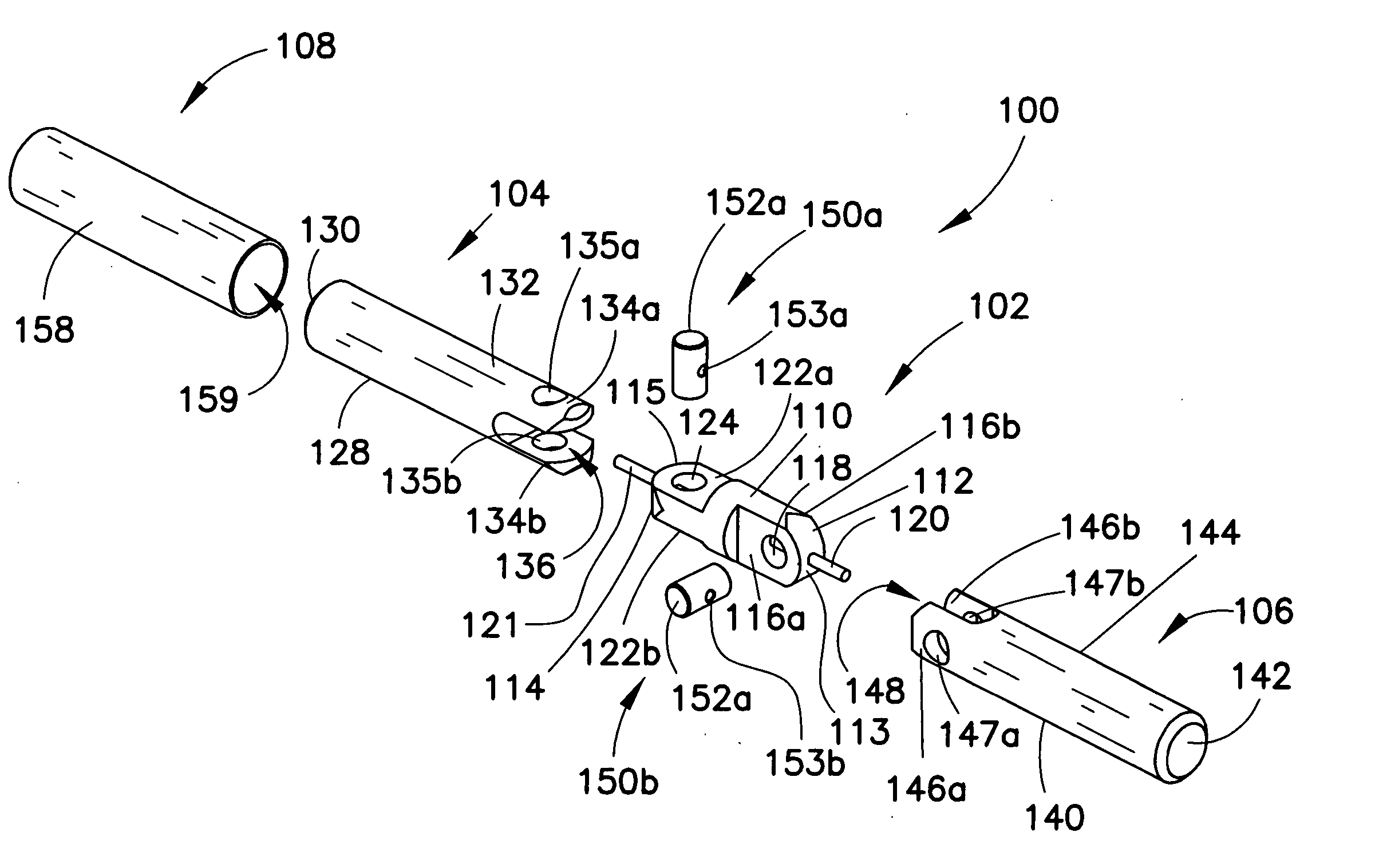
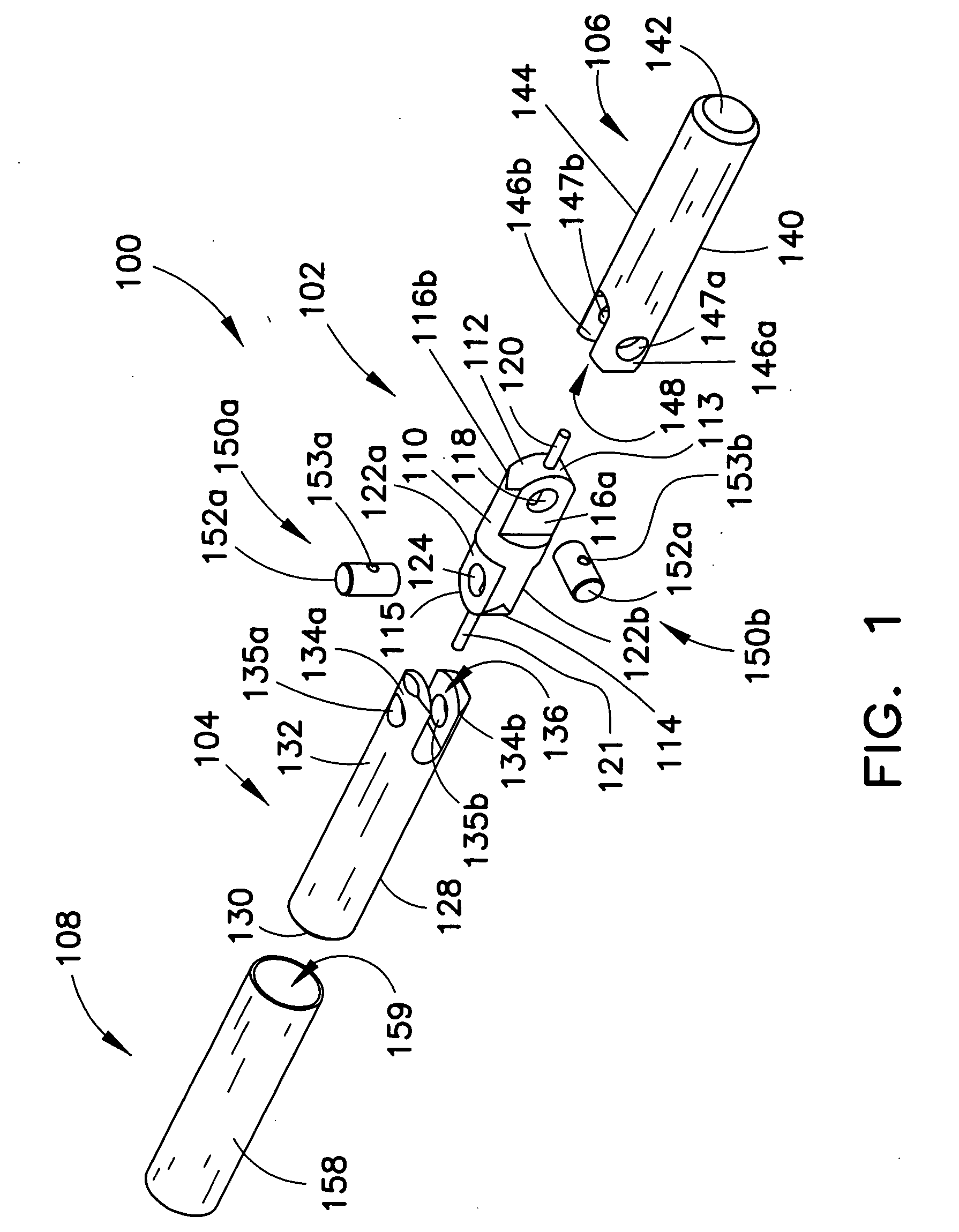
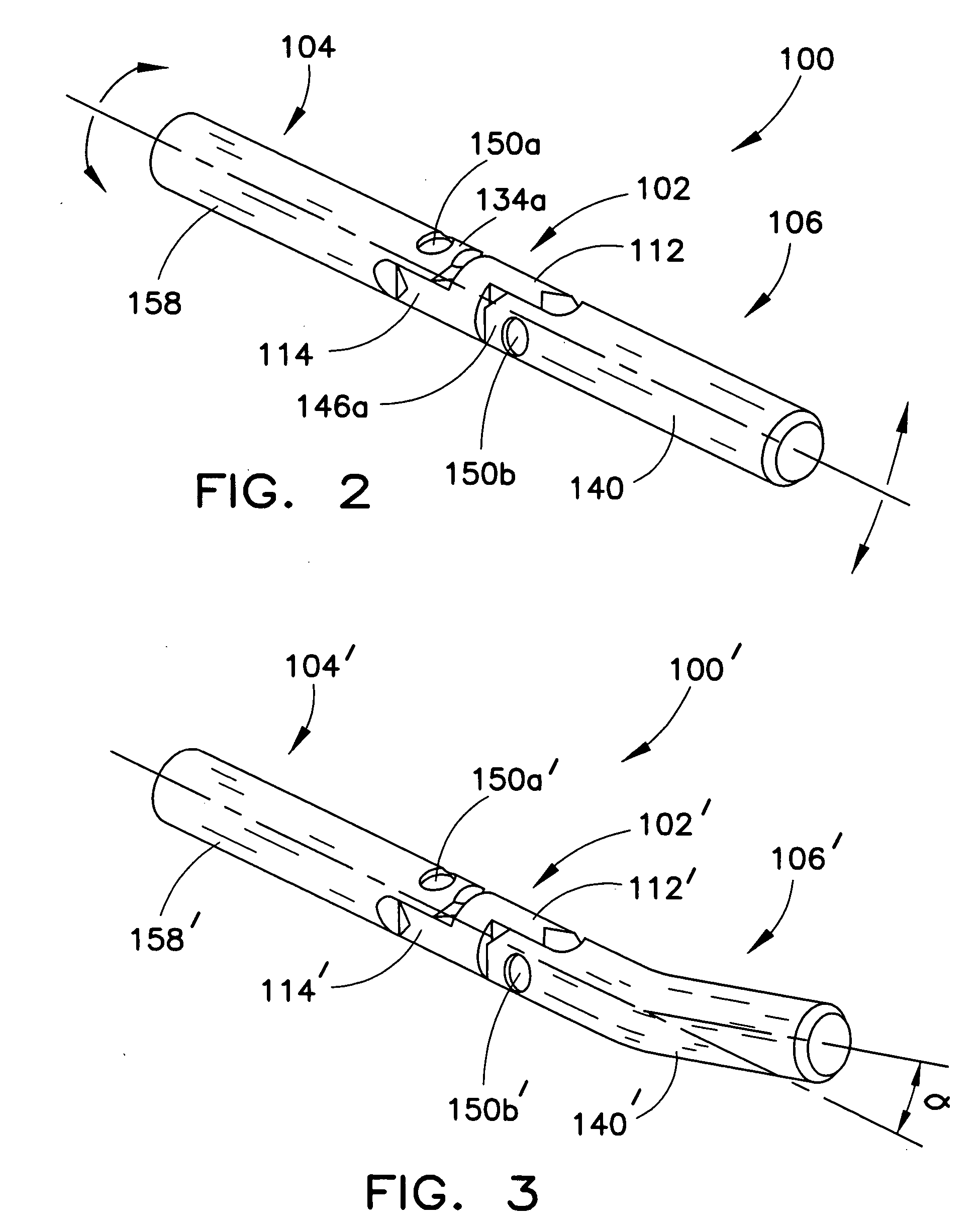
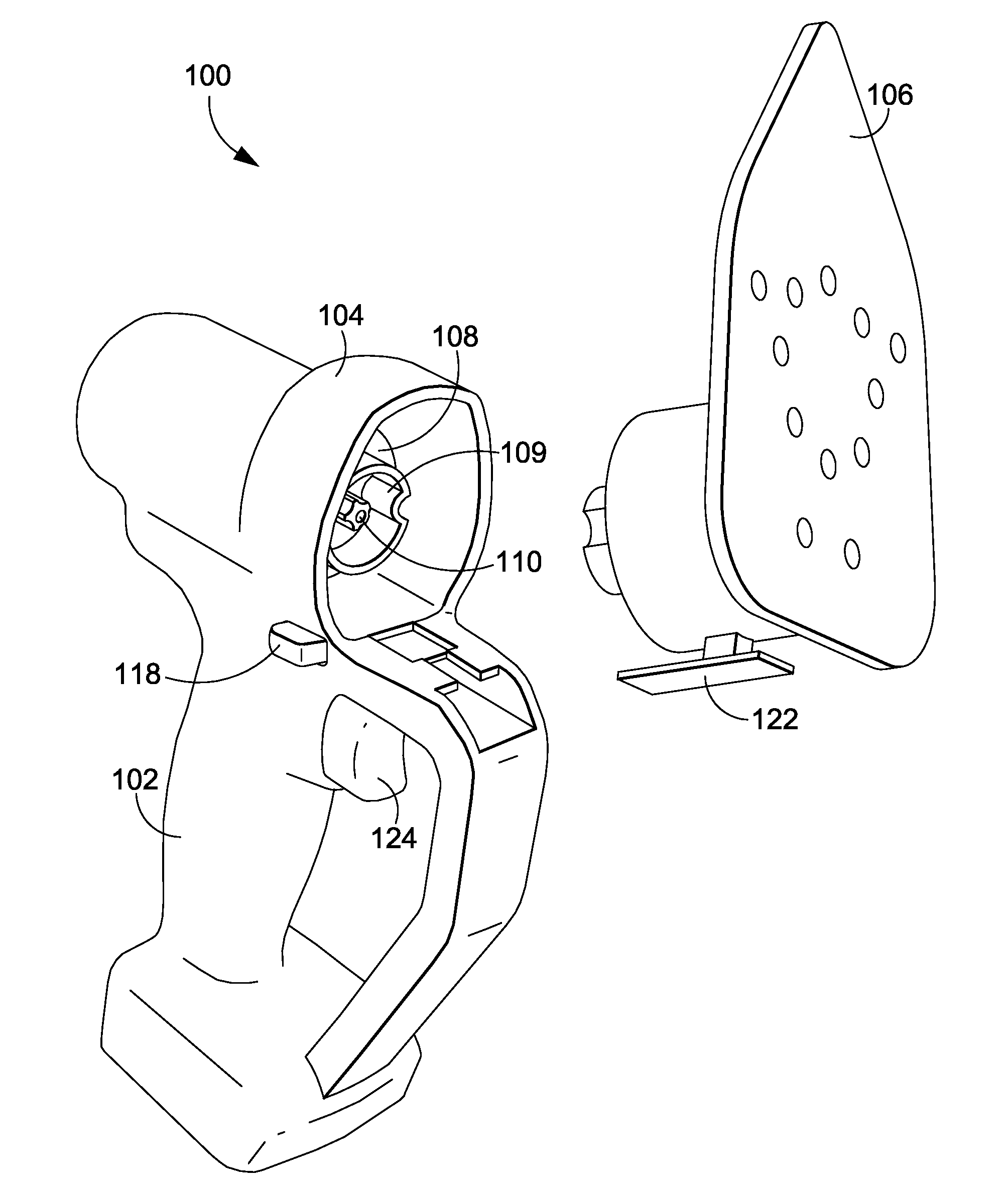
Patents
Literature
2958results about How to "Restrict movement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
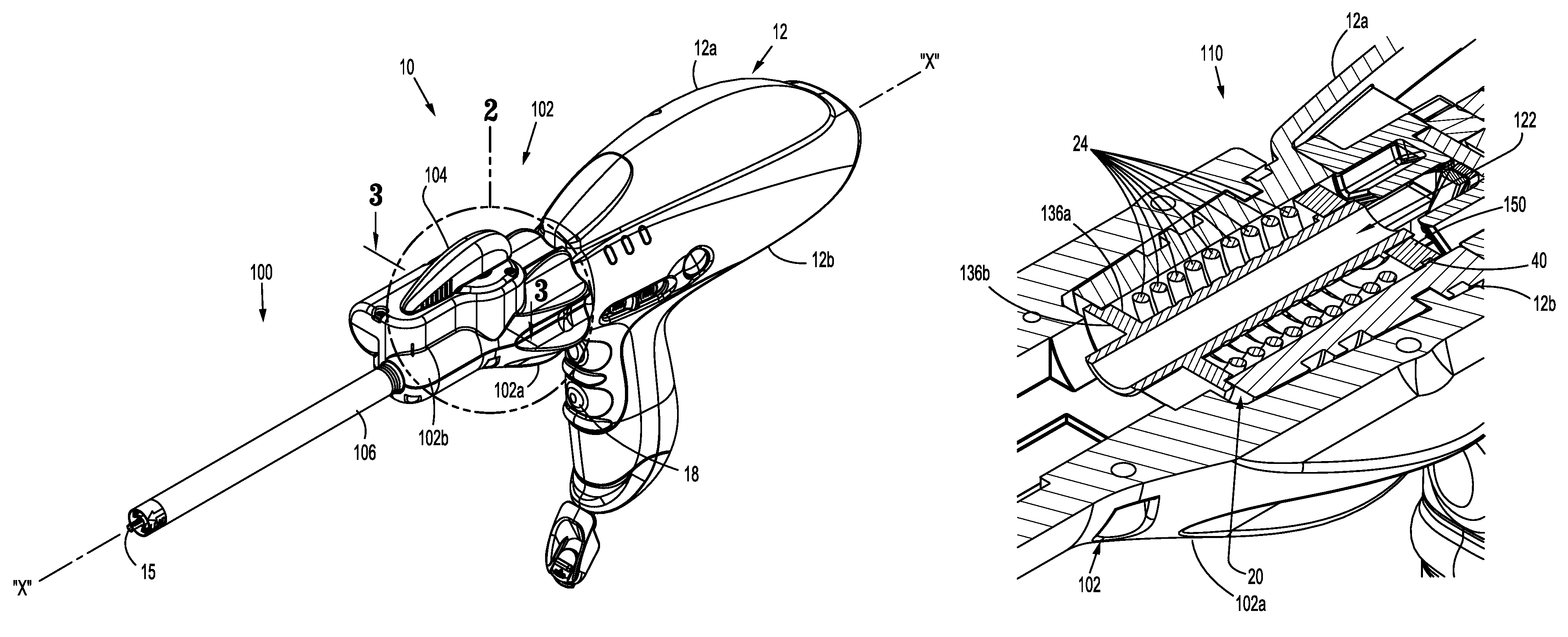
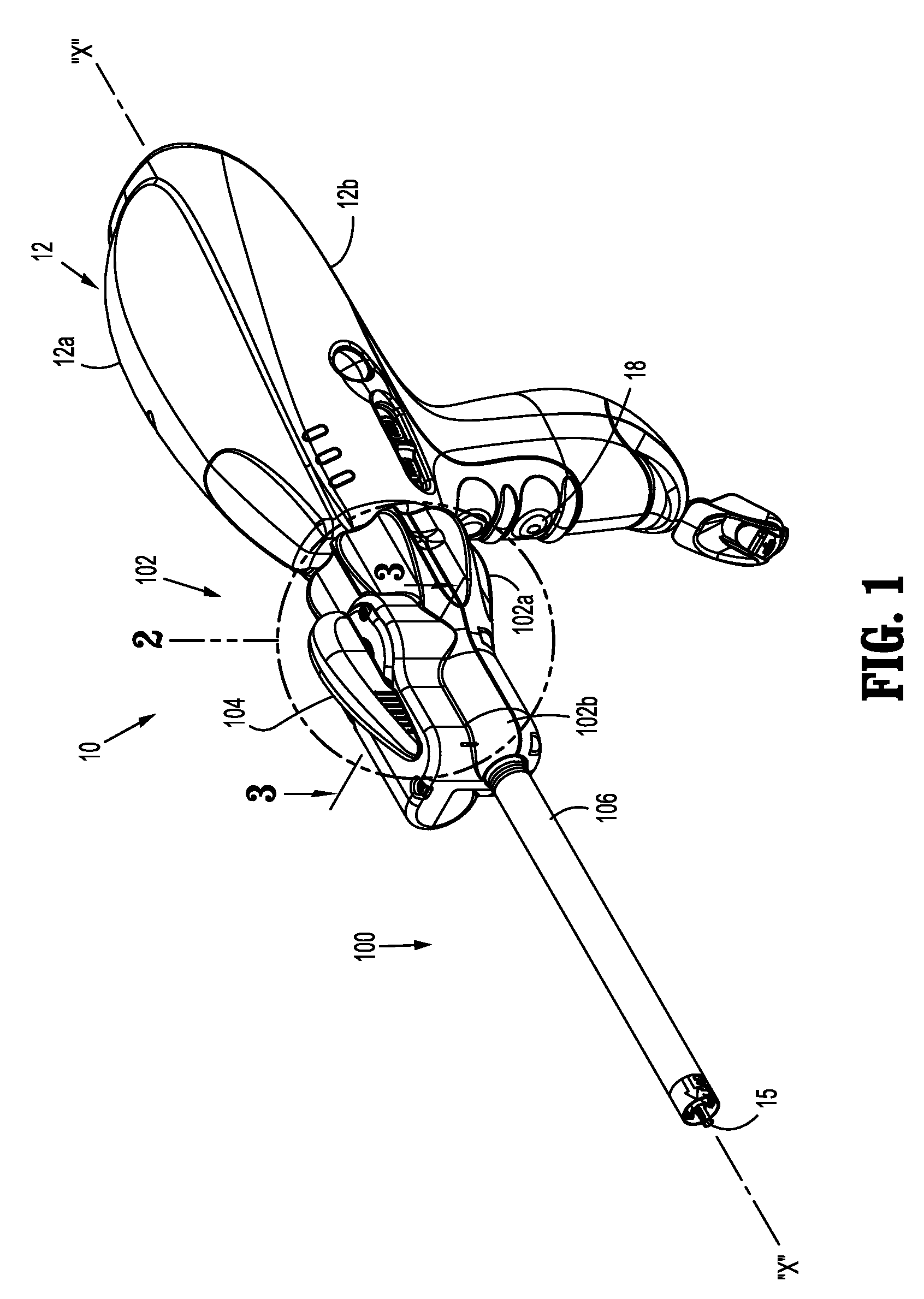
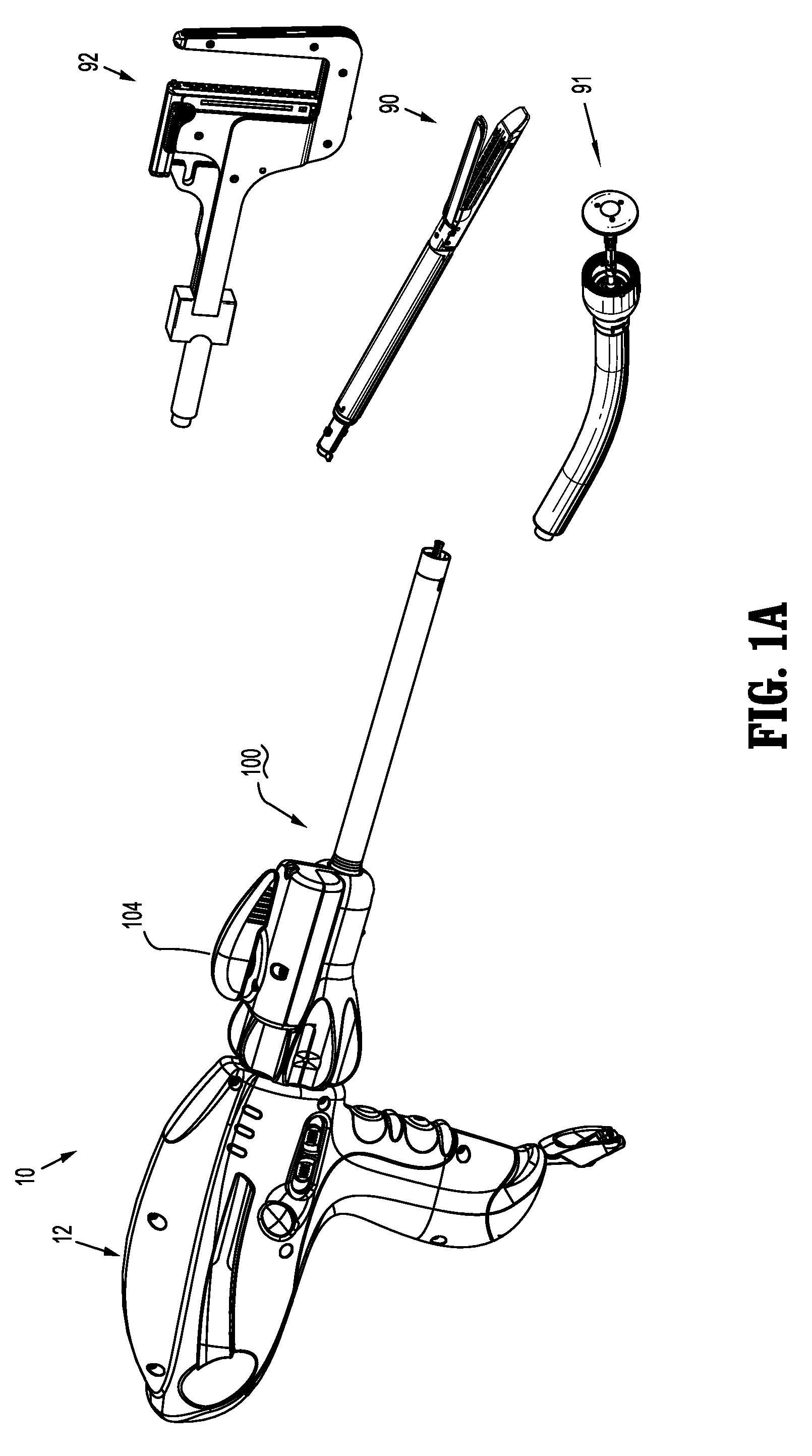
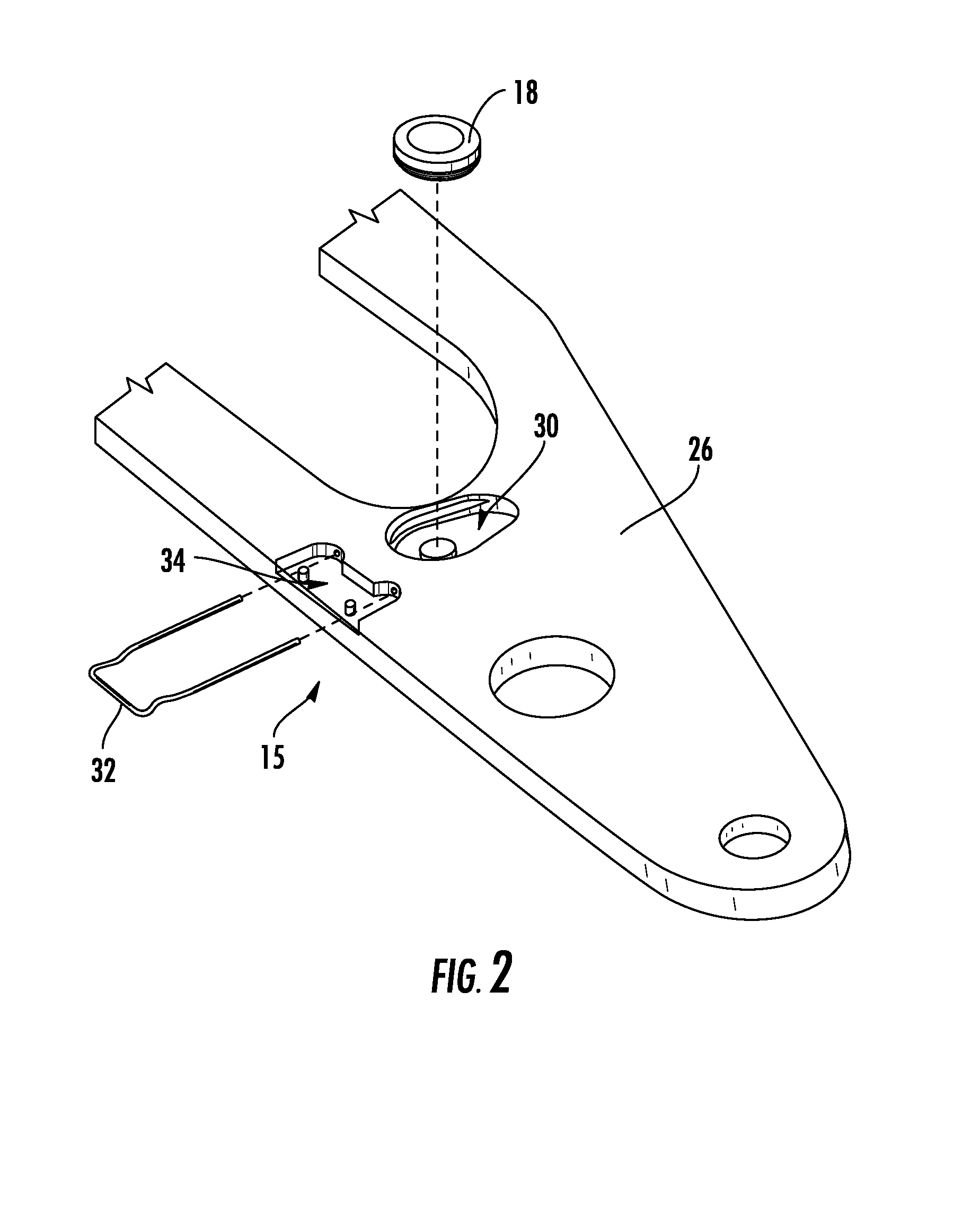
Wire spool for passing of wire through a rotational coupling
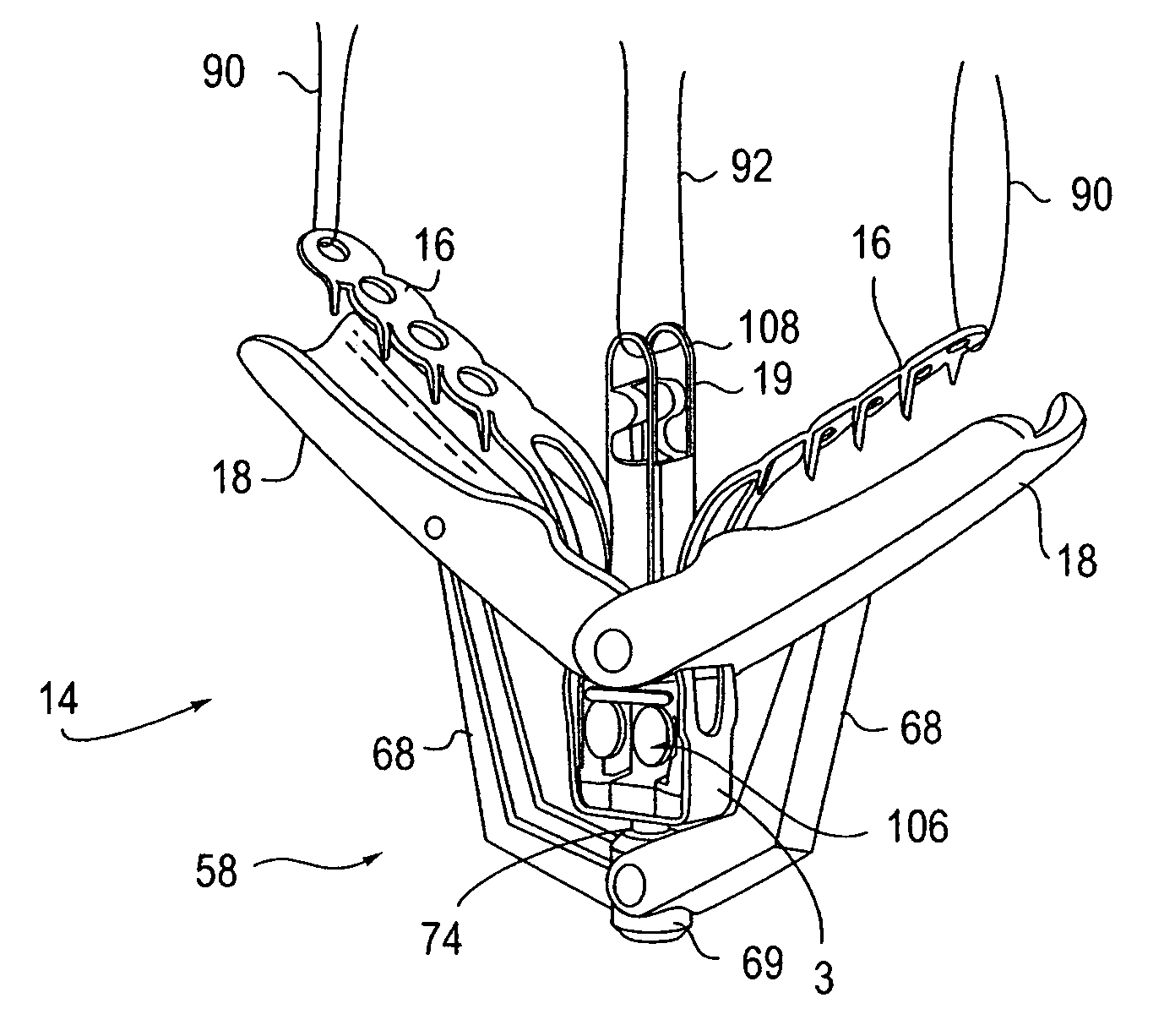
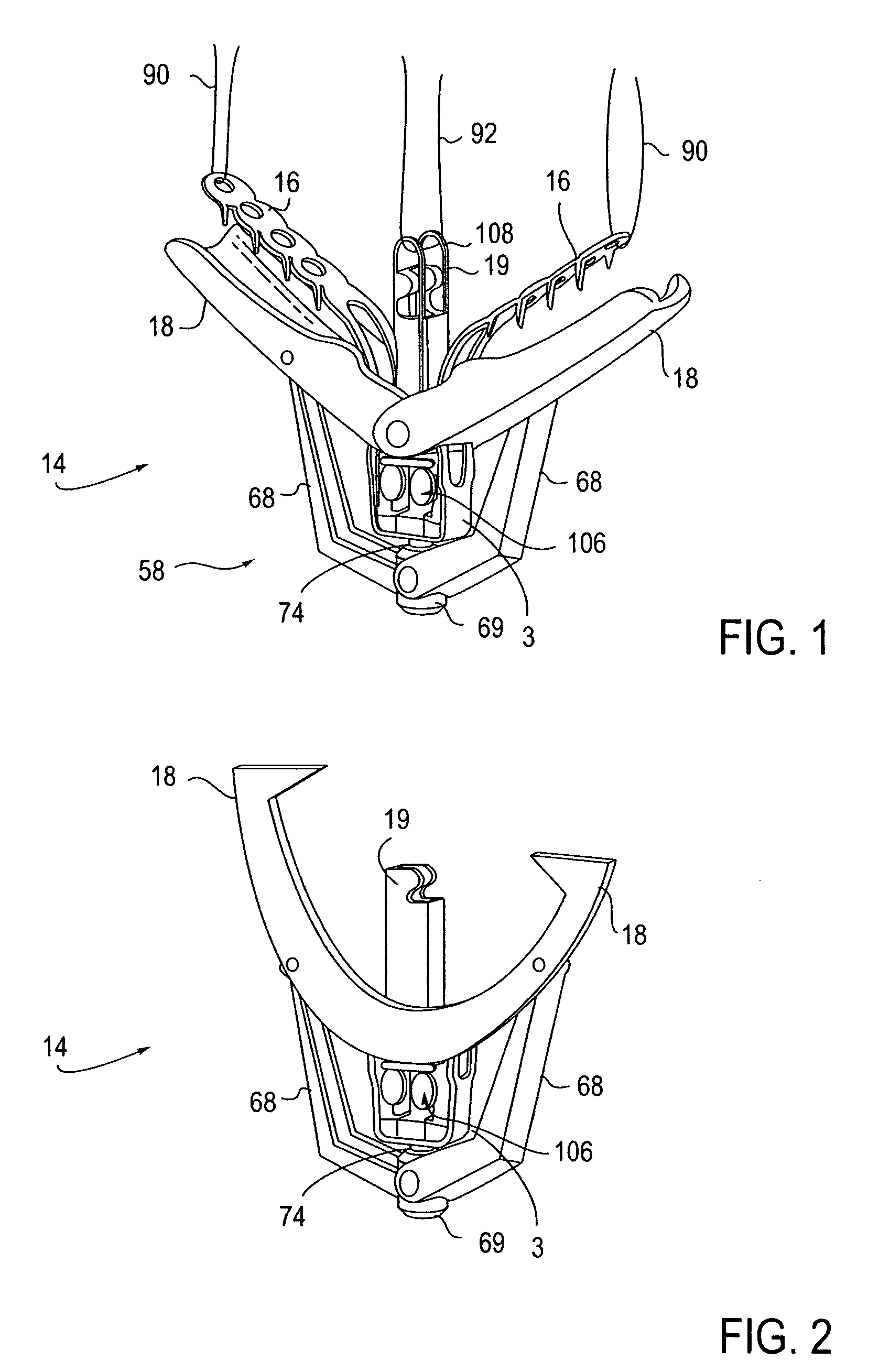
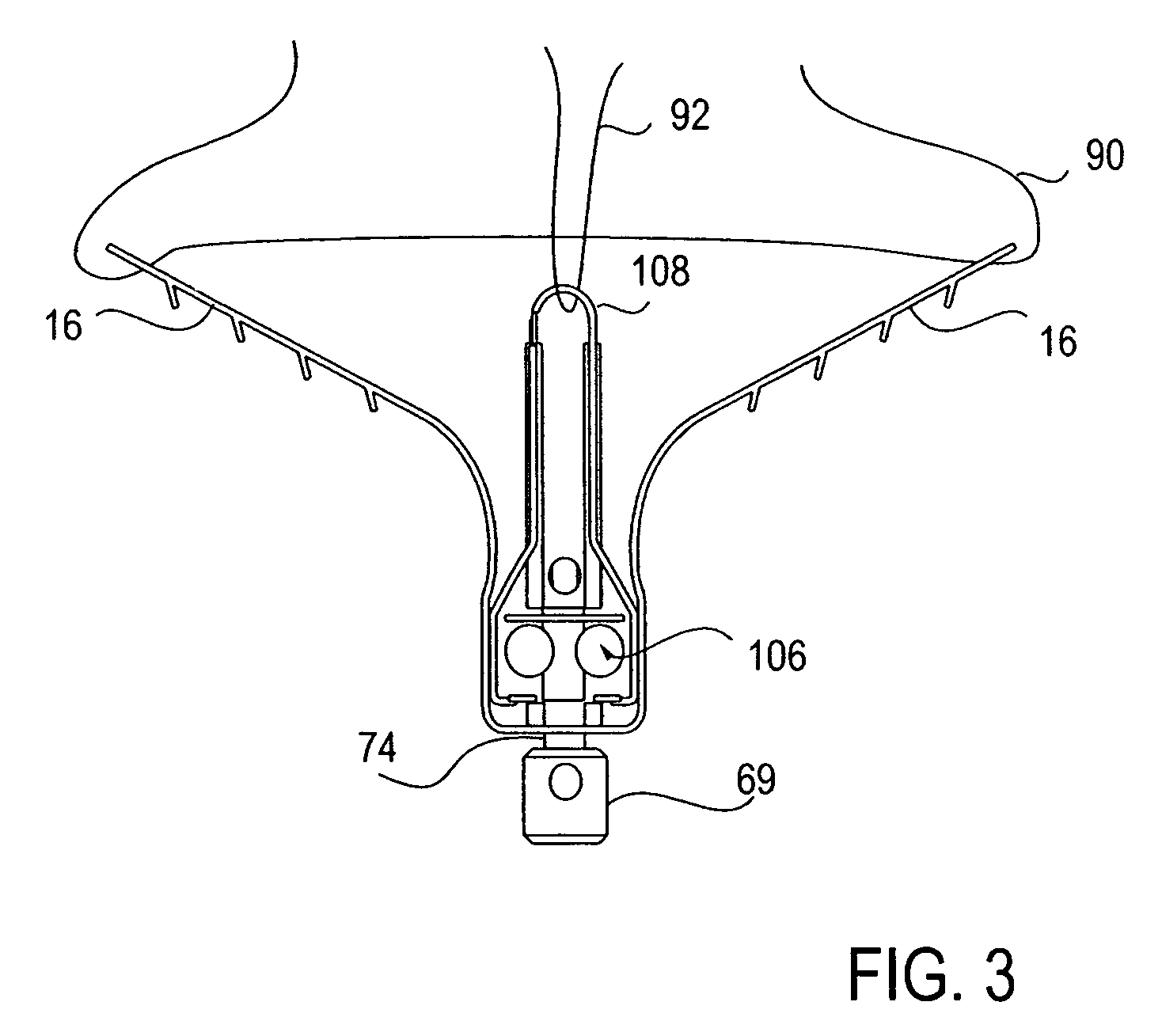
ActiveUS8568425B2Restrict movementPrevent further rotationSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringElectric wire
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
In-vivo visualization system
ActiveUS20050272975A1Prevent movementRestrict movementGastroscopesOesophagoscopesFiberscopeEndoscope
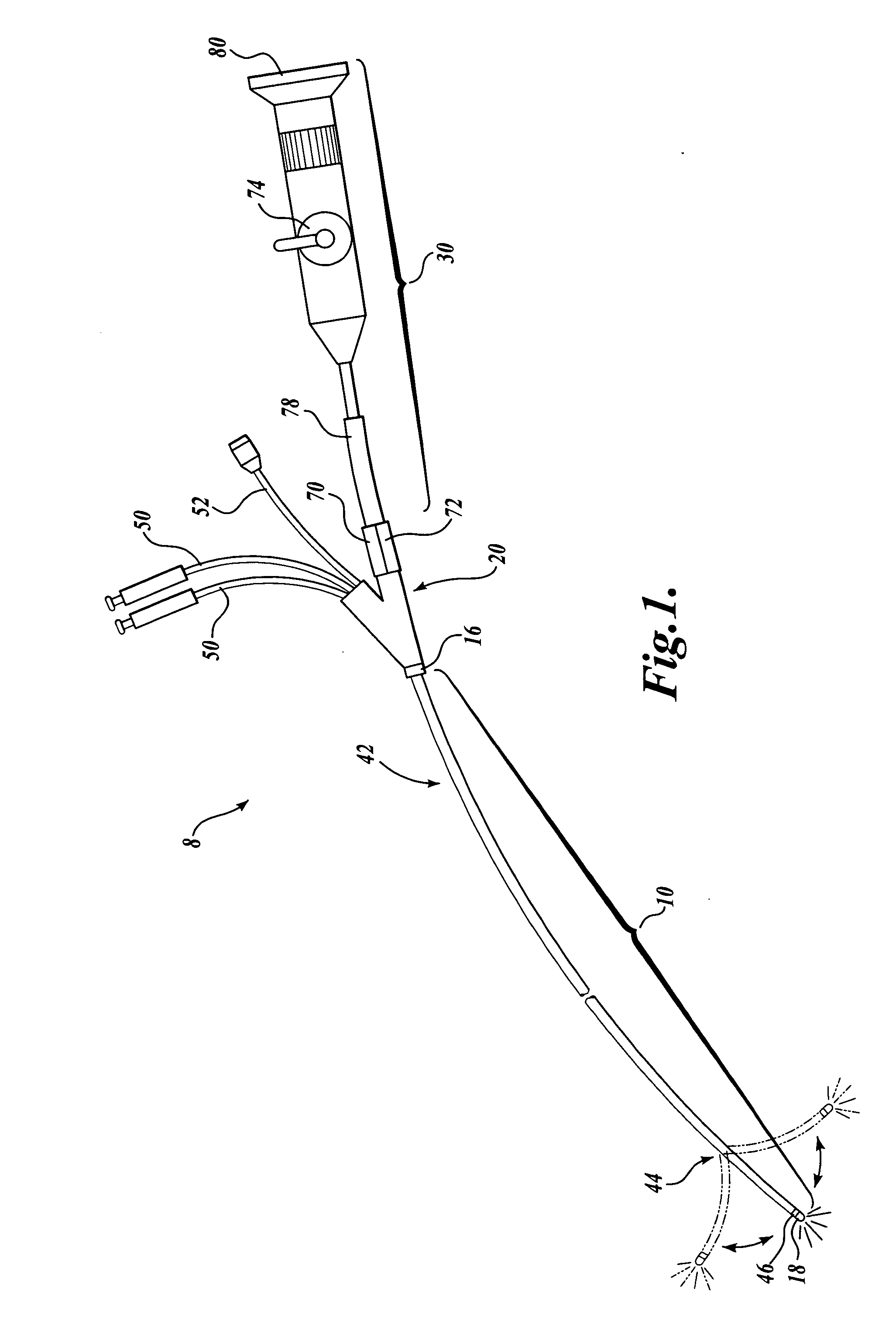
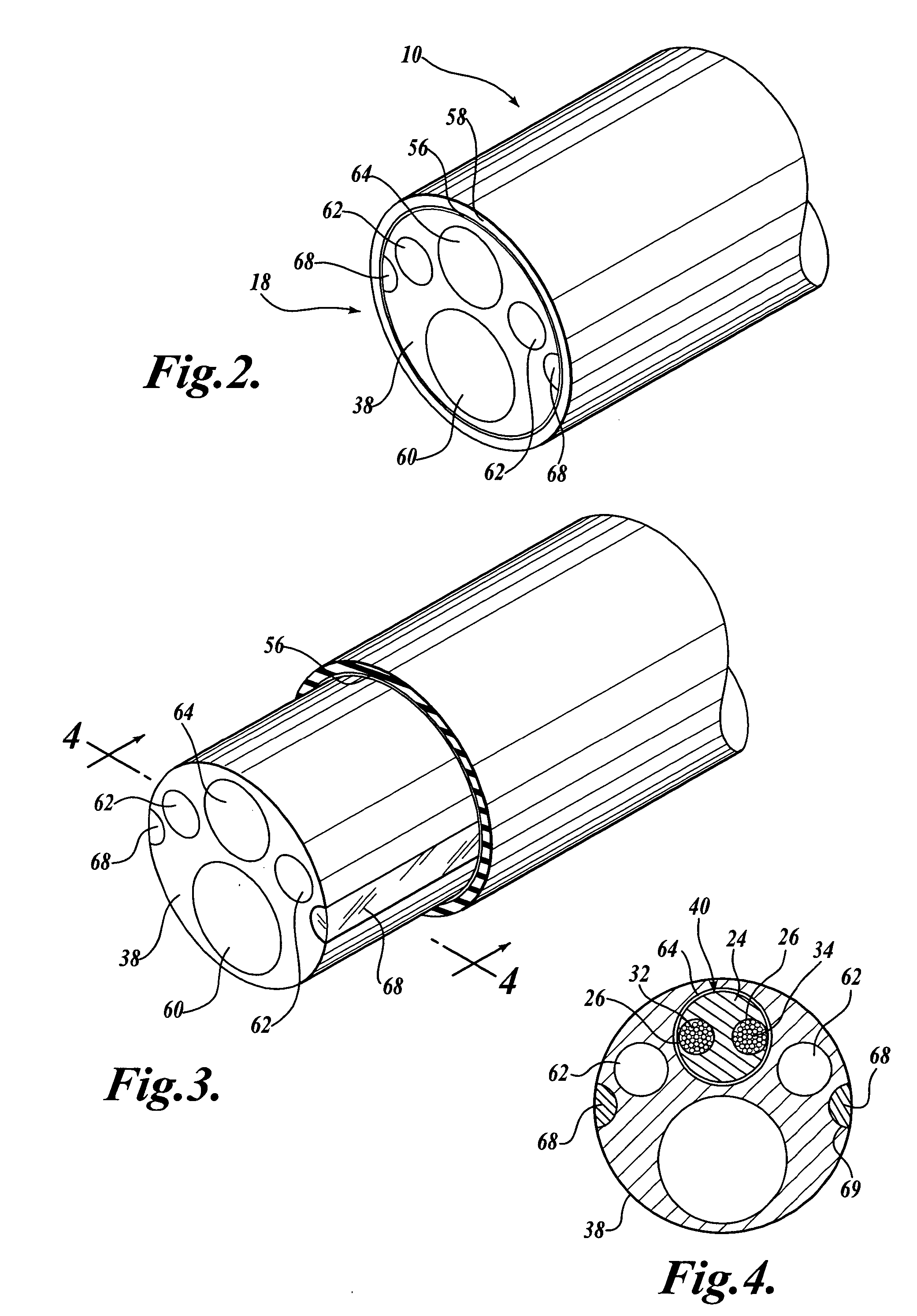
Several embodiments of the present invention are generally directed to medical visualization systems that comprise combinations of disposable and resuable components, such as catheters, functional handles, hubs, optical devices, etc. Other embodiments of the present invention are generally directed to features and aspects of an in-vivo visualization system that comprises an endoscope having a working channel through which a catheter having viewing capabilities is routed. the catheter may obtain viewing capabilities by being constructed as a vision catheter or by having a fiberscope or other viewing device selectively routed through one of its channels. The catheter is preferably of the steerable type so that the distal end of the catheter may be steered from its proximal end as it is advanced with the body. A suitable use for the in-vivo visualization system includes but is not limited to diagnosis and / or treatment of the duodenum, and particularly the biliary tree.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Operation unit and treatment tool for endoscope provided with the same
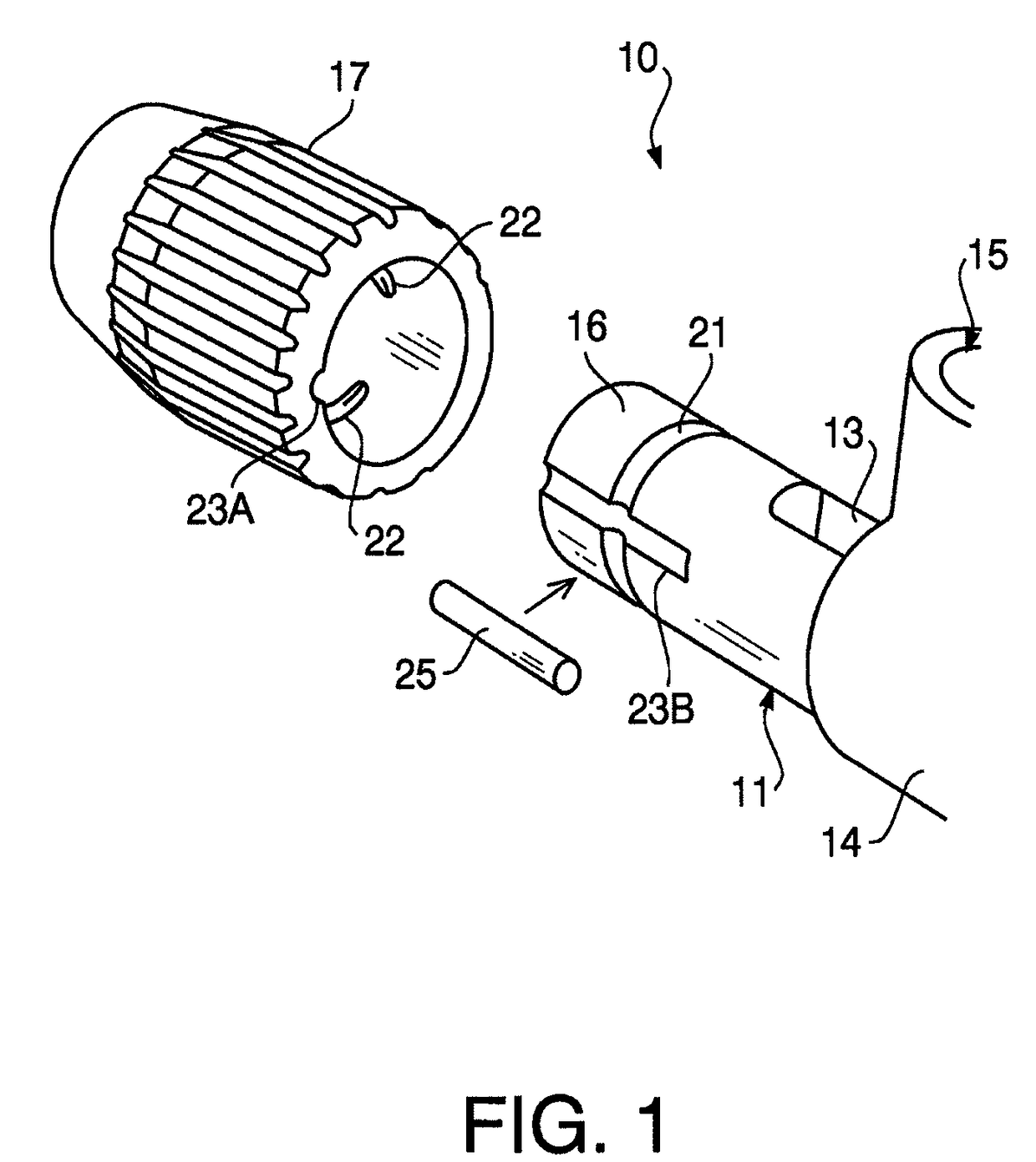
ActiveUS8469946B2Low production costLow costVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsEngineeringEndoscope
An operation unit of a treatment tool for an endoscope includes a first joining member configured to be joined to a rear end of a flexible sheath of the treatment tool, a second joining member configured such that the first joining member is fitted therearound rotatably around an axis line of the first joining member relative to the second joining member, and a pin fit hole formed between the first joining member and the second joining member such that a pin is fitted therein, the pin fit hole being configured to restrict rotational movement of the first joining member around the axis line relative to the second joining member when the pin is fitted in the pin fit hole.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Prosthetic spinal disc replacement
