Patents
Literature
136 results about "Acid-fast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Acid-fastness is a physical property of certain bacterial and eukaryotic cells, as well as some sub-cellular structures, specifically their resistance to decolorization by acids during laboratory staining procedures. Once stained as part of a sample, these organisms can resist the acid and/or ethanol-based decolorization procedures common in many staining protocols, hence the name acid-fast.
Enteric-coated multilayer encapsulated probiotic microcapsule and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1969889AGrowth inhibitionPromote formationMetabolism disorderBacteria material medical ingredientsAcid-fastSolubility
The invention discloses an enteric-solubility multilayer encysted bacterium microcapsule and making method in the biological agent technical domain, which is characterized by the following: adopting sodium alginate, calcium chloride and chitose as clad material of microcapsule; making lactic acid bacteria or bifidobacteria as core-clad material; proceeding ionic exchange for sodium alginate and calcium chloride; forming second clad on the surface of calcium alginate through different isoelectric points of calcium alginate and chitose; freezing at low temperature to obtain the product.
Owner:JINAN SYNBIOTICS BIOENG
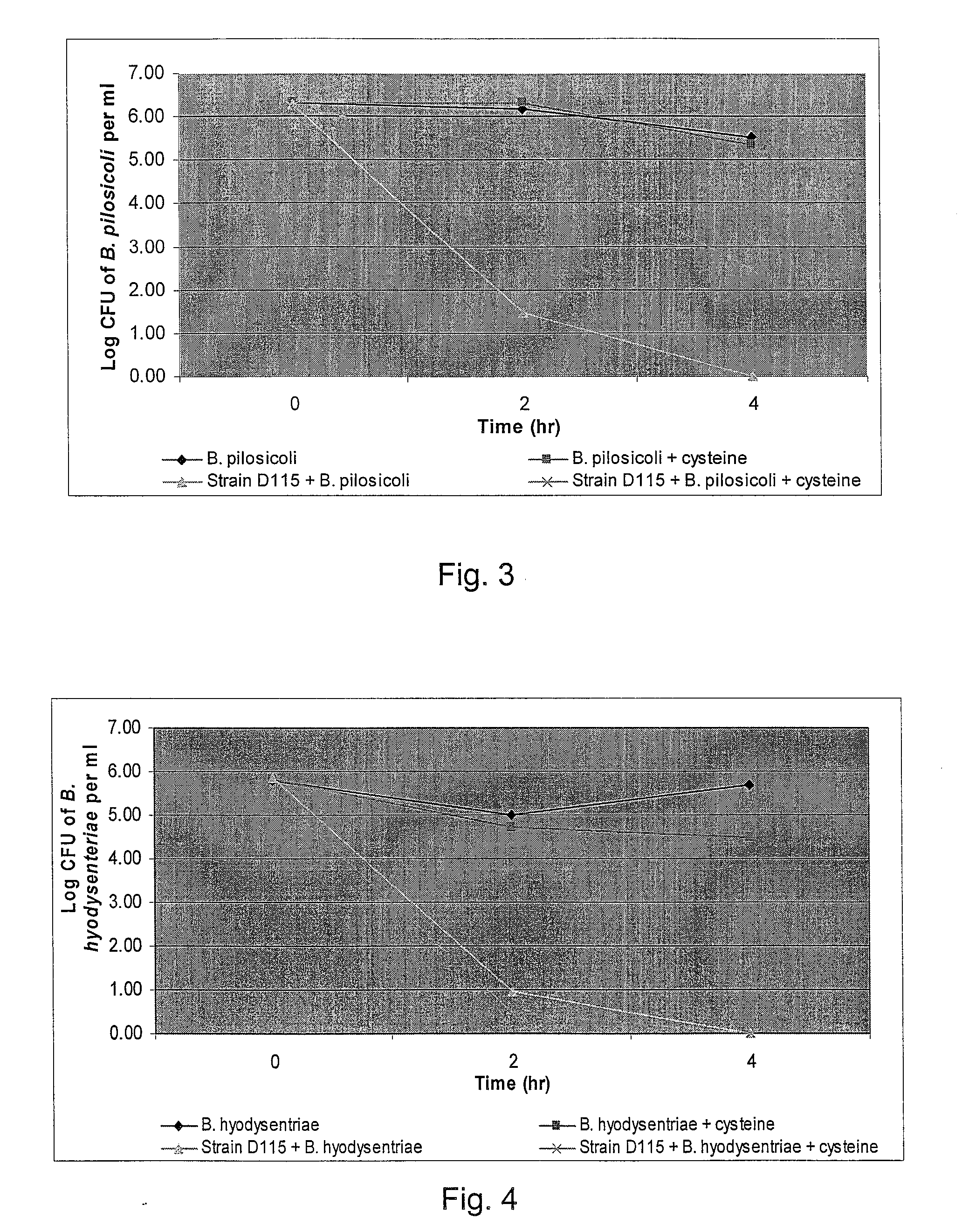
Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of Lactobacillus Johnsonii D115
The present invention demonstrated the potential use of Lactobacillus johnsonii D115 as a probiotic, as a prophylactic agent or as a surface treatment of materials against human and animal pathogens such as Brachyspira pilosicoli, Brachyspira hyodysenteriae, Shigella sonnei, Vibrio cholera, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Campylobacter jejuni, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, Clostridium perfringens, Yersinia enterocolitica, Escherichia coli, Klebbsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella spp., Bacillus cereus, Aspergillus niger and Fusarium chlamydosporum. The proteineous antimicrobial compound was partially characterized and found to be heat tolerant up to 121° C. for 15 min, and acid tolerant up to pH1 for 30 min at 40° C. The compound is also stable to enzymatic digestion, being able to retain more than 60% antimicrobial activity when treated with pepsin and trypsin.
Owner:KEMIN IND INC
Tubercle bacillus target recognizing and counting algorithm based on diverse characteristics
InactiveCN101877074AFully automatedRealize intelligenceImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionAcid-fastColor image
The invention relates to the field of medical image processing and mode recognition, in particular to a tubercle bacillus target recognizing and counting algorithm based on diverse characteristics. The algorithm comprises the following steps of: image preprocessing: carrying out image reinforcement and constructing median filter and Gaussian filter on a tubercle bacillus microimage; color image partition: carrying out fixed threshold partition based on HSV (Hue-Saturation-Value) color space on a preprocessed image and then carrying out adaptive threshold partition which is based on CIE L*a*b* color space and keeps a geometric shape of a target; communication block morphological analysis and target recognition: carrying out communication block analysis on the partitioned image; and tubercle bacillus target counting: estimating the quantity of tubercle bacillus targets in the image by utilizing a histogram statistics and multistrategy calculation method. The invention can effectively extract the bacillus targets in the tubercle bacillus microimage subjected to acid-fast stain from background and impurities and carry out accurate counting, thereby realizing the automation and the intellectualization of the detection of tubercle bacilli.
Owner:常州超媒体与感知技术研究所有限公司
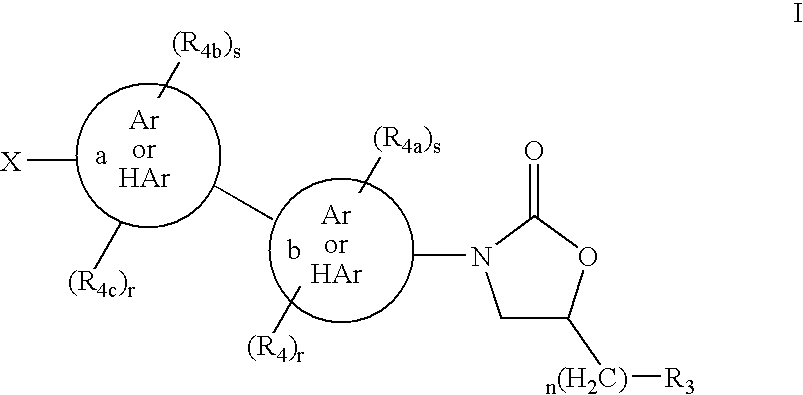
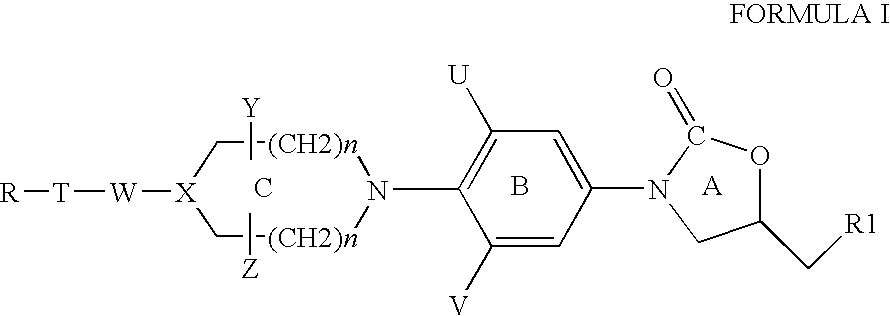
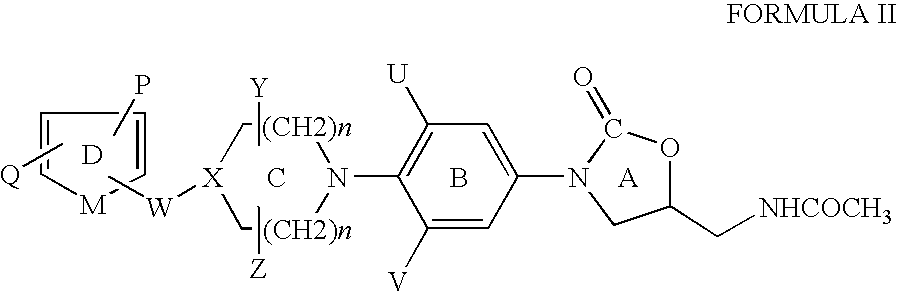
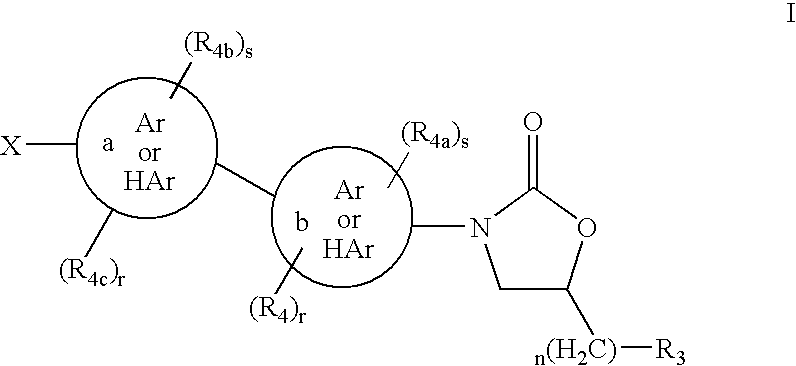
Cyclopropyl group substituted oxazolidinone antibiotics and derivatives thereof
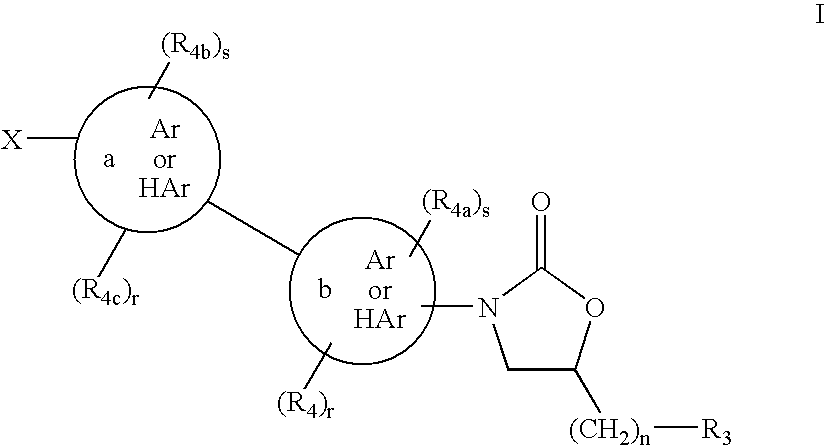
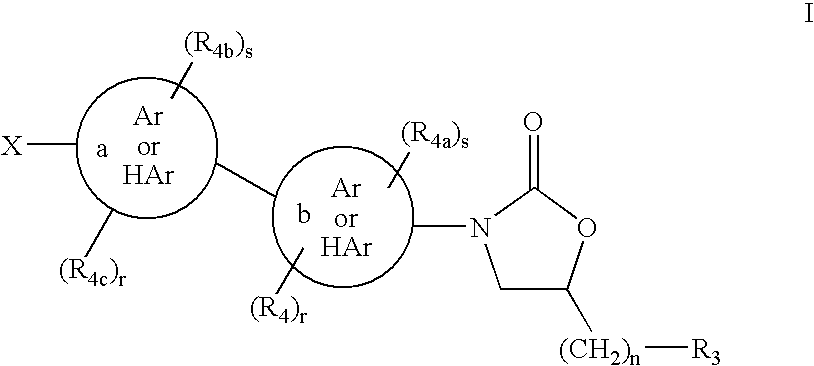
This invention relates to new oxazolidinones having a cyclopropyl moiety, which are effective against aerobic and anerobic pathogens such as multi-resistant staphylococci, streptococci and enterococci, Bacteroides spp., Clostridia spp. species, as well as acid-fast organisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other mycobacterial species. The compounds are represented by structural formula I: its enantiomer, diastereomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or ester thereof.
