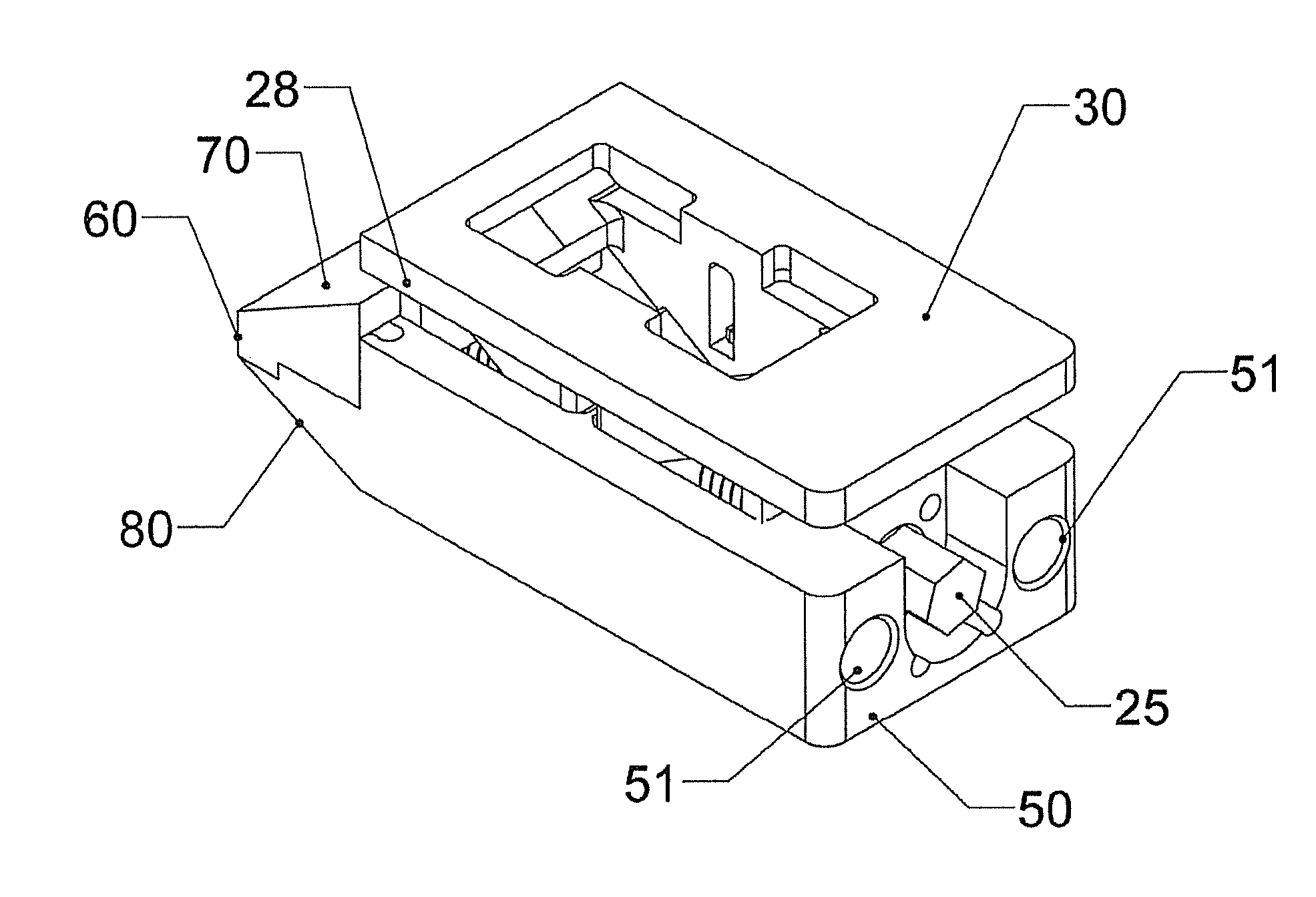
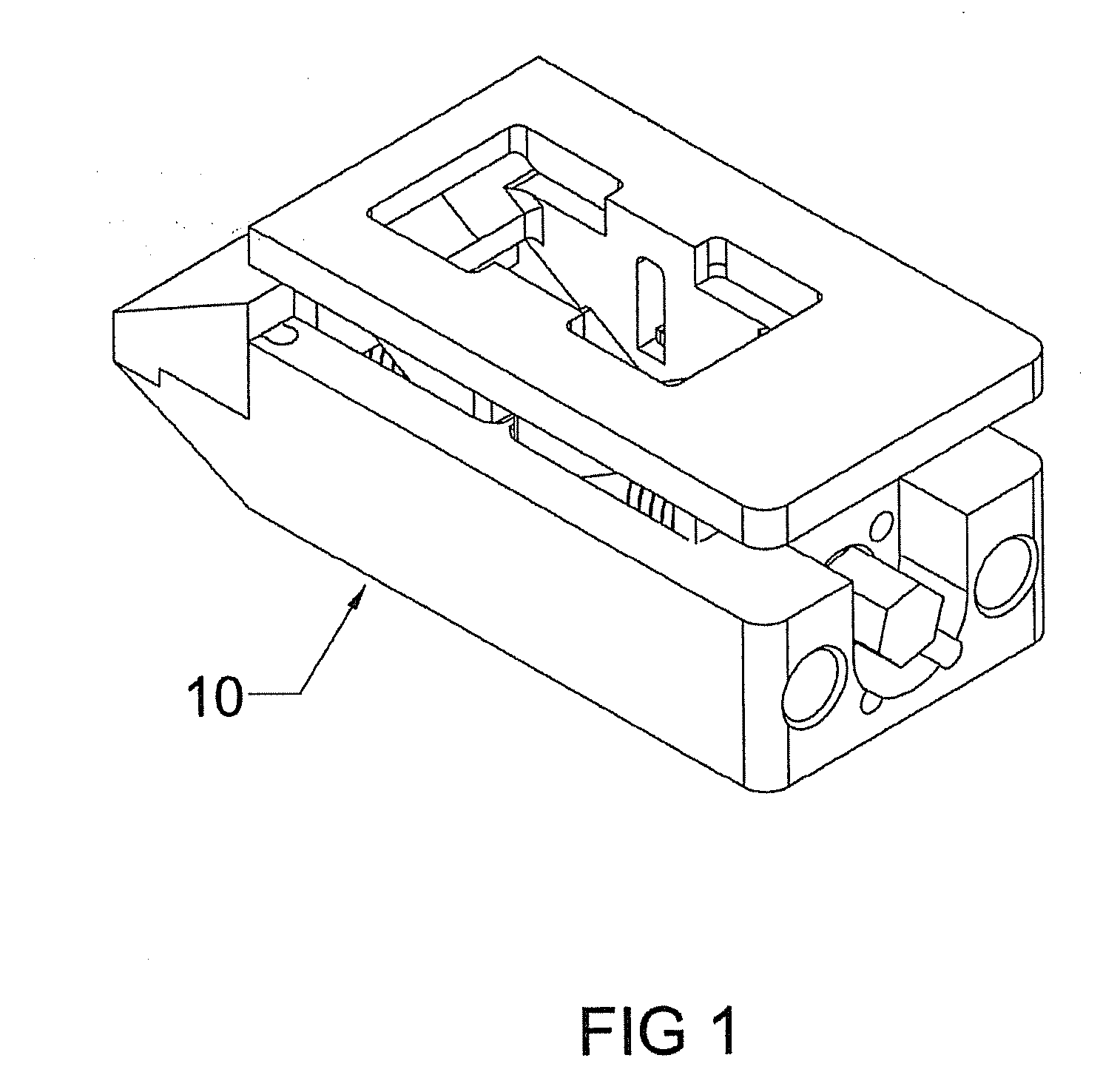
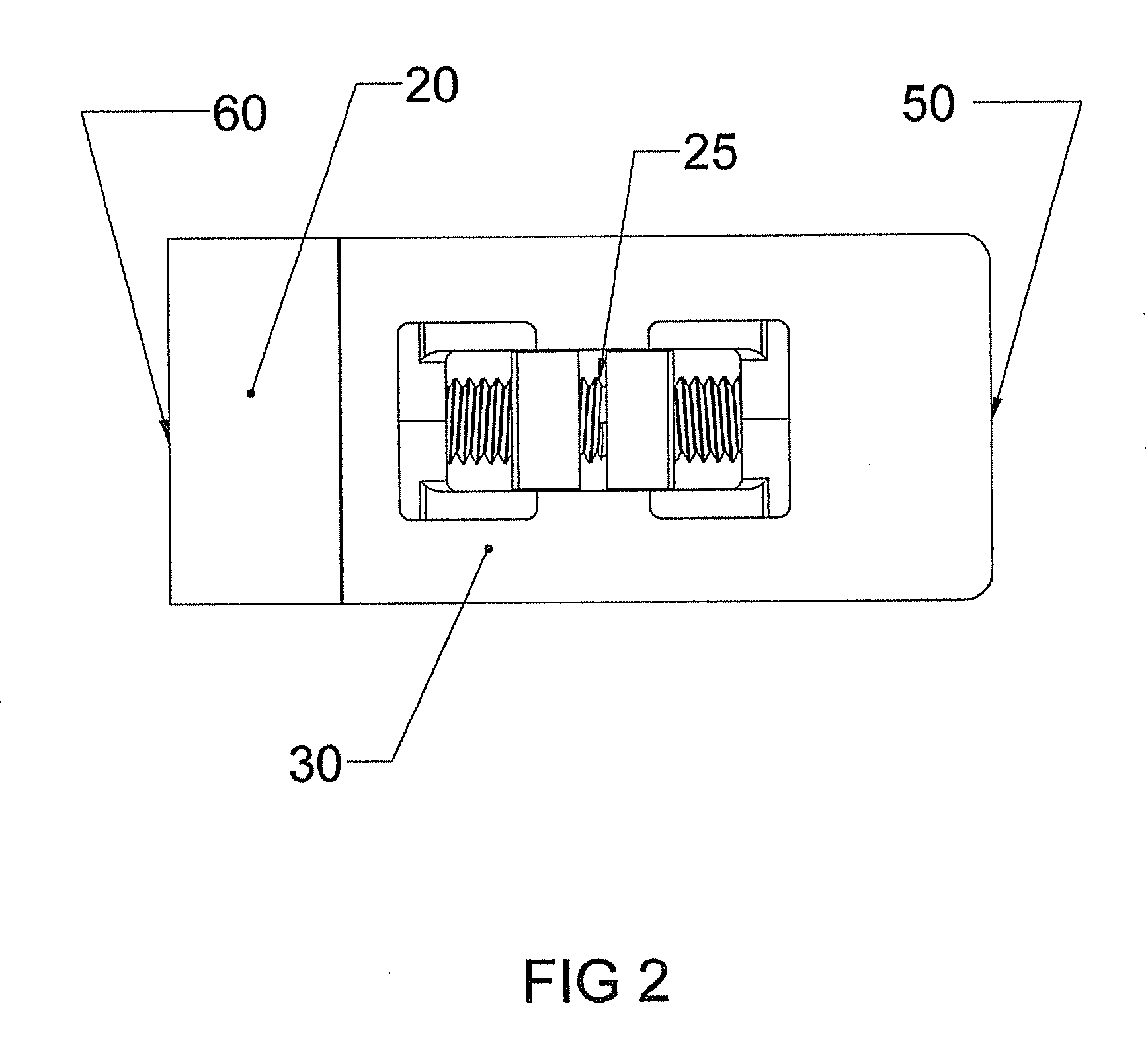
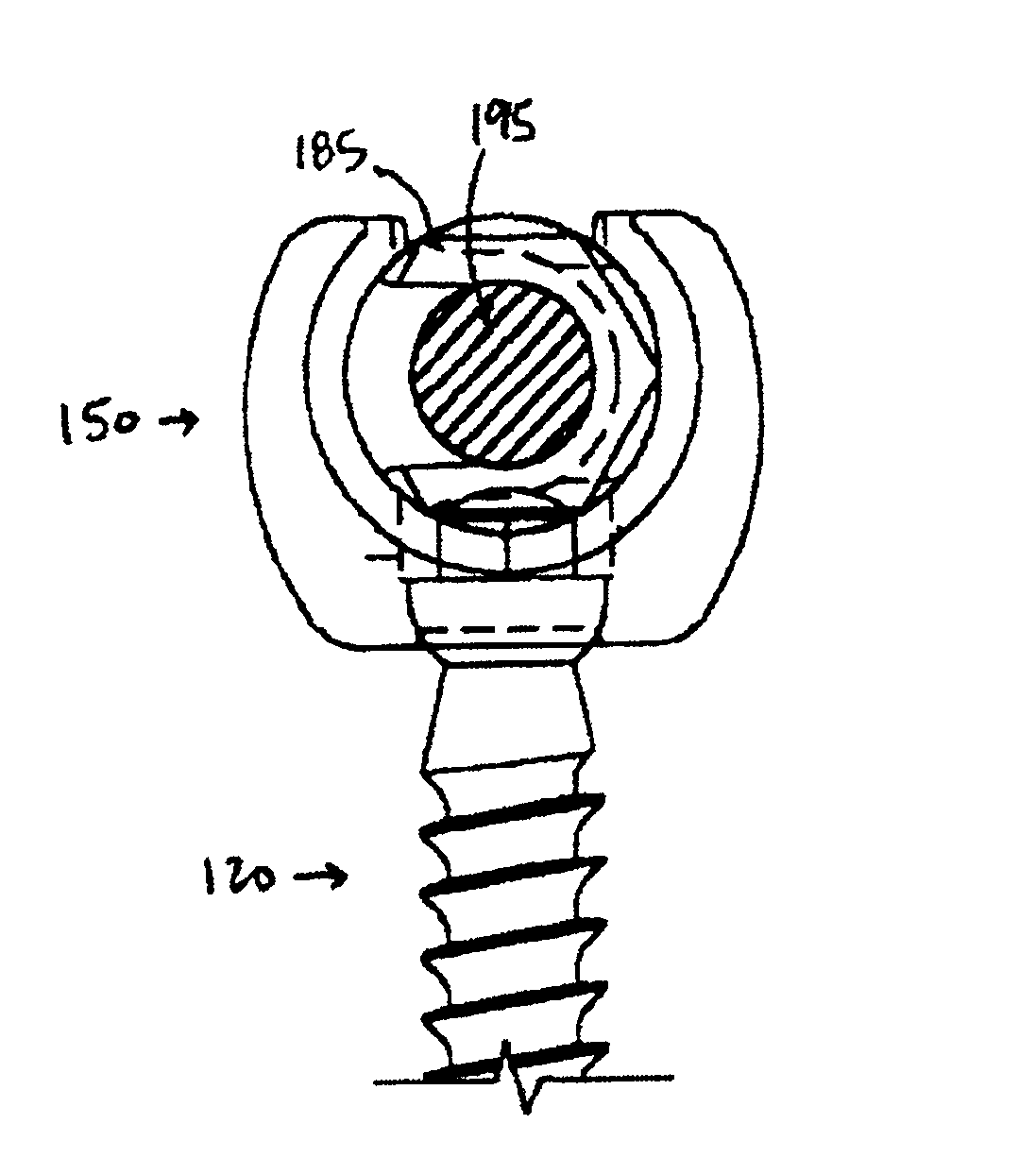
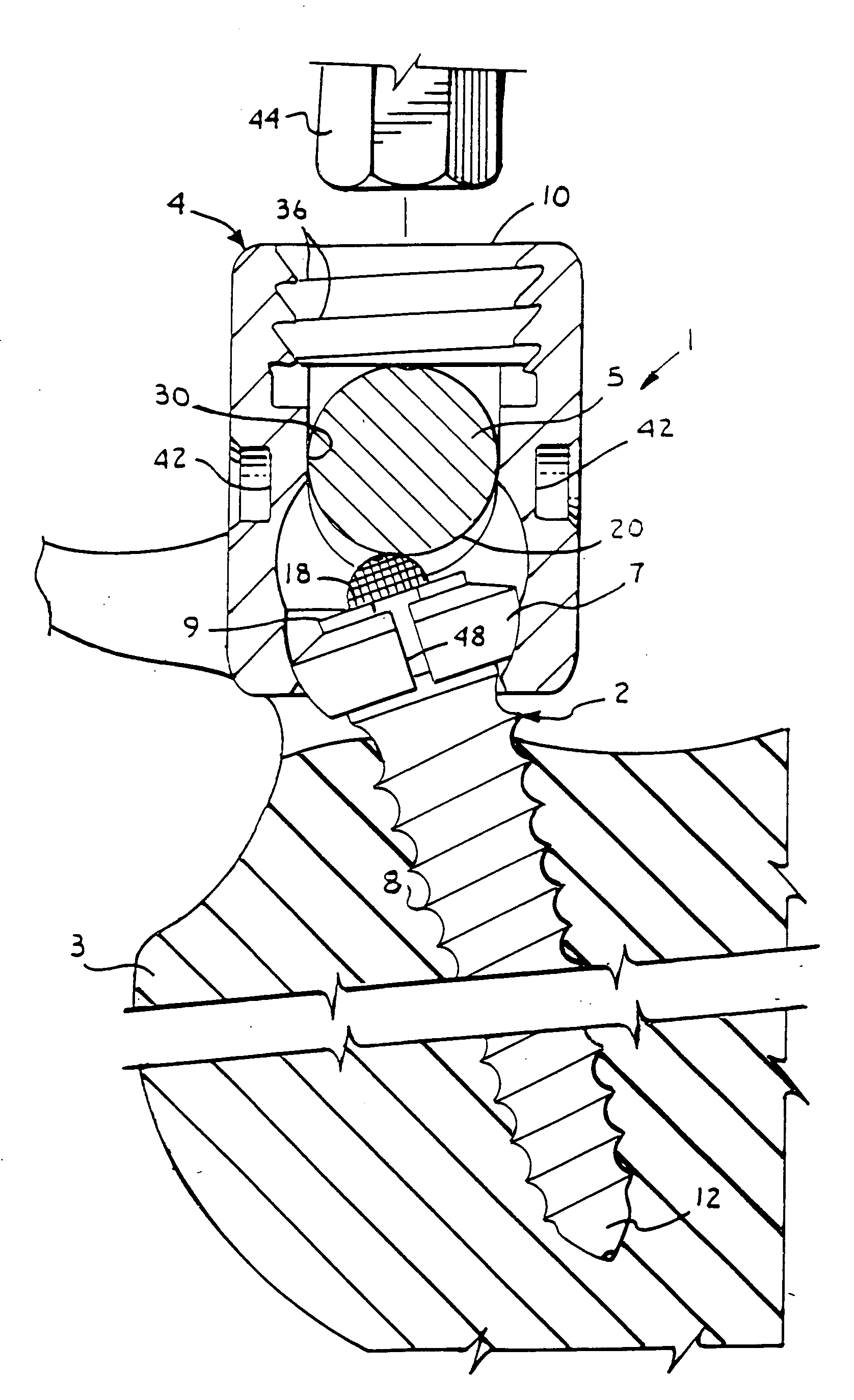
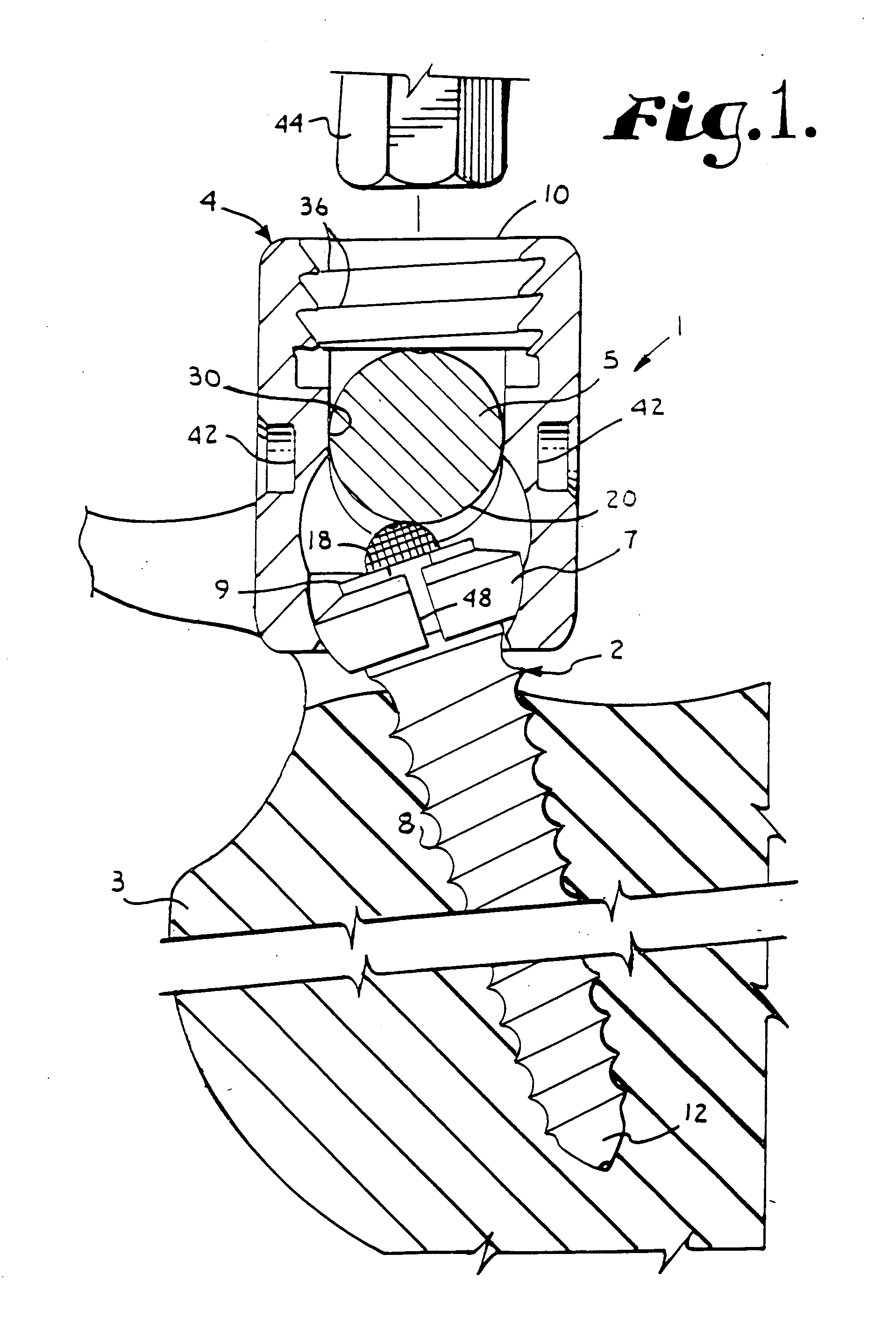
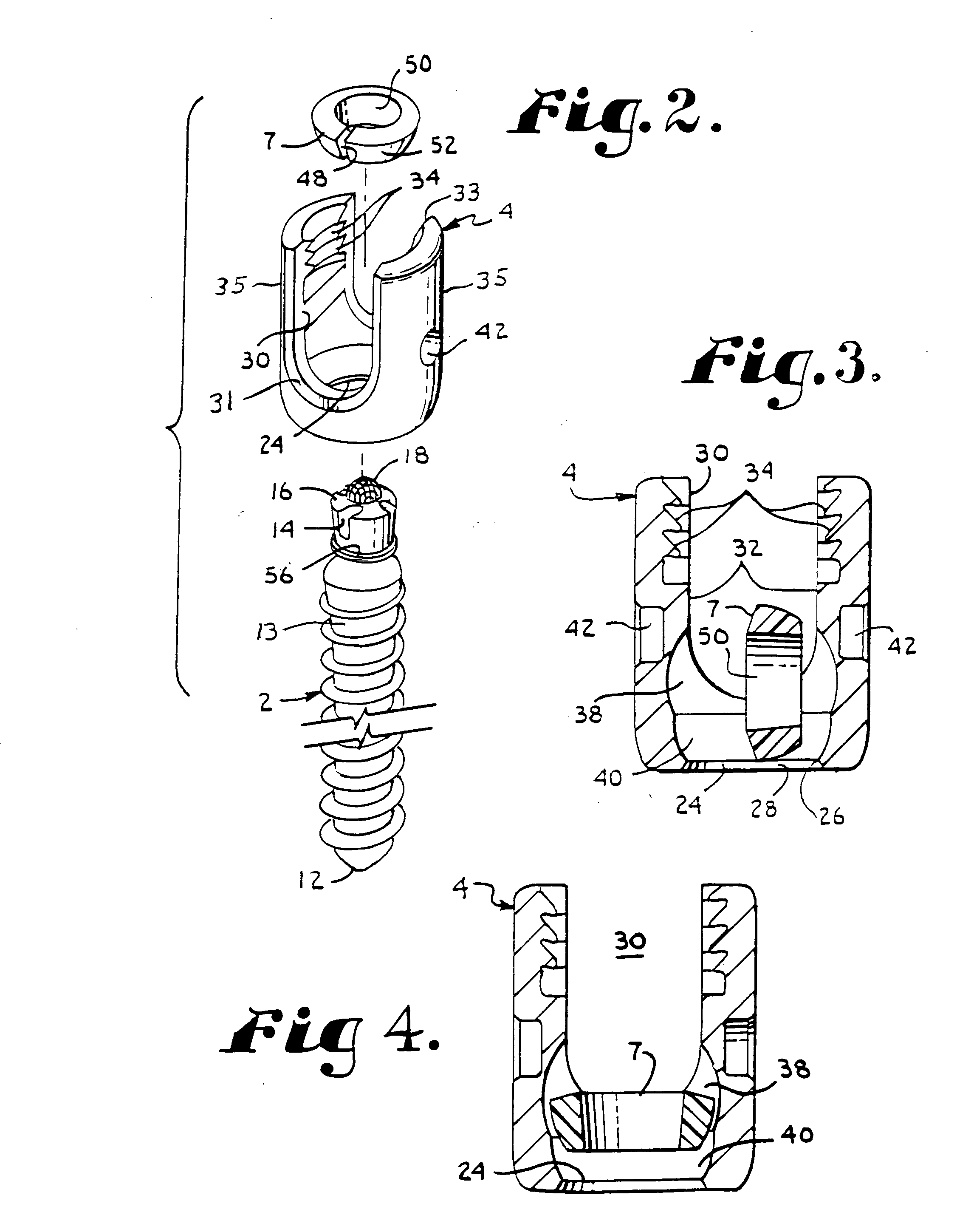
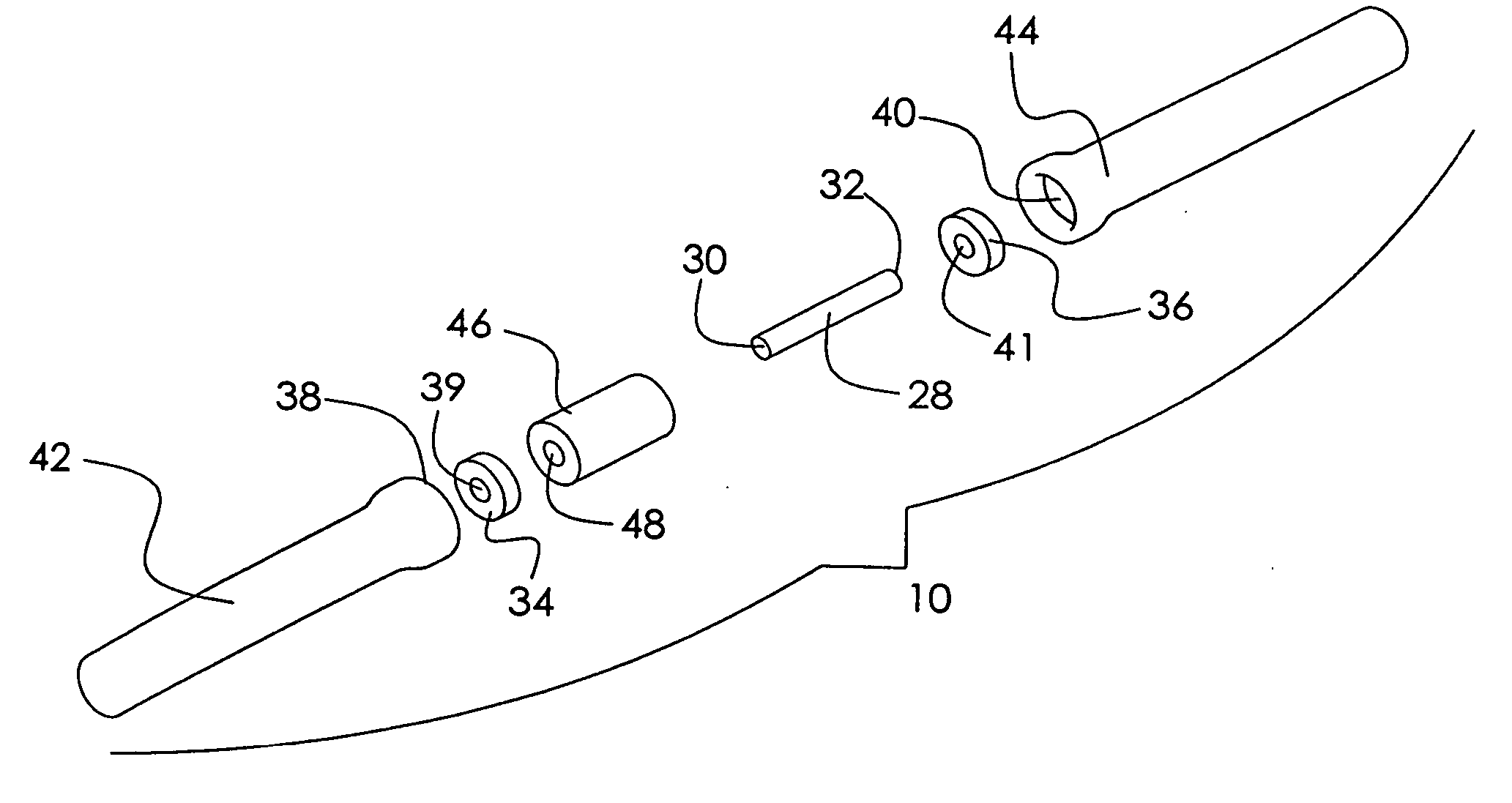
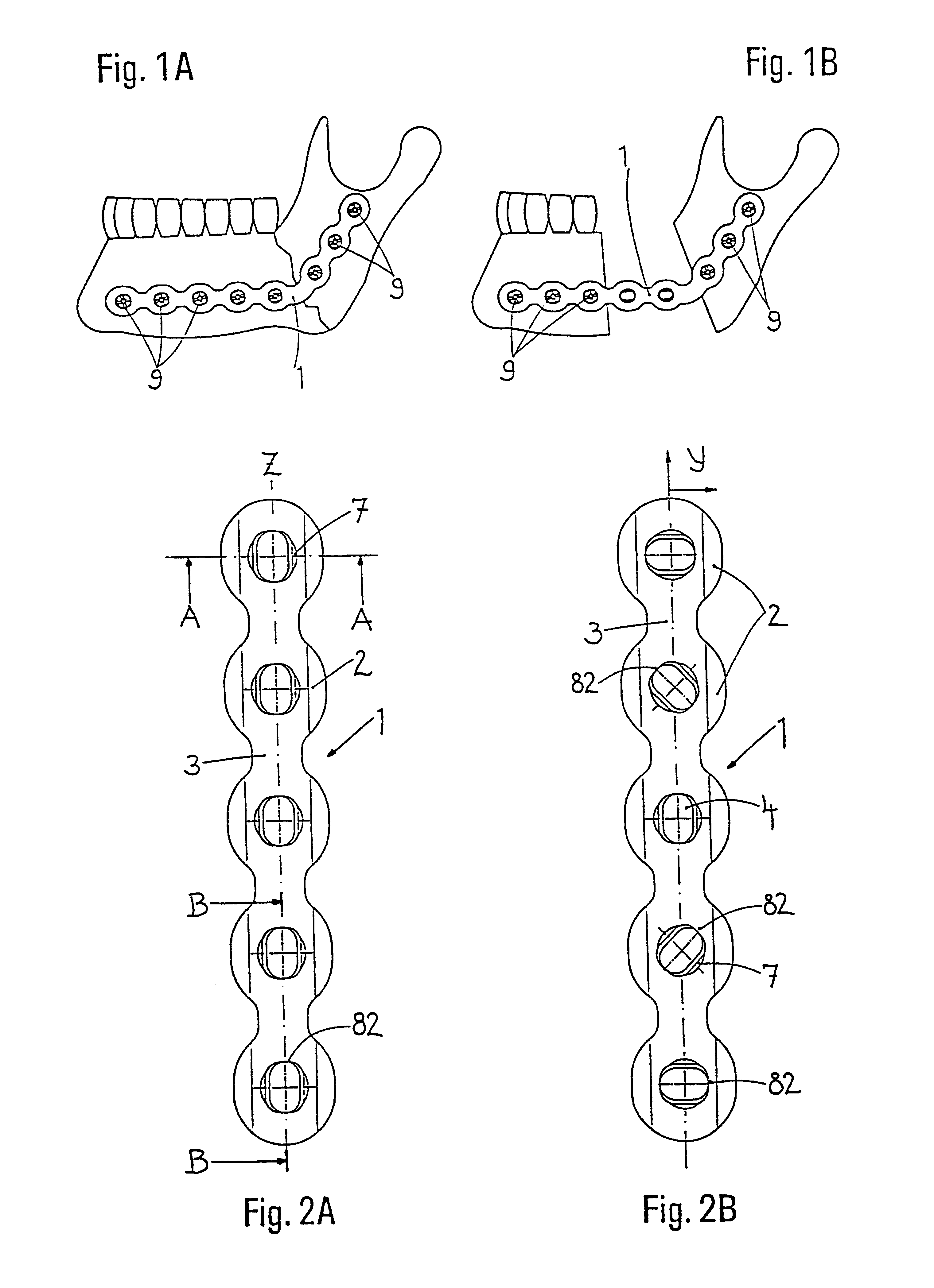Patents
Literature
5424 results about "Iliac screw" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6838493B2High porosityReduce probabilitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
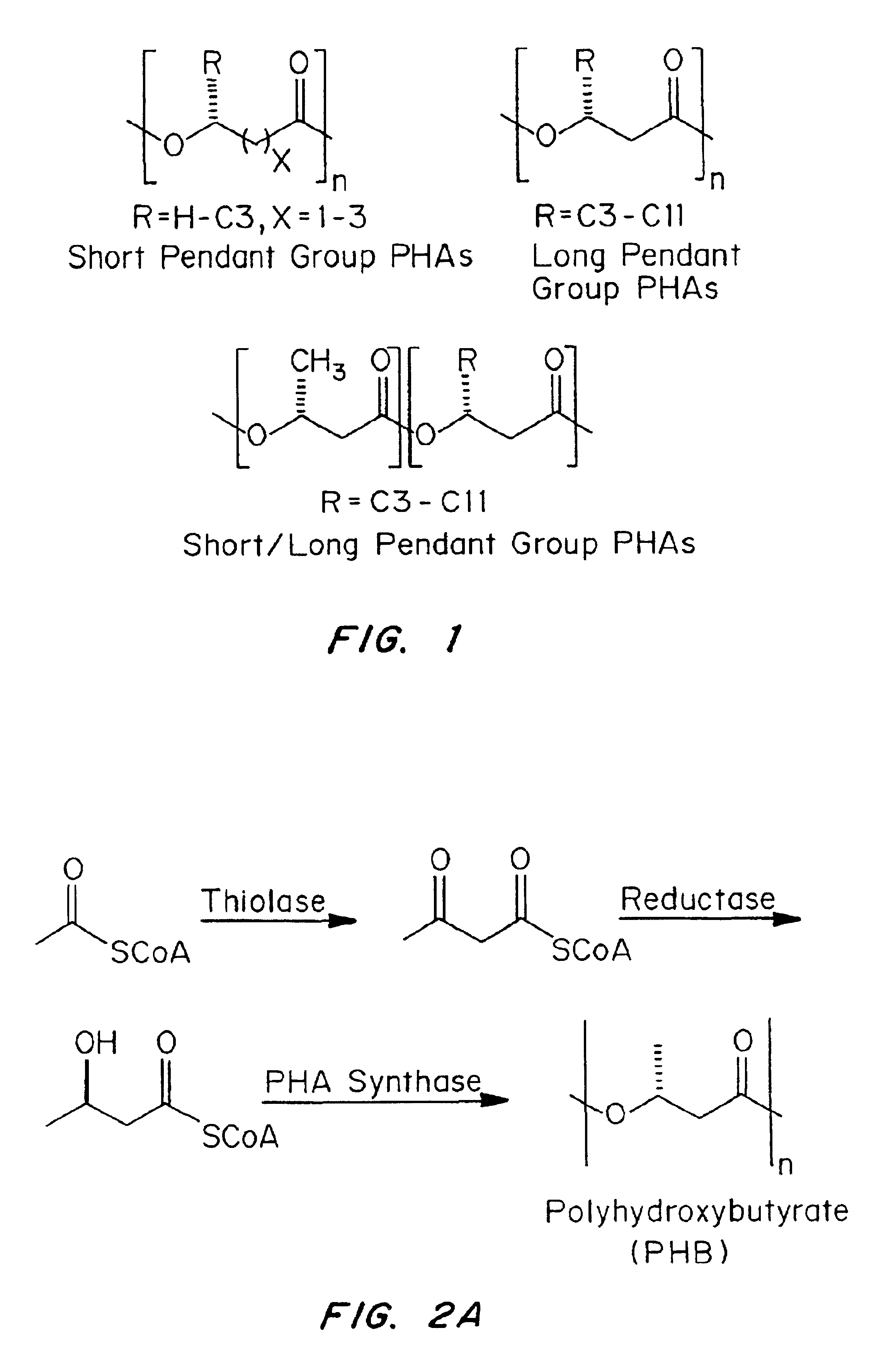
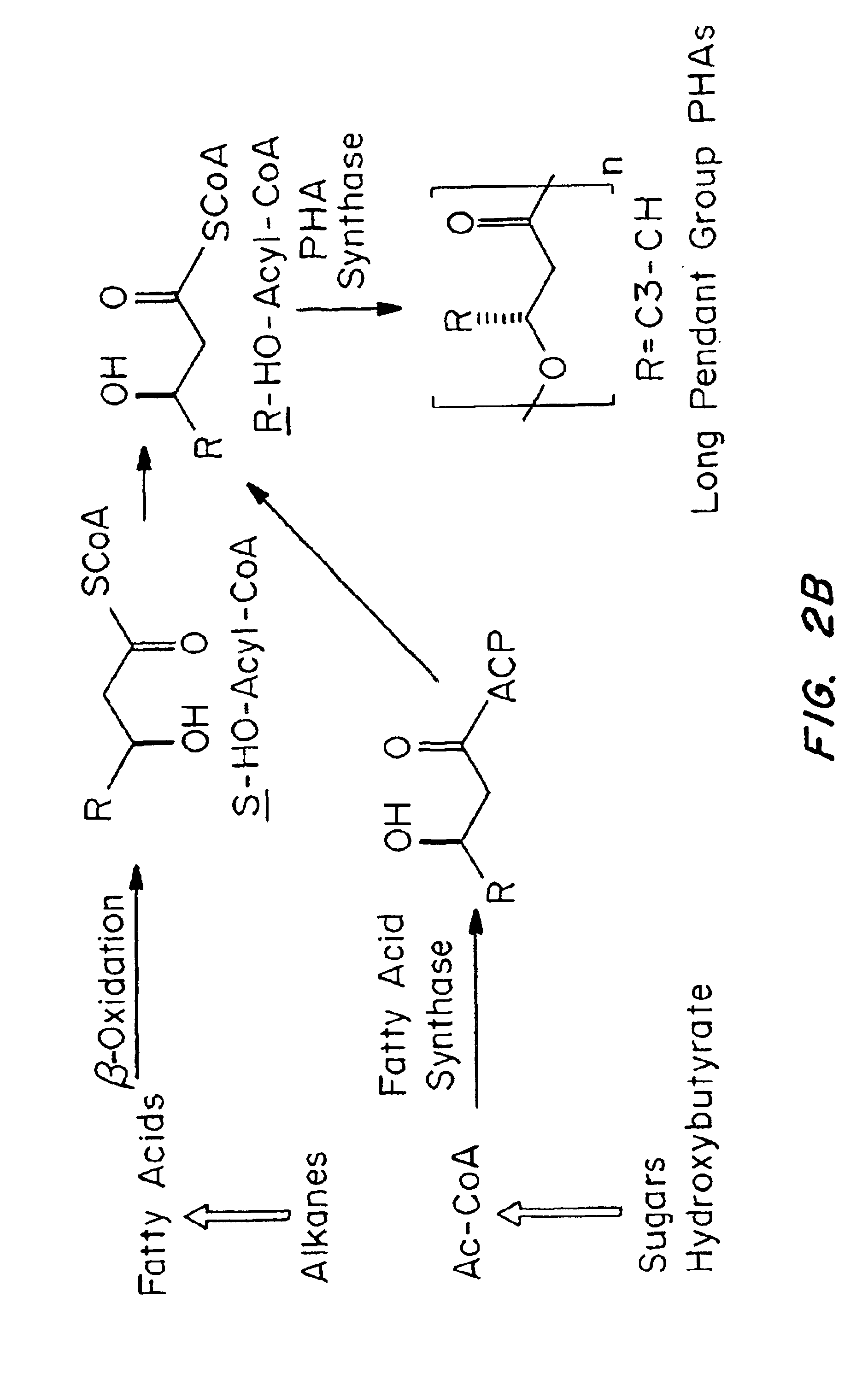
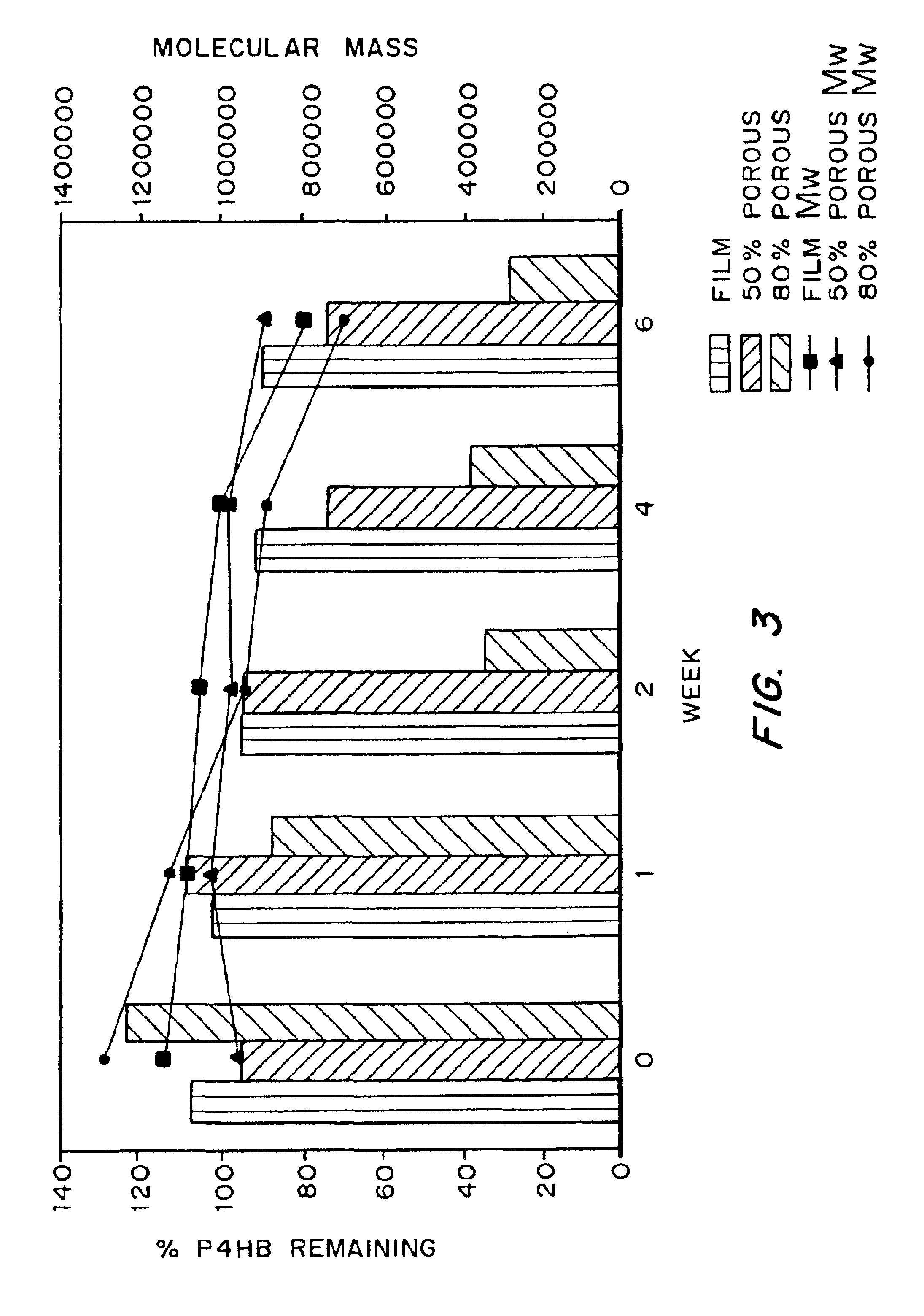
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Methods and devices for fastening bulging or herniated intervertebral discs
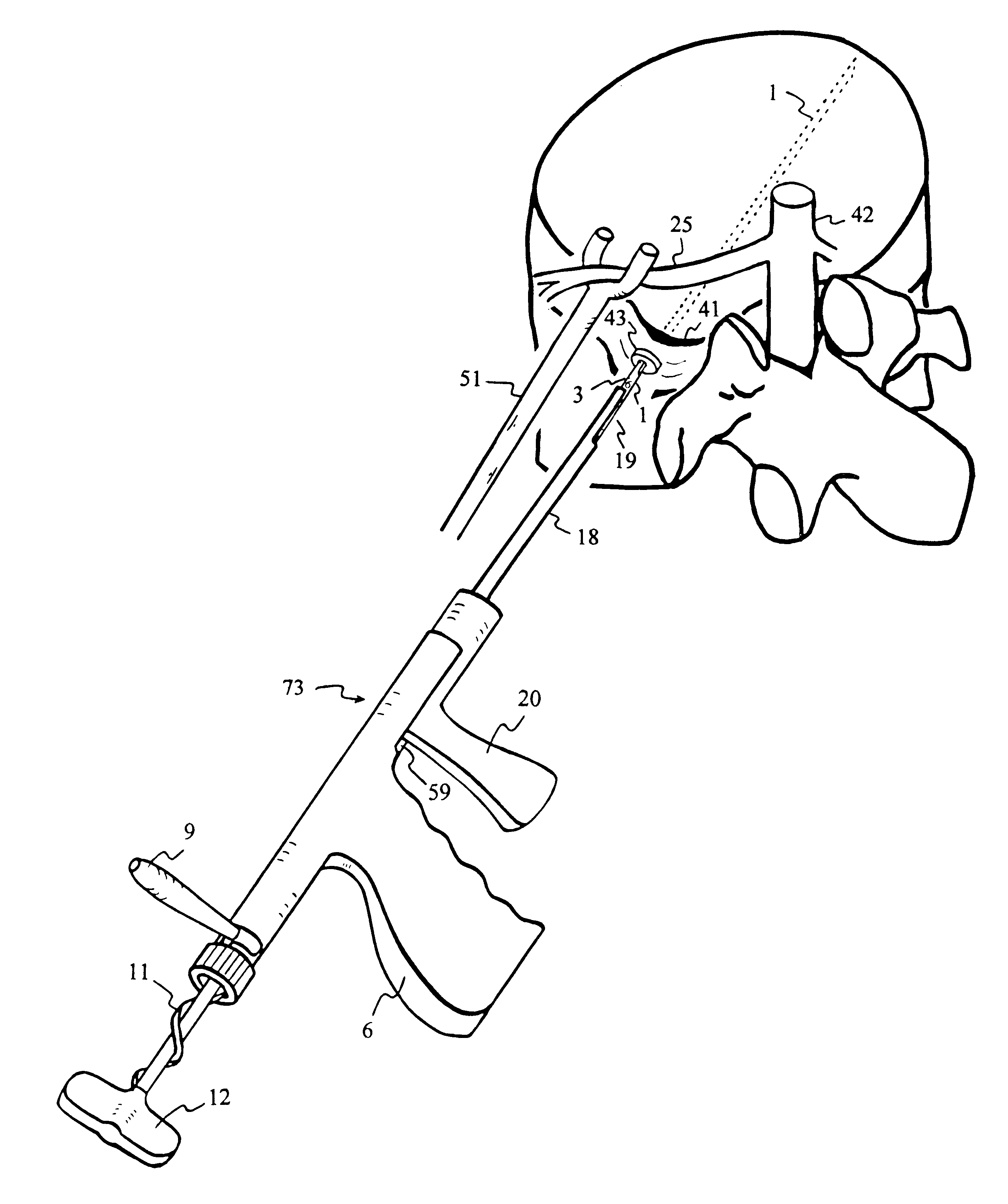
InactiveUS6530933B1Increase speedShorten post-surgical hospital staysSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsEngineeringIliac screw
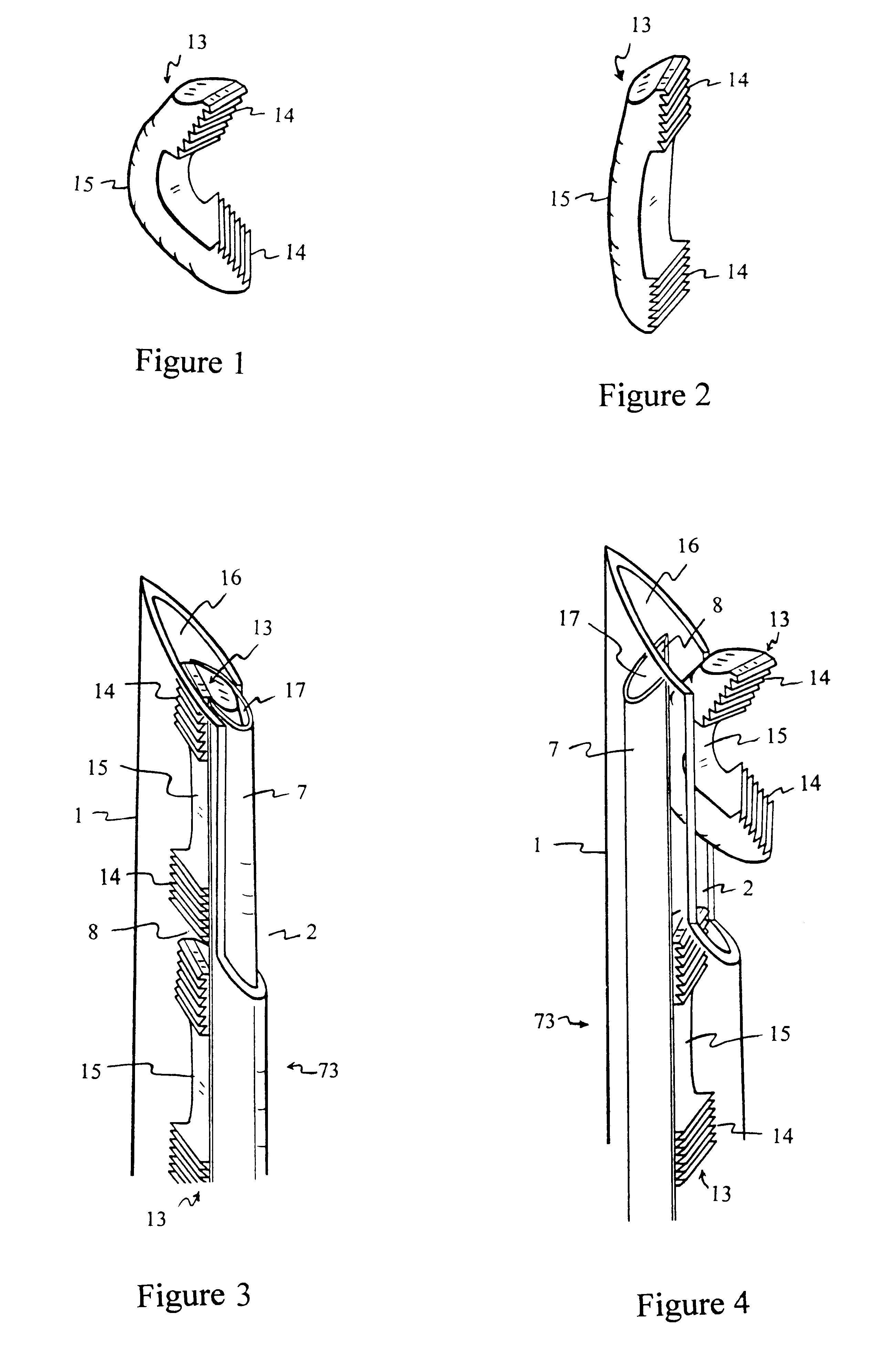
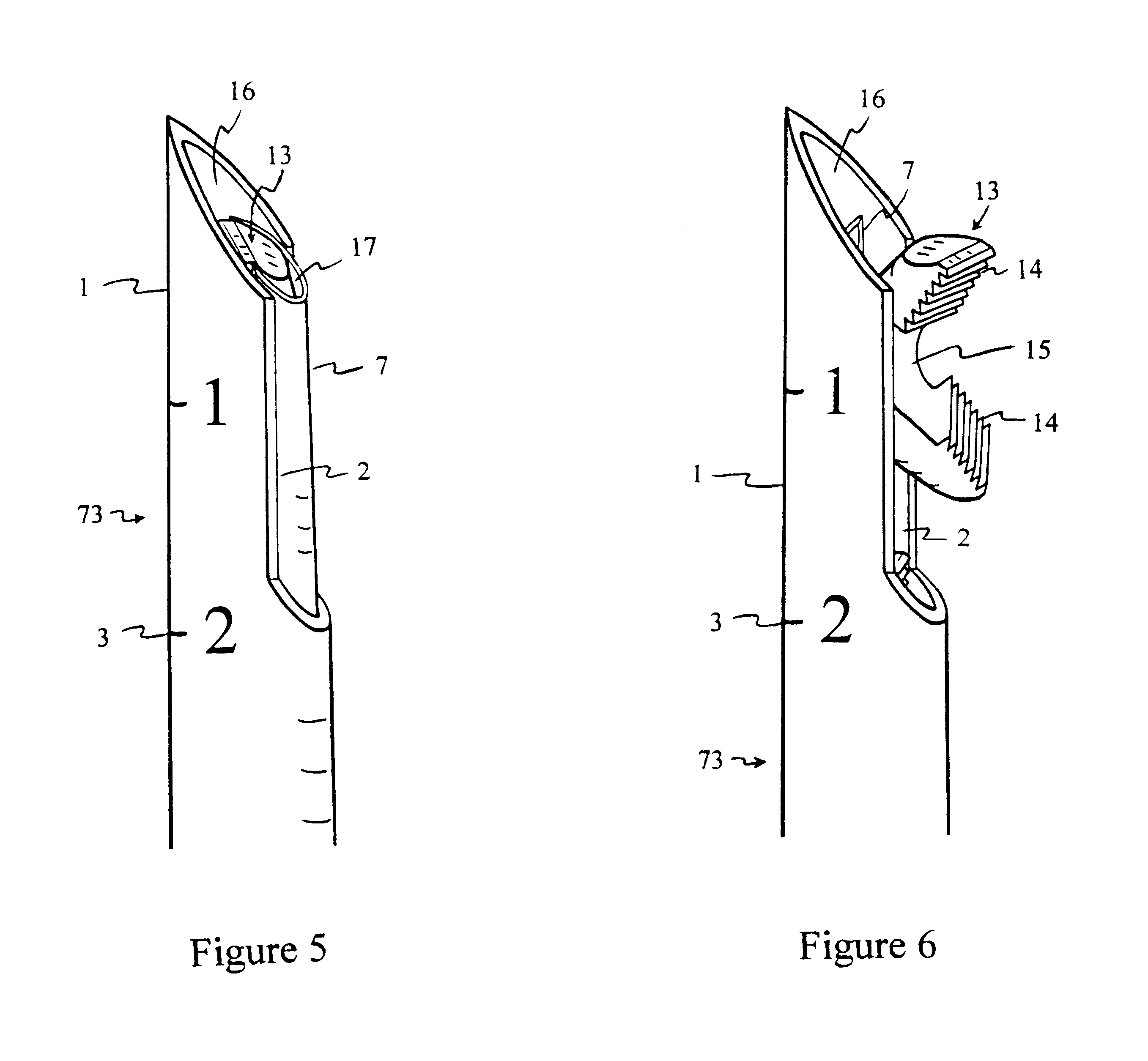
Methods and apparatuses for compressing and holding a bulging or herniated intervertebral disc. A number of fastener embodiments are disclosed, including a resiliently curved fastener, suture, screw, staple, tack and others. The curved fastener is resiliently straightened and loaded into a needle for