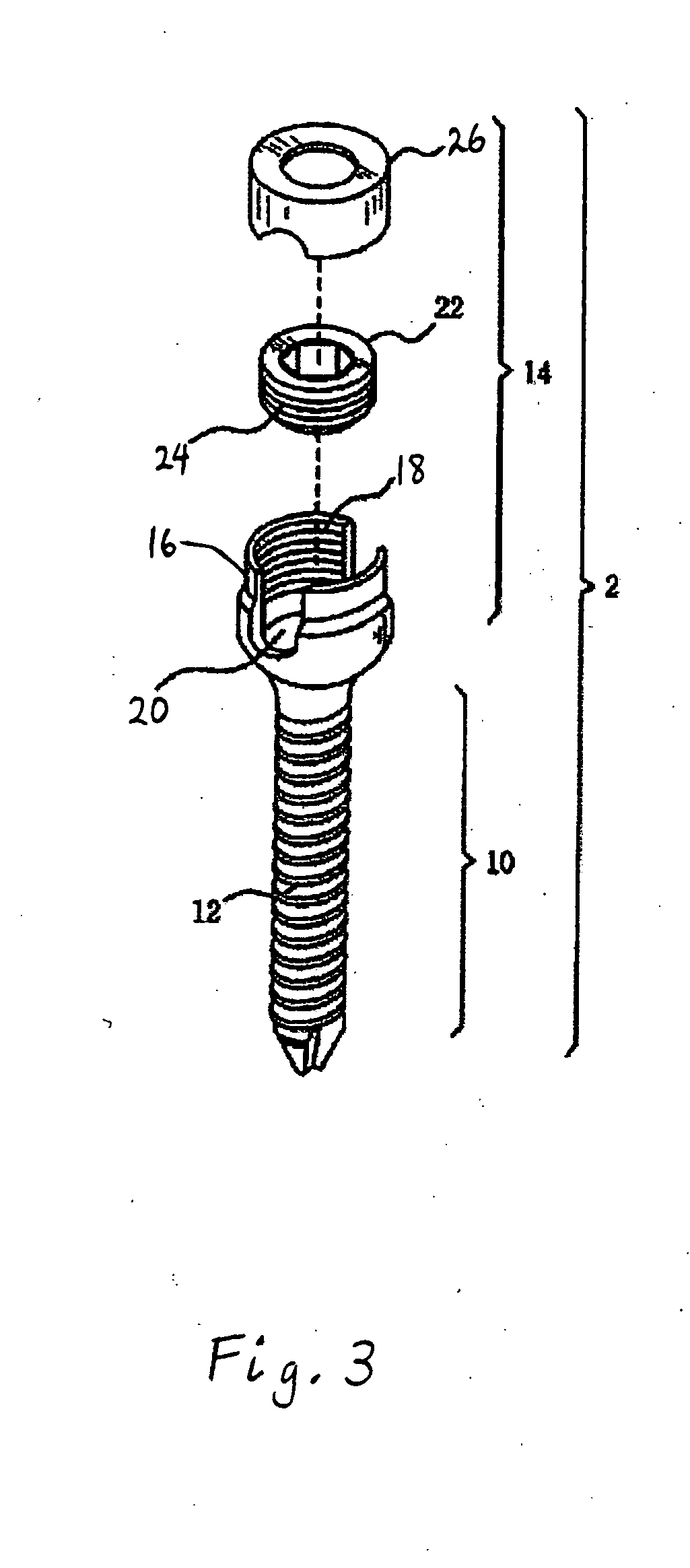
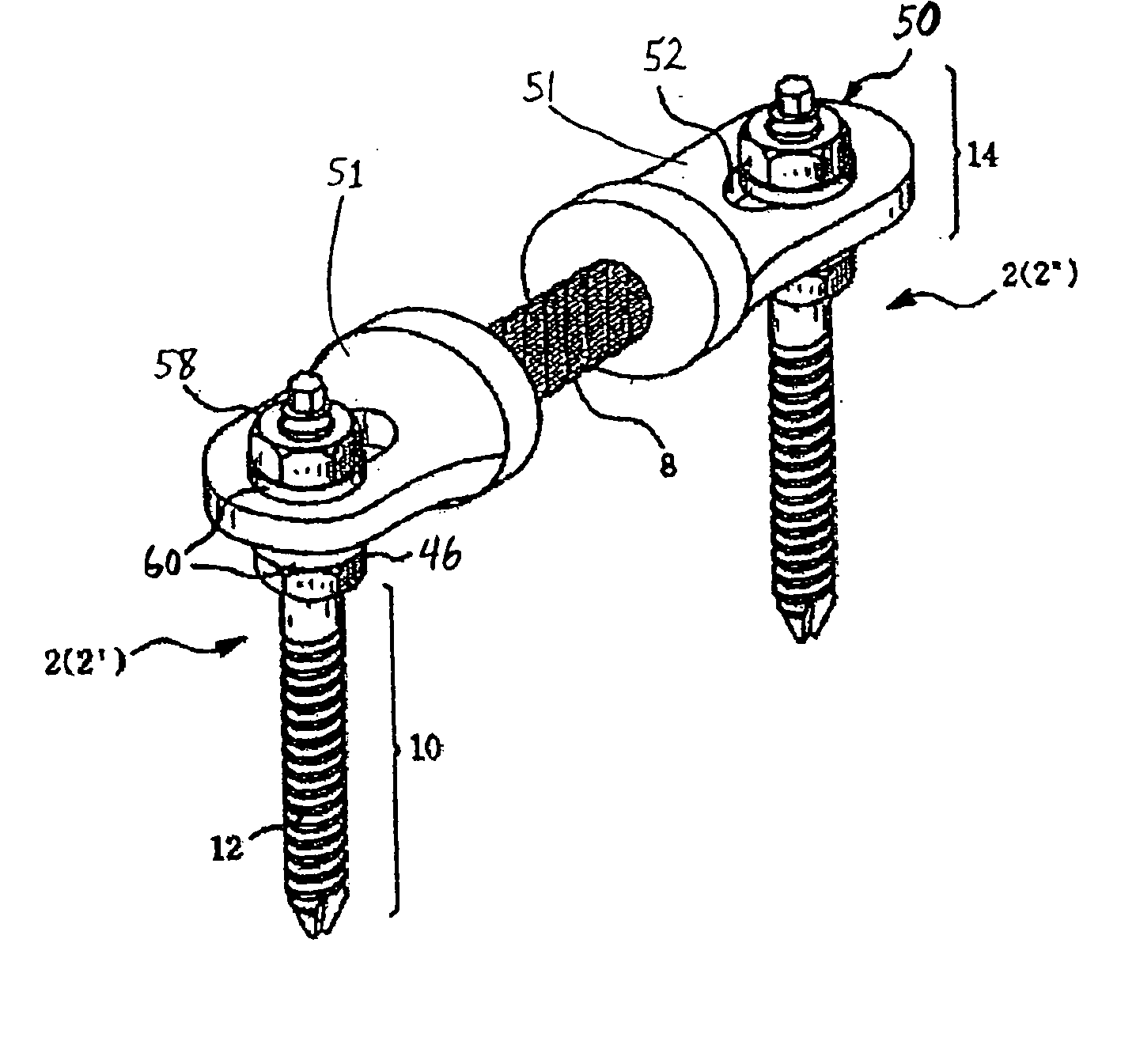
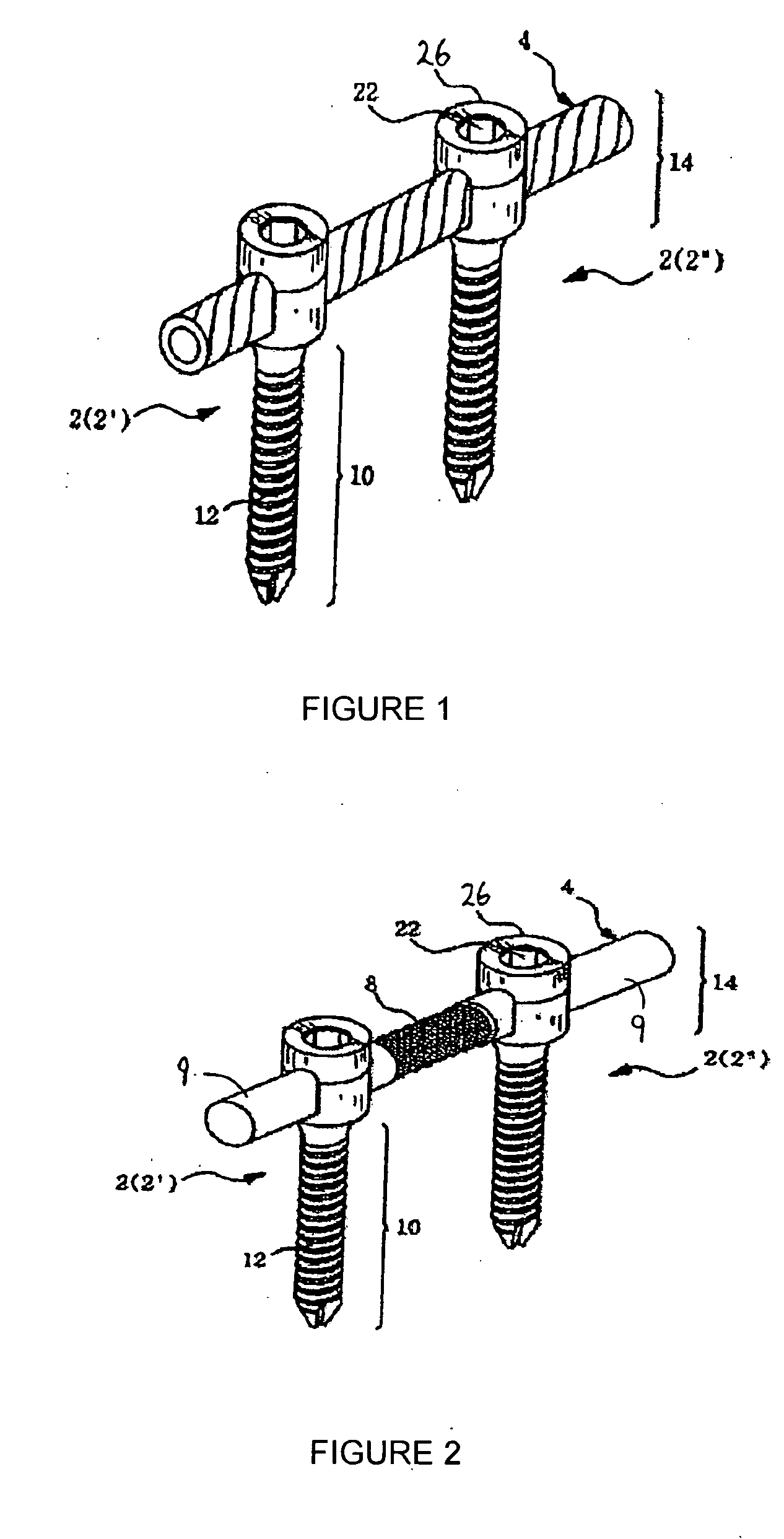
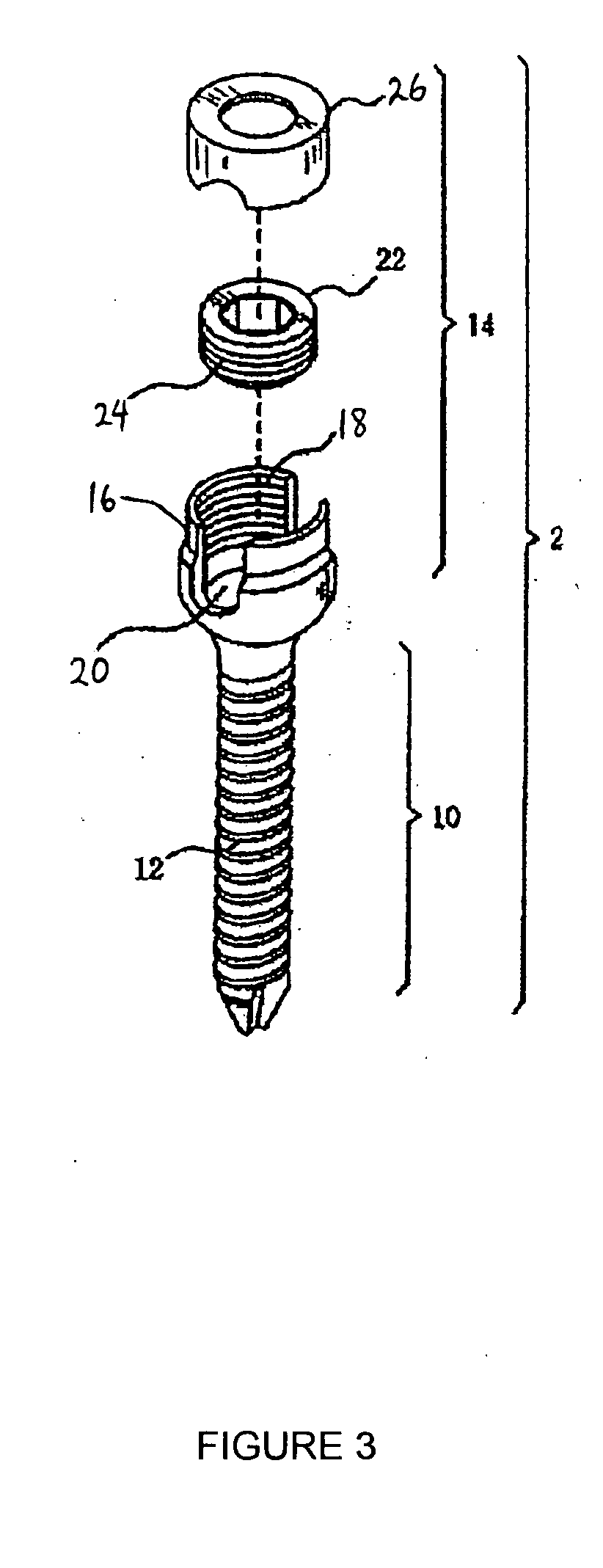
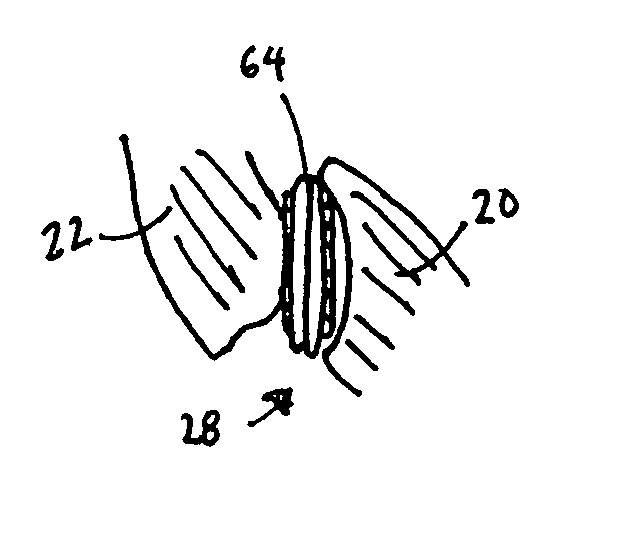
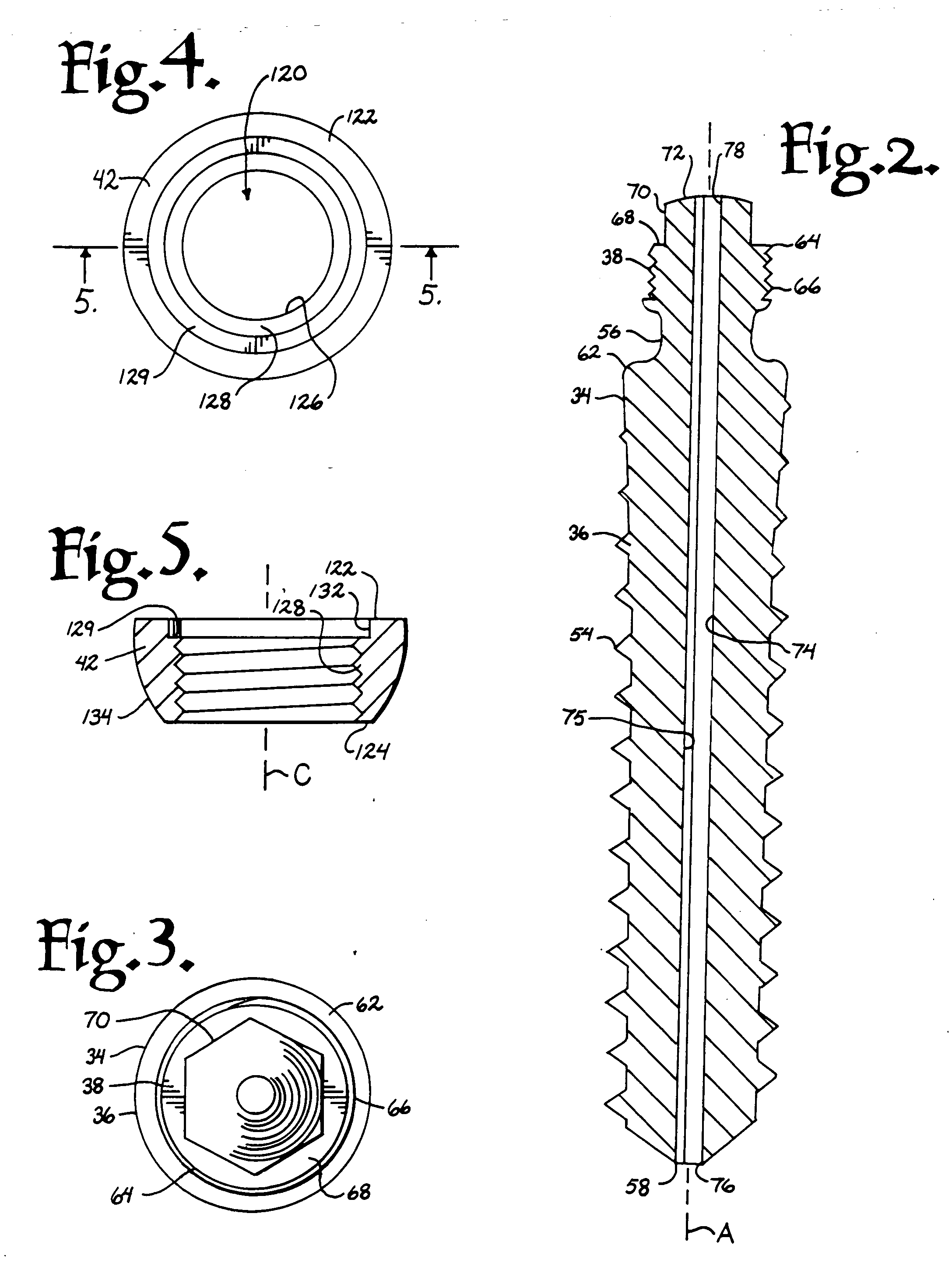
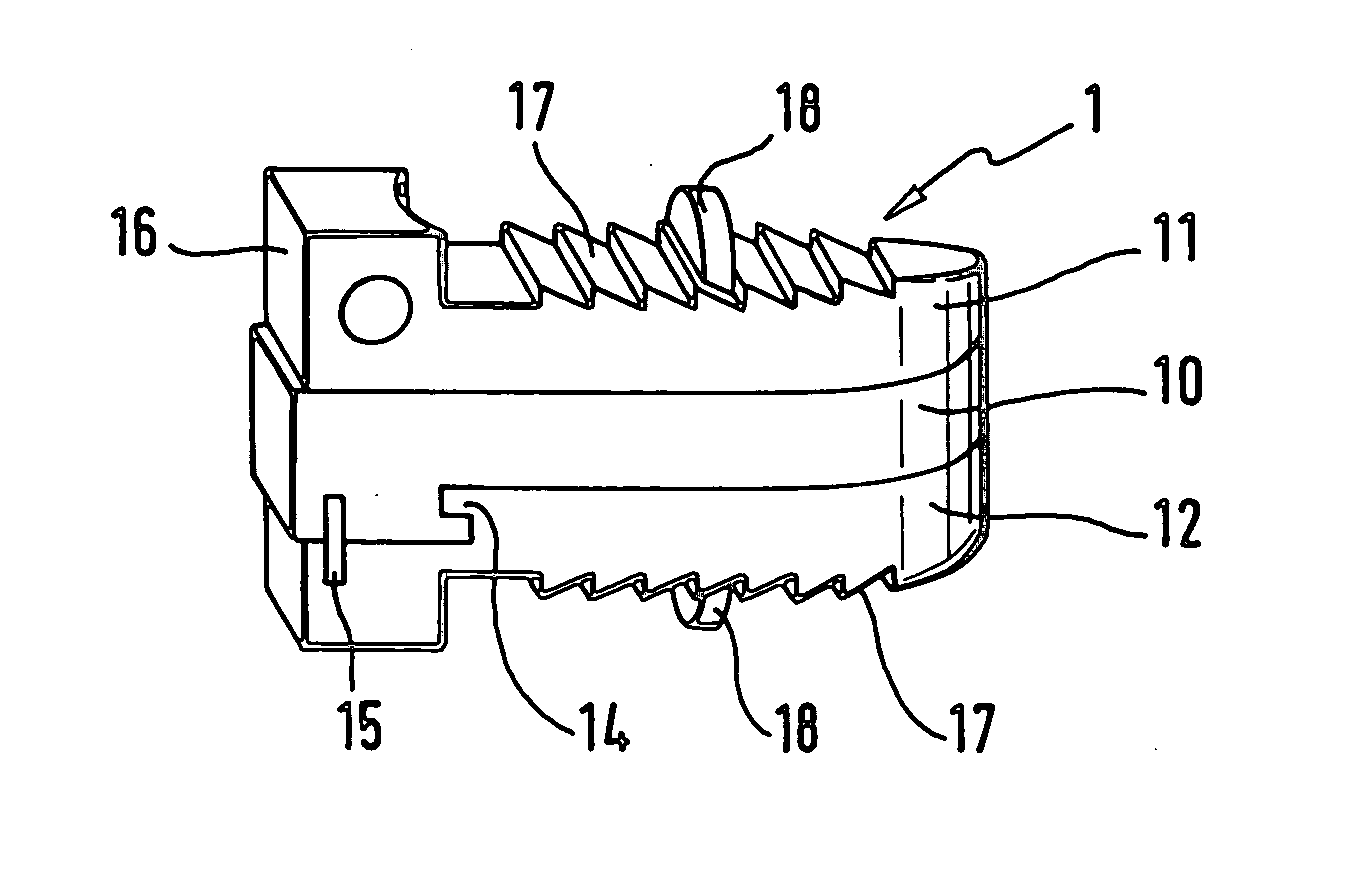
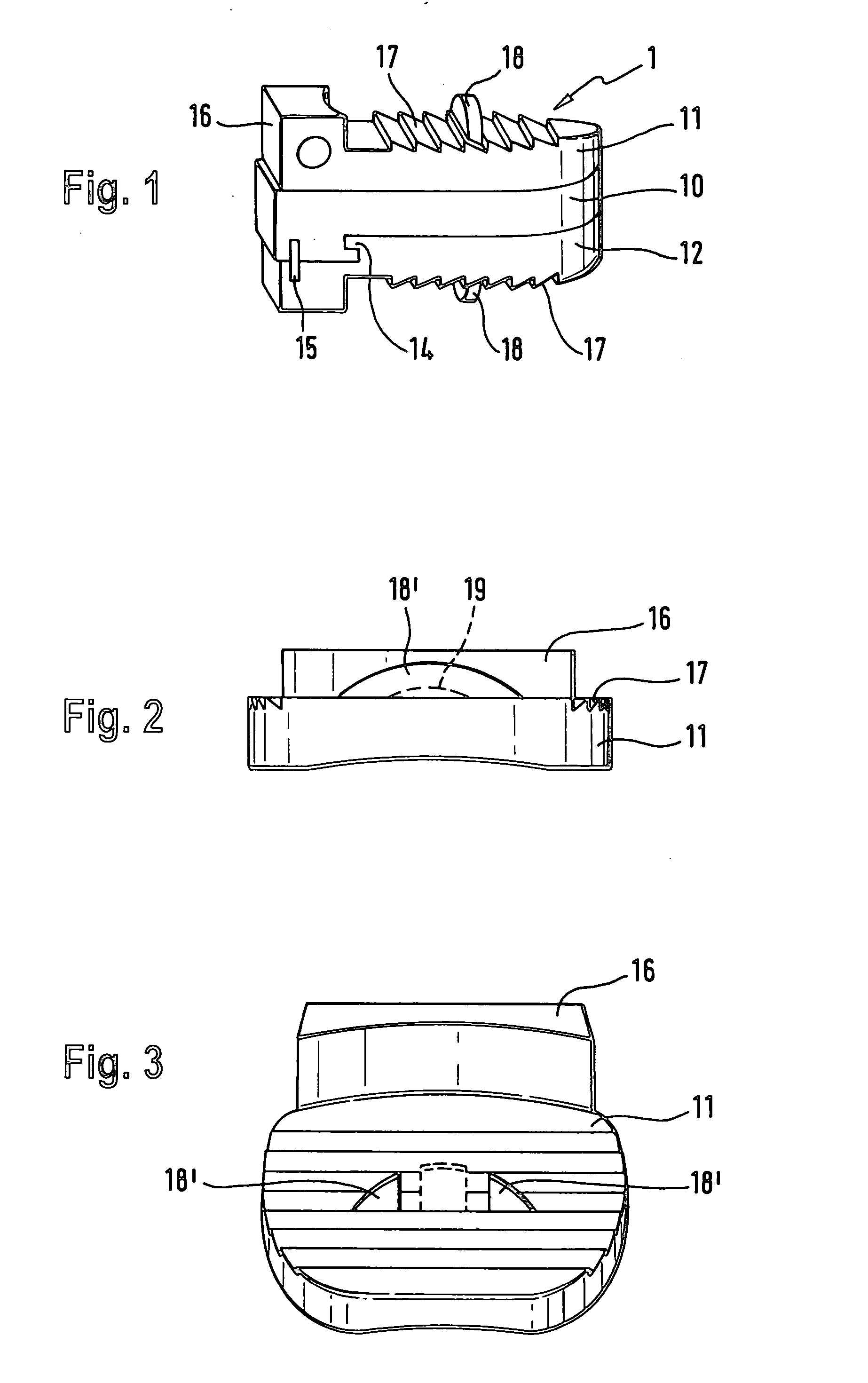
Anchoring element for securing a rod of a device for adjusting a human or animal vertrebal column on a vertreba
InactiveUS20060155277A1Lower clamping surfaceLower requirementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBiomedical engineeringLumbar vertebral column
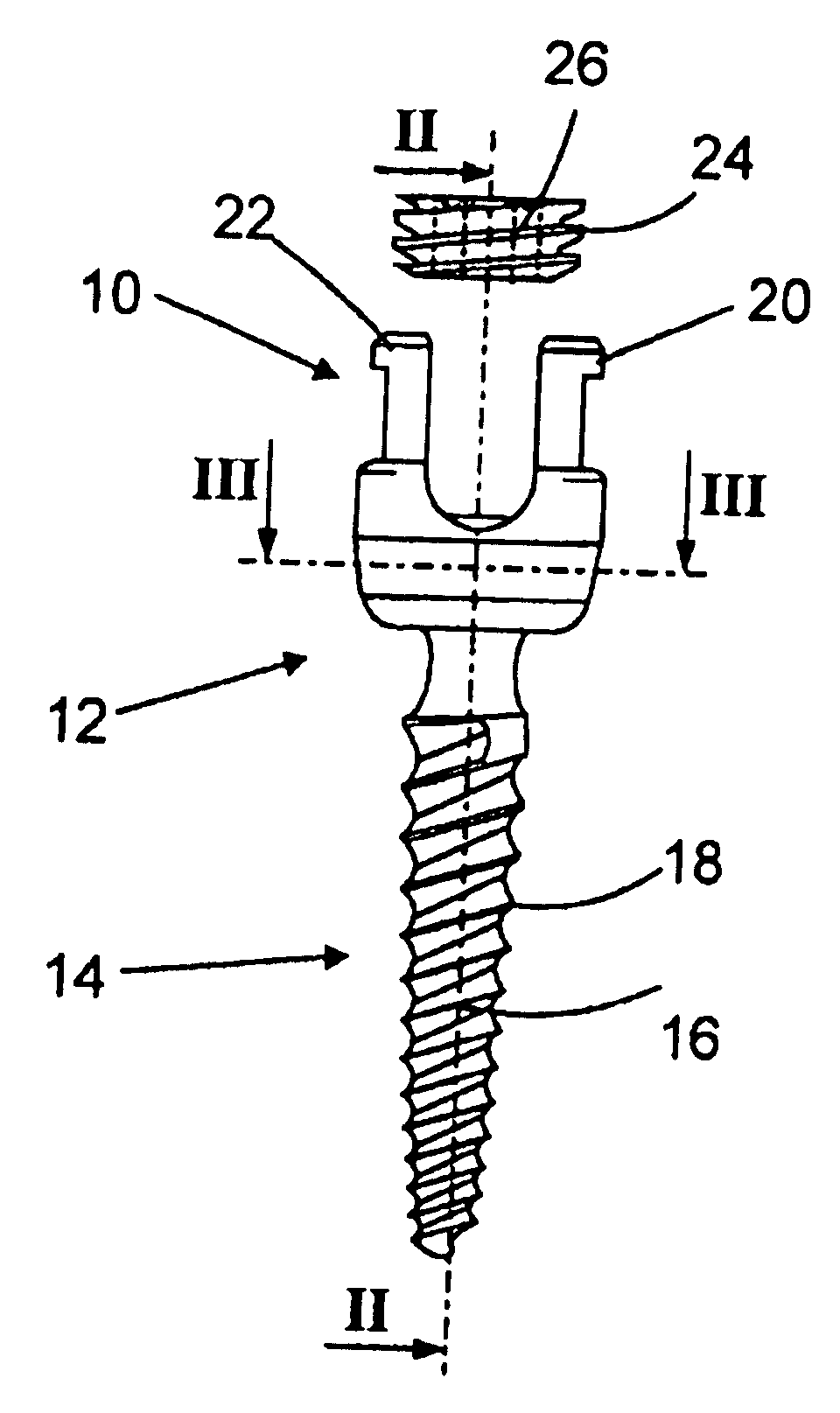
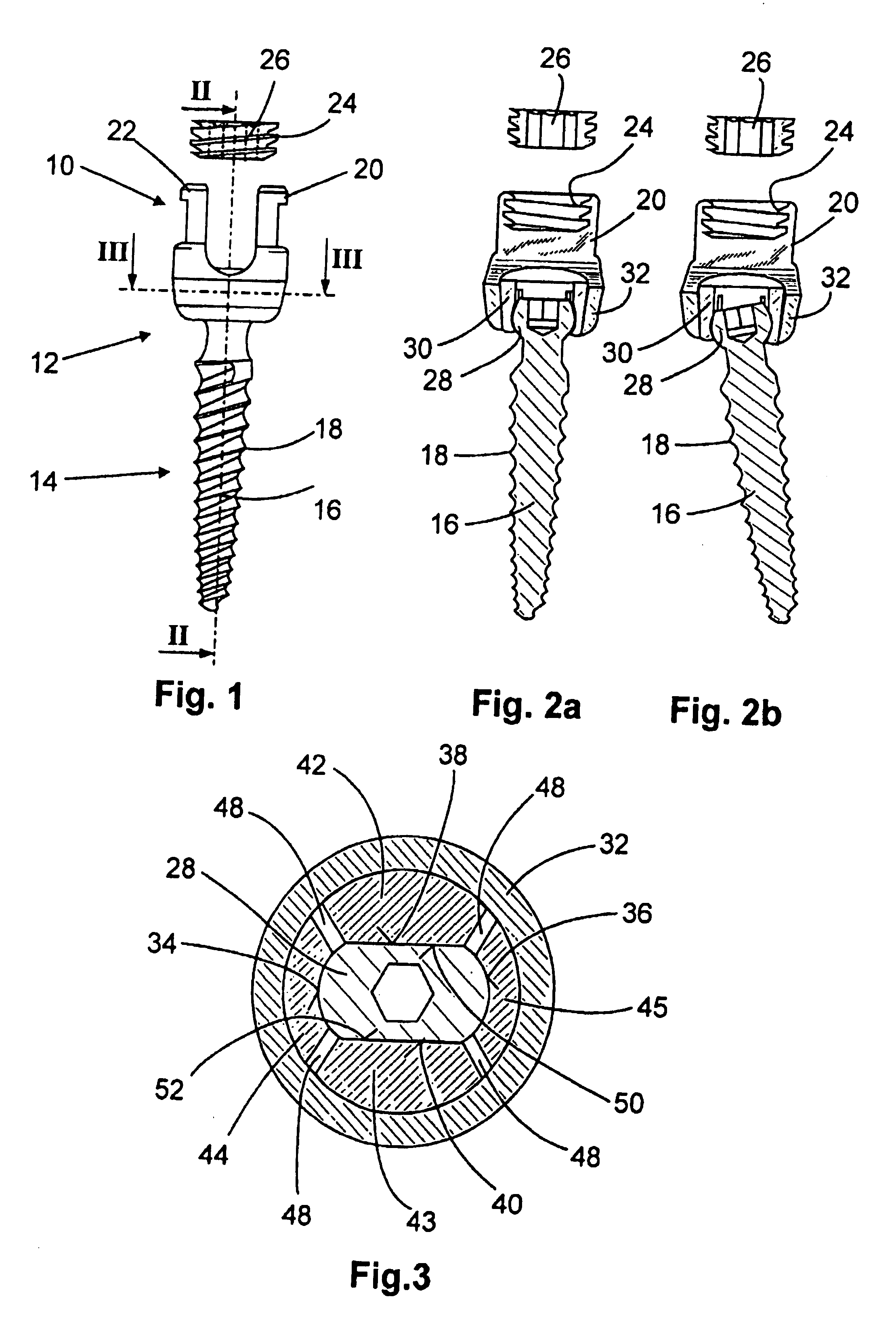
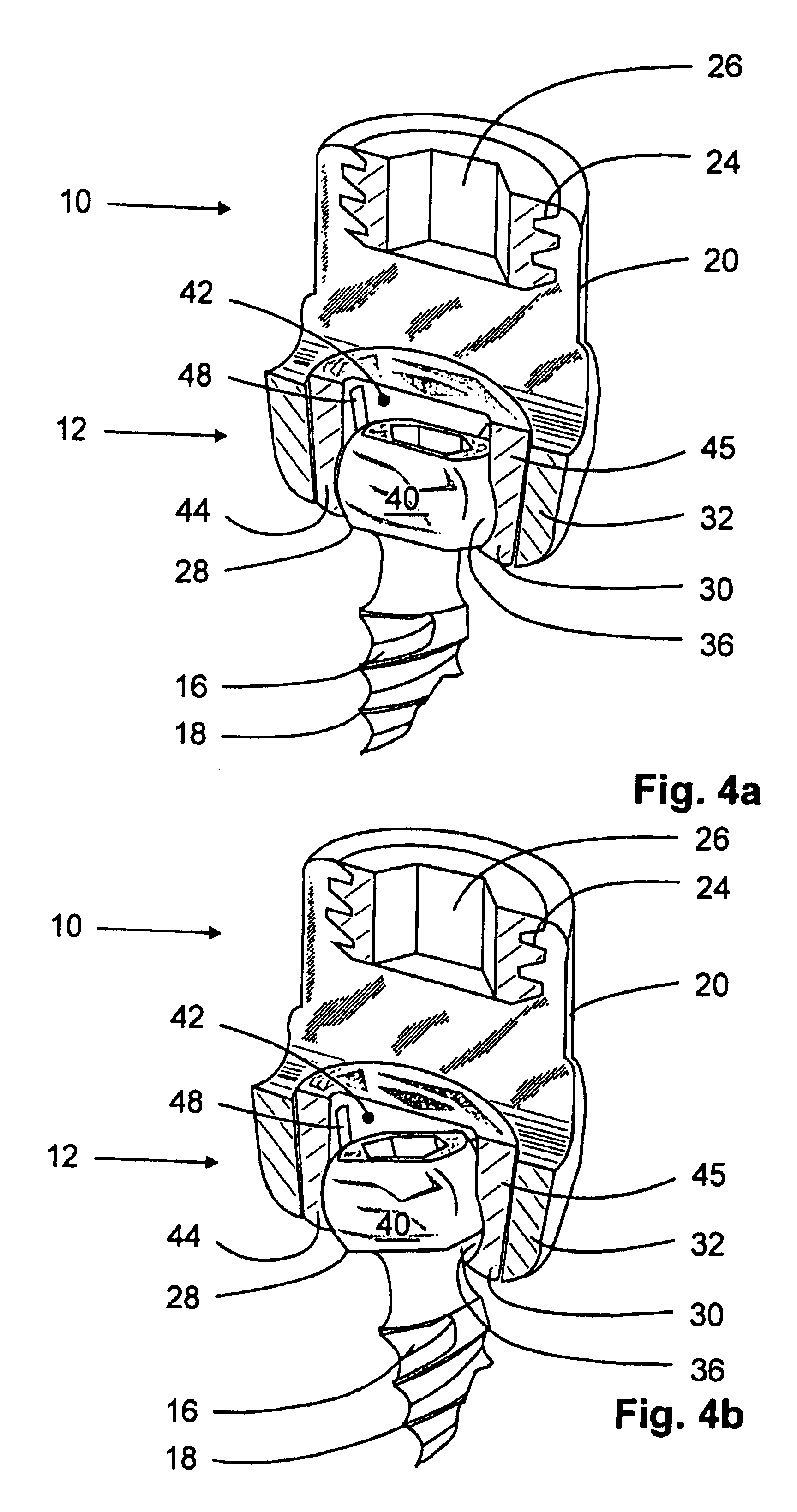
The invention relates to an anchoring element for securing a rod of a device for adjusting a human or animal vertebral column on a vertebra, comprising a retaining means (10) for receiving the rod, a safety element (26) placed on the retaining means and working against the rod, a securing element (14) which can be placed on the body of the vertebra, and a clamping device (12) which is arranged between the retaining means (10) and the securing element (14), comprising a ring-shaped mount (32), a partially conical-segment shaped bearing (28) and an intermediate element (30) which is embedded in the mount (32) and which engages the bearing, whereby the mounting (32) is moveable in a removed state in relation to the bearing (28), whereas the mount (32) is maintained in a clamped state on the bearing (28) by means of the intermediate element (30). The mount (32) is rigidly connected to the retaining means (10) and the bearing (28) is rigidly connected to the securing element (14). In order to enable said type of anchoring element, despite the fact that it is displaceably retained, to transmit relatively large amounts of force from the rod to the body of the vertebra without causing slipping, the bearing (28) comprises flat guiding surfaces (38, 40) which are formed laterally on two opposite sides (34, 36), and the intermediate element (30) is provided with corresponding counter surfaces (50, 52).
