Patents
Literature
2511 results about "Bacteriophage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A bacteriophage (/bækˈtɪərioʊfeɪdʒ/), also known informally as a phage (/feɪdʒ/), is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν (phagein), "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm.
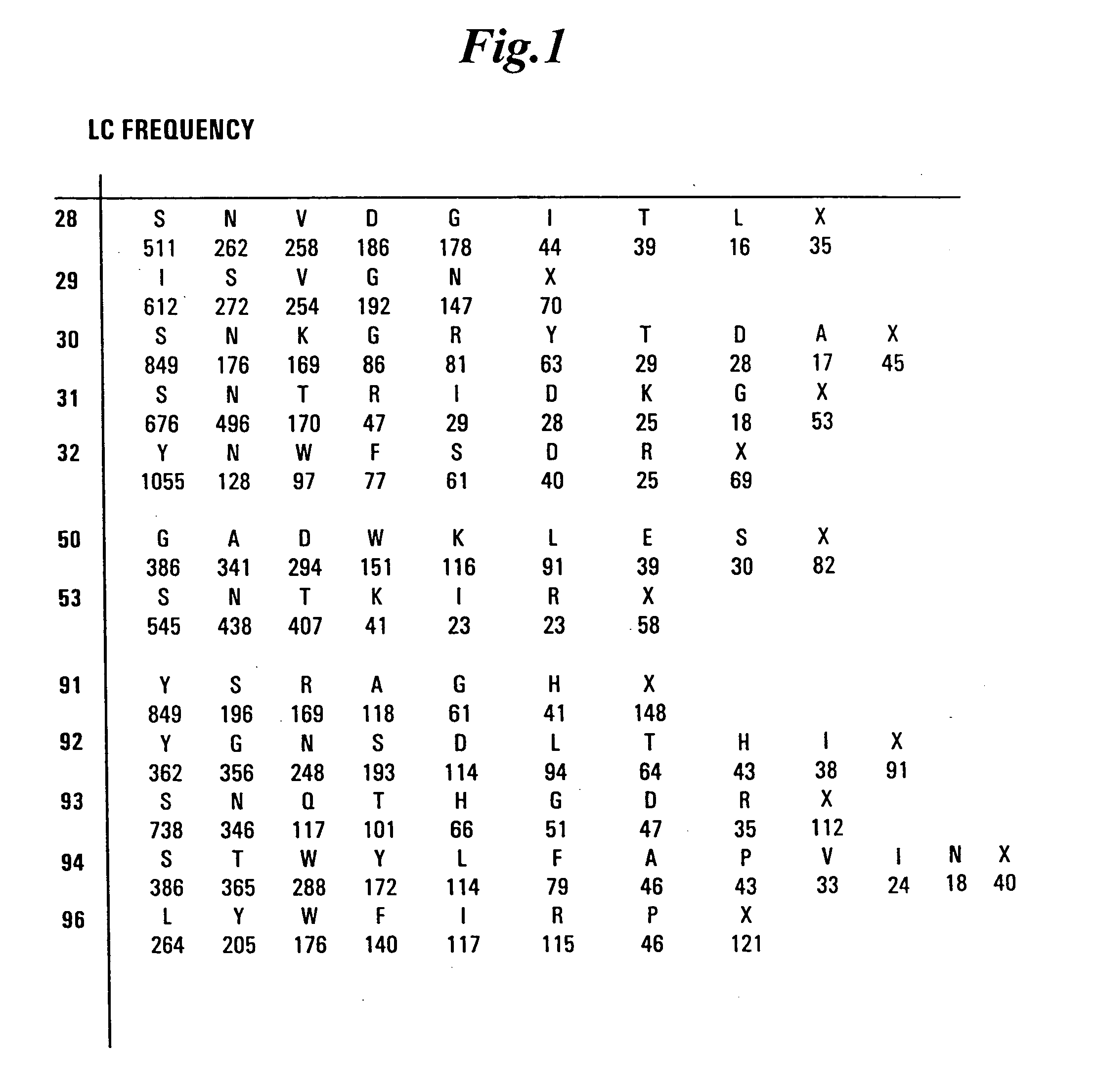
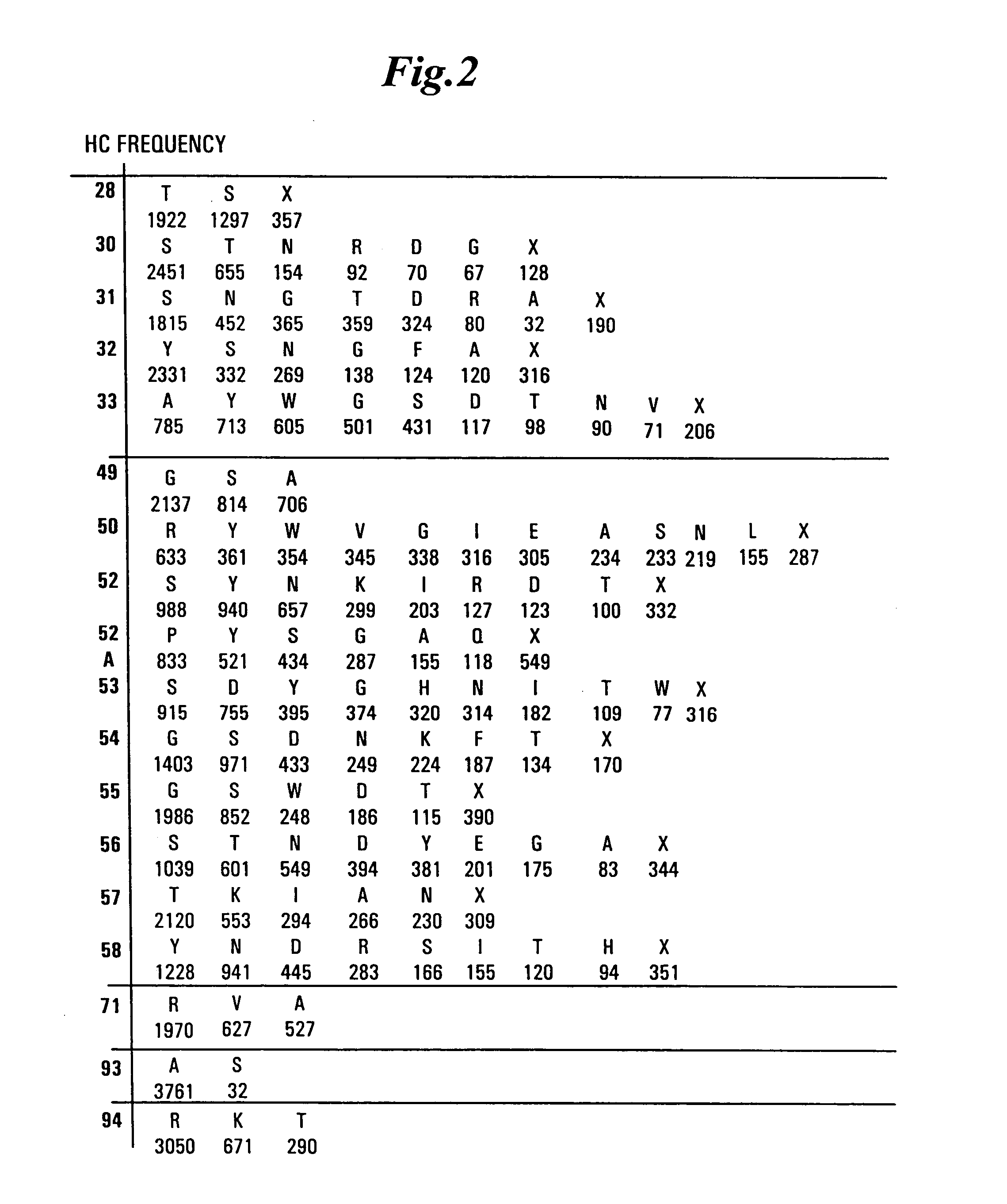
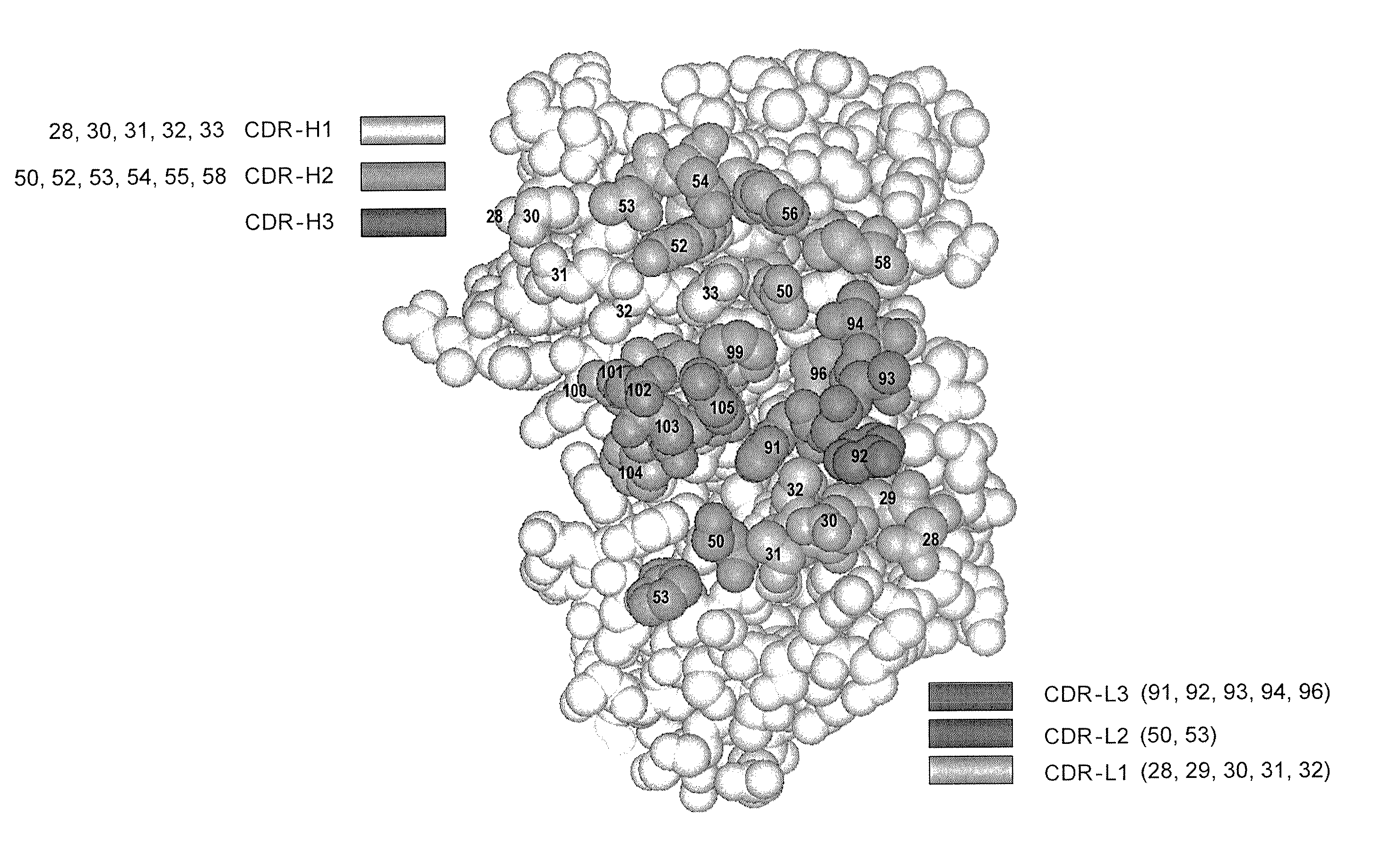
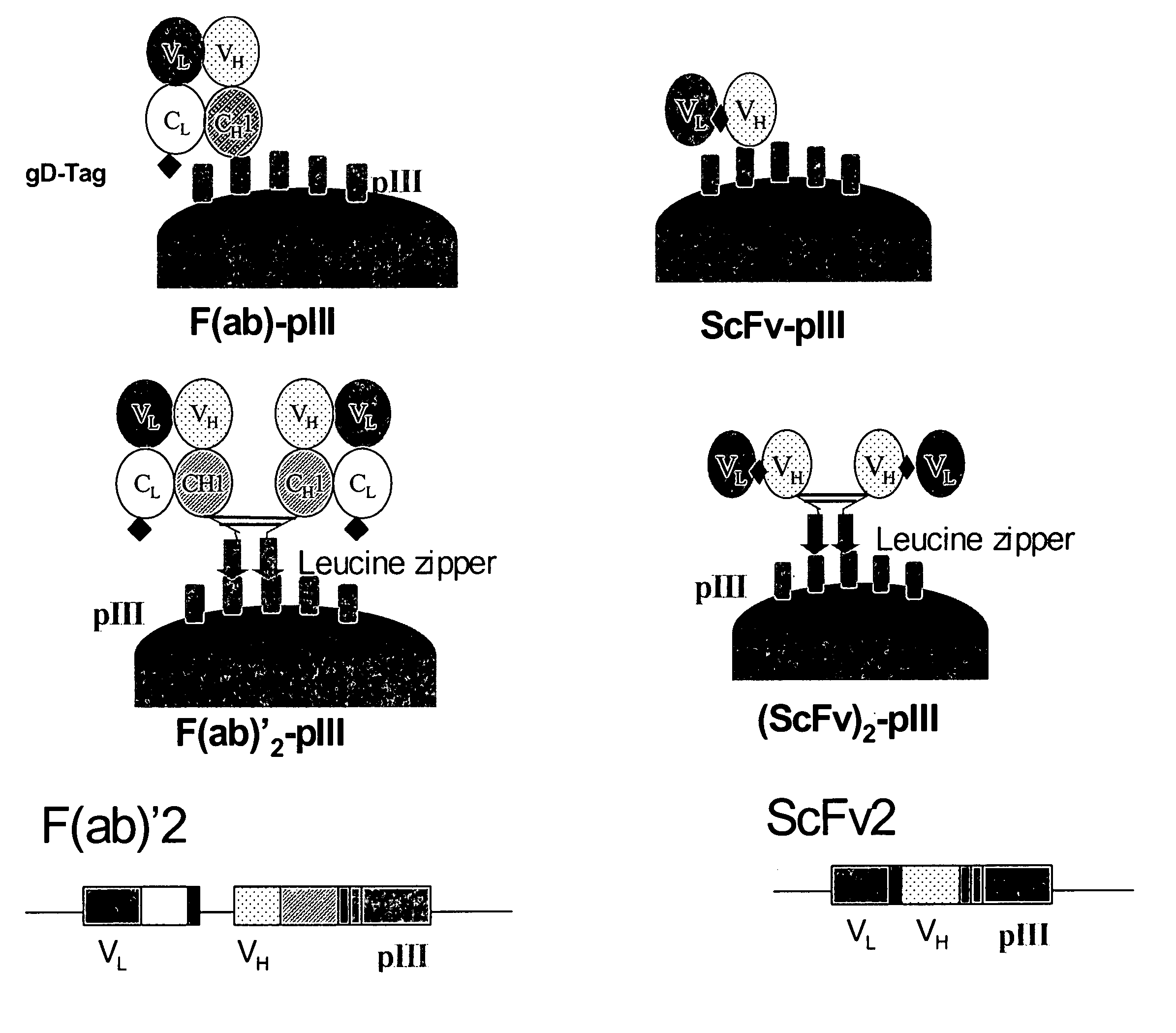
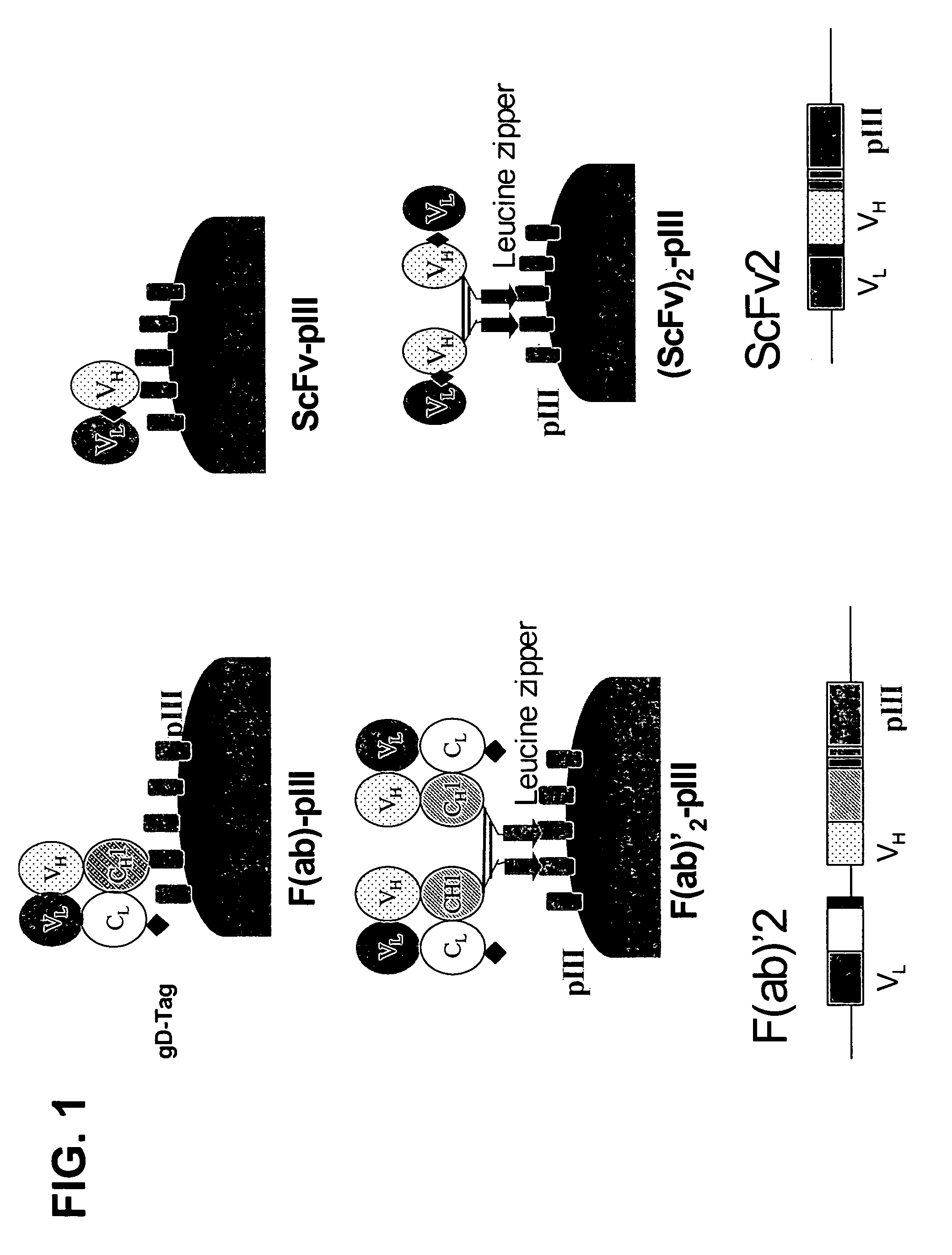
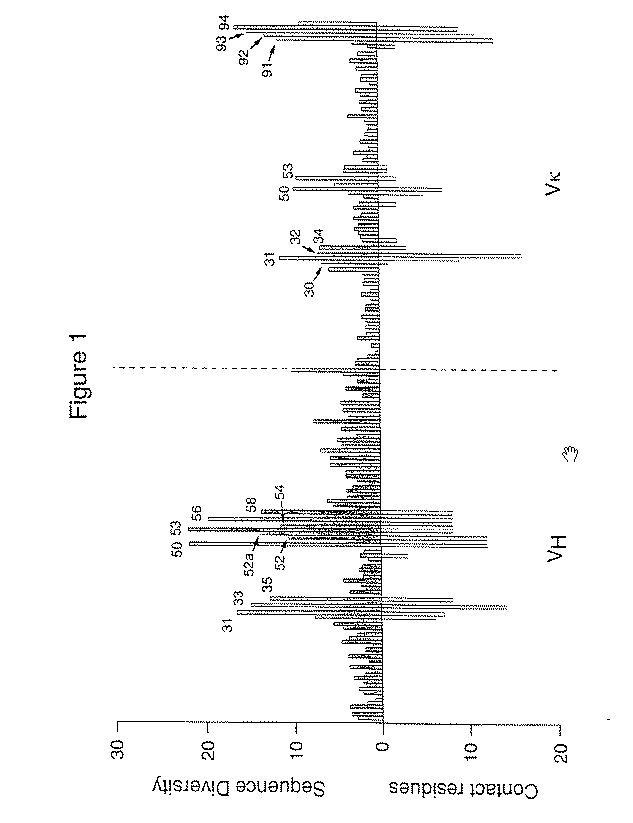
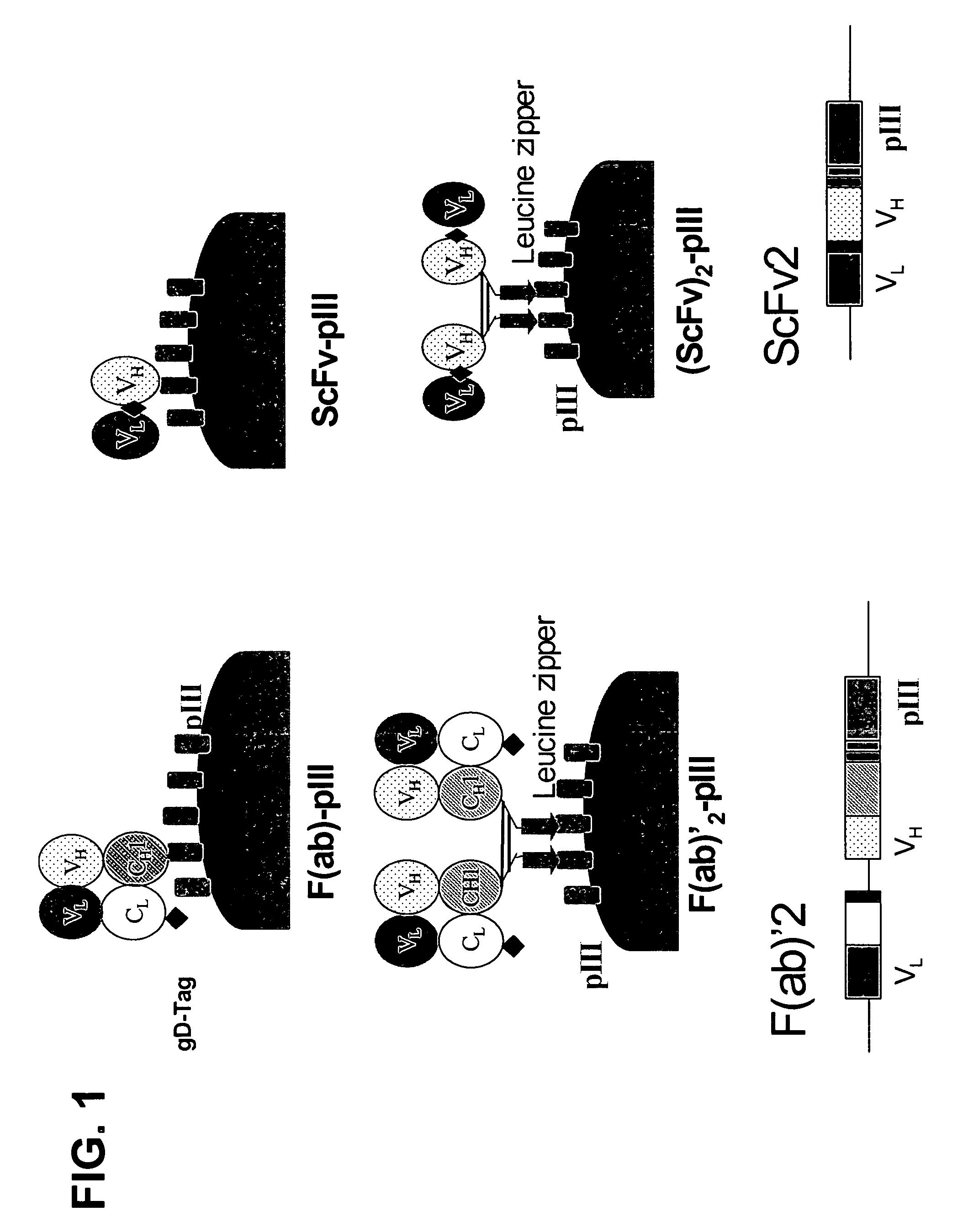
Synthetic antibody phage libraries
InactiveUS20050079574A1High-quality target binding characteristicGenerate efficientlyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeterologousIntravenous gammaglobulin
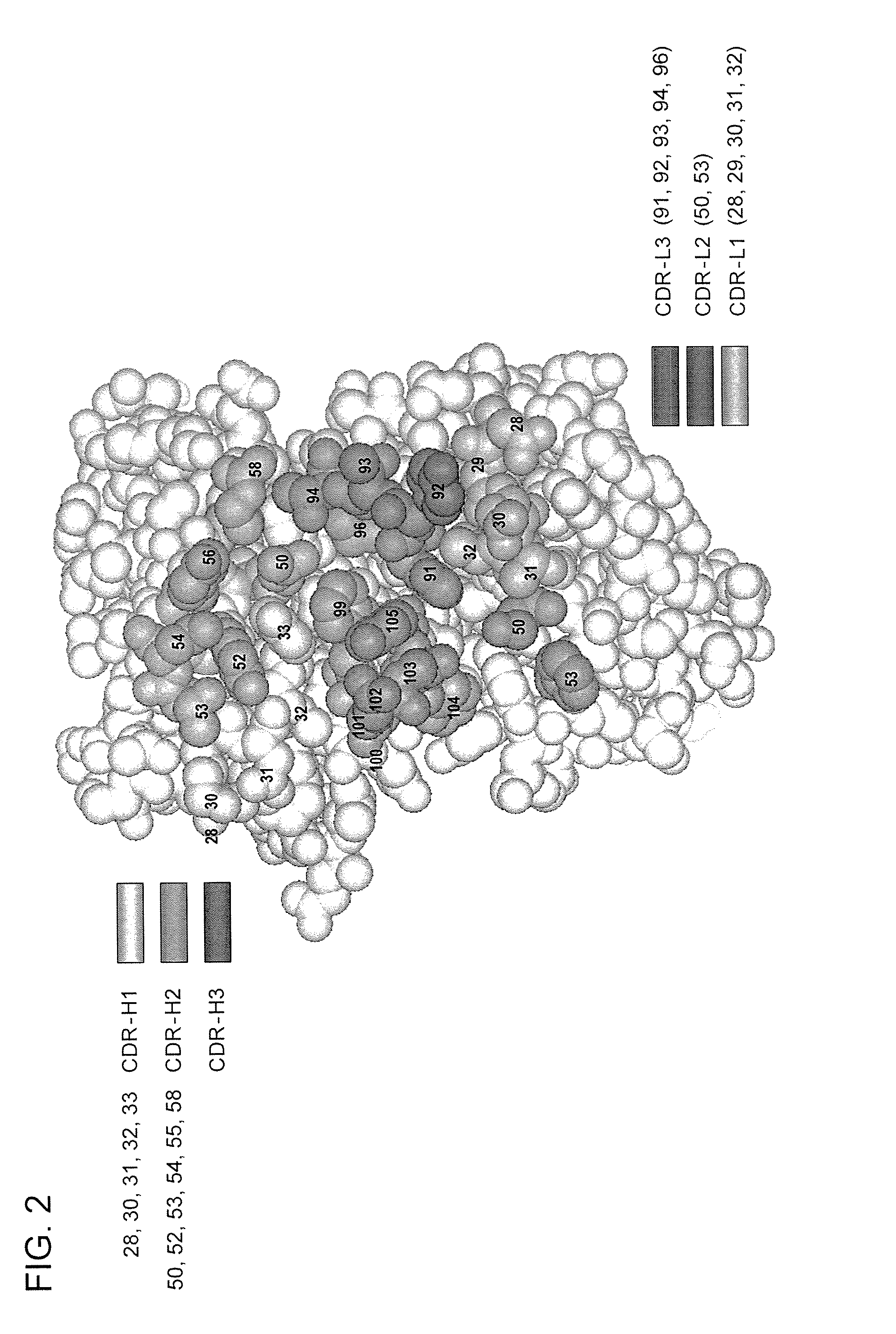
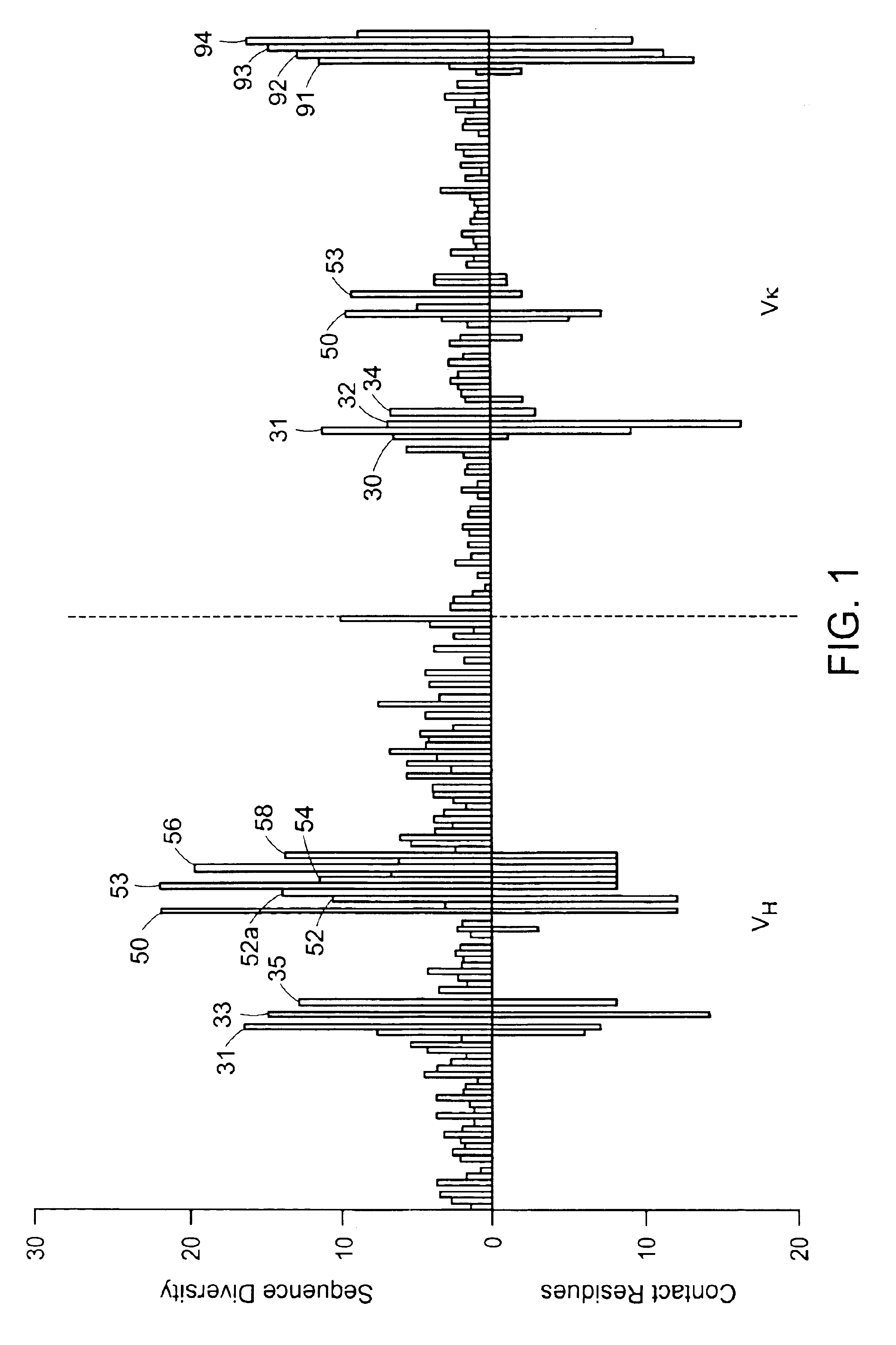
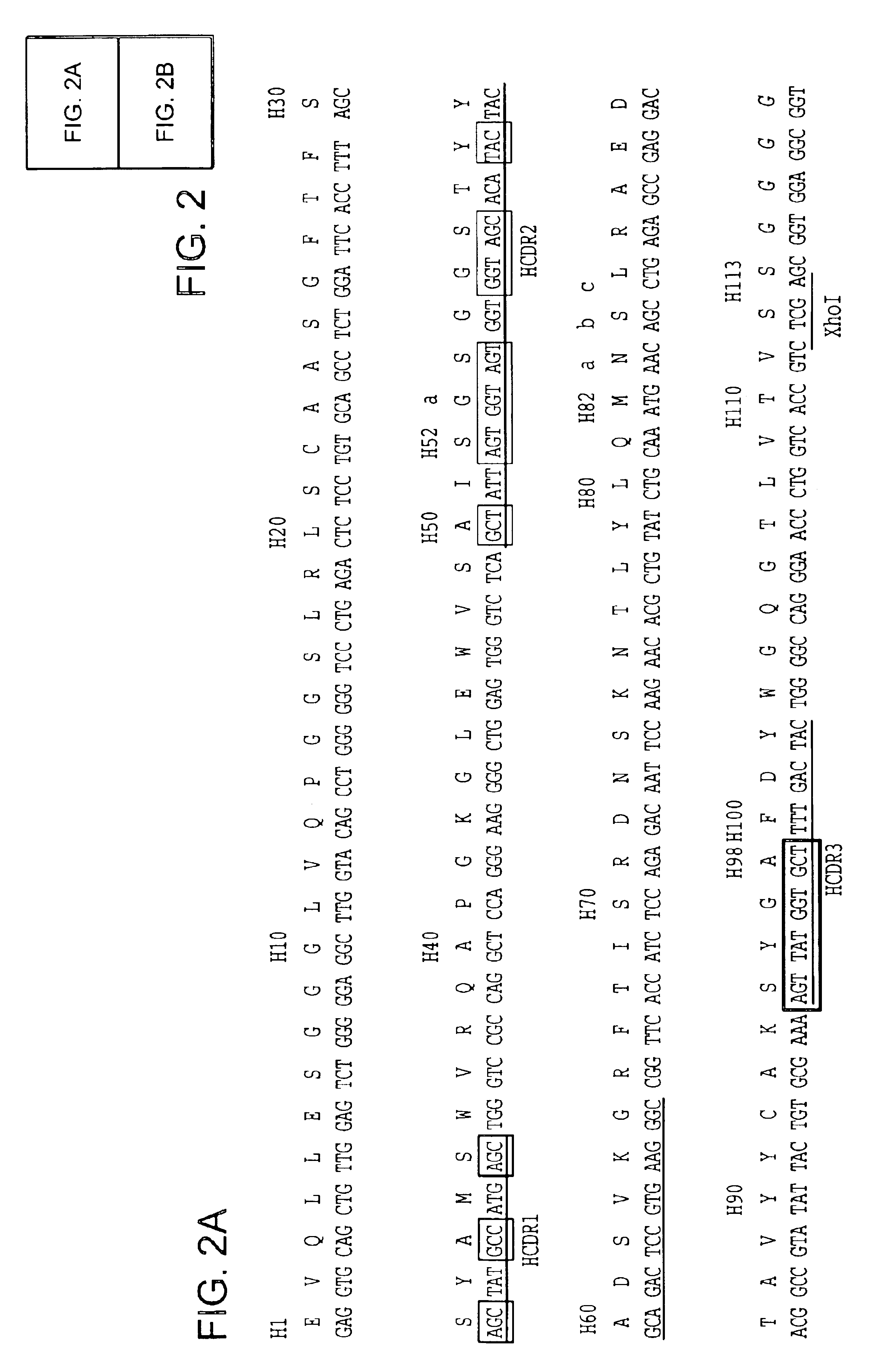
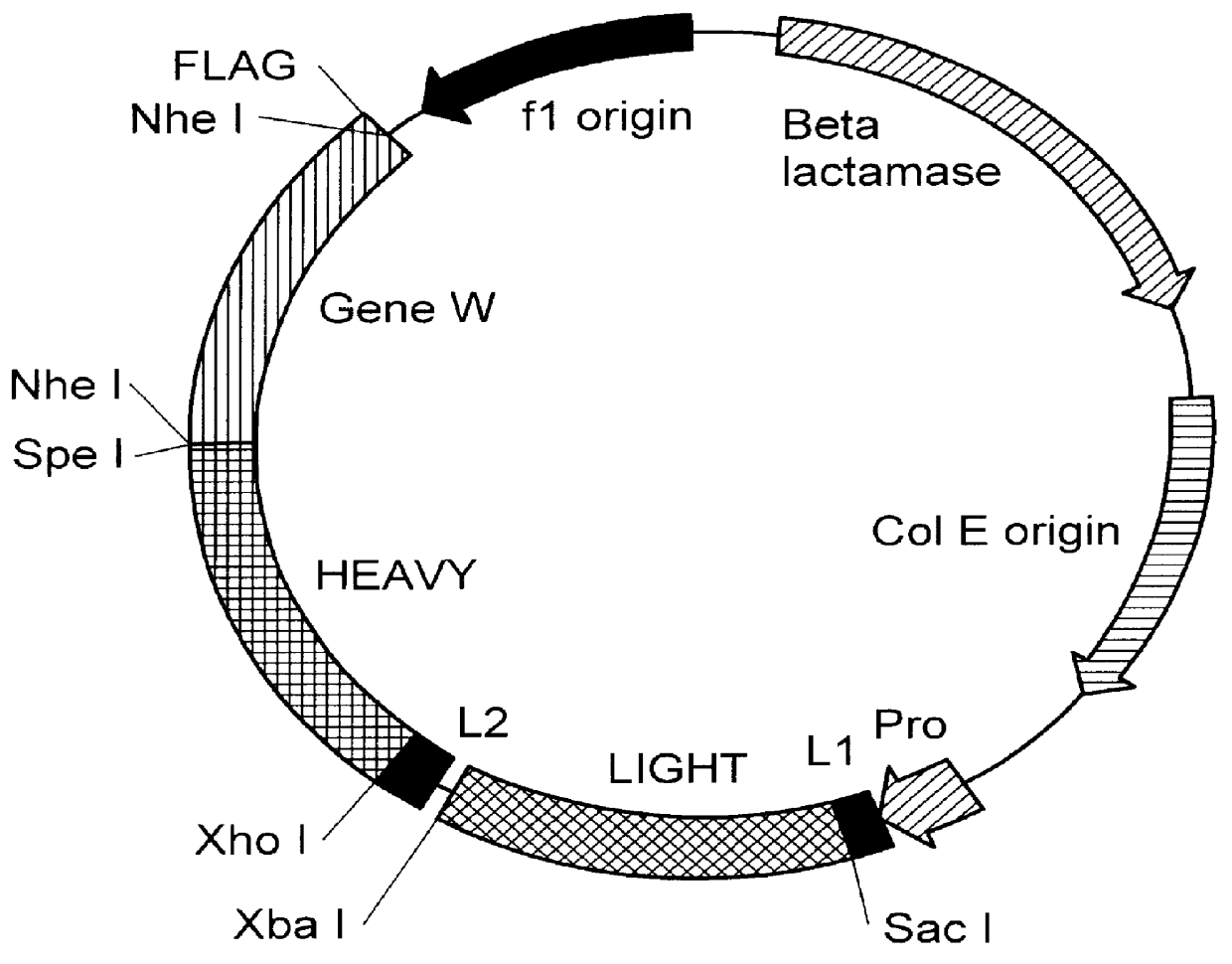
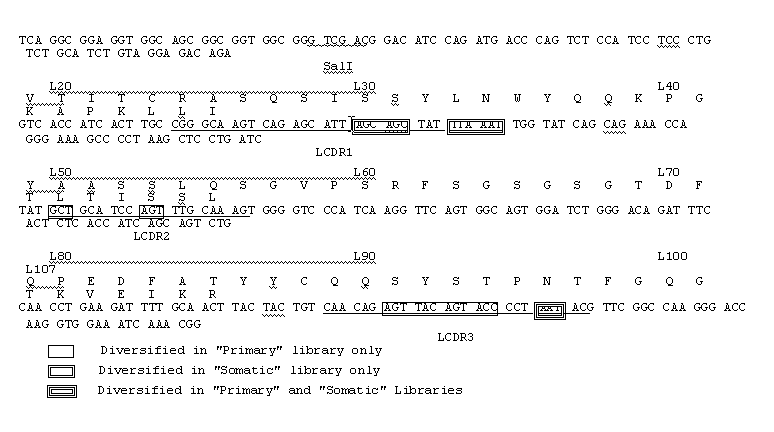
The invention provides immunoglobulin polypeptides comprising variant amino acids in CDRs of antibody variable domains. In one embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant CDRH3 region. These polypeptides provide a source of great sequence diversity that can be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides. The invention also provides these polypeptides as fusion polypeptides to heterologous polypeptides such as at least a portion of phage or viral coat proteins, tags and linkers. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
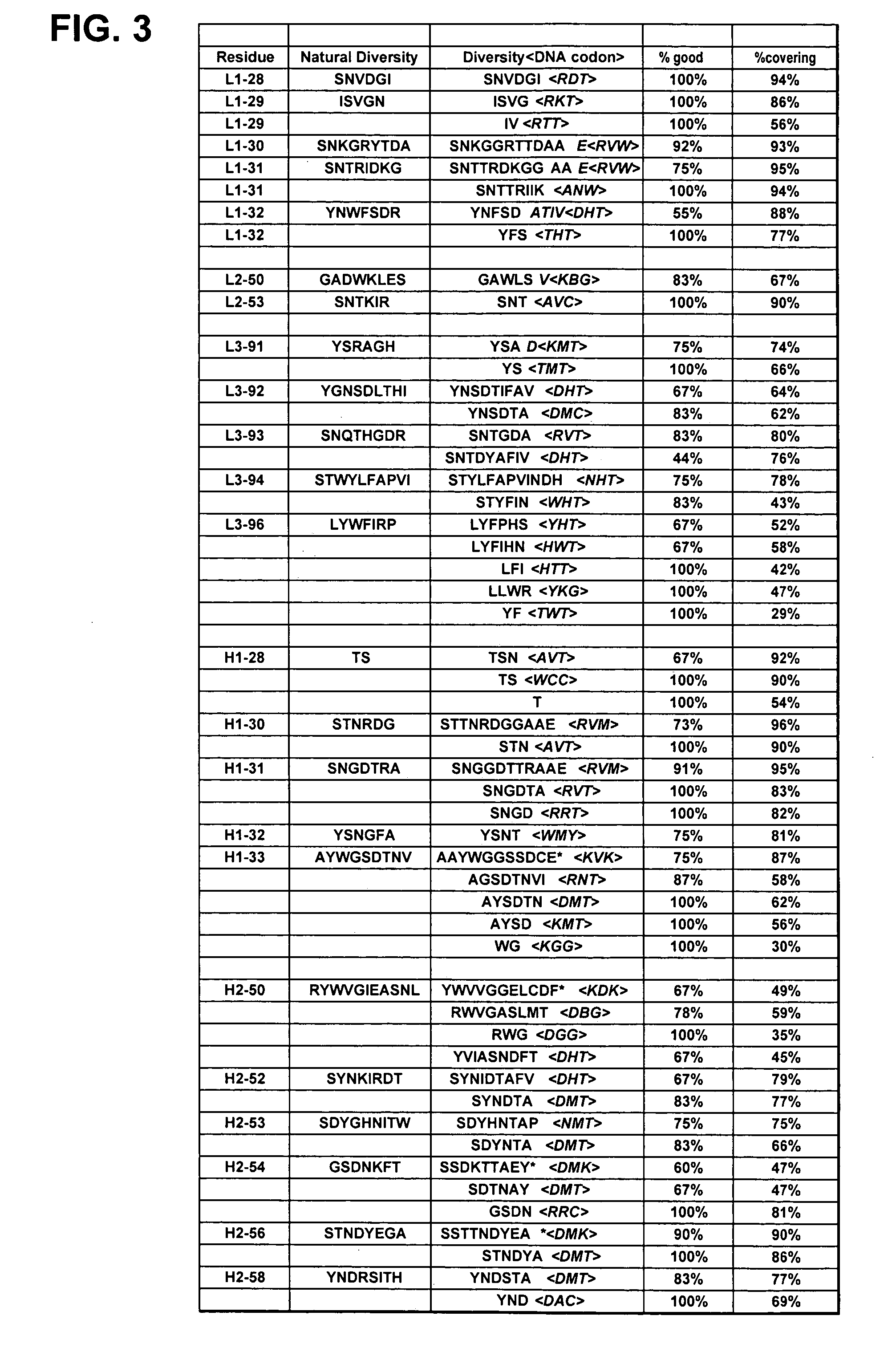
Binding polypeptides with restricted diversity sequences
InactiveUS20070237764A1Small sizeHigh-quality target binding characteristicFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousAntigen binding
The invention provides variant CDRs comprising highly restricted amino acid sequence diversity. These polypeptides provide a flexible and simple source of sequence diversity that can be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides. The invention also provides these polypeptides as fusion polypeptides to heterologous polypeptides such as at least a portion of phage or viral coat proteins, tags and linkers. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Phage antibodies
