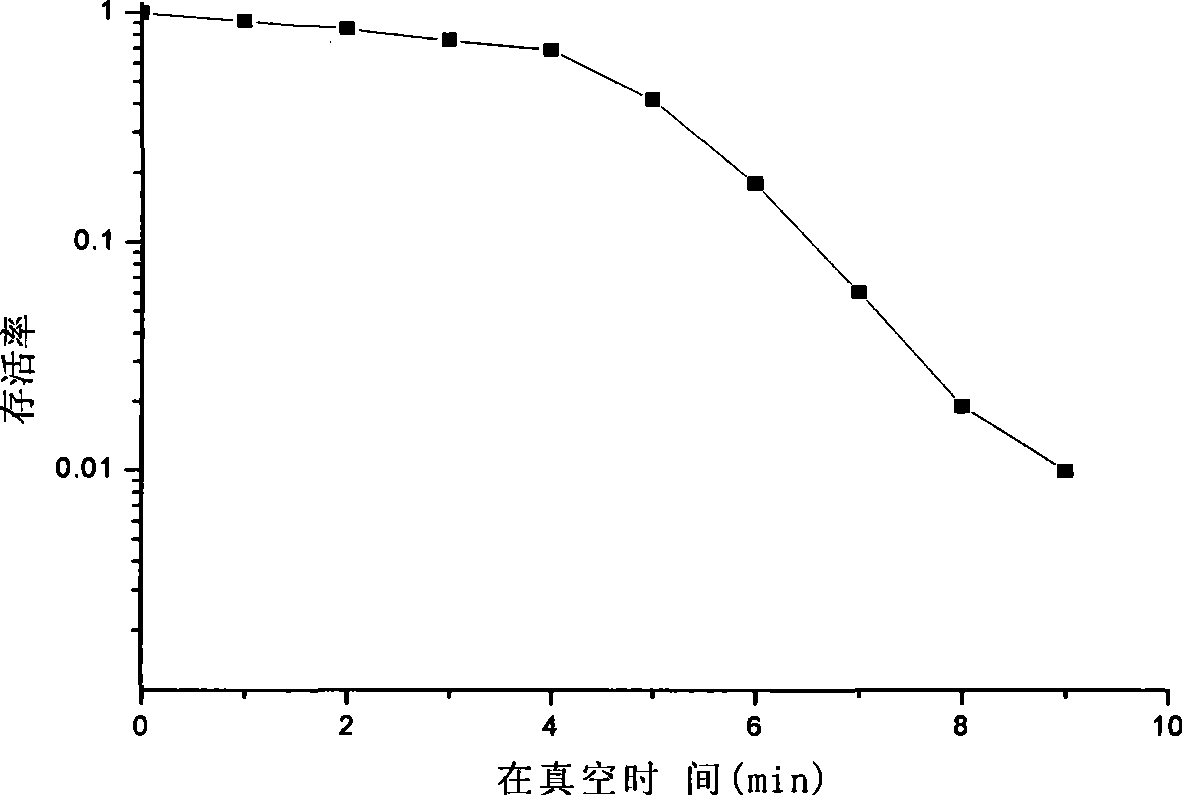
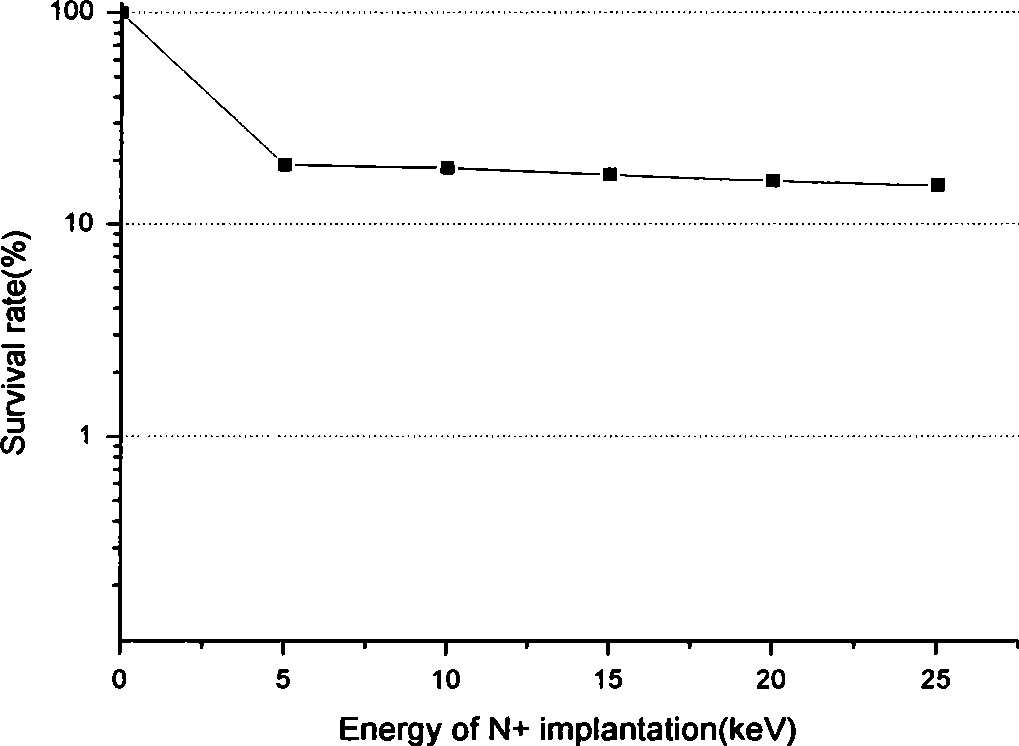
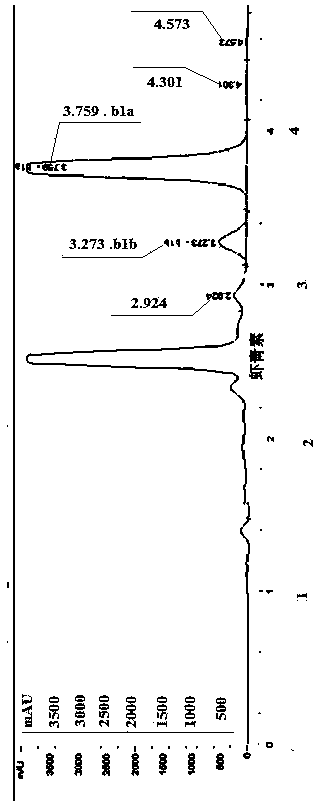
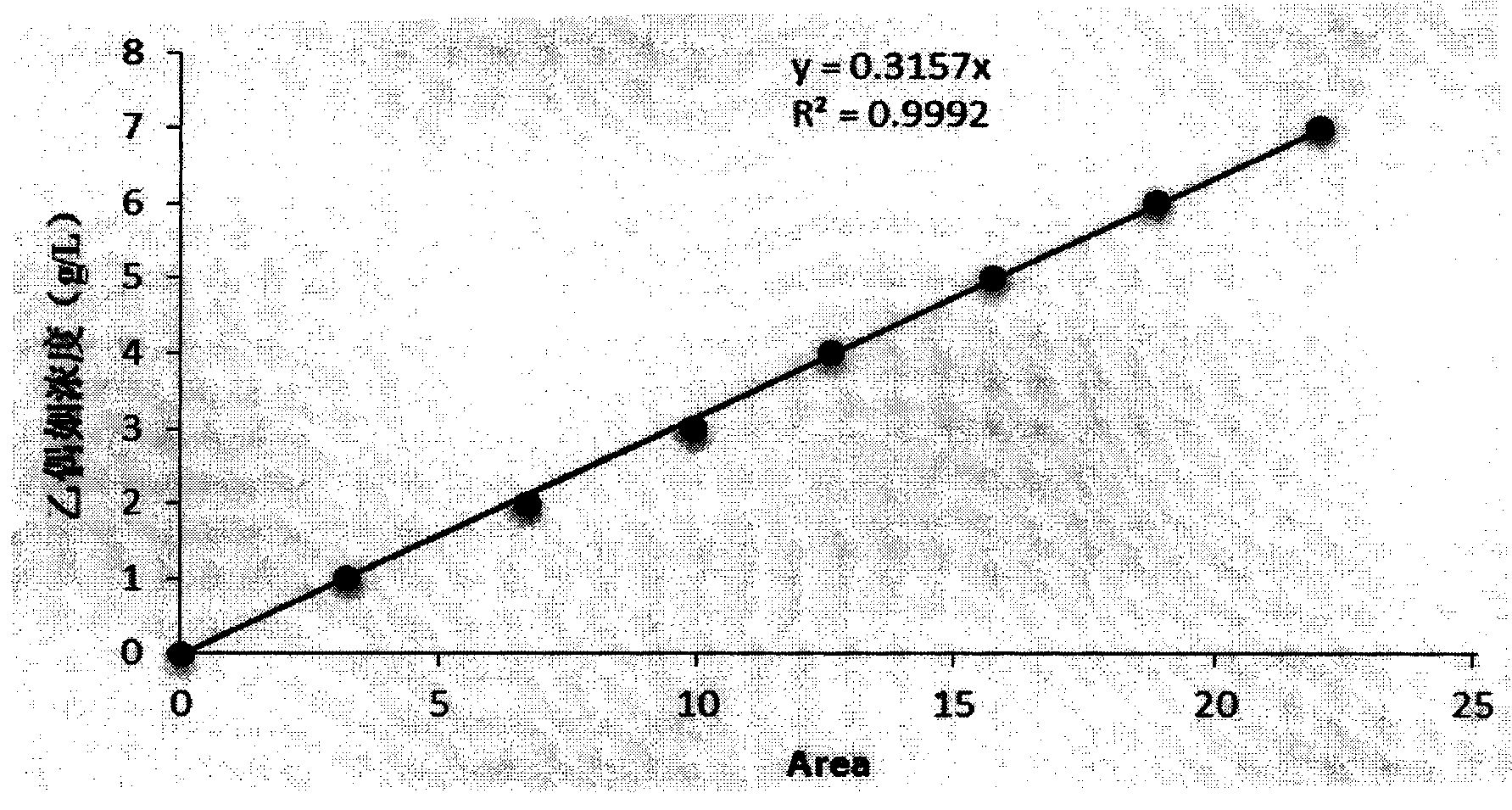
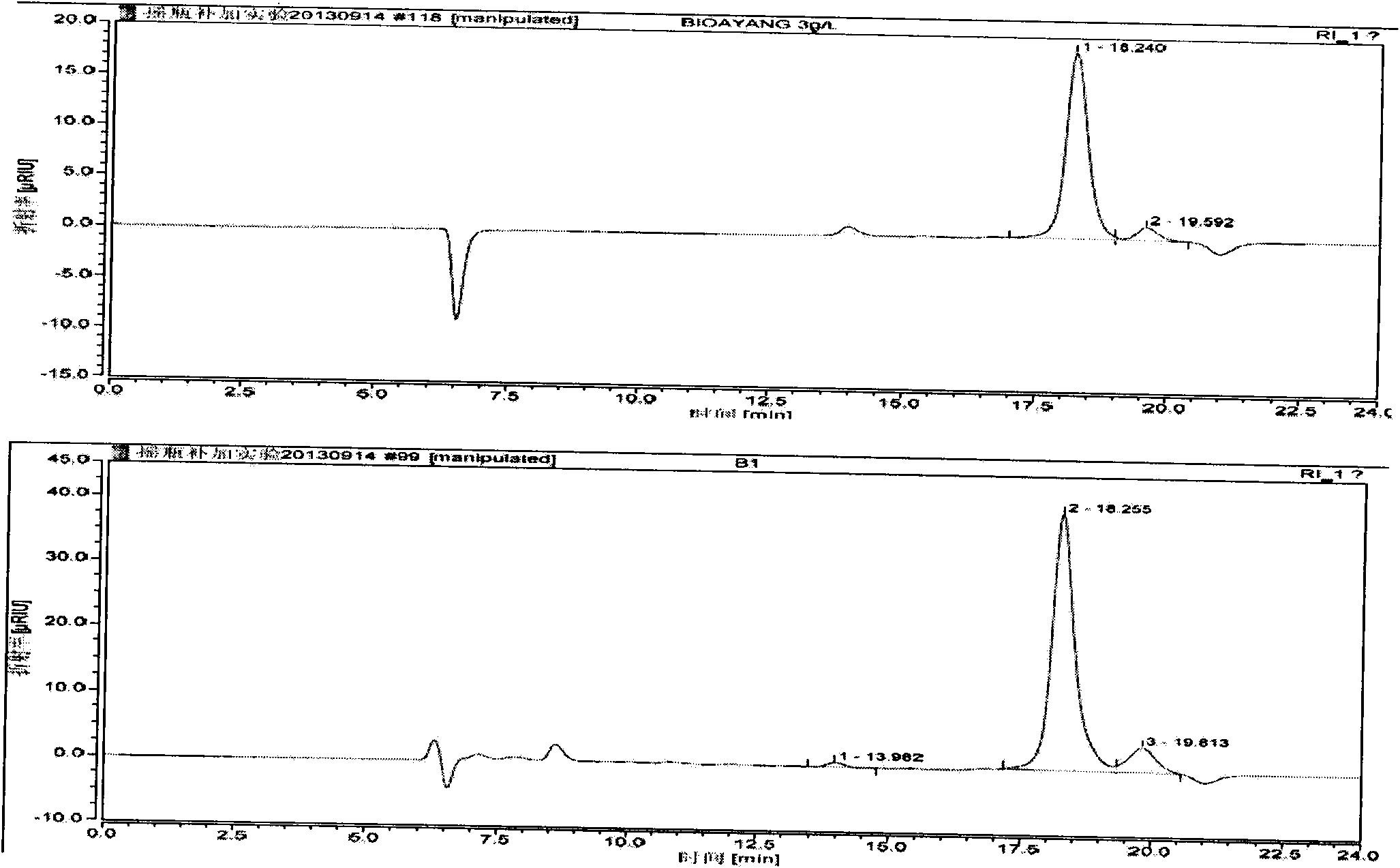
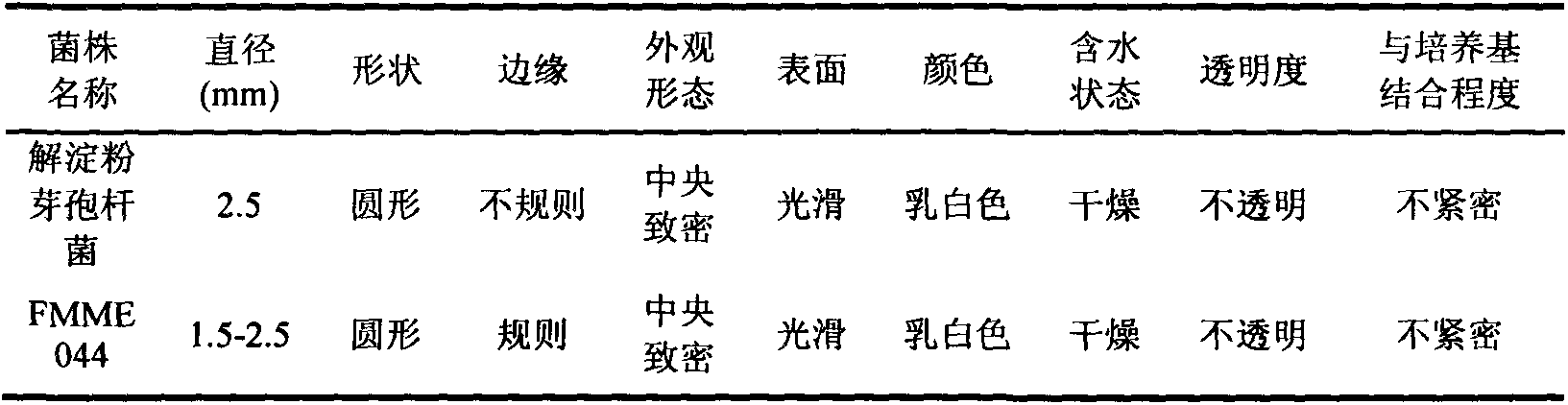
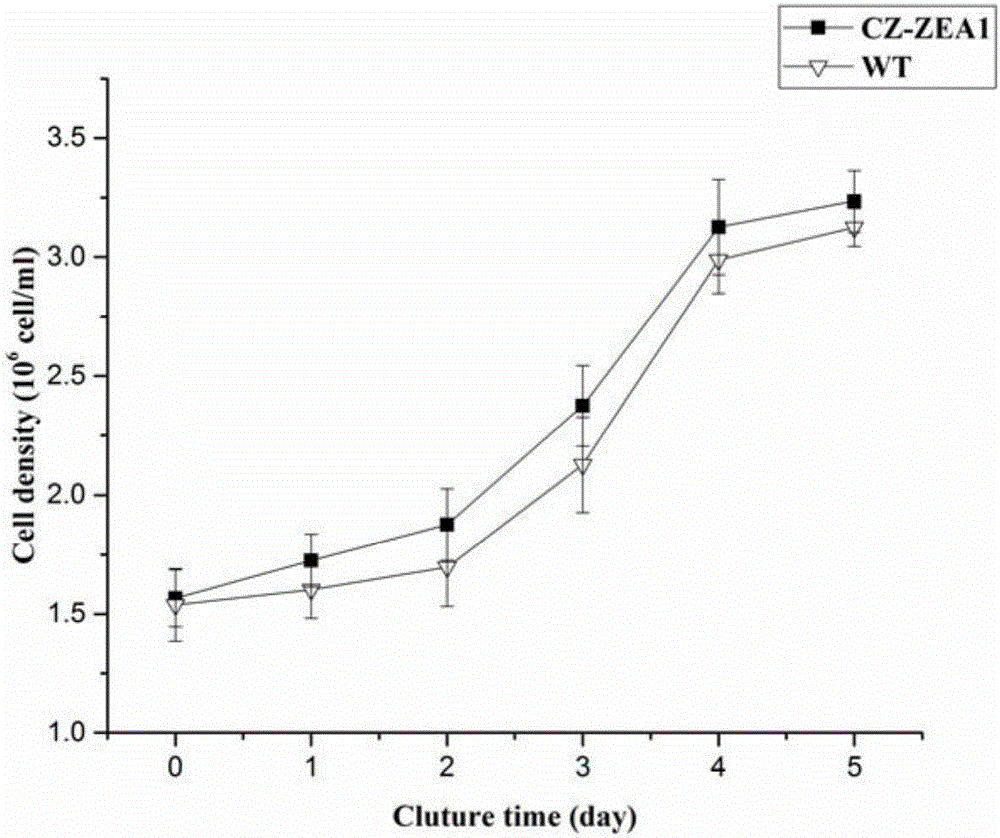
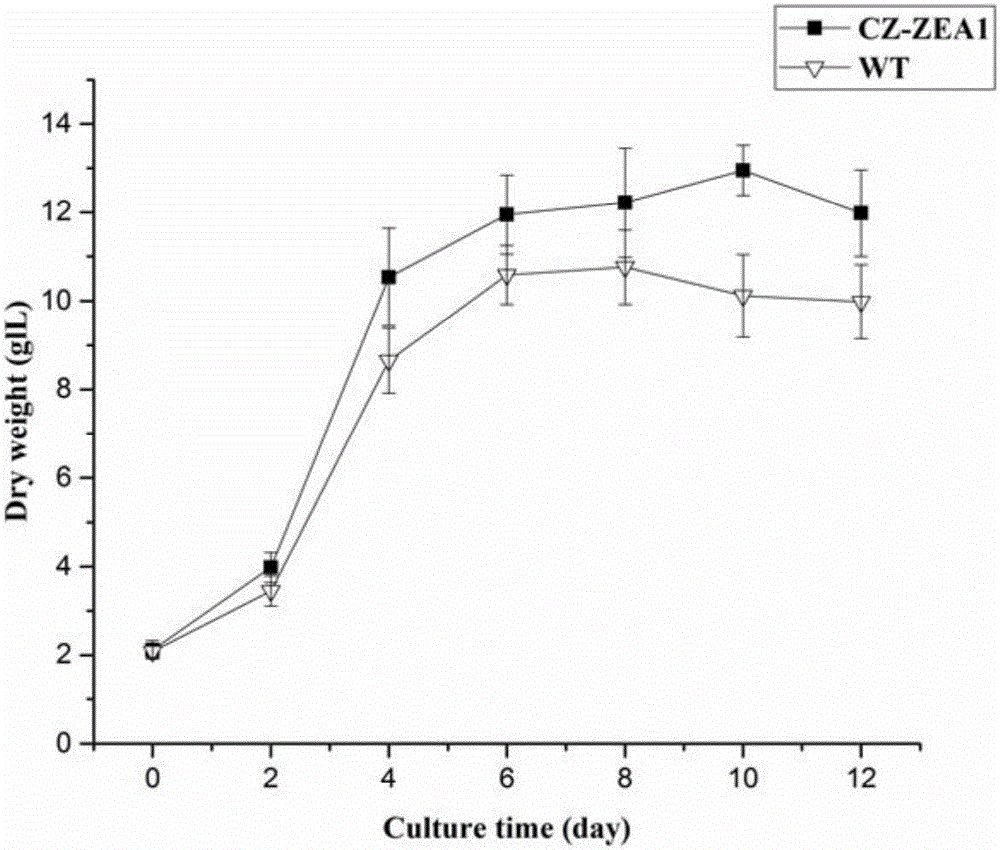
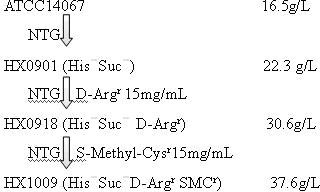Patents
Literature
88 results about "Nitrosoguanidines" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nitrosylated derivatives of guanidine. They are used as MUTAGENS in MOLECULAR BIOLOGY research.
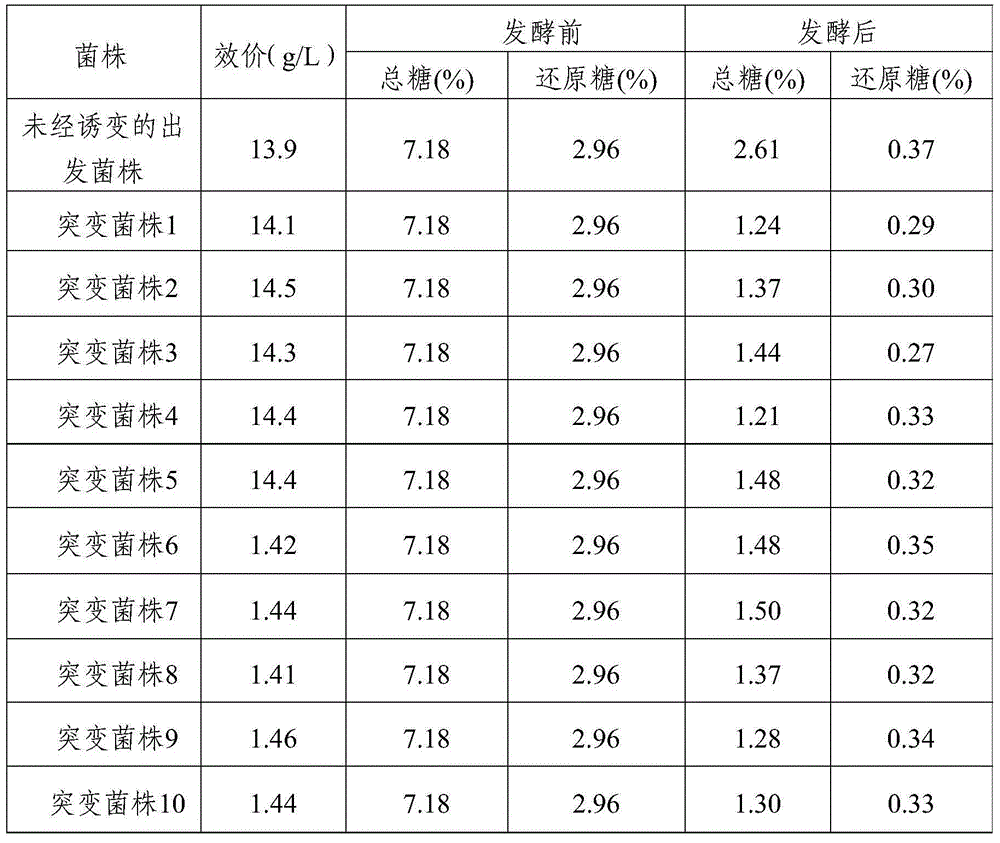
Strain capable of producing L-arginine and method for producing L-arginine by same
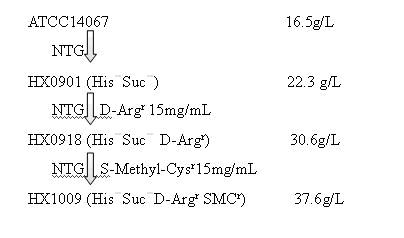
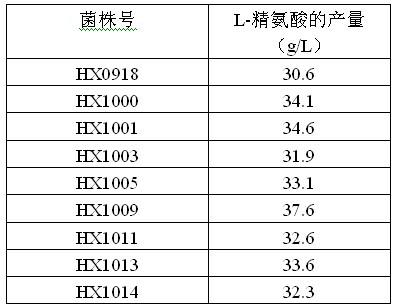
The invention relates to a strain capable of producing L-arginine and a method for producing the L-arginine by the strain and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. For the strain, Brevibacterium flavum ATCC 14067 is used as a starting strain; nitrosoguanidine is adopted to carry out mutagenesis step by step; mutant strains with histidine and succinic acid auxotrophic strains are screened out so as to cut off a competitive metabolic pathway; and mutant strains (His-, Suc-, D-Argr, SMCr) with resistances of arginine structural analogs and cysteine structural analogs are screened out. The strain is named as Brevibacterium flavum HX1009, is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center, has the preservation number of CGMCC No.4464 and has the genetic characters of histidine auxotroph His-, succinic acid auxotroph Suc-, D-arginine resistance D-Argr and S-methyl cysteine resistance SMCr for improving the yield of the L-arginine. Under the optimized condition, the L-arginine is produced by fermentation on a fermentation tank with the volume of 5L to 5M3 and the arginine production level achieves 50 to 70g / L.
