Patents
Literature
54 results about "Biotechnological process" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biotech uses biological processes such as fermentation and harnesses biocatalysts such as enzymes, yeast, and other microbes to become microscopic manufacturing plants. Biotech is helping to fuel the world by: Streamlining the steps in chemical manufacturing processes by 80% or more;
Heterocyclic compounds based on n6-substituted adenine, methods of their preparation, their use for preparation of drugs, cosmetic preparations and growth regulators, pharmaceutical preparations, cosmetic preparations and growth regulators containing these compounds
Novel heterocyclic derivatives based on N6-substituted adenine, having anticancer, mitotic, immunosuppressive and antisenescent properties for plant, animal and human cells and methods of their preparation. Included are also pharmaceutical compositions, cosmetic preparations and growth regulators, which contain these derivatives as active compound and the use of these derivatives for the preparation of drugs, cosmetic preparations, in biotechnological processes, in cosmetics and in agriculture.
Owner:INST OF EXPERIMENTAL BOTANY ACAD OF SCI OF THE CZECH REPUBLIC
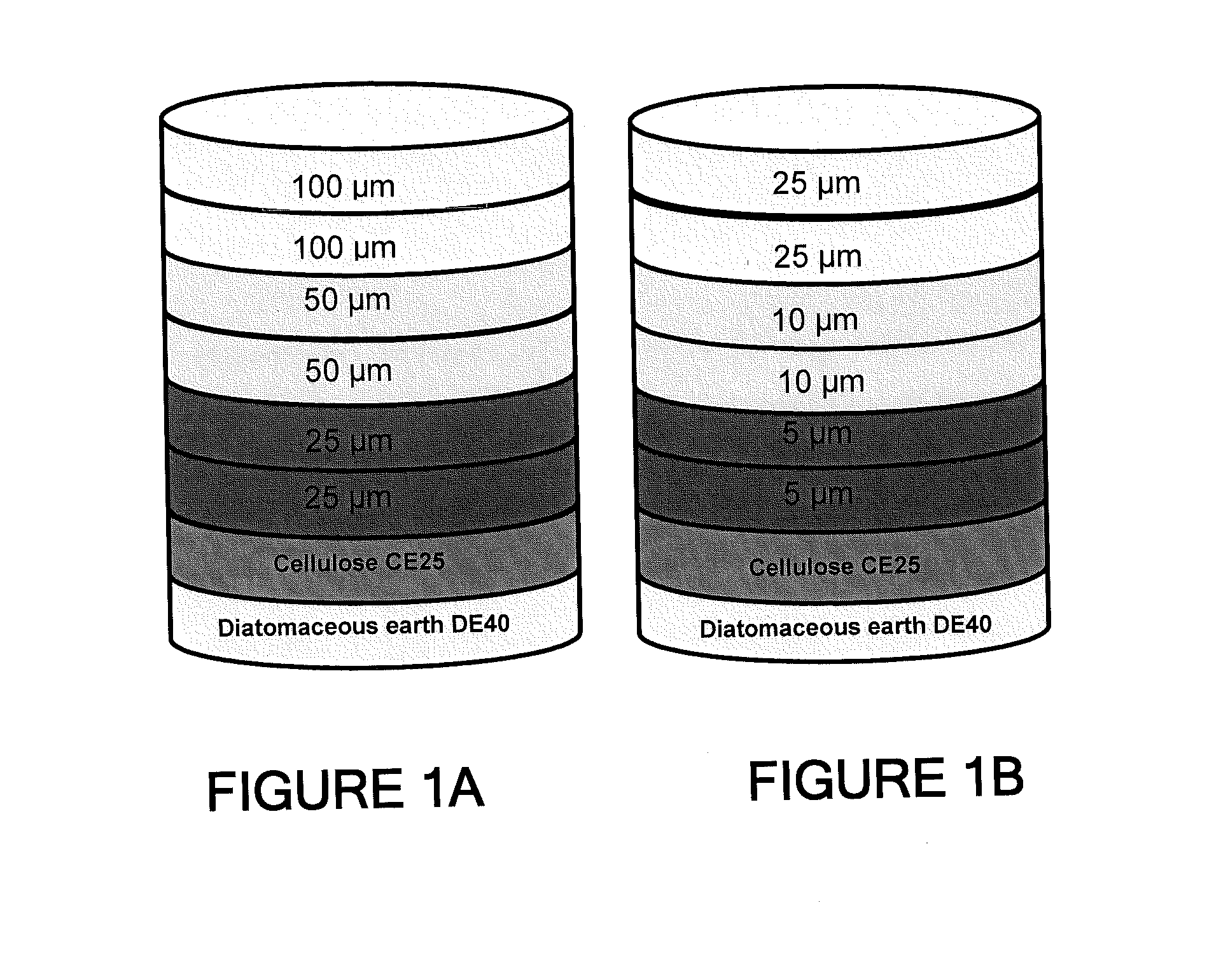
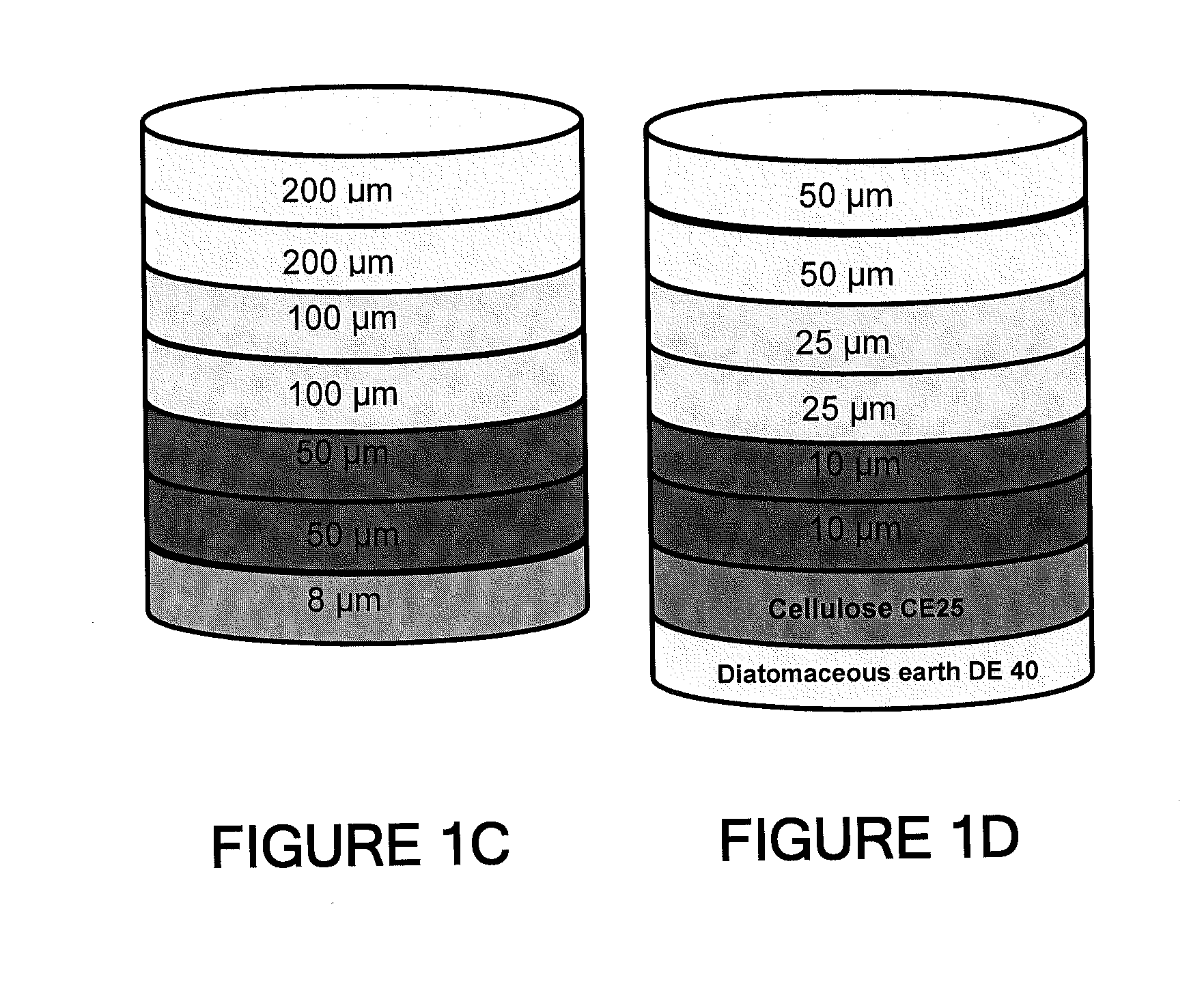
Depth Filters For Disposable Biotechnological Processes