Owner:METZ STAVENHAGEN PETER
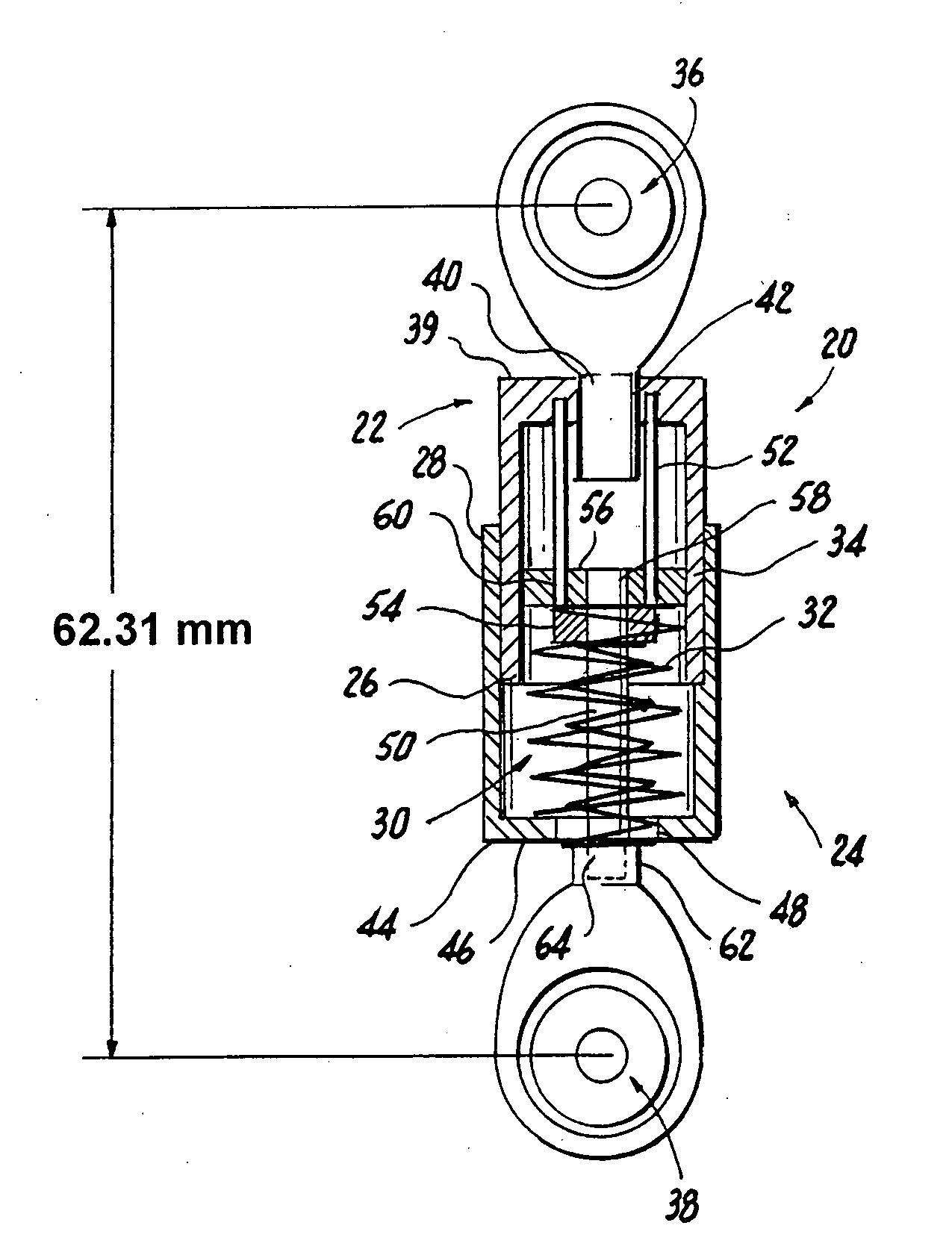
Dynamic stabilization device including overhanging stabilizing member
ActiveUS20050288670A1Reduced space requirementsStable responseMechanical apparatusInternal osteosythesisEngineeringAbutment
Spine stabilization devices, systems and methods are provided in which a single resilient member or spring is disposed on an elongate element that spans two attachment members attached to different spinal vertebrae. The elongate element passes through at least one of the two attachment members, permitting relative motion therebetween, and terminates in a stop or abutment. A second resilient member is disposed on the elongate element on an opposite side of the sliding attachment member, e.g., in an overhanging orientation. The two resilient members are capable of applying mutually opposing urging forces, and a compressive preload can be applied to one or both of the resilient members.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
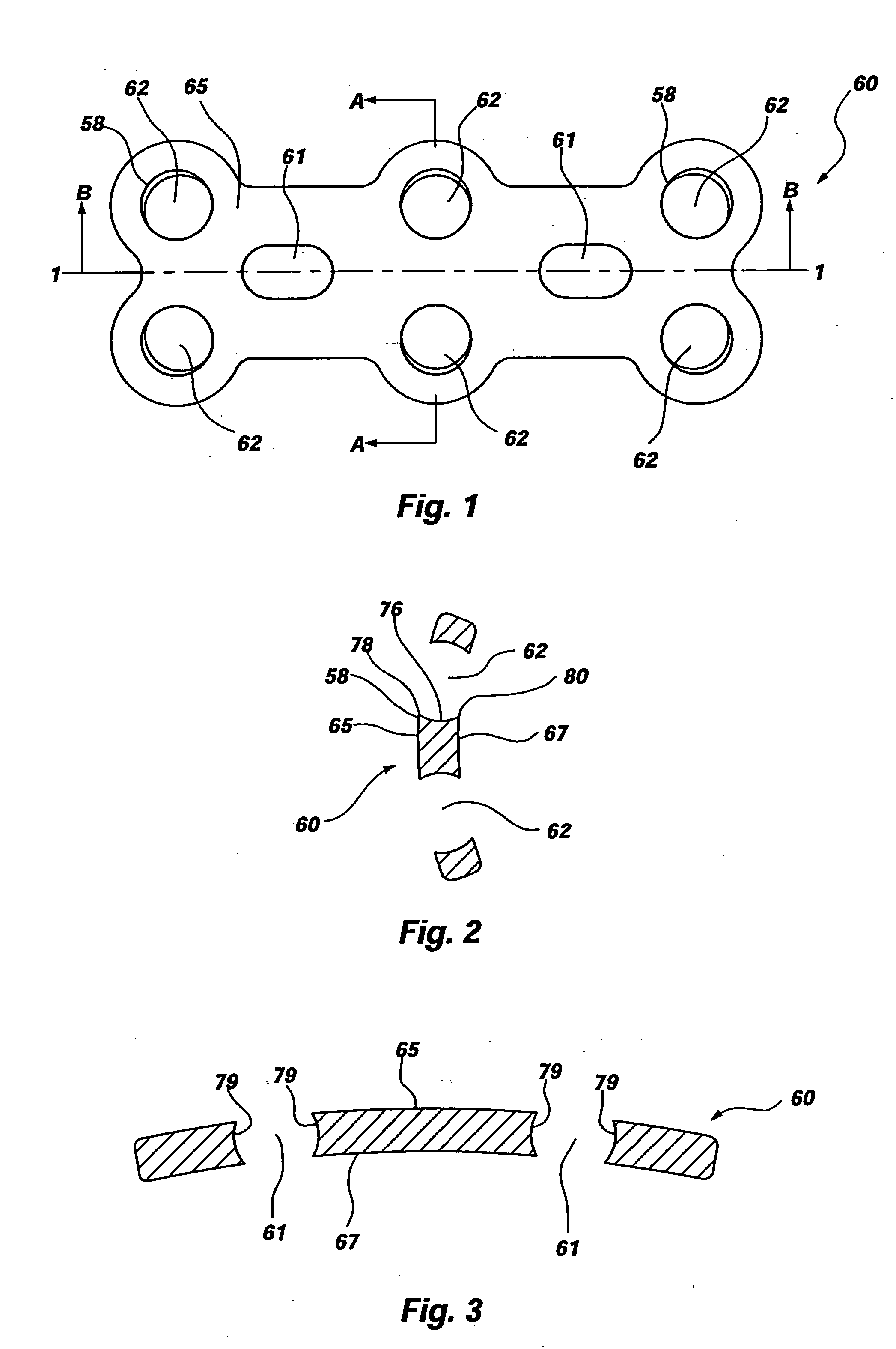
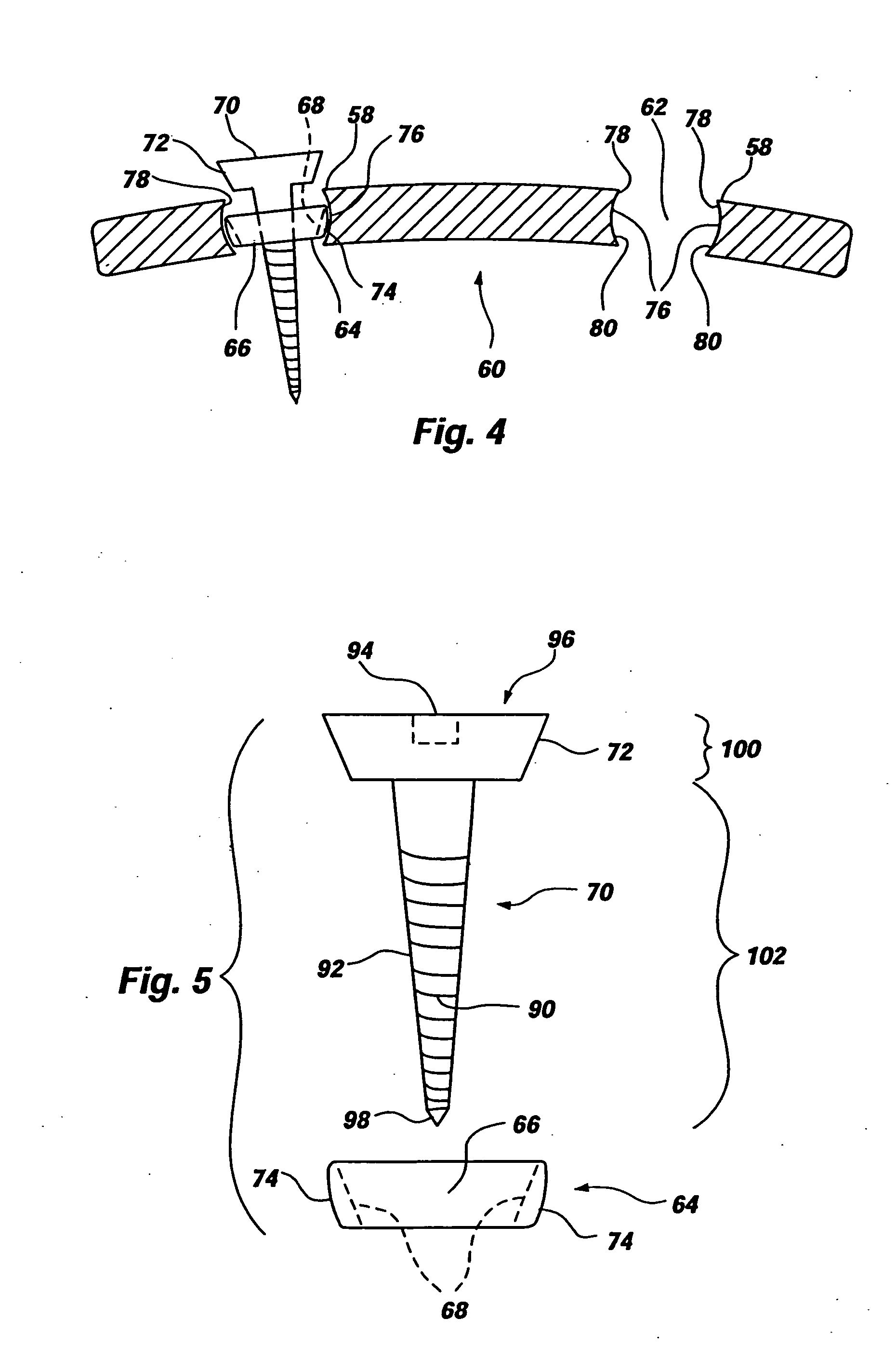
Cervical plate for stabilizing the human spine
A dynamic spinal fixation plate assembly includes a spinal plate, a receiving member, and a fastener resulting in a low profile orthopedic device. The plate may comprise a hole for maintaining the receiving member. The relationship between the receiving member and the plate may allow the plate to adjust during graft settling. The receiving member may be locked to the plate utilizing the mechanical or chemical properties of the device, or the receiving member may be configured to move and rotate freely within the plate hole, even after the fastener has been secured to the bone. The receiving member may have a tapered sidewall defining a through hole to matingly engage the fastener, which may also have a tapered portion forming a tapered lock-fit therebetween. The receiving member may comprise a lip for retaining the fastener within said receiving member.