Owner:KYORIN PHARMA CO LTD +1
Antimicrobial hexapeptides
ActiveUS20060229252A1Growth inhibitionPrevent microbial infectionAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryAcid-fastMammal
The invention encompasses hexapeptides consisting of alternating hydrophobic residues (B) at positions 2, 4, and 6, hydrophilic, hydrophilic, charged residues (X) at positions 1 and 3, and a naphthylalanine (Nal), an aliphatic or aromatic residue (O) at position five, represented generally by the formula XBXBOB, which exhibit antimicrobial activity against infections caused by a variety of pathogens. These pathogens may include gram positive or negative bacteria, acid-fast bacteria such a mycobacteria, parasites, dermatophytes, or fungal pathogens. Typical fungal pathogens include Candida albicans and typical dermatophytes include Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. The hexapeptides of the present invention exhibit antifungal activity, antibacterial activity, desirable stability, and lack toxicity to the mammal receiving treatment.
Owner:HELIX BIOMEDIX INC
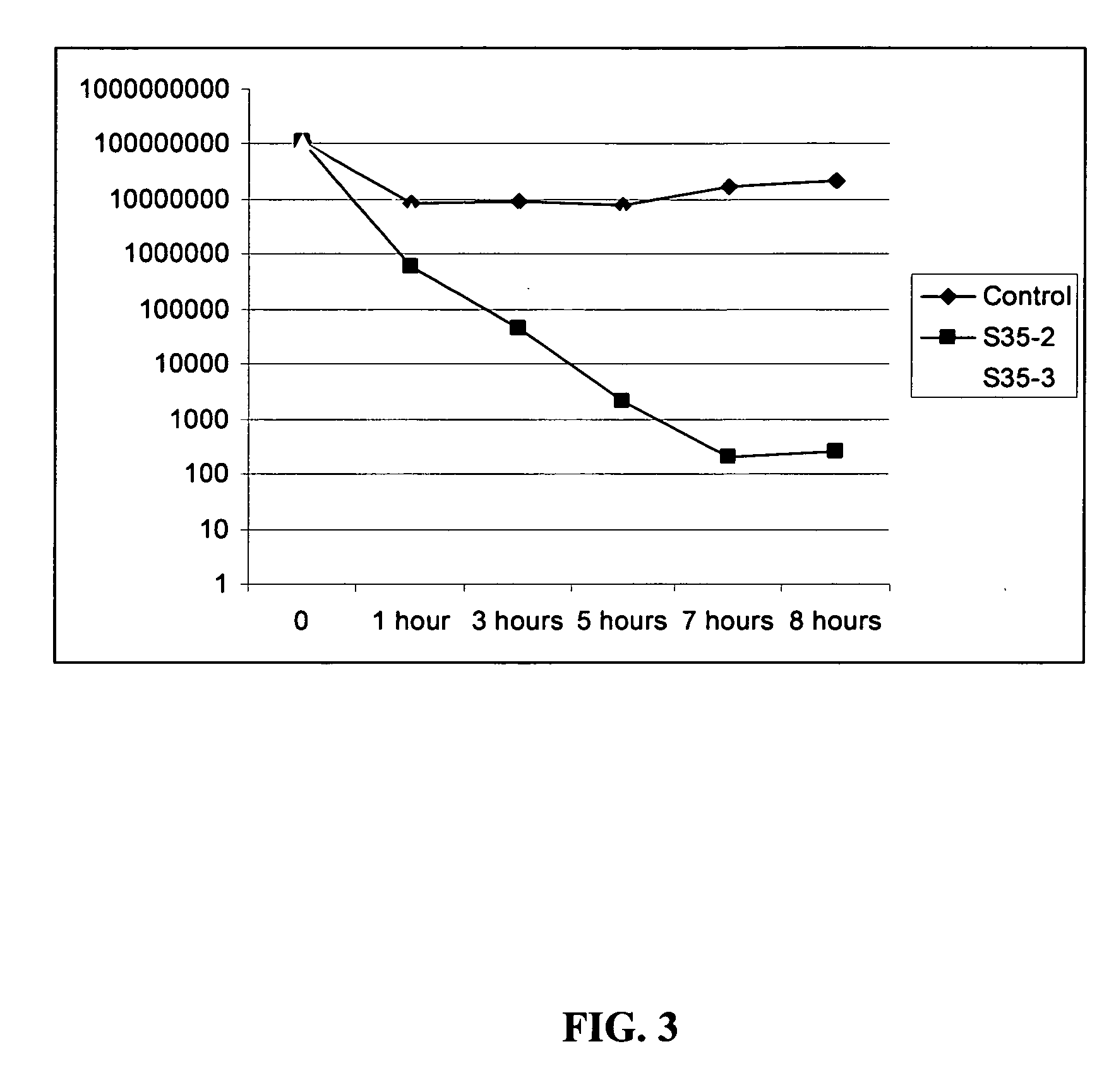
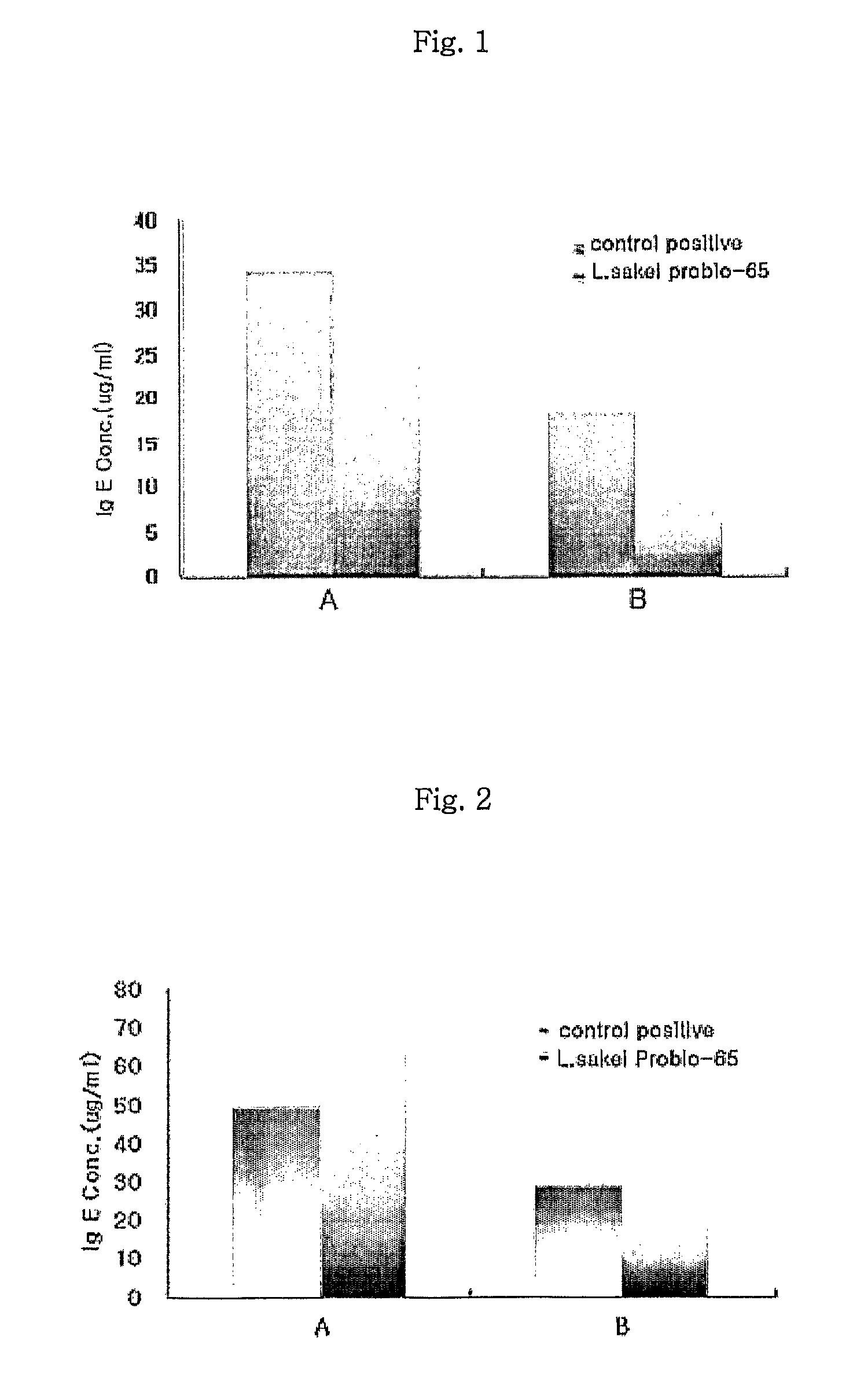
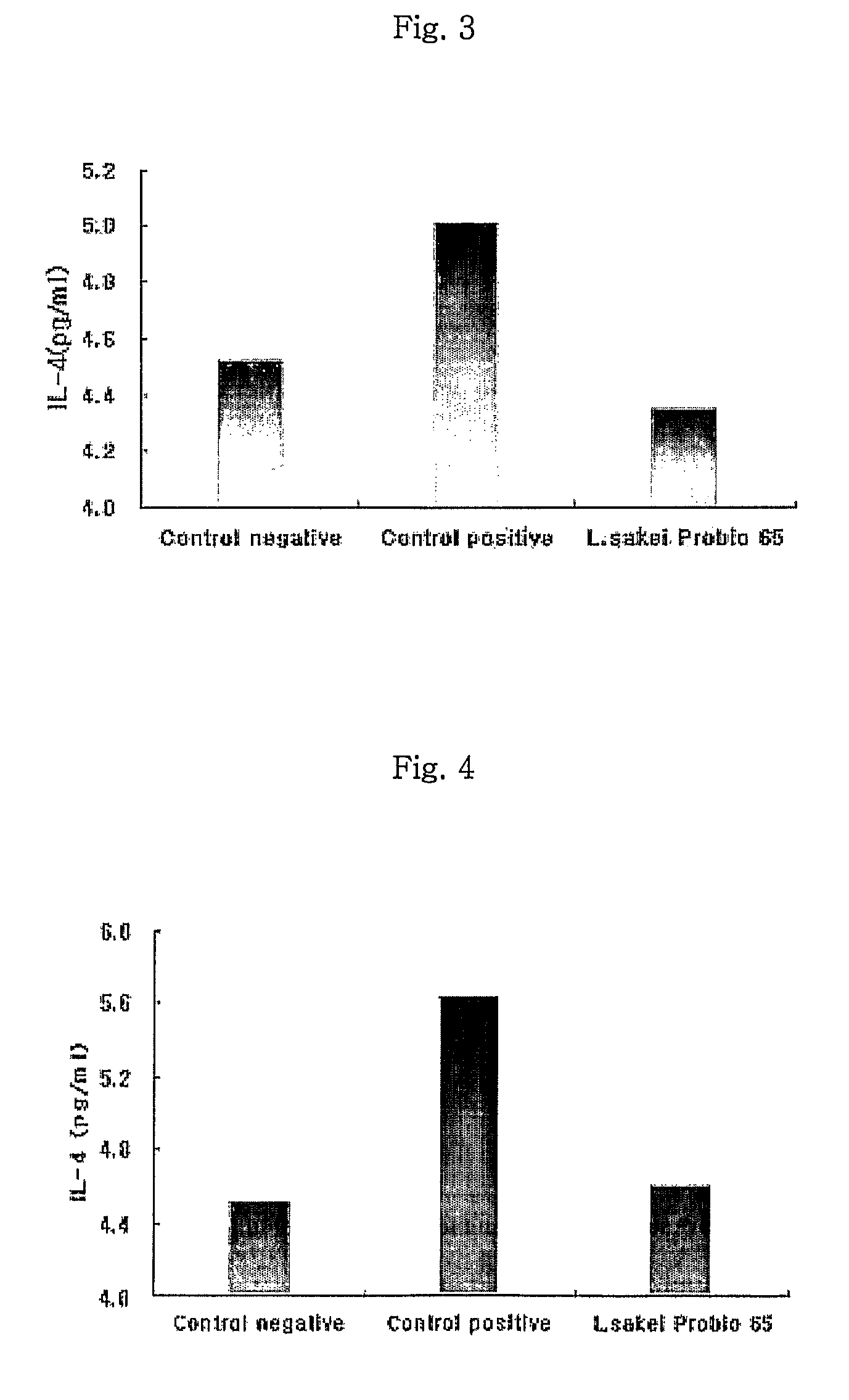