InactiveUS20130012689A1Avoid concentrationEfficient separationIon-exchanger regenerationUltrafiltrationChemical treatmentColloidal particle
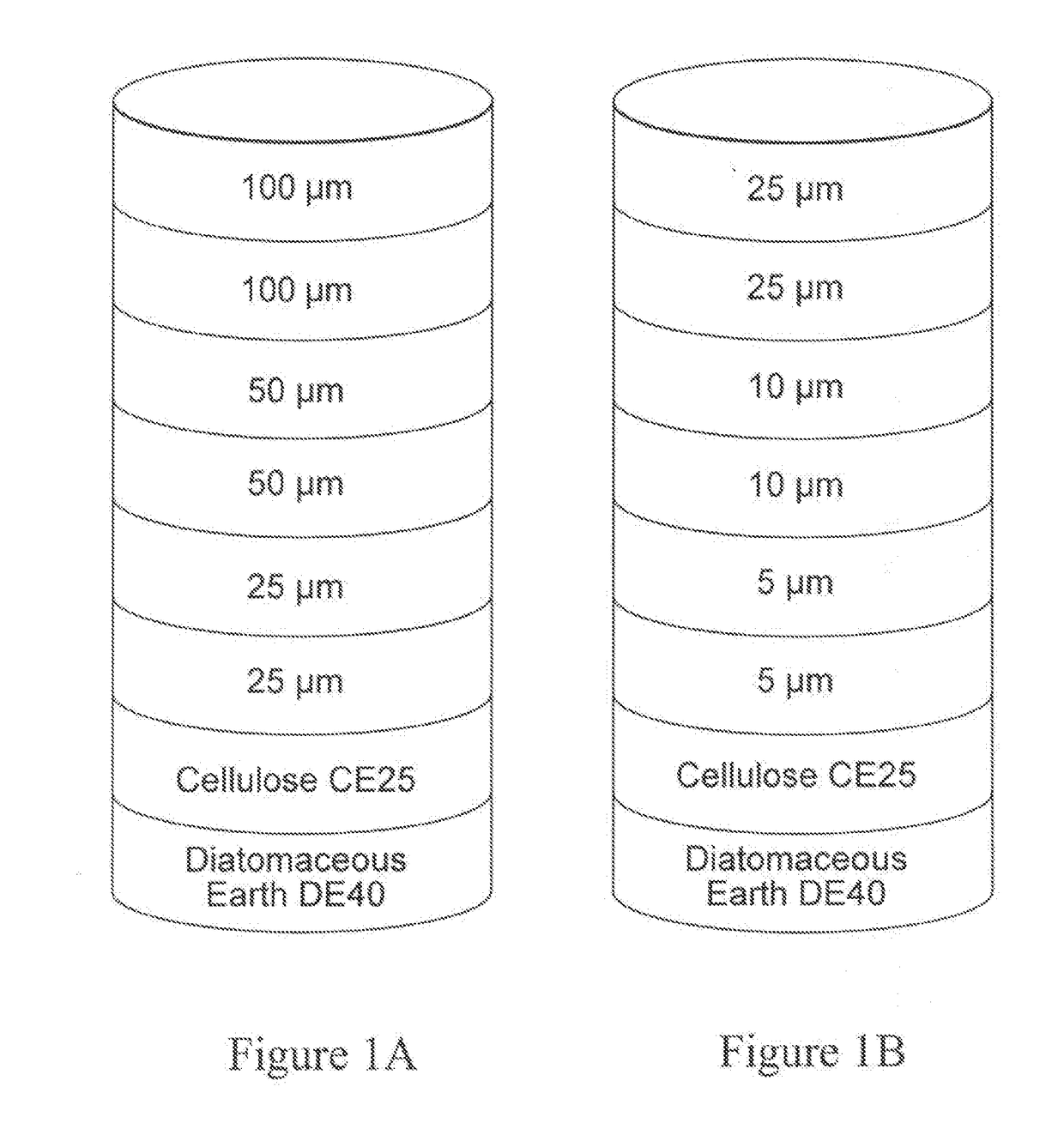
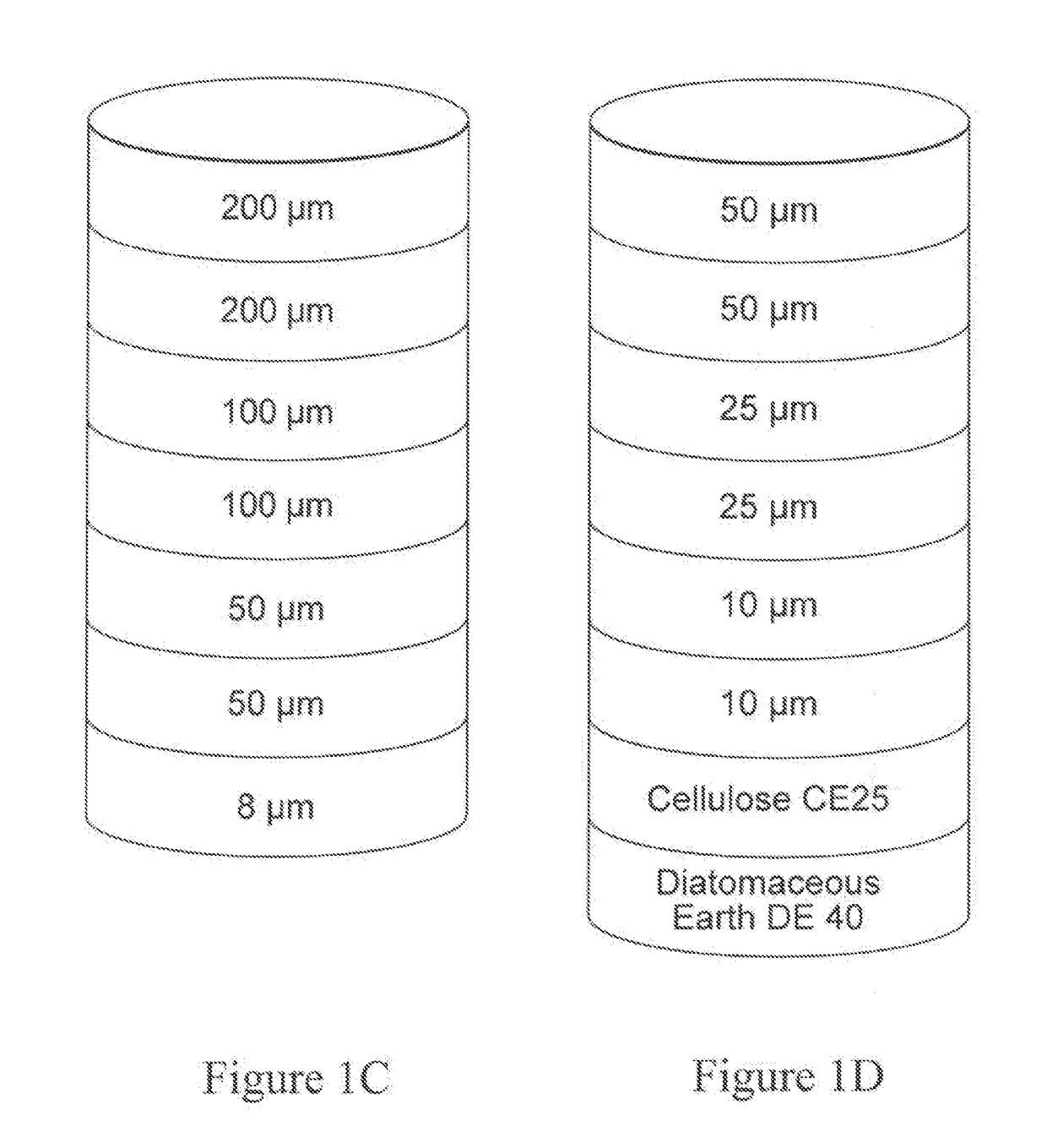
A process for the primary clarification of feeds, including chemically treated flocculated feeds, containing the target biomolecules of interest such as mAbs, mammalian cell cultures, or bacterial cell cultures, using a primary clarification depth filtration device without the use of a primary clarification centrifugation step or a primary clarification tangential flow microfiltration step. The primary clarification depth filtration device contains a porous depth filter having graded porous layers of varying pore ratings. The primary clarification depth filtration device filters fluid feeds, including chemically treated flocculated feeds containing flocculated cellular debris and colloidal particulates having a particle size distribution of approximately about 0.5 μm to 200 μm, at a flow rate of about 10 litres / m2 / hr to about 100 litres / m2 / hr. Kits and methods of using and making the same are also provided.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
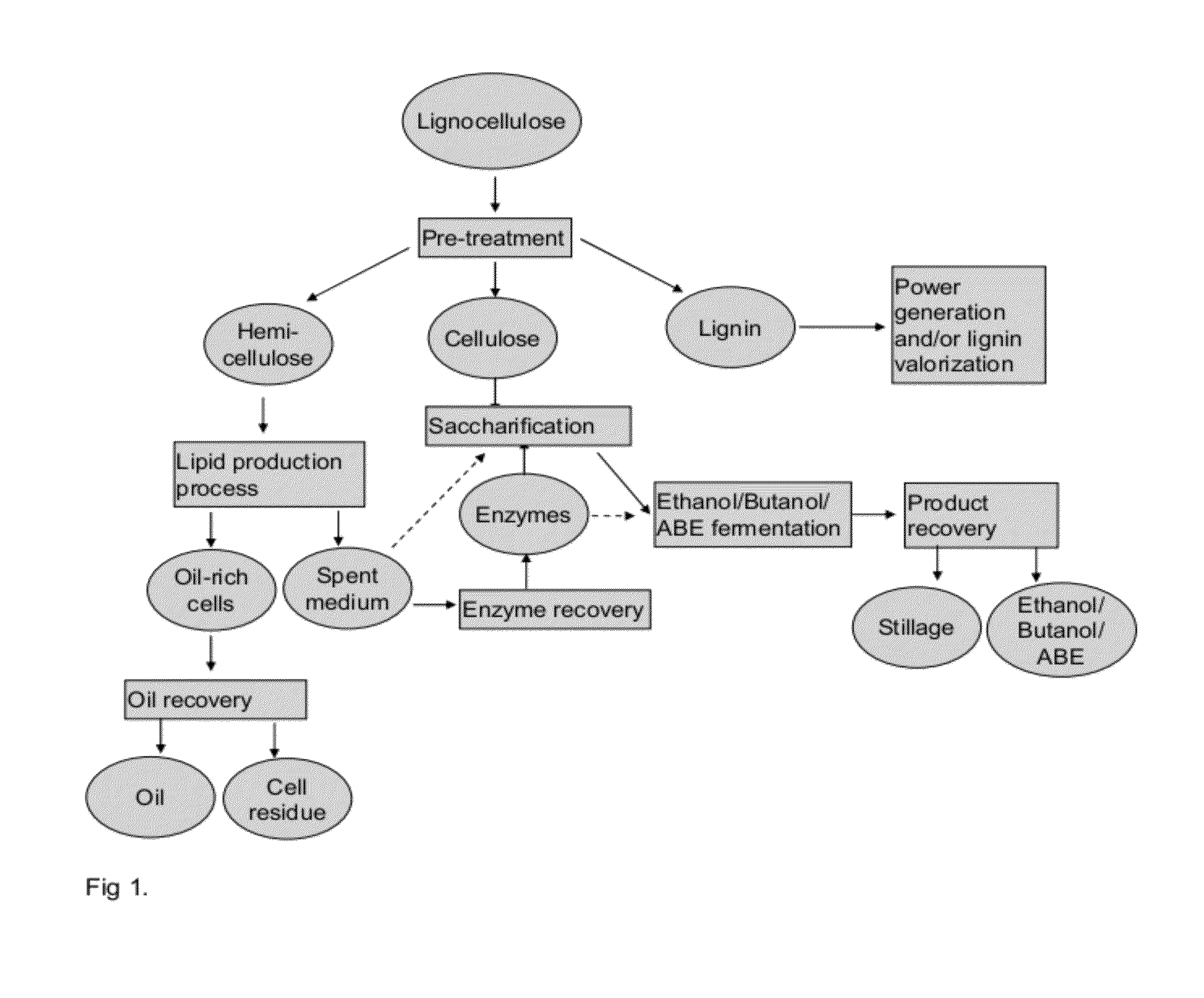
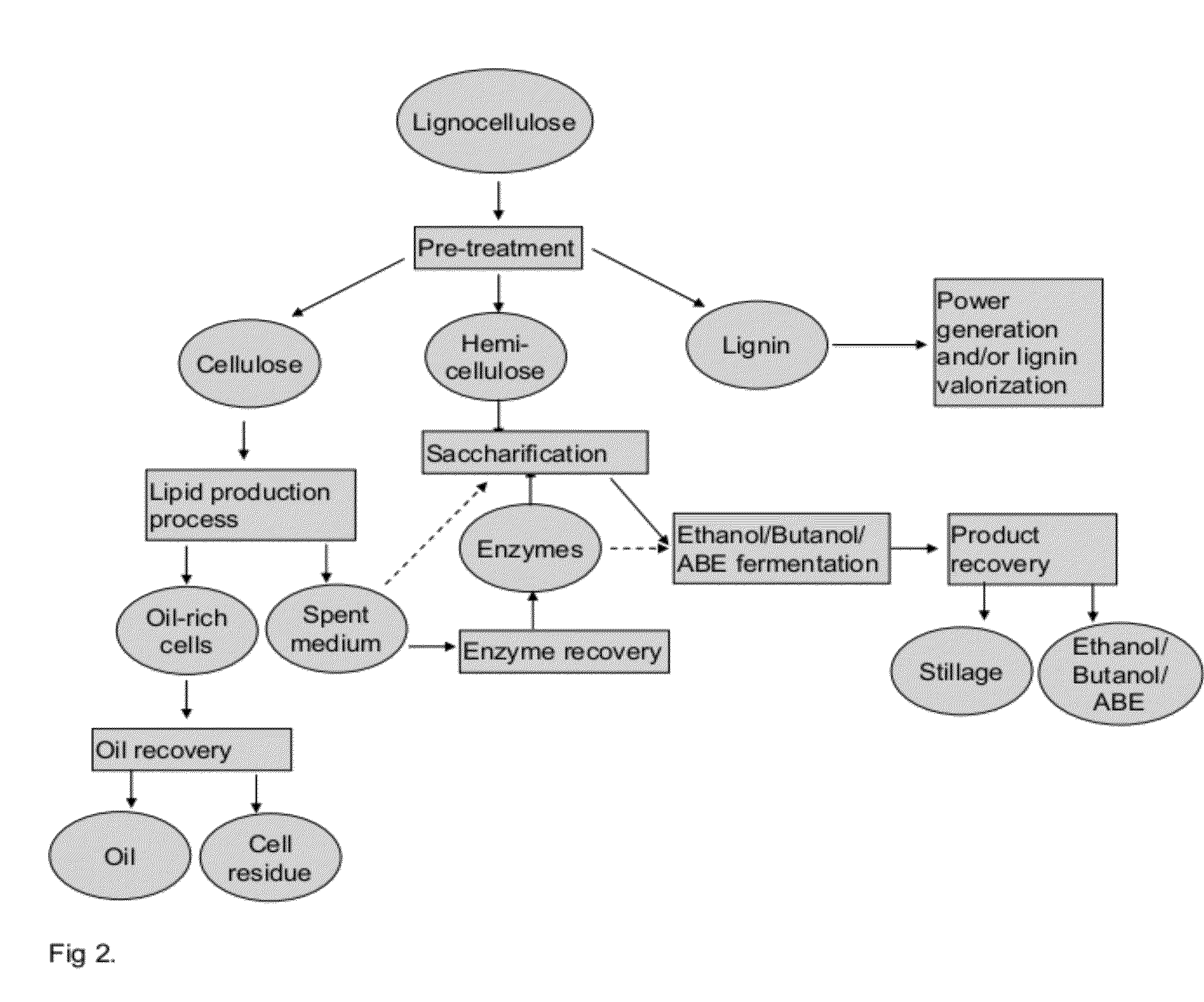
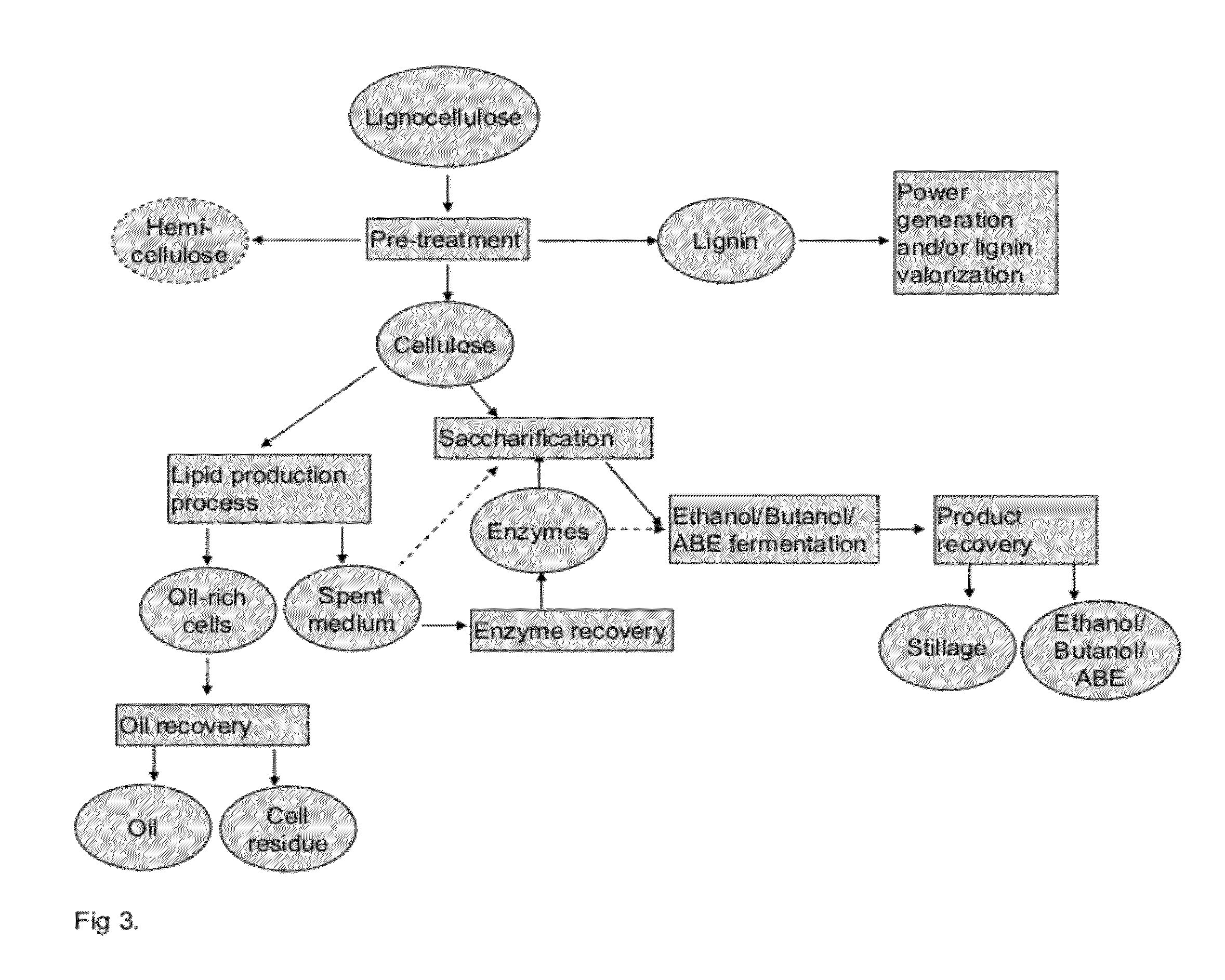
Integrated Process for Producing Biofuels
