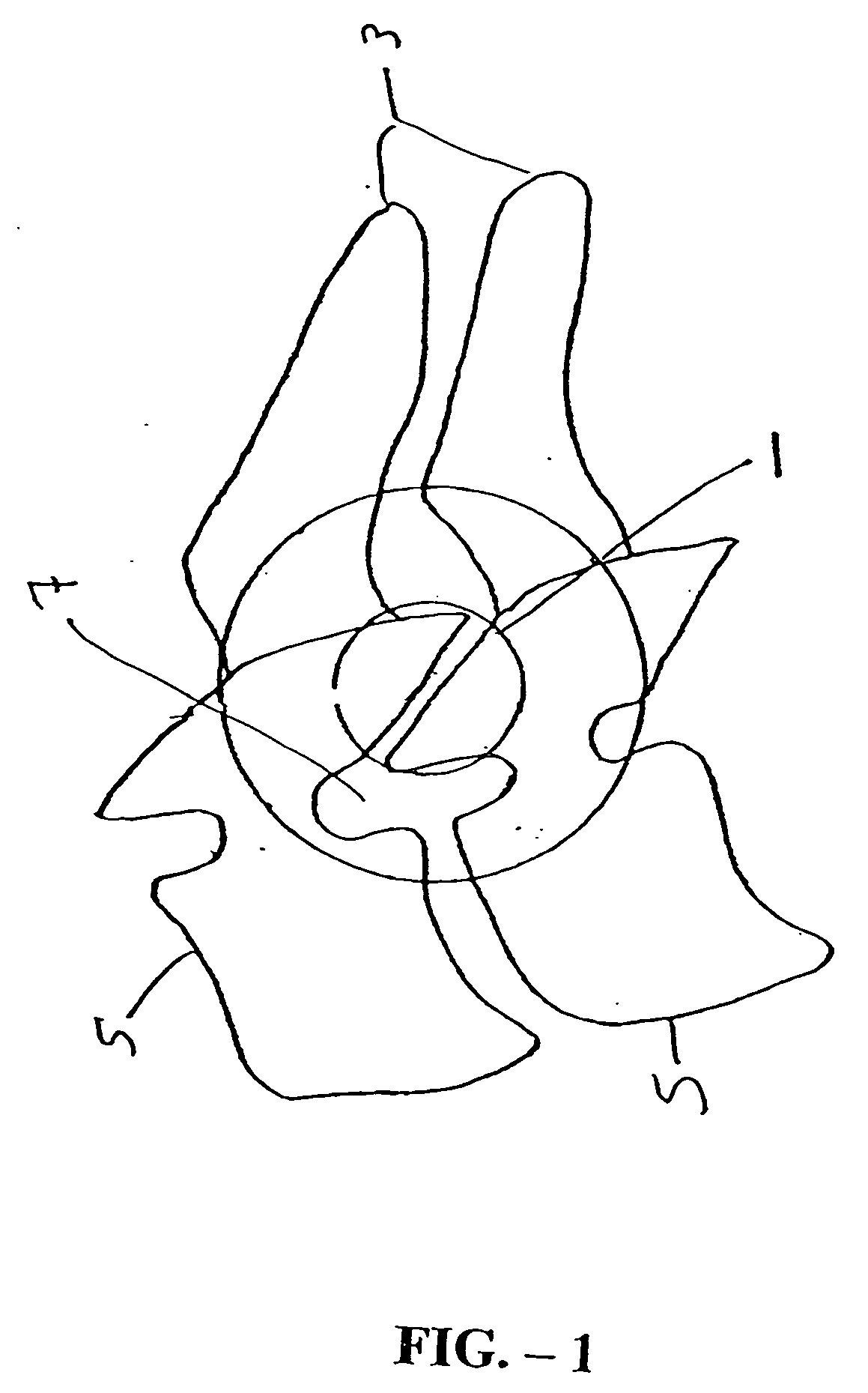
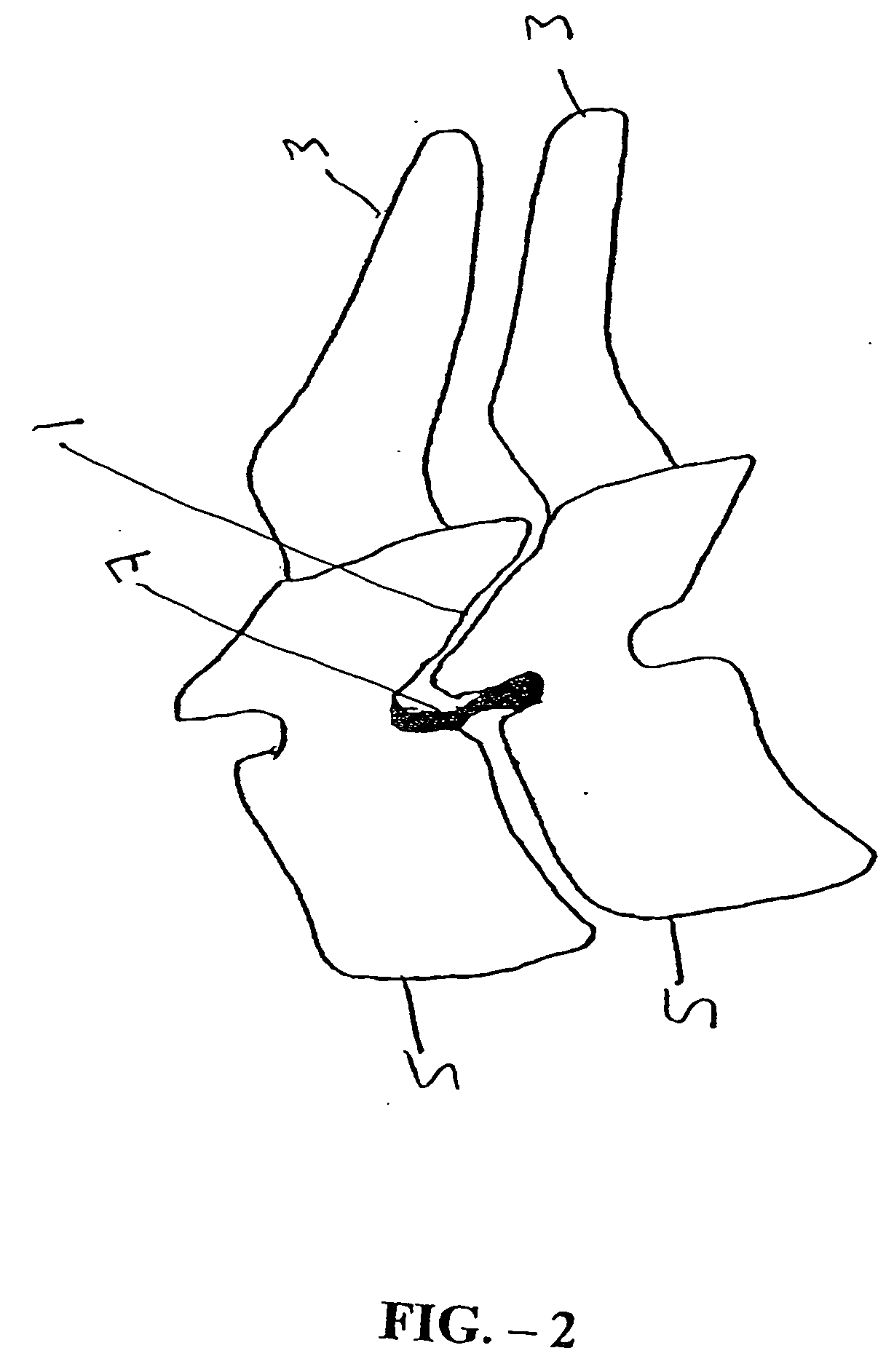
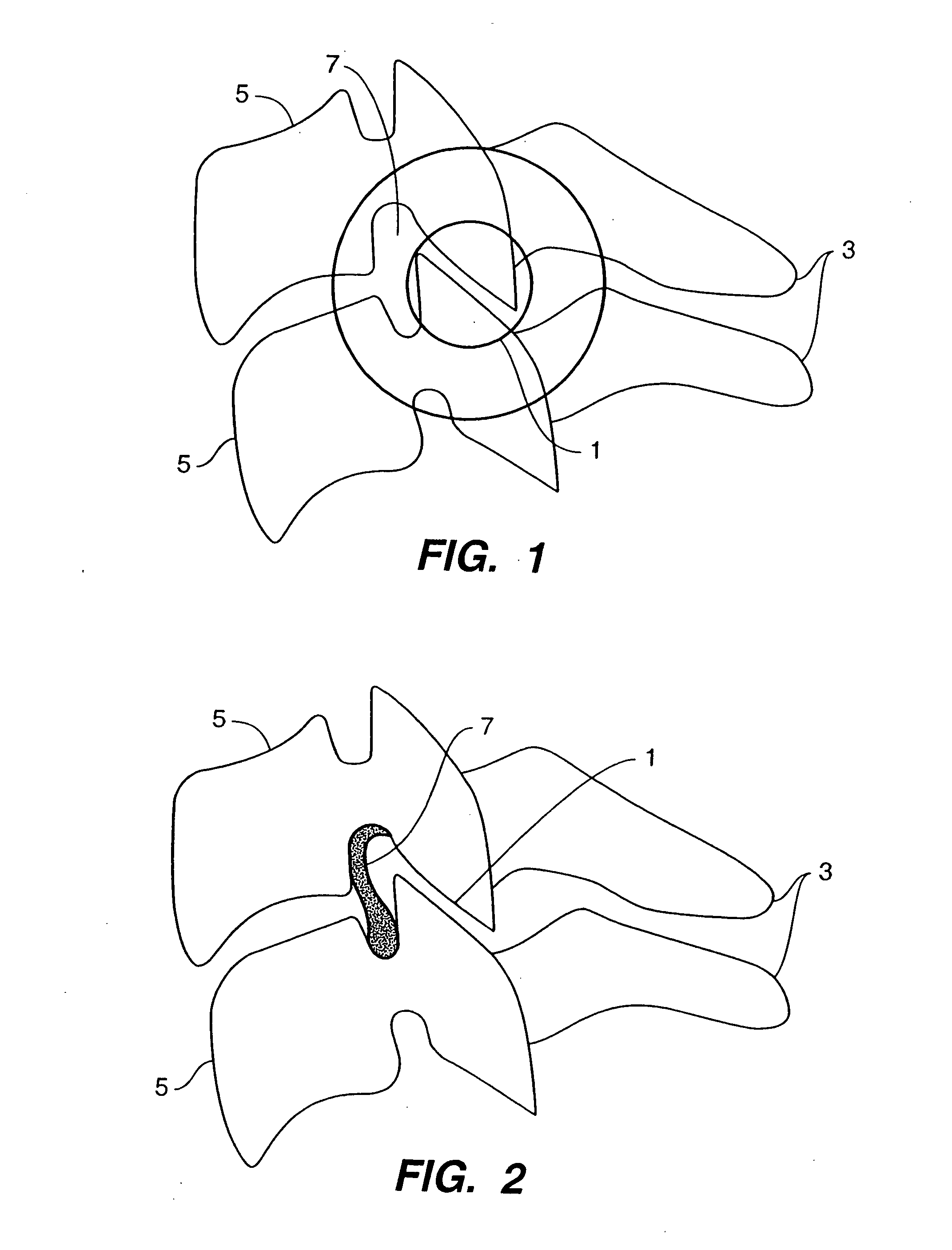
Patents
Literature
1181 results about "Cervical vertebrae" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
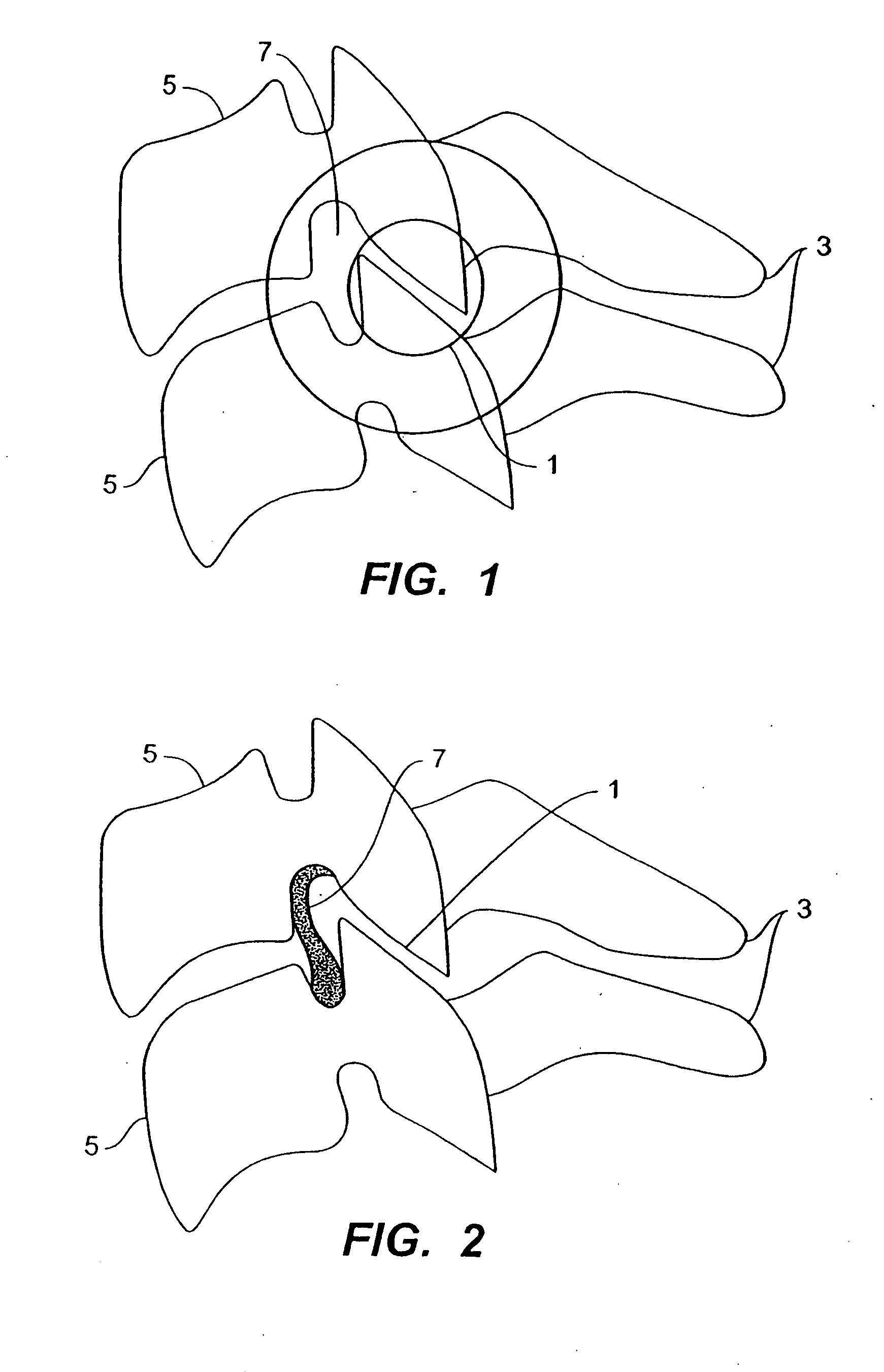
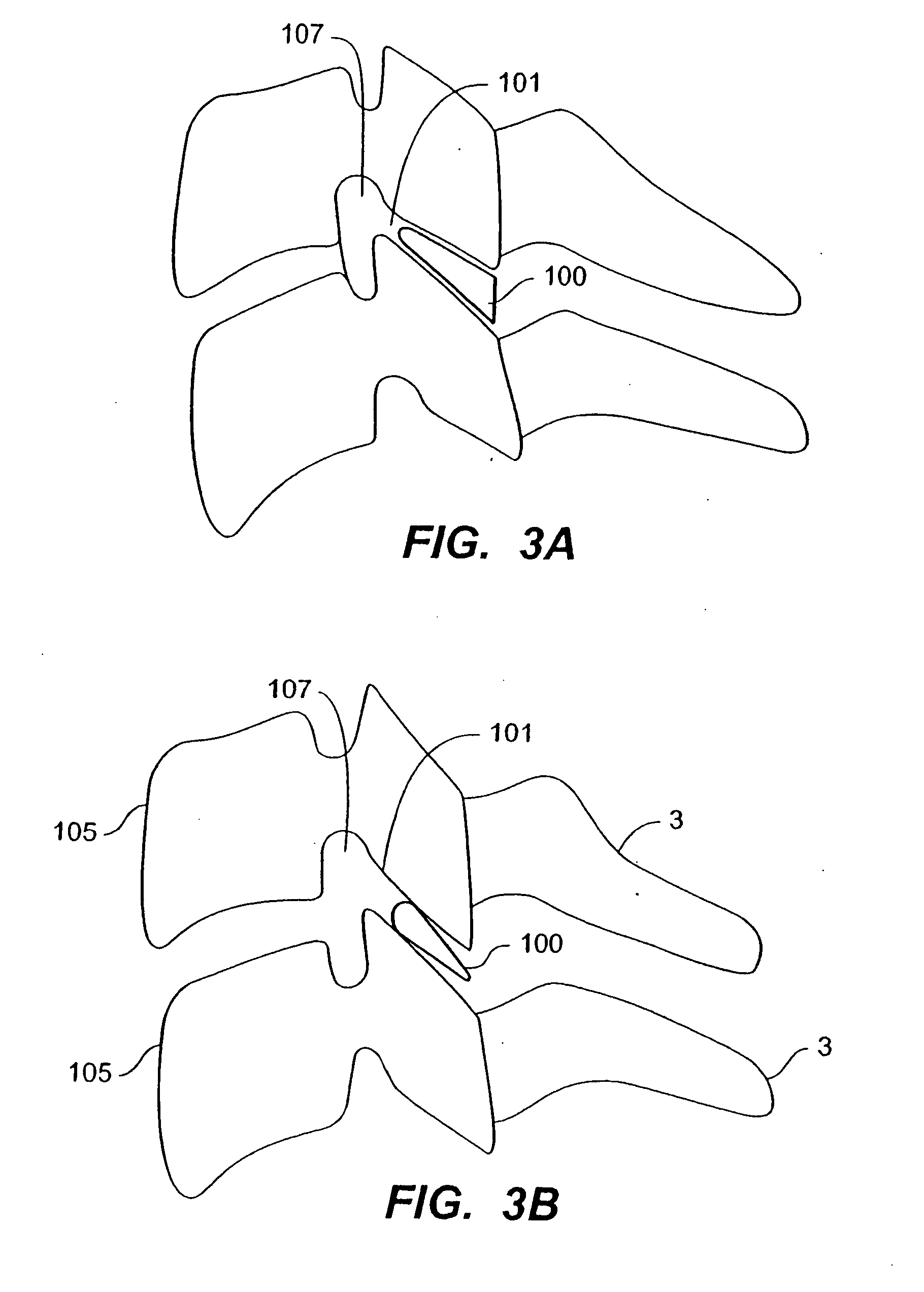
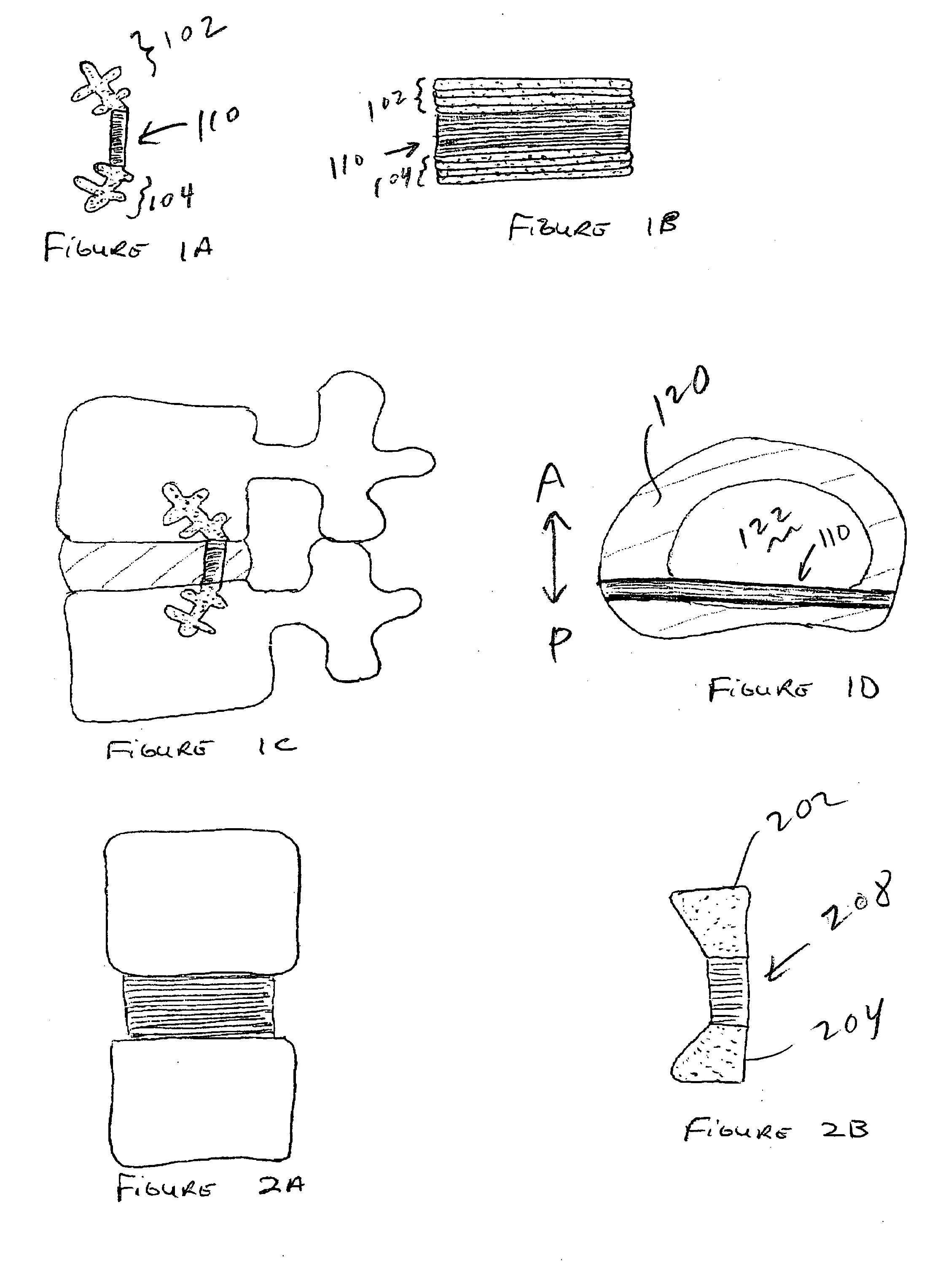
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have 7 cervical vertebrae, with the only 3 known exceptions being the manatee with 6, the two-toed sloth with 5–6, and the three-toed sloth with 9.
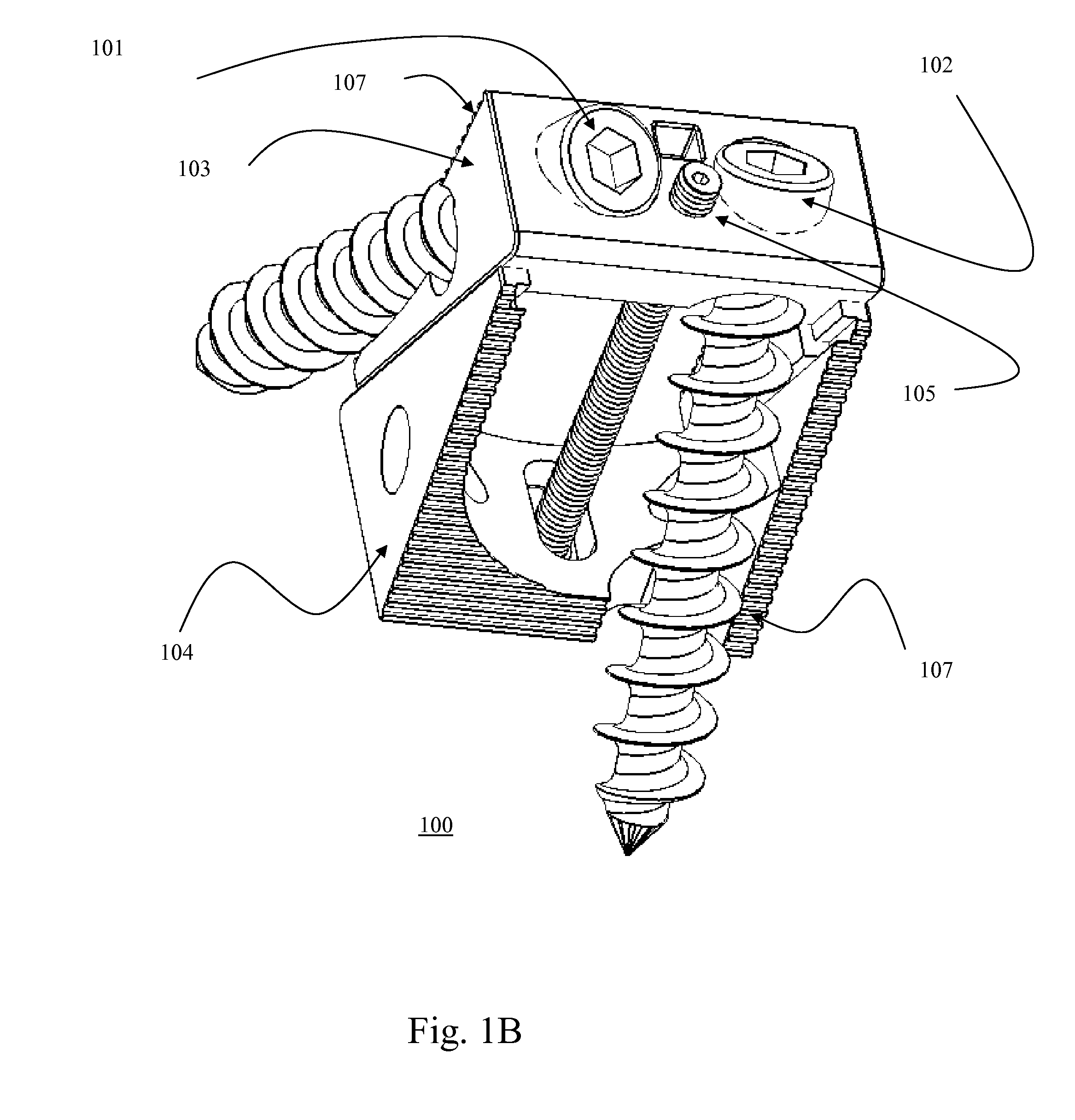
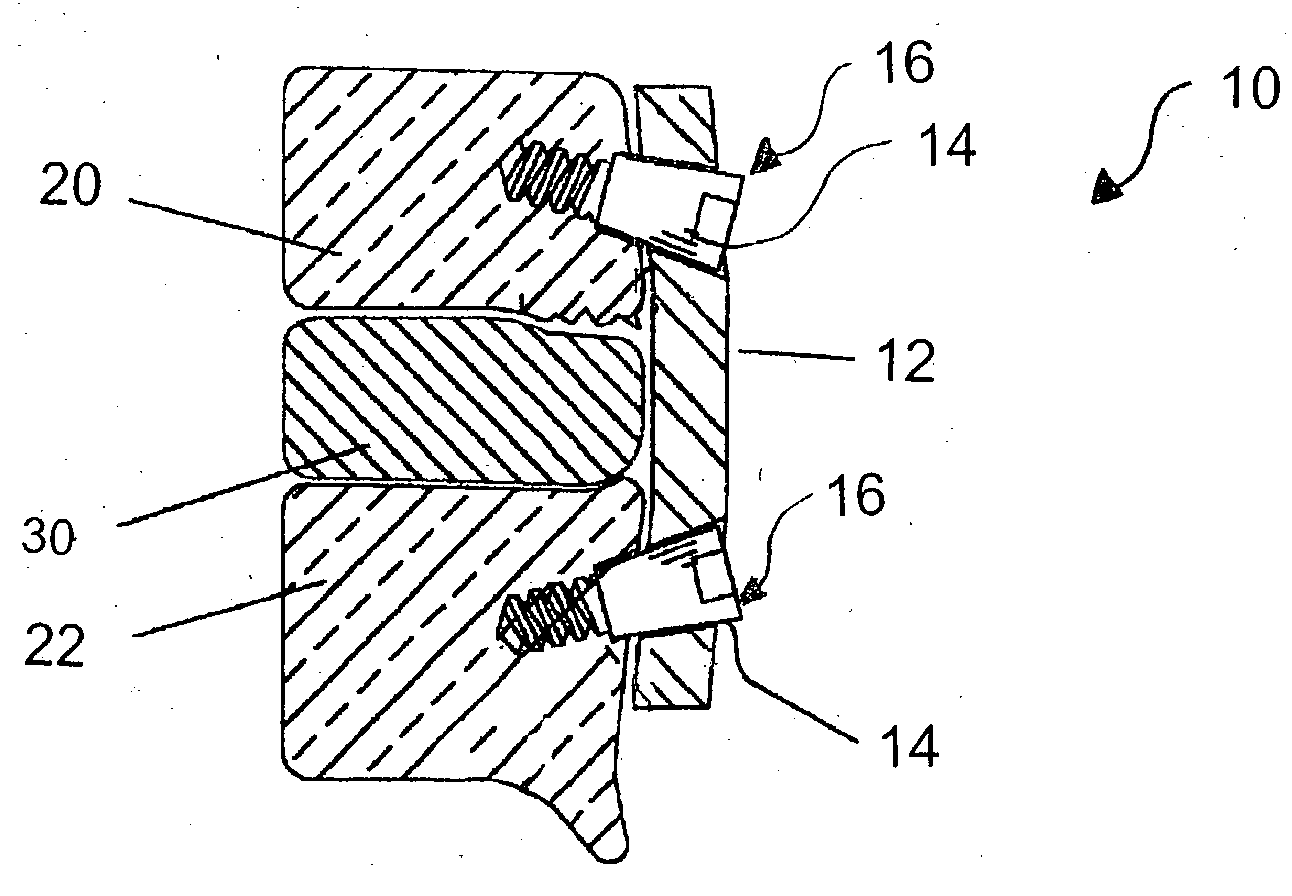
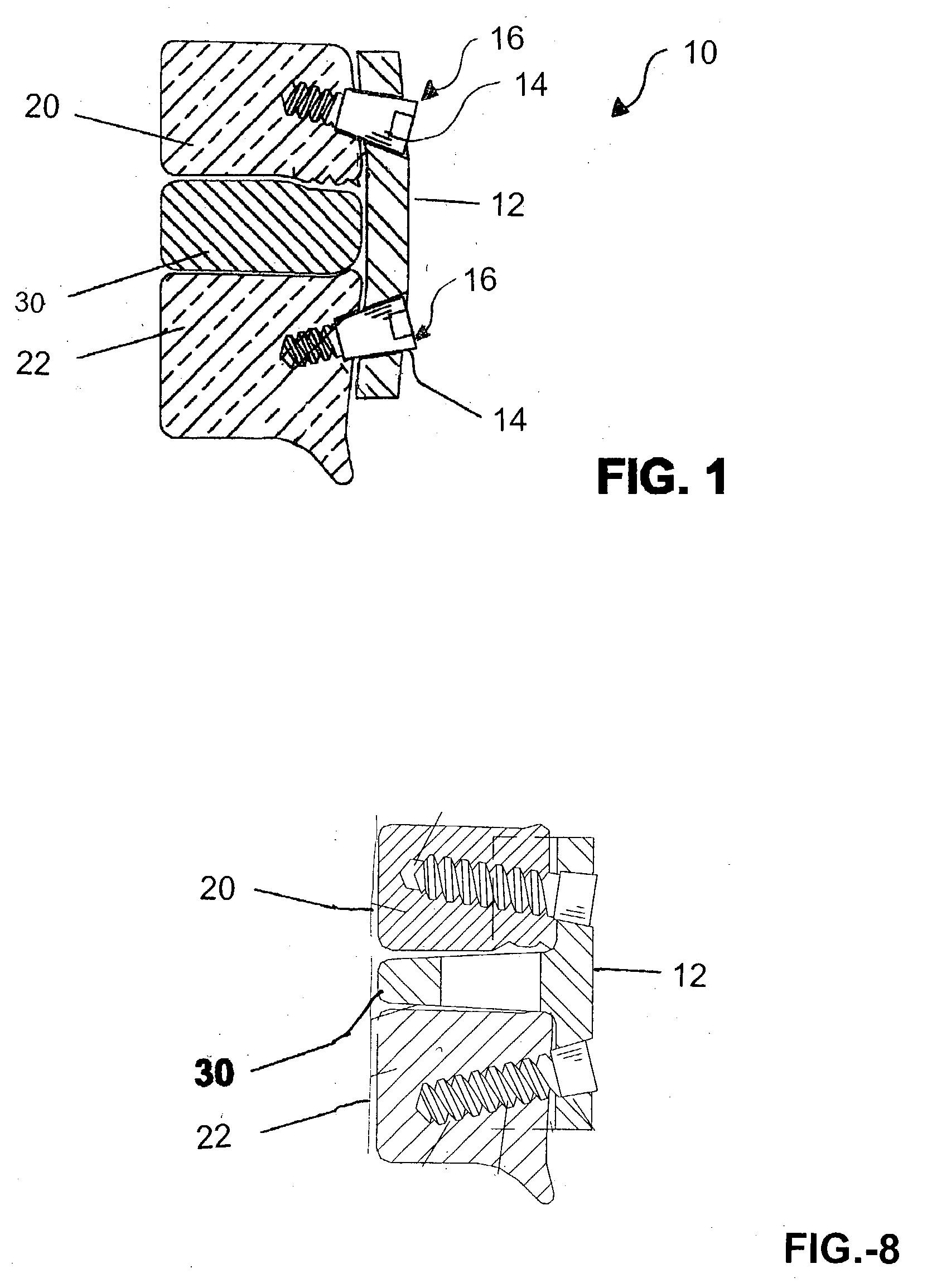
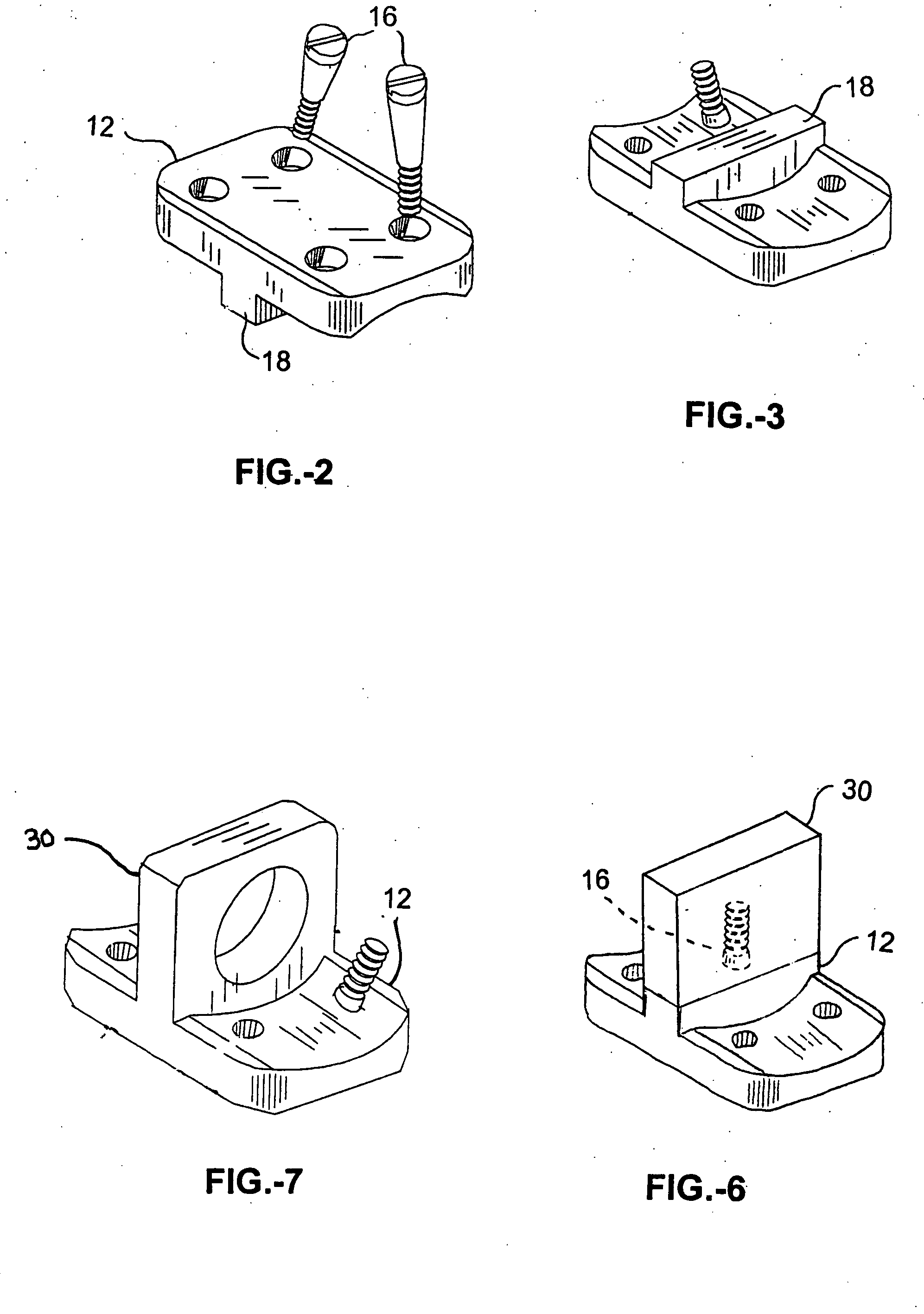
Methods and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis
InactiveUS20060106381A1Effective treatmentPermit flexionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnDevice form
Surgical implants are configured for placement posteriorly to a spinal canal between vertebral bodies to distract the spine and enlarge the spinal canal. In the preferred embodiments the device permits spinal flexion while limiting spinal extension, thereby providing an effective treatment for treating spinal stenosis without the need for laminectomy. The invention may be used in the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spine. Numerous embodiments are disclosed, including elongated, length-adjustable components coupled to adjacent vertebral bodies using pedicle screws. The preferred embodiments, however, teach a device configured for placement between adjacent vertebral bodies and adapted to fuse to the lamina, facet, spinous process or other posterior elements of a single vertebra. Various mechanisms, including shape, porosity, tethers, and bone-growth promoting substances may be used to enhance fusion. The tether may be a wire, cable, suture, or other single or multi-filament member. Preferably, the device forms a pseudo-joint in conjunction with the non-fused vertebra. Alternatively, the device could be fused to the caudal vertebra or both the cranial and caudal vertebrae.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Bioactive spinal implants and method of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS7238203B2Facilitating radiographic assessmentEnhance bone contact and stability and fusionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsLumbar vertebraeCervical fusions
A bioactive spinal implant used in cervical fusion, Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF), Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF), and Transforaminal Interbody Fusion (TLIF), having properties and geometries that enhance bone contact, stability, and fusion between adjacent vertebral bodies.
