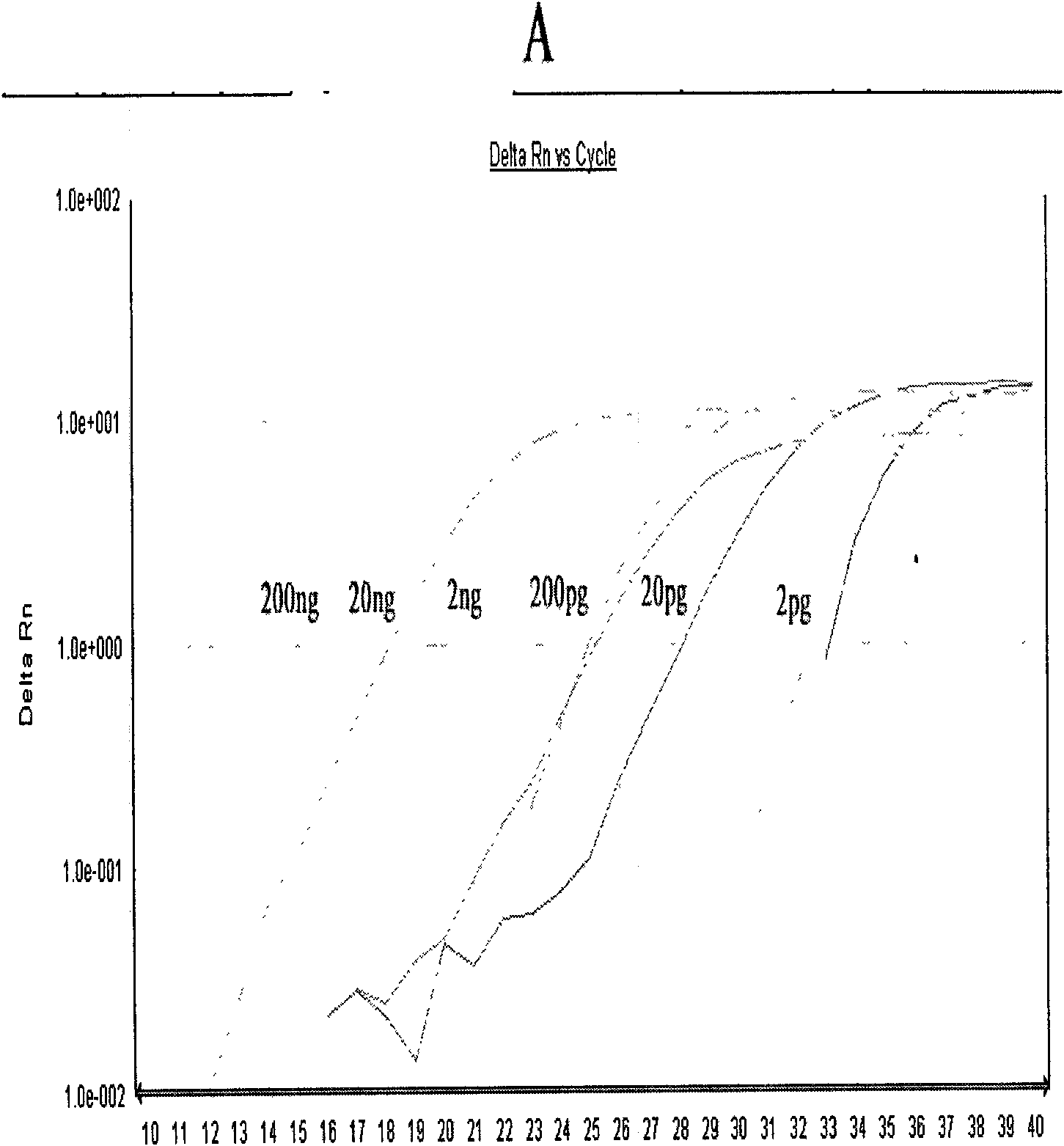
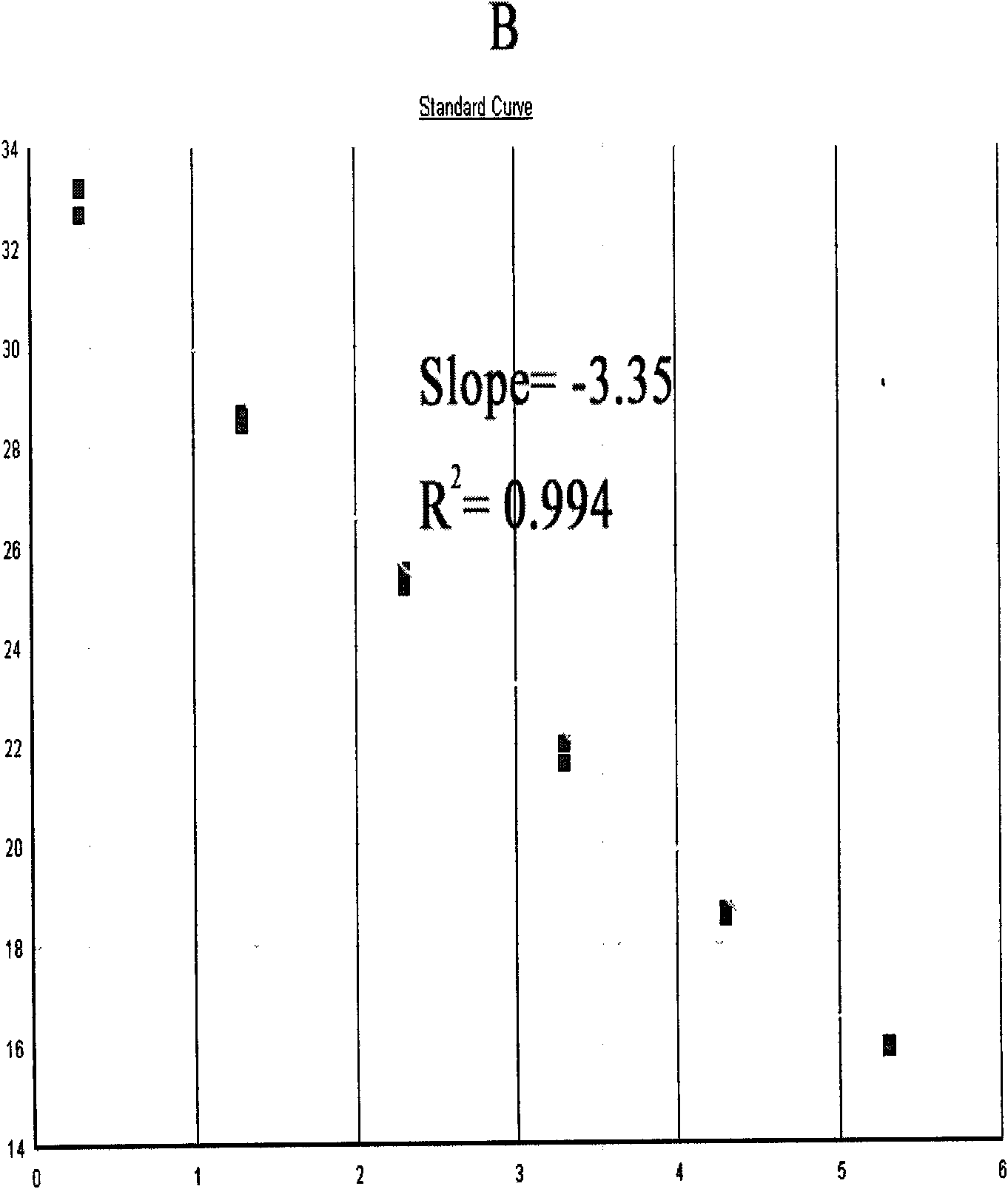
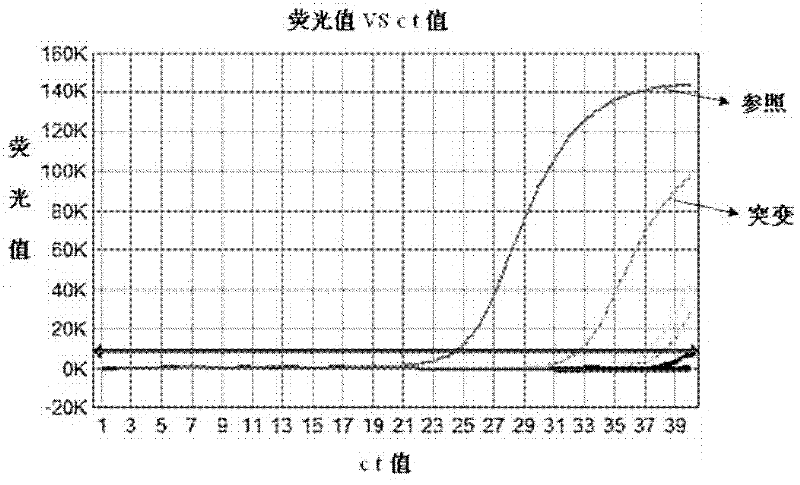
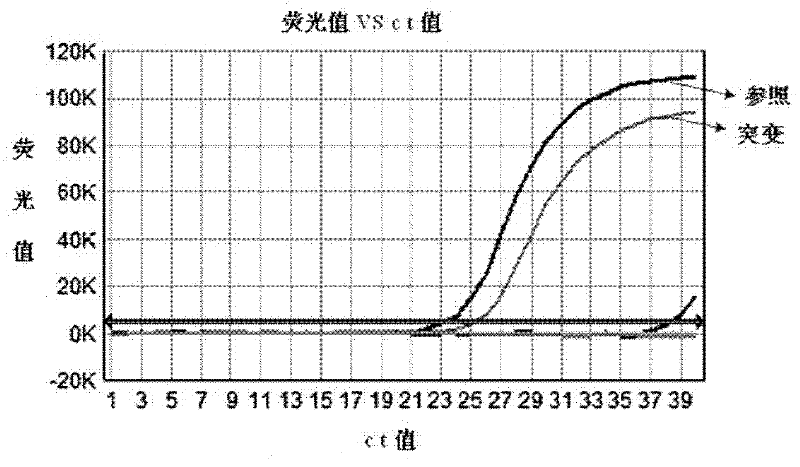
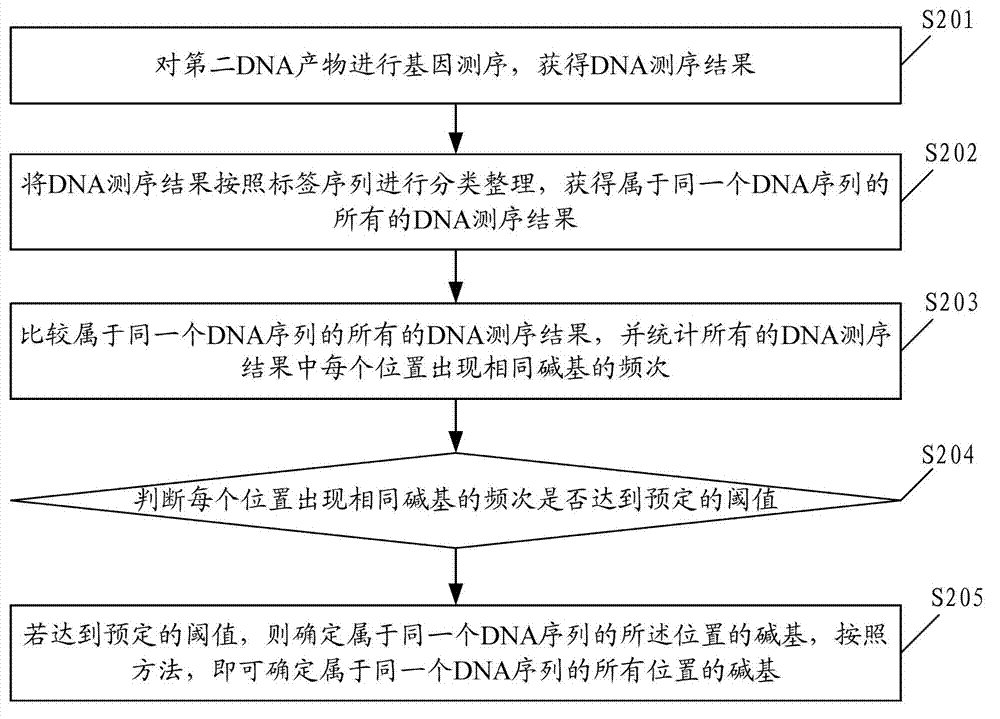
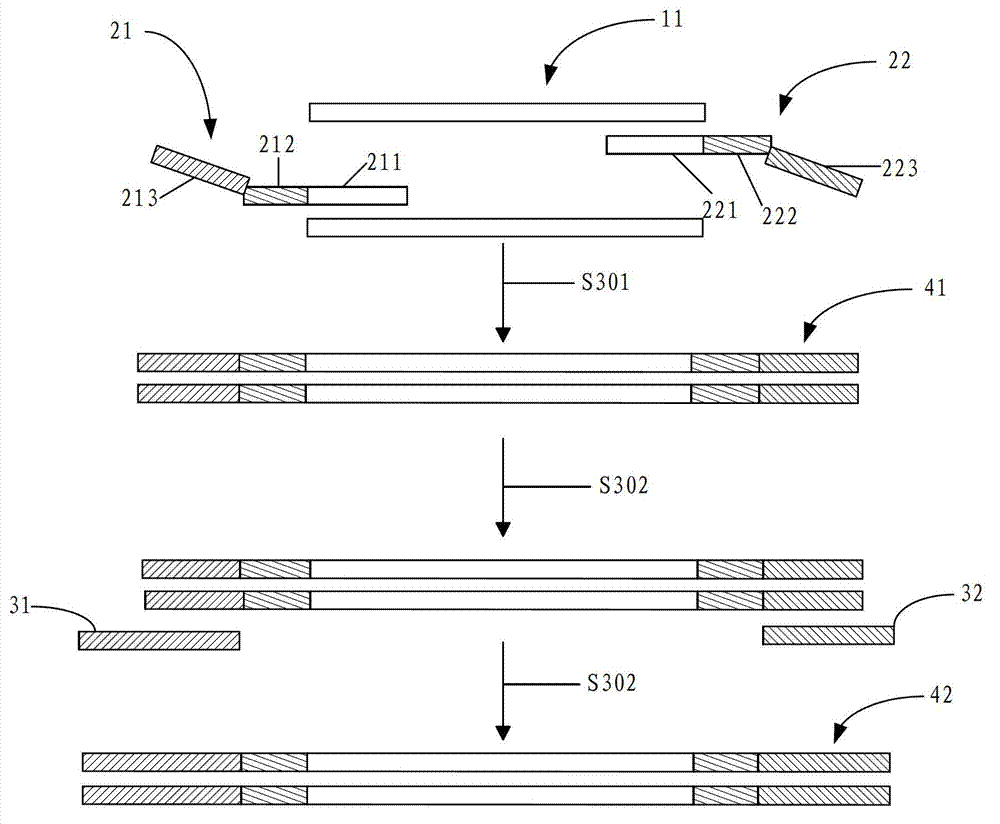
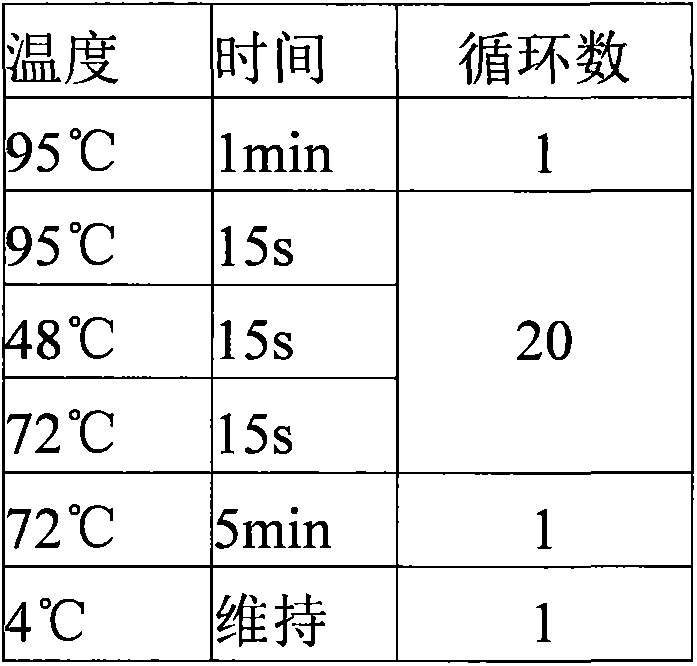
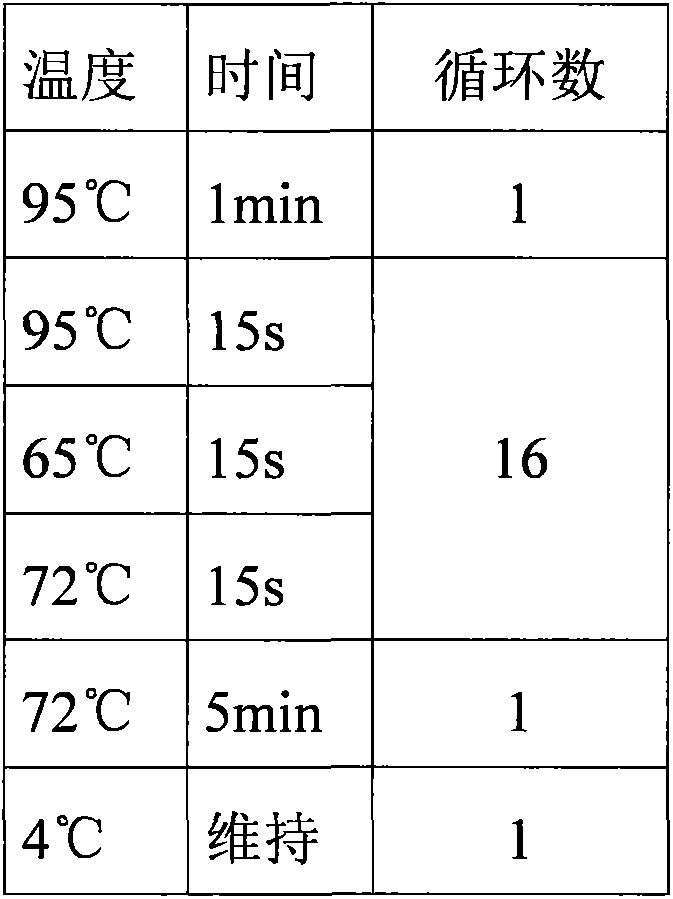
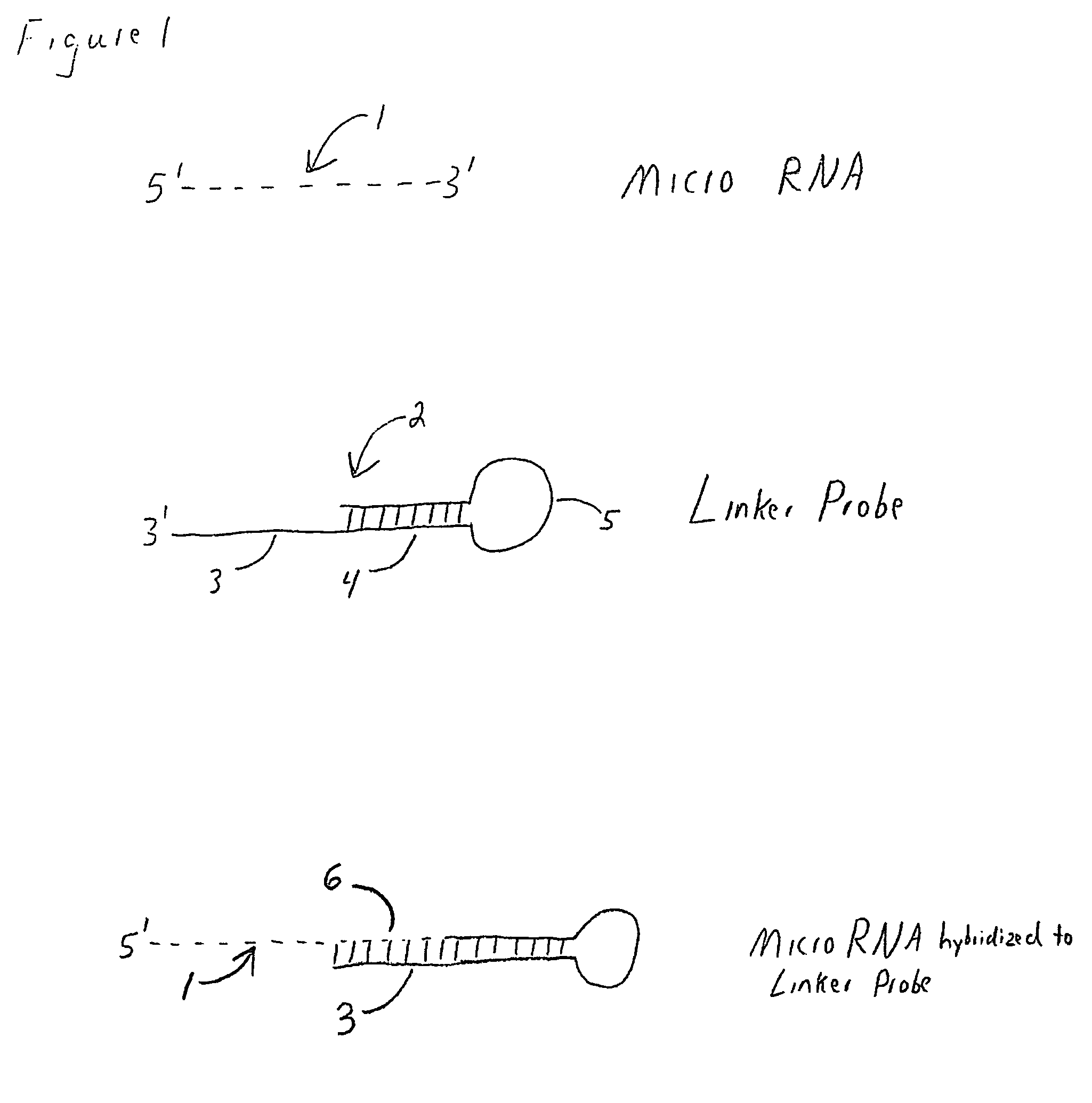Patents
Literature
2365 results about "Reverse primer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
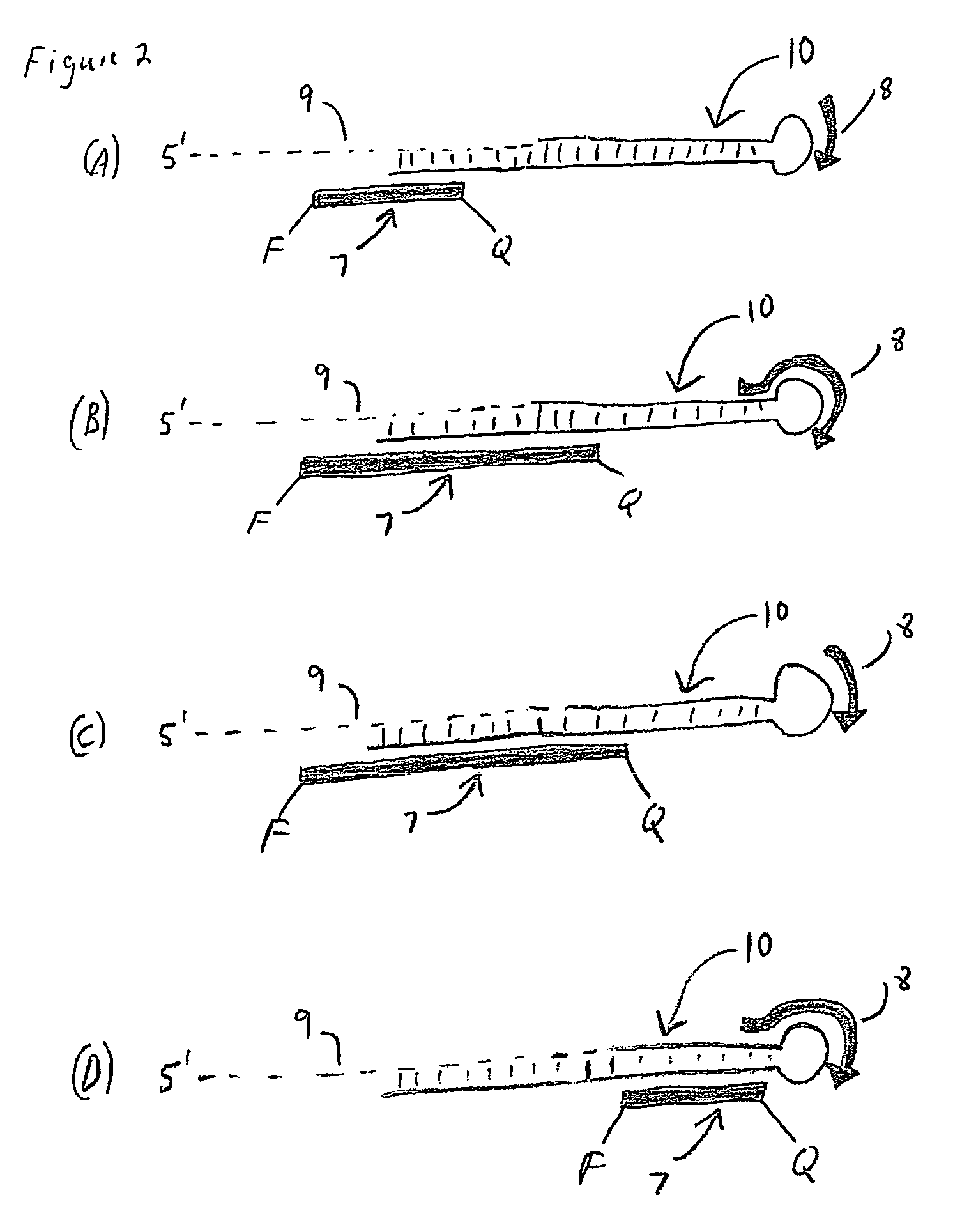
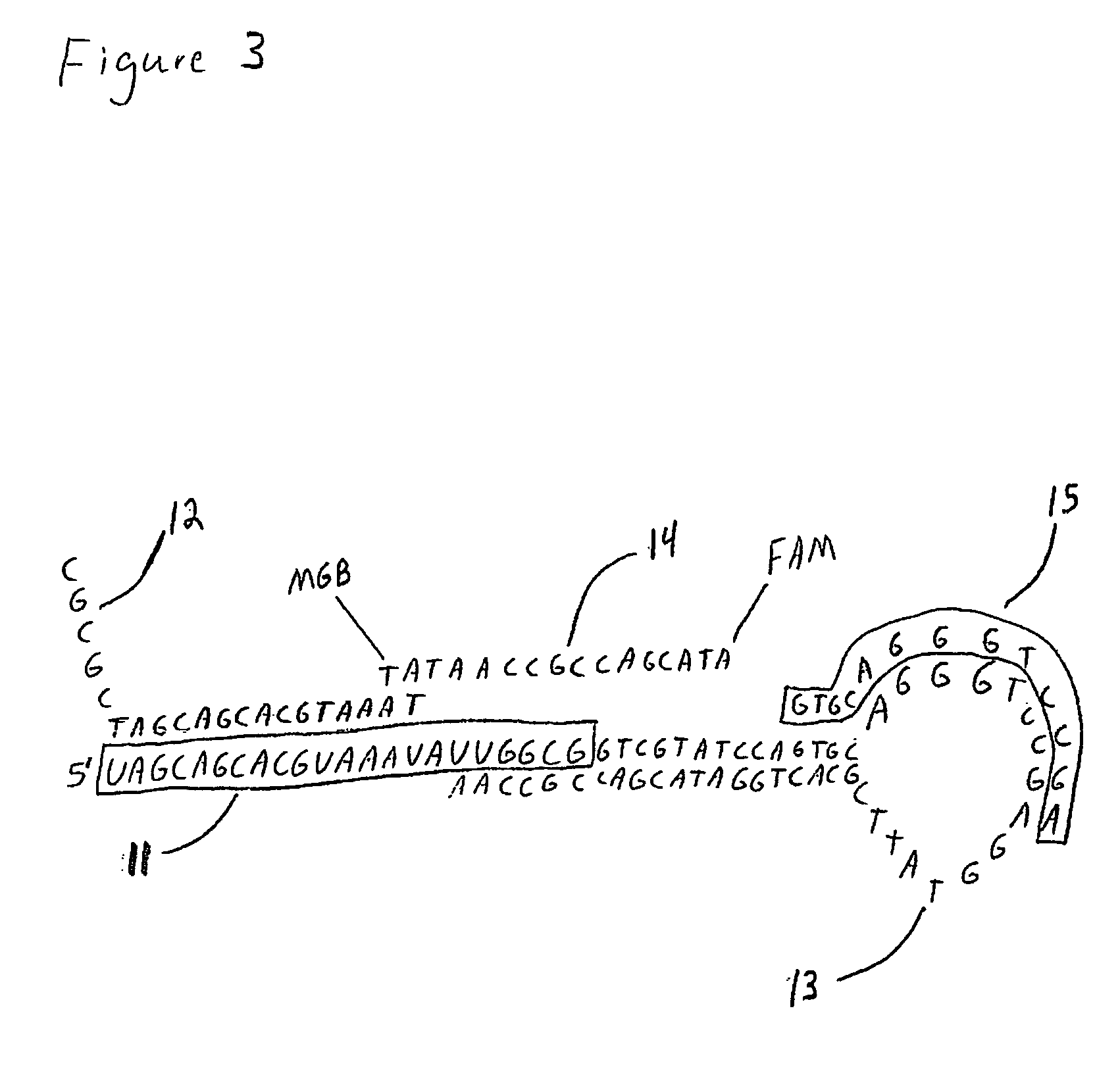
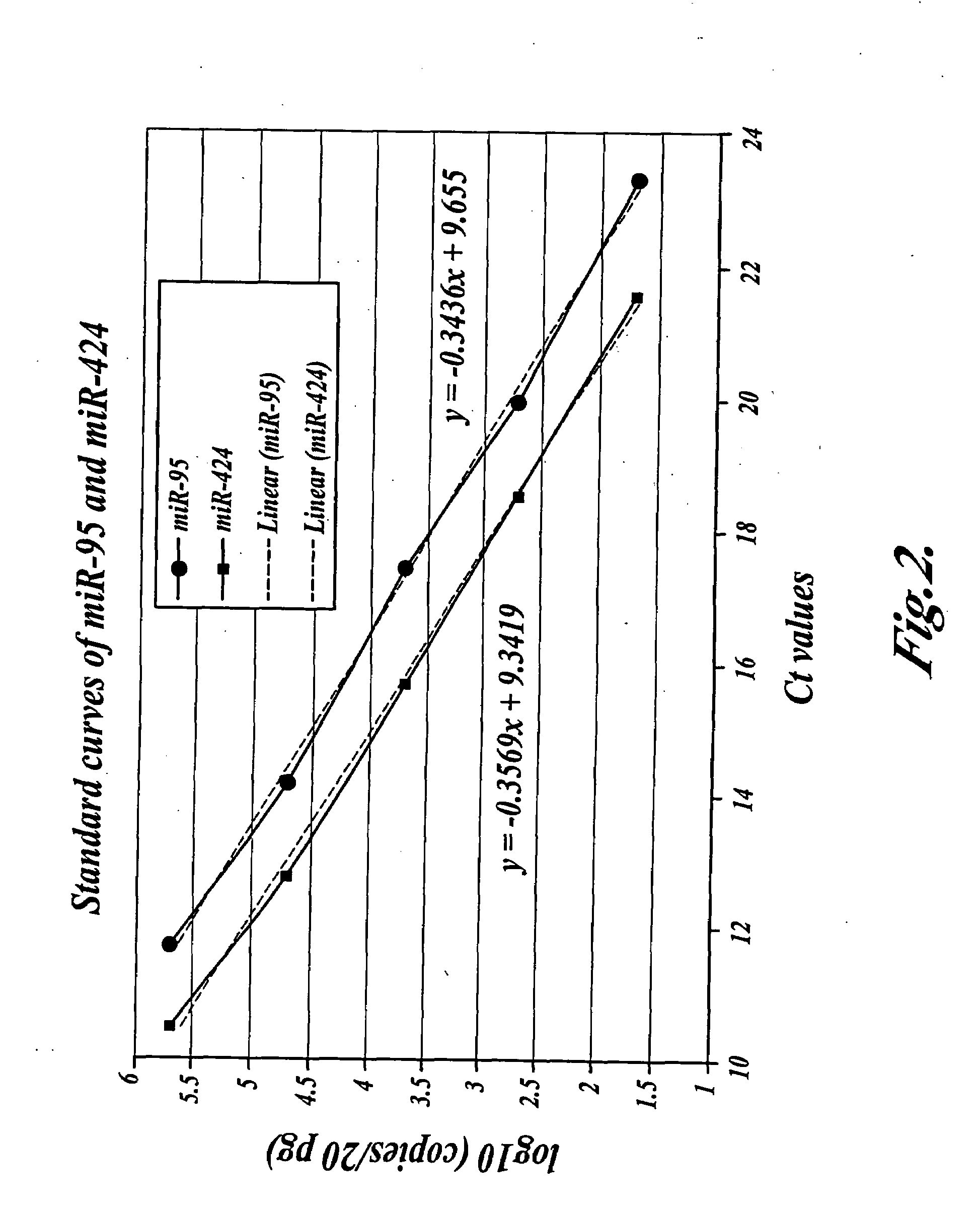
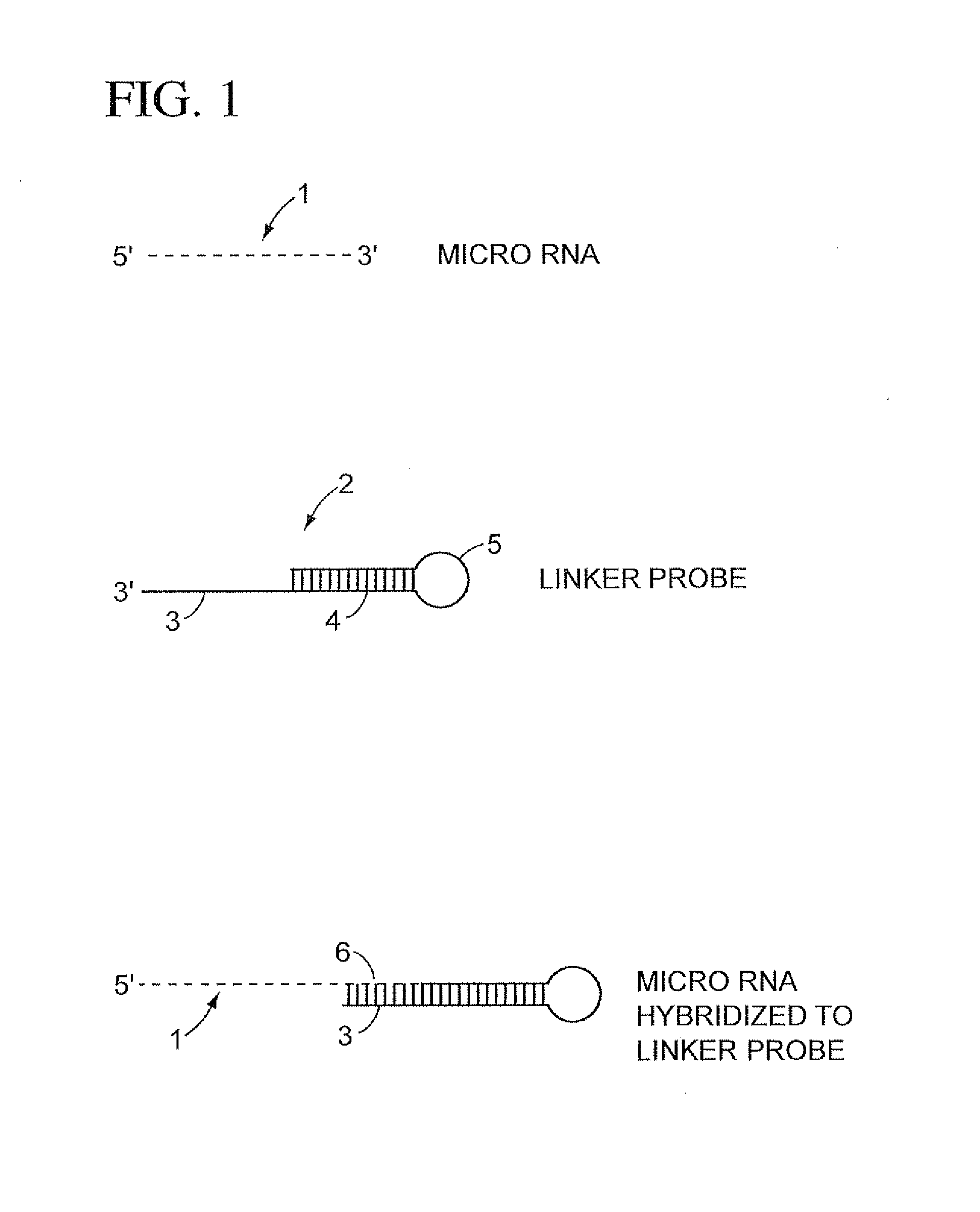
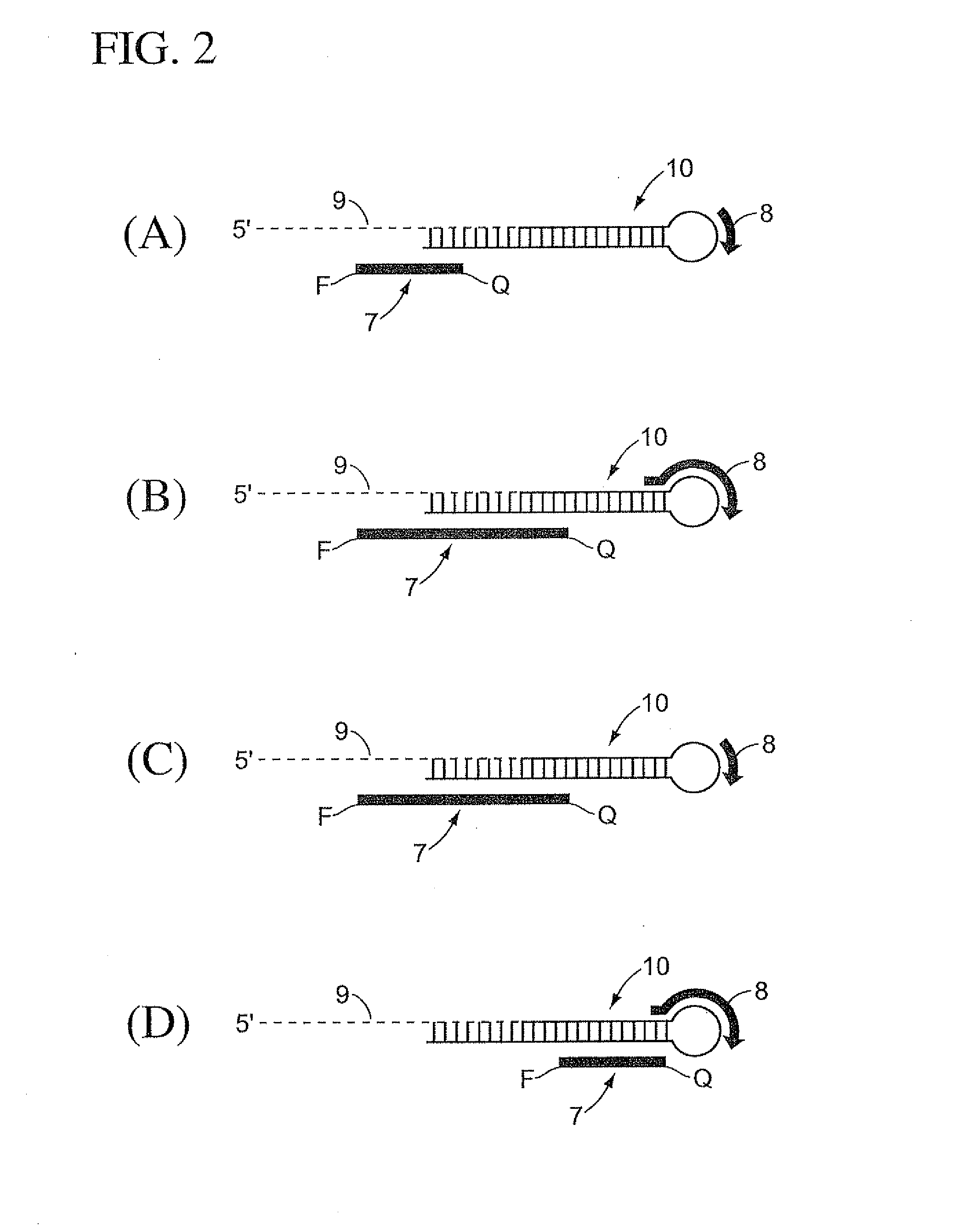
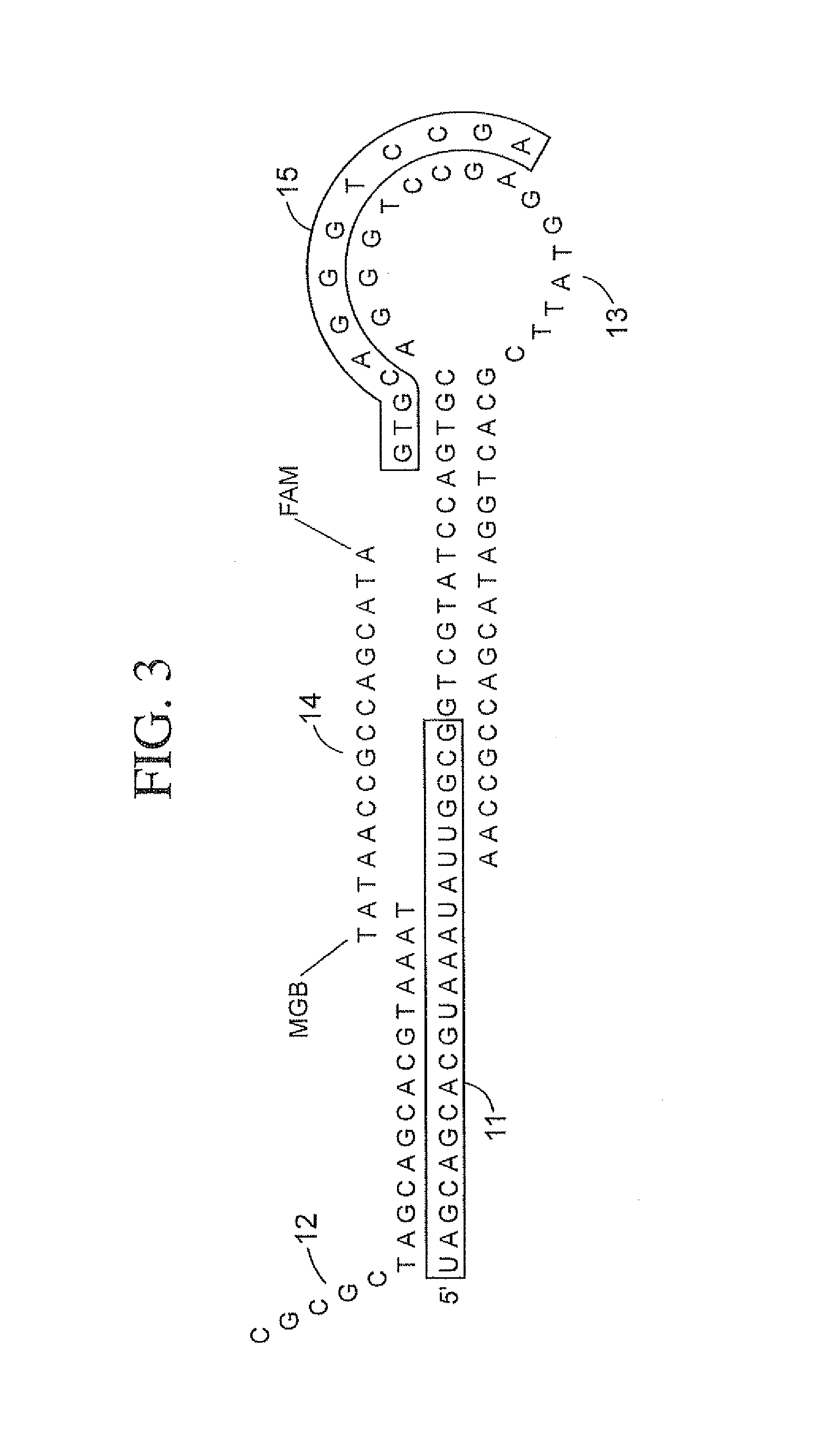
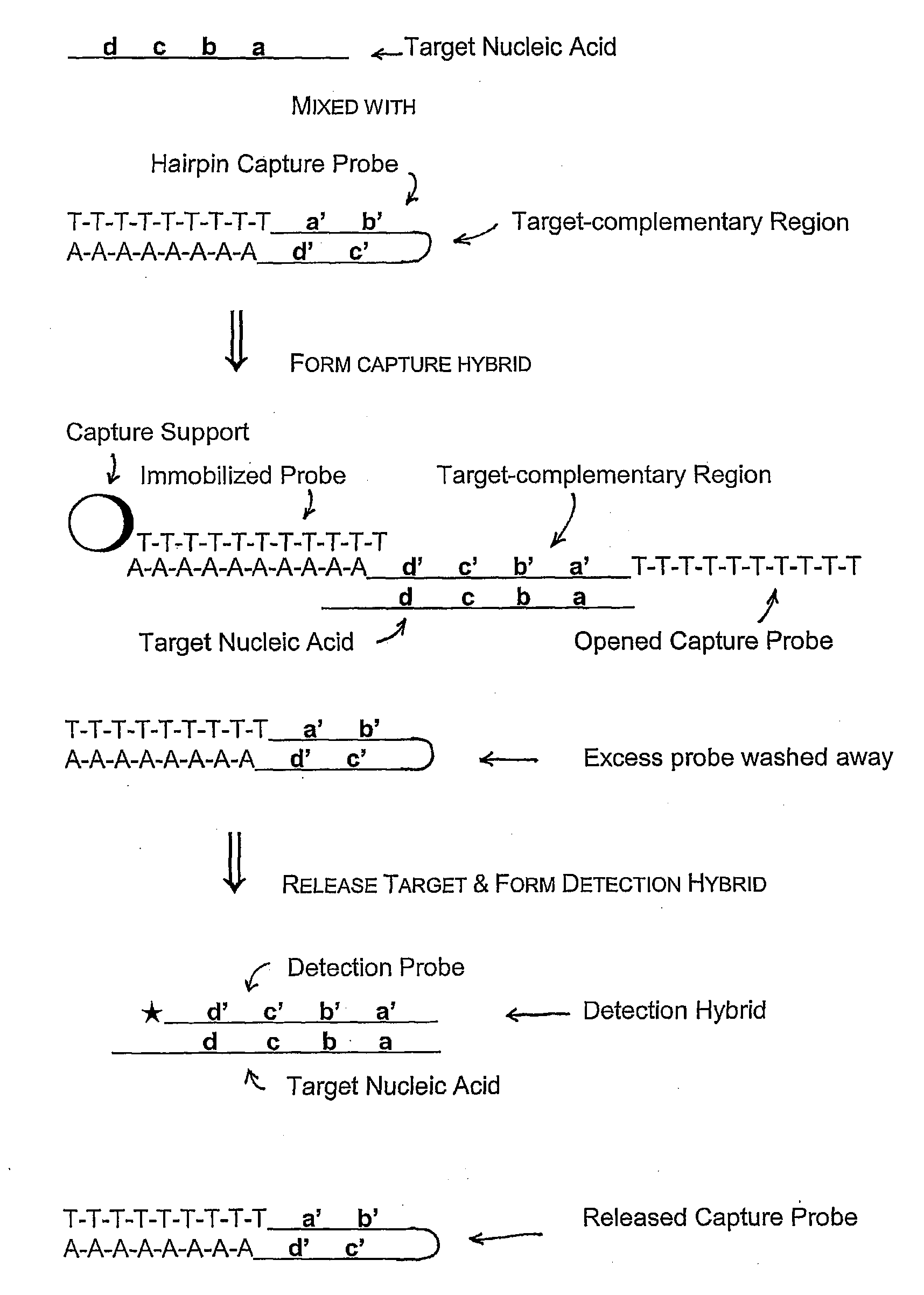
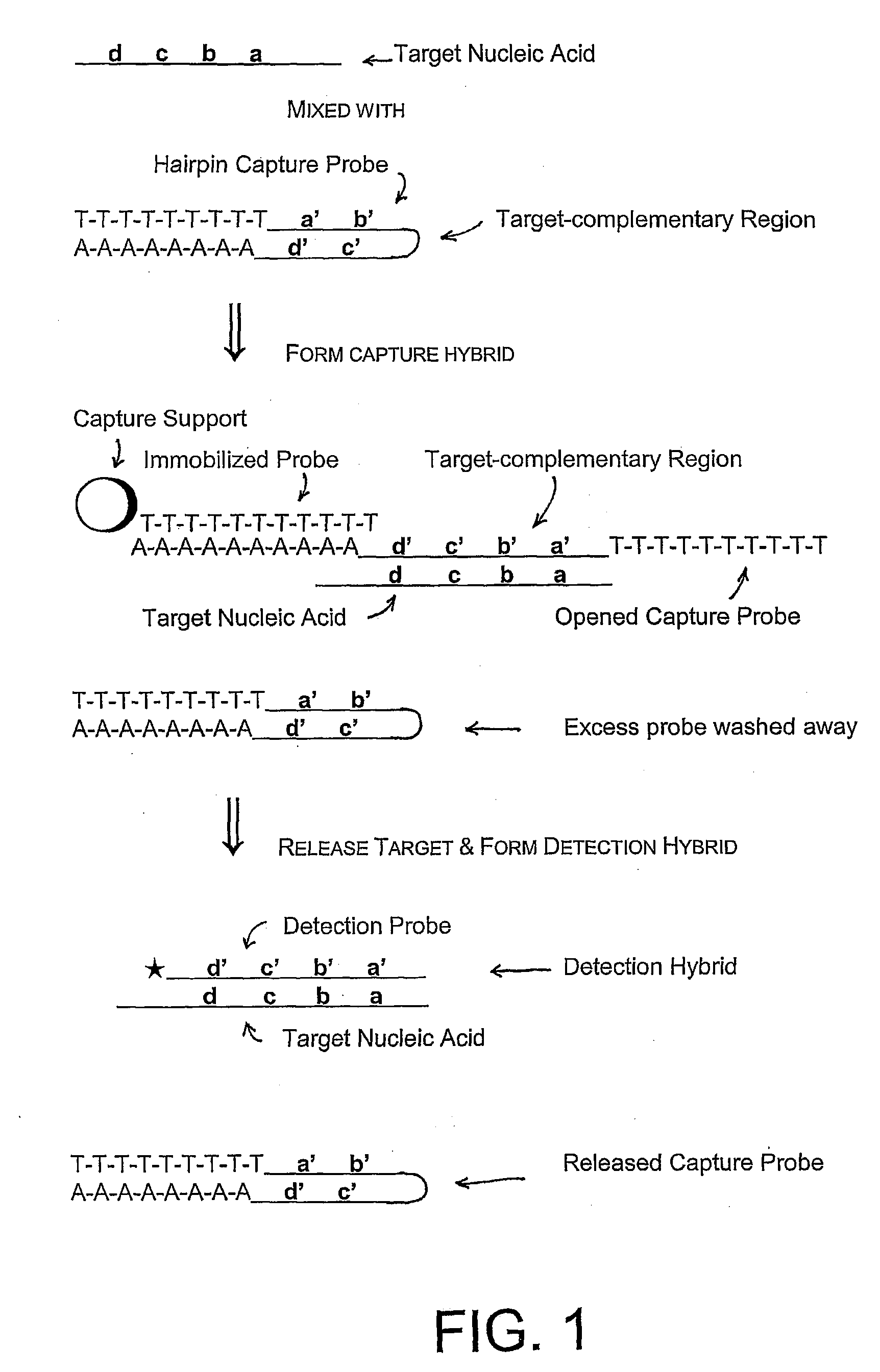
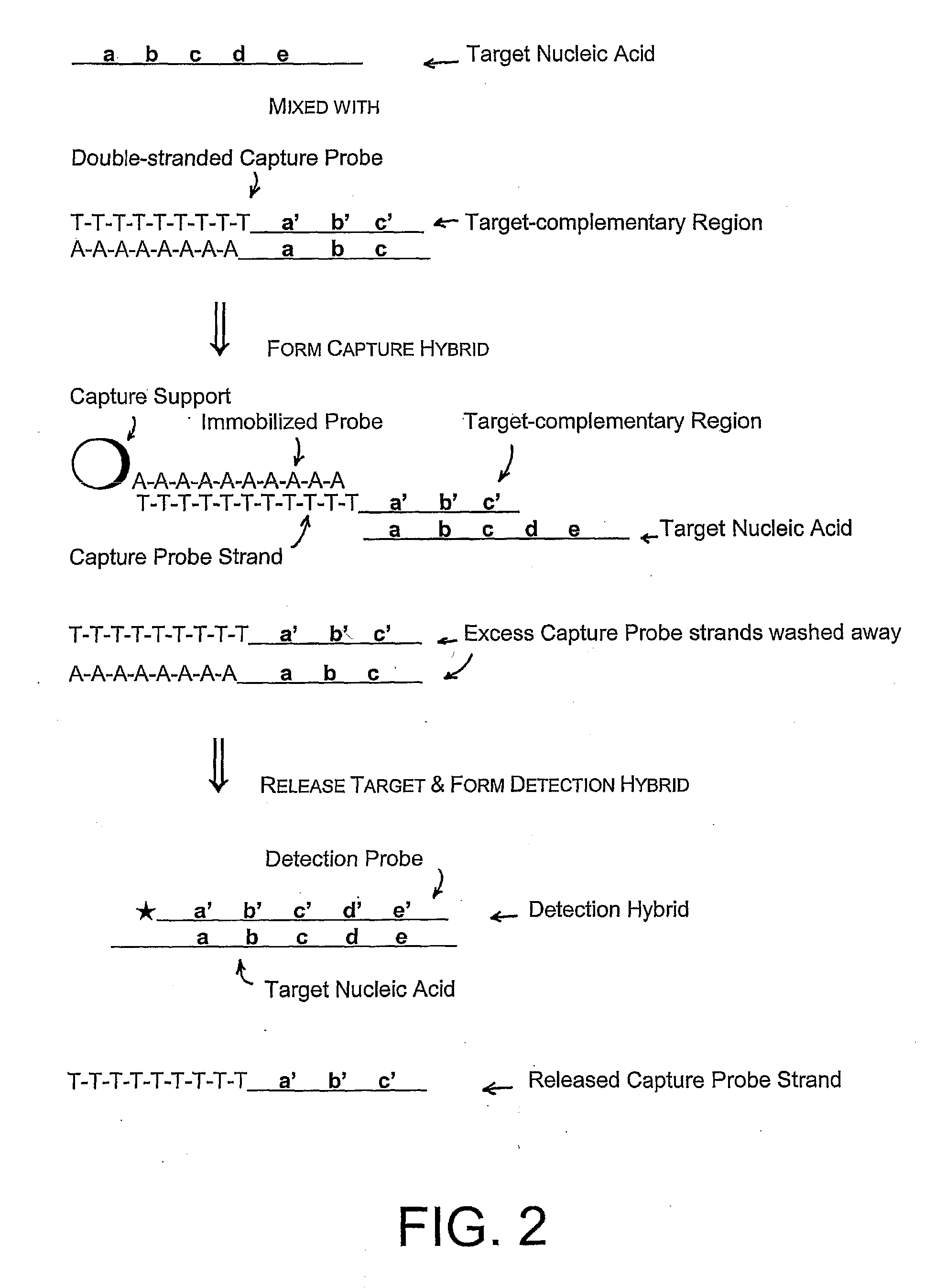
Methods, compositions, and kits comprising linker probes for quantifying polynucleotides
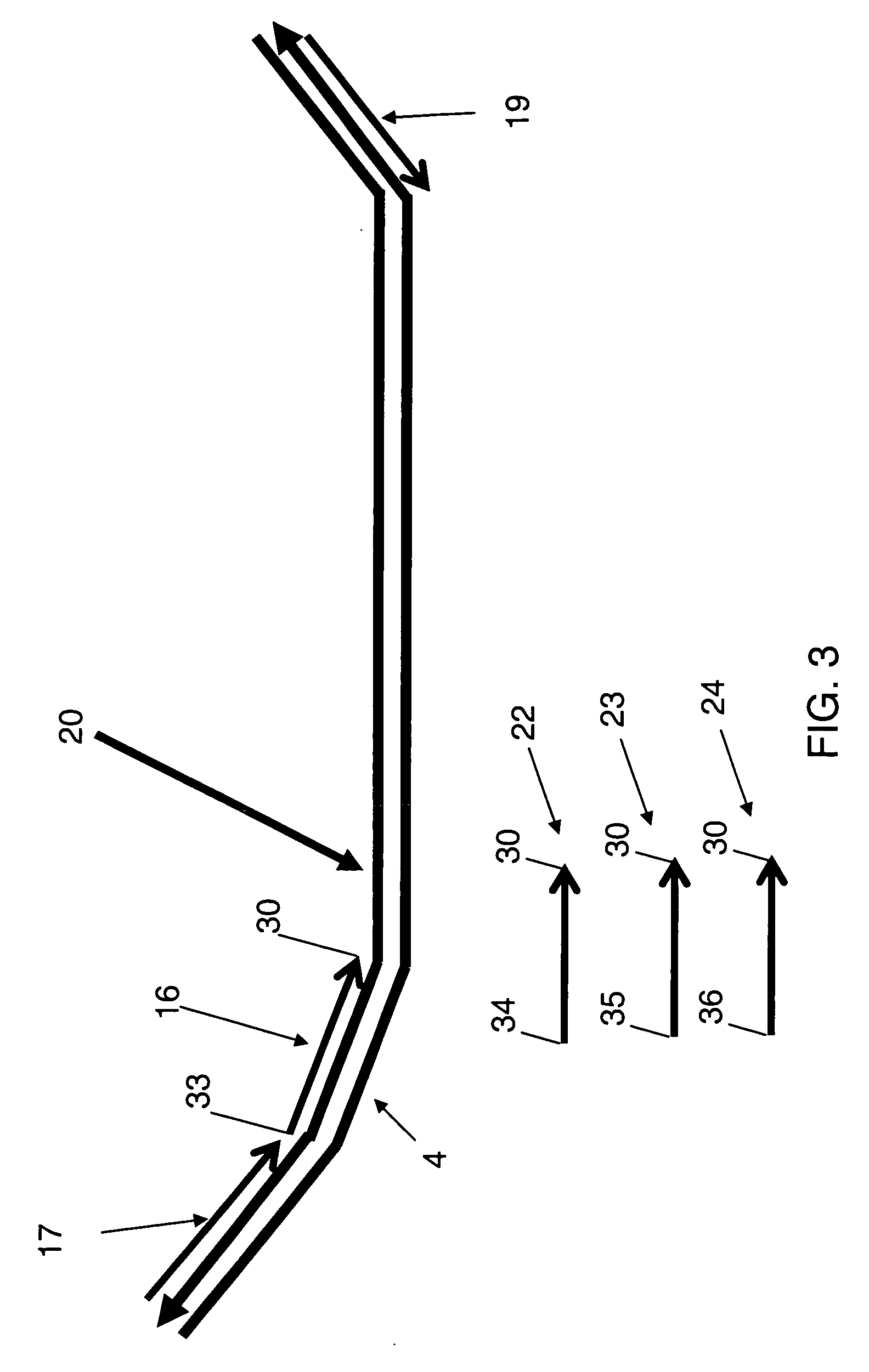
ActiveUS20050266418A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerPolynucleotide
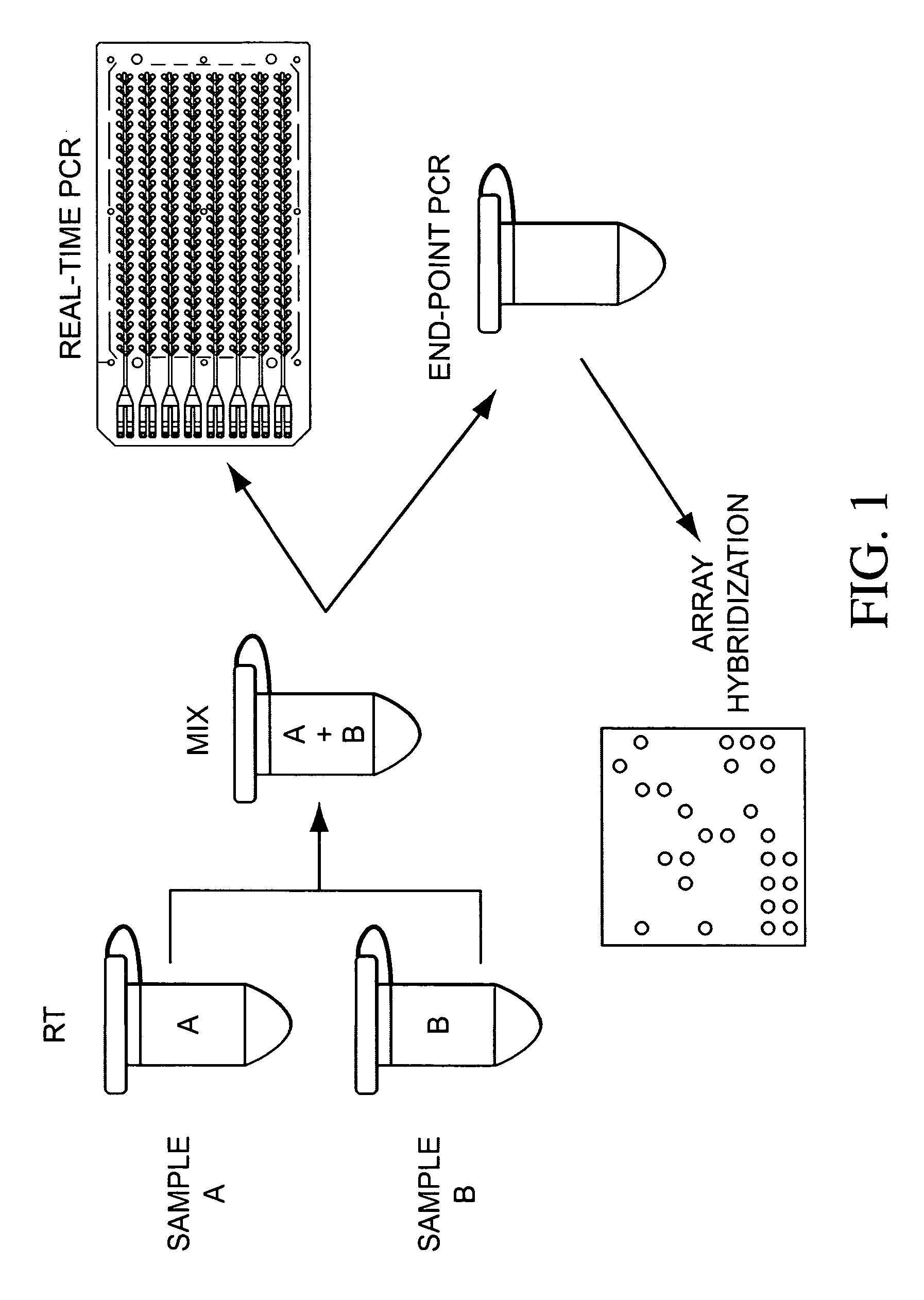
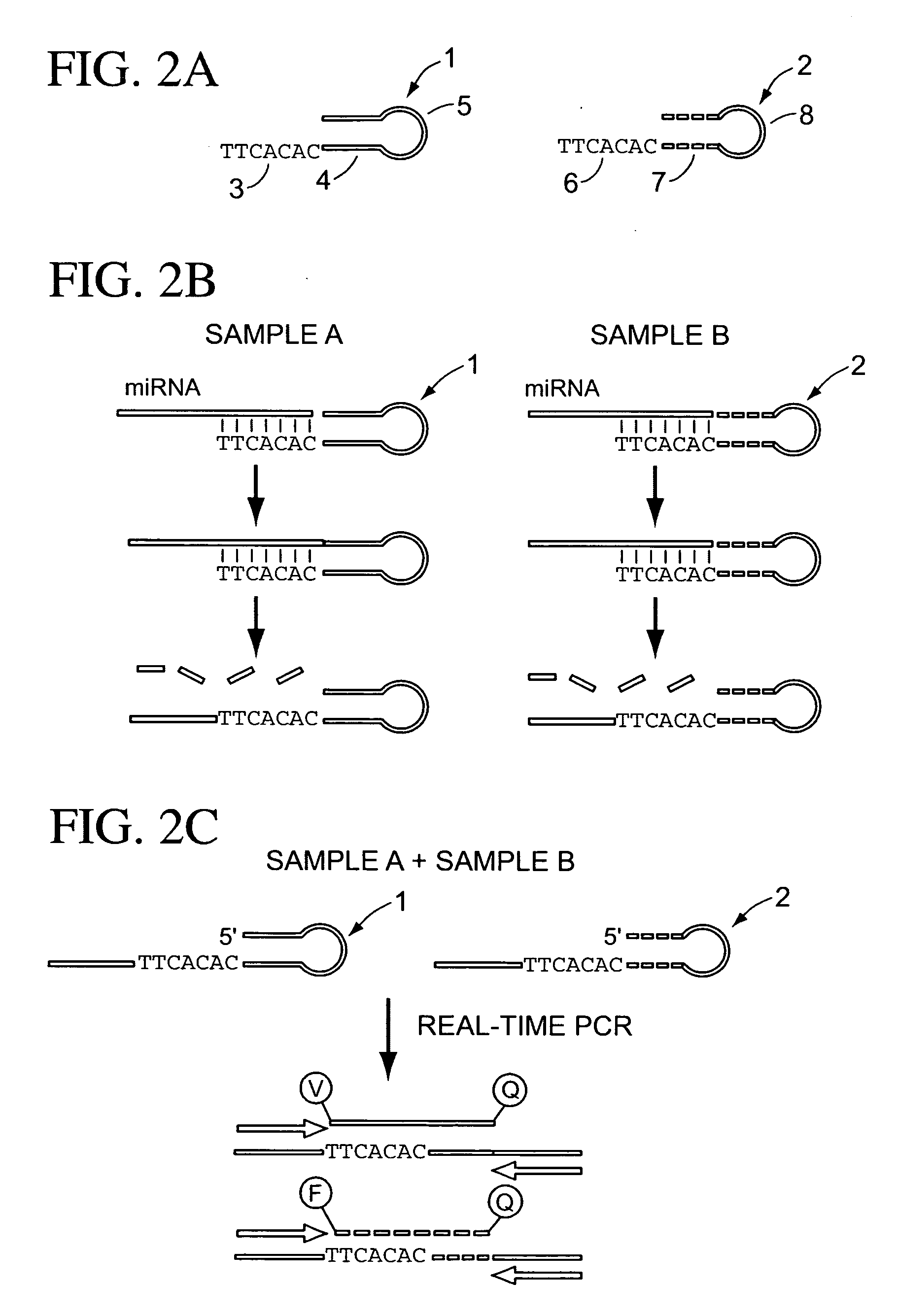
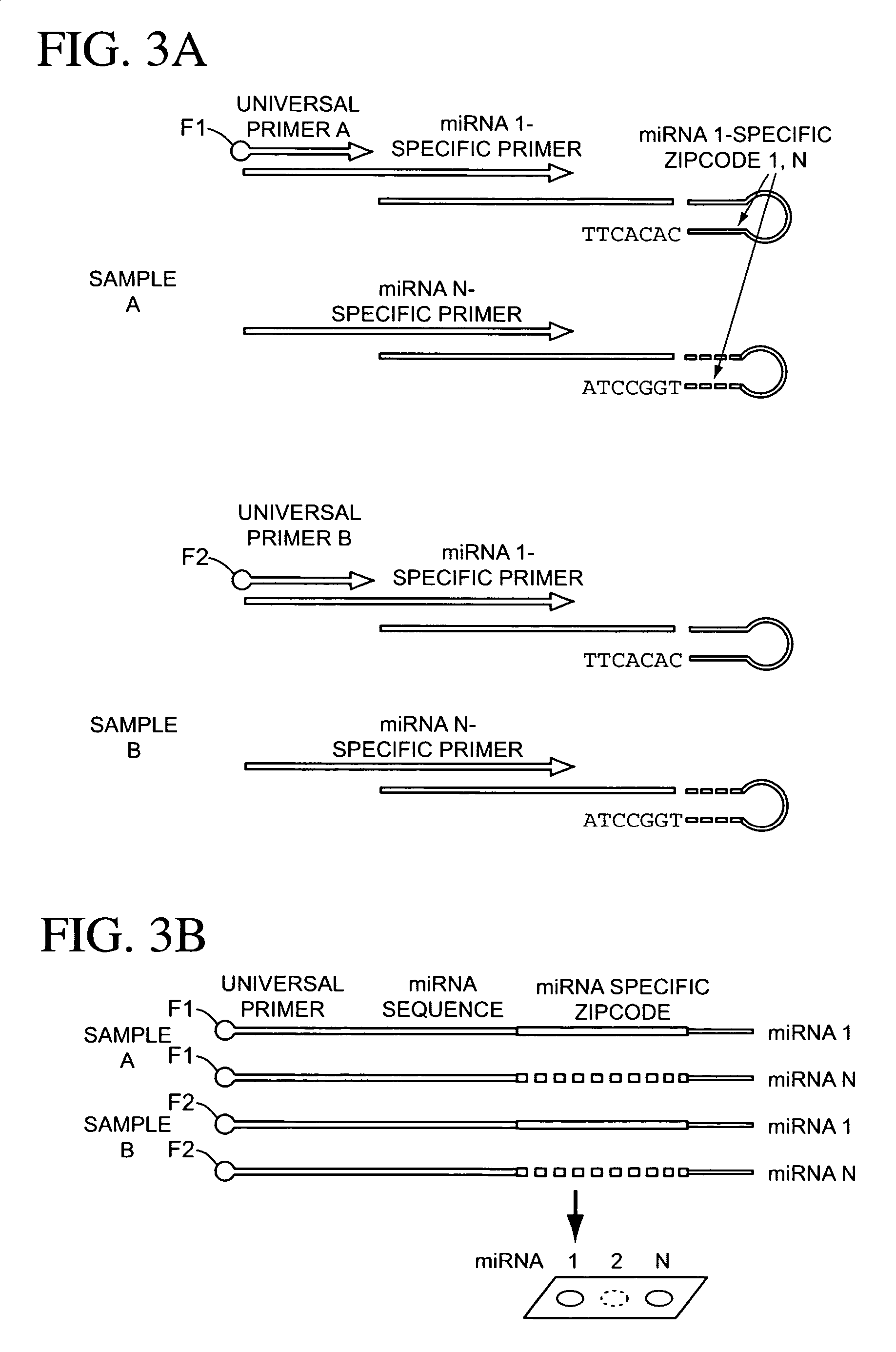
The present invention is directed to methods, reagents, kits, and compositions for identifying and quantifying target polynucleotide sequences. A linker probe comprising a 3′ target specific portion, a loop, and a stem is hybridized to a target polynucleotide and extended to form a reaction product that includes a reverse primer portion and the stem nucleotides. A detector probe, a specific forward primer, and a reverse primer can be employed in an amplification reaction wherein the detector probe can detect the amplified target polynucleotide based on the stem nucleotides introduced by the linker probe. In some embodiments a plurality of short miRNAs are queried with a plurality of linker probes, wherein the linker probes all comprise a universal reverse primer portion a different 3′ target specific portion and different stems. The plurality of queried miRNAs can then be decoded in a plurality of amplification reactions.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Compositions and Methods to Control Insect Pests
ActiveUS20140275208A1Lower Level RequirementsPest controlBiocideSugar derivativesSequence controlNucleotide
