Patents
Literature
45 results about "Equine influenza virus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Equine influenza (horse flu) is the disease caused by strains of influenza A that are enzootic in horse species. Equine influenza occurs globally, previously caused by two main strains of virus: equine-1 (H7N7) and equine-2 (H3N8).
Vaccines and methods to treat canine influenza
The present invention relates to providing new vaccines and treatments for the diseases related to canine influenza virus. It discloses influenza viral antigens, and methods of presenting these antigens to canines, especially dogs. It relates to attenuated and killed vaccines. The present invention relates to experimentally generated canine and equine influenza viruses. The invention also includes influenza A, including H3, N8, H3N8, H7N7 and viruses which contain at least one genome segment from an canine or equine influenza virus. The present invention also relates to the use of these viruses in therapeutic compositions to protect canines, dogs in particular, from diseases caused by influenza viruses.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
H3 equine influenza A virus
ActiveUS20060153871A1Efficient yieldPrevent and inhibit infectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseMicroorganismsEquine influenza virusGene
The invention provides an isolated H3 equine influenza A virus, as well as methods of preparing and using the virus, and genes or proteins thereof.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
H3 equine influenza A virus
The invention provides an isolated H3 equine influenza A virus, as well as methods of preparing and using the virus, and genes or proteins thereof.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Cold-adapted equine influenza viruses
The present invention provides experimentally-generated cold-adapted equine influenza viruses, and reassortant influenza A viruses comprising at least one genome segment of such an equine influenza virus, wherein the equine influenza virus genome segment confers at least one identifying phenotype of the cold-adapted equine influenza virus, such as cold-adaptation, temperature sensitivity, dominant interference, or attenuation. Such viruses are formulated into therapeutic compositions to protect animals from diseases caused by influenza A viruses, and in particular, to protect horses from disease caused by equine influenza virus. The present invention also includes methods to protect animals from diseases caused by influenza A virus utilizing the claimed therapeutic compositions. Such methods include using a therapeutic composition as a vaccine to generate a protective immune response in an animal prior to exposure to a virulent virus, and using a therapeutic composition as a treatment for an animal that has been recently infected with a virulent virus, or is likely to be subsequently exposed to virulent virus in a few days whereby the therapeutic composition interferes with the growth of the virulent virus, even in the absence of immunity. The present invention also provides methods to produce cold-adapted equine influenza viruses, and reassortant influenza A viruses having at least one genome segment of an equine influenza virus generated by cold-adaption.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Intranasal delivery system
InactiveUS7204822B1Minimize cuttingMinimize scoringMedical devicesInhalatorsDose deliveryCold adapted
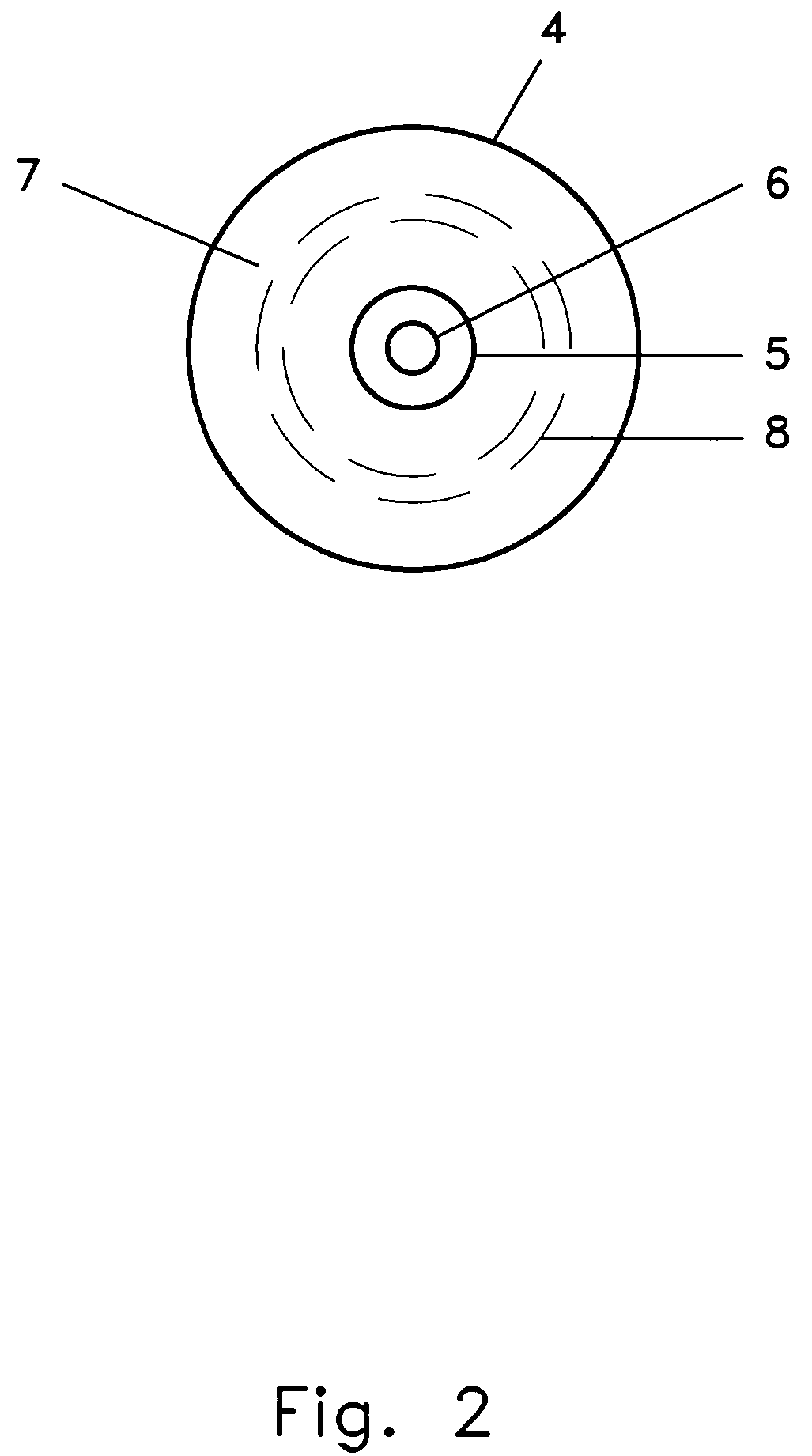
This invention relates to apparatus and methods of delivering various compositions including medicaments to a variety of targets. The invention includes a dose administrator (1) which may be used for intranasal delivery of compositions or medicaments, such as live virus vaccines, to both humans and animals. An axial collapse prevention element (2) to prevent excessive axial deflection of the dose administrator (1) or a dose-location coordinate indicator (3) to facilitate the delivery of a dose to the desired target location may be coupled to the dose administrator (1). An intranasal probe (4) having a force dissemination contact surface (7) may be responsive to a first end of the dose administrator (1). The dose may be delivered from a conformable dose sequestration element (10) through an aperture which penetrates the dose delivery aperture element (5) and the dose may be caused to stream by coupling a stream delivery element (6) to the dose delivery aperture element (5). The force application element (12) which acts upon the dose may be separated from the dose by a fluid dose propellent (13). While the invention may be used for numerous applications, it specifically addresses the difficulties of delivering cold-adapted live equine influenza viruses intranasally to equids.
