Patents
Literature
43 results about "Amycolatopsis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Amycolatopsis is a genus of high GC-content bacteria within the family Pseudonocardiaceae.
Process for obtaining HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors of high purity
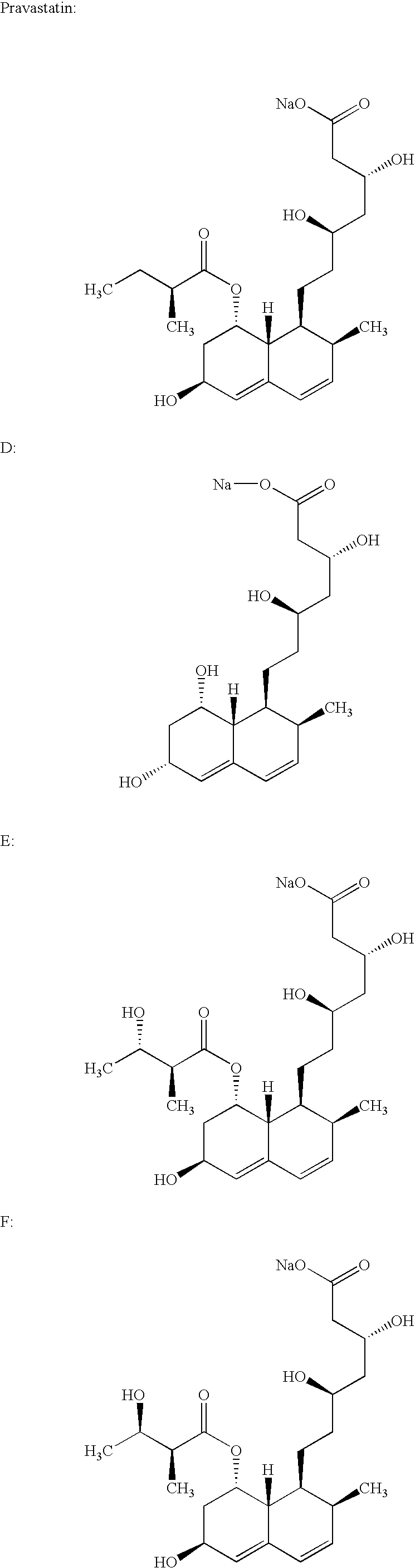
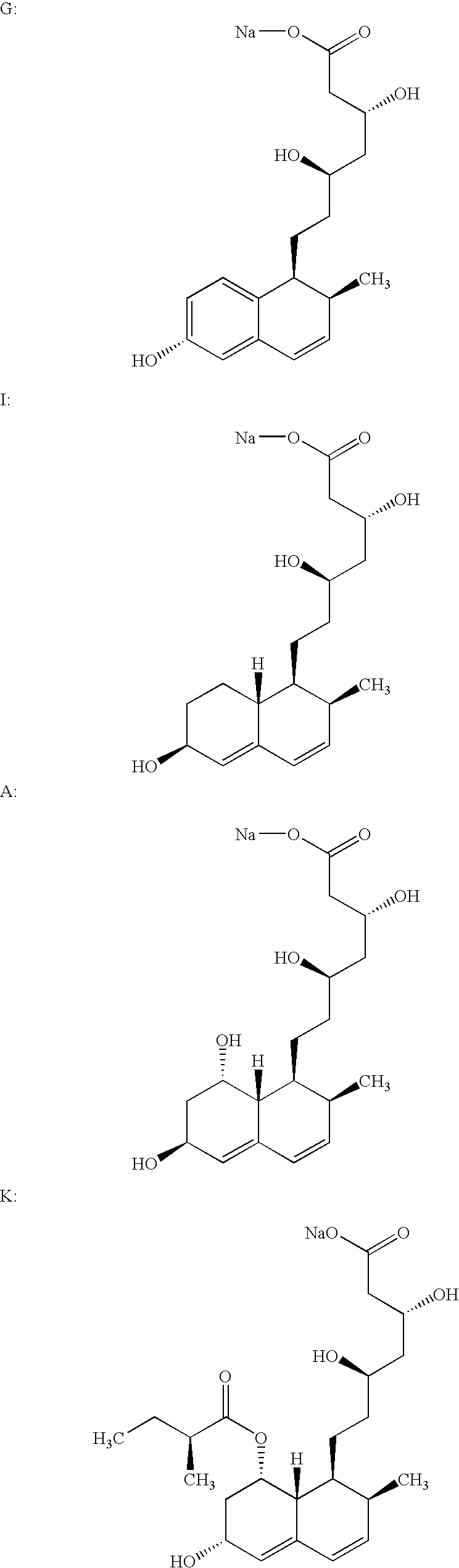
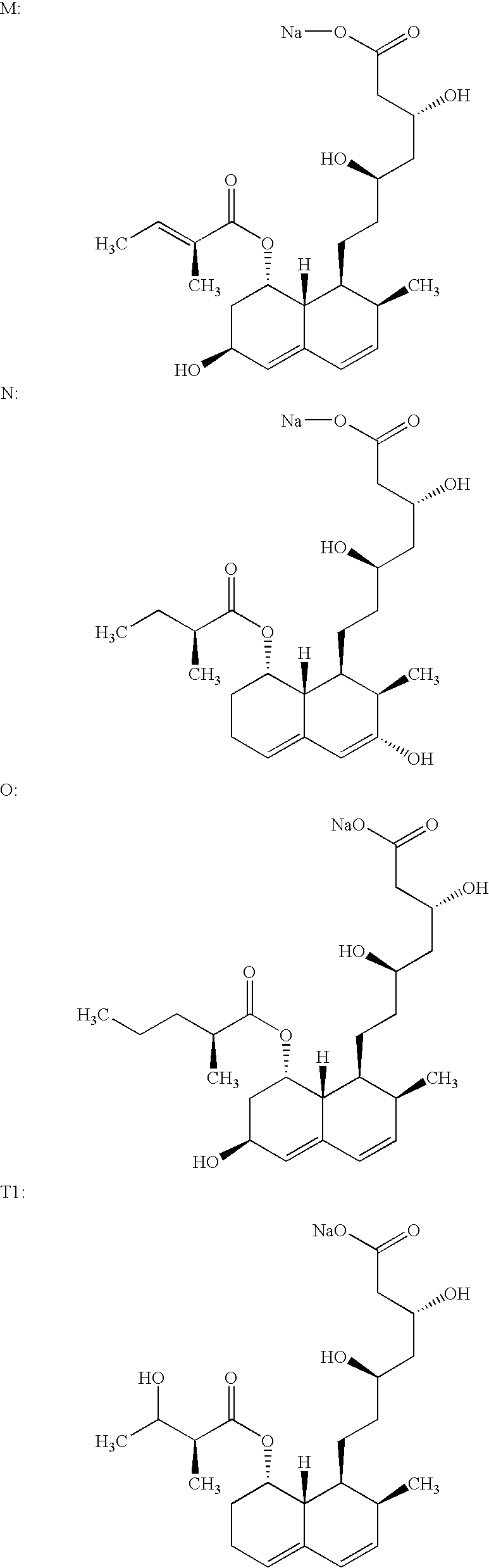
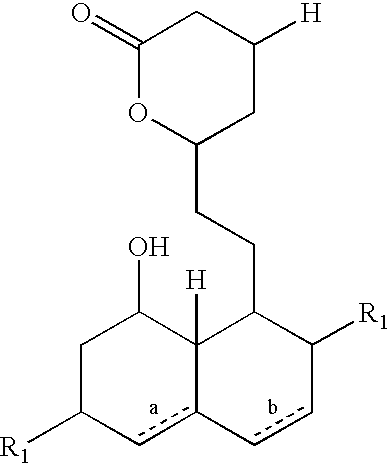
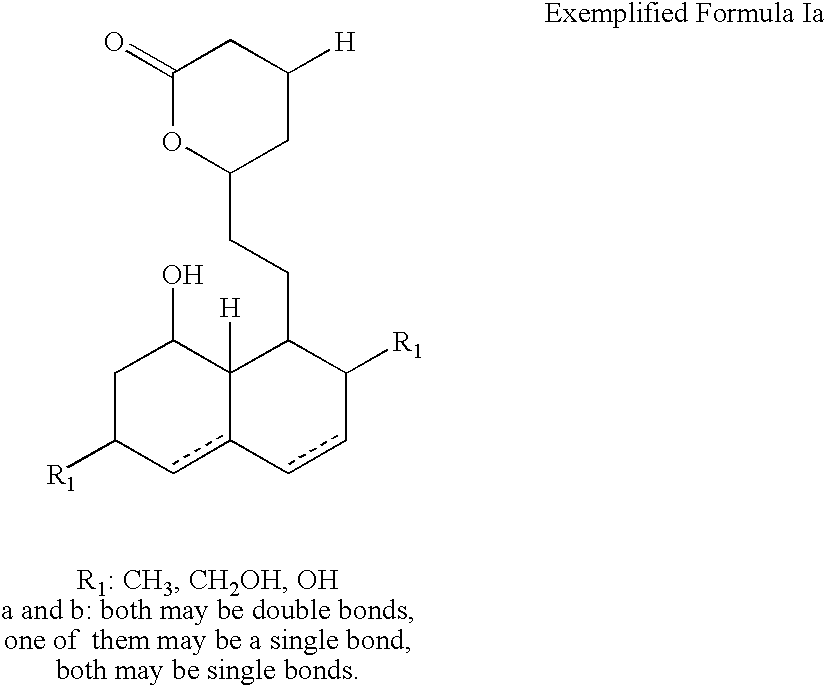
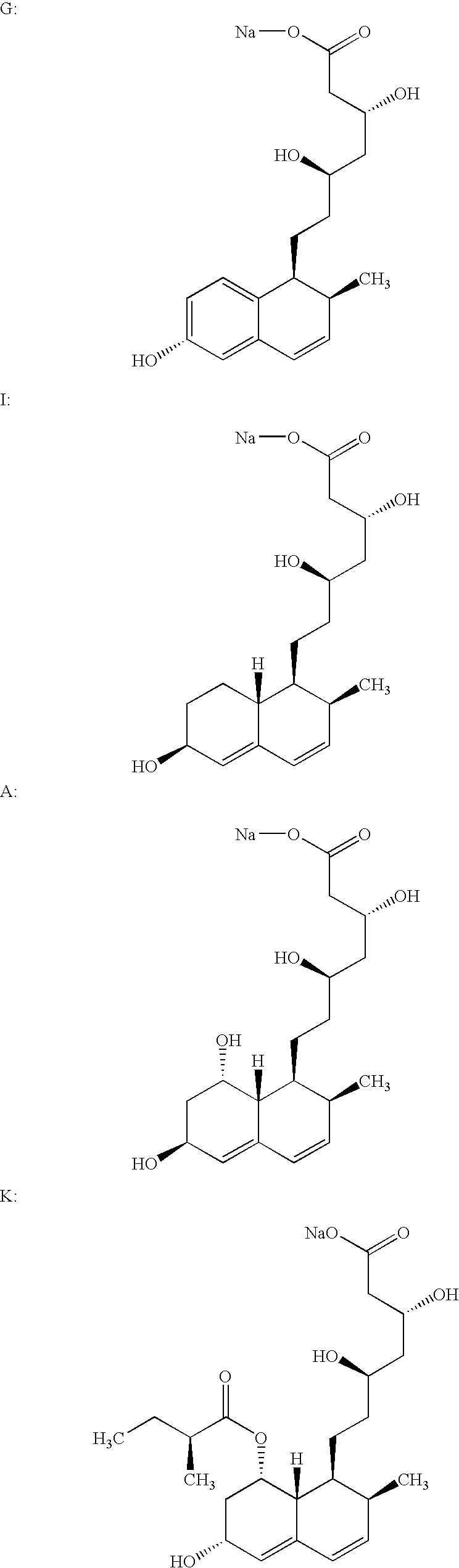
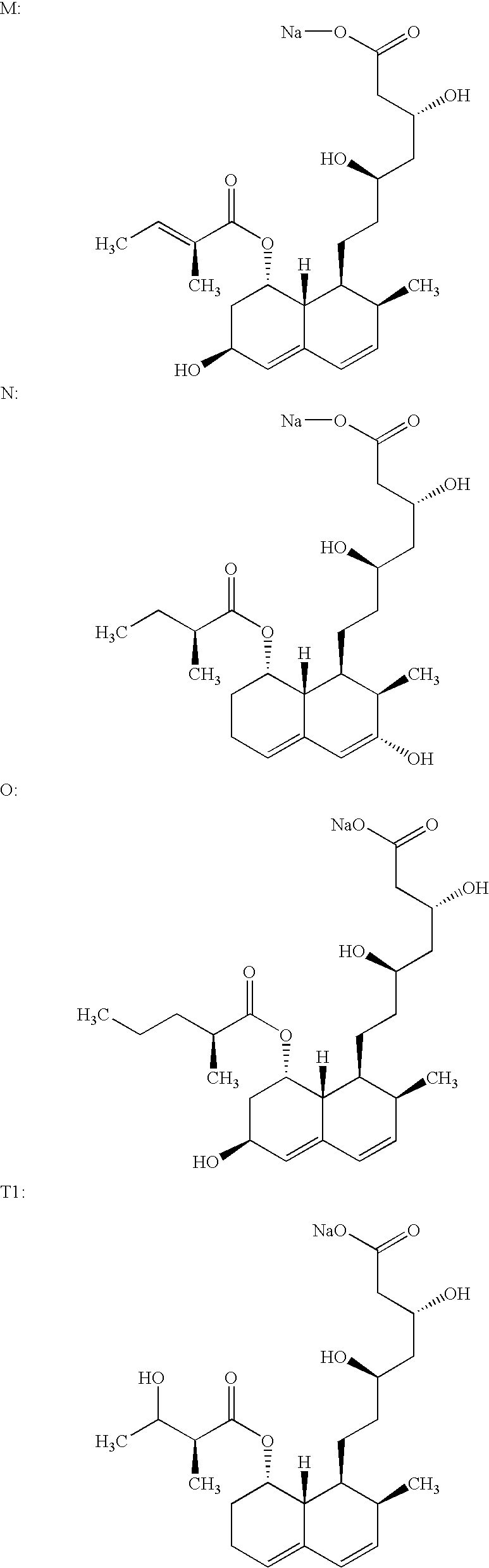
Lovastatin, pravastatin, simvastatin, mevastatin, atorvastatin, and derivatives and analogs thereof are known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and are used as antihypercholesterolemic agents. The majority of them are produced by fermentation using microorganisms of different species identified as species belonging to Aspergillus, Monascus, Nocardia, Amycolatopsis, Mucor or Penicillium genus, Streptomyces, Actinomadura, Micromonospora, some are obtained by treating the fermentation products using the method of chemical synthesis or they are the products of total chemical synthesis. The purity of the active ingredient is an important factor for manufacturing the safe and effective pharmaceutical, especially if the pharmaceutical product must be taken on a longer term basis in the treatment or prevention of high plasma cholesterol. The accumulation of the impurities from the pharmaceuticals of lower purity may cause many side effects during the medical treatment. The present invention relates to a new industrial process for the isolation of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors using so-called displacement chromatography. Use of the invention enables one to obtain HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors of high purity, with high yields, lower production costs and suitable ecological balance.