Methods and compositions are provided which employ a silencing element that, when ingested by a pest, such as a Coleopteran plant pest or a Diabrotica plant pest, decrease the expression of a target sequence in the pest. In specific embodiments, the decrease in expression of the target sequence controls the pest and thereby the methods and compositions are capable of limiting damage to a plant. The present invention provides various target polynucleotides set forth in any one of SEQ ID NOS: disclosed herein, (but not including the forward and reverse primers.) or active variants and fragments thereof, or complements thereof, wherein a decrease in expression of one or more of the sequences in the target pest controls the pest (i.e., has insecticidal activity). Further provided are silencing elements which when ingested by the pest decrease the level of the target polypeptide and thereby control the pest. In specific embodiments, the pest is D. virgifera virgifera, D. barberi, D. virgifera zeae, D. speciosa, D. speciosa, or D. undecimpunctata howardi. Plants, plant parts, bacteria and other host cells comprising the silencing elements or an active variant or fragment thereof of the invention are also provided.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC +1
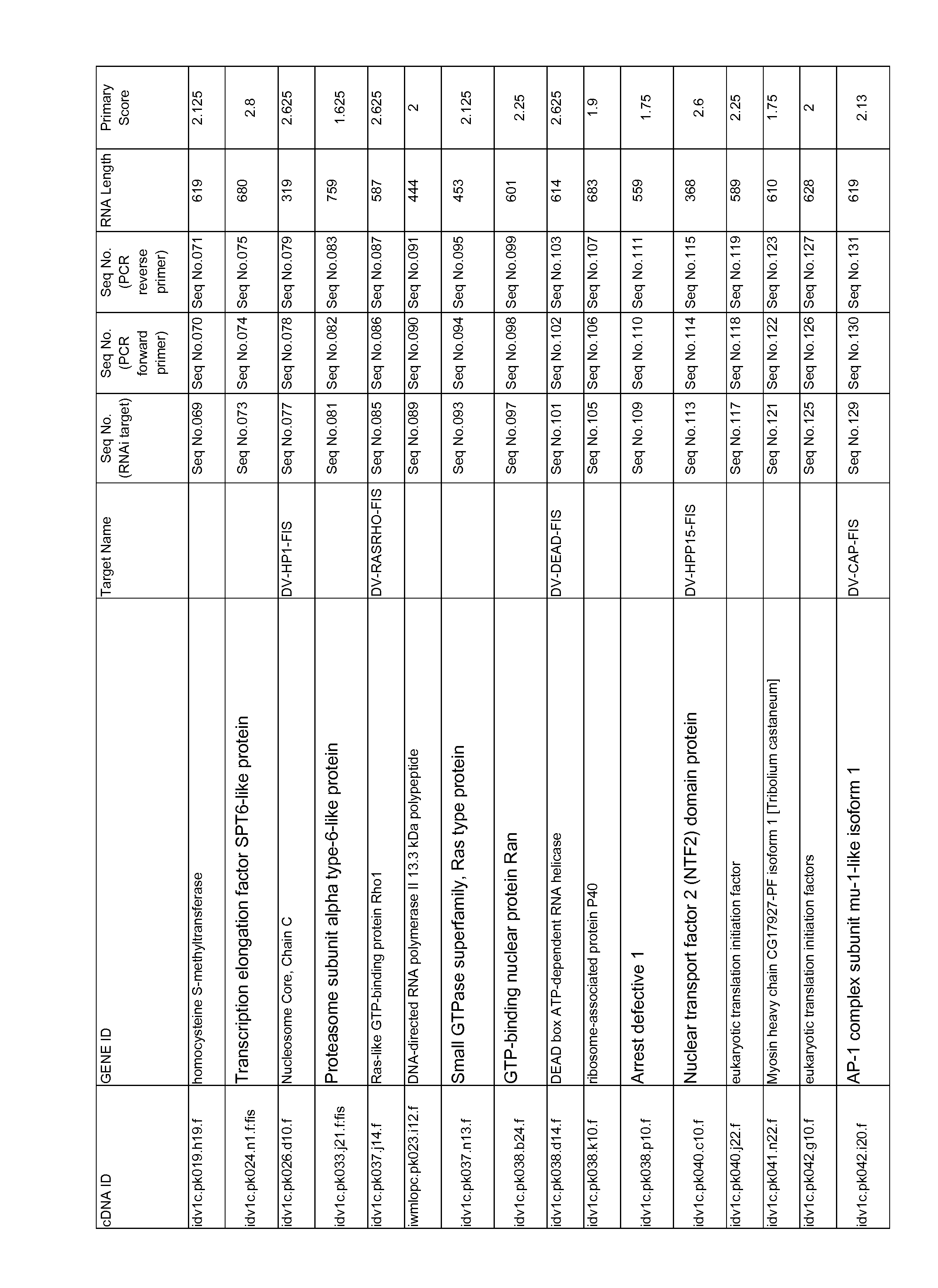
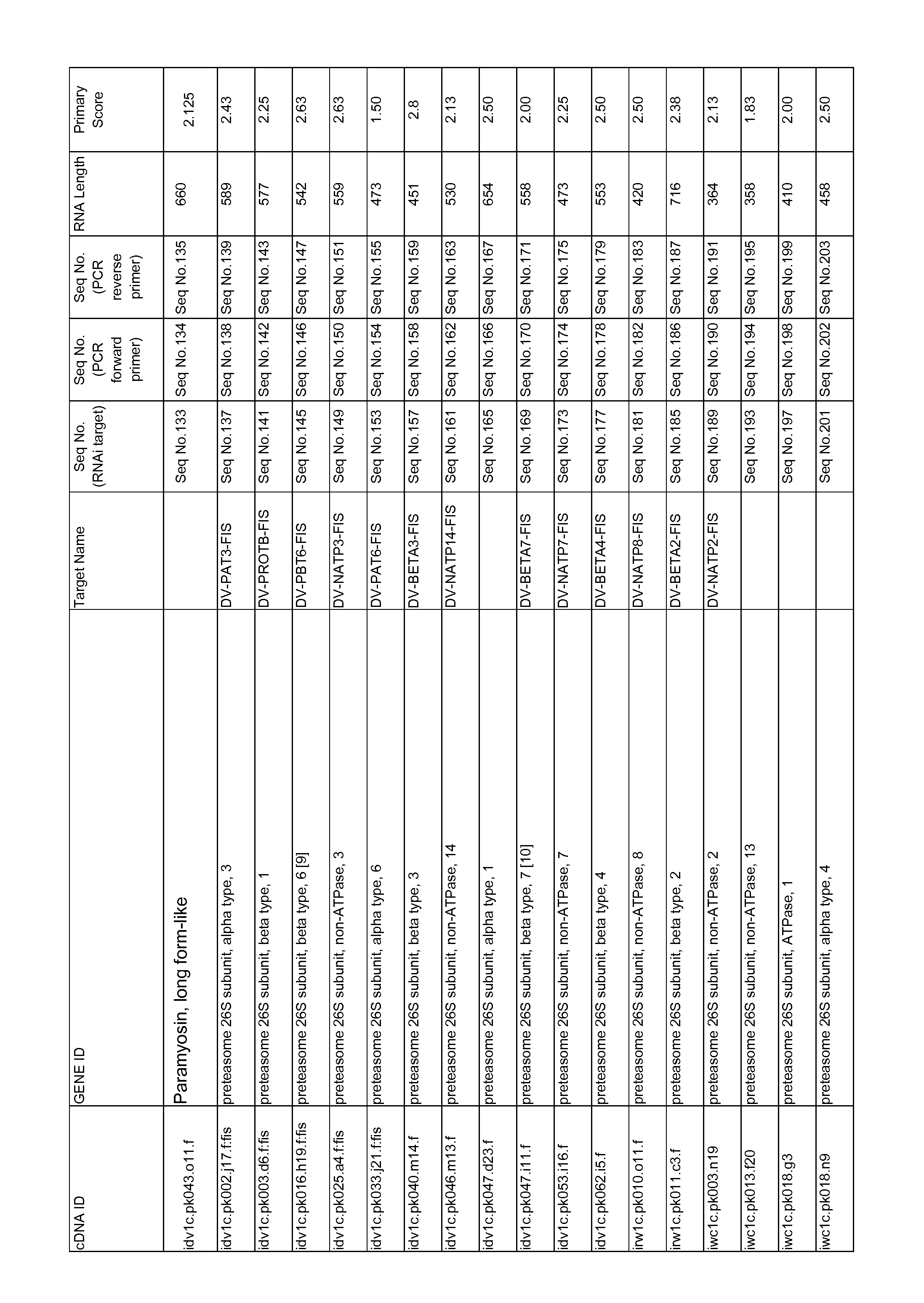
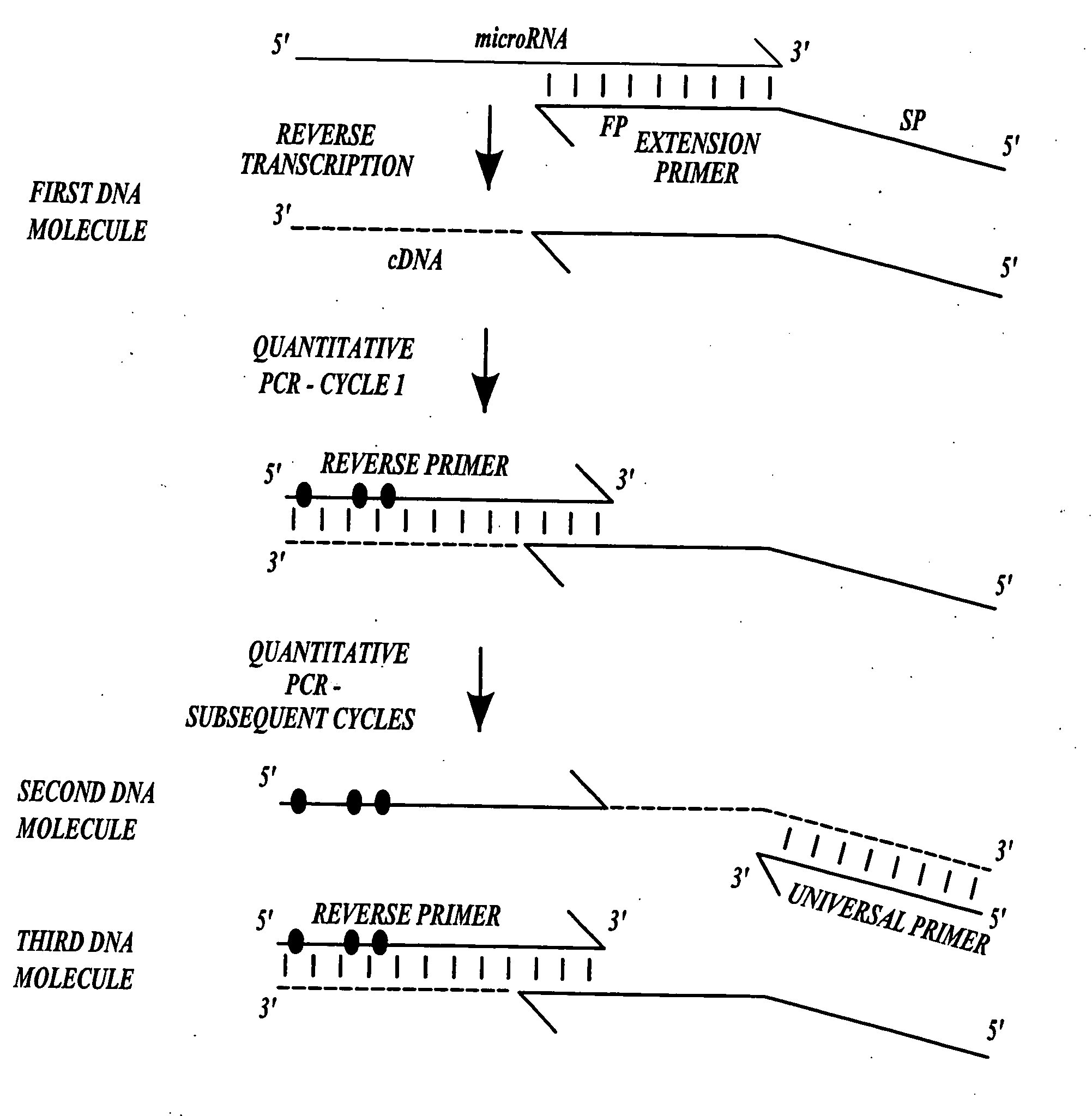
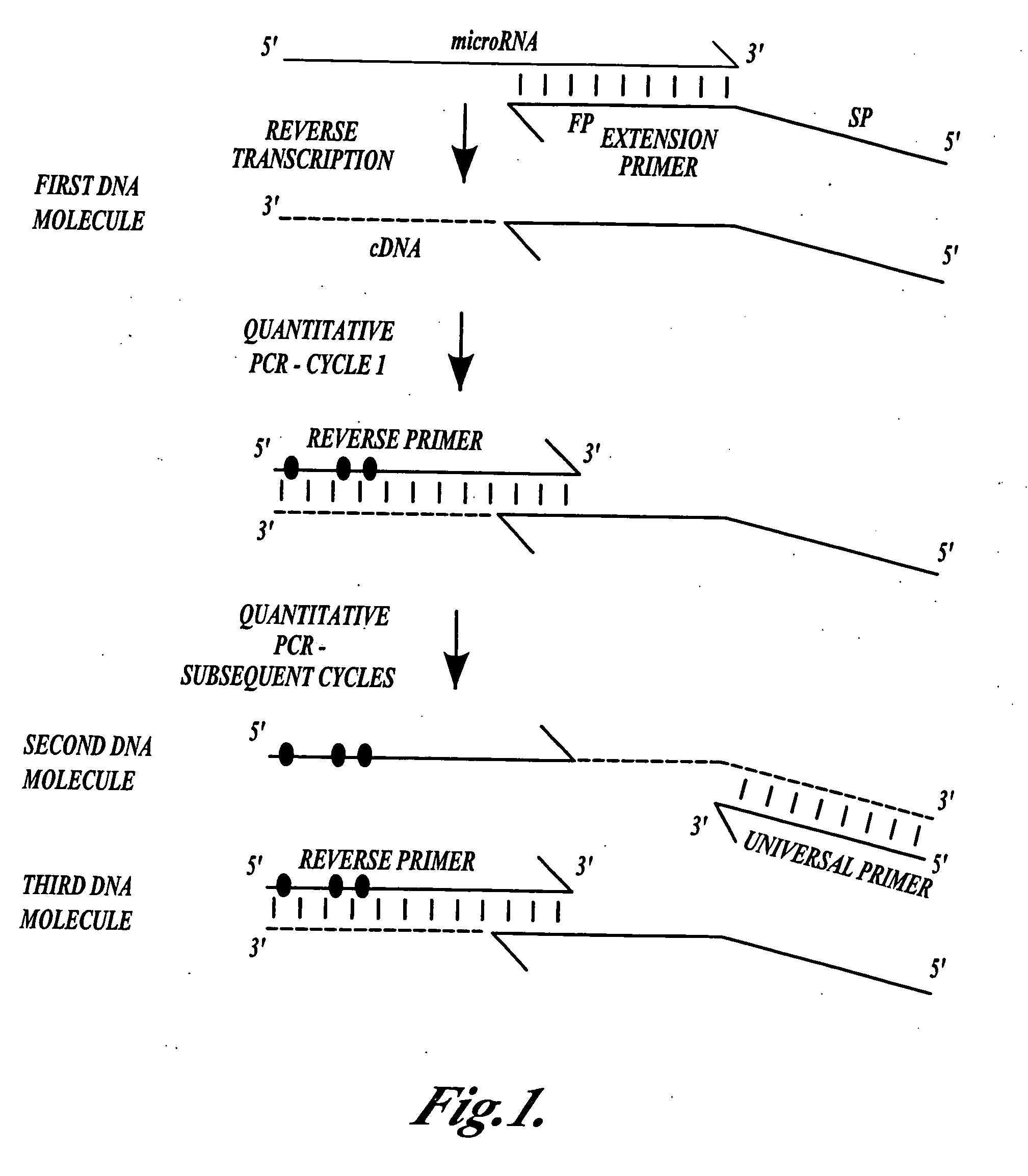
Methods for quantitating small RNA molecules
In one aspect, the present invention provides methods for amplifying a microRNA molecule to produce DNA molecules. The methods each include the steps of: (a) using primer extension to make a DNA molecule that is complementary to a target microRNA molecule; and (b) using a universal forward primer and a reverse primer to amplify the DNA molecule to produce amplified DNA molecules. In some embodiments of the method, at least one of the forward primer and the reverse primer comprise at least one locked nucleic acid molecule.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Methods, compositions, and kits comprising linker probes for quantifying polynucleotides
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Identifying and quantifying small RNAs
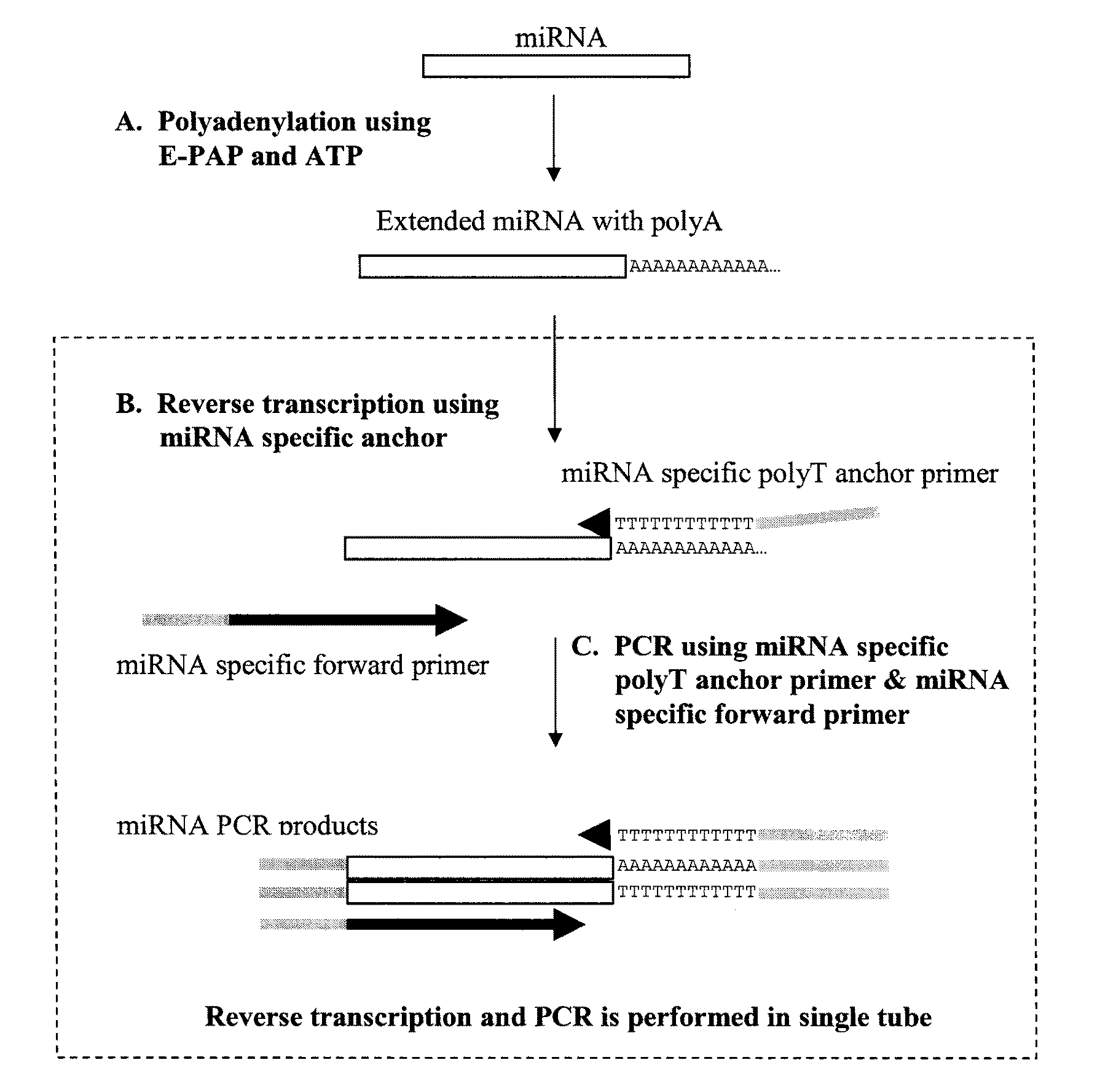
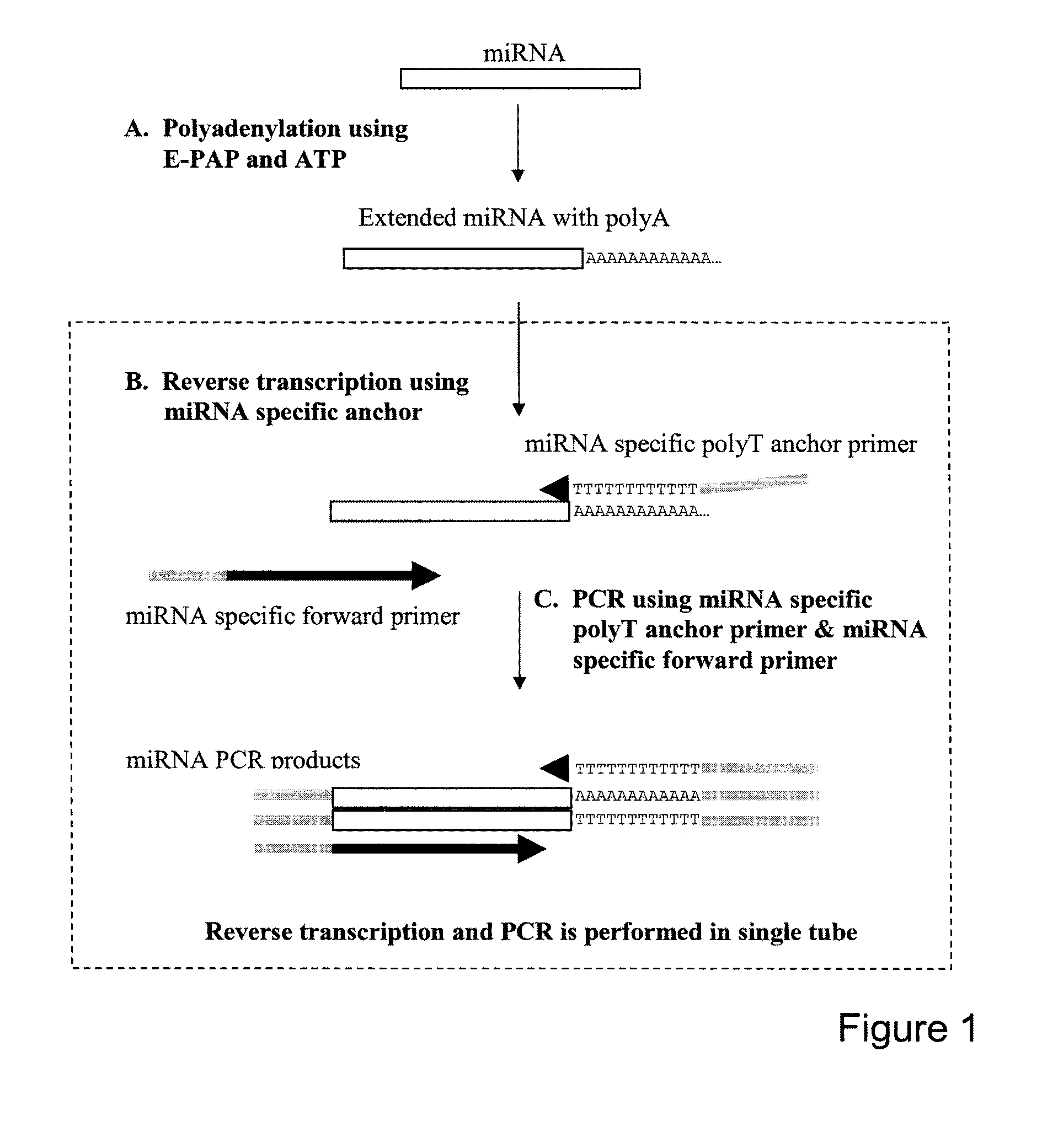