Owner:HESKA
Genetically Engineered Equine Influenza Virus and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20080254060A1Reduce capacityLow toxicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsUltrasound attenuationVirulent characteristics
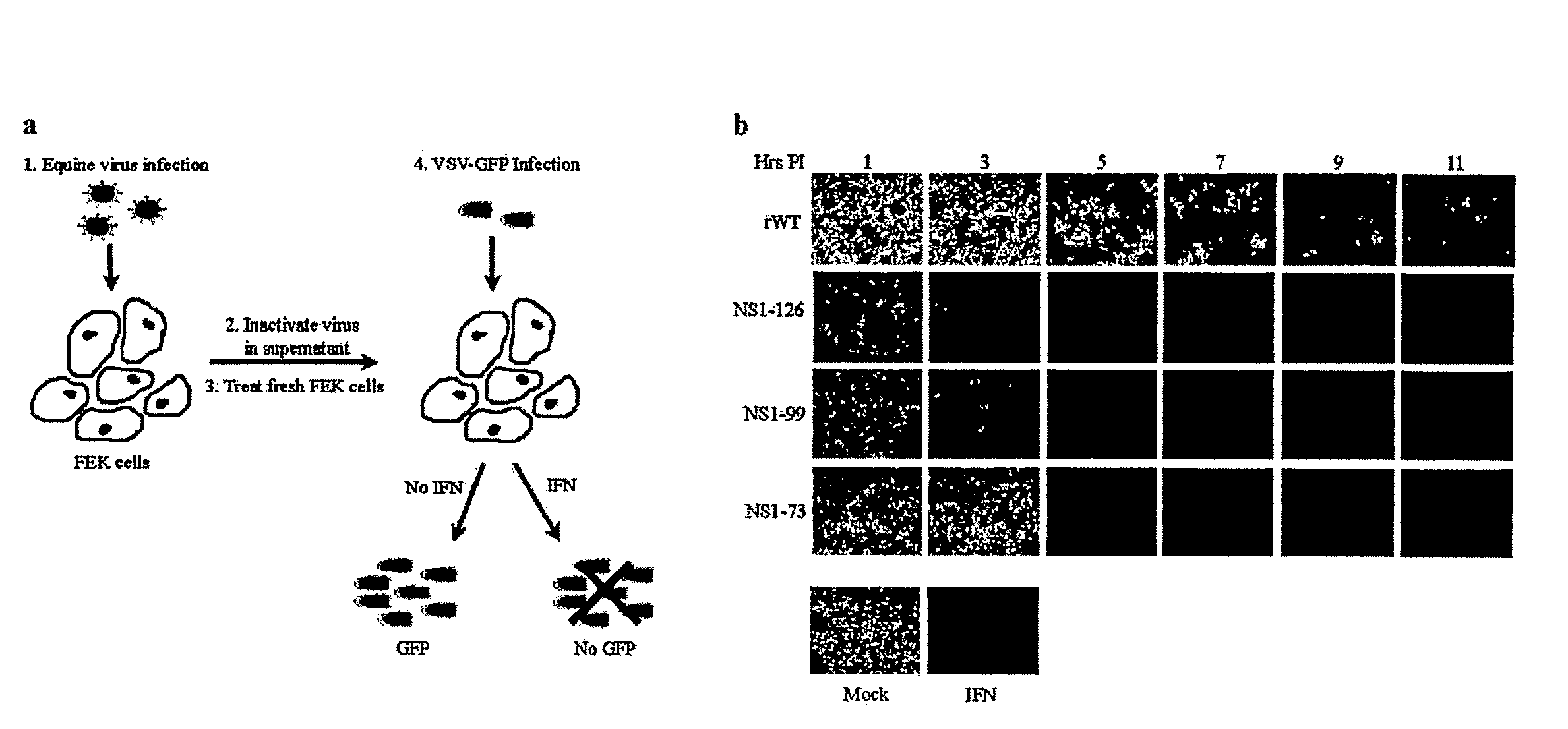
The present invention relates, in general, to attenuated equine influenza viruses having an impaired ability to antagonize the cellular interferon (IFN) response, and the use of such attenuated viruses in vaccine and pharmaceutical formulations. In particular, the invention relates to attenuated equine influenza viruses having modifications to an equine NS1 gene that diminish or eliminate the ability of the NS1 gene product to antagonize the cellular IFN response. These viruses replicate in vivo, but demonstrate decreased replication, virulence and increased attenuation, and therefore are well suited for use in live virus vaccines, and pharmaceutical formulations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY +1
Production method for influenza virus vaccines
InactiveCN101818131ASolve yourselfSolve pollutionAntiviralsViruses/bacteriophagesEquine influenza vaccineBioreactor
The invention discloses a production method for vaccines of avian influenza virus and other influenza virus such as swine influenza, dog influenza and equine influenza, which comprises the following steps of: (1) transfer of culture and cultivation of vaccine-made cells; (2) reproduction of vaccine-made virus seeds; (3) microcarrier suspension culture of MDCK cells in a bioreactor; (4) reproduction of vaccine-made virus liquid; and (5) harvest of the virus liquid. The production method has the advantages of reducing the production cost greatly and improving the yield and quality of the vaccines obviously, along with short production period, no restriction to raw material supply, small occupied area, easy and quick expansion of production scale, light environmental pollution, easy processing, high automaticity, low employment and easy realization of balanced and stable quality.
