Patents
Literature
431 results about "Porous sheet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
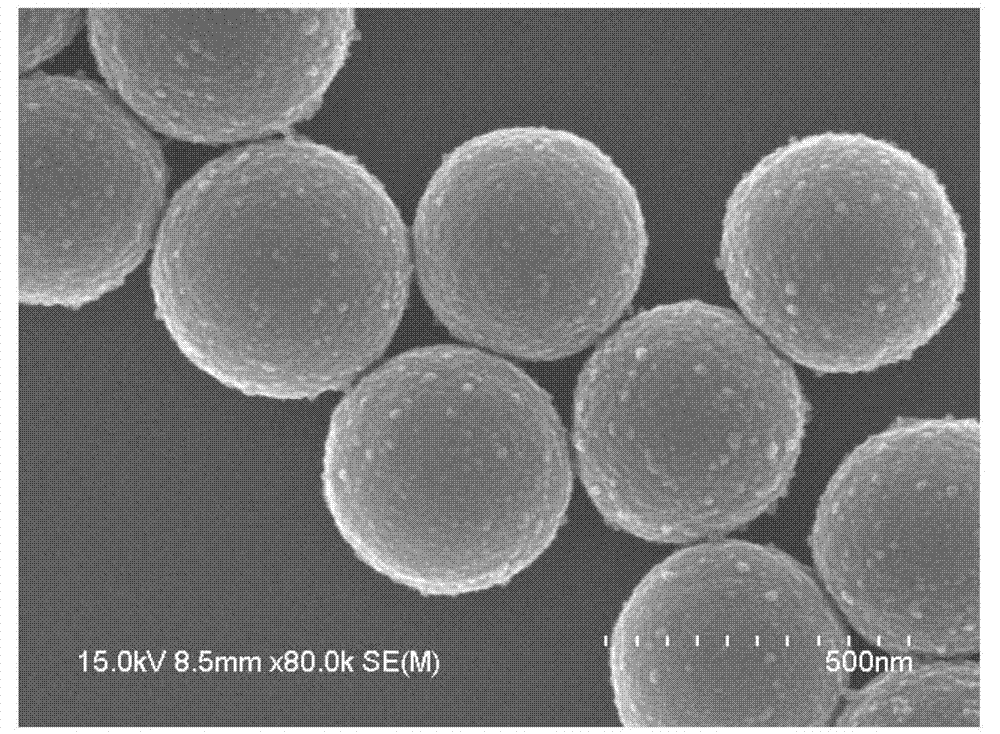
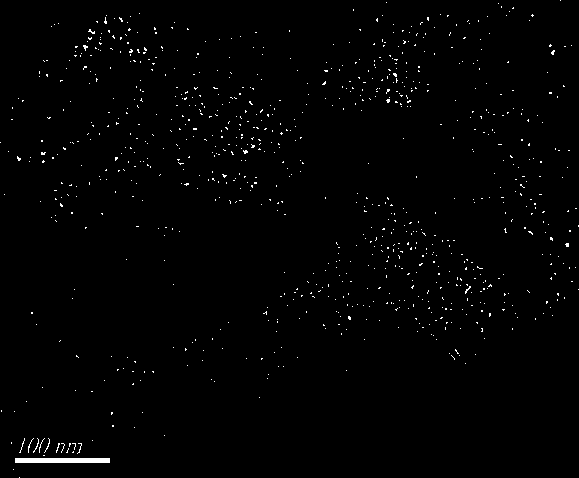
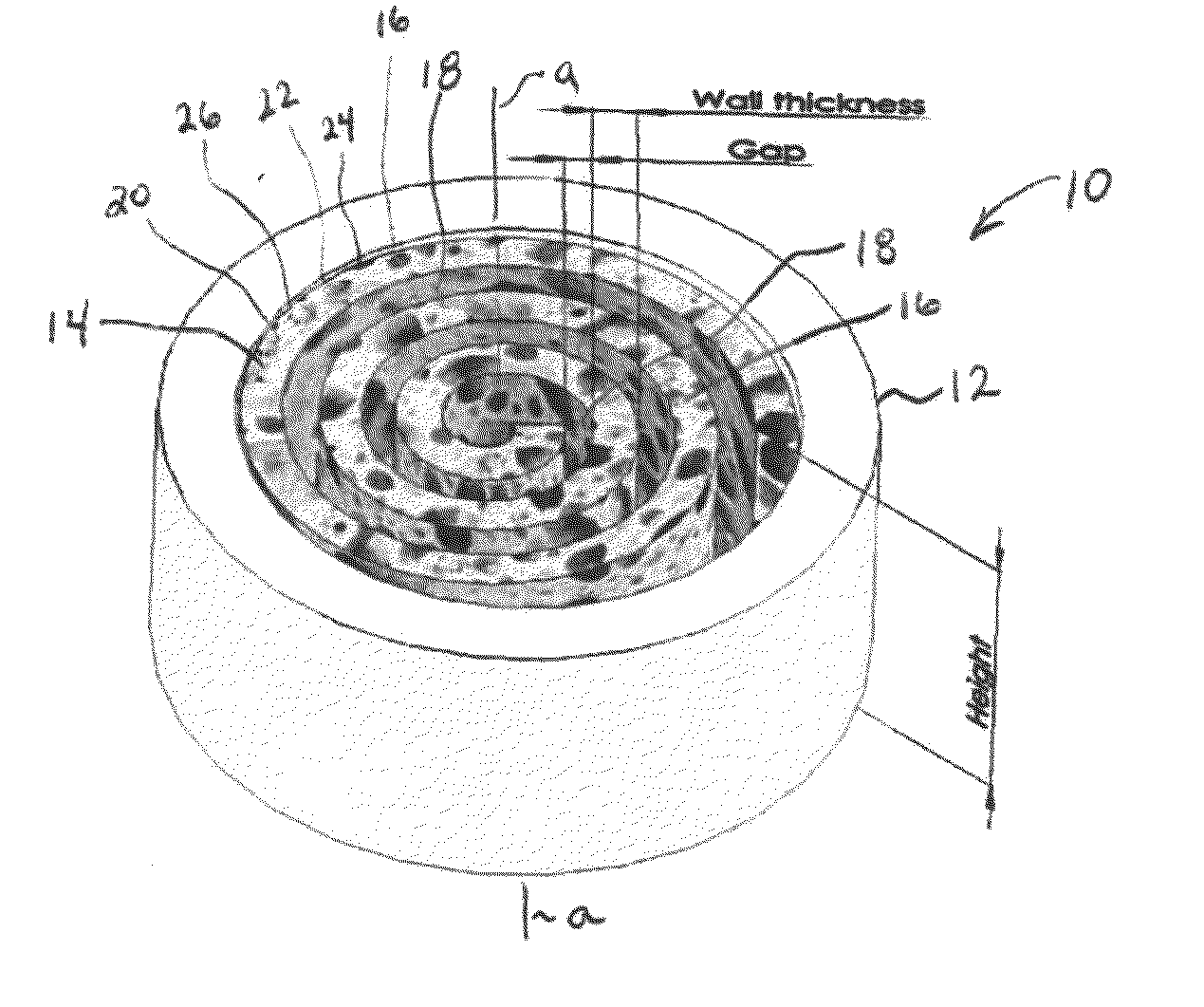
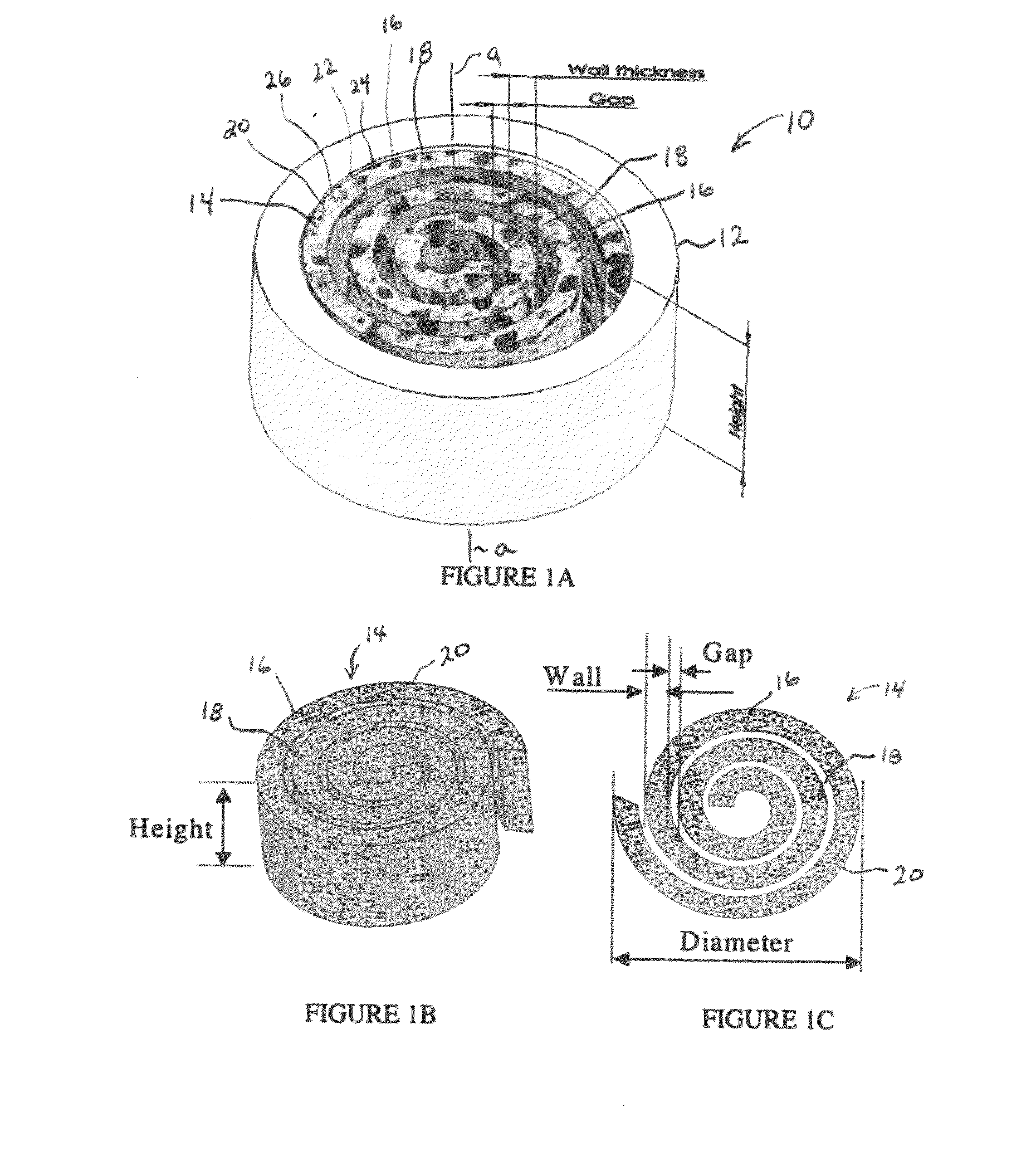
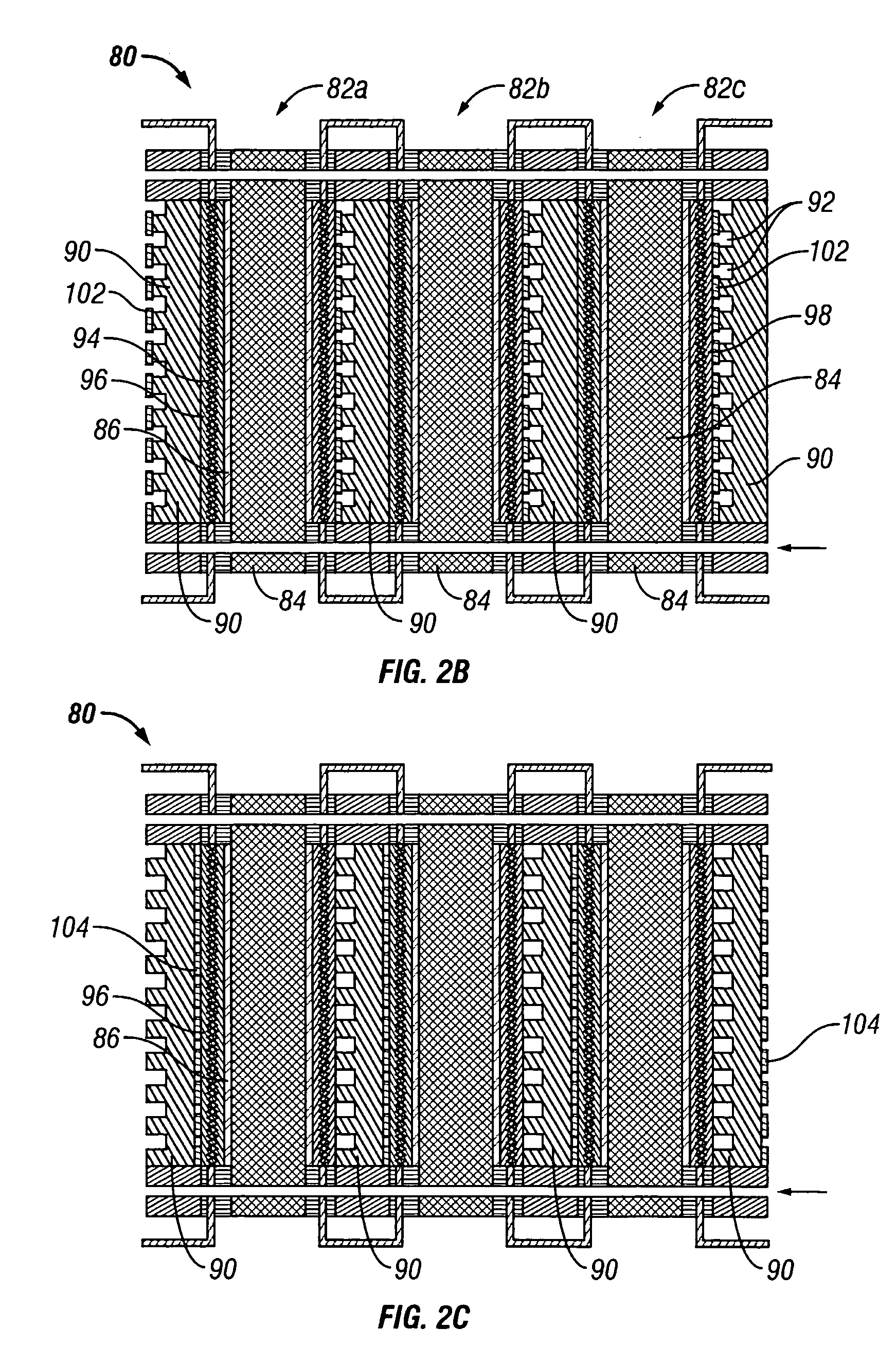
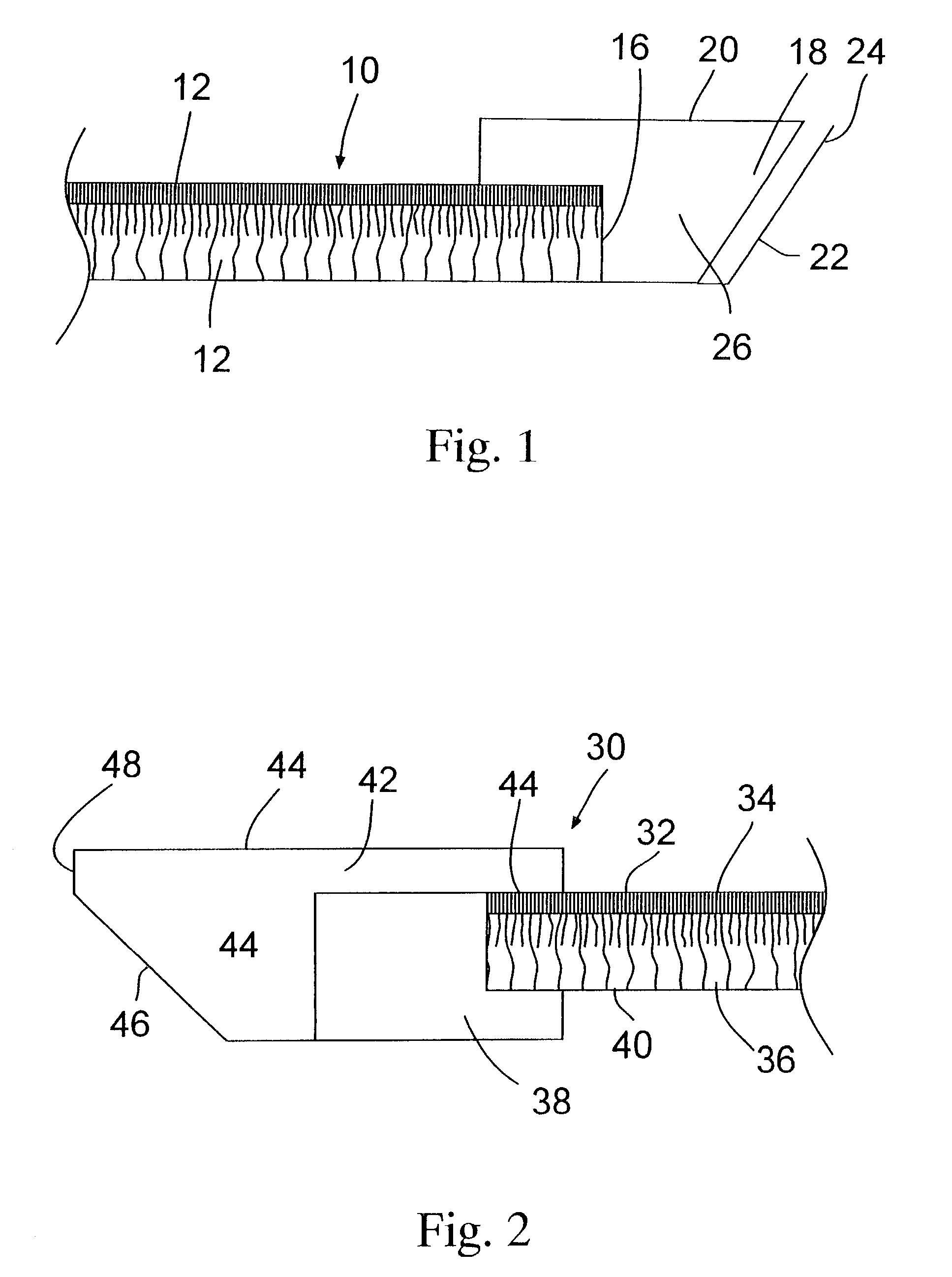
Synergetic functionalized spiral-in-tubular bone scaffolds
InactiveUS20100310623A1Increase the number ofIncrease alkaline phosphatase activityPeptide/protein ingredientsBone implantPorous sheetCell seeding
An integrated scaffold for bone tissue engineering has a tubular outer shell and a spiral scaffold made of a porous sheet. The spiral scaffold is formed such that the porous sheet defines a series of spiral coils with gaps of controlled width between the coils to provide an open geometry for enhanced cell growth. The spiral scaffold resides within the bore of the shell and is integrated with the shell to fix the geometry of the spiral scaffold. Nanofibers may be deposited on the porous sheet to enhance cell penetration into the spiral scaffold. The spiral scaffold may have alternating layers of polymer and ceramic on the porous sheet that have been built up using a layer-by-layer method. The spiral scaffold may be seeded with cells by growing a cell sheet and placing the cell sheet on the porous sheet before it is rolled.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Bone and tissue scaffolding and method for producing same
InactiveUS20050100578A1Improves orthopedic implant performanceLow costBiocideBone implantPorous sheetMaterials science
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
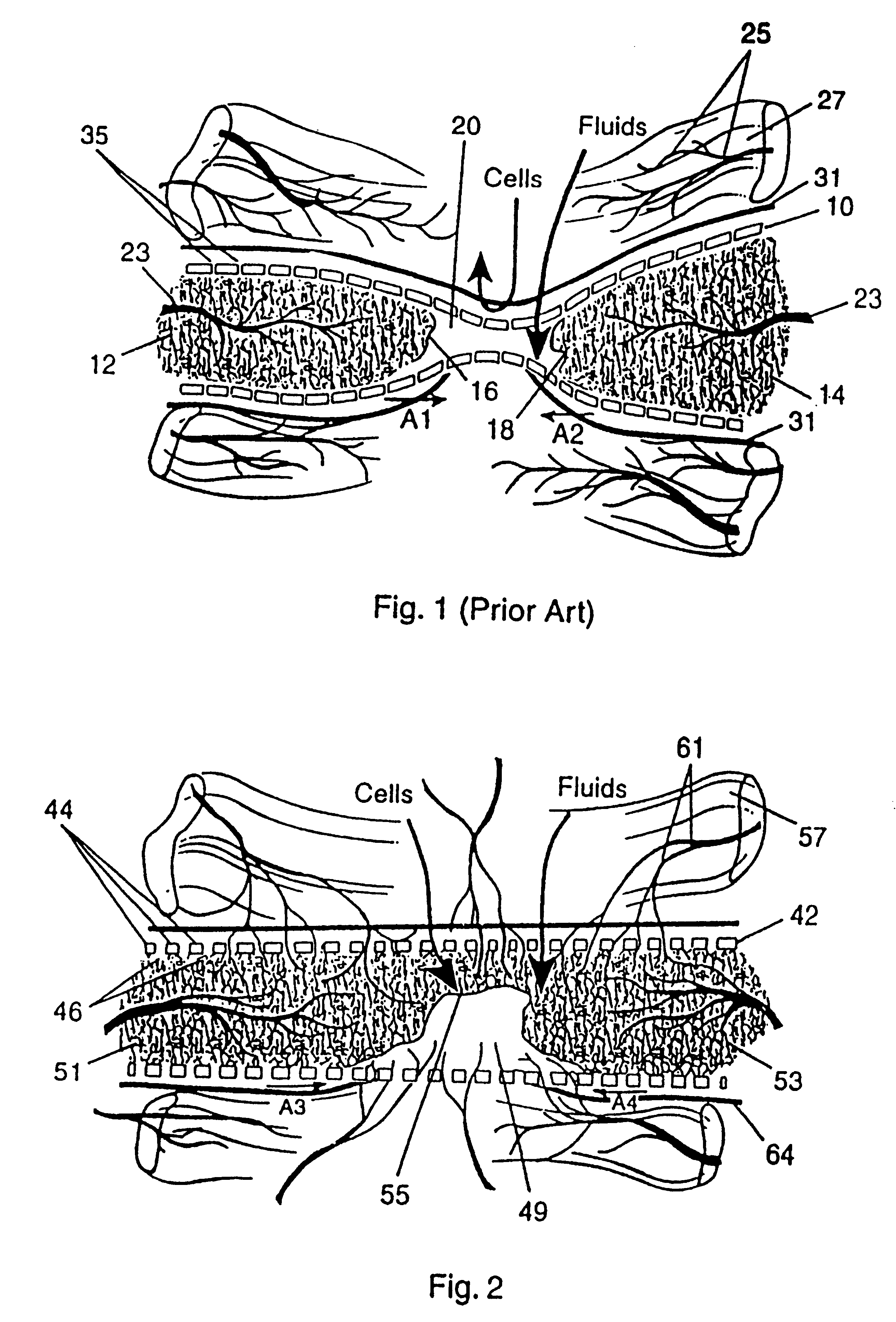
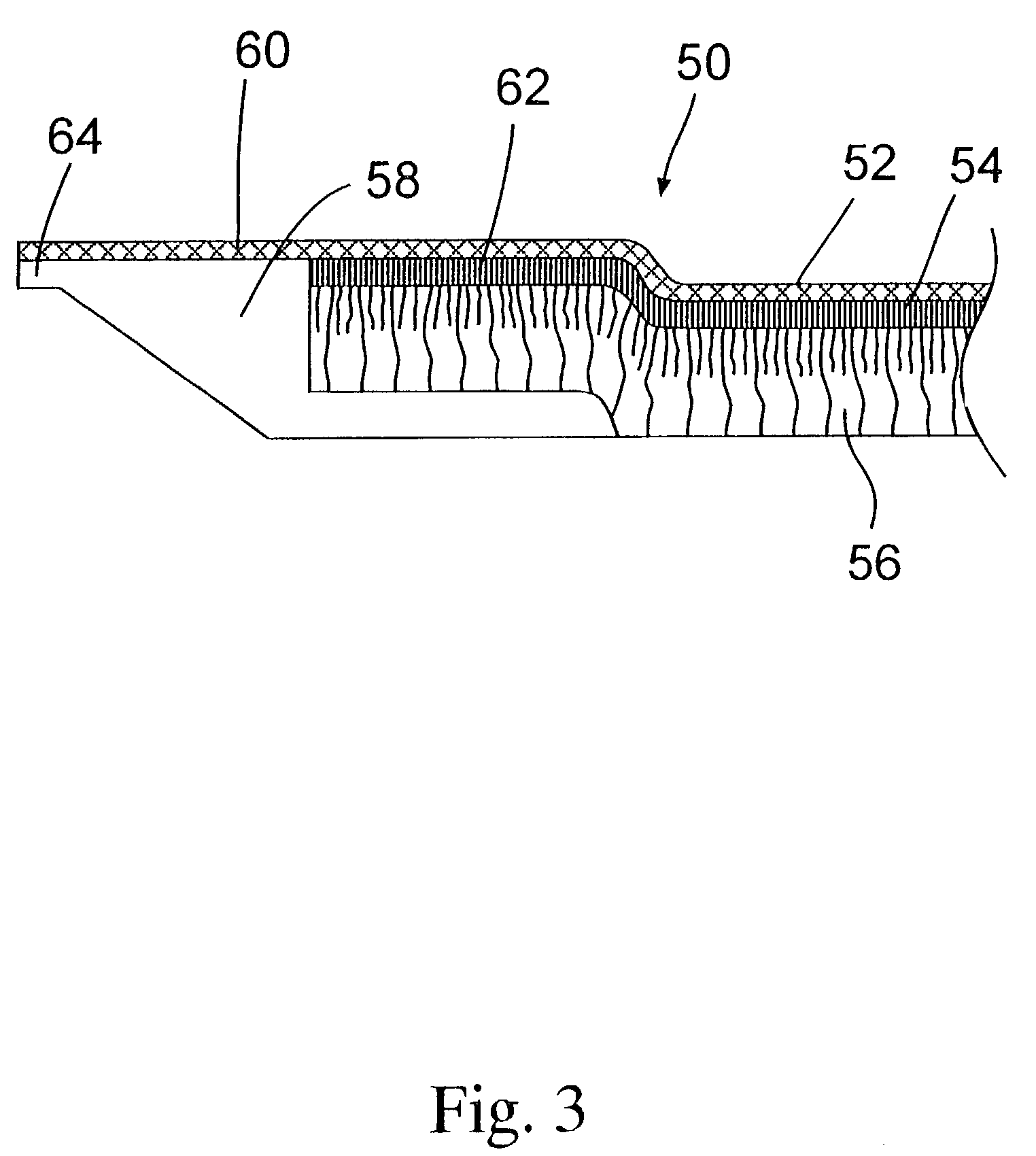
Resorbable, macro-porous, non-collapsing and flexible membrane barrier for skeletal repair and regeneration
A resorbable, flexible implant in the form of a continuous macro-porous sheet is disclosed. The implant is adapted to protect biological tissue defects, especially bone defects in the mammalian skeletal system, from the interposition of adjacent soft tissues during in vivo repair. The membrane has pores with diameters from 20 microns to 3000 microns. This porosity is such that vasculature and connective tissue cells derived from the adjacent soft tissues including the periosteum can proliferate through the membrane into the bone defect. The thickness of the sheet is such that the sheet has both sufficient flexibility to allow the sheet to be shaped to conform to the configuration of a skeletal region to be repaired, and sufficient tensile strength to allow the sheet to be so shaped without damage to the sheet. The sheet provides enough inherent mechanical strength to withstand pressure from adjacent musculature and does not collapse.