Disclosed is an integrated process comprising first and second biotechnical processes. The first process produces biofuel and / or starting material for biofuel and uses a microorganism capable of producing enzymes. The second process produces biofuel and / or starting material for biofuel. In the integrated process, the microorganisms are cultivated and biofuel and / or starting material for biofuel and enzymes are produced. The microorganism culture, supernatant or a protein enriched fraction or a dilution of the supernatant comprising catalytically active enzyme(s) are introduced into the first and / or into the second process, or feedstock for the process(es) is treated. The invention relates also to use of the produced enzymes in biofuel production process or in other applications as an enzyme preparation or a source of enzymes. The invention relates also to use of the produced lipids and alcohols as biofuel, a component of biofuel or a starting material for biofuel production.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
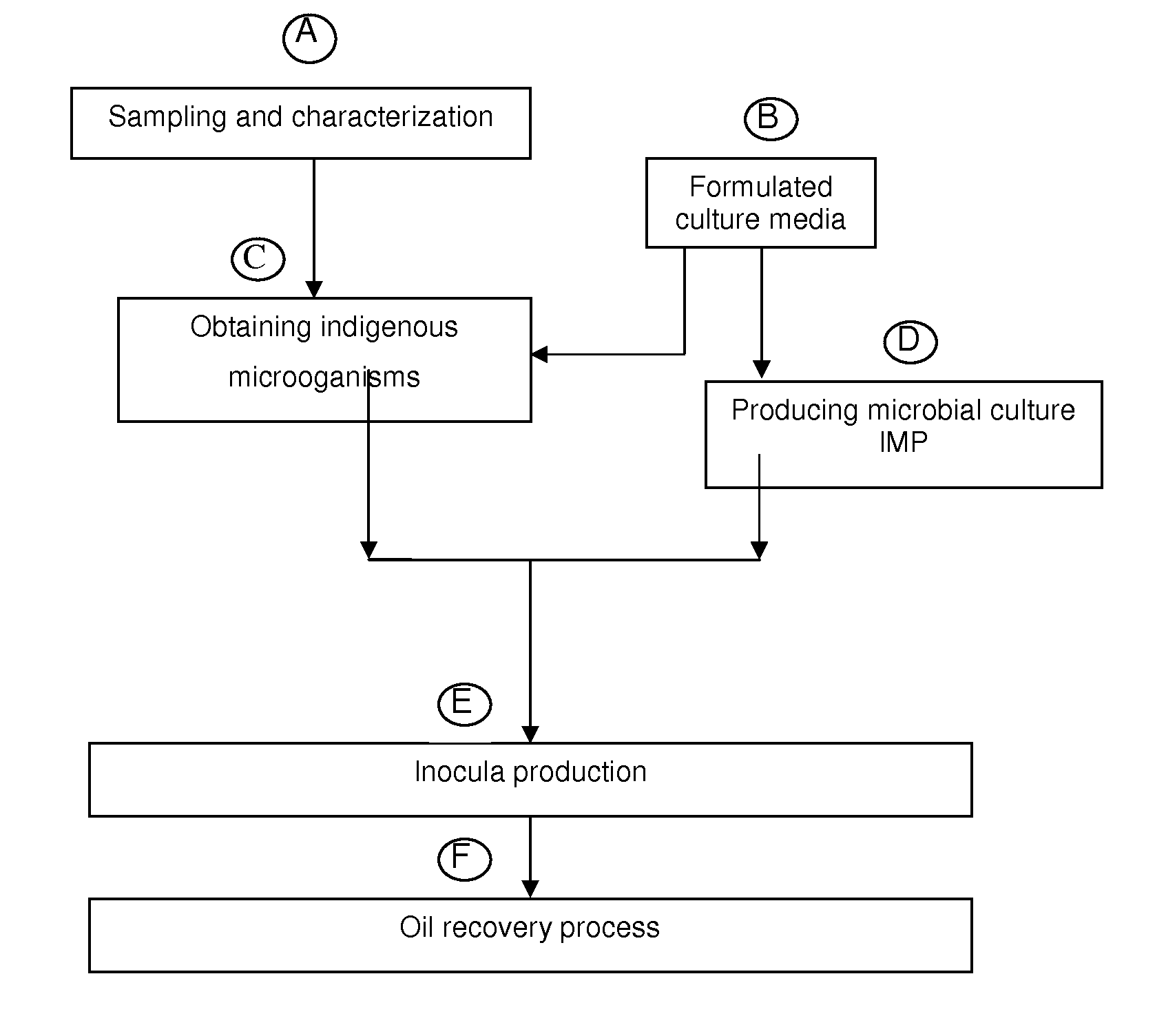
Biotechnological process for hydrocarbon recovery in low permeability porous media
ActiveUS20110146973A1Enhanced overall recoveryImprove mobilityFluid removalDrilling compositionMetaboliteAPI gravity
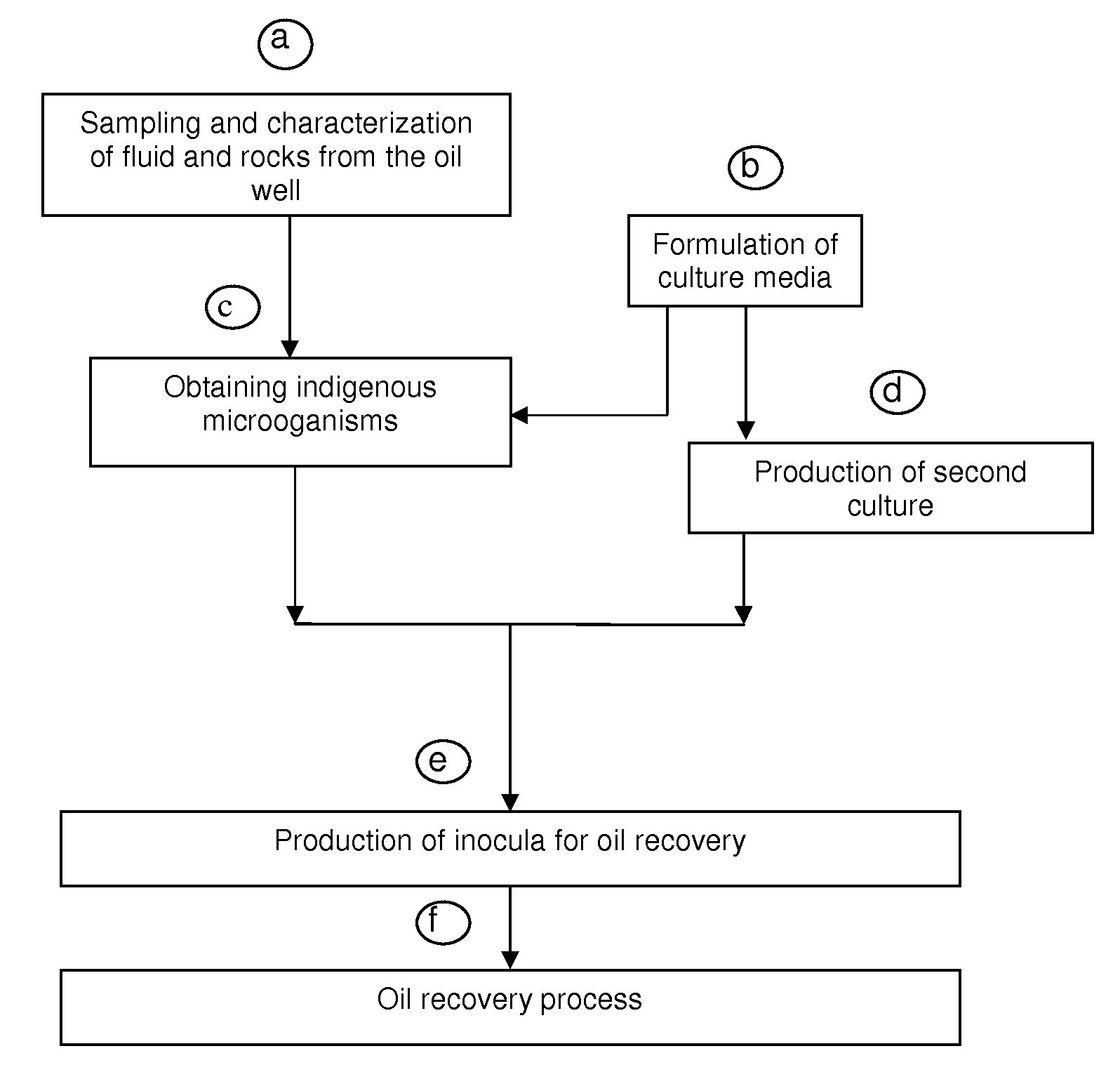
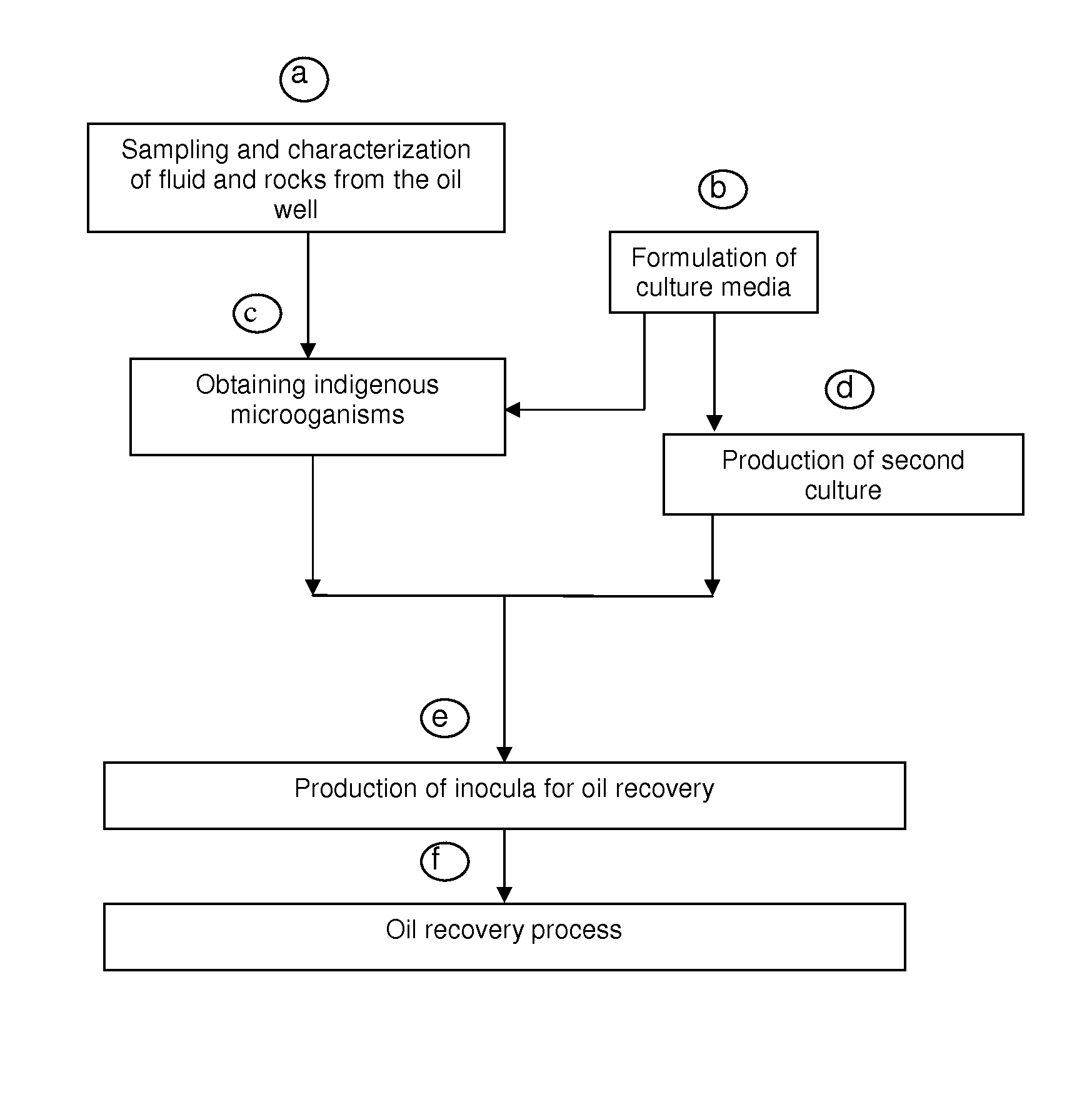
The present invention refers to a biotechnological process that enhances oil recovery of a 14 to 25 API Gravity oil contained in carbonate-containing and / or clayey sandstone porous rock systems with low permeability (7 to 100 mD), thus focused to petroleum wells associated to zones with low recovery factor. The process utilizes the indigenous extremophile microorganisms activity from the oil reservoir and an IMP culture, as well as its metabolites (gases, acids, solvents and surfactants), which improve oil mobility and are able to develop at 60 to 95° C. temperatures, 7 to 154.6 Kg / cm2 (100 to 2,200 psi) pressures and NaCl content from 5,000 to 45,000 ppm, in anaerobic conditions. The biotechnological process of the present invention includes: indigenous microorganisms sampling, collecting and characterization from the reservoir; formulation of culture media; selection, enrichment, activation and preservation of such microorganisms, as well as biostimulation (indigenous microorganisms) and bioaugmentation (IMP culture) to increase the metabolite production, useful for oil recovery in a porous media impregnated with oil in carbonate-containing and / or clayey sandstone porous systems, with one or several cycles and confinement periods from 5 to 10 days, to increase oil recovery. Experimental tests show that the biotechnological process of the present invention supplies an oil recovery increase up to 30%, additional to that obtained in secondary recovery processes.
