Patents
Literature
303 results about "Venom" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Venom is a secretion containing one or more toxins produced by an animal. Venom has evolved in a wide variety of animals, both predators and prey, and both vertebrates and invertebrates. Venoms kill through the action of at least four major classes of toxin, namely necrotoxins and cytotoxins, which kill cells; neurotoxins, which affect nervous systems; and myotoxins, which damage muscles. Biologically, venom is distinguished from poison in that poisons are ingested, while venom is delivered in a bite, sting, or similar action. Venomous animals cause tens of thousands of human deaths per year. However, the toxins in many venoms have potential to treat a wide range of diseases.
Method for producing swine fever live vaccine with cell line
ActiveCN101181637AGuaranteed to be pureEnsure safetyAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsQuality controlSeedling
The invention discloses a method for producing a live swine fever vaccine by using a cell line. The present invention comprises the following technical steps: (1) selecting a cell line as the cells for making seedlings; (2) subculture and cultivation of cells for making seedlings; (3) breeding of cytotoxic species; (4) breeding of venom for making seedlings; 5) Mixing seedlings, subpackaging and freeze-drying. The invention has the advantages of simple and stable production process, easy operation, high virus content, small difference between batches, easy quality control, and can significantly improve the yield and quality of vaccines. The live swine fever vaccine produced by the invention has good safety and high immune efficacy, and has complete immune protection against the virulent attack of swine fever.
Owner:CHINA INST OF VETERINARY DRUG CONTROL +1
Preparation method of Muscovy duck parvo novel vaccines
ActiveCN101880651AGenetically stableImprove securityMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsFibroblastCells fibroblast
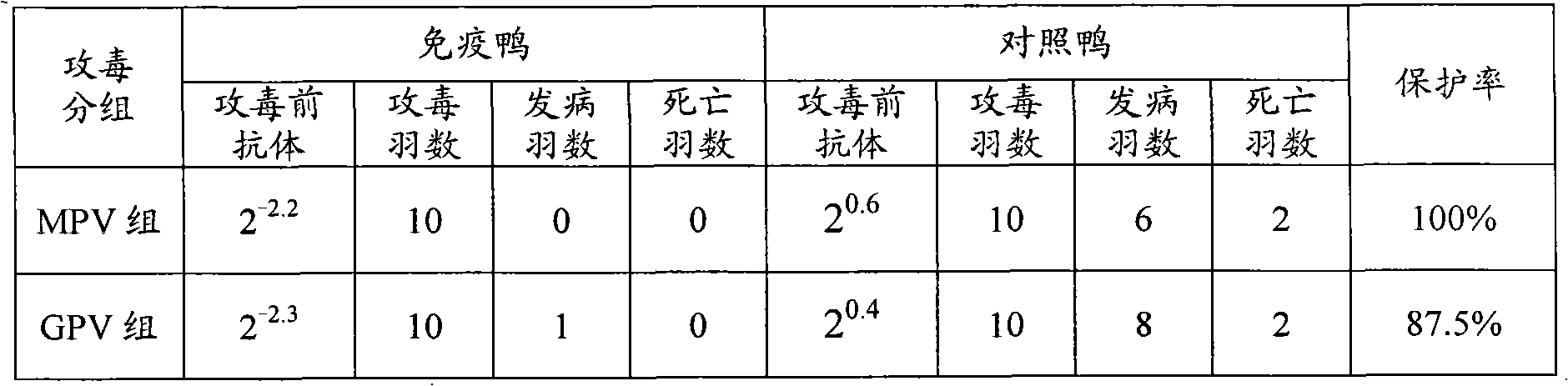
The invention relates to a preparation method of Muscovy duck parvo novel vaccines, which comprises the following steps of: using Muscovy duck parvovirus attenuated virus P1 strain (MPV-P1 strain with a preservation number of CCTCC NO:V201013) and Muscovy duck origin goose parvovirus attenuated virus D strain ( GPV-D strain with a preservation number of CCTCC NO:V201014) as seed viruses; proliferating viruses by applying the muscovy duck embryone fibroblast spinner culture technology to obtain cell toxic liquids; mixing the cell toxic liquids according to the proper proportion and freezing a dry protective agent to freeze and dry to research safe and effective Muscovy duck parvo novel vaccines. The young Muscovy ducks are inoculated once so as to prevent and control the Muscovy duck parvovirus infection and the Muscovy duck gosling blast dieases at the same time, thereby the stress reaction of the Muscovy ducks caused by immunization for many times is solved. The invention is suitable for scale production under the GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) condition, and saves the production cost of the vaccines.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
