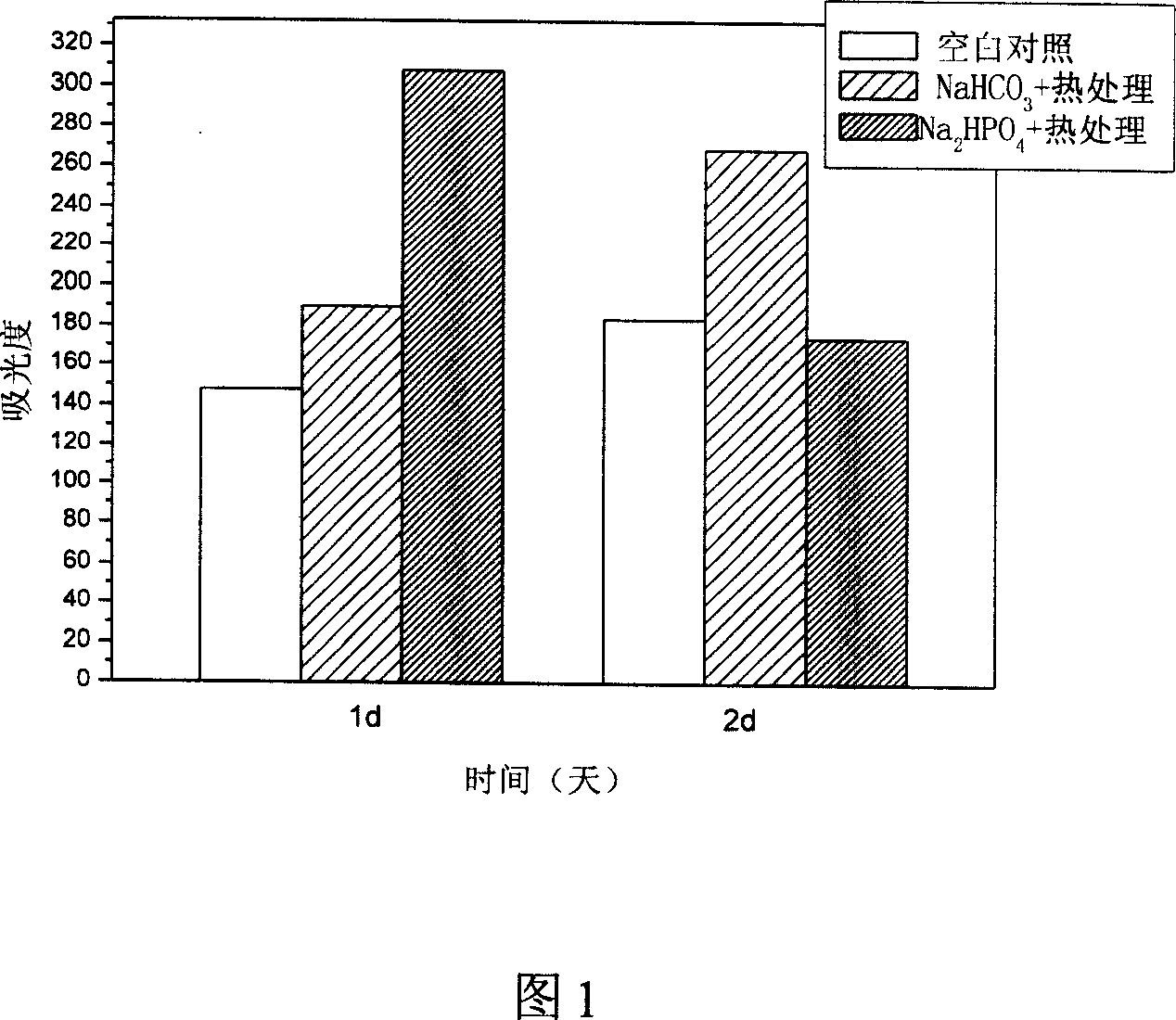
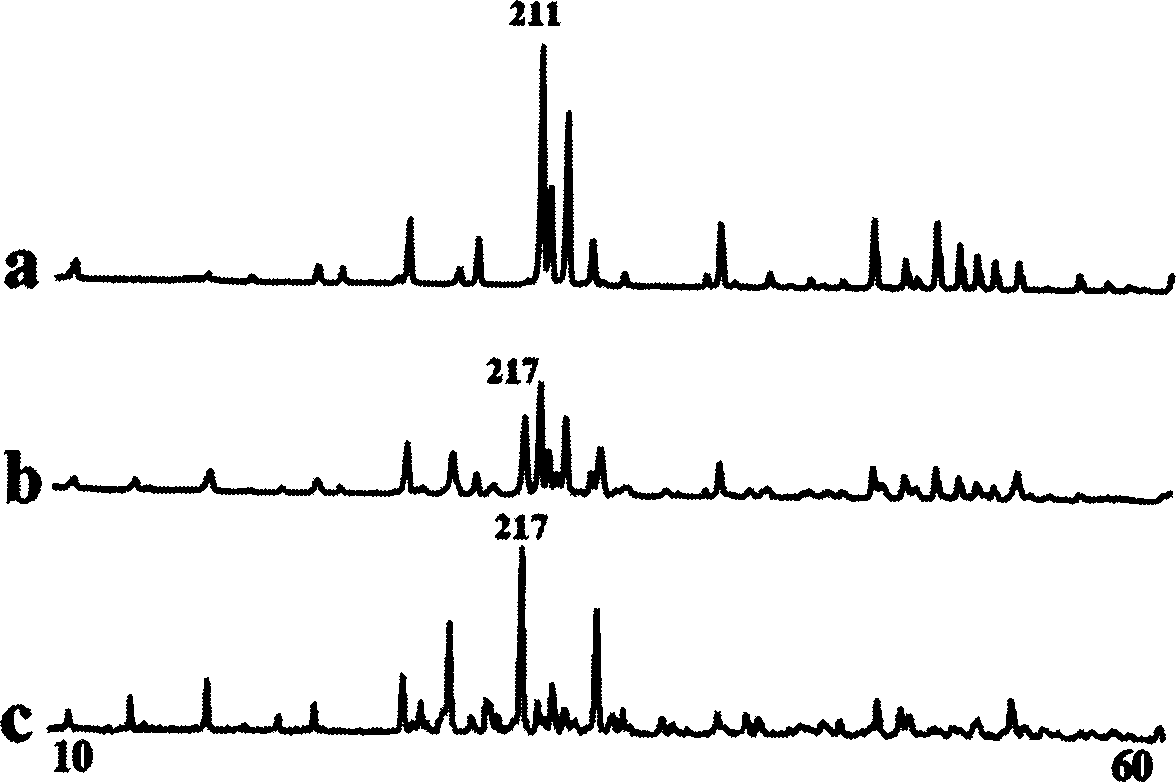
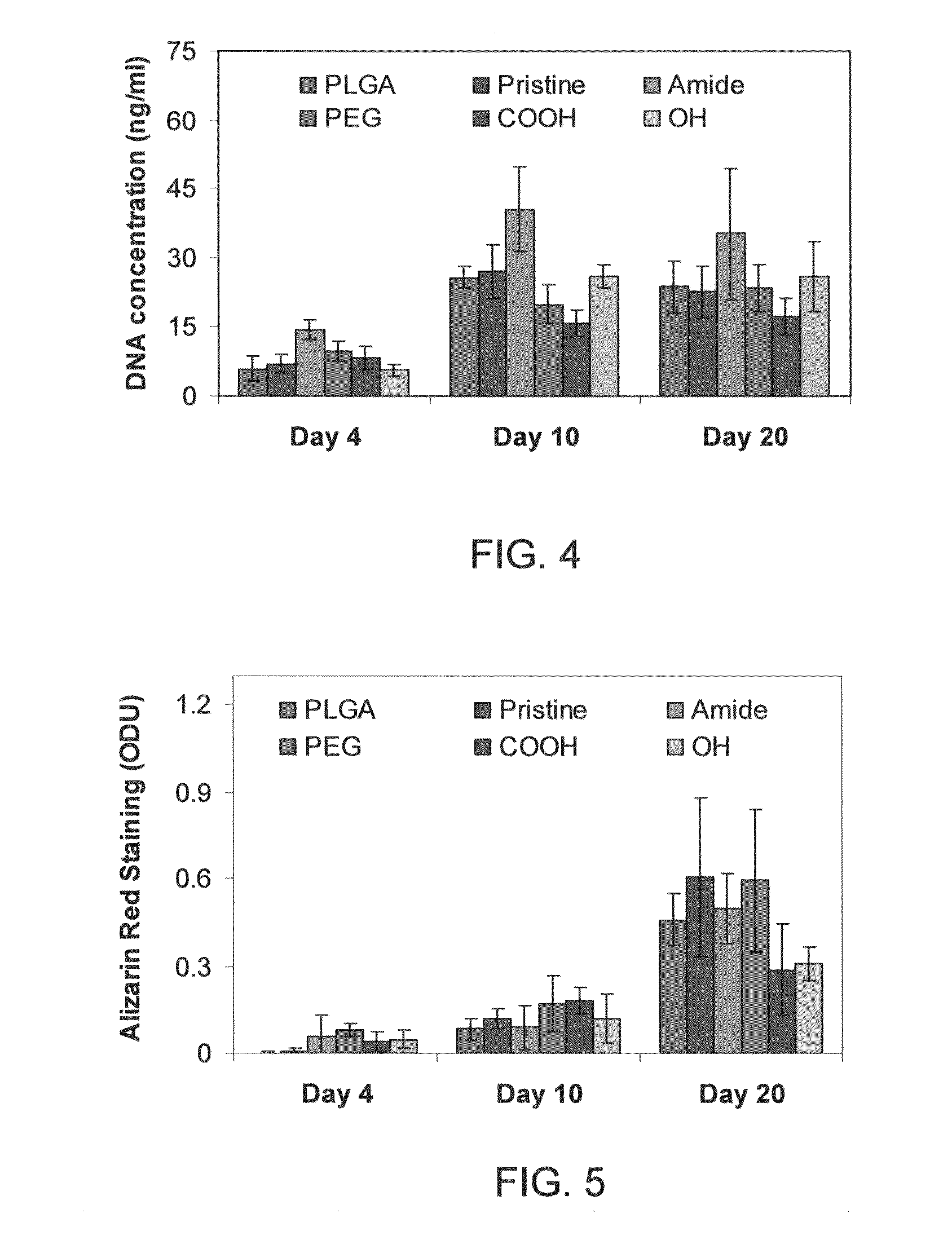
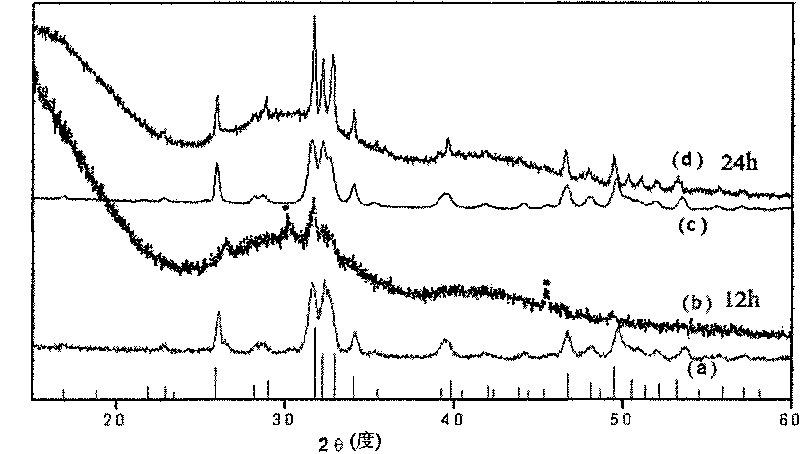
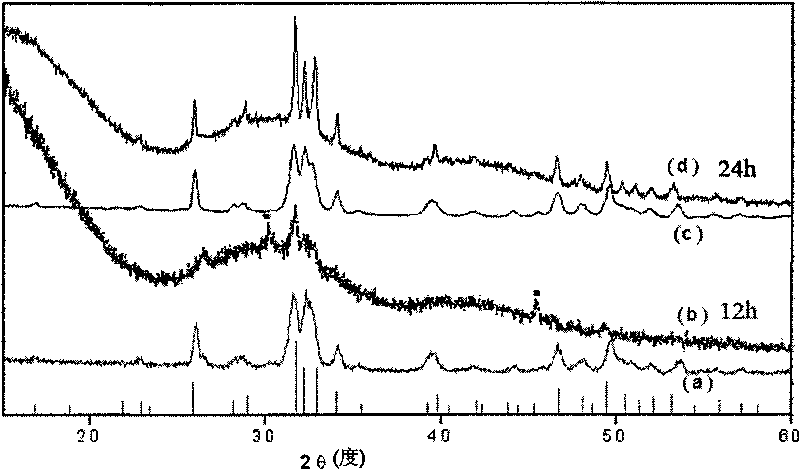
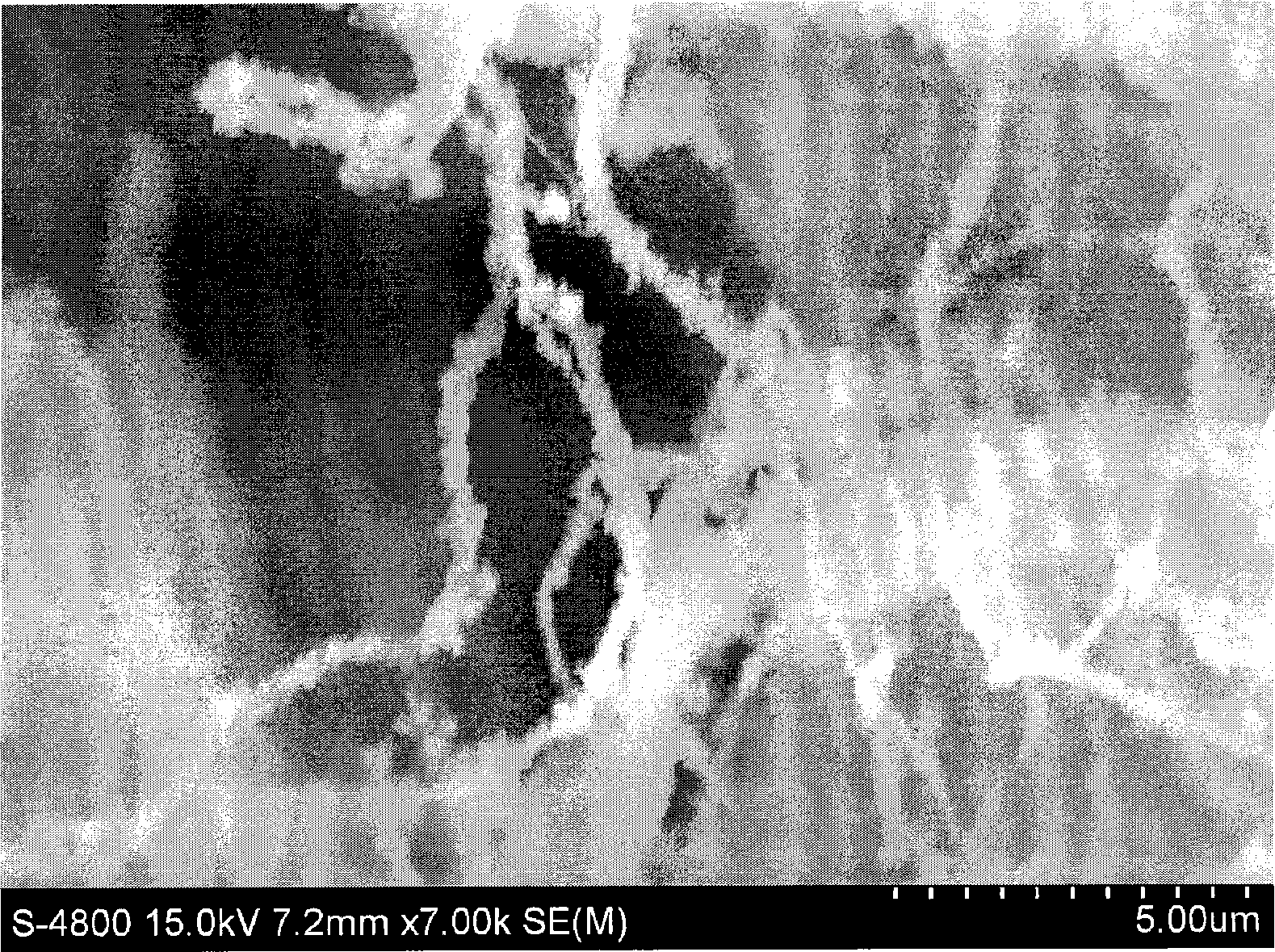Patents
Literature
639 results about "Bone tissue engineering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
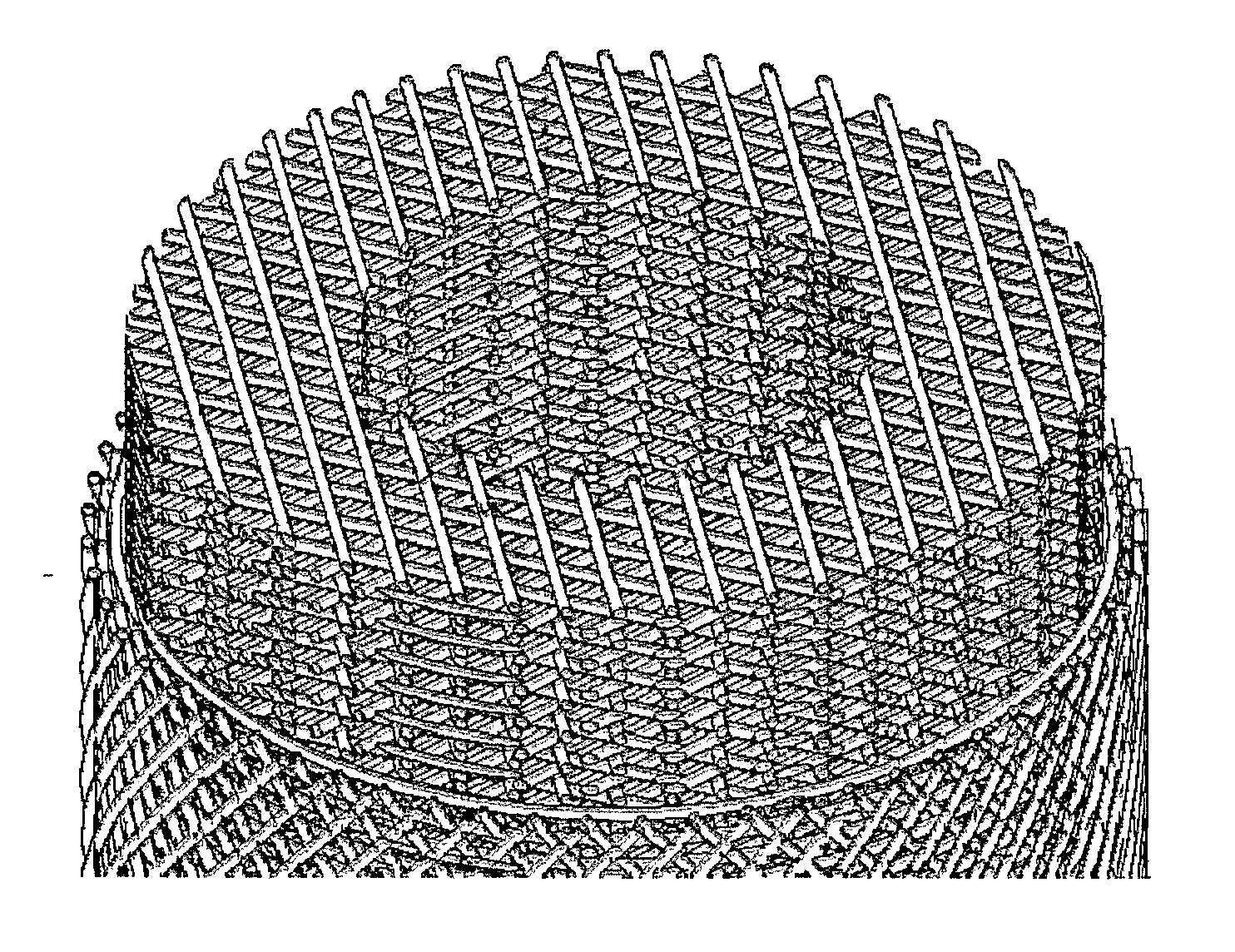
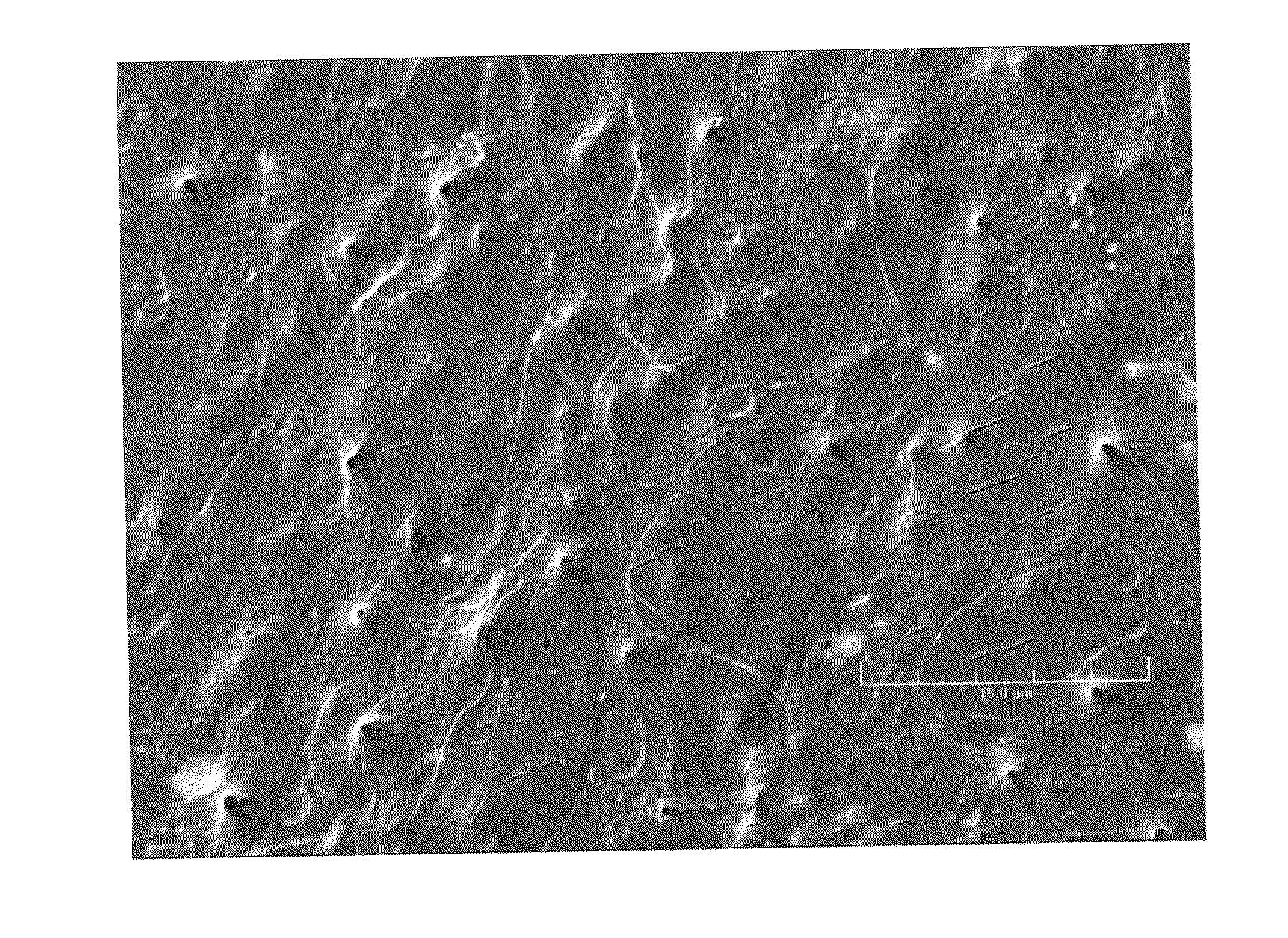
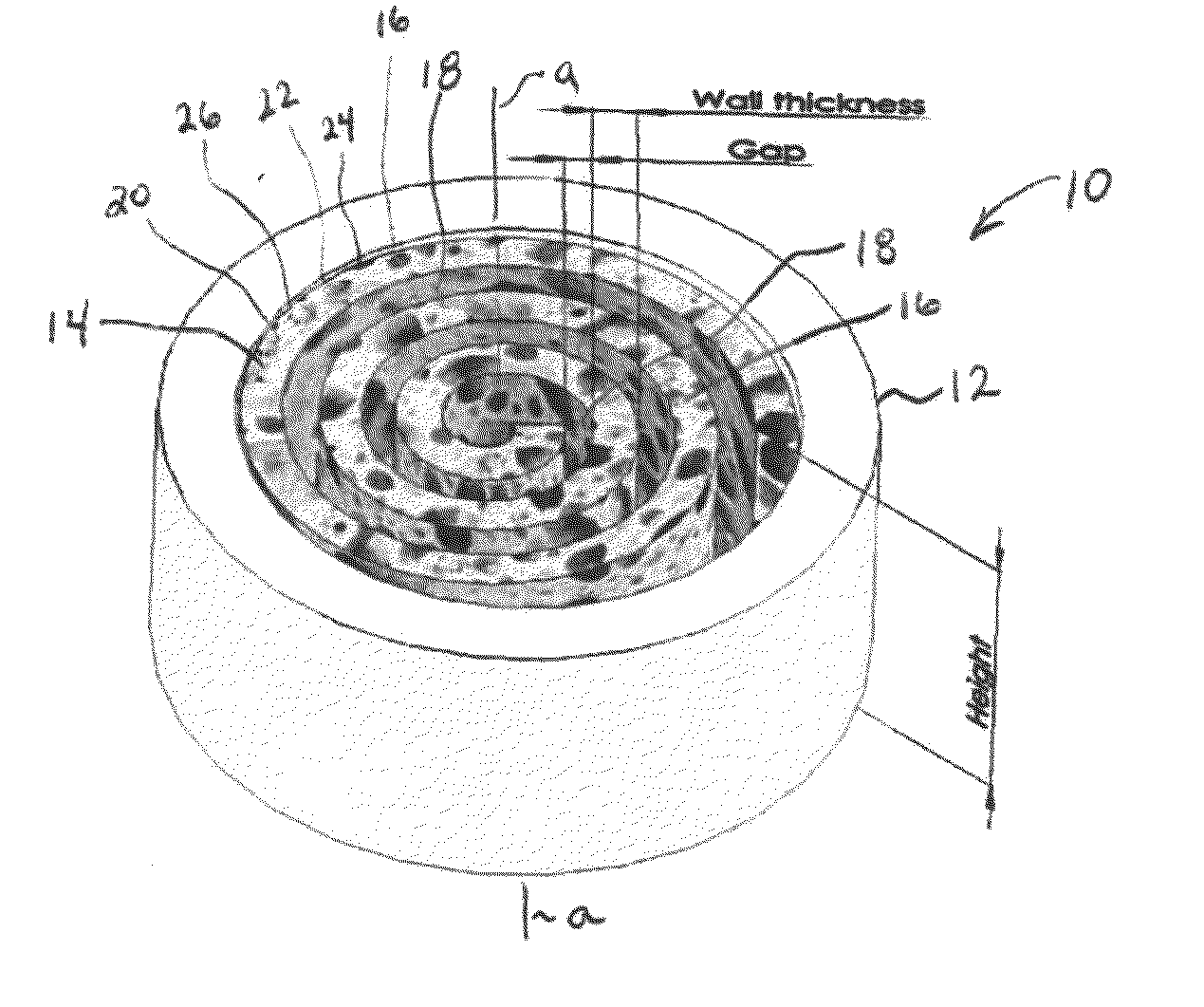
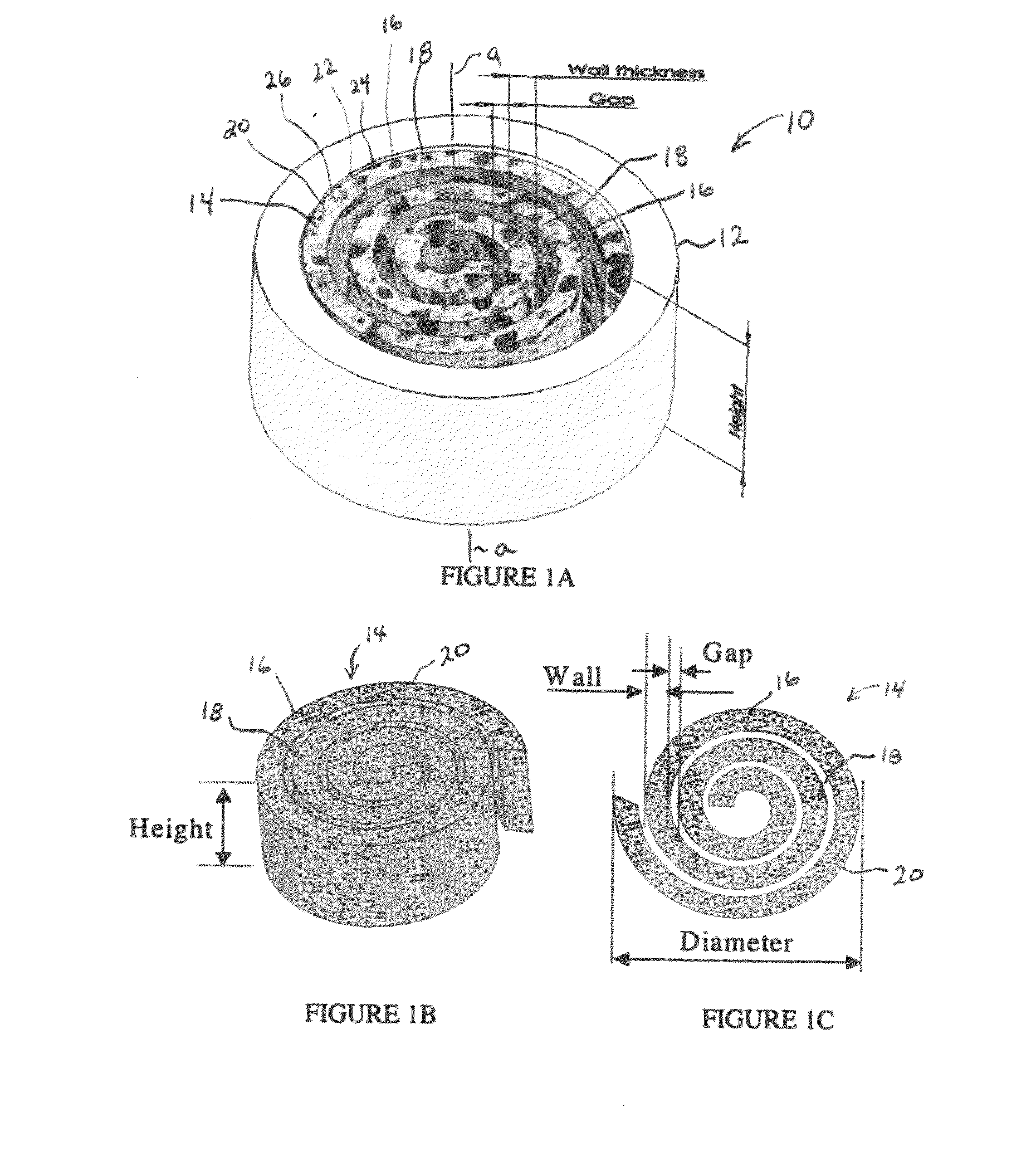
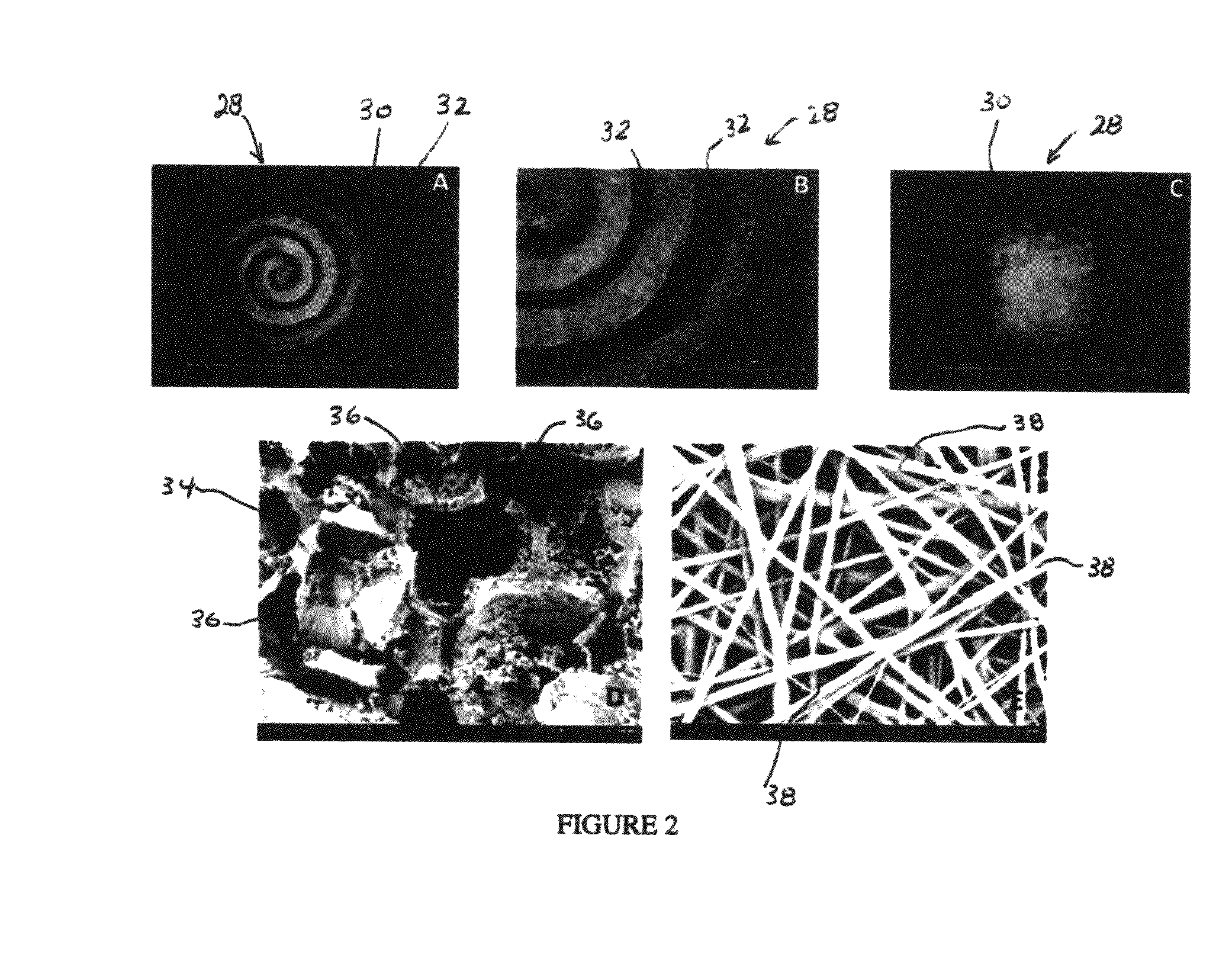
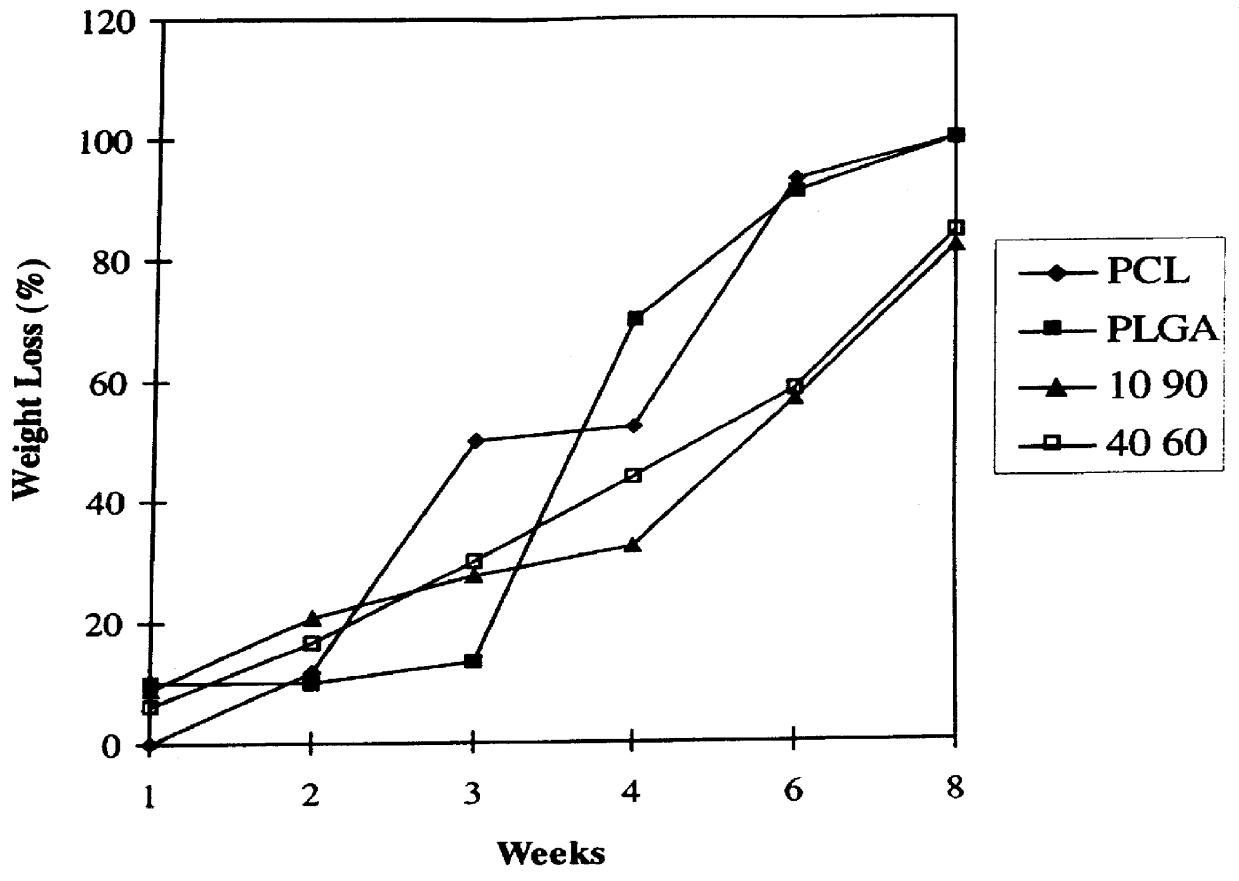
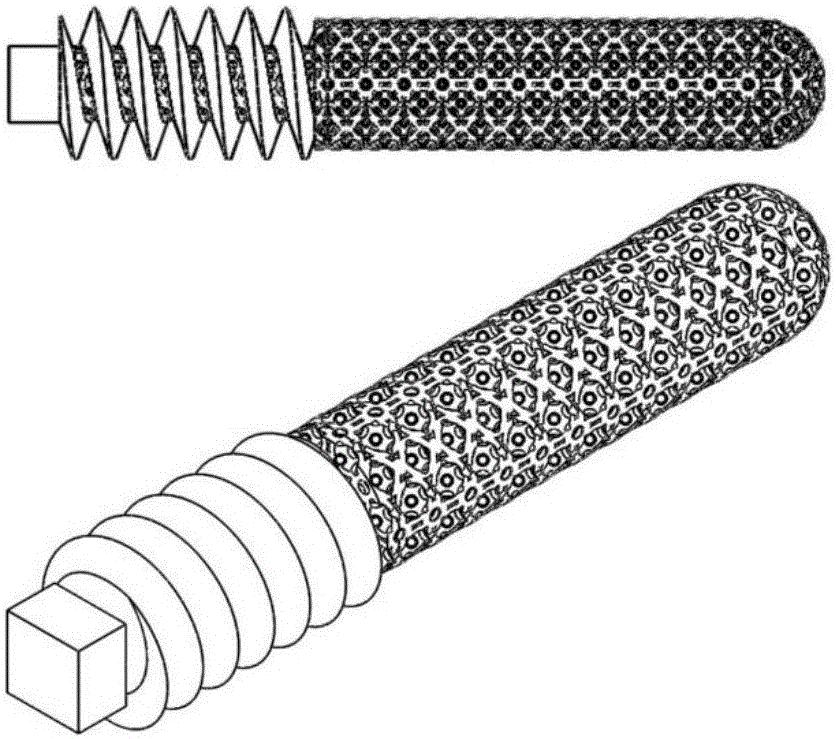
Synergetic functionalized spiral-in-tubular bone scaffolds
InactiveUS20100310623A1Increase the number ofIncrease alkaline phosphatase activityPeptide/protein ingredientsBone implantPorous sheetCell seeding
An integrated scaffold for bone tissue engineering has a tubular outer shell and a spiral scaffold made of a porous sheet. The spiral scaffold is formed such that the porous sheet defines a series of spiral coils with gaps of controlled width between the coils to provide an open geometry for enhanced cell growth. The spiral scaffold resides within the bore of the shell and is integrated with the shell to fix the geometry of the spiral scaffold. Nanofibers may be deposited on the porous sheet to enhance cell penetration into the spiral scaffold. The spiral scaffold may have alternating layers of polymer and ceramic on the porous sheet that have been built up using a layer-by-layer method. The spiral scaffold may be seeded with cells by growing a cell sheet and placing the cell sheet on the porous sheet before it is rolled.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Biocompatible compositions and methods of using same
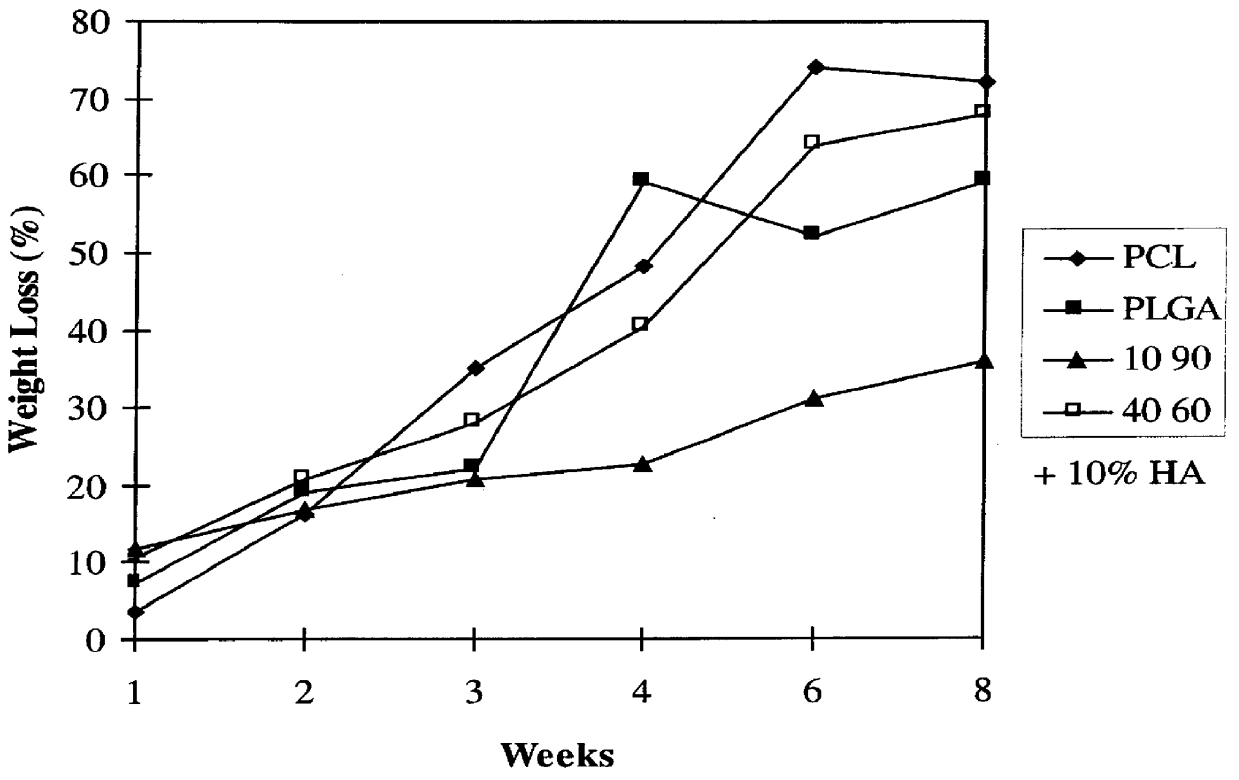
Blends of biodegradable polymers, preferably poly(caprolactone) and poly(D,L-lactic-co-glycolic) acid are discussed as well as their applications in the medical field, particularly with regard to bone tissue engineering. Preferably, hydroxyapatite ("HA") granules are incorporated into the blends and the resulting blends have desirable mechanical, physical, and biological characteristics. Even more preferably the compositions of the present invention are utilized to form osteoconductive composites that supported bone cell growth on the surface as well as throughout the scaffold.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV +1
Bone replacement materials
ActiveUS20070203584A1Easy adhesionFacilitate cell growthAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantBone tissueBone tissue engineering