Owner:成都史纪生物制药有限公司
Compositions and methods for the treatment of canine influenza virus disease
InactiveUS20070092537A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsEquine influenza virusVirus diseases
Compositions, including vaccine compositions, and methods for treating, preventing or ameliorating canine influenza virus (CIV) disease by utilizing one or more canine influenza virus (CIV) or equine influenza virus (EIV) strain or immunogens thereof are set forth herein. Also set forth are challenge models useful in assessing the efficacy of a composition against canine influenza virus, comprising an equine influenza virus (EIV) or canine influenza virus (CIV) strain or immunogens thereof.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Genetically engineered equine influenza virus and uses thereof
ActiveUS8137676B2Reduce capacityLow toxicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsVirus influenzaIn vivo
The present invention relates, in general, to attenuated equine influenza viruses having an impaired ability to antagonize the cellular interferon (IFN) response, and the use of such attenuated viruses in vaccine and pharmaceutical formulations. In particular, the invention relates to attenuated equine influenza viruses having modifications to an equine NS1 gene that diminish or eliminate the ability of the NS1 gene product to antagonize the cellular IFN response. These viruses replicate in vivo, but demonstrate decreased replication, virulence and increased attenuation, and therefore are well suited for use in live virus vaccines, and pharmaceutical formulations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY +1
Cold-adapted equine influenza viruses
InactiveUS20060121521A1Antibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus influenzaRespiratory disease
The present invention provides experimentally-generated cold-adapted equine influenza viruses, and reassortant influenza A viruses comprising at least one genome segment of such an equine influenza virus, wherein the equine influenza virus genome segment confers at least one identifying phenotype of the cold-adapted equine influenza virus, such as cold-adaptation, temperature sensitivity, dominant interference, or attenuation. Such viruses are formulated into therapeutic compositions to protect animals from diseases caused by influenza A viruses, and in particular, to protect horses from disease caused by equine influenza virus. The present invention also includes methods to protect animals from diseases caused by influenza A virus or other infectious agents utilizing the claimed therapeutic compositions. Such methods include using a therapeutic composition as a vaccine to generate a protective immune response in an animal prior to exposure to an infectious agent, as well as using a therapeutic composition as a treatment for an animal that has been recently infected with an infectious agent leading to respiratory disease, or is likely to be subsequently exposed to such an agent in a few days whereby the therapeutic composition reduces such respiratory disease, even in the absence of antibody-mediated immunity. The present invention also provides methods to produce cold-adapted equine influenza viruses, and reassortant influenza A viruses having at least one genome segment of an equine influenza virus generated by cold-adaptation.
Owner:DOWLING PATRICIA W +1
Method for producing influenza virus vaccine
ActiveCN101955915ASolve pollutionGuaranteed to be pureAntiviralsViruses/bacteriophagesCanine kidneyEquine influenza vaccine
The invention discloses a method for producing a vaccine for avian influenza viruses and other influenza viruses such as a swine influenza virus, a canine influenza virus and an equine influenza virus. The method comprises the following steps of: subculturing cells for preparing the vaccine; (2) reproducing cytotoxic varieties; (3) performing microcarrier suspension culture on darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells in a bioreactor; (4) reproducing venom for preparing the vaccine; and (5) harvesting virus liquid. The method has the advantages of great reduction in production cost, short production period, no restriction to raw material supply, small occupied area, easy and quick expansion in production scale, low and readily treated environmental pollution, high degree of automation, few labors, easy equilibrium and stabilization in quality and obvious improvement on the yield and the quality of the vaccines.