Owner:ORTHO DEV CORP
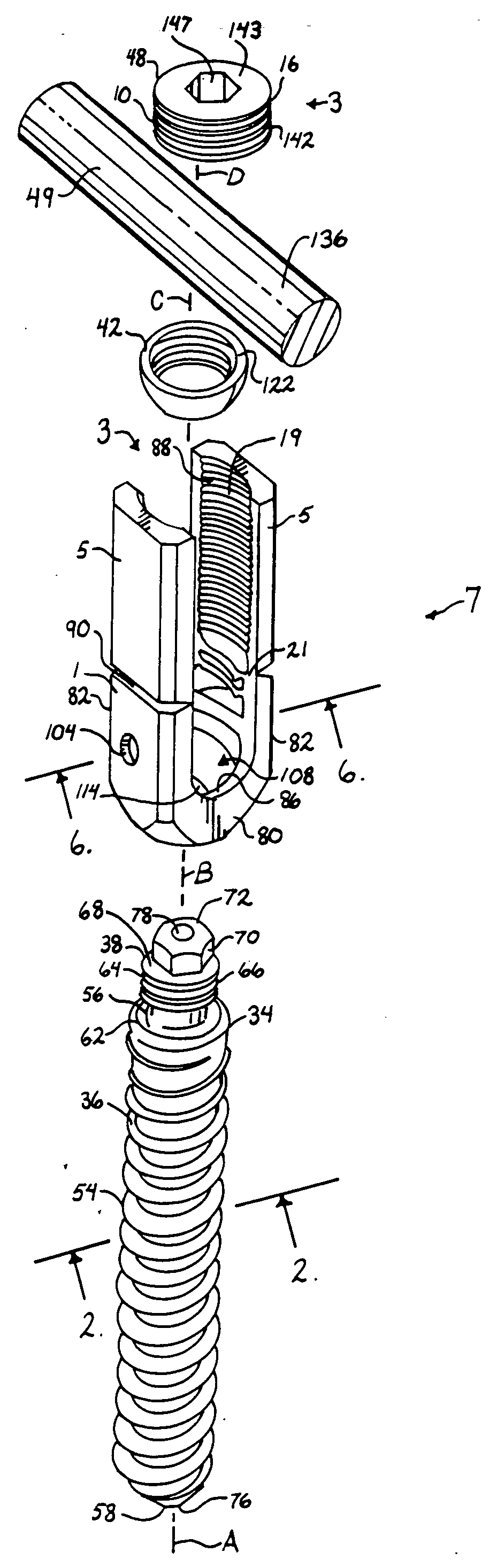
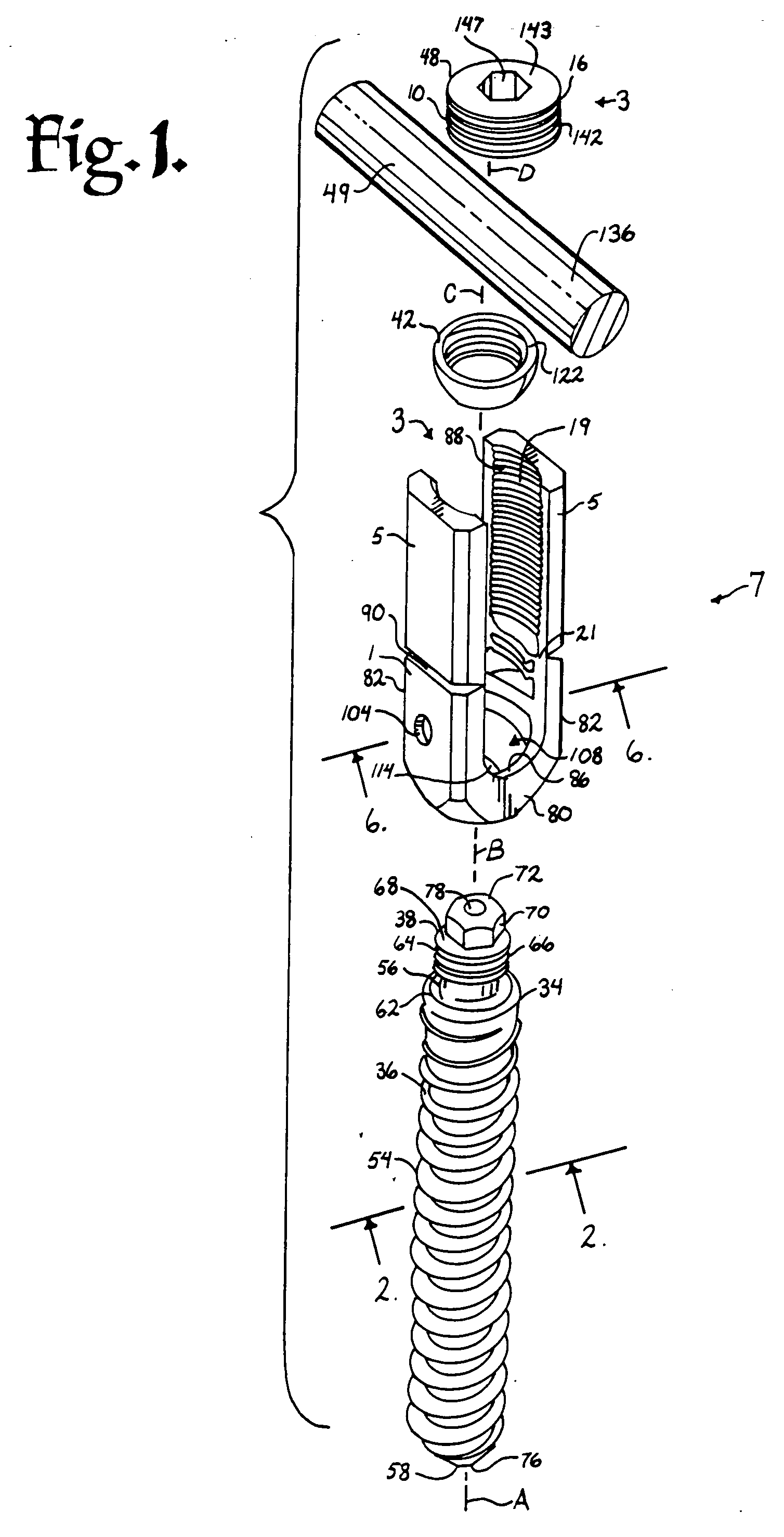
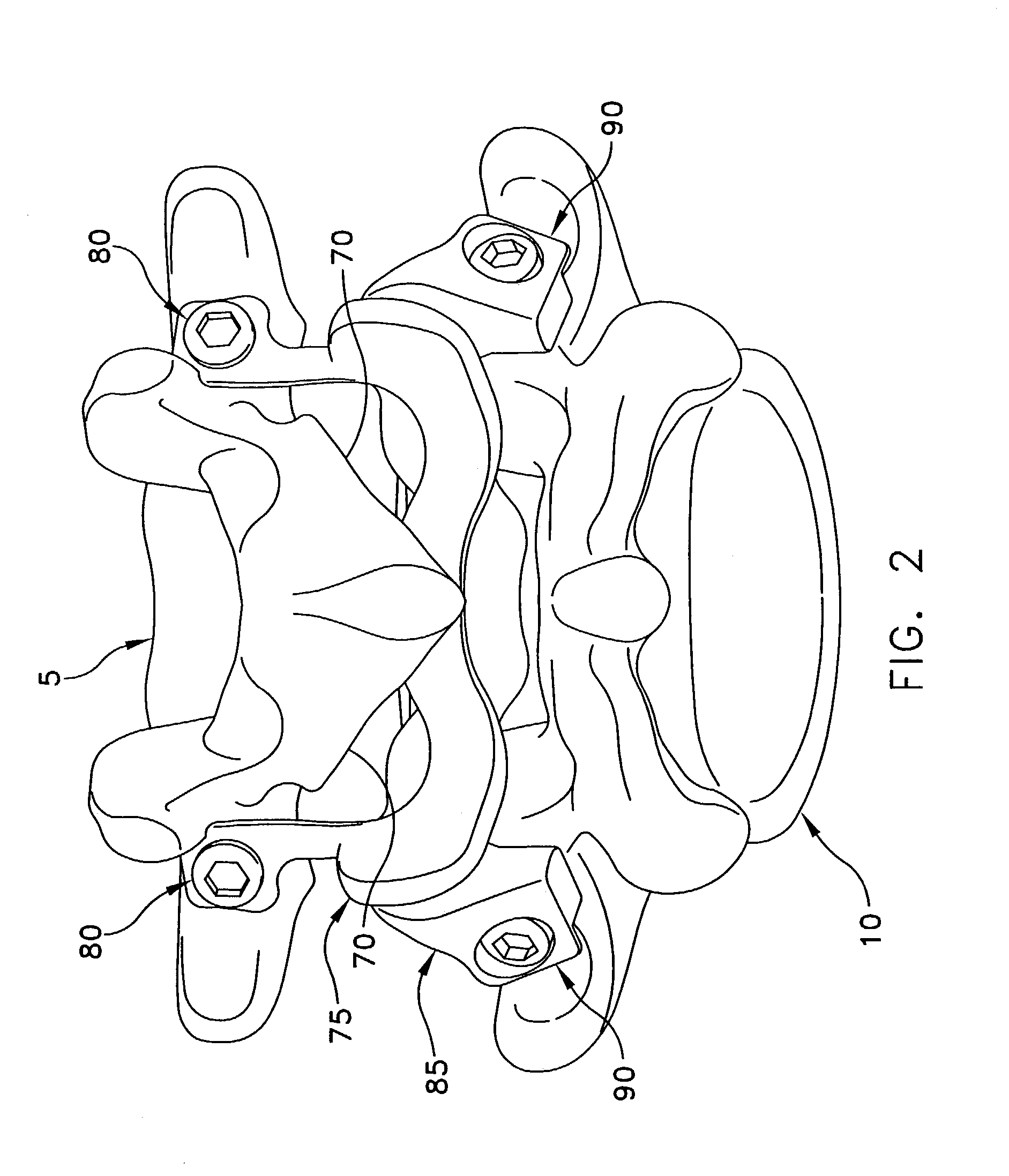
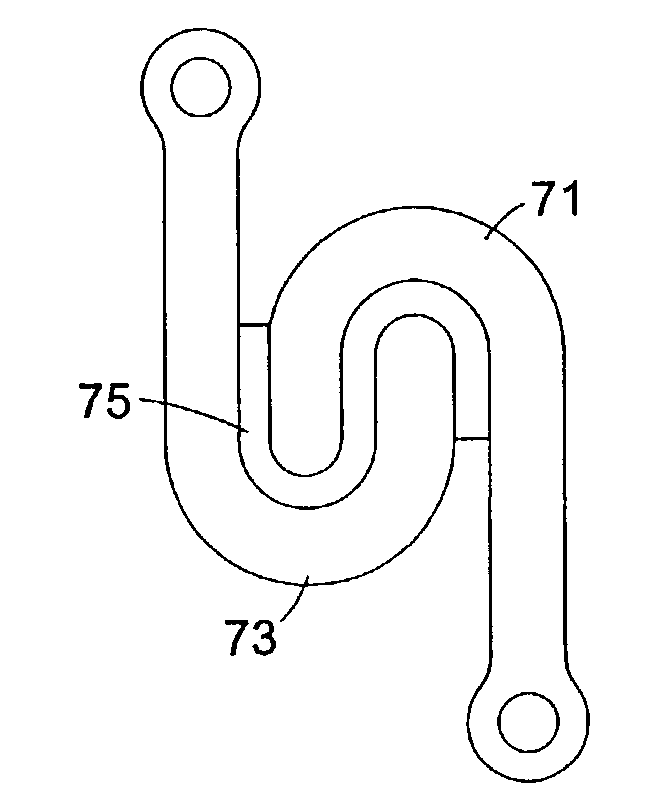
Helical reverse angle guide and advancement structure with break-off extensions
A spinal fixation device combines an anchor member with an open receiver, such as a polyaxial bone screw or a hook, with a rotatable closure that operably clamps a spinal fixation rod to the anchor member. The anchor member has spaced apart arms forming a rod receiving channel. The arms have arm extensions or tabs connected to main portions of the arms by weakened regions to enable the extensions to be broken off or separated after the rod is clamped. The closure and inner surfaces of the arms and tabs have mating helical, anti-splay, reverse angle guide and advancement structure formed thereon that mechanically cooperate to prevent splaying of the arms and the extensions as the closure is advanced into the rod receiving channel. The increased length of the arms with the extensions enables the rod to be captured at a greater distance from the seat of the channel and allows the rod to be urged toward the seat by helical advancement of the closure into the channel, starting between the extensions. Separation of the break-off extensions results in an implant with a desirable low profile.
Owner:JACKSON
Method and apparatus for flexible fixation of a spine
InactiveUS20050149020A1Improved construction and designMinimize injuryInternal osteosythesisCannulasSpinal columnCoupling
A flexible spinal fixation device having a flexible connection unit for non-rigid stabilization of the spinal column. In one embodiment, the fixation device includes at least two securing members configured to be inserted into respective adjacent spinal pedicles, each securing member each including a coupling assembly. The fixation device further includes a flexible connection unit configured to be received and secured within the coupling assemblies of each securing member so as to flexibly stabilize the affected area of the spine.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
System for stabilizing the vertebral column including deployment instruments and variable expansion inserts therefore
InactiveUS6905512B2Stabilize spineStabilizing the being's vertebral columnJoint implantsSpinal implantsIntervertebral spaceLigament structure
A system is provided for stabilizing adjacent vertebra without excision of bone or resection of ligaments comprising an expansion device and a deployment system which includes a hollow expandable insert and an expansion insert. The expandable insert includes a cylindrical body having a pair of slots having a threaded outer surface. The expandable insert is located with the slots oriented perpendicular to the vertebral column between the vertebrae. The thread cuts into the cortical bone contiguous to the intervertebral space but not substantially into the cancellous bone. The expandable insert is internally threaded. The expansion insert is externally threaded and arranged to be screwed into a bore in the expandable insert by the deployment system, whereupon the slots open to spread the vertebrae apart. The deployment system includes a tool having projecting fingers located within the slots to enable the expandable insert to be screwed into the intervertebral space.