delivery and deployment. In the intervertebral disc, the deployed fastener resumes the curvature to grip and hold the bulge. Alternatively, the suture is anchored and used to tie down the bulging tissue. The screw, staple or tack can also be used to securely fasten, compress and hold the bulge from impinging upon adjacent nerves or tissues.
Owner:KENSEY NASH CORP
Methods and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis
InactiveUS20060106381A1Effective treatmentPermit flexionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnDevice form
Surgical implants are configured for placement posteriorly to a spinal canal between vertebral bodies to distract the spine and enlarge the spinal canal. In the preferred embodiments the device permits spinal flexion while limiting spinal extension, thereby providing an effective treatment for treating spinal stenosis without the need for laminectomy. The invention may be used in the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spine. Numerous embodiments are disclosed, including elongated, length-adjustable components coupled to adjacent vertebral bodies using pedicle screws. The preferred embodiments, however, teach a device configured for placement between adjacent vertebral bodies and adapted to fuse to the lamina, facet, spinous process or other posterior elements of a single vertebra. Various mechanisms, including shape, porosity, tethers, and bone-growth promoting substances may be used to enhance fusion. The tether may be a wire, cable, suture, or other single or multi-filament member. Preferably, the device forms a pseudo-joint in conjunction with the non-fused vertebra. Alternatively, the device could be fused to the caudal vertebra or both the cranial and caudal vertebrae.
Owner:NUVASIVE
System and method for stabilizing of internal structures
There is shown a system and method for reducing the difficulty in percutaneous placement of a spine stabilization brace by coupling the brace to a pedicle screw in a single assembly. The brace-screw assembly is delivered along with an anchor extension through a cannula for anchoring in the vertebrae pedicle. The anchor extension becomes a cannula for working on the brace from the exterior of the patient, as constructed with a slot opening along two sides. Once the screw portion of the brace-screw assembly is locked in place with respect to the first vertebra, the proximal end of the brace is below the skin line. The brace is then repositioned so that the proximal end leaves the cannula through one slot and is captured by a corresponding slot positioned in a second cannula coupled to a second anchor. Once captured, the proximal end of the brace is guided by the second cannula to a receptacle positioned in the second vertebra.
