Patents
Literature
6373 results about "Vertebra" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
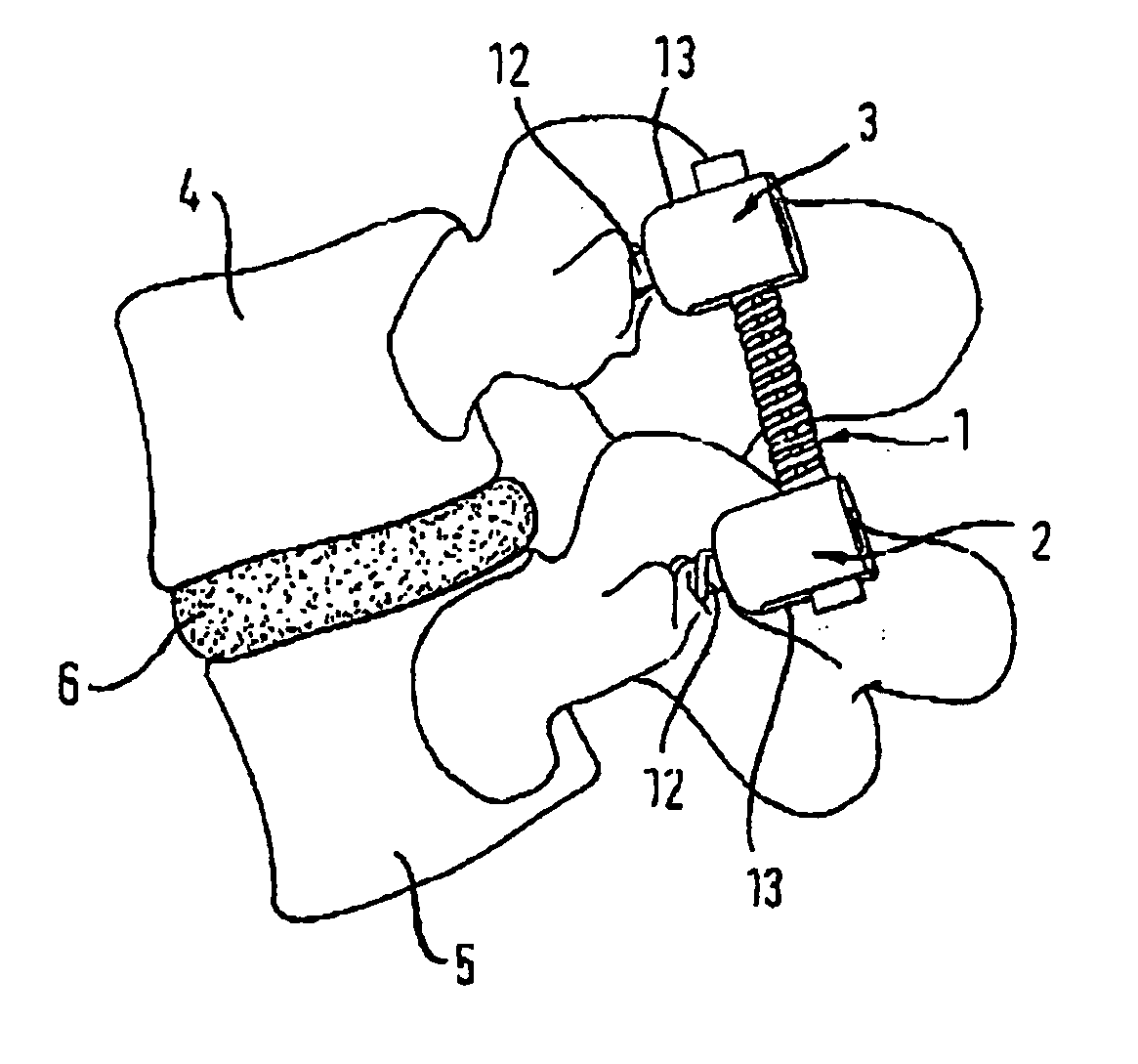
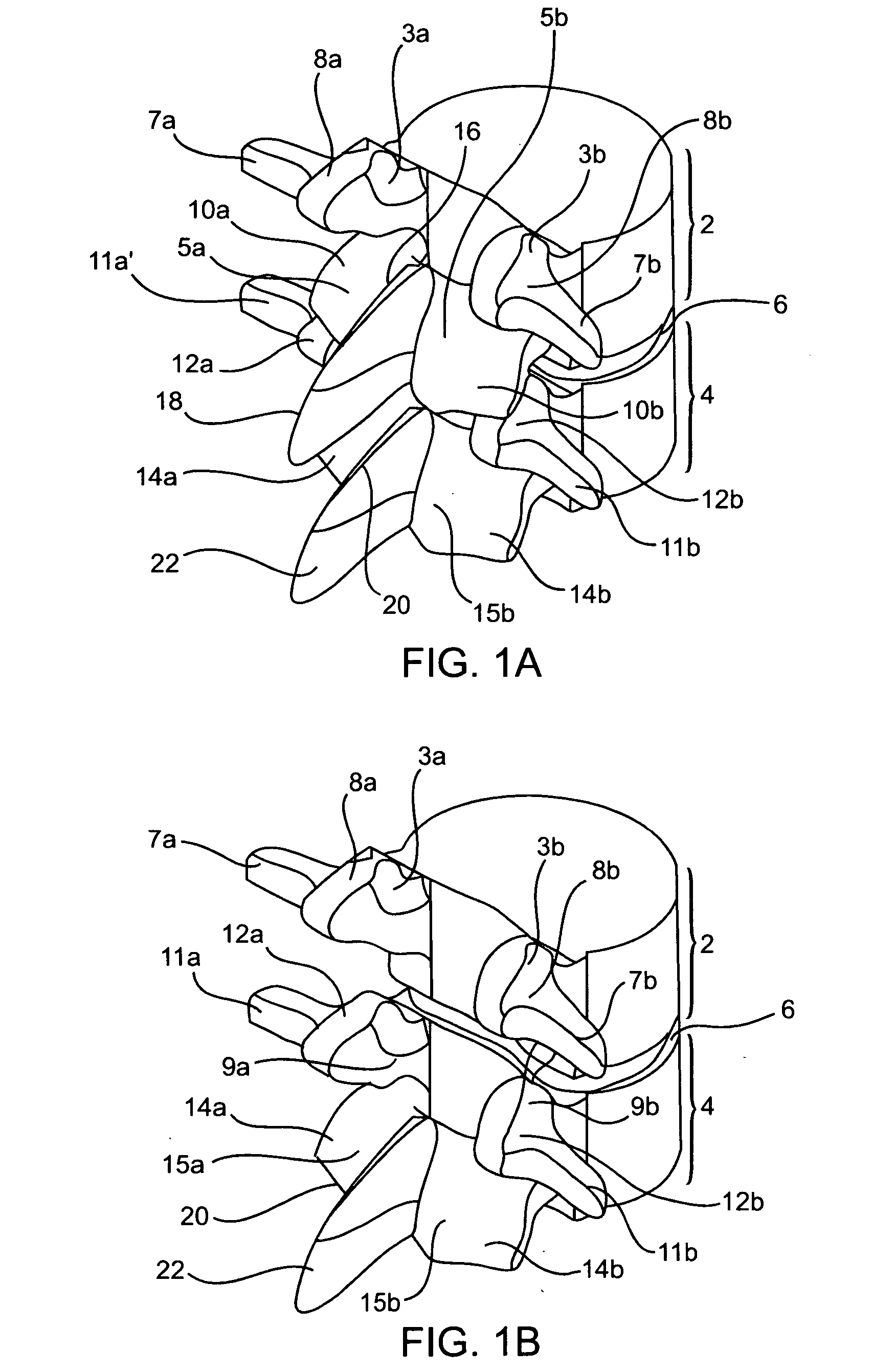
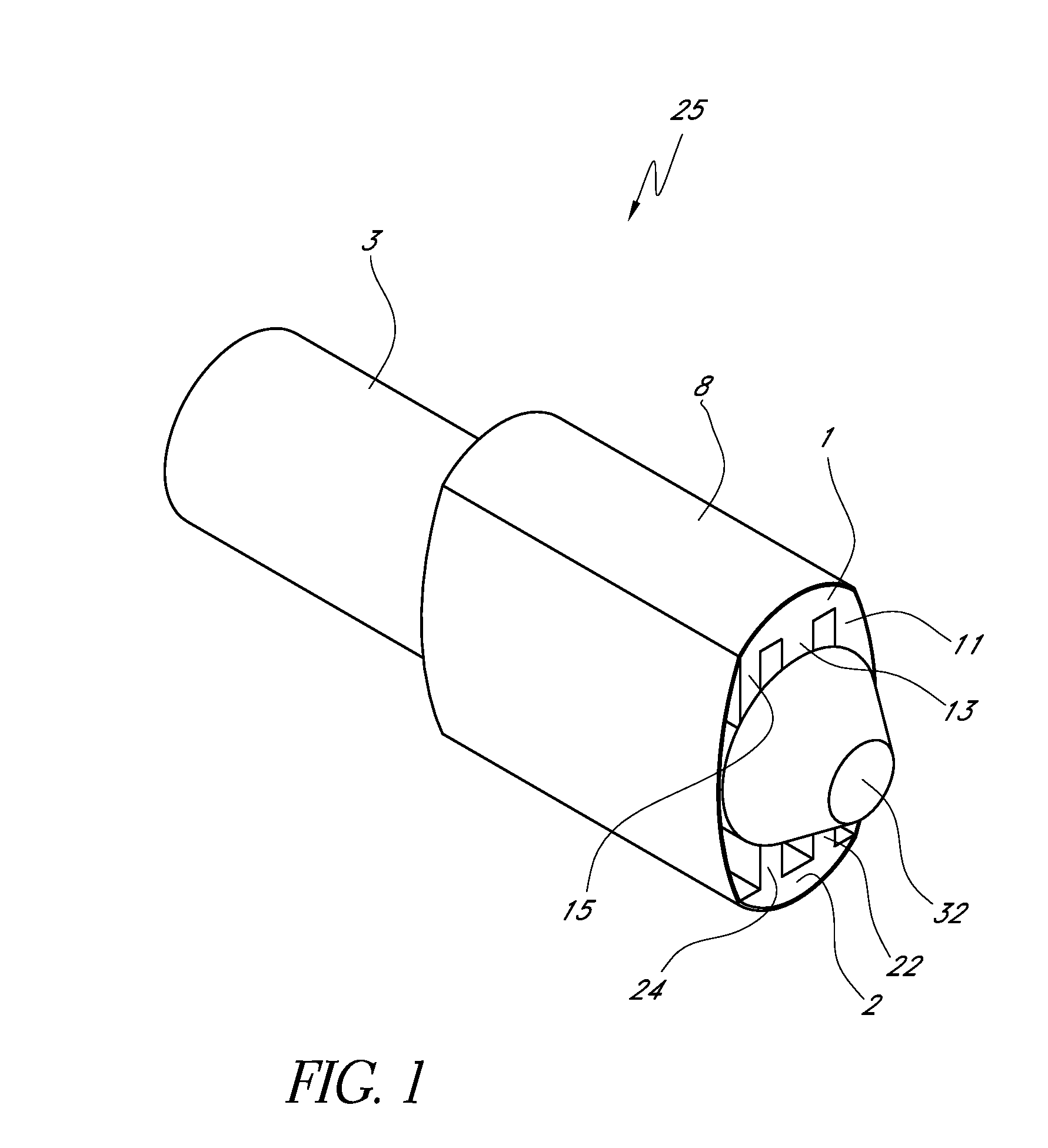
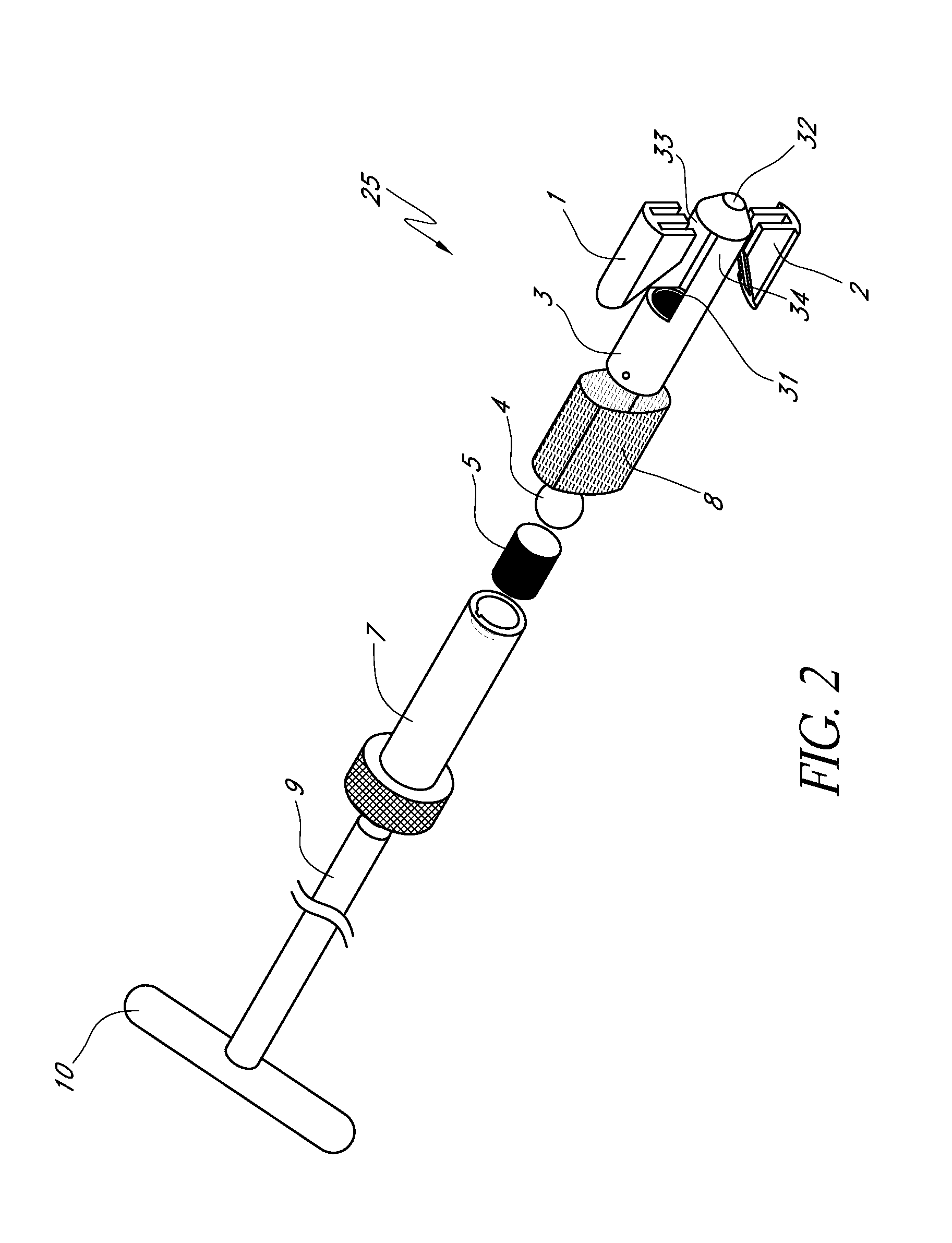
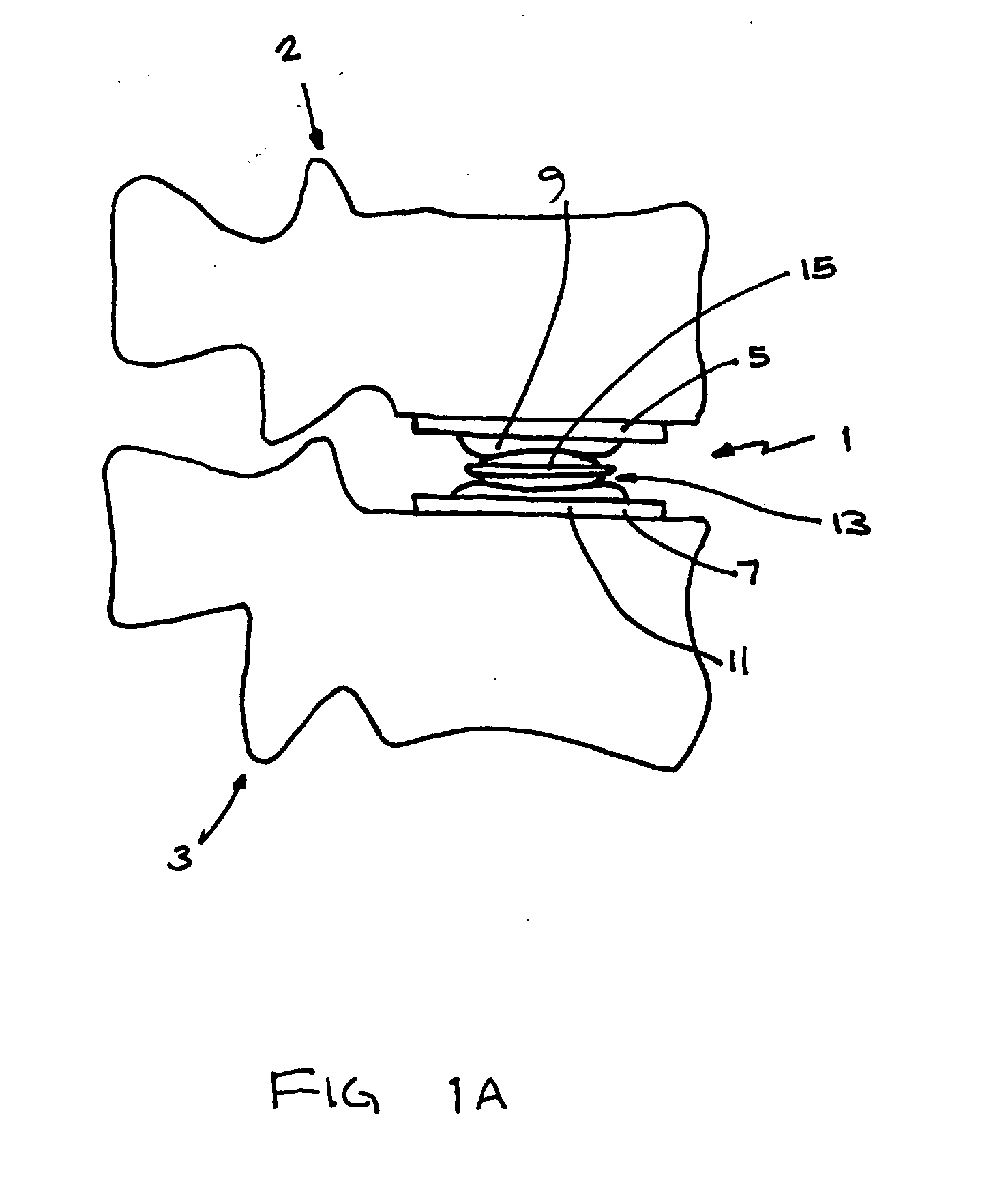
In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate.