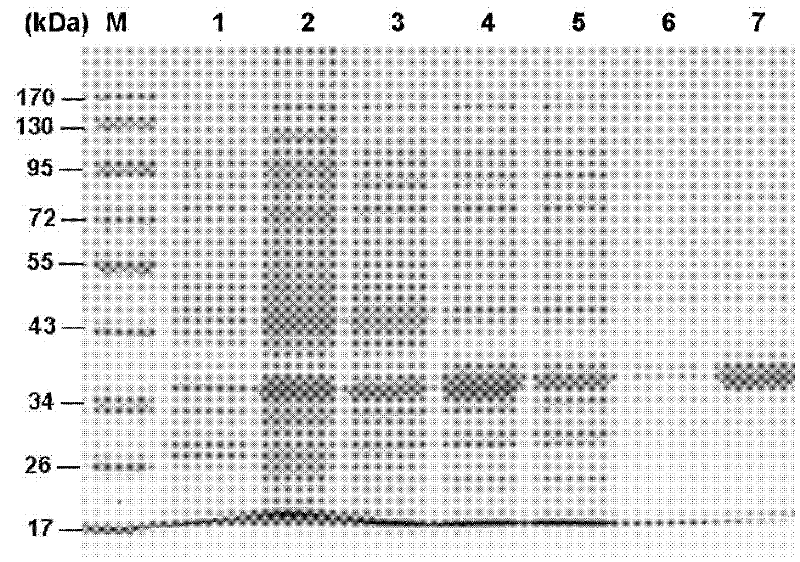
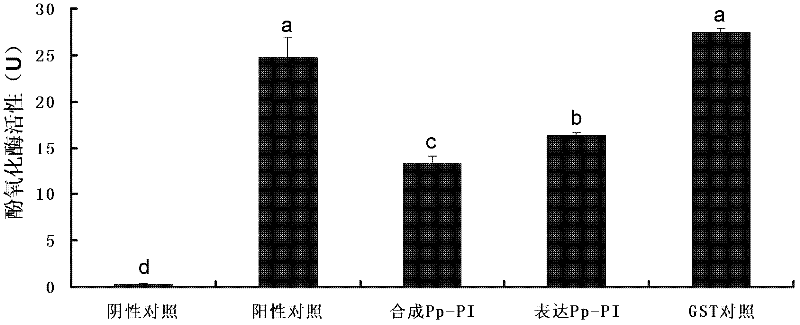
Serine protease inhibitor pp-pi polypeptide from chrysalis chrysalis chrysalis venom and its application
ActiveCN102260348AMicroorganism based processesRecombinant DNA-technologySerine Protease InhibitorsSymbiotic bacteria
The invention discloses a Pteromalus puparum venom serine protease inhibitor Pp-PI polypeptide which has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. At the same time, the invention also discloses a gene for encoding the Pteromalus puparum venom serine protease inhibitor Pp-PI polypeptide. The gene has a nucleotide sequence from the 126th nucleotide to the 290th nucleotide in SEQ ID NO: 1; or the gene has at least 70% homology with the nucleotide sequence from the 126th nucleotide to the 290th nucleotide in SEQ ID NO: 1; or the gene has a nucleotide sequence which can hybridize with the nucleotide sequence from the 126th nucleotide to the 290th nucleotide in SEQ ID NO: 1 at 40-55 DEG C. The Pteromalus puparum venom serine protease inhibitor Pp-PI polypeptide can be used to prepare a Pteromalus puparum venom serine protease inhibitor for genetically modifying crops or altering plant symbiotic bacteria.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
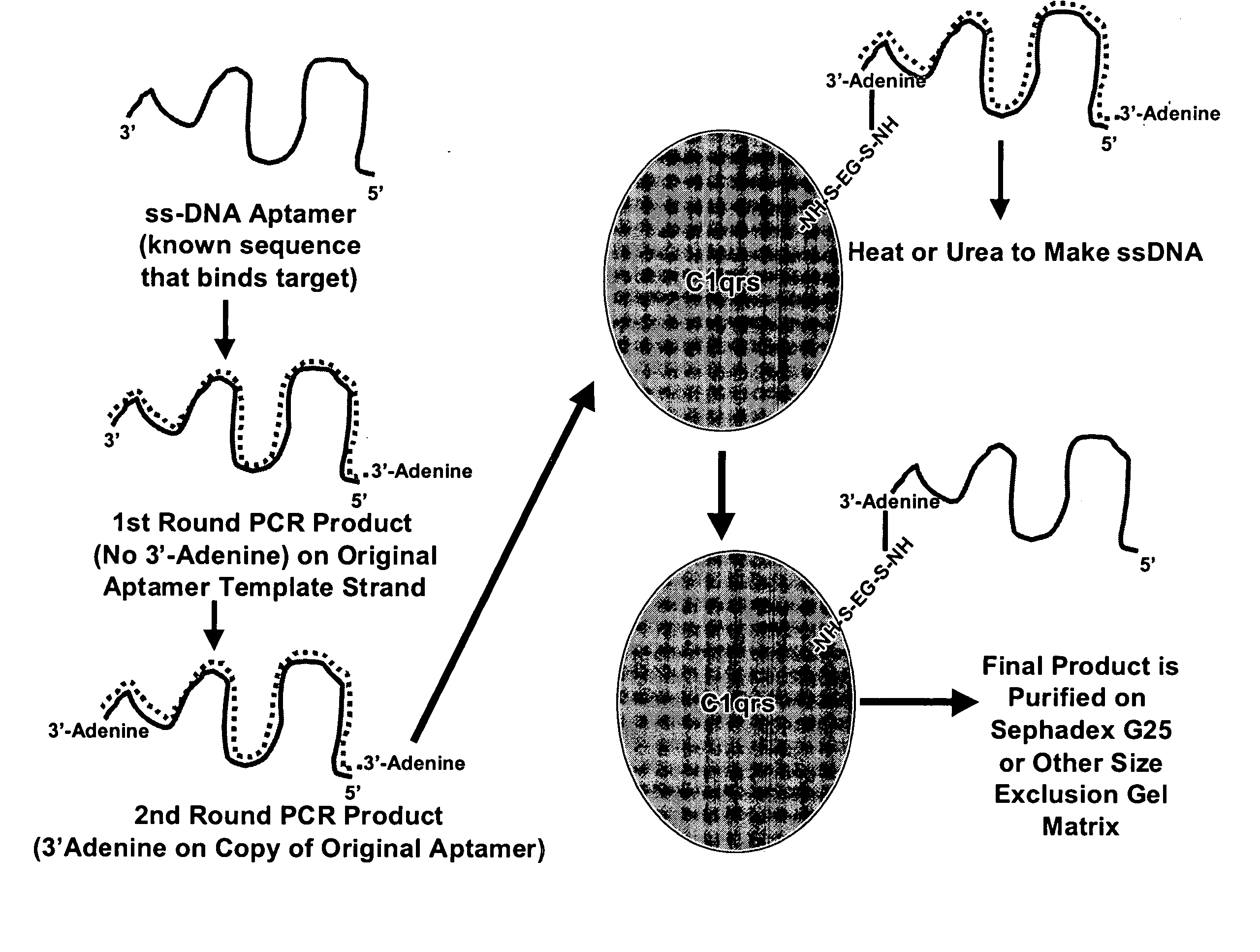
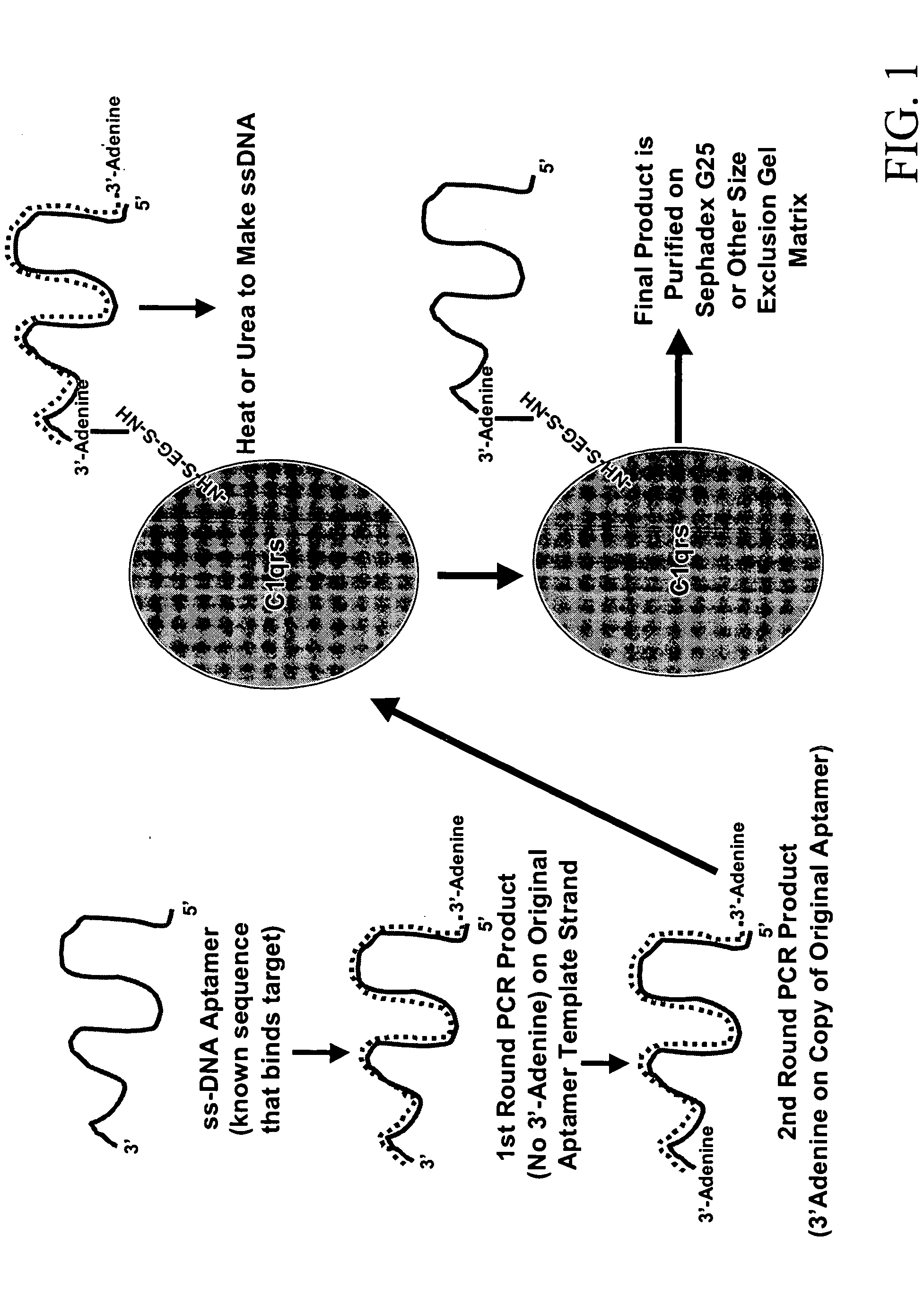
Therapeutic nucleic acid-3' -conjugates
InactiveUS20050191680A1Efficient killingPrevent breakdownMaterial nanotechnologyActivity regulationHalf-lifeWhite blood cell
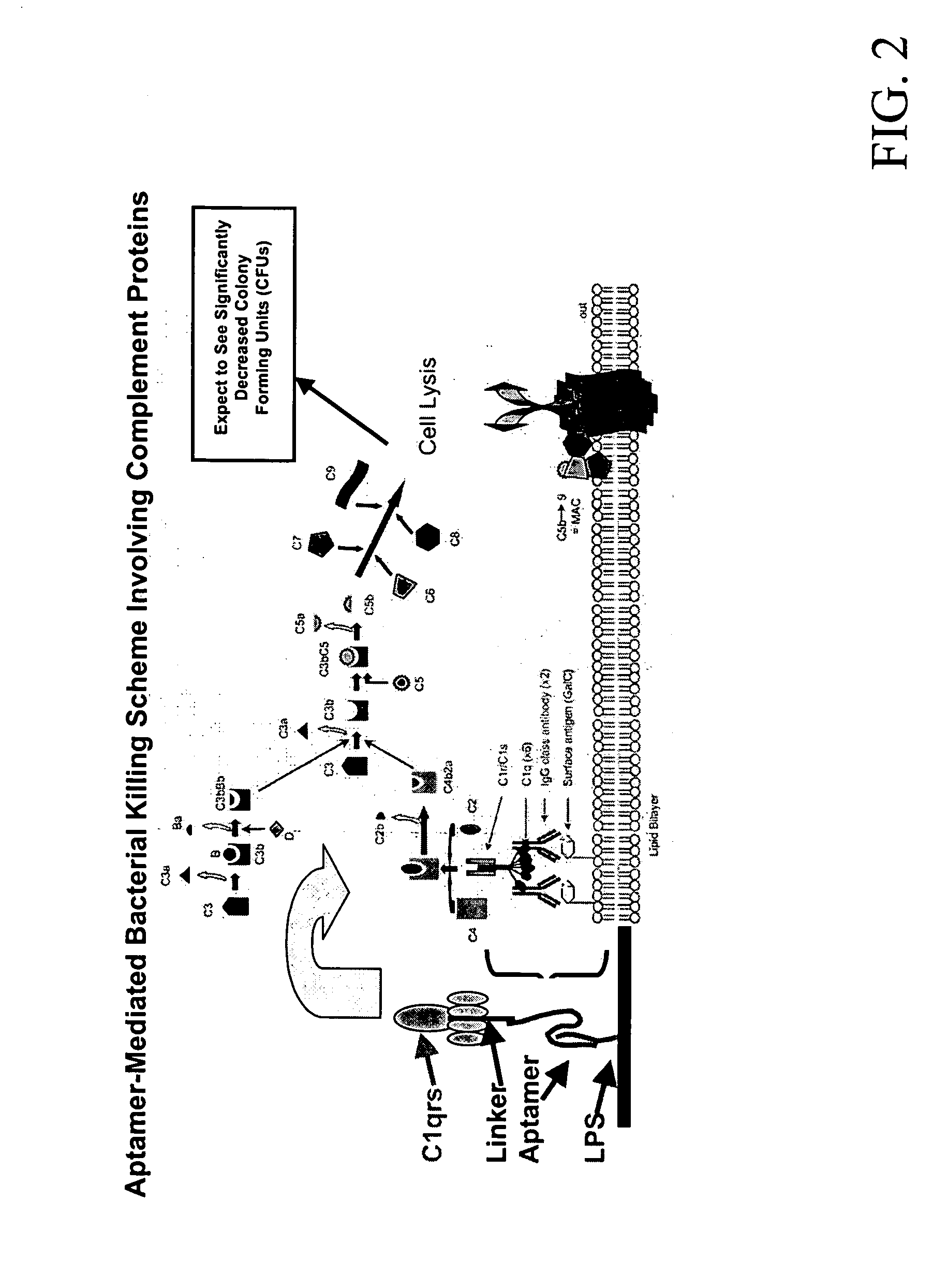
Methods are described for improvement of the serum half life of therapeutic nucleic acids by 3′ conjugation to useful target proteins, or other large molecules with useful function. In one embodiment, a 3′ A, C or G overhang is added to ds-DNA and the primary amines conjugated using biocompatible bifunctional linkers to proteins. The resulting nucleic acid-3′-conjugates are serum nuclease-resistant and retained in vivo for long periods without rapid kidney clearance. Further, the choice of conjugate imparts additional functionality to the nucleic acid-3-conjugate. For example, if the protein in the DNA-protein conjugate is the first component of the complement cascade (Clq or Clqrs) and the DNA aptamer has been developed against surface components of a target cell, it can be used to treat bacterial or parasitic infections and cancers. If the protein is serum albumin or another common (nonimmunogenic) blood protein and the aptamer is directed against a toxin or venom, the aptamer-protein conjugate can be used as an antidote that binds and neutralizes the toxin or venom. Similar DNA (aptamer)-nanotube, -enzyme, and -toxin conjugates could also be used to target and selectively kill bacteria, parasites, and cancer cells in vivo. If the protein is an Fc antibody fragment or C3b protein from the complement system and the aptamer is developed against a bacterial cell capsular material, other cell surface component or viral cell surface component, then the aptamer-3′-protein conjugate can aid in opsonization of the target cells or viruses by phagocytic leukocytes.