Owner:THEKEN SPINE
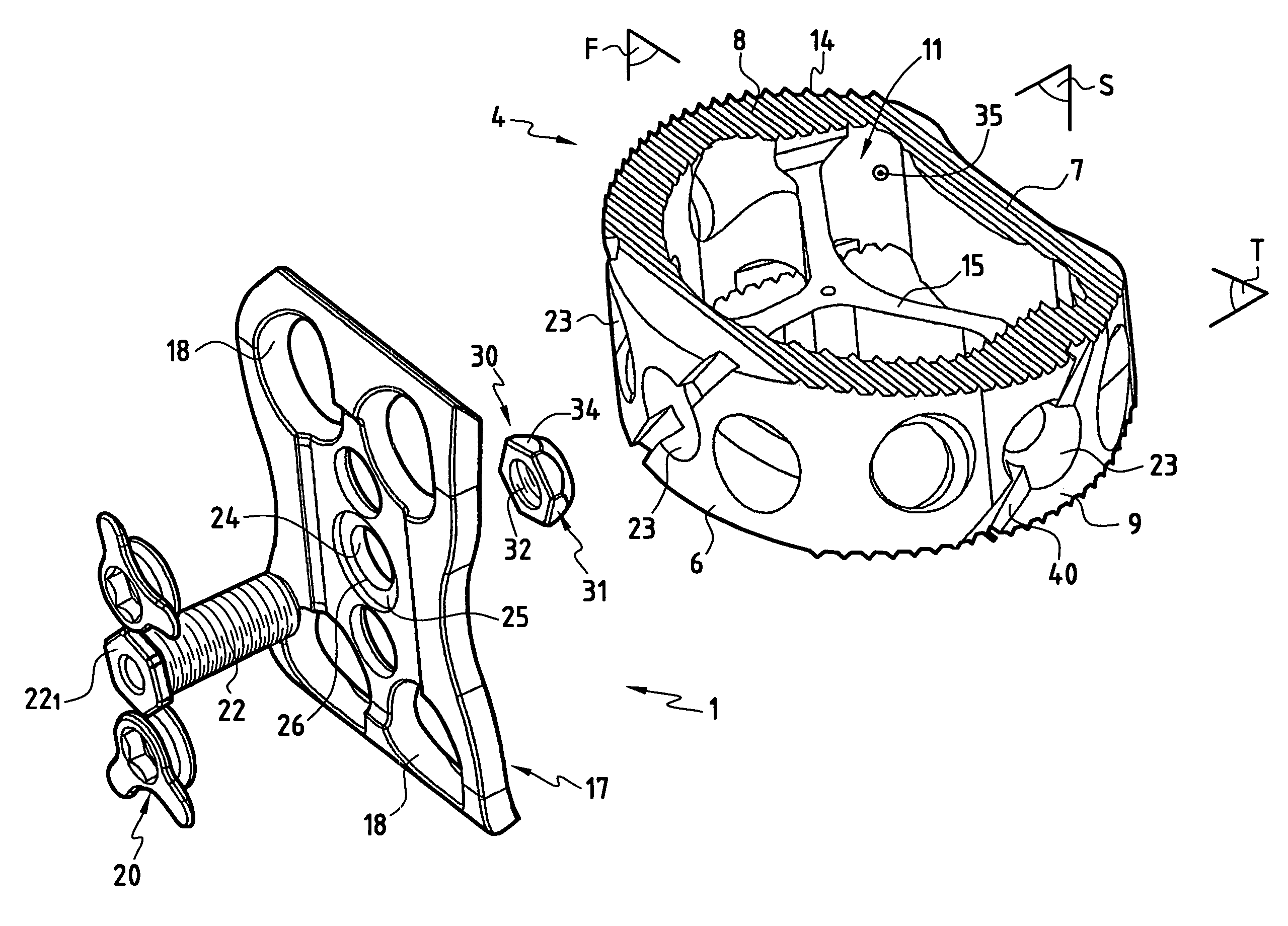
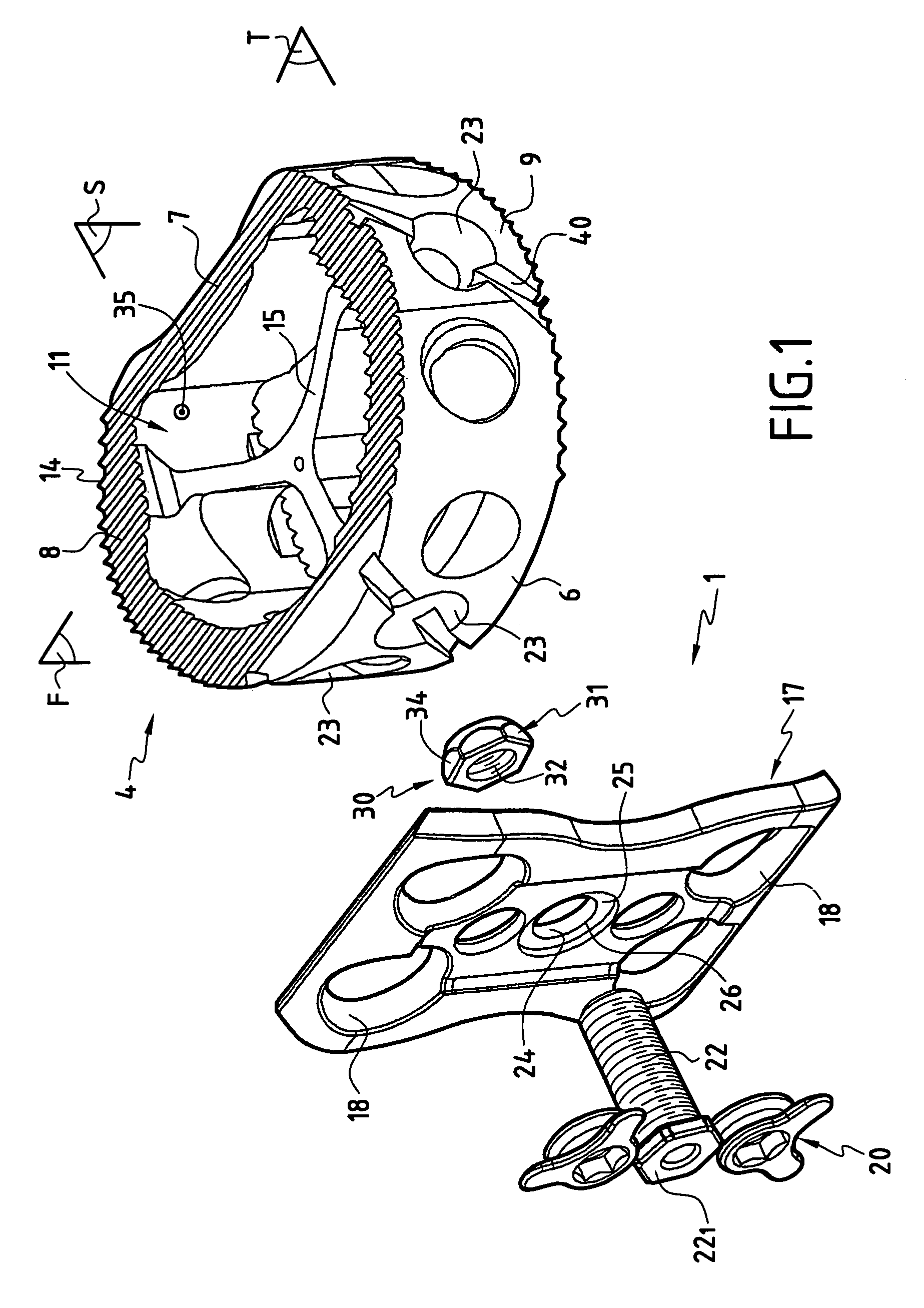
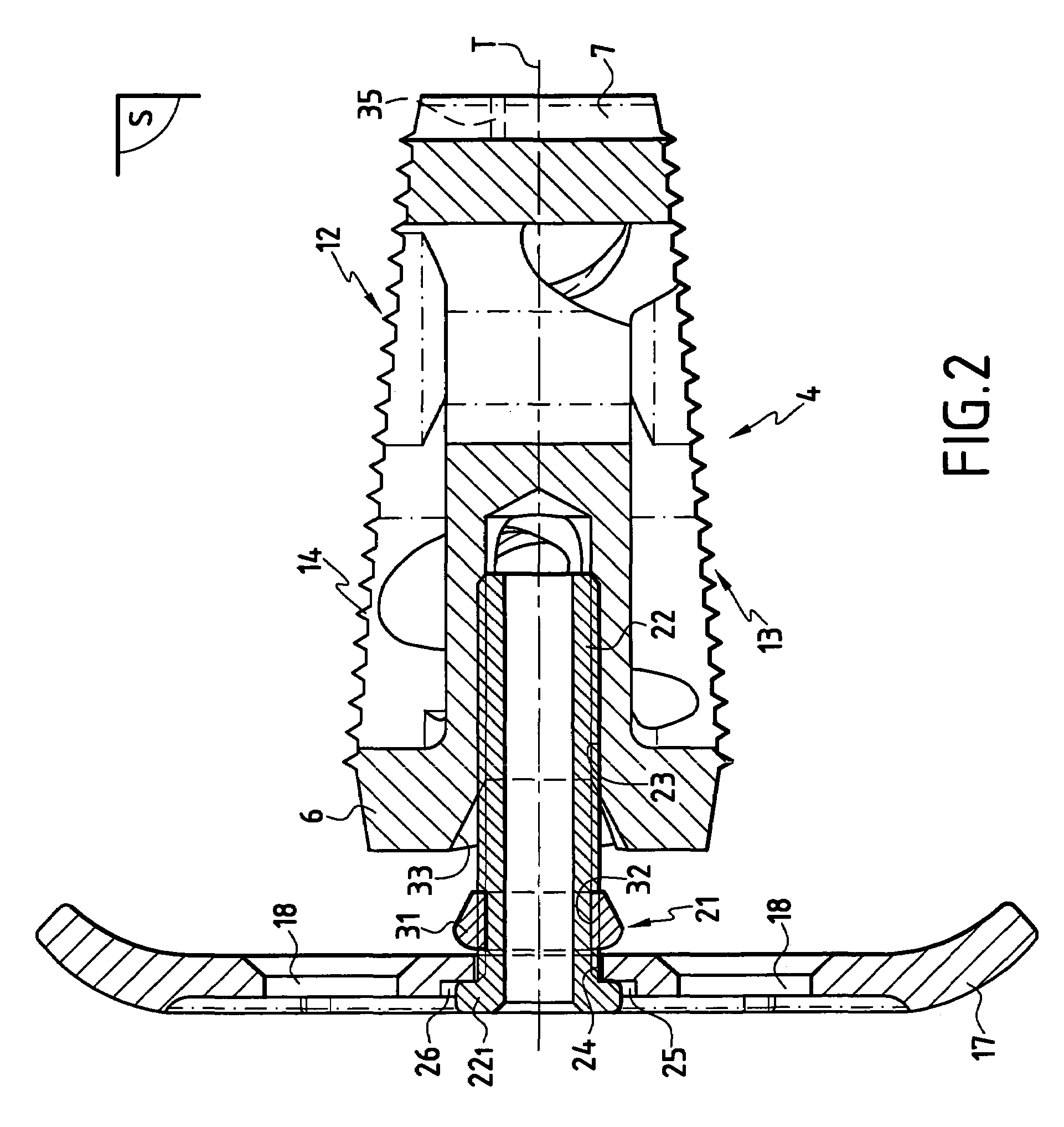
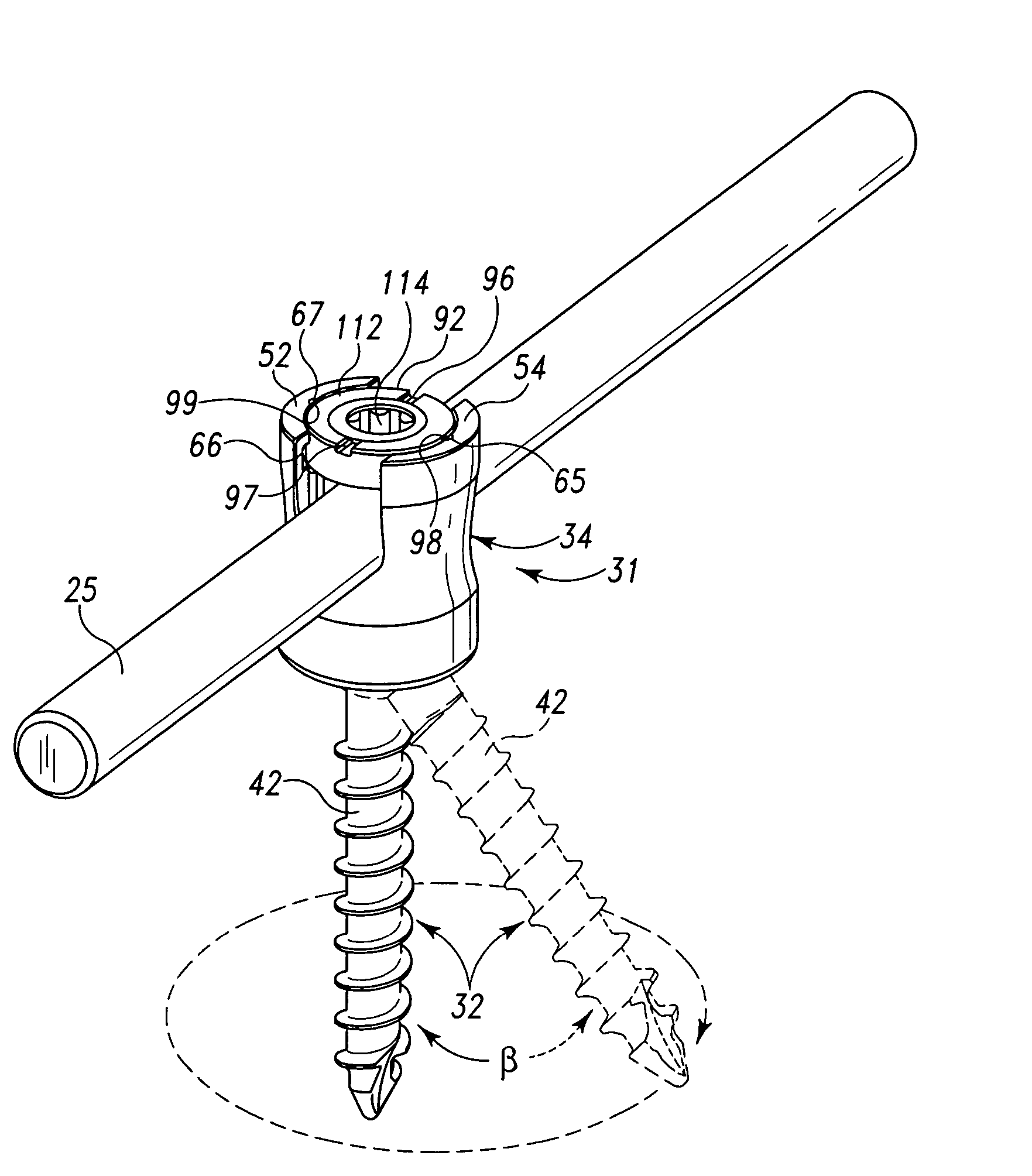
Stabilized interbody fusion system for vertebrae
The invention concerns a stabilized interbody fusion system for vertebrae, of the type comprising an interbody implant (4) designed to be inserted in the intervertebral space defined between two neighboring vertebrae to be mutually secured, so as to restore the height and the angle of the lordosis of the vertebral segment defined by the two neighboring vertebrae and a stabilizing plate (17) provided, at each of its ends, with at least a passage hole (18) for an anchoring screw, the plate (17) and the implant (4) being provided with mutual assembly means, such that after assembly, the stabilizing plate (17) extends on each side of the implant to enable the stabilizing plate to be anchored on the neighboring vertebrae through the screws, characterized in that it comprises spacing means (30), interposed between the stabilizing plate (17) and the implant (4), to enable the stabilizing plate to be positioned at a specific distance relative to the implant.
Owner:SCIENTX
Pedicle screw constructs for spine fixation systems
A pedicle screw coupling construct for a pedicle screw construct provides fixation of angular orientation thereof relative to a pedicle screw independent of fixation of a received spinal rod to the coupling construct. The pedicle screw construct forms one component or element in a spinal fixation system. The independent fixation coupling construct also provides for fixation of the angular orientation of the coupling construct while the coupling construct has received the spinal rod. In another form, a coupling head or construct is configured to allow a pedicle screw shaft to pass therethrough but retain the pedicle screw head for rotation of the coupling head about the pedicle screw head. The coupling head or construct is also configured to allow at least a 45° arc of pivot or articulation about a pedicle screw shaft relative to a longitudinal axis of a spinal rod received in the body. This allows the head with a received spinal rod to fold, bend or pivot relative to the pedicle screw shaft, particularly to a greater degree than the prior art.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
Graft fixation using a screw or plug against suture or tissue
InactiveUS6544281B2Excellent pull-out strengthHigh strengthSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisDistal portionSurgical department
A method for securing soft tissue to bone with excellent pull-out strength which does not require the surgeon to tie suture knots to secure the tissue to the bone. A blind hole or socket is created in the bone at the location the graft is to be secured. Preferably, suture is then passed through the graft at desired points. A cannulated driver is pre-loaded with a cannulated plug or screw slidably disposed onto the distal portion of the driver. In a preferred embodiment, a separate piece of suture is passed through the cannula of the driver with a loop end of that suture exposed at the distal end of the driver. The ends of the suture attached to the graft are fed through the suture loop at the end of the driver. Alternatively, the graft itself may be fed through the suture loop, in which case it is not necessary to attach suture through the graft. In another embodiment, the suture loop exposed at the distal end of the cannula of the driver may be omitted, and the sutures attached to the graft may then be fed through the driver cannula from the distal end to position the graft relative to the driver. The driver is inserted into the hole with the screw or plug just outside the hole. Tension is then placed on the suture. Once adequate tension is achieved on the suture, the driver is pressed into the hole, which engages the first thread or bump of the screw or plug on the bone. The screw or plug is then fully advanced into the hole using the driver. When the screw or plug is fully inserted, the suture loop is freed and the driver is removed. The loose ends of the sutures protruding from the anchor site can be cleaned up by clipping them short.
Owner:ARTHREX
Orthopedic implant rod reduction tool set and method
A tool set for implanting a rod in a human spine in conjunction with bone screws. The tool set includes a pair of end guide tools that receive opposite ends of the rod in channels and under manipulation by a surgeon facilitate transport of the rod toward the bone screws attached to the guide tools. Intermediate guide tools having guiding pass through slots are utilized to guide intermediate locations along the rod toward associated bone screws. An attachment structure operably connects the guide tools to the bone screws. The guide tools each include a lower guide and advancement structure to allow a closure top with mating structure to be rotated and driven downward against the rod and to cooperate with similar structure in the bone screw to seat and lock the rod therein. A method utilizing the tool set allows a surgeon to percutaneously implant the rod in the patient.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Biodegradable interference screw and tool for attaching a transplant to a bone
InactiveUS7261716B2Enhanced interactionEasy to handleSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsInterference screwsEngineering
A biodegradable interference screw for directly affixing a transplant to a bone, the interference screw being provided with at least one longitudinal groove designed to co-act with a tool for insertion of and if necessary, removal of the interference screw from an opening provided in the bone to receive both the transplant and the interference screw.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
Device for fixing the sacral bone to adjacent vertebrae during osteosynthesis of the backbone
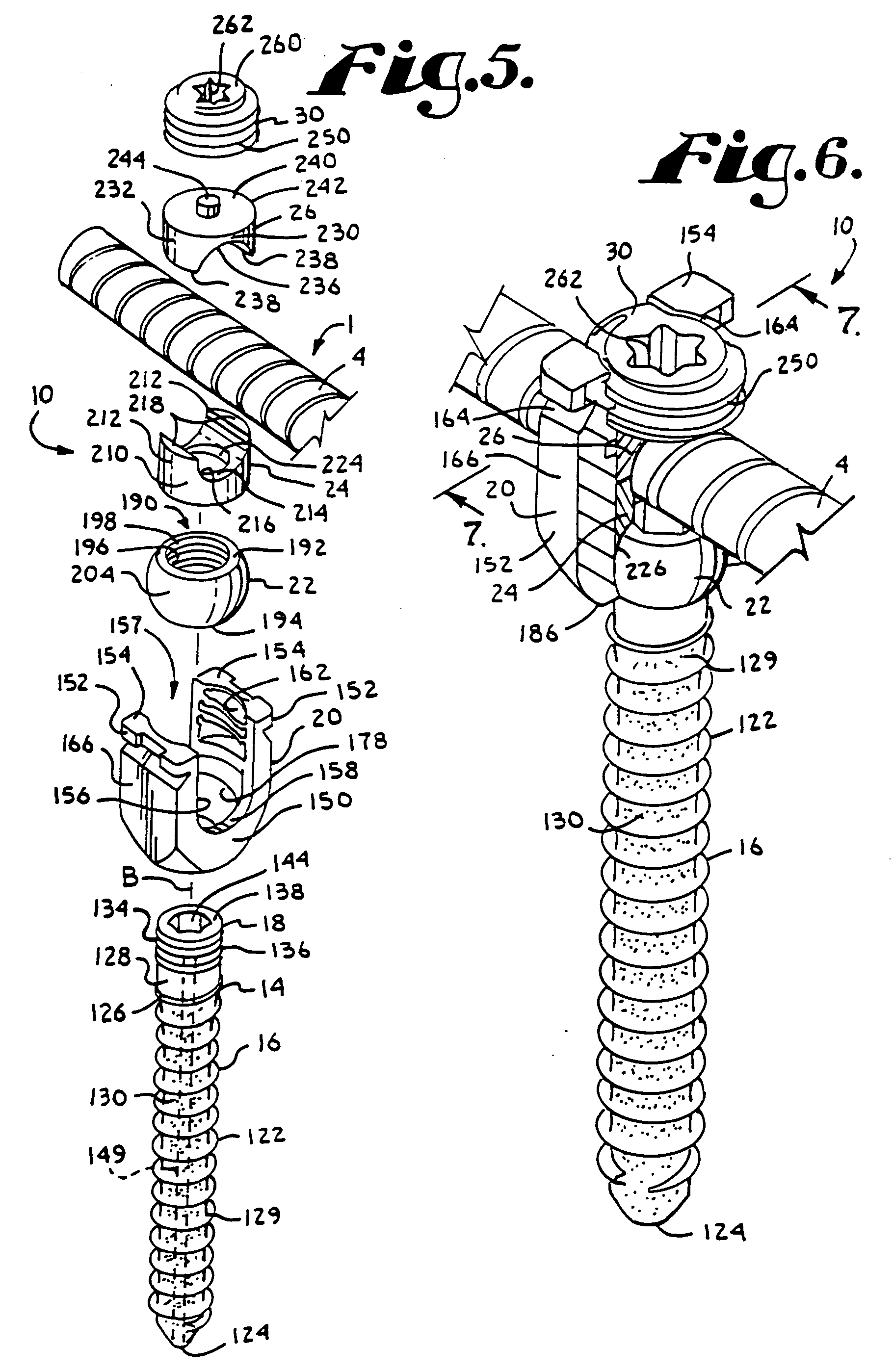
InactiveUS6290703B1Degree of stiffness attenuationReduce frictionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSacral BoneBone fixation devices
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Variable angle locked bone fixation system
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Surgical screw system and related methods
A surgical screw system for use with implantation rods includes a screw member, a receiver member, a pressure cap and a locking device. The screw member has a shaft and a head with a spherical undersurface and a conical tapered recess. The receiver member has an upper and lower portion, a u-shaped rod receiving channel and an axial bore. The u-shaped channel has two lateral legs at the upper portion and forms an opening leading to the axial bore. The axial bore near the lower portion includes an inwardly conical tapered surface which has a diameter larger than the shaft of the screw member but smaller than the head of the screw member. The conical surface forms a support upon which the spherical undersurface of the head of the screw member rests when the screw member is guided through the bore of the lower portion of the receiver member. The pressure cap is positioned within the axial bore and situated upon the head of the screw member. The locking device is designed for securing the rod within the u-shaped channel of the receiver member by applying a tightening torque upon the rod when positioned within the opening and the bore near the upper portion of the receiver member.
