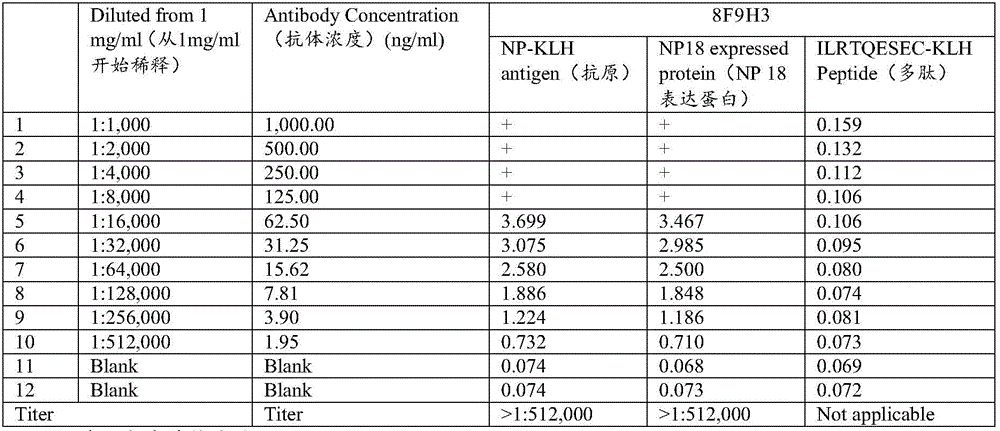
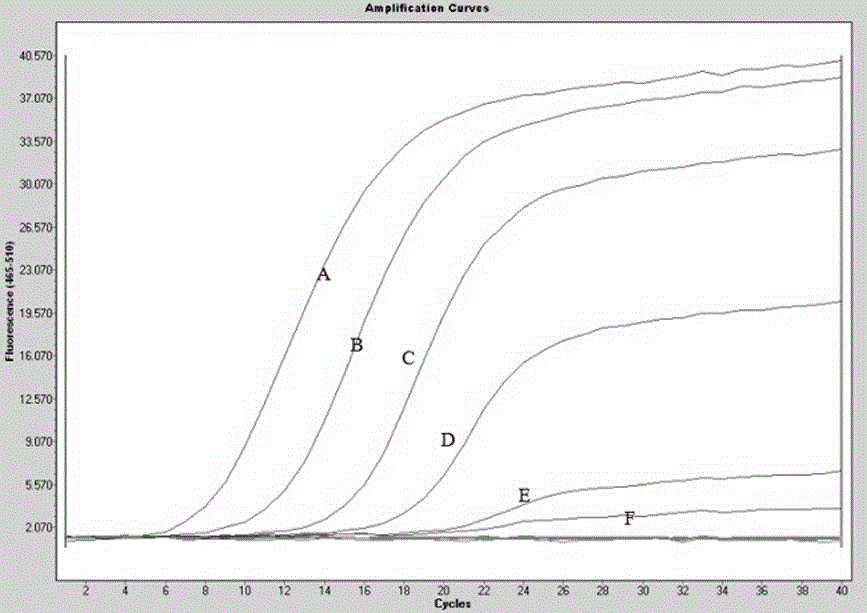
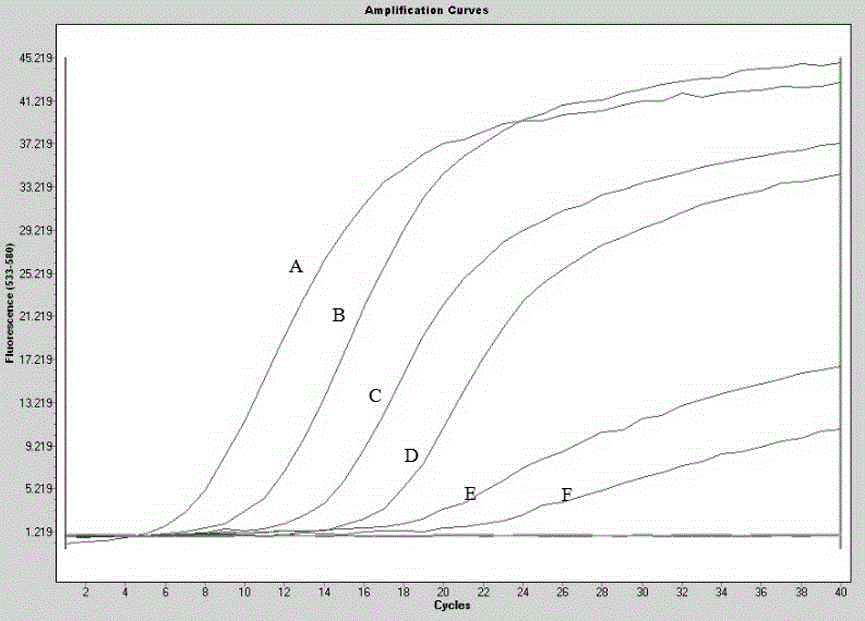
Patents
Literature
561 results about "Newcastle disease virus NDV" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Newcastle disease virus (NDV), a member of the Avulavirus genus in the Paramyxoviridae family, has a ribonucleic acid (RNA) genome that is negative sense, nonsegmented and single‐stranded.
Newcastle Disease Viruses and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20140271677A1Reduce severityPrevent relapseSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsNewcastle disease virus NDVAgonist
Described herein are chimeric Newcastle disease viruses engineered to express an agonist of a co-stimulatory signal of an immune cell and compositions comprising such viruses. Also described herein are chimeric Newcastle disease viruses engineered to express an antagonist of an inhibitory signal of an immune cell and compositions comprising such viruses. The chimeric Newcastle disease viruses and compositions are useful in the treatment of cancer. In addition, described herein are methods for treating cancer comprising administering Newcastle disease viruses in combination with an agonist of a co-stimulatory signal of an immune and / or an antagonist of an inhibitory signal of an immune cell.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Chimeric Newcastle disease viruses and uses thereof
ActiveUS8591881B2Prevents progression and worseningReduce severitySsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideNewcastle disease virus NDVAntagonist
Described herein are chimeric Newcastle disease viruses engineered to express a heterologous interferon antagonist and compositions comprising such viruses. The chimeric Newcastle disease viruses and compositions are useful in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Recombinant Newcastle disease virus RNA expression systems and vaccines
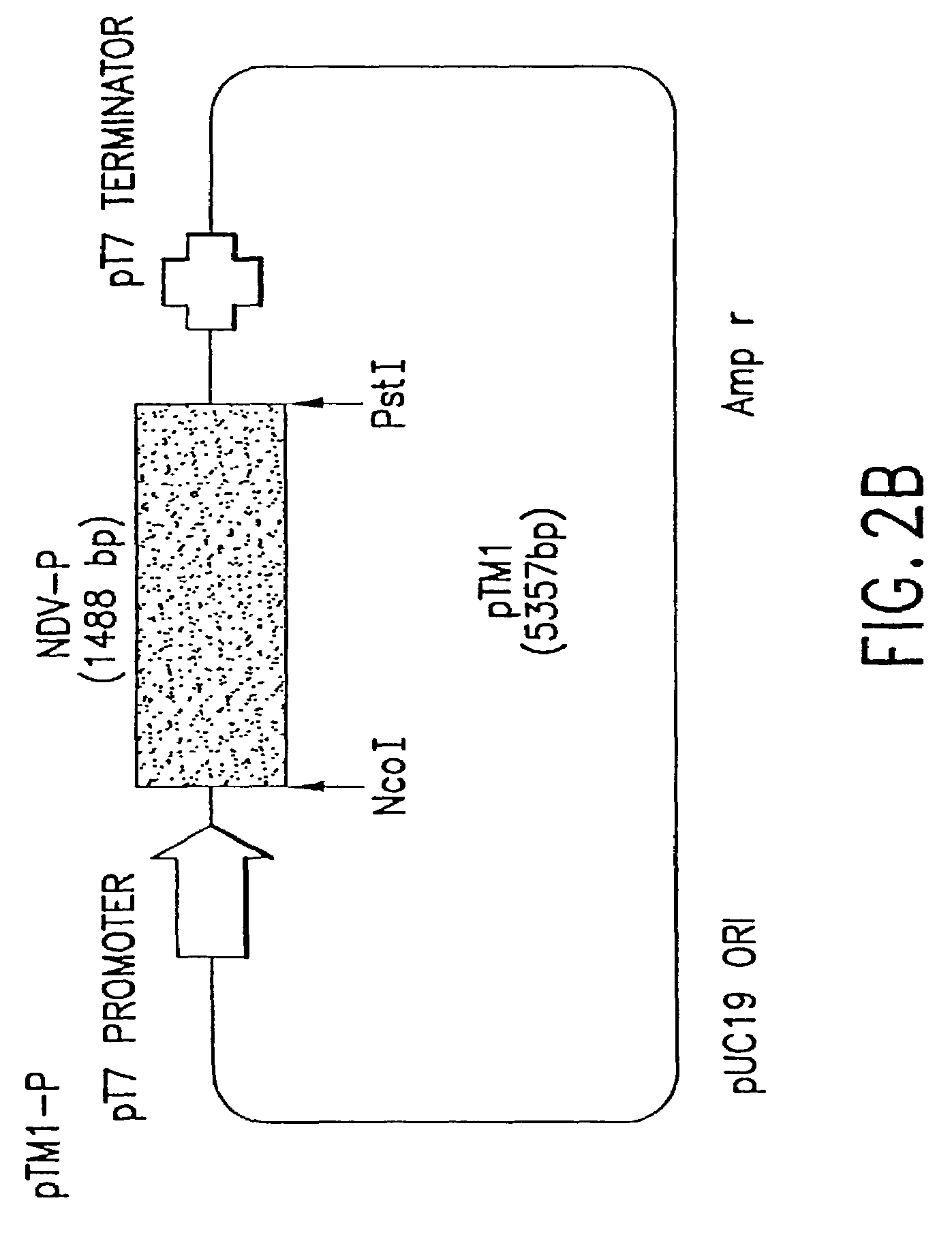
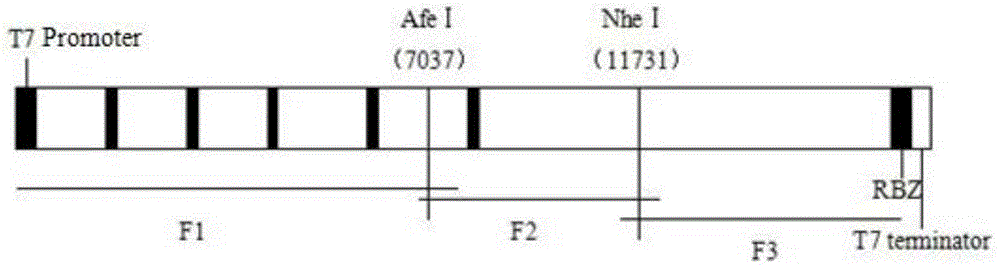
This invention relates to genetically engineered Newcastle disease viruses and viral vectors which express heterologous genes or mutated Newcastle disease viral genes or a combination of viral genes derived from different strains of Newcastle disease virus. The invention relates to the construction and use of recombinant negative strand NDV viral RNA templates which may be used with viral RNA-directed RNA polymerase to express heterologous gene products in appropriate host cells and / or to rescue the heterologous gene in virus particles. In a specific embodiment of the invention, the heterologous gene product is a peptide or protein derived from the genome of a human immunodeficiency virus. The RNA templates of the present invention may be prepared by transcription of appropriate DNA sequences using any DNA-directed RNA polymerase such as bacteriophage T7, T3, SP6 polymerase, or eukaryotic polymerase I.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods of treating and detecting cancer using viruses
