Patents
Literature
160 results about "Phosphoprotein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A phosphoprotein is a protein that is posttranslationally modified by the attachment of either a single phosphate group, or a complex molecule such as 5'-phospho-DNA, through a phosphate group. The target amino acid is most often serine, threonine, or tyrosine residues (mostly in eukaryotes), or aspartic acid or histidine residues (mostly in prokaryotes).
Pox virus containing DNA encoding a cytokine and/or a tumor associated antigen
InactiveUS6265189B1Improve securityImprove security levelVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman tumorWild type
Attenuated recombinant viruses containing DNA coding for a cytokine and / or a tumor associated antigen, as well as methods and compositions employing the viruses, are disclosed and claimed. The recombinant viruses can be NYVAC or ALVAC recombinant viruses. The DNA can code for at least on of: human tumor necrosis factor; nuclear phosphoprotein p53, wildtype or mutant; human melanoma-associated antigen; IL-2; IFNgamma; IL-4; GNCSF; IL-12; B7; erb-B-2 and carcinoembryonic antigen. The recombinant viruses and gene products therefrom are useful for cancer therapy.
Owner:VIROGENETICS
Vaccina virus comprising cytokine and/or tumor associated antigen genes
InactiveUS6537594B1Improve securityImprove security levelVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman tumorWild type
Owner:VIROGENETICS
Pox virus comprising DNA sequences encoding CEA and B7 antigen
Attenutated recombinant viruses containing DNA coding for a cytokine and / or a tumor associated antigen, as well as methods and compositions employing the viruses, are disclosed and claimed. The recombinant viruses can be NYVAC or ALVAC recombinant viruses. The DNA can code for at least one of: human tumor necrosis factor; nuclear phosphoprotein p53, wiltype or mutant; human melanoma-associated antigen; IL-2; IFNgamma; IL-4; GMCSF; IL-12; B7; erb-B-2 and carcinoembryonic antigen. The recombinant viruses and gene products therefrom are useful for cancer therapy.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR LTD
Biomarkers for differentiating melanoma from benign nevus in the skin
Disclosed is a method for diagnosing melanoma in a human subject, as well as a method for providing a prognosis to a human subject who is at risk of developing melanoma recurrence, and a method for determining the stage of melanoma in a human subject, comprising the step of determining the level of expression of phosphatase and actin regulator 1 (PHACTR1) gene, or fragments thereof, either alone or in combination with the level of expression of secreted integrin-binding phosphoprotein (SPP1), preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma (PRAME), growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF 15), and chemokine C-X-C motif ligand 10 (CXCL10) genes. Further, the invention relates to a diagnostic kit, comprising at least one substance for detection of the expression of PHACTR1, or fragments thereof, either alone or in combination with the detection of SPP1, PRAME, GDF15, and CXCL10, for the diagnosis or prognosis of melanoma.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL DIAGNOSTICS INC
Production of attenuated parainfluenza virus vaccines from cloned nucleotide sequences
InactiveUS7208161B1SsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesPolymerase LParainfluenza virus vaccine
Isolated polynucleotide molecules provide recombinant PIV genomes and antigenomes for production of recombinant PIV vaccines. The recombinant genome or antigenome can be expressed with a nucleoprotein (N), phosphoprotein (P), and a large (L) polymerase protein to produce isolated infectious PIV particles. The recombinant PIV genome and antigenome can be modified to produce desired changes, for example to incorporate attenuating mutations from biologically derived PIV mutants or to create chimeric PIV clones, to generate attenuated, immunogenic viruses for vaccine use.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF
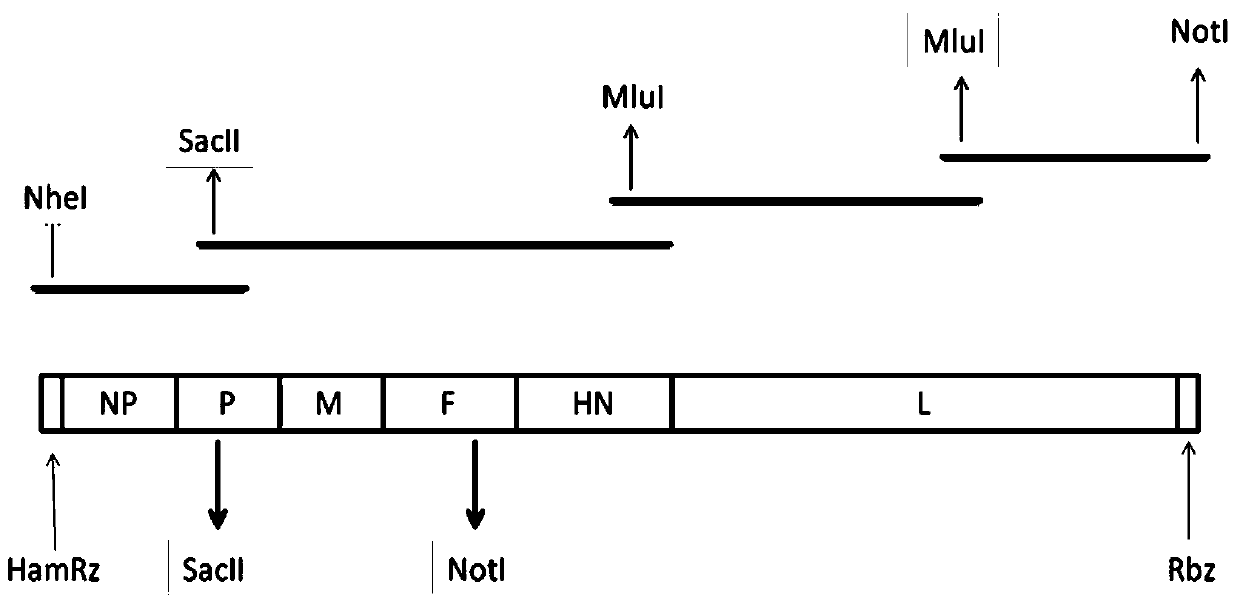