Owner:BLACKSTONE MEDICAL
Blockable bone plate
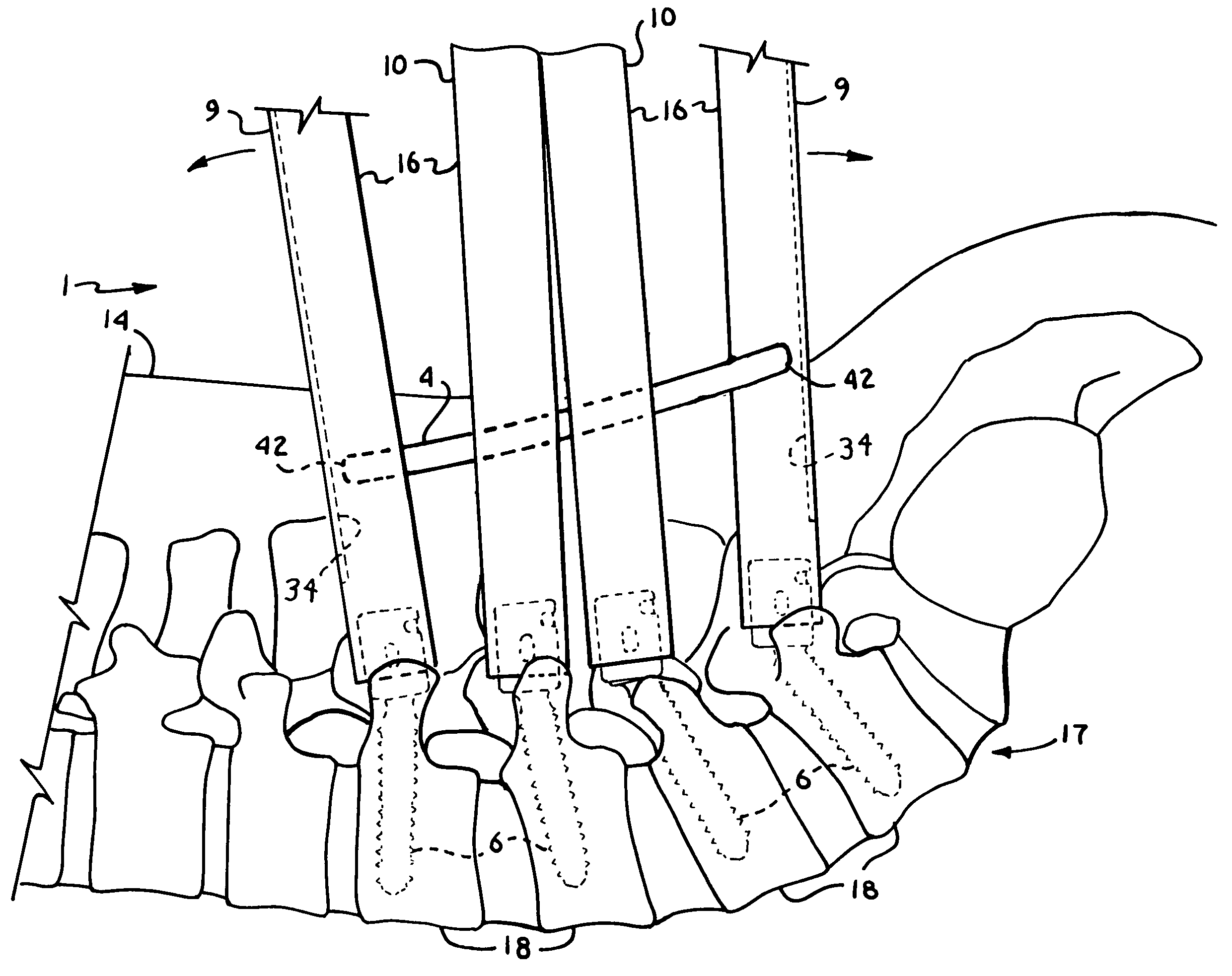
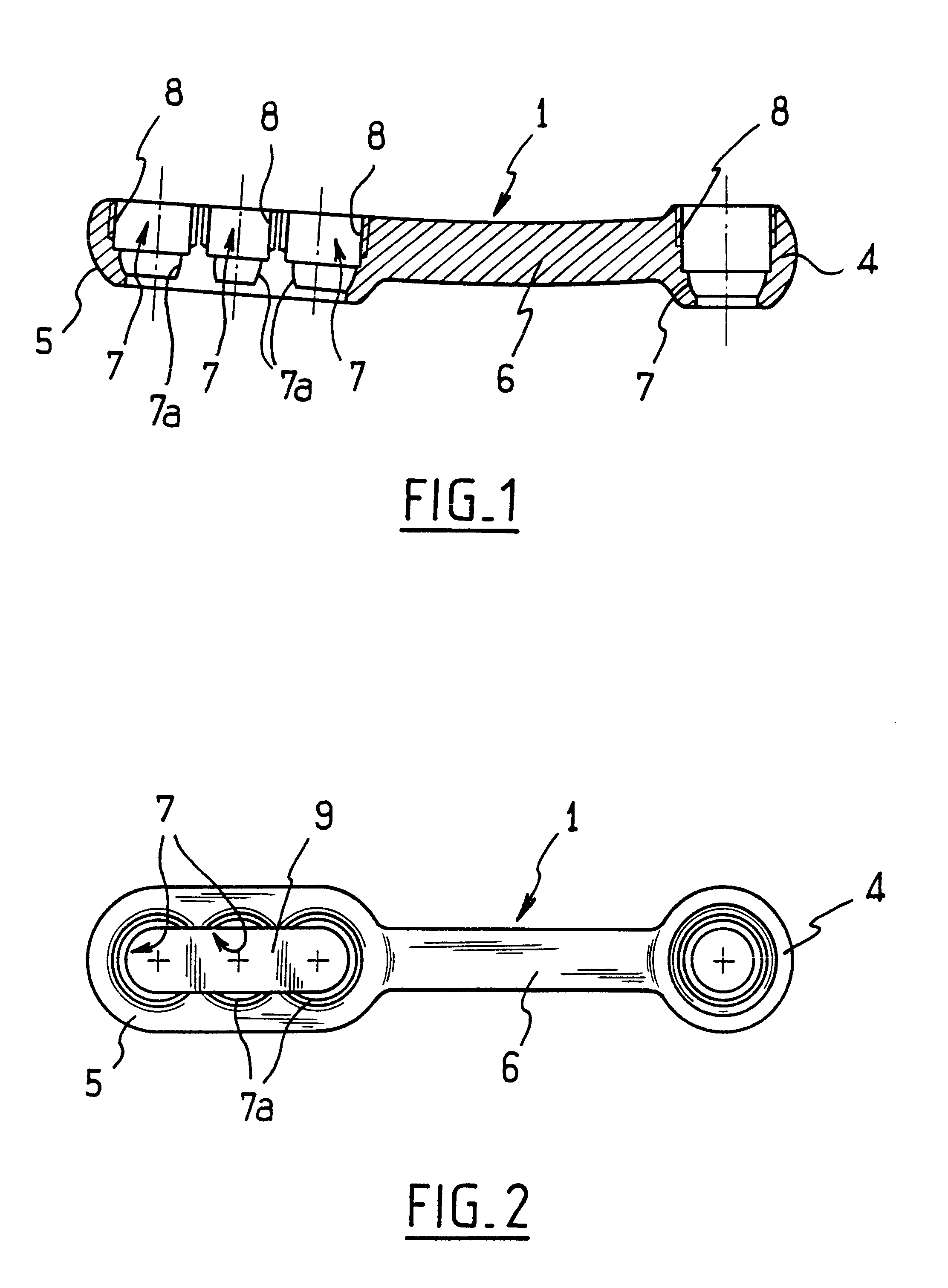
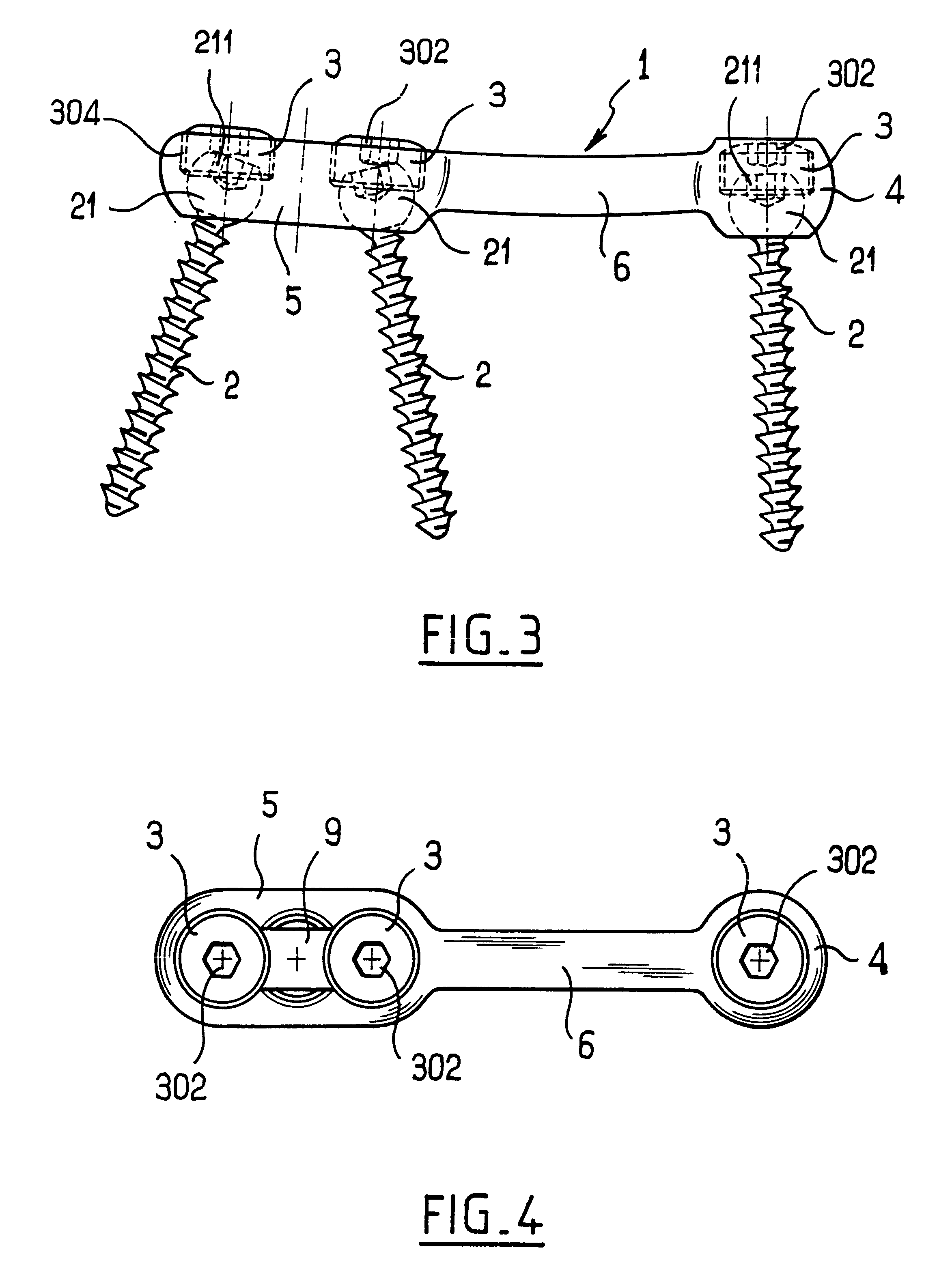
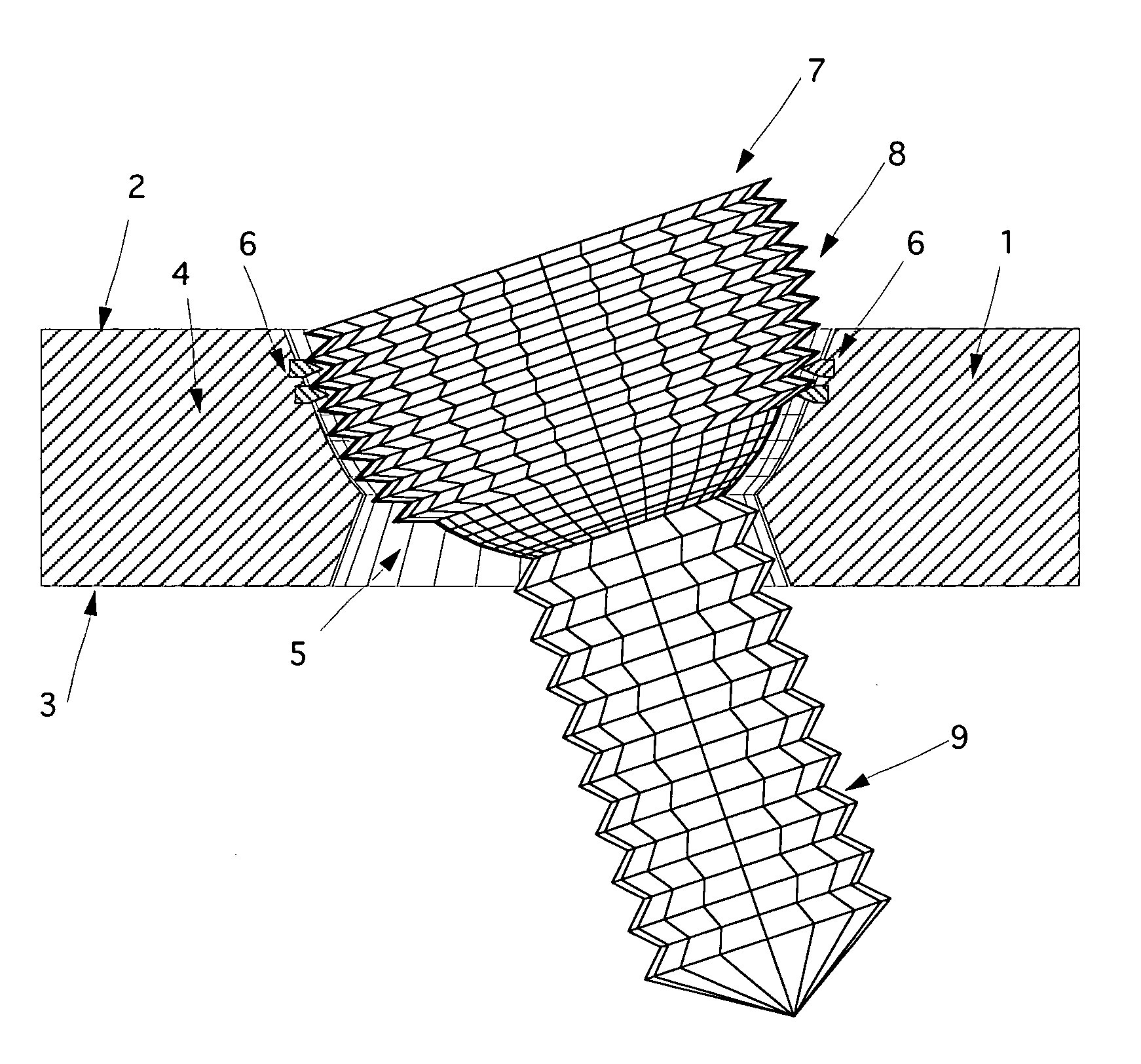
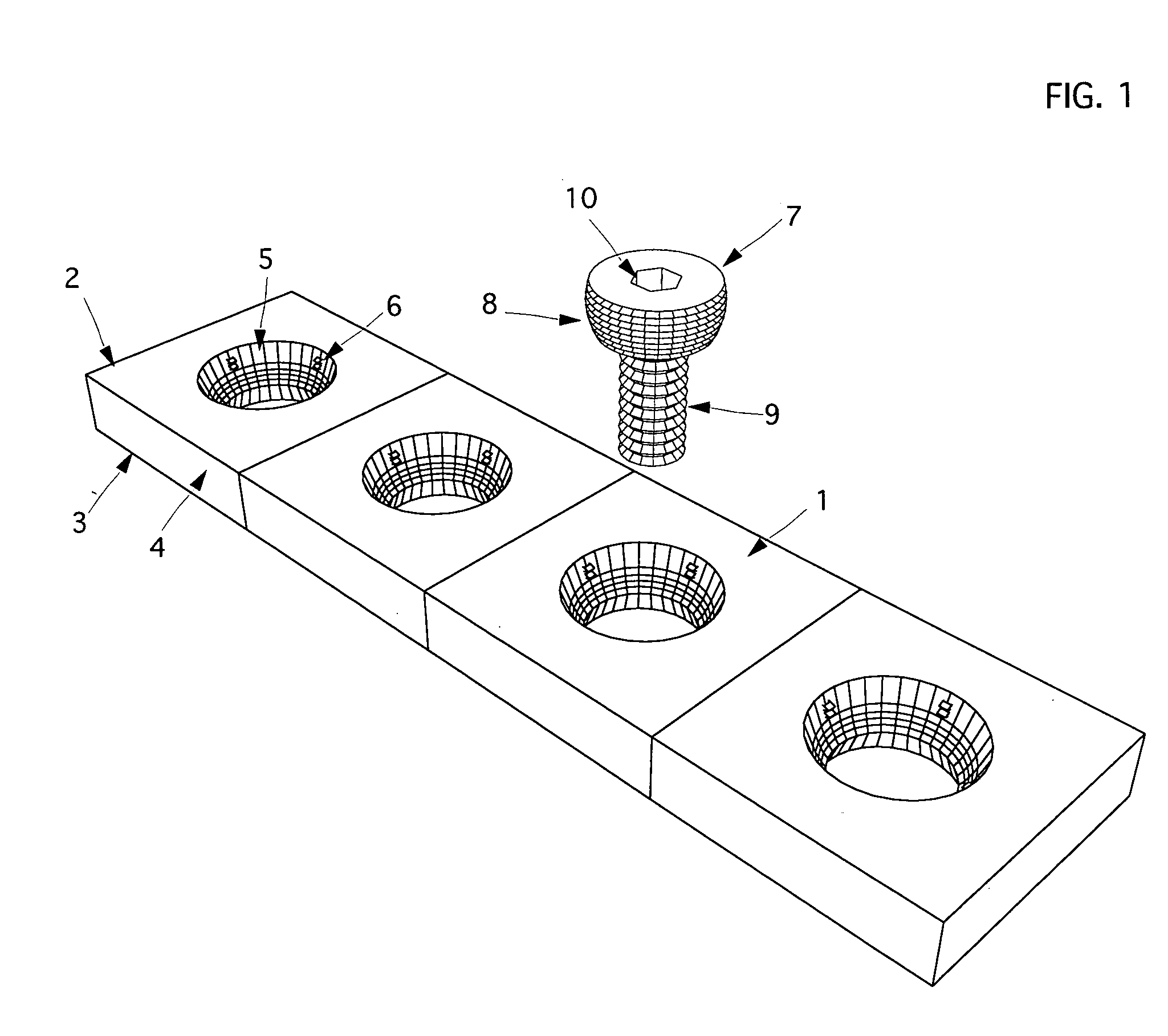
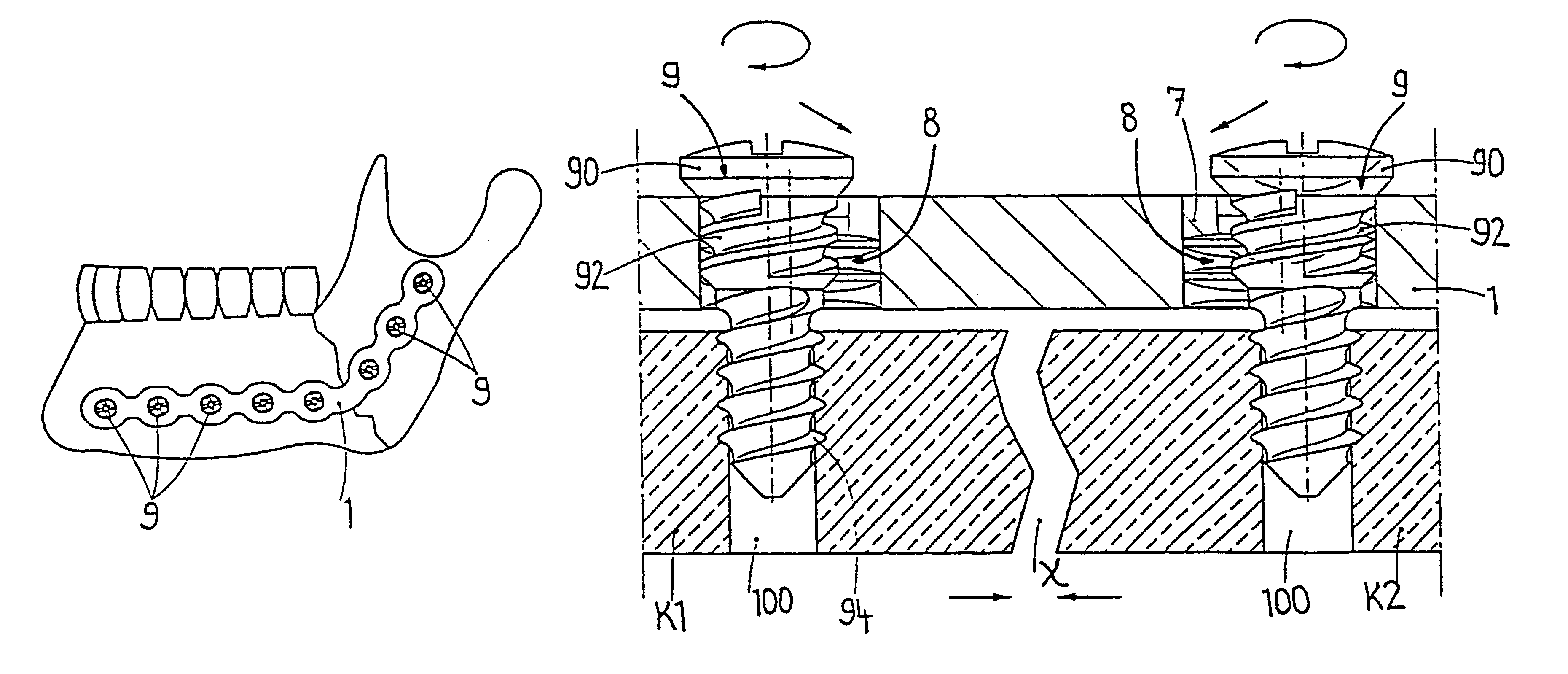
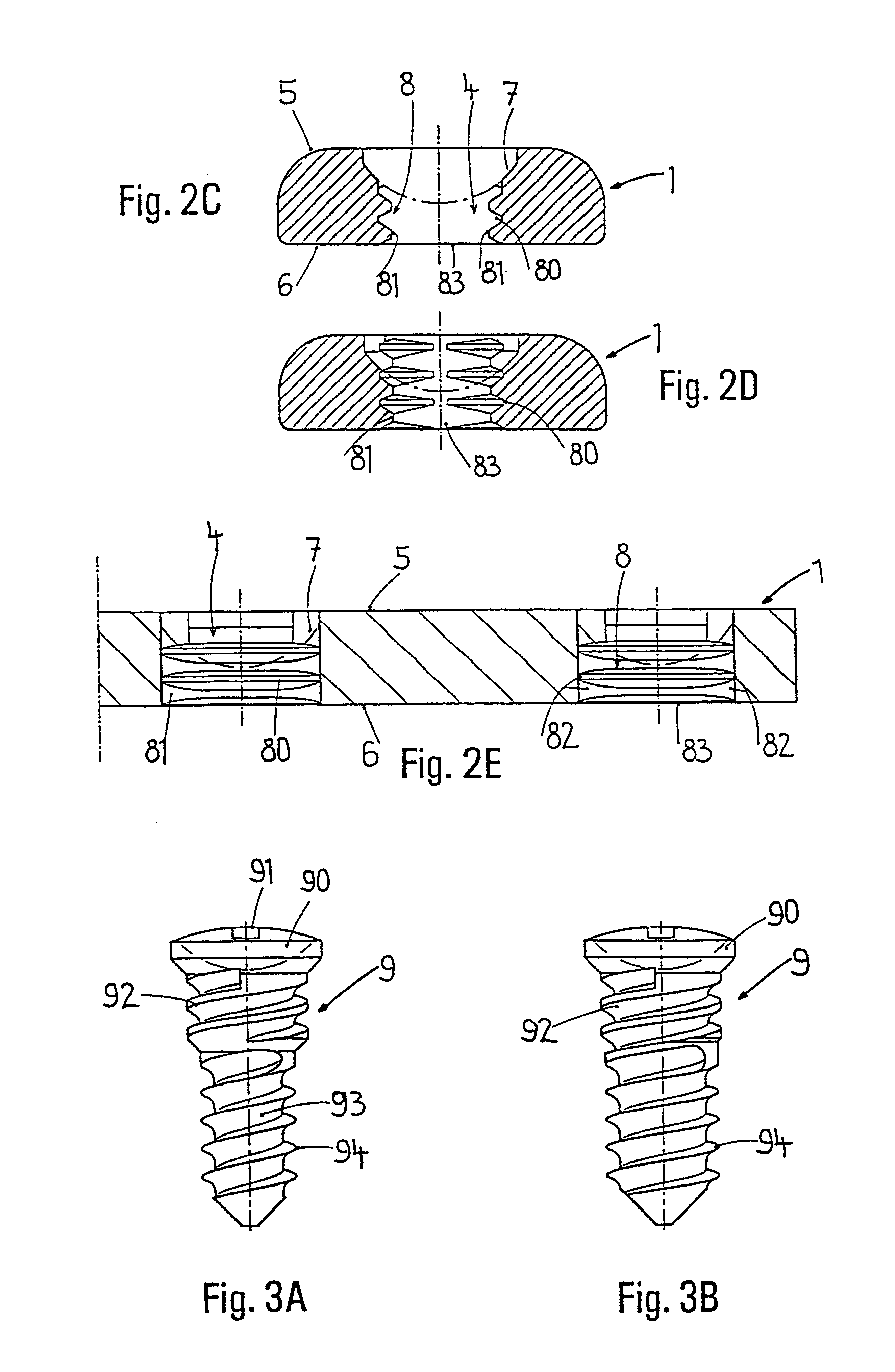
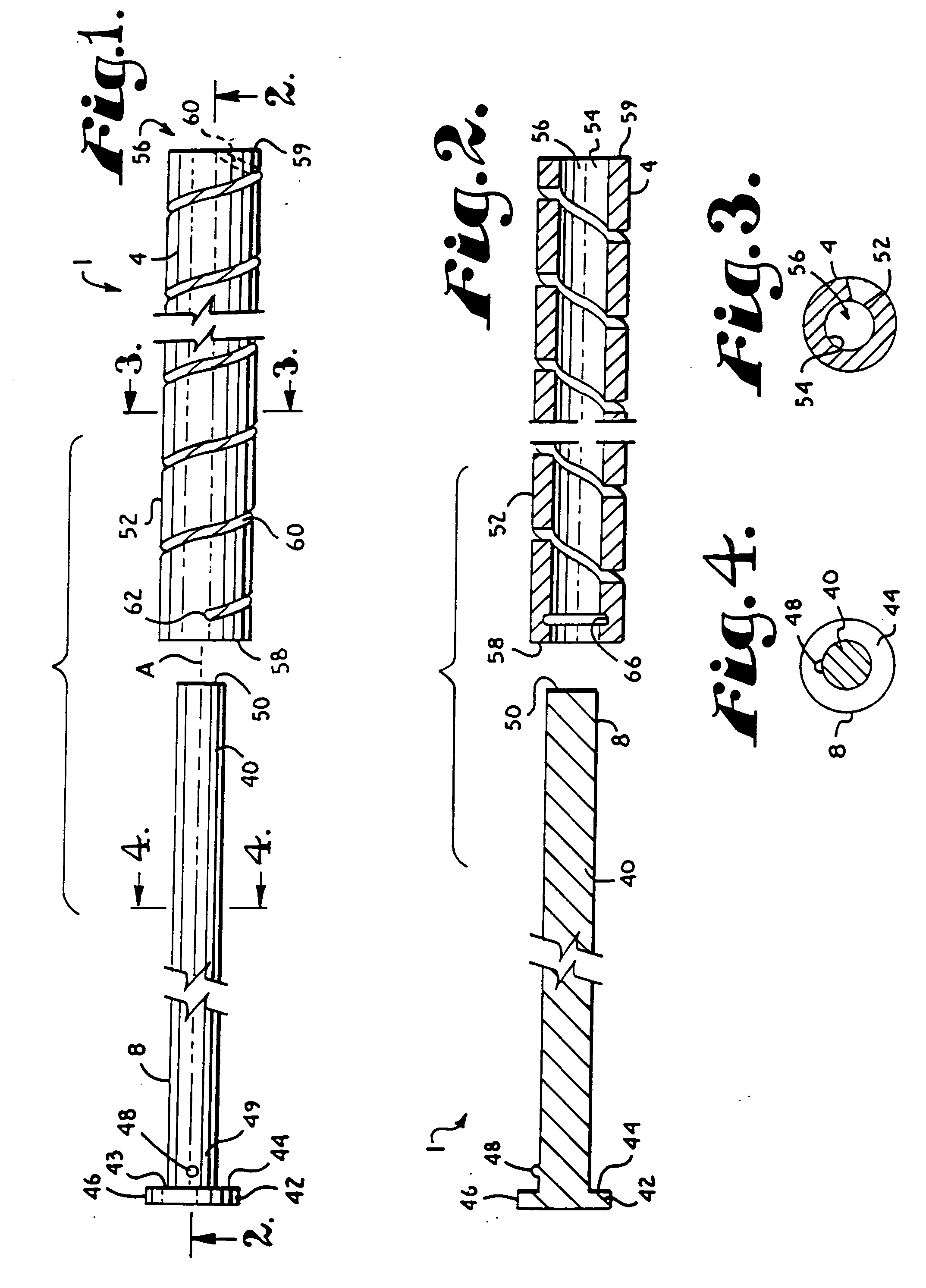
InactiveUS6730091B1Cost effective productionLow costSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEngineeringIliac screw
The blockable bone plate consists of a plurality of plate members which are connected to each other via webs. A screw hole is provided in at least some plate members, preferably in each plate member. The screw hole is surrounded by a spherical countersink on the upper surface of the plate. Provided internally in the screw hole there is an engagement contour which consists of contour valleys and contour peaks partially running in a horizontal and radial peripheral direction on the wall of the screw hole. The engagement contour is preferably produced by milling and has for example a pointed, round, trapezoidal or serrated configuration. A blocking thread is provided under the screw head of the screw intended for blocking. As the screw is screwed in, the blocking thread engages in the engagement contour. The particular advantages lie in increased security against the screw coming loose and in the possibility of also inserting the screw through the plate at an inclination. Furthermore, a bone plate is proposed which has the shape of an arc of a circle in the longitudinal axis of the plate and which requires less bending, particularly on the human lower jaw, and adapts to the bone in a more ideal manner.
Owner:MEDARTIS AG
Systems and methods for spine stabilization including a dynamic junction
InactiveUS20050182401A1Easy to installImprove clinical outcomesSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisRotational freedomUniversal joint
Spinal stabilization devices, systems and methods are provided that include at least one pedicle screw and at least one mechanism that supports three degrees of rotational freedom relative to the pedicle screw. The mechanism may include a universal joint mechanism or a ball and socket mechanism. In the case of the ball and socket mechanism, at least one spherical element is mounted with respect to the at least one pedicle screw and a socket member cooperates with the spherical element. The spherical element and the socket member cooperate to define a dynamic junction that allows the socket member to move relative to the ball element while remaining engaged therewith. The dynamic junction is advantageously incorporated into a spinal stabilization system that includes additional pedicle screw(s), spherical element(s) and socket member(s). The spinal stabilization system may incorporate dynamic stabilizing member(s) to so as to provide clinically efficacious results.
Owner:APPLIED SPINE TECH
Method and device for fixing and correcting spondylolisthesis anteriorly
A method and apparatus for fixation and correction of spondylolisthesis anteriorly includes a disk cage which is inserted into the space between adjacent vertebrae, a drill guide for guiding and aligning a drill bit to angle an opening anteriorly between adjacent vertebrae, a distractor for temporarily aligning the vertebrae to position a disk cage and an elongated hollow screw positioned in said drilled opening through one vertebra, said disk cage and into said adjacent vertebra.
Owner:SPINEOLOGY
Bio-flexible spinal fixation apparatus with shape memory alloy
ActiveUS20060064090A1Easily simply achieveAccurate operationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsShape-memory alloyEngineering
The present invention relates to a spinal fixation apparatus having a segment flexible rod for connecting pedicle screws and a transverse link for spacing out the rods, which are made from a shape memory alloy, thereby easily and simply connecting the rods and the pedicle screws. According to the present invention, it can easily and simply fit the rods to the misaligned pedicle screw, even if it may be a failure of alignment of the pedicle screws in surgery. Also, it can easily set up the transverse link on a pair of the longitudinal rods, even if the longitudinal rods are declined or are not in parallel.
Owner:PARK KYUNG WOO
Expandable Self-Anchoring Interbody Cage for Orthopedic Applications
ActiveUS20130158669A1Maintain and create lordosisEasy to useBone implantSpinal implantsSpinal cageInterbody cage