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO
Biotechnological synthesis process of organic compounds with the aid of an alkl gene product
InactiveUS20140186905A1Reduce inhibitionImprove processing yieldBacteriaBiofuelsGene productSubject matter
Subject matter of the invention is a biotechnological process for the production of organic compounds with the aid of at least one alkL gene product.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Protein feed stuff and processing method thereof
InactiveCN1788598AIncrease payGuaranteed Bioactive IngredientsAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsBiotechnologyAnimal science
The biotechnological process of producing polypeptide and protein feed is superior to traditional fish meal producing process, which has high protein loss rate, high power consumption, high cost, serious pollution and other demerits. The present invention produces polypeptide paste, polypeptide powder, protein paste or protein powder with fresh low value fishes and shrimp and aquatic animal leftover and through the process including the steps of eliminating impurity, steam to eliminate fat, oil-water separation, crushing, sterilizing, enzymolysis, inactivating enzyme, concentration, drying and others. The present invention has the advantages of high protein content in the products, high bioavailability, no environmental pollution, low power consumption, etc. The products have the effects of promoting animal growth, regulating immunity, preventing and treating diseases, etc. and are used mainly in raising animal and as nitrogen source for biological culture.
Owner:韩福山
Methods for high-throughput screening of cell lines
InactiveCN101472947AEfficient productionImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMaterial analysisBiotechnologyDrug development
Owner:WYETH LLC
Fungal micro-organism having an increased ability to carry out biotechnological process(es)
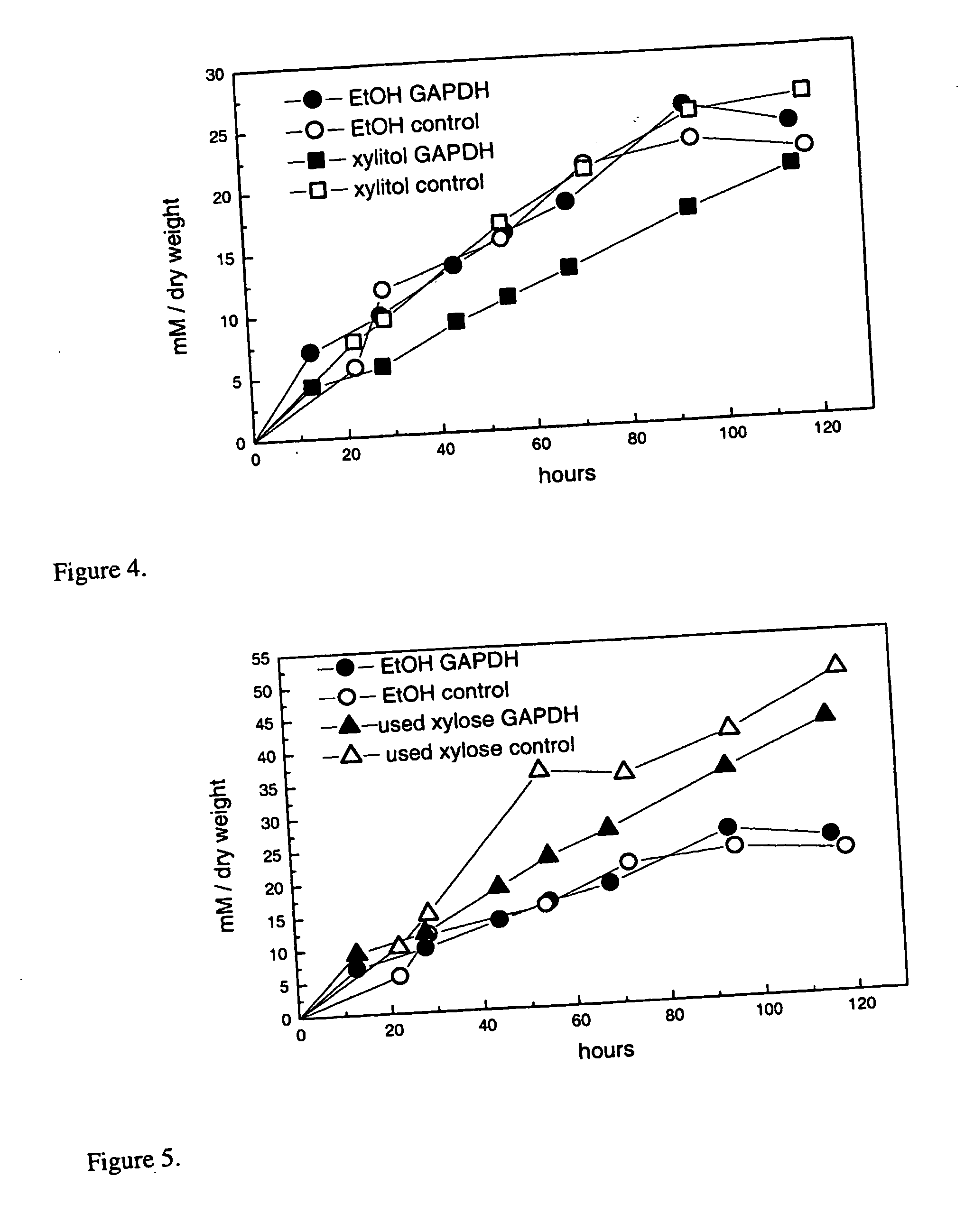
InactiveUS20050106734A1Easy to useDecreasing and eliminating needFungiBiofuelsNucleotideGlyceraldehyde
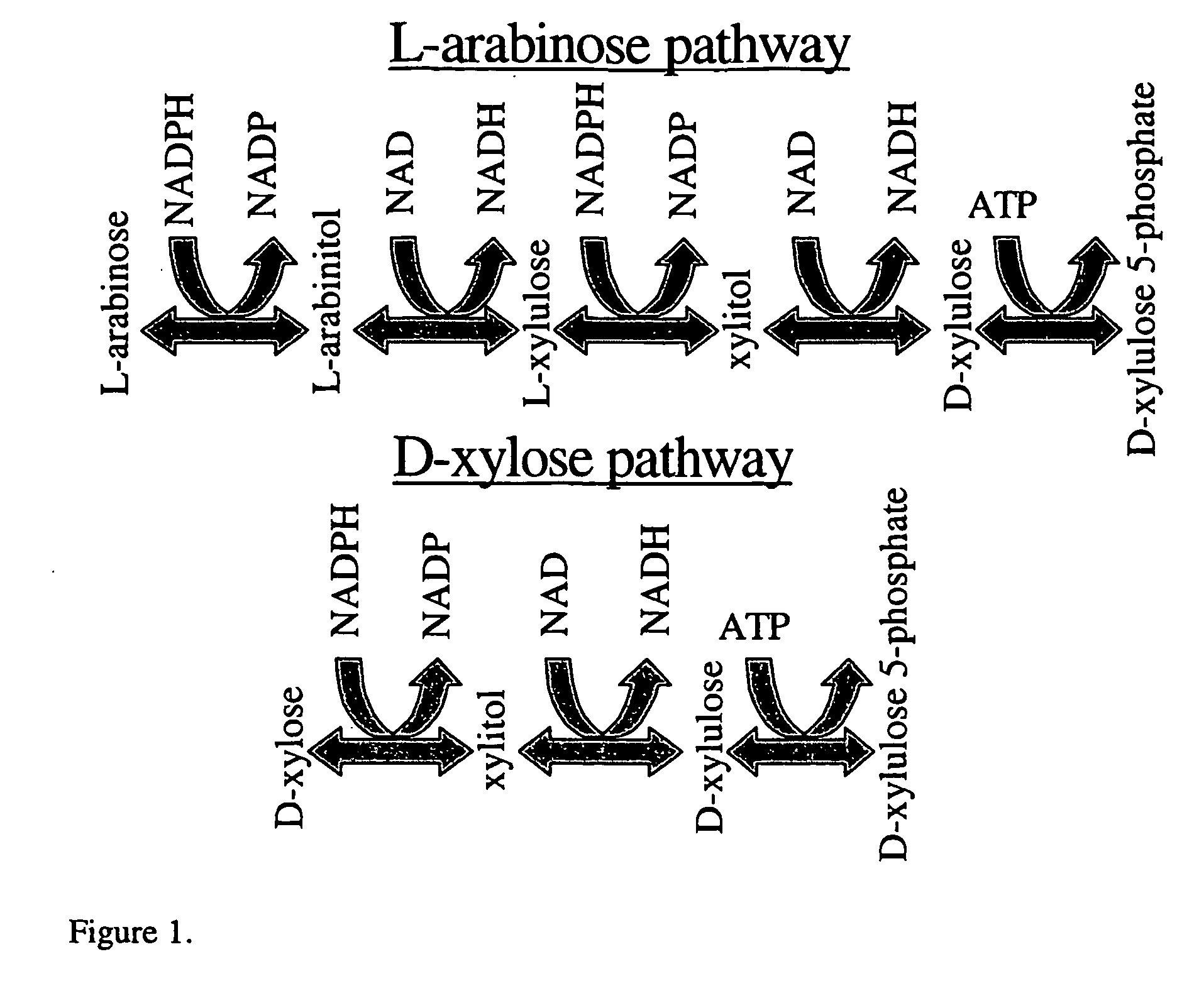
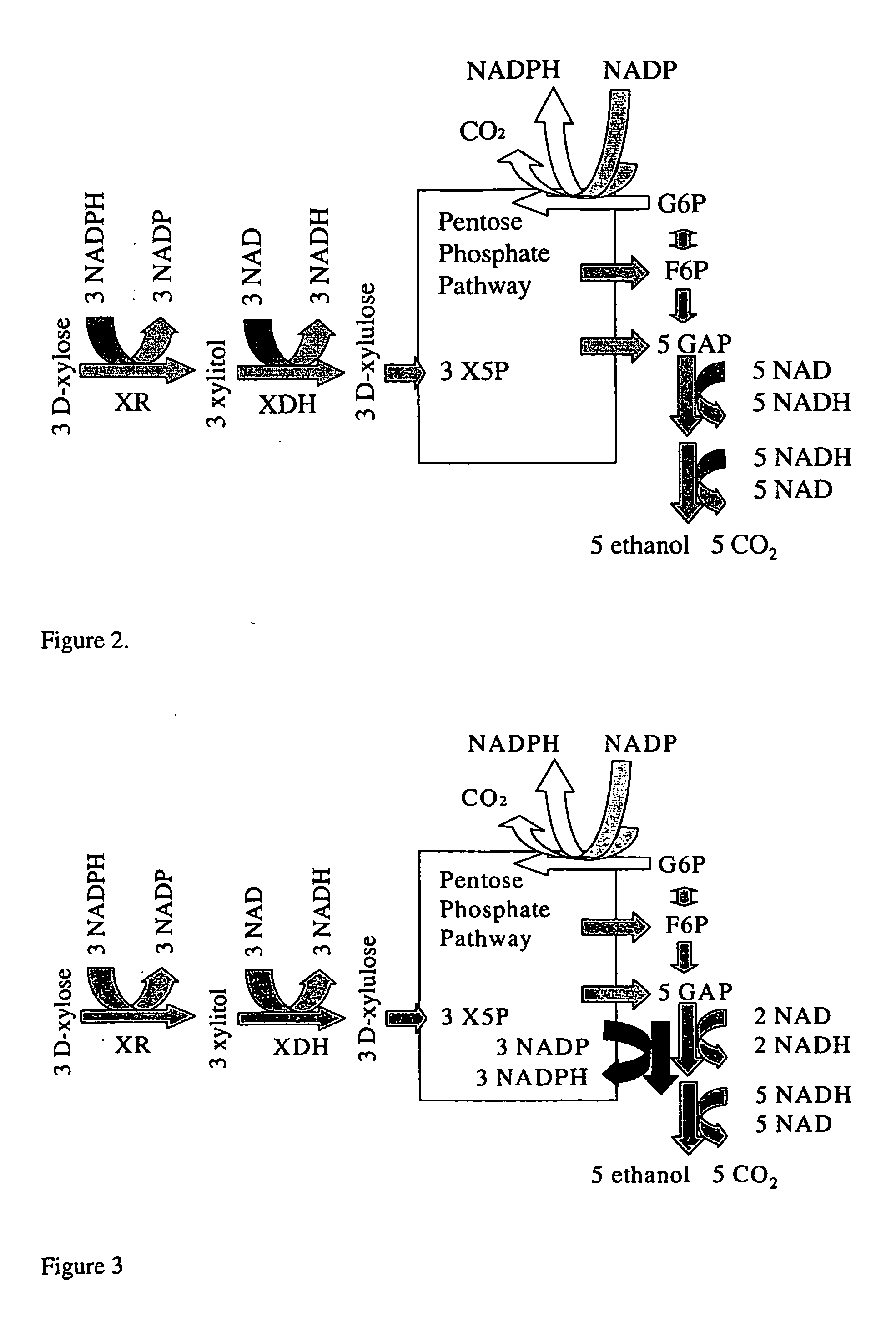
