Patents
Literature
142 results about "Controlled degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6838493B2High porosityReduce probabilitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6867247B2Reduce probabilityHigh porositySuture equipmentsStentsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions having controlled degradation rates
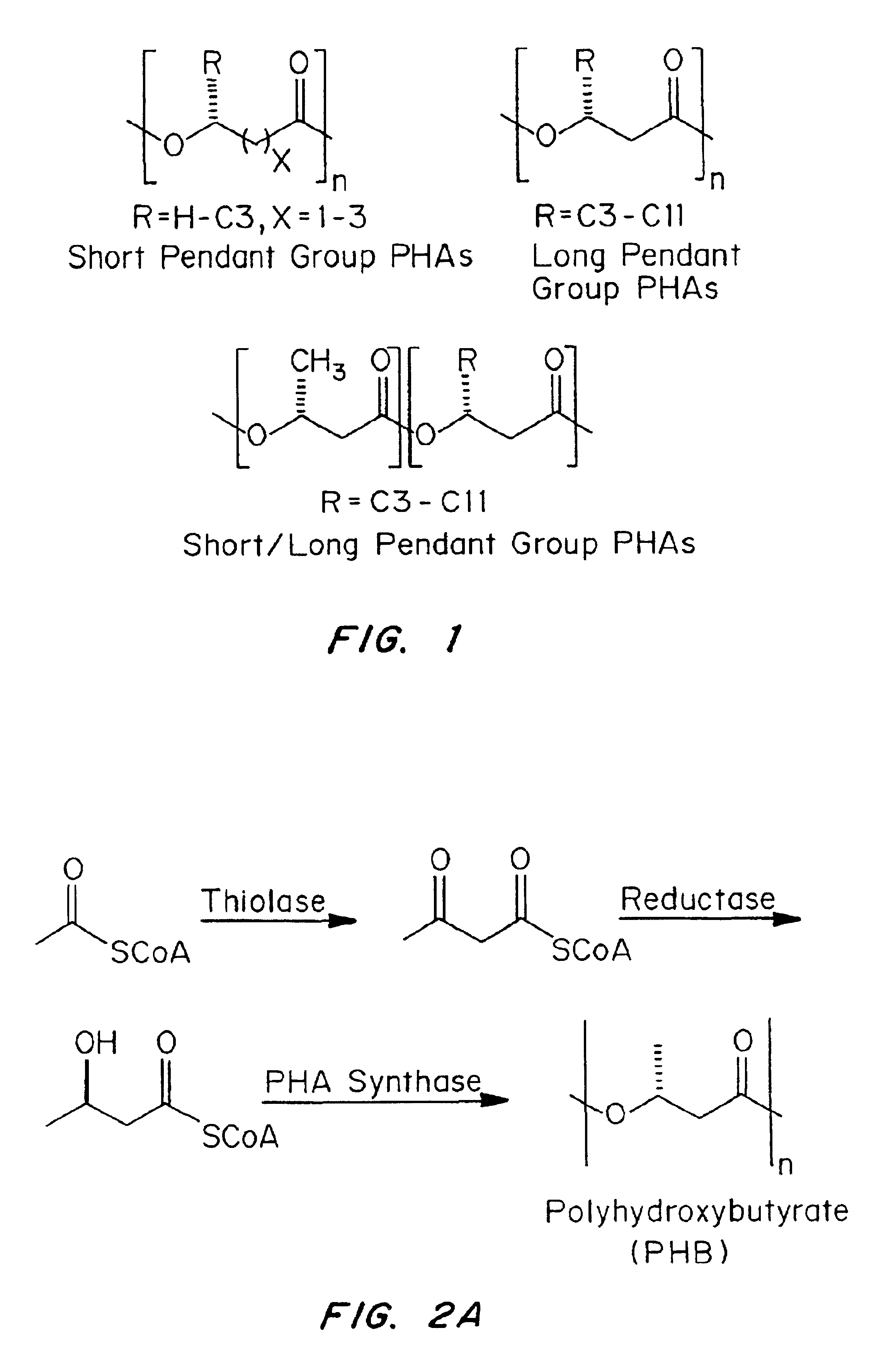
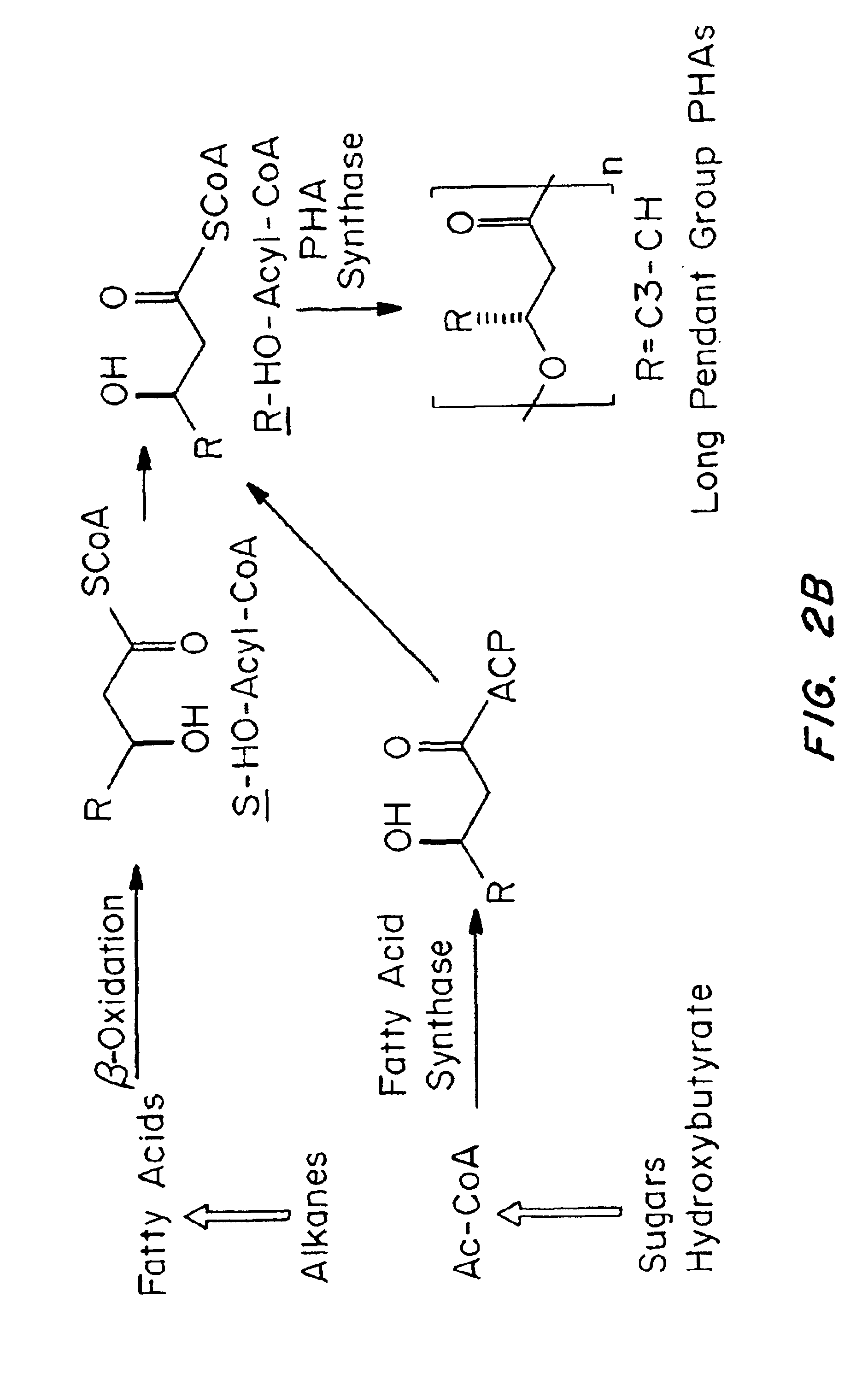
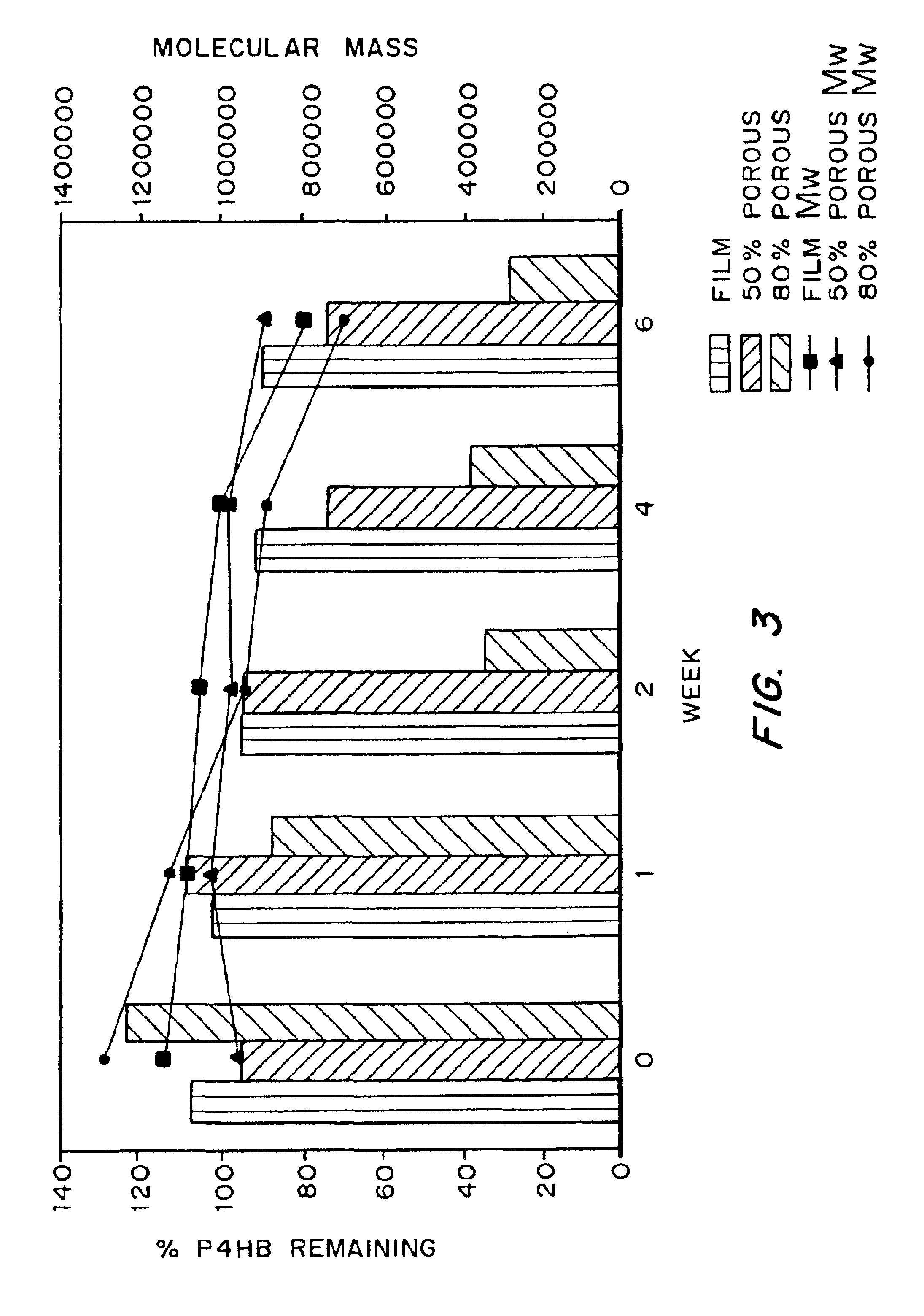
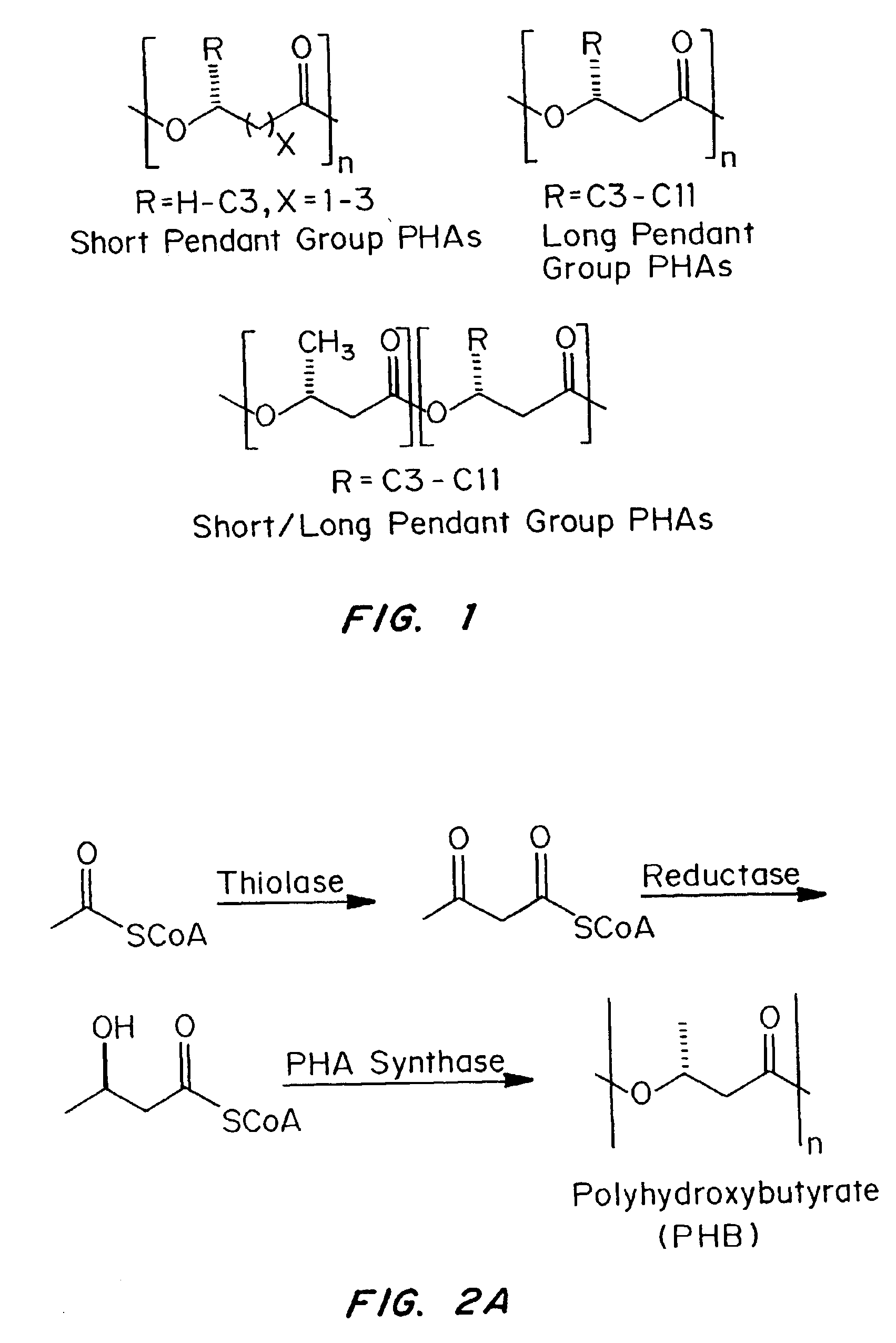
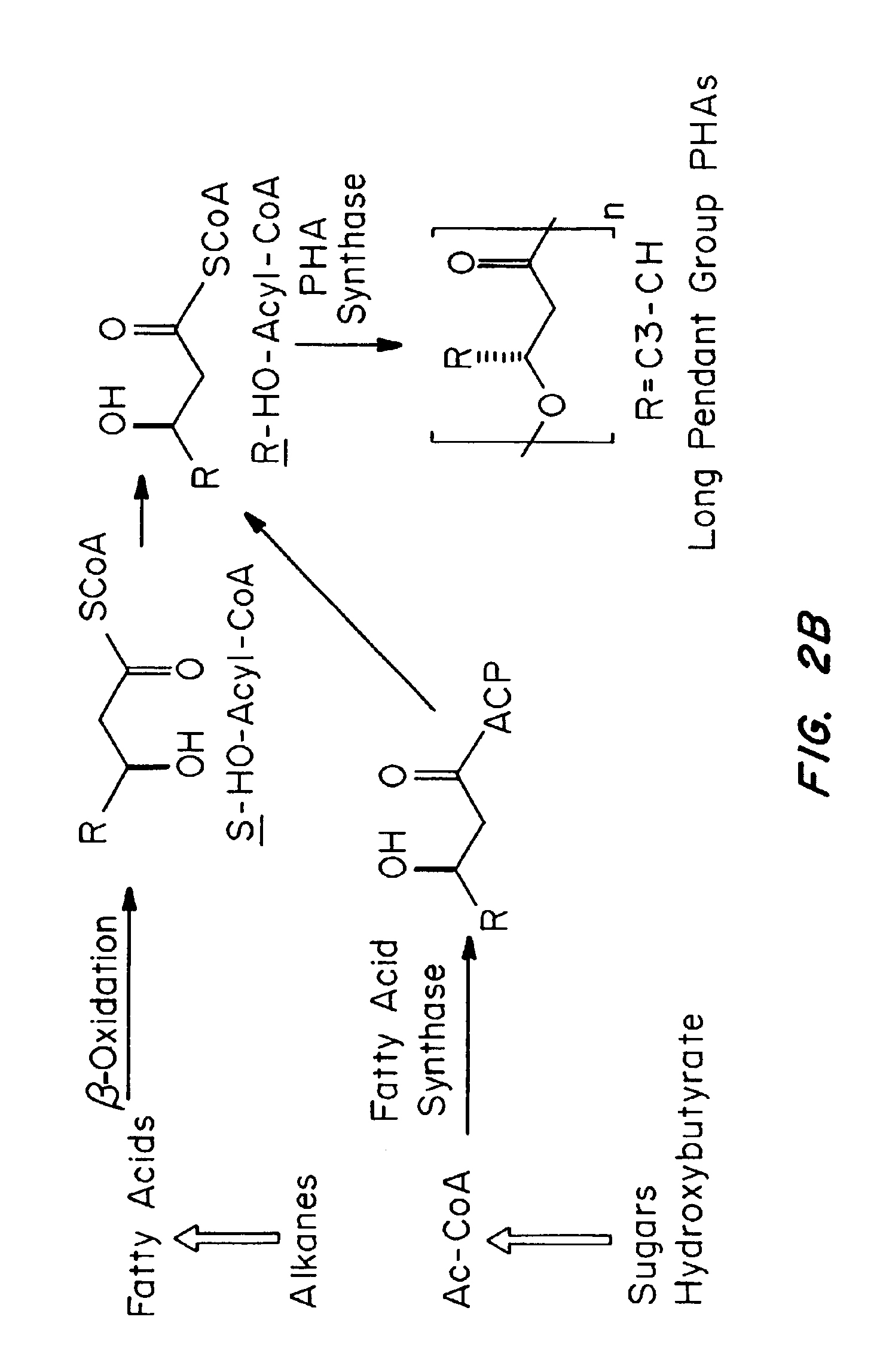
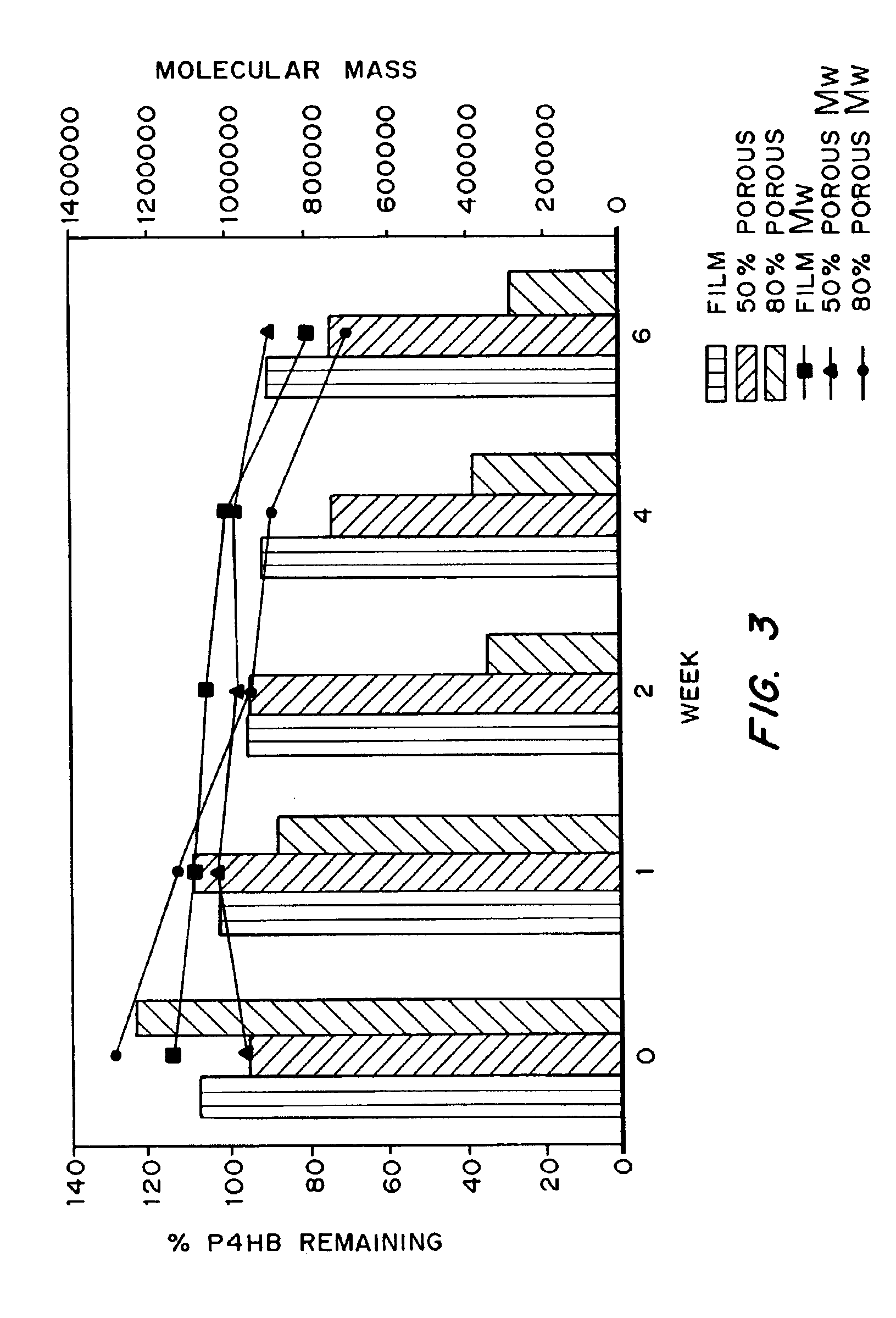
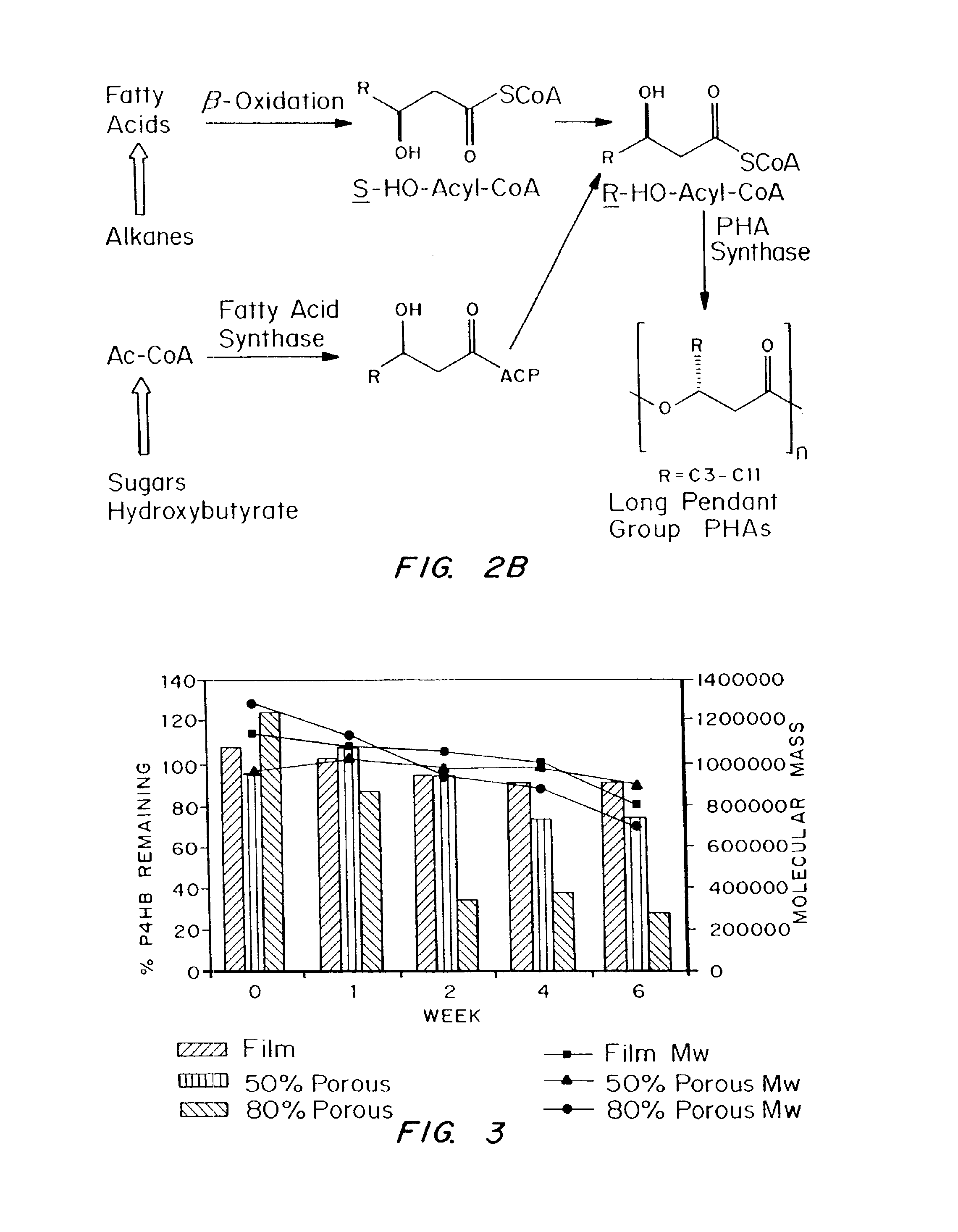
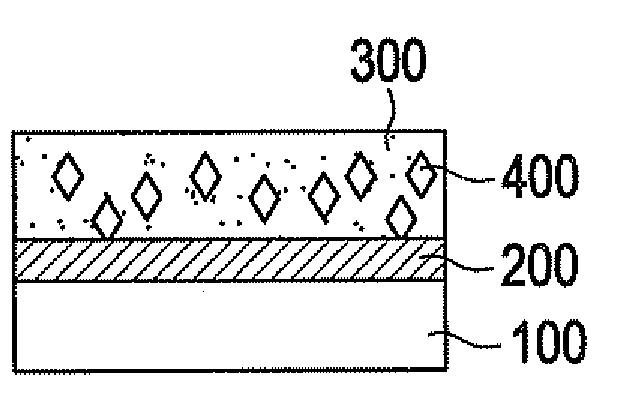
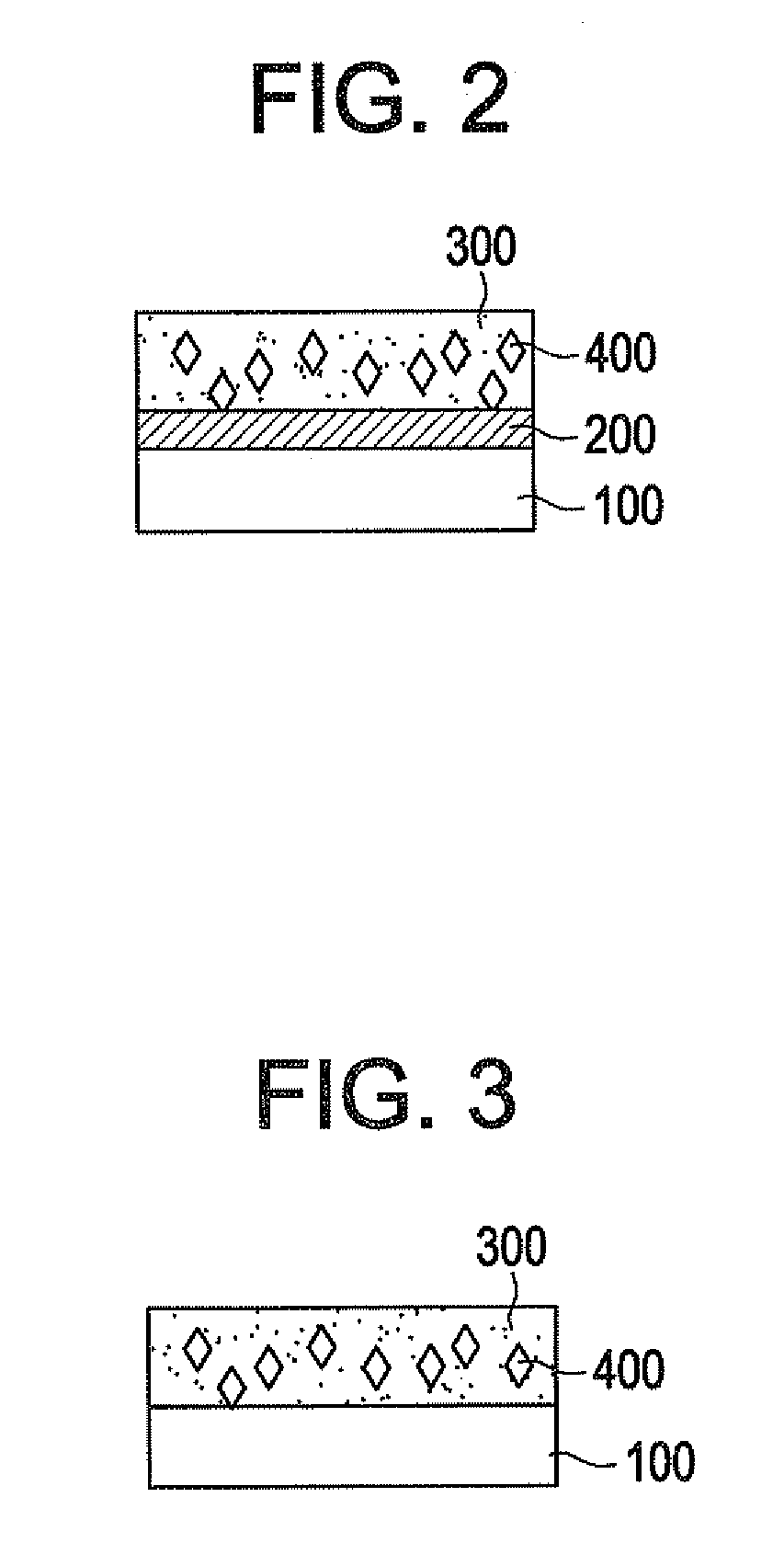
Biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions with controlled degradation rates have been developed. In one embodiment, the polyhydroxyalkanoates contain additives to alter the degradation rates. In another embodiment, the polyhydroxyalkanoates are formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones to alter their degradation rates. In still another embodiment, the polyhydroxyalkanoates are chemically modified. Methods for manufacturing the devices which increase porosity or exposed surface area can be used to alter degradability. For example, as demonstrated by the examples, porous polyhydroxyalkanoates can be made using methods that creates pores, voids, or interstitial spacing, such as an emulsion or spray drying technique, or which incorporate leachable or lyophilizable particles within the polymer. Examples describe poly(4HB) compositions including foams, coatings, meshes, and microparticles. As demonstrated by the examples, these polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions have extremely favorable mechanical properties, as well as are biocompatible and degrade within desirable time frames under physioogical conditions. These polyhydroxyalkanoate materials provide a wider range of polyhydroxyalkanoate degradation rates than are currently available. Methods for processing these materials, particularly for therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic applications, or into devices which can be implanted or injected, are also described.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Absorbable stent comprising coating for controlling degradation and maintaining pH neutrality
InactiveUS20070135908A1Simple designImprove the environmentSurgeryCoatingsMedicineMetallic materials