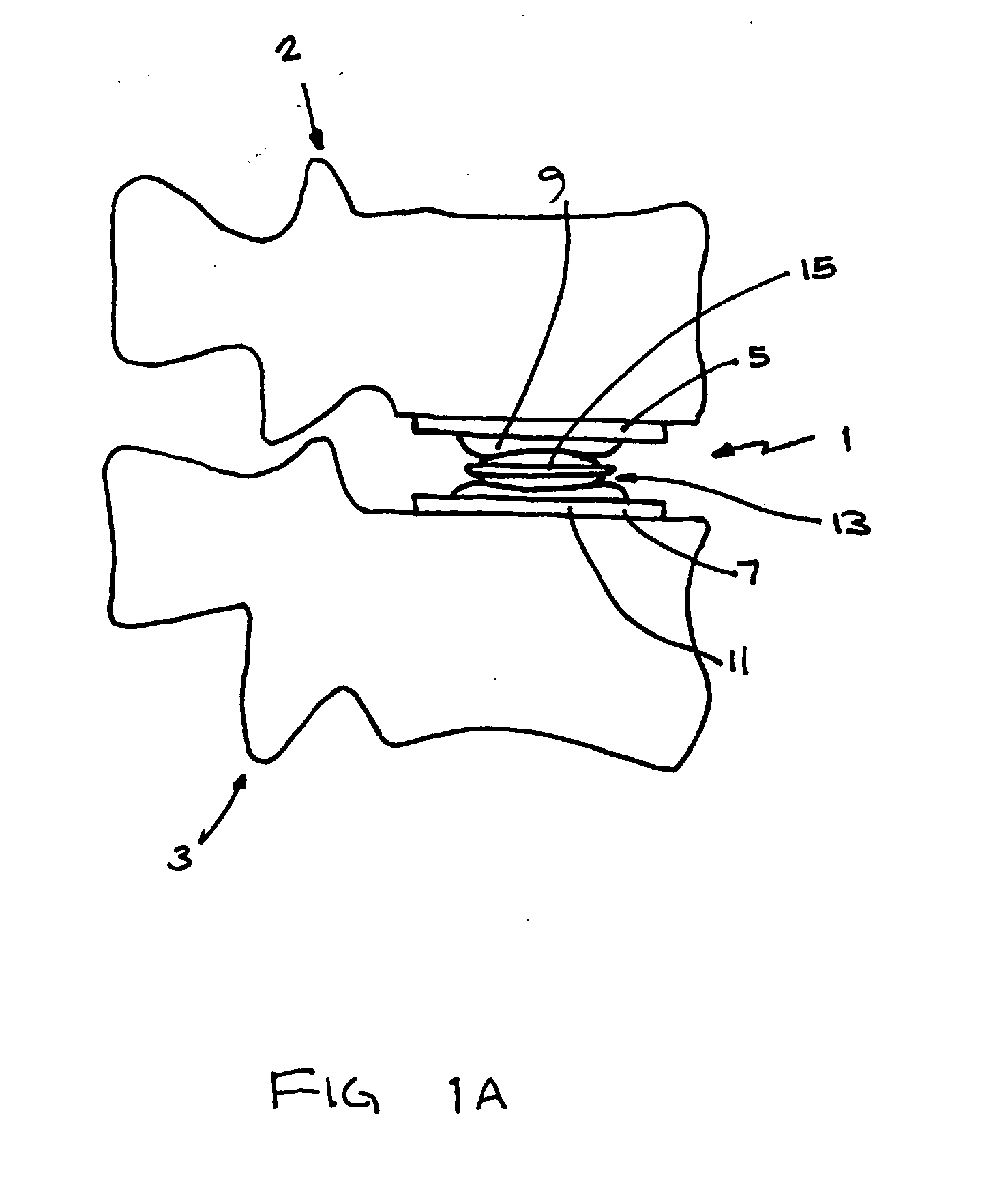
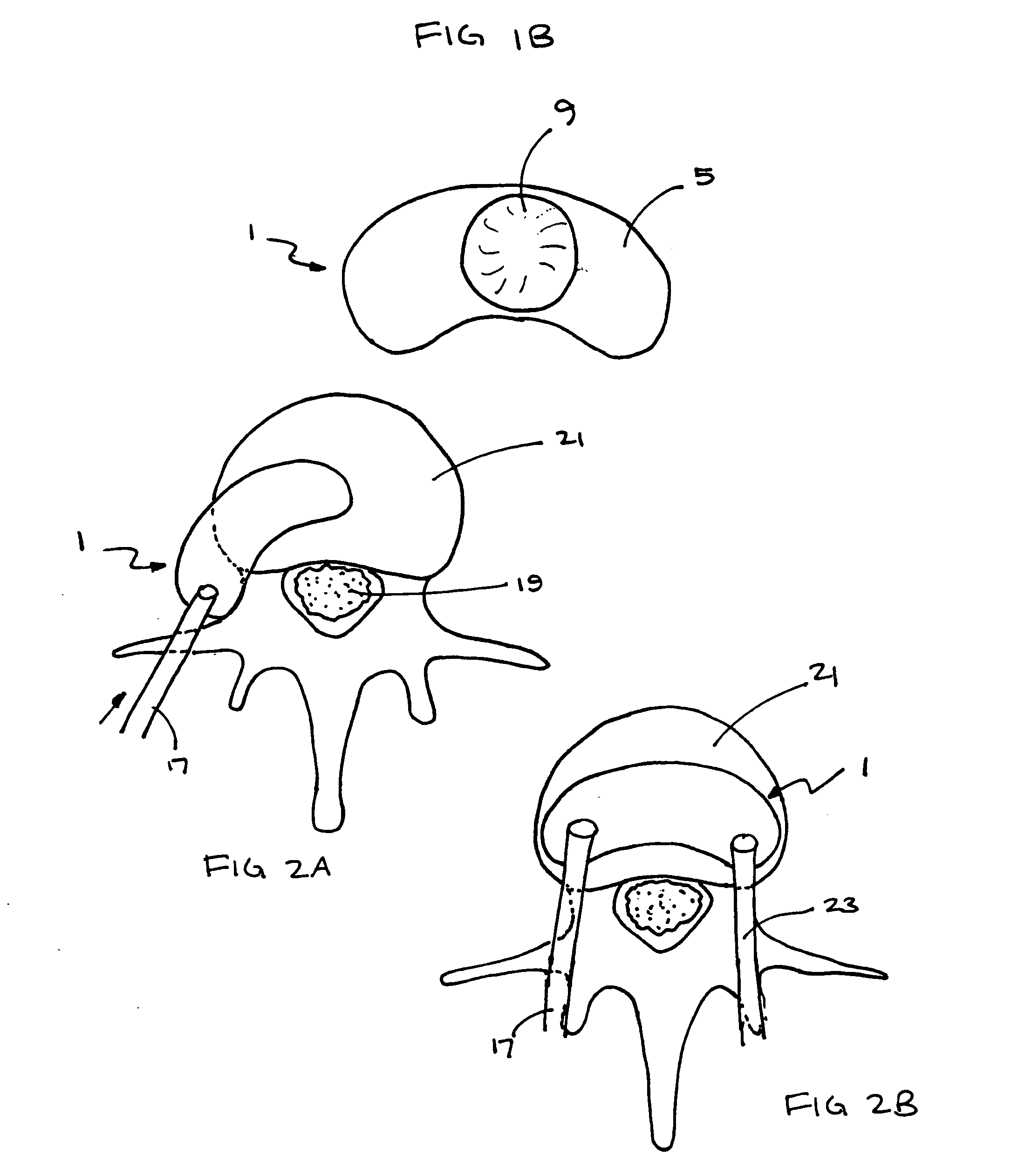
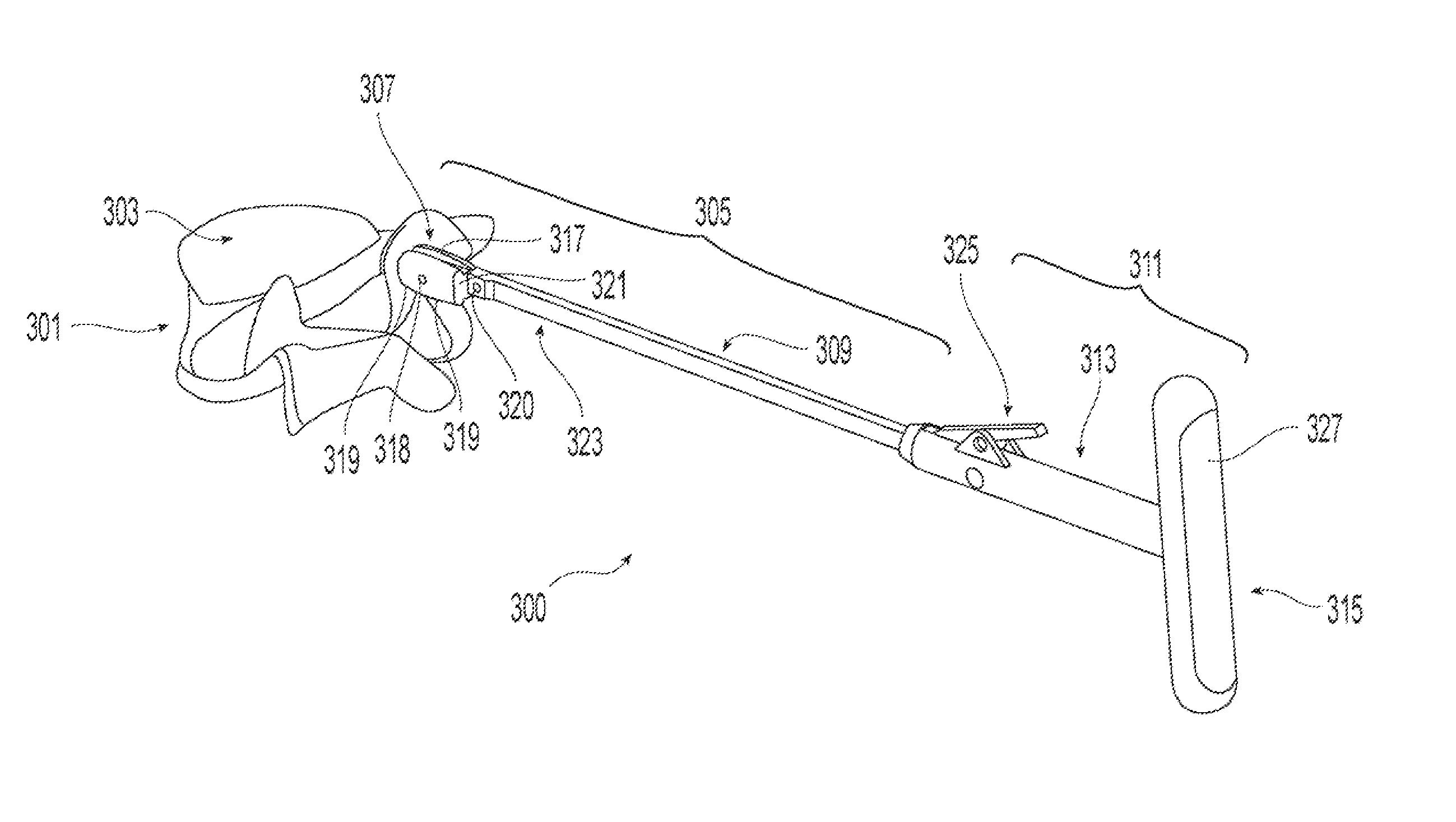
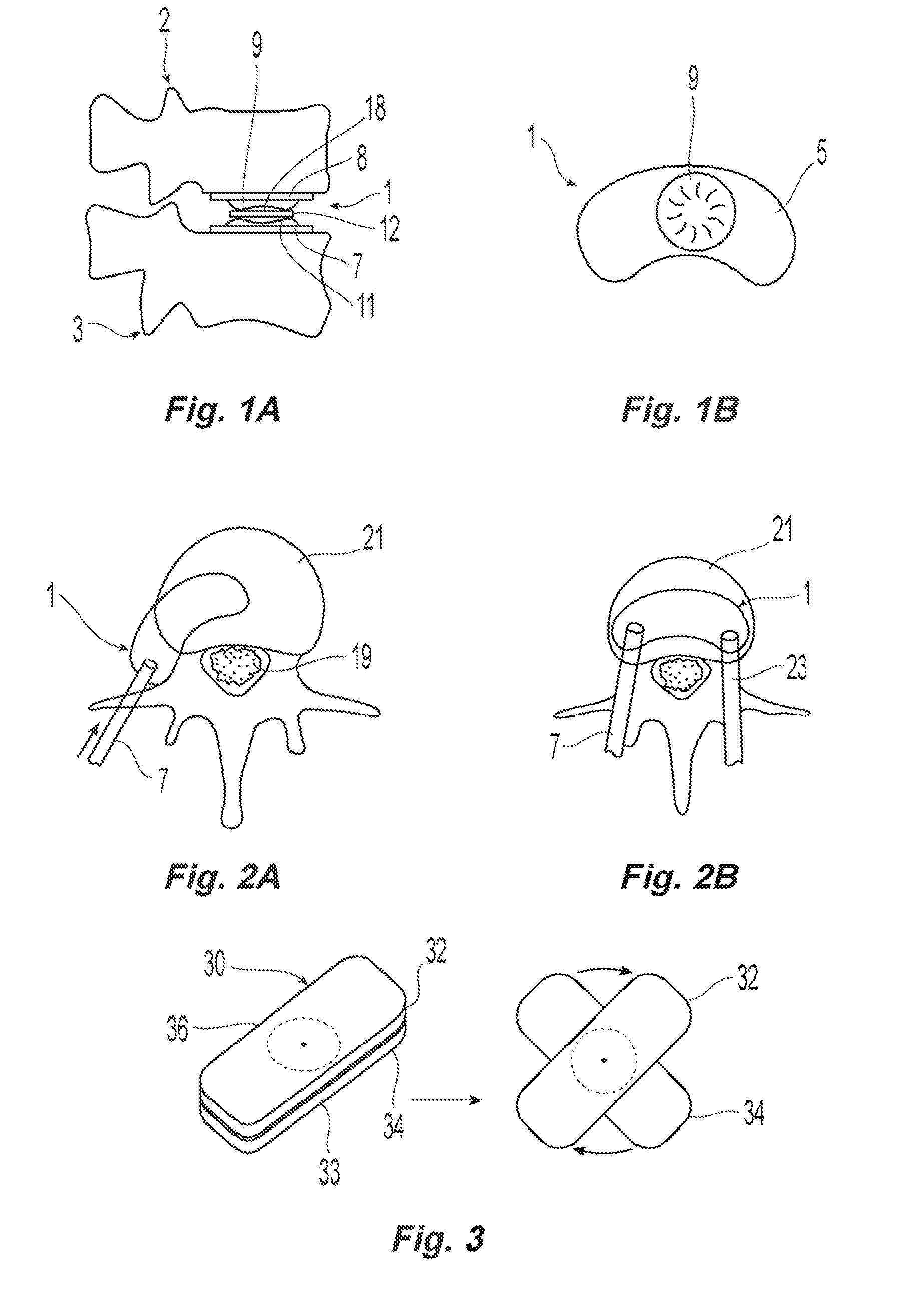
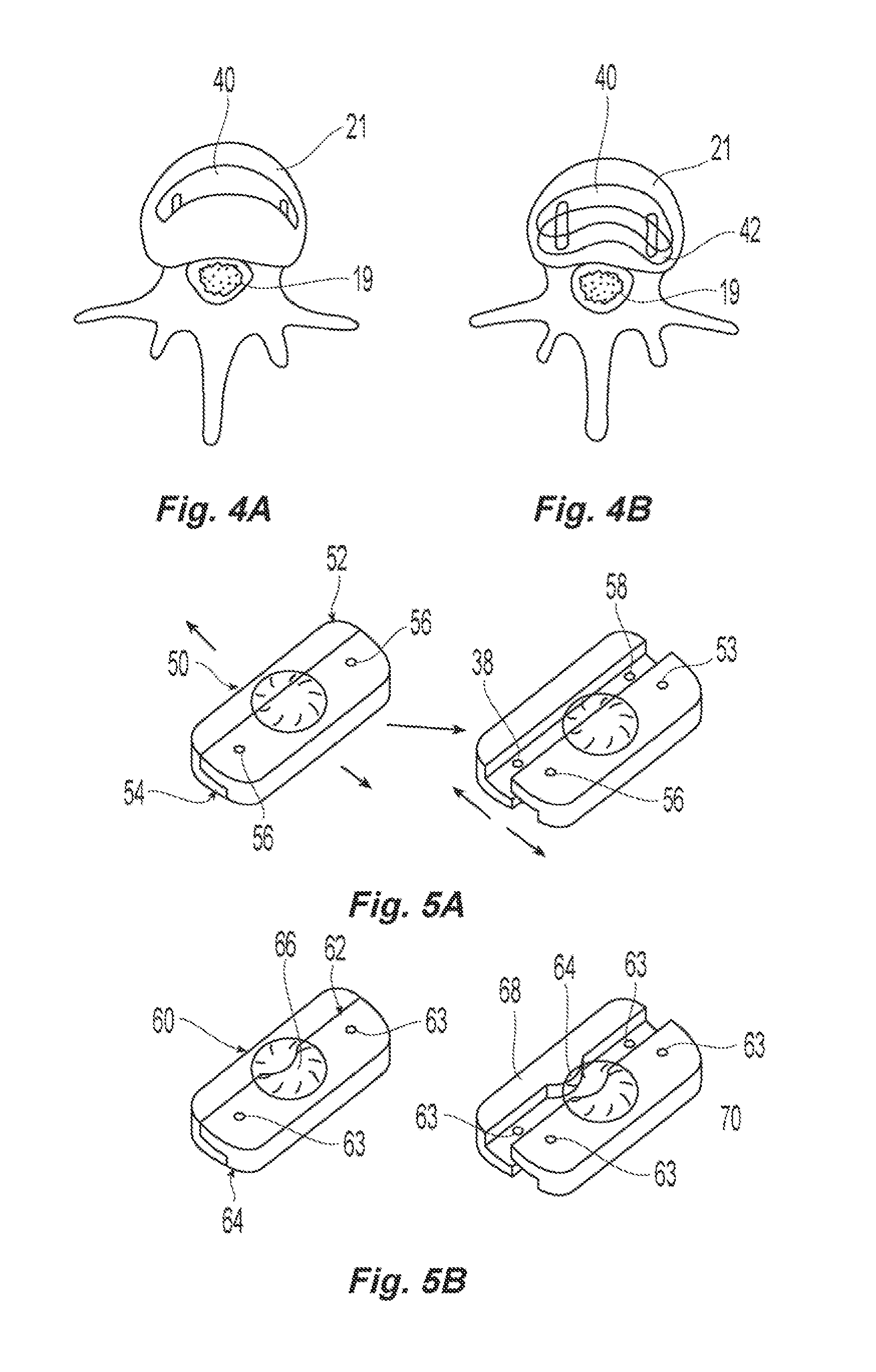
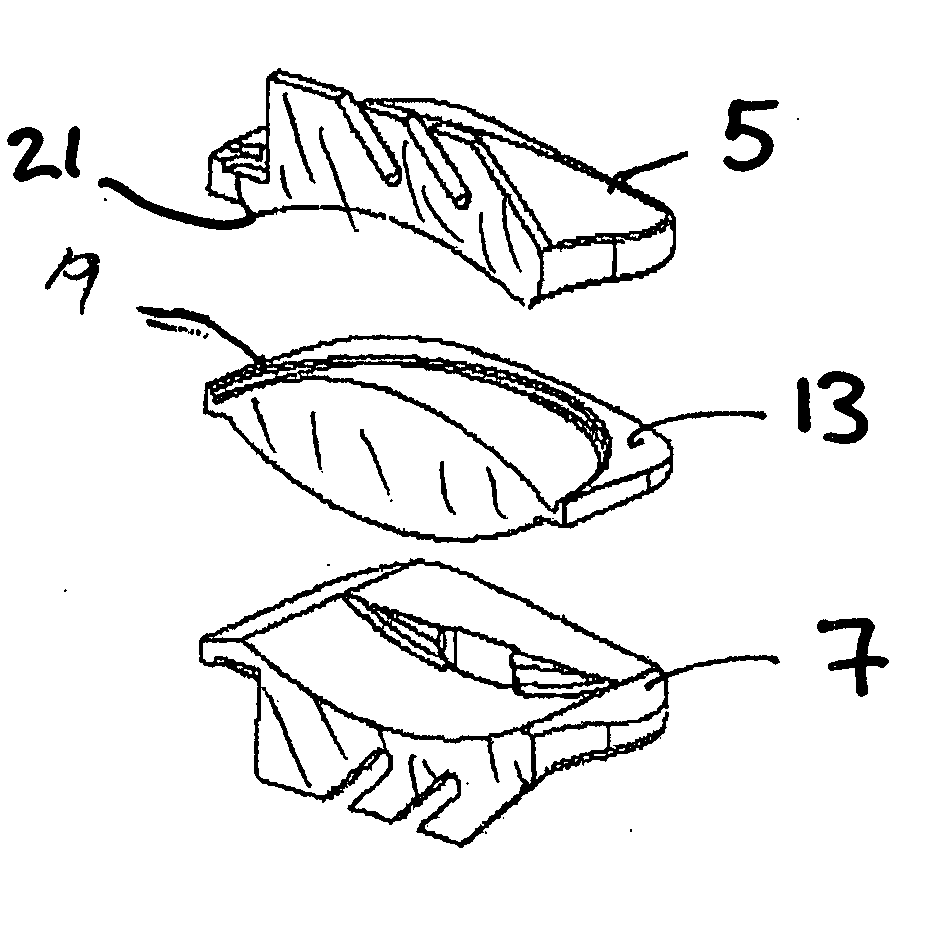
ActiveUS20050043800A1Restrict movementJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSpinal columnSurgical approach
The present invention relates generally to a prosthetic spinal disc for replacing a damaged disc between two vertebrae of a spine. The present invention also relates to a method for implanting a prosthetic spinal disc via posterior or posterior lateral implantation. Other surgical approaches for implanting the prosthetic disc may also be used. The present invention also involves a method for implanting the prosthetic spinal disc while either avoiding or minimizing contact with the spinal cord and nerve rootlets, or reducing the time and extent that they need to be repositioned during implantation.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
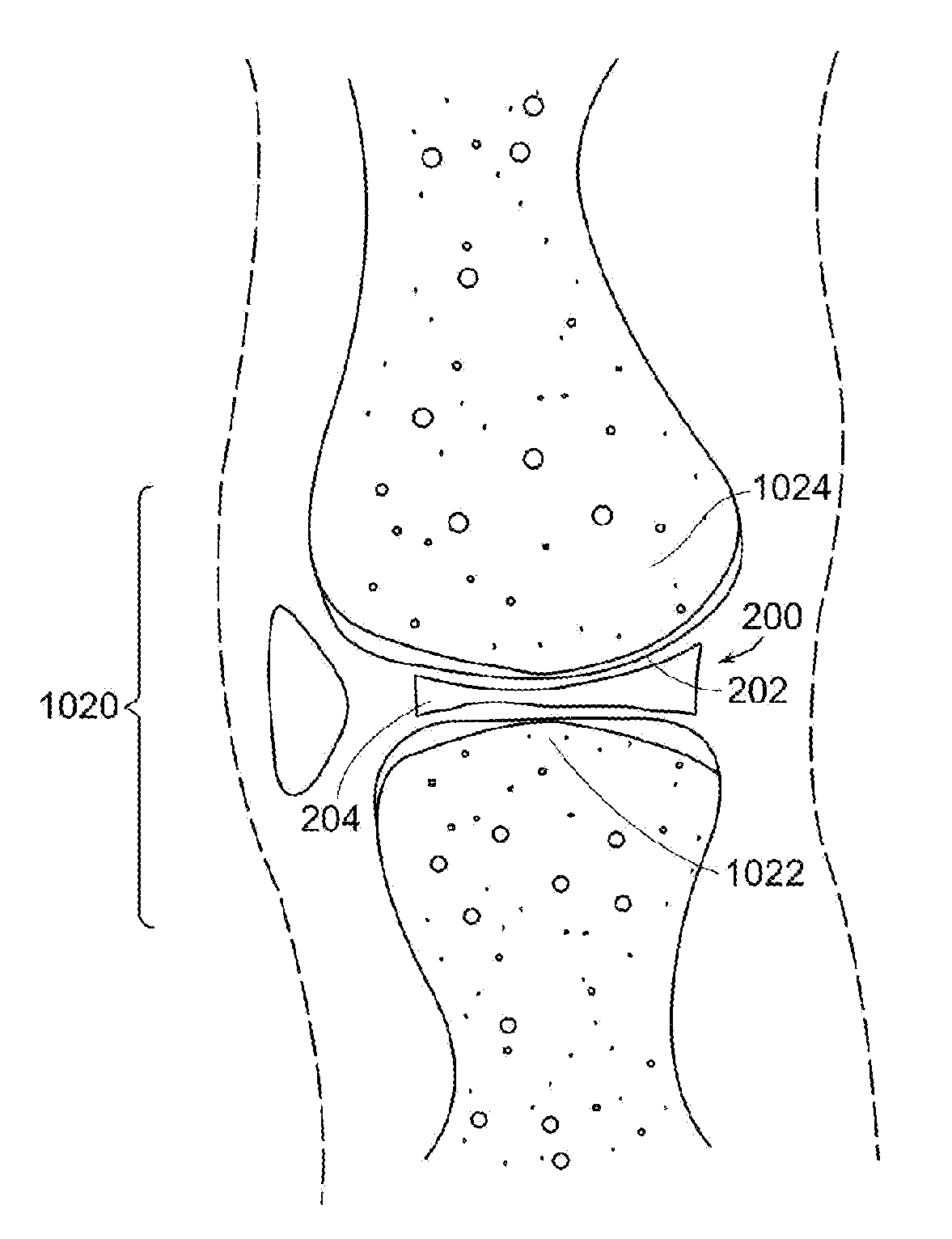
Interpositional Joint Implant
InactiveUS20070233269A1Improve anatomic functionalityPromote resultsJoint implantsDiagnostic recording/measuringTibiaTibial surface
A method of preparing an interpositional implant suitable for a knee. The method includes determining a three-dimensional shape of a tibial surface of the knee. An implant is produced having a superior surface and an inferior surface, with the superior surface adapted to be positioned against a femoral condyle of the knee, and the inferior surface adapted to be positioned upon the tibial surface of the knee, The inferior surface conforms to the three-dimensional shape of the tibial surface. The implant may be inserted into the knee without making surgical cuts on the tibial surface. The tibial surface may include cartilage, or cartilage and bone.
Owner:CONFORMIS
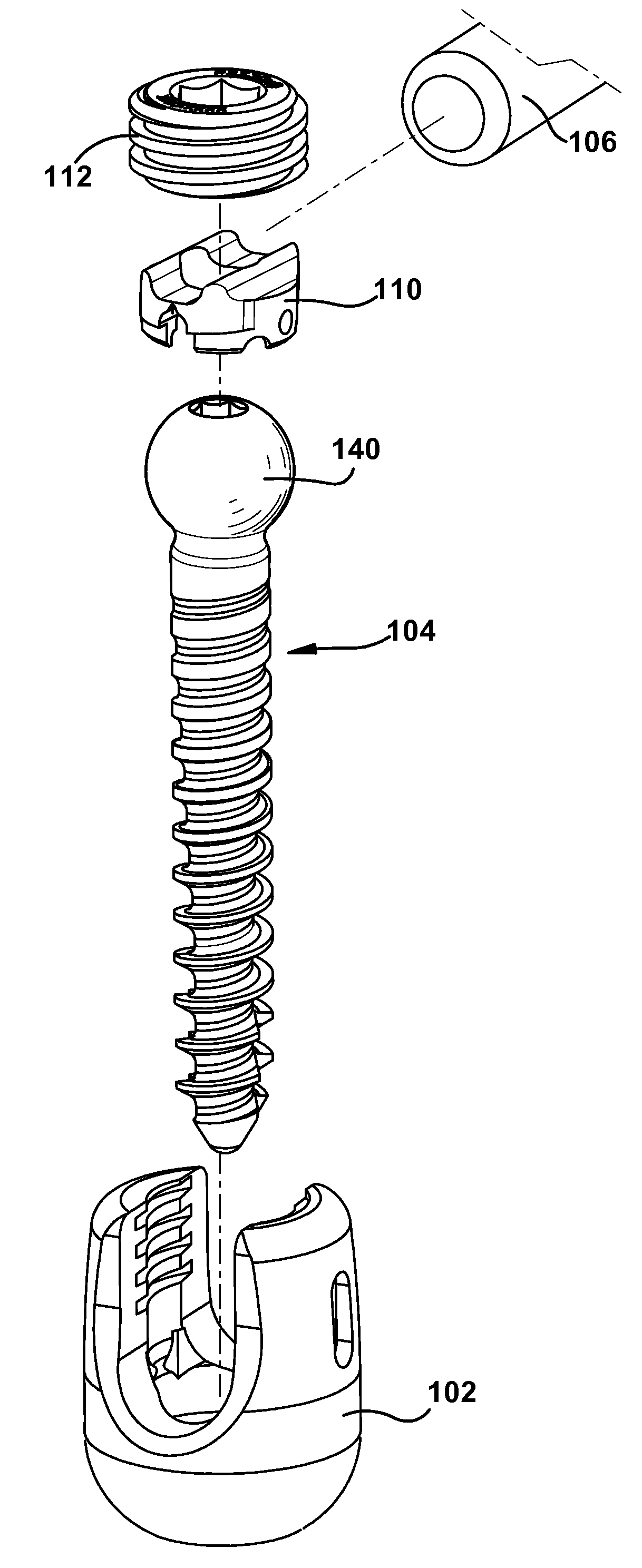
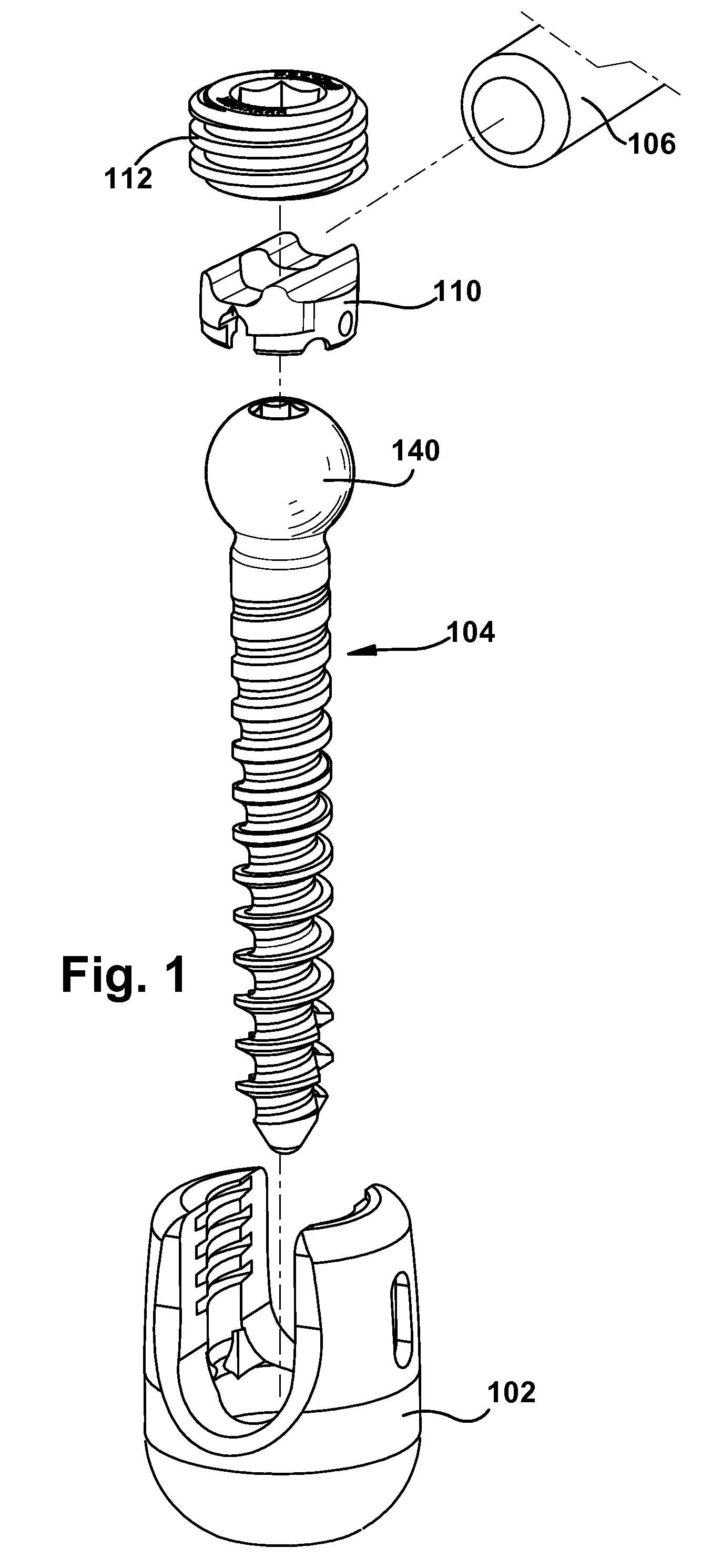
Constrained motion bone screw assembly
ActiveUS20060200131A1Prevent rotationRestrict movementSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisCompression memberBiomedical engineering