Reverse genetic operation system of New castle disease LaSota vaccine strain and its applciation
The present invention is reverse genetic operation system of Newcastle disease Lasota low virulent vaccine strain and its application. The system includes one transcription plasmid including the genome cDNA sequence of the low virulent vaccine strain; one or several transcription aiding plasmids including the cDNA sequence coding the nucleoprotein of the low virulent vaccine strain, the cDNA sequence coding the phosphoprotein of the low virulent vaccine strain and the cDNA sequence coding the large polymerase protein of the low virulent vaccine strain; and the host cell of the Newcastle disease Lasota low virulent vaccine strain. Wild viral strain is obtained by means of the reverse genetic operation system. The present invention lays firm foundation for further development of Newcastle disease virus live carrier vaccine and Newcastle disease virus related research.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Selective labeling and isolation of phosphopeptides and applications to proteome analysis
InactiveUS7052915B2Easy to separateImprove isolationComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhosphatePhosphoric acid
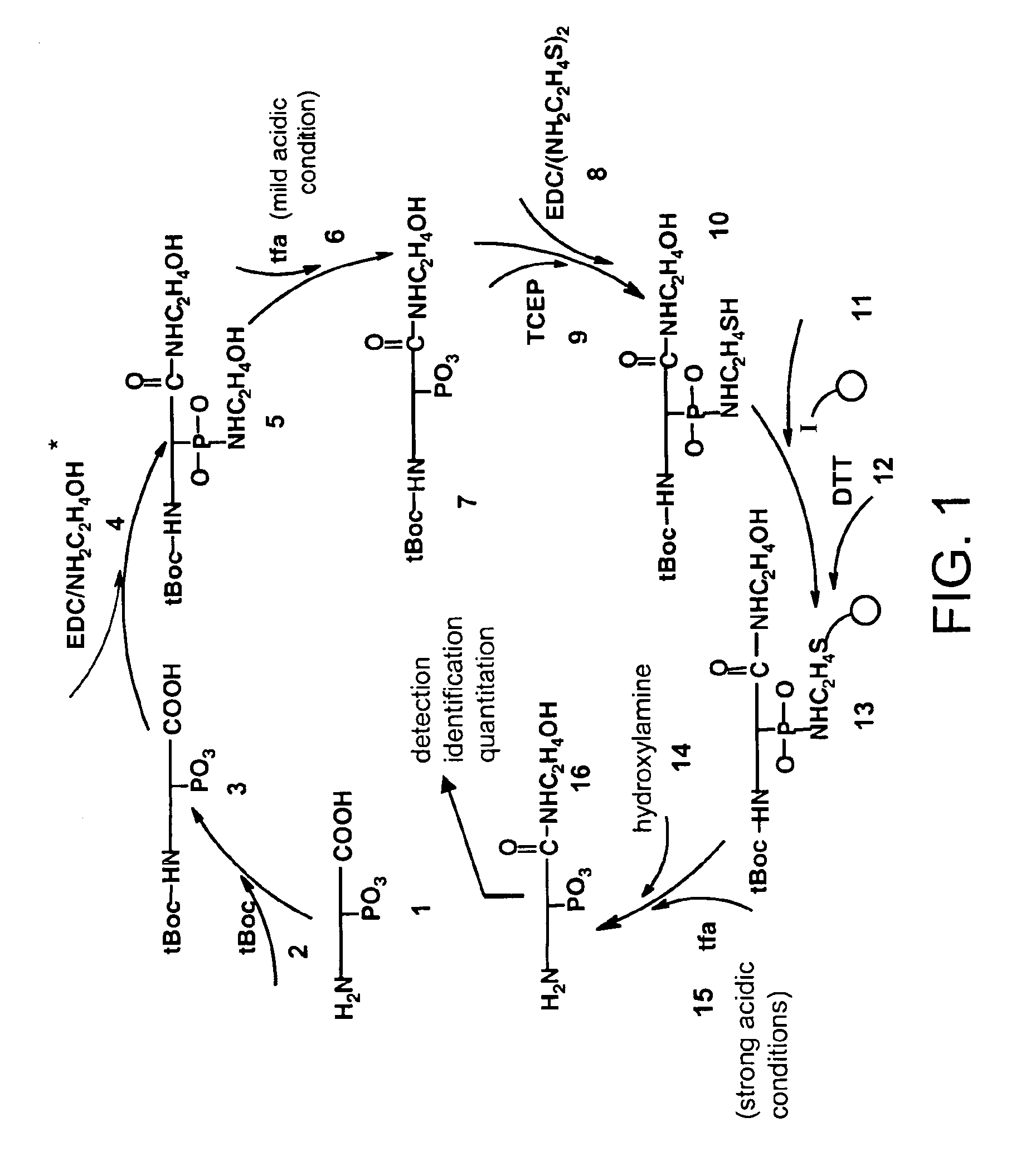
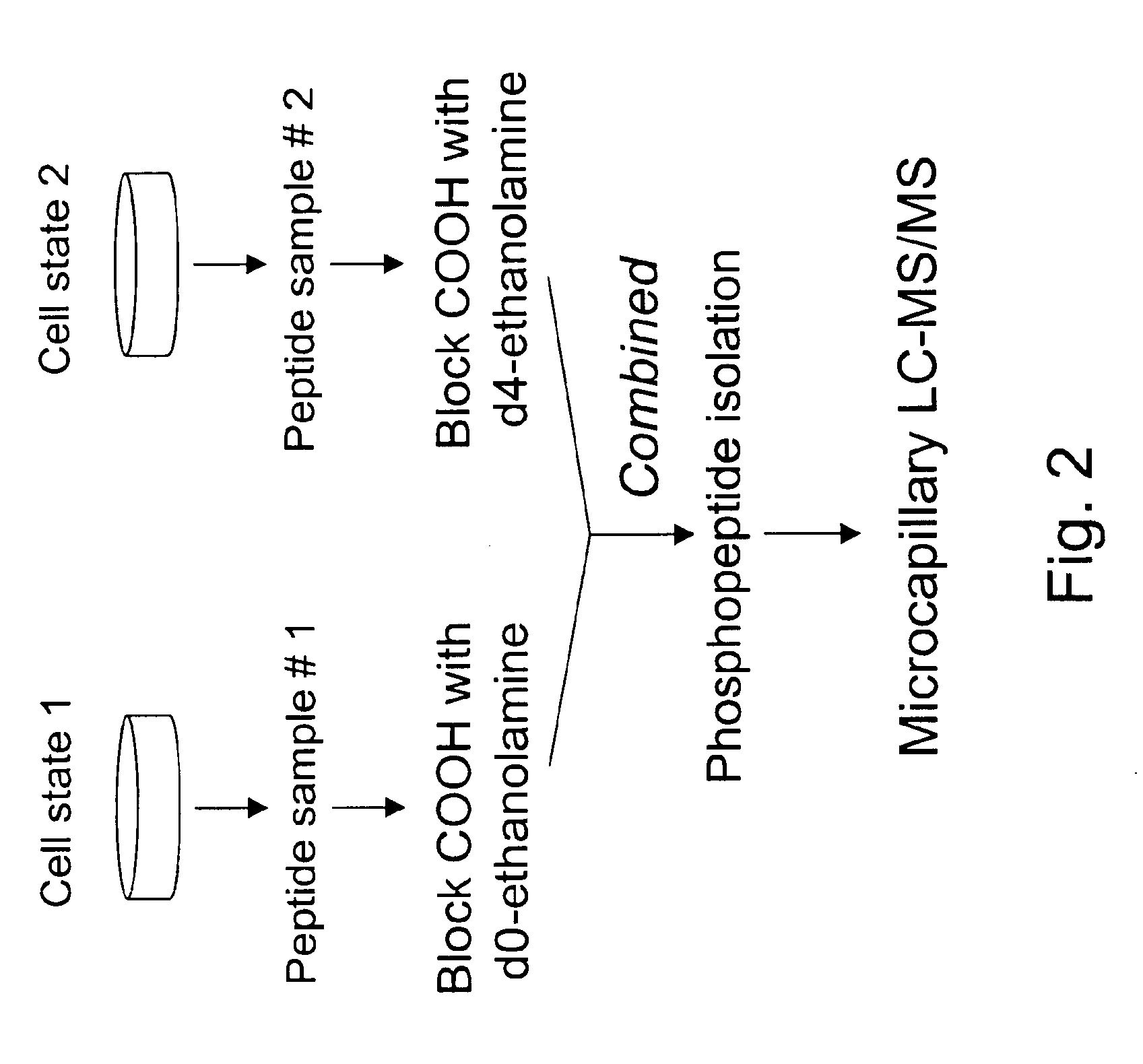
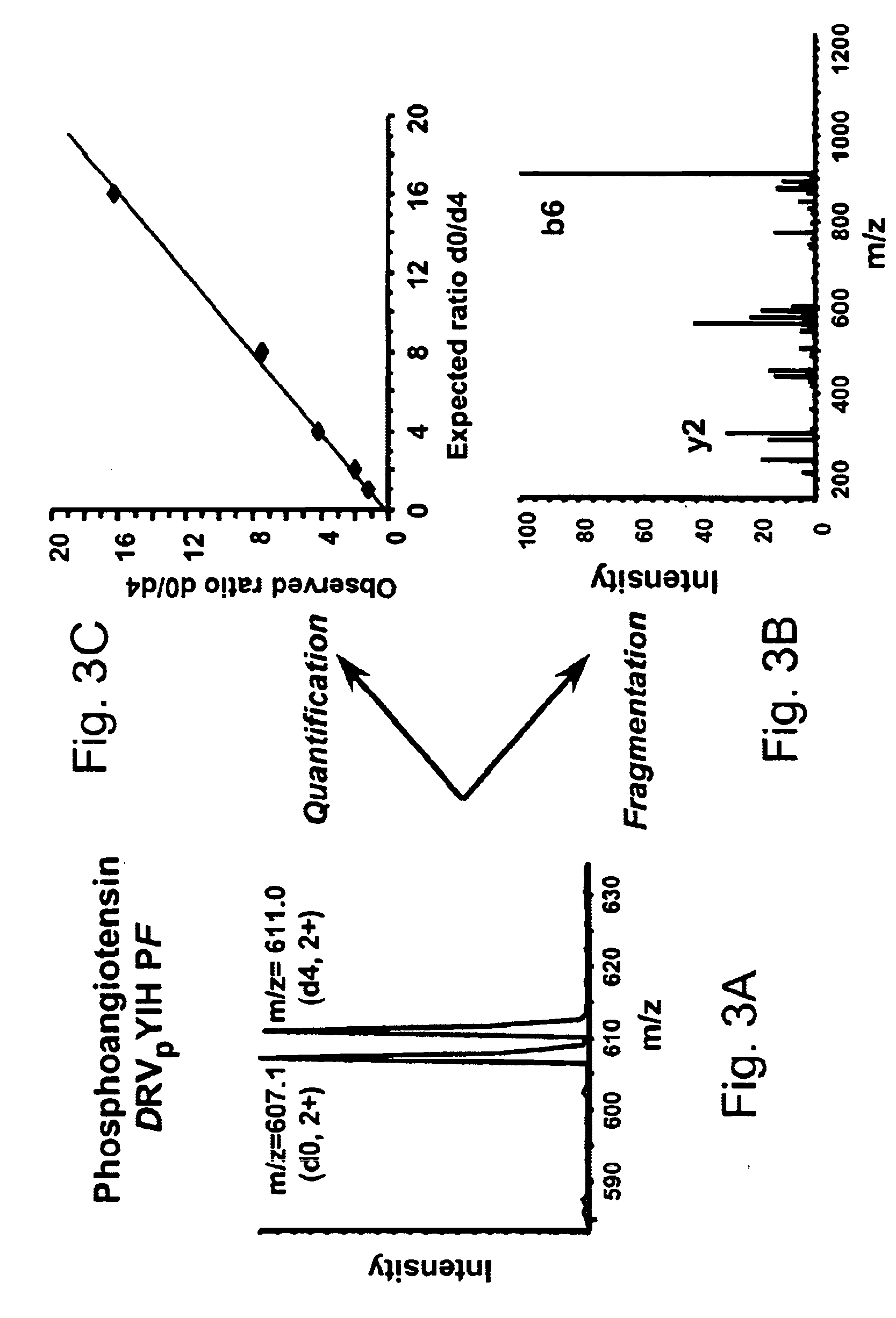
A method for selective labeling of phosphate groups in natural and synthetic oligomers and polymers in the presence of chemically related groups such as carboxylic acid groups. The method is specifically applicable to biological oligomers and polymers, including phosphopeptides, phosphoproteins and phospholipids. In a specific embodiment, selective labeling of phosphate groups in proteins and peptides, for example, facilitates separation, isolation and detection of phosphoproteins and phosphopeptides in complex mixtures of proteins. Selective labeling can be employed to selectively introduce phosphate labels at phosphate groups in an oligomer or polymer, e.g., in a peptide or protein. Detection of the presence of the label, is used to detect the presence of the phosphate group in the oligomer or polymer. The method is useful for the detection of phosphoproteins or phosphopeptides. The phosphate label can be a colorimetric label, a radiolabel, a fluorescent or phosphorescent label, an affinity label or a linker group carrying a reactive group (or latent reactive group) that allows selective attachment of the oligomer or polymer (protein or peptide) to a phosphate label, to an affinity label or to a solid support. The method can be combined with well-known methods of mass spectrometry to detect and identify phosphopeptides and phosphoproteins.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
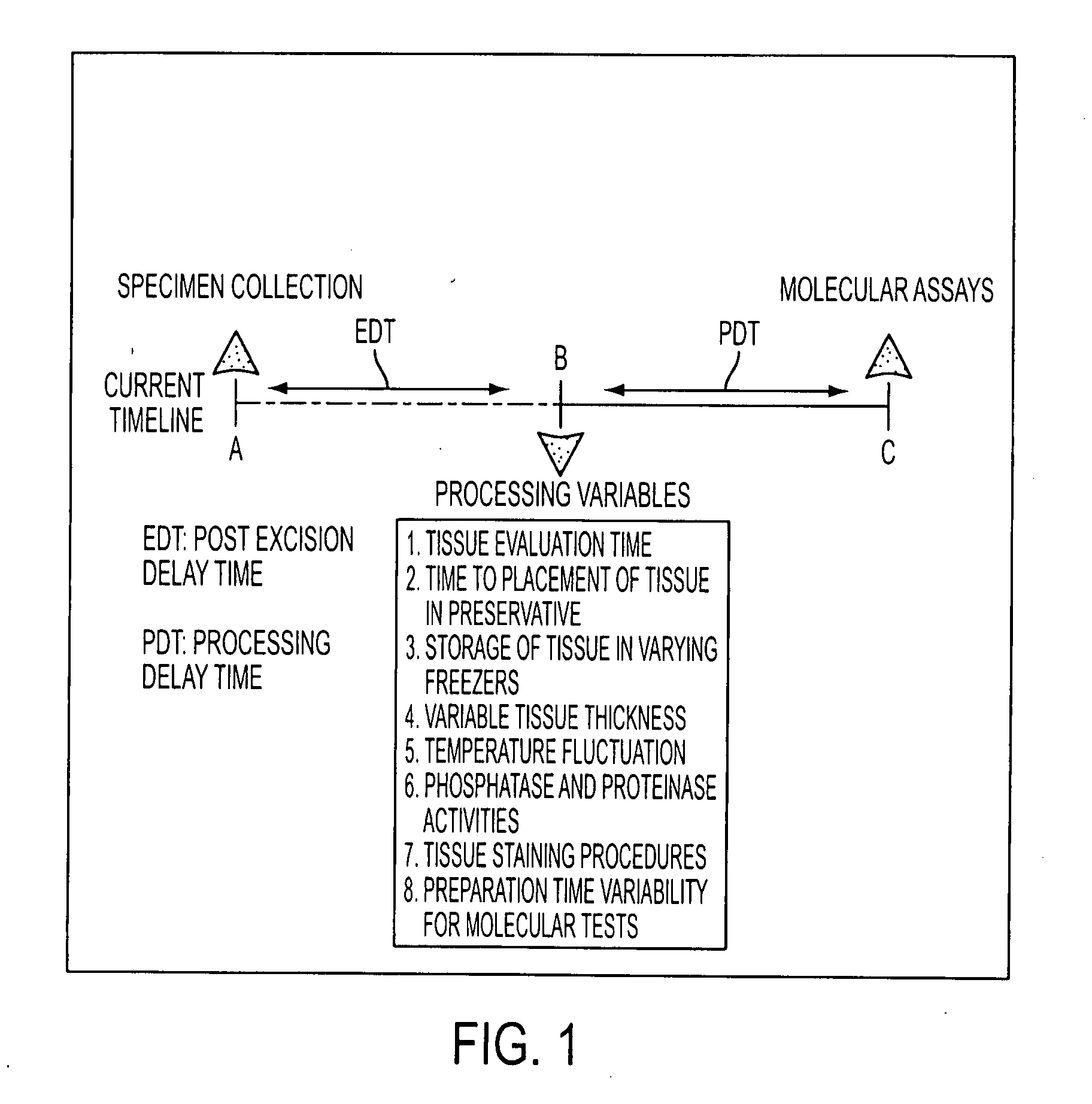
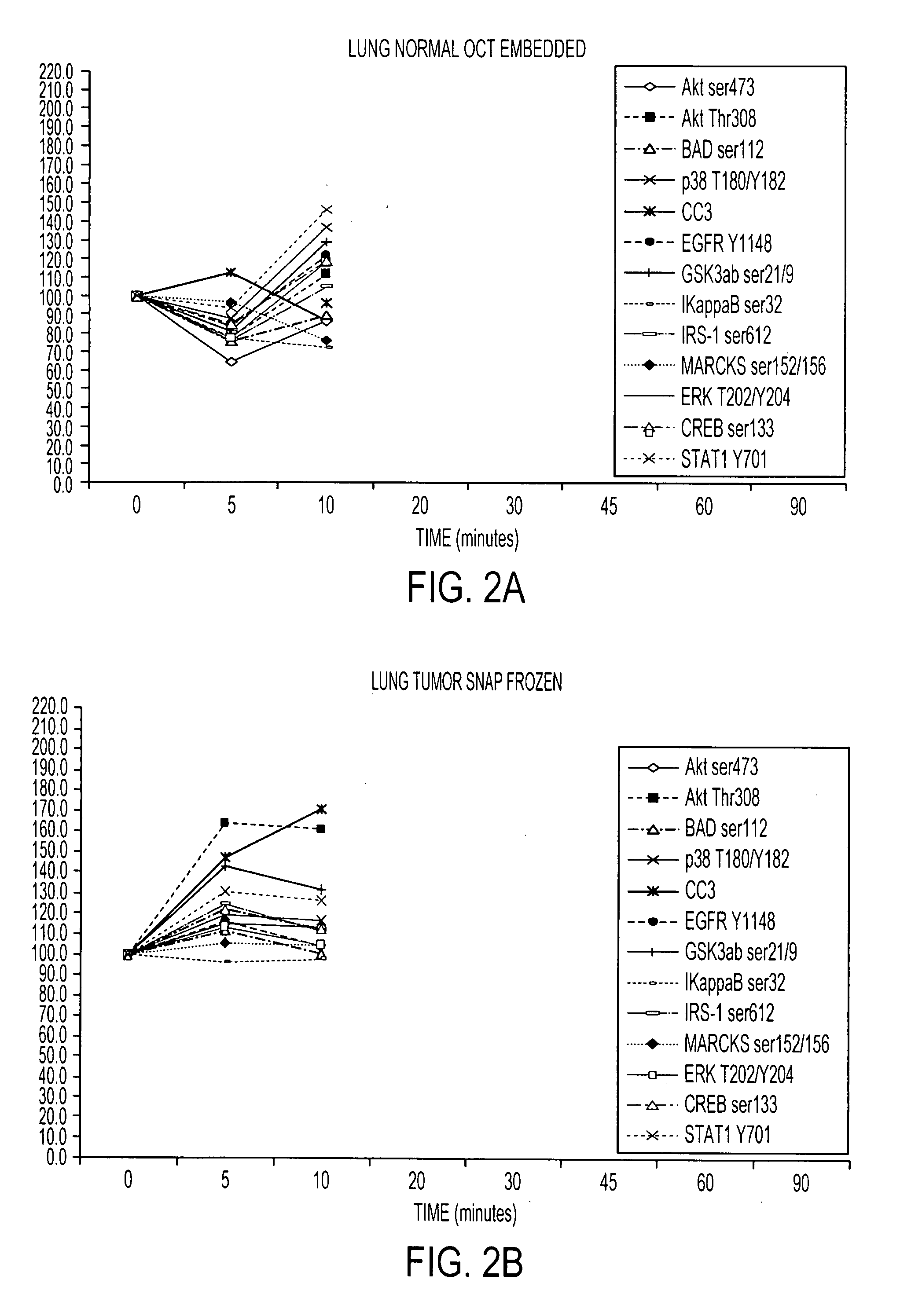
Tissue preservation and fixation method
ActiveUS20100068690A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyPopulation sampleMolecular analysis
This invention relates, e.g., to a composition that, at room temperature, when contacted with a sample comprising phosphoproteins, can fix and stabilize cellular phosphoproteins, preserve cellular morphology, and allow the sample to be frozen to generate a cryostat frozen section suitable for molecular analysis. The composition comprises (1) a fixative that is effective to fix the phosphoproteins, and that has a sufficient water content to be soluble for a stabilizer and / or a permeability enhancing agent); (2) a stabilizer, comprising (a) a kinase inhibitor and (b) a phosphatase inhibitor and, optionally, (c) a protease (e.g., proteinase) inhibitor; and (3) a permeability enhancing agent (e.g. PEG). Methods are described for preserving phosphoproteins, using such a composition. Also described are endogenous surrogate markers for monitoring protein degradation, including the loss of posttranslational modifications (such as phosphorylation), e.g. the following removal of a cell or tissue from a subject; and exogenous molecular sentinels (e.g. phosphoproteins attached to magnetic nanoparticles) that allow one to evaluate the processing history of a cellular or tissue population sample.
