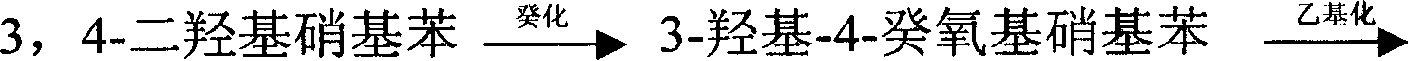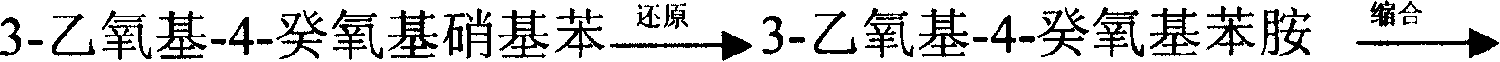Patents
Literature
148 results about "Diethyl sulfate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diethyl sulfate is a highly toxic and likely carcinogenic chemical compound with formula (C₂H₅)₂SO₄. It occurs as a colorless, oily liquid with a faint peppermint odor and is corrosive. Diethyl sulfate is used as an alkylating agent to prepare ethyl derivatives of phenols, amines, and thiols. It is used to manufacture dyes and textiles.
Method for preparing (Z)-5-amino-alpha-(ethoxy imino group)-1, 2, 4-thiadiazole-3-acetic acid
ActiveCN103804321AShort synthetic routeFew synthetic stepsOrganic chemistryAcetic acidPotassium thiocyanate
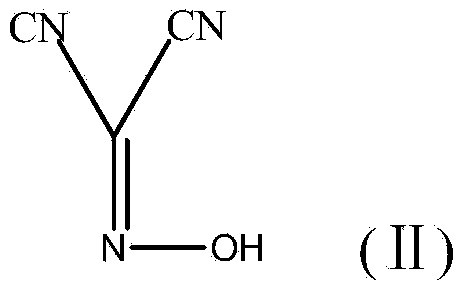
The invention discloses a method for preparing (Z)-5-amino-alpha-(ethoxy imino group)-1, 2, 4-thiadiazole-3-acetic acid. The method comprises steps of firstly, carrying out oximation reaction on malononitrile and sodium nitrite under the action of acetic acid so as to obtain a compound A, then carrying out Williamson synthesis on the compound A and bromoethane or diethyl sulfate under alkaline condition, so as to obtain a compound B, then carrying out amidine reaction on the compound B and ammonia water, so as to obtain a compound C, carrying out cyclization reaction on the compound C and potassium rhodanide for ring closing so as to obtain a compound D, and finally, hydrolyzing the compound D under the action of a strong base, so as to obtain (Z)-5-amino-alpha-(ethoxy imino group)-1, 2, 4-thiadiazole-3-acetic acid. The method has few synthesis steps, has low cost, uses the materials which are cheap and easy to obtain, is beneficial to industrial production, and has light contamination; the purity of the product can reach 99%, so that synthesis of high-purity ceftaroline fosamil in the subsequent step is guaranteed.
Owner:山西海泰电子材料有限公司
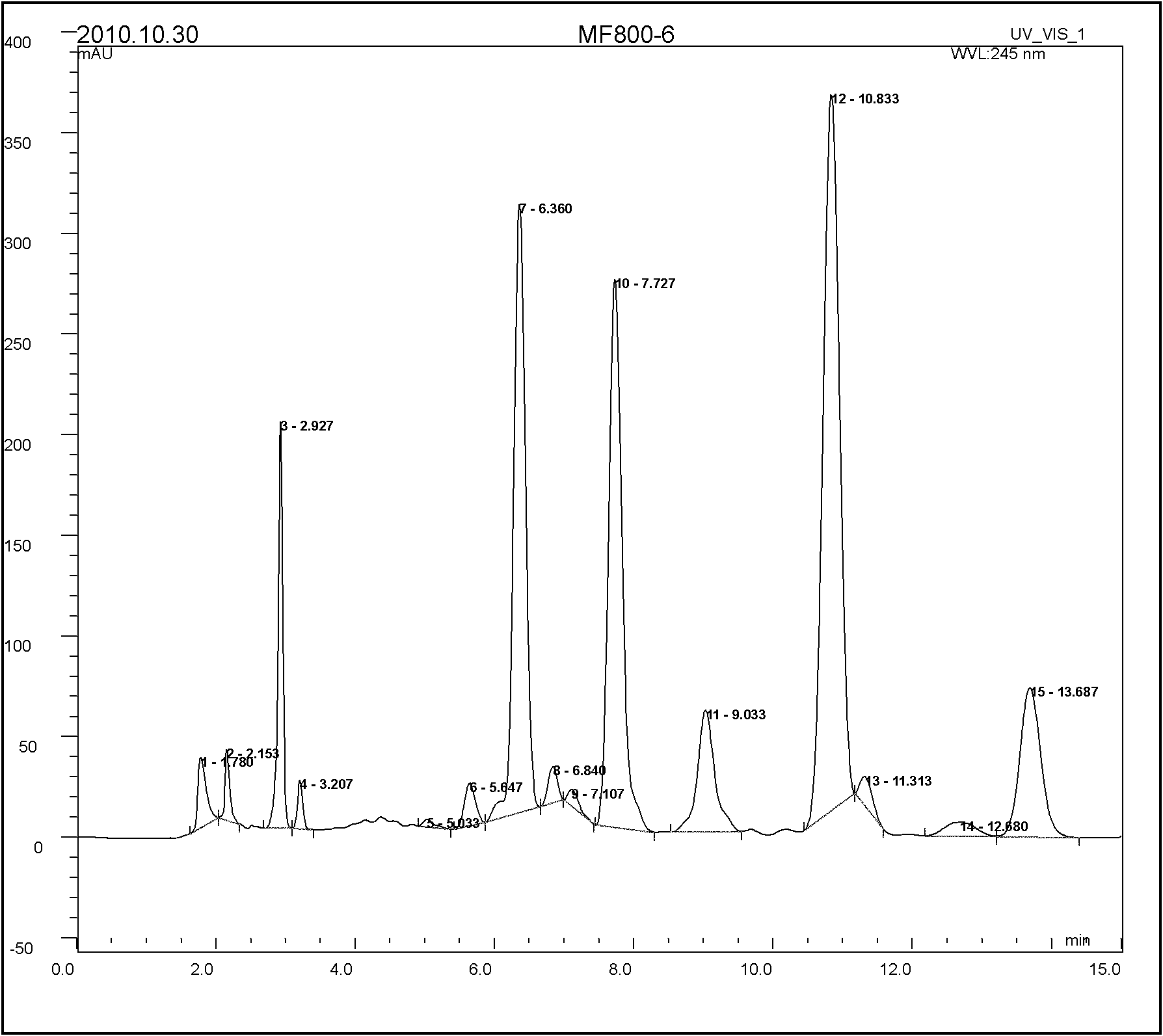
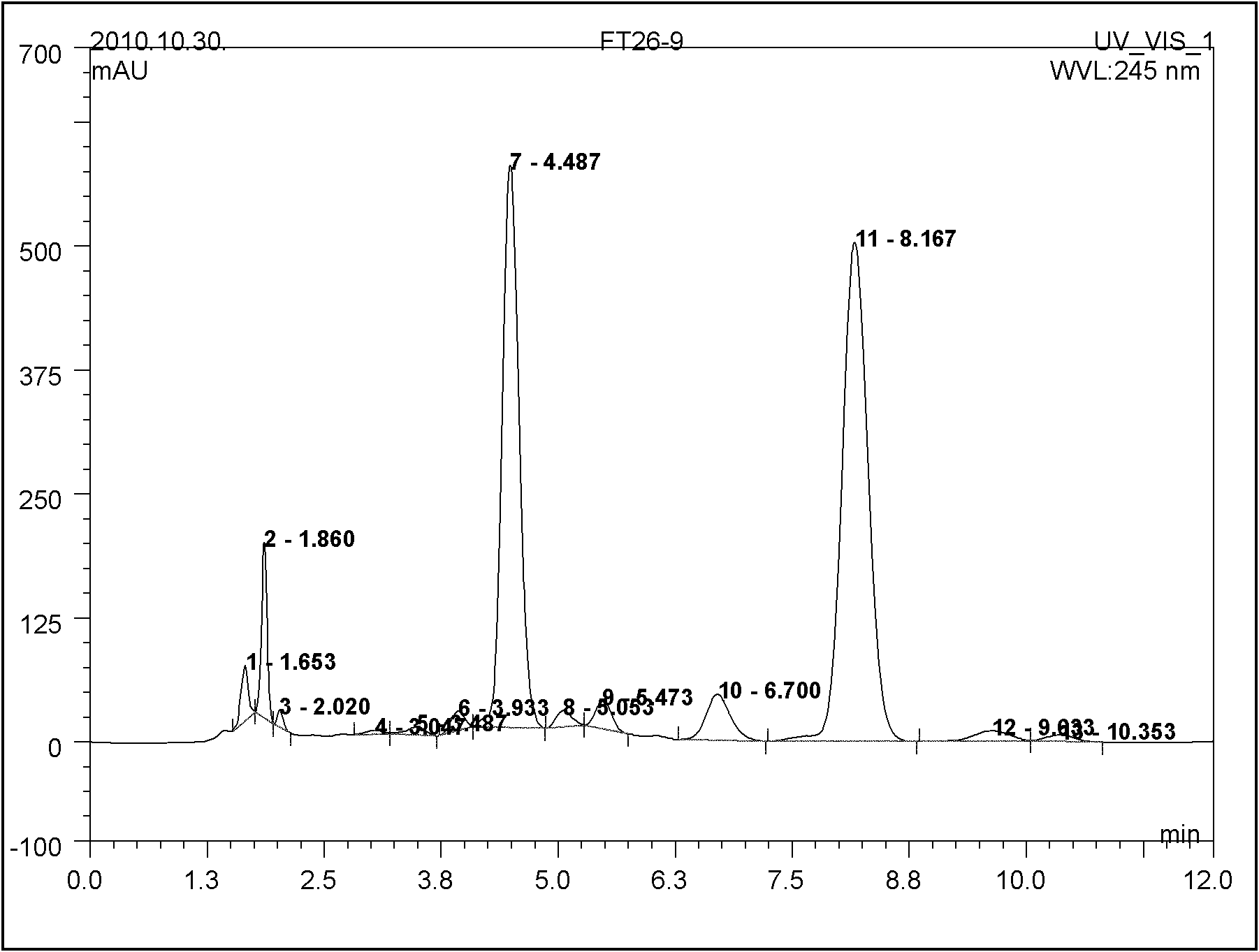
Abamectin producing bacterium and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102154168AImprove Abamectin B ComponentLess componentsBacteriaMutant preparationLithium chlorideHydroxylamine
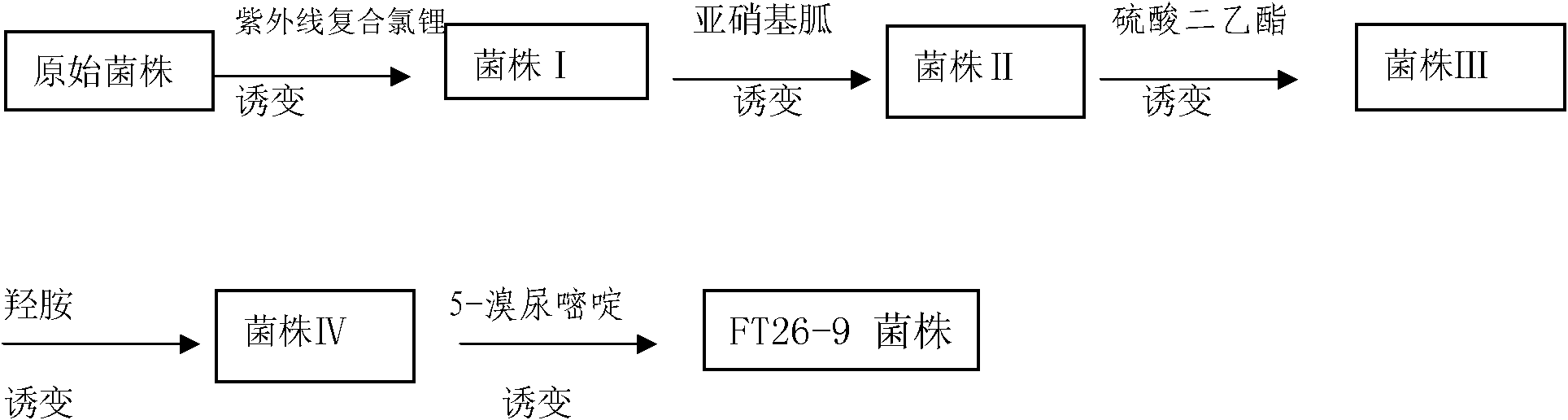
The invention discloses abamectin producing bacterium and a preparation method thereof. The collection name of the bacterium is FT26-9 and the collection number of the bacterium is CGMCC No.4341. The bacterium was collected on November 12th, 2010. The preparation method comprises: performing ultraviolet and lithium chloride combined mutation induction treatment of a starting strain; screening an induced-mutation strain; performing mutation induction by nitrosoguanidine and screening; performing mutation induction by diethyl sulfate and screening; performing mutation induction by hydroxylamine and screening; performing mutation induction by 5-bromouracil and ultraviolet and screening; and finally obtaining the FT26-9 strain which can greatly improve the abamectin B component content in a fermentation product and reduce the abamectin A component content in the fermentation product. When the bacterium is used in industrial production of abamectin, the fermentation unit is improved by about 40 percent, and the product cost is reduced by about 35 percent.
Owner:HEBEI XINGBAI AGRI SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing Bi2S3/BiOCl heterojunction photocatalyst
ActiveCN103316701ASimple operating parameters for preparationImprove photocatalytic activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsThio-Engineering
The invention belongs to the preparation field of inorganic material bismuth oxychloride heterojunction photocatalysts and particularly relates to a method for preparing a Bi2S3 / BiOCl heterojunction photocatalyst. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) dropwise adding diethyl sulfate water solution into triethylene tetramine water solution to carry out neutral reaction, stirring, and removing water out of the mixed liquid, so as to prepare triethylene tetramine diethyl sulfate type ionic liquid; (2) dissolving imidazole in water, then dropwise adding hydrochloric acid, and separating out imidazole chloride ion liquid; (3) dissolving bismuth nitrate in deionized water, additionally dissolving imidazole chloride in the deionized water, dropwise adding prepared imidazole chloride water solution into bismuth nitrate water solution, and separating to obtain BiOCl; and (4) preparing triethylene tetramine diethyl sulfate type ionic liquid water solution, and dissolving the BiOCl and thioacetamide into the water solution, so as to prepare Bi2S3 / BiOCl. The photocatalyst disclosed by the invention has good activity, low cost and high purity and can be produced in large scale.