One-step RT-PCR methods, compositions and kits for the detection and quantification of small RNAs in a sample are disclosed. The one-step RT-PCR approach involves polyadenylation of a small RNA followed by reverse transcription with a first primer containing a poly(T) sequence and at least two 3′ nucleotides complementary to the 3′ terminal end nucleotides of the small RNA, to produce a cDNA. This may be followed by PCR amplification using the same first primer as the revere primer and a second, forward primer in which a portion of its sequence is complementary to the 3′ terminal end of the cDNA. This may be then followed by detection and / or quantification of the amplified product.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Method and primers for detecting mi ribonucleic acid (miRNA) and application of method
ActiveCN102154505AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerDisease
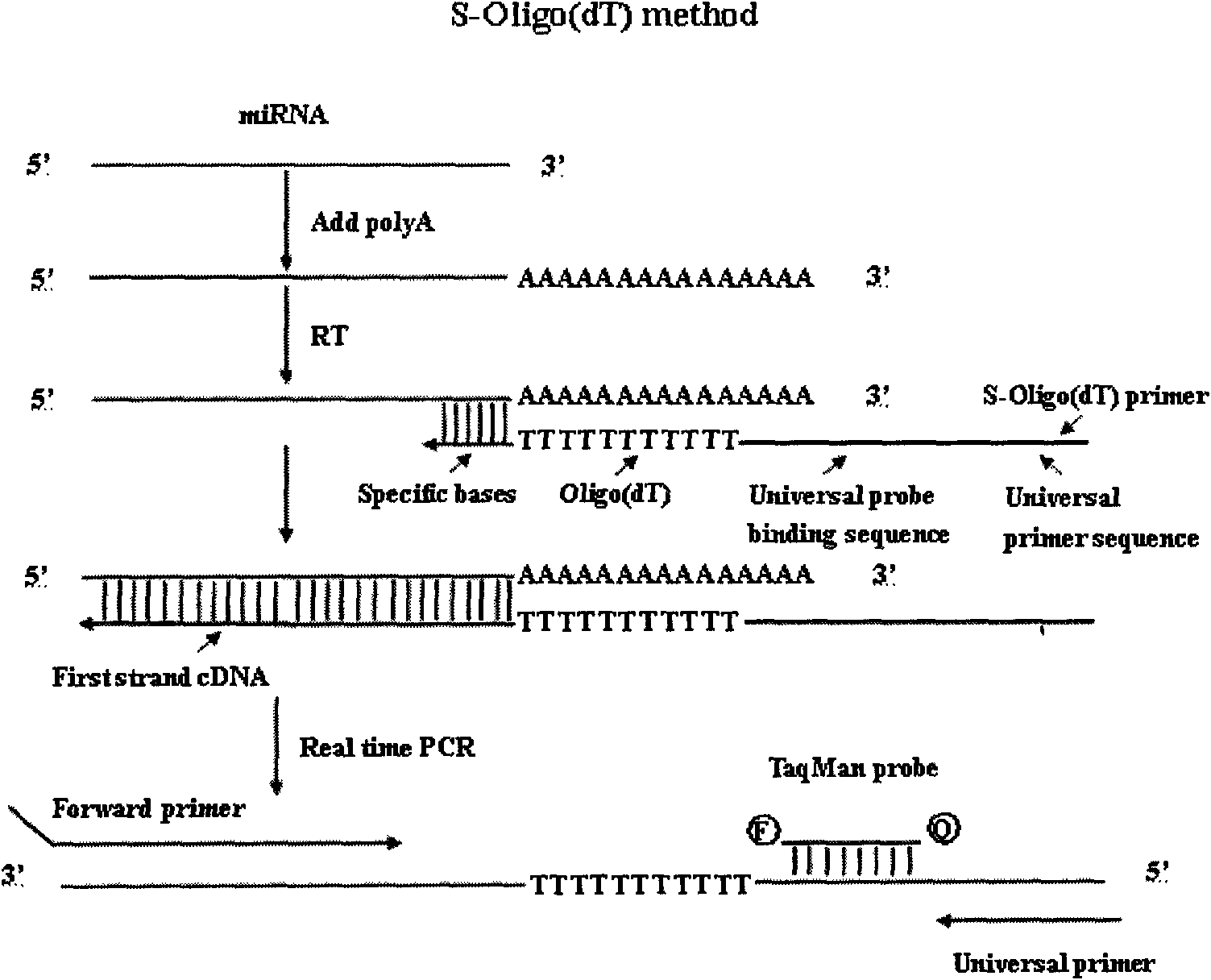
The invention discloses a method and primers for detecting mi ribonucleic acid (miRNA) and application of the method. The method comprises the following steps of: performing reverse transcription on the miRNA in a sample by using a reverse transcription primer formed by specific basic groups and Oligo (dT); and performing real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) quantitative detection on the miRNA by using a specific forward primer, a general reverse primer and a general probe. The invention has the characteristics that: the sensitivity and the specificity of the method are obviously higher than those of the conventional method; high-throughput analysis can be performed; and the method is simply and quickly operated, is low in cost, and can be widely used for early diagnosis and prediction of critical diseases such as tumors and the like.
Owner:苟德明 +1
ARMS-qPCR (Allele Refractory Mutation System-quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for KRAS (Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog) gene mutation subtype and detection method
InactiveCN102367478AIncreased sensitivityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementViral OncogenePositive control
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and aims to provide an ARMS-qPCR (Allele Refractory Mutation System-quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for KRAS (Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog) gene mutation subtype and a detection method. The kit comprises a qPCR hybrid reaction solution, a locked nucleic acid retardant probe, a reference primer, an ARMS primer and a positive control sample, wherein the qPCR hybrid reaction solution comprises a PCR buffer solution, dNTPs (Deoxynucleotide Triphosphates), MgCl2, GoldStarbest Taq