Owner:FUJIAN GUTIAN PHARMA
Strain for producing L-leucine and method for producing L-leucine
The invention relates to the technical field of biological engineering, in particular to a strain for producing L-leucine and a method for producing the L-leucine. According to the method, corynebacterium glutamicum is induced by using ultraviolet rays and nitrosoguanidine, then key mutants leuAG561D and ilvBG235S which are beneficial to generation of the L-leucine can be generated, research shows that under mutation conditions of leuAG561D and / or ilvBG235S, feedback inhibition of synthesis routes of the L-leucine can be released, the yield of the L-leucine can be greatly increased, a strain which can generate a great deal of the L-leucine can be obtained, the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC NO.13408, the strain is capable of achieving efficient accumulation of the L-leucine in the fermentation process, and the L-leucine can be up to 4.7g / L.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
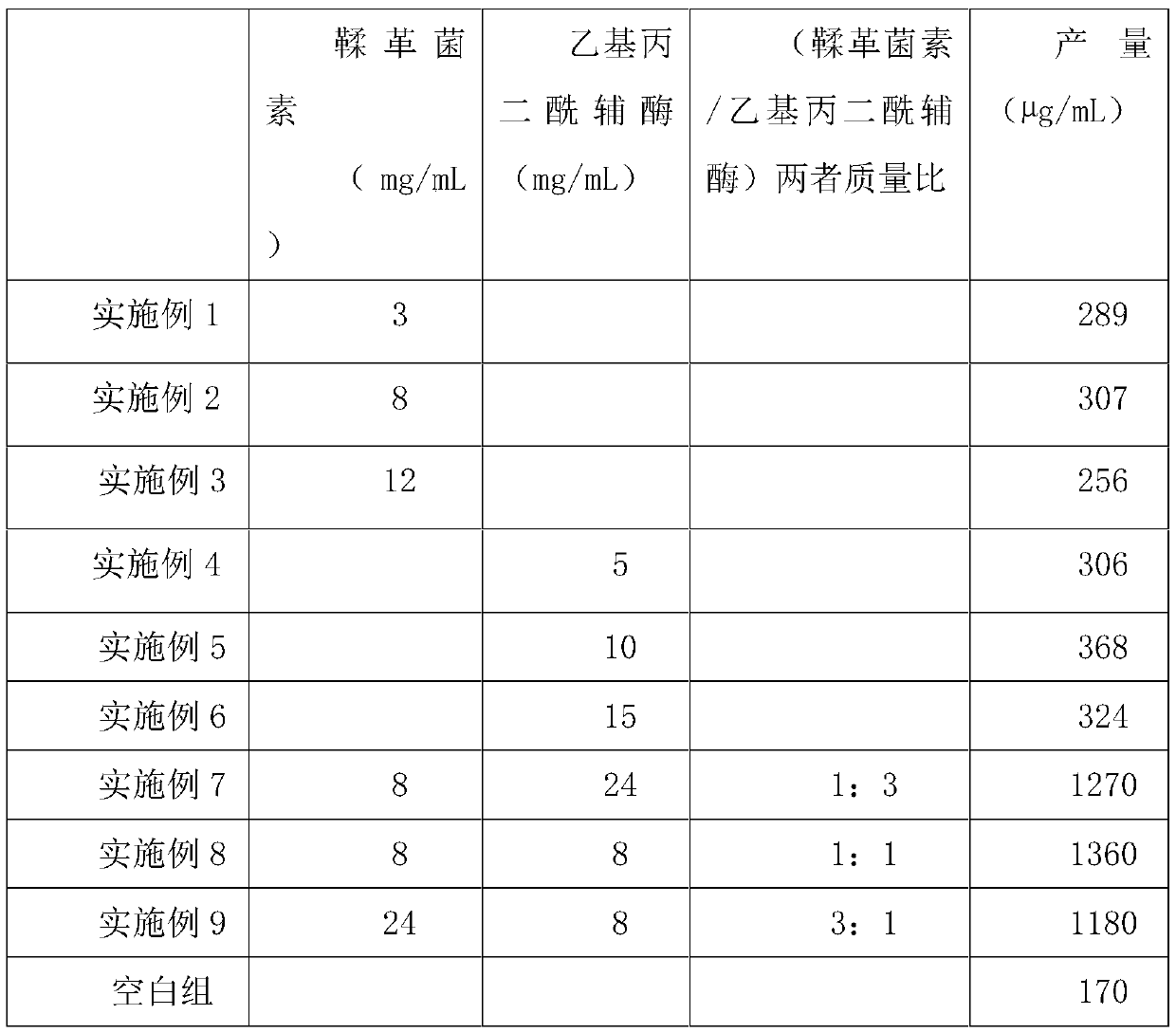
Abamectin producing bacterium and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102154168AImprove Abamectin B ComponentLess componentsBacteriaMutant preparationLithium chlorideHydroxylamine
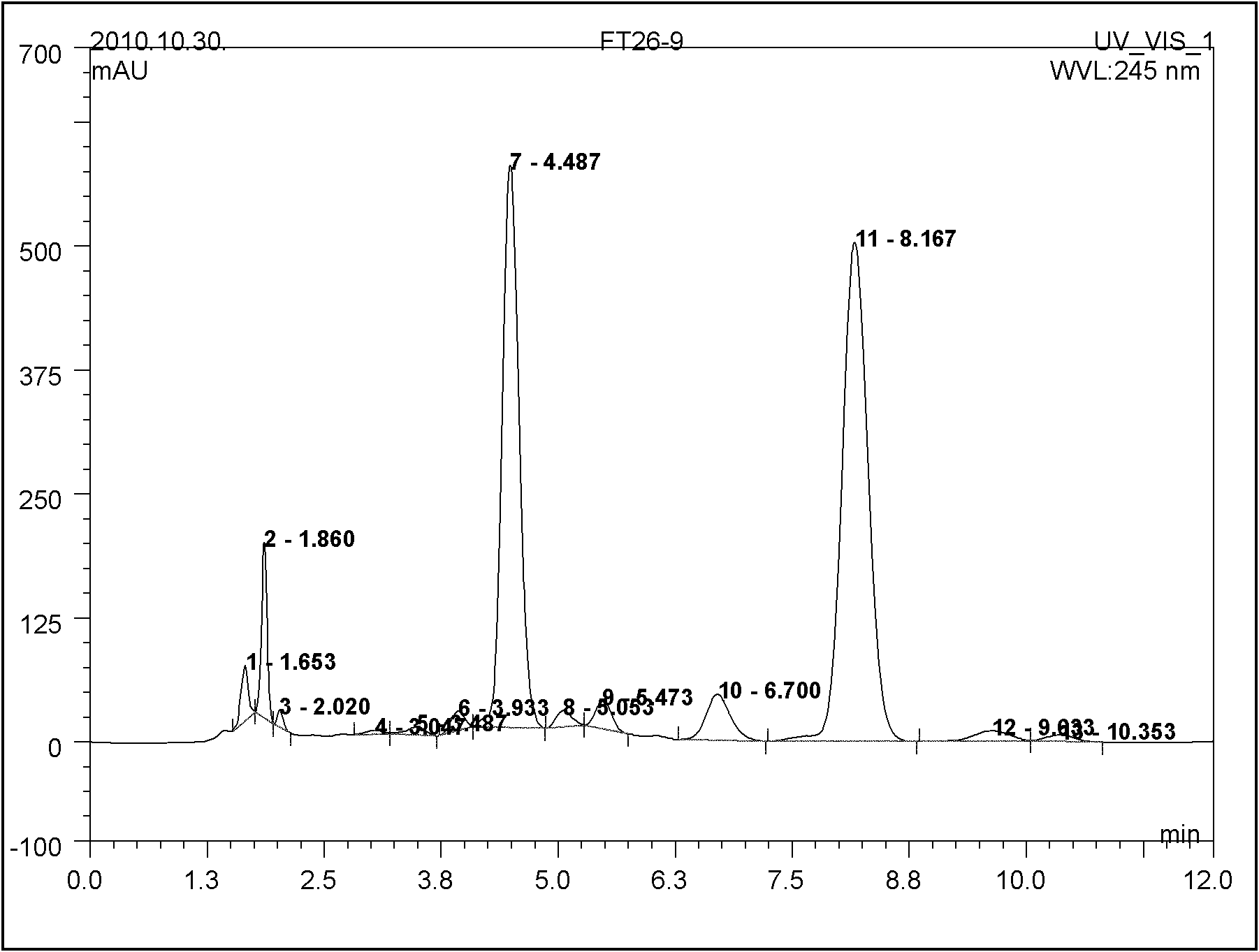
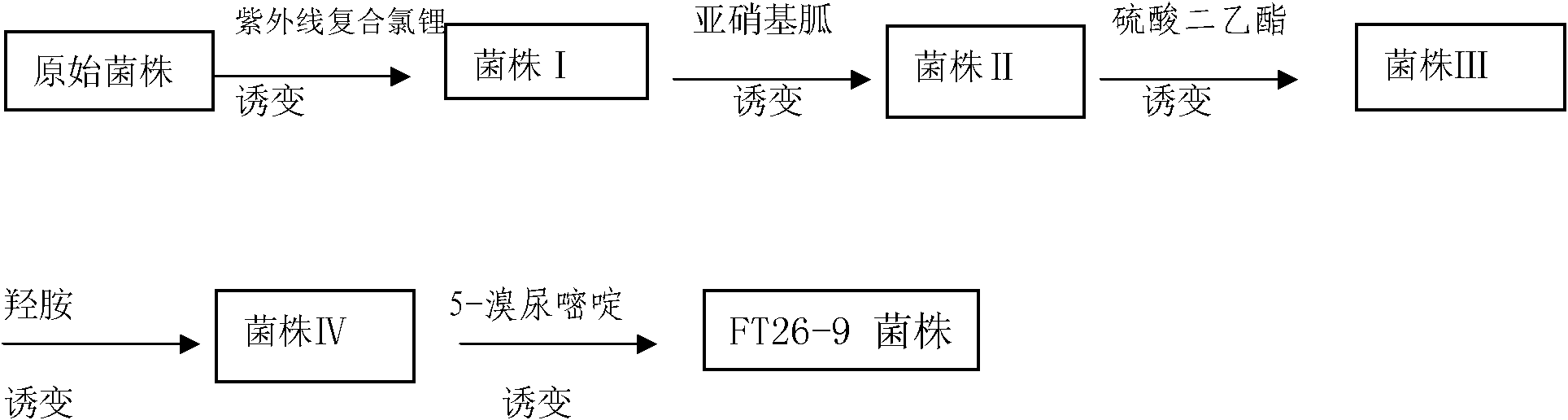
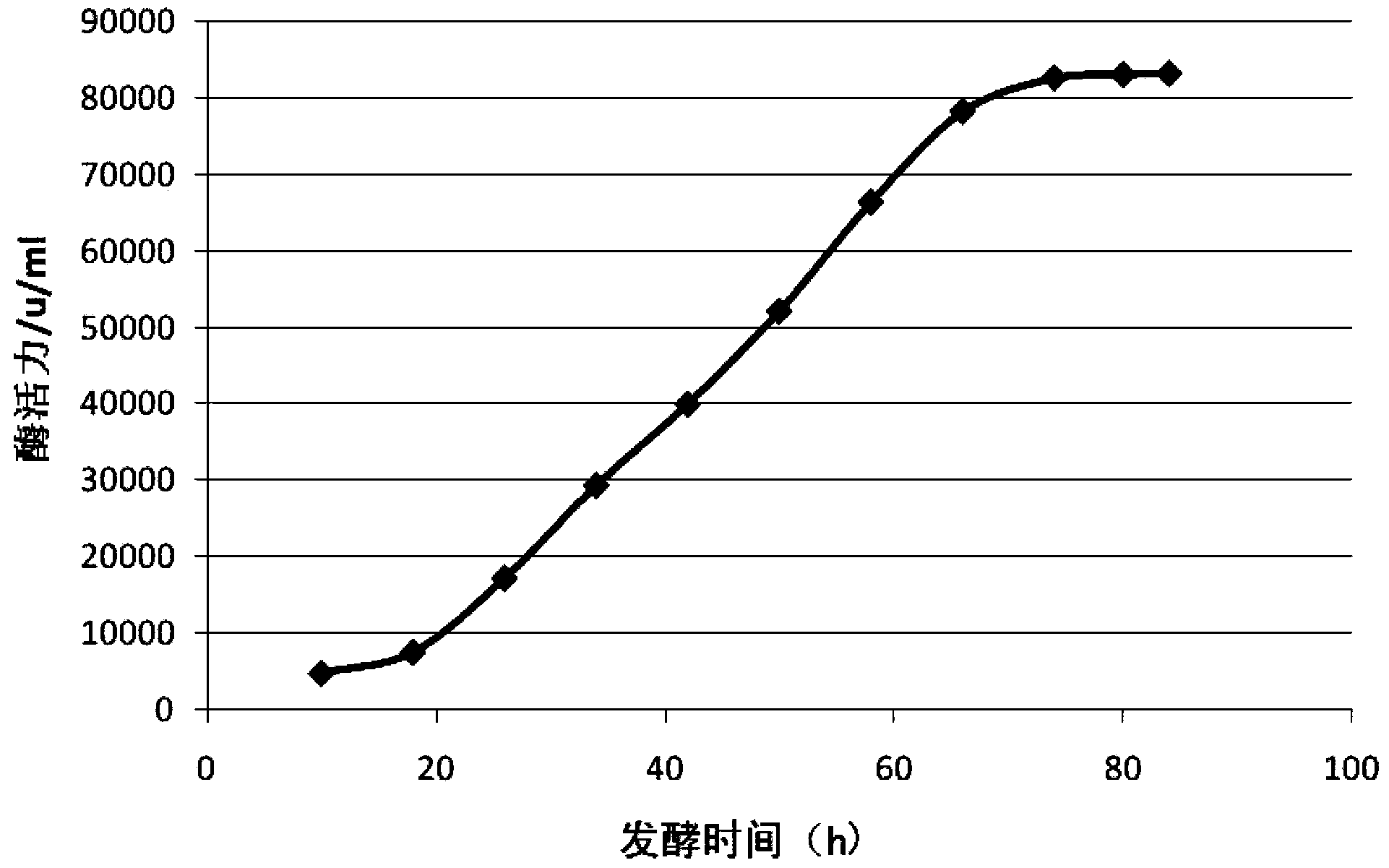
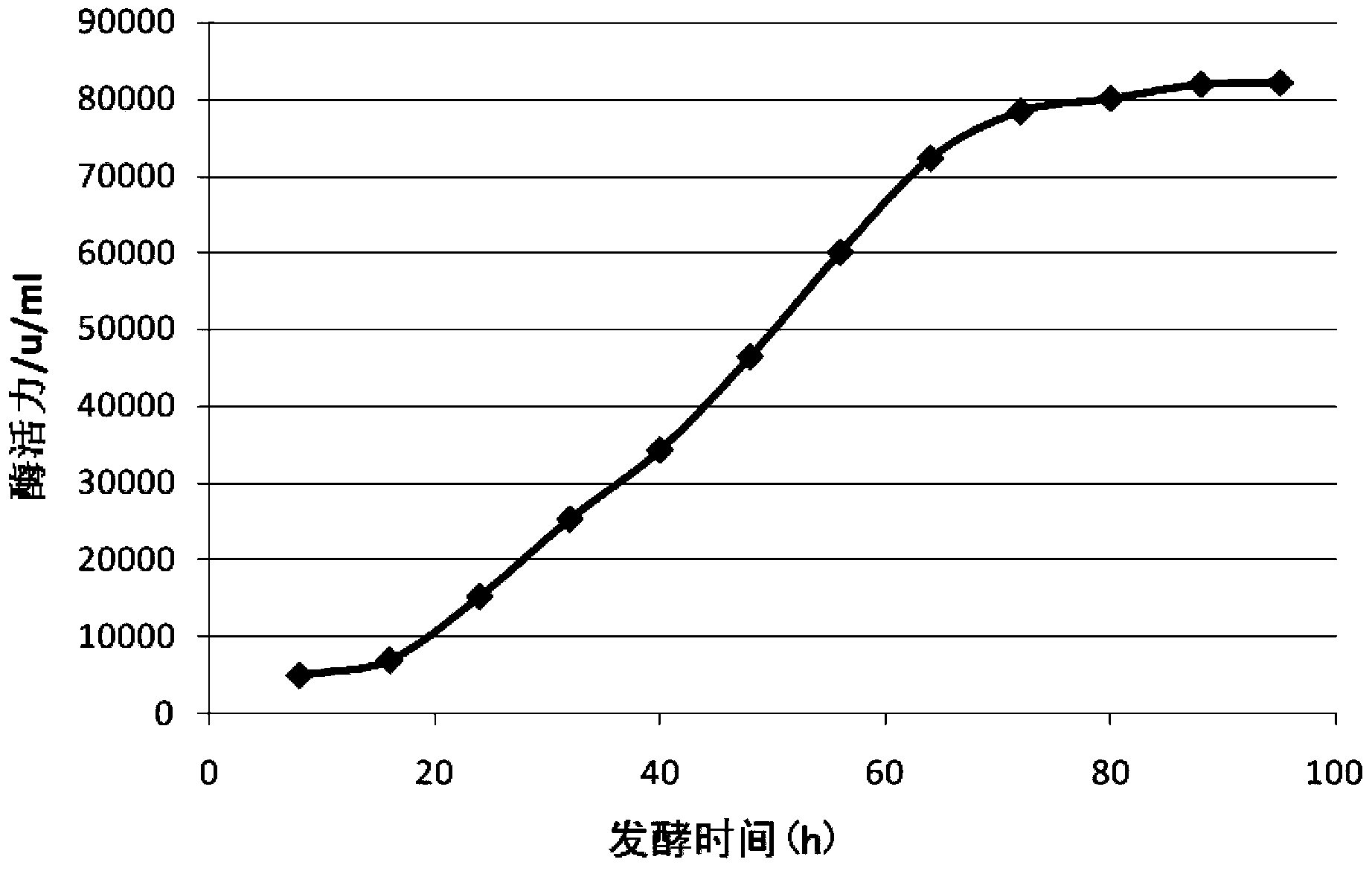
The invention discloses abamectin producing bacterium and a preparation method thereof. The collection name of the bacterium is FT26-9 and the collection number of the bacterium is CGMCC No.4341. The bacterium was collected on November 12th, 2010. The preparation method comprises: performing ultraviolet and lithium chloride combined mutation induction treatment of a starting strain; screening an induced-mutation strain; performing mutation induction by nitrosoguanidine and screening; performing mutation induction by diethyl sulfate and screening; performing mutation induction by hydroxylamine and screening; performing mutation induction by 5-bromouracil and ultraviolet and screening; and finally obtaining the FT26-9 strain which can greatly improve the abamectin B component content in a fermentation product and reduce the abamectin A component content in the fermentation product. When the bacterium is used in industrial production of abamectin, the fermentation unit is improved by about 40 percent, and the product cost is reduced by about 35 percent.