Peripheral blood leucocytes incubated with a semi-synthetic phage antibody library and fluorochrome-labeled CD3 and CD20 antibodies were used to isolate human single chain Fv antibodies specific for subsets of blood leucocytes by flow cytometry. Isolated phage antibodies showed exclusive binding to the subpopulation used for selection or displayed additional binding to a restricted population of other cells in the mixture. At least two phage antibodies appeared to display hithereto unknown staining patterns of B lineage cells. This approach provides a subtractive procedure to rapidly obtain human antibodies against known and novel surface antigens in their native configuration, expressed on phenotypically defined subpopulations of cells. Importantly, this approach does not depend on immunization procedures or the necessity to repeatedly construct phage antibody libraries.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Method of sequencing genomes by hybridization of oligonucleotide probes
InactiveUS6018041ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMammalian genomeHomologous sequence
The conditions under which oligonucleotides hybridize only with entirely homologous sequences are recognized. The sequence of a given DNA fragment is read by the hybridization and assembly of positively hybridizing probes through overlapping portions. By simultaneous hybridization of DNA molecules applied as dots and bound onto a filter, representing single-stranded phage vector with the cloned insert, with about 50,000 to 100,000 groups of probes, the main type of which is (A,T,C,G)(A,T,C,G)N8(A,T,C,G), information for computer determination of a sequence of DNA having the complexity of a mammalian genome are obtained in one step. To obtain a maximally completed sequence, three libraries are cloned into the phage vector, M13, bacteriophage are used: with the 0.5 kb and 7 kbp insert consisting of two sequences, with the average distance in genomic DNA of 100 kbp. For a million bp of genomic DNA, 25,000 subclones of the 0.5 kbp are required as well as 700 subclones 7 kb long and 170 jumping subclones. Subclones of 0.5 kb are applied on a filter in groups of 20 each, so that the total number of samples is 2,120 per million bp. The process can be easily and entirely robotized for factory reading of complex genomic fragments or DNA molecules.