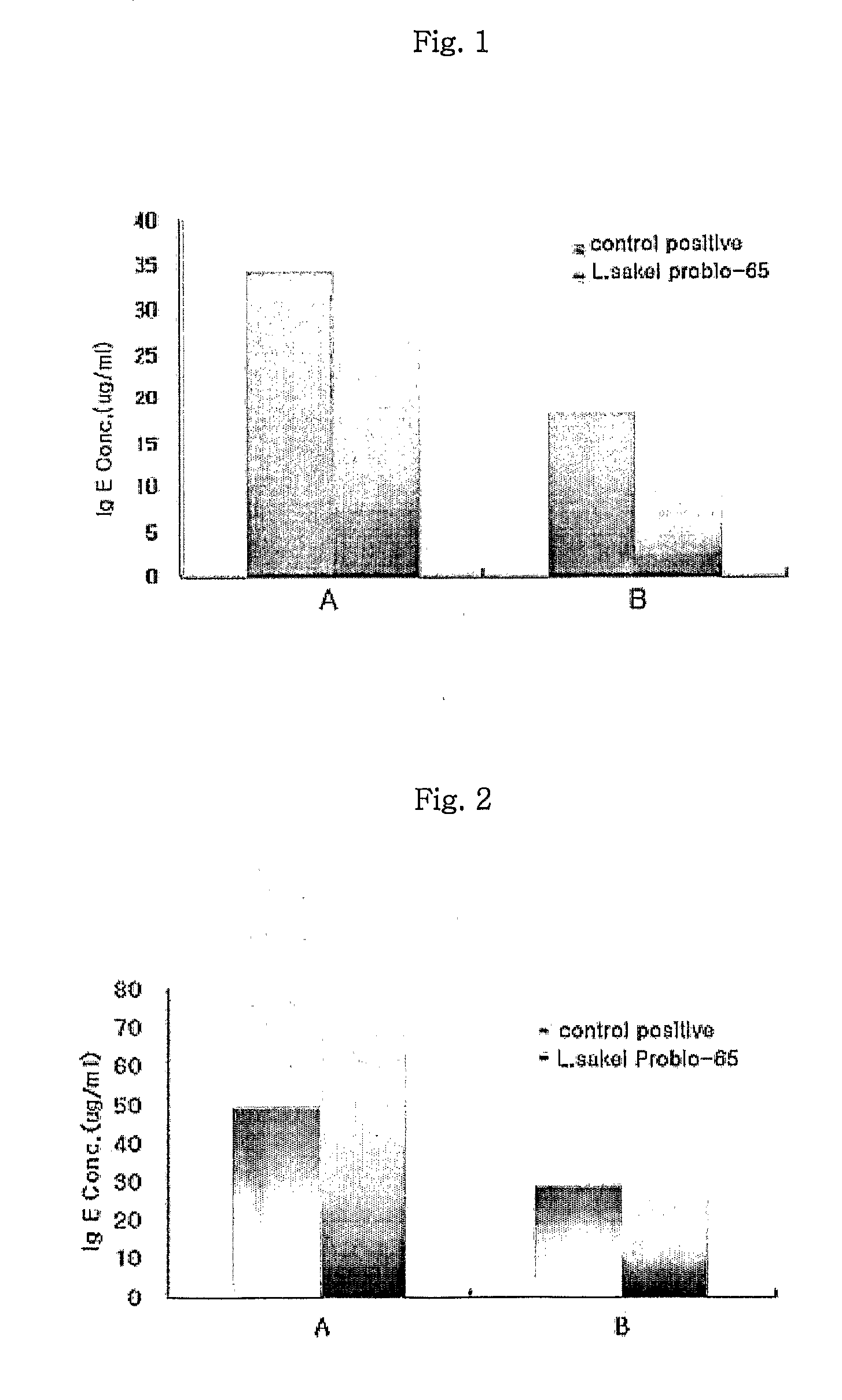
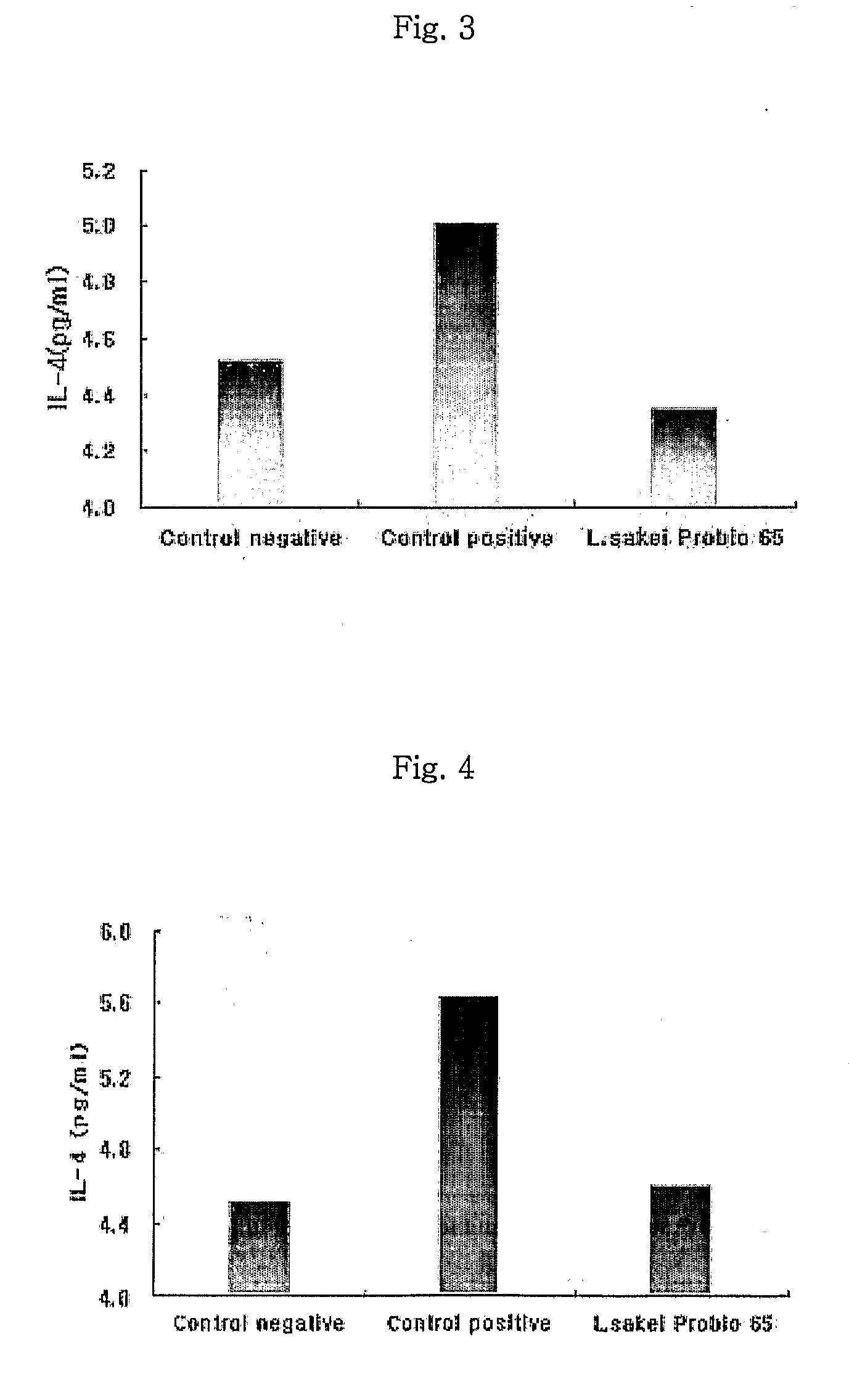
Acid tolerant Lactobacillus sakei probio-65 with the ability of growth suppression of pathogenic microorganisms and the anti-allergic effect
ActiveUS8034606B2Growth inhibitionEffectively inhibit harmful microorganismsBiocideCosmetic preparationsAcid-fastDisease
Disclosed are a novel tactic acid bacterium, Lactobacillus sakei Probio-65, and the use thereof. The L. sakei Probio-65 strain has acid tolerance, bile acid tolerance and antibiotic resistance, inhibits the growth of harmful pathogenic microorganisms in the body and the intestine of animals, and has immunuenhancing activity. In particular, the novel strain inhibits the growth of Staphylocccus aureus, which is known to be a factor aggravating atopic dermatitis. Thus, the novel strain is useful for preventing or treating atopic dermatitis and allergy-related disorders. Also, the novel strain stabilizes intestinal microflors by inhibiting the abnormal proliferation of harmful microorganisms in the intestine. The L. sakei Probio-65 strain or a culture thereof is useful in pharmaceutical, feed, food, and cosmetic compositions.