Particular aspects provide novel devices for bone tissue engineering, comprising a metal or metal-based composite member / material comprising an interior macroporous structure in which porosity may vary from 0-90% (v), the member comprising a surface region having a surface pore size, porosity, and composition designed to encourage cell growth and adhesion thereon, to provide a device suitable for bone tissue engineering in a recipient subject. In certain aspects, the device further comprises a gradient of pore size, porosity, and material composition extending from the surface region throughout the interior of the device, wherein the gradient transition is continuous, discontinuous or seamless and the growth of cells extending from the surface region inward is promoted. Additional aspects provide a device for bone tissue engineering, comprising a metal or metal-based composite member / material comprising an interior porous structure, wherein the pore size, porosity and material composition is selected to provide a device having an optimal density and / or elastic modulus and / or compression strength for a specific recipient. Novel methods for fabricating the devices are also provided.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
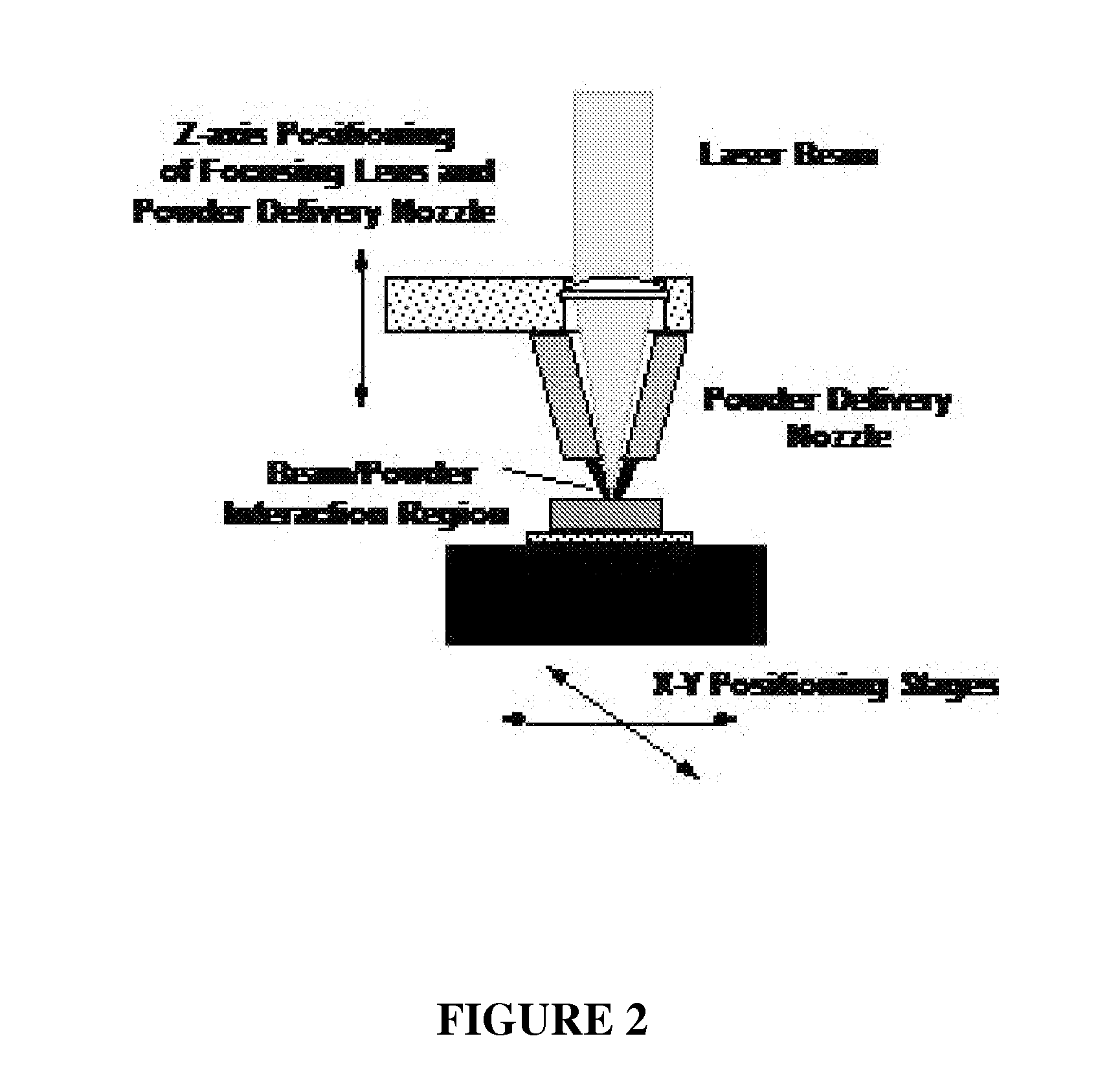
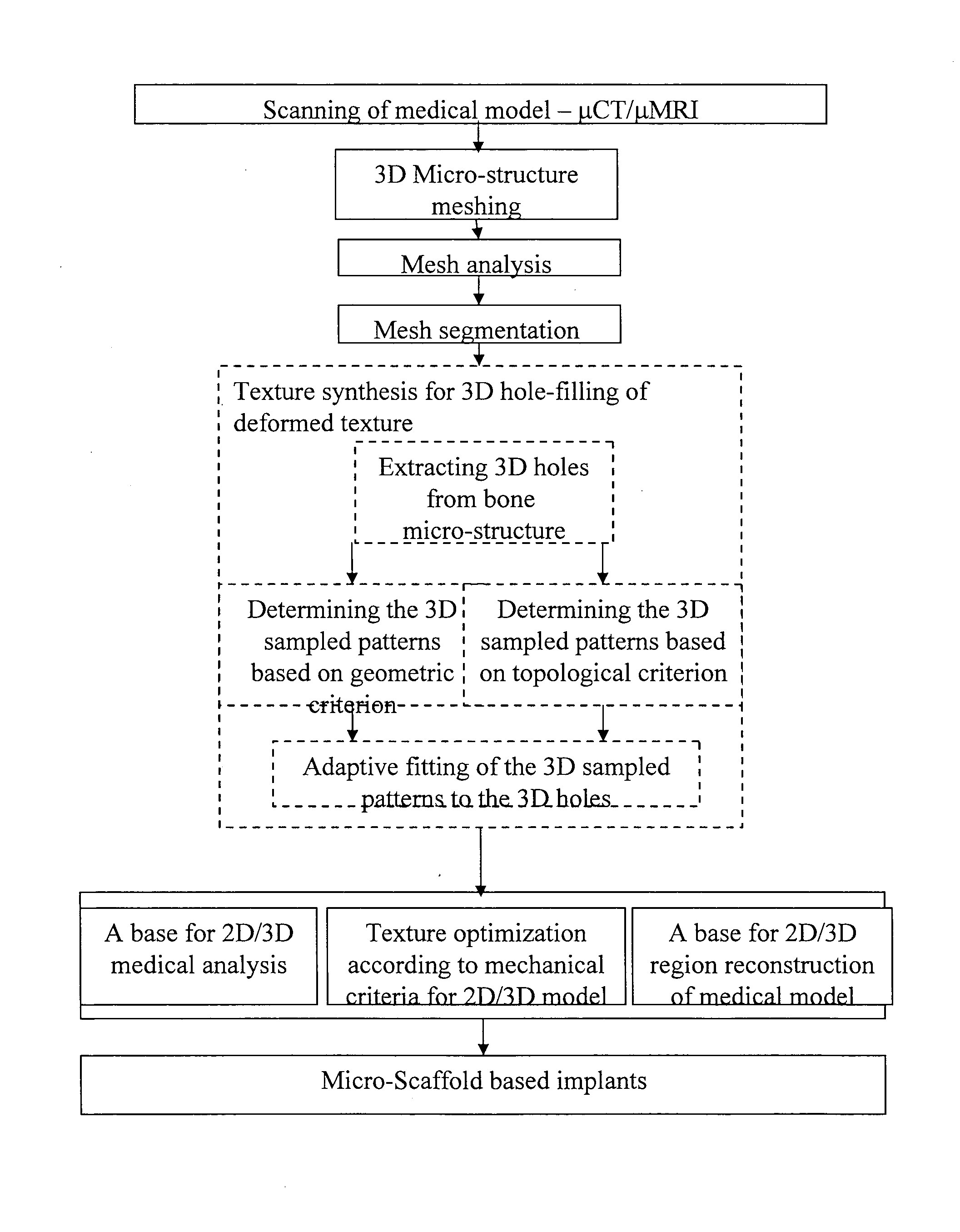
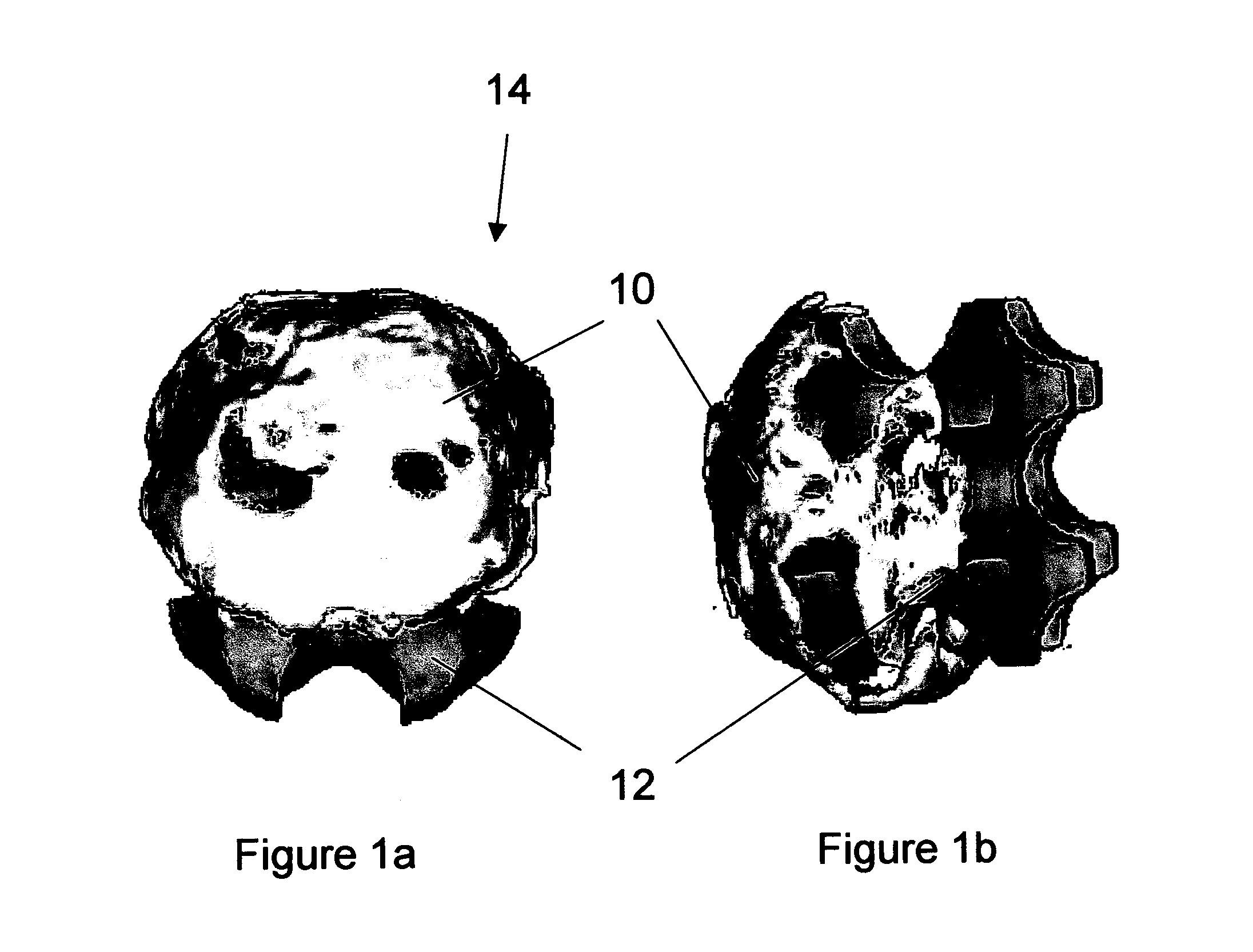
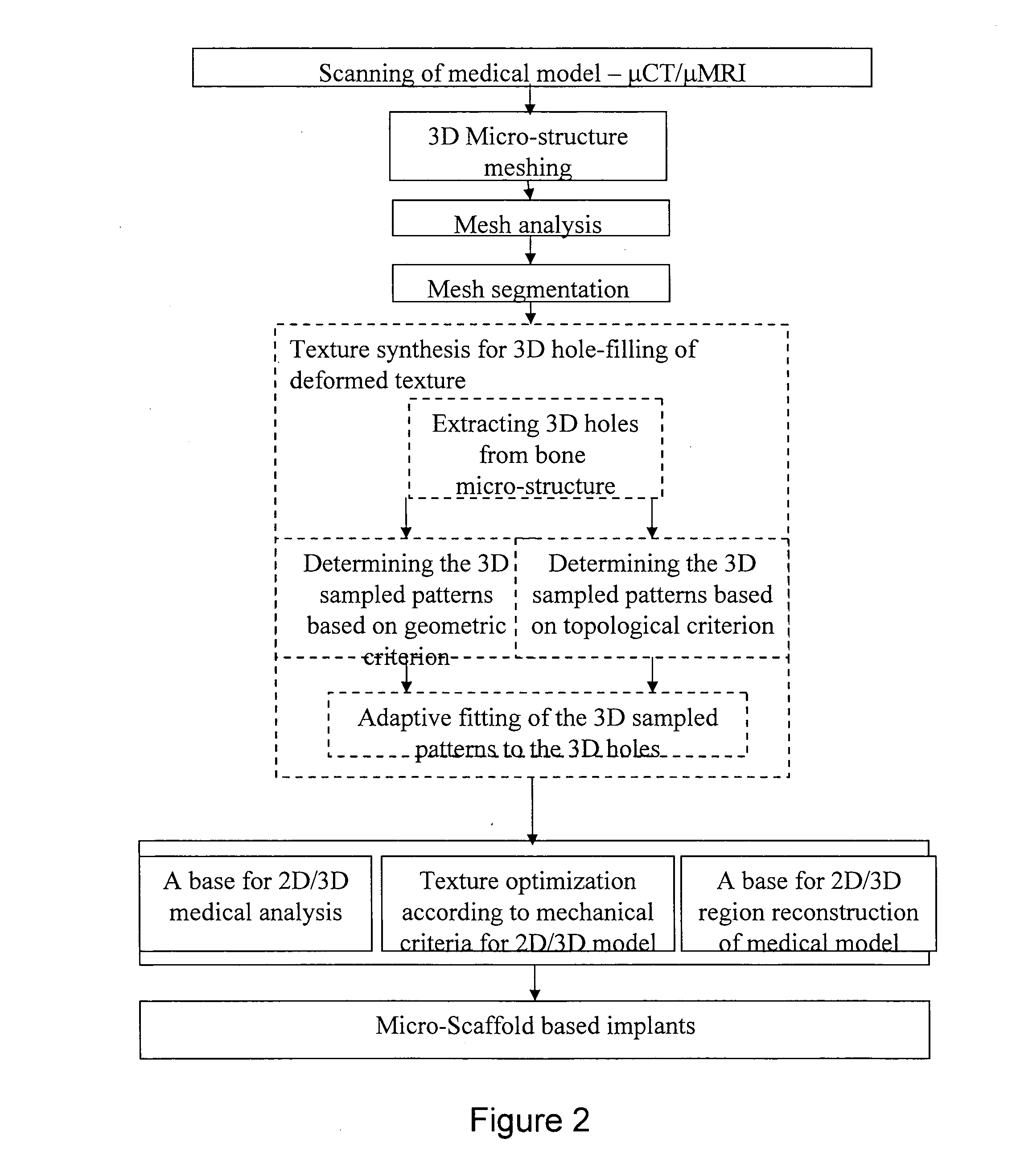
Modeling micro-scaffold-based implants for bone tissue engineering
InactiveUS20110022174A1Easy to integrateSimple processBone implantCharacter and pattern recognitionMicro structureNatural bone
A new conceptual biomedical method is presented for designing scaffold-based bone implants and using these implants in treating deteriorated bones. These implants have micro-architectural bone structures that are capable of mimicking the stochastic micro-structure as in natural bone bio-mineral structures. Moreover, they can be adapted as specific tailor-made compatible bone-repair mediator implants to be used as effective substitutes for natural damaged bone fracture structures.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Bioactive, resorbable scaffolds for tissue engineering
InactiveUS20050118236A1High porosityImprove manufacturabilityBiocideSynthetic resin layered productsPorosityFiber
Flexible, bioactive glass meshes and scaffolds made therefrom are provided. The meshes comprise interwoven bioactive glass fibers that can be coated with resorbable polymers. Meshes can also be woven from glass fibers and resorbable polymers. Scaffolds can be constructed by a plurality of meshes, which can have varying porosities to create porosity gradients in the scaffold. Methods of making scaffolds are provided which can comprise pulling bioactive glass fibers, winding the fibers, forming the fibers into bundles, coating the fibers with a resorbable polymer, and creating a biaxial weave with the bundles. Soft tissue engineering methods are also provided for creating scaffolds for incubating cells such as fibroblasts and chondroblasts. Meshes and scaffolds are suitable for tissue engineering, such as bone tissue engineering and cartilage tissue engineering.