Owner:OTC BIOTECH
Hemostatic compositions, devices and methods
InactiveUS7094428B2Lower Level RequirementsReduce concentrationPowder deliveryFactor VIIFactor VIIaBiopolymer
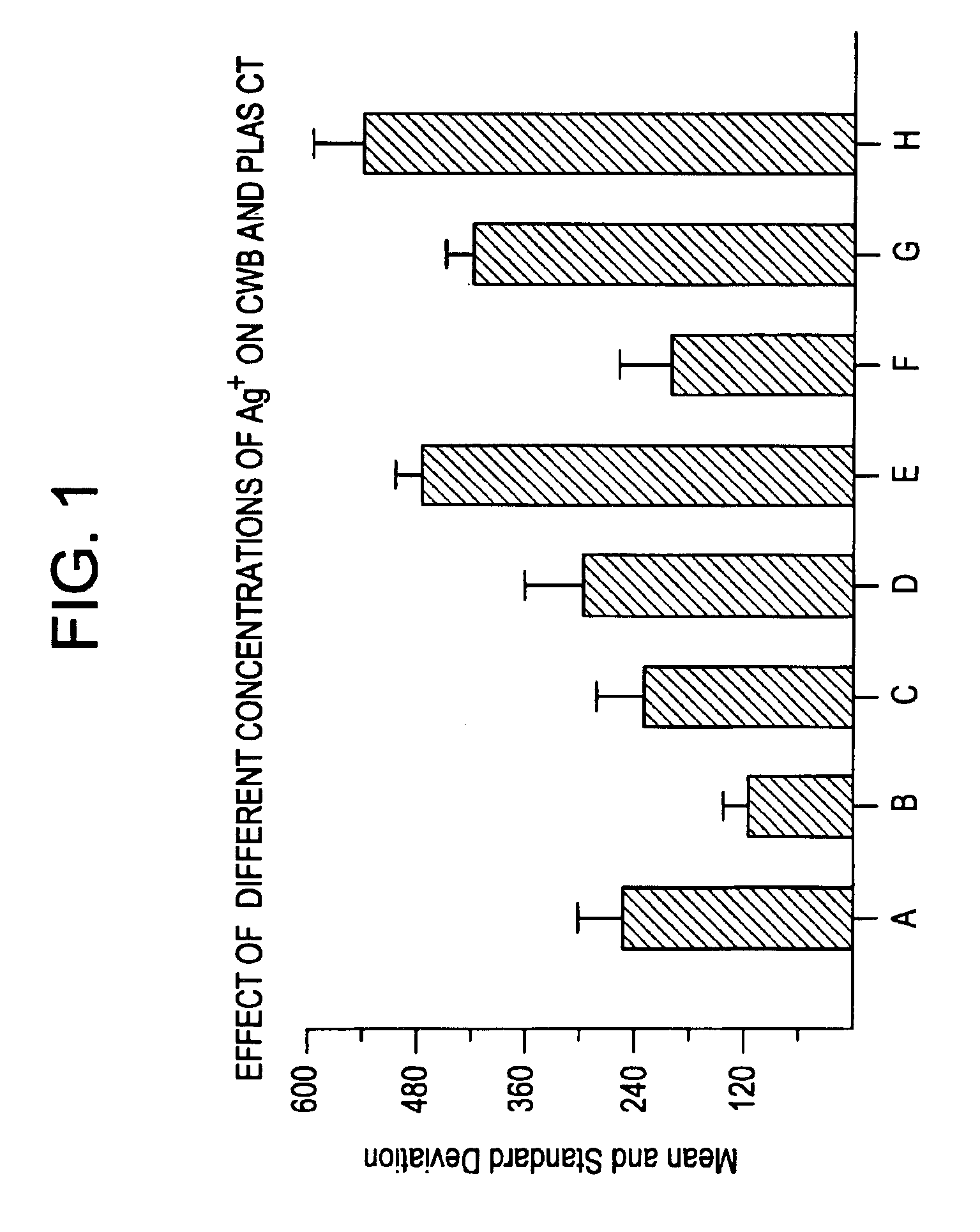
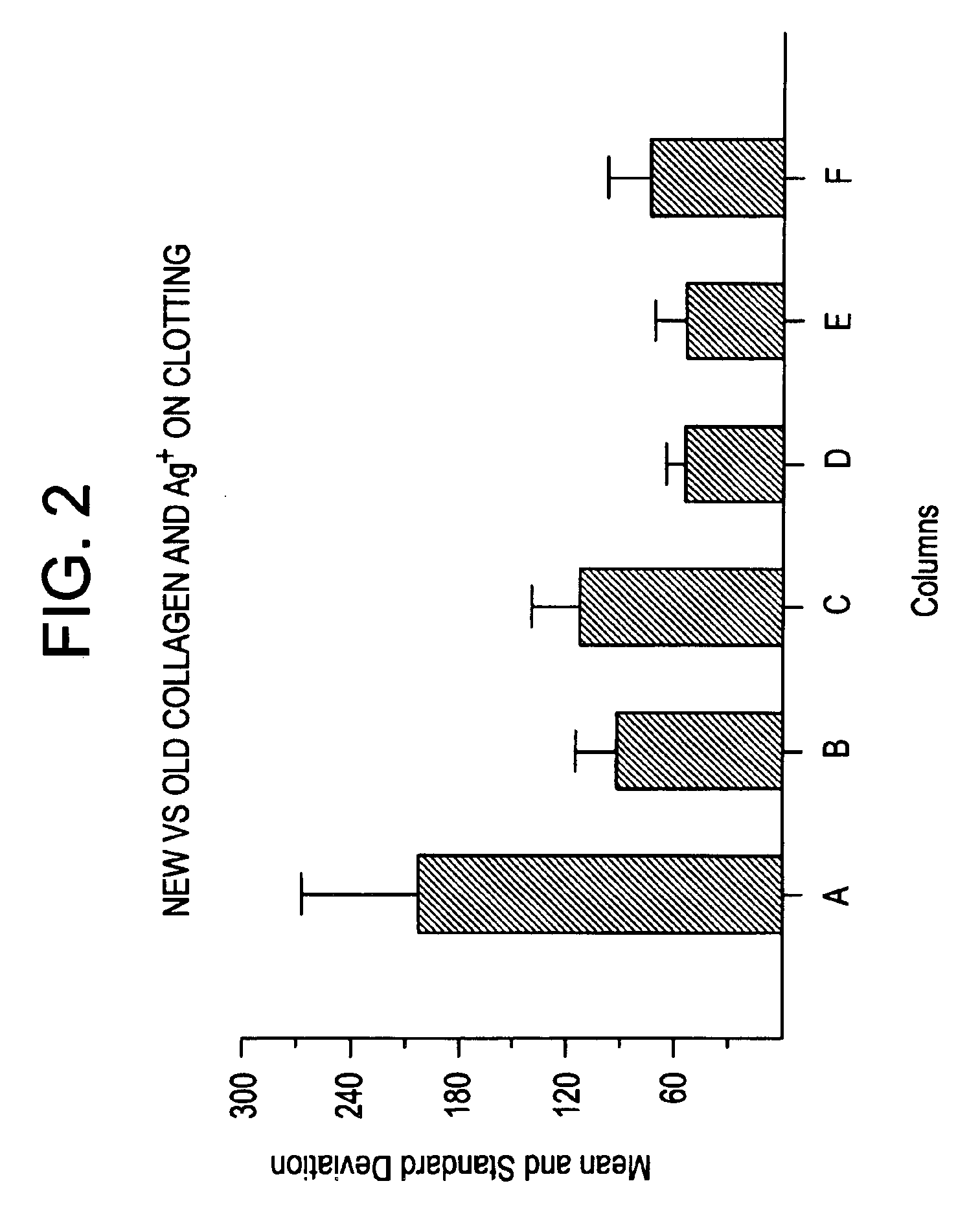
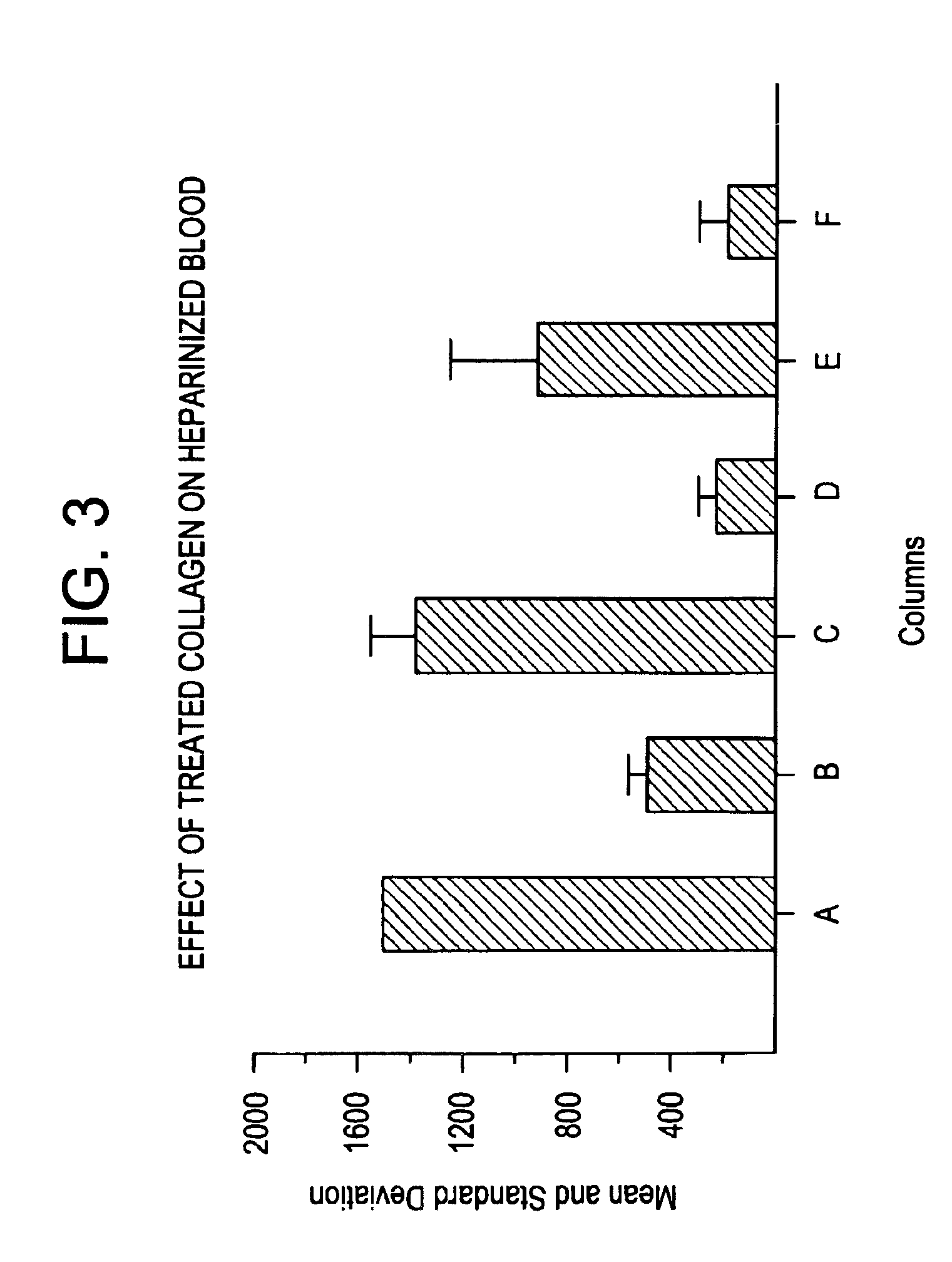
A hemostatic composition which comprises at least one procoagulant metal ion, such as silver (I) or mercury (II), and at least one procoagulant biopolymer, such as collagen, thrombin, prothrombin, fibrin, fibrinogen, heparinase, Factor VIIa, Factor VIII, Factor IXa, Factor Xa, Factor XII, von Willebrand Factor, a selectin, a procoagulant venom, a plasminogen activator inhibitor, glycoprotein IIb-IIIa, a protease, or plasma. The composition in the form of a paste, dough, glue, liquid, lyophilized powder or foam, may be provided, for application to a wound. A hemostatic device is also described which comprises a hemostatic composition as described above. The device may be in the form of, for example, a plug, bandage, gauze, cloth, tampon, membrane or sponge. Methods are also provided for prophylaxis or treatment of bleeding at a site by application to the site of the composition or device as described.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Α-conotoxin peptides
InactiveUS6855805B2Quick effectPromote recoverySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineMuscle relaxant
The invention relates to relatively short peptides (termed α-conotoxins herein), about 10-25 residues in length, which are naturally available in minute amounts in the venom of the cone snails or analogous to the naturally available peptides, and which preferably include two disulfide bonds. The α-conotoxins, as described herein, are useful for as neuromuscular blocking agents, such as muscle relaxants.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND +1
Preparatino method of low-molecular chitosar quaternary ammonium salt complex iodine clear venom
InactiveCN1470167AImprove antibacterial propertiesMaintain concentrationBiocideAnimal repellantsQuaternary ammonium cationDisinfectant
The invention is a preparing method of the low-molecular chitosan quaternary-ammonium-salt complex iodine sterilizing solution, its character: mixing and agitating the low-molecular chitosan quaternary-ammonium-salt or low-molecular chitosan solution with one, two or all of dialkyl diquaterary ammonium salt, dialkyl quaterary ammonium salt, and methyl quaterary ammonium salt, then heating the mixed solution, adding with iodine, or iodine and iodate, preserving heat to react, and cooling to room temperature. It is an environmental-protection, strong-efficiency disinfectant, irritation and the toxicity lower, and the sterilizing effect more stable and permanent.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Application of baby hamster kidney(BHK)-21 cell serum-free suspension culture technology in foot-and-mouth disease vaccine production
ActiveCN102178946AShort cycleIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsSerum igeSerum free