Owner:GEORGE MASON UNIVERSITY
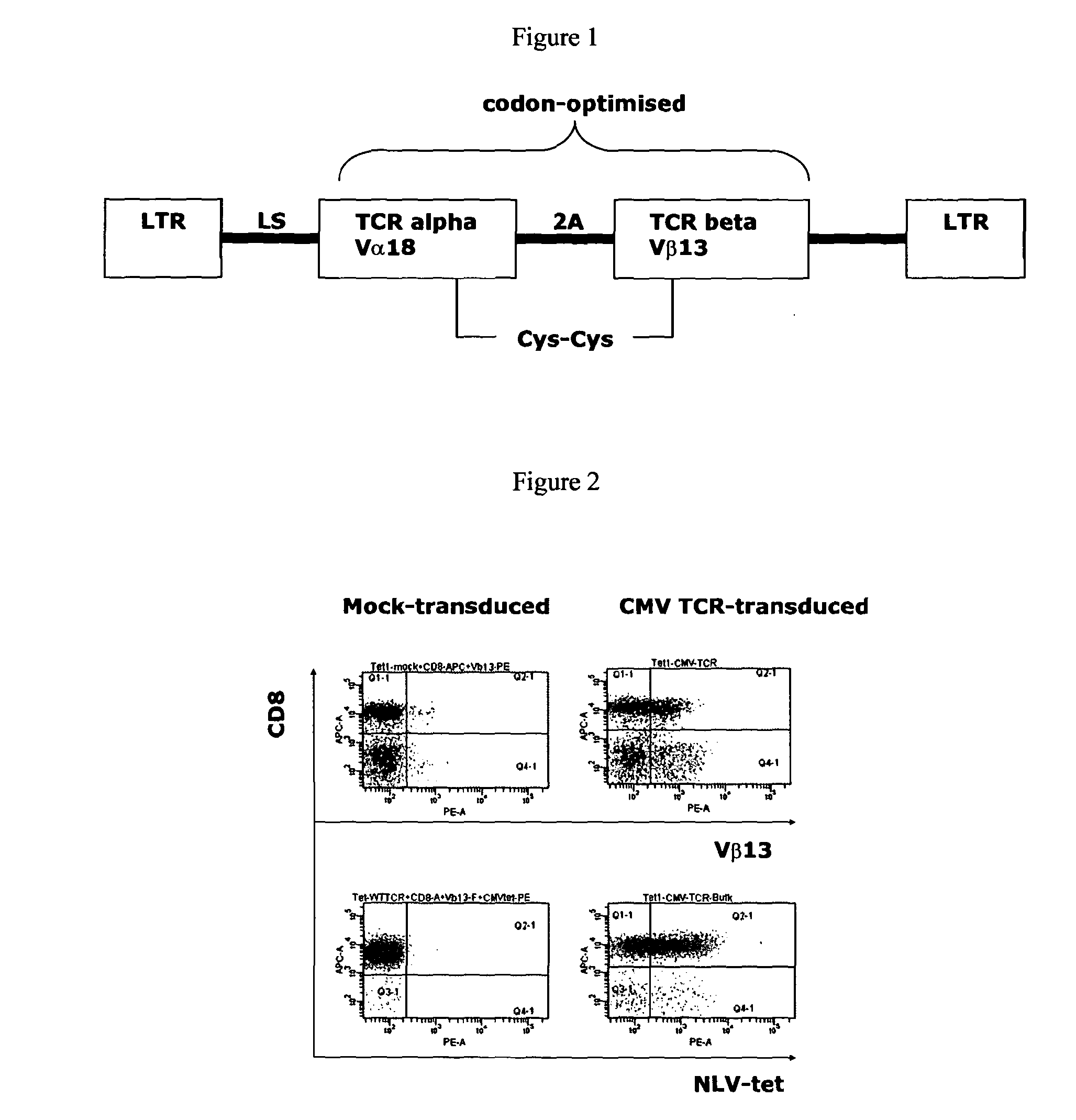
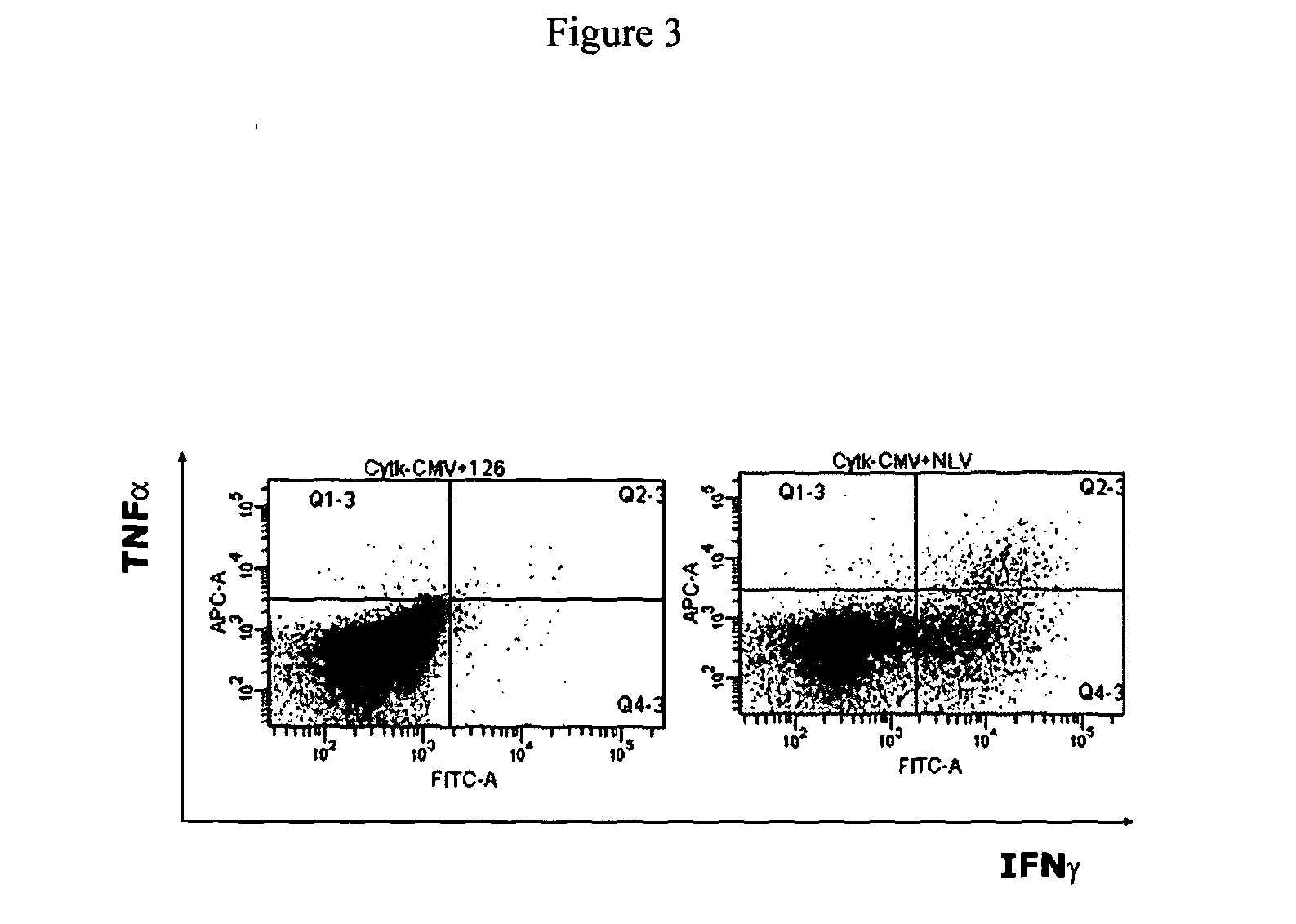
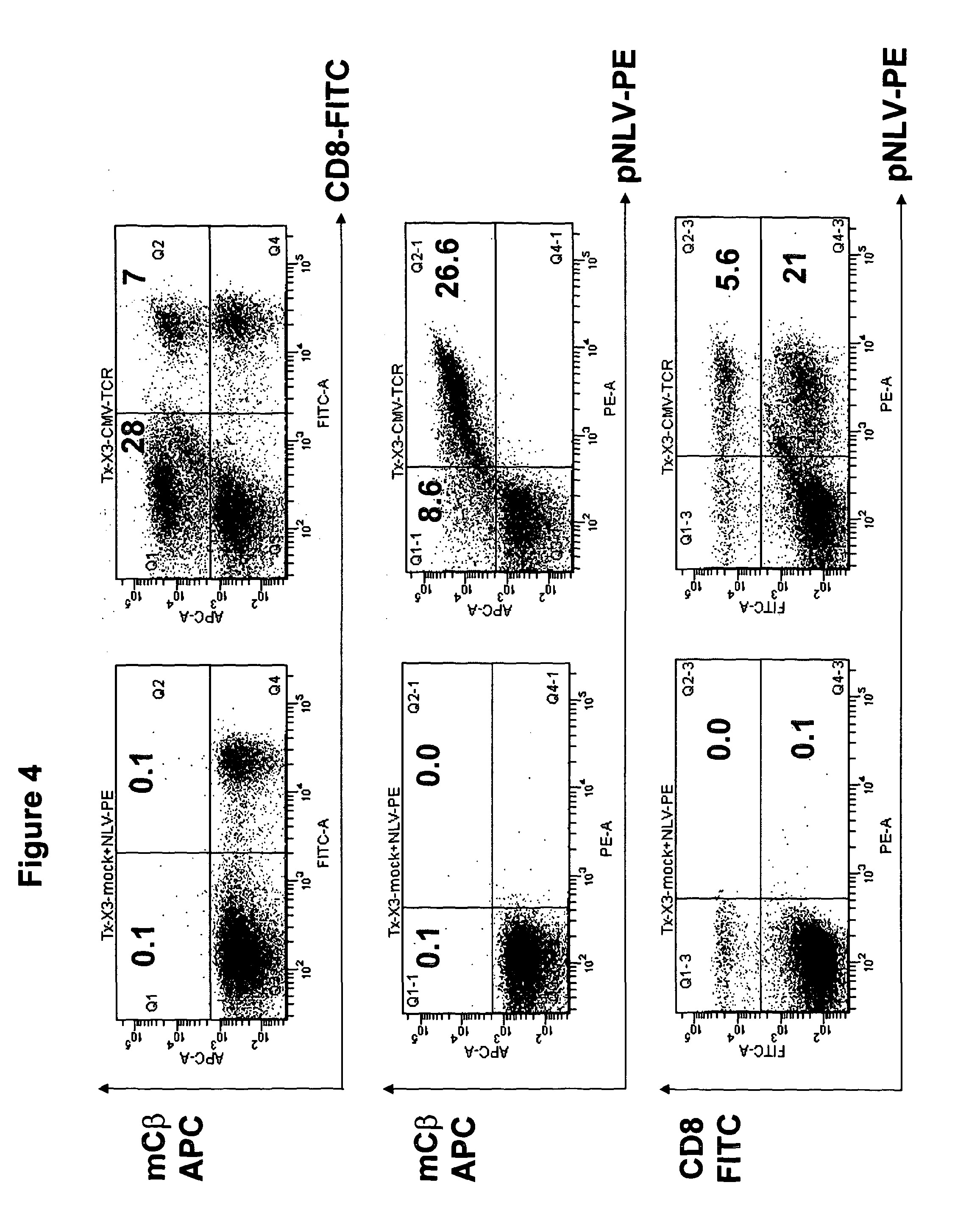
T-cell receptor capable of recognising an antigen from cytomegalovirus
The present invention provides a T-cell receptor (TCR) which binds to a peptide from the cytomegalovirus (CMV) phosphoprotein pp65 having the amino acid sequence NLVPMVATV (SEQ ID No. 1) when presented by a major histocompatability complex (MHC) molecule. The present invention also provides a nucleotide sequence encoding such a TCR, a vector comprising such a nucleotide sequence and its use to produce a CMV-specific T-cell. The present invention also provides the use of CMV-specific T-cell for cellular immunotherapy.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
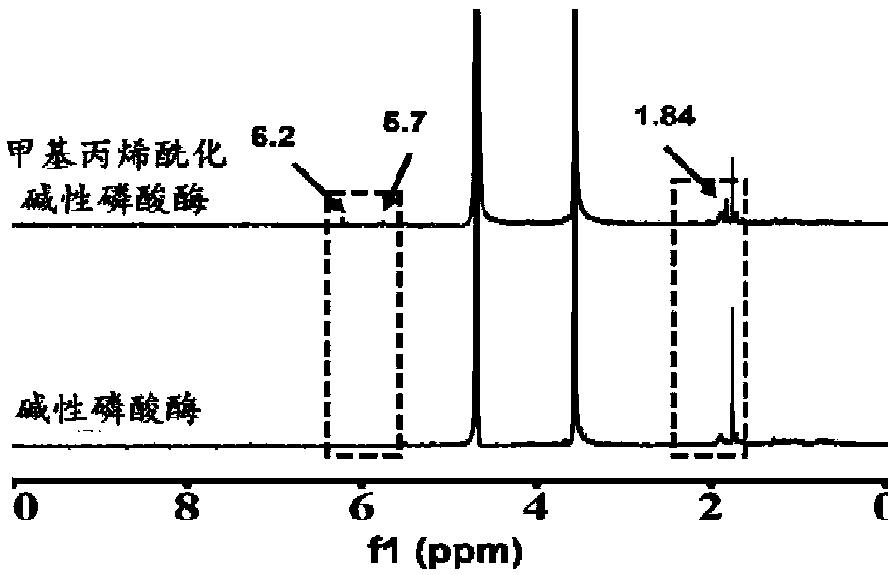
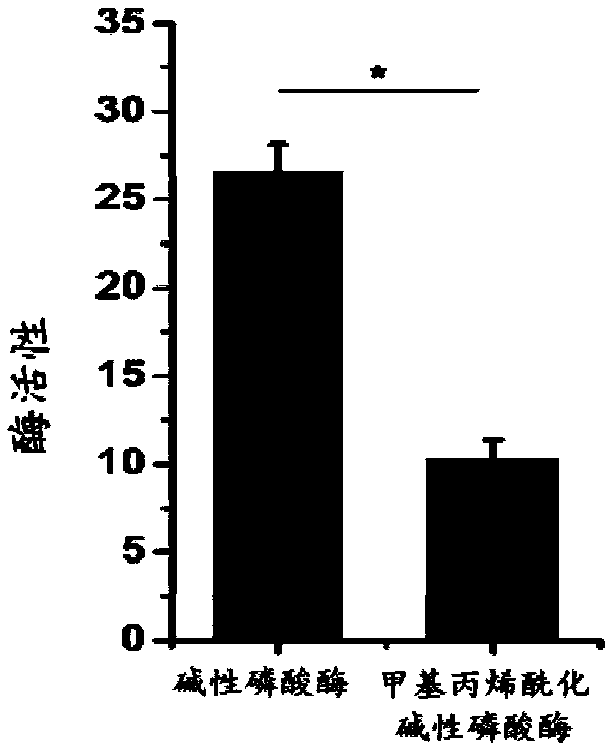
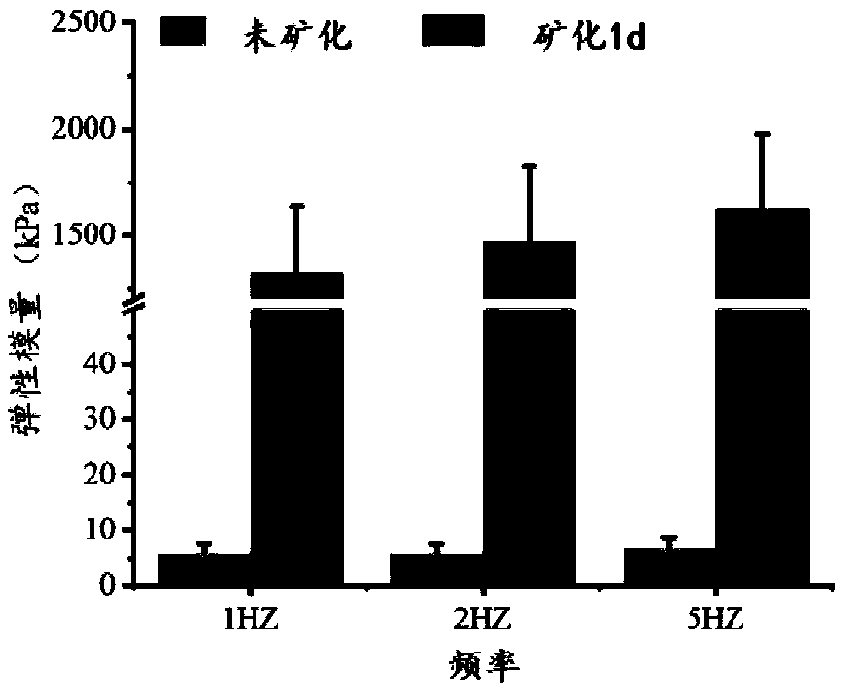
Preparation methods of mineralized hydrogel and biomimetic mineralized bone repair material
The invention discloses preparation methods of mineralized hydrogel and a biomimetic mineralized bone repair material. The mineralized hydrogel is prepared by using a photoactivated biomacromoleculesand a photoactivated phosphatase as raw materials; hydrogel is formed by initiating cross-linking by means of light irradiation or initiating polymerization cross-linking by means of a radical initiator; when the hydrogel is put into mineralized liquid, phosphatase can promote the uniform deposition of phosphate in the gel, so that the uniformly mineralized hydrogel is obtained. Phosphoprotein-like molecules are added during the preparation of the hydrogel; the phosphoprotein-like molecules can promote the uniform deposition of phosphate along a molecular network of biomacromolecules, so thatthe high-strength mineralized hydrogel can be obtained. When the phosphoprotein-like molecules and cells are added during the preparation of the hydrogel, the in-situ loading of the cells can be realized, and the enzyme in a process of bone physiological mineralization can be simulated so as to promote a phosphate mineralization process, so that the biomimetic mineralized bone repair material withhigh strength can be obtained, and the personalized customization of the bionic mineralized bone repair material can be realized; therefore, the preparation methods have a broad application prospectin the field of bone tissue engineering.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
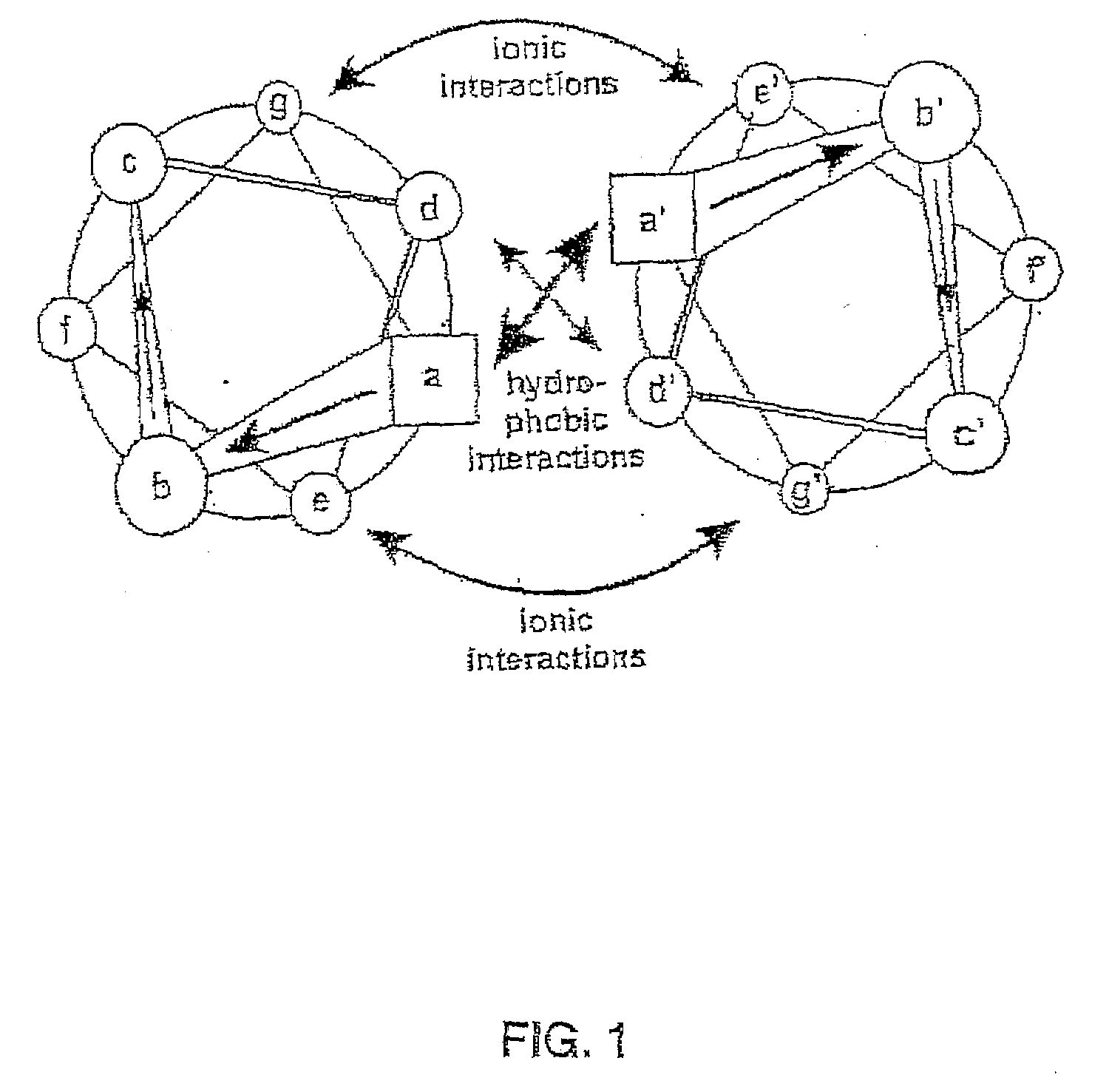
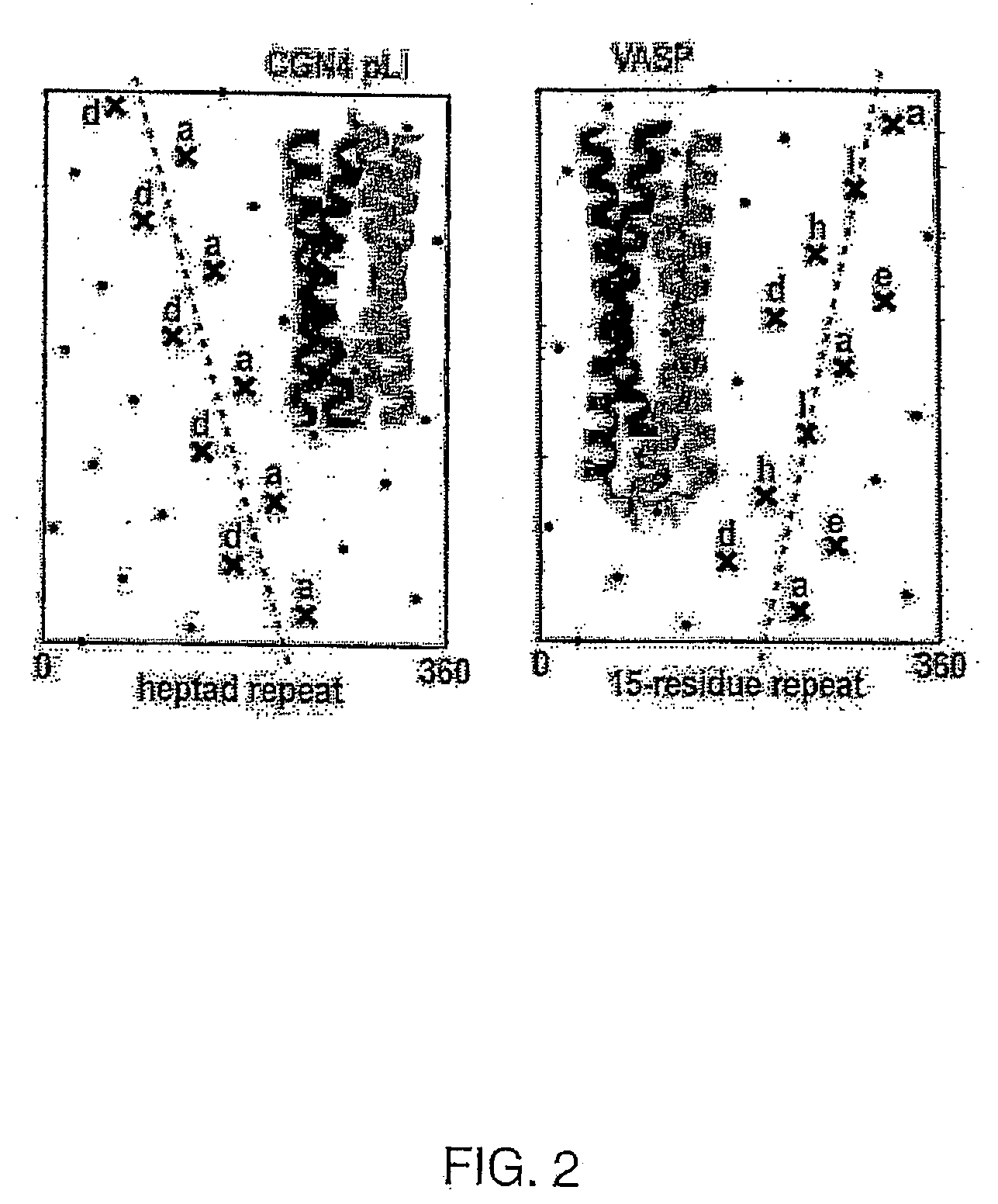
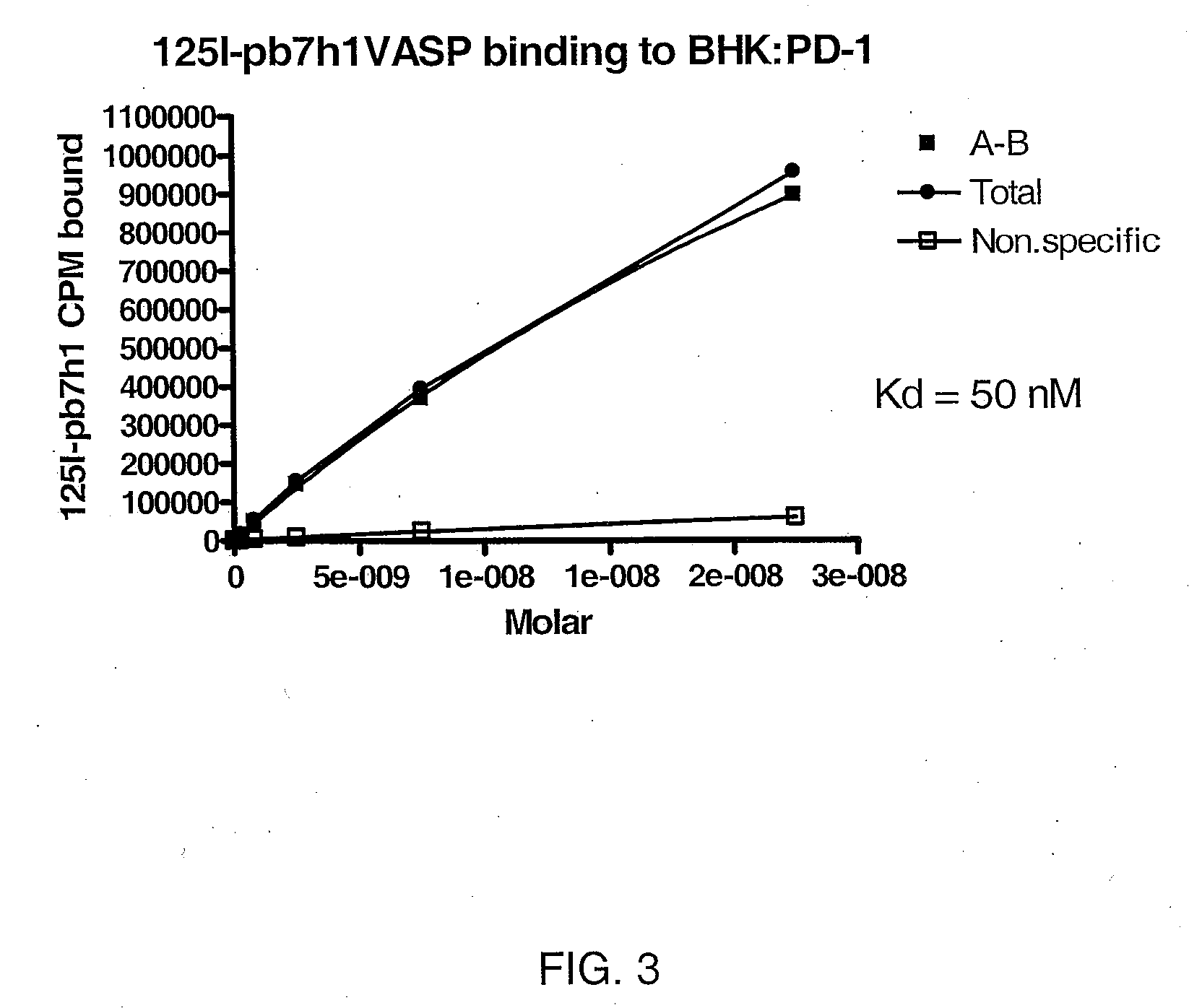
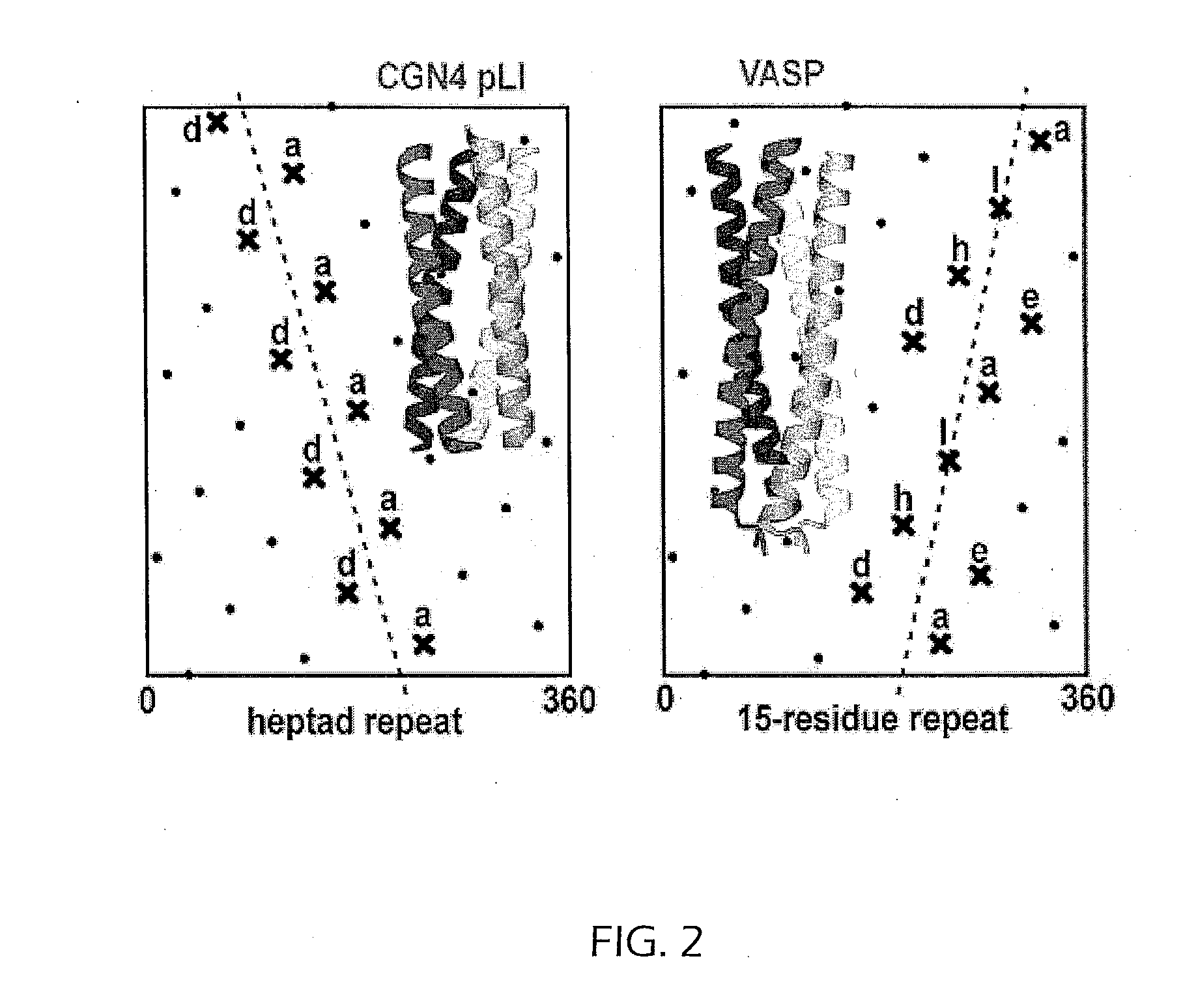
Tetramerizing polypeptides and methods of use
InactiveUS20070243584A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousPresent method
The present invention relates to a method of preparing a tetrameric protein comprising culturing a host cell transformed or transfected with an expression vector encoding a fusion protein comprising a vasodialator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) domain and a heterologous protein. In one embodiment, the heterologous protein is a membrane protein, the portion of the heterologous protein that included in the fusion protein is the extracellular domain of that protein, and the resulting fusion protein is soluble. The method can be used to produced homo- and hetero-tetrameric proteins. The present invention also encompasses DNA molecules, expression vectors, and host cells used in the present method and fusion proteins produced by the present method.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Tetramerizing polypeptides and methods of use
InactiveUS20070254339A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousPresent method