InactiveUS7056689B1Useful in detectionSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsCancer cellMammal
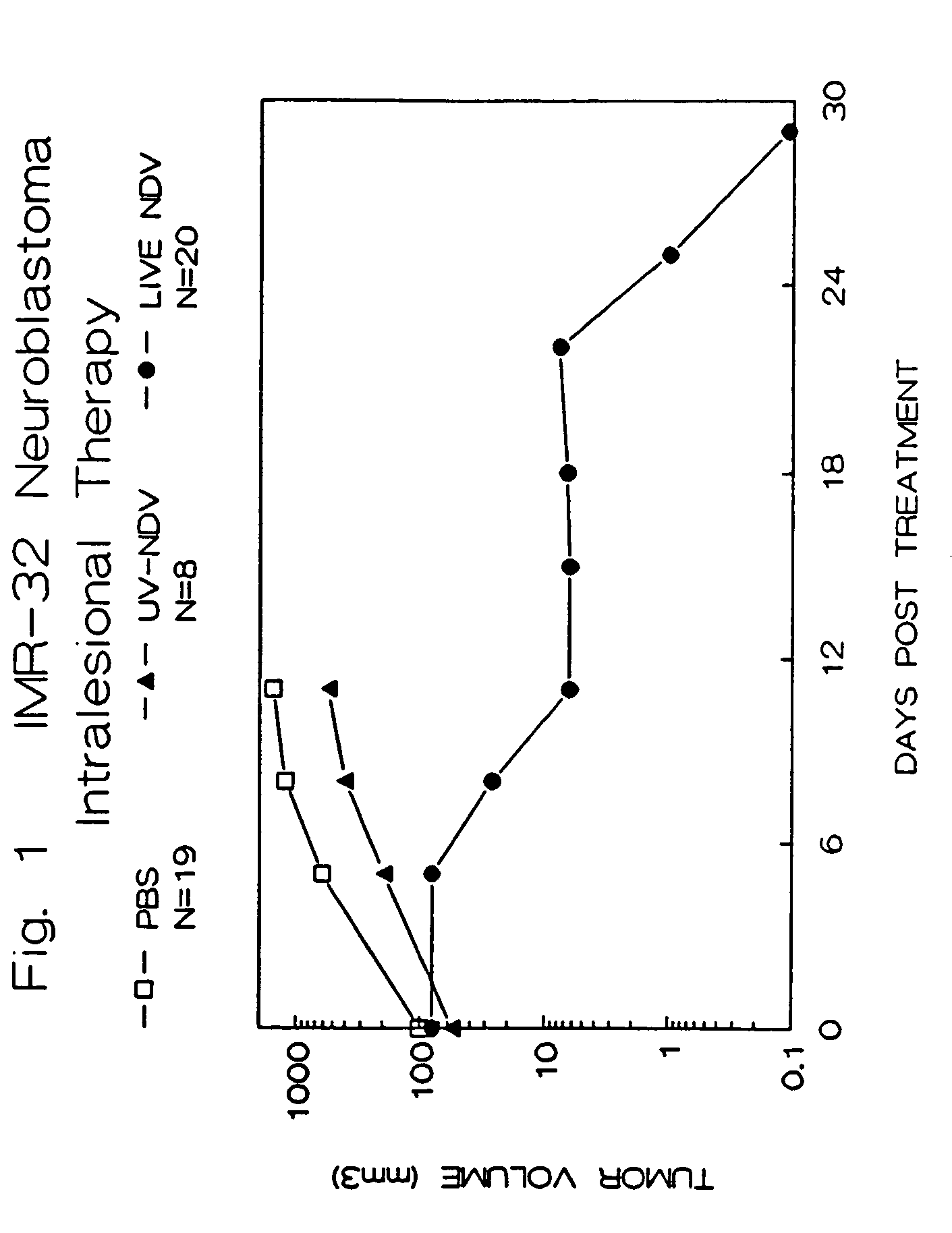
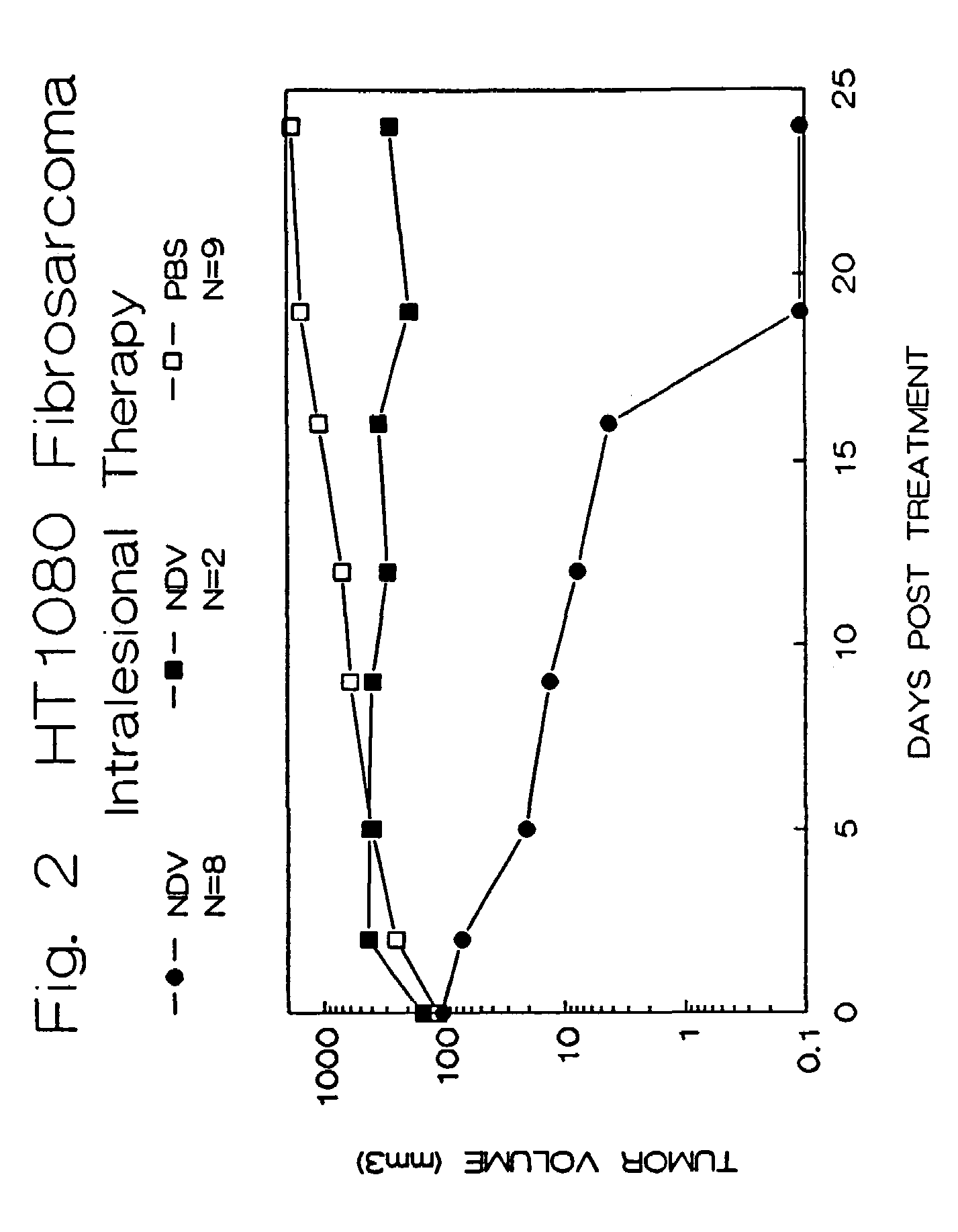
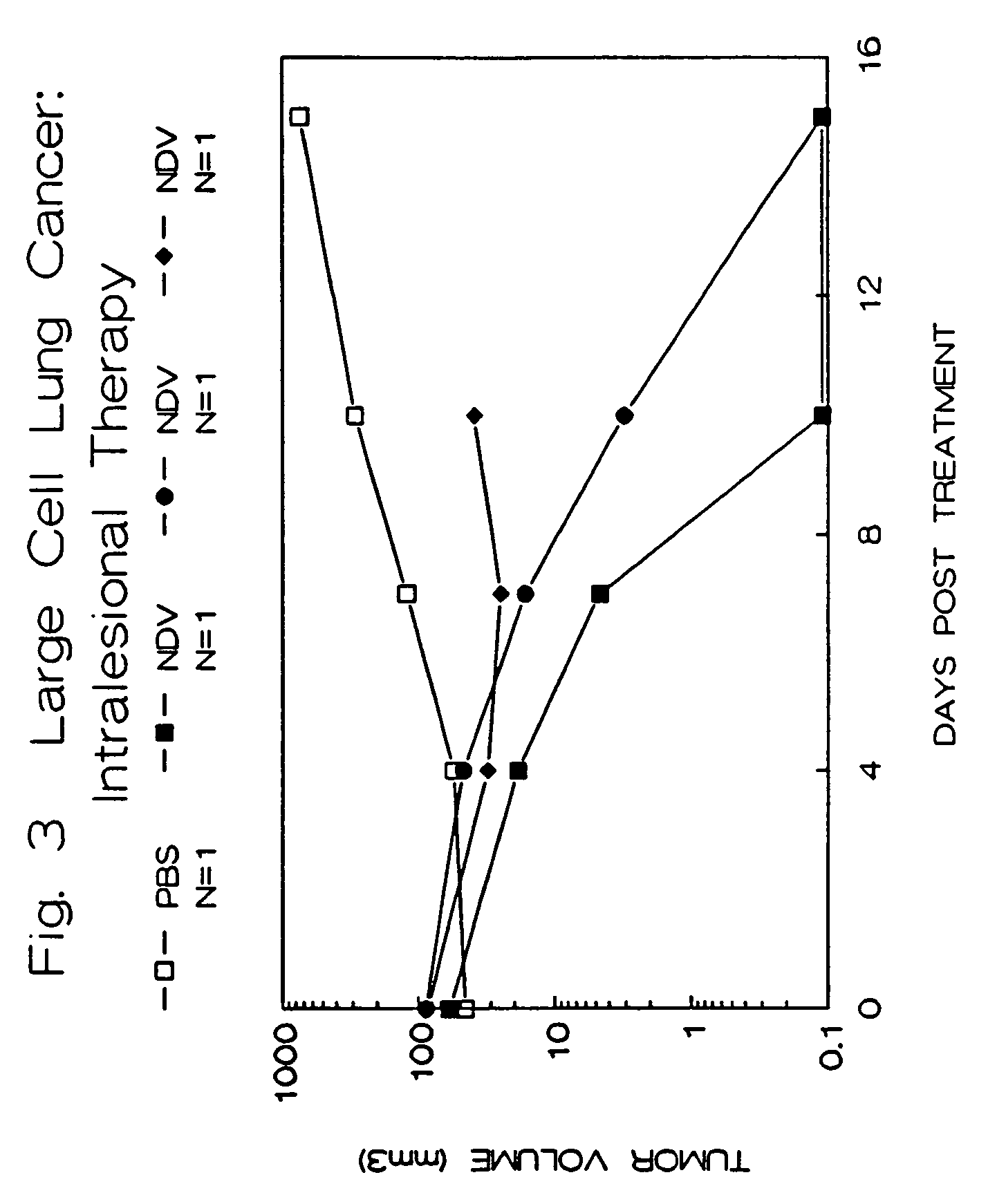
The invention provides a method of treating cancer in a mammal comprising administering to the mammal an effective amount of virus, particularly Newcastle Disease Virus or other Paramyxovirus. The invention also provides a method of treating cancer in a mammal comprising administering such viruses to the mammal in combination with another agent such as a chemotherapeutic compound, immunoadjuvant, cytokine, or immunosuppressive agent. The invention further provides a method of detecting cancer cells in a mammal using Paramyxovirus as an imaging agent and as an indicator of cancer cell growth in the mammal. The invention further provides genetically engineered Paramyxoviruses, and kits containing the viral compositions disclosed by the invention.
Owner:WELLSTAT BIOLOGICS CORP
Genetically-engineered newcastle disease virus as an oncolytic agent, and methods of using same
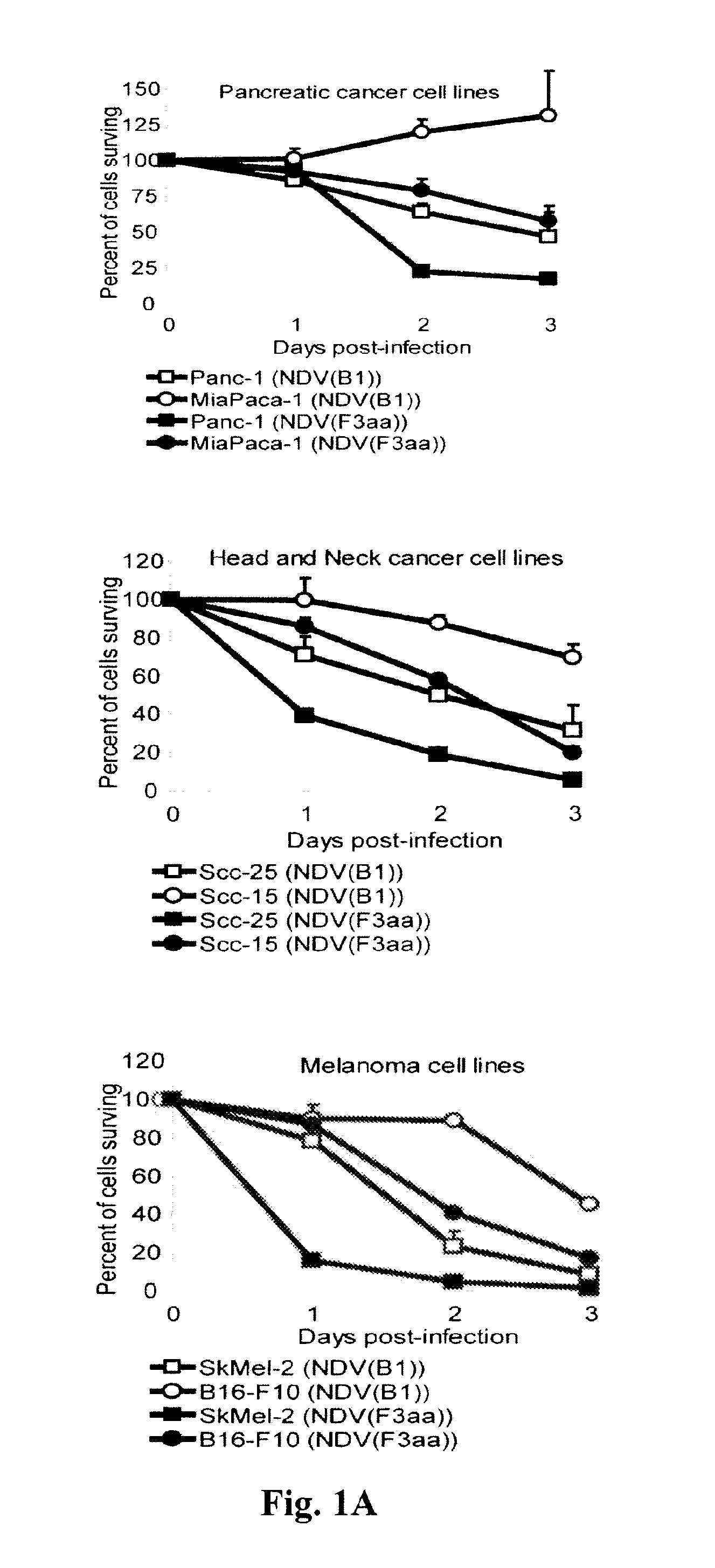
Recombinant strains of avian paramyxovirus (APMV), such as Newcastle disease virus (NDV), are provided. Also provided are compositions comprising them, and methods of using them to lyse tumor cells and to treat cancer. In certain aspects, genetically-engineered viral strains that incorporate therapeutic transgenes are also provided. The recombinant viruses may be used in accordance with methods of providing enhanced oncolytic efficacy and delivering an oncolytic virus to tumors present in a patient. Also provided are methods for identifying a recombinant virus as an oncolytically-effective agent.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND OFFICE OF TECH COMMLIZATION
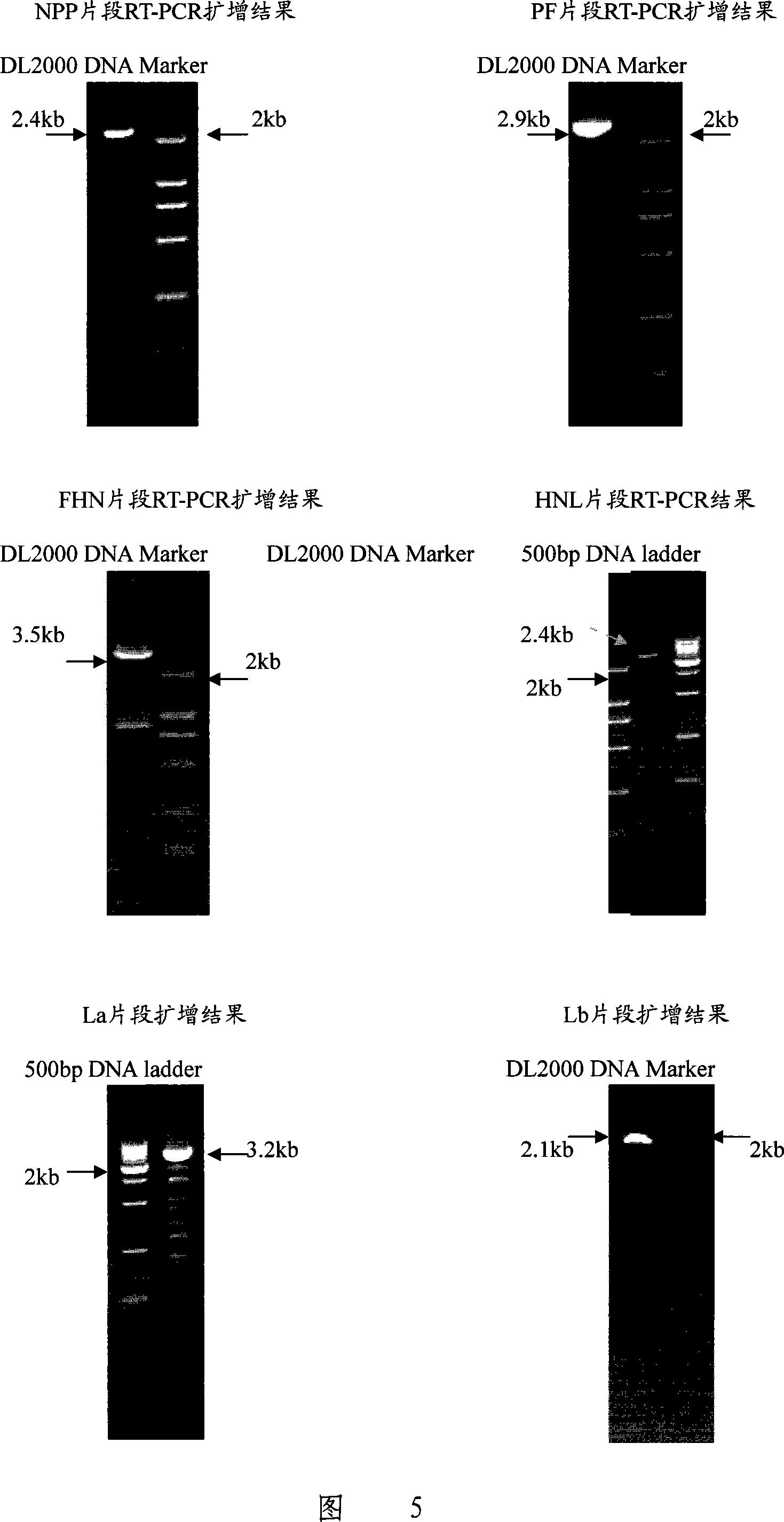
Gene ó¸ type new castle disease virus weakening strain A-NDV-ó¸ and construction method thereof
ActiveCN101182494AHigh reproductive titerSuitable for mass productionInactivation/attenuationNewcastle disease virus NDVGene type
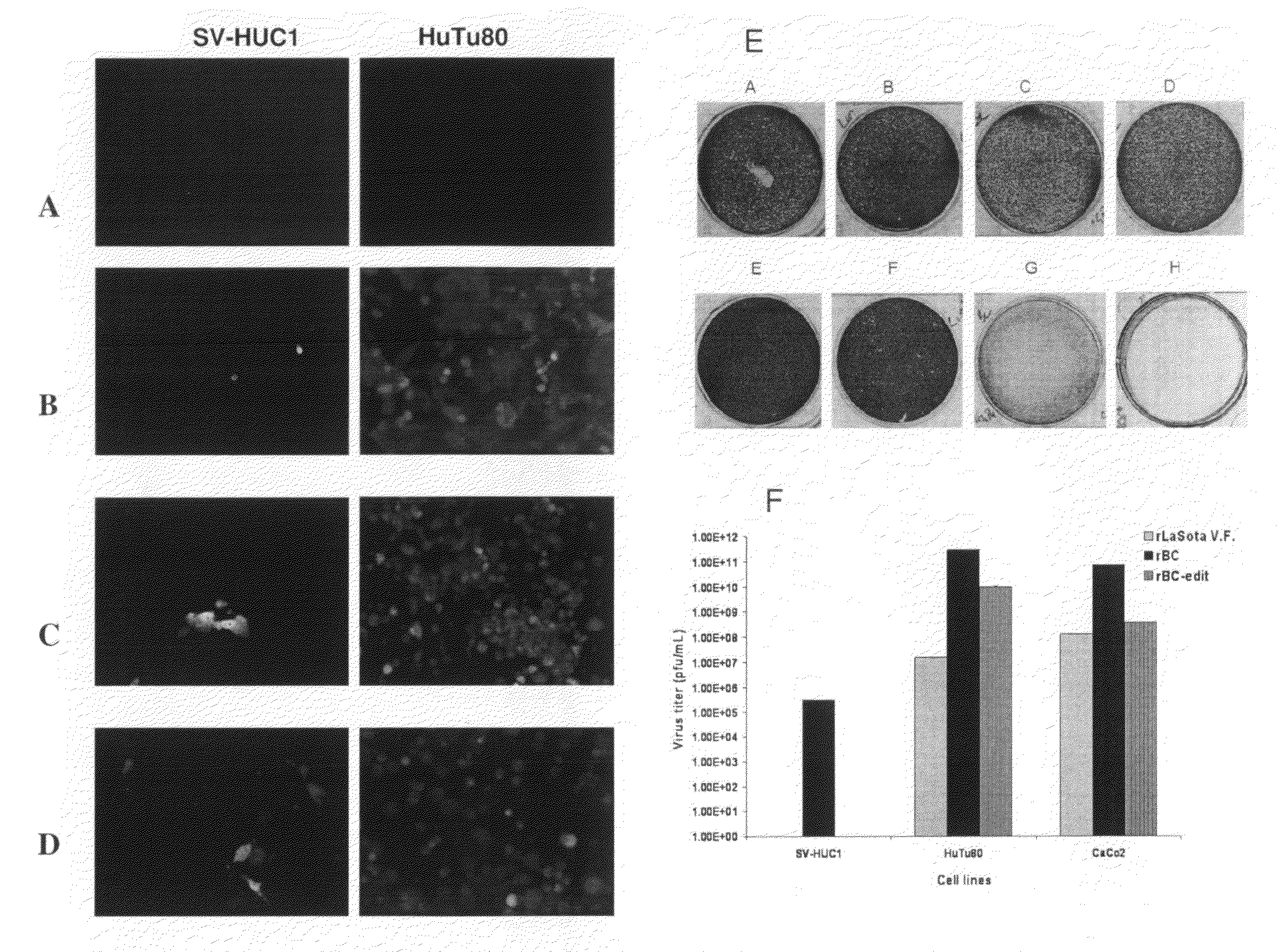
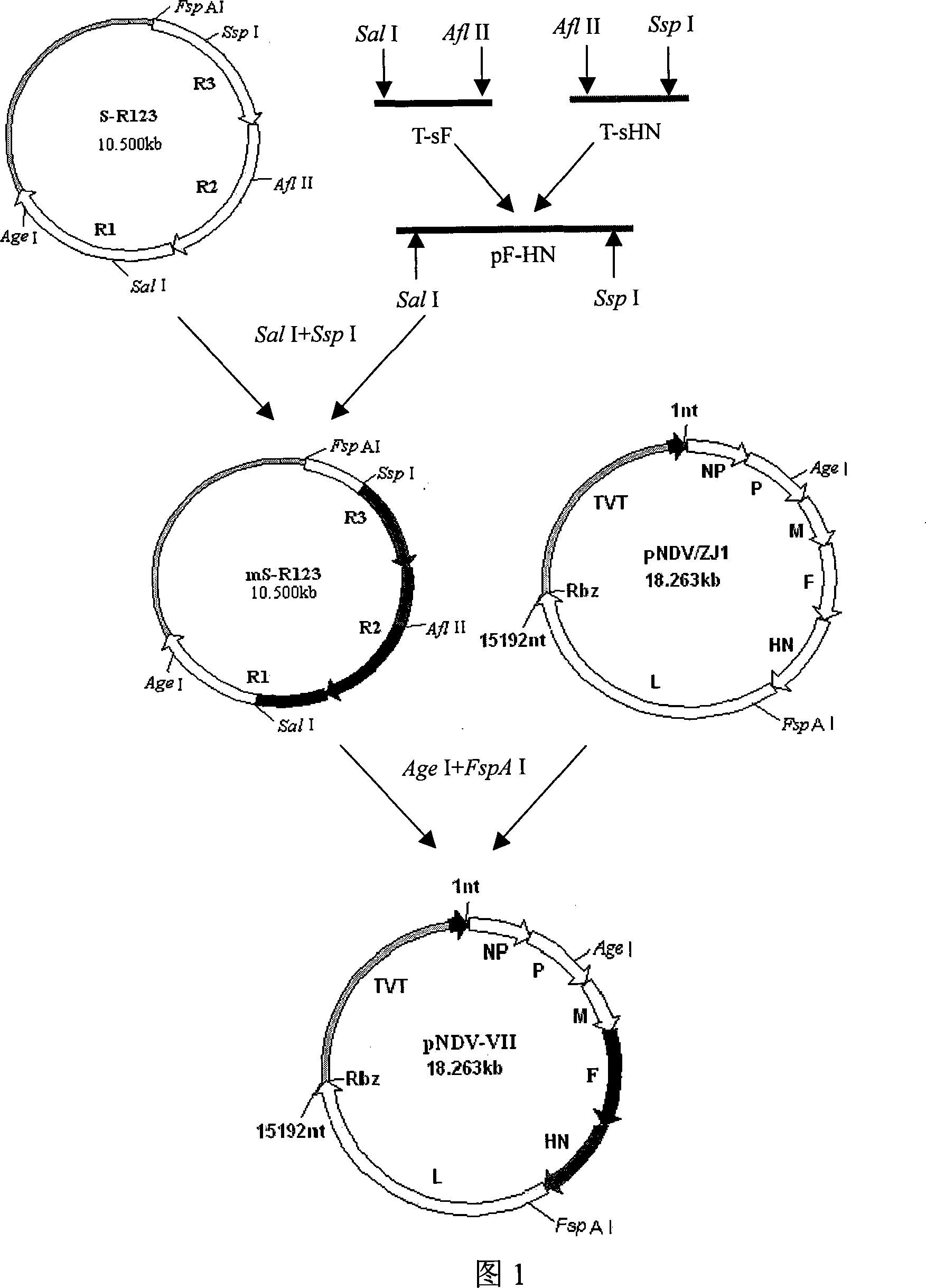
A VII gene type of an attenuated strain of Newcastle disease virus A-NDV-VII and a construction method are disclosed. The invention relates to the application of reverse genetics technique. The invention uses the constructed reverse genetics platform of ZJ1 strain of Newcastle disease virus of goose origin. The invention replaces two envelope glycoprotein gene fragments F and HN of an isolated strain JS-5-05-Go of Newcastle disease virus with high reproductive performance with the corresponding fragments of the ZJ1 strain of Newcastle disease virus of goose origin, so that the recombinant virus NDV-VII is obtained. The VII gene type of Newcastle disease virus A-NDV-VII which is highly attenuated is rescued after the attenuated mutation of the F gene of the recombinant virus. And the virus has a higher reproduction titer on chicken embryo. The invention is suitable for a mass production of vaccine, which can be used for the manufacture of vaccine.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Reverse genetic operation system of New castle disease LaSota vaccine strain and its applciation