Owner:MACROPORE
Particle-containing fibrous web
InactiveUS20060096911A1Lower overall pressure dropLow carbon shedding tendencyBreathing filtersDispersed particle separationPolymer scienceSorbent
A porous sheet article comprising a self-supporting nonwoven web of polymeric fibers and at least 80 weight percent sorbent particles enmeshed in the web, the fibers having sufficiently greater elasticity or sufficiently greater crystallization shrinkage than similar caliper polypropylene fibers and the sorbent particles being sufficiently evenly distributed in the web so that the web has an Adsorption Factor A of at least 1.6×104 / mm water. The articles have low pressure drop and can provide filter elements having long service life and an Adsorption Factor approaching and in some instances exceeding that of a packed carbon bed.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
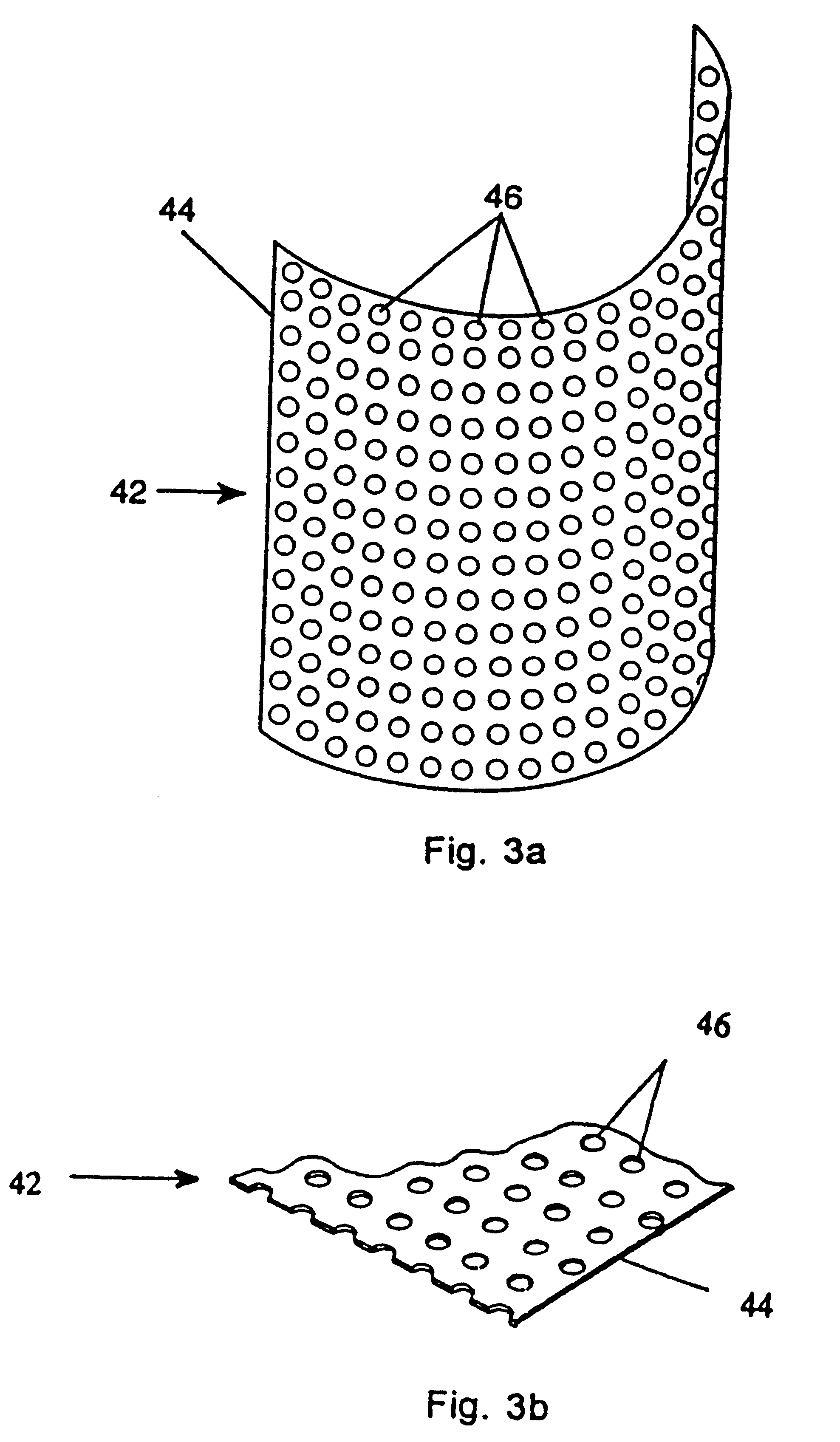
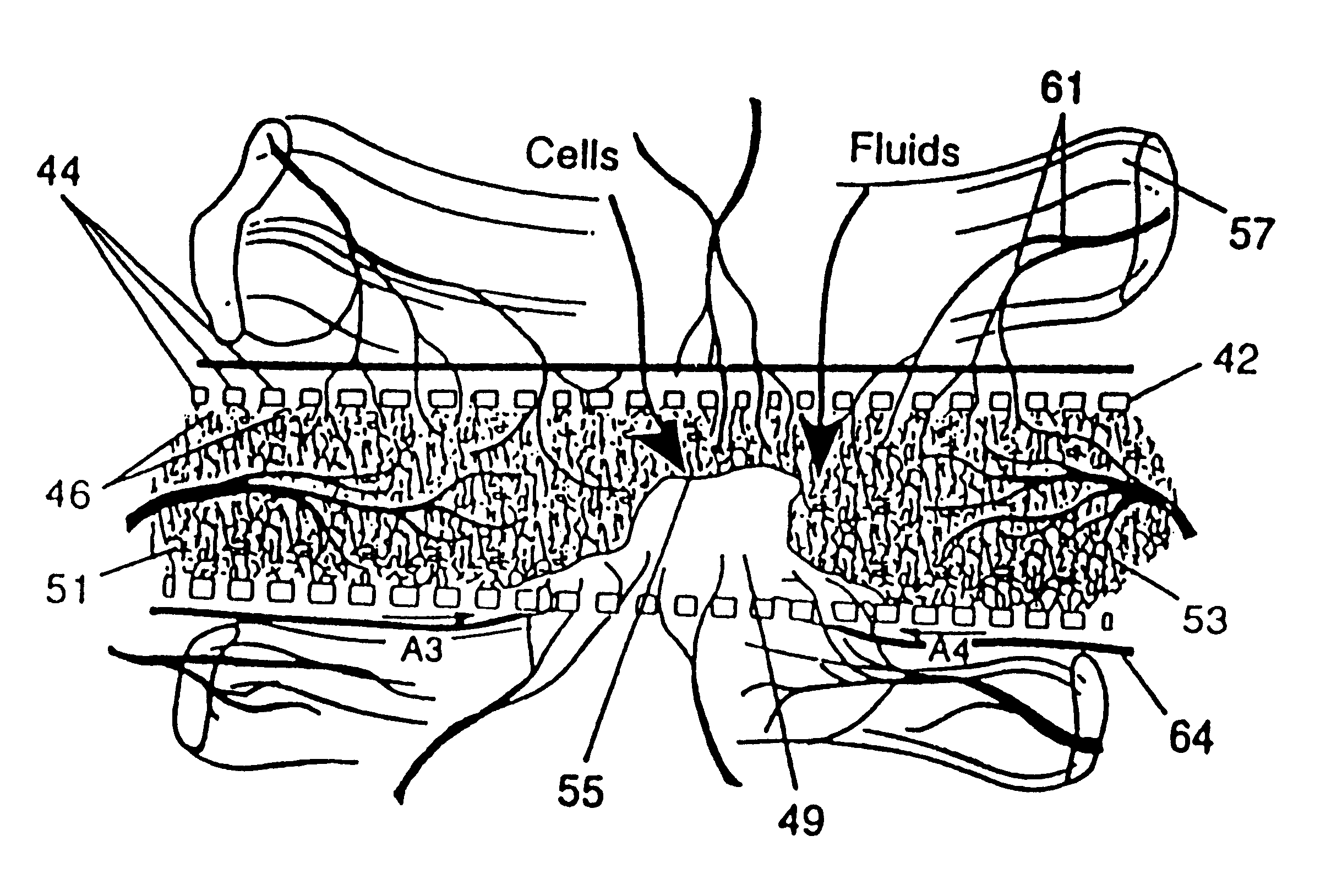
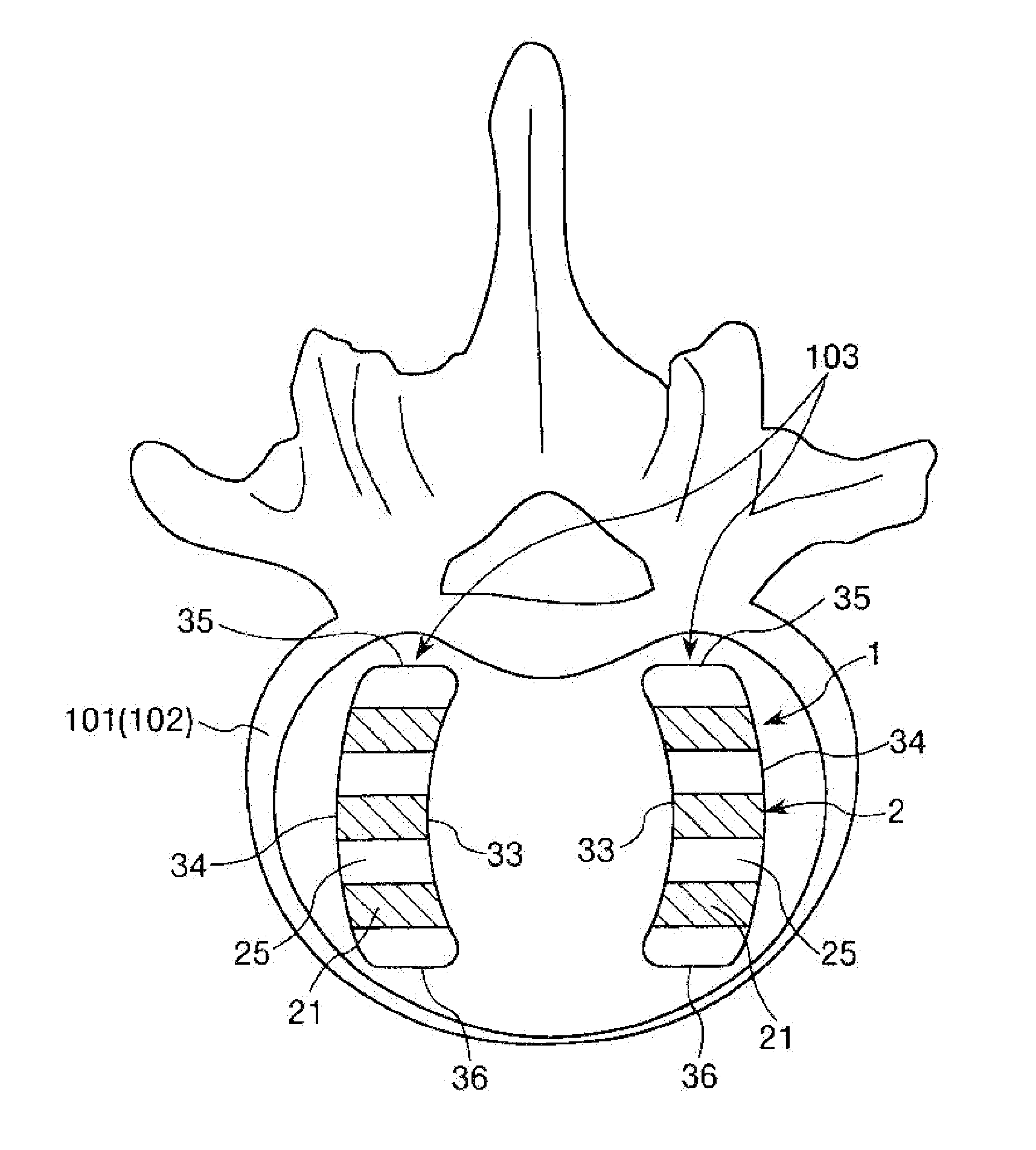
Membrane with tissue-guiding surface corrugations
A resorbing, flexible implant in the form of a continuous macro-porous sheet (42) is disclosed. The implant is adapted to protect biological tissue defects, especially bone defects in the mammalian skeletal system, from the interposition of adjacent soft tissues during in vitro repair. The membrane (42) has pores with diameters from 20 microns to 3000 microns. This porosity is such that vasculature, and connective tissue cells derived from the adjacent soft tissues including the periosteum, can proliferate through the membrane into the bone defect. The thickness of the sheet is such that the sheet has both sufficient flexibility to allow the sheet to be shaped to conform to the configuration of a skeletal region to be repaired, and sufficient tensile strength to allow the sheet to be so shaped without damage to the sheet. The sheet provides enough inherent mechanical strength to withstand pressure from adjacent musculature, and does not collapse.
Owner:MACROPORE
Resorbable, macro-porous non-collapsing and flexible membrane barrier for skeletal repair and regeneration
A resorbable, flexible implant in the form of a continuous macro-porous sheet is disclosed. The implant is adapted to protect biological tissue defects, especially bone defects in the mammalian skeletal system, from the interposition of adjacent soft tissues during in vivo repair. The membrane has pores with diameters from 20 microns to 3000 microns. This porosity is such that vasculature and connective tissue cells derived from the adjacent soft tissues including the periosteum can proliferate through the membrane into the bone defect. The thickness of the sheet is such that the sheet has both sufficient flexibility to allow the sheet to be shaped to conform to the configuration of a skeletal region to be repaired, and sufficient tensile strength to allow the sheet to be so shaped without damage to the sheet. The sheet provides enough inherent mechanical strength to withstand pressure from adjacent musculature and does not collapse.
Owner:MACROPORE BIOSURGERY INC
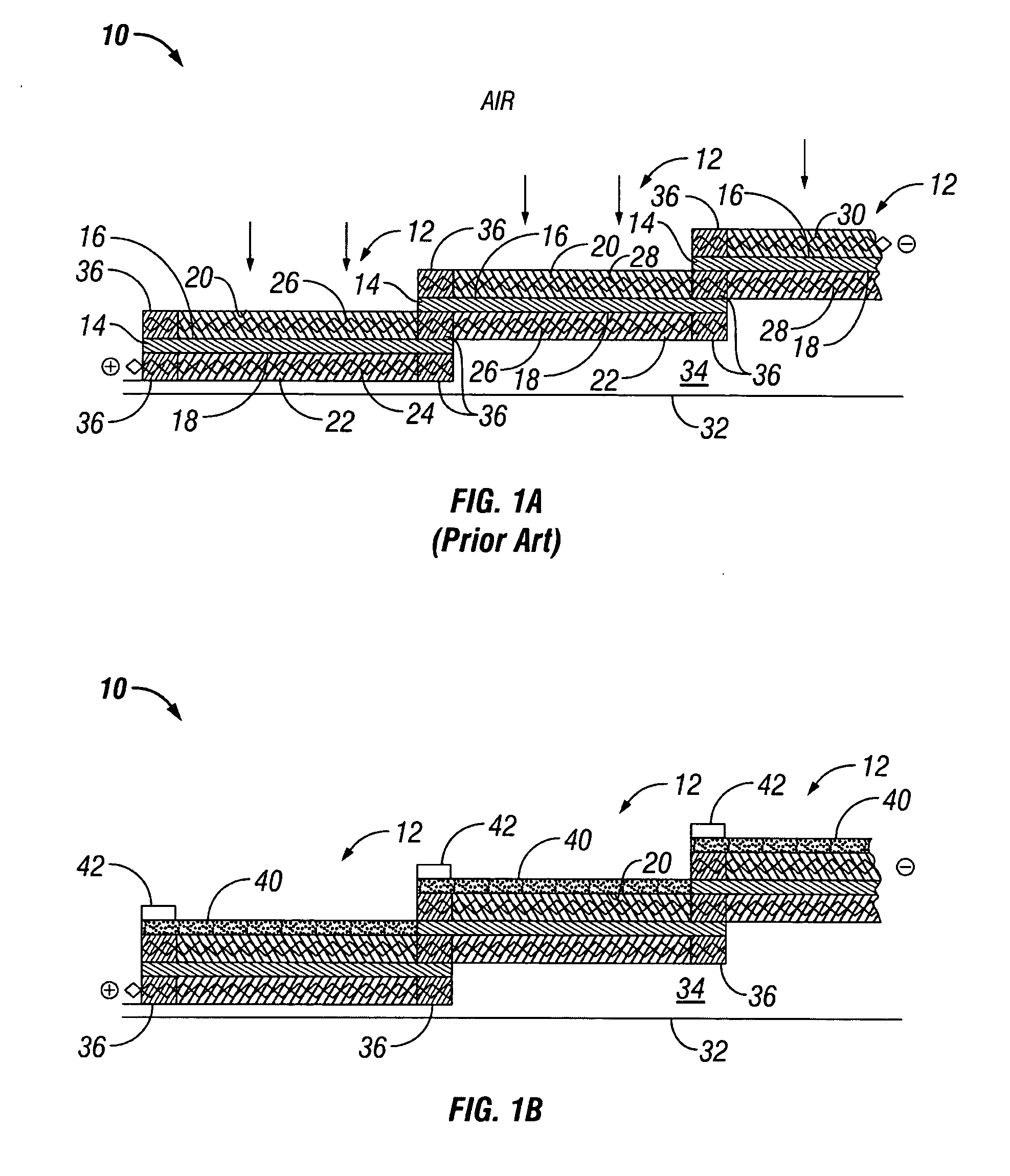
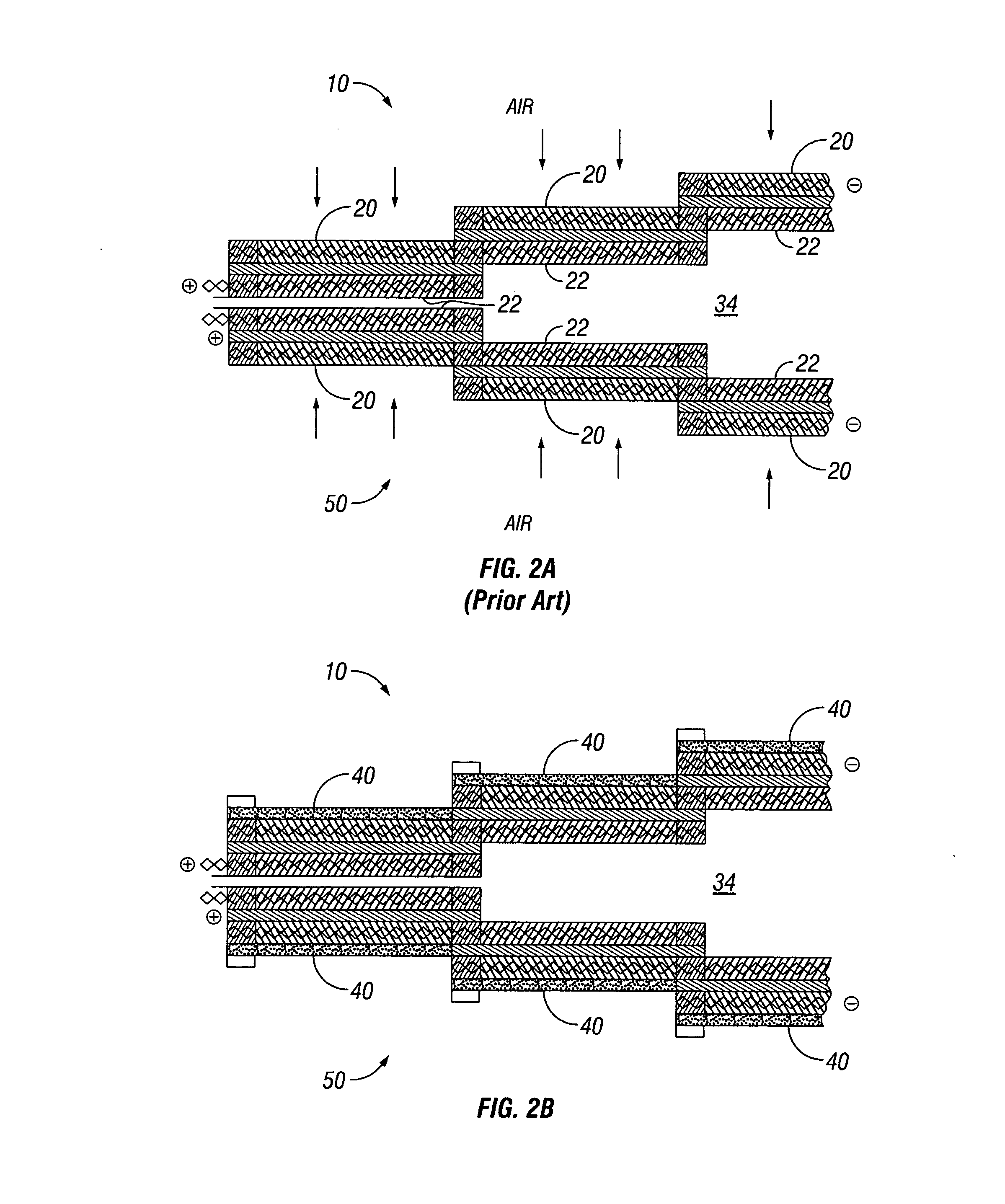
Water management in bipolar electrochemical cell stacks
InactiveUS20060199061A1Reduce probabilityPromote loss of waterFuel cells groupingWater management in fuel cellsPolymer electrolytesLiquid water
A bipolar, filter press-like electrochemical cell stack comprising a plurality of electrochemical cells, where each electrochemical cell is supplied with a gaseous anodic reactant and either supplied with a gaseous cathodic reactant or produces a gaseous cathodic product, and where each electrochemical cell avoids drying out the ion exchange membrane polymer electrolyte, avoids flooding at the cathode, facilitates recovery of liquid water at the anode, and reduces water losses from at least one of the electrodes. A water retention barrier is variously positioned, such as between a gas diffusion electrode and a fluid flow field. The barrier may be either: (i) a thin, gas permeable, liquid water impermeable membrane; (ii) a thin, porous sheet of material; or (iii) a thin, substantially solid sheet of material except for a plurality of small through-holes that penetrate from one side of the sheet to an opposing side of the same sheet. The barrier is advantageously used at the cathode and facilitates air cooling of the cell.