Owner:HYSEQ
Method to screen phage display libraries with different ligands
InactiveUS6846634B1Overcome inherent biasGuaranteed effective sizePeptide librariesLibrary screeningBinding siteBacteriophage
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Human B7.1-specific primatized antibodies and transfectomas expressing said antibodies
InactiveUS6113898AShrink tumorInhibit tumor growthPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticDiseaseOrgan transplant rejection
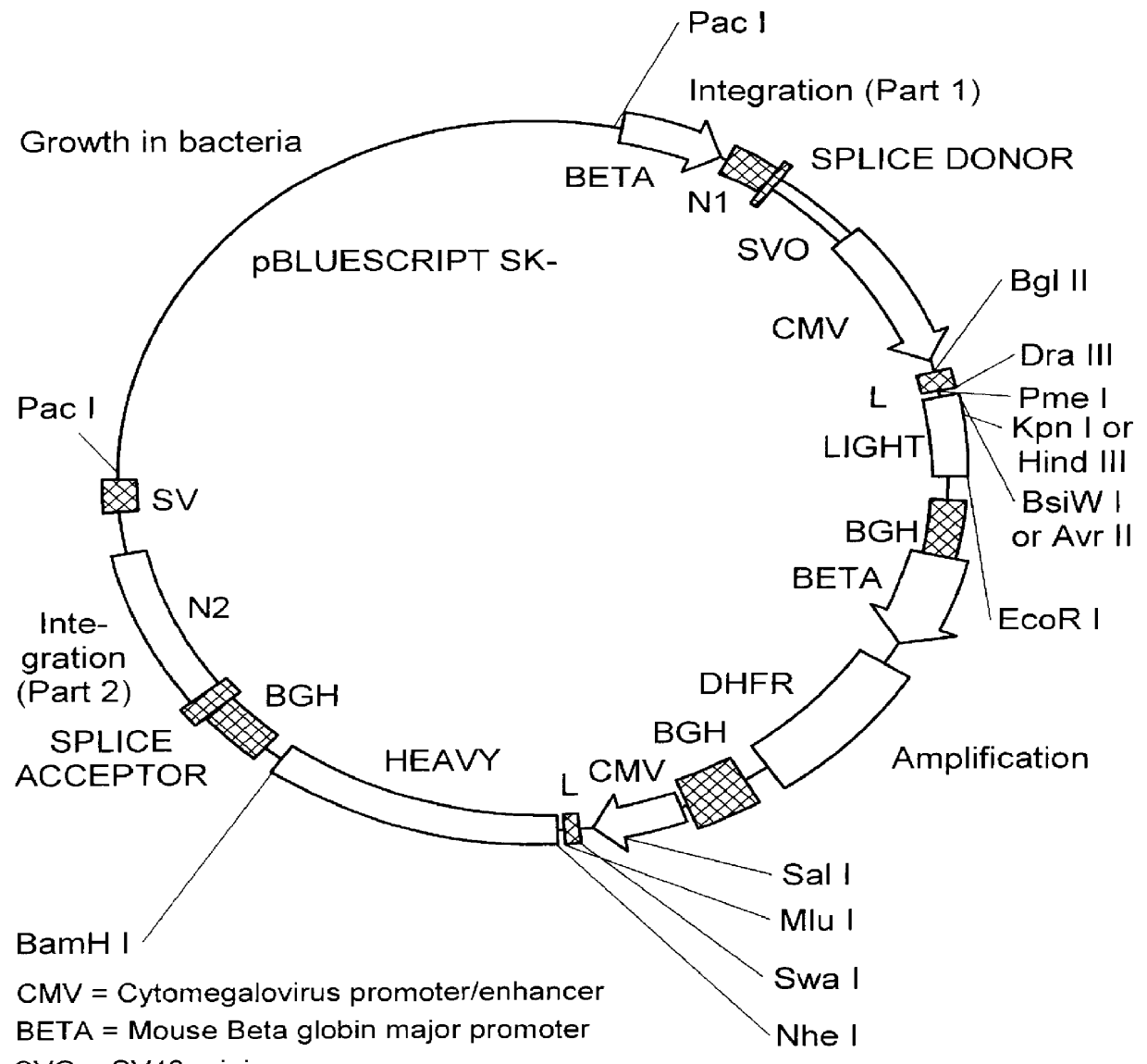
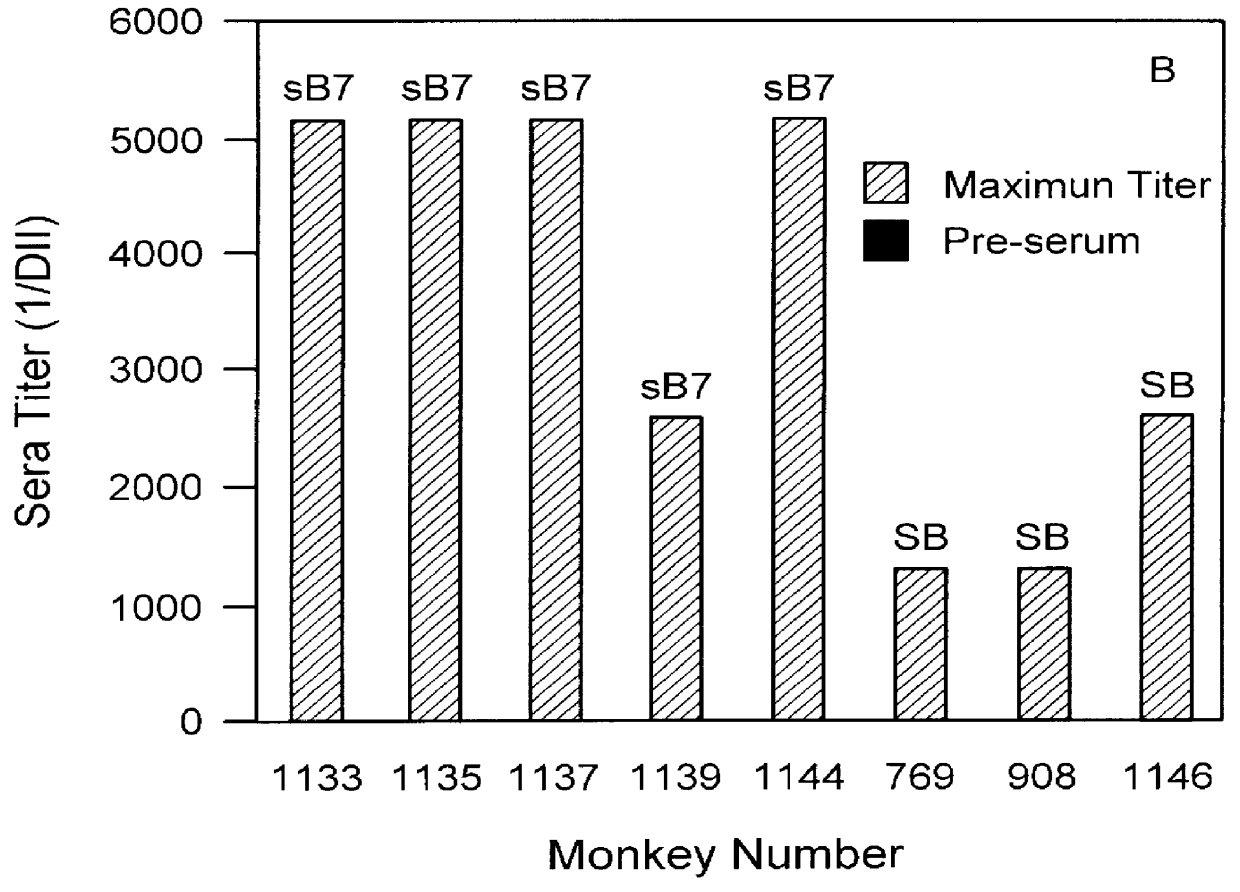
The present invention relates to the identification of macaque antibodies to human B7.1 and B7.2 by screening of phage display libraries or monkey heterohybridomas obtained using B lymphocytes from B7.1 and / or B7.2 immunized monkeys. More specifically, the invention provides four monkey monoclonal antibodies 7B6, 16C10, 7C10 and 20C9 which inhibit the B7:CD28 pathway and thereby function as effective immunosuppressants. The invention further provides the complete DNA and amino acid sequences of the light and heavy chain of three primatized antibodies derived from those monkey monoclonal antibodies which bind B7.1 and possibly B7.2, primatized 7C10, primatized 7B6 and primatized 16C10. These primatized and monkey antibodies may be used as specific immunosuppressants, e.g., for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and to prevent organ transplant rejection.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
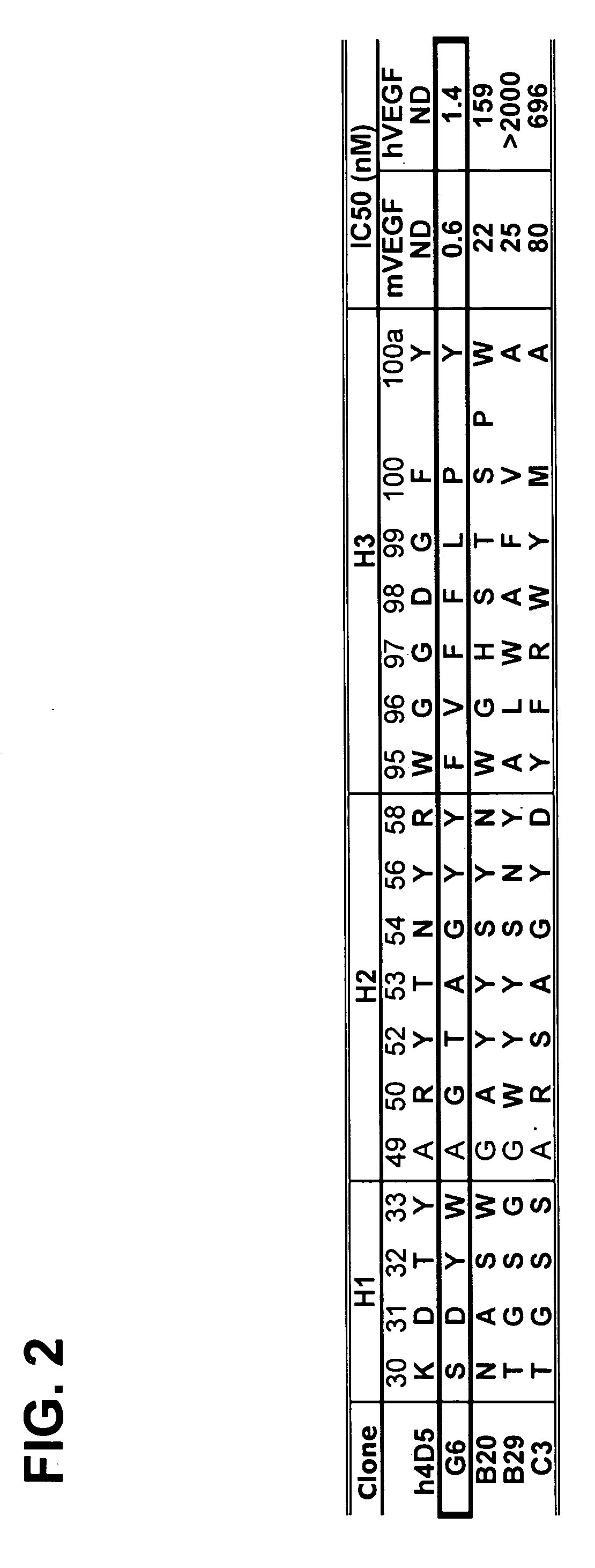
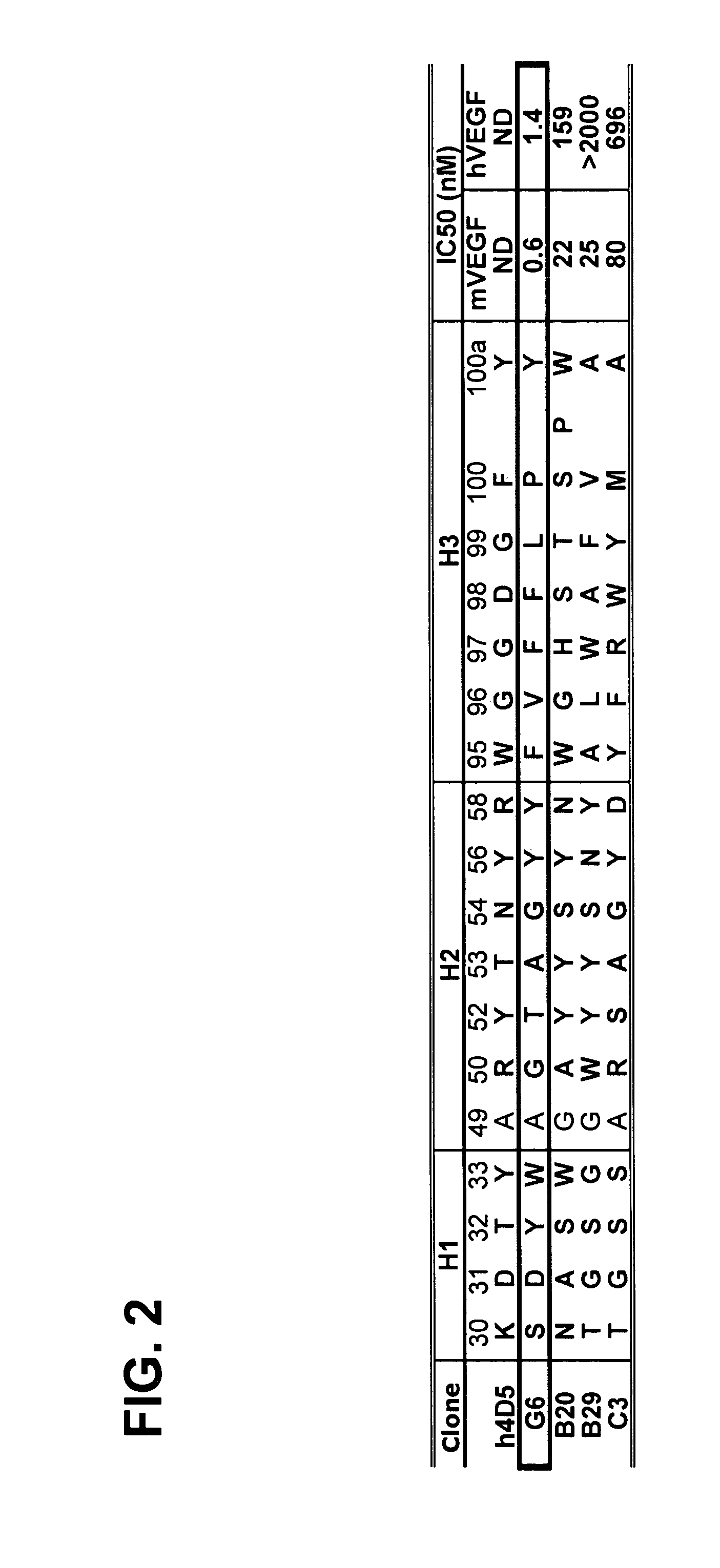
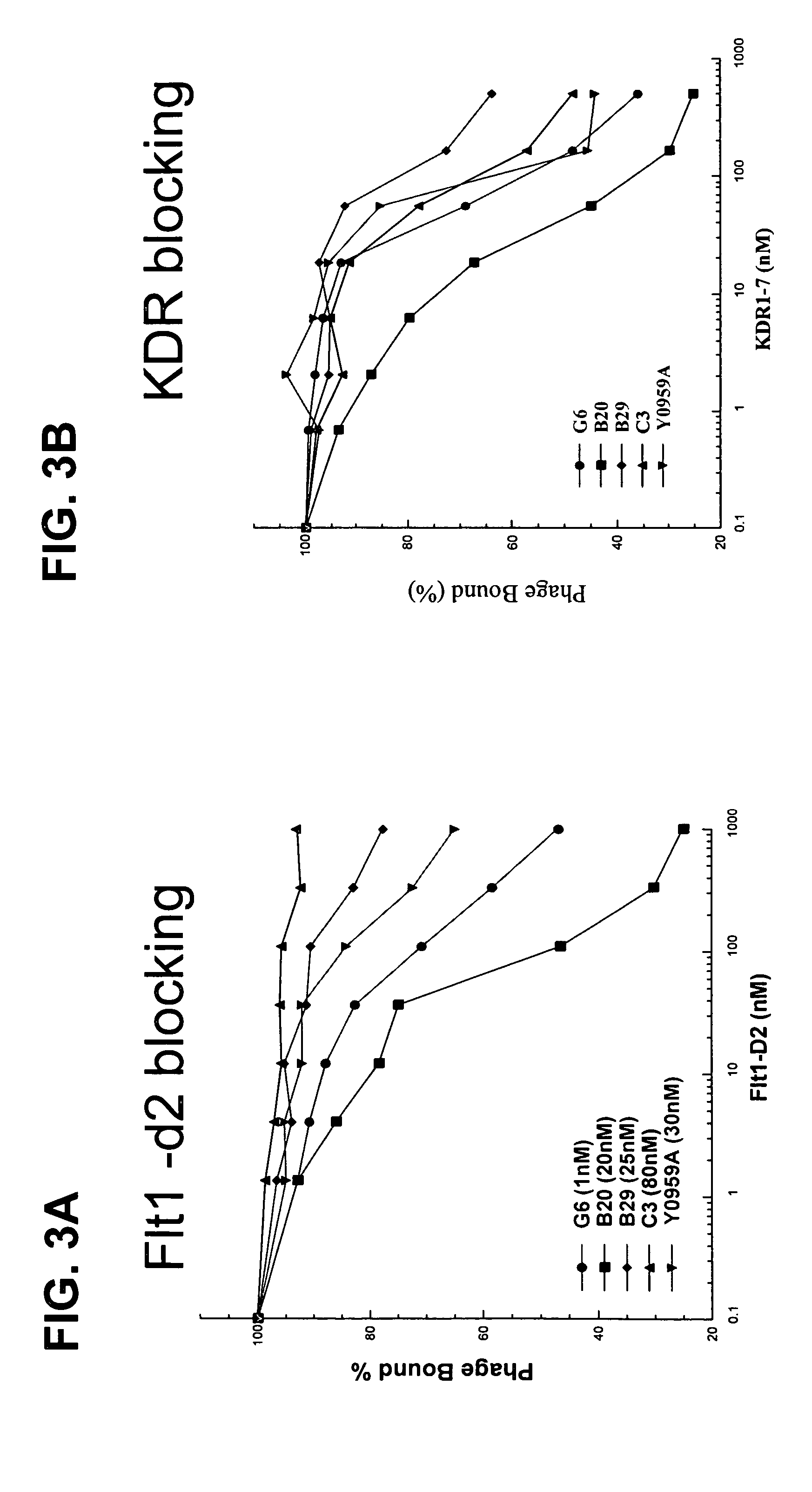
Anti-VEGF antibodies
Owner:GENENTECH INC
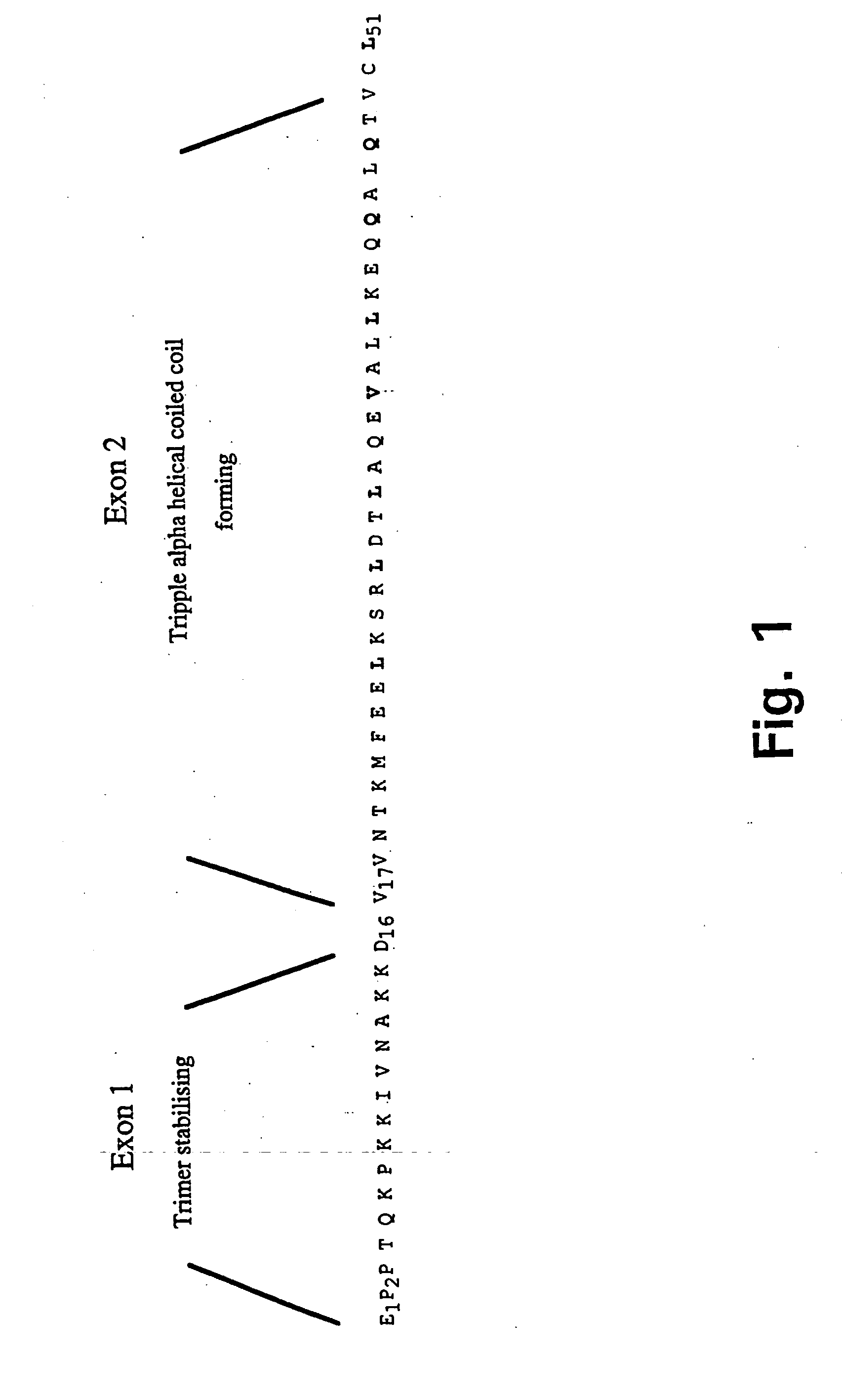
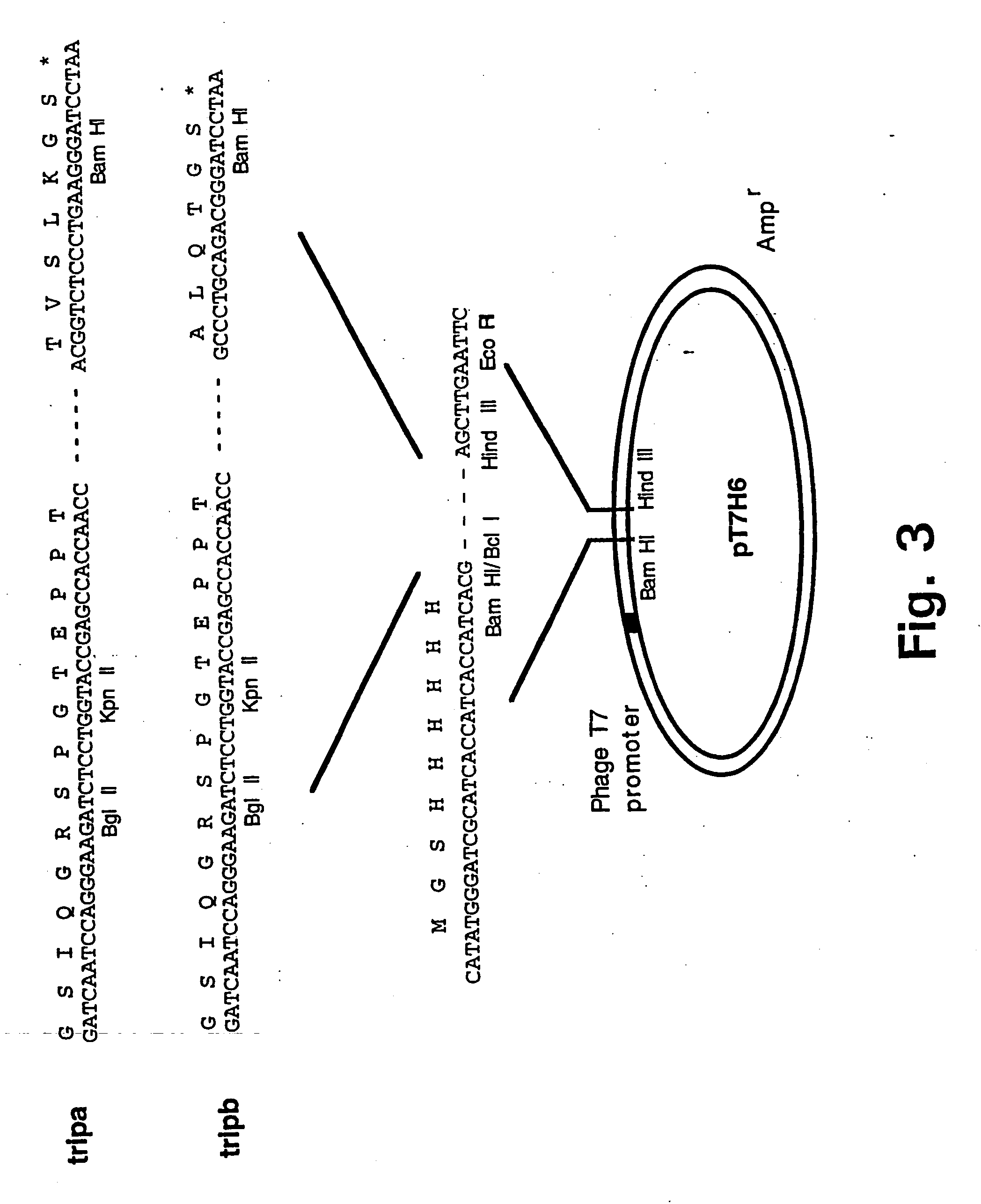
Trimerising module
The present invention relates to the design of trimeric polypeptides using polypeptide structural elements derived from the tetranectin protein family, and their use in rational de novo design and production of multi-functional molecules including the application of the multi-functional molecules in protein library technology, such as phage display technology, diagnostic and therapeutic systems, such as human gene therapy and imaging. The trimeric polypeptides being constructed as a monomer polypeptide construct comprising at least one tetranectin trimerising structural element (TTSE) which is covalently linked to at least one heterologous moiety, said TTSE being capable of forming a stable complex with two other TTSEs; or as an oligomer which is comprised of two monomer polypeptide constructs as mentioned above, and which comprises three TTSEs or a multiplum of three TTSEs, or which is comprised of three monomer polypeptide constructs.