A bone screw assembly includes an anchor portion and a head portion, such as a rod-receiving portion, movably mounted to the anchor portion to allow for controlled angulation between the anchor portion and the head portion. The anchor portion is pivotable in one or more selected directions about an axis relative to the head portion. A restriction member, which may be a rod seat, prevents the anchor portion from pivoting in one or more different directions about another axis relative to the head portion and / or a spinal fixation element received in the head portion. The restriction member may be inserted in the head portion to control direction that the anchor portion pivots relative to the head portion. The restriction member may also serve as a compression member and / or rod seat for seating a spinal rod coupled to the bone screw assembly.
Owner:SARL DEPUY SPINE +1
Spring retained end effector contact pad
ActiveUS8864202B1Reduce dispersionSecure attachmentGripping headsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContact padActuator
An end effector is disclosed for use in substrate processing. The end effector includes a effector body portion, a contact pad pocket formed in the end effector body, a spring retaining pocket formed in the end effector body adjacent the contact pad pocket and extending to an edge of the end effector body, and a pair of through-holes extending from the spring retaining pocket to the contact pad pocket. The end effector can include a contact pad seated within the contact pad pocket, the contact pad having at least one retaining channel formed therein, and a retaining spring having a pair of retaining arms extending from the retaining spring pocket through the through-holes and into the contact pad pocket. The retaining arms may extend at least partially into the at least one retaining channel of the contact pad and may thereby restrict movement of the contact pad.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Automatic surgical device and control assembly for cutting a cornea
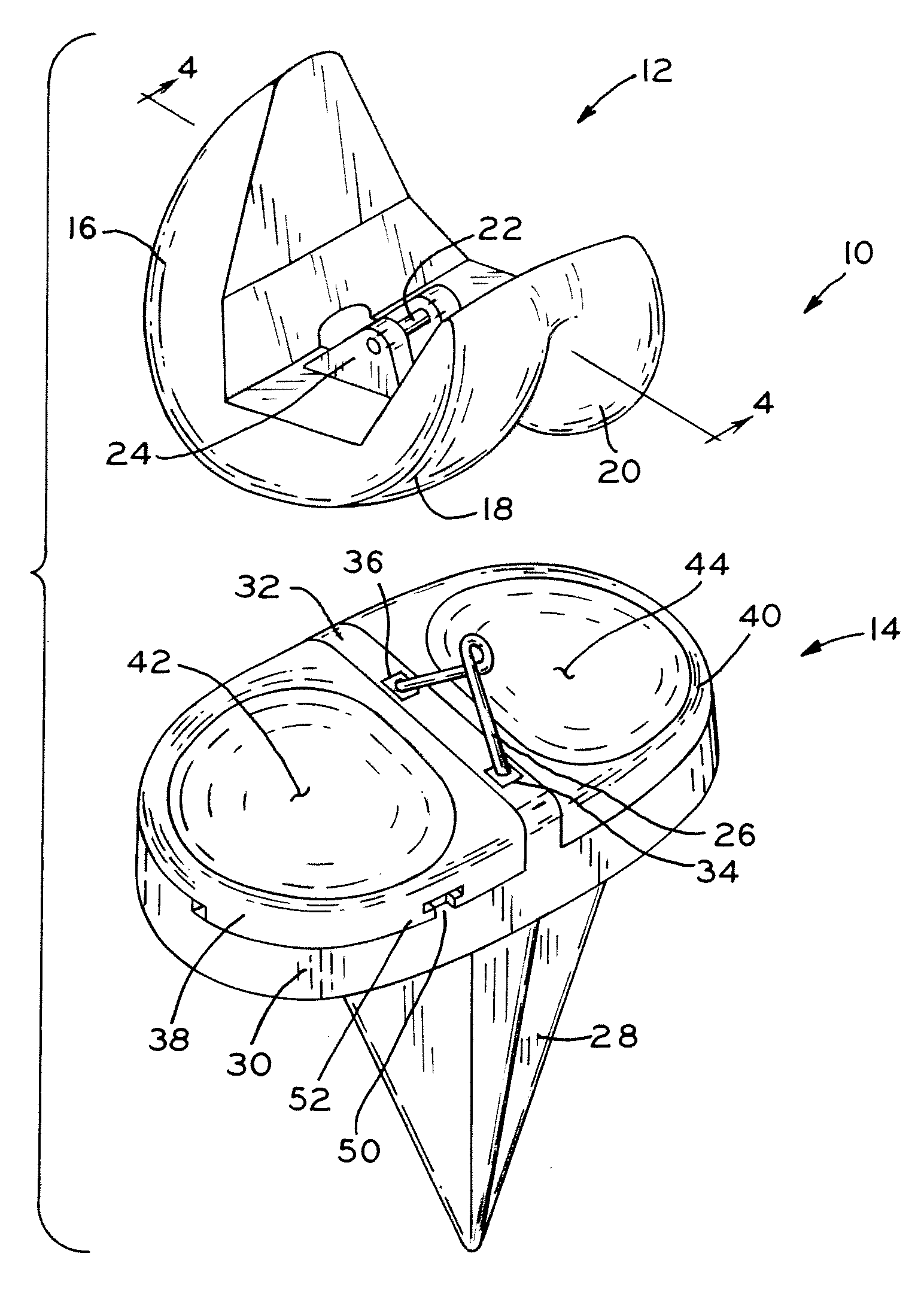
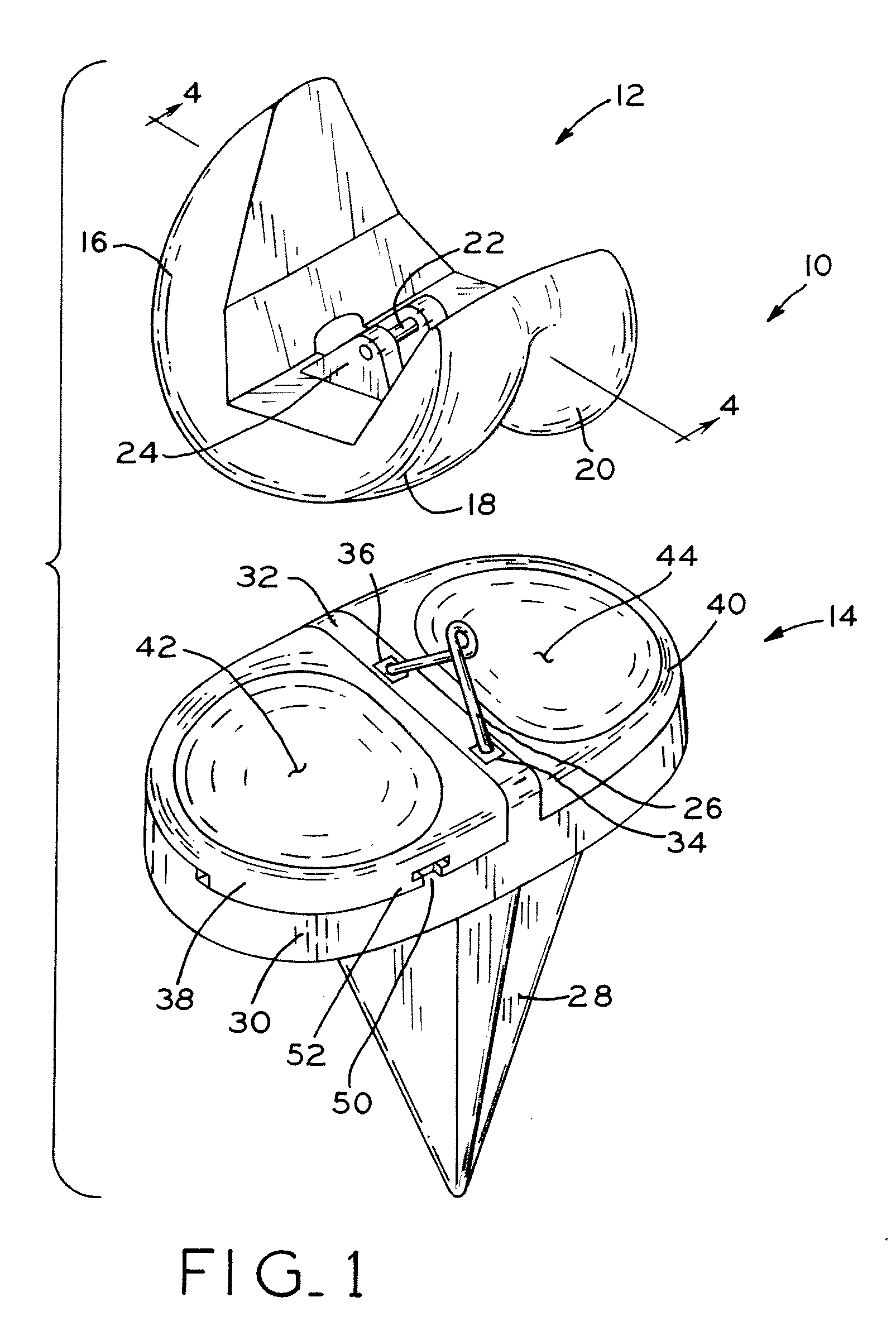
InactiveUS7166117B2Restrict movementQuick and easy installation and removalEye surgeryDiagnosticsSurgical departmentEngineering
A surgical device for cutting substantially across a cornea of an eye of a patient, the device including a positioning ring to be attached to an eye surrounding a cornea to be cut, and defining an aperture sized to receive and expose the cornea to be cut. The surgical device further includes a cutting head assembly structured to be guided and driven over an upper surface of the positioning ring in a generally arcuate path, and having a cutting element positioned therein and structured to oscillate laterally to facilitate smooth and effective cutting of the cornea. The cutting head assembly is structured to be detachably coupled to the positioning ring by a coupling member which permits movement of the cutting head assembly relative to the positioning ring along the generally arcuate path, but maintains sufficient engagement therebetween to ensure that smooth, steady, driven movement is maintained.