Owner:扬州天诗化工科技有限公司
Method of preparing yeast rich in copper
InactiveCN101508961AImprove absorption and utilizationResidue reductionFungiAnimal feeding stuffSurvival ratioFeed additive
The invention relates to a preparation method of copper-rich yeast. In the invention, high-copper resistant yeast strains are firstly prepared: yeast strains with different biochemical characteristics are cultivated in a culture medium in a gradient copper concentration, and the ones having maximal survival ratio are used as strains to be mutagenized; the strains to be mutagenized are inoculated on the culture medium of diethyl sulfate for mutagenesis; the strains after mutagenesis are inoculated in the culture medium in a gradient copper concentration for cultivation, fungus liquid collection, filtering and drying are carried out, and the strains after mutagenesis with biomass and copper content simultaneously higher than average values are used as the high-copper resistant yeast strains. And then the high-copper resistant yeast strains are used for preparing the copper-rich yeast, and the working procedures are as follows: slant strain cultivation; first-stage liquid seed cultivation; second-stage seed cultivation; fermentation cylinder cultivation; separation drying; grinding; and products of copper-rich yeast. The additives of the copper-rich yeast prepared in the invention greatly improves the absorption utility ratio of copper in animal organisms, increases the economic benefit, and can be applied to copper addition for beasts and birds, and aquatic livestock as feed additives.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for restructuring/breeding Actinobacillus succinogenes strain, and method for producing succinic acid by fermenting Actinobacillus succinogenes strain
InactiveCN101531972AImproved sodium toleranceImprove fermentation characteristicsBacteriaMutant preparationGenome shufflingX-ray
The invention relates to an Actinobacillus succinogenes strain CGMCC 2653 (namely F3-10) with better sodium-ion tolerance and acid-producing performance, a method for breeding the strain and a method for producing succinic acid by fermenting the strain. Actinobacillus succinogenes CGMCC 1593 is taken as an original strain and then subjected to X-ray mutation, ultraviolet mutation, diethyl sulfate (EMS) chemical mutation and nitrosoguanidine (NTG) chemical mutation respectively; three strains X-8, UV-17 and SE-6 with improved fermentative acid-producing performance and particularly improved sodium-ion tolerance, as well as a high-yield strain SF-9 with fluoroacetate resistance, are obtained by screening the obtained product; and a genome restructuring method is used for breeding the strains so as to obtain the strain F3-10 with high yield, sodium tolerance and fluoroacetate resistance. The strain F3-10 takes sugarcane molasses as raw material, adopts Na2CO3 to control fermentation pH, and performs fed-batch fermentation in a 5L fermenter, and produces 53.96 grams of succinic acid per liter in 48 hours; the yield of consumed sugar is 89.2 percent; the utilization rate of sugar is 94.0 percent; and the ratio of succinic acid to heteroacid is 6.58:1. Therefore, the strain F3-10 is remarkably improved as compared with the original strain CGMCC 1593.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Acid-producing Klebsiella bacterium and uses thereof
InactiveCN101063095AReduce outputIncrease profitBacteriaMicroorganism based processesUltravioletKlebsiella species
The invention discloses a generating acid klebsiella and appliance, which is characterized by the following: setting the preserved number at CCTCC NO: M 207023; adopting ultraviolet and diethyl sulfate; composite-treating strain CCTCC NO: M 207023; seeding on selective solid medium with bromide of sodium and sodium bromate; culturing; sorting single bacterial colony; yeasting; preparing 2, 3-butylene glycol. This invention possesses simple operation, low cost, high efficiency and short period, which can increase receiving ratio of 2, 3-butylene glycol.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for synthesizing nusaturated hydrophilic methyl or ethyl end capping polyether
In the synthetic method, allyl alcohol polyether and dimethyl sulfate or diethyl sulfate are etherified at temperature of 0-80 deg.C, under action of basic microcapsule catalyst in slow release and unsaturated hydrophilicity methyl or ethyl end capped polyether is obtained after neutralizing with acid-base and washing. The catalyst slowly releases alkali microcapsule prepard by alkali metal hydroxide or by mixed alkali metal chamicals.