A biocompatible metallic material may be configured into any number of implantable medical devices, including intraluminal stents. The biocompatible metallic material may comprise a magnesium alloy. The magnesium alloy implantable medical device may be designed to degrade over a given period of time. In order to control the degradation time, the device may be coated or otherwise have affixed thereto one or more coatings, one of which comprises a material for controlling the degradation time and maintain a pH neutral environment proximate the device. Additionally, therapeutic agents may be incorporated into one or more of the coatings on the implantable medical device.
Owner:WYETH LLC
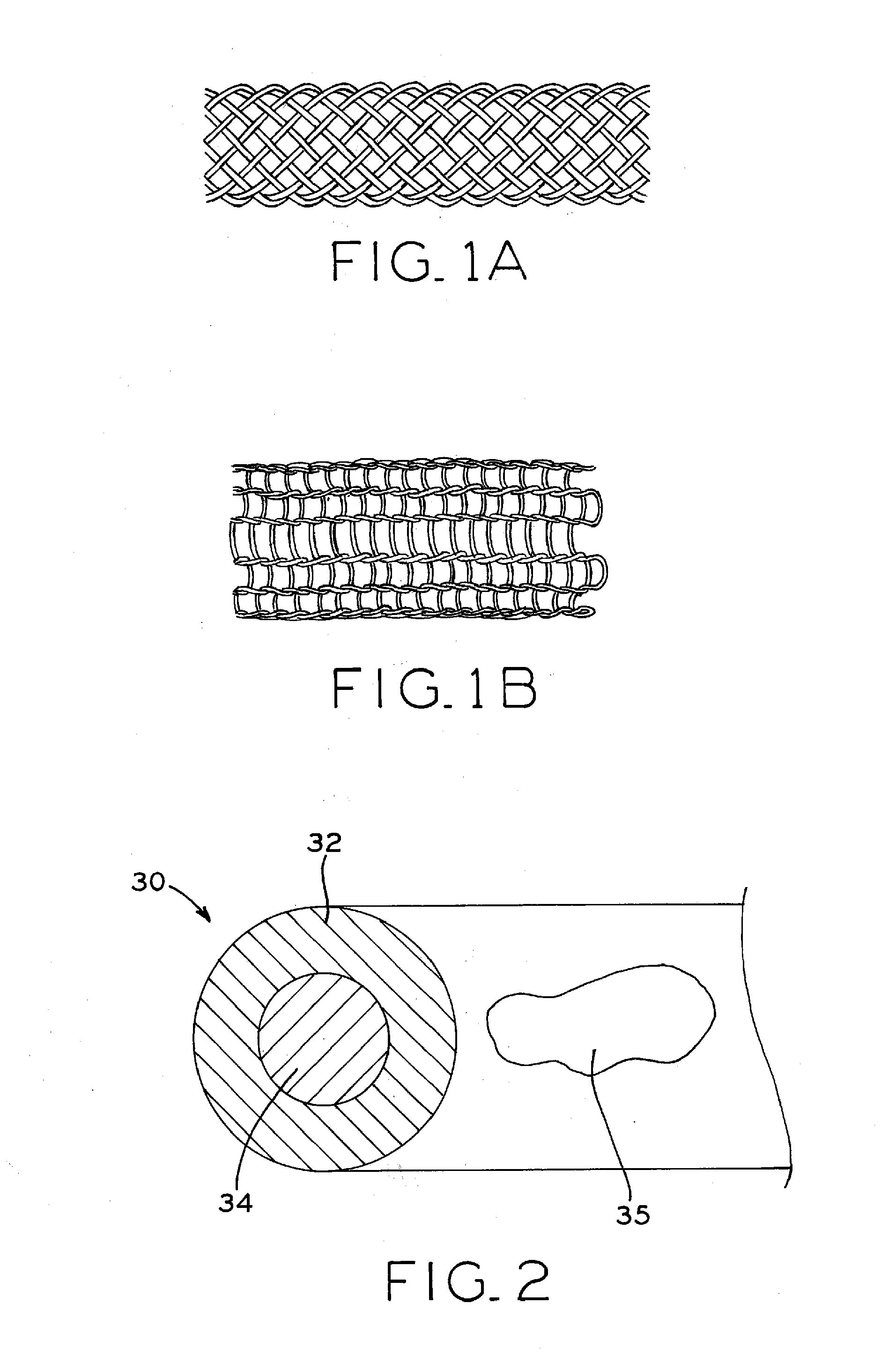
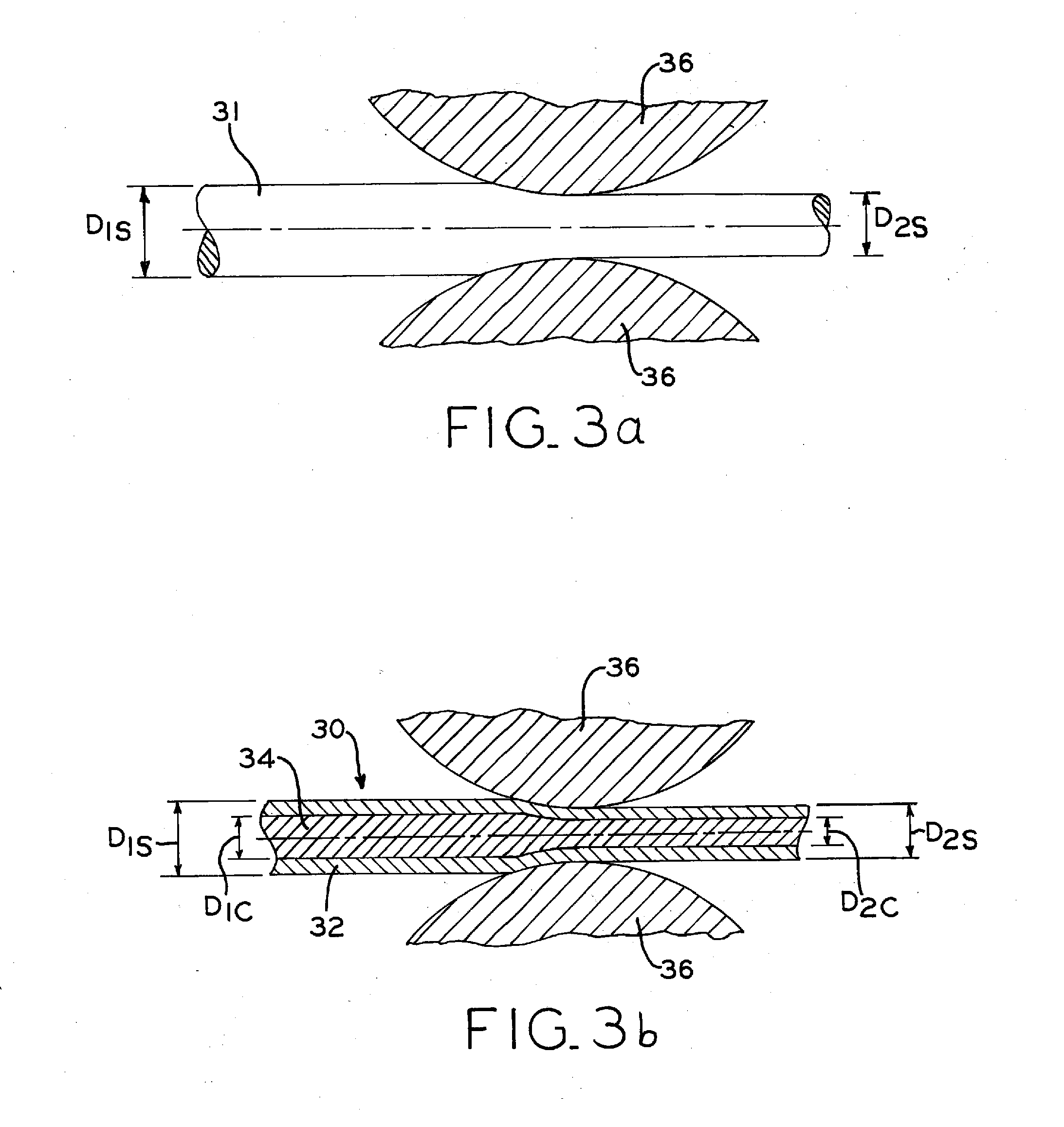
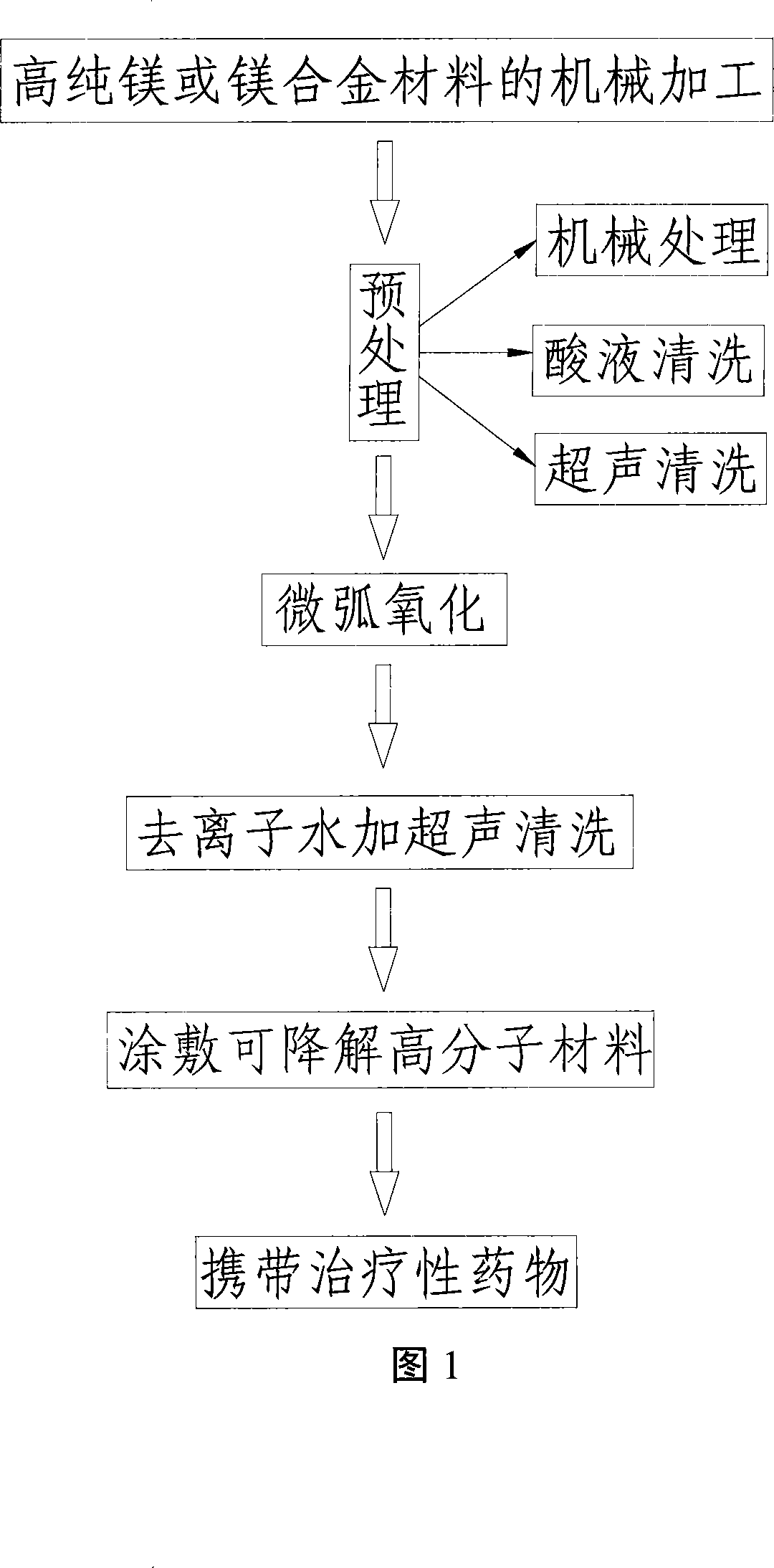
Controlled degradation magnesium alloy coating bracket and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101214396AImprove mechanical propertiesExcellent pharmacological propertiesAnodisationStentsSurface cleaningPolymer chemistry
The invention relates to a controlled degradation magnesium alloy coating stent and a preparation method. The stent body is made of medical high purity magnesium or magnesium alloy by mechanical processing or laser carving; the stent body is provided with a drug-loading coating which bears curative drug; the surface of the stent body is provided with an anti-corrosive coating; the surface of the anti-corrosive coating is provided with a degradable polymer film drug-loading coating; the preparation method includes surface cleaning, preparation of the degradable polymer film drug-loading coating, and application of curative drug; through (1)surface cleaning, (2)preparation of the degradable polymer film drug-loading coating, and (3)application of curative drug, an oxide film is formed on the surface; different drugs and dosage can be fixed by regulating the molecular weight and the thickness of the polymer layer, the drug-loading quantity is more than 30 percent, which improves the fixed stability of the drug, greatly reduces the degradation speed of the magnesium alloy and controls release of the drug, delays corrosion of the magnesium alloy, extends the service life of the stent, is safe in use, and meets the clinical requirement.
Owner:LEPU MEDICAL TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
ABSORBABLE STENT HAVING A COATING FOR CONTROLLING DEGRADATION OF THE STENT AND MAINTAINING pH NEUTRALITY
ActiveUS20100131050A1Simple designImprove the environmentStentsSurgeryMetallic materialsMedical device
A biocompatible metallic material may be configured into any number of implantable medical devices, including intraluminal stents. The biocompatible metallic material may comprise a magnesium alloy. The magnesium alloy implantable medical device may be designed to degrade over a given period of time. In order to control the degradation time, the device may be coated or otherwise have affixed thereto one or more coatings, one of which comprises a material for controlling the degradation time and maintain a pH neutral environment proximate the device. Additionally, therapeutic agents may be incorporated into one or more of the coatings on the implantable medical device.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Packaging system for transdermal drug delivery systems