Owner:HELLENKAMP JOHANN F
Locking mechanisms for fixation devices and methods of engaging tissue
InactiveUS7604646B2Prevent movementReduce frictional contactSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsEngineeringSurgical department
Owner:EVALVE
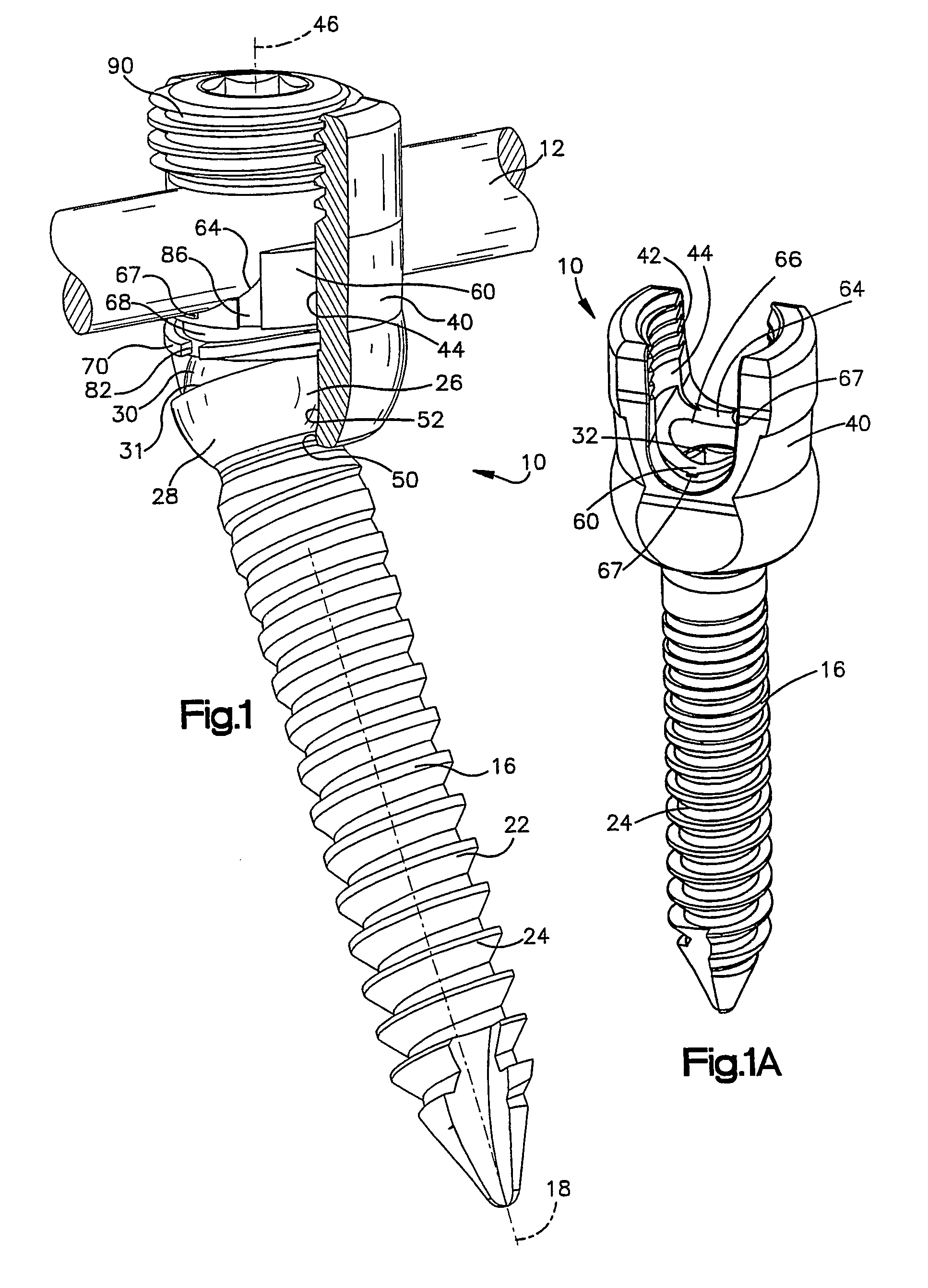
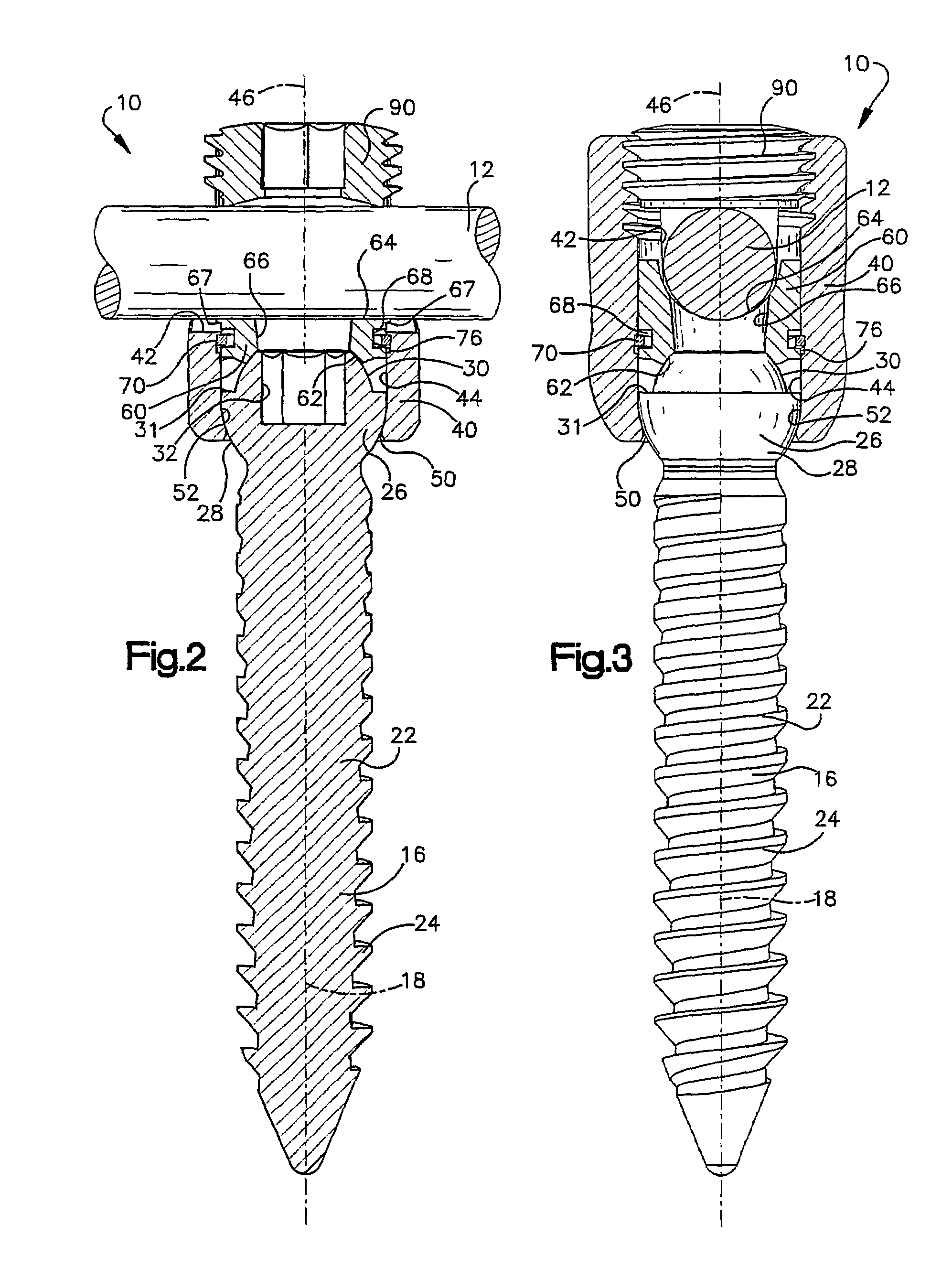
Apparatus for connecting a longitudinal member to a bone portion
InactiveUS7144396B2Prevent movementRestrict movementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringFastener
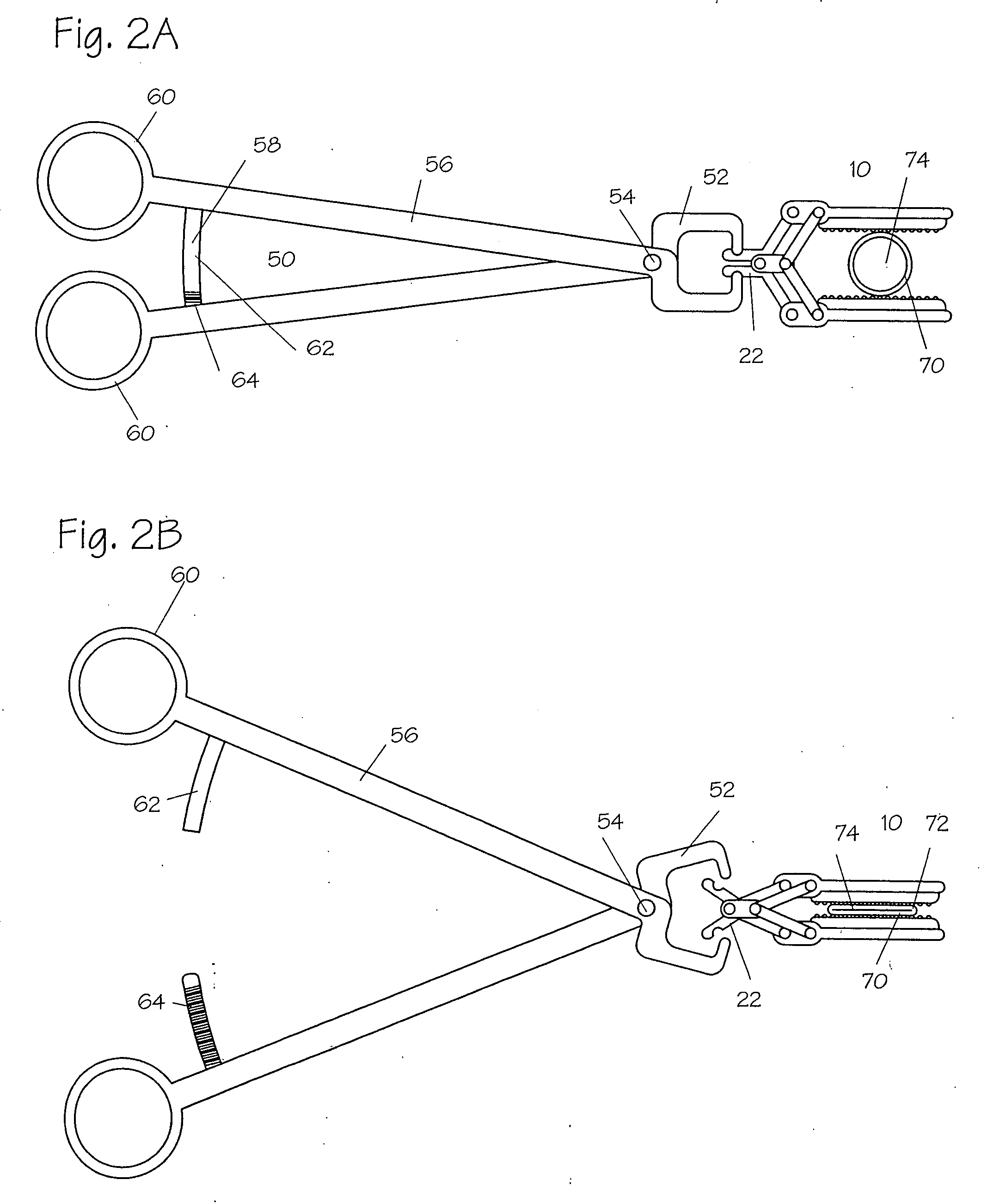
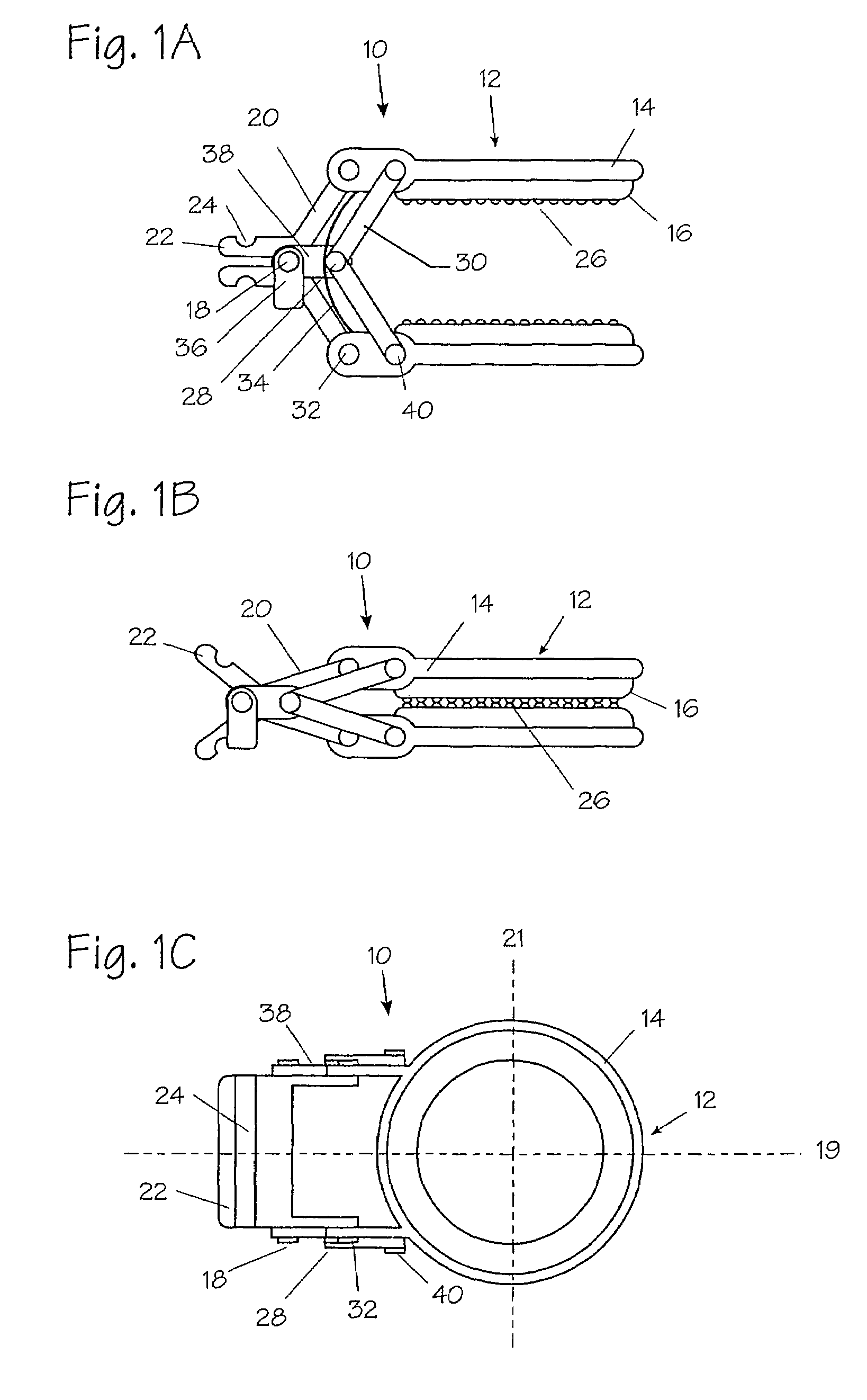
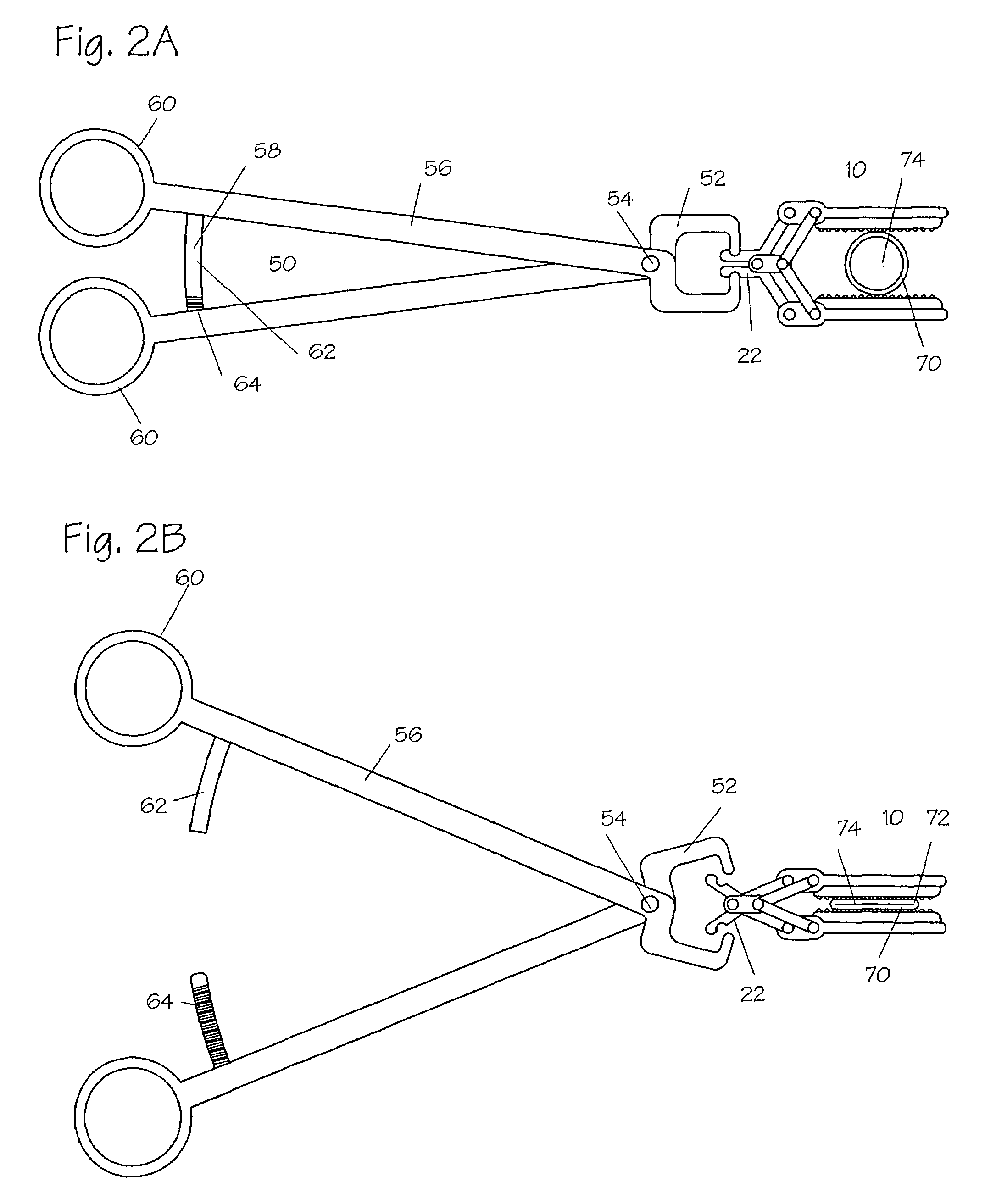
An apparatus (10) includes a fastener (16) engageable with a bone portion to connect a longitudinal member (12) to the bone portion. A housing (40) has a first passage (42) configured to receive the longitudinal member and a second passage (44) extending transverse to the first passage. The fastener extends through an opening (50) in the housing into the second passage. A longitudinal axis (18) of the fastener is positionable in any one of a plurality of angular positions relative to a longitudinal axis (46) of the second passage. A spacer (60) received in the second passage of the housing is engageable with the fastener and the longitudinal member. A positioning member (70) applies a force to prevent relative movement between the fastener and the housing and permit manual movement of the fastener relative to the housing against the force when the longitudinal member is disengaged from the spacer. A clamping mechanism (90) clamps the longitudinal member, the spacer, and the housing to the fastener to prevent movement of the fastener relative to the housing.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Method and apparatus for vascular and visceral clipping
InactiveUS20050251183A1Convenient treatmentMinimizing chanceSnap fastenersClothes buttonsTrauma surgeryLarge intestine
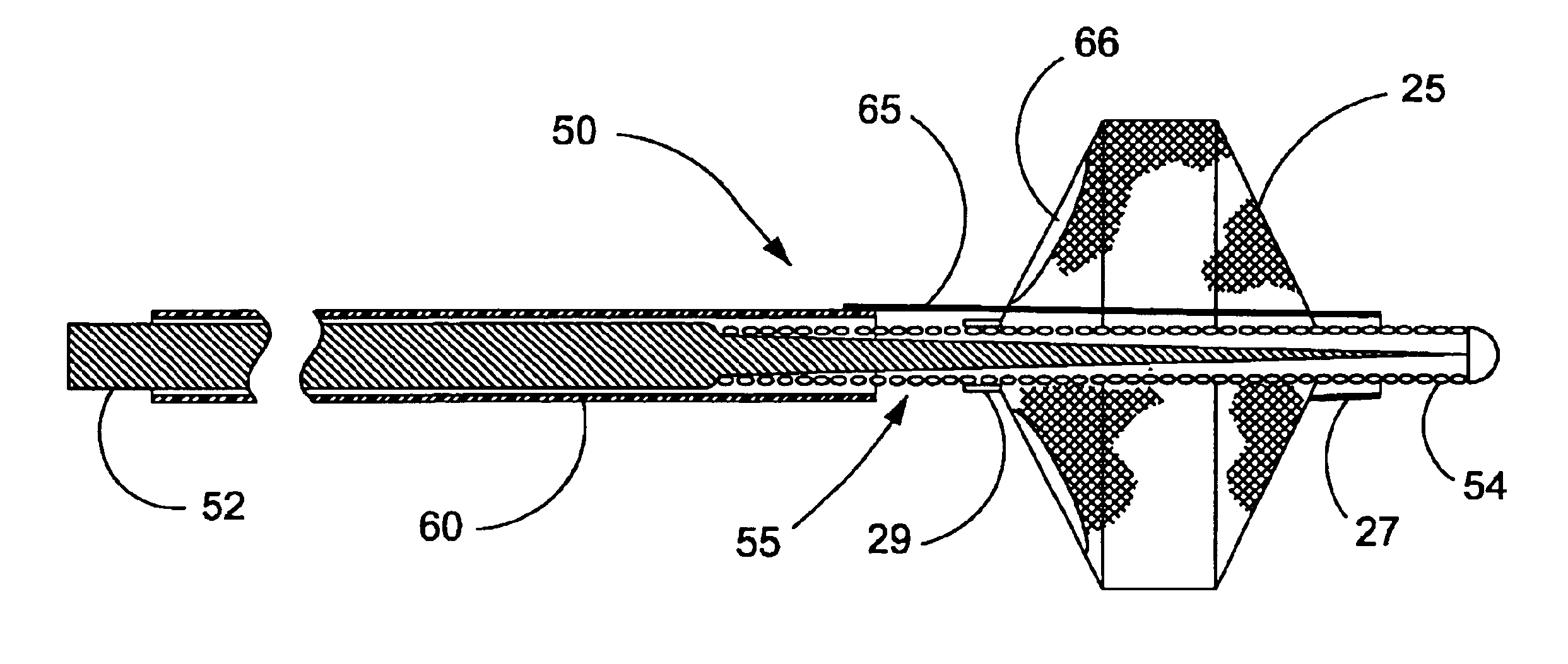
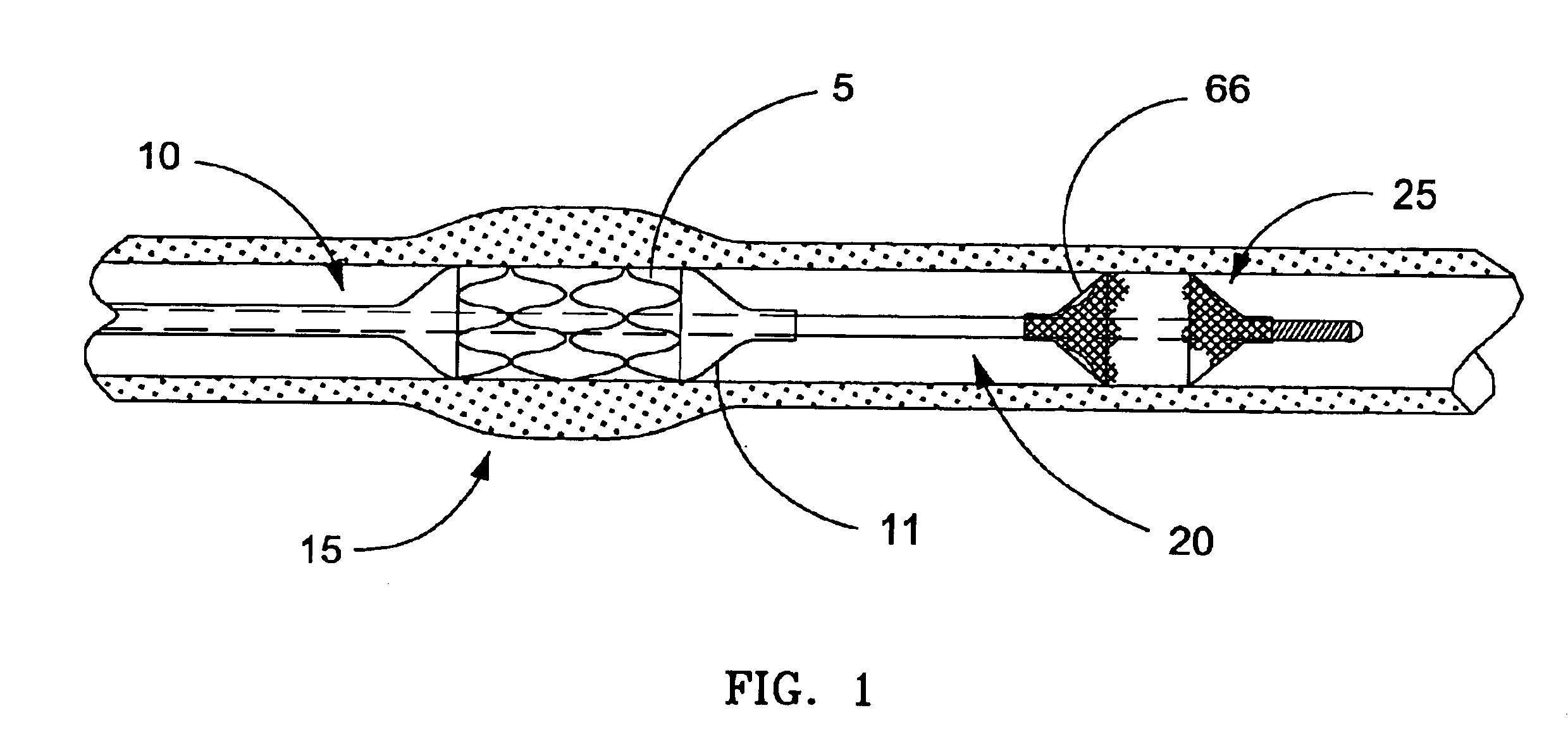
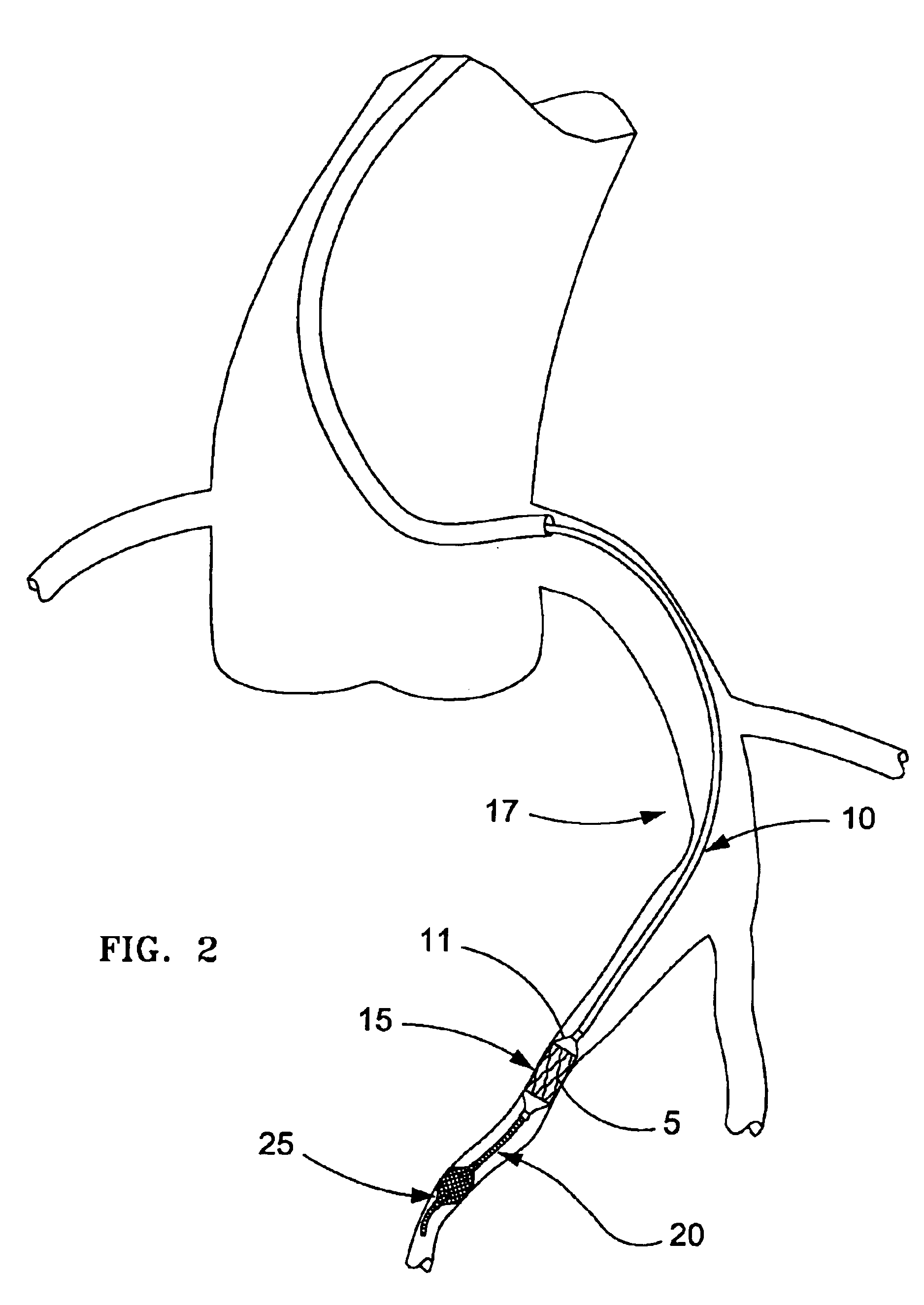
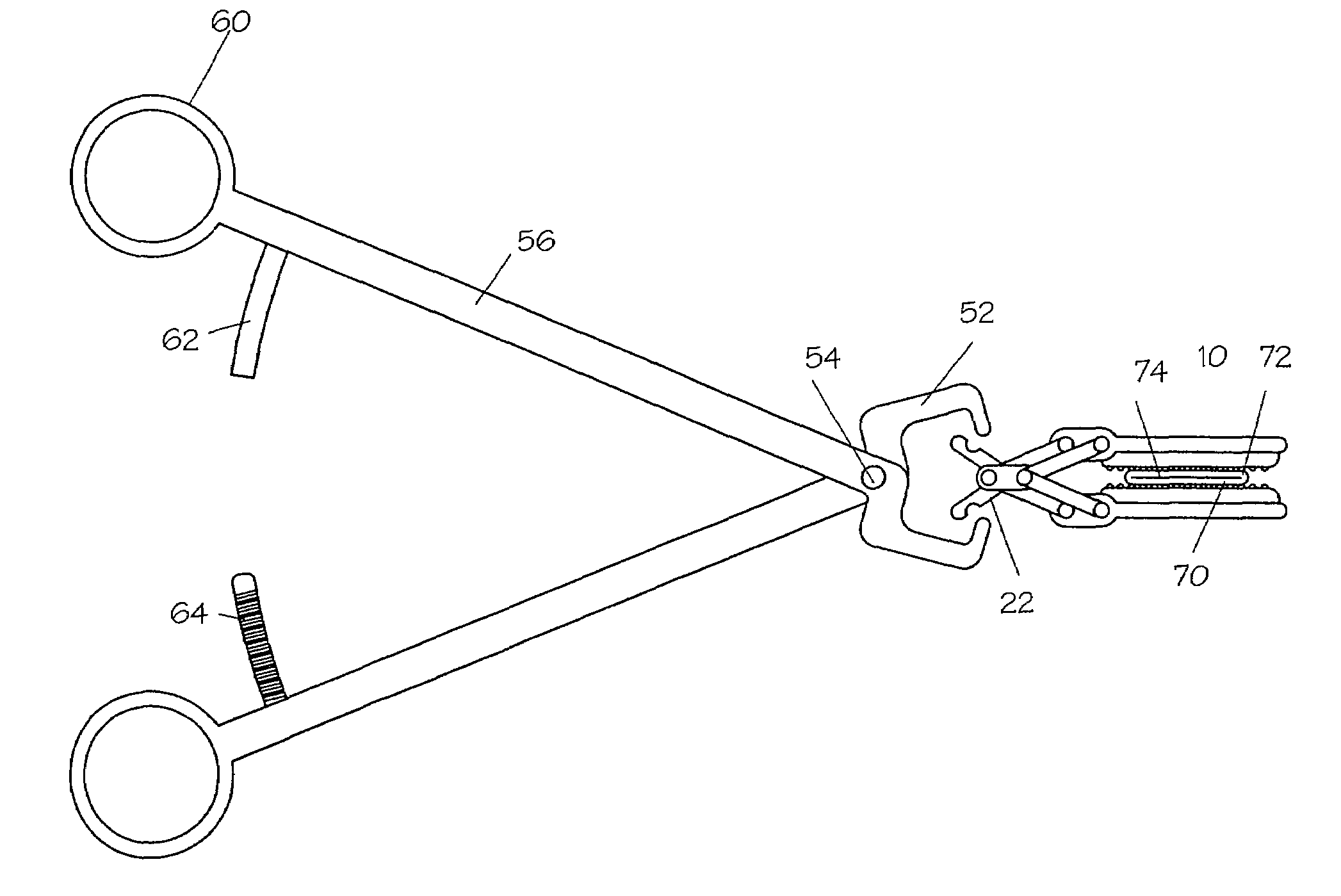
Devices and methods for achieving hemostasis and leakage control in hollow body vessels such as the small and large intestines, arteries and veins as well as ducts leading to the gall bladder and other organs. The devices and methods disclosed herein are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting, and most especially during damage control procedures. In such cases, the patient may have received trauma to the abdomen, extremities, neck or thoracic region. The devices utilize removable or permanently implanted, broad, soft, parallel jaw clips with minimal projections to maintain vessel contents without damage to the tissue comprising the vessel. These clips are applied using either standard instruments or custom devices that are subsequently removed leaving the clips implanted, on a temporary or permanent basis, to provide for hemostasis or leakage prevention, or both. These clips overcome the limitations of clips and sutures that are currently used for the same purposes. The clips come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The clips may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Posterior dynamic stabilizer devices
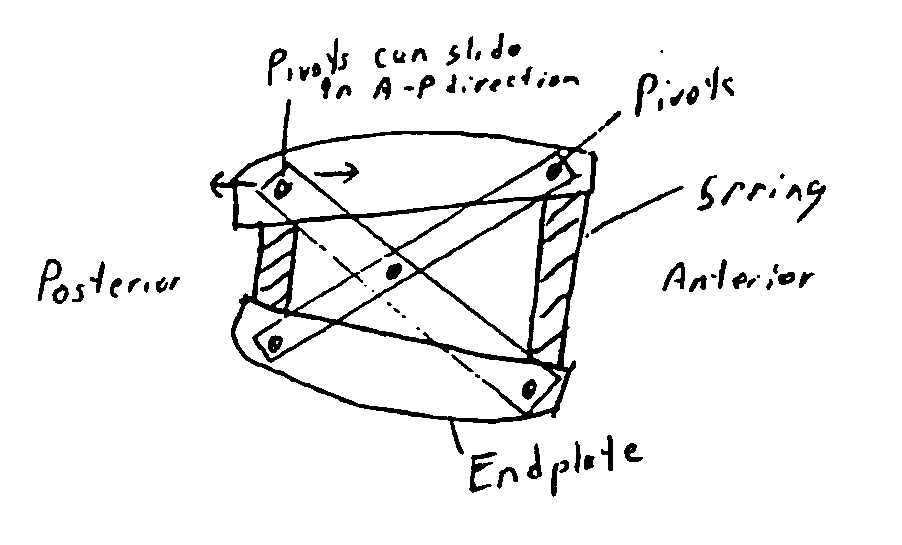
InactiveUS20060084991A1Restrict movementRepair and replacementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringPosterior stabilization
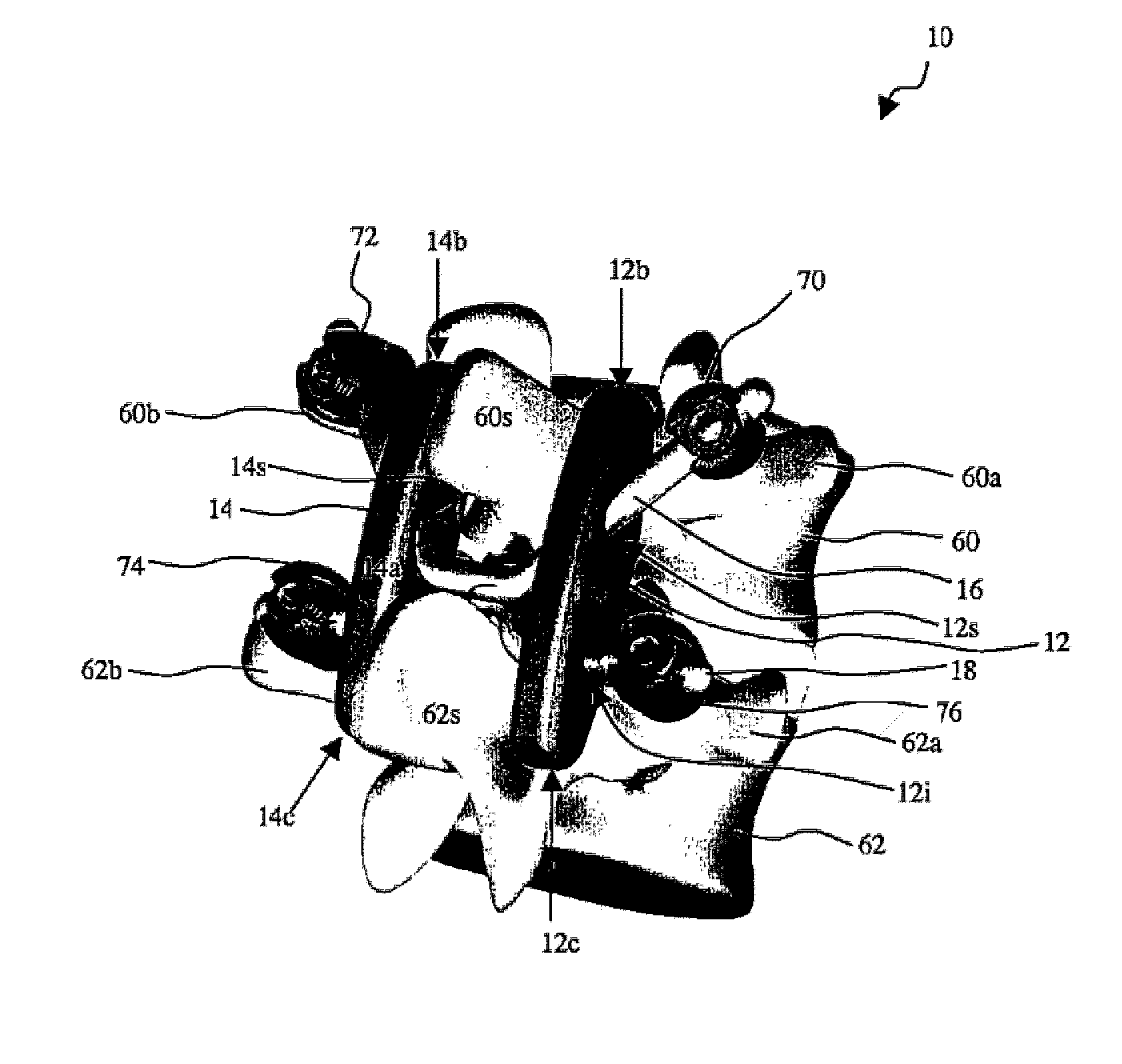
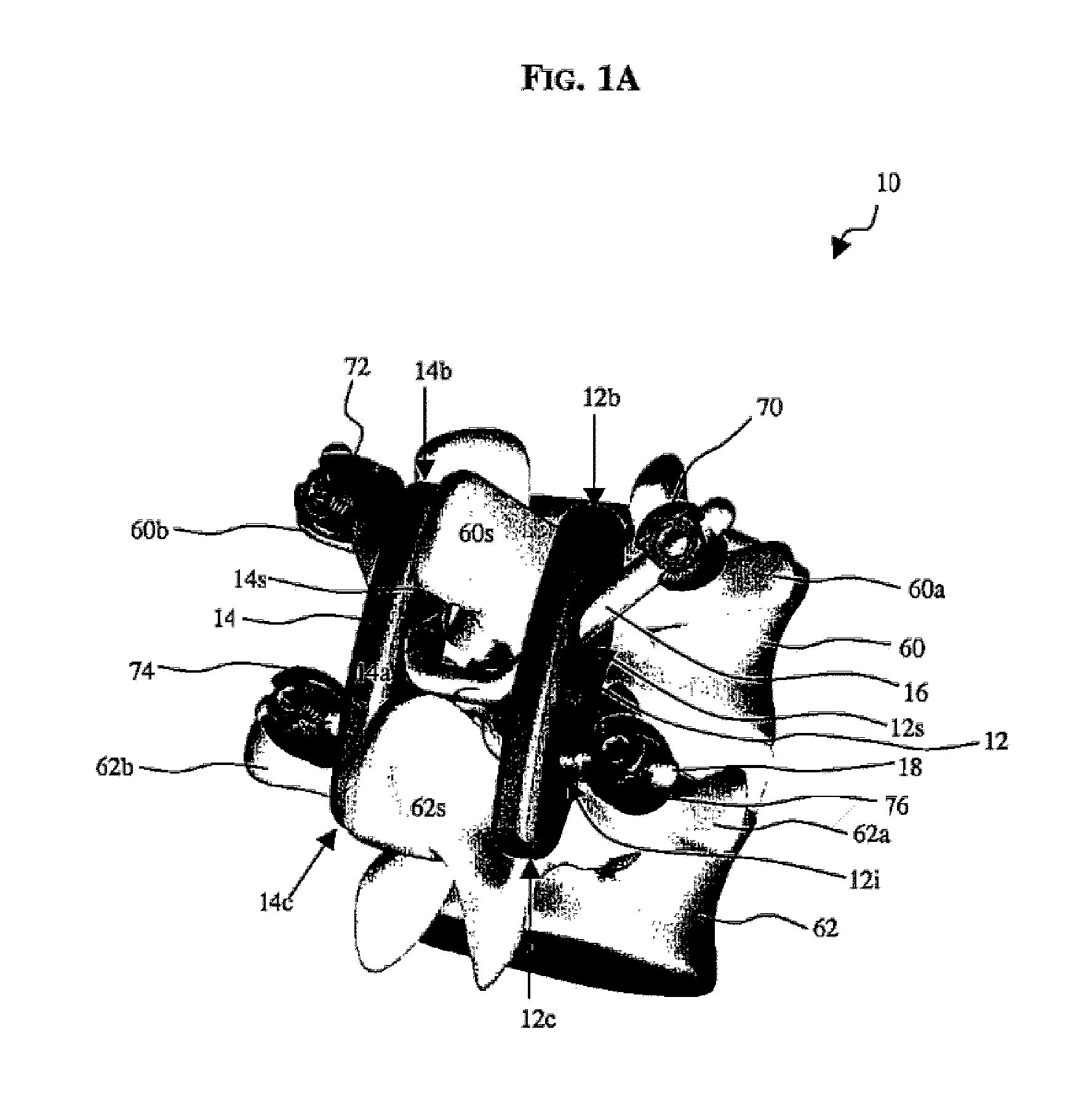
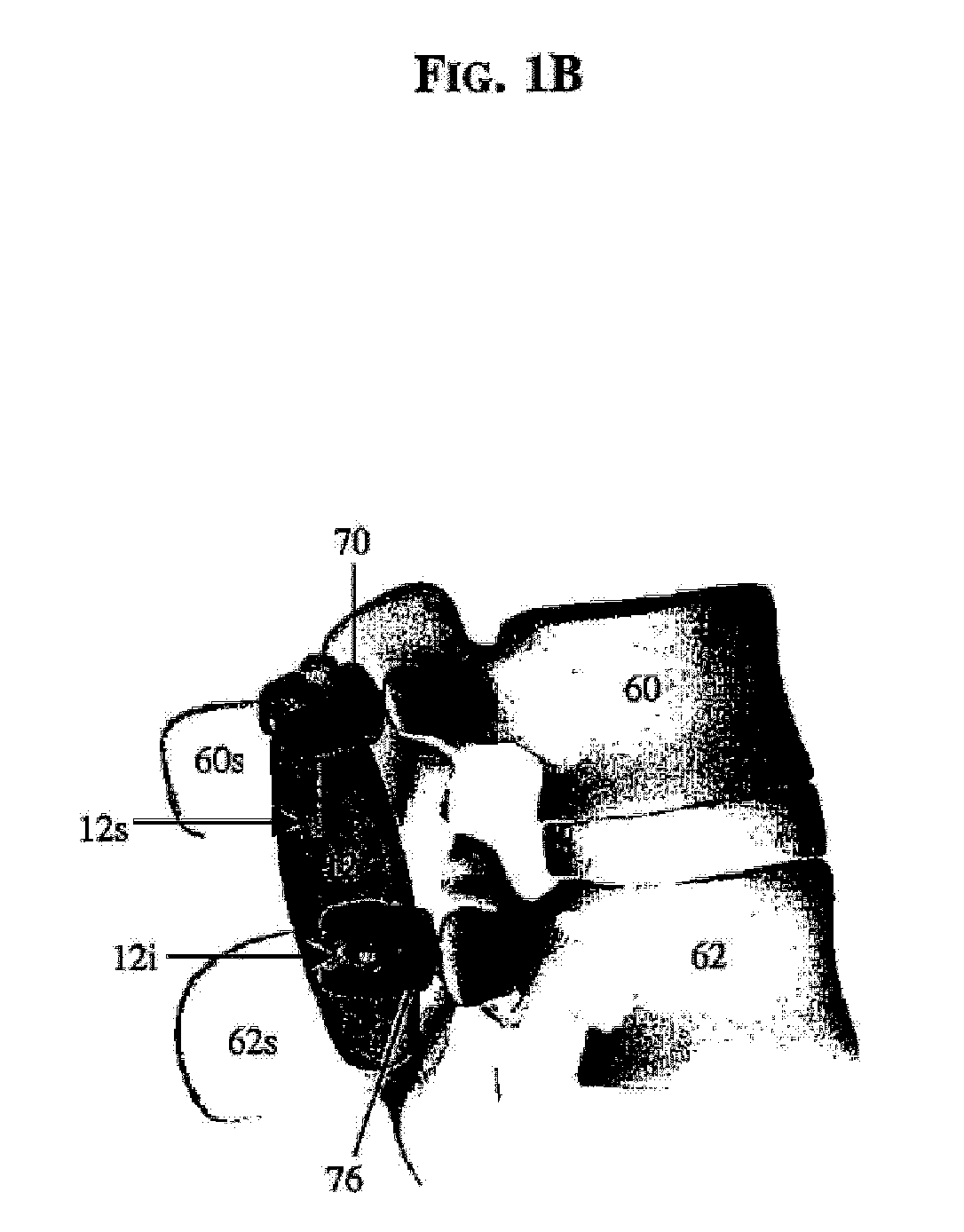
A posterior stabilization device is provided for controlling movement between adjacent vertebrae. In one exemplary embodiment, the stabilization device can include one or more joints that rely on rotational or sliding movement to allow flexion of adjacent vertebrae, and that control extension, lateral bending, axial rotation, and anterior-posterior shear, preferably by providing one or more flexible connectors and / or a flexible central spacer for connecting to the adjacent superior and inferior vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Dynamic spinal stabilization device and systems