Owner:LEK PHARMA D D
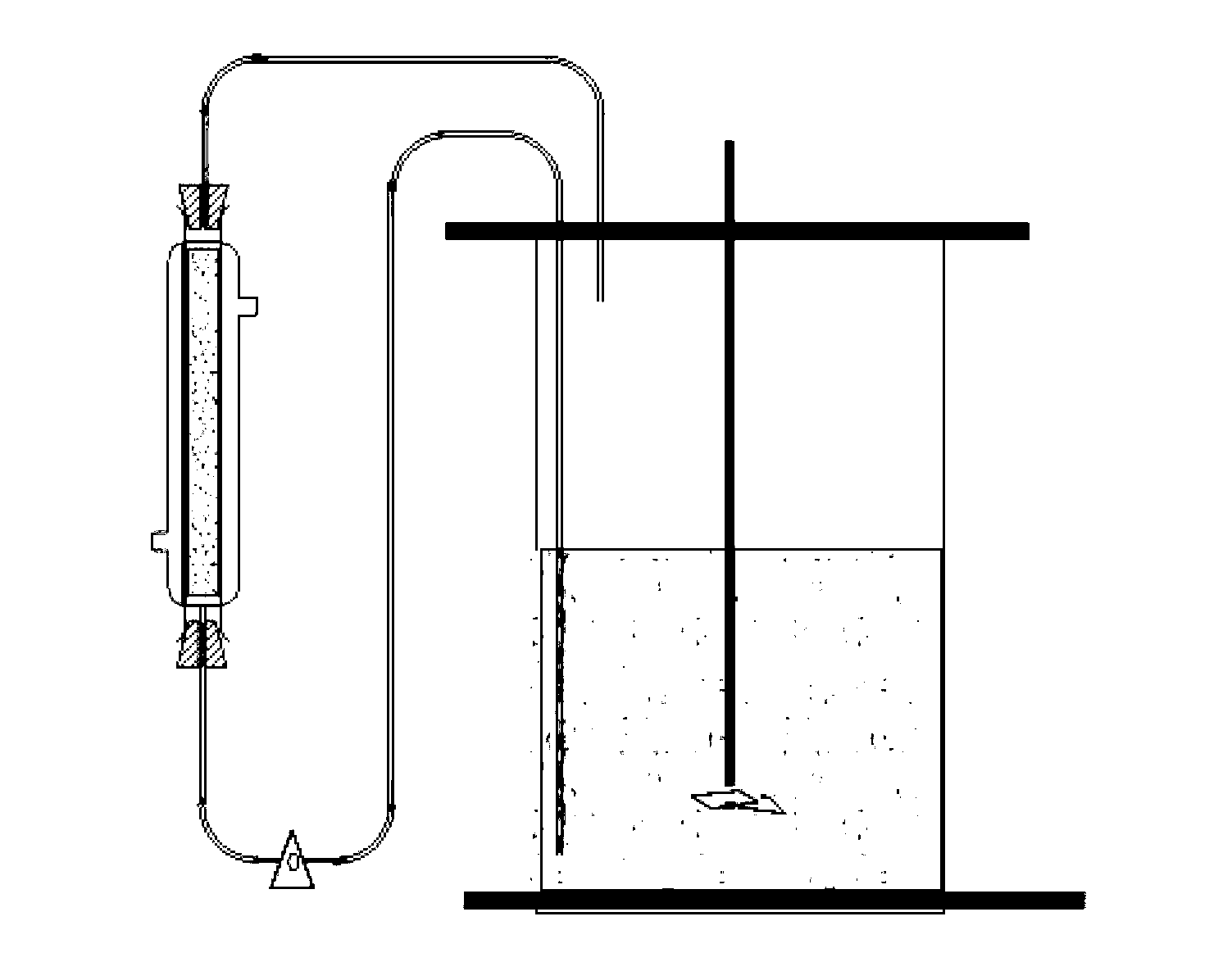
Amycolatopsis sp. Strain and Methods of Using the Same for Vanillin Production
ActiveUS20130115667A1Mild reaction conditionsLittle environmental pollutionBacteriaUnicellular algaeHigh concentrationAmycolatopsis
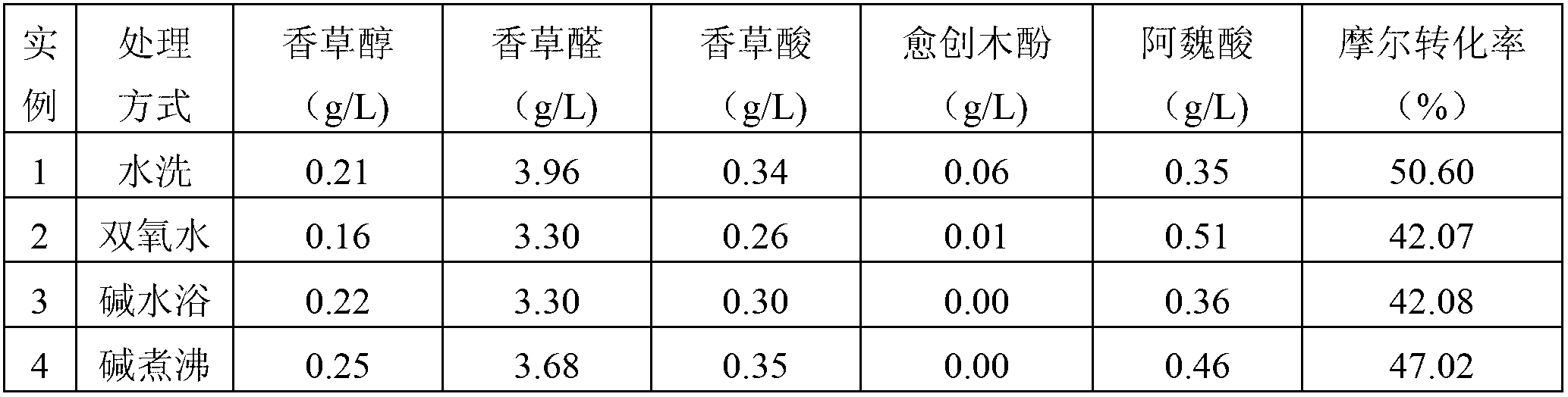
This invention provides an Amycolatopsis sp. strain (zhp06), and a method of using the whole cell preparation of the strain for vanillin production. The strain was deposited in China Center for Type Culture Collection on Jul. 26, 2011 with the number of CCTCC NO: M 2011265. Under high concentrations of ferulic acid substrate, the vanillin production by this method can reach more than 10 g / L. The molar conversion rate of ferulic acid is more than 50% and the purity of vanillin is from 80% to 95%. The advantage of this invention includes: repeated use of biocatalyst cells, mild biotransformation condition, low environmental pollution, short production cycle, high product purity and simple purification procedure. It has a great potential for industrial applications.
Owner:BGN TECH
Salts of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors
InactiveUS6838566B2Isolation and/or purificationLow toxicityOrganic compound preparationCrystallization separationChemical synthesisHMG-CoA reductase
Lovastatin, pravastatin, simvastatin, mevastatin, atorvastatin, and derivatives and analogs thereof are known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and are used as antihypercholesterolemic agents. The majority of them are produced by fermentation using microorganisms of different species identified as species belonging to Aspergillus, Monascus, Nocardia, Amycolatopsis, Mucor or Penicillium genus, some are obtained by treating the fermentation products using the methods of chemical synthesis or they are the products of total chemical synthesis. The present invention relates to the new amine salts of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, the preparation thereof, the preparation of pure HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors via amine salts thereof, use of the amine salts of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors in the process for semisynthetic preparation of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, use of the amine salts of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors in the process for biotechnological modification of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors as well as the conversion of the amine salts of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors into the pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and the conversion of the amine salts of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors into the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors in the lactone form.