Owner:VIA SPECIAL PURPOSE CORP +1
Controlled artificial intervertebral disc implant
ActiveUS20050251260A1Reduce the amount requiredProlong lifeBone implantJoint implantsMedicineAxial compression
The invention relates to an artificial intervertebral disc for placement between adjacent vertebrae. The artificial intervertebral disc is preferably designed to restore disc height and natural disc curvature, allow for a natural range of motion, absorb shock and provide resistance to motion and axial compression. Furthermore, the intervertebral disc may be used in the cervical, the thoracic, or the lumbar regions of the spine. The artificial intervertebral disc may include either singularly or in combination: an interior including at least one spring member preferably incorporating a arcuate surface member, a flexible core, the flexible core preferably being a slotted core, a ring spring, a winged leaf spring, or a leaf spring, or The articulating member preferably being attached to one of the endplate by an intermediate shock absorbing element.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Intervertebral disc implant
ActiveUS20050197702A1Reduce the amount requiredProlong lifeBone implantLigamentsCircular discAxial compression
The invention relates to an artificial intervertebral disc for placement between adjacent vertebrae. The artificial intervertebral disc is preferably designed to restore disc height and lordosis, allow for a natural range of motion, absorb shock and provide resistance to motion and axial compression. Furthermore, the intervertebral disc may be used in the cervical, the thoracic, or the lumber regions of the spine. The artificial intervertebral disc may include either singularly or in combination: an interior at least partially filled with a fluid; a valve for injecting fluid into the interior of the disk; a central region having a stiffness that is preferably greater than the stiffness of the outer regions thus enabling the disc to pivot about the central region. The central pivot may be formed by a center opening, a central chamber, an inner core or a central cable.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
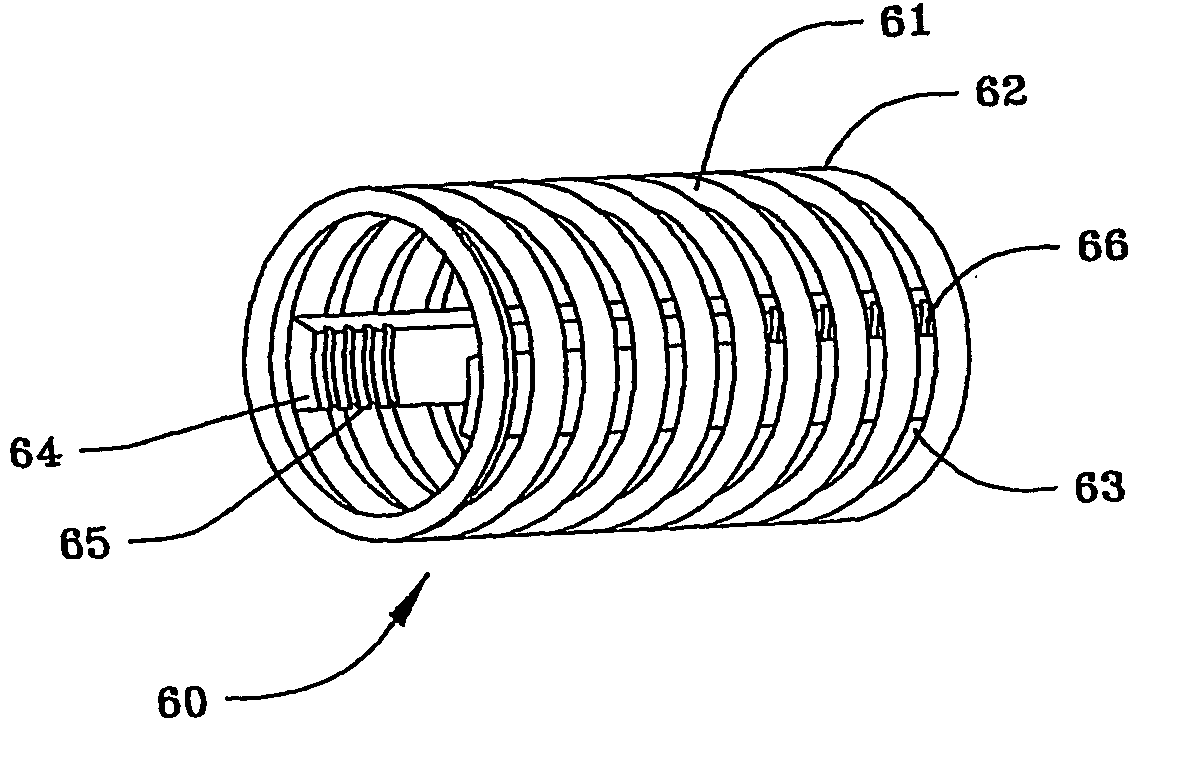
