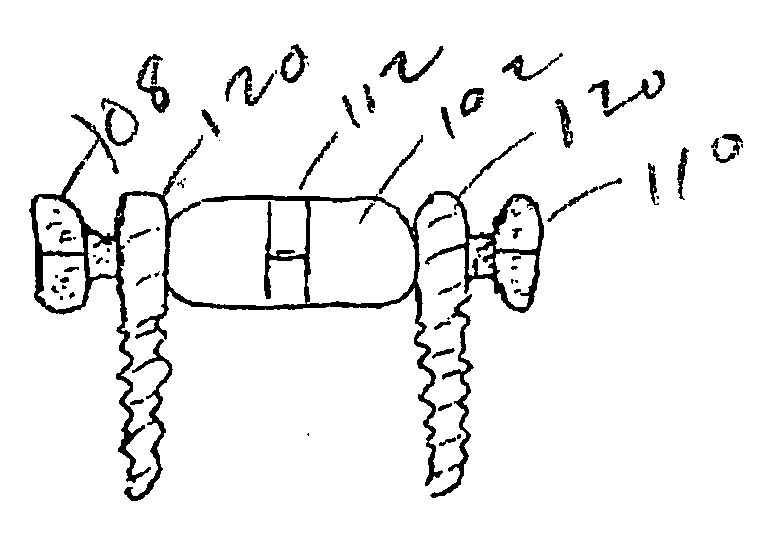
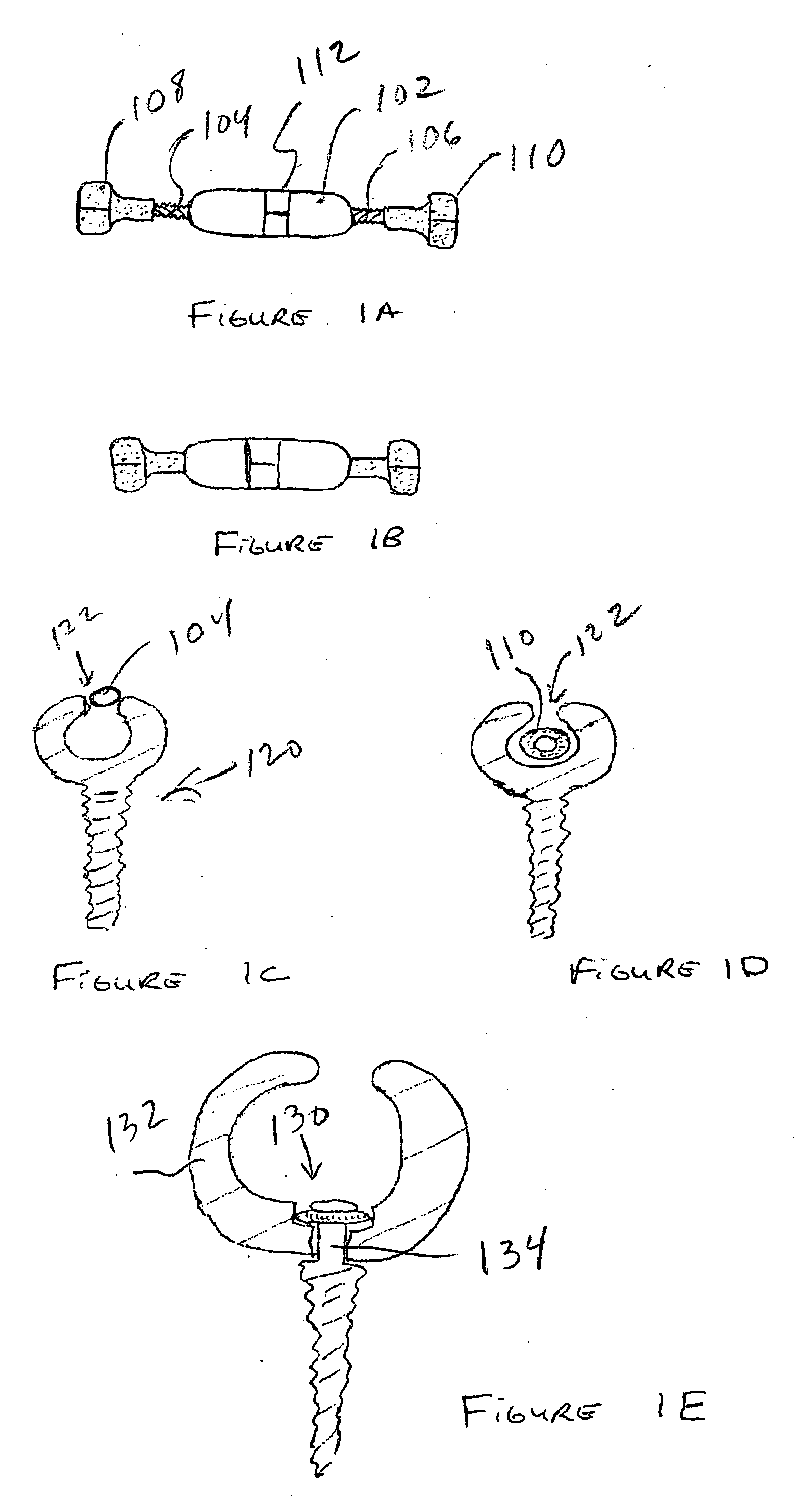
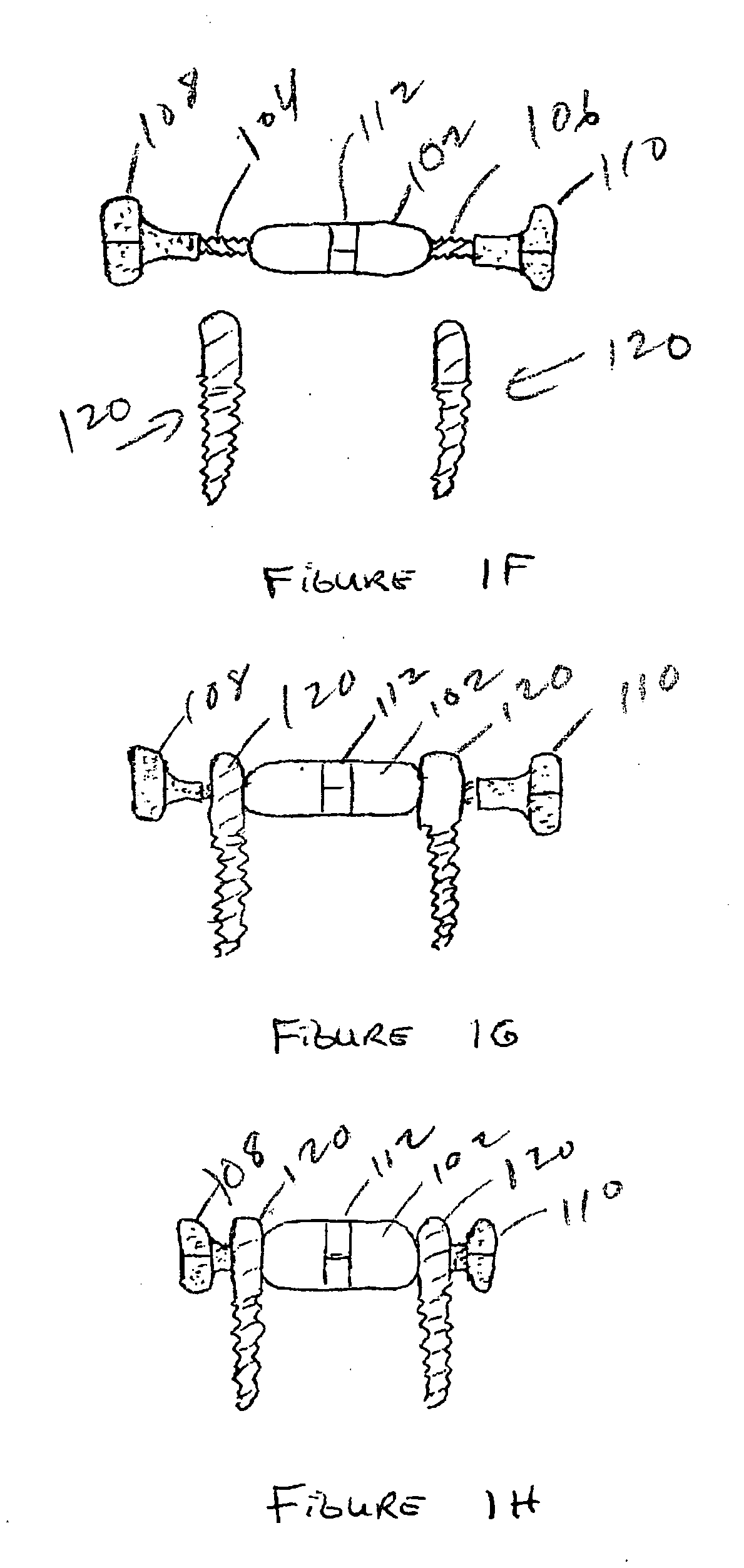
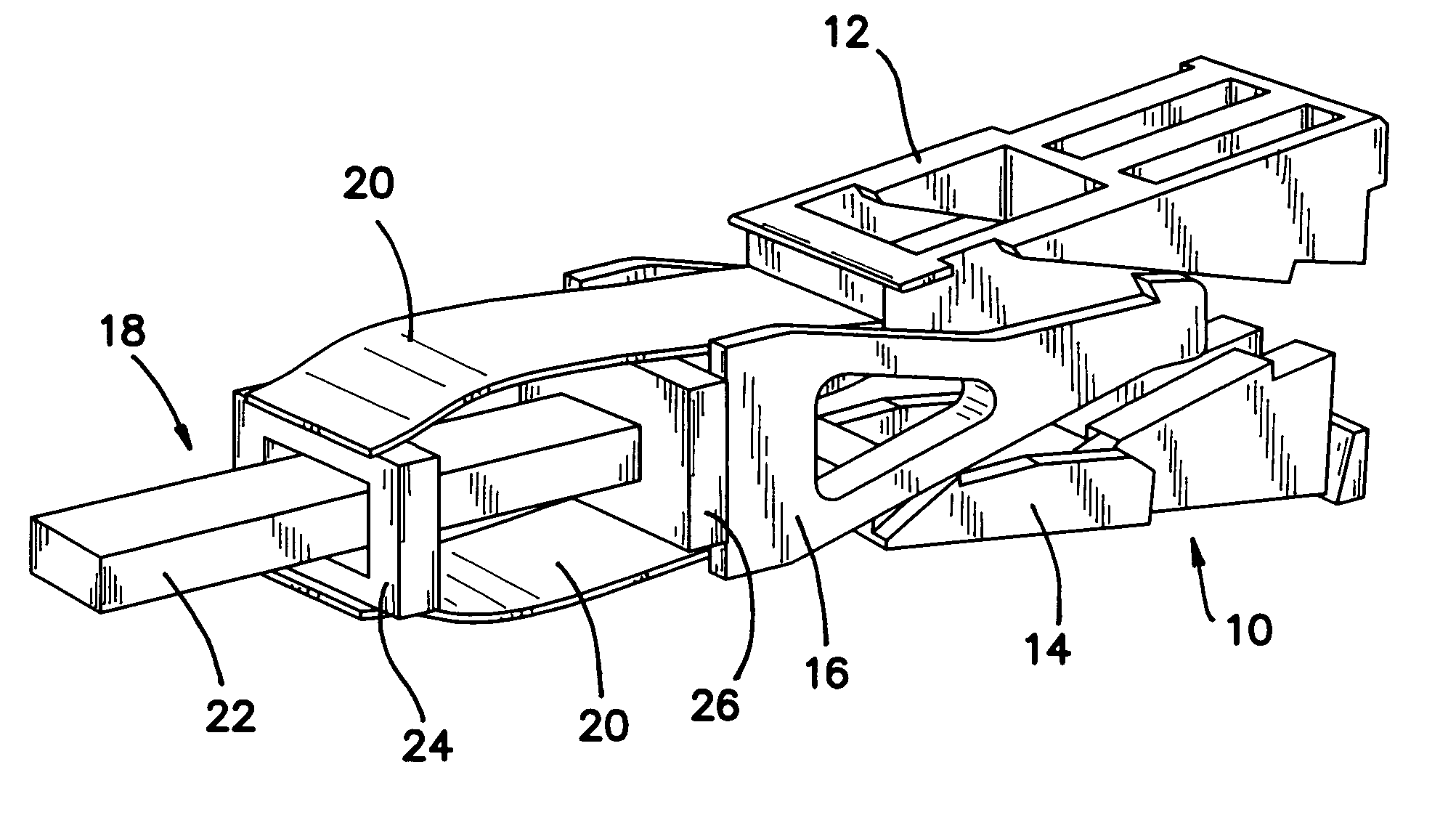
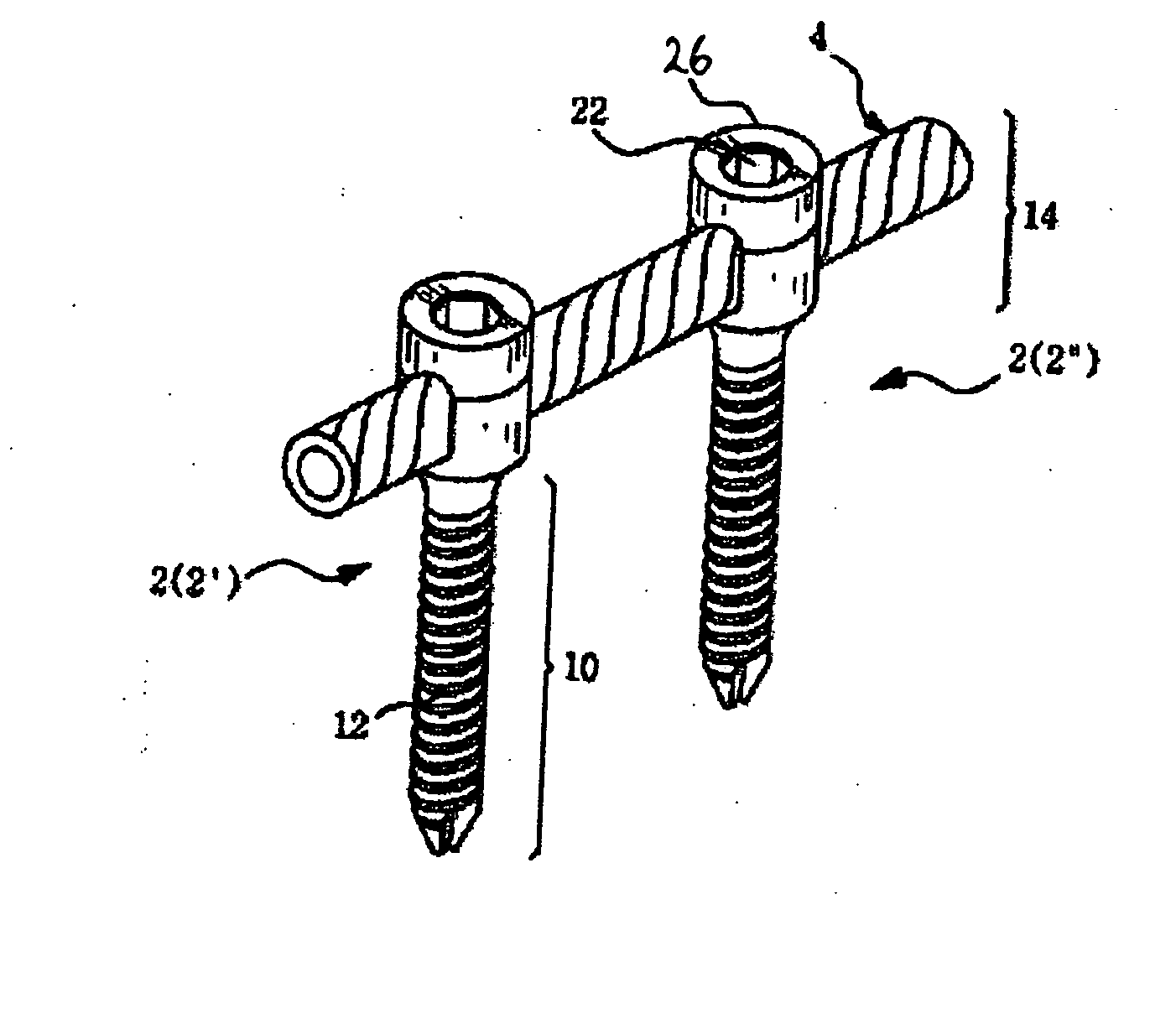
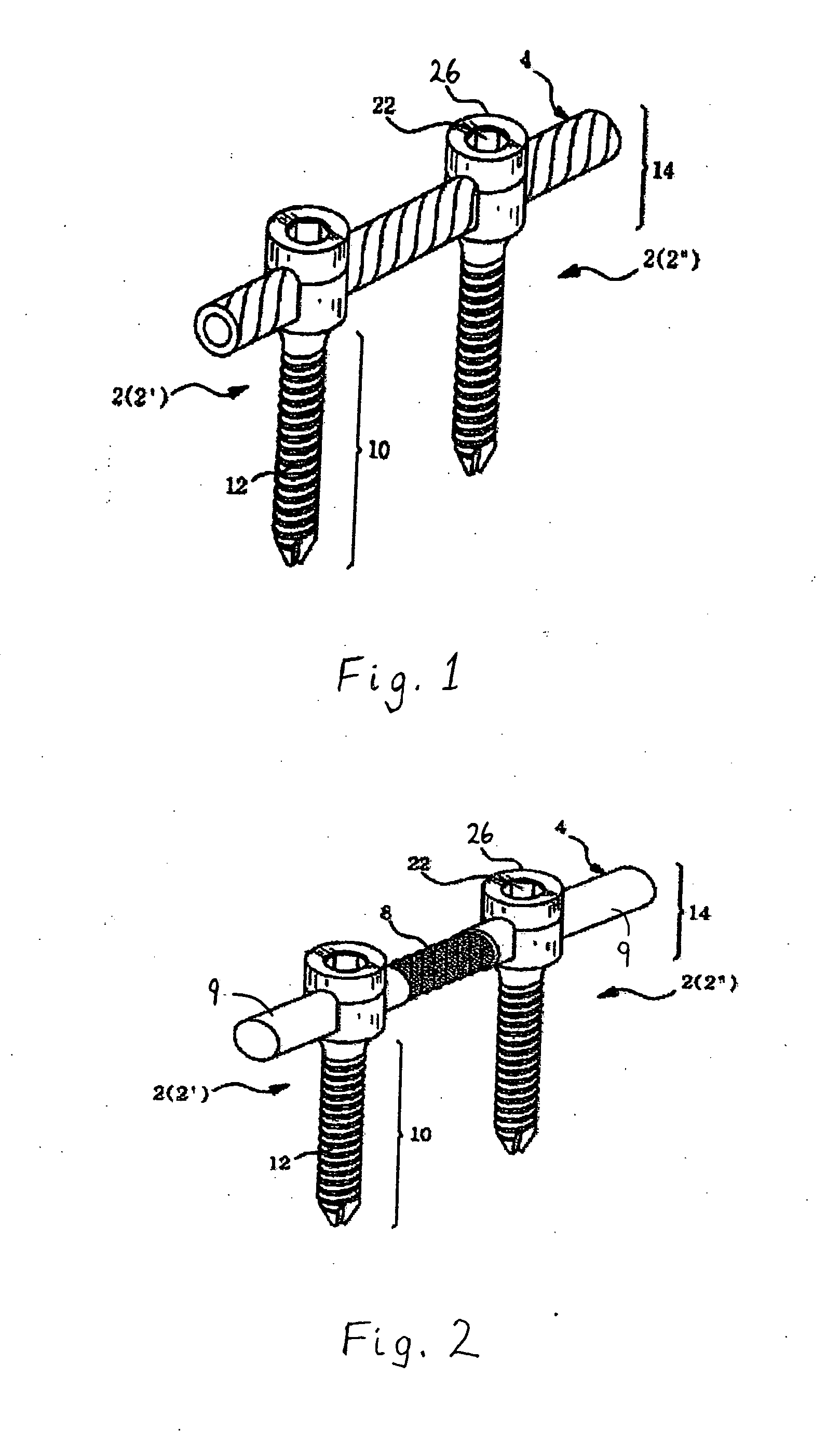
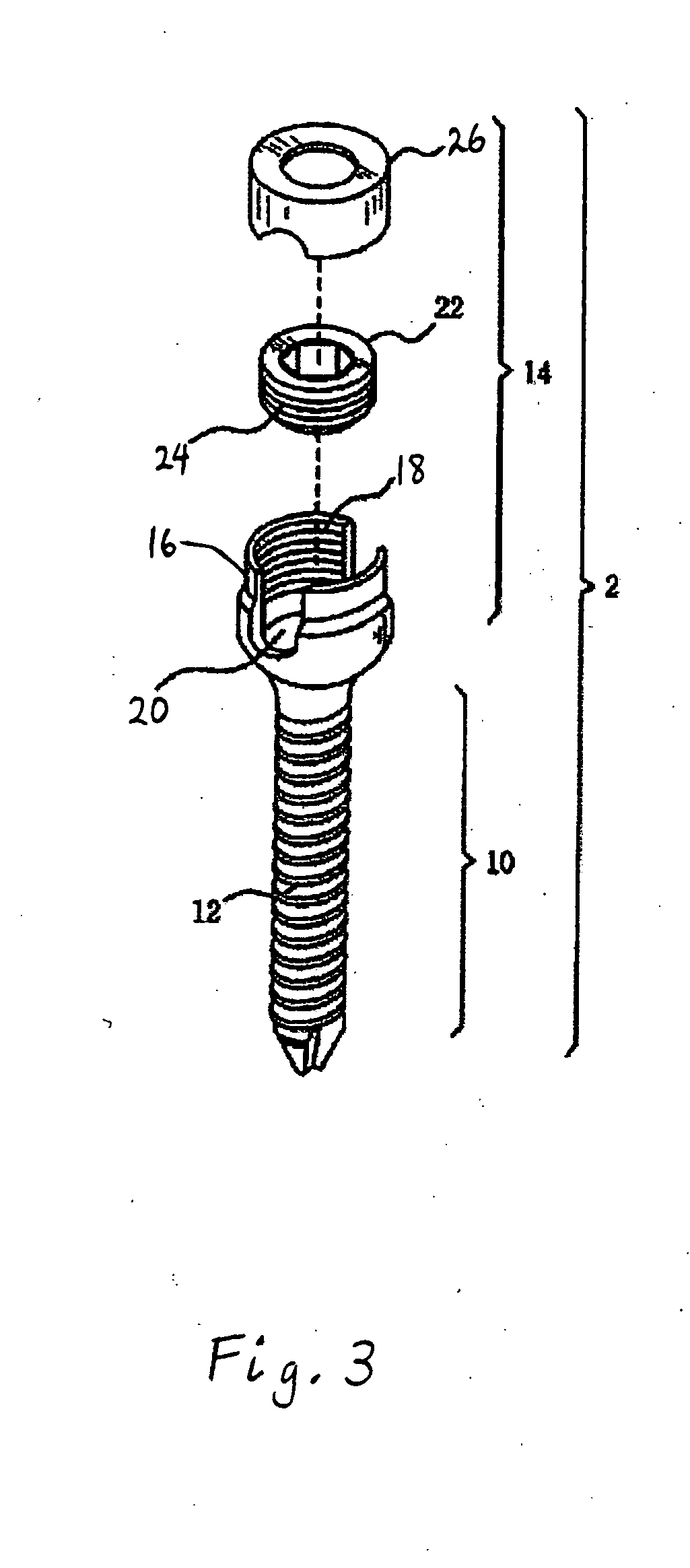
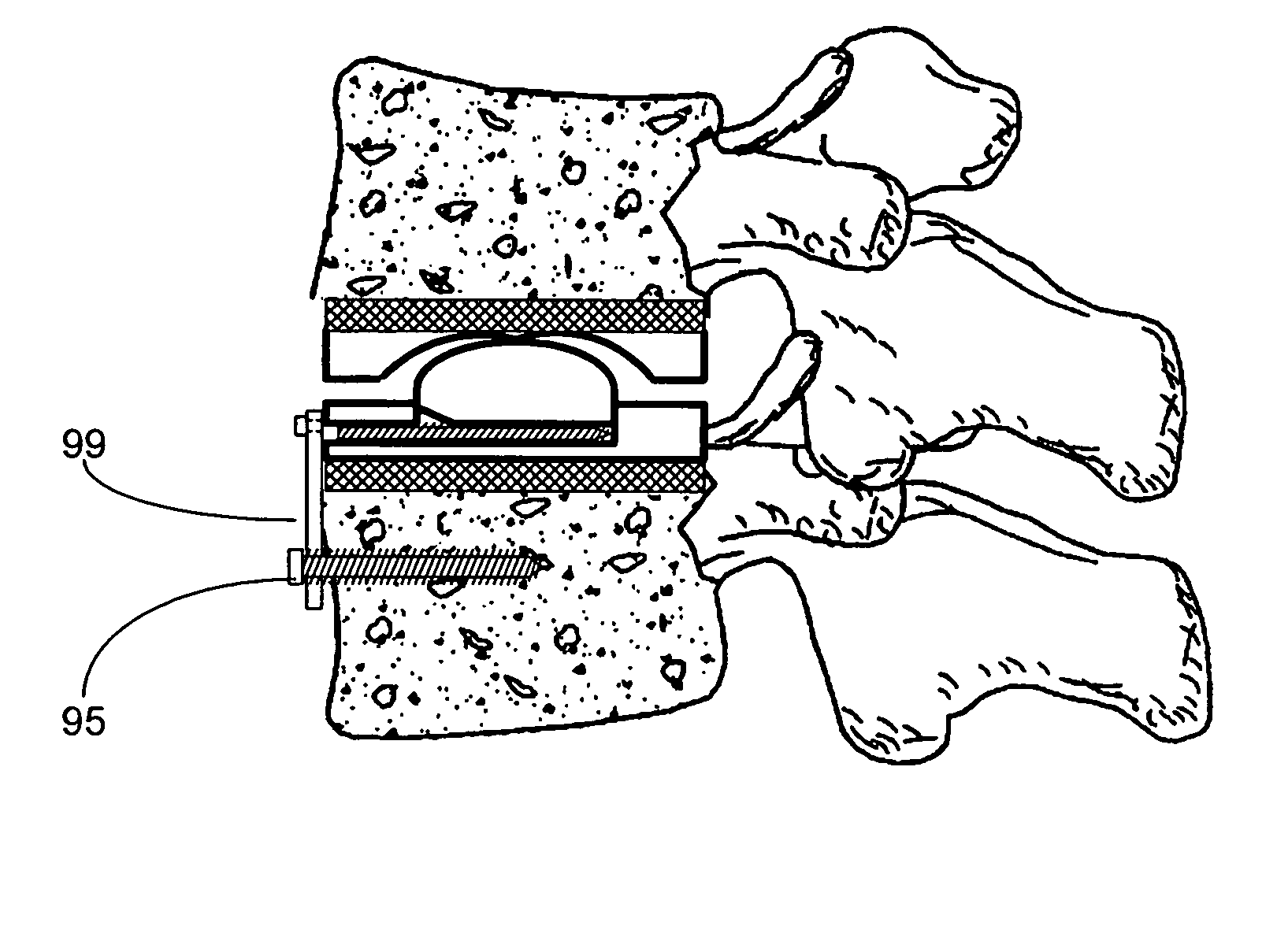
Patents
Literature
4376 results about "Spinal column" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6838493B2High porosityReduce probabilitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
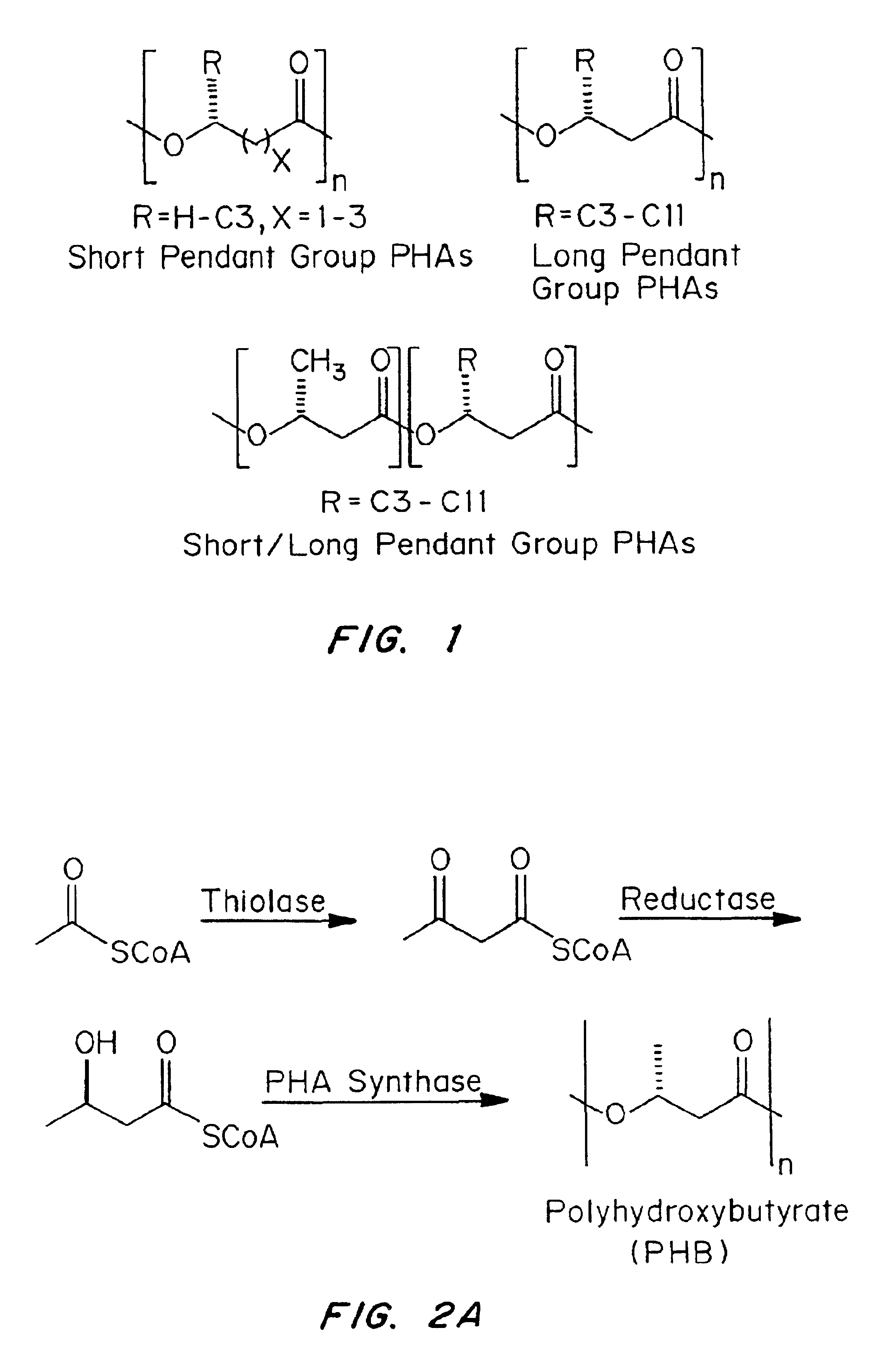
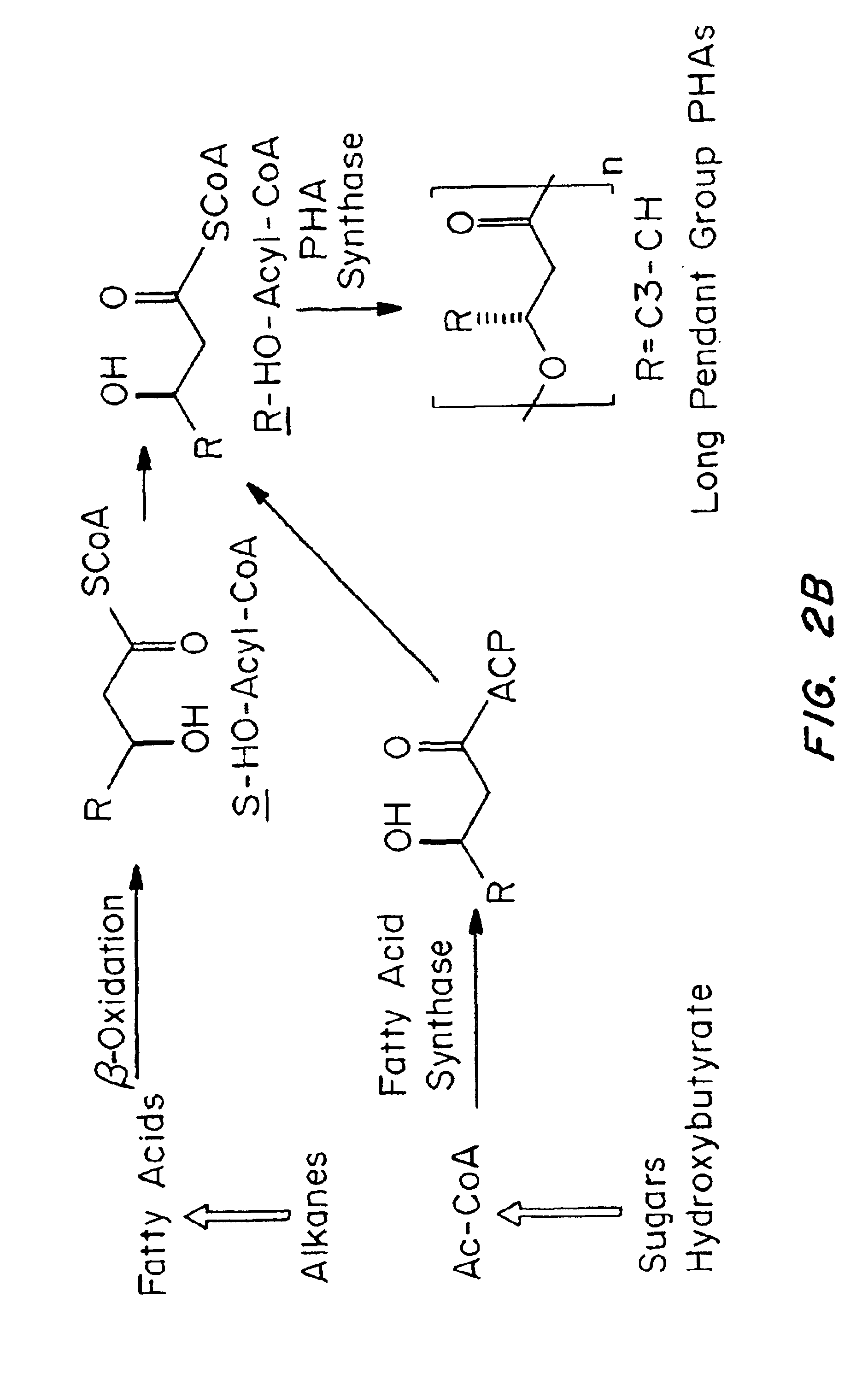
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Anterior buttress staple
An anterior buttress staple and screw system is provided that can be used to hold an implant such as a disc prosthesis in place and thereby prevent its migration out of the spinal column. The buttress staple comprises a screw locking plate having a screw locking design that prevents the screw from backing up and away from the plate. The screw is configured to provide an interference fit with the screw locking plate, and can be used as a staple removal tool during revision surgery when the screw locking plate needs to be lifted from the bone surface on which it is attached.
Owner:DEPUY ACROMED INC
Systems for percutaneous bone and spinal stabilization, fixation and repair
InactiveUS6127597ASize of wire can be enlarged and reducedEnlarging and reducing sizeInternal osteosythesisFluid pressure measurement using pistonsSpinal columnProsthesis