Owner:LYNNTECH
Potty training device
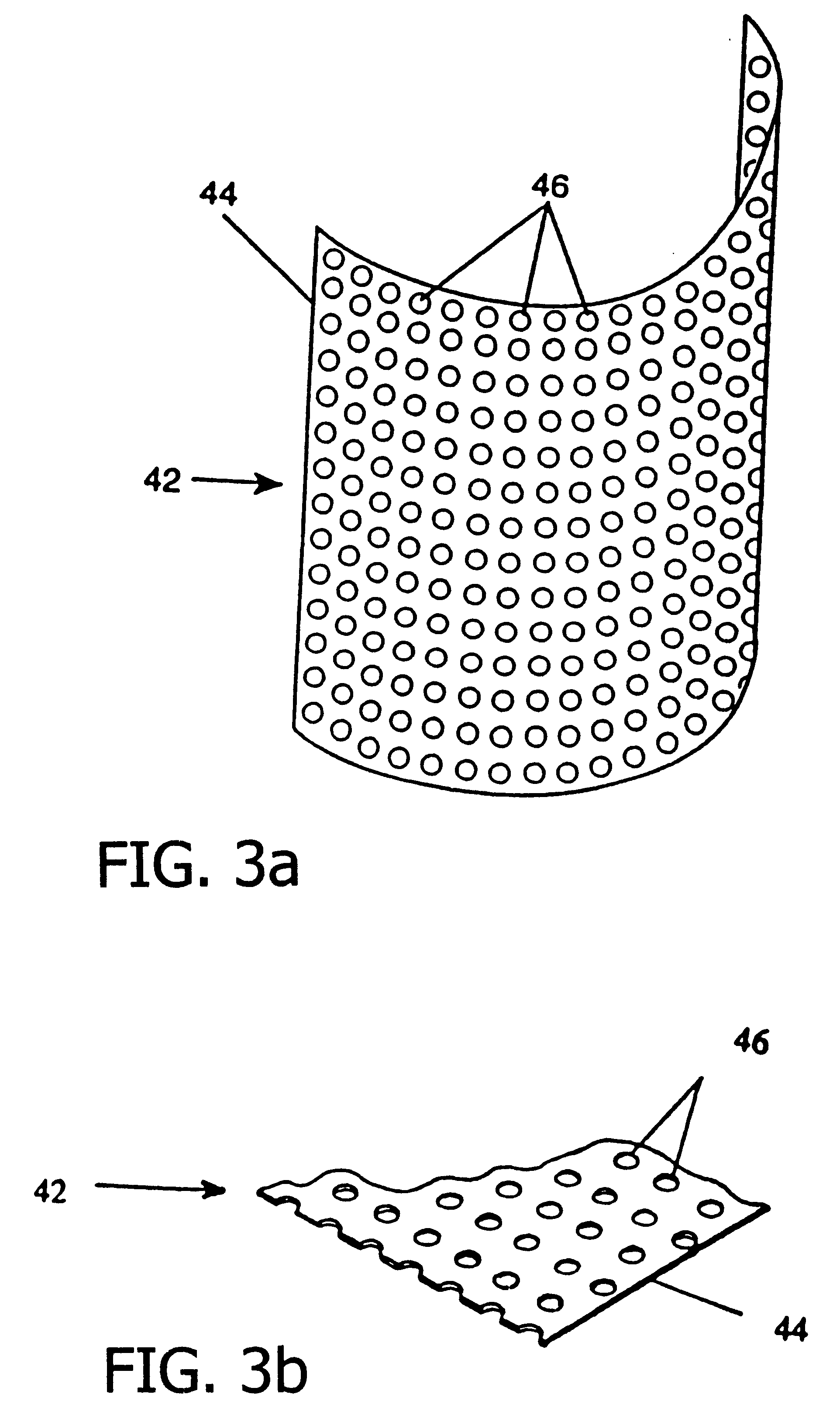
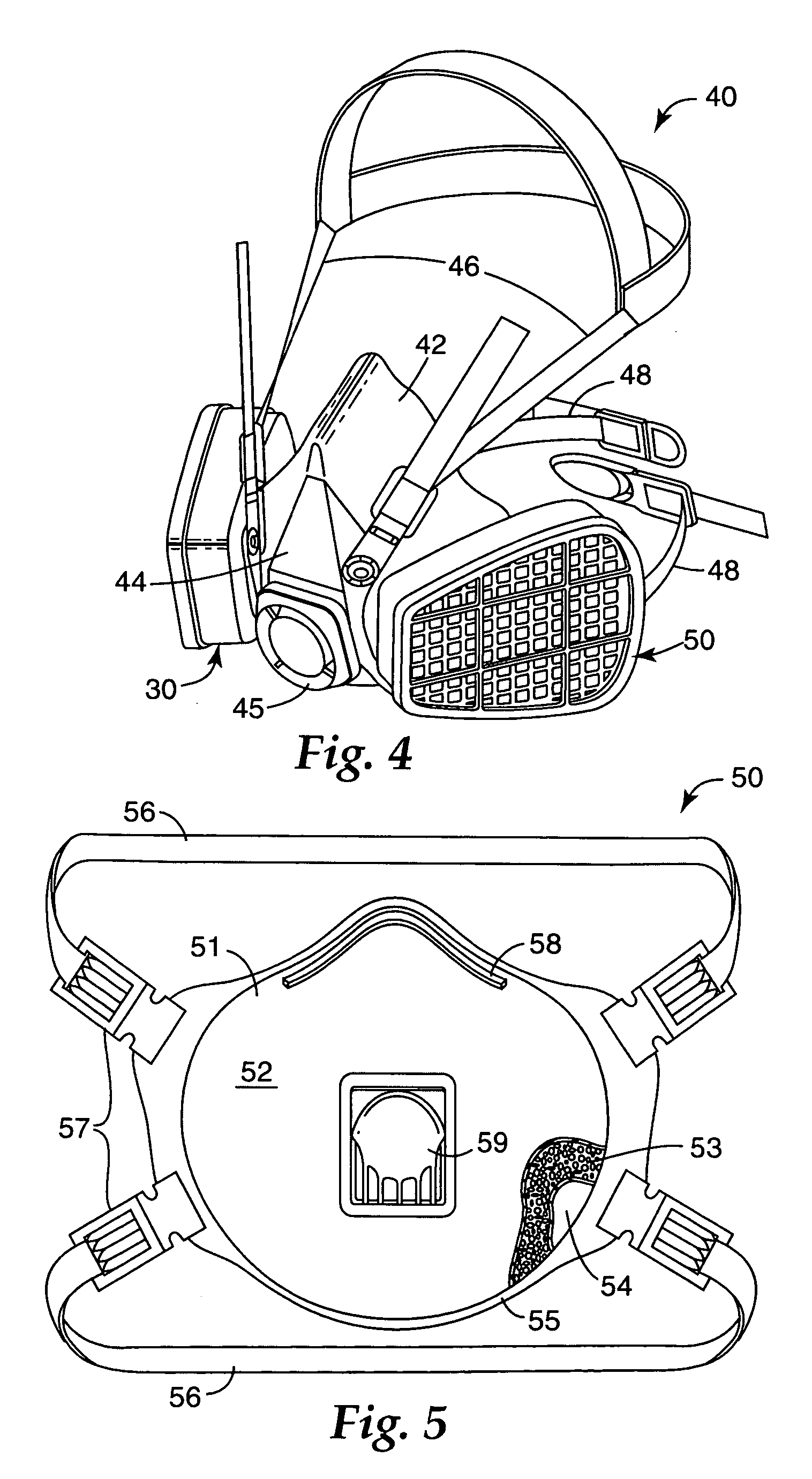
ActiveUS20070151009A1Simple and inexpensive solutionEffective blockingWater closetsFluid dynamicsPotty trainingPorous sheet
A potting training device for preventing a potty-training child's urine stream from passing through the opening formed between the toilet seat and the toilet bowl. The device is made of a flexible, water-resistant, preferably non-porous sheet material, having a folding seam separating a urine-deflecting surface and a plurality of attachment tabs. An adhesive material is applied to the surface of each attachment tab and attaches the attachment tabs to the underside of the toilet seat. The sheet material, in its unattached flat configuration, is manipulated into a curved configuration that matches the curvature of the toilet seat, and is attached thereto. The potty training device is also not visible to the observer unless the toilet seat is lifted up, in a vertical position or viewed from a position to the rear of the attachment point when the toilet seat is down.
Owner:CONRAD JOSEPH MICHAEL III
Particle-containing fibrous web
InactiveUS20060254427A1Lower overall pressure dropExtended service lifeBreathing filtersCellulosic plastic layered productsFiberDimethyl methylphosphonate
A porous sheet article including a self-supporting nonwoven web of less than 20 weight percent polymeric fibers exhibiting no more than about 1 weight percent dimethyl methyl phosphonate uptake and at least 80 weight percent sorbent particles enmeshed in the web, the sorbent particles being sufficiently evenly distributed in the web and the fiber polymer(s) being such that the web has an Adsorption Factor A of at least 1.6×104 / mm water. The articles have low pressure drop and can provide filter elements and other individual or collective protection devices having long service lives and an Adsorption Factor approaching and in some instances exceeding that of a packed carbon bed.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Water management in monopolar fuel cells
A monopolar fuel cell stack comprising proton exchange membrane fuel cells supplied with a gaseous anodic reactant, preferably hydrogen, and a gaseous cathodic reactant, preferably air. The monopolar fuel cell stack, forming at least one substantially planar array, includes a liquid water retention barrier disposed over an electrode to retain liquid water within the fuel cells. The barrier is preferably used over the cathode side of each fuel cell and allows excess air flow to cool the fuel cell stack without drying the membrane in each fuel cell. The liquid water retention barrier may be either: (i) a thin, gas permeable, liquid water impermeable membrane; (ii) a thin, porous sheet of material; or (iii) a thin, substantially solid sheet of material except for a plurality of small through-holes that penetrate from one side of the sheet to an opposing side of the same sheet.
Owner:LYNNTECH
Membrane/electrode assembly for polymer electrolyte fuel cells and polymer electrolyte fuel cell
ActiveUS20090246592A1Increase power generation capacityHigh mechanical strengthElectrolyte holding meansSolid electrolyte fuel cellsFiberEngineering
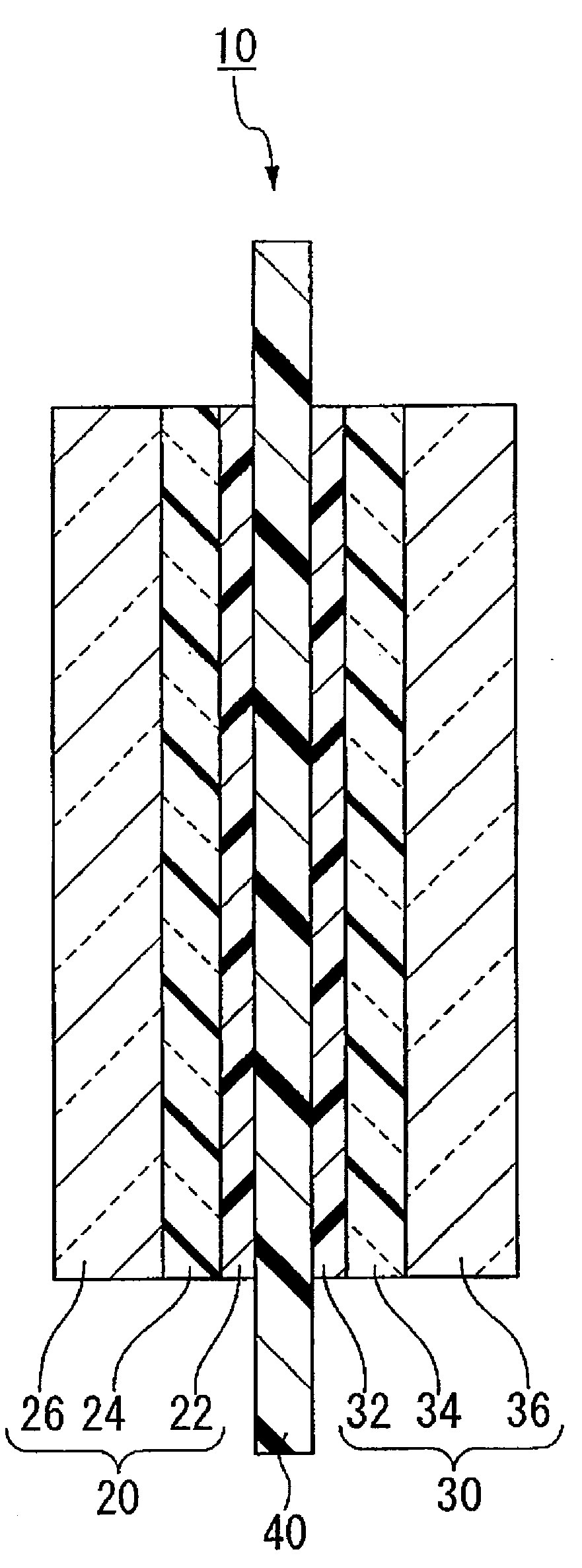