Owner:王伟松
Textile dye as well as preparation method and waterless dyeing method of textile dye
ActiveCN107541966AReduce the impactAvoid hydrolysisDyeing processSodium bicarbonateNuclear chemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of textile waterless dyeing and specifically discloses a textile dye as well as a preparation method and a waterless dyeing method of the textile dye. Thetextile dye is mainly prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 1-10 parts of toner, 3-30 parts of organic solvent, 3-5 parts of triethylene glycol, 2-4 parts of glycerin, 0.5-5 partsof sodium lignin sulfonate, 2-5 parts of sodium metanitrobenzene sulfonate, 1-10 parts of ammonium polyacryloyldimethyl taurate, 1-10 parts of triethanolamine alginate, 0.01-0.5 part of sodium bicarbonate, 1-2 parts of hexadecylpyridinium chloride, 0.5-1 part of coco-dimethylammonium diethyl sulfate and 50-90 parts of deionized water. According to the dye prepared by the invention and the waterless dyeing method, the dyeing effect is good; moreover, washing is not needed, thus any wastewater is not generated, environmental protection is facilitated, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:KUNSHAN KAIZHOU ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION MACHINERY CO LTD
Preparation method and product of functional red pitaya yeast
InactiveCN104195051ARich tasteReduce contentFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBlood sugar
The invention discloses a preparation method and product of functional red pitaya yeast. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing a pitaya culture medium; preparing a red yeast mycelium: culturing Monascus purpureus yang TY622 serving a strain in a slant culture medium and a liquid shake flask culture medium, meanwhile, carrying out compound mutation on the strain by using ultraviolet ray and diethyl sulfate, then, connecting the strain to a fermentation medium, and carrying out liquid fermentation culture to obtain the red yeast mycelium; and preparing the functional red pitaya yeast: connecting the red yeast mycelium, probiotics or lactic acid bacteria to a pitaya pulp culture medium, and carrying out liquid fermentation to obtain the functional red pitaya yeast. The functional red pitaya yeast disclosed by the invention simultaneously has various health-care functions of pitaya and red yeast, and not only has the red yeast effects of reducing blood fat, reducing blood pressure, reducing blood sugar and the like, but also has the pitaya effects of expelling toxins, beautifying the face, preventing senile lesion, eliminating heavy metal poisoning and the like, so that demands of more people can be met.
Owner:东莞市天益生物工程有限公司
Process of preparing alkyl dead-end polyether by polyether with parahydroxyl at molecular chain end
The process of preparing polyether with end capping alkyl group belongs to the field of polyether synthesis technology. The process includes the reaction of polyether with sec hydroxyl group in the end of molecular chain and strong nucleophilic reagent alkali, the further reaction with alkyl sulfate, neutralizing with alkali, water washing and filtering to obtain polyether with end capping alkyl group. The strong nucleophilic reagent alkali is alcohol solution of sodium methoxide, alcohol solution of potassium methoxide, solid sodium methoxide, solid potassium methoxide or their mixture; and the alkyl sulfate is dimethyl sulfate or diethyl sulfate. The present invention has very high reaction activity and effectively raised end capping rate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUANGMA TECH
Preparation method of ethylene sulfate
ActiveCN108610324AEliminate potential safety hazardsEasy to makeOrganic chemistrySodium methoxideLithium hydroxide
The invention discloses a preparation method of ethylene sulfate. The method comprises the steps of: reacting ethylene glycol with diethyl sulfate in the presence of an alkaline catalyst to produce ethylene sulfate, wherein the alkaline catalyst is one of or a combination of several of lithium hydroxide, sodium methoxide, sodium ethoxide, potassium carbonate, sodium carbonate and lithium carbonate. The preparation method provided by the invention can reduce environmental pollution, is more environmental friendly, and has the advantages of simple operation, safety, ideal yield and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU HUAYI NEW ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Bacillus subtilis producing high-temperature-resistance alpha-amylase
