Patents
Literature
264 results about "Antidote" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An antidote is a substance that can counteract a form of poisoning. The term ultimately derives from the Greek term φάρμακον ἀντίδοτον (pharmakon) antidoton, "(medicine) given as a remedy". Antidotes for anticoagulants are sometimes referred to as reversal agents.
Methods of generating novel peptides
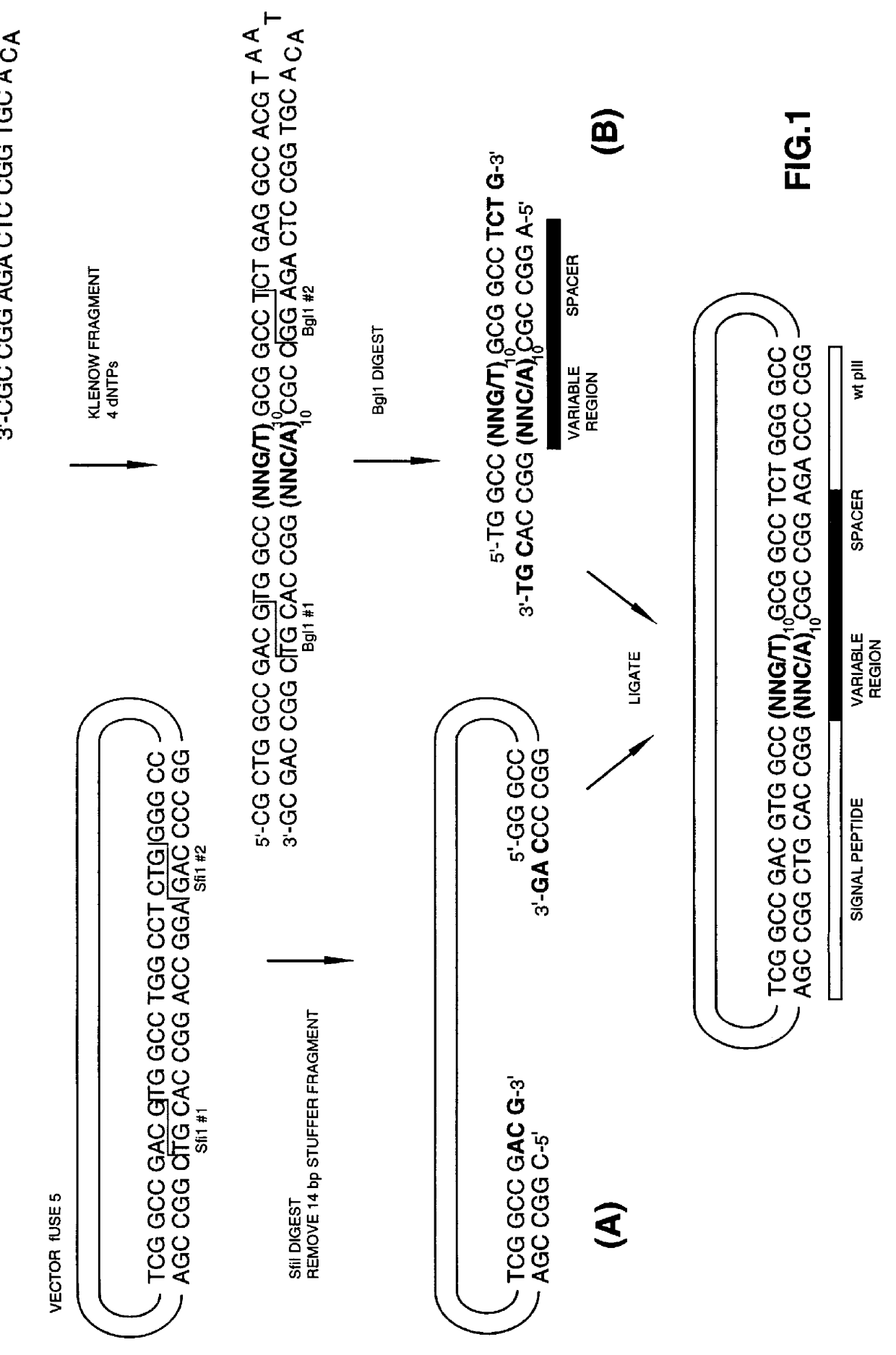
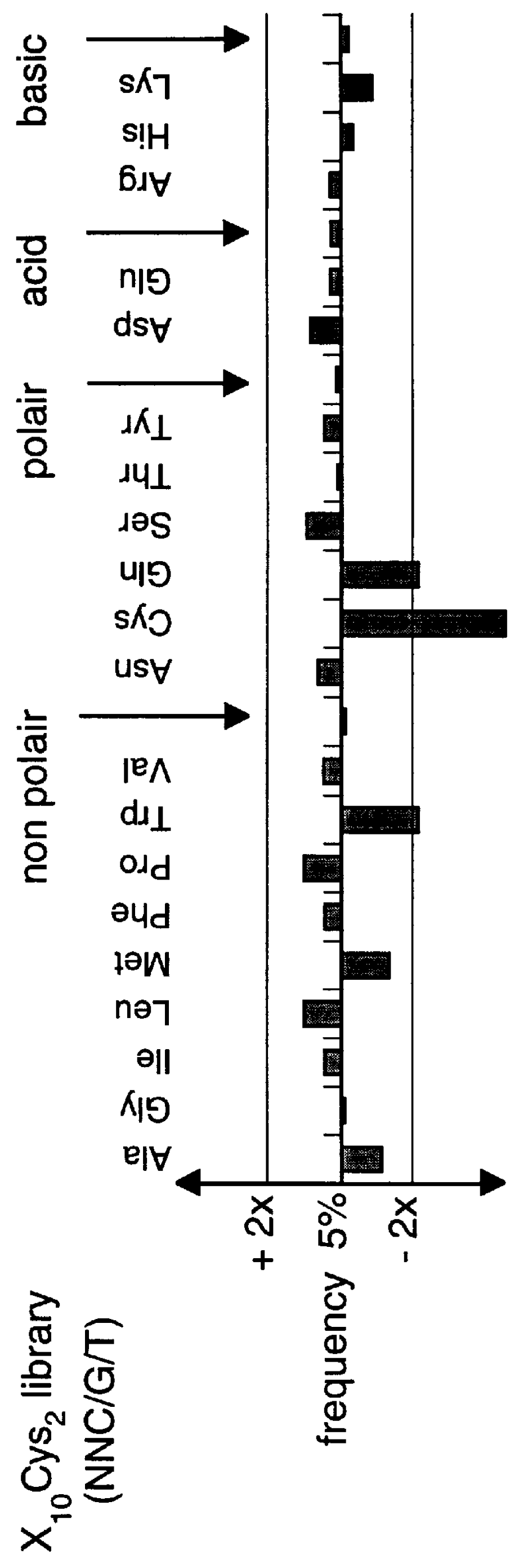
The present invention describes peptides capable of specifically binding to preselected micromolecules or to their natural receptor. The preselected molecules include but are not limited to drugs, vitamins, neuromediators and steroid hormones. Methods of using the phage display libraries to identify peptide compositions in preselected binding interactions are also disclosed. The retrieved peptides mimicking a natural receptor binding site to preselected molecules are used as is or as ligands to re-screen the same or different libraries to find and / or derive new receptor ligands, or are used to elicit the production of antibodies capable of binding to the natural receptor. The two categories of effector molecules (peptides or antibodies) may find diagnostic, therapeutic or prophylactic uses. The peptides directly derived from the phage display libraries may be used as drug detectors or antidotes. The others may be used to identify, target, activate or neutralize the receptor for the preselected micromolecules, the receptor being known or unknown.
Owner:BIOPHAGE
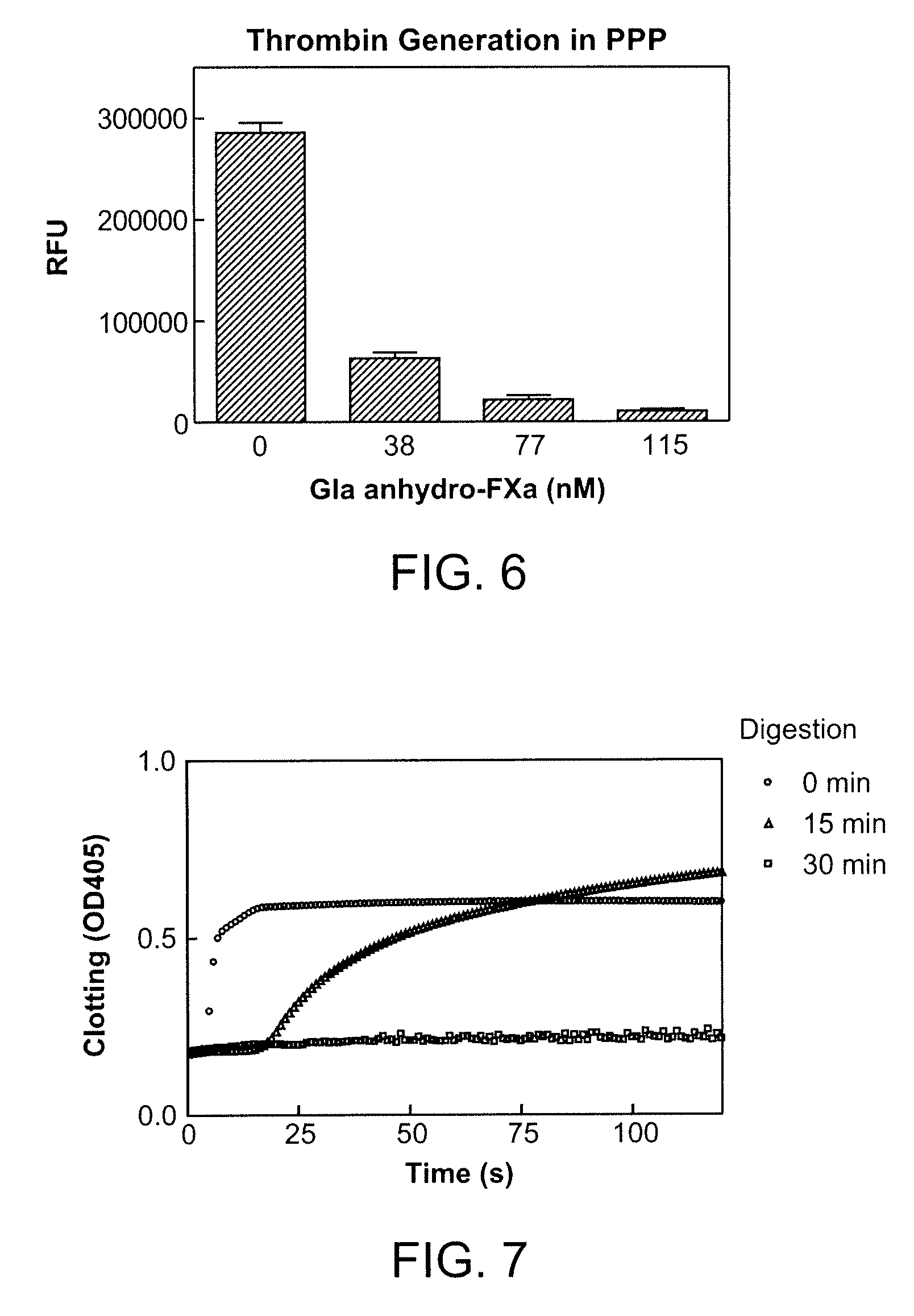
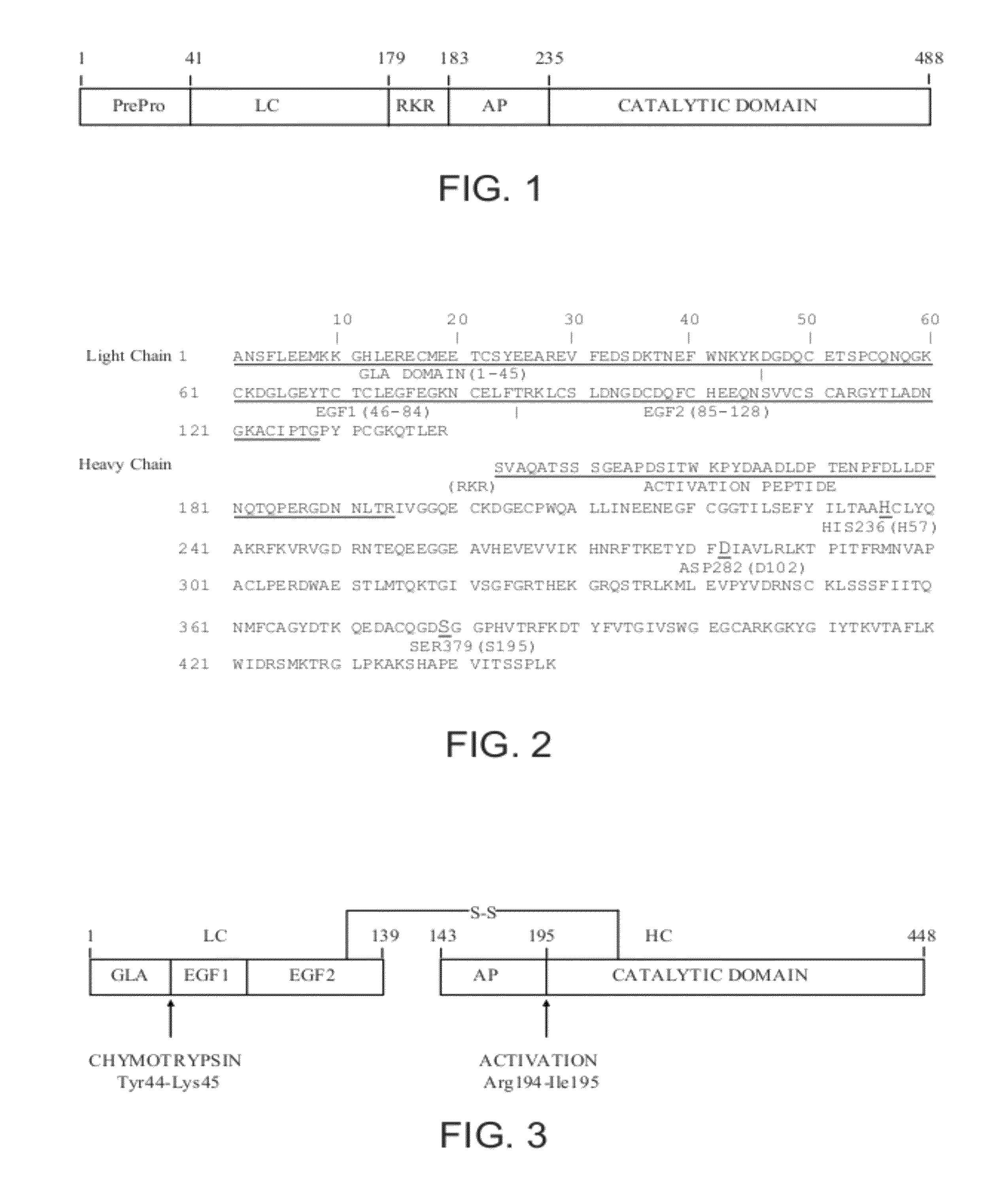
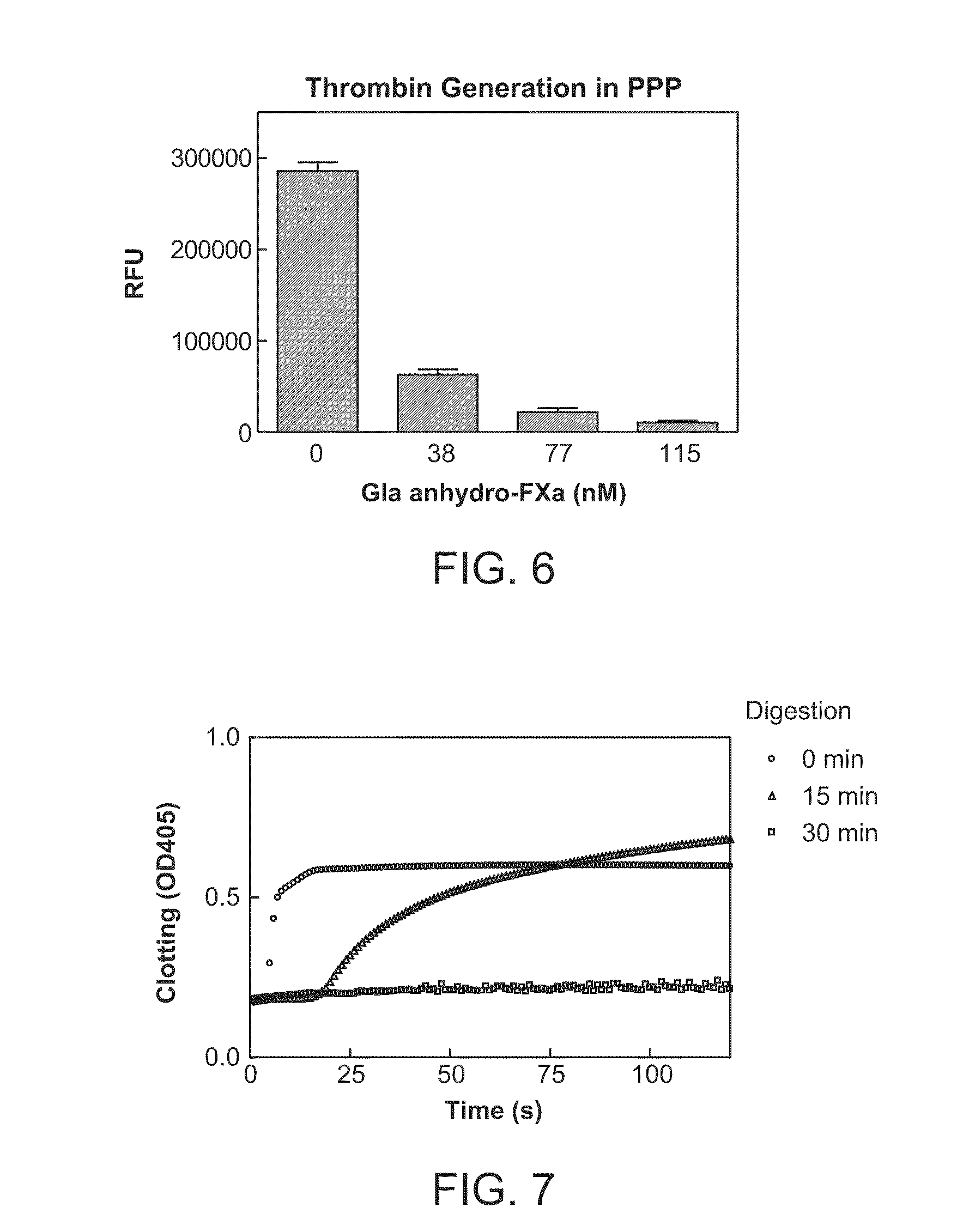
Antidotes for factor xa inhibitors and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20090098119A1Reduce and remove intrinsic procoagulantReduce and remove and anticoagulant activityOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesMedicineAntidote
The present invention relates antidotes to anticoagulants targeting factor Xa. The antidotes are factor Xa protein derivatives that bind to the factor Xa inhibitors thereby substantially neutralizing them but do not assemble into the prothrombinase complex. The derivatives describe herein lack or have reduced intrinsic coagulant activity. Disclosed herein are methods of stopping or preventing bleeding in a patient that is currently undergoing anticoagulant therapy with a factor Xa inhibitor.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
Antidotes for factor Xa inhibitors and methods of using the same
ActiveUS8153590B2Reduces and removes anticoagulant effectReduced activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsAntidoteFactor Xa Inhibitor
The present invention relates antidotes to anticoagulants targeting factor Xa. The antidotes are factor Xa protein derivatives that bind to the factor Xa inhibitors thereby substantially neutralizing them but do not assemble into the prothrombinase complex. The derivatives describe herein lack or have reduced intrinsic coagulant activity. Disclosed herein are methods of stopping or preventing bleeding in a patient that is currently undergoing anticoagulant therapy with a factor Xa inhibitor.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