Owner:HEBEI XINGBAI AGRI SCI & TECH CO LTD
Mutant Strain of Aspergillus sojae with Enhanced Protease Activity and Preparation Method of Natural Taste Enhancer Using the Same
The present invention relates to a mutant strain of Aspergillus sojae with an enhanced protease activity and a preparation method of a natural taste enhancer using the same. More specifically, the present invention relates to the mutant strain of Aspergillus sojae with an enhanced protease activity is obtained by selecting a strain with high protease activity and treating it with N-methyl-N′-Nitroso-N-nitrosoguanidine (NTG) and inducing a mutation through irradiating, and a preparation method of a natural taste enhancer using protein hydrolysate obtained by hydrolyzing the protein sources with their cultures.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Method of producing neutral beta-konjak mannase preparation
The invention discloses a preparing method of bacillus subtilis TQS6 CCTCC M207001 of highly effective expression neutral beta-mannase through adopting UV (ultraviolet mutagenesis ) and NTG (nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis) compositing mutagenesis, which comprises the following steps: bevel-culturing bacterial strain; proceeding ferment culture after one grade and two grade culture; choosing culture medium; adding into not exclusively degraded liquid from centrifuging sugar liquid; venting into oxygen-enriched air during the course of yeast; increasing dissolved oxygen; getting high active neutral beta-konjak mannase. The product possesses high enzyme production, high enzyme activator, short period of production and low cost, which can invert low mannan effectively.
Owner:WUHAN TAIYUAN INVESTMENT GUARANTEE
Biological fermentation extracting method for hyaluronic acid
InactiveCN101914594ASolve pollutionFix security issuesChemical industryMutant preparationIon exchangeBiology
The invention discloses a biological fermentation extracting method for hyaluronic acid. The method comprises the following steps of: A, taking streptococcus as an original strain, and taking ultraviolet rays and nitrosoguanidine as mutagens; B, inoculating mutagenic strains to an agar culture medium, and culturing slant strains; C, inoculating the slant strains to a triangular flask; D, inoculating the triangular flask strains to a seeding tank according to a proportion to perform spread culture; E, sterilizing and cooling culture solution in a fermentation tank, and inoculating seeds to the fermentation tank to perform fermentation; F, inactivating the fermentation solution with heating; G, adding active carbon into the fermentation solution to filter decarburized bacteria; H, adding CPB aqueous solution into the filtrate with stirring, and standing and settling the solution; I, adding sodium chloride solution of fermentation solution volume into the sediment, and stirring the solution; J, decolorizing dissociation solution by ion exchange; K, concentrating and purifying the decolorized solution by membrane separation; L, adding ethanol into the concentrate, and separating out the sediment; and M, drying the sediment to obtain the hyaluronic acid. The method has the advantages of feasibility, simple and convenient operation, short production period, low cost, high efficiency, energy conservation and environmental protection. The hyaluronic acid can be widely used in the fields of cosmetics, food, medicaments and the like.
Owner:湖北远成药业有限公司
Bacterial strain capable of producing alkali protease and industrialized liquid fermentation method of bacterial strain
ActiveCN103409347AReduce manufacturing costOptimizing the fermentation mechanismBacteriaHydrolasesLeather industryAlkaline protease
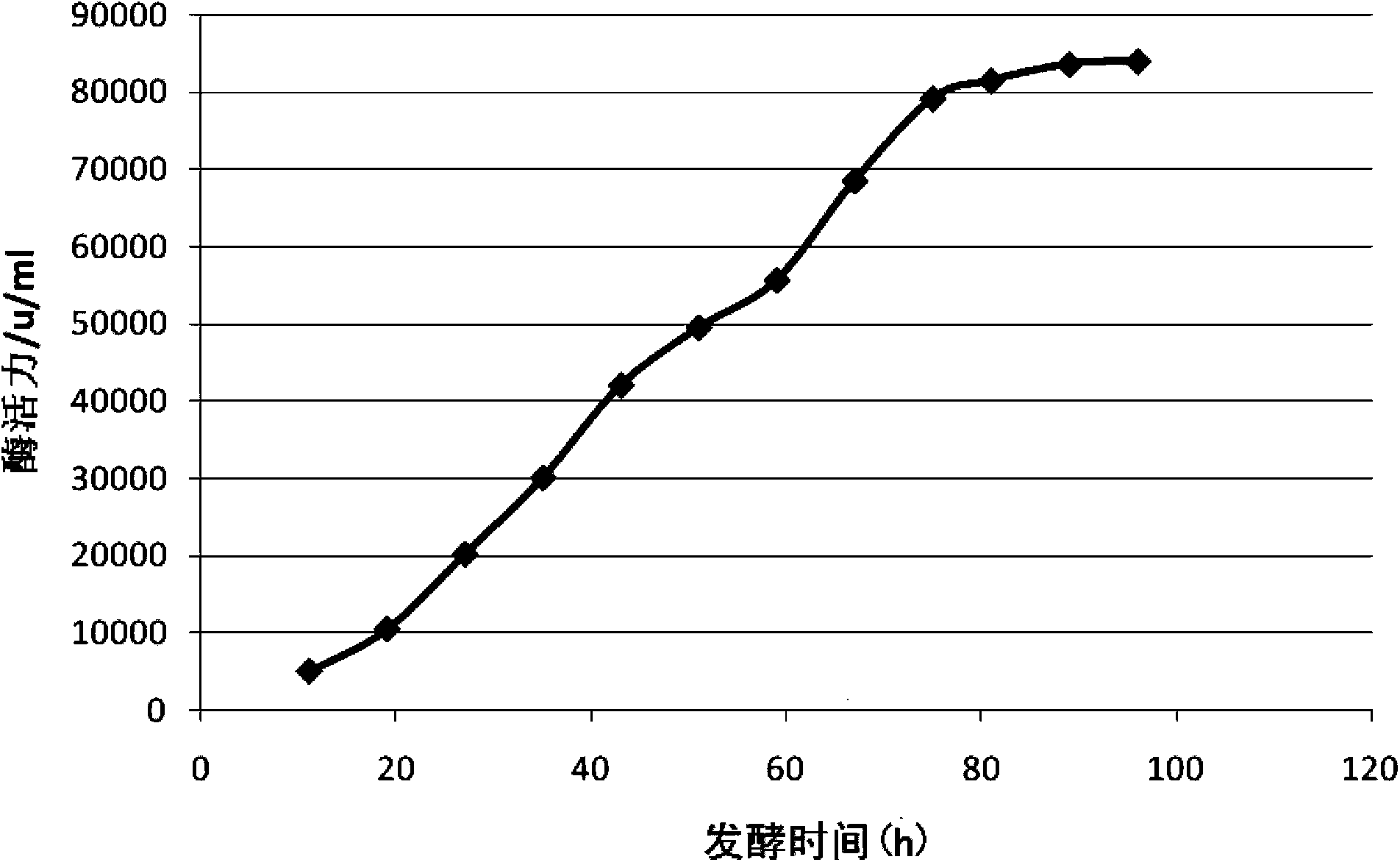
The invention discloses a bacterial strain capable of producing alkali protease and an industrialized liquid fermentation method of the bacterial strain, and belongs to the field of bioengineering technology. The bacterial strain is mutant strain Ap180 of Bacillus alcalophilus, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.7545. The bacterial strain is obtained by repeat UV-induced mutation, nitrosoguanidine-induced mutation and selection of a wild bacterial strain obtained from saline lands. Characteristics of the bacterial strain are that: efficiency of alkali protease production is high, and stability is excellent. The Bacillus alcalophilus strain, which is capable of producing alkali protease and is suitable for industrialized production , is provided in the invention, and related fermentation mechanism is optimized. According to the fermentation mechanism, operation processes are simple, cultivating conditions are mild, fermenting enzyme activity is more than 80000u / ml, production cost of enzyme activity per unit is reduced, and the requirements of market are met. Applications of the alkali protease in fields such as washing agent, forage, and leather industry are more extensive.
Owner:SHANDONG LONGKETE ENZYME PREPARATION
Method for restructuring/breeding Actinobacillus succinogenes strain, and method for producing succinic acid by fermenting Actinobacillus succinogenes strain
InactiveCN101531972AImproved sodium toleranceImprove fermentation characteristicsBacteriaMutant preparationGenome shufflingX-ray
The invention relates to an Actinobacillus succinogenes strain CGMCC 2653 (namely F3-10) with better sodium-ion tolerance and acid-producing performance, a method for breeding the strain and a method for producing succinic acid by fermenting the strain. Actinobacillus succinogenes CGMCC 1593 is taken as an original strain and then subjected to X-ray mutation, ultraviolet mutation, diethyl sulfate (EMS) chemical mutation and nitrosoguanidine (NTG) chemical mutation respectively; three strains X-8, UV-17 and SE-6 with improved fermentative acid-producing performance and particularly improved sodium-ion tolerance, as well as a high-yield strain SF-9 with fluoroacetate resistance, are obtained by screening the obtained product; and a genome restructuring method is used for breeding the strains so as to obtain the strain F3-10 with high yield, sodium tolerance and fluoroacetate resistance. The strain F3-10 takes sugarcane molasses as raw material, adopts Na2CO3 to control fermentation pH, and performs fed-batch fermentation in a 5L fermenter, and produces 53.96 grams of succinic acid per liter in 48 hours; the yield of consumed sugar is 89.2 percent; the utilization rate of sugar is 94.0 percent; and the ratio of succinic acid to heteroacid is 6.58:1. Therefore, the strain F3-10 is remarkably improved as compared with the original strain CGMCC 1593.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
High yield antibiotics producing fungus strain, preparation method and use thereof
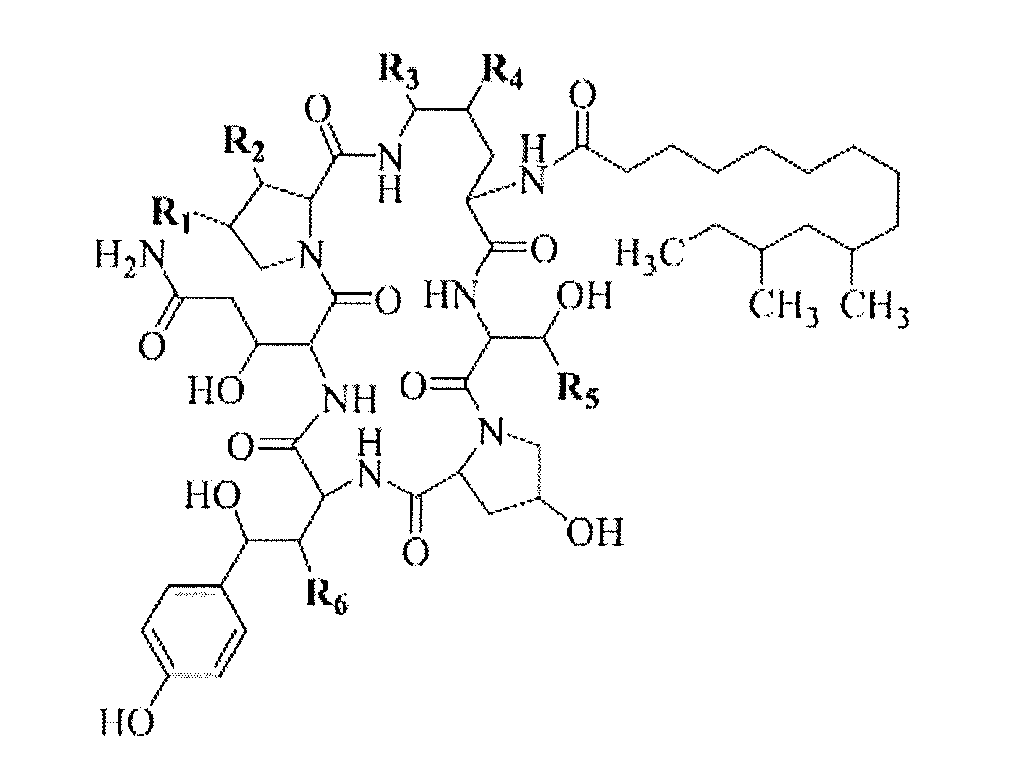
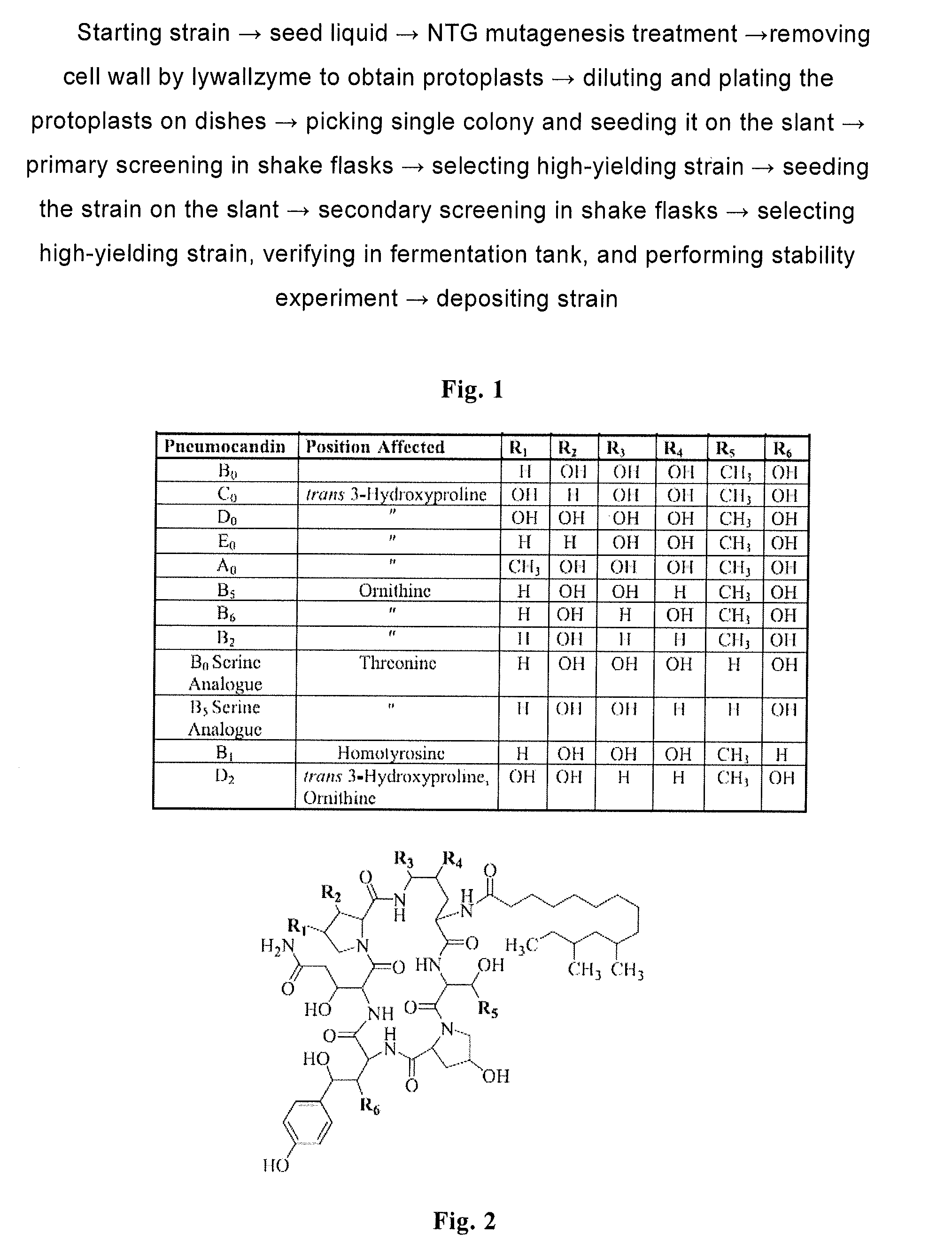
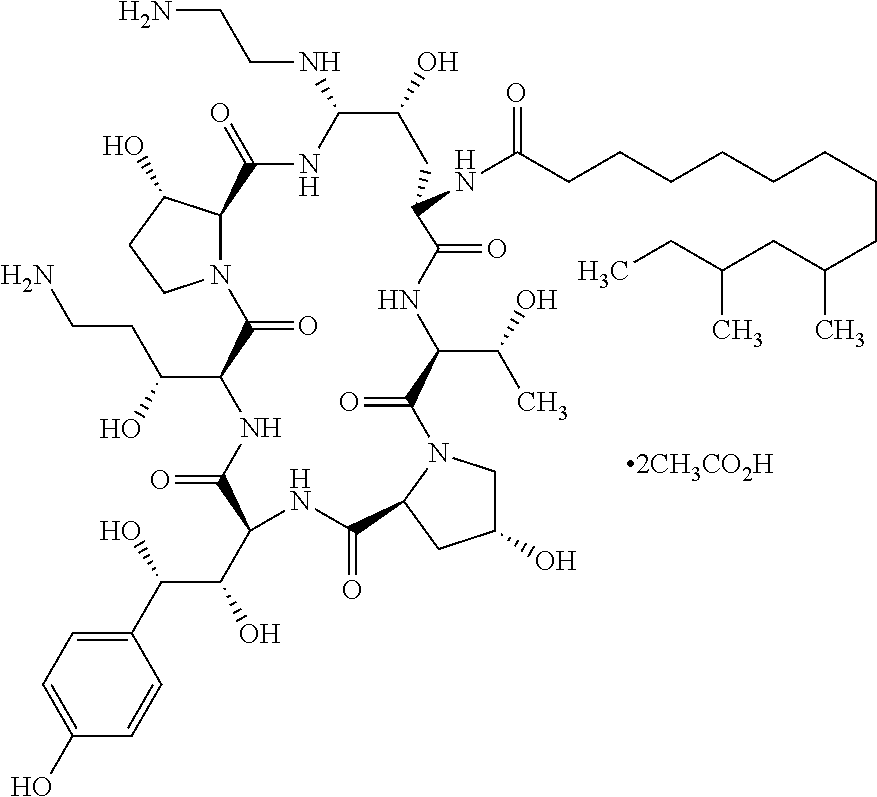
High yield antibiotics producing fungus strain, preparation method and use thereof are provided. The fungus strain is a mutant derived from Glarea lozoyensis, and deposited in CGMCC with the accession number of CGMCC 2933. The preparation method concludes following steps: (a) mixing the culture media of Glarea lozoyensis strain ATCC 20957 with nitrosoguanidine, and obtaining mixture a; (b) mixing lywallzyme with the mixture a, and obtaining protoplasts; (c) regenerating the protoplasts, and obtaining single clones; and (d) culturing the single clones, then obtaining the mutant strain. This fungus strain has stable genetic and producing property, produces little impurities in fermentation, and is suitable to be used in industry.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECHWELL BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD
White rot fungi, breeding method and use thereof
InactiveCN101469312AStable enzyme productionShort cycleFungiMutant preparationFiberAutomatic control
The invention relates to Trametes Versicolor YS-L613 and a breeding method and application thereof. The Trametes Versicolor YS-L613 is prepared by the method through mutation breeding. The breeding method is to take Trametes Versicolor as a starting strain, adopt composite mutation breeding technology which combines UV, 60 CO, ultraviolet rays, nitrosoguanidine, ion implantation and microwave treatment, and breed the YS-L613 strain for high-yield production of laccase. The invention performs breeding operation through physiochemical treatment methods such as ion implantation, the ultraviolet rays and mutagen, finally obtains the YS-L613 strain for high-yield production of the laccase, and adopts experimental automatic control technology, strain fermentation control technology and strain extraction technology to develop laccase products. As proved by experiments of the laccase in pulp bleaching, fiber modification and pulp deinking, utilization of the laccase in the paper-making industry can improve the quality of paper, reduce environmental pollution and save the cost.
Owner:HENAN YANGSHAO BIOCHEM ENG
Astaxanthin high-yield strain and application thereof
InactiveCN104178430AEnhanced Astaxanthin ComponentsHigh compositionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNitroso
