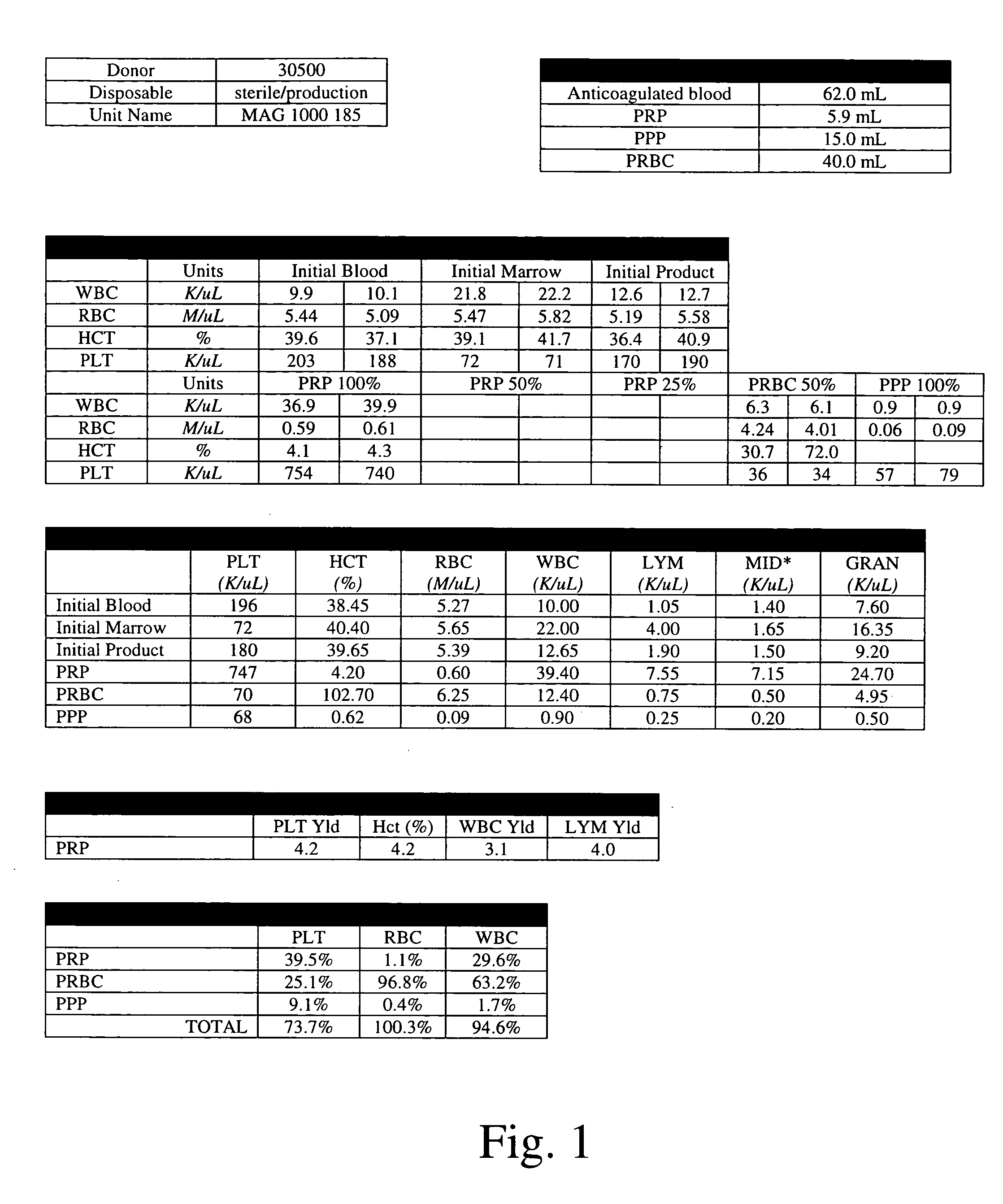
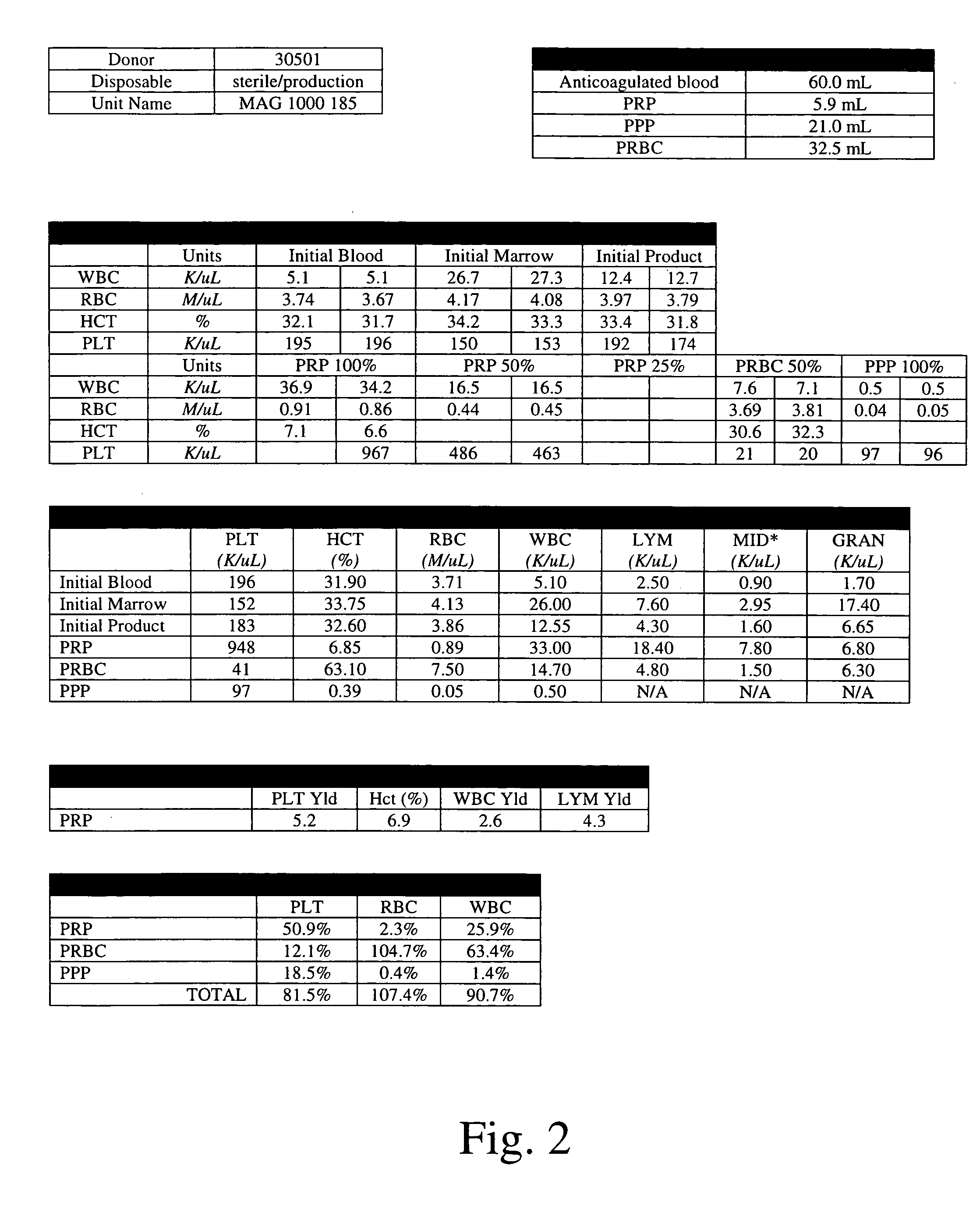
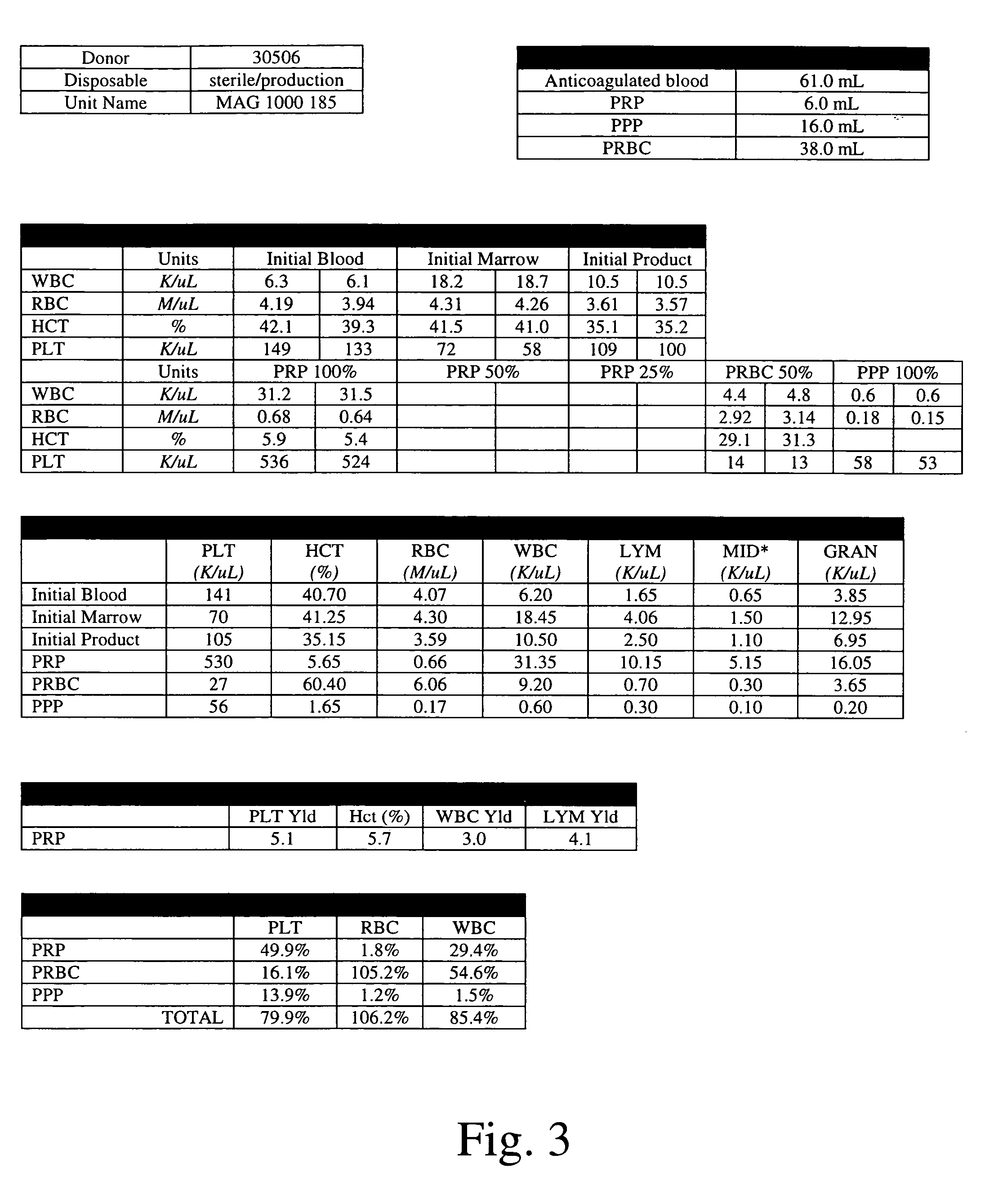
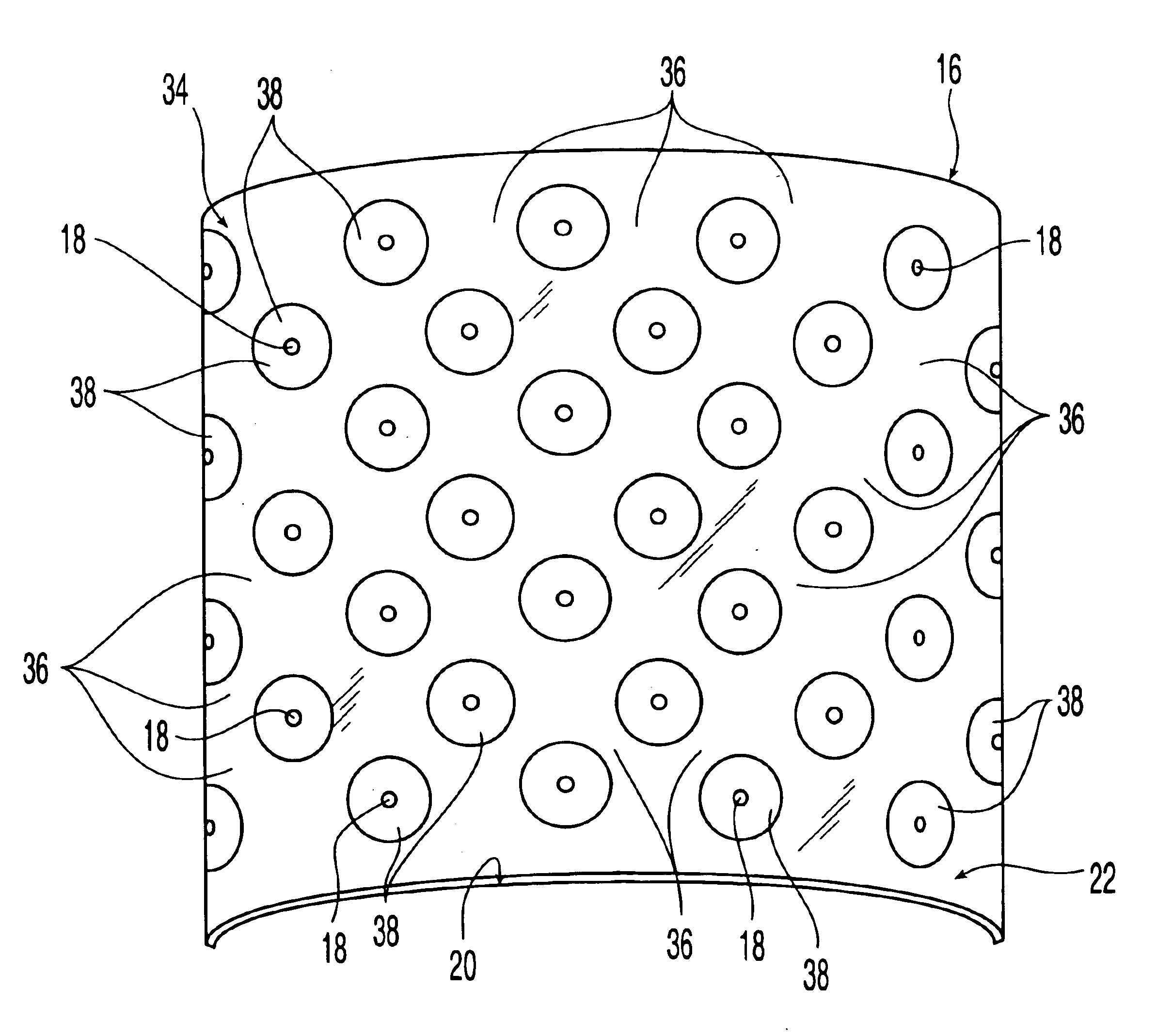
Patents
Literature
1504 results about "Bone defect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
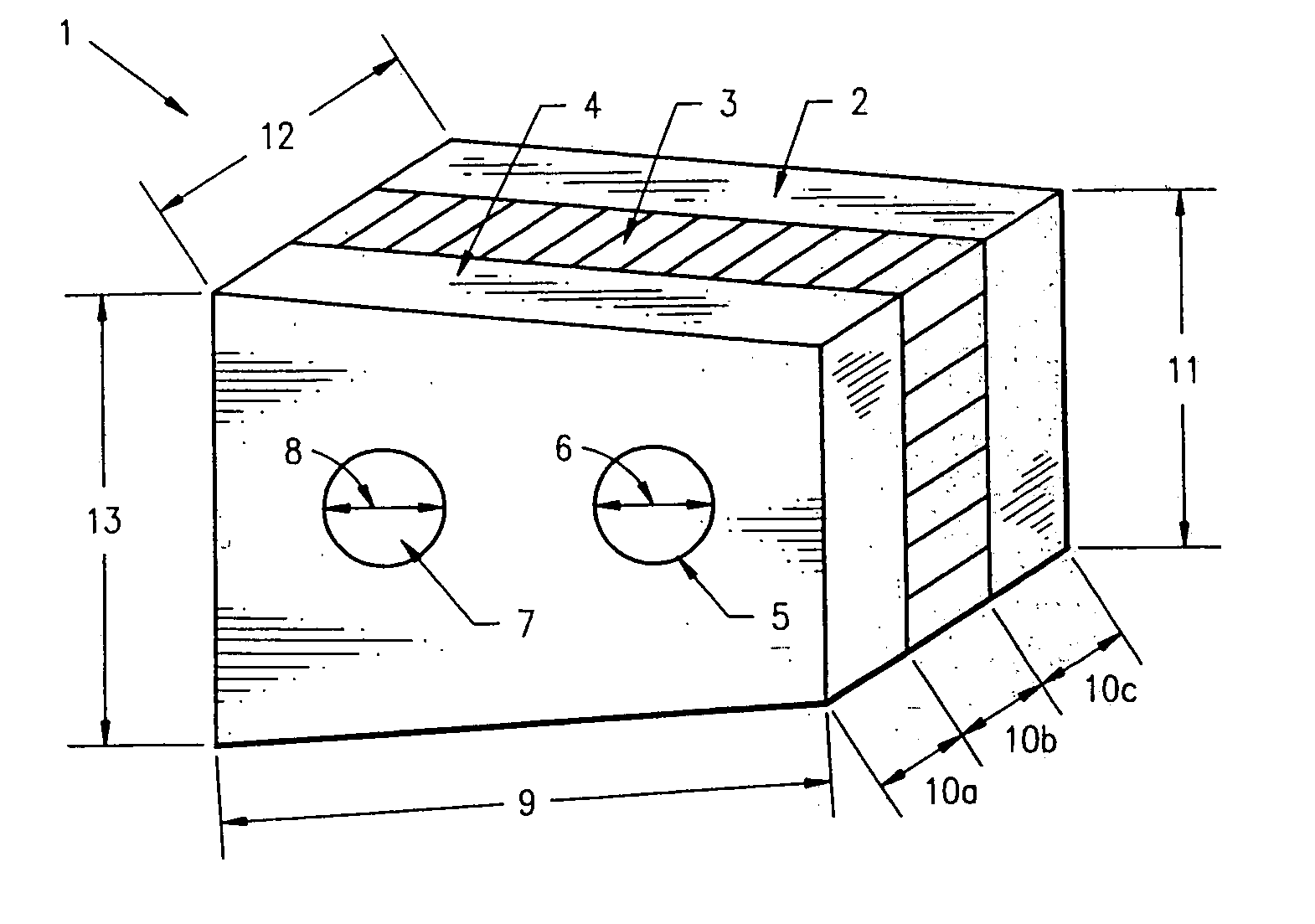
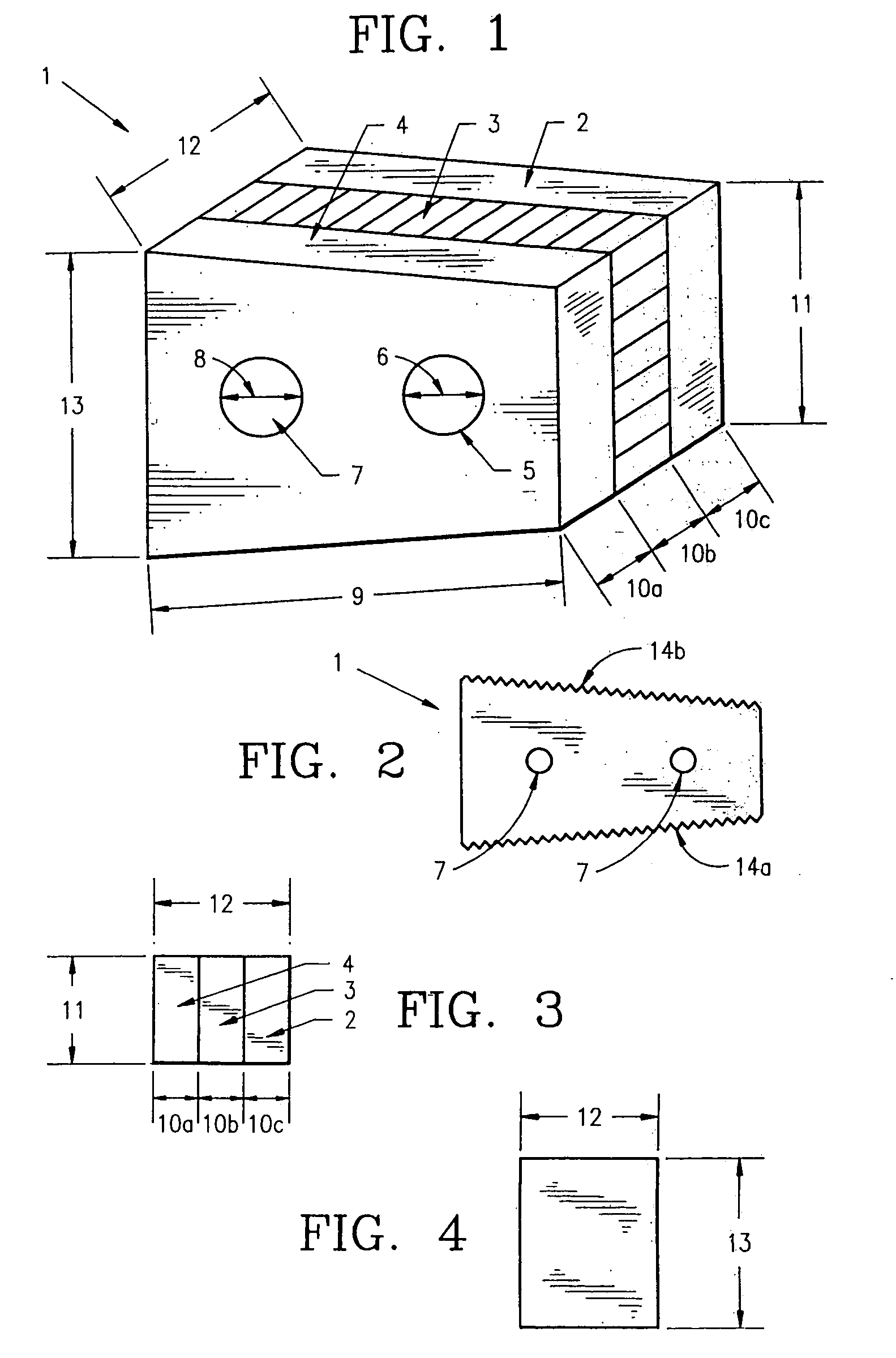
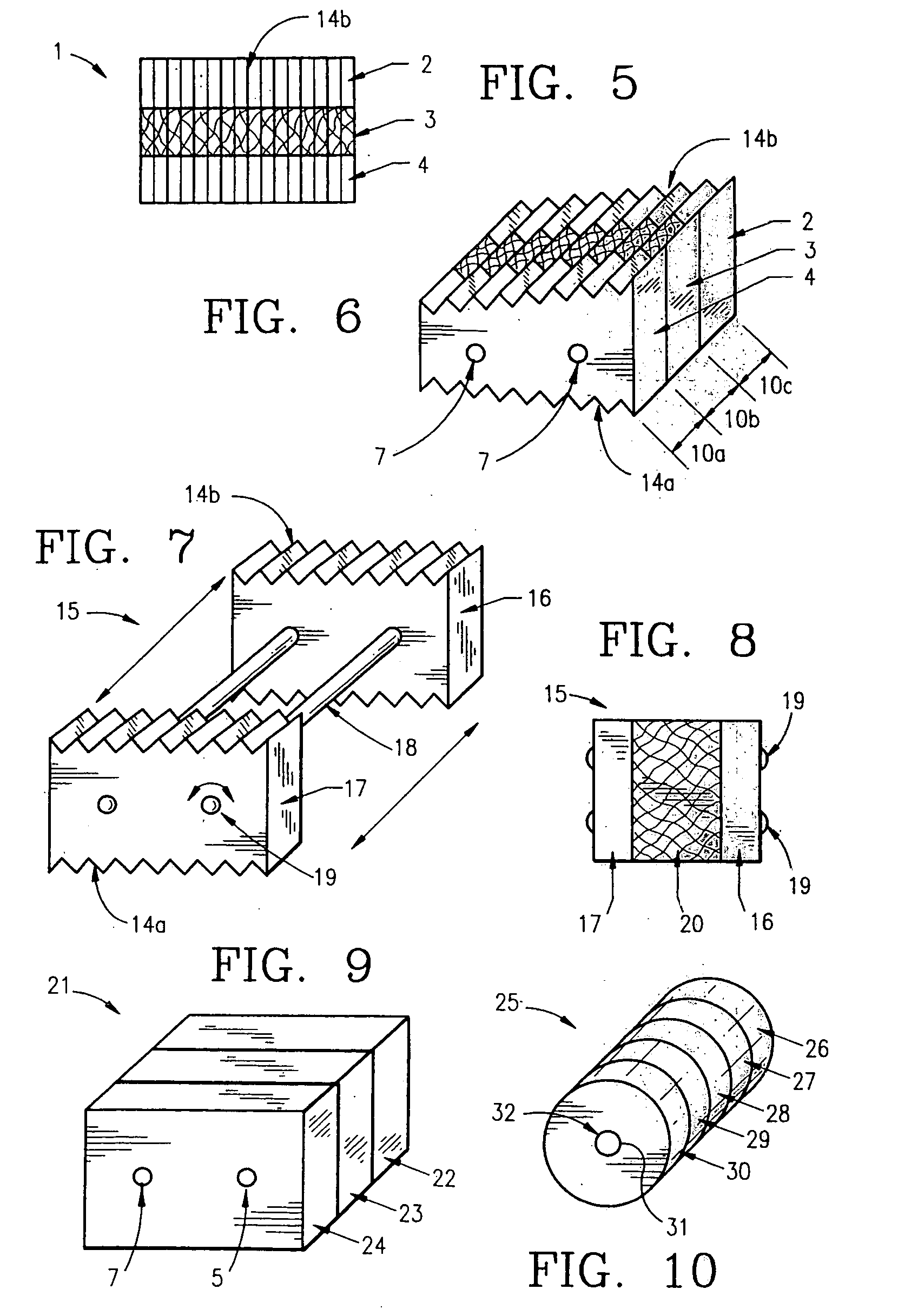
Bone defects may arise due to a number of congenital or acquired conditions. Congenital bone anomalies are commonly due to the absence of or maldevelopement of bones (such as zygomatic hypoplasia in Treacher Collins syndrome (TCS) or fibular hemimelia).