enzyme, a universal PCR reverse primer and a universal TaqMan probe. The kit provided by the invention can be used for rapidly and accurately detecting specific locus mutation of KRAS genes in various cancer tissues with high sensitivity, has high sensitivity, and can be used for detecting genome DNA with various tissue origins, specially free DNA segments adopting cell-free systems, such as blood serum and blood plasma, orother body fluid origins, wherein the genome DNA is derived from cell systems. Compared with direct sequencing and other mutation detection technologies, the kit and the detection method thereof havethe advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, simplicity and rapidness in operation, high throughput, safety, definiteness and objectivity in result identification and the like for detecting the KRAS gene mutation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
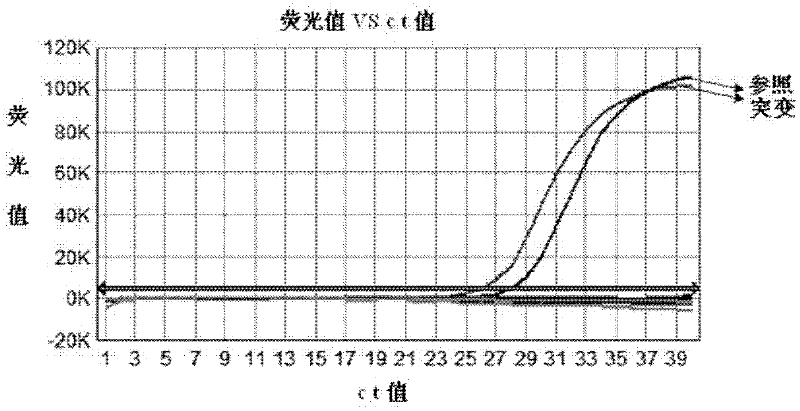
Two-color real-time/end-point quantitation of micrornas (miRNAs)
The present invention is directed to methods, reagents, kits, and compositions for detecting target polynucleotide sequences, especially small target polynucleotides such as miRNAs, between two samples. A pair of linker probes can be employed in two different reactions to query a particular species of target polynucleotide. A pair of detector probes, a single forward primer specific for the target polynucleotide, and a reverse primer can be employed in an amplification reaction to query the difference in expression level of the target polynucleotide between the two samples. In some embodiments a plurality of small miRNAs are queried with a plurality of linker probes. The plurality of queried miRNAs can then be decoded in a plurality of amplification reactions.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
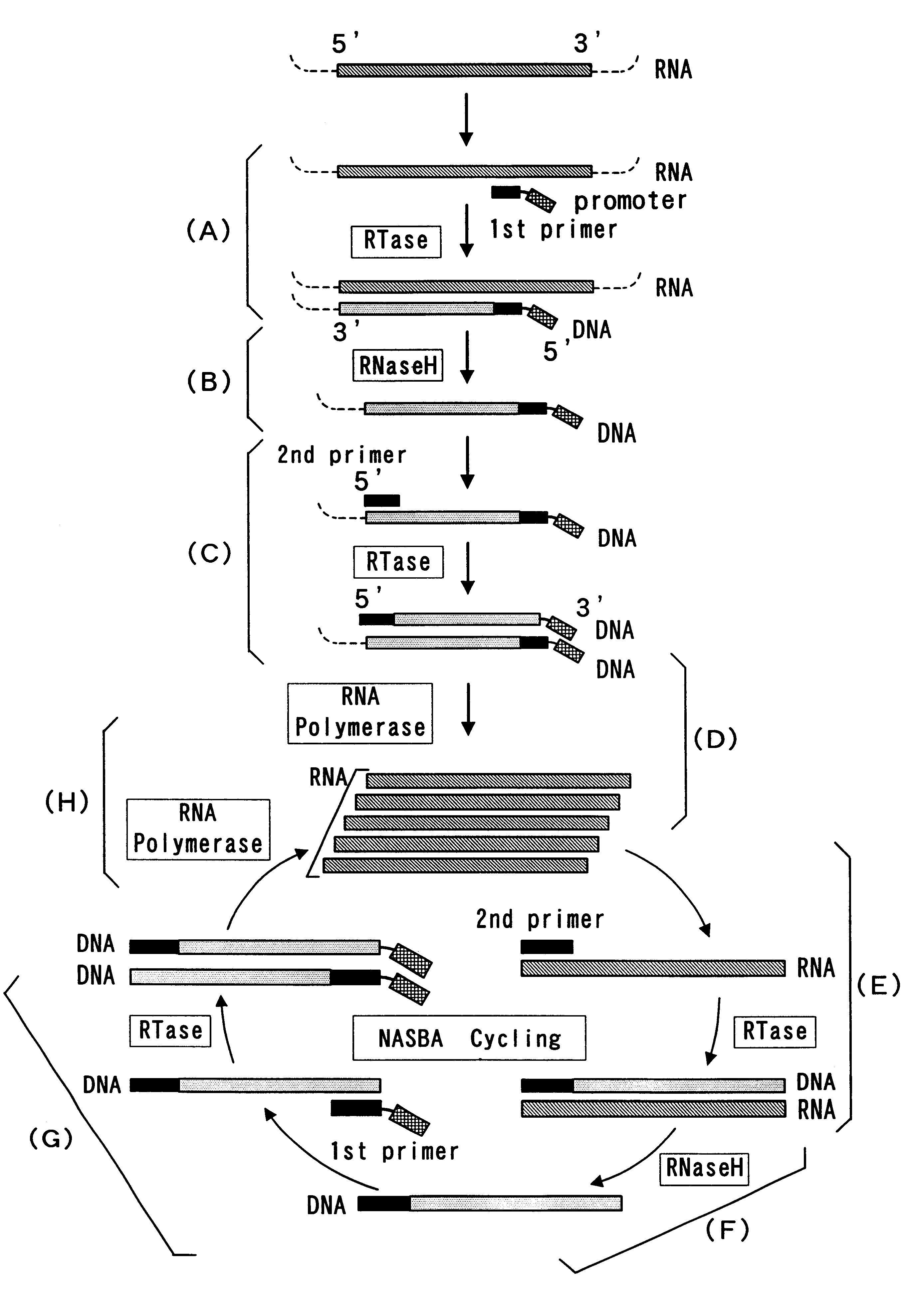
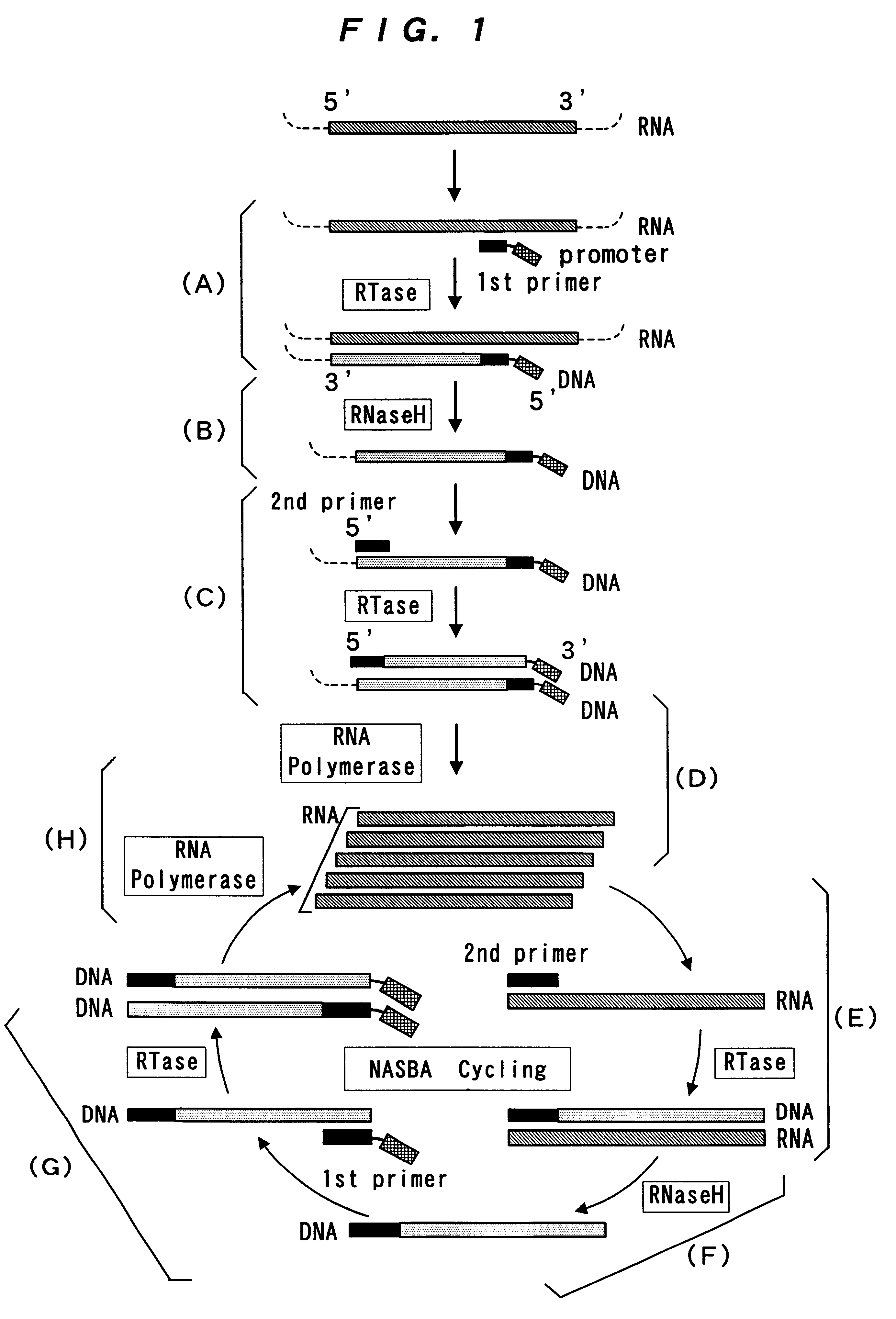
Reagent for nucleic acid amplification and process for nucleic acid amplification
InactiveUS6261773B1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyForward primerPolymerase L
The present invention provide a process for sequence-specific nucleic acid amplification capable of improving the detection sensitivity and increasing the signal. In particular, the present invention provides a reagent for nucleic acid amplification containing at least one member selected from the group consisting of EDTA, NTA, UDA, CyDTA, DTPA, GEDTA, TTHA and their