The invention discloses application of a baby hamster kidney(BHK)-21 cell serum-free suspension culture technology in foot-and-mouth disease vaccine production, which comprises the following steps of: 1) performing cell recovery; 2) performing reactor culture and cell amplification culture; and 3) inoculating foot-and-mouth disease virus seed venom and collecting the venom. A process for producing foot-and-mouth disease inactivated vaccines by culturing the BHK-21 cells through serum-free suspension culture and a step-by-step cell amplification method make the production period f the foot-and-mouth disease vaccines shortened and yield increased, and ensure stable quality and obvious benefit. The production process reduces the using amount of a culture medium, and the amount of the collected virus liquid is the culture medium consumption amount, while the culture medium consumption amount in a roller bottle production process is 2 times higher than the amount of the collected virus liquid, and bovine serum which is about 5 percent of the culture medium amount is needed.
Owner:马忠仁 +5
Method for producing pseudorabies living vaccines by using subculture cell source and product thereof
ActiveCN101695573AImprove securityImprove immune efficiencyAntiviralsViruses/bacteriophagesPig kidneyAntibiotic Y
The invention provides a method for producing pseudorabies living vaccines by using a subculture cell source and a pseudorabies living vaccine product thereof. The method comprises the following steps: culturing pseudorabies virus low-virulent strains by using subculture cells; harvesting the strains to obtain cell culture venom; and then adding a stabilizing agent and an antibiotic into the cellculture venom, and freezing and vacuum-drying the mixture to obtain the pseudorabies living vaccines of the subculture cell source. The subculture cells are subculture cells ST of pig testicle or subculture cells PK15 or IBRS-2 of pig kidney. The method for producing the pseudorabies living vaccines by using the subculture cell source has the advantages of simple and stable production process, easy operation, high virus content, little batch difference and controllable quality, can remarkably improve the yield and quality of the vaccines and reduce the anaphylactic reaction and the like. The pseudorabies living vaccines obtained by using the production method of the invention have good safety and high immune efficacy, and have better immune protection effect on pseudorabies virulent attack.
Owner:广东永顺生物制药股份有限公司
Microbial delivery system
InactiveUS8153414B2Reduce exposureReduce riskBacterial antigen ingredientsProtozoa antigen ingredientsAntigenDelivery system
The present invention provides methods and compositions for treating or preventing allergic responses, particularly anaphylactic allergic responses, in subjects who are allergic to allergens or susceptible to allergies. Methods of the present invention utilize administration of microorganisms to subjects, where the microorganisms produce allergens and protect the subjects from exposure to the allergens until phagocytosed by antigen-presenting cells. Particularly preferred microorganisms are gram-negative bacteria, gram-positive bacteria, and yeast. Particularly preferred allergens are proteins found in foods, venoms, drugs and latex that elicit allergic reactions and anaphylactic allergic reactions in individuals who are allergic to the proteins or are susceptible to allergies to the proteins. The proteins may also be modified to reduce the ability of the proteins to bind and crosslink IgE antibodies and thereby reduce the risk of eliciting anaphylaxis without affecting T-cell mediated Th1-type immunity.
Owner:N FOLD LLC
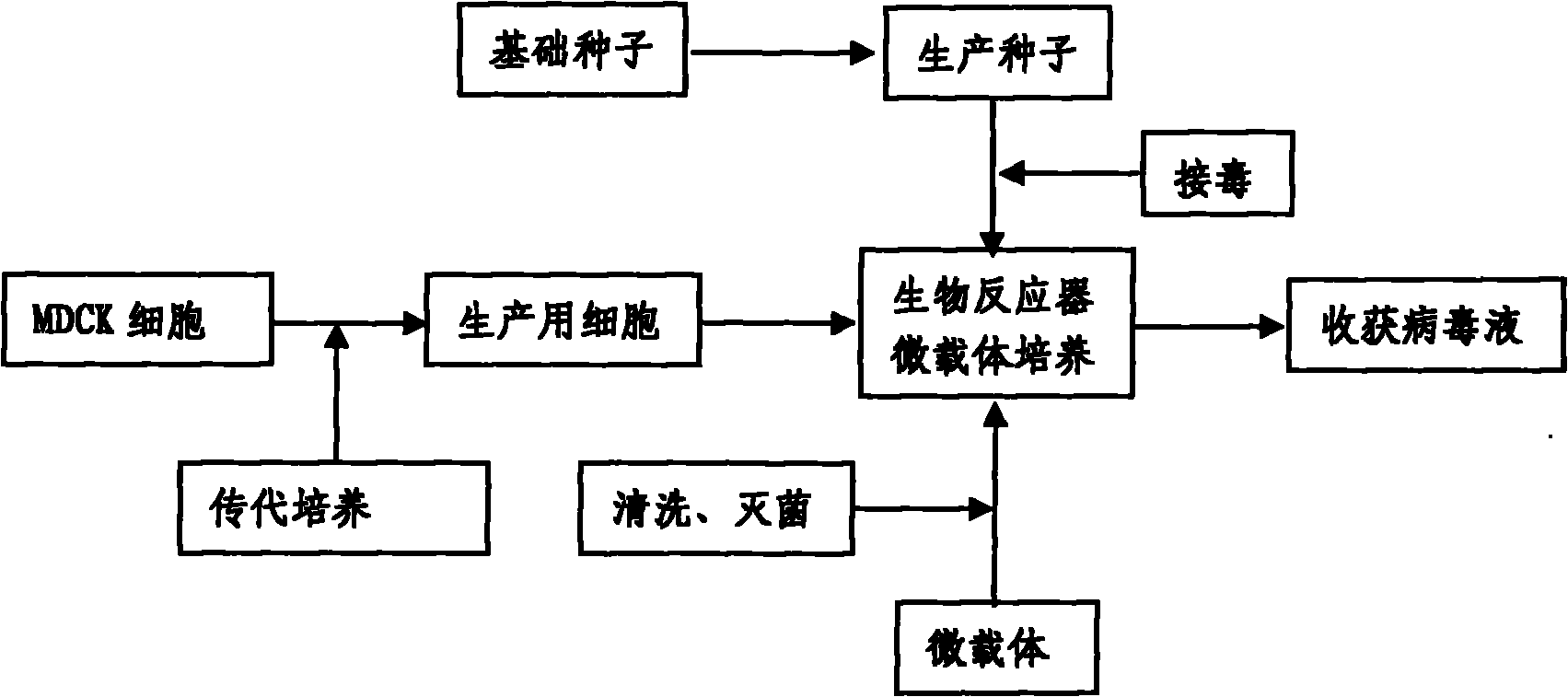
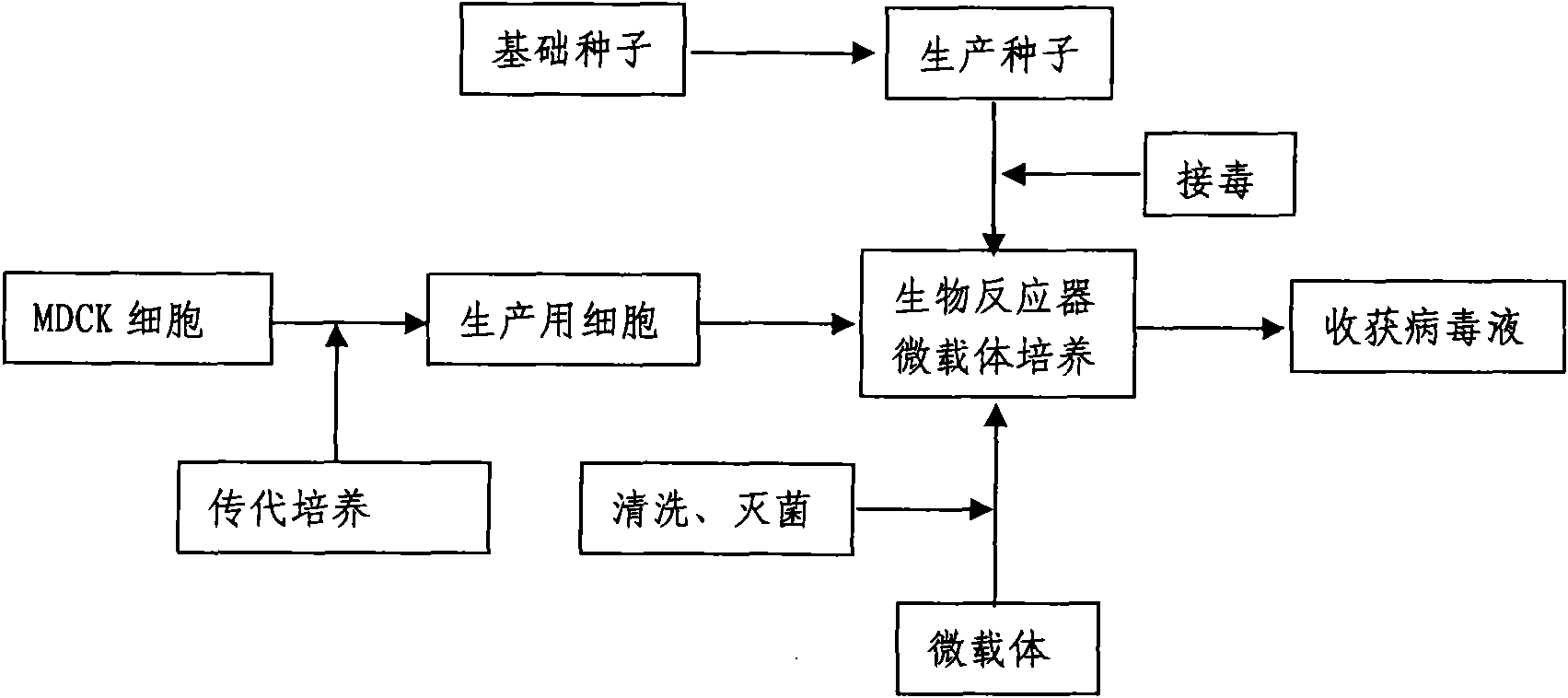
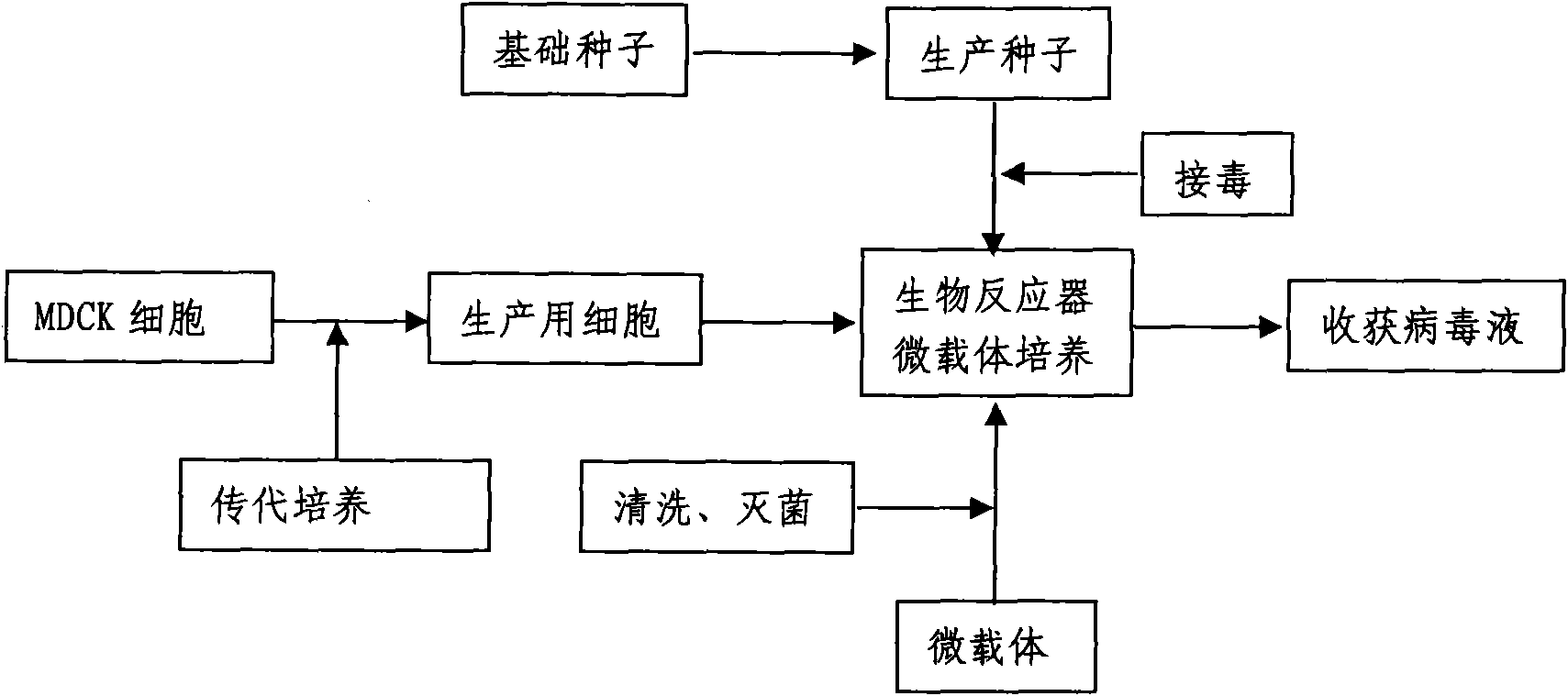
Production method for influenza virus vaccines
InactiveCN101818131ASolve yourselfSolve pollutionAntiviralsViruses/bacteriophagesEquine influenza vaccineBioreactor