Devices and methods for minimally invasive treatment of degenerated spinal discs
InactiveUS20050222681A1Accurate spacingBone debris is eliminatedBone implantJoint implantsExpandable cageRadio frequency
Spinal stabilization devices and their methods of insertion and use to treat degenerated lumbar, thoracic or cervical spinal discs in minimally invasive, outpatient procedures are described. In one embodiment, the spinal stabilization device is an expandable cage made of a coil or perforated cylindrical tube with a bulbous or bullet-shaped distal end and a flat or rounded proximal end. In a preferred embodiment, the spinal stabilization device is mechanically expanded to a larger diameter or is made of a superelastic nickel-titanium alloy which is thermally programmed to expand to a relatively larger diameter when a pre-determined transition temperature below body temperature is reached. To treat a degenerated disc, a guide wire is inserted into the disc and an endoscope is inserted through a posterolateral puncture in the back and advanced up to the facet of the spine. Mechanical tools or laser energy, under endoscopic visualization, are used to remove or vaporize a portion of the facet bone, creating an opening into the foraminal space in the spine for insertion of an endoscope, which enables the disc, vertebra and nerves to be seen. The passageway is expanded, mechanical tools or laser of RF energy are used to make a tunnel into the disc, and a delivery cannula is inserted up to the opening of the tunnel. An insertion tool is used to insert one or more spinal stabilization devices into the tunnel in the disc, preserving the mobility of the spine, while maintaining the proper space between the vertebra. Laser or radio frequency (RF) energy is used to coagulate bleeding, vaporize or remove debris and shrink the annulus of the disc to close, at least partially, the tunnel made in the disc.
Owner:TRIMEDYNE
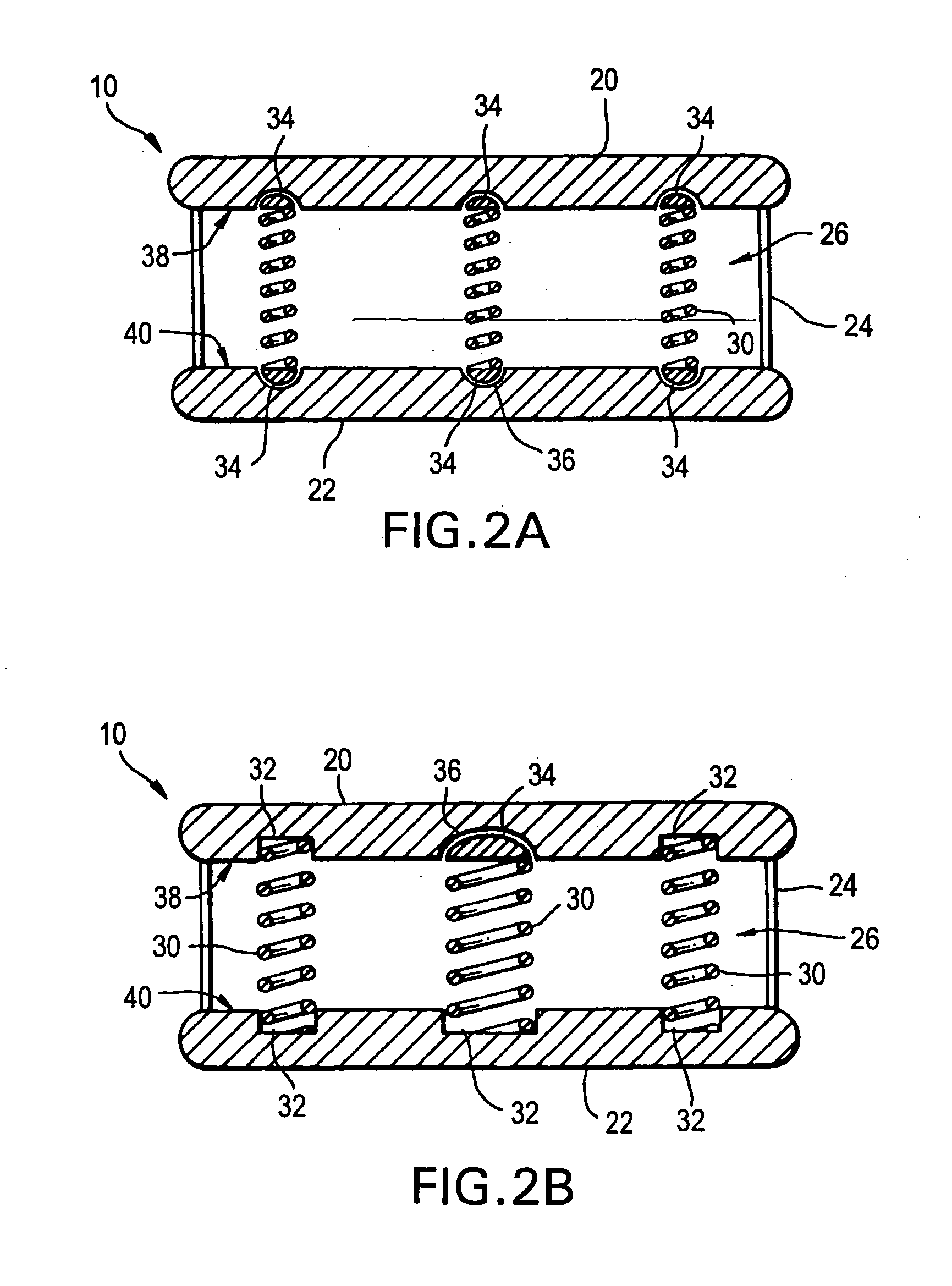
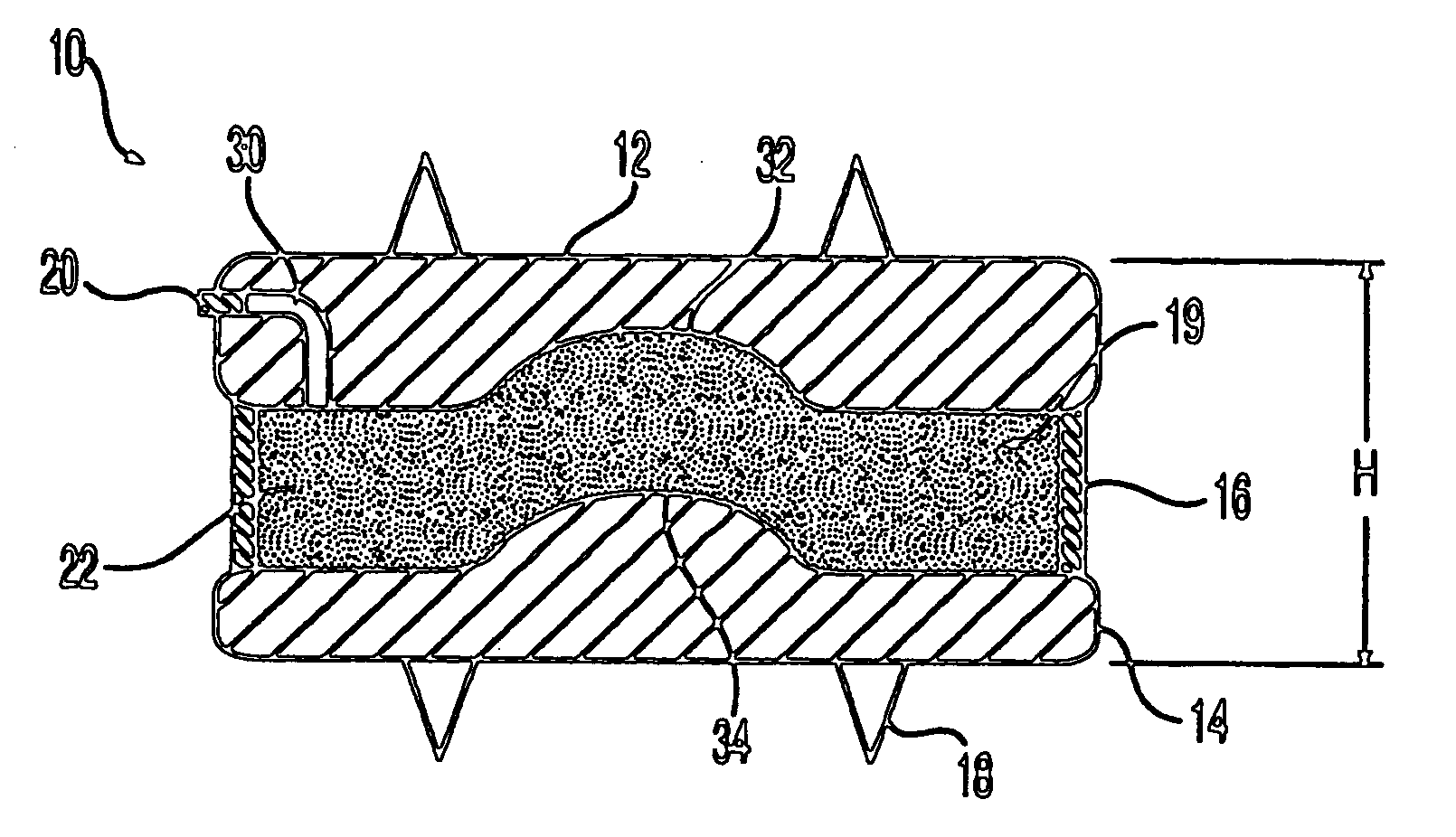
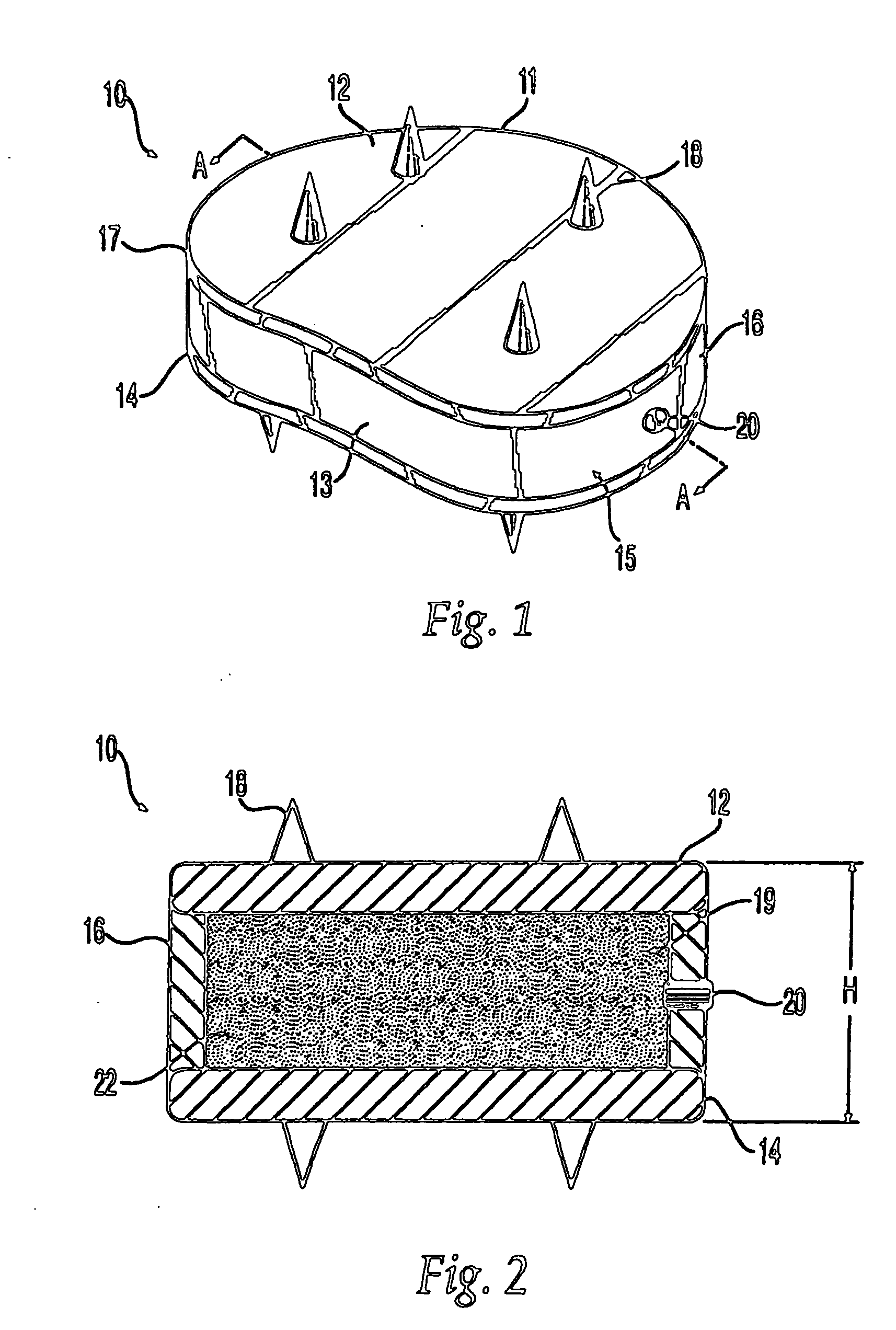
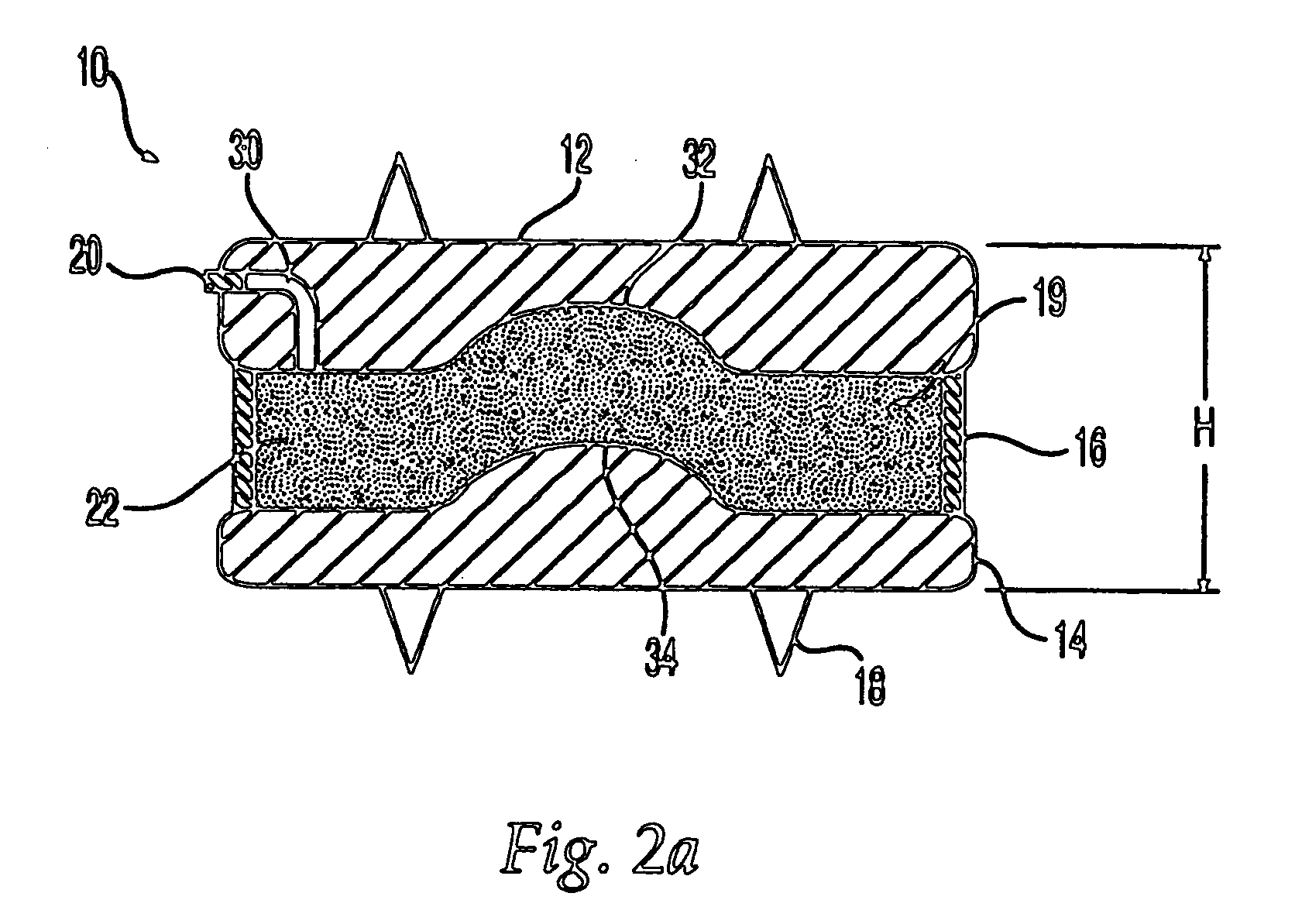
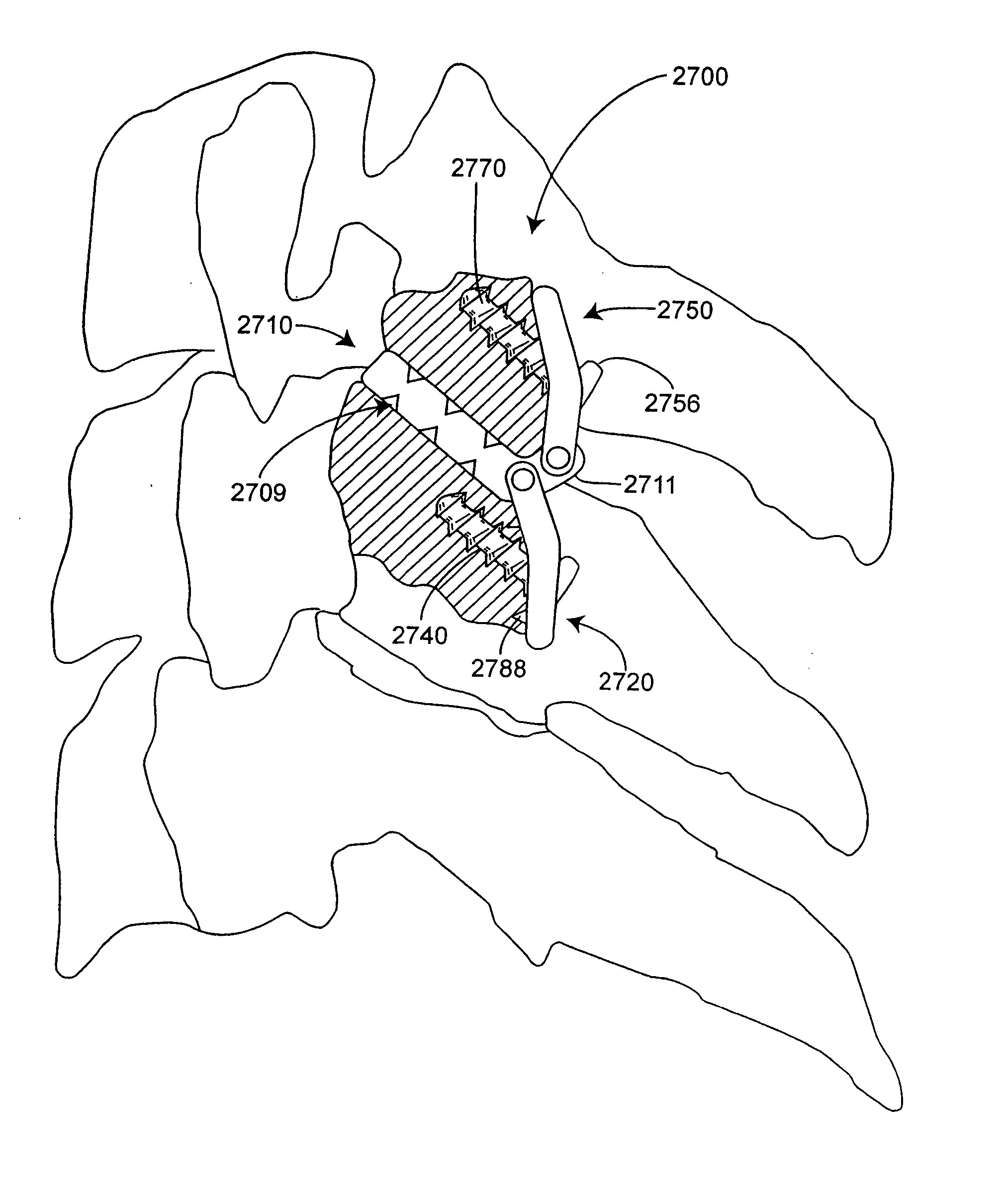
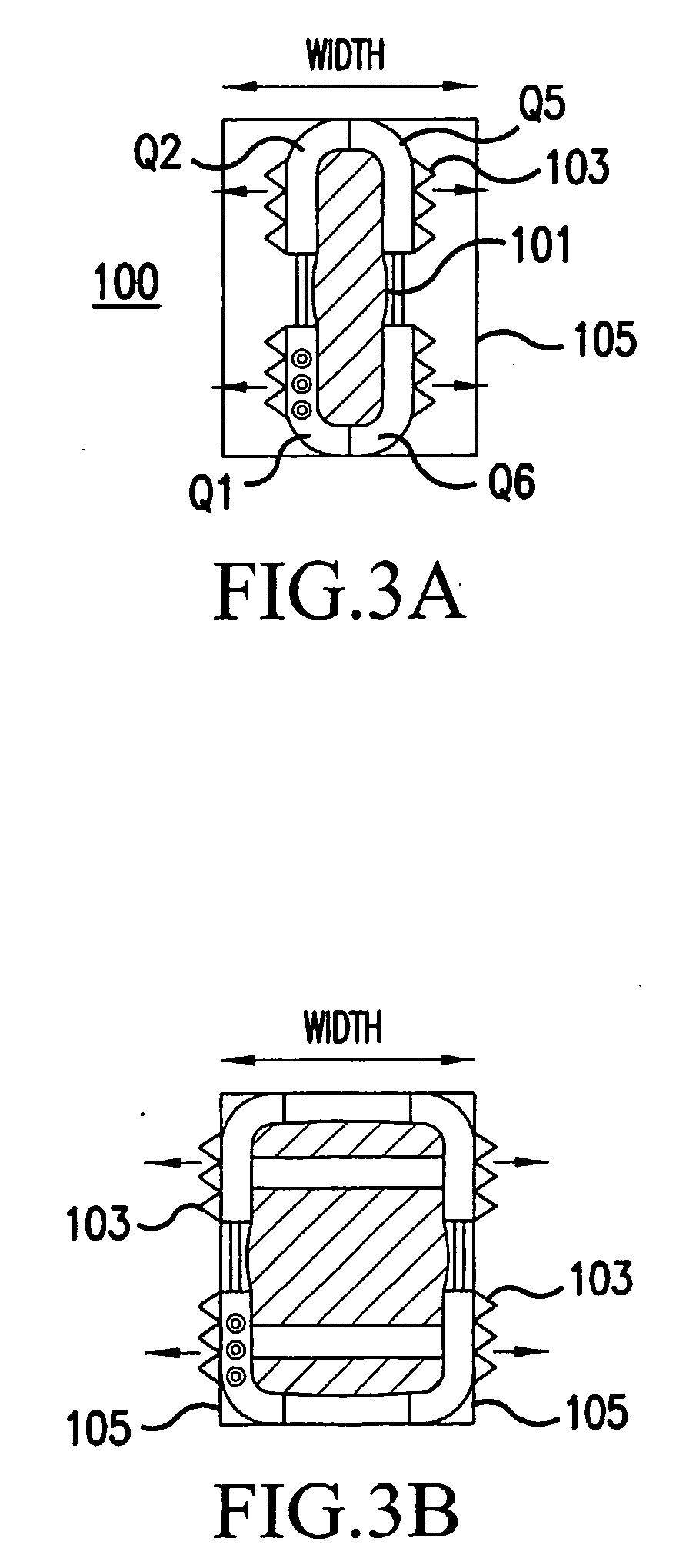
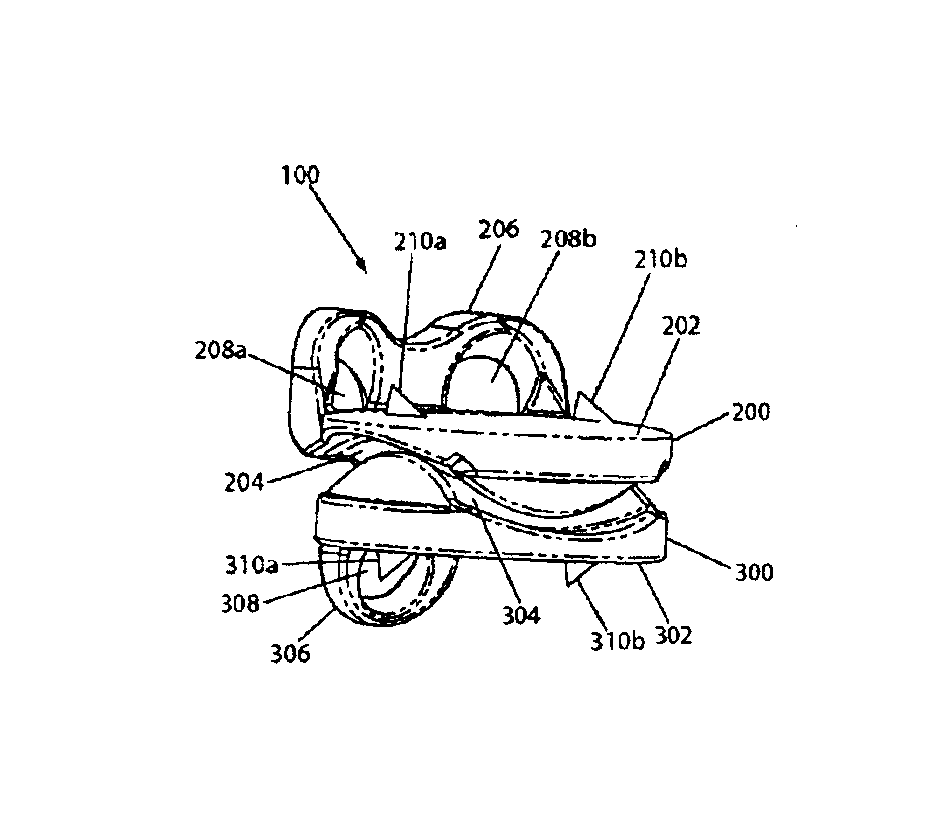
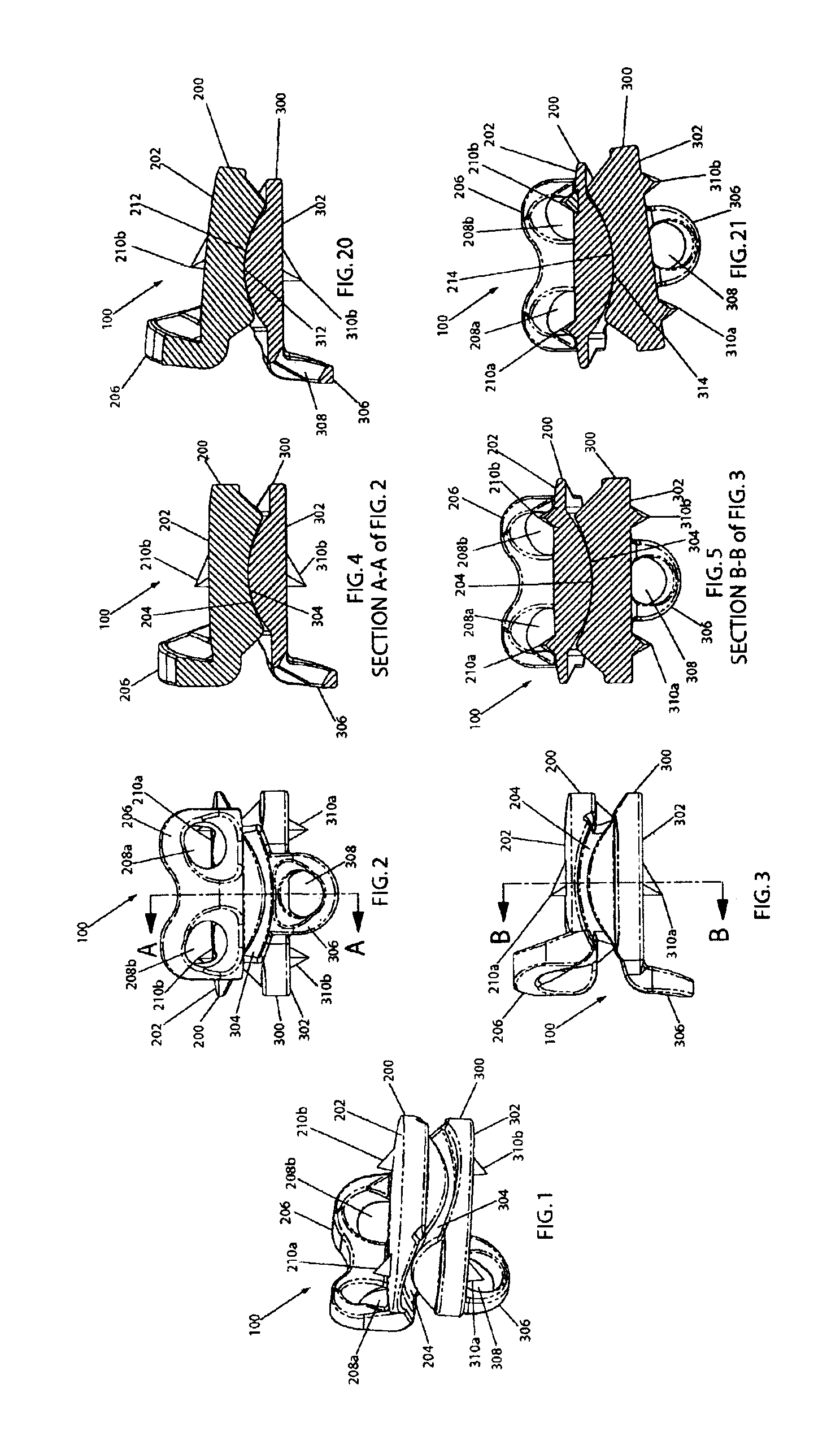