Owner:ANAPHORE INC +1
Method to screen phage display libraries with different ligands
InactiveUS20040038291A2Immunoglobulin superfamilyLibrary screeningPolyphageImmunoglobulin superfamily
Abstract of the Disclosure The present invention relates to methods for selecting repertoires of polypeptides using generic and target ligands. In particular, the invention relates to a library comprising a repertoire of polypeptides of the immunoglobulin superfamily, wherein the members of the repertoire have a known main chain conformation.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Anti-VEGF antibodies
ActiveUS20070020267A1Inhibit bindingSenses disorderImmunoglobulins against growth factorsAnti vegf antibodyBacteriophage
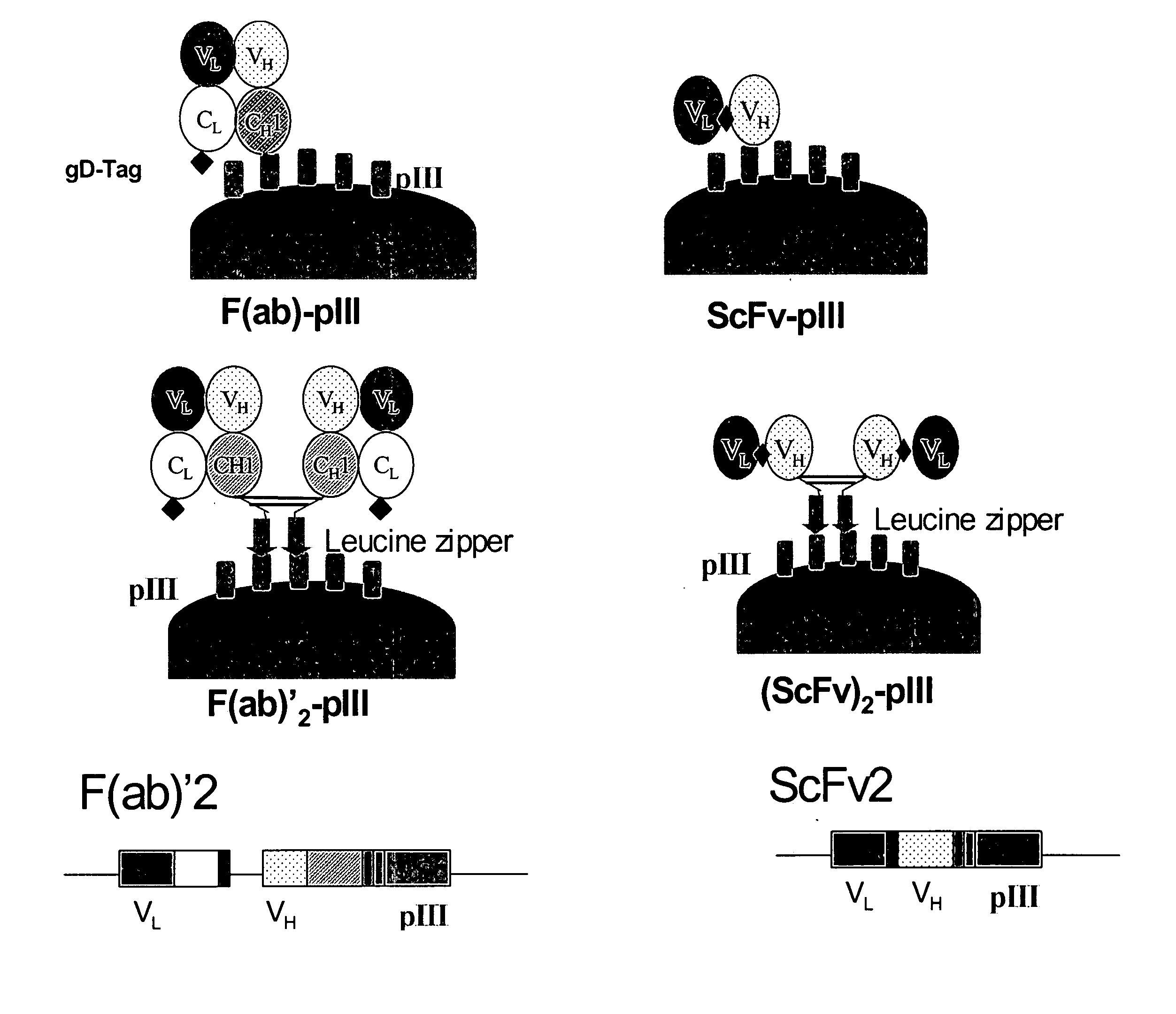
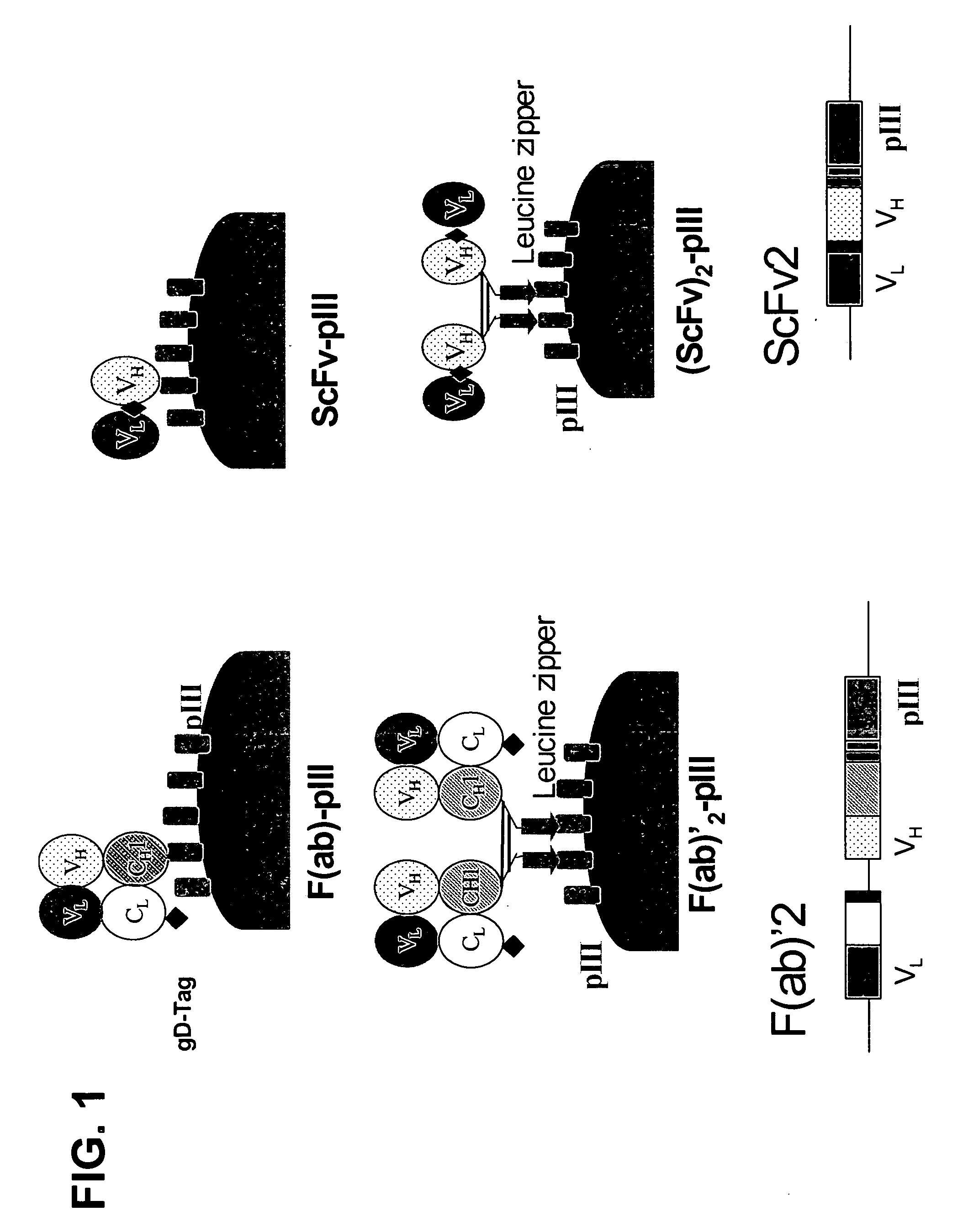
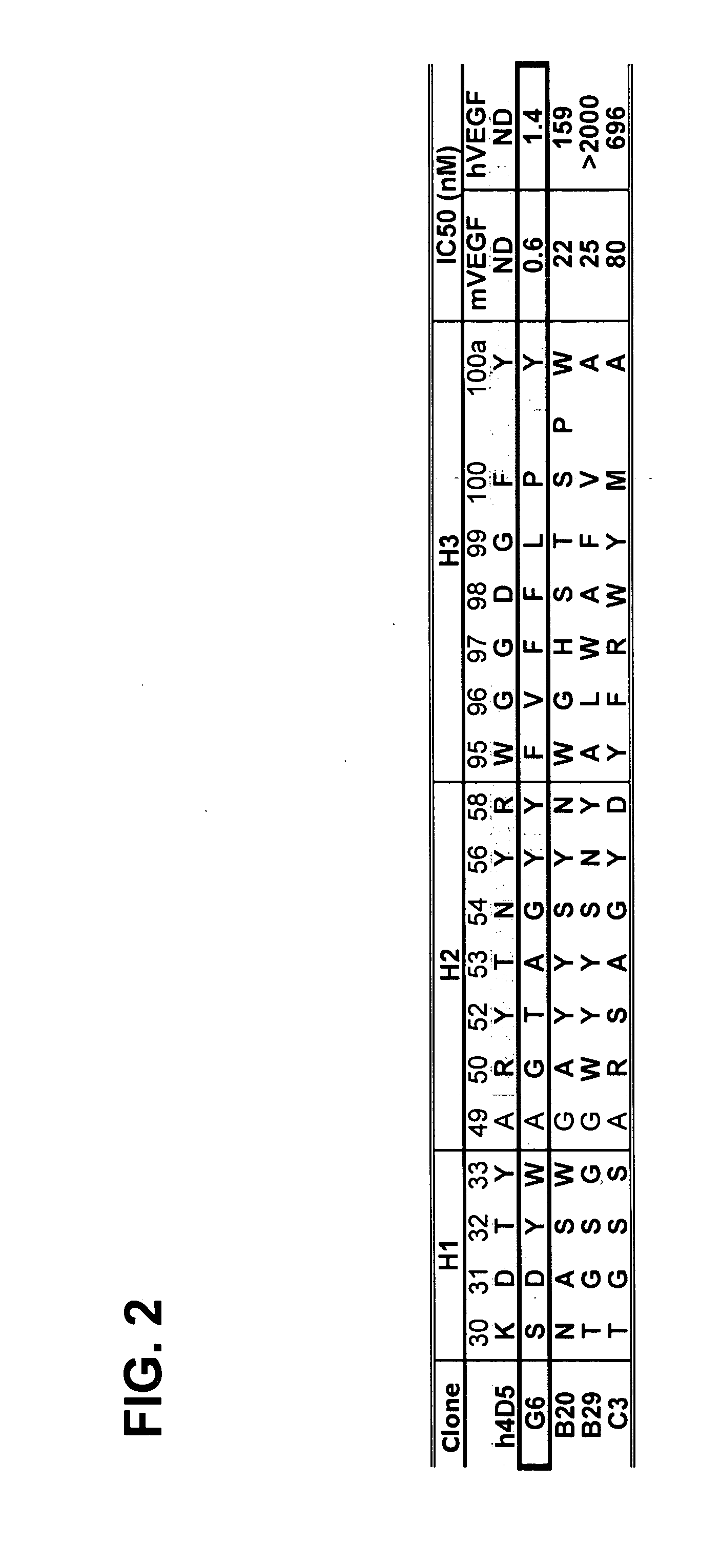
Anti-VEGF antibodies and variants thereof, including those having high affinity for binding to VEGF, are disclosed. Also provided are methods of using phage display technology with naïve libraries to generate and select the anti-VEGF antibodies with desired binding and other biological activities. Further contemplated are uses of the antibodies in research, diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Antibodies that block receptor protein tyrosine kinase activation, methods of screening for and uses thereof
ActiveUS20050147612A1Reduce usageUseful in treatmentFungiSenses disorderProtein-Tyrosine KinasesAntibody fragments
Molecules comprising the antigen-binding portion of antibodies that block constitutive and / or ligand-dependent activation of a receptor protein tyrosine kinase, such as fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3), are found through screening methods, where a soluble dimeric form of a receptor protein tyrosine kinase is used as target for screening a library of antibody fragments displayed on the surface of bacteriophage. The molecules of the present invention which block constitutive activation can be administered to treat or inhibit skeletal dysplasia, craniosynostosis disorders, cell proliferative diseases or disorders, or tumor progression associated with the constitutive activation of a receptor protein tyrosine kinase.
Owner:FIBRON
Methods of generating novel peptides
The present invention describes peptides capable of specifically binding to preselected micromolecules or to their natural receptor. The preselected molecules include but are not limited to drugs, vitamins, neuromediators and steroid hormones. Methods of using the phage display libraries to identify peptide compositions in preselected binding interactions are also disclosed. The retrieved peptides mimicking a natural receptor binding site to preselected molecules are used as is or as ligands to re-screen the same or different libraries to find and / or derive new receptor ligands, or are used to elicit the production of antibodies capable of binding to the natural receptor. The two categories of effector molecules (peptides or antibodies) may find diagnostic, therapeutic or prophylactic uses. The peptides directly derived from the phage display libraries may be used as drug detectors or antidotes. The others may be used to identify, target, activate or neutralize the receptor for the preselected micromolecules, the receptor being known or unknown.
Owner:BIOPHAGE
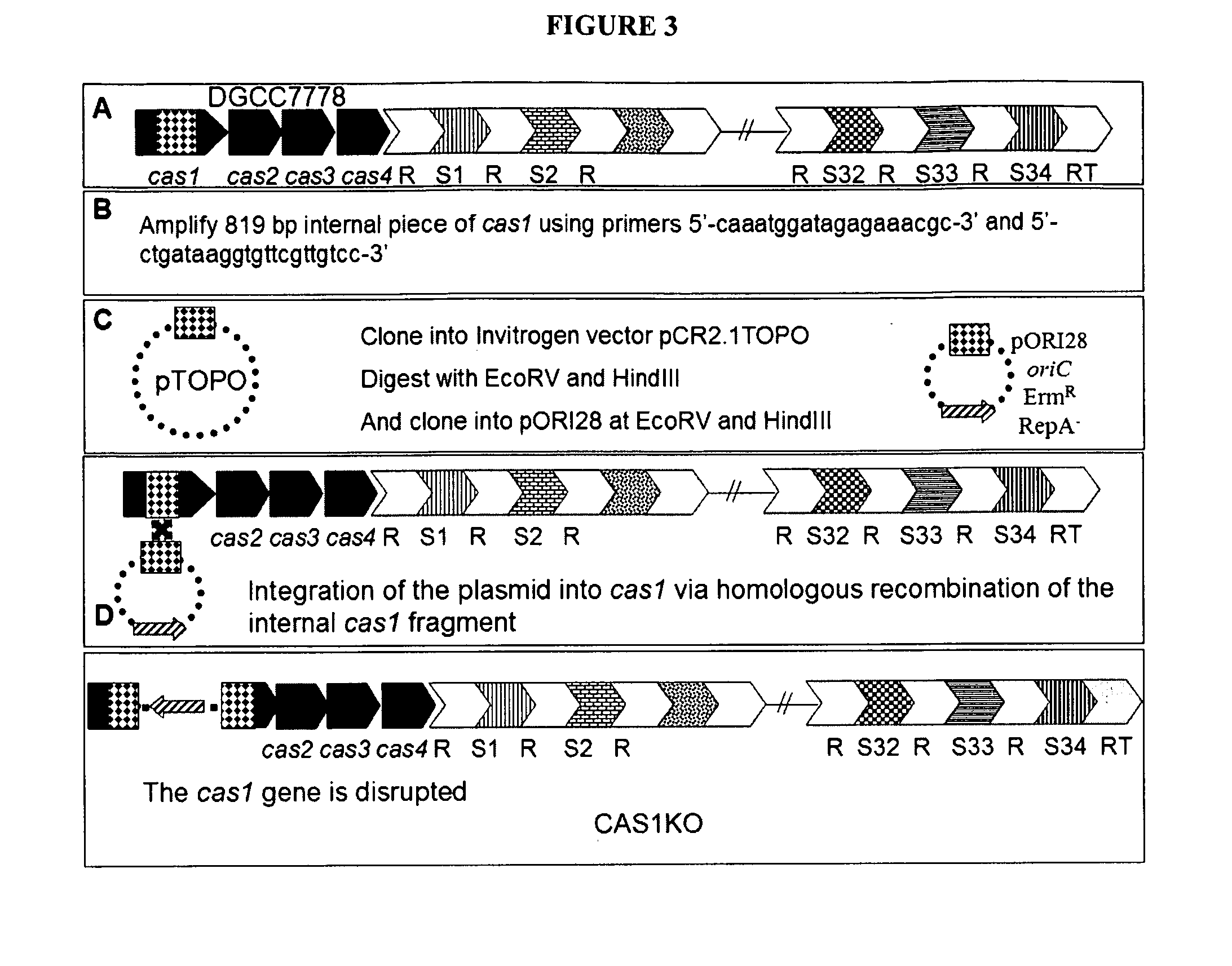
Cultures with Improved Phage Resistance
InactiveUS20110002889A1Reduced degree of homologyReduce decreaseBiocideBacteriaVirulent characteristicsBacteriophage
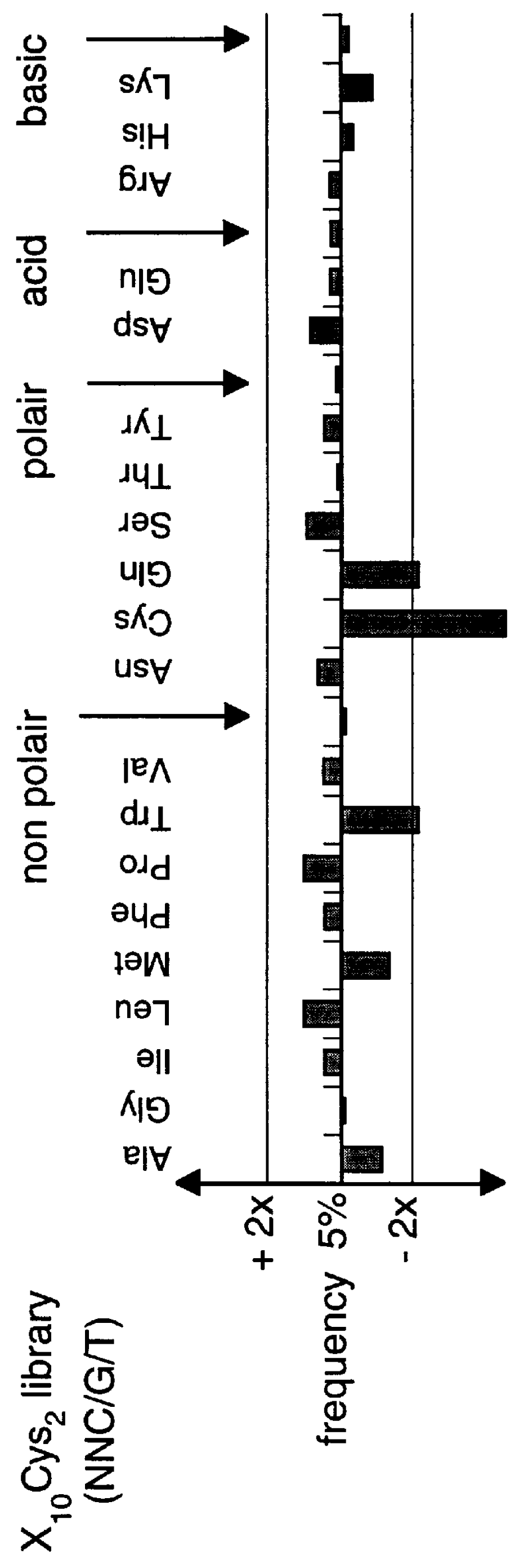
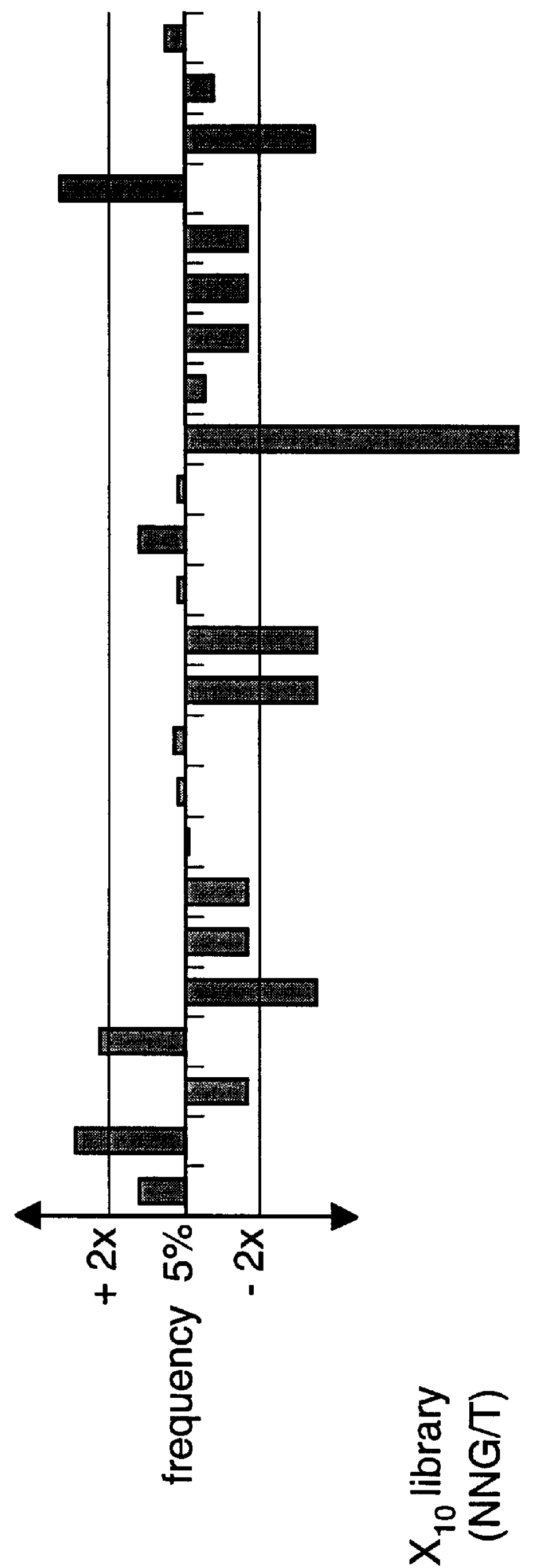
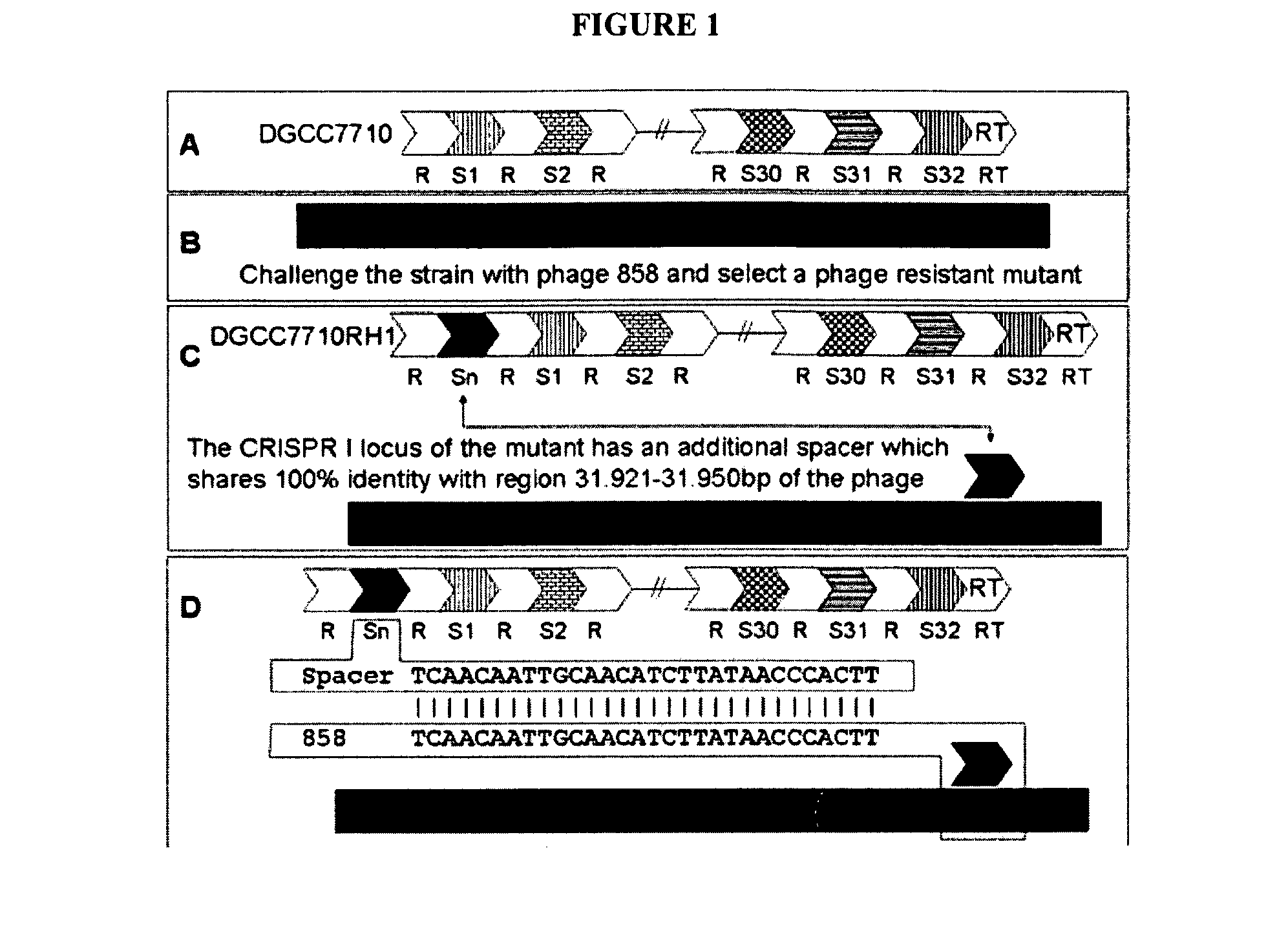
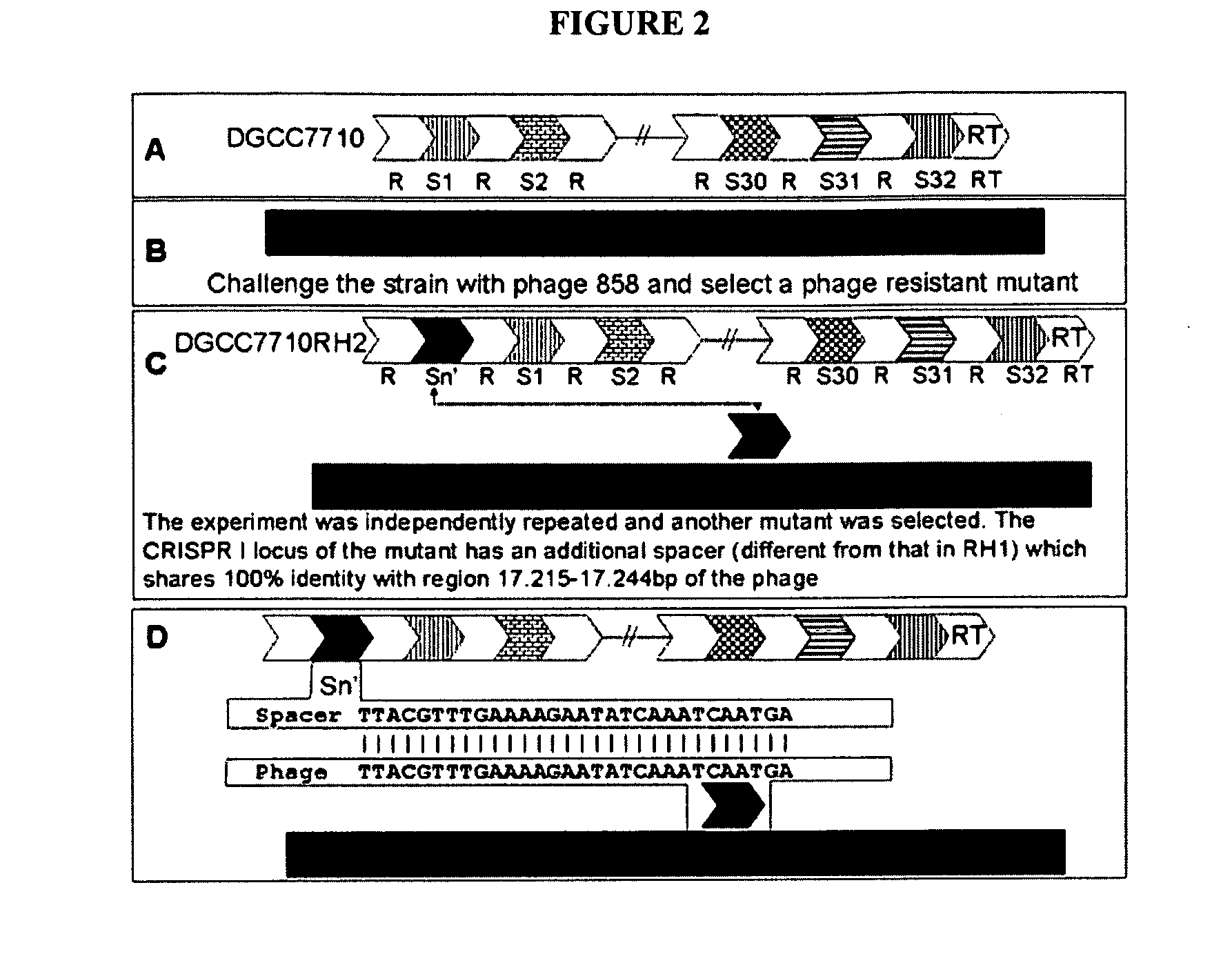
The present invention provides methods and compositions related to modulating the resistance of a cell against a target nucleic acid or a transcription product thereof. In some preferred embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods for the use of one or more cas genes or proteins for modulating the resistance of a cell against a target nucleic acid or a transcription product thereof. In some embodiments, the present invention provides methods and compositions that find use in the development and use of strain combinations and starter culture rotations. In additional embodiments, the present invention provides methods for labelling and / or identifying bacteria. In some preferred embodiments, the present invention provides methods for the use of CRISPR loci to determine the potential virulence of a phage against a cell and the use of CRISPR-cas to modulate the genetic sequence of a phage for increased virulence level. In still further embodiments, the present invention provides means and compositions for the development and use of phages as biocontrol agents.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Method of treating gastrointestinal diseases associated with species of genus clostridium
The invention includes a method of treating gastrointestinal diseases associated with species of genus Clostridium such as clostridium deficit in human patients with gastrointestinal disorders having an etiological component such as a microbial agent producing a toxin where treated with an antimicrobial composition an amount effective to inhibit or eliminate the microbial agent. The antimicrobial composition in a form of probiotic mixture can be administrated alone or in combination with an antimicrobial agent, such as a bacteriophage which is specific for a bacterium producing toxin or antibiotics which are then used to eliminate or inhibit the clostridial species overgrown in a patient's gastrointestinal tract. Disorders that can be treated by the method of the invention include diarrhea or inflammatory bowel diseases such as colitis or Crohn's disease.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Polyclonal antibody composition for treating allergy
InactiveUS6849259B2Efficient removalPotential clinical advantageImmunoglobulins against animals/humansImmunoglobulins against plantsMicrosphereBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
A pharmaceutical composition for treating allergy is described. The composition comprises as an active ingredient a recombinant polyclonal antibody or a mixture of different monoclonal antibodies capable of reacting with or binding to an allergen together with one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. The composition may be used topically as a solution, dispersion, powder, or in the form of microspheres. The polyclonal antibody is preferably a recombinant polyclonal antibody produced by phage display technology. The pairing of specific immunoglobulin variable region light chain and heavy chain maintained from the original polyclonal immune response or selected by panning using the allergen in question is preferably maintained by bulk transfer of the pairs into an expression vector.