Systems for bone and spinal stabilization, fixation and repair include intramedullar nails, intervertebral cages and prostheses, remotely activatable prostheses, tissue extraction devices, and electrocautery probes. The intramedullar nails, intervertebral cages and prostheses, are designed for expansion from a small diameter for insertion into place to a larger diameter which stabilizes, fixates or repairs the bone, and further can be inserted percutaneously. Remotely activatable prostheses can be activated from an external unit to expand and treat prosthesis loosening. Tissue extraction devices, and electrocautery probes are used to remove tissue from desired areas.
Owner:KYPHON
Method of inserting and preloading spinal implants
InactiveUS6080155ARestoring and maintaining normal angular relationshipFaster and safe and more efficaciousInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve. Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted to restore the normal angular relationship of the vertebrae adjacent to that disc space. An extended outer sleeve having extended portions capable of maintaining the vertebrae distracted in their normal angular relationship is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Apparatus for inserting spinal implants
InactiveUS6096038AEliminate separationEfficient removalInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Spinal stabilization system and method
A spinal stabilization system may include a pair of structural members coupled to at least a portion of a human vertebra with connectors. Connectors may couple structural members to spinous processes. Some embodiments of a spinal stabilization system may include fasteners that couple structural members to vertebrae. In some embodiments, a spinal stabilization system provides three points of fixation for a single vertebral level. A fastener may fixate a facet joint between adjacent vertebrae and couple a stabilization structural member to a vertebra. Connectors