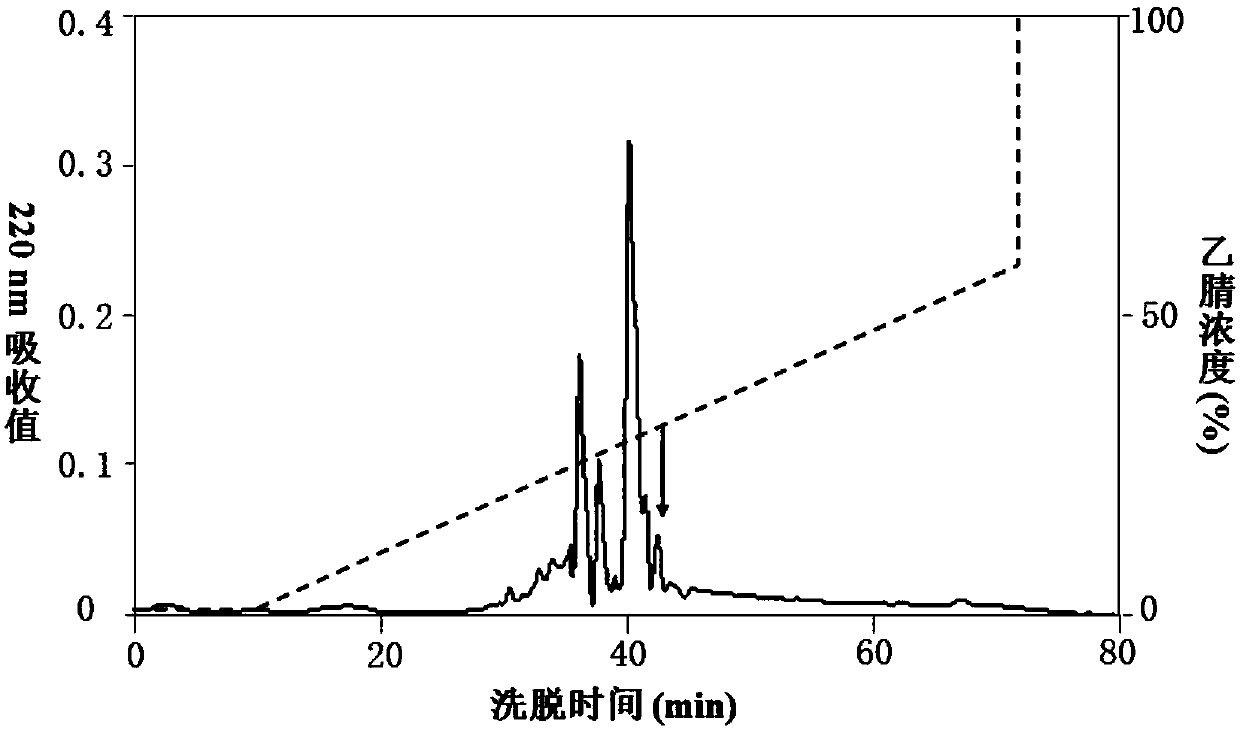
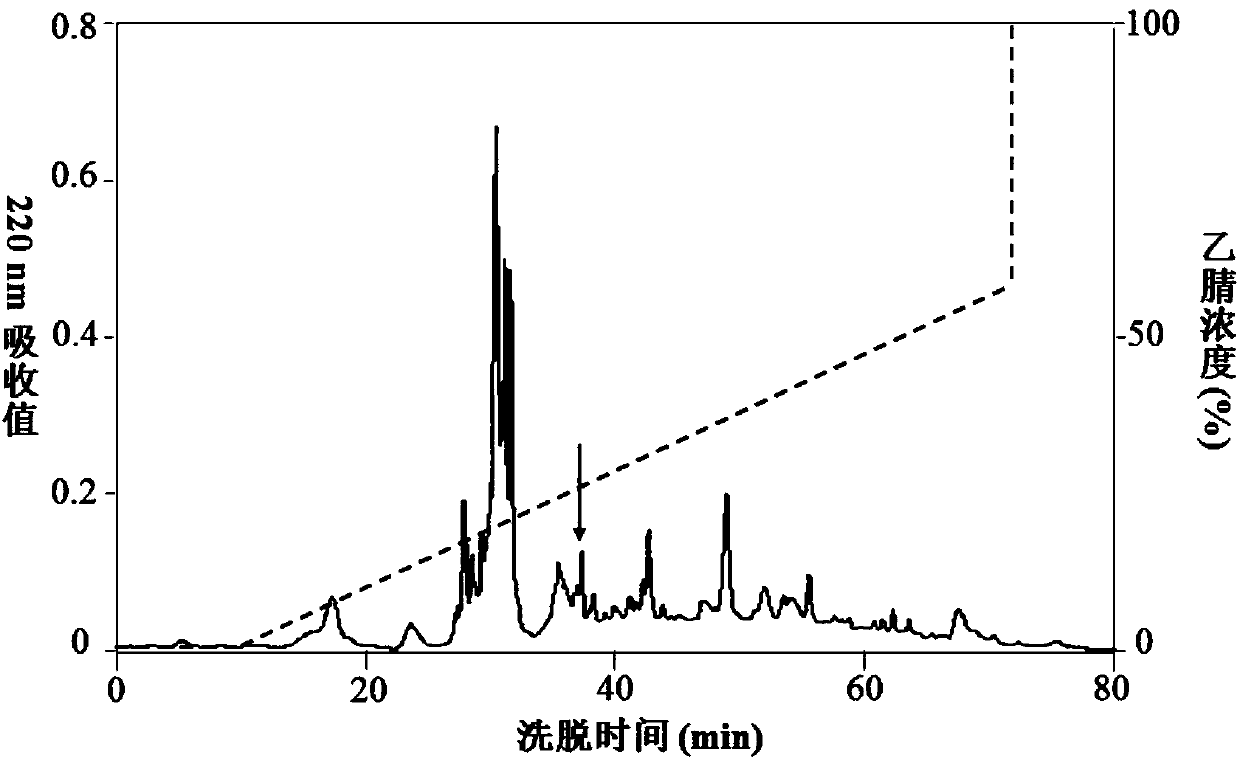
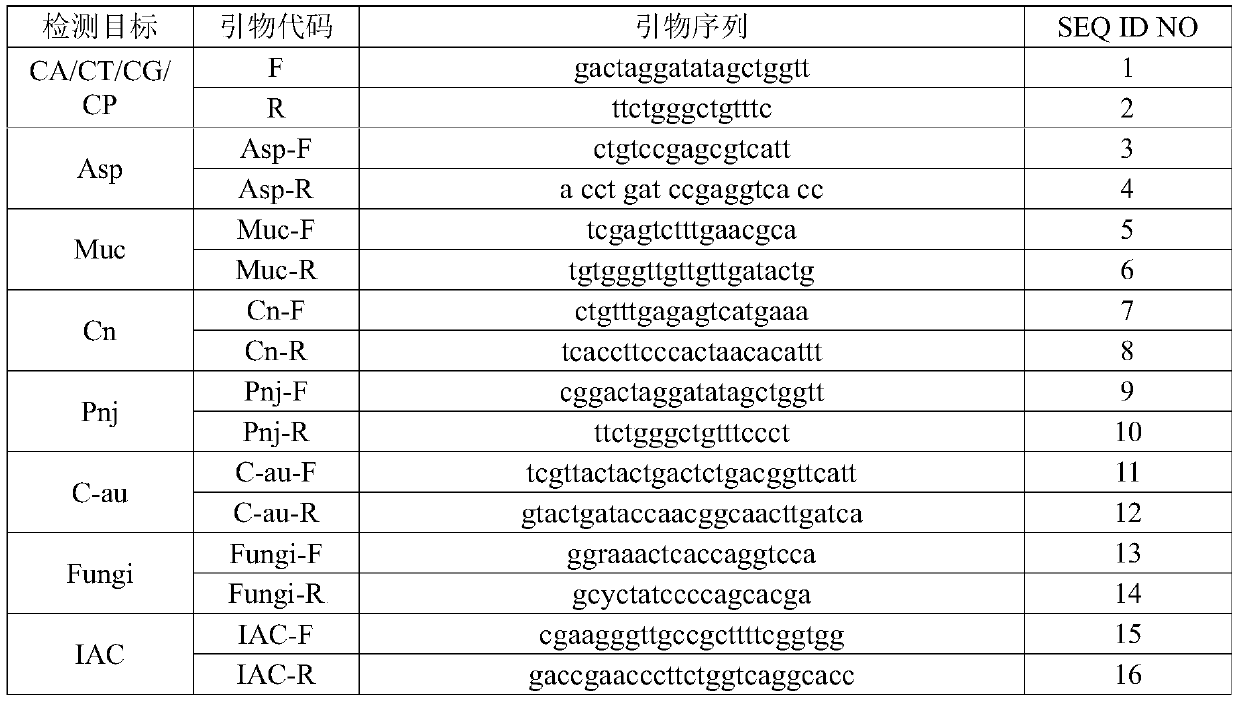
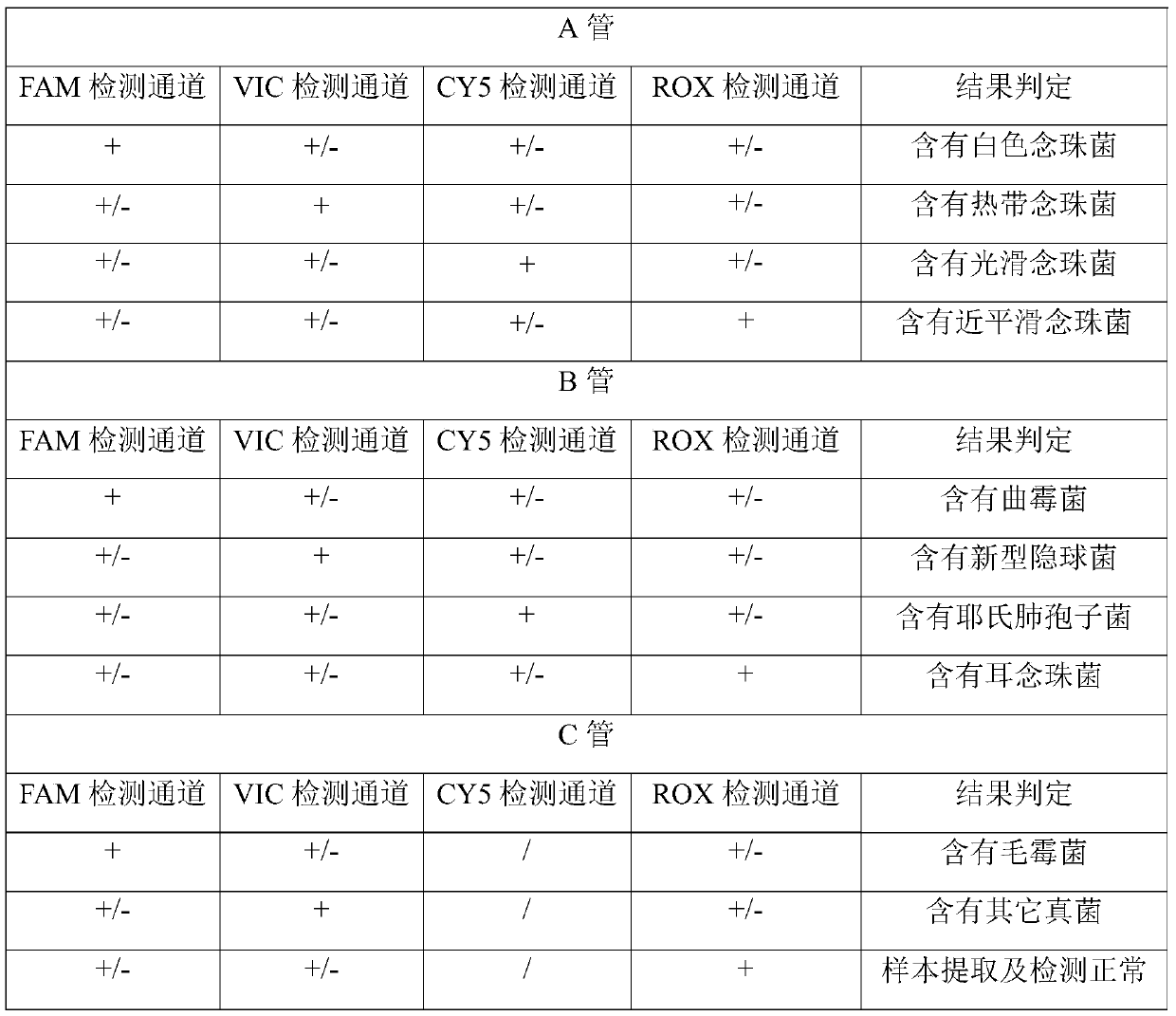
Patents
Literature
126 results about "Candida glabrata" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
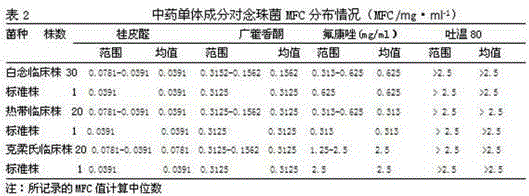
Candida glabrata is a species of haploid yeast of the genus Candida, previously known as Torulopsis glabrata. Despite the fact that no sexual life cycle has been documented for this species, C. glabrata strains of both mating types are commonly found. C. glabrata is generally a commensal of human mucosal tissues, but in today's era of wider human immunodeficiency from various causes (for example, therapeutic immunomodulation, longer survival with various comorbidities such as diabetes, and HIV infection), C. glabrata is often the second or third most common cause of candidiasis as an opportunistic pathogen. Infections caused by C. glabrata can affect the urogenital tract or even cause systemic infections by entrance of the fungal cells in the bloodstream (Candidemia), especially prevalent in immunocompromised patients.
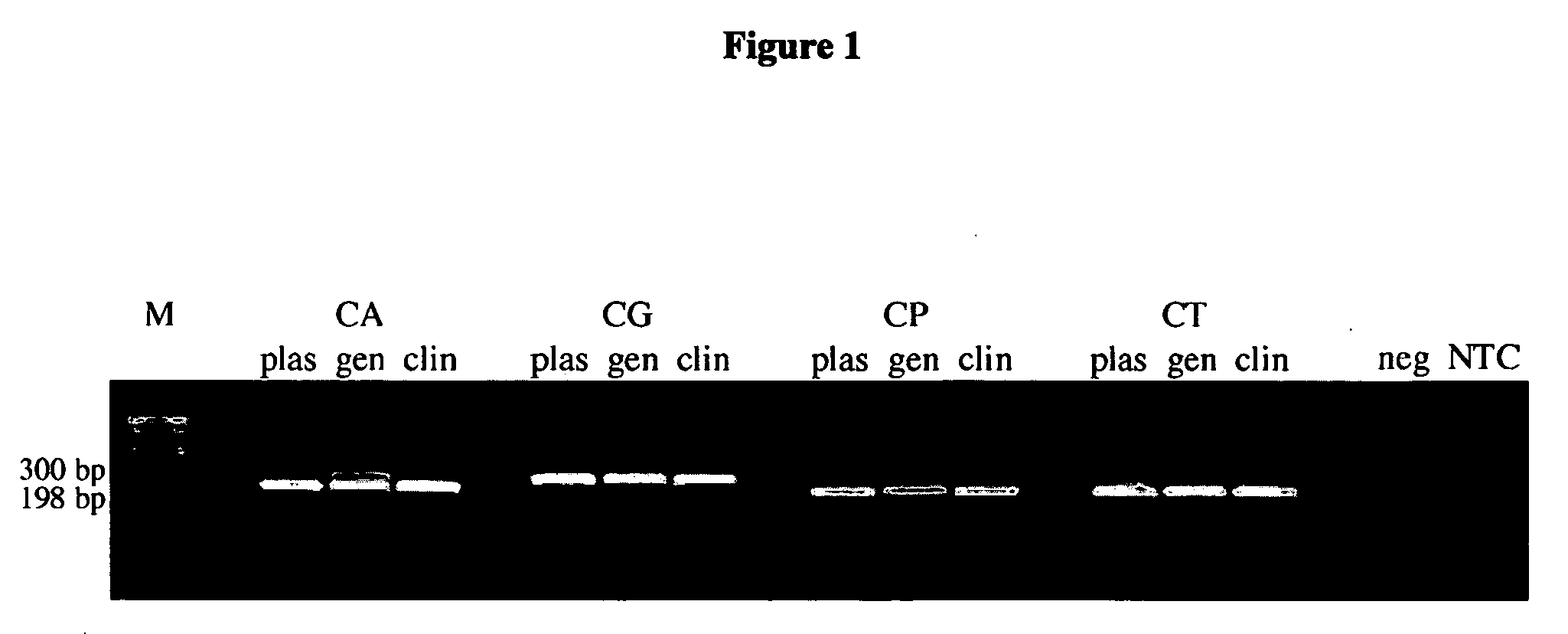
Nucleic acid probes and methods for detecting clinically important fungal pathogens
InactiveUS6858387B1Function increaseAttached with easeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesAspergillus flavus
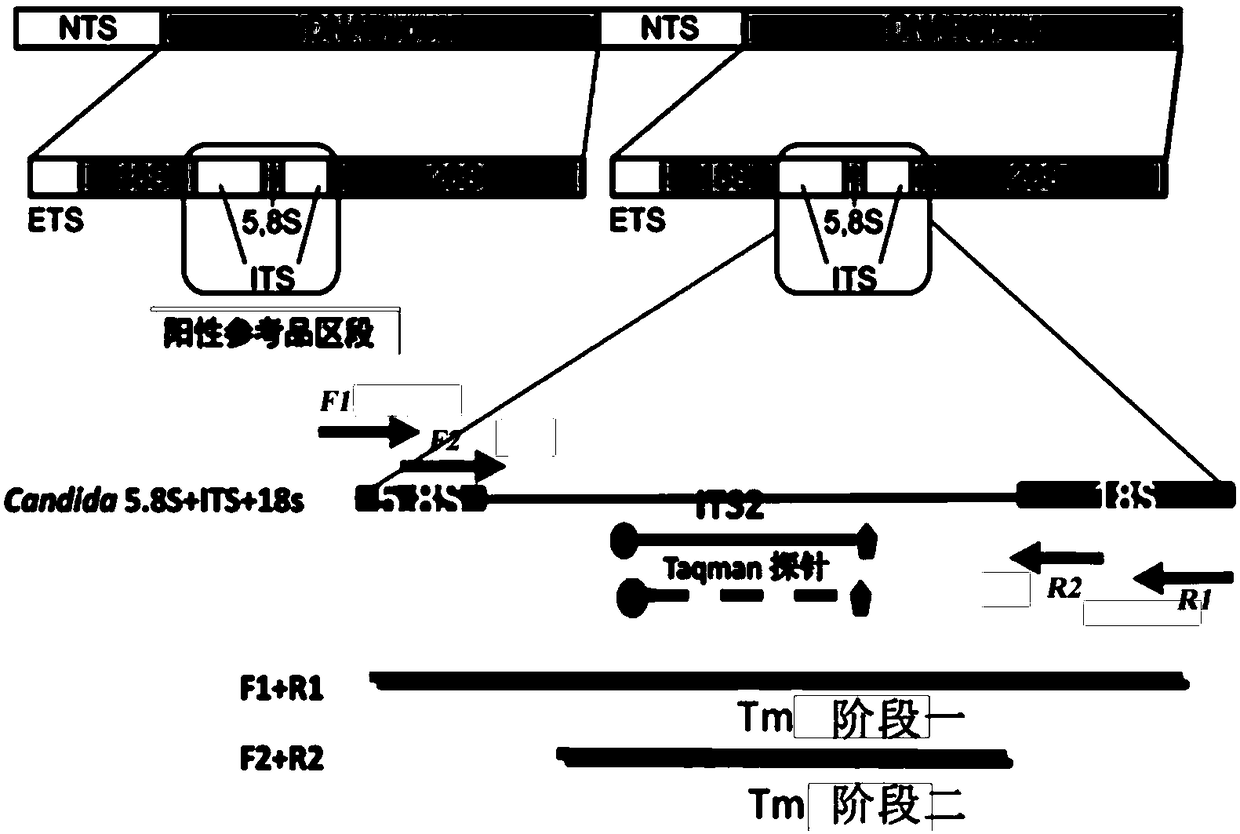
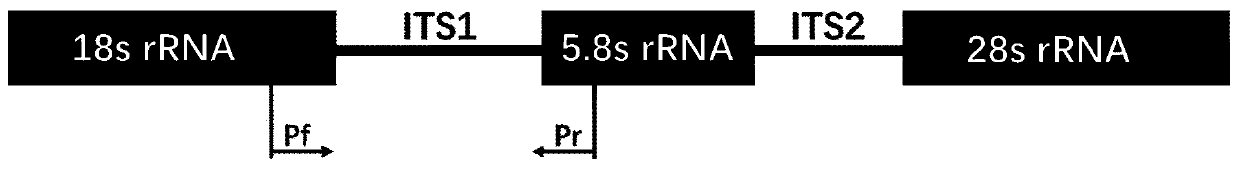
The current invention relates to the field of detection and identification of clinically important fungi. More particularely, the present invention relates to species specific probes originating from the Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) region of rDNA for the detection of fungal species such as Candida albicans, Candida parapsilosis, Candida tropicalis, Candida kefyr, Candida krusei, Candida glabrata, Candida dubliniensis, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus versicolor, Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus fumigatus, Cyptococcus neoformans and Pneumocystis carinii in clinical samples, and methods using said probes.