Owner:成都史纪生物制药有限公司
Influenza DNA vaccination and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20110171260A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsHeterologousDNA vaccination
The present invention relates to an influenza immunogen that includes one or more DNA constructs encoding at least two divergent influenza HAs, wherein each of such one or more DNA constructs encodes one or more of the at least two divergent influenza HAs. Such an immunogen, when administered to a subject, induces an immune response to a plurality of strains of influenza virus, wherein at least one strain of the plurality of strains does not encode any of the divergent influenza HAs encoded by the immunogen. The divergent influenza HAs can be swine influenza HAs or equine influenza HAs, such as influenza H1 HAs or influenza H3 HAs. The invention also relates to a method to use such an immunogen to induce such an immune response as well as to DNA constructs comprising such divergent influenza HAs. Such an immunogen can provide a heterologous as well as a homologous immune response. Such an immunogen can be used to induce an immune response against evolving influenza virus.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Cold-adapted equine influenza viruses
The present invention provides experimentally-generated cold-adapted equine influenza viruses, and reassortant influenza A viruses comprising at least one genome segment of such an equine influenza virus, wherein the equine influenza virus genome segment confers at least one identifying phenotype of the cold-adapted equine influenza virus, such as cold-adaptation, temperature sensitivity, dominant interference, or attenuation. Such viruses are formulated into therapeutic compositions to protect animals from diseases caused by influenza A viruses, and in particular, to protect horses from disease caused by equine influenza virus. The present invention also includes methods to protect animals from diseases caused by influenza A virus utilizing the claimed therapeutic compositions. Such methods include using a therapeutic composition as a vaccine to generate a protective immune response in an animal prior to exposure to a virulent virus, and using a therapeutic composition as a treatment for an animal that has been recently infected with a virulent virus, or is likely to be subsequently exposed to virulent viruses in a few days whereby the therapeutic composition interferes with the growth of the virulent virus, even in the absence of immunity. The present invention also provides methods to produce cold-adapted equine influenza viruses, and reassortant influenza A viruses having at least one genome segment of an equine influenza virus generated by cold-adaptation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Equine influenza detection kit and detection method
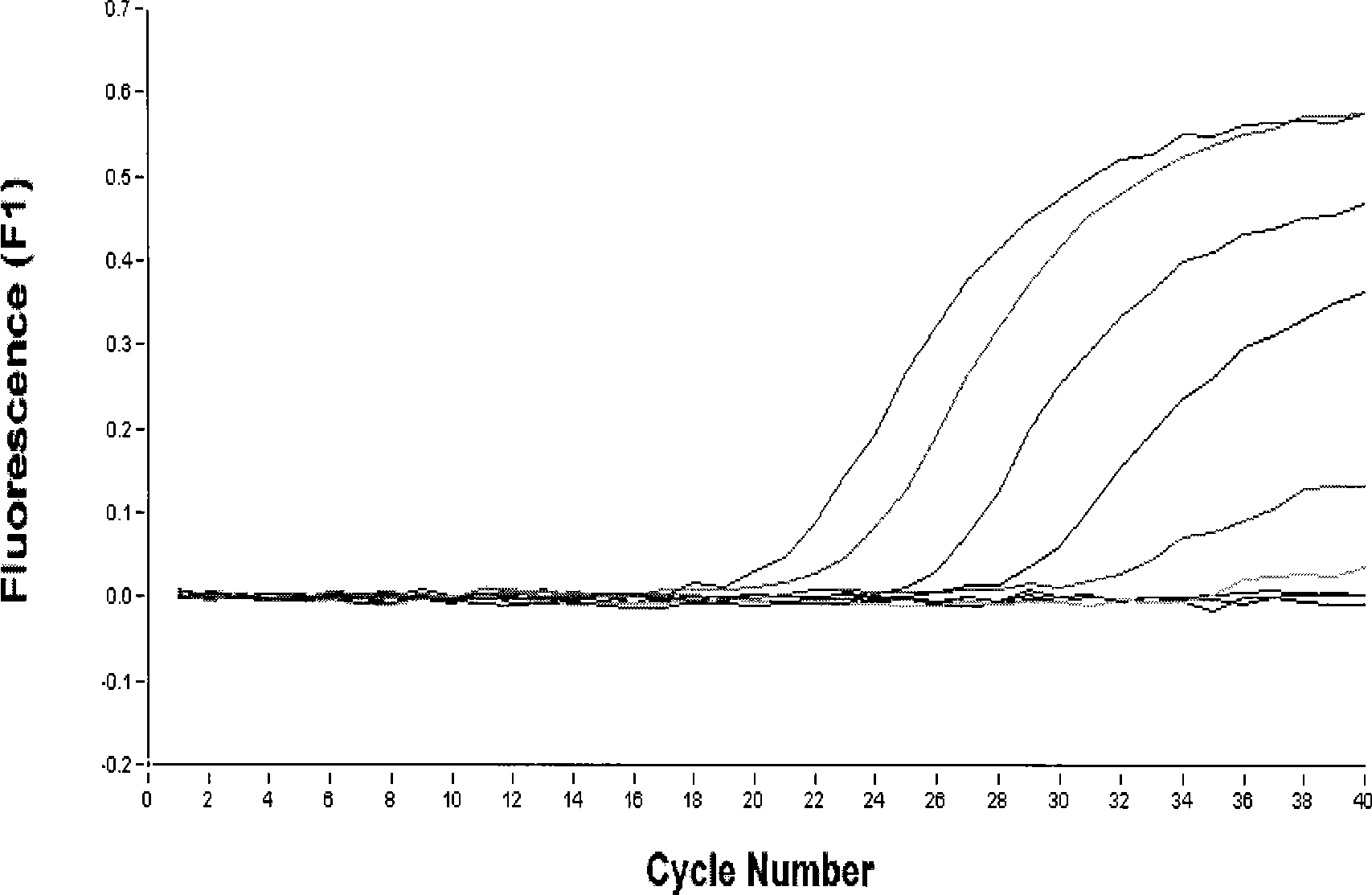
InactiveCN101392299AThe detection method is simpleShorten detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceNucleotideEquine influenza virus
The invention relates to a horse influenza detecting reagent kit and a detecting method, belonging to the inspection and quarantine field. A group of nucleotide sequences for detecting H3N8 subtype horse influenza virus is the nucleotide sequences showed in sequence lists from SEQ ID No: 1 to SEQ ID No: 6. The method has the advantages of: (1) fastness: the detecting time is shortened from 21 days which the traditional detecting method to 4 hours; (2) sensitivity: the H3N8 subtype horse influenza virus which is gradient-diluted for 10 times is detected and the results indicate positive while diluted to 10<-7> times by a single approach and negative while diluted to 10<-5> by double approaches; (3) specificity: when the established H3N8 subtype horse influenza virus single-approach and double-approach fluorescent RT-PCR detecting method is used for detecting equine arteritis virus and other subtype influenza viruses, the result is negative and no cross-reaction is found; (4) stability: results of repeated experiments show that the established method has good stability; and (5) being not easy for contamination: the totally closed-up reaction requires no PCR post-treatment, thus being safe in operation.