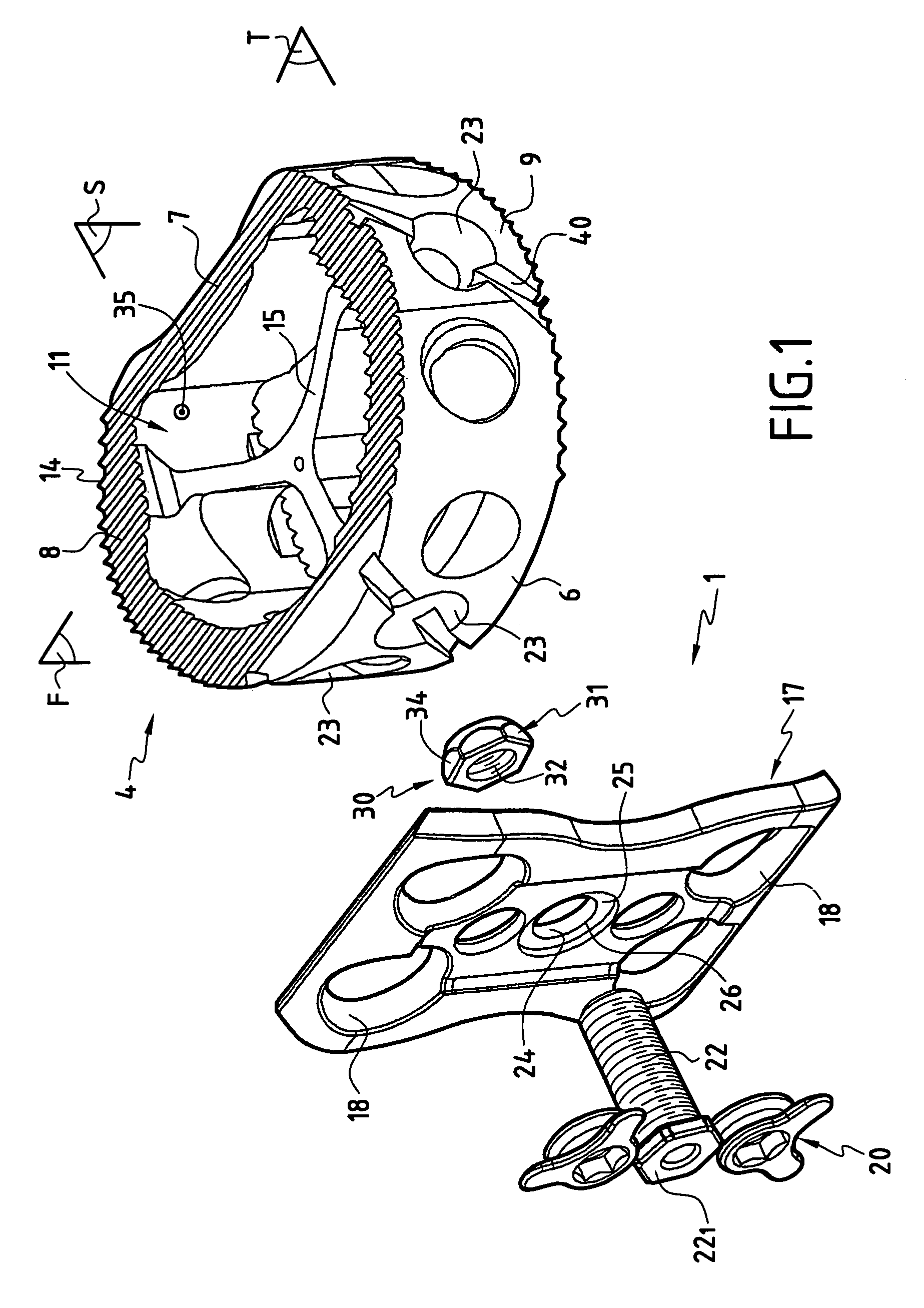
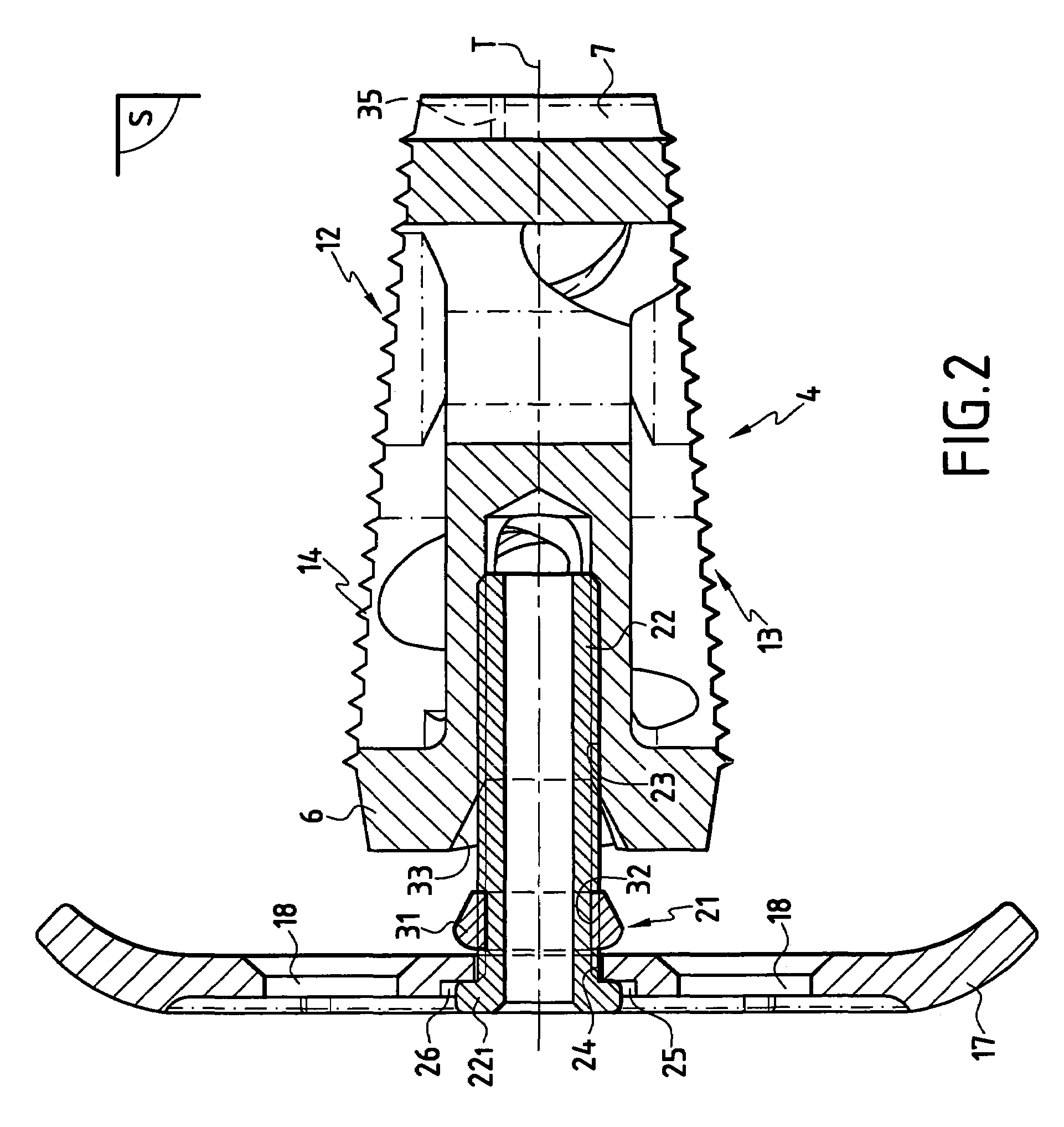
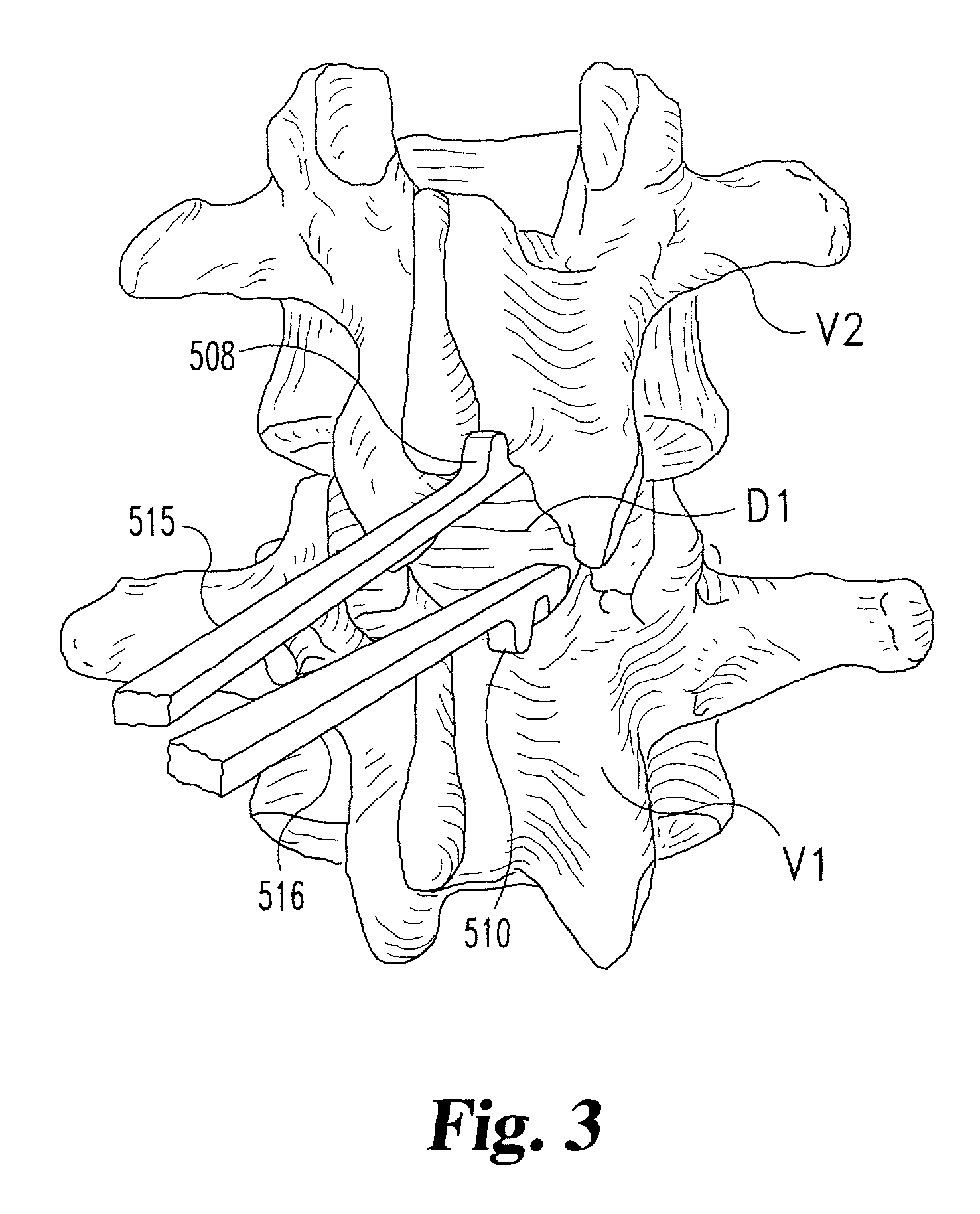
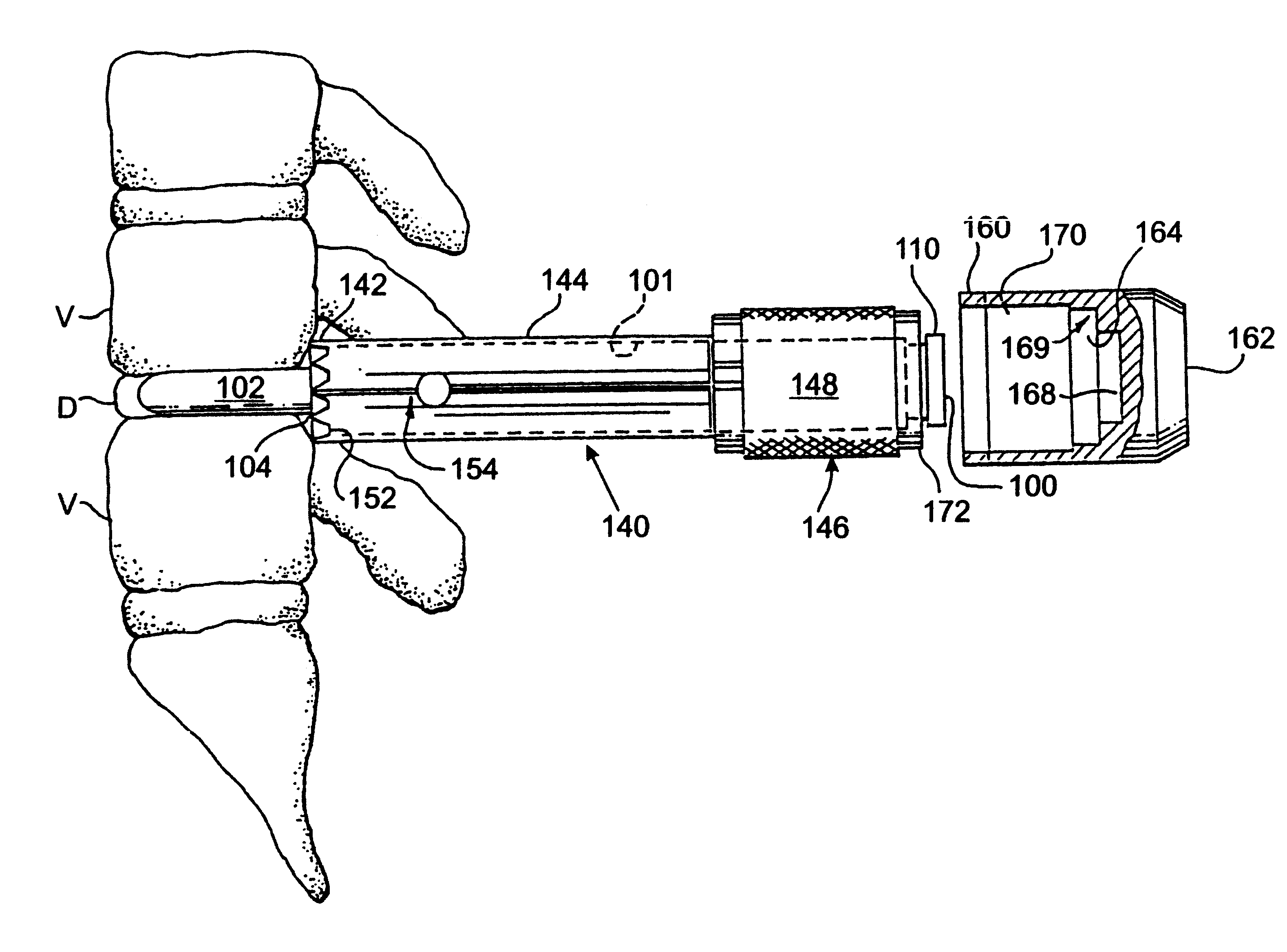
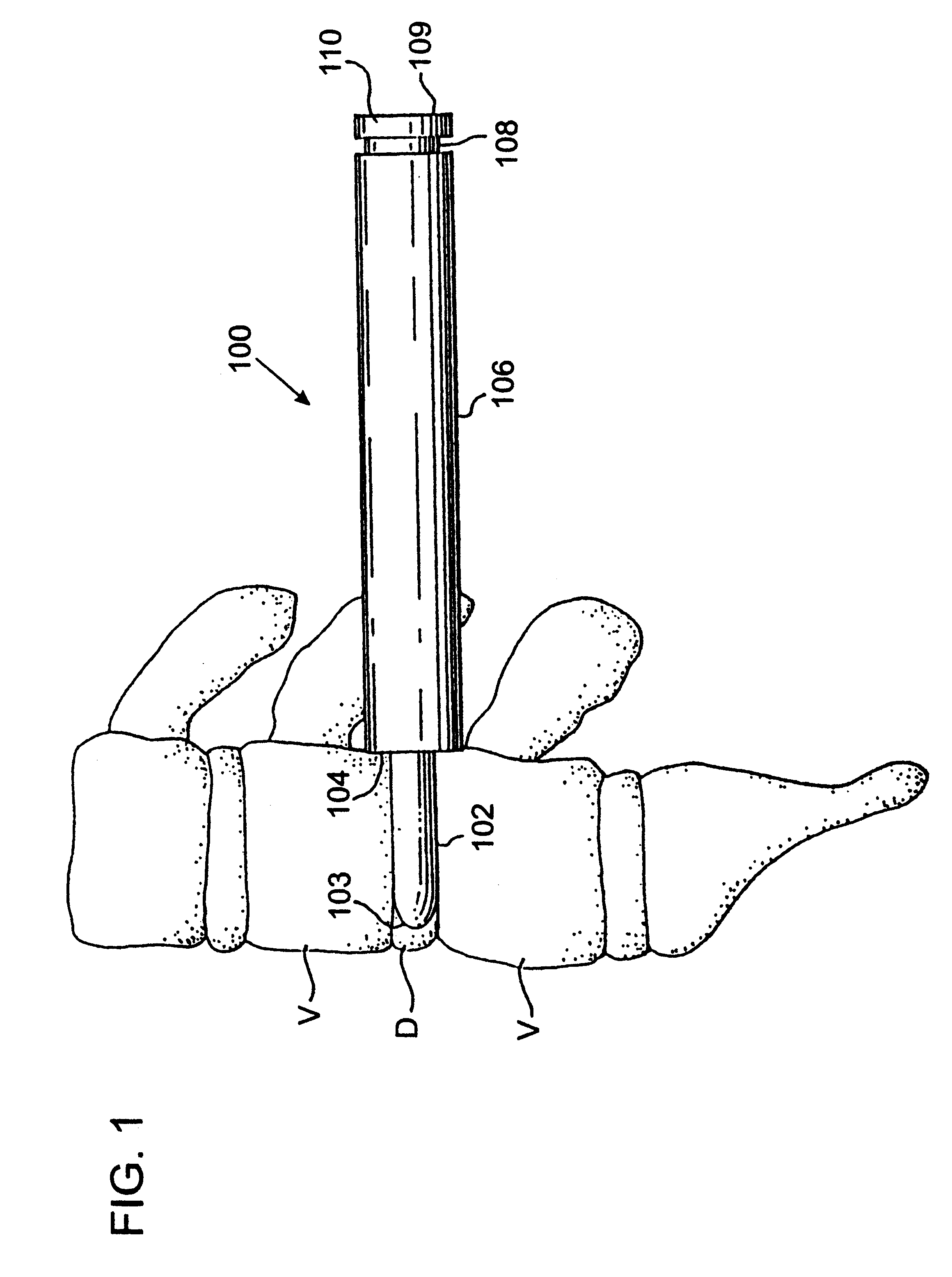
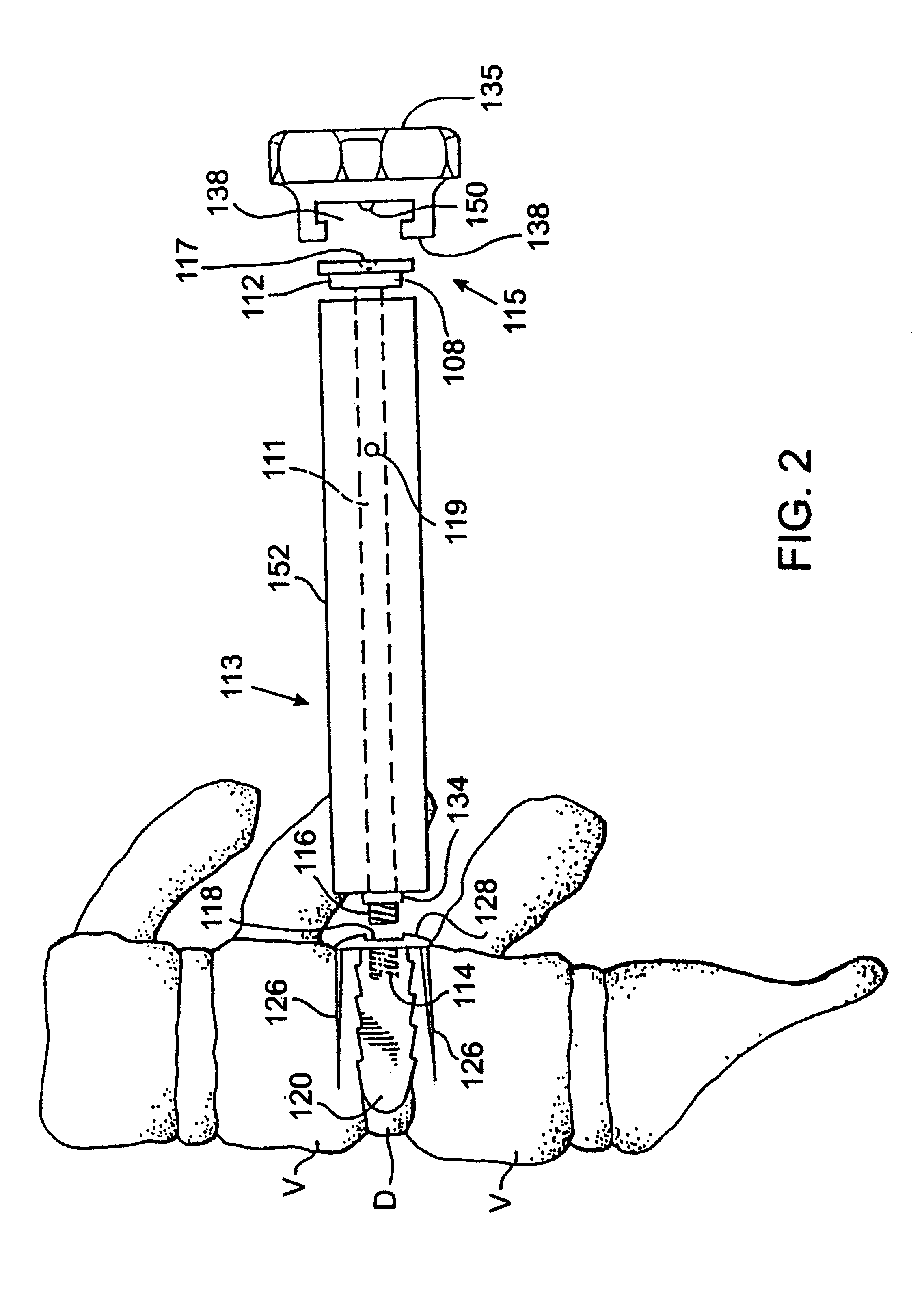
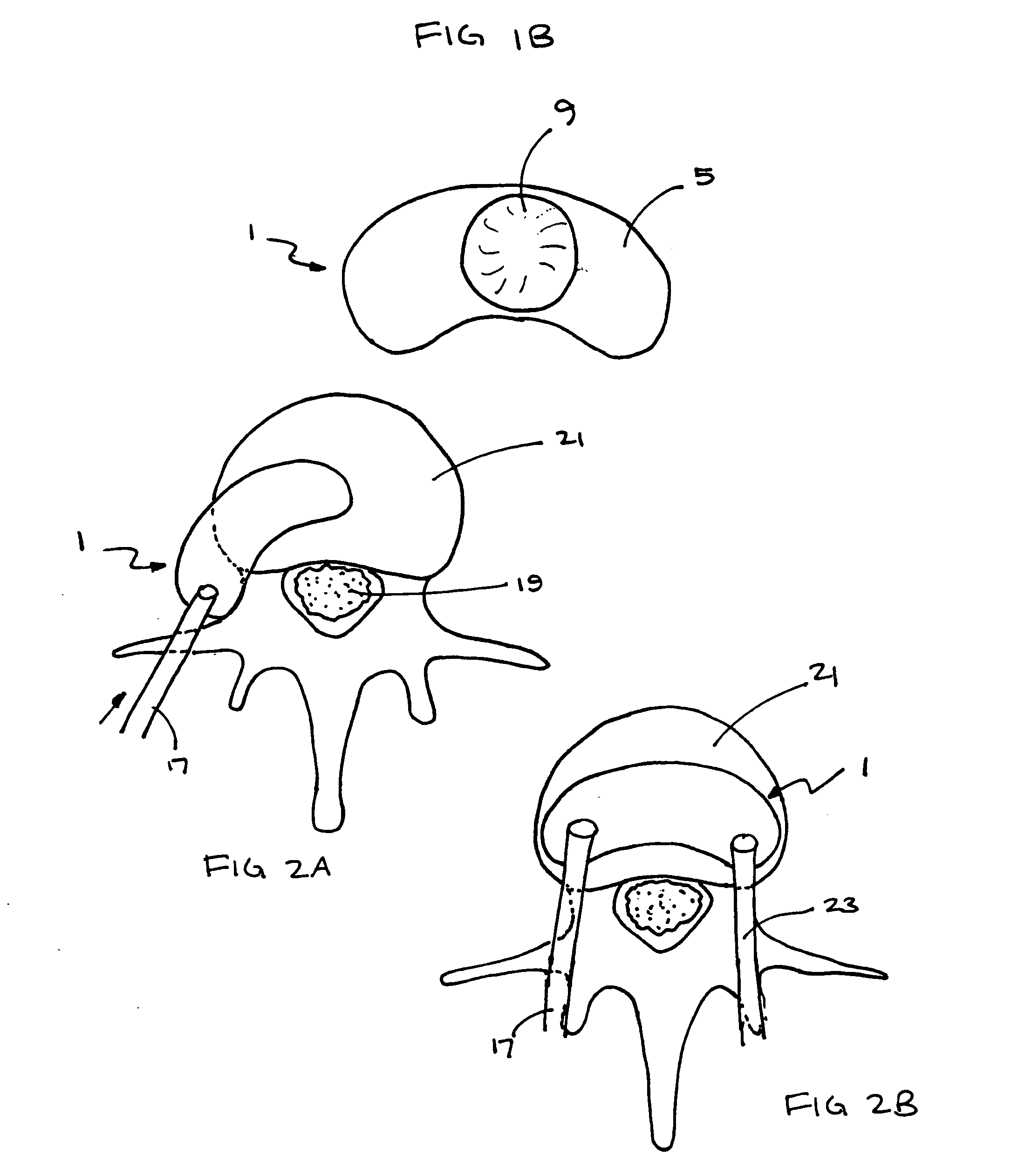
Methods and apparatus for performing therapeutic procedures in the spine
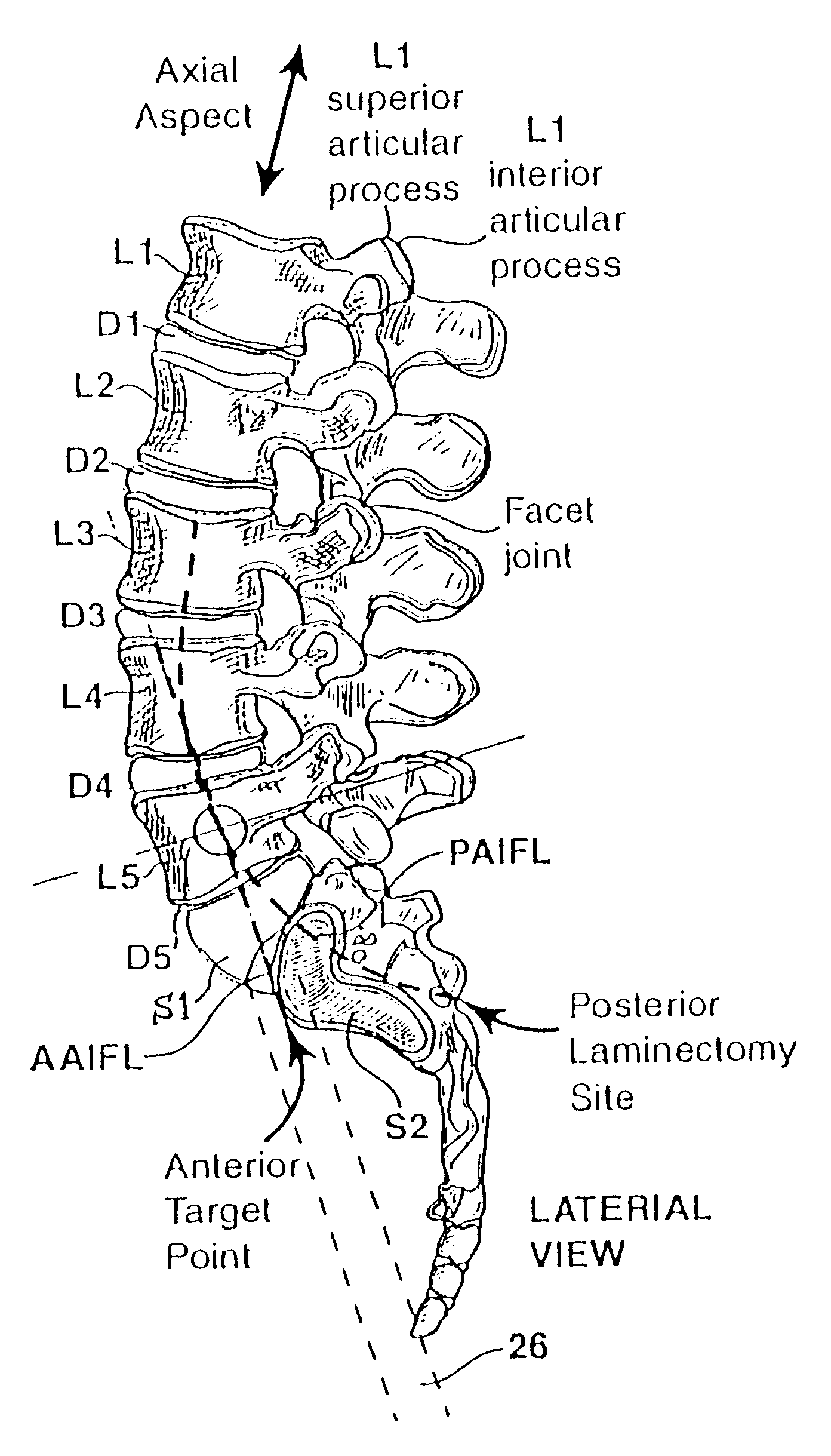
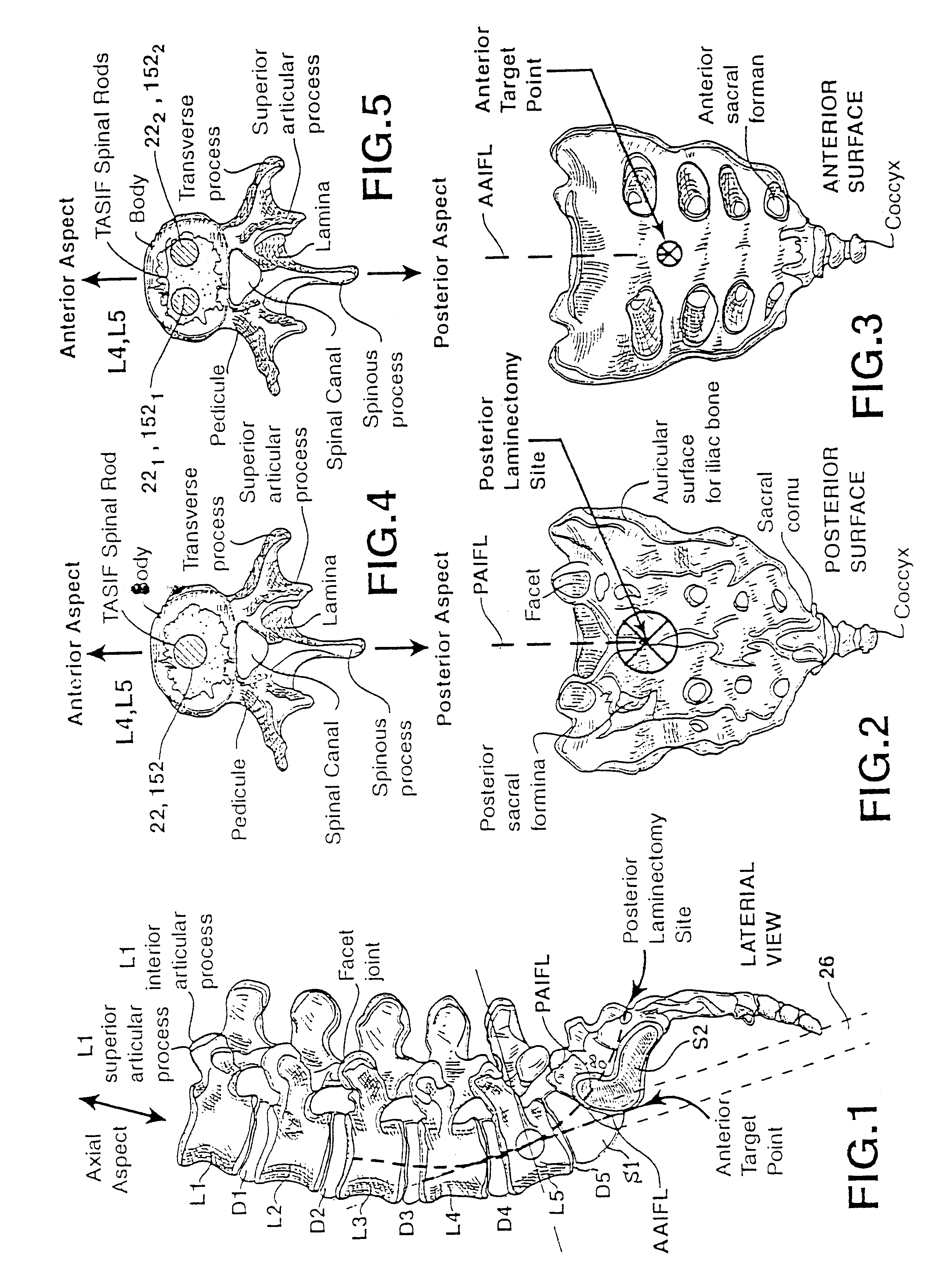
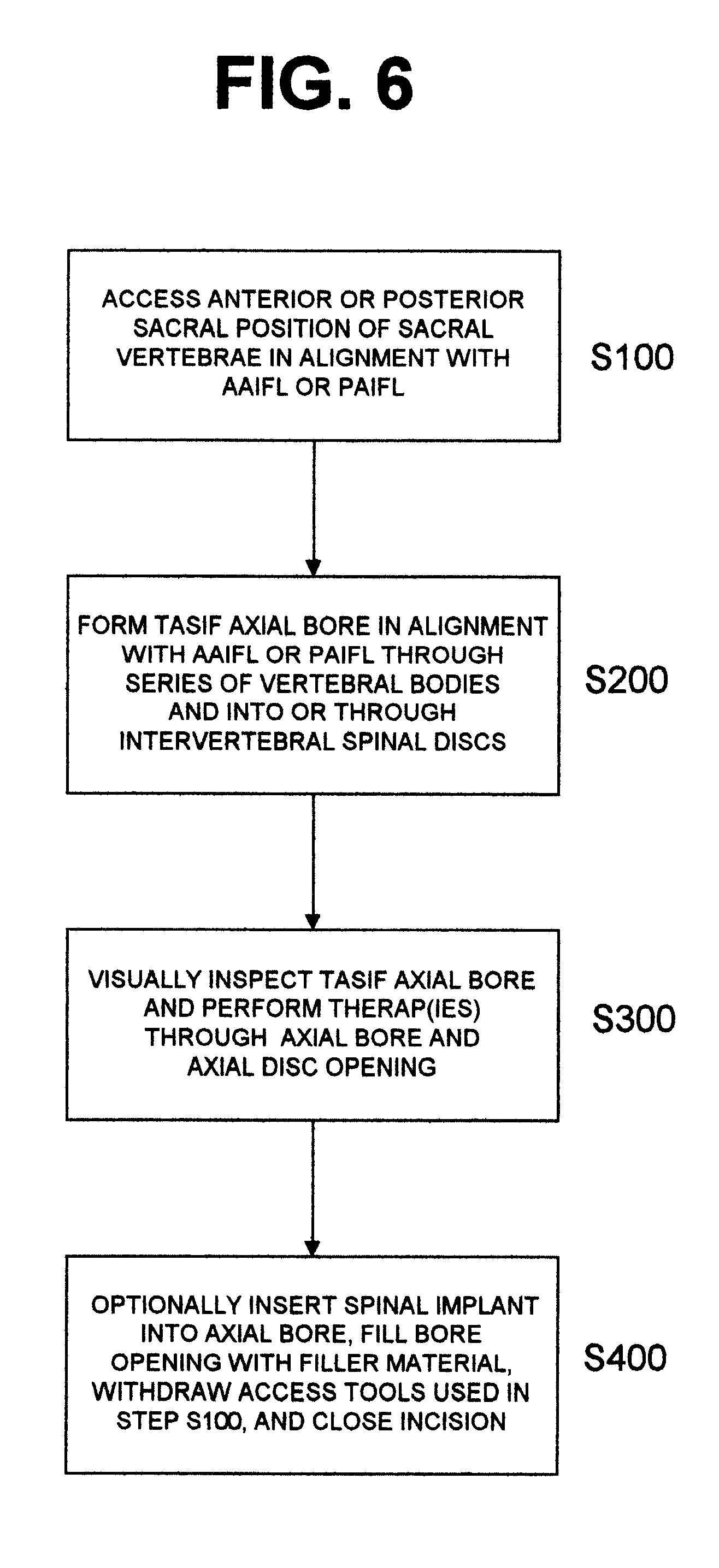
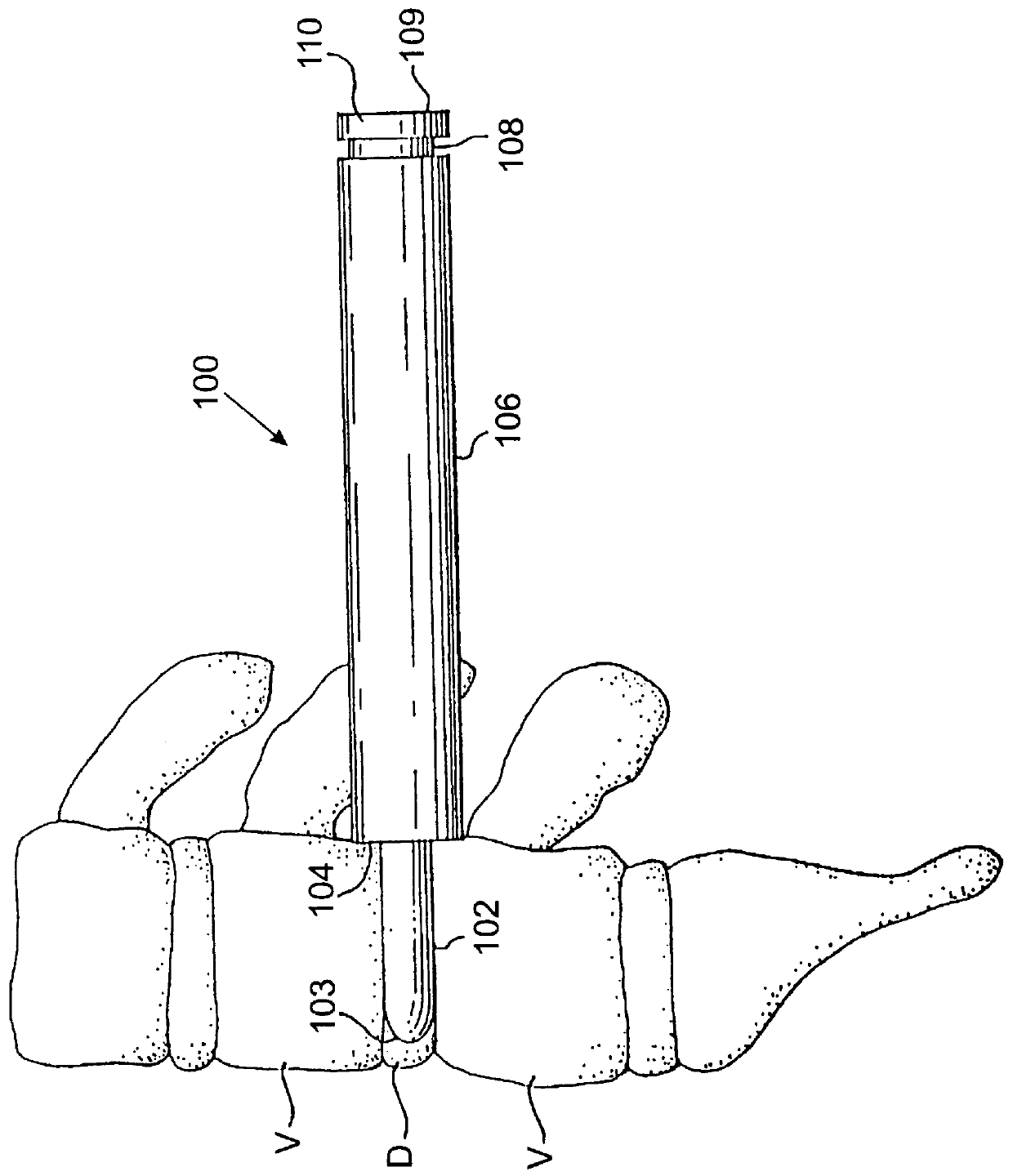
Methods and apparatus for forming one or more trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner and providing a therapy to the spine employing the axial bore. Anterior or posterior starting positions aligned with the AAIFL or PAIFL are accessed through respective anterior and posterior tracts. Curved or relatively straight anterior and curved posterior TASIF axial bores are formed from the anterior and posterior starting positions. The therapies performed through the TASIF axial bores include discoscopy, full and partial discectomy, vertebroplasty, balloon-assisted vertebroplasty, drug delivery, electrical stimulation and various forms of spinal disc cavity augmentation, spinal disc replacement, fusion of spinal motion segments and implantation of radioactive seeds. Axial spinal implants and bone growth materials can be placed into single or multiple parallel or diverging TASIF axial bores to fuse two or more vertebrae, or distract or shock absorb two or more vertebrae.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
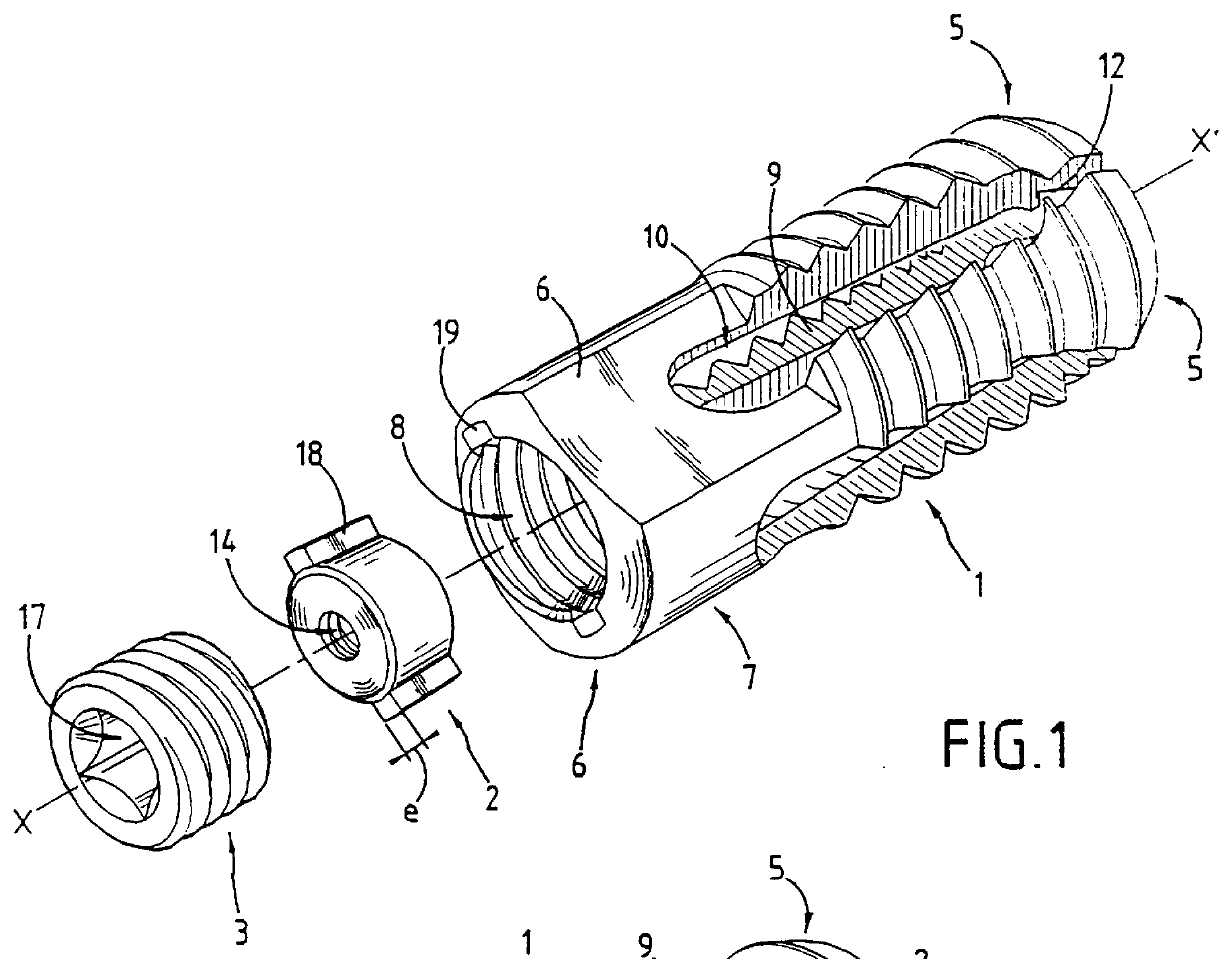
