Imitated extracellular matrix injectable in-situ hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of hydrogel and extracellular matrix, which is applied in the field of in situ hydrogel which imitates extracellular matrix and can be injected and its preparation and application, can solve the problem of single release rate, complicated steps, no controllable degradation, controllable Issues such as release and/or regulation of cell behavior, to achieve controllable release and/or regulation of cell behavior, to meet the requirements of different release rates, and to have broad clinical application prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
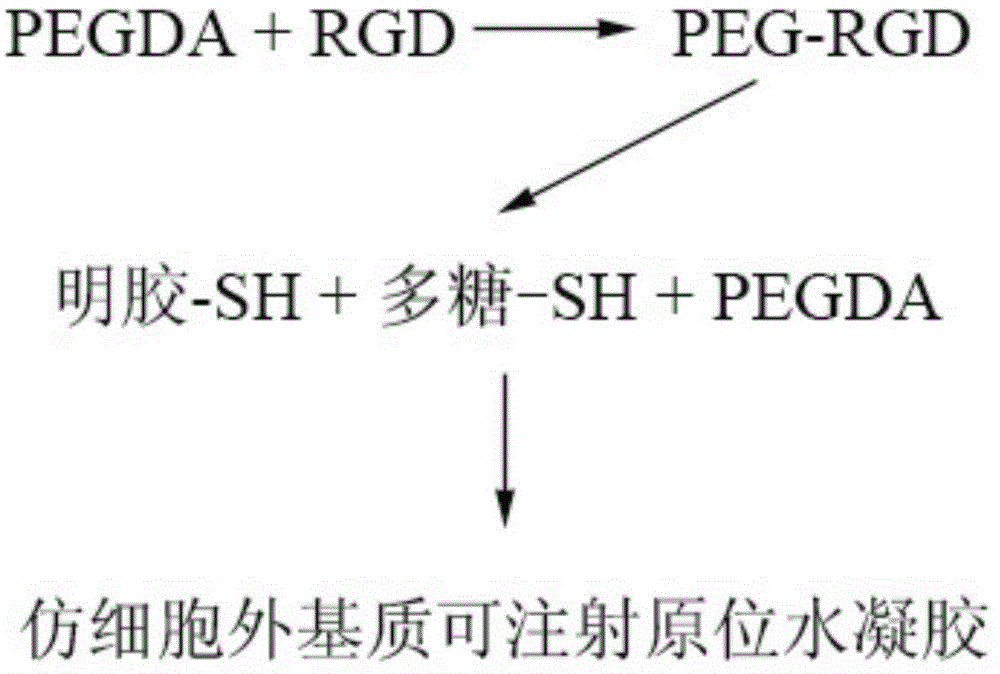
[0072] Example 1 Preparation of injectable in situ hydrogel imitating extracellular matrix
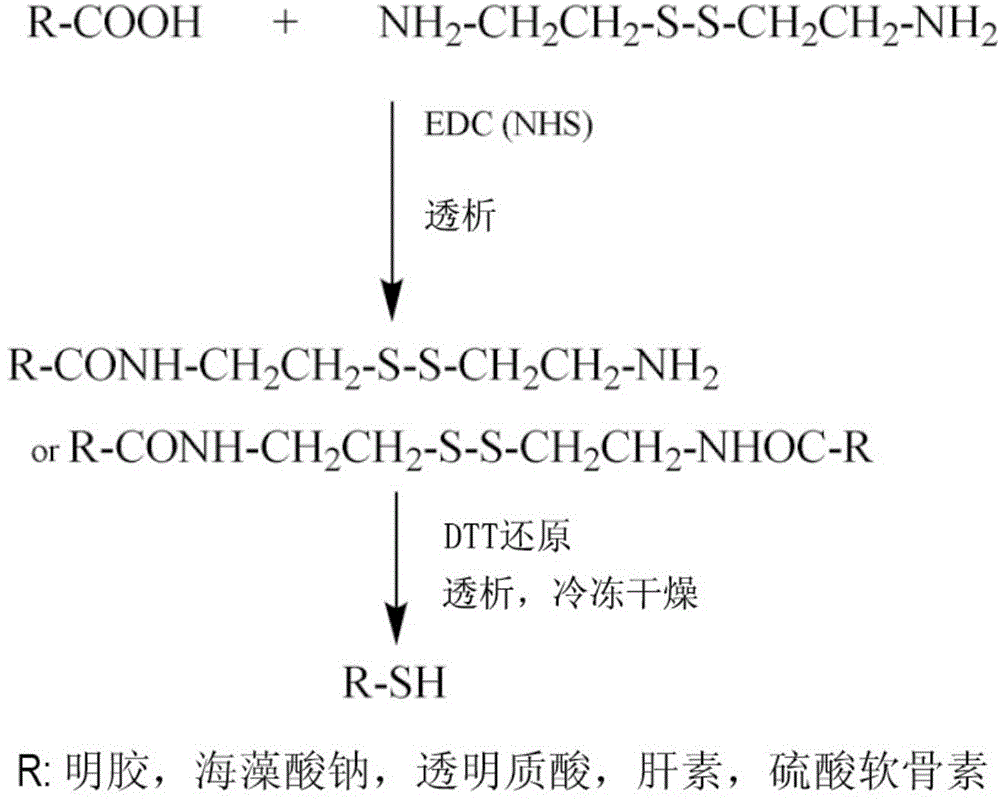
[0073] (1) Preparation of thiolated gelatin
[0074] Add 1 g of gelatin into 100 ml of ultrapure water, heat to 40°C, stir to dissolve, and then cool to room temperature. Cystamine dihydrochloride, EDC (1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiethylene amine hydrochloride) and NHS (N-hydroxysuccinimide), adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 4.75, start dialysis after 4 hours of reaction at room temperature, change the dialysate every 24 hours, add 0.5gDTT (dithiothreose) after 3 days of dialysis Alcohol), adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 8.5, adjust the pH to 4.0 after 2 hours of reaction, dialyze under nitrogen protection for 3 days, and change the dialysate once a day. After the dialysis is completed, filter sterilization and freeze-dry to obtain thiolated gelatin. The schematic diagram of its preparation is as follows: figure 1 .