Owner:PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA BEIJING ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Multiplex RT-PCR method for diagnosing equine influenza virus and identifying subtype thereof
InactiveCN101328508ARapid diagnosisRapid subtypingMicrobiological testing/measurementEquine influenza virusRibonucleotide synthesis
The invention discloses a method for diagnosticating an EIV and evaluating a multiple RT-PCR of the EIV subtype. The method comprises the following steps that: a RNA of a sample to be detected is taken as a template, two groups of ribonucleotide sequences of SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2 as well as SEQ ID NO:3 and SEQ ID NO:4 are taken as primers to perform the RT-PCR reaction; if only the product of 227bp is amplified in the sample, the sample is H7N7 subtype of the EIV; if the products of both 227bp and 595bp are amplified simultaneously, the sample is H3N3 subtype of the EIV; if the product of 227bp is not amplified, the sample does not contain the EIV. According to the RT-PCR technical theory, the multiple RT-PCR detection method is established according to the characteristic that the EIV only has two HA subtypes. The method has strong sensitivity and high specificity and can be applied to the rapid diagnosis and the subtype verification of the EIV.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Recombinant equine influenza virus strain, preparation method thereof and vaccine prepared from recombinant equine influenza virus strain
InactiveCN103602638AImproving immunogenicityViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsMicroorganism based processesCanine kidneyChick embryos
The invention discloses a recombinant equine influenza virus strain, a preparation method thereof and a vaccine prepared from the recombinant equine influenza virus strain. The recombinant influenza virus strain contains genes HA and NA of an equine influenza virus A / equine / xinjiang / 3 / 07 (H3N8) strain and six internal genes PB2, PB1, PA, NP, M and NS of an influenza virus A / Puerto Rico / 8 / 34 / Mount Sinai (H1N1) or A / PR / 8 / 34 (H1N1 short for PR8 virus). The recombinant equine influenza virus strain disclosed by the invention is named as rH3N8-PR and is preserved with the number of CGMCC NO.8161. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the recombinant equine influenza virus strain and a vaccine prepared from the recombinant equine influenza virus strain. Compared with a parental strain, the recombinant equine influenza virus strain disclosed by the invention can generate very high virus titer and blood clotting titer on both chick embryos and MDCK (Madin Darby Canine Kidney) cells, and the pathogenicity of the recombinant equine influenza virus strain to mice is remarkably reduced; experiments prove that the vaccine prepared from the recombinant equine influenza virus strain disclosed by the invention has favorable immunogenicity and protective effect.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
H3N8 subtype equine influenza recombinant virus-like particle vaccine as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103898070AGood protective immune responseDoes not interfere with epidemiological investigationsInactivation/attenuationAntiviralsEpidemiologic surveyEquine influenza virus