The invention discloses an astaxanthin high-yield strain and application thereof. The astaxanthin high-yield strain is classified to be named as Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous VR-032 and collected in CCTCC (China Center For Type Culture Collection), and the collection number is CCTCCM2014190. According to the invention, a target strain VR-032 is finally screened by virtue of nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis by adopting a strain which is obtained by fermentation and screening based on a shake flask and has high astaxanthin yield as an initial strain of a next round of mutagenesis, and the strain can be used for more greatly increasing astaxanthin components contained in a fermentation product and decreasing other components and has good hereditary stability. According to the astaxanthin high-yield strain disclosed by the invention, the sugar cane is utilized as a fermentation carbon source, the yield of the astaxanthin obtained by fermentation by utilizing the low-cost sugar cane as the carbon source in a 5L fermentation tank is up to 68.7mg / L, the yield of the astaxanthin is increased by 20.8% compared with that of an original initial strain, and the astaxanthin high-yield strain can be applied to industrial production, greatly improving the fermentation unit and achieving significant economic application value.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Production technology for fermentatively producing sodium hyaluronate by utilizing bacterium
InactiveCN103173507ATo satisfy the market's needsImprove mutagenesis efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationStreptococcus zooepidemicusHydrogen
The invention relates to a production technology for fermentatively producing sodium hyaluronate by utilizing bacterium. The production technology comprises the following steps of: using streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus (Streptococcus Zooepidemicus) as an original strain; mutagenizing by virtue of nitrosoguanidine, and also mutagenizing by virtue of a protoplast in the presence of ultraviolet rays; introducing a special culture medium; carrying out submerged fermentation to produce high-output hyaluronic acid; and then carrying out a relative separation and purification technology to obtain a high-purity sodium hyaluronate product. According to the production technology for fermentatively producing the sodium hyaluronate by utilizing the bacterium, under the culture conditions that the culture temperature is 32 to 38 DEG C, the pH (Potential Of Hydrogen) of fermentation liquor is maintained within the range of 5.0 to 9.0, and a fermentation tank is at speed of stirring of 150 to 600rev / min, the output of the hyaluronic acid is greatly increased; and the production technology is suitable for being applied to industrial production.
Owner:宁波林叶生物科技有限公司
Gene engineering bacteria for producing crown bacterin and its construction method
ActiveCN1900269AIncrease productionSolve outputBacteriaElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentDiseaseMicrobiology
The present invention relates to gene engineering bacterial strain, and is especially one kind of soybean disease causing variety (P.syringae pv.Glycinea) of pseudomonas syringae for producing crown bacterin and its construction process. The gene engineering pseudomonas strain is prepared through mutagenizing initial pseudomonas strain with nitrosoguanidine for genetic mutation, so as to screen out pseudomonas strain with high crown bacterin yield. Experiment proves that the gene engineering pseudomonas strain of the present invention may be used in industrial production of crown bacterin through fermentation at 18deg.c to reach the yield of 84.7-112 mg / L.
Owner:CHENGDU NEWSUN CROPSCI
Breeding of acetoin high-tolerance bacterial strain and acetoin fermentation production with bacterial strain
The invention discloses breeding of an acetoin high-tolerance bacterial strain and acetoin fermentation production with the bacterial strain, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering (the field of microorganism). The breeding procedures are as follows: (1) nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis: taking Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FMME044 screened and stored by the laboratory as an original strain to prepare a bacterial suspension, taking reaction with nitrosoguanidine in different concentrations, after a while, stopping reaction and then carrying out post-cultivation; (2) domestication: adding acetoin with different concentrations in domestication culture media to prepare acetoin fermentation liquors with different concentrations, gradually increasing the acetoin concentrate to carry out domesticating cultivation, and directly coating the domesticated bacterial suspensions on a panel containing high-concentration acetoin; (3) screening: obtaining the acetoin high-tolerance bacterial strain which is the single colonies grown on the panel containing the high-concentration acetoin, and then selecting the single colonies to carry out fermentation verification, performing secondary verification on the high-producing strains to screen out a bacterial strain with higher concentration of acetoin than the original strain, and naming the bacterial strain B. amyloliquefaciens E-11. The invention further discloses a method for producing acetoin with the bacterial strain. The yield of acetoin produced by the method with 40 h fermentation is 63 g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Mutant chlorella strain capable of producing zeaxanthine and beta-carotene and culturing method thereof
The invention provides a mutant chlorella strain capable of realizing high yield of zeaxanthine and other carotenoids essential to the human body, and a culturing method thereof. The culturing method comprises the following steps: subjecting Chlorella zofingiensis ATCC 30412 to nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis; then coating a Kuhl solid medium containing DPA with treated chlorella cells for culture; selecting a single chlorella colony from the Kuhl solid medium and culturing the single chlorella colony on a Kuhl liquid medium; adding glucose in the middle and later periods of logarithm for induction of carotenoid synthesis; and detecting the variety changes and content of carotenoids in the obtained chlorella body so as to obtain the strain which can realize high yield of zeaxanthine, xanthophyll and beta-carotene and is named as CZ-ZEA1. Under the induction condition that the concentration of glucose is 30 g / L, the biomass of the CZ-ZEA1 is 12.95 g / L, and the contents of zeaxanthine, xanthophyll and beta-carotene reach 2.176 mg / g, 1.10 mg / g and 1.211 mg / g, respecitively. The mutant chlorella strain is an edible alga species and contains high-content optimally-proportioned carotenoids essential to the human body, especially zeaxanthine rare in nature; so the mutant chlorella strain is an ideal new-resource functional foodstuff for preventing deterioration and lesion of the eyes of middle aged and old people and has good development and application prospects.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
White rot Inonotus hispidus mutant strain T906 for laccase production and preparation method thereof
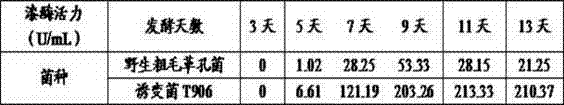
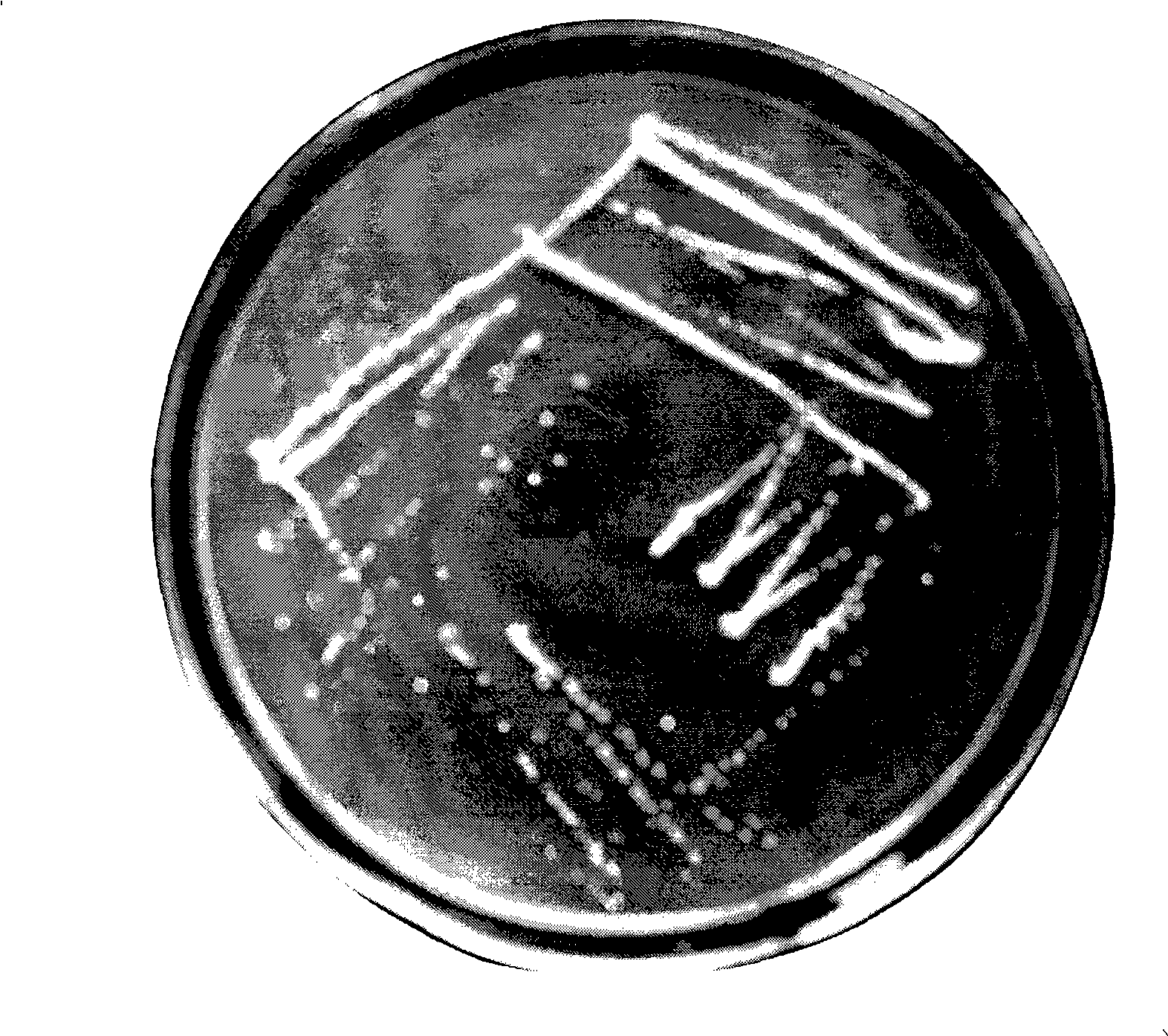
The invention discloses a white rot Inonotus hispidus mutant strain T906 for laccase production and a preparation method thereof. The mutant strain T906 (CoriolopsisgallicaT906) mentioned in the invention is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection. The preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2011317, the preservation date is September 15, 2011 and it is preserved in Wuhan University, Wuhan, China. Wild Inonotus hispidus (preservation number being cfcc88387) purchased from China Forestry Culture Collection Center is used as an original strain, and the mutant strain is obtained by ultraviolet and nitrosoguanidine combined mutation screening. Under an optimum condition, the laccase production of the mutant strain reaches 213U / mL. The mutant strain has mycelial morphology and cultural characteristics which are obviously different from the original strain, does not degenerate after serial passages for over 30 times and has genetic stability.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
L-leucine high-yield bacterium and fermentation method using the same for L-leucine production
It is an L-leucine high-yield bacterium and the production of L-leucine with invoice method, belonging to biological engineering field. The invented bacterial is a corynebacterium glutamicum JH-27, using corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032 as starting strain, mutagenizing separately with diethyl sulfate, nitrosoguanidine and ultraviolet, adding separately analogue of branched chain amino acid into minimum medium and sulfaguanidine into complete medium and breeding to prepare, being an L-leucine high-yield bacterium resistant sulfaguanidine and branched chain amino acid, compared with starting strain, producing L-leucine with the strain and invoice method, it expresses the ability of accumulation of highly qualified L-leucine. Shaking flask and culturing JH-27 for 60 hours, the yield of L-leucine is 30-32 g / l. Fermenting in fermenter of 5L for 55 hours, the yield of L-leucine is 40g / l.