The present invention relates to fungal microorganism having an increased ability to carry out biotechnological process(es). In particular, the invention relates to improving the regeneration of redox cofactors in biotechnological processes where useful products are produced from biomass containing pentoses. According to the invention, the microorganism is transformed with a DNA sequence encoding an NADP linked glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. The invention can be used to provide useful products for mankind from biological materials, including e.g. agricultural and forestry products, municipal waste. Examples of such useful products are ethanol, lactic acid, polyhydroxyalkanoates, amino acids, fats, vitamins, nucleotides and a wide variety of enzymes and pharmaceuticals.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
Processing method of portable chicken soup
ActiveCN104223212AIncrease concentrationSimple processing methodFood preparationAdditive ingredientWarm water
The invention discloses a processing method of portable chicken soup. A processing operation flow combining a traditional soup production method and a modern biotechnological process is adopted, and preferably-selected frozen fresh chicken bones, purified water, fresh shallot, gingers and natural spices are added into a special digestion interlayer high-pressure tank to be subjected to digestion, standing, concentration and seasoning to obtain concentrated chicken soup; then the chicken soup is sub-packaged into disposable small boxes and packaging bags, so that the chicken soup is convenient to eat at home and when people go out and travel; 20-30 times of warm water or hot water can be added into the concentrated chicken soup according to individual tastes to be directly taken; and the chicken soup can be used as nutritional chicken soup for frying dishes at home and boiling noodles. The product keeps the natural nutritional ingredients in bones and bone marrows to the greatest extent, is rich in proteins, a plurality of types of amino acids and microelements needed by a human body, and has natural and mellow flavor.
Owner:HENAN YONGDA MEIJI FOOD CO LTD
Integral fungus deodorizing reactor and its operation method
InactiveCN1486777ACompact structureSimple structureDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementBiochemical engineeringProduct gas
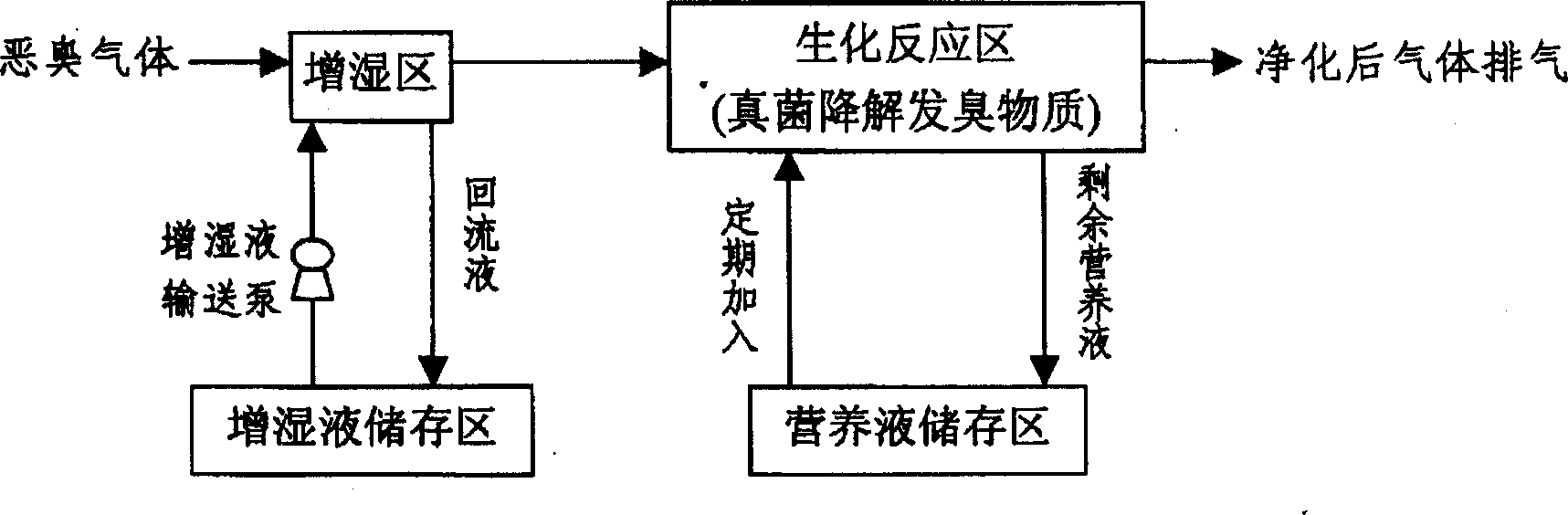
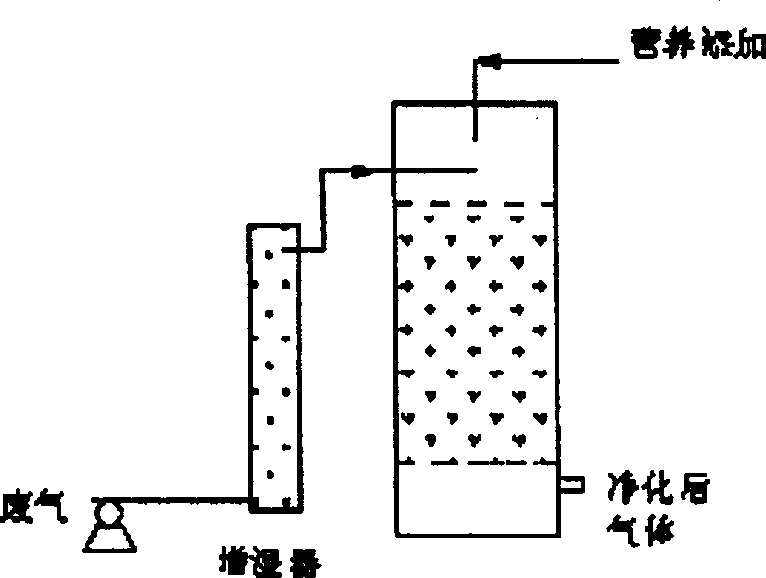