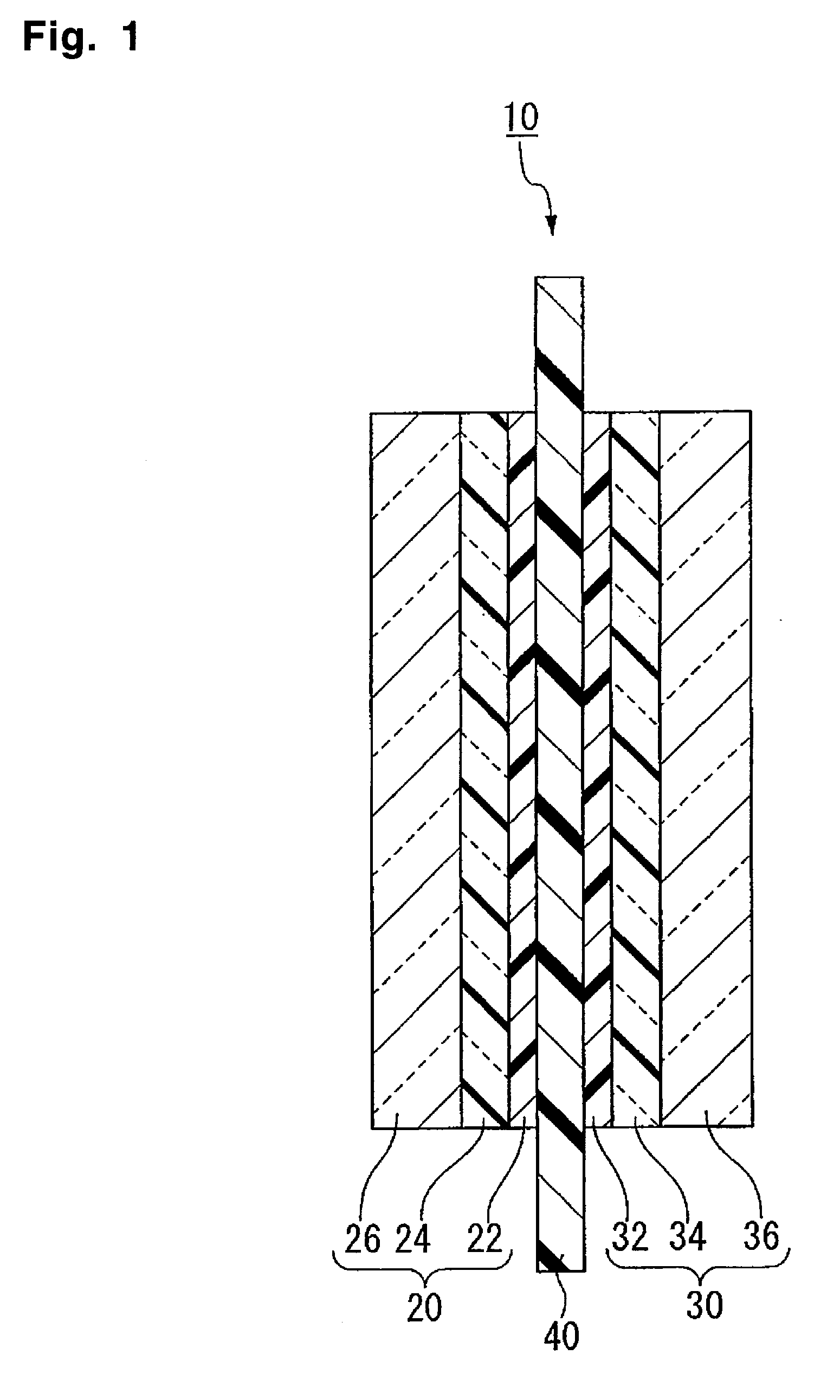
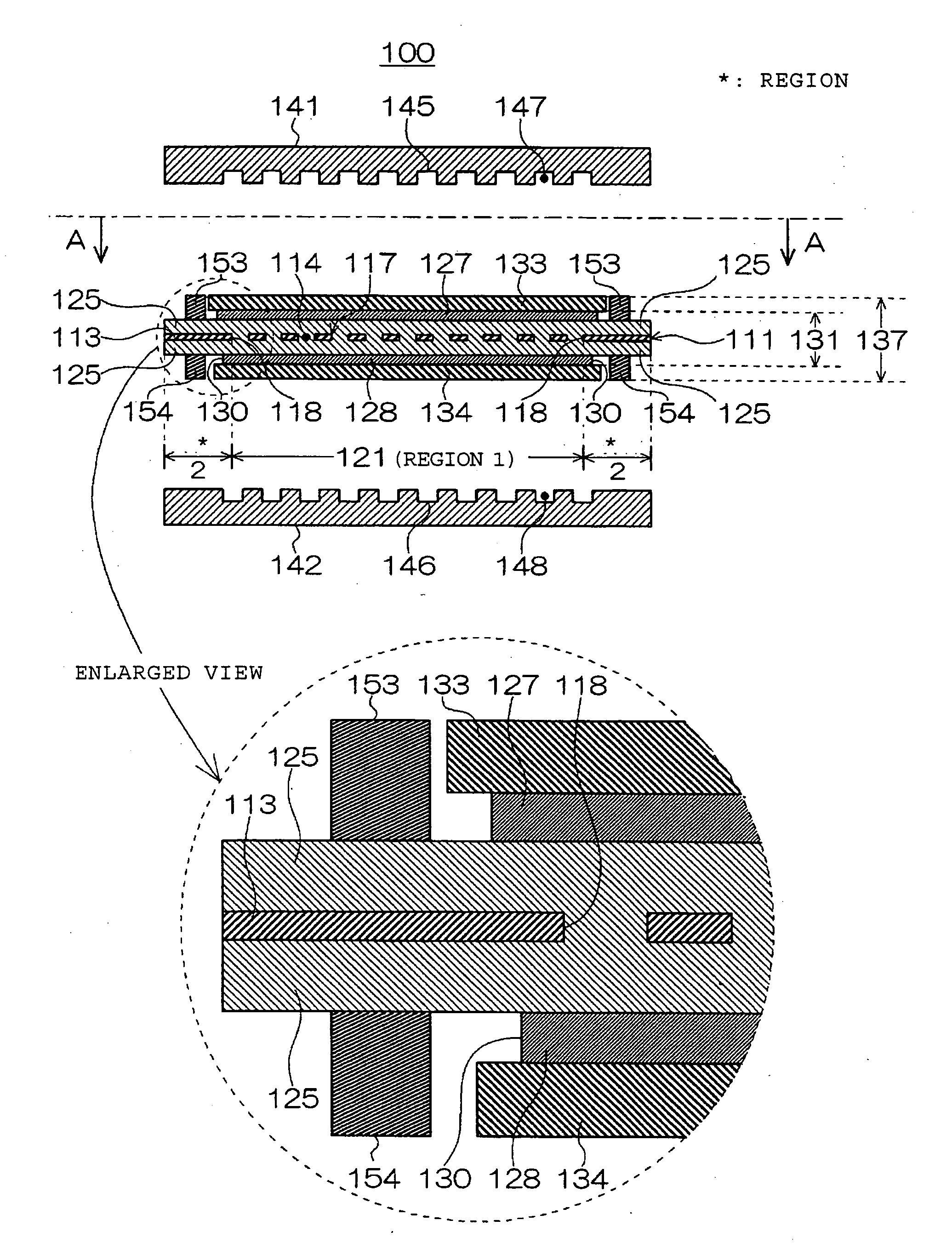
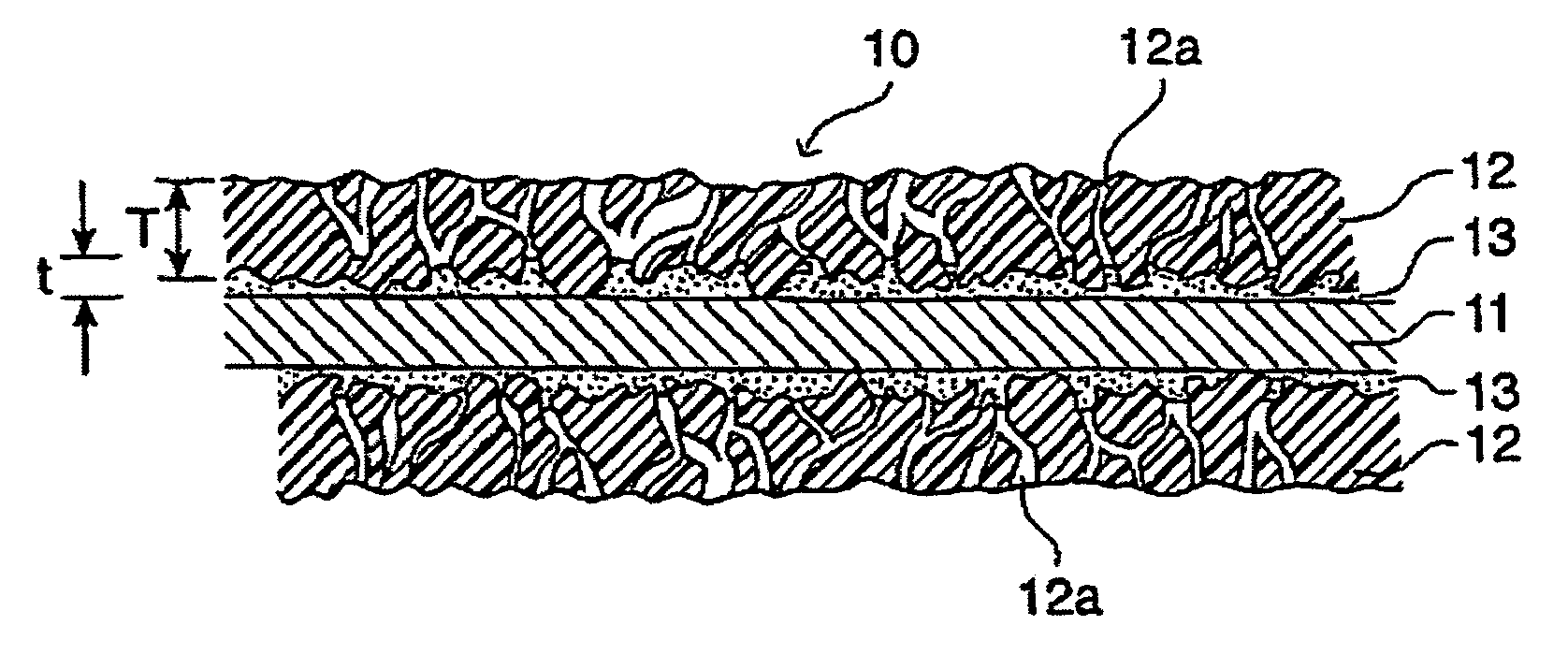
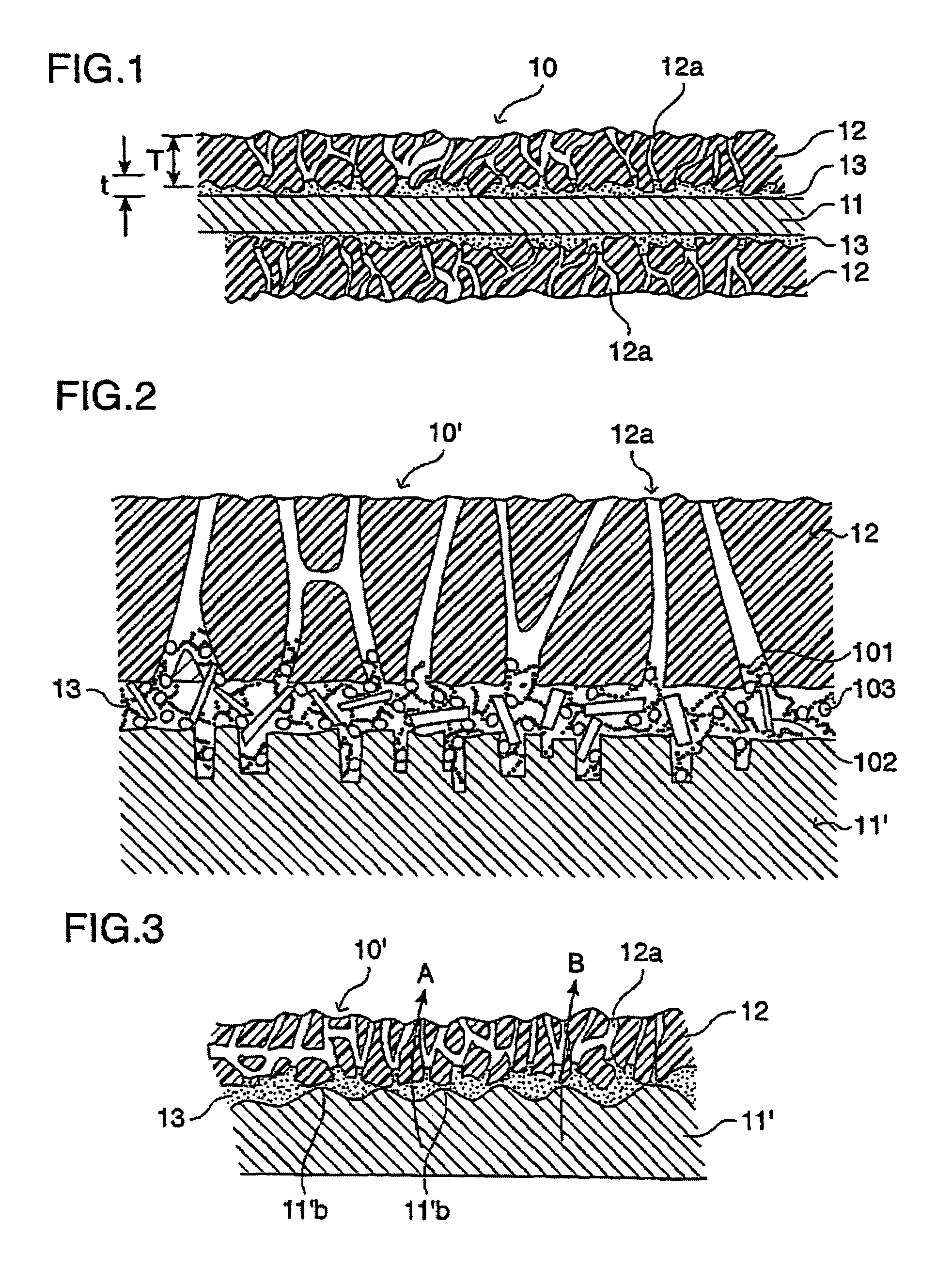
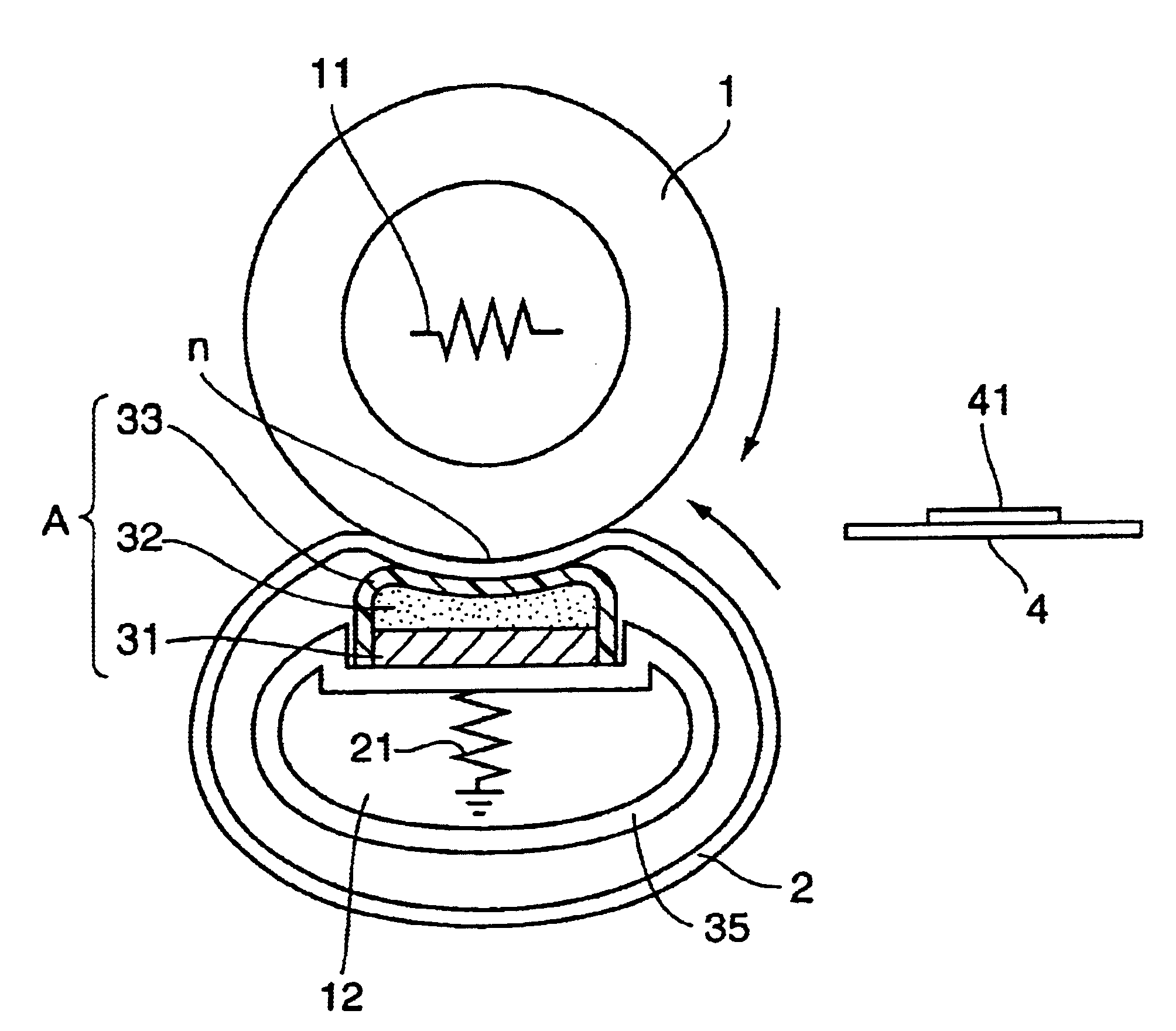
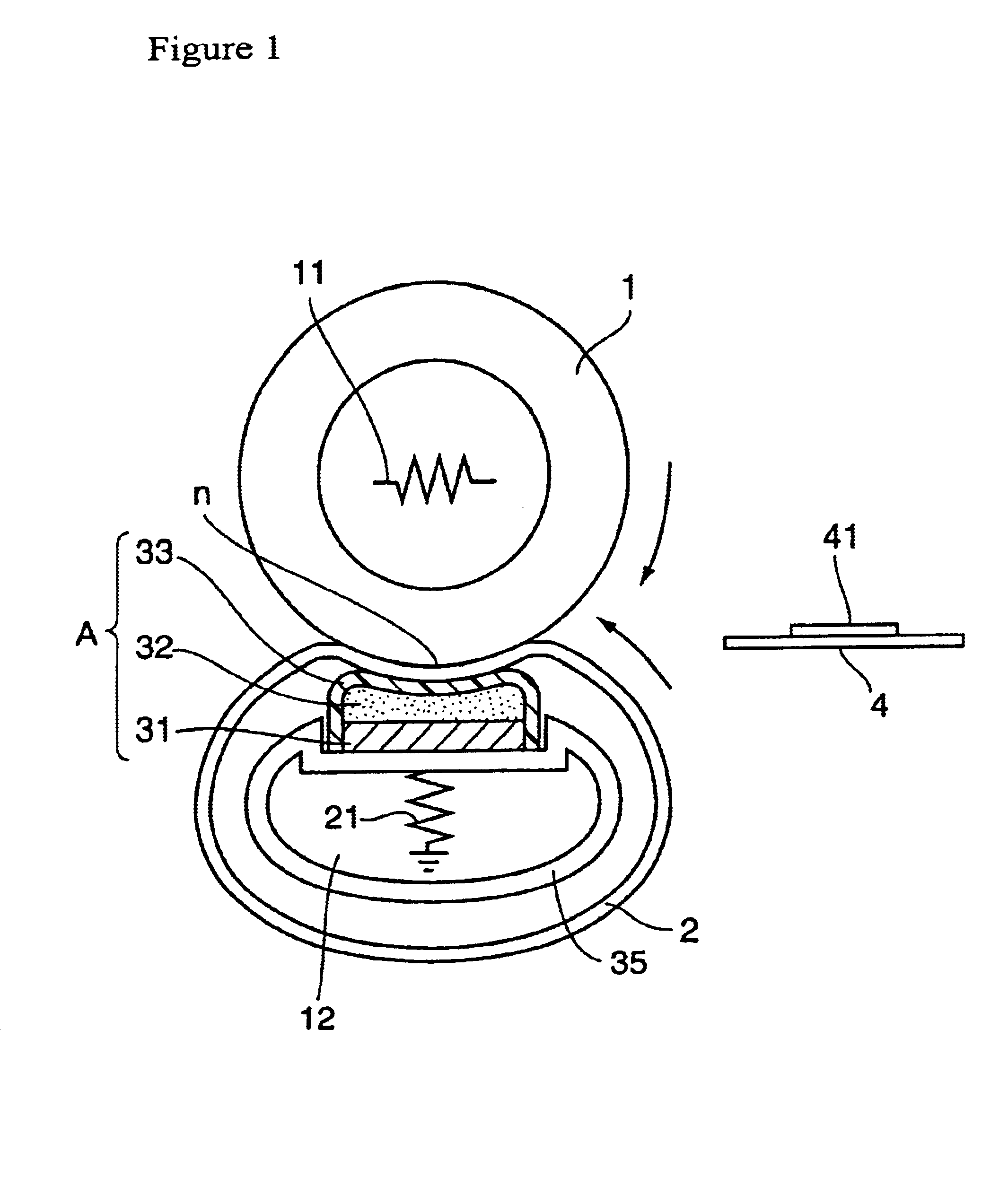
To provide a membrane / electrode assembly for polymer electrolyte fuel cells, which is capable of providing high power generation performance even under a low humidity condition and has sufficient mechanical strength and dimensional stability, and which has an excellent durability even in an environment where moistening and drying are repeated, and a polymer electrolyte fuel cell which is capable of providing high power generation performance even under a low humidity condition.A membrane / electrode assembly 10 is used, which comprises a cathode 20 having a catalyst layer 22, an anode 30 having a catalyst layer 32, and a polymer electrolyte membrane 40 interposed between the catalyst layer 22 of the cathode 20 and the catalyst layer 32 of the anode 30, wherein at least one of the cathode 20 and the anode 30 further has a reinforcing layer 26 comprising a porous sheet-form reinforcing material made of a polymer, and an electrically conductive fiber.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
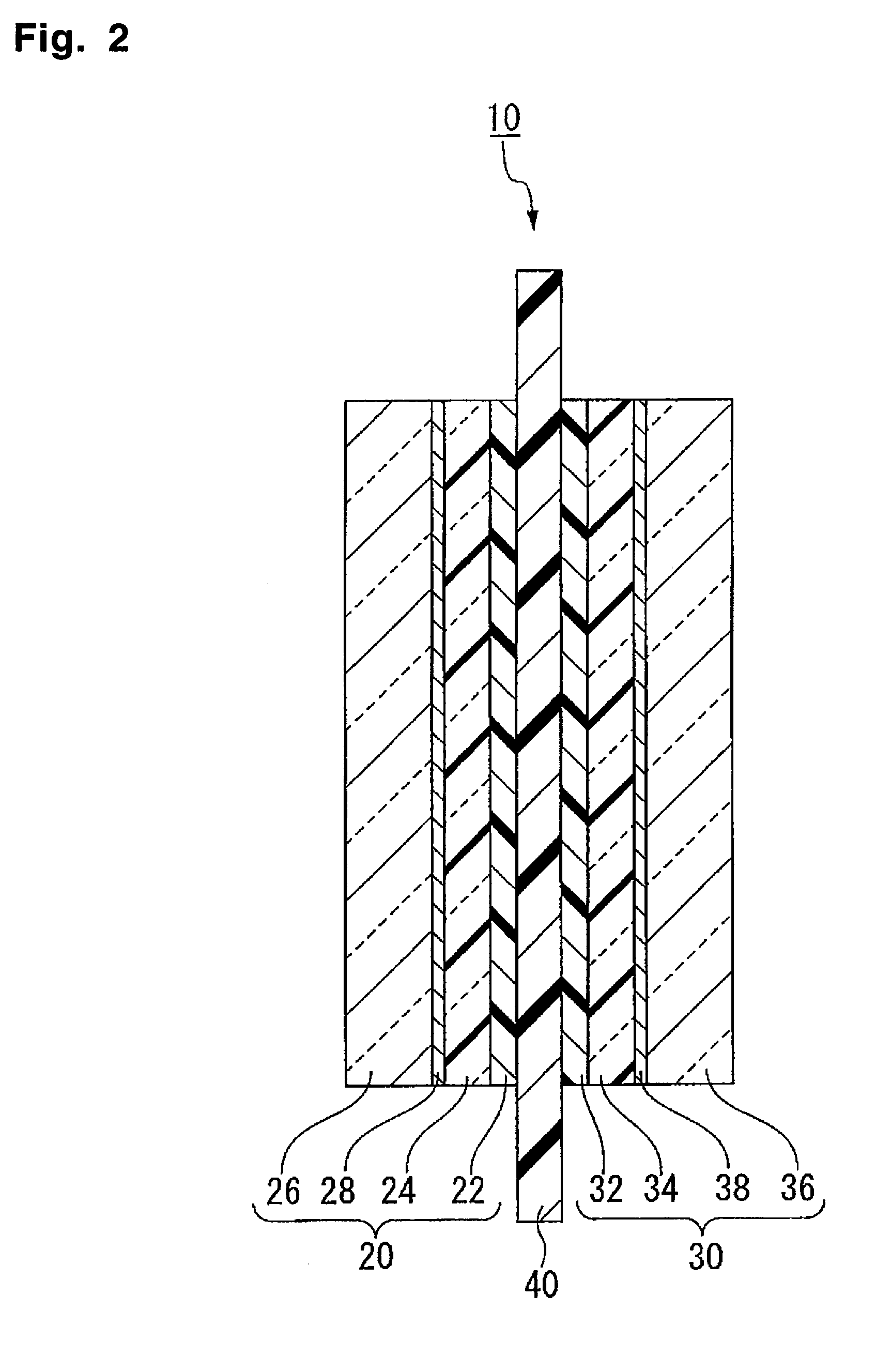
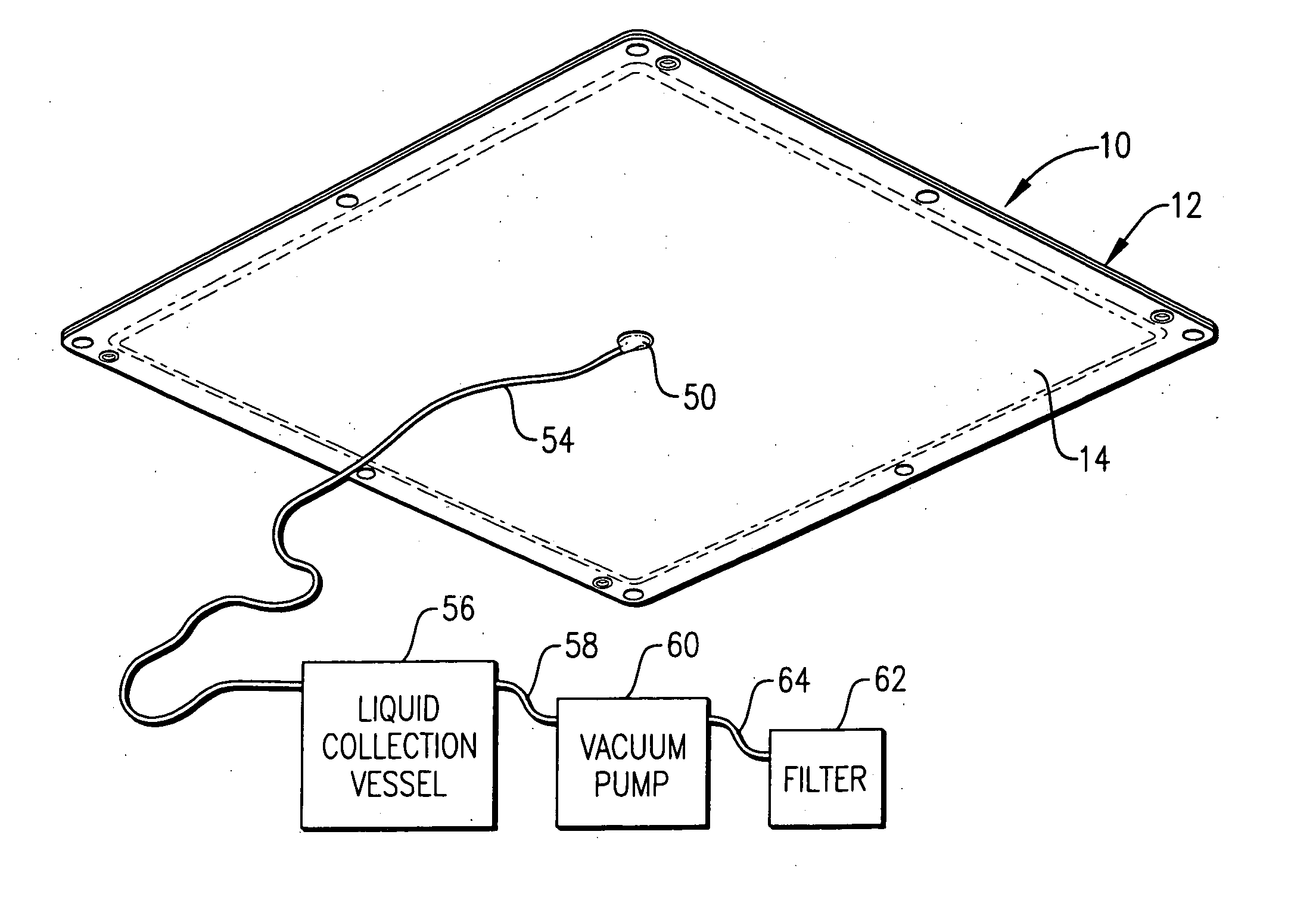
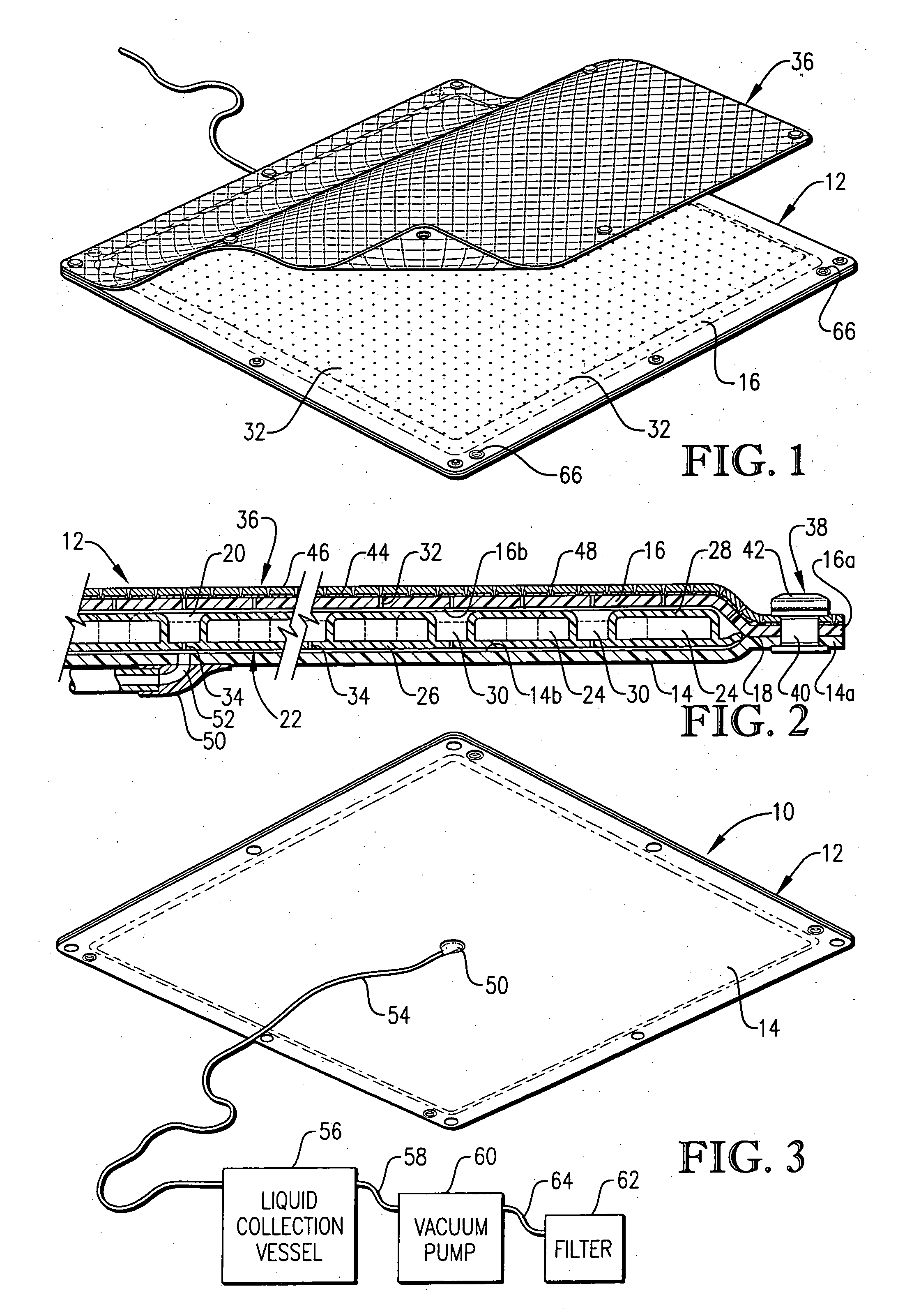
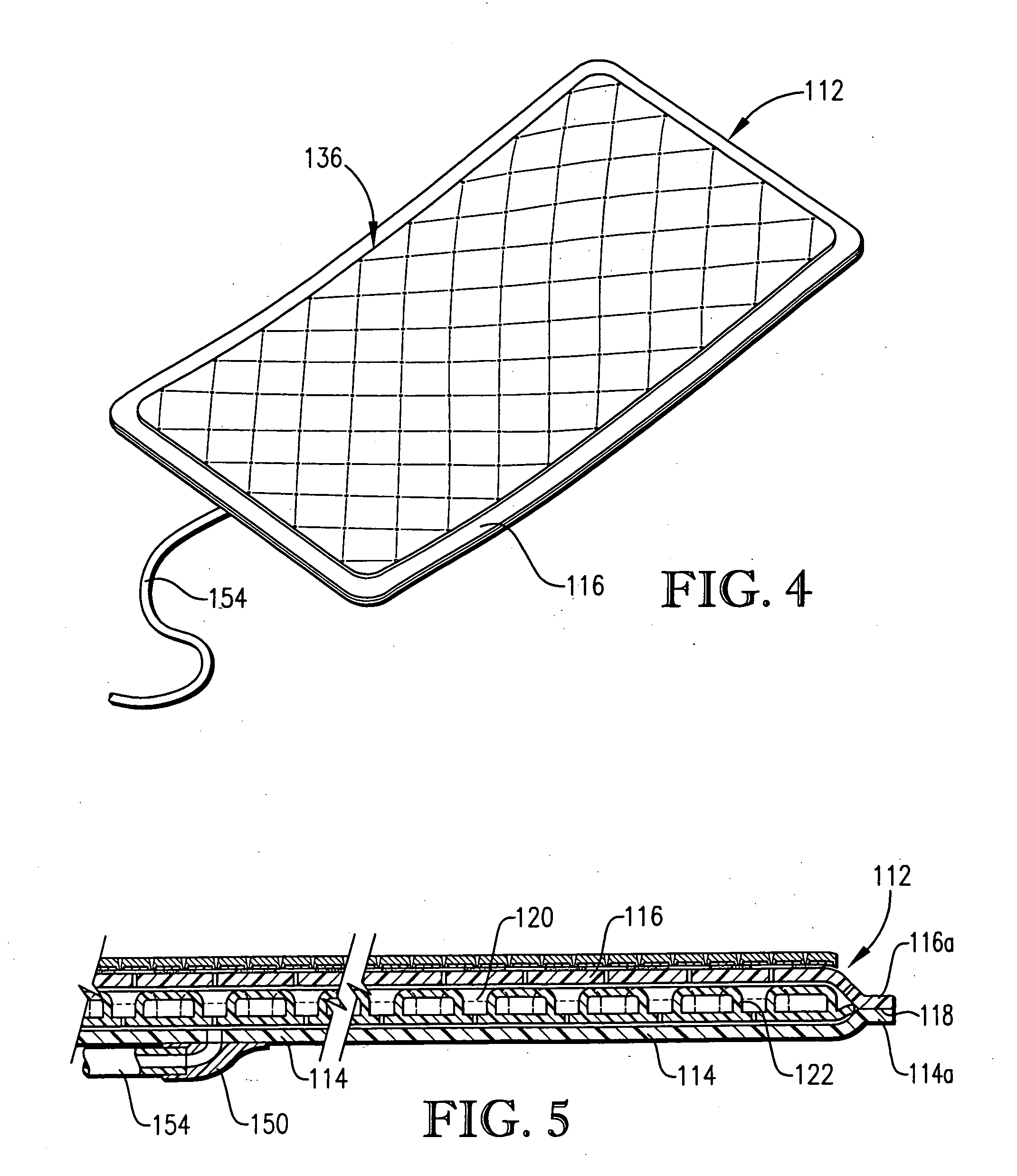
Fluid collection and aspiration unit for management of urinary incontinence
A flexible unit for collecting and transporting liquid to a collection point or to an area of use, and especially for facilitating management of urinary incontinence is provided which includes a flexible pad adapted to be positioned under an incontinent patient or worn under an undergarment. The pad is provided with an outer liquid permeable polymeric film layer, an outer liquid impermeable polymeric film layer and an intermediate cellular layer made up of a series of individual, spaced, thin wall, liquid impermeable polymeric cells. An aspiration assembly is connected to the pad for removing urine from the interior of the pad, which collects in the spaces between the individual cells. A disposable porous sheet, preferably comprising Dry-Weave® material, is releasably positioned over the outer permeable film layer of the pad. The pad may be sanitized and reused multiple times with only replacement of the Dry-Weave® sheet being required.
Owner:MAHNENSMITH MICHAEL
Separator and method of manufacturing non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery using the same
A separator includes a porous sheet, a heat-resistant porous layer, and a metal lithium layer. The heat-resistant porous layer is provided on one of surfaces of the porous sheet. The metal lithium layer is provided on the surface of the heat-resistant porous layer. The separator is disposed between a negative electrode that includes an active material capable of reversibly storing and emitting lithium ions and having a theoretical capacity density of 400 mAh / g or higher, and a positive electrode capable of reversibly storing and emitting lithium ions, so that the metal lithium layer faces the negative electrode.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Membrane-electrode assembly for polymer electrolyte fuel cells, and polymer electrolyte fuel cell