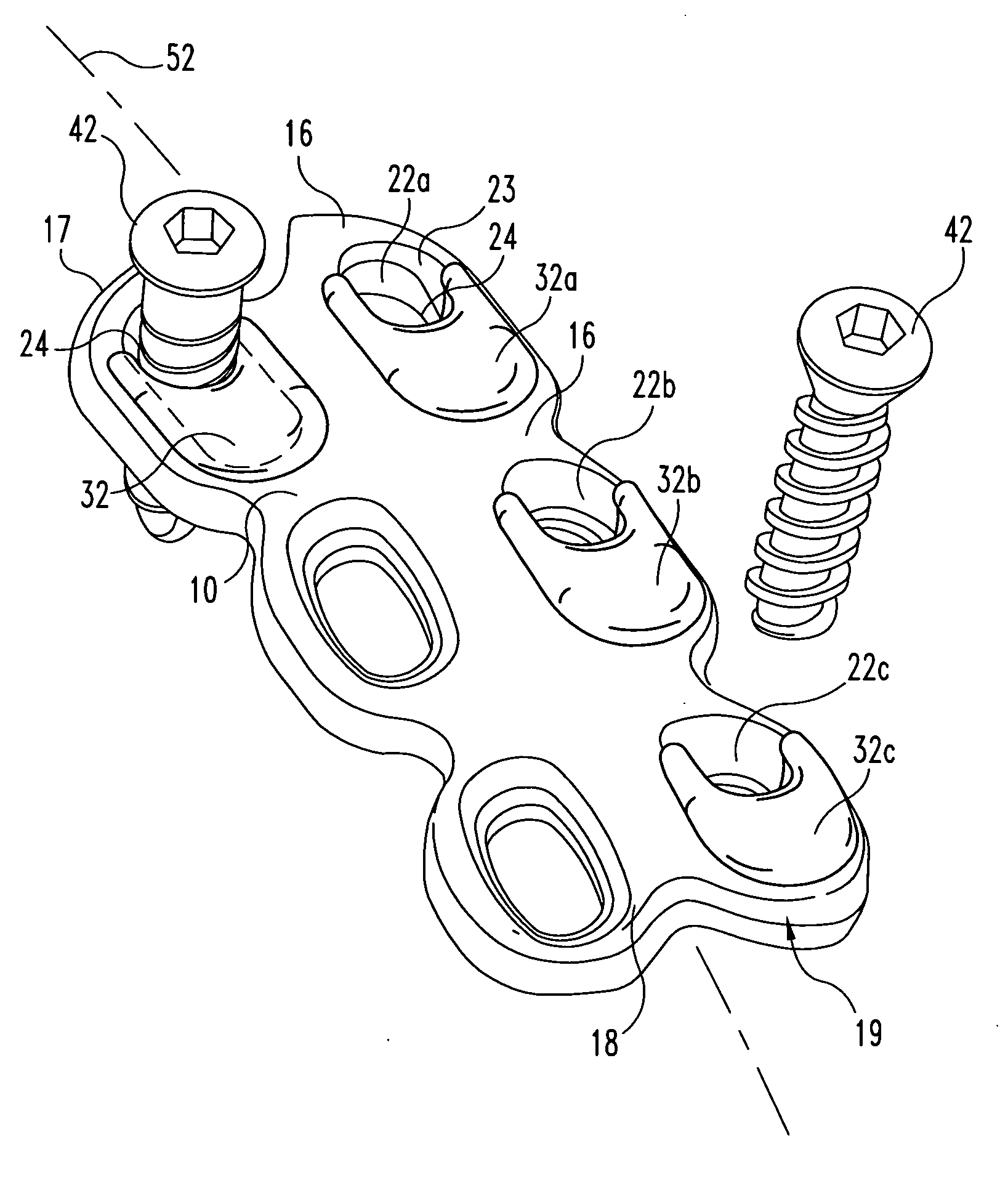
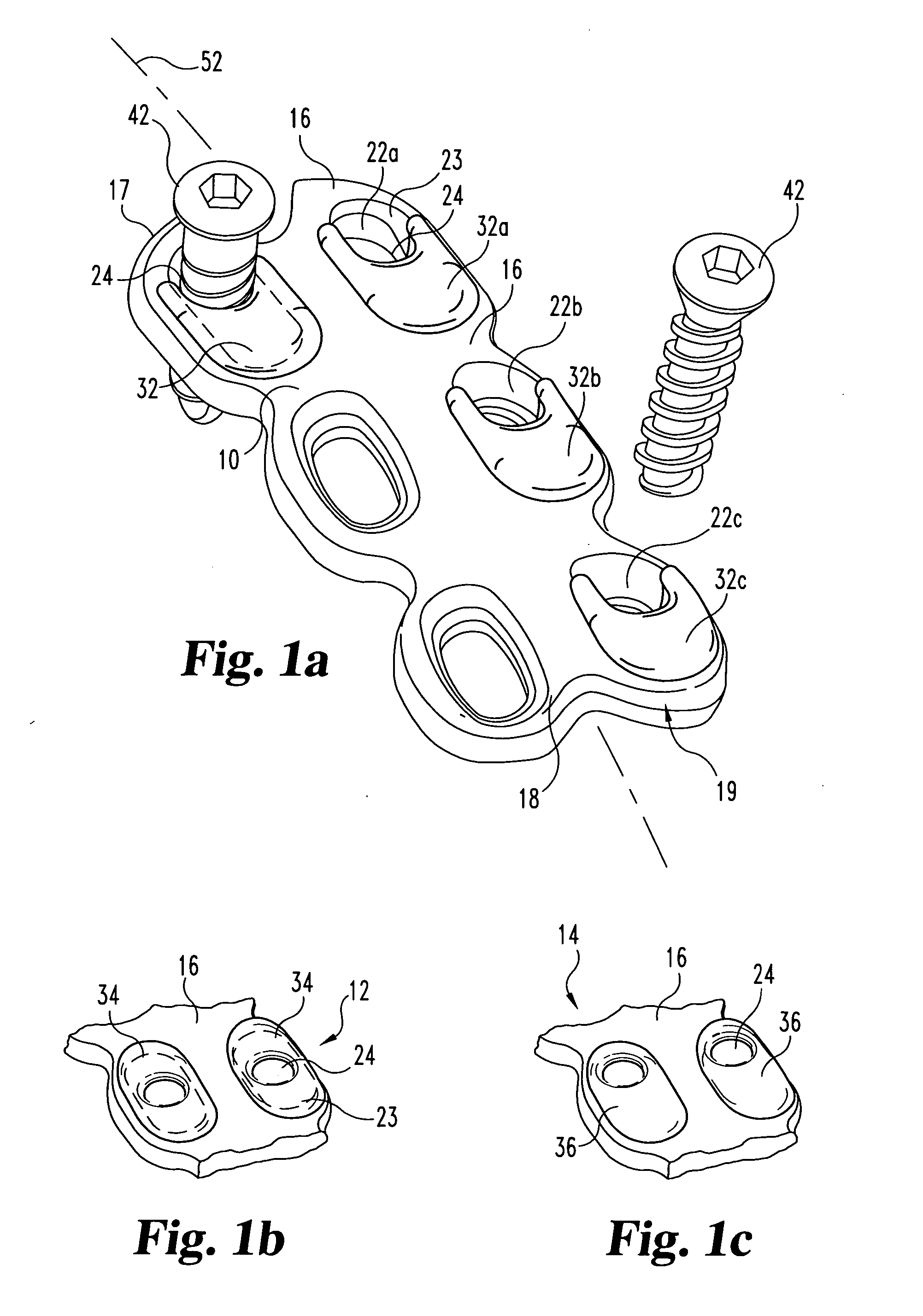
ActiveUS20070118122A1Restrict movementLimit angulationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBiomedical engineeringVertebra
A dynamic spine stabilization element of a spine stabilization assembly includes first and second spinal rod segments that are coupled to one another via a connector. The connector allows movement of a spinal rod segment with respect to the coupling device and / or with respect to another spinal rod segment. This provides limited angulation (e.g. bending) between spinal rod segments allowing for limited movement of the vertebra connected by the present dynamic stabilization element. The connector may allow pivoting motion of the rod segments relative to the coupling device and relative to the other rod segment such as pivoting motion of one rod segment in a first plane and pivoting motion of the other rod segment in a second plane that is perpendicular to the first plane. The connector may also be bendable or flexible. In this form, the connector allows limited flexing, bending or angulation as between the associated spinal rod segments during use. Moreover, ends of the spinal rod segments may be configured to prevent or limit rotation of the spinal rod segments. The configured ends may cooperate with the coupling device to achieve the limitation on rotational movement.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
Multi-head power tool with reverse lock-out capability
ActiveUS9421682B2Selection is limitedRestrict movementMechanical apparatusOperator-supported drilling machinesPower toolEngineering
A handheld power tool having a detachable tool head is disclosed in which, depending on the type of tool head used, selection of reverse movement of the rotary assembly of the power tool can be prevented. Where reverse movement of the tool head is undesirable, such as for a saw blade, the tool head contains a contact plate that slides a plate member to a position to prevent selection of the reverse direction by the user. However, where reverse movement of a tool head is desired, such as for a drill head, the plate member remains in its original position such that forward and reverse directions can be selected by a user.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
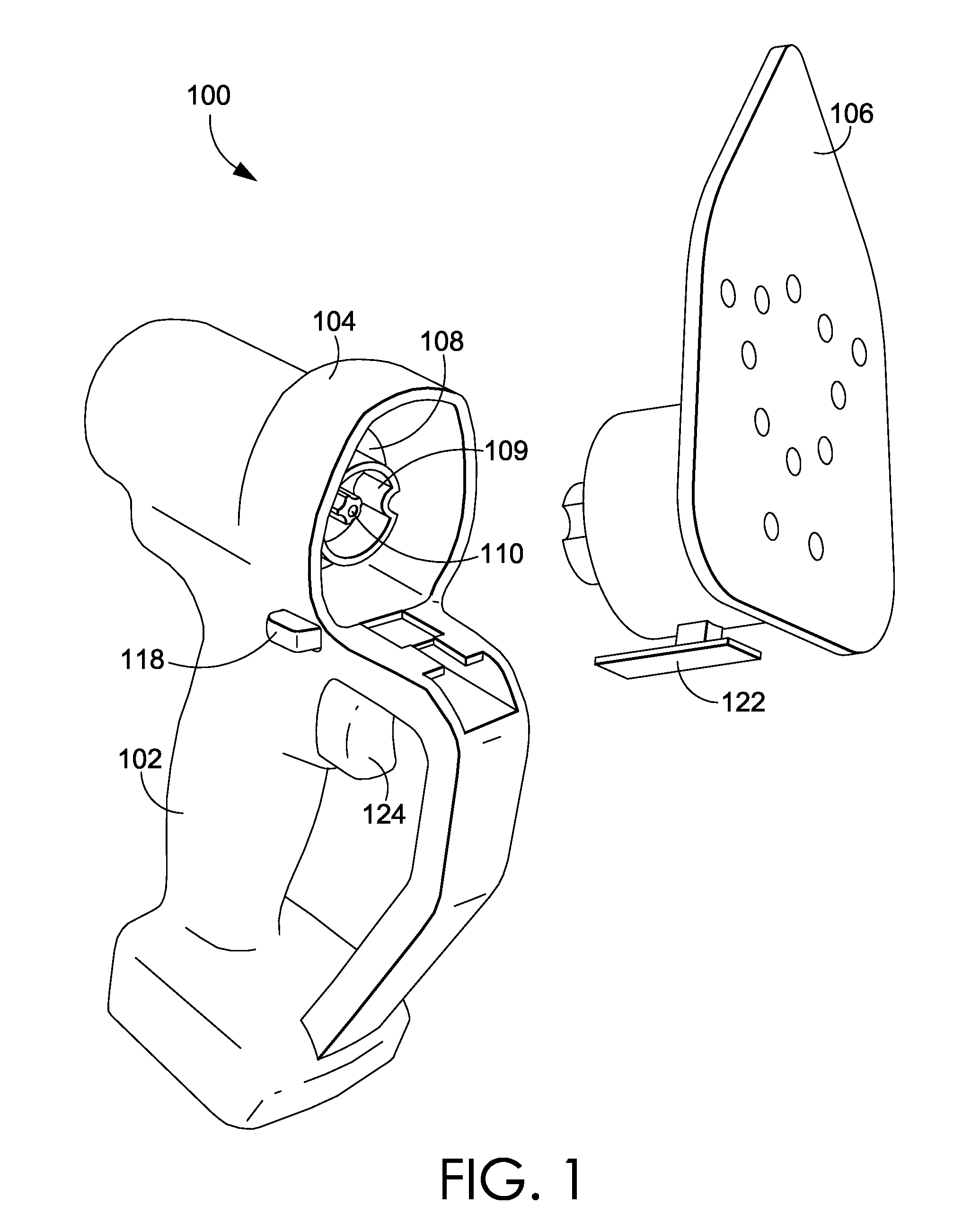
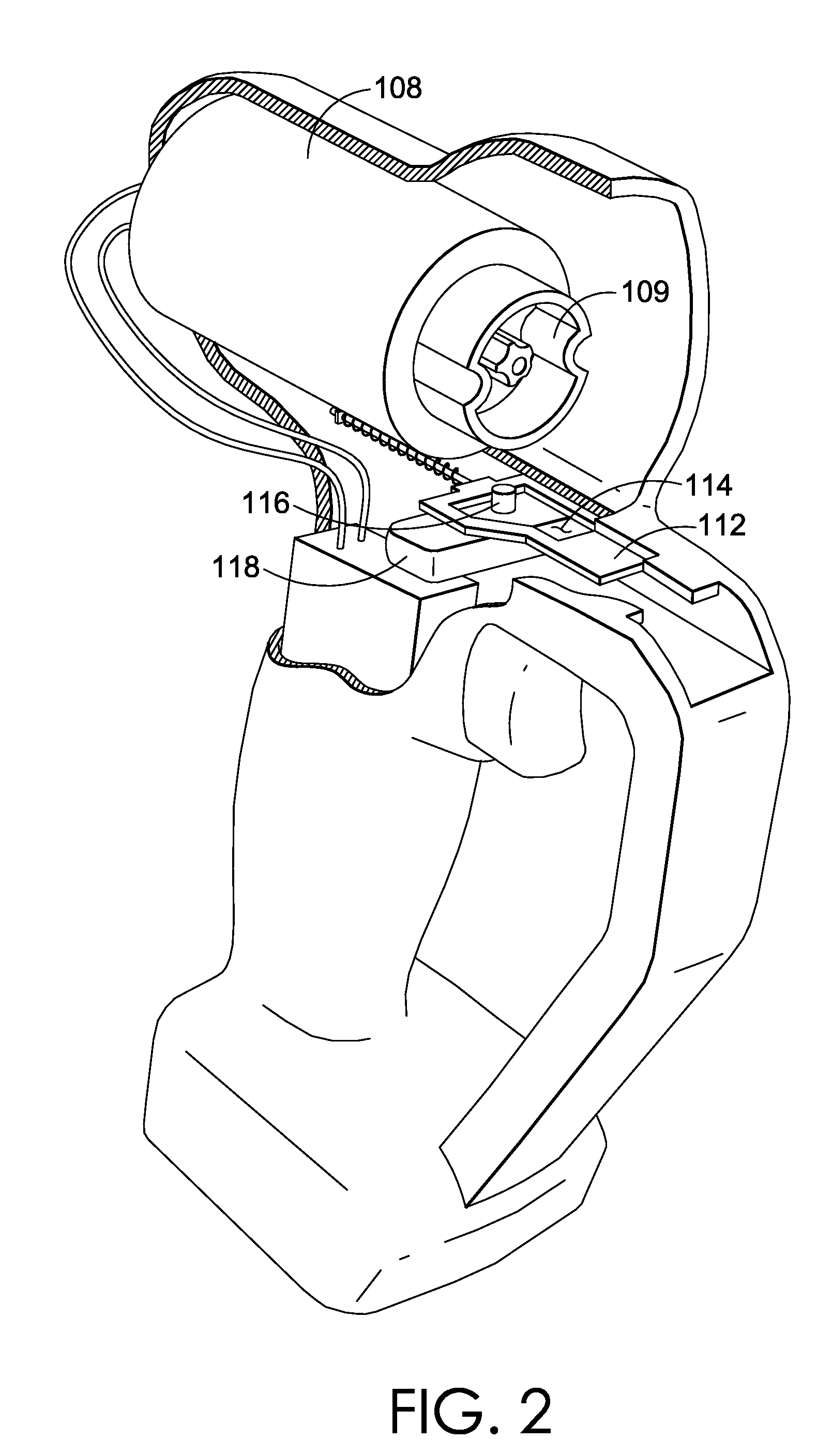
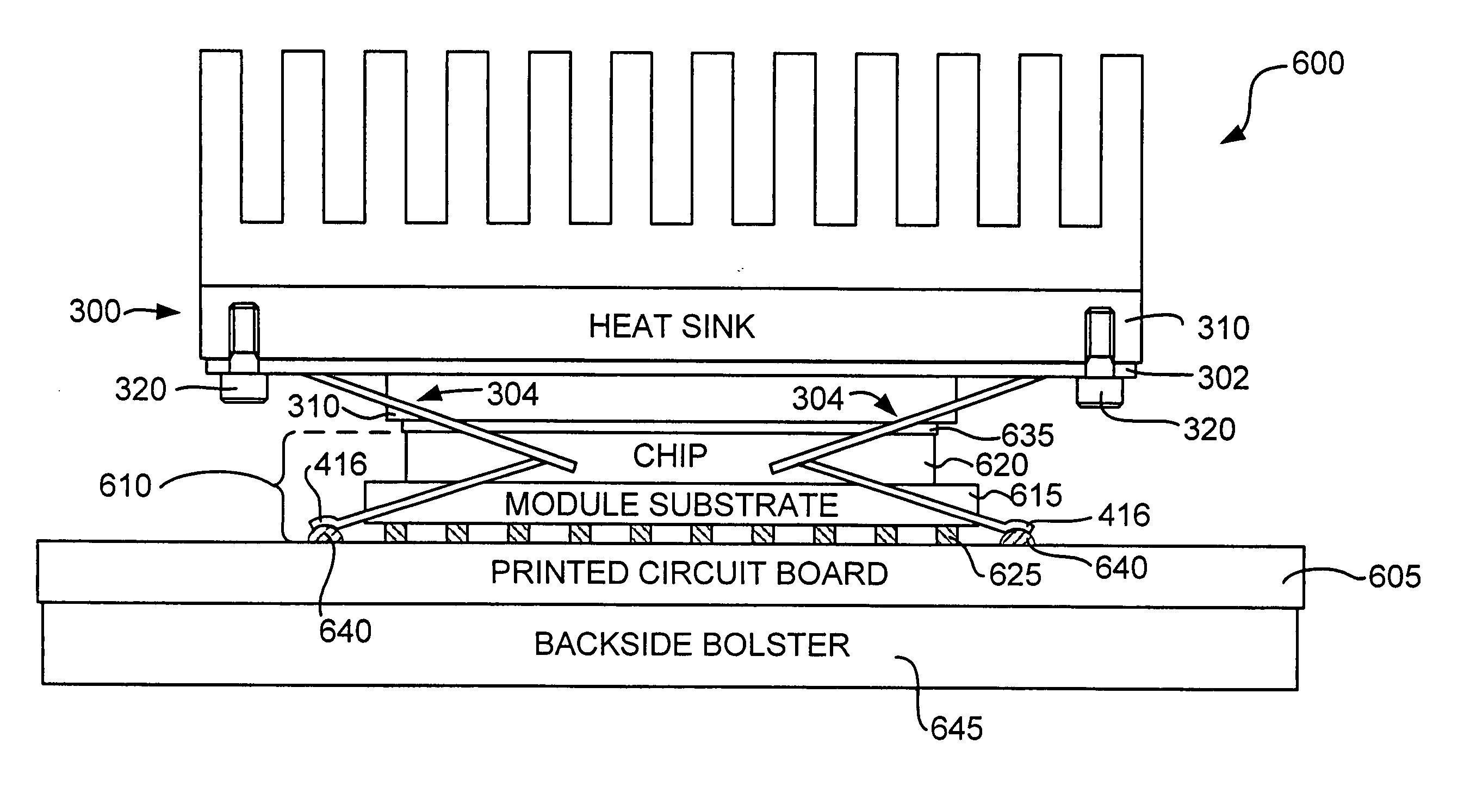
Method and apparatus for grounding a heat sink in thermal contact with an electronic component using a grounding spring having multiple-jointed spring fingers
InactiveUS20070097653A1Not easy to slipRestrict movementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityElectromagnetic interference
A grounding spring for electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression is interposed between a heat sink and a printed circuit board (PCB). The grounding spring comprises a conductive material having an opening formed at its base through which the heat sink makes thermal contact with an electronic module mounted on the PCB. The base makes electrical contact with a peripheral surface of the heat sink, and multiple-jointed spring fingers extend from the base to make electrical contact with conductive pads on the PCB. During compression, the movement of each spring finger's tip is substantially limited to the z-axis. Accordingly, the final installed location of the tip can be precisely controlled even when the grounding spring must accommodate a wide variety of installed heights of the heat sink relative to the PCB. Preferably, the spring fingers terminate with a concave tip that is less susceptible to sliding off the conductive pads.