Owner:SYMPHOGEN AS
Synthetic antibody phage libraries
The invention provides comprising variant amino acids in CDRs of antibody variable domains. These polypeptides provide a source of great sequence diversity that can be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides. The invention also provides these polypeptides as fusion polypeptides to heterologous polypeptides such as at least a portion of phage or viral coat proteins, tags, and linkers. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Selective posttranslational modification of phage-displayed polypeptides
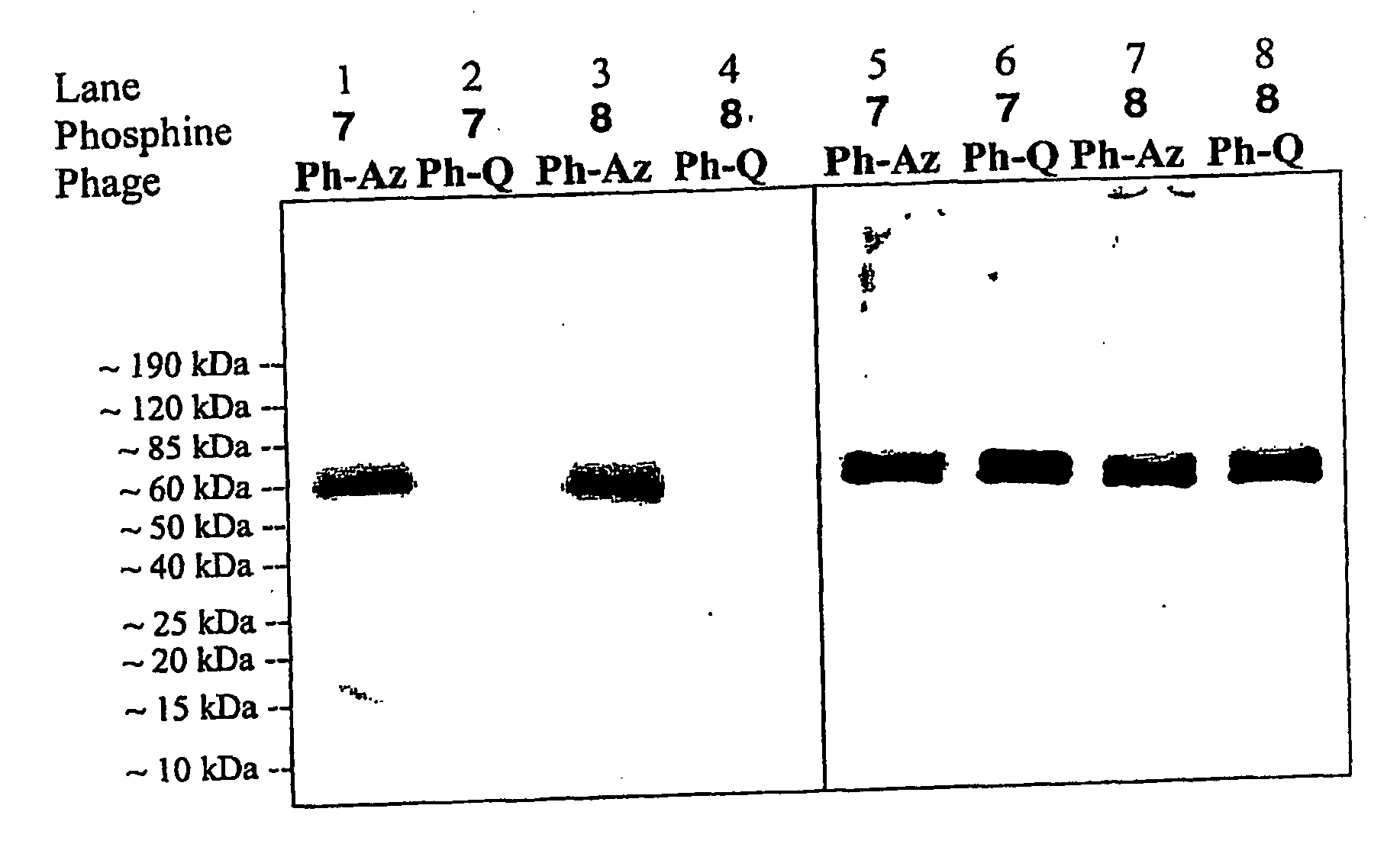
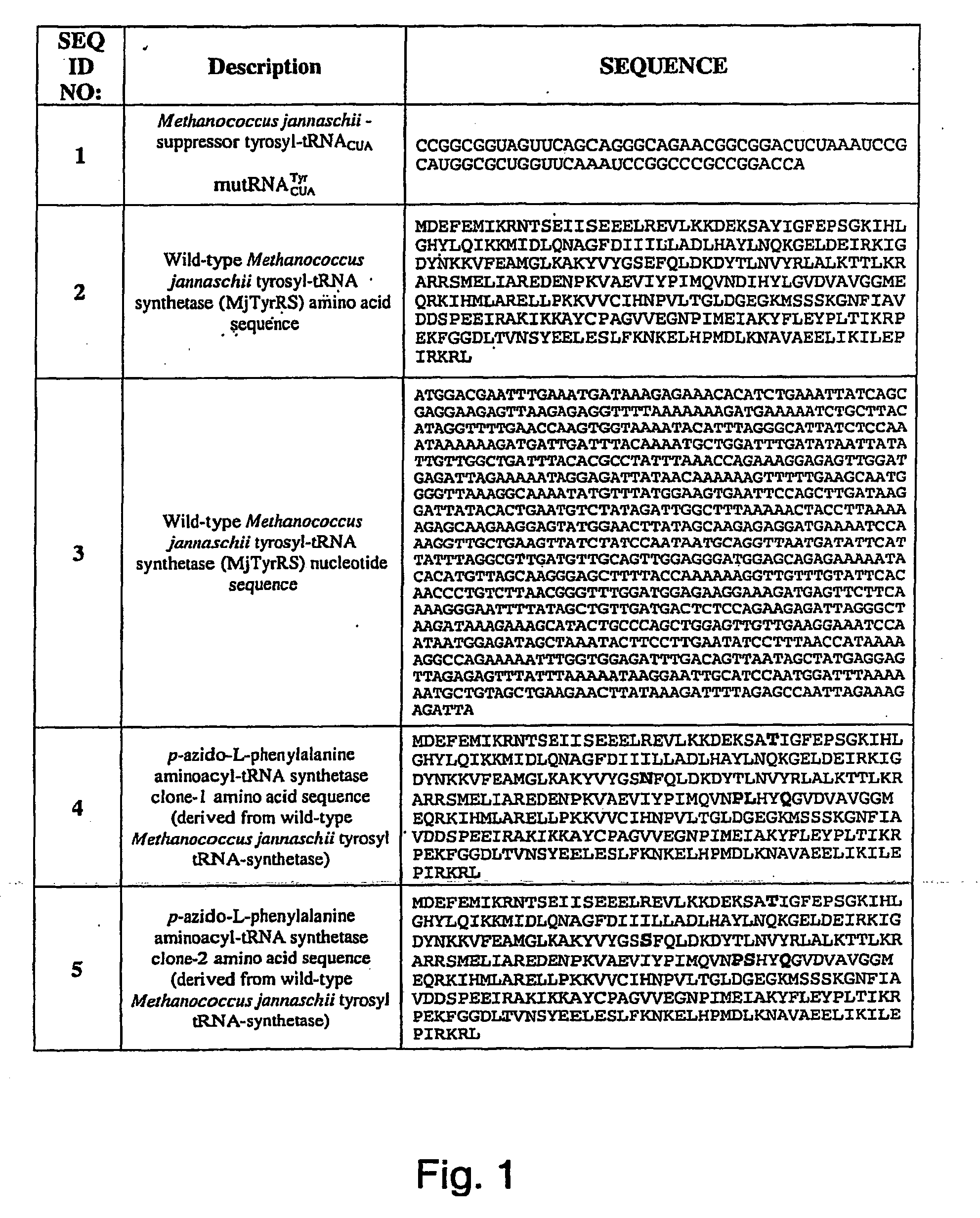
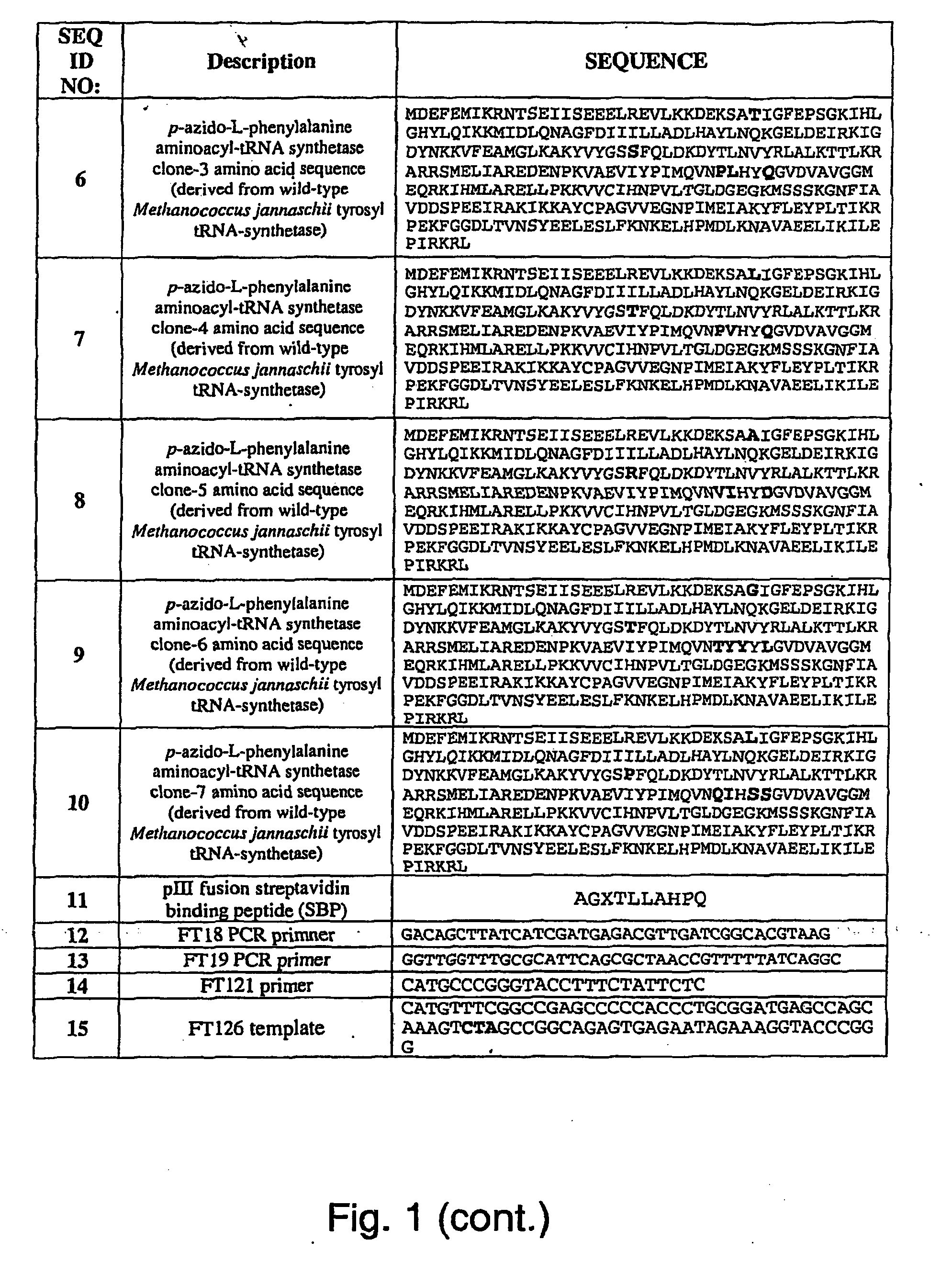
ActiveUS20070178448A1Easy to detectEasy to quantifyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesArylCycloaddition
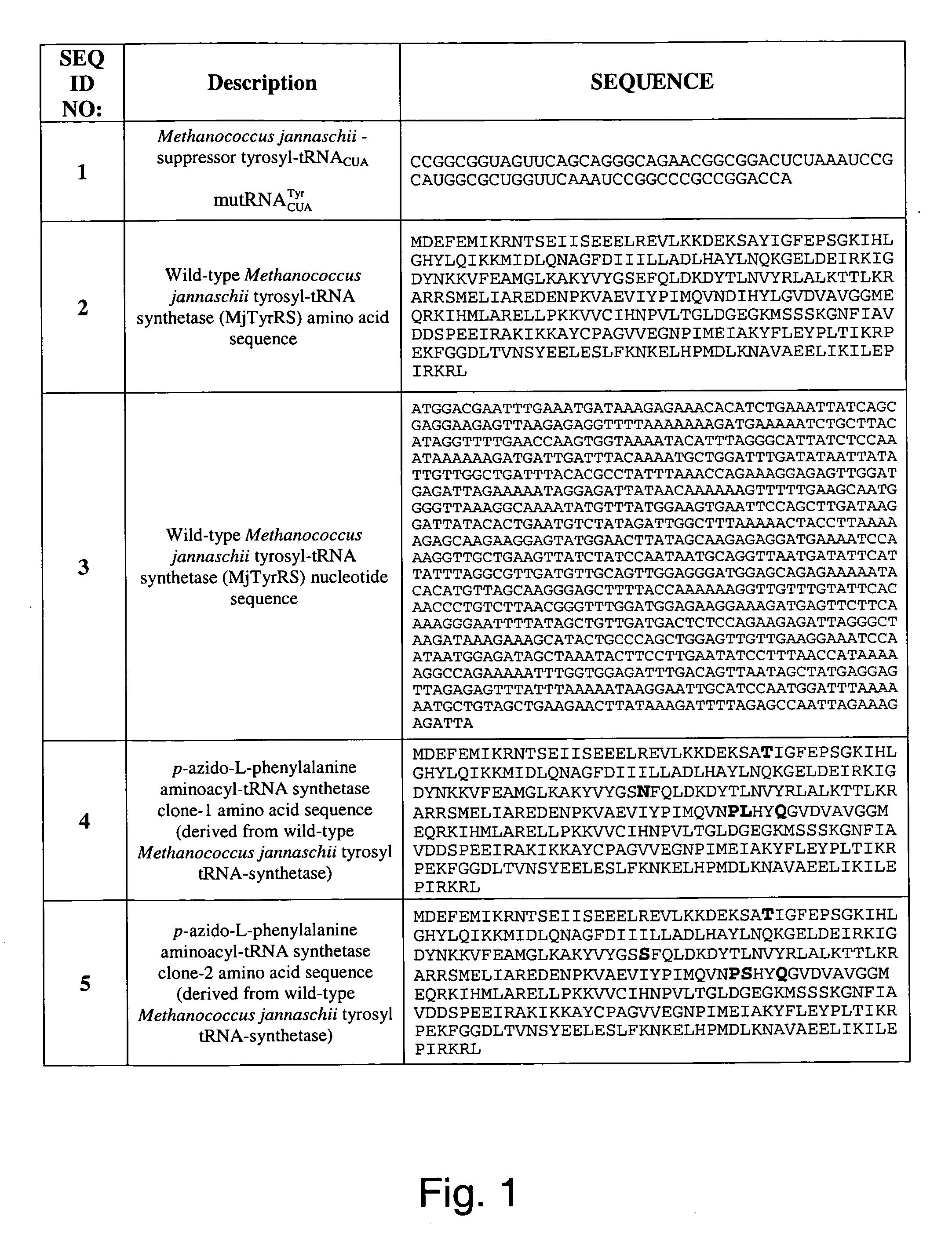
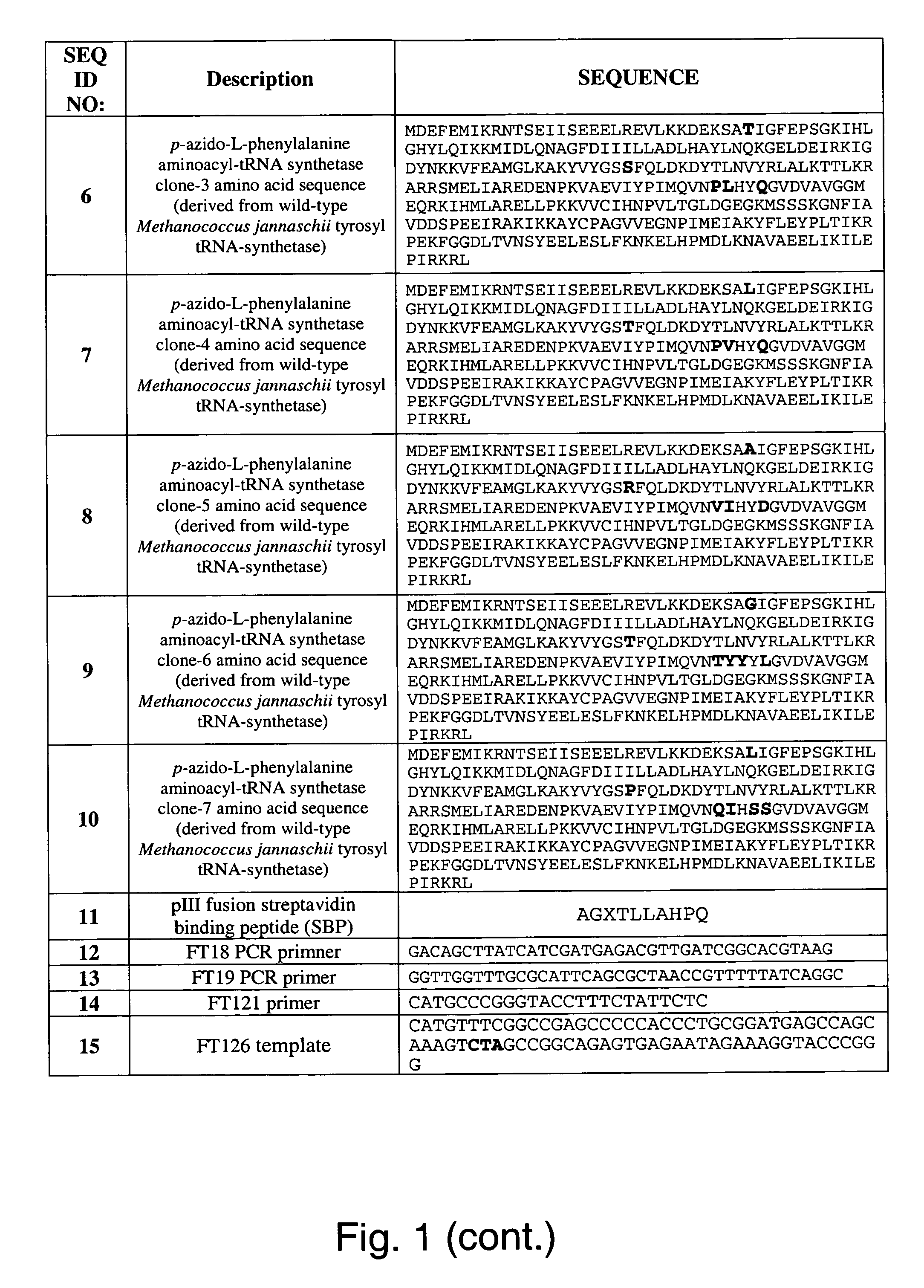
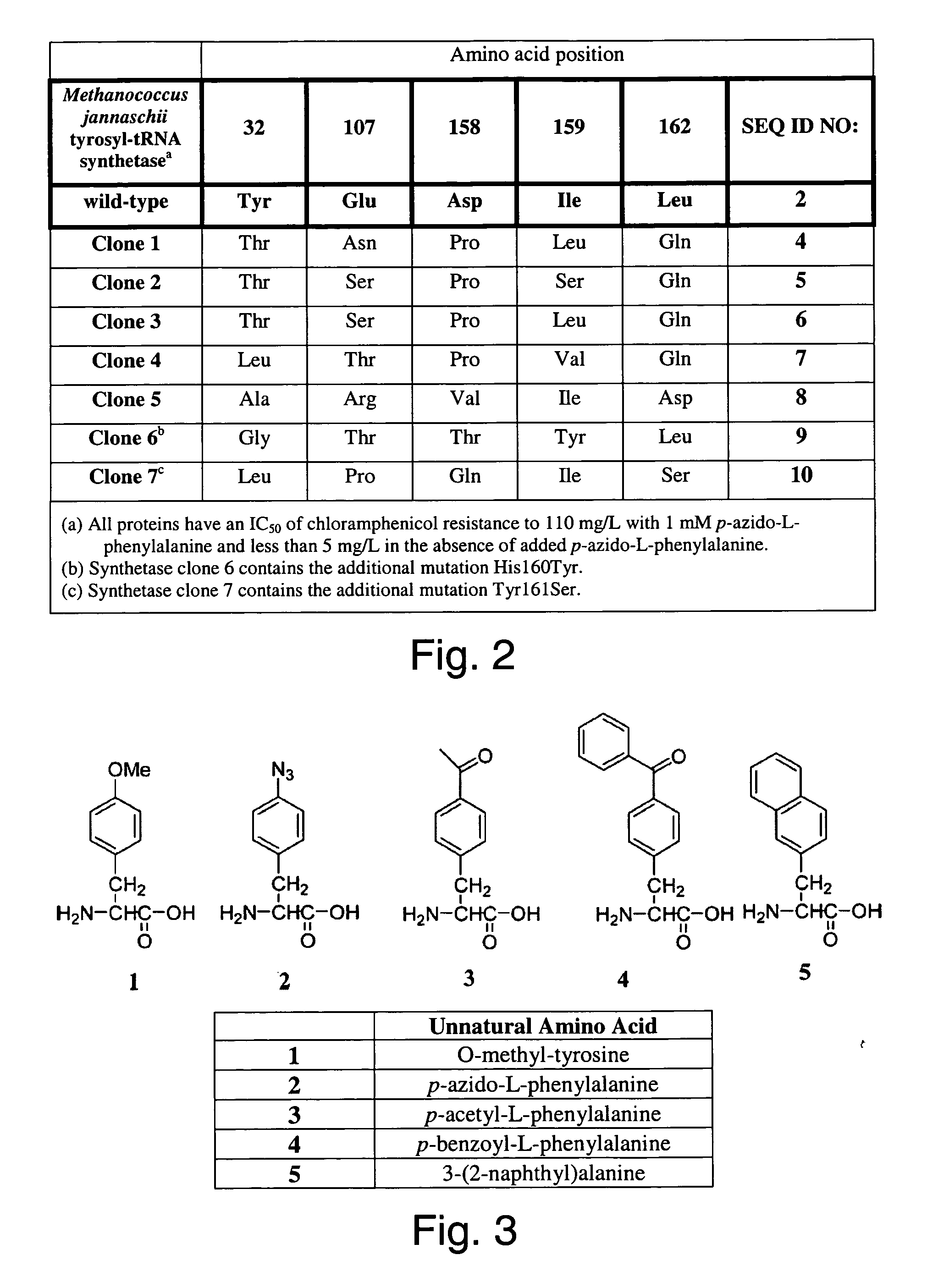
The invention relates to posttranslational modification of phage-displayed polypeptides. These displayed polypeptides comprise at least one unnatural amino acid, e.g., an aryl-azide amino acid such as p-azido-L-phenylalanine, or an alkynyl-amino acid such as para-propargyloxyphenylalanine, which are incorporated into the phage-displayed fusion polypeptide at a selected position by using an in vivo orthogonal translation system comprising a suitable orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and a suitable orthogonal tRNA species. These unnatural amino acids advantageously provide targets for posttranslational modifications such as azide-alkyne [3+2] cycloaddition reactions and Staudinger modifications.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Microbial production of nuclease resistant DNA, RNA, and oligo mixtures
Owner:FRAYNE CONSULTANTS
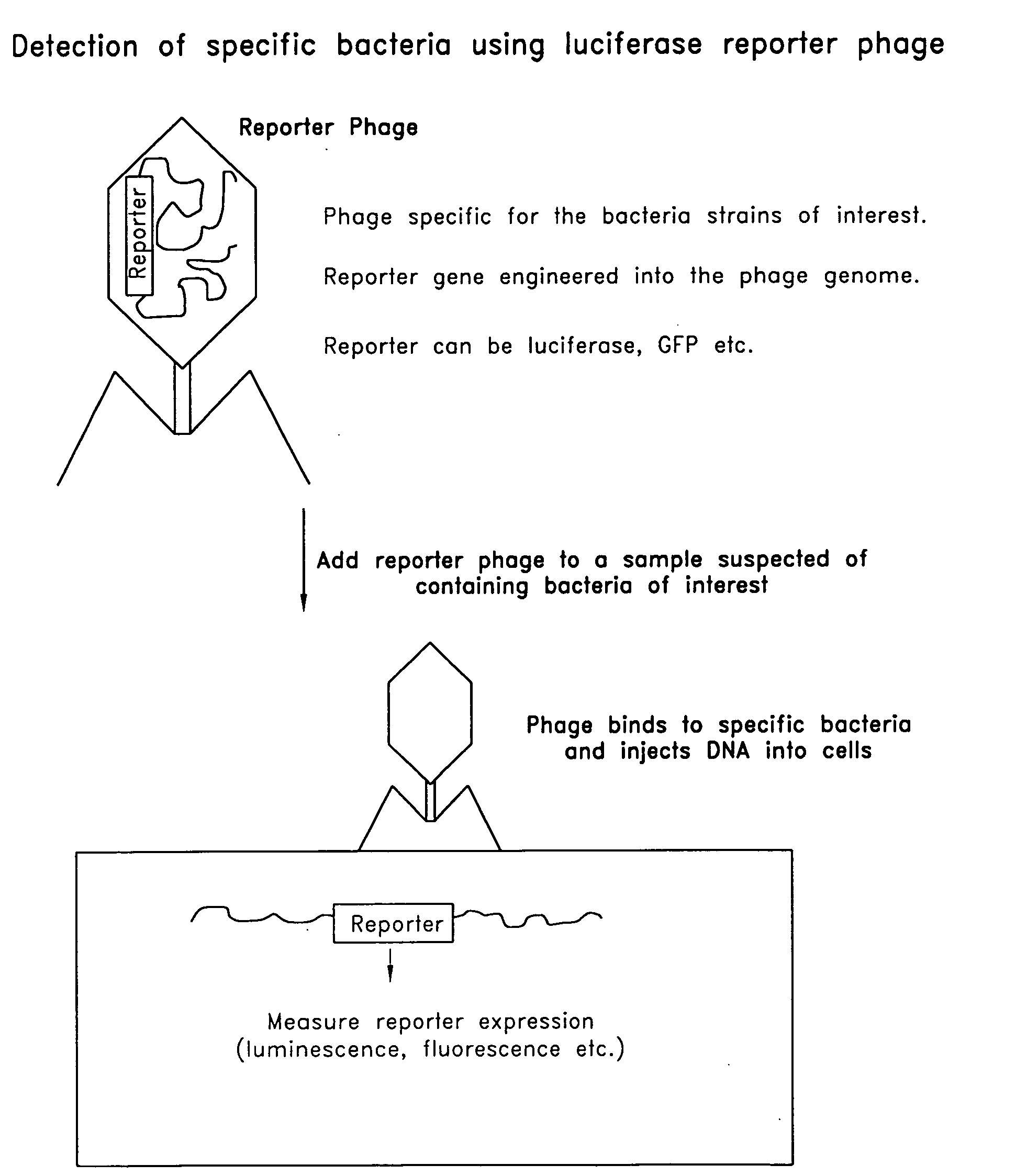
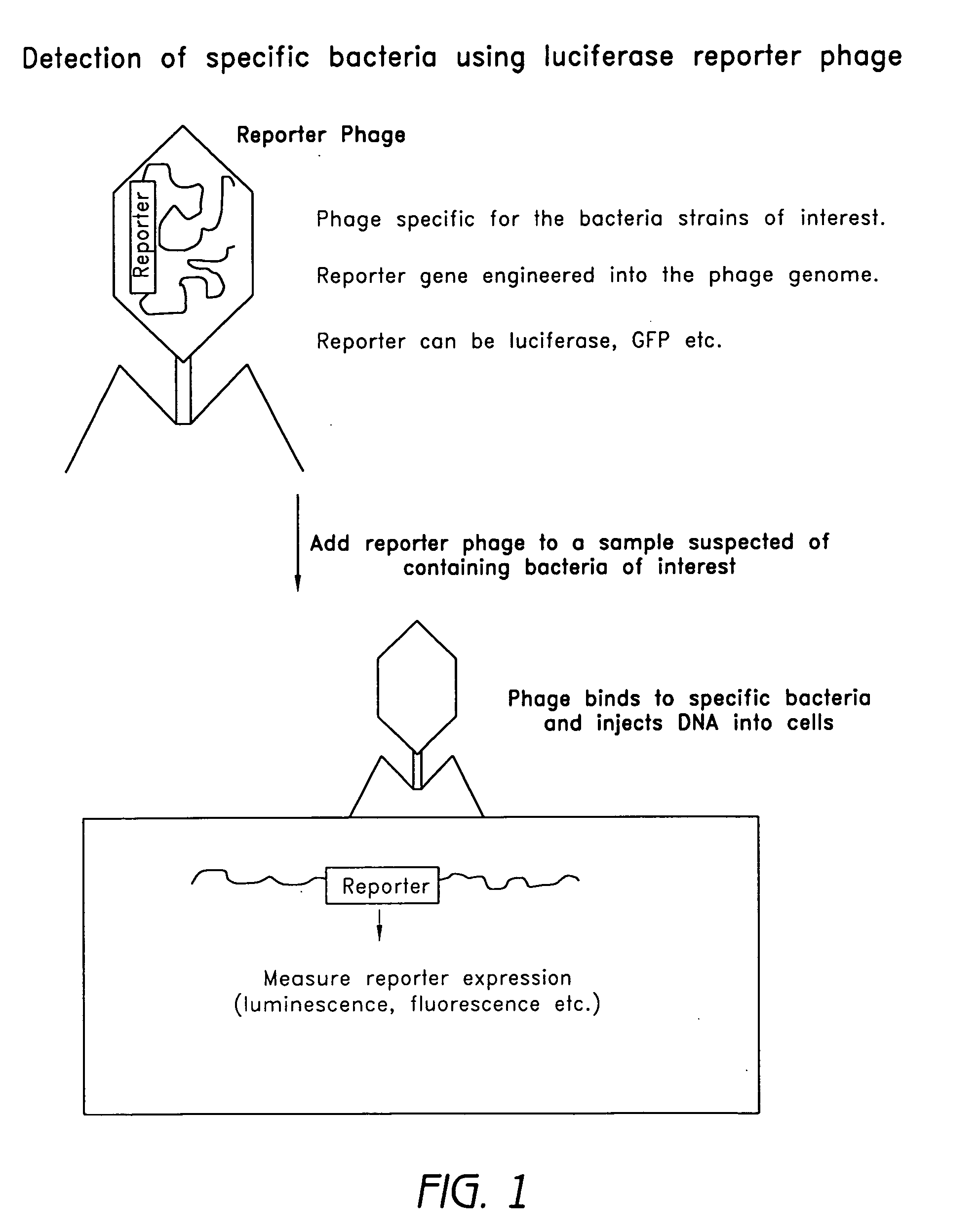
Reporter plasmid phage packaging system for detection of bacteria
InactiveUS20090155768A1Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesBacteroidesOrigin of replication