The present invention is reverse genetic operation system of Newcastle disease Lasota low virulent vaccine strain and its application. The system includes one transcription plasmid including the genome cDNA sequence of the low virulent vaccine strain; one or several transcription aiding plasmids including the cDNA sequence coding the nucleoprotein of the low virulent vaccine strain, the cDNA sequence coding the phosphoprotein of the low virulent vaccine strain and the cDNA sequence coding the large polymerase protein of the low virulent vaccine strain; and the host cell of the Newcastle disease Lasota low virulent vaccine strain. Wild viral strain is obtained by means of the reverse genetic operation system. The present invention lays firm foundation for further development of Newcastle disease virus live carrier vaccine and Newcastle disease virus related research.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Newcastle disease virus vectored avian vaccines
The present invention encompasses engineered Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) vaccines or compositions. The vaccine or composition may be a recombinant vaccine. The invention also encompasses recombinant vectors encoding and expressing avian pathogen antigens, more specifically avian influenza proteins, epitopes or immunogens. Such vaccines or compositions can be used to protect animals, in particular avian, against disease.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM ANIMAL HEALTH USA INC
GeXP rapid detection kit capable of simultaneously identifying nine pathogens of chicken respiratory tract diseases
ActiveCN102899424AStrong specificityImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInfectious laryngotracheitisRespiratory tract disease
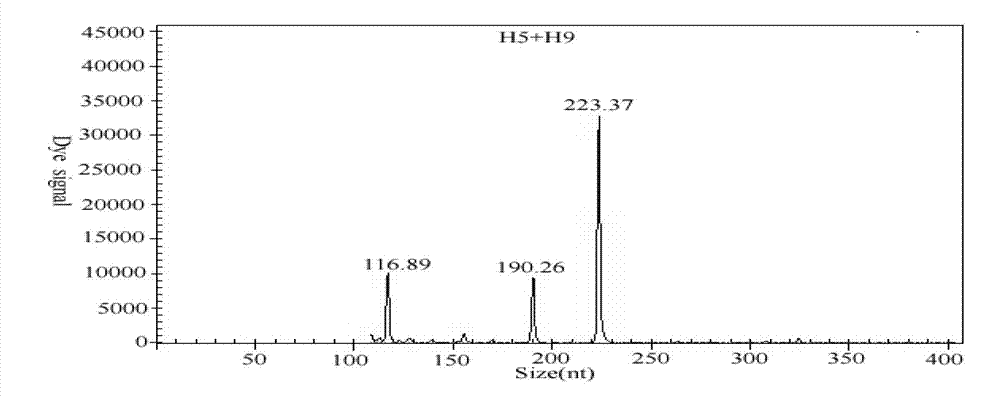
The invention discloses a GeXP rapid detection kit capable of simultaneously identifying nine pathogens of chicken respiratory tract diseases. The kit is used based on a GeXP system and comprises ten polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primer pairs; the kit is used for identifying and detecting avian influenza virus, H5, H7 and H9 subtype avian influenza virus, newcastle disease virus, infectious bronchitis, infectious laryngotracheitis, mycoplasma gallisepticum, bursa synovialis mycoplasma and haemophilus paragallinarum; and the kit is good in specificity, high in sensitivity and can detect 100 copy / mu l. Compared with an identifying result of the conventional experiment method of a pathogen separation and hemagglutination inhibition experiment or a serology experiment and the like, the GeXP rapid detection kit has the advantage that the coincidence rate reaches 100 percent. The kit is generally used for detecting the main chicken respiratory tract diseases and the pathogens thereof, so that a simple and high-flux detection kit and a detection system are provided, an actual requirement is met, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:GUANGXI VETERINARY RES INST