InactiveUS20060046121A1Increase of gas leakage is suppressedInhibit deteriorationElectrolyte holding meansFuel cells groupingPolymer electrolytesFuel cells
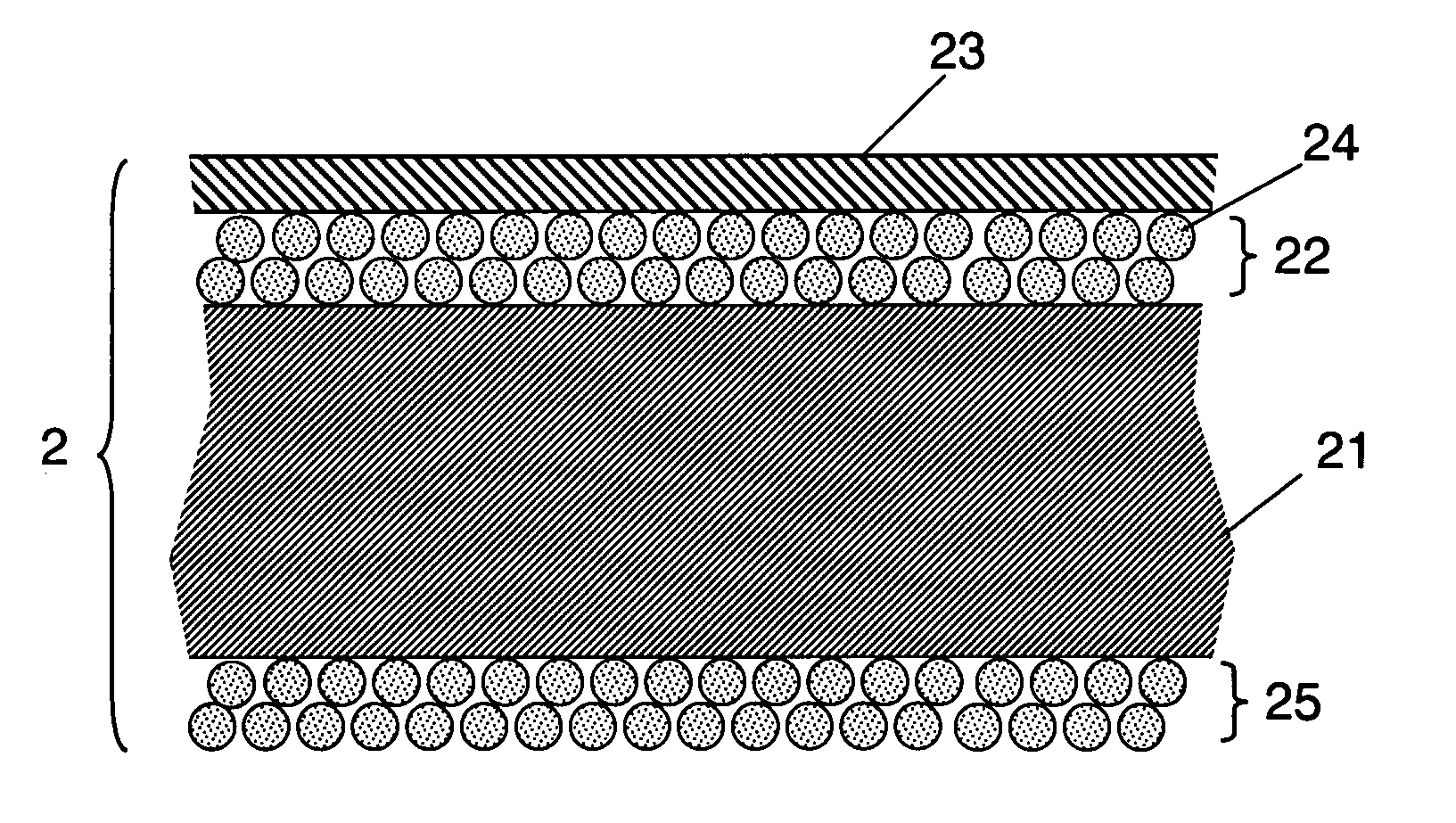
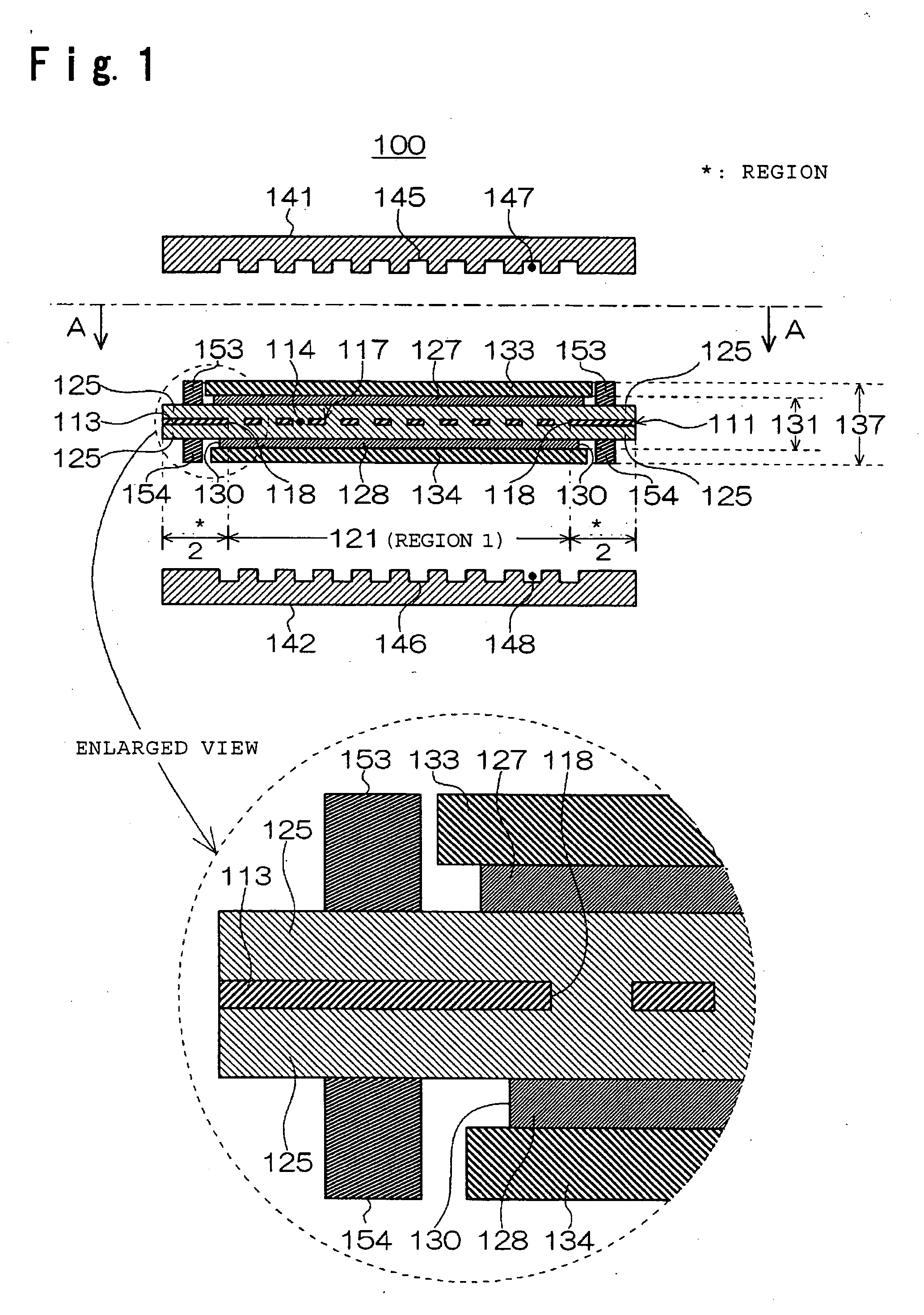
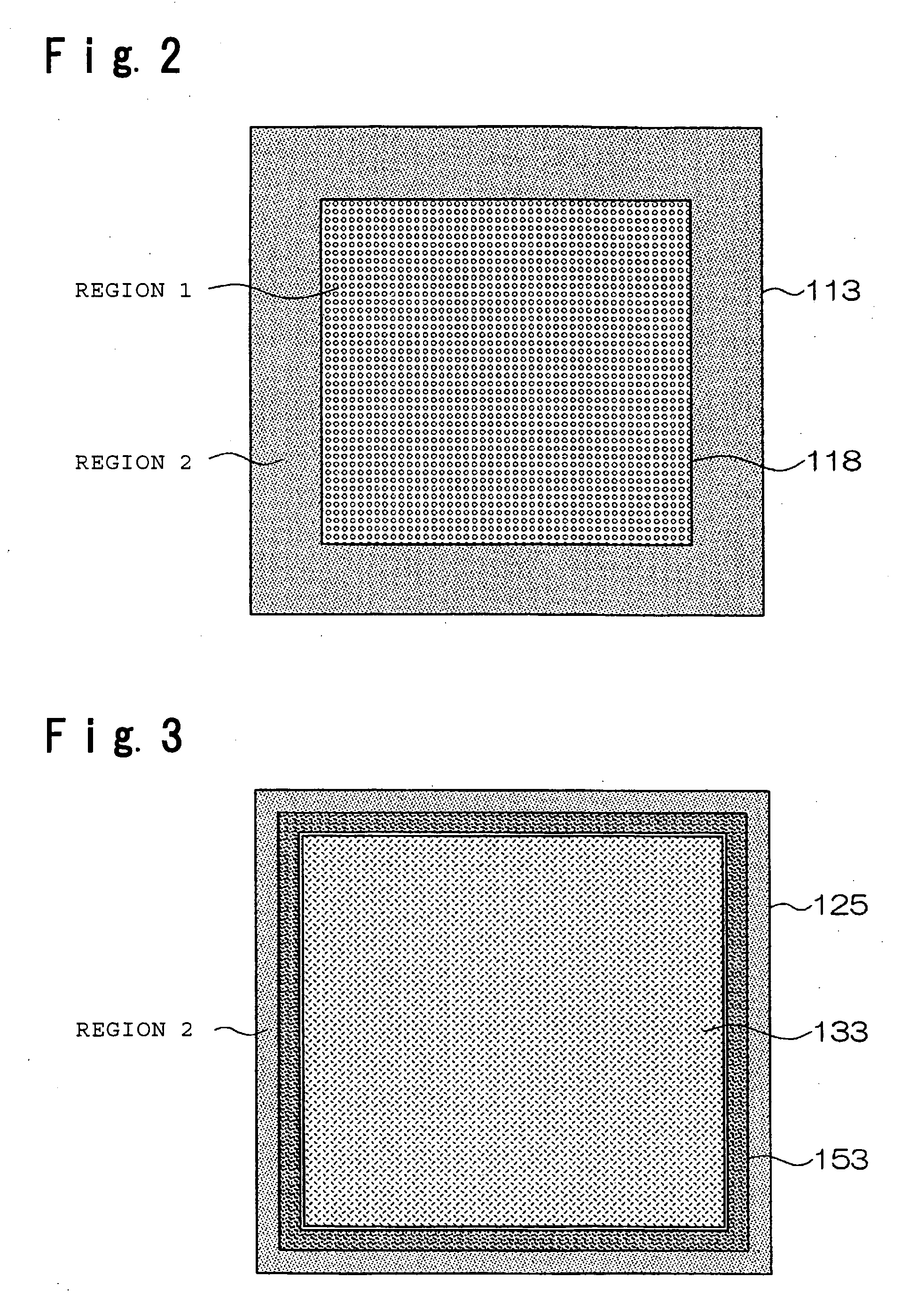
The present invention provides a membrane-electrode assembly for polymer electrolyte fuel cells and a polymer electrolyte fuel cell having excellent dimensional stability and mechanical strength, and having high durability at the time of a power generation. Each of polymer electrolyte membranes (111, 211, 311) have a region 1 having proton conductivity over the entirety in the thickness direction of the membrane and a region 2 located at the outer peripheral portion of the region 1 and having a non-porous sheet disposed so that the region 2 has no proton conductivity over the entirety in the thickness direction of the membrane, and outer edges of the catalyst layers (127, 128) are disposed so as to be located in the area 2.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Porous sheet, separator for electrochemical element, and method for manufacturing porous sheet
ActiveUS20100252426A1Improve balanceExcellent in high-rate propertyDouble layer capacitorsPretreated surfacesElectrolytic agentPorous substrate
A porous sheet which has good balance between electrolytic solution permeability and dry-up resistance, is superior in high-rate property, and is suitable for a separator for an electrochemical element, and a manufacturing method thereof are provided.The present invention relates to a porous sheet comprising a porous substrate containing non-fibrillar fibers having an average fiber diameter of 0.01-10 μm and a net-like structural body composed of a polymer, the net-like structural body having penetrating pores with a pore diameter of 0.01-10 μm, wherein the net-like structural body is present at the surface and at the internal of the porous substrate and the non-fibrillar fibers having an average fiber diameter of 0.01-10 μm and the net-like structural body are entangled; to a separator for an electrochemical element comprising the porous sheet; and to a method for manufacturing the porous sheet.
Owner:MITSUBISHI PAPER MILLS LTD
Fluid collection and aspiration unit for management of urinary incontinence
A flexible unit for collecting and transporting liquid to a collection point or to an area of use, and especially for facilitating management of urinary incontinence is provided which includes a flexible pad adapted to be positioned under an incontinent patient or worn under an undergarment. The pad is provided with an outer liquid permeable polymeric film layer, an outer liquid impermeable polymeric film layer and an intermediate cellular layer made up of a series of individual, spaced, thin wall, liquid impermeable polymeric cells. An aspiration assembly is connected to the pad for removing urine from the interior of the pad, which collects in the spaces between the individual cells. A disposable porous sheet, preferably comprising Dry-Weave® material, is releasably positioned over the outer permeable film layer of the pad. The pad may be sanitized and reused multiple times with only replacement of the Dry-Weave® sheet being required.