Owner:WUXI JINGHAI AMINO ACID
Bacillus thermophilus capable of producing high-temperature and alkali resistant xylanase and application of bacillus thermophilus
ActiveCN103667151AEnzyme stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismReaction temperature
The invention discloses a bacillus thermophilus 701 capable of producing high-temperature and alkali resistant xylanase and belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation. The bacillus thermophilus is obtained through the steps that a soil sample is collected from a paper mill, a bacillus thermophilus is separated from the soil sample, and ultraviolet mutagenesis and nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis, and screening are performed repeatedly. The xylanase produced by the bacillus thermophilus has the characteristics of strong high-temperature resistance and alkali resistance. The bacillus thermophilus is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on October 12, 2013, the preservation No. is CCTCC M2013537. The high-temperature and alkali resistant xylanase prepared from the bacillus thermophilus 701 is 350-420 IU / ml in specific activity, 40-75 DEG C in applicable temperature range, 65 DEG C in optimum reaction temperature, completely stable in enzyme activity at the temperature of 75 DEG C, 5.0-11.0 in applicable reaction pH value, completely stable in enzyme activity at the pH value of 11.0, and is 10.0 in optimum reaction pH value.
Owner:HUNAN HONGYING BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Breeding method of strong-acid resistant lactic acid bacteria strain
InactiveCN105925561ANo biosecurity riskMeet production needsBacteriaMutant preparationChemical mutagensLactic acid bacterium
The invention discloses a breeding method of strong-acid resistant lactic acid bacteria strain. The breeding method includes inducing common probiotic lactic acid bacteria by chemical mutagen such as nitrosoguanidine, exploring massive mutation colony of lactic acid as a new lactic acid genetic germplasm resource library, screening mutant strains, which are capable of growing on lactobacillus culture medium MRS and have regular shape and distinctive characteristics, from the resource library, and screening strains that could multiply fast after being treated by simulated gastric fluid from the mutant strains, which are the novel high-quality and strong-acid resistant lactic acid bacteria strain.
Owner:SUZHOU JIANSHIXING BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Screening and application of beer microzyme containing CMP kinase and CDP kinase
ActiveCN101265453AEasy to manufactureReduce leakageFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyCarrageenan
The invention relates to a method for screening Saccharomyces cerevisiae with high-activity CMP kinase and CDP kinase, and the use of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the production of cytidine triphosphate, and belongs to the technology field of biological engineering. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with accession number of CGMCC NO.2448. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with high-activity CMP kinase and CDP kinase are screened by means of nitrosoguanidine (NTG) mutagenesis. In the production of the cytidine triphosphate, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains are used to be prepared into immobilized cells of various grain diameters with carrageenan as carriers by different controlled stirring speeds realized through embedding. Compared with manual cutting, the screening method of the invention has the advantages of small cell leakage, regular grains with high strength, low labor intensity, simple grain-producing procedure, no complicated equipment and instrument, and is suitable for industrialized production. Furthermore, bean oil used in the invention is safe and nontoxic solvent, suitable for various requirements and easy to recycle.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV +1
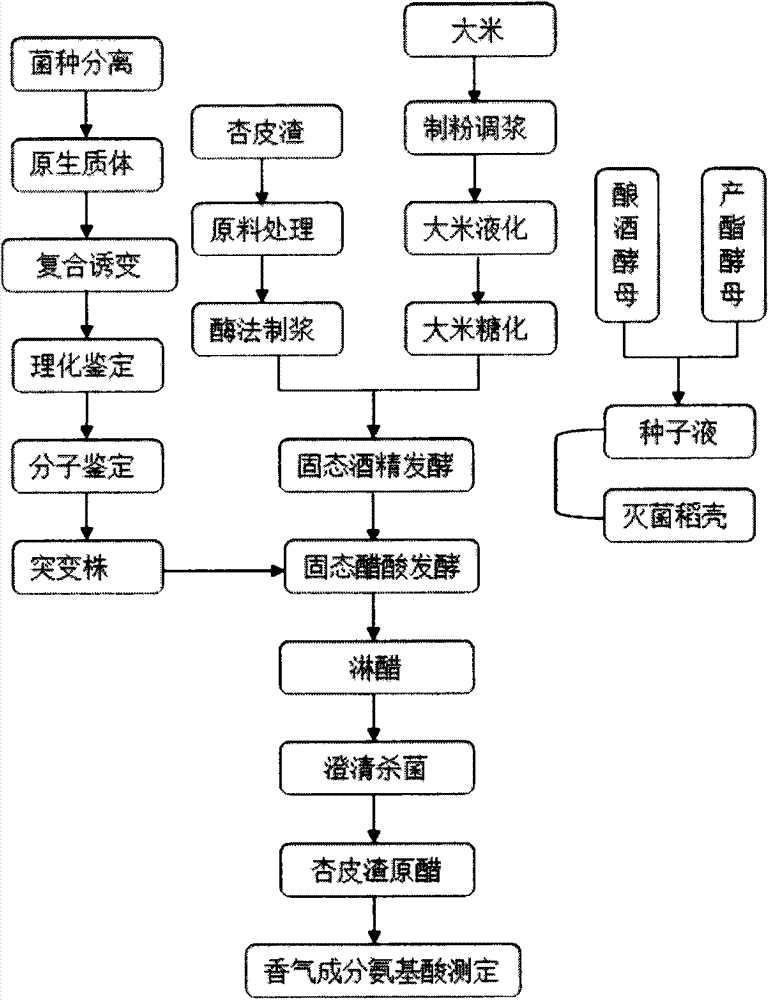
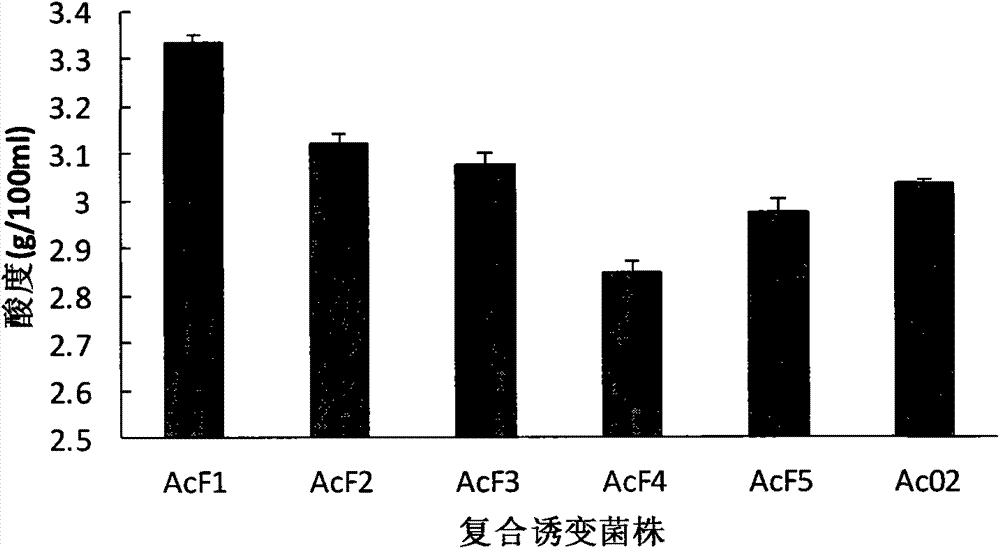
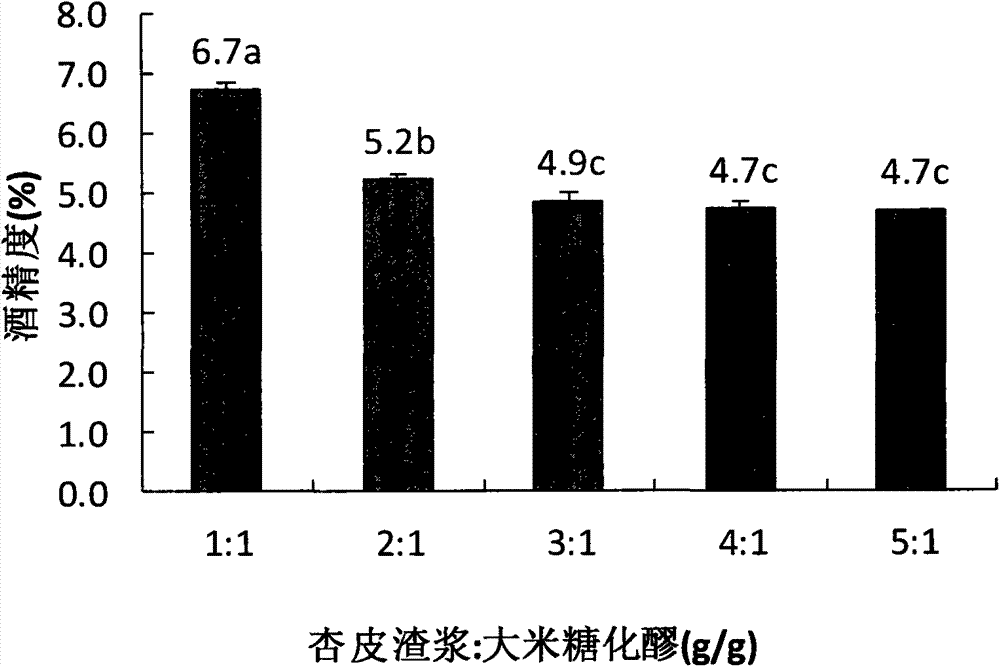
Acetobacter aceti and fruit vinegar prepared from Acetobacter aceti through solid-state fermentation of apricot bark slag
InactiveCN103865841AGood sensory evaluationImprove alcohol resistanceBacteriaMutant preparationSlagBacterial strain
The invention discloses Acetobacter aceti and fruit vinegar prepared from Acetobacter aceti through solid-state fermentation of apricot bark slag. Acetobacter pomorum AcF1 with the preservation number: CCTCC No: M2013554 which is stable in heredity and excellent in fermentation performance is obtained by carrying out compound mutation on acetic acid bacterial strain through nitrosoguanidine and ultraviolet rays, wherein under conditions that initial alcoholic strength is 6%, acetic acid inoculation amount is 14%, fermentation time is 25 days, fermentation temperature is 31 DEG C and acetic acid content is 8.16g / 100ml, alcohol resistance and high acid resistance are excellent; the apricot bark slag vinegar which can be produced by a solid-state mixed culture fermentation process has excellent qualities on sensorial, physical and chemical, and sanitary indexes, is brown-yellow and clear in color, thicker in fruity flavor and sour, comfortable in sweet and full in body, so that varieties of fruit vinegar products are enriched, and therefore, the Acetobacter aceti has wide practicability and product typicality.