salts, specifically a reagent for nucleic acid amplification comprising, in addition to the at least one compound, a forward primer having a DNA sequence homologous to a sequence of a target RNA; a reverse primer having a DNA sequence complementary to a sequence of the target RNA and having a promoter for RNA polymerase attached to its 5' end; ribonucleotides; deoxyribonucleotides; a reverse transcriptase or RNA-directed DNA polymerase; a RNase H; a DNA polymerase or a reverse transcriptase having DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity; and a RNA polymerase. The present invention also provides a process for nucleic acid amplification characterized by carrying out a nucleic acid amplification reaction in the presence of at least one member selected from the group consisting of EDTA, NTA, UDA, CyDTA, DTPA, GEDTA, TTHA and their salts.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Detection of gene expression
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
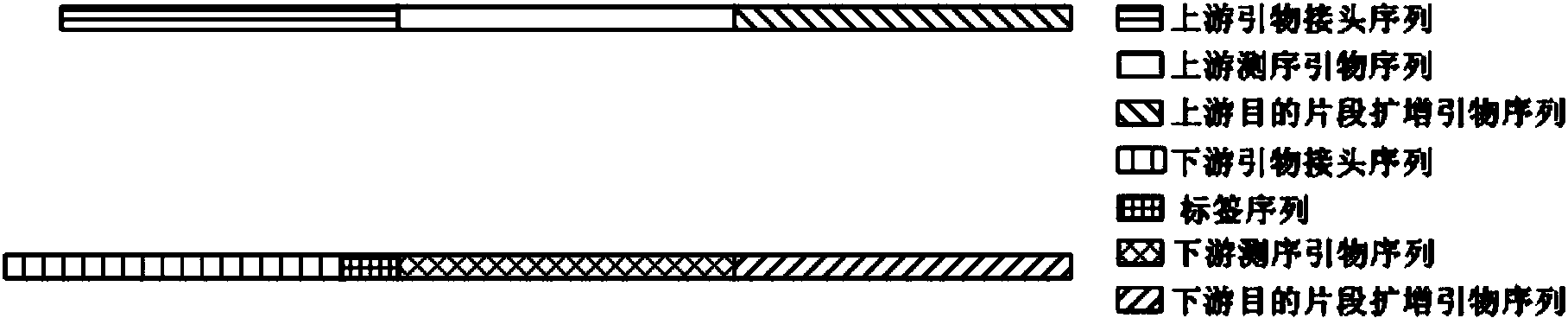
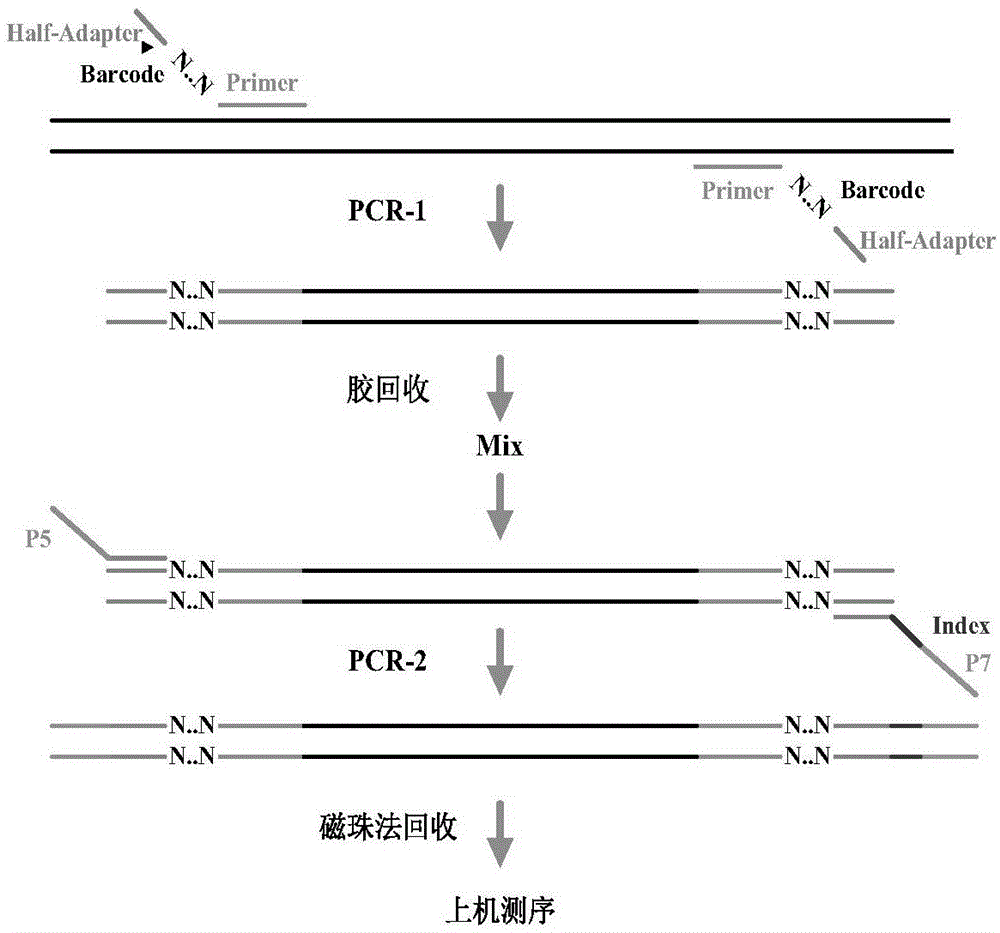
Primer applied to amplicon sequencing library construction and method for constructing amplicon sequencing library
InactiveCN104263726AQuality improvementImprove efficiencyLibrary creationDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerOn board
The invention discloses a primer applied to amplicon sequencing library construction and a method for constructing an amplicon sequencing library. The primer consists of a forward primer and a reverse primer, and the forward primer and the reverse primer comprise a joint sequence, a sequencing primer sequence and a target fragment amplification primer sequence from a sequence from the 5' end to the 3' end. According to the primer provided by the invention, the joint sequence, the sequencing primer sequence and the target fragment amplification primer sequence are integrated on a pair of primers, so that library construction can be finished in one step by utilizing the primer. The sequencing library quality and library construction efficiency are improved, the constructed amplicon sequencing library can perform high-throughput sequencing due to the joint sequence and the sequencing primer sequence used on a conventional sequencing platform by utilizing a common reagent for on-board sequencing, and the phenomena that an extra sequencing primer is provided and the mixed sequencing primers of the PHiX library are changed are avoided.