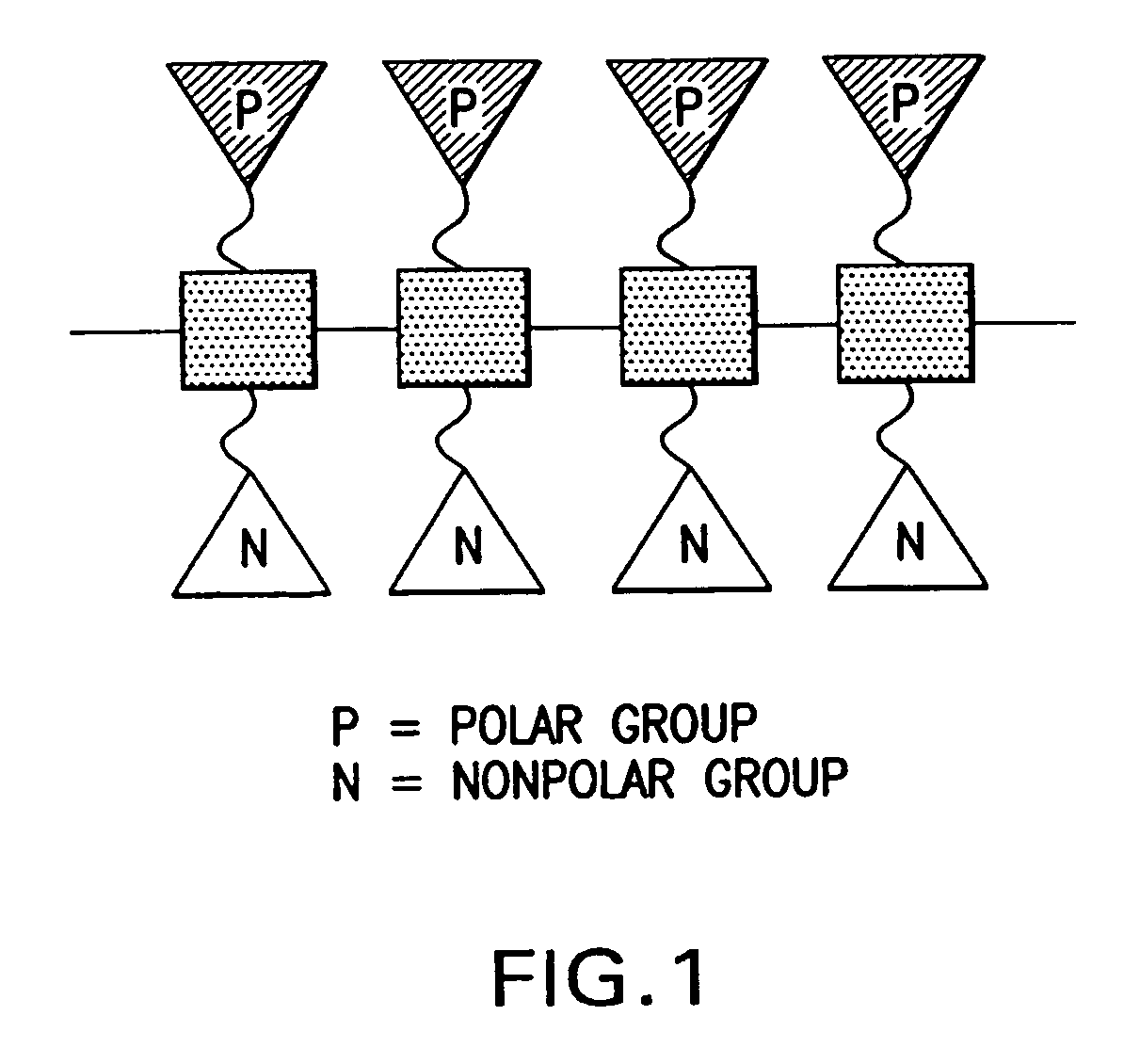
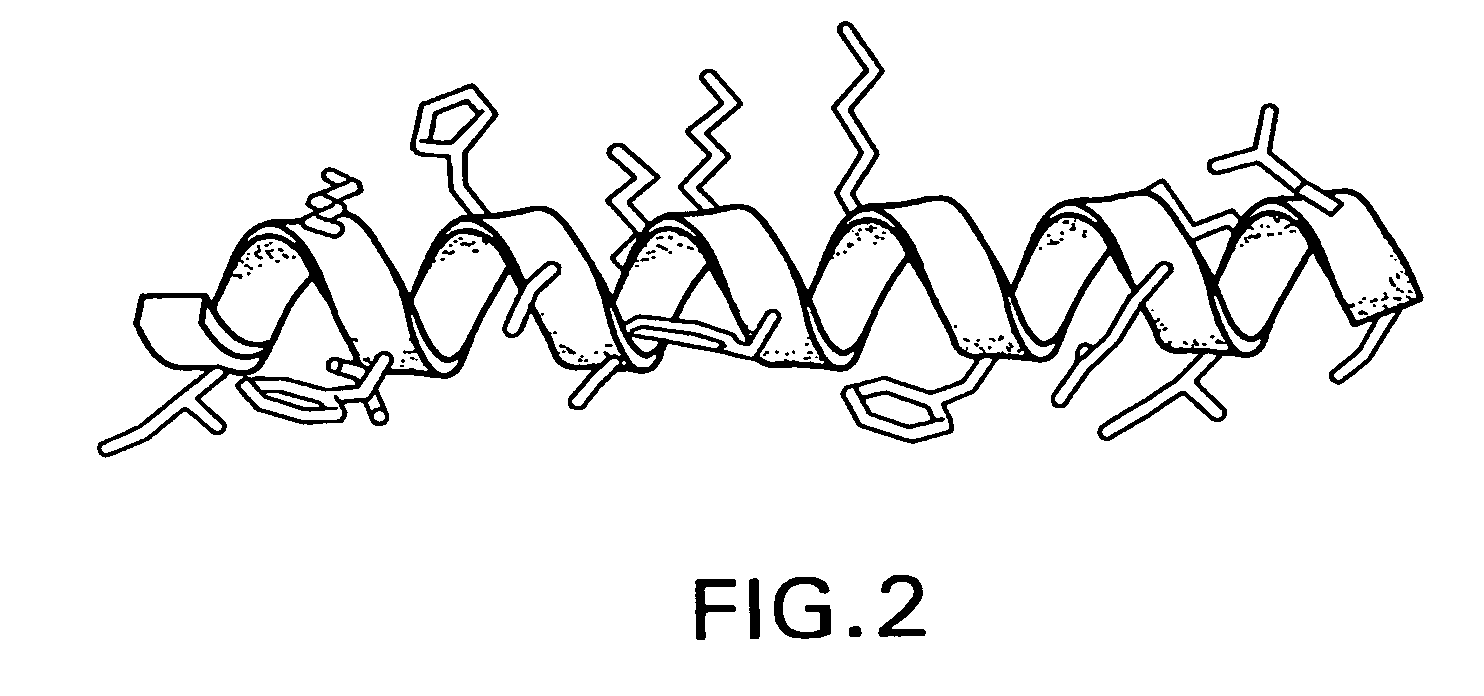
Facially amphilic polymers and oligomers and uses thereof
The present invention discloses methods of use of facially amphiphilic polymers and oligomers, including pharmaceutical uses of the polymers and oligomers as antimicrobial agents and antidotes for hemorrhagic complications associated with heparin therapy. The present invention also discloses novel facially amphiphilic polymers and oligomers and their compositions, including pharmaceutical compositions. The present invention further discloses the design and synthesis of facially amphiphilic polymers and oligomers.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Antidotes for factor Xa inhibitors and methods of using the same
ActiveUS8268783B2Reduces and removes anticoagulant effectReduced activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsFactor XAntidote
The present invention relates antidotes to anticoagulants targeting factor Xa. The antidotes are factor X and factor Xa protein derivatives that bind to the factor Xa inhibitors thereby substantially neutralizing them but do not assemble into the prothrombinase complex. The derivatives describe herein lack or have reduced intrinsic coagulant activity. Disclosed herein are methods of reversing anticoagulation, stopping or preventing bleeding in a patient that is currently undergoing anticoagulant therapy with a factor Xa inhibitor.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
Genetically engineered clostridial genes, proteins encoded by the engineered genes, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060204524A1Optimized biological propertyOptimized therapeutic propertyAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHeavy chainAntidote
The present invention relates to an isolated Clostridial neurotoxin propeptide having a light chain region, a heavy chain region, where the light and heavy chain regions are linked by a disulfide bond, and an intermediate region connecting the light and heavy chain regions. An isolated nucleic acid molecule encoding a Clostridial neurotoxin propeptide is also disclosed. Also disclosed is an isolated, physiologically active Clostridial neurotoxin produced by cleaving a Clostridial neurotoxin propeptide, a vaccine or antidote thereof, and methods of immunizing against or treating for toxic effects of Clostridial neurotoxins. Methods of expressing recombinant physiologically active Clostridial neurotoxins are also disclosed. Also disclosed is a chimeric protein having a heavy chain region of a Clostridial neurotoxin and a protein with therapeutic functionality. A treatment method is also disclosed.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Facially amphiphilic polyaryl and polyarylalkynyl polymers and oligomers and uses thereof