Owner:LEK PHARMA D D
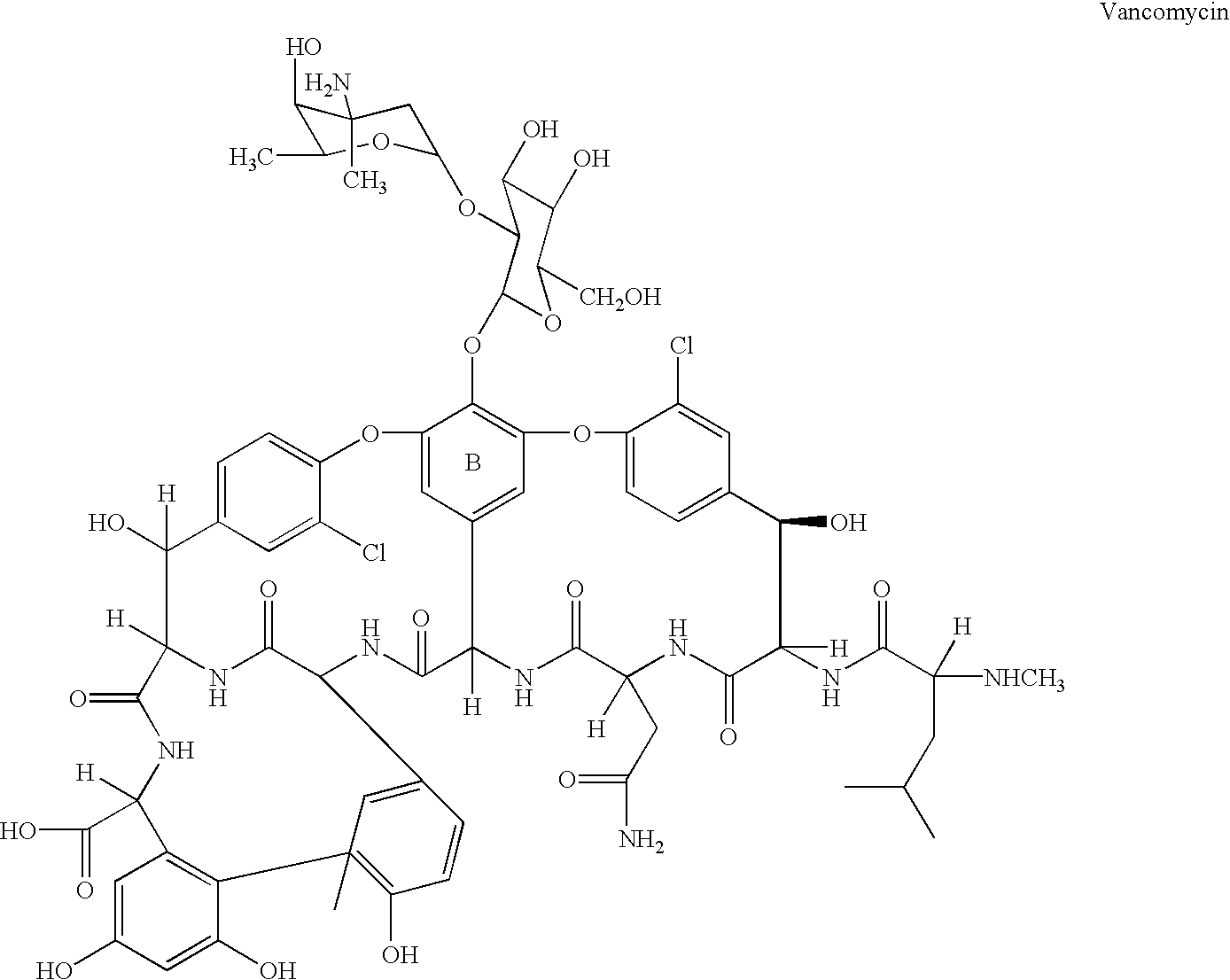
Ribosome resistance mutagenesis breeding vancomycin production bacterial strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101608209AIncrease productionGood yield stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesInhibition zoneHplc method
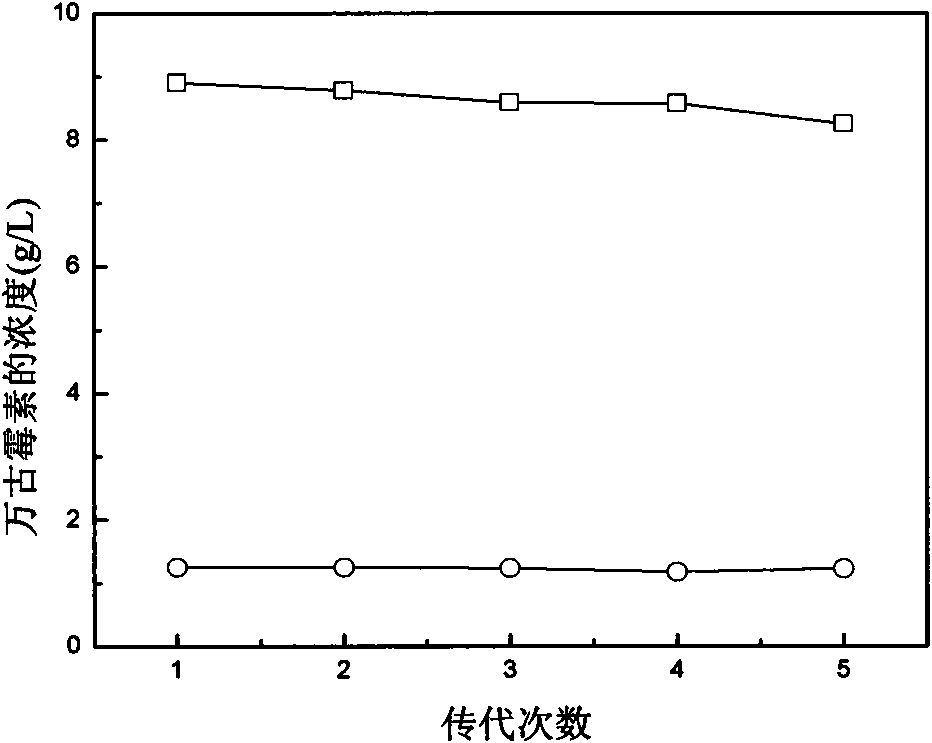
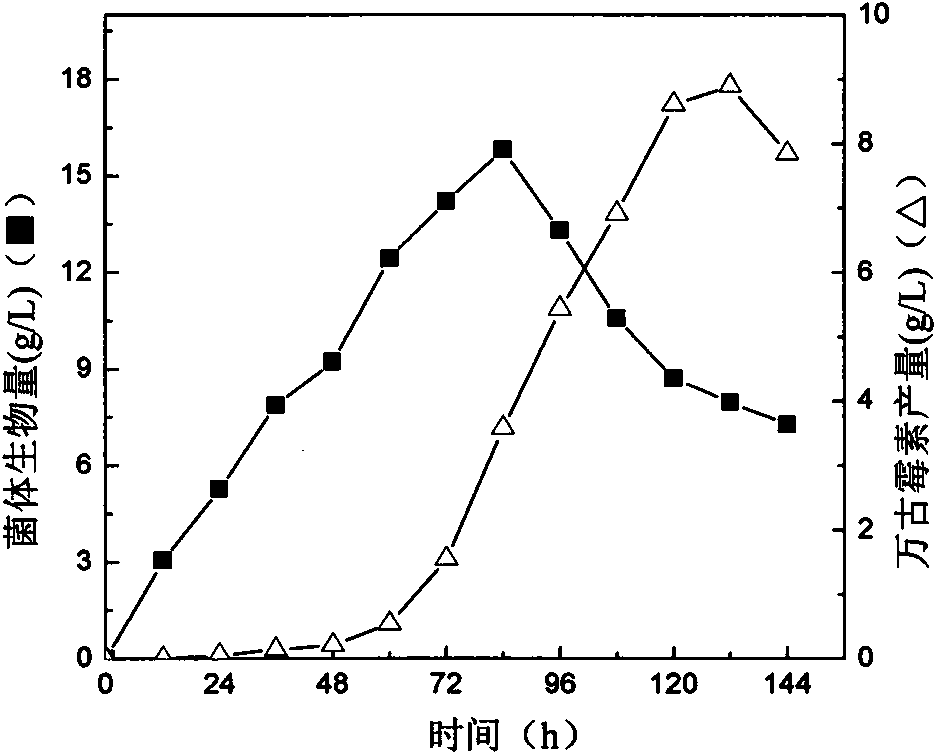
The invention provides ribosome resistance mutagenesis breeding vancomycin production bacterial strain and an application thereof, specifically the mutagenesis breeding method of mutagenesis bacterial strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis and the application thereof in preparing vancomycin, relating to breeding of microorganism. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating the Amycolatopsis orientalis to Gause-1 agar culture medium panel to be cultured; taking out spore and using sterile water to prepare spore suspension and coating the spore suspension in Gause-1 agar culture medium panel featuring mixing resistance of vancomycin and streptomycin to be cultured; randomly selecting produced single bacterial colony and streak-inoculating the single bacterial colony to the Gause-1 agar culture medium panel to be cultured, carrying out biological activity determination on produced mutagenesis bacterial strain; selecting mutagenesis bacterial strain with inhibition zone diameter thereof being 2mm larger than the inhibition zone diameter of original strain and inoculating the mutagenesis bacterial strain to liquid fermentation medium to be cultured; determining the content of vancomycin in fermentation liquor by HPLC method to verify the obtained vancomycin mutagenesis bacterial strain; subjecting the obtained vancomycin mutagenesis bacterial strain to 5 times of continuous passage stability inspection to obtain the vancomycin production bacterial strain.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Glycosyltransferase gene gtfC from Amycolatopsis orientalis