The present invention relates to a method of preparing a tetrameric protein comprising culturing a host cell transformed or transfected with an expression vector encoding a fusion protein comprising a vasodialator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) domain and a heterologous protein. In one embodiment, the heterologous protein is a membrane protein, the portion of the heterologous protein that included in the fusion protein is the extracellular domain of that protein, and the resulting fusion protein is soluble. The method can be used to produced homo- and hetero-tetrameric proteins. The present invention also encompasses DNA molecules, expression vectors, and host cells used in the present method and fusion proteins produced by the present method.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Newcastle disease virus heat resistant live vaccine vector system and application thereof
ActiveCN104059942AHeat resistantHigh heat resistanceSsRNA viruses negative-senseMicroorganism based processesDiseasePBR322
The invention belongs to the field of virus genetic operation, and in particular to a Newcastle disease virus (NDV) heat resistant live vaccine vector system and application thereof. The Newcastle disease virus (NDV) heat resistant live vaccine vector system comprises a) a transcription plasmid, b) three auxiliary plasmids and c) host cells. The transcription plasmid is obtained by cloning genomic full-length cDNA of a NDV heat resistant vaccine strain to pBR322 vector; and the three auxiliary plasmids are obtained by cloning nucleoprotein, phosphoprotein and large polymerase protein gene of the NDV heat resistant vaccine strain to pcDNA3.1 vector. The artificial recombinant Newcastle disease virus has the characteristic of heat resistance, and the Newcastle disease virus (NDV) heat resistant live vaccine vector system is established for the first time. The artificial recombinant Newcastle disease virus has great application prospect in the aspects of research and development of multiple (multivalent) heat resistant genetic engineering live vaccines of the NDV, avian influenza and other major diseases of poultry, research on virus heat-resistant mechanism, and the like.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
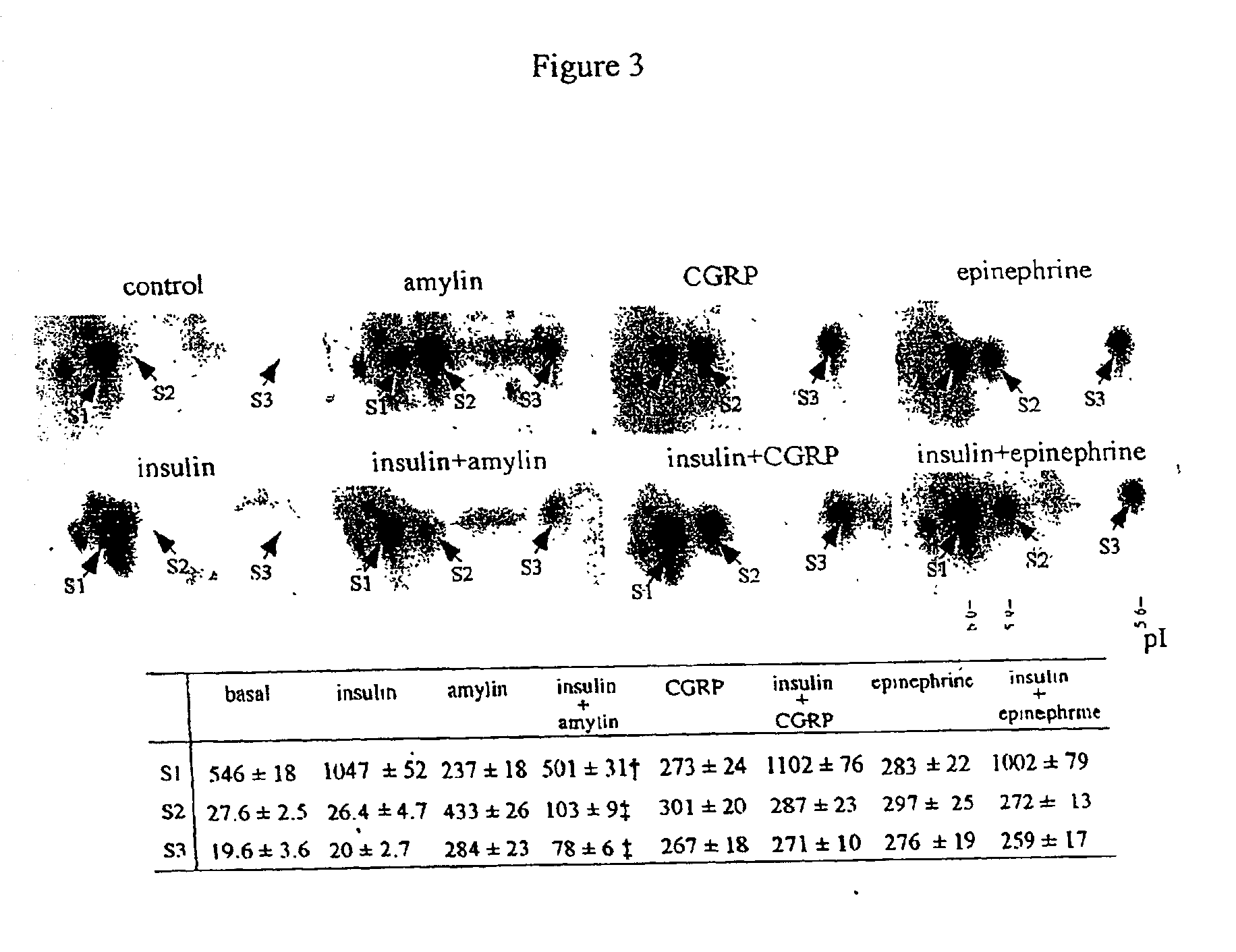
Phosphoprotein target for insulin and its antagonists
InactiveUS6884575B2Lower Level RequirementsCompound screeningApoptosis detectionInsulin resistanceProtein C
Owner:PROTEMIX DISCOVERY LTD
Selective labeling agent for phosphoproteome analysis and phosphorylated site analysis
InactiveUS20050176093A1High detection sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsPhosphopeptideSlurry
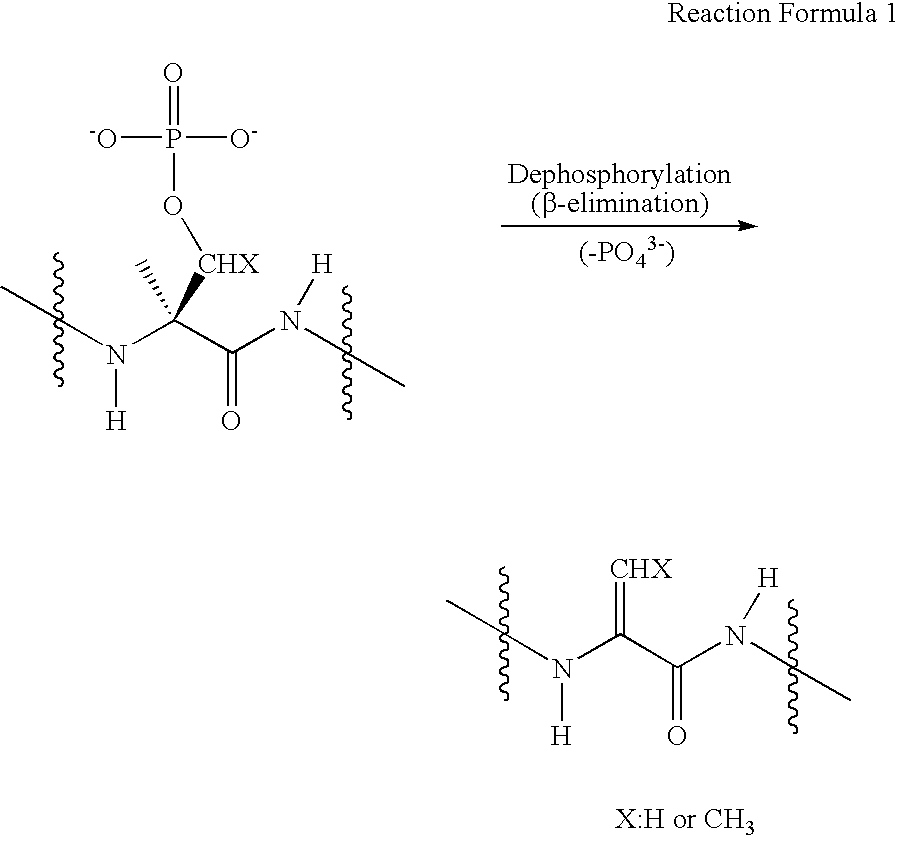
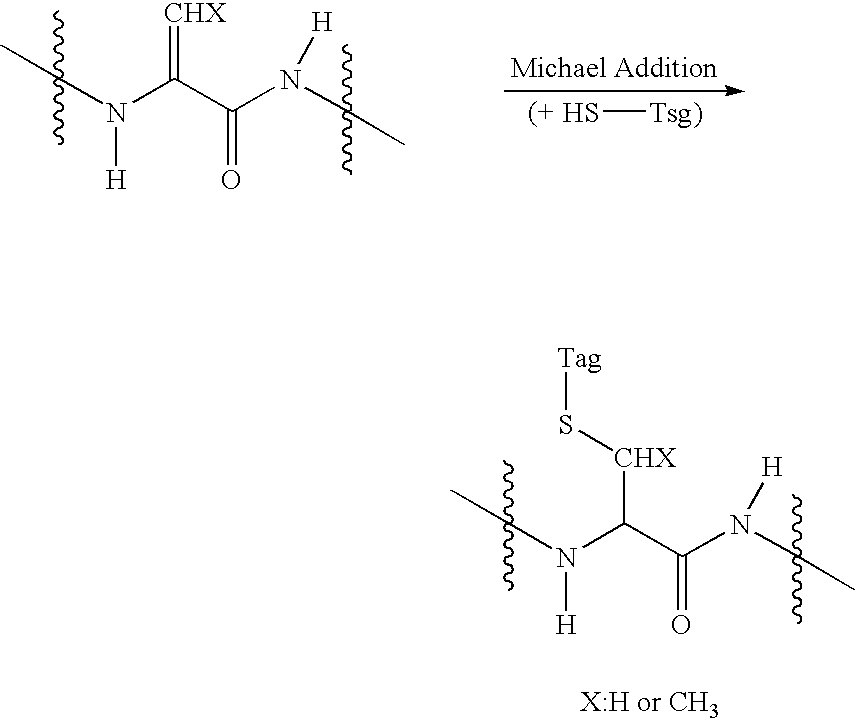
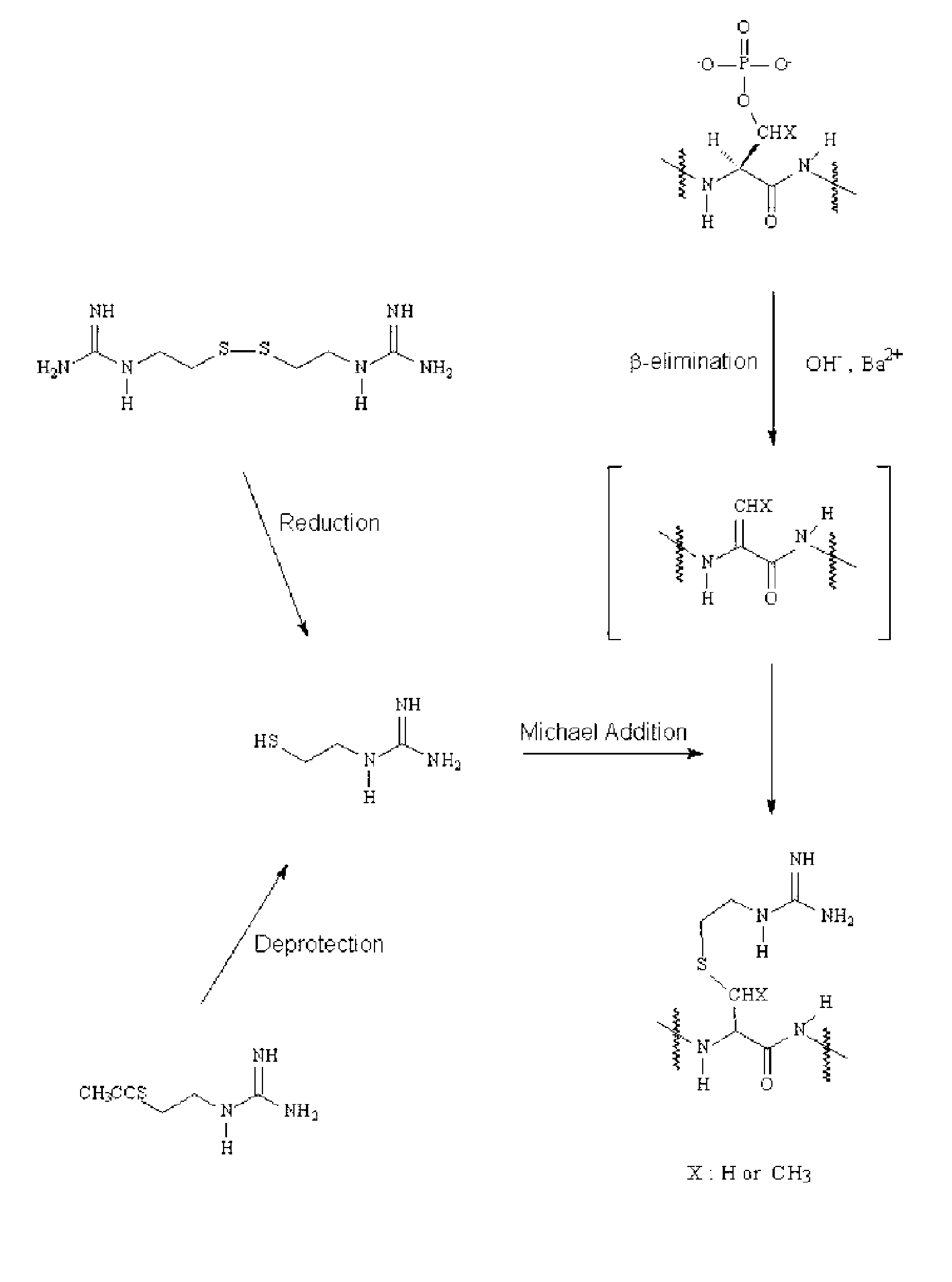
Disclosed is a method of analyzing mass of the phosphoproteins or phosphopeptides and of analyzing phosphorylated positions at a phosphoprotein or phosphopeptide, comprising the steps of: 1) dephosphorylating at least one Ser and / or Thr residue of the phosphoprotein or phosphopeptide; 2) tagging the dephosphorylated amino acid residues with a tag having a R-L-G moiety wherein R is a nucleophilic functional group that selectively bind with dephosphorylated amino acid residues, G is selected from the group consisting of guanidine moiety or protected guanidine moiety such as a mono-N-protected guanidino group, a di-N,N′-protected guanidino group and an N′-protected guanidino group, and L is a linker linking the R and the G; and 3) subjecting the tagged proteins or peptides to mass spectrometry. The method is capable of precisely analyzing mass of phosphoproteins of trace amounts as well as positions of phosphoryated amino acids.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
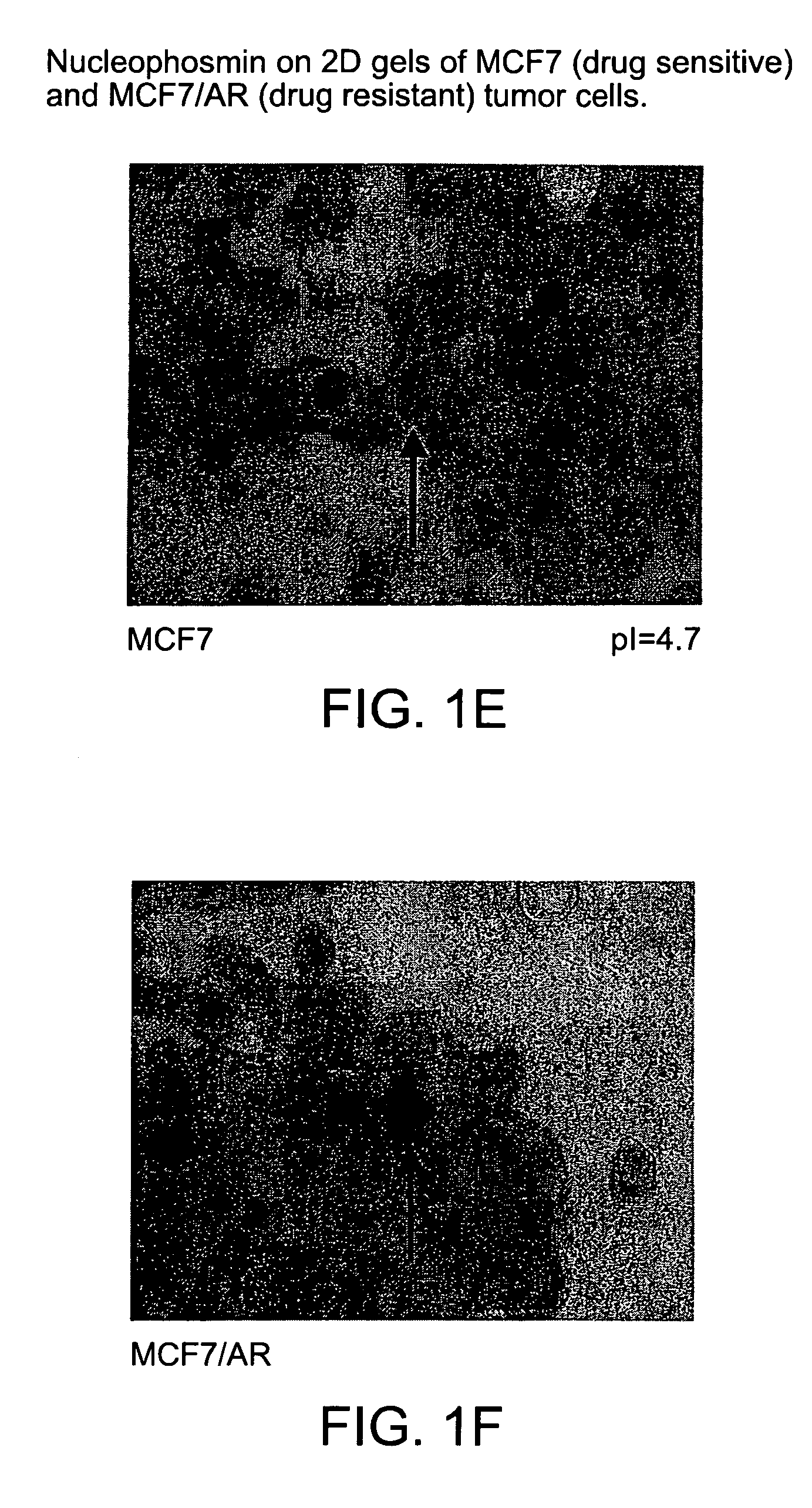
Nucleophosmin directed diagnostics and therapeutics for multidrug resistant neoplastic disease
Disclosed are methods for detecting neoplastic or damaged cells and for detecting multidrug resistance in neoplastic or damaged cells by detecting an increase in the cell surface expression of a nucleophosmin (NPM) protein on the surface of such a multidrug resistant neoplastic or damaged cells as compared to the level of expression of the nucleophosmin protein on the surface of a normal cell.