Owner:MAHNENSMITH MICHAEL
Electrode for electric double layer capacitor, method for manufacturing same, electric double layer capacitor, and conductive adhesive
InactiveUS7486497B2Lower internal resistanceIncrease capacitanceNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesHybrid capacitor electrodesInternal resistanceAdhesive
The present invention is an electrode for electric double layer capacitors wherein a polarizable porous sheet composed of constituent materials including a carbonaceous electric double layer-forming material, a carbon material for ensuring conductivity, and a binder is integrated to at least one surface of a collector via a conductive intermediate layer; and is characterized in that the conductive intermediate layer contains a synthetic rubber and two more kinds of carbon materials having different particle diameters. According to the present invention, the electrode can be readily manufactured in a continuous manner with high heat resistant adhesion between the polarizable porous sheet and the collector and a low internal resistance; and when used in an electric double layer capacitor, it is possible to obtain an electrode capable of ensuring a higher capacity and lower internal resistance than is conventionally achieved.
Owner:JAPAN GORE TEX INC
Janus nano material with double properties and preparation method of Janus nano material
The invention discloses a Janus nano material with double properties and a preparation method of the Janus nano material. The preparation method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: taking polymer colloidal particles as templates and acquiring organic and / or inorganic hybrid Janus particles based on the interface self-assembly and separation mechanism through a seed emulsion polymerizing method; and removing the template polymer colloidal particles and then directly acquiring the Janus nano particles or porous sheet materials. The controlling of the size, the micro structure and the chemical composition of the Janus nano particles or the porous sheet materials is realized by controlling the conditions of concentration and varieties of reactants. The Janus nano particles or the porous sheet materials have great application prospects in particle emulsifying agents, self-assembly, compatibilizer and nano motors.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sliding member for electrophotographic apparatus and fixing device using the same
ActiveUS6895208B2Reduce frictionImprove heat stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsElectrographic process apparatusEngineeringPorous sheet
The present invention relates to a sliding member for an electrophotographic apparatus using a non-porous sheet having a sliding surface including at least a fluorocarbon resin as a sheet-like member interposed between a press member A and a resin film tubular body. The invention also relates to an image fixing device using the sliding member.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
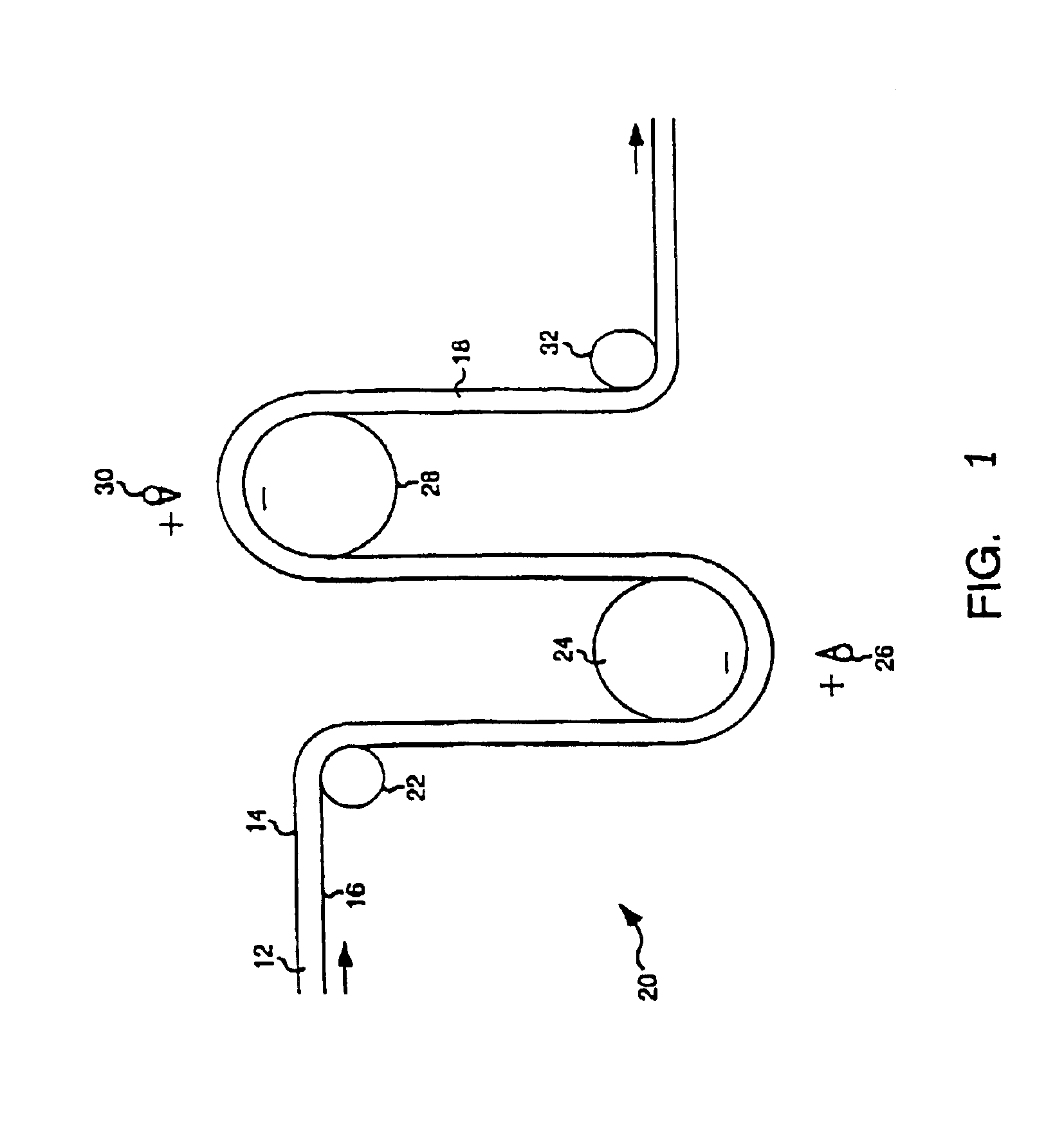
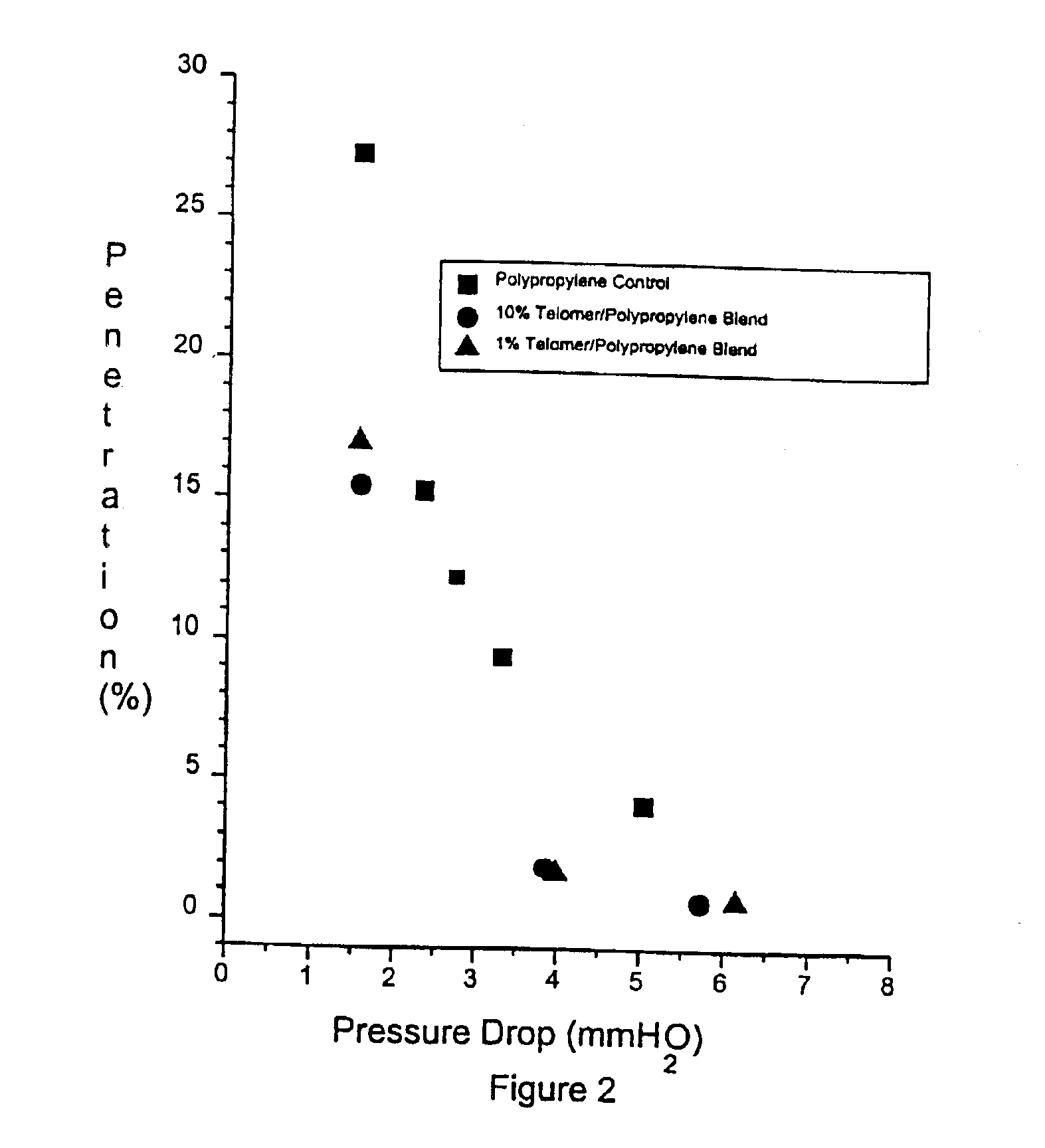
Stable electret polymeric articles
InactiveUS6893990B2Material efficiencyImprove filtration efficiencyElectrostatic separationDigital storagePolymer sciencePolyolefin
A porous polymeric sheet is provided having an electrostatic charge and comprising a zero-three composite of a polymeric matrix and a ferroelectric material dispersed therein. The polymeric component comprises a non-polar thermoplastic polymer, such as a polyolefin, and a second thermoplastic polymer having polar functional units, such as a telomer. The composite material is formed into a porous sheet and is electrically or corona poled to create an electret material which is well suited four use in various filtration, air-masking and dust wipe applications.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Composite materials
ActiveUS20120114899A1High in fiberEliminate the problemFinal product manufactureBaby linensTurbine bladeWork in process
A curable prepreg or semipreg material comprising a layer of fibres and a substantially non-flowable curable resin having a layer of porous sheet material on an outer surface, the material allows automatic lay-up of high fibre content prepregs or semiprepregs typically used in industrial applications such as wind turbine blades.
Owner:HEXCEL COMPOSITES LTD (GB)
Fire resistant article, and associated production method
ActiveUS20160243789A1Improve cohesionFlat surfaceSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationCelluloseFiber
A method of forming an article and associated article are provided. Multi-fiber cellulose strips are interacted with a bonding agent and layered in a plurality of layers, the layered cellulose strips collectively defining opposed major surfaces. A porous sheet member, interacted with a fire-retarding solution, is engaged with at least one of the major surfaces of the layered cellulose strips, such that the porous sheet member substantially covers the at least one major surface. The layered cellulose strips and the porous sheet member are collectively exposed to an actuating element, configured to actuate the bonding agent to facilitate cohesion of the layered cellulose strips and the porous sheet member, to form a board member, wherein the at least one major surface cooperates with the porous sheet member engaged therewith, in response to the actuating element, such that the porous sheet member forms a substantially smooth and uniform surface.
Owner:BLH TECH
Method for preparing porous flake-like graphite phase carbon nitride on large scale, and application thereof
InactiveCN105289684AEasy to operateImprove controllabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationPollutantUrea
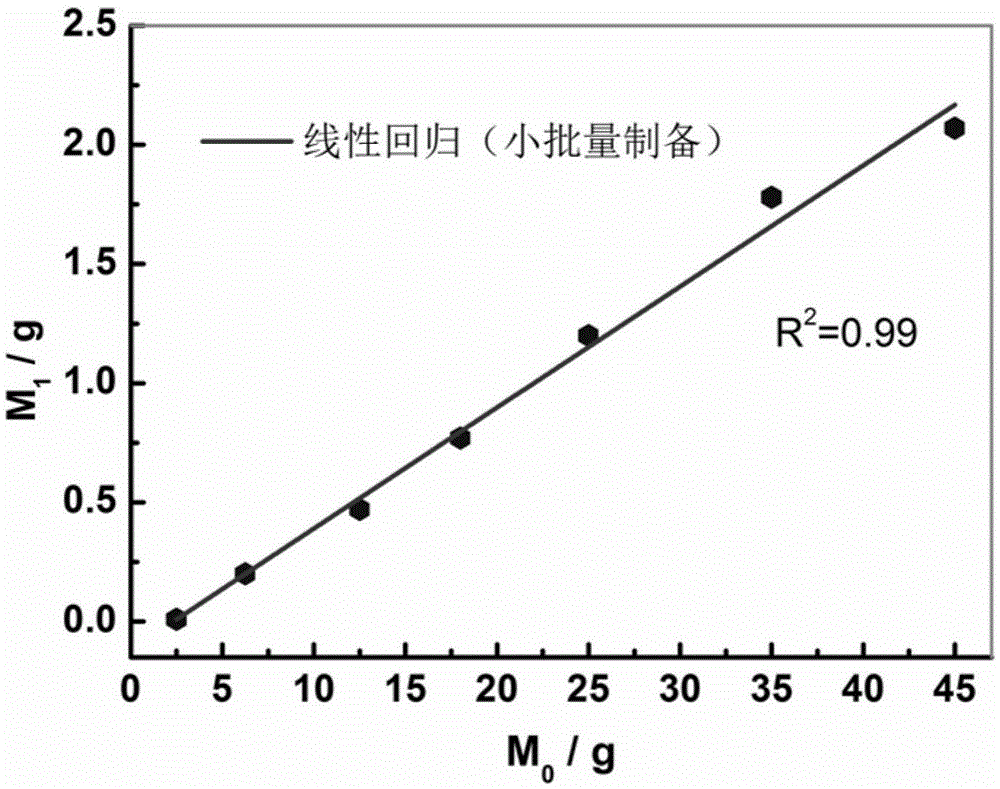
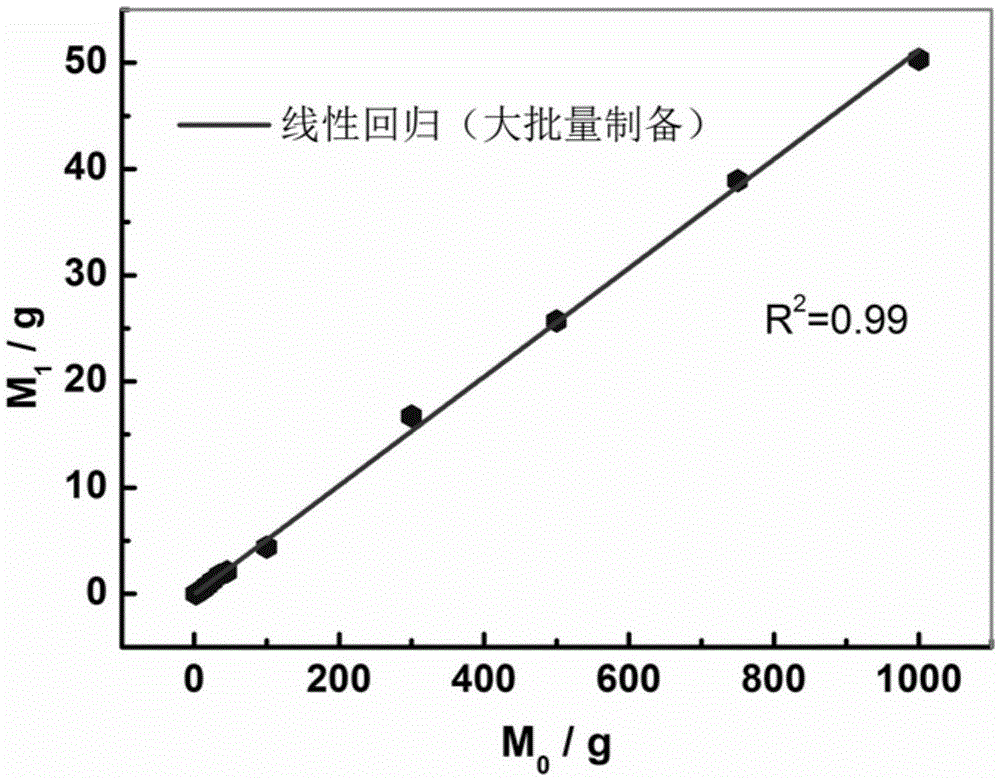
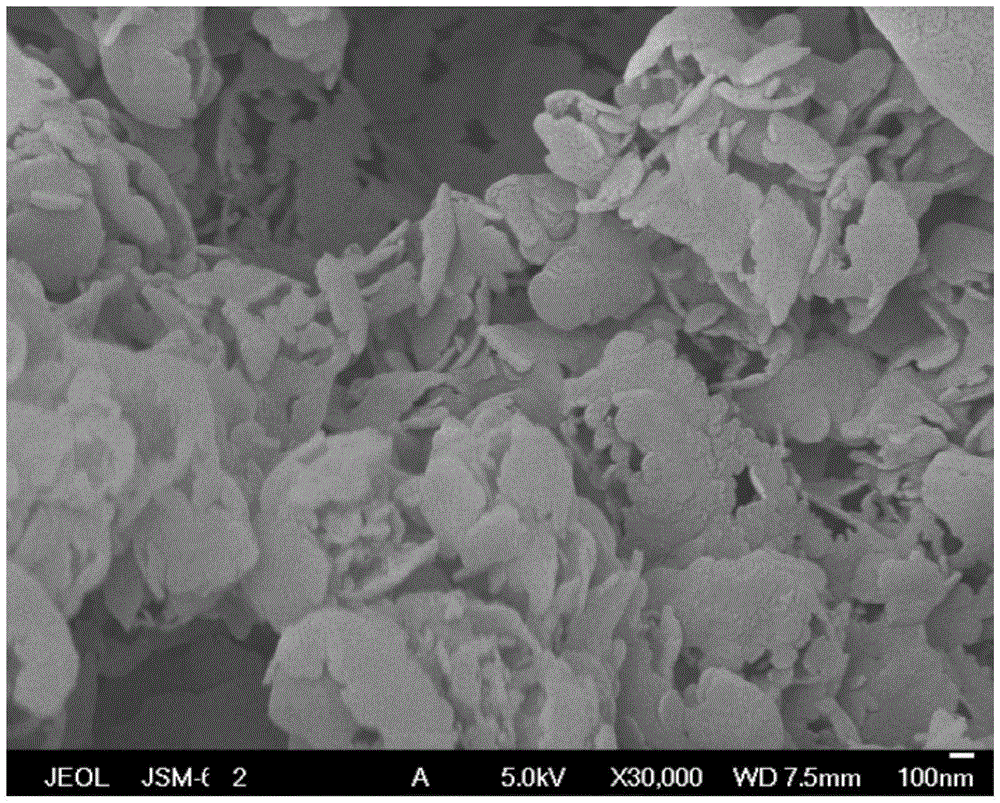
The invention discloses a method for preparing porous flake-like graphite phase carbon nitride with efficient visible light photocatalytic degradation activity of pollutants on a large scale, and belongs to the technical field of polymeric materials and photocatalysis. A thermopolymerization method is adopted, and urea is taken as raw materials and is subjected to certain processing through a direct calcination method in an aluminum reactor to obtain efficient porous flake-like graphite phase carbon nitride photocatalyst. The yield and an input raw material amount have a good linear relationship, and mass preparation can be simply realized. The obtained graphite phase carbon nitride is flake like, has a large specific surface area and favorable visible light absorption capability and especially has efficient visible light photocatalytic degradation capability of organic pollutants. The technology of the invention can be used for the purification processing of organic maters in industrial wastewater and municipal domestic wastewater.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
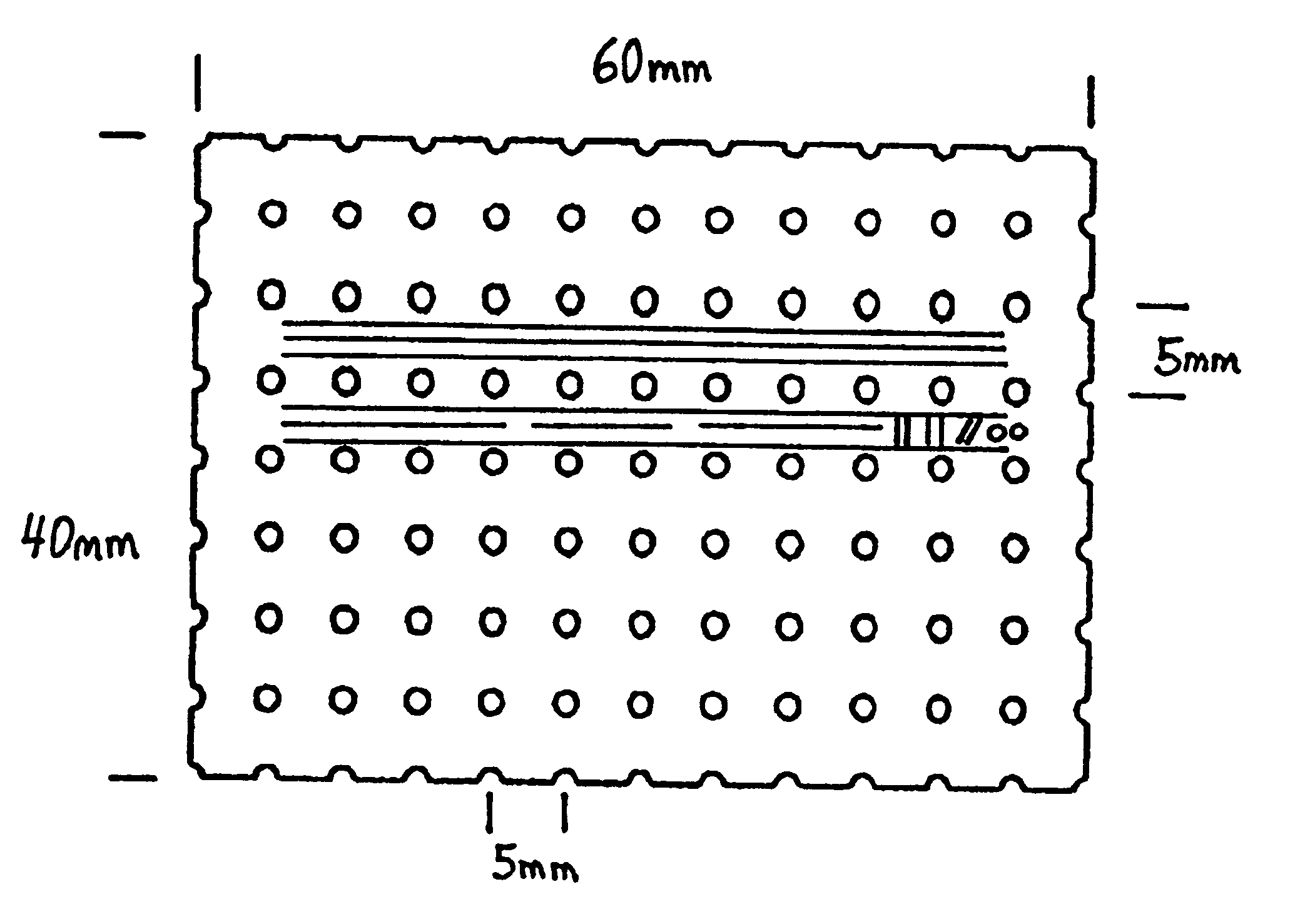
Vacuum clamp for machining porous sheet and using method thereof
InactiveCN101733651AImprove machining accuracyLow costWork holdersPositioning apparatusPorous sheetMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a vacuum clamp for machining a porous sheet and a using method thereof and belongs to the technical field of conveying thin appliances. The vacuum clamp comprises a baseplate, a positioning device, an air guide device, a vacuum generating device and a sealing device; the vacuum clamp is characterized in that: shallow cavities adaptive to the shape of a machined part are distributed on the baseplate; air guide holes are distributed in each shallow cavity; each shallow cavity and the underside of the machined part form a vacuum cavity, so the machined part is adsorbed on the baseplate; the positioning device limits the movement of the machined part on the baseplate so as to make the machined part in a clamping state; the air guide device is connected with the baseplate and the vacuum generating device; the sealing device comprises sealing bars and through hole sealing elements; the sealing bars are distributed on the peripheral edges of the shallow cavities; and the through hole sealing elements are distributed in the shallow cavities. The vacuum clamp adopts a reliable positioning mode, the shape of the vacuum cavities is matched with the shape of the part, and the adsorption area can be farthest utilized.