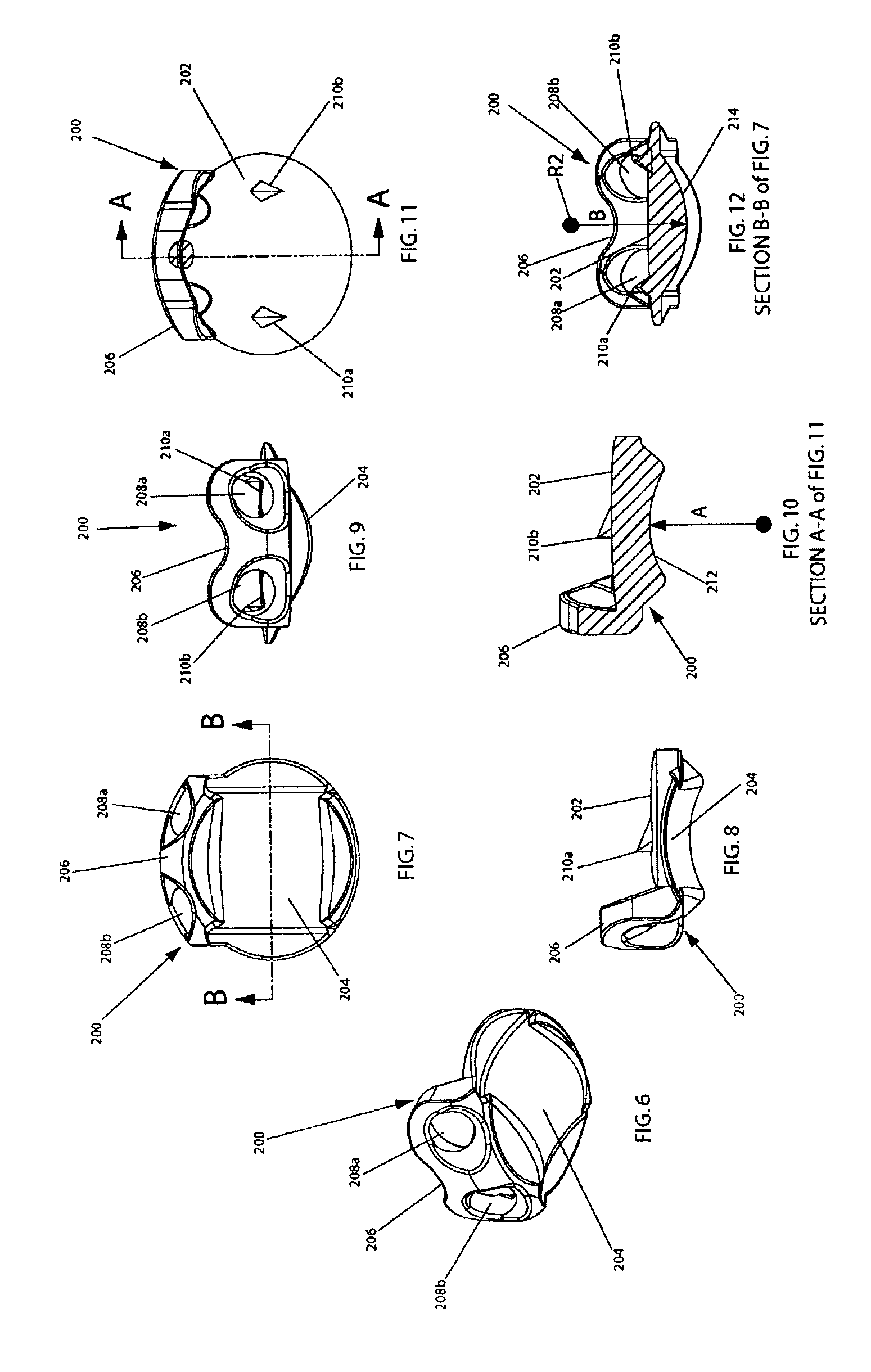
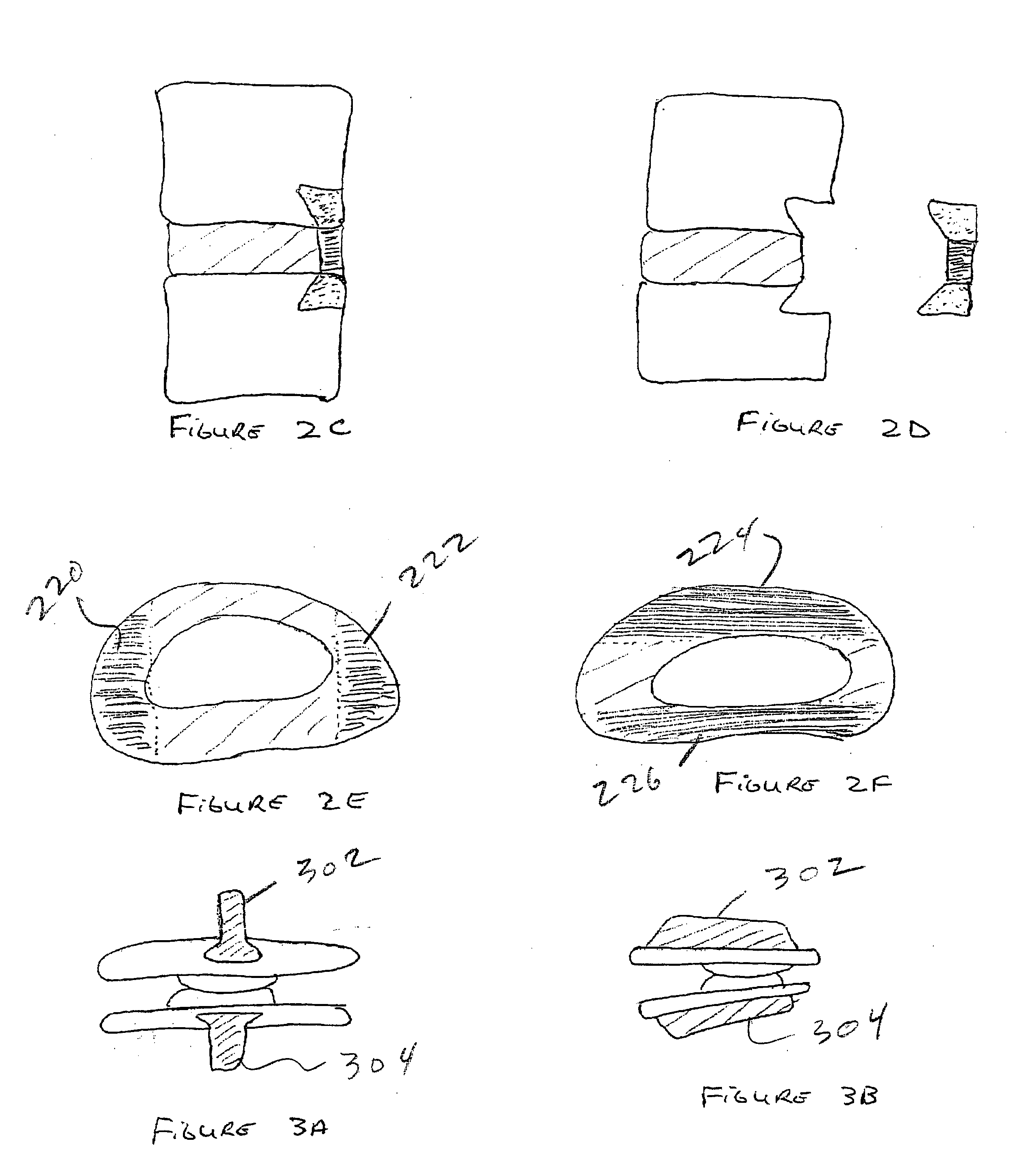
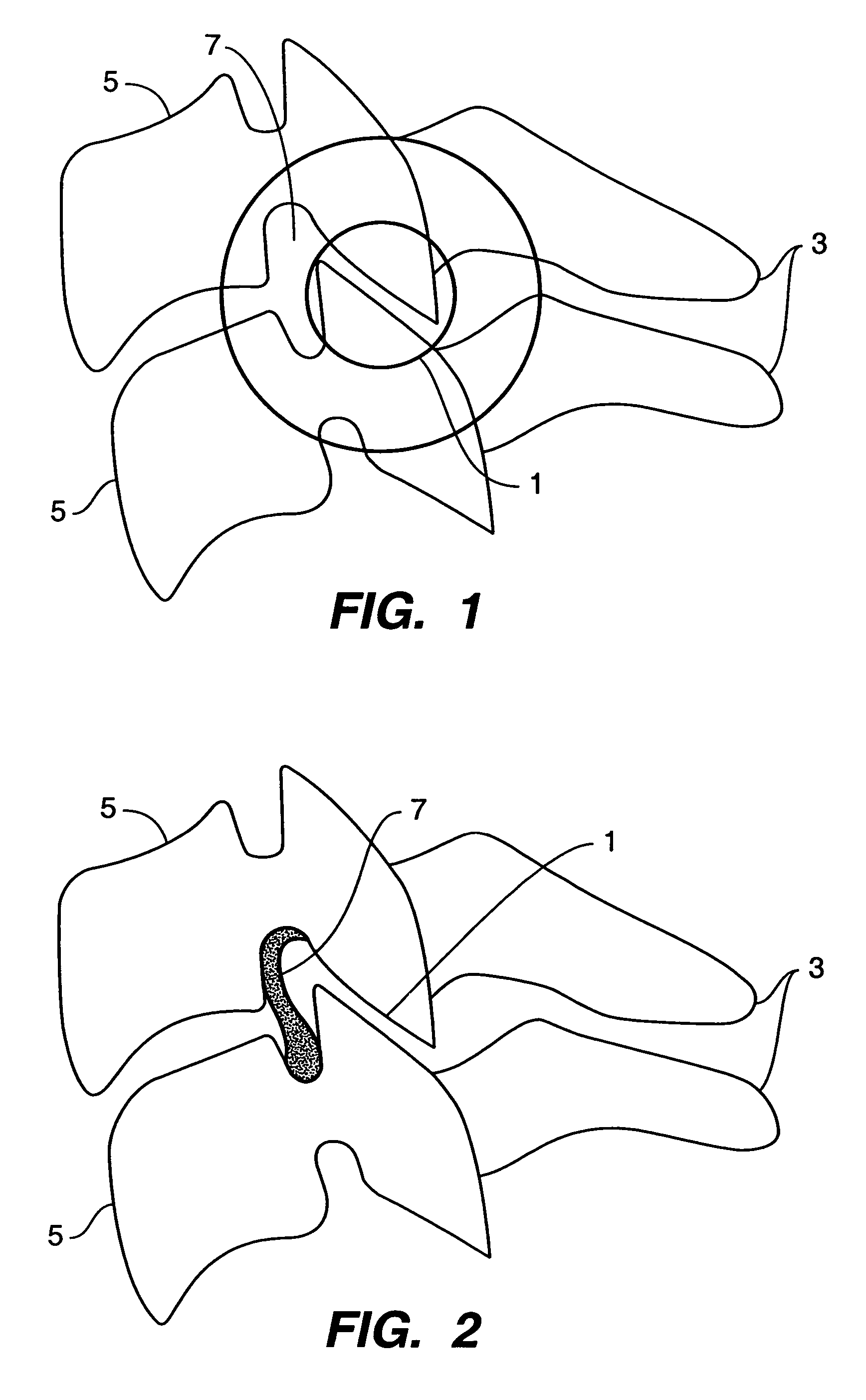
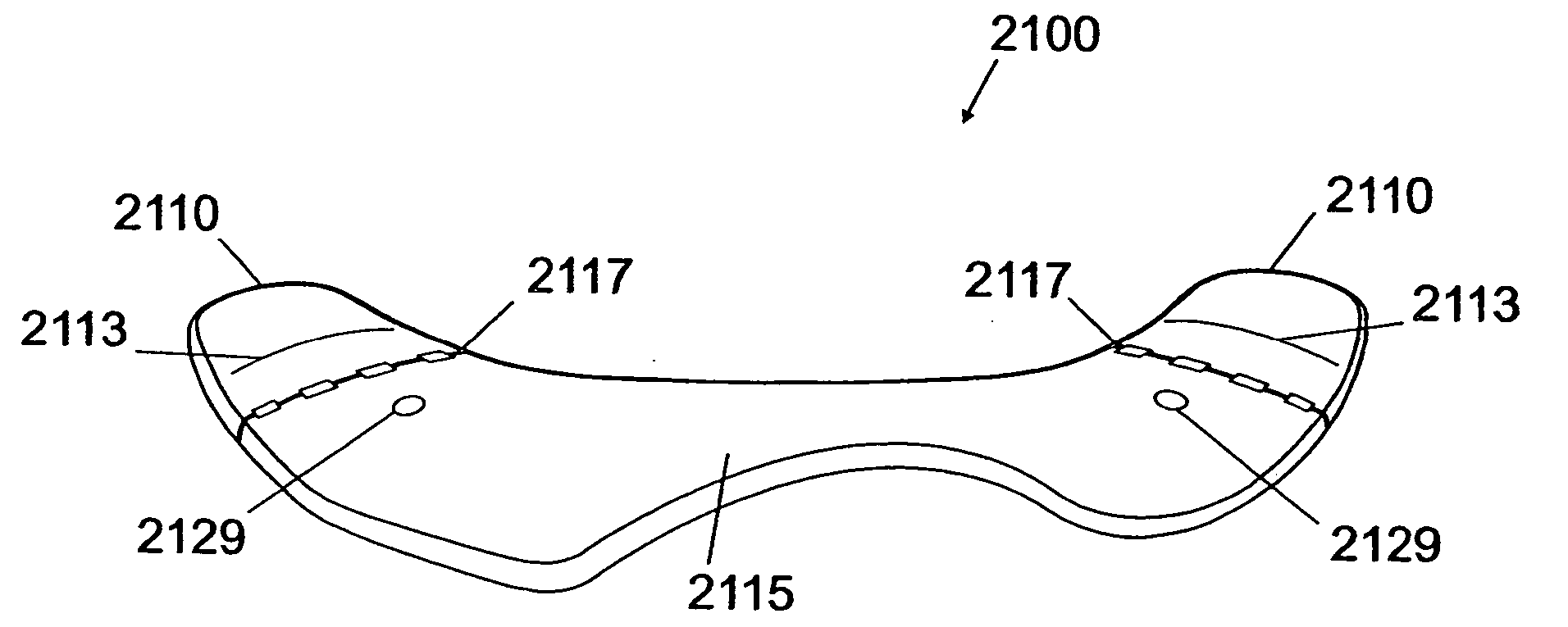
Inter-cervical facet implant with surface enhancements
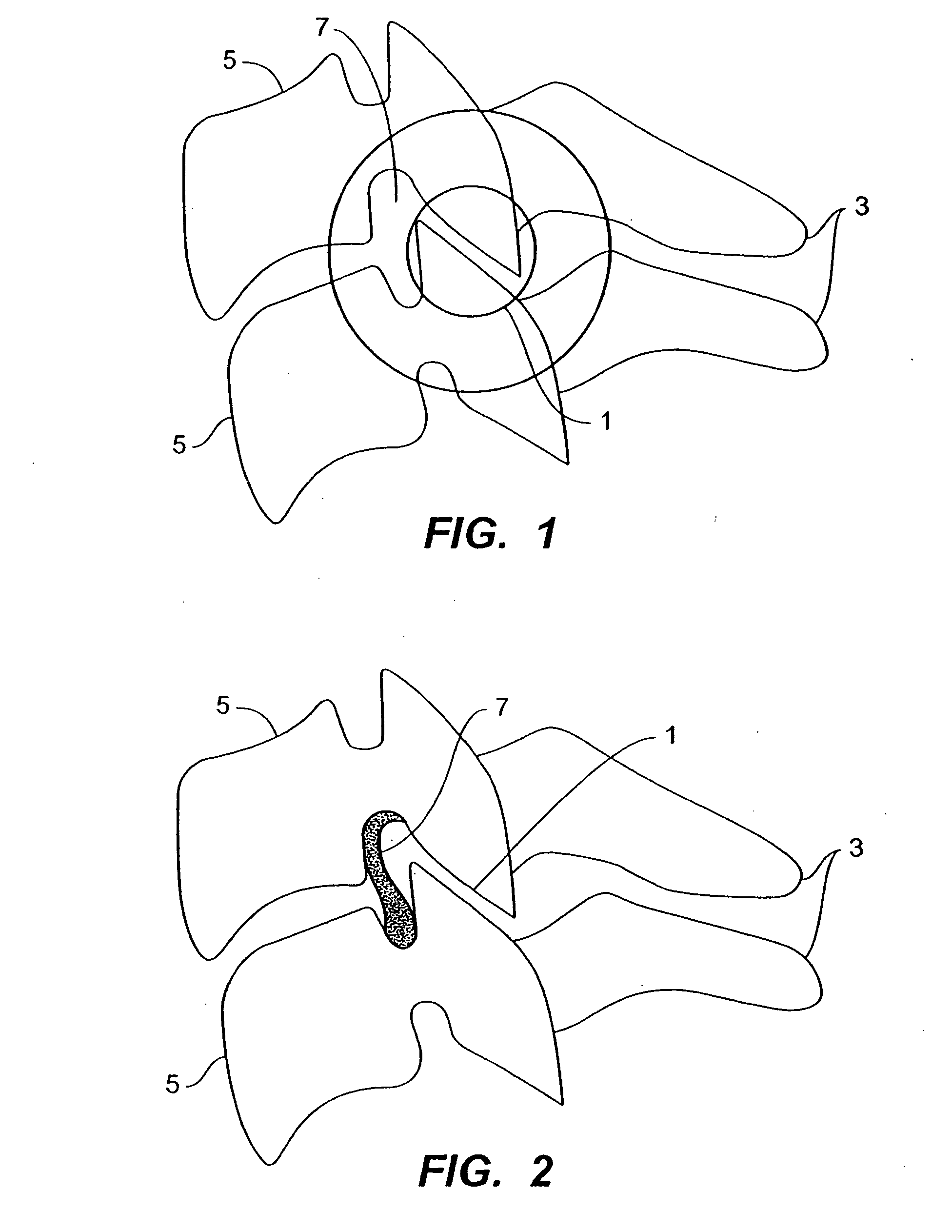
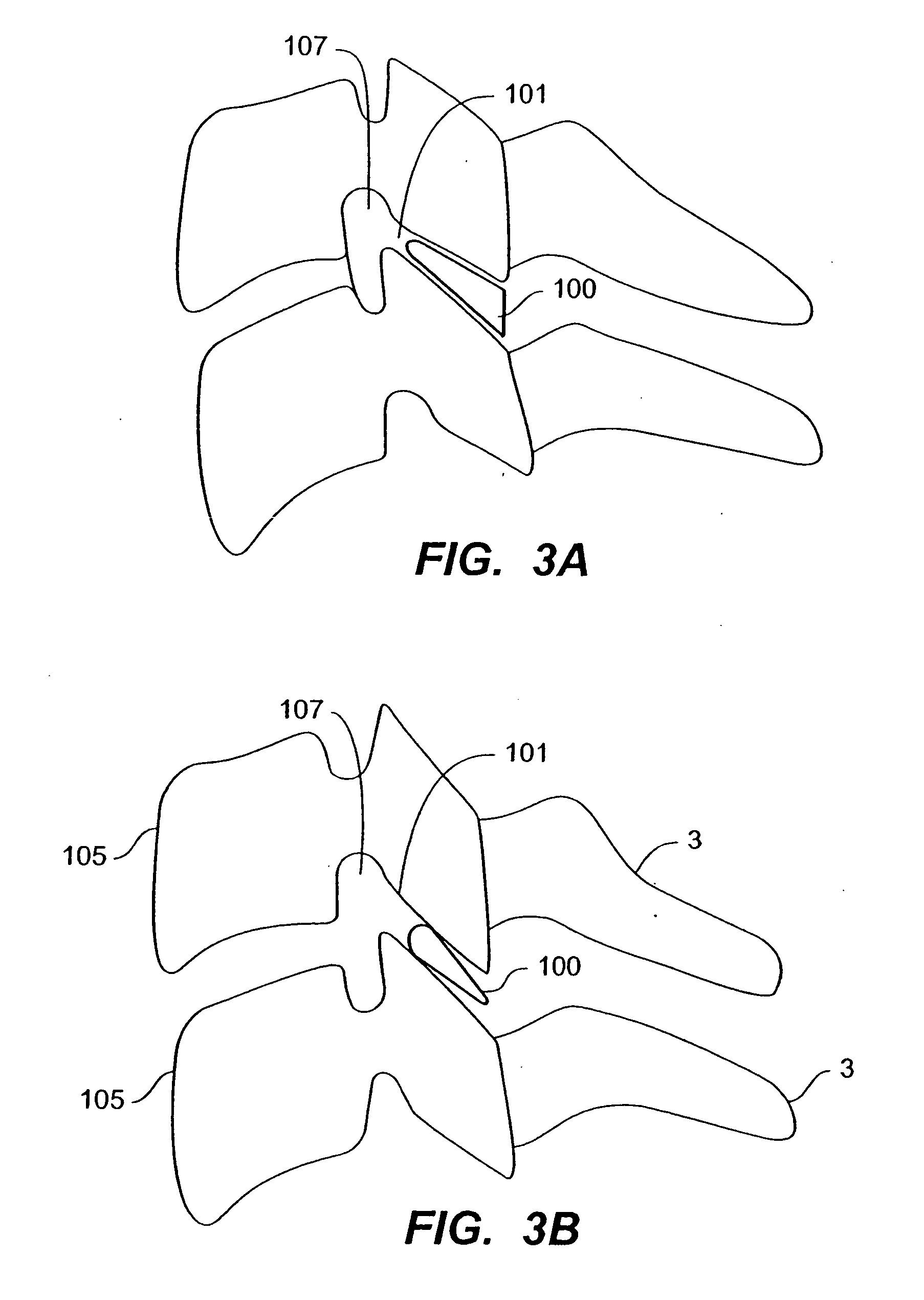
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
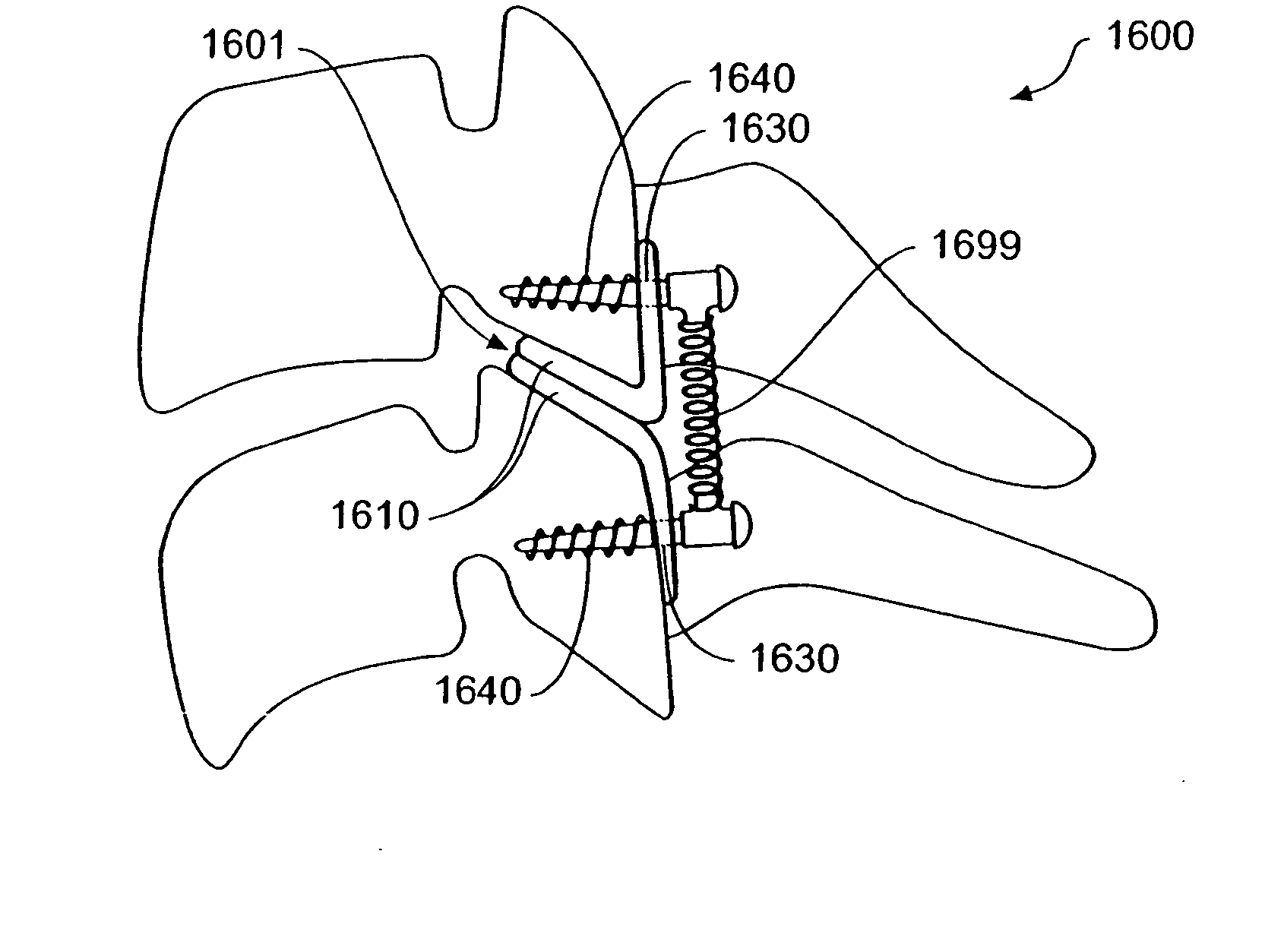
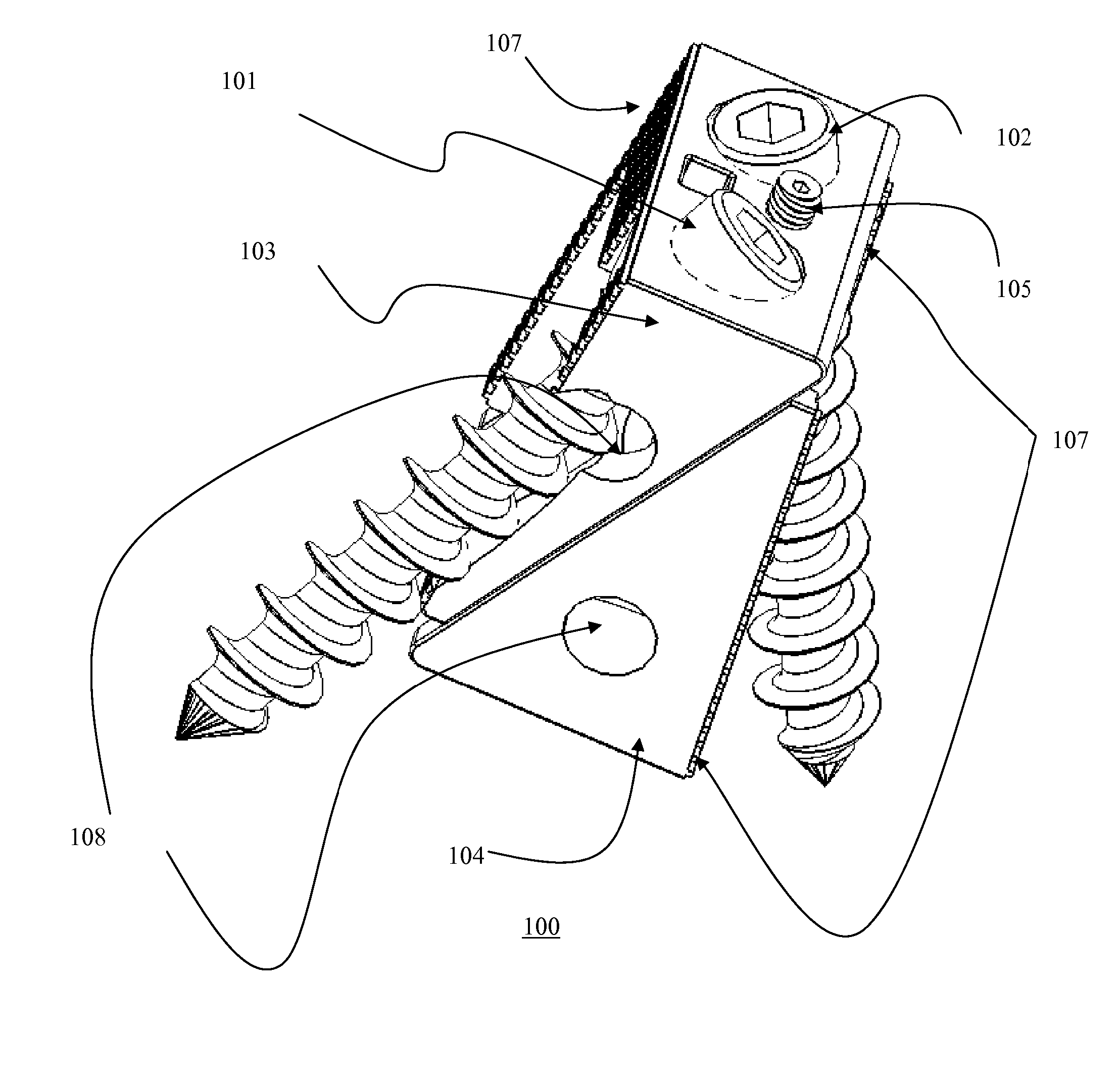
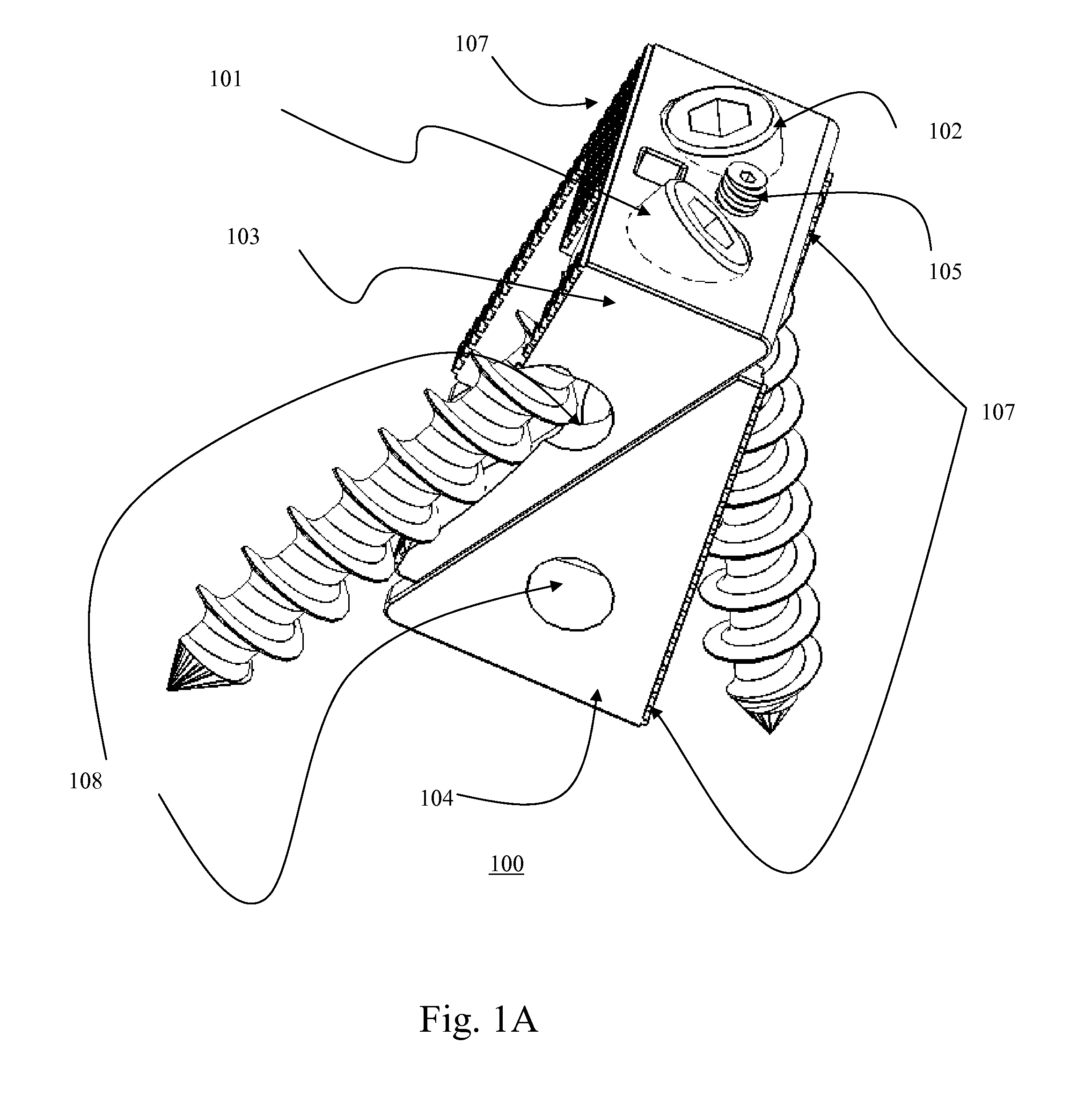
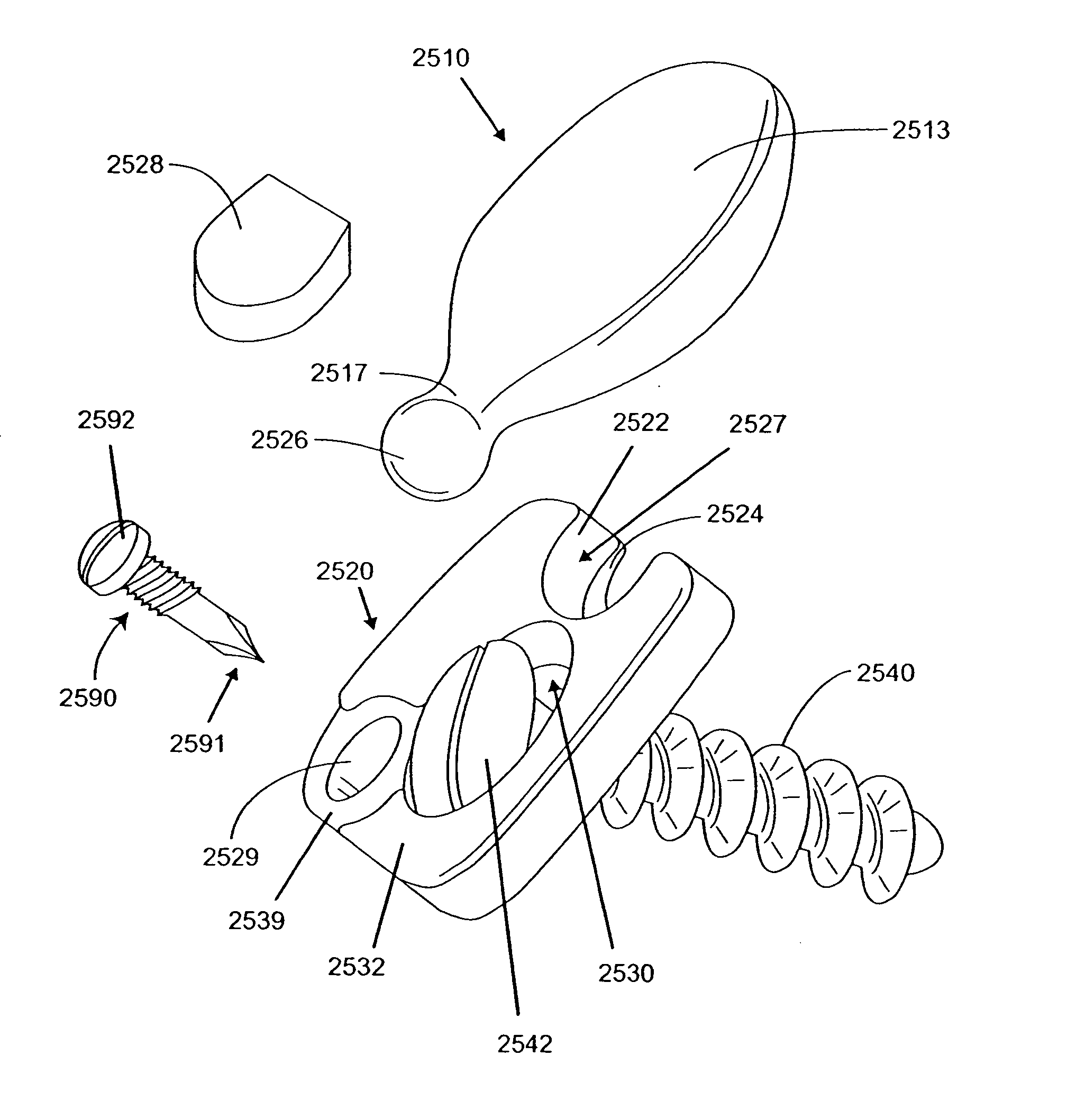
Bi-directional fixating transvertebral body screws and posterior cervical and lumbar interarticulating joint calibrated stapling devices for spinal fusion
ActiveUS20080033440A1Reduce widthAvoid excessive retractionInternal osteosythesisBone implantBones fusionLumbar vertebrae
A self-drilling bone fusion screw apparatus is disclosed which includes at least first and second sliding boxes. A first screw member having a tapered end and a threaded body is disposed within the first sliding box, and a second screw member having a tapered end and a threaded body disposed within the second sliding box. An adjuster adjusts the height of the sliding boxes. The screw members are screwed into vertebral bodies in order to fuse the vertebral bodies together. A plurality of the self-drilling bone fusion screw apparatuses may be attached together and / or integrated via a plate or cage. Also disclosed is a cervical facet staple that includes a curved staple base and at least two prongs attached to the bottom surface of the curved staple base.
Owner:MOSKOWITZ FAMILY LLC
Inter-cervical facet joint fusion implant
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
Artificial expansile total lumbar and thoracic discs for posterior placement without supplemental instrumentation and its adaptation for anterior placement of artificial cervical, thoracic and lumbar discs
Owner:MOSKOWITZ NATHAN C
Bi-directional fixating transvertebral body screws and posterior cervical and lumbar interarticulating joint calibrated stapling devices for spinal fusion
ActiveUS7942903B2Traversing and exciting nerve rootsSame functionInternal osteosythesisBone implantCervical facet jointsLumbar vertebrae
Owner:MOSKOWITZ FAMILY LLC