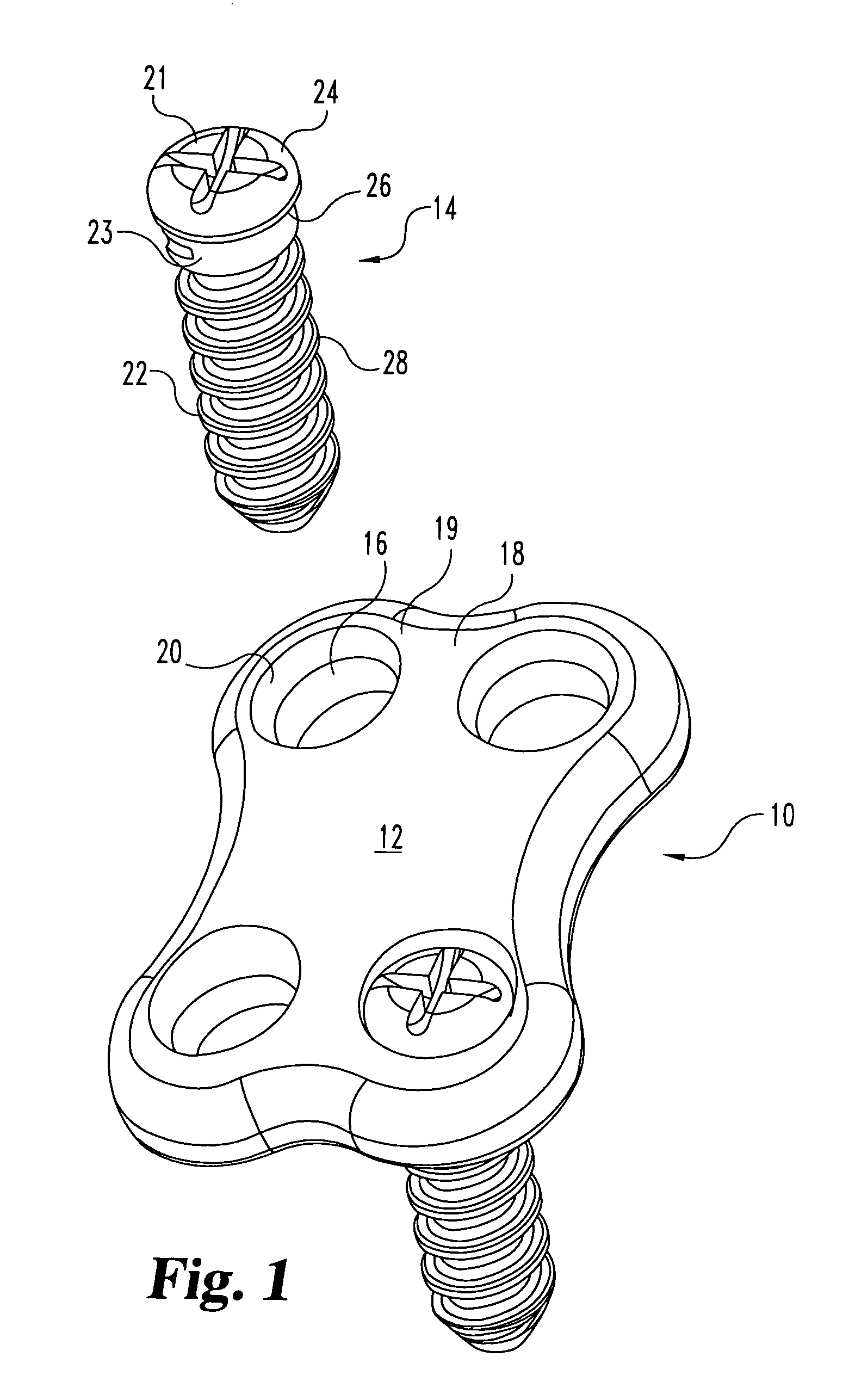
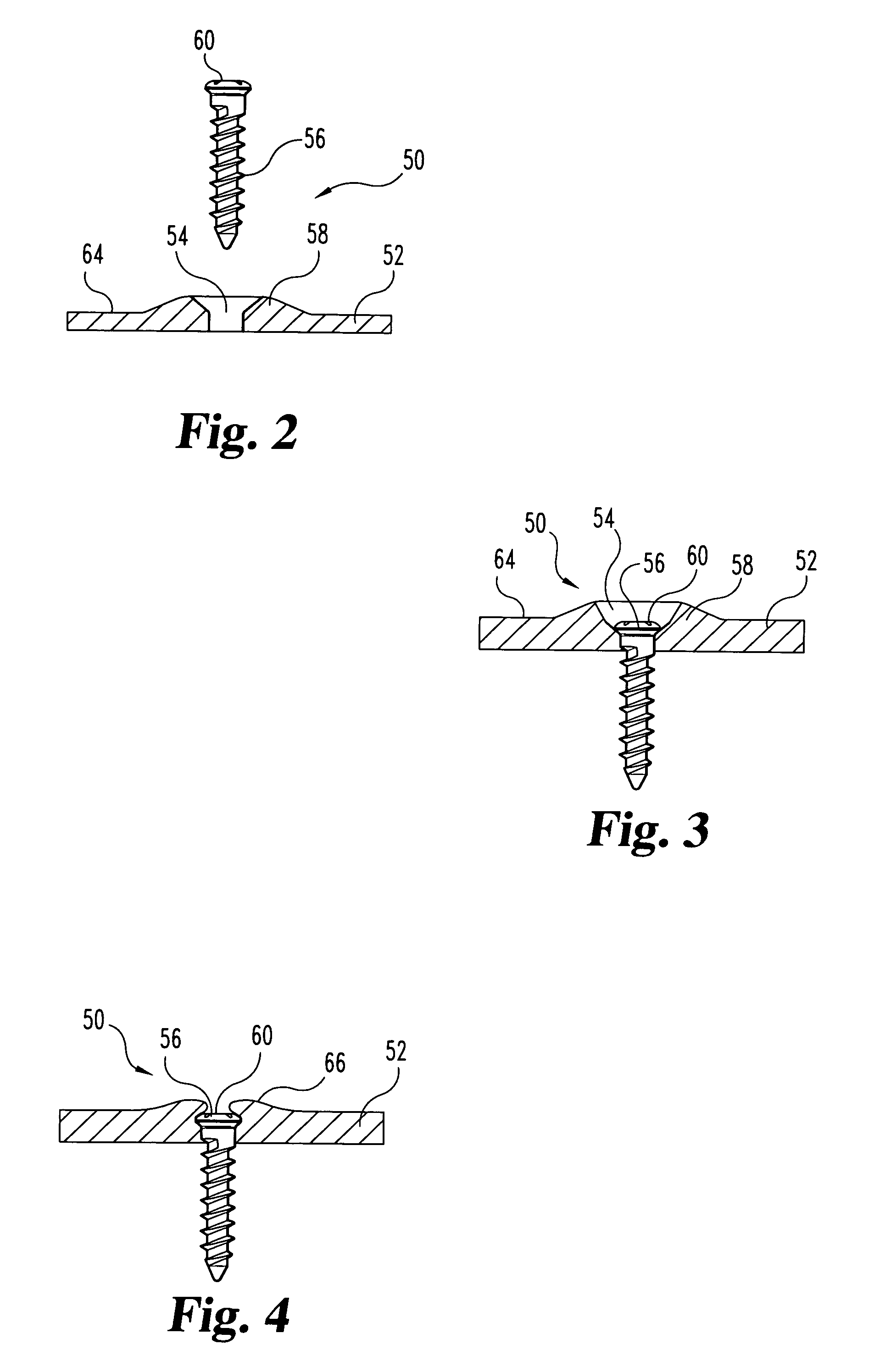
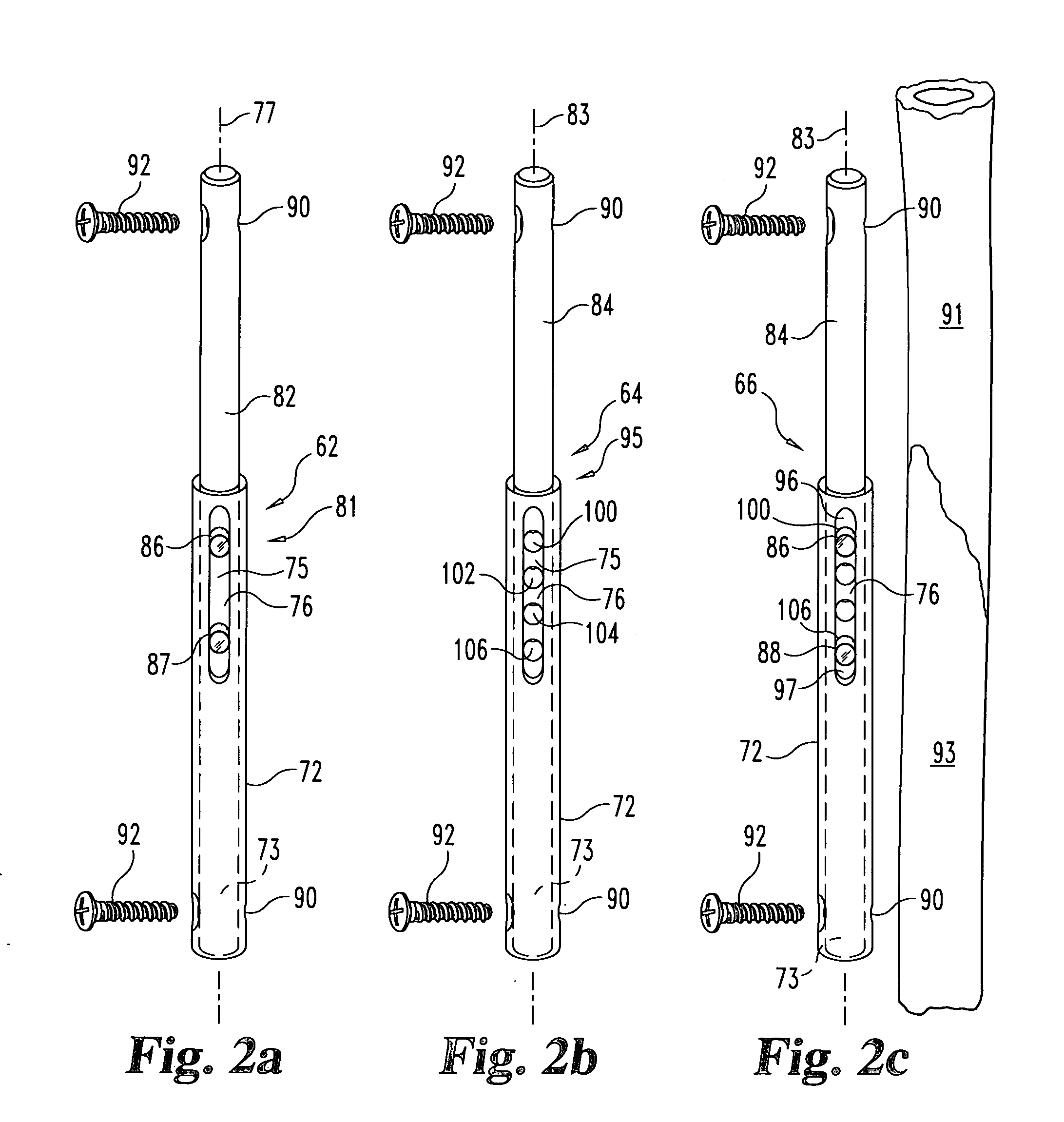
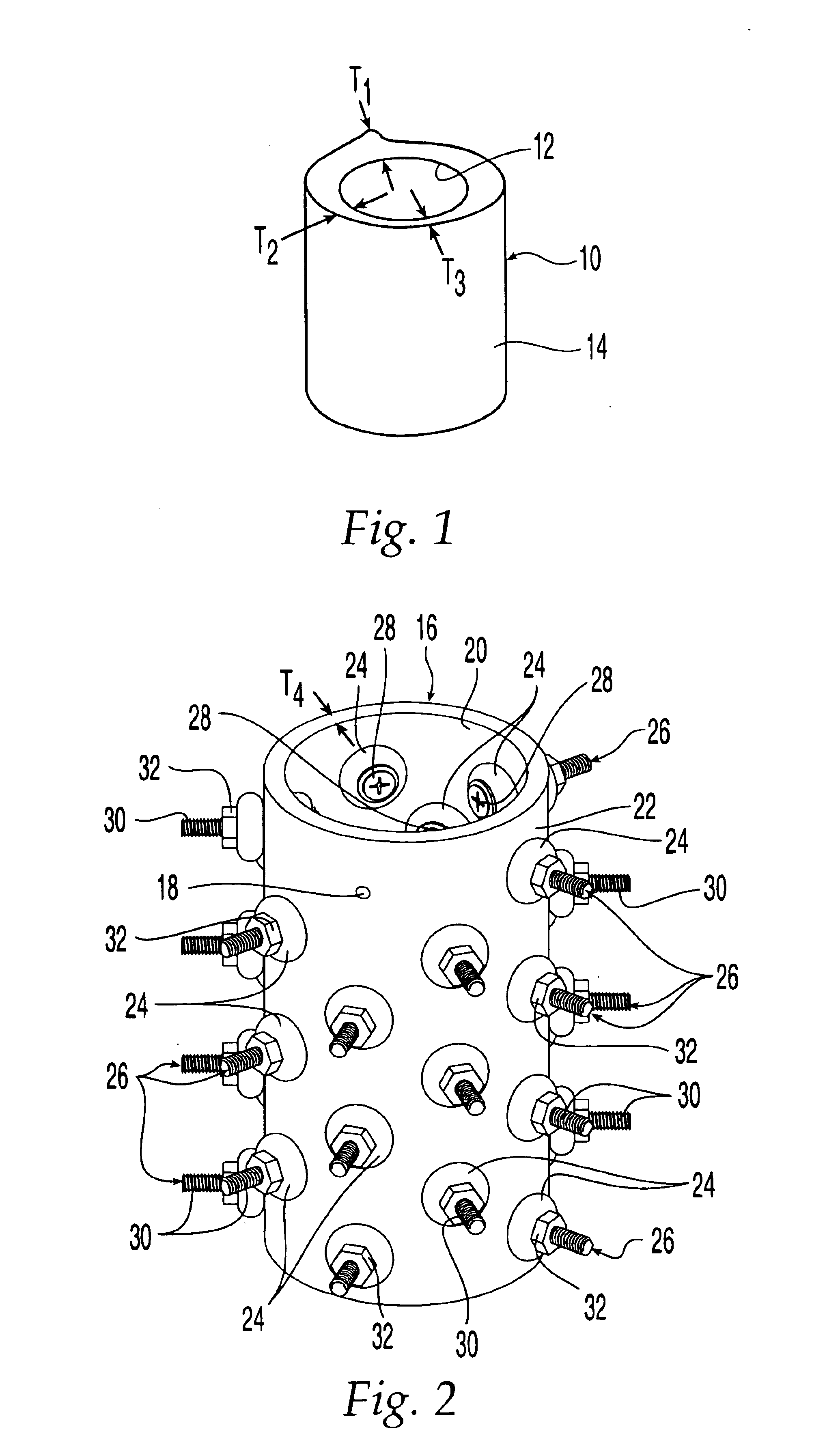
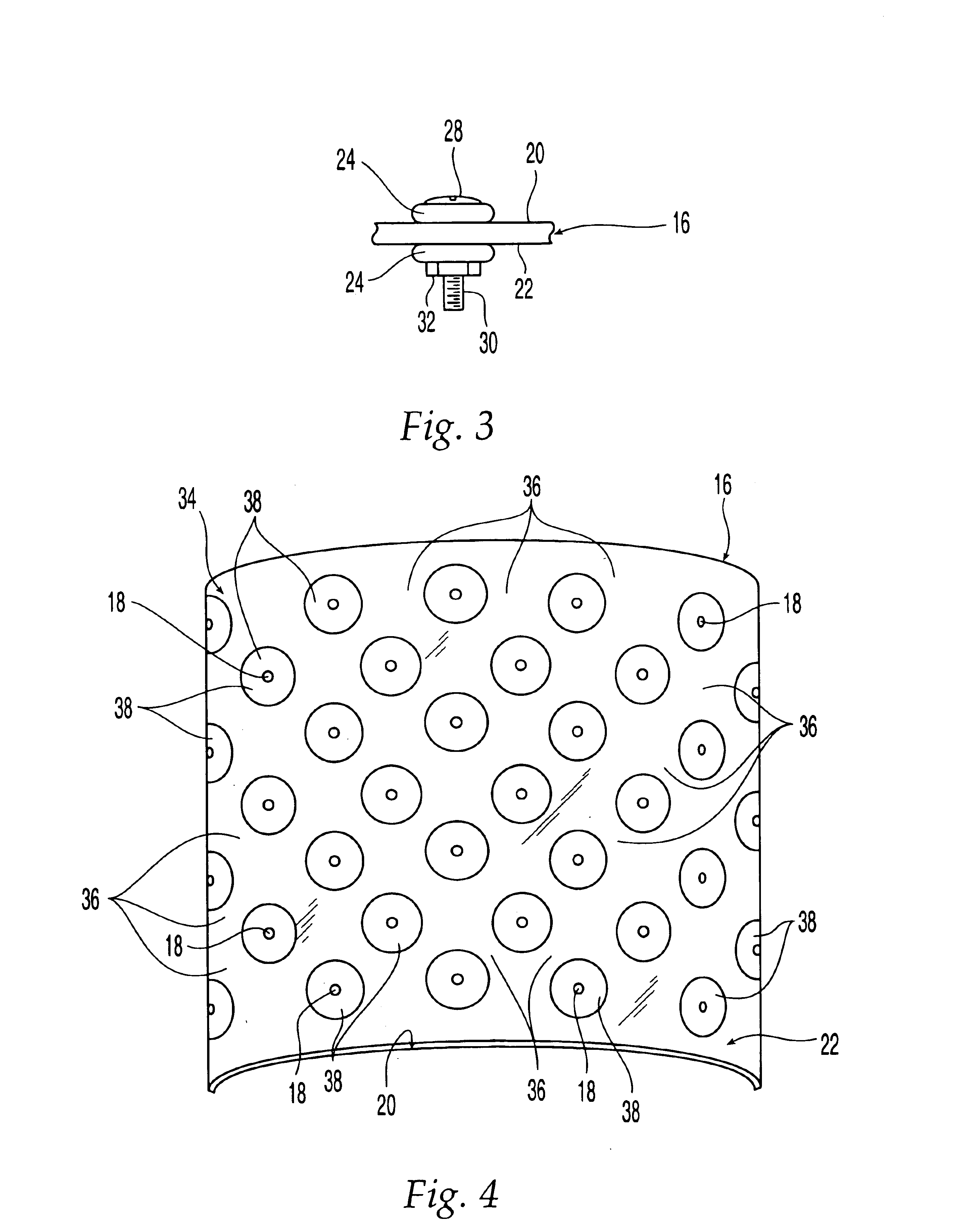
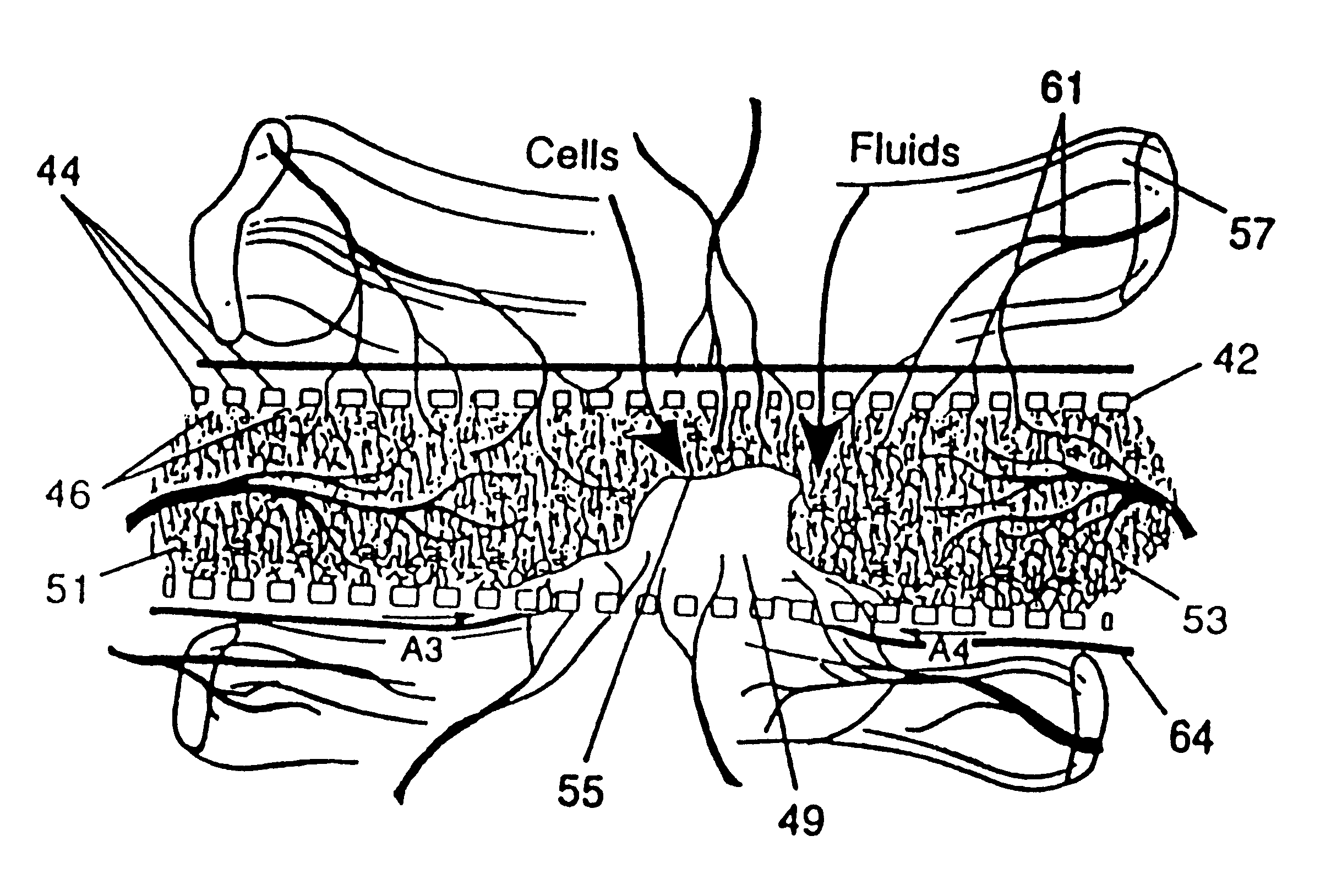
Non-metallic implant devices and intra-operative methods for assembly and fixation
This invention relates to orthopedic implants and to methods of treating bone defects. More specifically, but not exclusively, the present invention is directed to non-metallic implants and to methods for intra-operative assembly and fixation of orthopedic implants to facilitate medical treatment. The non-metallic implant assembly can be secured to underlying tissue by a fastener, such as a bone screw, that is capable of swelling on contact with fluid in the underlying tissue. Alternatively, the non-metallic implant assembly can be assembled intra-operatively using a fastener that is adhesively bonded to a bone plate or the bone plate can be deformed using heat, force, or solvents to inhibit withdrawal of the fastener. In preferred embodiments, both the fastener and the bone plate are formed of biodegradable material.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
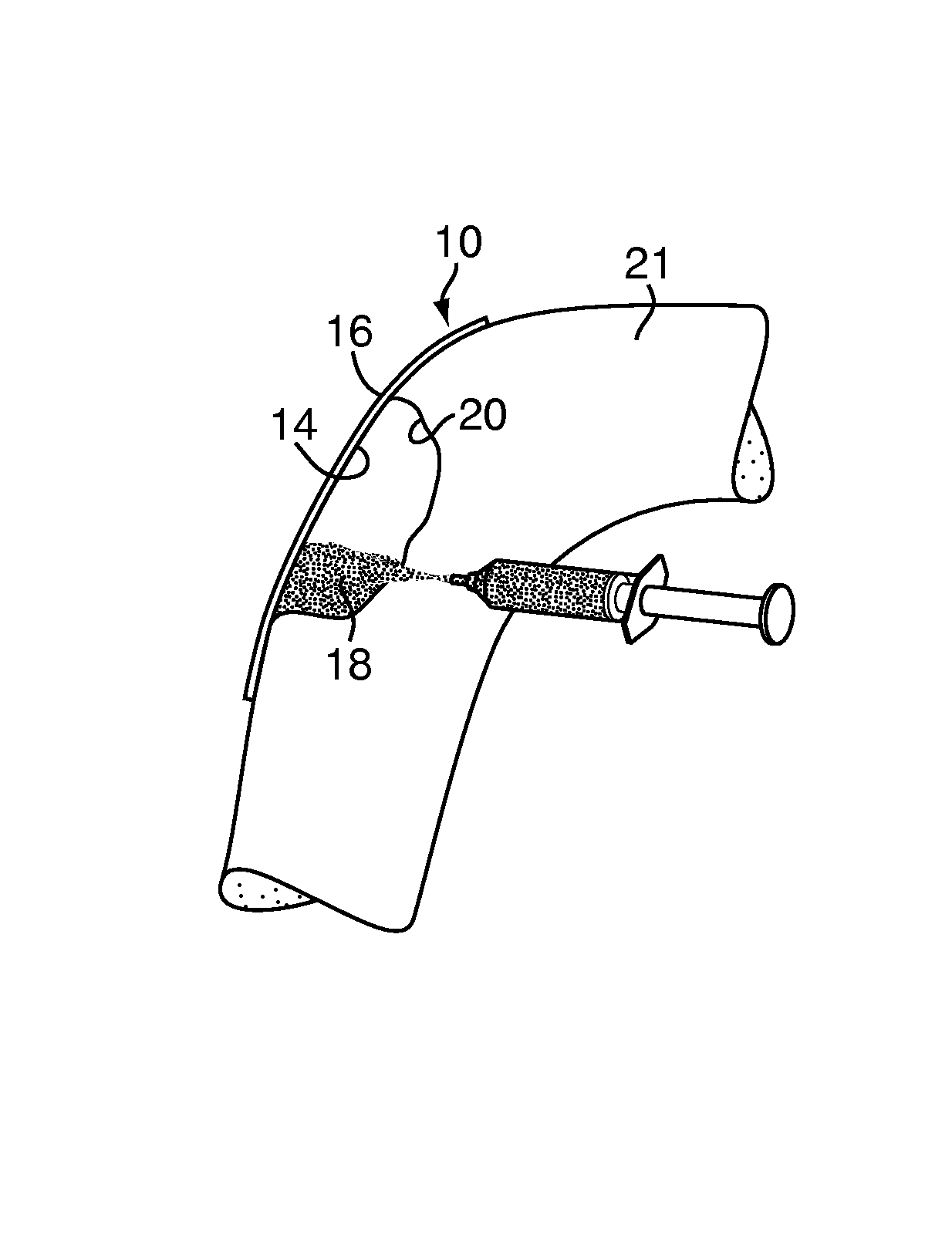
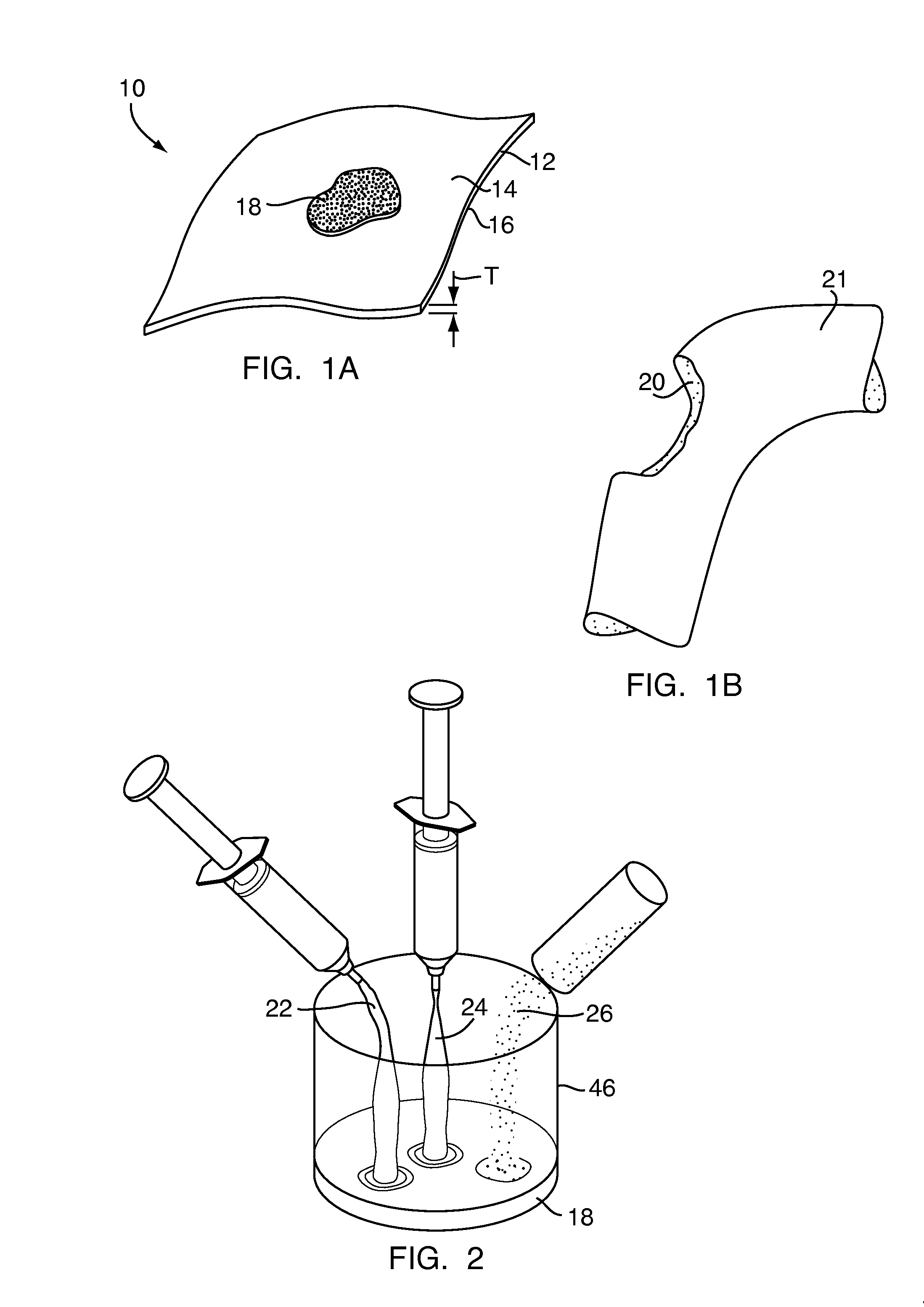
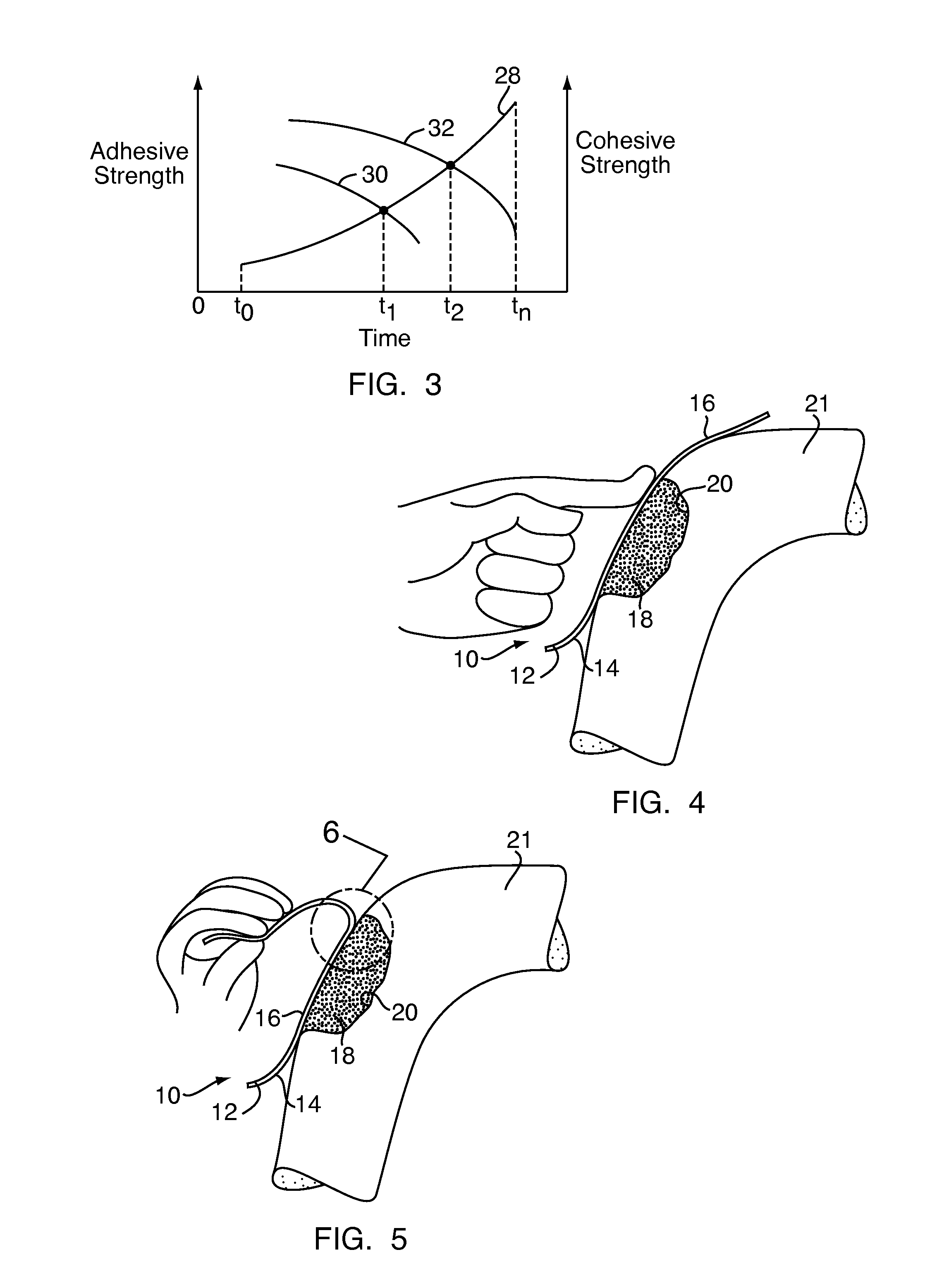
Method and device for handling bone adhesives
A bone adhesive application device has a pliable structure with an application surface upon which a bone adhesive may be applied. The application surface has a surface energy substantially equal to or less than a surface energy of the bone adhesive to reduce adhesion between the bone adhesive and the bone adhesive application device. The bone adhesive application device may be included in a kit for repairing bone defects having a bone adhesive formed from a reactive biocompatible polyurethane material. The bone adhesive may be applied to a bone defect by positioning the pliable structure over at least a portion of the bone defect, delivering the bone adhesive to the bone defect and removing the pliable structure from the bone adhesive.