Owner:SUZHOU CHUNXING PRECISION MECHANICAL
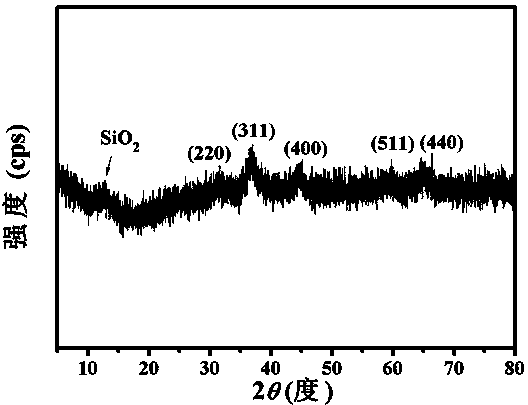
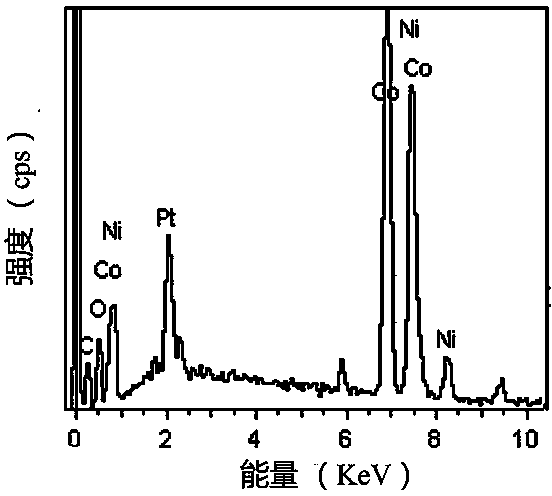
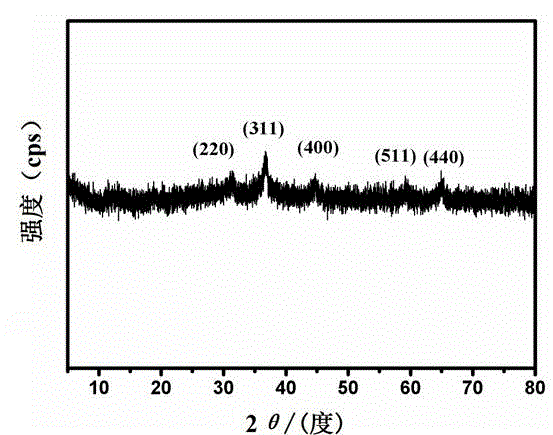
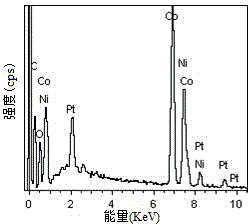
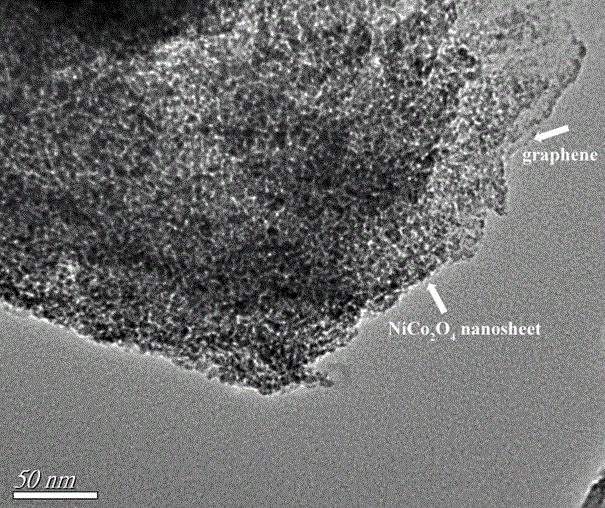
Method for manufacturing porous flaky NiCo2O4 and grapheme composite capacitive material
ActiveCN104240972AHigh specific capacitanceImprove electrochemical stabilityHybrid/EDL manufactureAir atmosphereCapacitance
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a porous flaky NiCo2O4 and grapheme composite capacitive material, and belongs to the field of nano composite material manufacturing. According to the method, a graphite oxide, cobalt nitrate and nickel nitrate are dissolved in deionized water in an ultrasonic mode and stirred, a certain amount of hexamethylene tetramine is added, a reflux reaction is carried out for 3-4 hours at the temperature of 90 DEG C, sediments are collected, the collected sediments are calcined in an air atmosphere for 2 hours at the temperature of 330 DEG C, and the porous flaky NiCo2O4 and grapheme nano composite material is obtained. In the manufactured porous flaky NiCo2O4 and grapheme composite capacitive material, porous flaky NiCo2O4 is completely attached to the surface of a grapheme piece. By means of the composite structure, conductivity of the material is improved, and the contact area of the material and an electrolyte solution is greatly improved, so that the composite material has high specific capacitance and good electrochemical stability and can be possibly used as a super-capacitor electrode material.
Owner:江阴智产汇知识产权运营有限公司
Stack-type lithium-ion polymer battery
InactiveUS20070117008A1Improve production yieldCapacity degradation can be preventedFinal product manufactureLi-accumulatorsEngineeringPorous sheet
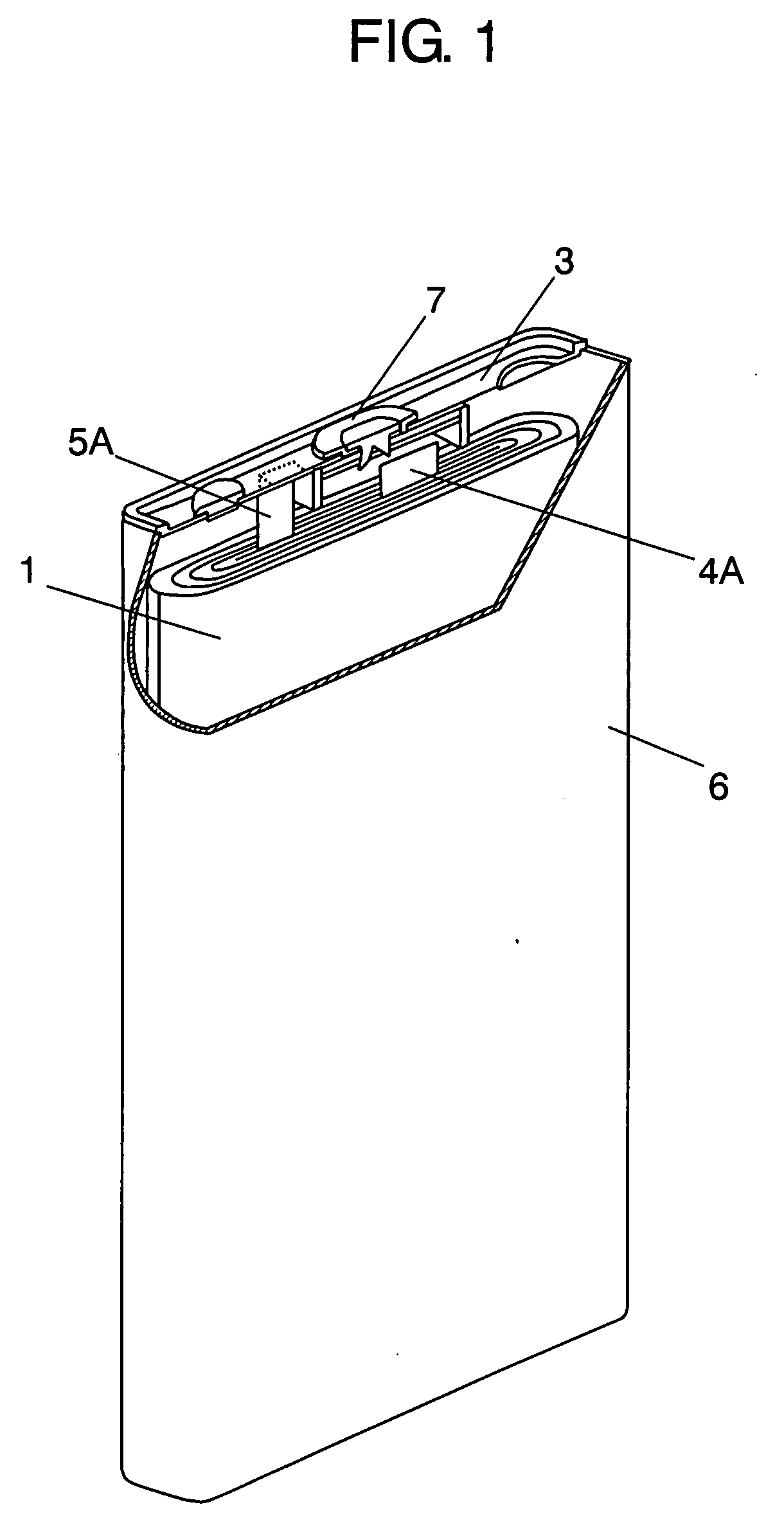
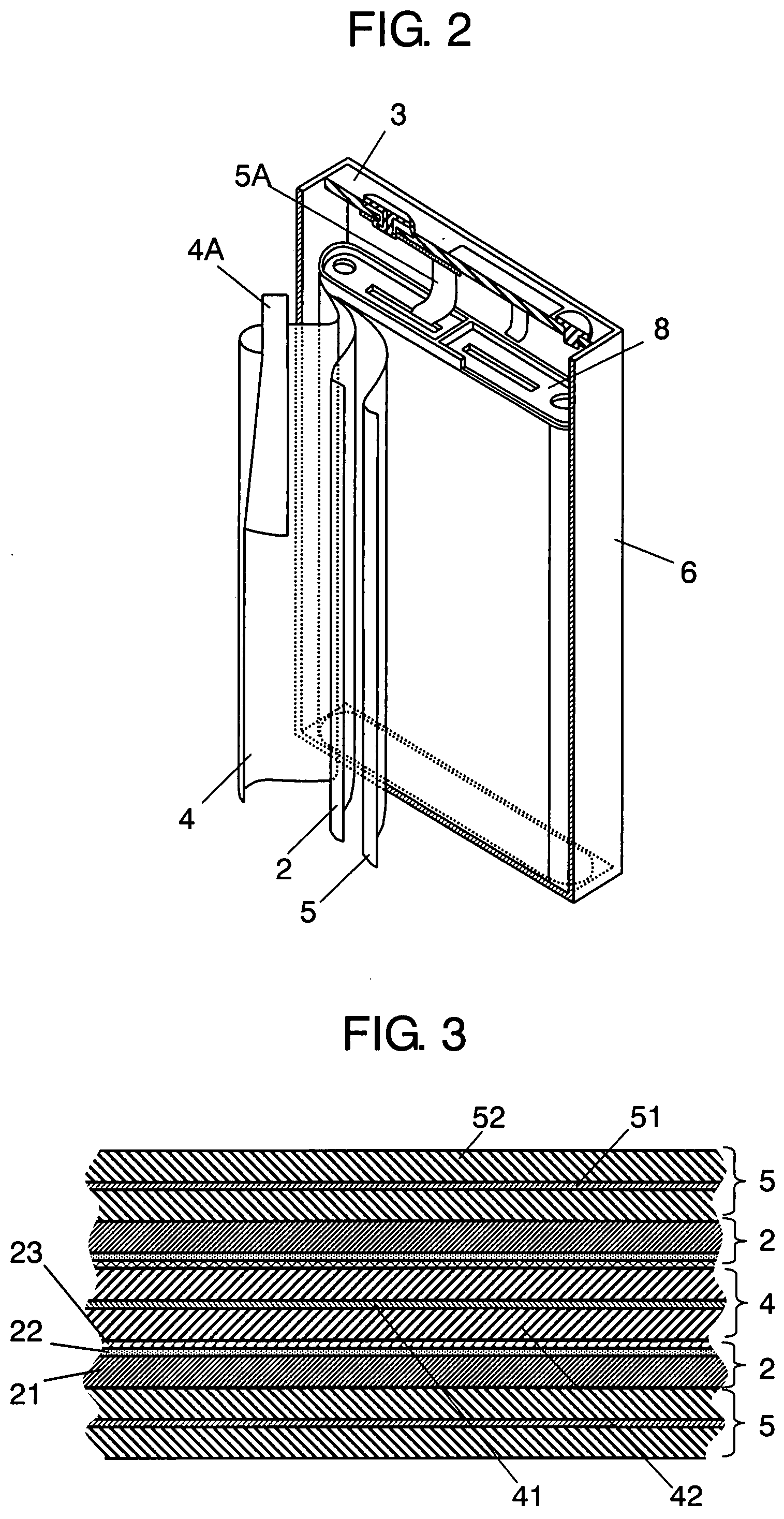
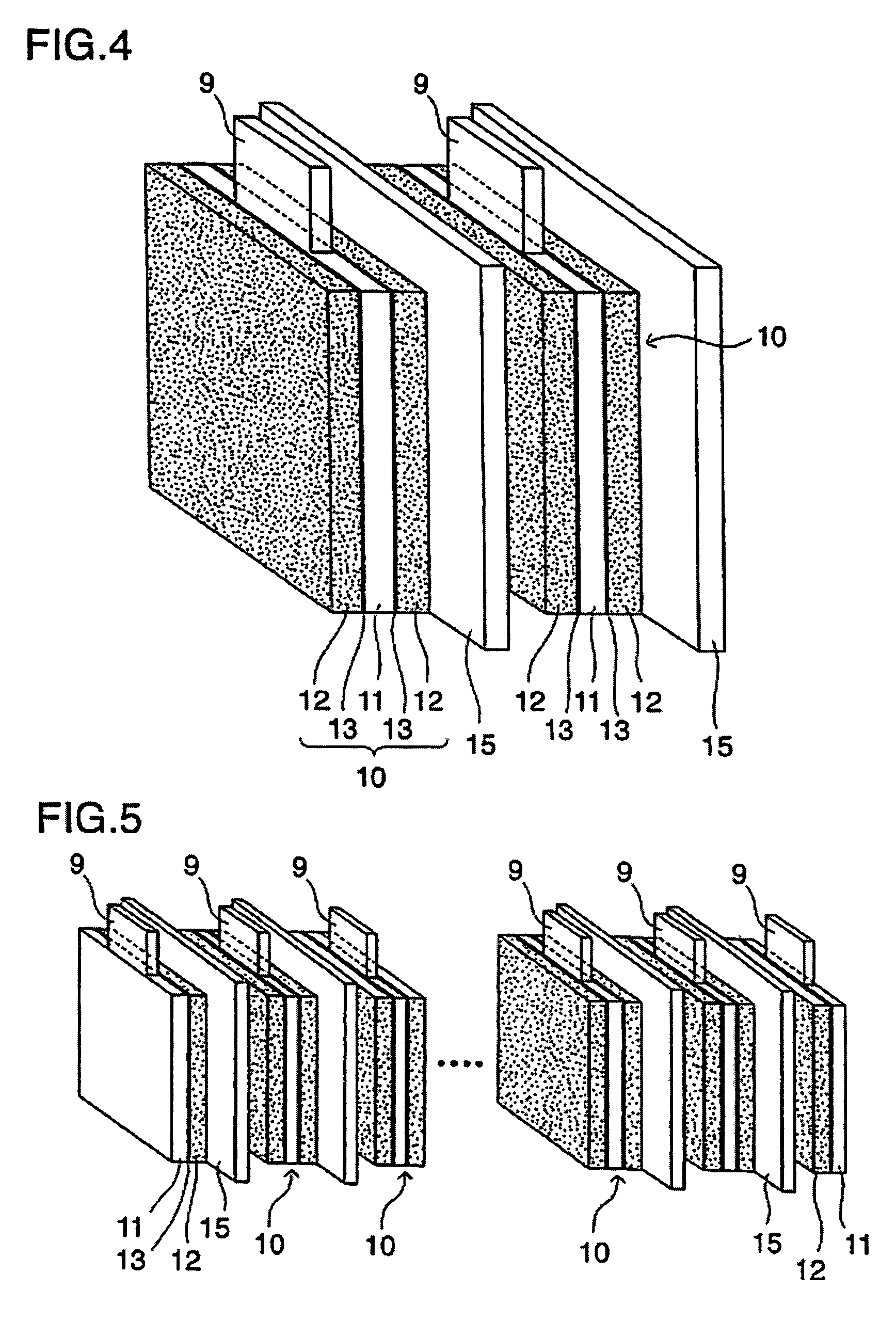
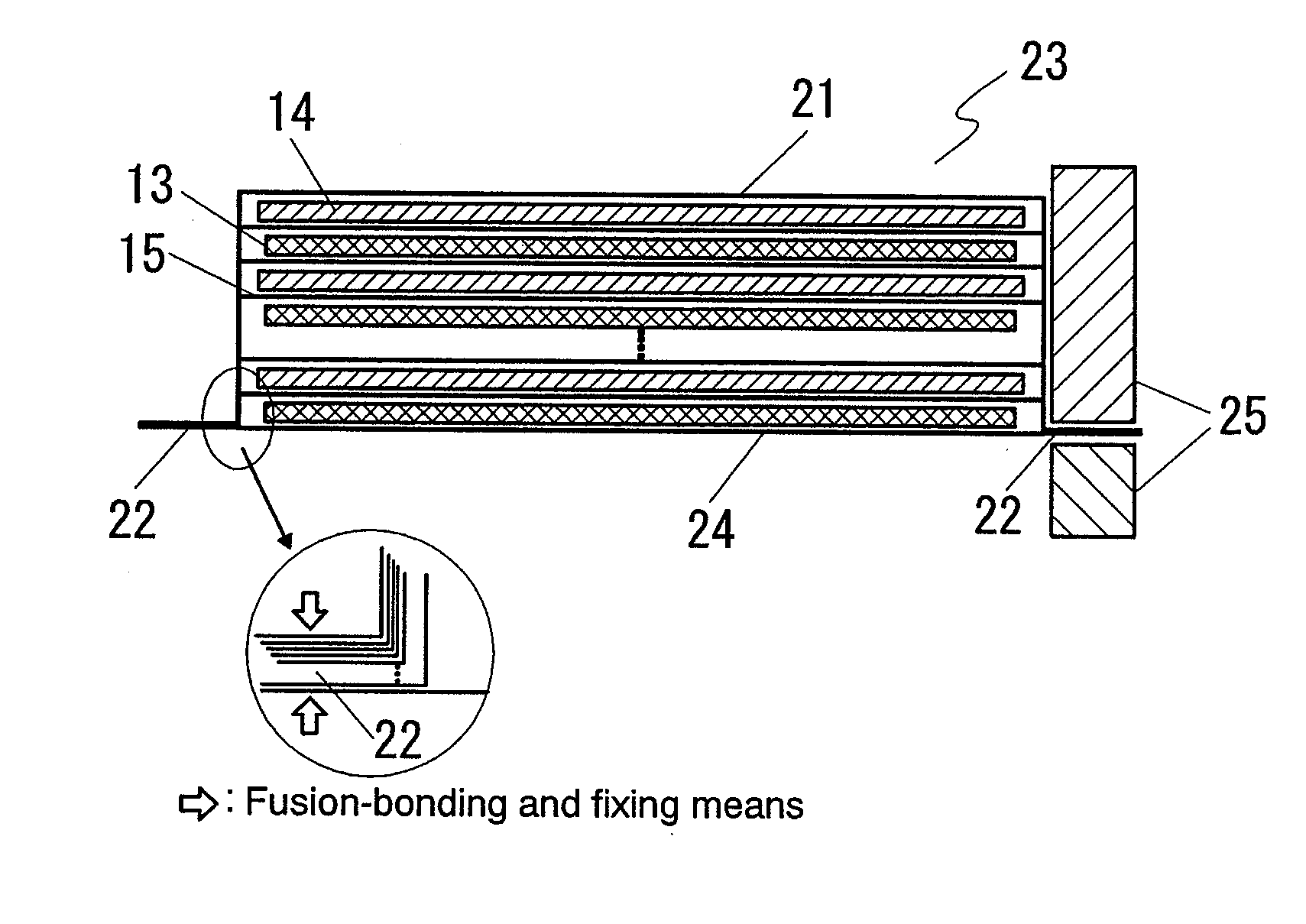
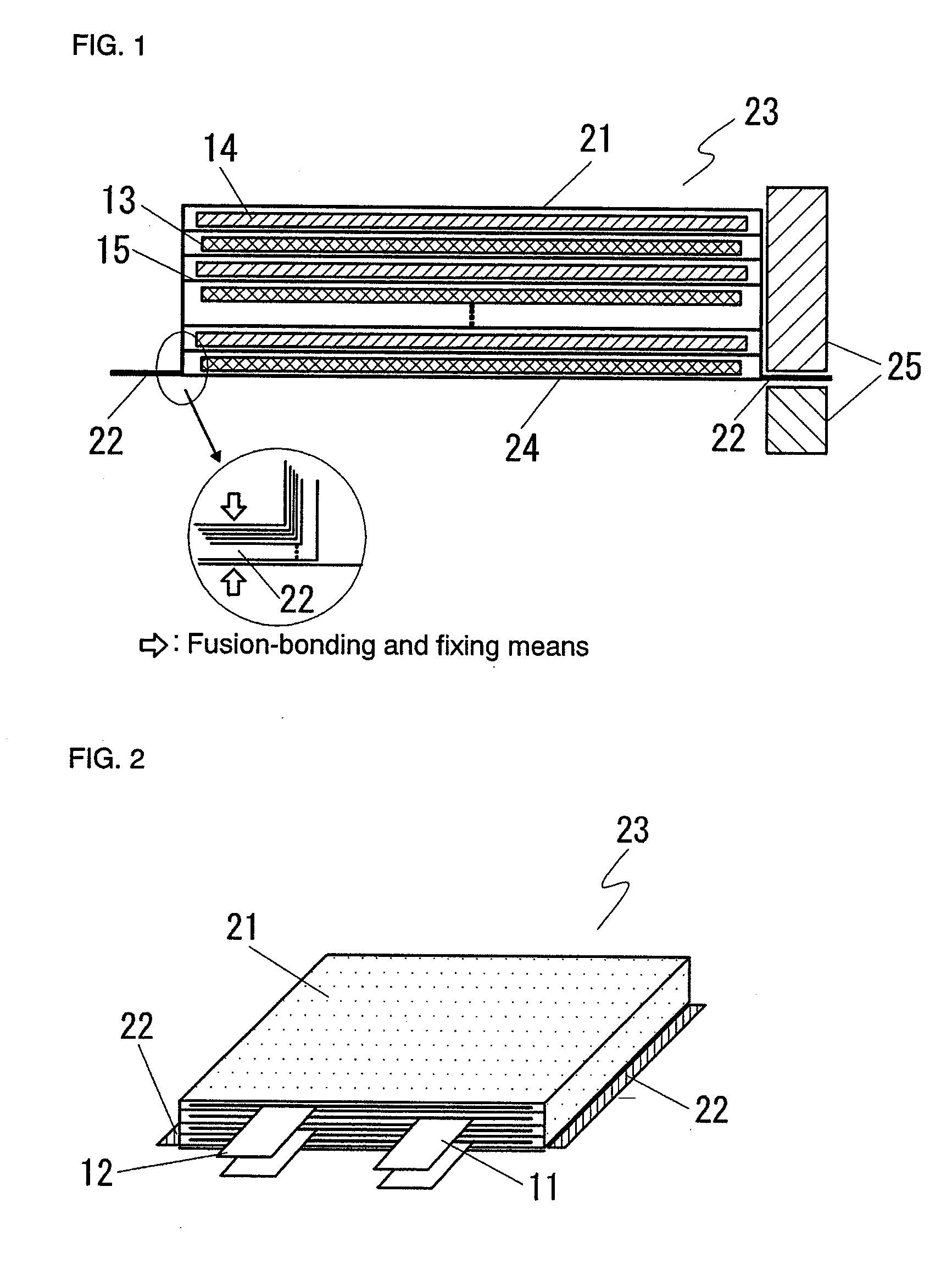
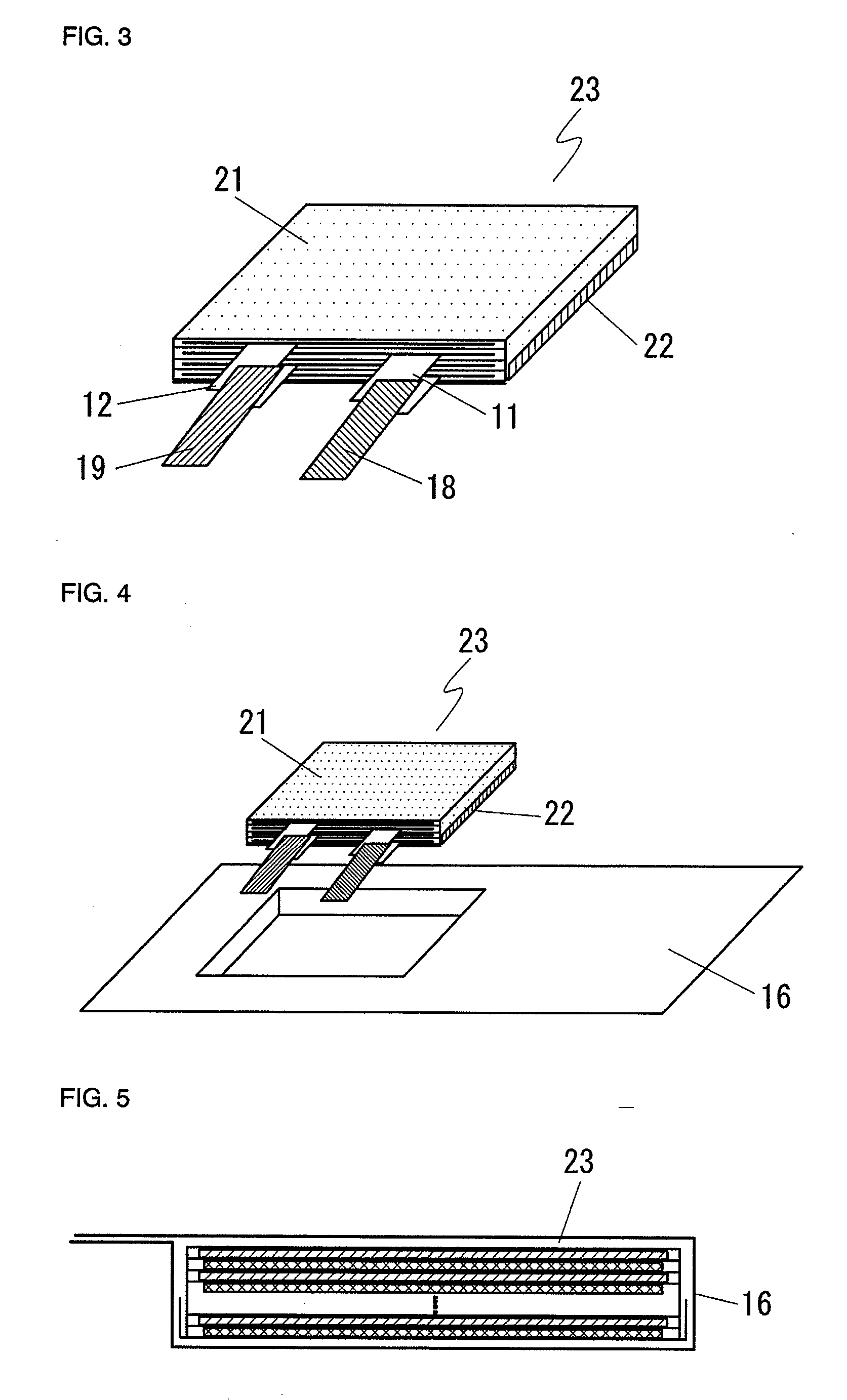
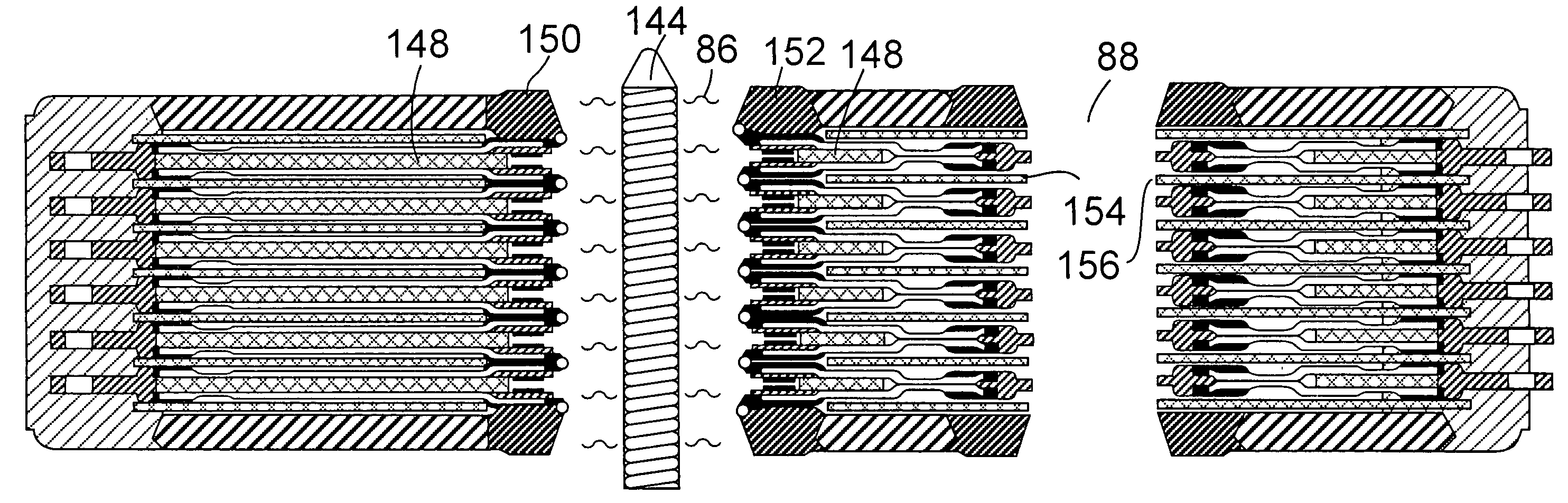
The present invention provides a stack-type lithium-ion polymer battery wherein: the battery capacity is not being degraded; the generation of the wrinkles and fracture of the separator is being suppressed; the battery has gas releasing paths; the displacement of an electrode stack hardly occurs; and the workability at the time of placing the electrode stack in a package body is improved by fixing the electrode stack. A stack-type lithium-ion polymer battery of the present invention comprises: a cathode 13; an anode 14; a separator 15; and a gel electrolyte; wherein an electrode stack 23 in which the cathode 13 and the anode 14 are stacked through the separator 15 is enclosed and fixed by insulating porous sheets 21 and 24, and is packaged with a laminate material.
Owner:NEC ENERGY DEVICES LTD
Process for making a fluid processing module
InactiveUS7097800B2Improve sealingAvoid degradation of mechanical propertiesSemi-permeable membranesOther chemical processesPorous layerFiltration
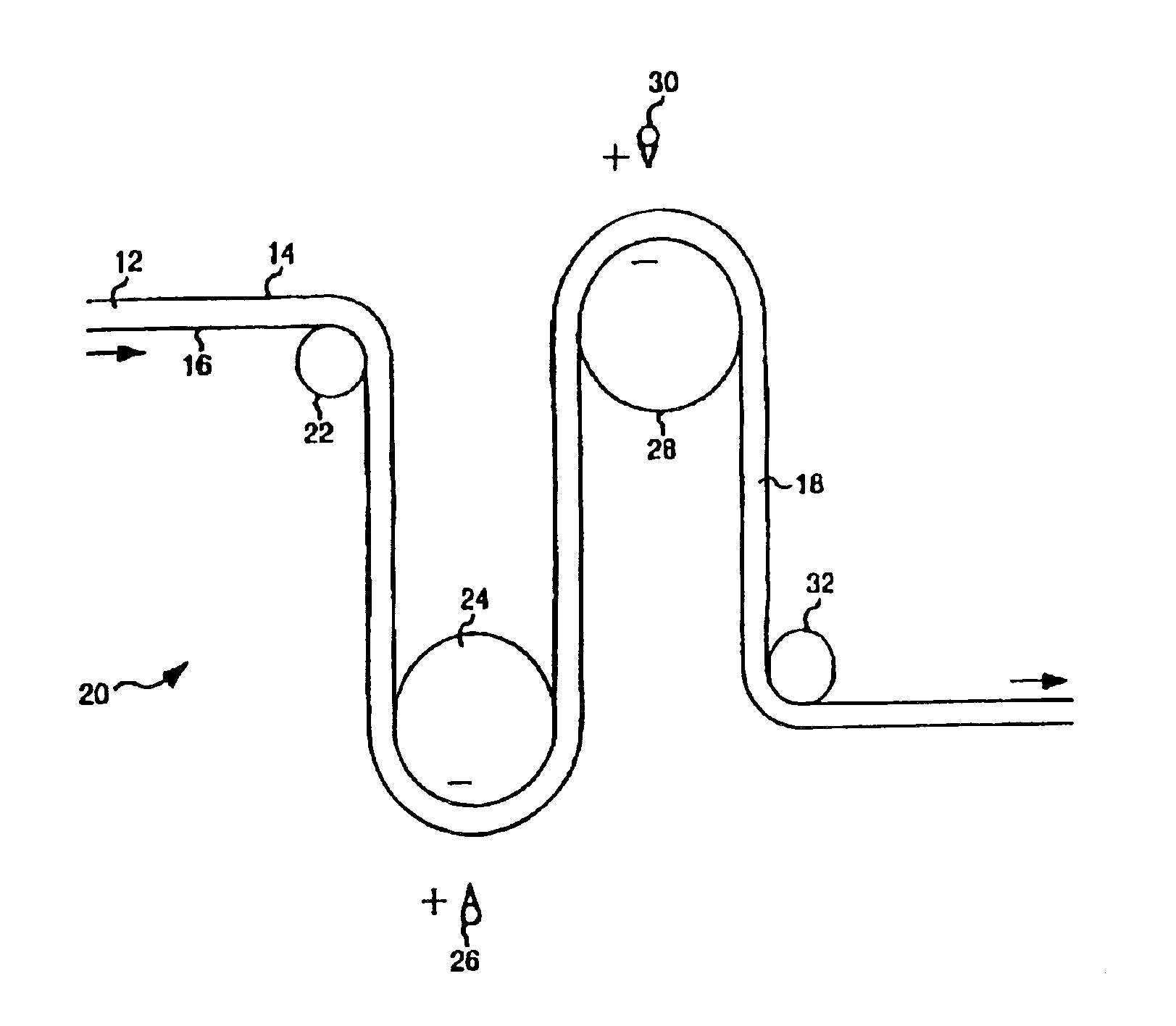
A process for making a fluid processing module is provided wherein a plurality of filtration elements is alternated with a fluid porous layer to form a stack. The filtration elements comprise a membrane sheet having a thermoplastic element bonded to a portion of an edge of the membrane. An opening is provided either through the membrane or through the thermoplastic element. A portion of the thermoplastic element extends into the opening and can be sealed to an adjacent positioned thermoplastic element to seal the porous sheet positioned between adjacently positioned membranes from fluid communication with the opening. Sealing can be effected by extending a heating element through the opening of the stack to effect simultaneous sealing of a plurality of thermoplastic elements.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