Owner:ENTERPRISE IRELAND +2
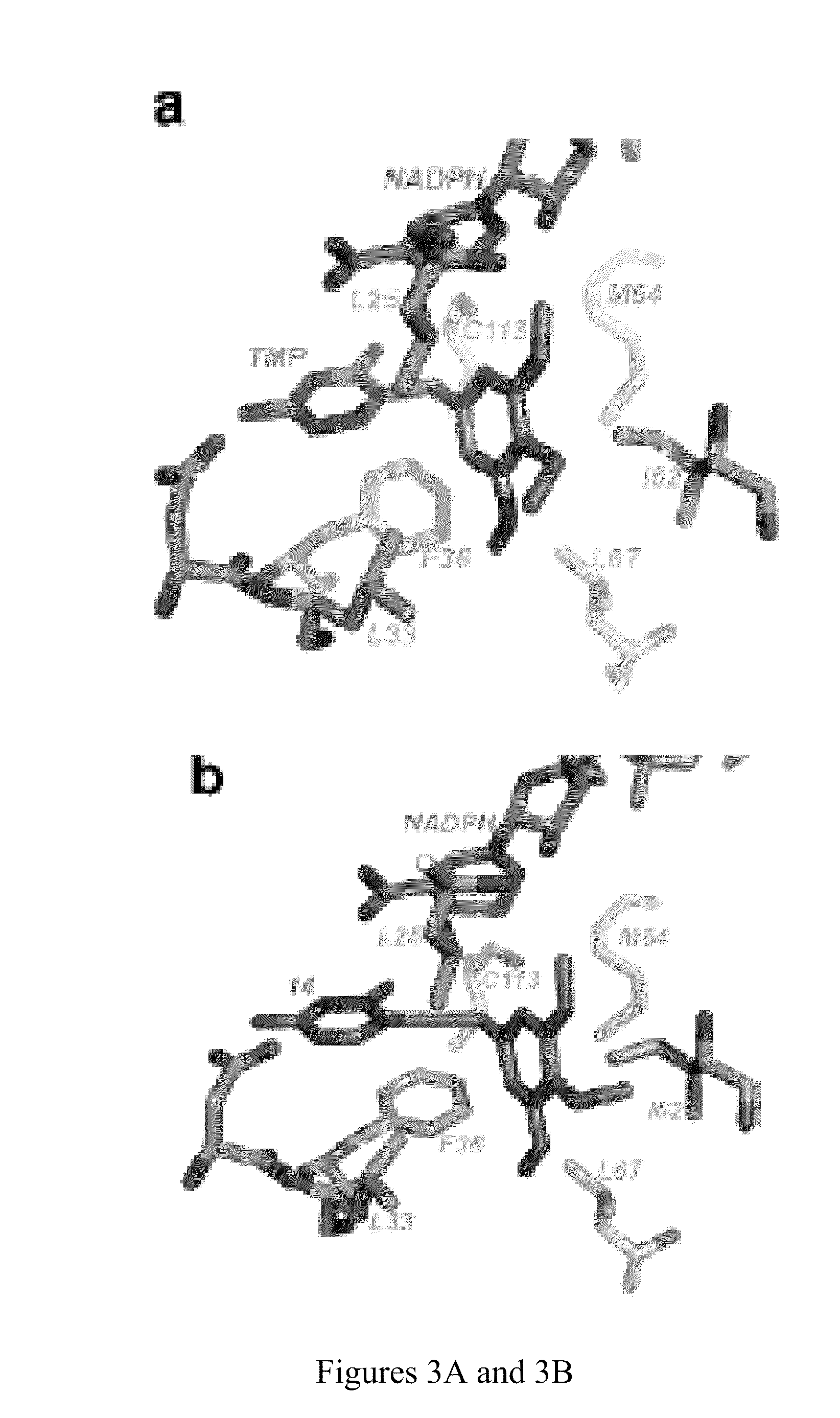
Carbonyl reductase, gene and mutant and application thereof to asymmetrical reduced carbonyl compound
ActiveCN102618513AHigh optical purityMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationMethyl o-chloromandelate
The invention discloses a novel carbonyl reductase, a gene, a mutant thereof, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene and the mutant, a recombinant expression transformant, a recombinase preparation method, and applications of the carbonyl reductase and recombinase to preparation of active chiral alcohols with a chiral carbonyl compound before asymmetrical reduction. The carbonyl reductase is derived from candida glabrata, is applied to preparation of a plurality of optically-active chiral alcohols such as (R)-chloromandelic acid methyl ester, (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate, (R)-4-chlorin-3-phenyl ethyl butyrate and the like. Compared with other preparation methods, a product prepared through the method has high concentration, does not require additionally or slightly adding any expensive coenzyme, has high optical purity, and has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, easiness and convenience for operating, easiness for amplifying and the like, and has a good industrial application prospect in the production of clopidogrel, L-carnitine and perindopril antihypertensive medicinal intermediates.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Methods and compositions for detecting and identifying species of Candida
ActiveUS20080102449A1Avoid disadvantagesMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationForward primerNucleotide
Methods and compositions useful in the detection and identification of species of Candida are disclosed. These species include Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis, each of which is a causative agent for vaginal candidiasis. The compositions of the invention are combinations of oligonucleotides. These oligonucleotides include pairs of forward and reverse primers for polymerase chain reactions, wherein each primer pair is capable of priming the synthesis of an amplicon specific to one of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis, but preferably is not capable of priming the synthesis of an amplicon specific to any of the other three species. In preferred embodiments, the forward primers of the primer pairs have identical sequences, while each reverse primer of the primer pairs has a unique sequence relative to all of the other reverse primers; or the reverse primers of the primer pairs have identical sequences, while each forward primer of the primer pairs has a unique sequence relative to all of the other forward primers. These unique primer sequences account for the species specificity of the resultant amplicons. The oligonucleotides also include probes capable of detecting these amplicons, and sequencing primers for determining, in primer extension reactions, the nucleotide sequences contained within the amplicons. In preferred methods of the invention, a biological sample is tested for the presence of at least one isolate of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis by isolating nucleic acid from the sample, attempting a polymerase chain reaction in a mixture containing this nucleic acid and a plurality of these primer pairs, ascertaining whether any amplicon is produced in the mixture using an oligonucleotide probe, and determining the sequence of any resultant amplicon using the sequencing primers. The detection of an amplicon indicates that the sample contains at least one isolate of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, or Candida tropicalis, and the nucleotide sequence data is used to determine which of these four Candida species is present.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
Fluorescence quantitative PCR primer, probe and kit for detecting ordinary pathogenic fungi
InactiveCN104450936AOvercome limitationsSolve the problem of fungal infectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceCandida tropicalis
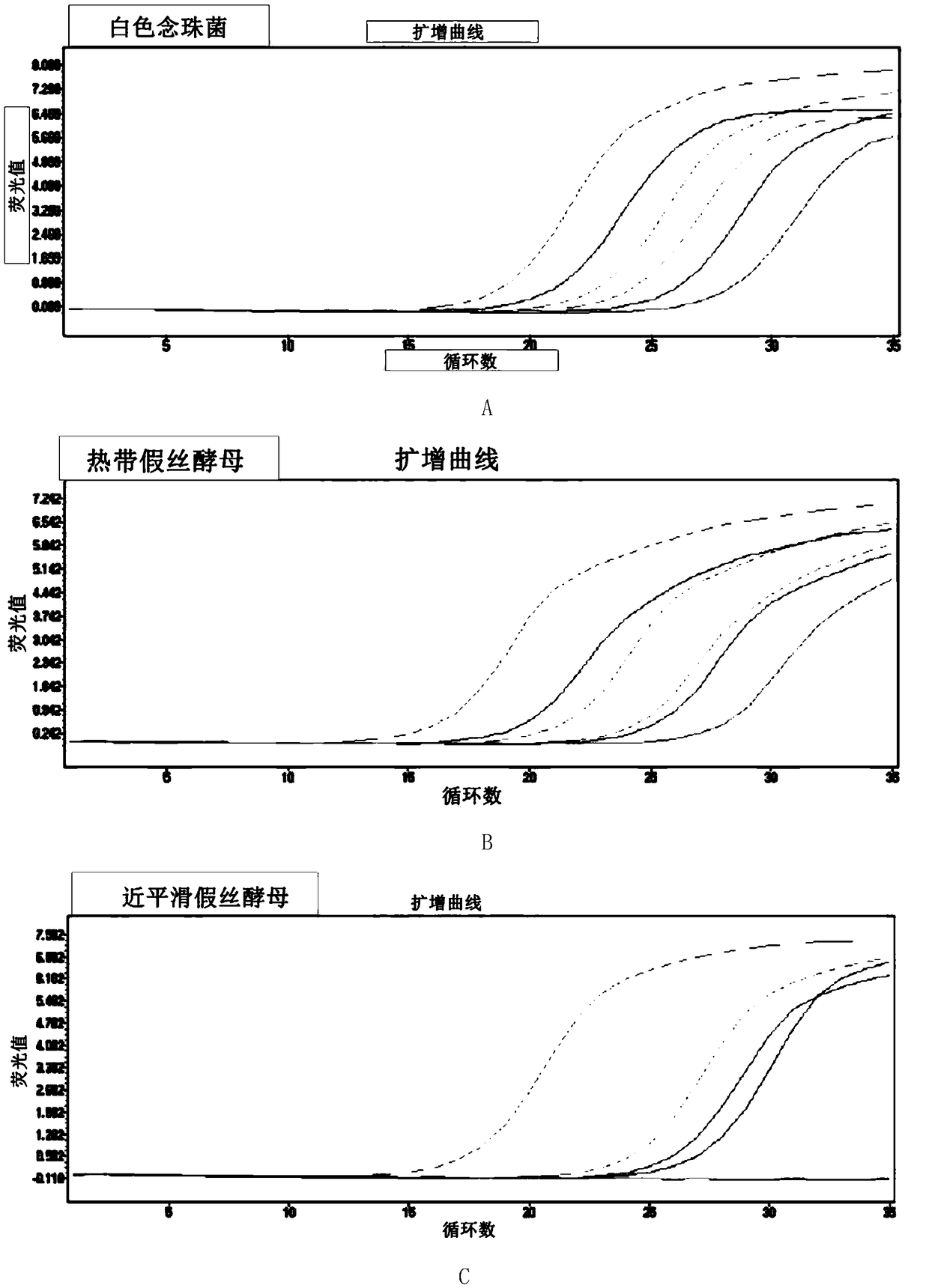
The invention discloses a fluorescence quantitative PCR primer, a probe and a kit for detecting ordinary pathogenic fungi. A specific primer and a TaqMan probe are independently designed, and a fluorescence PCR detection method which can be used for simultaneously detecting 15 clinically ordinary pathogenic fungi, including 8 candida mycoderma bacteria (candida albicans, candida glabrata, candida parapsilosis, candida kefyr, candida sake, candida kruse, candida guilliermind and candida tropicalis), four aspergilli (aspergillus niger, aspergillus flavus, aspergillus terreus and aspergillus fumigates), cryptococcus, rhizopus oryzae and mucor circinelloides, is established. The method is relatively high in sensitivity and specificity, and has significant meanings for early diagnosis and treatment on invasive infections with fungi.
Owner:天津宝瑞生物技术有限公司
Detection method of invasive fungus infection, detection kit and application
ActiveCN109055502ASimplify detectionSimplify operabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCell freeFluorescence
The invention provides a fast multiplex PCR identification diagnosis detection method of invasive fungus infection based on cfDNA (cell free DNA). The method can be used for identifying the invasive infection caused by clinic common and high-incidence Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis, Candida krusei, Candida glabrata and Aspergillus fumigtus. An amplification primer is designed according to characteristic genome segments of each fungus category and species; a detection fluorescence probe of a strain can be distinguished according to the amplification segment design; the real time PCR can be performed on a sample to be tested; high sensitivity of nested PCR and high specificity and multi-target performance advantages of multiple fluorescent hybrid probe PCR are integrated for identifying the fungus strain. The invention also provides a PCR diagnosis kit for the invasive fungus infection and application thereof.
Owner:DIASYS DIAGNOSTIC SYST SHANGHAI
Nucleic acid probes and methods for detecting clinically important fungal pathogens
InactiveUS20050164243A1Faster and simpler to performSuitable for automationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesAspergillus flavus
The current invention relates to the field of detection and identification of clinically important fungi. More particularely, the present invention relates to species specific probes originating from the Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) region of rDNA for the detection of fungal species such as Candida albicans, Candida parapsilosis, Candida tropicalis, Candida kefyr, Candida krusei, Candida glabrata, Candida dubliniensis, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus versicolor, Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus fumigatus, Cryptococcus neoformans and Pneumocystis carinii in clinical samples, and methods using said probes.