Owner:ABYRX
Apparatus and method for providing dynamizable translations to orthopedic implants
InactiveUS20050085812A1Avoid stress shieldingLimited supportSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBone structureJoint arthrodesis
The present invention generally relates to orthopedic devices and methods for treating bone defects. The orthopedic devices can provide sufficient support to the bone defect while allowing bone ingrowth and minimizing the risk to stress shield and / or pseudo-arthrodesis. The bone fixation devices include a biodegradable material or component that further resists relative motion of attached bones and allows the device to gradually transfer at least some load from the device to the growing bone structure in vivo and permitting an increase in the relative motion of bones attached to the device.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Malleable putty and flowable paste with allograft bone having residual calcium for filling bone defects
The invention is directed toward a malleable bone putty and a flowable pastel composition for application to a bone defect site to promote new bone growth at the site which comprises a new bone growth inducing compound of partially demineralized lyophilized allograft bone material having a residual calcium content ranging from 4 to 8% dry weight. The bone powder has a particle size ranging from about 100 to about 800 microns and is mixed in a high molecular weight hydrogel carrier containing a sodium phosphate saline buffer, the hydrogel component of the carrier ranging from about 1.00 to 50% of the composition and having a molecular weight of about at least 700,000 Daltons. The composition has a pH between 6.8-7.4 contains about 25% to about 35% bone powder and can be additionally provided with BMP's.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Resorbable, macro-porous, non-collapsing and flexible membrane barrier for skeletal repair and regeneration
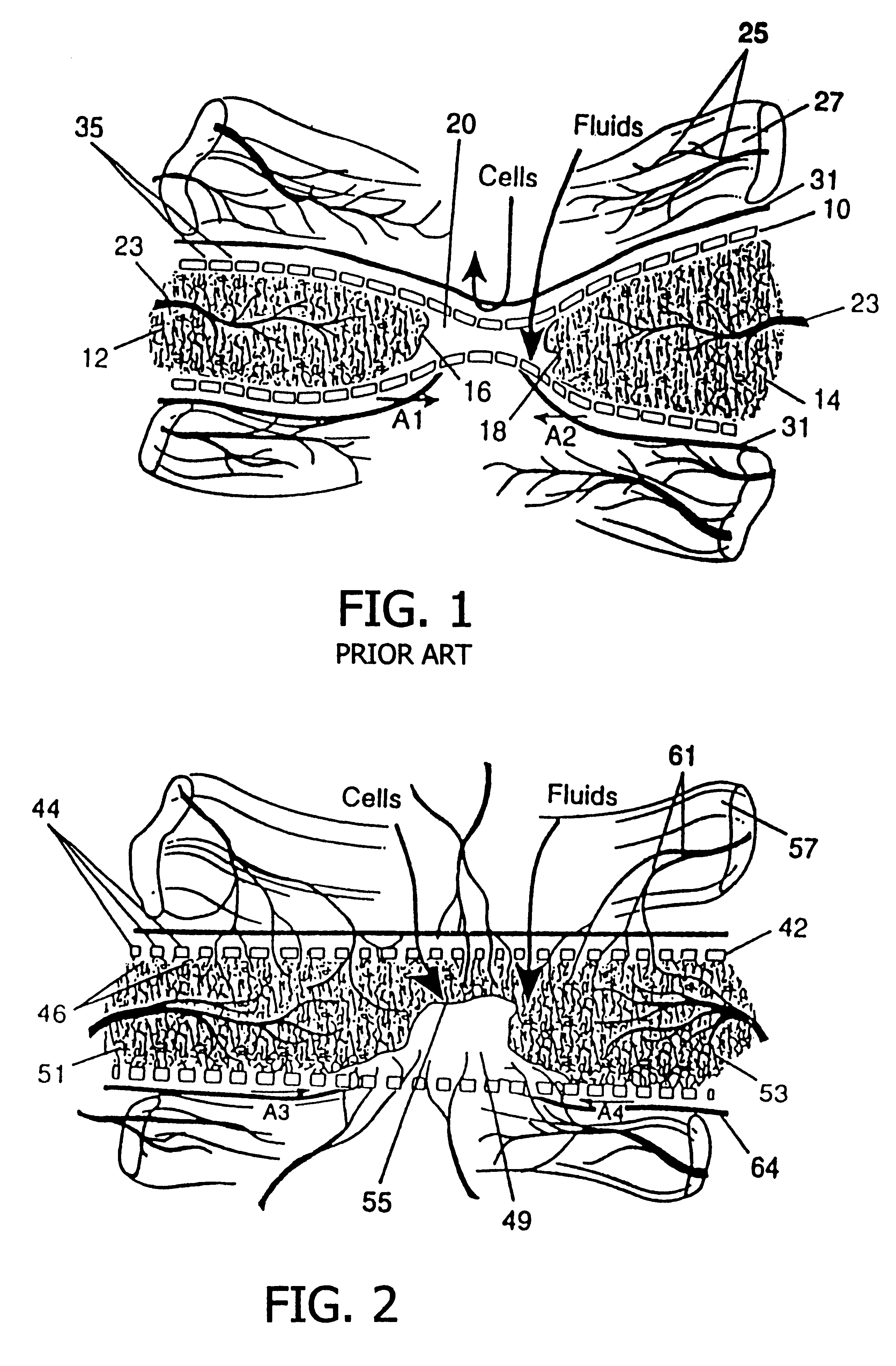
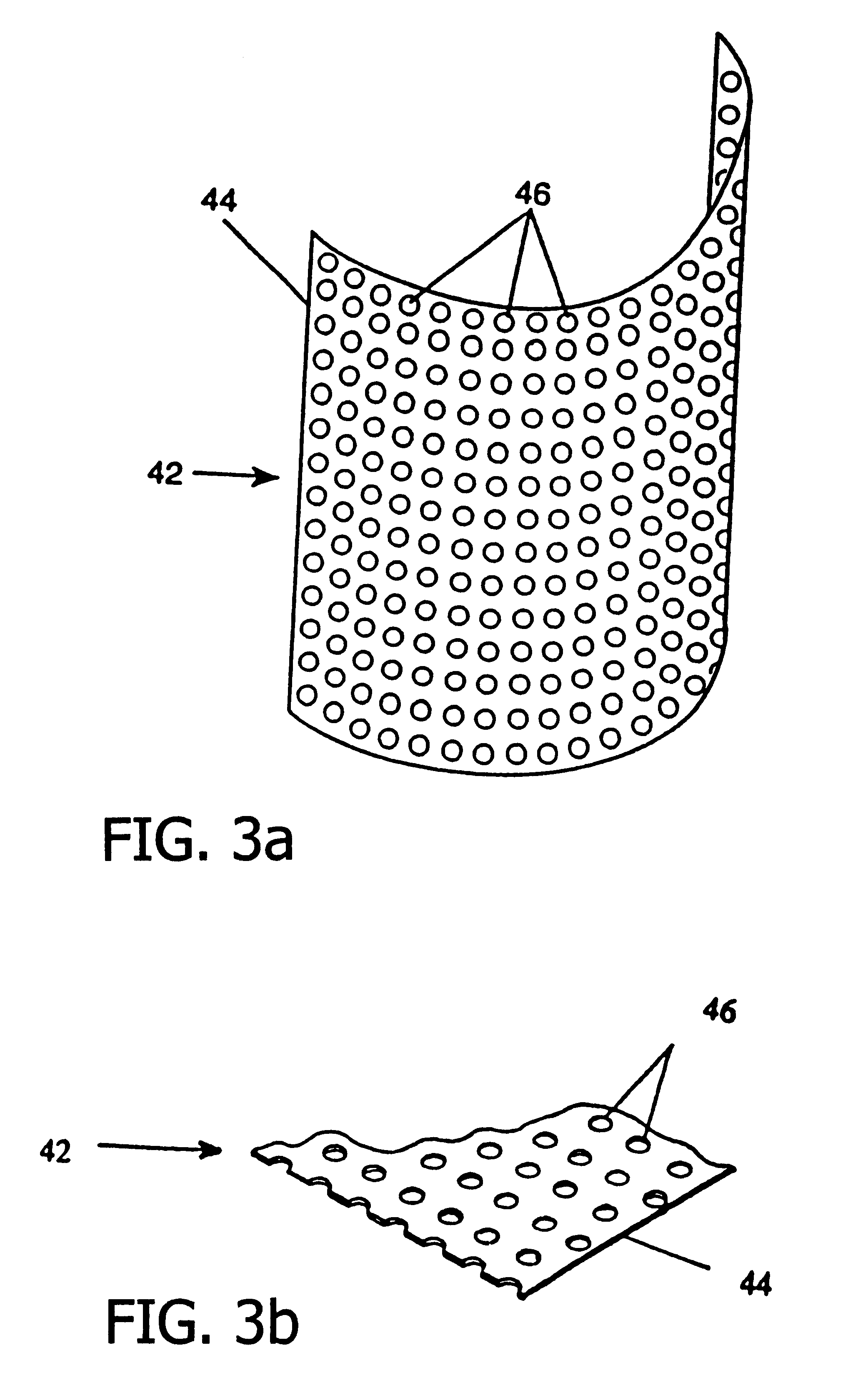
A resorbable, flexible implant in the form of a continuous macro-porous sheet is disclosed. The implant is adapted to protect biological tissue defects, especially bone defects in the mammalian skeletal system, from the interposition of adjacent soft tissues during in vivo repair. The membrane has pores with diameters from 20 microns to 3000 microns. This porosity is such that vasculature and connective tissue cells derived from the adjacent soft tissues including the periosteum can proliferate through the membrane into the bone defect. The thickness of the sheet is such that the sheet has both sufficient flexibility to allow the sheet to be shaped to conform to the configuration of a skeletal region to be repaired, and sufficient tensile strength to allow the sheet to be so shaped without damage to the sheet. The sheet provides enough inherent mechanical strength to withstand pressure from adjacent musculature and does not collapse.
Owner:MACROPORE
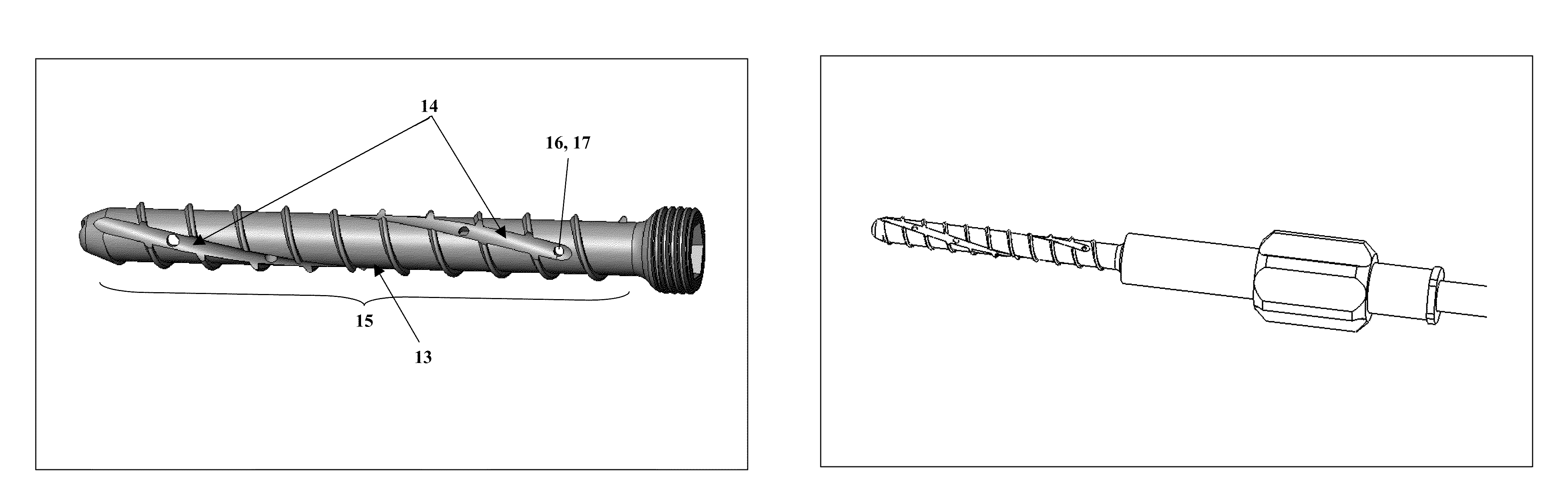
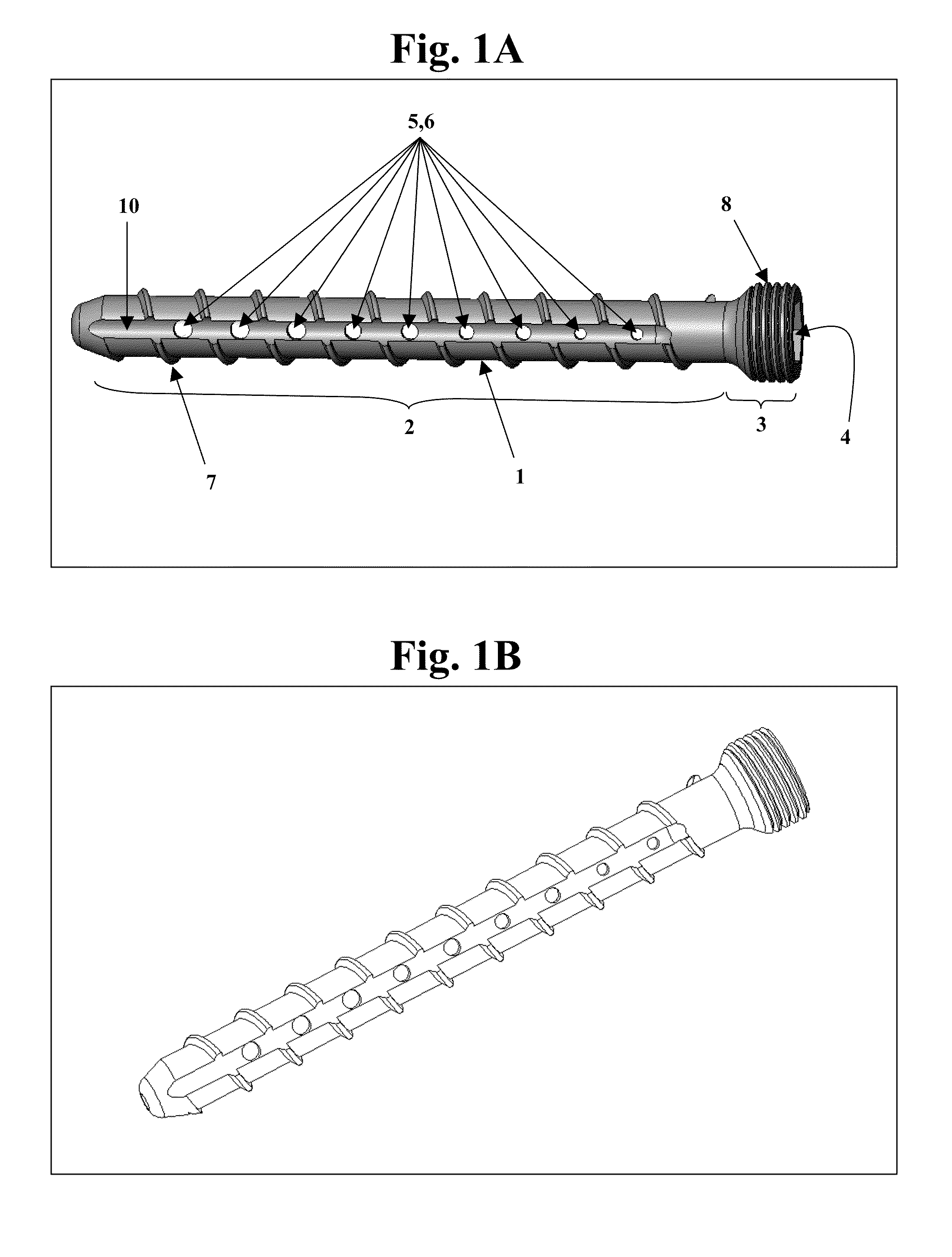
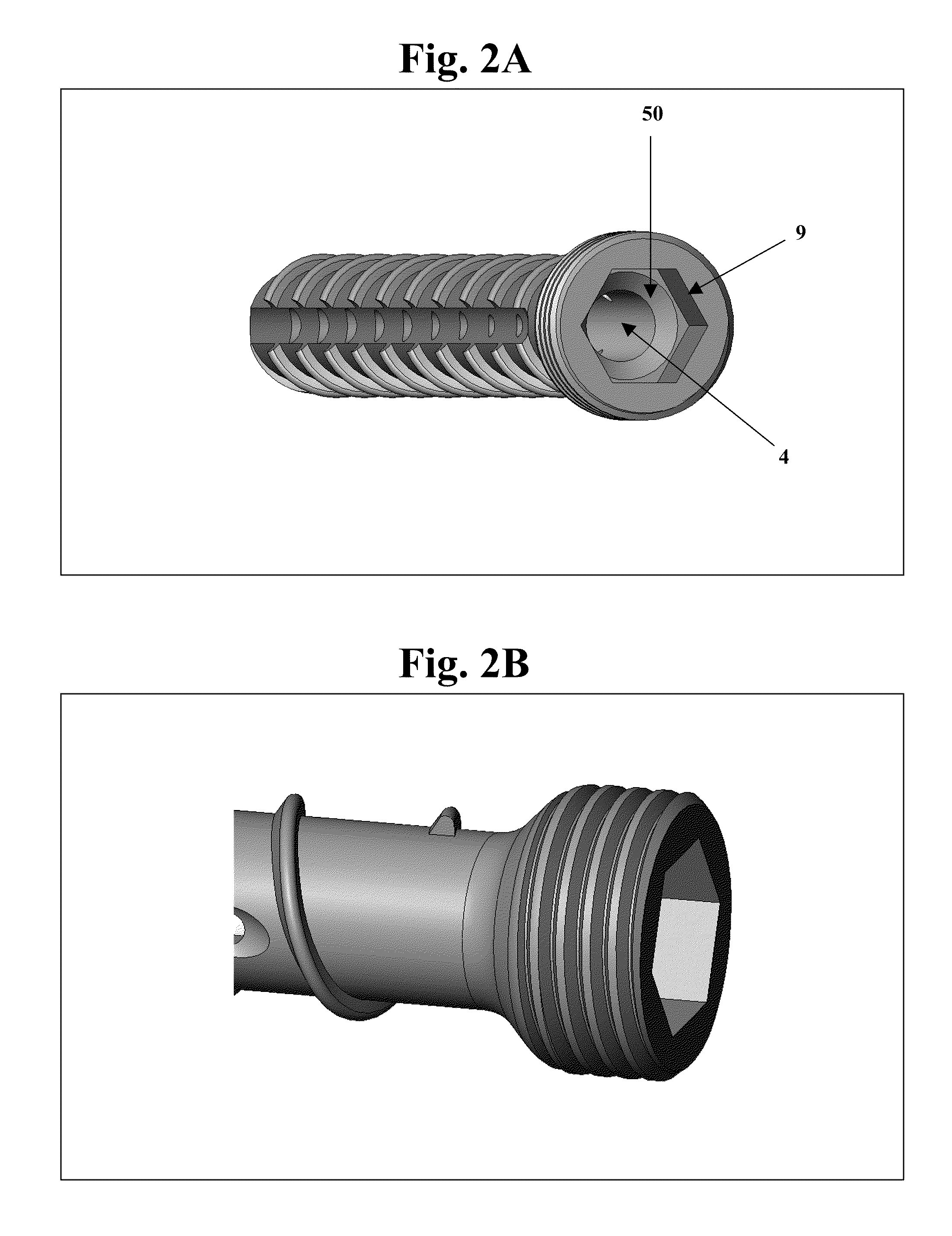
Bone screws and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20110060373A1Prevent escapeFaster advanceSuture equipmentsDental implantsBone defectBiomedical engineering
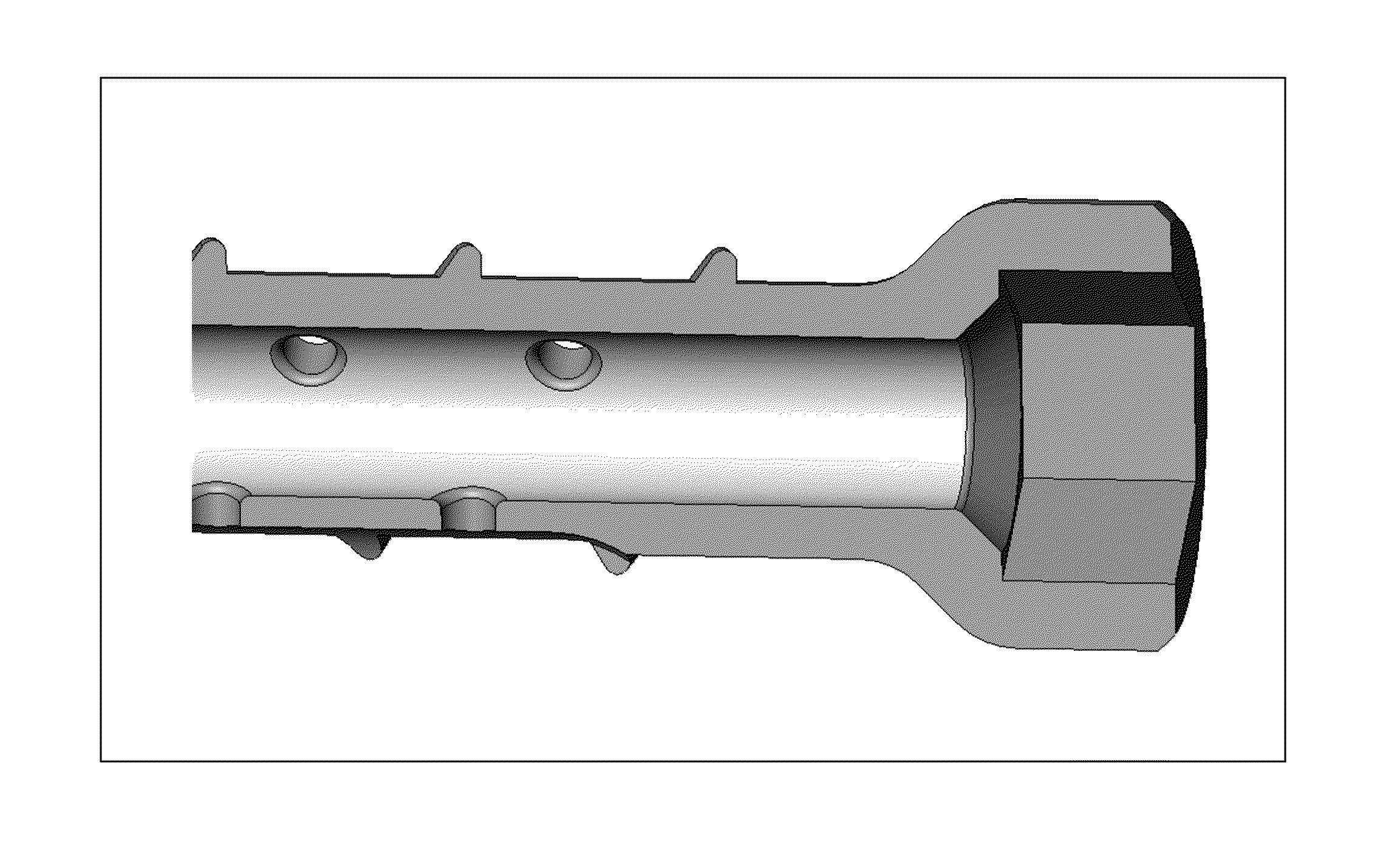