InactiveUS6905016B2Improve protectionCost efficientSmall article dispensingDiagnosticsEnantiomerPack material
A device and method for stabilizing a drug, particularly a chiral drug or the active enantiomer(s) thereof, in a carrier composition of a transdermal delivery system prior to the systems use by providing a product packaging system to prevent or control degradation reactions that can result from certain packaging materials and moisture contamination, while at the same time providing a child-resistant wrapping for the transdermal system.
Owner:NOVEN PHARMA
Controlled degradation type full-biodegrade agricultural mulching film
ActiveCN104072953AGuaranteed stiffnessGood physical propertiesClimate change adaptationPlant protective coveringsPolyesterPlastic mulch
The invention discloses a controlled degradation type full-biodegrade agricultural mulching film, belonging to the technical field of agricultural mulching films. The full-biodegrade agricultural mulching film comprises the following raw materials by weight percent: 0.5%-50% of a processing aid A, 0.1%-0.5% of a processing aid B, 2%-10% of a functional aid A, 0.3%-2% of a functional aid B, 0.1%-5% of a functional aid C and the balance of full-biodegrade polyester. The full-biodegrade agricultural mulching film is reasonable in design, and the stiffness of the mulching film is kept by compounding flexible full-biodegrade resin with rigid full-biodegradable resin; good physical performance of the mulching film is ensured by reasonably combining various aids with full-biodegrade polyester; in addition, the mulching film does not contain non-biodegradable resin, is good in comprehensive performance, can meet the requirements on the degradation time caused by crops, and cannot affect subsequent farm operation after being degraded.
Owner:HANGZHOU XINFU TECH CO LTD
Controlled Degradation of Magnesium Stents
InactiveUS20090240323A1Prolong lifeAvoid rapid degradationSurgeryPharmaceutical containersActive agentTherapeutic effect
Implantable medical devices, more specifically stents, are described herein comprising magnesium based core structures whose elimination times are slowed by the appropriate polymer coating. Appropriate biodegradable polymers are selected which are suitable to provide a specific degradation time for the magnesium based core structure. Bioactive agents are incorporated into the polymer coating in order to aid in the therapeutic effect of the stent.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Controlled degradation of stents
