Patents
Literature
114 results about "Joint arthrodesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
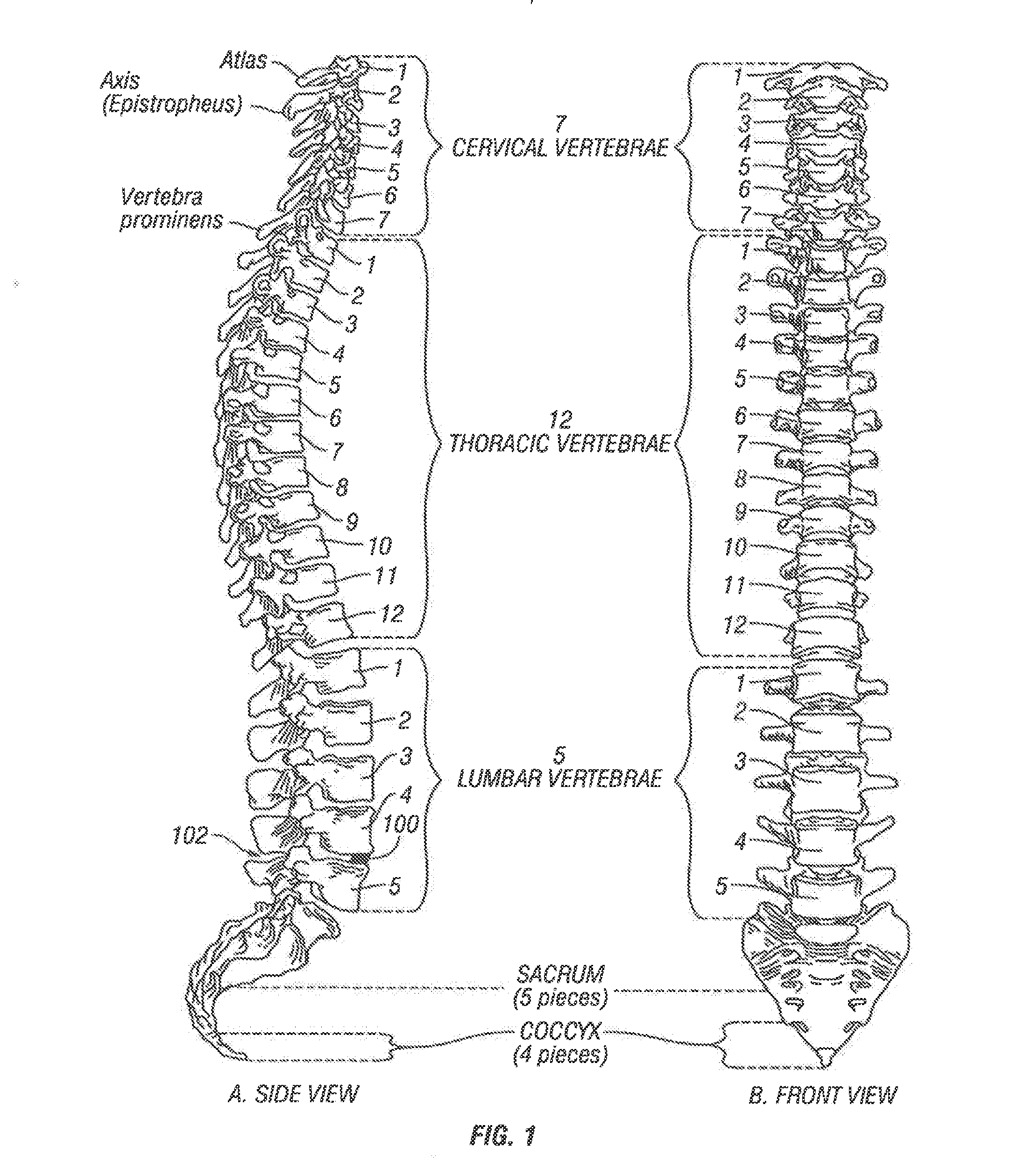
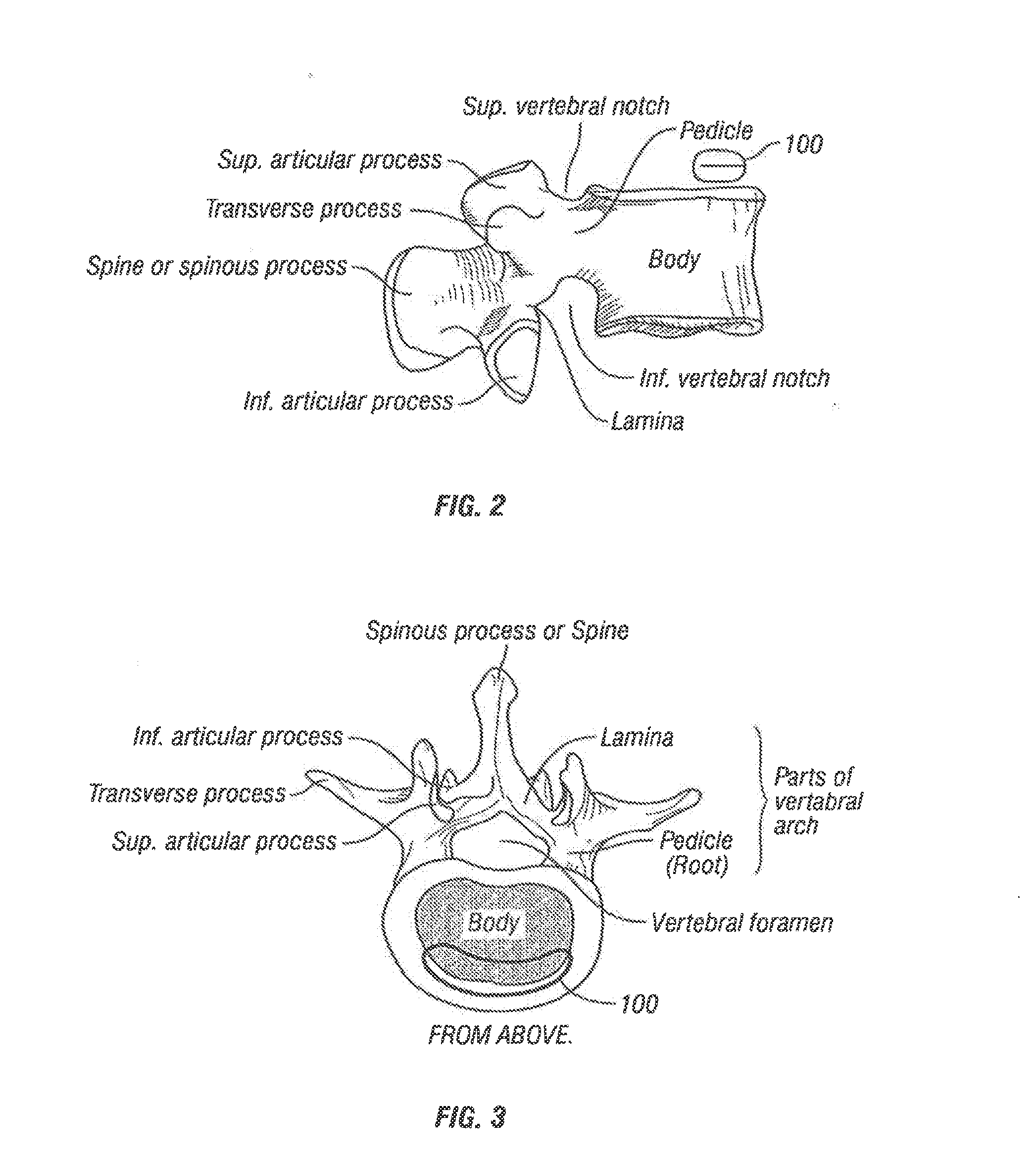
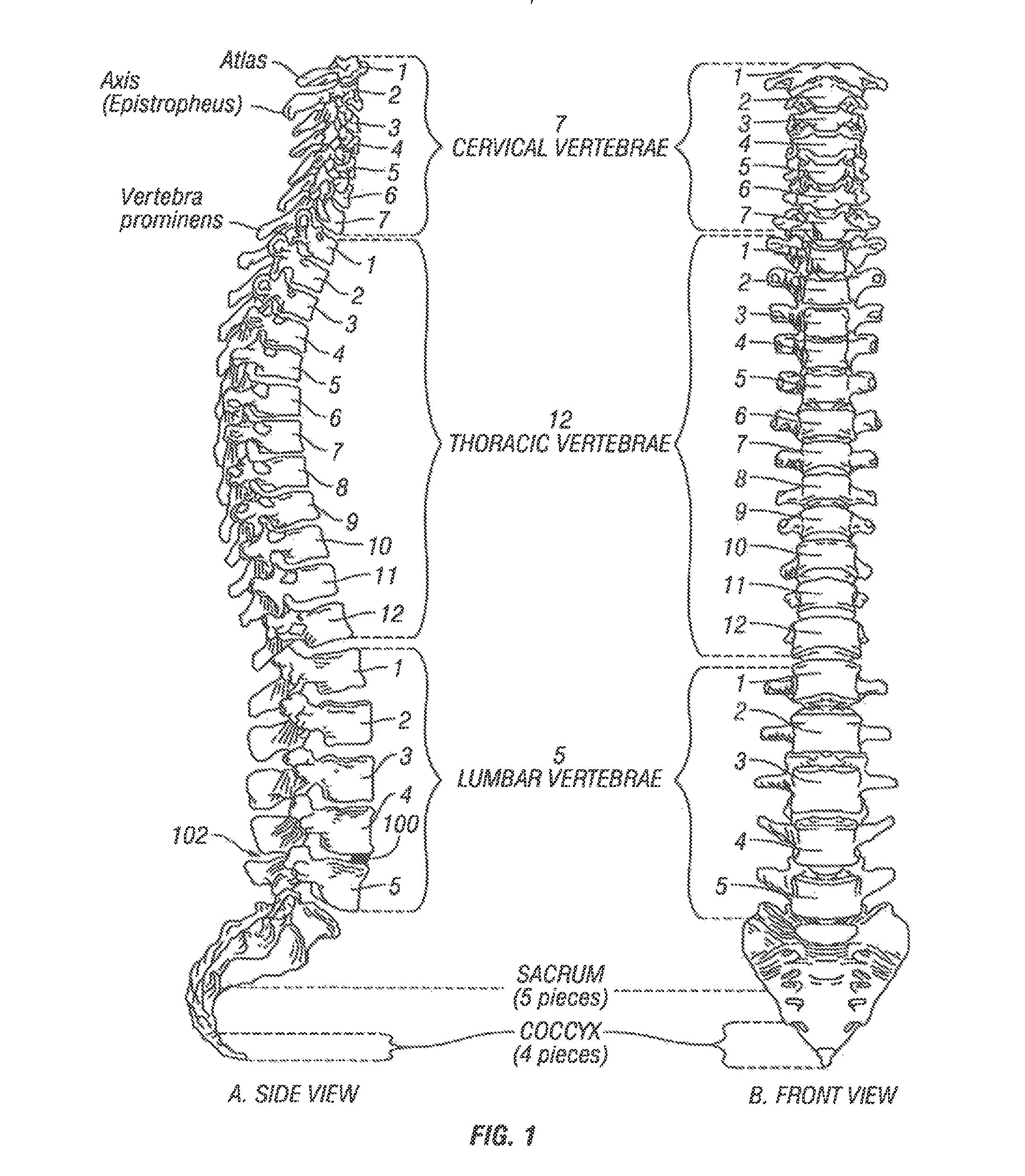
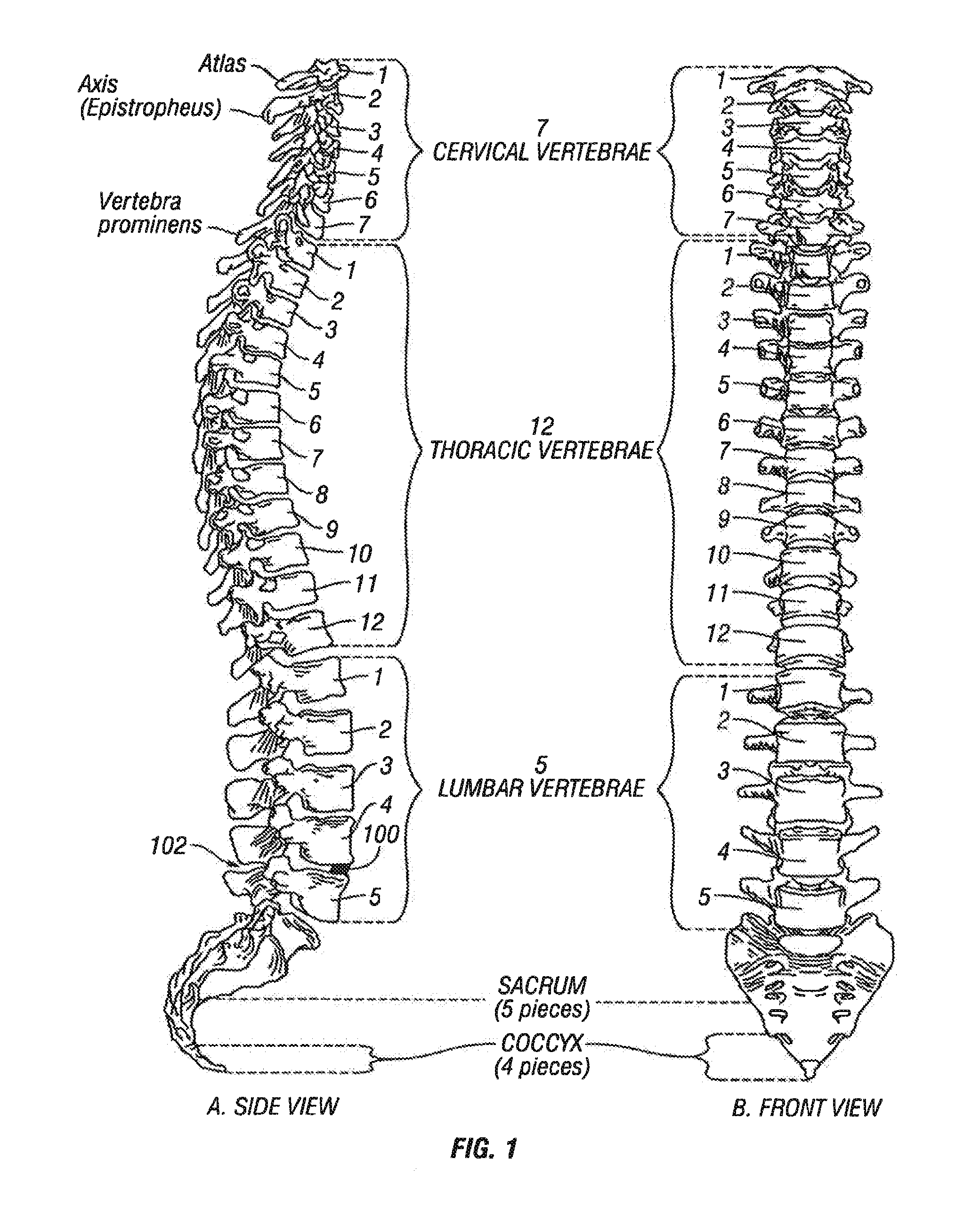
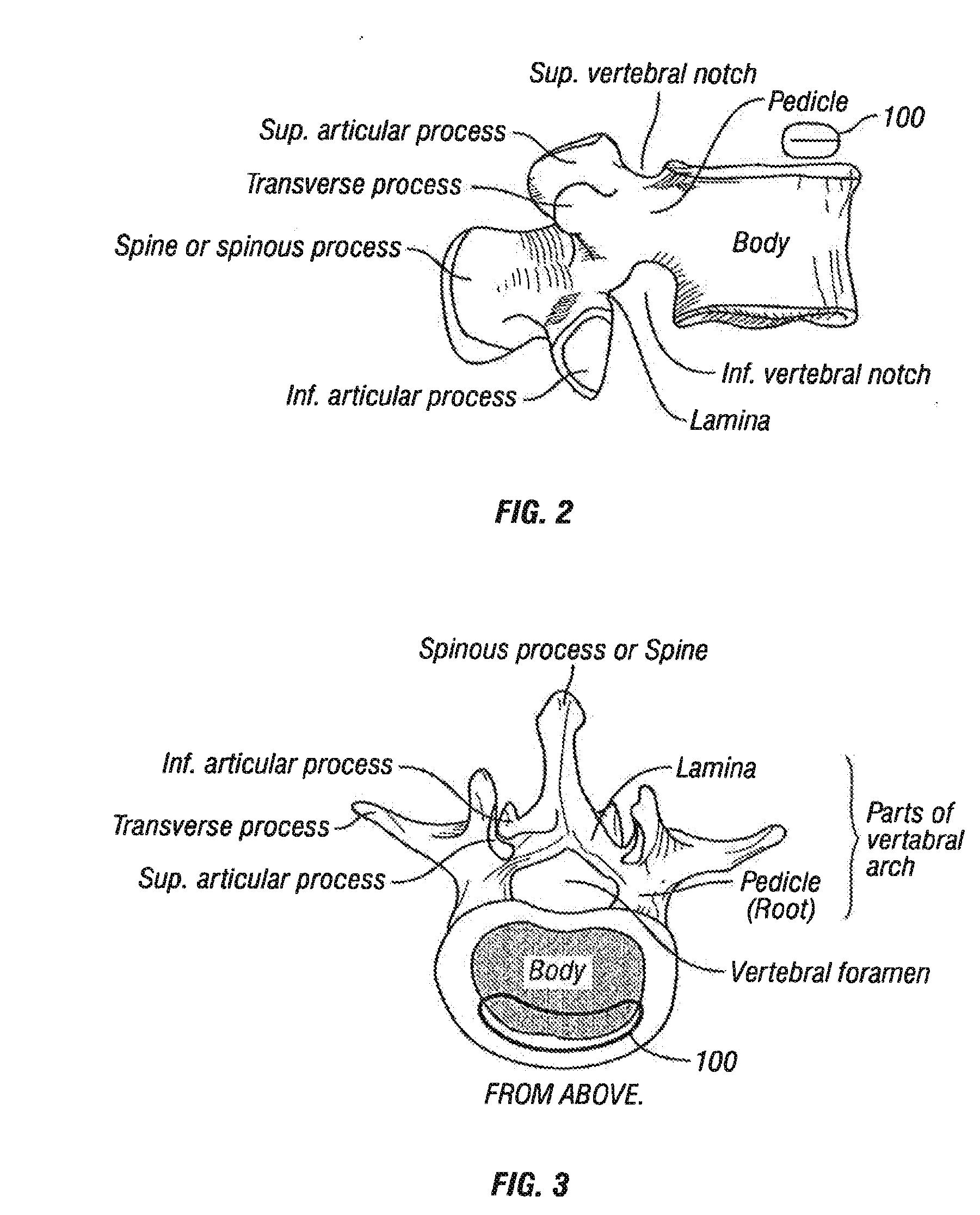
Arthrodesis, also known as artificial ankylosis or syndesis, is the artificial induction of joint ossification between two bones by surgery. This is done to relieve intractable pain in a joint which cannot be managed by pain medication, splints, or other normally indicated treatments.
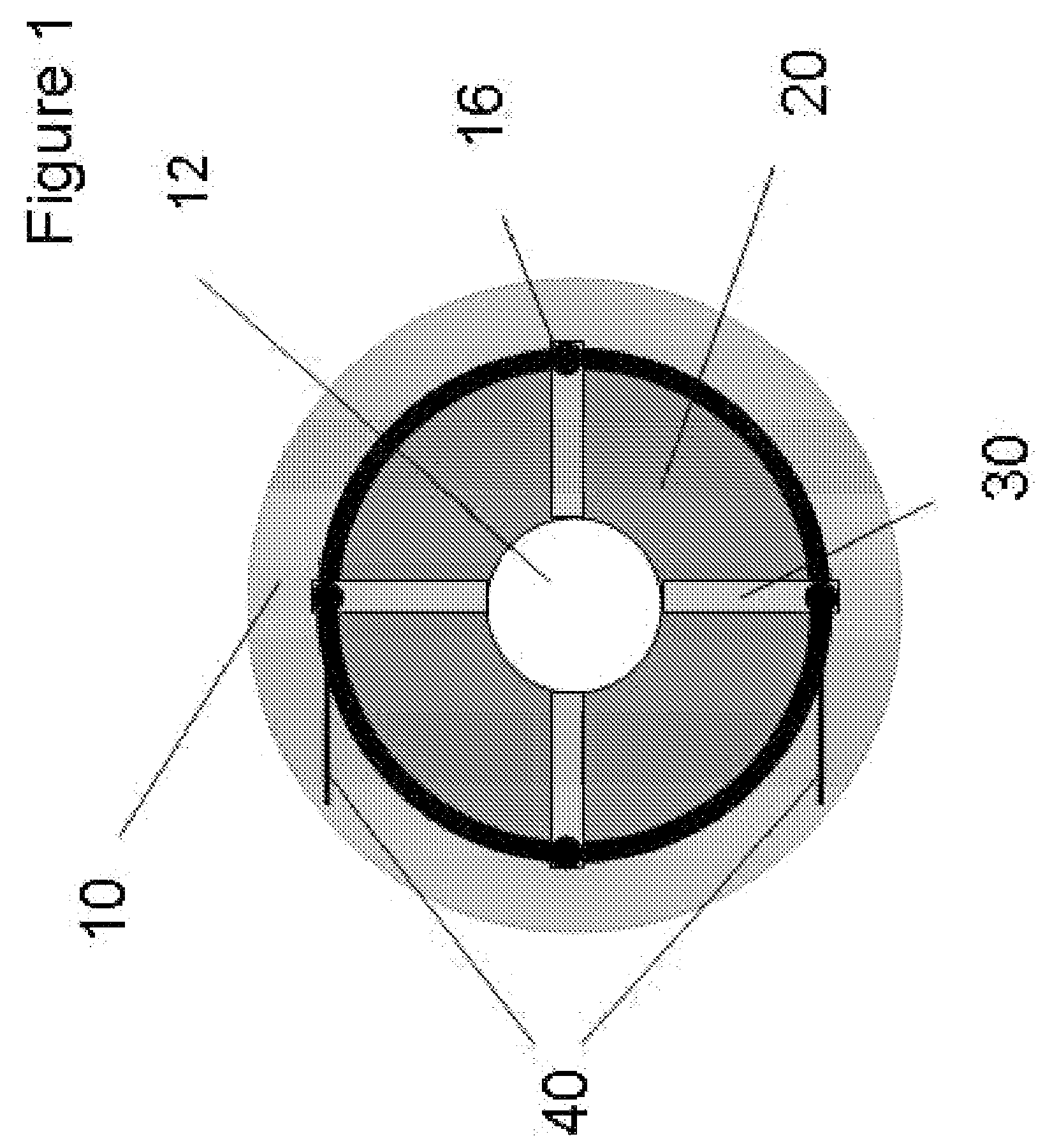
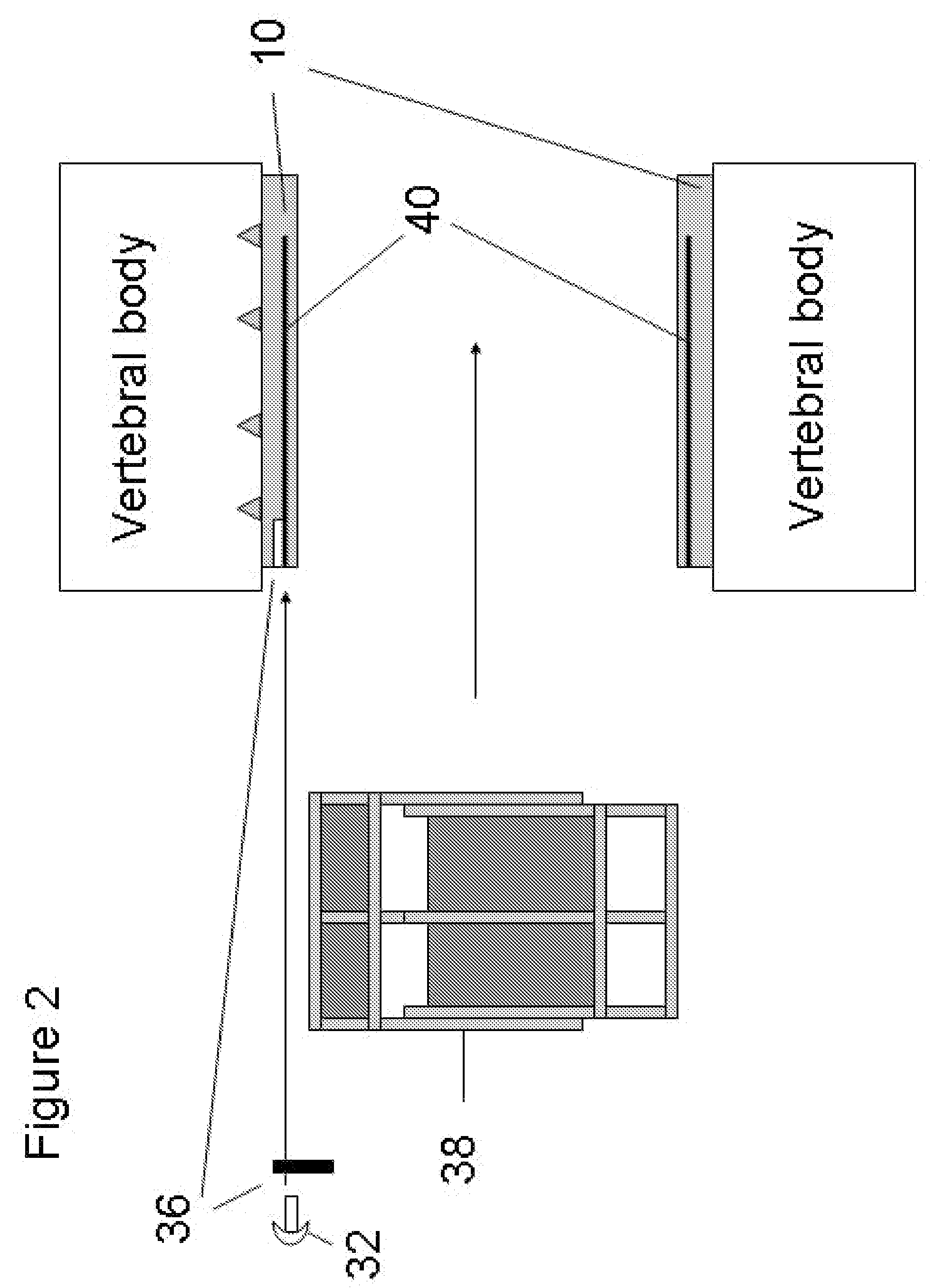
Bone implants and methods
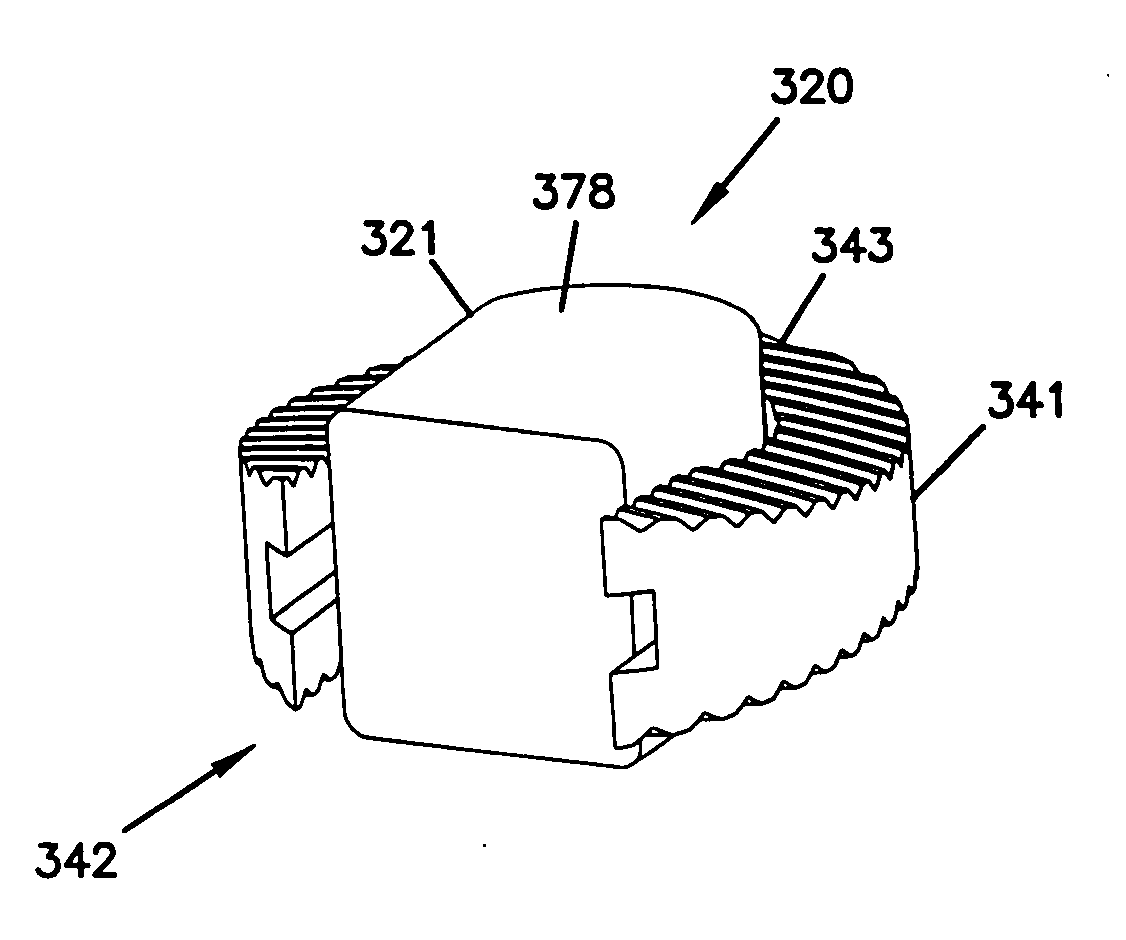
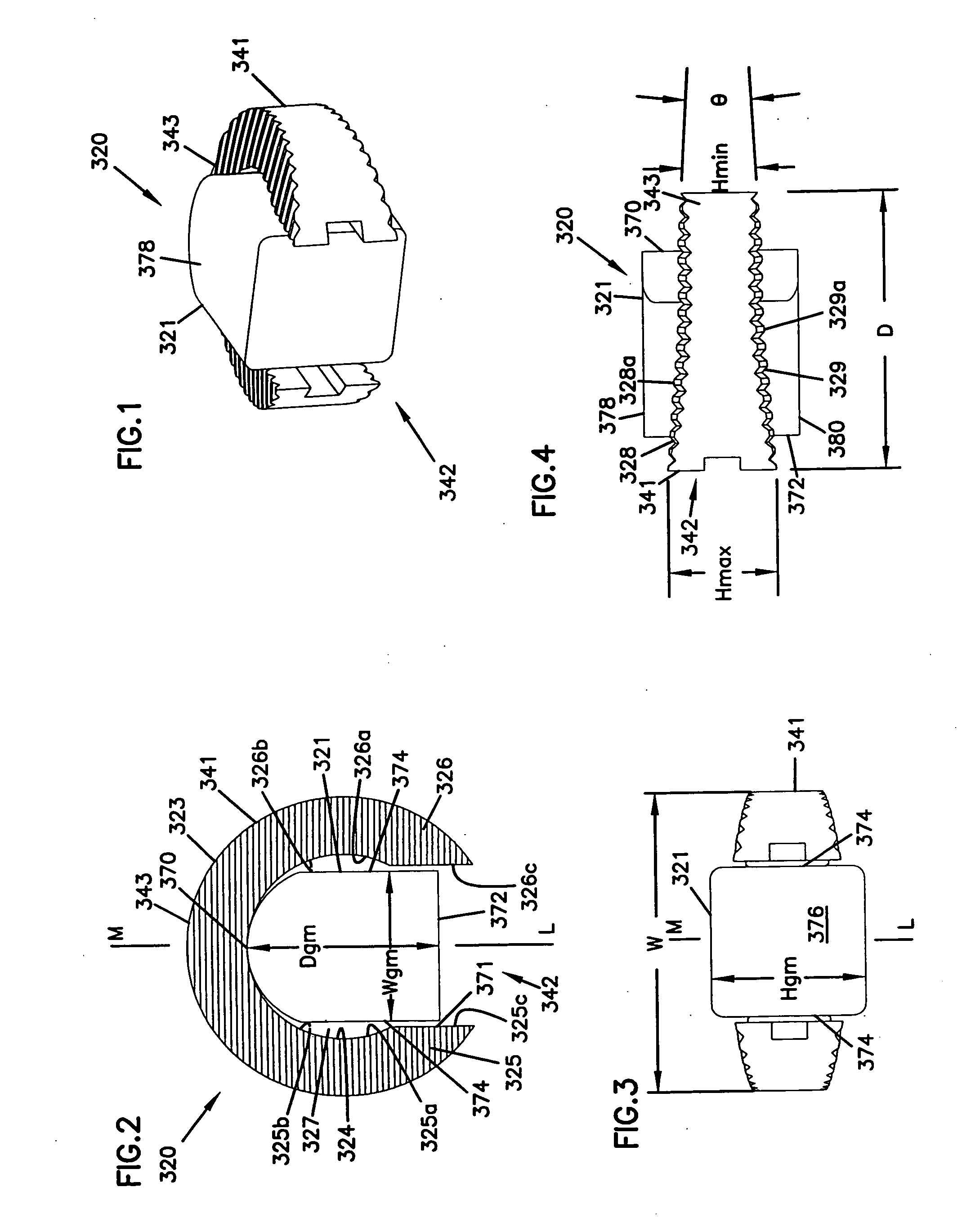
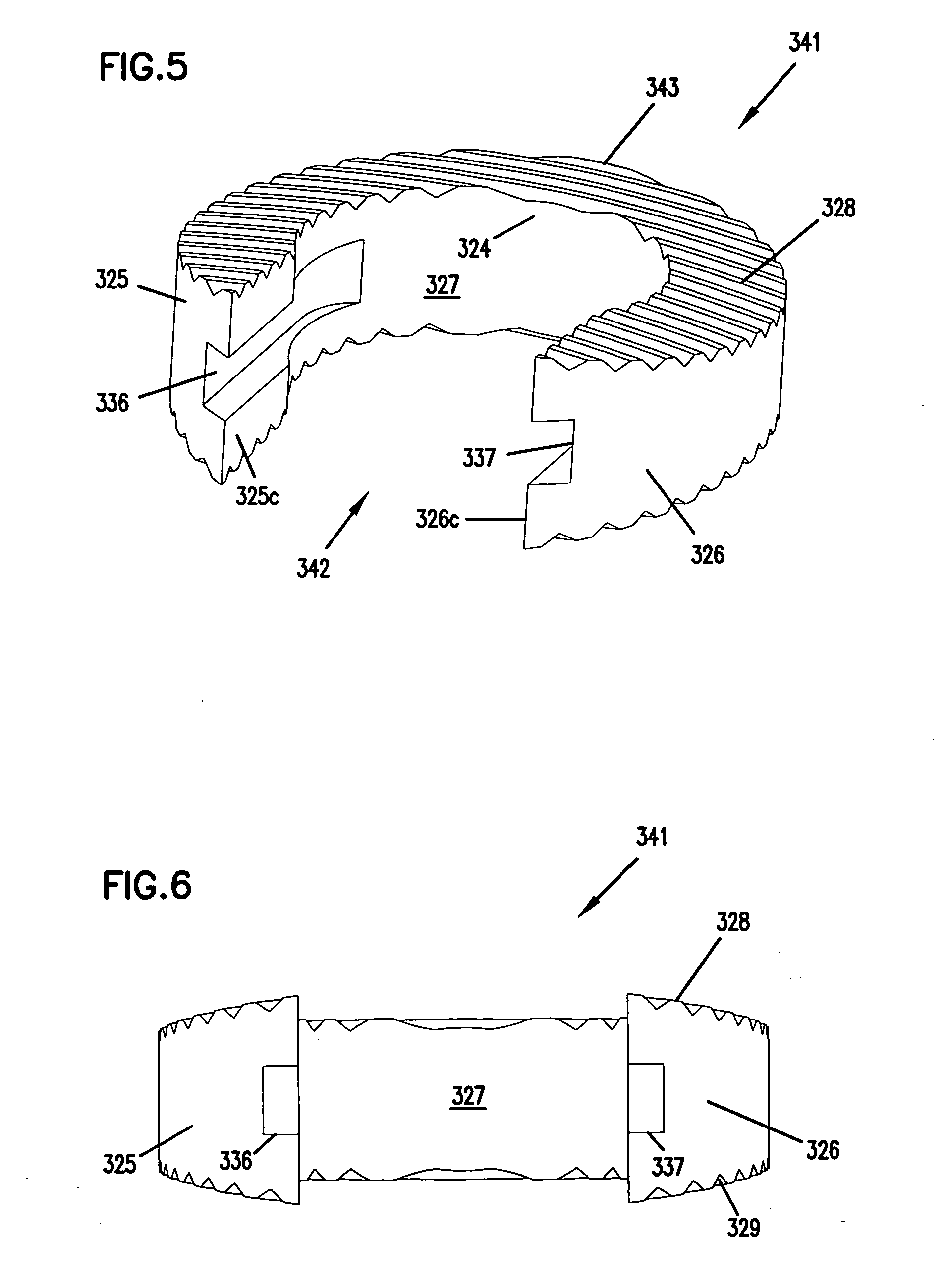
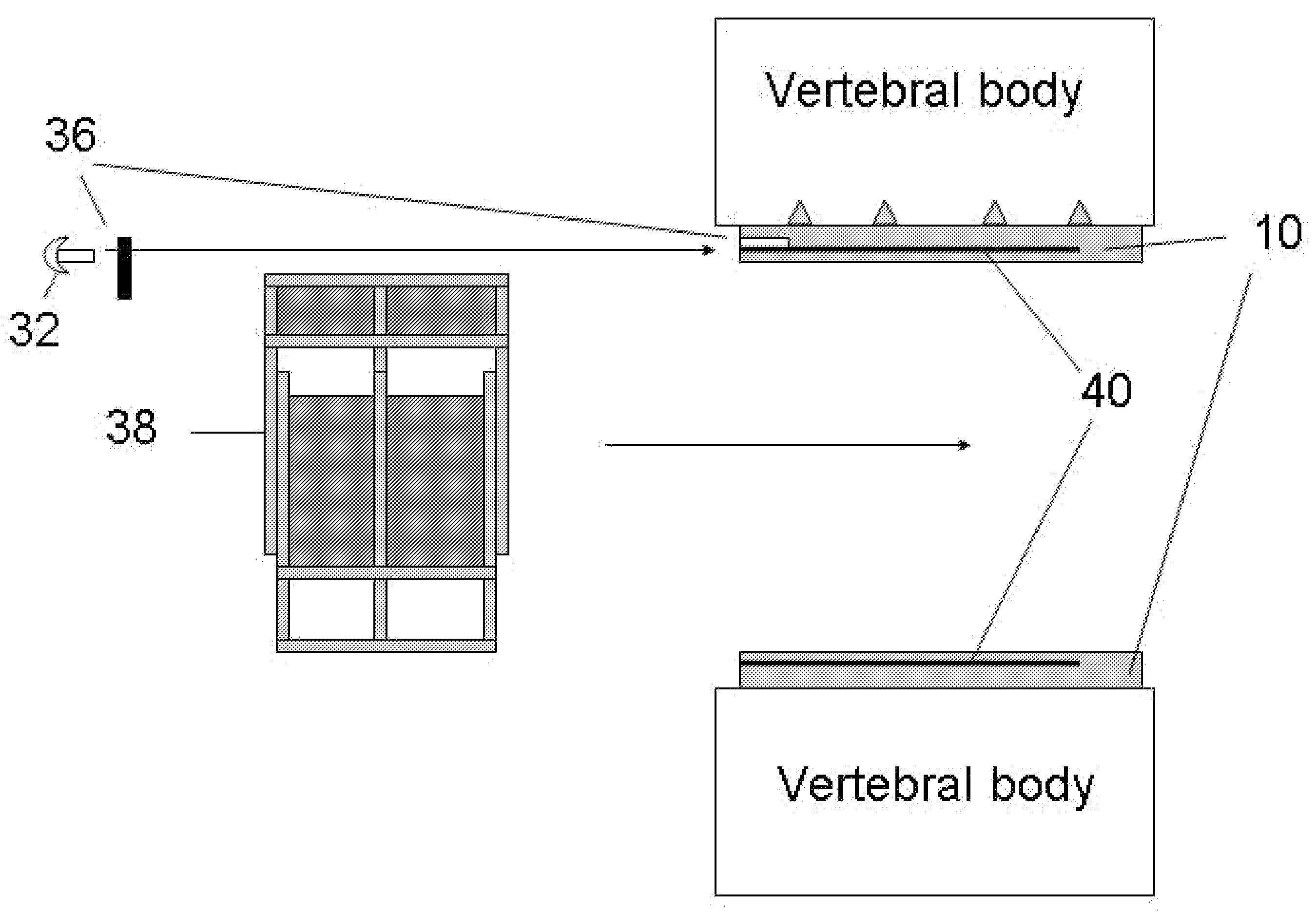
Implants, instruments and methods for bone fusion procedures are disclosed. In some embodiments, the implants are particularly advantageous for use between opposing vertebral bodies to facilitate stabilization or arthrodesis of an intervertebral joint. The implants include, at least, a support component that provides structural support during fusion. In a typical embodiment, the implants also include a growth component. A growth component provides an environment conducive to new bone growth between the bones being fused. Several unique configurations to enhance fusion, instruments for insertion and methods for insertion are also disclosed.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Implants formed of shape memory polymeric material for spinal fixation
ActiveUS20050033295A1Absorb energySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisJoint arthrodesisImplanted device
This invention relates to a orthopedic implant that comprises a shape memory polymeric material. The orthopedic implant can be fabricated or molded in a desired configuration selected to provide support or tension to bony structures. Examples of implantable devices include spinal rods, bone plates, and bone fixation cords. The orthopedic implant can be deformed to a second configuration different from the first configuration either prior to implantation or after implantation. When desired, the shape memory polymeric material can be induced to revert to it original molded configuration. This can compress the attached bony structure and / or promote arthrodesis.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Bone implants and methods
The disclosure provides implants and methods for bone fusion procedures. In some embodiments, the implants are particularly advantageous for use between opposing vertebral bodies to facilitate stabilization or arthrodesis of an intervertebral joint. The implants includes, at least, a support component that provides structural support during fusion. In a typical embodiment, the implants also include a growth component. A growth component provides an environment conductive to new bone growth between the bones being fused. Several unique configuration to enhance fusion, instruments for insertion and methods for insertion use are also disclosed.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Apparatus and method for providing dynamizable translations to orthopedic implants