The invention discloses an H3N8 subtype equine influenza recombinant virus-like particle vaccine as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The vaccine in the invention contains recombinant virus-like particle protein which is obtained by expressing nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2 through an insect / baculovirus expression system, a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, an adjuvant or an excipient. The recombinant virus-like particle has a morphological structure similar with that of a natural virus particle, and has good immunogenicity; the vaccine prepared by the recombinant virus-like particle can induce a mouse to generate good protective immune response after immunizing the mouse, and is free of any risk of live virus; and meanwhile, naturally infected persons and immune persons can be distinguished, so that epidemiological investigation is not affected, and therefore, the H3N8 subtype equine influenza recombinant virus-like particle vaccine disclosed by the invention can be used as a candidate vaccine for preventing and treating the equine influenza.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Cold-adapted equine influenza viruses
InactiveUS20050175985A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesGenomic SegmentUltrasound attenuation
The present invention provides experimentally-generated cold-adapted equine influenza viruses, and reassortant influenza A viruses comprising at least one genome segment of such an equine influenza virus, wherein the equine influenza virus genome segment confers at least one identifying phenotype of the cold-adapted equine influenza virus, such as cold-adaptation, temperature sensitivity, dominant interference, or attenuation. Such viruses are formulated into therapeutic compositions to protect animals from diseases caused by influenza A viruses, and in particular, to protect horses from disease caused by equine influenza virus. The present invention also includes methods to protect animals from diseases caused by influenza A virus utilizing the claimed therapeutic compositions. Such methods include using a therapeutic composition as a vaccine to generate a protective immune response in an animal prior to exposure to a virulent virus, and using a therapeutic composition as a treatment for an animal that has been recently infected with a virulent virus, or is likely to be subsequently exposed to virulent viruses in a few days whereby the therapeutic composition interferes with the growth of the virulent virus, even in the absence of immunity. The present invention also provides methods to produce cold-adapted equine influenza viruses, and reassortant influenza A viruses having at least one genome segment of an equine influenza virus generated by cold-adaptation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Efficient bidirectional transcription/expression plasmid and application thereof in influenza virus reverse genetics
InactiveCN105861555AEasy to insertHigh Toxic YieldSsRNA viruses negative-senseNucleic acid vectorEnzyme digestionEquine influenza virus
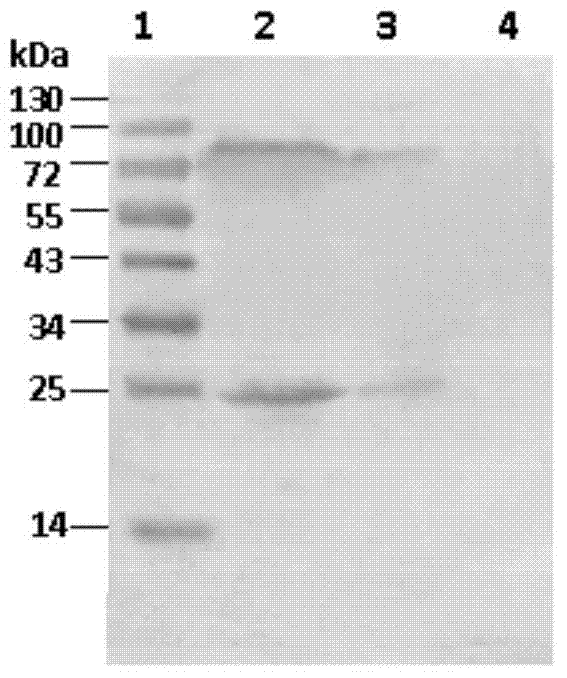
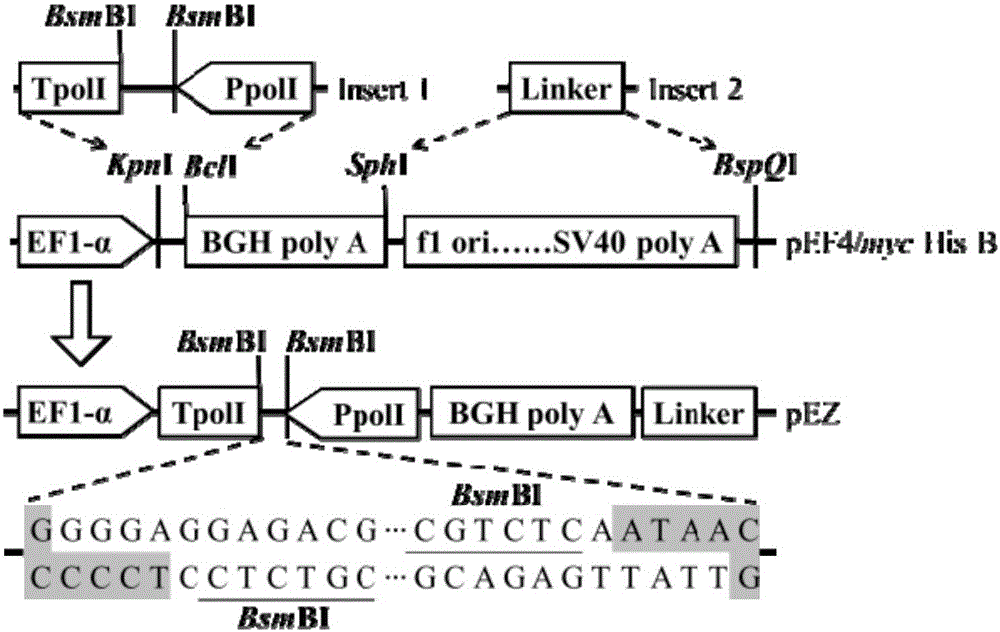
The invention discloses an efficient bidirectional transcription / expression plasmid and application thereof in influenza virus reverse genetics. The bidirectional transcription / expression plasmid is obtained by transformation by taking a eukaryotic expression vector pEF4 / myc-His B as a skeleton. In order to create a reverse genetic system of EIVs (Equine influenza viruses), the bidirectional transcription / expression plasmid obtained by structuring is used for respectively expressing EIVs PB2, PB1, PA, HA, NP, NA and NS and M genes, and a strain of the EIV and mutants thereof are successfully saved by means of cotransfection, sequencing, drawing of growth curves and enzyme digestion are obtained. Compared with existing pBD systems, the created reverse genetic system is superior to the pBD systems in toxigenic quantity. A novel technical means is provided for research on reverse genetics of the influenza viruses, and a solid foundation is laid for future in-depth study on transmission of the EIVs, pathogenesis and even screening of vaccine candidates.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Anti-H3N8 subtype equine influenza virus monoclonal antibody and application thereof
InactiveCN101892200ANo cross reactionMicroorganism based processesImmunoglobulins against virusesSerodiagnosesEquine infectious anemia