InactiveUS20080015686A1Fast degradationImprove degradation rateSurgeryBlood vesselsPolymerMaterials science
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Degradable synthetic paper material and preparation method thereof
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of controlled-degradation high-hygroscopicity resin
The invention discloses a preparation method of controlled-degradation high-hygroscopicity resin. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding an acrylic acid monomer, a host / guest identification monomer and a functional monomer to a dispersion medium, uniformly mixing, then adding a cross-linking agent and an initiator, and polymerizing under a certain condition to obtain the high-hygroscopicity resin. The preparation method has the advantages that: the identification effect among the host and guest molecules in the polymer chain of the prepared resin can be controlled by changing the external conditions, and the degradation speed of the high-hygroscopicity resin is further controlled, therefore, the degradation time of the high-hygroscopicity resin can be adjusted to be adapted to different completion time during the oil-gas field construction; and under certain conditions, the host and guest molecules in the molecular chain of the degraded resin are compounded to form the high-hygroscopicity resin, thereby achieving the recycling effect. The obtained product can be applied to oil-gas field plugging agents, agricultural water-retaining corrosion inhibitors, soil improvement agents and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
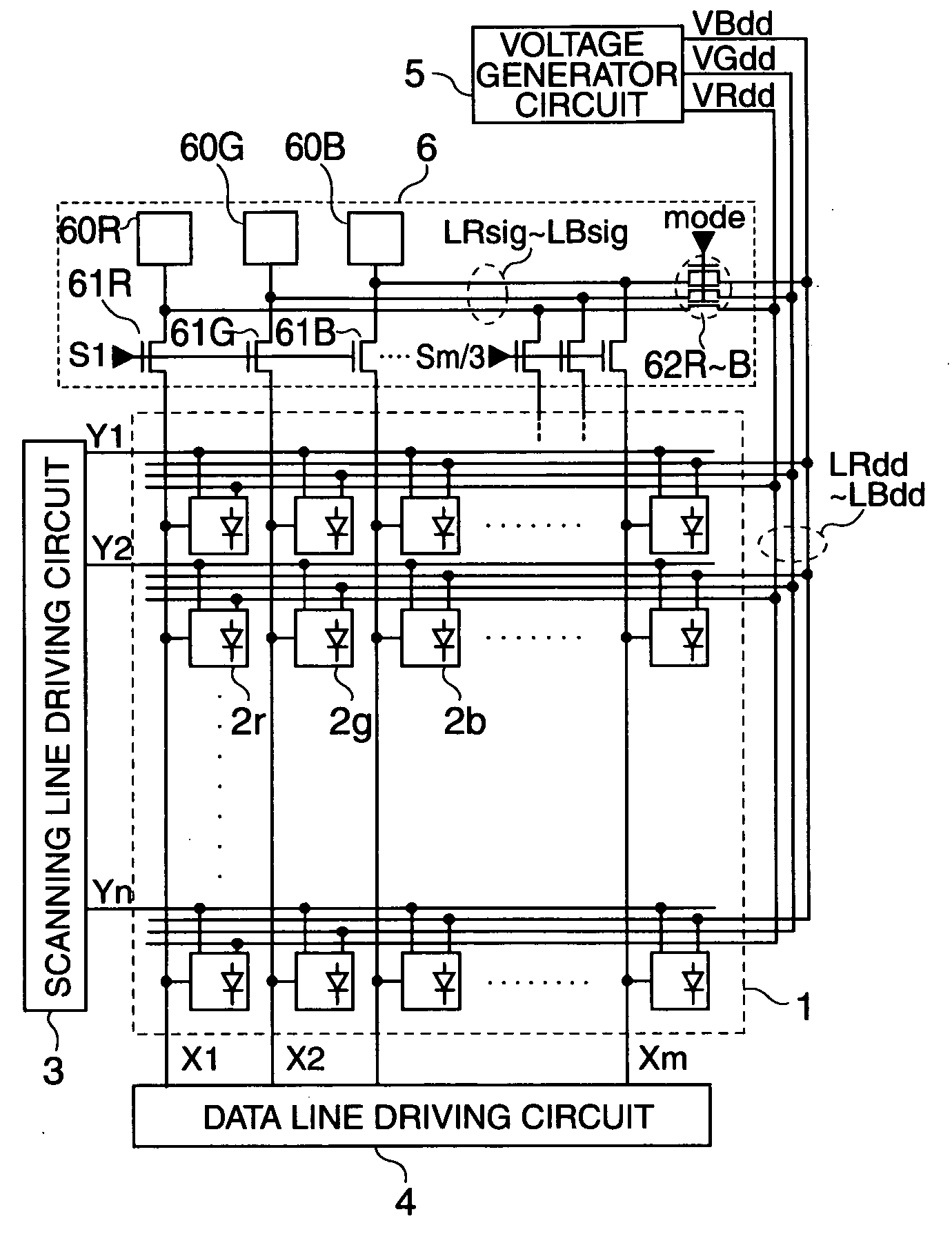
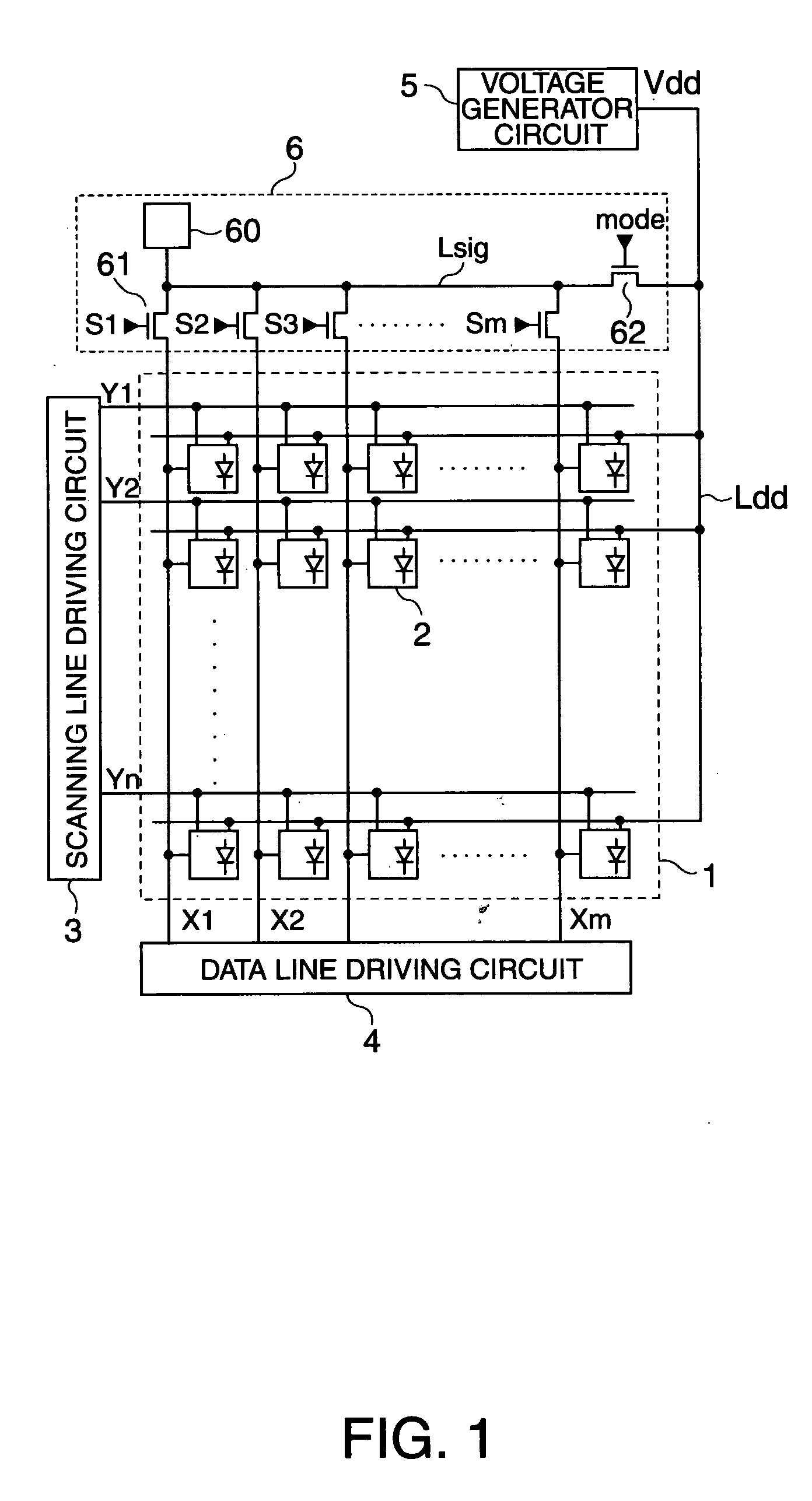
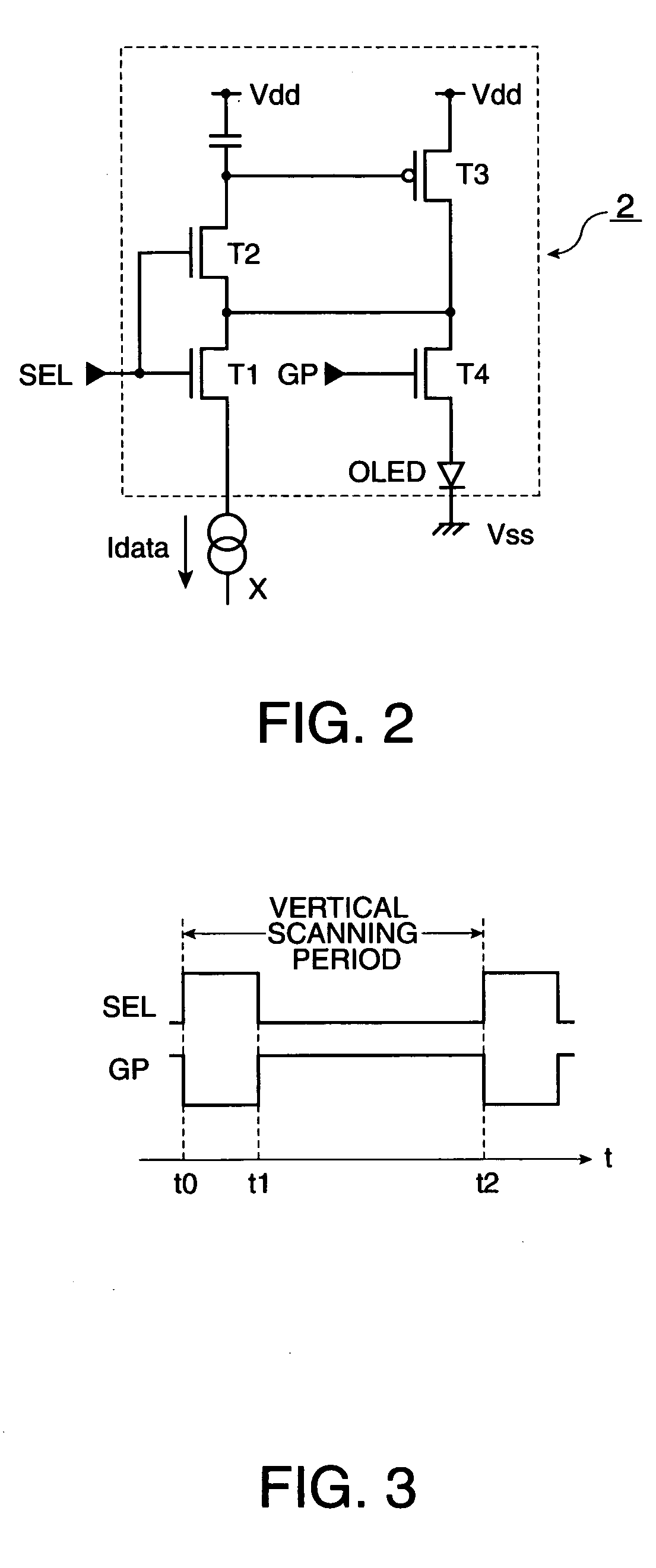
Electro-optical device, method to drive the same, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20050001794A1Prevent degradationSuppresses an off-leak currentPipe supportsElectroluminescent light sourcesNormal modeOrganic electroluminescence
To suppress an off leak current of a switching element arranged along a data line to control degradation of tonal gradation in an arrangement in which an organic electro-luminescent element OLED is driven using a current programming method, a first switching element is set to be in a non-conductive state and a second switching element is set to be in a conductive state during a normal mode. During a test mode, the first switching element is set to be in a conductive state while the second switching element is set to be in a non-conductive state.
Owner:ELEMENT CAPITAL COMMERCIAL CO PTE LTD
Biodegradable composite wire for medical devices