The present invention discloses methods of use of facially amphiphilic polyaryl and polyarylalkynyl polymers and oligomers, including, but not limited to, pharmaceutical uses of the polymers and oligomers as antimicrobial agents and as antidotes for hemorrhagic complications associated with heparin therapy. The present invention also discloses novel facially amphiphilic polyaryl and polyarylalkynyl polymers and oligomers, compositions of the novel polymers and oligomers, including pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of designing and synthesizing the facially amphiphilic polyaryl and polyarylalkynyl polymers and oligomers.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
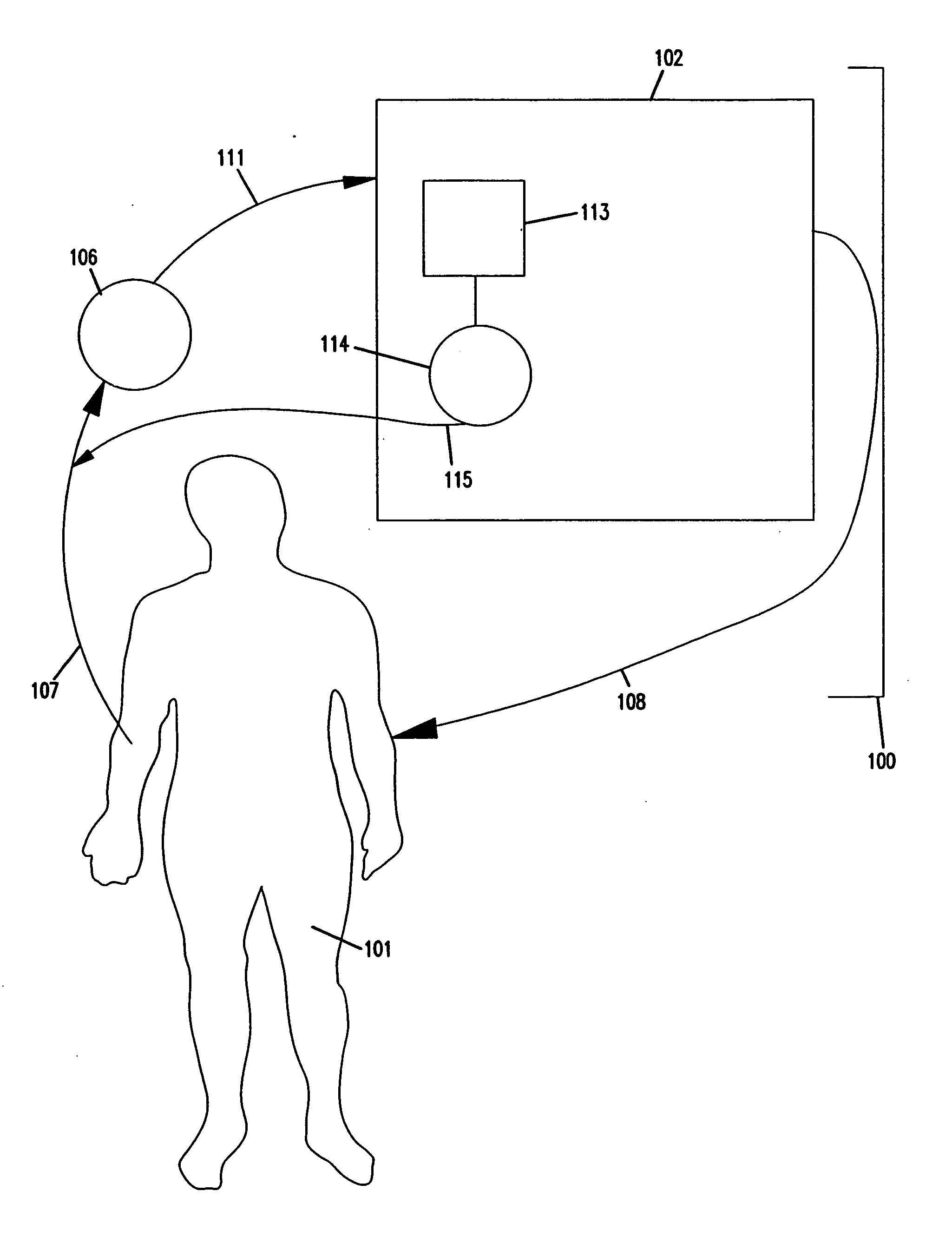
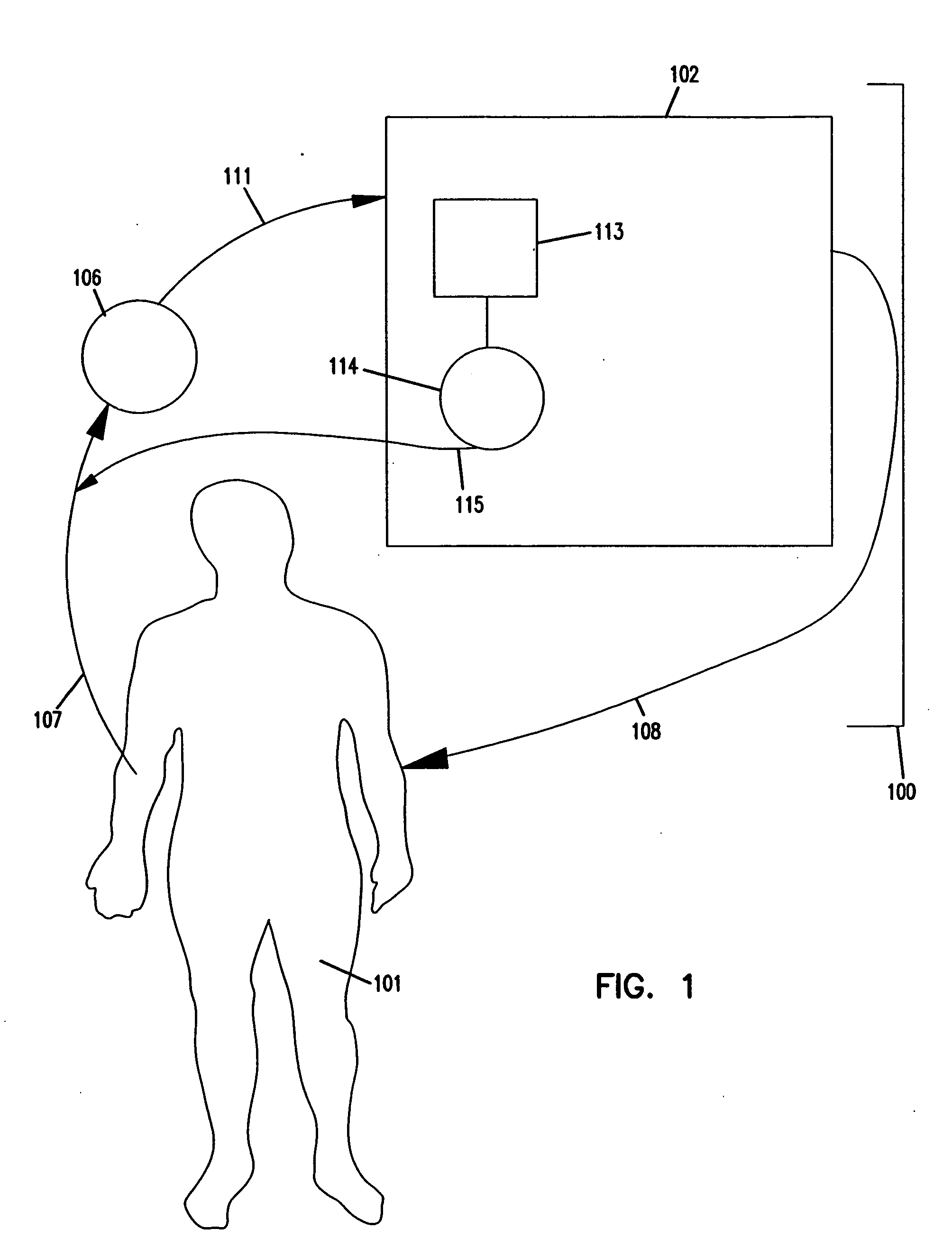
Method and system for detecting and treating biological and chemical warfare agents
InactiveUS20130178791A1Maximizes neutralizationMinimize side effectsMedical devicesPressure infusionRadio equipmentSide effect
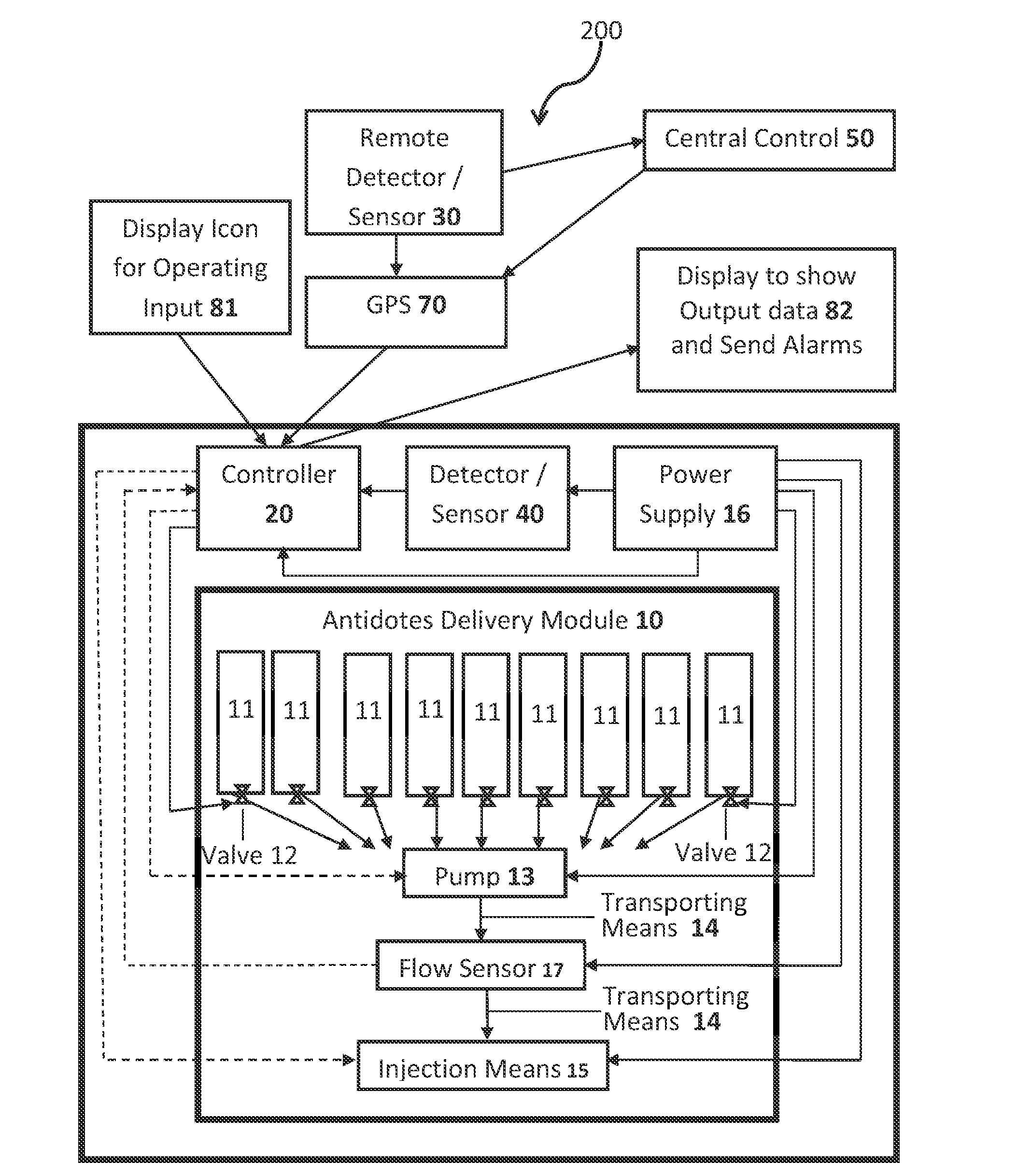
The present invention generally relates to radio-enabled devices for detection and remedy of biological and chemical warfare attack. More particularly, this invention relates to an on-body apparatus that provides a means of treatment which is innocuous to the wearer, but capable of injecting antidotes within seconds and preferably also combines multiple means of sensing chemical and biological agents as well as monitoring user's physiological response to the antidotes thereby to enable tailored and continuous infusion of antidotes while minimizing the side effect of the antidotes themselves. A key embodiment of this invention is the incorporation of an electronically-controlled needle or cannula that will deploy only when commanded to. When not deployed, the device sits inertly against the patient's skin, affixed by adhesive and or elastic materials.
Owner:JAVITT JONATHAN C
Antidotes for factor xa inhibitors and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20100255000A1Preventing and reducing bleedingReduces and removes anticoagulant effectPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesMedicineAntidote
The present invention relates antidotes to anticoagulants targeting factor Xa. The antidotes are factor X and factor Xa protein derivatives that bind to the factor Xa inhibitors thereby substantially neutralizing them but do not assemble into the prothrombinase complex. The derivatives describe herein lack or have reduced intrinsic coagulant activity. Disclosed herein are methods of reversing anticoagulation, stopping or preventing bleeding in a patient that is currently undergoing anticoagulant therapy with a factor Xa inhibitor.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
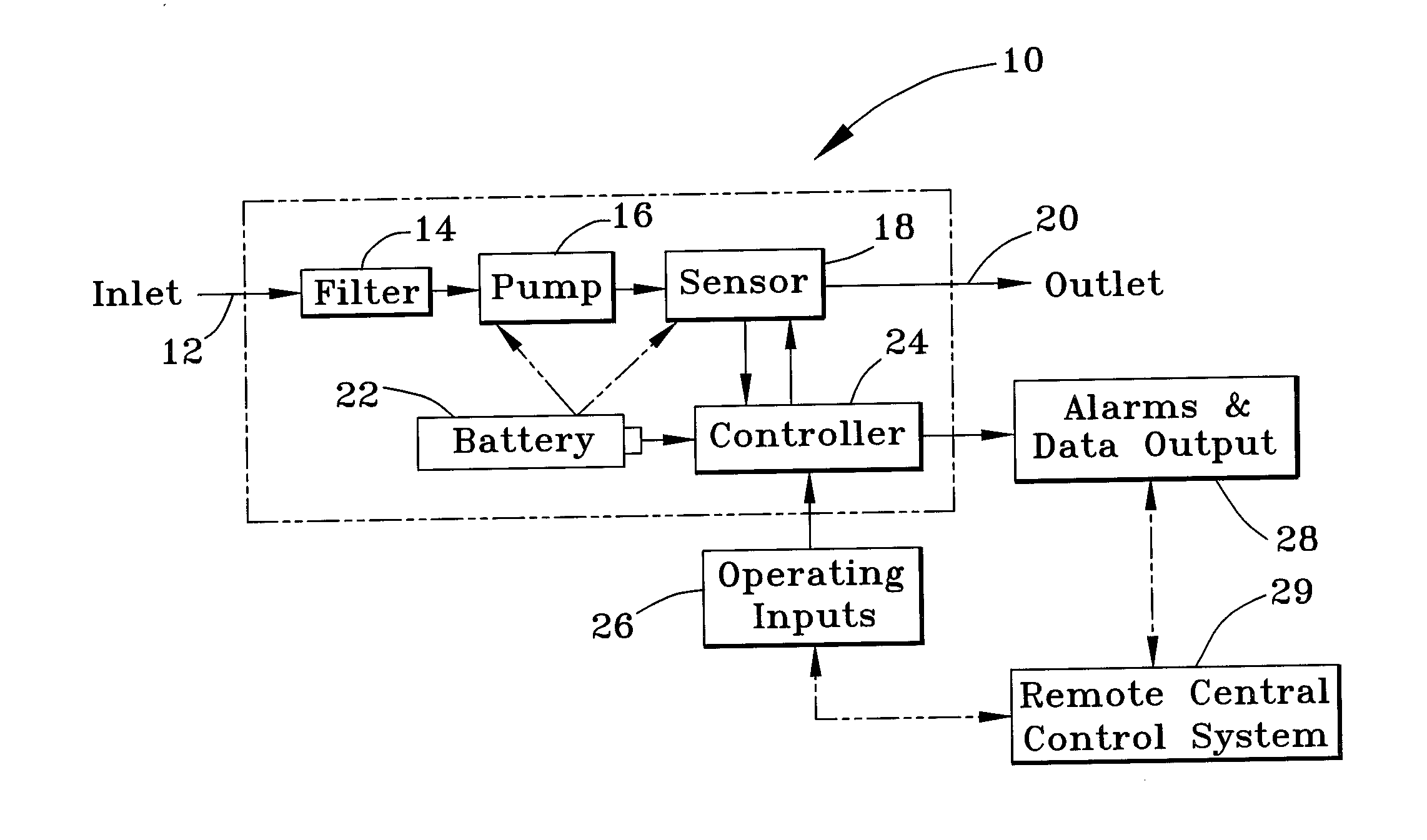
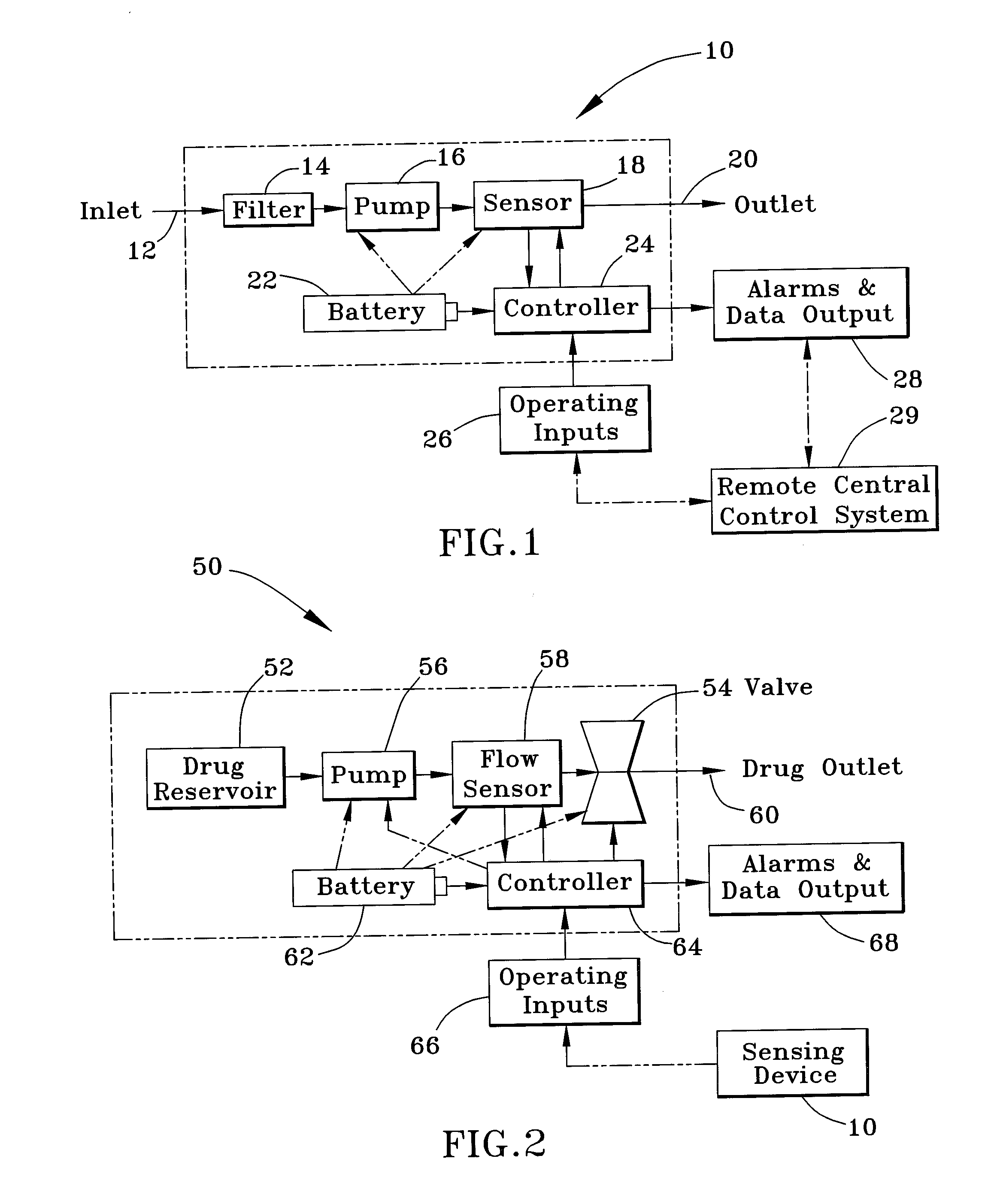
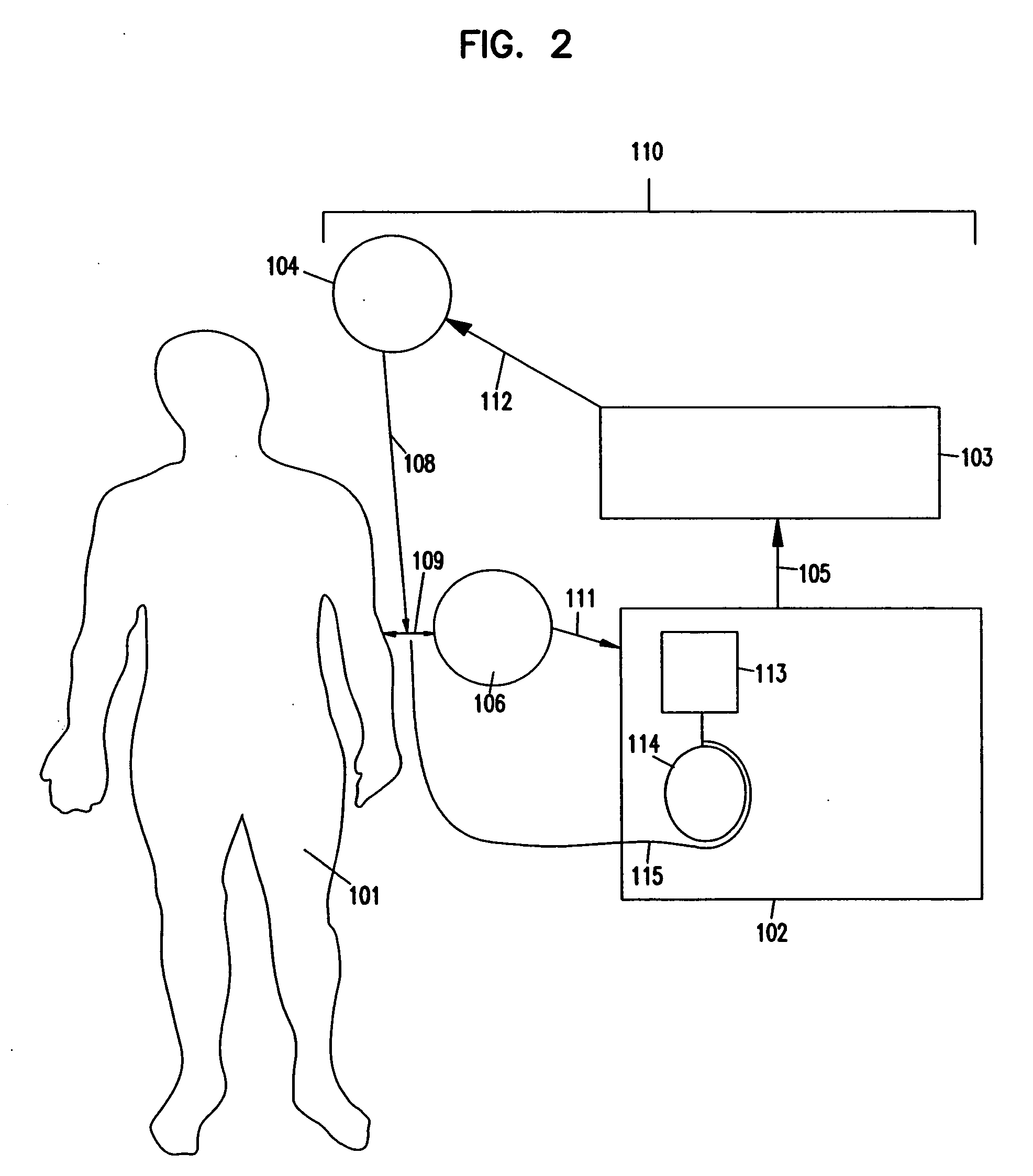
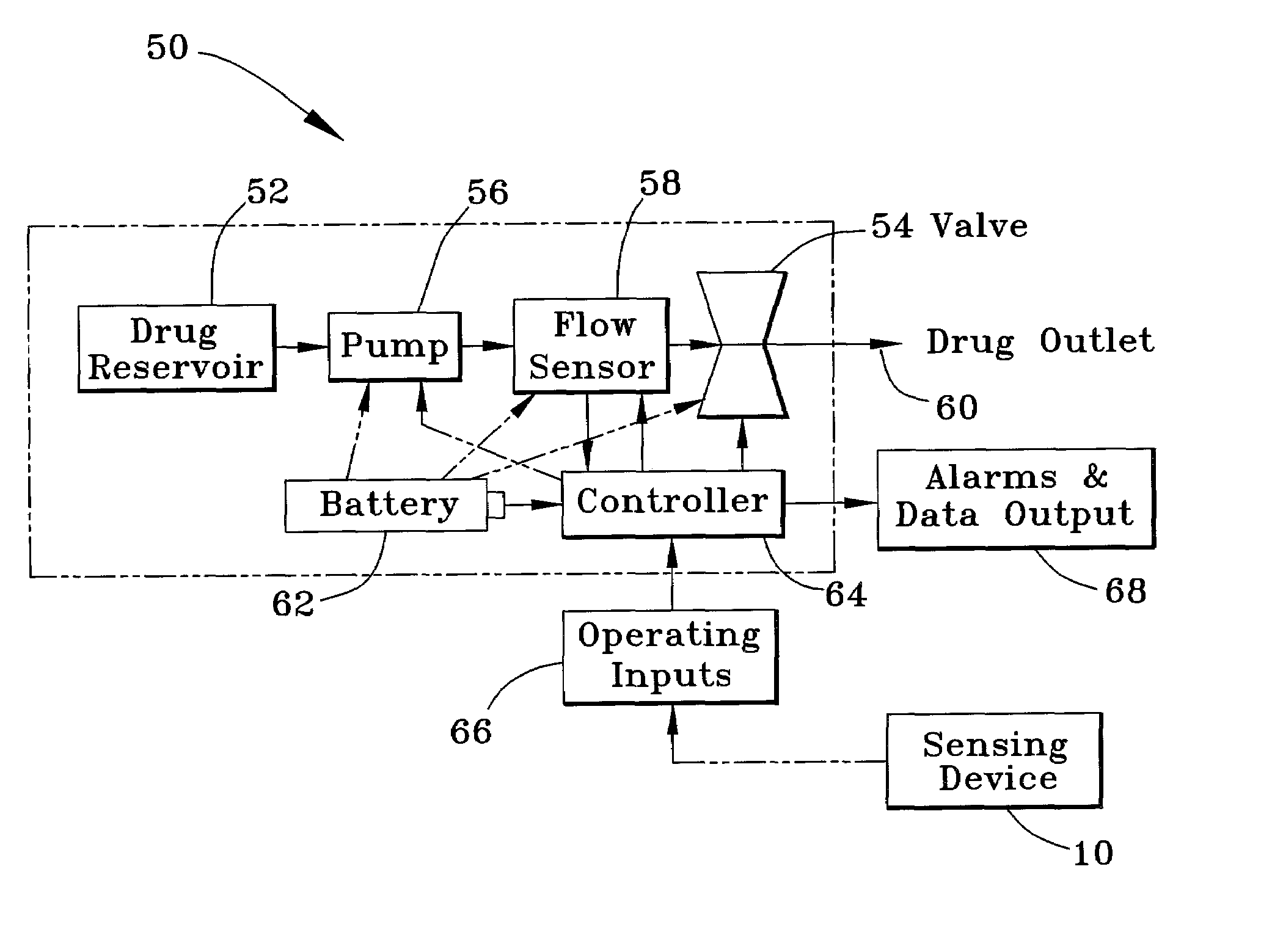
Device and method for detecting and treating chemical and biological agents