Owner:INNOGENETICS NV +2
Method for microbial fermentation synthesis of ª‡- ketoglutaric acid
InactiveCN1544642AIncrease carbon molar ratioIncrease concentrationFermentationHigh concentrationIncreased biotin
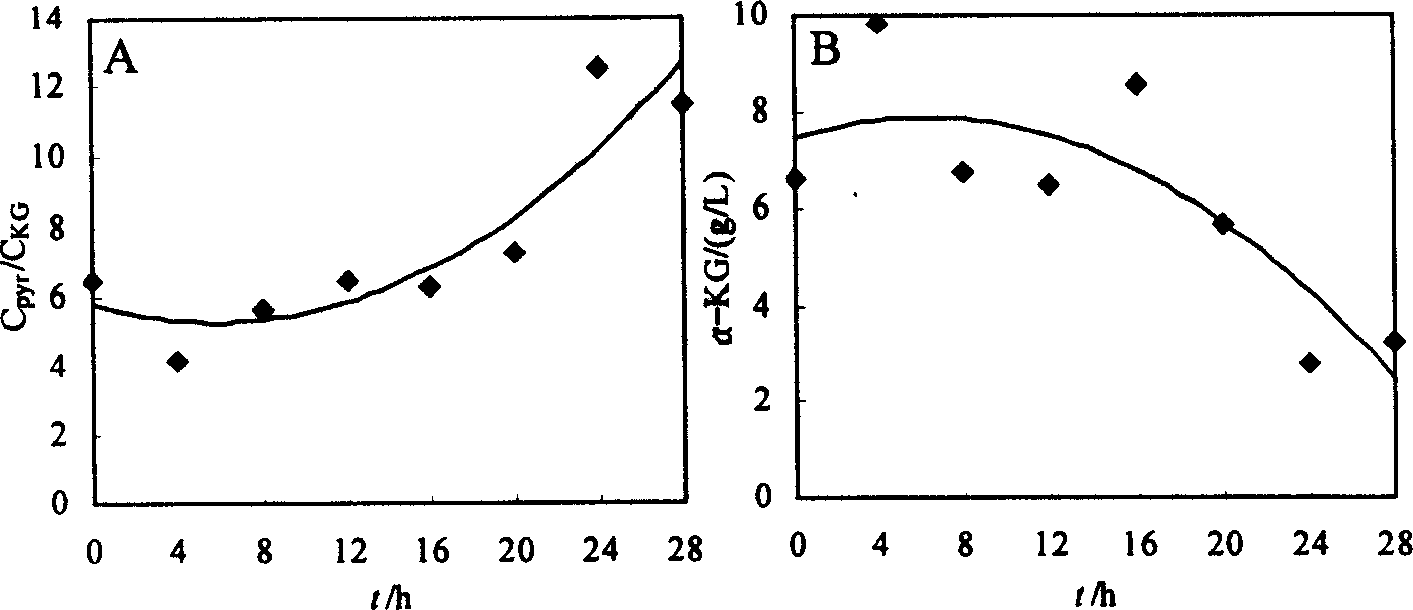
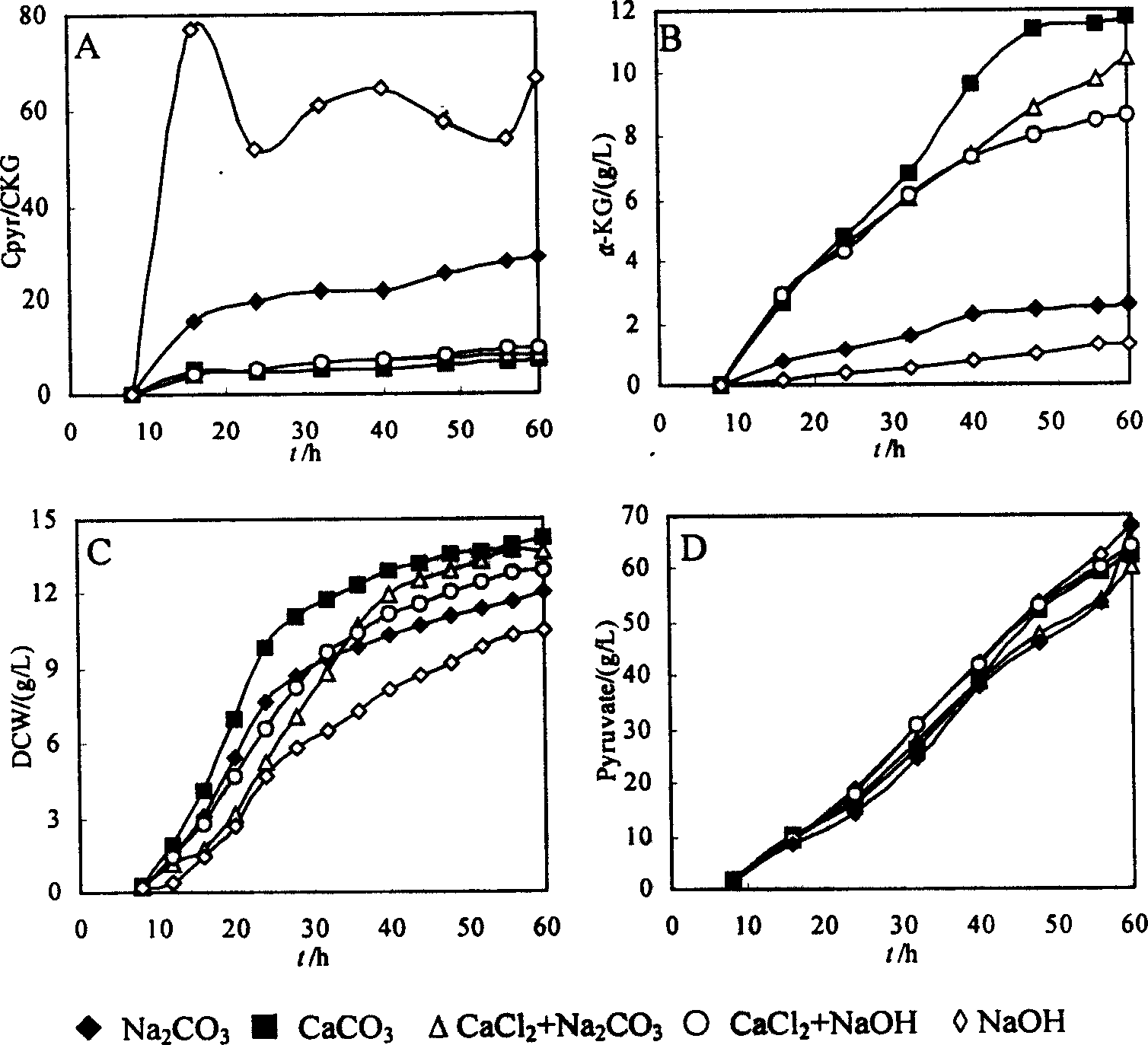
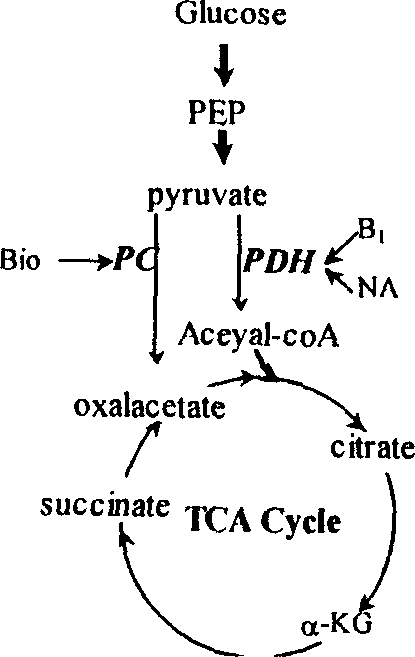
The invention is a method of synthesizing alpha-ketoglutarate by fermenting microbes, promoting to produce a large amount of alpha-ketoglutarate in fermenting course by adding CaCO3 to the culture medium and increasing biotin concentration. in the course of fermenting candida glabrata CCTCC M202019 to producing pyruvic acid, the delay of time of adding CaCO3 will inhibit the generation of alpha-ketoglutarate and increase the carbon mole ratio of pyruvic acid to alpha-ketoglutarate (CPYR / CKG), and increase of CaCO3 concentration in the culture medium will promote accumulation of a large amount of alpha-ketoglutarate, when the CaCO3 concentration is 40g / L, it is most beneficial to alpha-ketoglutarate generation. Keeping the CaCO3 concentration in the culture medium but increasing biotin concentration in the culture medium so as to promote the continuous increase of the alpha-ketoglutarate concentration but continuous decrease of CPYR / CKG value, and when biotin concentration is 60mum g / L, accumulated quantity of alpha- ketoglutarate is 23.5g / L. when Ca2+ exists, in-cell phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity can be increased by 40%, and the activity of pyruvic acid dehydrogenase system does not change obviously. The increase of the Ca2+ and biotin concentration can remarkably the activity of enhance pyruvic acid dehydrogenase, thus making T.glabrata transfer from production of pyruvic acid by fermenting to synthesis of high-concentration alpha-ketoglutarate.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Primer probe combination for simultaneously detecting four types of candida and kit thereof
ActiveCN108034745AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismFluorescence
The invention provides a primer probe combination for simultaneously detecting four types of candida, which belongs to the technical field of microbe detection. The primer probe combination comprisesprimers and a probe, the primer is an upstream primer and a downstream primer, a sequence of the upstream primer is shown as SEQ ID No.1; the sequence of the downstream primer is shown as SEQ ID No.2,and the probe is the sequence labeled with a report fluorescence group and a quenching fluorescence group shown as SEQ ID No.3. The invention provides a pair of primers and a probe which specificallyand simultaneously detect four types of candida such as Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis, candida glabrata and candida parapsilosis.
Owner:杭州缔蓝生物技术有限公司
Carbonyl reductase and gene thereof as well as application of carbonyl reductase in asymmetrical reductive carbonyl compound
ActiveCN102492668AHigh optical purityMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAngiotensin-converting enzymeAlcohol
The invention discloses a new carbonyl reductase and gene thereof, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene and a recombinant expression transformant containing the gene, a recombinase of the carbonyl reductase and a preparation method of the recombinase as well as an application of the recombinase serving as a catalyst in preparation of chiral alcohol from prochiral carbonyl compoundssuch as asymmetrical reductive 2-carbonyl-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate. The carbonyl reductase gene disclosed by the invention is derived from candida glabrata, can be used as a catalyst to be applied to preparation of multiple chiral alcohols with optical activities, such as (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate. Compared with the other methods for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate, a product obtained by catalysis with the method disclosed by the invention is high in concentration without additional expensive coenzyme; the product is high in optical purity, reaction condition is mild, operation is convenient and easy to amplify. Thus, the carbonyl reductase has a good industrial application prospect in production of an ACEI (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor) medicament intermediate.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Defensin cathelicidin-PP of polypedates puerensis as well as gene and application thereof
The invention relates to defensin cathelicidin-PP of polypedates puerensis as well as a gene and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biomedicine. The defensin cathelicidin-PP is a cyclic polypeptide encoded by a gene of defensin of Chinese amphibian polypedates puerensis, and has a molecular weight of 3,366.08 daltons and an isoelectric point of 10.05; the amino acid sequence of the defensin cathelicidin-PP is as shown by SEQ ID NO: 1. A gene GenBank Accession KY610282 for encoding a precursor of the defensin cathelicidin-PP of the polypedates puerensis consists of 615 nucleotide sequences; the nucleotide sequence of the gene GenBank Accession KY610282 is as shown by SEQ ID NO: 2, wherein nucleotides at No. 346 to No. 441 sites are encoding genes of defensin cathelicidin-PP of mature polypedates puerensis. The invention relates to the application of the defensin cathelicidin-PP of the polypedates puerensis to the preparation of a therapeutic medicine for infectious diseases caused by escherichia coli, salmonella paratyphi A, pseudomonas aeruginosa and candida glabrata. The defensin cathelicidin-PP has the obvious effects of inhibiting the growth of a bacterium and a fungus for the escherichia coli, the salmonella paratyphi A, the pseudomonas aeruginosa and the candida glabrata.
Owner:KUNMING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Nucleic acid reagent, kit, system and method for detecting invasive fungi
InactiveCN110551840AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCandida tropicalisCandida famata
The invention relates to a nucleic acid reagent, kit, system and method for detecting invasive fungi. The nucleic acid reagent comprises a primer shown in SEQ ID NO.1-14 and a probe shown in SEQ ID NO.17-26, and the primer and the probe are stored independently with each other correspondingly or mixed with each other at will. Through the primer and the probe, the nucleic acid reagent, the kit, thesystem and the method of at least 9 invasive fungi of candida albicans, candida tropicalis, candida glabrata, candida parapsilosis, mucor, aspergillus, cryptococcus neoformans, pneumocystis jeroveciand candida auris, fast, comprehensive, sensitive, specific and automatic detection result determination can be achieved, and the sensitivity, specificity, simplicity and convenience of simultaneous detection of the detection target genome are significantly improved.
Owner:北京卓诚惠生生物科技股份有限公司
Degrading bacterium agent for kitchen waste treatment and application thereof
InactiveCN111548963AImprove biological activityImprove degradation rateFungiBio-organic fraction processingCelluloseBacillus licheniformis
The invention provides a degrading bacterium agent for kitchen waste treatment. The degrading bacterium agent is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 20 to 30 parts of bacillus subtilis, 10 to 15 parts of lysine bacillus, 10 to 20 parts of bacillus licheniformis, 15 to 25 parts of trichoderma viride, 5 to 10 parts of candida glabrata, 5 to 10 parts of yersinia lipolytica and1 to 5 parts of a biological surfactant. The invention further provides an application of the degrading bacterium agent in kitchen waste integrated treatment equipment. The degradation microbial inoculum can rapidly decompose proteins, grease, starch polysaccharides, cellulose, hemicellulose and other macromolecular organic matters in the kitchen waste, so that the macromolecular organic matters are rapidly stabilized, the degradation efficiency of the kitchen waste is improved, the space utilization rate of a fermentation bin is further improved, and the quality of the kitchen waste degradation product organic fertilizer is improved.
Owner:中铁环境科技工程有限公司
Novel wide-spectrum bacillus resisting clinical and plant pathogenic fungi and application thereof
InactiveCN103087939ABroad antifungal spectrumGood antibacterial effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesBacterial strain
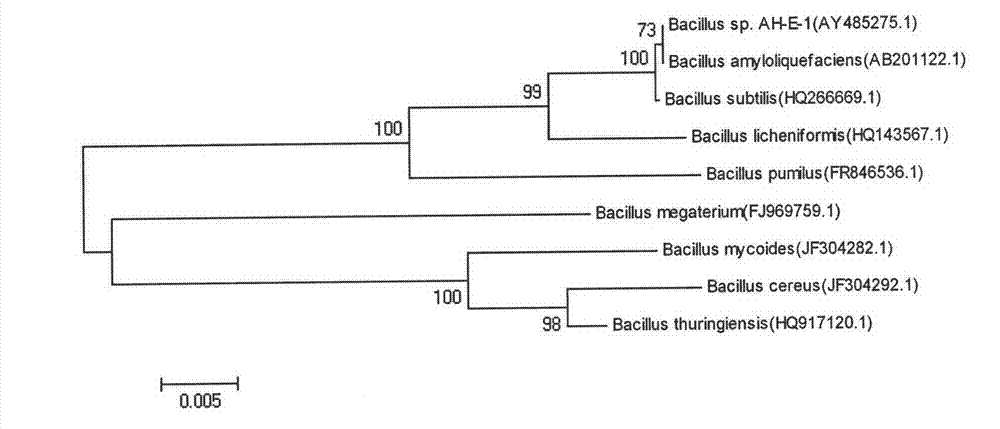
The invention relates to a novel wide-spectrum bacterial strain Bacillus sp. AH-E-1 inhibiting clinical and plant pathogenic fungi, and an application thereof. The main content comprises: (1) Bacillus sp. AH-E-1 is a newly-discovered bacillus strain or subspecies; (2) Bacillus sp. AH-E-1 can produce anti-fungus substances after fermentation under appropriate conditions; (3) Bacillus sp. AH-E-1 can significantly inhibit 20 clinical pathogenic fungi such as aspergillus flavus, aspergillus fumigates, trichophyton rubrum, trichophyton mentagrophyte, candida glabrata, cryptococcus neoformans, and the like; (4) Bacillus sp. AH-E-1 can significantly inhibit 13 plant pathogenic fungi such as staphylococcus, magnaporthe oryzae, rhizopusstolonife, and the like. The invention provides an excellent novel anti-fungus substance producing bacterial strain which has the advantages of wide fungus-inhibiting spectrum, obvious effect, and the like.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Candida categorized detection primer and probe composition, kit, detection method and application of composition
ActiveCN109971883AImprove featuresHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesFluorescenceCandida famata
The invention provides a Candida categorized detection primer and probe composition, a kit, a detection method and an application of the composition. The Candida categorized detection primer and probecomposition comprises specific primers, detection probes and complementary probes which are used for Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis, Candida krusei and Candida glabrata, and the complementary probes and the detection probes are incompletely complemented and paired. The primer and probe composition can detect and determine presence and absence of Candida infection onceand can distinguish the Candida albicans, the Candida tropicalis, the Candida parapsilosis, the Candida krusei and the Candida glabrata in the same fluorescent light channel.