Owner:IBM CORP
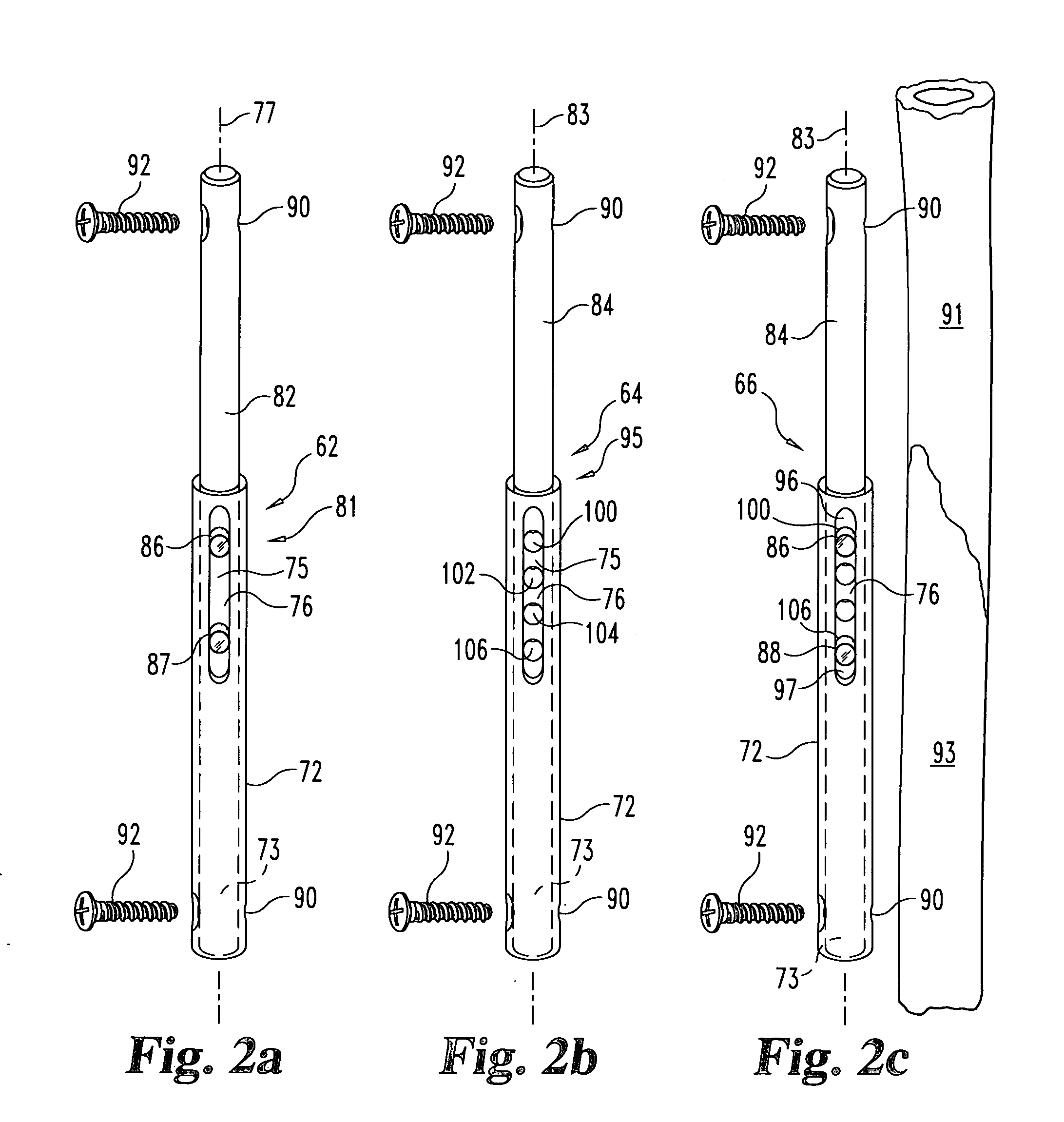
Apparatus and method for providing dynamizable translations to orthopedic implants
InactiveUS20050085812A1Avoid stress shieldingLimited supportSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBone structureJoint arthrodesis
The present invention generally relates to orthopedic devices and methods for treating bone defects. The orthopedic devices can provide sufficient support to the bone defect while allowing bone ingrowth and minimizing the risk to stress shield and / or pseudo-arthrodesis. The bone fixation devices include a biodegradable material or component that further resists relative motion of attached bones and allows the device to gradually transfer at least some load from the device to the growing bone structure in vivo and permitting an increase in the relative motion of bones attached to the device.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Posterior prosthetic spinal disc replacement and methods thereof
The present invention relates generally to a prosthetic spinal disc for replacing a damaged disc between two vertebrae of a spine. The present invention also relates to a method for implanting a prosthetic spinal disc via posterior or posterior lateral implantation. Other surgical approaches for implanting the prosthetic disc may also be used. The present invention also involves a method for implanting the prosthetic spinal disc while either avoiding or minimizing contact with the spinal cord and nerve rootlets, or reducing the time and extent that they need to be repositioned during implantation.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Anterior prosthetic spinal disc replacement
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
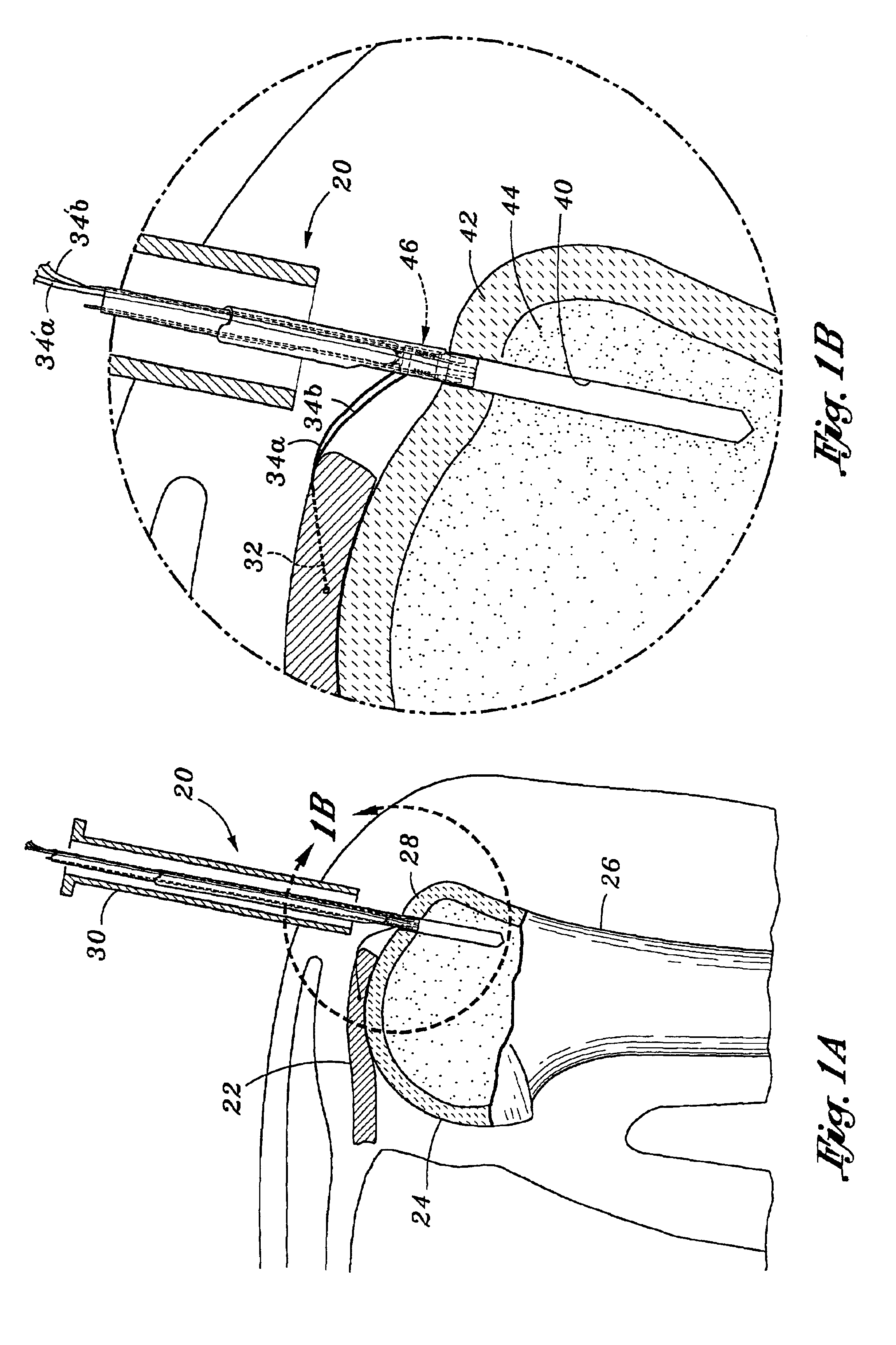
Automatic injector
ActiveUS20060030819A1Increase surface areaRelieve pressureAutomatic syringesMedical devicesBiomedical engineeringAuto-Injector
An auto-injector for dispensing a predetermined dose of medicament is disclosed. The auto-injector includes a needle cover that is configured to move from a retracted position to an extended locked position. The auto-injector includes a first locking assembly to hold the needle cover in a locked retracted position and a second locking assembly to hold the needle cover in a locked extended position.
Owner:MYLAN SPECIALTY
Lens delivery system
A lens delivery system having a plunger, an injector body and a nozzle portion connected to the injector body, the nozzle portion having a hinged lid and a hollow body with a lens holding platform formed beneath the hinged lid. The cartridge has an elongated nozzle tube or tip with a bore, the bore communicating with the lens holding platform. The bottom of the bore is rounded, which causes the edges of the lens between the lens haptics to fold upwardly as the lens is pushed down the bore from the platform by the plunger. A removable pin fits into the lid and prevents the lens from moving down the bore of the tip during shipment and storage.
Owner:ALCON INC
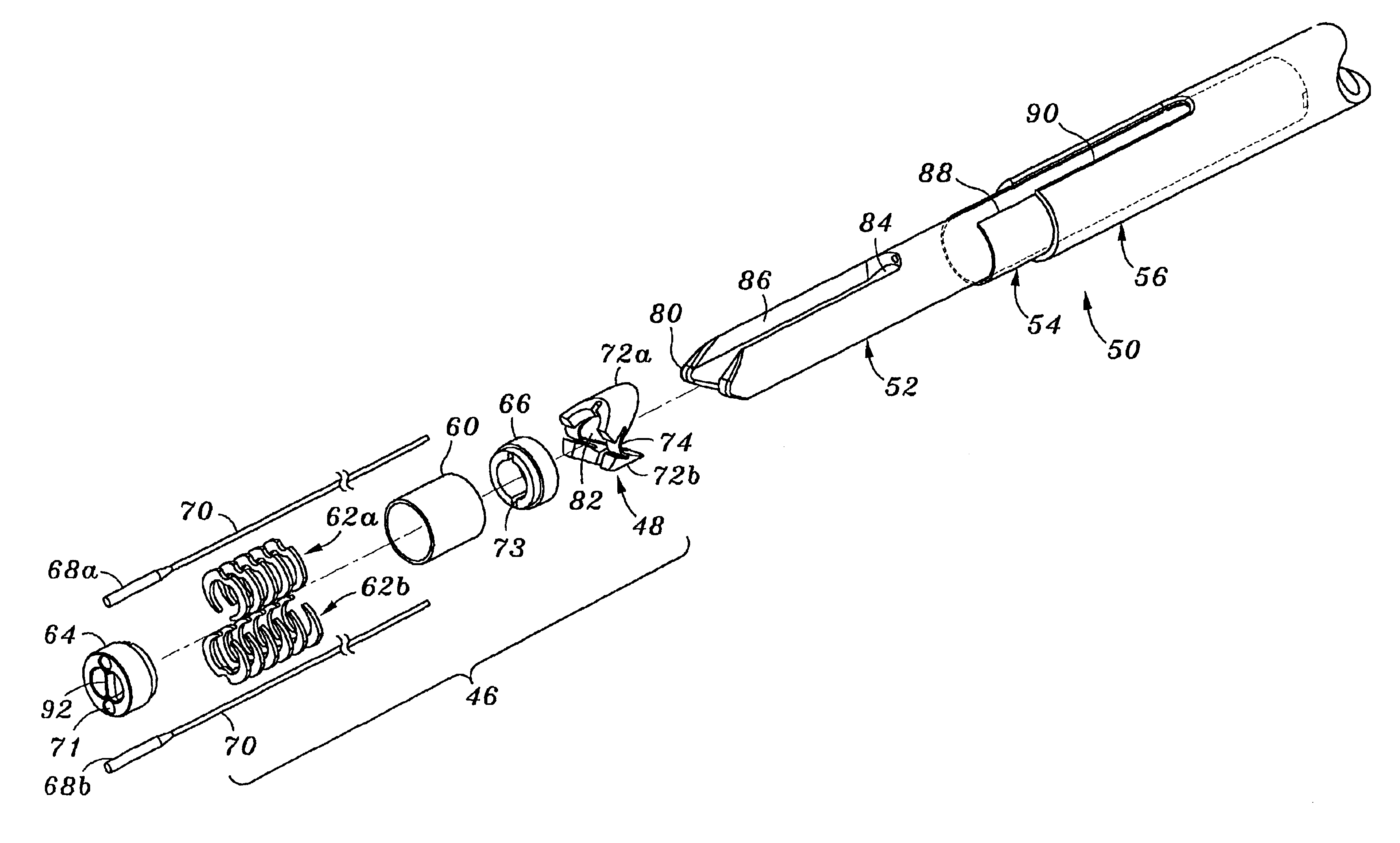
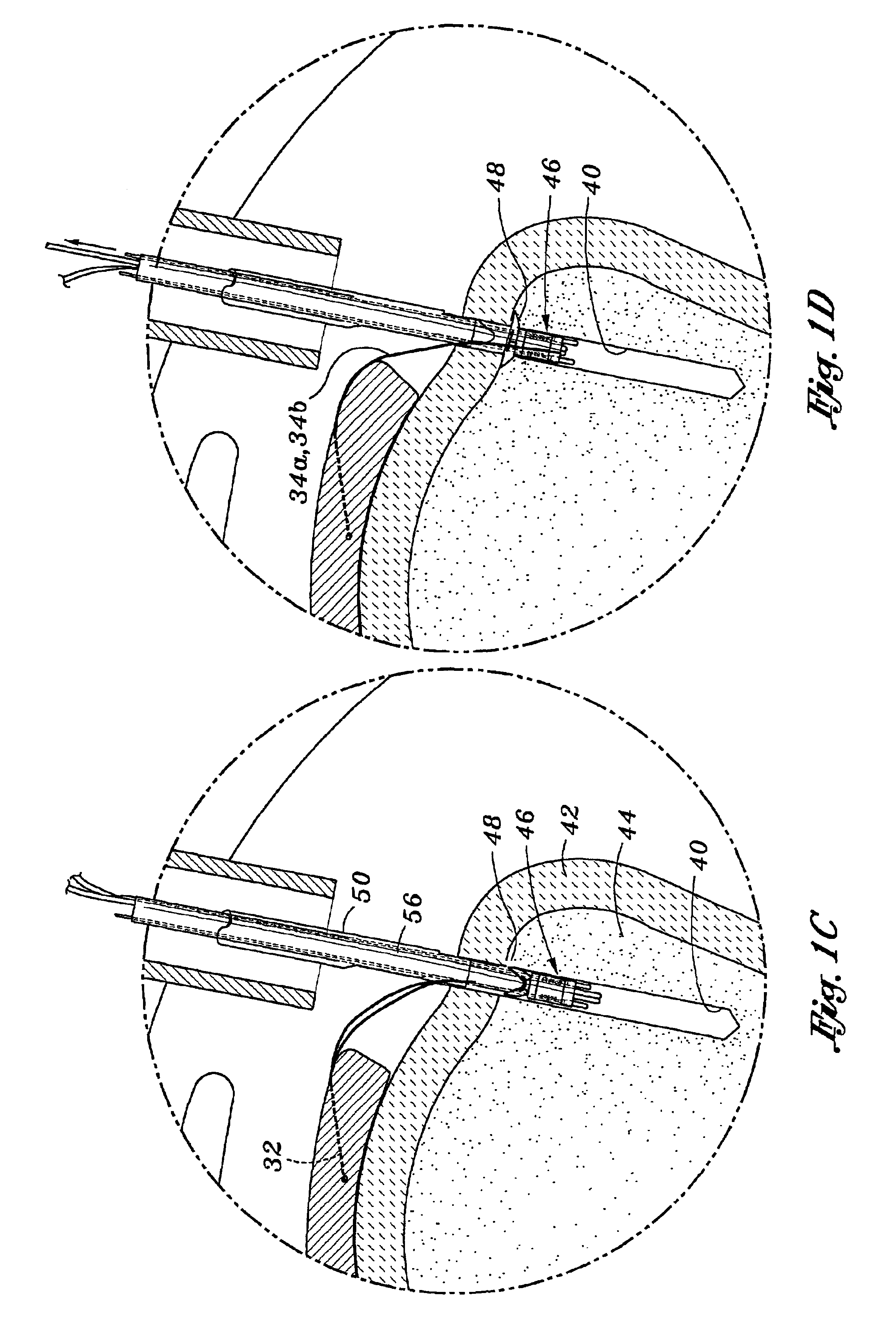
Temporary intraluminal filter guidewire and methods of use
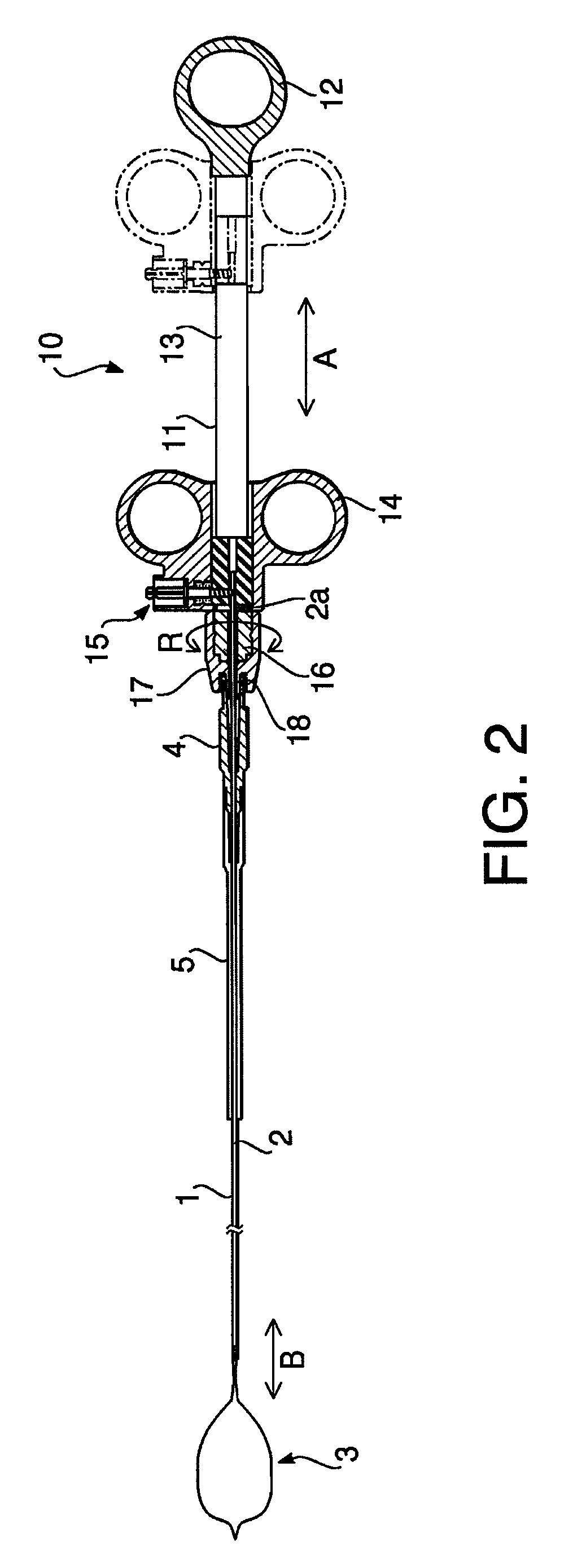
InactiveUS6866677B2Restrict movementPrevent movementDilatorsCatheterRelative displacementEngineering
The present invention is a temporary intraluminal filter guidewire for use during interventional procedures, such as angioplasty or stent deployment. A braided filter is mounted near the distal end of a steerable guidewire, which guides a therapeutic catheter. An actuator rod slides over the guidewire and is removably connected to the filter. The rod controls relative displacement of the filter ends, causing transformation of the filter between a deployed configuration and a collapsed configuration. Wire having enhanced radiopacity is included in the filter to provide visualization under fluoroscopy.