Owner:天津诺禾致源生物信息科技有限公司
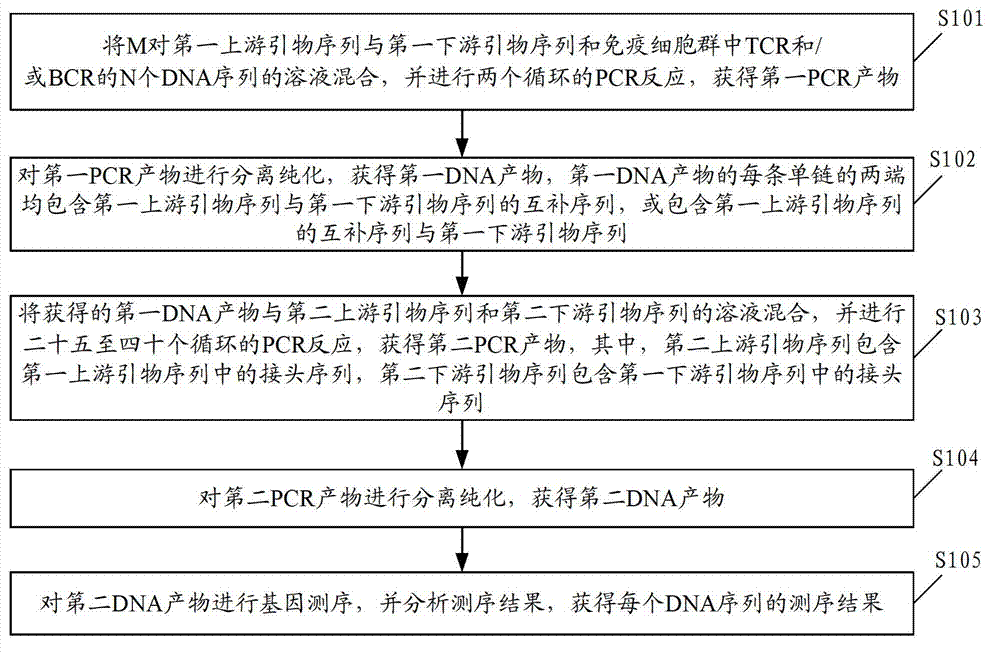
Method and device for gene sequencing of plurality of mixed DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) or RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) sequences
InactiveCN103045726AImprove accuracyReduce error rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsForward primerRNA Sequence
The invention discloses a method and a device for gene sequencing of a plurality of mixed DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) or RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) sequences, which is mainly characterized by adding random labels at two ends of each DNA or RNA template sequence before establishing a bank. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing a first forward primer containing the random label and a connector, a first reverse primer and the DNA sequences, performing multiple PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on two PCR circulations, and purifying the PCR product to obtain a first DNA product; mixing the first DNA product, a second forward primer containing a sample indexing sequence and the connector, and a second reverse primer, performing PCR reaction to obtain a second PCR product; purifying to obtain a second DNA product; and sequencing the second DNA product to obtain a sequencing result of each DNA sequence. According to the method disclosed by the invention, by introducing the random labels to each DNA molecule, the sequencing precision is improved, the error rate of the sequencing is obviously reduced, and the copy number of each DNA is precisely detected.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA +1
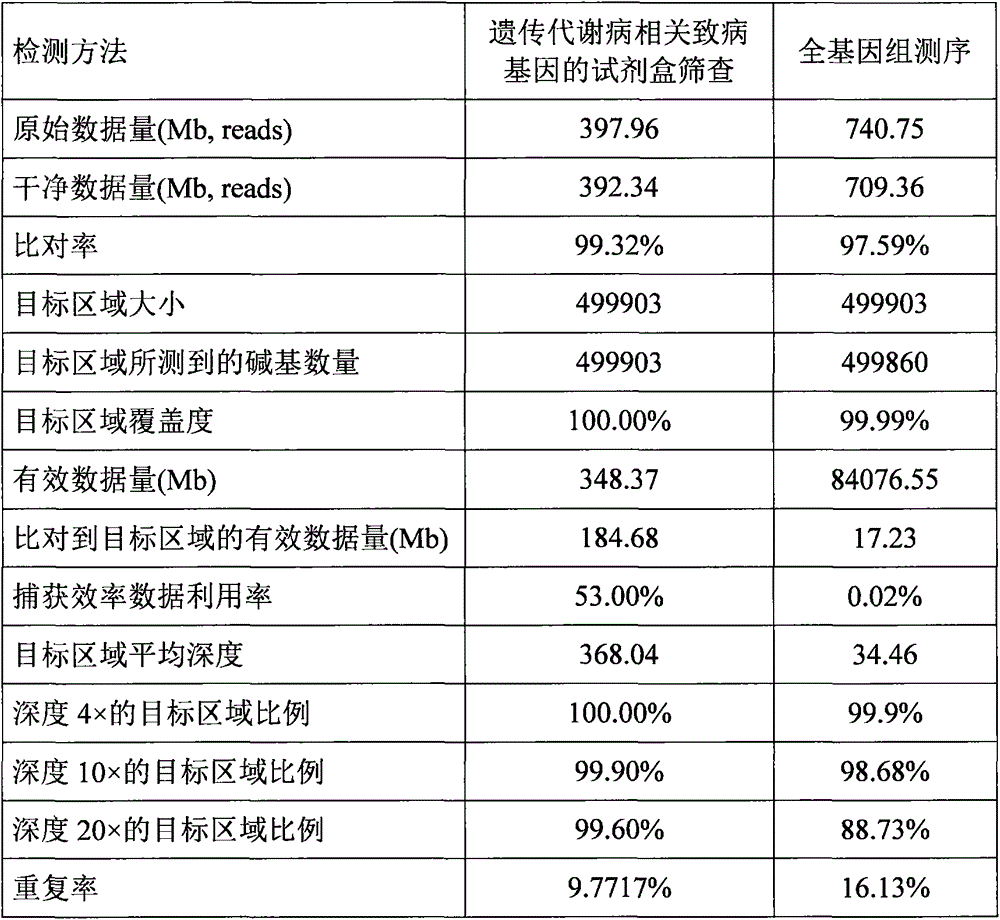
Inherited metabolic disease screening method and reagent kit
ActiveCN105297145ASave the amount of sequencing dataGuaranteed therapeutic effectNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseForward primer
The invention provides an inherited metabolic disease screening method and a reagent kit. The method includes the steps that following libraries are built, according to each encoding sequence of inherited metabolic disease associated disease-causing genes and the principle of sequence reverse complement, from 5' to 3', a probe sequence with the length being 120 bp starts to be designed from the first basic group, and besides, 60 bp superposition exists between every two adjacent probe sequences; a TAGGTGTGTAGGCGC sequence and a GTCAGCTAGTACGCA sequence are added to the 5' end and the 3' end of each probe sequence respectively; by the adoption of the oligonucleotide in-situ synthesis technology, large-scale synthesis of oligonucleotides is carried out on a chip; the oligonucleotides on the chip are eluted through ammonia water and dissolved in water to form an oligonucleotide mixture; through the PCR method, forward primers (TTAGATAGGTGTGTAGGCGC) and reverse primers (TAAGGTGCGTACTAGCTGAC) provided with biotin labels at the 5' ends are adopted, the oligonucleotide mixture is amplified, and an inherited metabolic disease associated disease-causing gene DNA probe library with the biotin labels is formed.
Owner:艾吉泰康(嘉兴)生物科技有限公司
Database-building method for amplicon sequencing
The invention relates to the technical field of high-flux sequencing and discloses a database-building method for amplicon sequencing. The database-building method comprises the following steps of 1, object region enrichment based on PCR amplification: designing primer sequences aiming at an object region of genome DNA of a sample to be detected, wherein ends 5' of a forward primer and a reverse primer in the primer sequences are provided with random base sequences and linking sequences, carrying out PCR amplification and recovering the PCR product, and 2, sequencing linker introduction based in PCR amplification: carrying out mixing on the PCR product obtained by the step 1, designing primer sequences comprising sequences complementary with the linking sequences obtained by the step 1, carrying out PCR amplification on the mixture, and recovering the PCR product so that a DNA database for amplicon sequencing is obtained. The database-building method reduces building time and cost of the DNA database for amplicon sequencing, reduces error of bioinformatics analysis of the sequencing result and improves accuracy and authenticity of the analysis result.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAJORBIO BIO PHARM TECH
Multiplex PCR method for distinguishing four meat components in food at the same time
InactiveCN102605090ARapid identificationAvoid cross interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerGenomic DNA
The invention belongs to the technical field of food quality and safety detection and particularly relates to a method for rapidly detecting pork, beef, mutton and chicken components in food at the same time through animal genomic DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) extraction, primer design and UP-M-PCR (universal primers-multiplex-PCR). The four meat components can be distinguished rapidly at the same time according to differential sites of mitochondrial cytochrome b of the animal by using the forward primer sharing and reverse primer specificity strategy and an M-PCR system including five primers. The result shows that the method has the advantages that the detection limit can be up to the pictogram level, the components of the reaction system are free from cross interference and the meat products on market can be detected, verified and distinguished accurately by sampling 80 meat products randomly according to the specificity of the four target meat components. In a word, the invention provides a specific, sensitive and practical multiplex PCR method for rapidly screening four common meat components in food at the same time.
Owner:NANJING INST OF PROD QUALITY INSPECTION
CRISPR (Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)/Cas12 one-step nucleic acid detection method and 2019-nCoV detection kit
ActiveCN111593145AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerNucleic acid detection
The invention relates to the technical field of gene detection, in particular to a CRISPR (Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) / Cas12 one-step nucleic acid detection method and a2019-nCoV detection kit. The 2019-nCoV detection kit comprises crRNA, Cas protein, a primer, a buffer system and single stranded DNA reporter molecules; the primer is obtained as follows: 5'-TTTN-3'sequence is sought in a to-be-detected target molecule area, a forward primer is designed in the position near 5' area 0-200bp, a reverse primer is designed in the position near 3' area 25-200bp, theobtained primer is subjected to chemical modification to prevent decomposition of DNA enzyme or Cas12 protein after activation. The method has the benefits that compared with existing PCR-based nucleic acid detection technologies, the nucleic acid detection method and the 2019-nCoV detection kit can allow synchronous amplification and detection, thus, operation is more convenient.
Owner:亚能生物技术(深圳)有限公司
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) kit for rapidly detecting vibrio parahaemolyticus
InactiveCN102864228AQuick checkThe detection process is fastMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesSerodiagnosesForward primer
The invention discloses a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) kit for rapidly detecting vibrio parahaemolyticus. The LAMP kit is composed of LAMP reaction liquid, a standard positive template and a negative quality control standard substance. The LAMP reaction liquid contains a Bst DNA polymerase big fragment, a primer, LAMP10*buffer, dNTPs solution, MgSO4 solution and glycine betaine. The primer is divided into a forward primer and a reverse primer. The LAMP kit has the advantages of being good in specificity, high in sensitivity, rapid and convenient, high in repeatability, capable of judging results by using eyes and the like, can conduct rapid qualitative detection on vibrio parahaemolyticus in industrial foods, and can replace continuously-used traditional culture method and serological diagnosis method.
Owner:WUHAN ZHENFU PHARMA CO LTD
PCR primer used for amplifying human breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1 and BRCA2 coding sequence and application thereof
ActiveCN105779636AExperiment operation is simpleLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationForward primerHuman breast
The invention relates to a PCR primer for a human breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1 and BRCA2 coding sequence based on a NGS technology and application thereof. The PCR primer for the human breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1 and BRCA2 coding sequence comprises at least one capturing primer pair, and sequences of a forward primer and a reverse primer of each capturing primer pair respectively comprise a specific sequence and a linker sequence connected with a terminal 5' of the specific sequence. The PCR primer used for amplifying the human breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1 and BRCA2 coding sequence based on the NGS technology and application thereof have the advantages that experiment operations related in the whole method are simple, only a PCR reagent and a primer combination are related, cost is low, and a ditag sequencing linker sequence is introduced for distinguishing different samples, so that high throughput sample sequencing detection can be realized, and gene detection support can be effectively provided for risk assessment on human breast cancer and other BRCA susceptible gene-related hereditary tumours or targeted medication specific to BRCA mutation.
Owner:GUANGZHOU LBP MEDICINE SCI & TECH
Methods and compositions for detecting and identifying species of Candida
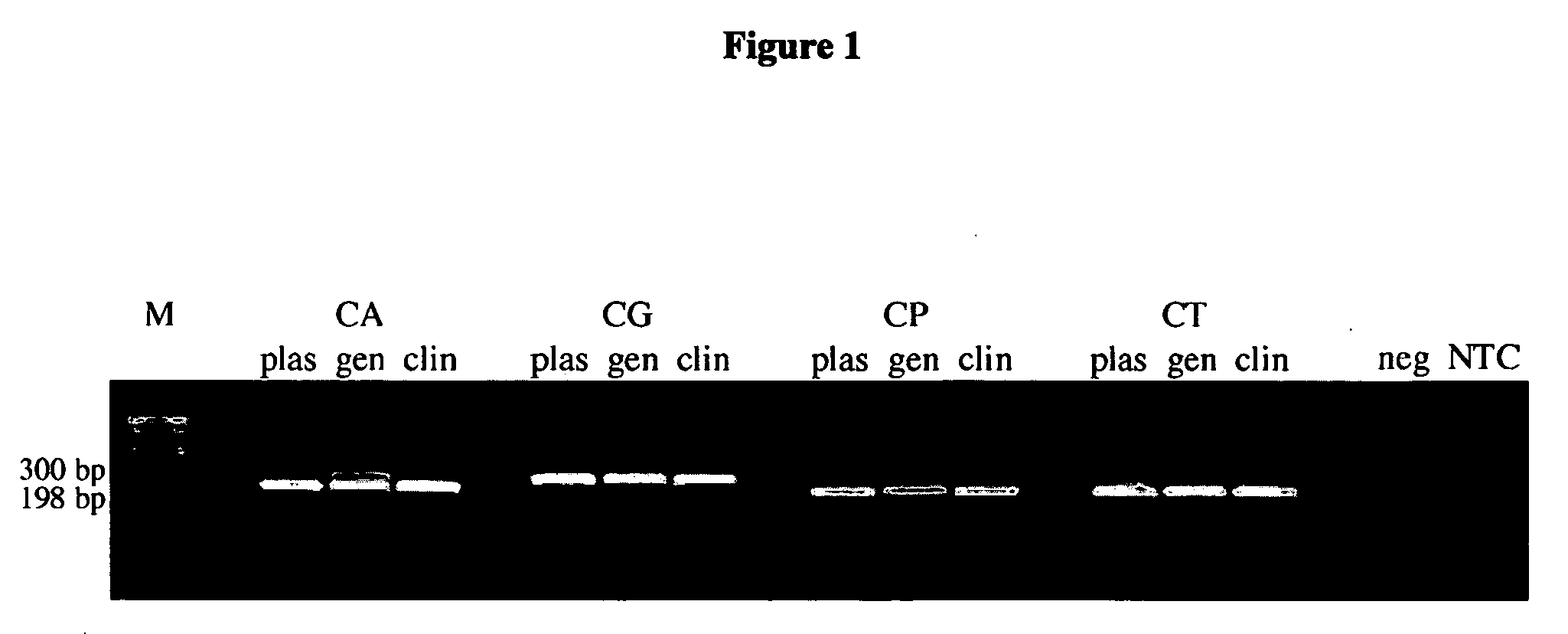
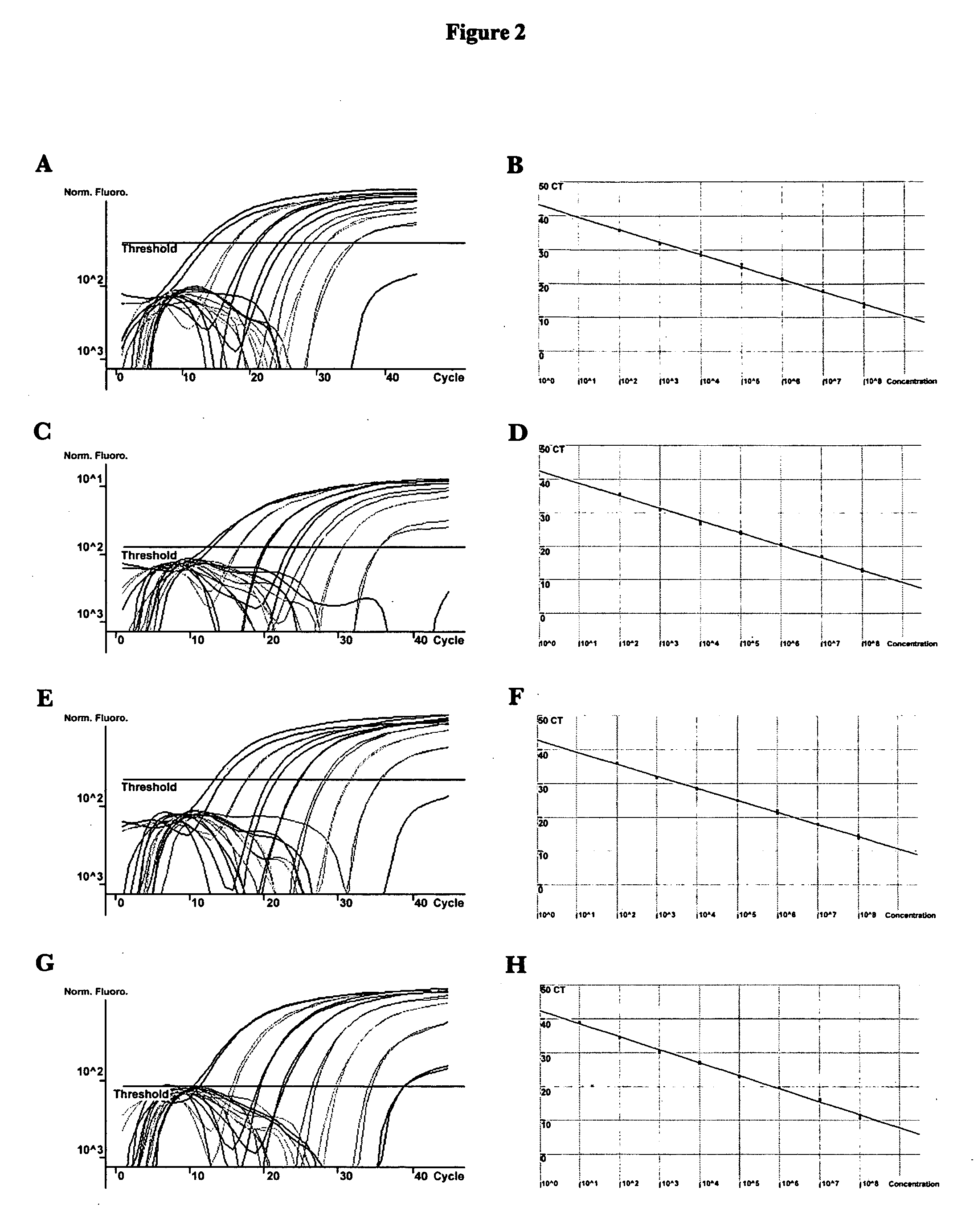
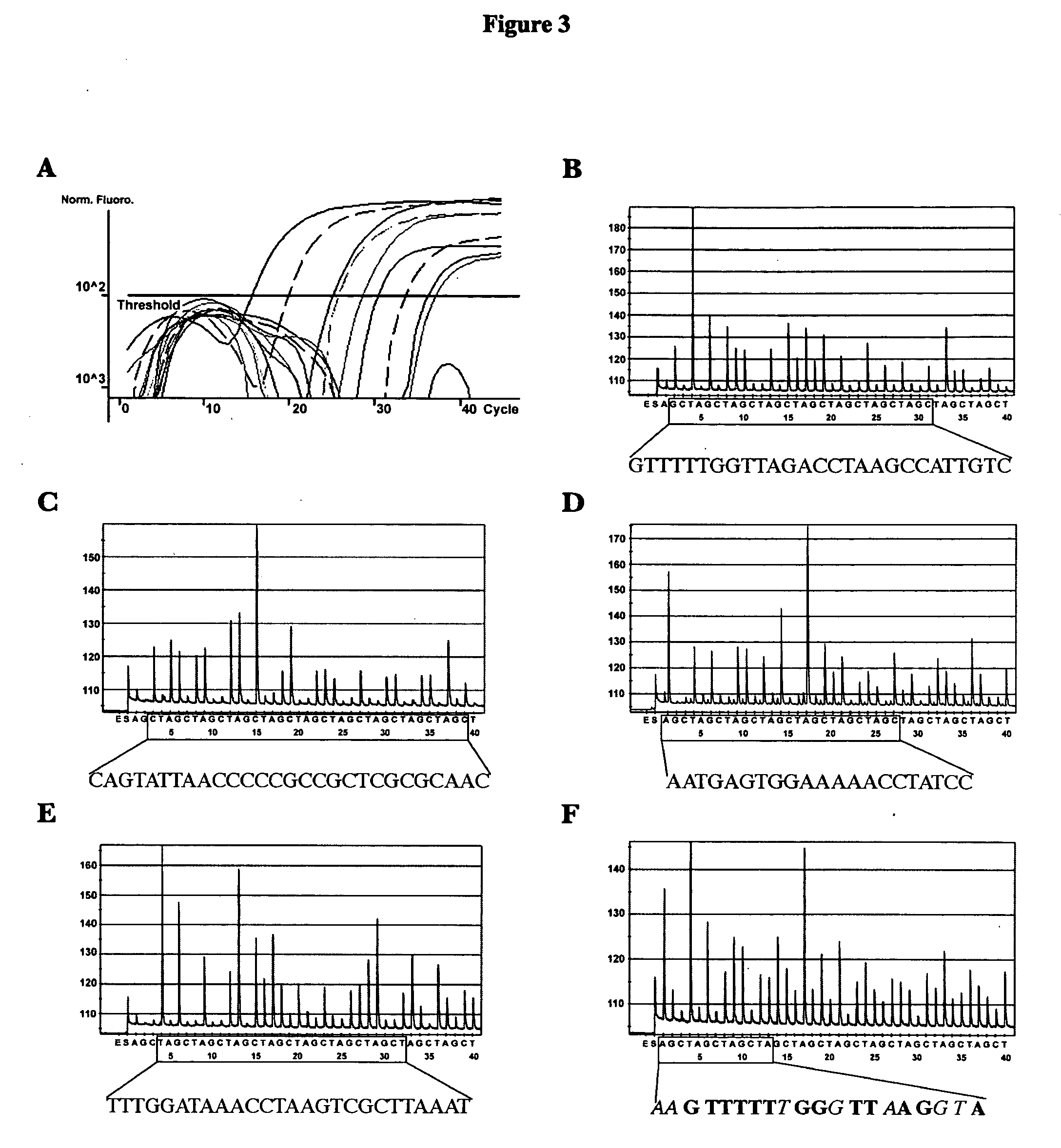
ActiveUS20080102449A1Avoid disadvantagesMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationForward primerNucleotide
Methods and compositions useful in the detection and identification of species of Candida are disclosed. These species include Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis, each of which is a causative agent for vaginal candidiasis. The compositions of the invention are combinations of oligonucleotides. These oligonucleotides include pairs of forward and reverse primers for polymerase chain reactions, wherein each primer pair is capable of priming the synthesis of an amplicon specific to one of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis, but preferably is not capable of priming the synthesis of an amplicon specific to any of the other three species. In preferred embodiments, the forward primers of the primer pairs have identical sequences, while each reverse primer of the primer pairs has a unique sequence relative to all of the other reverse primers; or the reverse primers of the primer pairs have identical sequences, while each forward primer of the primer pairs has a unique sequence relative to all of the other forward primers. These unique primer sequences account for the species specificity of the resultant amplicons. The oligonucleotides also include probes capable of detecting these amplicons, and sequencing primers for determining, in primer extension reactions, the nucleotide sequences contained within the amplicons. In preferred methods of the invention, a biological sample is tested for the presence of at least one isolate of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis by isolating nucleic acid from the sample, attempting a polymerase chain reaction in a mixture containing this nucleic acid and a plurality of these primer pairs, ascertaining whether any amplicon is produced in the mixture using an oligonucleotide probe, and determining the sequence of any resultant amplicon using the sequencing primers. The detection of an amplicon indicates that the sample contains at least one isolate of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, or Candida tropicalis, and the nucleotide sequence data is used to determine which of these four Candida species is present.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
A real-time isothermal recombinase-polymerase amplification detection kit for African swine fever viruses
ActiveCN106521027AQuick checkRapid diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerAfrican swine fever
A real-time isothermal recombinase-polymerase amplification detection kit for African swine fever viruses is disclosed. A forward primer sequence for detecting the African swine fever viruses through a method provided by the kit is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, a reverse primer sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:2 and a probe sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:3. A real-time isothermal recombinase-polymerase amplification method provided by the invention for ASFV detection is simple and convenient in operation, rapid in reaction and low in detection cost, can be used for ASFV detection in a laboratory and on site, particularly ASFV detection in quarantine ports, airports and epidemic disease outbreak sites, and provides a novel and reliable technique support for ASF control in China.