Owner:DYNAMIKER BIOTECH TIANJIN
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods to vaccinate against disseminated candidiasis
InactiveUS20060083750A1Treating preventingInhibit bindingAntibacterial agentsFungiCell adhesionAdjuvant
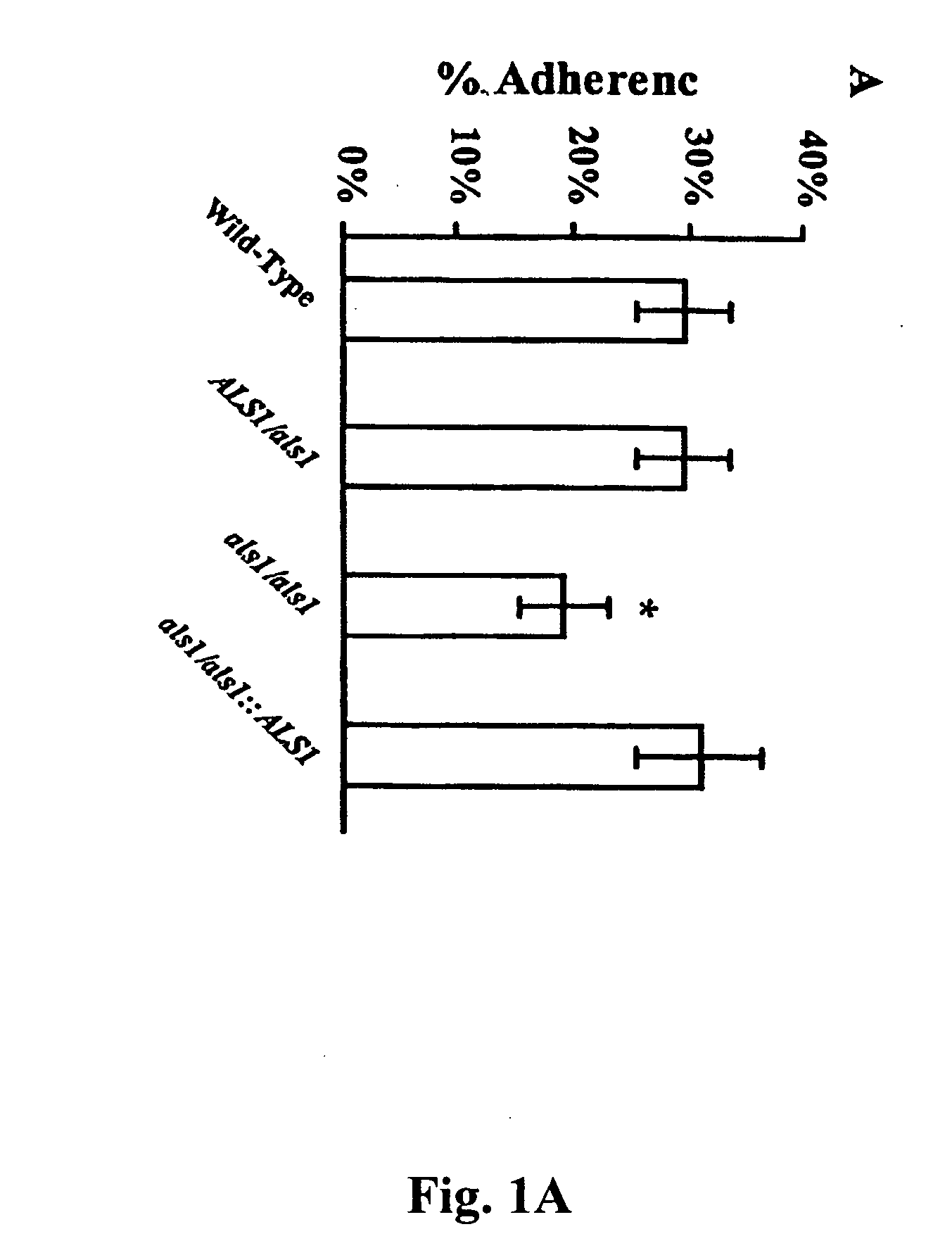
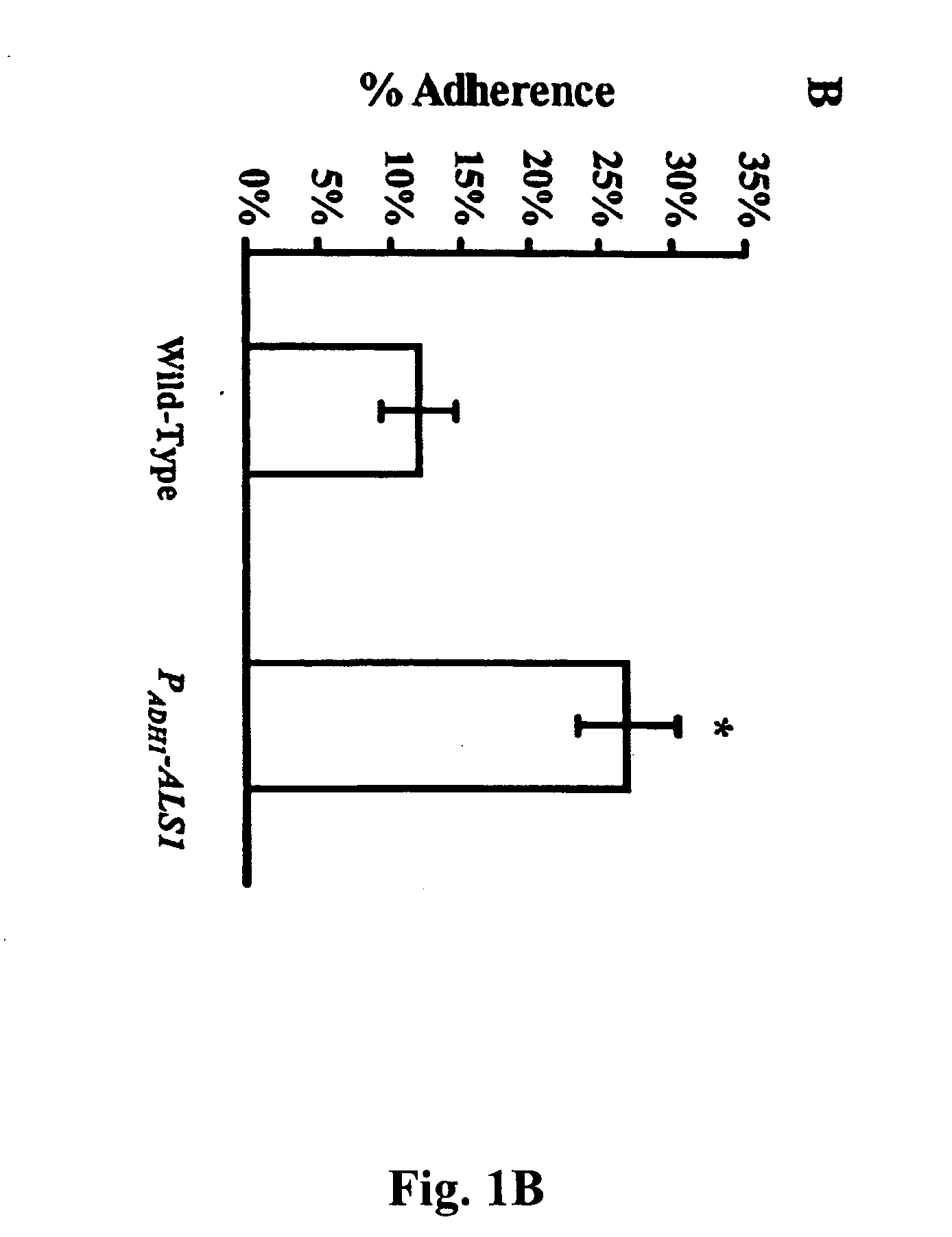
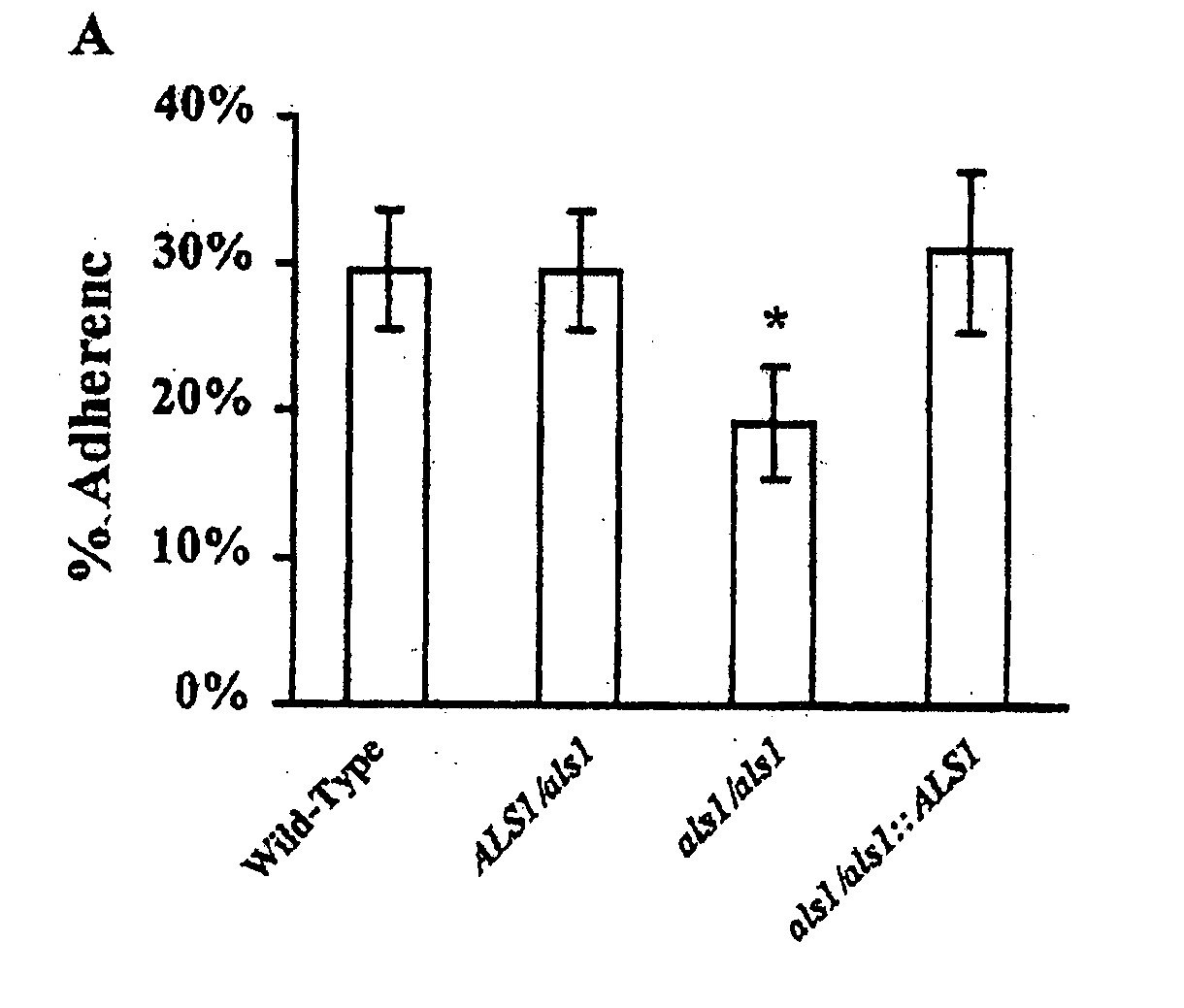
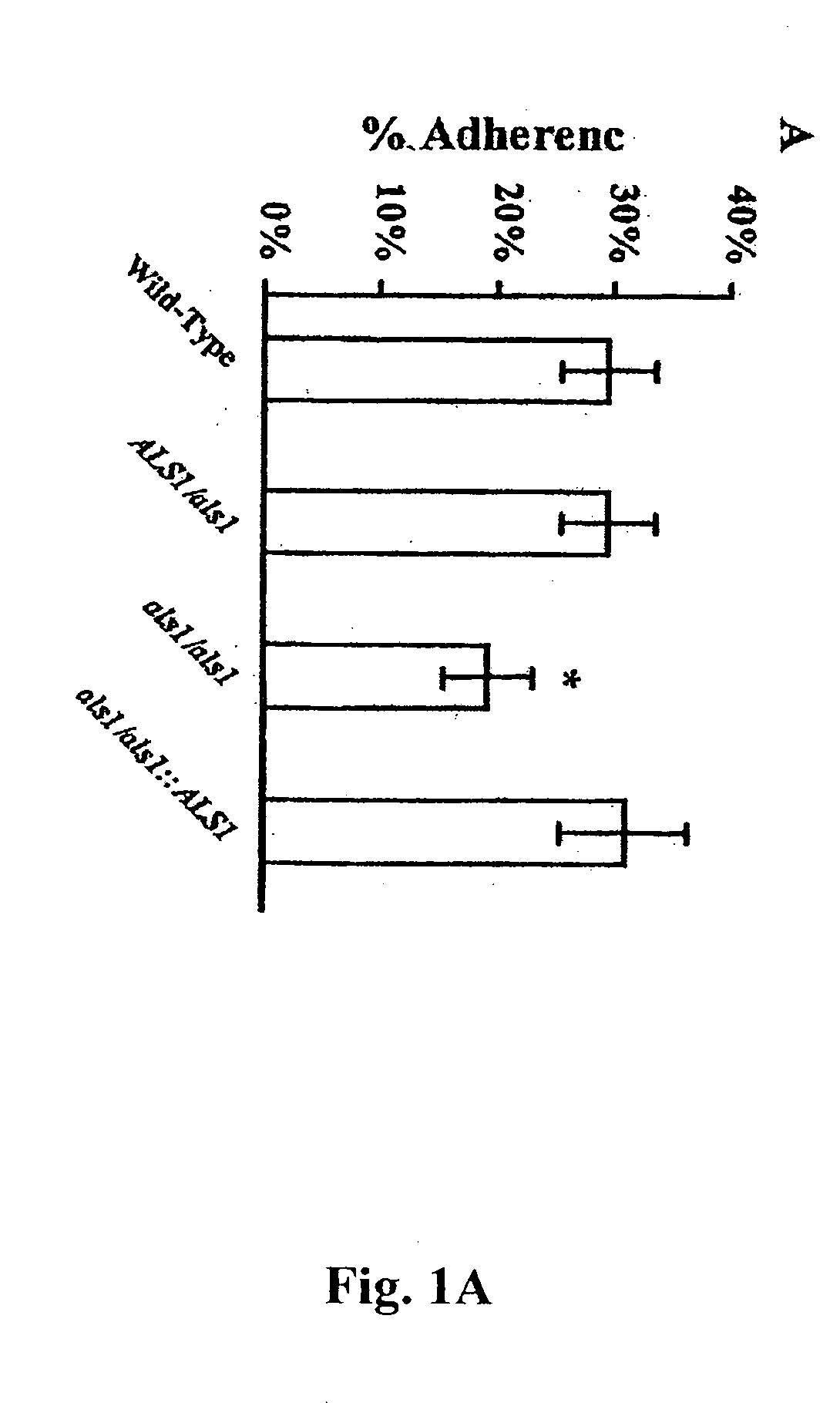
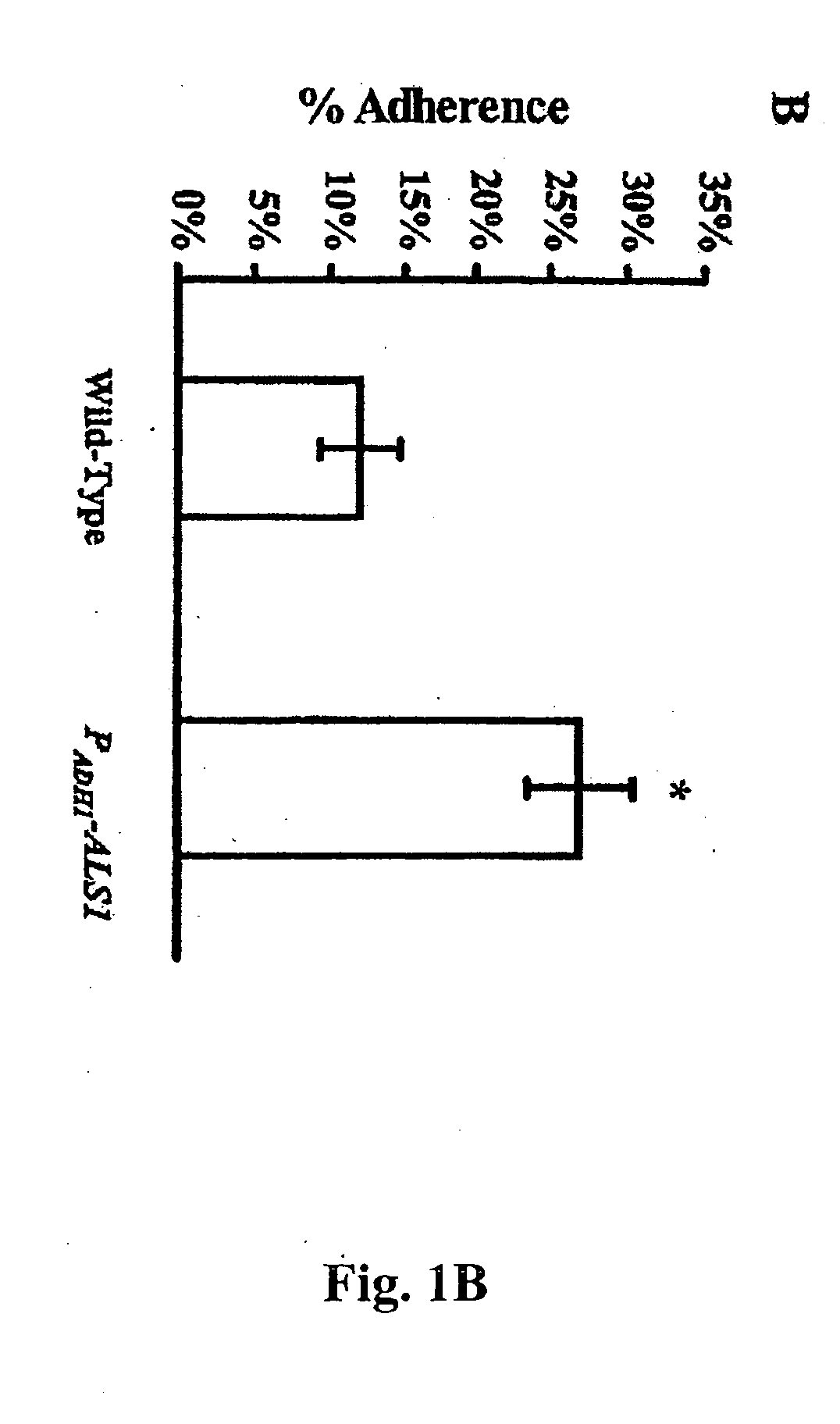
The invention provides a vaccine including an isolated Als protein family member having cell adhesion activity, or an immunogenic fragment thereof, with an adjuvant in a pharmaceutically acceptable medium. The invention also provides a method of treating or preventing disseminated candidiasis. The method includes administering an immunogenic amount of a vaccine an isolated Als protein family member having cell adhesion activity, or an immunogenic fragment thereof, in a pharmaceutically acceptable medium. A method of treating or preventing disseminated candidiasis also is provided that includes administering an effective amount of an isolated Als protein family member having cell adhesion activity, or an functional fragment thereof, to inhibit the binding or invasion of Candida to a host cell or tissue. The Als protein family member can be derived from a Candida strain selected from the group consisting of Candida albicans, Candida krusei, Candida tropicalis, Candida glabrata and Candida parapsilosis and the Als protein family member includes Als1p, Als3p, Als5p, Als6p, Als7p or Als9p.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods to vaccinate against disseminated candidiasis and other infectious agents
InactiveUS20070077256A1Treating preventingInhibit bindingAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsCell adhesionAdjuvant
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for preparing Candida resisting medicines
ActiveCN104083361AHigh antibacterial activityGood synergyAntimycoticsAldehyde active ingredientsCandida famataCandida glabrata
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine composition for preparing Candida resisting medicines. The traditional Chinese medicine composition contains the ingredients in parts by weight: 40-80 parts of cinnamaldehyde and 30-60 parts of pogostone. The traditional Chinese medicine composition for preparing the Candida resisting medicines, provided by the invention, can be used for treating deep or systemic fungal infections caused by Candida, including deep or systemic fungal infections caused by Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis, Candida krusei or Candida glabrata. According to the traditional Chinese medicine composition, the pogostone is screened from numerous ingredients of ageratum oil, has relatively high bacteriostasis activity and has a good synergistic effect with the cinnamaldehyde; the cinnamaldehyde and the pogostone are suitable for being used after being combined; compared with the bacteriostasis activity after the cinnamaldehyde and the ageratum oil are combined, the bacteriostasis activity after the pogostone and the cinnamaldehyde are combined is remarkably improved, and the safety is good.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF HEBEI MEDICAL UNIV
Fungus rapid culture, identification and susceptibility detection kit and detection method thereof
ActiveCN101886111AGrowth inhibitionGrow fastMicrobiological testing/measurementCandida famataAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses a fungus rapid culture, identification and susceptibility detection kit for rapidly and effectively identifying multiple fungi and testing the susceptibility. The invention also discloses a method for directly detecting a clinical sample by using the kit. The kit has the advantages that the multiple fungi are simultaneously identified and different pores are favorable for growing different fungi by coating various sugars or inhibitors on a susceptibility test board, so that the most common fungi in clinic use, such as candida albicans, candida tropicalis, candida glabrata, candida krusei, cryptococcus neoformans, candida guilliermondii and the like, can be identified and effective guidance is provided for the clinical use. The detection method is simple and suitable for detecting pure fungi, can be further directly applied to fungus identification of the clinical sample and the susceptibility detection of antibiotics and has a short detection period, namely thefungi to be detected can be simultaneously identified and the susceptibility can be detected at one time and the result can be given in 24 hours; and thus the detection method greatly shortens the clinical detection period and is favorable for early diagnosis and early therapy of patients.
Owner:AUTOBIO DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Gene chip for detecting 15 clinical common pathogenic microorganisms
ActiveCN102080127AWith monitoring functionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceCandida tropicalisRhizopus oryzae
The invention discloses a gene chip for detecting 15 clinical common pathogenic microorganisms. The gene chip comprises specific detection probes fixed on a solid phase vector, wherein the probes are designed for 16SrRNA gene and ITS gene sequences of staphylococcus aureus, klebsiella pneumoniae, pseudomonas aeruginosa, proteus mirabilis, Escherichia coli, shigella, enterobacter aerogenes, pseudomonas fluorescens, candida albicans, candida glabrata, candida tropicalis, candida parapsilosis, aspergillus terreus, aspergillus flavus and rhizopus oryzae, and screened and verified by repeated tests, and have high hybridization specificity and accuracy. The chip provided by the invention ensures simple detection operations and relatively lower cost, saves time, is applied to the screening of the clinical common pathogenic microorganisms, the early rapid diagnosis of critical patients and the diagnosis of suddenly occurring infection event pathogens and favorable for clinically rapidly diagnosing infection sources and functions in the early detection and early diagnosis of clinical diseases.