Genetic engineering marked attenuated vaccine strain of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and application thereof
ActiveCN102250843AMeet the differential diagnosisEasy to solveViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsNucleotideGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a genetic engineering marked attenuated vaccine strain of a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV). The attenuated vaccine strain comprises a genomic nucleic acid of a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus attenuated vaccine strain HuN4-F112; the HuN4-F112 genome includes a mutation in a genetic region for coding an Nsp2 protein, and the mutation is as follows: a nucleotide sequence for coding a Newcastle disease virus NP protein is inserted to a lacking region of a nucleotide sequence for coding 480-532-site amino acid of the Nsp2 protein; or the nucleotide sequence for coding the Newcastle disease virus NP protein is inserted to the lacking region of a nucleotide sequence for coding 508-532-site amino acid of the Nsp2 protein. The invention also discloses an application of the genetic engineering marked attenuated vaccine strain. The genetic engineering marked attenuated vaccine strain of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus provided by the invention not only can provide completely safe immune protection to resist high-pathogenicity PRRSV after the porcine is immunized, but also can effectively distinguish the immunized porcine of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome vaccine with the naturally infected porcine of the field virus.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
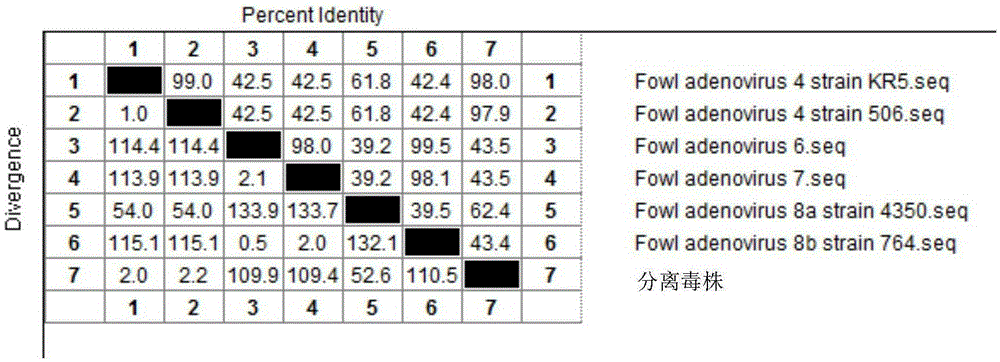
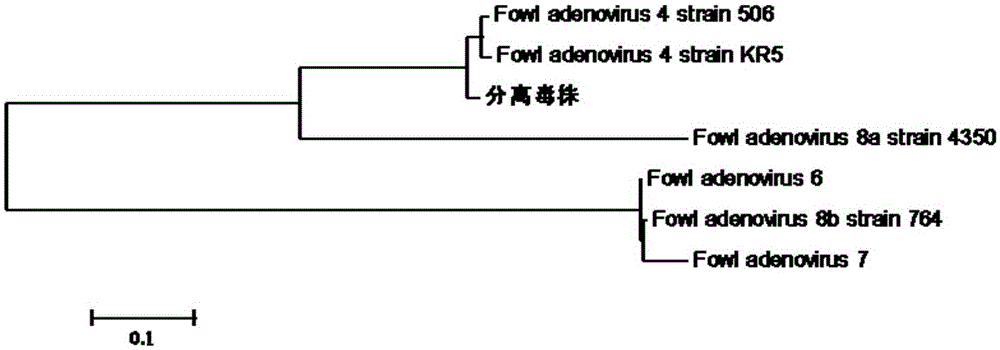
I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 strain and application thereof
ActiveCN105368795AImprove featuresImproving immunogenicityViral antigen ingredientsBiological material analysisInfected cellLaryngotracheitis virus
The invention aims at providing an I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 strain, which is preserved with preservation number of CCTCC No. V201541. The I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 YBAV-4 strain disclosed by the invention is excellent in specificity and immunogenicity; a specific precipitation line does not appear in specific positive serum chicken SPF chicken serum such as infected cell sap and egg drop syndrome resisting virus, chicken infectious bursal disease virus, Newcastle disease virus, chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus, chicken Marek's disease virus, avian influenza and the like, while an obvious specific precipitation line appears in I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 specific serum. The strain disclosed by the invention, as a vaccine strain which is good in manufacturing effect, is capable of preventing chicken hydropericardium syndrome, and the strain is applicable to identification of virus serotype and investigation on epidemiology.