The present invention is directed to an expandable spinal fusion intervertebral implant that provides for maintaining and creating lordosis in the human spine that can be filled with biologics while in situ to encourage spinal fusion. A threaded rod that traverses an insertion / injection handle can be rotated to operate a screw within the interbody cage that displaces opposing vertical tapped sliding wedges, causing them to converge towards each other. Such contact causes the operation of a horizontal wedge that acts as a lift to expand the interbody cage to one of various dimensions in a preferred range. At its desired expansion, the spinal fusion implant of the present invention is sized to fit within the disc space between two vertebral bodies and fill all voids left while the vertical and horizontal wedges operate within, due to the biologics being contained within the interbody cage.
Owner:BLUE TIP BIOLOGICS
Polyaxial pedicle screw having a rotating locking element
InactiveUS6840940B2Avoid couplingEffective movementSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisCouplingOrthopedic department
A screw and coupling element assembly for use with an orthopedic rod implantation apparatus includes a screw with a head and a shaft extending from the head, a coupling element with a seat within which the head is seatable such that the shaft protrudes from the coupling element, and a locking element mateable with the coupling element and when mated is selectively movable through a plurality of positions including unlocked and locked positions. When in the unlocked position, the locking element presents a rod-receiving channel and the head is movable in the seat such that the shaft is directable in a plurality of angles relative to the coupling element. When in the locked position, a rod disposed within the rod-receiving channel is fixed relative to the coupling element and the head is immovable in the seat such that the shaft is fixed at an angle relative to the coupling element.
Owner:K2M
Orthopedic implant rod reduction tool set and method
ActiveUS20050192570A1Good adhesionEasy to disengageInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsEngineeringBone staple
A tool set for implanting a rod in a human spine in conjunction with bone screws. The tool set includes a pair of end guide tools that receive opposite ends of the rod in channels and under manipulation by a surgeon facilitate transport of the rod toward the bone screws attached to the guide tools. Intermediate guide tools having guiding pass through slots are utilized to guide intermediate locations along the rod toward associated bone screws. An attachment structure operably connects the guide tools to the bone screws. The guide tools each include a lower guide and advancement structure to allow a closure top with mating structure to be rotated and driven downward against the rod and to cooperate with similar structure in the bone screw to seat and lock the rod therein. A method utilizing the tool set allows a surgeon to percutaneously implant the rod in the patient.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Adjustable rod and connector device and method of use
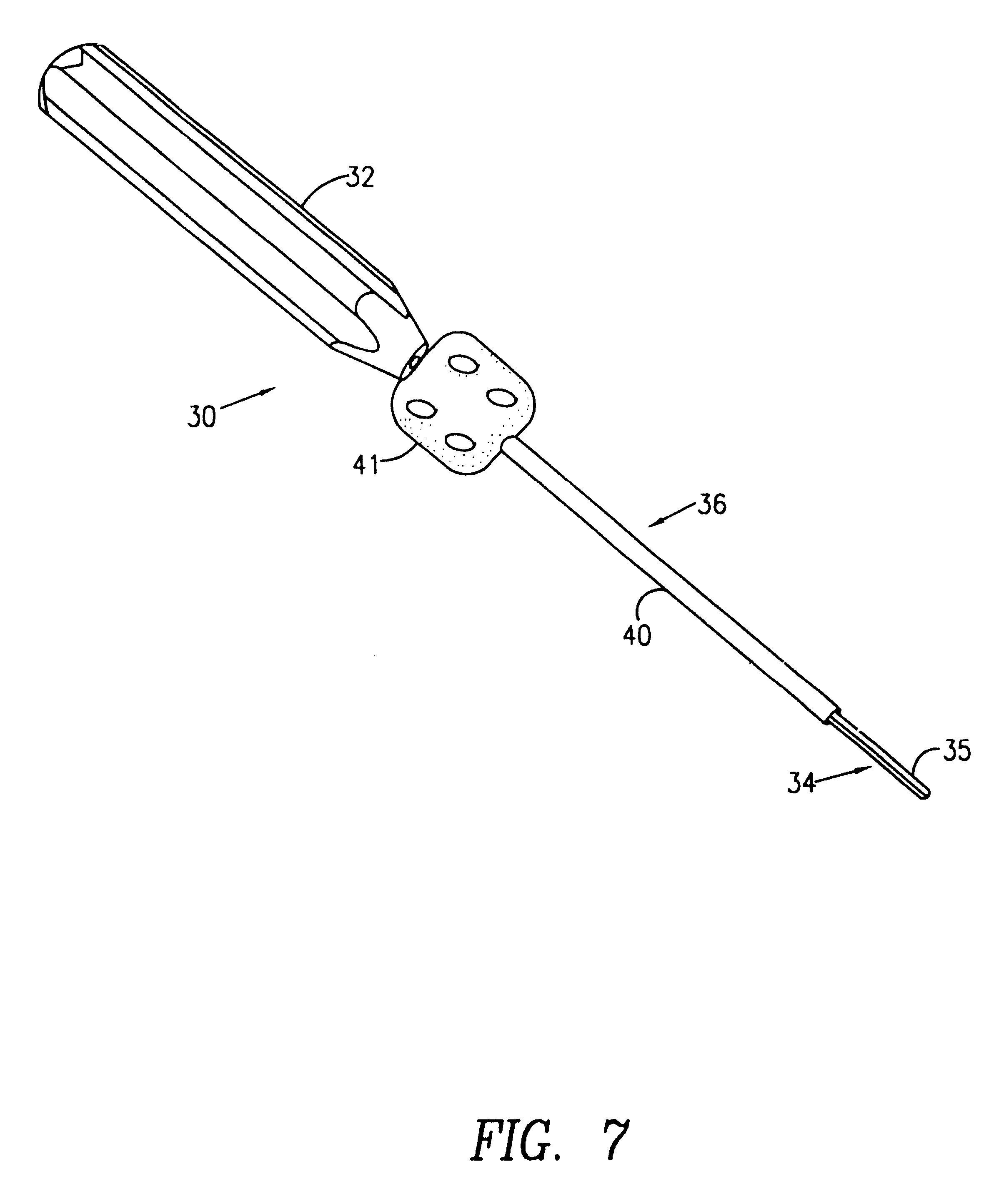
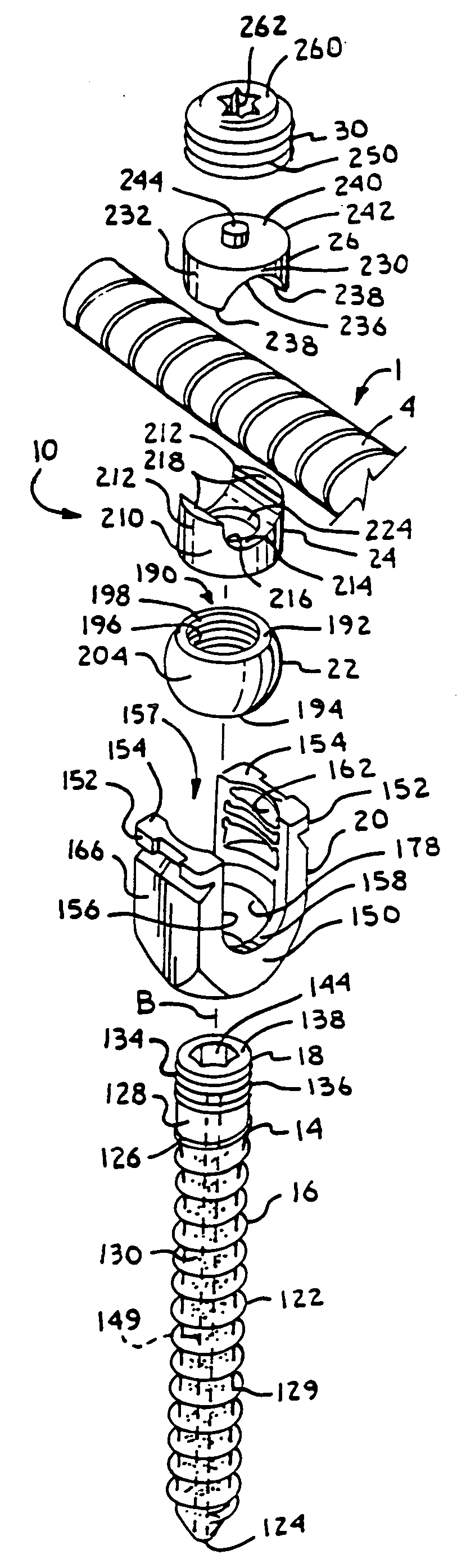
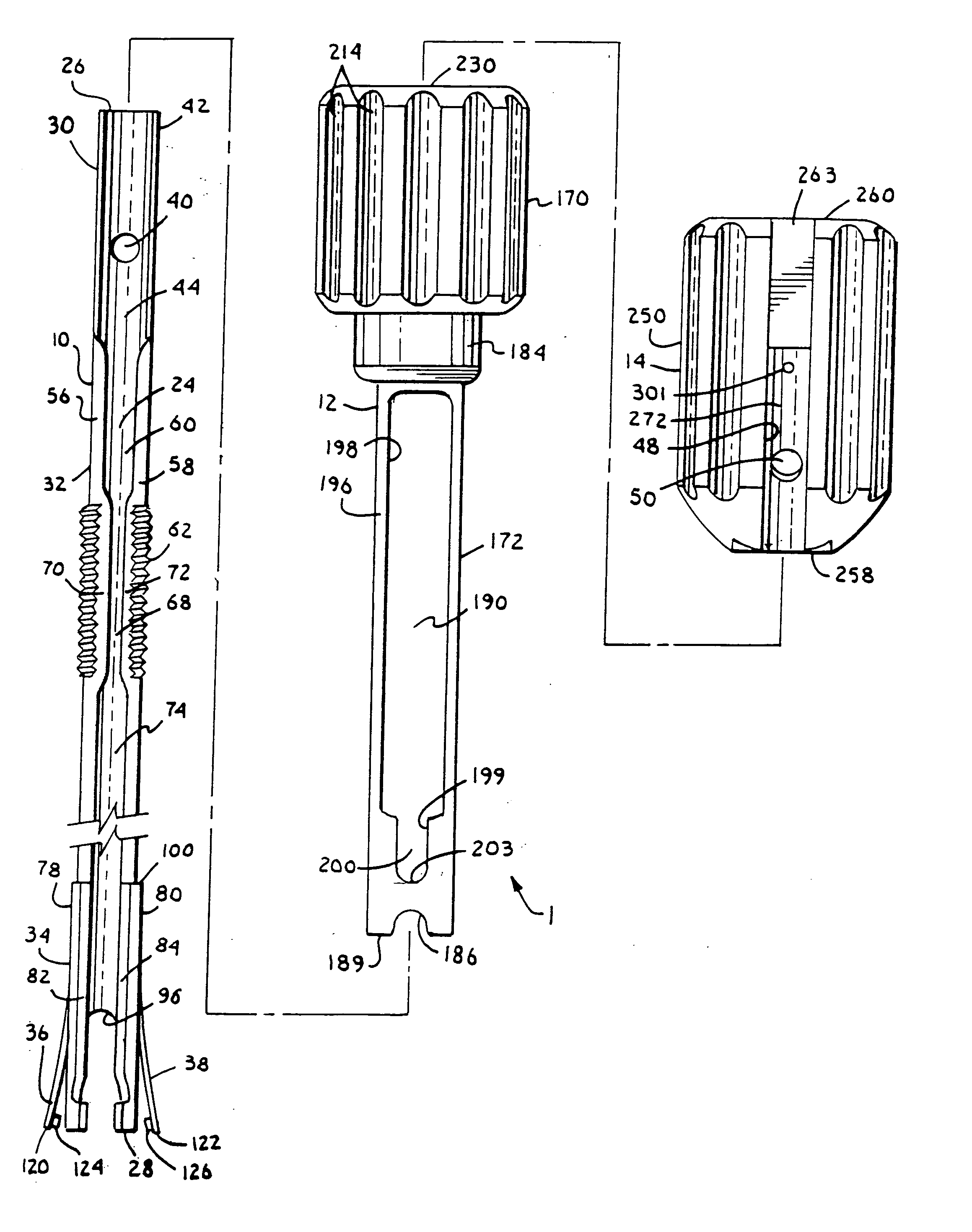
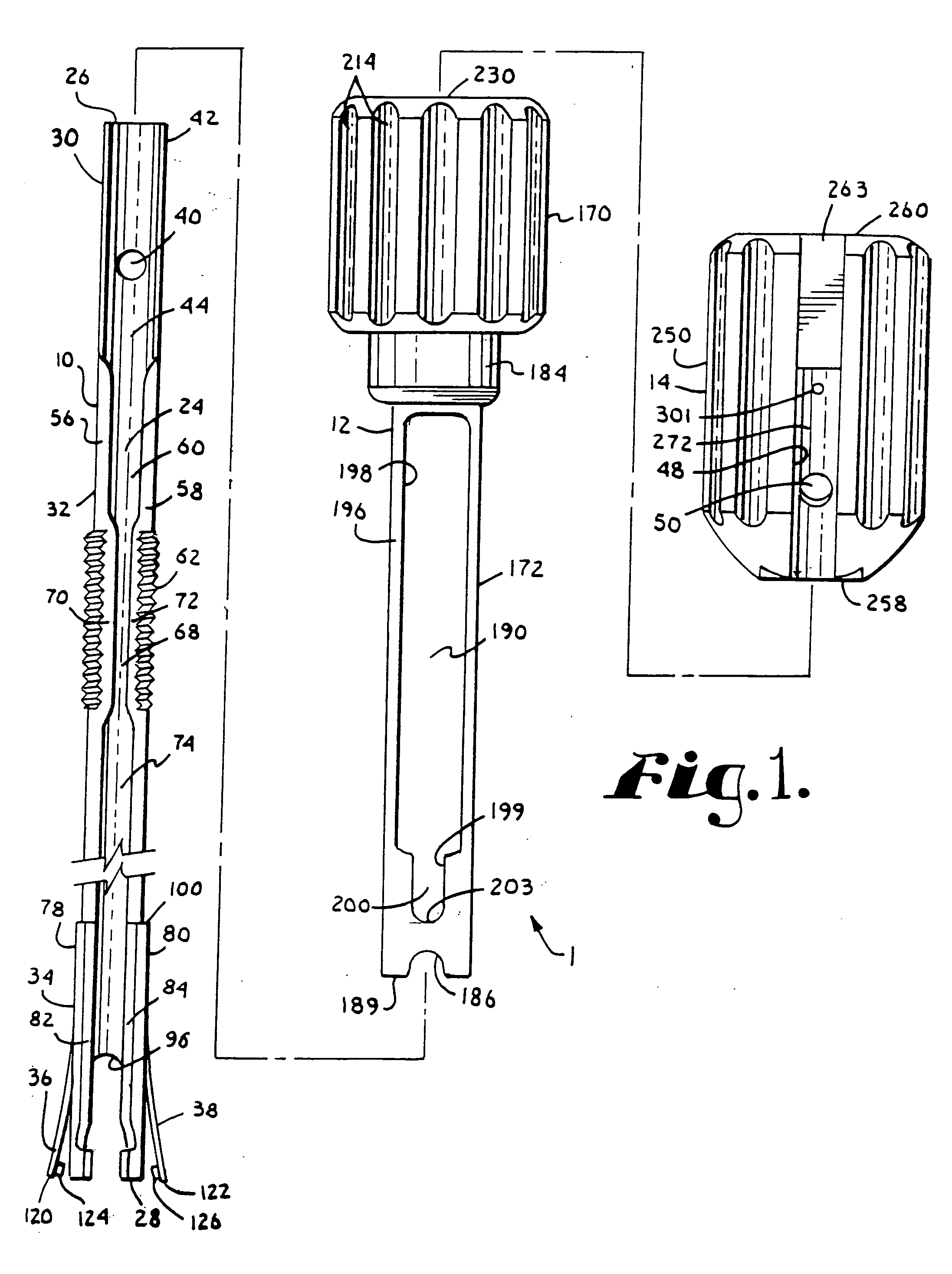
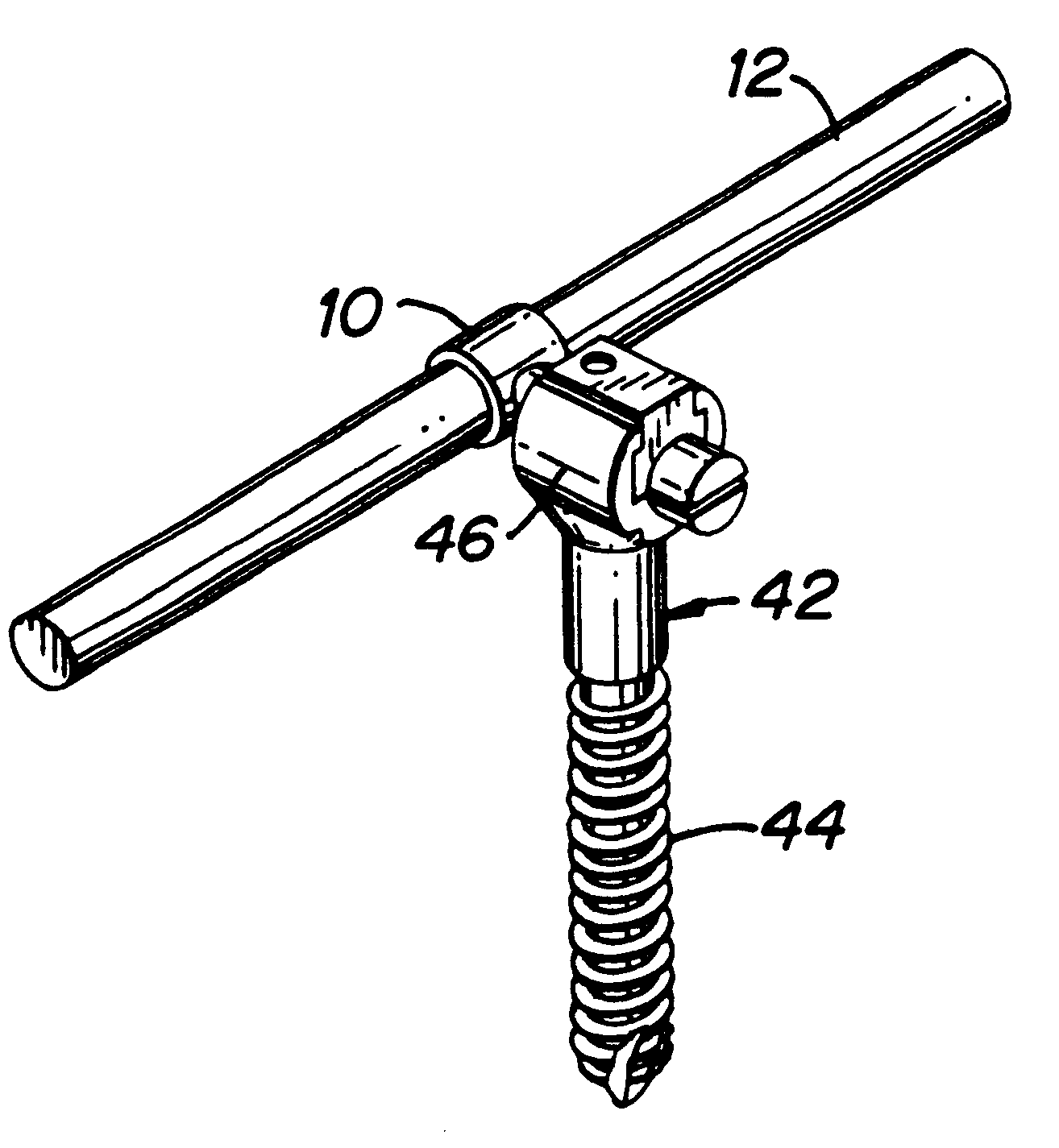
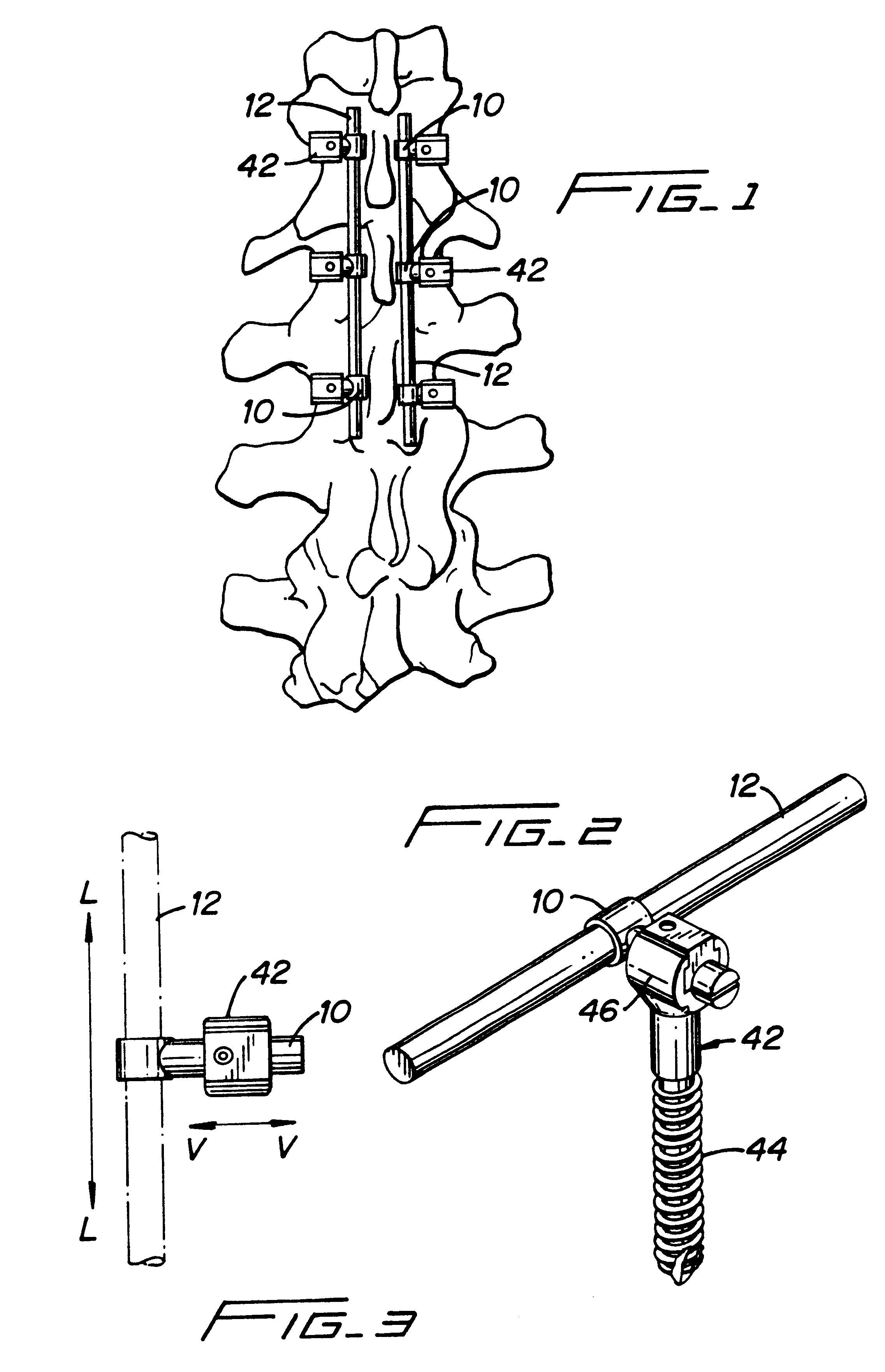
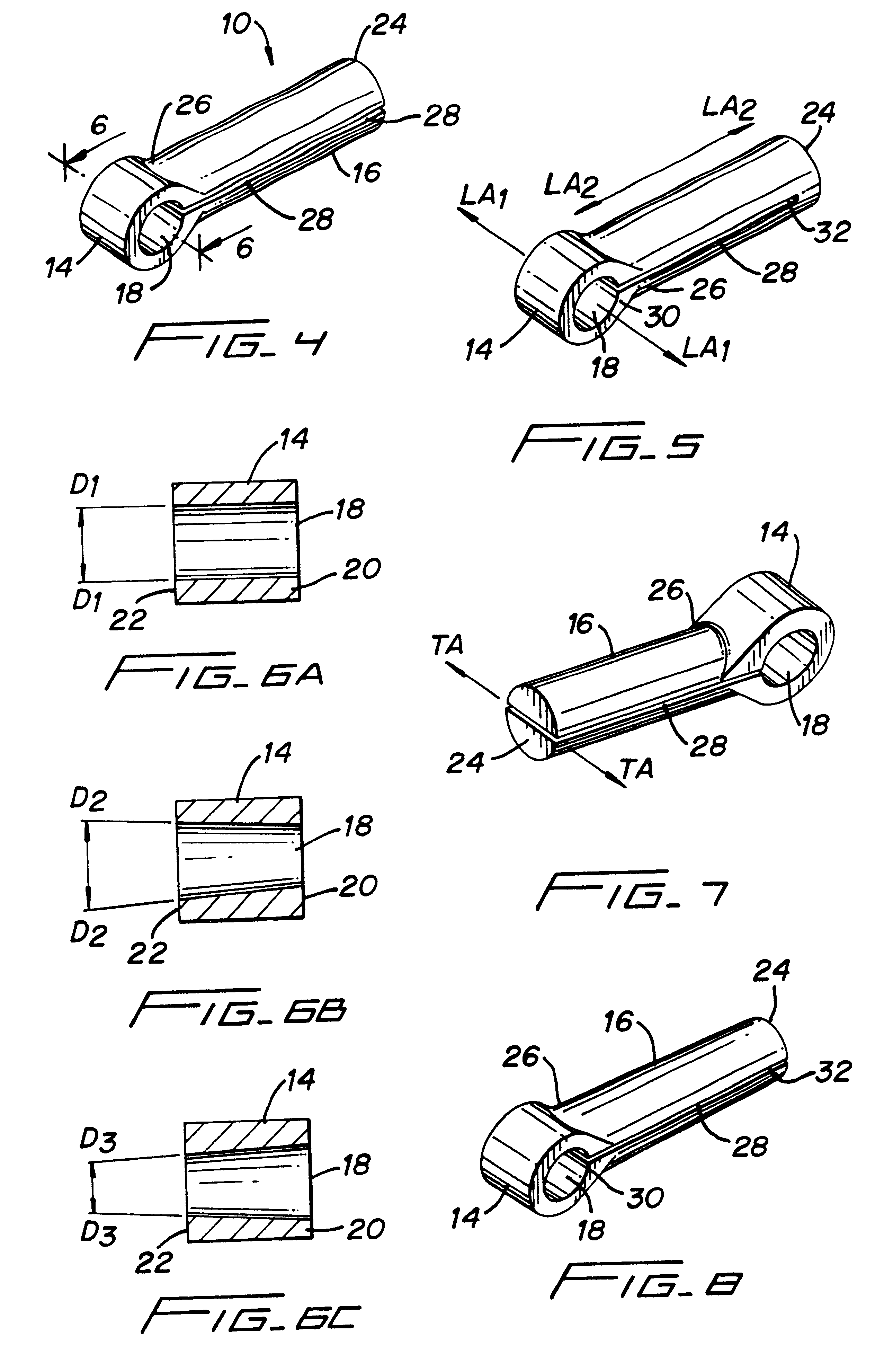
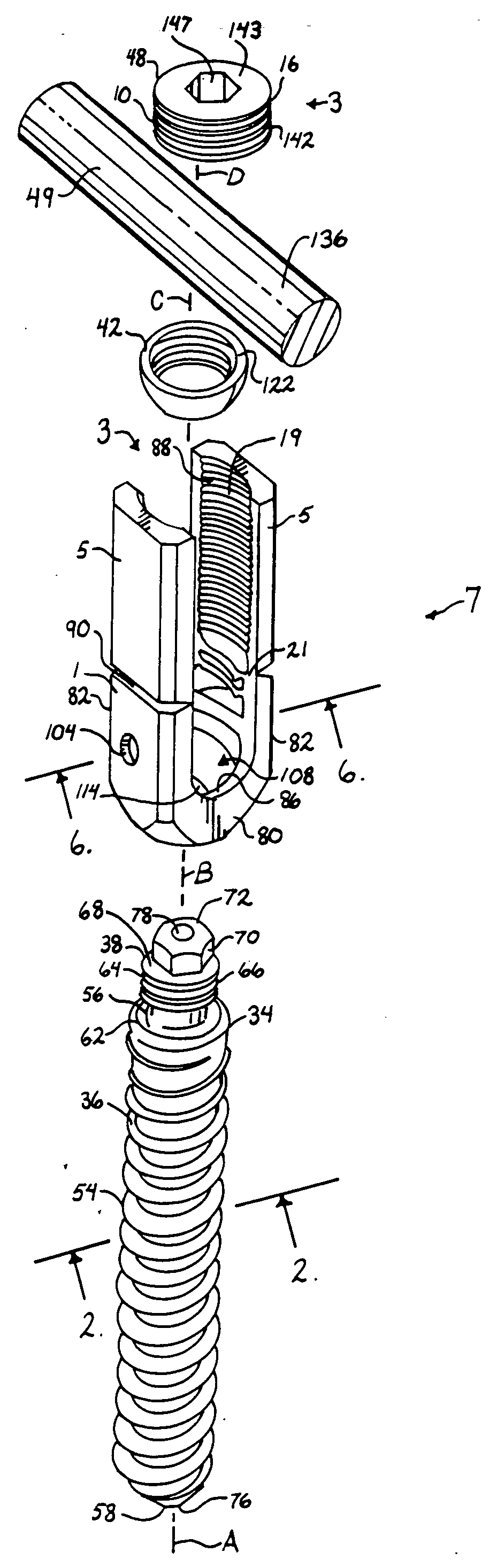
InactiveUS6991632B2Minimal displacementEasy to useInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsImplanted deviceIliac screw
Owner:RITLAND STEPHEN
Surgical power drill including a measuring unit suitable for bone screw length determination
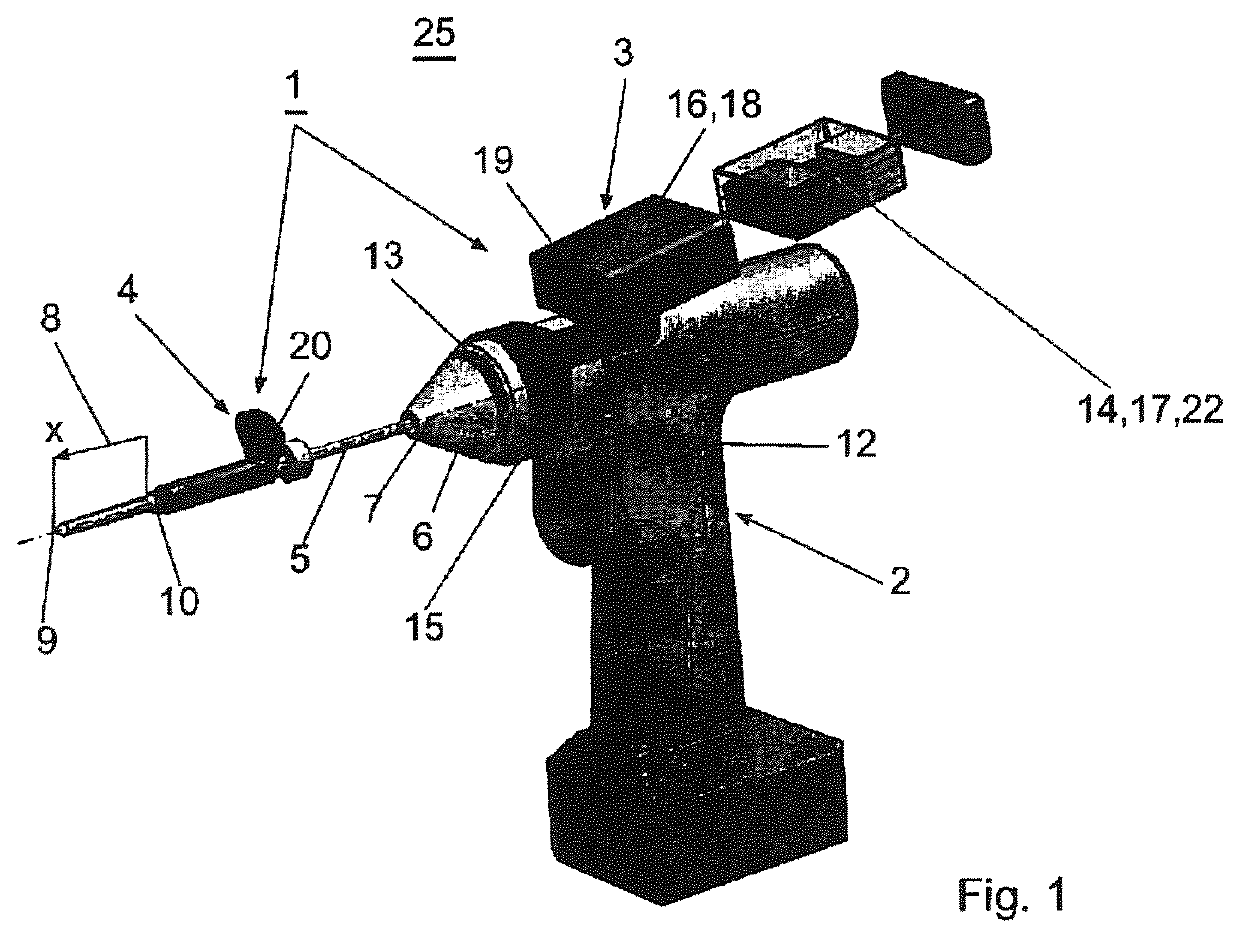
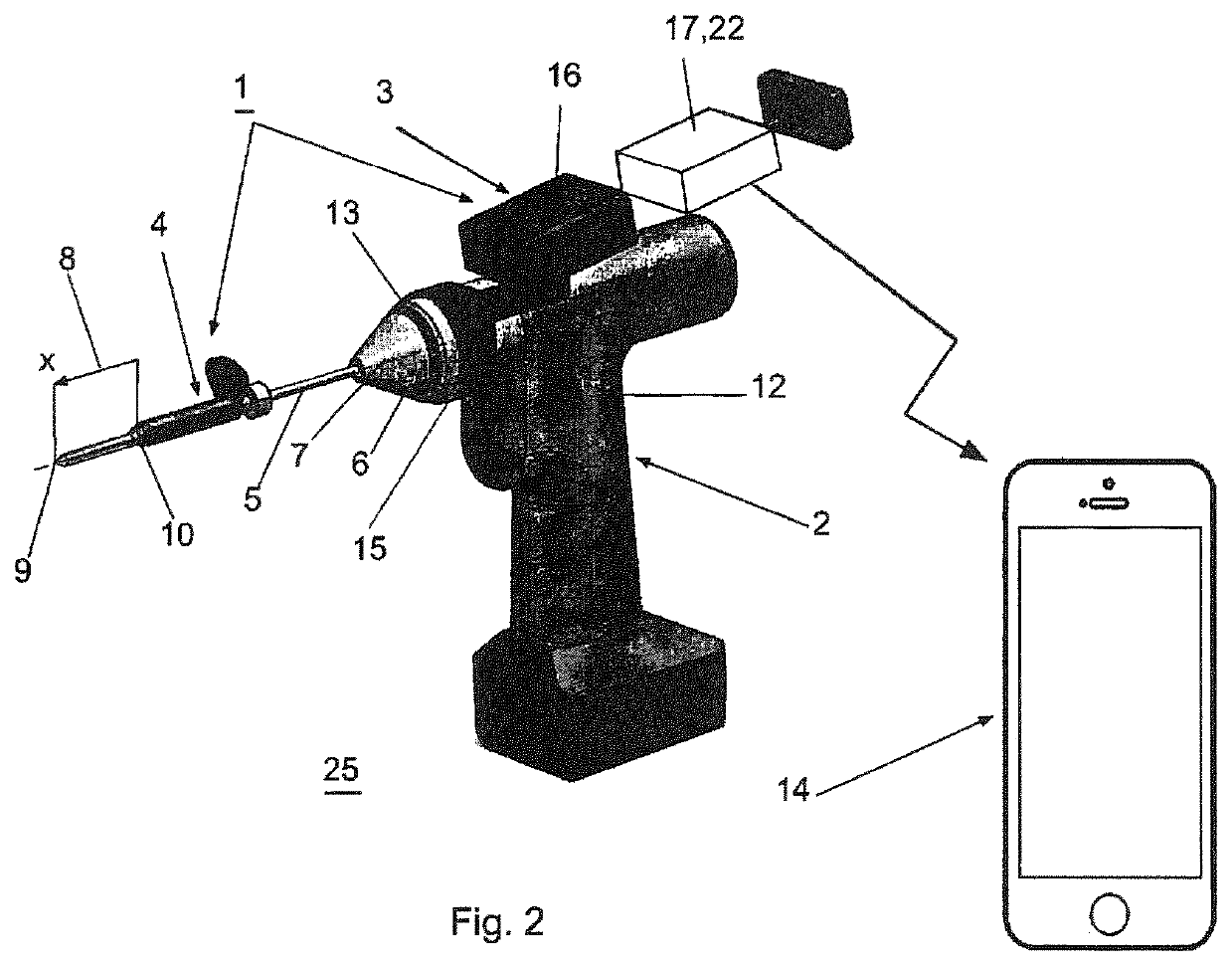
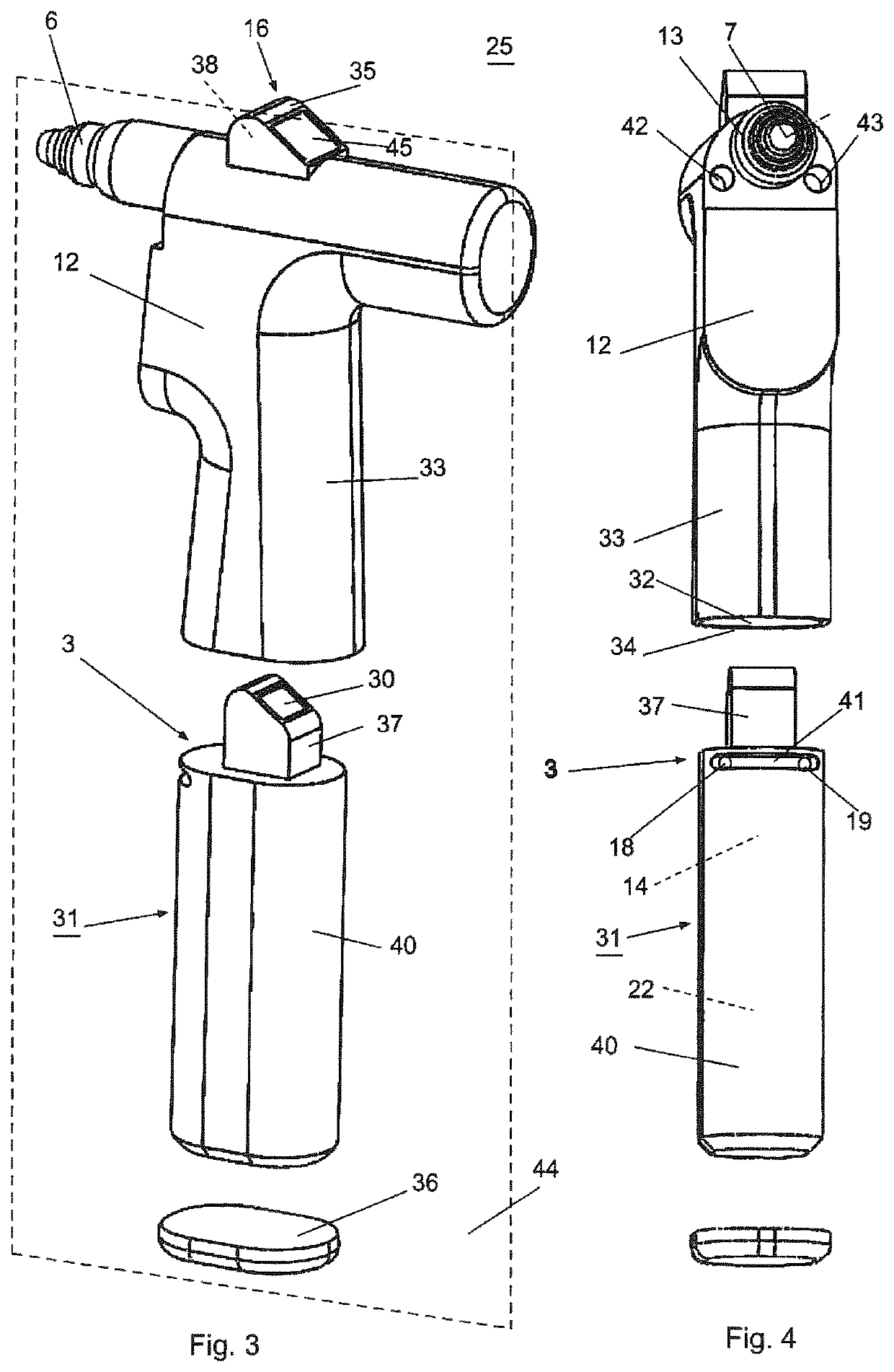
A device (25) for drilling holes in bone and configured to determine bone screw length, the device (25) including a surgical power drill (2) comprising: a) a housing (12) and; b) a measuring device (1) releasably attached or fixed to the housing (12), wherein the measuring device (1) is configured to measure the distance (x) covered by the housing (12) in the direction of the longitudinal axis (7) and relative to a surface of an implant (26) or a bone during a drilling process, wherein the measuring device (1) comprises a processing unit (14) to record the distance (x) covered with respect to time; the processing unit (14) comprises one or more differentiators to determine at least the first and second derivatives of the distance (x) covered with respect to time; and the processing unit (14) further comprises a peak detector to analyze one or more peaks occurring in the graph of the highest derivative with respect to time, and wherein the measuring device (1) comprises a laser device or an ultrasound position sensor for displacement assessment.
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
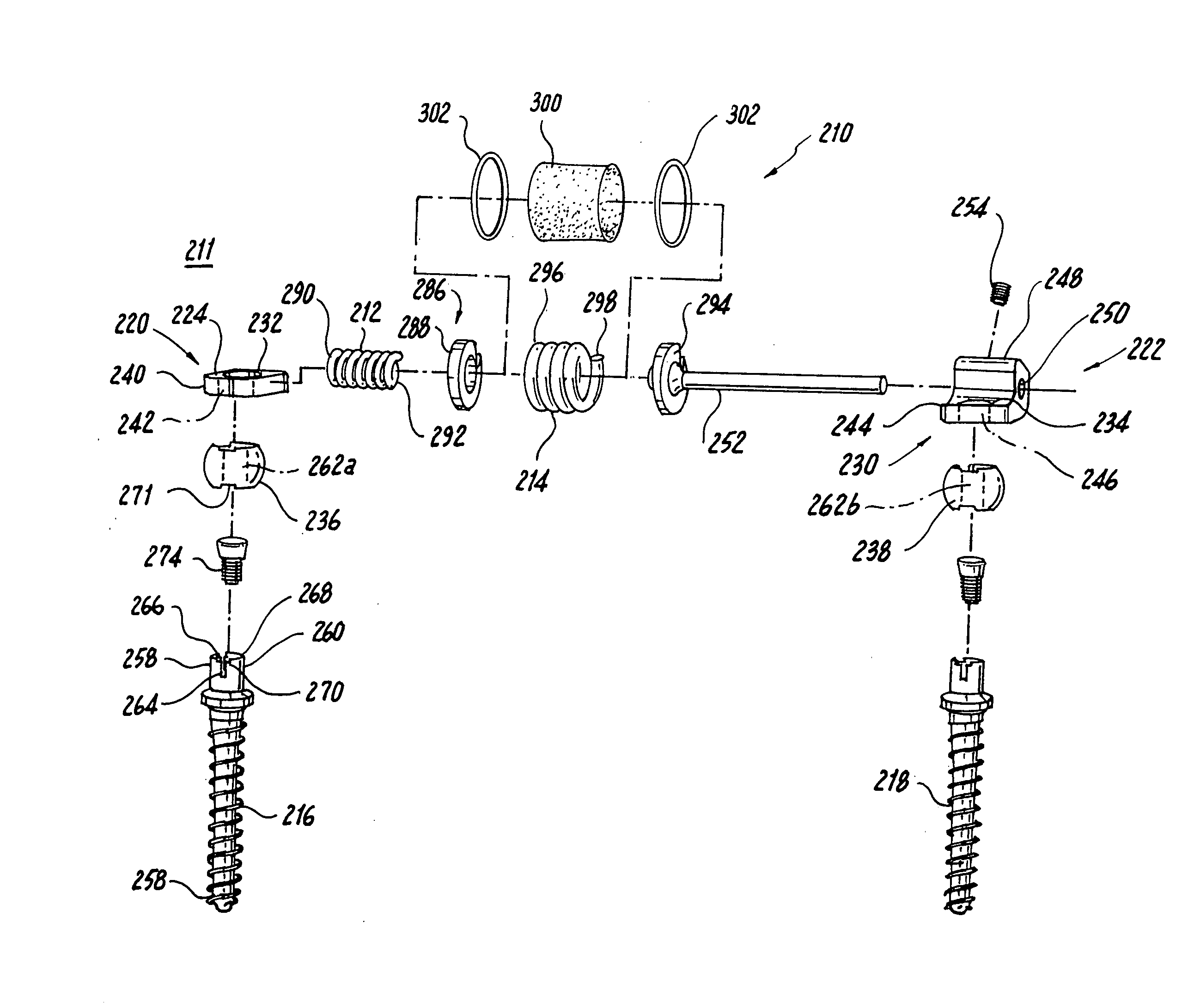
Dynamic fixation assemblies with inner core and outer coil-like member