Owner:GENTIS
Material for bone tissue engineering scaffold and making method thereof
InactiveCN101032632AImprove mechanical propertiesGood biocompatibilityBone implantBiocompatibility TestingBiological materials
The present invention relates to biological material technology, and is especially porous magnesium, magnesium alloy and composite magnesium material used as high strength biomedicine rack material for human body hard tissue defection and its preparation process. The porous magnesium, magnesium alloy and composite magnesium material used in bone tissue engineering rack has porosity of 5-99 % and pore diameter of 50-900 microns. Owing to easy degradation and absorption of magnesium inside body, the bone tissue engineering rack of porous magnesium, magnesium alloy and composite magnesium material has excellent mechanical performance and excellent biocompatibility and can provide 3D space for cell to grow.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composite material for porous material and gel use thereof
InactiveCN1644221AImprove stabilityGood adhesionProsthesisCalcium biphosphateAlpha-tricalcium phosphate
A composition of porous material and gel for preparing artificial bone is prepared from collagen and porous material chosen from alpha-tricalcium phosphate / hydroxy apatite, beta-tricalcium phosphate / hydroxy apatite-coral, calcium phosphate / hydroxy apatite, calcium carbonatel tricalcium phosphate, etc.
Owner:徐小良
Multiplex composite bone tissue engineering bracket material capable of degrading gradiently and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a multiplex composite engineering scaffold material capable of gradually decomposing bone tissue and a preparation method thereof. The composite scaffold material consists of calcium phosphate bone cement, biological compatible degradable synthetic high polymer and biological compatible degradable natural high polymer, has better mechanical property and gradient degradation characteristic, and can achieve the aim of regenerating and repairing bone tissue defect by implanting a bone growth factor to induce in-vivo stem cells to be differentiated into bone cells, thereby obviously improving initial strength and toughness of the scaffold material, and ensuring enough strength and toughness of the scaffold material during operating and implanting. After compounded with the high polymer material, the scaffold has excellent flexibility, so that the scaffold can be subjected to certain machining, such as cutting and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Bracket material for bone tissue engineer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101417145AImprove mechanical propertiesGood biocompatibilityProsthesisDrug biological activityProtein C