may couple the structural members to the spinous processes of the vertebrae. Use of a spinal stabilization system may improve the stability of a weakened or damaged portion of a spine. When used in conjunction with an implant or other device, the spinal stabilization system may immobilize vertebrae and allow for fusion of the implant or other device with vertebrae.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Systems and methods for posterior dynamic stabilization of the spine
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
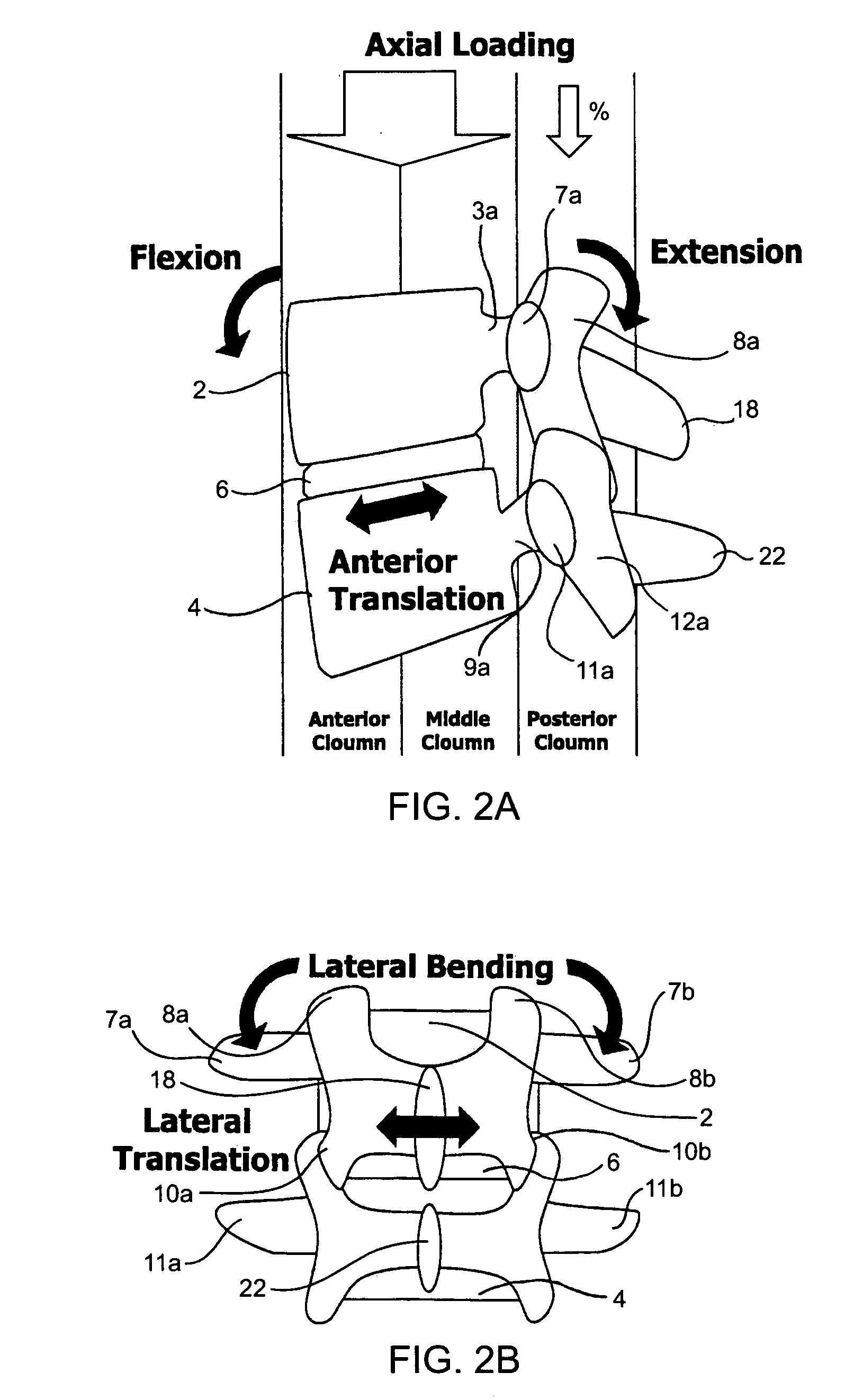
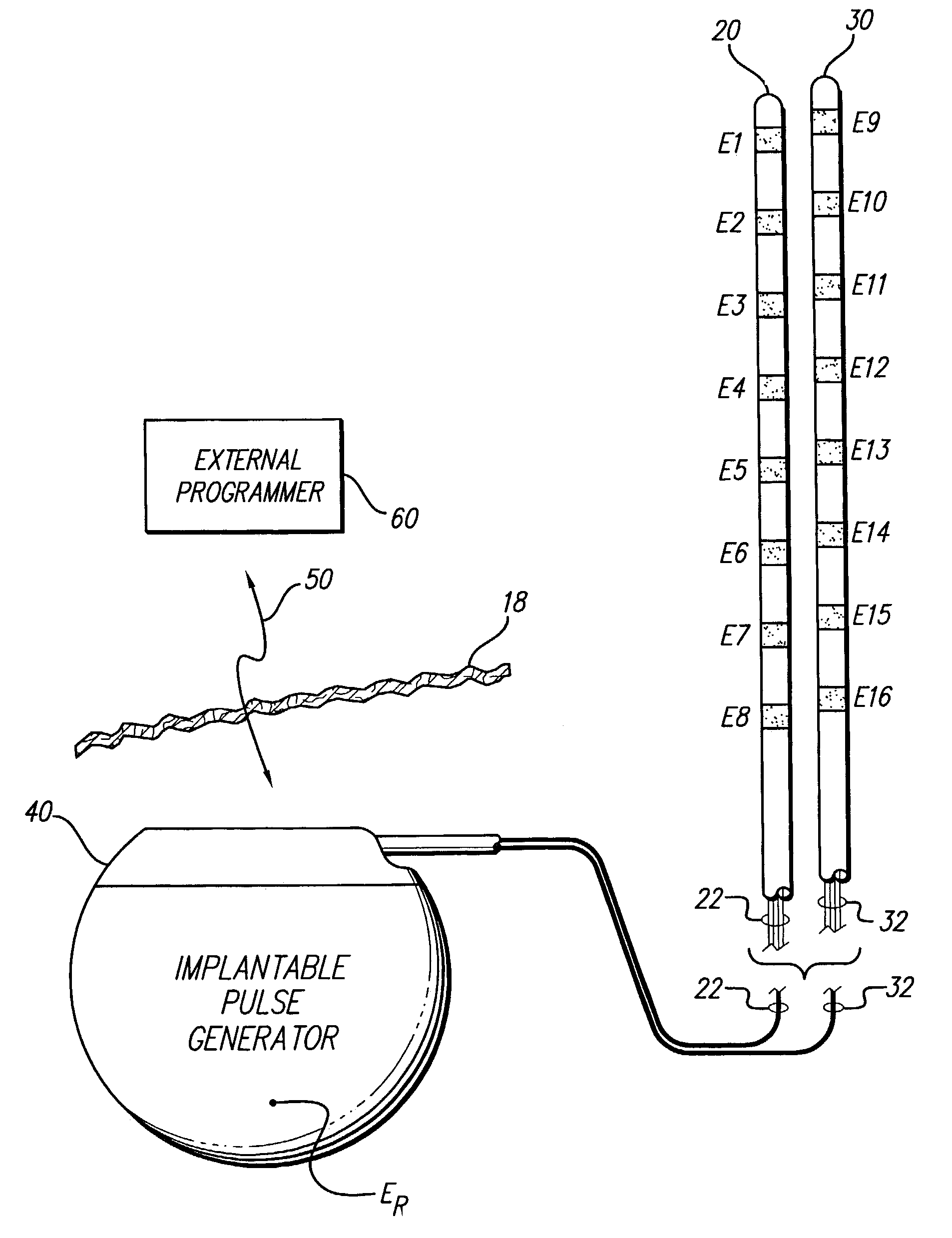
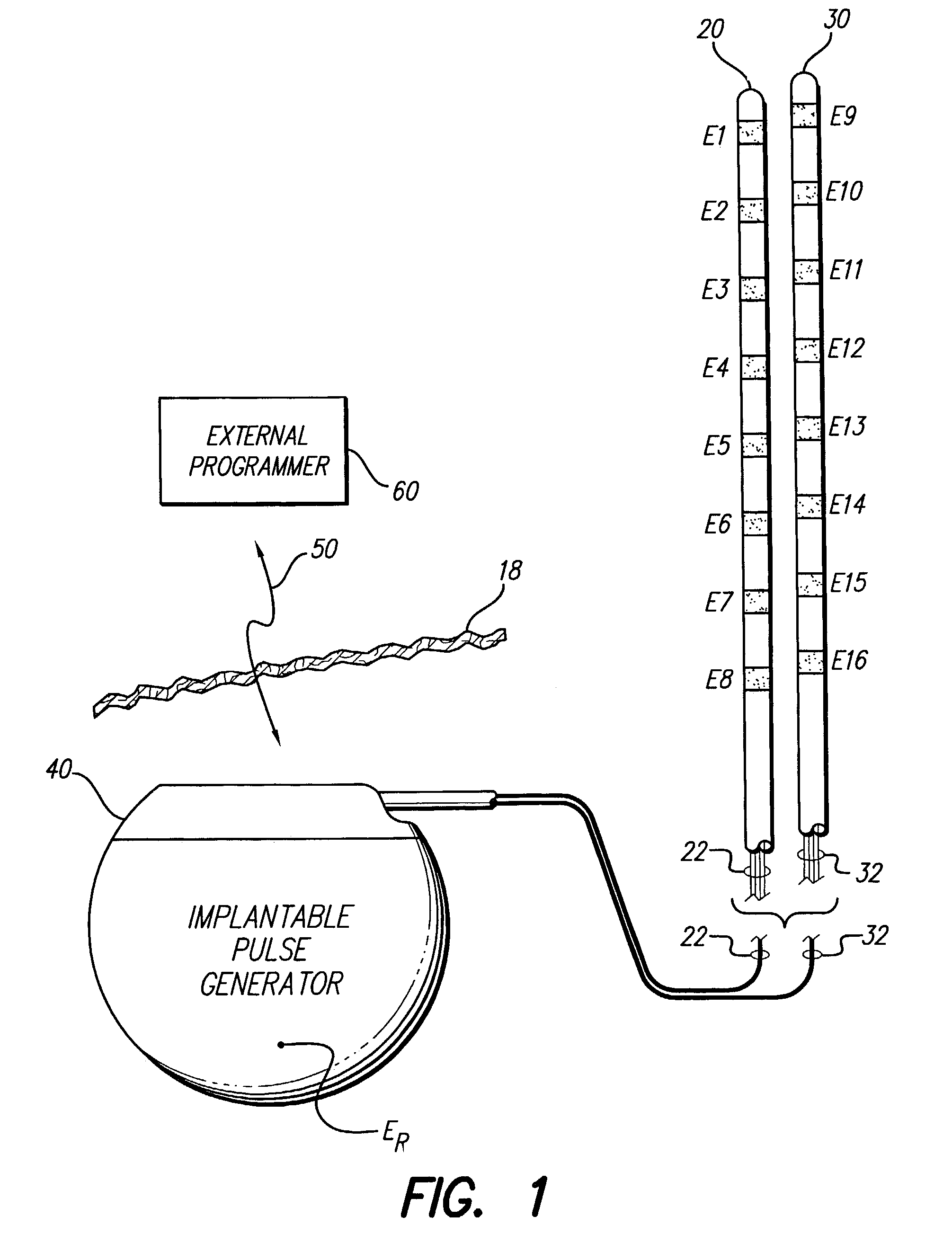
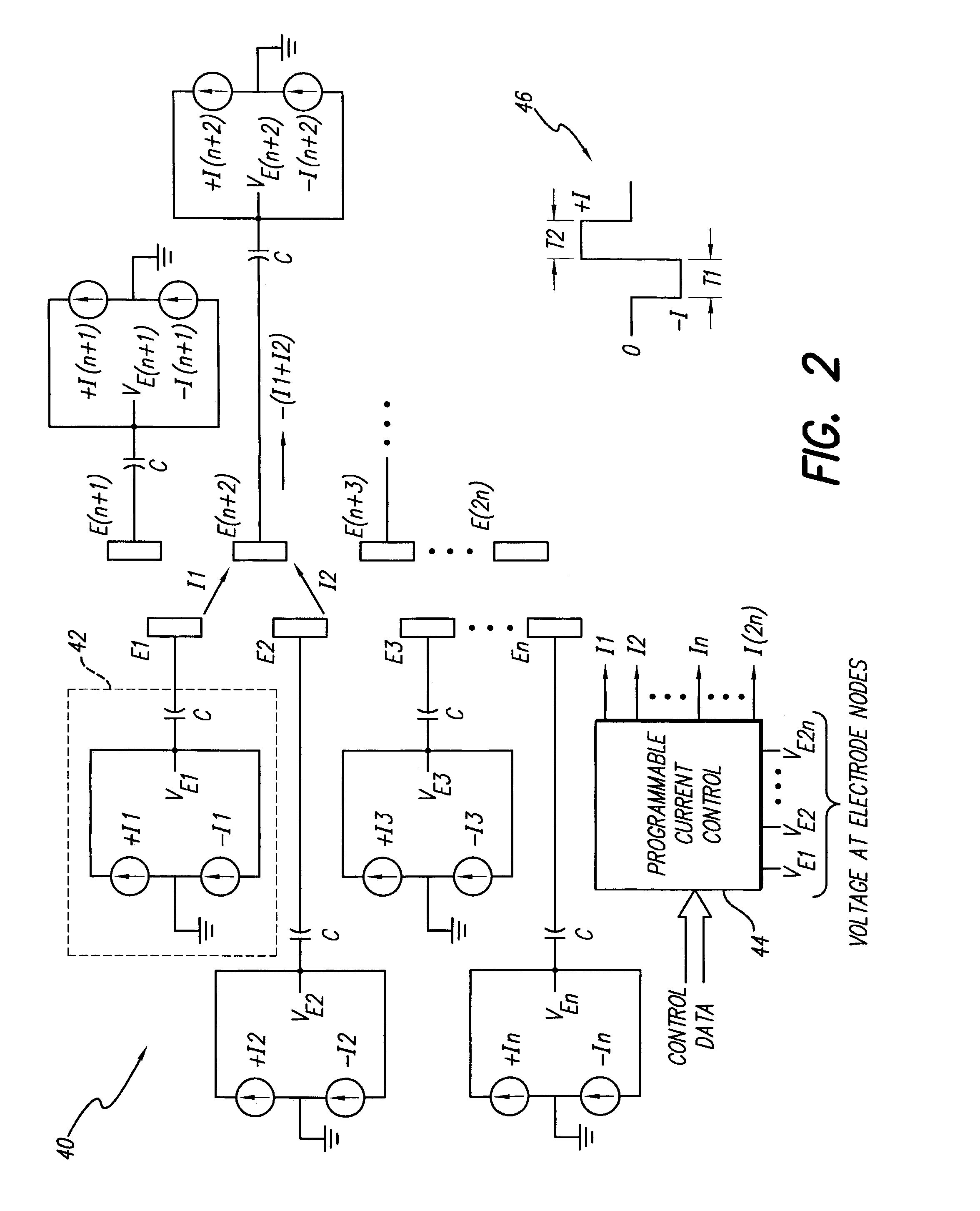
Apparatus and method for determining the relative position and orientation of neurostimulation leads
ActiveUS6993384B2Sure easySpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringPotential measurementSpinal column
Interelectrode impedance or electric field potential measurements are used to determine the relative orientation of one lead to other leads in the spinal column or other body / tissue location. Interelectrode impedance is determined by measuring impedance vectors. The value of the impedance vector is due primarily to the electrode-electrolyte interface, and the bulk impedance between the electrodes. The bulk impedance between the electrodes is, in turn, made up of (1) the impedance of the tissue adjacent to the electrodes, and (2) the impedance of the tissue between the electrodes. In one embodiment, the present invention makes both monopolar and bipolar impedance measurements, and then corrects the bipolar impedance measurements using the monopolar measurements to eliminate the effect of the impedance of the tissue adjacent the electrodes. The orientation and position of the leads may be inferred from the relative minima of the corrected bipolar impedance values. These corrected impedance values may also be mapped and stored to facilitate a comparison with subsequent corrected impedance measurement values. Such comparison allows a determination to be made as to whether the lead position and / or orientation has changed appreciably over time. In another embodiment, one or more electrodes are stimulated and the resulting electric field potential on the non-stimulated electrodes is measured. Such field potential measurements provide an indication of the relative orientation of the electrodes. Once known, the relative orientation may be used to track lead migration, to setup stimulation configurations and parameters for nominal stimulation and / or navigation. Also, such measurements allow automatic adjustment of stimulation energy to a previously-defined optimal potential field in the case of lead migration or postural changes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Spinal stabilization systems
ActiveUS20050113927A1Preserving and simulating flexionPreserving and simulating and extensionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnFacetectomy
Spinal stabilizing elements and spinal stabilization systems composed of spinal stabilizing elements in combination with disc prostheses or disc nucleus replacements are provided. The stabilizing elements and stabilization systems are designed to preserve the natural mobility of vertebral discs and facet joints in patients with facet joint disease or patients who has undergone a prior destabilizing procedure, such as a facetectomy. The stabilizing elements may be pivoting elements or dynamic elements.