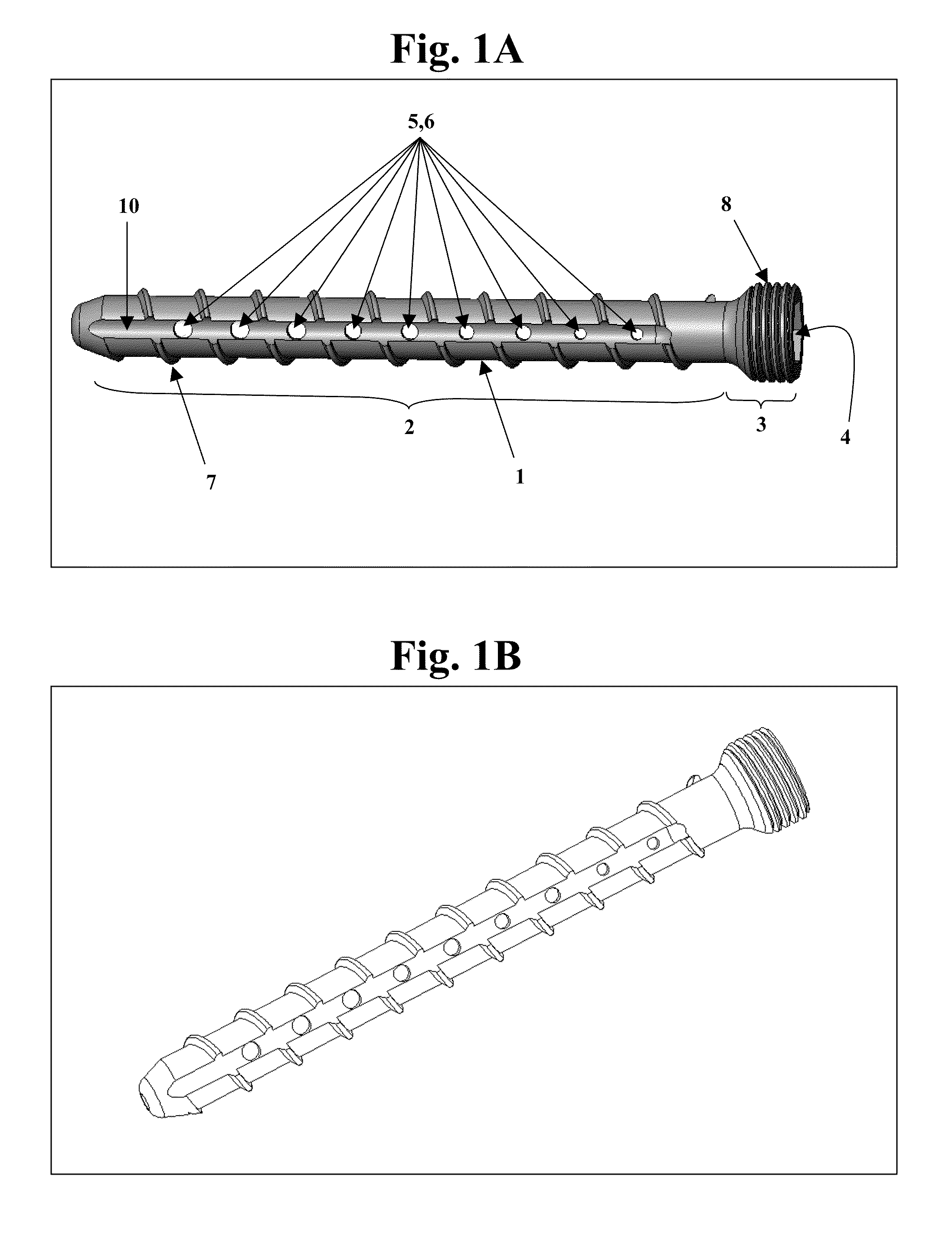
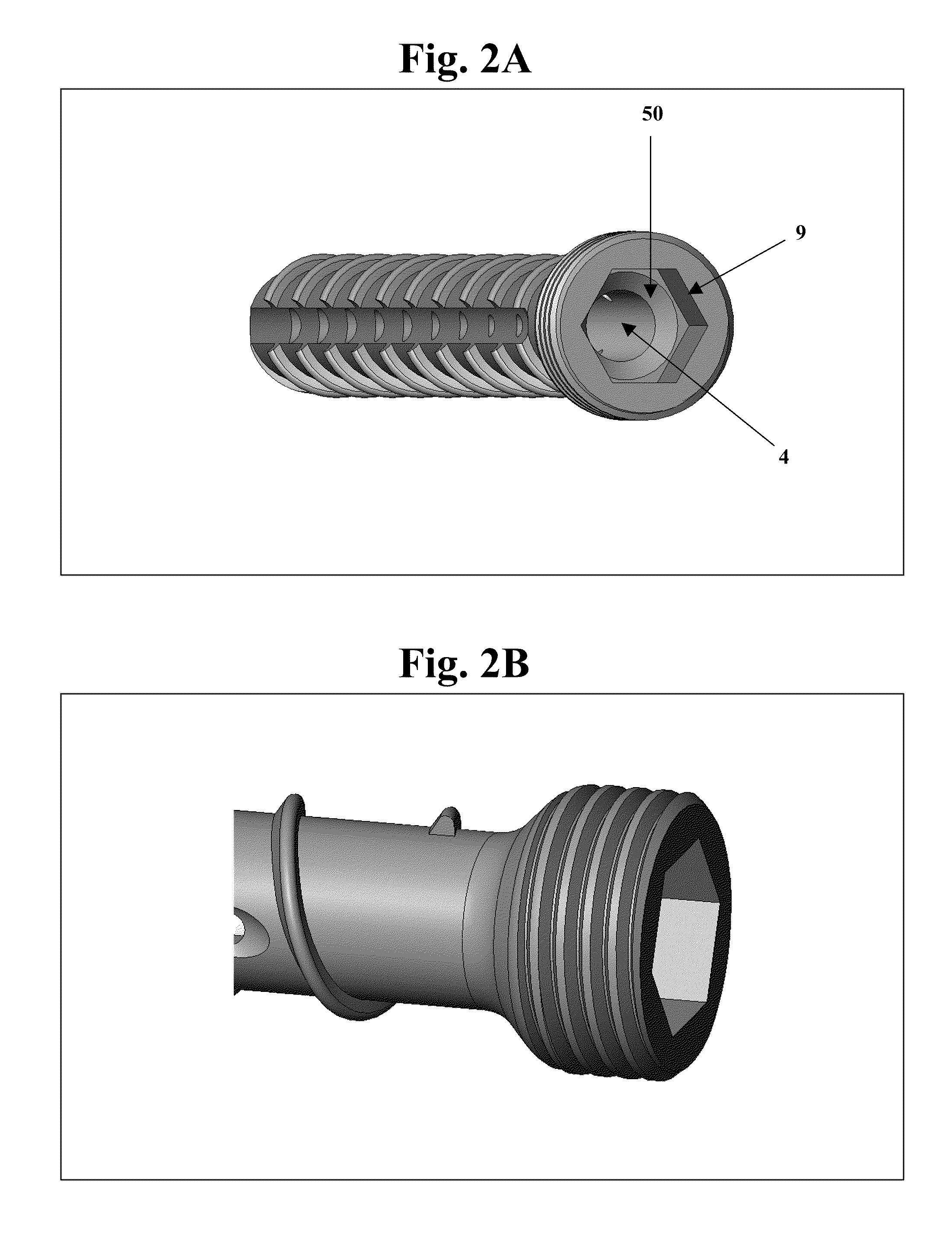
The invention features bone screws having a threaded screw body and a screw head attached to one end of the screw body, the bone screw further including: a) an interior channel extending longitudinally through the screw head and through at least a portion of the screw body, wherein the interior channel has a width of less than 5.0 millimeters; and b) a plurality of radially-disposed delivery channels connecting the interior channel to the exterior of the screw body, each delivery channel having exterior openings. The invention further features devices that include a bone screw and a delivery manifold detachably attached to the screw head of the bone screw. In addition, the invention features methods of treating a patient having a bone defect by using a bone screw described herein.
Owner:INNOVISION CO LTD
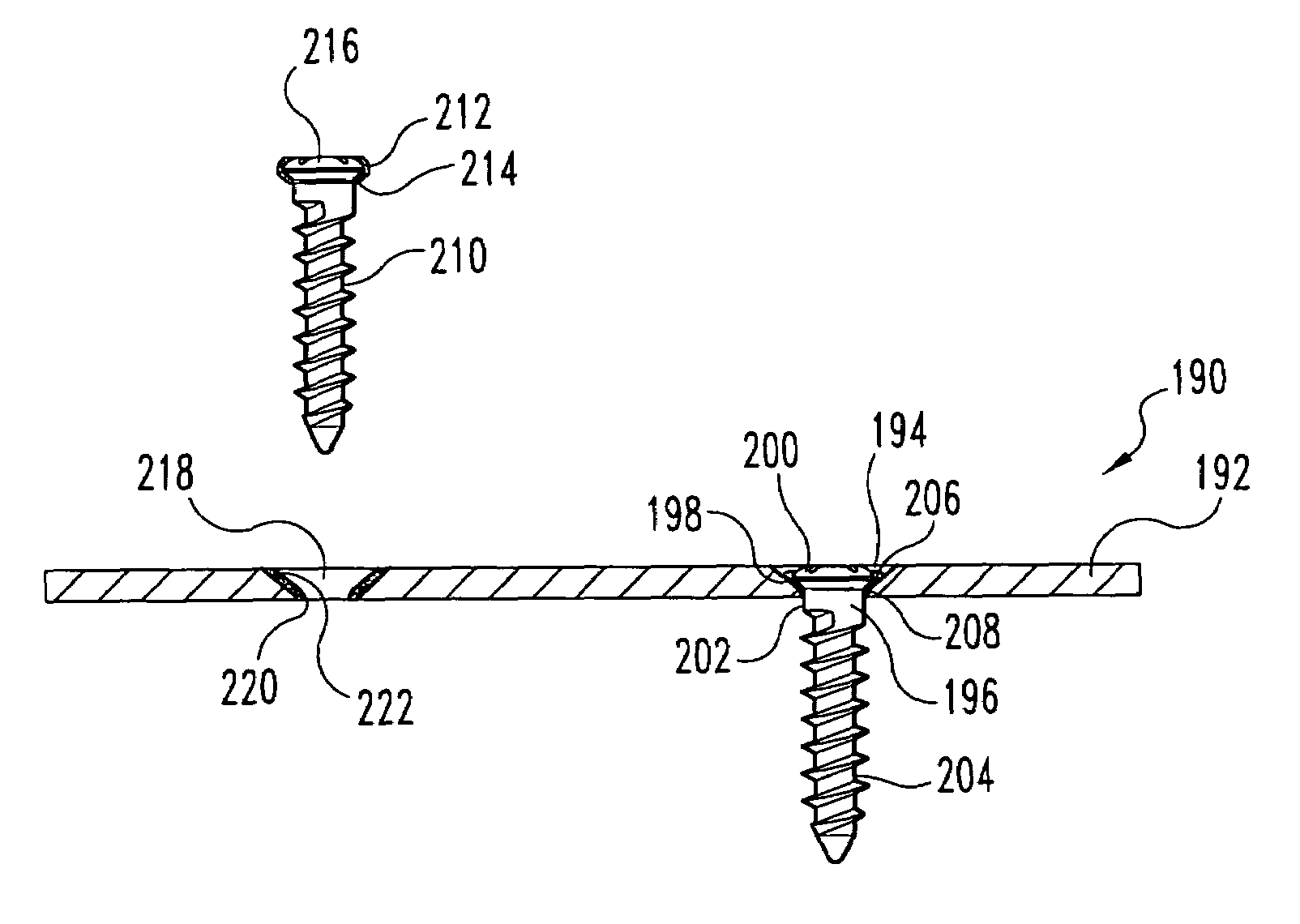
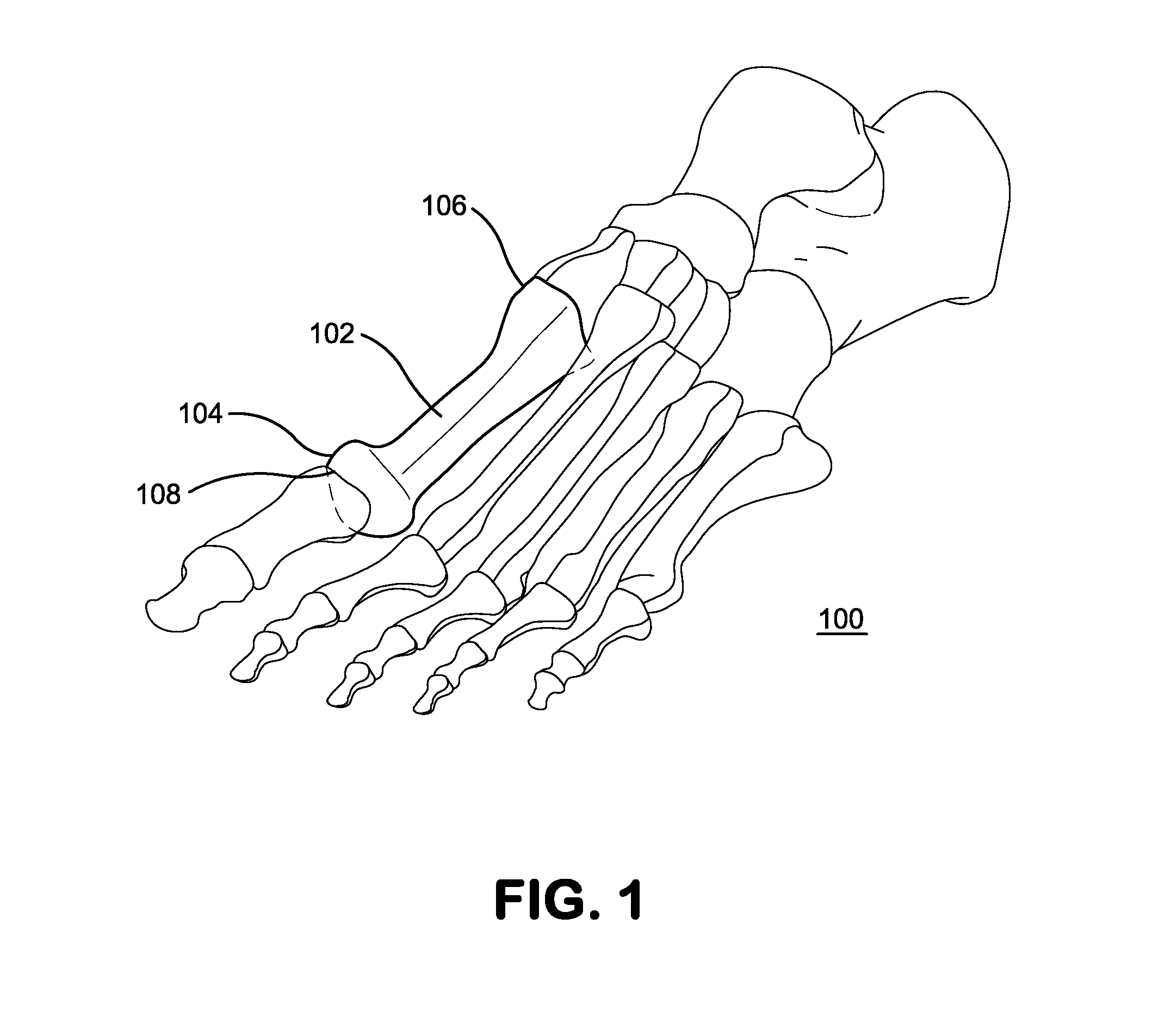
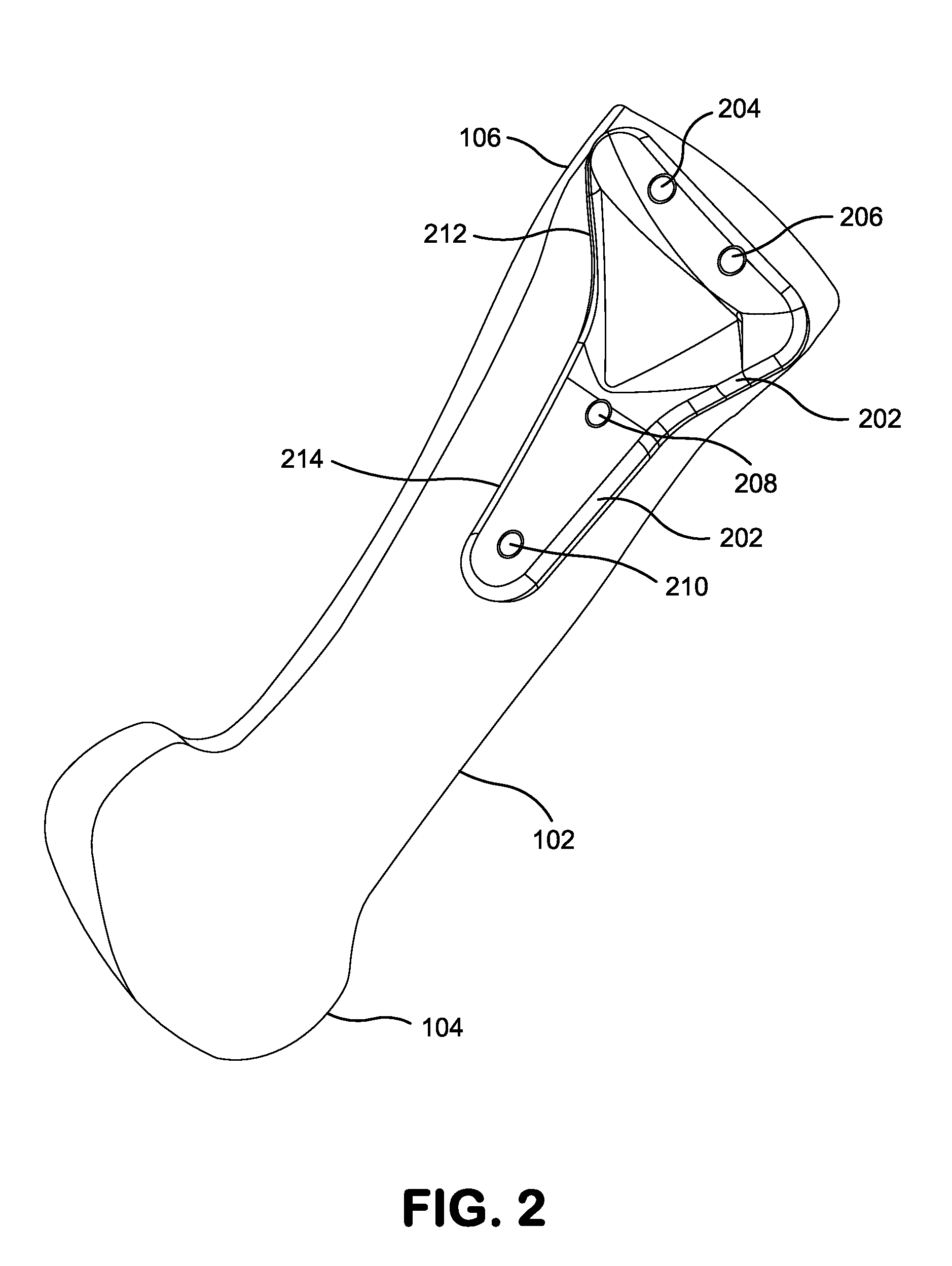
Bone defect repair device and method
In a method and system for corrective bunionectomy surgery of a bone, a saw template is positioned at a proximal portion of the bone. The saw template has a plurality of pin holes, for the insertion of pins. The saw template is replaced with a saw block placed over a portion of the plurality of pins. The bone is cut into first and second bone segments based on a position of the saw block. The saw block is removed. A corrective angle is applied to the second bone segment relative to the first bone segment. A mating plate compatible with the corrective angle is positioned over the plurality of pins to join the first bone segment and the second bone segment. A plurality of bone screws is screwed into the mating plate to secure the first bone segment and the second bone segment to form a corrective construct.
Owner:MEDARTIS AG
Composite bone graft, method of making and using same
InactiveUS6902578B1Avoid significant donor site morbidityHigh mechanical strengthBone implantJoint implantsDiseaseOssicular Prosthesis Implantation
The invention is directed to a composite bone graft for implantation in a patient, and methods of making and using the composite bone graft, along with methods for treating patients by implanting the composite bone graft at a site in a patient. The composite bone graft includes two or more connected, discrete, bone portions, and includes one or more biocompatible connectors which hold together the discrete bone portions to form the composite bone graft. The composite bone graft may include one or more textured bone surfaces. The textured surface preferably includes a plurality of closely spaced protrusions, preferably closely spaced continuous protrusions. The composite bone graft is useful for repairing bone defects caused by congenital anomaly, disease, or trauma, in a patient, for example, for restoring vertical support of the anterior and / or posterior column. Implantation of the composite bone graft results in improved graft stability and osteoinductivity, without a decrease in mechanical strength. The composite bone graft does not shift, extrude or rotate, after implantation. The present composite bone graft can be appropriately sized for any application and can be used to replace traditional non-bone prosthetic implants.