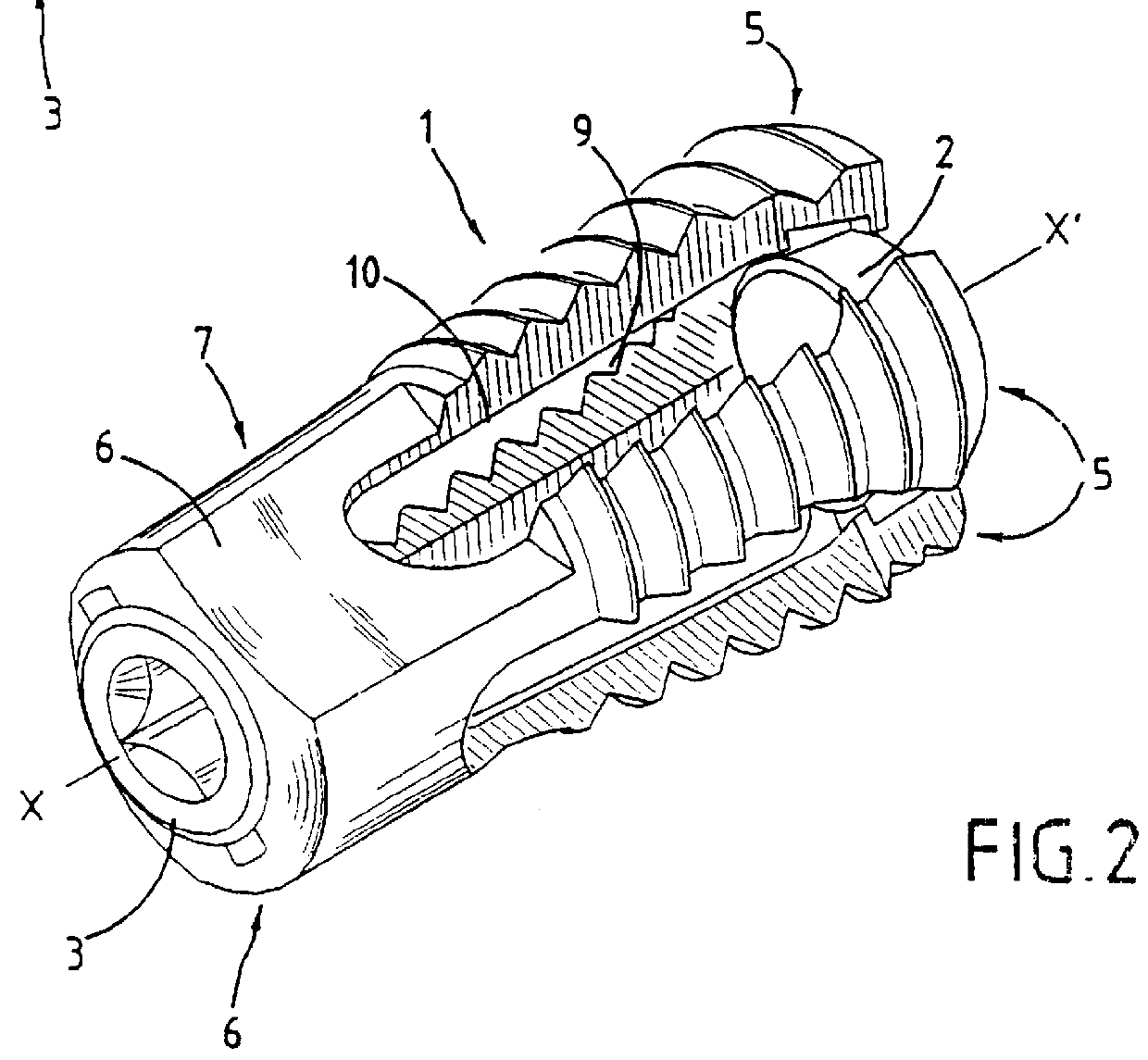
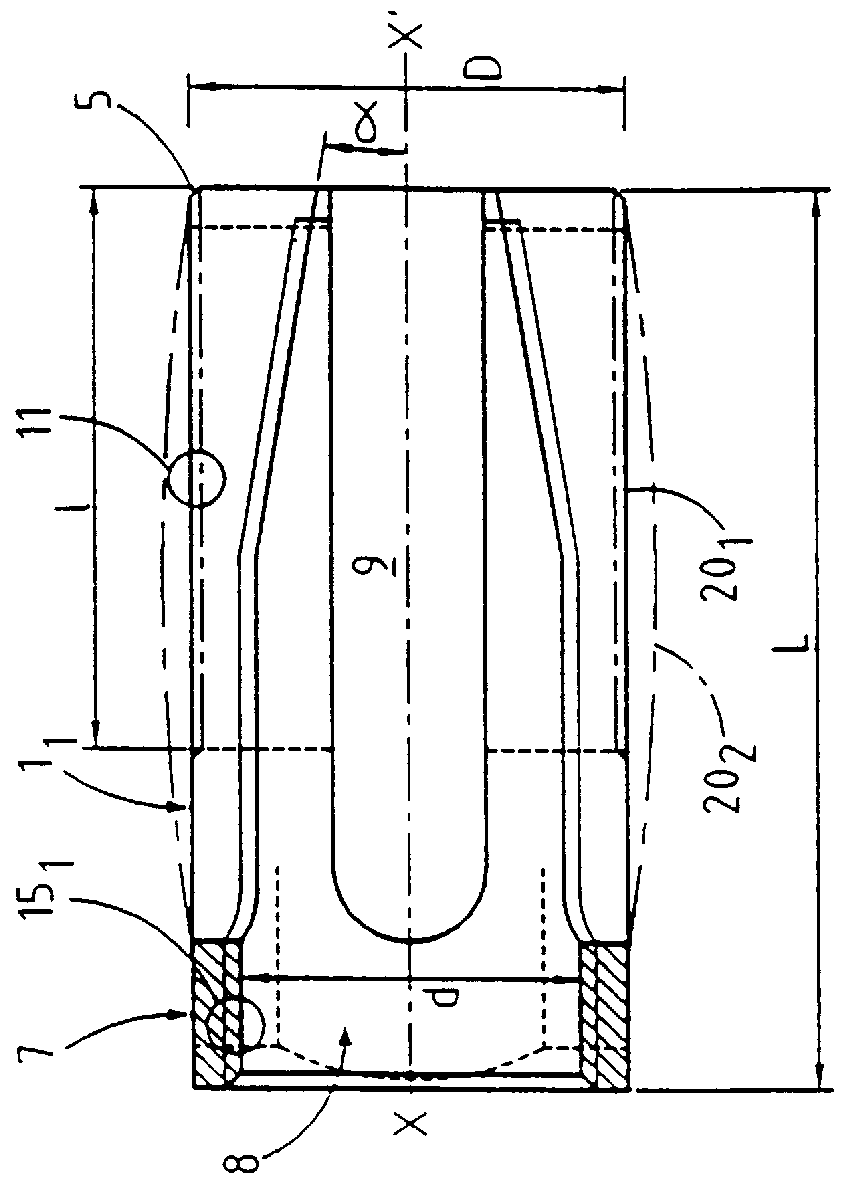
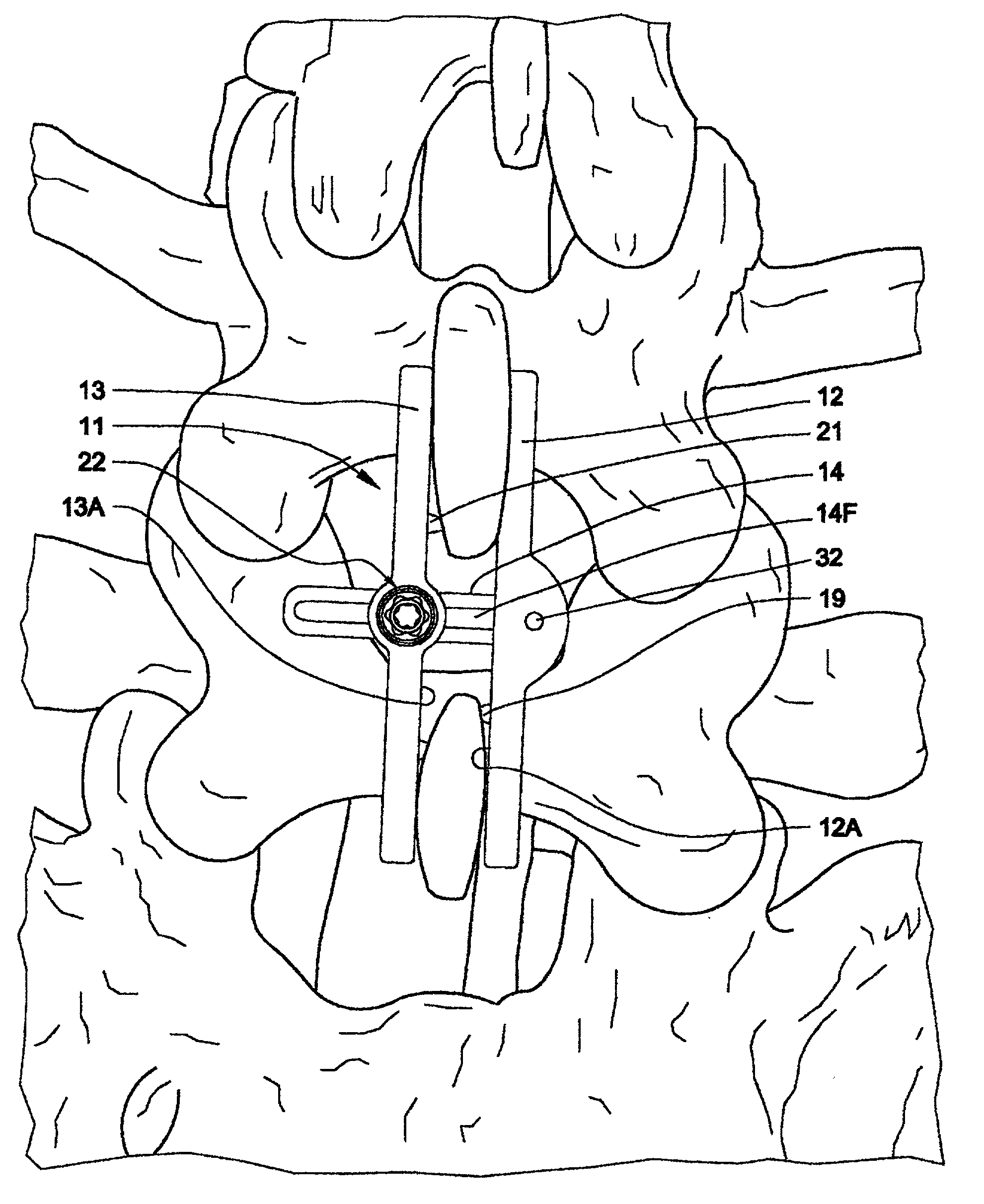
Method of inserting and preloading spinal implants
InactiveUS6080155ARestoring and maintaining normal angular relationshipFaster and safe and more efficaciousInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve. Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted to restore the normal angular relationship of the vertebrae adjacent to that disc space. An extended outer sleeve having extended portions capable of maintaining the vertebrae distracted in their normal angular relationship is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
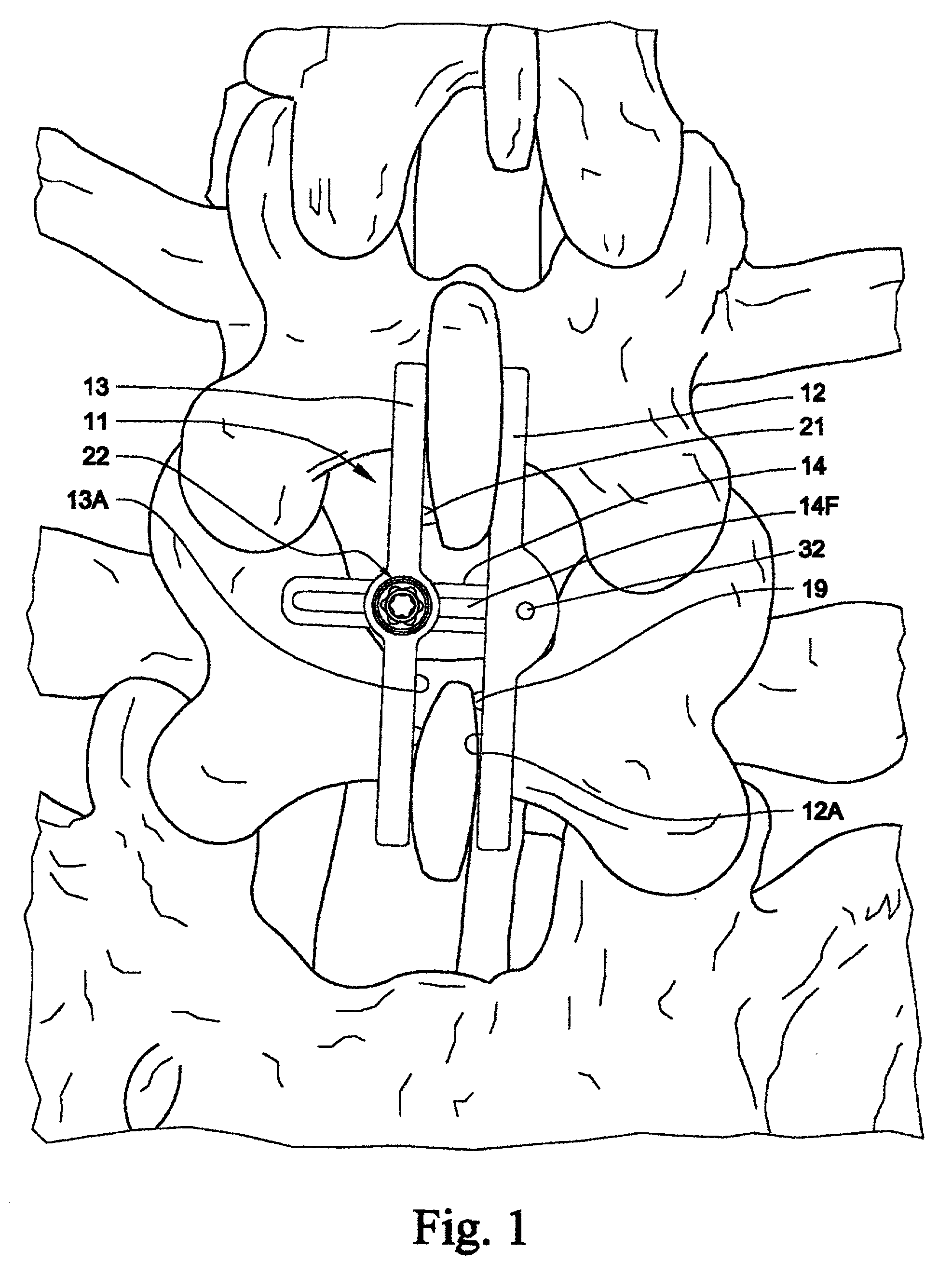
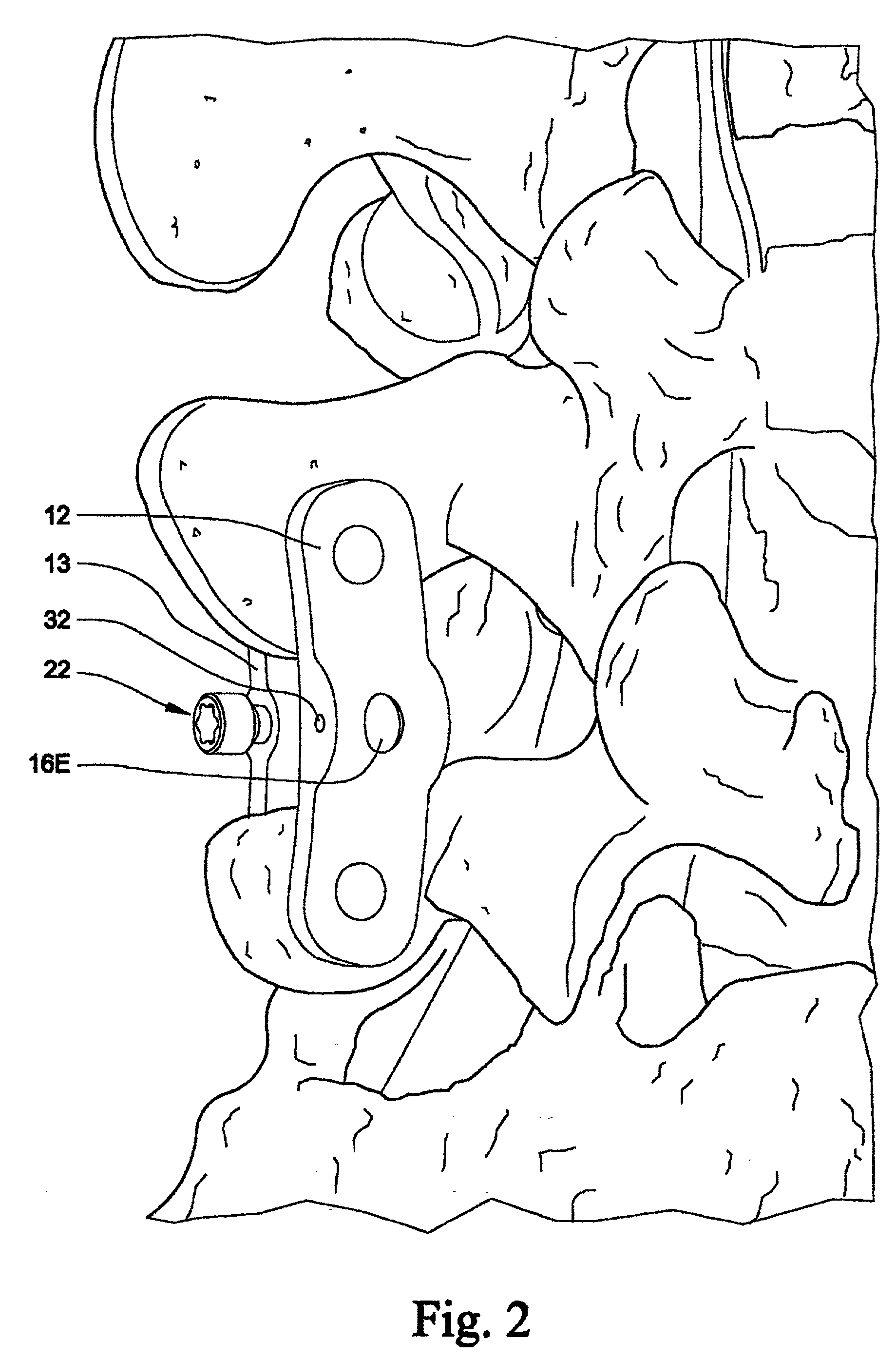
Spinal stabilization system and method
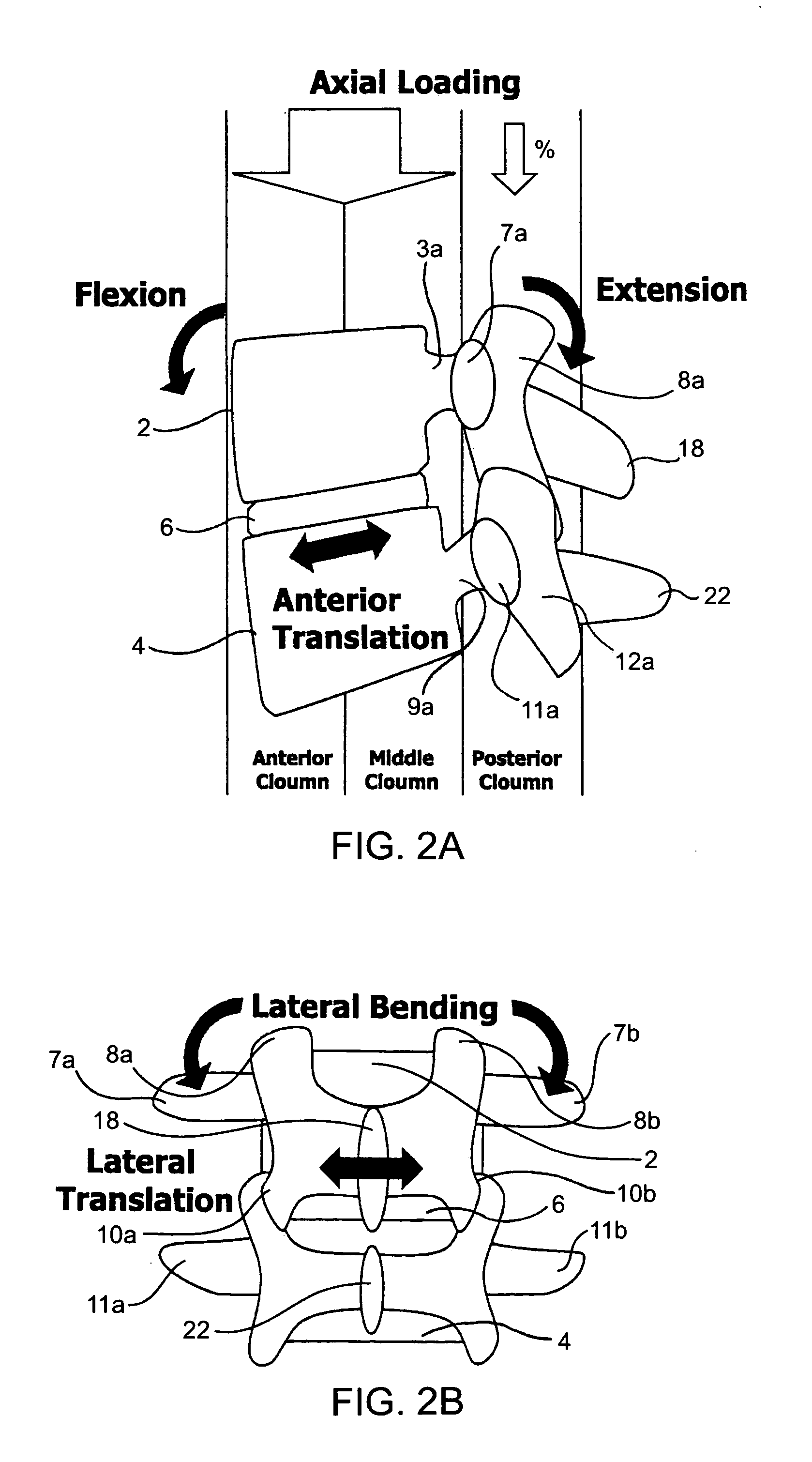
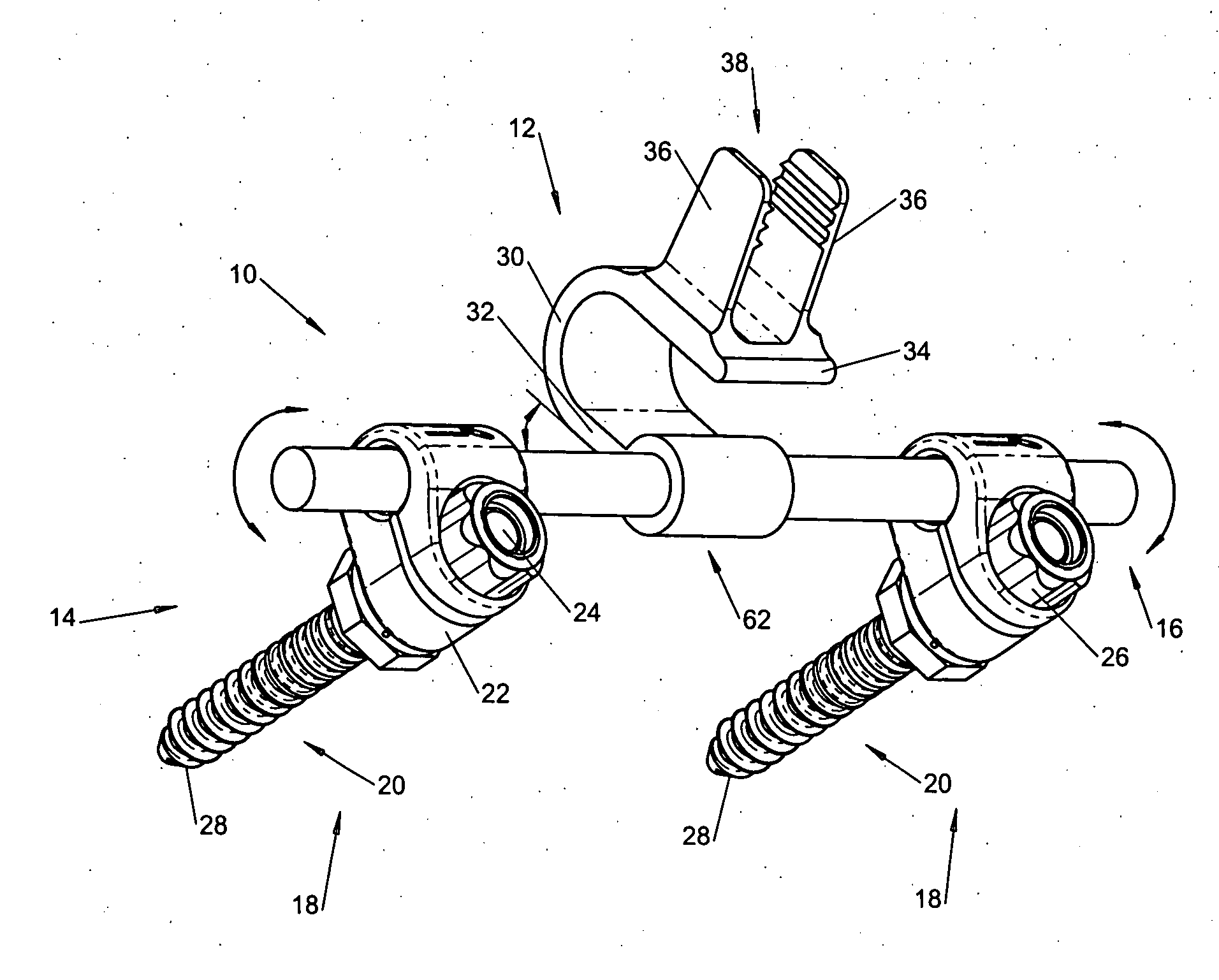
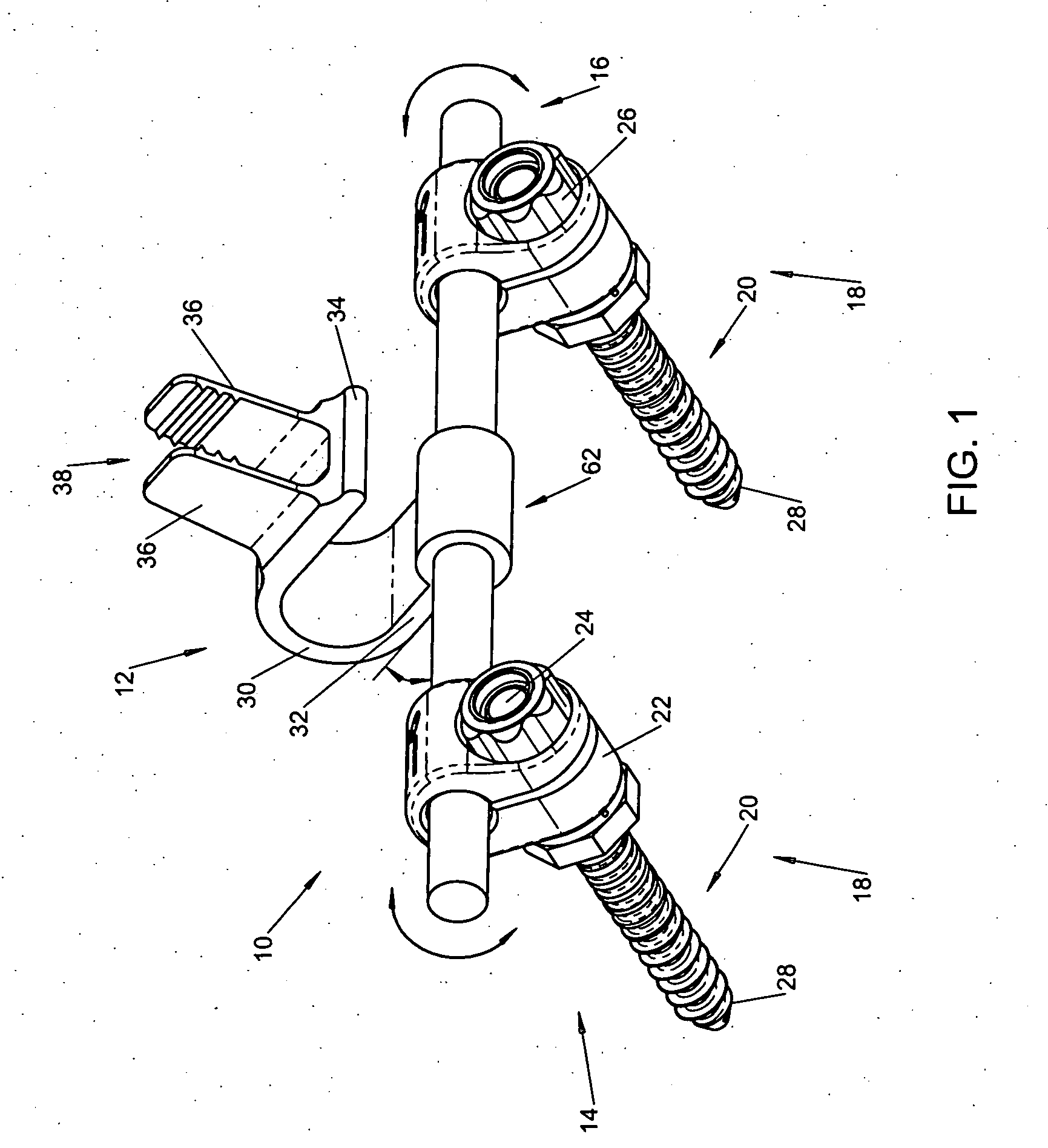
A spinal stabilization system may include a pair of structural members coupled to at least a portion of a human vertebra with connectors. Connectors may couple structural members to spinous processes. Some embodiments of a spinal stabilization system may include fasteners that couple structural members to vertebrae. In some embodiments, a spinal stabilization system provides three points of fixation for a single vertebral level. A fastener may fixate a facet joint between adjacent vertebrae and couple a stabilization structural member to a vertebra. Connectors may couple the structural members to the spinous processes of the vertebrae. Use of a spinal stabilization