Owner:ST CLOUD CAPITAL PARTNERS III SBIC LP
Systems and methods for posterior dynamic stabilization of the spine
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Expandable osteosynthesis cage
InactiveUS6129763AGood jamLarge inside volumeBone implantJoint implantsSpinal columnBiomedical engineering
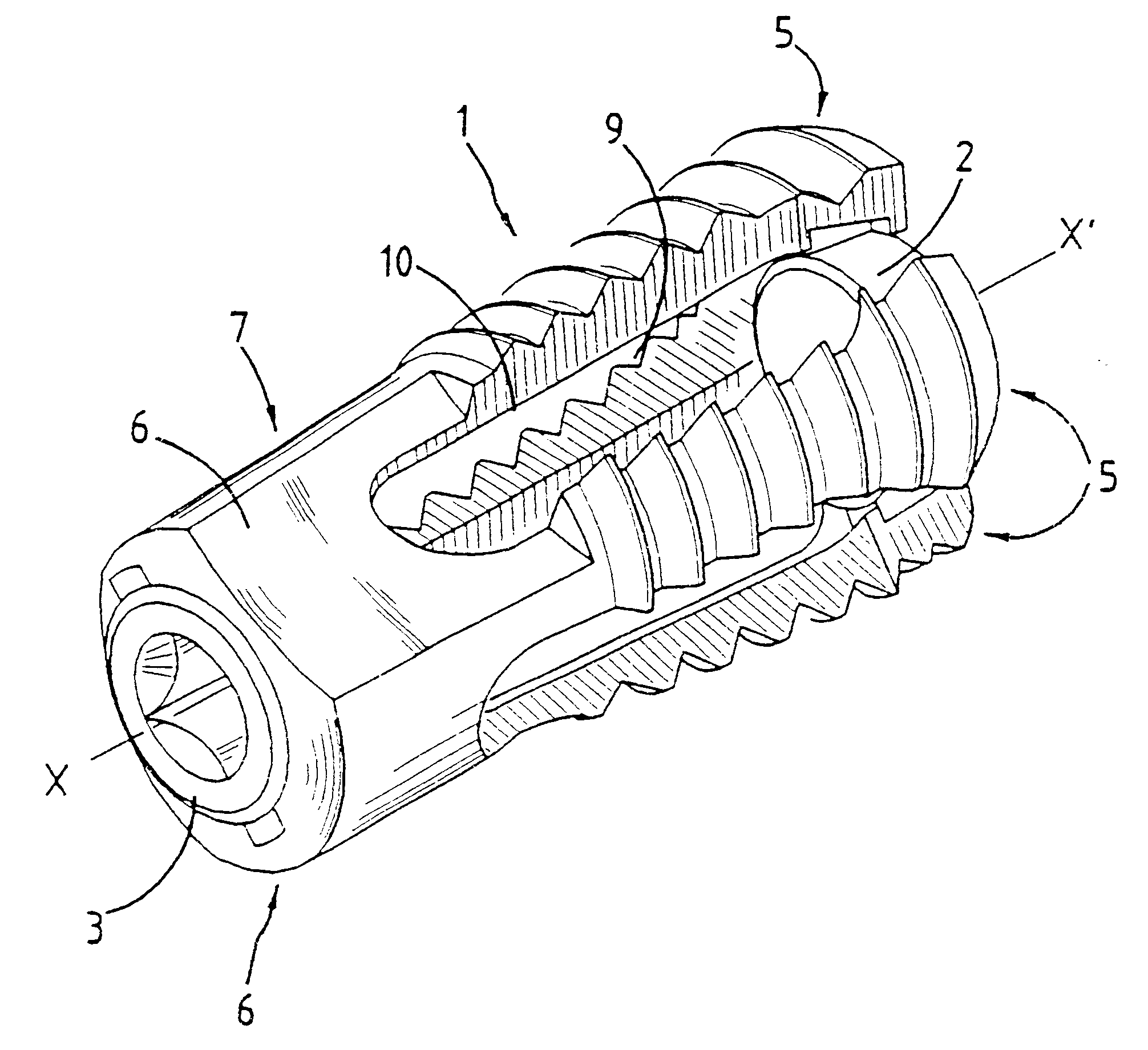
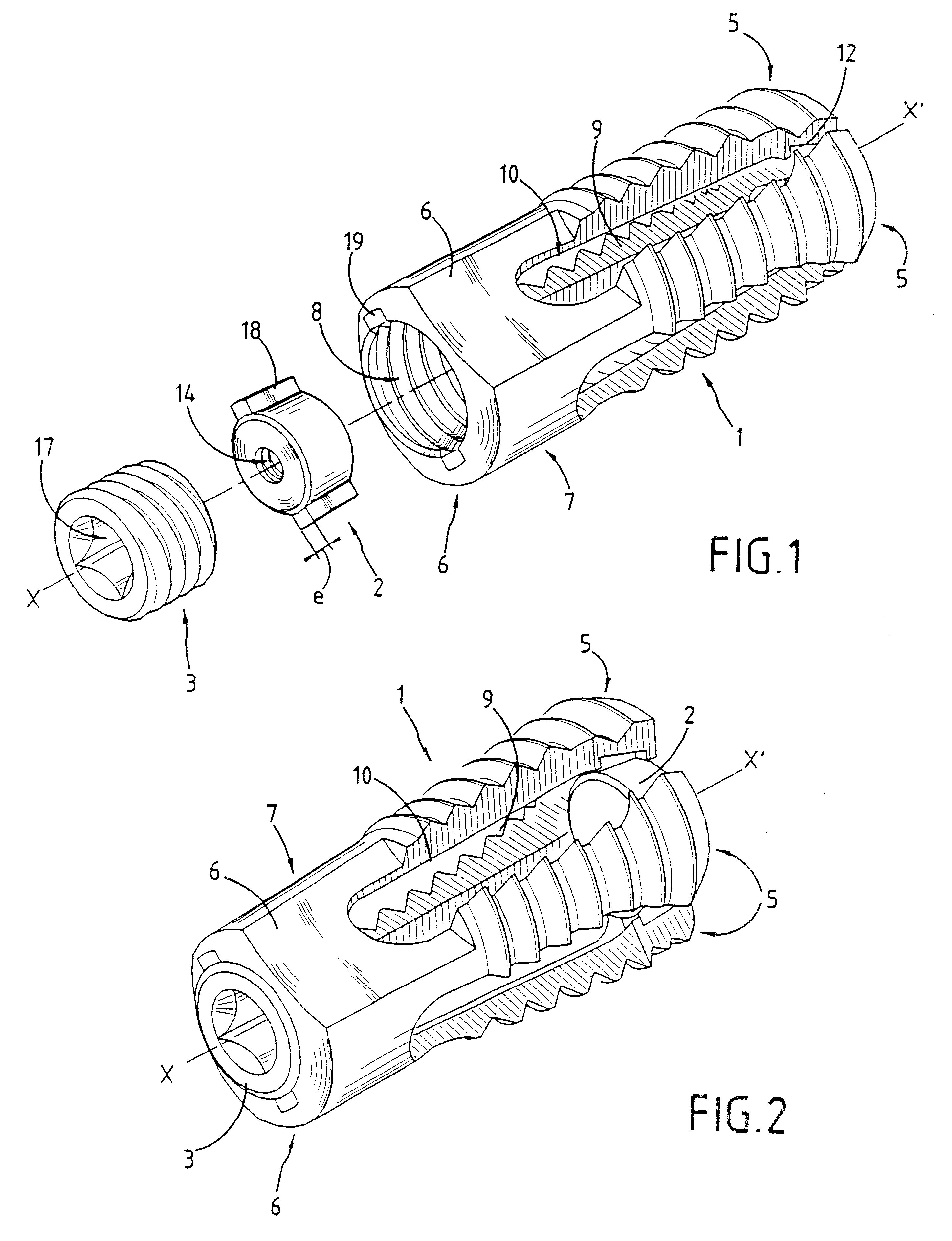
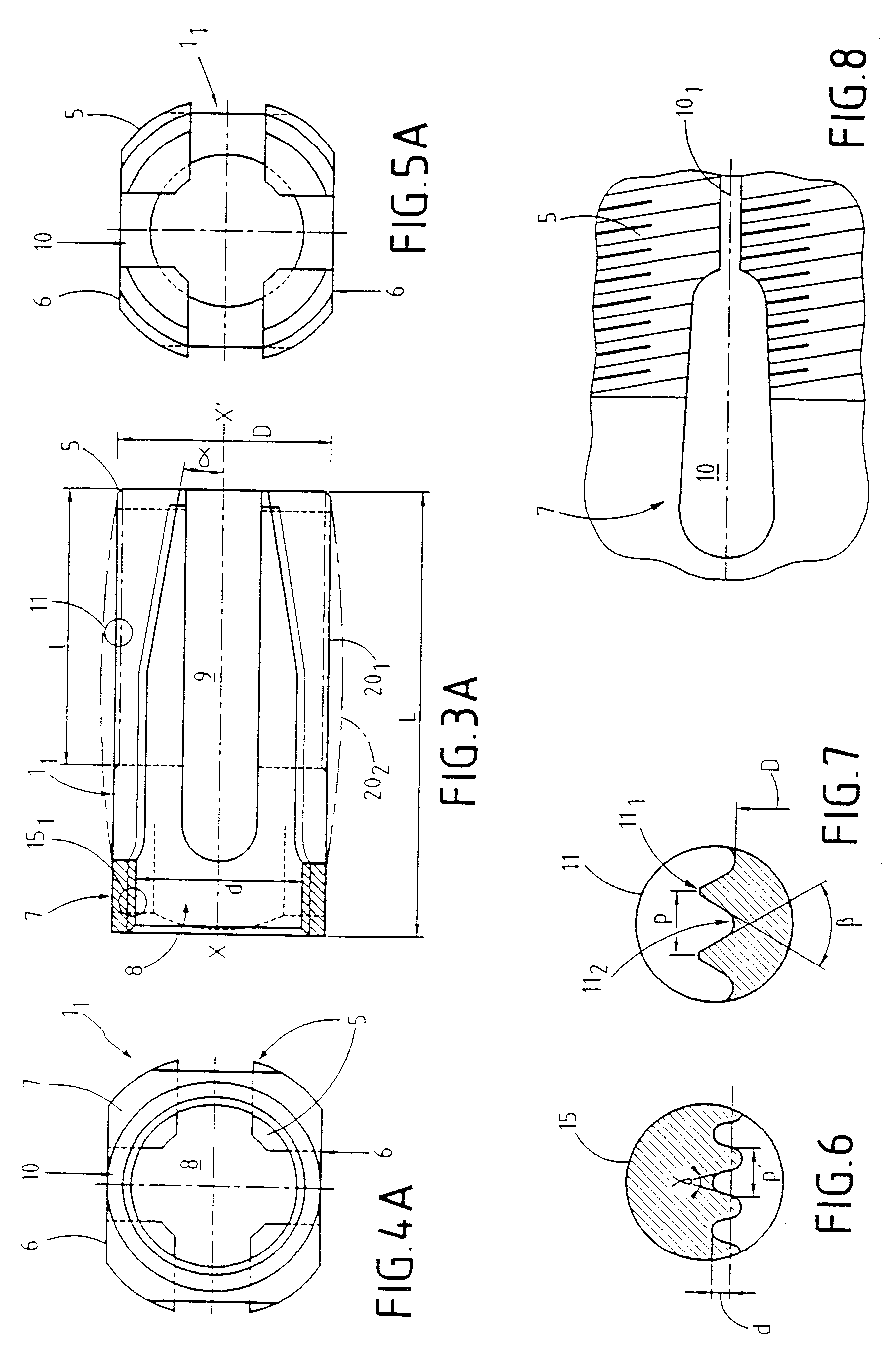
PCT No. PCT / FR97 / 01617 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 28, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 28, 1998 PCT Filed Sep. 12, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 10722 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 19, 1998An expandable osteosynthesis implant has branches (5) each connected at one end to a seat (7) which is pierced by an orifice (8), suitable for being slid from a posterior direction between the facing faces of two consecutive vertebrae in order to hold them a given distance apart and restore stability of the spinal column. According to the invention, the branches (5) and the seat (7) define a hollow cage (1) which, in a "rest" position, has an outside general shape that is a cylinder of circular section, and a portion at least of the inside volume (9) of the cage (1) towards the distal ends of the branches (5) is in the form of a circular truncated cone whose large base is towards the seat (7), which implant has at least three branches (5) and, inside the inside volume (9) at least one spacer (2) suitable for passing through the orifice (8) and the large base of the truncated cone.
Owner:OSTEOIMPLANT TECH
Expandable spinal fusion device and methods of promoting spinal fusion
InactiveUS7018415B1Promoting osteogenic fusionMinimal exposureBone implantJoint implantsSpinal columnBone growth
An intervertebral disc space implant includes spaced-apart bone engagement portions that define an intermediate chamber that holds bone growth inducing material into contact with adjacent vertebral bodies. The implant is expandable to establish and maintain desired intervertebral spacing during fusion. The implant includes a first member and a second member arranged to move relative to each other by action of an expansion member, the first member being engageable with the vertebral body below the disc space.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Methods and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis
InactiveUS20060106381A1Effective treatmentPermit flexionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnDevice form
Surgical implants are configured for placement posteriorly to a spinal canal between vertebral bodies to distract the spine and enlarge the spinal canal. In the preferred embodiments the device permits spinal flexion while limiting spinal extension, thereby providing an effective treatment for treating spinal stenosis without the need for laminectomy. The invention may be used in the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spine. Numerous embodiments are disclosed, including elongated, length-adjustable components coupled to adjacent vertebral bodies using pedicle screws. The preferred embodiments, however, teach a device configured for placement between adjacent vertebral bodies and adapted to fuse to the lamina, facet, spinous process or other posterior elements of a single vertebra. Various mechanisms, including shape, porosity, tethers, and bone-growth promoting substances may be used to enhance fusion. The tether may be a wire, cable, suture, or other single or multi-filament member. Preferably, the device forms a pseudo-joint in conjunction with the non-fused vertebra. Alternatively, the device could be fused to the caudal vertebra or both the cranial and caudal vertebrae.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Posterior lumbar interbody fusion expandable cage with lordosis and method of deploying the same
A spinal fusion cage comprises an upper half-cage, a lower half-cage, and a plunger with a cam. The upper half-cage and lower half-cage have a first collapsed configuration which has a thin, flat, rectangular envelope and a second expanded configuration. The half-cages have at least one ramped surface on which the cam of the plunger rides. The cam bears against the ramped surface and spreading the two half-cages apart. A method of deploying a spinal fusion cage comprises the steps of disposing in a spinal space an upper half-cage and lower half-cage in a first collapsed configuration which has a thin, flat, rectangular envelope and a second expanded configuration. The method continues with the step of distally advancing a plunger between the upper half-cage and lower half-cage and spreading the two half-cages apart.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
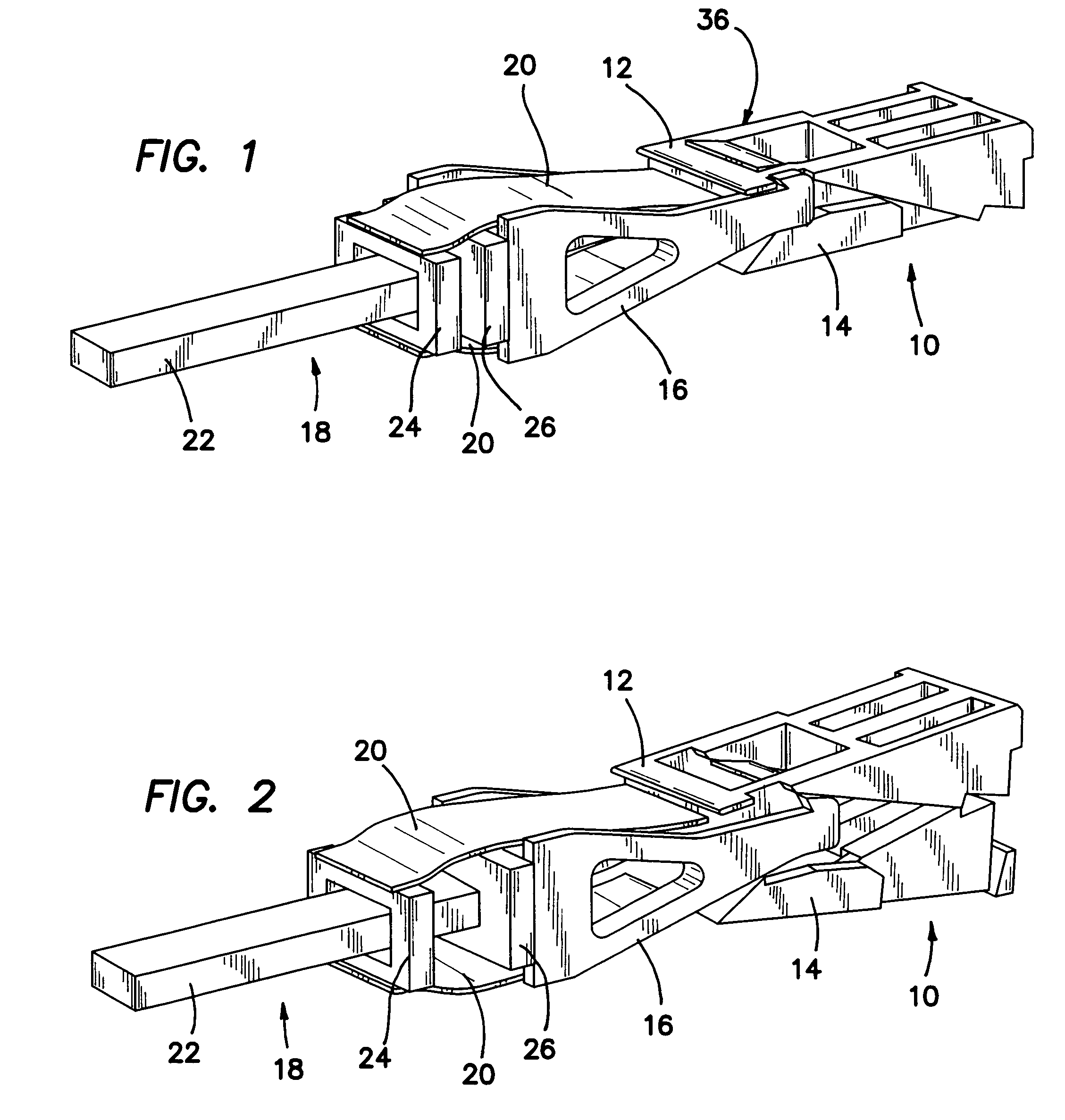
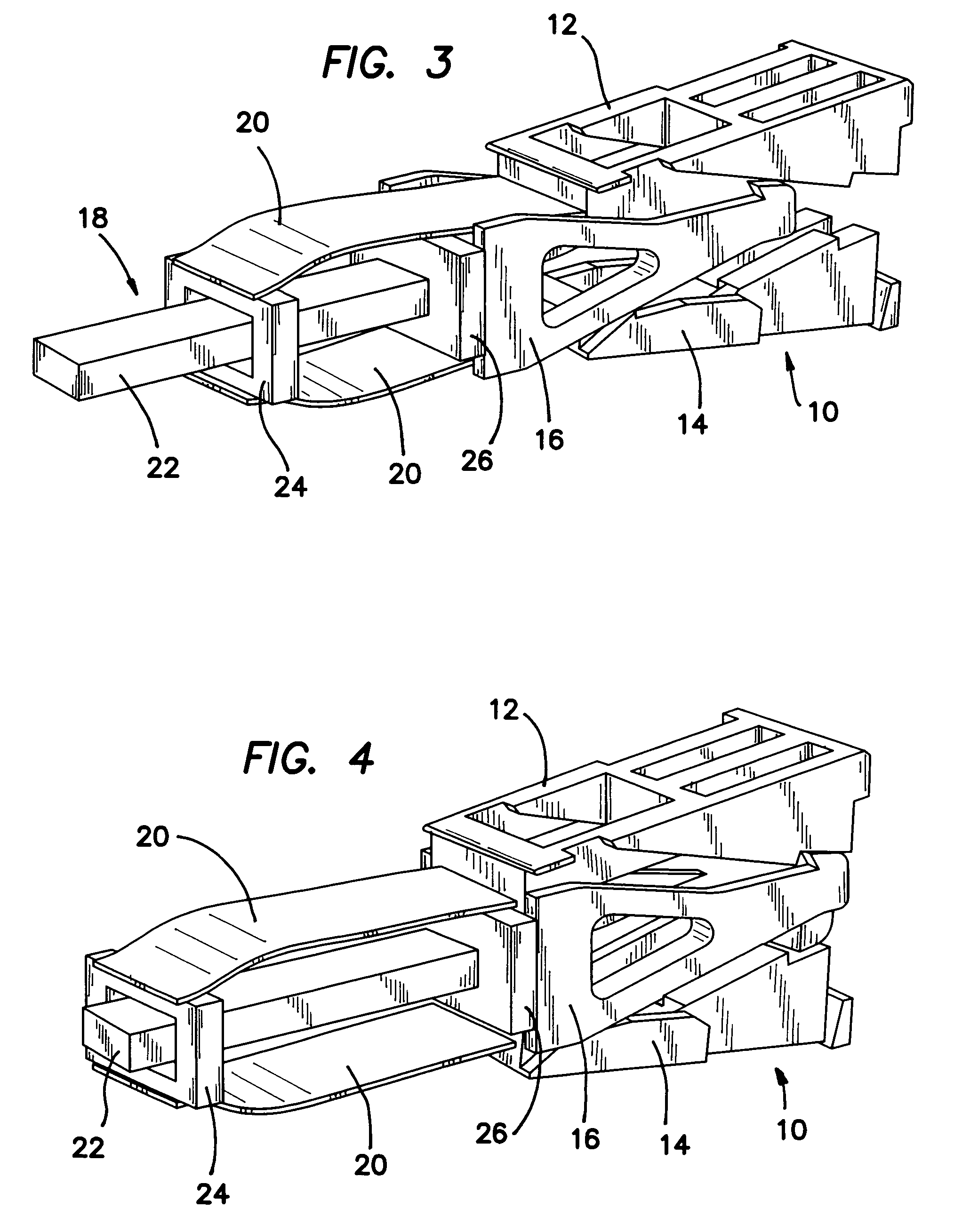
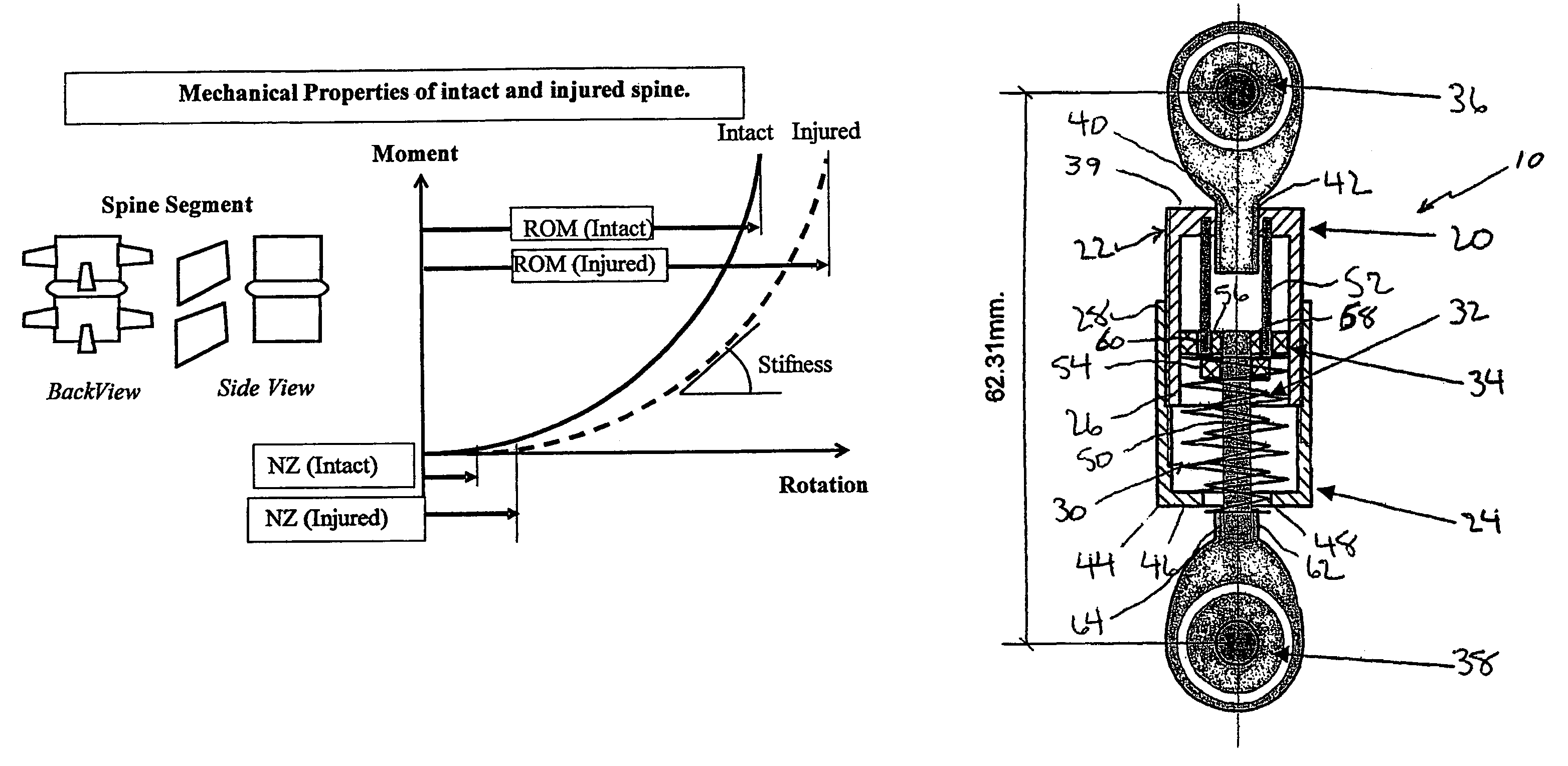
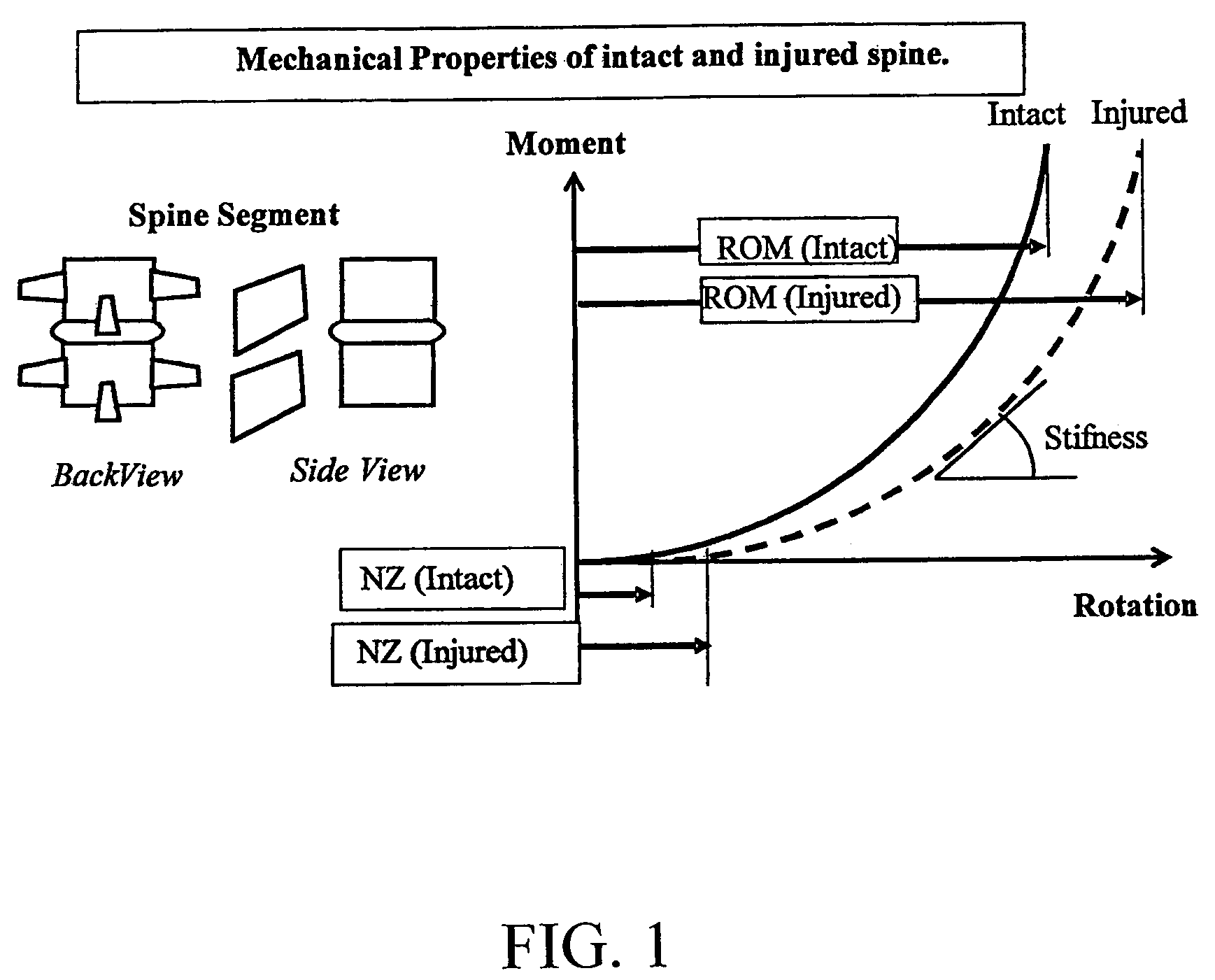
Spinal stabilization method