The invention discloses a production method for vaccines of avian influenza virus and other influenza virus such as swine influenza, dog influenza and equine influenza, which comprises the following steps of: (1) transfer of culture and cultivation of vaccine-made cells; (2) reproduction of vaccine-made virus seeds; (3) microcarrier suspension culture of MDCK cells in a bioreactor; (4) reproduction of vaccine-made virus liquid; and (5) harvest of the virus liquid. The production method has the advantages of reducing the production cost greatly and improving the yield and quality of the vaccines obviously, along with short production period, no restriction to raw material supply, small occupied area, easy and quick expansion of production scale, light environmental pollution, easy processing, high automaticity, low employment and easy realization of balanced and stable quality.
Owner:成都史纪生物制药有限公司
Preparation method of swine pseudorabies vaccine
The invention relates to a preparation method of a swine pseudorabies vaccine, which comprises the following steps of: culturing a virus by using a swine testicle cell, and when one layer of cells grows, inoculating a swine pseudorabies virus; then adding into a cell maintenance medium, statically or rotatably culturing, when the cell suffers from more than 80 percent of pathological changes, harvesting a cell culture, repeatedly freeze-thawing to obtain a cell venom containing supernate, and mixing the cell venom qualified in toxic valence detection with formaldehyde for inactivating; and mixing with an emulsifying agent for emulsifying to obtain the swine pseudorabies vaccine. Compared with the prior art, a strain used for preparing the vaccine has the advantages of stronger toxicity and high virus valence; the swine pseudorabies vaccine has good immunogenicity and long immunization period; and the preparation method has the advantages of reasonable process and lower cost, thereby greatly lowering the cost load of the fish breeding and poultry raising industry.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELITE AGRI SCI TECH GROUP +1
Method for producing pseudorabies attenuated vaccine by using bioreactor and pseudorabies attenuated vaccine product
ActiveCN101695572AImprove immune efficiencyIncrease growth densityMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsVaccine ProductionAntibiotic Y
The invention provides a method for producing a pseudorabies attenuated vaccine by using a bioreactor and a pseudorabies attenuated vaccine product. After being sterilized, the bioreactor and a micro carrier are inoculated with cells for producing the vaccine, and a cell growth medium is added for culture. A maintenance medium containing attenuated strains of pseudorabies viruses are inoculated into the bioreactor to continue culturing the cells. 2 to 3 days after virus inoculation, cell culture virus liquid is obtained and added with a stabilizer and antibiotics, and the cell culture virus liquid is refrigerated and dried under vacuum to obtain the pseudorabies attenuated vaccine. In the method, the cell density and virus concentration are improved greatly, the titer of the vaccine is improved, the side reactions, labor intensity and product cost are reduced, the monitoring performance of vaccine production is improved and uniform and stable product quality is guaranteed. The pseudorabies attenuated vaccine produced by the method has high safety, immune efficacy and good immune and protective effect against the attack by the virulent pseudorabies viruses.