Owner:GUANGZHOU IMPROVE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +1
Preparation method of degrading bacterium agent for kitchen waste treatment
InactiveCN111394287AHigh biological activityImprove degradation rateFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyFermentation
The invention provides a preparation method of a degrading bacterium agent for kitchen waste treatment. The degrading bacterium agent comprises Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus lysine, Bacillus licheniformis, Trichoderma viride, Candida glabrata, Yarrowia lipolytica and a biological surfactant. The method comprises the following steps: step A, activation culture; step B, domestication culture: respectively performing domestication culture on the six strains, specifically, performing step-by-step domestication culture for gradually increasing the concentration of sodium chloride for culture on eachmicroorganism; step C, liquid fermentation enlarged culture; step D, dehydrating and drying; step E, uniform mixing. The degrading bacterium agent prepared by the method can rapidly decompose proteins, grease, starch polysaccharides, cellulose, hemicellulose and other macromolecular organic matters in the kitchen waste, so that the macromolecular organic matters are rapidly stabilized, the degradation efficiency on the kitchen waste is improved, the space utilization rate of a fermentation bin is further improved, and the organic fertilizer quality of degradation products of the kitchen wasteis improved.
Owner:中铁环境科技工程有限公司
Inhibitors of dihydrofolate reductase with antibacterial antiprotozoal, antifungal and anticancer properties
ActiveUS8426432B2Increase capacityStraightforward to synthesizeAntibacterial agentsBiocideProtozoaBacteroides
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Candida glabrata and application in kitchen waste
ActiveCN105950483AImprove salt toleranceImprove acid resistanceFungiSolid waste disposalAcid-fastHigh activity
The invention provides candida glabrata. The candida glabrata is named as Candida glabrata CY-9 and preserved in Common Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, the address is Institute of Microbiology of Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, No.1 yard, Beichenxi road, Chaoyang District, Beijing City, the postal code is 100101, the preservation number is CGMCC NO.12449, and the preservation date is May 13, 2016. The invention further provides application of the candida glabrata in kitchen waste treatment. The candida glabrata has the high activity of protease, amylase and fat hydrolase, can produce acid by degrading glucose, belongs to thermophilic bacteria with the high salt tolerance and the high acid resistance and can quickly and efficiently decreasing 85% of the weight of input kitchen waste by being effectively combined with a carrier.
Owner:BIOMAX ECOLOGICAL ENG
Inhibitors of Dihydrofolate Reductase With Antibacterial Antiprotozoal, Antifungal and Anticancer Properties
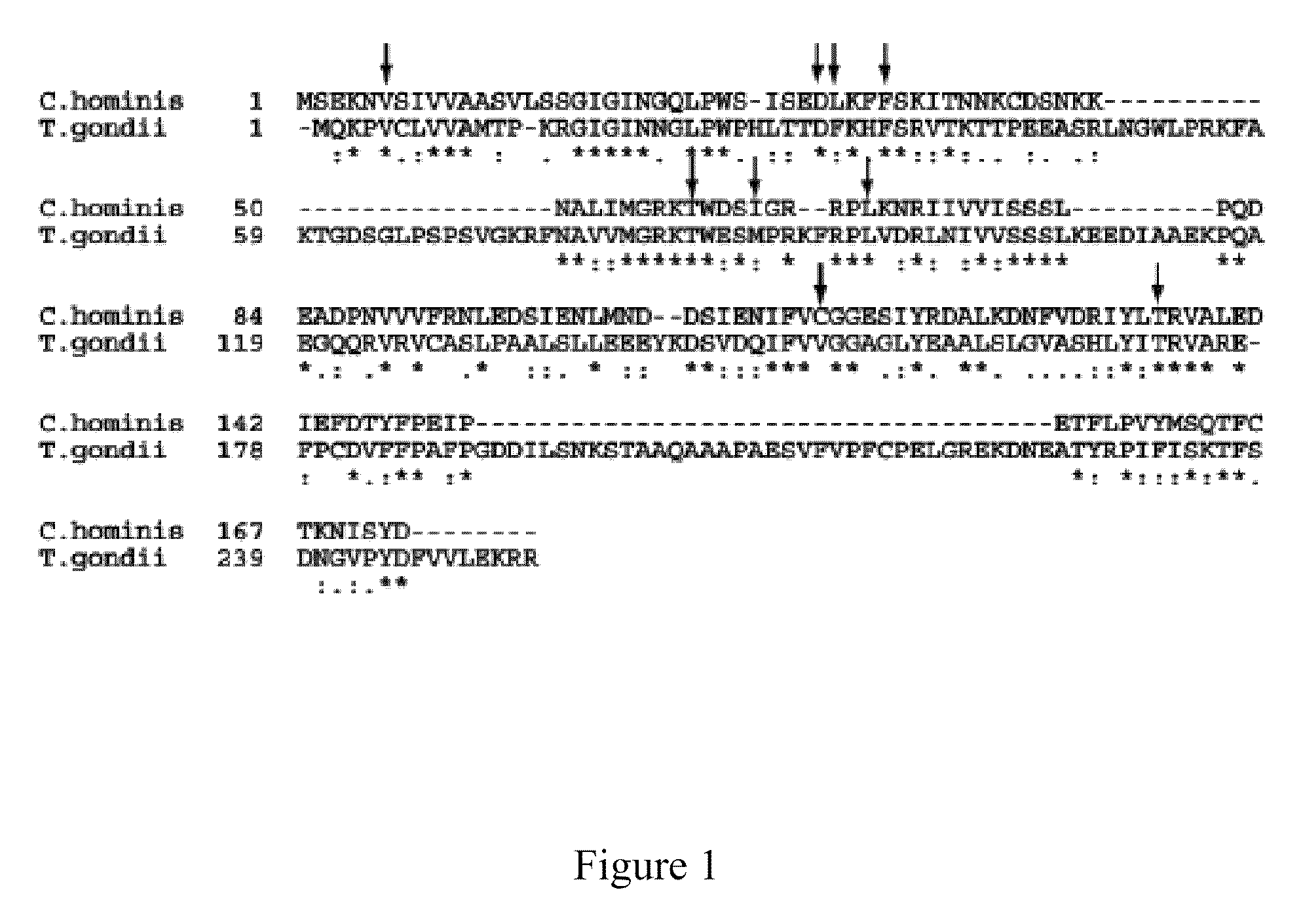
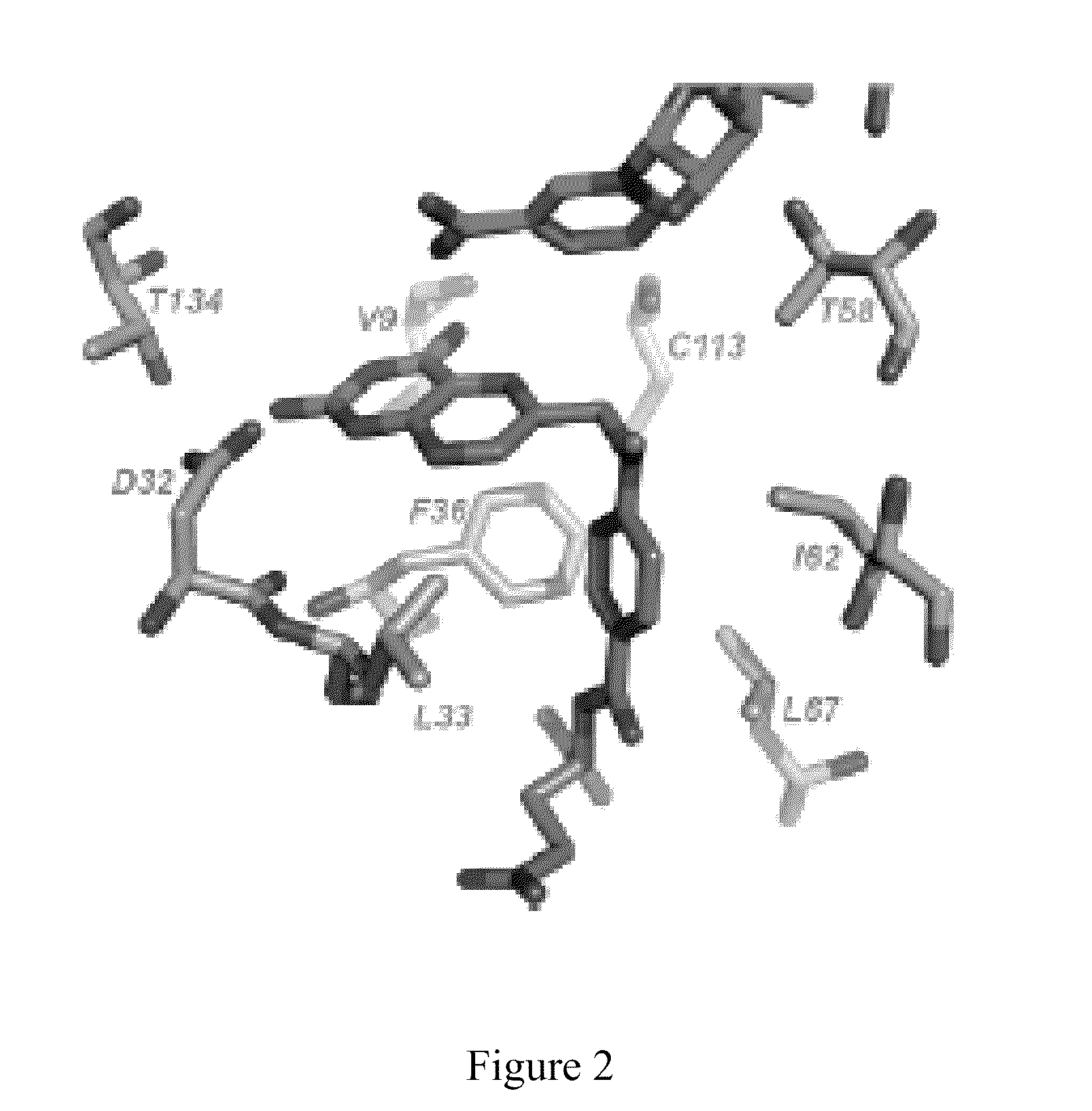
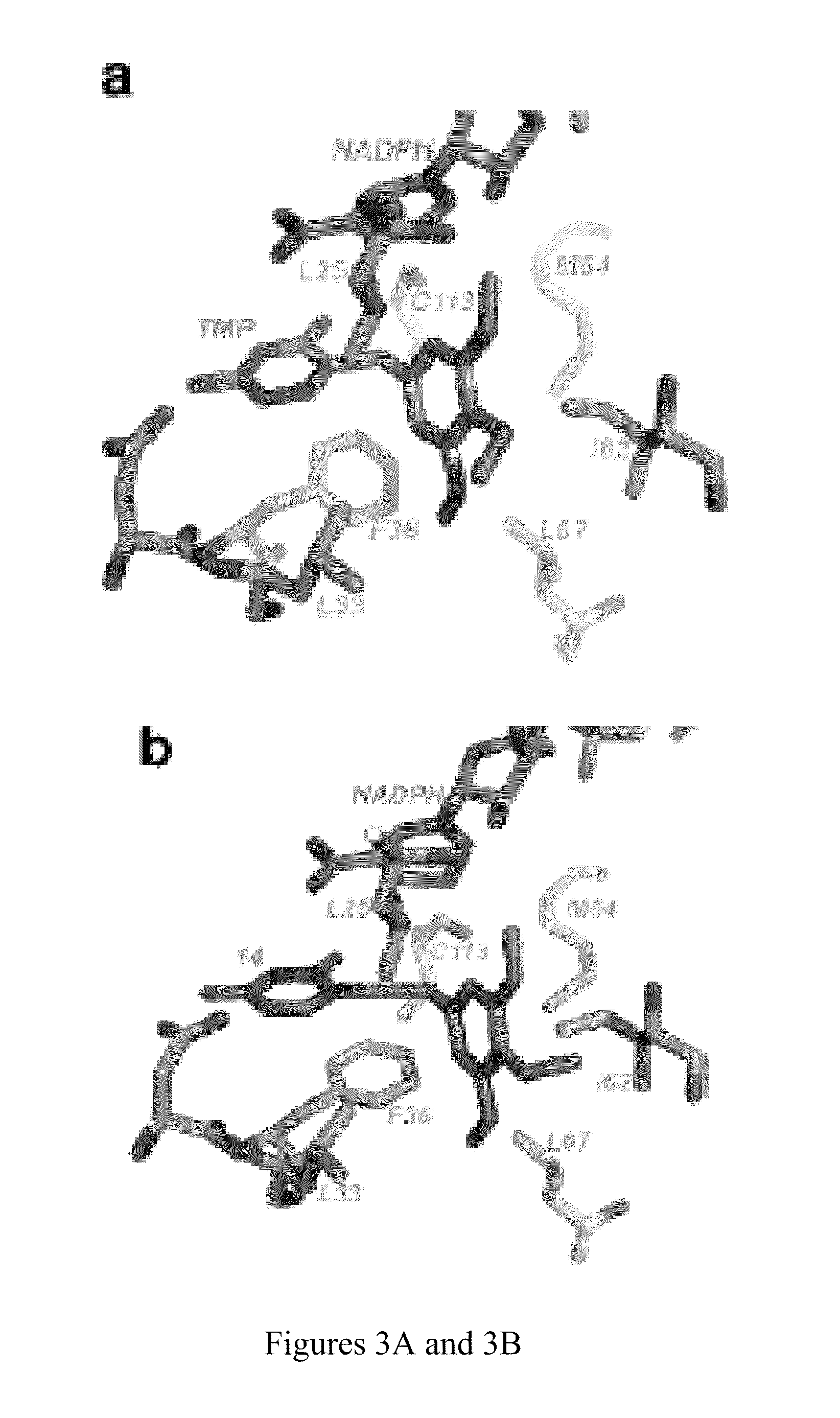
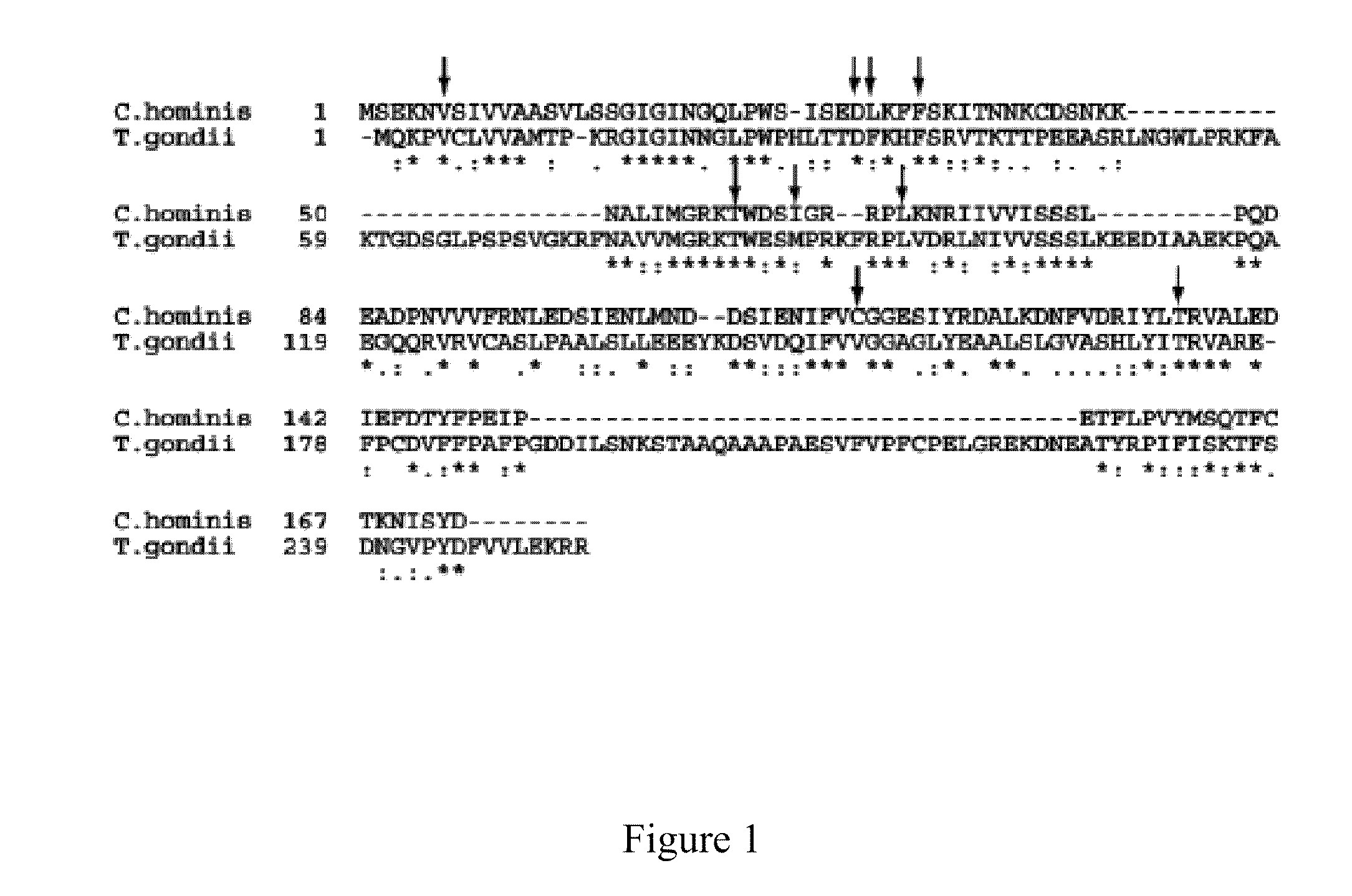
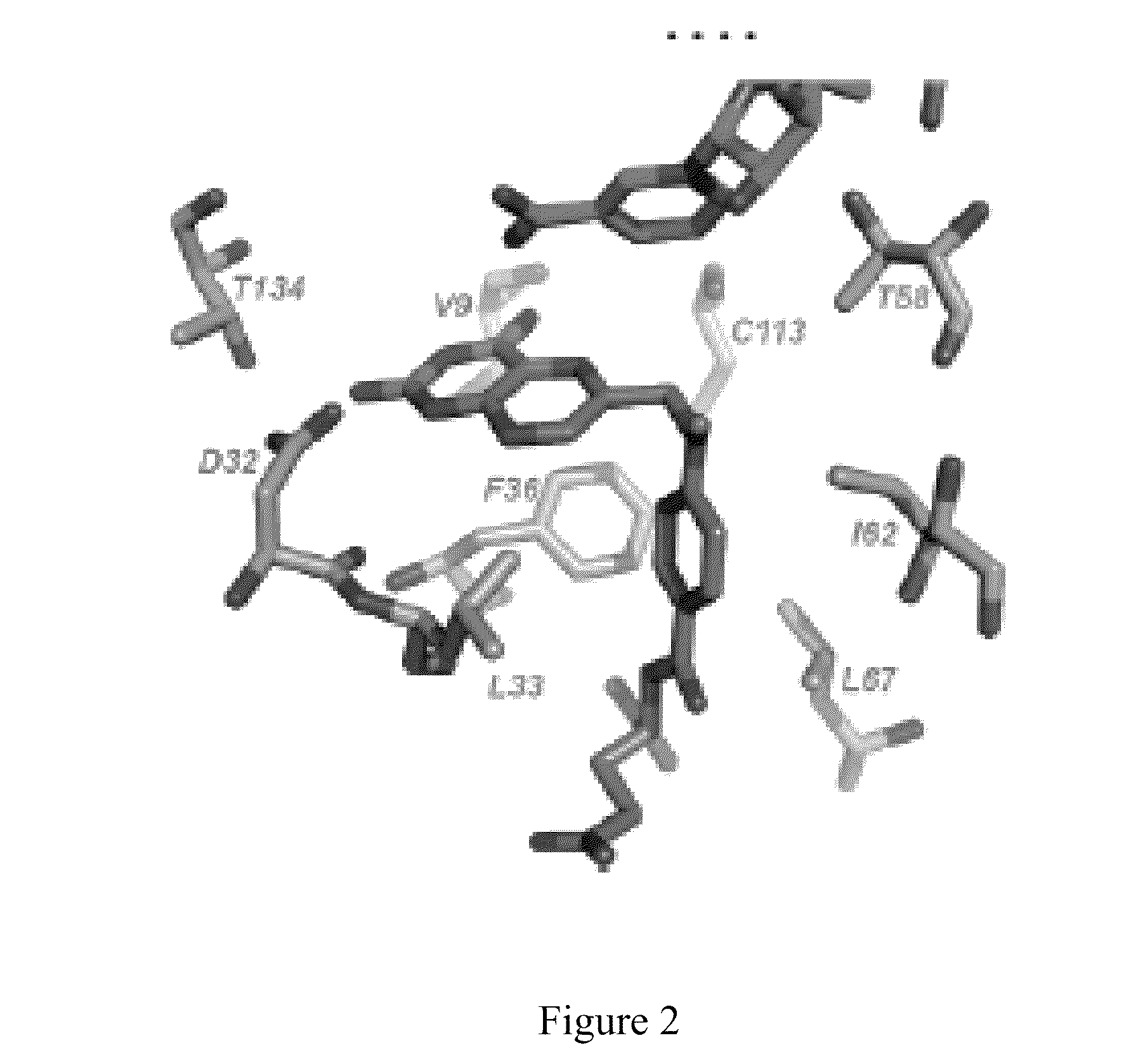