A bioabsorbable wire material includes manganese (Mn) and iron (Fe). One or more additional constituent materials (X) are added to control corrosion in an in vivo environment and, in particular, to prevent and / or substantially reduce the potential for pitting corrosion. For example, the (X) element in the Fe—Mn—X system may include nitrogen (N), molybdenum (Mo) or chromium (Cr), or a combination of these. This promotes controlled degradation of the wire material, such that a high percentage loss of material the overall material mass and volume may occur without fracture of the wire material into multiple wire fragments. In some embodiments, the wire material may have retained cold work for enhanced strength, such as for medical applications. In some applications, the wire material may be a fine wire suitable for use in resorbable in vivo structures such as stents.
Owner:FORT WAYNE METALS RES PROD CORP
Controlled degradation differential arc oxidized metallic support and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN101239009AImprove stabilityIncrease varietyStentsAnodisationPlasma electrolytic oxidationMicro arc oxidation
The invention relates to a micro arc oxidation metal bracket capable of controlling degradation and the preparing method. The bracket is provided with a micro arc oxidation film and a degradable polymer coating. The method comprises the steps showed as follows: processing a degradable metal into a bracket; pretreating the bracket to remove the oxide at the surface of the bracket; putting the bracket into the micro arc oxidation electrolyte, as the anode of an electrobath, the bracket is put in the direct current or alternating current to have micro arc oxidation treatment, ensuring the surface of the bracket have the micro arc oxidation film; cleaning the bracket after the micro arc oxidation treatment; spraying degradable polymer material at the bracket surface after being cleaned and the degradable polymer material carries therapeutic medicine. The micro arc oxidation film at the bracket can reduce the erosion speed of the bracket remarkably, can prolong the service life of the bracket and simultaneously guarantee the mechanical property of materials in the degradation process.
Owner:LEPU MEDICAL TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
Implantable medical devices comprising bio-degradable alloys
The invention provides medical devices comprising high-strength alloys which degrade over time in the body of a human or animal, at controlled degradation rates, without generating emboli. In one embodiment the alloy is formed into a bone fixation device such as an anchor, screw, plate, support or rod. In another embodiment the alloy is formed into a tissue fastening device such as staple. In yet another embodiment, the alloy is formed into a dental implant or a stent.