InactiveUS20050085812A1Avoid stress shieldingLimited supportSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBone structureJoint arthrodesis
The present invention generally relates to orthopedic devices and methods for treating bone defects. The orthopedic devices can provide sufficient support to the bone defect while allowing bone ingrowth and minimizing the risk to stress shield and / or pseudo-arthrodesis. The bone fixation devices include a biodegradable material or component that further resists relative motion of attached bones and allows the device to gradually transfer at least some load from the device to the growing bone structure in vivo and permitting an increase in the relative motion of bones attached to the device.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Expandable Spacer and Method For Use Thereof
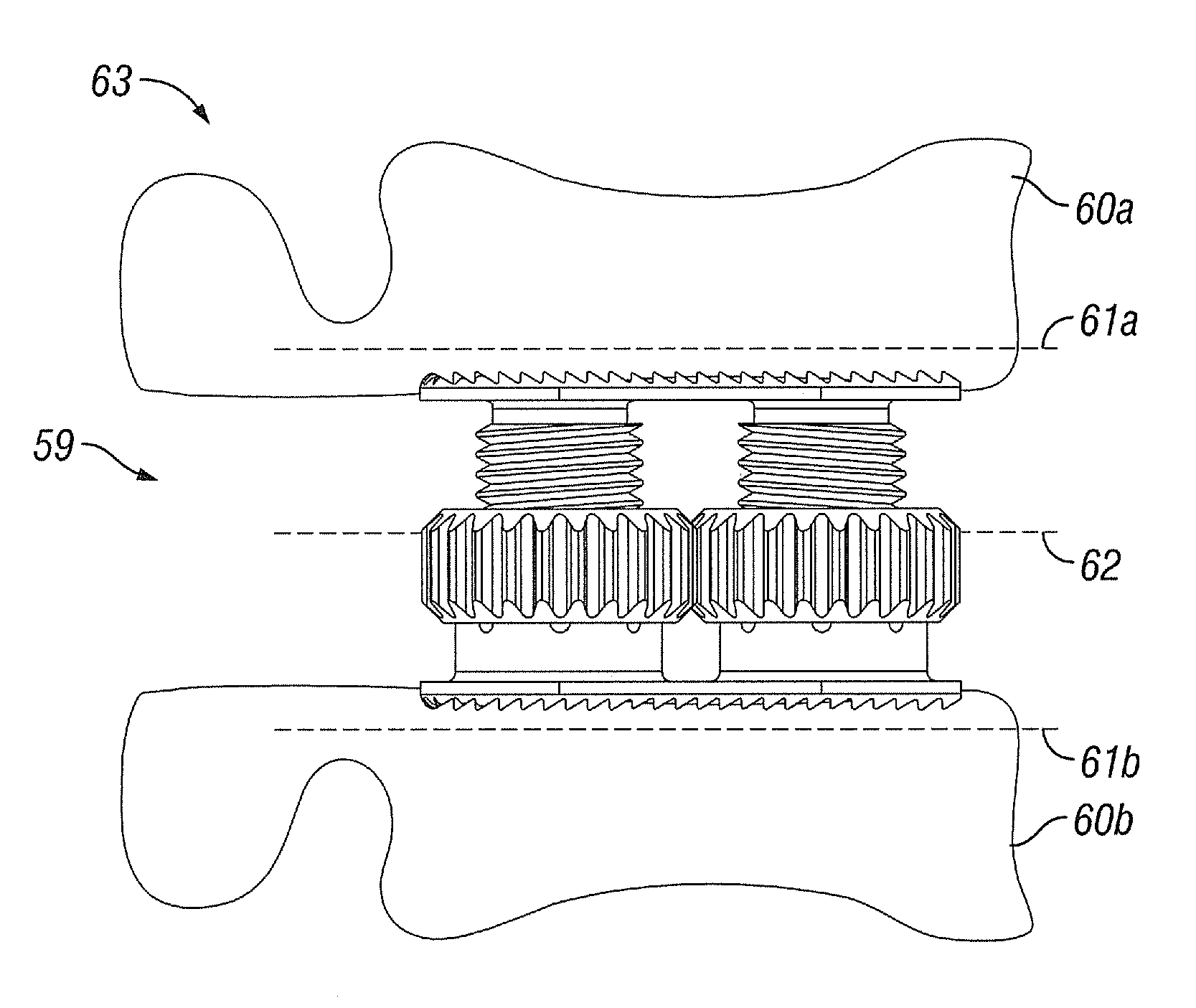
ActiveUS20110172716A1Facilitates arthrodesisEasy to fuseBone implantJoint implantsArticular surfacesJoint arthrodesis
An expandable implant is disclosed having an adjustable height for insertion between two adjacent bony structures or joint surfaces, for example between two adjacent spinal vertebrae. The implant includes at least one gear associated with at least one threaded shaft. Rotation of the gear engages the threaded shaft to expand the implant. The implant can be inserted in a collapsed configuration and expanded in situ. The invention also provides methods for using the implant to facilitate arthrodesis or fusion of adjacent joint surfaces or spinal vertebrae.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Expandable spacer and method for use thereof
ActiveUS8353963B2Facilitates arthrodesis and fusionEasy to adjustBone implantJoint implantsArticular surfacesJoint arthrodesis
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Vertebral implant for promoting arthrodesis of the spine
This invention provides a vertebral implant for impaction in a disc space to restore and / or maintain desired disc space height and spinal orientation. The implant has an elongated basis body having a generally lens-shape provided by convex upper and lower surfaces. Bearing surfaces are provided on the cross-edge surfaces of the endwalls. Grooves are provided in the upper and lower surfaces positioned between the bearing surfaces. The implant can be prepared from a wide variety of materials including metallic materials, synthetic materials, polymeric materials, ceramic materials, and composite materials including reinforced materials