Owner:AURELIUM BIOPHARMA
Peste des petits ruminants virus (PPRV) reverse genetic operating system and application thereof
ActiveCN102071218ALow costReduce labor costsInactivation/attenuationVector-based foreign material introductionComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidFull length cdna
The invention relates to a peste des petits ruminants virus (PPRV) reverse genetic operating system and an application thereof. The PPRV reverse genetic operating system comprises a transcription plasmid and one or more helper plasmids, wherein the transcription plasmid can express the genome full-length cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of the PPRV; and the helper plasmid(s) can express nucleoprotein (N), phosphoprotein (P) and polymerase large protein (L) of the PPRV, and virus replication-permitting host cells of the PPRV. By using the PPRV reverse genetic operating system, the recombined PPRV is successfully saved. The establishment of the PPRV reverse genetic operating technical platform provides an excellent technical platform for the development of PPRV live vector vaccines and the fundamental research related to PPRV.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
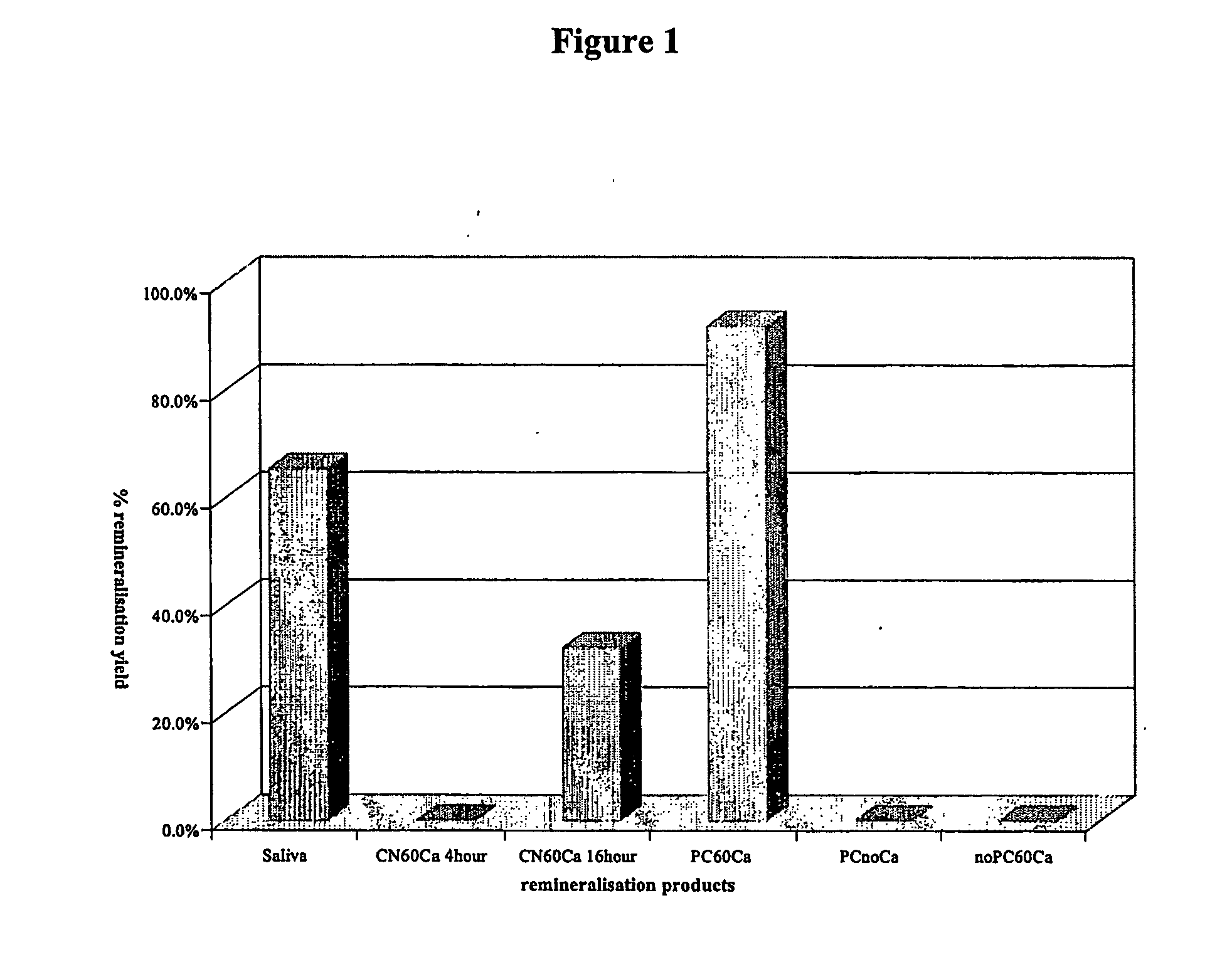
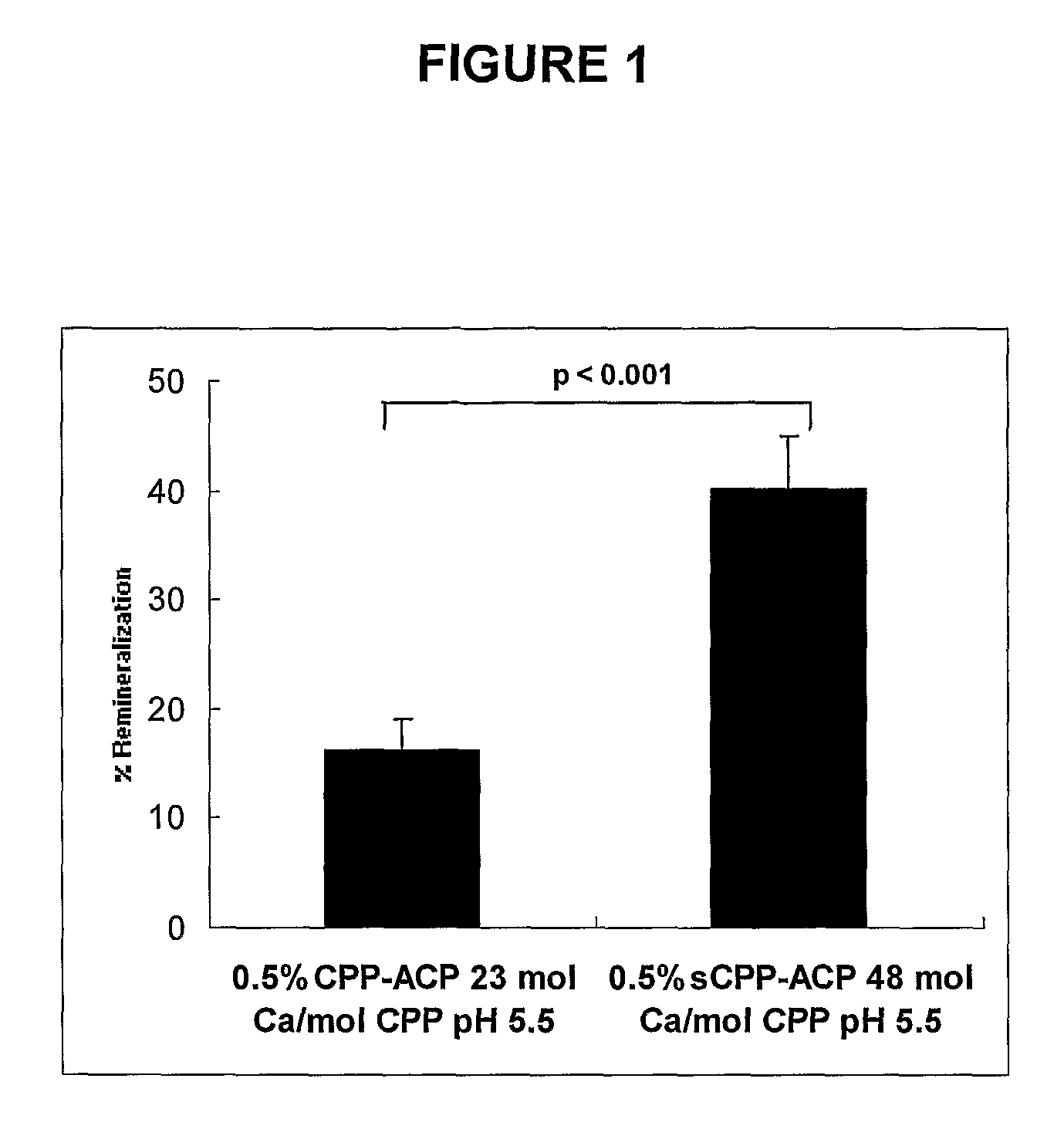
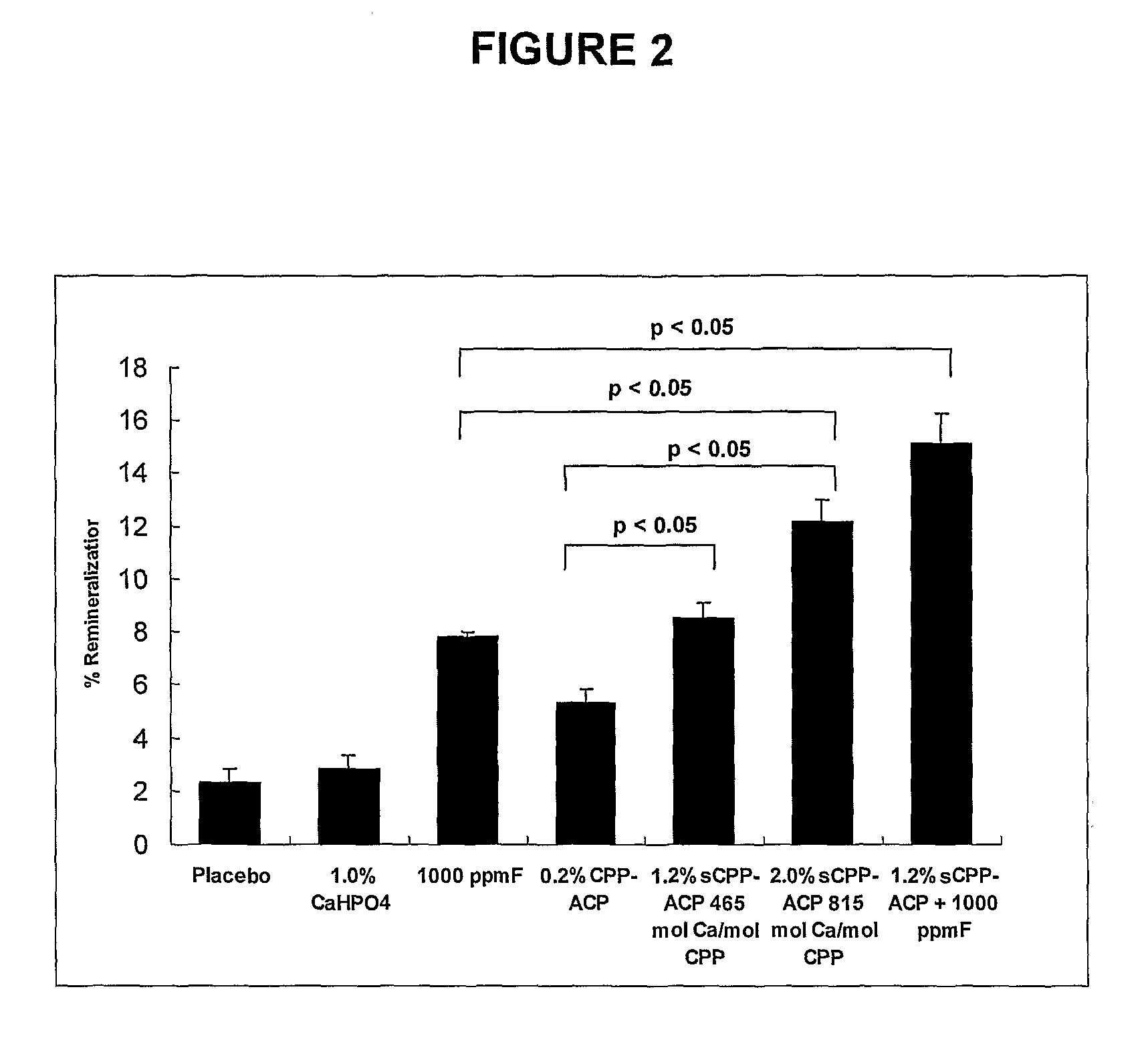
Phosphoprotein preparations for bioactive metal ion delivery and teeth remineralisation
The invention provides, in one aspect, compositions for delivering a bioactive metal ion to a mammal, the compositions comprising (a) an effective amount of a source of the bioactive metal ion, (b) a phosphoprotein preparation obtained by partially cross linking a partial hydrolysate of casein or a caseinate, and (c) one or more physiologically acceptable diluents or carriers. Also provided are compositions for remineralising tooth enamel and / or for treating or preventing dental caries, tooth erosion, dentinal hypersensitivity or gingivitis in a mammal, wherein the compositions comprise an effective amount of such a phosphoprotein preparation, in combination with one or more carriers or diluents. In related aspects, the invention provides methods of using such compositions. Also provided are novel phosphoprotein preparations suitable for use in such compositions and methods.