A dynamic fixation medical implant includes a longitudinal connecting member assembly having an elongate coil-like outer member and an inner cylindrical core attached to the outer member at only one end thereof. Some assemblies include a second longitudinal connecting member in the form of a rod that is fixed to the inner core and extends outwardly from the assembly. Certain assemblies include a threaded core or threaded inserts that cooperate with a helical slit of the coil-like outer member. Two or more cooperating bone screw assemblies attach to the connecting member assembly. The bone screw assemblies may include upper and lower compression members for affixing to and cradling the coil-like outer member only, allowing relative movement between the outer member and the inner cylindrical core. Press fit or snap-on features attach one end of the coil-like outer member to one end of the inner cylindrical core.
Owner:JACKSON
Spinal fixation tool set and method for rod reduction and fastener insertion
A tool for implantation of a rod into a bone screw implanted in a human spine includes a guide member having a laterally opening channel disposed along an entire length thereof for side loading and receiving an implant fastener. A rod pushing member and a handle with a laterally opening channel are coaxial with the guide member, with the rod pushing member being rotatingly mateable to the guide member and the handle having a spring attachment mechanism for attaching the handle to the guide member. The guide member includes spring tabs for attachment to a bone screw, the tabs biased away from the bone screw. The rod pushing member includes a sleeve that extends substantially about the guide member, pressing the spring tabs toward the bone screw and into apertures on the bone screw arms. The rod pushing member sleeve also operatively functions as a rod pusher that abuts a rod as the sleeve is translated along the guide member and toward the bone screw. The handle lateral opening receives and supports a manipulation tool for inserting and installing an implant fastener for attaching the rod to the bone screw.
Owner:JACKSON
Dynamic spine stabilization device with travel-limiting functionality
InactiveUS20070043356A1Enhance alignment and durabilityLimit distanceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnClassical mechanics
Spinal stabilization devices, systems and methods are provided that include a stabilization member including a first structural member that mounts to a pedicle screw, a second structural member adjacent the first structural member and that can move away therefrom, a resilient element mounted between the structural members and that elongates to accommodate relative movement therebetween, and a travel-limiting structure mounted between the structural members and that defines and imposes upon the stabilization member a maximum distance by which the first and second structural members may be separated. The travel-limiting structure can include an axially inextensible, laterally flexible elongate element, e.g., wire-rope cable, disposed between the structural members. The resilient element extends between respective first ends of the structural members, while the travel-limiting structure can include terminations at opposite ends of the elongate element and mounted to respective second ends of the structural members opposite the first ends thereof.
Owner:RACHIOTEK
Clamping connector for spinal fixation systems
InactiveUS6706045B2Relieve pressureClamp firmlyInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsTransverse axisLocking mechanism
The present invention is directed to one piece connector for connecting angularly misaligned implanted pedicle screws to transverse spinal rods in spinal fixation systems. The body portion includes a bore having an inside diameter and a longitudinal axis, with the longitudinal axis of the bore being positioned perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the leg portion. The leg portion includes a slot placed through a section of the leg portion, along the transverse axis of the leg portion and parallel to the longitudinal axis of the leg portion. The slot intersects the bore of the body portion perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the bore. The slot allows the one piece connector to be securely clamped around a longitudinal spinal rod when a pedicle screw is implanted at variable distances from the longitudinal spinal rod. The one piece connector allows for angular misalignment of an implanted pedicle screw in relation to a longitudinal spinal rod and the one piece connector, and for the attachment of the one piece connector to both the longitudinal spinal rod and to the implanted pedicle screw with a single locking mechanism when the one piece connector is used in a spinal fixation system.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Helical reverse angle guide and advancement structure with break-off extensions