Owner:PROBIONIC CO LTD
Oxazolidinone piperazinyl derivatives as potential antimicrobials
InactiveUS6956040B2High antibacterial activityTreatment safetyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAcid-fastGram
The present invention relates to certain substituted phenyl piperazinyl oxazolidinones, for example, to those having the structure of Formula I with the variables as defined within, and to processes for the synthesis of the same. This invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds of the present invention as antimicrobials. The compounds are useful antimicrobial agents, effective against a number of human and veterinary pathogens, including gram-positive aerobic bacteria such as multiply-resistant staphylococci, streptococci and enterococci as well as anaerobic organisms such as Bacterioides spp. and Clostridia spp. species, and acid fast organisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium spp.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
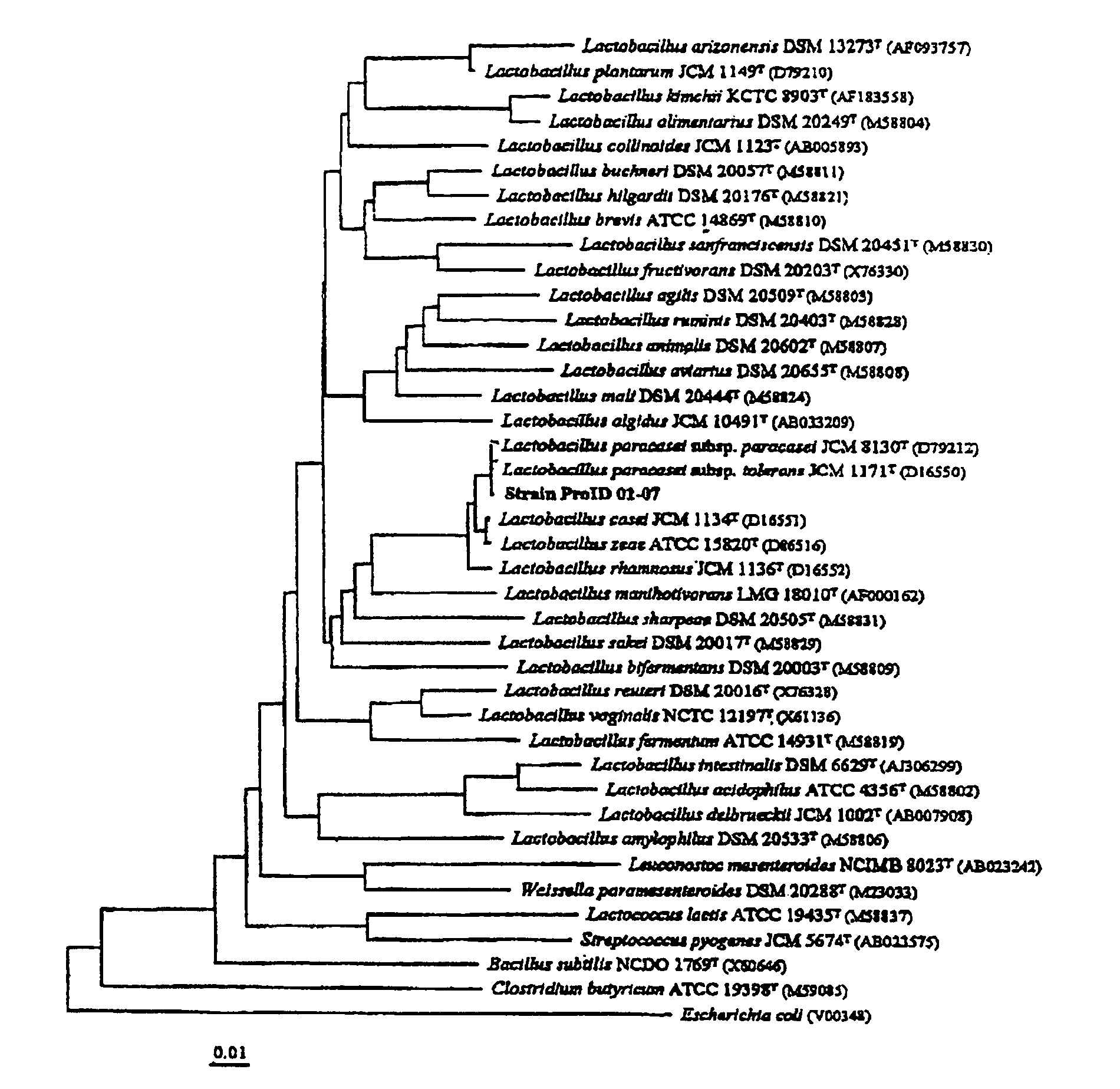
Novel lactobacillus sp. strain and use thereof
InactiveUS20050019894A1Maintain good propertiesNon toxicAntibacterial agentsBiocideAcid-fastFood additive
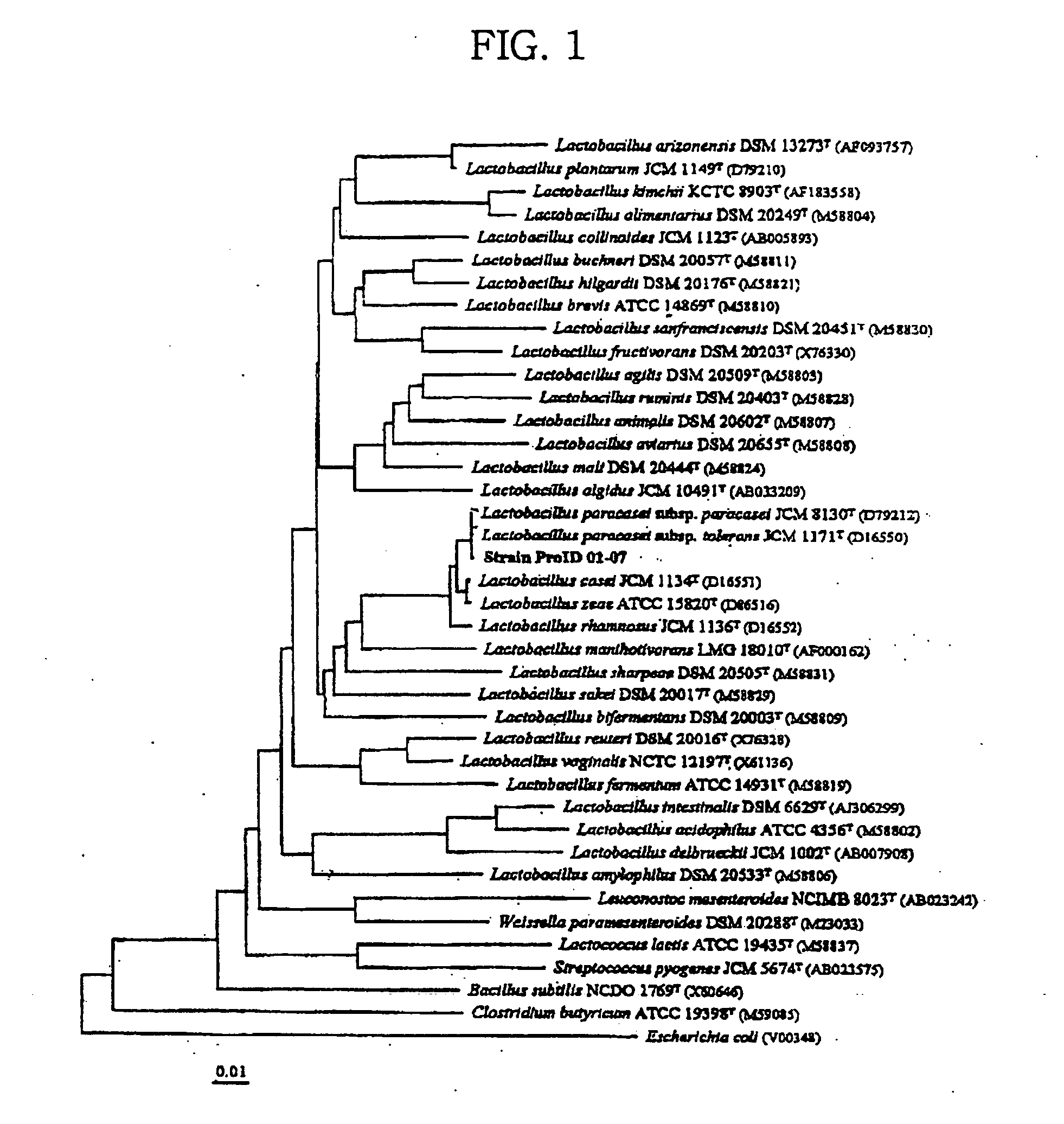
The present invention relates a novel Lactobacillus sp. Strain and usc thereof. More specifically, the present invention relates to a novel Lactobacillus sp. Strain, Lactobacillus paracasei, isolated and identified from Kimchi fermentation liquid and uses thereof as probiotics, feeding additive, deodorizing agent and food additive. Lactobacillus paracasei of the present invention has good acid-resistance, bile acid-resistance and stability in the human body, has pathogenic bacteria inhibiting activity, increases numbers of beneficial bacteria by changing intestinal microflora and decreases diarrhea incidence, deodorizes offensive odor, and has effectes of softening and deodorizing in meat and fish.