The invention discloses an anti-H3N8 subtype equine influenza virus monoclonal antibody and an application thereof. The anti-H3N8 subtype equine influenza virus monoclonal antibody is secreted by hybridoma cell strains with the microbial collection number of CGMCC No.3543. EL1SA, and Western-bolt methods prove that the monoclonal antibody of the invention has no cross reaction with equine infectious anemia virus, equine arteritis virus and normal chick embryo allantois fluid; and the abdominal dropsy ELISA valence of the H3N8 / 10 of the invention is 1:1.6*104. The anti-H3N8 subtype equine influenza virus monoclonal antibody of the invention can be applied to antigenicity analysis on A-type equine influenza virus, serodiagnosis, vaccine quality monitoring, epidemiological survey and other aspects.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
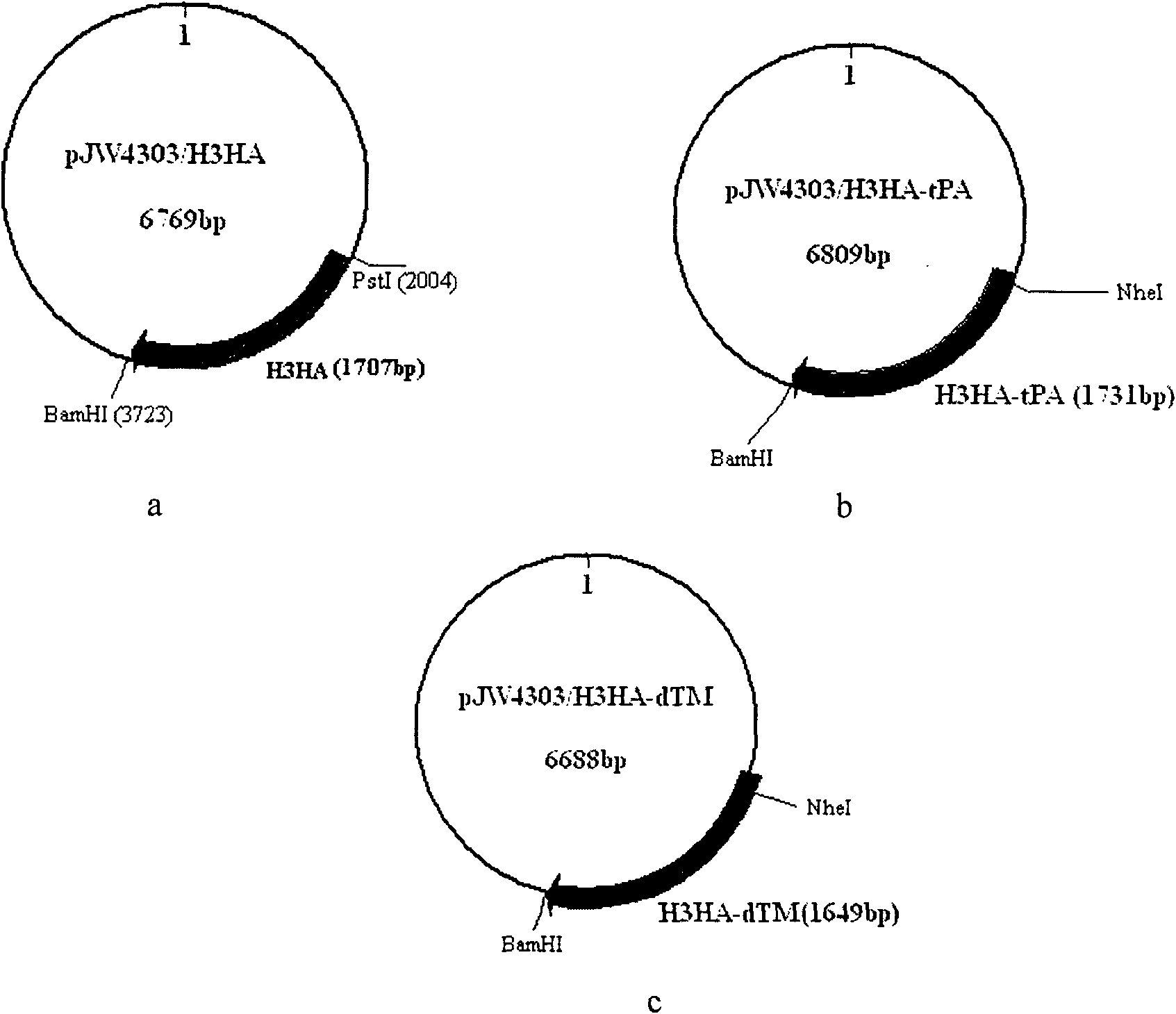
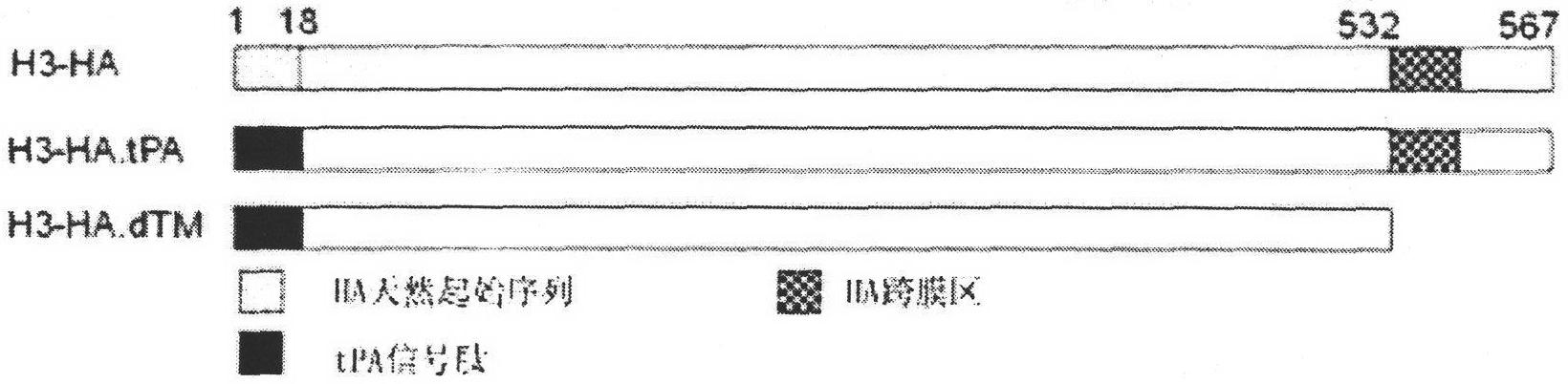
Codon-optimized H3HA/XJ3-07 gene and nucleic acid vaccine thereof
InactiveCN101886084AEfficient expressionStimulate the immune systemGenetic material ingredientsAntiviralsChemical synthesisNew Zealand white rabbit
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical biology, and relates to a codon-optimized H3HA / XJ3-07 gene and a nucleic acid vaccine thereof. In the invention, according to an HA protein sequence of an equine A-type influenza virus A / Equine / Xinjiang / 3 / 07 (H3N8), an H3HA / XJ3-07 gene segment which can express a corresponding protein is chemically synthesized after codon optimization, and the segment is cloned into a nucleic acid vaccine vector pJW4303 to construct an equine influenza H3HA nucleic acid vaccine; and further, HA genes are modified, an H3-XJ HA natural signal peptide is replaced by a human tPA signal peptide or the gene segments of part of the HA genes are removed to make the HA genes only express an extracellular domain of the HA protein. The experimental result shows that three H3HA nucleic acid vaccines can be expressed in a 293T cell with high efficiency, and can induce the generation of specific anti-H3HA antibodies in New Zealand white rabbits.
Owner:王世霞 +4
Equine Influenza Virus Live Attenuated Vaccines
ActiveUS20190125860A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseImmunoglobulinsEquine influenza virusAttenuated vaccine
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Equine intranasal delivery system
InactiveUS20050039739A1Minimize cuttingMinimize scoringMedical devicesMedical atomisersDose deliveryCold adapted
This invention relates to apparatus and methods of delivering various compositions including medicaments to a variety of targets. The invention includes a dose administrator (1) which may be used for intranasal delivery of compositions or medicaments, such as live virus vaccines, to both humans and animals. An axial collapse prevention element (2) to prevent excessive axial deflection of the dose administrator (1) or a dose-location coordinate indicator (3) to facilitate the delivery of a dose to the desired target location may be coupled to the dose administrator (1). An intranasal probe (4) having a force dissemination contact surface (7) may be responsive to a first end of the dose administrator (1). The dose may be delivered from a conformable dose sequestration element (10) through an aperture which penetrates the dose delivery aperture element (5) and the dose may be caused to stream by coupling a stream delivery element (6) to the dose delivery aperture element (5). The force application element (12) which acts upon the dose may be separated from the dose by a fluid dose propellent (13). While the invention may be used for numerous applications, it specifically addresses the difficulties of delivering cold-adapted live equine influenza viruses intranasally to equids.