InactiveUS20080065050A1Volume/mass flow measurementVolume measurement and fluid deliveryAntidoteResonance
A device and method capable of sensing the presence of biochem agents, and preferably also capable of delivering precise amounts of one or more antidotes to treat a victim exposed to the agents. The device includes a freestanding tube portion having an internal passage containing a substance selective to a chemical or biological agent so that matter accumulates within the freestanding tube portion when a fluid drawn through the tube portion contains the agent. When vibrated at resonance, the resonant frequency of the tube portion is indicative of the accumulation of matter and thereby the presence of the agent to which the substance is selective. The device then preferably delivers precise amounts of one or more appropriate antidotes to treat the victim. The device is a sufficiently small and lightweight unit to permit being carried by an individual.
Owner:INTEGRATED SENSING SYST INC
Facially amphiphilic polymers and oligomers and uses thereof
The present invention discloses methods of use of facially amphiphilic polymers and oligomers, including pharmaceutical uses of the polymers and oligomers as antimicrobial agents and antidotes for hemorrhagic complications associated with heparin therapy. The present invention also discloses novel facially amphiphilic polymers and oligomers and their compositions, including pharmaceutical compositions. The present invention further discloses the design and synthesis of facially amphiphilic polymers and oligomers.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Composition, synthesis and therapeutic applications of polyamines
InactiveUS20050085555A1Chromium concentration were decreasedIncrease excretionBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAntidoteRisk stroke
This invention relates to a process of synthesis and composition of open chain (ring), closed ring, linear branched and or substituted polyamines, polyamine derived tyrosine phosphatase inhibitors and PPAR partial agonists / partial antagonists via a series of substitution reactions and optimizing the bioavailability and biological activities of the compounds. Polyamines prevent the toxicty of neutoxins and diabetogenic toxins including paraquat, methyphenyl pyridine radical, rotenone, diazoxide, streptozotocin and alloxan. These polyamines can be to treat neurological, cardiovascular, endocrine acquired and inherited mitochondrial DNA damage diseases and other disorders in mammalian subjects, and more specifically to the therapy of Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Lou Gehrig's disease, Binswanger's disease, Olivopontine Cerebellar Degeneration, Lewy Body disease, Diabetes, Stroke, Atherosclerosis, Myocardial Ischemia, Cardiomyopathy, Nephropathy, Ischemia, Glaucoma, Presbycussis, Cancer, Osteoporosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Multiple Sclerosis and as Antidotes to Toxin Exposure.