Owner:MEDTRONIC AVE
Method and apparatus for vascular and visceral clipping
InactiveUS7322995B2Convenient treatmentMinimizing chanceSnap fastenersClothes buttonsTrauma surgeryChest region
Devices and methods for achieving hemostasis and leakage control in hollow body vessels such as the small and large intestines, arteries and veins as well as ducts leading to the gall bladder and other organs. The devices and methods disclosed herein are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting, and most especially during damage control procedures. In such cases, the patient may have received trauma to the abdomen, extremities, neck or thoracic region. The devices utilize removable or permanently implanted, broad, soft, parallel jaw clips with minimal projections to maintain vessel contents without damage to the tissue comprising the vessel. These clips are applied using either standard instruments or custom devices that are subsequently removed leaving the clips implanted, on a temporary or permanent basis, to provide for hemostasis or leakage prevention, or both. These clips overcome the limitations of clips and sutures that are currently used for the same purposes. The clips come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The clips may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
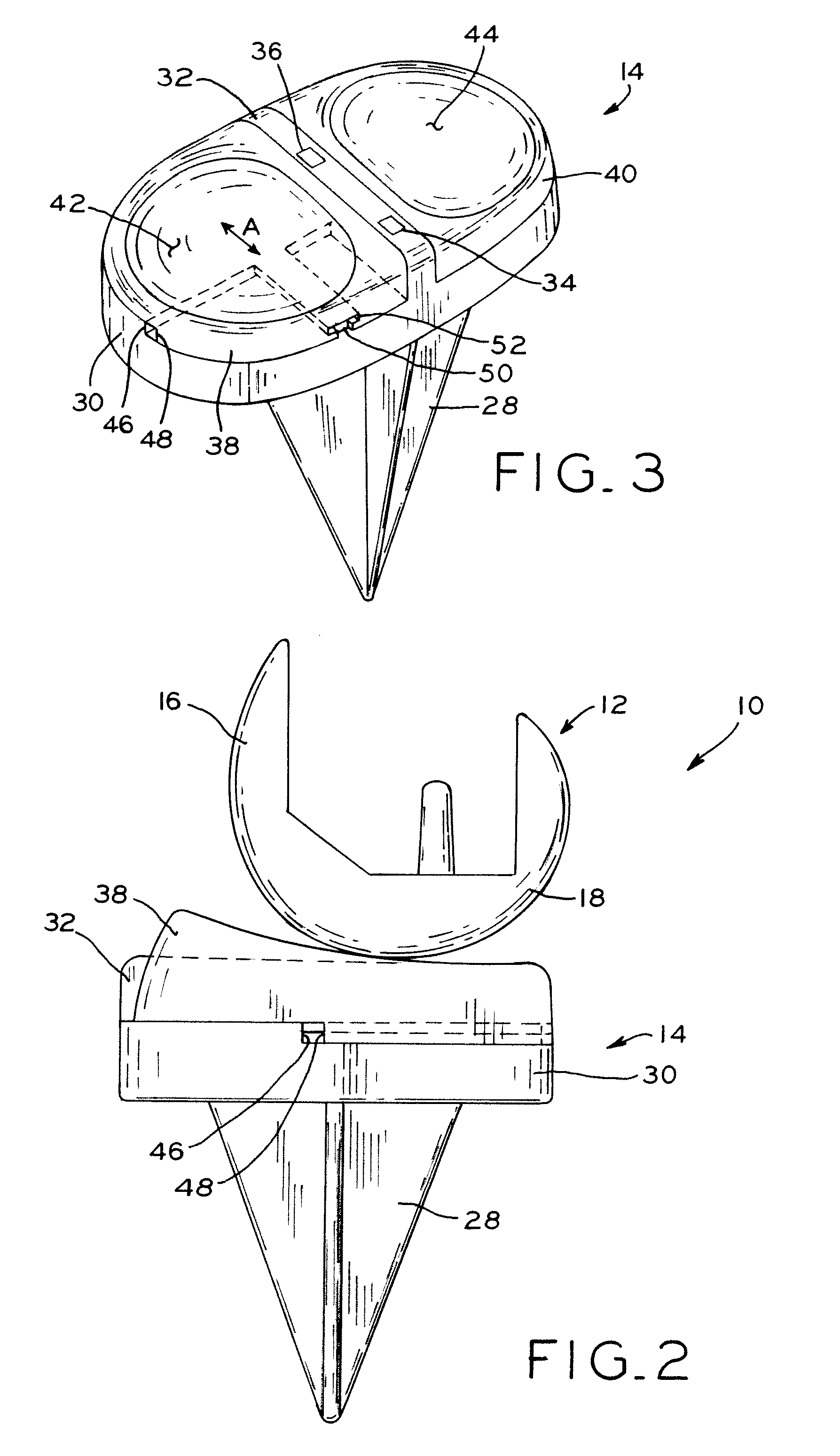
Total knee implant
A knee prosthesis is provided for use in knee arthroplasty. In one exemplary embodiment, the present invention provides a tibial prosthesis having a tibial baseplate with a fixed medial bearing component and a mobile lateral bearing component. In one exemplary embodiment, the lateral bearing component is secured to the lateral portion of the tibial baseplate utilizing at least one prosthetic ligament. Additionally, in one exemplary embodiment, a stop is provided to limit anterior or posterior movement of the lateral bearing component relative to the tibial baseplate. For example, the stop may be defined by cooperating shoulders formed on the lateral bearing and the tibial baseplate.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Method and apparatus for attaching connective tissues to bone using a knotless suture anchoring device
InactiveUS6855157B2Restrict movementSmall sizeSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSuture anchorsBone Cortex
An innovative bone anchor and methods for securing soft tissue, such as tendons, to bone, which permit a suture attachment that lies entirely beneath the cortical bone surface. Advantageously, the suturing material between the soft tissue and the bone anchor is secured without the need for tying a knot. The suture attachment to the bone anchor involves the looping of a length of suture around a pulley within the bone anchor, tightening the suture and attached soft tissue, and clamping the suture within the bone anchor. The bone anchor may be a tubular body having a lumen containing a plurality of suture-locking elements that clamp the suture therein. The locking elements may be thin and C-shaped. One or more locking plugs attached to separable actuation rods displace axially within the lumen and act on the locking elements to displace them radially. A generally uniform passage through the locking elements in their first positions converts to a smaller irregular passage after the locking plug displaces the elements to their second positions, thus effectively clamping the suture. The bone anchor further may include locking structure for securing itself within a bone cavity.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
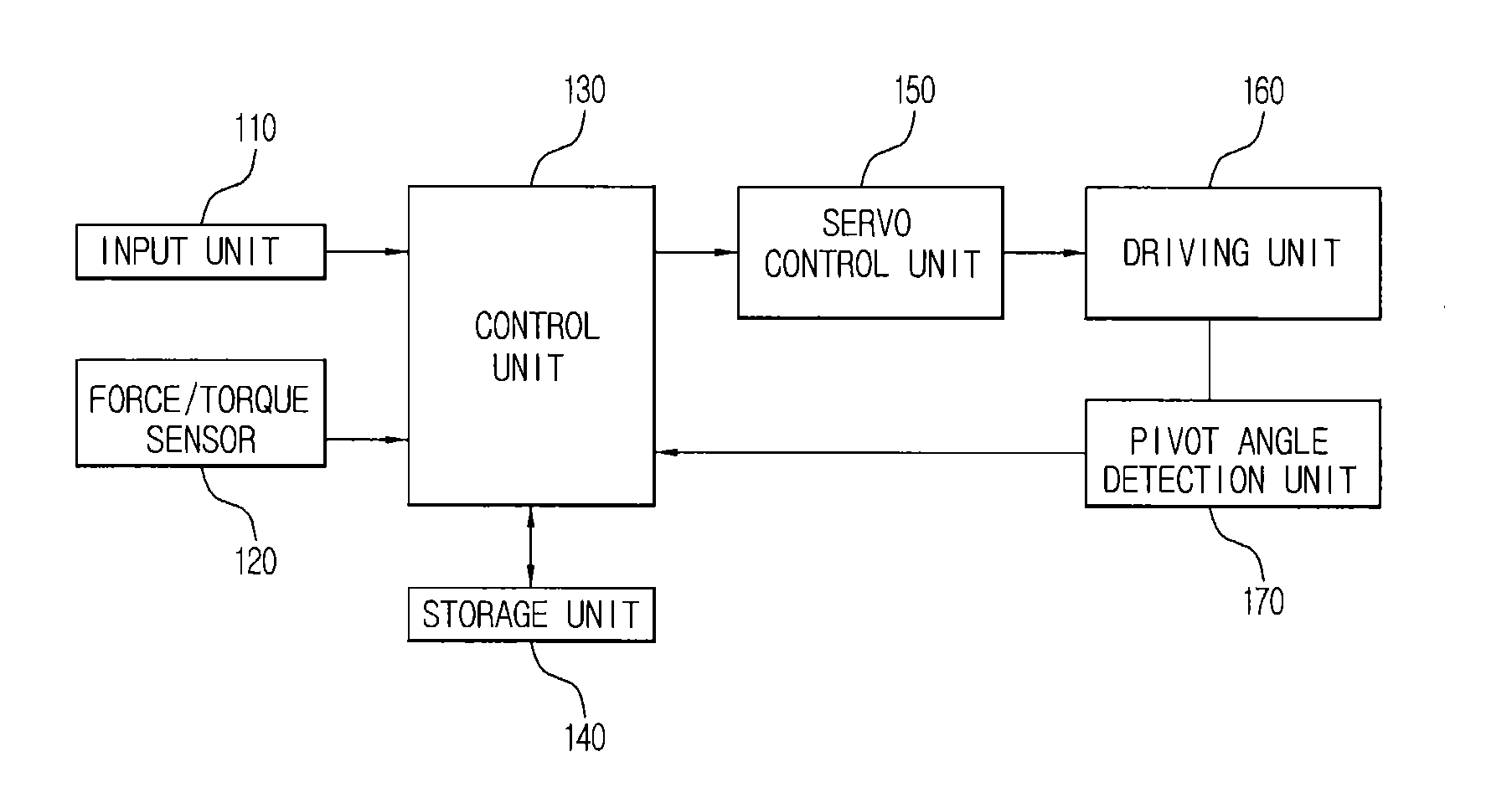
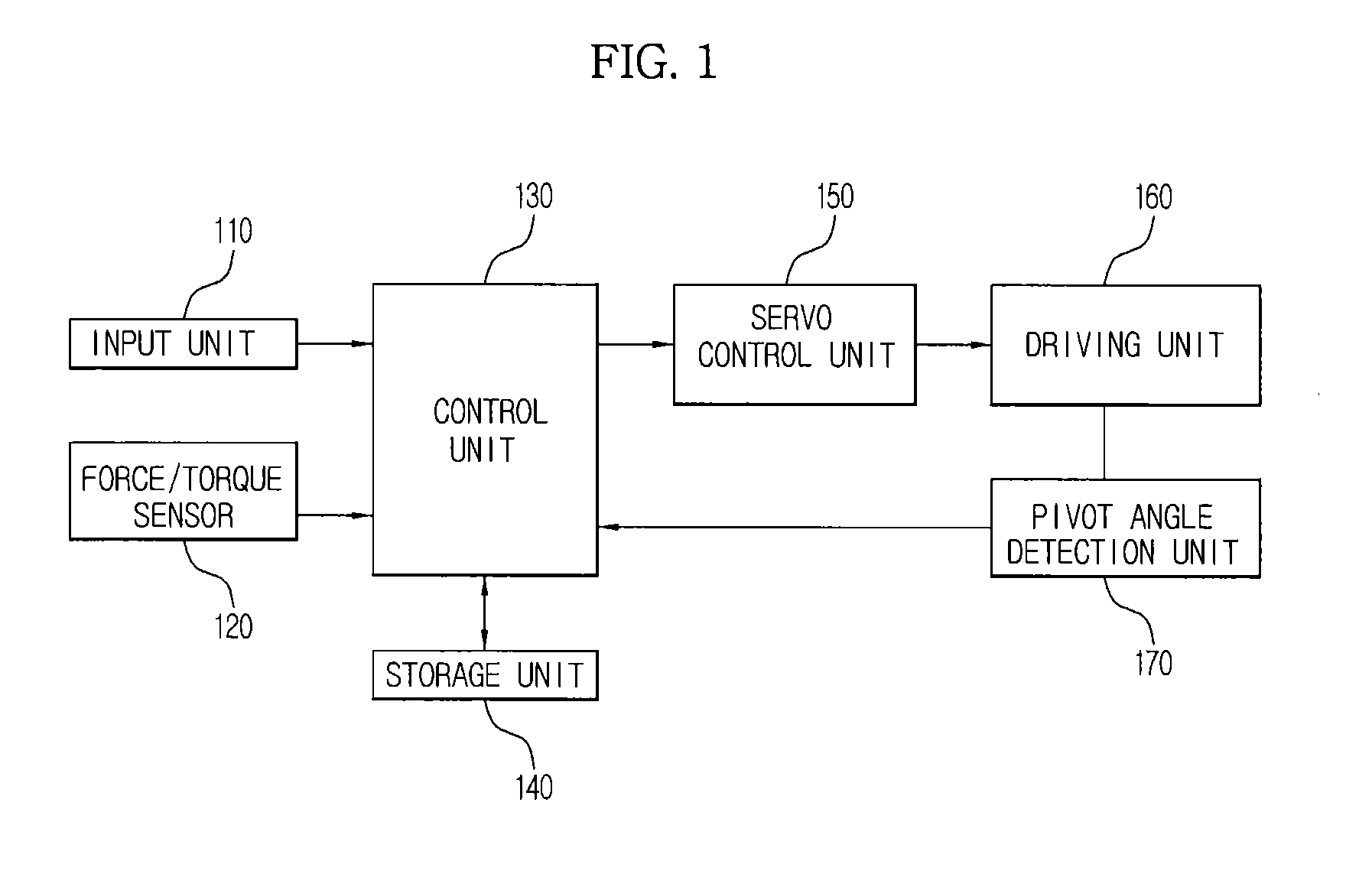
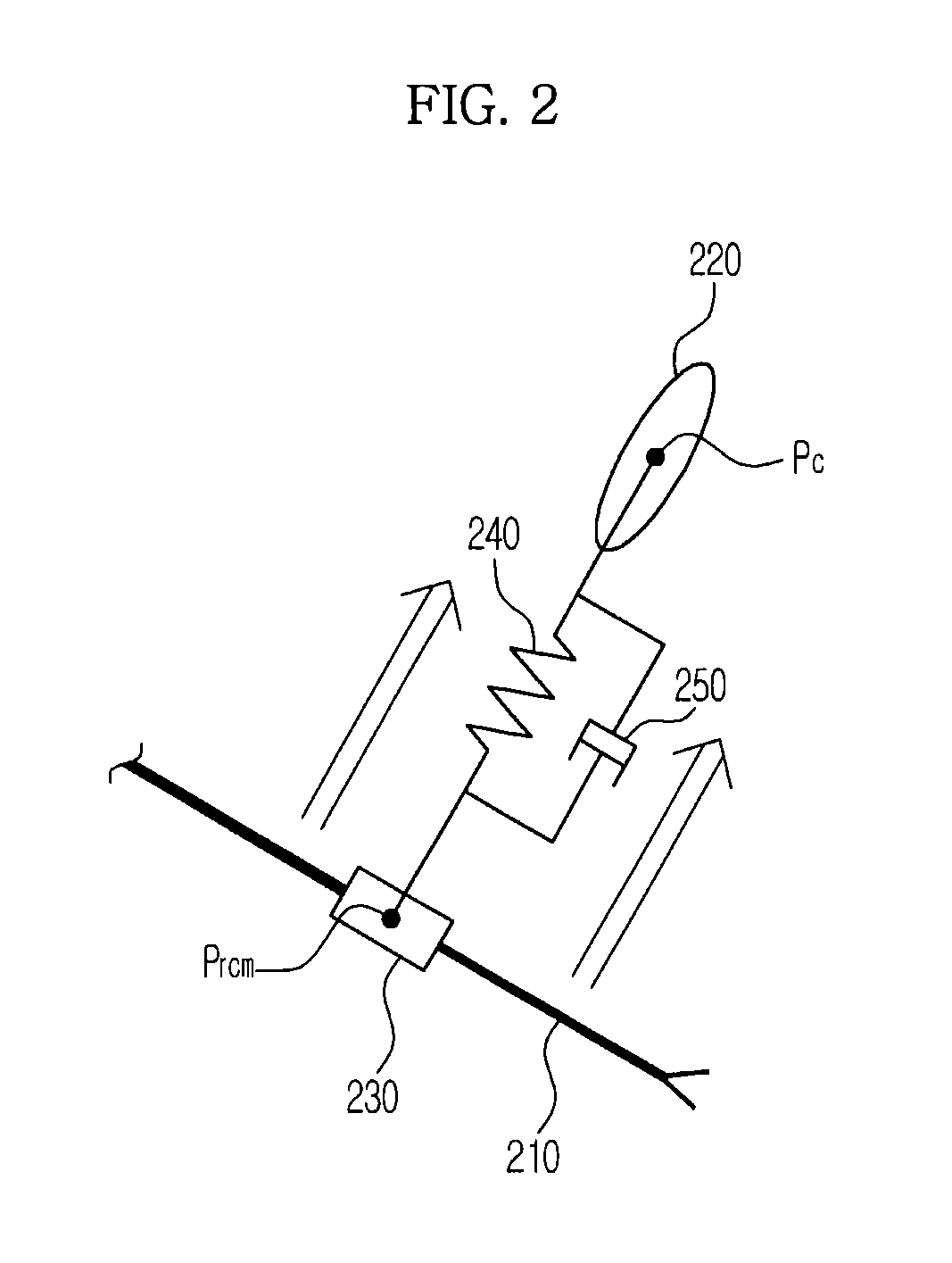
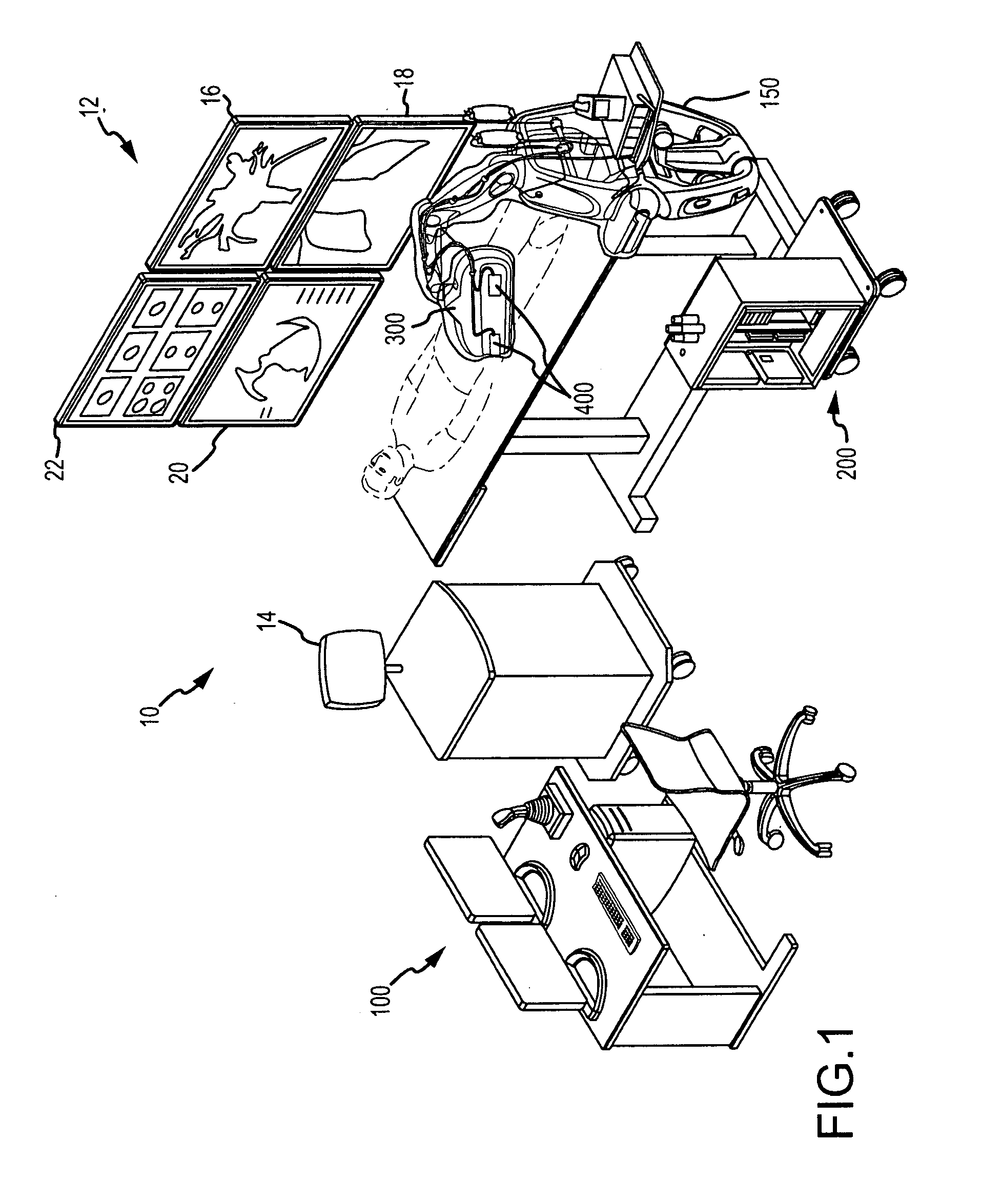
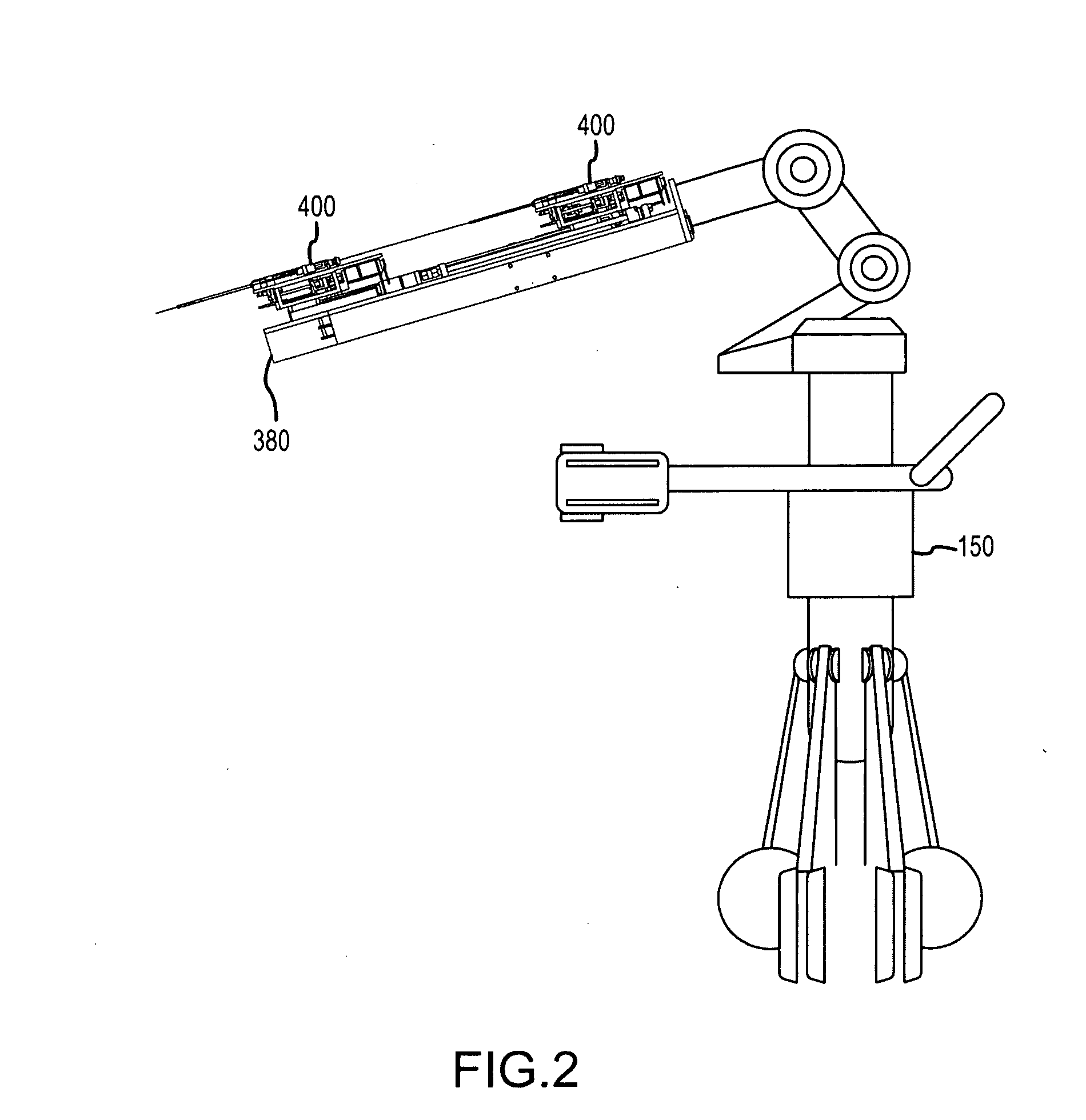
Surgical robot and control method thereof
InactiveUS20130116706A1Lower the volumeCompact designProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsSurgical robotEngineering
A method for controlling a surgical robot includes calculating an external force acting on a robot arm mounted with a surgical instrument, filtering the external force acting on the robot arm when a central point of an incision is set, calculating a virtual force to enable the surgical instrument which is positioned away from the central point of the incision to return to the central point of the incision, and applying the calculated virtual force to the filtered external force, to control movement of the robot arm. As a result, it is possible to compactly design the surgical robot and thereby reduce the volume of the surgical robot.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
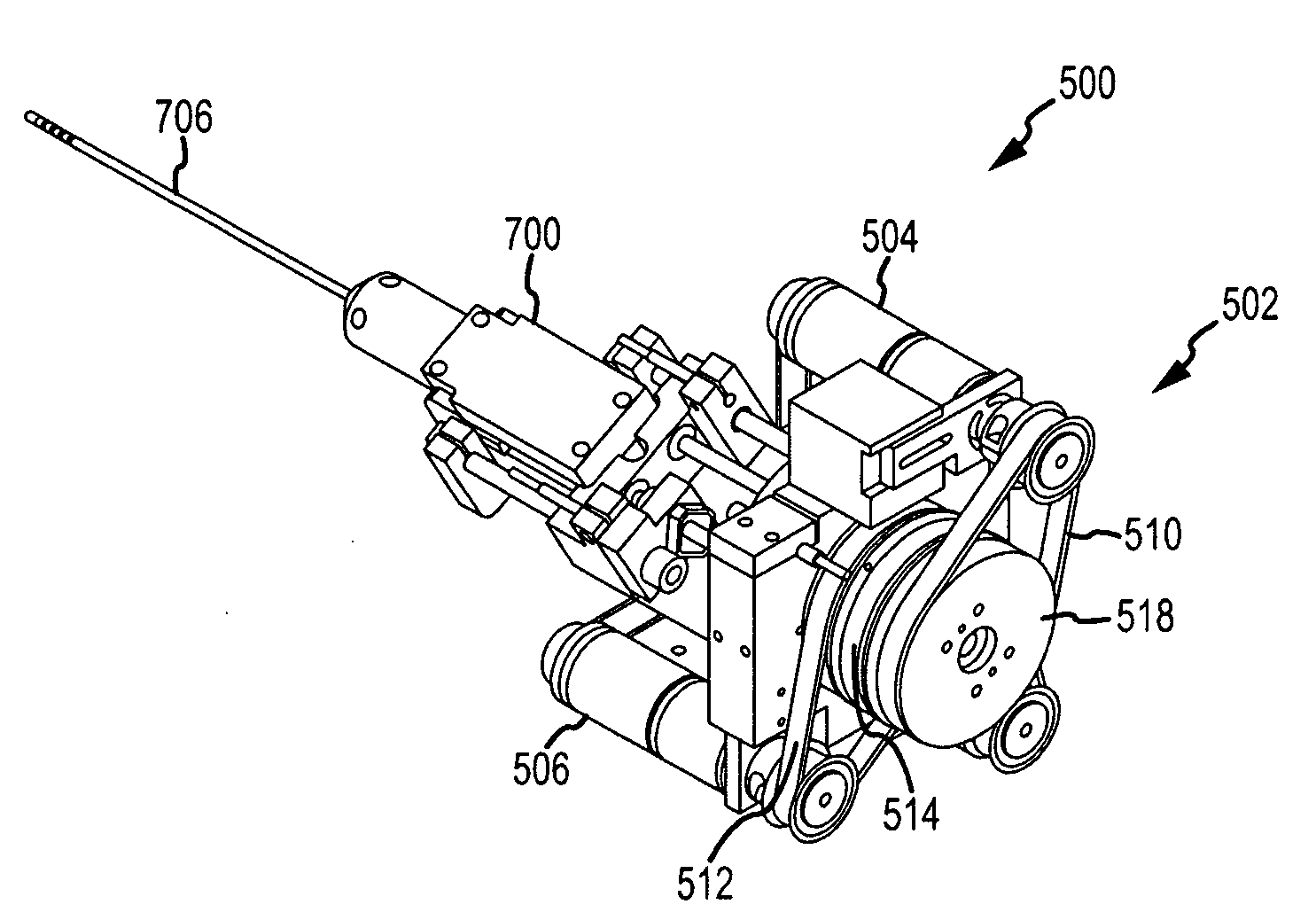
Robotic catheter rotatable device cartridge
InactiveUS20090247944A1Minimize and eliminate procedural variabilityEliminate backlashDiagnosticsMedical devicesEngineeringSteering Wire
A robotic catheter rotatable device cartridge may include a housing member attachable to a drive mechanism for rotating the cartridge and a catheter attached to the cartridge along an axial direction of the catheter. A slider block may be generally slidable relative to the housing and engaged with one or more steering wires for controlling movement of the catheter in a transverse direction relative to the axial direction. The catheter may include the steering wire(s) engaged therewith and movable in the transverse direction when the slider block is linearly driven in a predetermined direction.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Locking mechanism with two-piece washer
InactiveUS20100023061A1Restrict movementStrong lockSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSet screwLocking mechanism
Locking mechanisms and methods of fixation, such as the fixation of a fixation device like a bone screw and of a rod to the spine. The locking mechanism includes a body, a rod seat and a set screw. The rod seat is configured to separate into two pieces when the rod exerts force on the top portion of the washer and the set screw limits movement of the washer toward the bottom of the locking mechanism.