The present invention relates to equipment for treating foul gas via biotechnological process, and is especially one kind of integral fungus deodorizing reactor and its operation method. The integral fungus deodorizing reactor consists of four parts, humidifying area, biochemical reaction area, humidifying liquid storing area and nutritive liquid storing area. The biochemical reaction area is provided with stuffing for fungus microbe to adsorb and grow. In the reactor, foul gas is passed through a central pipe as the humidifying area to be humidified and then made to enter biochemical reaction area directly. The reactor provides fungi and bacteria of different types with habitat for stable growth, and this raises the deodorzing effect effectively. The present invention may be used in treating foul gas from sewage treatment and solid water treatment as well as other type of foul gas.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Peach gum hydrolase producing strain and application in preparation of peach gum polysaccharide thereof
InactiveCN101701198ARich in economic valueShort hydrolysis cycleBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHydrolysisHydrolase
The invention discloses a peach gum hydrolase producing strain and an application in preparation of peach gum polysaccharide thereof. The peach gum hydrolase producing strain belongs to microbacterium, is named microbacterium A5. The microbacterium was conserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on august 7, 2009 and the CCTCC NO is M209174. The strain of the invention can be used to effectively produce peach gum hydrolase used for degrading peach gum so as to obtain peach gum polysaccharide with large economic value. The strain of the invention can be utilized to produce peach gum through enzyme method, wherein the hydrolysis period is short, the relative molecular mass distribution of the product is narrow, no environmental pollution is caused, and the method is easy to control. The invention provides a new gum biotechnological process with more environmental friend and uniform product quality so as to facilitate the sustainable development of the society, promote the comprehensive utilization of wastes of Chinese agricultural culture and have wide market prospect.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
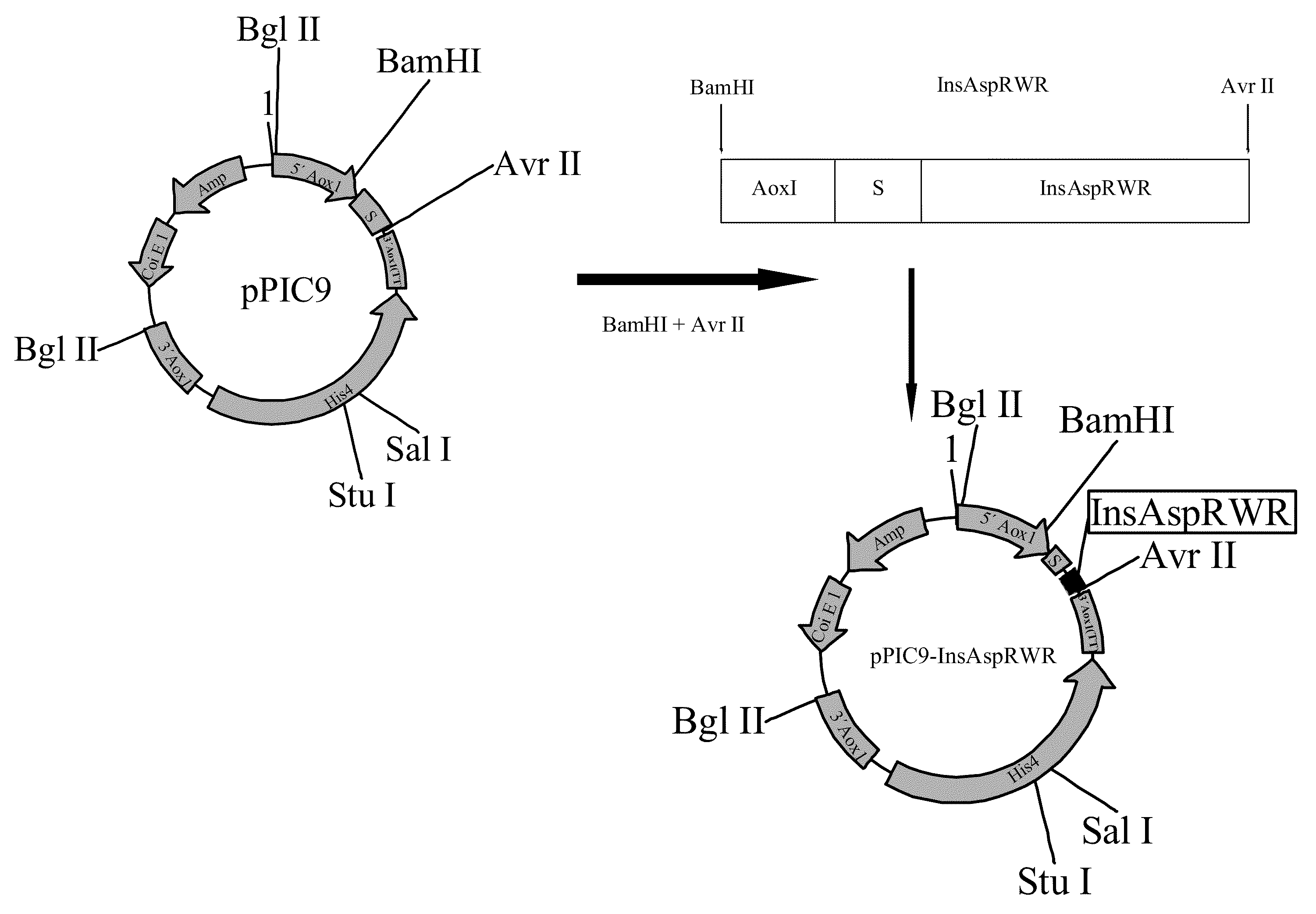
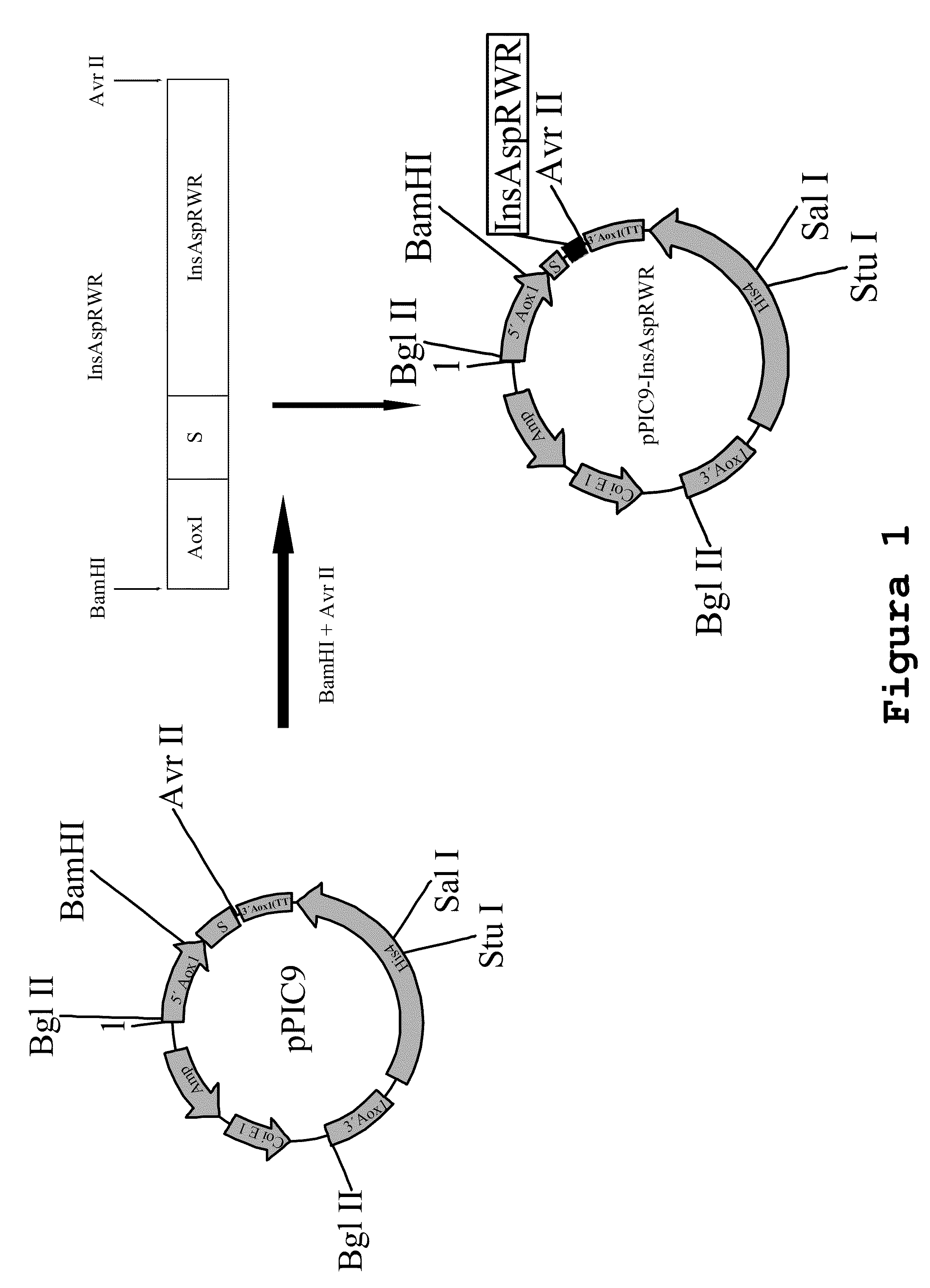
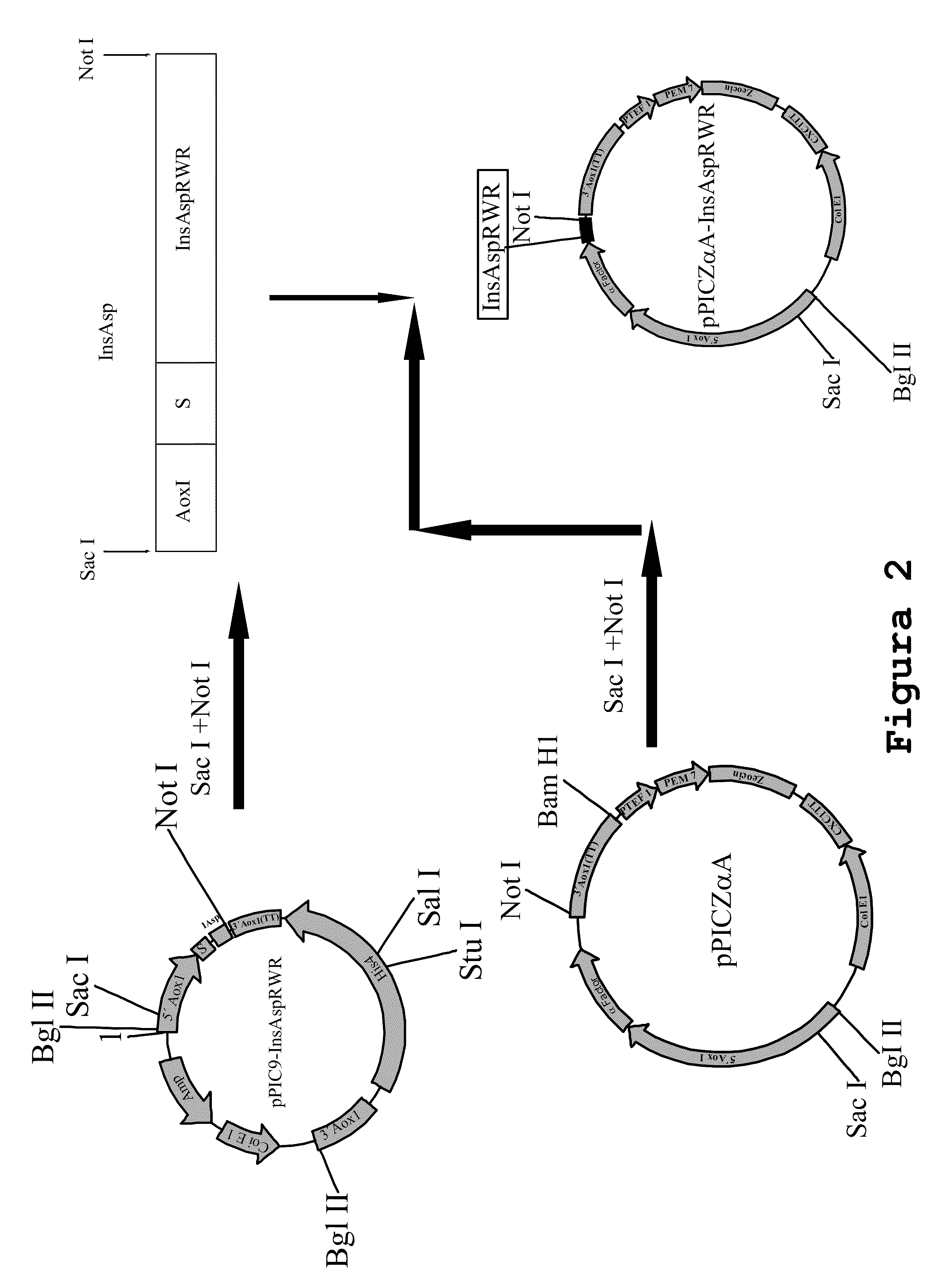
Process for obtaining aspart insulin using a pichia pastoris yeast strain
The present invention refers to a method for producing a human insulin analogue with high efficiency and excellent yield, by means of a biotechnological process comprising transformation of a Pichia pastoris yeast strain. In particular, the invention refers to a biotechnological process for obtaining aspart insulin.