Owner:MURPHY MICHAEL A
Antidotes for factor Xa inhibitors and methods of using the same in combination with blood coagulating agents
ActiveUS8455439B2Low effective doseReduce potential side effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsAntidoteFactor Xa Inhibitor
The present invention relates to antidotes of anticoagulants targeting factor Xa which antidotes are used in combination with blood coagulating agents or other heparin antidotes to prevent or reduce bleeding in a subject. The antidotes described herein have reduced or no intrinsic coagulant activity. Disclosed herein are methods of stopping or preventing bleeding in a patient that is or will be undergoing anticoagulant therapy with a factor Xa inhibitor.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
Antidotes for factor xa inhibitors and methods of using the same in combination with blood coagulating agents
ActiveUS20100125052A1Reduce potential side effectsLow effective dosePeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsMedicineAntidote
The present invention relates to antidotes of anticoagulants targeting factor Xa which antidotes are used in combination with blood coagulating agents or other heparin antidotes to prevent or reduce bleeding in a subject. The antidotes described herein have reduced or no intrinsic coagulant activity. Disclosed herein are methods of stopping or preventing bleeding in a patient that is or will be undergoing anticoagulant therapy with a factor Xa inhibitor.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
Apheresis methods and devices
InactiveUS20050143684A1Low toxicityAlter metabolismOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesMedicineAntidote
An apheresis method that includes drawing blood from a mammal, adding an amount of an agent effective in preventing coagulation, wherein the agent is an anticoagulant, extracting one or more constituent components from the blood, wherein an extracted blood and constituent component result therefrom, and diminishing the activity of said anticoagulant by introducing an antidote, wherein the amount of antidote introduced is coupled with the amount of anticoagulant added. The antidote is provided either to the processed blood prior to reintroduction to the donor or directly to the donor. The invention also includes an apheresis machine that includes an antidote delivery conduit, wherein the antidote delivery conduit delivers an amount of antidote that is coupled with an amount of anticoagulant delivered.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES +1
Preparation and compositions of highly bioavailable zerovalent sulfur and uses thereof
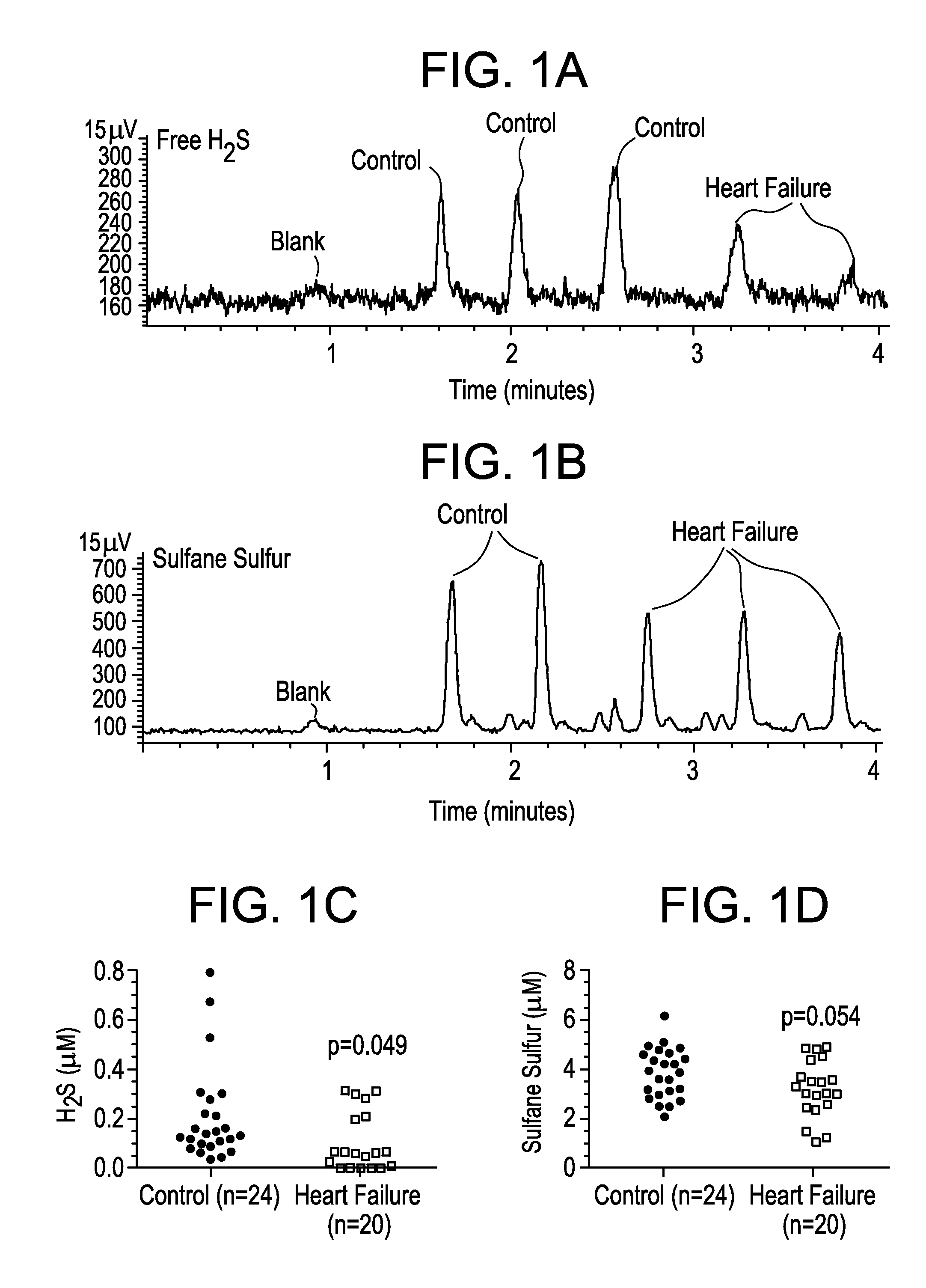
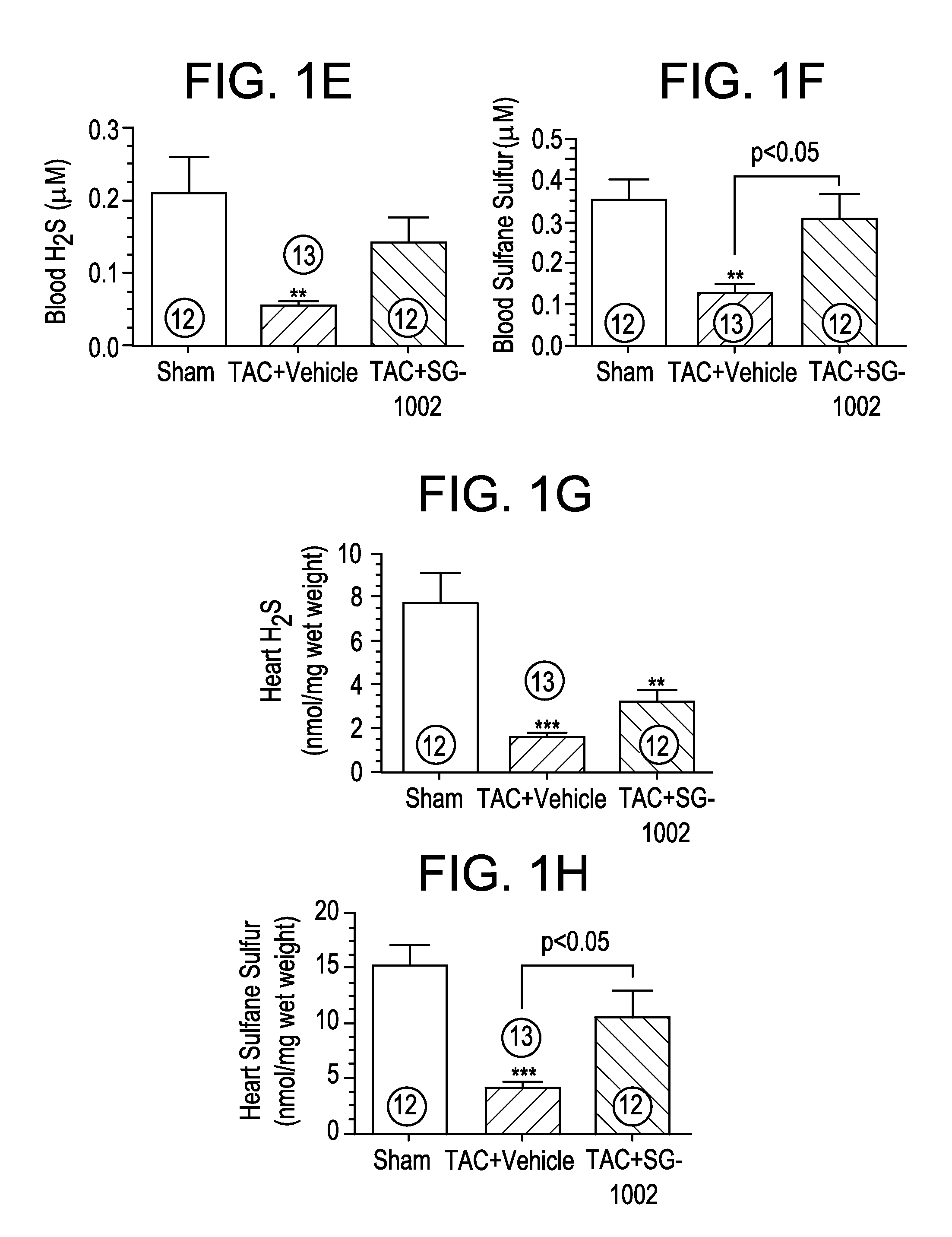
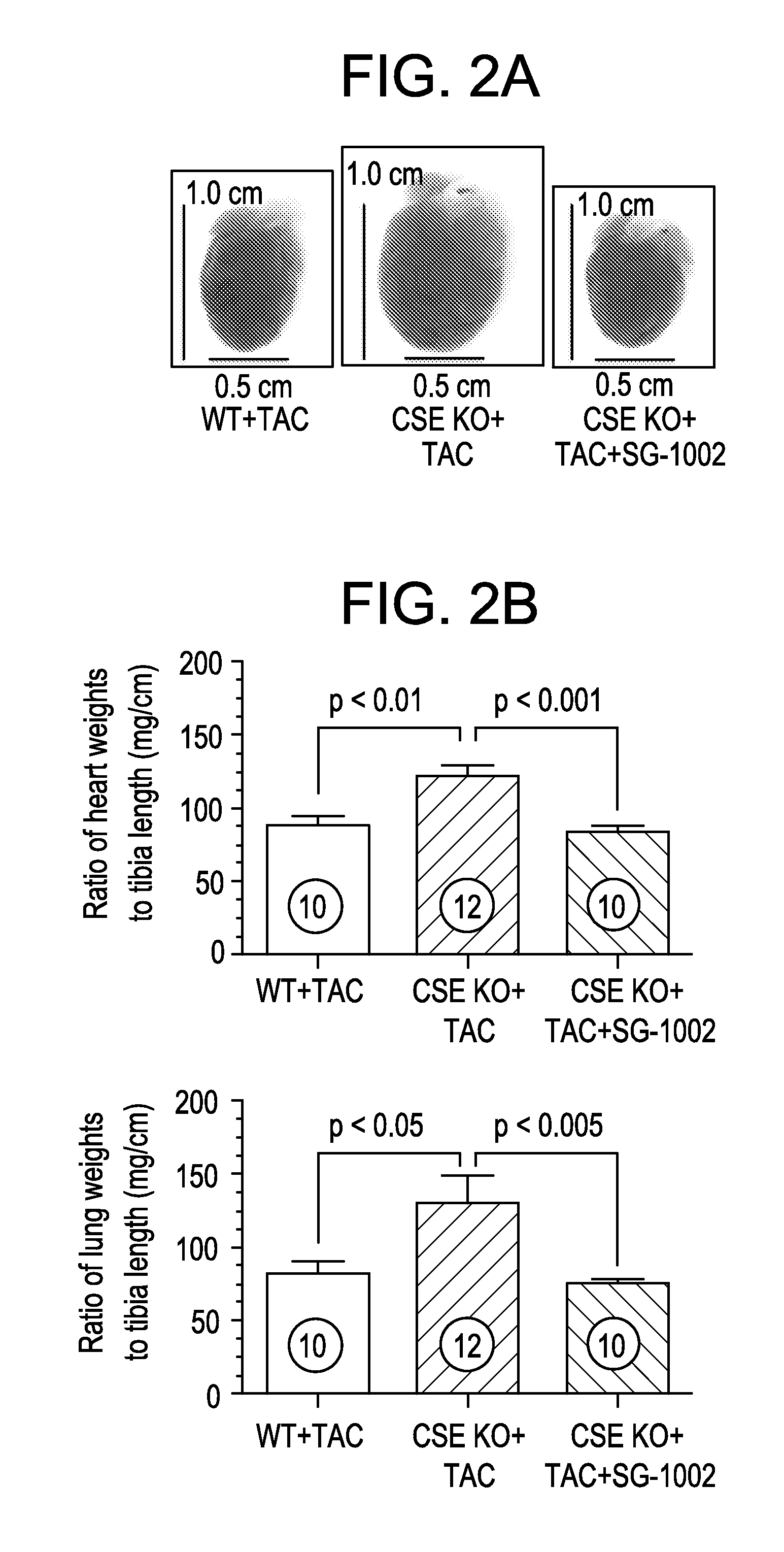
ActiveUS20130064904A1Increase in in vivoImprove responseBiocideSenses disorderOxidative stressAntidote
The present invention features sulfur-rich compositions and preparations thereof that are safe and effective as hydrogen sulfide prodrugs of high bioavailability. The invention also includes methods of treating pathological conditions associated with oxidative stress using sulfur-rich compositions. The invention further includes sulfur-rich compositions as antidotes and medical food for preserving and promoting general health.
Owner:SULFAGENIX
Oxidation type antidote for residual agricultural chemicals in fruits and vegetables
The invention discloses an oxidization type fruit and vegetable pesticide residue toxicide which belongs to the field of agro-chemistry, the toxicide is prepared from solid peroxodisulfate, peroxocarbonate or ferrate or other strong oxidisability substance in the form of powdery, sheet-like or granular form, when used in immersing vegetable and fruit with water, it can not only eliminate the pesticide residue on vegetable and fruit through oxidation degradation, but also be used for sterilization and disinfection, and fresh-keeping storage.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
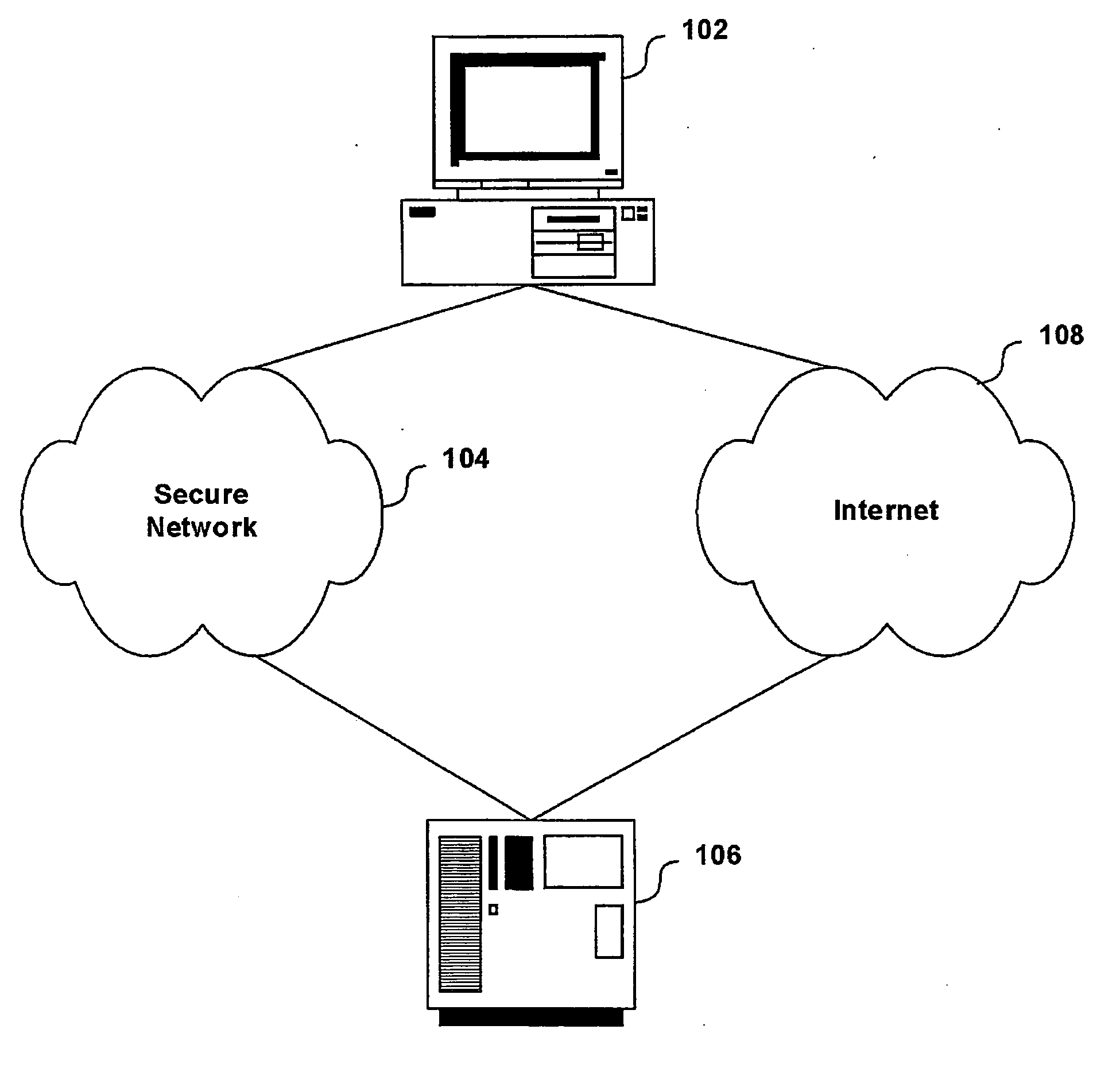
Packet filtering in a NIC to control antidote loading
A method and system is described for selectively downloading antidotes onto a client computer. The client computer is connected via a network interface card (NIC) to a network that contains an anti-virus server. The NIC is initially logically isolated from the client computer, thus permitting the NIC to autonomously examine packets to and from the client computer and the network. The NIC selectively accepts packets only from trusted Internet Protocol (IP) addresses that conform to a security format such as Internet Protocol Security (IPSec).