Owner:PHOENIX BIOMEDICAL
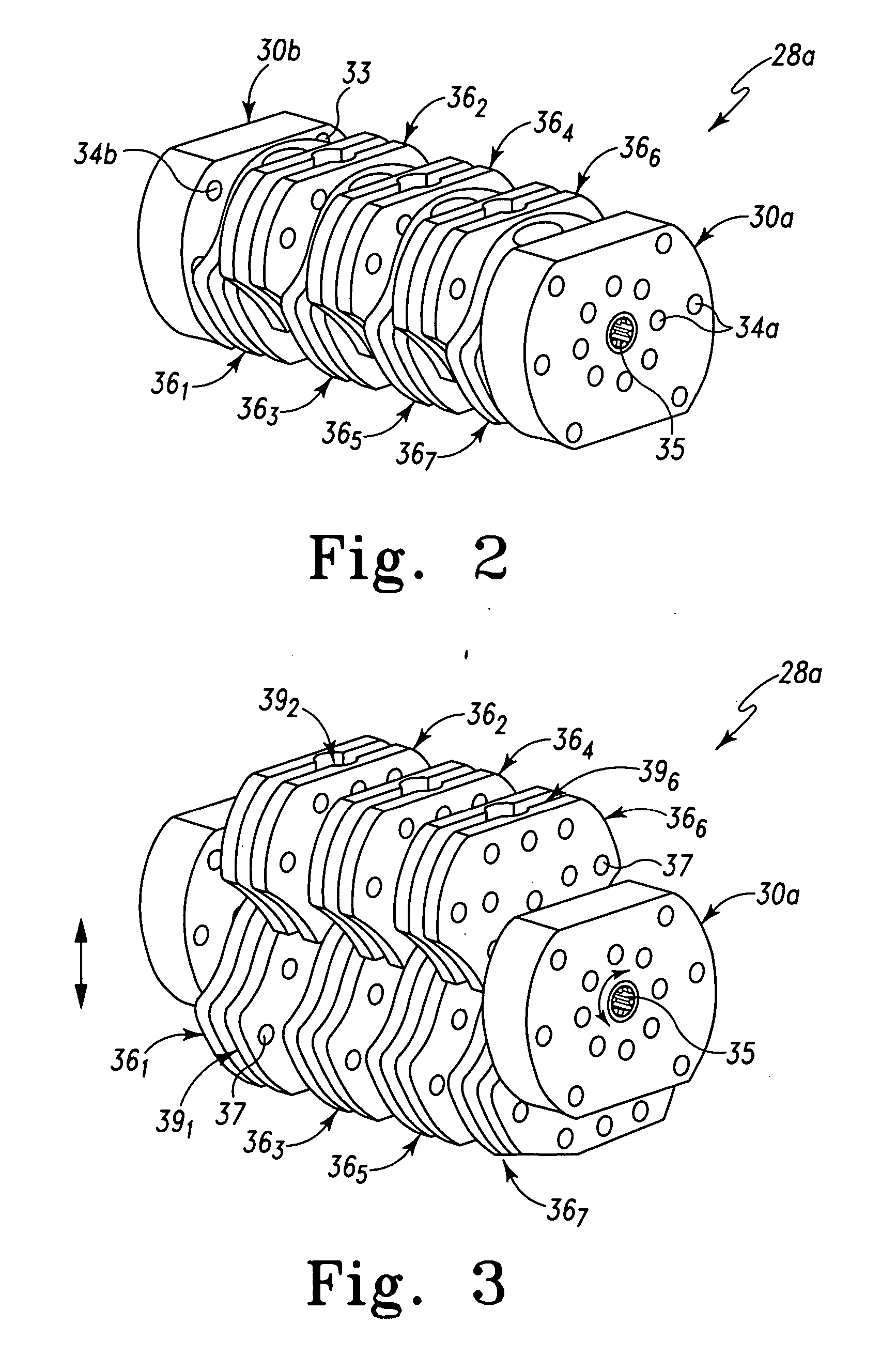
Expandable spinal interbody and intravertebral body devices
ActiveUS20060224241A1Simple definitionJoint implantsSpinal implantsAxial compressionBiomedical engineering
An expandable vertebral interbody / intravertebral (spinal) body device for insertion into a spinal (intervertebral or intravertebral) space is provided. The interbody / intravertebral body device is expandable from a first circumference to a second circumference through axial compression of segments of the vertebral interbody / intravertebral body device, particularly once the interbody / intravertebral body device has been properly situated within a vertebral space. The interbody / intravertebral body device is characterized by a plurality of axially stacked, individual segments that are provided on a central insertion and deployment rod. Each segment includes a central plate or body to which are pivotally attached plate or leaf structures. Pivoting of the structures provides a collapsed or unexpanded position of the first circumference and an open or expanded position of the second circumference. The vertebral interbody / intravertebral body device may be formed of a bio-compatible radiolucent material. The radial profile of an interbody / intravertebral body device is easily defined by plate or leaf structures of the segments.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
Multiple facet joint replacement
InactiveUS7074237B2Precise and tight attachmentFixation strengthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsProsthesisSacroiliac joint
A prosthesis for the replacement of multiple diseased or traumatized spinal facets comprises a portion that replaces at least a bony portion of the facets to be replaced and where the prosthesis attaches to the vertebra in a manner that does not require attachment to, or abutment against, the lamina. Multiple configurations of the prosthesis provide for replacement of the two inferior facets, the two superior facets, a superior and inferior facet, or all four facets. A method of installing the prosthesis is provided that is comprised of the steps of resecting at least a portion of the facets that carry the diseased or traumatized spinal facets and attaching the prosthesis in a manner that does not require attachment or abutment against the lamina.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Prosthetic facet joint ligament
InactiveUS7101398B2Relief the painProcess stabilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisProsthesisLigament structure
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Cervical Intervertebral Disc Prosthesis Comprising An Anti-Dislocation Device And Instruments
InactiveUS20080027550A1Easily advancedImprove connection reliabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsUnintended MovementSpinal column
A cervical intervertebral prosthesis includes lower and upper anchoring plates with a prosthesis core arranged between them to create an articulated connection. The anchoring plates are designed to bear with their anchoring plate surfaces on adjacent vertebral bodies. At least one anchoring plate surface has a rib-like projection thereon which can be used to engage in the vertebral body with a form fit. In order to produce a corresponding recess in the vertebral body, an instrument having a handle, a stem, a head part and an excavating element that can be retracted into the head part may be used. This permits considerably improved securing of the cervical intervertebral prosthesis against unintended movement. The medullary canal running along the posterior margin of the vertebral column is in this way protected from damage.