Owner:SILCOCK PATRICK JOSEPH +4
Method for identifying phosphoprotein
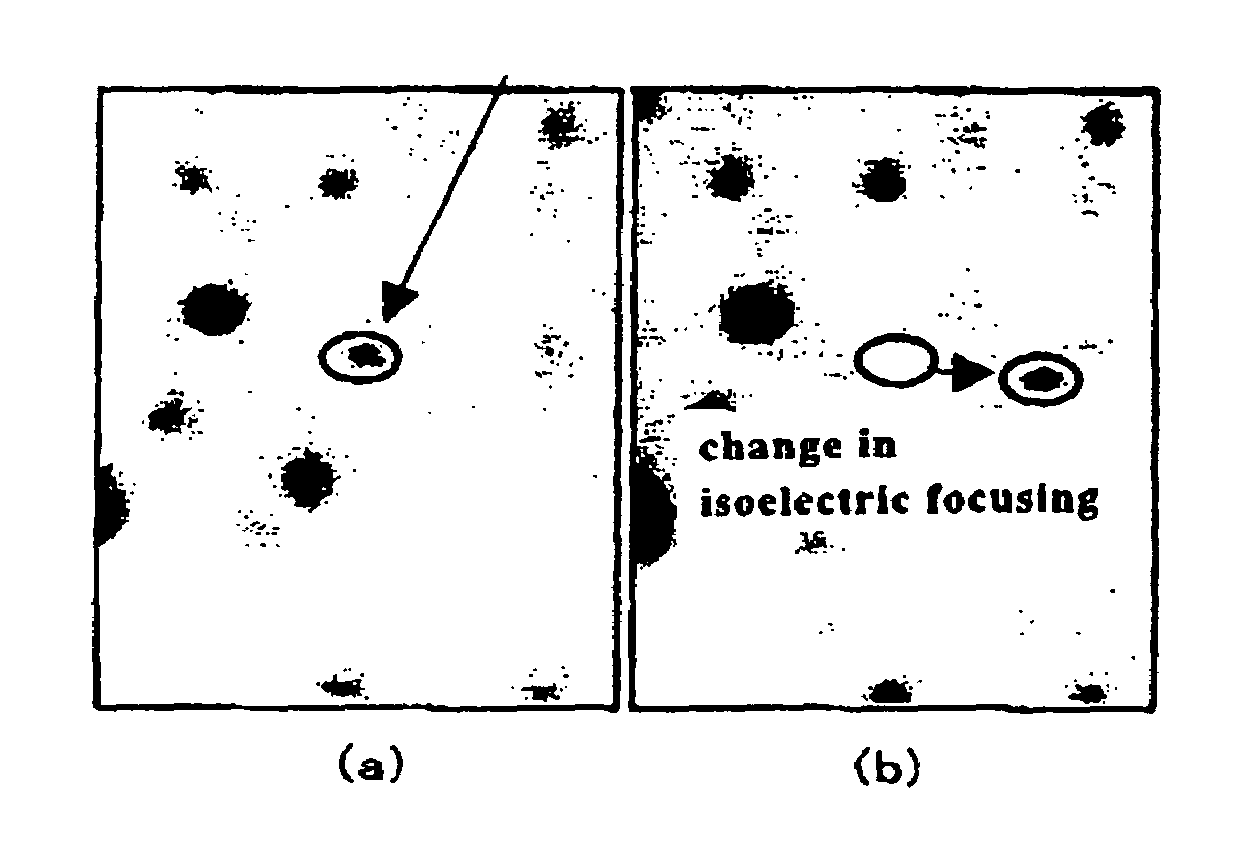
InactiveUS7074583B2Avoid deactivationPrevent precipitationElectrolysis componentsHydrolasesBioinformaticsProtein C
A method for identifying phosphoprotein, which comprises: subjecting a sample protein to two-dimensional electrophoresis; dephosphorylating the sample protein with phosphatase; once again performing the two-dimensional electrophoresis under the same conditions; and detecting the spot that migrates to the alkaline side of the isoelectric focusing as the phosphoprotein is provided as a convenient method for identifying phosphoprotein with high accuracy.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Biomarkers for differentiating melanoma from benign nevus in the skin
InactiveUS20160115555A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigenBiomarker (petroleum)
Disclosed is a method for diagnosing melanoma in a human subject, as well as a method for providing a prognosis to a human subject who is at risk of developing melanoma recurrence, and a method for determining the stage of melanoma in a human subject, comprising the step of determining the level of expression of phosphatase and actin regulator 1 (PHACTR1) gene, or fragments thereof, either alone or in combination with the level of expression of secreted integrin-binding phosphoprotein (SPP1), preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma (PRAME), growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15), and chemokine C-X-C motif ligand 10 (CXCL10) genes. Further, the invention relates to a diagnostic kit, comprising at least one substance for detection of the expression of PHACTR1, or fragments thereof, either alone or in combination with the detection of SPP1, PRAME, GDF15, and CXCL10, for the diagnosis or prognosis of melanoma.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL DIAGNOSTICS INC
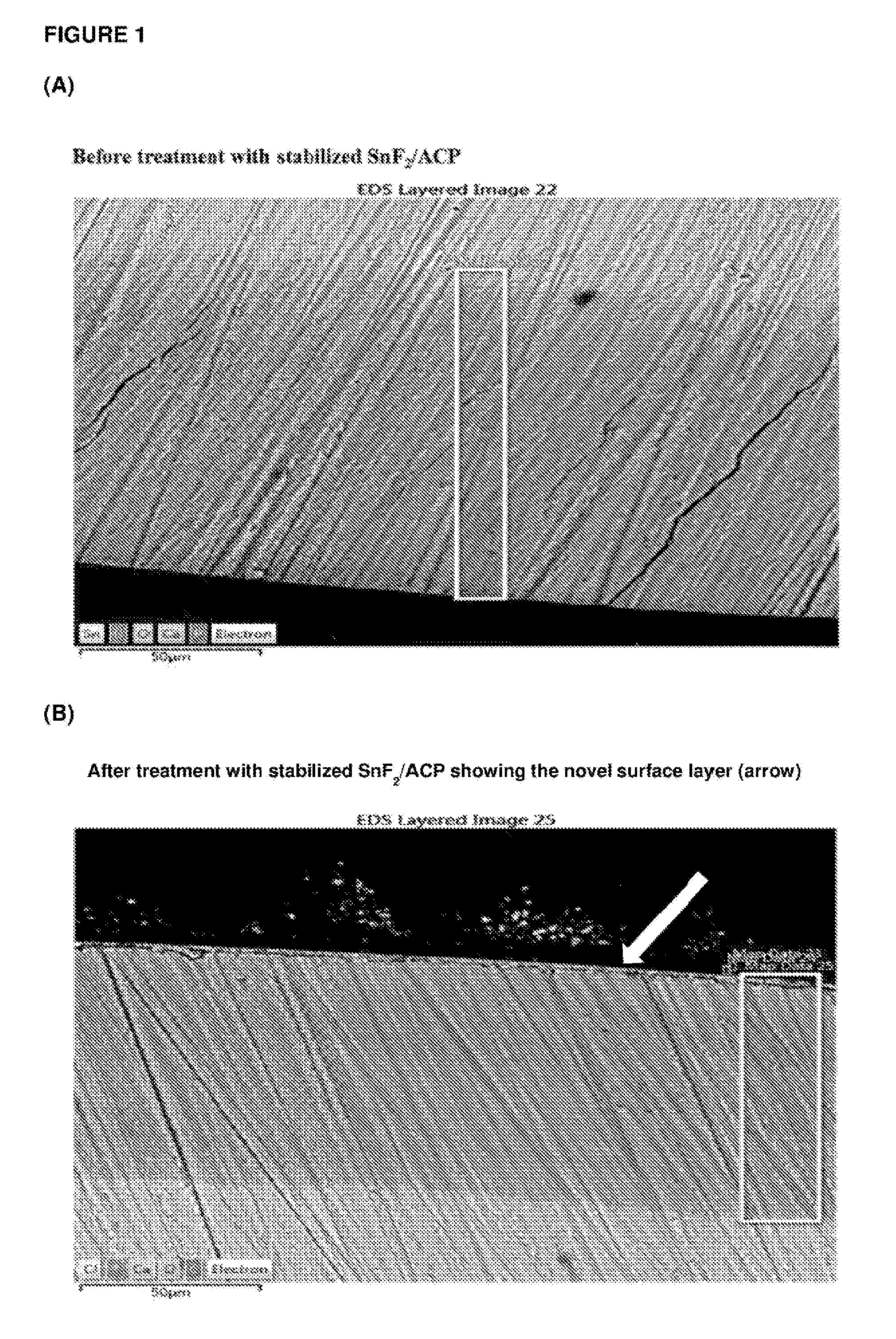
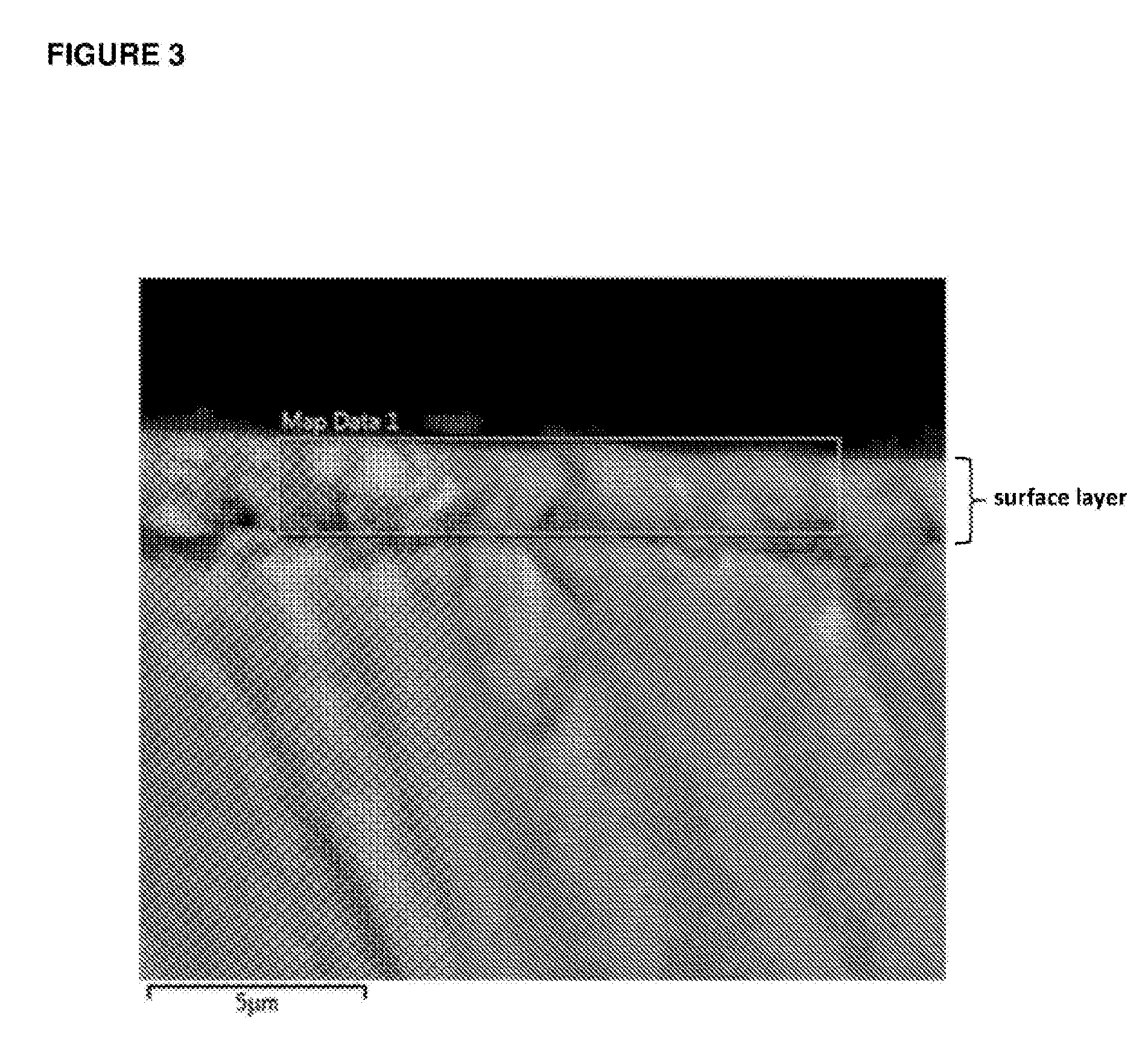
Stabilized stannous compositions
ActiveUS20160317404A1Reduced bioavailabilityReduced activityCosmetic preparationsHeavy metal active ingredientsPhosphopeptidePhases of clinical research
The present invention relates to improved complexes of amorphous calcium phosphate and / or amorphous calcium fluoride phosphate stabilised by phosphopeptides / phosphoproteins by addition of stannous ions. These complexes have anticariogenic properties useful to protect tooth structures as they remineralize (repair) early stages of dental caries and have other dental / medical applications (including anti-calculus, anti-erosion / corrosion and anti-dentinal hypersensitivity). Methods of making the complexes of the invention and of treatment or prevention of various dental conditions including dental caries, dental calculus, dental erosion / corrosion and dental hypersensitivity are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
Ionic complexes
ActiveUS8603988B2Growth inhibitionReduce and prevent formationCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsNuclear chemistryAmorphous calcium phosphate
The present invention provides a phosphopeptide or phosphoprotein (PP) stabilized amorphous calcium phosphate or amorphous calcium fluoride phosphate complex having a calcium ion greater than about 30 moles of calcium per mole of PP.
Owner:MELBOURNE UNIV OF THE
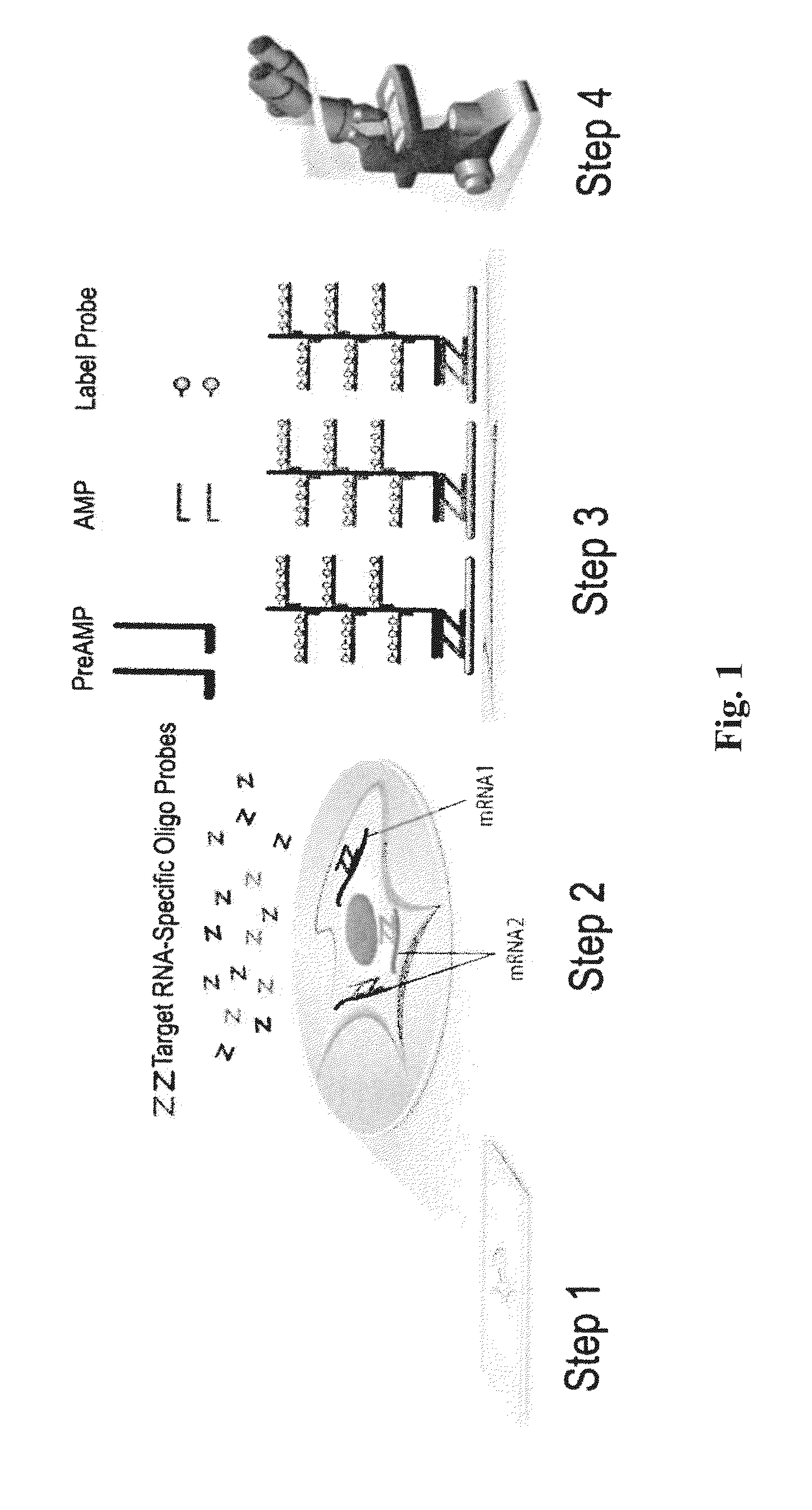
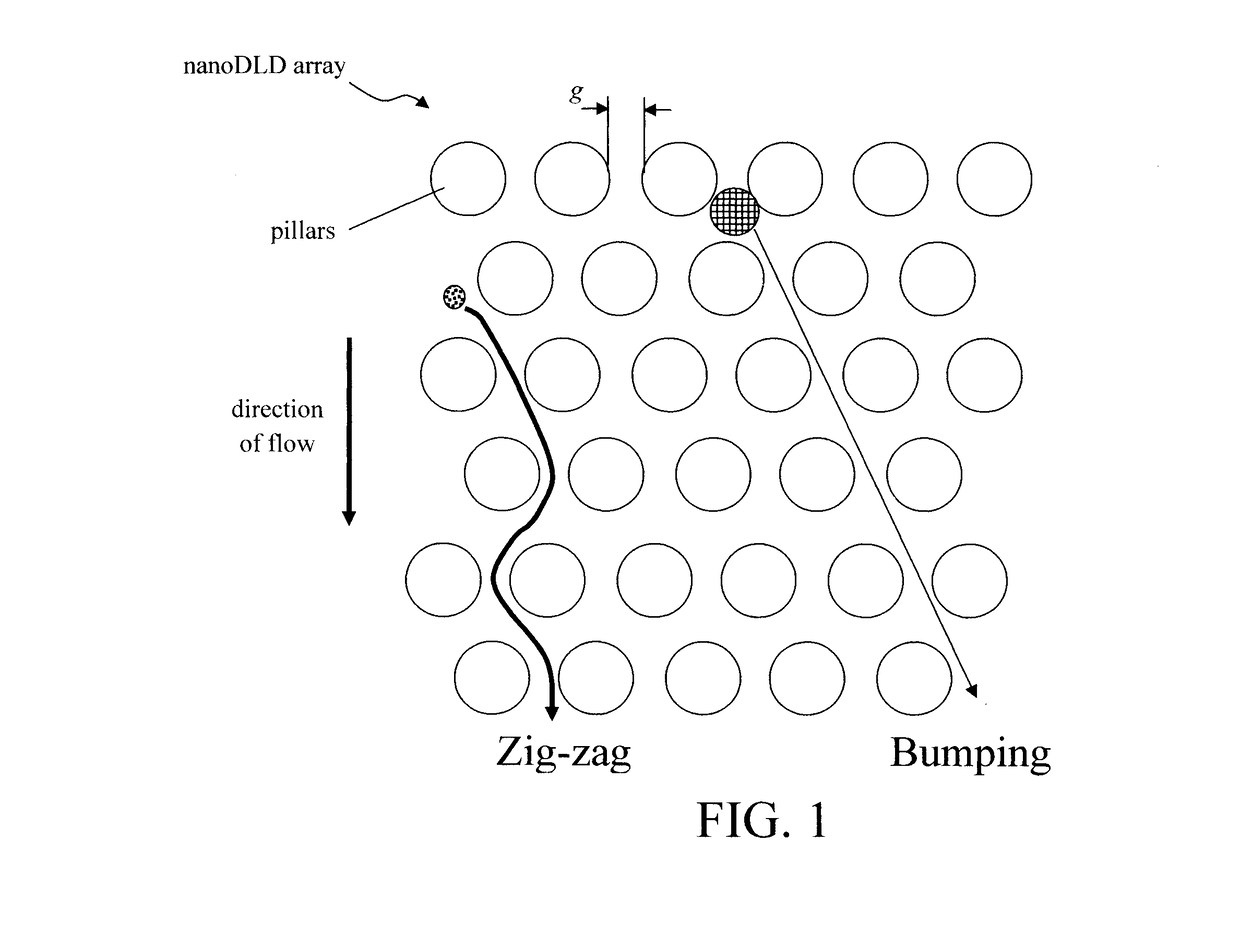
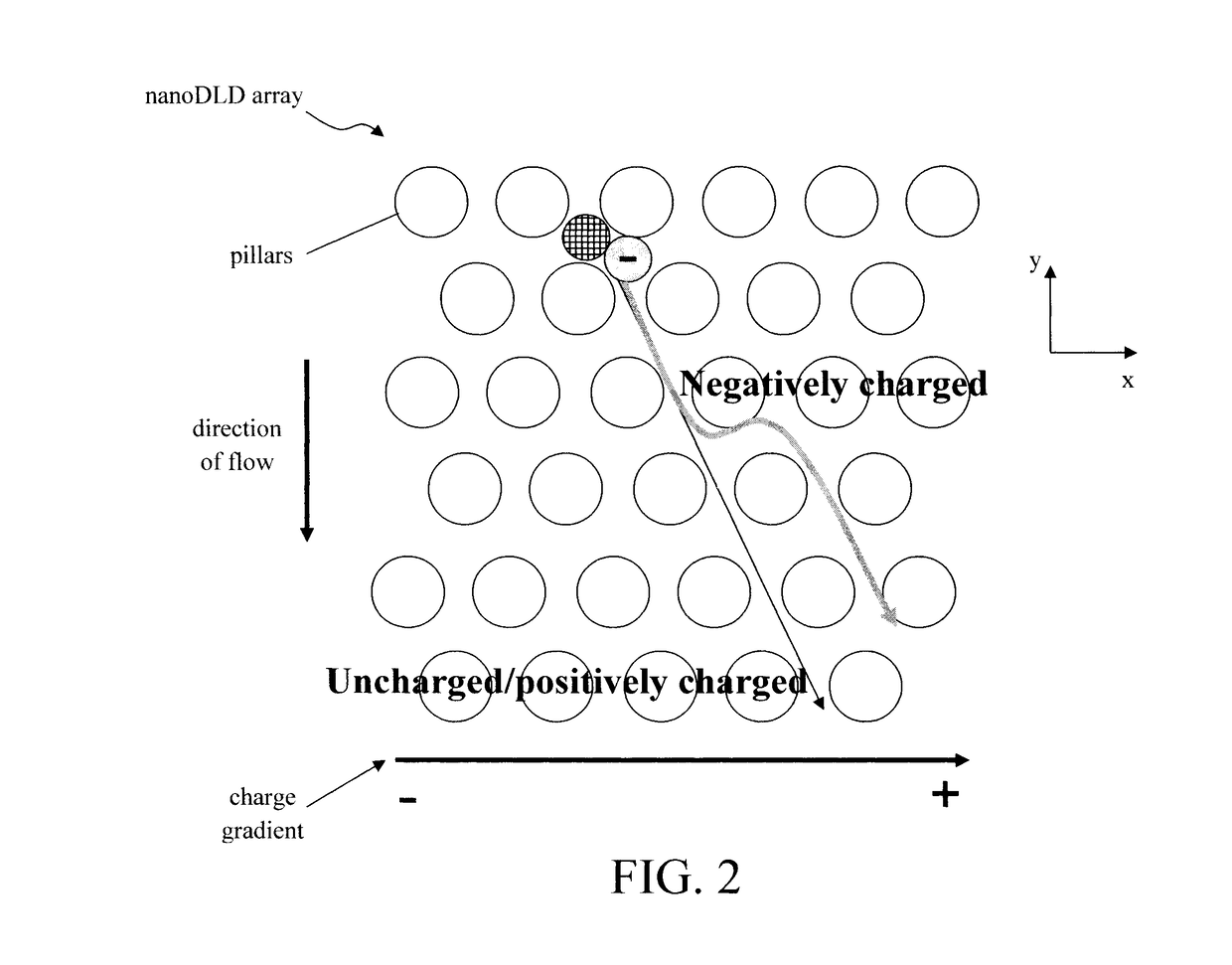
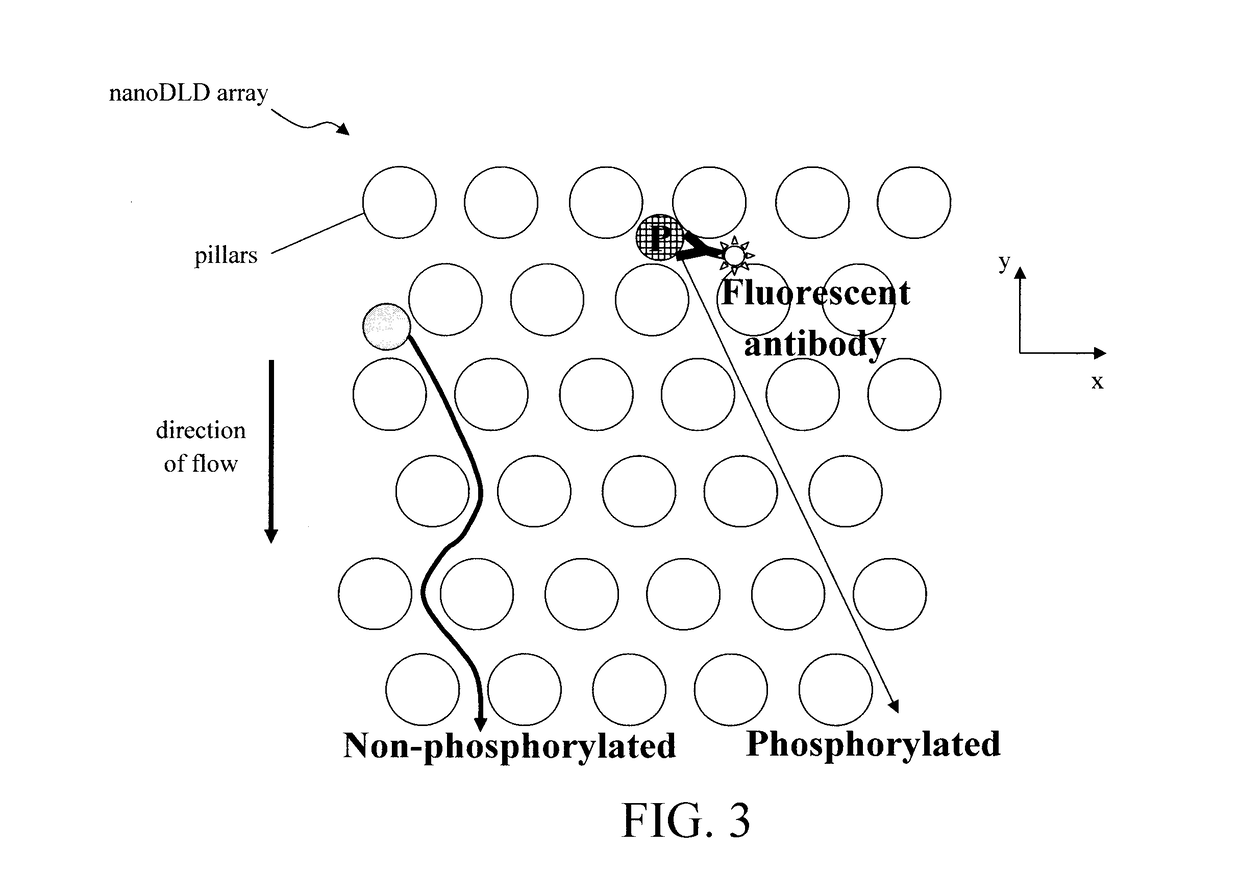
Phosphoprotein Detection Using a Chip-Based Pillar Array