i.e. glass, fiber, and / or carbon fiber reinforced materials (CFRP). These preferred materials for fabricating implants in the present invention reduce costs, increase service life and provide excellent physiological compatibility. The non-metallic material can be selected to be either a substantially permanent material, a biodegradable material or a bioerodable material. Further, the implant material can be provided to be radio opaque to facilitate monitoring of bone ingrowth both into the implant and between the opposing endplates of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Implants formed of shape memory polymeric material for spinal fixation
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
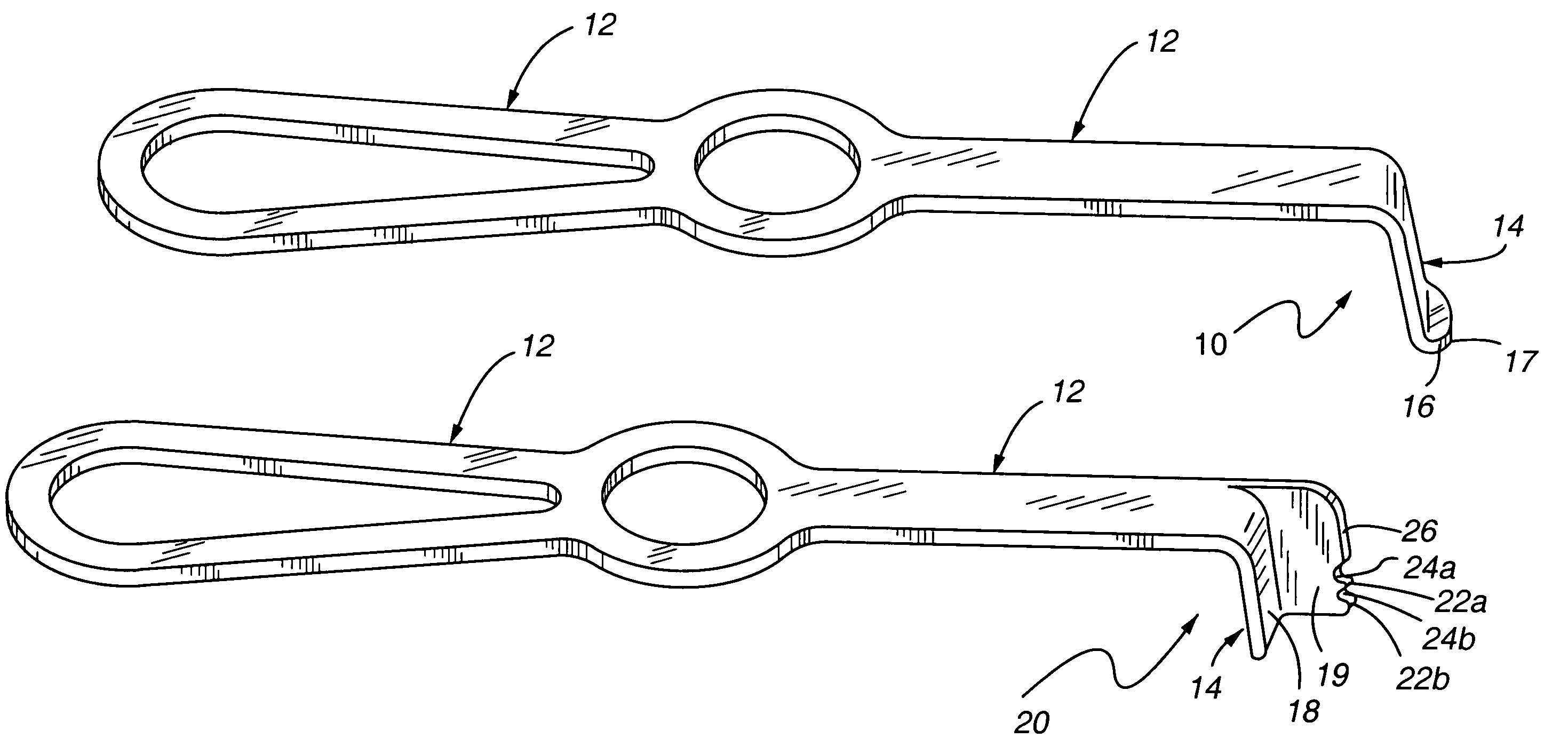
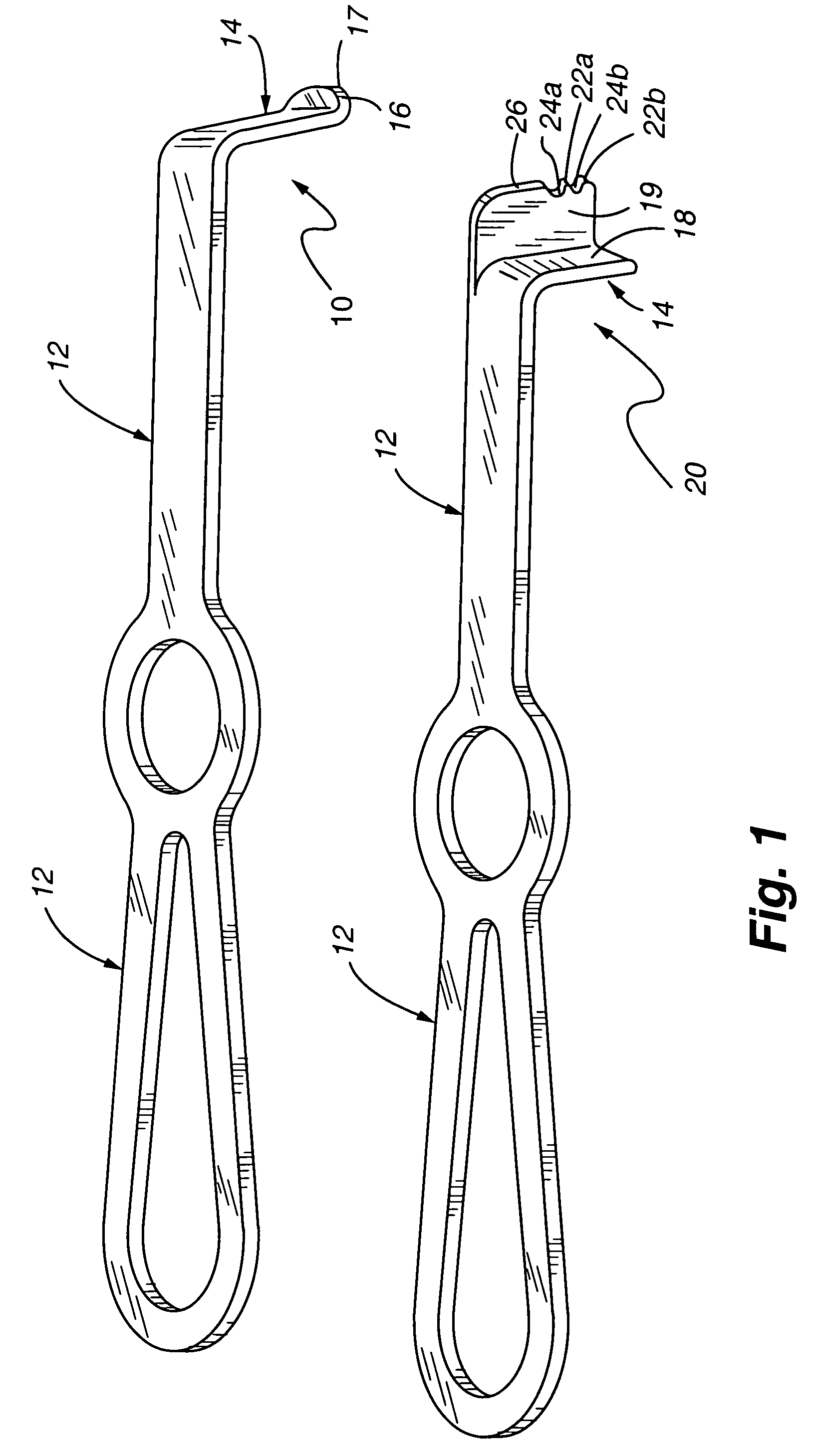
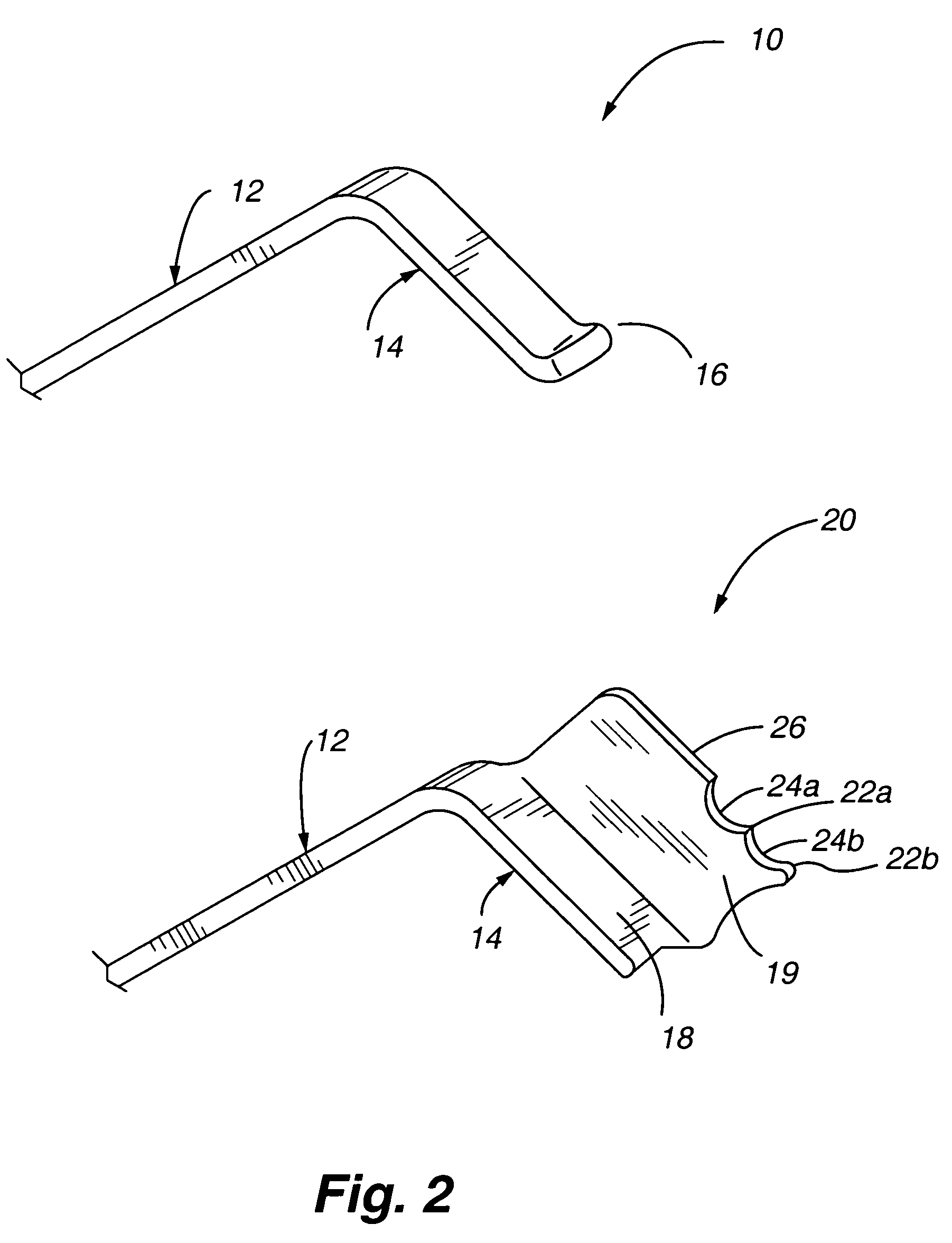
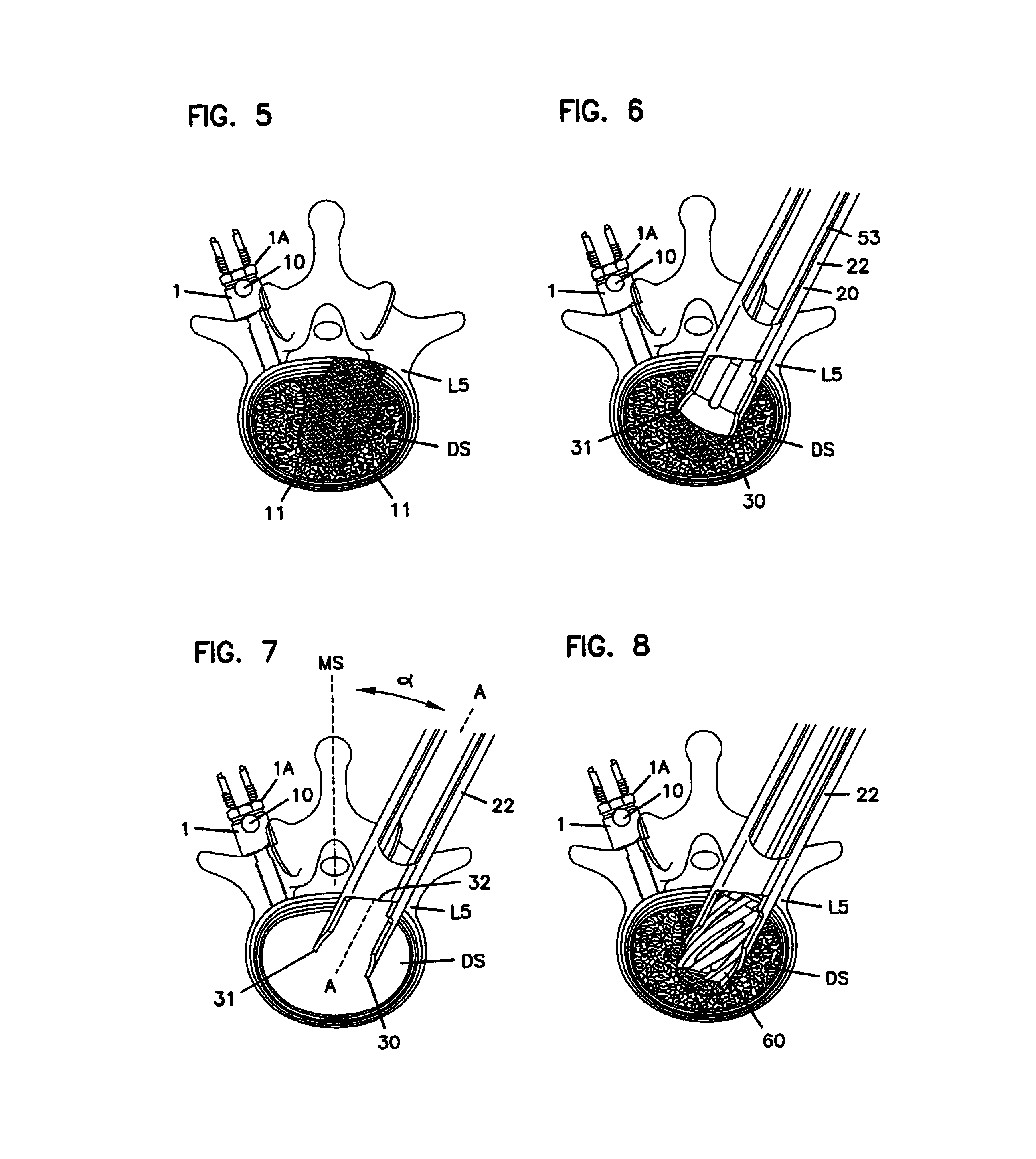
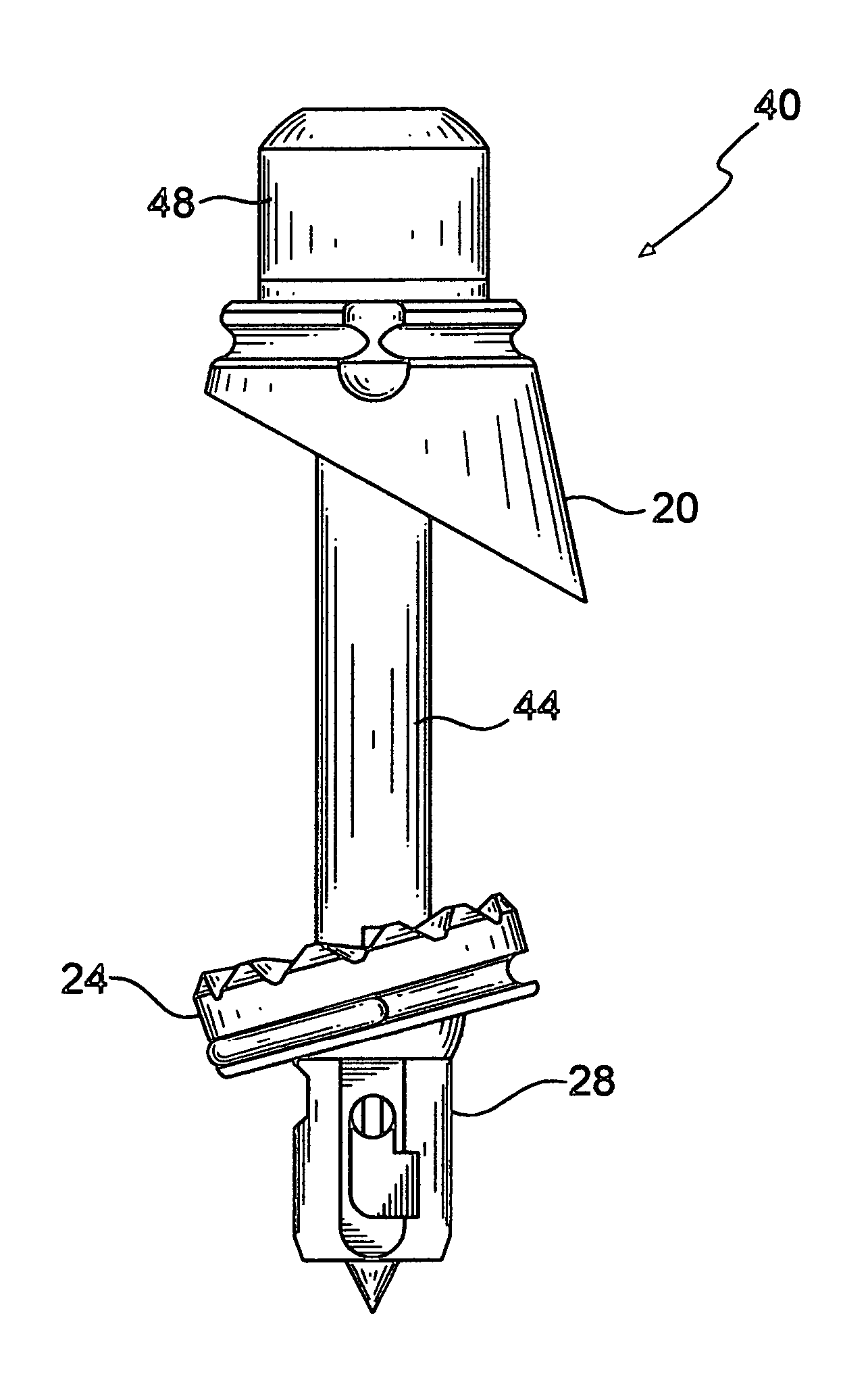
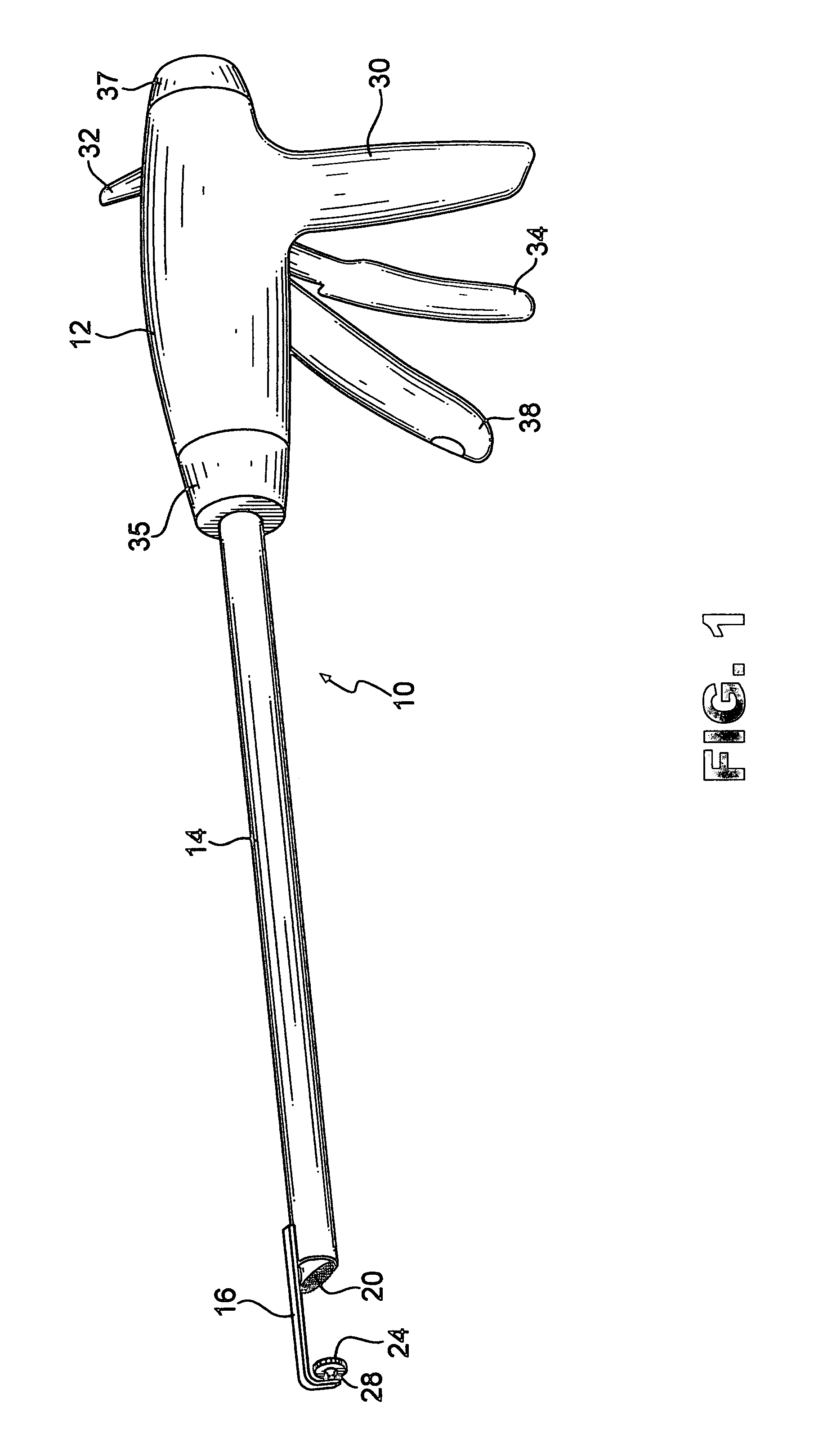
Method and device for retractor for microsurgical intermuscular lumbar arthrodesis
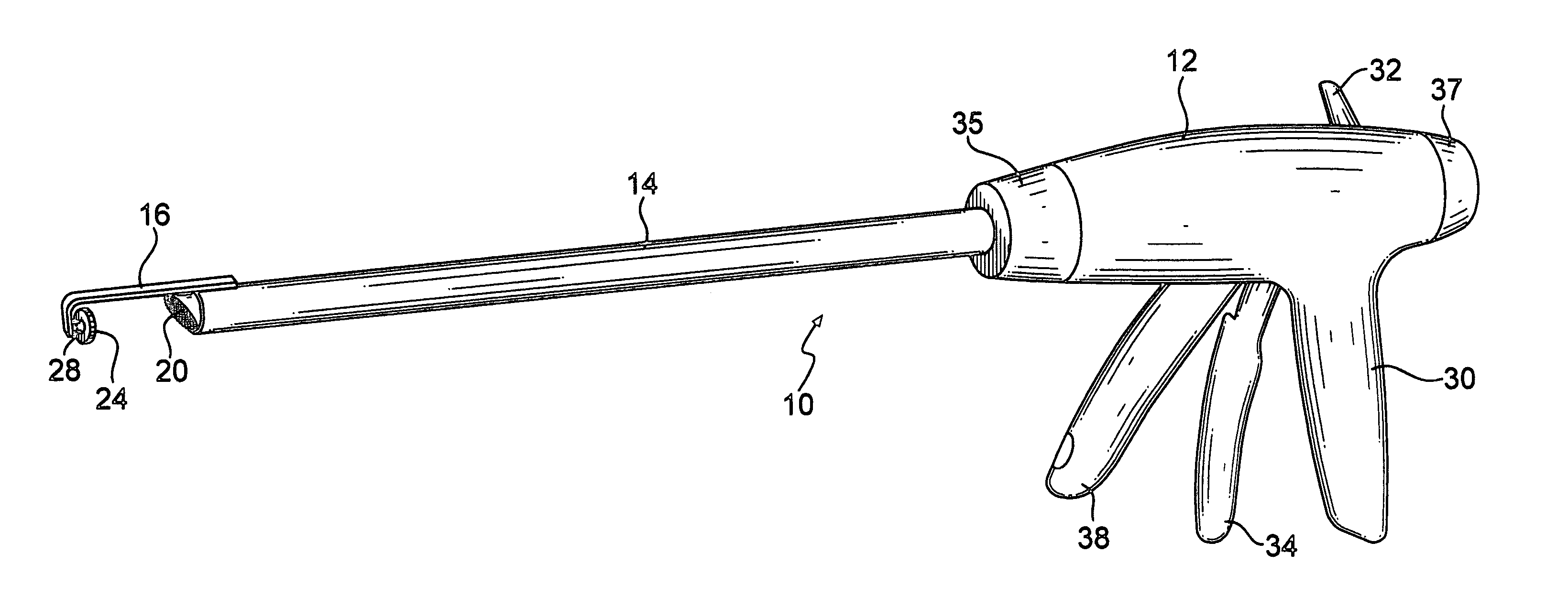
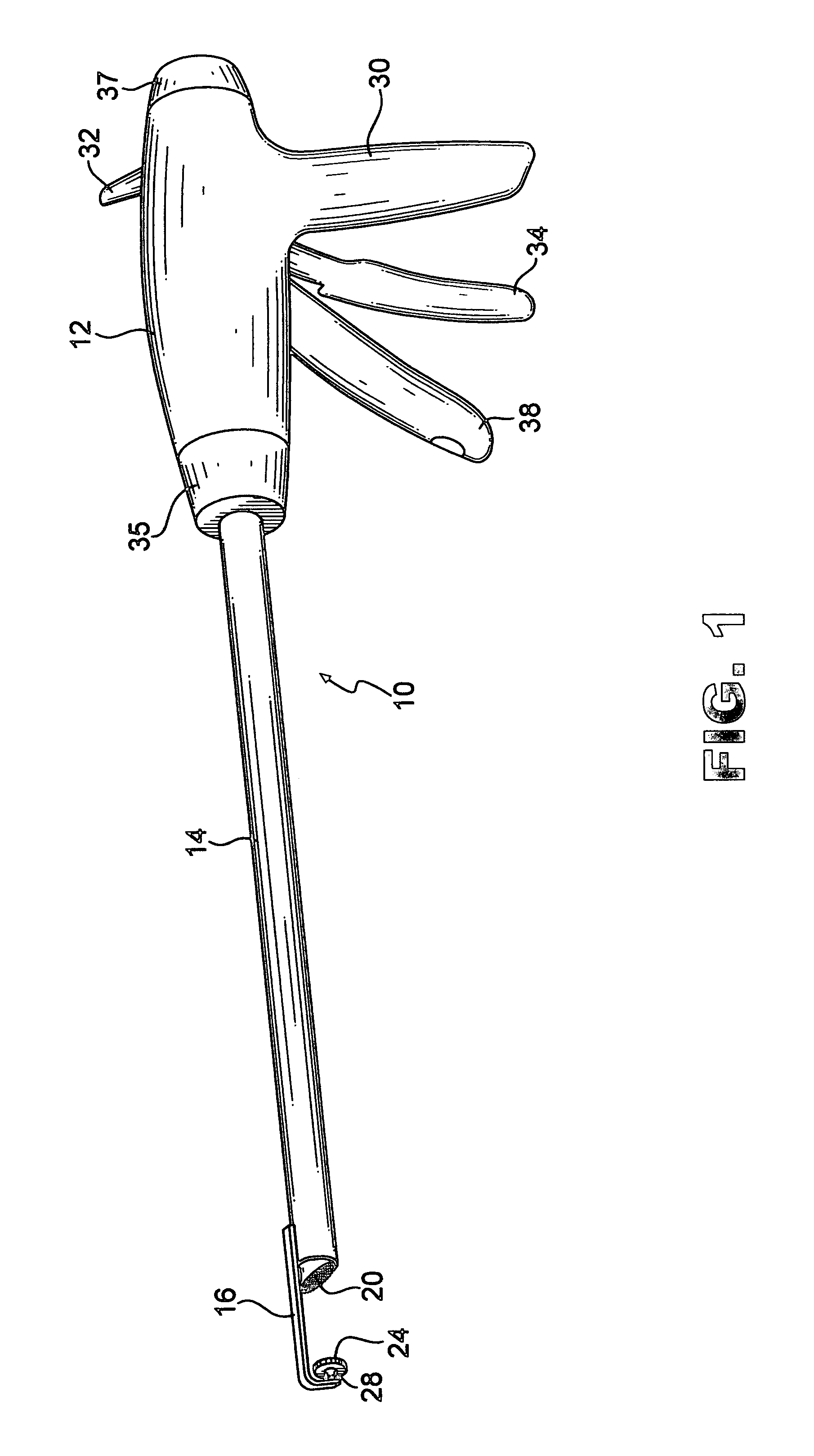
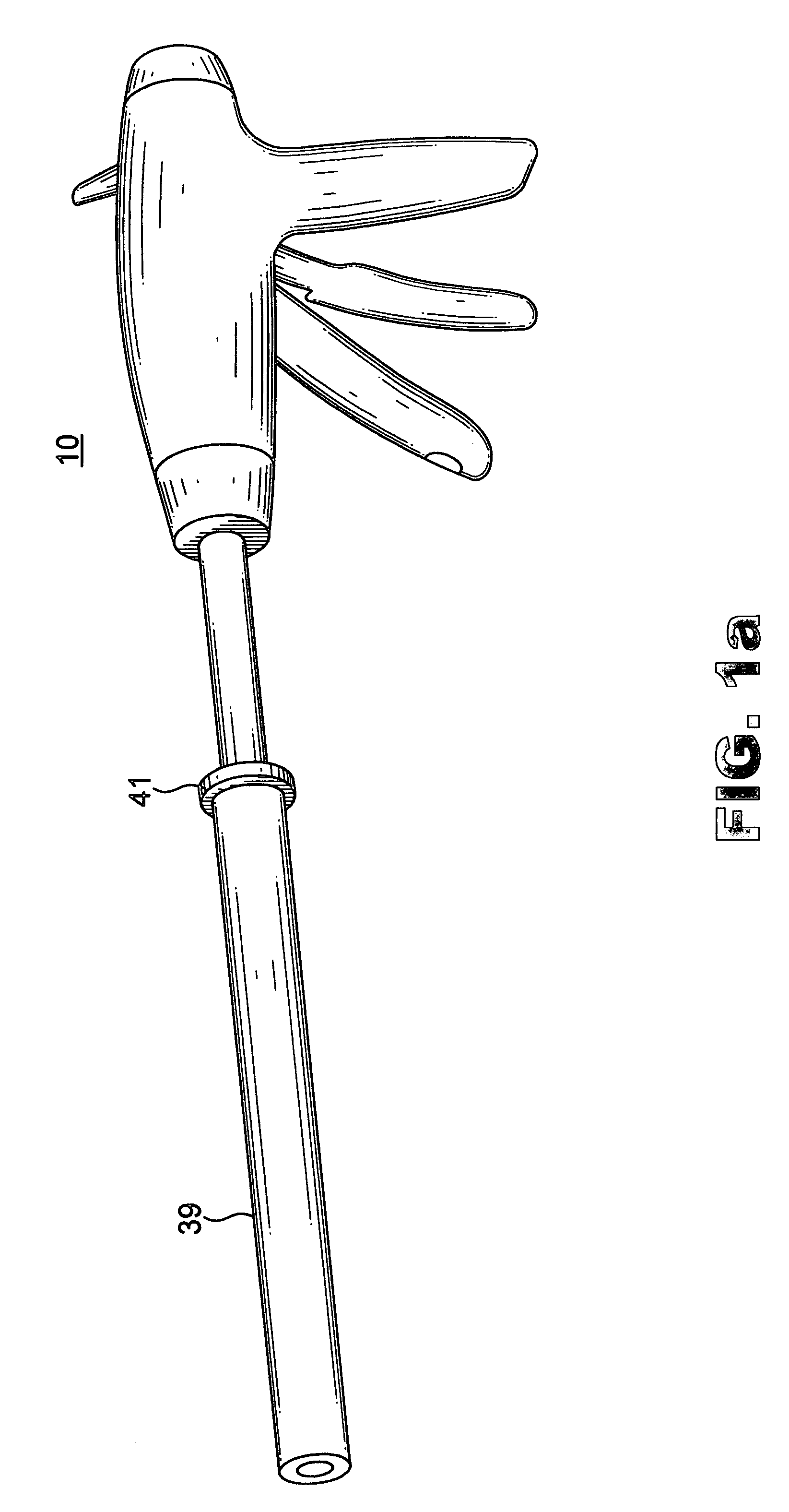
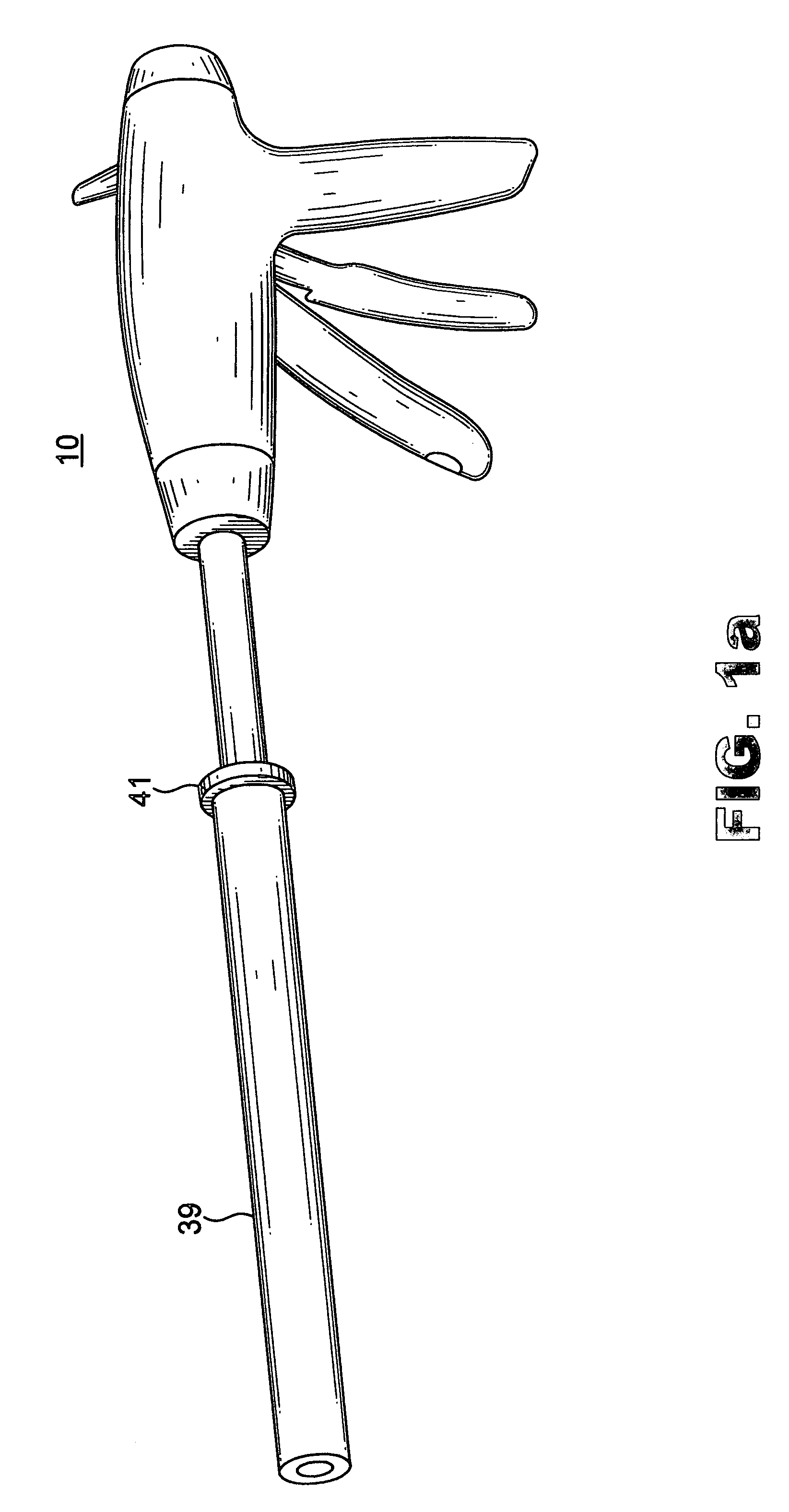
An instrument useful in performing lumbar arthrodesis with a minimal approach which spares the lumbar muscles from surgical disruption and includes one of two retractor designs having blades angled approximately 90° with respect to each respective retractor handle. One blade is bent at an end portion thereof in a direction away from the handle portion. The other blade has first and second blade faces, with the second face having at least two toothed structures located thereon.
Owner:RITLAND STEPHEN
Selectively Expanding Spine Cage With Enhanced Bone Graft Infusion
A selectively expanding spine cage has a minimized cross section in its unexpanded state that is smaller than the diameter of the neuroforamen through which it passes in the distracted spine. The cage conformably engages between the endplates of the adjacent vertebrae to effectively distract the anterior disc space, stabilize the motion segments and eliminate pathologic spine motion. Expanding selectively (anteriorly, along the vertical axis of the spine) rather than uniformly, the cage height increases and holds the vertebrae with fixation forces greater than adjacent bone and soft tissue failure forces in natural lordosis. Stability is thus achieved immediately, enabling patient function by eliminating painful motion. The cage shape intends to rest proximate to the anterior column cortices securing the desired spread and fixation, allowing for bone graft in, around, and through the implant for arthrodesis whereas for arthroplasty it fixes to endpoints but cushions the spine naturally.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Posterior oblique lumbar arthrodesis