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
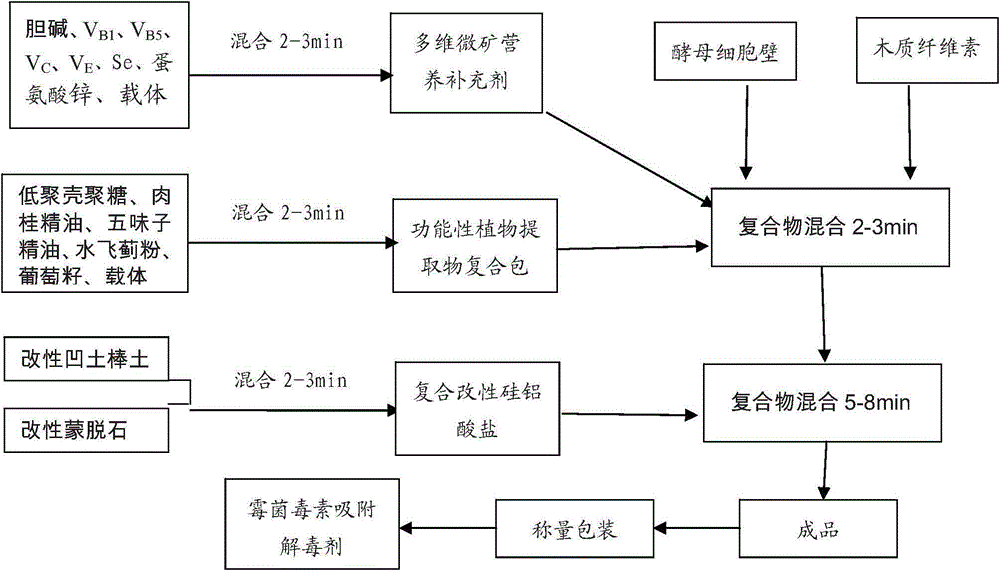
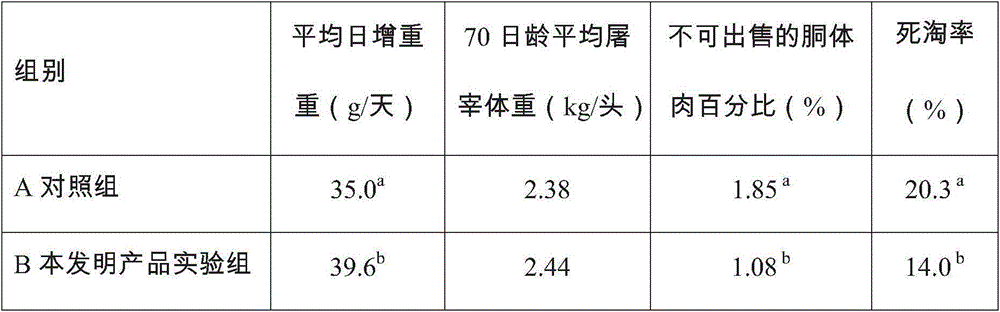
Adsorption antidote capable of eliminating harm done by mycotoxins to livestock
InactiveCN105166420AOptimize spatial structureReduce adsorptionAnimal feeding stuffAntidoteCell wall
The invention provides a toxin adsorption antidote capable of eliminating harm done by mycotoxins to livestock. The toxin adsorption antidote is prepared from 45-55% of modified attapulgite, 20-28% of modified montmorillonite, 5-10% of lignocelluloses, 5-15% of yeast cell walls, 1-2% of multi-vitamin micro-mineralization nutritious supplementary and 3-5% of functional extract superpacket. The toxin adsorption antidote can adsorb common mycotoxins, including aflatoxin, zearalenone, vomitoxin, ochratoxin and fumonisins, in feed so as to reduce the harm done by mycotoxins to animals; meanwhile, adsorption detoxication function is realized through nutrition enhancement and immunity improvement of livestock, and livestock breeding effect is improved.
Owner:ANYOU BIOTECH GRP
Ricin inhibitors and methods for use thereof
Ricin A-chain is an N-glycosidase that attacks ribosomal RNA at a highly conserved adenine residue. Crystallographic studies show that not only adenine and formycin, but also pterin-based rings can bind in the ricin active site. For a better understanding of the recognition mode between ricin, and adenine-like rings, the interaction energies and geometries were calculated for a number of complexes. Shiga toxin, a compound essentially identical to the protein originally isolated from Shigella dysenteriae, has an active protein chain that is a homologue of the ricin active chain, and catalyzes the same depurination reaction. The present invention is drawn to identifying inhibitors of ricin and Shiga toxin, using methods molecular mechanics and ab initio methods and using the identified inhibitors as antidotes to ricin or Shiga toxin, or to facilitate immunotoxin treatment by controlling non-specific cytotoxicity.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Disease prevention and detoxification feed for fish and shrimps in fresh water, and preparation method of feed
InactiveCN104381641AStrong disease prevention abilityGood detoxification effectAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a disease prevention and detoxification feed for fish and shrimps in fresh water, and a preparation method of the feed. The feed is prepared from the following raw materials: corn flour, wheat bran, fermented blood meal, an antidote and the like. The feed is capable of effectively removing harmful toxins such as escherichia coli, intestinal toxins, heavy metal ions and the like in the bodies of the fish and the shrimps by absorption, thus having the functions of epidemic prevention, cure of diseases, disinsection and sterilization; the feed is also capable of providing trace elements which are necessary for the growth of the fish and the shrimps, promoting the metabolism of organisms, improving the feed conversion ratio, promoting the fish and the shrimps to have strong appetite and promoting growth and weight gain. The feed is a puffed product, and the antidote has strong absorption and detoxification functions, so that the feed can be used for purifying the water in a pool, improving the breathability of the water in the pool and increasing the dissolved oxygen of the water. Furthermore, Indian bread cyrtomium rhizome, fineleaf schizonepeta herb, coptis root, rhubarb and baikal skullcap root which are fed into the feed also have good functions of antibiosis and disinsection, and are capable of improving the efficacy and thoroughly controlling after being matched with the antidote for use.
Owner:安徽华亿农牧科技发展有限公司
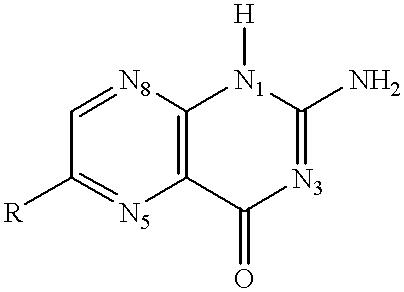
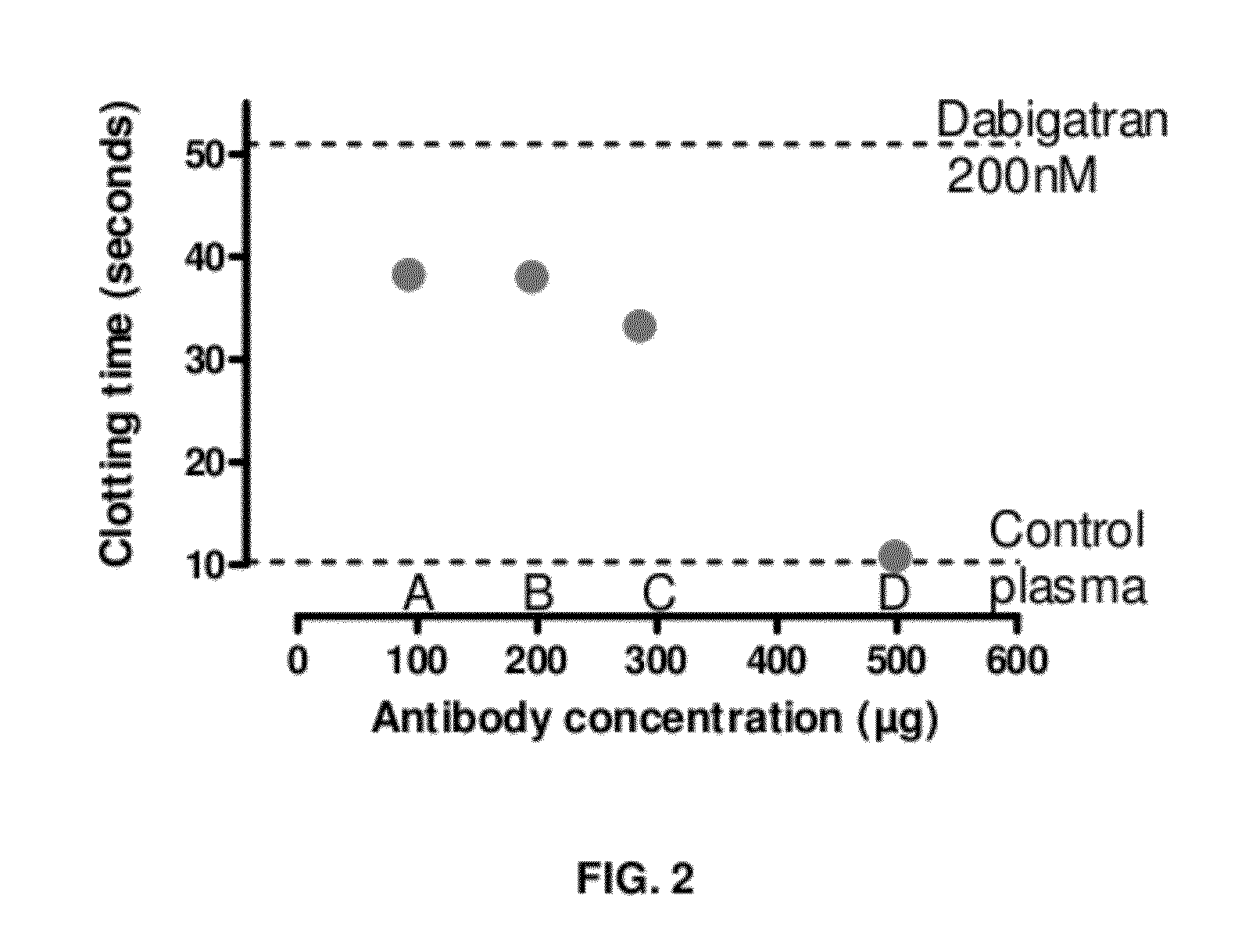
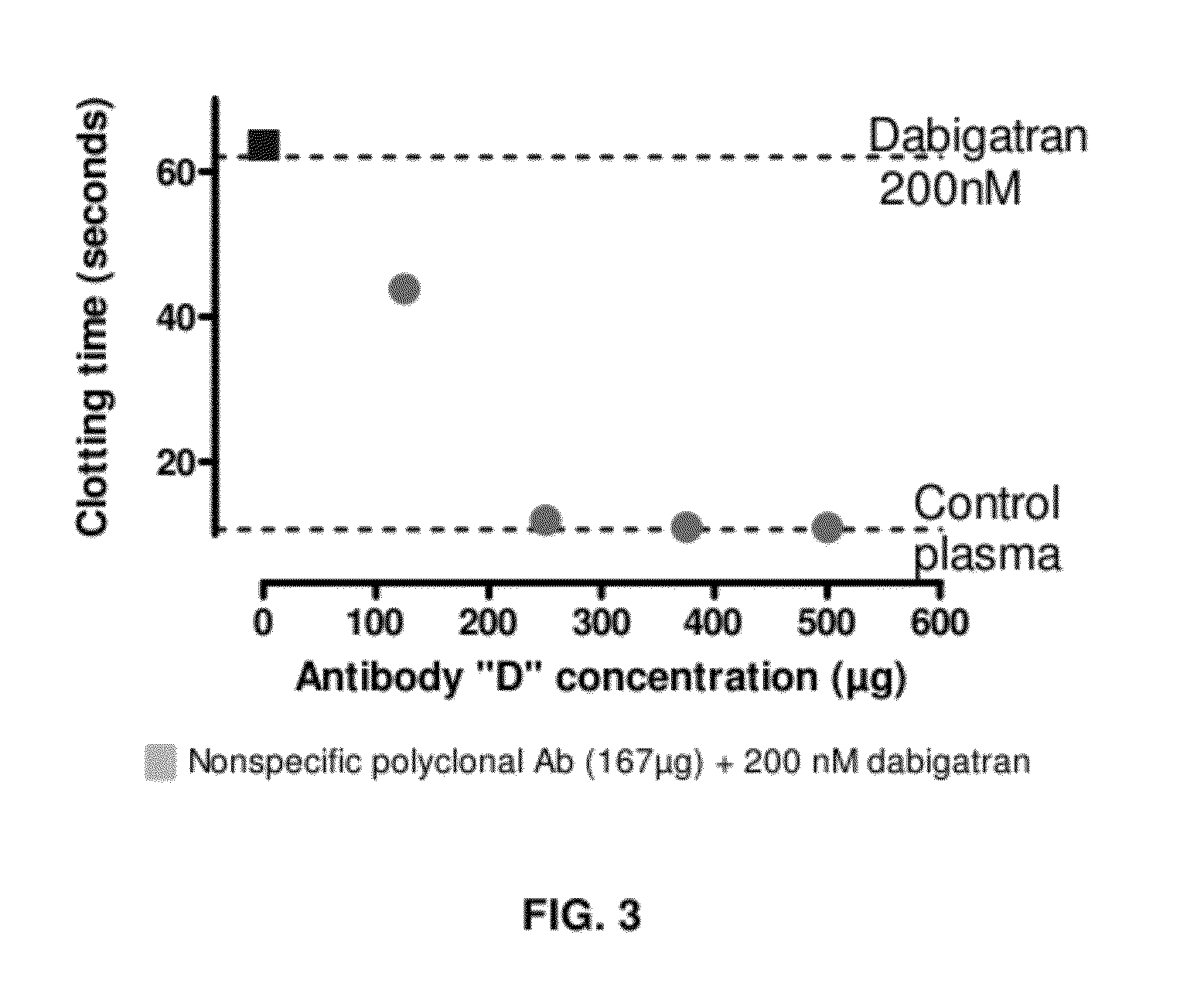
Anticoagulant antidotes comprising antibodies that bind dabigatran and/or related compounds
The present invention relates to antibody molecules against anticoagulants, in particular dabigatran, and their use as antidotes of such anticoagulants.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
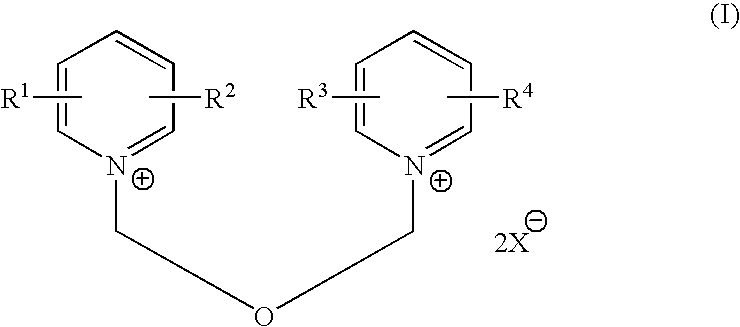
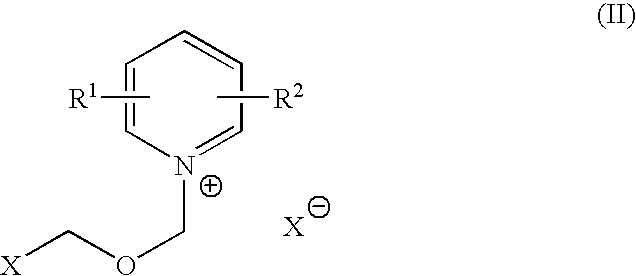
Process for halomethyl ethers of hydroxyiminomethyl quaternary pyridinium salts
A halide salt of a 1-(hydroxyiminomethyl-1-pyridino)-3-(halomethyl)-2-oxapropane is prepared by adding a pyridinealdoxime to a bis-halomethylether in such a manner that the bis-halomethylether is maintained in excess throughout the addition. This procedure produces the halide salt of a 1-(hydroxyiminomethyl-1-pyridino)-3-(halomethyl)-2-oxapropane in high yield and purity, which facilitates its use as an intermediate in the manufacture of an asymmetrically substituted 1,3-di (1-pyridino)-2-oxapropane, a class of compounds that are generally useful antidotes to various toxic agents. A prominent member of the class is the dimethylsulfonate salt of 1-(2-hydroxyiminomethyl-1-pyridino)-3-(4-carbamoyl-1-pyridino)-2-oxapropane. The use of mercaptoalkyl-functionalized polymers is disclosed as a preferred metal ion scavenger for a final purification step in the manufacture of these compounds.