InactiveCN104630084AIncrease enzyme activityStrong heat resistanceBacteriaMutant preparationLithium chlorideStrong acids
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis producing high-temperature-resistance alpha-amylase. The bacillus subtilis Li-2013-02 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on July 15, 2013, and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.7926. The strain is prepared from bacillus subtilis Li-2010 producing high-temperature-resistance alpha-amylase by means of ultraviolet ray-lithium chloride-diethyl sulfate combined mutation screening, has the characteristics of strong acid resistance, heat resistance and high enzyme production activity, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:邵素英
Paecilomyces thermophila mutant strain and mutation induction method and application thereof
InactiveCN107201315ASimple screening methodFast screening methodFungiMutant preparationAcid-fastBiotechnology
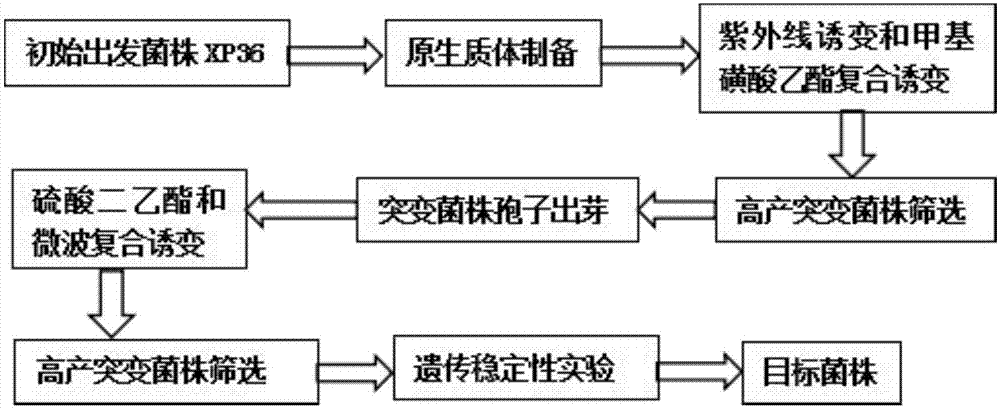
The invention discloses a Paecilomyces thermophila mutant strain and a mutation induction method and application thereof. The mutation induction method includes: Paecilomyces thermophila screened from high-temperature-fermented compost and used for producing high-temperature-resistant and acid-resistant glucose oxidase is used as the original strain, protoplast ultraviolet and ethyl methane sulfonate compound mutation induction is performed, and the screened strain is subjected to budding spore diethyl sulfate-microwave compound mutation induction to obtain the Paecilomyces thermophila mutant strain. The Paecilomyces thermophila mutant strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on January 11th, 2016, and the preservation number of the mutant strain is CGMCC No. 13182. Compared with a conventional mutation induction method, the mutation induction method has the advantages that the method is high in efficiency and simple in fast in screening, the productivity of the mutant strain is high, the yield of the mutant stain is 277.65% of that of the Paecilomyces thermophila original strain, fermentation liquor enzyme activity reaches 185U / ml, production cost is lowered, and the glucose oxidase produced by the mutant strain is good in high-temperature resistance and acid resistance and can be used as feed enzyme applied to feed industry.
Owner:XUZHOU UNIV OF TECH
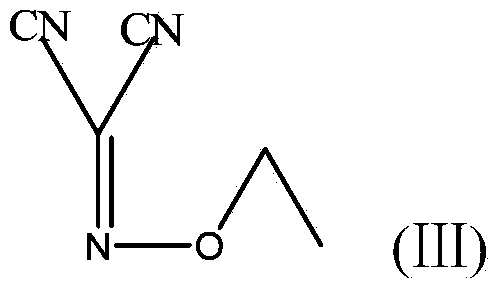
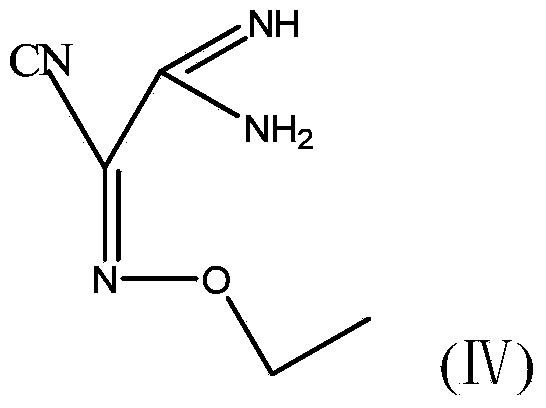
4-[2-(substituted benzylidene) hydrazino]-5, 6, 7-trialkoxy quinazoline compound and preparation method and application
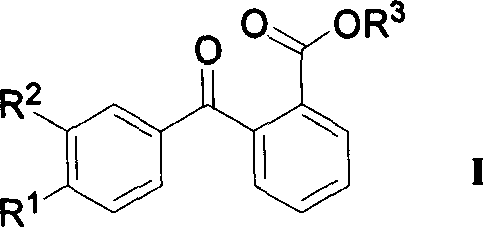
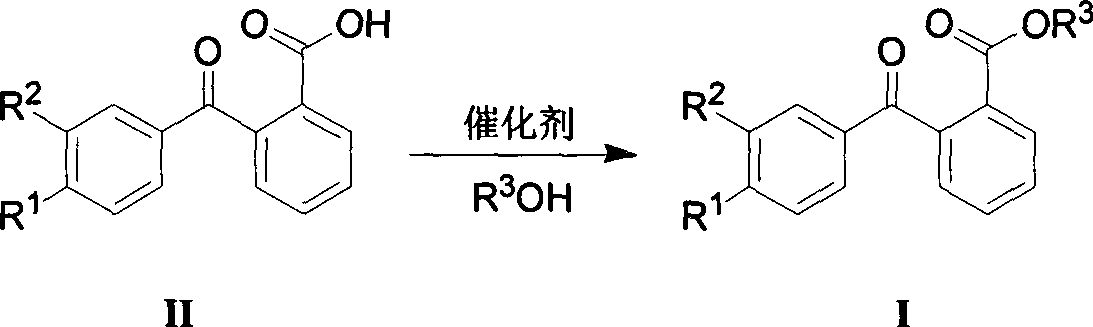
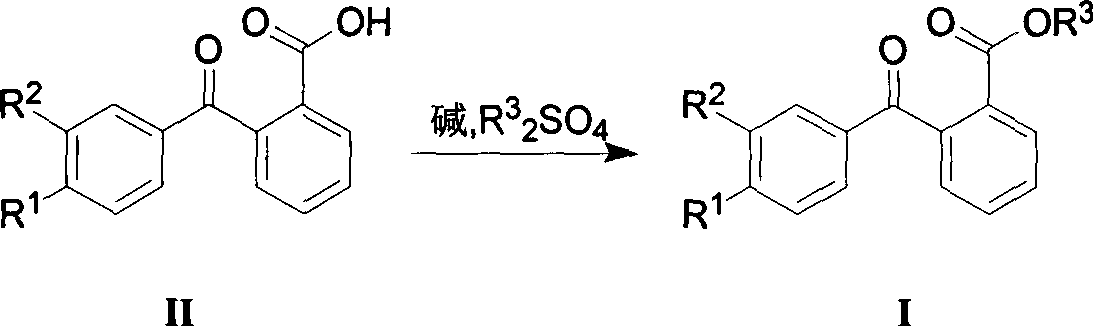
The invention discloses a 4-[2-(substituted benzylidene) hydrazino]-5, 6, 7-trialkoxy quinazoline compound and a preparation method and application thereof. 4-[2-(substituted benzylidene) hydrazino]-5, 6, 7-trialkoxy quinazoline compound has the structure shown as the following general form (I). According to the preparation method, 2, 3, 4-trihydroxybenzoic acid, dimethyl sulfate, diethyl sulfate, carbinol, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrogen, formamide, phosphorus oxychloride, 80% of hydrazine hydrate and aromatic aldehyde are adopted as raw materials, and synthesized to obtain a series of novel 4-[2-(substituted benzylidene) hydrazino]-5, 6, 7-trialkoxy quinazoline compounds through eight steps; and such compounds have excellent antitumous effects and high effects on restraining the fungi of plant, and can be applied to preparing anti-cancer drugs and anti-plant fungal pesticides.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
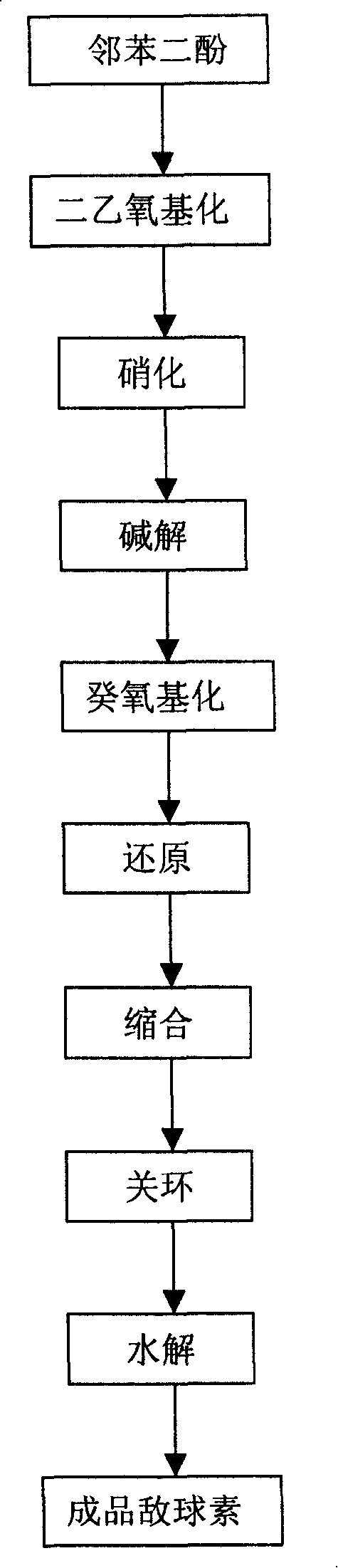
Method for preparing decoquinate premix