The compositions and methods described herein discloses the design, synthesis and testing of compounds that act as inhibitors of DHFR. The basic scaffold of these inhibitors includes a 2,4-diaminopyrimidine ring with a propargyl linker to another substituted aryl, bicyclo or heteroaryl ring. These DHFR inhibitors are potent and selective for many different pathogenic organisms, including the DHFR enzyme from bacteria such as Bacillus anthracis and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, fungi such as Candida glabrata, Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans and protozoa such as Cryptosporidium hominis and Toxoplasma gondii. These compounds and other similar compounds are also potent against the mammalian enzyme and may be useful as anti-cancer therapeutics.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
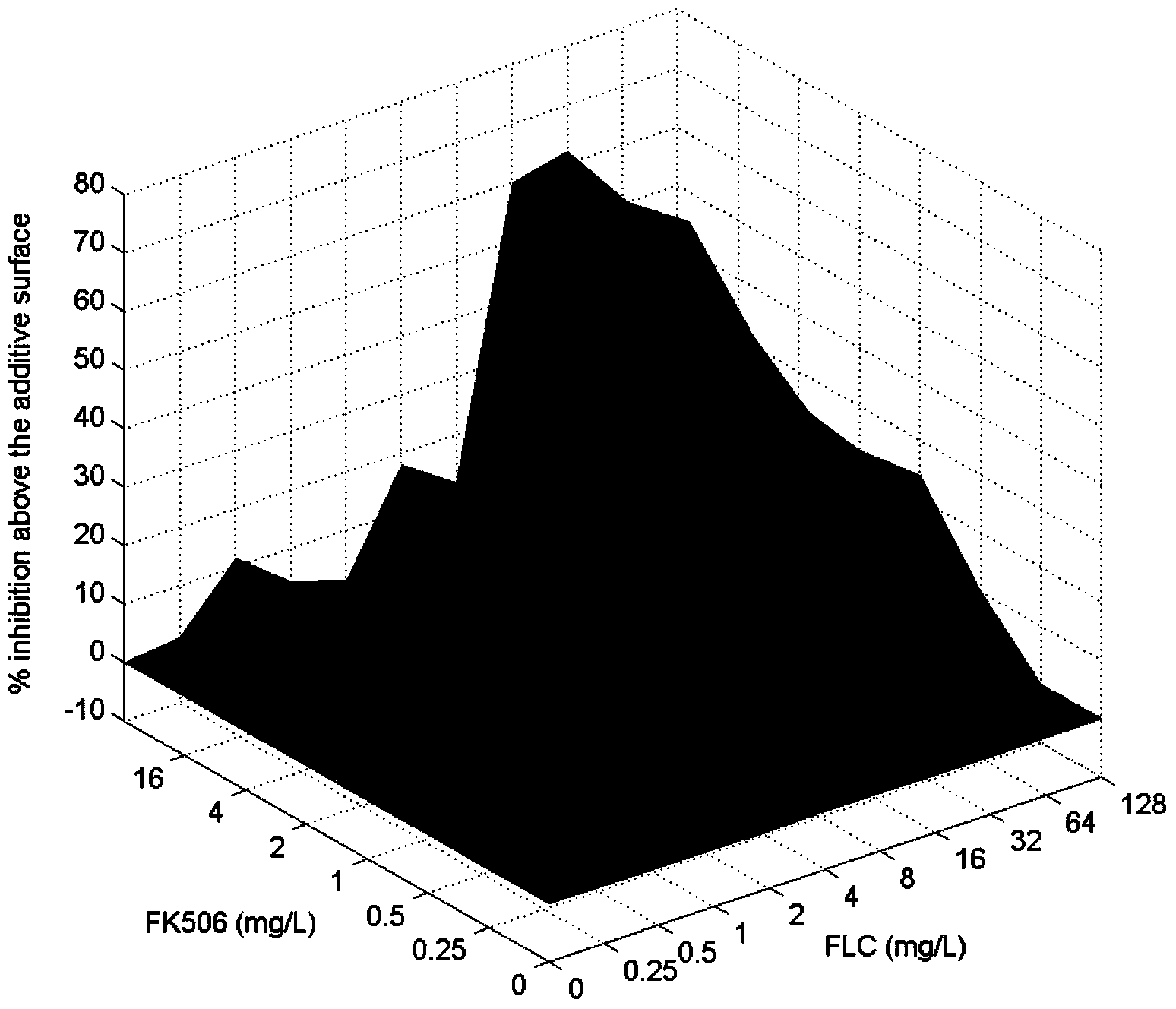
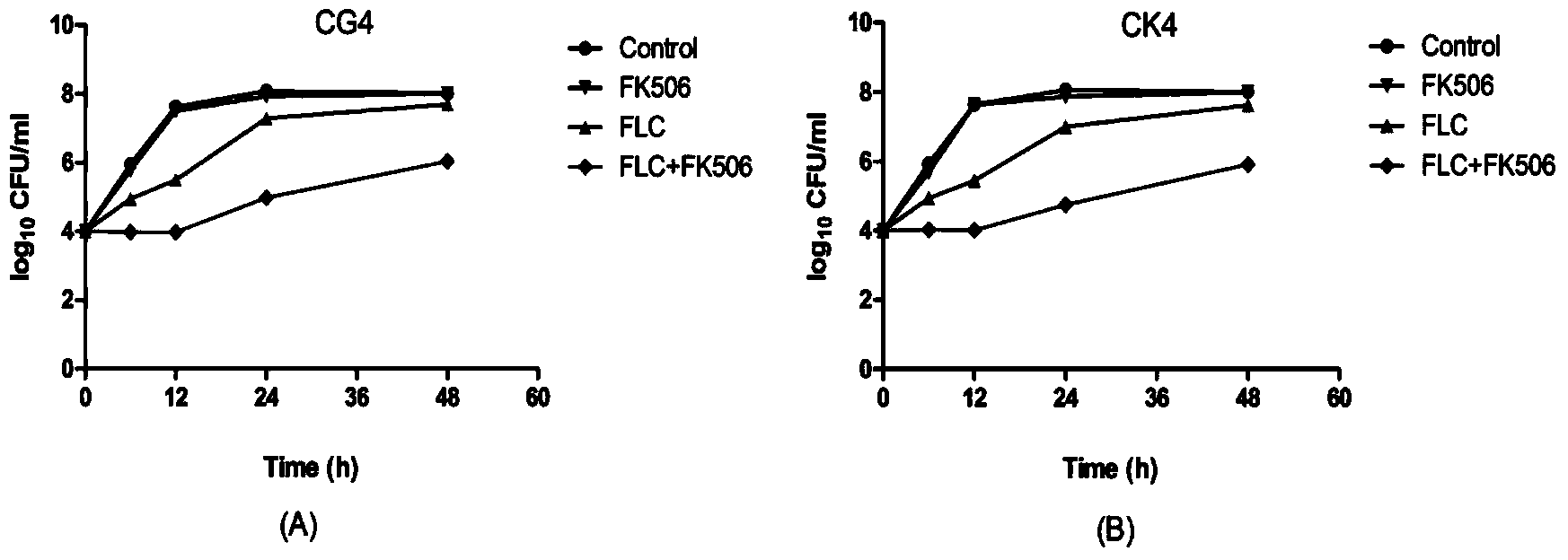
Application of combination of tacrolimus and fluconazole in preparing antifungal drugs
InactiveCN103520157AReverse drug resistanceHigh antibacterial activityOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsAntifungal drugsCandida famata
The invention discloses application of combination of tacrolimus and fluconazole in preparing antifungal drugs. According to the invention, static and dynamic combined antifungal effects of combination of tacrolimus and fluconazole to common non-albicans candida species are researched by various methods. The researches show that combination of tacrolimus and fluconazole has a remarkable synergic antifungal effect to common non-albicans candida species (candida glabrata and candida krusei). Predictably, combination of tacrolimus and fluconazole can be used for preparing antifungal drugs. According to the invention, tacrolimus and fluconazole are applied in a combined way to enhance the antimicrobial activity of fluconazole to non-albicans candida species so as to generate the synergic antifungal effect. Combination of tacrolimus and fluconazole can reverse the drug resistance of non-albicans candida species to fluconazole, thereby providing a research direction for development of new drugs and new use of old drugs.
Owner:QIANFOSHAN HOSPITAL OF SHANDONG
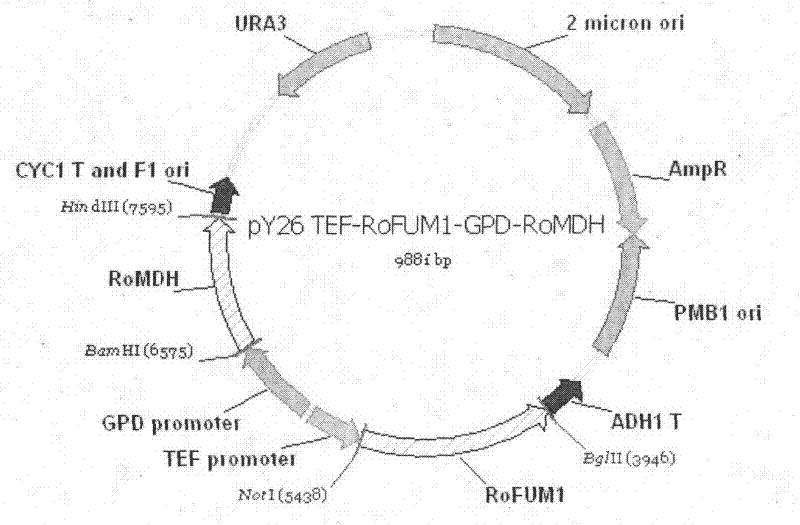
Construction method and use of fumaric acid producing candida glabrata engineering strain
The invention discloses a construction method and use of a fumaric acid producing T.glabrata candida glabrata engineering strain and belongs to the field of fermentation engineering. In the invention, a recombinant T.glabrata FMME045 strain is obtained by overexpression of a malic dehydrogenase (RoMDH) gene and a fumarase (RoFUM1) gene from rhizopus oryzae in a uracil deficient (Ura) T.glabratadeltaura3 strain of a pyruvic acid producing strain T.glabrata in a free expression mode. When the strain is used for fermentation production of fumaric acid, the fumaric acid yield after the fermentation is performed for 60 hours is increased by 6 times to 35mg / L compared with that of a starting strain. Thus, a new approach is provided for producing fumaric acid by a microbial fermentation process. The method has a bright application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
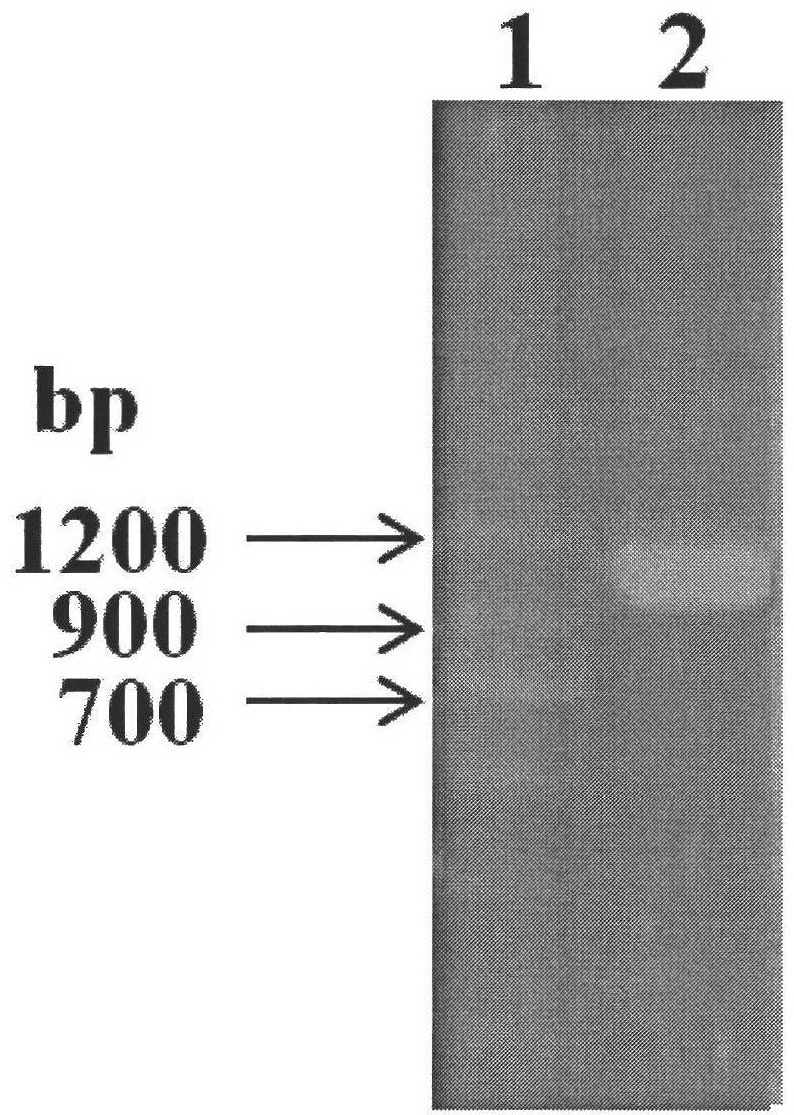