The invention relates to a bracket material used for an osseous tissue project, and a preparation method thereof. Firstly, the bracket of a type I collagen is extracted from a small fresh pigskin by a mature extracting technique. Then, the bracket is further expanded in a Tris cushion liquid, the pH of which is equal to 8.8 to obtain a natural porous collagen bracket by the treatments of freezing and drying. The bracket is respectively and repeatedly mineralized in a CaCl2 liquid and in (NH4)2HPO4 liquid or mineralized in simulated body fluid for a long period to lead the weakly crystallized HA to be uniformly settled into the collagen bracket; and then a pigskin collagen-hydroxyapatite ossein is obtained by the treatments of freezing and drying to replace the natural bracket material. The invention not only maintains the natural bracket structure of the collagen in an organism, but also has the advantages of low material cost, simple devices, short period and easy operation. The obtained compound bracket material used for the pigskin collagen-hydroxyapatite osseous tissue project has the characteristics of high intensity, large toughness, non-antigenicity, higher biological activity as well as degradation and releasing control.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Calcium phosphate/collagen composite biologic ceramic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103055352AImprove mechanical propertiesPromote repair and regenerationProsthesisCalcium biphosphateBone tissue engineering
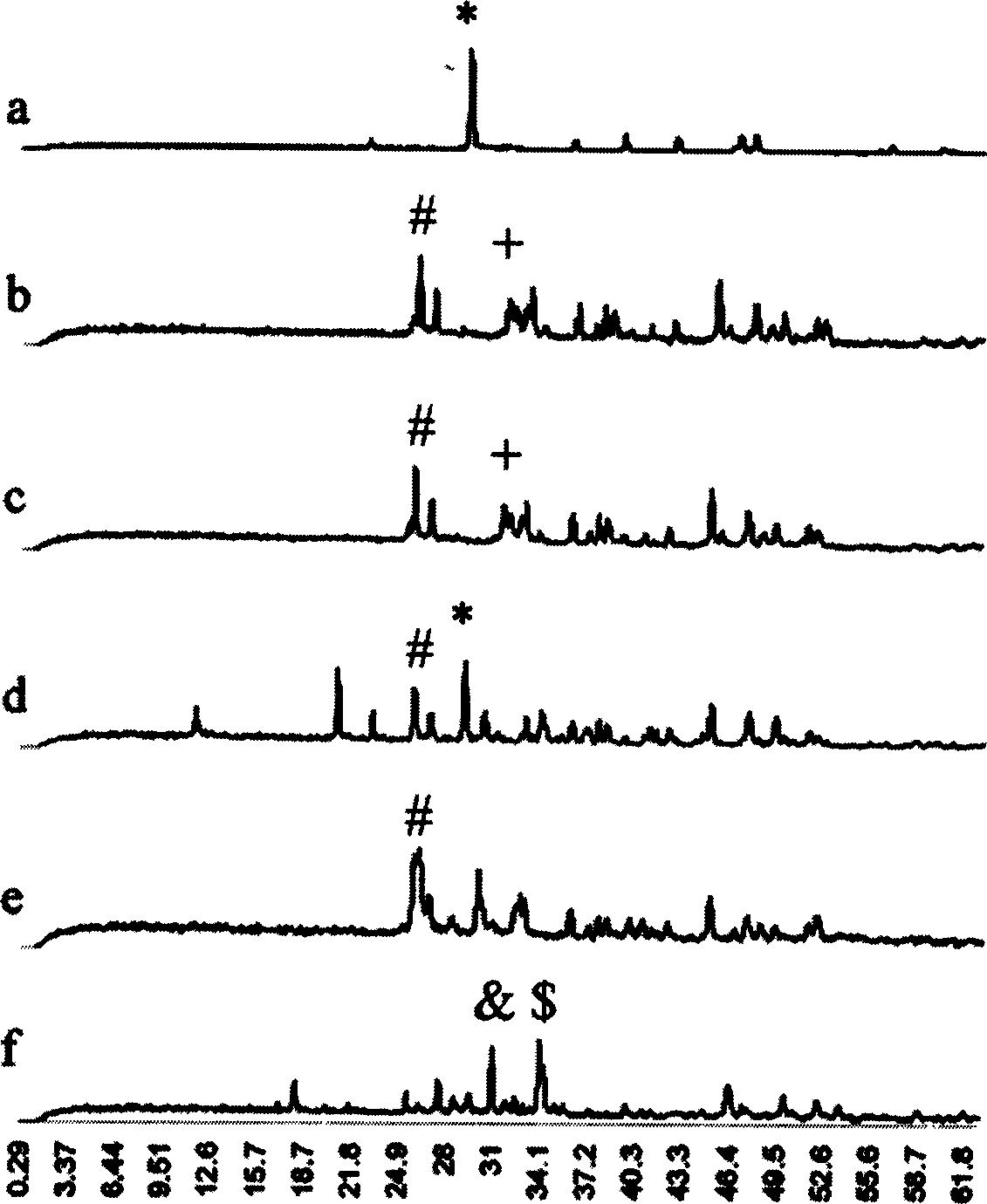
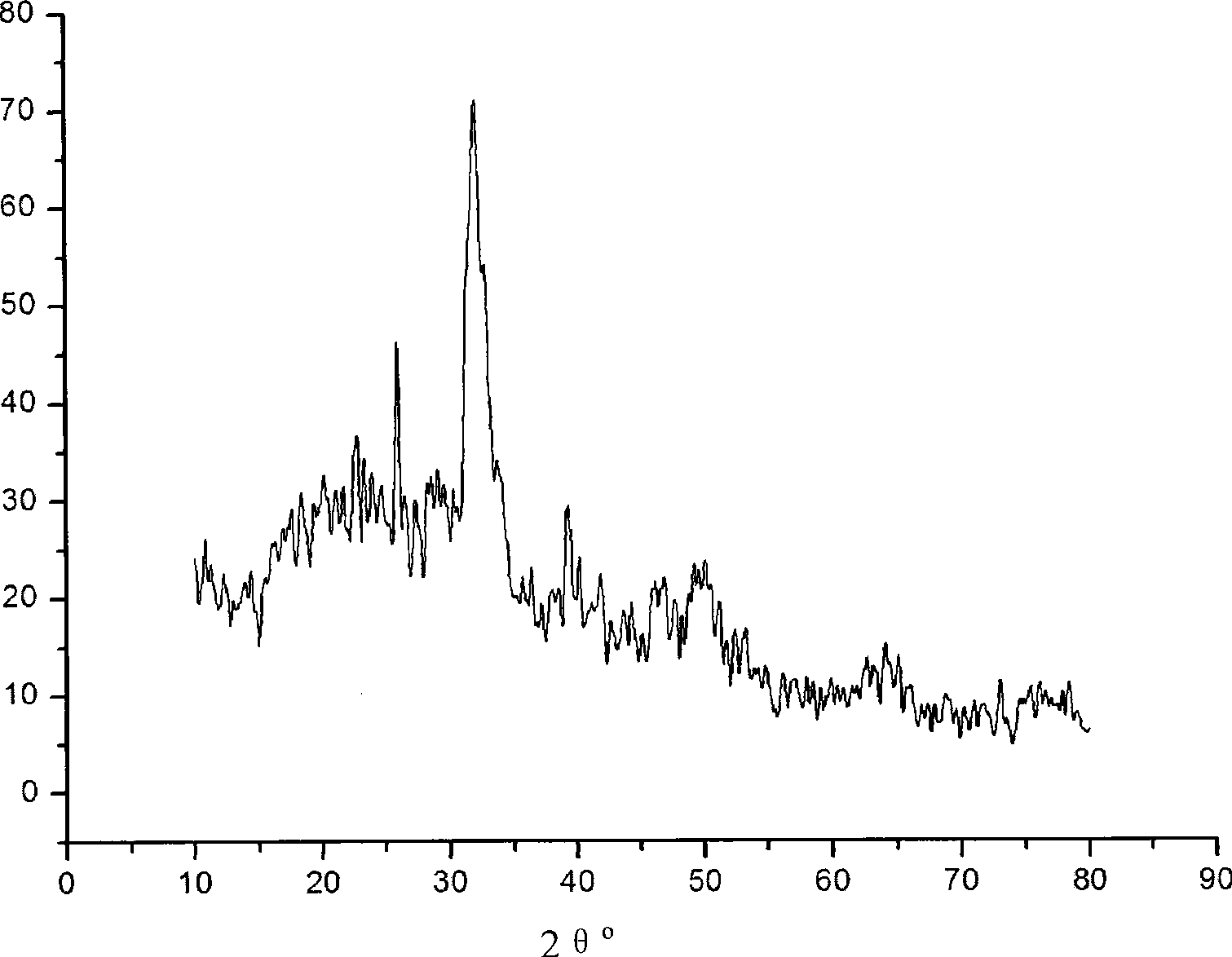
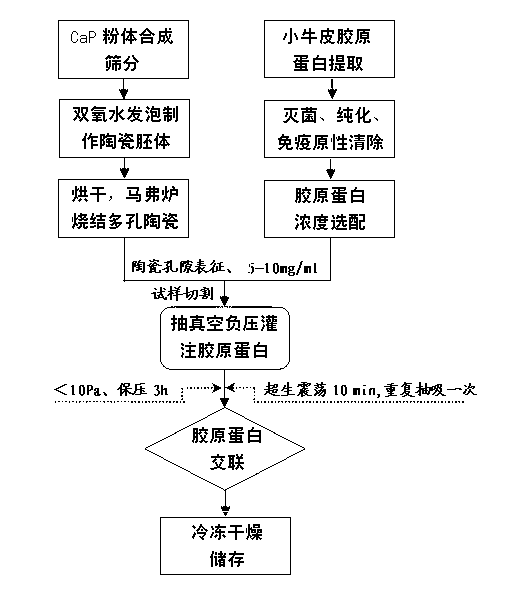
The invention relates to a CaP (Calcium Phosphate) / collagen composite biologic ceramic material and a preparation method thereof. The composite biologic ceramic is prepared by adopting a porous calcium phosphate ceramic as the substrate and I-type collage as the toughening reinforcing phase in a vacuum negative pressure pouring and crosslinking mode. The process is as follows: firstly, preparing the first type through porous calcium phosphate ceramic, wherein the porosity is 60-95%; dipping the porous calcium phosphate ceramic into a collagen solution of which the concentration is 5-20mg / ml; and vacuuming to 0-10Pa at normal temperature and pouring, keeping the pressure for 1-3 hours and carrying out ultrasonic oscillation. The vacuum negative pressure pouring process can be repeated according to demands. The calcium phosphate ceramic poured with the collagen is frozen and dried to prepare the composite biologic ceramic after being subjected to crosslinking. The prepared biologic ceramic has good biocompatibility and biological activity, and at the same time has a mechanical strength better than that of a pure calcium phosphate ceramic material, so that the biologic ceramic can be used as artificial bones and bone tissue engineering bracket materials, and has wide clinical application prospects in orthopedics.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Resorbable Scaffolds For Bone Repair And Long Bone Tissue Engineering