Artificial expansile total lumbar and thoracic discs for posterior placement without supplemental instrumentation and its adaptation for anterior placement of artificial cervical, thoracic and lumbar discs
A total artificial expansible disc having at least two pairs of substantially parallel shells, which move in multiple directions defined by at least two axes, is disclosed. Several methods for implanting the total artificial expansile disc are also disclosed. The total artificial expansile disc occupies a space defined by a pair of vertebral endplates. An expansion device, which preferably includes a jackscrew mechanism, moves the pairs of shells in multiple directions. A core is disposed between the pairs of shells, and the core permits the vertebral endplates to move relative to one another.
Owner:MOSKOWITZ NATHAN C
Cervical disc replacement
InactiveUS6908484B2Immediate and short-term relief from painInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsArticular surfacesSpinal column
An articulating joint implant for use in the cervical spine includes a pair of opposing upper and lower elements having nested articulation surfaces providing a center of rotation of the implant above the adjacent vertebral body endplate surfaces in one mode of motion lateral bending and a center of rotation of the implant below those surfaces in flexion / extension, and that further permit axial rotation of the opposing elements relative to one another about the longitudinal axis of the spinal column through a range of angles without causing them to move in opposing directions along the longitudinal axis within that range. In preferred embodiments, the articulation surfaces further cause such opposite movement of the opposing elements beyond that range.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Inter-cervical facet joint implant with locking screw system
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
Inter-cervical facet implant and method
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
Inter-cervical facet implant with multiple direction articulation joint and method for implanting
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
Bioactive Spinal Implants and Method of Manufacture Thereof