Owner:YEBIO BIOENG OF QINGDAO
Immunological adjuvant, and its application in preparing vaccine and medicine for anti-virus
InactiveCN1718243AImprove immune activityReach clearAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsAnti virusDisease
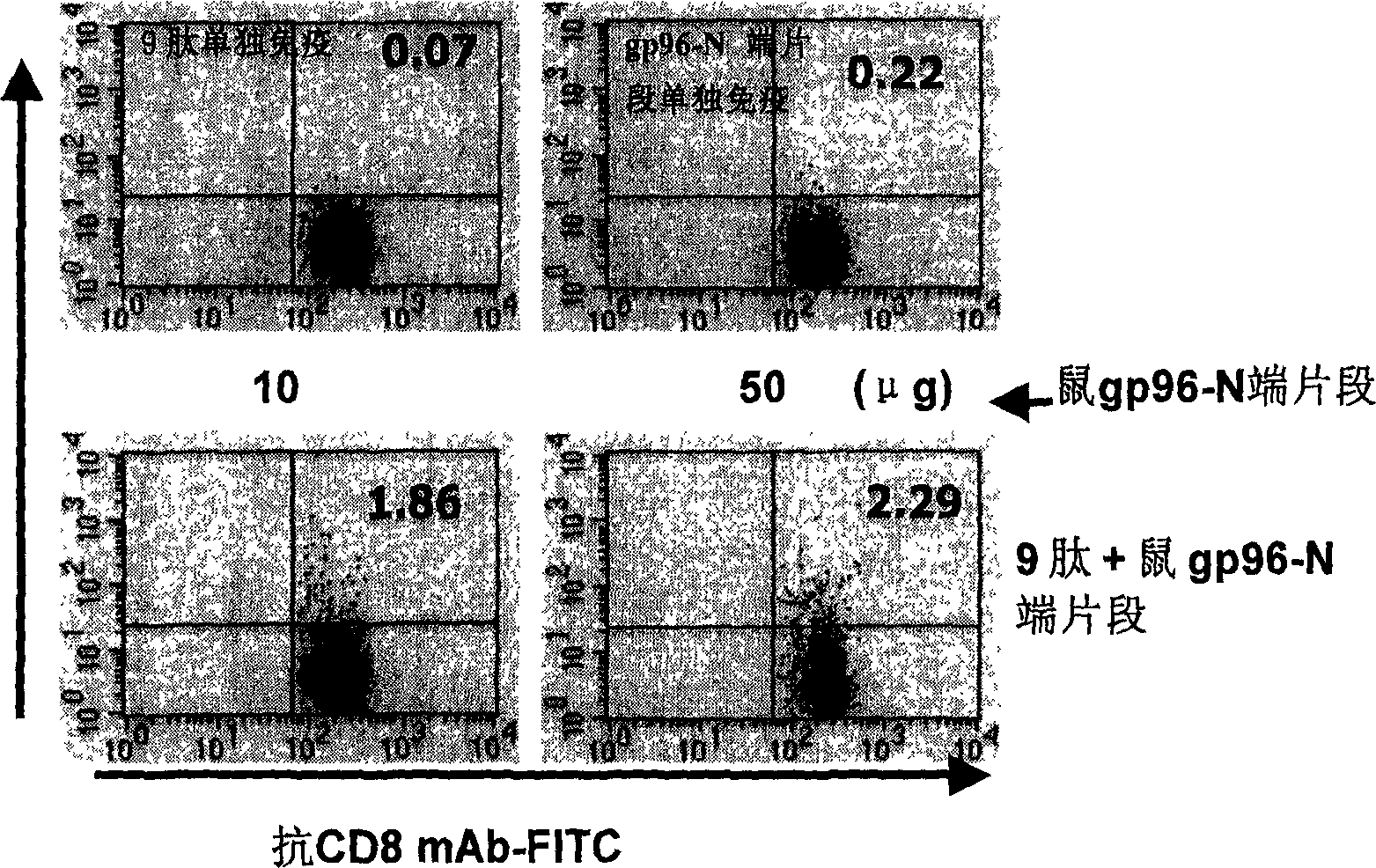
An immunoadjuvant used to prepare the antiviral vaccine or medicine for increasing the immune activity of the antigens for HBV, HCV, SARS coronavirus, fowl influenza virus, etc is a kind of human or animal's novel heat shock proteins gp96, hsp108 and hsp70.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
GeXP (Gene Expression) rapid detection kit capable of simultaneously identifying six virus of chicken respiratory disease
ActiveCN102899423AStrong specificityImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBovine respiratory diseaseInfectious bronchitis virus
The invention discloses a GeXP (Gene Expression) rapid detection kit capable of simultaneously identifying six virus of chicken respiratory disease. The GeXP rapid detection kit is used basing on a CeXP system and contains seven PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer pairs, the specificity for simultaneously detecting avian influence virus, H5, H7 and H9 sub type of the avian influence virus, Newcastle disease virus, infectious bronchitis virus and infectious laryngotracheitis virus is strong, the sensitivity can be up to 100 copy / mu l, and compared with an identifying result of regular test methods such as virus isolation and hemagglutination inhibition, the coincidence rate is up to 100%. According to the GeXP rapid detection kit disclosed by the invention, a simple and high-throughput detection kit and a detection system are provided for the detection of common main chicken viral respiratory disease, the actual needs are accordant, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:GUANGXI VETERINARY RES INST
Chimeric newcastle disease viruses and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120058141A1Reduce severityPrevent relapseSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideNewcastle disease virus NDVAntagonist
Described herein are chimeric Newcastle disease viruses engineered to express a heterologous interferon antagonist and compositions comprising such viruses. The chimeric Newcastle disease viruses and compositions are useful in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Blocking ELISA kit for detecting NDV (Newcastle disease virus) antibody
ActiveCN106596933ASimple and fast operationEasy to operateBiological material analysisElisa kitPositive control