Owner:LIFENET HEALTH
Porous osteoimplant
ActiveUS20080069852A1Accelerate the remodeling processImprove permeabilityBone implantSkeletal disorderBone growthBone defect
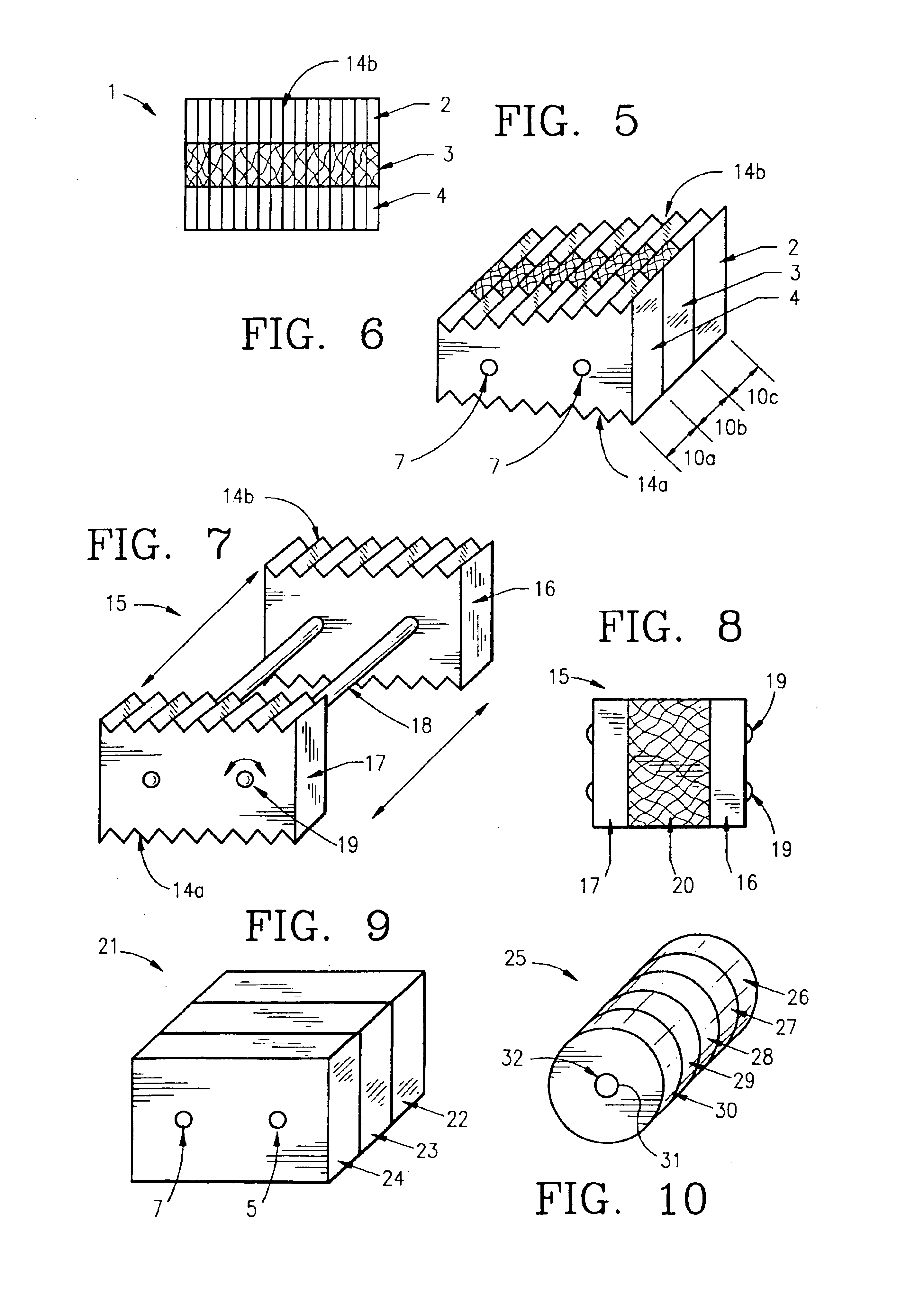
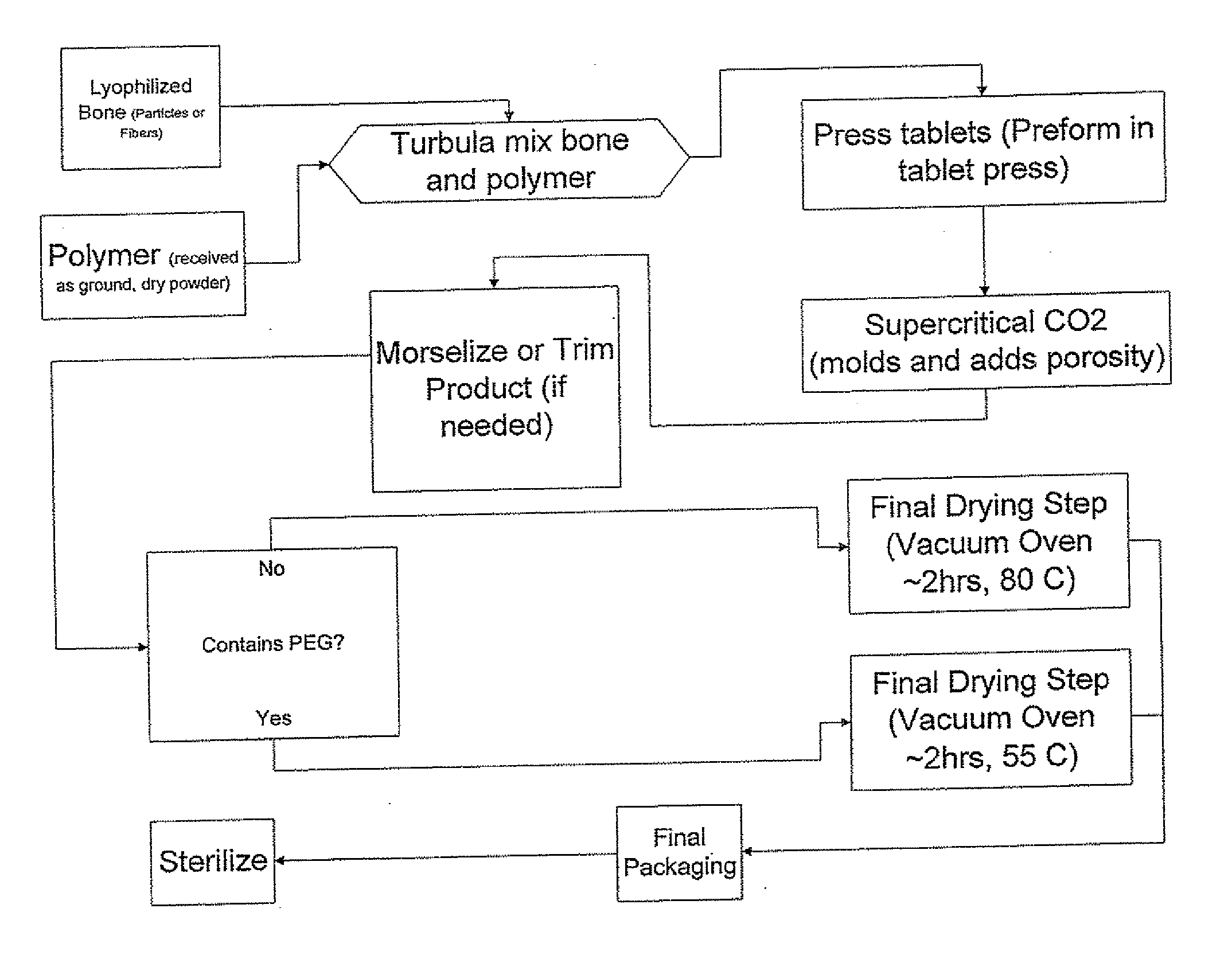
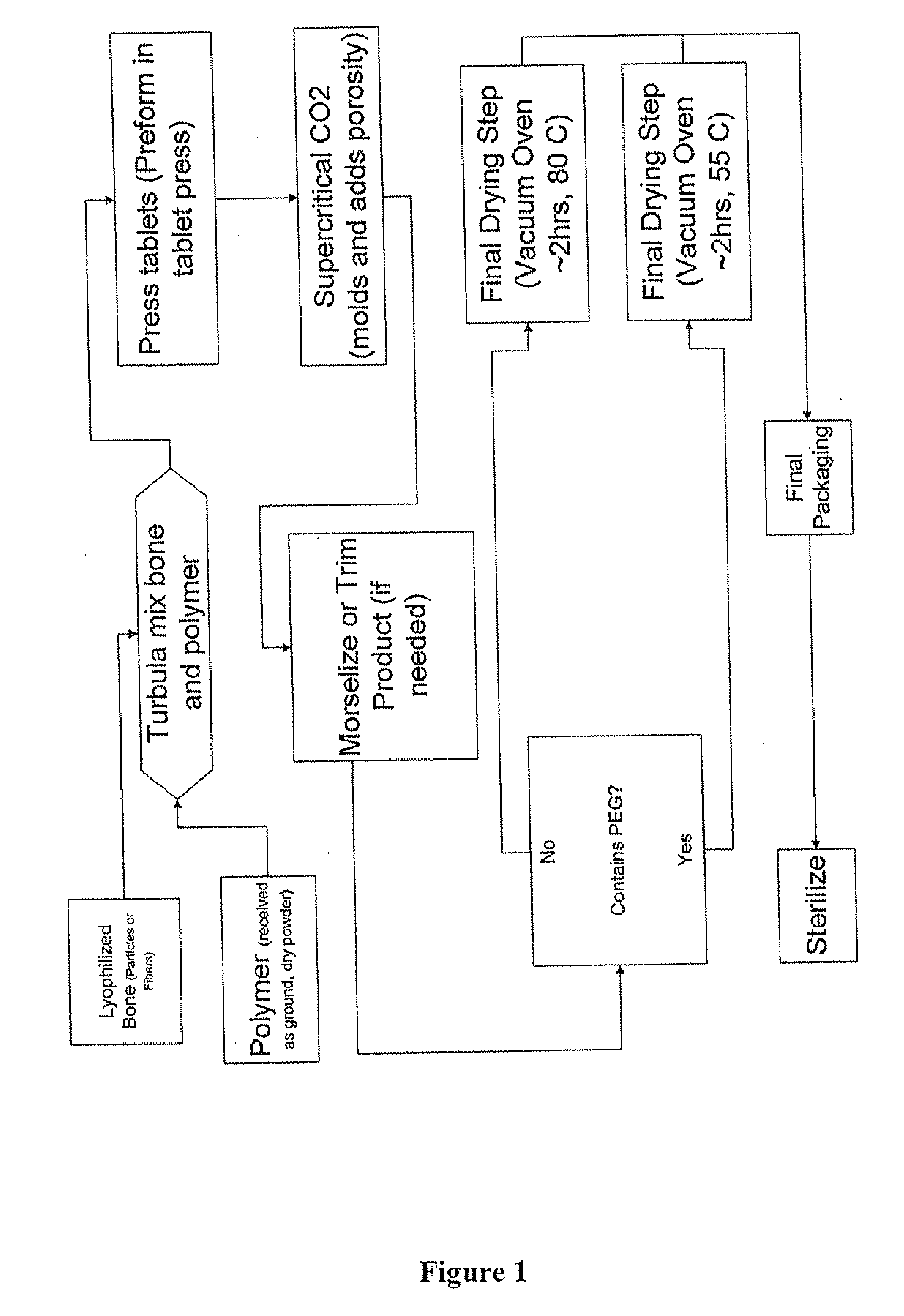
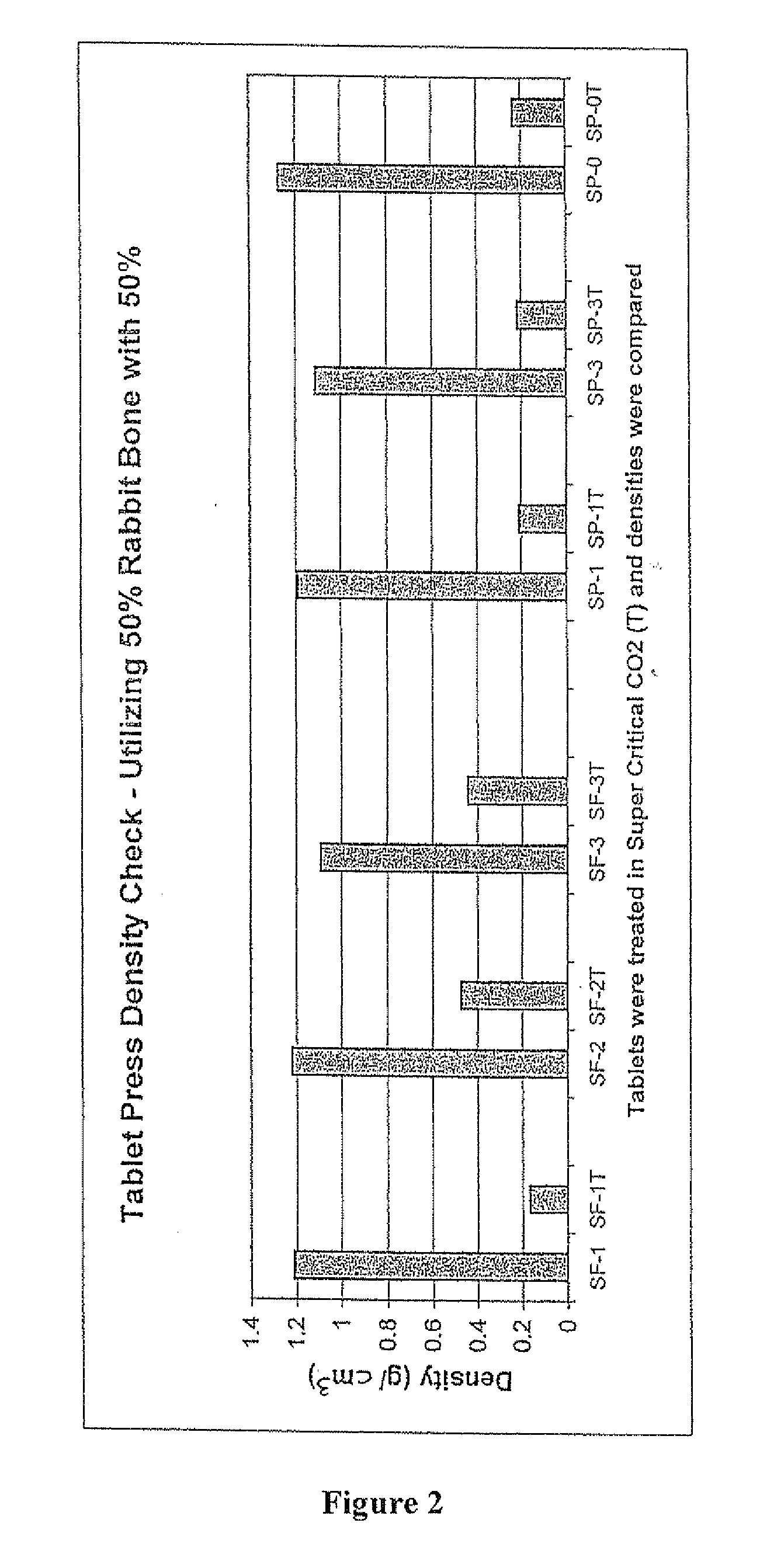
The invention is directed toward porous composites for application to a bone defect site to promote new bone growth. The inventive porous composites comprise a biocompatible polymer and a plurality of particles of bone-derived material, inorganic material, bone substitute material or composite material. In certain embodiments, the porous composites are prepared using a method that includes a supercritical fluid (e.g., supercritical carbon dioxide) treatment. The invention also discloses methods of using these composites as bone void fillers.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Isolation of bone marrow fraction rich in connective tissue growth components and the use thereof to promote connective tissue formation
InactiveUS20050130301A1Peptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderConnective tissue fiberTissue defect
A bone marrow isolate rich in one or more connective tissue growth components, methods of forming the isolate, and methods of promoting connective tissue growth using the isolate are described. A biological sample comprising bone marrow is centrifuged to separate the sample into fractions including a fraction rich in connective tissue growth components. The fraction rich in connective tissue growth components is then isolated from the separated sample. The isolate can be used directly or combined with a carrier and implanted into a patient at a tissue (e.g., bone) defect site. The biological sample can comprise bone marrow and whole blood. The isolate can be modified (e.g., by transfection with a nucleic acid encoding an osteoinductive polypeptide operably linked to a promoter) prior to application to the tissue defect site. The isolate can be made and applied to the tissue defect site in a single procedure (i.e., intraoperatively).
Owner:MCKAY WILLIAM F +1
Demineralized bone-derived implants
Selectively demineralized bone-derived implants are provided. In one embodiment, a bone sheet for implantation includes a demineralized field surrounding mineralized regions. In another embodiment, a bone defect filler includes a demineralized cancellous bone section in a first geometry. The first geometry is compressible and dryable to a second geometry smaller than the first geometry, and the second geometry is expandable and rehydratable to a third geometry larger than the second geometry.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Polymer-bioceramic composite for orthopaedic applications and method of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20040002770A1Promote ingrowthImprove toughnessBone implantJoint implantsCompression moldingPolymer science
Polymer-bioceramic structures are described for use in the repair of bone defects. The composites of the present disclosure are characterized by a polymer disposed in a porous bioceramic matrix. Processes for preparing the composites of the present invention by compression molding are described, including compression molding to induce orientation of the polymer is multiple directions. The composites of the present invention are also useful as drug delivery vehicles to facilitate the repair of bone defects.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Allograft bone composition having a gelatin binder
InactiveUS7045141B2Low tensile strengthIncrease delayImpression capsSurgical adhesivesCross-linkSolid structure
The invention is directed toward an osteoimplant for application to a bone defect site to promote new bone growth at the site which comprises a new bone growth inducing composition of demineralized allograft bone material mixed with an aqueous phosphate buffered gelatin which when lyophilized to remove water from the composition cross links the gelatin to form a solid structure.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT
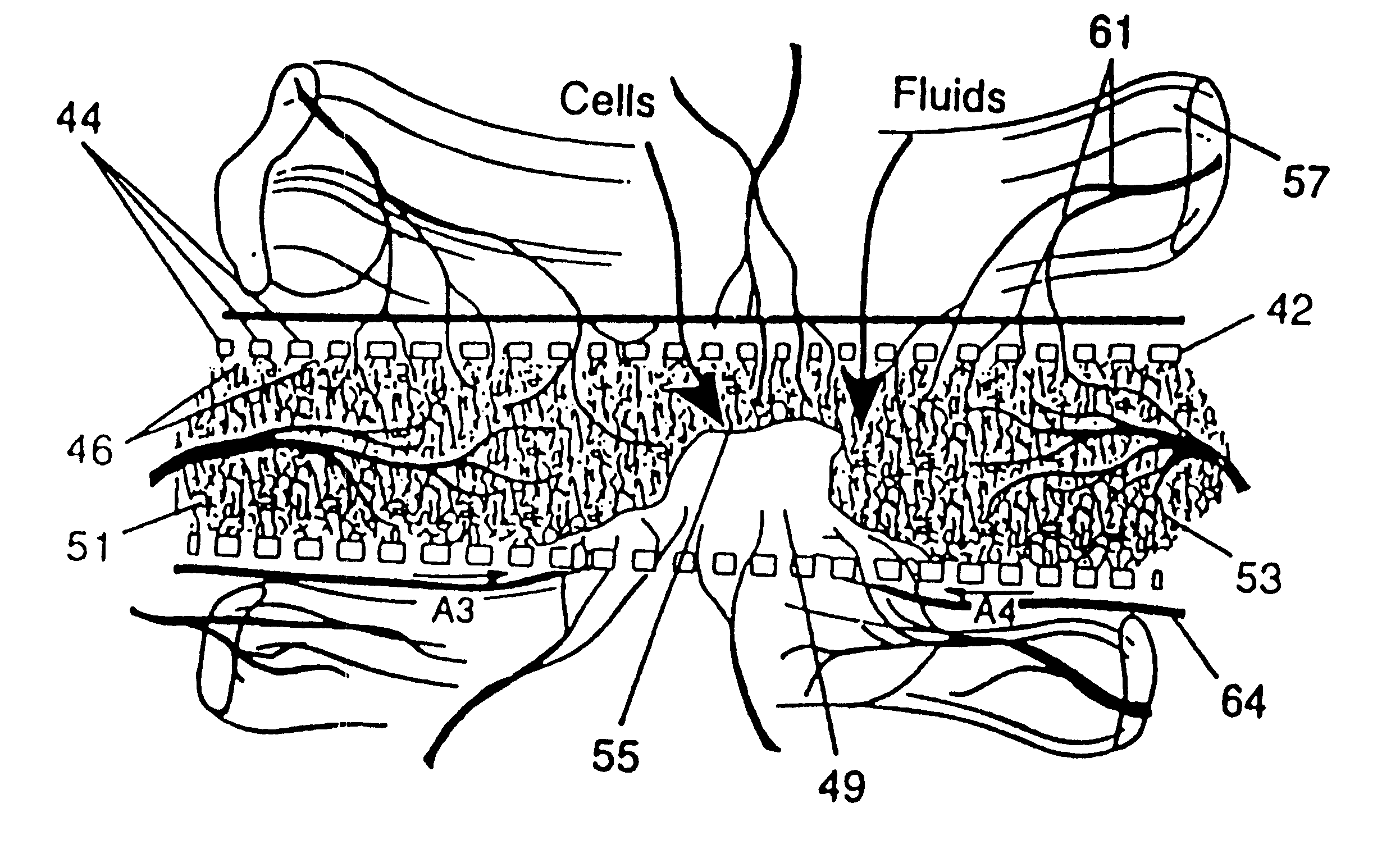
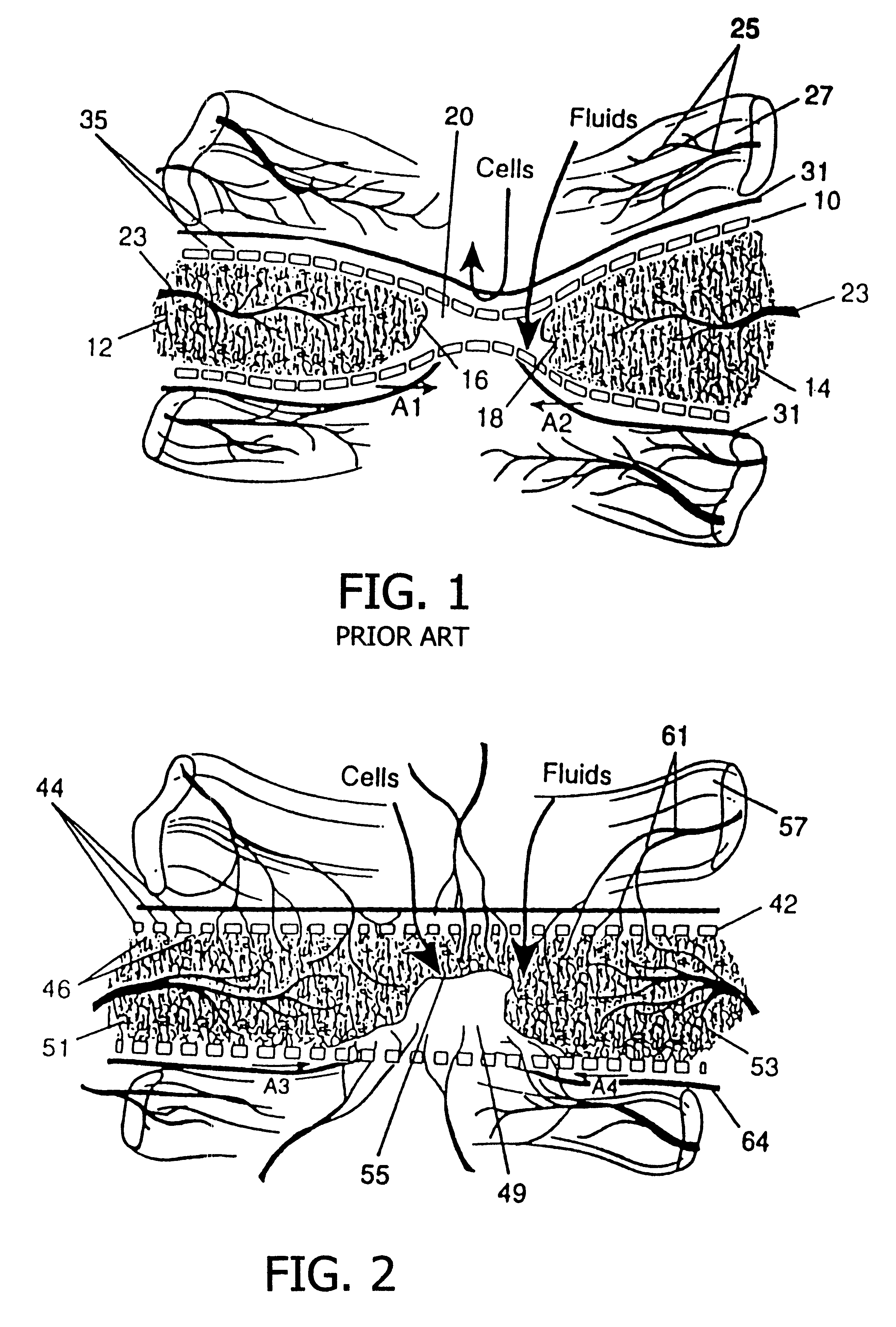
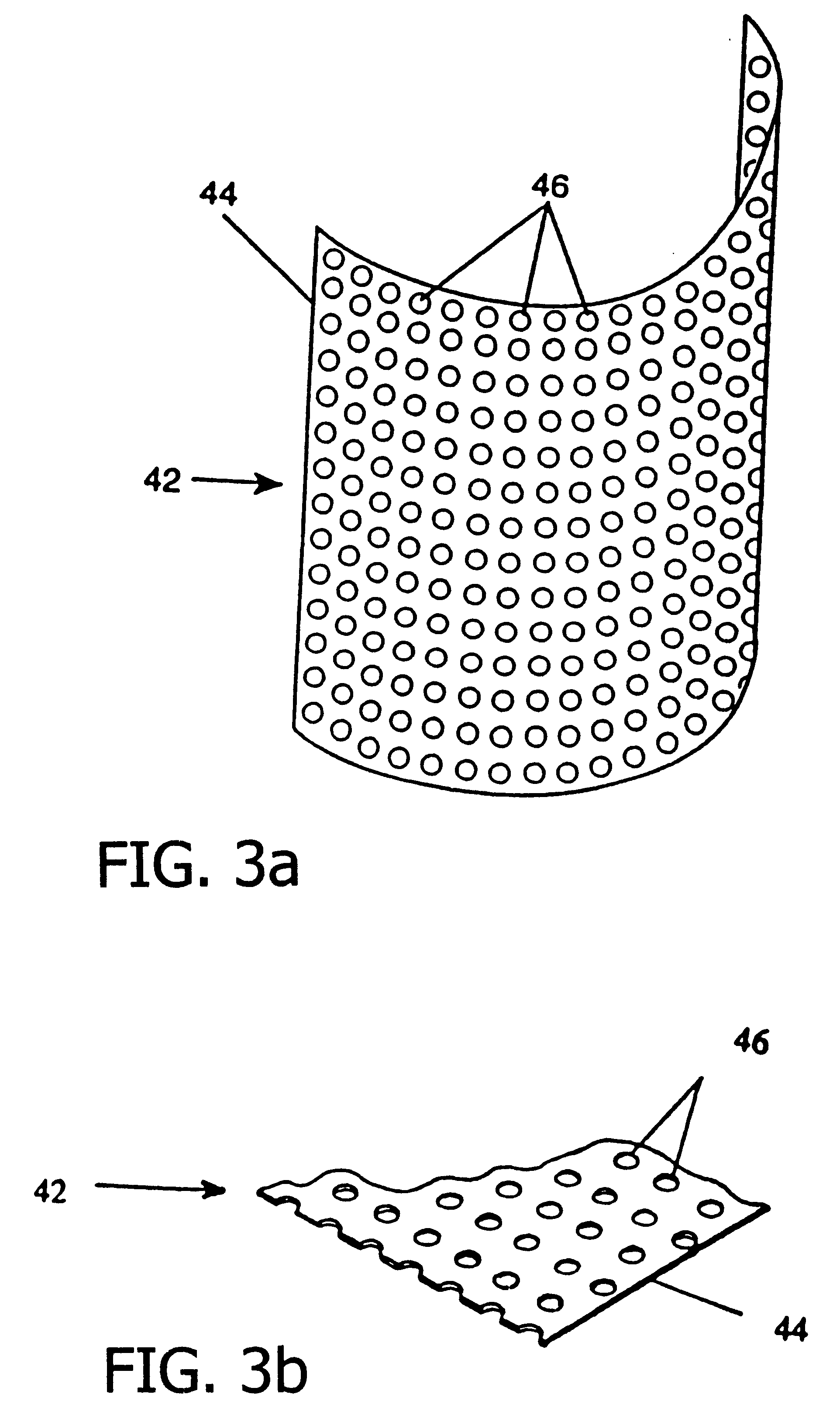
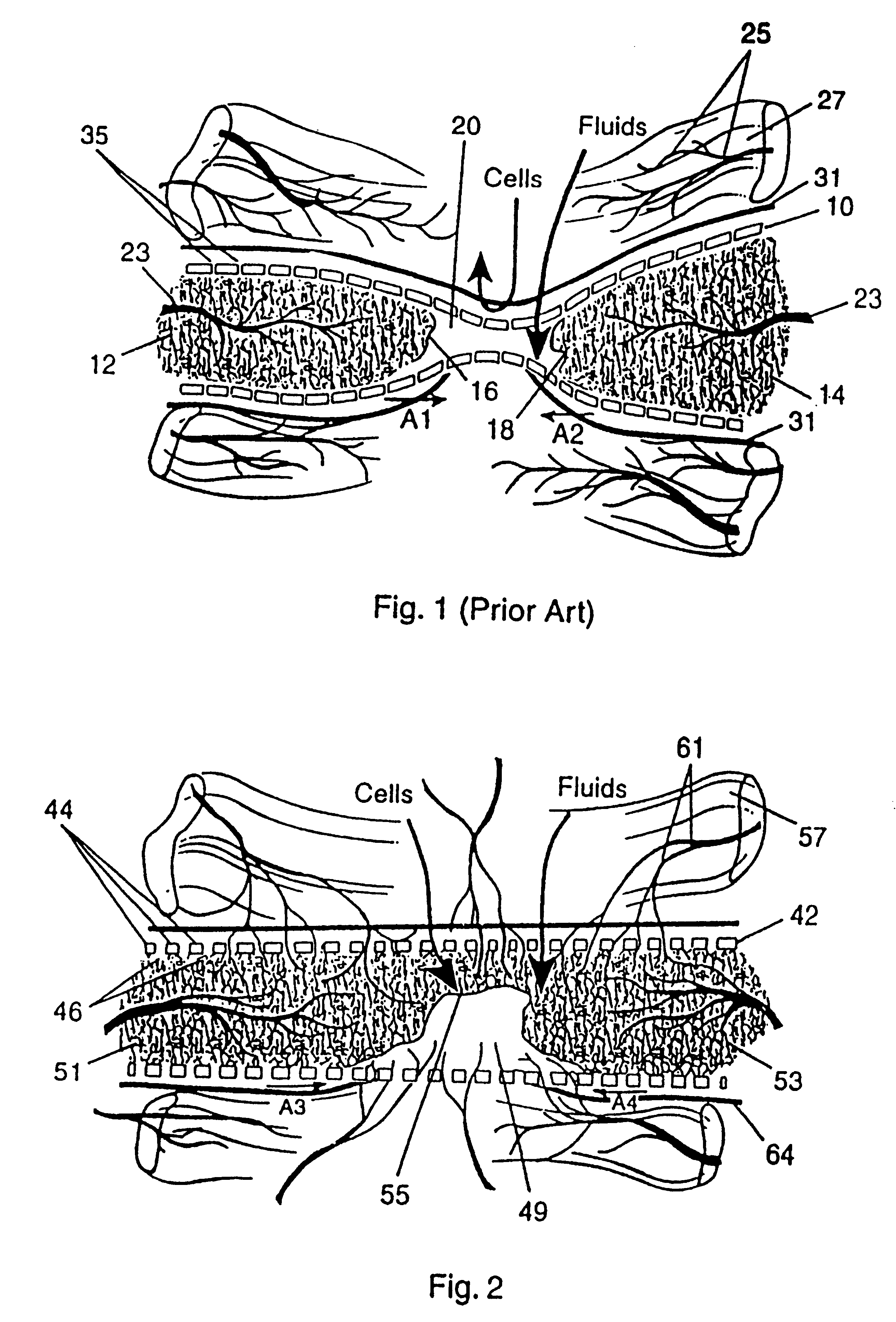
Membrane with tissue-guiding surface corrugations
A resorbing, flexible implant in the form of a continuous macro-porous sheet (42) is disclosed. The implant is adapted to protect biological tissue defects, especially bone defects in the mammalian skeletal system, from the interposition of adjacent soft tissues during in vitro repair. The membrane (42) has pores with diameters from 20 microns to 3000 microns. This porosity is such that vasculature, and connective tissue cells derived from the adjacent soft tissues including the periosteum, can proliferate through the membrane into the bone defect. The thickness of the sheet is such that the sheet has both sufficient flexibility to allow the sheet to be shaped to conform to the configuration of a skeletal region to be repaired, and sufficient tensile strength to allow the sheet to be so shaped without damage to the sheet. The sheet provides enough inherent mechanical strength to withstand pressure from adjacent musculature, and does not collapse.