InactiveUS20070293948A1Facilitating radiographic assessmentEnhance bone contact and stability and fusionJoint implantsSpinal implantsLumbar vertebraeCervical fusions
A bioactive spinal implant used in cervical fusion, Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF), Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF), and Transforaminal Interbody Fusion (TLIF), having properties and geometries that enhance bone contact, stability, and fusion between adjacent vertebral bodies.
Owner:ORTHOVITA INC
Inter-cervical facet implant and method
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
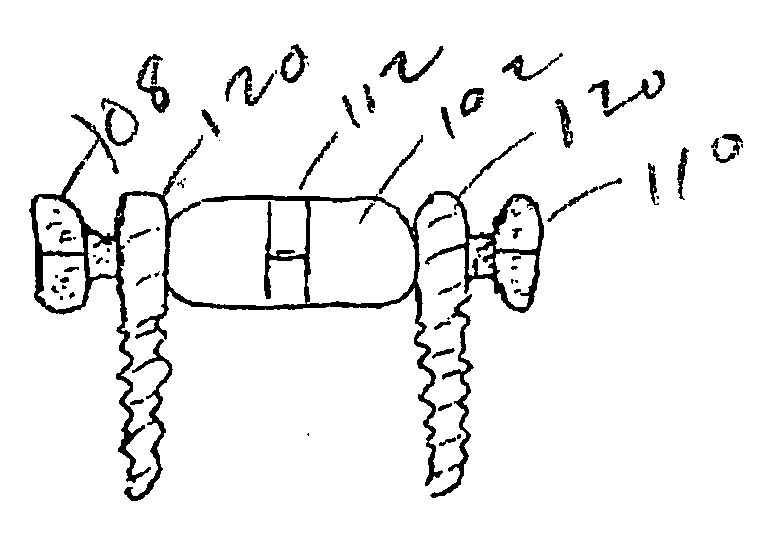
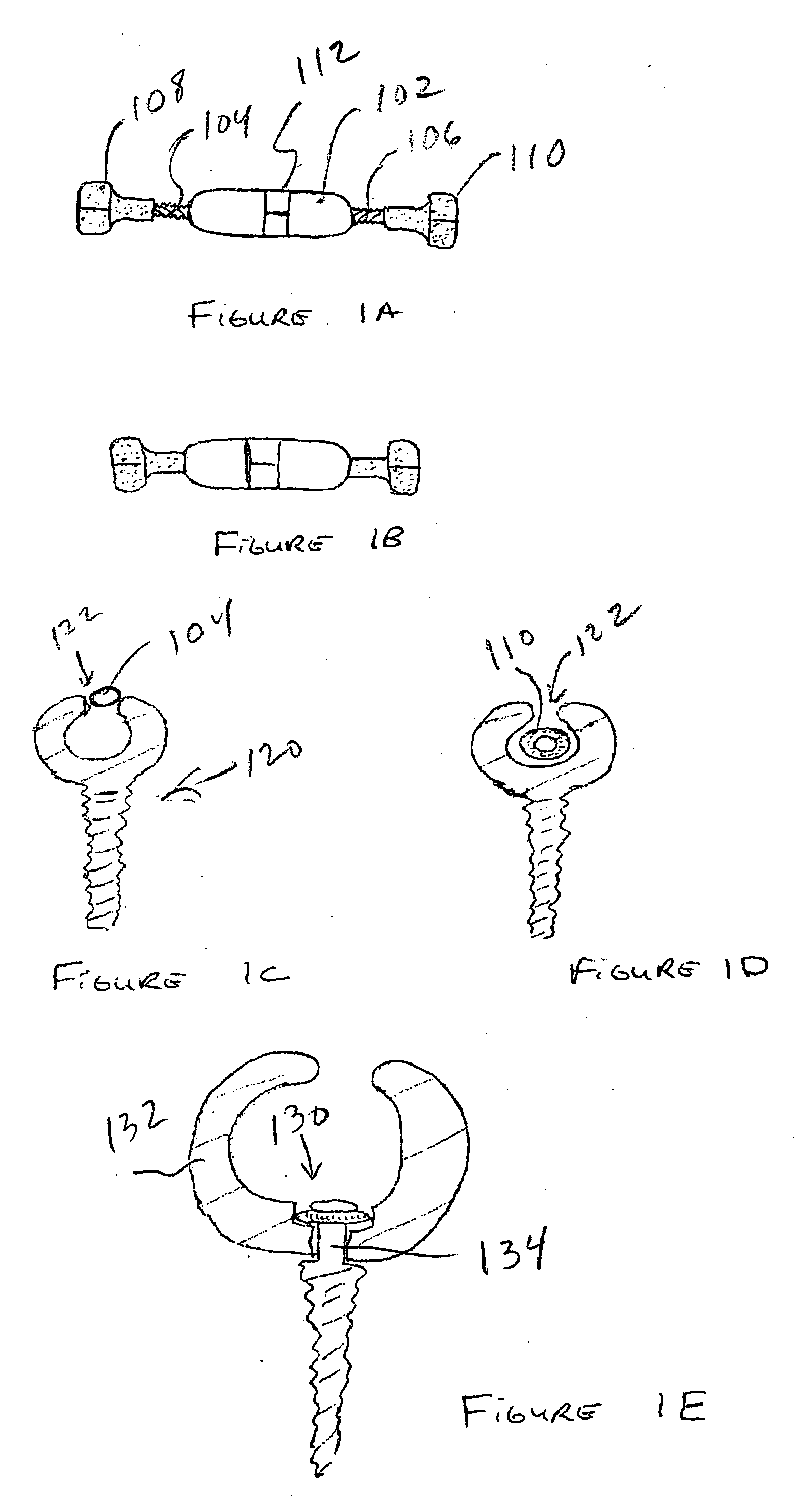
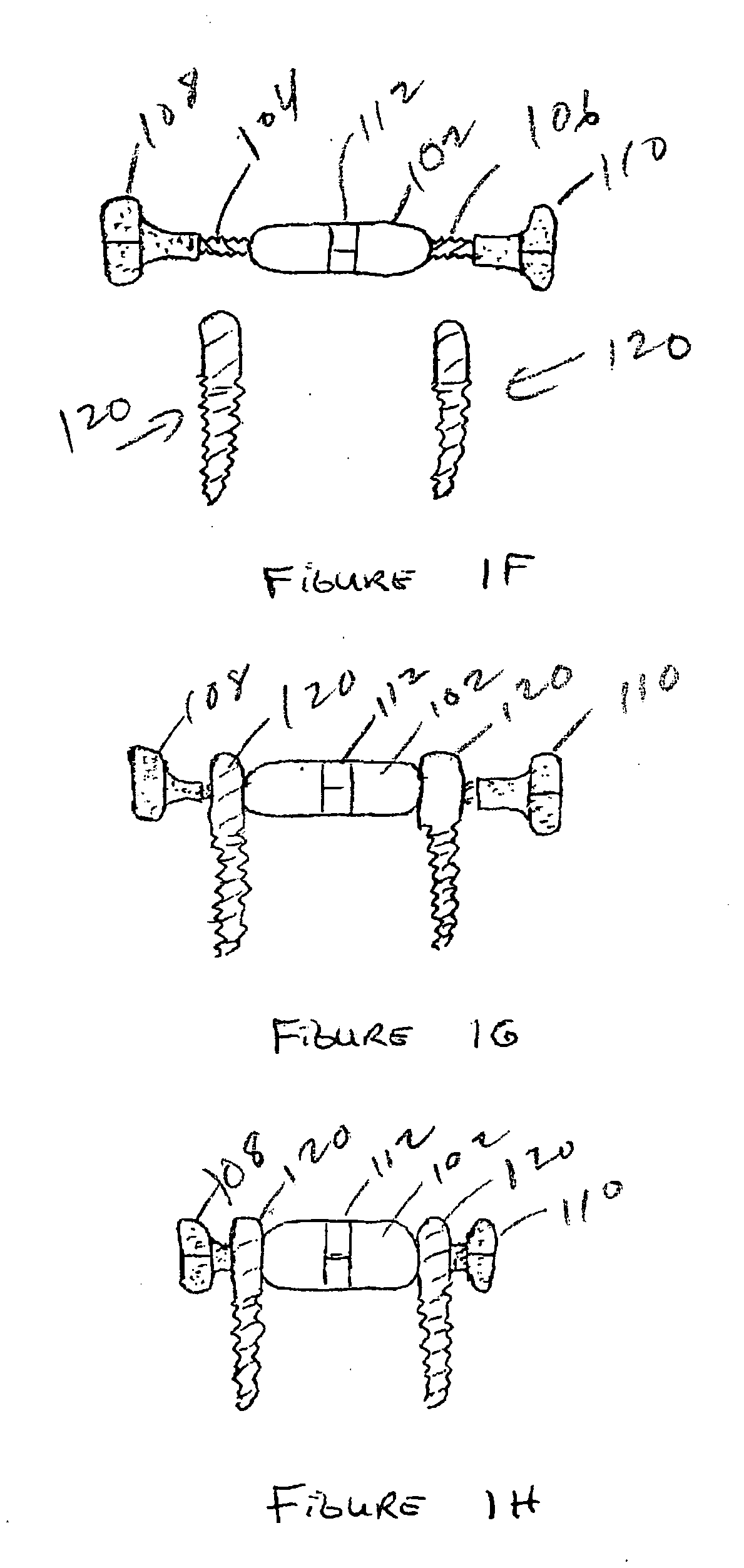
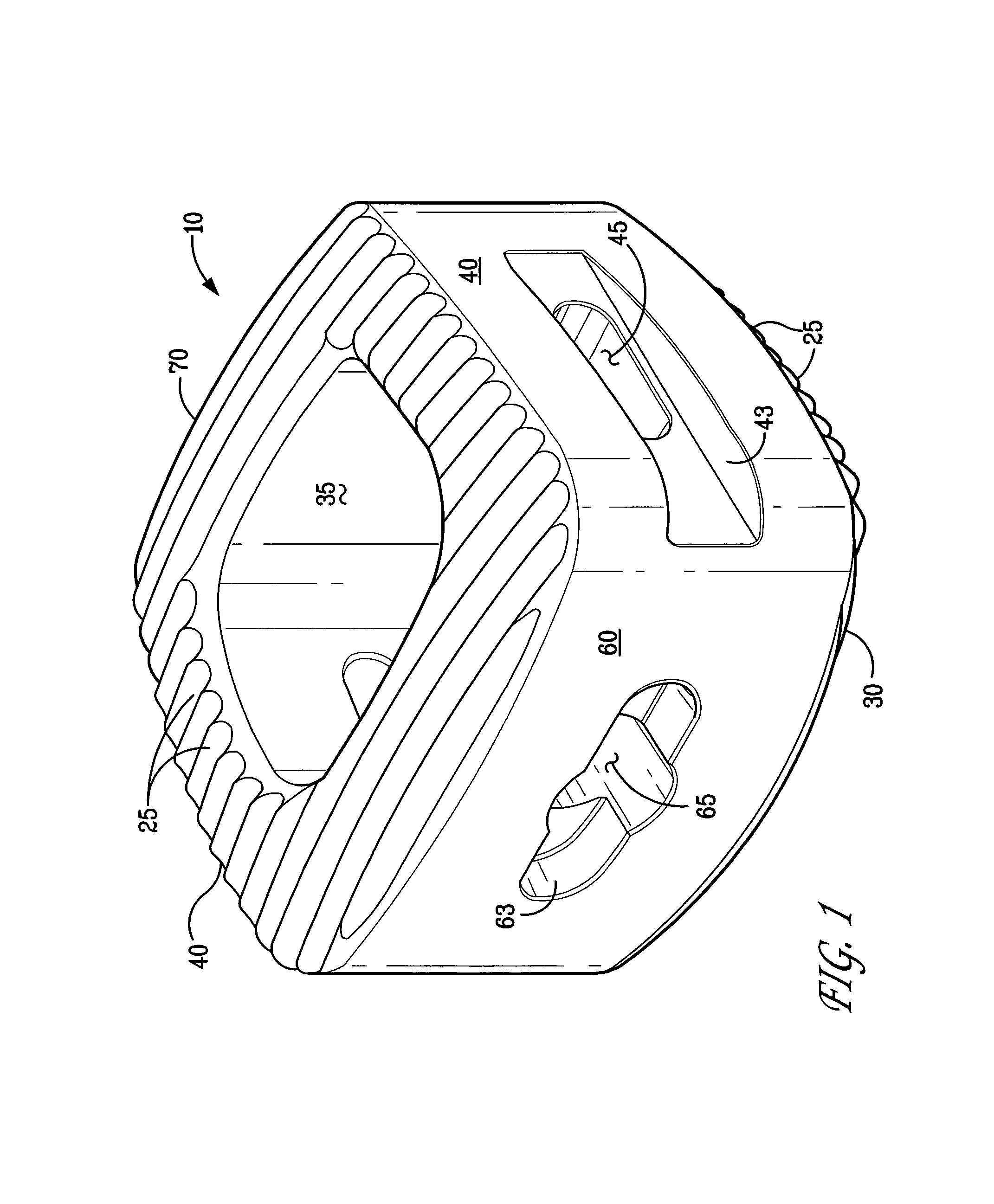
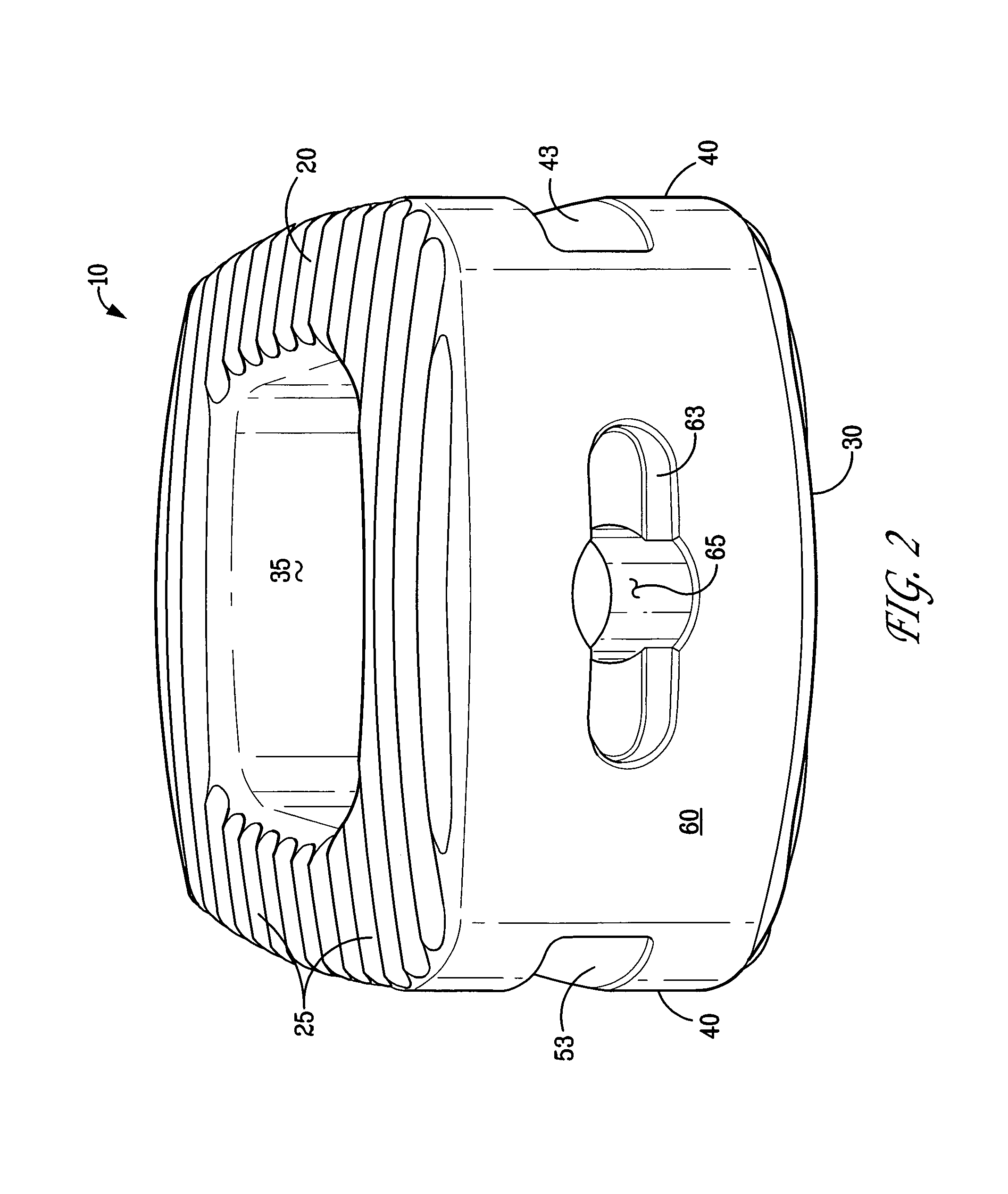
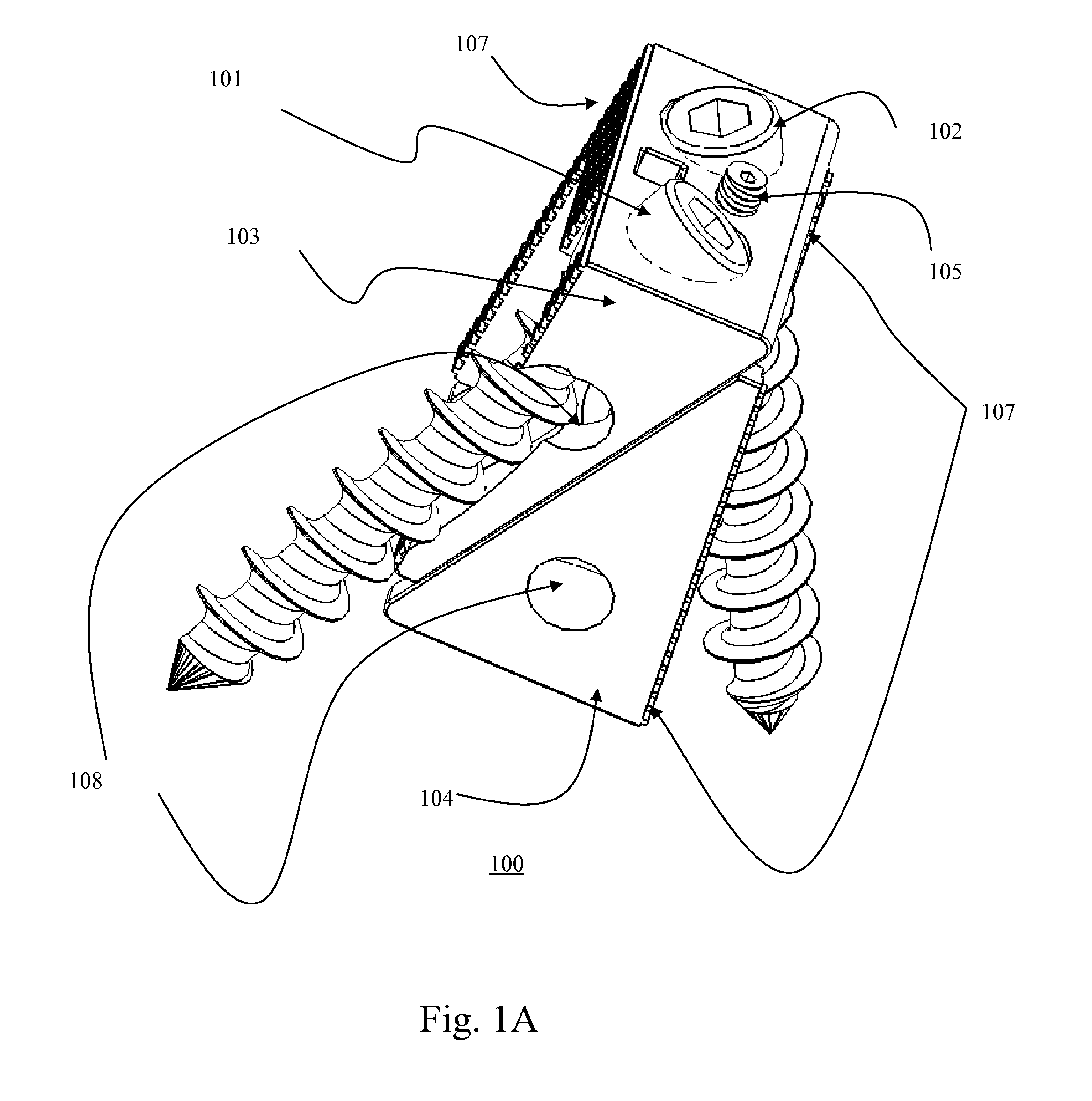
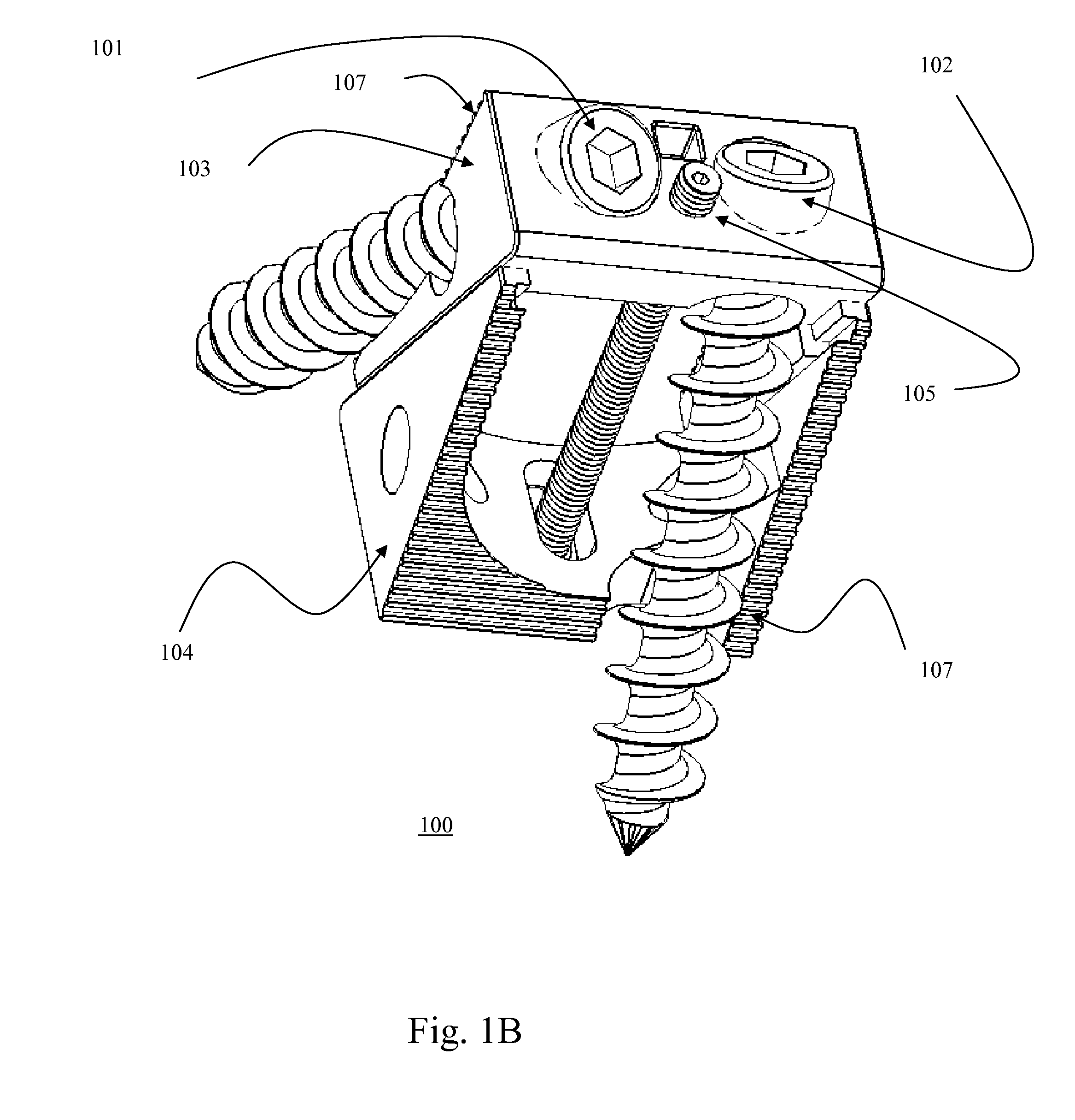
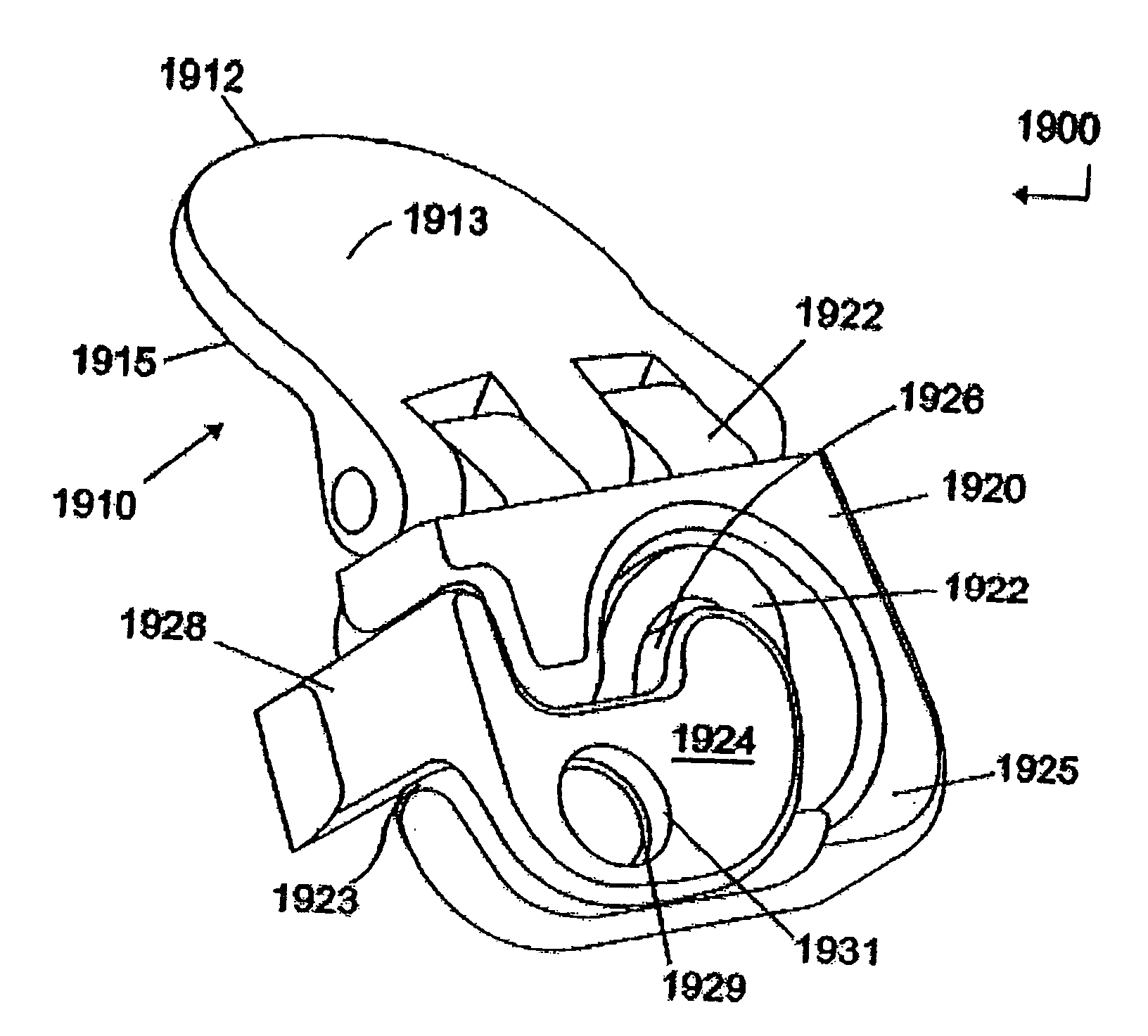
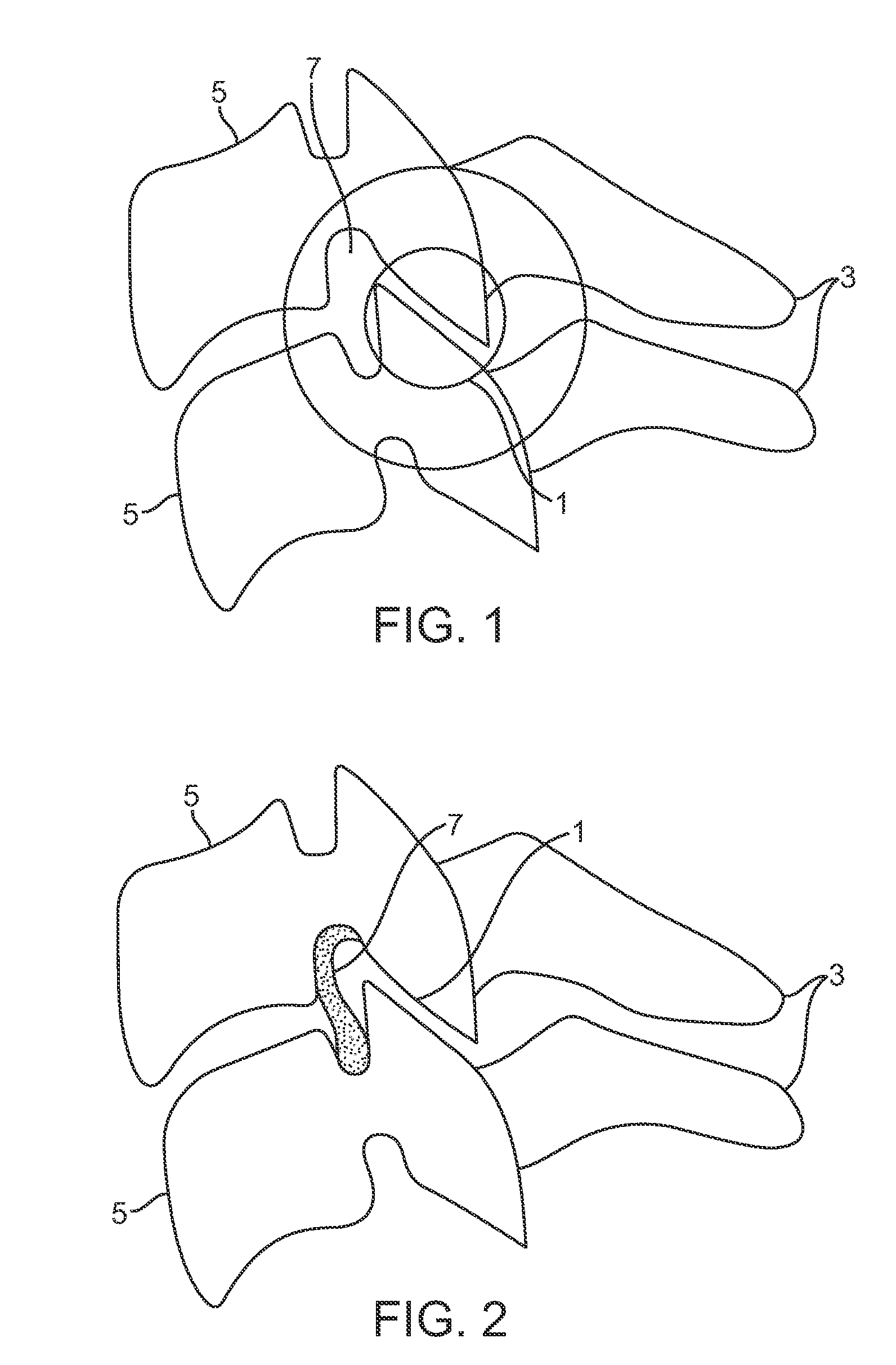
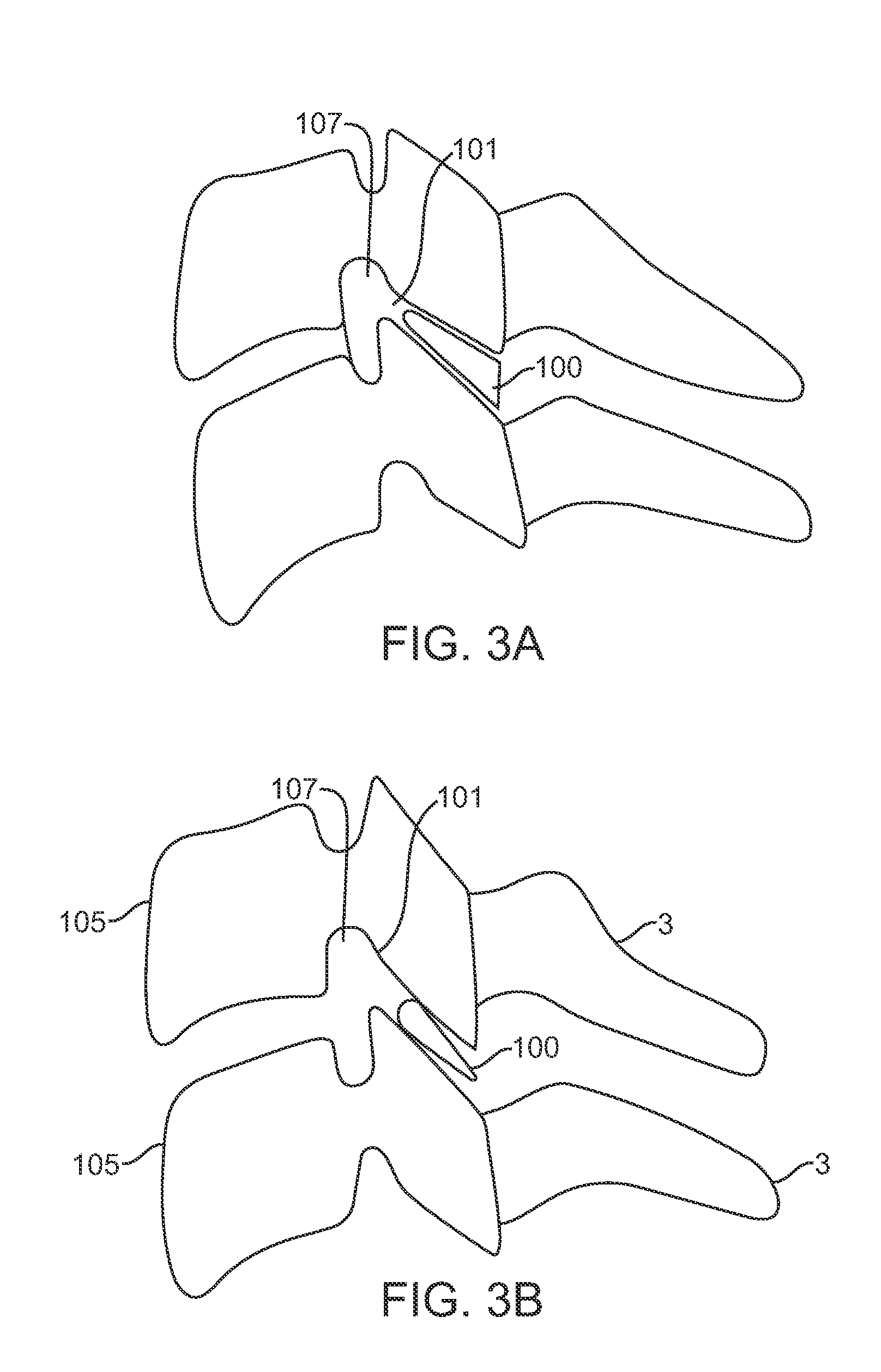
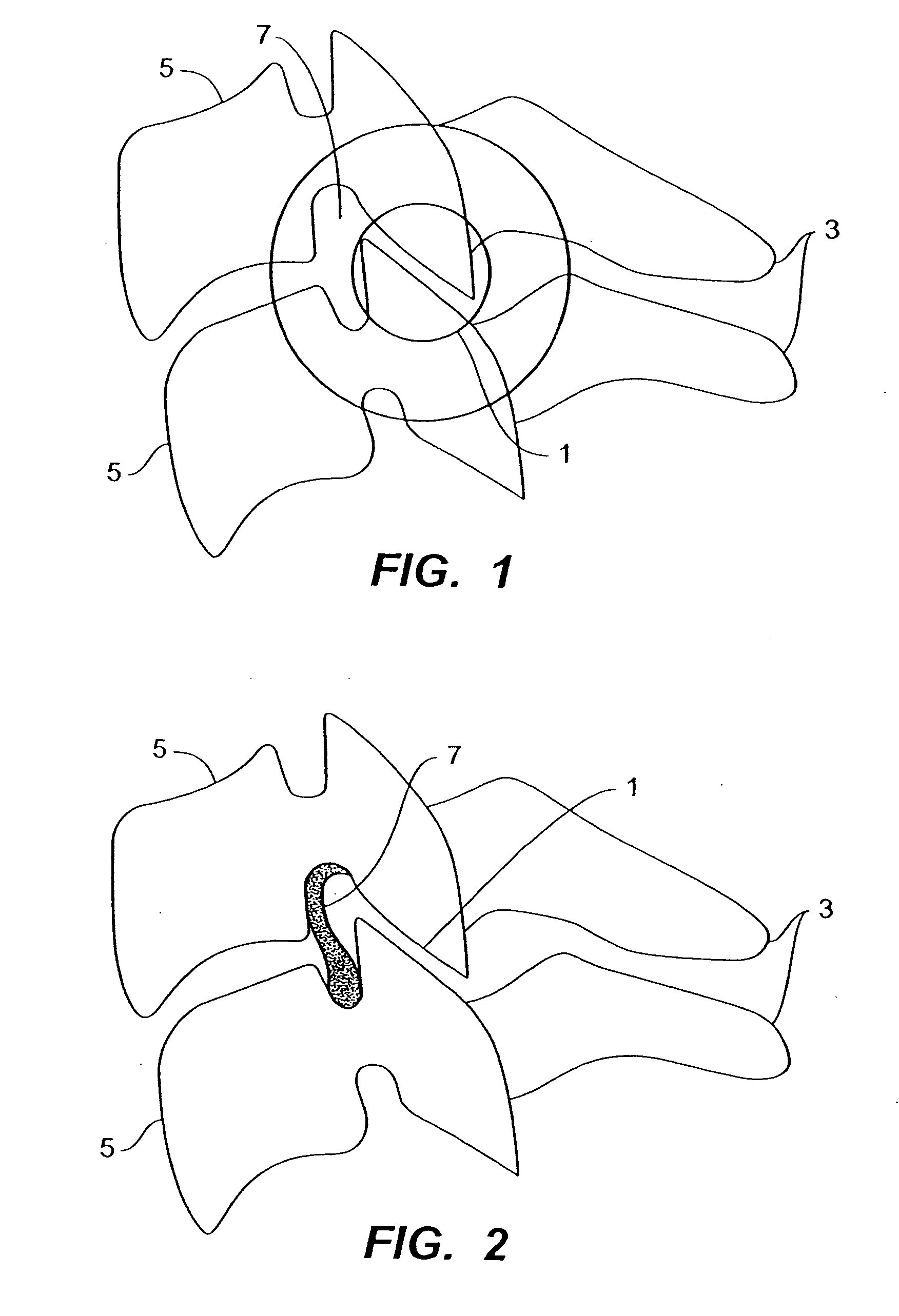
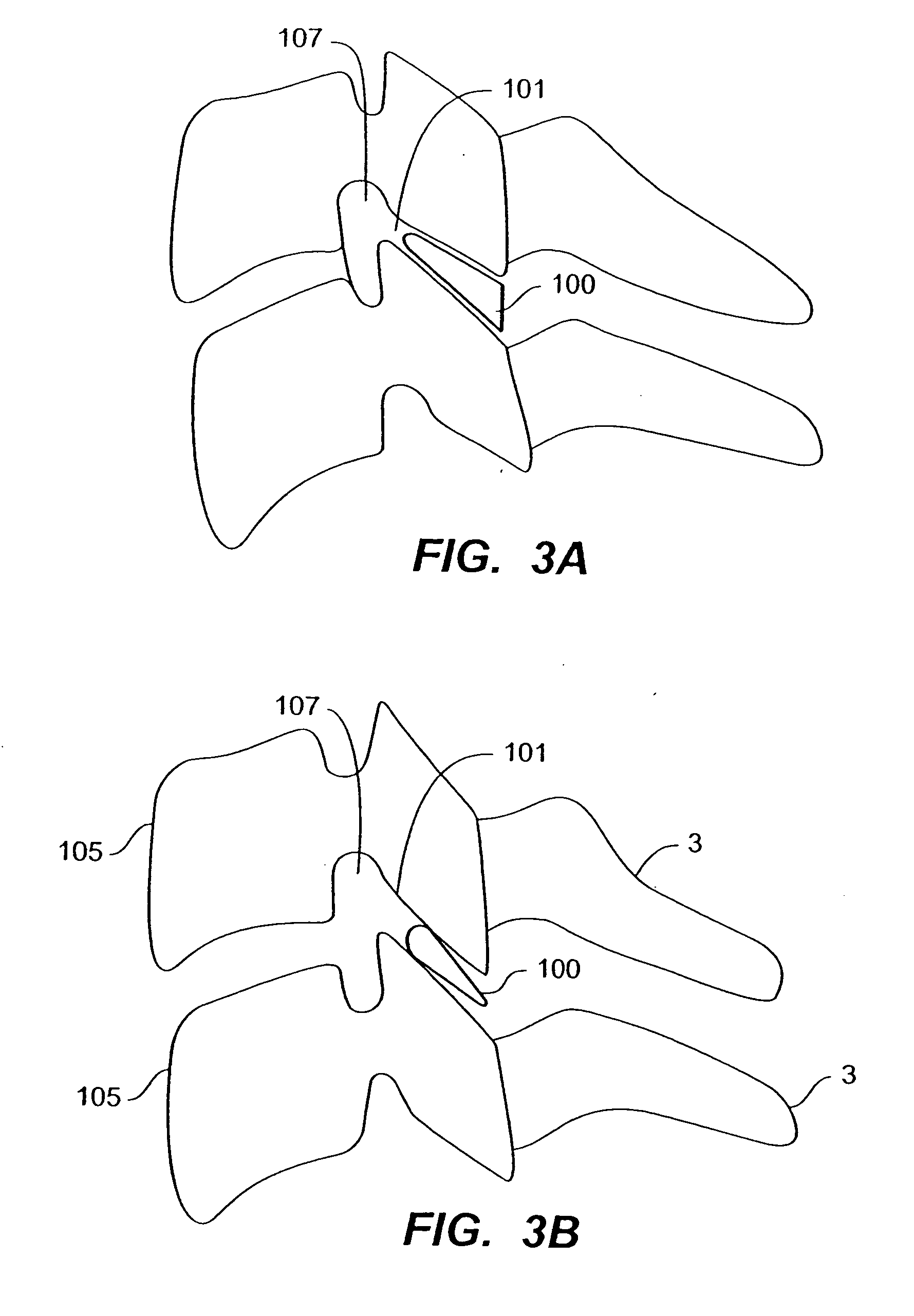
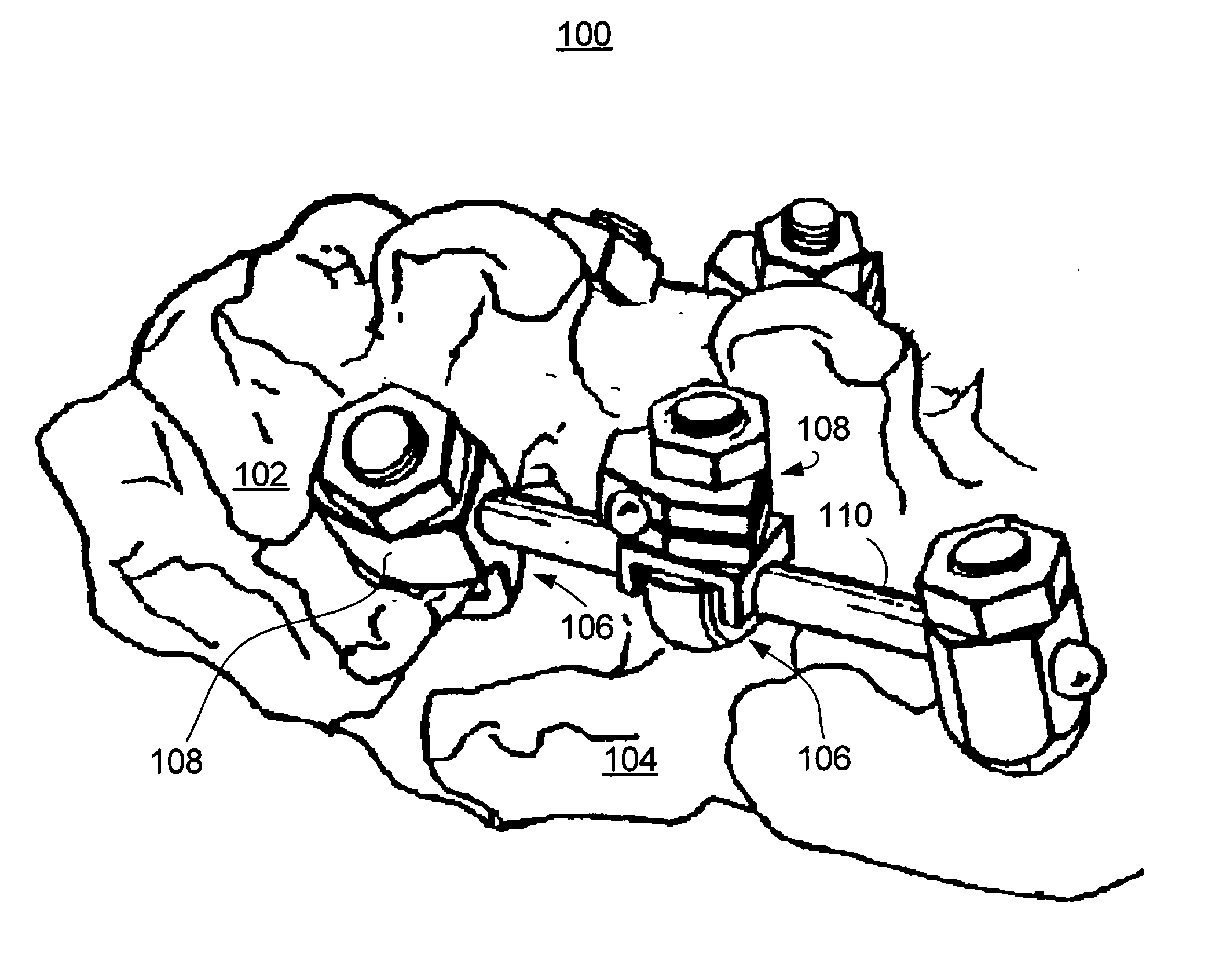
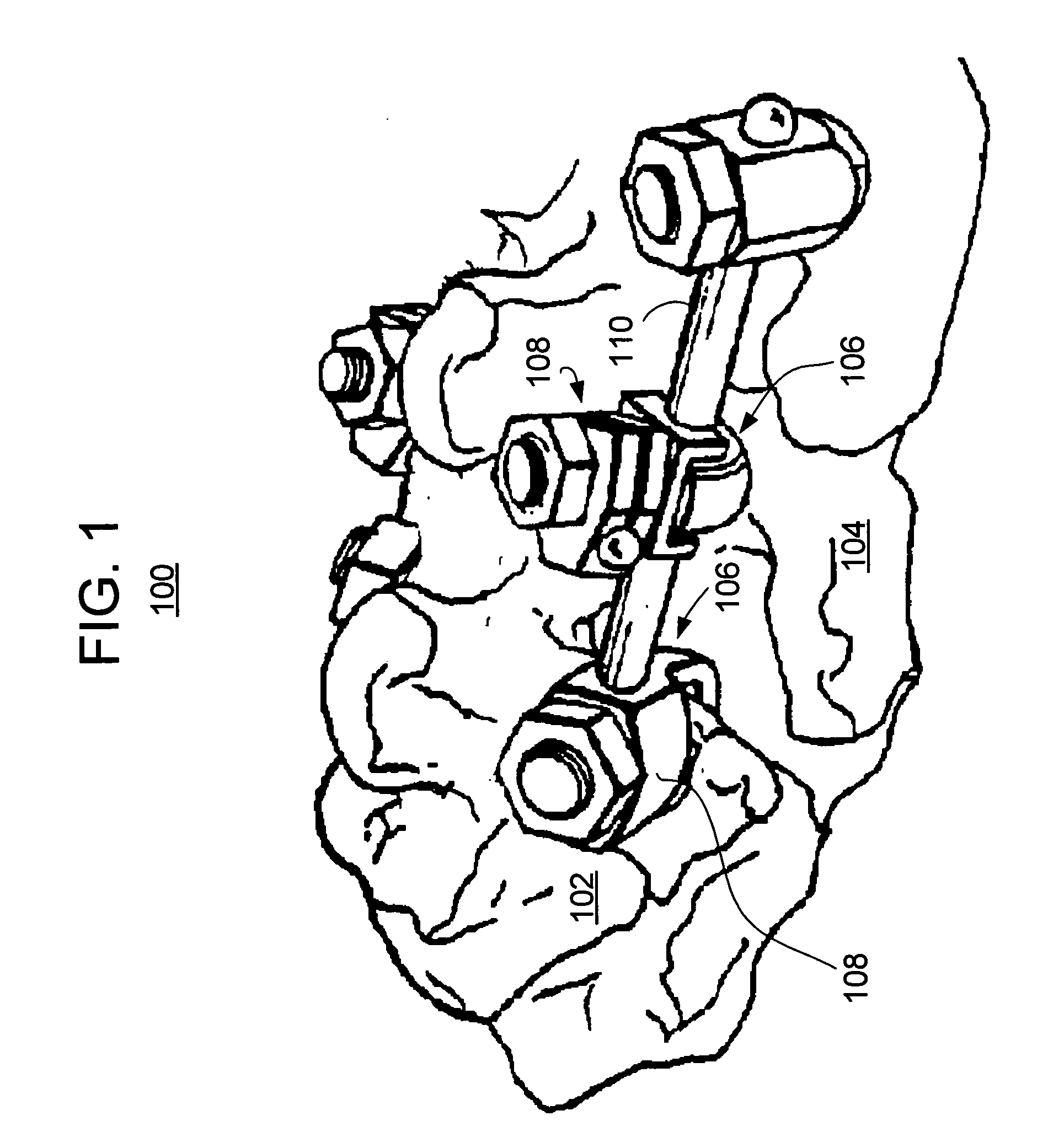
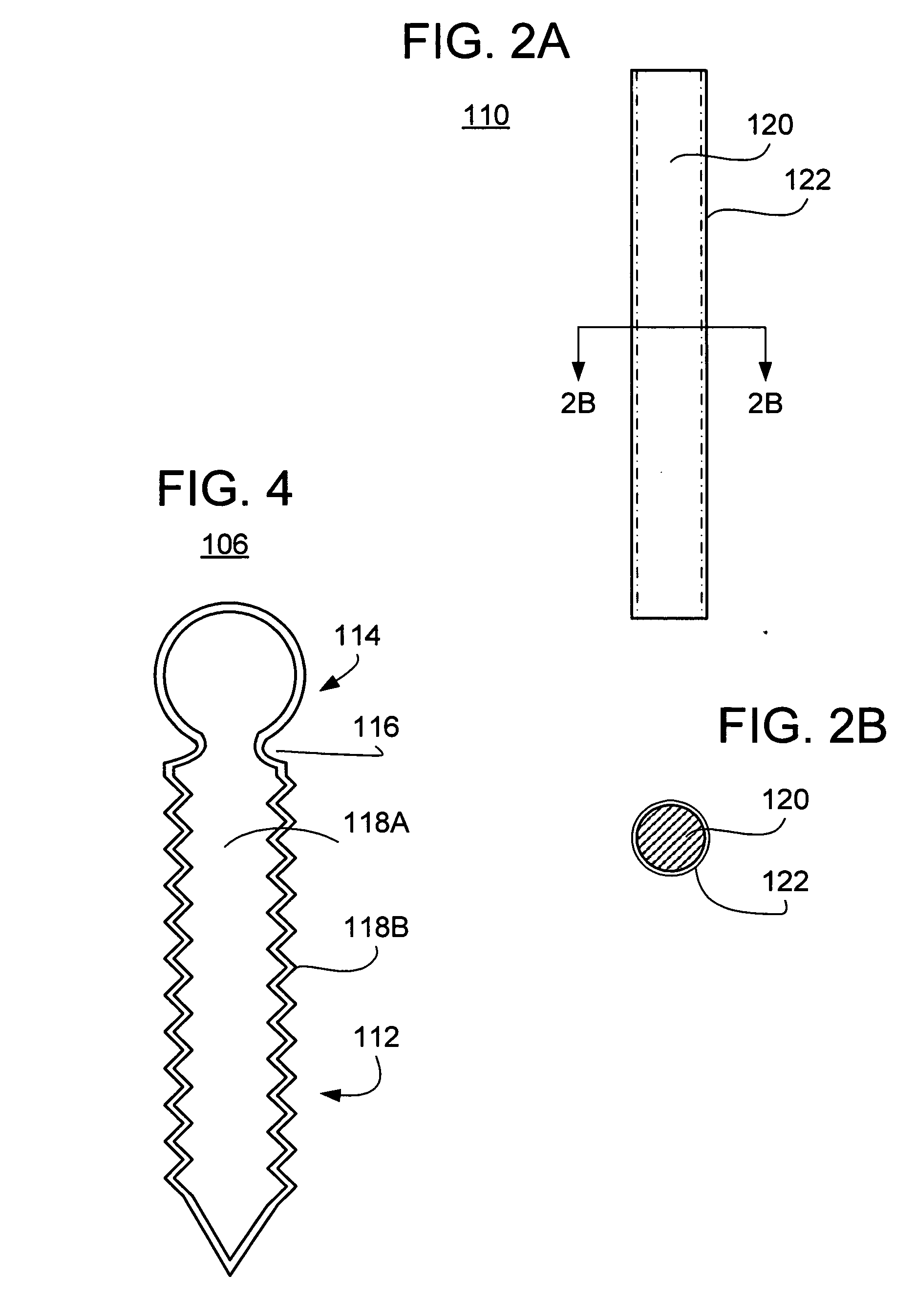
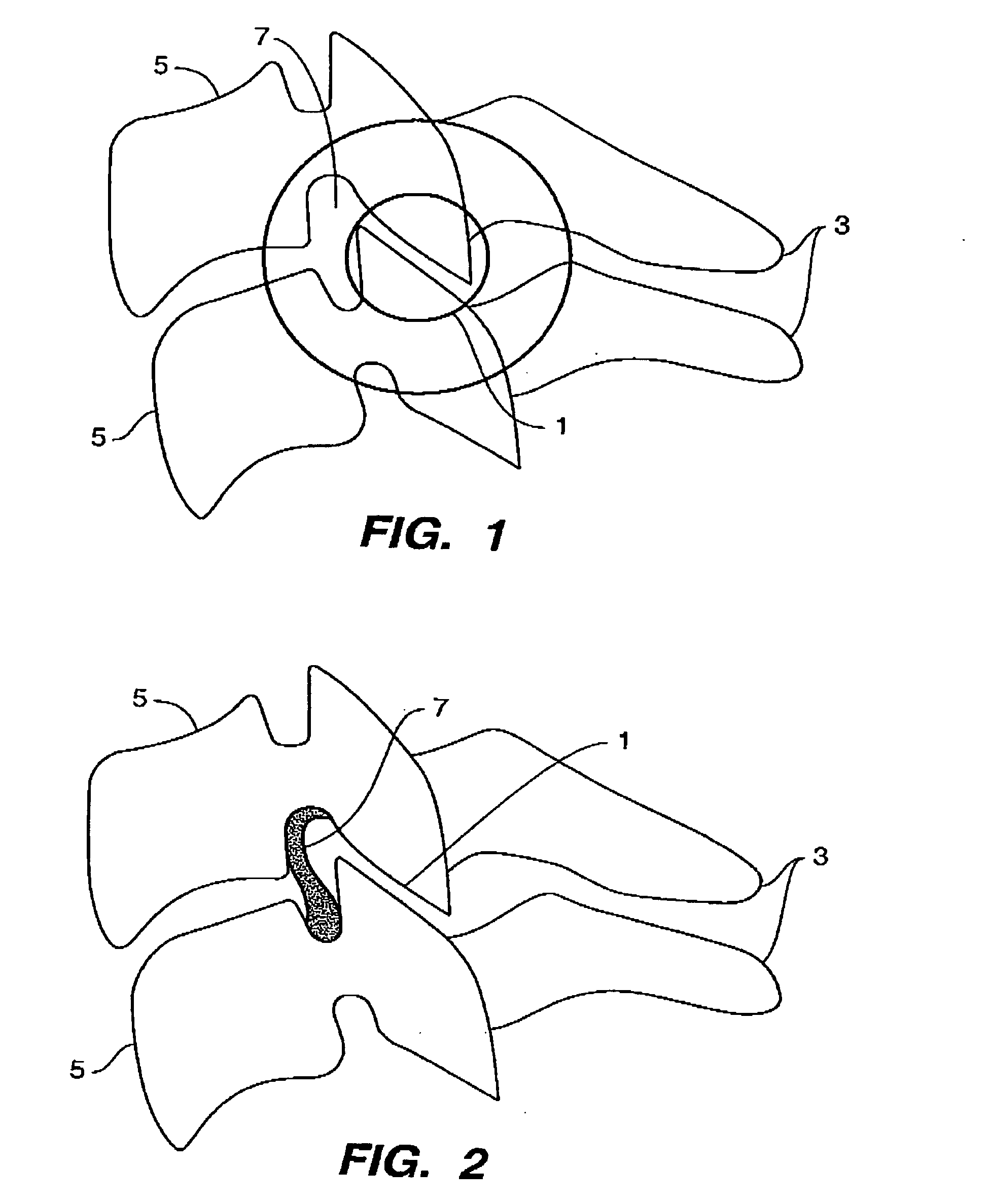
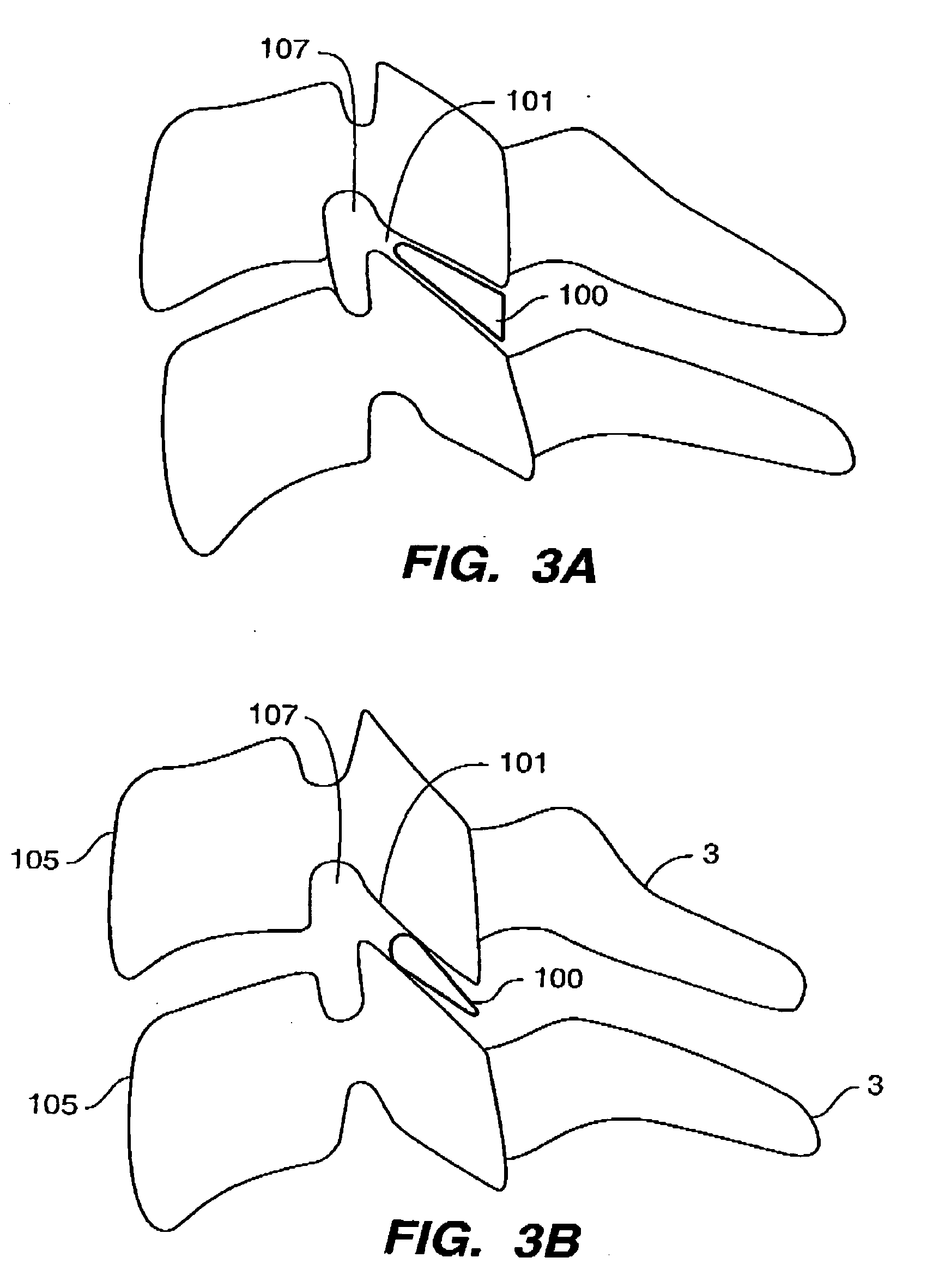
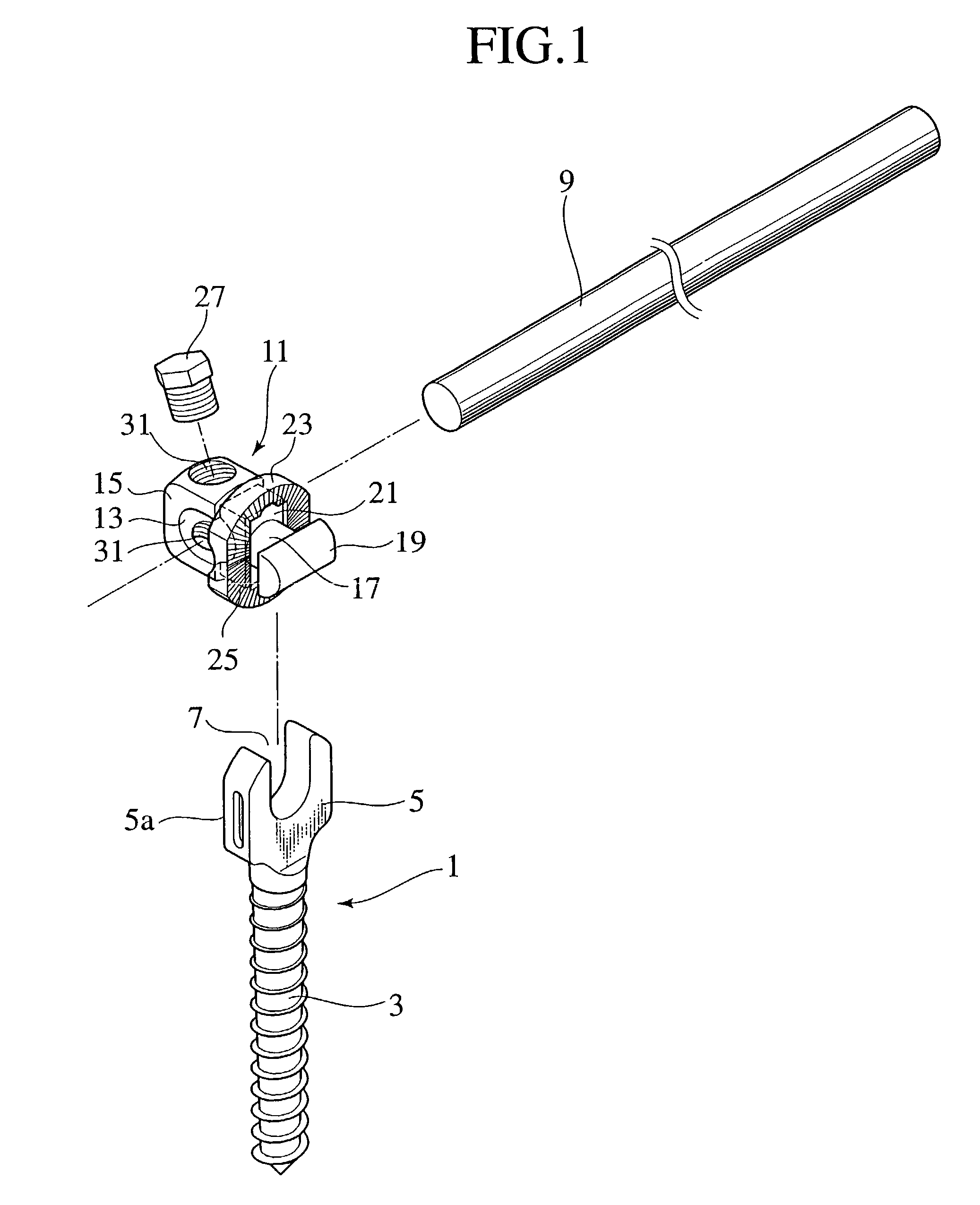
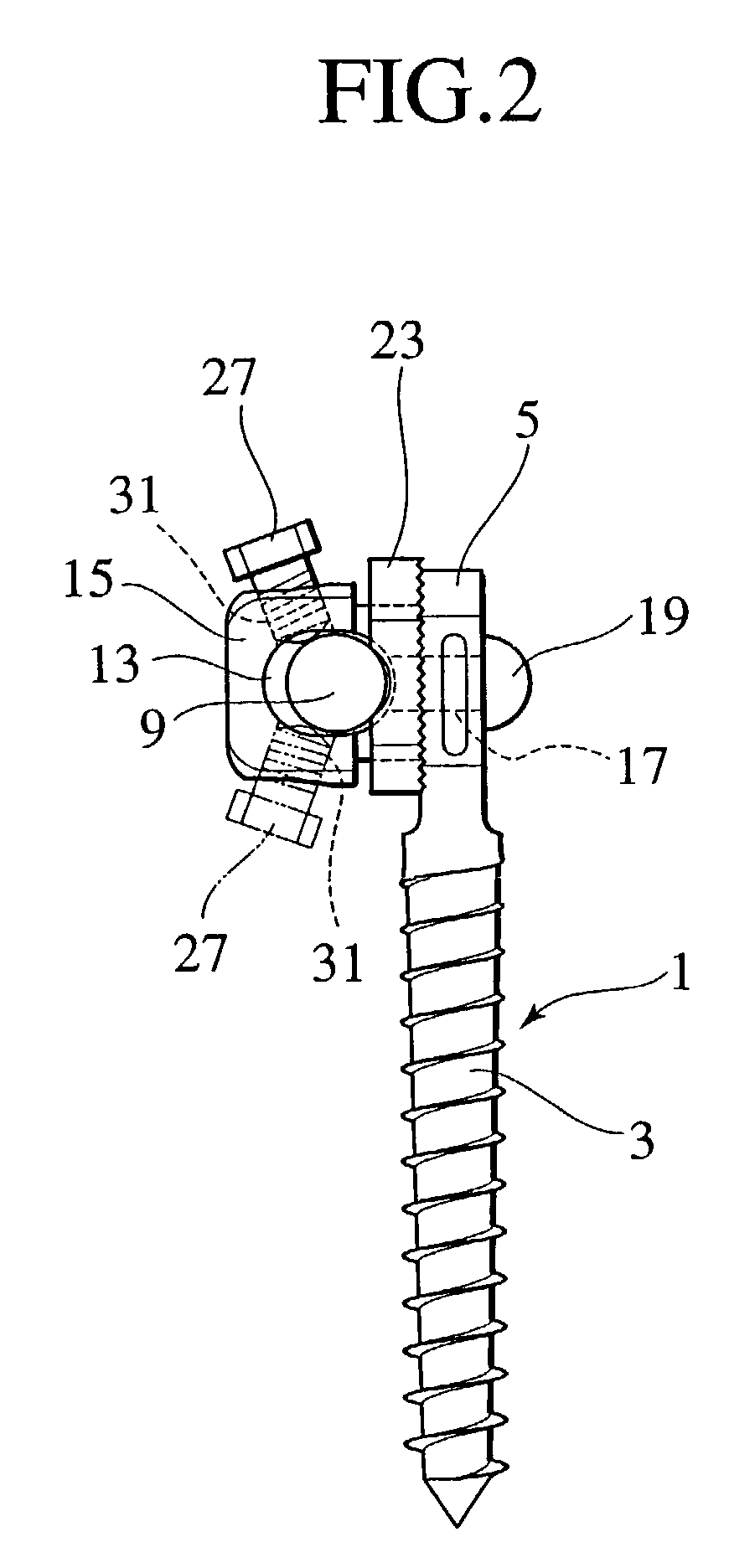
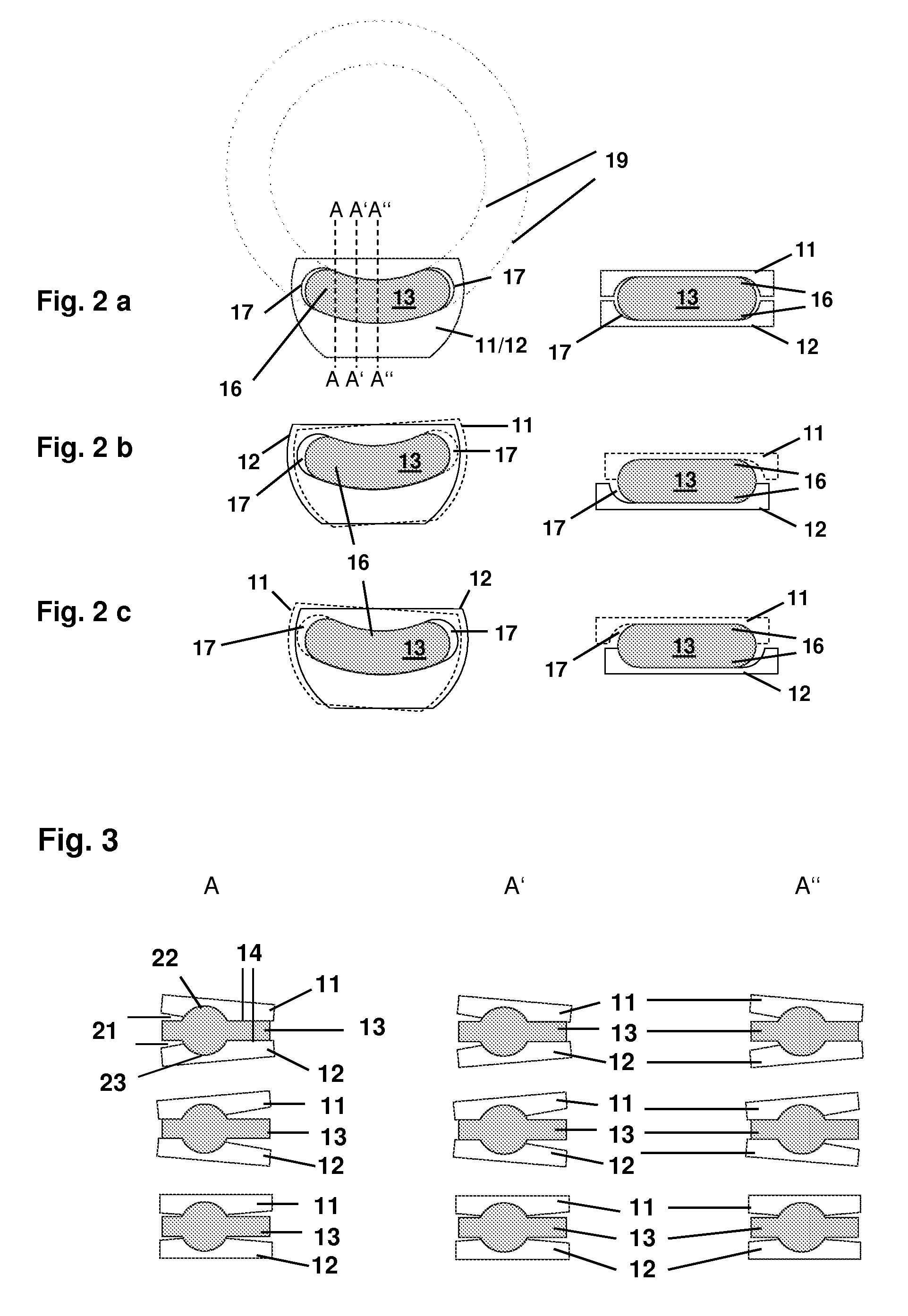
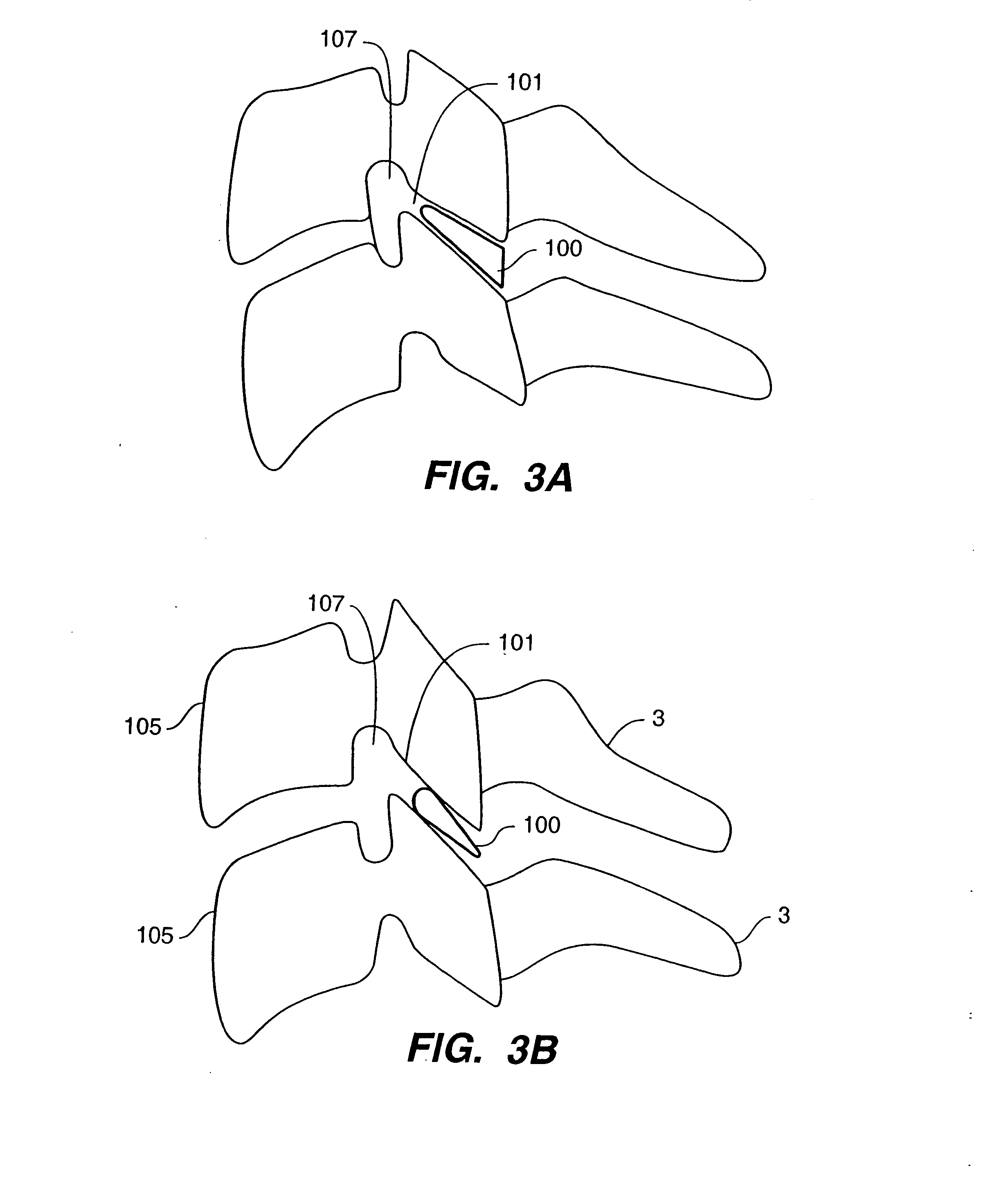
Rod for cervical vertebra and connecting system thereof
A connector is provided with a first fastening member 55 having an engagement hole 53 freely engaging with a head portion of an implant 41 screwed and inserted to a body of vertebra and a fastening groove 57, a second fastening member 63 having an insertion hole 61 freely inserting a rod 49 therethrough and a fastening groove 65, and a fastening device 69 freely penetrating a through hole 59 crossing to the fastening groove 57 in the first fastening member 55 and a through hole 67 crossing to the fastening groove 65 in the second fastening member 63, and an angle adjusting and engaging portion is provided on connecting surfaces 55a and 63a between the first fastening member 55 and the second fastening member 63.