ActiveUS7029475B2Improve machineryLower resistance to movementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnBiomedical engineering
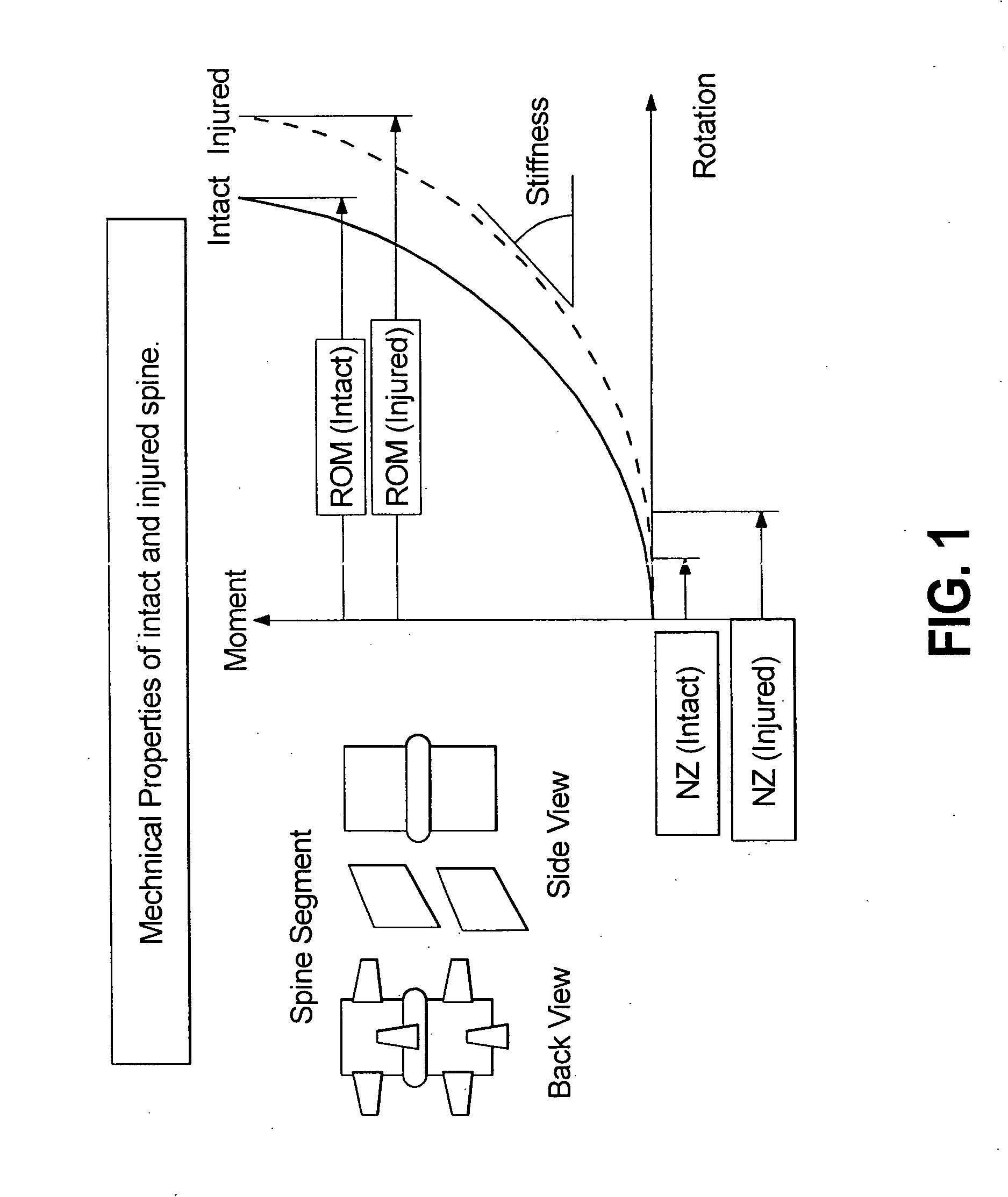
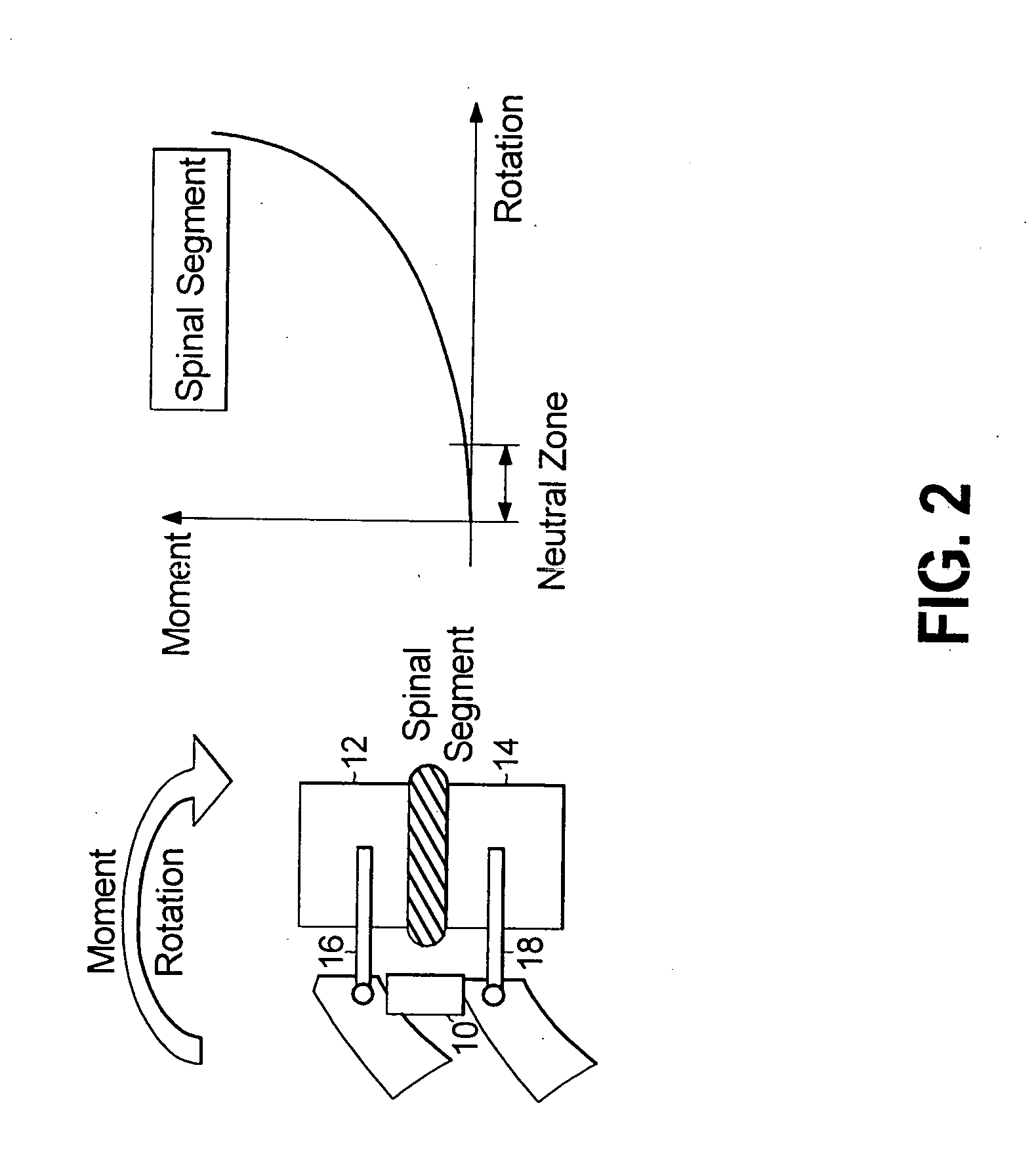
A dynamic spine stabilizer moves under the control of spinal motion providing increased mechanical support within a central zone corresponding substantially to the neutral zone of the injured spine. The dynamic spine stabilizer includes a support assembly and a resistance assembly associated with the support assembly. The resistance assembly generates greater increase in mechanical force during movement within the central zone and lesser increase in mechanical force during movement beyond the central zone. A method for using the stabilizer is also disclosed.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Articulating spinal fixation rod and system
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for aligning and implanting orthopedic fixation or stabilization implants within the body. In one embodiment, the system includes at least two bone anchors, at least one of which is provided with a transverse portal and a locking member. In one aspect, the system also includes at least one linkage rod, for linking two or more bone anchors through their respective locking members. The linking rod may include at least one angularly adjustable joint, which may be fixed by actuating the locking member. The bone anchors and the linkage rod may be locked into place to form a spinal fusion or fixation prosthesis.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Method of providing proper vertebral spacing
InactiveUS6371989B1Easy to anchorInhibit migrationBone implantJoint implantsSpinal columnBiomedical engineering
An expandable osteosynthesis implant has branches (5) each connected at one end to a seat (7) which is pierced by an orifice (8), suitable for being slid from a posterior direction between the facing faces of two consecutive vertebrae in order to hold them a given distance apart and restore stability of the spinal column. According to the invention, the branches (5) and the seat (7) define a hollow cage (1) which, in a "rest" position, has an outside general shape that is a cylinder of circular section, and a portion at least of the inside volume (9) of the cage (1) towards the distal ends of the branches (5) is in the form of a circular truncated cone whose large base is towards the seat (7), which implant has at least three branches (5) and, inside the inside volume (9) at least one spacer (2) suitable for passing through the orifice (8) and the large base of the truncated cone.
Owner:OSTEOIMPLANT TECH
Percutaneous spine distraction implant systems and methods
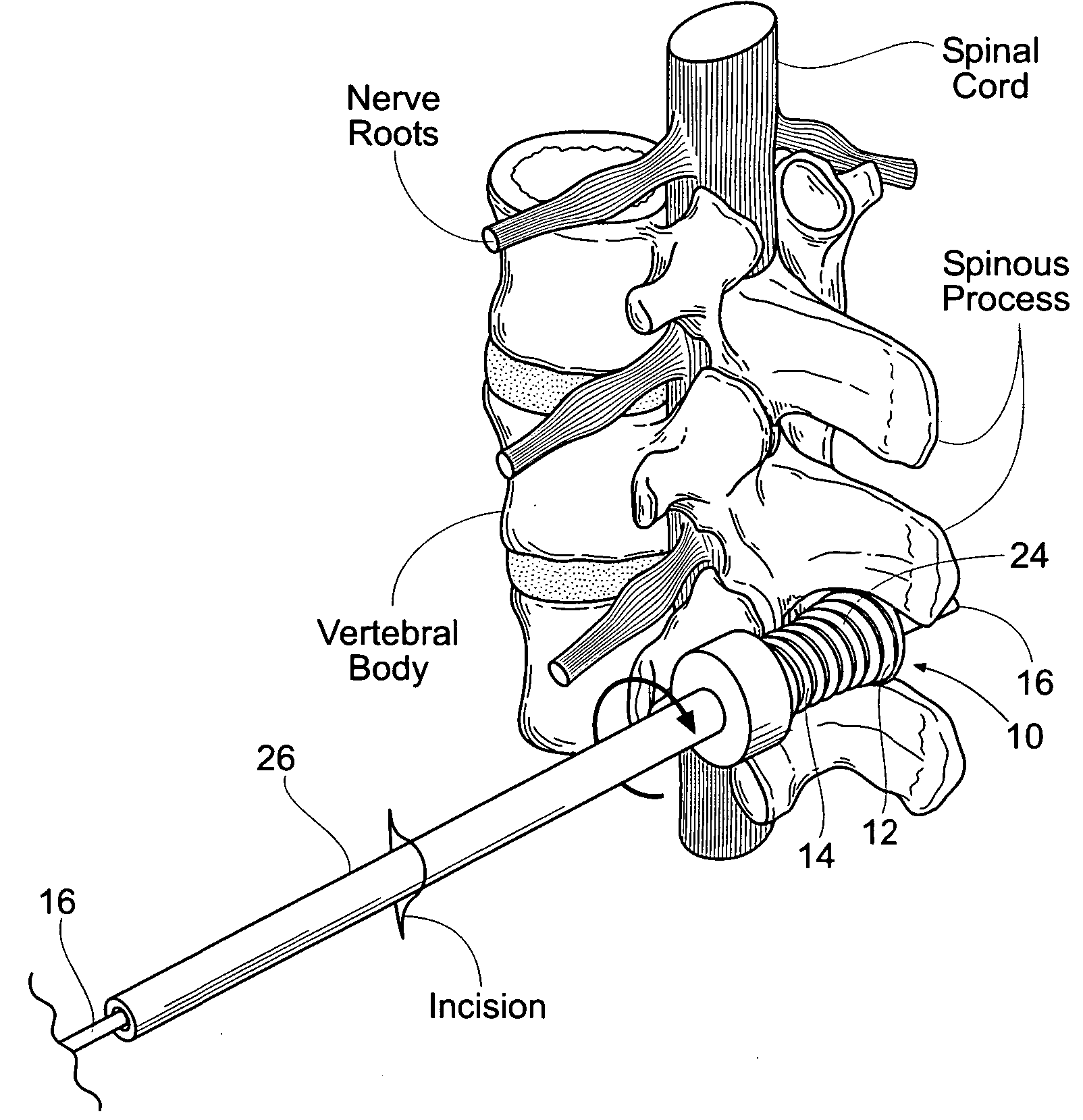
Systems and methods for treating spinal stenosis insert a guide element percutaneously into proximity with the adjacent spinous processes. The systems and methods direct an implant device over the guide element to a position resting between the adjacent spinous processes. The device is sized and configured to distend the adjacent spinous processes. The implant device itself can be variously constructed. It can, e.g., possess threaded lands and / or a notched region in which a spinous process can rest. The implant device has a lumen to accommodate passage of the guide element, so that the device can be passed percutaneously over the guide element for implantation between adjacent spinous processes.
Owner:REILEY MARK A
Methods and devices for minimally invasive spinal fixation element placement
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Methods and apparatus for forming curved axial bores through spinal vertebrae
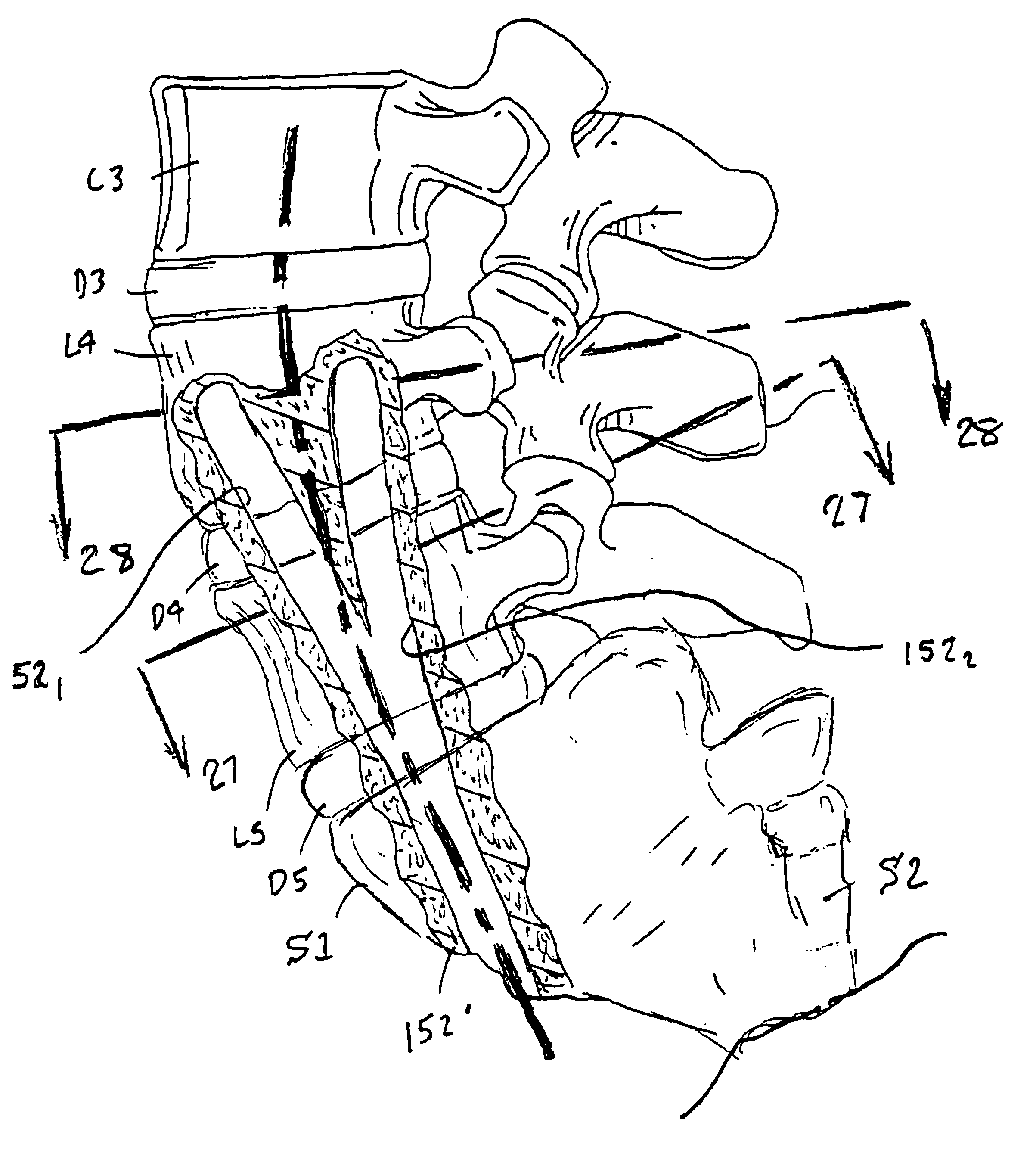
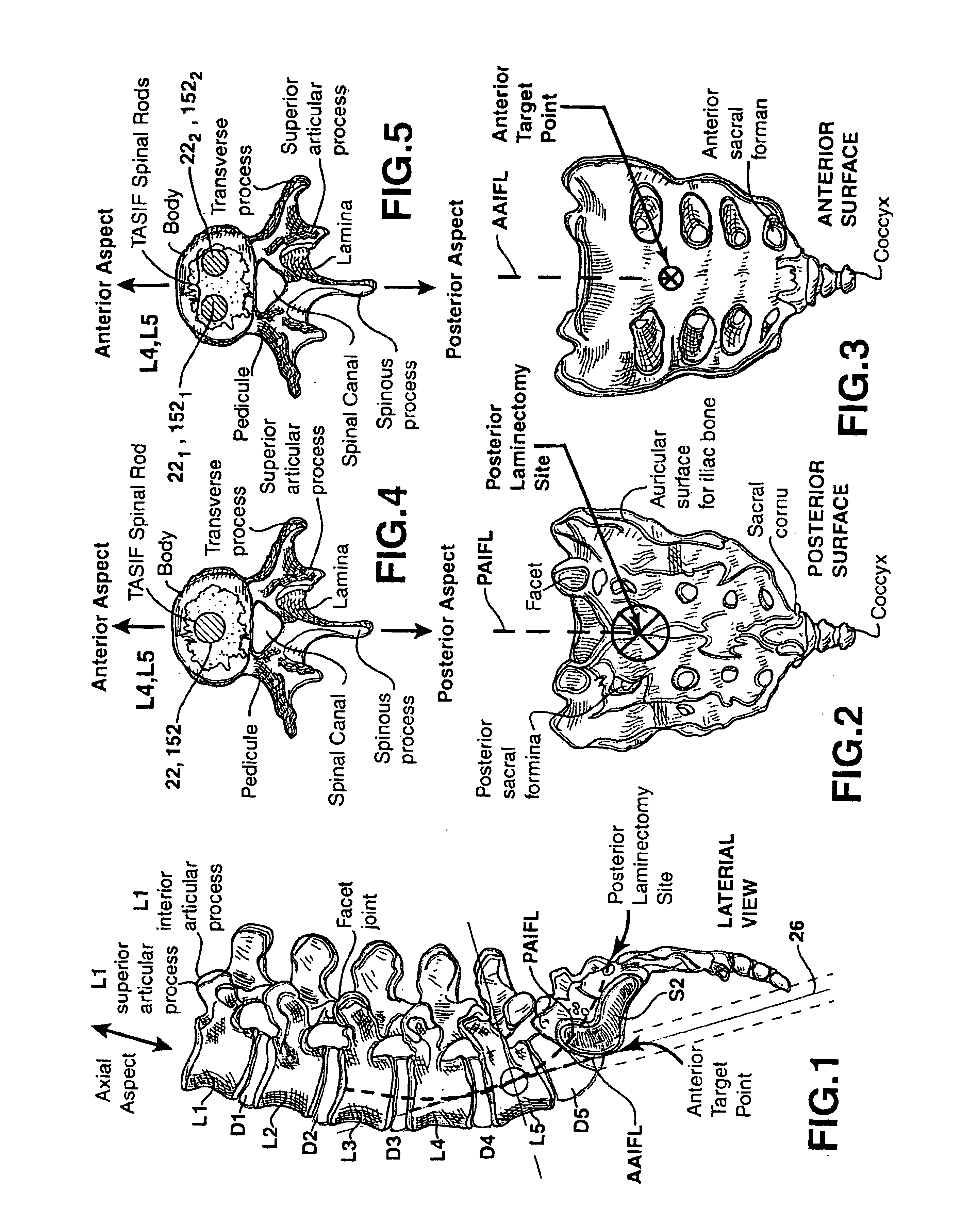
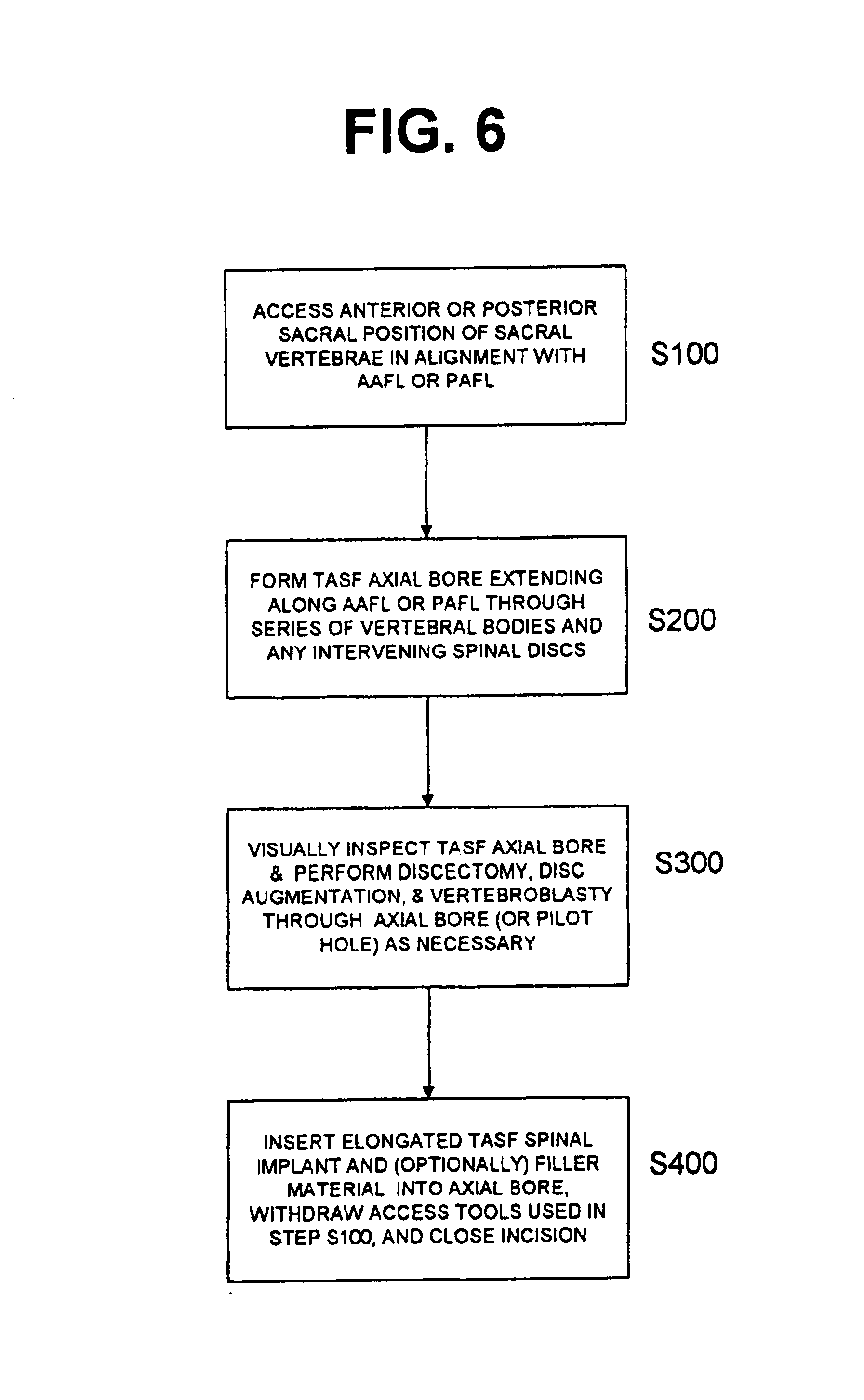
One or more curved axial bore is formed commencing from an anterior or posterior sacral target point and cephalad through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) line in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner. An anterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL) or a posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (PAIFL) that extends from the anterior or posterior target point, respectively, in the cephalad direction following the spinal curvature through one or more vertebral body is visualized by radiographic or fluoroscopic equipment. Generally curved anterior or posterior TASIF axial bores are formed in axial or parallel or diverging alignment with the visualized AAIFL or PAIFL, respectively. The anterior and posterior TASIF axial bore forming tools can be manipulated from proximal portions thereof to adjust the curvature of the anterior or posterior TASIF axial bores as they are formed in the cephalad direction. The boring angle of the distally disposed boring member or drill bit can be adjusted such that selected sections of the generally curved anterior or posterior TASIF axial bores can be made straight or relatively straight, and other sections thereof can be made curved to optimally traverse vertebral bodies and intervening disc, if present.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