Owner:MACROPORE
Composition for filling bone defects
InactiveUS7019192B2Low tensile strengthIncrease delayBiocideSurgical adhesivesSodium phosphatesDemineralized bone
The invention is directed toward a formable bone composition for application to a bone defect site to promote new bone growth at the site which comprises a new bone growth inducing compound of demineralized lyophilized allograft bone particles. The particle size ranges from about 0.1 mm to about 1.0 cm and is mixed in a hydrogel carrier containing a sodium phosphate saline buffer, the hydrogel component of the carrier ranging from about 1.0 to 5.0% of the composition and a pH between 6.8–7.4 with one or more additives of a cellular material, growth factor, demineralized bone chips or mineralized bone chips.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Impacted orthopedic bone support implant
InactiveUS7537616B1Promote bone growthProvide supportBone implantJoint implantsDiseaseBone structure
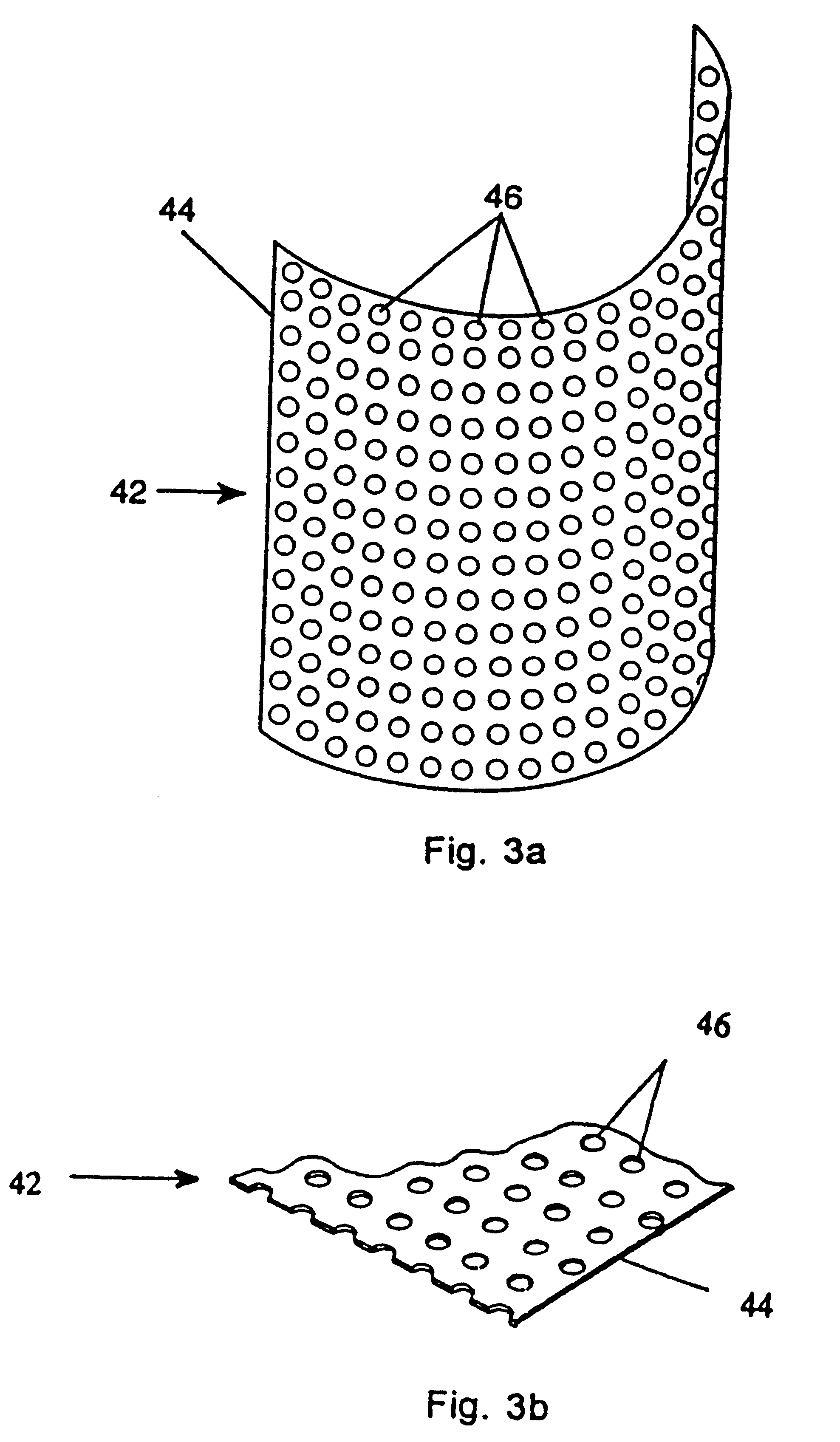
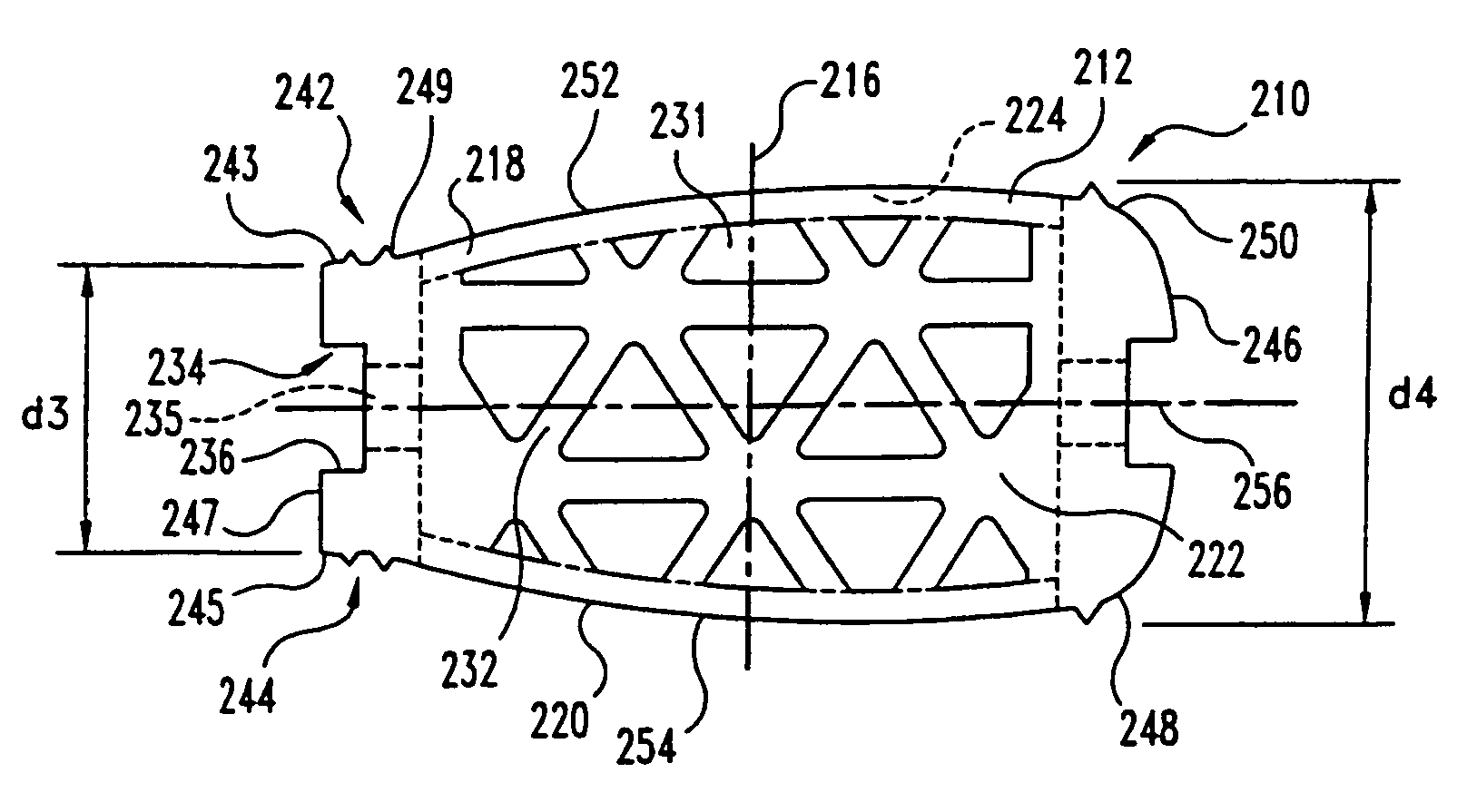
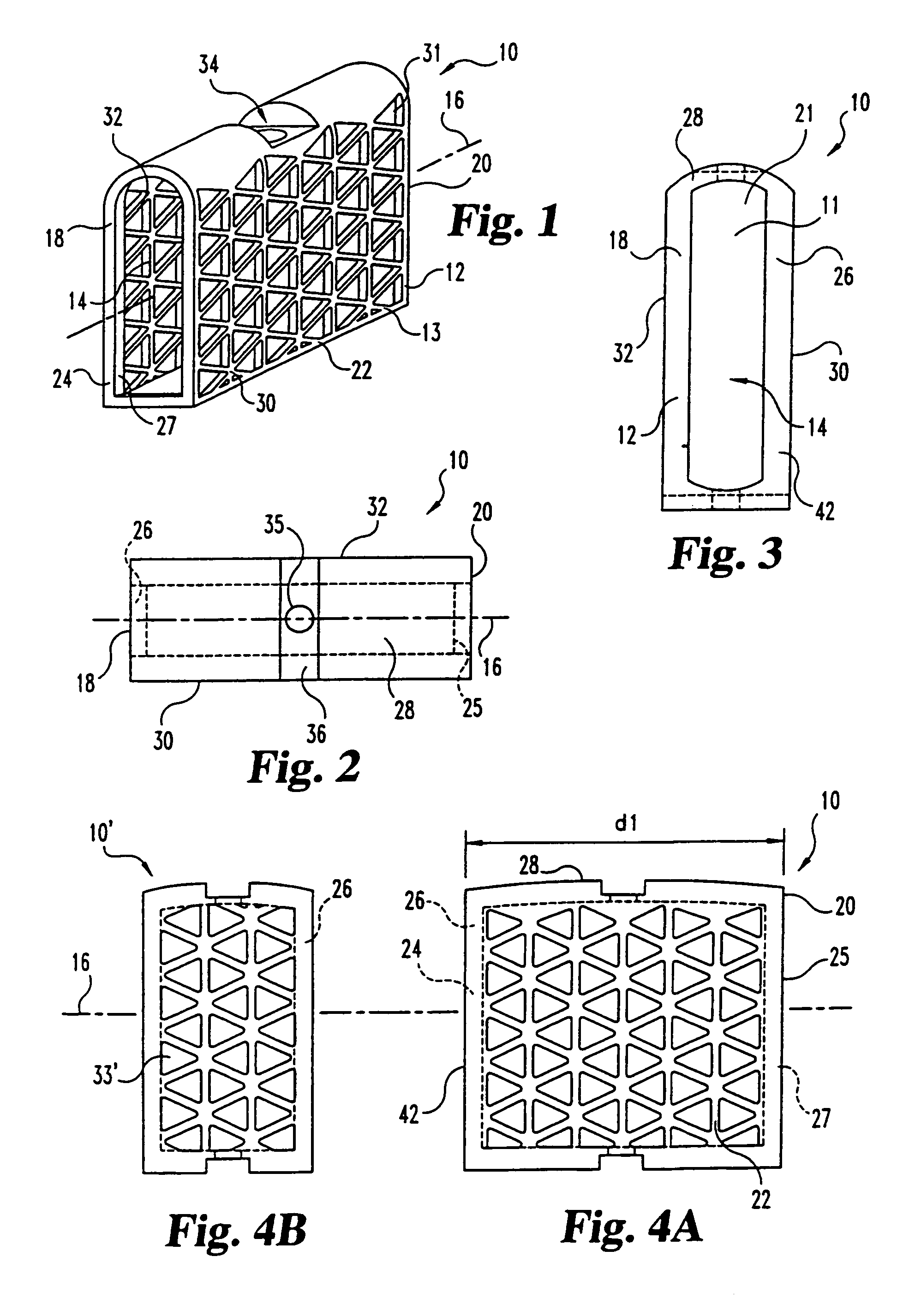
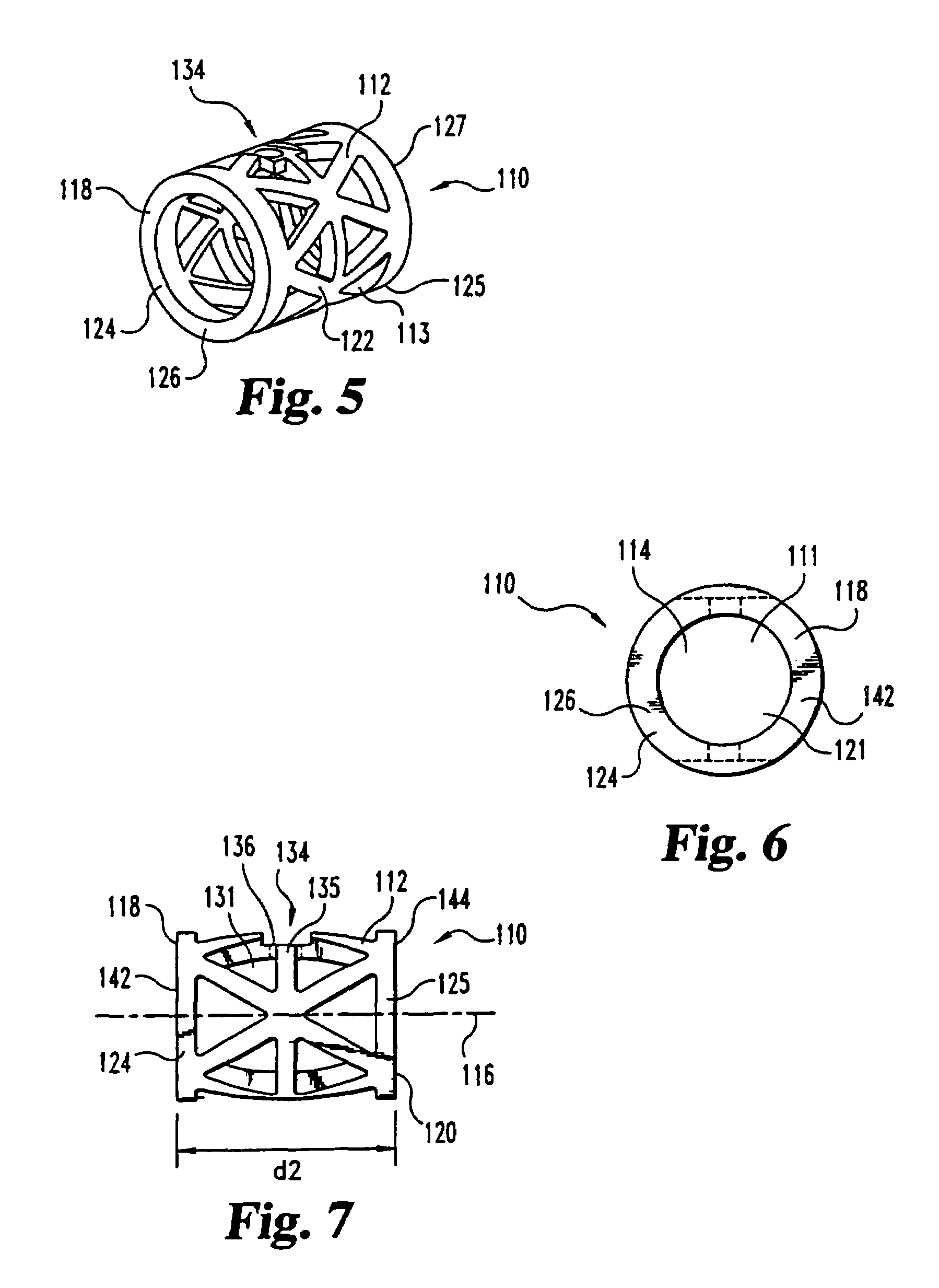
This invention relates to a porous bone implant (10, 110, and 210), a method of manufacturing the implant and a method of orthopedic treatment. The mesh implant can be manufactured using extrusion techniques and a variety of cutting and machining processes to provide the implant with the desired structural features and in the required dimensions to be matingly received within the bone defect or cavity. The implant can be used to strengthen bone structures and support bone tissue adjacent to a defect of cavity. Thus, the implant can be used to provide improved treatment of patients having bone defects or diseases with decreased postoperative pain and a shorter recovery time.
Owner:SDGI HLDG
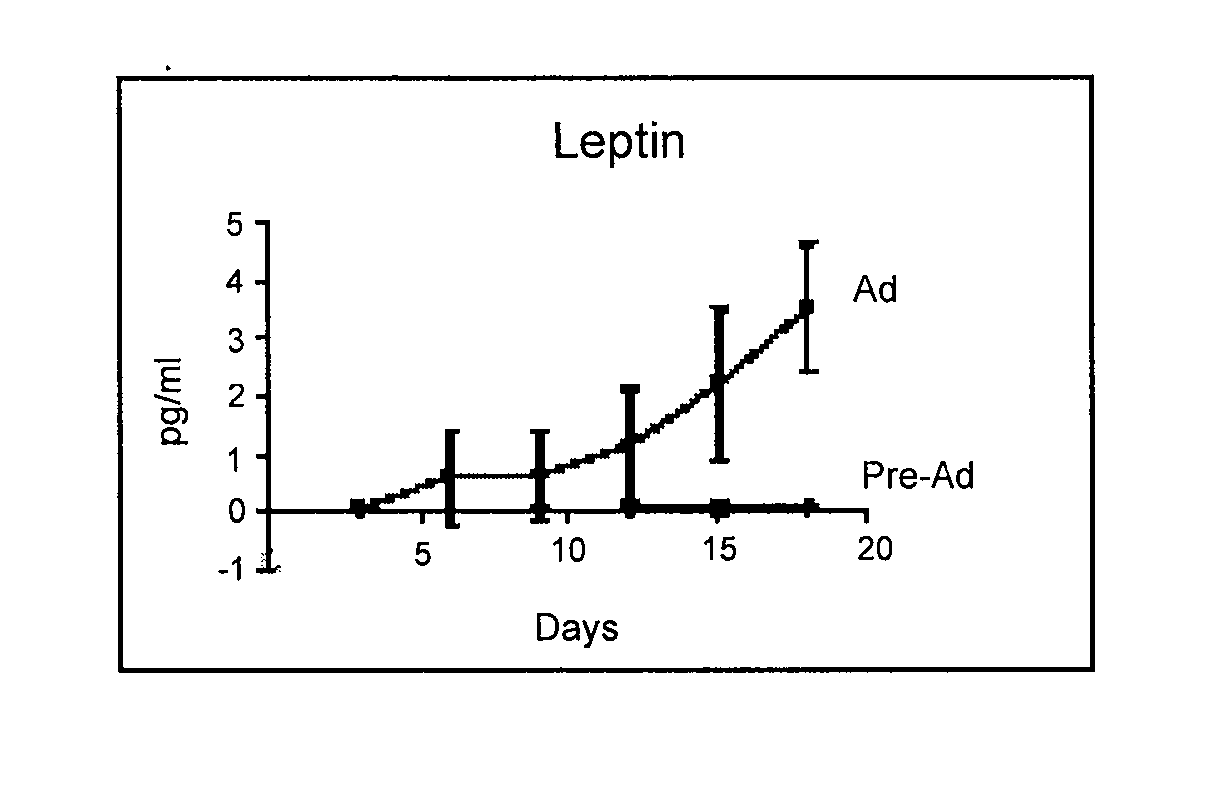
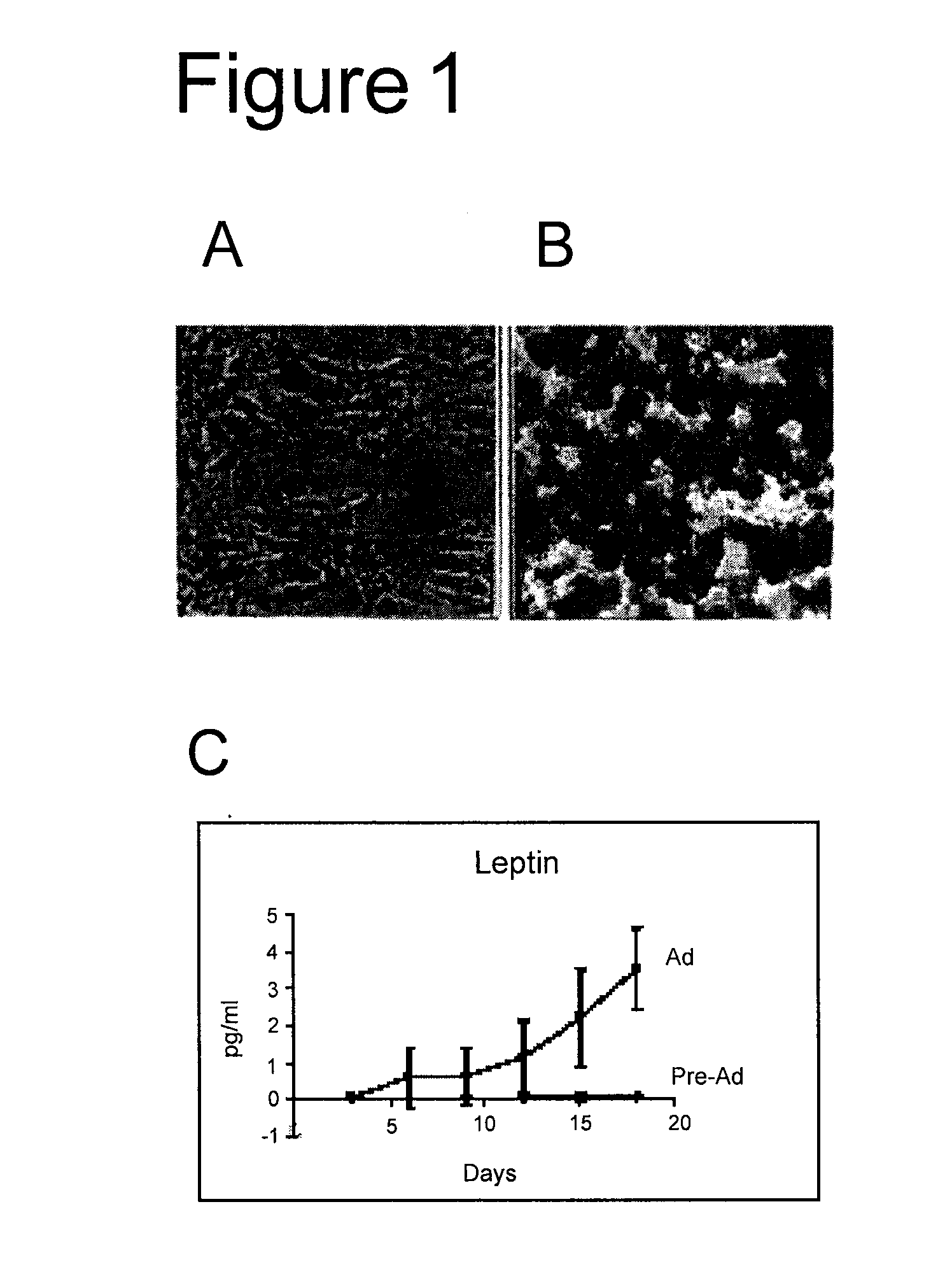
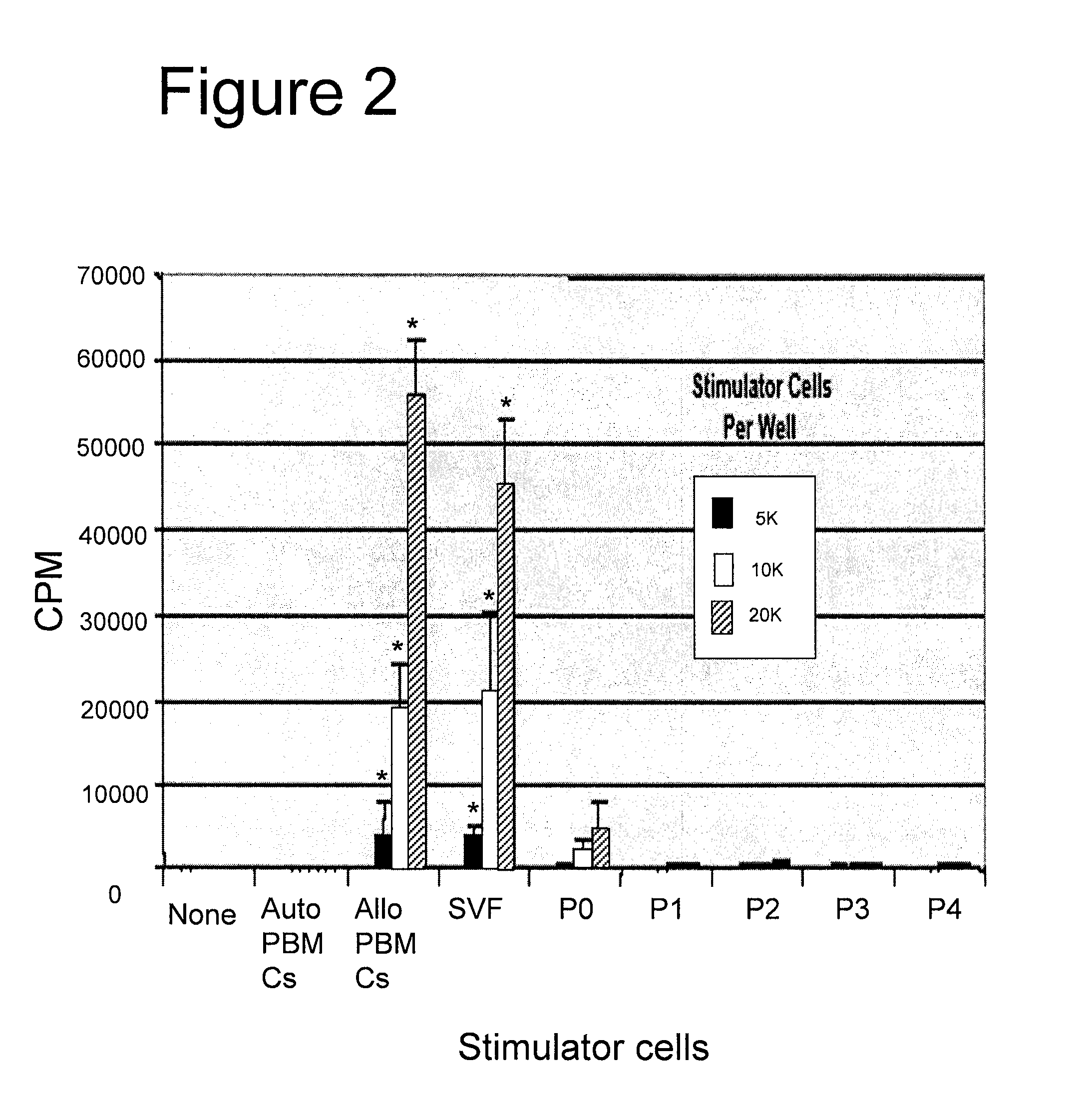
Biocompatible scaffolds and adipose-derived stem cells
The present invention relates to compositions of biocompatible materials and adult stem cells. The present invention also provides methods of alleviating or treating bone defects or soft tissue defects using the compositions.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE +1
Malleable paste for filling bone defects
InactiveUSRE38522E1Easy to packFast absorptionSurgical adhesivesPeptide/protein ingredientsBone defectBiomedical engineering
The invention is directed toward a malleable bone putty and a flowable gel composition for application to a bone defect site to promote new bone growth at the site which comprises a new bone growth inducing compound of demineralized lyophilized allograft bone powder. The bone powder has a particle size ranging from about 100 to about 850 microns and is mixed in a high molecular weight hydrogel carrier, the hydrogel component of the carrier ranging from about 0.3 to 3.0% of the composition and having a molecular weight of about at least 10,000 Daltons. The composition contains about 25% to about 40% bone powder and can be additionally provided with BMP's and a sodium phosphate buffer.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Resorbable, macro-porous non-collapsing and flexible membrane barrier for skeletal repair and regeneration
A resorbable, flexible implant in the form of a continuous macro-porous sheet is disclosed. The implant is adapted to protect biological tissue defects, especially bone defects in the mammalian skeletal system, from the interposition of adjacent soft tissues during in vivo repair. The membrane has pores with diameters from 20 microns to 3000 microns. This porosity is such that vasculature and connective tissue cells derived from the adjacent soft tissues including the periosteum can proliferate through the membrane into the bone defect. The thickness of the sheet is such that the sheet has both sufficient flexibility to allow the sheet to be shaped to conform to the configuration of a skeletal region to be repaired, and sufficient tensile strength to allow the sheet to be so shaped without damage to the sheet. The sheet provides enough inherent mechanical strength to withstand pressure from adjacent musculature and does not collapse.