Owner:CERVITECH INC
Posterior vertebral joint prosthesis
InactiveUS20050015146A1Easy to slideConserve high degree of mobilityJoint implantsSpinal implantsProsthesisVertebral Joint
The present invention relates to a posterior vertebral joint prosthesis. The left or right posterior vertebral joint prosthesis of the invention presents a smooth bearing surface and said surface presents antero-posterior curvature.
Owner:LOUIS CHRISTIAN +1
Method and device for treating scoliosis
This invention relates to a spinal facet cap for treating scoliosis, the facet cap comprising a shim portion for inserting into a facet joint of a spine, and an alignment portion for maintaining alignment of the shim portion within the facet joint. The invention also provides a method for treating scoliosis, comprising implanting at least one spinal facet cap into at least one facet joint of a subject in need thereof.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
Method and device for fixing spondylolisthesis posteriorly
A method and apparatus for fixation of spondylolisthesis includes an elongated, threaded, hollow shaft which is threaded into a bore hole correctly formed between correctly aligned vertebrae posteriorly. The shaft includes a plurality of openings therethrough in the distal and proximal ends to allow bone and fibrous through growth to stabilize the vertebrae to decrease associated pain.
Owner:SPINEOLOGY
Helical guide and advancement flange with radially loaded lip
ActiveUS20050182410A1Low profileReduce manufacturing costSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEngineeringBone screws
A spinal fixation device combines an open-headed anchor member, such as a bone screw or a hook, with a closure member to thereby clamp a spinal fixation rod to the anchor member. The anchor member has spaced apart arms forming a rod receiving channel. The arms have arm extensions or tabs connected to main portions of the arms by weakened regions to enable the tabs to be broken-off or separated after the rod is clamped. The closure member and inner surfaces of the arms and tabs have helical anti-splay guide and advancement interlocking flanges formed thereon which cooperate to prevent splaying the arms and extensions as the closure member is advanced into the rod receiving channel. The flanges have anti-splay contours which can be formed on load flanks or stab flanks of the flanges. The load flanks can be oriented in such a manner as to aid in the anti-splay characteristics of the flanges or to control the proportioning of axial stresses between the flanges.
Owner:JACKSON
Methods and apparatus for placing intradiscal devices
An osteotomy of a portion of a vertebral endplate and / or vertebral body allows for easier insertion of a device that fits tightly into a disc space. A different aspect of the invention resides in a mechanical device to hold the osteotomized portion of the vertebra against the vertebral body after the intradiscal device is placed. The device may be removed after the pieces of vertebra heal and fuse together.
Owner:ANOVA
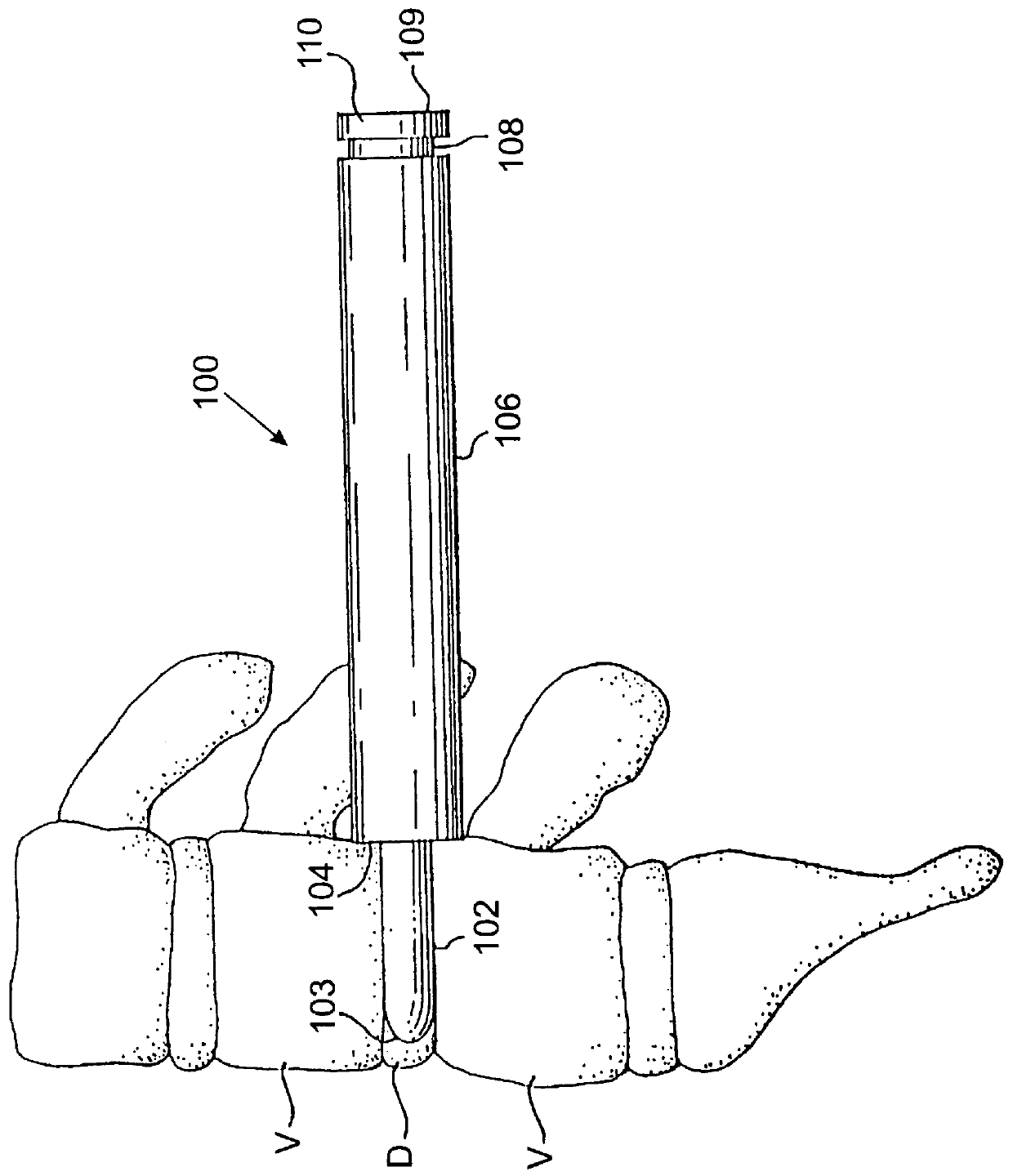
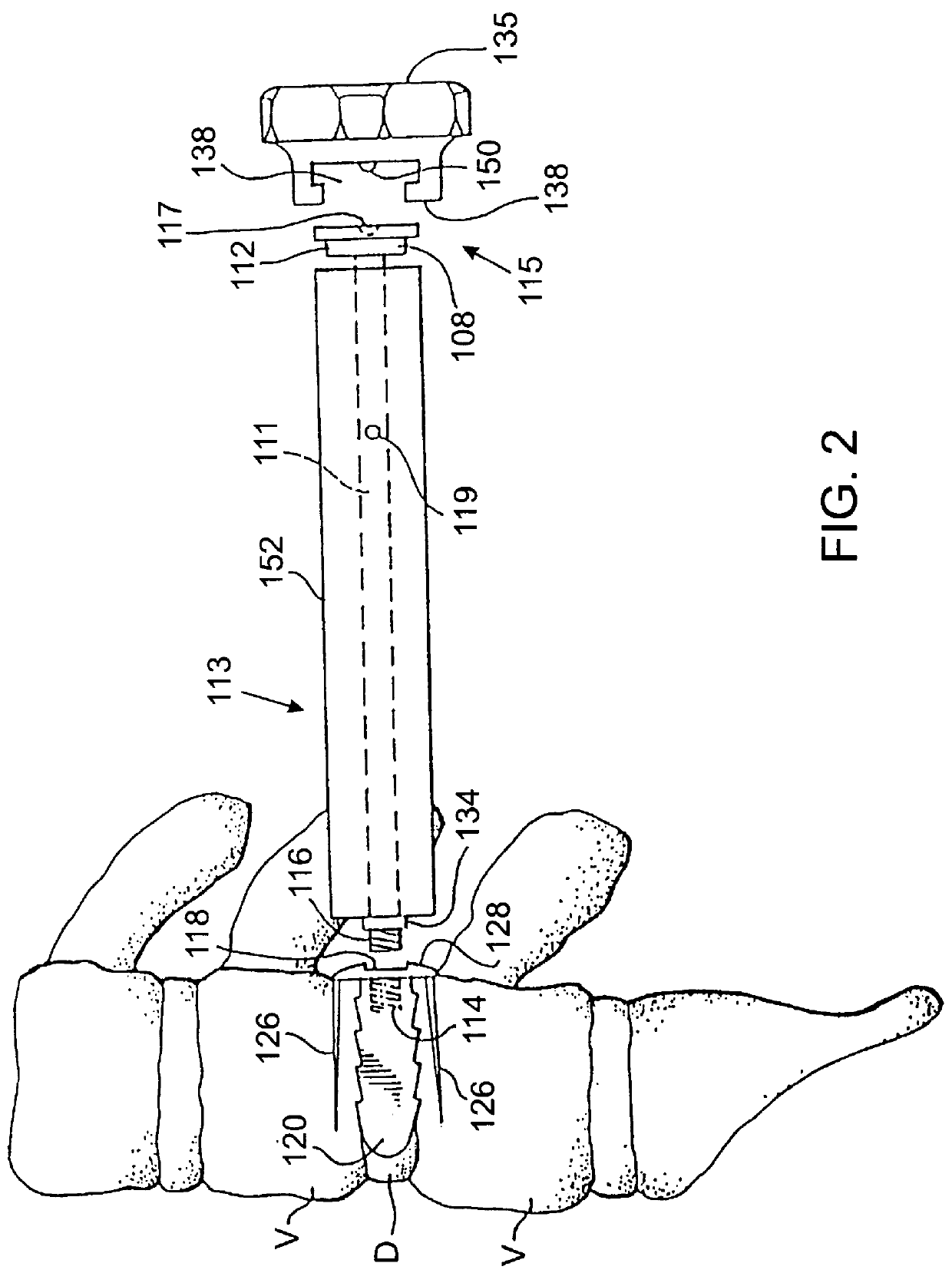
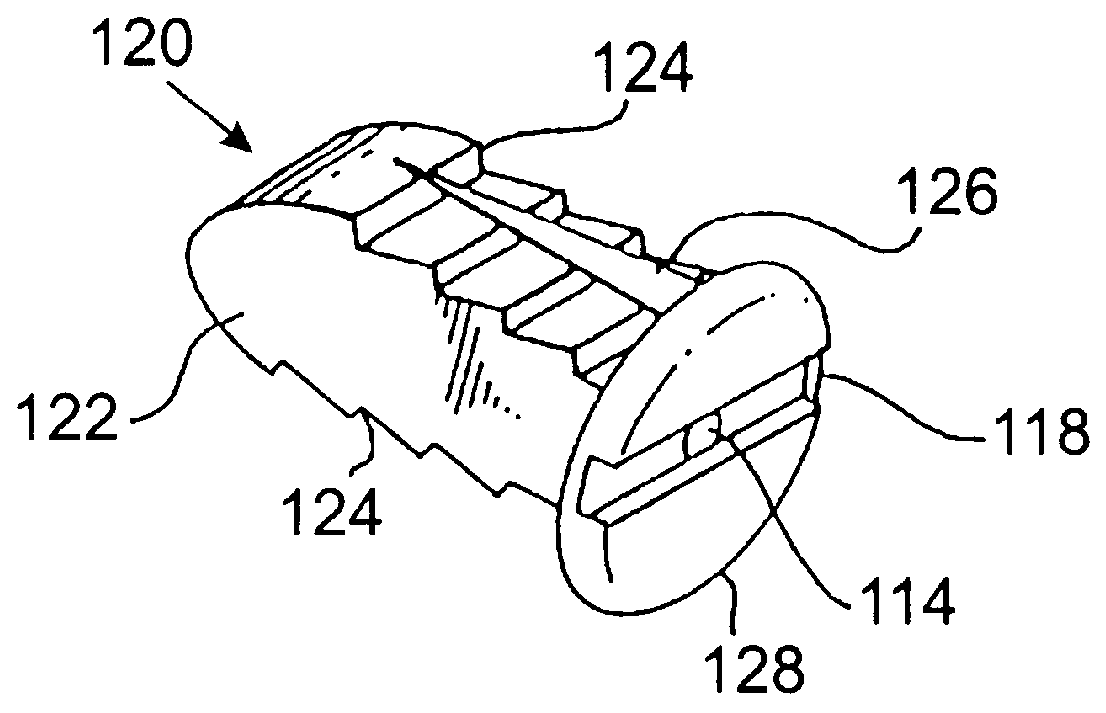