ActiveUS20110307073A1Sufficient bendingAvoid insufficient compressionBone implantMechanical propertyPolycaprolactone
Bioresorbable scaffolds for bone engineering, such as repair of bone defects, particularly long bone defects, or augmentation of bone length are described. Scaffolds are porous and comprise multiple side channels. In one embodiment, scaffolds are made from layers of micro-filament meshes comprising polycaprolactone (PCL) or a PCL-composite sequentially laid in incremental 60 degrees of rotation to produce a 0 / 60 / 120 degree layering pattern, providing for the formation of interconnected pores. The scaffold can comprise a central channel filled, packed or infused with suitable agents such as bioactive agents. Furthermore, the scaffolds are stiff but yet fracture resistant and with sufficient bending, compressive and torsional strength suitable for bone engineering. The slow degradation of the scaffold is sufficient for the 3D matrix to maintain structure integrity and mechanical properties during the remodelling process.
Owner:OSTEOPORE KOREA +2
Porous calcium phosphate bioceramic material and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN1488602AEasy to manufactureTo avoidBone implantCeramicwareCalcium biphosphateRestorative material
The invention is porous calcium phosphate ceramic material and the manufacturing method. It takes the calcium source and phosphate source according to Ca / P=1.00í½2.00 / 1.00 and computes the quantity of water according to the mol ratio Ca / H2O=1.00.3.00í½20.00, the hole agent / Ca=0.011í½6.00 / 1.00. adds in 0.1í½2.0mm hole agent, upgrades the temperature to 50í½1000íµ fro about 0í½24 hours, and carries on hydro-thermal process. The parameters are: pH is 5í½14, temperature 140í½360íµ, pressure 0.4í½20MPa, the insulated time 0í½24 hours.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Degradable open porous magnesium and magnesium alloy biomaterial and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a degradable open porous magnesium and magnesium alloy biomaterial and a preparation method thereof. The magnesium and magnesium alloy biomaterial is in a completely open structure, the hole shape and size are controllable, holes are communicated by virtue of communicating holes, and the number and size of the communicating holes in hole walls are controllable; the holes are uniformly distributed and the porosity is adjustable. The preparation method comprises the following steps: sintering sodium chloride crystal particles to obtain an open porous sodium chloride prefabricated structure; pouring molten magnesium or magnesium alloy into a mould cavity with a sodium chloride