Owner:广东永顺生物制药股份有限公司
Oil emulsion vaccine for broilers and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102579339APromote absorptionQuick resultsViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsOil emulsionOil phase
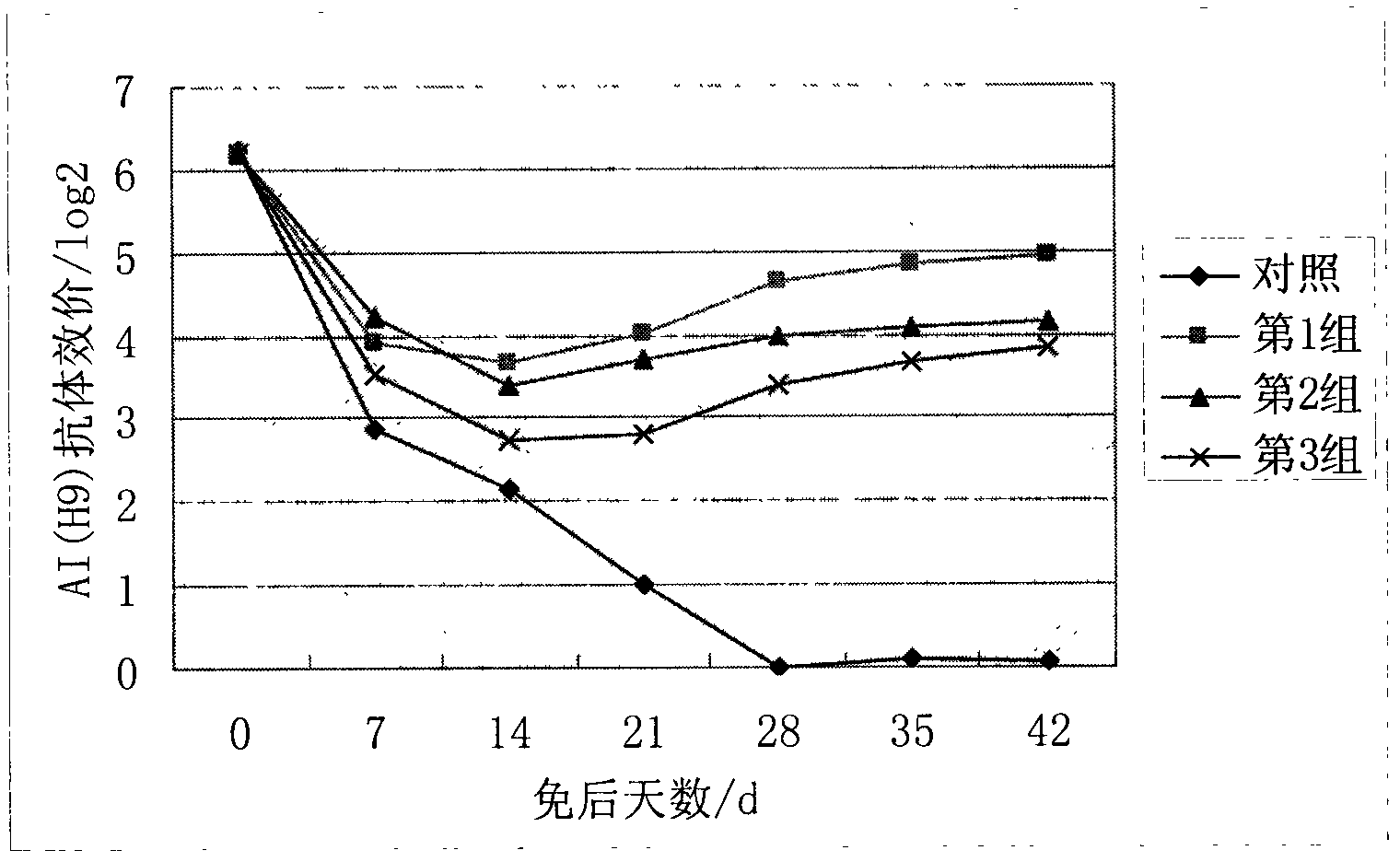
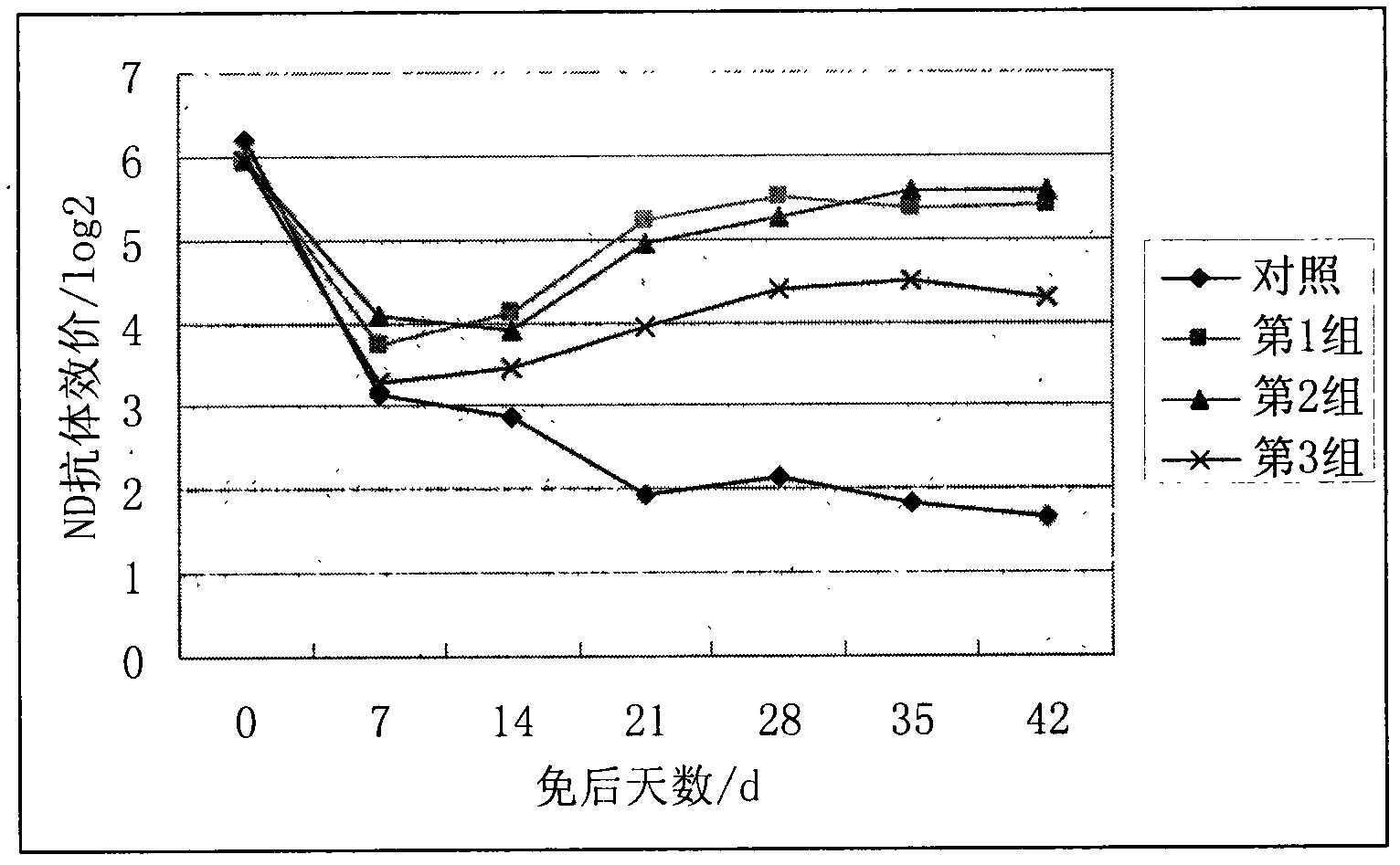
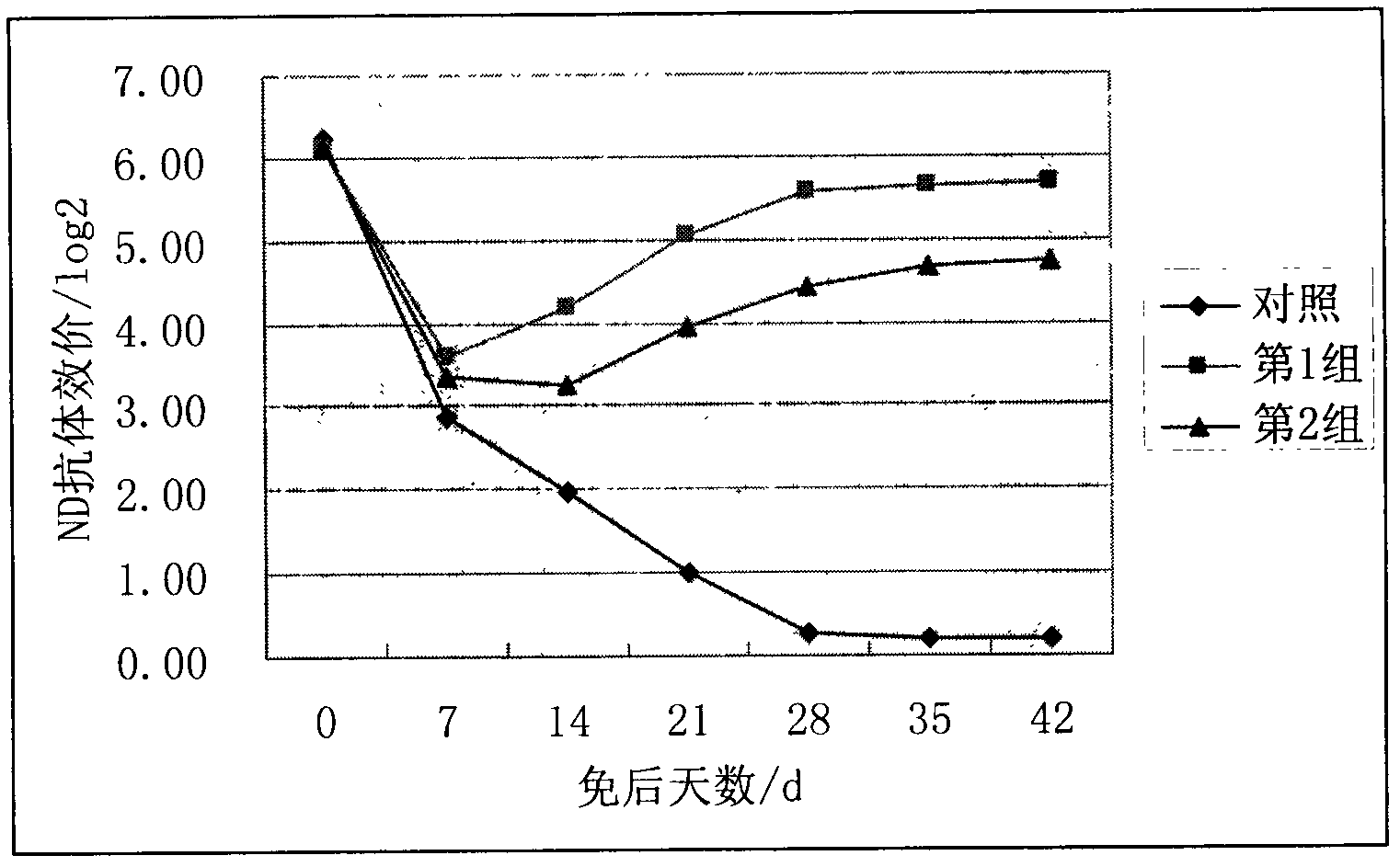
The invention discloses an oil emulsion vaccine for broilers and a preparation method thereof. The oil emulsion vaccine comprises a water phase and an oil phase, wherein the water phase contains concentrated and inactivated ND (newcastle disease) and H9 AI (avian influenza) venom and Tween-80; the oil phase contains an oil adjuvant formed by white oil, Span-80 and aluminium stearate; the volume ratio of the water phase to the oil phase is (1:1.6) to (1:2); and the kinematic viscosity (40 DEG C) of the selected white oil is 4-8mm<2> / s. The oil emulsion vaccine has the characteristics of easiness in absorption, quick effect and high level of the generated antibodies, is suitable for growth of the broilers, can effectively increase the immune levels of the broilers, can effectively protect the broilers from being invaded by ND and H9 AI viruses and avoids ND and H9 AI in the immune phase.