Owner:HANGZHOU ZHONGCE BIO SCI&TECH CO LTD
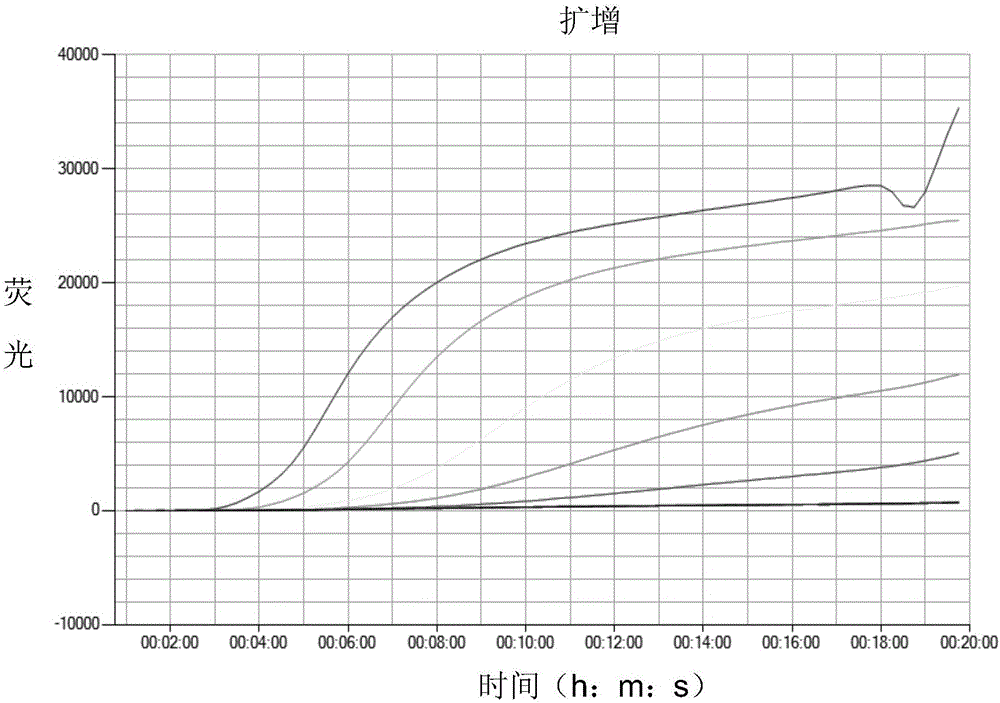
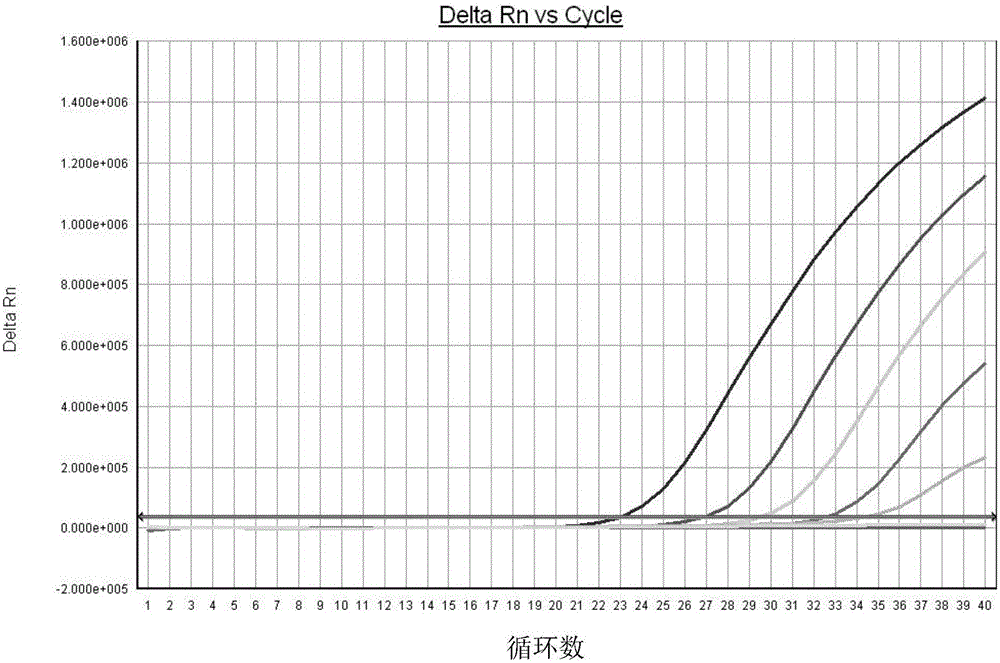
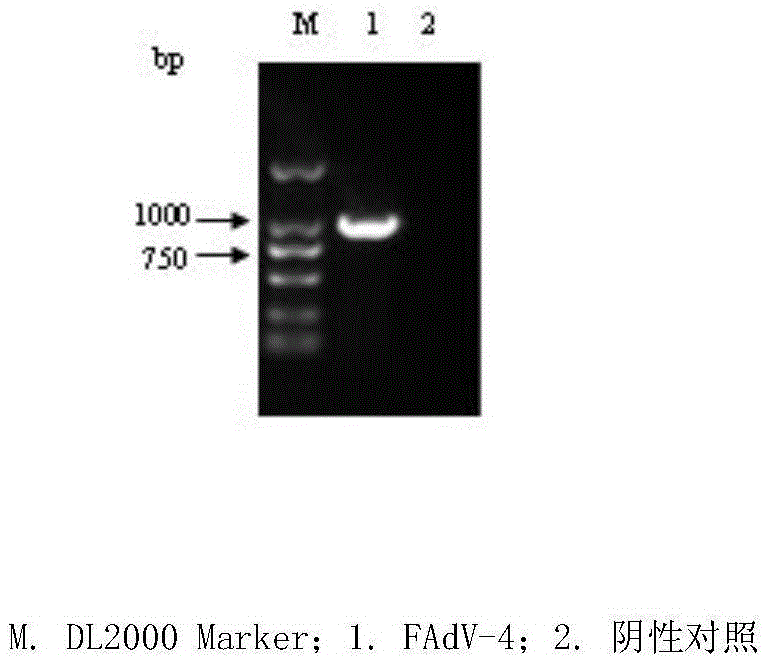
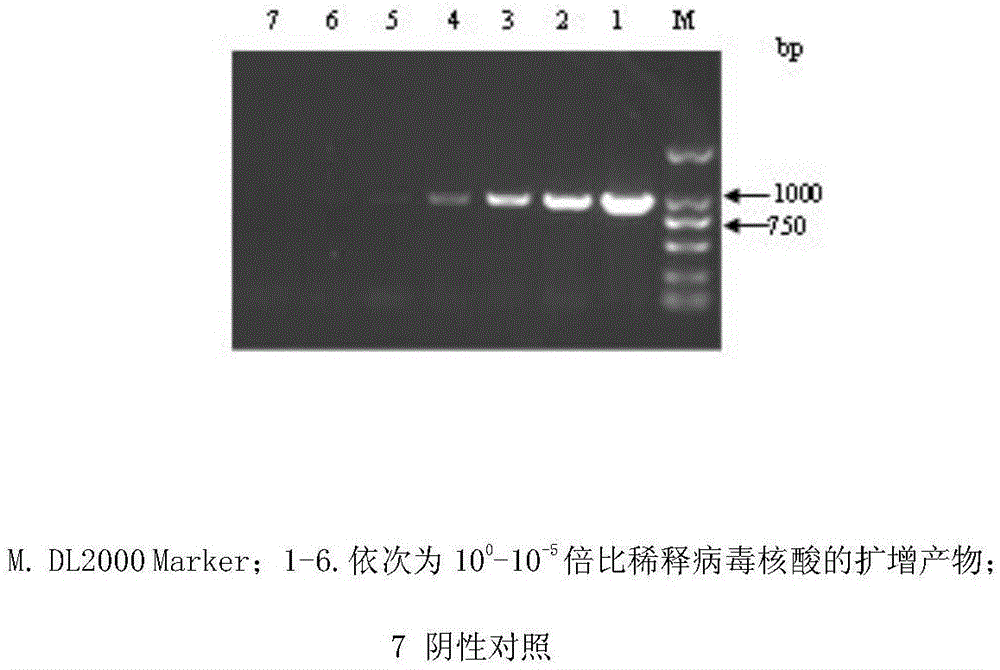
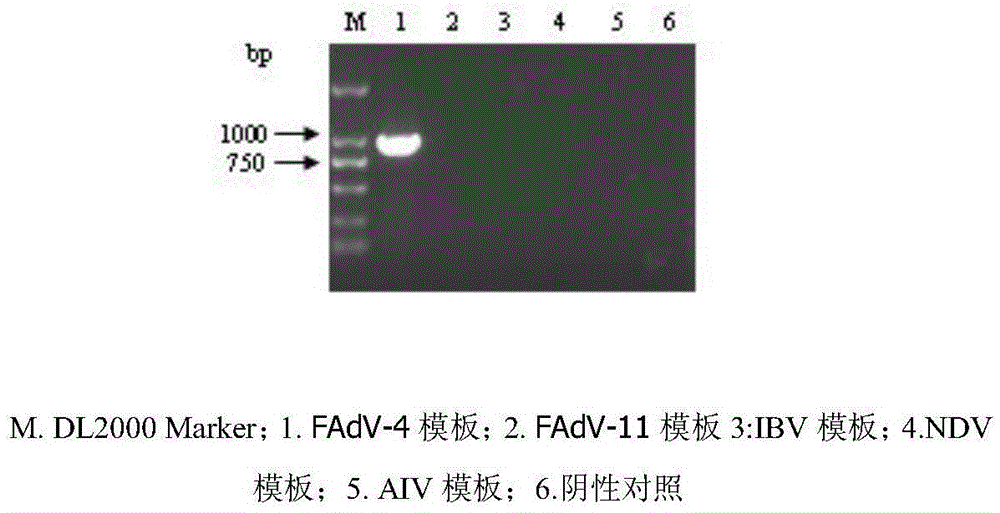
FAdV-4 PCR detection kit and detection method
ActiveCN105483292ASpecific detectionQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementSodium acetateDistilled water
The invention discloses an FAdV-4 PCR detection kit and detection method. The kit comprises protease K, a lysing solution, sodium acetate, saturated phenol, chloroform, isoamylol, anhydrous ethanol and sterile distilled water, and is characterized by comprising 2*TaqPCR Mix, a sense primer and a reverse primer, wherein the sequence of the sense primer is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and the sequence of the reverse primer is shown as SEQ ID No.2. The kit can be used for detecting FAdV-4. The method for detecting FAdV-4 by adopting the kit is also provided, and FAdV-4 can be detected quickly and specifically.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG SHIMU ANIMAL HUSBANDRY PHARMA CO LTD
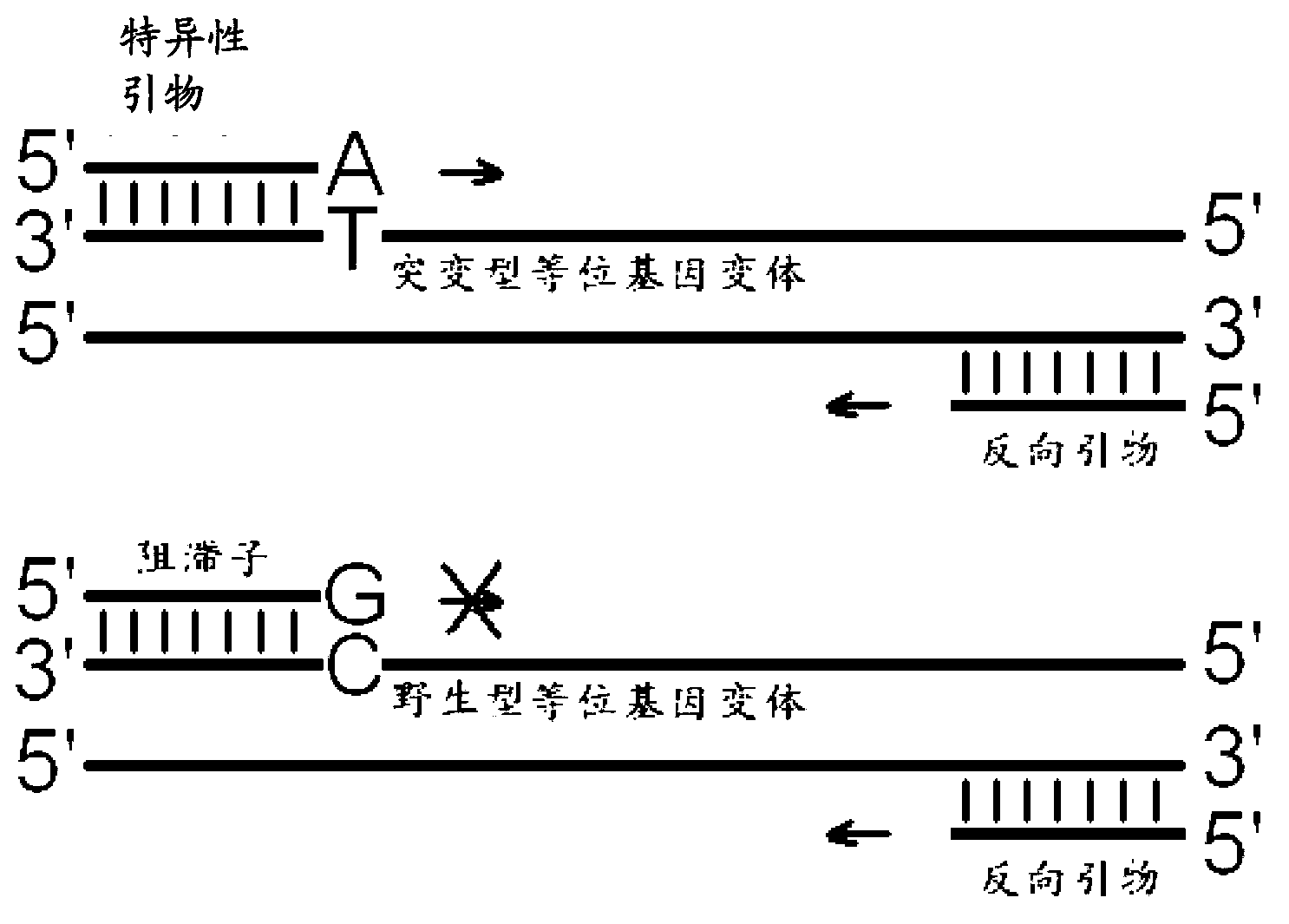
Allele variant detection method, kit and composition
InactiveCN103215361AImprove efficiencyGrowth inhibitionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSpecific detectionFluorescence
The invention provides a method for carrying out allele variant specific detection by utilizing an inhibitor, a kit and a composition. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: adding a primer pair and an inhibitor the terminal 3' of which can not be extended by polymerase in a hybridization process into a nucleic acid sample, wherein the primer pair comprises a specific primer and a reverse primer; hybridizing the specific primer and the reverse primer respectively with target sequence mutant type oligonucleotide in the nucleic acid sample to produce an amplicon; hybridizing the inhibitor with a target sequence wild type oligonucleotide in the nucleic acid sample; and carrying out real-time specific detection on a mutant type allele by utilizing a fluorescent dye or a detection pointer. The added inhibitor can not extend in an amplification process, and amplification of a wild type allele variant is inhibited, so that the amplification efficiency of a mutant type allele variant is improved, and the sensitivity and specificity of detection are improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNI MEDICA TECH
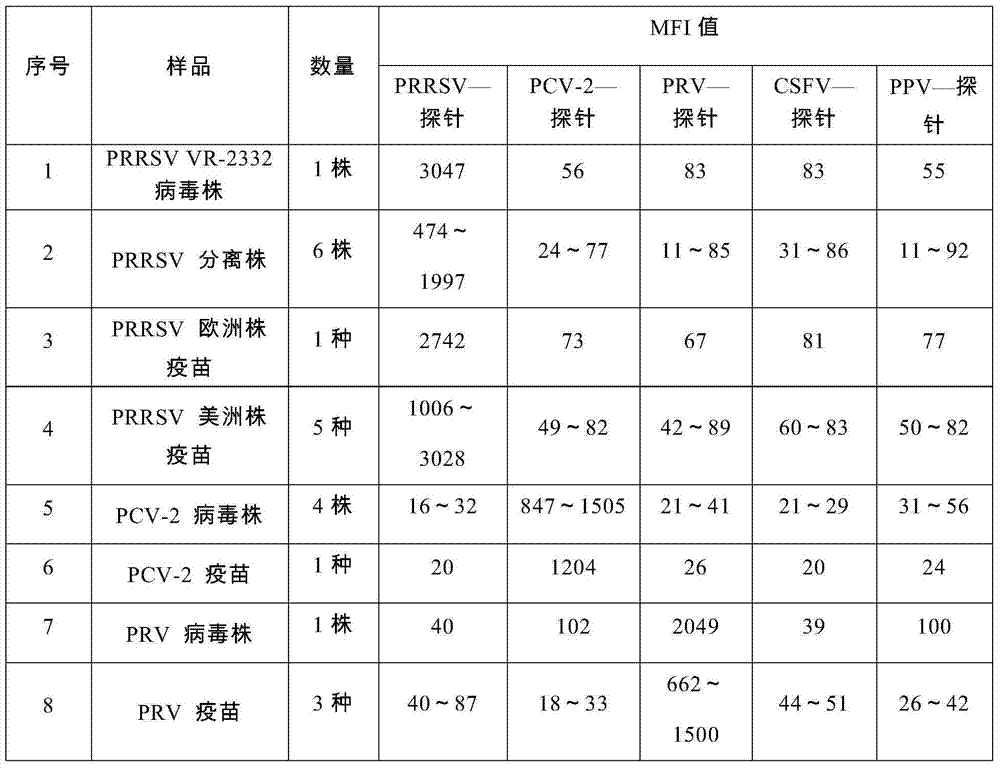
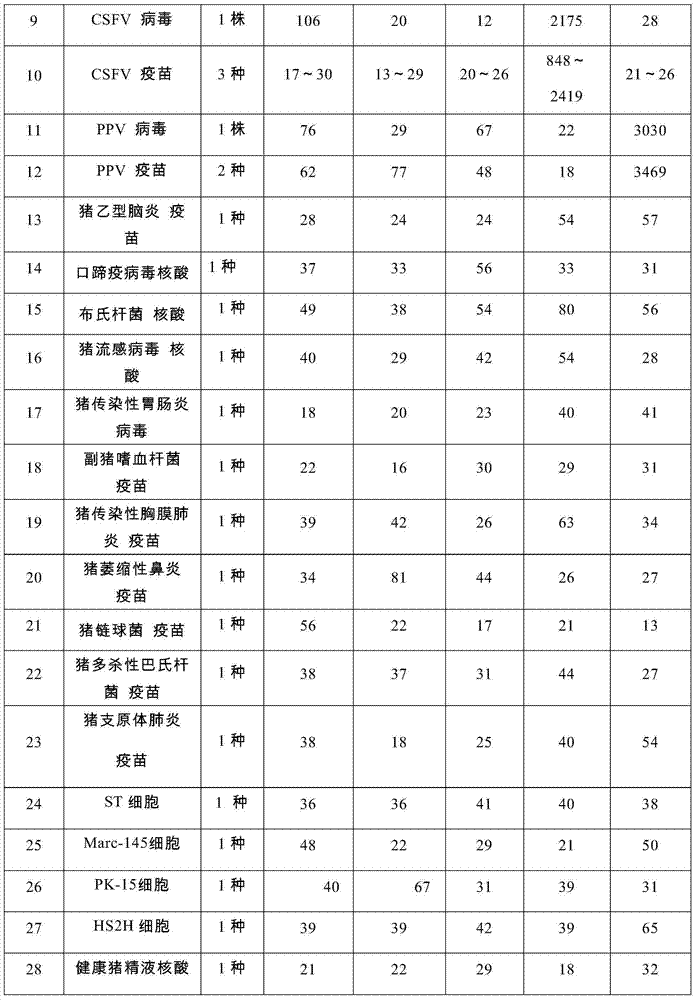
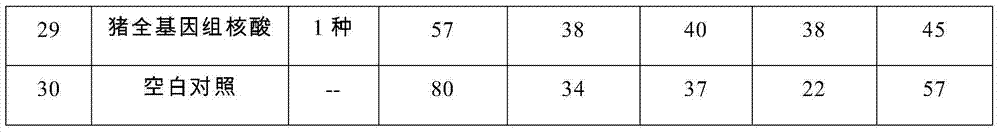
Nucleic acids of liquid-phase gene chip for synchronously detecting five porcine viruses and detection method thereof
ActiveCN104328218AHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesClassical swine fever virus CSFVMultiplex
The invention provides a set of nucleic acids of a liquid-phase gene chip for synchronously detecting five porcine viruses, which comprise forward and reverse primers and hybrid probes for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV), porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2), porcine pseudorabies virus (PRV), classical swine fever virus (CSFV) and porcine parvovirus (PPV). The invention also provides a multiplex liquid-phase chip high-flux molecular biology detection method of the five porcine viruses. According to the method, porcine virus nucleic acids in the sample to be detected are extracted to perform multiplex unsymmetric nucleic acid amplification / multiplex liquid-phase gene chip (suspension chip) combined detection, thereby synchronously and accurately detecting and identifying the five porcine viruses in the sample to be detected. The method has the advantages of high specificity, high sensitivity, high stability, high flux and high detection speed, and is simple to operate.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF GUANGDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Compositions and methods for detecting small rnas, and uses thereof
Compositions and methods are provided for the detection of small RNA target nucleic acids, preferably miRNA target nucleic acids, wherein the compositions and methods provide for sensitive and specific detection of the target nucleic acids. The compositions and methods include using one or more of a first amplification oligomer that is preferably an extender primer, a target capture oligomer that is preferably at least partially double stranded, a promoter primer / provider, a reverse primer that is preferably a universal primer and a detection probe. The compositions and methods are useful for diagnostics, prognostics, monitoring the effectiveness of treatment and / or determining a treatment.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
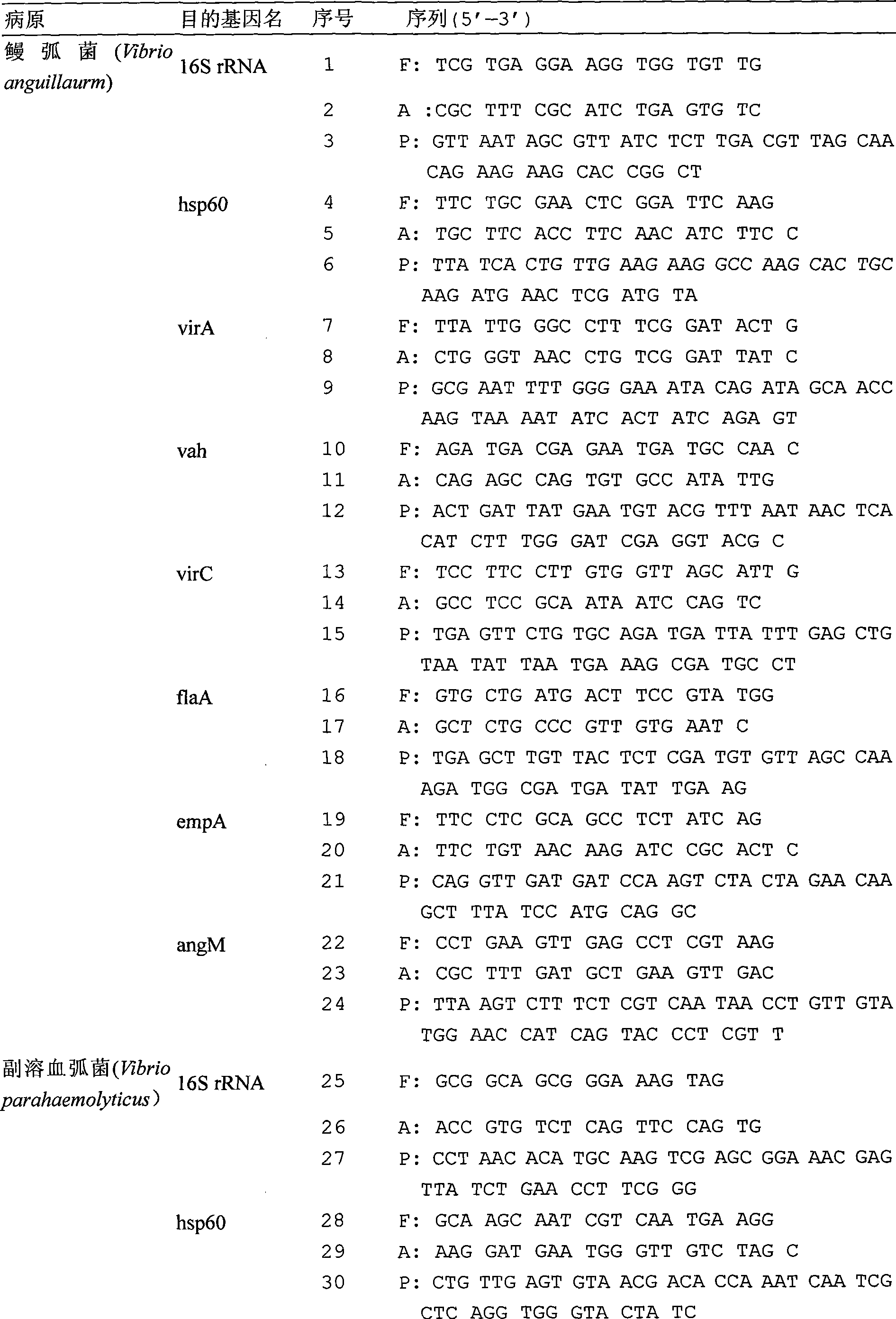
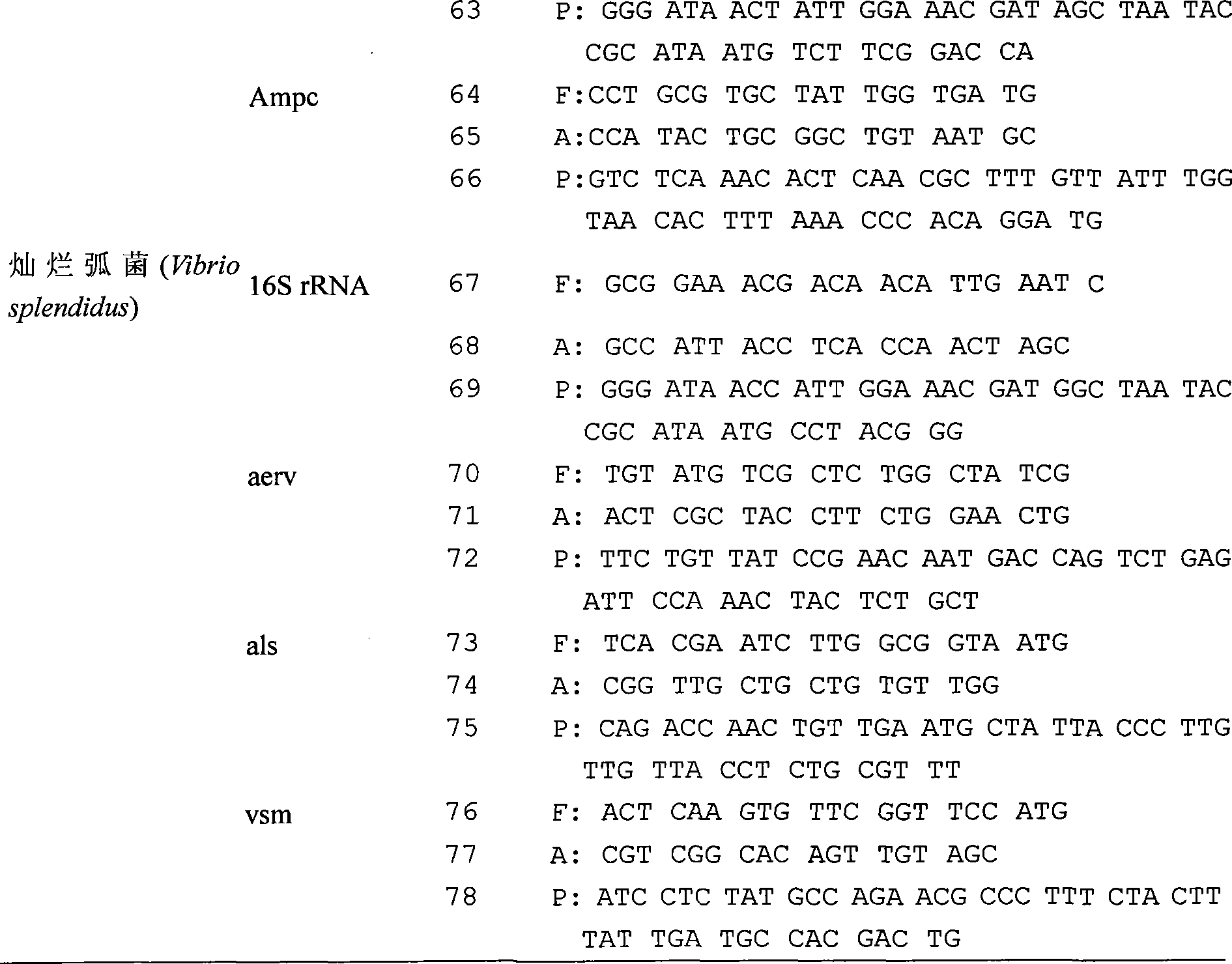
Chip for gene detection of multiple vibrios at the same time, and detection and use thereof
ActiveCN101475986AEffective guidanceEffectively guide productionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerVirulent characteristics
The present invention relates to a detection chip for performing gene detection to various vibrio and its detection and applications. The invention provides 16S rRNA sequences corresponding to each vibrio of vibrio anguillarum, vibrio harveyi, vibrio alginolyticus, vibrio parahaemolyticus, brilliant vibrio and Fisher vibrio; heat shock protein hsp60 probe sequence; virulence gene probe sequence; 16S rRNA forward primer sequence; 16S rRNA reverse primer sequence; heat shock protein hsp60 forward primer sequence; heat shock protein hsp60 reverse primer sequence; virulence gene forward primer sequence and virulence gene reverse primer sequence. The present invention has specific, sensitive and high-throughput features, can simultaneously detect six kinds of bacteria virulence genes, and the invention will effectively guide the production as an important disease early-warning detection method used in clinical diagnosis of aquatic animals.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
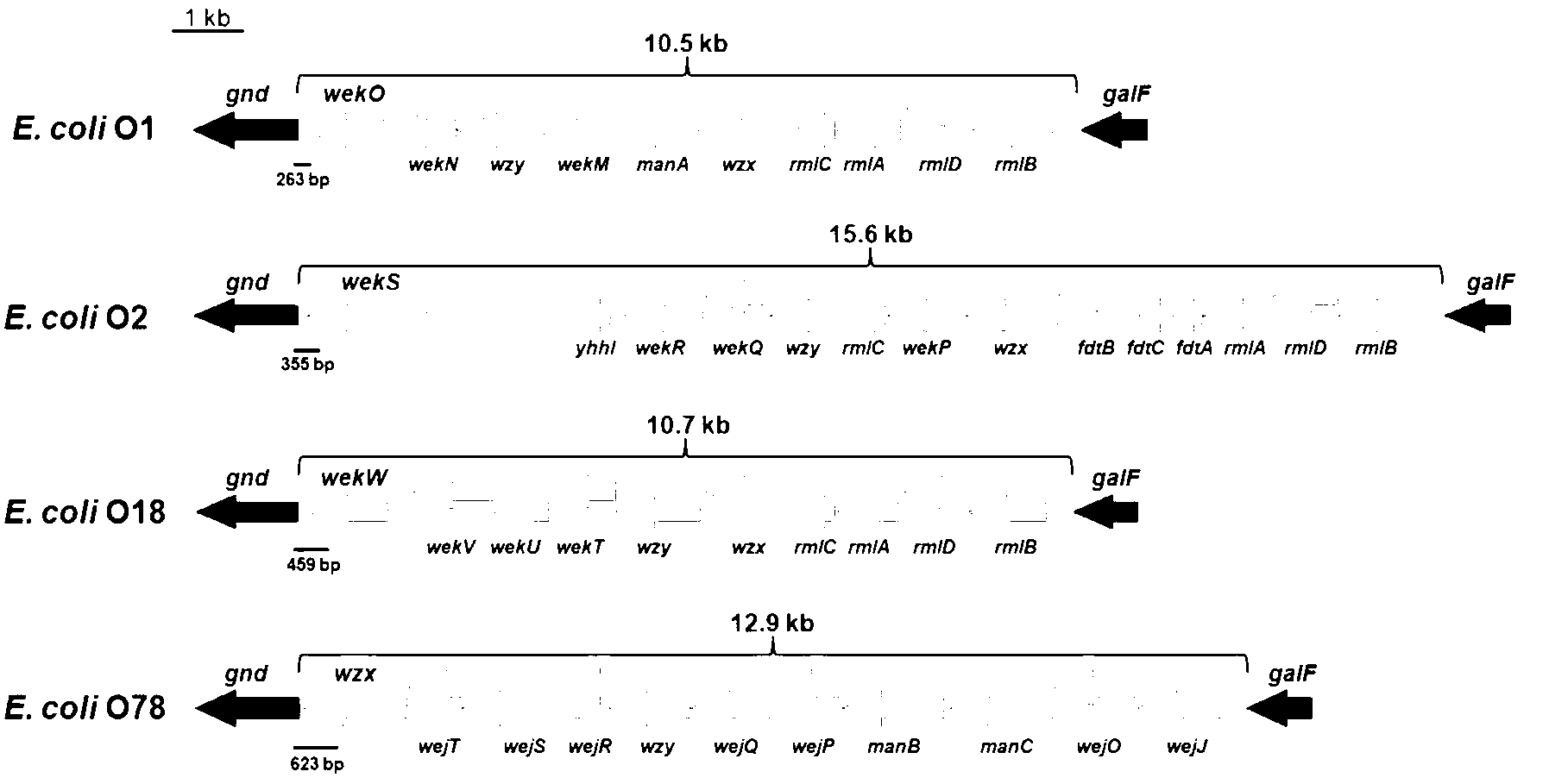
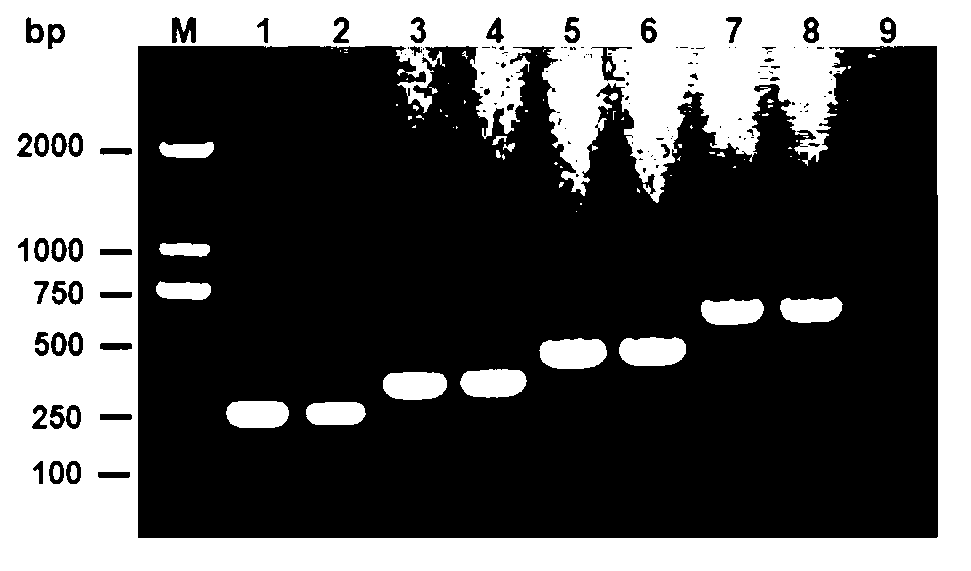
Escherichia coli O1, O2, O18 and O78 serotype detection kit and detection method thereof