prefabricated body, and performing seepage pressure casting; and removing magnesium or magnesium alloy block outer skin with the sodium chloride prefabricated body, washing with alkali, and filtering to remove sodium chloride to obtain the degradable open porous magnesium and magnesium alloy biomaterial. The preparation process is simple, convenient to perform and pollution-free; the prepared open porous structure is provided with the communicated and uniformly distributed holes, is controllable in hole shape and size, relatively high in porosity and strength, free of pore former residues and pore closing phenomenon and adjustable in degradation rate, and can serve as a new-generation degradable bone tissue engineering scaffold.
Owner:SHANGHAI INNOVATON MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Preparing method for heteroossein base materials
A process for preparing collagen matrix with heterogeneous bone, used as the bone repairing material and the extracellular matrix of bone tissue engineering, includes such steps as treating ox bone or pig bone, defatting, partial decalcifying, removing non-collagen, proteinas digesting, disinfecting and packing. It has better porosity and pore canal structure.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
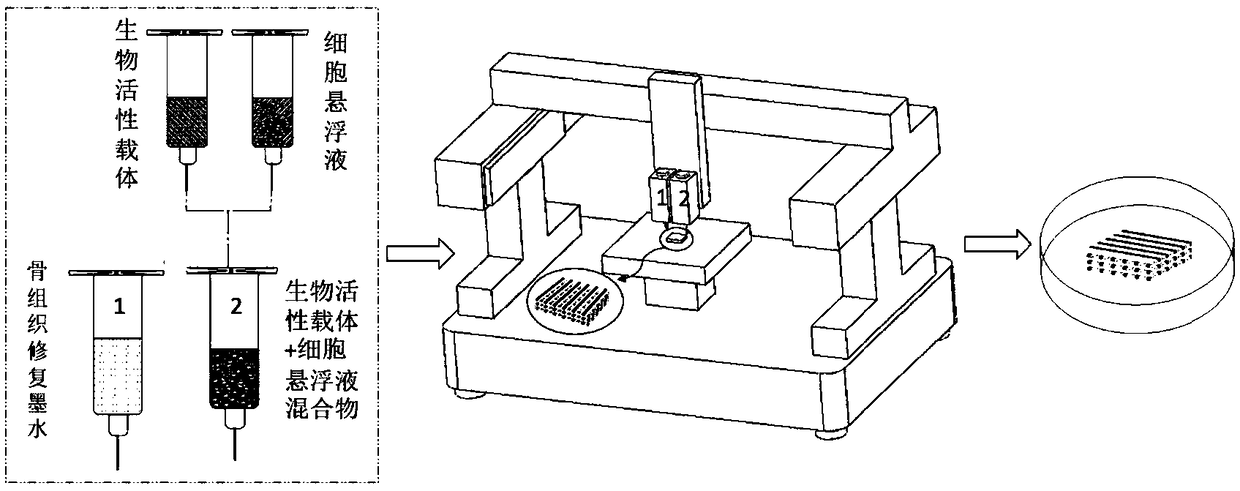
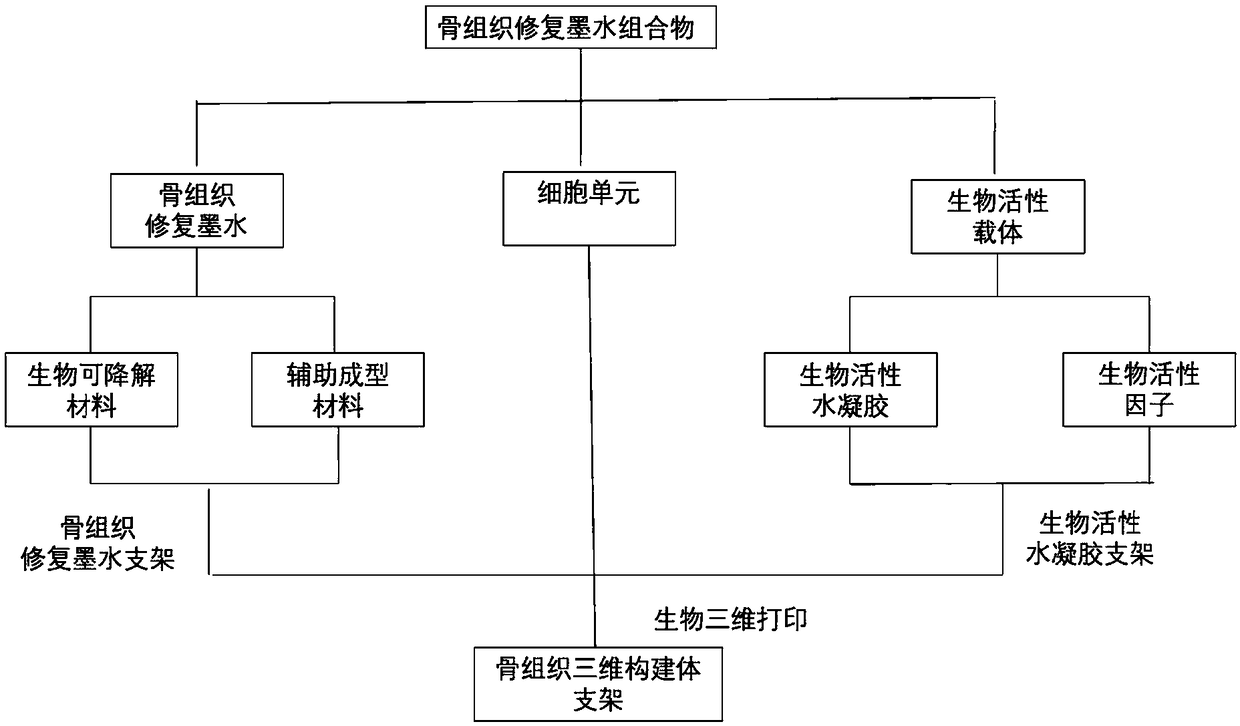
Bone tissue repair ink, composition and bracket, and preparation methods thereof as well as kit
ActiveCN109381749APromote proliferationPromote directed differentiationAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationBone tissueBone tissue engineering
The invention relates to the field of bone tissue engineering, in particular to bone tissue repair ink, a bone tissue repair composition and a bone tissue repair bracket, and preparation methods thereof as well as a kit. The bone tissue repair ink and a bioactive carrier wrapping cells are used as raw materials, and the bone tissue repair bracket is printed according to a preset three-dimensionalstructure by adopting a biological printer. Meanwhile, living cell printing is realized by adopting the bone tissue repair ink and the bioactive carrier as the raw materials. The cells are uniformly distributed on a bracket model formed by the bone tissue repair ink and difficultly slide down to the bottom of the bracket, so that the problem that the expression of some characteristic proteins of the cells is easily lost in the prior art is effectively solved. The growth of the cells on the bracket is facilitated. A human body bone cell growth environment is better simulated, the cell proliferation, the directional differentiation and the specific protein expression are promoted, the extension and the migration of the cells in the bone tissue bracket and the cell junction establishment arefacilitated, and an organic construction body is formed.