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid compounds encoding the glycosyltransferase protein GtfC of Amycolatopsis orientalis. Also provided are vectors carrying the gtfC gene, transformed heterologous host cells for expressing the GtfC protein, and methods for producing glycopeptide compounds using the cloned gtfC gene.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
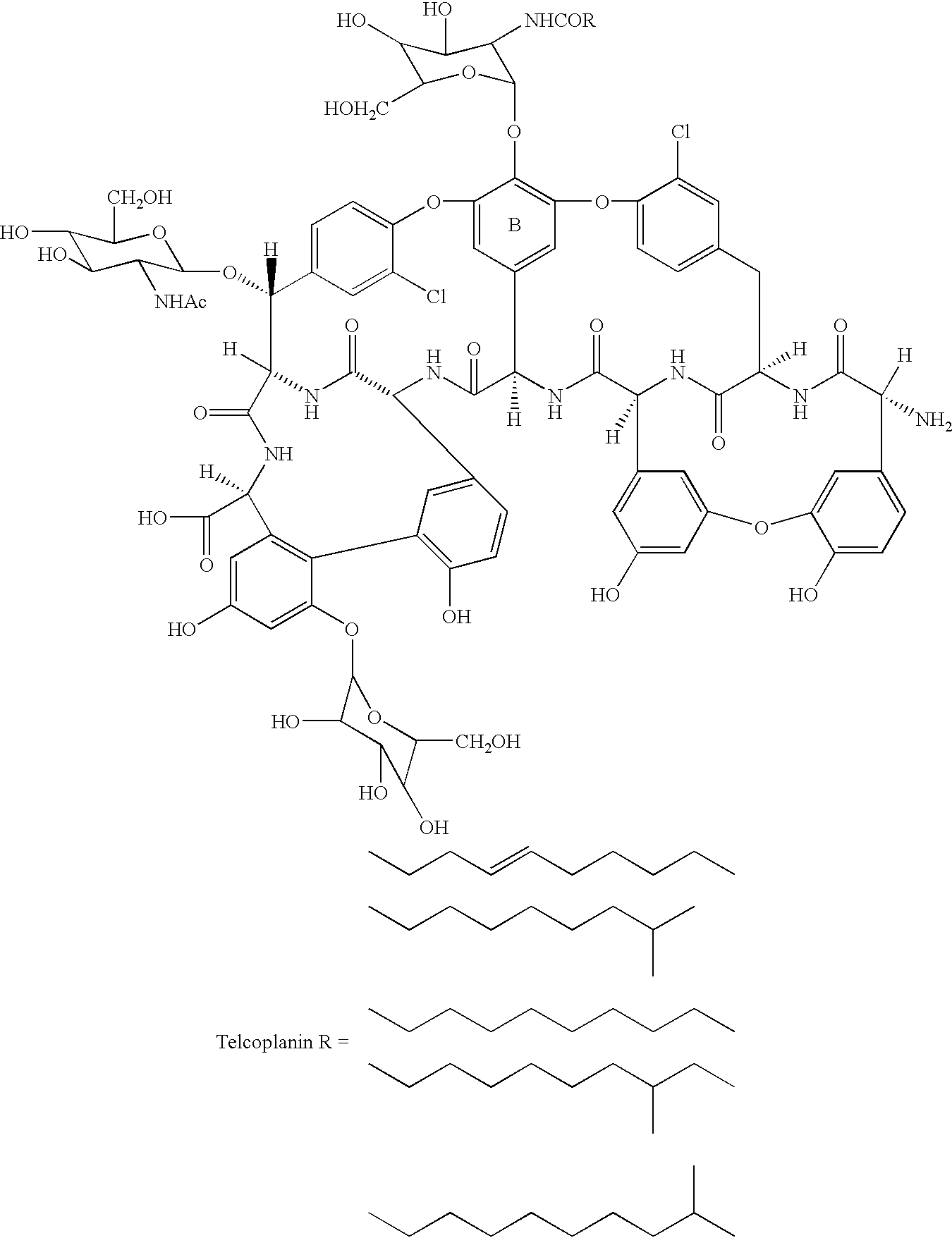
Glycosyltransferase gene GFTD from amycolatopsis orientalis
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid compounds encoding the glycosyltransferase protein GtfD of Amycolatopsis orientalis. Also provided are vectors carrying the gtfD gene, transformed heterologous host cells for expressing the GtfD protein, and methods for producing glycopeptide compounds using the cloned gtfD gene.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Glycosyltransferase gene gtfB from Amycolatopsis orientalis
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid compounds encoding the glycosyltransferase protein GtfB of Amycolatopsis orientalis. Also provided are vectors carrying the gtfB gene, transformed heterologous host cells for expressing the GtfB protein, and methods for producing glycopeptide compounds using the cloned gtfB gene.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
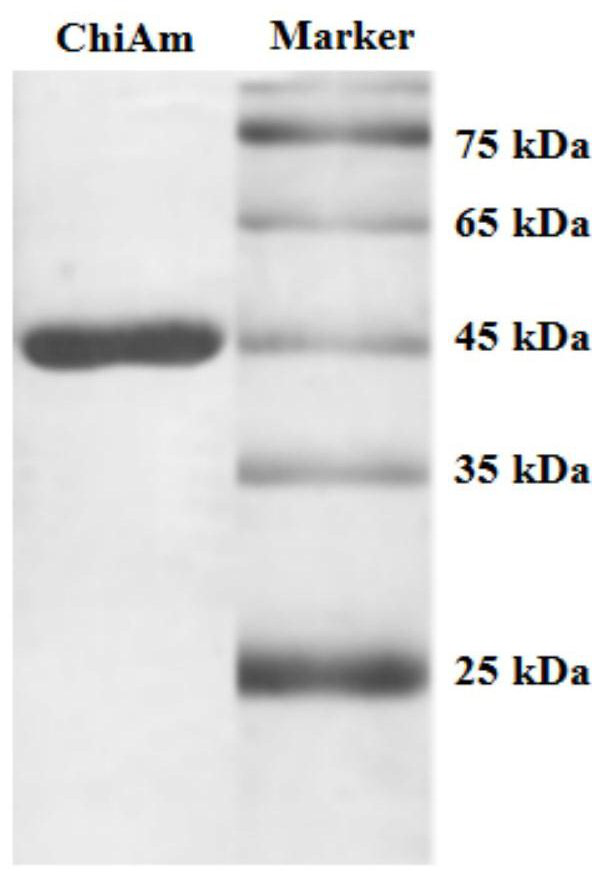
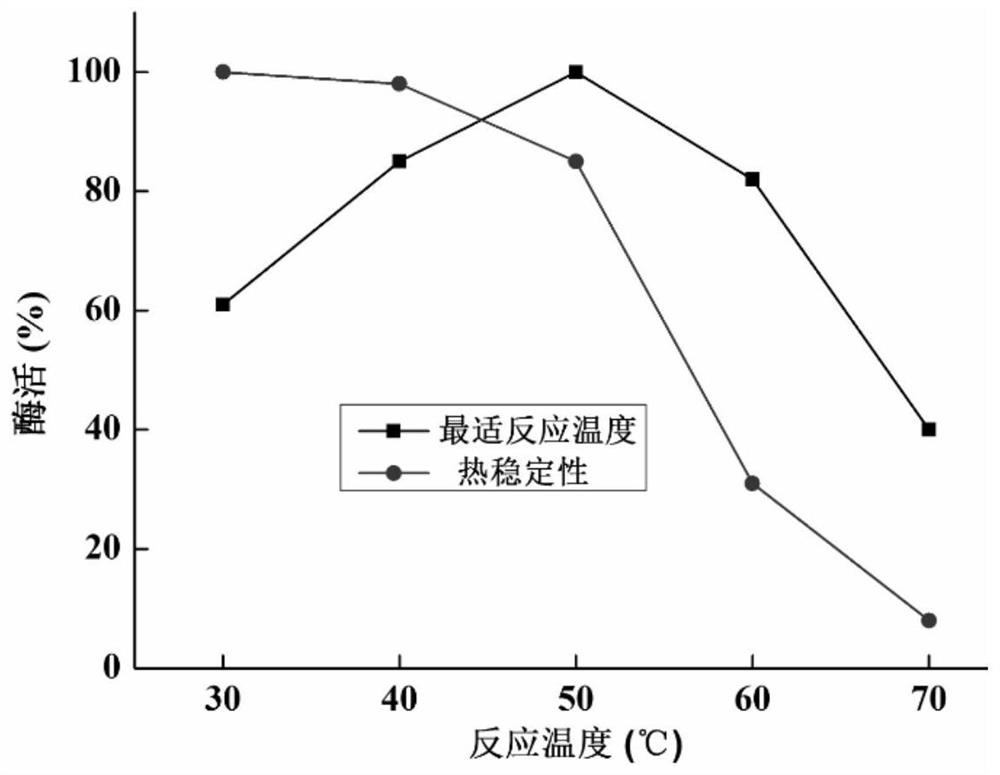
Chitinase gene, chitinase and preparation method and application of chitinase
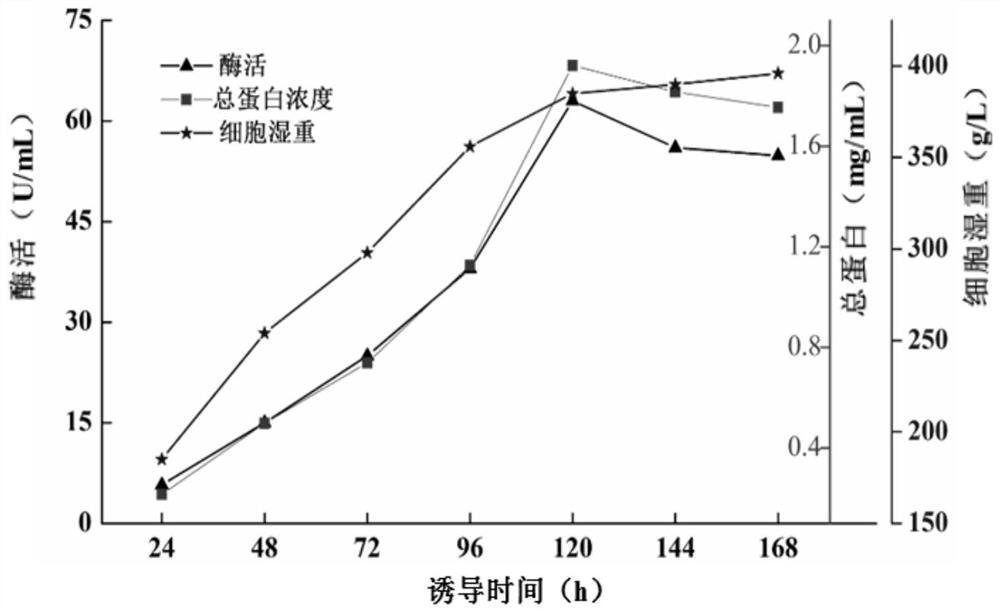
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to a chitinase gene, chitinase and a preparation method and application of the chitinase. The nucleotide sequence of the chitinase gene chiam is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and the chitinase gene chiam is obtained by comprehensively optimizing the sequence of the chitinase derived from the Amycolatopsis mediterranei. The amino acid sequence of the chitinase ChiAm is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. The types and source ways of the chitinase are enriched, the enzyme specific activity is 48U / mg, the chitinase has good stability in a wide temperature range and a wide pH range, and the chitinase has good application prospects and industrial value.