ActiveCN103305627ACross reactionReduce sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesESCHERICHIA COLI ANTIGENEscherichia coli serotype
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology detection and relates to an escherichia coli O1, O2, O18 and O78 serotype detection kit and a detection method thereof. Forward primers of a primer group of the kit are highly conservative escherichia coli O antigen combined relative gene sequences, and backward primers are four serotype specific primers designed on the basis of four O1, O2, O18 and O78 serotype escherichia coli O antigen synthesis relative genes. The detection kit containing the primer group and the detection method of the detection kit have the advantages of being fast, sensitive, specific, low in cost, easy to operate and capable of well overcoming the shortcomings in the current escherichia coli O1, O2, O18 and O78 serotype detection method, can meet the requirements for the current escherichia coli O1, O2, O18 and O78 serotype detection, can be popularized and used easily in a wide range and have wide market prospect and large economic benefit.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
InDel molecular marker for identifying clubroot-resistant QTL (quantitative trait locus) located on Chinese cabbage A03 chromosome and application thereof
InactiveCN105543391AAccurate and reliable identification resultsReduce labor costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyForward primer
The invention discloses an InDel molecular marker for identifying clubroot-resistant QTL (quantitative trait locus) located on Chinese cabbage A03 chromosome and application thereof. The invention provides a method for identifying or auxiliarily identifying whether a Chinese cabbage is a clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage, which comprises the following steps: carrying out amplification by using genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of the Chinese cabbage to be identified as a template, a single-stranded DNA disclosed as SEQ ID No.2 as a forward primer and a single-stranded DNA disclosed as SEQ ID No.3 as a reverse primer; detecting the size of the amplification product; and determining whether the Chinese cabbage to be identified is a clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage according to the size of the amplification product: if the amplification product of the Chinese cabbage to be identified contains a 201bp strip, the Chinese cabbage to be identified is a clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage or candidate clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage; and if the amplification product of the Chinese cabbage to be identified does not contain any 201bp strip, the Chinese cabbage to be identified is a non-clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage or non-candidate clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Onion cytoplasmic male sterility SCAR mark and uses thereof
InactiveCN101492738ASimple and fast operationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerIntellectual property
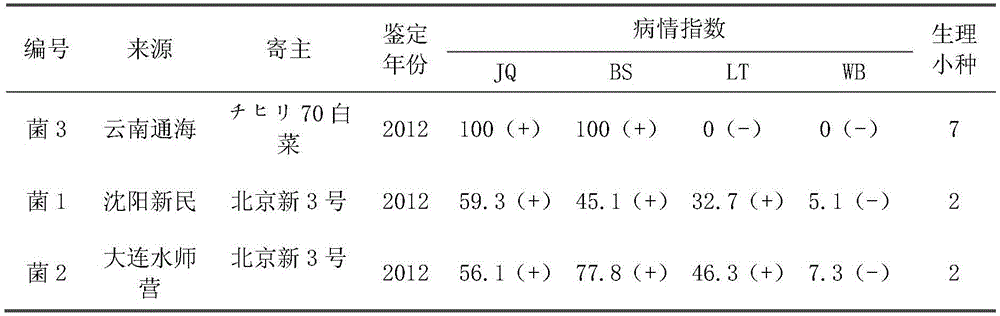
The invention discloses an onion cytoplasm male sterility SCAR marker, wherein the length of the specific fragment of the SCAR marker is 339bp, and the nucleotide sequence thereof is shown as SEQ ID No.2. The invention further discloses a primer of the SCAR maker, wherein the forward primer is Zt339-u:5'-GTTCTCAAGCAGATTCCGCAC-3', and the reverse primer is Zt339-d:5'-AGGACCAAACCGAGAGTGAGC-3'. Quick and accurate selection for onion cytoplasm fertility can be realized by using the obtained SCAR marker, thereby quickening the seed selection for new breed strain of onion cytoplasm male sterility, and establishing novel onion coenospecies parent selection system; first-filial generation breeds with independent intellectual property are selected and bred, thereby solving the difficult problems that conventional seeds are mainly used in the current production in China and large sums of foreign exchange is used for buying foreign coenospecies.
Owner:VEGETABLE RES INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Sturgeon sexuality difference molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN105861642AReliable methodEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerAgricultural science
The invention discloses a sturgeon sexuality difference molecular marker and an application thereof; the marker has the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1; a DNA sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO.1 is detected by PCR primers, and according to a PCR detection result, the sturgeon sexuality is identified; a forward primer F of the PCR primers is 5'-CACACTGATGCTCTACATGT-3', a reverse primer R is 5'-AGGCTGGACAGTGATGCTGT-3', and the forward primer F and the reverse primer R are respectively shown in SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.3. The invention provides a nucleic acid fragment for detecting the sturgeon sexuality and the PCR primers for detecting the molecular marker related to sturgeon; the molecular marker is not limited by the age of the sturgeon, is accurate and reliable, is easy to operate, and has important application value in production.
Owner:深圳华大海洋科技有限公司
Feature sequences, tag primer and identification method of carya illinoensis variety Nacono
ActiveCN107557369ALower requirementImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationForward primerMolecular Technique
The invention relates to feature sequences and a molecular specificity tag primer of a pair of high-specificity feature sequences of carya illinoensis variety Nacono, a molecular specificity tag primer, and a method capable of being used for fast identifying the carya illinoensis variety Nacono. The molecular specificity tag primer has the sequence that a forward primer is 5'-GTCACTTCCCTTTCTCGGCA-3', and a reverse primer is 5'-CCCCGGGTGCAGGTATAAAA-3'. The molecular specificity tag primer provided by the invention can be used for performing fast early-stage identification on the carya illinoensis variety Nacono; the method is simple, fast and accurate, and belongs to an irreplaceable molecular technique for distinguishing the carya illinoensis variety through appearance features.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY ACAD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com