Owner:SESANG L & C
Method for assembling foot and mouth disease virus hollow capsid in insect with acidproof improvement
The present invention discloses a method for assembling foot-and-mouth disease virus empty capsids in insect cells via the alteration of acid-resistance. The method for assembling foot-and-mouth disease virus empty capsids in insect cells includes the following steps: (1) the altered P12A gene and the non-structural protein gene 3C of foot-and-mouth disease virus are introduced into bacteria via baculovirus vectors for recombination to produce recombinant rhabdovirus A; (2) the DNA of the recombinant rhabdovirus A is used to transfect the insect cells, so that the foot-and-mouth disease virus empty capsids are obtained. The method assembles the integral foot-and-mouth disease virus empty capsids in the insect cells for the first time, lays a foundation for the research and the development of gene-engineered subunit vaccines and novel diagnostic reagents.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bacillus adhaerens and its use in preparing health food having thrombolysis property
InactiveCN1464046AHigh activityStrong thrombolytic effectBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsAcid-fastSolubility
Bacilliis natto NLSSc with the preservation number CGMCC No. 0724 is Gram staining positive, non-acid fast, straight or near straight, (0.6-0.8)x(1.5-2.0) micron sized and aerobic; has mesial and un-swelled spore with the spore number inside one sporange cell not more than one, meso diamino heptane diacid and glycin contained in the cell wall, no characteristic saccharum and peripheral flagellum; and can be grown well in five kinds of natural organic culture medium and can form relatively thick mycoderm and butter fat colored colony with smooth edge in soybean cake powder culture medium. Bacilliis natto can be cultured in culture medium with nitrogen source to obtain thrombus dissolving matter natto kinase and the cultured matter may be extracted to obtain powdered matter as the additive for thrombolytic health food.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Antimicrobial hexapeptides
The invention encompasses hexapeptides consisting of alternating hydrophobic residues (B) at positions 2, 4, and 6, hydrophilic, charged residues (X) at positions 1 and 3, and a naphthylalanine (Nal), an aliphatic or aromatic residue (O) at position five, represented generally by the formula XBXBOB, which exhibit antimicrobial activity against infections caused by a variety of pathogens. These pathogens may include gram positive or negative bacteria, acid-fast bacteria such as mycobacteria, parasites, dermatophytes, or fungal pathogens. Typical fungal pathogens include Candida albicans and typical dermatophytes include Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. The hexapeptides of the present invention exhibit antifungal activity, antibacterial activity, desirable stability, and lack toxicity to the mammal receiving treatment.
Owner:HELIX BIOMEDIX INC
Cyclopropyl group substituted oxazolidinone antibiotics and derivatives thereo
This invention relates to new oxazolidinones having a cyclopropyl moiety, which are effective against aerobic and anerobic pathogens such as multi-resistant staphylococci, streptococci and enterococci, Bacteroides spp., Clostridia spp. species, as well as acid-fast organisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other mycobacterial species. The compounds are represented by structural formula I: its enantiomer, diastereomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or ester thereof.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Compositions and methods for treating or ameliorating mycobacterial infections
InactiveUS20100137192A1Inhibit functioningAvoid symptomsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAcid-fastMycobacterium Infections
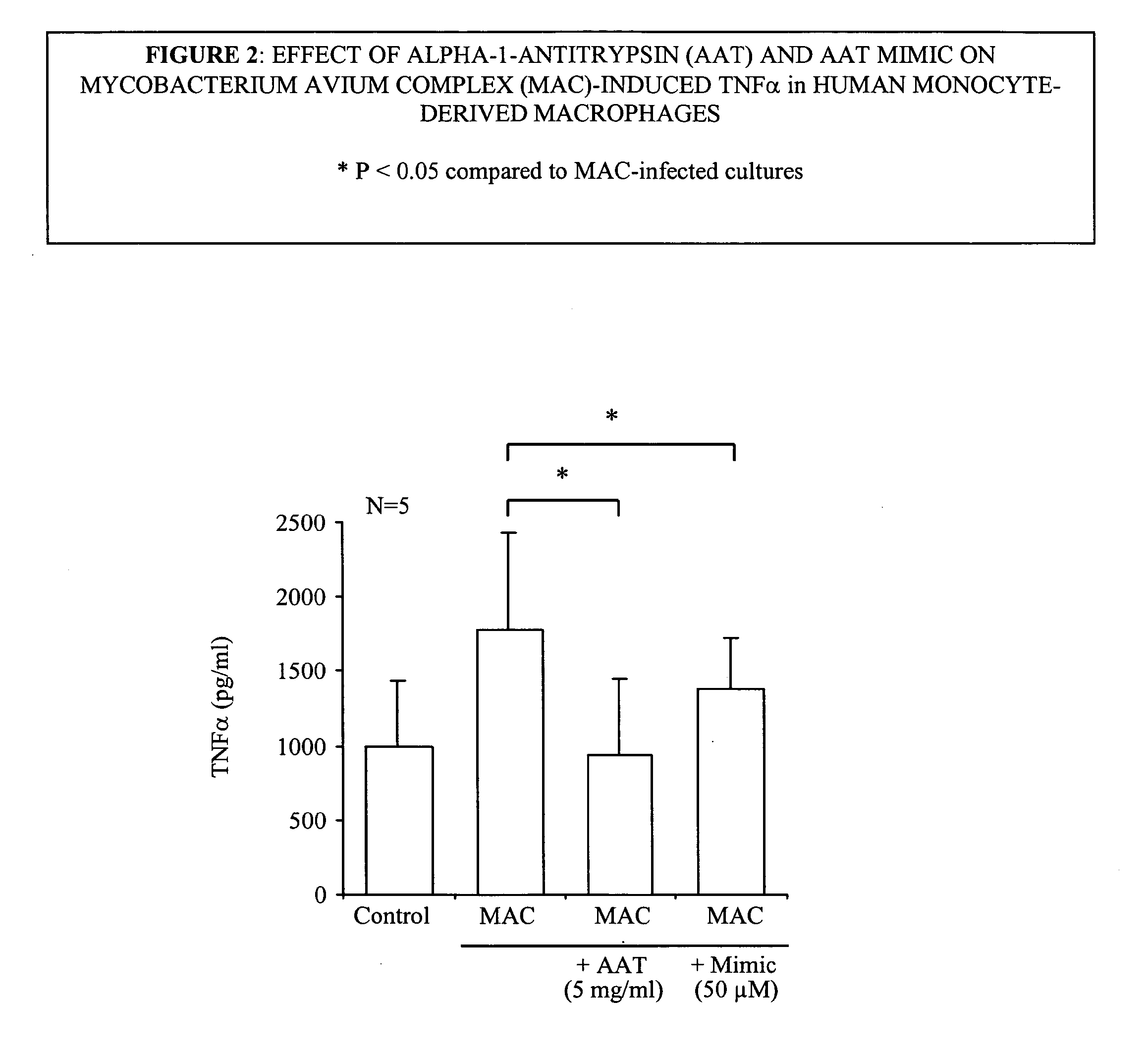
A novel method of treating and preventing bacterial diseases is provided. In particular, the present invention relates to compositions and methods for inhibition of Gram negative, Gram poitive and acid fast bacilli in general and tuberculosis (TB), mycobacterium avium complex (MAC), and anthrax in particular. Thus, the invention relates to modulation of cellular activities, including macrophage activity, and the like. More particularly, the present invention relates to the inhibitory compounds comprising naturally occurring and man-made inhibitors of serine protease.
Owner:SHAPIRO LELAND
Bacillus licheniformis and applications thereof in kitchen waste
ActiveCN106190900AHigh activity proteaseHigh lipohydrolase activityBacteriaSolid waste disposalAcid-fastBacillus licheniformis
The invention provides bacillus licheniformis, wherein the classification name is bacillus licheniformis CY-1, the bacillus licheniformis CY-1 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), the address is the Institute of Microbiology of Chinese Academy of Sciences located in 3, Courtyard 1, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, the postal code is 100101, the accession number is CGMCC NO.12448, and the preservation date is May 13, 2016. The invention further provides applications of bacillus licheniformis in kitchen waste treatment. The bacillus licheniformis has the activities of high-activity protease, amylase and oil hydrolase, can degrade glucose for generating acid, and is a thermophilic bacterium with high salt tolerance and high acid tolerance, and through effective combination of the bacillus licheniformis with a carrier, the weight of the fed kitchen waste is rapidly and efficiently reduced by 85%.
Owner:BIOMAX ECOLOGICAL ENG
Cyclopropyl group substituted oxazolidinone antibiotics and derivatives thereof
This invention relates to new oxazolidinones having a cyclopropyl moiety, which are effective against aerobic and anerobic pathogens such as multi-resistant staphylococci, streptococci and enterococci, Bacteroides spp., Clostridia spp. species, as well as acid-fast organisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other mycobacterial species. The compounds are represented by structural formula I: its enantiomer, diastereomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or ester thereof.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Exopolysaccharides-producing lactobacillus plantarum for adsorbing monophthalate effectively
The invention relates to the biotechnical field, particularly relates to the field of production and development of functional lactic acid bacteria, more particularly relates to exopolysaccharides-producing lactobacillus plantarum for adsorbing monophthalate effectively. The strain number of the exopolysaccharides-producing lactobacillus plantarum for adsorbing monophthalate effectively is RS20D, and the exopolysaccharides-producing lactobacillus plantarum for adsorbing monophthalate effectively is registered and preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with the preservation number of CGMCC No.13272 and the preservation date of November 14, 2016. The lactobacillus plantarum RS20D provided by the invention is functional lactic acid bacteria which has acid resistance, grows well in an environmental condition of pH 3.0-9.0, and particularly has the characteristic of adsorbing monophthalate and producing exopolysaccharides, for example, the lactobacillus plantarum RS20D is developed to a health-care food or drug which is taken for a long time to improve intestinal flora, and the damage of a phthalate plasticizer on a human body is reduced; or, the lactobacillus plantarum RS20D is input to a fermenting diary product or a cheese product, so that the sensory characteristic of the product can be improved.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Cyclopropyl group substituted oxazolidinone antibiotics and derivatives thereof
This invention relates to new oxazolidinones having a cyclopropyl moiety, which are effective against aerobic and anerobic pathogens such as multi-resistant staphylococci, streptococci and enterococci, Bacteroides spp., Clostridia spp. species, as well as acid-fast organisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other mycobacterial species.The compounds are represented by structural formula I:its enantiomer, diastereomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or ester thereof.