Owner:深圳润康生态环境股份有限公司
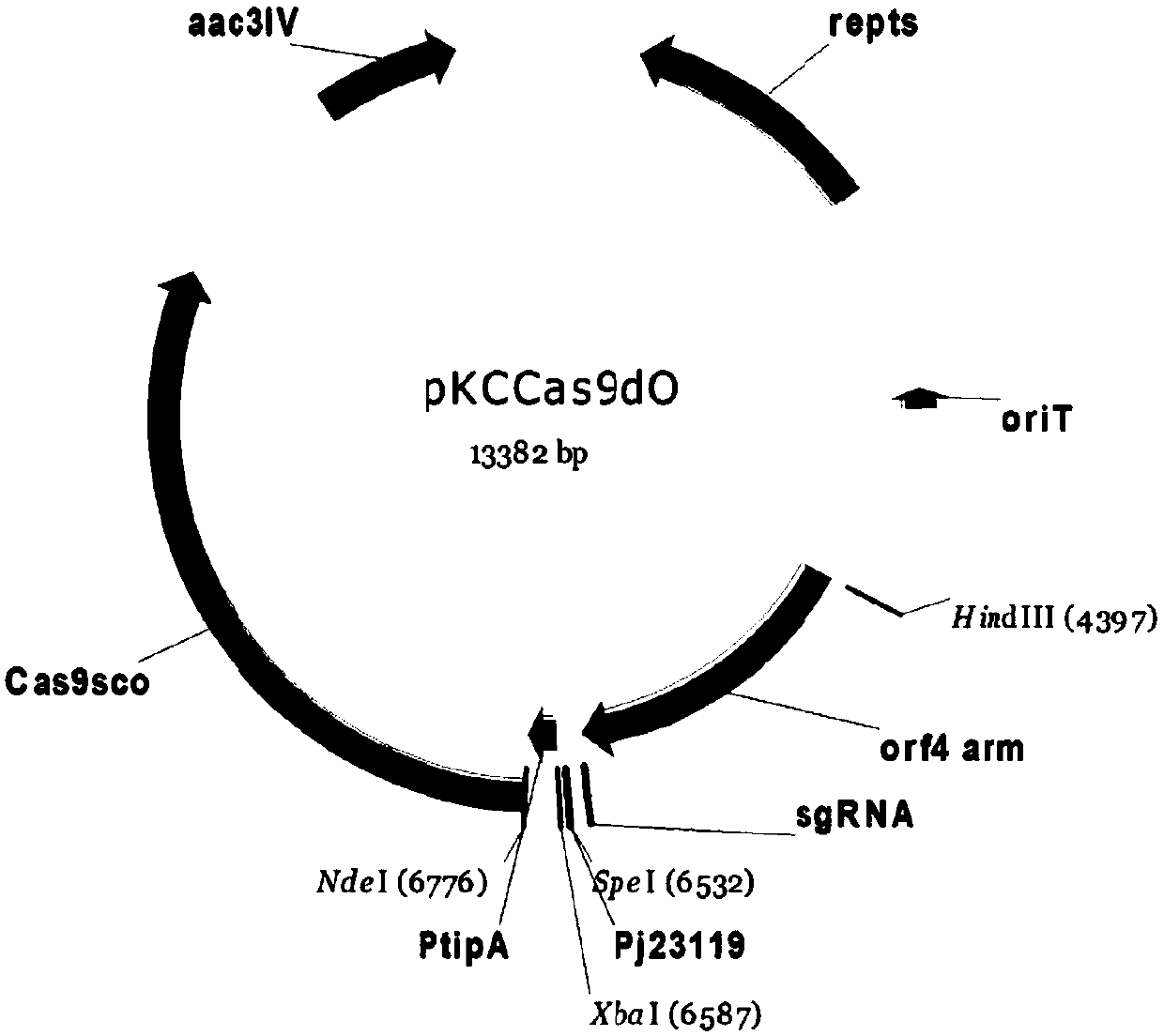
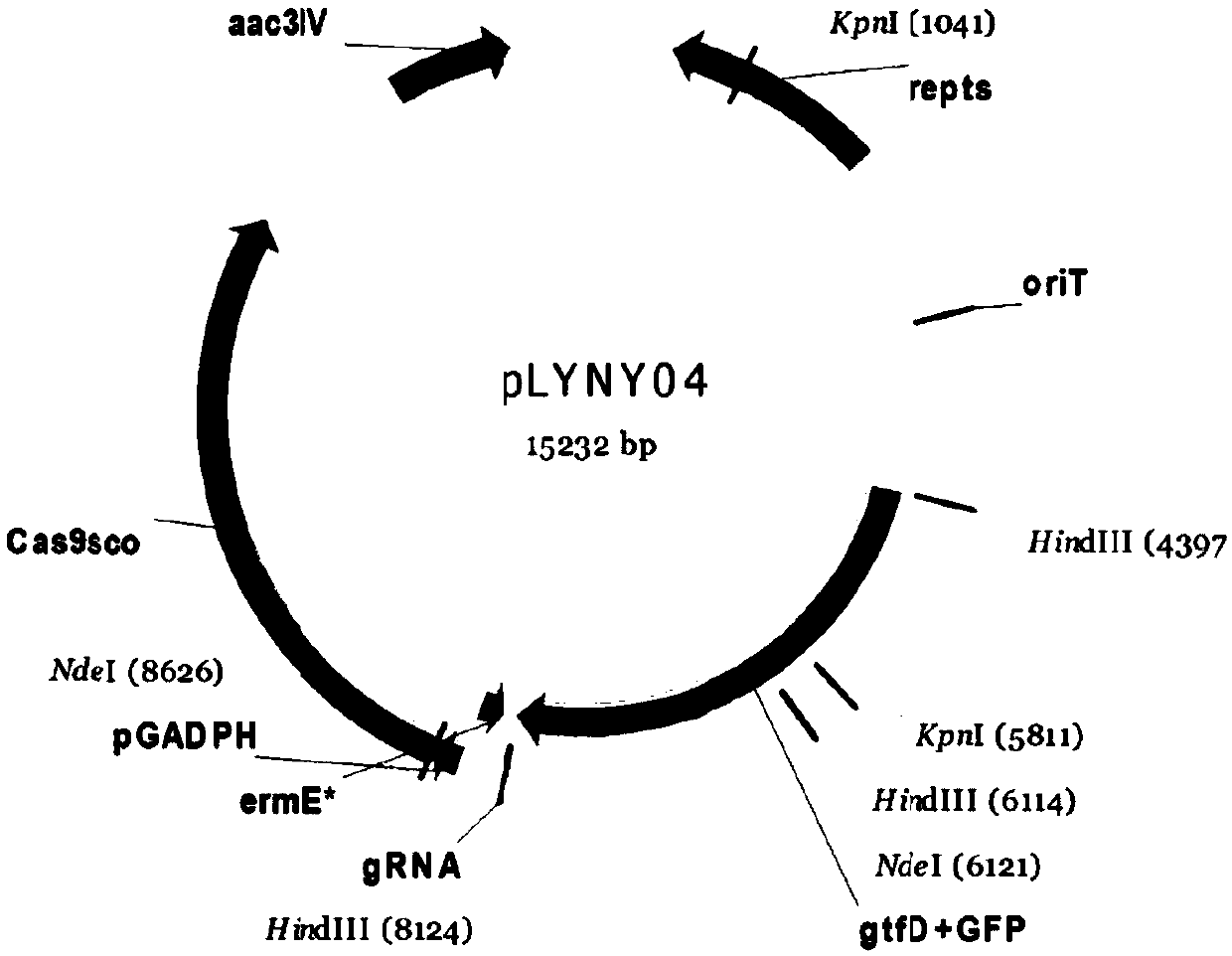
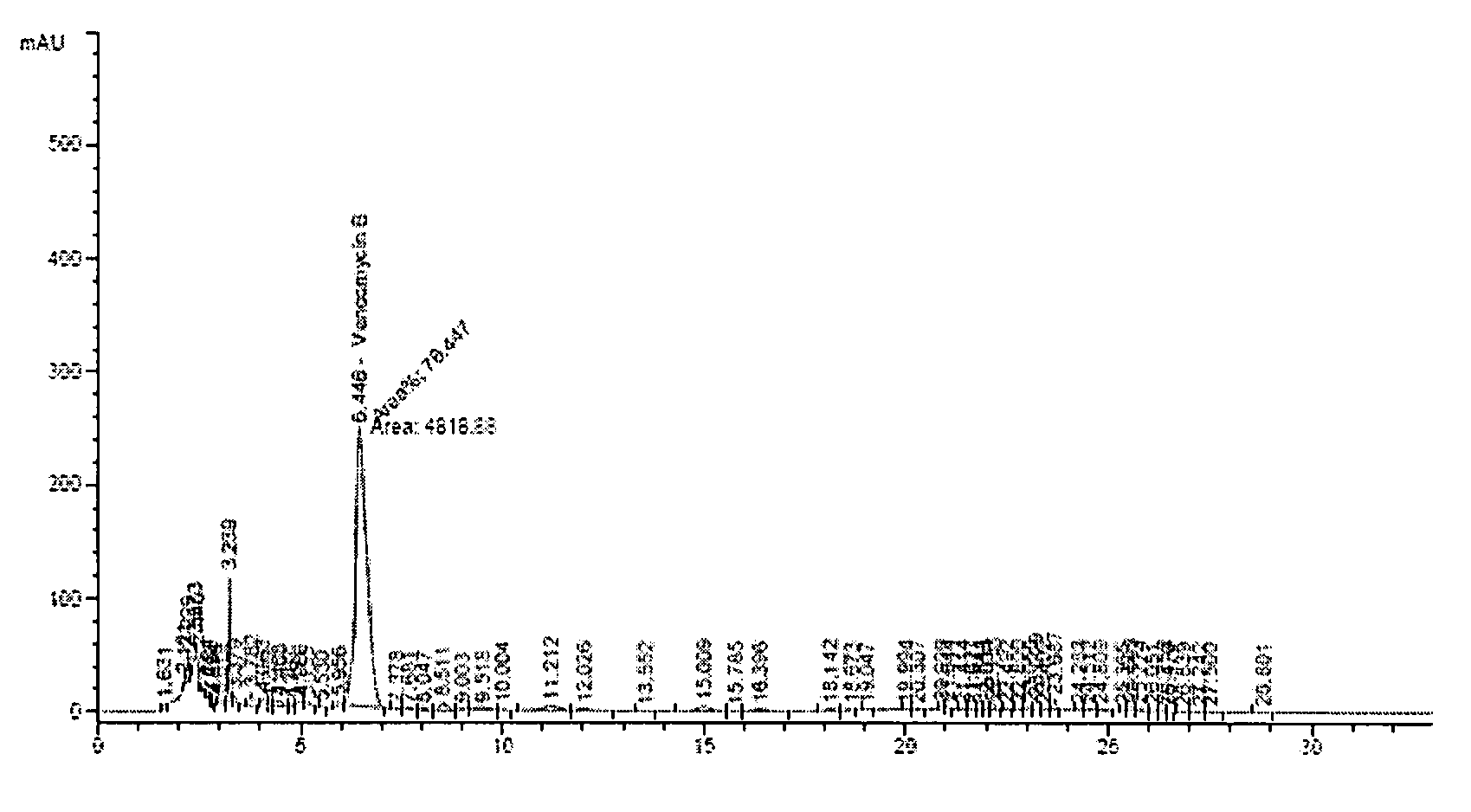
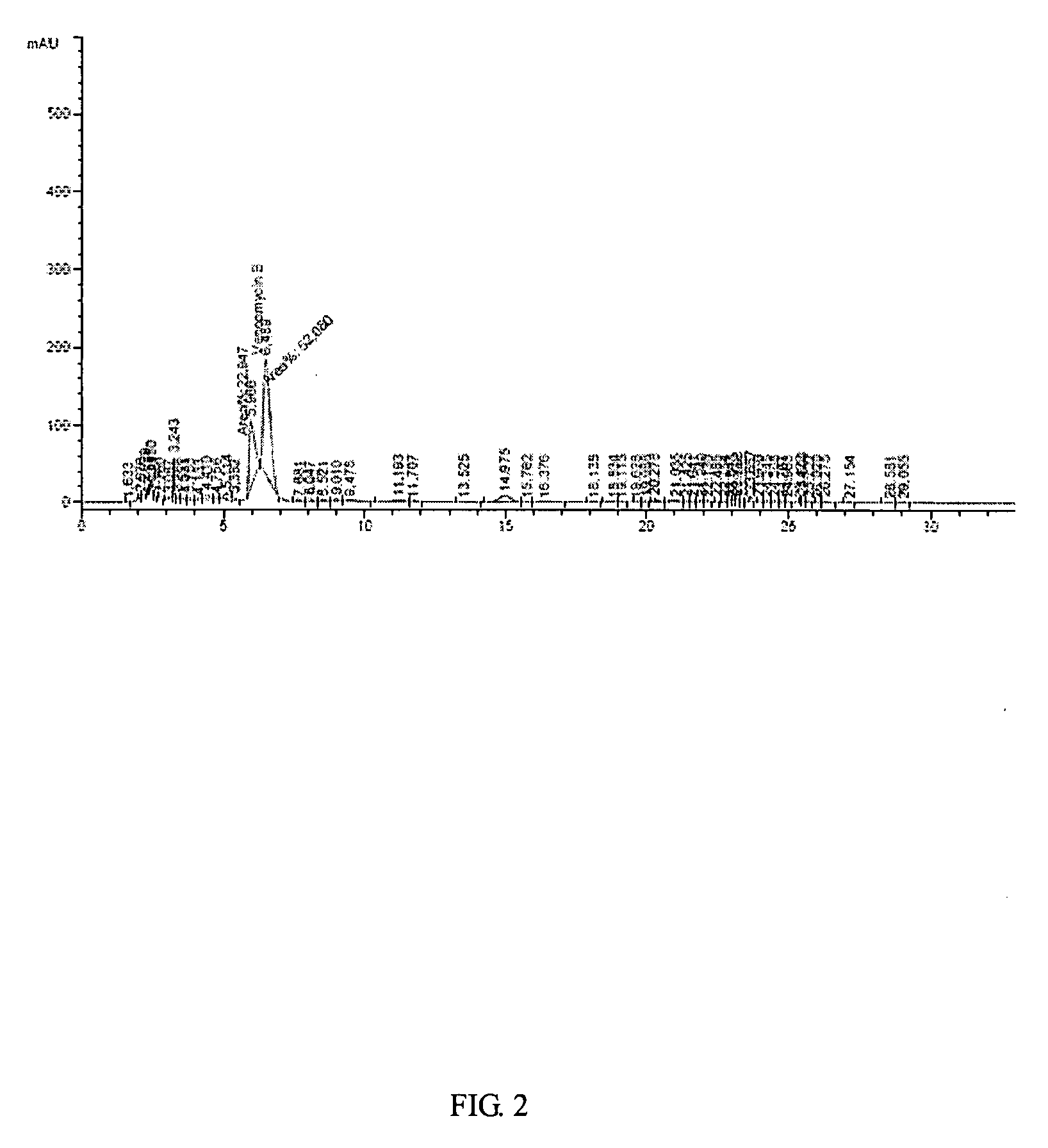
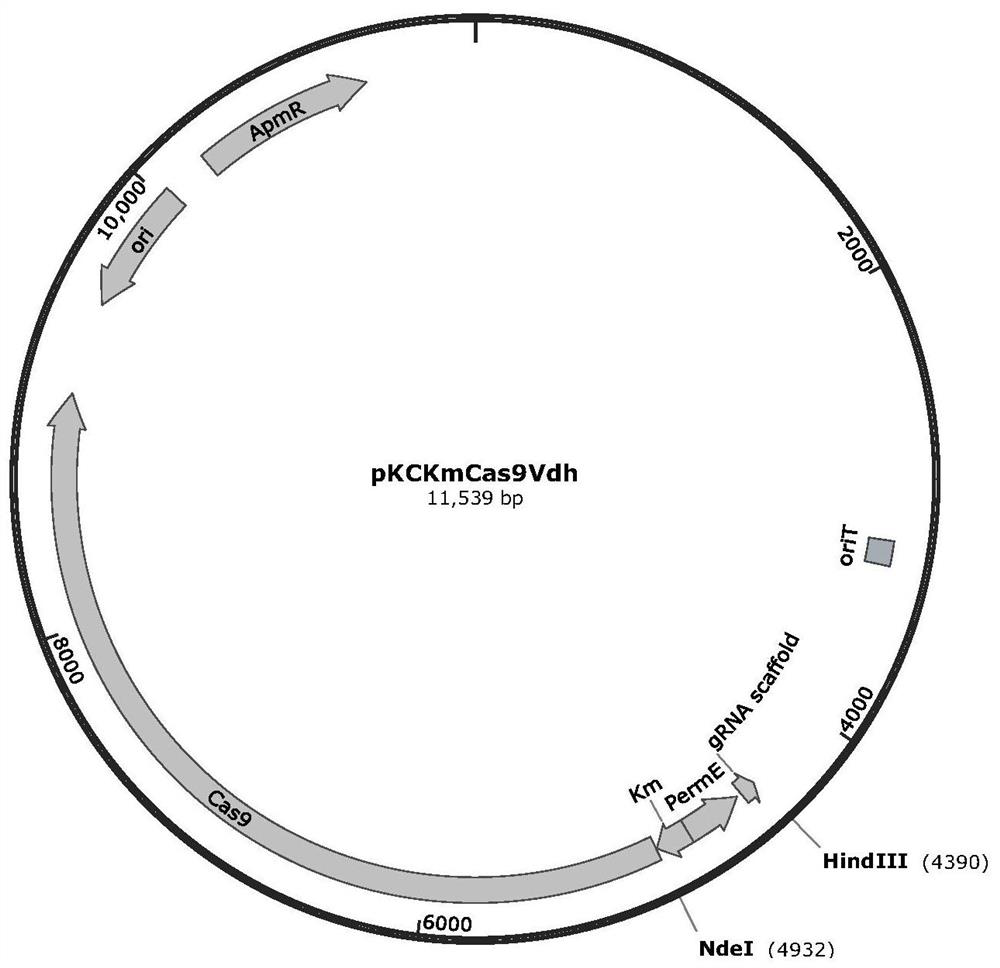
Application of gene editing method in Amycolatopsis orientalis
InactiveCN109609537AEasy to detectImprove integration efficiencyVectorsBacteriaAmycolatopsisAmycolatopsis orientalis
The invention discloses a CRISPR / Cas9 editing system based method for gene knockout and gene knock-in in Amycolatopsis orientalis. The method introduces a CRISPR / Cas9 edited plasmid pLYNY04 into Amycolatopsis orientalis HCCB10007, realizes gene knockout and gene knock-in, simplifies genetic operation and improves the integration efficiency of the Amycolatopsis orientalis. The invention also discloses a CRISPR / Cas9 edited plasmid pLYNY04 containing a gtfD gene homologous arm; and eGFP is inserted into a target sequence of the Amycolatopsis orientalis to facilitate detection of gene editing results. The invention also discloses application of the CRISPR / Cas9 edited plasmid pLYNY04 containing the gtfD gene homologous arm.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Mutant strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis and process for preparing vancomycin hydrochloride
The present invention provides a process for preparing vancomycin hydrochloride using a mutant strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis (accession No. KCCM-10836P) comprising the steps of i) mutating and isolating a strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis (accession No. KCCM-10836P) for producing vancomycin from mother strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis (accession No. ATCC-19795) using NTG(N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine) in the selection medium; ii) seed culturing the isolated mutant strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis (accession No. KCCM-10836P); iii) cultivating and fermenting said mutant strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis in the fermentation medium consisting of 12˜18 (w / v) % of dextrin, 2.2˜3.8 (w / v) % of bean powder, 1.9˜2.9 (w / v) % of potato protein, 0.10˜0.14 (w / v) % of sodium chloride and a small amount of minerals; iv) filtering vancomycin using microfilter in the cultivation broth by removing mycelia; v) purifying obtained vancomycin using column system compacted with cation exchange resin, anion exchange resin and absorbent resin; and vi) crystallizing the purified vancomycin with hydrochloric acid.
Owner:BIONGENE
Preparation of vanillin from microbial transformation media by extraction by means supercritical fluids or gases
Crude solid vanillin-containing material is precipitated from a solution obtained by biotransformation, and purified by a process comprising contacting it with a purification fluid selected from (a) a liquefied gas whose pressure exceeds its critical pressure and whose temperature is below its critical temperature; (b) a supercritical fluid; (c) a gas. The fluid is preferably liquid carbon dioxide. The temperature is maintained below 25°. The product may be further purified by treatment with CO2 in a fluid bed drier. The crude material is preferably one precipitated from a solution resulting from biotransformation of ferulic acid. A new strain of Amycolatopsis capable of generating high concentrations of vanillin with minimal odoriferous by-products (e.g. guaiacol) is also disclosed.