The invention discloses a blocking ELISA kit for detecting an NDV (Newcastle disease virus) antibody. The blocking ELISA kit for detecting the NDV antibody comprises an ELISA plate coated with an NDV inactivated antigen, an NDV positive control serum, an NDV negative control serum and a horseradish peroxidase labeled NDV NP protein monoclonal antibody, wherein the horseradish peroxidase labeled NDV NP protein monoclonal antibody is secreted by a hybridoma cell strain with the preservation number being CCTCC NO: C2016180. The blocking ELISA kit for detecting the NDV antibody can detect serum samples which are infected with the suspected NDV and are from different species, can distinguish an MG7-deficient vaccine from an NDV serum after being infected with a wild virus, and has no cross reaction with a common avian viral pathogen positive serum, thereby being high in sensitivity and specificity, good in reproducibility and suitable for high-throughput detection of serum samples.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Composite kit for detecting avian influenzas and Newcastle disease viruses and detection method
InactiveCN101798602AQuality improvementEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceBiology
The invention relates to a composite kit for detecting avian influenzas and Newcastle disease viruses and a detection method, characterized in that the kit comprises a lysis solution, an RT-PCR buffer solution, primers and a probe mixture solution, particularly a primer and a probe sequenc for detecting various subtype avian influenzas viruses, a primer and a probe sequenc for detecting Newcastle medium and strong viruses, enzyme mixture, DEPC water and negative and positive contrasts. The detection method comprises the following steps of: carrying out an RT-PCR reaction and judging a quality control standard and results. The invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity and simple operation. The process from processing samples to getting a result only needs 4 hours. The invention overcomes the defects of single fluorescence and realizes the aim of simultaneously detecting two viruses by one real-time fluorescent quantification PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) reaction.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT SHANDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Gene VII-type newcastle disease virus strain, vaccine composition thereof and preparing method and application of vaccine composition
The invention discloses a gene VII-type newcastle disease virus strain with good immunogenicity and a low virulent strain subjected to passage attenuation through the newcastle disease virus strain. A newcastle disease virus strain F gene comprises a nucleotide sequence of a protein sequence shown by substantially-coded SEQ ID NO.2, and a virus strain HN gene comprises a nucleotide sequence of a protein sequence shown by substantially-coded SEQ ID NO.6. The newcastle disease virus strain is high in toxicity, and the growth rate on a chicken embryo is high; compared with a conventional newcastle disease virus strain, the gene VII-type newcastle disease virus strain has the advantages of being good in safety, high in immune protection capacity and immune efficacy and the like.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Genotype VII Newcastle disease virus marker vaccine strain and application thereof