Owner:BIO DG INC
Implantable medical devices comprising bio-degradable alloys
Owner:BIO DG INC
Preparation method for super-absorbent resin with sensitivity to pH value
InactiveCN102311517AAchieve controlled degradationEasy to controllable degradationSuper absorbentSoil conditioner
The invention discloses a preparation method for a super-absorbent resin with sensitivity to pH values. According to the method, groups with sensitivity to pH values are introduced into an absorbent resin system, and reversible fragmentation or combination of sensitive groups is controlled through adjusting pH values, thereby further controlling degradation / recovery of an absorbent resin. The advantages of the invention are as follows: controlling degradation of the super-absorbent resin by changing pH values enables convenient operation and is easy to realize; the changing of pH values of the system in a range of between weak acid and weak base does not cause obvious influence on surrounding environment in which the super-absorbent resin is used. The obtained product of super-absorbent resin is applicable to oil and gas field leak stopping agents, agricultural water retention corrosion inhibitors, soil amendments, packaging materials, daily absorbing articles, etc.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
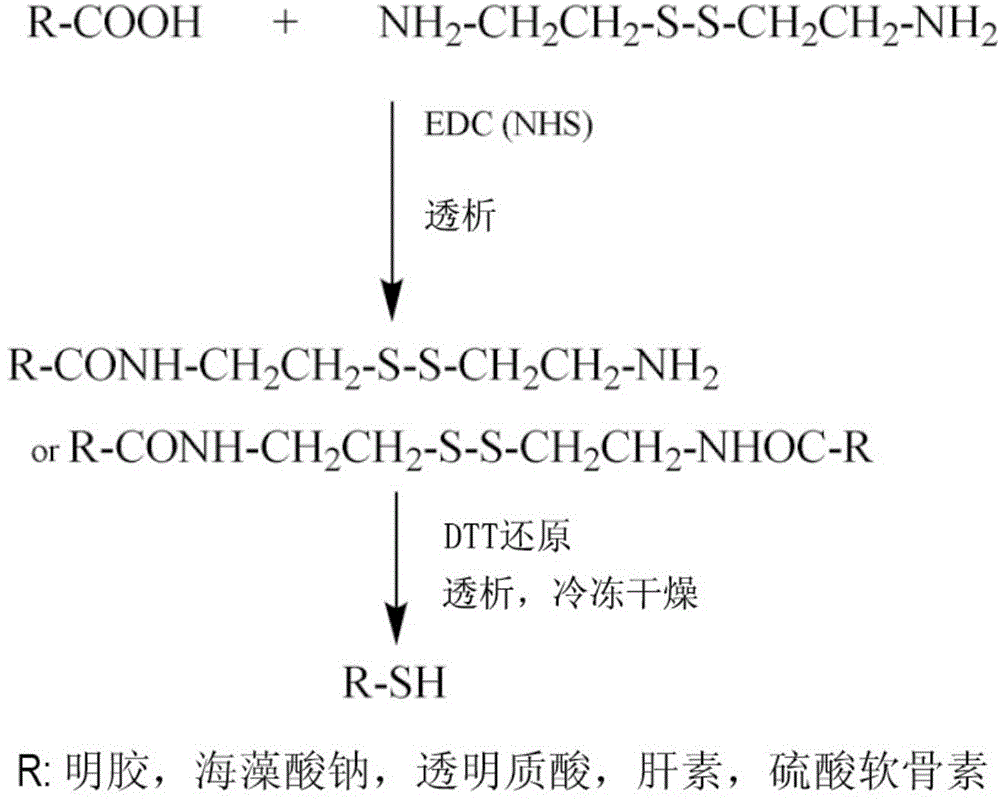
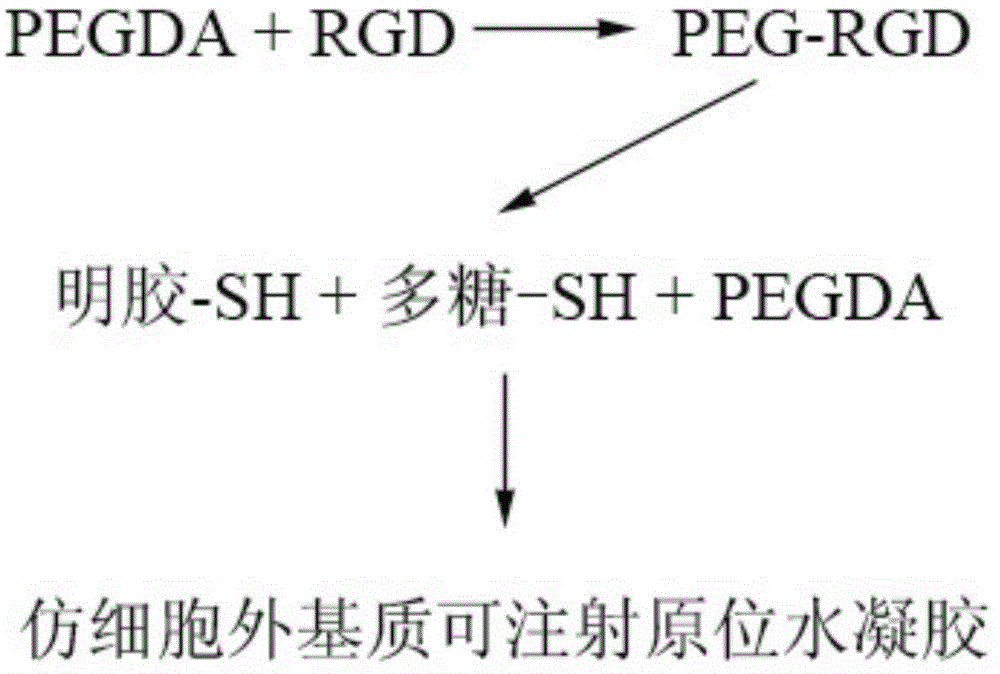
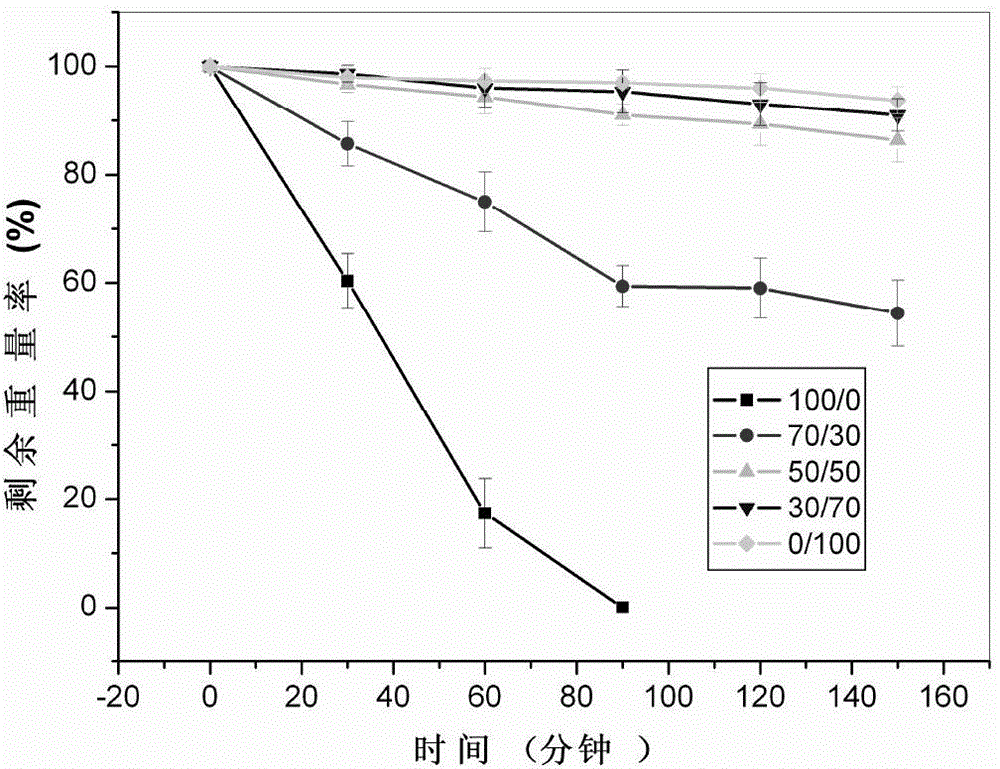
Imitated extracellular matrix injectable in-situ hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104307049ADegradation controllableControl releaseAnimal cellsPeptide/protein ingredientsCross-linkCell adhesion
The invention discloses imitated extracellular matrix injectable in-situ hydrogel and a preparation method and application thereof. The hydrogel is prepared by carrying out a cross-linking reaction between sulfhydrylation gelatin, sulfhydrylation polysaccharides or RGD-containing cell adhesion peptides and polyethylene glycol diacrylate. The composition of the hydrogel is similar to that of the extracellular matrix, so that the hydrogel has high biocompatibility, has the effects of controlled degradation, controlled release and / or cell behavior regulation in performance and can conveniently meet the requirements on different release rates of growth factors or medicines. Meanwhile, the clinical injectable and in-situ forming operation requirements can be met, and the hydrogel has good application prospects in tissue repair and regeneration.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Controlled degradation of stents
InactiveUS7794495B2Fast degradationImprove degradation rateSurgeryBlood vesselsPolymerMaterials science
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Absorbing Solution, Method and Device for Absorbing CO2 or H2S or Both
ActiveUS20080078292A1Avoid performance degradationLow costCombination devicesGas treatmentOxygenDiamine
An absorbing solution according to the present invention is an absorbing solution that absorbs CO2 or H2S in gas or both of CO2 and H2S. The absorbing solution is formed by adding desirably 1 to 20 weight percent of tertiary monoamine to a secondary-amine composite absorbent such as a mixture of secondary monoamine and secondary diamine. Consequently, it is possible to control degradation in absorbing solution amine due to oxygen or the like in gas. As a result, it is possible to realize a reduction in an absorption loss, prevention of malfunction, and a reduction in cost. This absorbing solution is suitably used in an apparatus for removing CO2 or H2S or both of CO2 and H2S.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND ENG LTD +1
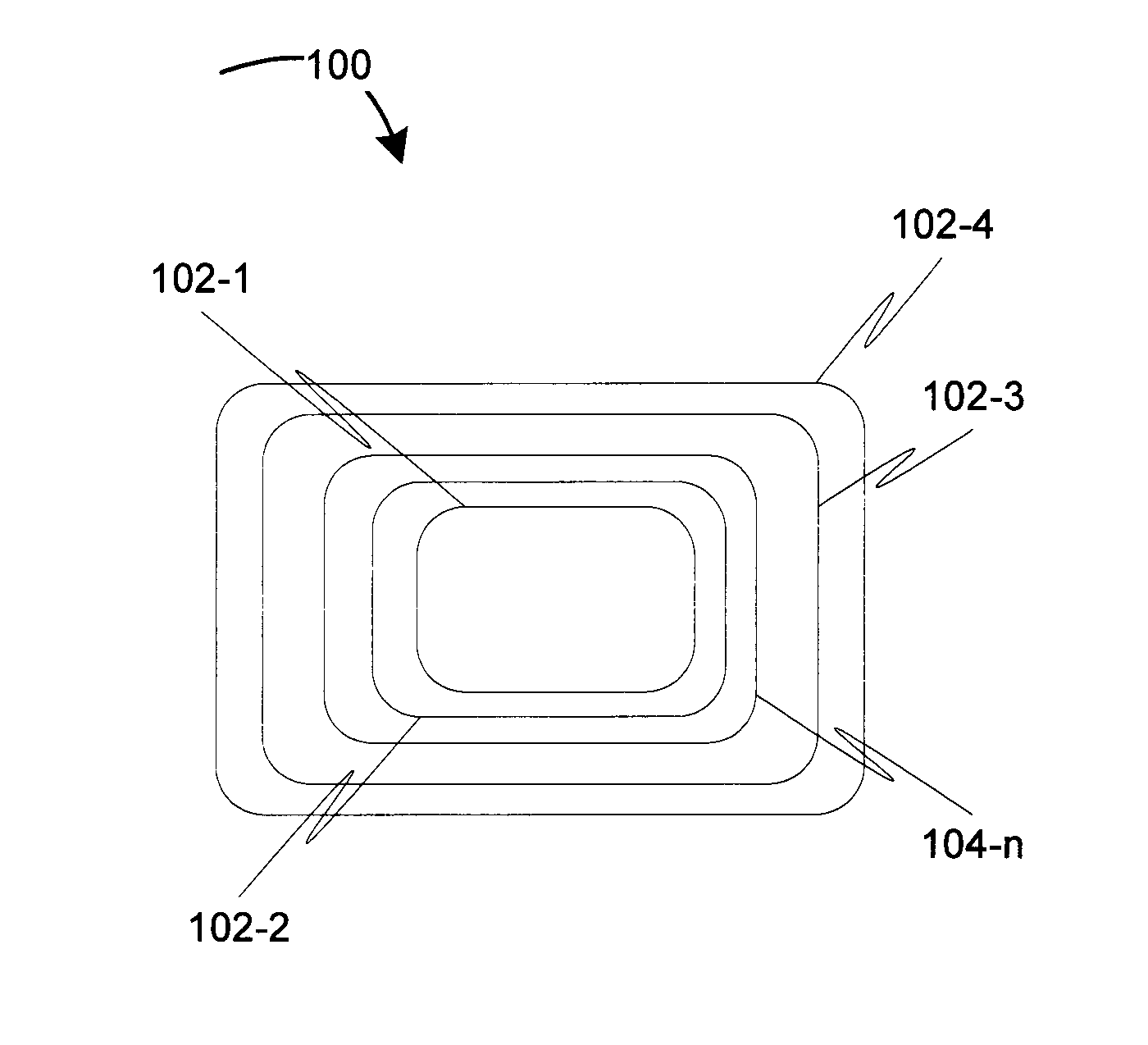
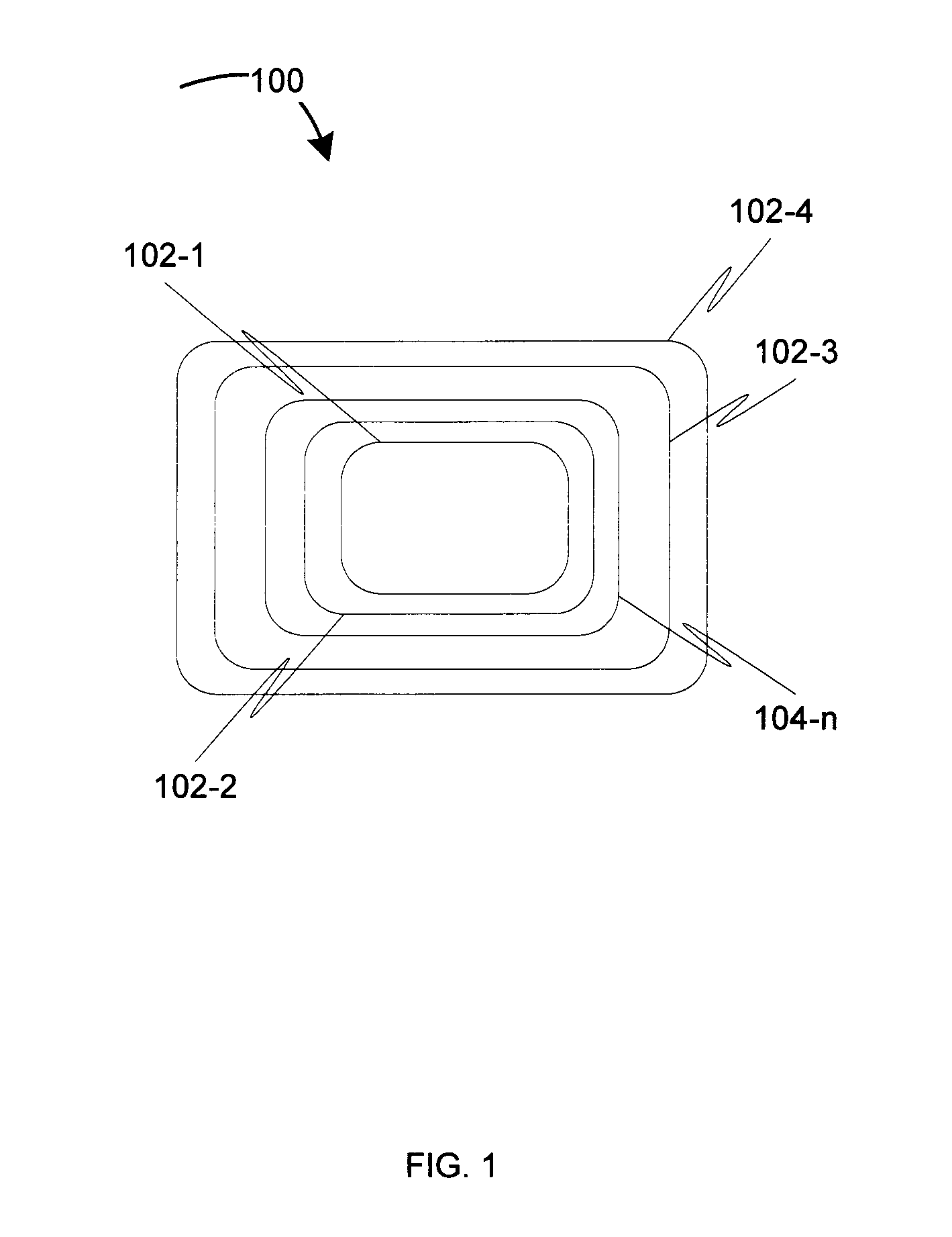
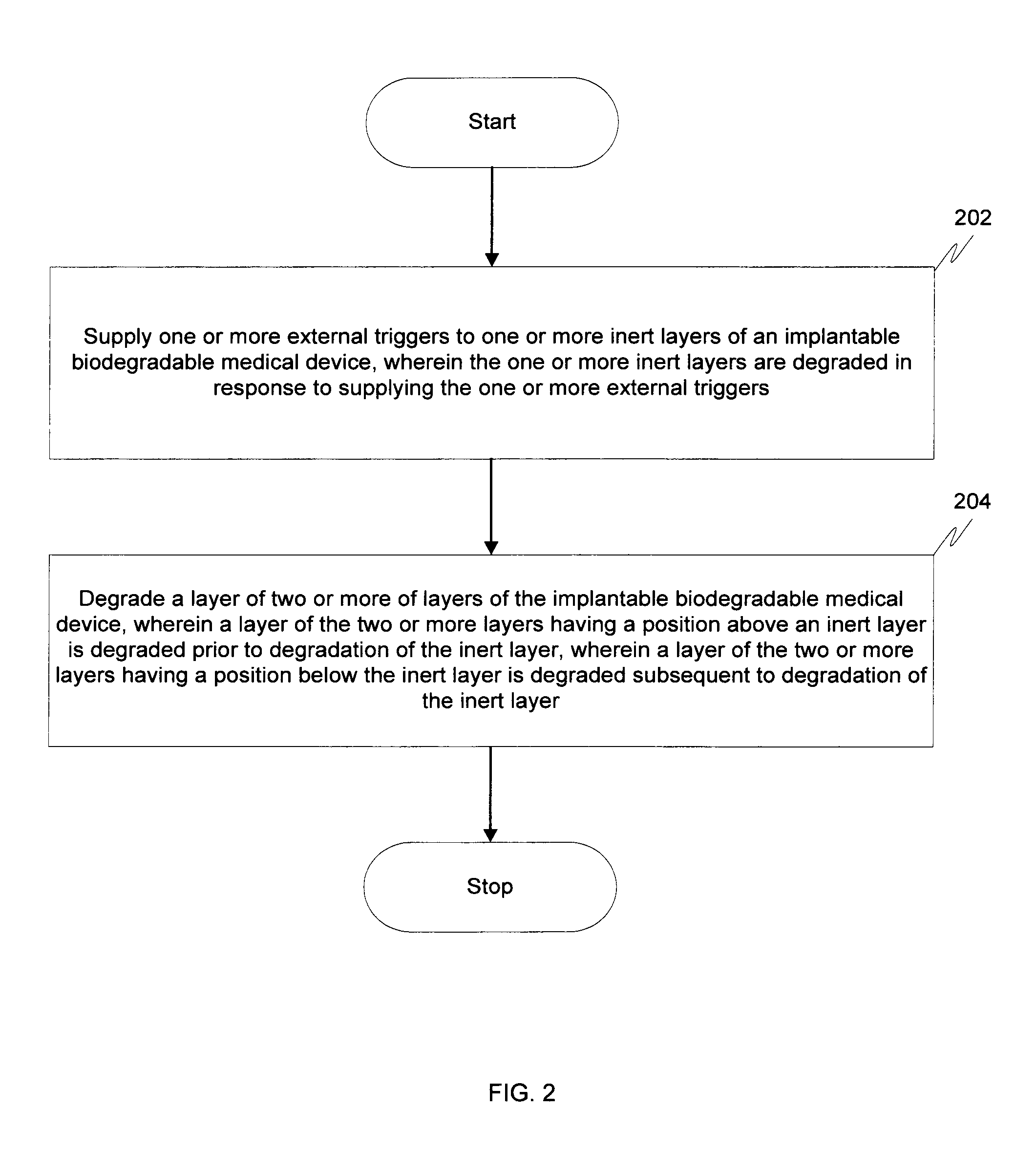
Biodegradable medical devices and method to control degradation of the biodegradable medical devices
An implantable biodegradable device having two or more layers composed of one or more biodegradable materials is disclosed. The two or more layers are coated with one or more drugs. The implantable biodegradable device further having one or more inert layers is composed of a biodegradable material. The one or more inert layers of the implantable biodegradable device are degraded in response to introduction of one or more external triggers when the implantable biodegradable medical device is placed within a living organism. Further, a layer of the two or more layers having a position above an inert layer is degraded prior to degradation of the inert layer. Subsequently, a layer of the two or more layers having a position below the inert layer is degraded subsequent to degradation of the inert layer.