system may improve the stability of a weakened or damaged portion of a spine. When used in conjunction with an implant or other device, the spinal stabilization system may immobilize vertebrae and allow for fusion of the implant or other device with vertebrae.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Apparatus for inserting spinal implants
InactiveUS6096038AEliminate separationEfficient removalInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
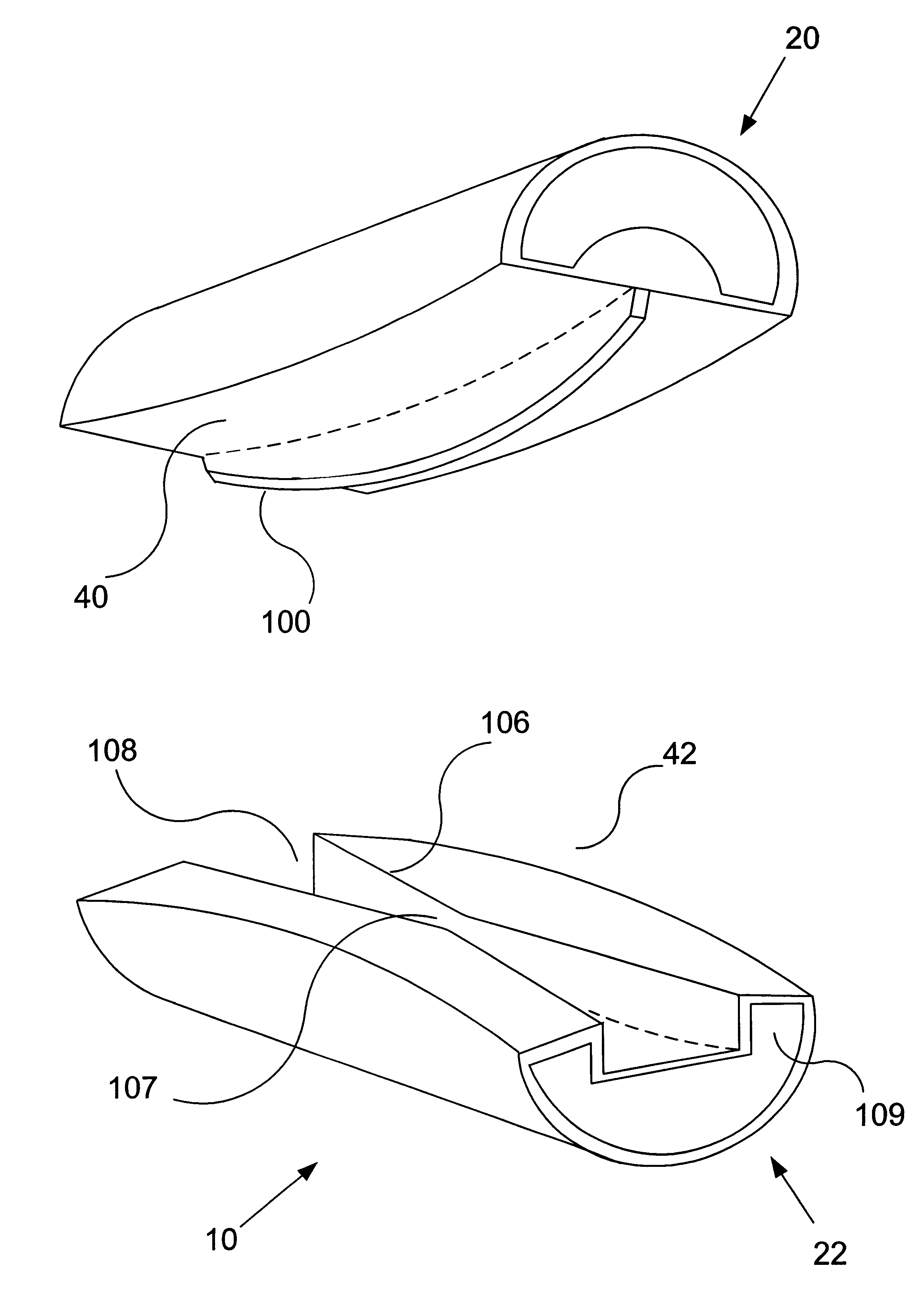
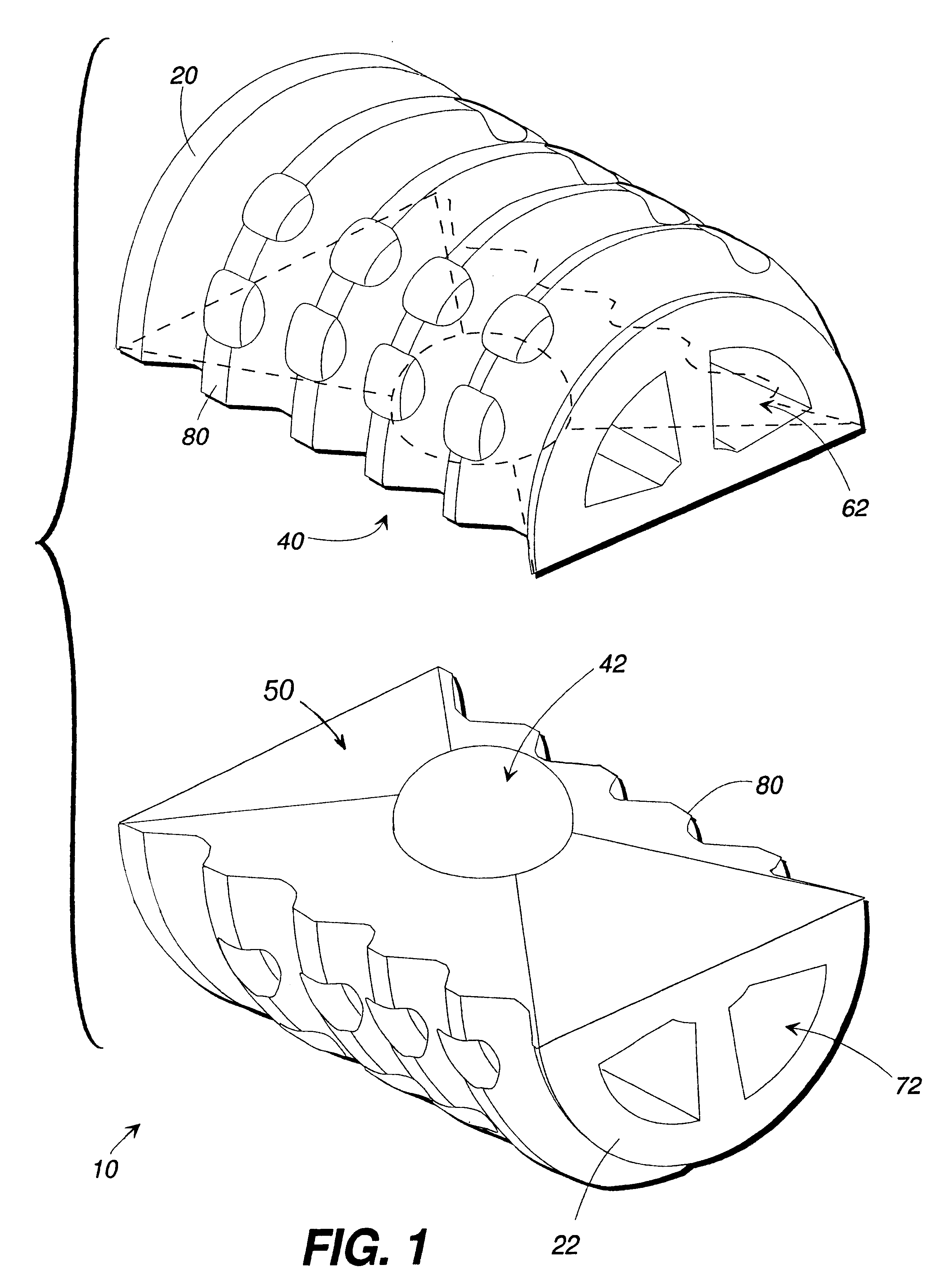
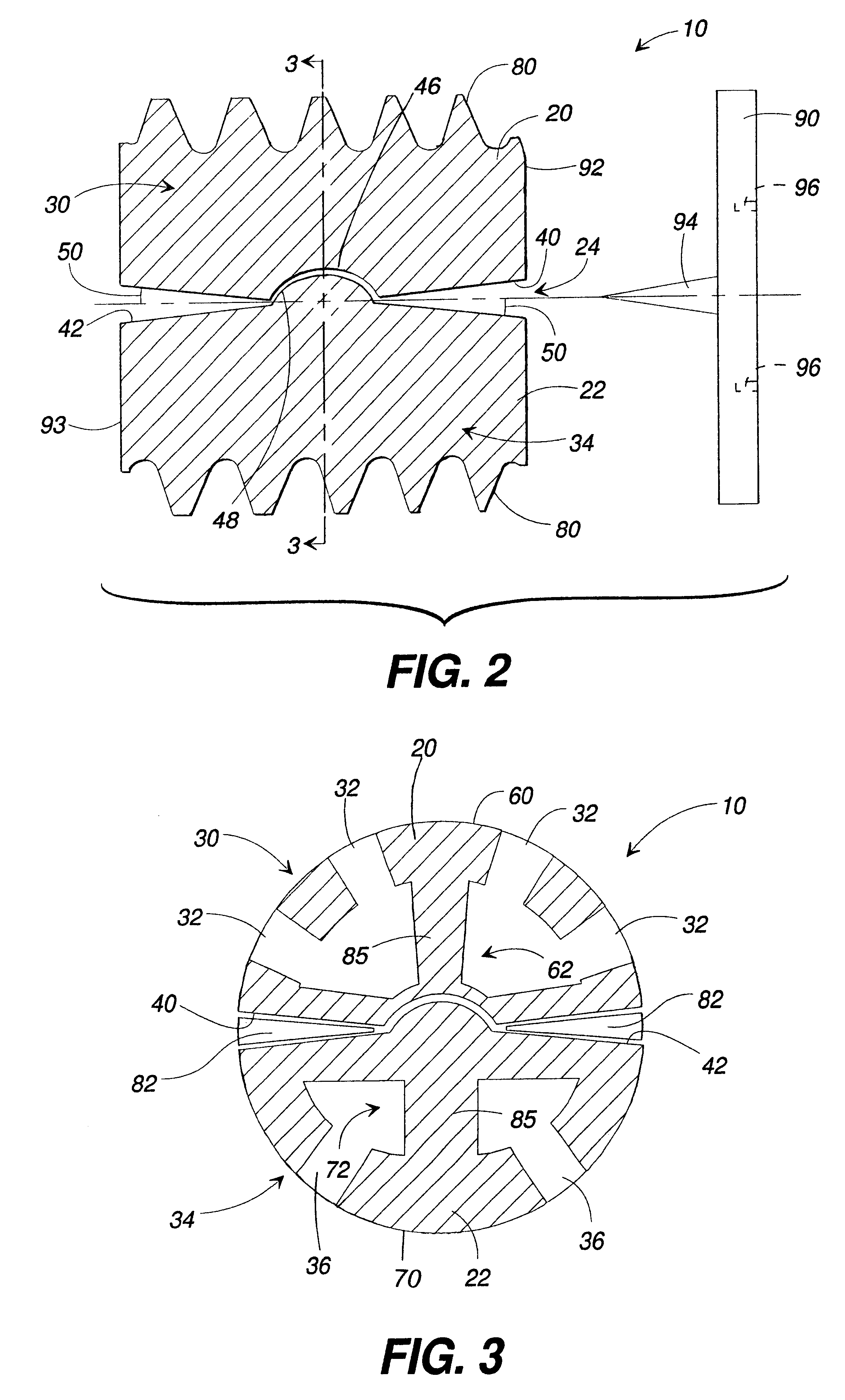
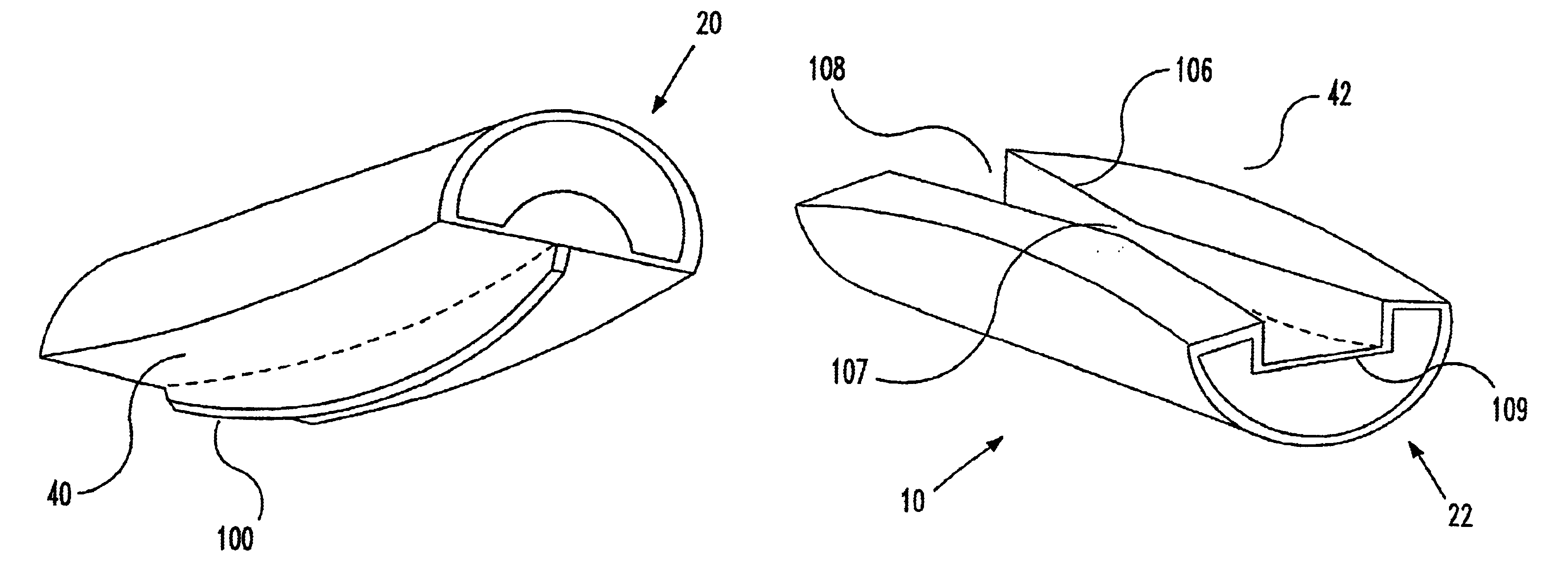
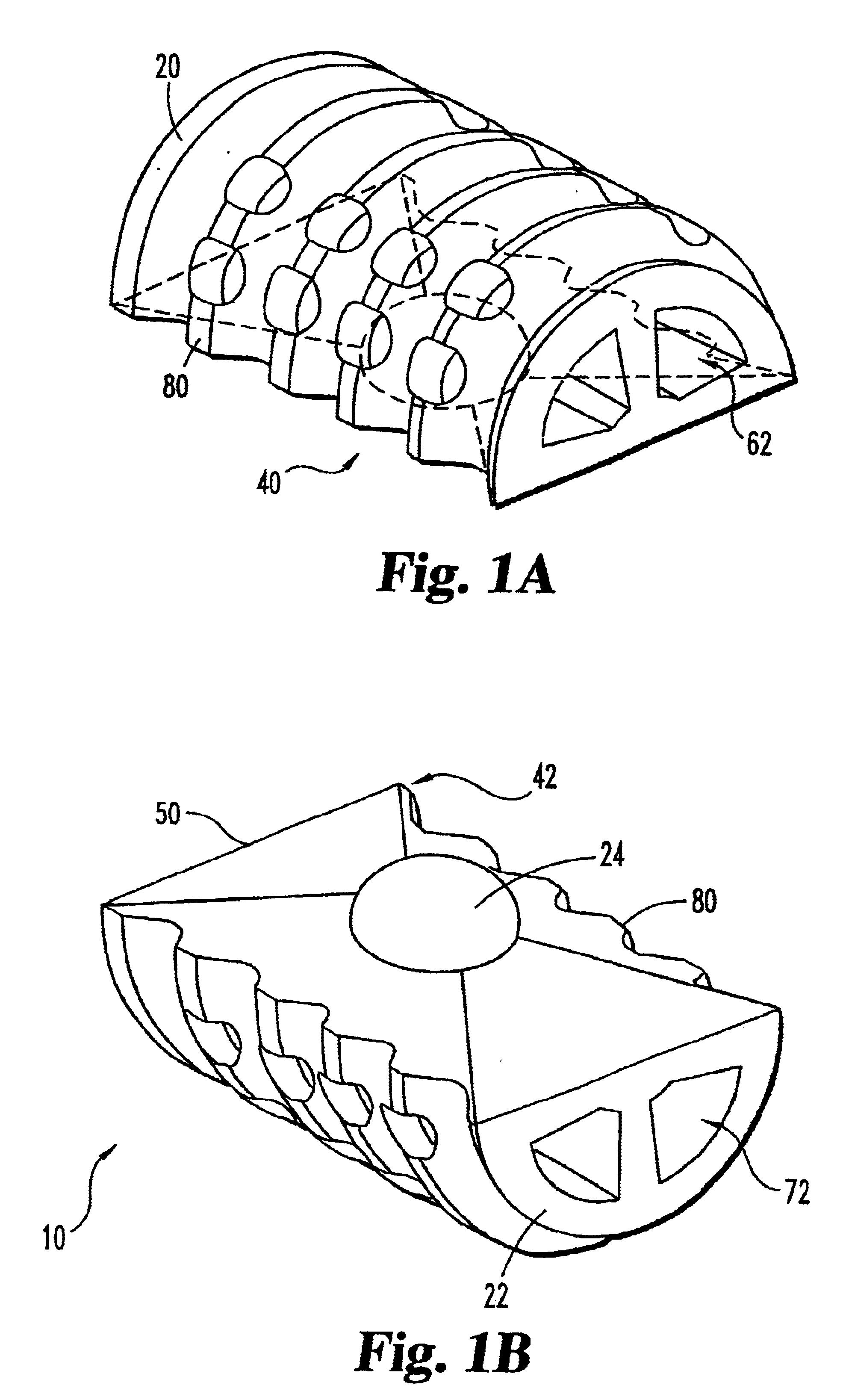
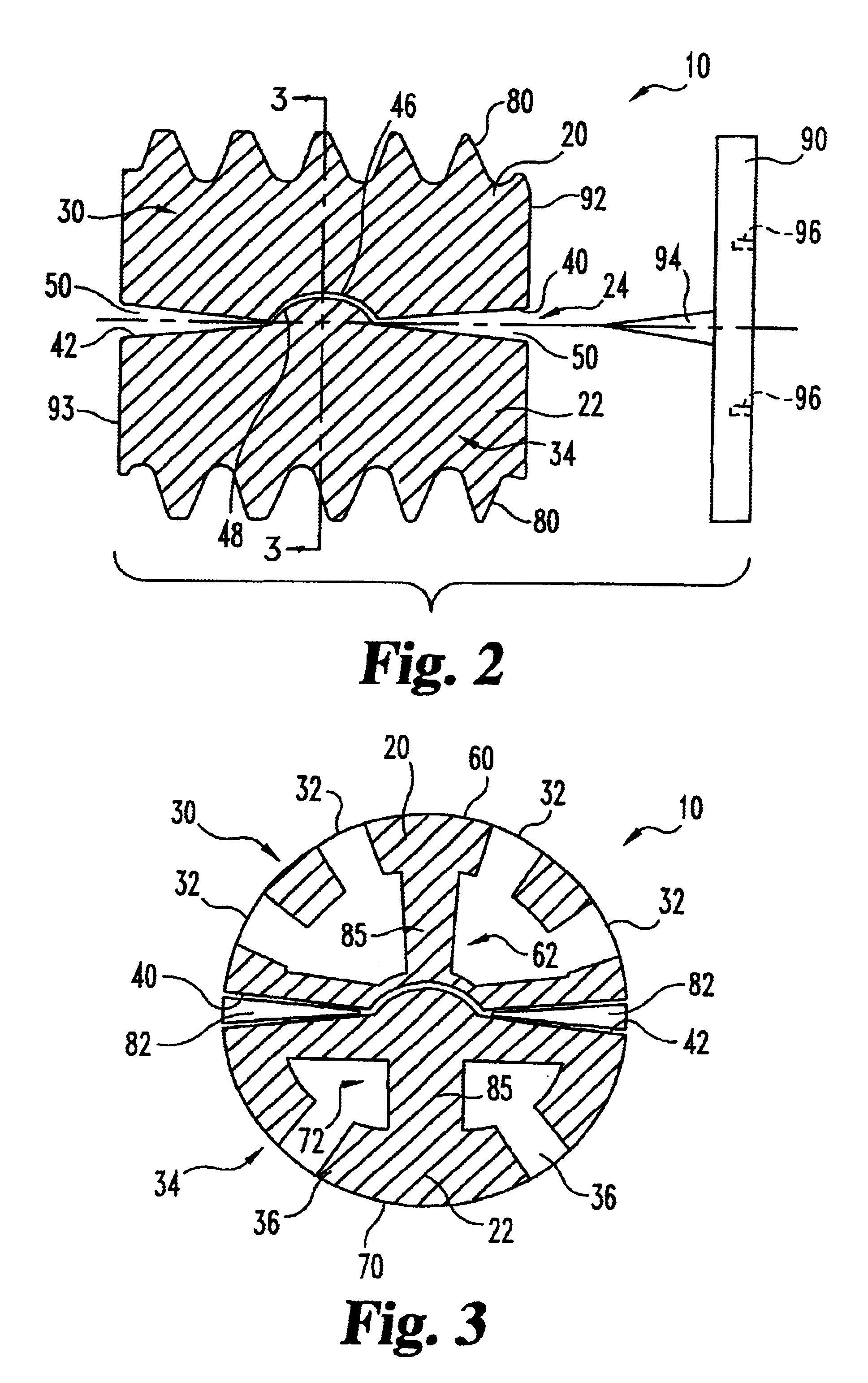
Articulating spinal implant
A spinal implant for intervertebral disc replacement. The implant is formed from two hemicylindrical elements, each engaging one of an adjacent pair of vertebrae. An articulating ball-and-socket joint between the two elements resists compression and lateral movement between the vertebra, but allows pivotal movement, thereby preserving mobility. Fusion chambers are provided for allowing bone ingrowth to fuse the elements to the vertebrae. Biocompatible, bioreabsorbable struts, shims, fillers and / or end caps are provided for temporary stabilization of the first and second hemicylindrical elements. Bone chips removed from the vertebrae during implantation or bone growth stimulators can be inserted into the fusion chamber or otherwise applied to the implant to enhance bone ingrowth.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Devices and methods for the treatment of spinal disorders