Instruments and methods for spinal stabilization are disclosed. In preferred embodiments, the invention provides greater stabilization of vertebral bodies through methods including combinations of external fixation systems and intervertebral implants to provide greater fusion stability, greater motion segment stability, faster fusion, reduced pain, reduced chance of migration, reduced chance of subsidence, etc.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC +1
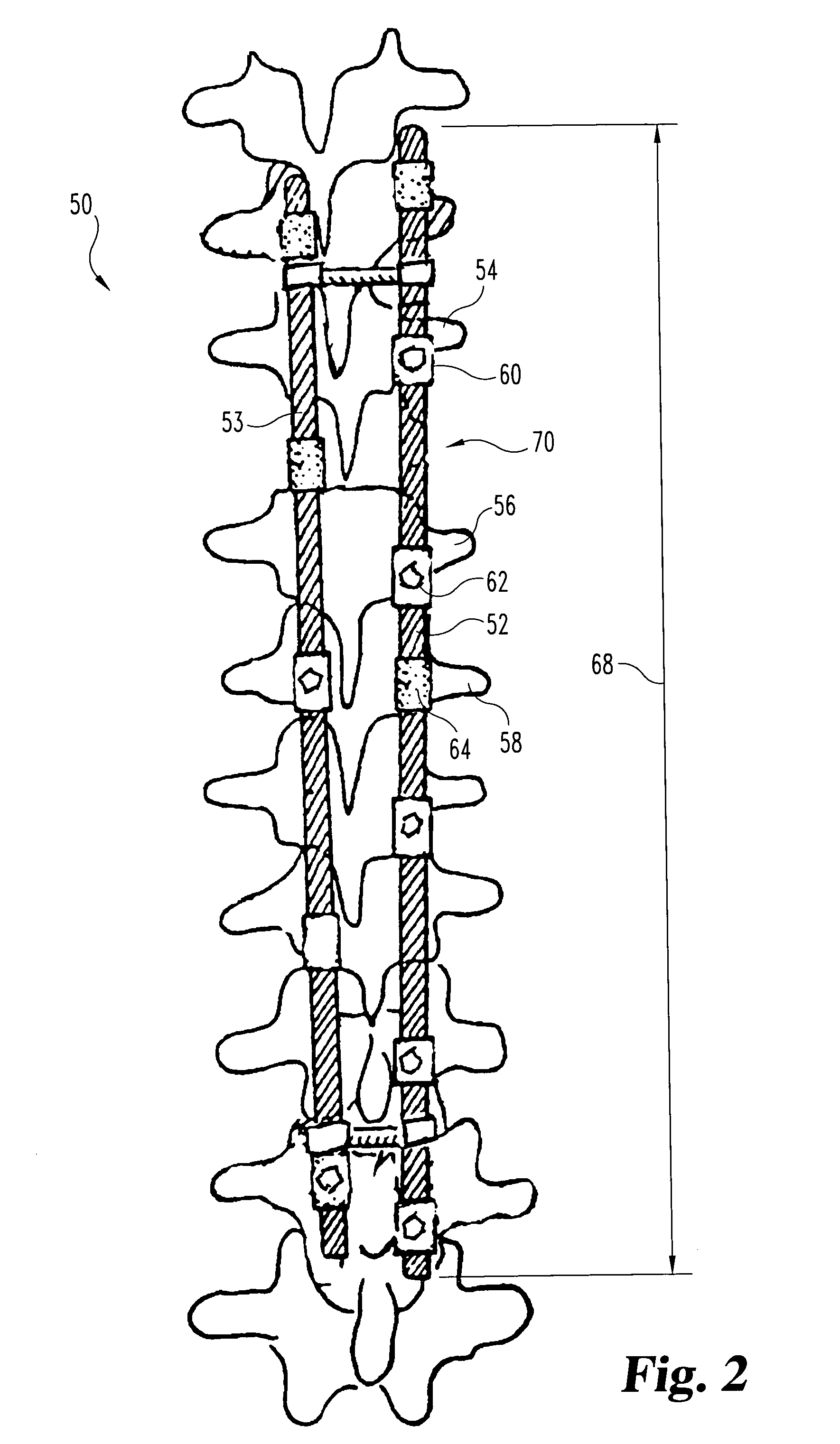
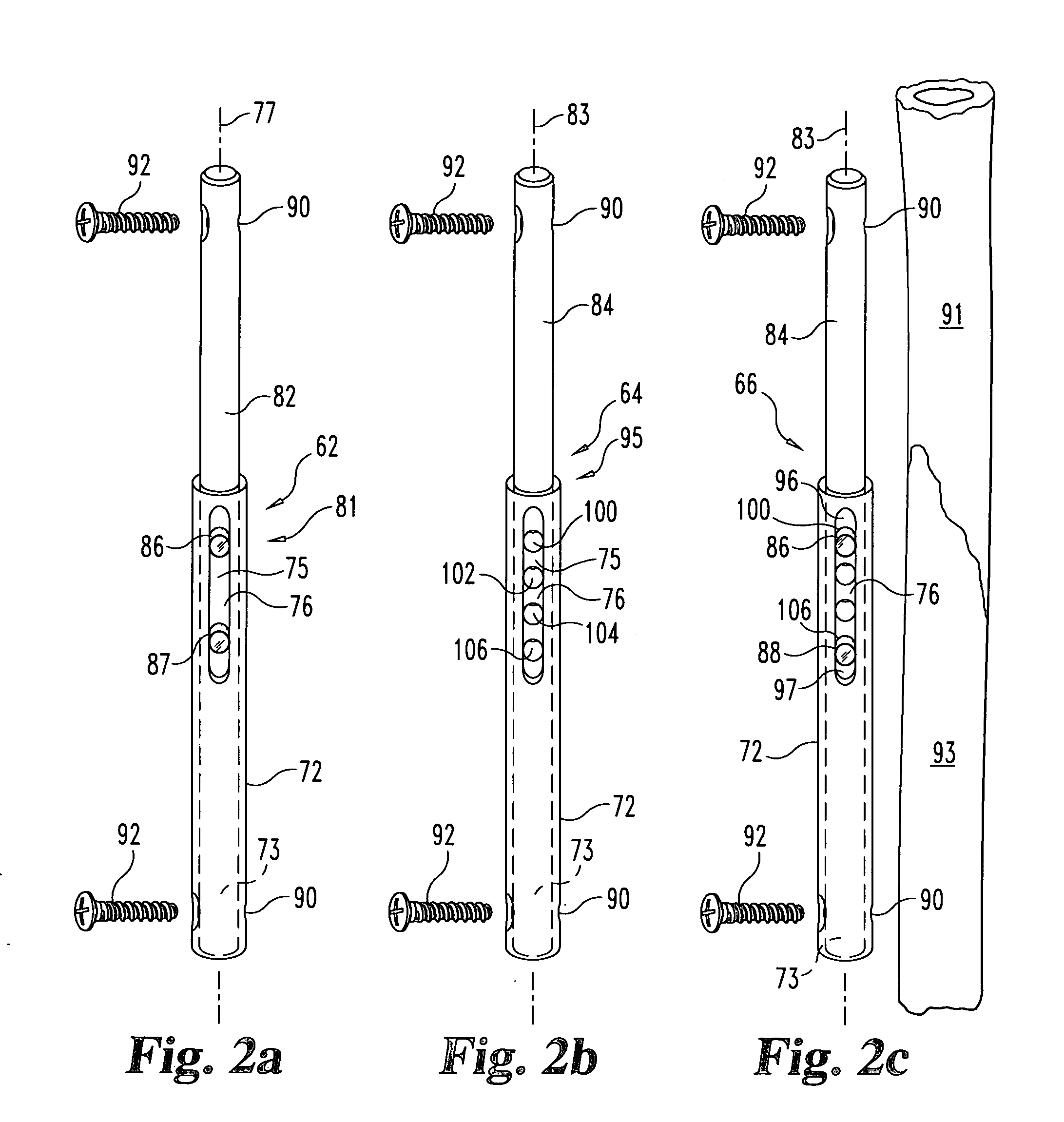
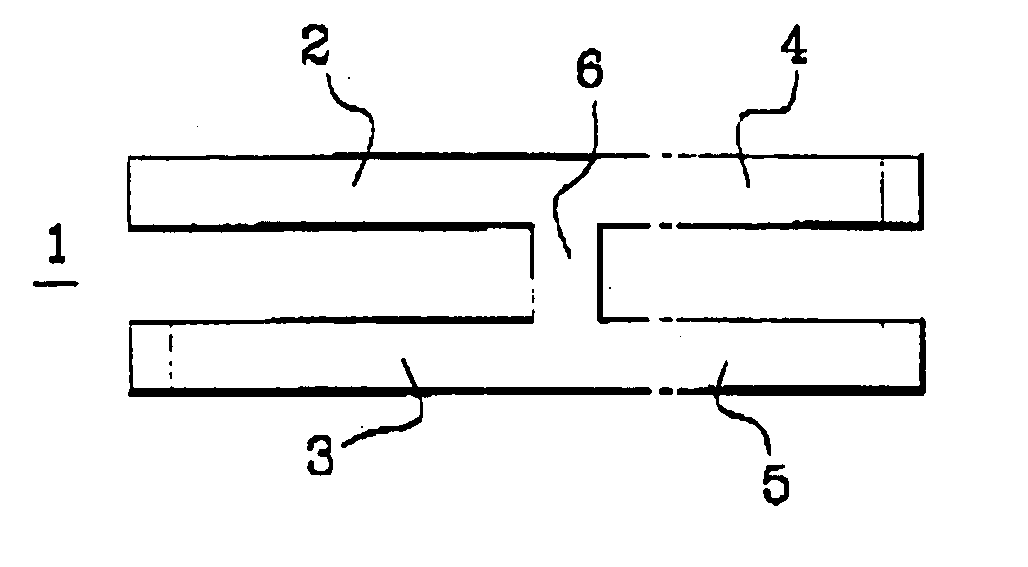
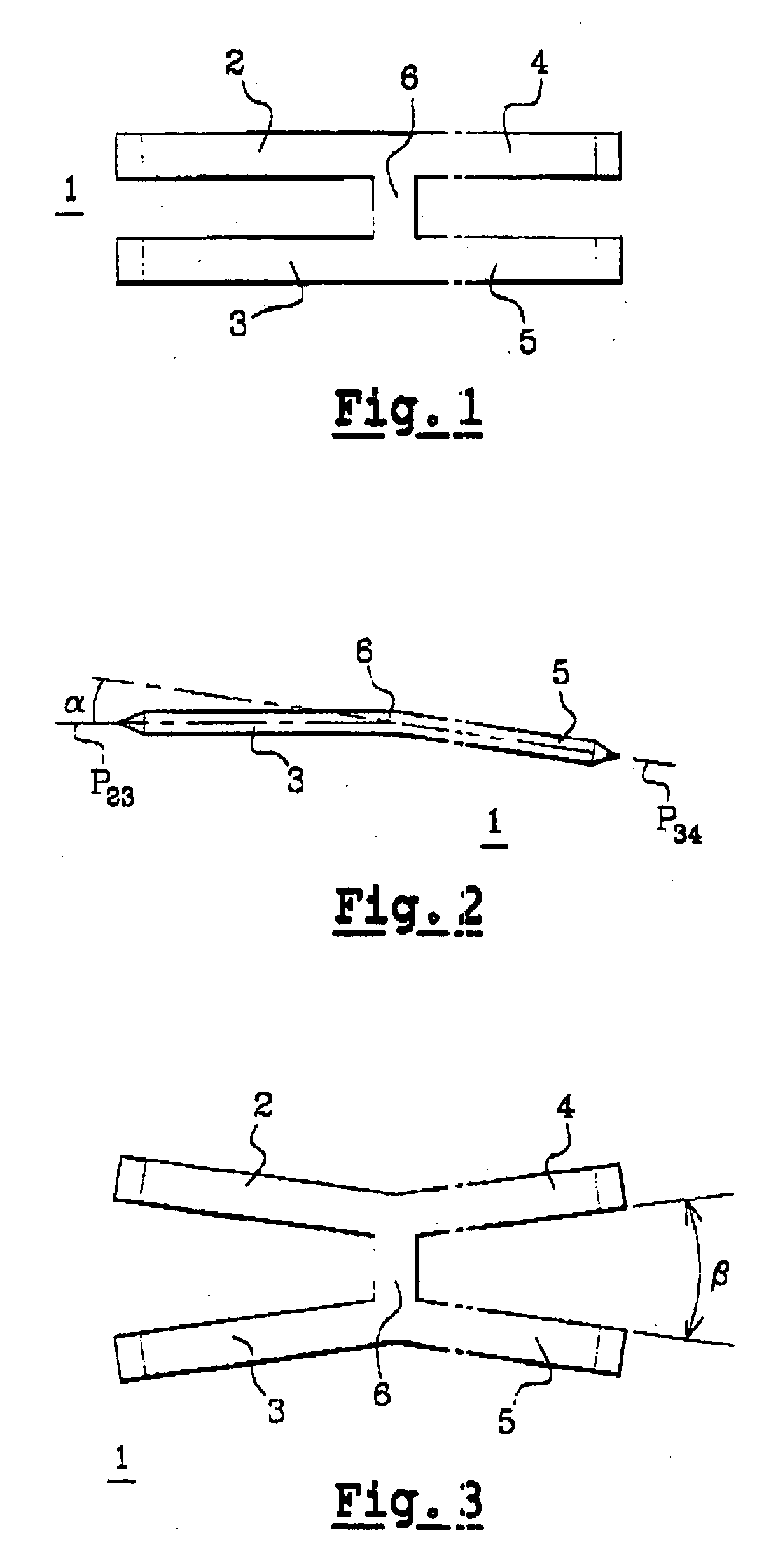
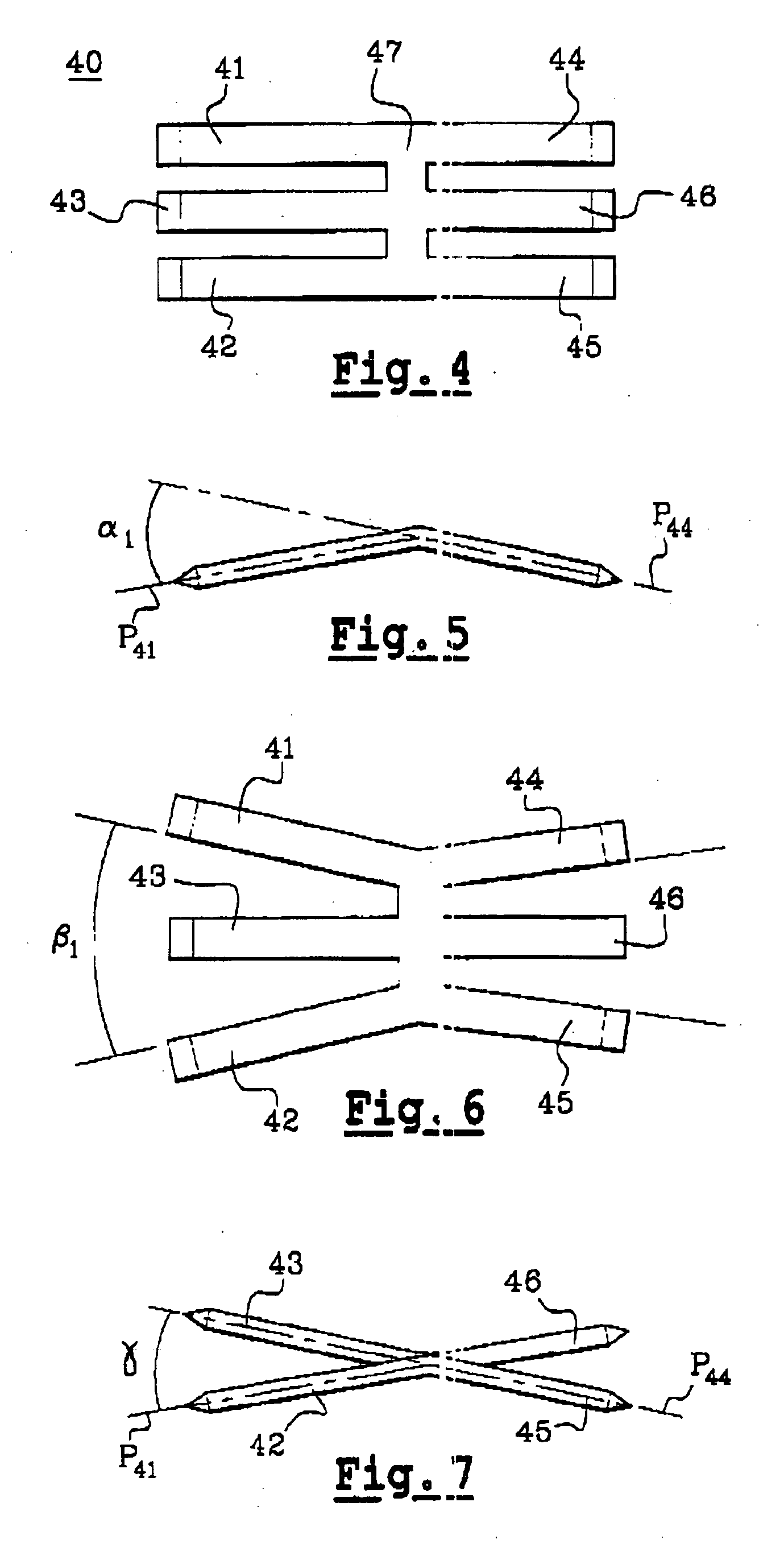
Intramedullary osteosynthesis implant
InactiveUS20050283159A1Stable osteosynthesisRegulate flexumSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisJoint arthrodesisDiaphysis
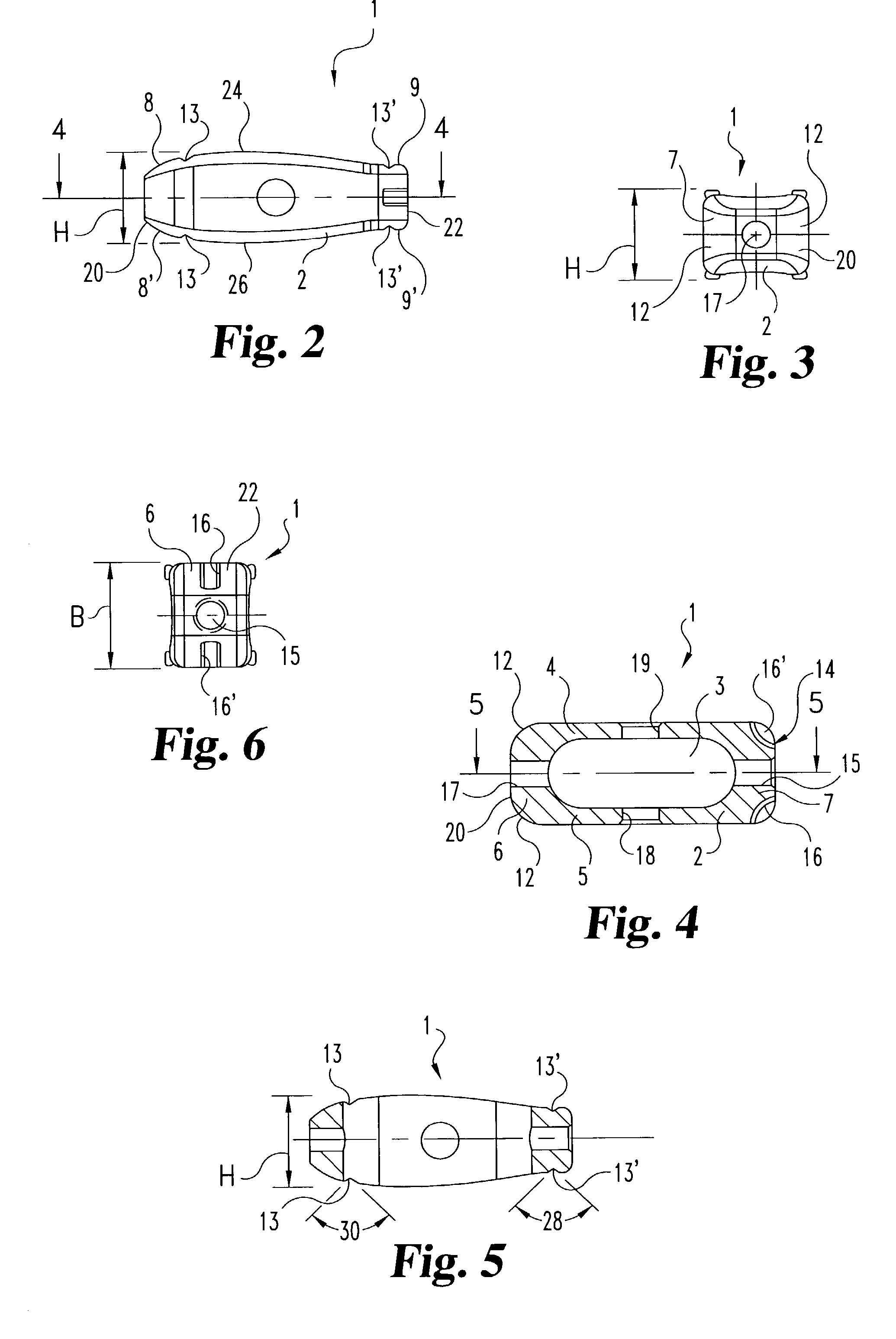
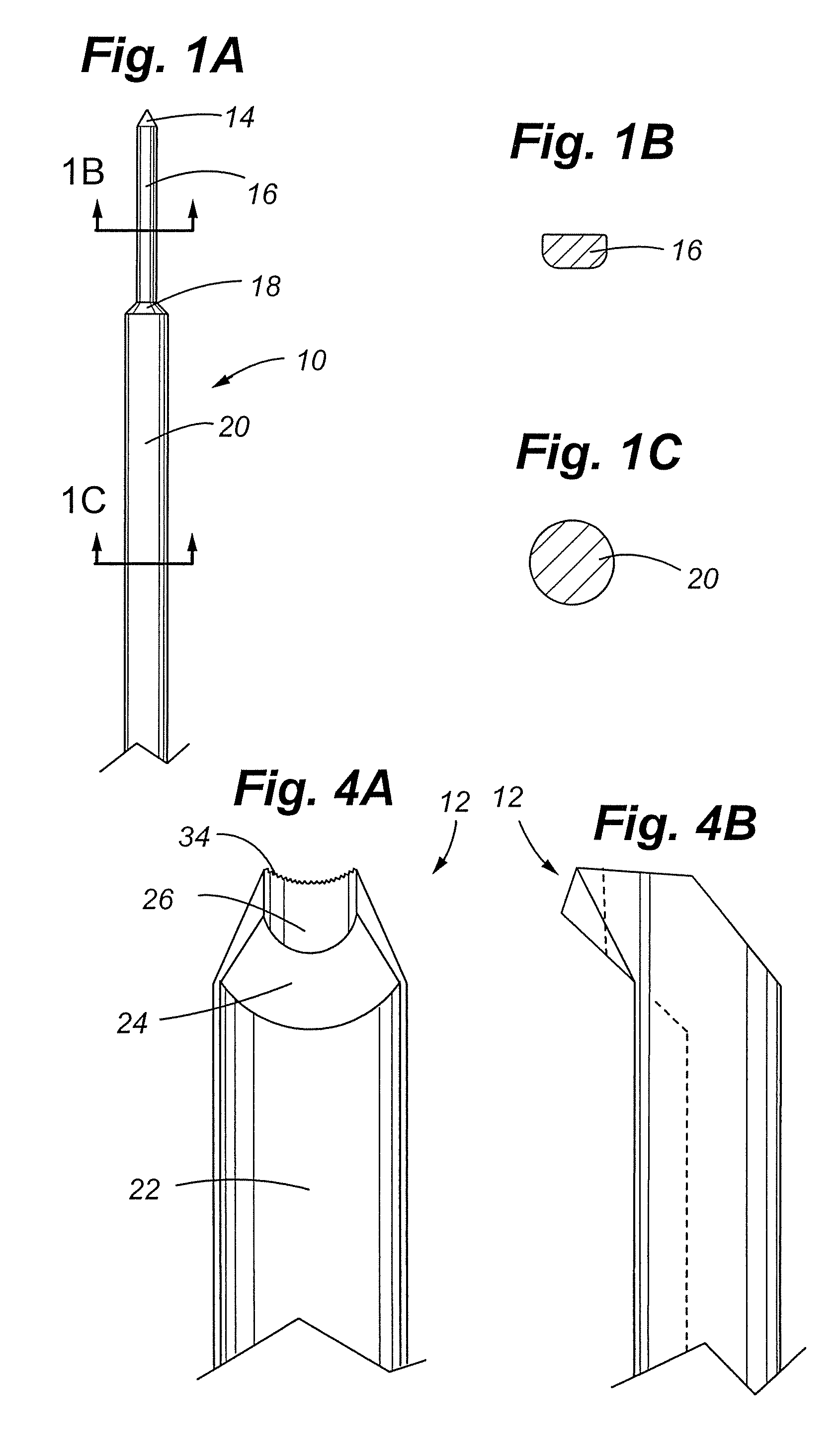
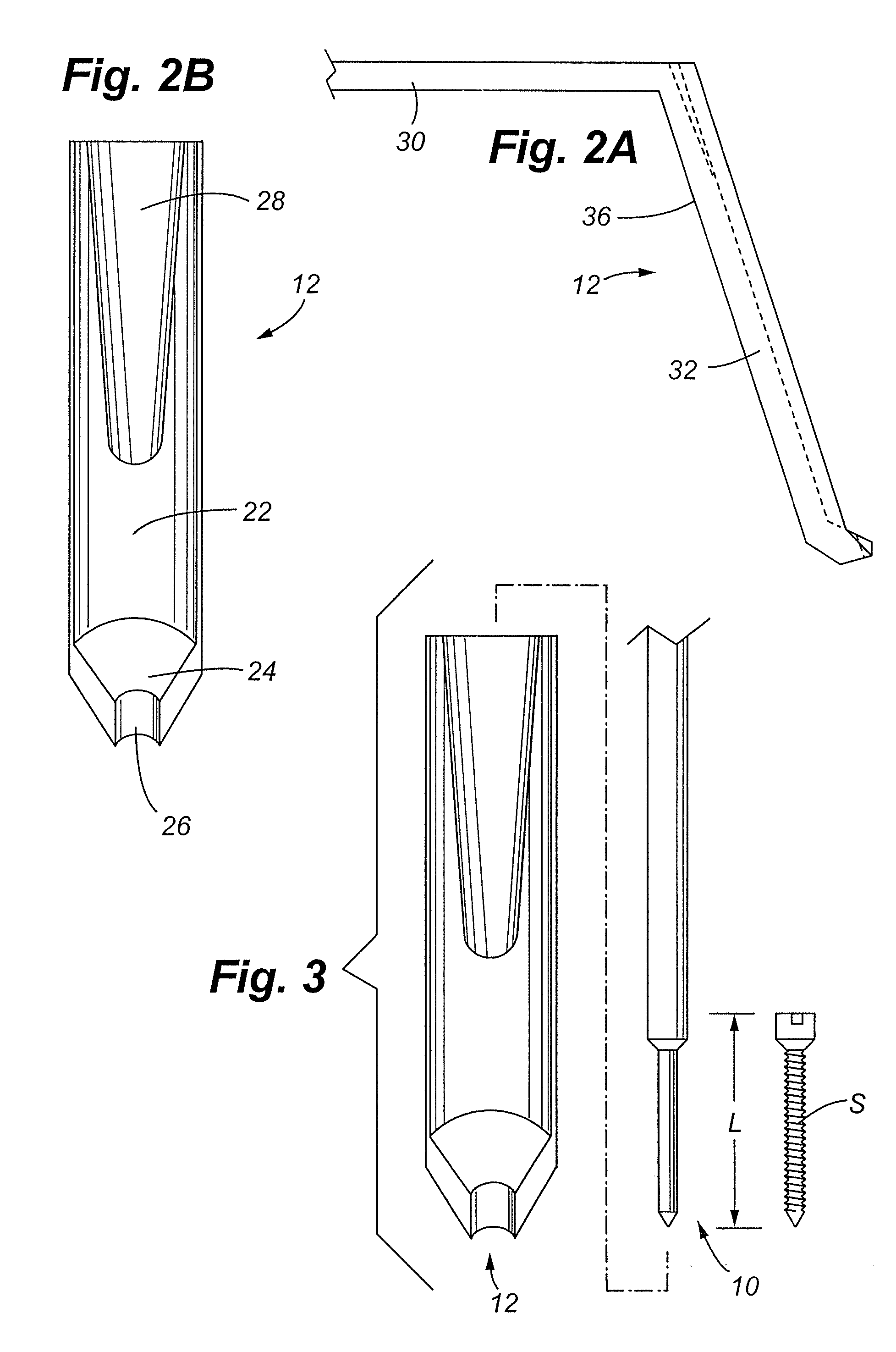
Intramedullary osteosynthesis implant, permitting in particular arthrodesis (1) of a joint, for example an interphalangeal joint, or diaphyseal osteosynthesis of the upper limb or of the lower limb, comprising two sets of at least two rods (2, 3, 4, 5) each extending on either side of a central zone (6), said rods (2, 3; 4, 5) being substantially parallel at ambient temperature within the same set, each set of rods being intended to be impacted in the medullary canal of a diaphysis, said implant being made from a shape-memory material so that, at body temperature, the rods (2, 3; 4, 5) of the same set spread apart so as to be able to immobilize themselves in said medullary canal.
Owner:AMADEX
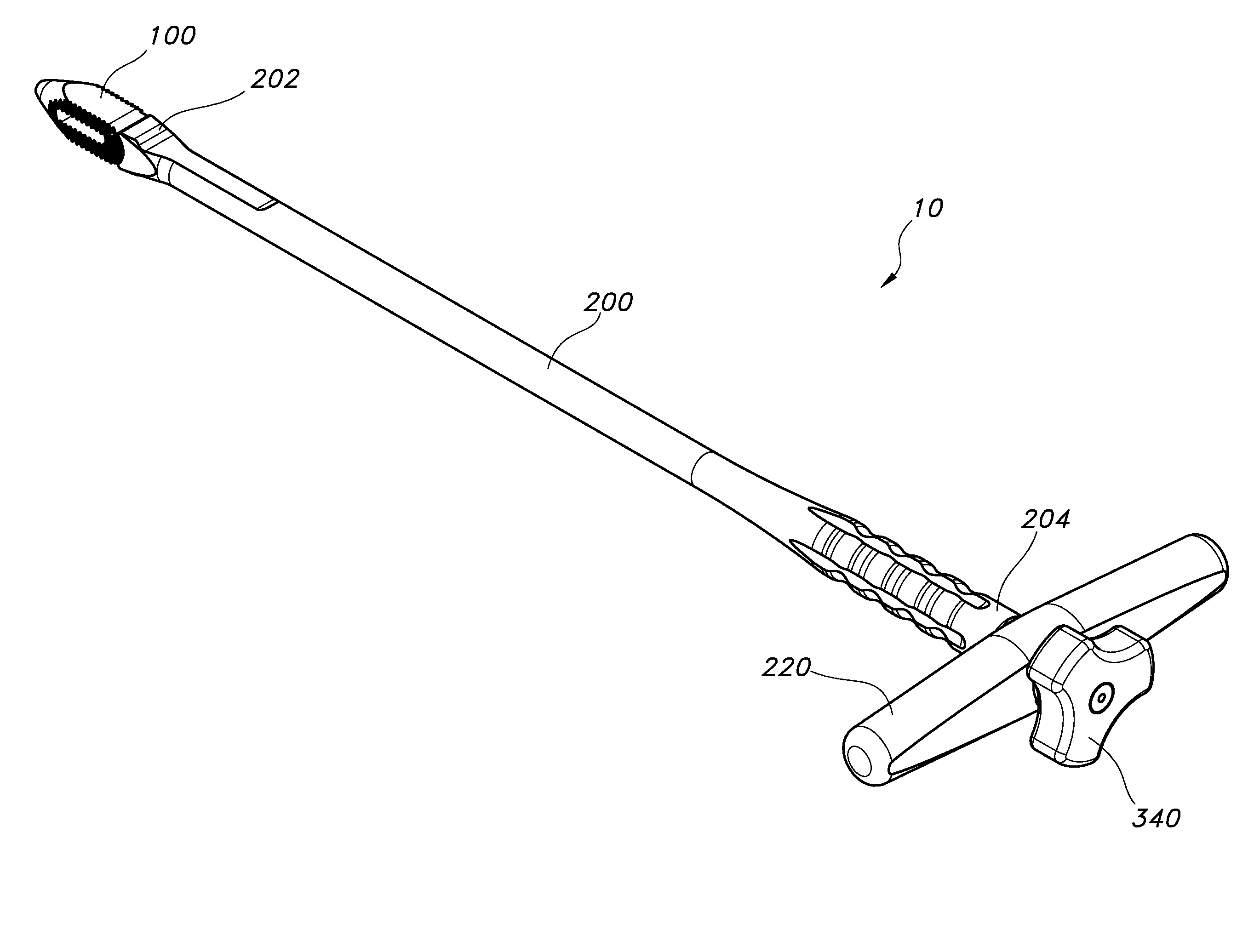
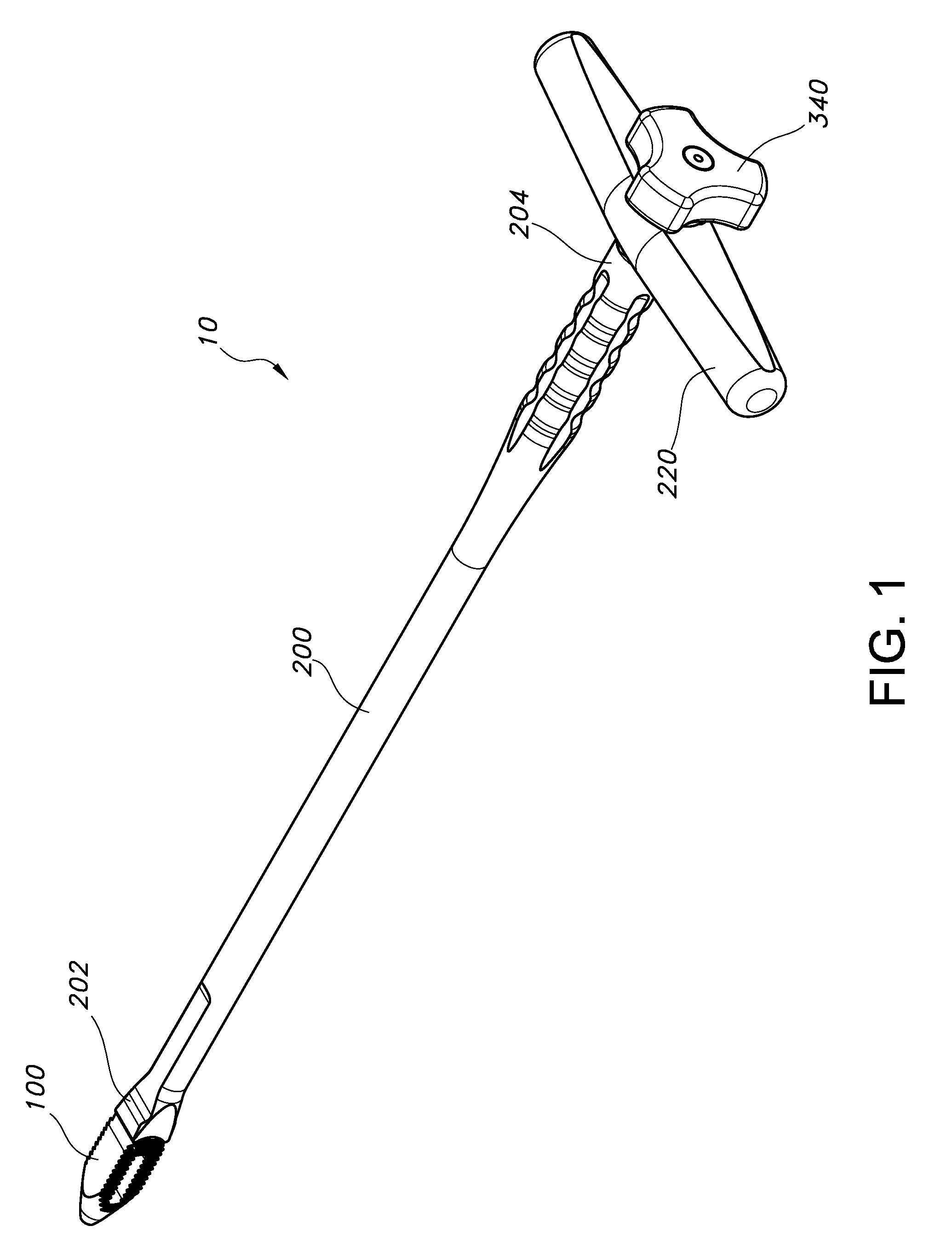
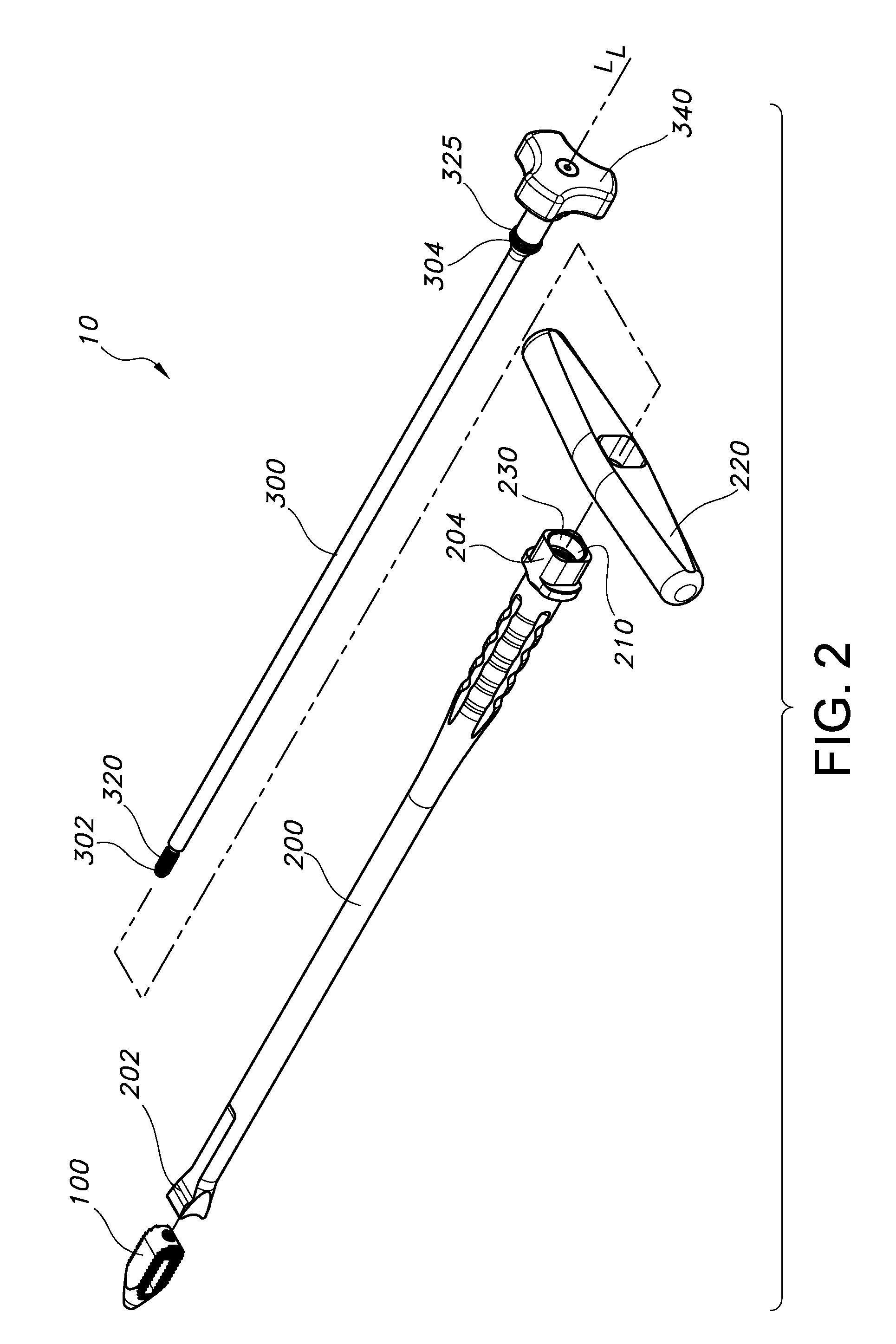
Arthrodesis implant apparatus and method
InactiveUS20120089197A1Length minimizationSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisJoint arthrodesisEngineering
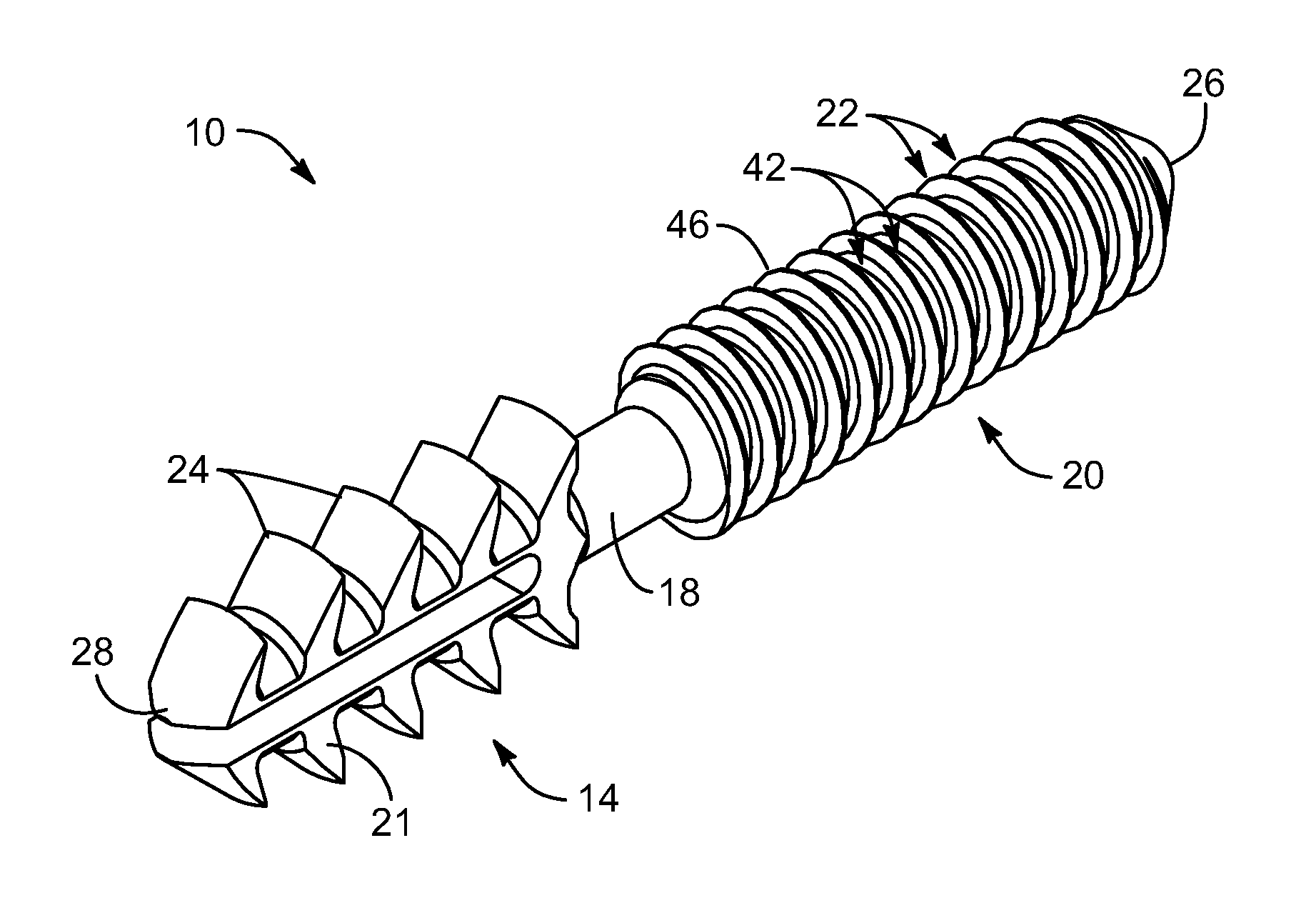
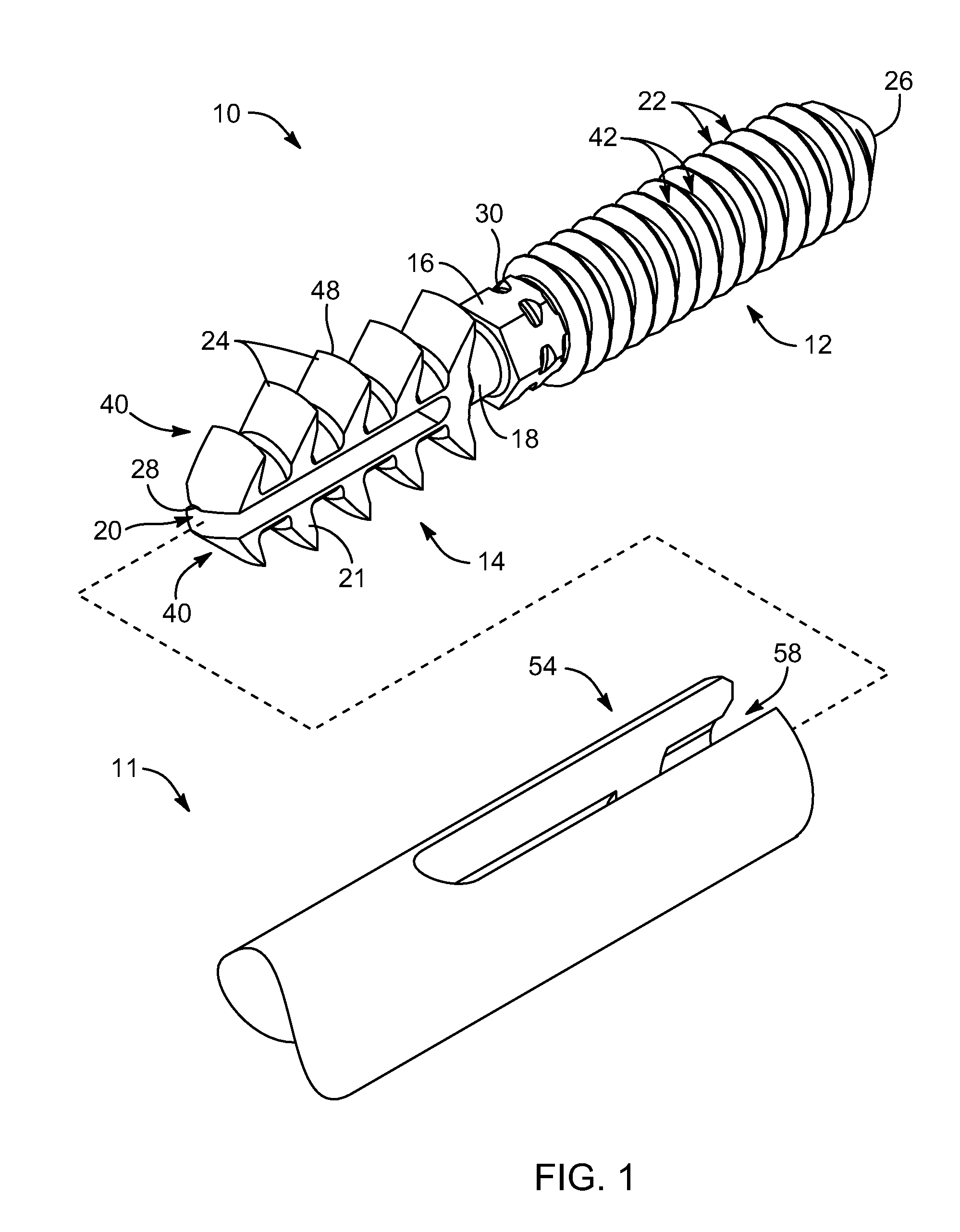
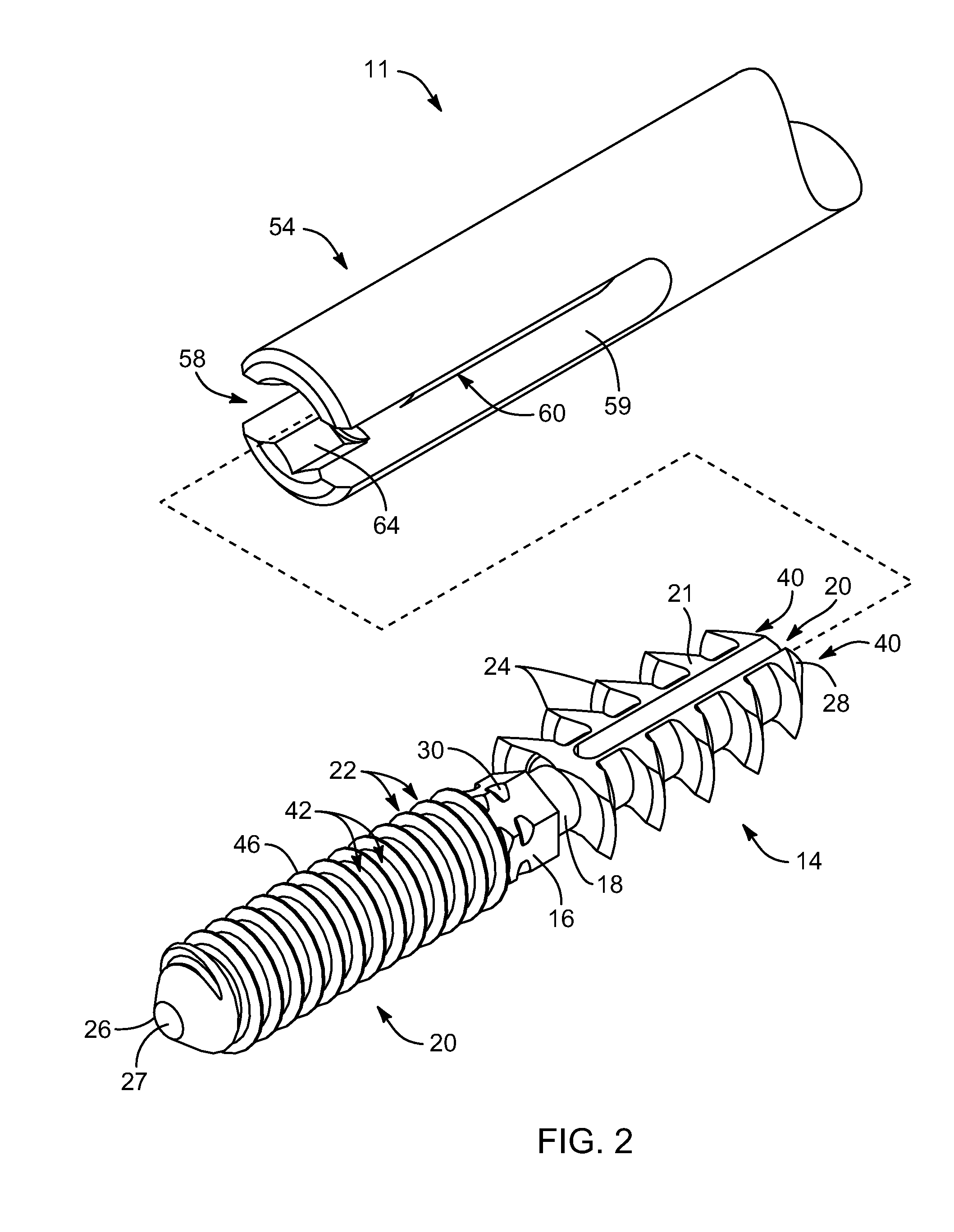
An arthrodesis anchor is formed as a monolithic piece for ease of handling and use, having two ends, one of which has prongs supporting barbs extending radially therefrom. The other end may have threads or barbs. A neck between may circular in cross section and be sized from about 0.045 inches to about 0.08 inches and may be conveniently sized at 0.062 inches for bending to accommodate final alignment of joints to be bonded. Optionally, a shank next to the neck may receive a tool for threading the anchor into a joint. The proximal and intermediate phalangial joints may be trimmed and pilot drilled, after which a first end may be inserted by a tool, typically into the proximal joint by threading or linear insertion of barbed prongs. The second end having barbed prongs may then be inserted into a pilot drilled into the base of the intermediate joint.