The invention is related to a transducing particle that comprises a bacteriophage coat and a DNA core that comprises plasmid DNA comprising: a) a host-specific bacteriophage packaging site wherein the packaging site is substantially in isolation from sequences naturally occurring adjacent thereto in the bacteriophage genome, b) a reporter gene, c) a bacteria-specific promoter operably linked to said reporter gene, d) a bacteria-specific origin of replication, and optionally e) an antibiotic resistance gene. The invention includes phage transducing particles, methods of making transducing particles, and methods of using the transducing particles in bacterial detection.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
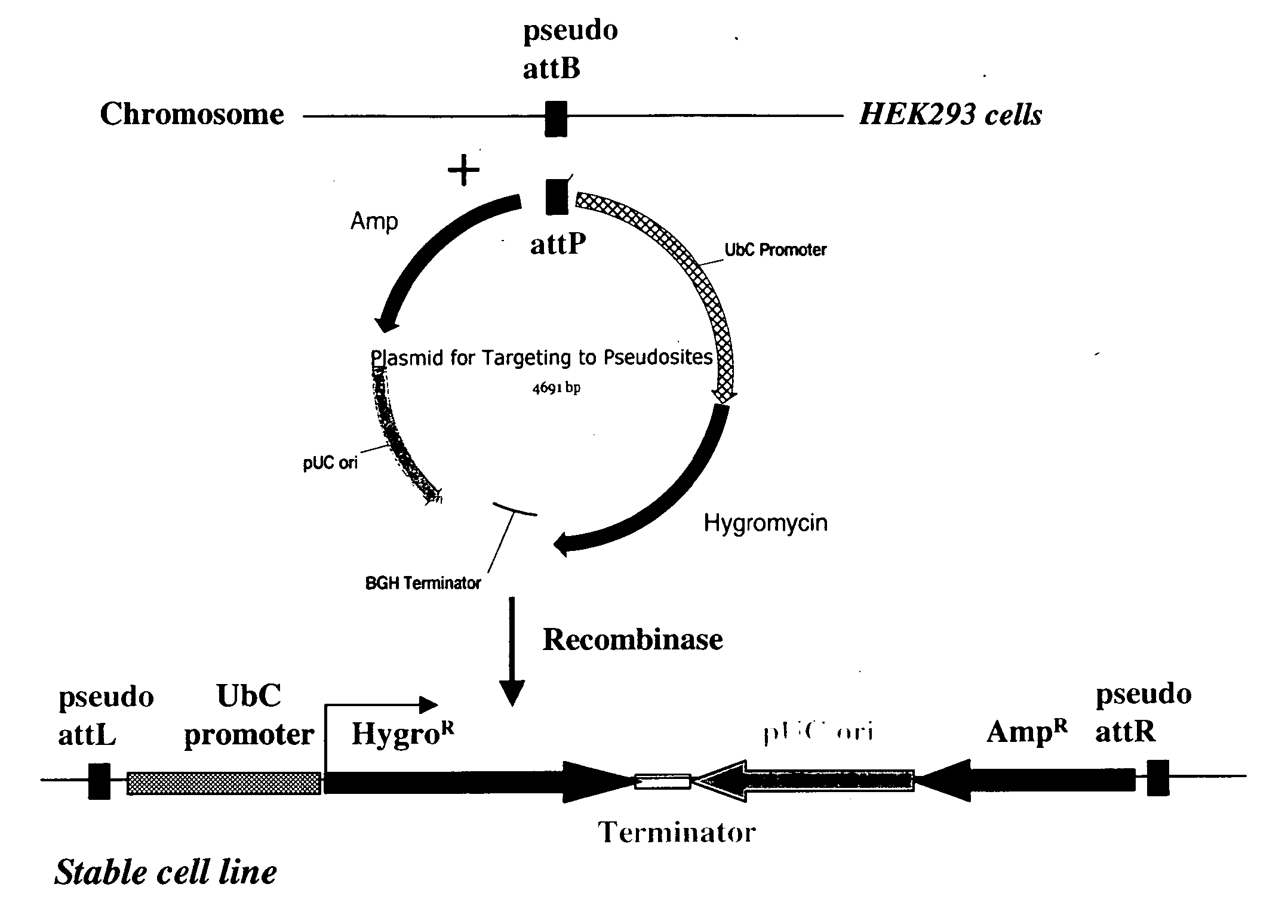
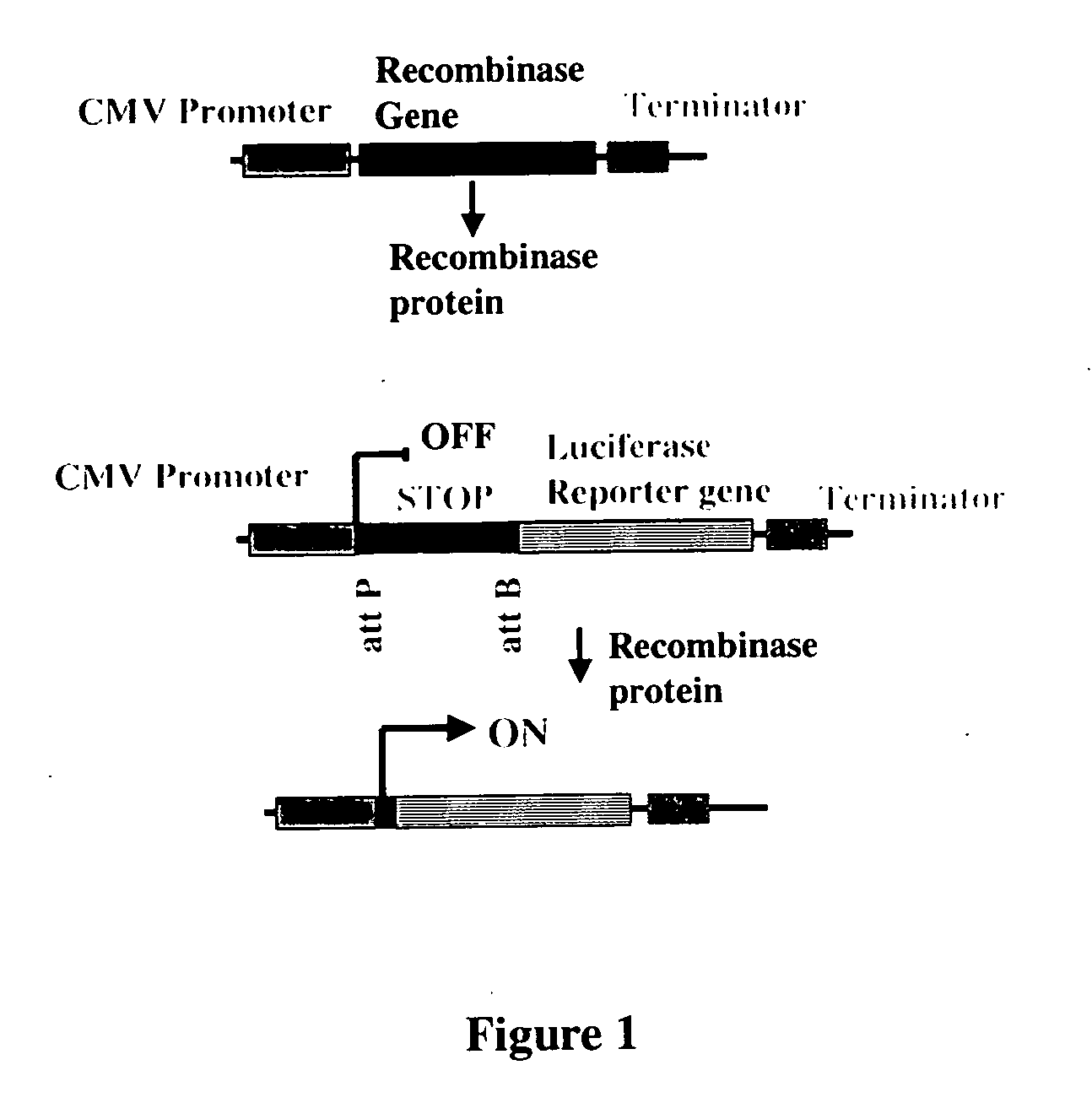
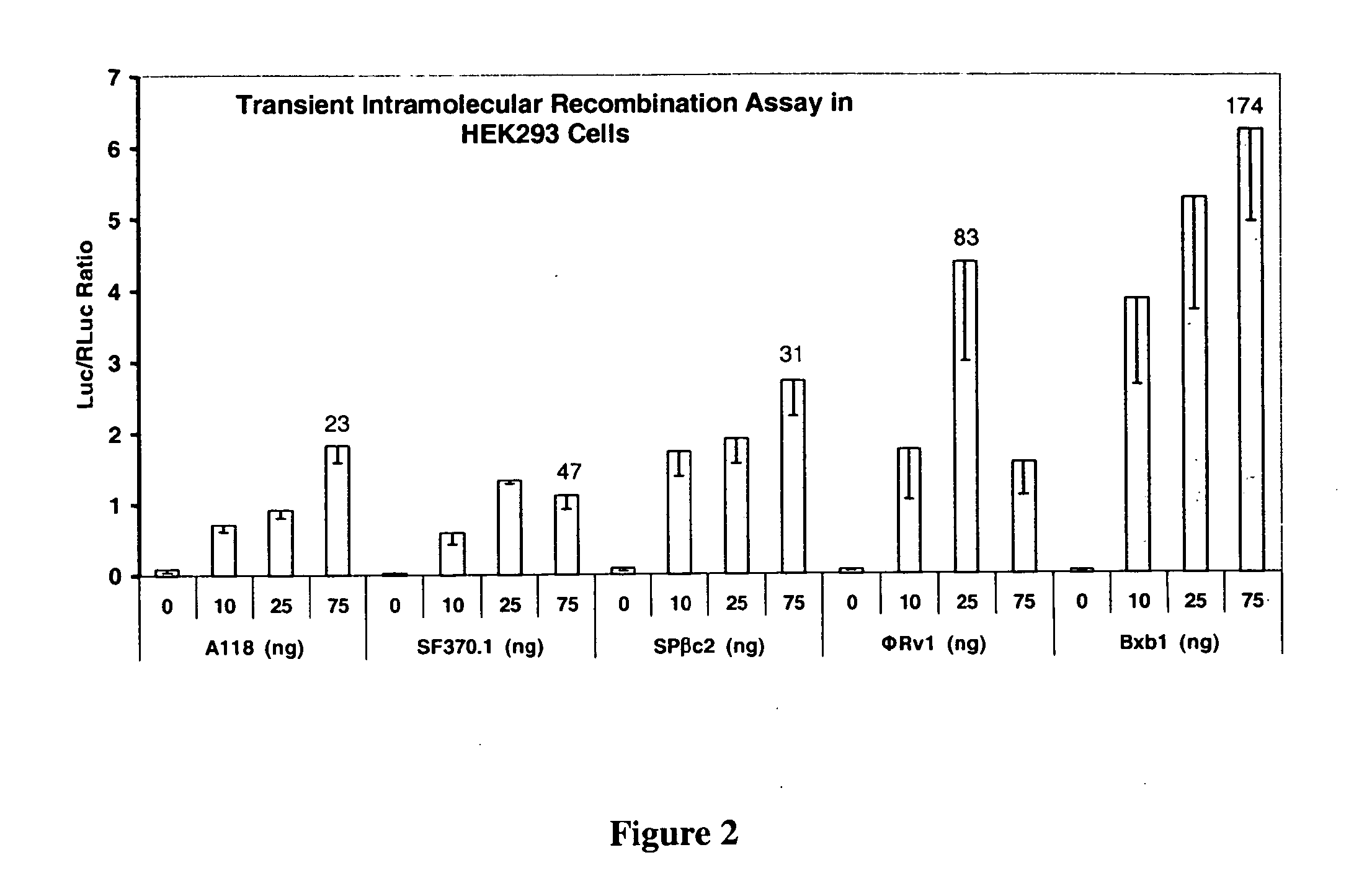
Site-specific serine recombinases and methods of their use
InactiveUS20080020465A1Antibacterial agentsHydrolasesStreptococcus pyogenesSite-specific recombination
The present invention provides a method for obtaining site-specific recombination in a eukaryotic cell, the method comprising providing a eukaryotic cell that comprises a first recombination attachment site and a second recombination attachment site; contacting the first and second recombination attachment sites with a prokaryotic recombinase polypeptide, resulting in recombination between the recombination attachment sites, wherein the recombinase polypeptide can mediate recombination between the first and second recombination attachment sites, the first recombination attachment site is a phage genomic recombination attachment site (attP) or a bacterial genomic recombination attachment site (attB), the second recombination site is attB or attP, and the recombinase is selected from the group consisting of a Listeria monocytogenes phage recombinase, a Streptococcus pyogenes phage recombinase, a Bacillus subtilis phage recombinase, a Mycobacterium tuberculosis phage recombinase and a Mycobacterium smegmatis phage recombinase, provided that when the first recombination attachment site is attB, the second recombination attachment site is attP and when the first recombination attachment site is attP, the second recombination attachment site is attB. The invention also describes compositions, vectors, and methods of use thereof, for the generation of transgenic cells, tissues, plants, and animals. The compositions, vectors and methods of the present invention are also useful in gene therapy applications.