ActiveCN104988124AHigh growth titerHigh biological propertiesViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesViral MarkersChick embryos
The invention discloses a genotype VII Newcastle disease virus marker vaccine strain and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of genotype VII Newcastle disease virus marker vaccine strain rescue and application. A built Newcastle disease virus reverse genetic operating platform is utilized for enabling NP protein of a G7 strain to miss 18 amino acids and conducting mutation on F-protein cleavage loci, and the highly-weak virulence and high-virus titer genotype VII Newcastle disease virus marker vaccine strain MG7-NPdelta18+Fmut is rescued through screening. The microbial preservation serial number is CCTCC NO: V201505. The marker vaccine strain has the biological characteristics of high growth titer and low virulence in chick embryos and is genetically stable. The immune protection test result shows that the marker vaccine strain is good in immunogenicity, capable of inducing high-level protective antibodies, and capable of completely protecting immunized chicken, can be used for preventing and controlling a currently-popular genotype VII Newcastle disease virus and lays the foundation of identifying vaccine immunity and wild virus infection.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
New castle disease and H9 subtype bird flu bivalent vaccine
ActiveCN104922663AImproving immunogenicitySmall dose of immunizationViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsDiseaseOil adjuvant
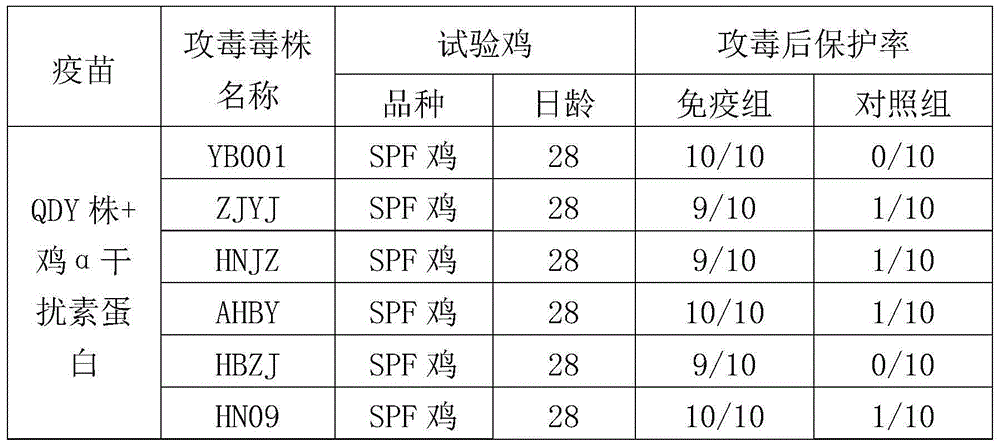
The invention aims at providing a new castle disease and H9 subtype bird flu bivalent vaccine. The new castle disease and H9 subtype bird flu bivalent vaccine contains antigens and adjuvant. The antigens are inactivated H9 subtype bird flu viruses and new castle disease viruses. The H9 subtype bird flu viruses are QDY strains, and the preservation number of the H9 subtype bird flu viruses is CCTCC v201517. The QDY strains of the H9 subtype bird flu viruses and a Lasota strain of the new castle disease viruses are inoculated to chick embryos respectively, and then virus liquid is collected; the virus liquid and the oil adjuvant are mixed and emulsified into the vaccine after the virus liquid is inactivated through a formaldehyde solution. The new castle disease and bird flu bivalent inactivated vaccine is good in immunogenicity, antibody production is fast after immunity, the produced antibody titer is high, the produced antibody holding time is long, the retention period is long, the immunizing dose is small, the selected adjuvant is easy to inject, and two kinds of diseases can be prevented through one-time injection. The vaccine has the advantages of being efficient and good in safety.