Owner:SAF ISIS
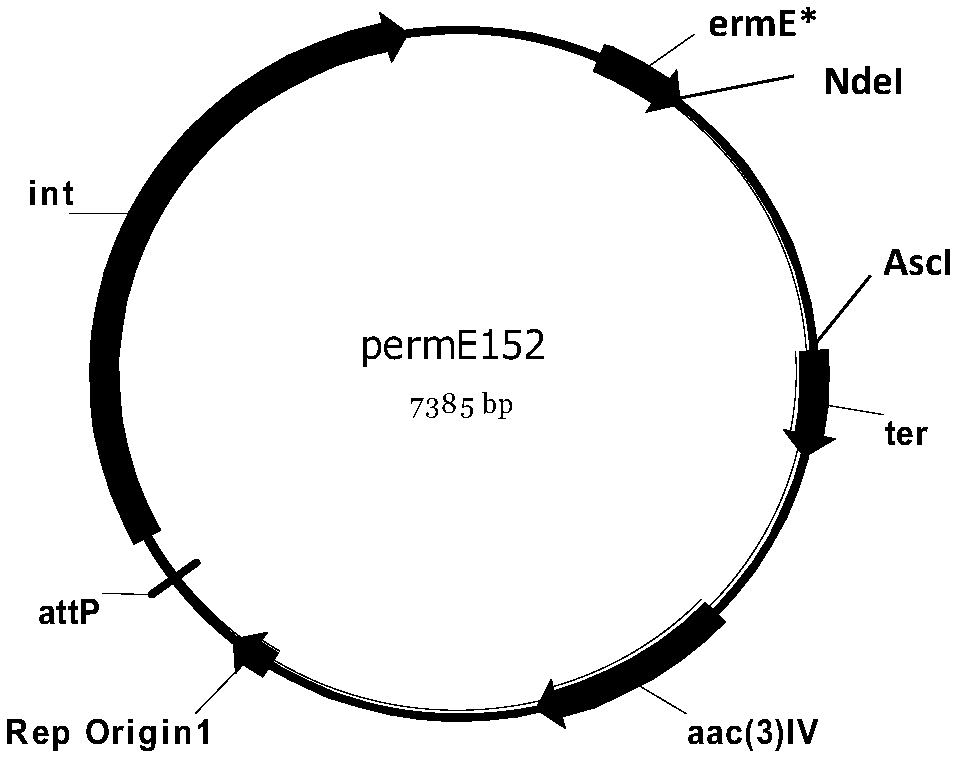
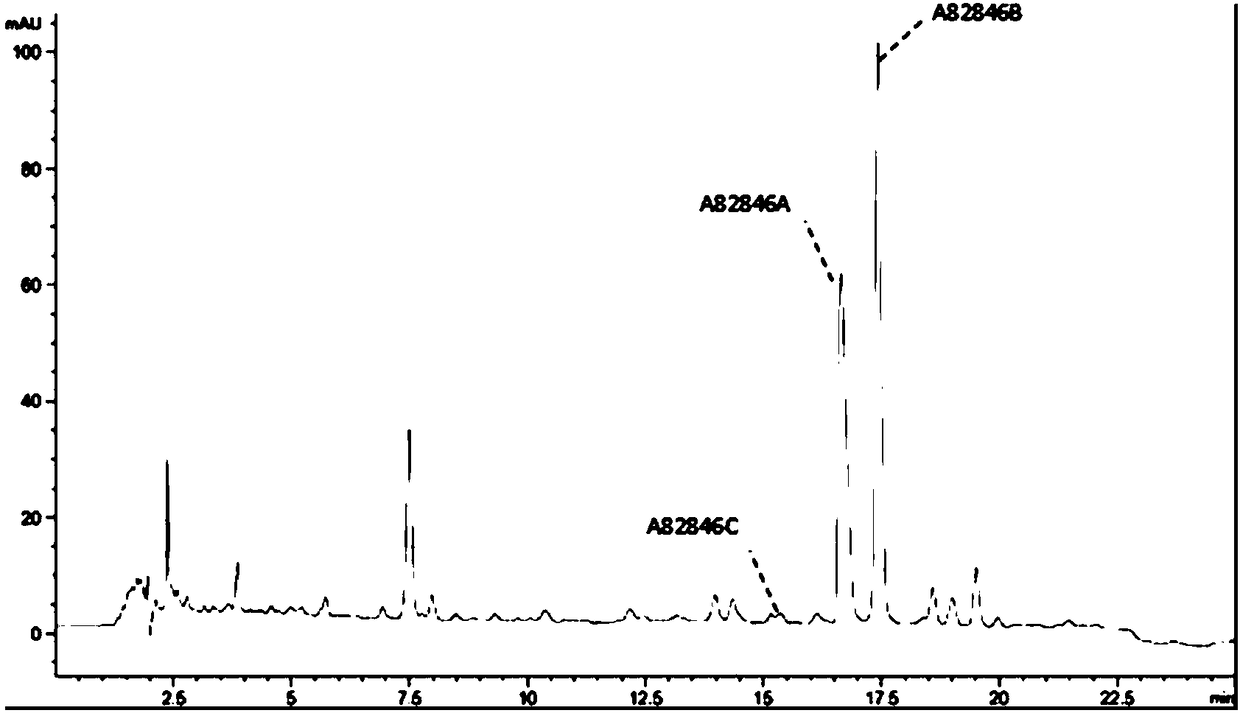
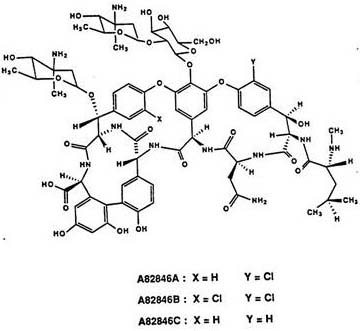
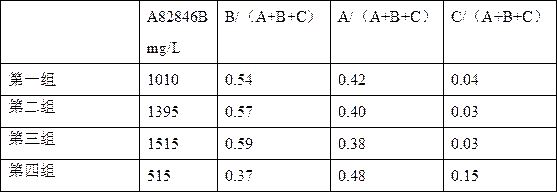
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing A82846B as well as preparation method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for producing A82846B. The genetically engineered bacterium is an engineering bacterium which integrates an endogenous halogenase gene chaA or an exogenous halogenase gene whose homology with the endogenous halogenase gene chaA is not less than 84% into a genome of amycolatopsis orientalis. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the genetically engineered bacterium, and a method for fermenting the genetically engineered bacterium and obtaining the A82846B from a fermentation liquid. According to the invention, the genetically engineered bacterium over-expresses the introduced halogenase gene and produces the A82846B, and the yield (mg / L) of the A82846B or the proportion of a target product in total products is remarkably improved; the production efficiency is improved, the production cost is reduced, and the environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD +1
New salts of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors
InactiveUS20050049422A1Isolation and/or purificationLow toxicityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationHMG-CoA reductaseChemical synthesis
Lovastatin, pravastatin, simvastatin, mevastatin, atorvastatin, and derivatives and analogs thereof are known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and are used as antihypercholesterolemic agents. The majority of them are produced by fermentation using microorganisms of different species identified as species belonging to Aspergillus, Monascus, Nocardia, Amycolatopsis, Mucor or Penicillium genus, some are obtained by treating the fermentation products using the methods of chemical synthesis or they are the products of total chemical synthesis. The present invention relates to the new amine salts of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, the preparation thereof, the preparation of pure HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors via amine salts thereof, use of the amine salts of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors in the process for semisynthetic preparation of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, use of the amine salts of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors in the process for biotechnological modification of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors as well as the conversion of the amine salts of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors into the pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and the conversion of the amine salts of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors into the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors in the lactone form.
Owner:LEK PHARMA D D
Amycolatopsis sp. strain and methods of using the same for vanillin production
ActiveUS9115377B2Mild reaction conditionsLittle environmental pollutionOrganic chemistryBacteriaHigh concentrationAmycolatopsis
This invention provides an Amycolatopsis sp. strain (zhp06), and a method of using the whole cell preparation of the strain for vanillin production. The strain was deposited in China Center for Type Culture Collection on Jul. 26, 2011 with the number of CCTCC NO: M 2011265. Under high concentrations of ferulic acid substrate, the vanillin production by this method can reach more than 10 g / L. The molar conversion rate of ferulic acid is more than 50% and the purity of vanillin is from 80% to 95%. The advantage of this invention includes: repeated use of biocatalyst cells, mild biotransformation condition, low environmental pollution, short production cycle, high product purity and simple purification procedure. It has a great potential for industrial applications.
Owner:BGN TECH
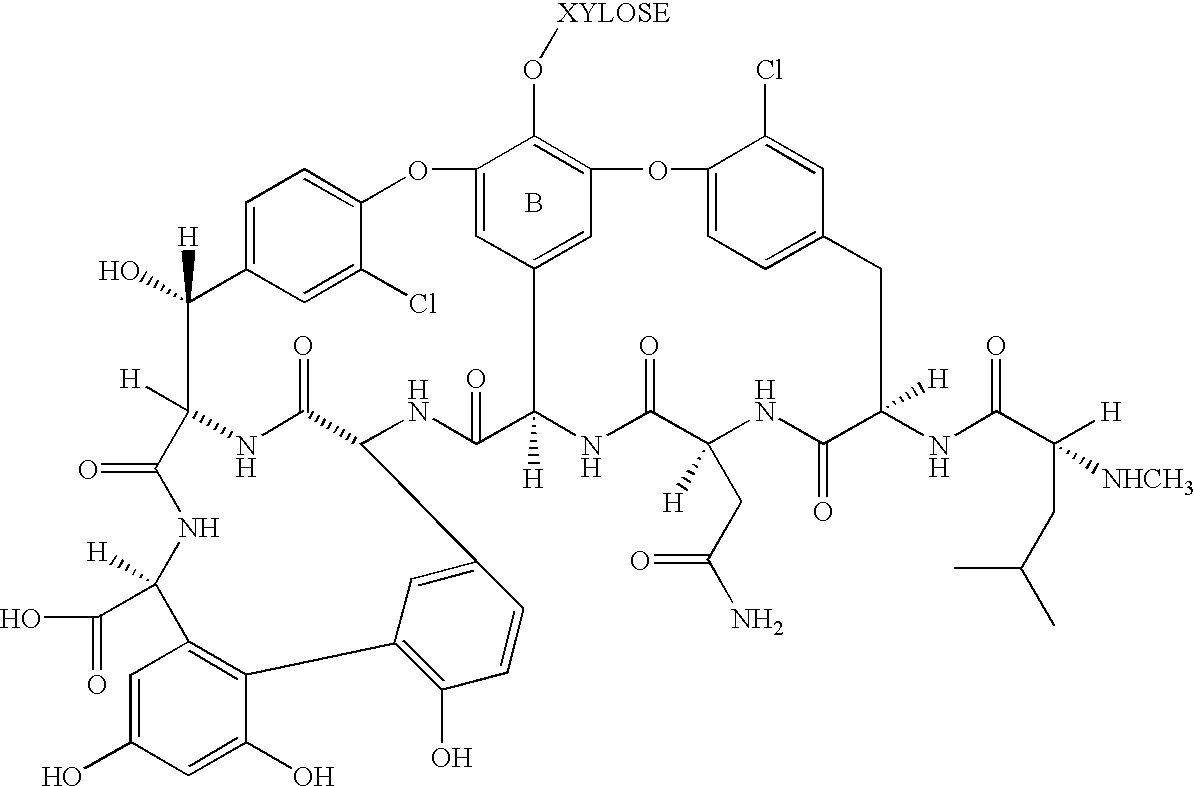
Method for improving yield of ECO-0501 produced by fermenting Amycolatopsis orientalis
ActiveCN101545000AIncrease productionInhibit synthesisMicroorganism based processesFermentationVancomycin synthesisCombinatorial chemistry
The invention discloses a method for improving the yield of ECO-0501 produced by fermenting Amycolatopsis orientalis, which is achieved by interdicting the Amycolatopsis orientalis to synthesize vancomycin, wherein the synthesis of the interdicted vancomycin comprises interdicting or knocking out vancomycin synthetase genes or vancomycin precursor synthetase genes. The method for improving the yield of the compound ECO-0501 produced by fermenting the Amycolatopsis orientalis interdicts the synthesis of the vancomycin while improving the yield of the ECO-0501, thus the method is particularly favorable for the downstream separation steps.
Owner:SHANGHAI LAIYI BIOMEDICAL RES & DEV CENT +1
Method for converting ferulic acid to produce vanillin by immobilized amycolatopsis
InactiveCN103060392ANo pollution in the processReduce contentMicroorganism based processesOn/in organic carrierCelluloseBio engineering
The invention discloses a method for converting ferulic acid to produce vanillin by immobilized amycolatopsis, and belongs to the technical field of biology engineering. Cellulosic materials such as sawdust, bagasse and the like are used as carriers, and an amycolatopsis cell is fixed by an adsorption way. An immobilized cell can be recycled for 10 times, and the mole conversion rate for converting ferulic acid into vanillin is kept at more than 50%. A resin is coupled and adsorbed in a conversion system. The output of vanillin reaches 19.65g / L, and the production strength of vanillin is 0.131g / L.h. The method is mild in conversion reaction condition, little in environmental pollution, short in production period, low in cost and easily separates and purifies converted products, so that the method has a good application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Process for obtaining HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors of high purity
Lovastatin, pravastatin, simvastatin, mevastatin, atorvastatin, and derivatives and analogs thereof are known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and are used as antihypercholesterolemic agents. The majority of them are produced by fermentation using microorganisms of different species identified as species belonging to Aspergillus, Monascus, Nocardia, Amycolatopsis, Mucor or Penicillium genus, Streptomyces, Actinomadura, Micromonospora, some are obtained by treating the fermentation products using the method of chemical synthesis or they are the products of total chemical synthesis. The purity of the active ingredient is an important factor for manufacturing the safe and effective pharmaceutical, especially if the pharmaceutical product must be taken on a longer term basis in the treatment or prevention of high plasma cholesterol. The accumulation of the impurities from the pharmaceuticals of lower purity may cause many side effects during the medical treatment. The present invention relates to a new industrial process for the isolation of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors using so-called displacement chromatography. Use of the invention enables one to obtain HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors of high purity, with high yields, lower production costs and suitable ecological balance.