Owner:ENVISION SCI PVT LTD
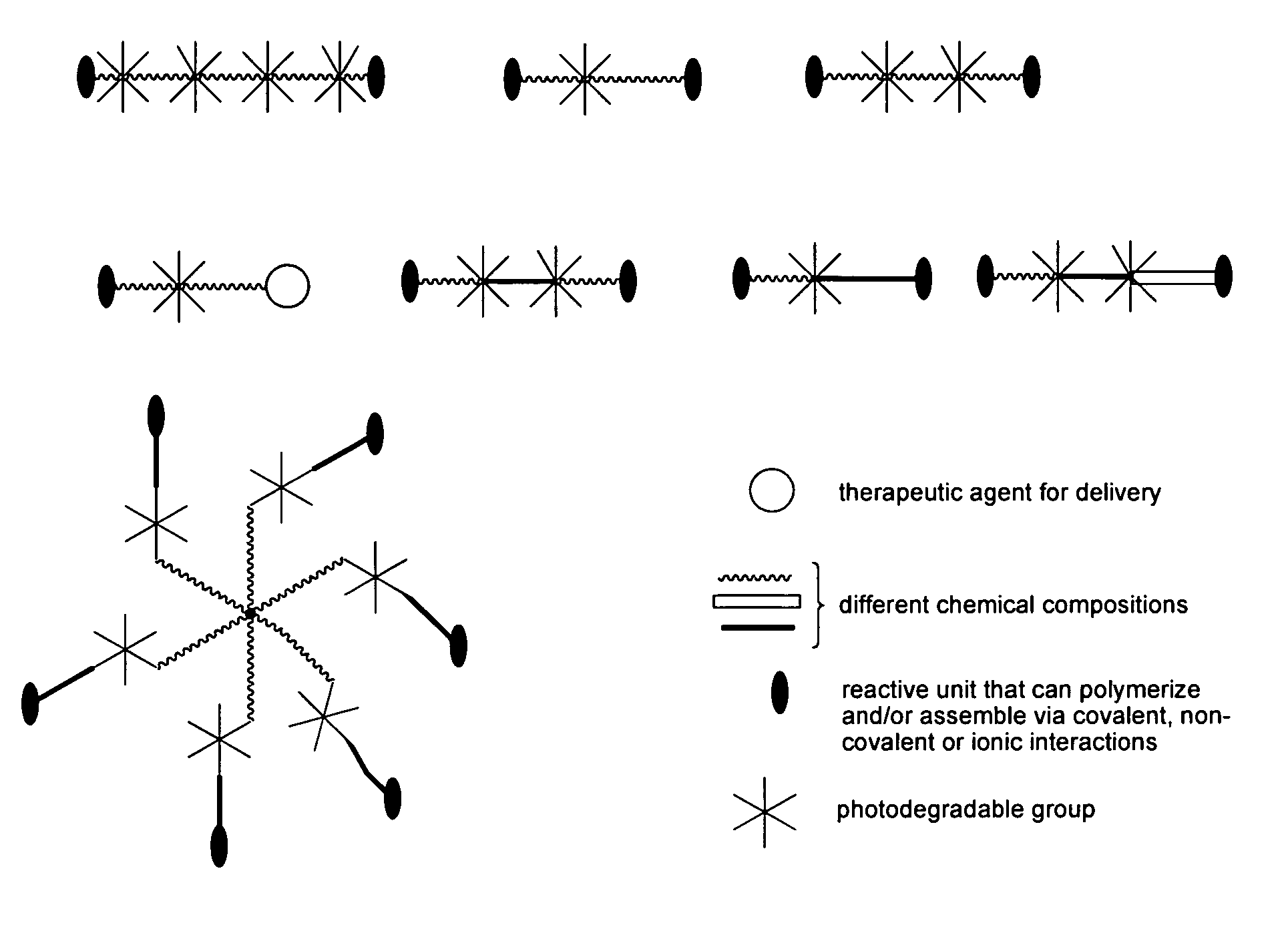
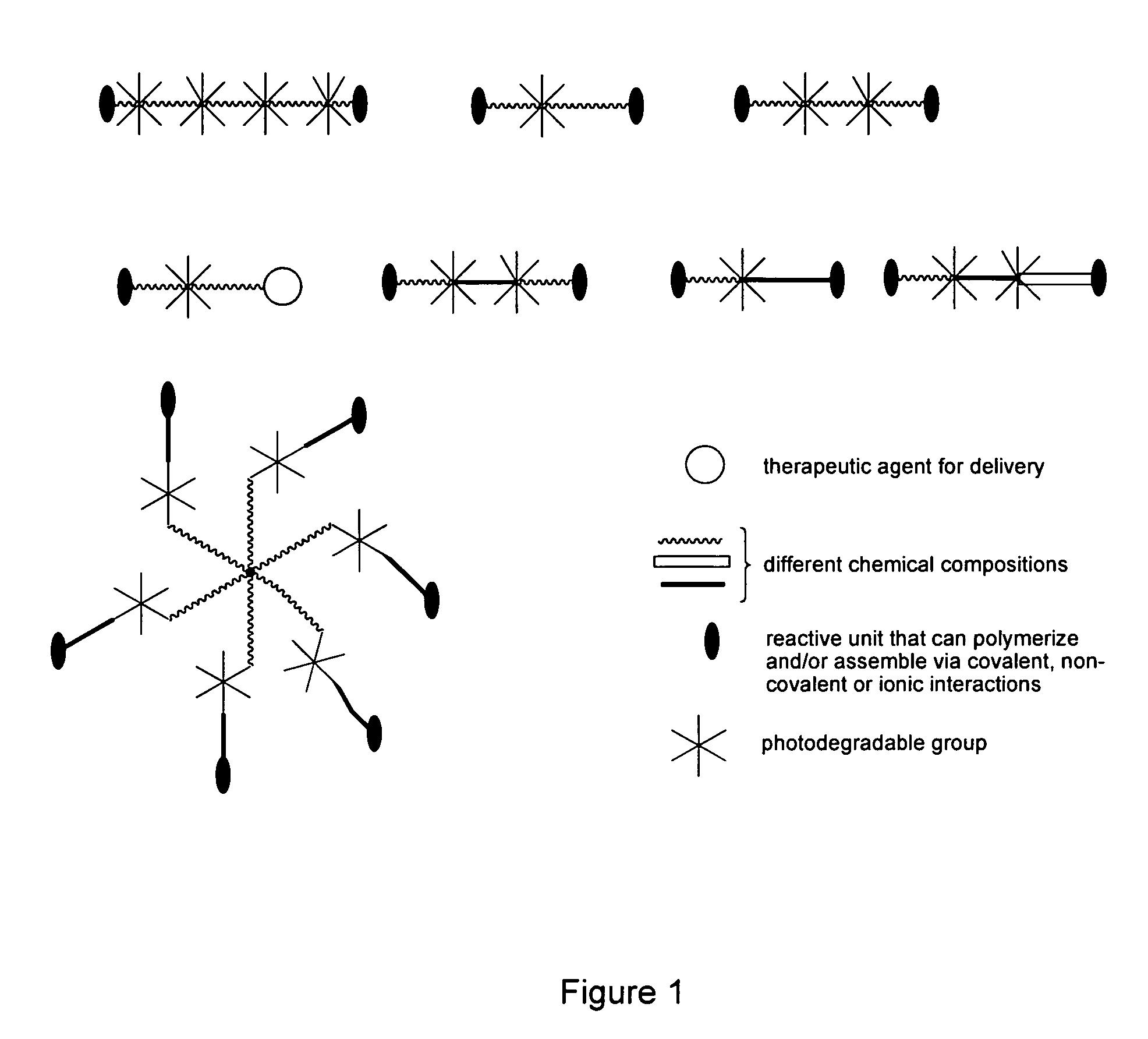
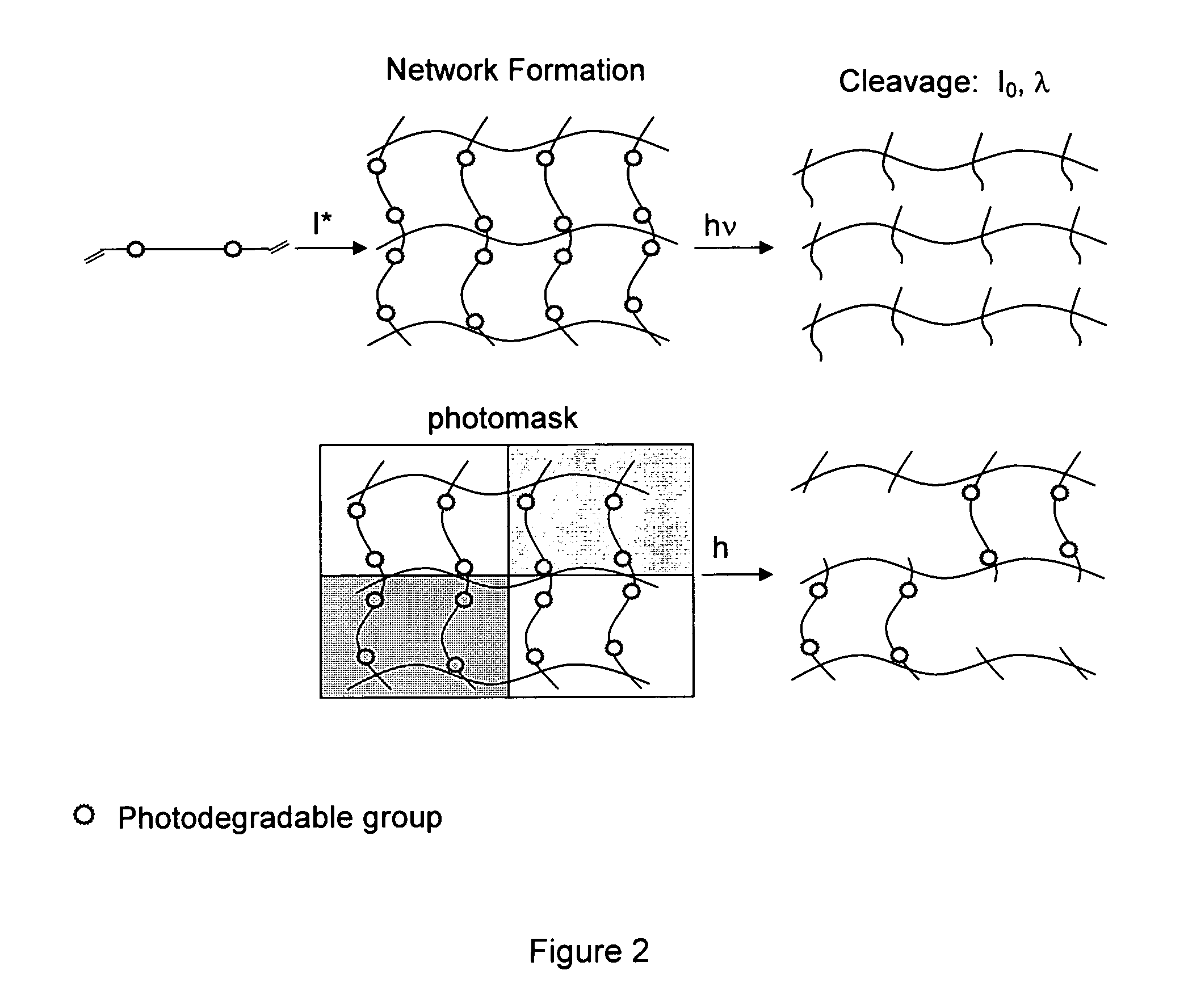
Photodegradable groups for tunable polymeric materials
ActiveUS8343710B1Sure easyEasy to useOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsPolymer scienceEnd-group
Provided is a method that provides both spatial and temporal control of a polymer degradation process using mono- and multifunctional macromolecular monomers (“macromers”) that degrade via single- and multi-photon photolysis mechanisms over a broad range of wavelengths. The macromers can form or be incorporated into networks via covalent, non-covalent and / or ionic interactions. The spatial and temporal degradation of these networks can be controlled. More specifically, provided is a photodegradable macromer, comprising: (a) a photodegradable group; (b) a backbone structure comprising one or more repeating units that may be the same or different, which backbone structure is attached to the photodegradable group directly or through a linker; (c) one or more reactive end groups at one or more ends of the macromer; and optionally, (d) one or more therapeutic agents; and optionally (e) one or more caged groups. Also provided are polymers and networks incorporating macromers of the invention and optionally other substituents such as other polymeric structures. Also provided is a method of controlled degradation of a polymer comprising: providing a photodegradable polymer as described herein and exposing the photodegradable polymer to photoradiation of the appropriate wavelength and energy to cause one or more of the photodegradable groups to photodegrade.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Degradable environment-friendly type polypropylene(PP) foam plastic and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an environment-friendly-type polypropylene (pp) aerated plastics and a process for preparation, and the aerated plastics utilizes plastic projectile body to be basis material, a third monomer is led in to be auxiliary crosslinking agent to crosslink and control degradation products, aerated plastics section products are made by processing graft copolymerization and cross-linking reaction to polypropylene, and closely welding, openly welding, tabletting, and foaming to shape with compatibilizer, filling material, nucleating agent, cross linking agent and inflating agent. The invention modifies the shortcomings that the traditional homopolymerized polypropylene can not get higher breakpoint extension force, high melt intensity and viscosity to foam and shape in the process of thermal foaming and shaping. The polypropylene (pp) aerated plastics products which are provided by the invention have excellent fire-resisting property and little heat distortion degree, and the softening point is between 100 DEG C and 130 DEG C. The invention can be used for long term in the temperature scope, and the application area is wide, wastes can be recycled, and can be automatically degraded, and the invention has no pollution to environment.
Owner:FUJIAN ZHENGYI IND
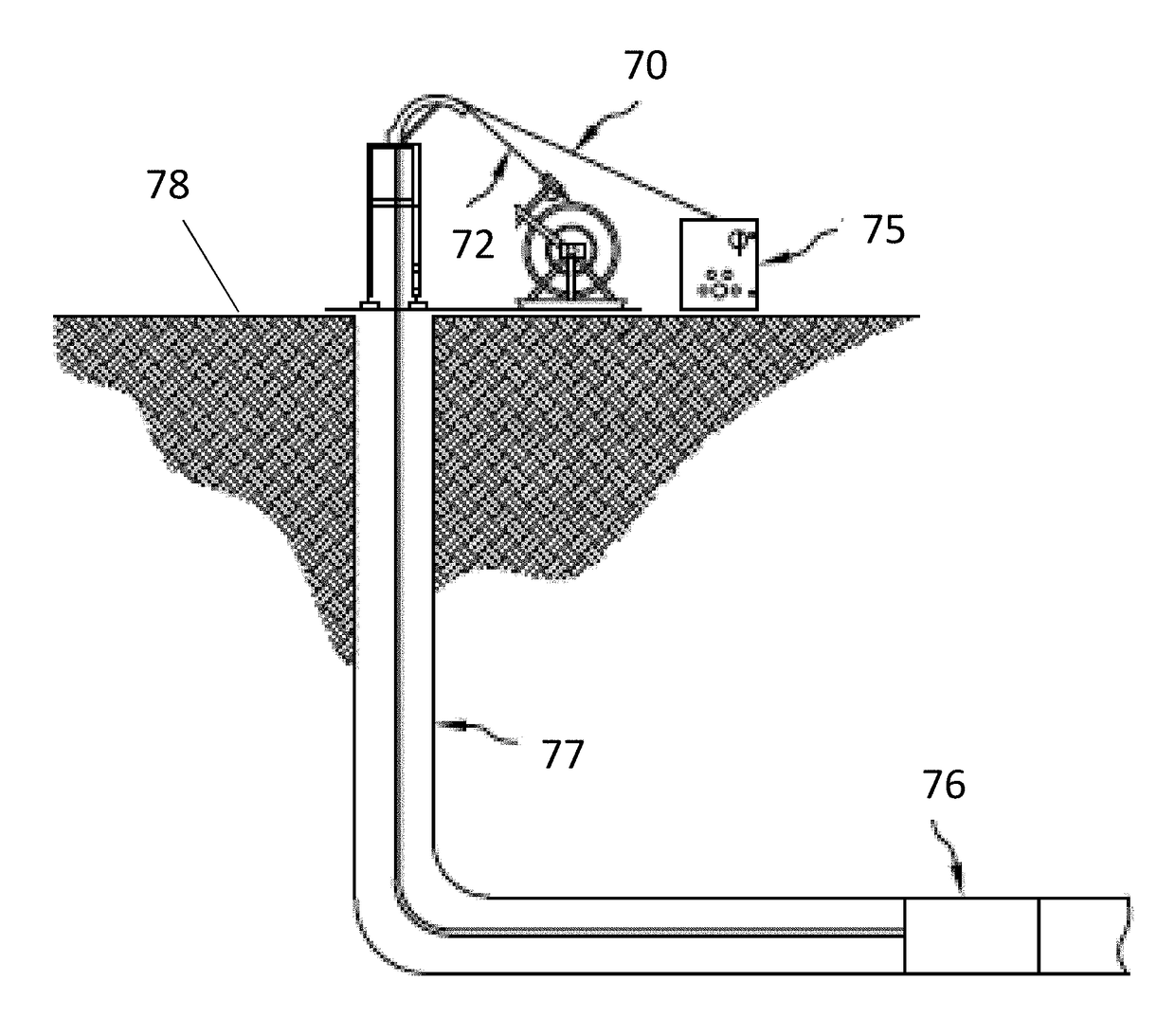
Downhole tools having controlled degradation and method
ActiveUS20180283121A1Improve the degradation problemSurveyConstructionsEngineeringBiological activation
A downhole assembly includes a downhole tool including a degradable-on-demand material, the degradable-on-demand material including a matrix material, and a unit in contact with the matrix material, the unit including a core comprising an energetic material configured to generate energy upon activation to facilitate degradation of the downhole tool and, an activator disposed in contact with the core, the activator having a triggering system including an electrical circuit, an igniter in the electrical circuit arranged to ignite the energetic material, a sensor configured to sense a target event or parameter within the borehole, and a control unit arranged to receive sensed signals from the sensor and to deliver a start signal to the electrical circuit in response to the sensed signals indicating an occurrence of the target event or parameter wherein, after the start signal is delivered from the control unit, the electrical circuit is closed and the igniter is initiated.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Downhole tools having controlled degradation and method