Owner:MACROPORE BIOSURGERY INC
Bioactive bone graft substitute
The invention relates to biocompatible bone graft materials for repairing bone defects and the application of such bone graft materials.
Owner:ORTHOVITA INC
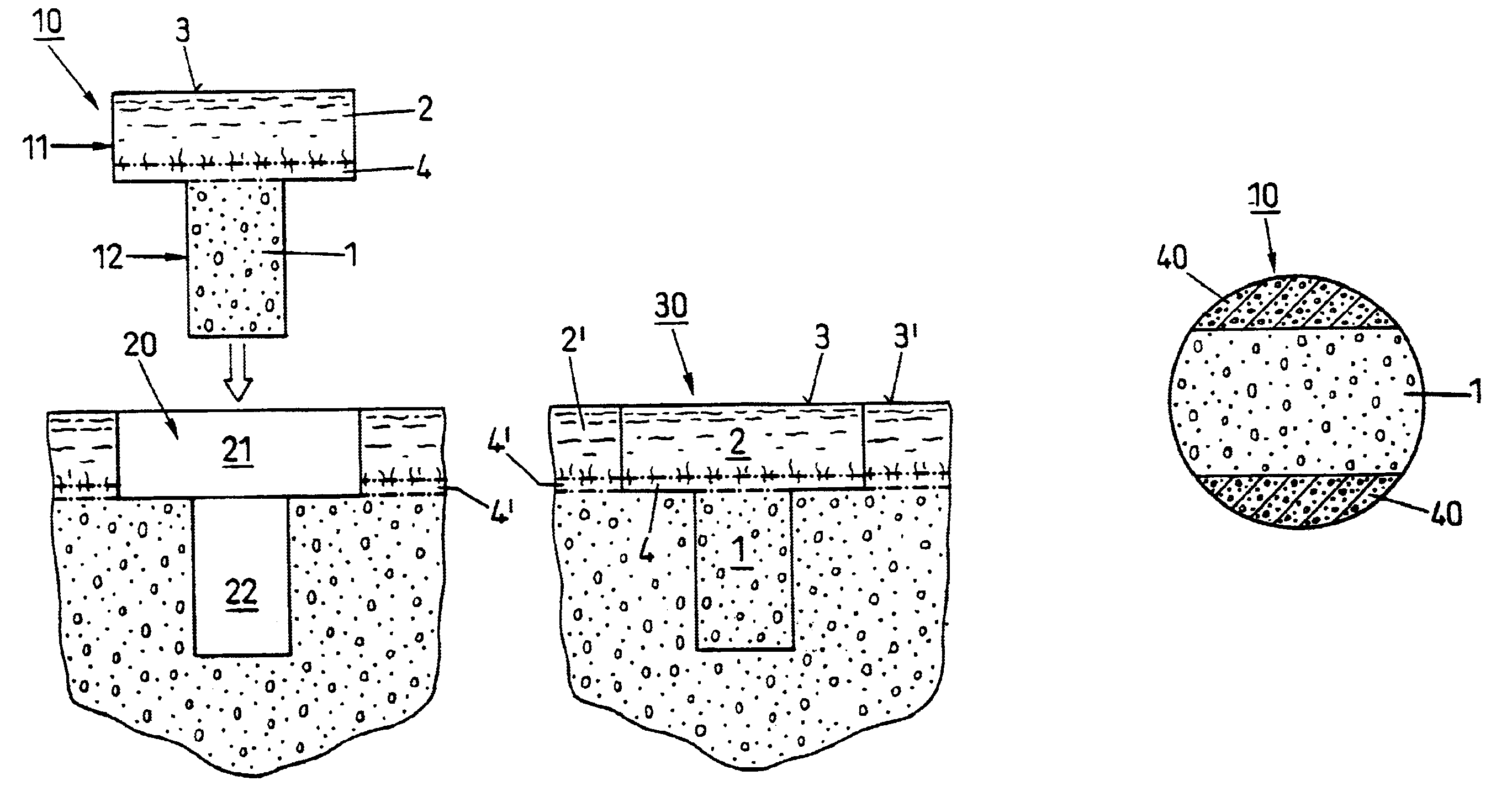
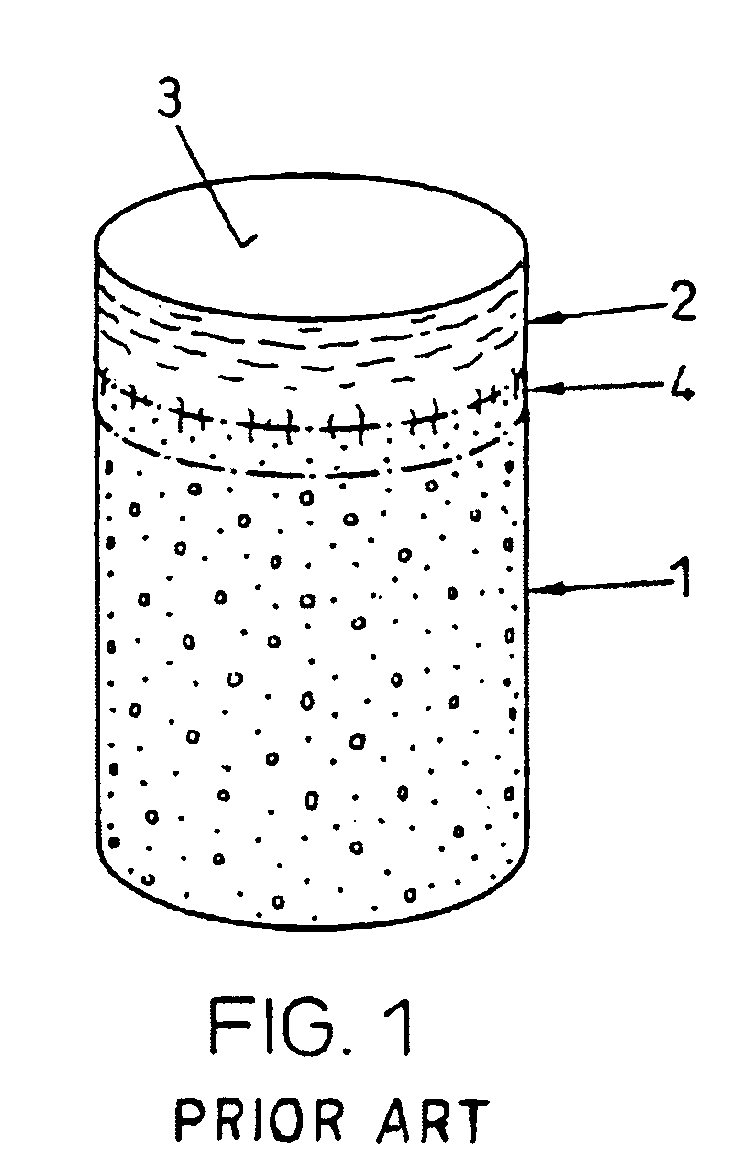
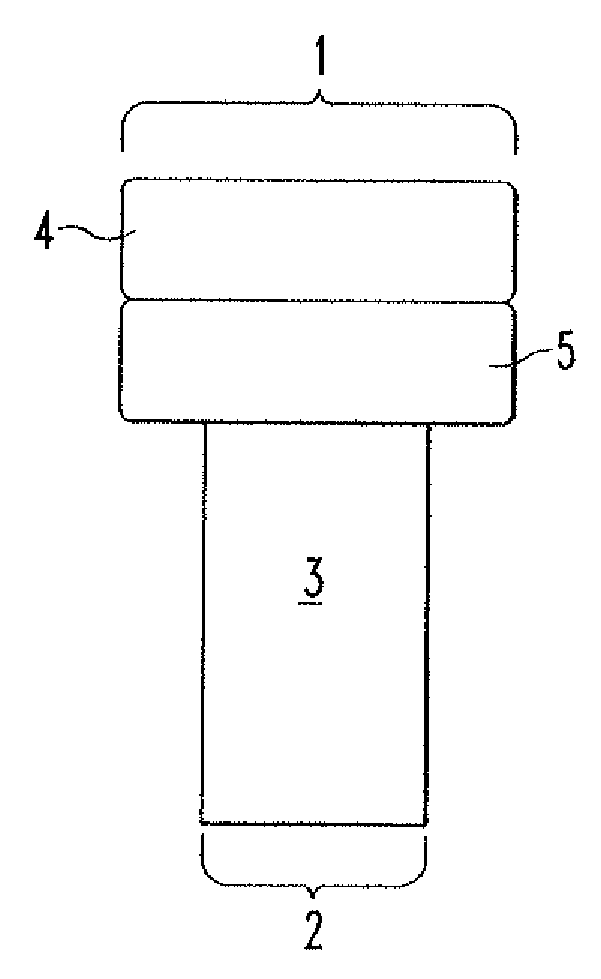
Preparation for repairing cartilage defects or cartilage/bone defects in human or animal joints
InactiveUS6858042B2Reduce absorptionResistant to resorptionBone implantJoint implantsRepair tissueCyst
Repairs of cartilage defects or of cartilage / bone defects in human or animal joints with the help of devices including a bone part (1), a cartilage layer (2) and a subchondral bone plate (4) or an imitation of such a plate in the transition region between the cartilage layer (2) and the bone part (1). After implantation, the bone part (4) is resorbed and is replaced by reparative tissue only after being essentially totally resorbed. In a critical phase of the healing process, a mechanically inferior cyst is located in the place of the implanted bone part (1). In order to prevent the cartilage layer (2) from sinking into the cyst space during this critical phase of the healing process the device has a top part (11) and a bottom part (12), wherein the top part (11) consists essentially of the cartilage layer (2) and the subchondral bone plate (4) and the bottom part (12) corresponds essentially to the bone part (1) and wherein the top part (11) parallel to the subchondral bone plate (4) has a larger diameter than the bottom part (12). After implantation in a suitable opening or bore (20), the cartilage layer (2) and the subchondral bone plate (4) are supported not only on the bone part (1) but also on native bone tissue having a loading capacity not changing during the healing process. Therefore, the implanted cartilage layer cannot sink during the healing process.
Owner:ZIMMER GMBH
Implant Scaffold Combined With Autologous Tissue, Allogenic Tissue, Cultured Tissue, or combinations Thereof
InactiveUS20070185585A1Reduce and prevent immune responseReducing and preventing inflammationSuture equipmentsSkin implantsAutologous tissueTissue defect
The present disclosure relates to an implant for insertion into a tissue defect, such as a cartilage defect or a cartilage and bone defect. The implant includes a plug including a porous polymeric material having at least one channel therein, wherein the plug is sized to fit the tissue defect; and tissue. The tissue substantially fills the channel and is selected from a group including autologous tissue, allogenic tissue, cultured tissue, or combinations thereof. In an embodiment, the plug includes a plurality of porous polymeric phases. In another embodiment, the plug includes a plurality of channels wherein the channels are longitudinal and / or transverse. A method for repairing defective tissue is also disclosed.
Owner:BRACY BRAT +2
Absorbable implants and methods for their use in hemostasis and in the treatment of osseous defects
ActiveUS20050065214A1Stimulate bone healing processLower potentialBiocidePowder deliveryBarium saltTG - Triglyceride
Two (or more), -component, body-implantable, absorbable, biocompatible, putty, and non-putty hemostatic tamponades for use in surgery. Component 1 is a finely powdered bulking material, preferably less than 50 microns, e.g. the calcium, magnesium, aluminum, or barium salts of saturated or unsaturated carboxylic acids containing about 6 to 22 carbon atoms, hydroxyapatite, DBM, polyglycolide, polylactide, poldioxinones, polycaprolactones, absorbable glasses, gelatin, collagens, mono, and polysaccharides starches. Component 2, a dispersing vehicle, may be esters of C8-C18 monohydric alcohols with C2-C6 aliphatic monocarboxylic acids; C2-C18 monohydric alcohols with polycarboxylic acids; C8-C30 monohydric alcohols; tocopherol and esters thereof with C2-C10 aliphatic monocarboxylic acids or polycarboxylic acids; absorbable 10-14C hydrocarbons; free carboxylic acids such as oleic, capric, and lauric; dialkyl ethers and ketones; alkyl aryl ethers and ketones, polyhydroxy compounds and esters and ethers thereof; (ethylene oxide / propylene oxide copolymers), oils e.g. olive oil, castor oil and triglycerides.
Owner:ABYRX
Mesenchymal precursor cell and use thereof in the repair of bone defects and fractures in mammals
InactiveUS20050158289A1Increase ratingsEasy to transplantBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAntigenVCAM-1
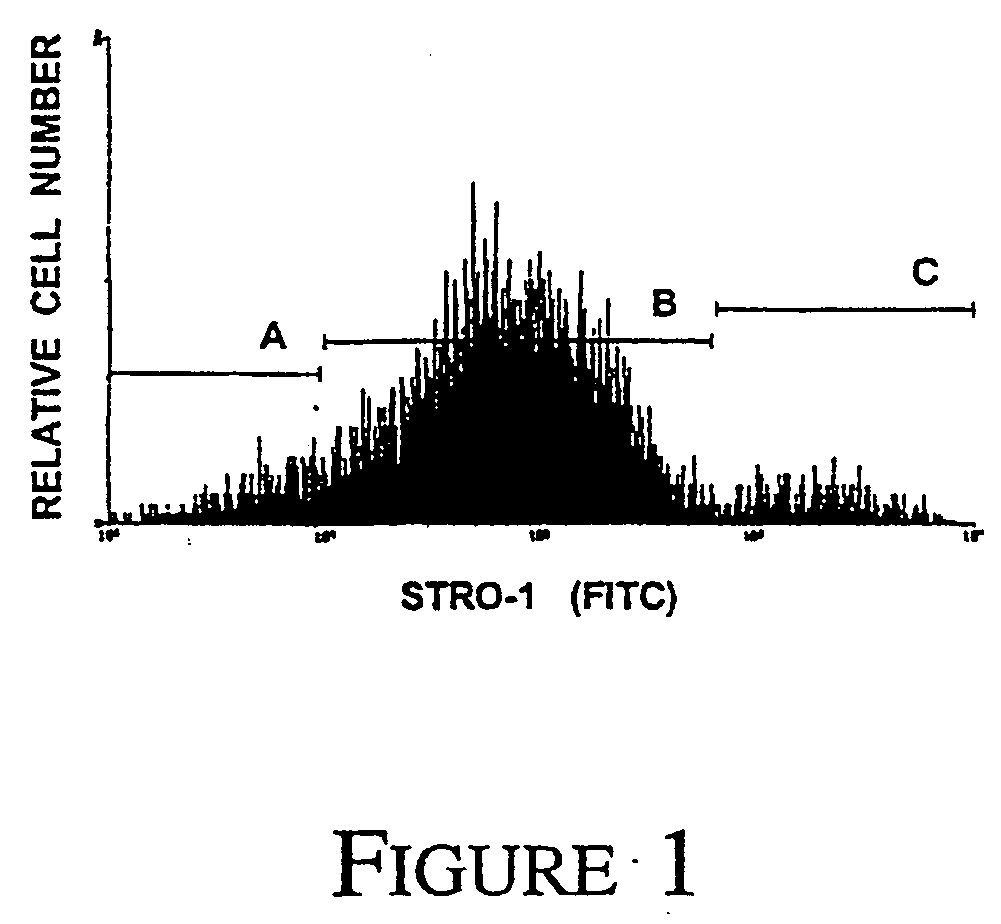
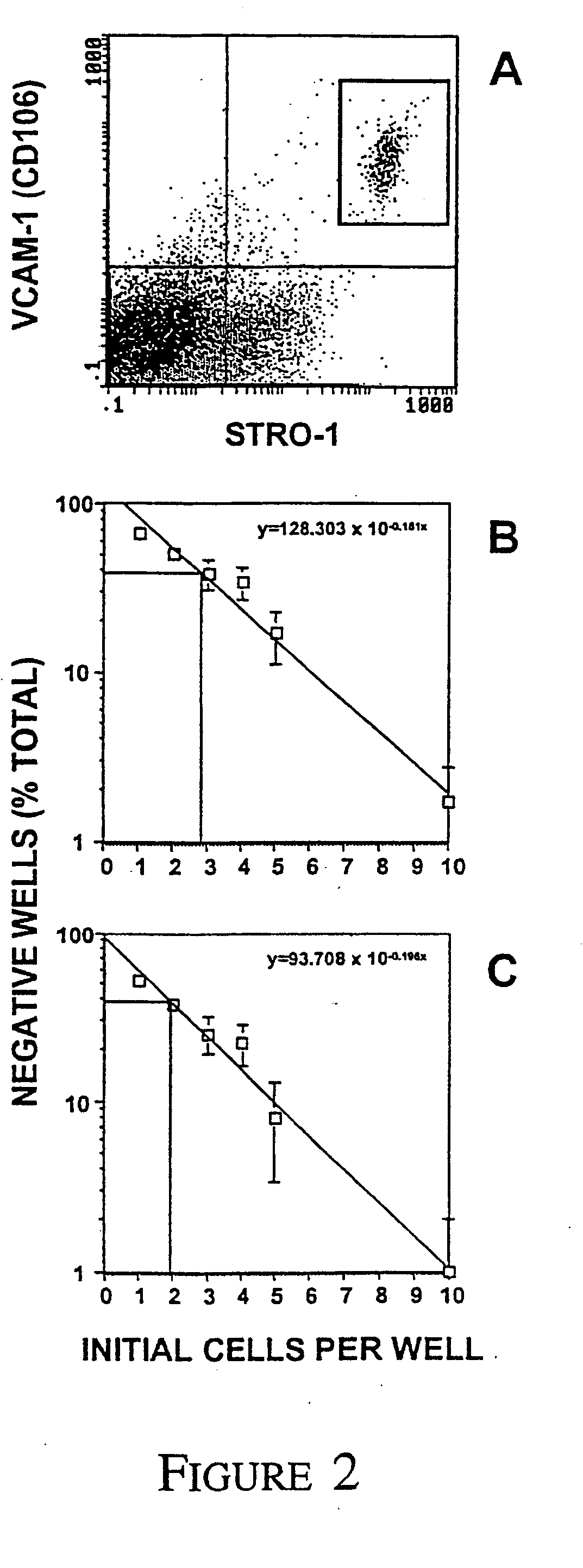
A method of enriching mesenchymal precursor cells including the step of enriching for cells based on at least two markers is provided, as well as enriched populations of mesenchymal precursor cells and compositions comprising the cells. The markers may be either i) the presence of markers specific for mesenchymal precursor cells, ii) the absence of markers specific for differentiated mesenchymal cells, or iii) expression levels of markers specific for mesenchymal precursor cells. The method may include a first solid phase sorting step utilizing MACS recognizing expression of the antigen to the STRO-1 Mab, followed by a second sorting step utilising two colour FACS to screen for the presence of high level STRO-1 antigen expression as well as the expression of VCAM-1.
Owner:MESOBLAST
Composite bone graft, method of making and using same
InactiveUS20050261767A1High mechanical strengthAvoid significant donor site morbidityBone implantJoint implantsDiseaseOssicular Prosthesis Implantation
The invention is directed to a composite bone graft for implantation in a patient, and methods of making and using the composite bone graft, along with methods for treating patients by implanting the composite bone graft at a site in a patient. The composite bone graft includes two or more connected, discrete, bone portions, and includes one or more biocompatible connectors which hold together the discrete bone portions to form the composite bone graft. The composite bone graft may include one or more textured bone surfaces. The textured surface preferably includes a plurality of closely spaced protrusions, preferably closely spaced continuous protrusions. The composite bone graft is useful for repairing bone defects caused by congenital anomaly, disease, or trauma, in a patient, for example, for restoring vertical support of the anterior and / or posterior column. Implantation of the composite bone graft results in improved graft stability and osteoinductivity, without a decrease in mechanical strength. The composite bone graft does not shift, extrude or rotate, after implantation. The present composite bone graft can be appropriately sized for any application and can be used to replace traditional non-bone prosthetic implants.
Owner:LIFENET HEALTH
Method of preparing a poorly crystalline calcium phosphate and methods of its use
InactiveUS7517539B1Readily injectableHigh strengthBiocideSurgical adhesivesOsteoporotic boneIntervertebral spaces
The present invention provides a novel process for producing a calcium phosphate cement or filler which hardens in a temperature dependent fashion in association with an endothermic reaction. In the reaction a limited amount of water is mixed with dry calcium phosphate precursors to produce a hydrated precursor paste. Hardening of the paste occurs rapidly at body temperature and is accompanied by the conversion of one or more of the reactants to poorly crystalline apatitic calcium phosphate. The hardened cements, fillers, growth matrices, orthopedic and delivery devices of the invention are rapidly resorbable and stimulate hard tissue growth and healing. A composite material is provided including a strongly bioresorbable, poorly crystalline apatitic calcium phosphate composite and a supplementary material. The supplementary material is in intimate contact with the hydroxyapatite material in an amount effective to impart a selected characteristic to the composite. The supplemental material may be biocompatible, bioresorbable or non-resorbable. A method for treating a bone defect also is provided by identifying a bone site suitable for receiving an implant, and introducing a strongly resorbable, poorly crystalline apatitic calcium phosphate at the implant site, whereby bone is formed at the implant site. The implant site may be a variety of sites, such as a tooth socket, non-union bone, bone prosthesis, an osteoporotic bone, an intervertebral space, an alveolar ridge or a bone fracture.