Owner:LEK PHARMA D D
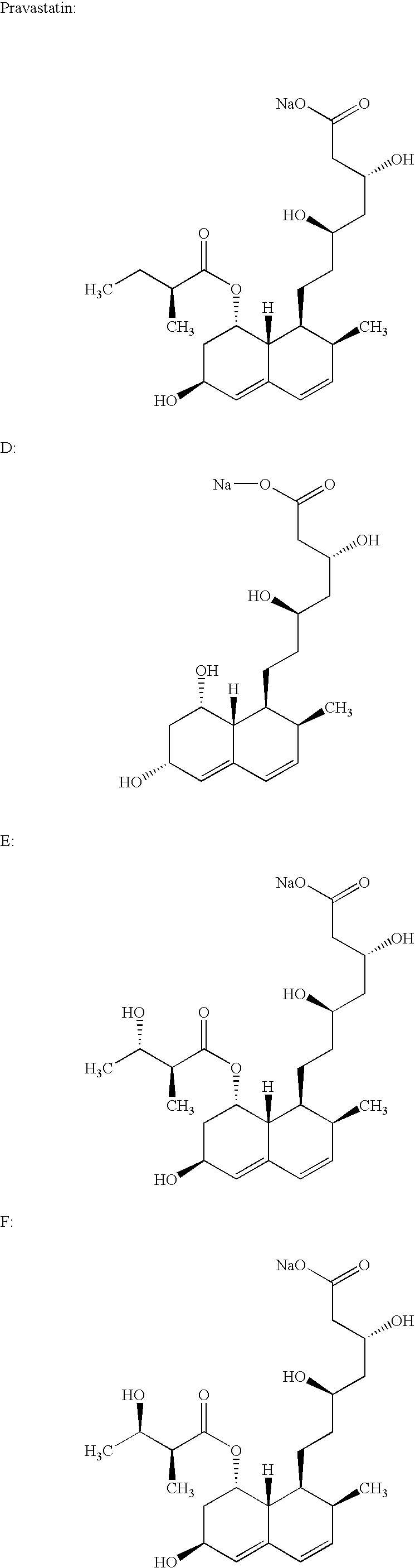
Crystals of the sodium salt of pravastatin
InactiveUS20060183929A1High purityImprove stabilityOrganic compound preparationMetabolism disorderChemical synthesisHMG-CoA reductase
Lovastatin, pravastatin, simvastatin, mevastatin, atorvastatin, fluvastatin and cervastatin and derivatives and analogs thereof are known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and are used as antihypercholesterolemic agents. The majority of them are produced by fermentation using microorganisms of different species identified as species belonging to Aspergillus, Monascus, Nocardia, Amycolatopsis, Mucor or Penicillium genus, some are obtained by treating the fermentation products using the methods of chemical synthesis (simvastatin) or they are the products of total chemical synthesis (fluvastatin, atorvastatin and cervastatin). The present invention relates to a crystalline form of the sodium salt of pravastatin, which is known by the chemical name 1-naphthaleneheptanoic acid, 1,2,6,7,8,8a-hexahydro-β,δ,6-trihydroxy-2-methyl-8-(2-methyl-1-oxobutoxy)-, mono sodium salt, which is useful as a pharmaceutical substance. The present invention further relates to the method for its preparation and isolation, to a pharmaceutical formulation containing the sodium salt of pravastatin in the crystalline form and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and to a pharmaceutical method of treatment. The novel crystalline form of the sodium salt of pravastatin is useful in the treatment of hypercholesterolemia and hyperlipidemia.
Owner:LEK PHARMACEUTICAL & CHEMICAL CO D D
Method for producing chlorine-free vancomycin
InactiveCN101724645AEasy to transformBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAmycolatopsis
The invention provides a method for producing chlorine-free vancomycin, which comprises the following steps: (i) interdicting a gene of encoding halogenase in amycolatopsis orientalis for producing vancomycin, constructing gene engineering bacteria for producing the chlorine-free vancomycin; and (ii) fermenting the gene engineering bacteria for producing the chlorine-free vancomycin so as to prepare the chlorine-free vancomycin. The invention also provides a method for constructing the gene engineering bacteria for producing the chlorine-free vancomycin and the gene engineering bacteria obtained through the method. The invention opens up a new approach for the preparation of the chlorine-free vancomycin.
Owner:SHANGHAI LAIYI BIOMEDICAL RES & DEV CENT +1
Preparation of Vanillin from Microbial Transformation Media by Extraction by Means Supercritical Fluids or Gases
Crude solid vanillin-containing material is precipitated from a solution obtained by biotransformation, and purified by a process comprising contacting it with a purification fluid selected from (a) a liquefied gas whose pressure exceeds its critical pressure and whose temperature is below its critical temperature; (b) a supercritical fluid; (c) a gas. The fluid is preferably liquid carbon dioxide. The temperature is maintained below 25°. The product may be further purified by treatment with CO2 in a fluid bed drier. The crude material is preferably one precipitated from a solution resulting from biotransformation of ferulic acid. A new strain of Amycolatopsis capable of generating high concentrations of vanillin with minimal odoriferous by-products (e.g. guaiacol) is also disclosed.
Owner:SAF ISIS
Amycolatopsis sp. YIM M13163 and method for preparing efrotomycin pivalate by adopting same
ActiveCN105886421AHigh antibacterial activitySimple methodBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEngineering
The invention discloses Amycolatopsis sp. YIM M13163 and a method for preparing efrotomycin pivalate by adopting the strain through fermentation. Amycolatopsis sp. YIM M13163 is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on July 10, 2015, the preservation number is CCTCC M 2015445, and the preservation address is Wuhan University in Wuhan city of China. The Amycolatopsis sp. YIM M13163 provided by the invention can generate antibiotic, namely, efrotomycin pivalate through fermentation; meanwhile, the method for preparing efrotomycin pivalate by adopting the strain is simple, the yield is high, thus sufficient sample support is provided for the development of the medicinal value of efrotomycin pivalate, and therefore, the application prospects are wide.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
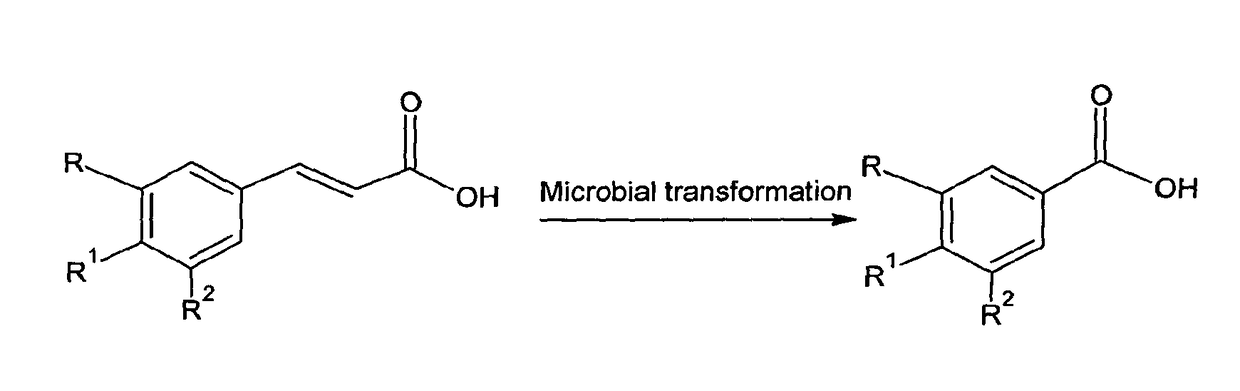
Microbial biotransformation of aromatic acids to their reduced carbon aromatic acids
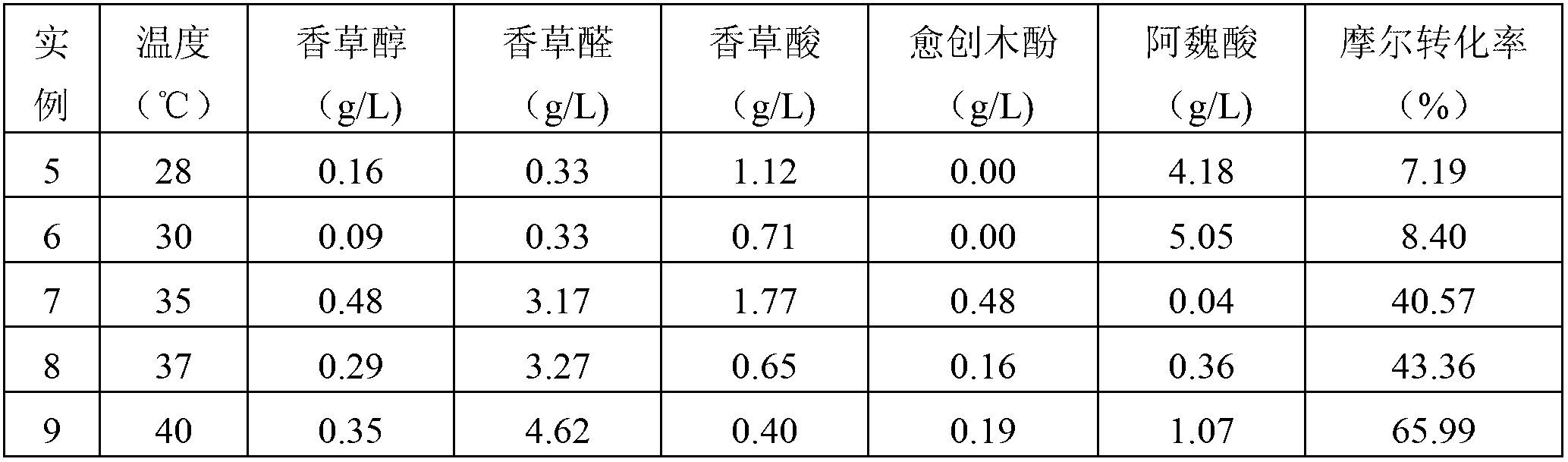
The present invention relates to a method for microbial fermentation and biotransformation of aromatic acids to aromatic acids with reduced carbon atoms of wide commercial importance using a culture of actinomycete species. Amycolatopsis sp or the mutant thereof is employed in the present invention to convert natural as well as synthetic aromatic acids to reduced carbon aromatic acids with wide applications. The said culture in the disclosed invention is adapted to grow at 37-46° C. to achieve the biotransformation of aromatic acid to reduced carbon aromatic acid is accomplished at 37-46° C. to obtain a higher yield of the product.
Owner:PRIVI BIOTECH
Detection method for identifying amycolatopsis
ActiveCN112899382AQuick checkSensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPcr methodAmycolatopsis
The invention discloses a detection method for identifying amycolatopsis, and belongs to the field of molecular biology. The invention provides a primer pair capable of specifically identifying the amycolatopsis. The primer pair is designed based on a specific conserved gene AMETH_3452 in the amycolatopsis and homologous gene segments in the amycolatopsis and has strong specificity; a PCR method for rapidly detecting the amycolatopsis is established through optimization of PCR parameters, and it is repeatedly proved that the method is rapid and sensitive, a plurality of strains can be detected at the same time, the detection cost is low, consumed time is short, and the effect is good. A basis is provided for further research on environment detection and animal or clinical actinomycetes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Process for the preparation of amides
A novel biotechnological process for the preparation of nitriles, starting from amides, is described. Micro-organisms of the genus Amycolatopsis, Actinomadura or Rhodococcus are employed for this process.