Owner:ORTHOPRO
Pedicle seeker and retractor, and methods of use
InactiveUS7959564B2Quantity minimizationApproach can be quite invasiveInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsJoint arthrodesisSurgical site
Owner:RITLAND STEPHEN
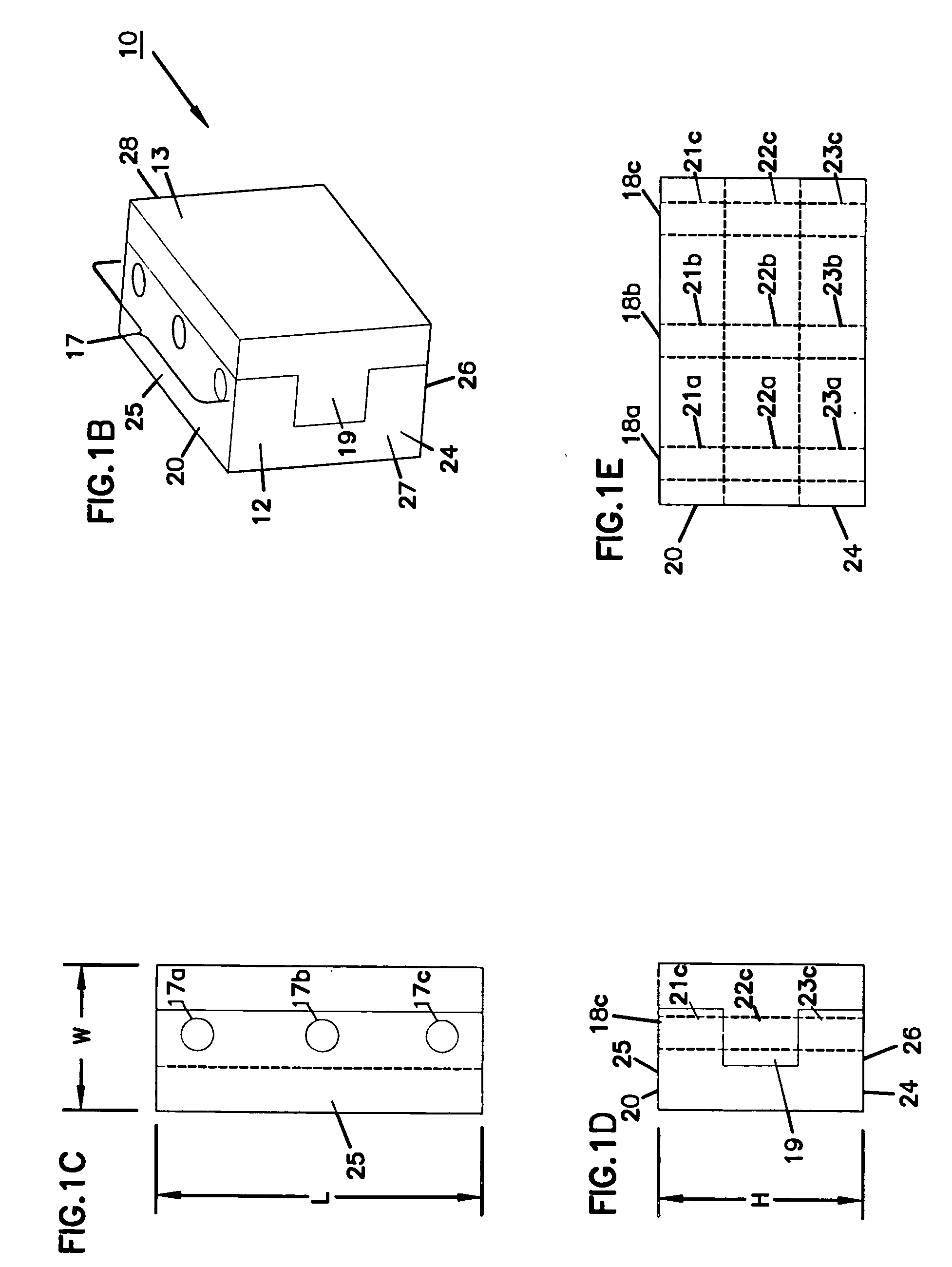
Plate for fixing the bones of a joint, in particular a metatarso-phalangeal joint
InactiveUS20030060827A1Improve accuracyEasy to placeJoint implantsBone platesJoint arthrodesisVertical plane
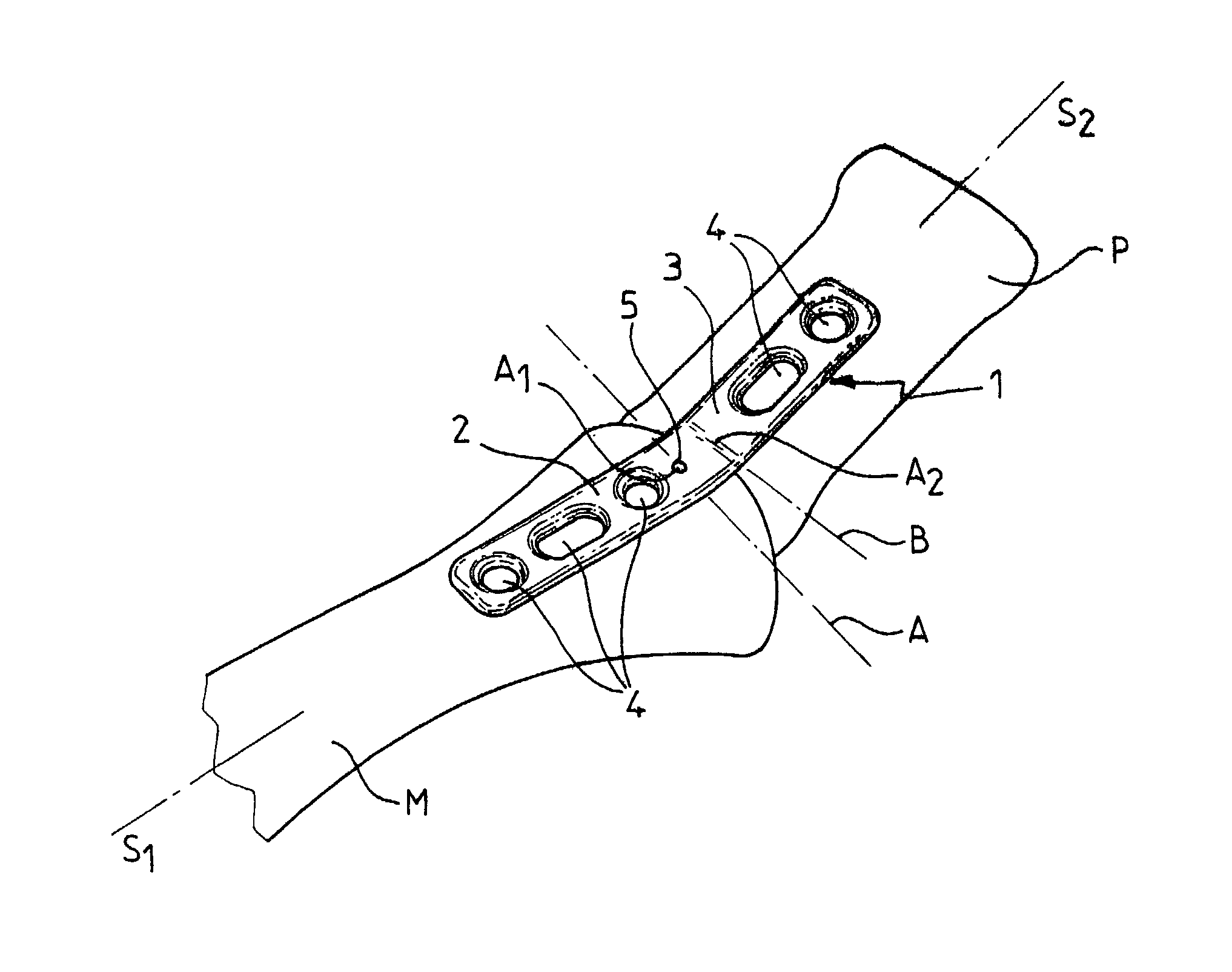
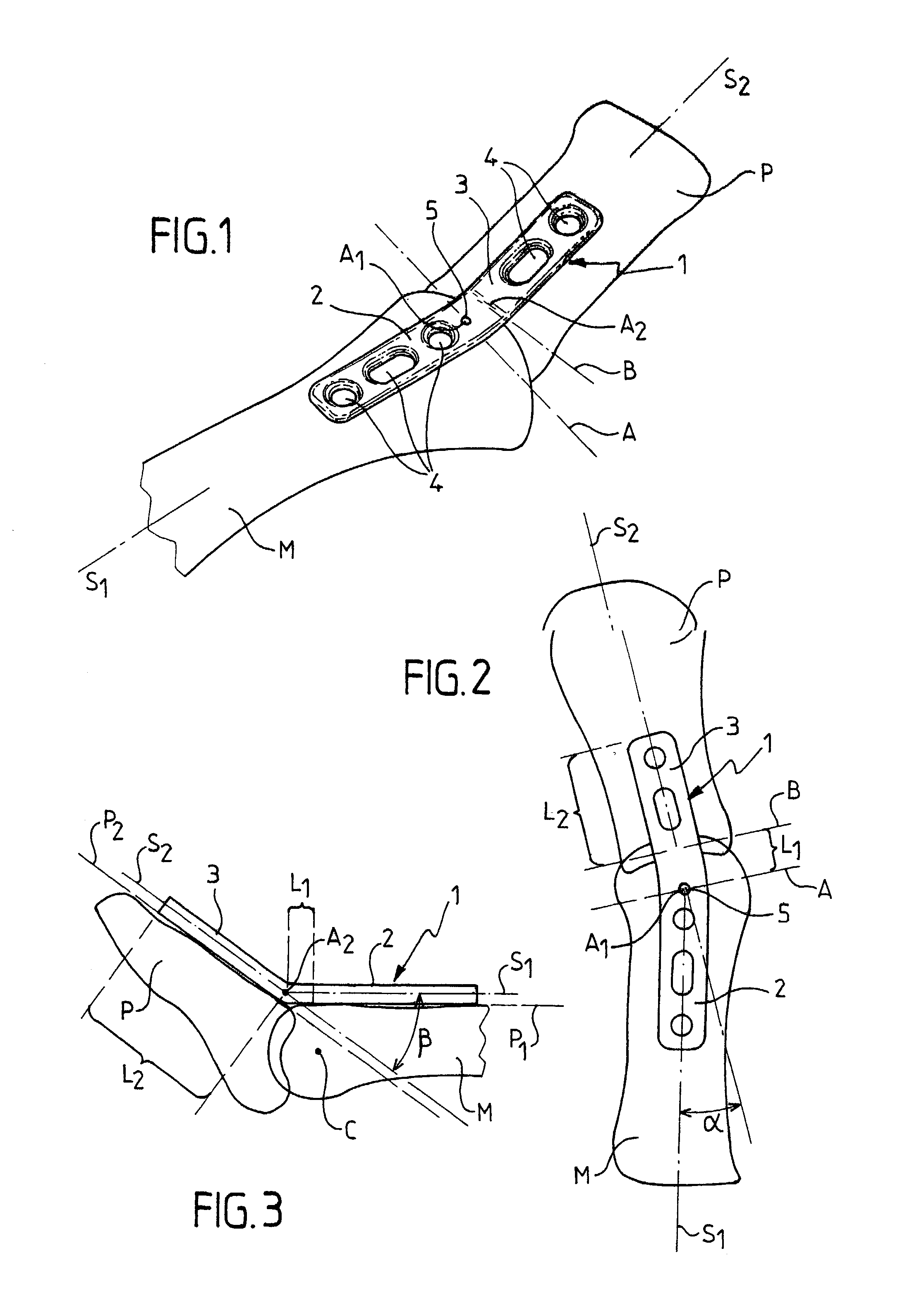
The invention relates to a plate for fixing the bones of a joint, in particular of a metatarso-phalanageal joint, for the purpose of performing arthrodesis, wherein: the plate comprises two sections, respectively a proximal section and a distal section, each section having a respective longitudinal axis of symmetry S1, S2 such that the projection onto a horizontal plane of tie axis of symmetry S2 of the distal section presents an angle of inclination relative to the projection of the axis of symmetry S1 of the proximal portion, the projections intersecting at a point A; and the projection onto a vertical plane of the axis of symmetry S2 presents an angle of inclination relative to the projection of the axis of symmetry S1, their intersection taking place at a point A2 which is distinct from the point A1
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
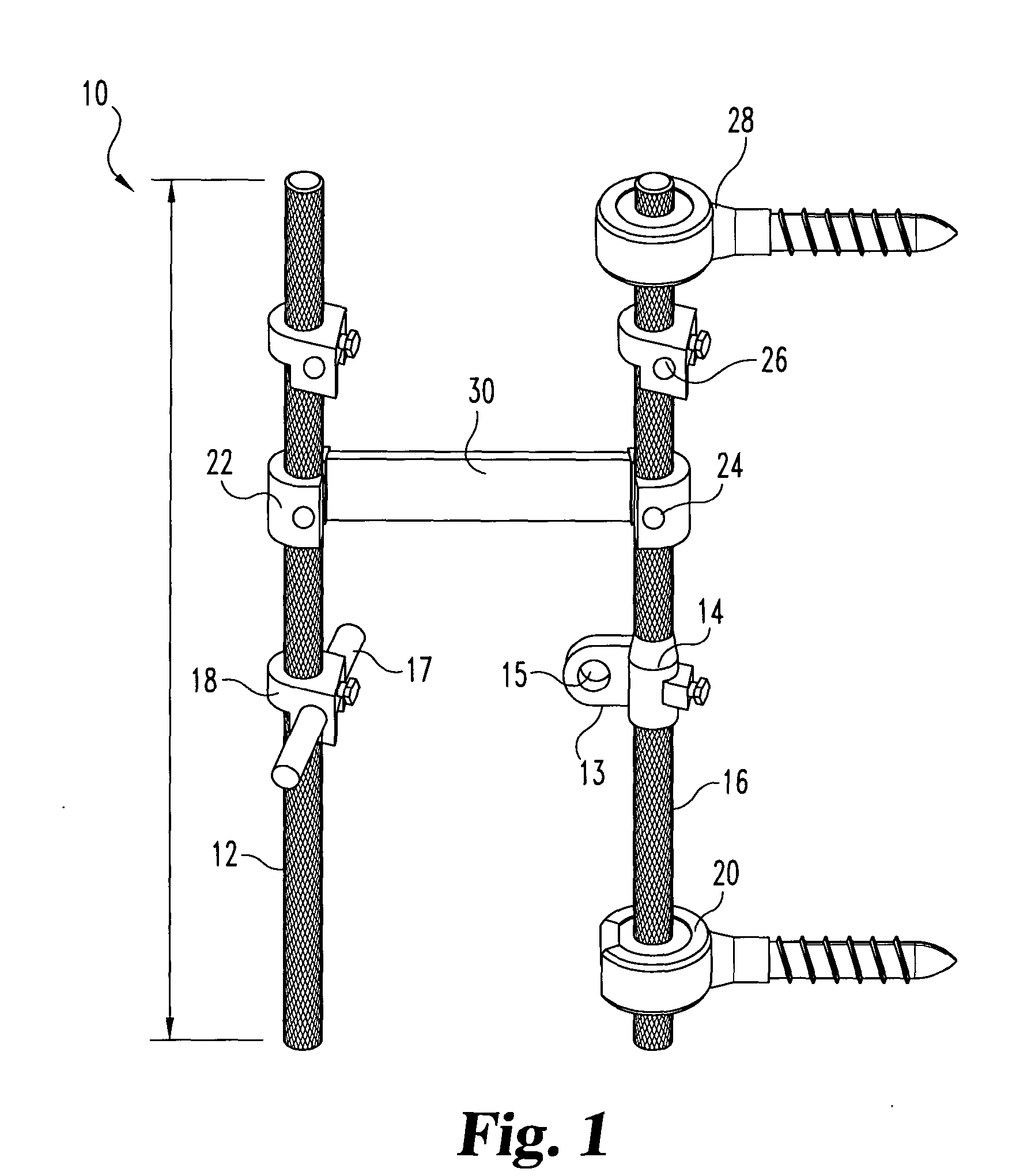
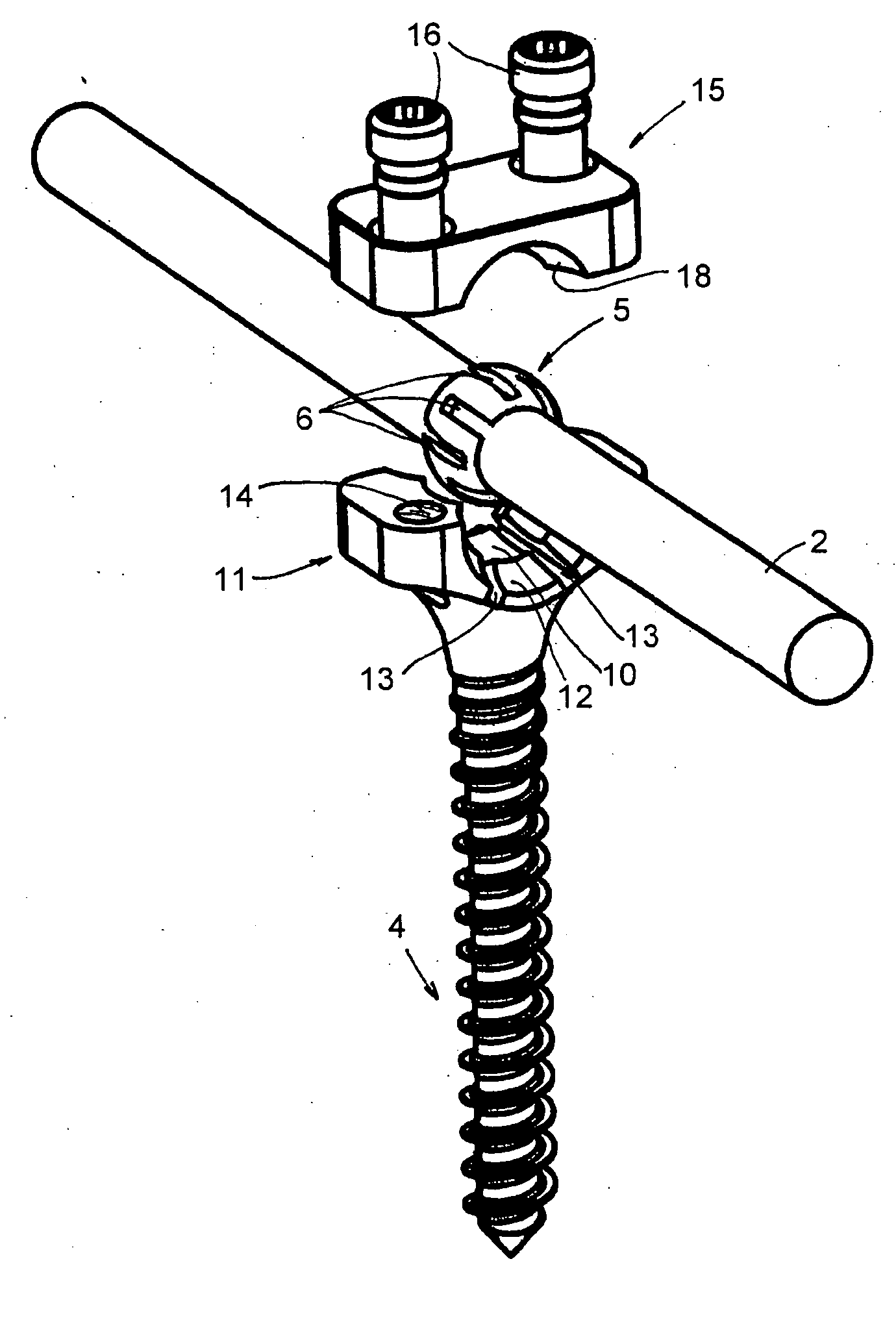
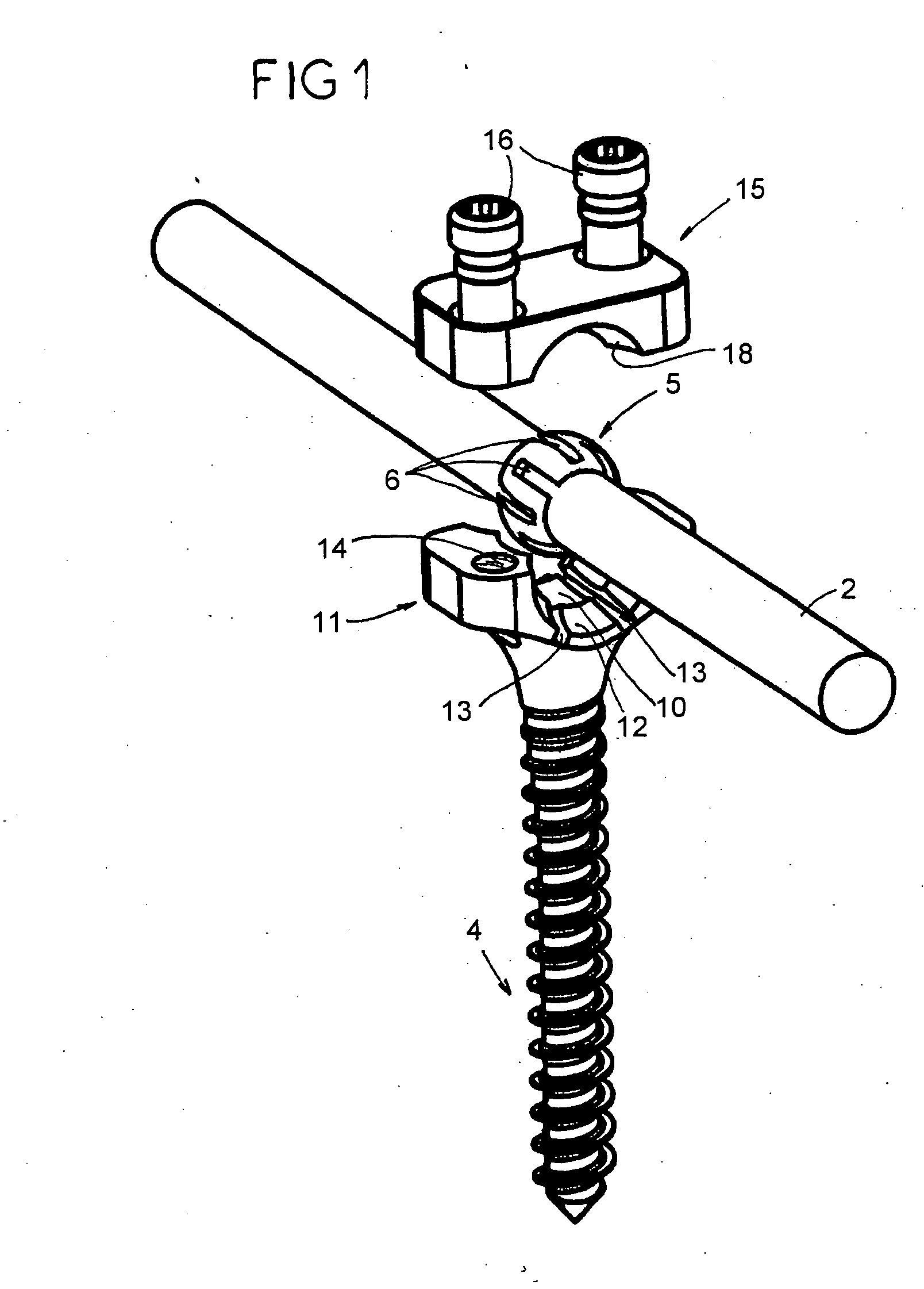
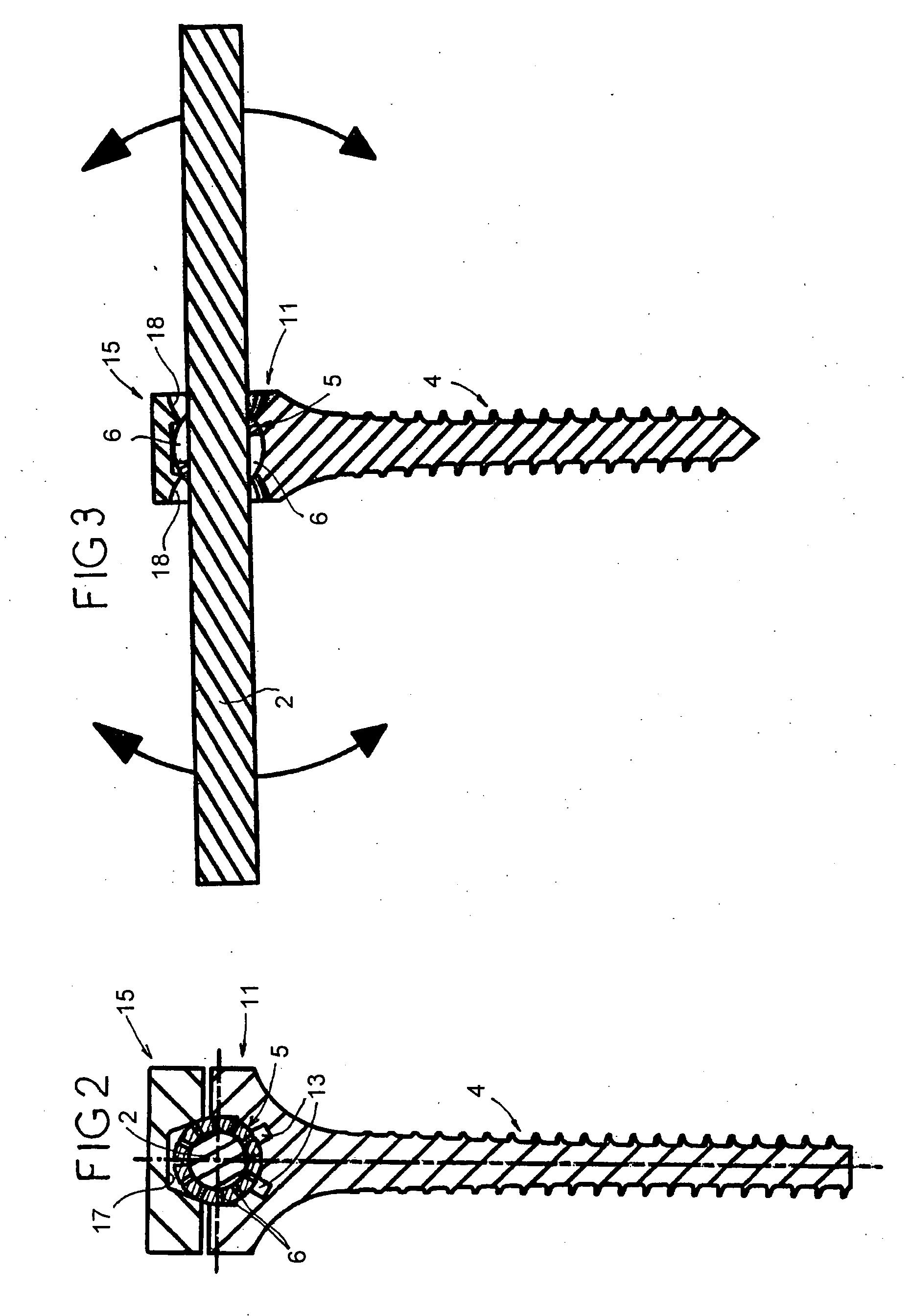
Vertebral arthrodesis equipment
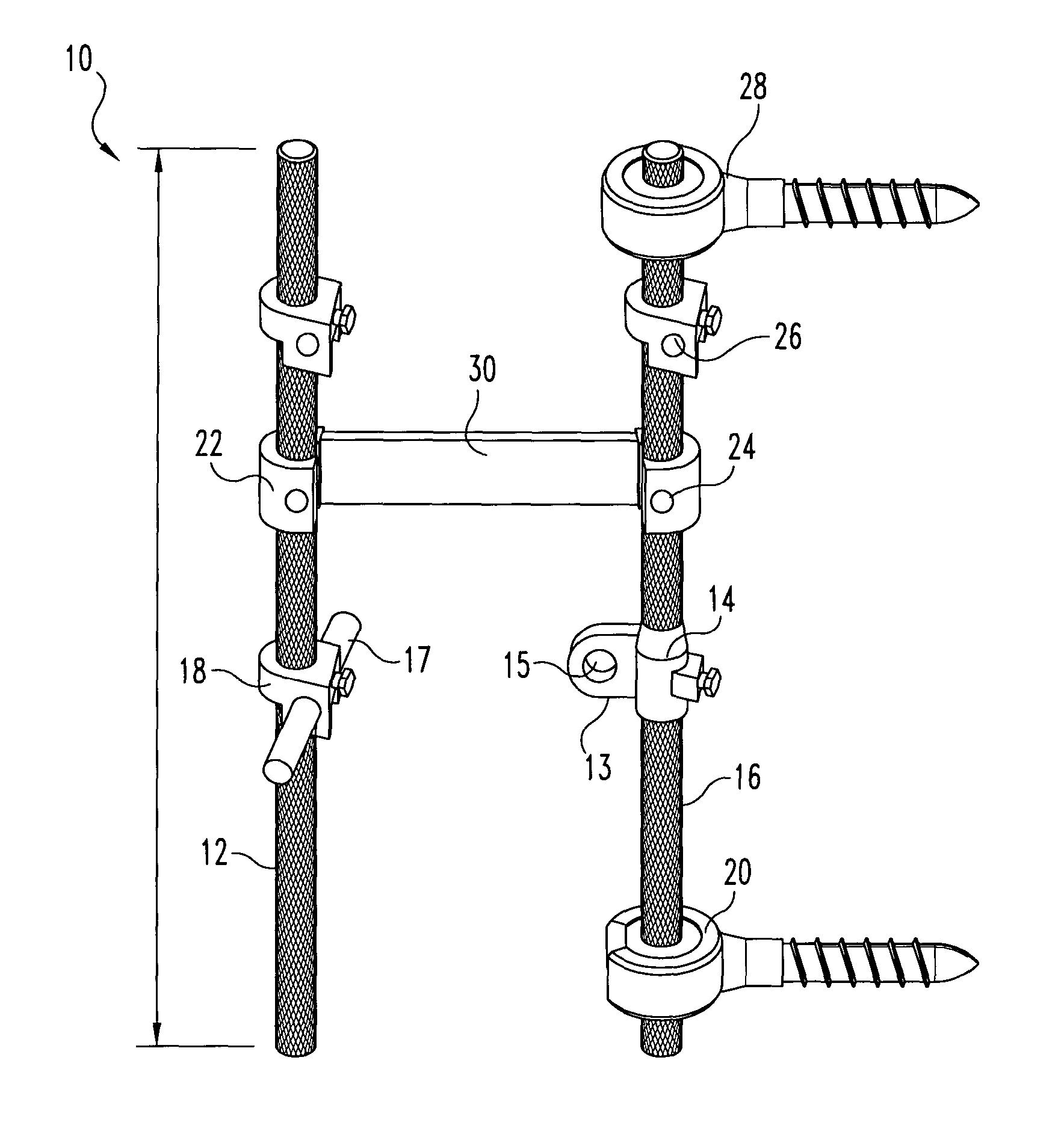
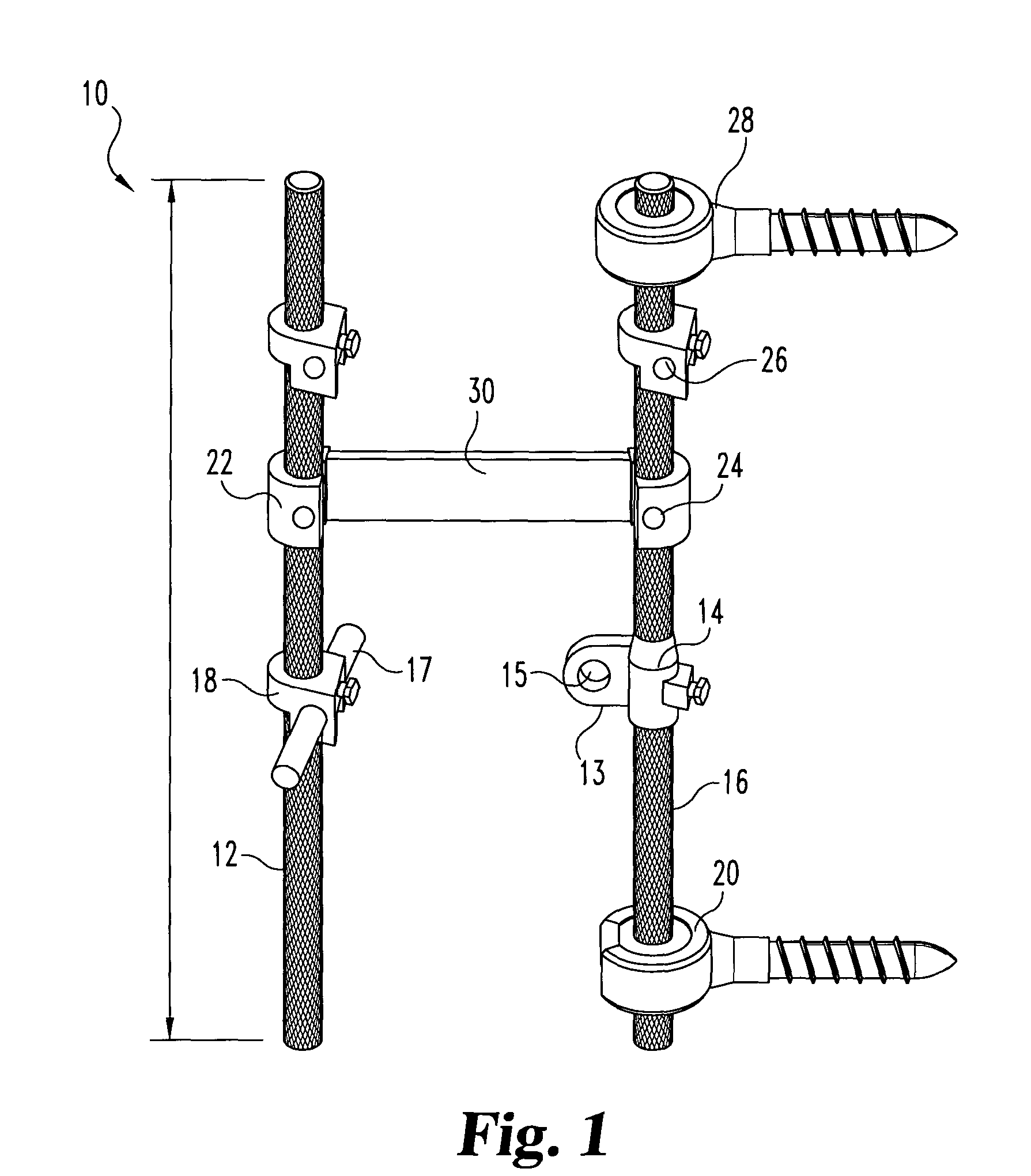
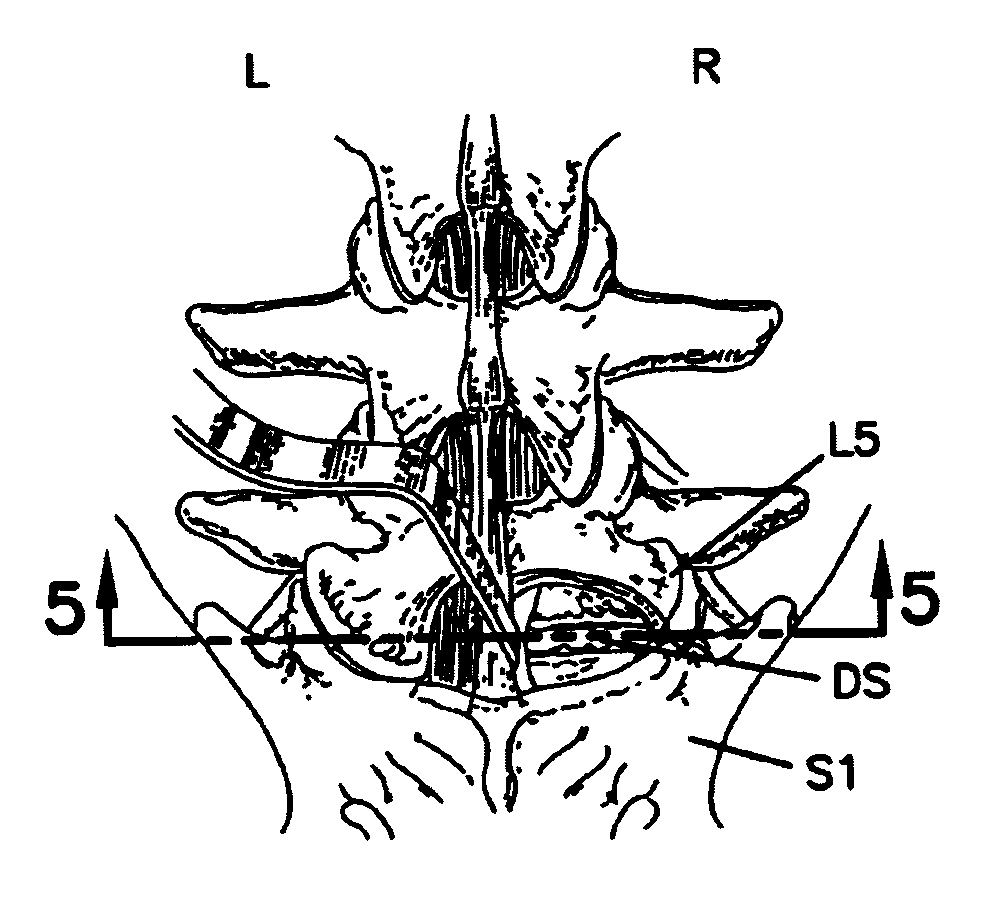
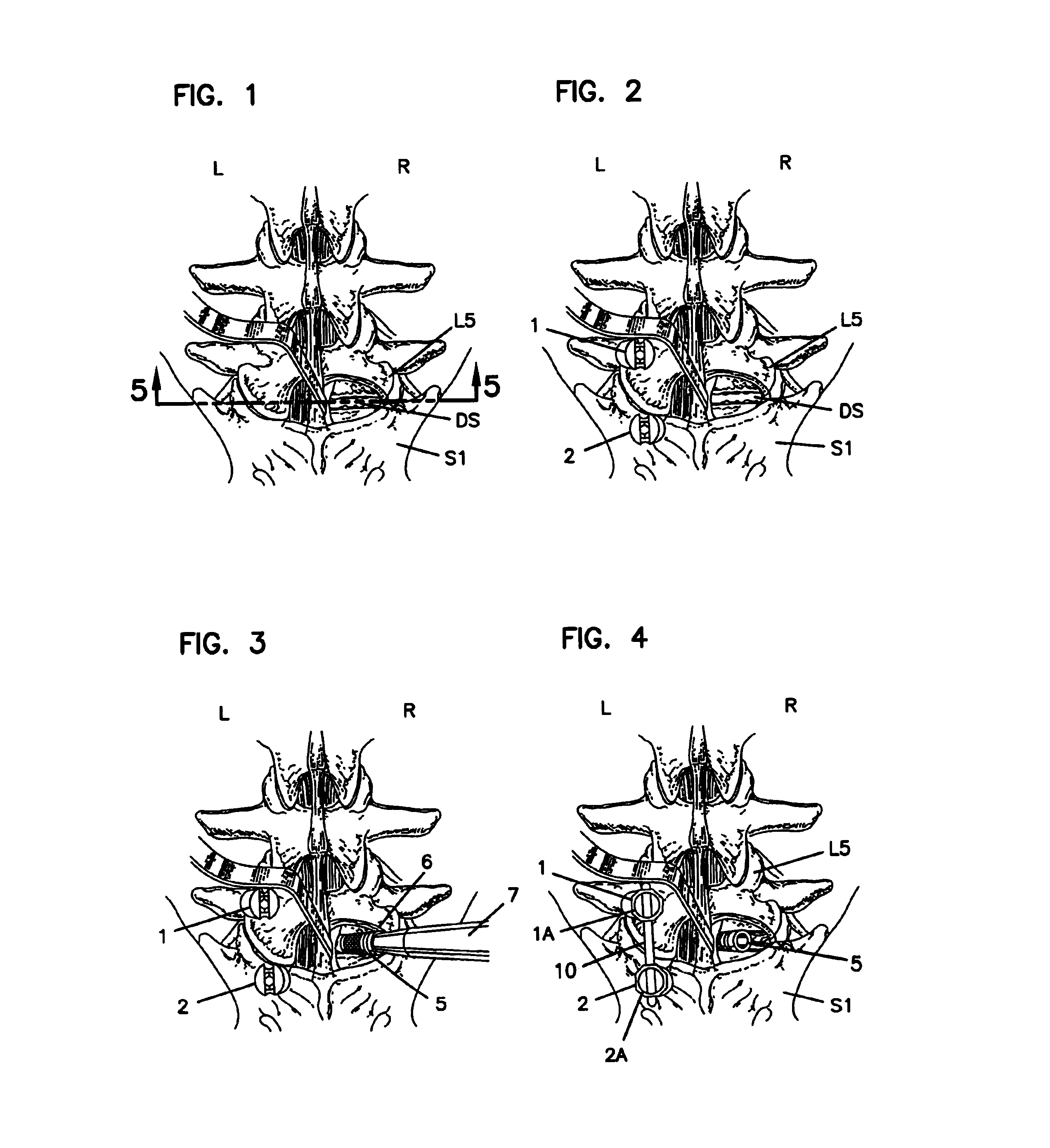
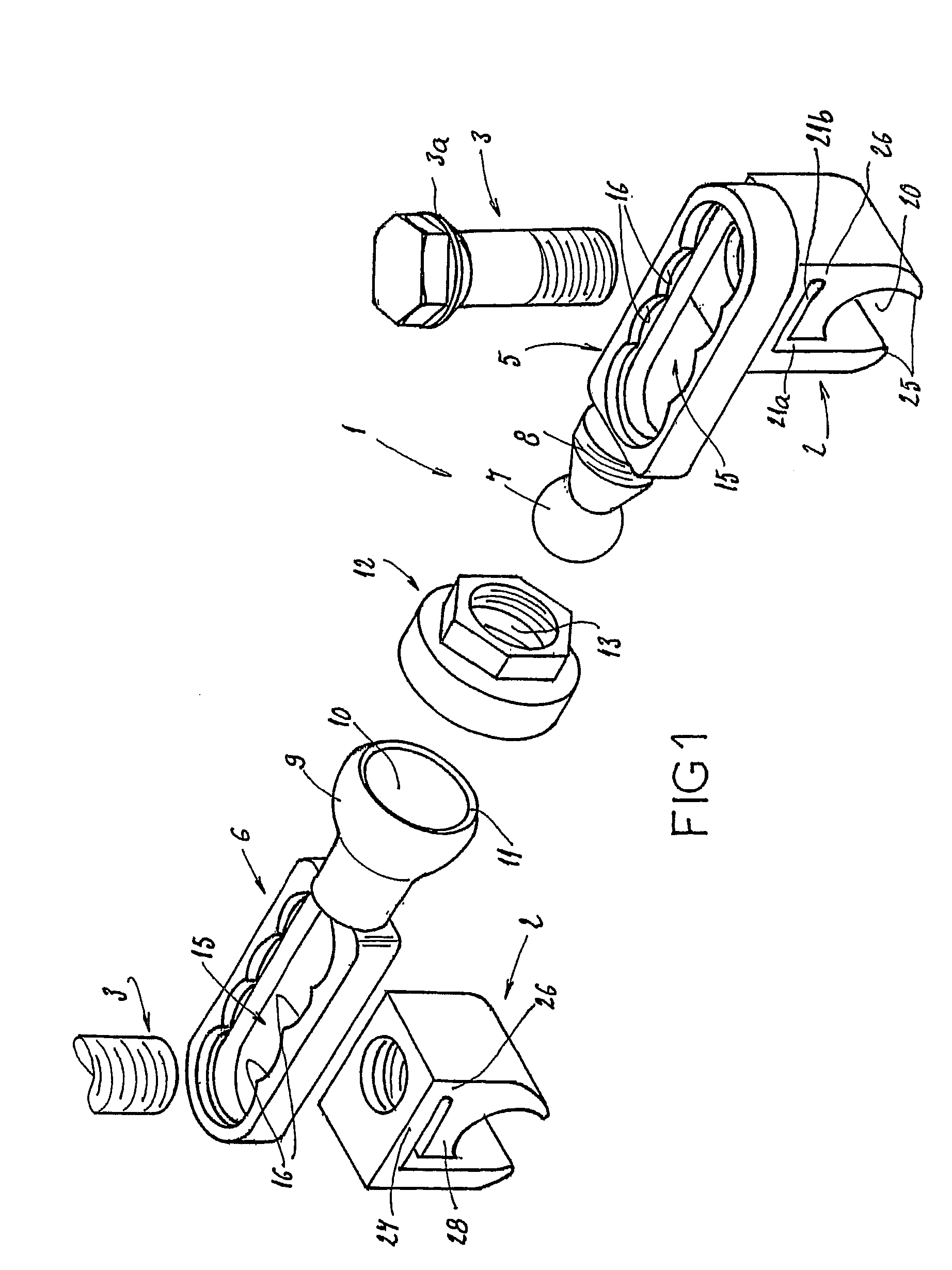
InactiveUS7033358B2Easy to engageEasy to implantInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsJoint arthrodesisIliac screw
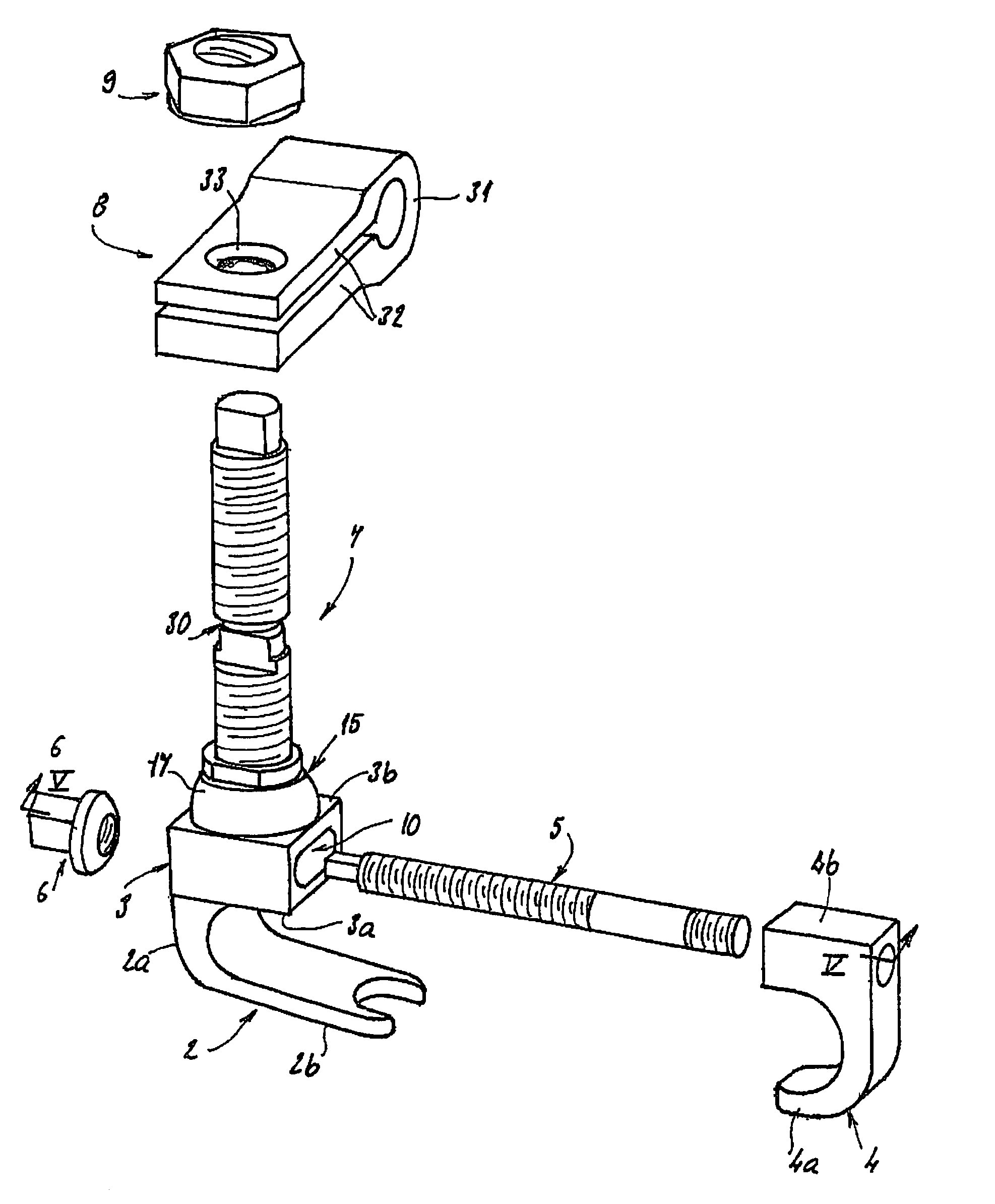
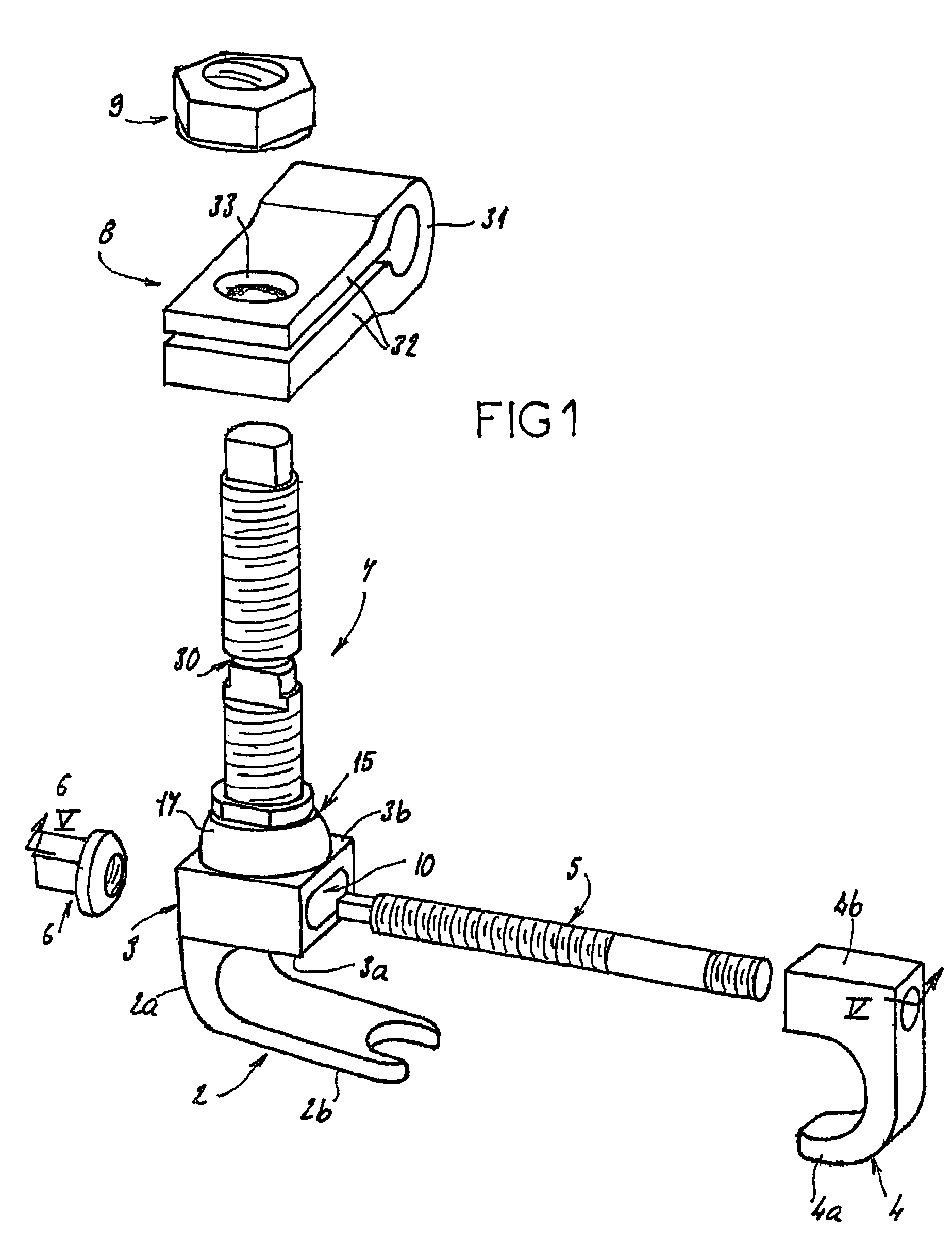