ActiveUS20180080857A1Component separationPreparing sample for investigationProtein insertionLab-on-a-chip
Techniques for phosphoprotein detection, quantification, and purification using a chip-based pillar array are provided. In one aspect, a method for purifying a protein sample includes: introducing a mixture including the protein sample and an antibody to a nanoDLD array having a plurality of pillars separated by a gap g, wherein the antibody and proteins in the protein sample form antibody-protein complexes having a size that is greater than a size threshold of the nanoDLD array created by the gap g which permits size-based separation of the antibody-protein complexes as the mixture flows through the nanoDLD array; and collecting a purified protein sample containing the antibody-protein complexes from the nanoDLD array. A lab-on-a-chip (LOC) device including the nanoDLD array is also provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
Yak myeloid calcium tablets
InactiveCN1679628AUnique formulaGreat tasteMetabolism disorderUnknown materialsCalcium in biologyCoronary artery disease
A nutritive health-care calcium tablet for providing Ca and trace elements to human body, and preventing arteriosclerosis, coronary heart disease, constipation and diabetes is prepared from the bone marrow powder of yak, chocolate powder, granular white sugar, defatted milk powder and magnesium stearate. It is rich in nutrients: P. phosphoprotein, amino acid, VA, VB1, VD, bone glue, etc.
Owner:吴东
Composition for recovering measles virus, and kit, purpose and method thereof
ActiveCN103160473ARescue is easy and convenientAcquire infectivityAntiviralsViruses/bacteriophagesGenomeNucleocapsid Proteins
The present invention provides a composition for recovering measles virus, and a kit, a purpose and a method thereof. The composition for recovering measles virus of the present invention comprises: 1) a recombinant transcription vector, which contains the measles virus whole genome cDNA, wherein the 5' and 3' ends of the measles virus whole genome respectively includes a ribozyme sequence with self-cleavage function; 2) a first recombinant expression vector, which includes an encoding gene of nucleocapsid protein of measles virus; 3) a second recombinant expression vector, which includes the encoding gene of measles virus phosphoprotein; and 4) a third recombinant expression vector, which includes an encoding gene of RNA polymerase of measles virus. The composition of the present invention can simply and easily recover measles virus, and the recovered measles virus can be used for preparing a measles vaccine. The composition is suitable for industrial applications.
Owner:NAT VACCINE & SERUM INST
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer assays for sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium atpase and phospholamban
ActiveUS20120021926A1Compound screeningApoptosis detectionEnergy transferHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
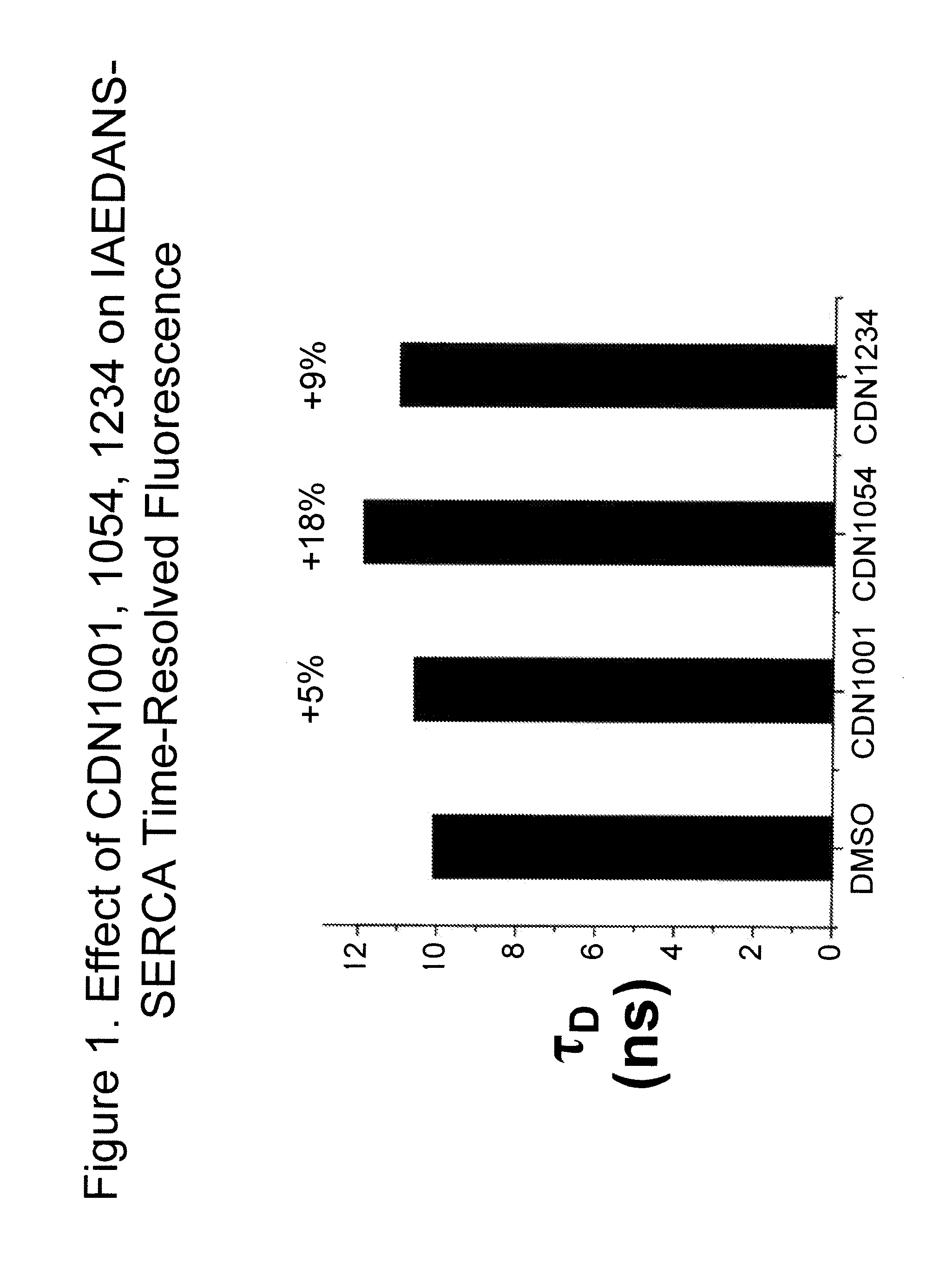
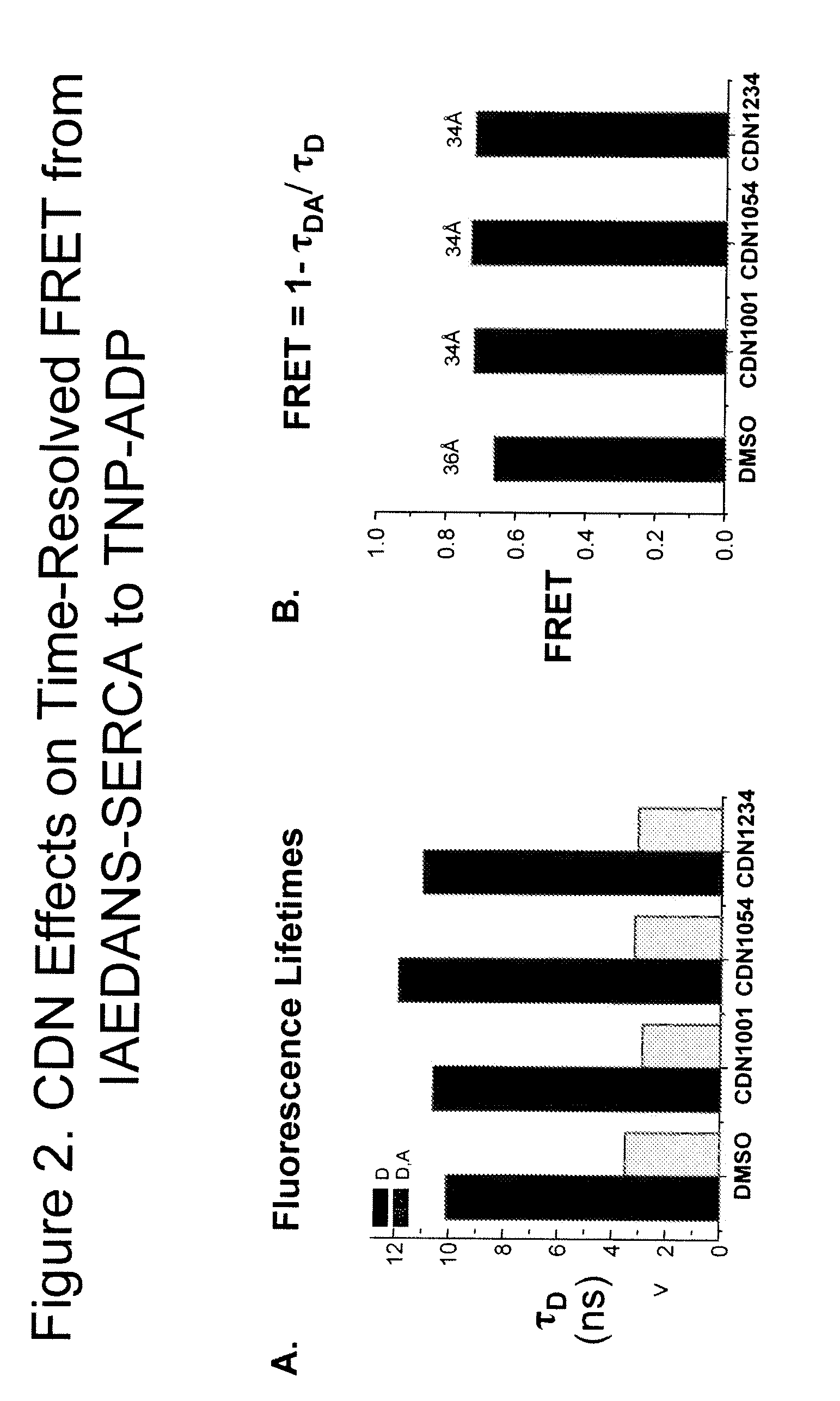
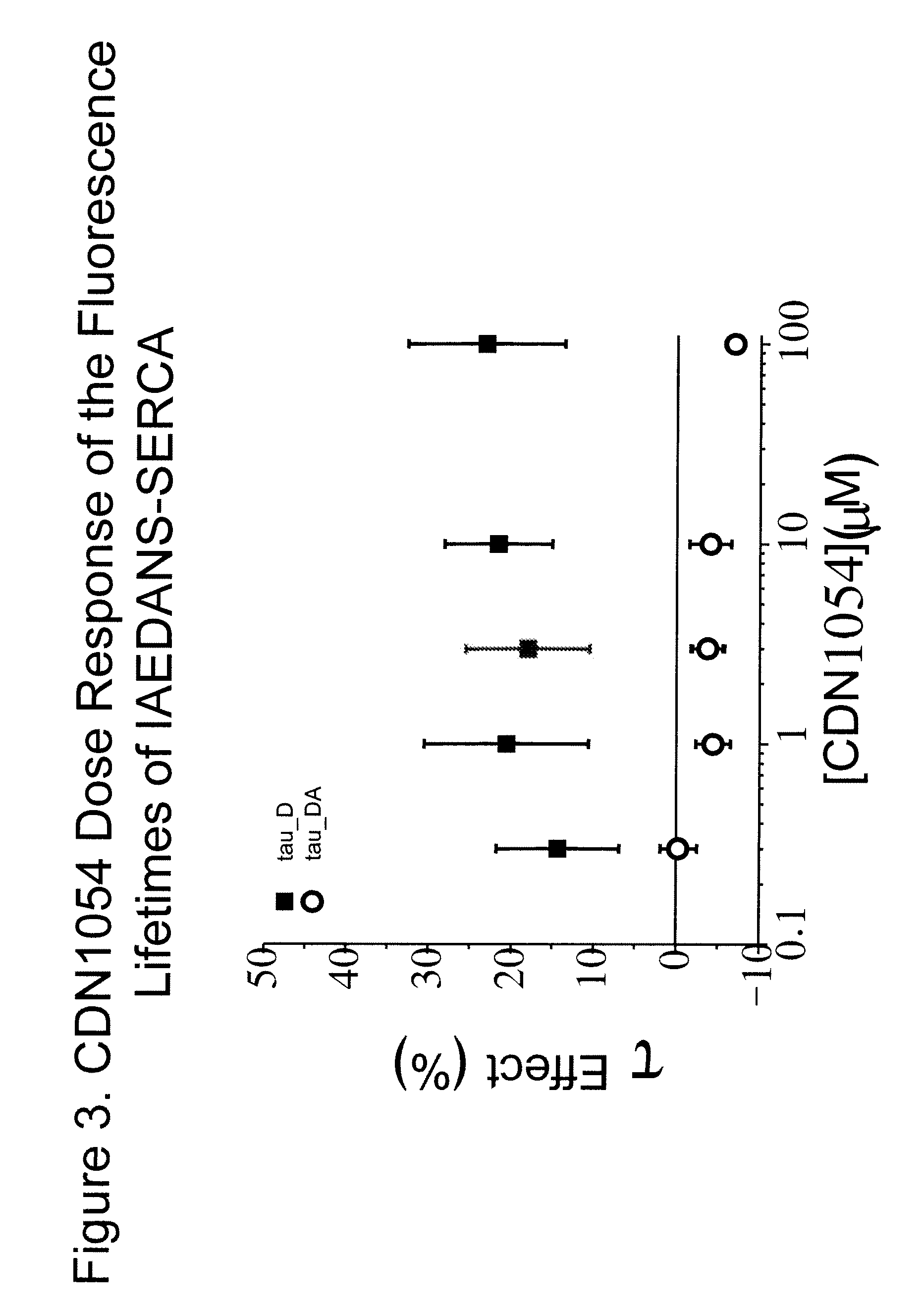
Provided herein are methods for identifying molecules capable of modulating SERCA, the SERCA-PLB complex or the microenvironment of the complex. An exemplary assay provided herein is fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). Also provided herein are FRET assays that are optimized for high-throughput screening (HTS) for identifying small molecules that modulate SERCA or the SERCA-PLB complex. Further provided are kits for carrying out said methods for identifying molecules.