Owner:SHOWA IKA KOHGYO
Inter-cervical facet implant with implantation tool
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
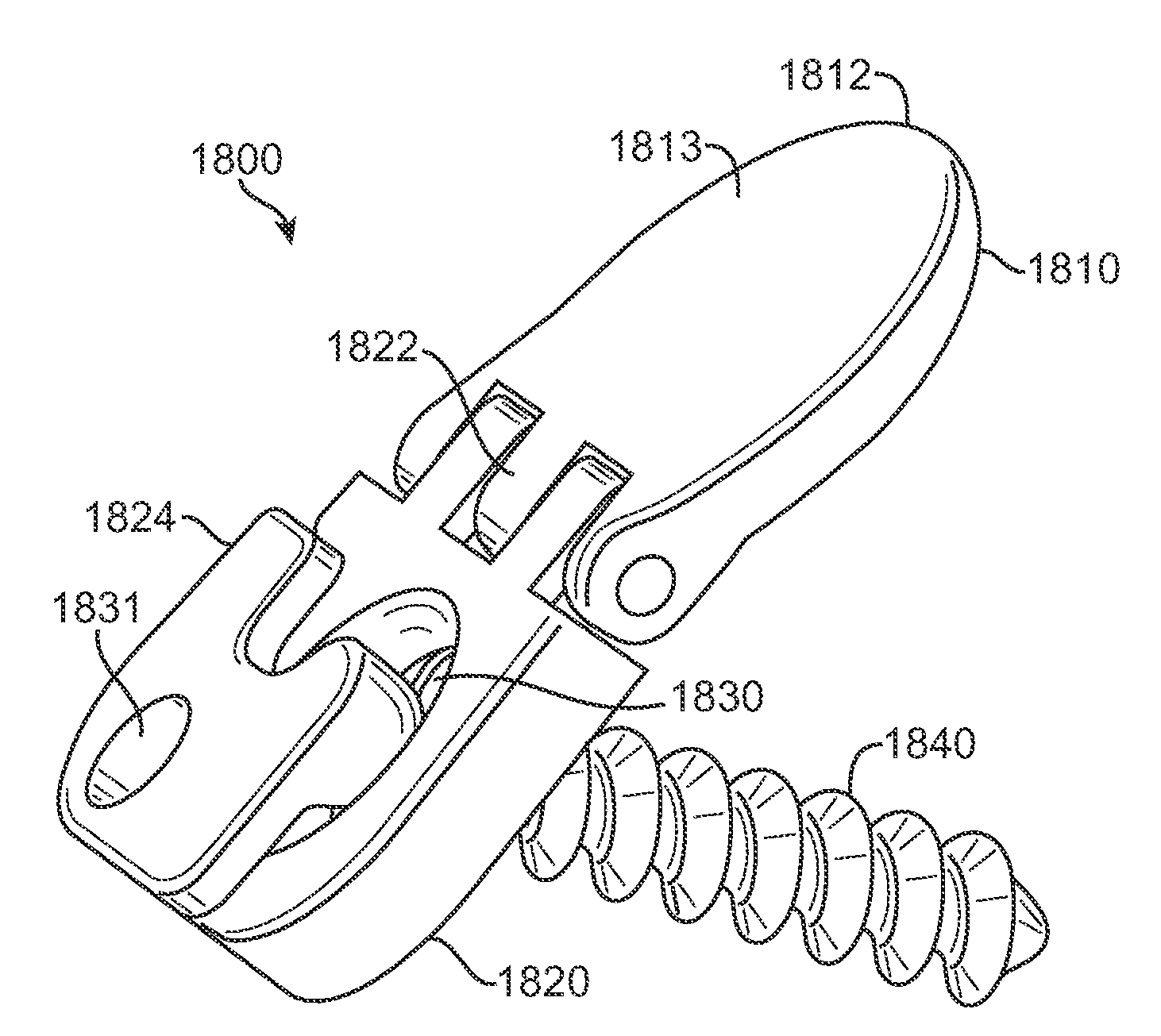
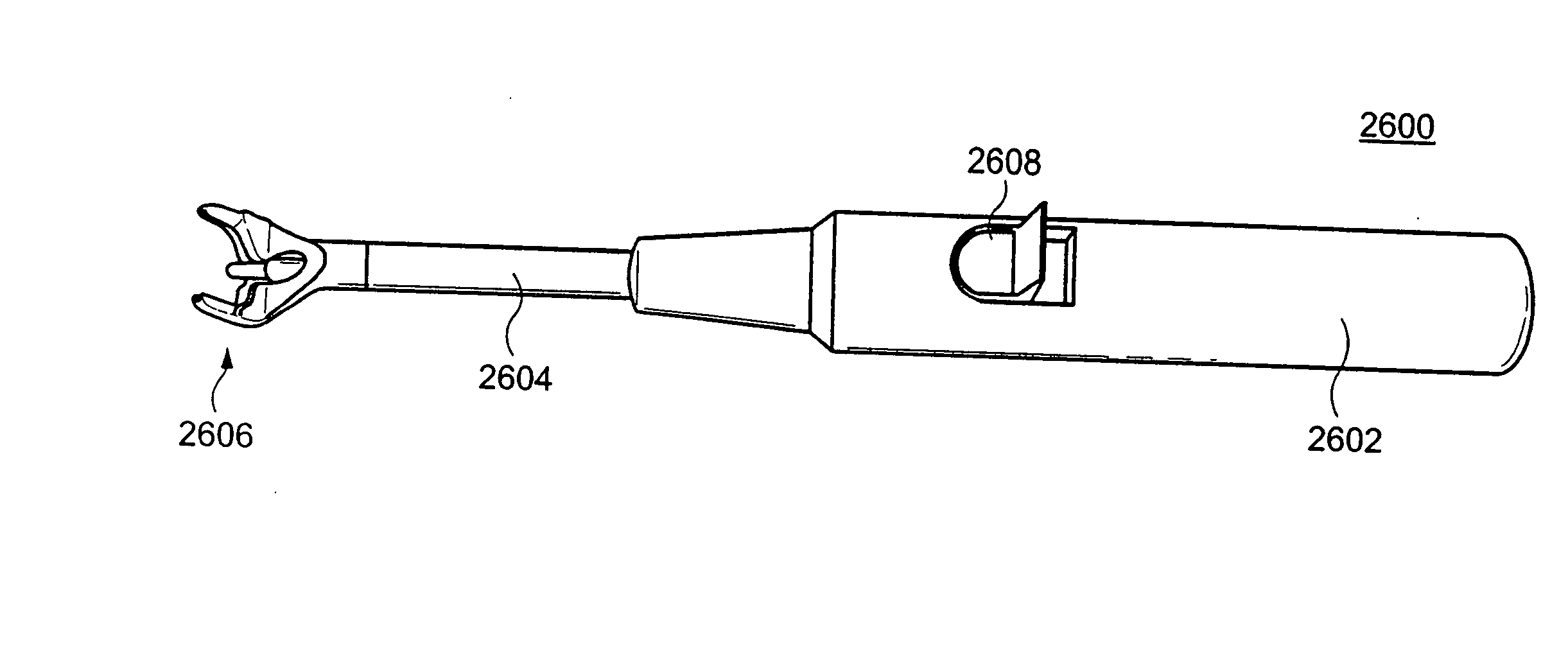
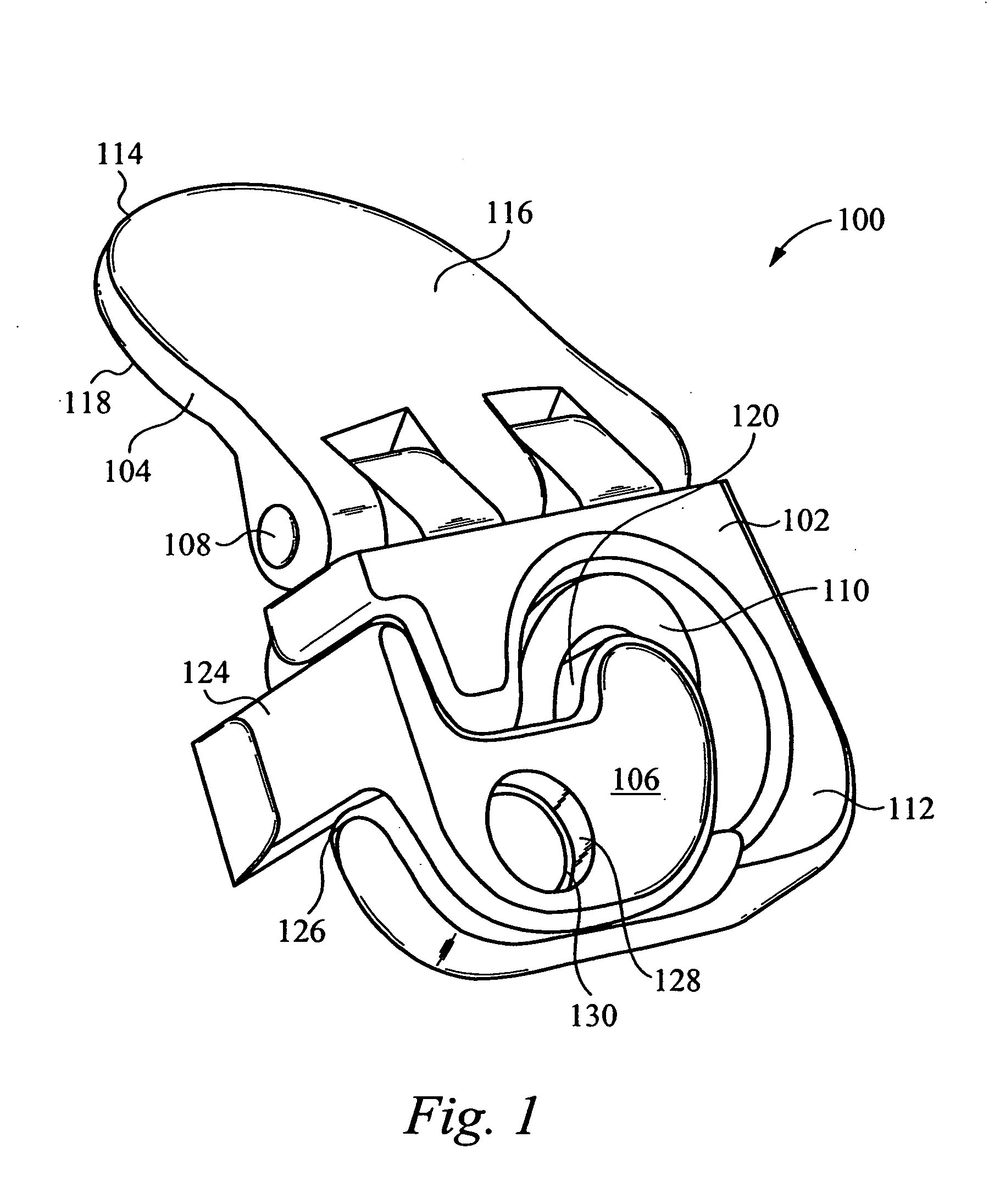
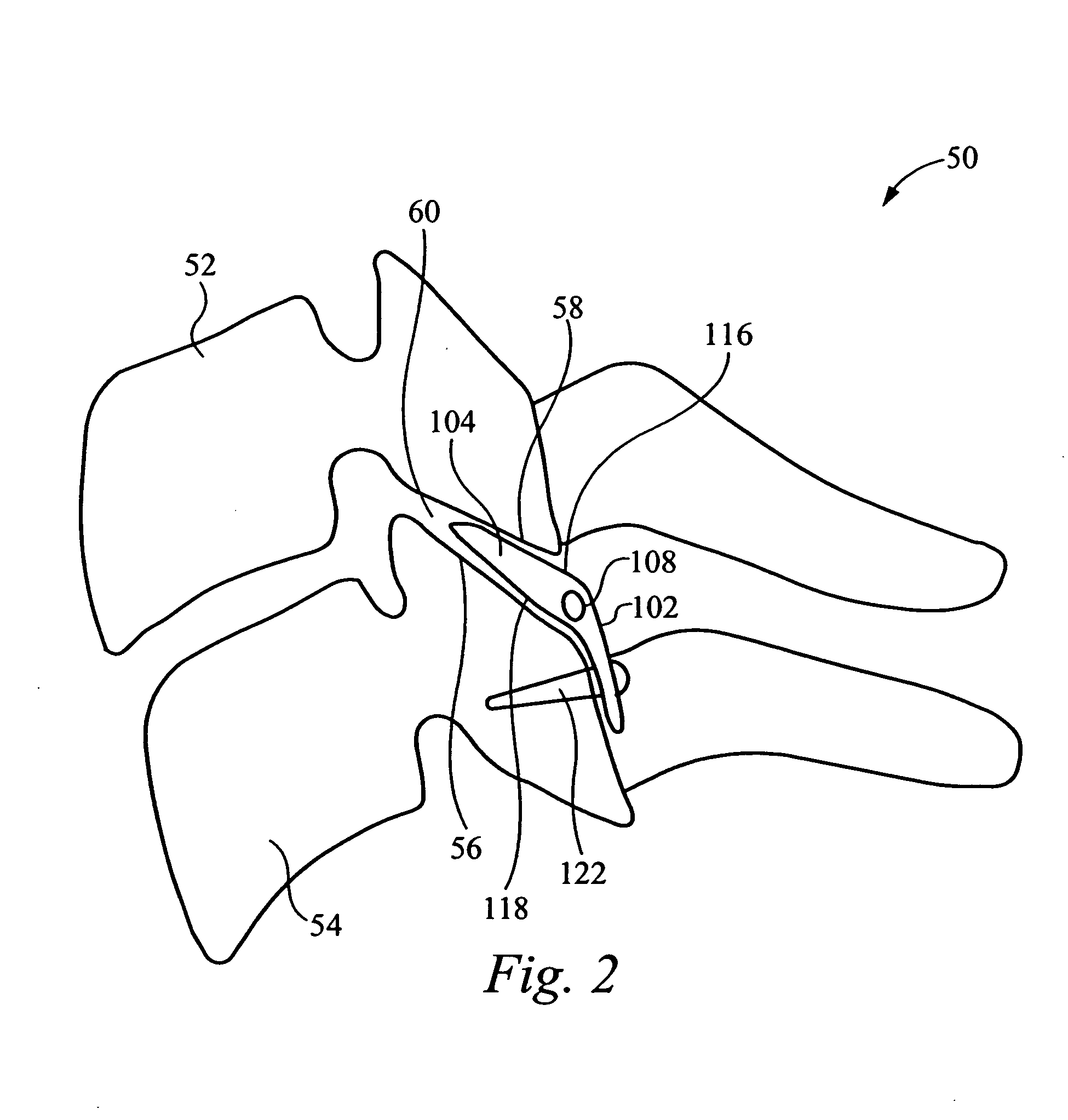
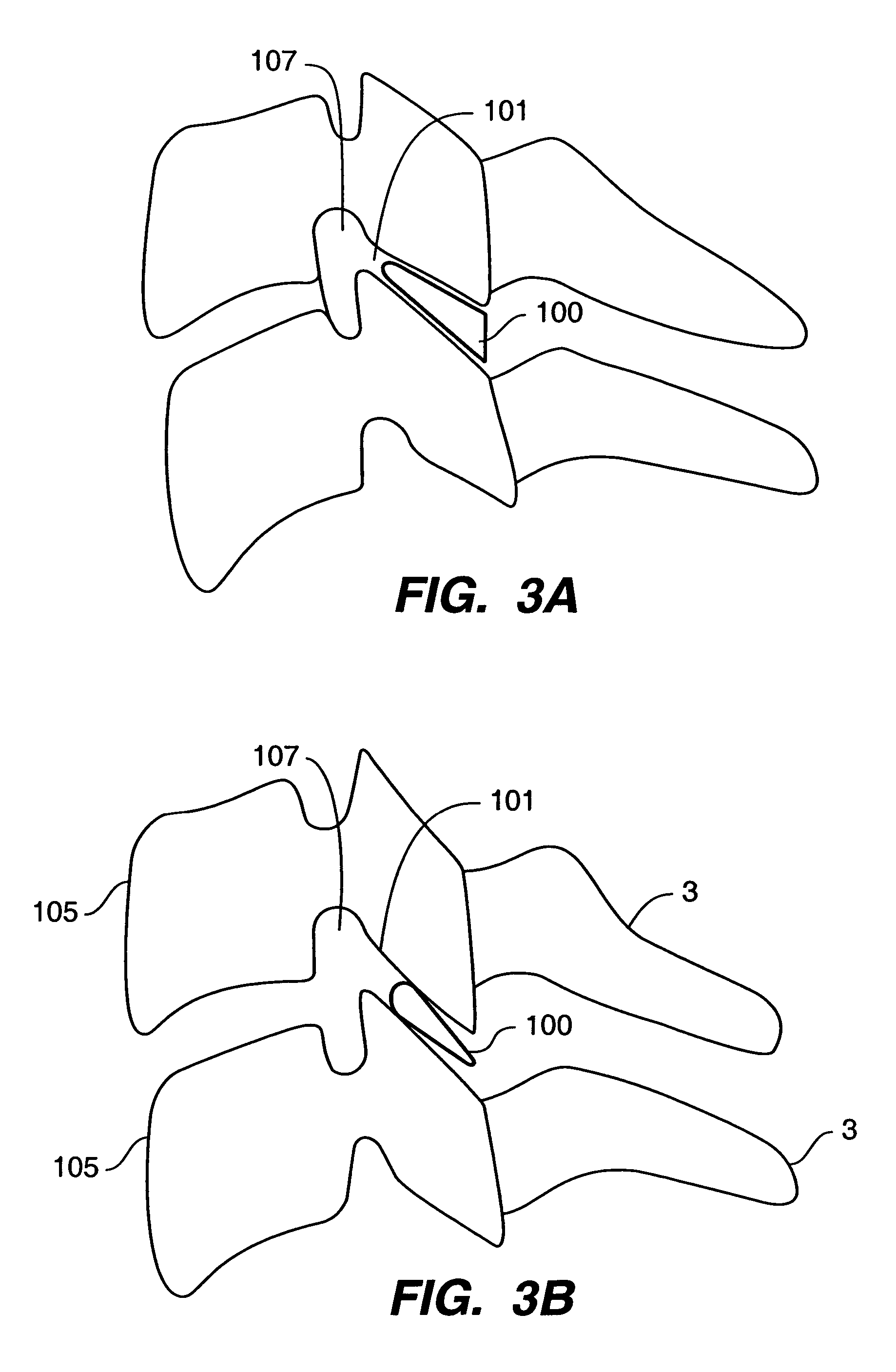
Inter-cervical facet implant distraction tool
A distraction tool is disclosed which distracts, and preferably sizes, adjoining facets of a spine for an implant. The tool preferably includes a distraction head that has a first and a second head component. The first head component and the second head component preferably include inter-digitated fingers when the distraction head is in a non-distracted position. The tool includes a handle which is actuatable to move the distraction head to a distracted position, whereby the first set and second set of fingers are separated from one another. The tool can include a distraction gauge as well as a locking mechanism. The tool can also include a movement limitation mechanism to control the amount of distraction which the tool undergoes when actuated. The tool can include an insertion feature to allow the implant to be inserted into the facet joint while the tool is distracting the facets apart.
Owner:KYPHON
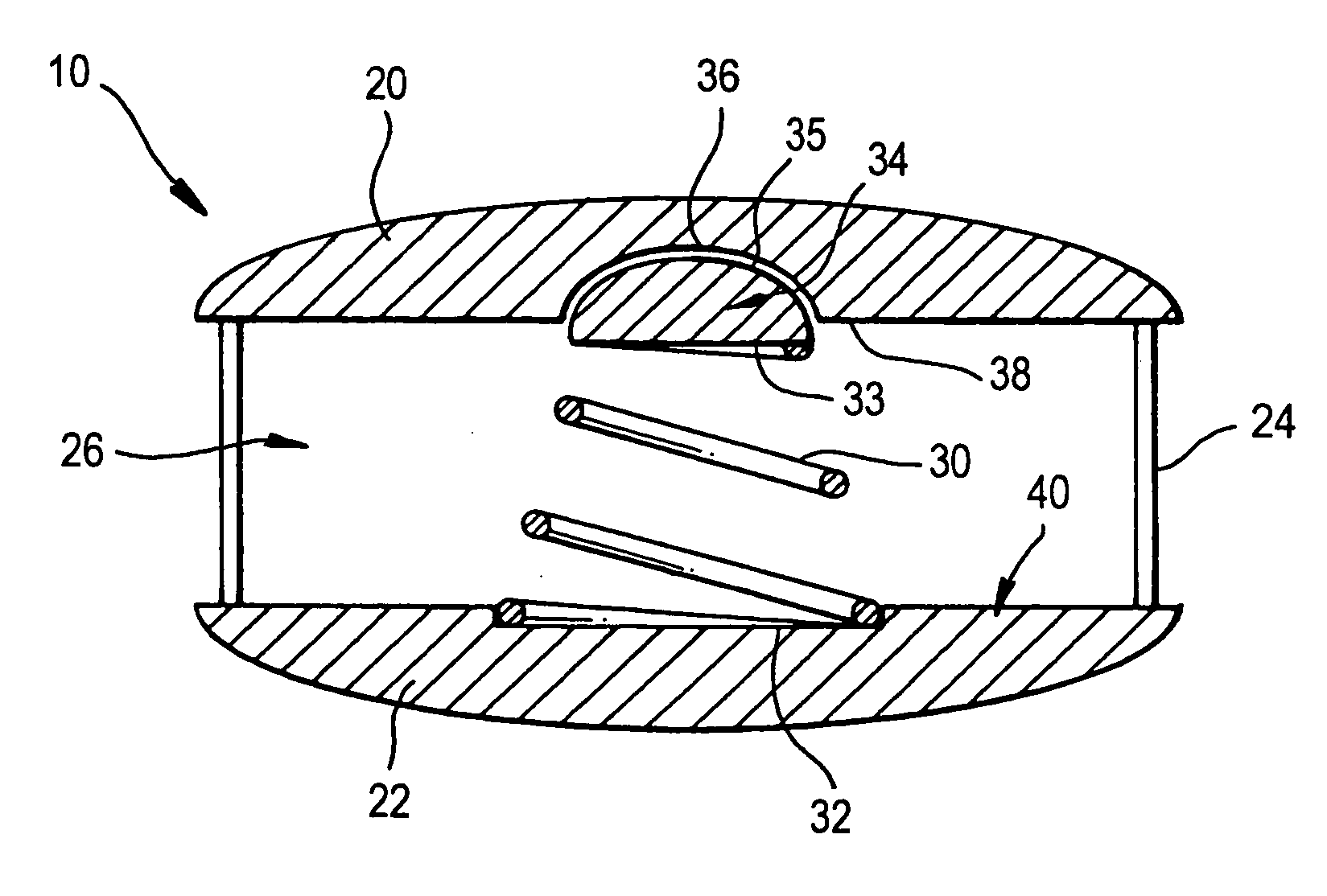
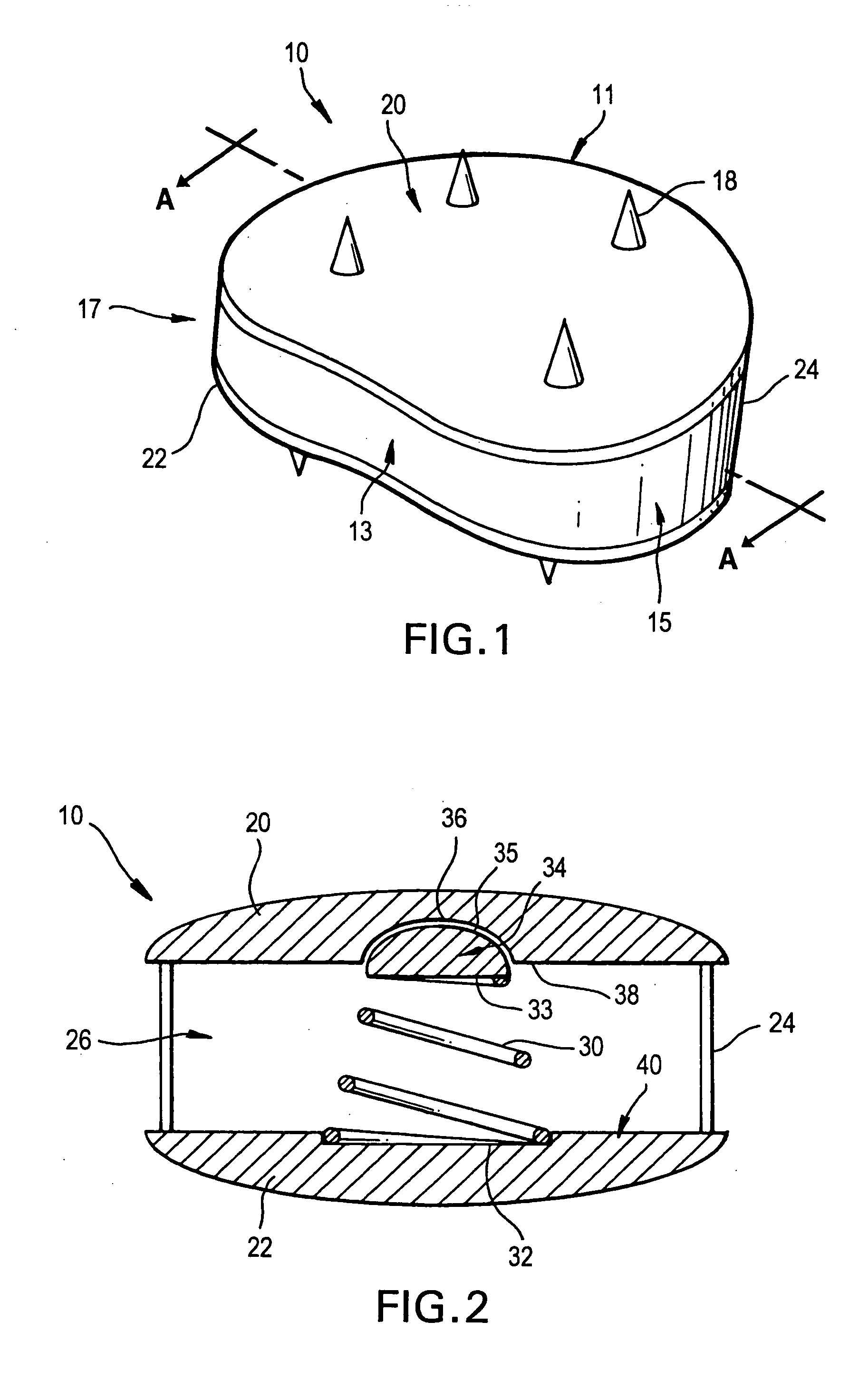
Spinal implants, including devices that reduce pressure on the annulus fibrosis
InactiveUS20050256582A1Promote reconstructionPrevents herniationInternal osteosythesisBone implantFibrosisDiscectomy
The invention broadly facilitates reconstruction of the Annulus Fibrosus (AF) or the AF and the Nucleus Pulposus (NP). Such Reconstruction prevents recurrent herniation following Microlumbar Discectomy (MLD) other procedures. The invention may also be used in the treatment of herniated discs, annular tears of the disc, or disc degeneration, while enabling surgeons to preserve the contained NP. The methods and apparatus may be used to treat discs throughout the spine including the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spines of humans and animals. In the preferred embodiment, a spinal repair system according to the invention comprises a first end portion adapted for placement within an intervertebral body, a second end portion adapted for placement within an adjacent intervertebral body, and a bridge portion connecting the first and second end portions, the bridge portion being adapted to span a portion of an intervertebral disc space and prevent excessive outward bulging.
Owner:ANOVA
Intervertebral disc prosthesis with transversally arched, curved cylindrical articulation surfaces for the lumbar and cervical spine
ActiveUS20060235531A1Easy to integrateMinimize risk of fracturingSpinal implantsCoatingsIntervertebral discLumbar vertebrae
The invention relates to an intervertebral disc prosthesis for the total replacement of a natural intervertebral disc within the lumbar and cervical spine, comprising articulating sliding partners, where the upper sliding partner has means for a firm assembly to an upper vertebral body and the lower sliding partner has means for a firm assembly to a lower vertebral body and at least one sliding surface that is between two sliding partners. According to the invention, functional two- and three part designs are planned and both prostheses have in common, that only a dorsoventral- and rotation movement is possible as a result of laterolaterally aimed, transversally arched, ventrally curved cylindrical convexity(ies) and corresponding concavity(ies), however without an inclination of the sliding partners in a lateral direction. In a further design, the cylindrical articulation surfaces are un-curved, enabling a motion of the sliding partners in only a ventrodorsal direction. According to the invention, the intervertebral disc prostheses are suited for an implantation from lateral and ventrolateral, particularly in revision surgeries.
Owner:BUETTNER JANZ KARIN
Intradiscal devices including spacers facilitating posterior-lateral and other insertion approaches