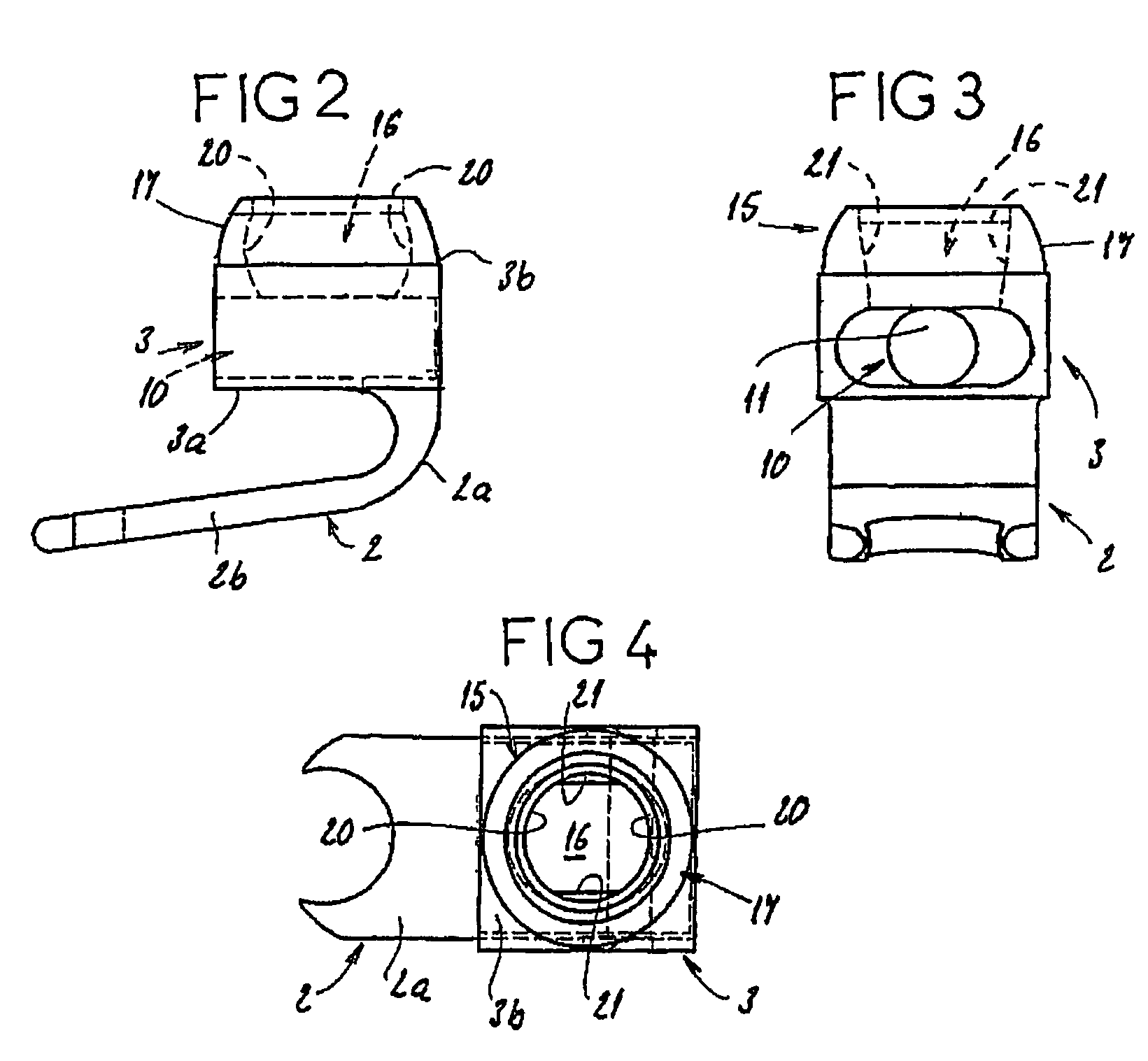
An equipment includes at least a shoring rod and at least an anchoring assembly of the shoring rod to a vertebra; each anchoring assembly comprises a base integral with a hook which has substantially planar part, extending in a parallel plane, or forming a slight angle, less than 15 degrees, with the base. The base has a hole which runs right through it, having an oblong cross-section, and the anchoring assembly comprises a hook-shaped component whereof the part corresponding to the base of the hook is linked to a threaded rod capable of being engaged in the hole with the possibly of pivoting about an axis and of displacement in the plane, and capable of receiving a screw.
Owner:TAYLOR AS +4
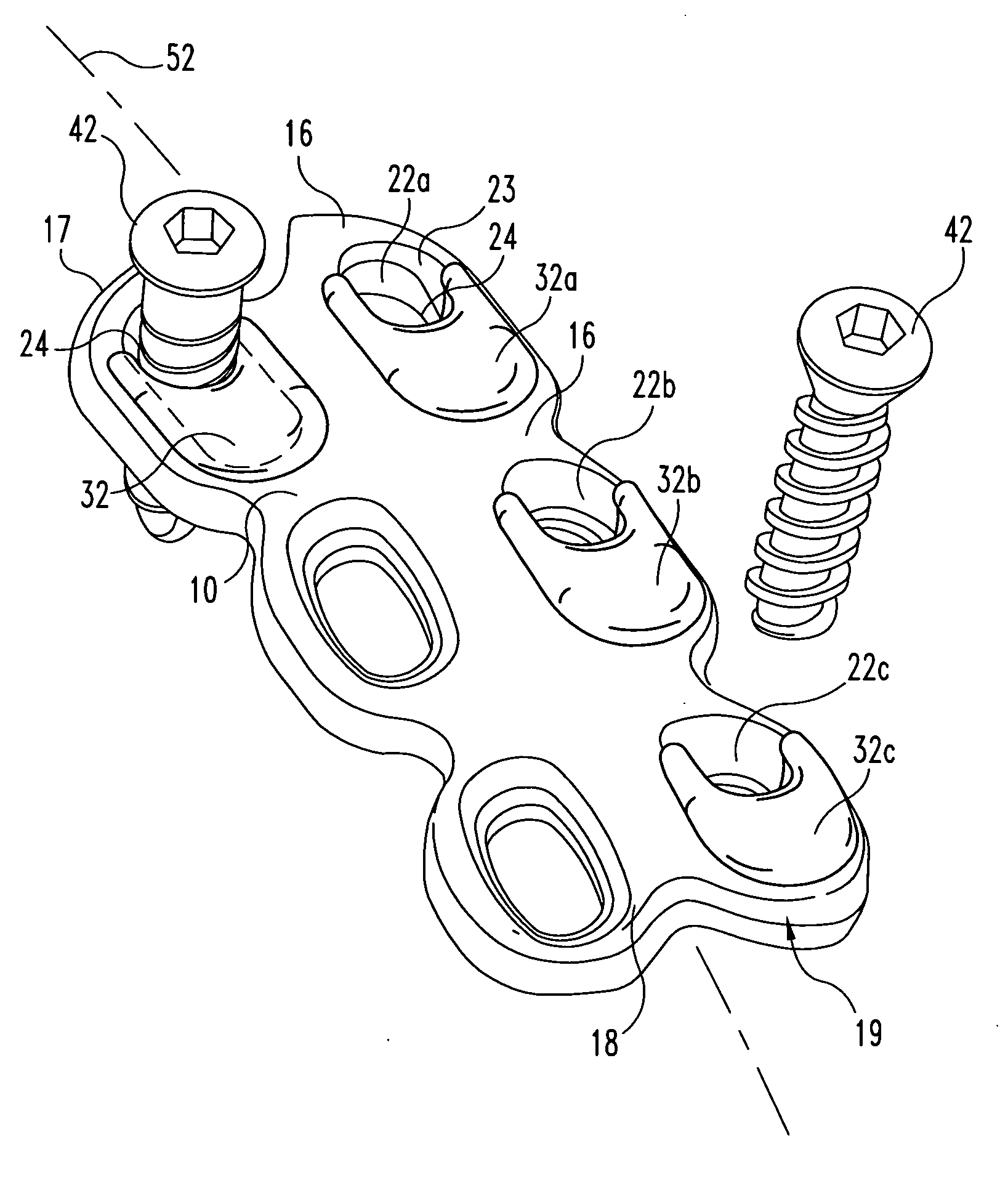
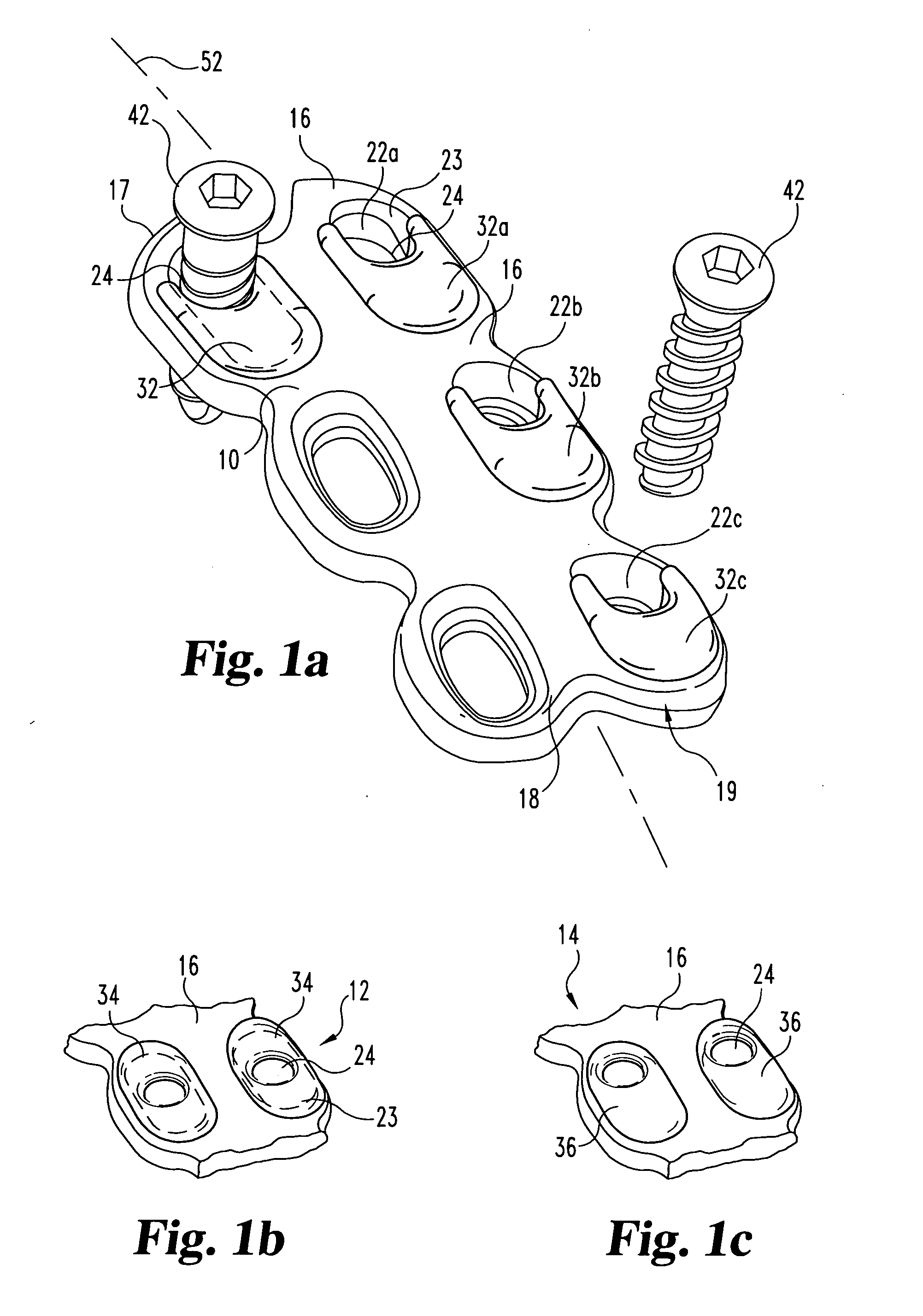
Bone fixation implant system and method
A system for performing bone arthrodesis includes an implant for bone arthrodesis and a bone fastening device. The implant includes a fastener with an elongated shaft having a head at one end and a bone-piercing point at the opposite end. A first washer has structure for engaging the head of the shaft so as to be polyaxially pivotable with respect to the head. A locking member has structure for engaging the shaft. The locking member can have a second washer pivotally engaged thereto. The bone fastening device can include an elongated cannula with a collet for detachably engaging the first washer and for advancing the first washer. Structure is provided for engaging the fastener and for advancing and rotating the fastener through the collet and through the first washer. The bone arthrodesis device further includes a lower end portion extending from the cannula. The lower end portion has structure for detachably engaging the locking member. The fastener, first washer, and locking member are aligned such that the advancing fastener will advance through the first washer, drill through the bone, and move into the locking member. A method for performing bone arthrodesis is also disclosed.