The invention discloses a preparing method of deccox, which uses cheap pyrocatechol as material to obtain deccox products with good quality and low cost by diethoxylation, nitration, alkali hydrolysis, decyloxylation, reduction, condensation, ring closing and hydrolyzation. Compared with the prior art, materials such as 3,4-dihydroxynitrobenzene or catechol ethylether, which are expensive and not easy to buy, are replaced by chemical materials, such as plate caustic soda, pyrocatechol, diethyl sulfate, glacial acetic-acid, nitric acid, glycol monoethyl ether, potassium hydroxide, bromodecane, phosphorus oxychloride, ethoxymethylene, sodium hydroxide, etc., which are cheap and easy to obtain, the reaction condition is gental, the integration cost is 50% lower than that of the prior art.
Owner:凌青云
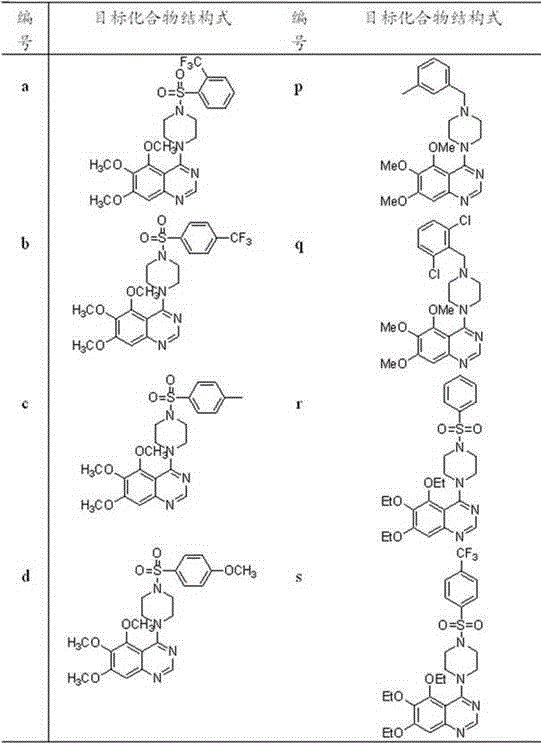
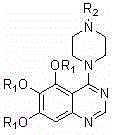
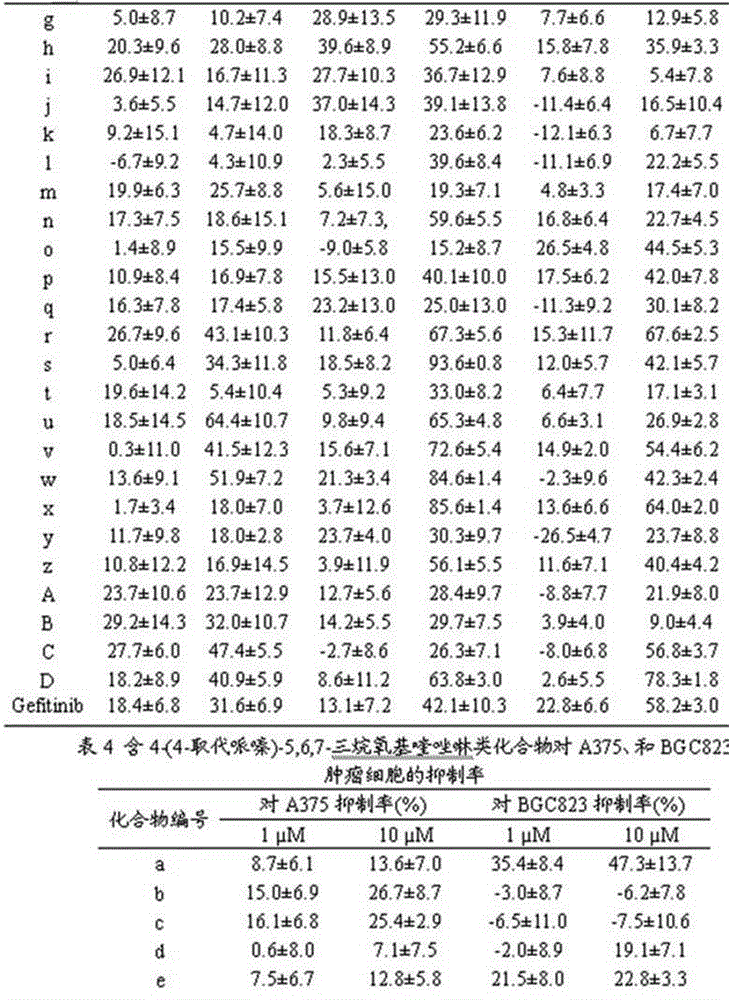
4-(4-substituted piperazine)-5,6,7-trialkoxy quinazoline type compound as well as preparation method and application of 4-(4-substituted piperazine)-5,6,7-trialkoxy quinazoline type compound
The invention discloses a 4-(4-substituted piperazine)-5,6,7-trialkoxy quinazoline type compound as well as a preparation method and application of the 4-(4-substituted piperazine)-5,6,7-trialkoxy quinazoline type compound, wherein the compound structure is shown as the following general formula (I). A series of novel 4-(4-substituted piperazine)-5,6,7-trialkoxy quinazoline type compounds are synthesized by using 2,3,4-trihydroxy benzoic acid, dimethyl sulfate, diethyl sulfate, methanol, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrogen gas, formamide, phosphorus oxychloride, N-Boc piperazine, hydrochloric acid, aryl sulfonyl chloride and 4-aromatic (benzyl, pyridine and morpholine propyl) substituted piperazine as raw materials through multiple steps. The compound has a better anticancer effect and a plant fungus inhibition effect and can be used for preparing anticancer medicine and plant fungus resistance pesticide. (I) is shown as the accompanying drawing.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
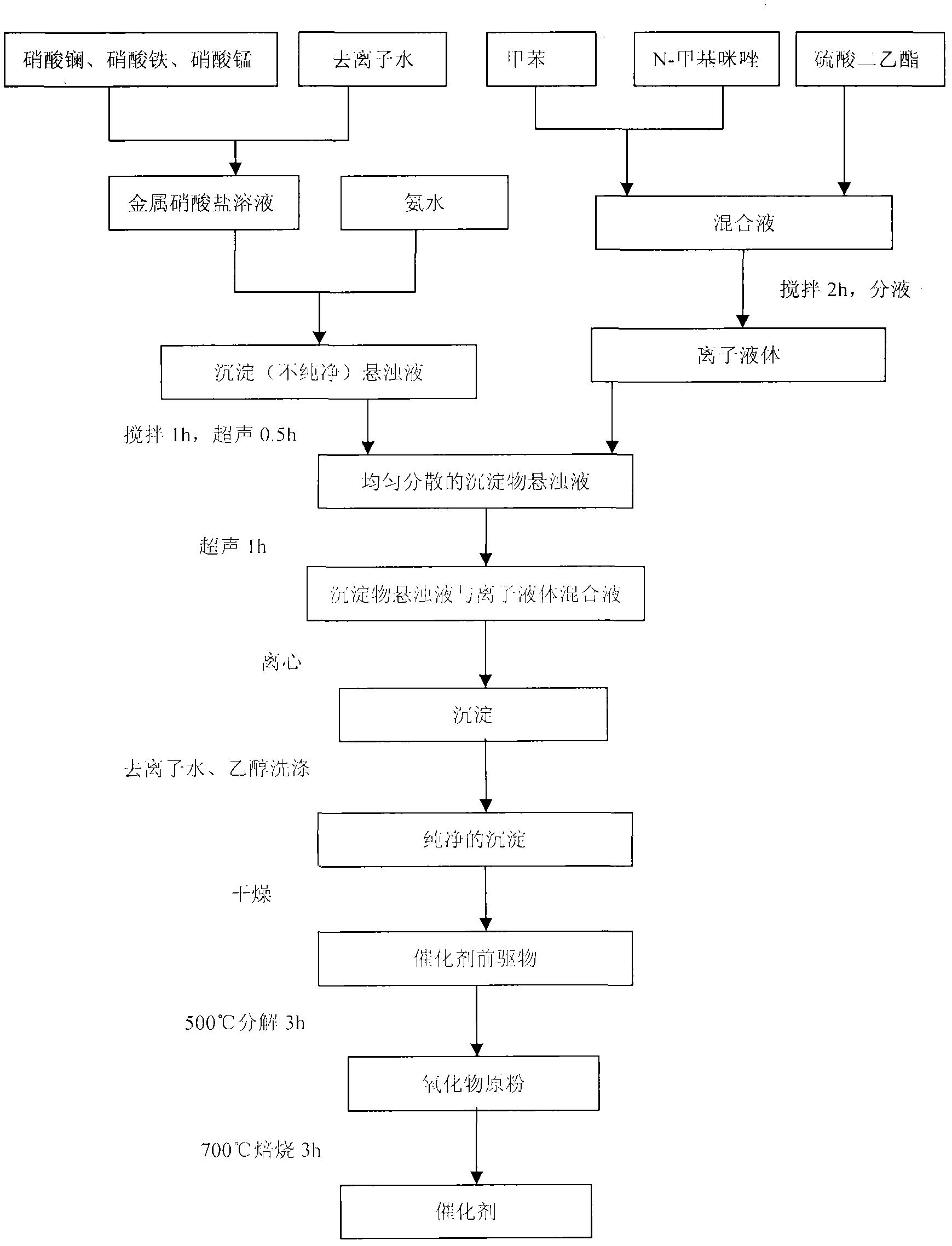
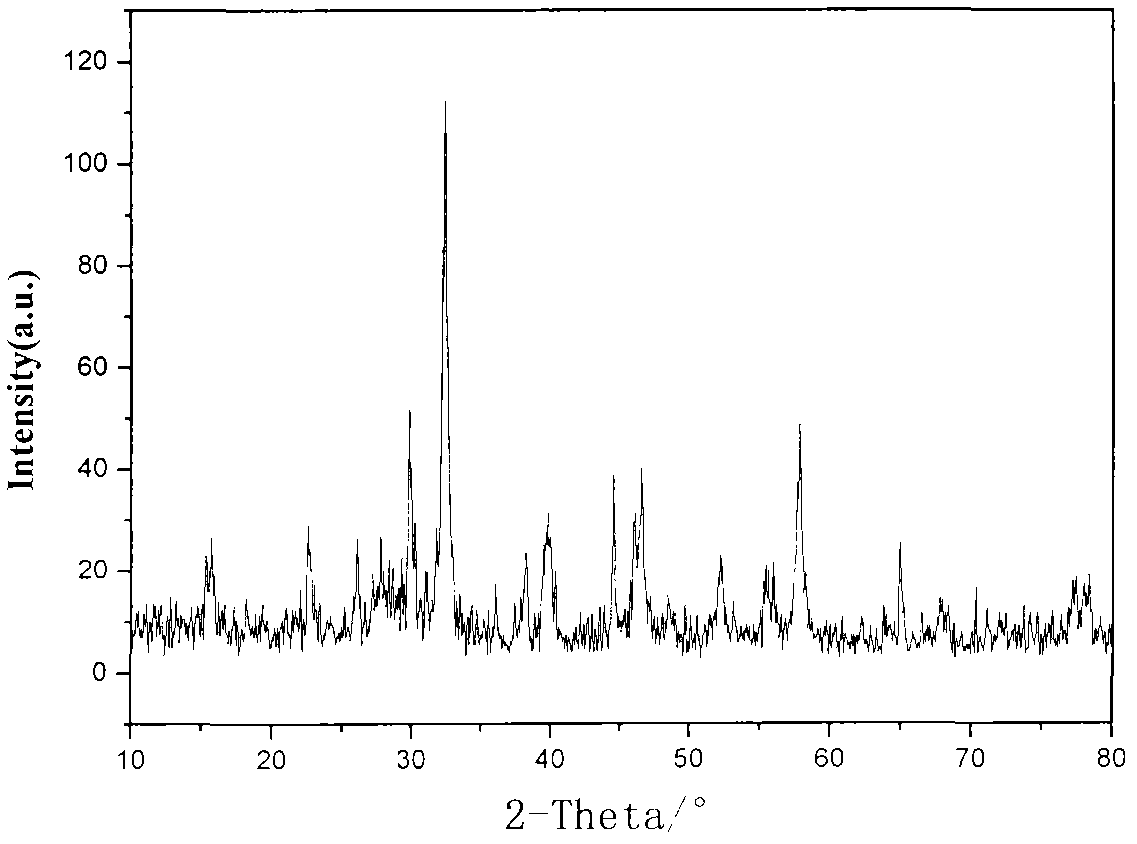
Preparation method of rare-earth composite oxide photocatalyst
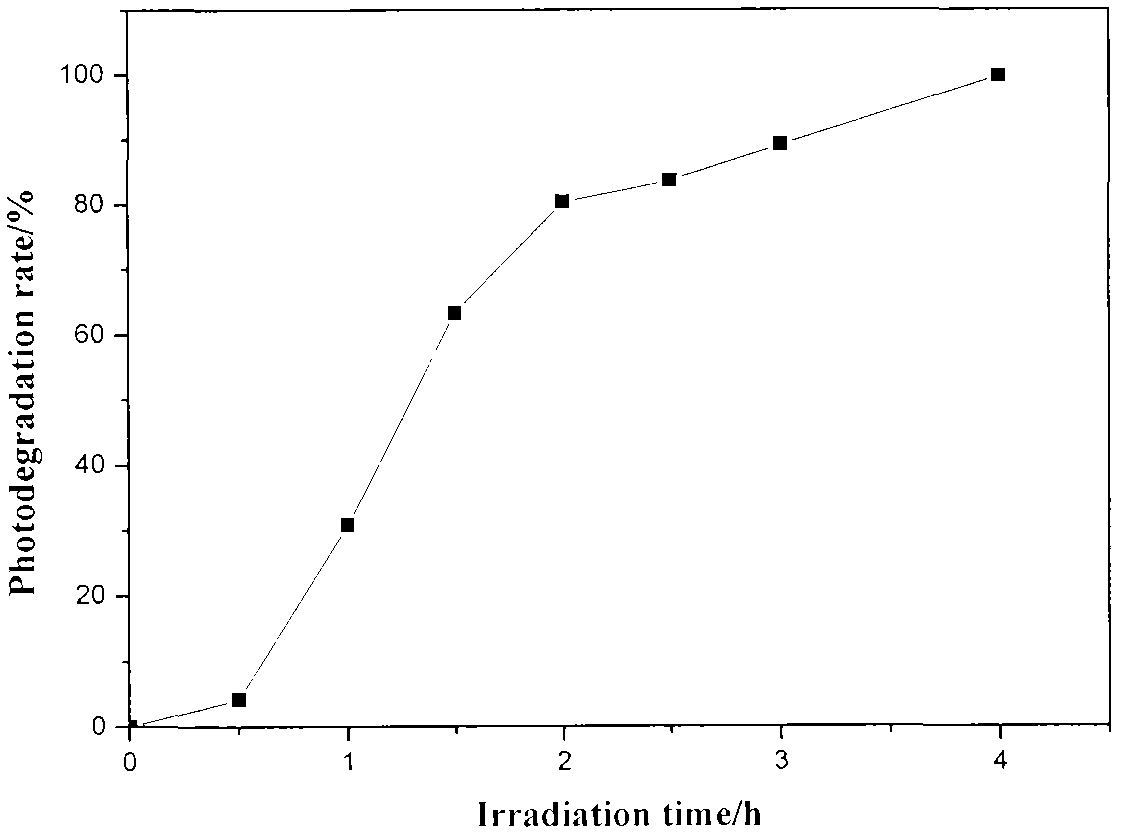
InactiveCN102078815AFully adsorbedPromote resultsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAir atmosphereRare earth
The invention discloses a preparation method of a rare-earth composite oxide photocatalyst. The main preparation technology comprises the following steps: dissolving La(NO3)3.nH2O, Fe(NO3)3.9H2O and 50% Mn(NO3)2 in deionized water to prepare the mixed solution of metal nitrates; adding ammonia water in the mixed solution to adjust the pH value, stirring, performing ultrasonic dispersion, adding ionic liquid prepared from N-methylimidazole, toluene and diethyl sulfate, performing ultrasonic dispersion continuously; and performing centrifugal separation, washing the obtained precipitate, dryingthe precipitate in an oven, roasting in a muffle furnace to obtain oxide raw powder, and roasting in air atmosphere to finally prepare the new La-Fe-Mn catalyst. The preparation method has simple process and mild reaction conditions; and the prepared catalyst has better catalytic activity in the reaction that the catalytic degradation of phenol is performed under visible light.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
L-leucine high-yield bacterium and fermentation method using the same for L-leucine production
It is an L-leucine high-yield bacterium and the production of L-leucine with invoice method, belonging to biological engineering field. The invented bacterial is a corynebacterium glutamicum JH-27, using corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032 as starting strain, mutagenizing separately with diethyl sulfate, nitrosoguanidine and ultraviolet, adding separately analogue of branched chain amino acid into minimum medium and sulfaguanidine into complete medium and breeding to prepare, being an L-leucine high-yield bacterium resistant sulfaguanidine and branched chain amino acid, compared with starting strain, producing L-leucine with the strain and invoice method, it expresses the ability of accumulation of highly qualified L-leucine. Shaking flask and culturing JH-27 for 60 hours, the yield of L-leucine is 30-32 g / l. Fermenting in fermenter of 5L for 55 hours, the yield of L-leucine is 40g / l.