InactiveUS20050049708A1Permit some movementReducing nerve impingementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsDiseaseSpine disorder
Devices and methods for treating a damaged intervertebral disc to reduce or eliminate associated back pain. Dynamic bias devices and reinforcement devices are disclosed, which may be used individually or in combination, to eliminate nerve impingement associated with the damaged disc, and / or to reinforce the damaged disc, while permitting relative movement of the vertebrae adjacent the damaged disc.
Owner:ANULEX TECH
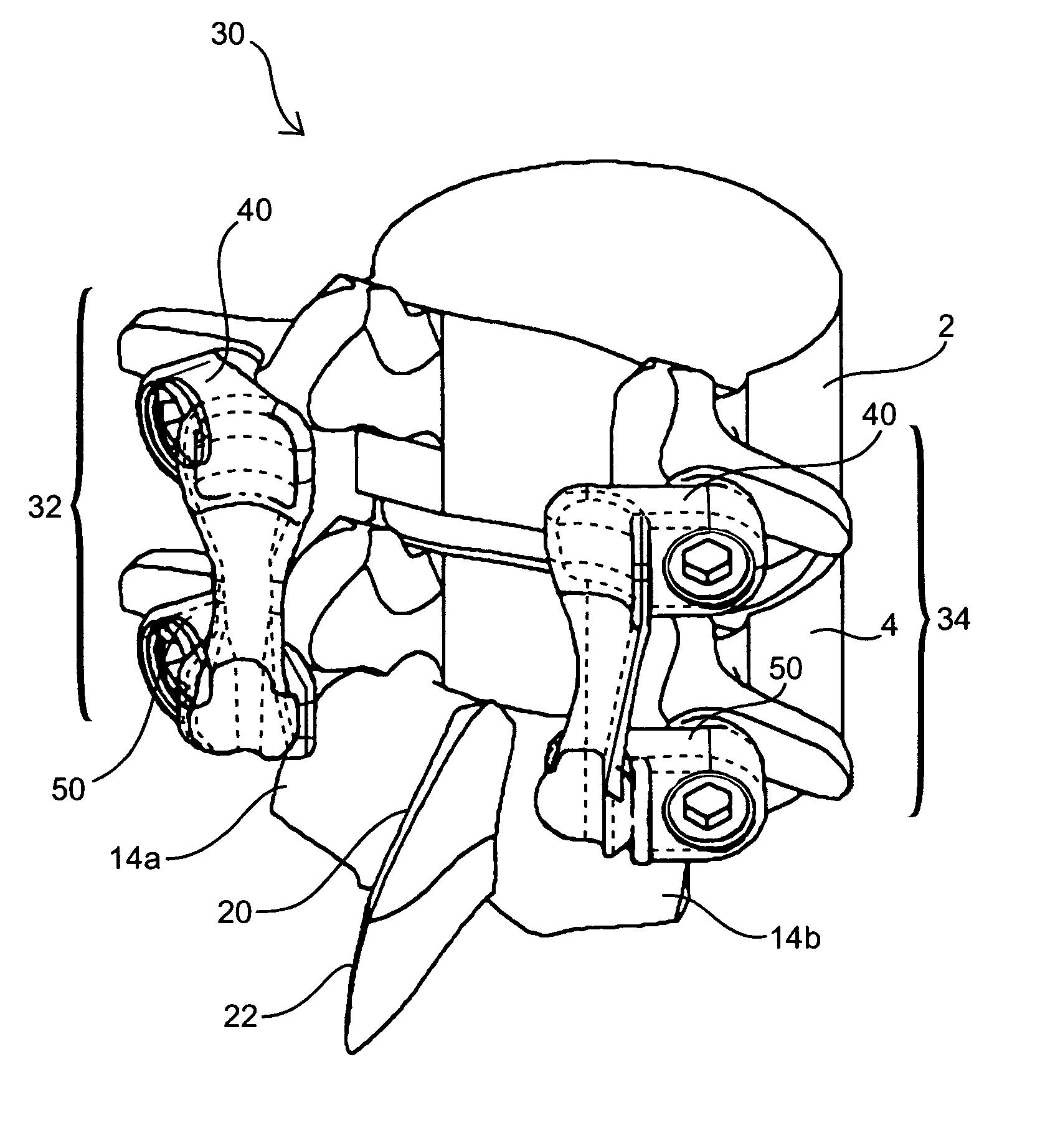
Spinal stabilization systems and methods
InactiveUS7250052B2Minimize damageProvide stabilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisMinimally invasive proceduresSkin incision
A spinal stabilization system may be formed in a patient. In some embodiments, a minimally invasive procedure may be used to form a spinal stabilization system in a patient. Bone fastener assemblies may be coupled to vertebrae. Each bone fastener assembly may include a bone fastener and a collar. The collar may be rotated and / or angulated relative to the bone fastener. Detachable members may be coupled to the collar to allow for formation of the spinal stabilization system through a small skin incision. The detachable members may allow for alignment of the collars to facilitate insertion of an elongated member in the collars. An elongated member may be positioned in the collars and a closure member may be used to secure the elongated member to the collars.