Adjustable posterior spinal column positioner
ActiveUS20060004447A1Alter heightAvoid fusesInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsSpinal columnBiomedical engineering
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Pedicle screw constructs for spine fixation systems
A pedicle screw coupling construct for a pedicle screw construct provides fixation of angular orientation thereof relative to a pedicle screw independent of fixation of a received spinal rod to the coupling construct. The pedicle screw construct forms one component or element in a spinal fixation system. The independent fixation coupling construct also provides for fixation of the angular orientation of the coupling construct while the coupling construct has received the spinal rod. In another form, a coupling head or construct is configured to allow a pedicle screw shaft to pass therethrough but retain the pedicle screw head for rotation of the coupling head about the pedicle screw head. The coupling head or construct is also configured to allow at least a 45° arc of pivot or articulation about a pedicle screw shaft relative to a longitudinal axis of a spinal rod received in the body. This allows the head with a received spinal rod to fold, bend or pivot relative to the pedicle screw shaft, particularly to a greater degree than the prior art.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
Articulating spinal fixation rod and system
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for aligning and implanting orthopedic fixation or stabilization implants within the body. In one embodiment, the system includes at least two bone anchors, at least one of which is provided with a transverse portal and a locking member. In one aspect, the system also includes at least one linkage rod, for linking two or more bone anchors through their respective locking members. The linking rod may include at least one angularly adjustable joint, which may be fixed by actuating the locking member. The bone anchors and the linkage rod may be locked into place to form a spinal fusion or fixation prosthesis.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Orthopedic implant rod reduction tool set and method
A tool set for implanting a rod in a human spine in conjunction with bone screws. The tool set includes a pair of end guide tools that receive opposite ends of the rod in channels and under manipulation by a surgeon facilitate transport of the rod toward the bone screws attached to the guide tools. Intermediate guide tools having guiding pass through slots are utilized to guide intermediate locations along the rod toward associated bone screws. An attachment structure operably connects the guide tools to the bone screws. The guide tools each include a lower guide and advancement structure to allow a closure top with mating structure to be rotated and driven downward against the rod and to cooperate with similar structure in the bone screw to seat and lock the rod therein. A method utilizing the tool set allows a surgeon to percutaneously implant the rod in the patient.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Method and apparatus for flexible fixation of a spine
InactiveUS20050065516A1Easy constructionSimple designInternal osteosythesisEar treatmentSpinal columnCoupling
A flexible spinal fixation device having a flexible metallic connection unit for non-rigid stabilization of the spinal column. In one embodiment, the fixation device includes at least two securing members configured to be inserted into respective adjacent spinal pedicles, each securing member each including a coupling assembly. The fixation device further includes a flexible metal connection unit configured to be received and secured within the coupling assemblies of each securing member so as to flexibly stabilize the affected area of the spine.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Artificial spinal unit assemblies
ActiveUS20050033432A1Prohibit some movementPrevent movementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnSurgical approach
An artificial functional spinal unit is provided comprising, generally, an expandable artificial intervertebral implant that can be placed via a posterior surgical approach and used in conjunction with one or more artificial facet joints to provide an anatomically correct range of motion. Expandable artificial intervertebral implants in both lordotic and non-lordotic designs are disclosed, as well as lordotic and non-lordotic expandable cages for both PLIF (posterior lumber interbody fusion) and TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) procedures. The expandable implants may have various shapes, such as round, square, rectangular, banana-shaped, kidney-shaped, or other similar shapes. By virtue of their posteriorly implanted approach, the disclosed artificial FSU's allow for posterior decompression of the neural elements, reconstruction of all or part of the natural functional spinal unit, restoration and maintenance of lordosis, maintenance of motion, and restoration and maintenance of disc space height.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE
Stent systems and methods for spine treatment
InactiveUS20060100706A1Prevent subsidenceRestore body heightInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsSpinal columnCardiac allograft
Stent systems and methods for expanding and deploying stents in hard tissue such as bone, more particularly within a vertebral body. One exemplary method includes using a stent body that is coupled to a high speed rotational motor with the stent expandable and detachable from an introducer working end. In one embodiment, the stent is a deformable metal body with zig-zag type struts in an expanded configuration that carries diamond cutting particles bonded to the strut surfaces. The “spin” stent is rotated at high rpm's to remove cancellous bone from the deployment site together with irrigation and aspiration at the end of the probe that carries the stent. The stent may be expanded asymmetrically, such as with first and second balloons or by using an interior restraint, to apply vertical distraction forces to move apart the cortical endplates and support the vertebra in the distracted condition. The cancellous bone about the expanded stent as well as the interior of the stent can be filled with a bone cement, allograft or other bone graft material. In one method of use, the spin stent is designed and adapted for (i) treating a vertebral compression fracture (VCF) or for (ii) reinforcing an osteoporotic vertebral body.
Owner:DFINE INC
Prosthetic spinal disc replacement
ActiveUS20050043800A1Restrict movementJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSpinal columnSurgical approach
The present invention relates generally to a prosthetic spinal disc for replacing a damaged disc between two vertebrae of a spine. The present invention also relates to a method for implanting a prosthetic spinal disc via posterior or posterior lateral implantation. Other surgical approaches for implanting the prosthetic disc may also be used. The present invention also involves a method for implanting the prosthetic spinal disc while either avoiding or minimizing contact with the spinal cord and nerve rootlets, or reducing the time and extent that they need to be repositioned during implantation.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Devices to prevent spinal extension
InactiveUS20050288672A1Avoid painPreventing other complicationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsPreventing painSpinal column
This invention resides in an apparatus for inhibiting full extension between upper and lower vertebral bodies, thereby preventing pain and other complications associated with spinal movement. In the preferred embodiment, the invention provides a generally transverse member extending between the spinous processes and lamina of the upper and lower vertebral bodies, thereby inhibiting full extension. Various embodiments of the invention may limit spinal flexion, rotation and / or lateral bending while preventing spinal extension. In the preferred embodiment, the transverse member is fixed between two opposing points on the lower vertebral body using pedicle screws, and a cushioning sleeve is used as a protective cover. The transverse member may be a rod or cable, and the apparatus may be used with a partial or full artificial disc replacement. To control spinal flexion, rotation and / or lateral bending one or more links may be fastened to an adjacent vertebral body, also preferably using a pedicle screw. Preferably a pair of opposing links are used between the upper and lower vertebral bodies for such purposes.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Systems and methods for spine stabilization including a dynamic junction
InactiveUS20050182401A1Easy to installImprove clinical outcomesSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisRotational freedomUniversal joint
Spinal stabilization devices, systems and methods are provided that include at least one pedicle screw and at least one mechanism that supports three degrees of rotational freedom relative to the pedicle screw. The mechanism may include a universal joint mechanism or a ball and socket mechanism. In the case of the ball and socket mechanism, at least one spherical element is mounted with respect to the at least one pedicle screw and a socket member cooperates with the spherical element. The spherical element and the socket member cooperate to define a dynamic junction that allows the socket member to move relative to the ball element while remaining engaged therewith. The dynamic junction is advantageously incorporated into a spinal stabilization system that includes additional pedicle screw(s), spherical element(s) and socket member(s). The spinal stabilization system may incorporate dynamic stabilizing member(s) to so as to provide clinically efficacious results.
Owner:APPLIED SPINE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com