Owner:LIFE SCI ENTERPRISES
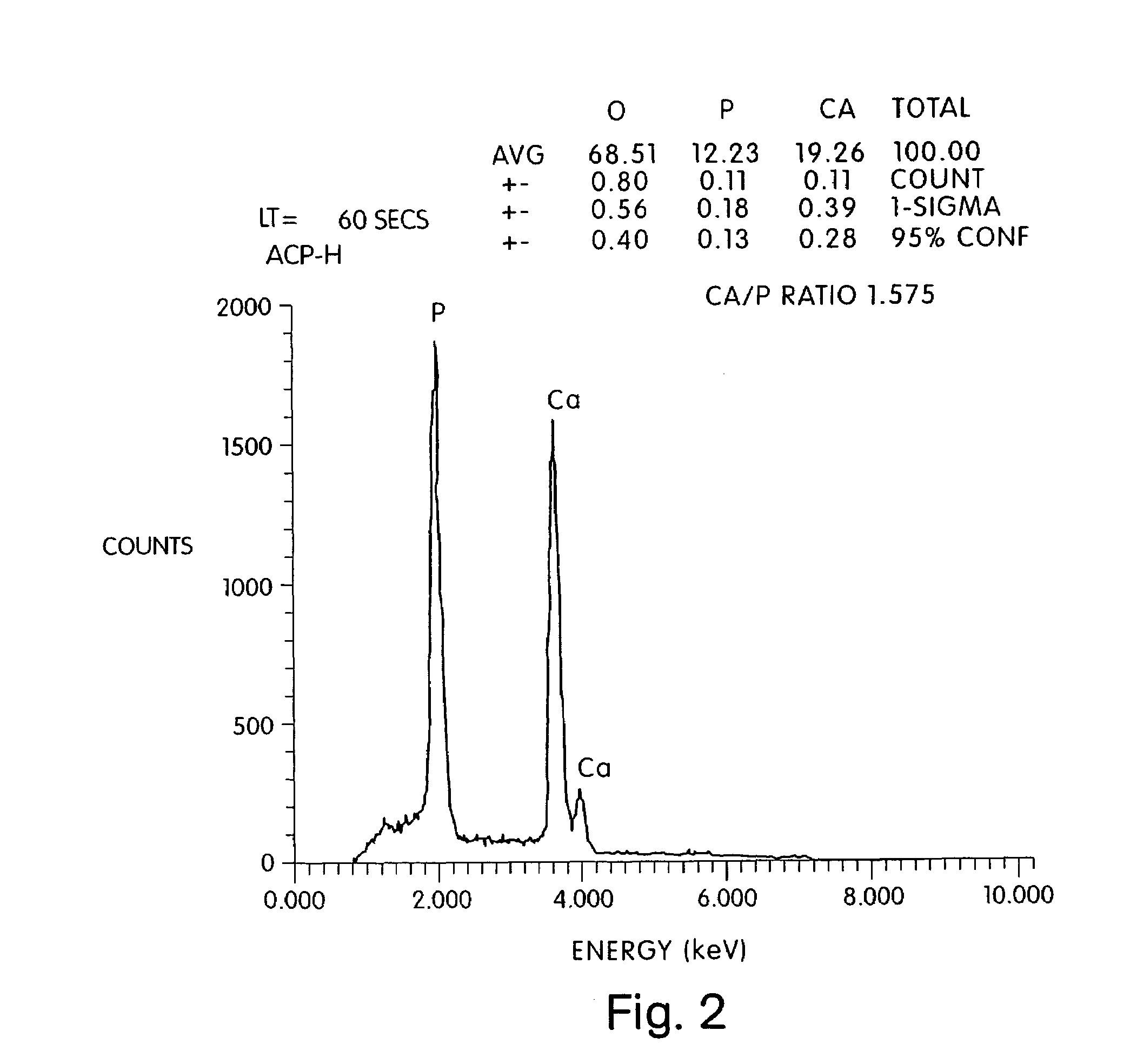
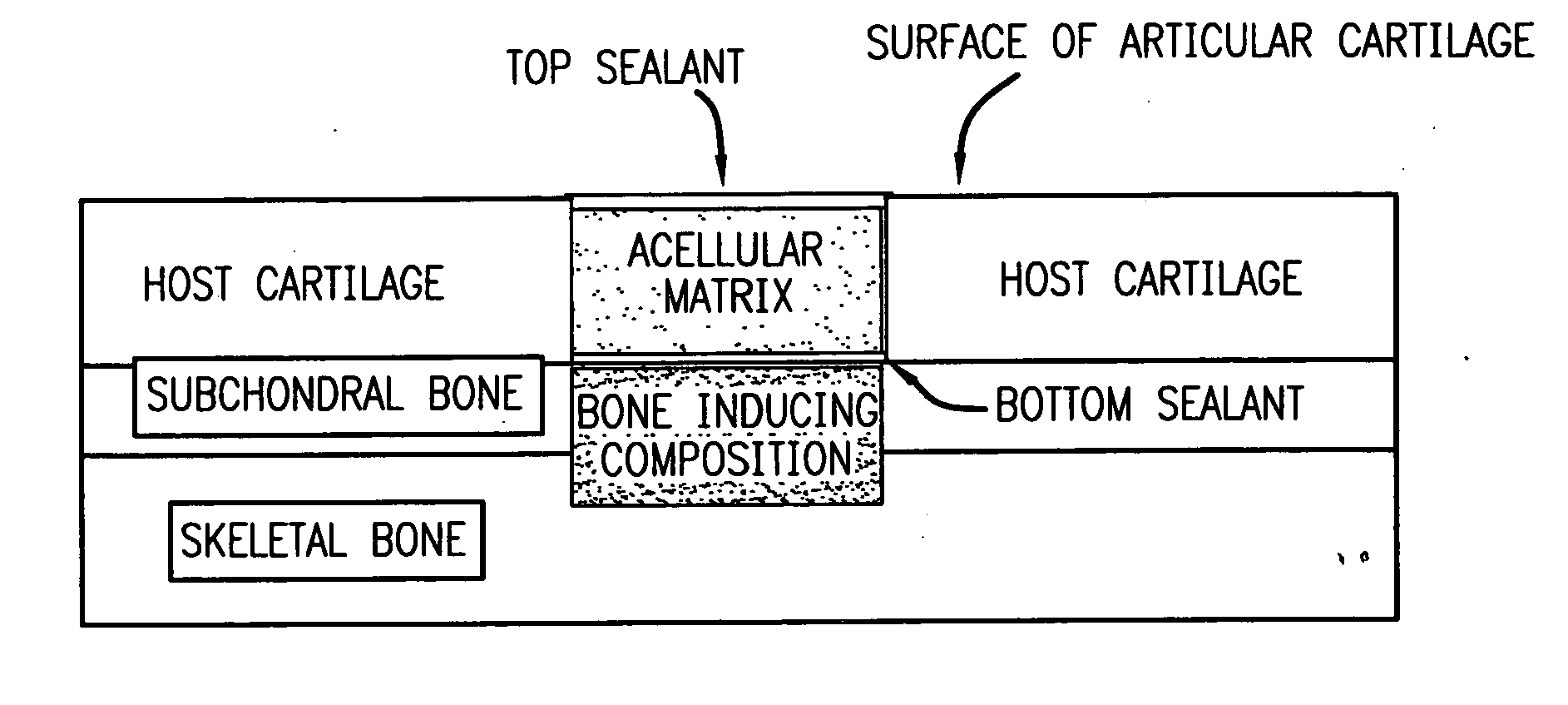
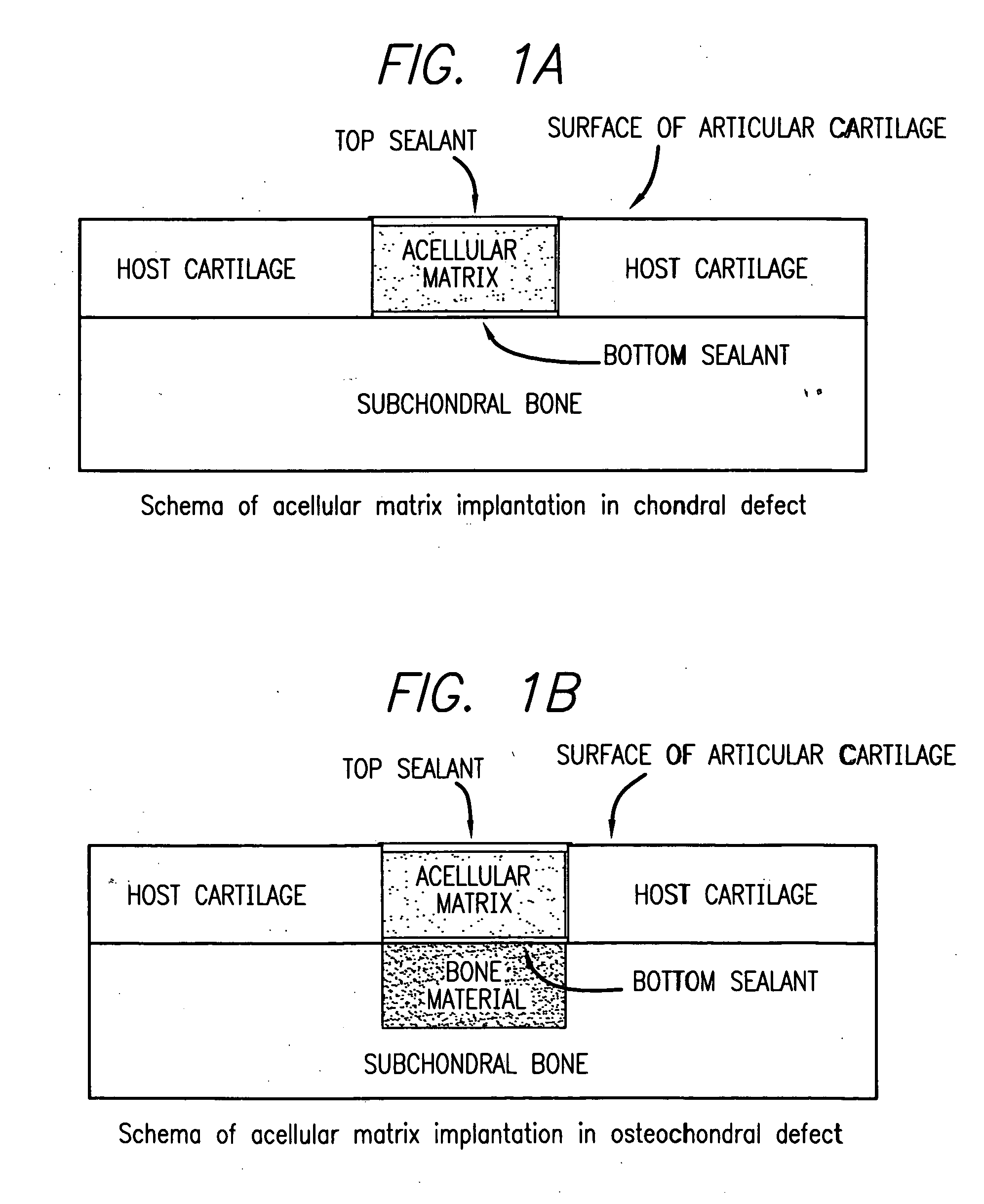
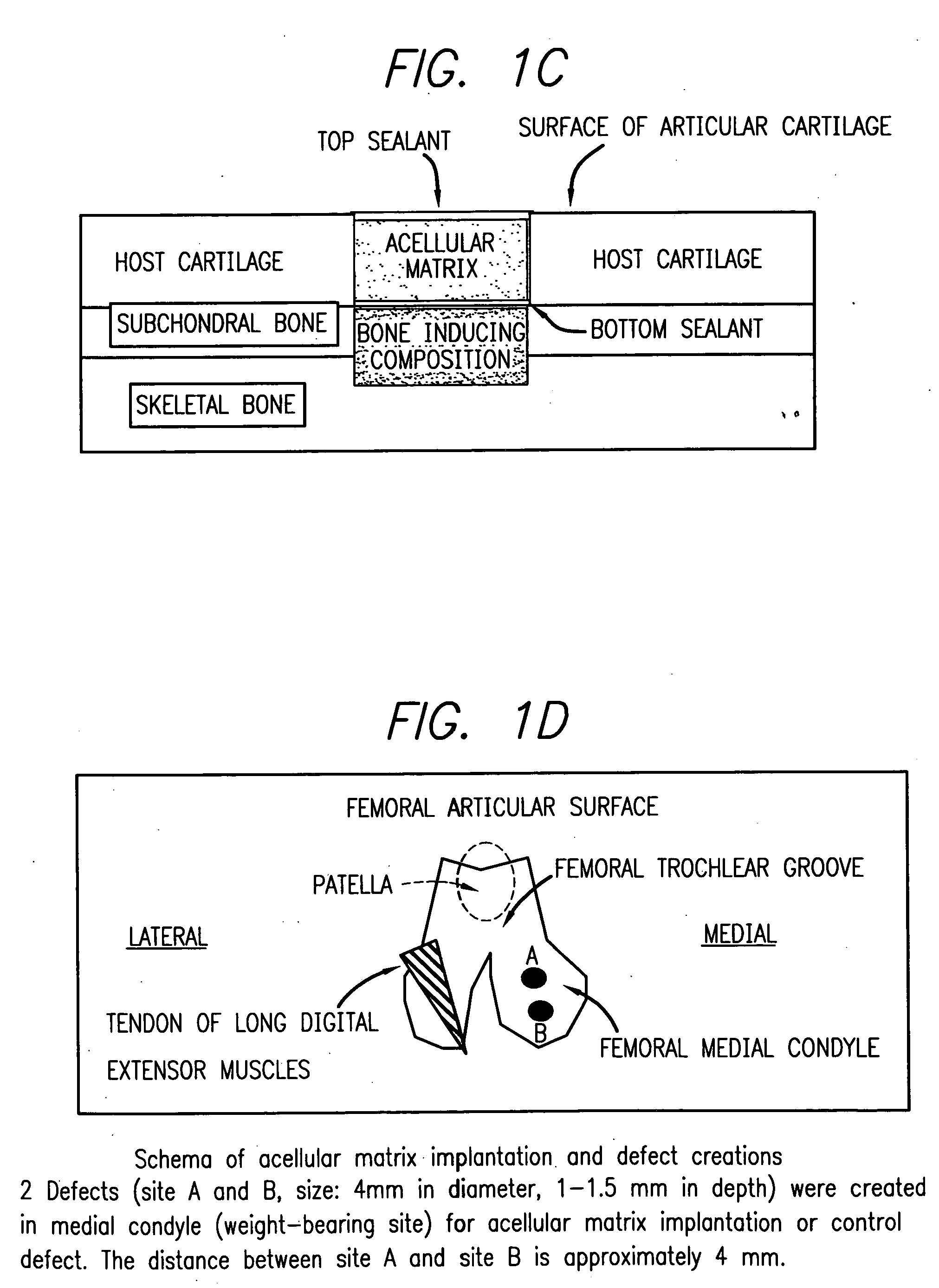
Acellular matrix implants for treatment of articular cartilage, bone or osteochondral defects and injuries and method for use thereof
ActiveUS20050043813A1Provide protectionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAcellular matrixMedicine
An acellular matrix implant for treatment of defects and injuries of articular cartilage, bone or osteochondral bone and a method for treatment of injured, damaged, diseased or aged articular cartilage or bone, using the acellular matrix implant implanted into a joint cartilage lesion in situ and a bone-inducing composition implanted into an osteochondral or bone defect. A method for repair and restoration of the injured, damaged, diseased or aged cartilage or bone into its full functionality by implanting the acellular matrix implant between two layers of biologically acceptable sealants and / or the bone-inducing composition into the osteochondral bone or skeletal bone defect. A method for fabrication of the acellular matrix implant of the invention. A method for preparation of bone-inducing composition.
Owner:PURPOSE CO LTD +1
EP4 receptor selective agonists in the treatment of osteoporosis
Owner:PFIZER INC
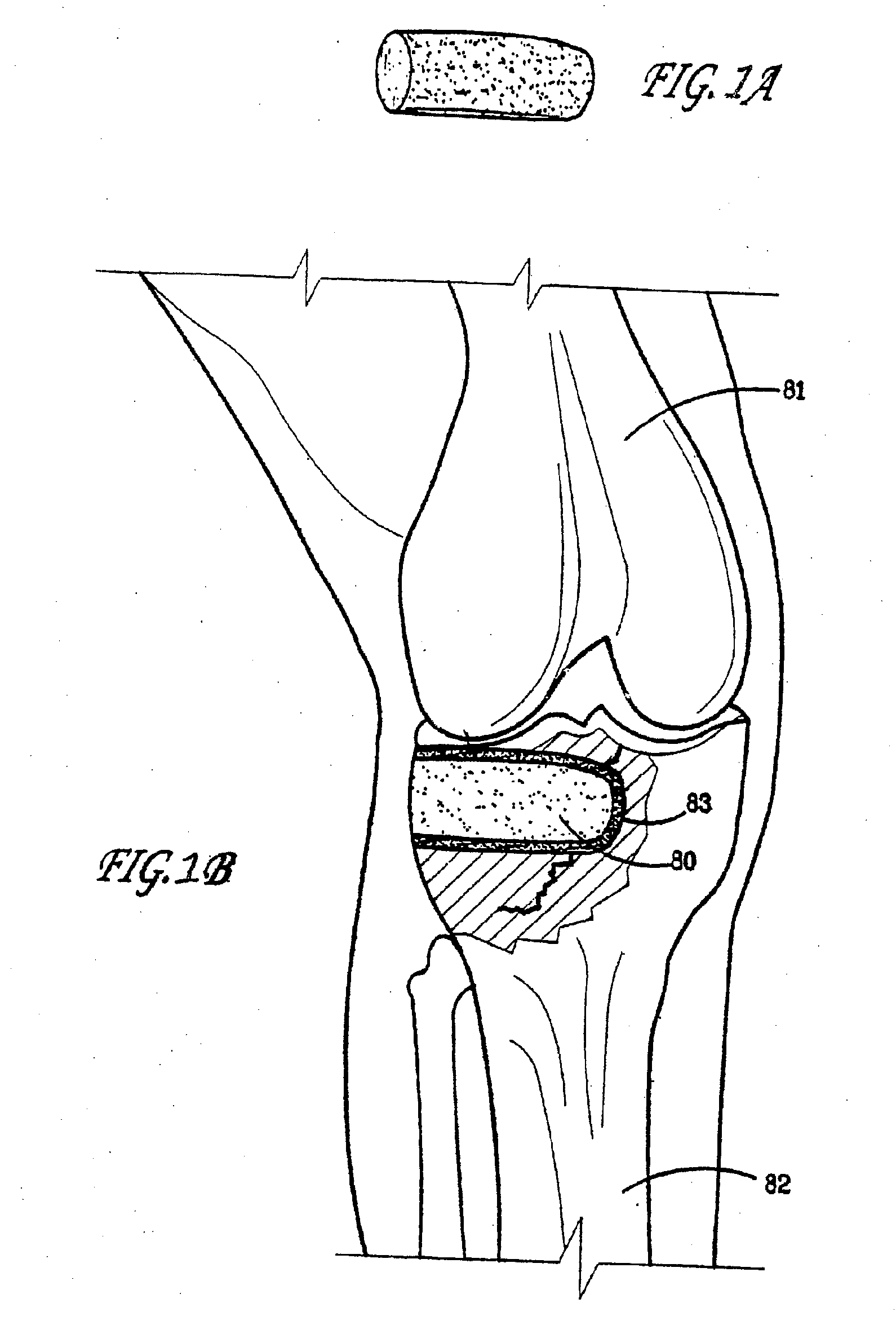
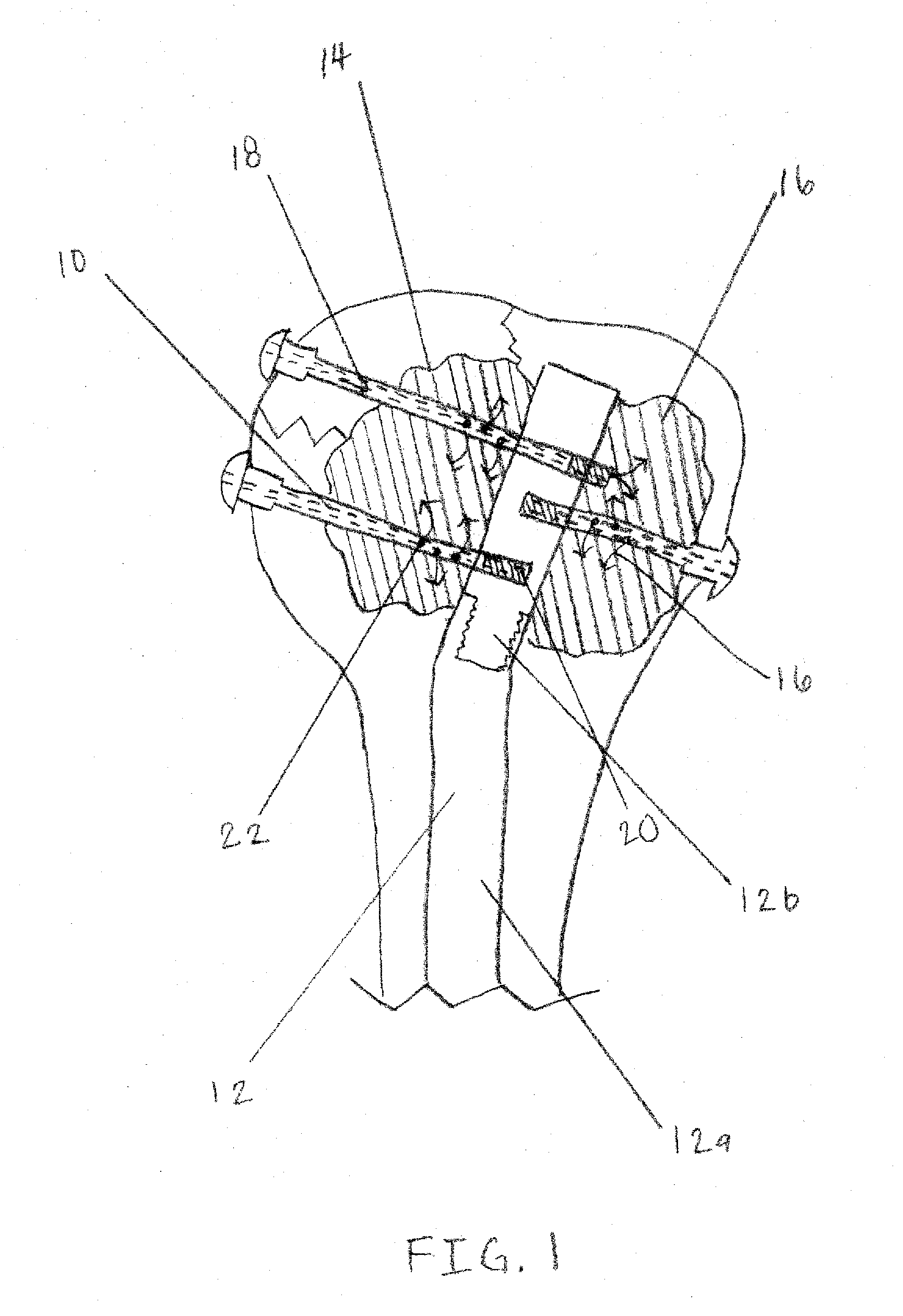
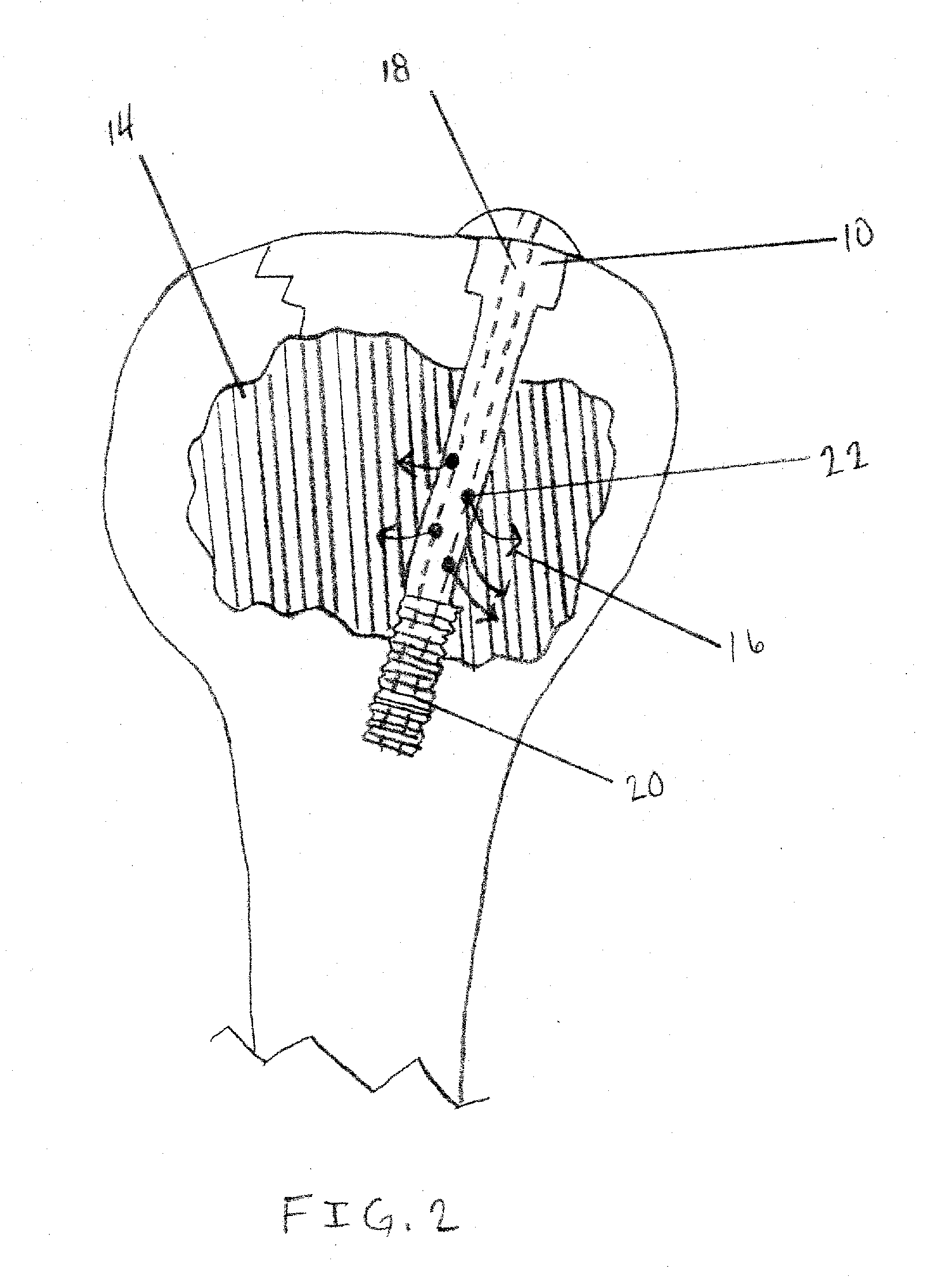
Apparatus and Methods of Repairing Bone Defects
InactiveUS20090157078A1Fixed securityFortifying the structural integrity of the boneInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBody of femurBone defect
An apparatus and method for repairing osseous defects in such bones as the humerus, femur, ulna and long bones. A first embodiment presents one or more cannulated screws affixed to an intramedullary nail, which is installed in a humerus having an intraosseous void. In a second embodiment, one or more cannulated screws alone are inserted into a proximal humerus having an intraosseous void. Other embodiments teach one or more cannulated screws inserted into a damaged femur and attached to a plate or medullary rod. Another embodiment presents a number of cannulated screws used to attach a plate to a fractured long bone. In a final embodiment, a cannulated screw is installed in damaged ulna. In all embodiments, a bioresorbable or non-bioresorbable cement is injected into a hollow channel of the cannulated screw and extruded into the bone to stabilize the weakened bone and secure the position of a fixation device.
Owner:MIKOL EDWARD J
Bone screws and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS8574273B2Prevent escapeFaster advanceSuture equipmentsDental implantsBone defectScrew thread
The invention features bone screws having a threaded screw body and a screw head attached to one end of the screw body, the bone screw further including: a) an interior channel extending longitudinally through the screw head and through at least a portion of the screw body, wherein the interior channel has a width of less than 5.0 millimeters; and b) a plurality of radially-disposed delivery channels connecting the interior channel to the exterior of the screw body, each delivery channel having exterior openings. The invention further features devices that include a bone screw and a delivery manifold detachably attached to the screw head of the bone screw. In addition, the invention features methods of treating a patient having a bone defect by using a bone screw described herein.
Owner:INNOVISION CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com