Owner:YEBIO BIOENG OF QINGDAO
Newcastle disease virus heat resistant live vaccine vector system and application thereof
ActiveCN104059942AHeat resistantHigh heat resistanceSsRNA viruses negative-senseMicroorganism based processesDiseasePBR322
The invention belongs to the field of virus genetic operation, and in particular to a Newcastle disease virus (NDV) heat resistant live vaccine vector system and application thereof. The Newcastle disease virus (NDV) heat resistant live vaccine vector system comprises a) a transcription plasmid, b) three auxiliary plasmids and c) host cells. The transcription plasmid is obtained by cloning genomic full-length cDNA of a NDV heat resistant vaccine strain to pBR322 vector; and the three auxiliary plasmids are obtained by cloning nucleoprotein, phosphoprotein and large polymerase protein gene of the NDV heat resistant vaccine strain to pcDNA3.1 vector. The artificial recombinant Newcastle disease virus has the characteristic of heat resistance, and the Newcastle disease virus (NDV) heat resistant live vaccine vector system is established for the first time. The artificial recombinant Newcastle disease virus has great application prospect in the aspects of research and development of multiple (multivalent) heat resistant genetic engineering live vaccines of the NDV, avian influenza and other major diseases of poultry, research on virus heat-resistant mechanism, and the like.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Tumor targeting recombinant newcastle disease viruses and construction method thereof
ActiveCN101205544AElimination of receptor binding sitesEliminate binding sitesGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTumor targetOpen reading frame
The invention relates to a tumor-targeted recombinant Newcastle virus and a construction method thereof, wherein, 3'of an HN gene open reading frame of an Italien strain virus genome of the Newcastle virus is connected with a tumor scFv sequence through a G4S linker, and fusion expression of the two proteins can be realized; simultaneously, relative sequences which are responsible for coding sialic acid acceptors in HN genes are mutated, and the virus loses identification and combining capacities on sialic acids, and finally the recombinant virus can only be combined with tumor cells which express tumor associated antigens and replicated in the tumor cells which are then caused to be dead. The invention has the advantages that the recombinant oncolytic Newcastle virus which can be combined with the tumor cells which express the tumor associated antigens by means of targeting and replicated in the tumor cells which are finally killed, and is avirulent to normal human histiocytes. The invention provides a possible proposal for therapy research of associated tumors.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Nucleic acid detection kit for synchronously identifying and diagnosing newcastle disease virus and avian influenza virus
InactiveCN101240352AAvoid potential risksEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementHighly pathogenicFluorescence
The invention belongs to the field of inspection and quarantine technology. Specifically, the invention is a nucleic acid detection reagent kit for synchronous discriminating and diagnosing avian influenza virus and newcastle disease virus. The detection reagents of the reagent kit include extraction reagent for extracting virus by silicon gel absorption column method, detection amplification reagent for detecting nucleic acid by RT-PCR Taq Man fluorescent probe method, and pretreatment liquid for solid tissue specimen for extracting virus RNA. Further, the invention employs in vitro transcription RNA as a positive contrast of the reagent kit. The reagent kit can rapidly and synchronously discriminate and diagnose avian influenza virus and newcastle disease virus which are highly infectious among avian plagues and have similar symptom, determine current major prevalent subtypes, such as H5, H7, H9, etc., and discriminate whether a infection source is an avian influenza having high pathogenicity, non-pathogenic avian influenza or mildly pathogenic avian influenza to human. The reagent kit is suitable for livestock and veterinarian station, import and export inspection and quarantine bureau, as well as other laboratories, and can be used for large-scale detection of influenza and epidemic surveillance.
Owner:SHANGHAI KEHUA BIO ENG
Preparation method and application of Newcastle disease virus infected immune complex vaccines
InactiveCN102233133AAvoid infectionSame characteristicsViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsYolkMicroorganism
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of Newcastle disease virus infected immune complex vaccines. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing antigens and inactivated vaccines by using Newcastle disease virus Shanghai strains as seed viruses; (2) transferring antibodies in chicken blood serum to yolk to form yolk antibodies IgY; and (3) mixing the prepared inactivated vaccines and the yolk antibodies IgY in equal volume, and hatching to obtain the immune complex vaccines. By combining passive immune (vaccine) and active immune (specific antibody) measures, animals are protected from the infection of pathogenic microbes in time for a long time.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Recombinant non-pathogenic marek's disease virus constructs encoding infectious laryngotracheitis virus and newcastle disease virus antigens
ActiveUS8932604B2Stable, safe, and efficacious immunogenic compositionsImproving immunogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideInfectious bronchitis virusBorna disease virus
Recombinant multivalent non-pathogenic Marek's Disease virus constructs that encode and express both Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus and Newcastle Disease virus protein antigens, and methods of their use in poultry vaccines.
Owner:INTERVET INC
Stable and Filterable Enveloped Virus Formulations
ActiveUS20080166784A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementNewcastle disease virus NDVAqueous solution
Envelope viruses (e.g. Newcastle disease virus (NDV)) are formulated for storage at moderately cold temperatures (e.g. −20 C). The formulation is an aqueous solution containing the enveloped virus at a concentration of from 106 PFU / mL to 1012 PFU / mL; and a non-reducing saccharide (e.g. sucrose). When the non-reducing saccharide is a disaccharide it is present in the solution at a concentration of from 5% (w / v) to 50% (w / v), and when it is a monosaccharide it is present in the solution at a concentration of from 2.5% (w / v) to 25% (w / v). The solution has an osmotic pressure of about 250 mOs or higher, and has a pH of from 5 to 10.
Owner:WELLSTAT BIOLOGICS CORP
Newcastle disease virus/avian influenza virus H9 subtype/infectious bronchitis virus triplex fluorescence quantification detection reagent and detection method
InactiveCN105671204AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceQuarantine
The invention relates to a newcastle disease virus / avian influenza virus H9 subtype / infectious bronchitis virus triplex fluorescence quantification detection reagent and a detection method and belongs to the technical field of animal quarantine. A newcastle disease virus M gene coding region specific sequence, an avian influenza virus H9 subtype H gene coding region specific sequence and a chicken infectious bronchitis virus M gene coding region specific sequence are selected as target regions, and on the basis of multi-sequence comparison, primer and probe design is conducted. The length of primers is about 20 basic groups, the GC content is 50-60%, a two-stage structure and repeatability do not exist in the primers, no complementary sequence exists between the primers or in the primers, and the melting temperature (Tm value) difference between the primers is smaller than 5 DEG C. In order to guarantee universal use of a newcastle disease virus probe, the length of the probe is only 13 basic groups, the probe is modified by LAN, and the Tm value of the probe is increased. The lengths of the other two virus probes are both about 25 basic groups, and the Tm values are about 5 DEG C higher than those of the primers.
Owner:山东省动物疫病预防与控制中心 +1
Synthetic method of N-2-hydroxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan and preparation method of Newcastle disease attenuated live vaccine-loaded nanoparticles of N-2-hydroxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan
ActiveCN102432695ARaw materials are easy to getEasy to operatePowder deliveryViral antigen ingredientsSide effectFreeze-drying
The invention provides a synthetic method of N-2-hydroxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan and a preparation method of Newcastle disease attenuated live vaccine-loaded nanoparticles of the N-2-hydroxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan, relating to a synthetic method of chitosan and a preparation method of vaccine-loaded nanoparticles of the chitosan. The synthetic method comprises the following steps of: deacelation of the chitosan; dip-treatment of the chitosan; crude preparation of the N-2-hydroxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan; and refined preparation of the N-2-hydroxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding a Newcastle disease virus solution into an N-2-hydroxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan solution to obtain a solution A; adding sodium tripolyphosphate, PBS (phosphate buffer solution) and span-80 into the solution A to obtain a solution B; and centrifuging the solution B to obtain a deposit, adding PBS for suspension, adding mycose skimmed milk, and performing freeze drying to finish the preparation. The nanoparticles prepared by using the method has the advantages of easiness in control of particle size, small particle size of drug-loaded nanoparticles, high entrapment efficiency, large drug-loading quantity, mild preparation conditions, low drug toxic or side effect, long slow release time, simple preparation process, lower production cost and easiness in large-scale production.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Gene VII type Newcastle disease virus attenuated strain, vaccine composition and application of vaccine composition
ActiveCN107281479AImproving immunogenicityGuaranteed not to detoxSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsAntigenNewcastle disease virus NDV
The invention relates to a vaccine composition. The vaccine composition comprises an immunizing dose gene VII type Newcastle disease virus attenuated strain or an antigen of a culture of the immunizing dose gene VII type Newcastle disease virus attenuated strain and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The vaccine composition completely protects against the attacking toxins of the classic virus strain and the existing prevalent strains, and a vaccine prepared for protecting the relatively classic virus strain is more comprehensive. The invention also provides a vaccine prepared by using the gene VII type Newcastle disease virus attenuated strain or the antigen of the culture of the gene VII type Newcastle disease virus attenuated strain and other pathogen antigens together, and various antigen ingredients in the vaccine respectively protect the corresponding pathogens.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG +1
Newcastle disease virus infectious clones, vaccines and new diagnostic assays
InactiveUS7332169B2Immune responseImprove propertiesSsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetic material ingredientsAntigenVirulent characteristics
The invention relates to a process for generating infectious Newcastle disease virus (NDV) entirely from cloned full-length cDNA and to the use of vaccines and diagnostic assays generated with and derived from the process. The process offers the possibility to modify the NDV genome by means of genetic modification and allows for the introduction of mutations, deletions and / or insertions. The process can be used to modify the virulence of NDV, thus generating new attenuated live vaccines with enhanced properties. The process can be used to modify the antigenic make-up of NDV, to allow the generation of live NDV marker vaccines that can be serologically distinguished from NDV field strains.
Owner:STICHTING DIENST LANBOUWKUNDIG ONDERZOEK
Recombinant non-pathogenic marek's disease virus constructs encoding infectious laryngotracheitis virus and newcastle disease virus antigens
ActiveUS20130101619A1Stable, safe, and efficacious immunogenic compositionsImproving immunogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBorna disease virusNewcastle disease virus NDV
The present invention discloses novel recombinant multivalent non-pathogenic Marek's Disease virus constructs that encode and express both Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus and Newcastle Disease virus protein antigens, and methods of their use in poultry vaccines.
Owner:INTERVET INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com