ActiveUS20180283142A1Improve the degradation problemWell/borehole valve arrangementsSealing/packingEngineeringBiological activation
A downhole assembly includes a downhole tool including a degradable-on-demand material including: a matrix material; and, a unit in contact with the matrix material. The unit includes a core including an energetic material configured to generate energy upon activation to facilitate degradation of the downhole tool; and, an activator disposed in contact with the core, the activator including a triggering system having an electrical circuit and an igniter within the electrical circuit, the electrical circuit having an open condition and a closed condition, the electrical circuit configured to be in the closed condition after movement of an object downhole that engages directly or indirectly with the triggering system, and the igniter arranged to ignite the energetic material in the closed condition of the electrical circuit. In the open condition of the electrical circuit the igniter is inactive, and in the closed condition of the electrical circuit the igniter is activated.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Stuffing of controllable degradative macropore cellulose for carrying microbe in use for treating wastewater and preparation
InactiveCN1562800ANo pollution in the processEasy to makeSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentCross-linkCellulose
Said filling is short cylinder-shaped, circular, block-shaped or schistose. The characteristics are: its specific superficial is 5m2 / g-10m2 / g, porosity is between 40 percent and 70 percent, carrier aperture is 100 um-1000 um. Said prepn. method includes macropore cellulose carrier prepn. and modifying process of carrier controlled degradation, the former is to make cellulose into cellulose viscose by alkalizing and yellowing, then to add in short cotton fibre and blowing agent to foam, macropore carrier filling of cellulose is produced by regenerating in weak sulphuric aci solution, the latter is to make the carrier and cross-linking agent ethanediol glycidyl ether cross-linked to realize controlled modifying of degradation speed.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
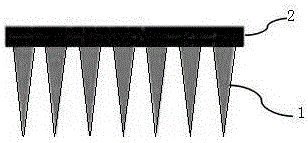
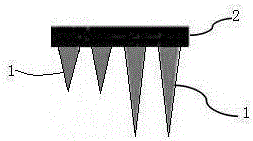
Micro-structure body and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a micro-structure body and a preparation method thereof. The micro-structure body is mainly composed of a microneedle and a substrate where the microneedle is vertically arranged. The preparation method comprises the steps of providing gel of the substrate and the microneedle; printing the substrate through a 3D printer, and printing the microneedle on the substrate; performing sterilization. The micro-structure body has the advantages of achieving controlled degradation and sustained release, being easy to prepare, meeting the individualized requirement and being applicable to the fields of biological medicine and medical cosmetology.
Owner:李媚
Oxo-biodegradable BOPP (biaxially-oriented polypropylene) film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102019736ANot easy to thermal cracking failureDoes not change appearanceSynthetic resin layered productsNon toxicitySurface layer
The invention discloses an oxo-biodegradable BOPP (biaxially-oriented polypropylene) film and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of the processing of BOPP films. The oxo-biodegradable BOPP film comprises an upper surface layer, a sandwich layer and a lower surface layer, and is prepared by the following steps of: adding 0.5-1.0 percent of an oxygen-containing biodegradable agent and other constituents into the upper surface layer, the sandwich layer and the lower surface layer, melting and extruding by utilizing a double-screw extruder at low temperature of 220-230DEG C, and then biaxially stretching on a Germany Bruckner machine. The structure of the traditional equipment is not changed in the invention, at the same time, the oxo-biodegradable BOPP film can solve the problem of white pollution, can not change the function and appearance of the traditional BOPP and produce harmful substances to the environment during decomposition process, and has the advantages of controlled degradation period, non-toxicity and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG KINLEAD PACKAGING MATERIAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com