A spinal fixation device combines an anchor member with an open receiver, such as a polyaxial bone screw or a hook, with a rotatable closure that operably clamps a spinal fixation rod to the anchor member. The anchor member has spaced apart arms forming a rod receiving channel. The arms have arm extensions or tabs connected to main portions of the arms by weakened regions to enable the extensions to be broken off or separated after the rod is clamped. The closure and inner surfaces of the arms and tabs have mating helical, anti-splay, reverse angle guide and advancement structure formed thereon that mechanically cooperate to prevent splaying of the arms and the extensions as the closure is advanced into the rod receiving channel. The increased length of the arms with the extensions enables the rod to be captured at a greater distance from the seat of the channel and allows the rod to be urged toward the seat by helical advancement of the closure into the channel, starting between the extensions. Separation of the break-off extensions results in an implant with a desirable low profile.
Owner:JACKSON
Slidable bone plate system
The invention is directed to a bone plate system. The bone plate system comprises a base plate having two generally parallel elongated screw slots extending therethrough. Two bone screws are provided that are capable of securing the base plate to a bone by insertion through the screw slots into the bone. Each bone screw has a screw head and a threaded portion extending therefrom. An interference device is attached to the base plate and retains the bone screws while permitting the bone screws to toggle and to controllably slide in the screw slots of the base plate. This design is particularly useful for joining adjacent vertebral bodies, as it permits controlled settling of the vertebral bodies, thereby enhancing the healing process.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Spinal fixation system having locking and unlocking devices for use with a multi-planar, taper lock screw
ActiveUS20070093817A1Easy to operateEasy to masterInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringBone fragment
Provided is a novel spinal fixation system that includes a novel multi-planar taper lock screw for connecting a connecting rod to bone as well as a novel locking device and a novel unlocking device, each being configured to selectively partially lock or fully the novel screw of the system. The screw is capable of multi-directional articulation while the connecting rod position can remain stable and aligned as needed. After the screw had been articulated and properly positioned, it can be locked such that the screw and the connecting rod will remain in relative position to the bone. The screw is configured for easy insertion and connection as well as easy removal and disconnection from the connecting rod. A method of fixing bones or bone fragments using the novel system is also provided.
Owner:K2M
Polyaxial bone screw apparatus
ActiveUS20050049589A1Reduce manufacturing costConvenient and secure in useSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEngineeringScrew thread
A polyaxial bone screw includes a head member and a shank member. The shank has a capture end and an opposite threaded end for threaded insertion into a vertebra. The head has a U-shaped cradle for receiving a spinal fixation rod and a central bore for receiving the capture end of the shank. An expandible retainer ring with a radial split is snapped onto the capture end of the shank to retain it within the head. The retainer ring has a spherical outer surface which forms a ball joint with a spherical socket cavity within the head to enable the head to be angled relative to the shank. A threaded closure plug is tightened within the cradle to clamp the rod into engagement with a knurled dome on the capture end of the shank to secure the rod relative to the vertebra.
Owner:JACKSON
Mobile spine stabilization device
InactiveUS20060264937A1Limit range of motionConstraining bending forceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnMedicine
An orthopedic device is described for stabilizing the spinal column between first and second vertebral bodies. The device has first and second screws adapted for fixation to the first and second vertebral bodies, respectively. The device further includes an elongated ligament with a first end connected to the first screw and the second end operatively connected with the second screw. The ligament is made preferably of a nickel titanium alloy selected to have ductile inelastic properties at body temperature and is capable of continuous plastic deformation to allow relative constrained motion between the vertebral bodies. In a preferred embodiment the second pedicle screw includes a bearing for receiving the ligament in a slideably engageable relationship. The device further includes optional first and second dampening members surrounding the ligament for restraining the spinal column during flexion and extension. Other preferred devices and kits containing such devices are also described.
Owner:WHITE PATRICK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com