Owner:TIANJIN RINGPU BIO TECH
Modified alpha-neurotoxins as painkillers
InactiveUS20050031608A1Long maintenance periodPeptide/protein ingredientsReptile material medical ingredientsDiseaseNervous system
The disclosed invention is a composition of matter, a process of production thereof, and a method for the treatment of chronic pain, especially to the treatment of heretofore intractable pain as associated with advanced cancer, neurological conditions and rheumatoid arthritis. The treatment of pain associated with viral infections and lesions are also within the contemplation of the present invention. The composition of matter comprises modified alpha-neurotoxins or modified venoms known to contain alpha-neurotoxins in an acceptable carrier for either parenteral, oral or topical administration.
Owner:RECEPTOPHARM +2
Medicine for curing malignant turnor and its preparation method
InactiveCN1399999APromote generationLess componentsAmphibian material medical ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsUltrasound attenuationSide effect
The present invention relates to a medicine for curing malignant tumor and its preparation method. It is made of asparagus tuber, Buddha's hand fruit, American ginseng, acanthopanax obovatus, hippophae rhmnoides fruit, Chinese gooseberry root, venom and bolbostemma tuber as raw material through the processes of removing dust and cleaning, decocting, alcohol precipitation extraction and alcohol impregnating extraction. Said medicine has no toxic side effect, has strong action of resisting tumor and raising immunity of body, and can possess synergistic action and attenuation when it is matched with radiotherapy and chemical medicine therapy to cure malignant tumor, and can obtain good therapeutic effect.
Owner:李新民
Method for preparing rainbow trout IHN(Infectious Haematopoietic Necrosis) inactivated vaccine
InactiveCN104189899ASafe preparationEfficient preparationMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsAntigenJuvenile fish
The invention discloses a method for preparing a rainbow trout IHN (Infectious Haematopoietic Necrosis) inactivated vaccine, which comprises the following steps: carrying out grinding, filtering and poison dipping processing on pancreas and livers of juvenile fish which is attacked, but is still alive, inoculating rainbow trout gonad (RTG) cells, carrying out blind passaging at 14 DEG C, keeping for 5 days when carrying out blind passaging on the tenth generation, and collecting cell poisonous fluid; inoculating chinook salmon embryonic (CHSE) cells, carrying out passaging at 14 DEG C, and raising the culture temperature by 1 DEG C when passaging for 5 generations each time until the culture temperature is raised to 20 DEG C; and adopting epithelioma papulosum cyprini (EPC) cells to continuously carry out passaging under the condition of 20 DEG C, passaging to the twelfth generation to obtain high-titer virus solution and carrying out inactivation to obtain the rainbow trout IHN inactivated vaccine. According to the preparation method, RTG-2, CHSE-214 and EPC cells are utilized to alternately culture rainbow trout IHN viruses at a specific environment temperature so as to obtain a high-titer IHNV (Infectious Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus) antigen and produce the inactivated vaccine; and the technical difficult problem that the high-titer IHNV antigen cannot be obtained through single cells is solved.
Owner:LANZHOU WEITESEN BIOTECH
Chinese medicinal herb additive for controlling porcine hyperthermia
InactiveCN101653494AImprove immunityImprove disease resistanceAmphibian material medical ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsSide effectGlycyrrhiza uralensis
The invention discloses a Chinese medicinal herb additive for controlling porcine hyperthermia. The Chinese medicinal herb additive comprises the following Chinese medicinal herb raw materials according to the parts by weight: 10 parts of milk vetch, 12 parts of codonopsis pilosula, 30 parts of raw hawthorn, 15 parts of banks' rose, 12 parts of honeysuckle, 12 parts of isatis root, 12 parts of echinacea, 9 parts of periostracum cicadae, 3 parts of dried venom of toads, 9 parts of glycyrrhiza uralensis, 6 parts of allicin and 60 parts of cactus. The effective rate of the medicine for preventingporcine hyperthermia is 94%, the effective rate of the medicine for curing is 96% and the recovery rate is 82%. The Chinese medicinal herb additive of the invention has obvious effect for preventingand curing porcine hyperthermia, the additive is convenient to take and has no toxity, side effect and residue, the resources of the raw materials are wide, the price is cheap, and the additive not only benefits the health of people, but also increases the economic benefit of the pig industry.
Owner:赵代良
Method for preparing swine fever-pseudorabies bigeminal live vaccine and product thereof
InactiveCN101690808AImprove securityImprove immune efficiencyMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsImmunologic paralysisBiologic Products
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological products for veterinary use, in particular to a method for preparing a swine fever-pseudorabies bigeminal live vaccine by using passage cells and a product thereof. The method for preparing the swine fever-pseudorabies bigeminal live vaccine by using the passage cells comprises the following steps: (1) culturing a swine fever lentogen strain and a pseudorabies lentogen strain by the passage cells; (2) harvesting cell culture venoms prepared in the step (1); and (3) mixing two kinds of cell culture venoms prepared in the step (2) in a ratio of 1:2 to prepare the passage cell swine fever-pseudorabies bigeminal live vaccine through cooling and vacuum drying. The invention also provides the swine fever-pseudorabies bigeminal live vaccine prepared by the preparation method. The swine fever-pseudorabies bigeminal live vaccine can be used for immunization, can reduce the workload of the immunization, reduce the number of immunization times, avoid immunologic paralysis caused by frequent immunizations, reduce stress on a swine herd correspondingly, and prevent and control the occurrence of the swine fever and the pseudorabies.
Owner:广东永顺生物制药股份有限公司 +1
Method for treating venomous bites and stings
InactiveUS20140087003A1Reduces local hemorrhage and tissue necrosisAvoid toxicityBiocideInorganic active ingredientsMedicinePoisonous effects
Owner:CISNEROS IGNACIO
Method for producing influenza virus vaccine
ActiveCN101955915ASolve pollutionGuaranteed to be pureAntiviralsViruses/bacteriophagesCanine kidneyEquine influenza vaccine
The invention discloses a method for producing a vaccine for avian influenza viruses and other influenza viruses such as a swine influenza virus, a canine influenza virus and an equine influenza virus. The method comprises the following steps of: subculturing cells for preparing the vaccine; (2) reproducing cytotoxic varieties; (3) performing microcarrier suspension culture on darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells in a bioreactor; (4) reproducing venom for preparing the vaccine; and (5) harvesting virus liquid. The method has the advantages of great reduction in production cost, short production period, no restriction to raw material supply, small occupied area, easy and quick expansion in production scale, low and readily treated environmental pollution, high degree of automation, few labors, easy equilibrium and stabilization in quality and obvious improvement on the yield and the quality of the vaccines.
Owner:成都史纪生物制药有限公司
Preparation method for duck viral hepatitis refine yolk antibody
ActiveCN101607994ADoes not affect antibody titerNo chemical residueEgg immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against virusesYolkAntigen
The invention relates to a preparation method for a duck viral hepatitis refine yolk antibody, which comprises the following steps: (1) preparation of virus seed for production; (2) preparation of venom for preparing antigen; (3) preparation of oil-emulsion inactivated vaccine; (4) preparation of eggs from hype-immunized chickens; (5) separation of yolk; (6) inactivation I and extraction; (7) inactivation II, collation and deep filtration; (8) inactivation III and degerming filtration; and (9) mixing and package, wherein the collected sterile filtered liquid is subject to liver neutralizing antibody titer determination; the antibody is diluted until the neutralizing antibody titer of the antibody is 1:256-1:1,024 by using 0.015mol / L of sterilized PBS with the pH of 7.2; 0.02 volume percent of tween-80 as a stabilizer is added in the antibody, and the mixture is evenly mixed and sub-packaged; and the obtained product is sterile and quantitative sub-packaged. The product has the advantages of high purity, strong specificity, easy preservation, no residue and the like, and has extremely good effect of preventing and treating the duck viral hepatitis.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Preparation method for vaccine of porcine circovirus II
InactiveCN101773667AHigh poison priceExpand production scaleViral antigen ingredientsBiological material analysisAdjuvantHigh density
The invention discloses mass production of inactivated vaccine of porcine circovirus II (PCV2) and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following technical steps: (1) high-density culture of cells for vaccine preparation; (2) reproduction of venom for vaccine preparation; and (3) addition of adjuvant to prepare the inactivated vaccine. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages that the virus yield is high, the virus titer is high, the production scale is large, the yield of a single batch is high, the production cost is relatively low, the product quality is high and stable, the operation is convenient, the operation space is small, the technological parameters are controlled accurately and the like. The inactivated vaccine has high safety, can induce pig bodies to generate immune protection and fully satisfies the national biological product standards.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Applications of BHK-21 cell full-suspension culture technology in production of newcastle disease vaccine
The invention relates to applications of a BHK-21 cell full-suspension culture technology in production of a newcastle disease vaccine. A process of producing the newcastle disease vaccine by BHK-21 cell full-suspension culturing includes steps as follows: (1) a step of viral strain seed selection, namely a step of inoculating a monolayer BHK-21 cell with a newcastle disease vaccine virus seed cultured by a chick embryo, adding a virus maintenance medium, culturing to obtain a newcastle disease vaccine adapted to the BHK-21 cell, and performing system identification; (2) a step of domestication and seed selection of a suspension cell strain, namely a step of domesticating a full-suspension BHK21 cell used for culturing of the newcastle disease vaccine virus and establishing a basic seed; (3) a step of subjecting the suspension cell to enlarged cultivation; (4) a step of virus inoculation and harvest, namely a step of inoculating the newcastle disease vaccine virus adapted to the BHK-21 cell and harvesting a virus solution; and (5) a step of measuring the viral titer of the multiplicated newcastle disease vaccine virus and preparing the vaccine. According to the applications, culturing and production with chick embryos of the newcastle disease vaccine are changed into to large-scale culture and production with mammalian cells of the newcastle disease vaccine, the process of producing the newcastle disease vaccine is simplified, the production cost is reduced, and the yield and quality of the vaccine are largely improved.