Owner:AMPAC FINE CHEM
Therapeutic nucleic acid-3' -conjugates
InactiveUS20050191680A1Efficient killingPrevent breakdownMaterial nanotechnologyActivity regulationHalf-lifeWhite blood cell
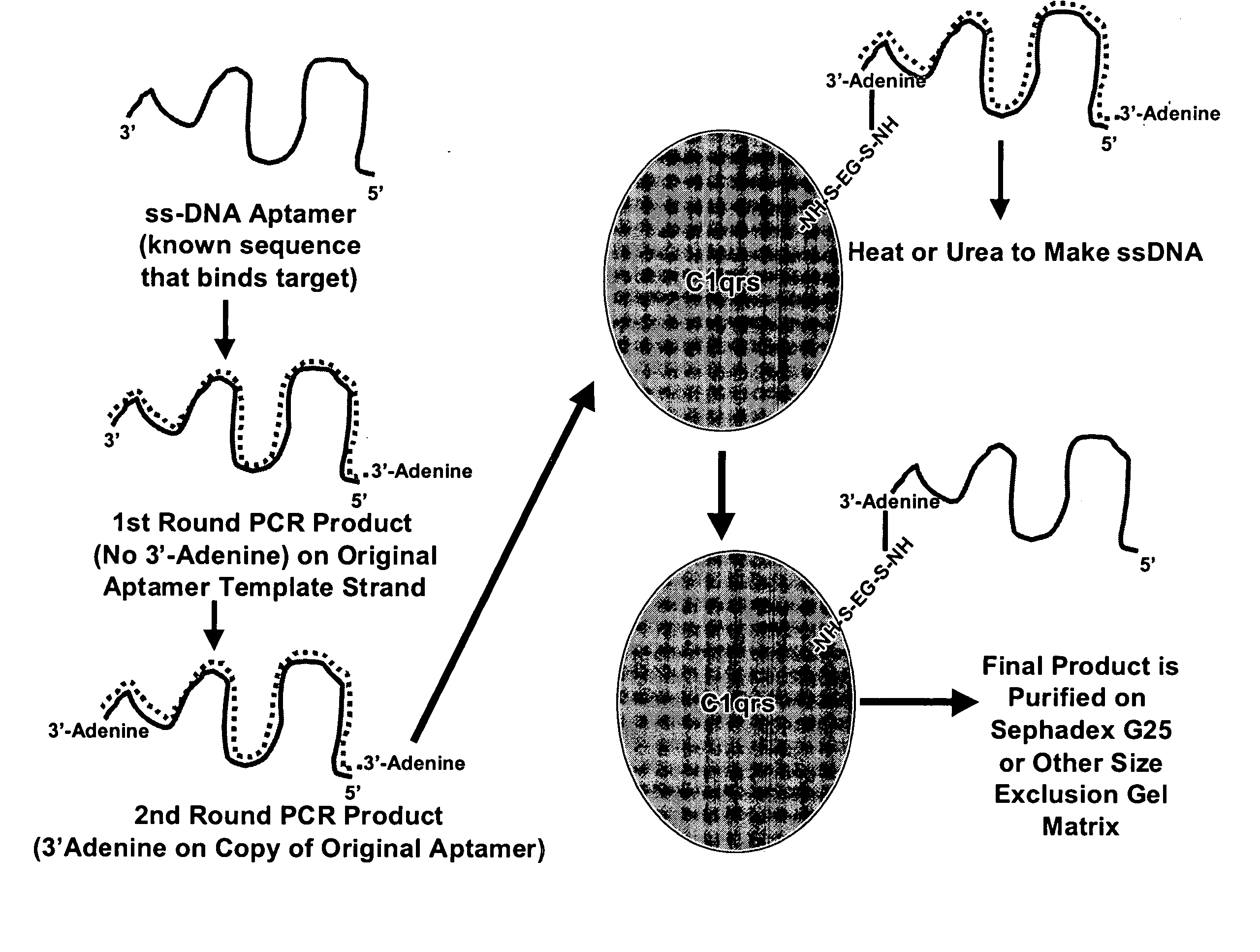
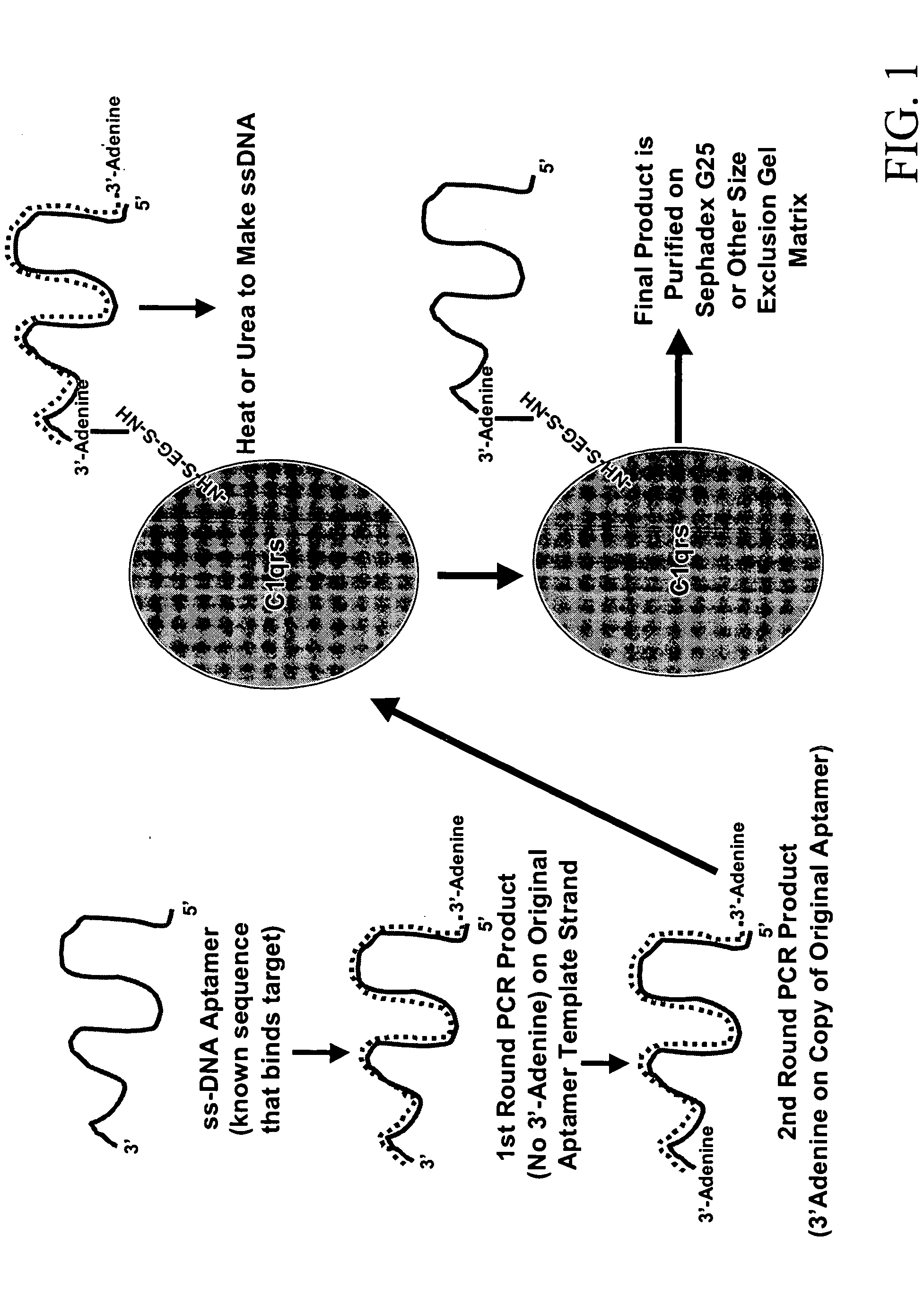
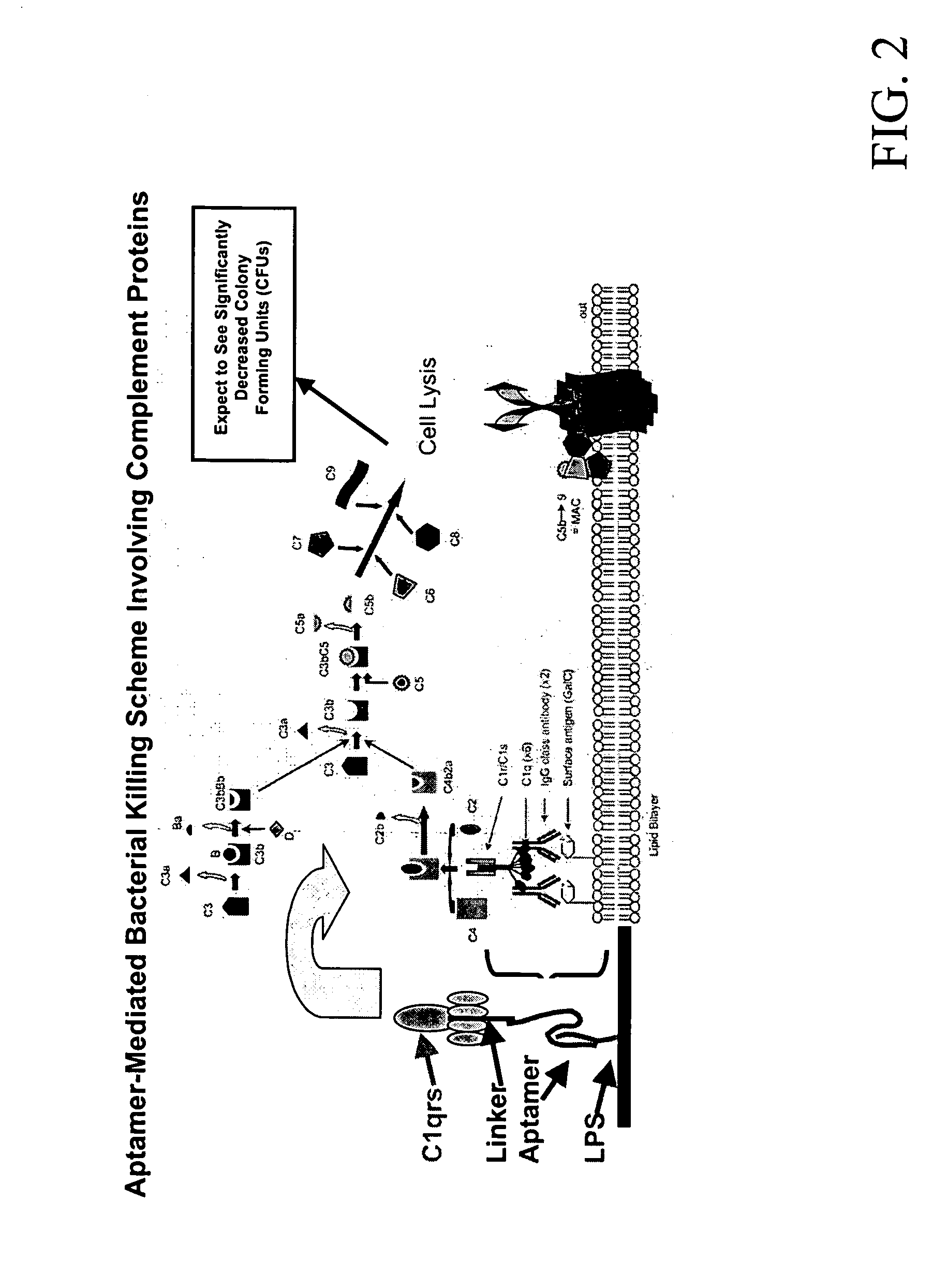
Methods are described for improvement of the serum half life of therapeutic nucleic acids by 3′ conjugation to useful target proteins, or other large molecules with useful function. In one embodiment, a 3′ A, C or G overhang is added to ds-DNA and the primary amines conjugated using biocompatible bifunctional linkers to proteins. The resulting nucleic acid-3′-conjugates are serum nuclease-resistant and retained in vivo for long periods without rapid kidney clearance. Further, the choice of conjugate imparts additional functionality to the nucleic acid-3-conjugate. For example, if the protein in the DNA-protein conjugate is the first component of the complement cascade (Clq or Clqrs) and the DNA aptamer has been developed against surface components of a target cell, it can be used to treat bacterial or parasitic infections and cancers. If the protein is serum albumin or another common (nonimmunogenic) blood protein and the aptamer is directed against a toxin or venom, the aptamer-protein conjugate can be used as an antidote that binds and neutralizes the toxin or venom. Similar DNA (aptamer)-nanotube, -enzyme, and -toxin conjugates could also be used to target and selectively kill bacteria, parasites, and cancer cells in vivo. If the protein is an Fc antibody fragment or C3b protein from the complement system and the aptamer is developed against a bacterial cell capsular material, other cell surface component or viral cell surface component, then the aptamer-3′-protein conjugate can aid in opsonization of the target cells or viruses by phagocytic leukocytes.