Owner:WUXI JINGHAI AMINO ACID
Method for cultivating Monascus strain for highly yielding Monacolin K
InactiveCN108165497AIncrease reproductive rateIncrease productionFungiMutant preparationRed yeast riceMallet
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a Monascus strain for highly yielding Monacolin K. The method comprises the following steps: separating and purifying red yeast rice to obtain a Monascus colony, adding the prepared Monascus colony to a medium prepared from agar, a potato juice, a mallet juice, lactic acid, anhydrous ethanol, sodium nitrate and potassium dihydrogen phosphate to prepare Monascus spores, flushing the medium with sterile sodium chloride water to obtain a Monascus spore bacterium suspension, performing ultraviolet irradiation on the Monascus spore bacterium suspension to achieve physical mutagenesis, adding a diethyl sulfate solution to achieve further mutagenesis, and mixing the obtained Monascus spore bacterium suspension with rice flour to rapidly breed the Monascus strain. An atomic irradiation mutagenesis technology is combined with a high-temperature piling cultivation technology, so the breeding rate of the Monascus strain in the medium is effectivelyincreased, the number of the Monascus strain is increased, and the metabolic Monacolin K is also increased, thereby the yield of the Monacolin K is increased.
Owner:吕玲
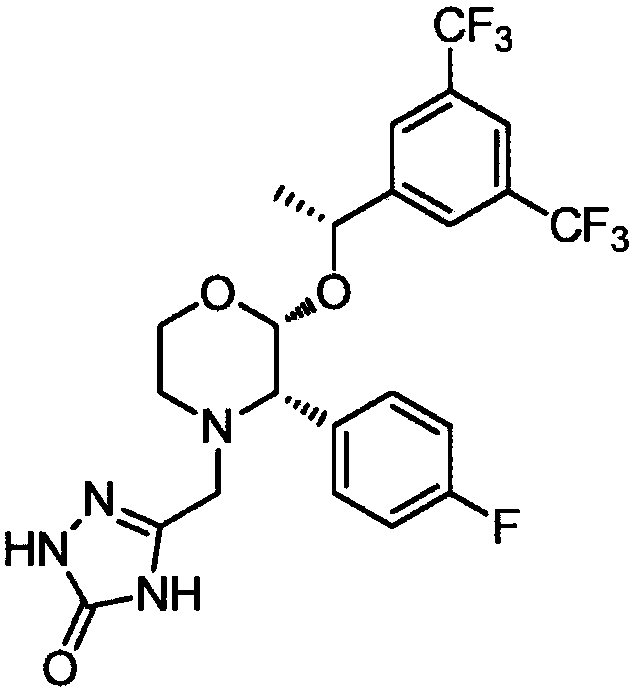
Preparation process of aprepitant
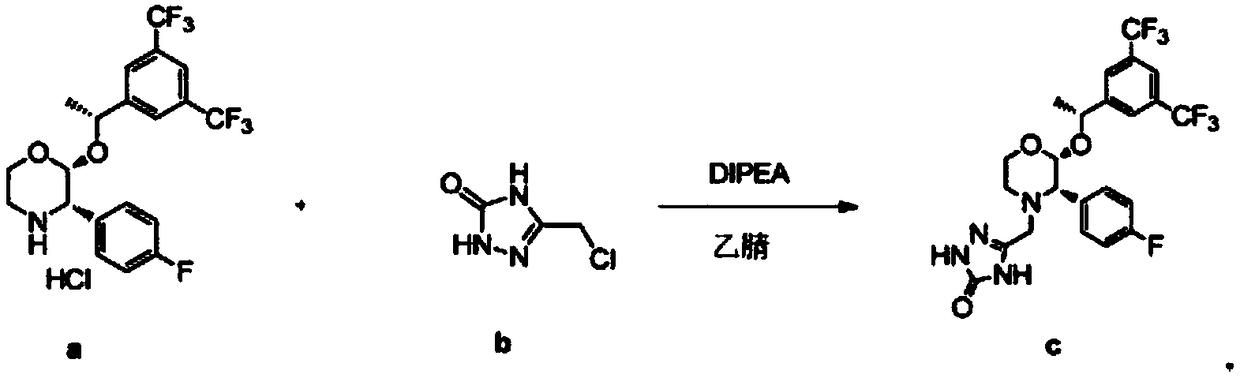
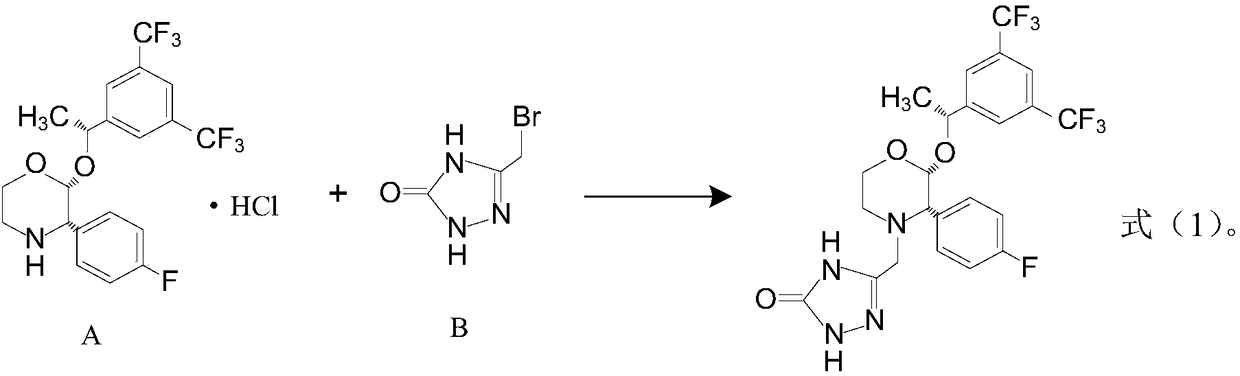
The invention discloses a preparation process of aprepitant. The process comprises the steps as follows: Step 1, a compound A and a compound B are firstly added to a mixed solvent of N,N-dimethylformamide and triethylamine to be stirred and dissolved to obtain a mixed solution; Step2, adding lithium diisopropylamide to the mixed solution in a nitrogen atmosphere and performing uniform mixing; Step3, dropwise adding a diethyl sulfate xylene solution under conditions of nitrogen shielding and stirring; Step 4, after addition, conducting a stirring reaction at 30-35 DEG C for 12-15 h under shielding of nitrogen; Step 5, separating and purifying a reaction product in Step 4 to obtain a final aprepitant product. By process improvement and formula optimization, the aprepitant synthesis processhas the characteristics of mild reaction condition, low cost and the like and is suitable for large-scale industrial production; the synthesized aprepitant product has low impurity content and high purity, and the yield of aprepitant is greatly increased.