Owner:CHINA INST OF VETERINARY DRUG CONTROL
Medicine for external application for treating pyogenic type contaminated wounds
InactiveCN101612278AEasy dischargeActive growthHeavy metal active ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsHalloysiteMyrrh
The invention discloses a medicine for external application for treating pyogenic type contaminated wounds, which is characterized by comprising the following raw materials in the proportion by weight: 20-60 of catechu, 15-45 of dragon blood, 25-60 of prepared frankincense, 25-60 of prepared myrrh, 50-150 of calcined dragon bone, 60-200 of calcined gypsum, 20-60 of red halloysite, 40-80 of pearl, 0.5-1.0 of musk, 2-5 of borneol and 2-5 of calomel. The medicine for external application has the efficacies of diminishing inflammation and relieving pain, removing necrosis and promoting granulation, promoting discharge of venom, increasing the amount of blood supply, activating cell growth, accelerating growth of granulation tissue and promoting wounds to heal quickly. The medicine for external application is used for treating various pyogenic type contaminated wounds of dermis, fat, muscle, aponeurosis and periosteum. After clinical application for many years, the medicine for external application has good treating effect, and the healing rate reaches 90 percent. The course of treatment is generally ten days to two months, the healed wounds have unobvious scars, and patients have slight or no functional disorder.
Owner:刘明林
Modified venom and venom components as anti-retroviral agents
InactiveUS20060088858A1Avoid infectionInhibition of replicationPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementFeline immunodeficiency virusAcquired immunodeficiency
The present invention relates to a class of proteins, and a method for treatment of neurological and viral diseases in humans and animals. More specifically it applies to the treatment of heretofore intractable diseases such as retro-viral infections including human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV), bovine immunodeficiency virus (BIV) and equine acquired immunodeficiency virus (EAIV). The method of treatment comprises administering to the subject a disease mitigating amount of a detoxified modified venom composition.
Owner:RECEPTOPHARM
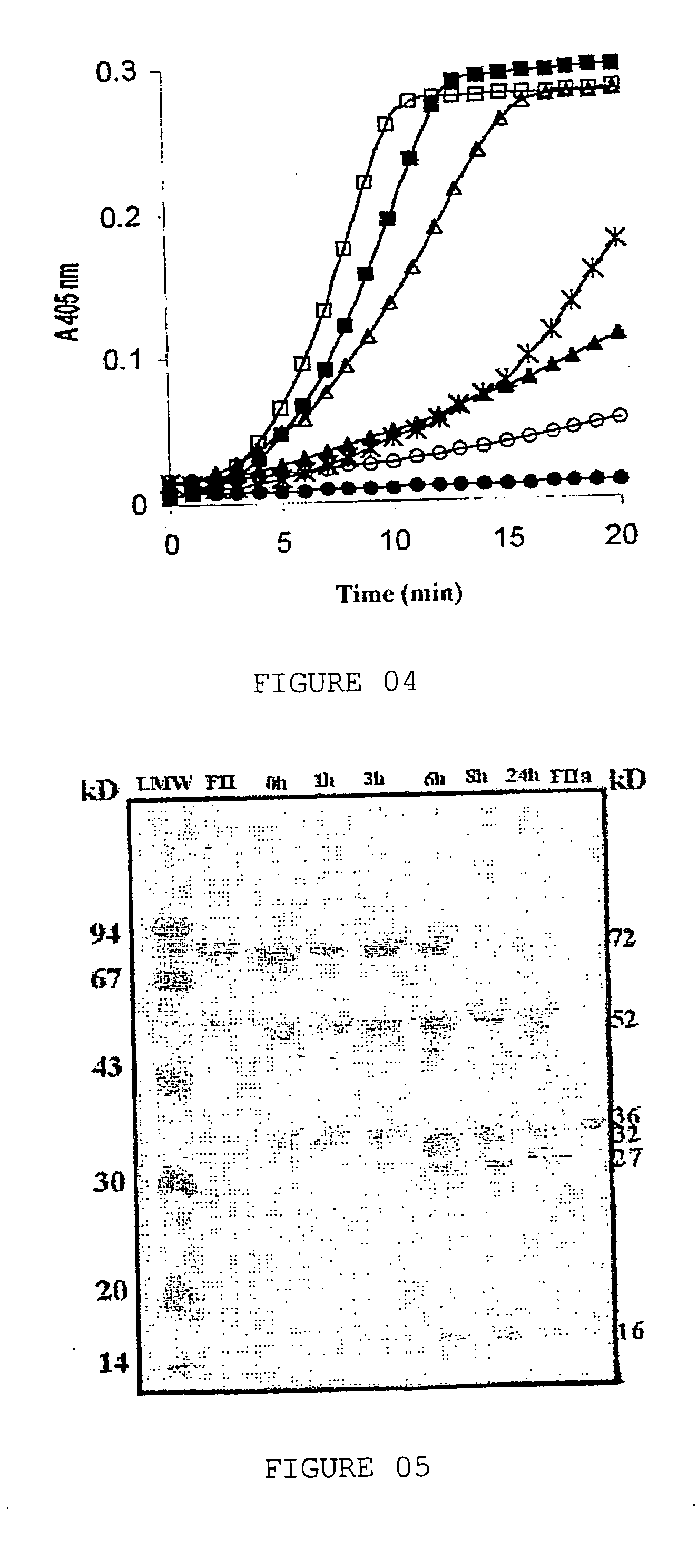
Purifying process of soluble proteins of the l.obliqua bristles through prothrombin activation: process for a partial determination of the amino acids sequence of the prothrombin activator; process for determining the prothrombin activation of fraction II, n-terminal and internal fragments sequences
InactiveUS20050130287A1Prolong coagulation timePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDysprothrombinemiaConsumption Coagulopathy
The herein invention refers to a purifying process of soluble proteins of the L. obliqua bristles through prothrombin activation; a partial deterrination of the amino acids sequence of the prothrombin activator; a process for determining the fraction II of the prothrombin activation as well as the N-terminal sequence and the sequence of internal fragments of the prothrombin activator fraction, the prothrombin activator and the utilization of the prothrombin activator through the homogenization of the L. obliqua bristles. The herein invention has shown that only one component of the Lonomia obliqua venom, the Lopap, causes the hemorrhagic syndrome directly by activating prothrombin and, therefore, a patient should be conducted to a therapy when in contact with the Lonomia obliqua venom. According to the herein invention, Lopap is a new prothrombin activator, showino to be a quite important factor responsible for consumption coagulopathy, found in patients exposed to the venom of the L. obliqua caterpillar. In low doses of purified protein, due to its capacity of activating prothrombin and generating thrombin, it is possible, in controlled conditions, to withdraw fibrinogen from circulation, transforming it in fibrin microthrombs. The decrease on the concentration of plasmatic fibrinogen promotes the increasing of blood coagulation time and therefore it will avoid acute vascular thrombosis. Since protein does not present proteolytic activity, it could maintain the coagulating capacity of the fibrinogen not consumed in the process. The fibrinogen plasmatic concentration would decrease, however there would not be predisposition for hemorrhagic state. Besides that, it could be used to produce diagnosis KITS for detecting dysprothrombinemias.
Owner:BIOLAB SANUS FARMACEUTICA LTD
Modified venom and venom components as anti-retroviral agents
InactiveUS20050255097A1Strong antiviral activityAvoid infectionBiocideNervous disorderFeline immunodeficiency virusAcquired immunodeficiency
The present invention relates to a class of proteins, a process of production thereof, and a method for treatment of neurological and viral diseases in humans and animals. More specifically it applies to the treatment of heretofore intractable diseases such as retro-viral infections including human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV), bovine immunodeficiency virus (BIV) and equine acquired immunodeficiency virus (EAIV). The
Owner:RECEPTOPHARM
Newcastle disease-H9 subtype avian influenza bivalent dual adjuvant inactivated vaccine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102416177APrevent immune failureAvoid immune failureViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsImmune effectsOil adjuvant
The invention discloses a Newcastle disease-H9 subtype avian influenza bivalent dual-adjuvant inactivated vaccine and a preparation method thereof. The bivalent vaccine consists of a concentrated and inactivated ND and AI (H9) venom, levamisole hydrochloride and an oil adjuvant, wherein every milliliter of inactivated vaccine contains 0.5-16 mg of levamisole hydrochloride immunopotentiator. When the synergic ND-AI (H9) bivalent dual-adjuvant inactivated vaccine prepared with the method is applied to immunized chicken, the humoral immunity and cell immune levels of table poultry and laying hens can be raised effectively, the growth is promoted, and rate of live weight growth is increased. The bivalent dual-adjuvant inactivated vaccine has an immune effect which is remarkably superior to that of the conventional chicken ND-AI bivalent oil emulsion inactivated vaccine, and can be used for effectively protecting chicken flocks from being intruded by the ND virus and AI (H9) virus and preventing the Newcastle disease and H9 subtype avian influenza at the immune period.
Owner:TIANJIN RINGPU BIO TECH
Triple vaccine special for Muscovy duck
ActiveCN103272230AGenetically stableImprove securityAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsDiseaseEmbryo
The invention discloses a triple vaccine special for Muscovy duck, and the triple vaccine special for Muscovy duck uses Muscovy duck liver white-spot disease attenuated MWCA strain, Muscovy duck parvovirus attenuated P1 strain and Muscovy duck goose-origin parvovirus attenuated D strain as seed viruses, and respectively uses SPF chicken embryo fibroblast or Muscovy duck embryo fibroblast spinner cultivation technology to propagate virus and obtain the cell toxic liquid, and after mixing according to a proper proportion, a freeze-drying protective agent is added for freeze drying, and the triple live vaccine of Muscovy duck reovirus disease, Muscovy duck parvovirus disease and Muscovy duck gosling plague special for Muscovy duck is prepared; the triple vaccine can be used in the Muscovy duck culture region where the Muscovy duck reovirus disease, the Muscovy duck parvovirus disease and the Muscovy duck gosling plague are prevalent, and the purpose for preventing and controlling three diseases above can be realized by one-time immunization.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com