Owner:OTC BIOTECH
Anti-cigarette herbal formulation as an antidote to tobacco
InactiveUS20060137702A1Good effectControl is complicatedBiocideTobacco treatmentNicotiana tabacumCinnamomum zeylanicum
The present invention provides a novel nicotine free anticigarette herbal formulation as an anti-dote to the poisoning effects of tobacco products such as Cigarettes, Gutka, Pan masala and other similar tobacco related products. Formulation(s) comprises of sterilized dried plant powder / extracts together with the conventional additives to form the oral dosage forms, which include tablets, capsules, syrup and powders ready for suspension and mouth spray. The anti tobacco addiction herbal formulation comprises of Sesbania grandiflora, Catharanthus roseus, Ocimum sanctum, Myristica fragrans, Elettaria cardamomum, Carum copticum, Syzgium aromaticum, Cinnamomum tamala, Acorus calamus, Zingiber officinale, Piper nigrum, Cinnamomum zeylanicum, Cuminum cyminum, Nigella sativum, Cinnamomum camphora, Piper longum Ocimum gratssimum and Hemidesmus indicus.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method for degrading zearalenone
ActiveCN102406098ARestoring application valueEfficient degradationFood preparationTerra firmaAntidote
The invention relates to a method for degrading zearalenone, which is characterized in that: a fermentation product of aspergillus niger is used for degrading zearalenone in musty grain, wherein the fermentation product of the aspergillus niger is the dry powder of fermentation liquor. In the invention, because the fermentation product of aspergillus niger is used for degrading zearalenone, zearalenone in the musty grain can be effectively degraded, thereby restoring the application value of the musty grain. Meanwhile, by measuring the effect of the fermentation product of aspergillus niger on degrading ZEN (zearalenone) in the in-vitro environment of simulating the gastrointestinal tract, optimal degrading conditions of the fermentation product of aspergillus niger on ZEN are obtained, thereby providing a solid foundation for further developing the fermentation product of aspergillus niger into a biological antidote for degrading ZEN in the grain and feed.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP +1
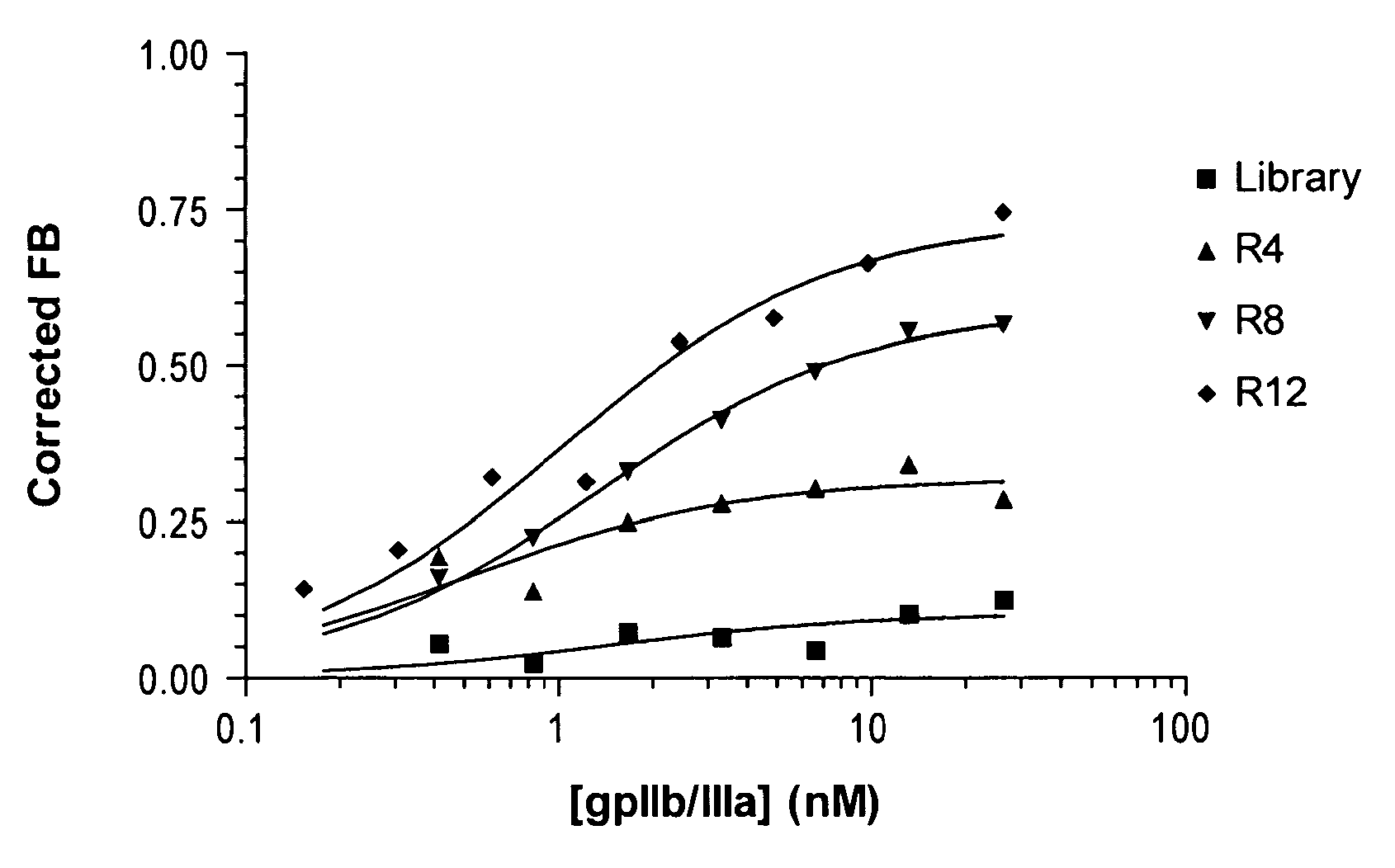
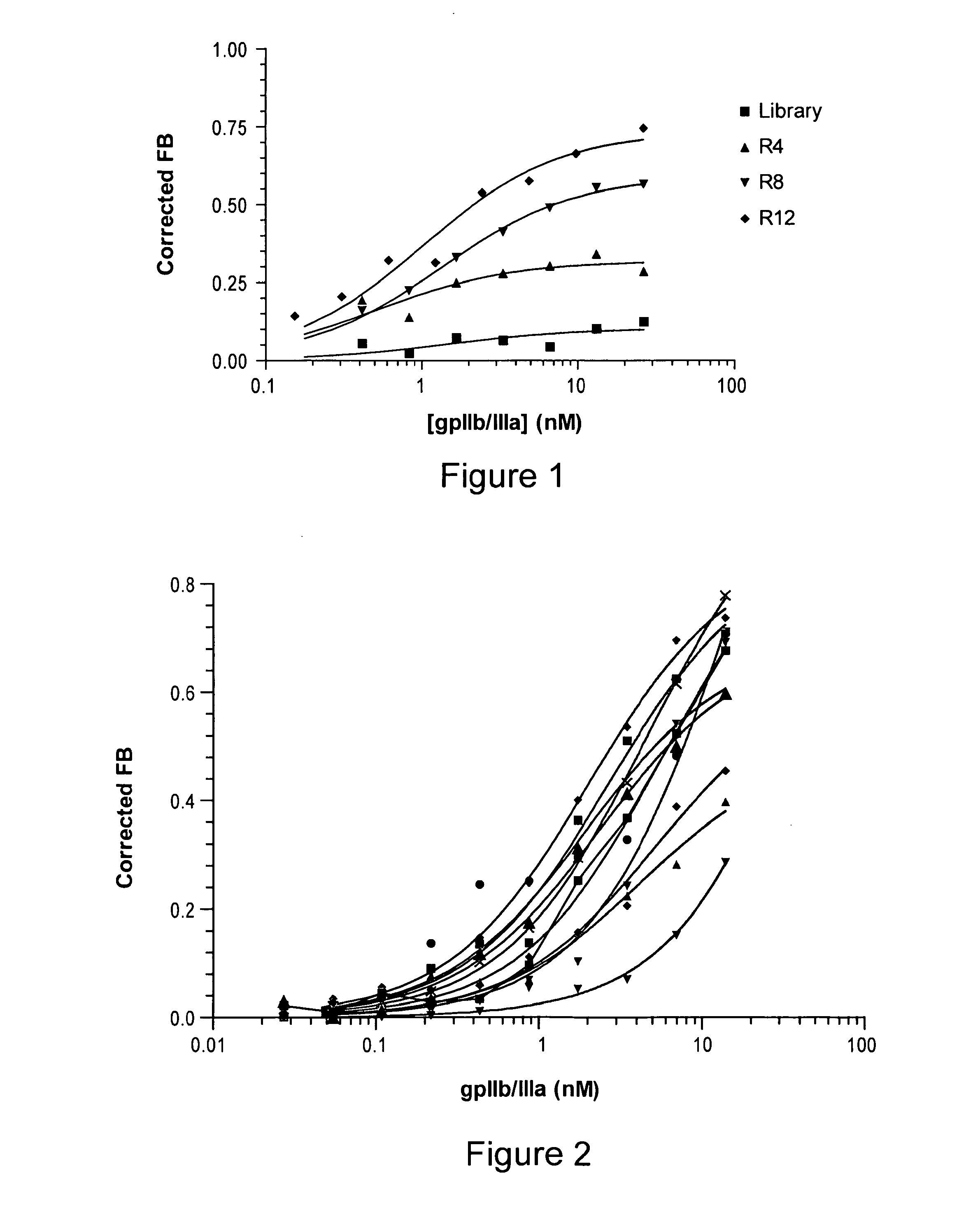
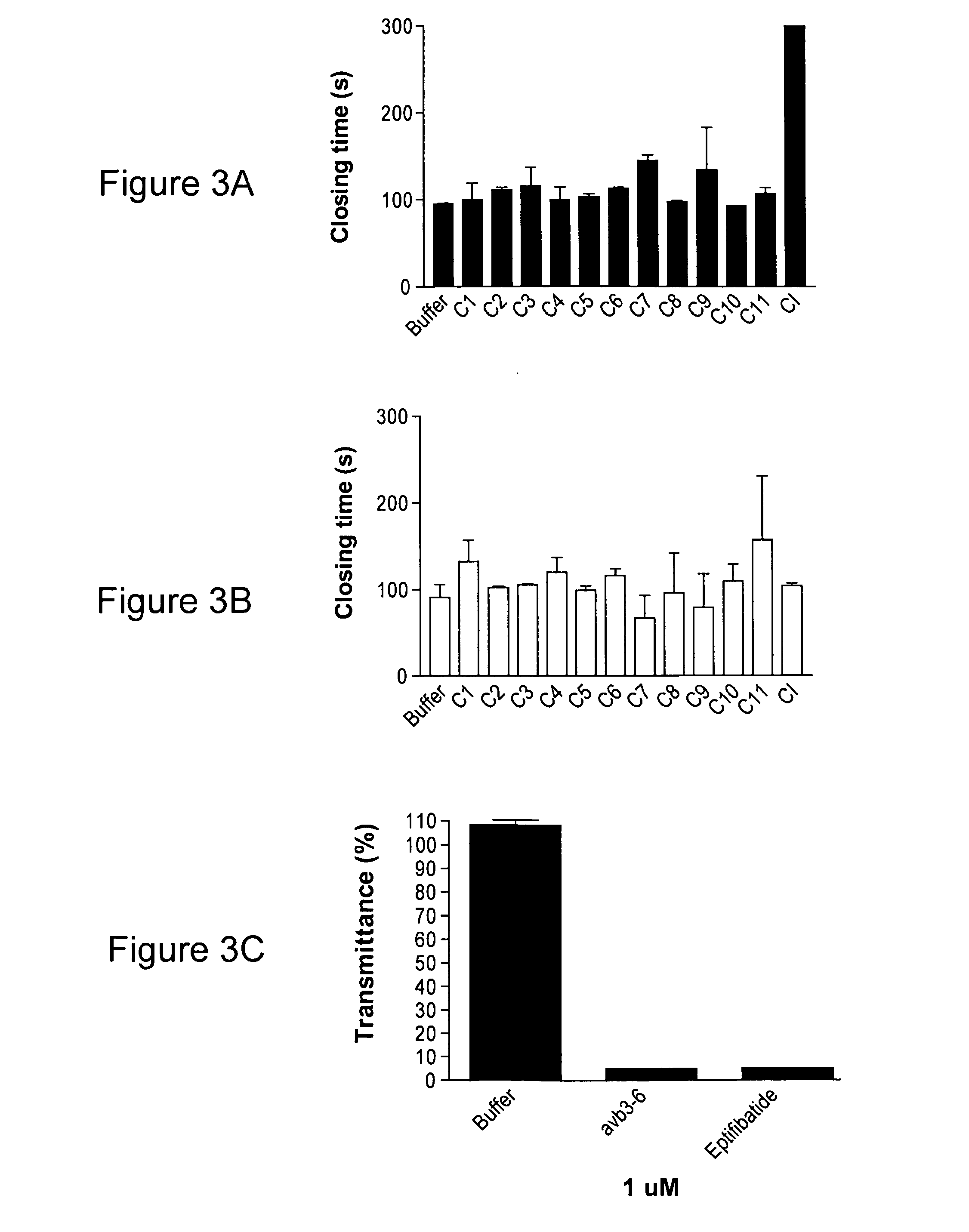
Reversible platelet inhibition
InactiveUS20110118187A1Inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesFactor VIII vWFAntidote
The present invention relates, in general, to receptors and to platelet aggregation and, in particular, to a method of inhibiting platelet aggregation using an aptamer that binds to and inhibits the activity of a receptor, such as glycoprotein IIb / IIIa (gpIIb / IIIa), and to aptamers suitable for use in such a method. The invention also relates to antidotes to antiplatelet agents and to methods of using such antidotes to reverse aptamer-induced platelet inhibition. The invention further relates to von Willebrand Factor (VWF) inhibitors, and antidotes therefore, and to methods of using same.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Water body antidote in field of freshwater aquaculture and preparing and using method thereof
InactiveCN104386837AEliminate hazardsImprove survival rateSpecific water treatment objectivesScale removal and water softeningSorbentFresh water organism
The invention discloses a water body antidote in the field of freshwater aquaculture and a preparing and using method thereof. The antidote is prepared by mixing a carrier material, an adsorbent, traditional Chinese herbs, organic acid and a metal-chelator. Under the combined effect of the adsorbent, active ingredients of the traditional Chinese herbs, the organic acid and the metal-chelator, the water body antidote can be used for decolorizing, deodorizing, softening, clarifying, sterilizing and detoxifying a water body, so that the water body can be clarified, foreign odors can be eliminated, dissolved oxygen can be increased, harm of heavy metal ions and pathogenic bacteria to aquatic products can be relieved, the survival rate of young aquatic animals can be improved, and development of the fresh water aquiculture industry can be promoted.
Owner:安徽华亿农牧科技发展有限公司
Compositions and methods for transepithelial molecular transport
The invention relates to fragments of Clostridium botulinum HC that can be linked with an entity (e.g., an antigen, a particle, or a radionuclide) and used to deliver the entity across a non-keratinized epithelial membrane of an animal. The fragments are useful, for example, for making vaccines, antidotes, and anti-toxins and in situations in which rapid uptake of an agent by an animal is desired.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Device and method for detecting and treating chemical and biological agents
InactiveUS7354429B2Volume/mass flow measurementVolume measurement and fluid deliveryResonanceAntidote
A device and method capable of sensing the presence of biochem agents, and preferably also capable of delivering precise amounts of one or more antidotes to treat a victim exposed to the agents. The device includes a freestanding tube portion having an internal passage containing a substance selective to a chemical or biological agent so that matter accumulates within the freestanding tube portion when a fluid drawn through the tube portion contains the agent. When vibrated at resonance, the resonant frequency of the tube portion is indicative of the accumulation of matter and thereby the presence of the agent to which the substance is selective. The device then preferably delivers precise amounts of one or more appropriate antidotes to treat the victim. The device is a sufficiently small and lightweight unit to permit being carried by an individual.
Owner:INTEGRATED SENSING SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com