Owner:KYORIN PHARMA CO LTD +1
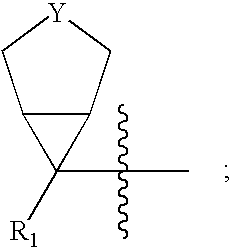
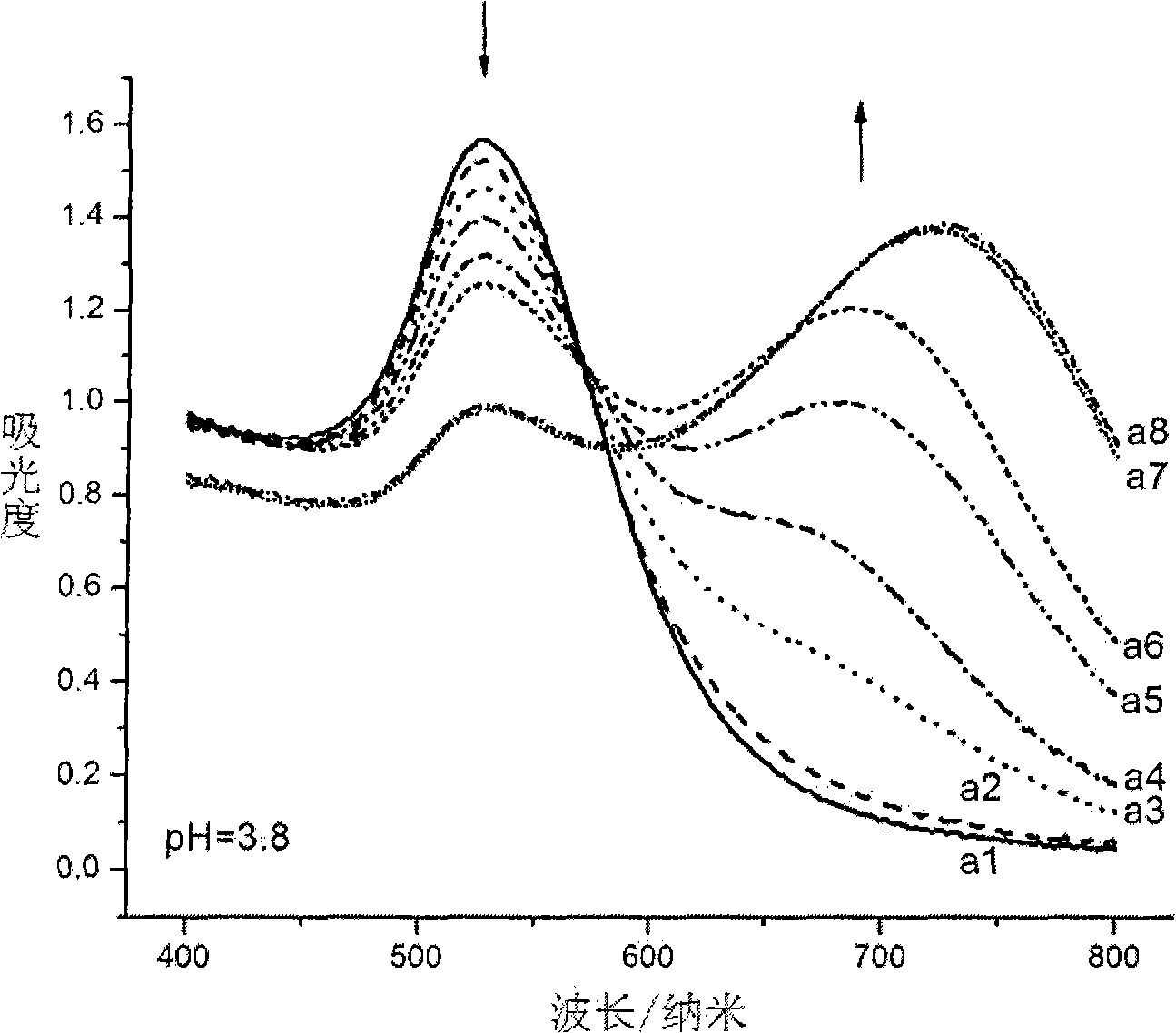
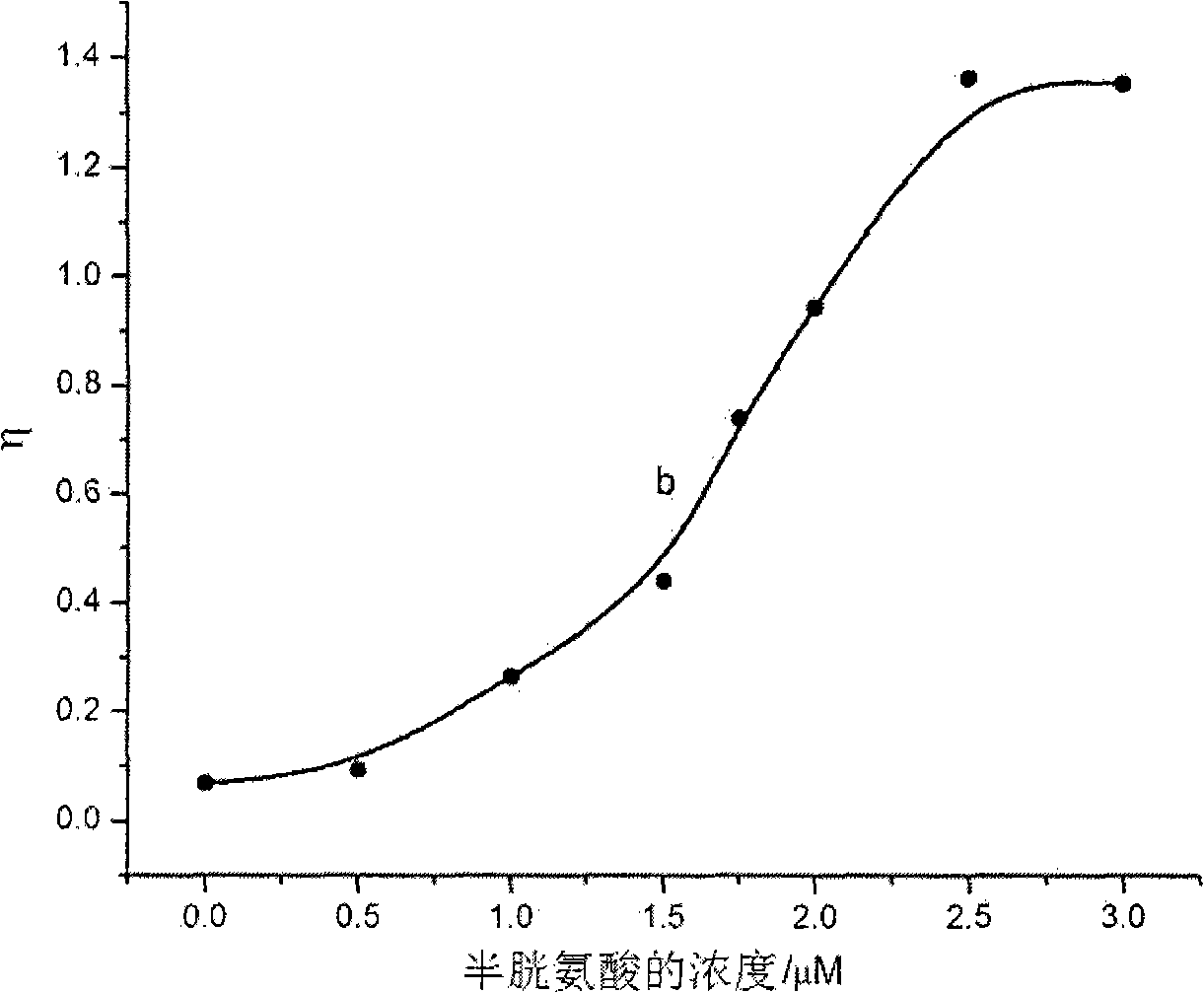
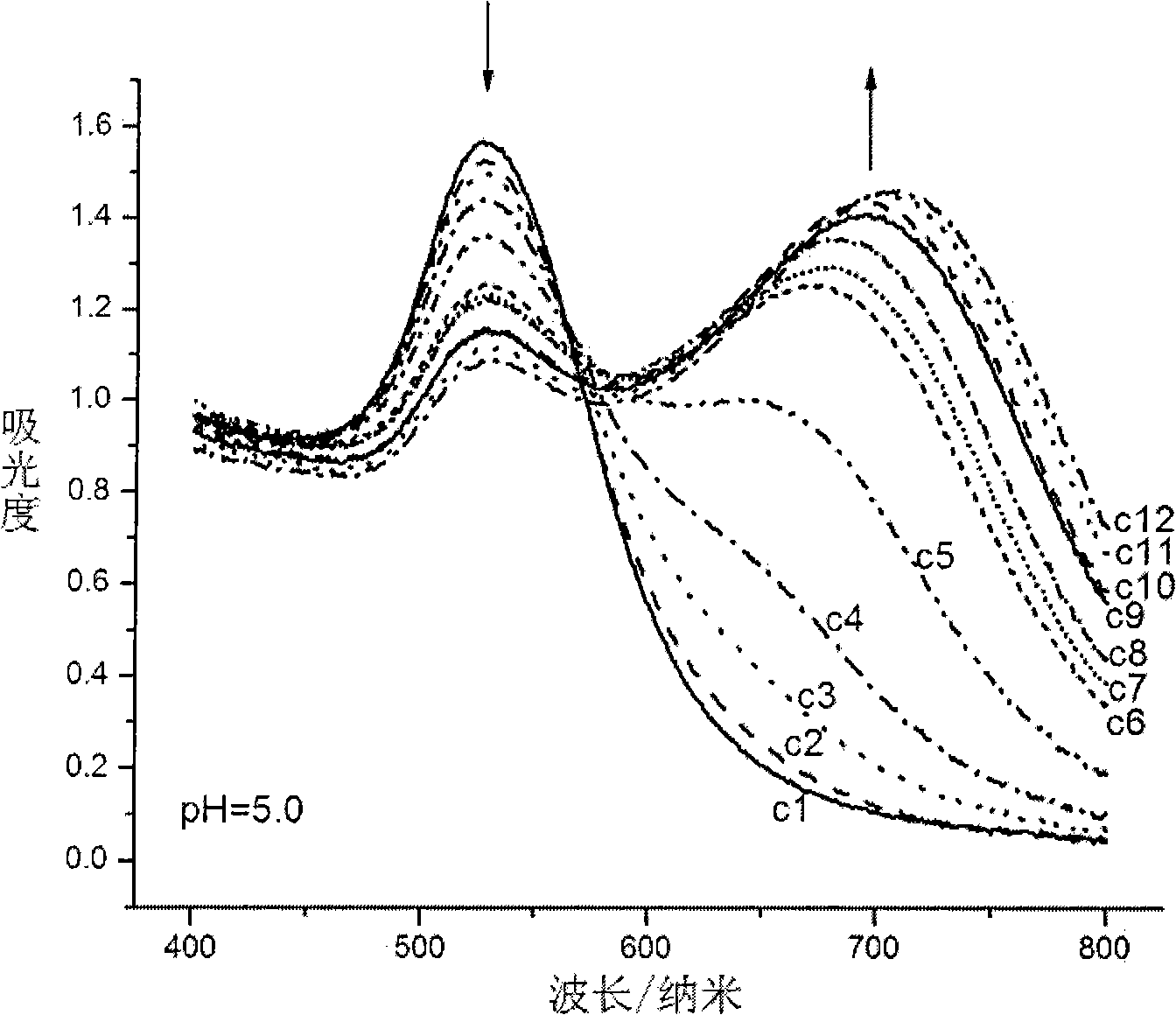
Aminothiopropionic acid fast detecting method based on gold nano particle colloidal sols absorption spectrum
InactiveCN101408509AShorten the timeEasy to operateColor/spectral properties measurementsAcid-fastCysteine thiolate
The invention discloses a cysteine quick detection method based on an absorption spectrum of Au nanoparticle collosol. The invention is characterized in that deionized water, buffer solution with 3.8 to 5.7 pH value and Au nanoparticle collosol stock solution are mixed to be prepared into detection solution, and the concentration of the buffer substance and the element Au in the detection solution is respectively 10 plus or minus 1mm and 0.9 plus or minus 0.1mm; the cysteine-containing liquid to be detected is added to the detection solution, the concentration of the cysteine in the formed detection system is 0.5 to 10mum, and the absorption spectrum is measured within ten minutes after even mixing; and according to the difference of the specific value eta of the absorbance of 700 nanometers and 525 nanometers of the wavelength in the absorption spectrum of the detection system, the concentration of the cysteine can be detected quantitatively. The method greatly reduces the time required for detecting the cysteine, and meanwhile, has the advantages of simple equipment, simple operation and mass detection.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Bacillus cereus and application of bacillus cereus as agricultural biological agent
The invention provides bacillus cereus and an application of the bacillus cereus as an agricultural biological agent and relates to the bacillus cereus and the application of the bacillus cereus in the agricultural field. The bacillus cereus solves the problem that microorganism engineering strains for degrading organophosphorus pesticide are single in function in the prior art. The bacillus cereus WSW-P05 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation number of the bacillus cereus WSW-P05 is CGMCC No: 10605. The bacillus cereus WSW-P05 serves as the agricultural biological agent. The bacillus cereus WSW-P05 serves as the agricultural biological agent so that crop growth can be promoted, and the crop yield can be increased; the organophosphorus pesticide in crops and soil is degraded; acid resistance is achieved; multiple pathogenic bacteria can be restrained; multiple functions are achieved.
Owner:哈尔滨绿洲之星生物科技有限公司
Acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis CLP-7, and applications thereof
The invention discloses an acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 which is capable of preventing diseases and promoting growth, and can be used for biocontrol. The acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is preserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, on 27th, October, 2016, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.13204. The antibacterial spectrum of the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is relatively large; the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is capable of inhibiting growth of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae, Ralstonia solanacearum, and Alternaria alternata Keissler; the antagonistic activity under acidic conditions is high, the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is capable of producing siderophore, possesses protease and glucanase activity, and potassium releasing capacity. The results of biocontrol pot experiment show that the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is capable of preventing under acidic soil conditions, and promoting growth and chlorophyll synthesis of tobacco seedlings in acidic soil, so that the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 and microorganism bacterium agents of the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 can be used for preventing tobacco fungi and bacterial root and stem diseases under continuous cropping or acidic soil conditions effectively, and is high in application value.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD +1