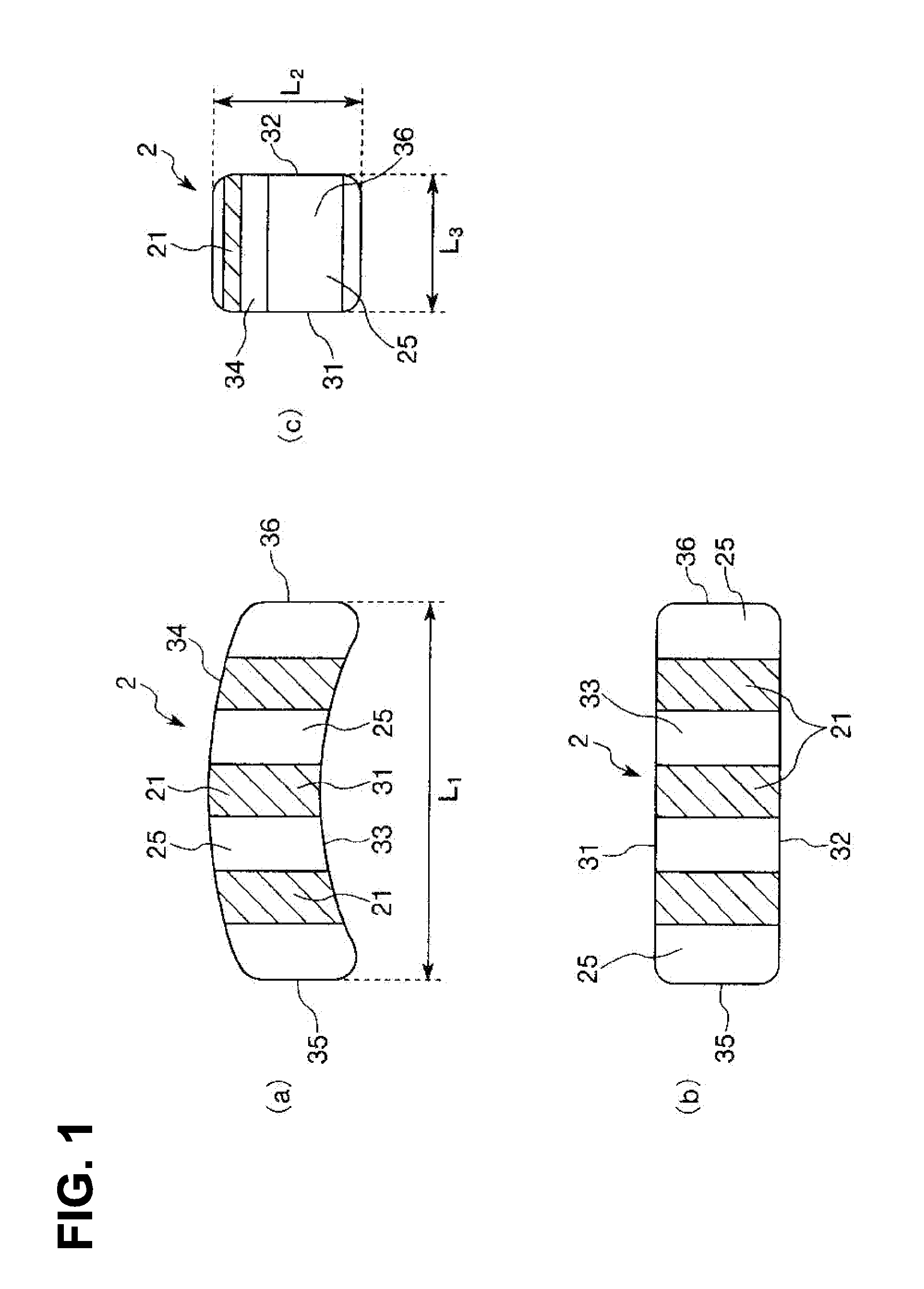
Vertebral body spacer
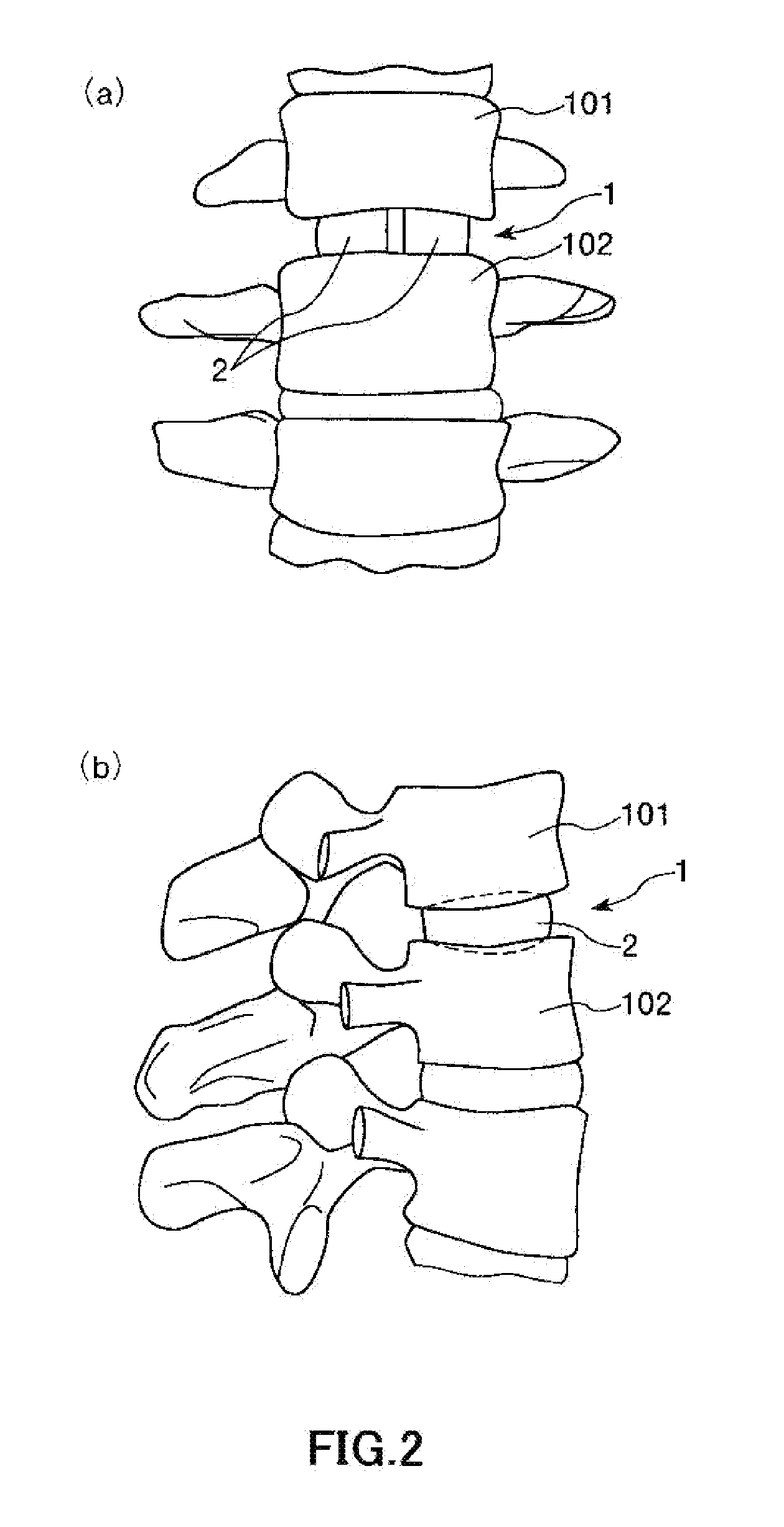
InactiveUS20130274886A1Small sizeEasy to implementSpinal implantsCoatingsIntervertebral spacePorous sheet
A vertebral body spacer of the present invention is used by being inserted between a vertebral body and a vertebral body (intervertebral space). The vertebral body spacer has a block body constituted of titanium or a titanium alloy as a main component thereof, and provided with a pair of contact surfaces to be made contact with the vertebral body and the vertebral body. The block body includes dense sheets having a dense part on at least a surface thereof and porous sheets having a porous part on at least a surface thereof. The porous part has a larger porosity than a porosity of the dense part. Each of the porous sheets is sandwiched between the pair of dense sheets. According to the present invention, it is possible to maintain an appropriate size between the vertebral bodies (intervertebral space).
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Lithium secondary cell, separator, cell pack, and charging method
InactiveUS6818352B2Improve securityLow costPrimary cell maintainance/servicingCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersChemical physicsCharge current
A lithium ion secondary battery including a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a separator and a nonaqueous electrolyte, where the separator essentially includes a porous sheet. The positive electrode active material and the negative electrode active material can be reversibly doped and dedoped such that, where Qp (mAh) is an electric charge necessary for causing total lithium contained in the positive electrode to be dedoped and Qn (mAh) is an electric charge necessary for causing lithium to fully dope the negative electrode, Qp>Qn. Further, when the battery is charged at a charging current Ic (mA) in a range of 0.2 Qn / h<Ic<2 Qn / h, in a range of an electric charge for charging Qc (mAh) of 1<Qc / Qn<Qp / Qn, doping of the positive electrode by lithium is initiated by producing lithium particles on the negative electrode by charging of the battery until Qc<Qp.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Method for preparing NiCo2O4/graphene supercapacitor material with microwave method
InactiveCN104882298AImprove electrochemical performanceSimple processHybrid/EDL manufactureAir atmosphereMicrowave method
The invention belongs to the field of preparation of nano composite materials, and relates to a method for preparing a NiCo2O4 / graphene supercapacitor material with a microwave method. The main steps includes: using natural graphite as a raw material, oxidizing with a Hummers method to obtain graphite oxide, ultrasonically dispersing the graphite oxide in water, then adding cobalt chloride and nickel chloride, stirring and then adding urea, continuing to stir, then heating the mixed solution in a microwave reactor to 100 DEG C and carrying out a reflux reaction for 5 to 25 min, thereby obtaining a precursor, and calcining the precursor in an air atmosphere at 300 DEG C for 2h, thereby obtaining a porous flaky NiCo2O4 / graphene supercapacitor material. The prepared composite supercapacitor material is synthesized through the microwave method, the preparation method is simple in technology, convenient to operate, high in feasibility, and rapid and efficient, and is easy to realize industrial implementation. The synthesized NiCo2O4 is tightly attached to the graphene, and excellent electrochemical performance is represented.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com