Owner:PADIDAM MALLA
A33 antigen specific immunoglobulin products and uses thereof
InactiveUS6342587B1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsImmunglobulin eBacteriophage
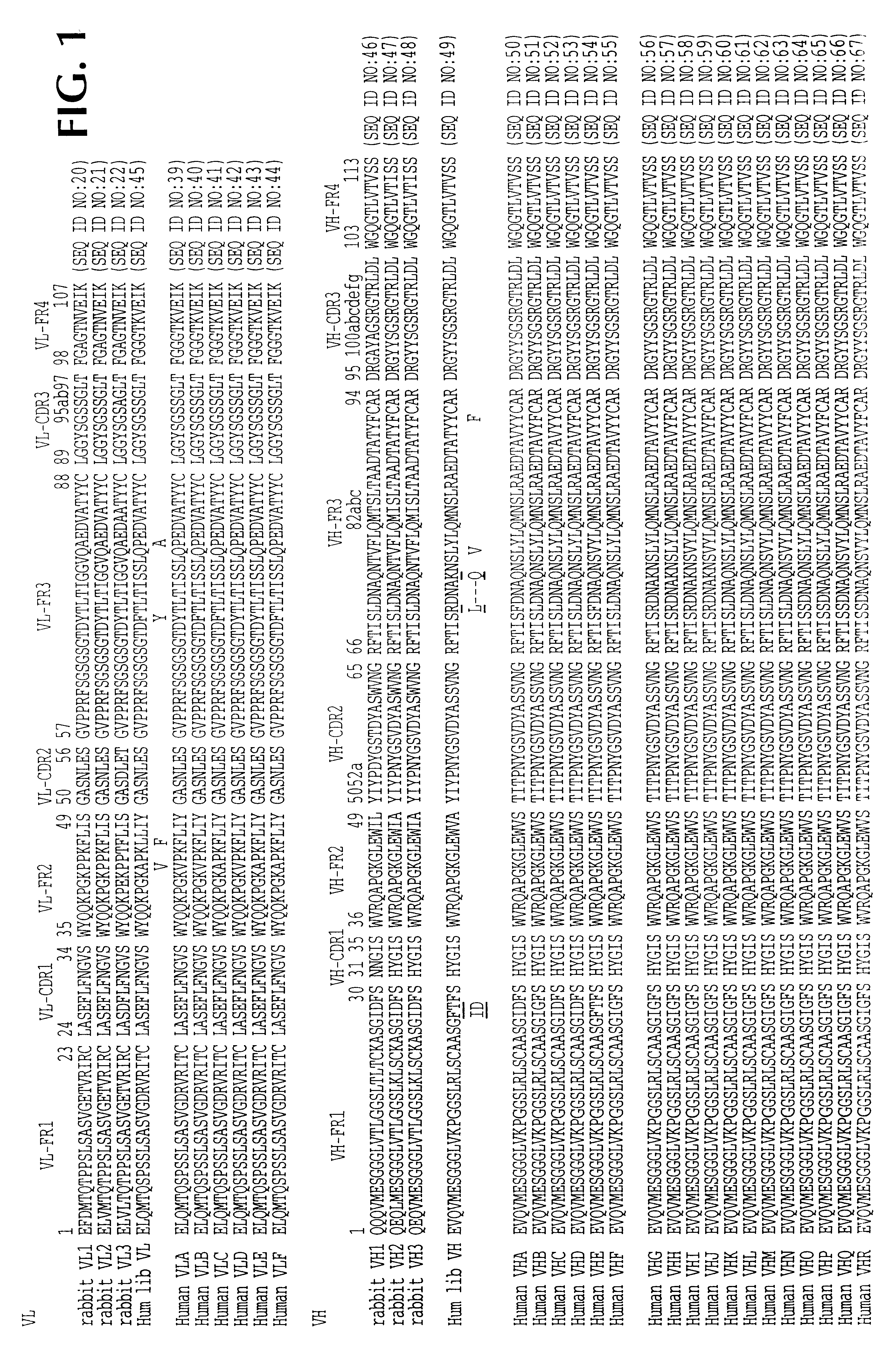
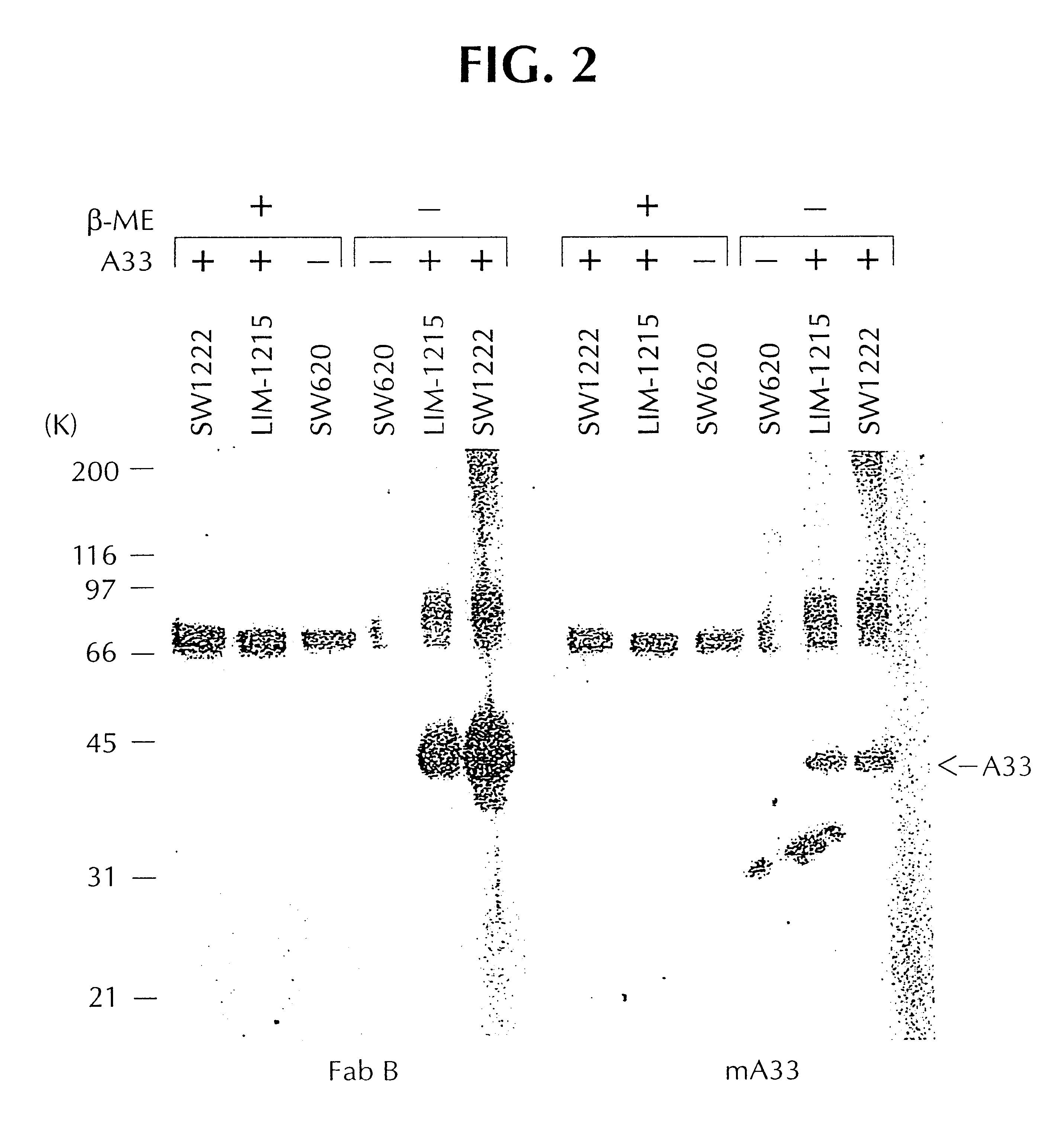
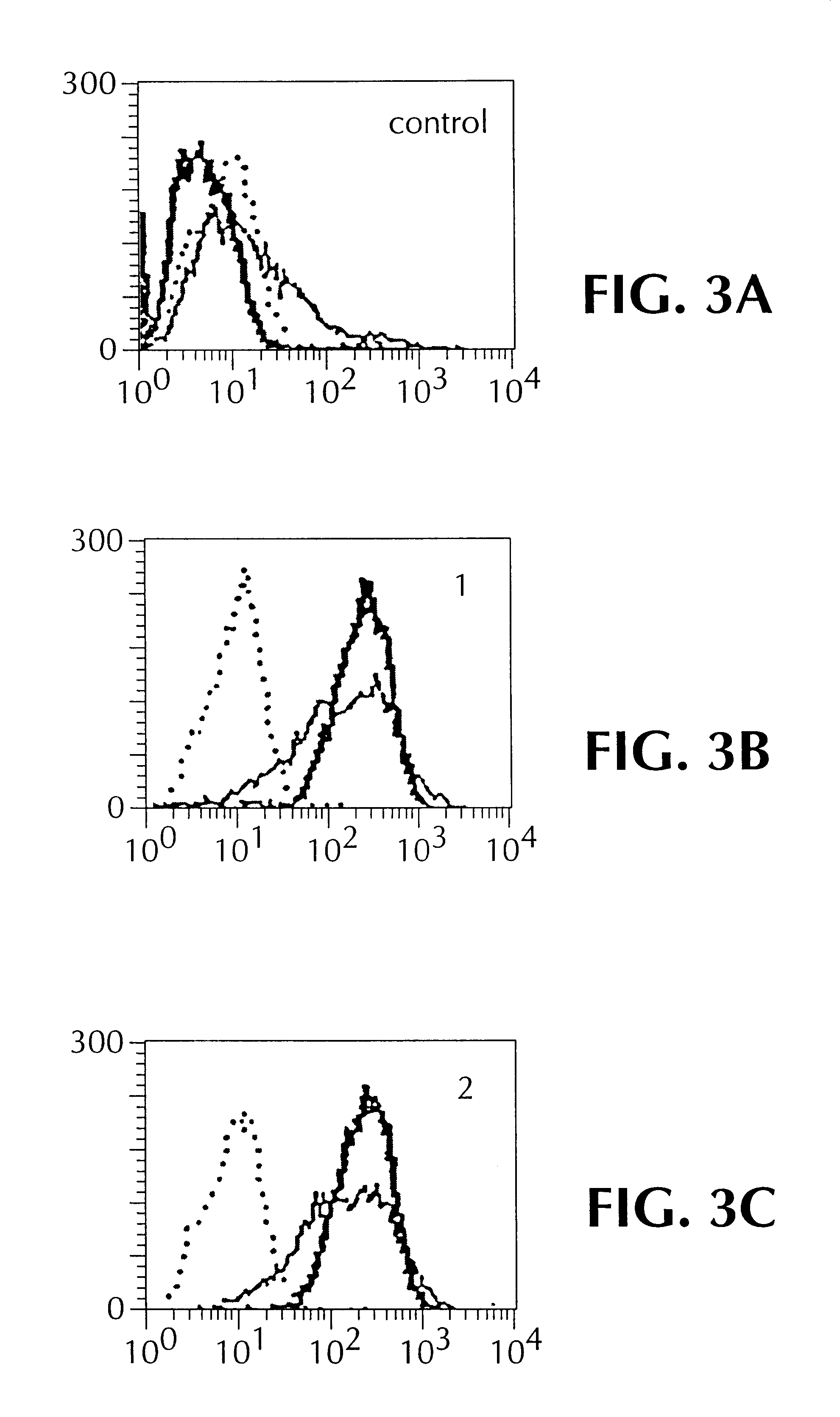
The invention is directed to novel CDRs and immunoglobulin products that bind to A33 antigens and methods for their use. The invention also involves a method for making humanized antibodies, using a rabbit as a host animal, and phage display library methodologies, and the antibodies themselves. The methodology is useful, for example, in generating humanized antibodies against molecules associated with cancer, such as A33, which is associated with colon cancer.
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES +2
Reagents and methods for diagnosing, imaging and treating atherosclerotic disease
The invention provides a novel human Mab Fab, cloned by phage display, and its use in diagnostic and therapeutic methods. In particular the invention provides a method for analyzing the OxLDL components of atherosclerotic plaques in vivo and a means to determine their relative pathology. As the method is based on a human Fab rather than a mouse Mab, the progress or regression of the disease may be monitored over time. The antibody may also be used for the analysis of surgical or serum samples ex vivo for the presence of OxLDL. The antibody may also be used to target therapeutic agents to the site of atherosclerotic plaques or may have use as a therapeutic agent itself.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Production of recombinant AAV virions
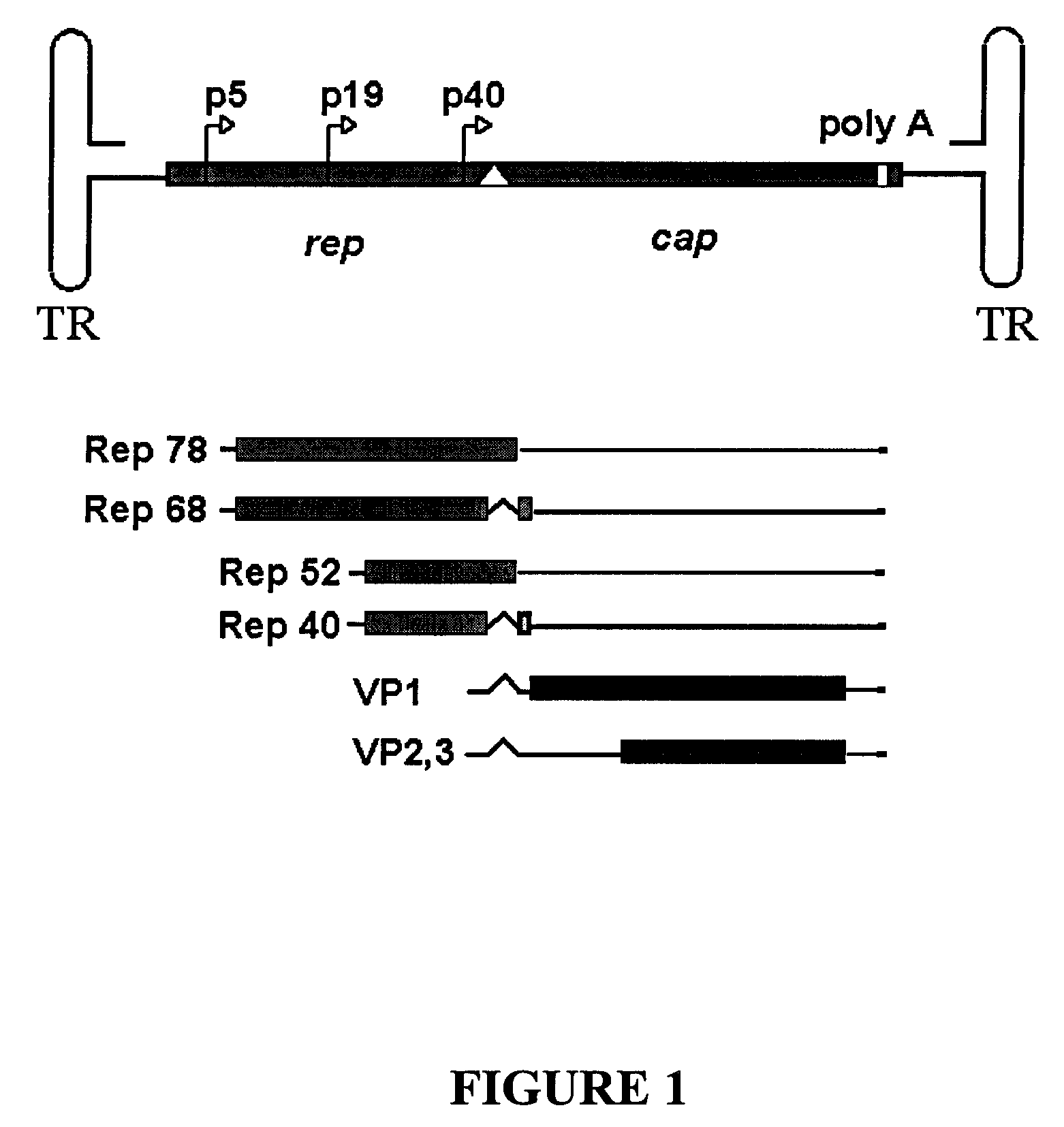
ActiveUS7927585B2Simple working processCost effective productionBiocideSugar derivativesYeastVirosome
Stocks of infectious rAAV are generated using yeast strains, bacterial strains, and bacteriophages engineered to express the required AAV proteins and harboring rAAV vector sequences. Stocks of rAAV virions of all serotypes and pseudotypes can be generated in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells using the methods described herein.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Selective Posttranslational Modification of Phage-Displayed Polypeptides
ActiveUS20090137424A1High selectivityPreserves viral infectivityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicrobiological testing/measurementArylCycloaddition
The invention relates to posttranslational modification of phage-displayed polypeptides. These displayed polypeptides comprise at least one unnatural amino acid, e.g., an aryl-azide amino acid such asp-azido-L-phenylalanine, or an alkynyl-amino acid such as para-propargyloxyphenylalanine, which are incorporated into the phage-displayed fusion polypeptide at a selected position by using an in vivo orthogonal translation system comprising a suitable orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and a suitable orthogonal tRNA species. These unnatural amino acids advantageously provide targets for posttranslational modifications such as azide-alkyne [3+2]cycloaddition reactions and Staudinger modifications.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Anti-VEGF antibodies
ActiveUS7758859B2Senses disorderImmunoglobulins against growth factorsAnti vegf antibodyBacteriophage
Anti-VEGF antibodies and variants thereof, including those having high affinity for binding to VEGF, are disclosed. Also provided are methods of using phage display technology with naïve libraries to generate and select the anti-VEGF antibodies with desired binding and other biological activities. Further contemplated are uses of the antibodies in research, diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
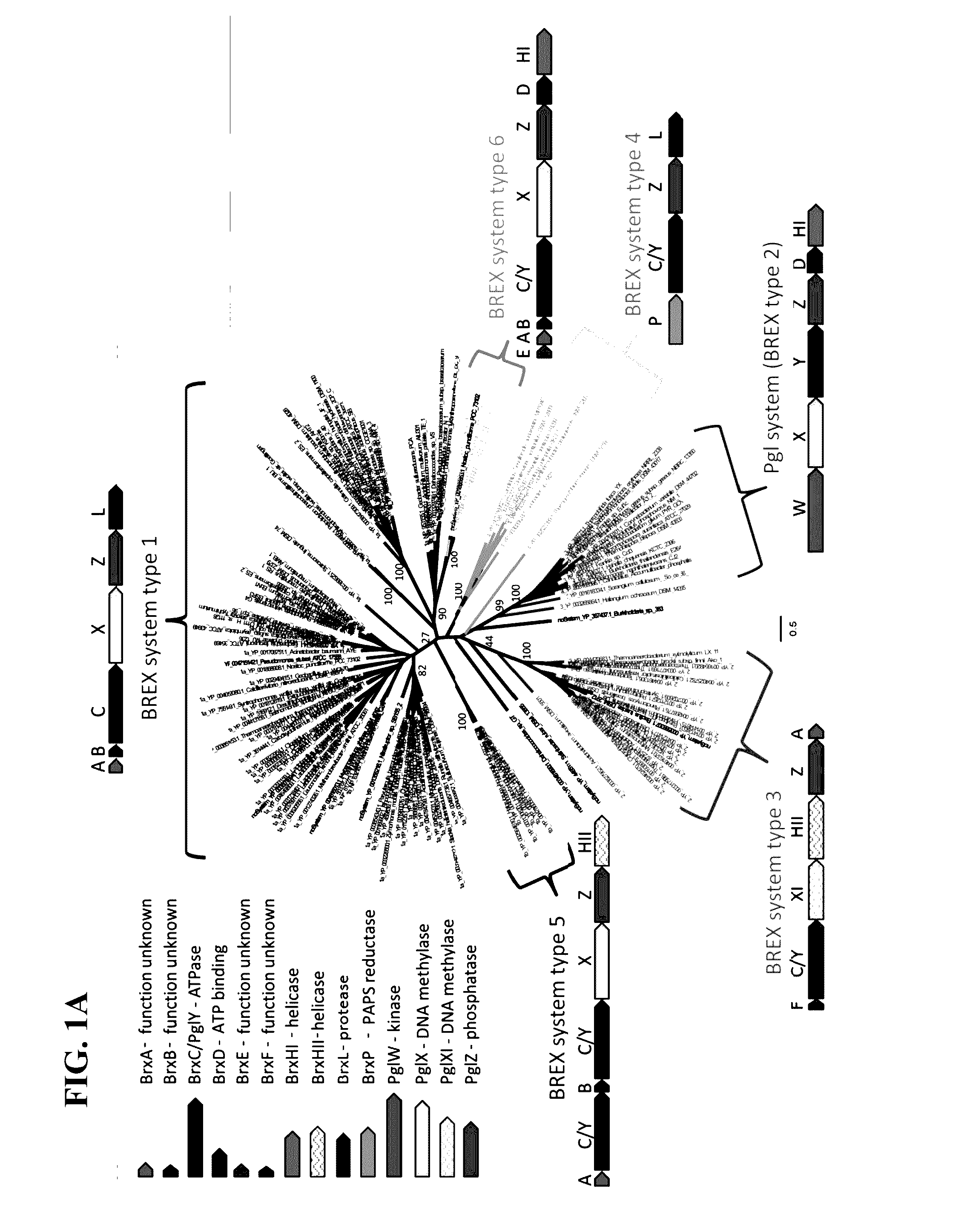
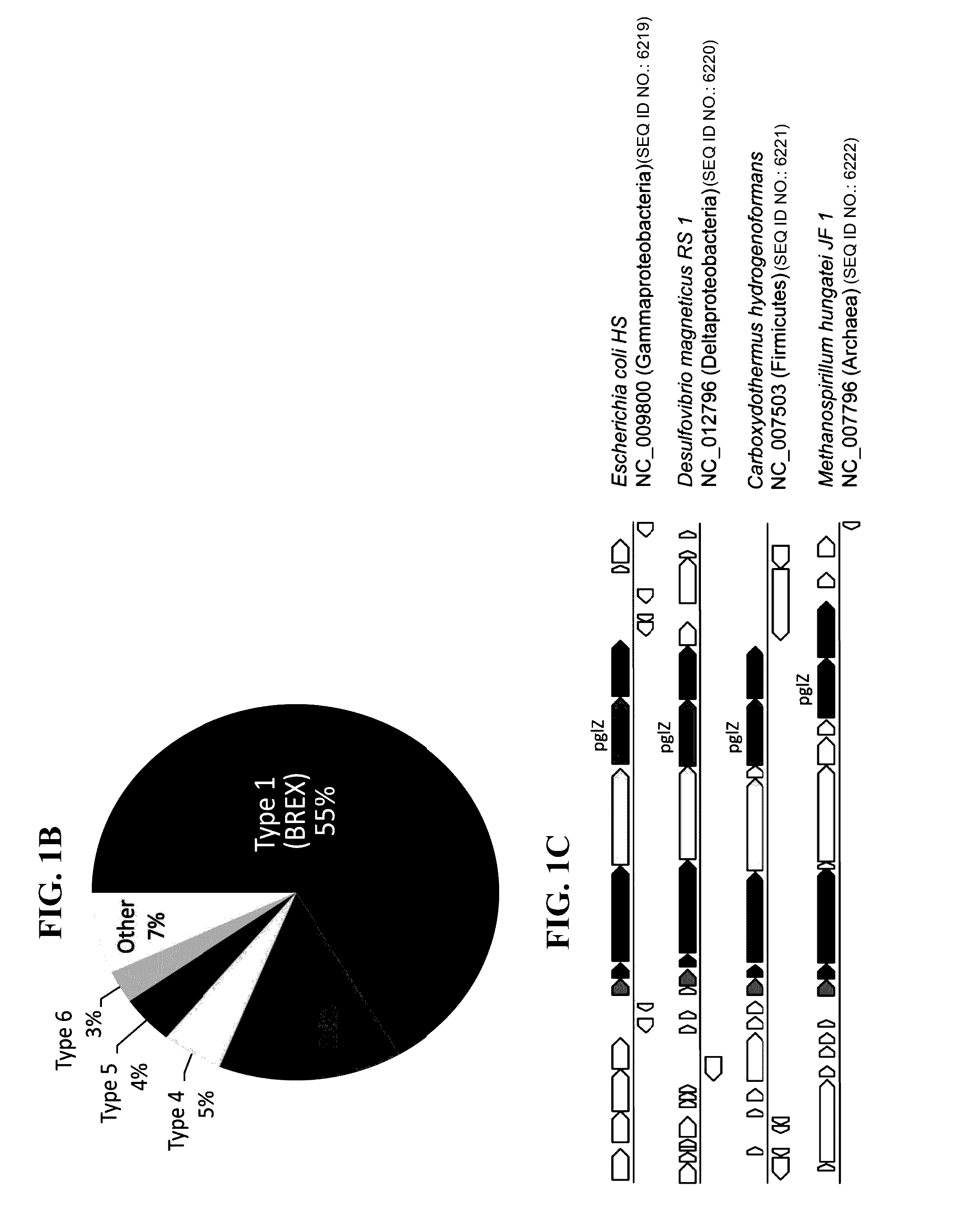
Polynucleotides encoding brex system polypeptides and methods of using same
Isolated polynucleotides encoding a BREX system are provided. Accordingly there is provided an isolated polynucleotide encoding a BREX system comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding the BREX system comprising brxC / pglY, pglZ and at least one of pglX, pglXI, brxP, brxHI, brxHII, brxL, brxD, brxA, brxB, brxF, and brxE, with the proviso that said BREX system does not comprise pglW, and wherein said BREX system confers phage resistance to a bacteria recombinantly expressing same; Also provided is an isolated polynucleotide encoding a BREX system comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding the BREX system comprising brxC / pglY, pglZ, pglX, pglW and at least one of brxD and brxHI, and wherein said BREX system confers phage resistance to a bacteria recombinantly expressing same. Also provided are compositions and methods for conferring phage resistance to bacteria or for conferring bacterial susceptibility to phages.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