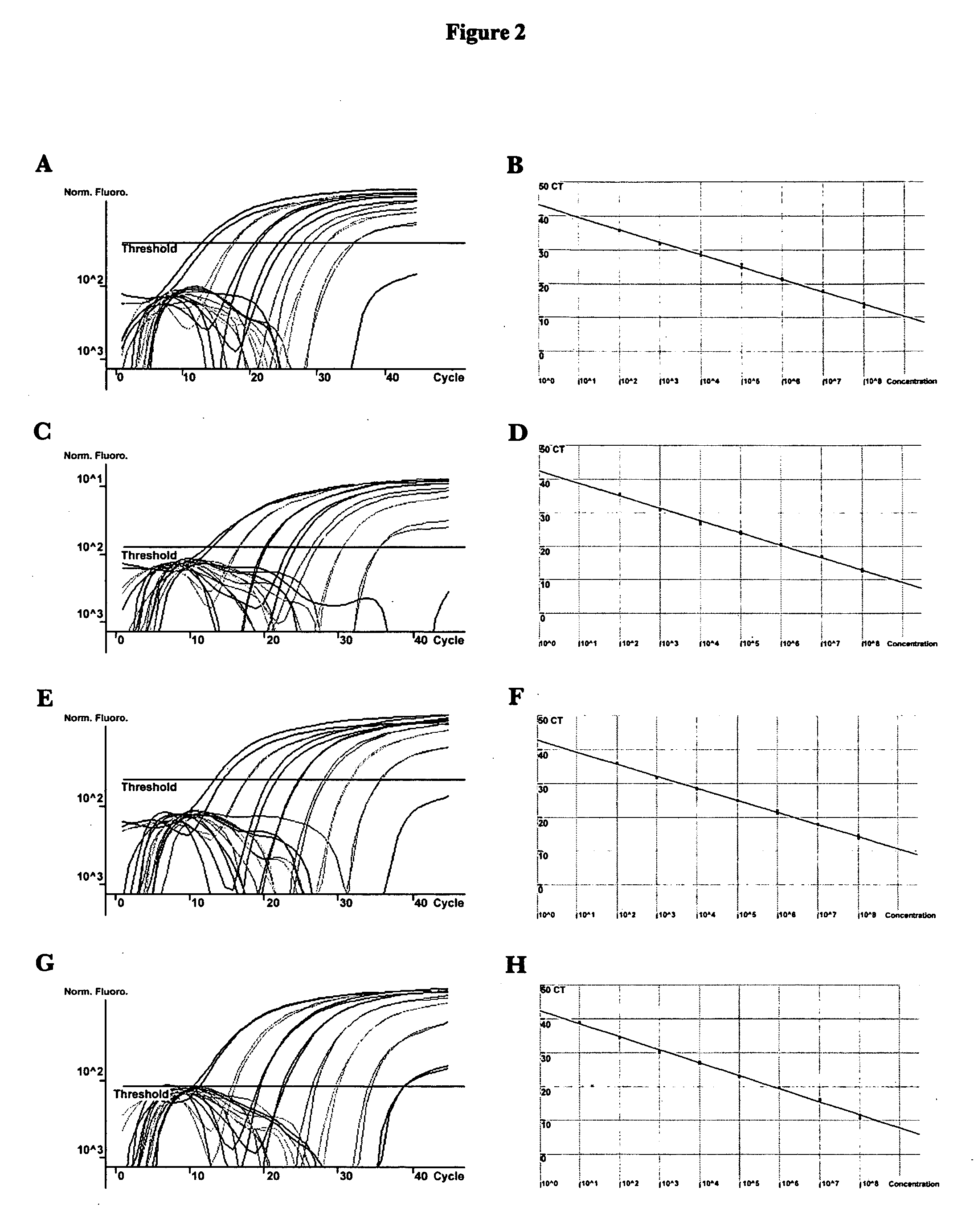
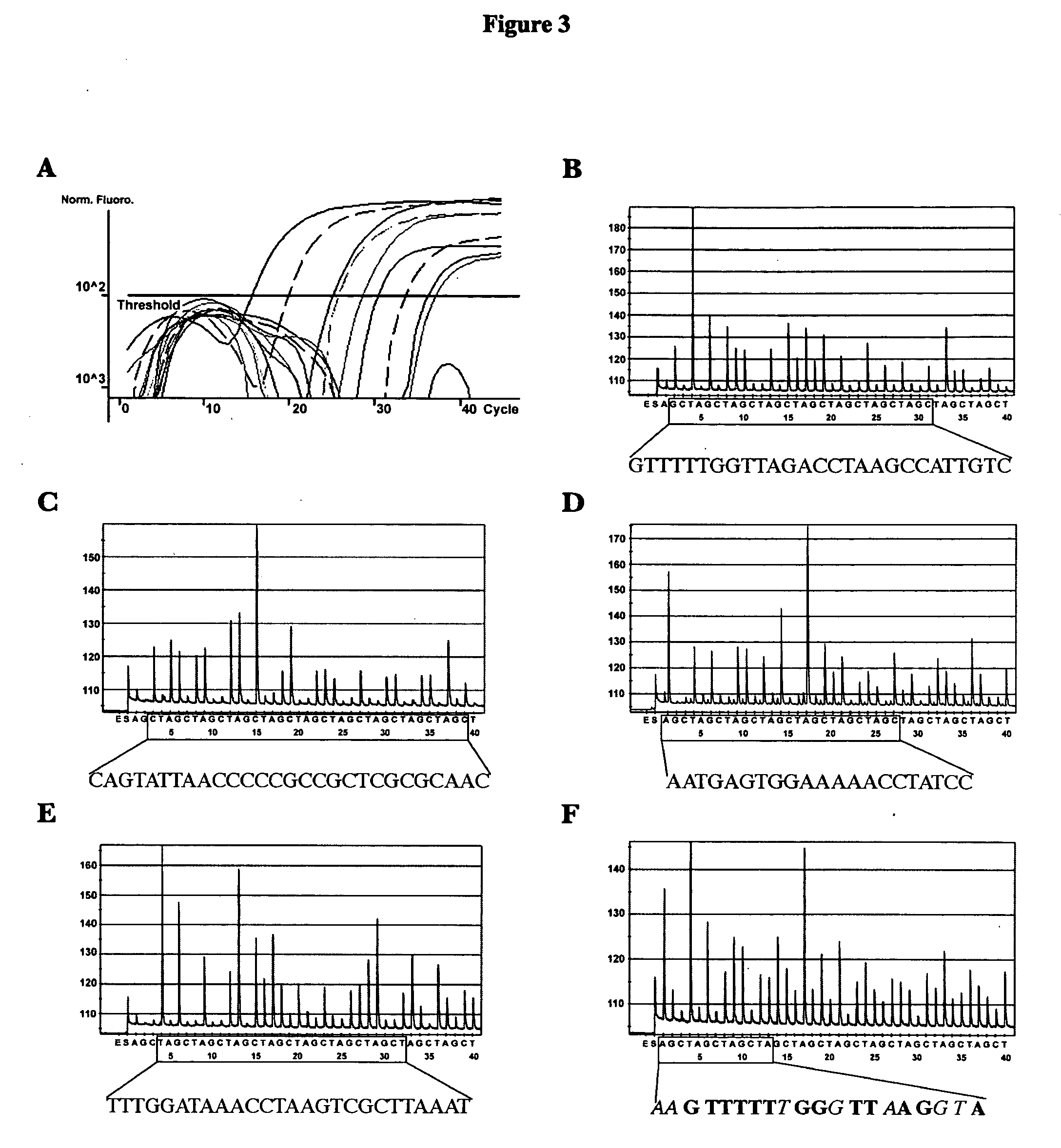
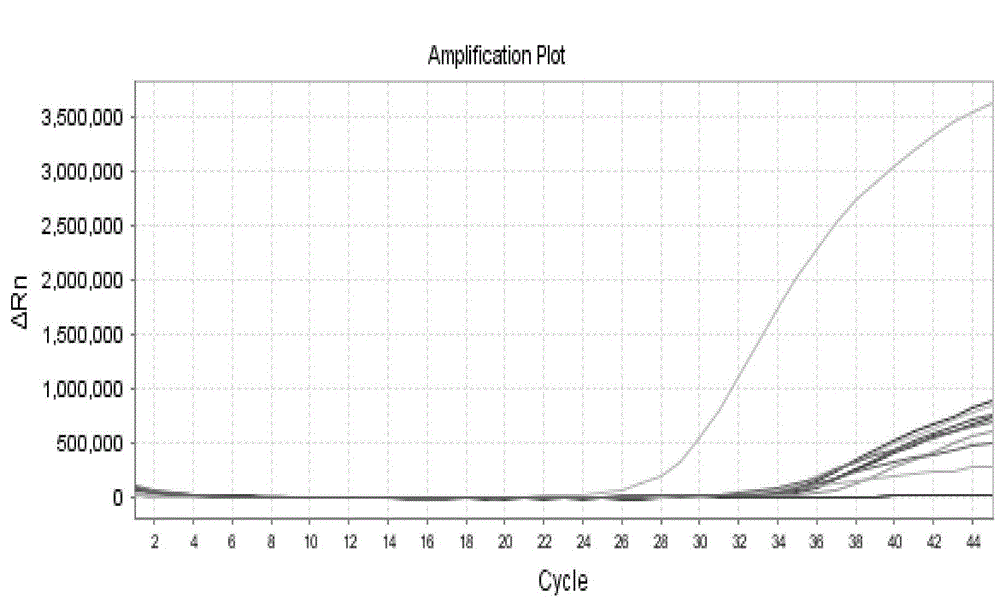
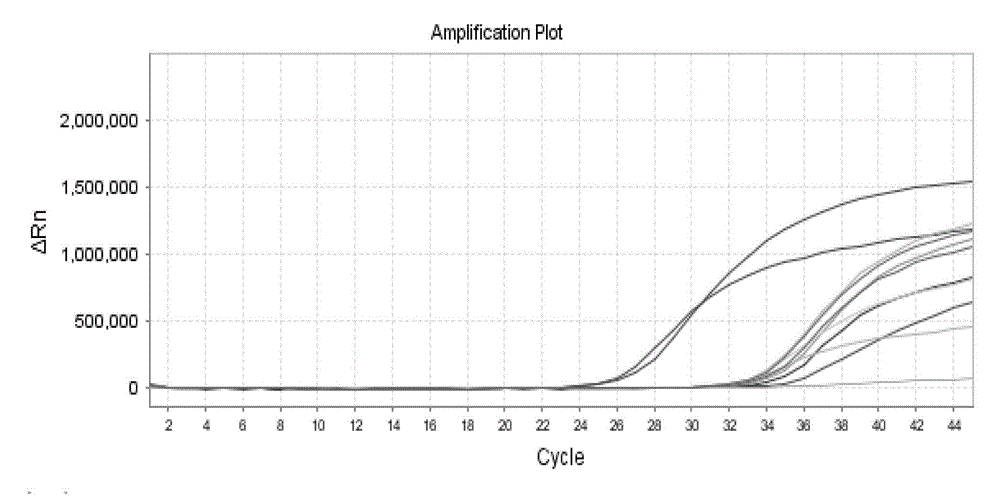
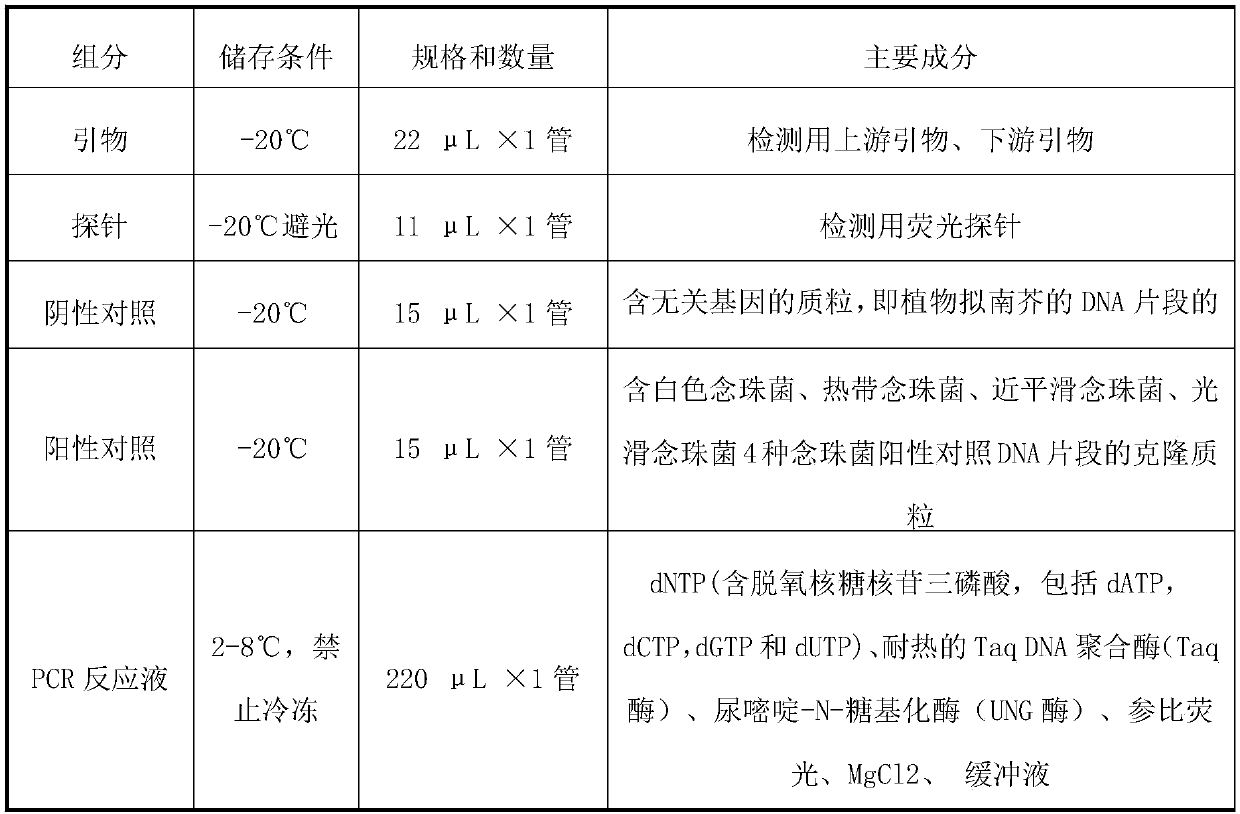
Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) kit for detecting candida glabrata
InactiveCN102181567AAid in early diagnosisAids in healingMicrobiological testing/measurementCandida glabrataPcr ctpp
The invention discloses a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) kit for detecting candida glabrata, which comprises the following substances: PCR reaction solution, primer and probe mixed solution, a PCR reaction enzyme, pure H2O and a positive quantitative standard product. The real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR kit is used for detecting the nucleic acid amplification level of the candida glabrata and can reflect the state of the infection of the candida glabrata in a patient body, be used for monitoring, preventing and treating fungal infection, and be conductive to early diagnosis and treatment of diseases; and the real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR technology designs a primer and a probe against the nucleic acid specificity sequence of the candida glabrata, the specificity is strong, the sensitivity is high, and the technology further has the advantages of higher flux, simpleness in operation and relatively low cost, and is applicable to detecting various samples of most of patients. The amplification of the samples to be detected by using the kit is completed by a commercial real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR instrument, the operation is simple, the consumed time is short, and the pollution can be reduced to the maximum extent.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for improving acid stress resistance of candida glabrata
ActiveCN104789600AImprove growth performanceImprove acid stress resistanceFungiStable introduction of DNAAcetic acidCandida glabrata
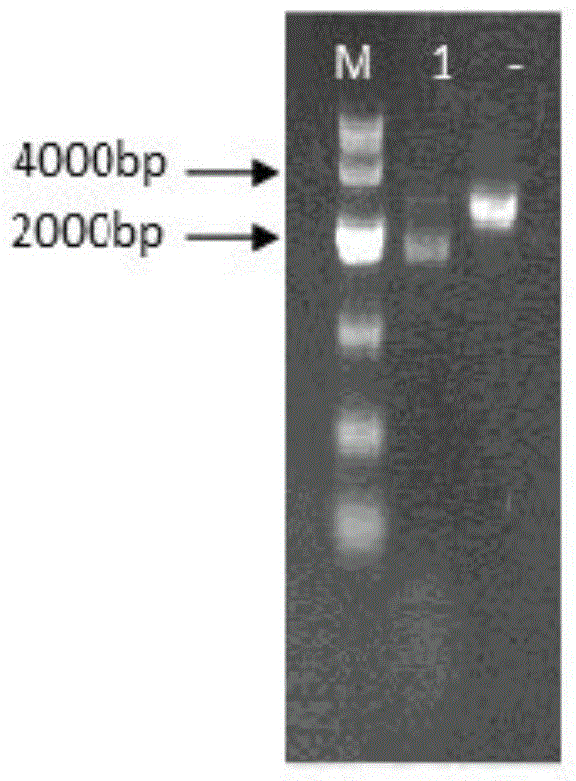
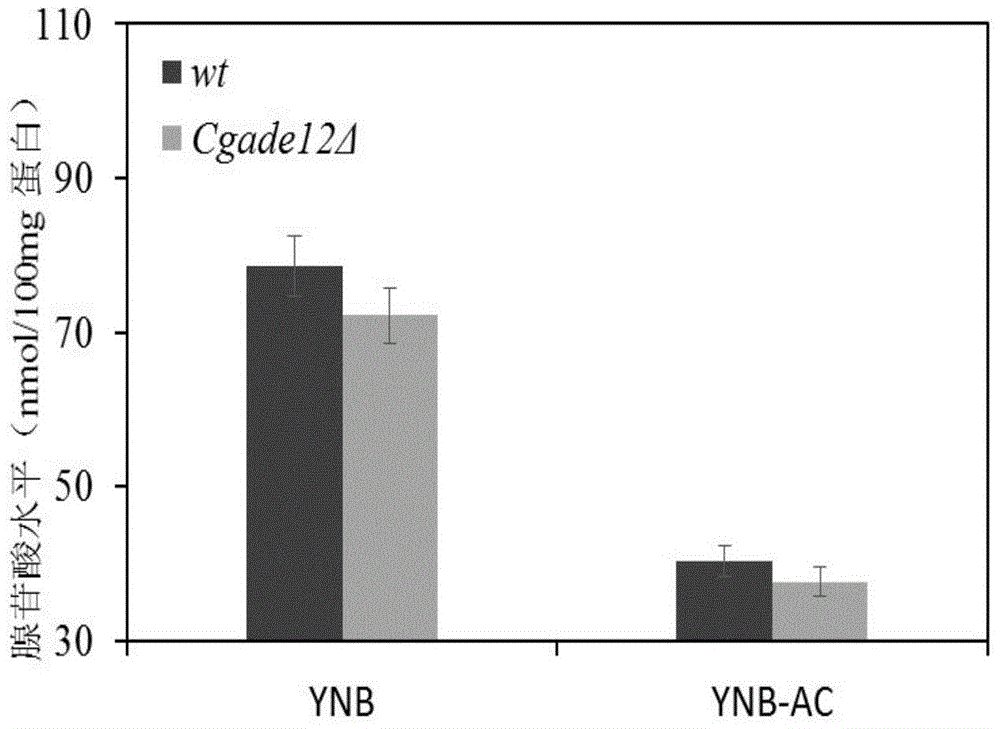
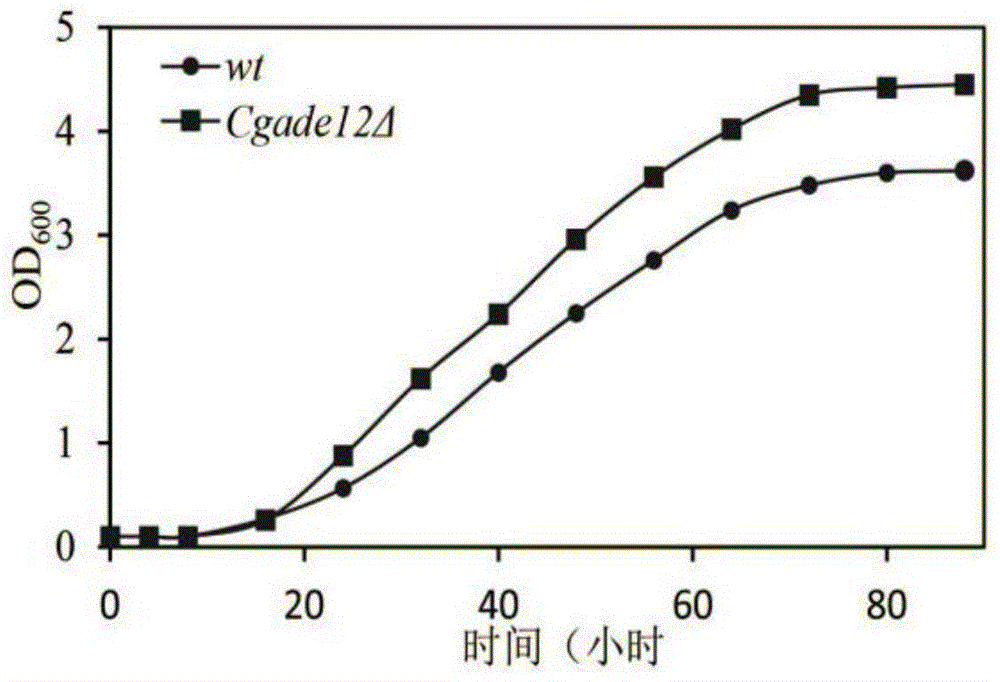
The invention discloses a method for improving the acid stress resistance of candida glabrata, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: improving the candida glabrata, constructing a gene-deleted mutant strain Cgade12Delta, measuring the intracellular ATP level of the constructed strain, and determining the organic acid tolerance of the strain by a plate growth experiment and cellular activity analysis. After the deletion of the gene CgADE12 is found out, the intracellular ATP level of the strain under the stress of 0.2 percent acetic acid is lowered, the growth capability under the stress of acetic acid is improved, and the acetic acid tolerance is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Use of rhizoma paridis chinensis for preparing antifungal drug
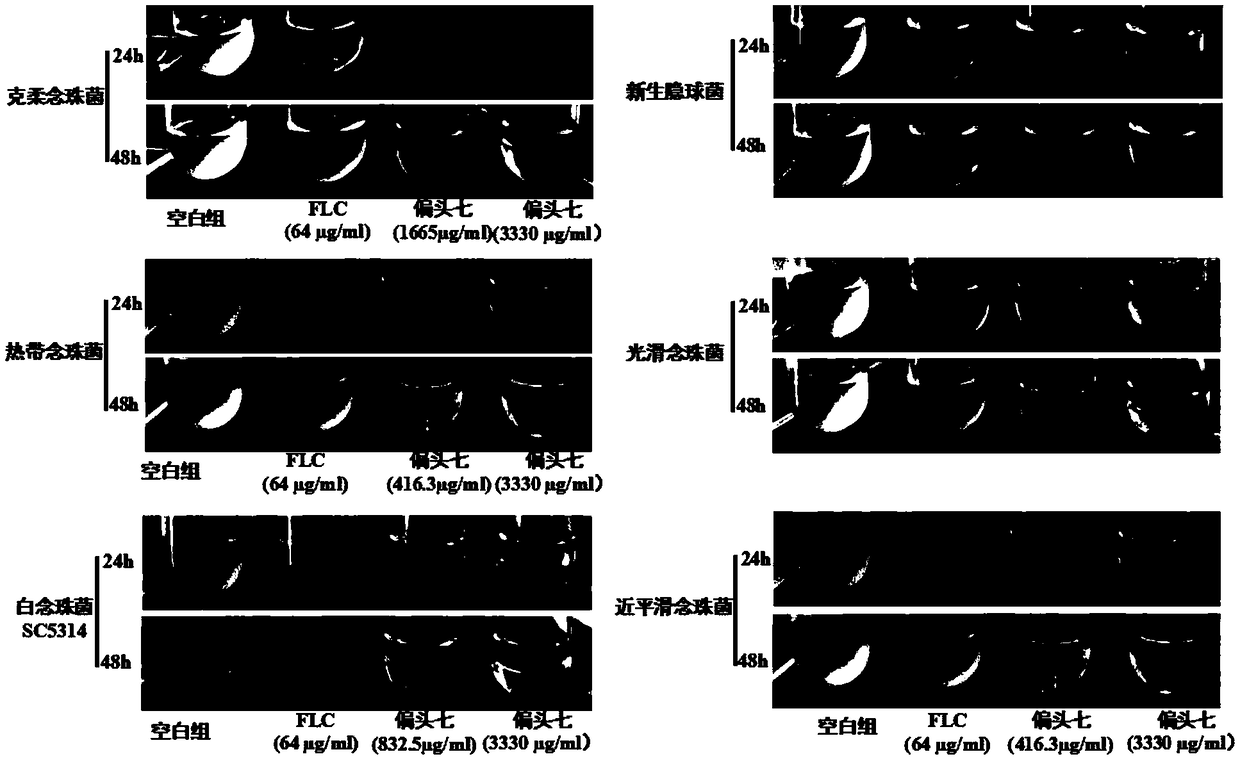
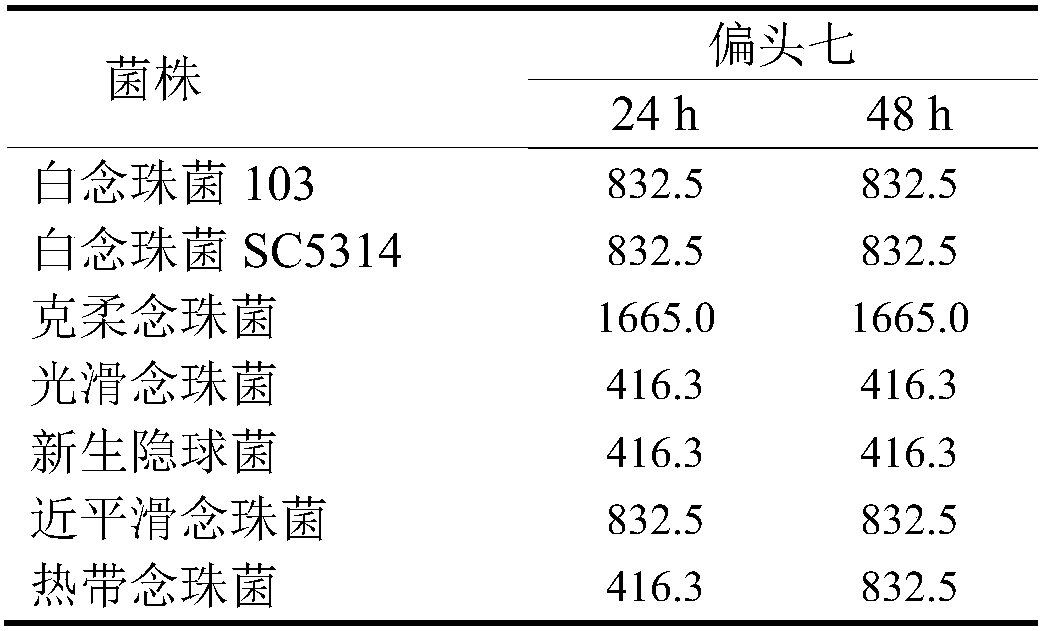
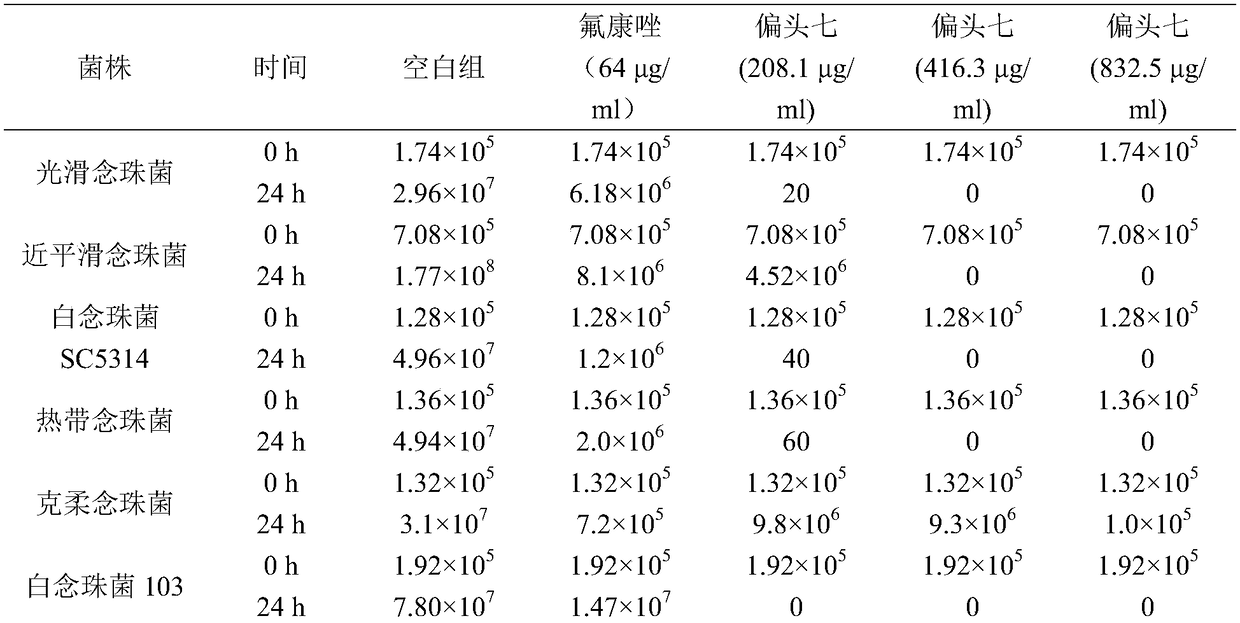
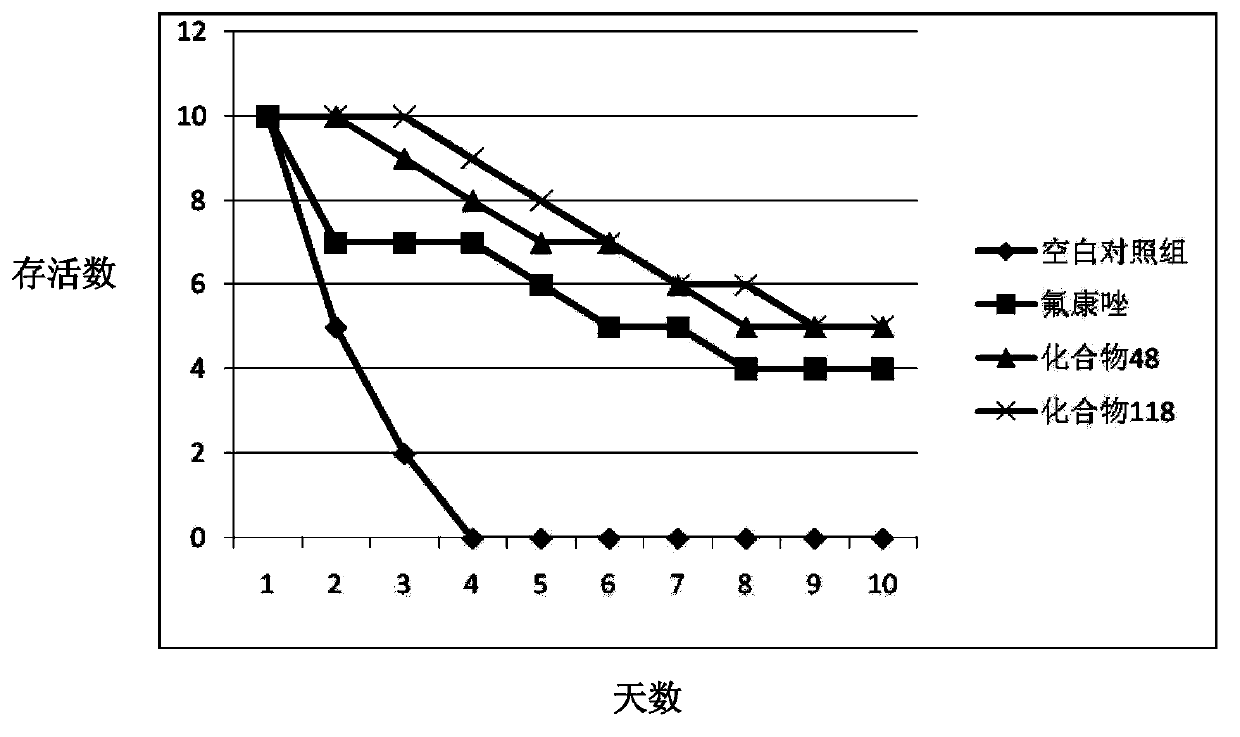