Owner:REGENOVO BIOTECH
Silk fibrin and hydroxyapatite compound material and preparation process thereof
The invention discloses a silk hydroxyapatite composite stock and making method, which is characterized by the following: taking the hydroxyapatite and silk protein as base; taking the degelatinized cultivated silk or cloth as reinforcement; solidifying HA power in more homogeneous solution rapidly by adapting solution blending-freezing gel method; elevating temperature above the glass transition temperature of silk solution; adding low-molecular-weight effumable organic reagent to rearrange the silk protein molecule in the freezing solution; gelifing to fix HA powder; formatting pore of certain structure after detaching the water and organic reagent by heating; forming silk hydroxyapatite composite stock with multipore. The invention qualifies good dynamical property, cellular compatibility and right degradation speed to satisfy the need of cell cultivation bracket as bone injuring renovation, medicine control releasing and bone tissue engineering stock with broad prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
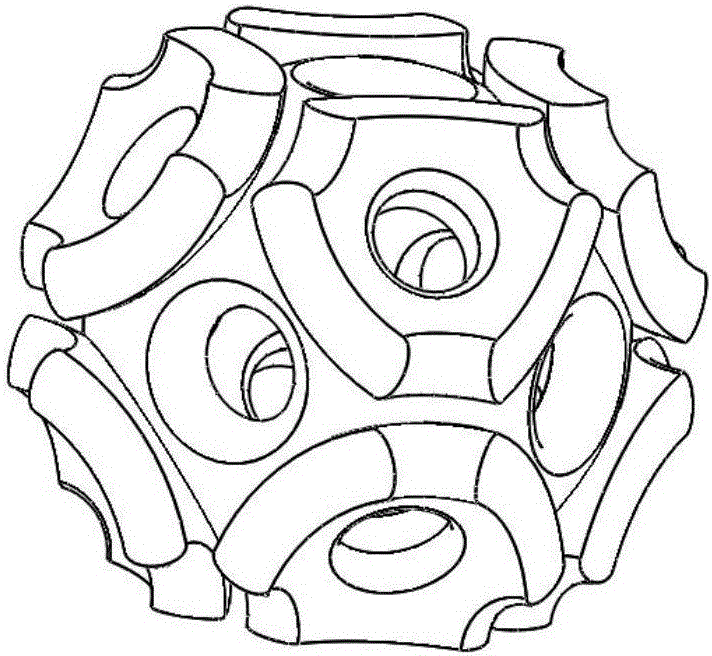
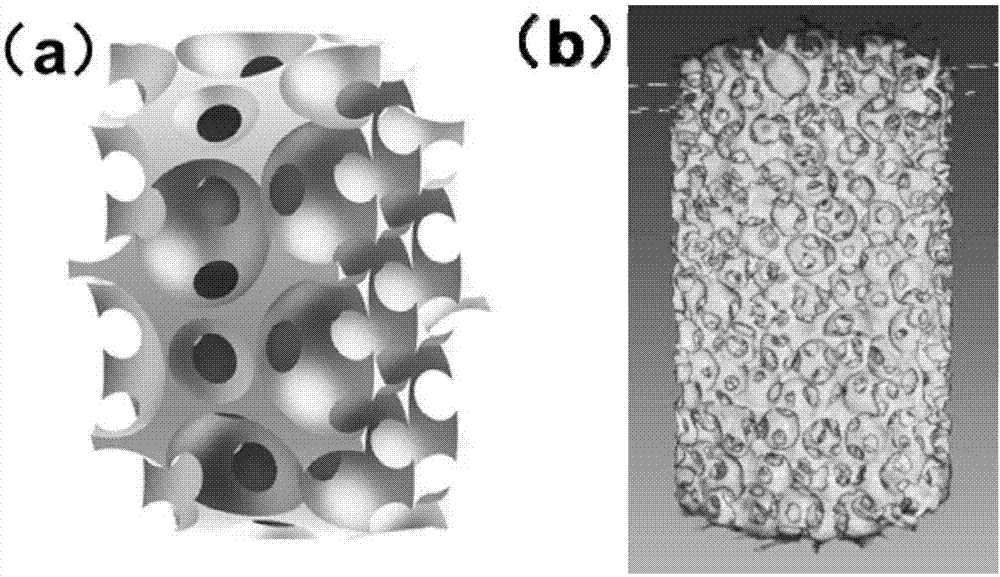
Bionics design bone-line porous bone product and preparation method and purpose thereof
ActiveCN105877874AImprove adhesionPromote growthAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantDefect repairSpatial structure
The invention relates to a bionics design bone-line porous bone product and a preparation method and a purpose thereof, and belongs to the field of biomedical materials. The bionics design bone-line porous bone product is of a body-centered three-dimensional lattice micropore space structure, the atom positions of a unit body of the micropore space structure are filled by geometries, each geometry is a sphere casing or a sphere body, and is crossed with the surrounding sphere casings or the sphere bodies, and a through circular hole is formed in each crossing part. The bionics design bone-line porous bone product has the advantages that by utilizing a three-dimensional printing quick forming manufacturing technique, the excessive cutting waste is avoided, the utilization rate of material is high, and the processing is rapid; the bone-line porous bone nails, bars and plates prepared by the bionics design bone-line porous bone product are used for the human body hard tissue defect repair, bone tissue engineering stents, and bearing part bone tissue wound repair and reconstruction, the good structure integrity and shape customizing capability are realized, various shapes can be processed according to the patient bone tissue defect repair requirements, and the personalized medical requirements of the patient are met.
Owner:成都百年贝雅医疗科技有限公司
Bone tissue filling material
InactiveCN1511595ALow priceGood biocompatibilitySurgeryProsthesisSpinal columnBiocompatibility Testing
The present invention provides a kind of bone tissue filling material. Spongy bone of ox is first treated to become inorganic matter, soaked in sodium pyrophosphate solution, dried and high temperature calcined to produce calcined bone tissue filling material. The filling material is soaked in suspension of zinc chloride, dried and high temperature calcined to obtain the zinc-containing calcined porous bone tissue filling material. The porous bone tissue filling material has low cost, good biocompatibility, homogeneous and communicated pores, certain mechanical strength, capacity of promoting bone growth and other features, and is suitable for filling bone deficiency, spinal column fusion and cell rack in bone tissue engineering, etc.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
Separating and culturing process of human amnion mesenchyme stem cell and its medical composition
ActiveCN1810959AWide variety of sourcesUnrestricted by ethicsMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSingle cell suspensionCulture mediums
The present invention is separating and culturing process of human amnion mesenchyme stem cell and its medical composition. The separating and culturing process includes digesting human amnion successively with trypsin, collagenase and deoxyribonuclease, and filtering to prepare single cell suspension; culturing in DMEM / F12 culture medium with VDMEM and VF12 in the equal ratio and containing ox embryo blood serum in 10-20 vol% and basic fibroblast growth factor of ultimate concentration 10-20 ng / ml inside a culture box at 37 deg.c, saturated humidity and CO2 in 5 vol%; and replacing liquid and culture passage to proliferate and purify human amnion mesenchyme stem cell. The process has wide material source no ethnic limitation and wide application foreground. The medical composition may be used in various kinds of treatment.
Owner:SHENZHEN BEIKE BIOTECH +4
Carbon nanotube composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering
InactiveUS20100075904A1High mechanical strengthSuitable propertyPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderBone tissue engineeringBone tissue
The present invention provides biocompatible composite materials that can be fabricated into a scaffold having properties suitable for bone repair and regeneration. These scaffolds have sufficient mechanical strength to be useful for the repair and regeneration of cortical bone.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Nanometer hydroxyapatite/chitosan/gelatin porous scaffold material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1799647AImprove mechanical propertiesGood biocompatibilityCoatingsProsthesisApatiteMass ratio
The invention discloses a nano hydroxyapatite / chitose / gelatine composite porous bone tissue engineering cradle material and the preparing method. The material comprises chitose and gelatine with their mass ratio being 3:7-7:3 and the nano hydroxyapatite of 40-80nm deposited on the porous cradle material formed by chitose and gelatine. Preparing the porous cradle material with pore diameter 100-300 ª–m and factor of porosity greater than 90% by using phase separation technique, then immersing it in the Tris buffer solution of Ca(NO3)2 for 10-12 hours, washing with deionized water three times and then immersing it in the Tris buffer solution of Na3PO4 for 10-12 hours, regulating pH value between 11 to 13, washing with deionized water three times and freezing for drying, then getting the nano hydroxyapatite / chitose / gelatine composite porous material by recycling the steps above several times, the size diameter of the hydroxyapatite is about 50nm, the material prepared in this invention possesses good mechanical property and biological compatibility.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Nanometer hydroxyapatite/natural polymer composite, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101693774AThe preparation method worksEasy to operateTissue regenerationProsthesisPolymer scienceHigh energy
The invention relates to tissue engineering materials and particularly discloses a nanometer hydroxyapatite / natural polymer composite, a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method includes the steps of putting the natural polymer composite into the mixed solution of alcohol, water and urea and adding monosodium phosphate solution and calcium chloride solution to conduct sealing reaction and obtain the composite, wherein the volume ratio of the alcohol and the water in the mixed solution is 2-6:1, the concentration of urea in the mixed solution is 1-3g / 100ml. The method is quick and effective, the conditions of the reaction system are mild, the reaction method and the reaction system are easy to operate and control, the cost is low and investment of high energy source is saved. The composite obtained by the method has a thicker mineralization layer and therefore higher tensile and compressive strength and also can be applied to the field of the tissue engineering materials requiring high mechanical strength, for example the manufacture of bone tissue engineering materials.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing nano hydroxyapatite/polylactic acid composite microspheres
InactiveCN101590388AEvenly dispersedImprove mechanical propertiesMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationMicrosphereFiltration
The invention discloses a method for preparing nano hydroxyapatite / polylactic acid composite microspheres, which uses nano hydroxyapatite (n-HA) and polylactic acid (PLA) as raw materials and adopts an ultrasonic blending composite process and an emulsification-solvent evaporation method to prepare the microspheres of a nano hydroxyapatite / polylactic acid composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: nano-crystallizing hydroxyapatite, proportionally preparing complex liquid, performing ultrasonic dissolving and blending, emulsifying the mixture into small liquid drops, reducing pressure to volatilize a solvent, performing refrigeration and filtration, performing washing, and performing freeze-drying to obtain the composite microspheres. Compared with like products, the composite microspheres have the characteristics that the method has simple and easy operation, the size of the microspheres is easy to control, and the prepared microspheres have large surface holes and specific area, and good mechanical property. The prepared nano hydroxyapatite / polylactic acid composite microspheres are mainly applied to microsphere bonding type brackets in bone tissue engineering and cell micro-carriers in cell engineering, and can be applied to conveying medicaments and bioactive molecules.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
Preparation methods of mineralized hydrogel and biomimetic mineralized bone repair material
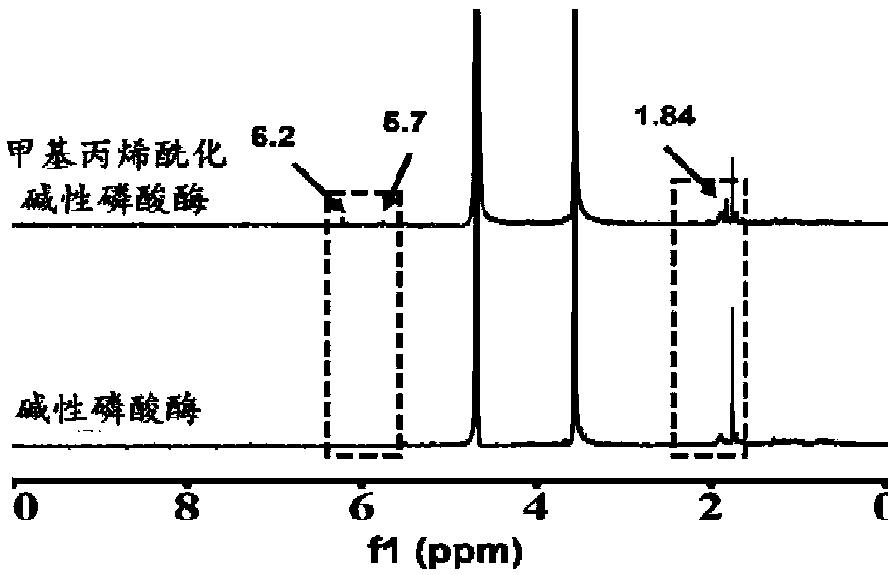
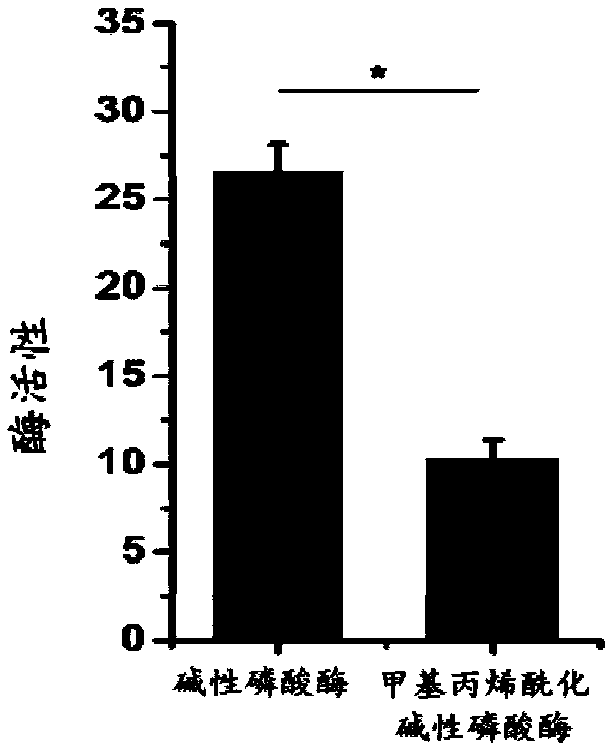
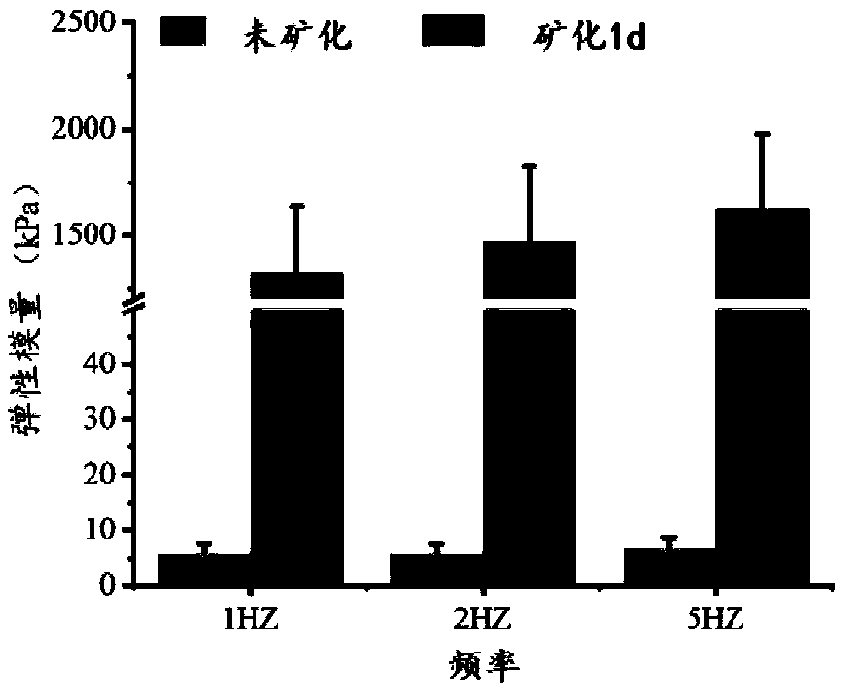
The invention discloses preparation methods of mineralized hydrogel and a biomimetic mineralized bone repair material. The mineralized hydrogel is prepared by using a photoactivated biomacromoleculesand a photoactivated phosphatase as raw materials; hydrogel is formed by initiating cross-linking by means of light irradiation or initiating polymerization cross-linking by means of a radical initiator; when the hydrogel is put into mineralized liquid, phosphatase can promote the uniform deposition of phosphate in the gel, so that the uniformly mineralized hydrogel is obtained. Phosphoprotein-like molecules are added during the preparation of the hydrogel; the phosphoprotein-like molecules can promote the uniform deposition of phosphate along a molecular network of biomacromolecules, so thatthe high-strength mineralized hydrogel can be obtained. When the phosphoprotein-like molecules and cells are added during the preparation of the hydrogel, the in-situ loading of the cells can be realized, and the enzyme in a process of bone physiological mineralization can be simulated so as to promote a phosphate mineralization process, so that the biomimetic mineralized bone repair material withhigh strength can be obtained, and the personalized customization of the bionic mineralized bone repair material can be realized; therefore, the preparation methods have a broad application prospectin the field of bone tissue engineering.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Preparation method of poly (lactic acid-glycolic acid)/hydroxyapatite nanofiber compound bracket for bone repair
InactiveCN101693126AMaintain crystalline structureGood biocompatibilityNanostructure manufacturePhosphorus compoundsFiberOsteoblast
The invention discloses a preparation method of a poly (lactic acid-glycolic acid) / hydroxyapatite nanofiber compound bracket for bone repair, which comprises the following steps: adding hydroxyapatite nanoparticles into a mixed solvent of tetrahydrofuran and dimethylformamide, and then, adding poly (lactic acid-glycolic acid) to obtain a mixed solution of the hydroxyapatite and the poly (lactic acid-glycolic acid); carrying out electrostatic spinning on the mixed solution; and obtaining the poly (lactic acid-glycolic acid) / hydroxyapatite nanofiber compound bracket for bone repair. The invention has simple and convenient preparation method and wide material sources, simulates the composition and the structure of natural bones of human bodies, introduces the bioactive ceramic material hydroxyapatite into a degradable poly (lactic acid-glycolic acid) substrate to form a compound nanofiber bracket, has the advantages of good biocompatibility, excellent comprehensive performance, convenient use and the like, can effectively promote the adhesion, growth and function expression of bone cells and meet the biological requirements of the bone tissue engineering.