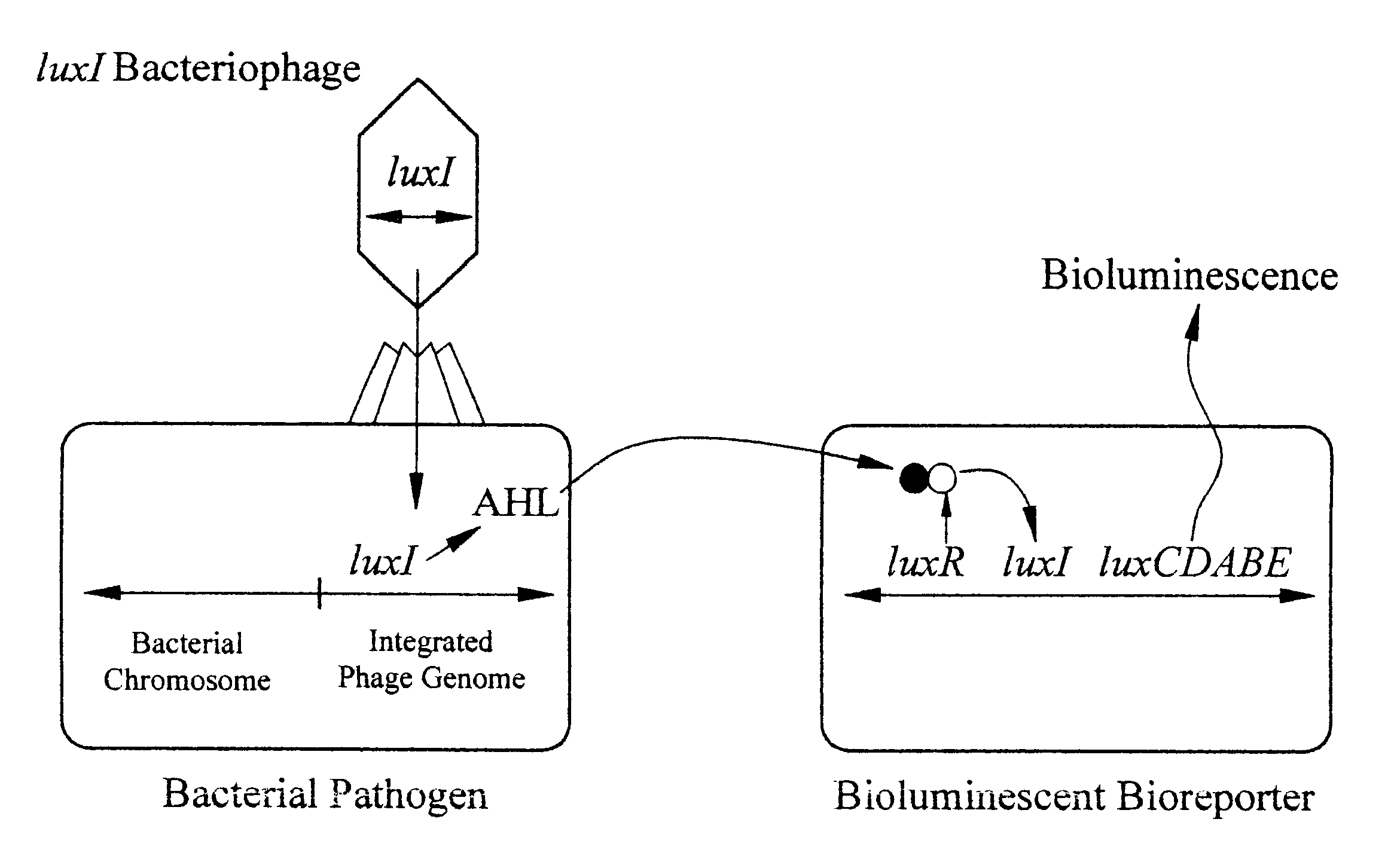
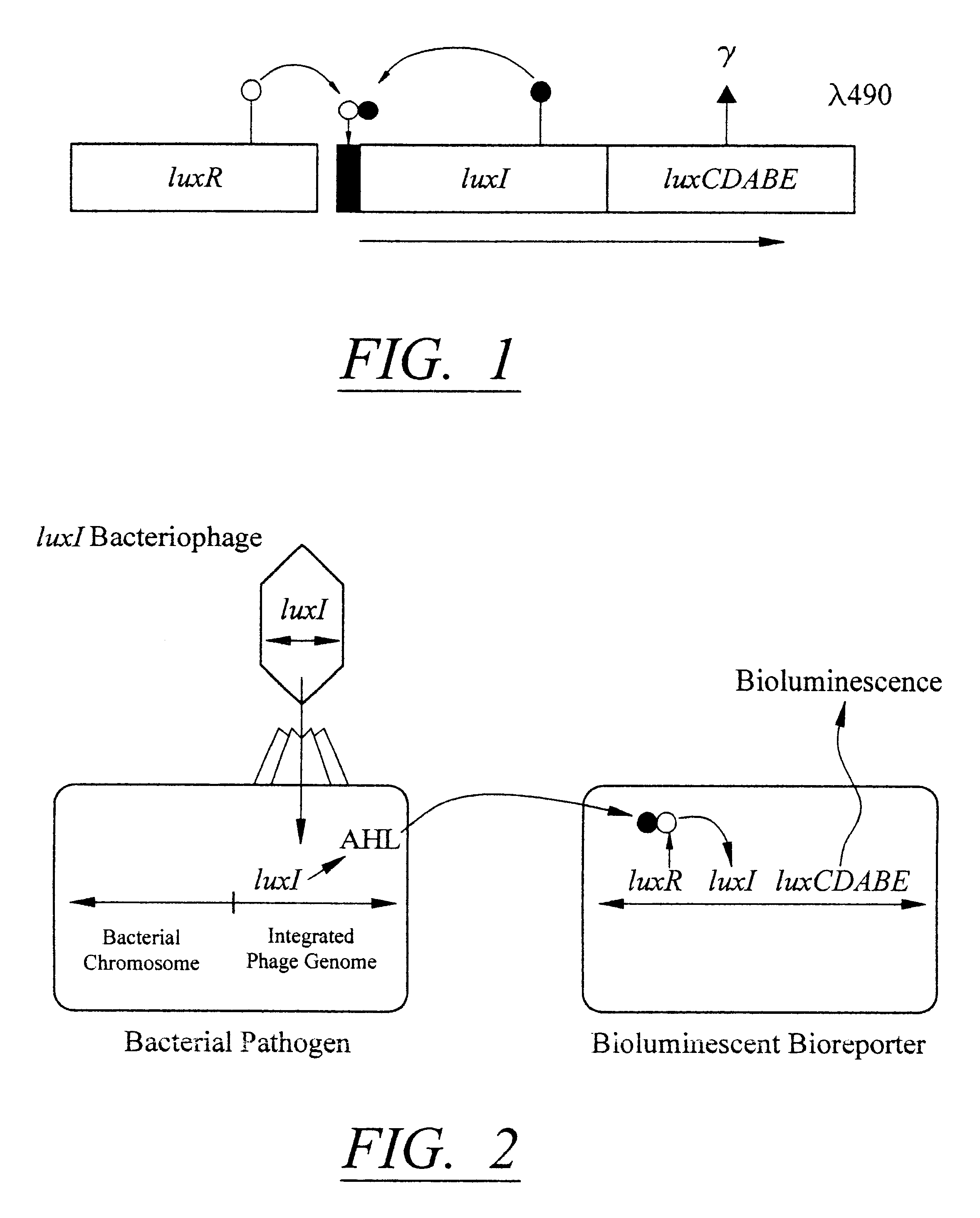
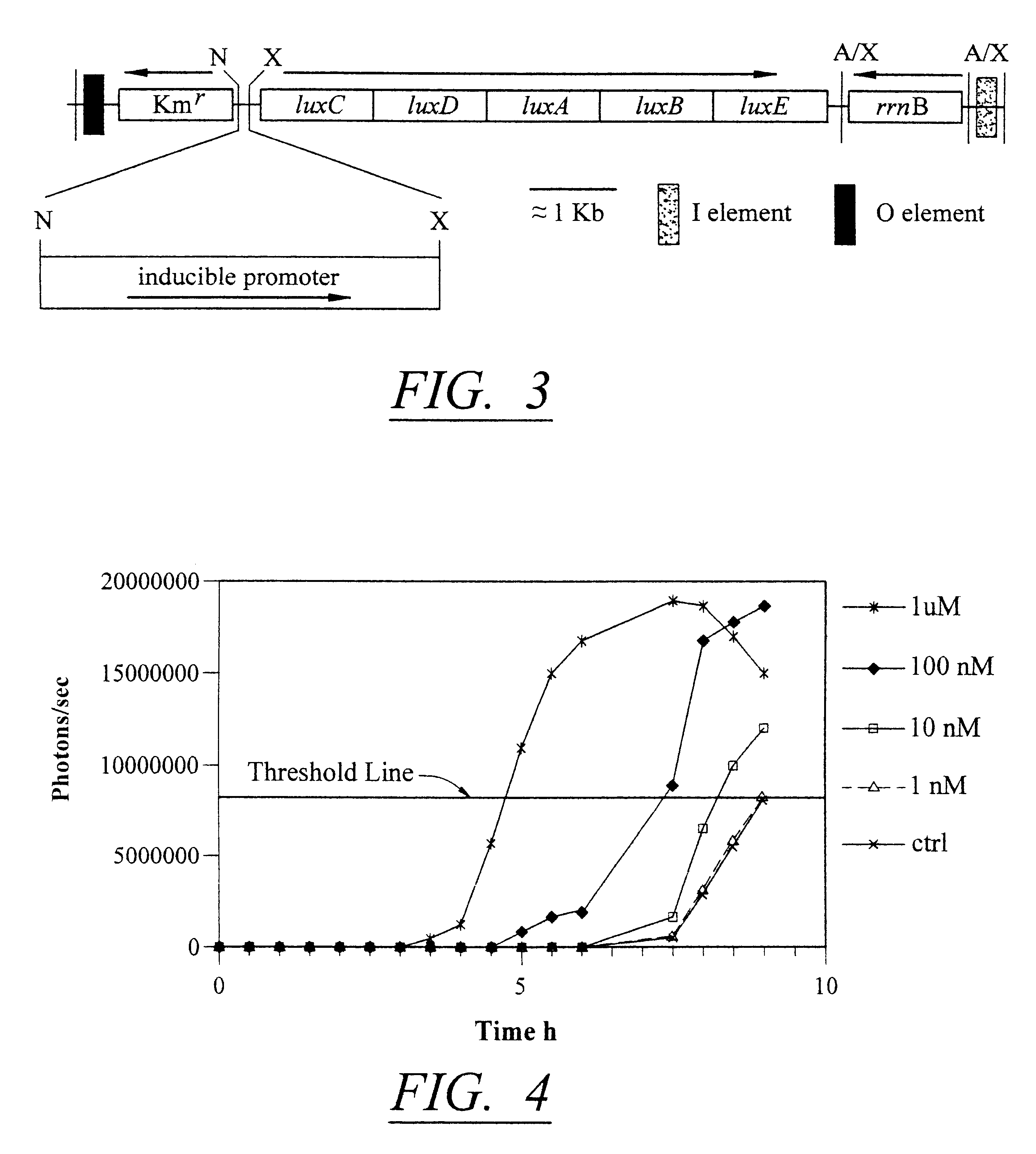
Bioluminescent biosensor device
InactiveUS6544729B2Less stressRapid and sensitive detectionAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSugar derivativesBacteroidesBacterial strain
Disclosed are methods and devices for detection of bacteria based on recognition and infection of one or more selected strains of bacteria with bacteriophage genetically modified to cause production of an inducer molecule in the bacterium following phage infection. The inducer molecule is released from the infected bacterium and is detected by genetically modified bacterial bioreporter cells designed to emit bioluminescence upon stimulation by the inducer. Autoamplification of the bioluminescent signal permits detection of low levels of bacteria without sample enrichment. Also disclosed are methods of detection for select bacteria, and kits for detection of select bacteria based on the described technology.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TENNESSEE +1
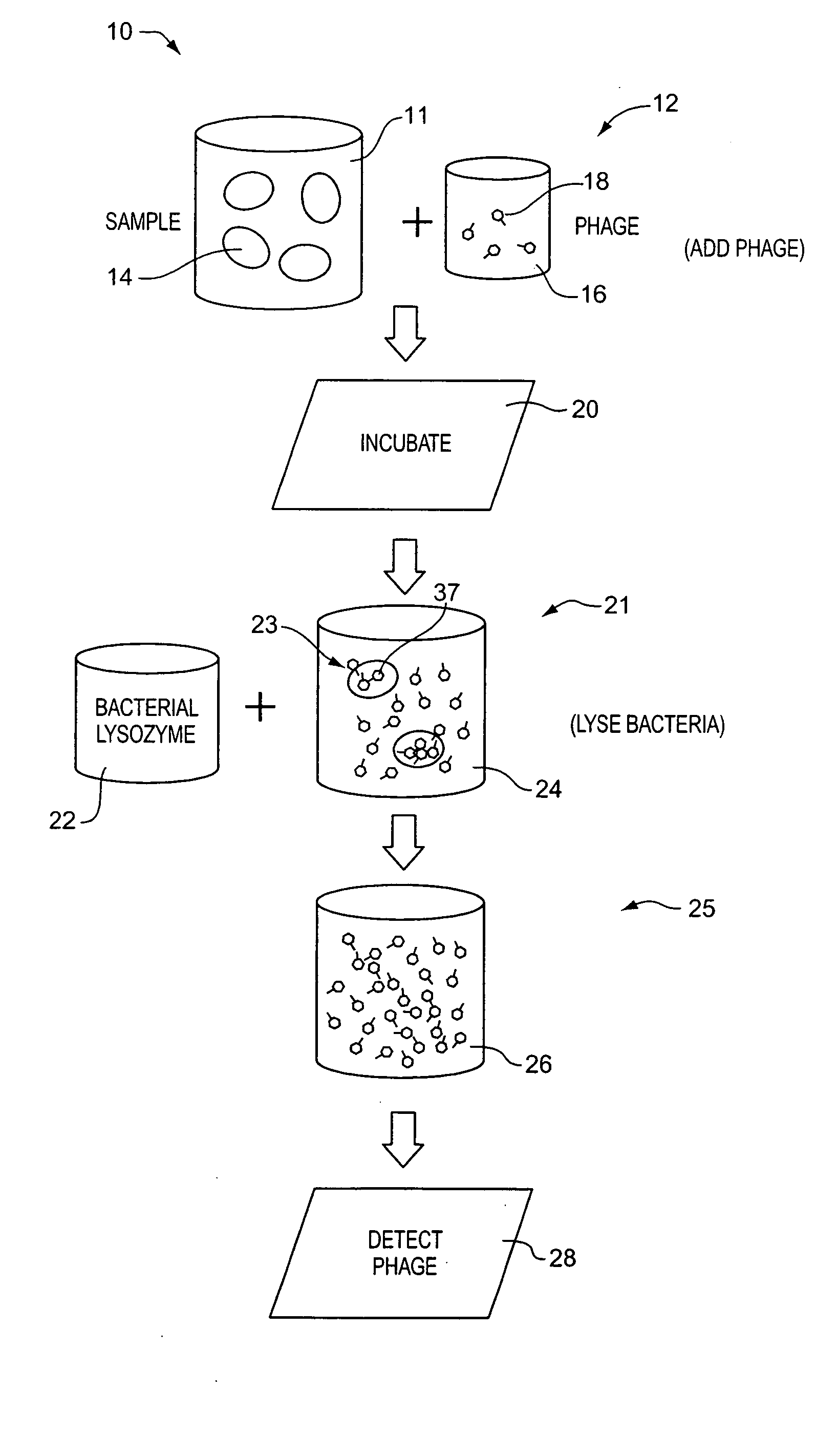
Apparatus and method for detecting microscopic living organisms using bacteriophage
InactiveUS20050003346A1Wide concentration rangeFast resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisBacteroidesAntibiotic resistance
A method for detecting one or more target bacteria in a raw sample where: 1) bacteriophage(s) specific to each target bacterium are added to the raw sample, 2) the test sample is incubated, and 3) the test sample is tested for the presence of each phage in sufficient numbers to indicate the presence of the associated target bacteria in the raw sample. In one embodiment, each phage is initially added to the raw sample in concentrations below the detection limit of the final phage detection process. In another embodiment, the parent phages are tagged in such a way that they can be separated from the progeny phage prior to the detection process. Preferred phage detection processes are immunoassay methods utilizing antibodies that bind specifically to each phage. Antibodies can be used that bind to the protein capsid of the phage. Alternatively, the phage can by dissociated after the incubation process and the sample tested for the presence of individual capsid proteins or phage nucleic acids. The invention can be used to test target bacteria for antibiotic resistance.
Owner:MICROPHAGE +1
Compositions and methods for delivery of an agent using attenuated Salmonella containing phage
The present application generally discloses delivery of an agent which can be therapeutic or prophylactic and, more particularly, the preparation and use of attenuated bacteria, such as Salmonella, containing a bacteriophage in which the genome of the bacteriophage has been modified to encode for a gene product of interest, e.g., an antigen or an anti-tumor protein. The bacteria functions as a vector for delivering the bacteriophage encoded gene product of interest to an appropriate site of action, e.g., the site of a solid tumor.
Owner:NANOTHERAPEUTICS INC
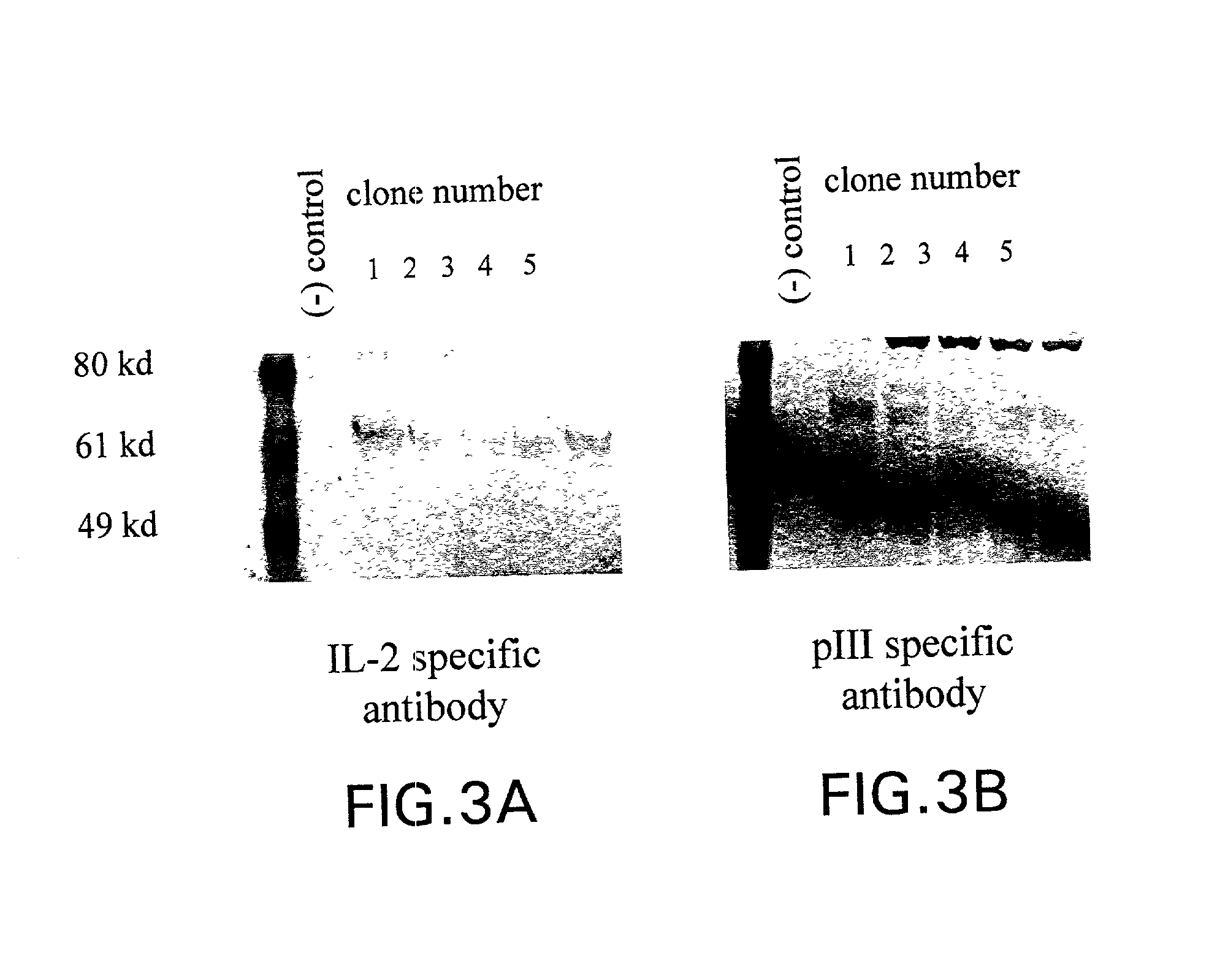
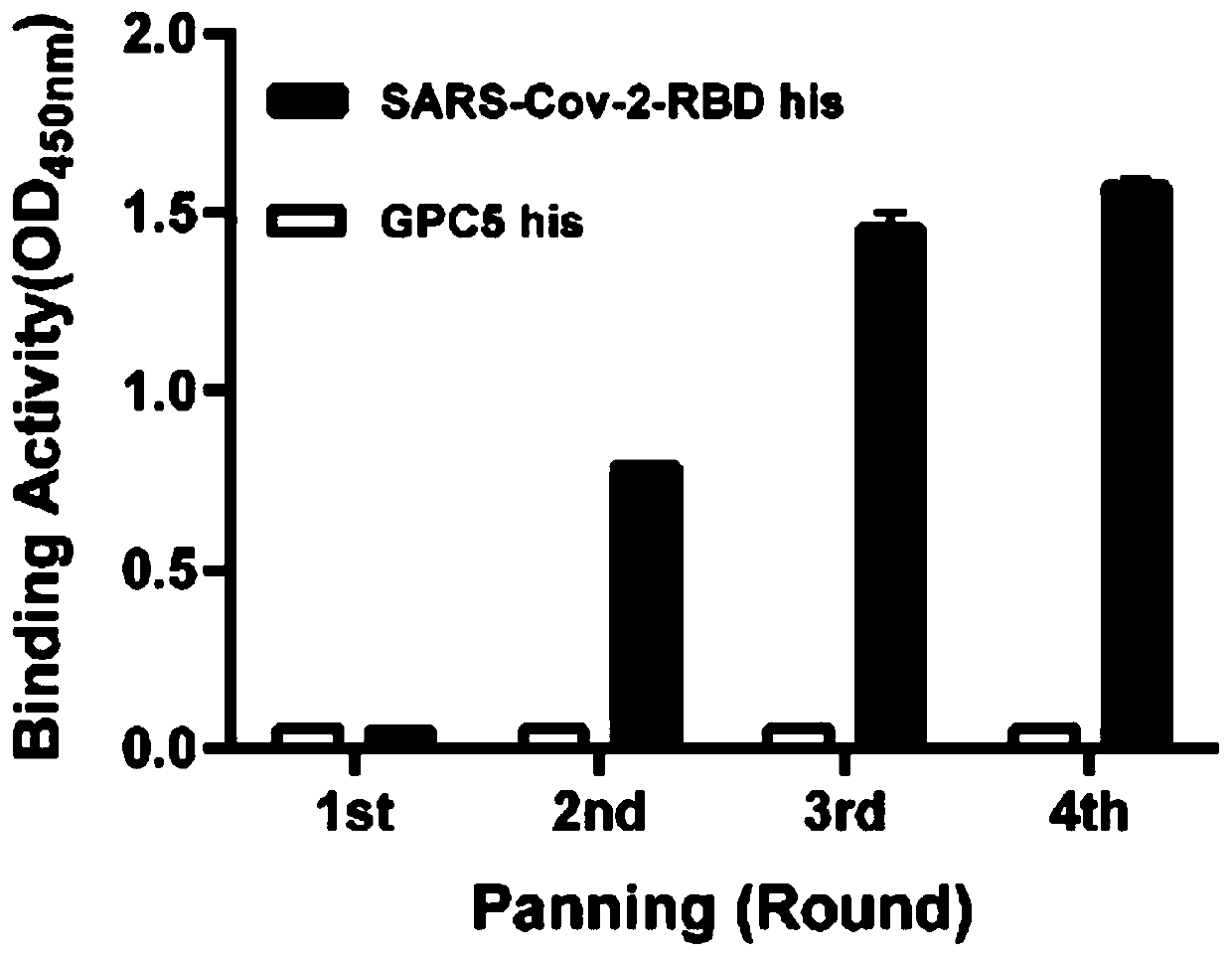
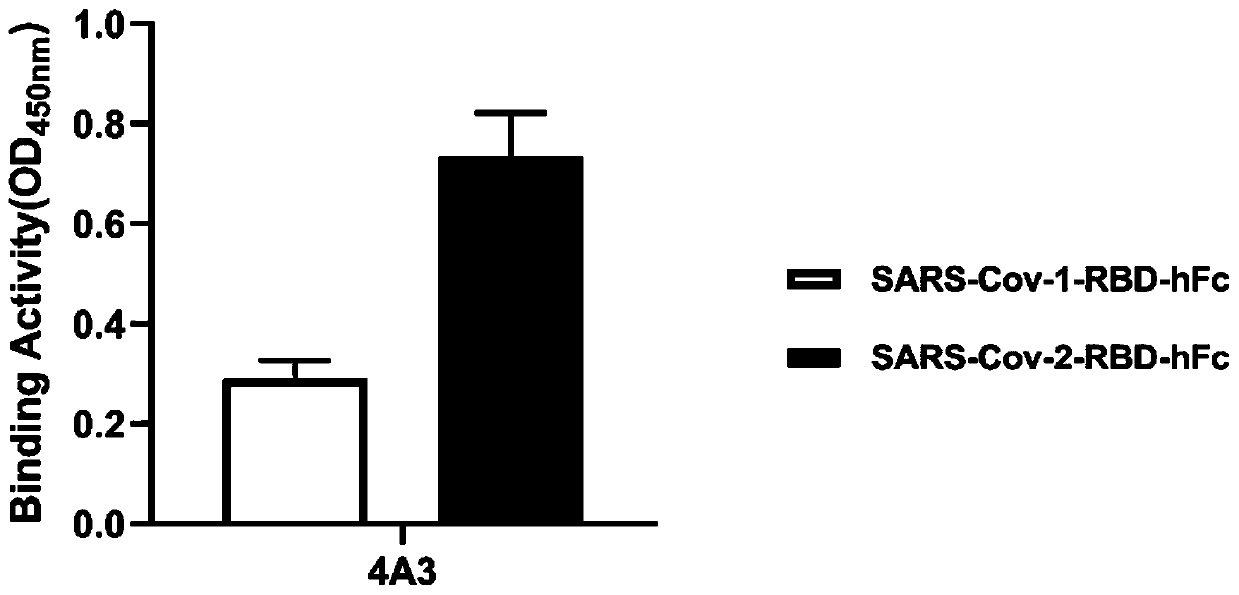
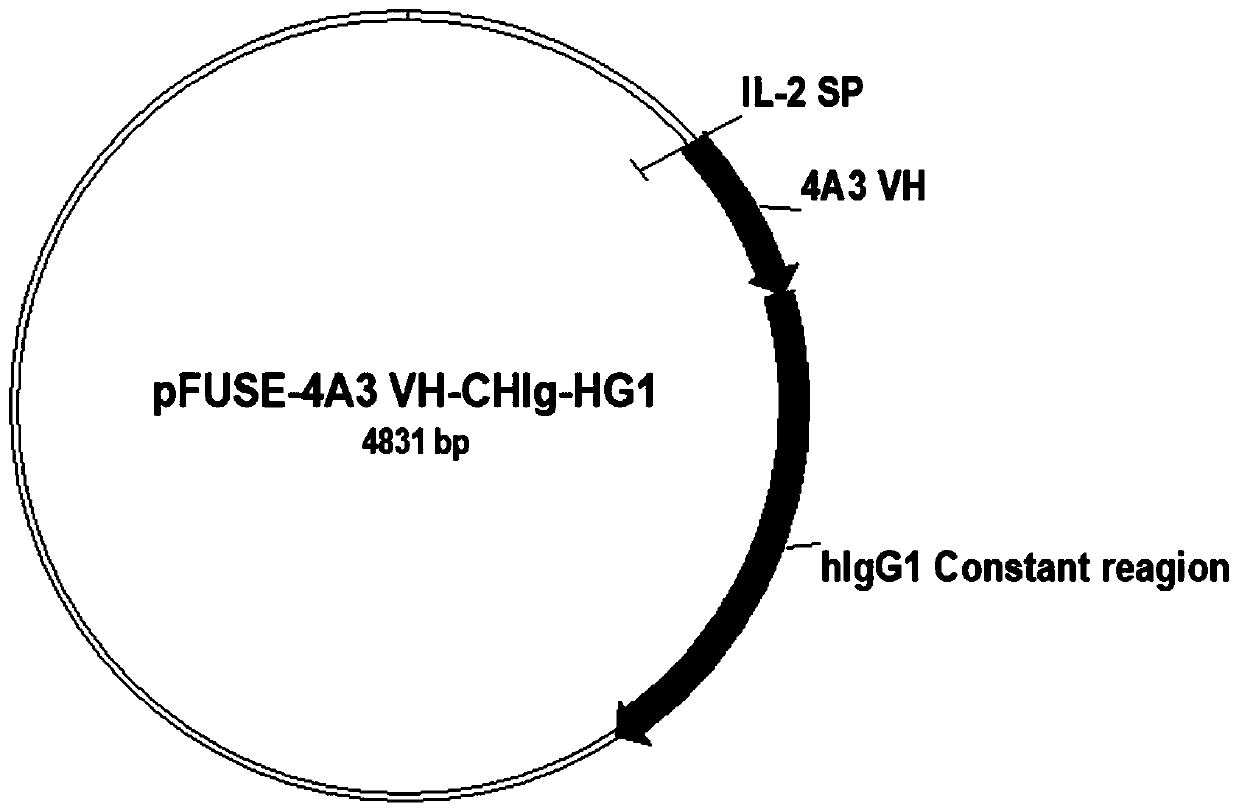
Neutralizing antibody for resisting novel coronavirus SARS-Cov-2 and application thereof
ActiveCN111592595ABlock bindingGood effectImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsNeutralizing antibodyPhage Display Techniques
The invention relates to a neutralizing antibody for resisting a novel coronavirus SARS-Cov-2 and an application of the neutralizing antibody. The antibody at least comprises one of a heavy chain CDR1, a heavy chain CDR2, a heavy chain CDR3, a light chain CDR1, a light chain CDR2 and a light chain CDR3. The antibody can be used for preparing a diagnostic reagent or a diagnostic kit, a drug or a pharmaceutical composition for detecting, preventing and treating a COVID-19. According to the neutralizing antibody, differential antibody screening is carried out through a phage display technology ina manner of targeting SARS-Cov-2-RBD and SARS-Cov-1-RBD; the neutralizing antibody for resisting the novel coronavirus SARS-Cov-2 is obtained; binding of the SARS-Cov-2-RBD and ACE2 positive cells can be blocked; and the neutralizing antibody has a remarkable virus neutralizing effect on an SARS-Cov-2 pseudo virus and provides an effective alternative antibody drug for prevention and treatment ofthe COVID-19.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com