The invention discloses use of rhizoma paridis chinensis for preparing an antifungal drug, belonging to the technical field of medicines. In-vitro cell experiments show that rhizoma paridis chinensishas different levels of antifungal effects and even fungus-killing effect to drug-resistant candida albicans 103, candida albicans SC5314, cryptococcus neoformans, candida krusei, candida parapsilosis, candida glabrata and candida tropicalis and therefore can be taken as the antifungal drug. According to the use, new use of rhizoma paridis chinensis is opened up, rhizoma paridis chinensis is usedfor preparing the antifungal drug, and a new candidate drug is provided for the treatment of fungal infection. Currently, drugs with wide antifungal spectrums and fungus-killing activity on clinic arevery few, and a new way is provided for the clinical and efficient treatment of infection of fungi and even drug-resistant fungi by virtue of the characteristics of wide antifungal spectrums and fungus-killing activity of rhizoma paridis chinensis under the conditions that clinical fungus drug resistance becomes common increasingly and the drug resistance level becomes serious increasingly.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel triazole antifungal compound, pharmaceutical composition and preparation method and application thereof
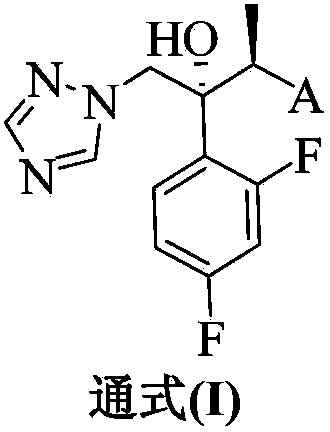
The invention provides a triazole compound shown as a general formula (I), optical isomers or the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, and application of the compound, optical isomers or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof to preparation of medicaments for resisting fungi, especially Candida albicans, Candida parapsilosis, Candida glabrata, Cryptococcus neoformans, Microsporum flavescens, Trichophyton rubrum and / or Aspergillus fumigatus. The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of one or more selected from the compound shown in the formula (I), optical isomers and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof and pharmaceutic adjuvants.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
DPO primer pair, detection method and kit of candida classification detection and application of kit of candida classification detection
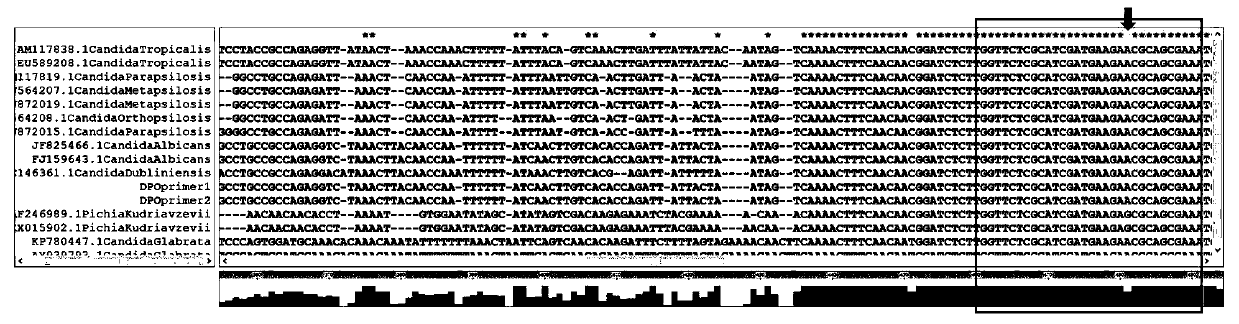
InactiveCN109811080AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEscherichia coliNucleotide
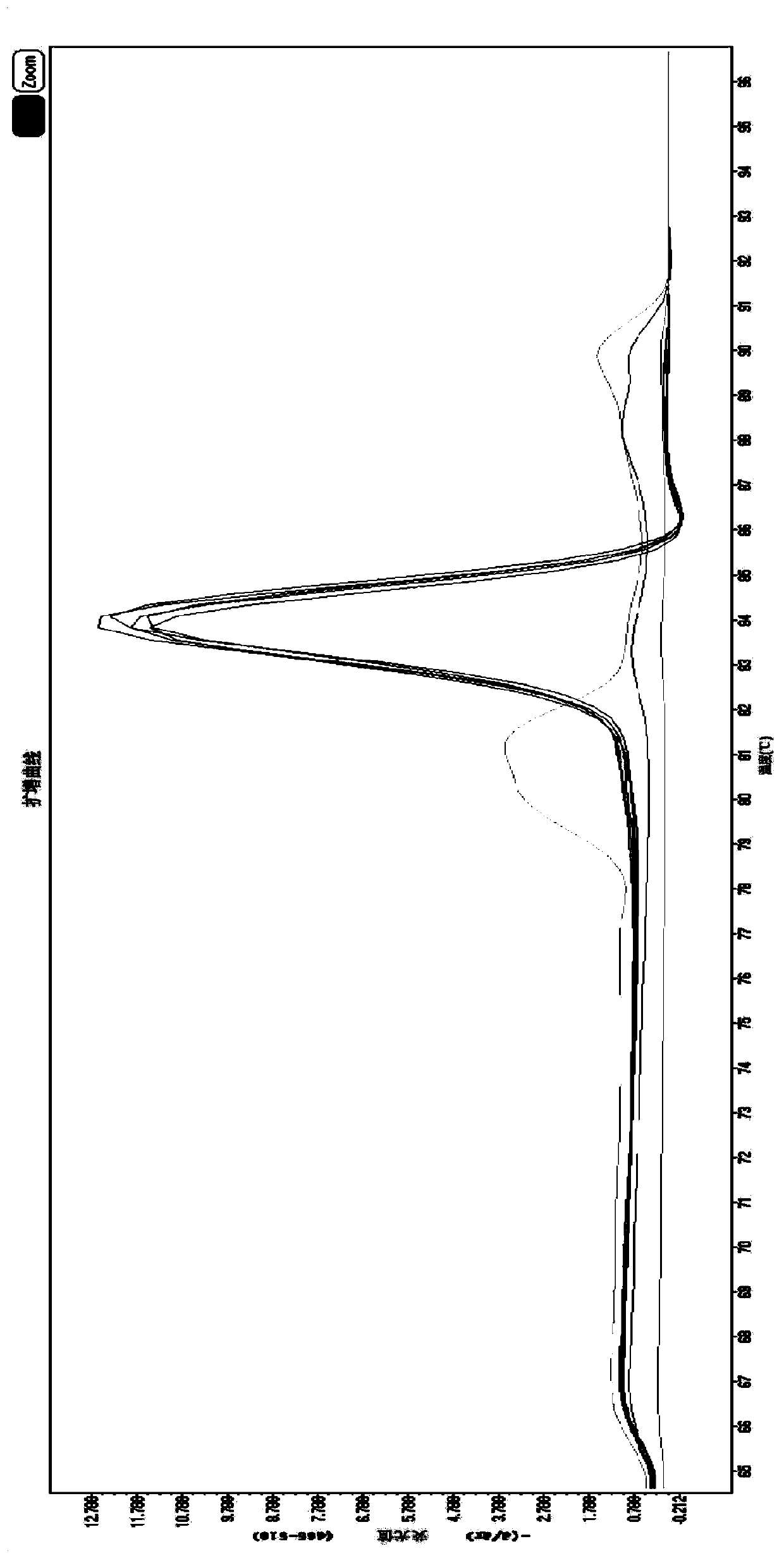
The invention provides a DPO primer pair, detection method and kit of candida classification detection and application of the kit of candida classification detection. Nucleotide sequences of the DPO primer pair are as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-2. The primer pair can specifically amplify candida, and is not crossed with other common pathogenic bacteria such as aspergillus, escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus, moreover, by designing the DPO primer pair, products of different candida strains have different annealing temperatures, through melting curve analysis of the products, candida albicans,candida tropicalis, candida parapsilosis, candida krusei and candida glabrata can be judged, only one pair of primers are used for achieving multiple detection, and compared with the prior art, the DPO primer pair is more simple, convenient and economic.
Owner:DYNAMIKER BIOTECH TIANJIN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com