Owner:HIGHRIDGE MEDICAL LLC
Intersomatic setting and fusion system
A system for intersomatic fusion and setting of vertebrae. The system includes at least one open internal cage arranged for receiving spongy bone or bone substitute and is designed to be interposed between two vertebrae during diskectomy. The cage (1) includes on its anterior face (5) an external element forming a plate (12) extending in a plane substantially perpendicular to the insertion plane of the cage (1), and has at each of its ends an anchor device (13,14) adapted for anchoring to at least two adjacent vertebrae to be secured to each other by the cage (1). The system can be separated into two parts, the cage and the plate.
Owner:SCIENTX
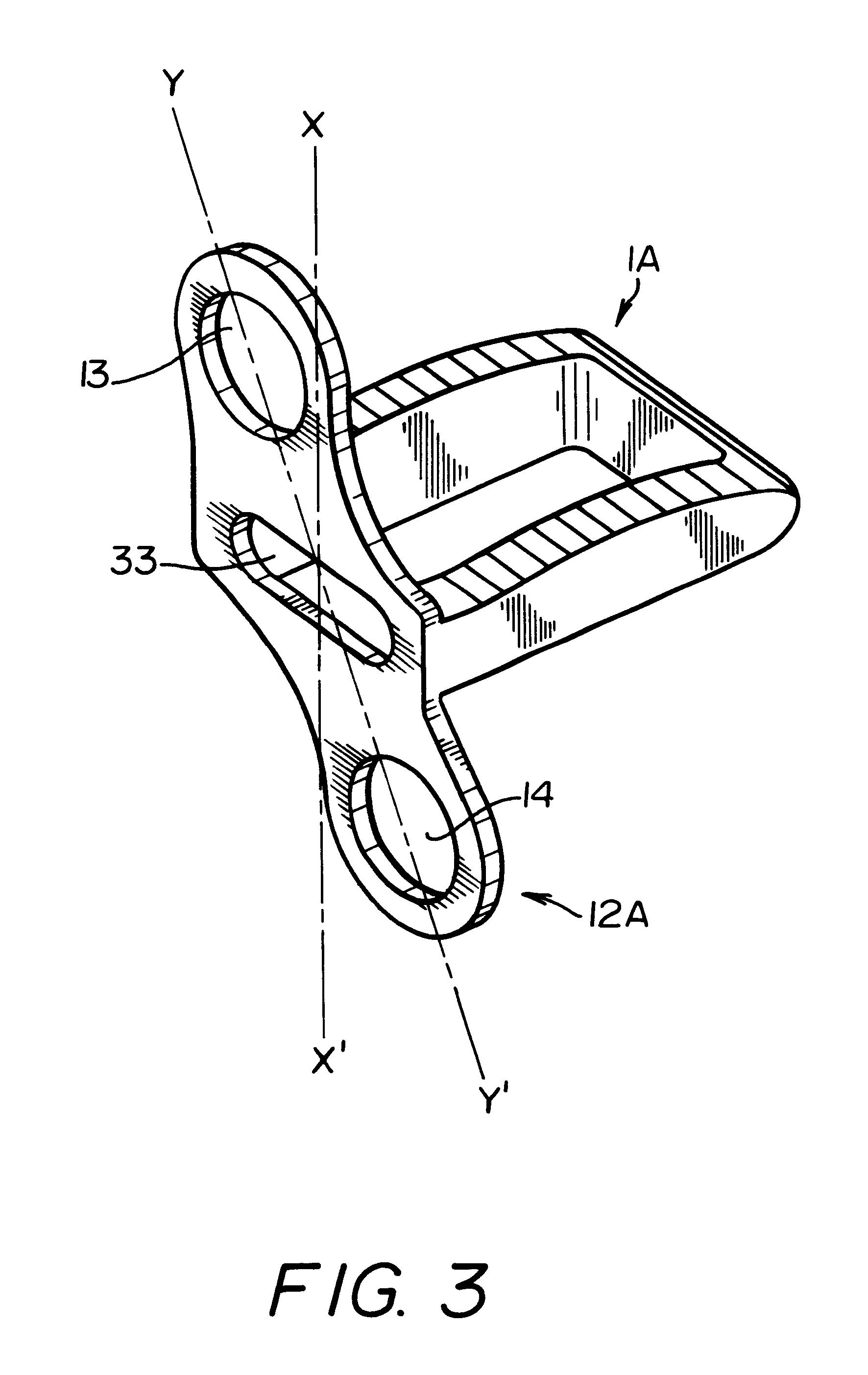
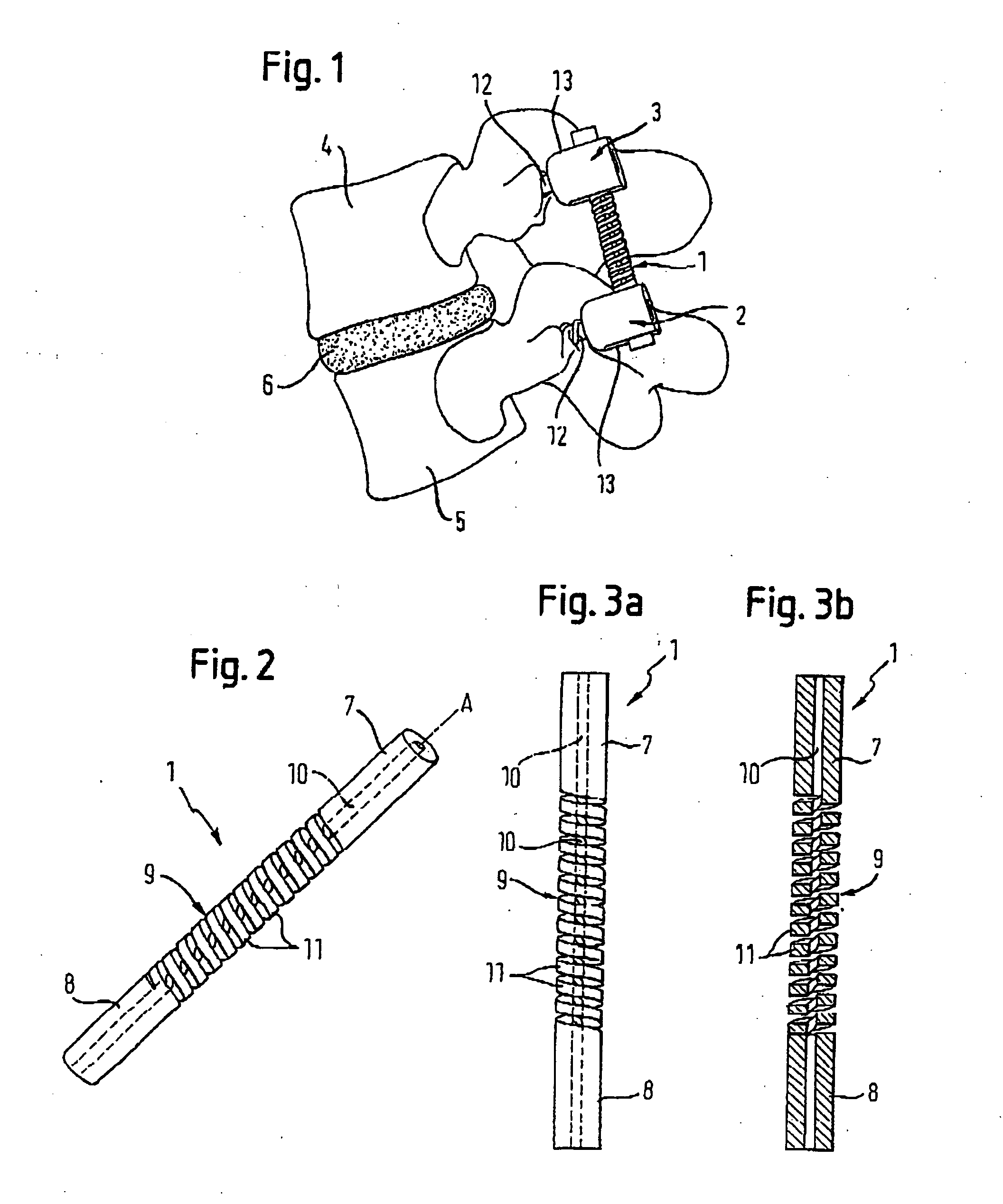
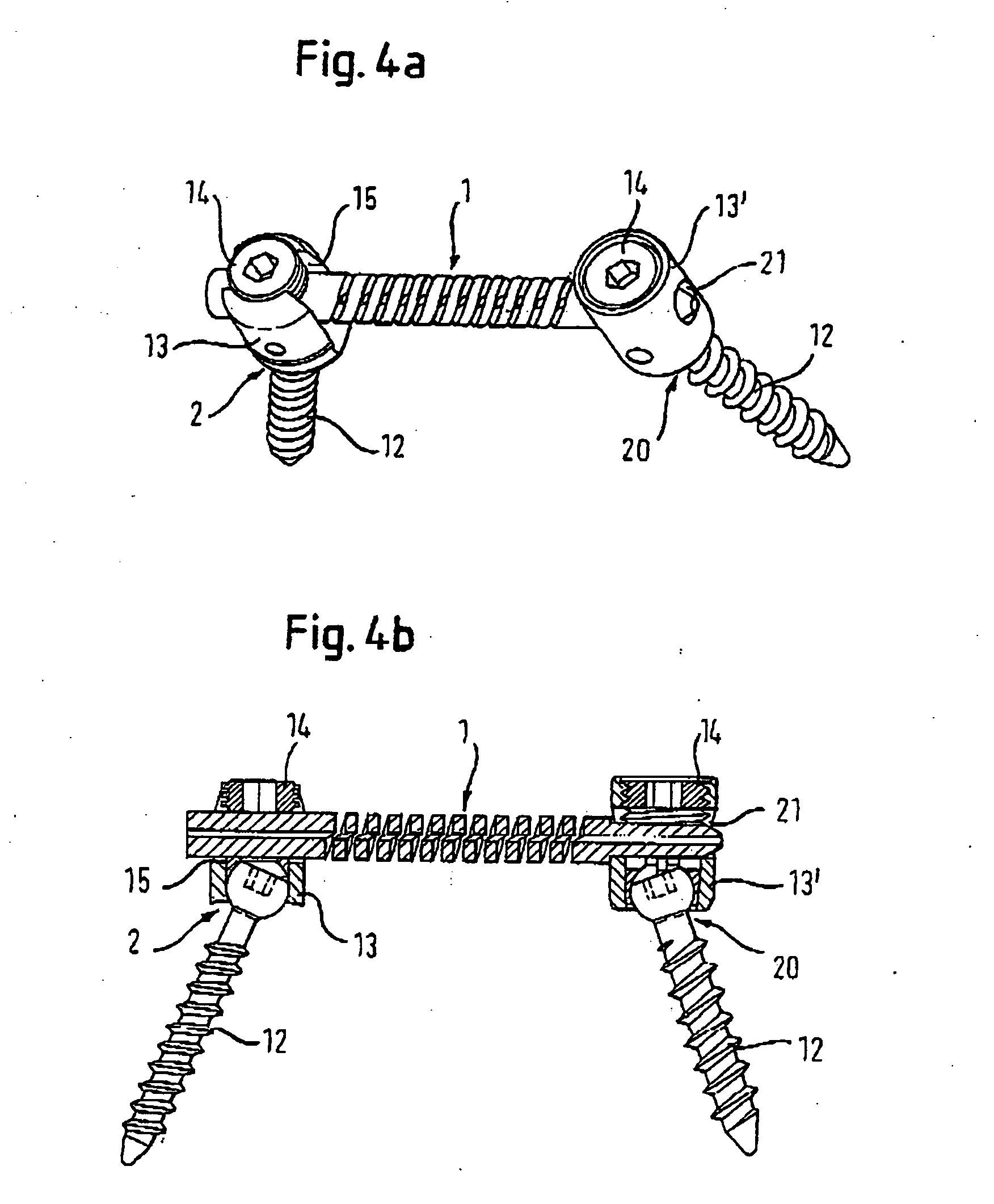
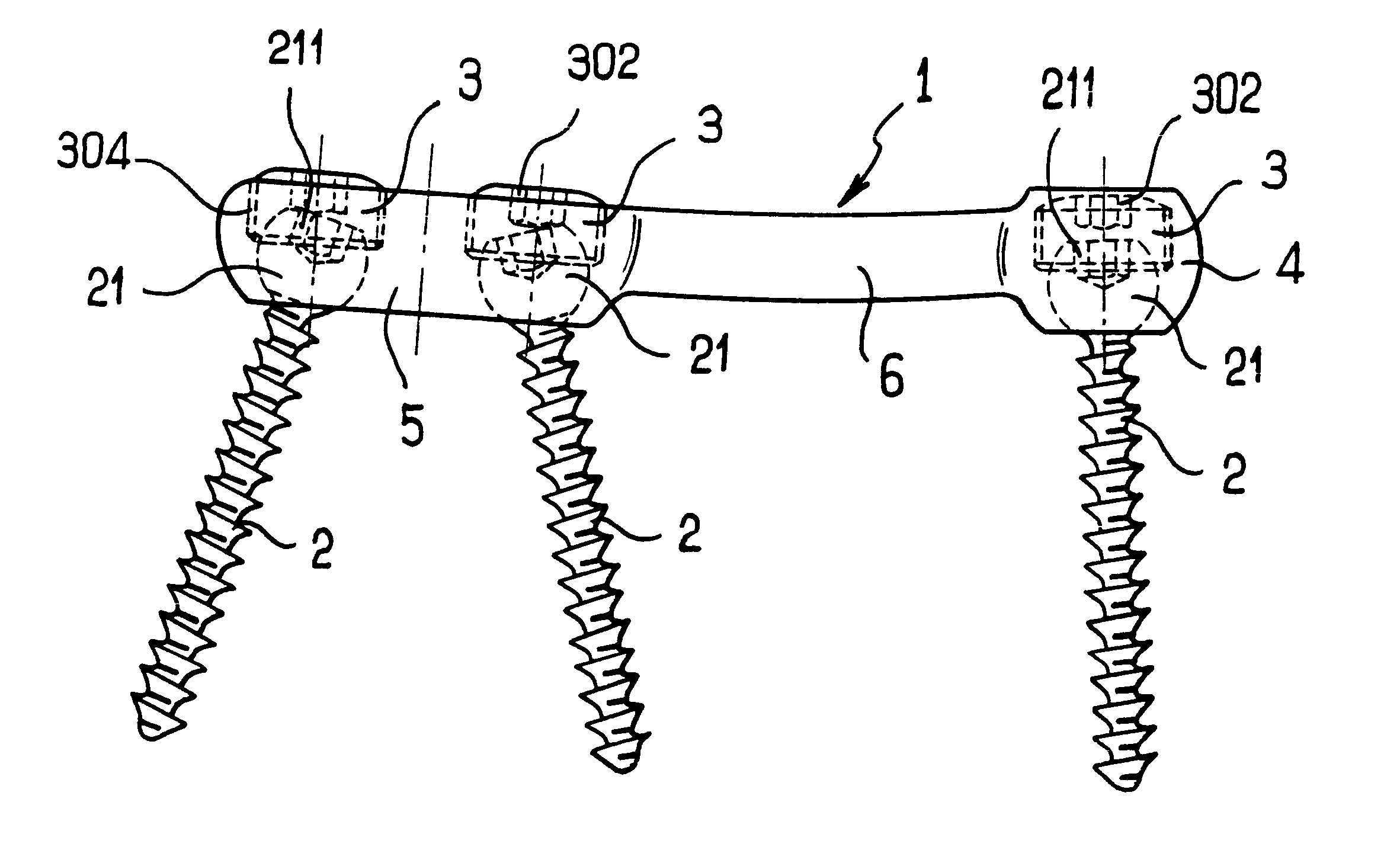
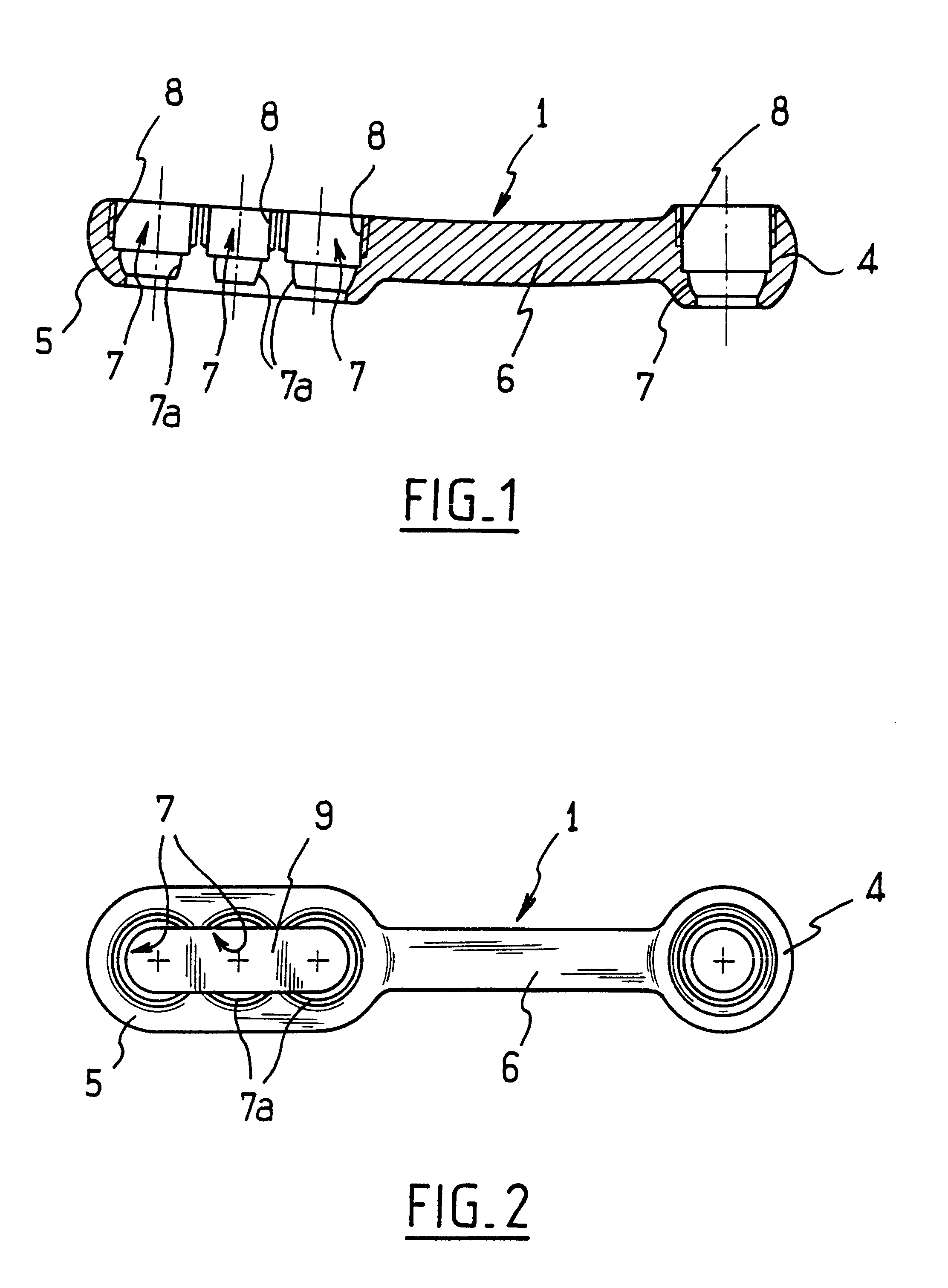
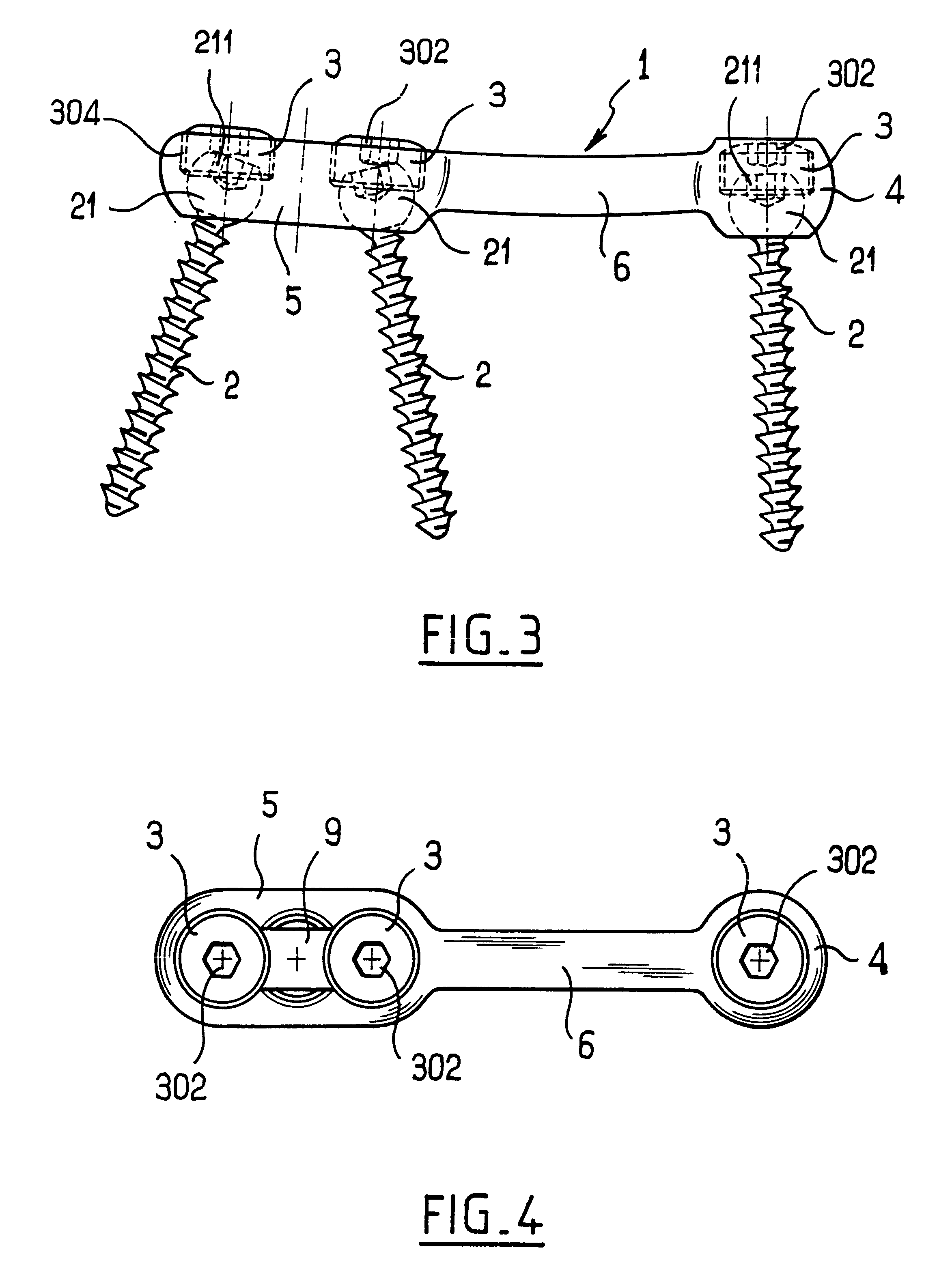
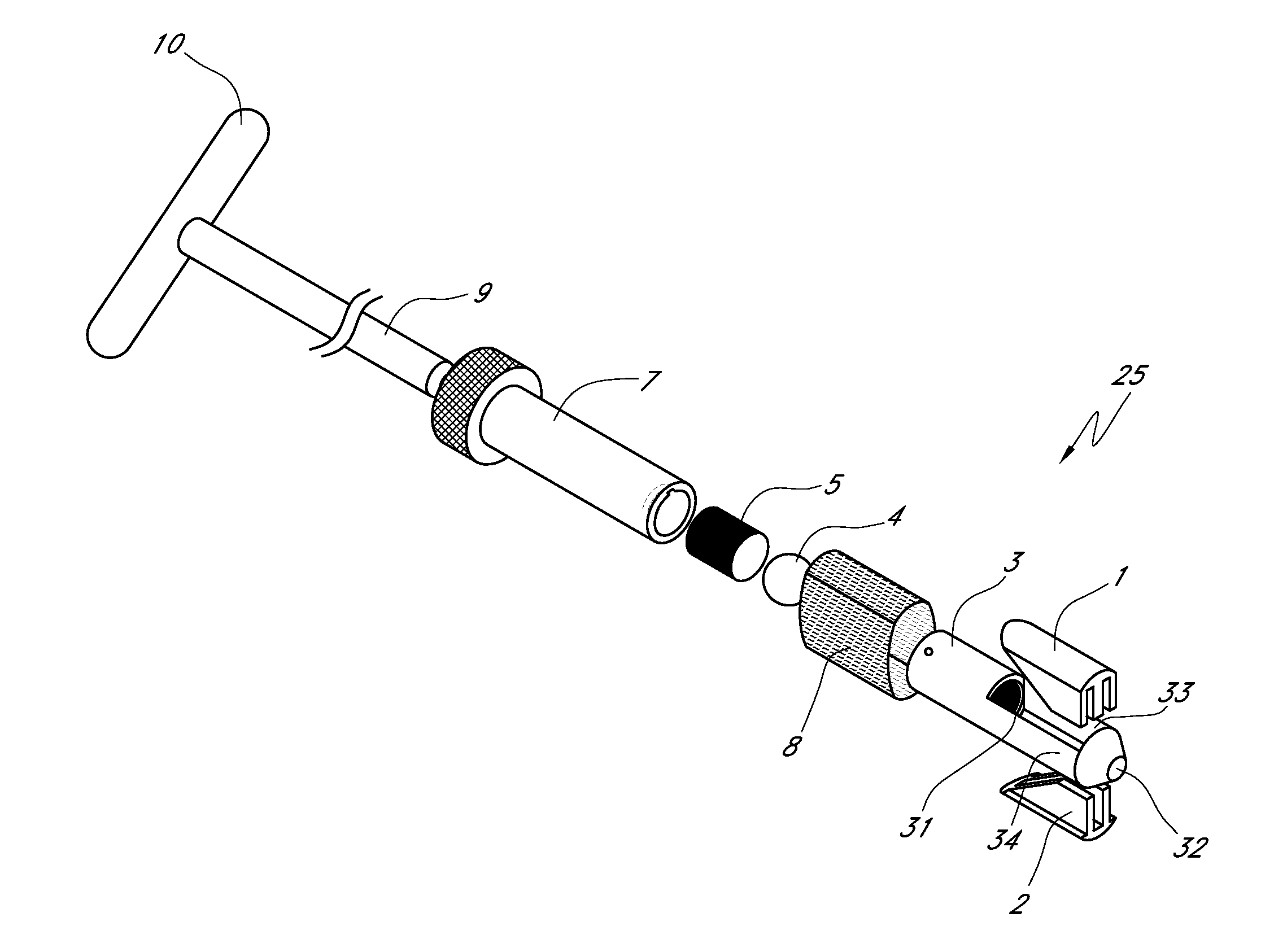
Rod-shaped implant element for application in spine surgery or trauma surgery, stabilization apparatus comprising said rod-shaped implant element, and production method for the rod-shaped implant element
ActiveUS20050085815A1Reliable fixed positioningEasily realizedSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisTrauma surgeryBone anchor
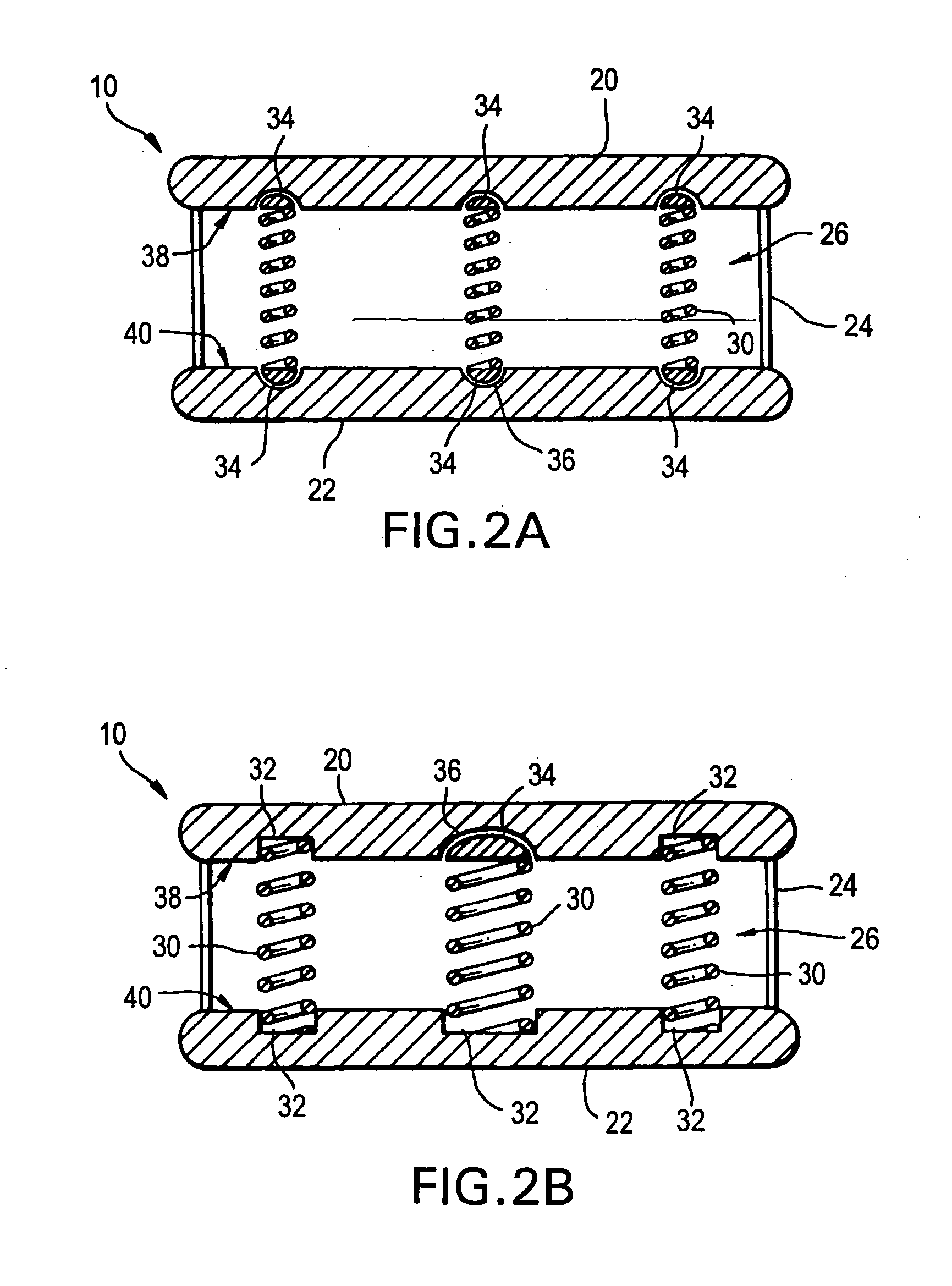
A rod-shaped implant element (1, 100, 101, 102, 300) is disclosed for the connection of bone anchoring elements, Each bone anchoring element has an anchoring section (12) to be anchored in the bone and a receiver member (13) to be connected to the rod-shaped implant element The rod-shaped implant element has at least one rigid section (7, 8) that is configured to be placed in the receiver member (13). It also has a flexible section (9, 90, 900, 902) that is adjacent to the rigid section. The flexible section and the rigid section are formed in one piece. Also disclosed is a stabilization apparatus using a rod-shaped implant element and at least two of the bone anchoring elements. The stabilization apparatus can limit the movement of two vertebrae or parts of a bone in relation to each other in a defined manner.
Owner:BIEDERMANN TECH GMBH & CO KG
Expandable osteosynthesis cage
InactiveUS6129763AGood jamLarge inside volumeBone implantJoint implantsSpinal columnBiomedical engineering
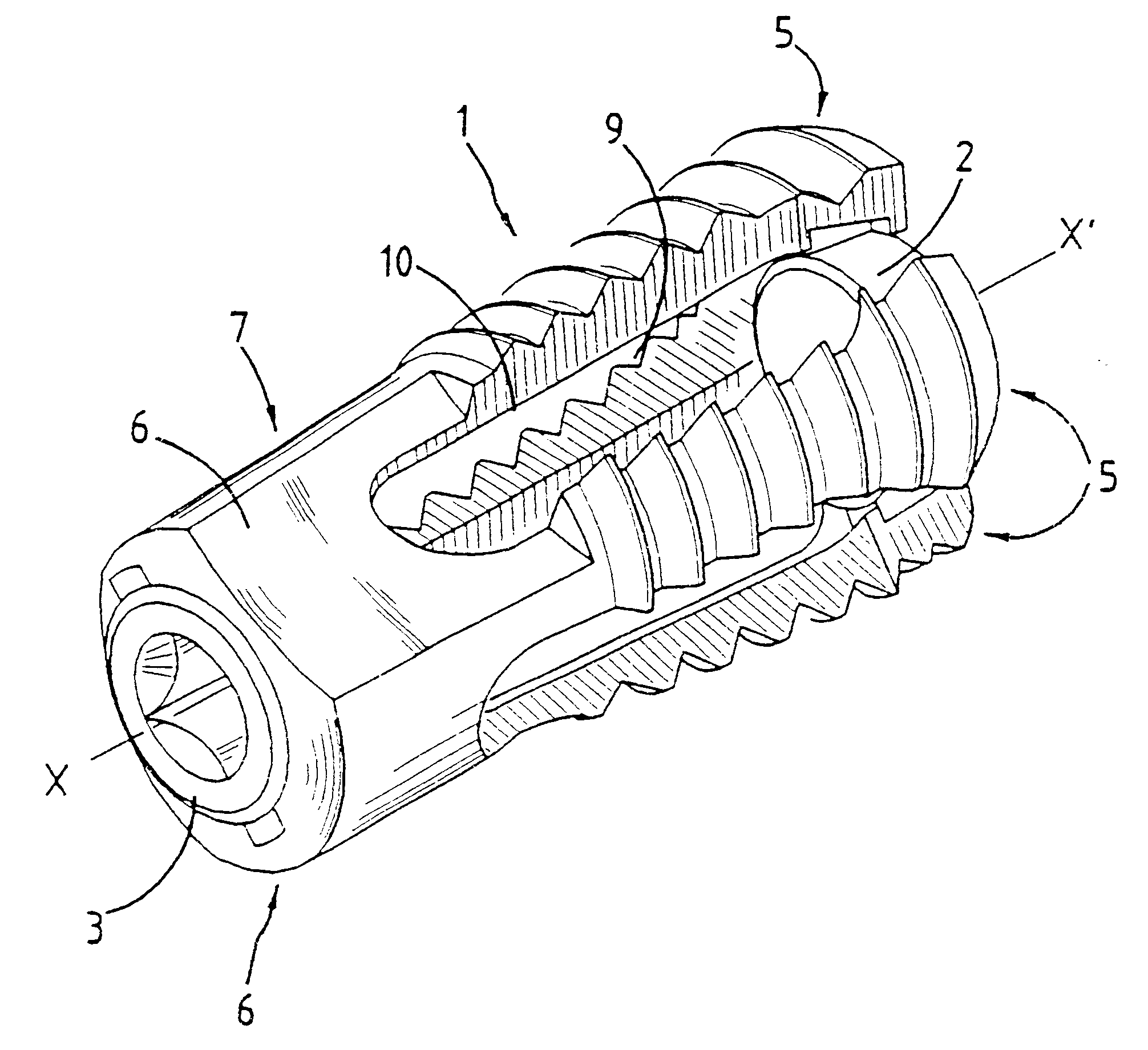
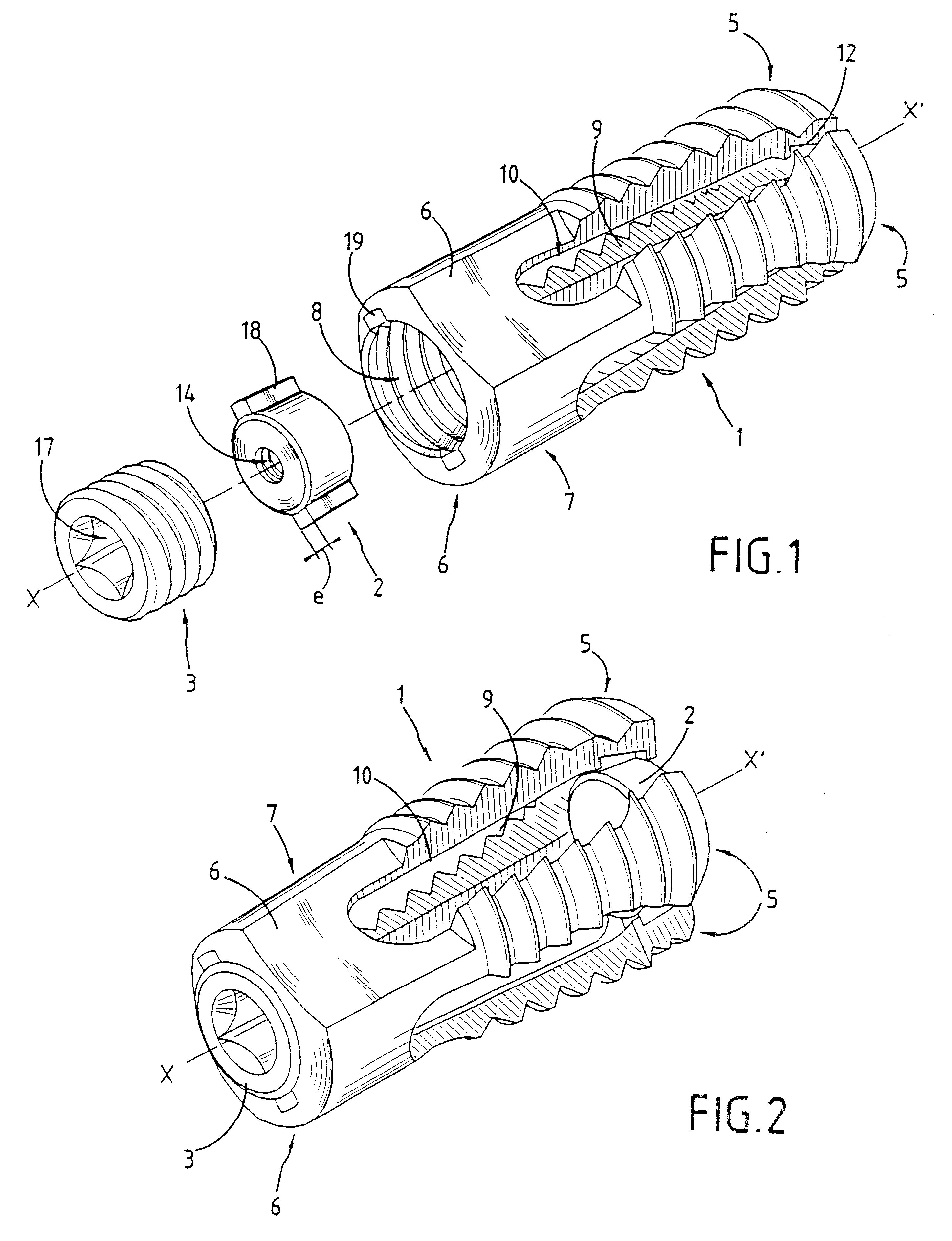
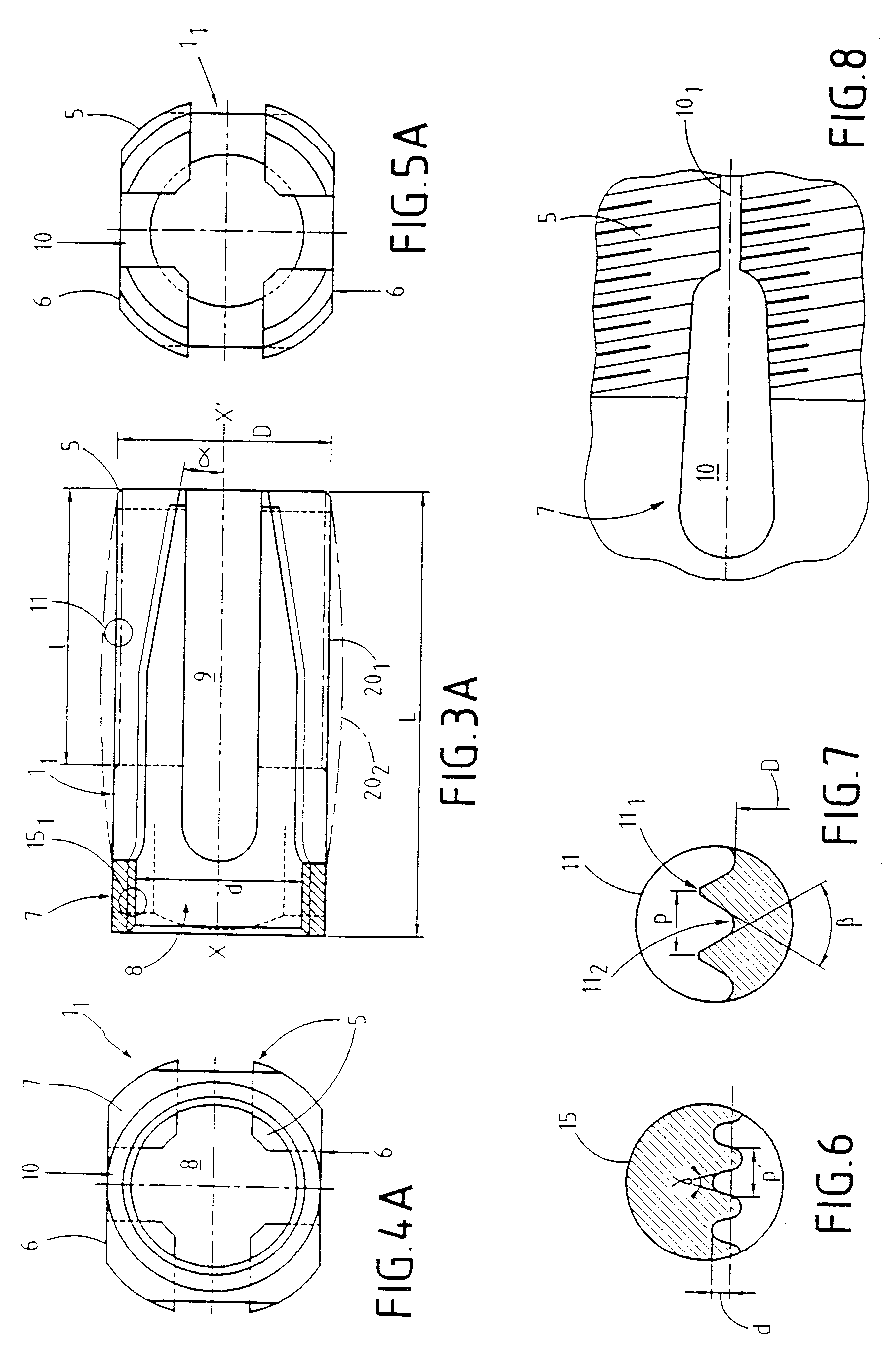
PCT No. PCT / FR97 / 01617 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 28, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 28, 1998 PCT Filed Sep. 12, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 10722 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 19, 1998An expandable osteosynthesis implant has branches (5) each connected at one end to a seat (7) which is pierced by an orifice (8), suitable for being slid from a posterior direction between the facing faces of two consecutive vertebrae in order to hold them a given distance apart and restore stability of the spinal column. According to the invention, the branches (5) and the seat (7) define a hollow cage (1) which, in a "rest" position, has an outside general shape that is a cylinder of circular section, and a portion at least of the inside volume (9) of the cage (1) towards the distal ends of the branches (5) is in the form of a circular truncated cone whose large base is towards the seat (7), which implant has at least three branches (5) and, inside the inside volume (9) at least one spacer (2) suitable for passing through the orifice (8) and the large base of the truncated cone.
Owner:OSTEOIMPLANT TECH
Device for fixation of spinous processes