Owner:CTL MEDICAL CORP
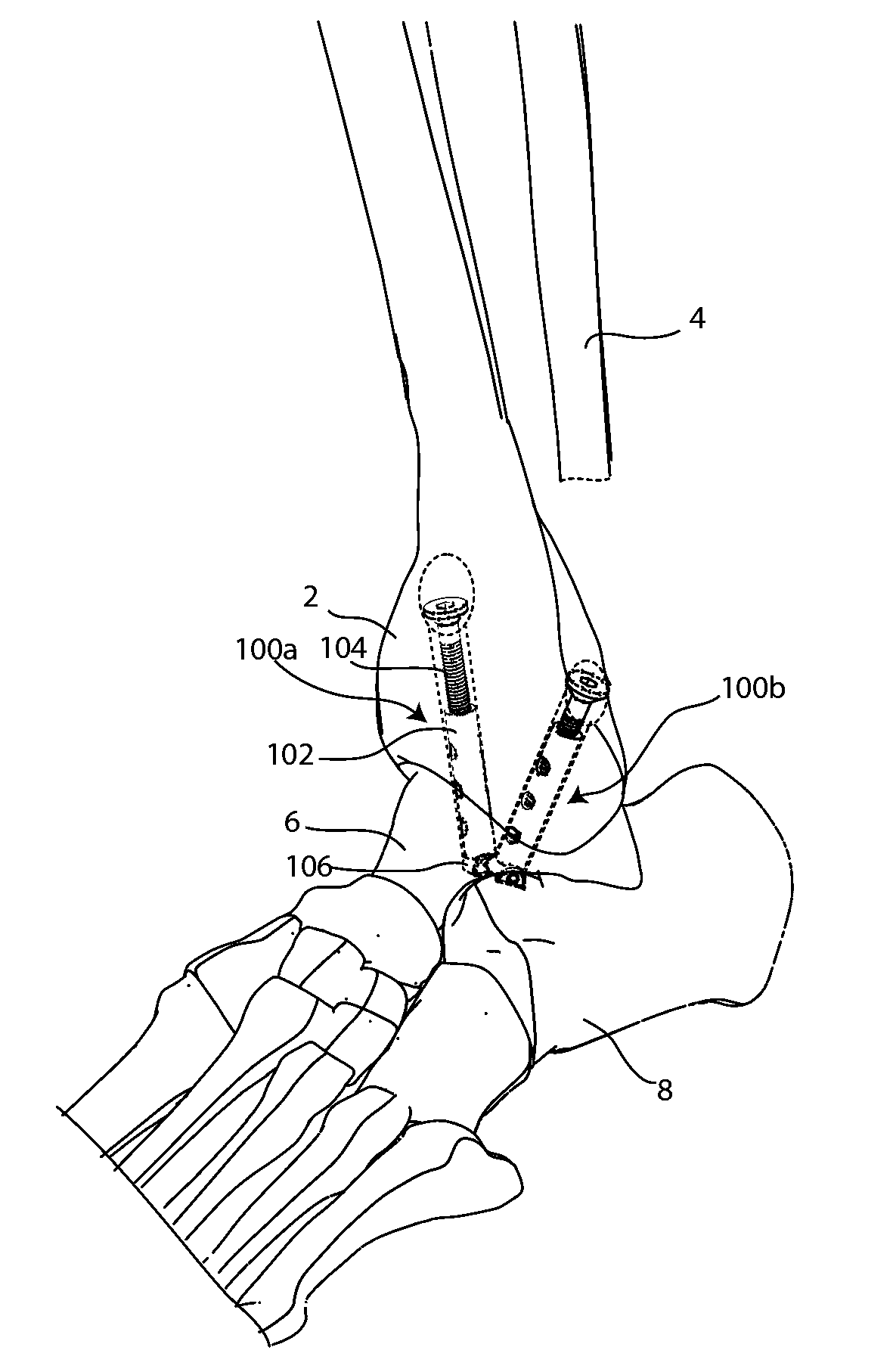
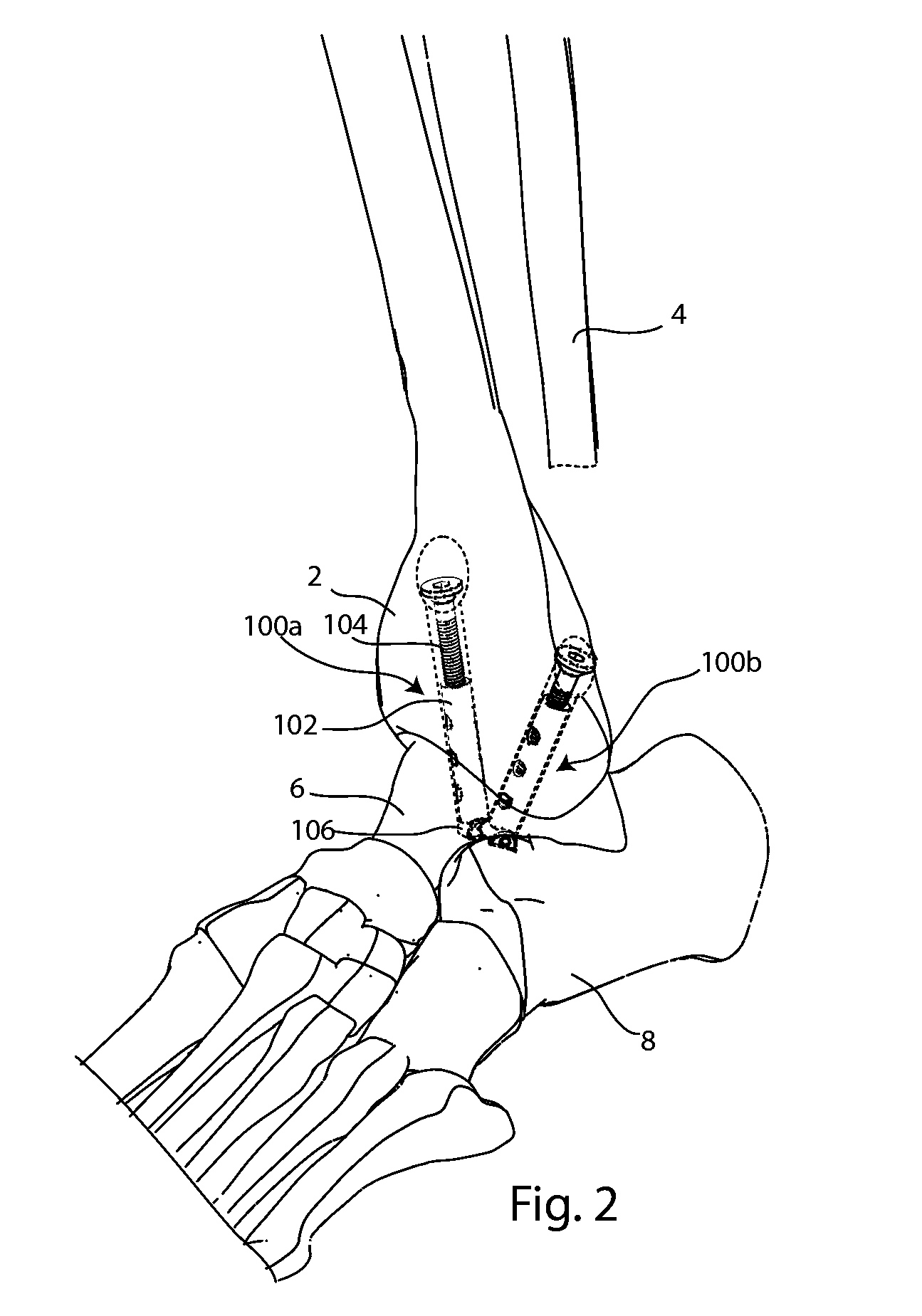
Joint Arthrodesis and Arthroplasty
An implantable fixation system for fusing a joint between a first bone and a second bone. The system may include an anchor, standoff, bolt, and cortical washer. The system may be implanted across the joint along a single trajectory, the length of the system adjustable to provide compressive force between the anchor and the cortical washer. The system may be implanted across a tibiotalar joint with the anchor positioned in the sinus tarsi. A spacing member may be inserted between the two bones and the fixation system implanted to extend through an opening in the spacing member. The spacing member may be anatomically shaped and / or provide deformity correction. An ankle arthroplasty system may include a tibial plate, a talar plate, and a bearing insert. The plates may be anchored to the tibia and talus along a single trajectory. The ankle arthroplasty system may be revisable to a fusion system.
Owner:MEDICINELODGE +1
Percutaneous arthrodesis method and system
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
Vertebral arthrodesis device
Owner:PARADIGM SPINE LLC
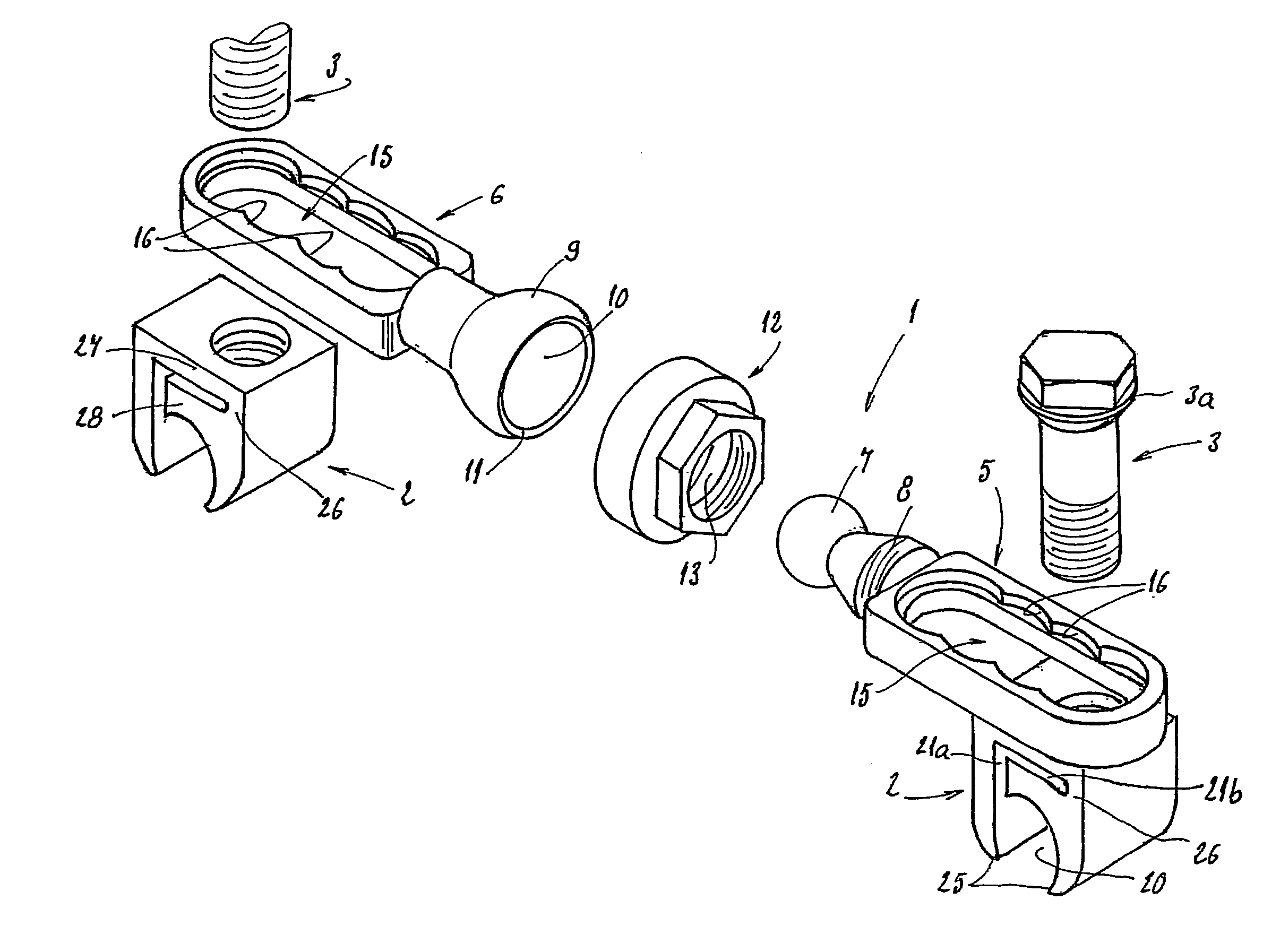
Vertebral arthrodesis equipment
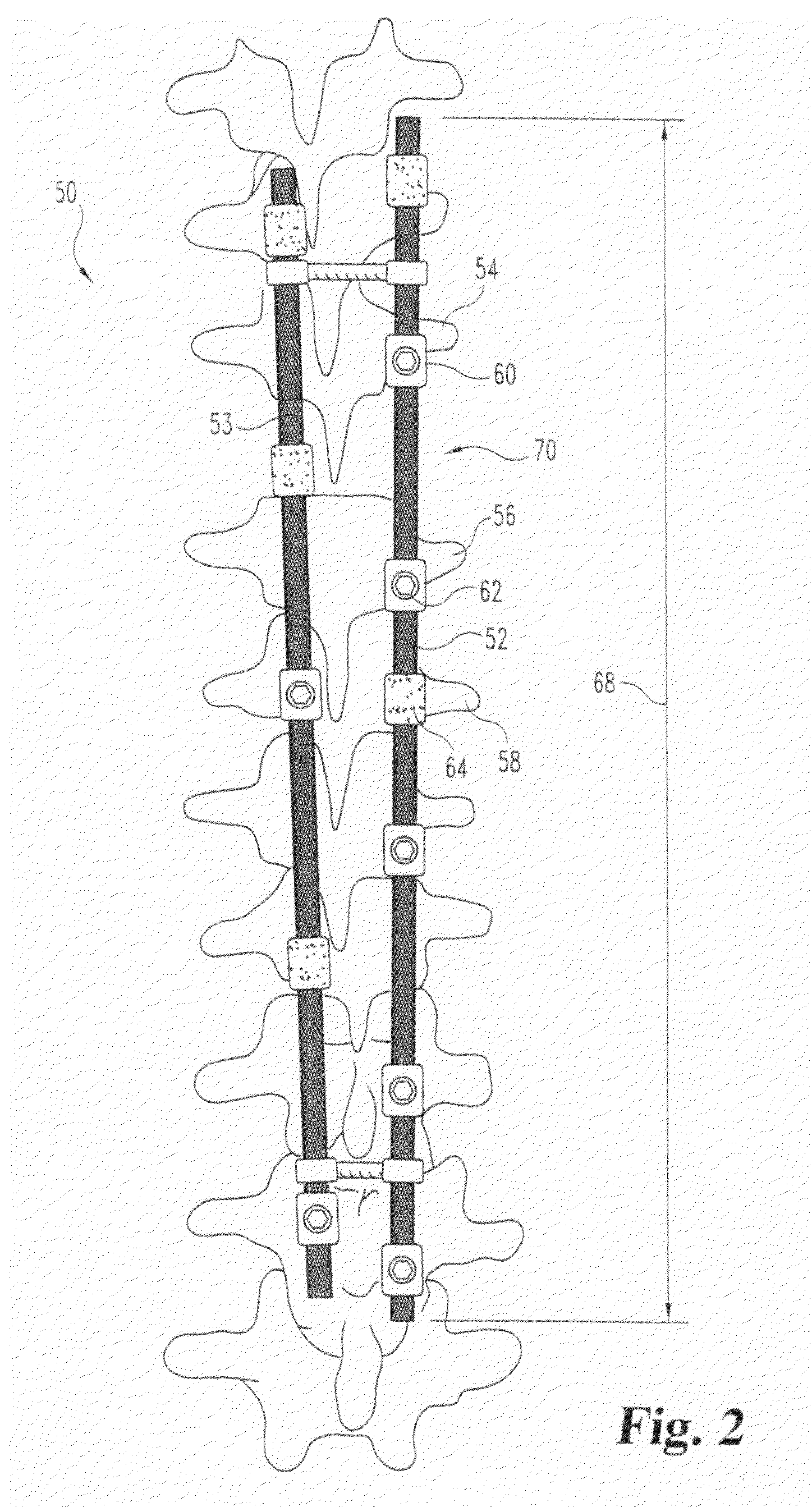
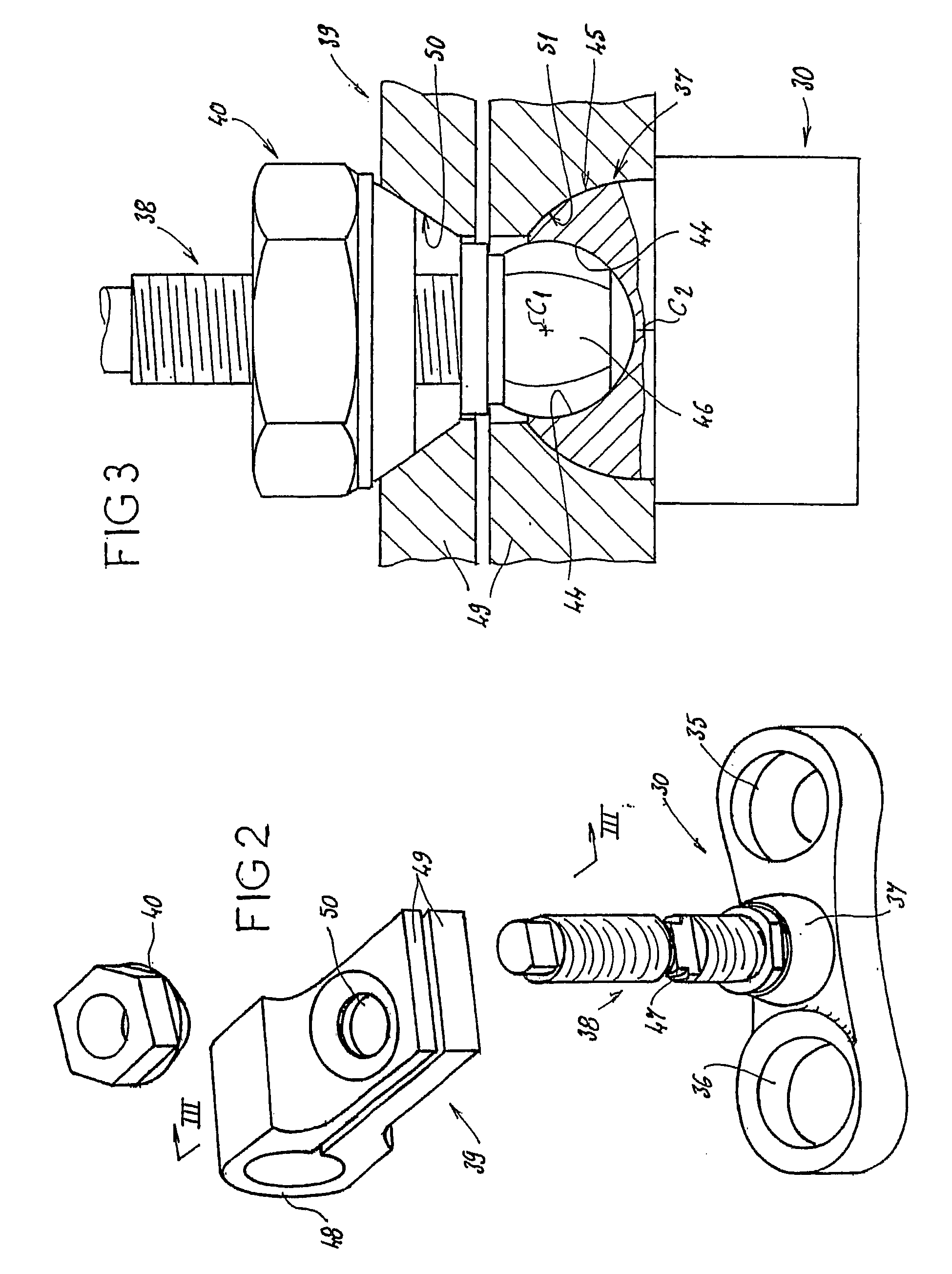
The invention concerns an equipment comprising two shoring rods, members for anchoring said two rods to the vertebrae, at least a crosspiece (1) in two parts (5, 6) and members (2) assembling said crosspiece (1) to the shoring rods. The invention is characterised in that one of the crosspiece parts (5) comprises a spherical head (7) and a thread (8) adjacent to said head (7); the other crosspiece part (6) comprises a spherical bulging end (9), defining internally a spherical cavity (10) adapted to receive said head (7), and each crosspiece (1) comprises a nut (12) designed to co-operate with said thread (8), including further a spherical seat (13) with a shape matching that of the wall (11) delimiting the cavity (10). The invention also concerns plates (30for anchoring the equipment to the sacrum.
Owner:TAYLOR JEAN +3
Selectively expanding spine cage with enhanced bone graft infusion
A selectively expanding spine cage has a minimized cross section in its unexpanded state that is smaller than the diameter of the neuroforamen through which it passes in the distracted spine. The cage conformably engages between the endplates of the adjacent vertebrae to effectively distract the anterior disc space, stabilize the motion segments and eliminate pathologic spine motion. Expanding selectively (anteriorly, along the vertical axis of the spine) rather than uniformly, the cage height increases and holds the vertebrae with fixation forces greater than adjacent bone and soft tissue failure forces in natural lordosis. Stability is thus achieved immediately, enabling patient function by eliminating painful motion. The cage shape intends to rest proximate to the anterior column cortices securing the desired spread and fixation, allowing for bone graft in, around, and through the implant for arthrodesis whereas for arthroplasty it fixes to endpoints but cushions the spine naturally.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Minimally invasive systems, devices, and surgical methods for performing arthrodesis in the spine
Systems, devices, and methods achieve percutaneous fusion of the spine. The systems, devices, and methods percutaneously manipulate instrumentation to achieve posterior percutaneous transpedicular access to an interior of a first targeted vertebral body through a pedicle of the vertebra. The systems, devices, and methods percutaneously manipulate instrumentation through the achieved percutaneous transpedicular access, to achieve percutaneous cephalad trans-disc access to an interior of a second targeted vertebral body at a next adjacent superior level to the first targeted vertebral body. The systems, devices, and methods percutaneously manipulate instrumentation through the achieved percutaneous transpedicular access and percutaneous cephalad trans-disc access, to achieve percutaneous disc cavity creation comprising forming an enlarged cavity in the intervertebral disc space between the first and second targeted vertebral bodies. The systems, devices, and methods percutaneously manipulate instrumentation through the achieved percutaneous transpedicular access and percutaneous cephalad trans-disc access, to place a support structure in the enlarged cavity that achieves disc cavity support, into which a volume of a filling material is conveyed that, over time, hardens to promote fusion of the targeted first and second vertebral bodies.
Owner:COBBS CHARLES S
Bone implants and methods
The disclosure provides implants, instruments and methods for bone fusion procedures. In some embodiments, the implants are particularly advantageous for use between opposing vertebral bodies to facilitate stabilization or arthrodesis of an intervertebral joint. The implants include, at least, a support component that provides structural support during fusion. In a typical embodiment, the implants also include a growth component. A growth component provides an environment conducive to new bone growth between the bones being fused. Several unique configurations to enhance fusion, instruments for insertion and methods for insertion are also disclosed.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Expandable intervertebral implant and method
Replaces anterior spinal column with an expandable lattice implant made of supportive material that includes use of fusion augmenting material. Allows ease of use while promoting both immediate spinal stability and eventual arthrodesis. May be utilized during anterior or retroperitoneal approaches to the spinal column, primarily addressing anterior spinal column pathology. May utilize fusion augmenting material of limited biomechanical strength compared to the strength of its rigid components. May be accompanied by additional anterior or posterior spinal instrumentation and fixation. Uses a pair of circular endplate discs that are distracted from each other by ribs of rigid support rods. Extension may be performed using an expansion tool once device is placed within intervertebral space. Hollow portions of device may be packed with bone or other materials to enhance eventual fusion. Shape of discs at each end may be manipulated prior to surgery to adapt to the specific spinal curvature desired.
Owner:BAMBAKIDIS NICHOLAS
Bone fixation implant system and method
Owner:CTL MEDICAL CORP
Fixation implant for a bone graft within a joint for the purpose of ensuring arthrodesis of the joint
InactiveUS20060058802A1Solid and comfortable maintenanceReduce operating errorsAnkle jointsBone implantJoint arthrodesisSacroiliac joint
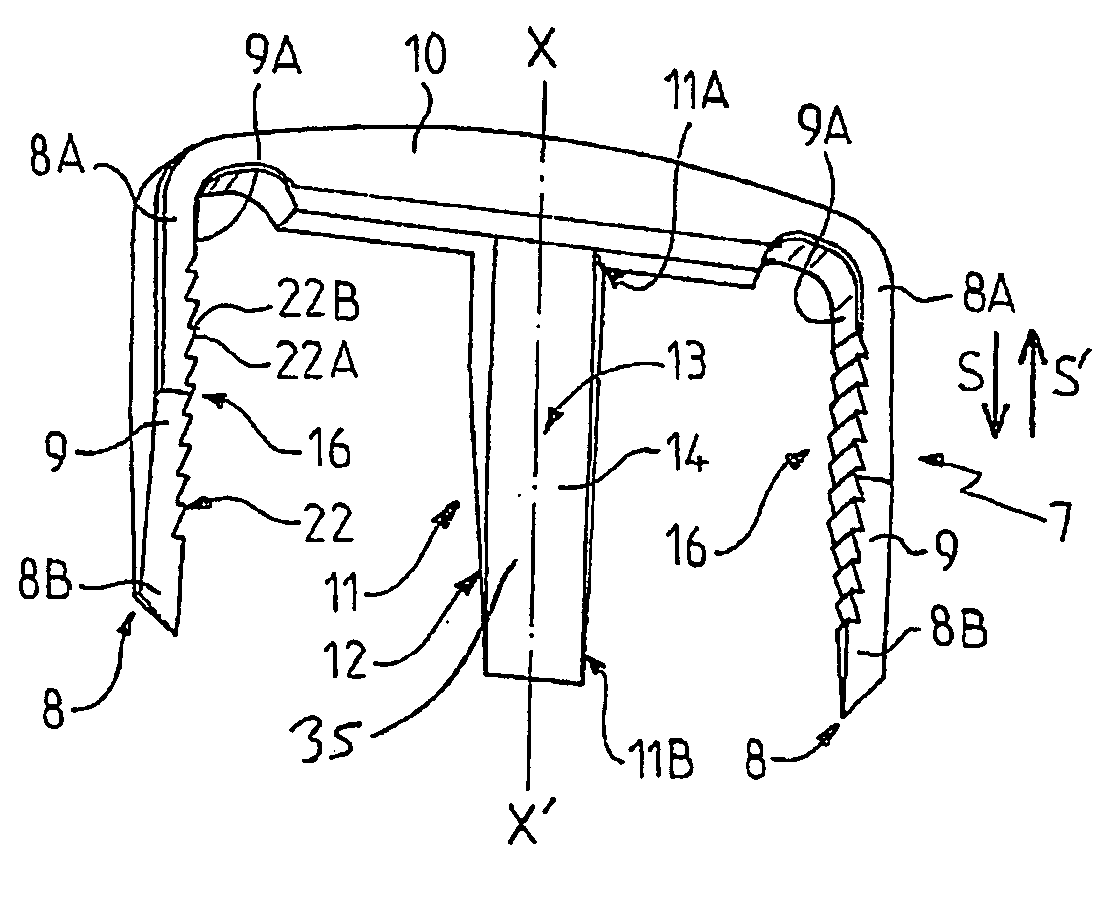
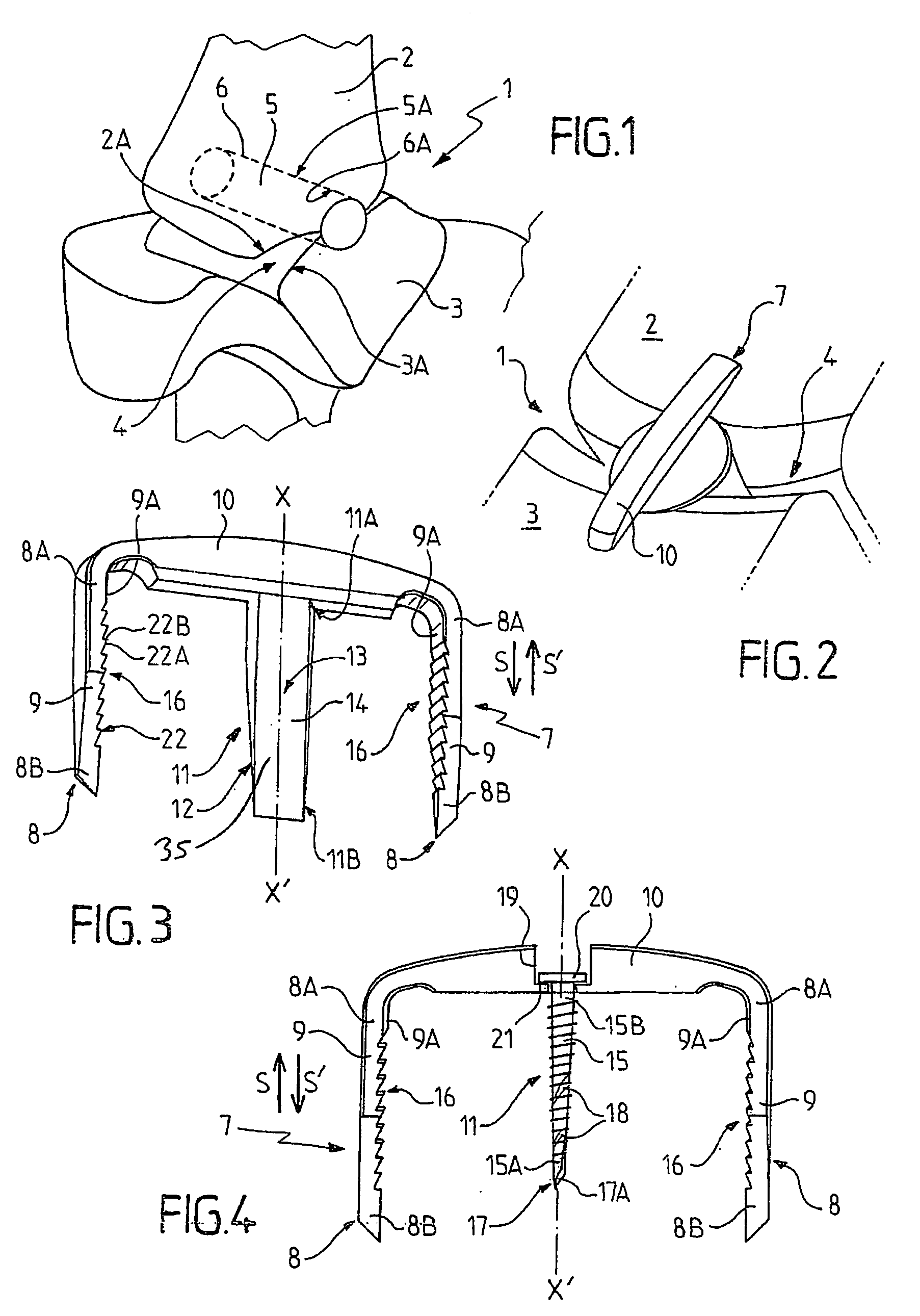
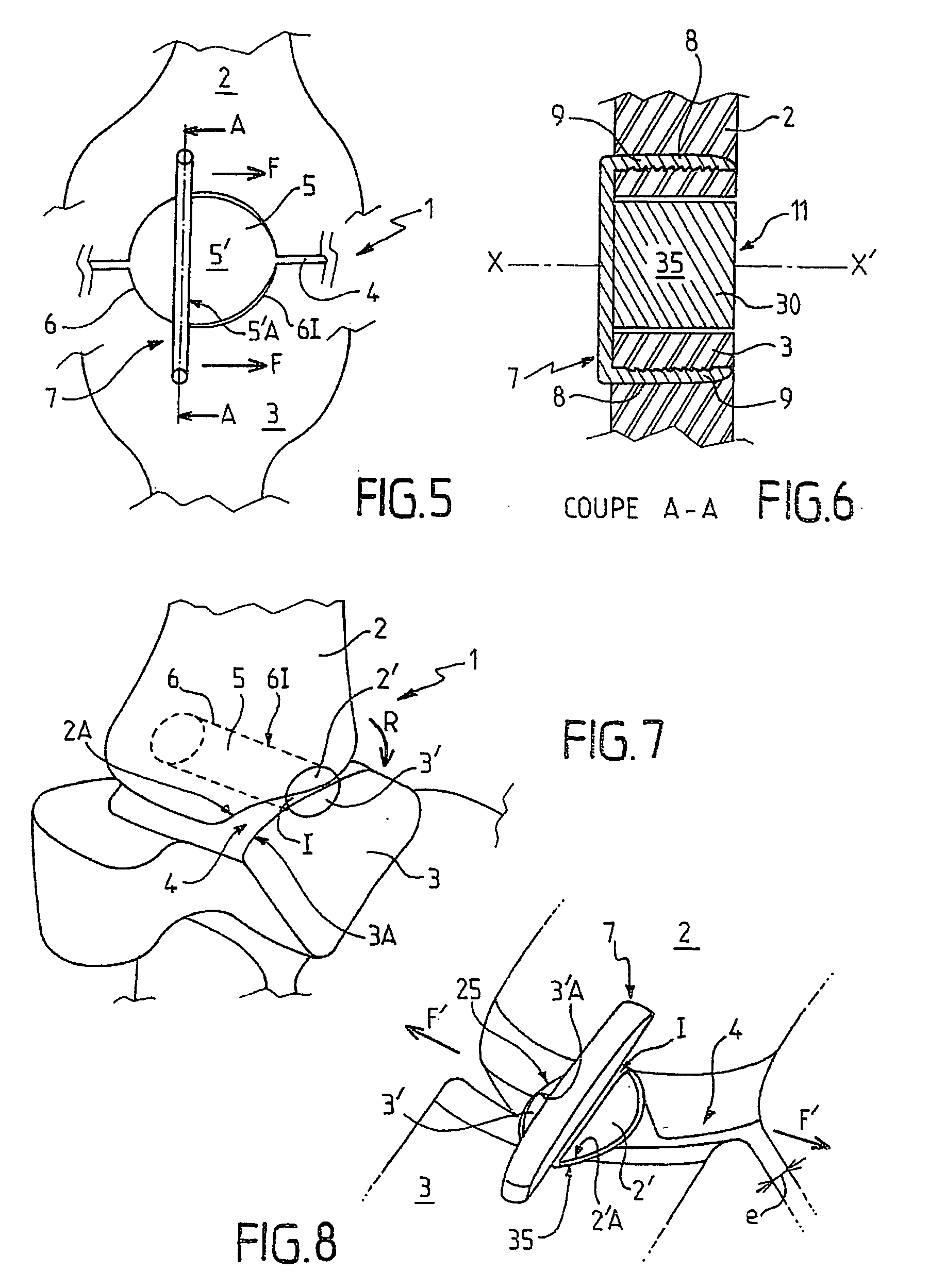
A fixation implant for a bone graft within a joint for the purpose of ensuring arthrodesis of the joint, and a surgical method for emplacement of the described fixation implant. The fixation implant for a bone graft is arranged between the bones located on both sides of an articular space, for the purpose of ensuring arthrodesis of a joint. The fixation implant (7) includes: at least two elements for anchoring (8) into the bones, connected to each other by at least one connection element (10) extending to the outside of the joint; and an immobilization means (11) for the bone graft, arranged between the anchoring elements (8) and connected to the connection element (10) in such a way as to ensure, in cooperation with the anchoring elements (8), blocking of the bone graft with respect to the bones of the joint and vice-versa.