Owner:HANSHAN NORMAL UNIV
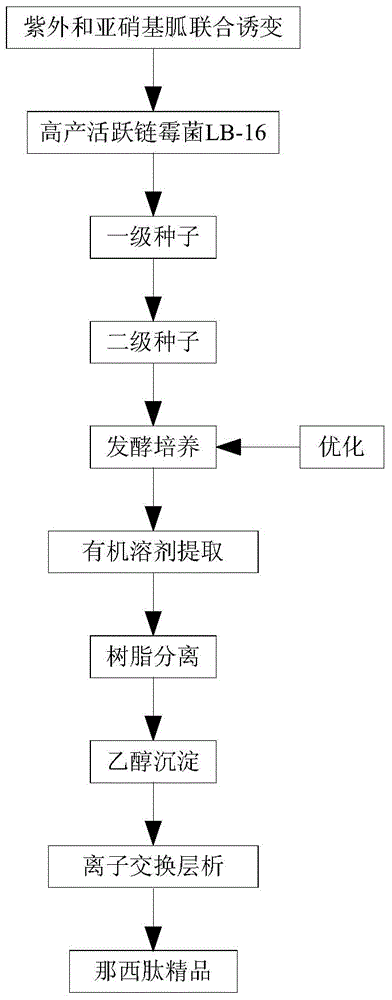
Streptomyces actuosus LB-16 and method for preparing nosiheptide from same
The invention relates to Streptomyces actuosus LB-16, and further relates to a method for producing Streptomyces actuosus LB-16 and a method for preparing nosiheptide from the Streptomyces actuosus LB-16. In the method for producing the Streptomyces actuosus LB-16, ultraviolet and nitrosoguanidine are adopted for achieving combined mutagenesis for Streptomyces actuosus CN10, and the Streptomyces actuosus LB-16 is obtained through screening. In the method for preparing the nosiheptide from the Streptomyces actuosus LB-16, temperature-variable culture is adopted, the ventilation flow is controlled in a staging mode, and an organic solvent method, resin separation, and ethyl alcohol and water mixed precipitation extraction separation are adopted, so that the nosiheptide is obtained, and the refined nosiheptide is obtained by the adoption of an ion exchange chromatography through separation and purification. The Streptomyces actuosus LB-16 has the advantages of being low in production cost, high in production extraction rate and high in product biological value.
Owner:西藏天虹科技股份有限责任公司
Mutation screening method and application of streptomyces strain SPC6-50-1
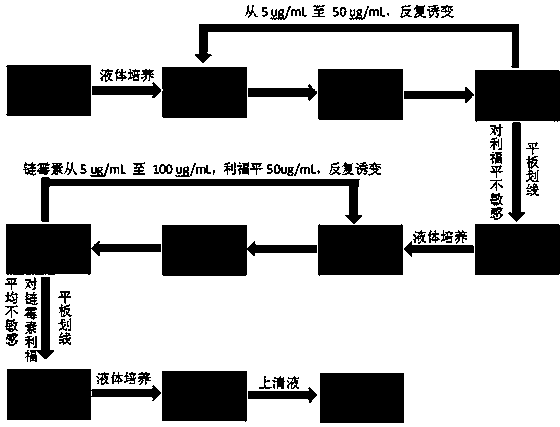
The invention discloses a mutation screening method of a streptomyces strain SPC6-50-1. The mutation screening method comprises the steps of inducing mutation of streptomyces coelicolor and streptomyces Lzsg6 through nitrosoguanidine to obtain a streptomyces mutant library, and screening the mutant library through rifampicin and streptomycin to obtain a strain with a transcription system and a translation system in mutation. The invention also discloses a streptomyces strain SPC6-50-1 and application thereof. The streptomyces strain SPC6-50-1 disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the strain contains substances having bacteriostatic activities, and the method of nitrosoguanidine (NTG) inducing as well as rifampicin and streptomycin screening can activate silent genes of the streptomyces to obtain a new metabolite, thus obtaining a new antibiotic; meanwhile, the mutation screening method has the advantages of simple operation, short cycle and high efficiency, and is not only applicable to streptomyces but also suitable for such microorganisms as myxobacteria rich in secondary metabolites; the mutation screening method has good popularization and application values.
Owner:COLD & ARID REGIONS ENVIRONMENTAL & ENG RES INST CHINESE
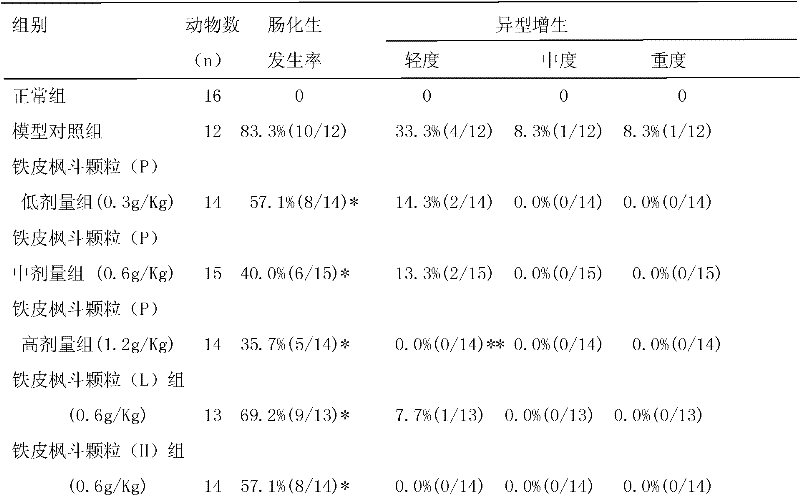
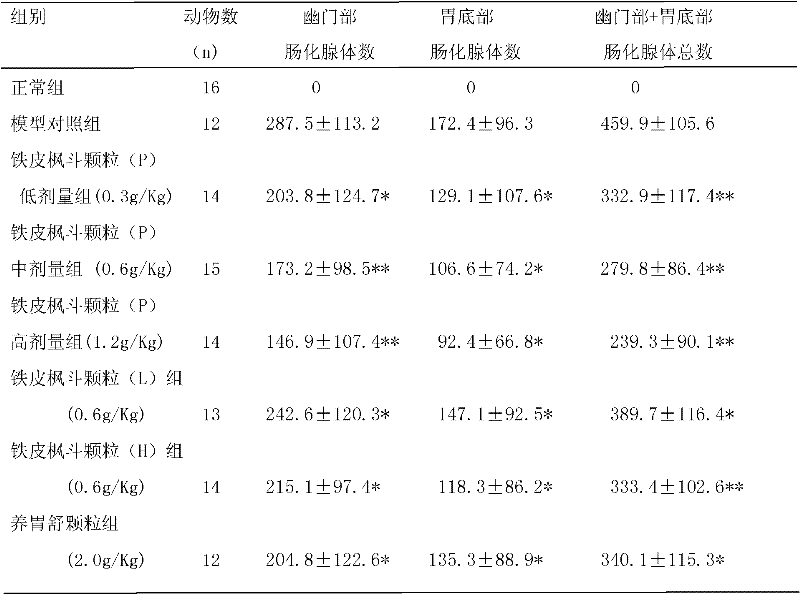
Application of dendrobium candidum to preparation of medicine for treating intestinal metaplasia
The invention relates to a novel purpose of dendrobium candidum, which aims at providing an application of the dendrobium candidum to the preparation of medicine for treating intestinal metaplasia. The invention discloses the application of the dendrobium candidum to the preparation of the medicine for treating the intestinal metaplasia and a preparation method of the medicine for treating the intestinal metaplasia on the basis of the dendrobium candidum. Both dendrobium candidum particles provided by the invention and Yangweishu particles have a certain reversing effect on the intestinal metaplasia caused by N- methyl-N'-nitryl-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG), but the effect of the dendrobium candidum particles is more obvious. Results show that the dendrobium candidum particles mixed with American ginseng has the potential application prospects on the intestinal metaplasia of clinic chronic atrophic castritis (CAG).
Owner:ZHEJIANG TIANHUANG MEDICINAL PLANT PHARMA
Aspergillus usamil high in yield of acid protease and application of aspergillus usamil high in yield of acid protease
The invention discloses aspergillus usamil 801-2 high in yield of acid protease and belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation. The aspergillus usamil is preserved with the preservation number CCTCC NO: M2013601 in China Center for Type Culture Collection on November 24, 2013. The aspergillus usamil 801-2 is obtained by subjecting aspergillus usamil 801 yielding the acid protease, preserved by a laboratory, to ultraviolet and lithium chloride compound mutagenesis, nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis and diethyl sulfate mutagenesis sequentially and subjecting a mutant to isolation and screening, and grows faster than a starting strain, the diameter of a colony is 82mm after the aspergillus usamil 801-2 grows at the temperature of 28 DEG C for four days, and enzyme activity of the acid protease in fermentation liquor can be up to 13000-14000U / mL which is 8 times of that of the starting strain. The acid protease secreted by the aspergillus usamil 801-2 is tolerable to high temperature, and under the same conditions, in order to reach same enzyme activity, tolerable temperature of the acid protease is averagely increased by 8-12 DEG C than that of the starting strain.
Owner:湖南新鸿鹰生物工程有限公司
Red steroid brevibacterium for highly yielding cholesterol oxidase
InactiveCN101186897AHigh fermentation enzyme activityBacteriaMutant preparationMicroorganismBrevibacillus borstelensis
Provided is red brevibacterium sp of high-yield cholesterol oxidase, which belongs to the technical field of microorganism bacterial strain. The bacterial strain of the invention is classified and named as brevibacterium sp. DGCDC-82 (choB), and is preserved in the Preservation Center of Chinese Typical Culture, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M207182. The bacterial strain of the invention is mutagenized and achieved by the process of combining nitrosoguanidine with ultrasonic on the basis of white brevibacterium sp. The fermentation study finds that the vitality for producing cholesterol oxidase of the red brevibacterium achieves 1.21U per milliliter, which is increased by 140%. The relation of the bacterial strain enzyme production and haematochrome is studied with the process of reverse mutation, finding that the content of the bacterial strain enzyme production has positive correlation with the content of haematochrome, the darker the red color of the bacteria is, the higher the vitality of fermentation and enzyme production is.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for improving saccharopolyspora spinosa spinosad fermentation yield
InactiveCN105624142AHigh potencyLower total sugarMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySaccharopolyspora
The invention relates to a method for improving a saccharopolyspora spinosa spinosad fermentation yield. The method utilizes mutagenesis treatment to screen a saccharopolyspora spinosa spinosad high-yield mutant strain with a good starch utilization capability. The mutagenesis treatment comprises at least two of UV-streptomycin combined mutagenesis, 5-fluorouracil mutagenesis, microwave-streptomycin combined mutagenesis and nitrosoguanidine-streptomycin combined mutagenesis. Preferably, the mutagenesis treatment comprises the above four mutagenesis methods. Preferably, the UV-streptomycin combined mutagenesis, 5-fluorouracil mutagenesis, microwave-streptomycin combined mutagenesis and nitrosoguanidine-streptomycin combined mutagenesis processes are orderly carried out. The broth of the obtained mutant strain has spinosad titer substantially higher than that of an original strain screened through mutagenesis and thus the method can improve a saccharopolyspora spinosa spinosad fermentation yield.
Owner:牡丹江佰佳信生物科技有限公司
Streptomycete strain mutagenesis preparation method for high-yield production of tacrolimus
InactiveCN111334500AIncrease productionStrong competitionMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesNitrosoNitrosoguanidines
The invention provides a streptomycete strain mutagenesis preparation method for high-yield production of tacrolimus. According to the invention, mutagenesis breeding is performed with nitrosoguanidine (NTG), and then active substances of vibralactone and ethyl malonyl coenzyme A are used as selection pressures to achieve the aim of increasing the yield of tacrolimus. According to the invention, the yield of tacrolimus prepared by taking the active substances of vibralactone and ethyl malonyl coenzyme A synergistically as selection pressures is obviously increased compared with the yield of mutagenesis breeding by using a single selection pressure. Streptomyces tsukubaensis prepared by taking the active substances of vibralactone and ethyl malonyl coenzyme A as selection pressures has thecharacteristics of high activity of ethyl malonyl coenzyme A and high activity of lipase, and the yield of tacrolimus is improved due to high activity of ethyl malonyl coenzyme A and high activity oflipase, and generation of by-products is reduced. The yield of combined use of vibralactone and ethyl malonyl coenzyme A is obviously higher than the yield of mutagenesis breeding by using a single selection pressure.