A fixation device for use in association with ALIF procedures includes a couple of spaced plates having integral spikes on facing surfaces thereof for pressing into spinal processes of adjacent vertebrae. One of the plates has a spherical socket which captures a spherical head end of a post whose other end is received through an aperture in the other plate. The socket mounting is arranged to enable the post to pivot therein for at least two degrees of freedom to a limited extent, enabling angulation between the two plates so as to accommodate the different thicknesses and orientations of the spinal processes on adjacent vertebrae. The reception of the post in the second plate enables adjustment of spacing between the plates to accommodate effective installation of the assembly on the spinal processes by a compression instrument, and permanent reliable maintenance of that spacing following removal of the compression instrument. The cross-sectional configuration of the post and a receiver aperture in the plate inhibits rotation of the plate relative to the post about the post axis, and a set screw in the apertured plate engages a flat on the post fixing the inter-plate space as adjusted.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Systems and methods for posterior dynamic stabilization of the spine
ActiveUS20060084987A1Adjustable lengthShape adjustableInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsInterconnectionSpinal locomotion
Systems and devices for dynamically stabilizing the spine are provided. The systems include a superior component for attachment to a superior vertebra of a spinal motion segment and an inferior component for attachment to an inferior vertebral of a spinal motion segment. The interconnection between the two components enables the spinal motion segment to move in a manner that mimics the natural motion of the spinal motion segment. Methods are also provided for stabilizing the spine and for implanting the subject systems.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method of providing proper vertebral spacing
InactiveUS6371989B1Easy to anchorInhibit migrationBone implantJoint implantsSpinal columnBiomedical engineering
An expandable osteosynthesis implant has branches (5) each connected at one end to a seat (7) which is pierced by an orifice (8), suitable for being slid from a posterior direction between the facing faces of two consecutive vertebrae in order to hold them a given distance apart and restore stability of the spinal column. According to the invention, the branches (5) and the seat (7) define a hollow cage (1) which, in a "rest" position, has an outside general shape that is a cylinder of circular section, and a portion at least of the inside volume (9) of the cage (1) towards the distal ends of the branches (5) is in the form of a circular truncated cone whose large base is towards the seat (7), which implant has at least three branches (5) and, inside the inside volume (9) at least one spacer (2) suitable for passing through the orifice (8) and the large base of the truncated cone.
Owner:OSTEOIMPLANT TECH
Interspinous vertebral and lumbosacral stabilization devices and methods of use
Implantable devices are provided for stabilizing adjacent vertebrae and the lumbosacral region of a patient. The devices can comprise an interspinous flexible spacer body having a substantially U-shape comprising a superior section, inferior section, and a midsection extending therebetween. The superior and / or inferior sections can include a pair of lateral walls configured to engage a spinous process of a vertebra. Fixation caps can be provided for securing a spinous process of a vertebra to the flexible spacer body. To secure the flexible spacer body between the lumbar vertebra and an adjacent vertebra, an anchor assembly is provided. Also provided are methods of using the implantable devices to stabilize a patient's spine.