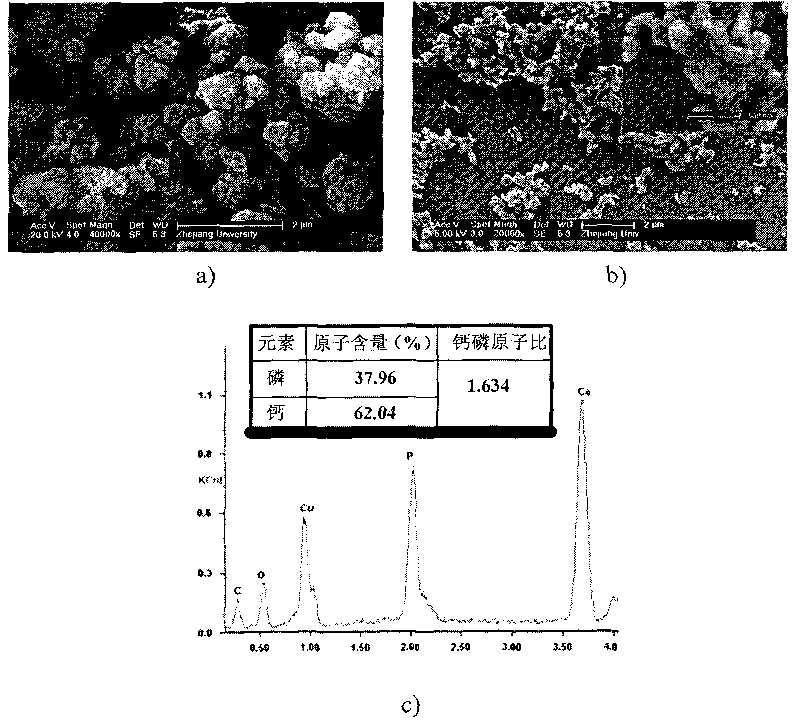
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
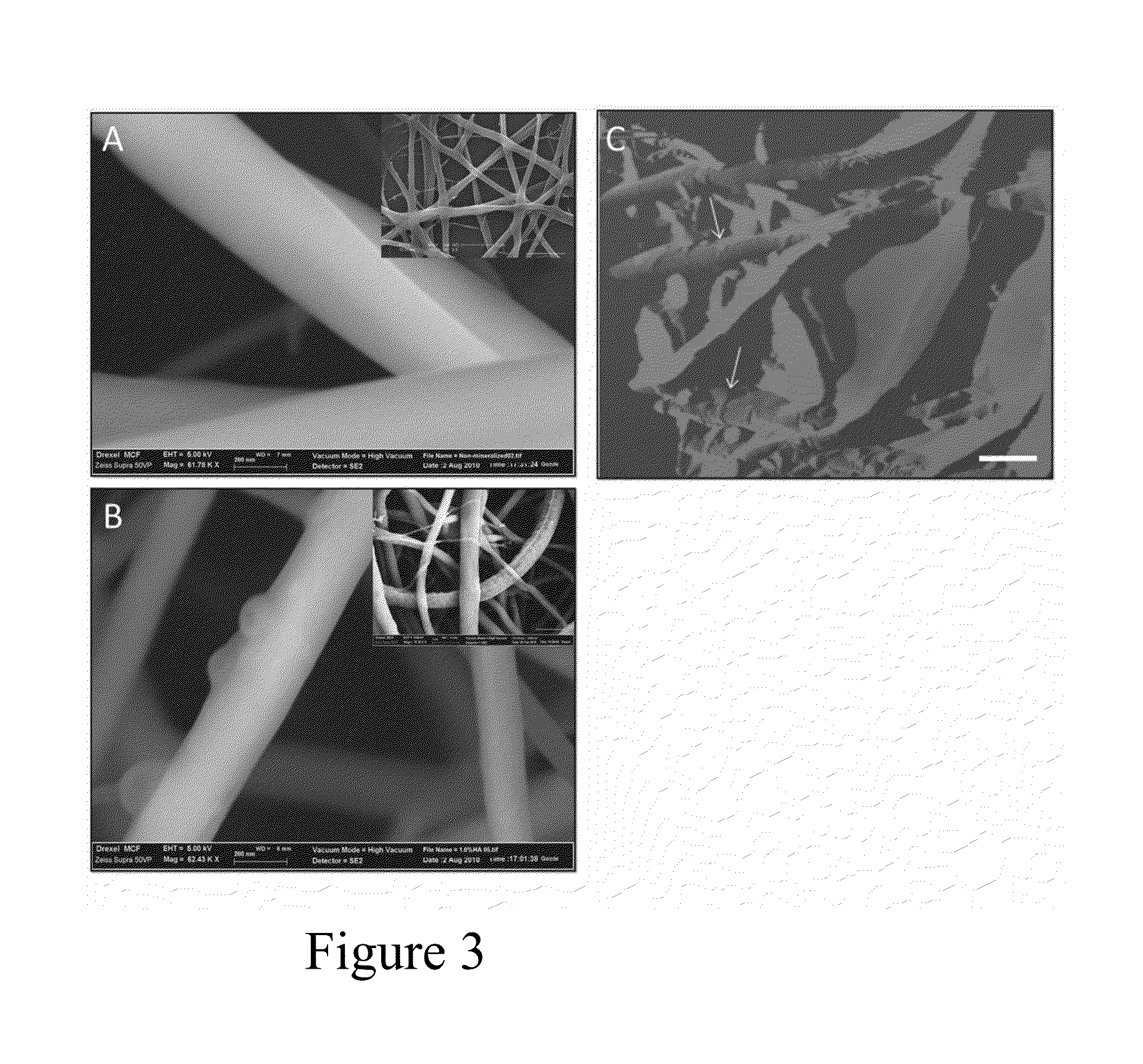
Electrospun Mineralized Chitosan Nanofibers Crosslinked with Genipin for Bone Tissue Engineering
The present invention relates to an electrospun chitosan scaffold. The scaffold mimics natural bone mechanical properties and structure through mineralization without hindering the biocompatibility for osteoblasts. The electrospun mineralized scaffold is useful in bone regeneration therapies.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Bone cartilage repair material and preparation method of scaffold for tissue engineering
InactiveCN109364302AEasy to prepareRealize the loadAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationOsteoblastSolvent
The invention discloses a bone cartilage repair material and a preparation method of a scaffold for tissue engineering. The material comprises a subchondral bone layer, an interface layer and a cartilage layer arranged in sequence, wherein the interface layer is positioned between the subchondral bone layer and the cartilage layer; the material contains the following components in parts by weight:10-40 parts of oil-soluble high polymer materials, 10-50 parts of biological ceramic powder, 50-100 parts of oily solvents, 0.1-1 part of a water-soluble bio-active material, 2-30 parts of water, more than 0 and less than 1 part of an emulsifier, 10-30 parts of a hydrogel material, 0-10 parts of seed cells and 50-100 parts of a culture medium. The preparation method comprises the following steps:preparing printing ink according to the ratio of the materials, and transferring into 3D printing equipment for printing molding. The bone cartilage scaffold having a personalized appearance can be prepared, load and controlled release of different growth factors or peptides in different zones of the scaffold can be realized, and directional differentiation of bone marrow stem cells at differentparts to osteoblast and chondrocyte can be promoted.
Owner:王翀
Degradable open-cell porous zinc/zinc alloy biomaterial and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104258458ANo residueUniform distribution throughoutProsthesisPorosityBone tissue engineering
The invention discloses a degradable open-cell porous zinc / zinc alloy biomaterial and a preparation method thereof. The degradable open-cell porous zinc / zinc alloy biomaterial is of a completely open-cell structure, wherein the hole pattern and the size are controllable, holes are communicated by use of communicating holes, and the number and the size of the communicating holes in the hole walls are controllable; the biomaterial is even in overall hole distribution and adjustable in porosity. The preparation method of the biomaterial comprises the following steps that sodium chloride crystal particles are sintered to obtain an open-cell porous sodium chloride prefabricated structure; a zinc or zinc alloy melt is poured into a die cavity in which a sodium chloride prefabricated body is put and pressure seepage casting is performed; the outer skin of a zinc or zinc alloy block containing the sodium chloride prefabricated body is removed, and then alkali wash is performed and the sodium chloride is performed to obtain the degradable open-cell porous zinc / zinc alloy biomaterial. The preparation method of the degradable open-cell porous zinc / zinc alloy biomaterial is simple in process, convenient to operate and pollution-free; the obtained open-cell porous structure has the advantages that the holes are communicated with each other and distributed evenly, the appearance and size of the holes are controllable, the porosity and the strength are relatively high, no hole forming agent is left and hole closure is prevented, and meanwhile, the degradation rate is adjustable; as a result, the biomaterial can be used as a new generation degradable bone tissue engineering stent.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method of antibacterial biological activity ceramic coating with magnetic responsiveness
InactiveCN105920668AGood osteoinductivityImprove antibacterial propertiesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationCeramic coatingBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a preparation method of an antibacterial biological activity ceramic coating with magnetic responsiveness, and belongs to the technical field of biological materials. The preparation method is combined with a layer-by-layer self-assembly technology by using ultrahigh adhesiveness of polydopamine so as to construct a coating of a multilayer film structure on the surface of a base material coated with a polydopamine film. A single layer film is prepared by coating polydopamine functionalized magnetic particle dispersion liquid, polydopamine functionalized antibacterial particle dispersion liquid or polydopamine functionalized biological activity ceramic particle dispersion liquid. The coating prepared through the preparation method has good biocompatibility, biological activity and antibacterial property, the coating can respond to an external magnetic field, and the effect of the external magnetic field can strengthen the osteoinductivity of the coating; the preparation method disclosed by the invention can effectively control the composition, thickness and shape of the coating according to actual requirements; the problems that the binding force between films formed by multilayer inorganic particles in the coating and the binding force between the coating and the base material are not strong are solved. The method has significant research value and clinical significance in bone tissue engineering.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Three-dimensional porous tissue engineering stand material and preparation thereof
A 3D porous scaffold material for tissue engineering to induce the generation of bone tissue is prepared from chitosan, gelatin, GPSM and calcium nitrate through sol-gel process, chemical treating and freeze drying. Its advantages are high bioactivity and degradability, proper porosity and pore diameter, and controllable properties.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com