Owner:浙江弘盛药业有限公司
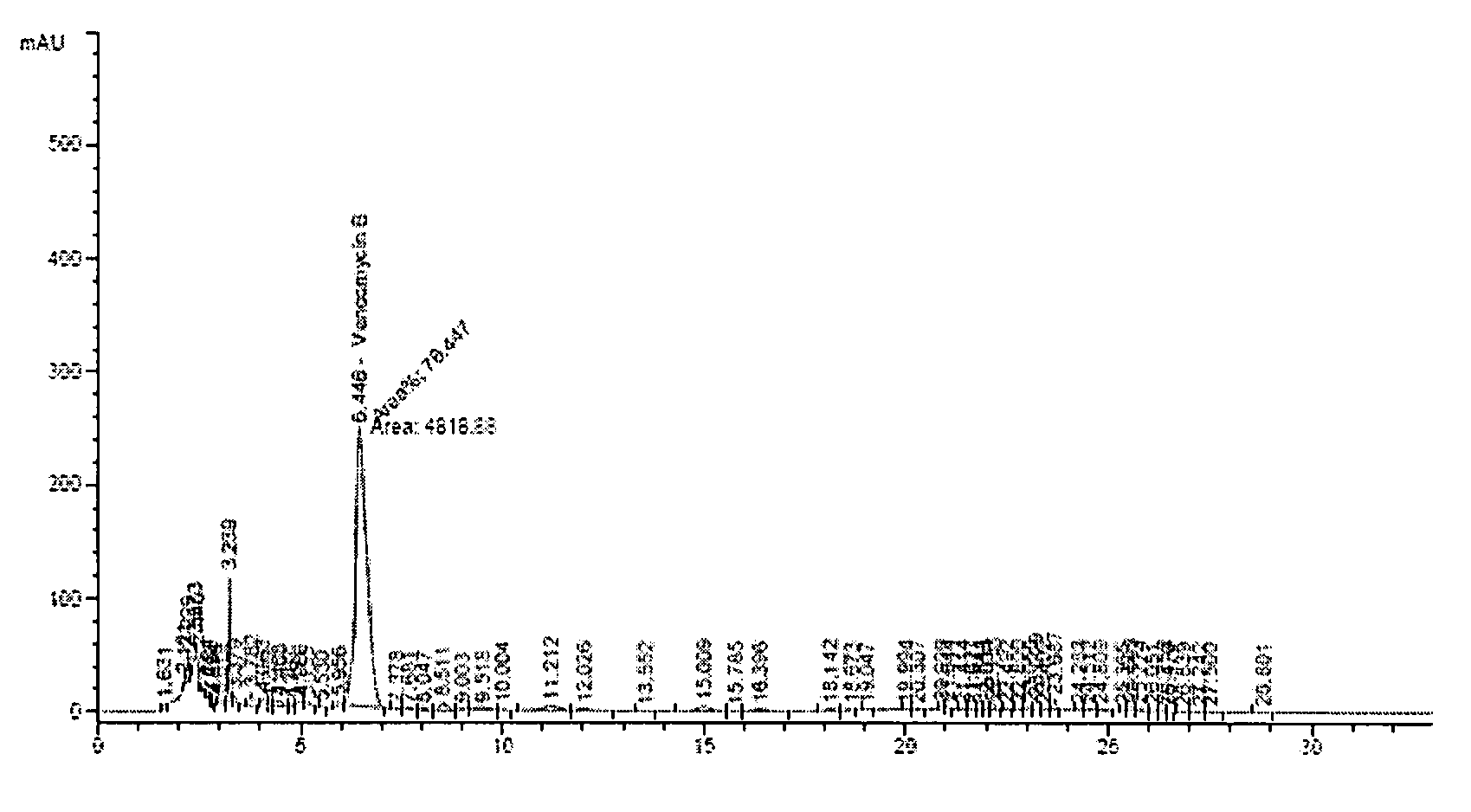
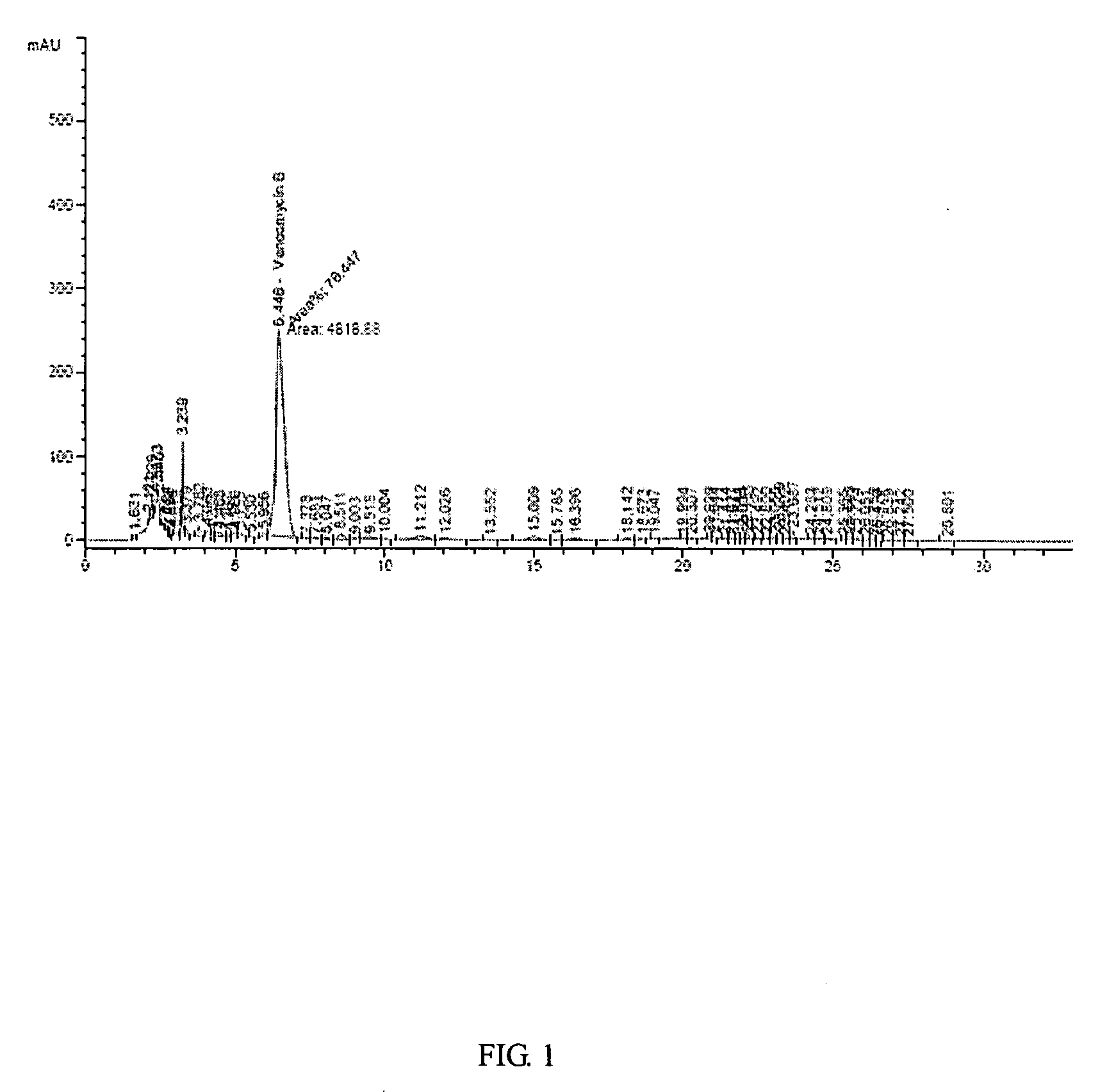
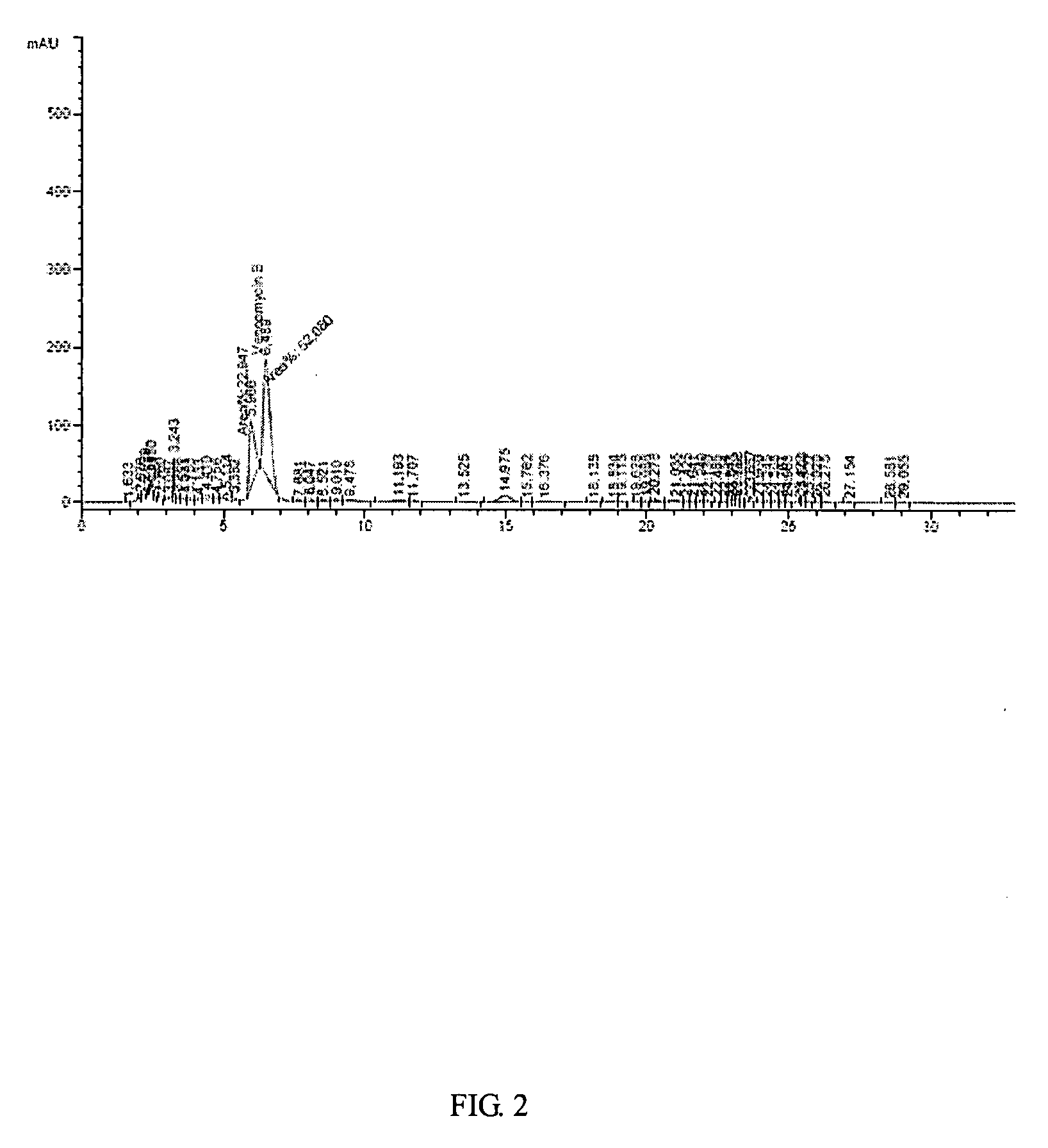
Mutant strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis and process for preparing vancomycin hydrochloride
The present invention provides a process for preparing vancomycin hydrochloride using a mutant strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis (accession No. KCCM-10836P) comprising the steps of i) mutating and isolating a strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis (accession No. KCCM-10836P) for producing vancomycin from mother strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis (accession No. ATCC-19795) using NTG(N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine) in the selection medium; ii) seed culturing the isolated mutant strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis (accession No. KCCM-10836P); iii) cultivating and fermenting said mutant strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis in the fermentation medium consisting of 12˜18 (w / v) % of dextrin, 2.2˜3.8 (w / v) % of bean powder, 1.9˜2.9 (w / v) % of potato protein, 0.10˜0.14 (w / v) % of sodium chloride and a small amount of minerals; iv) filtering vancomycin using microfilter in the cultivation broth by removing mycelia; v) purifying obtained vancomycin using column system compacted with cation exchange resin, anion exchange resin and absorbent resin; and vi) crystallizing the purified vancomycin with hydrochloric acid.
Owner:BIONGENE
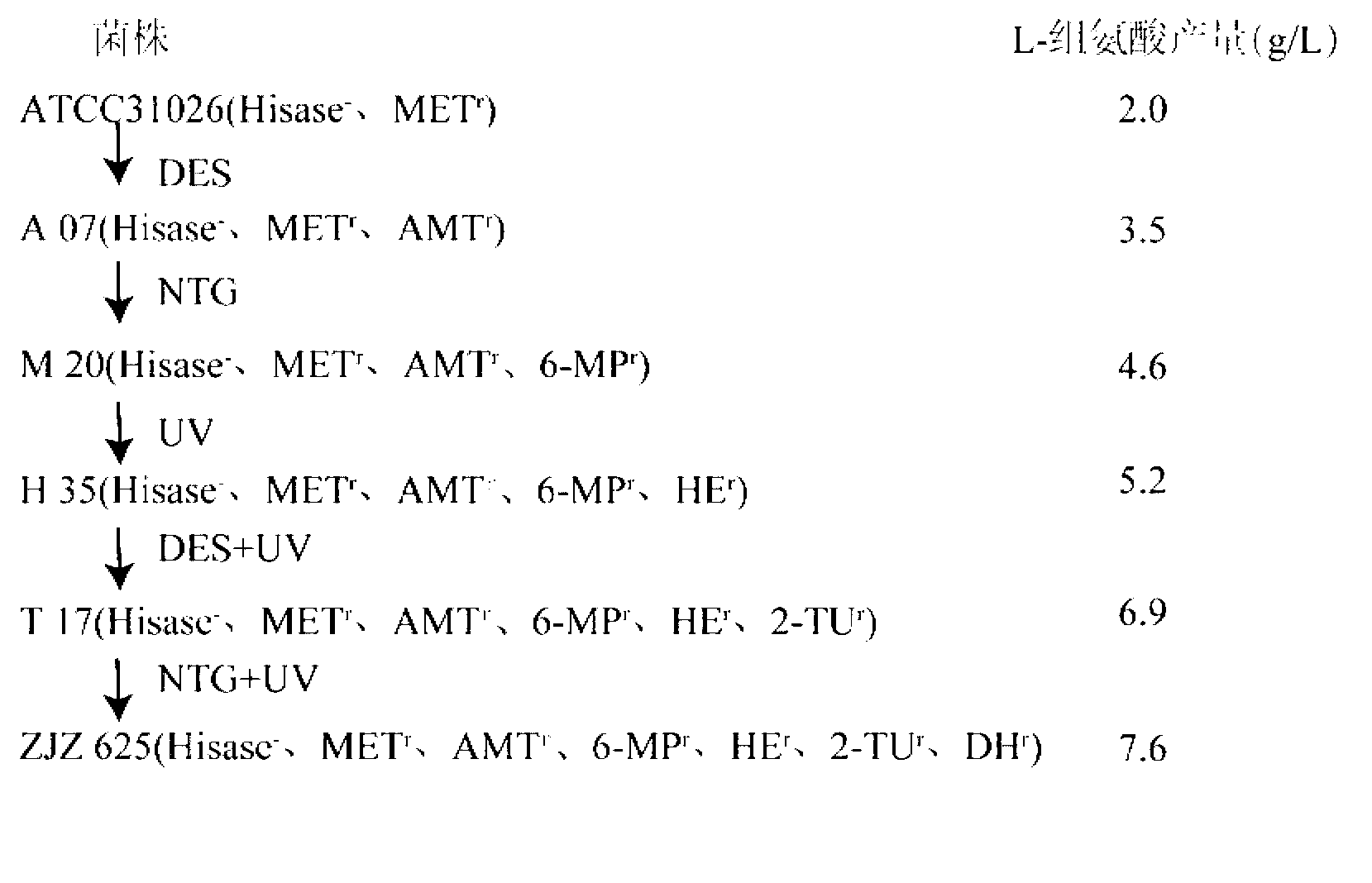
L-histidine high-yielding strain and application thereof
InactiveCN103013876ARelease feedback inhibitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCulture mediumsChemistry
The invention provides an L-histidine high-yielding strain and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of a bioengineering technology. The invention provides Serratia marcescens ZJZG25 which is obtained by the following steps of: by taking Serratia marcescens ATCC (American Type Culture Collection) 31026 as a starting strain, carrying out diethyl sulfate (DES), nitrosoguanidine (NTG) and ultraviolet (UV) gradual-grade mutation; and adding analogues of L-histidine including 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole, 6-purinethol, histidine methyl ester, 2-thiouracil, D-histidine and the like into a basic culture medium and screening. The L-histidine is produced by a strain fermentation method; and compared with the starting strain, the capability of the accumulating high-level L-histidine is expressed. The ZJZ 625 is subjected to shake-flask culture for 72 hours and the yield of the L-histidine can reach to 9.7 g / L. The fermentation is a 3-L fermentation tank is carried out for 60 hours and the yield of the L-histidine can reach to 18.1 g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com