Apparatus and methods are used to expand and / or connect disc replacement devices in situ, allowing such devices to be inserted through smaller openings including posterior as well as an anterior approaches to the spine. Other embodiments reside in nucleus replacements that do not expand within the disc space, providing improved longevity compared to existing NRs. Embodiments of the invention may be used in the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spine. The invention may also be used in other joints such as, the knee, prosthetic knees, prosthetic hips, or other joints in the body.
Owner:FERREE BRET A +1
Inter-cervical facet implant with locking screw and method
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
Inter-cervical facet implant and method
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
Inter-cervical facet implant with implantation tool
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
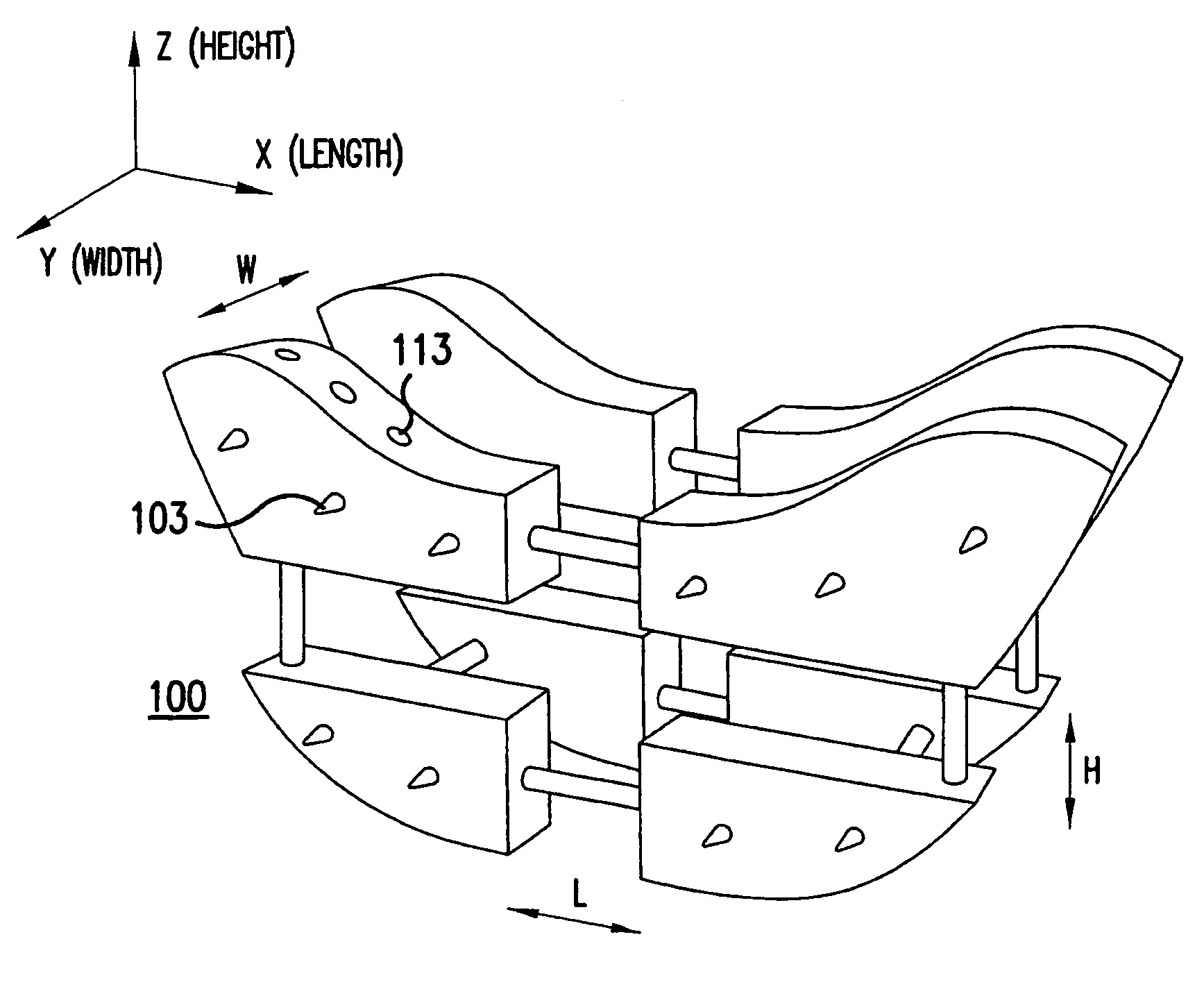
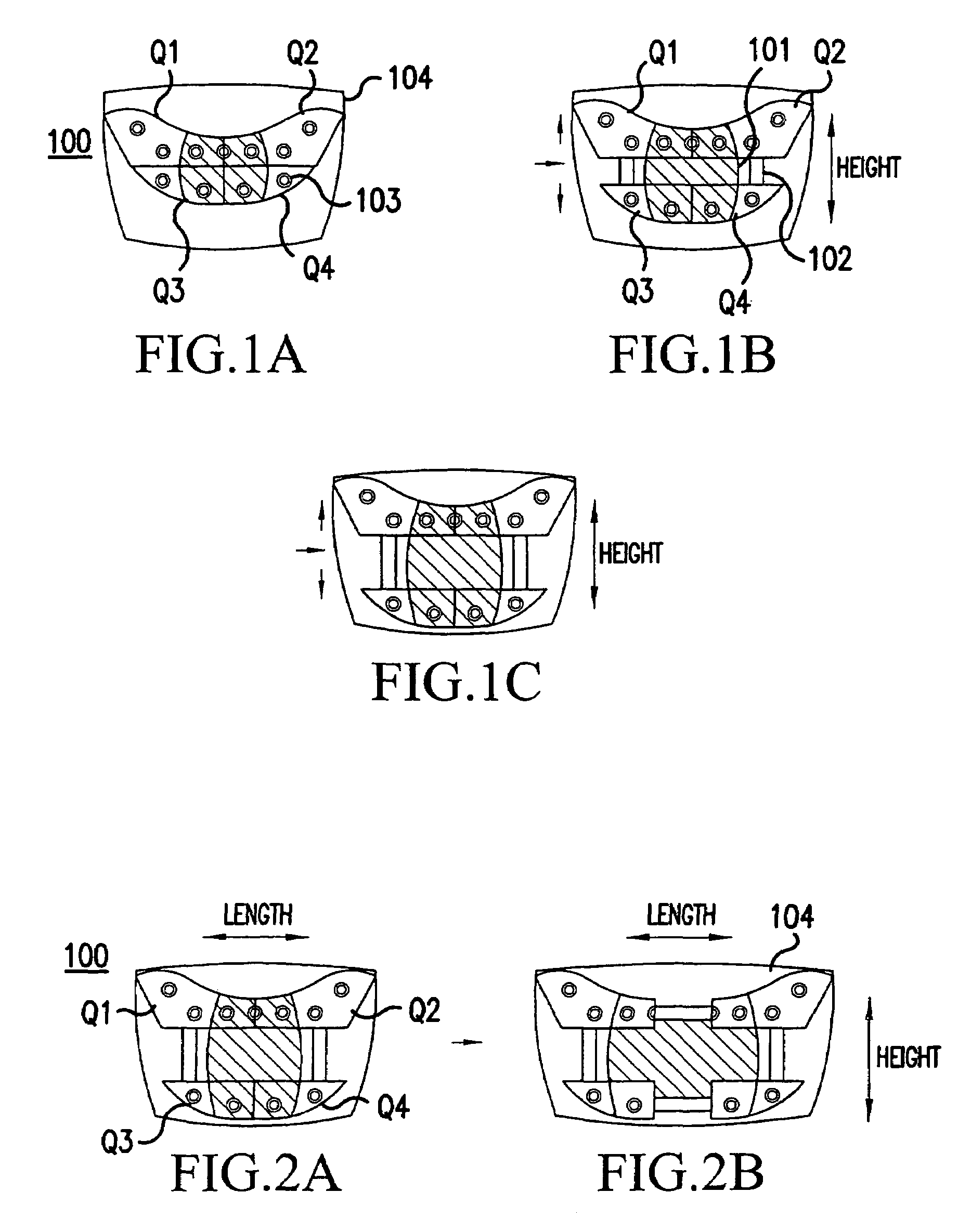
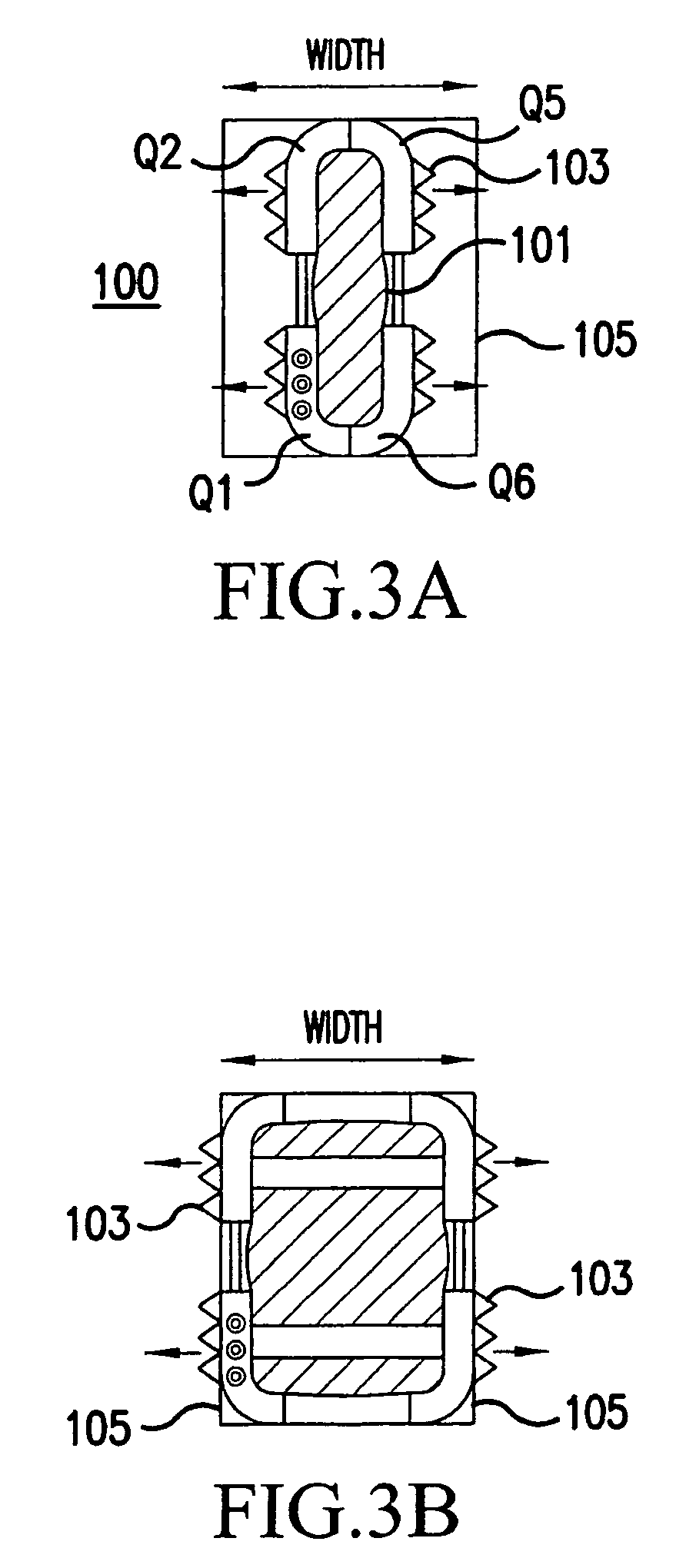
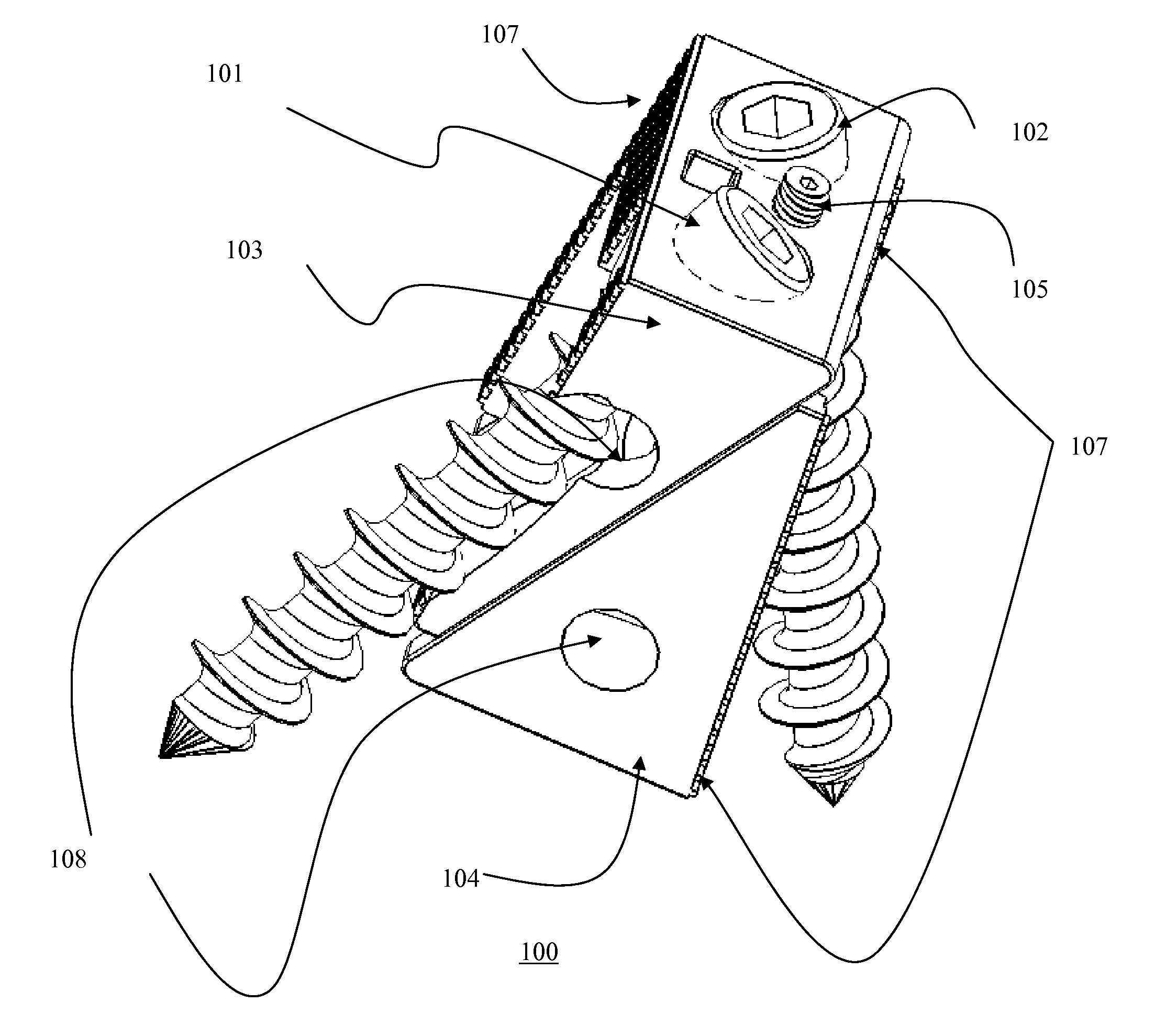
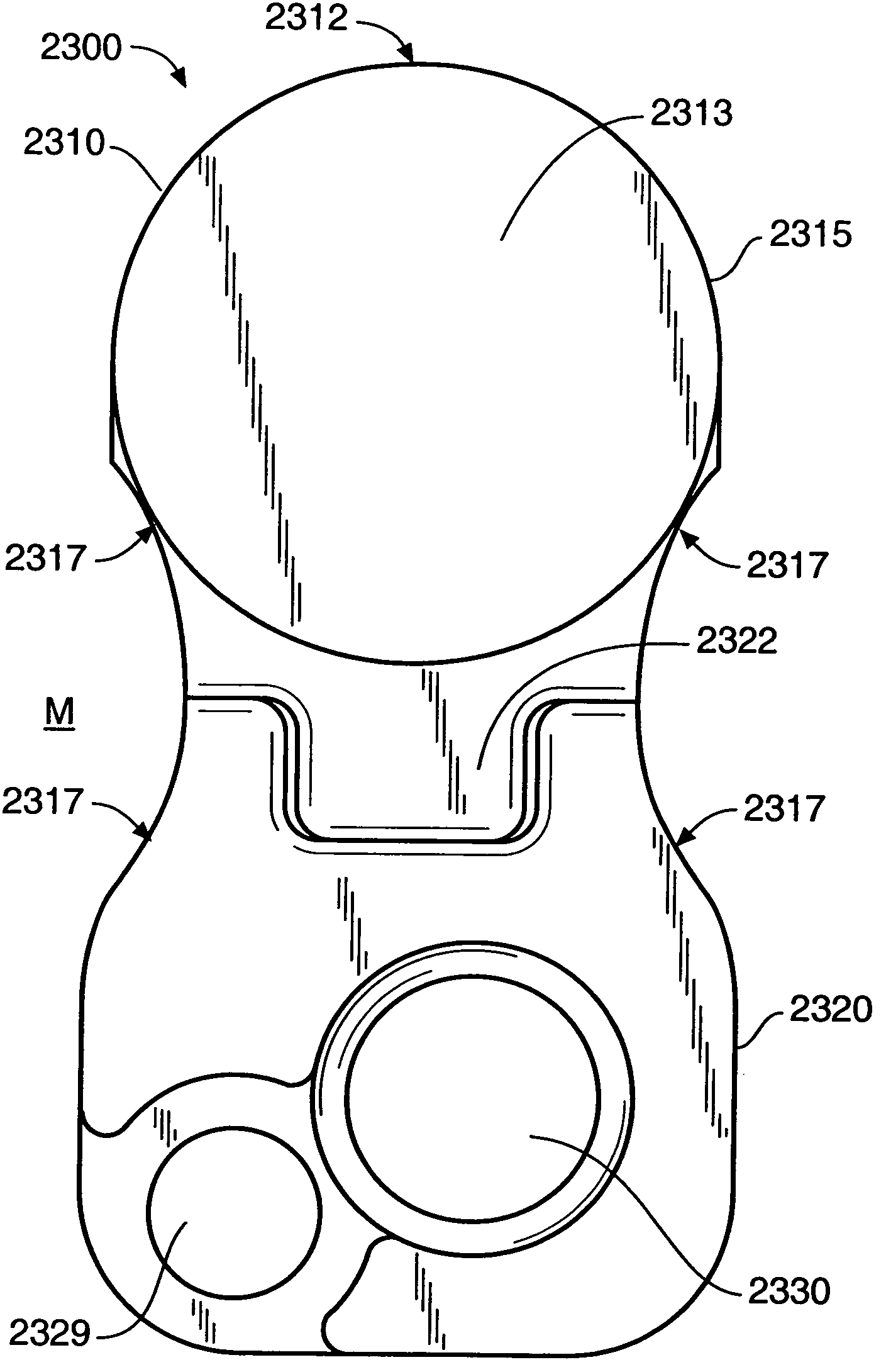
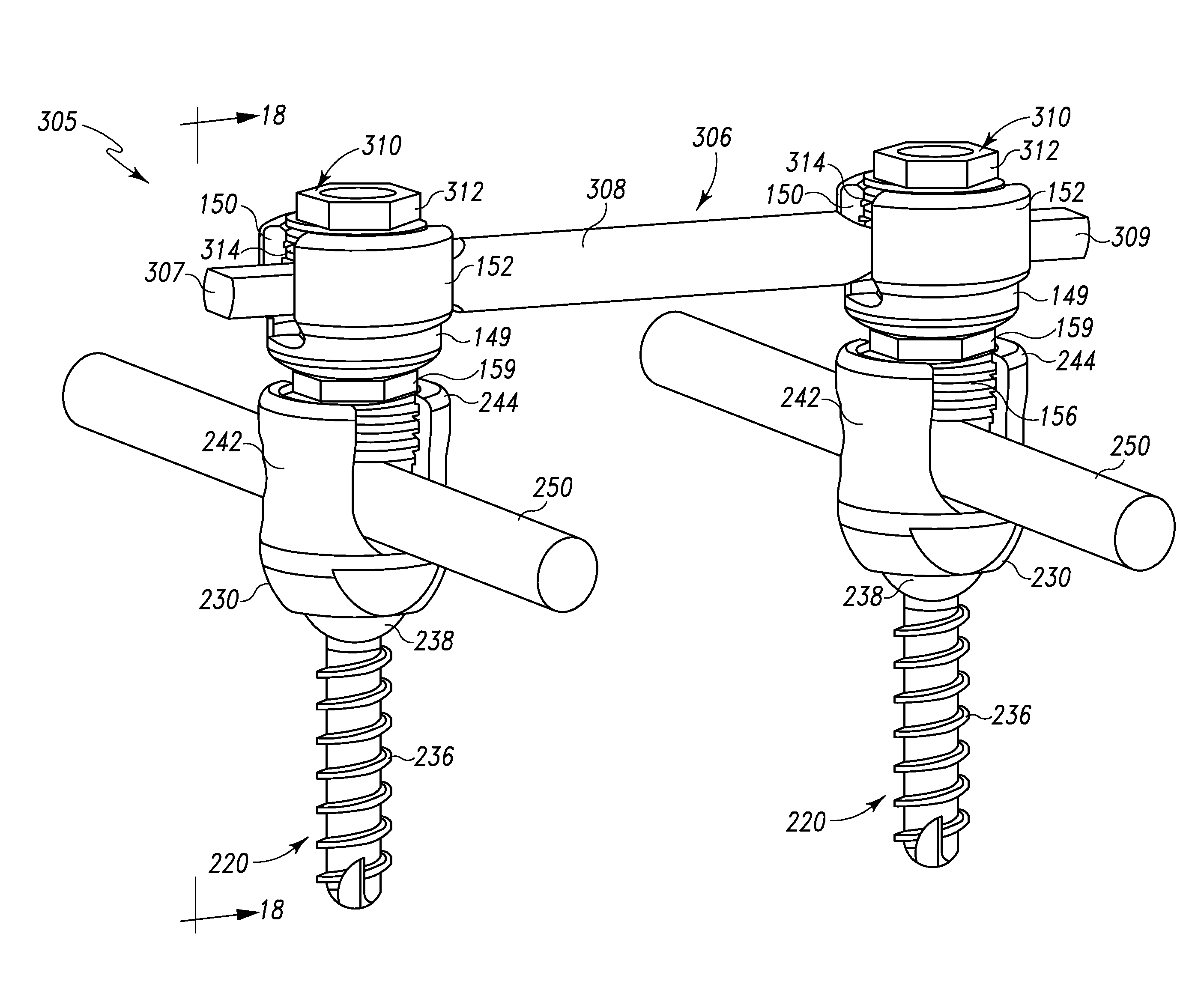
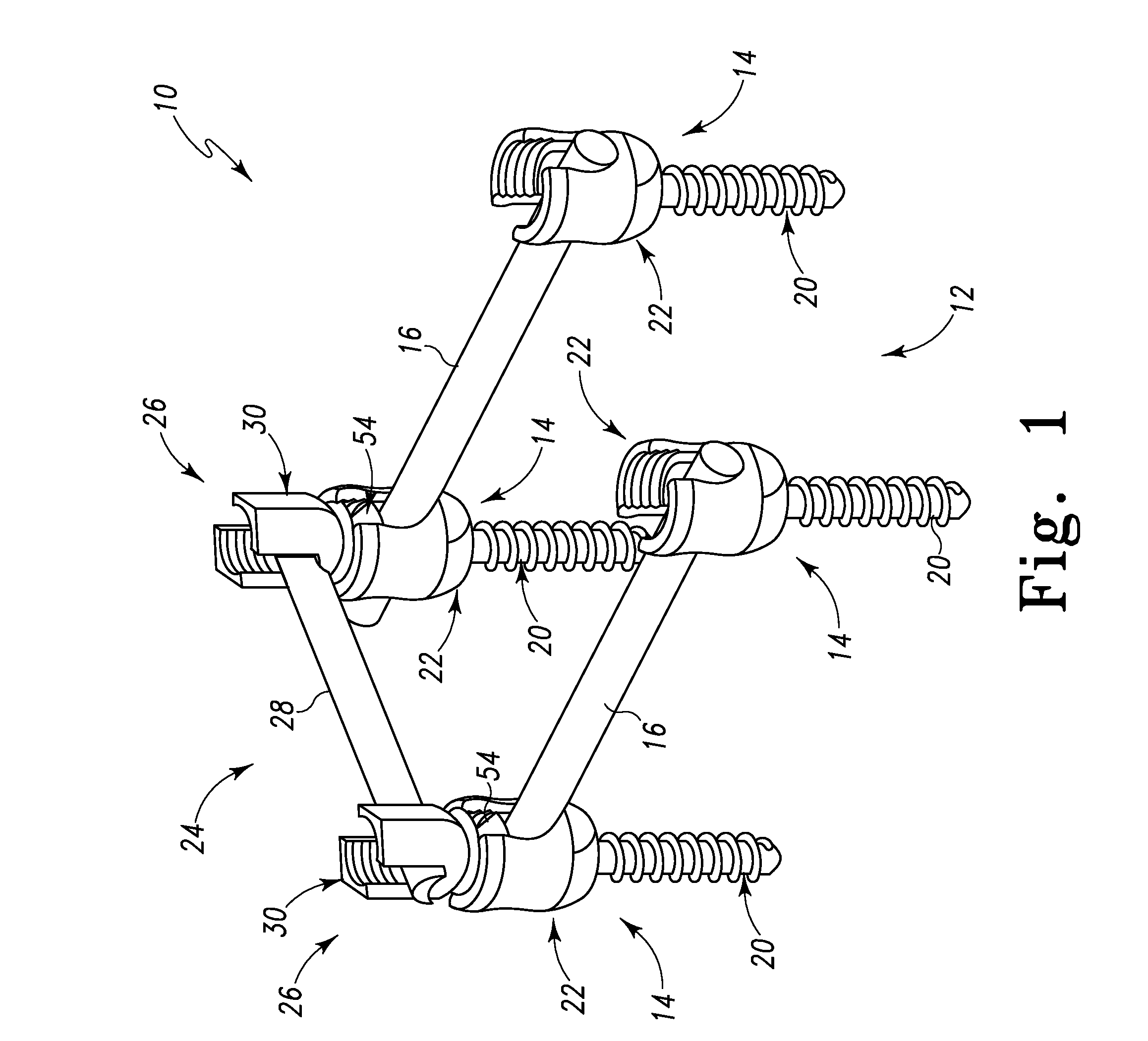
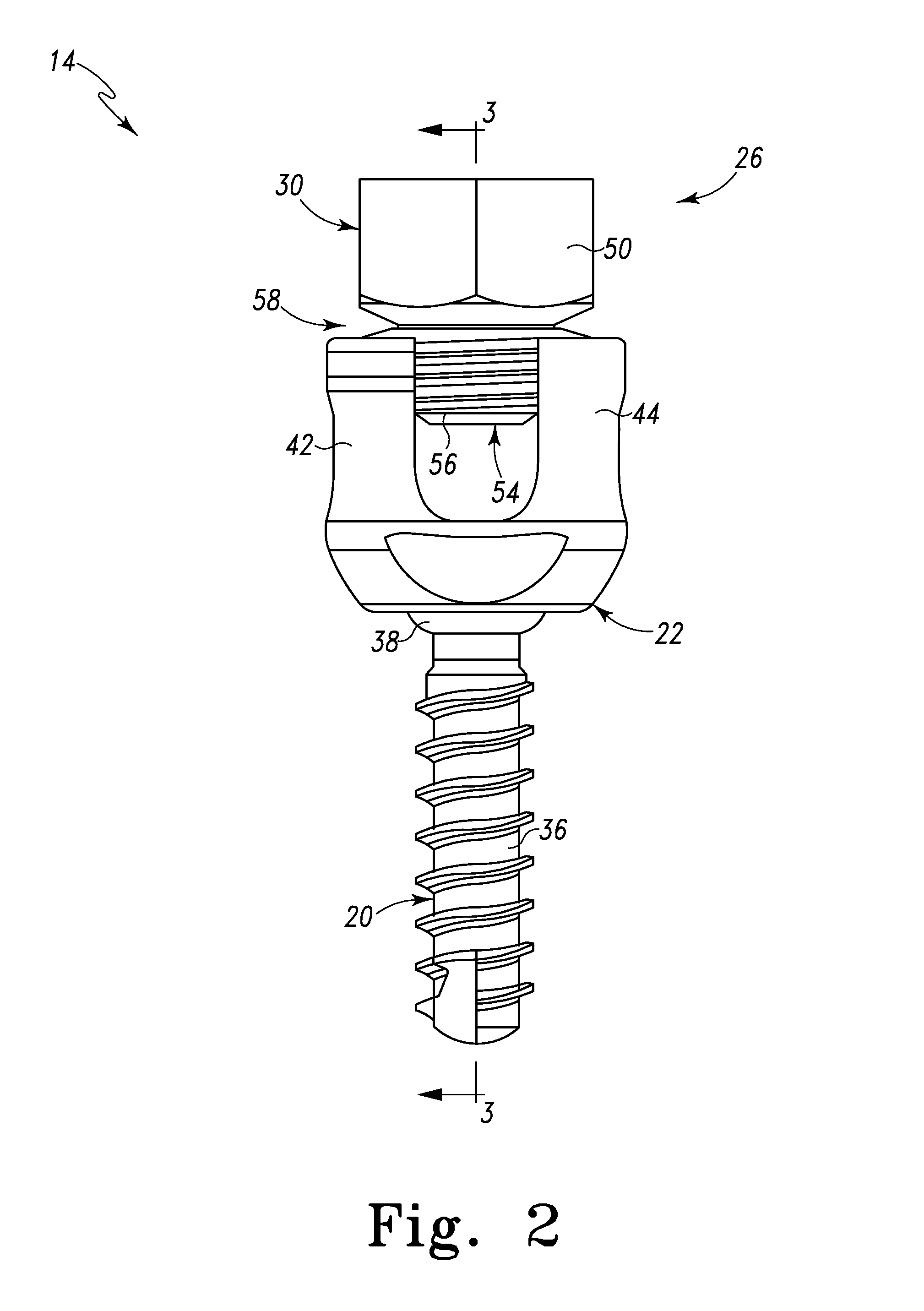
Posterior Cervical Cross Connector Assemblies
ActiveUS20100160981A1Increase construction heightSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSet screwCross connection
A spinal cross connector head assembly and a cross connector assembly utilizing the spinal cross connector head assembly are configured for fixation to an existing spinal rod bone screw head. The spinal cross connector head assembly has one or more components which incorporate one or more breakaway portions that aid in the installation of the cross connector head assembly onto a polyaxial spinal rod bone screw assembly. The spinal cross connector assembly includes first and second spinal cross connector head assemblies each of which is configured for fixation to existing, adjacent spinal rod screw heads and connection with a cross connector rod. Each spinal cross connector rod head assembly has a dual breakaway system including a cross connector head component having a breakaway collar that, once detached, provides a polyaxial cross connector head, and a set screw component having a breakaway set screw that, once detached, provides fixation of the orientation of the polyaxial cross connector head relative to the polyaxial spinal rod bone screw head.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
Vertebral implant for bone fixation or interbody use
InactiveUS20060142765A9Minimized reactivityOvercome limitationsInternal osteosythesisBone implantCouplingIliac screw
The present invention provides a biodegradable implant which can be used as fixation and / or interbody implants. The implant is formed of a biodegradable material and may be used as a cervical stabilizing system. The stabilizing system comprises a body constructed of a biodegradable, polymeric material, which when implanted within the body will maintain a predetermined structural integrity for at least a predetermined period of time while minimizing reactivity with adjacent tissues. In an embodiment of the invention, the stabilization system comprises a fixation member which includes apertures to allow selective coupling to bone segments by means of biodegradable screws. In another embodiment, the stabilization system includes a bone column implant which maintains space between at least two bone segments of a bone column. The body member is dimensioned to substantially maintain the distance, geometry and continuity between the at least two bone segments. The invention is also directed to a combination device comprising a fixation device along with an interbody implant and methods for using the stabilization system.
Owner:ALTUS PARTNERS
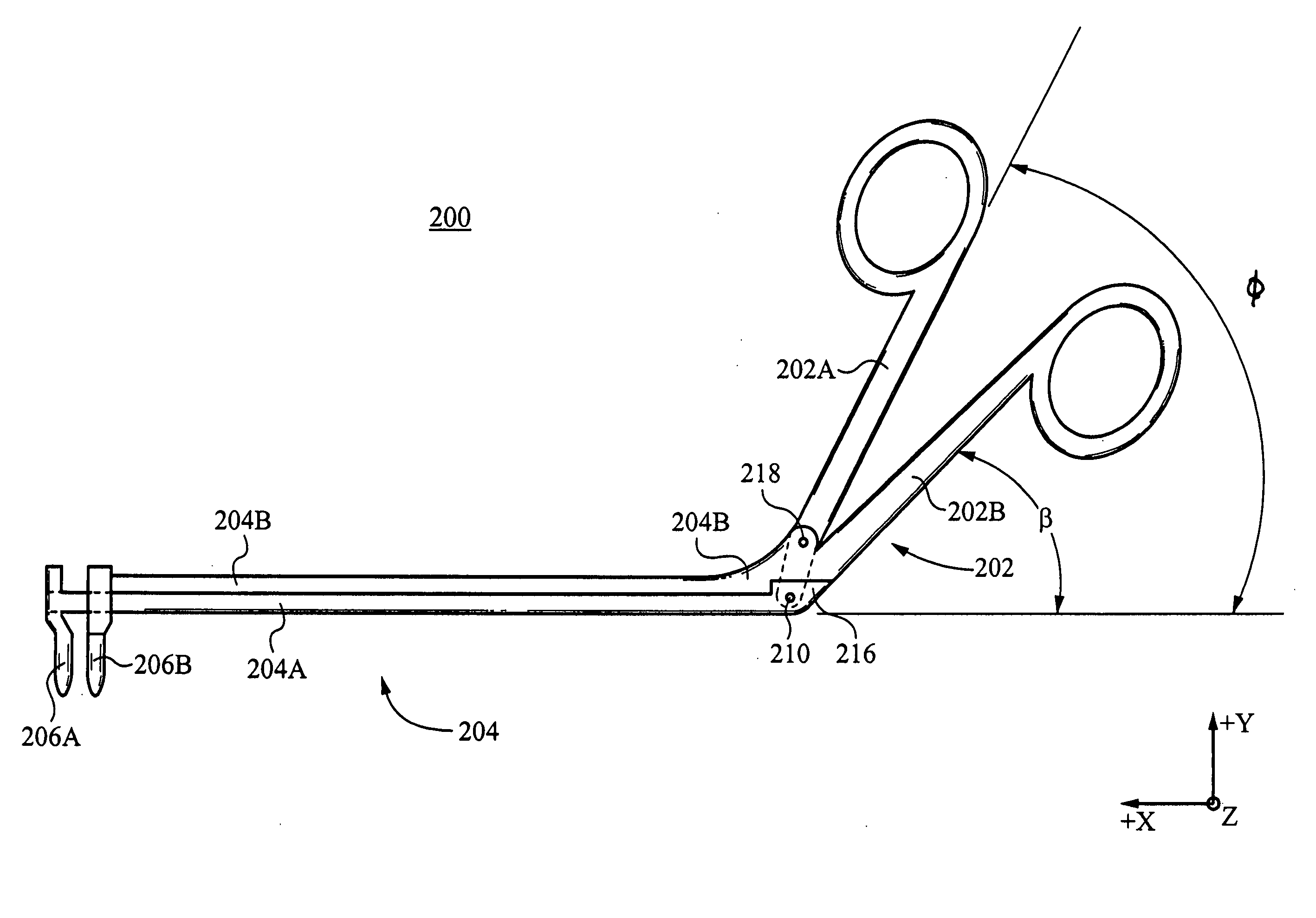
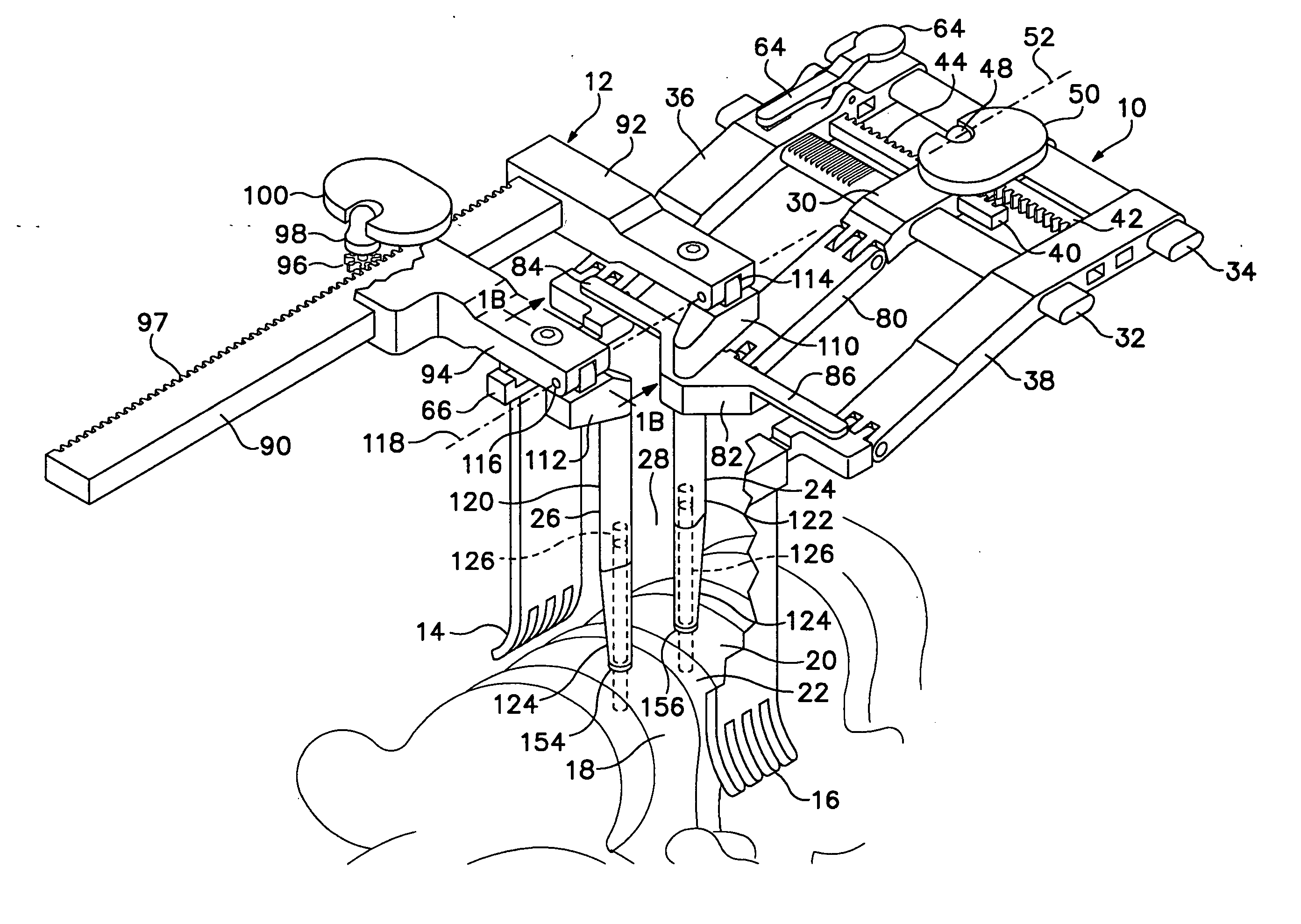
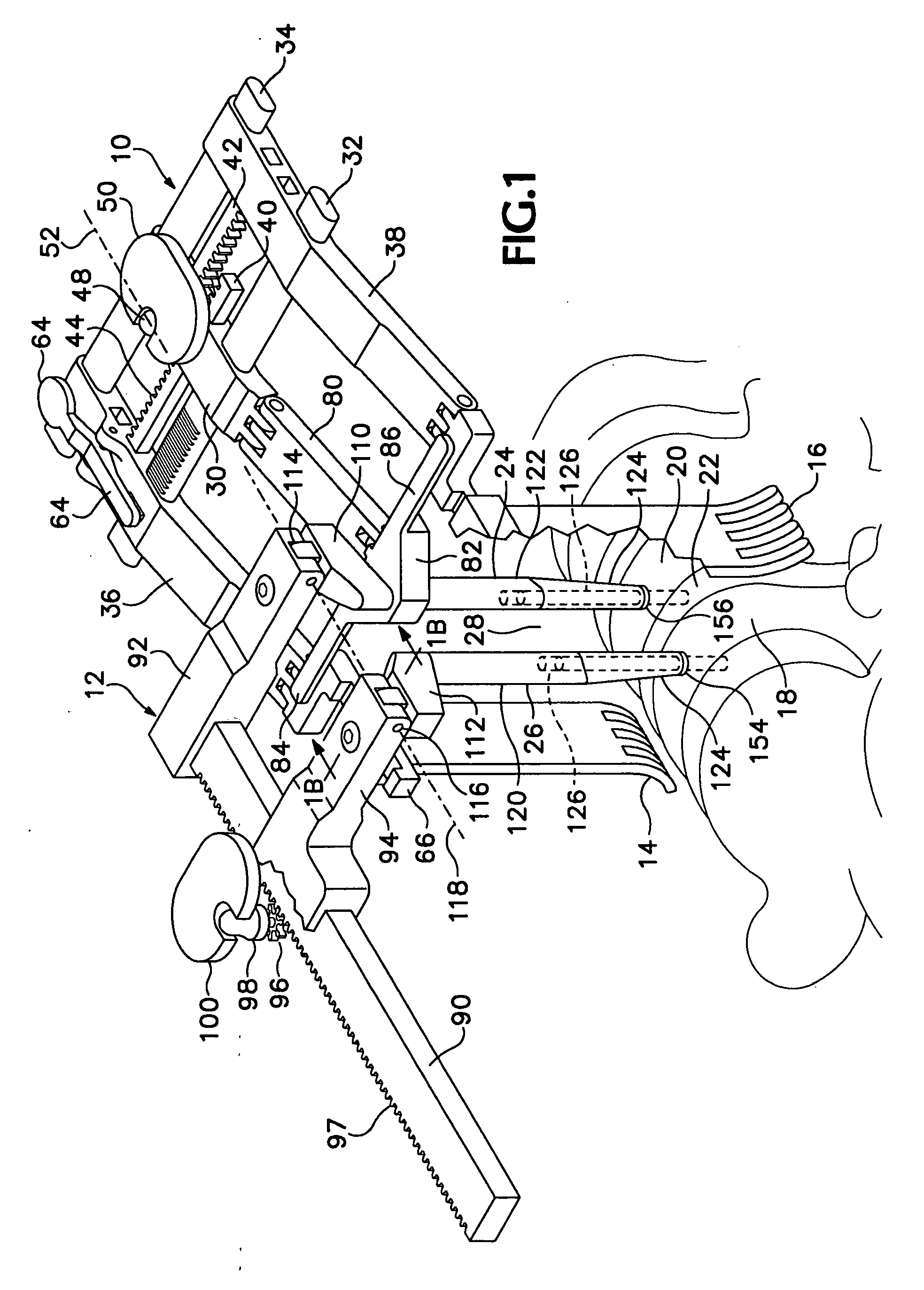
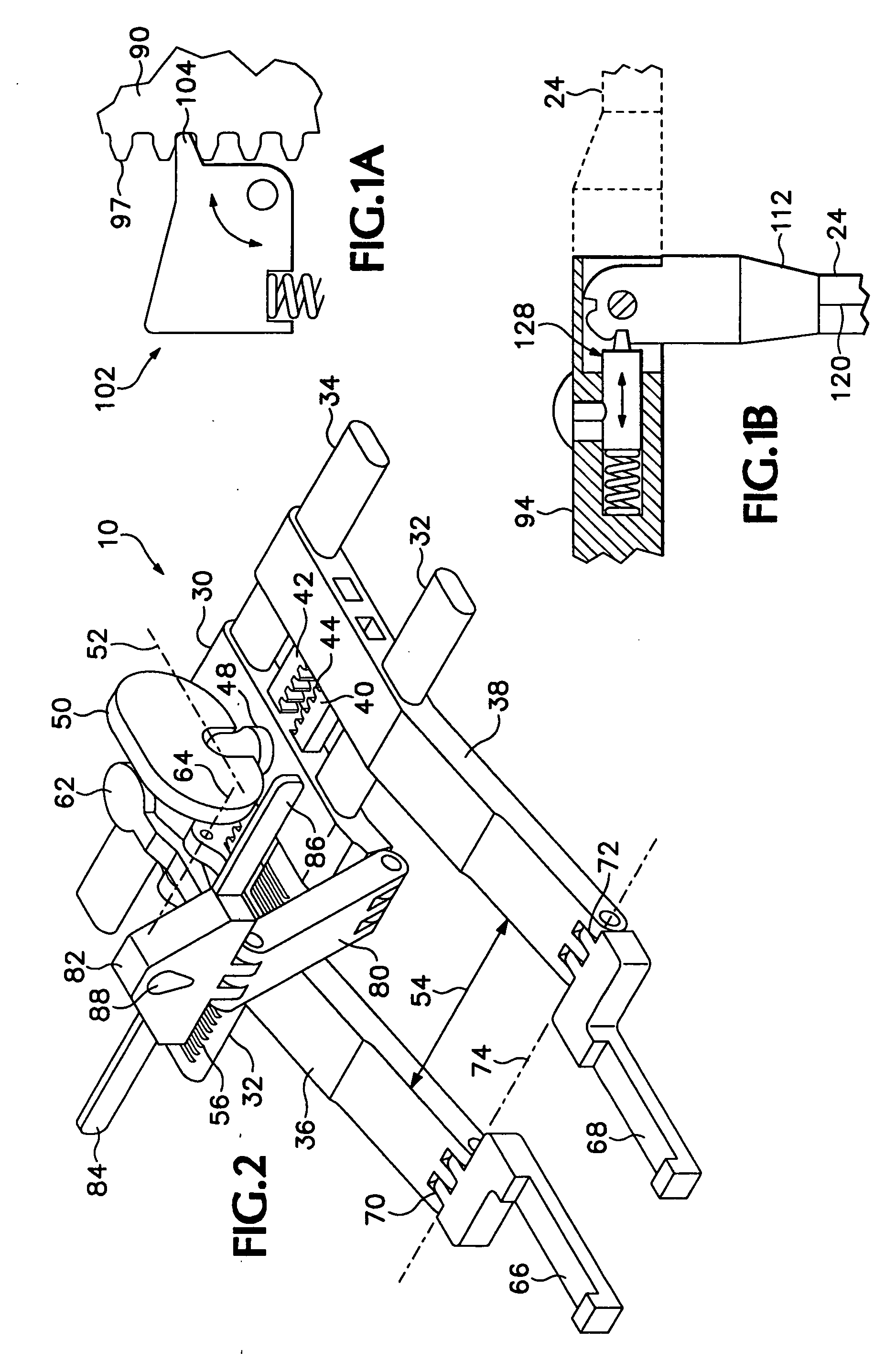
Retractor and distractor system for use in anterior cervical disc surgery
A retractor, a distractor, and a drill guide for use in performing anterior cervical discectomy and vertebral fusion. The distractor is located with respect to vertebrae to be fused by pins fastened in the vertebrae to be fused, and the retractor is mated mechanically with the distractor to hold the retractor in a required location. Blade carrying arms of the retractor are both moved toward or away from a central part of the retractor.
Owner:NEHLS DANIEL G
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com