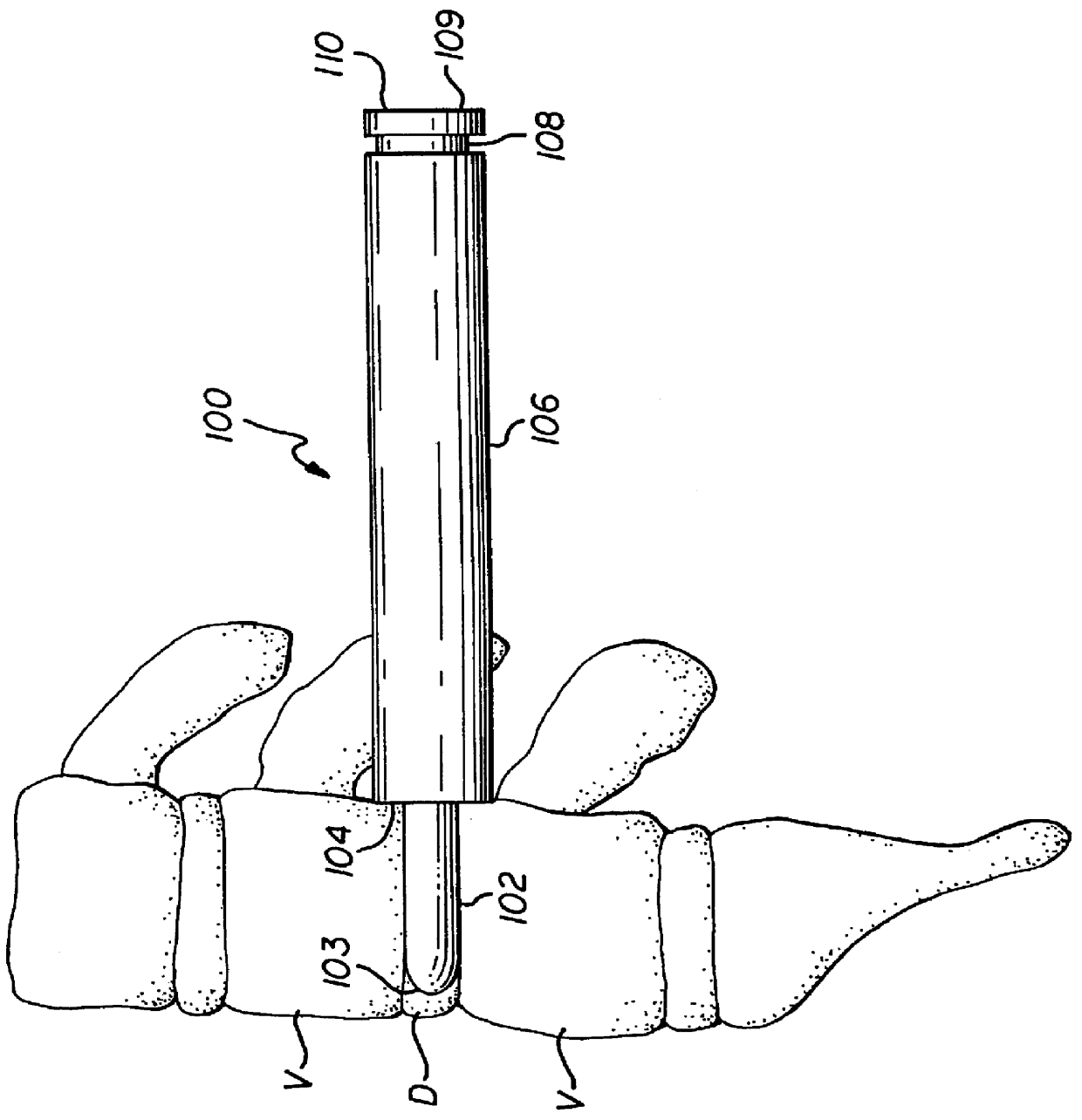
Spinal interbody system and method
ActiveUS8216312B2Avoid expulsionLimiting reducing and limiting impactInternal osteosythesisBone implantCouplingIntervertebral disk
Embodiments of the present invention provide spinal implant systems and methods. According to one embodiment, a plate attached to one or more vertebrae can prevent expulsion of an interbody device from a disc space. The plate and interbody device can be coupled by an attachment member. According to one embodiment, the attachment member is coupled to the plate and includes a portion inserted in a threaded or non-threaded cavity. Preferably, the coupling between the plate and attachment member allows rotation in three dimensions thereby allowing the plate to rotate relative to the interbody device. This allows the plate to be better positioned for attachment to the spine during an operation.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
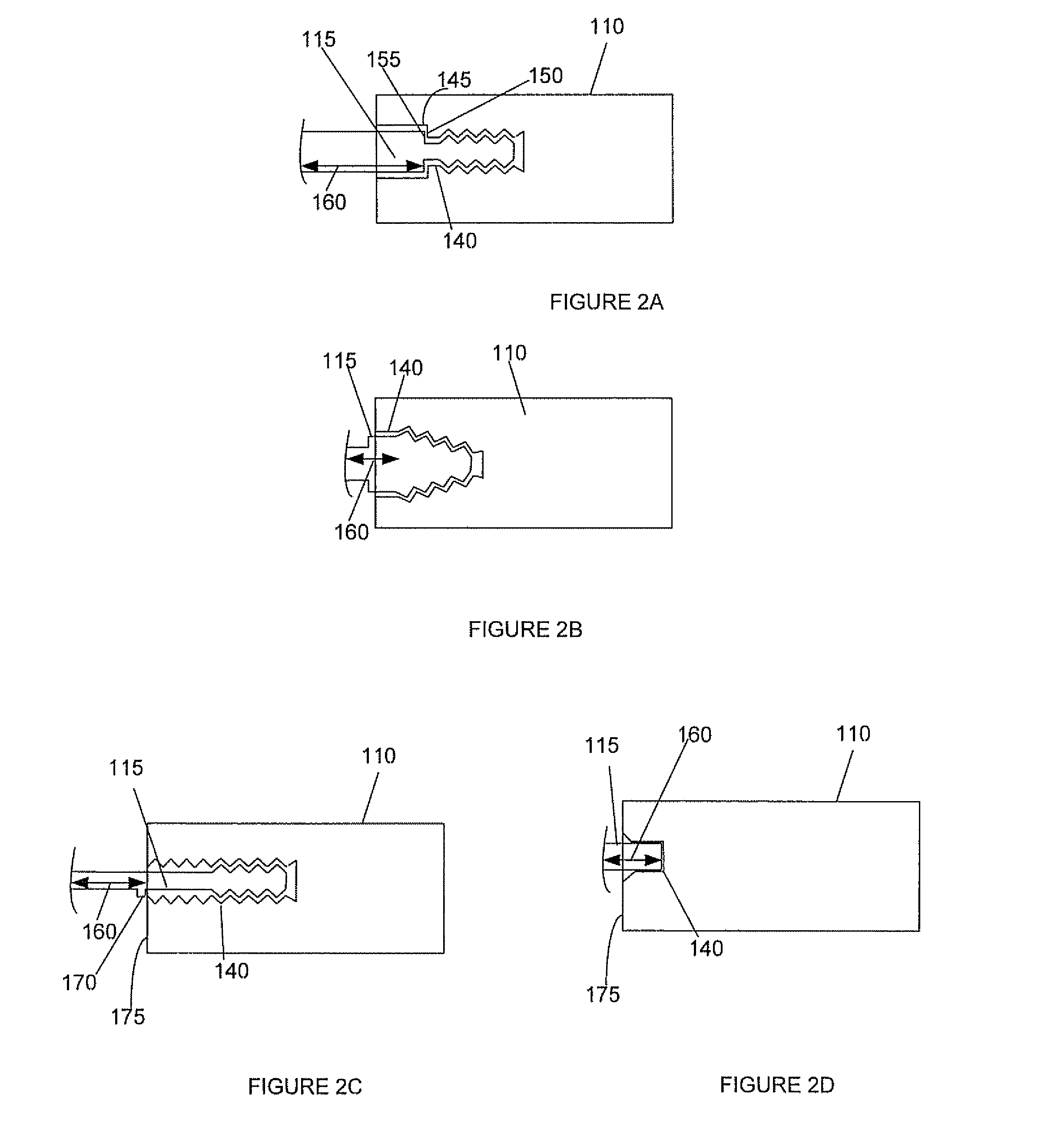
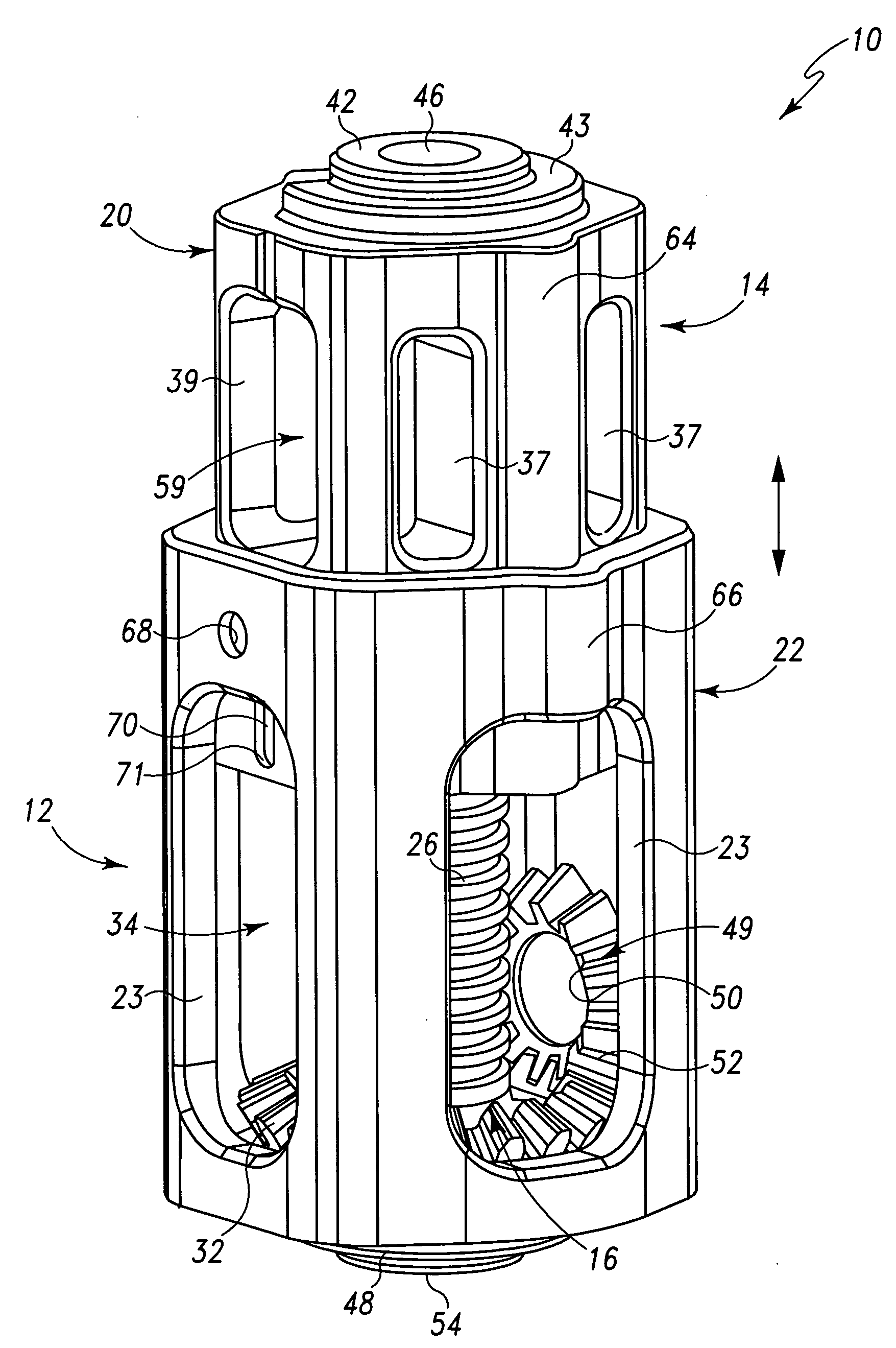
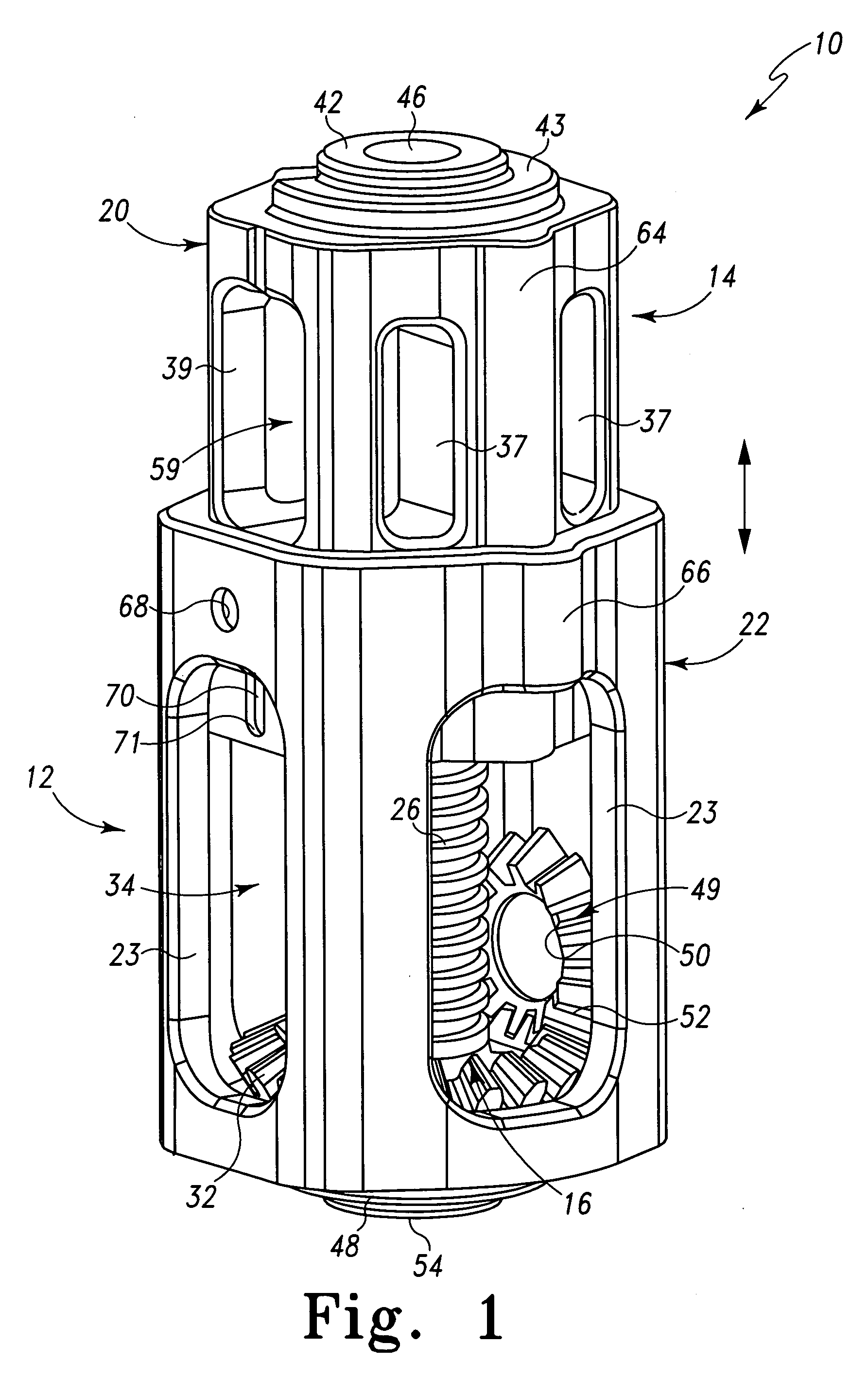
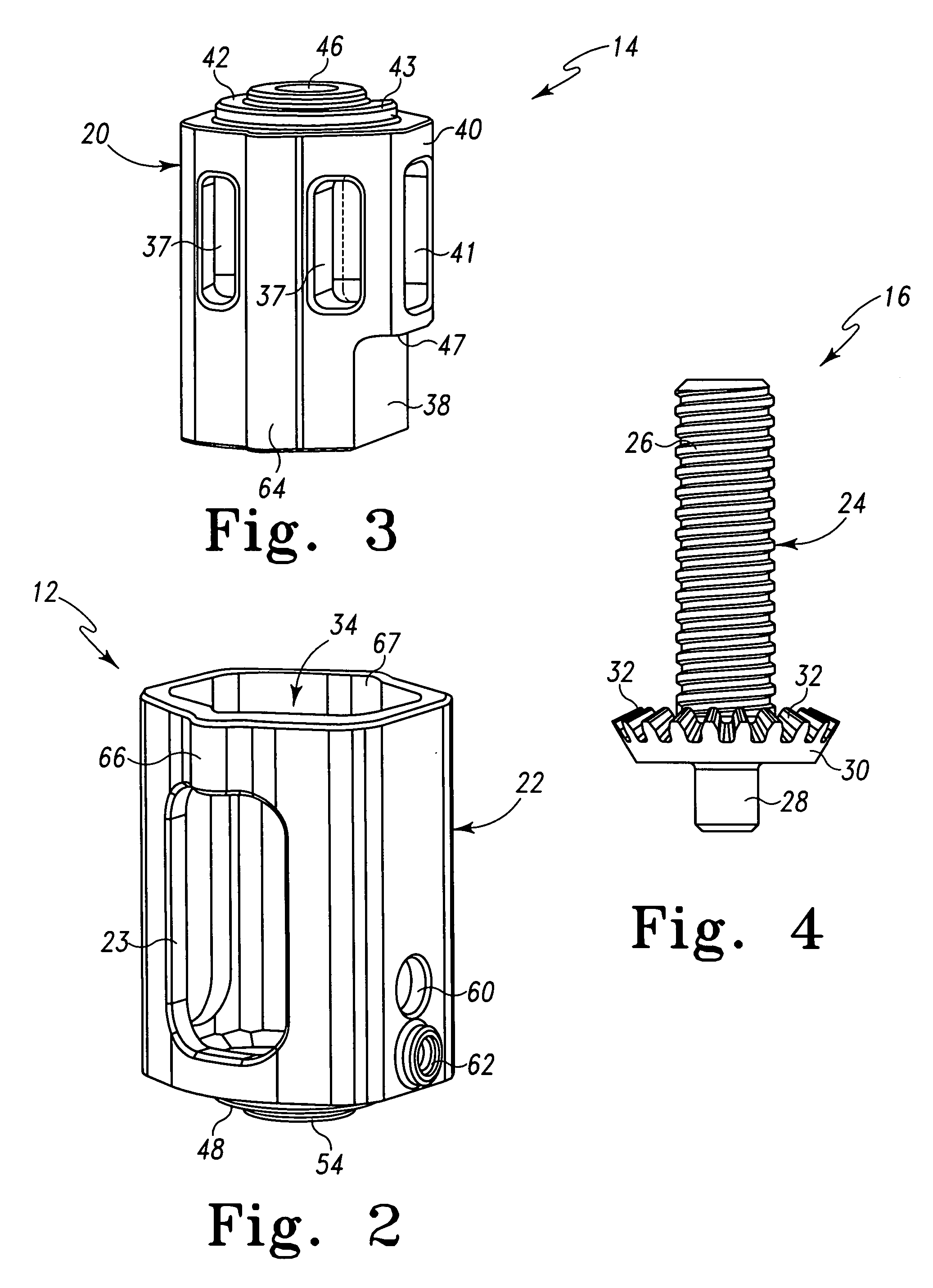
Height adjustable spinal prostheses
Dimensionally adjustable spinal prostheses are adjustable in an axial or superior to inferior dimension such that spinal prostheses may assume variations in height. The height adjustable spinal prostheses are characterized by first and second portions that are configured for adjustable coupling with one another. Spatial adjustment between the first and second portions is provided by an adjustment assembly. The adjustment mechanism preferably, but not necessarily, provides infinite adjustment over a minimum prosthesis height to a maximum prosthesis height. In one form, first and second ends of the height adjustable spinal prostheses are configured to receive an endplate. The endplates aid in attachment and / or anchoring of the spinal prosthesis within the spine. The endplates may be fashioned in various configurations such as circular or anatomical. In one form, the adjustment assembly utilizes rotational motion for varying the axial position of one prosthetic portion relative to the other prosthetic portion. Rotational movement of an adjustment mechanism of the adjustment assembly is translated into axial movement of one prosthetic portion relative to the other prosthetic portion. In another form, the adjustment mechanism is a screw and gearing assembly. In yet another form, the adjustment mechanism is a rack and pinion assembly.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
Spinal interbody spacer
Owner:K2M
Apparatus for Bone Restoration of the Spine and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20120071977A1Inhibition of contractionInternal osteosythesisBone implantMechanical resistanceBack pain
The subject disclosure is directed to systems, apparatuses, devices and methods for vertebral and spinal correction. In some embodiments, an expandable implant is provided which may be inserted inside the vertebral body and / or between two vertebrae, for instance, for maintenance and / or restoration of a space therein or there between. In certain embodiments, the implant includes a mechanical resistance that prevents the expandable implant from contracting once it has been expanded. Methods of treatment and methods of use of such implants for the alleviation of back pain (for example) are also provided herein.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com