Owner:成都晶富医药科技有限公司
Process for synthesizing diacetylmonoxime ethyl ether by continuous reactions in microtube
ActiveCN103304442AReduce operating costsThe concentration is basically constantOximes preparationPotassium hydroxideOil phase
The invention discloses a process for synthesizing diacetylmonoxime ethyl ether by continuous reactions in a microtube. In the process, diacetylmonoxime and diethyl sulfate are directly reacted to synthesize diacetylmonoxime ethyl ether in a condition that the temperature is 30-45 DEG C and the pressure is 0.1MPa in the presence of strong base with the adoption of a continuous reaction technology in the microtube, wherein the strong base is sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide or an alcamine compound. In the process, diethyl sulfate, the alkali liquor and diacetylmonoxime are respectively fed by a precise micro pump, wherein diacetylmonoxime sequentially mixed with the alkali liquor and diethyl sulfate reacts in a microtube reactor. The product through a heat exchanger is condensed and collected at low temperature, and is stewed and layered by a chromatographic separator. A water phase is extracted and separated by a micro extraction tower, and an oil phase containing diacetylmonoxime ethyl ether is rectified and purified by a rectifying tower, so that the final product diacetylmonoxime ethyl ether is obtained. The process is high in selectivity of diacetylmonoxime ethyl ether, mass transfer and heat transfer can be remarkably enhanced, and hydrolysis of diethyl sulfate is effectively avoided. The process is simple in process, long in stable transfer time, low in cost, easy to amplify and suitable for the industrialized production requirement.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Photoinitiator for ultraviolet light curing agent and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102993340AInitiation efficiency is highReduce the amount requiredOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAlcoholUltraviolet lights
The invention relates to an aromatic ester photoinitiator for ultraviolet light-like curing and a manufacturing method thereof. The preparation method of the photoinitiator comprises two ways: a first method is to react aromatic carboxylic acid with alcohol in the presence of a catalyst to prepare the aromatic ester photoinitiator; and a second method is to react in two steps, ensure that the aromatic carboxylic acid and the alkali are acted under a backflow condition to obtain corresponding carboxylate and react the carboxylate with the diethyl sulfate to prepare the aromatic ester photoinitiator at the temperature of 0-50 DEG C. Two manufacturing methods provided by the invention have the advantages of easy operation, rapid reaction, high yield and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN JIURI NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
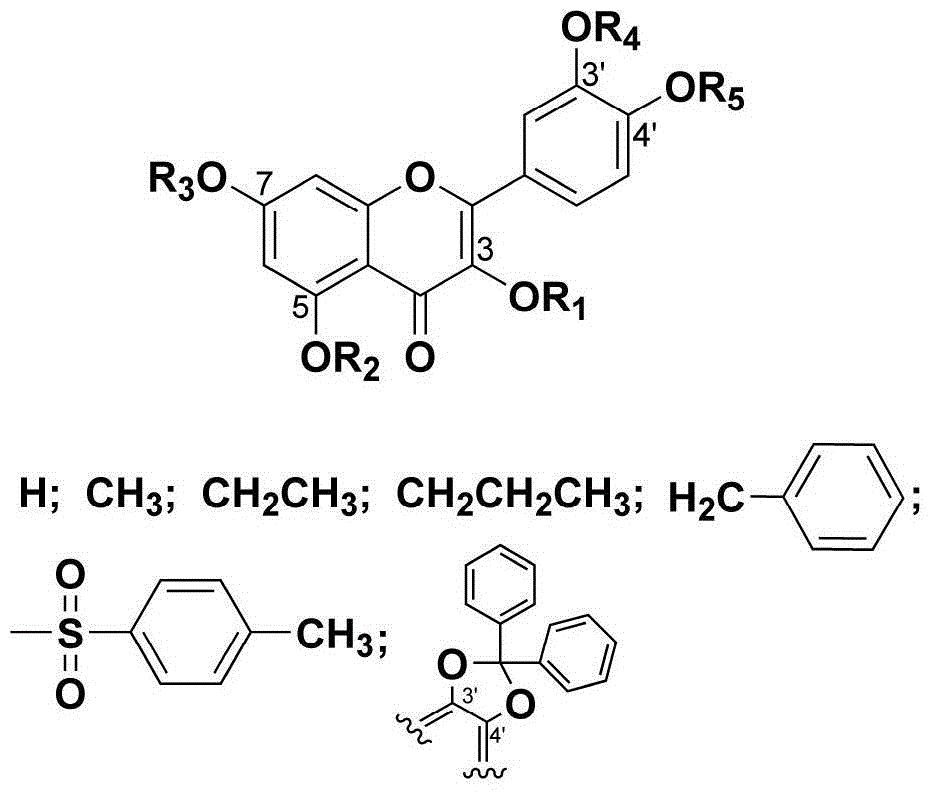
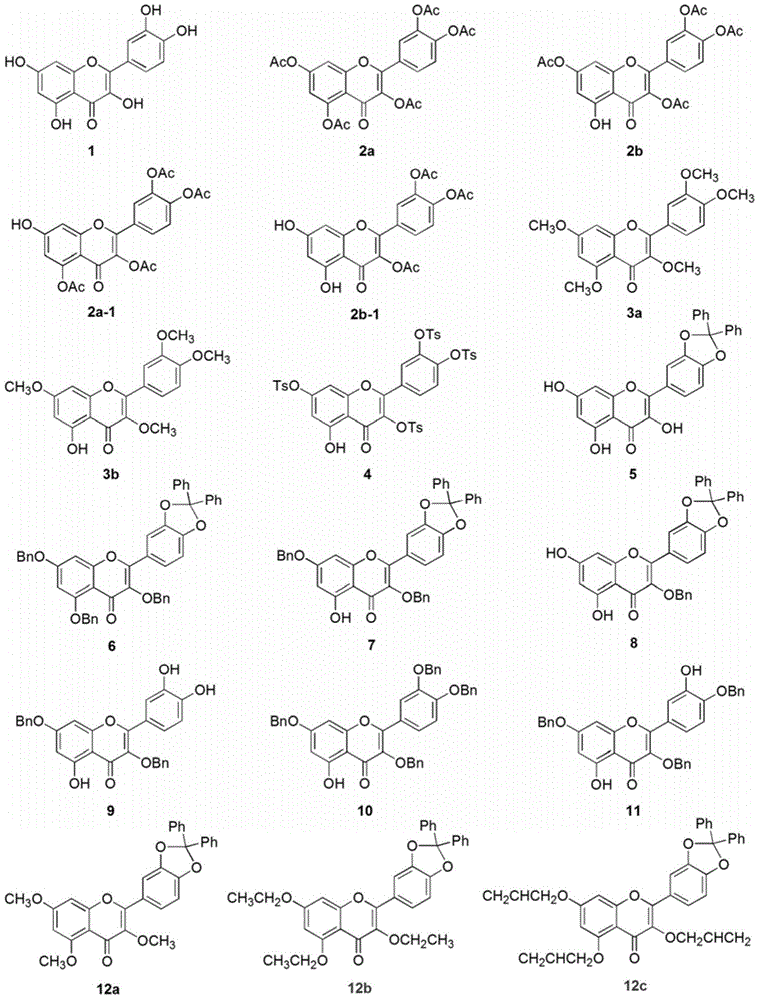
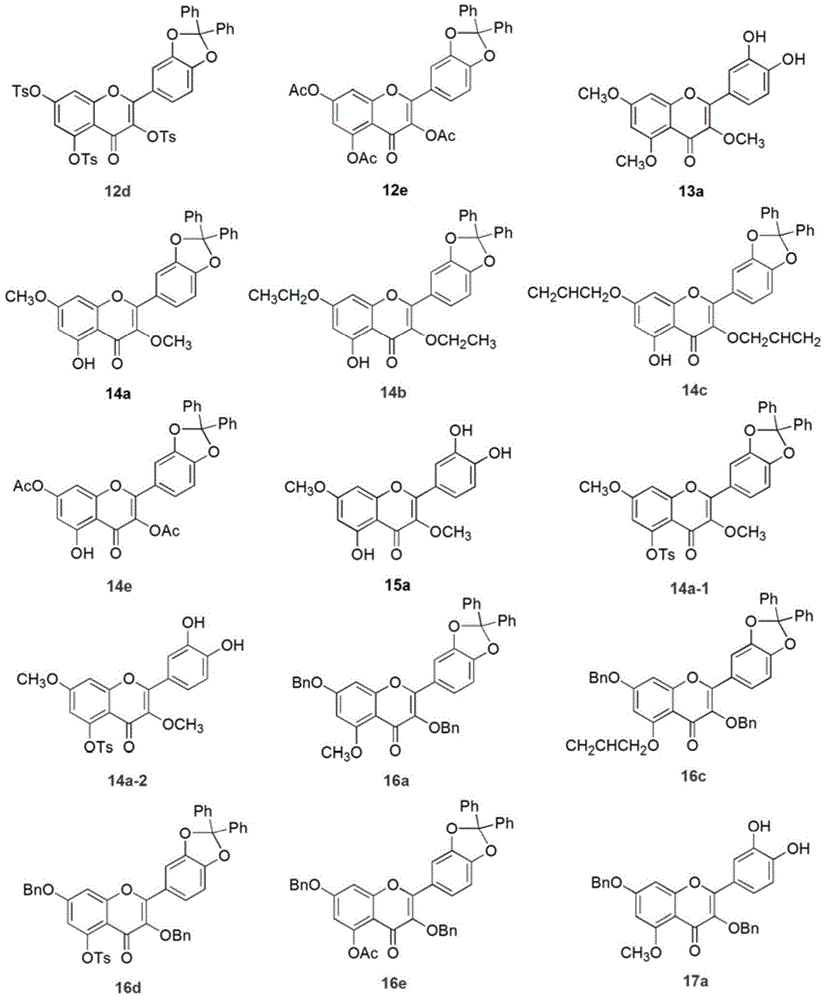
Quercetin derivative and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104557891AAntiproliferative activityIncrease proliferative activityOrganic chemistryDigestive systemAcetic anhydrideQuercetin derivatives
The invention discloses a quercetin derivative and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly using dichlorodiphenylmethane to protect quercetin o-diphenol hydroxyl, combining a benzyl protection group to obtain the selectively protected quercetin derivative, and then independently reacting with dimethyl sulfate, diethyl sulfate, allyl bromide, paratoluensulfonyl chloride and acetic anhydride respectively to generate corresponding quercetin derivatives. All of the prepared derivative compounds have NRK-49F proliferation activity inhibition superior to that of quercetin. The quercetin derivatives 20a-1, 14a-1 and 23d-1 compositely replaced by methyl and p-tosyl have higher inhibition NRK-49F proliferation activity, and the inhibition ratio respectively reaches 86.33%, 78.04% and 75.91%. Thus, the currently obtained quercetin derivative compounds have obvious inhibition effect on kidney fibroblast NRK-49F proliferation.
Owner:南京盈博医药生物技术创新研究院有限公司
Polyurethane retardant catalyst, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a polyurethane retardant catalyst, and a preparation method and application thereof. The polyurethane retardant catalyst is a reaction product of diethyl sulfate and triethylenediamine. Compared with the existing amine catalyst, the polyurethane retardant catalyst has better catalysis retarding effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAFON NEW MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Method for determining dimethyl sulfate and diethyl sulfate in electronic and electric products
InactiveCN103592377AEasy to separateAccurate measurementComponent separationInjection volumeHplc method
The invention discloses a method for determining dimethyl sulfate and diethyl sulfate in electronic and electric products. The method comprises the following steps: adding a certain amount of acetone into a prepared sample, carrying out ultrasonic extraction to obtain the target compounds, deriving the target compounds with p-nitrophenol under alkaline conditions, extracting the derivation products with diethyl ether, and separating and detecting the ethyl ether extraction solution with a high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) system. The chromatographic column uses an octadecyl bonded silica gel as the filler; the detector is a diode array detector; the mobile phase is a mixed solvent composed of 40-60 vol% of methanol and 60-40 vol% of water; the detection wavelength is 305nm; the column temperature is 40-60 DEG C; and the sample injection volume is 5-20 muL. After the systemic comparative studies, the invention establishes an HPLC method for determining contents of dimethyl sulfate and diethyl sulfate in electronic and electric products for the first time; and the method has the technical characteristics of favorable separating effect, high determination accuracy, high sensitivity, high specificity, simple and quick analysis and the like.