Owner:PARADIGM SPINE LLC
Distractible interspinous process implant and method of implantation
ActiveUS20050010293A1Internal osteosythesisSpinal implantsCervical vertebral bodyBiomedical engineering
Systems and method in accordance with embodiment of the present invention can includes a distractible implant comprising a distracting insert and a body having a first part and a second part adapted to be positioned between adjacent spinous processes of cervical vertebrae. The distracting insert can be inserted into cavities of the body, thereby urging apart the first part and second part, and distracting the adjacent spinous processes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC EURO SARL
Methods and devices for minimally invasive spinal fixation element placement
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Apparatus for inserting spinal implants
InactiveUS6270498B1Eliminate separationEfficient removalInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve. Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted to restore the normal angular relationship of the vertebrae adjacent to that disc space. An extended outer sleeve having extended portions capable of maintaining the vertebrae distracted in their normal angular relationship is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
System and method for stabilizing of internal structures
There is shown a system and method for reducing the difficulty in percutaneous placement of a spine stabilization brace by coupling the brace to a pedicle screw in a single assembly. The brace-screw assembly is delivered along with an anchor extension through a cannula for anchoring in the vertebrae pedicle. The anchor extension becomes a cannula for working on the brace from the exterior of the patient, as constructed with a slot opening along two sides. Once the screw portion of the brace-screw assembly is locked in place with respect to the first vertebra, the proximal end of the brace is below the skin line. The brace is then repositioned so that the proximal end leaves the cannula through one slot and is captured by a corresponding slot positioned in a second cannula coupled to a second anchor. Once captured, the proximal end of the brace is guided by the second cannula to a receptacle positioned in the second vertebra.
Owner:THEKEN SPINE
Stabilized interbody fusion system for vertebrae
The invention concerns a stabilized interbody fusion system for vertebrae, of the type comprising an interbody implant (4) designed to be inserted in the intervertebral space defined between two neighboring vertebrae to be mutually secured, so as to restore the height and the angle of the lordosis of the vertebral segment defined by the two neighboring vertebrae and a stabilizing plate (17) provided, at each of its ends, with at least a passage hole (18) for an anchoring screw, the plate (17) and the implant (4) being provided with mutual assembly means, such that after assembly, the stabilizing plate (17) extends on each side of the implant to enable the stabilizing plate to be anchored on the neighboring vertebrae through the screws, characterized in that it comprises spacing means (30), interposed between the stabilizing plate (17) and the implant (4), to enable the stabilizing plate to be positioned at a specific distance relative to the implant.
Owner:SCIENTX
Devices and techniques for a posterior lateral disc space approach
This invention relates to devices and instruments for implant insertion through a posterior lateral opening to the disc space. The instruments include an implant inserter, and the devices include a spinal fusion implant engageable by the implant inserter. The implant provides bilateral support of the adjacent vertebrae when inserted into the disc space from a postero-lateral approach.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Apparatus for use in inserting spinal implants
InactiveUS6770074B2Eliminate separationEfficient removalBone implantDiagnosticsMedicineIntervertebral space
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve. Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted to restore the normal angular relationship of the vertebrae adjacent to that disc space. An extended outer sleeve having extended portions capable of maintaining the vertebrae distracted in their normal angular relationship is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
System and method for spinal fusion
The current invention is directed to a system and method for fusing two adjacent vertebrae. In one embodiment, the vertebrae are fused by inserting a self-broaching interbody apparatus into a disc space without the need for separately drilling and broaching. The self-broaching interbody apparatus may include cutting flutes or other broaching means capable of cutting through the cartilaginous endplates of the vertebrae. In another embodiment, an interbody apparatus with an expanding means capable of distracting the disc space between the adjacent vertebrae is inserted into the disc space. Another embodiment includes a sleeve that fits around an interbody apparatus that has at least one opening in its outer surface leading to a cavity filled with bone and / or ortho-biological materials.
Owner:AEOLIN
Multi-Directional fasteners or attachment devices for spinal implant elements
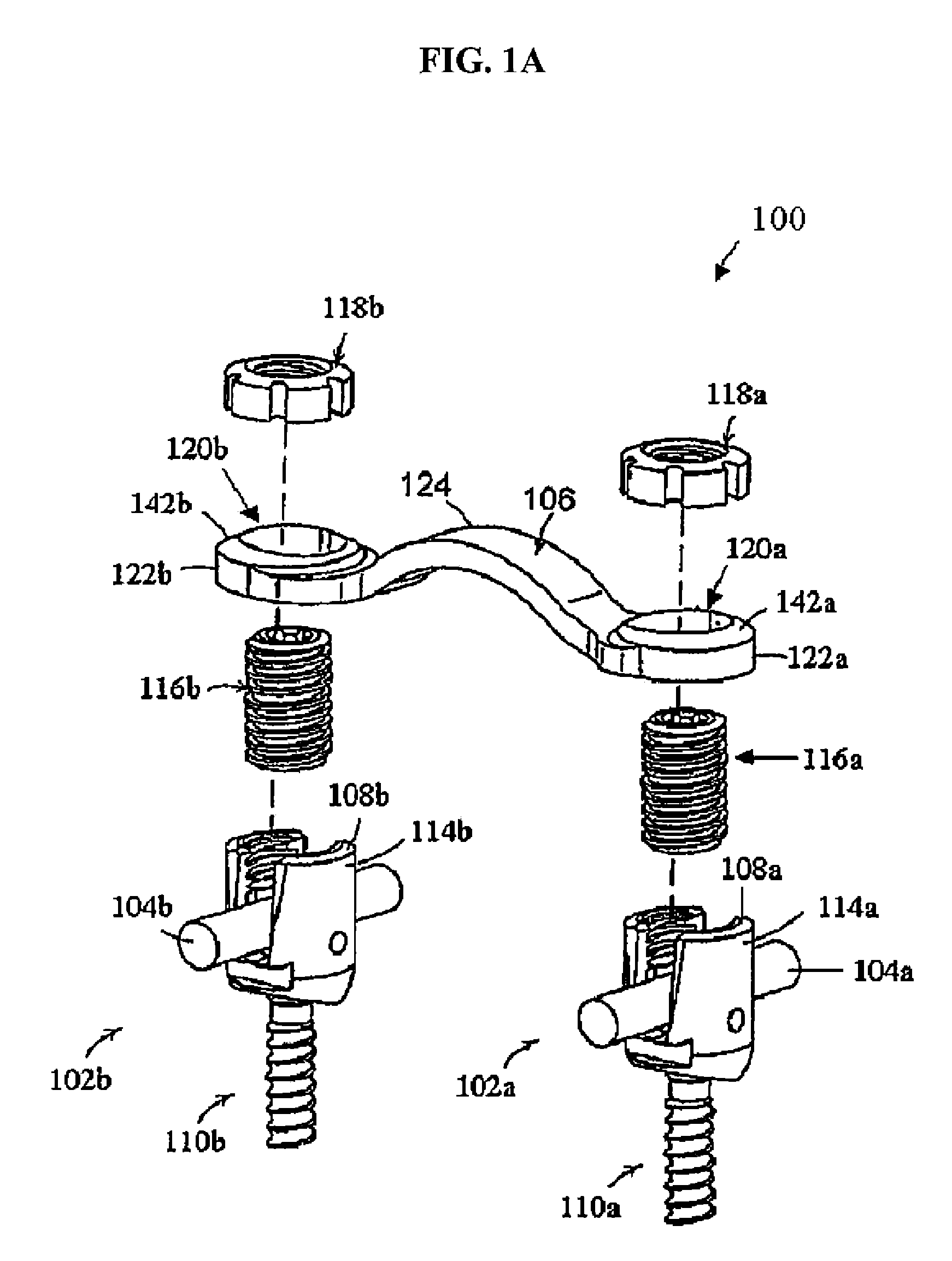
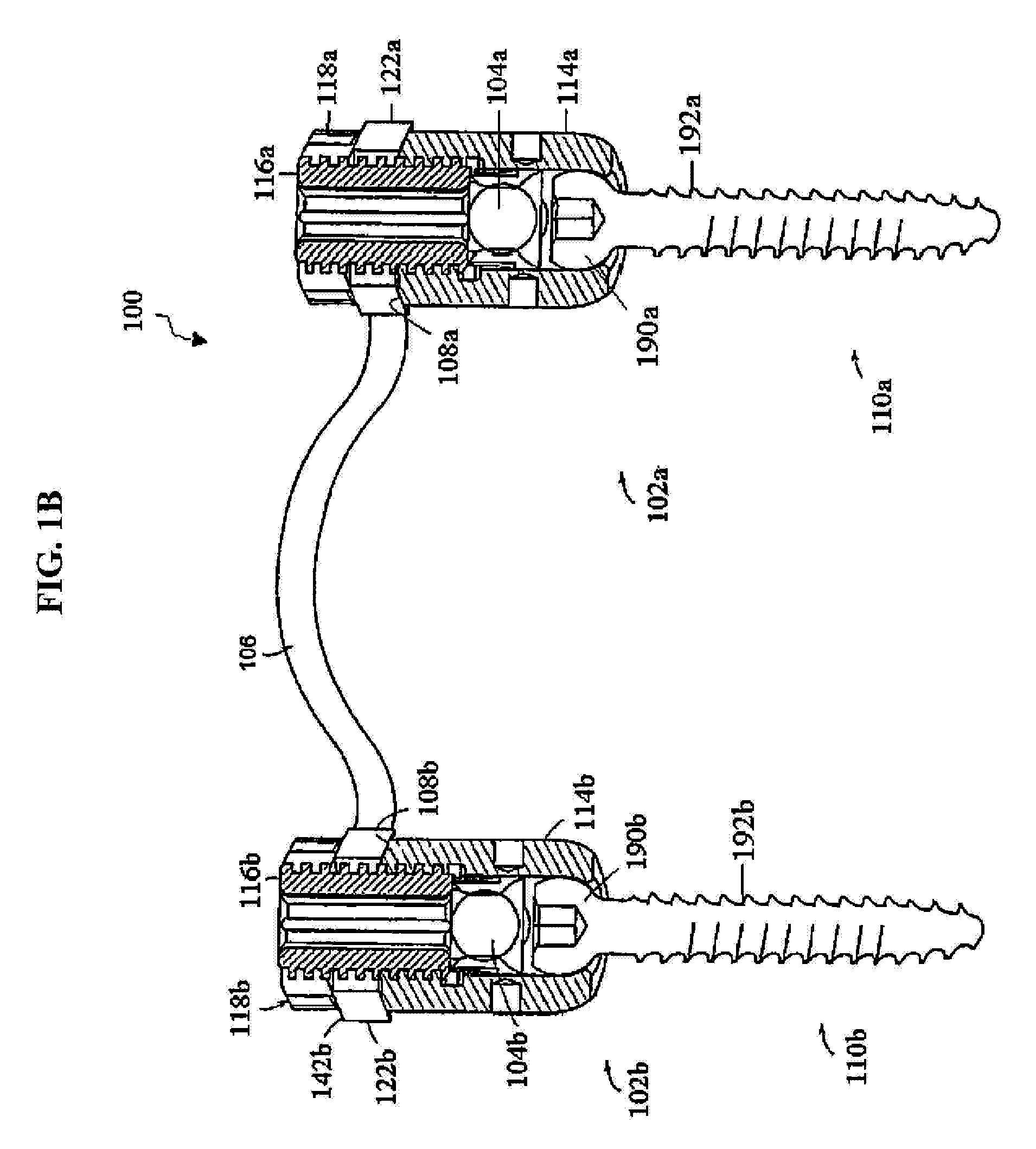
InactiveUS6019759AIncreased bone volumeAvoid damageSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisMultiple pointSpinal implant
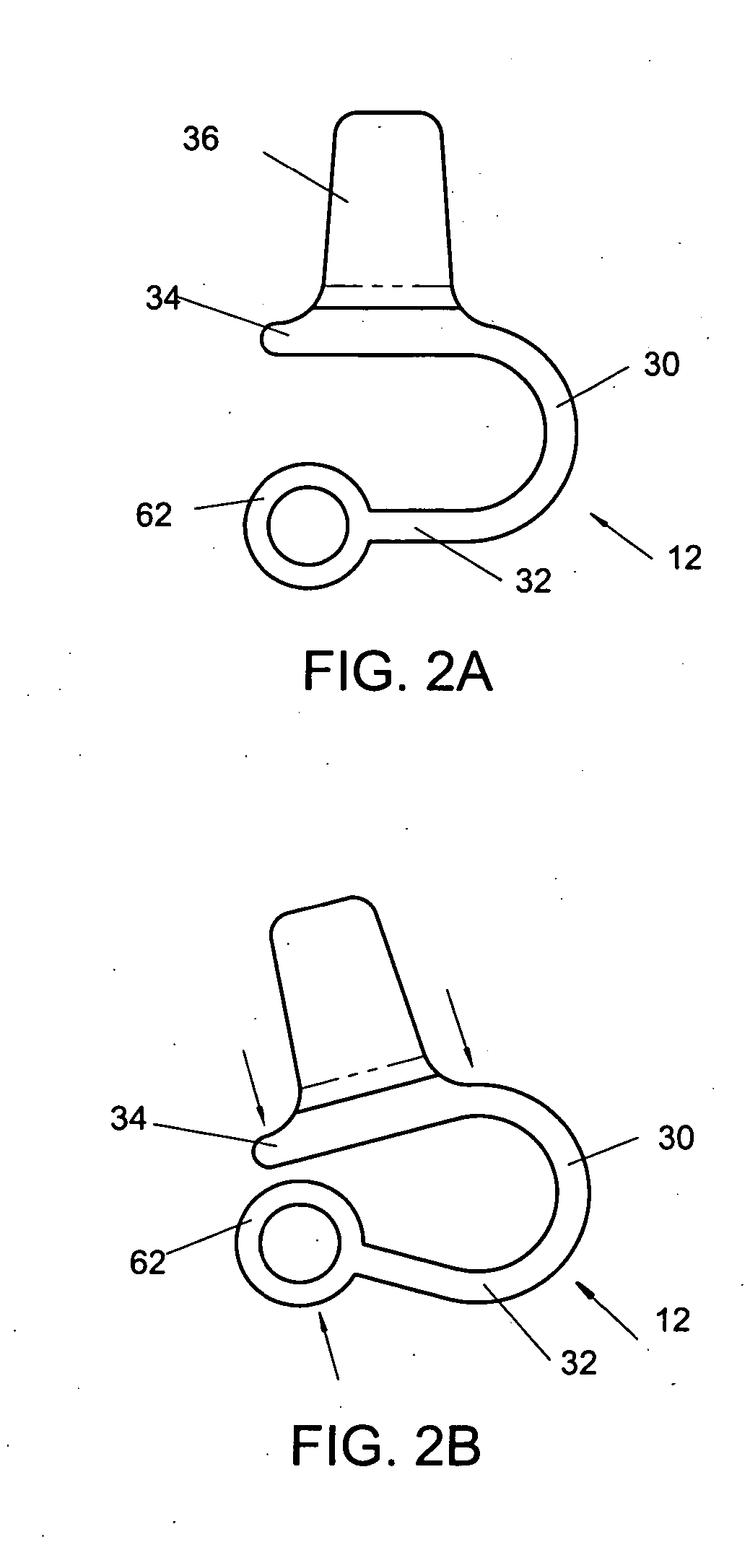
An apparatus, method and system for treating spinal conditions by moving or spatially fixing at least one vertebra relative to another vertebra. The invention includes a link member the ends of which are configured to be secured to adjacent vertebrae and which are offset from a central portion of the link member. The link members can be in the form of a C-shaped or V-shaped rod or plate to form the offset. The offset provides increased bone volume that can be used for grafts or fusion. Attachment structure in the form of bone screws, bolts, or hook members are provided to secure the link members to respective vertebrae or other bones. A plurality of link members can be connected in chain-like fashion to connect multiple points on a plurality of vertebrae or other bones even though those points are nonlinear. In another aspect of the invention, a multi-directional attachment member is provided and may be used with the link members to form a spinal implant or external bone fixation system.
Owner:ROGOZINSKI CHAIM
Controlled artificial intervertebral disc implant
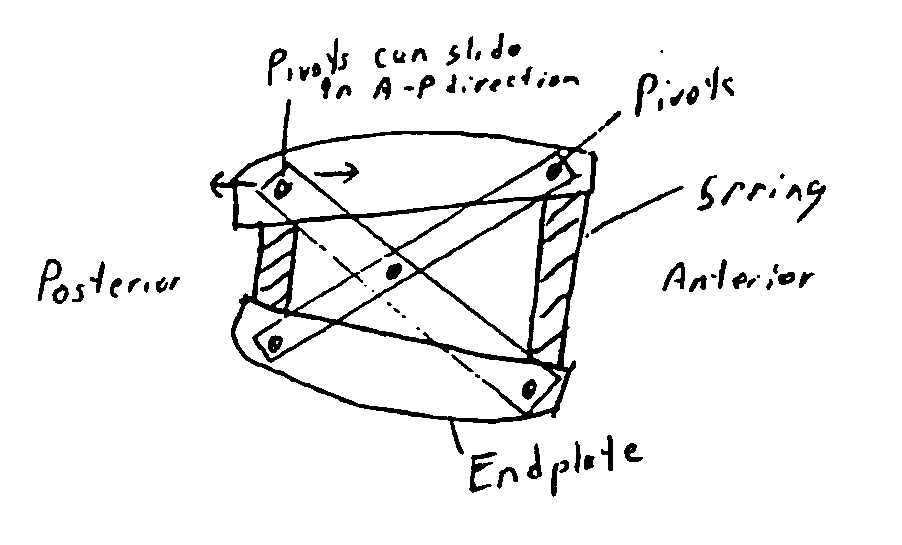
ActiveUS20050251260A1Reduce the amount requiredProlong lifeBone implantJoint implantsMedicineAxial compression
The invention relates to an artificial intervertebral disc for placement between adjacent vertebrae. The artificial intervertebral disc is preferably designed to restore disc height and natural disc curvature, allow for a natural range of motion, absorb shock and provide resistance to motion and axial compression. Furthermore, the intervertebral disc may be used in the cervical, the thoracic, or the lumbar regions of the spine. The artificial intervertebral disc may include either singularly or in combination: an interior including at least one spring member preferably incorporating a arcuate surface member, a flexible core, the flexible core preferably being a slotted core, a ring spring, a winged leaf spring, or a leaf spring, or The articulating member preferably being attached to one of the endplate by an intermediate shock absorbing element.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Facet joint replacement
InactiveUS7041136B2Precise and tight press fitExcellent long-term fixation strengthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsProsthesisSacroiliac joint
A prosthesis for the replacement of a diseased or traumatized facet of a mammalian vertebra includes a surface that articulates with another prosthetic facet or a natural facet, a portion that replaces at least a bony portion of the diseased or traumatized spine facet which is to be replaced, and an element to attach the prosthesis to the vertebra in a manner that does not require attachment to or abutment against the posterior arch. A method of installing the prosthesis includes the steps of resecting at least a portion of a facet and attaching the prosthesis in a manner that does not require attachment or abutment against the posterior arch.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Device for fixing the sacral bone to adjacent vertebrae during osteosynthesis of the backbone
InactiveUS6290703B1Degree of stiffness attenuationReduce frictionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSacral BoneBone fixation devices
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Intervertebral implant and installation tool
InactiveUS20090292361A1Increase heightImprove shock absorptionSpinal implantsOsteosynthesis devicesEngineeringBiomedical engineering
An intervertebral implant, an installation tool, and related methods are provided for ensuring a minimum distance between two vertebrae. The implant can comprise a pair of opposing body portions and an expansion component. The expansion component can rotate relative to the body portions in order to urge a head portion thereof against one or more inclined contact surfaces of at least one of the body portions. In this manner, the body portions can be separated, thereby increasing a height of the implant. The installation tool can comprise a plurality of components that can be moved relative to each other to facilitate expansion or contraction of the implant.
Owner:LOPEZ RUDOLF MORGENSTERN
Prosthetic spinal disc replacement
ActiveUS20050043800A1Restrict movementJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSpinal columnSurgical approach
The present invention relates generally to a prosthetic spinal disc for replacing a damaged disc between two vertebrae of a spine. The present invention also relates to a method for implanting a prosthetic spinal disc via posterior or posterior lateral implantation. Other surgical approaches for implanting the prosthetic disc may also be used. The present invention also involves a method for implanting the prosthetic spinal disc while either avoiding or minimizing contact with the spinal cord and nerve rootlets, or reducing the time and extent that they need to be repositioned during implantation.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Rod attachment for head to head cross connector
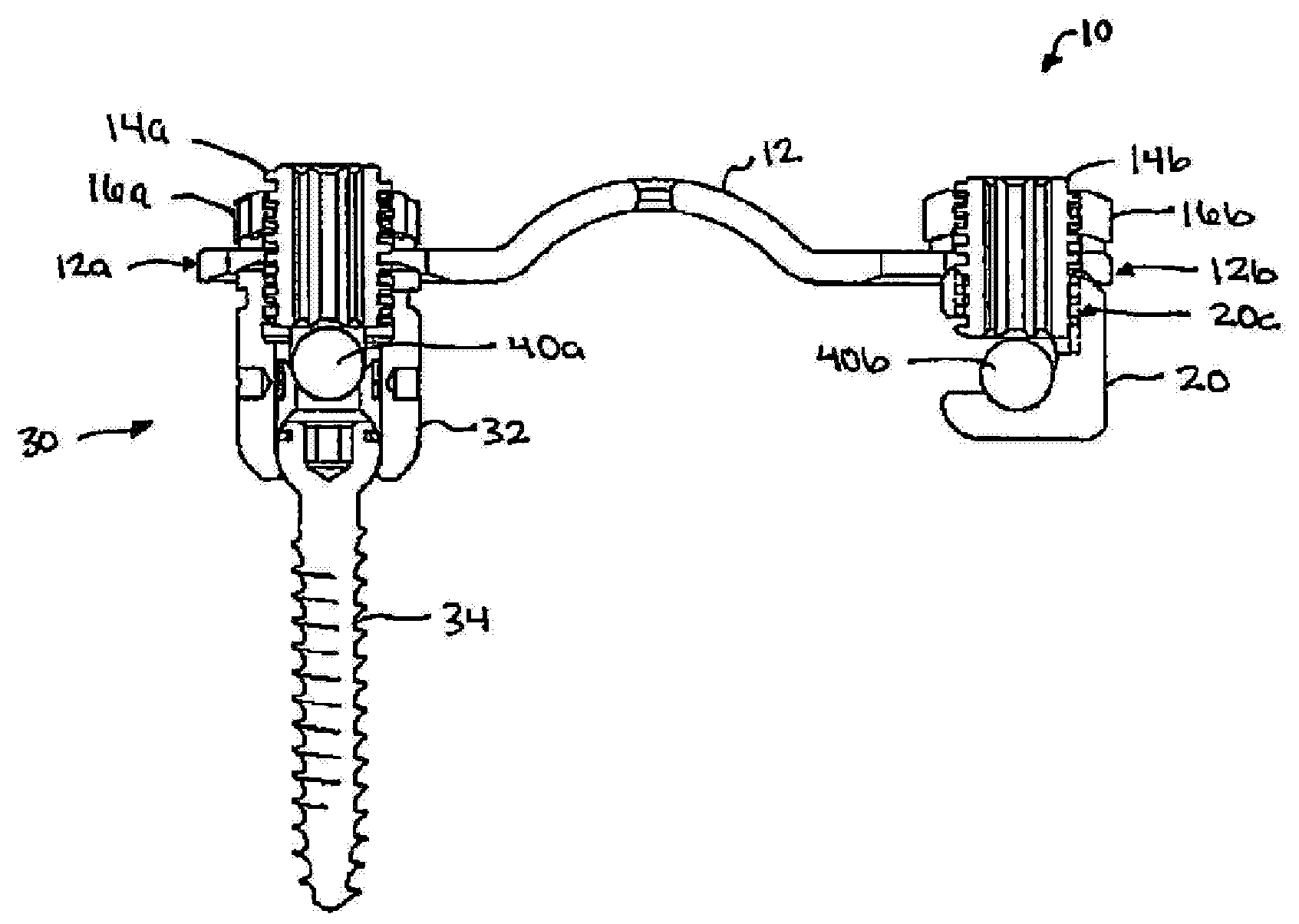
Exemplary spinal fixation devices, systems, and method are provided for stabilizing vertebrae in a patient's spine. In one exemplary embodiment, methods and devices are provided for coupling one or more bone anchors, such as hooks, screws, etc., and / or one or more spinal fixation elements, such as spinal rods, cables, plates, etc. In certain exemplary embodiments, a cross connector is provided for connecting and stabilizing two bone anchors, a bone anchor and a spinal fixation element, or a bone anchor and bone.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Articulating spinal implant
An articulating spinal implant for intervertebral disc replacement. The articulating spinal implant is formed from two elements, each engaging one of an adjacent pair of vertebra. Articulation features between the two elements resist compression and lateral movement between the vertebra, but allow the adjacent vertebra to articulate about an instantaneous axis of rotation.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com