Lactobacillus fermentum strain suo for adjusting intestinal tract motion and preventing constipation and use thereof
ActiveCN104498383AStrong acid resistanceIncrease the push rateMilk preparationBacteriaAcid-fastFeces
The invention discloses Lactobacillus fermentum suo for adjusting intestinal tract motion and preventing constipation and a use thereof. The Lactobacillus fermentum suo has a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2013511, has strong acid resistance, has a survival rate of 92.46+ / -4.06% after being arranged in an artificial gastric juice with a pH value of 3.0 for 3h, can slowly grow in cholate with a concentration of 1.0%, has a growth rate 17.36+ / -1.19% that of cholate-free culture, has cell hydrophobicity of 68.44+ / -2.48% and can normally grow in the human intestinal tract. Lactobacillus fermentum suo can relieve constipation-caused mouse weight reduction, reduce tarry stool excretion time, improve a small intestine propulsion rate, improve serum MTL, Gas, ET, AchE, SP and VIP factor levels to different degrees, reduce a SS factor, improve food intake and water intake, relieve reduction of a stool excretion mount, the number of stool particles and stool water content and can produce a certain constipation prevention effect similar to those of constipation treatment drugs.
Owner:江苏新申奥生物科技有限公司
Acid and high temperature resistant alpha-amylase and genes and engineering bacteria of alpha-amylase and preparation method
ActiveCN106086048AHigh expressionEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcid-fastChemical industry
The invention discloses genes and engineering bacteria of acid and high temperature resistant alpha-amylase and a preparation method of the genes and engineering bacteria. Compared with a mutant reported by literature, under the condition that the pH ranges from 4.2 to 4.6, and the temperature is 95 DEG C, the thermostability of the acid and high temperature resistant alpha-amylase is enhanced, the expression quantity is 50 times that of existing acid and high temperature resistant alpha-amylase, the alpha-amylase is applied to the fields of chemical industry, food, medicine and the like, starch can be efficiently degraded under the conditions of strong acidity and high temperature, the process can be simplified, environmental pollution is reduced, and a wide application prospect is achieved. Meanwhile, according to genes and engineering bacteria of the acid and high temperature resistant alpha-amylase and the preparation method of the genes and engineering bacteria, rational design of applied combined construction prediction has important guiding significance in improving thermostability of an industrial enzyme.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Novel Acid Tolerant Lactobacillus Sakei Probio-65 with the Ability of Growth Suppression of Pathogenic Microorganisms and the Anti-Allergic Effect
ActiveUS20090214497A1Prevent proliferationGrowth inhibitionBiocideCosmetic preparationsDiseaseIntestinal structure
Disclosed are a novel tactic acid bacterium, Lactobacillus sakei Probio-65, and the use thereof. The L. sakei Probio-65 strain has acid tolerance, bile acid tolerance and antibiotic resistance, inhibits the growth of harmful pathogenic microorganisms in the body and the intestine of animals, and has immunuenhancing activity. In particular, the novel strain inhibits the growth of Staphylocccus aureus, which is known to be a factor aggravating atopic dermatitis. Thus, the novel strain is useful for preventing or treating atopic dermatitis and allergy-related disorders. Also, the novel strain stabilizes intestinal microflors by inhibiting the abnormal proliferation of harmful microorganisms in the intestine. The L. sakei Probio-65 strain or a culture thereof is useful in pharmaceutical, feed, food, and cosmetic compositions.