Owner:INGENIUM
Navigation arm system and methods
InactiveUS20170304020A1Position be accurate and stableFacilitate positioningCannulasSurgical needlesCartStructural stability
A navigation arm system for supporting a navigation device of a navigation system, capable of coupling with a navigation display cart, the navigation arm system involving: an arm assembly configured to position the navigation device, the arm assembly including a first arm linkage having a tension adjustment feature and releasably connectable to the navigation device; a second arm linkage capable of connecting the arm assembly to the navigation display cart; and at least one joint coupling at least the first and second arm linkages; and a locking mechanism configured to maintain a disposition of the arm assembly in relation to the navigation display cart in a locked stored position and a unlocked deployed position, the locking mechanism configured to lockably couple the arm assembly in relation to the navigation display cart, the locking mechanism including a plurality of locking modes, whereby structural stability is providable
Owner:SYNAPTIVE MEDICAL INC
Robotic surgery system including position sensors using fiber bragg gratings
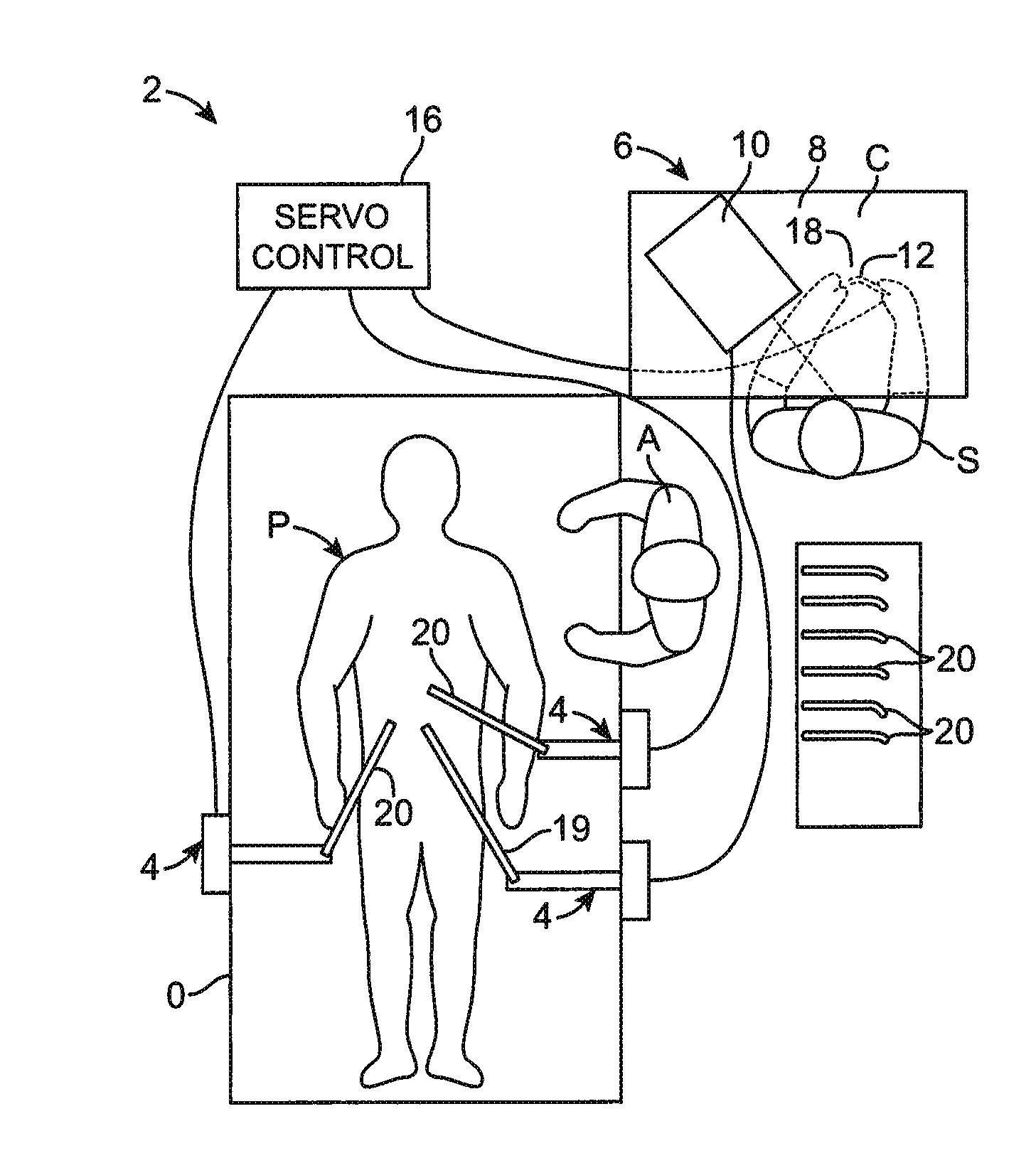
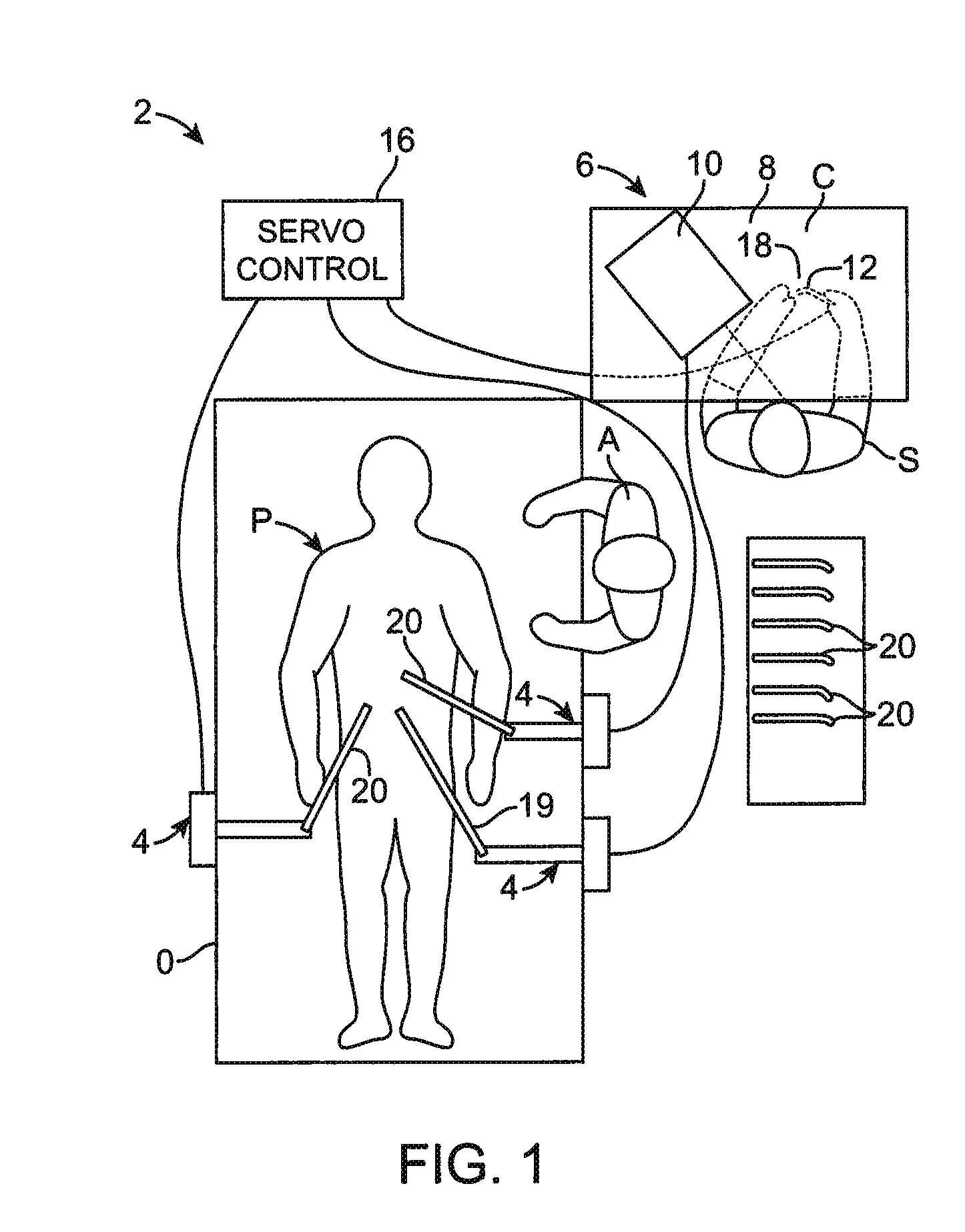
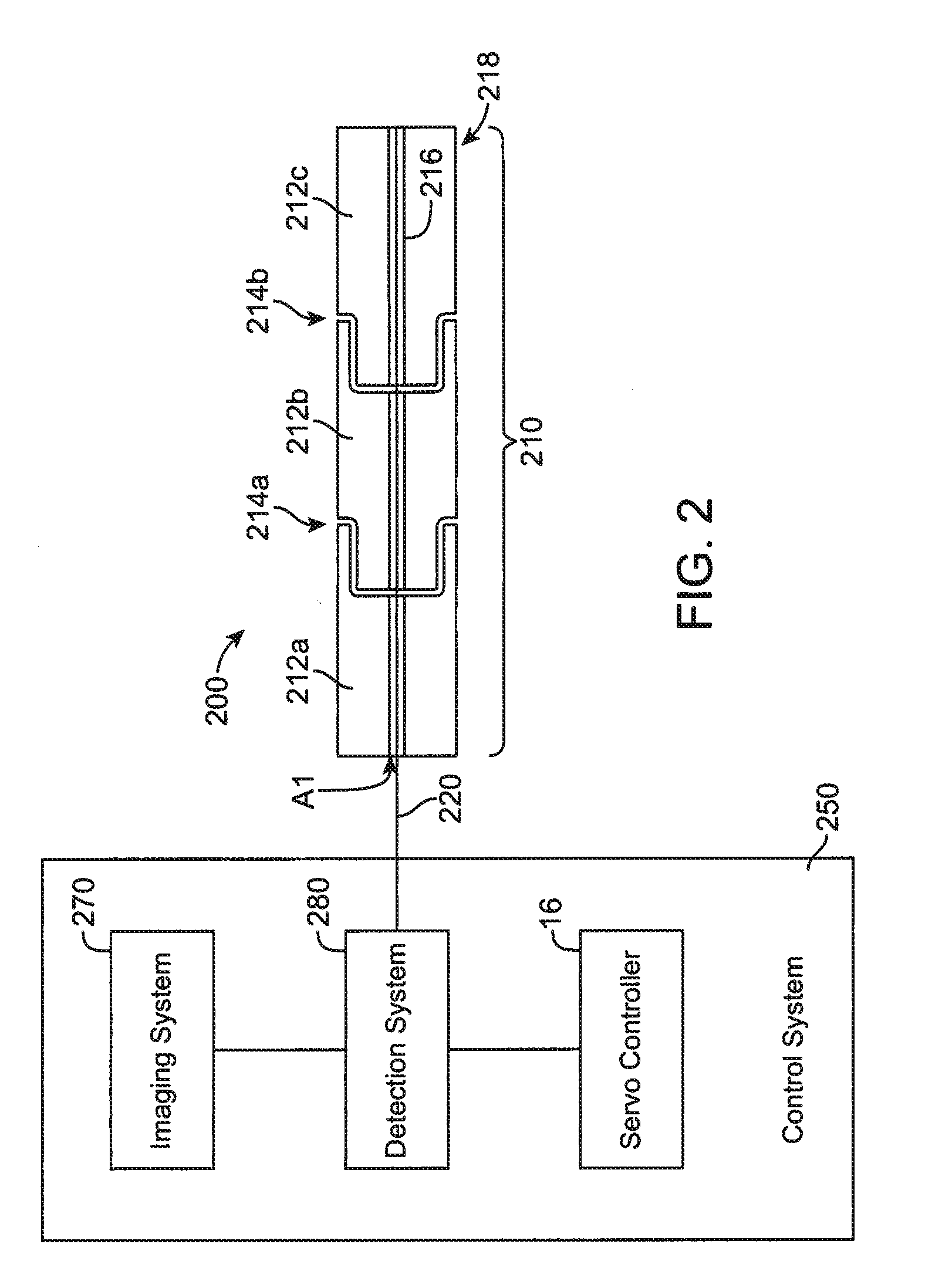
A surgical instrument is provided, including: at least one articulatable arm having a distal end, a proximal end, and at least one joint region disposed between the distal and proximal ends; an optical fiber bend sensor provided in the at least one joint region of the at least one articulatable arm; a detection system coupled to the optical fiber bend sensor, said detection system comprising a light source and a light detector for detecting light reflected by or transmitted through the optical fiber bend sensor to determine a position of at least one joint region of the at least one articulatable arm based on the detected light reflected by or transmitted through the optical fiber bend sensor; and a control system comprising a servo controller for effectuating movement of the arm.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
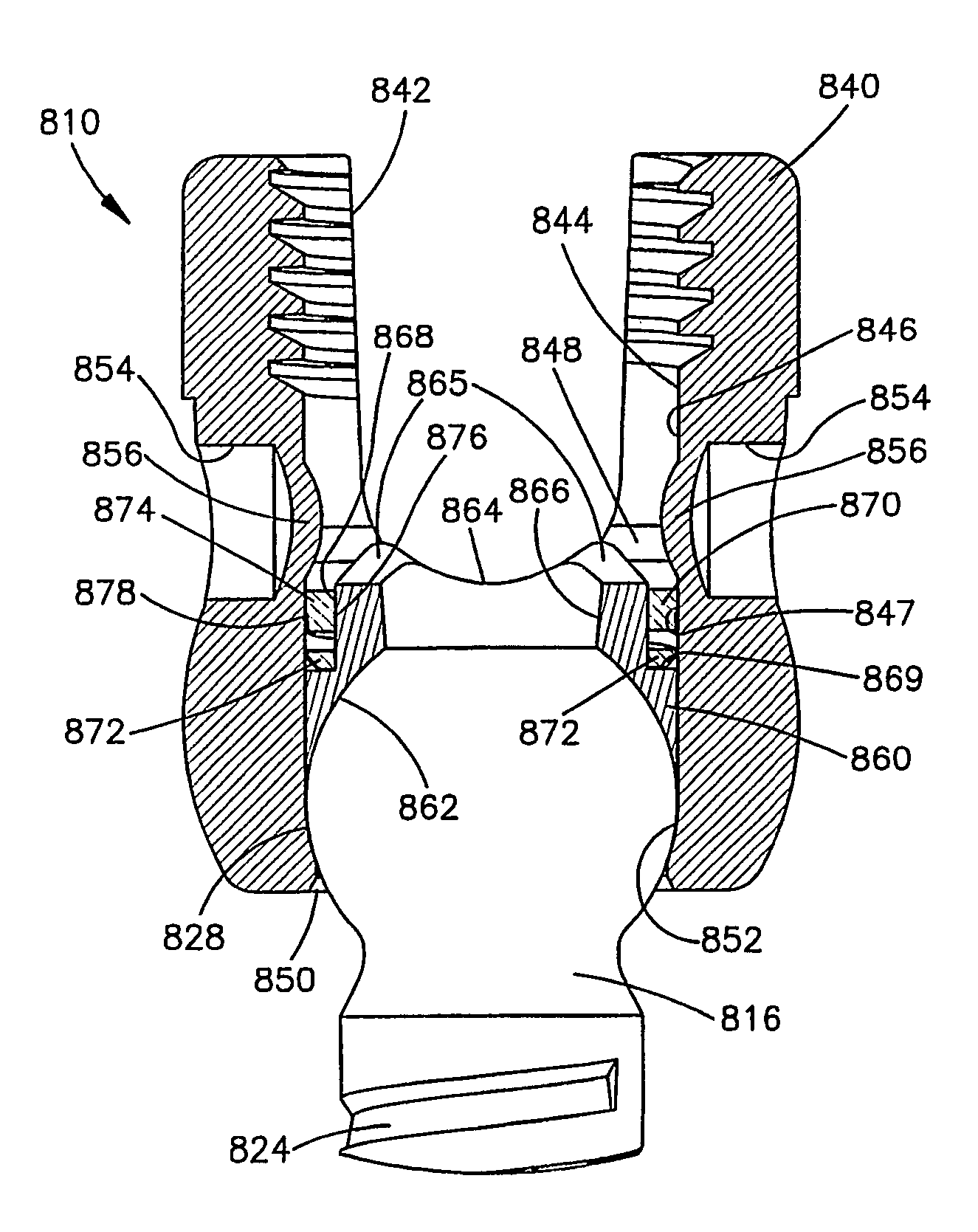
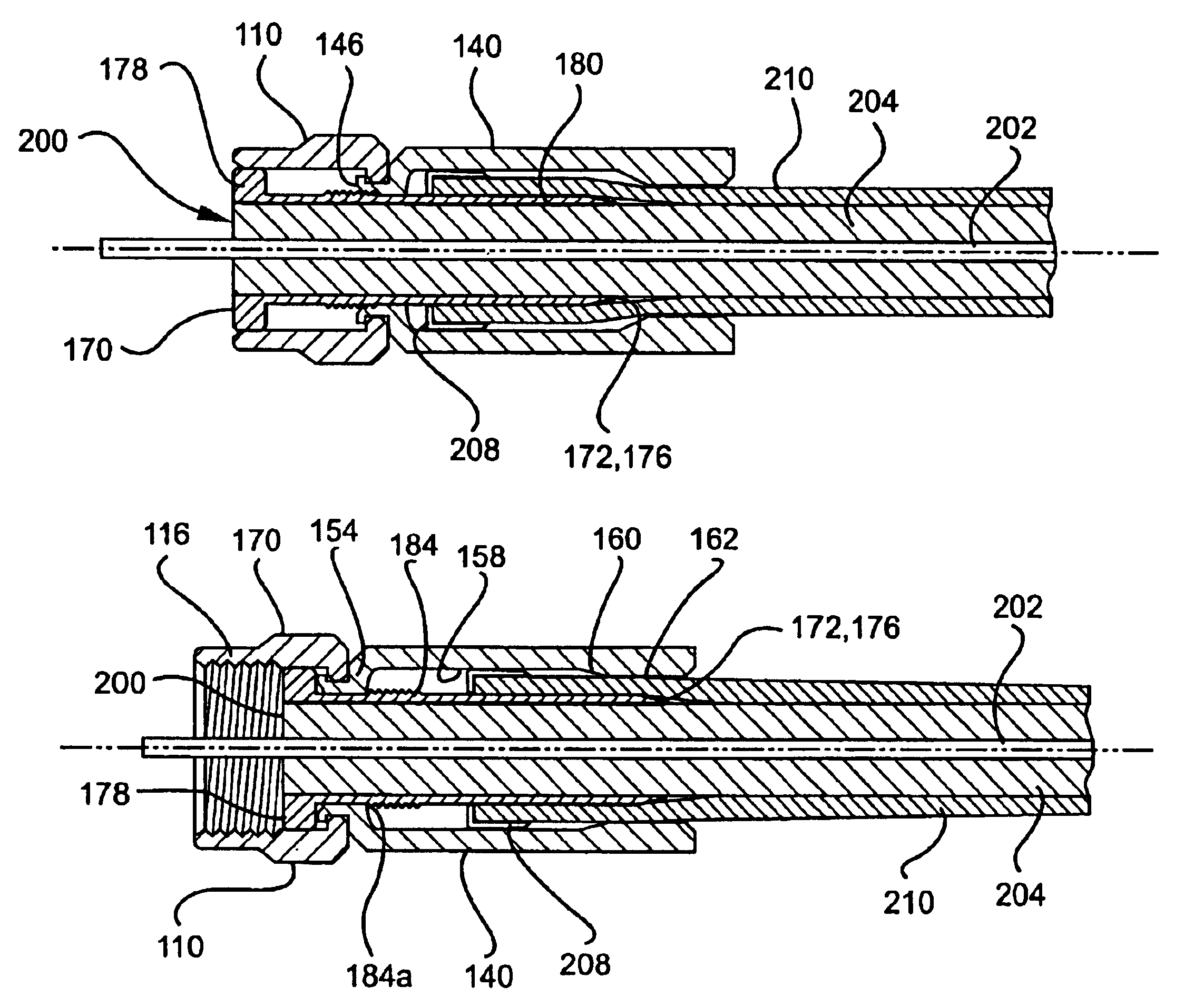
Sealed coaxial cable connector and related method
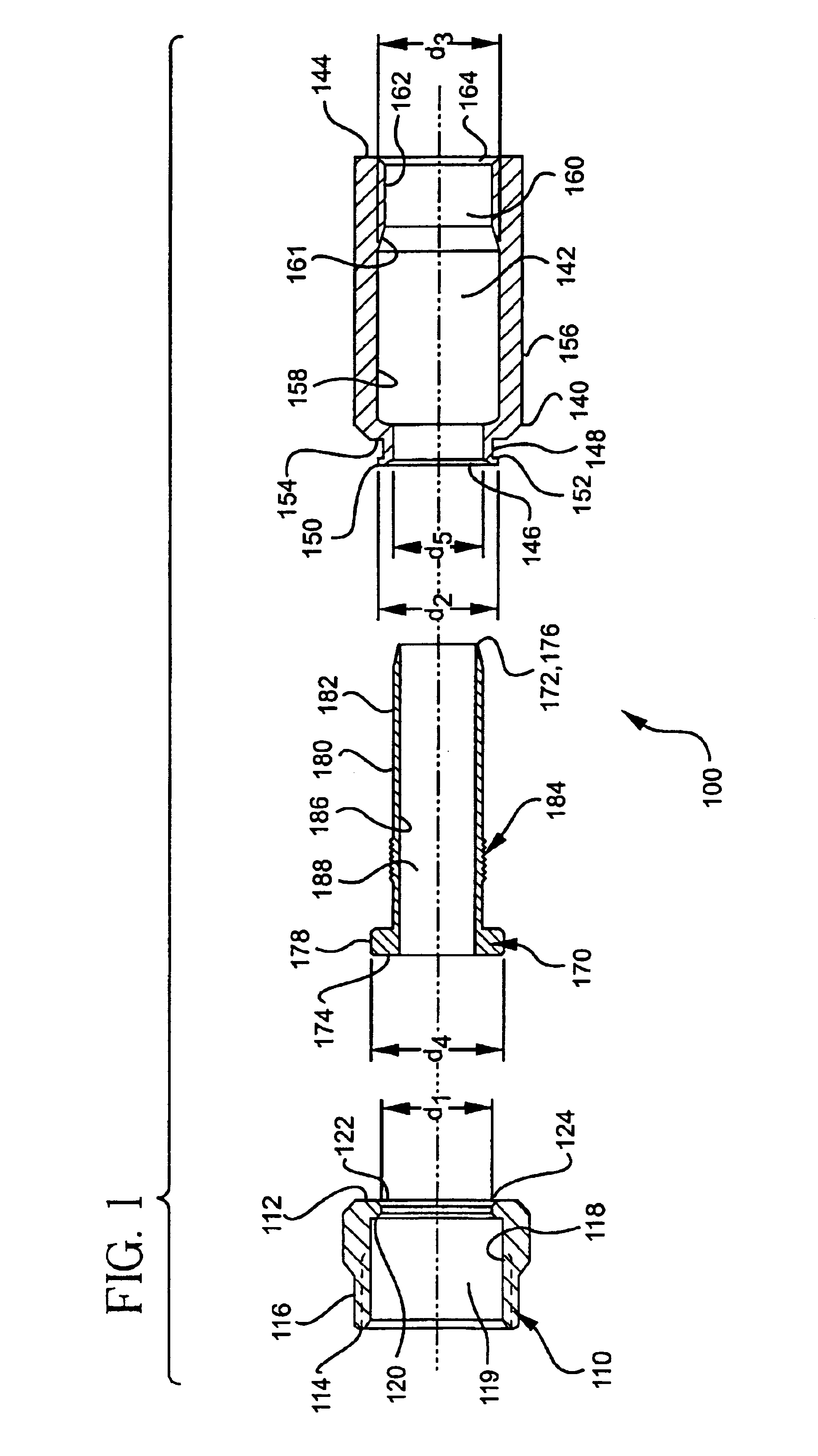
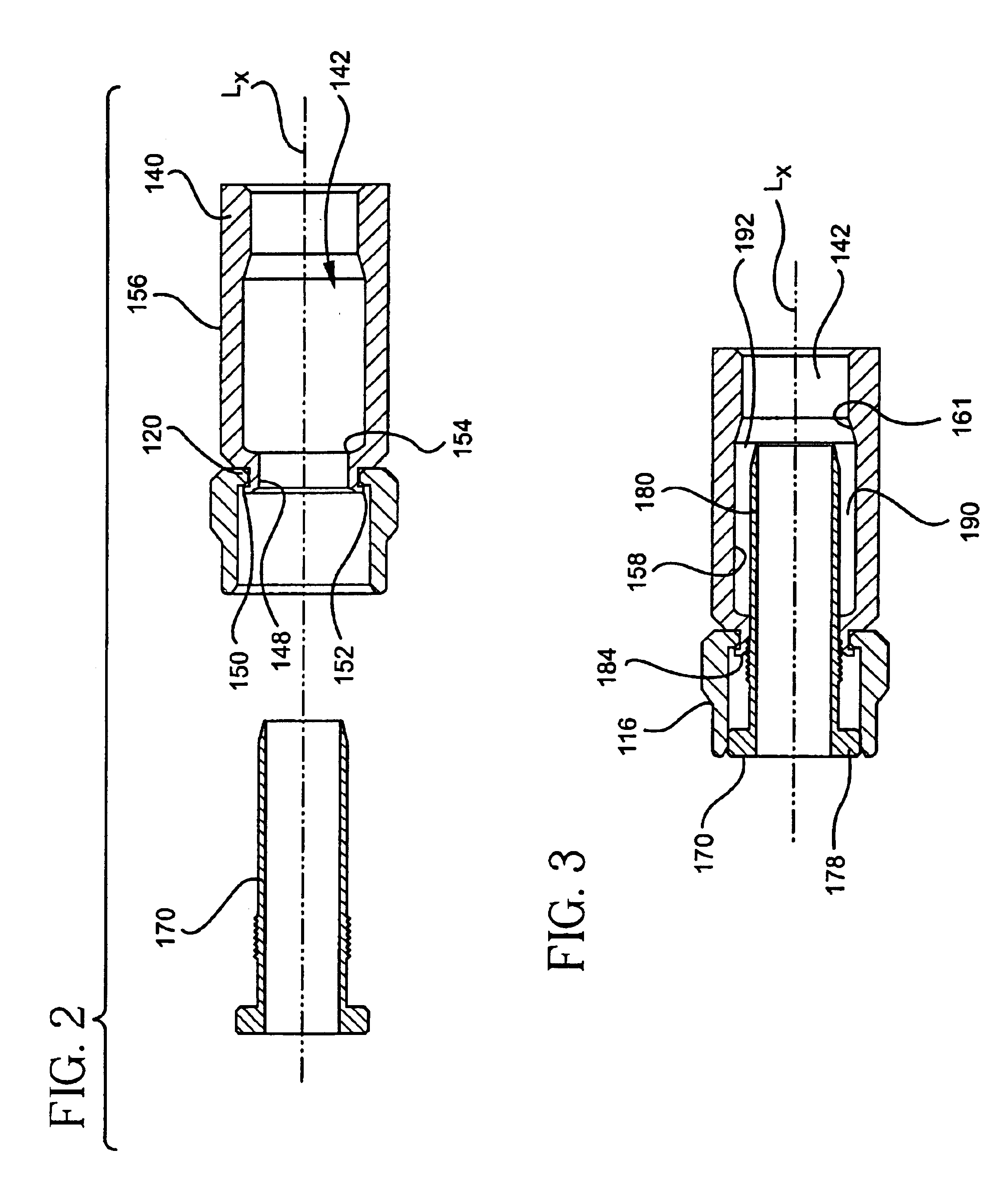
InactiveUS6790081B2Maximum engagementPermit some movementElectrically conductive connectionsSecuring/insulating coupling contact membersCoaxial cableElectrical conductor
A coaxial cable connector includes a coupler, a post and a body member. One end of the body member includes a lip that is inserted through the opening in an annular collar of the coupler. In a cable-installed position, the shank of the post is received in the body member to form an annular chamber which is sufficiently narrow to compress the outer conductor and the jacket of a coaxial cable to establish a distal seal. Tightening of the coupler to the terminal compresses the lip between the flange of the post and the annular collar for establishing a proximal seal. Related methods also are provided.
Owner:PPC BROADBAND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com