Owner:THERAGENE PHARMA INC +1
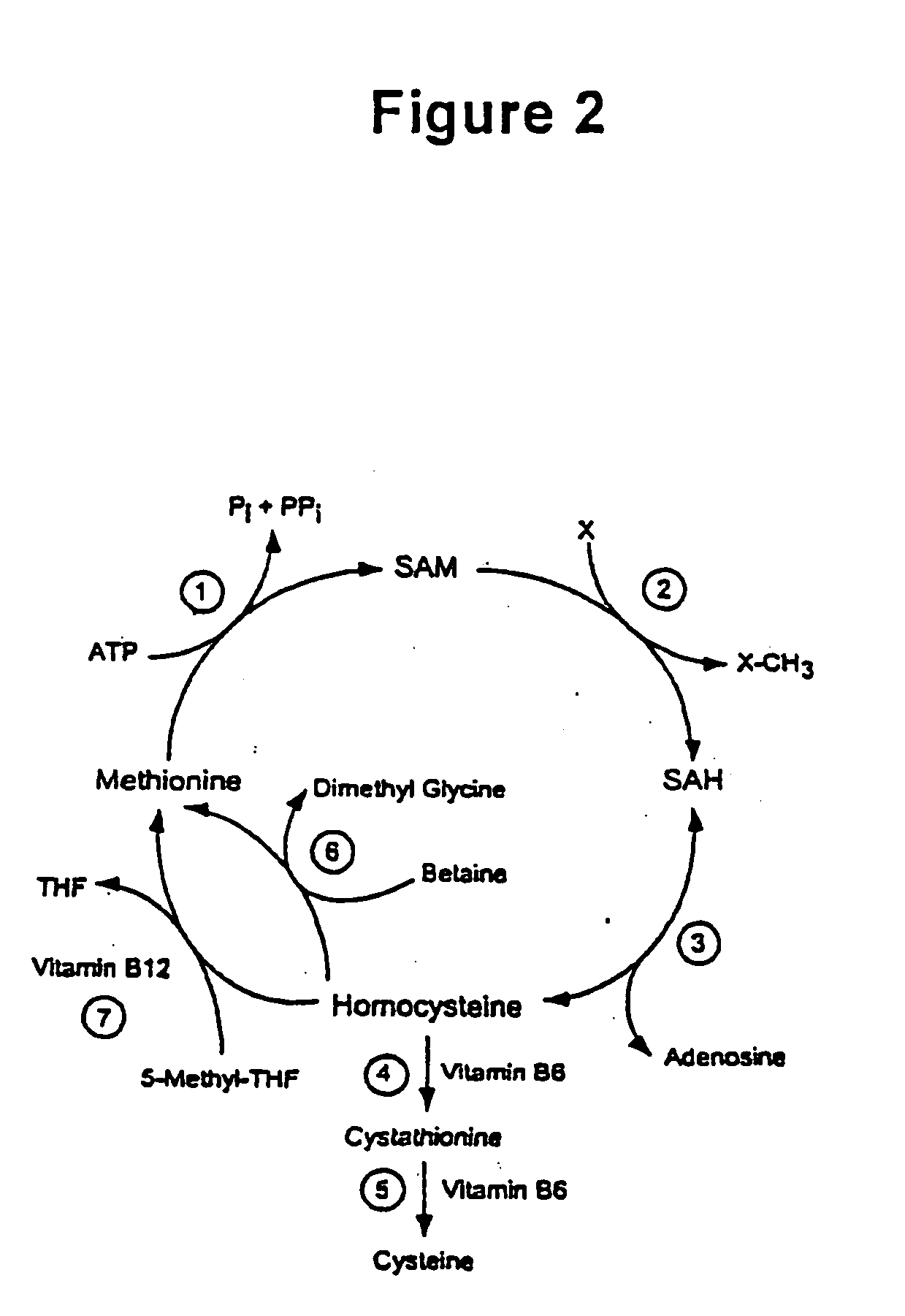
Modulation of protein methylation and phosphoprotein phosphate
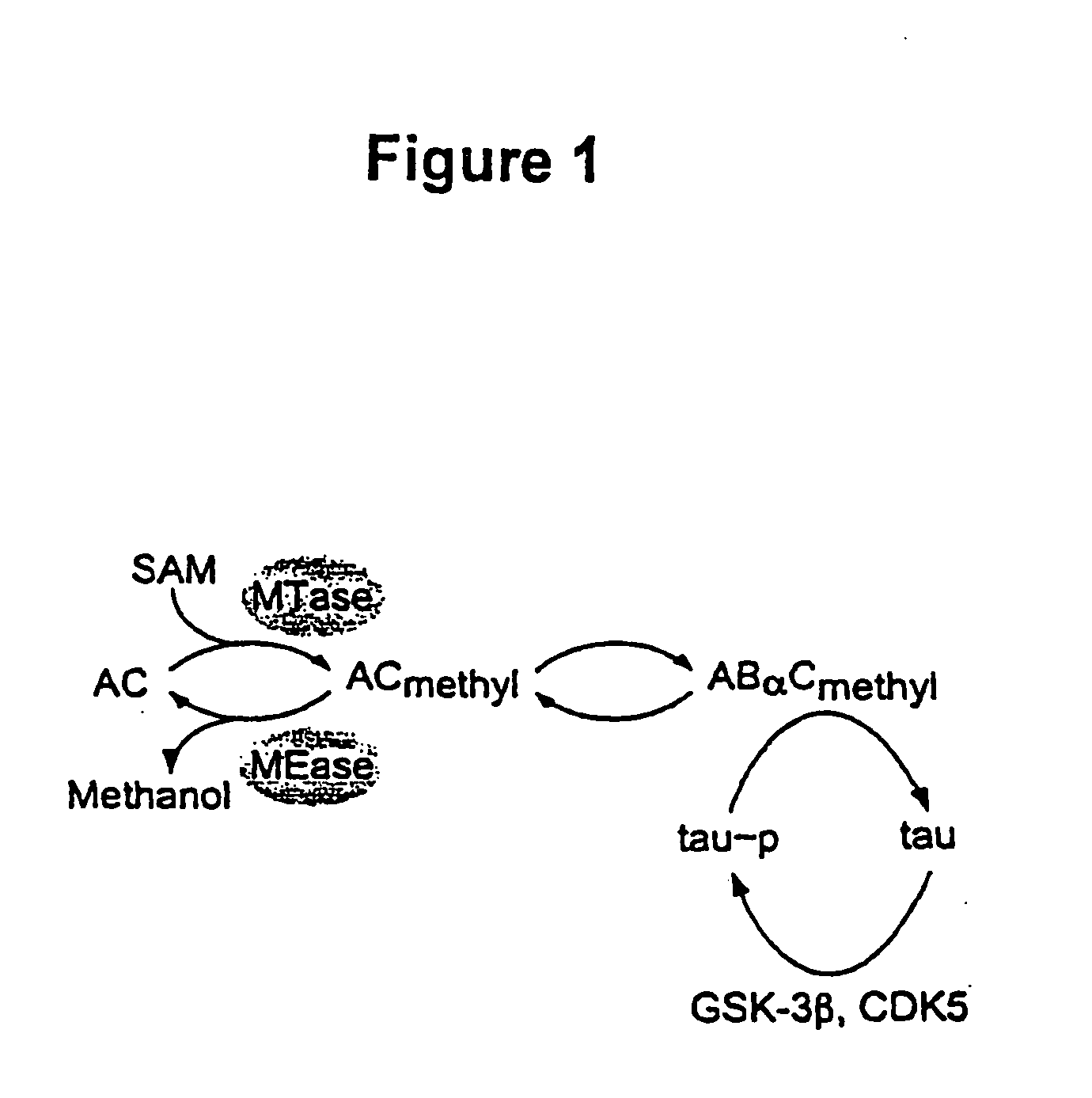
InactiveUS20070031909A1Reduces overall methylation rateReduction in methylation rateBiocideCompound screeningEtiologyPhosphate
The invention relates to methylated proteins that control protein phosphorylation, particularly phosphoesterases, such as PP2A. It relates to screening methods for determining agents that affect methylation of these proteins and thus also modulate the level of phosphorylation of phosphoproteins. It relates as well to the agents and to compositions comprising the agents. In a particular aspect in this regard the invention relates to agents that alter PP2A methylation and that thereby affect phosphorylation of phosphoproteins that play an important role in health or disease, such as the tau protein which is implicated in the etiology of Alzheimer's Disease. The invention further relates to diagnostic methods based on protein methylation levels, to compositions comprising agents for affecting methylation of proteins and for controlling the phosphate complement of phosphoproteins. Additionally, the invention relates to methods for administering the agents and compositions to affect methylation of proteins physiologically and to modulate the phosphate complement of phosphoproteins. Examples in this regard include agents and compositions that affect physiological activity of PP2A and alter the phosphate complement of phosphoproteins that are altered in disease.
Owner:SIGNUM BIOSCIENCES INC +1
Iron-enriched yolk powder and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical filed of agricultural by-product deep-processing and comprehensive utilization of by-products thereof, and relates to iron-enriched yolk powder and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the iron-enriched yolk powder comprises the following technological processes: preparing a main ingredient, preparing a phosvitin peptide iron compound, blending the main ingredient and the auxiliary ingredients, carrying out vacuum deodorization and cooling, and carrying out vacuum freeze-drying. Yolk liquid is used as the main ingredient; and maltose, pectin, milk powder, soybean powder and the phosvitin peptide iron compound are used as the auxiliary ingredients. The main ingredient and the auxiliary ingredients are processed so as to prepare the iron-enriched yolk powder which has the functions of supplementing iron, and is light yellow in color, uniform in texture, appropriate in taste, free of peculiar smell of the egg, and easy for the human body to absorb. The percentage by weight of each auxiliary ingredient compared with the main ingredient is as follows: 3-8% of the maltose, 5-10% of the pectin, 40-60% of the milk powder, 40-60% of the soybean powder, 2.6-3.8% of the phosvitin peptide iron compound, and 30-40% of water.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
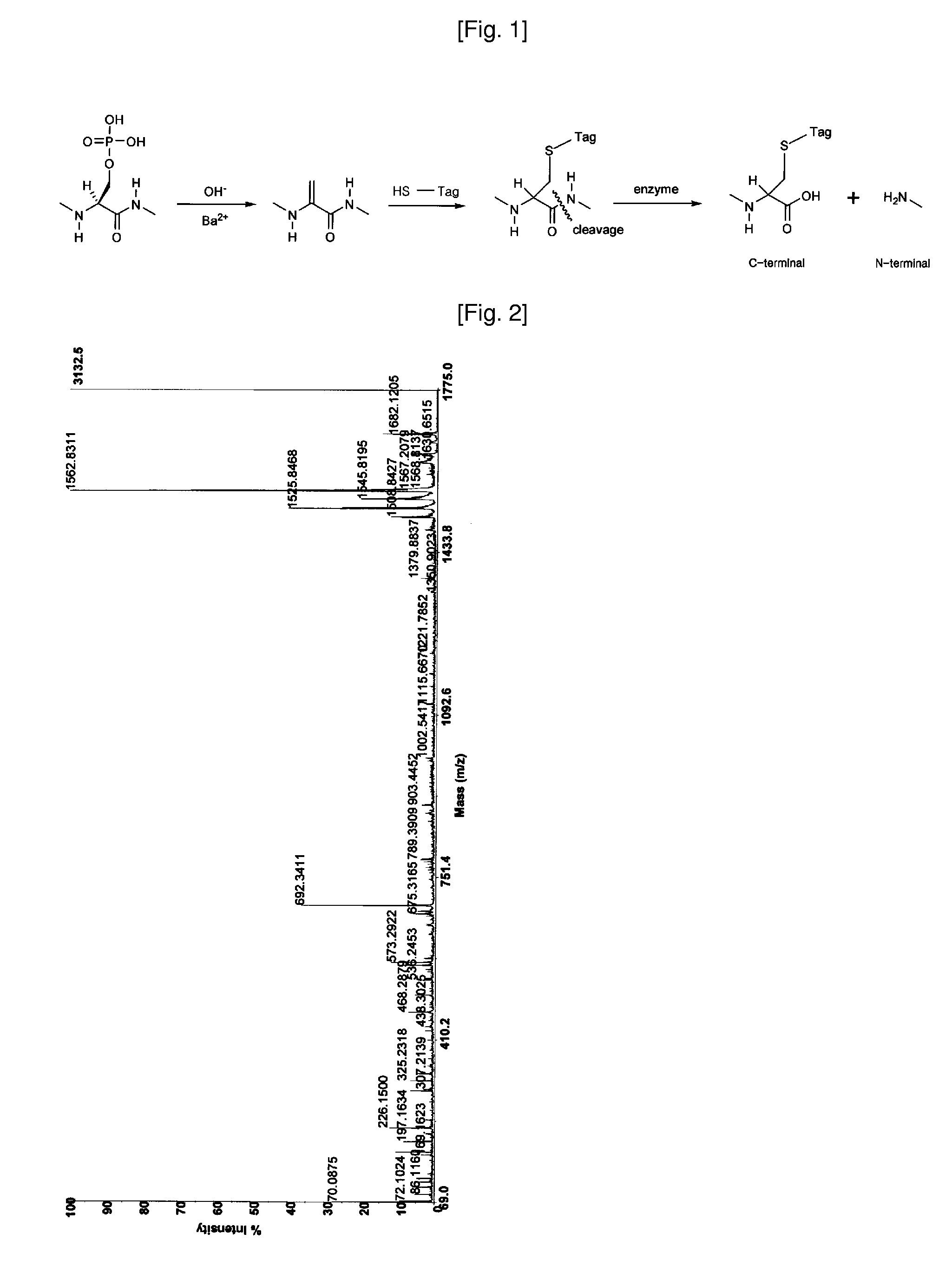
In-gel tagging and in-gel digestion for phosphoproteins analysis and phosphorylation site identification
The present invention relates to a method for phosphorylation site-specific labeling of phosphoproteome with a site-specific tagging reagent and analyzing of the resulting labeled one, more especially, a method for in-situ tagging of phosphorylation sites of phosphoproteins retained in polymeric gel with a nucleophilic tagging reagent. It also relates a method for generating new proteolytic cleavable sites at formerly phosphorylation sites by a proper choice of a nucleophilic tagging reagent. It also relates to a method for phosphopeptides analysis and phosphorylation site identification by in-gel digestion of the previously in-gel tagged proteins and subsequent mass analysis of the resulting peptides. The invention provides in-gel chemical tagging method for phosphoaminoacid residue of phosphoproteins retained in polymeric gel matrix. Phosphoprotein can be immobilized into gel matrix by a variety of methods such as gel electrophoresis. The immobilized phosphoproteins are retained in gel matrix during tagging reaction to phosphorylated aminoacid residue of phosphoproteins, and the resulting tagged proteins are also retained in gel matrix till following purification steps like washing of the tagging reagents are accomplished. The tagged proteins is digested by protease, and the resulting digested peptides is released from gel into solution and applied for peptide mass analysis.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
Reverse genetic operation system of Newcastle disease virus Mukteswar medium-toxicity vaccine strain and application of reverse genetic operation system
ActiveCN104195154AViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesNewcastle disease virus NDVWild type
The invention relates to a reverse genetic operation system of a Newcastle disease virus Mukteswar medium-toxicity vaccine strain and an application of the reverse genetic operation system. The system comprises a transcription plasmid and three transcription auxiliary plasmids, wherein the transcription plasmid comprises a whole genome cDNA sequence of the Newcastle disease virus Mukteswar medium-toxicity vaccine strain which is controlled by an eukaryotic promoter; the three transcription auxiliary plasmids are controlled by the eukaryotic promoter; and each transcription auxiliary plasmid comprises a cDNA sequence which is used for encoding the nucleoprotein (NP) of the Newcastle disease virus Mukteswar medium-toxicity vaccine strain, a cDNA sequence which is used for encoding the phosphoprotein (P) of the Newcastle disease virus Mukteswar medium-toxicity vaccine strain and a cDNA sequence which is used for encoding the large polymerase (L) of the Newcastle disease virus Mukteswar medium-toxicity vaccine strain. According to the reverse genetic operation system, the wild type recombined Newcastle disease virus is successfully rescued, and a foundation is laid for the further development of the vaccine development by taking the Newcastle disease virus as a carrier and the fundamental researches related to the tumor oncolytic treating virus and the NDV (Newcastle Disease Virus).
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com