Owner:PROBIONIC CO LTD
Acid-resistant pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 and application thereof
ActiveCN108570433AAcid resistantEnhance disease preventionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAcid-fastNicotiana tabacum
The invention provides acid-resistant pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 and application thereof. According to the acid-resistant pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 and the application thereof, the bacterial strainof the pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on October 27th, 2016, and the biological preservation number of the pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 is CGMCC No.13205; the bacterial strain of the pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 has acid resistance, is good in disease prevention and plant growth promotion effects and high in stress resistance, hasthe antagonistic activity of pathogenic bacteria, is wide in soil acidity tolerance range and wide in antibacterial spectrum, and has application and development potential in prevention and treatmentof bacterial wilt, black shanks and brown spots; and meanwhile, under the general background that the acidification conditions in China is increasingly severe, the research on the bacterial strain ofthe pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 has reference significance in prevention and treatment of plant diseases under various soil qualities, a microbial resource is provided for green prevention and control over the bacterial wilt, the black shanks and the brown spots in acid soil, and secondary metabolites of microorganisms are excavated, so that an important foundation can be laid for the biocontrolefficacy on the bacterial wilt, the black shanks and the brown spots in the acid soil.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
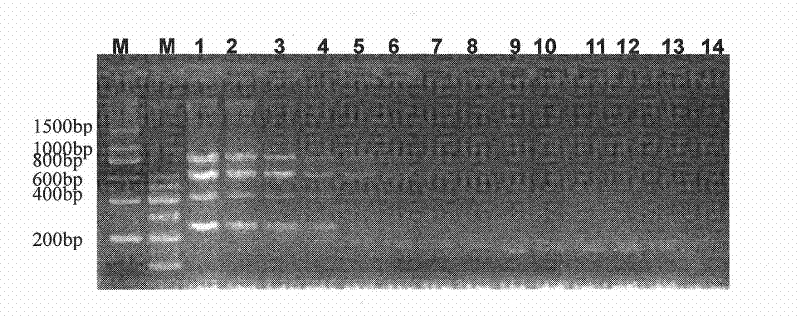
Multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) kit for identifying mycobacterium tuberculosis
InactiveCN102533959ASimple and fast operationEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence designAcid-fast
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
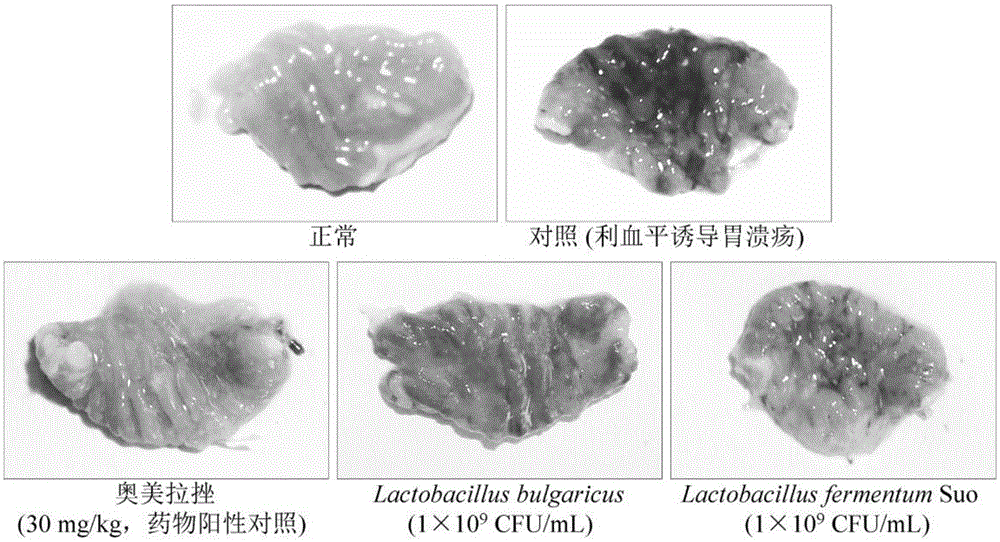
Lactobacillus fermentum strain suo capable of preventing gastric ulcers and application of lactobacillus fermentum strain suo
The invention discloses lactobacillus fermentum strain suo capable of preventing gastric ulcers and application of the lactobacillus fermentum strain suo. A bacterial strain of which the preservation number CCTCC NO is M2013511 has strong acid resistance, and the survival rate in artificial gastric juice of which the pH value is 3.0 for three hours reaches 92.46 plus or minus 4.06%, and the bacterial strain can slowly grow in cholate of which the concentration is 1.0%, and the growth efficiency reaches 17.36 plus or minus 1.19% of cholate-free cultivation; the hydrophobicity of lactobacillus fermentum strain suo cells also reaches 68.44 plus or minus 2.48%, and the lactobacillus fermentum strain suo cells can normally grow in human intestines. By adopting the lactobacillus fermentum strain suo, the areas and degrees of the gastric ulcers can be reduced; motilin (MOT) and P substances (SP) are reduced by different degrees; somatostatin (SS) and vasoactive intestinal peptides (VIP) are increased, and tumor necrosis factors-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-12 (IL-12) and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) can be lowered; the lactobacillus fermentum strain suo has a good gastric ulcer inhibiting effect, and the effect similar to omeprazole is achieved.
Owner:江苏新申奥生物科技有限公司
Lactobacillus sp. strain and use thereof
The present invention relates a novel Lactobacillus sp. strain and use thereof. More specifically, the present invention relates to a novel Lactobacillus sp. strain, Lactobacillus paracasei, isolated and identified from Kimchi fermentation liquid and uses thereof as probiotics, feeding additive, deodorizing agent and food additive. Lactobacillus paracasei of the present invention has good acid-resistance, bile acid-resistance and stability in the human body, has pathogenic bacteria inhibiting activity, increases numbers of beneficial bacteria by changing intestinal microflora and decreases diarrhea incidence, deodorizes offensive odor, and has effectes of softening and deodorizing in meat and fish.
Owner:SESANG L & C
Antimicrobial Peptides and Methods of Use
InactiveUS20100099614A1Reduce morbidityReduce severityAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesAcid-fast
Disclosed herein are antimicrobial peptides with useful and / or superior properties such as specificity, resistance to degradation, antimicrobial activity, desirably low levels of hemolytic activity, and a therapeutic index against a broad range of microorganisms including gram-negative, gram-positive and acid-fast bacteria, fungi and other organisms. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions comprising these peptides and methods of using such peptides to control microbial growth or to treat or reduce incidence of infections caused by such microorganisms. Also disclosed are peptides at least one or all amino acids in the D configuration. Compositions disclosed herein are useful in the treatment of bacterial, mycobacterial and / or fungal infections or for reducing microbial cell numbers or growth on surfaces or in materials.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
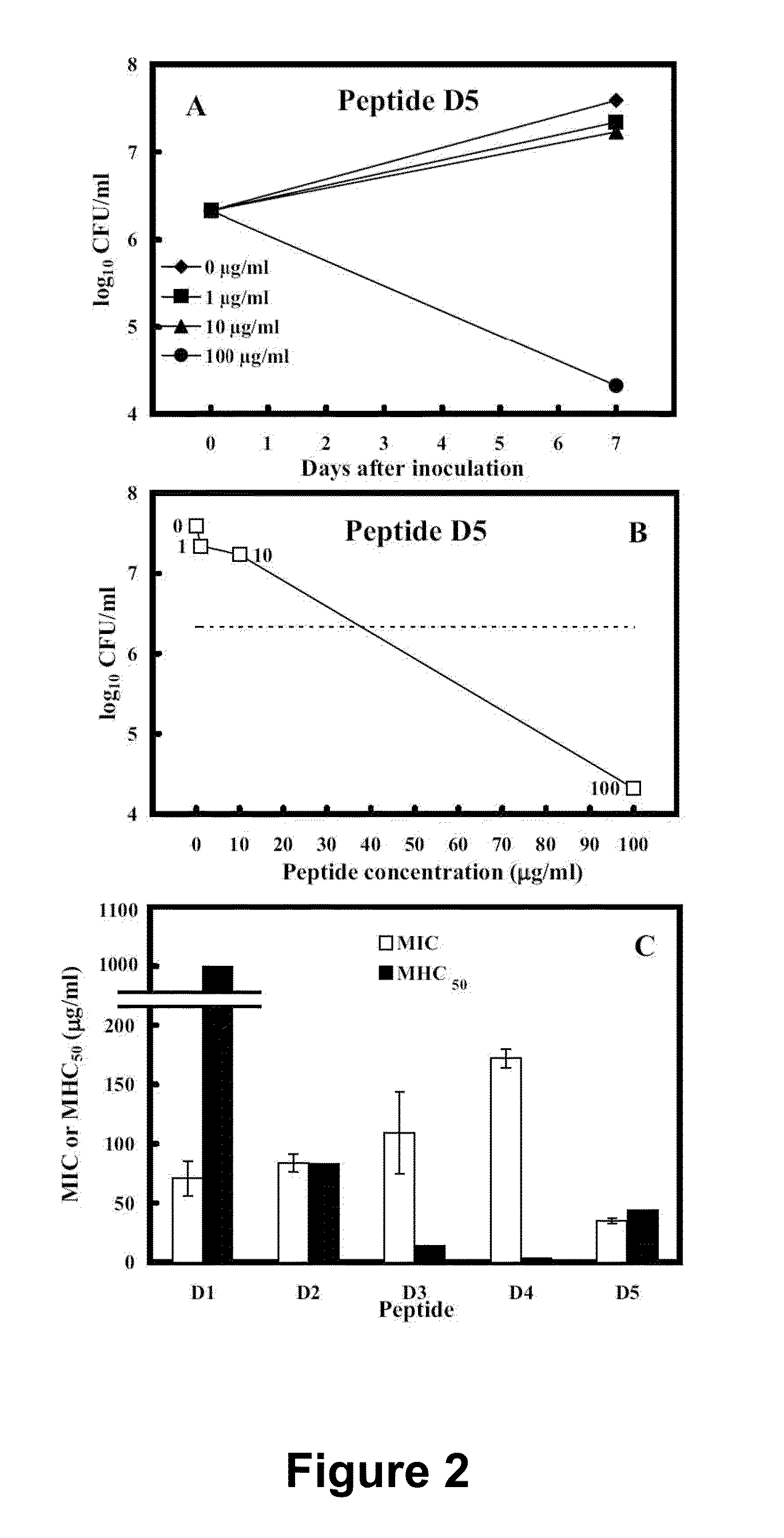
Paecilomyces thermophila mutant strain and mutation induction method and application thereof
InactiveCN107201315ASimple screening methodFast screening methodFungiMutant preparationAcid-fastBiotechnology
The invention discloses a Paecilomyces thermophila mutant strain and a mutation induction method and application thereof. The mutation induction method includes: Paecilomyces thermophila screened from high-temperature-fermented compost and used for producing high-temperature-resistant and acid-resistant glucose oxidase is used as the original strain, protoplast ultraviolet and ethyl methane sulfonate compound mutation induction is performed, and the screened strain is subjected to budding spore diethyl sulfate-microwave compound mutation induction to obtain the Paecilomyces thermophila mutant strain. The Paecilomyces thermophila mutant strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on January 11th, 2016, and the preservation number of the mutant strain is CGMCC No. 13182. Compared with a conventional mutation induction method, the mutation induction method has the advantages that the method is high in efficiency and simple in fast in screening, the productivity of the mutant strain is high, the yield of the mutant stain is 277.65% of that of the Paecilomyces thermophila original strain, fermentation liquor enzyme activity reaches 185U / ml, production cost is lowered, and the glucose oxidase produced by the mutant strain is good in high-temperature resistance and acid resistance and can be used as feed enzyme applied to feed industry.
Owner:XUZHOU UNIV OF TECH
Method for microencapsulating cholesterol-degrading lactic acid bacteria
InactiveCN101724589ALow priceImprove acid resistanceBacteriaMetabolism disorderAcid-fastNon toxicity
The invention discloses a method for microencapsulating cholesterol-degrading lactic acid bacteria, which comprises the steps of the activation of the cholesterol-degrading lactic acid bacteria, the preparation of immobilized cholesterol-degrading lactic acid bacteria, the preparation of microcapsules by a W / O / W multiphase emulsion method, and freeze-drying. The cholesterol-degrading lactic acid bacteria microcapsules prepared by adopting the multiphase emulsion method (W / O / W) have the characteristics of stability, non-toxicity and the like due to the fact that wall materials thereof all belong to natural polymer materials; the release rate of the microcapsules in intestinal juice within 2h is over 87.4 percent, and the viable count can reach 7.03*109cfu / mL; the viable count can still reach 6.81*106cfu / mL after the microcapsules are placed for 3h at the temperature of 50 DEG C, and can still reach 6*108cfu / mL after the microcapsules are stored for 30d; in vitro cholesterol degradation tests, the degradation rate of cholesterol is over 36.07 percent; and the microcapsules have better acid resistance, enteric property, high temperature resistance and cholesterol degradation, and the yield is about 86.62 percent. Capsule materials and carrier materials have low cost, so the cost is reduced.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com