Owner:HESKA
Cold-adapted equine influenza viruses
InactiveUS7169397B2SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsUltrasound attenuationCold adapted
The present invention provides experimentally-generated cold-adapted equine influenza viruses, and reassortant influenza A viruses comprising at least one genome segment of such an equine influenza virus, wherein the equine influenza virus genome segment confers at least one identifying phenotype of the cold-adapted equine influenza virus, such as cold-adaptation, temperature sensitivity, dominant interference, or attenuation. Such viruses are formulated into therapeutic compositions to protect animals from diseases caused by influenza A viruses, and in particular, to protect horses from disease caused by equine influenza virus. The present invention also includes methods to protect animals from diseases caused by influenza A virus utilizing the claimed therapeutic compositions. Such methods include using a therapeutic composition as a vaccine to generate a protective immune response in an animal prior to exposure to a virulent virus, and using a therapeutic composition as a treatment for an animal that has been recently infected with a virulent virus, or is likely to be subsequently exposed to virulent virus in a few days whereby the therapeutic composition interferes with the growth of the virulent virus, even in the absence of immunity. The present invention also provides methods to produce cold-adapted equine influenza viruses, and reassortant influenza A viruses having at least one genome segment of an equine influenza virus generated by cold-adaptation.
Owner:UNIV OF PITTSBURGH OF THE COMMONWEALTH SYST OF HIGHER EDUCATION
Vaccines and Methods to Treat Canine influenza
The present invention relates to providing new vaccines and treatments for the diseases related to canine influenza virus. It discloses influenza viral antigens, and methods of presenting these antigens to canines, especially dogs. It relates to attenuated and killed vaccines. The present invention relates to experimentally generated canine and equine influenza viruses. invention also includes influenza A, including H3, N8, H3N8, H7N7 and viruses which contain at least one genome segment from an canine or equine influenza virus. The present invention also relates to the use of these viruses in therapeutic compositions to protect canines, dogs in particular, from diseases caused by influenza viruses.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
DNA vaccine expressing HA1 of equine-2 influenza virus
InactiveUS20050032732A1Enhance immune responsePromote proper rate of absorptionSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsHemagglutininInfluenza virus A hemagglutinin
The invention is for a DNA vaccine expressing the hemagglutinin (HA1) gene of equine-2 influenza virus. By engineering a stop codon within HA1, expression of HA1 is ensured. By encapsulation of the DNA vaccine in liposome and by intranasal inoculation, it is sufficient to elicit protective immunity at a significantly lower dosage compared to a DNA vaccine expressing the full length HA gene. Lower dosage reduces the risk of induction of anti-DNA antibodies. Intranasal inoculation directly to the respiratory epithelial cells reduces the risk of DNA integration. The inventive vaccine is advantageous over current inactivated or live attenuated vaccines, as updating of the vaccine requires only the replacement of the encoding sequence with the new virus.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
Molecular beacon probe and kit for detecting equine influenza virus pathogens
InactiveCN111485037AStrong specificityStrong conservativeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerBenzoic acid
The invention provides a molecular beacon probe and a kit for detecting equine influenza virus pathogens. The molecular beacon probe and the kit belong to the field of biotechnology. The kit comprisesa primer pair for detecting a PB1-D sequence of H3N8 and a molecular beacon probe, nucleotide sequence of upstream primer of primer pair is SEQ: 1; wherein the nucleotide sequence of the forward primer is SEQ: 1, the nucleotide sequence of the reverse primer is SEQ: 2, the nucleotide sequence of the molecular beacon probe is SEQ: 3, the 5'end of the molecular beacon probe is subjected to fluorescence labeling with 5 (6)-carboxyl fluorescein (FAM), and the 3 'end of the molecular beacon probe is subjected to fluorescence labeling with quenched fluorescence 4-(4'-oxane aminobenzene azo) benzoicacid (DABCYL). The kit can inhibit generation of fluorescence signals caused by non-specific binding of the molecular beacon probe and reduce the signal-to-background ratio, so that detection signalscan accurately reflect the number of templates, and the specificity, sensitivity, repeatability and accuracy of detection are improved.
Owner:SHANDONG VOCATIONAL ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY COLLEGE
Equine intranasal delivery system
InactiveUS7678087B2Minimize cuttingMinimize scoringMedical devicesMedical atomisersDose deliveryCold adapted
Owner:HESKA
A Bidirectional Transcription/Expression Plasmid and Its Application in Influenza Virus Reverse Genetics
InactiveCN105861555BEasy to insertHigh Toxic YieldSsRNA viruses negative-senseNucleic acid vectorEnzyme digestionEquine influenza virus
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Universal mammalian influenza vaccine
ActiveUS20190321459A1Highly effective in inducing HA specific antibodyEnhance cross-protectionSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsAdjuvantMammal
The present invention provides vaccine or immunogenic compositions comprising novel antigens derived from the equine strain of influenza H3N8. These proteins and specific immunogenic domains are effective as primary universal influenza antigens. The disclosed vaccines or immunogenic compositions are highly effective in inducing HA specific antibodies reactive to different influenza viruses, mucosal and systemic immune responses, and cross-protection regardless of influenza virus subtypes. In some embodiments, the vaccine is cross-protective against two or more (e.g., 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6) subtypes of influenza with or without the use of an adjuvant.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com