Owner:青岛谱尼测试有限公司
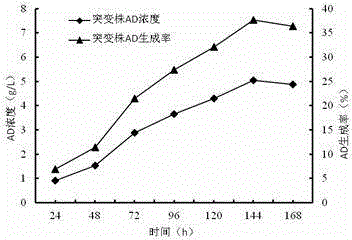
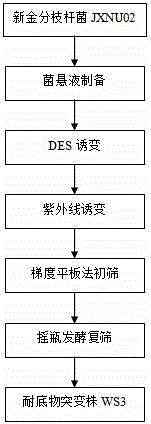
Androstenedione substrate-tolerant mutant strain and mutation breeding method thereof
InactiveCN104531548AImprove the ability to degrade phytosterolsStrong conversion potentialBacteriaMutant preparationMycobacterium neoaurumPhytosterol
The invention discloses an androstenedione substrate-tolerant mutant strain and a mutation breeding method thereof. A mutant strain of mycobacterium neoaurum WS3 is preserved in China center for type culture collection with an accession number of CCTCC NO: M 2014322, and the preservation date is July 4, 2014. According to the invention, mycobacterium neoaurumJXNU02 is used as a starting strain; compound mutation is carried out by diethyl sulfate and an ultraviolet mutation method; primary screening is performed by a gradient plate method; secondary screening and verification are carried out by a shake flask fermentation method; and thus the mutant strain of mycobacterium neoaurum WS3 with high substrate tolerance and genetic stability is bred. The method of the invention effectively improves the capability of mycobacteria for degrading phytosterol to generate androstenedione, provides an excellent strain for producing androstenedione by a microbiological method, and has important significance on the pharmaceutical industry of our country.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
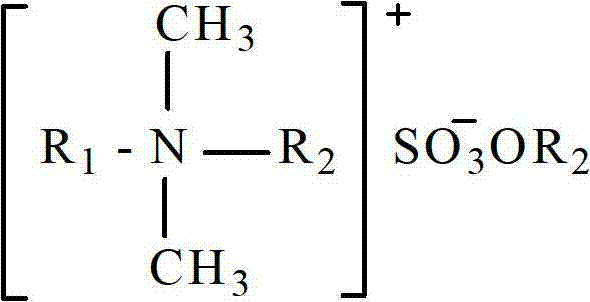
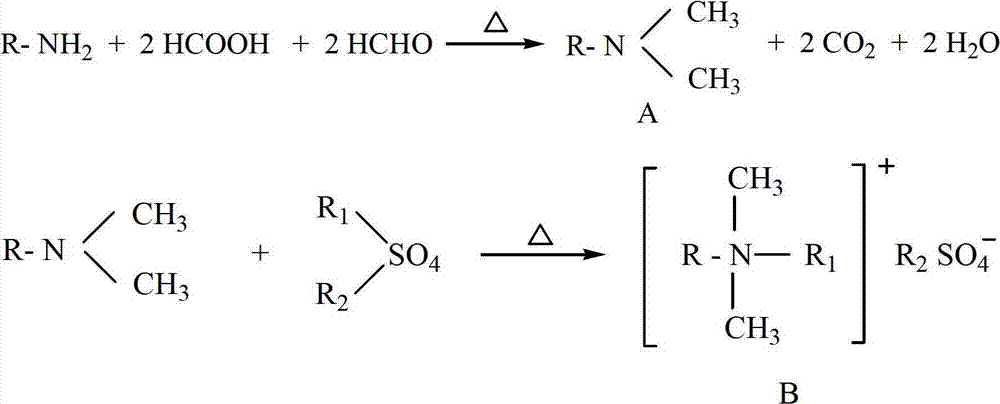
Halogen-free environmentally-friendly cationic antistatic agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102775697AEffective AntistaticSimple preparation processOrganic compound preparationSulfuric acid esters preparationFiberTemperature resistance
The invention discloses a halogen-free environmentally-friendly cationic antistatic agent and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: reacting alkyl primary amine with formic acid and formaldehyde in a solvent to obtain tertiary amine and then reacting with dimethyl sulfate or diethyl sulfate to prepare the cationic antistatic agent. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps of: adding the alkyl primary amine, the solvent and the formic acid into a reaction kettle, adding formaldehyde solution while strongly mixing at a temperature of 50-100 DEG C, reacting for 5-25 hours, neutralizing a solvent removing agent and drying to obtain alkyl tertiary amine; and reacting the alkyl tertiary amine with the dimethyl sulfate or the diethyl sulfate for 1-10 hours at a temperature of 50-100 DEG C to obtain the cationic antistatic agent. The halogen-free environmentally-friendly cationic antistatic agent has the advantages of stable and good anti-antistatic agent effect, easily-available raw materials, simple process, temperature resistance, low cost and convenience in use and can be widely applied to coatings, plastics and fibers, and other properties of products are not affected in the use process.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Pseudonocardia and application thereof
ActiveCN110527650AFully tap the application valueAvoid the many downsides of convertingBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial transformationProtoplast
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, and in particular to an application of pseudonocardia in catalyzing microbial transformation of sterol compounds by hydroxylation. The pseudonocardia is Pseudonocardia HRW001 obtained by isolating and purifying an original strain from soil of Laoshan National Forest Park in Nanjing, subjecting the original strain to compound mutagenesis through ultraviolet, microwave, diethyl sulfate and protoplast fusion technology, and screening. As identified by the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the pseudonocardia isclassified and named Pseudonocardia sp. HRW001, and has a deposit number of CGMCCC No. 17524. According to the application, after liquid fermentation of the pseudonocardia, a large number of bacterialcells are obtained, and the microbial transformation of sterol compounds by hydroxylation is catalyzed. The pseudonocardia has high catalytic activity and specificity. The Pseudonocardia HRW001 of the invention is an important microorganism for catalyzing the microbial transformation of sterol compounds by hydroxylation, can catalyze the hydroxylation of various sterol compounds, and has great application value.
Owner:NANJING HERON PHARMA SCI & TECH CO LTD
Aspergillus usamil high in yield of acid protease and application of aspergillus usamil high in yield of acid protease
The invention discloses aspergillus usamil 801-2 high in yield of acid protease and belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation. The aspergillus usamil is preserved with the preservation number CCTCC NO: M2013601 in China Center for Type Culture Collection on November 24, 2013. The aspergillus usamil 801-2 is obtained by subjecting aspergillus usamil 801 yielding the acid protease, preserved by a laboratory, to ultraviolet and lithium chloride compound mutagenesis, nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis and diethyl sulfate mutagenesis sequentially and subjecting a mutant to isolation and screening, and grows faster than a starting strain, the diameter of a colony is 82mm after the aspergillus usamil 801-2 grows at the temperature of 28 DEG C for four days, and enzyme activity of the acid protease in fermentation liquor can be up to 13000-14000U / mL which is 8 times of that of the starting strain. The acid protease secreted by the aspergillus usamil 801-2 is tolerable to high temperature, and under the same conditions, in order to reach same enzyme activity, tolerable temperature of the acid protease is averagely increased by 8-12 DEG C than that of the starting strain.
Owner:湖南新鸿鹰生物工程有限公司
Method for preparing 3-N,N-dimethylamino-ethyl acrylate
ActiveCN101293850ALow reaction temperatureReduce manufacturing costOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationOrganic layerRoom temperature
The invention provides a preparation method of 3-N,N-dimethylaminoethyl acrylate. The preparation process comprises adding diethyl sulfate to dimethylformamide (DMF) at a molar ratio of 1:(1.1-1.3) for reacting to generate condensated salt; mixing with diethyl malonate, solvent and catalyst, heating until refluxing and reacting for 3-10 hours, and cooling to room temperature; filtering to remove the salt, washing the filtrate with water, mixing the organic layer, and depressing and distilling to remove solvent; and high vacuum distilling the residue, and collecting fraction of 80-85 DEC C / 5mmHg. The obtained 3-N,N-dimethylaminoethyl acrylate has yield and purity higher than that of optimal values in prior art.
Owner:SUZHOU KAIYUAN MINSHENG SCI & TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



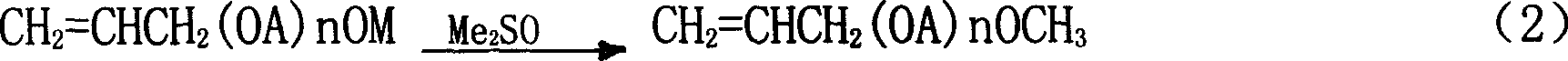
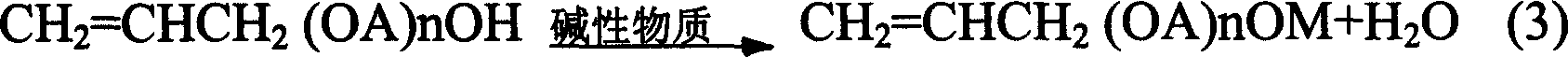
![4-[2-(substituted benzylidene) hydrazino]-5, 6, 7-trialkoxy quinazoline compound and preparation method and application 4-[2-(substituted benzylidene) hydrazino]-5, 6, 7-trialkoxy quinazoline compound and preparation method and application](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/290c5d53-41fe-44a3-b517-f07f5c094786/119717DEST_PATH_IMAGE007.PNG)
![4-[2-(substituted benzylidene) hydrazino]-5, 6, 7-trialkoxy quinazoline compound and preparation method and application 4-[2-(substituted benzylidene) hydrazino]-5, 6, 7-trialkoxy quinazoline compound and preparation method and application](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/290c5d53-41fe-44a3-b517-f07f5c094786/2012104354735100001DEST_PATH_IMAGE002.PNG)
![4-[2-(substituted benzylidene) hydrazino]-5, 6, 7-trialkoxy quinazoline compound and preparation method and application 4-[2-(substituted benzylidene) hydrazino]-5, 6, 7-trialkoxy quinazoline compound and preparation method and application](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/290c5d53-41fe-44a3-b517-f07f5c094786/2012104354735100002DEST_PATH_IMAGE002.PNG)