Owner:LONZA AG
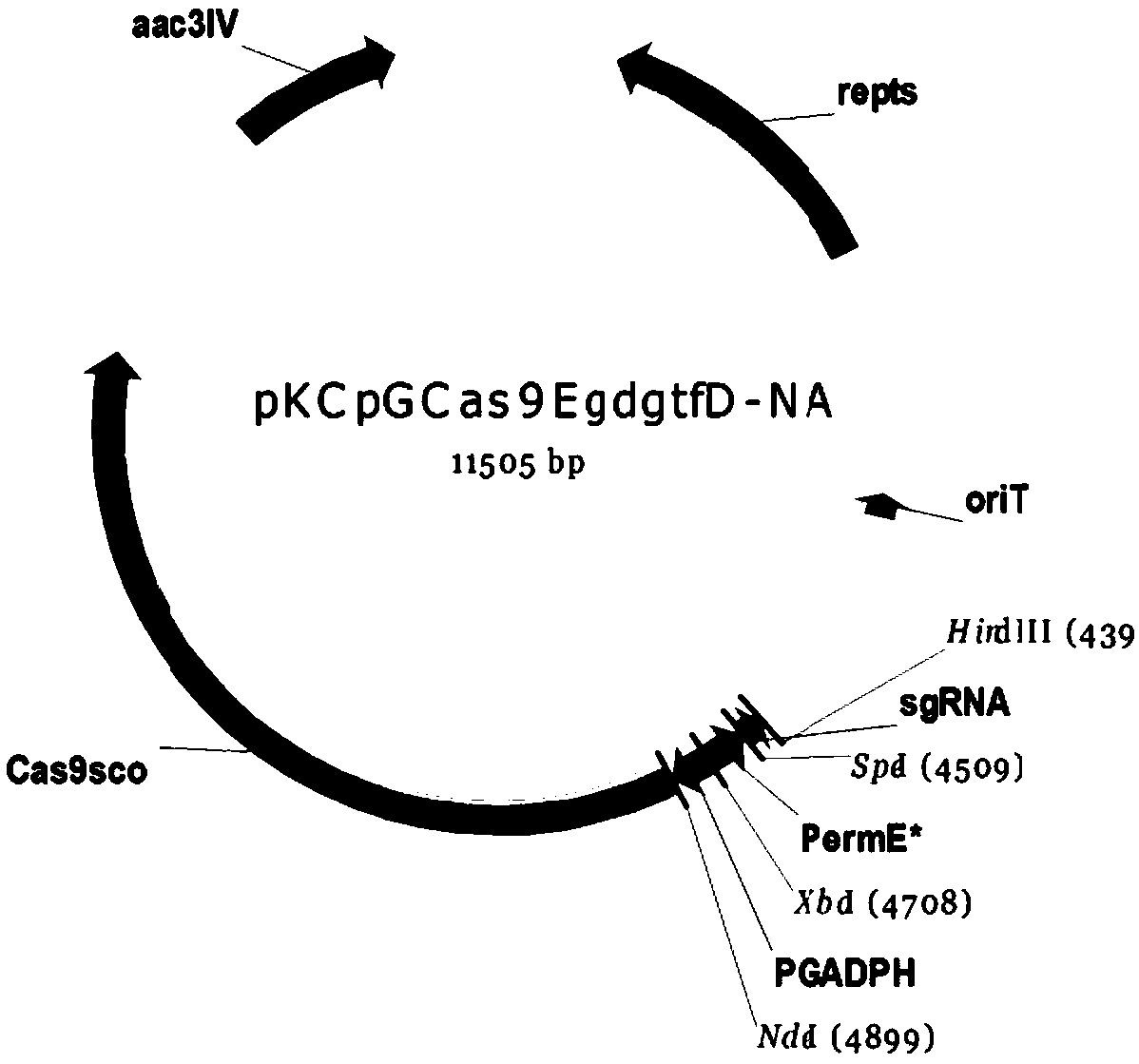
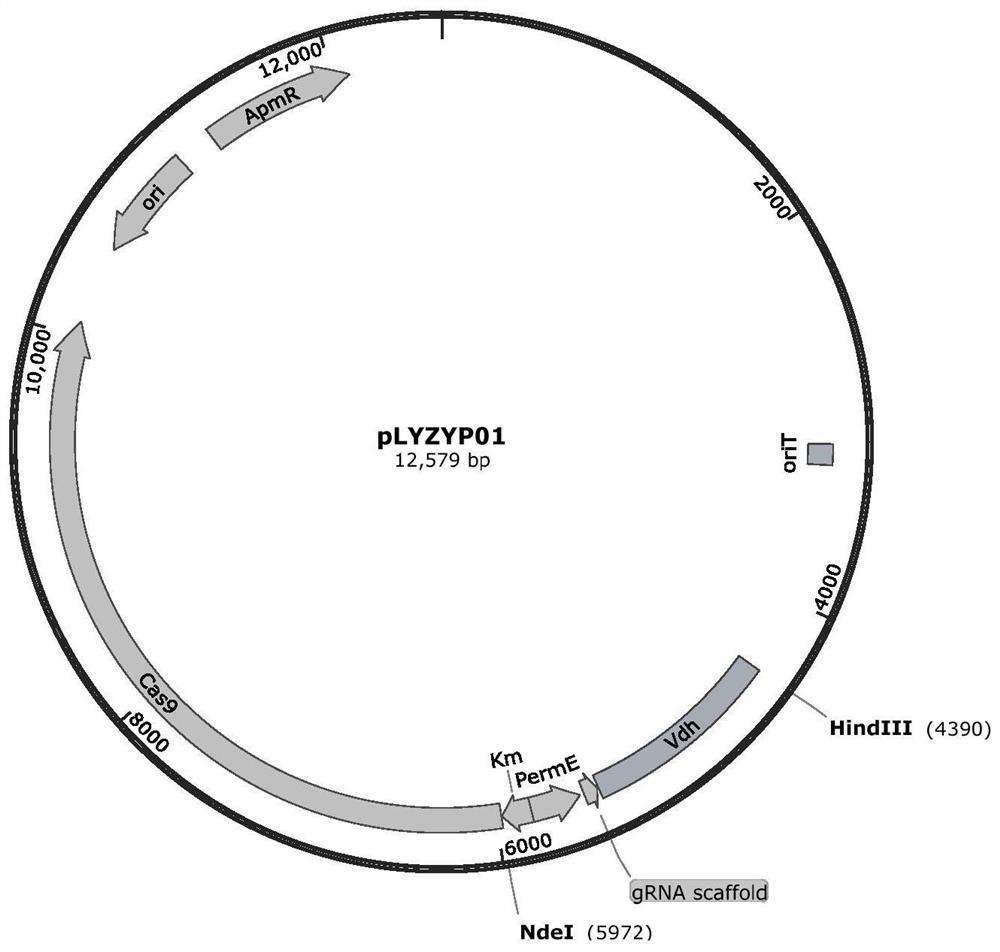
Gene engineering strain of amycolatopsis, construction method and application thereof
PendingCN113061560AImprove conversion rateReduce concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAmycolatopsis
The invention discloses a gene engineering strain of amycolatopsis, a construction method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to a method for performing gene knockout in amycolatopsis producing vanillin by using a CRISPR / Cas9 editing system, a CRISPR / Cas9 editing plasmid pLYZYP01 containing a Vdh gene homologous arm is introduced into amycolatopsis CCTCCM 2011265 to achieve vdh gene knockout, and under the condition that 12 g / L of substrate ferulic acid is added into the obtained genetic engineering strain Amycolatopsis sp.delta vdh, the yield of vanillin reaches 9.19 g / L, and the molar conversion rate is 97.7, so that good industrial application value is shown.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing oritavancin intermediate by fermentation
ActiveCN109811024BIncrease the proportion of componentsHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesPeptidesBiotechnologyOritavancin
Owner:JIANGSU SENRAN CHEM
High efficient homologous recombination engineering strain of Amycobacter, its construction method and application
Owner:SHAANXI HEALTHFUL BIOLOGICAL ENG
A method for preparing echinosporin antibiotics by fermentation
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Glycosyltransferase gene gtfE from amycolatopsis oreintalis
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid compounds encoding a glycosyltransferase enzyme of Amycolatopsis orientalis. Also provided are vectors carrying genes that encode said enzyme, transformed heterologous host cells for expressing said enzyme, and methods for producing glycopeptide compounds using the cloned genes that encode said enzyme.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
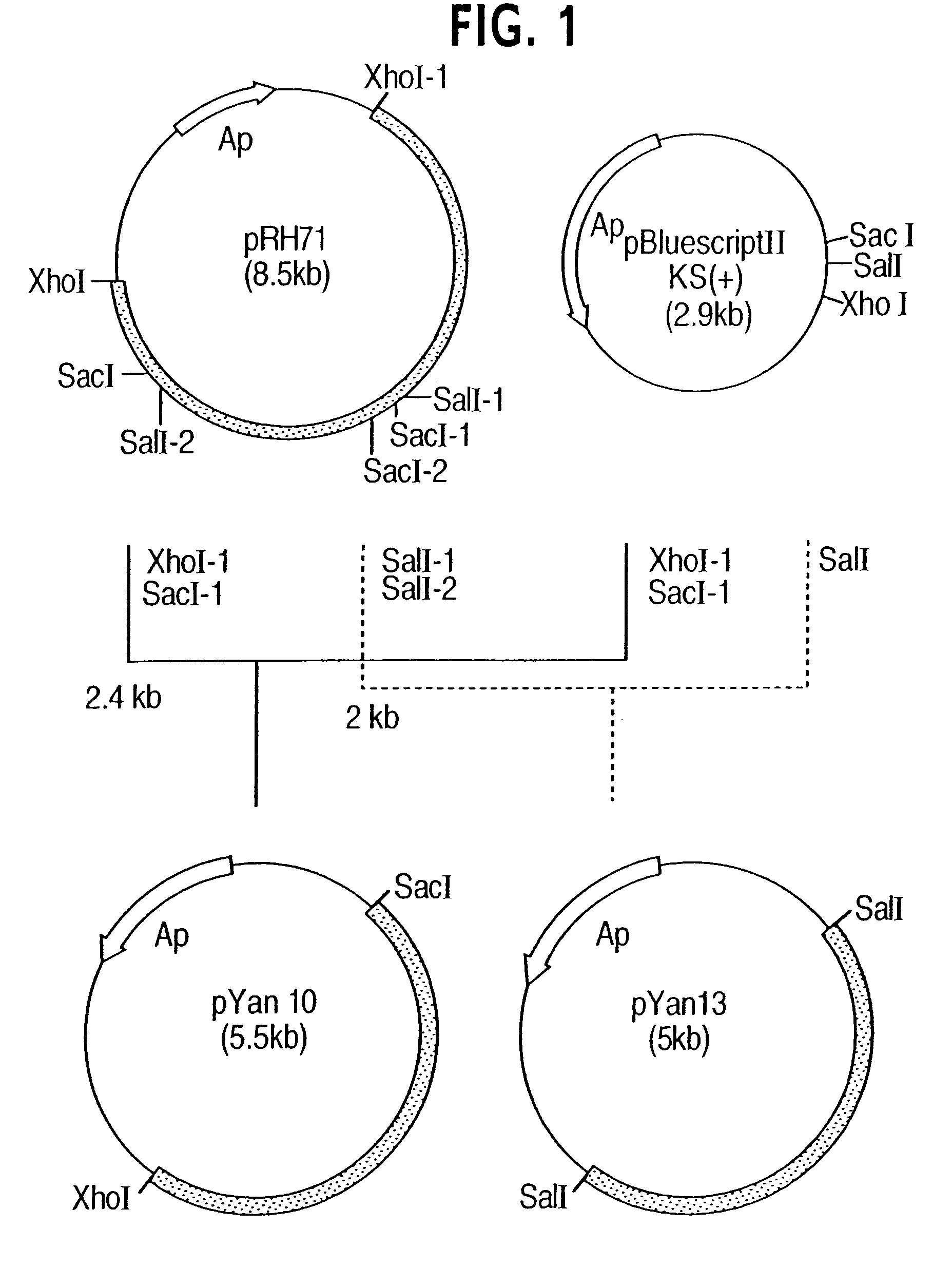
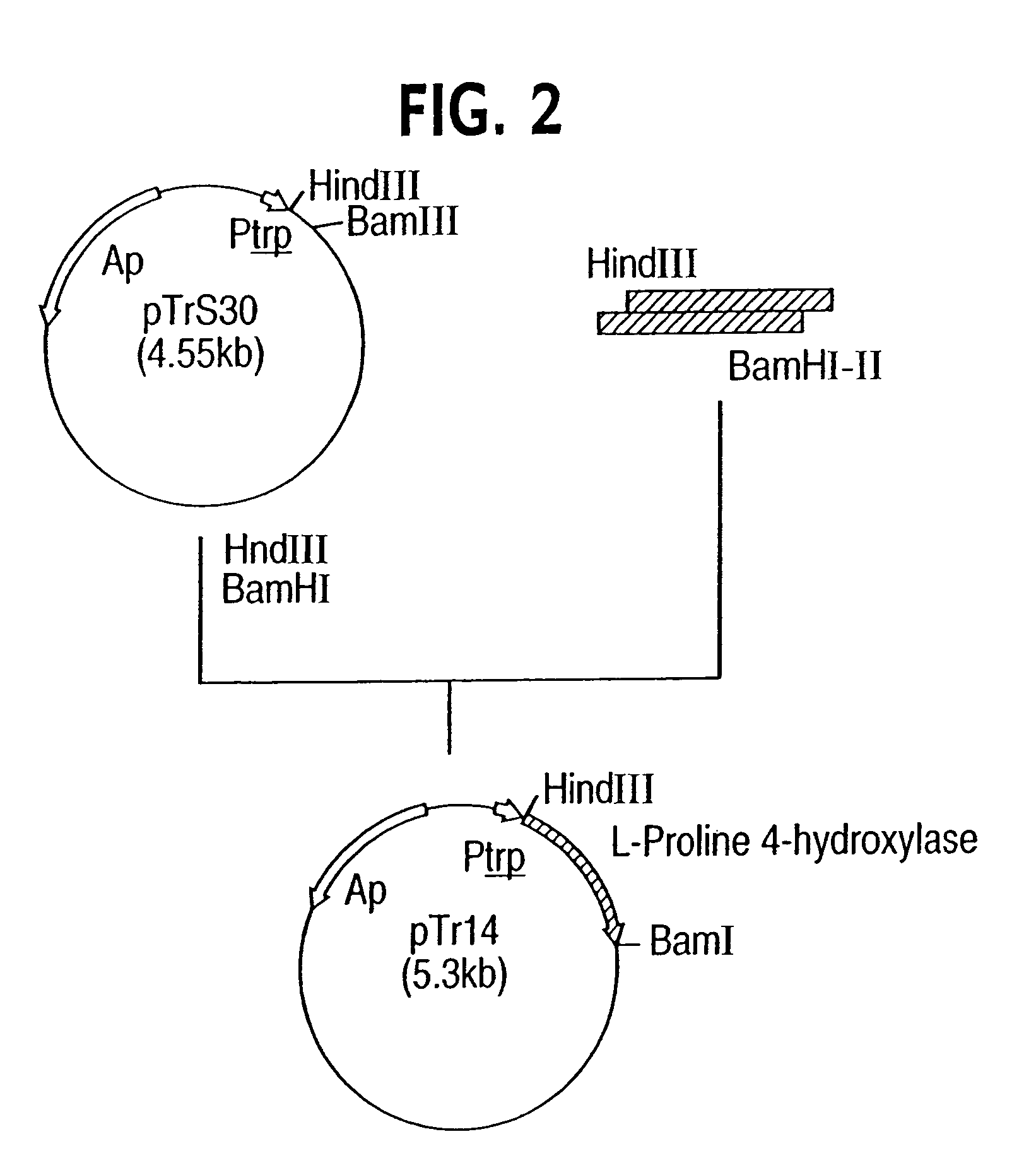
Process for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline
InactiveUS7238501B2Low costLow cost productionSugar derivativesBacteria2-ketoglutaric acidAmycolatopsis
The present invention is directed to a process for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline, which is useful as a raw material for medicines or as an additive to foods. In the process, L-proline is converted into trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline in the presence of an enzyme source which is derived from a microorganism belonging to the genus Dactylosporangium, Amycolatopsis or Streptomyces and which catalyzes the hydroxylation of L-proline into trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline, a divalent iron ion and 2-ketoglutaric acid, in an aqueous medium, and the produced trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline is collected from the aqueous medium. In addition, the present invention is directed to a process for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline, wherein the L-proline biosynthesis activity of the host cell of the transformant is reinforced.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO BIO CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com