Owner:NEWDEAL
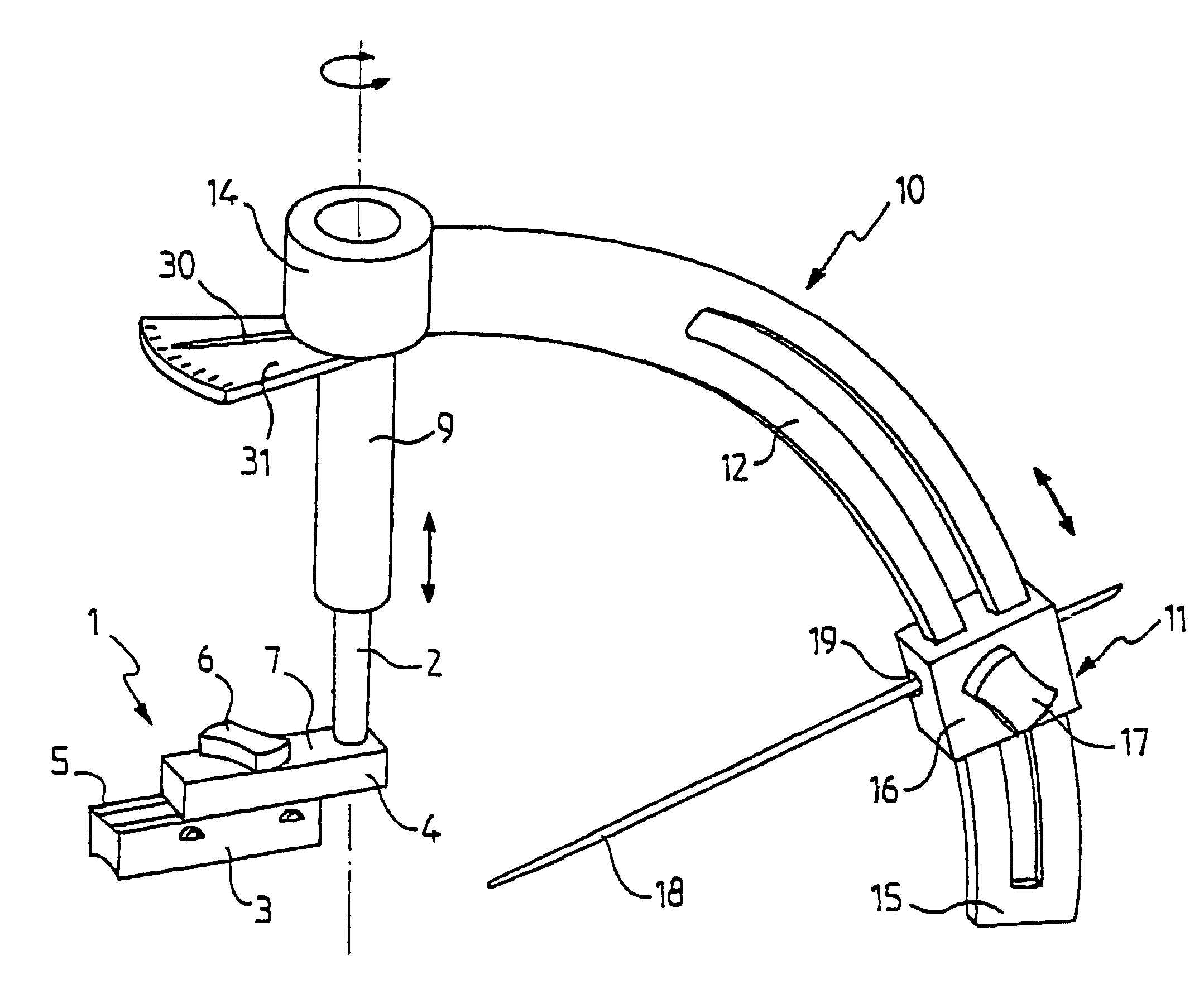
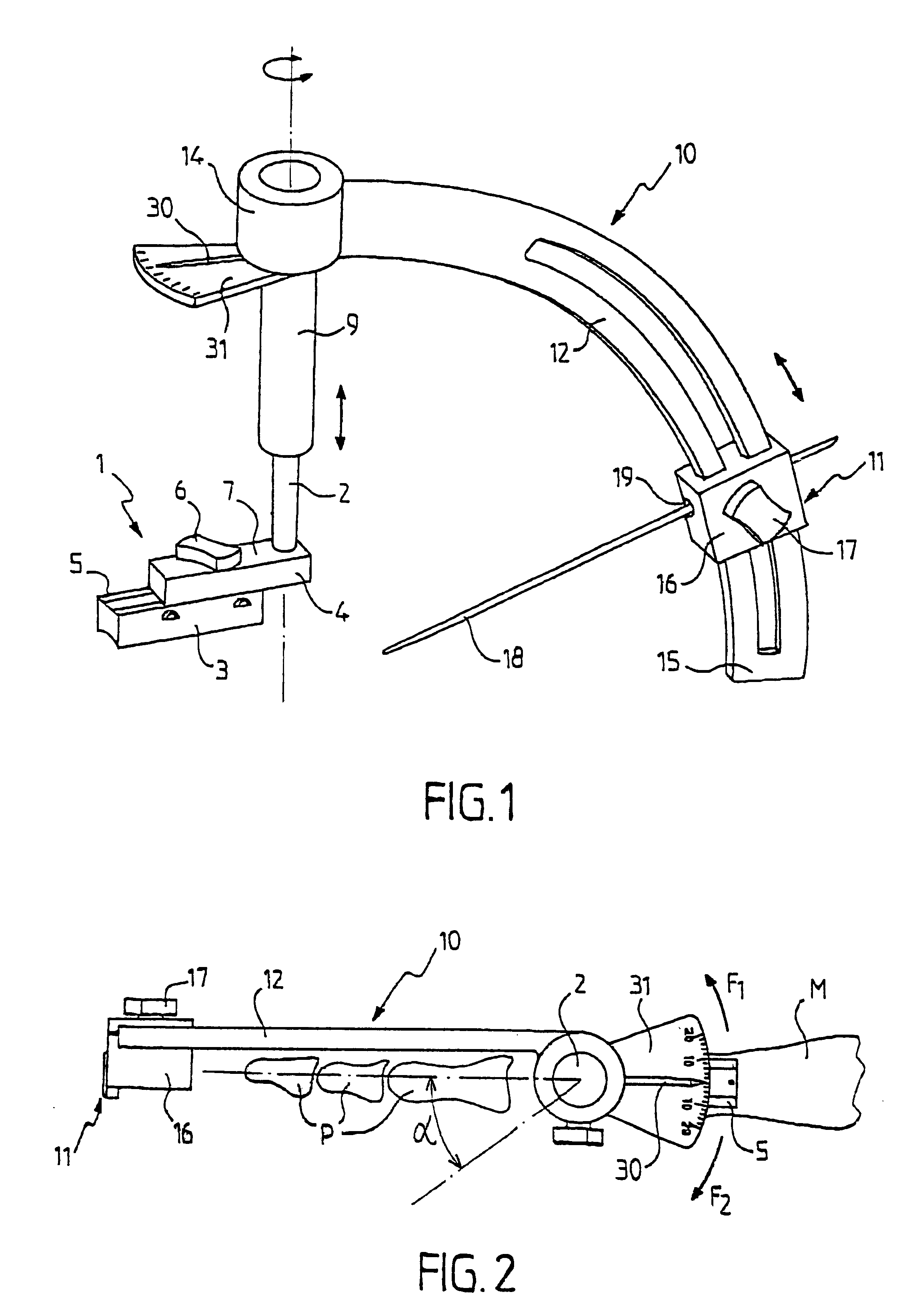
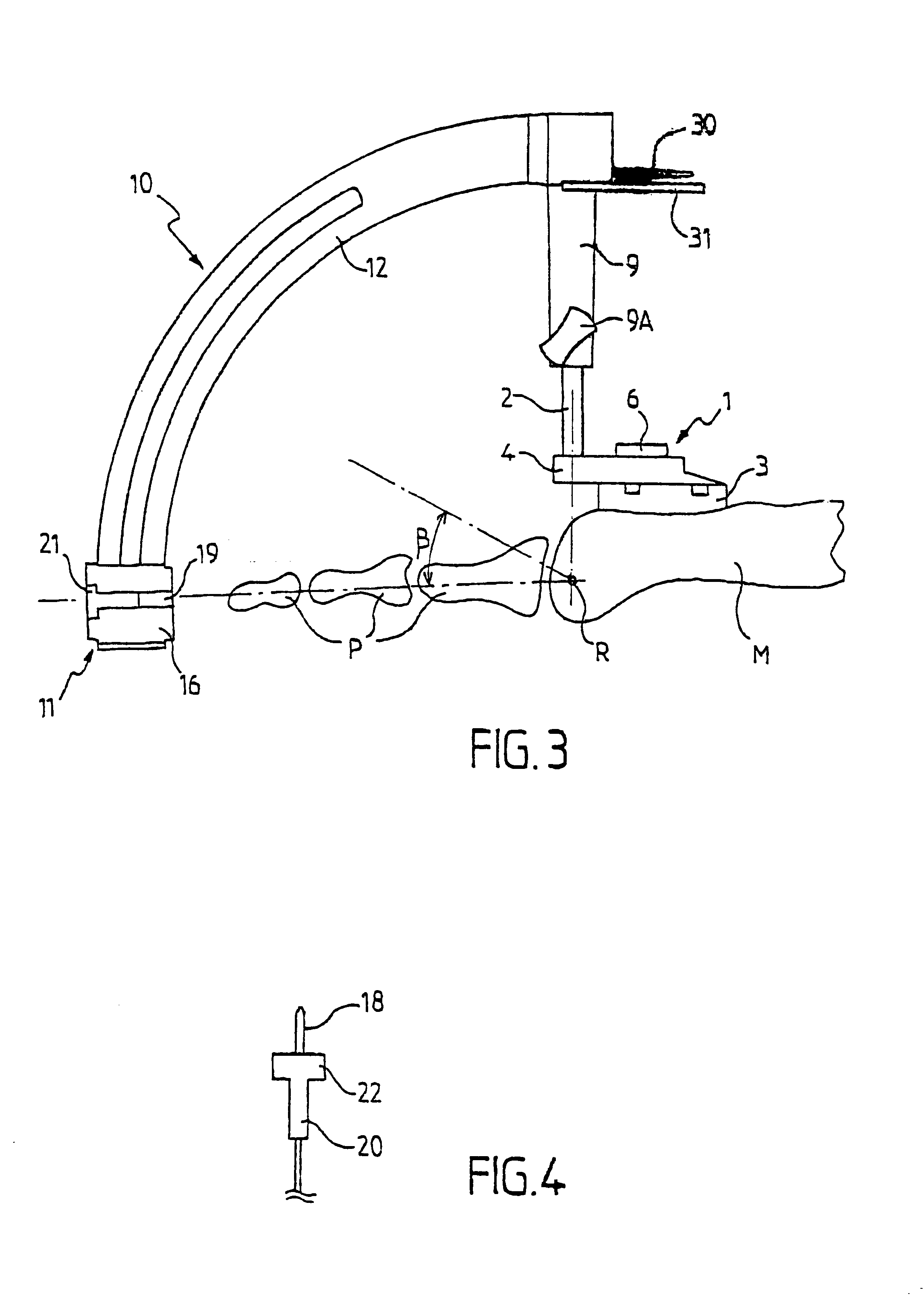
Arthrodesis guide for angularly positioning joint bones
InactiveUS6755838B2Simple and reliable processEasy to adjustJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesJoint arthrodesisEngineering
The invention provides a guide for angularly positioning bones in a joint in order to perform arthrodesis, the guide comprising:a base for positioning on the joint, and having an adjustment shaft whose position is designed to be adjusted so as to be substantially vertically above a fixed first geometrical reference point R of the joint; andan adjustment assembly mounted to slide axially and in rotation on the adjustment shaft to adjust respectively a height for the assembly relative to the first geometrical reference point R and a first angle alpha for the assembly about said axis, said adjustment assembly being formed by an angular adjustable member which can be positioned on a graduated piece to adjust a second angle beta centered on the first geometrical reference point R, but situated in a plane different from the first angle alpha.The guide is suitable for metatarso-phalangeal positioning.
Owner:NEWDEAL
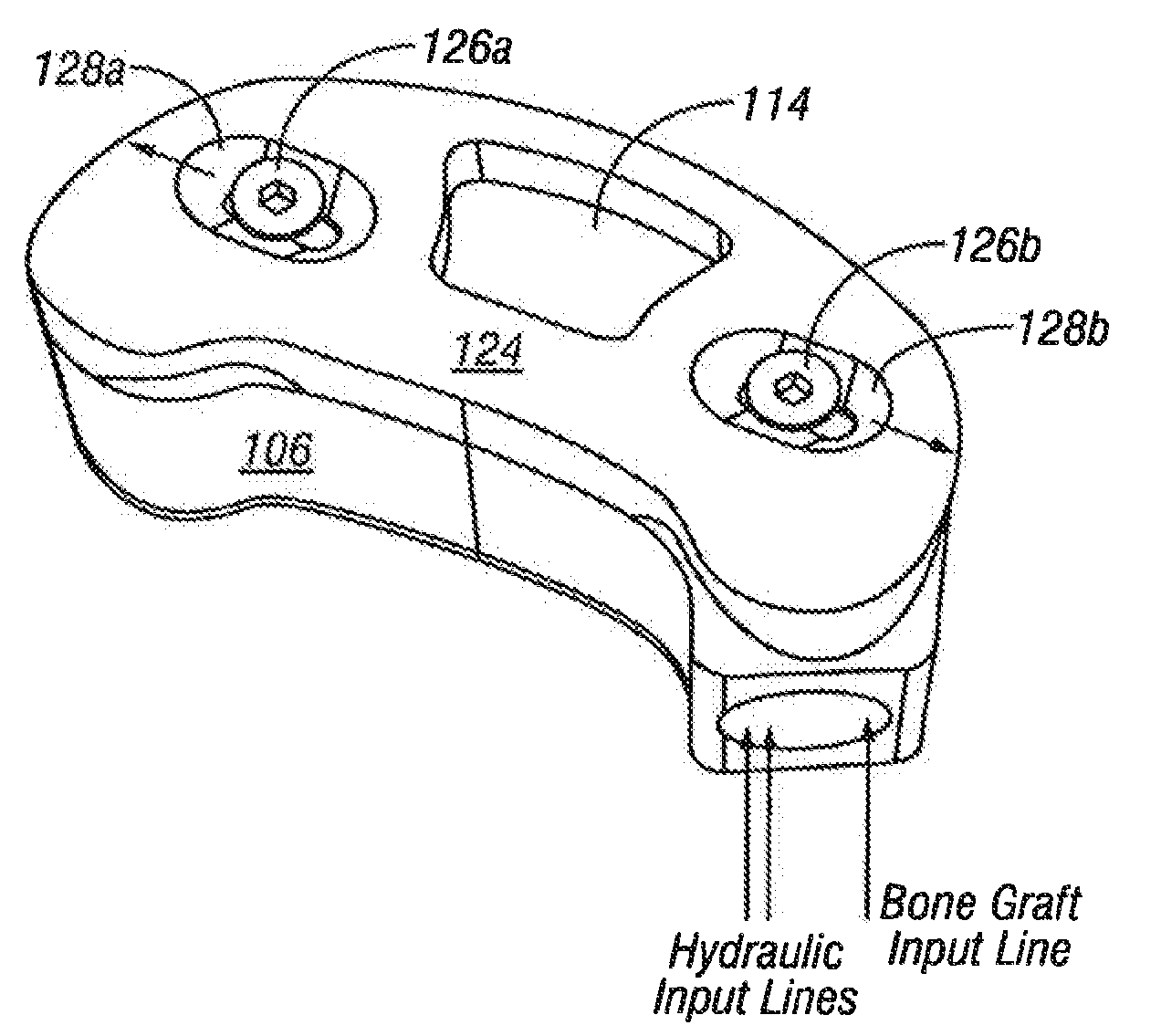
Selectively Expanding Spine Cage, Hydraulically Controllable In Three Dimensions For Enhanced Spinal Fusion
A selectively expanding spine cage has a minimized diameter in its unexpanded state that is smaller than the diameter of the neuroforamen through which it passes in the distracted spine. The cage conformably engages between the endplates of the adjacent vertebrae to effectively distract the anterior disc space, stabilize the motion segments and eliminate pathologic spine motion. Angular deformities can be corrected, and natural curvatures restored and maintained. The cage enhances spinal arthrodesis by creating a rigid spine segment, or if filled with compressible substances, the cage can be used for motion preservation between vertebral bodies. Expanding selectively (anteriorly, along the vertical axis of the spine) rather than uniformly, the cage height increases and holds the vertebrae with fixation forces greater than adjacent bone and soft tissue failure forces in natural lordosis. Stability is thus achieved immediately, enabling patient function by eliminating painful motion. The cage shape intends to rest proximate to the anterior column cortices securing the desired spread and fixation, allowing for bone graft in, around, and through the implant for arthrodesis whereas for arthroplasty it fixes to endpoints but cushions the spine naturally.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
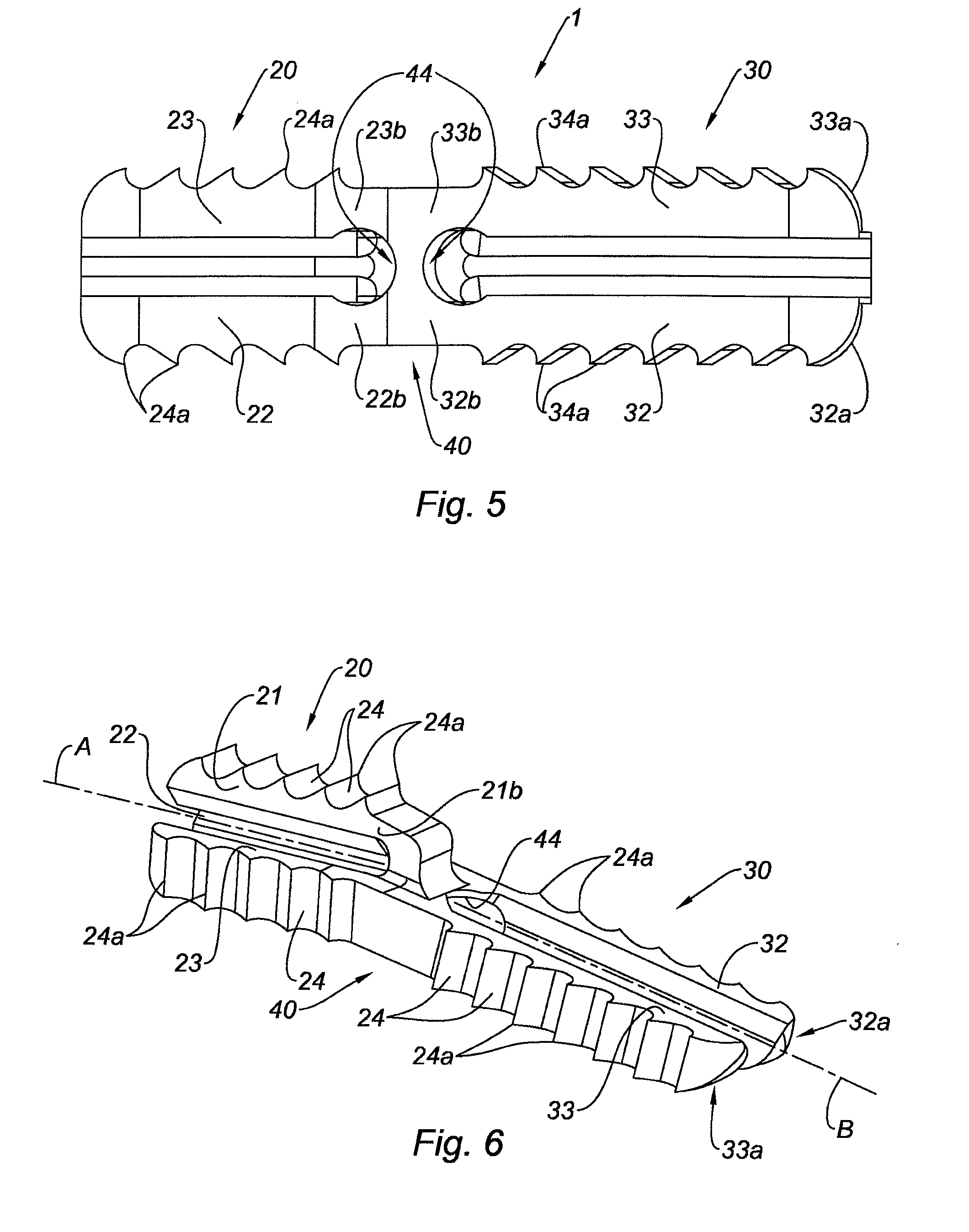
Arthrodesis implant
ActiveUS20130066435A1Assures rigidityAssures flexibilityFinger jointsInternal osteosythesisJoint arthrodesisSacroiliac joint
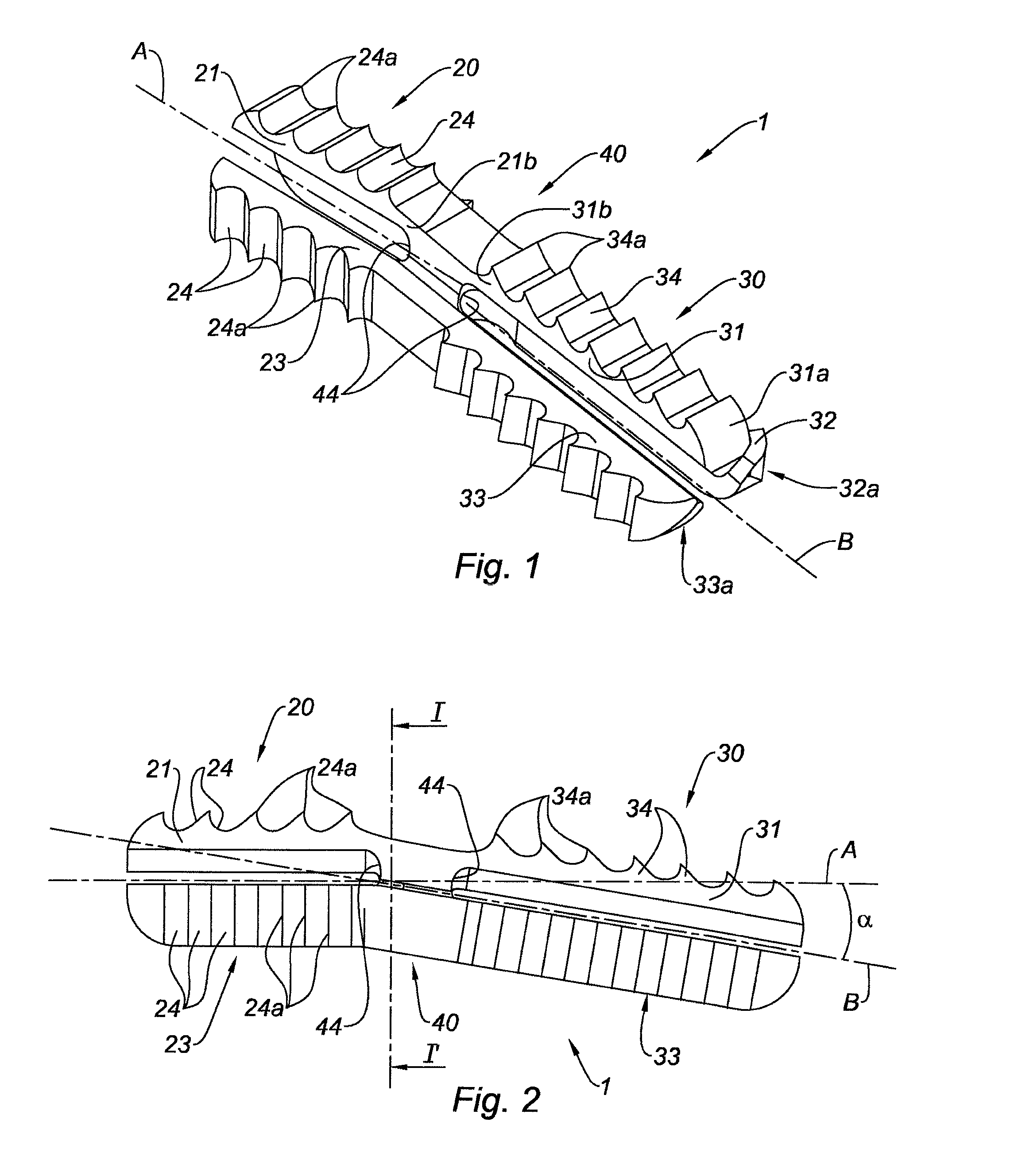
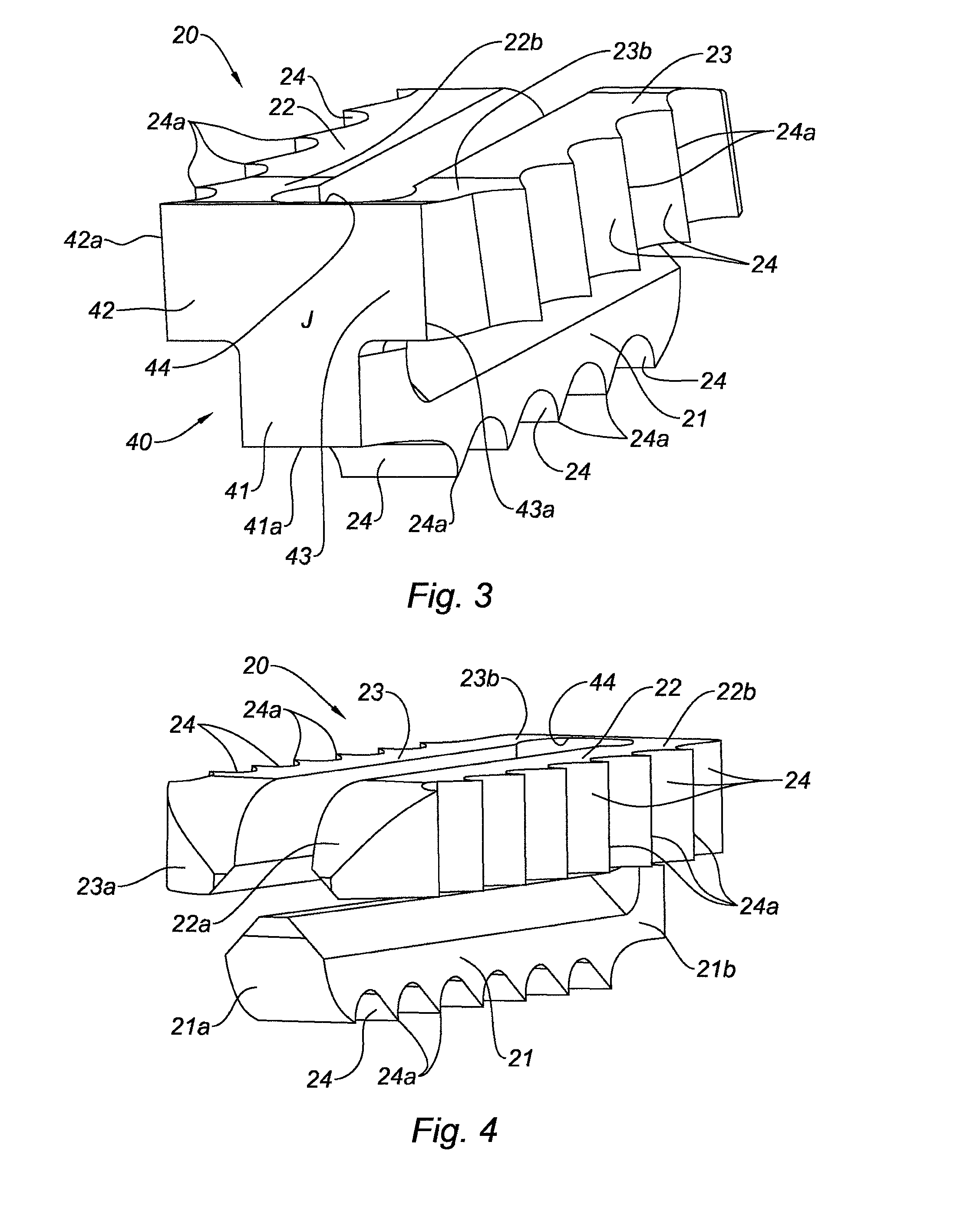
The invention relates to an implant (1) for osseous fusion between two bones, including a first portion (20) having a longitudinal axis A, for being inserted in the first bone and including a first means (24) for attaching said implant in said first bone, and a second portion (30) having a longitudinal axis B, for being inserted in the second bone and including a second means (34) for attaching said implant in said second bone, said first and second portions (20, 30) being connected by a central core (40), said central core being a solid body, the cross-section of which, in a plane perpendicular to said longitudinal axis A, has the shape of a star having at least three points (41, 42, 43), said first portion having three tabs (21, 22, 23), each tab extending along said longitudinal axis A from the free end (41a, 42a, 43a) of one of the points of said central core.
Owner:ADSM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com