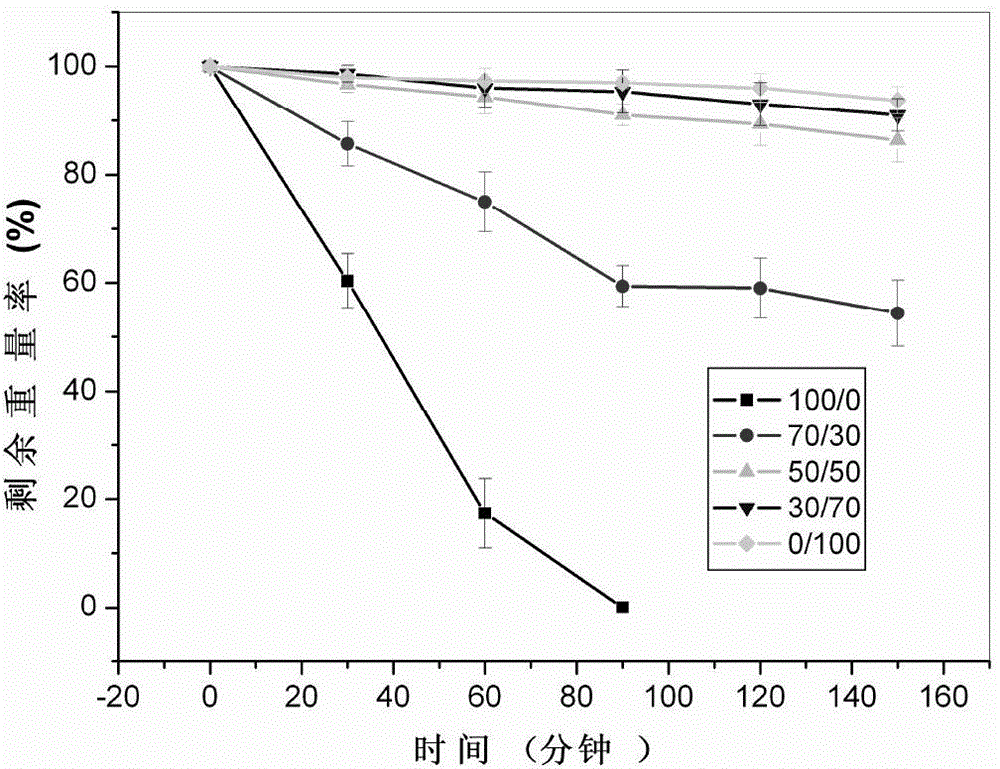
[0075] The thiol content was deter...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Example 2: Preparation of injectable in situ hydrogel imitating extracellular matrix
[0085] (1) Preparation of thiolated gelatin
[0086] Add 1 g of gelatin into 100 ml of ultrapure water, heat to 40°C, stir to dissolve, and then cool to room temperature. Add cystamine dihydrochloride, EDC and NHS according to the molar ratio of 1:1:2:2 (the molar ratio of carboxyl groups in gelatin is 1), adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 4.75, and start dialysis after 4 hours of reaction at room temperature, every 24 hours Change the dialysate once, add 0.5g DTT after 3 days of dialysis, adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 8.5, react for 2 hours, adjust the pH to 4.0, dialyze for 3 days under nitrogen protection, and change the dialysate once a day. After the dialysis is completed, filter sterilization and freeze-drying to obtain thiolated gelatin.
[0087]The mercapto group content was determined to be 0.42 mmol / g by the Ellman method.
[0088] (2) Preparation of t...
Embodiment 3
[0096] Example 3: Preparation of injectable in situ hydrogel imitating extracellular matrix
[0097] (1) Preparation of thiolated gelatin
[0098] Add 1 g of gelatin into 100 ml of ultrapure water, heat to 40°C, stir to dissolve, and then cool to room temperature. Add cystamine dihydrochloride, EDC and NHS according to the molar ratio of 1:3:3:3 (the carboxyl molar ratio in gelatin is 1), adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 4.75, and start dialysis after 4 hours of reaction at room temperature, every 24 hours Change the dialysate once, add 0.5g DTT after 3 days of dialysis, adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 8.5, react for 2 hours, adjust the pH to 4.0, dialyze for 3 days under nitrogen protection, and change the dialysate once a day. After the dialysis is completed, filter sterilization and freeze-drying to obtain thiolated gelatin.
[0099] The mercapto group content was determined to be 0.6 mmol / g by the Ellman method.
[0100] (2) Preparation of mercaptohep...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com