Owner:LAB BETA SA
Biological neutralization of highly alkaline textile industrial wastewater
ActiveUS20060141605A1Bring downGuaranteed economic efficiencyBacteriaSolid waste disposalIndustrial effluentCompound (substance)
The present invention provides a novel process of neutralizing textile industrial wastewater by a bacterial strain isolated in India. The isolated bacterial strain is capable to bring down the pH of wastewater from 12.00 to 7.00 units within two hours. The neutralization of alkaline textile industrial wastewater by such biotechnological process is highly effective and economical as compared to conventional neutralization by chemical means. This biotechnological process may find wide commercial application in textile industries emanating alkaline wastewater.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
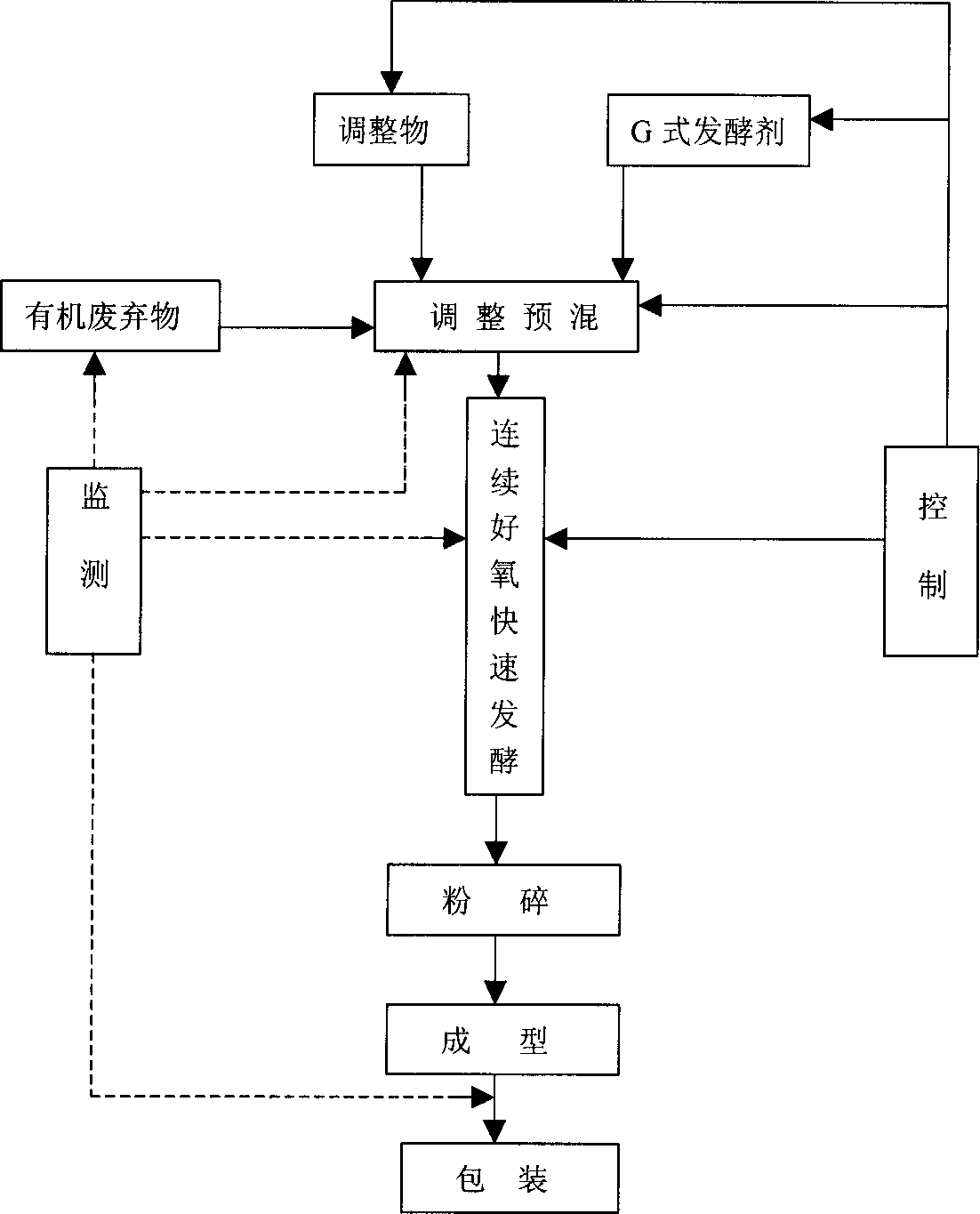
Comprehensive biotechnological process of producing organic fertilizer with organic waste
This invention relates to a comprehensive liological technique for producing organic fertilizer by utilizing organic waste discards. Firstly, organic waste discards are inspected, they are regulated for portion mix according to inspection results, G-type fermentation agent is injected, and they are commercially produced under monitored condition so that they are required to make into different types of suitable and special-purpose G-type organic fertilizers. This invention by use of the said technique can quickly change the environmental-pollution waste discards to become the high-effective organic fertilizer.
Owner:北京六合新星生物技术有限公司
Process for urban fecal treatment using engineering earthworm
The present invention relates to environment science and technology, and is especially biotechnological process of treating excrement from city. The technological process includes treating excrementin fermenting pond, producing feed medium with excrement and soil, setting feed medium in culture plate, setting fermented organic matter to the surface of the culture plate, separating mature earthworm, young earthworm, earthworm egg from the earthworm dung, feeding mature earthworm to processing area for making high-protein feed and producing medicine, producing organic fertilizer with earthworm dung, and backing young earthworm and earthworm egg to culture plate. The present invention is one high-utility green engineering.
Owner:吴玉春
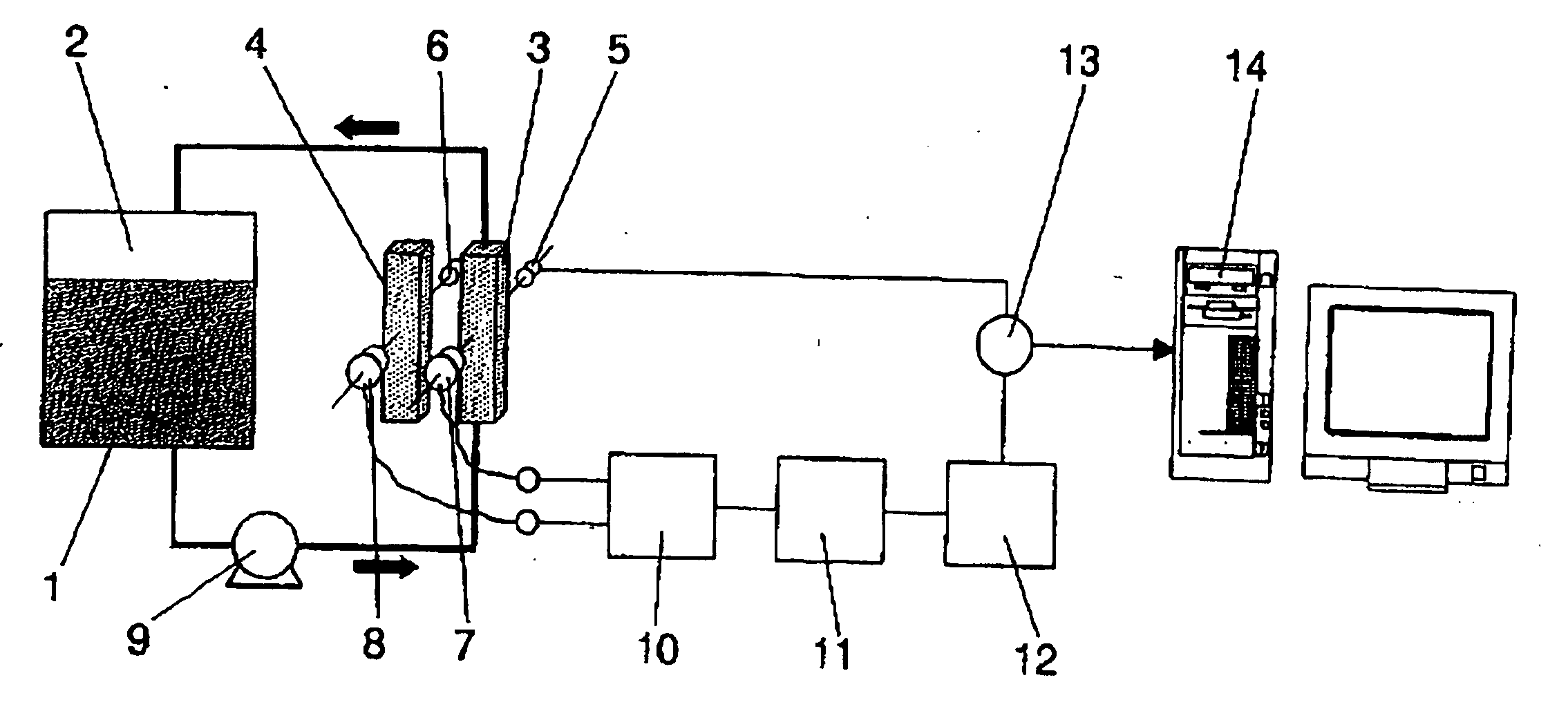
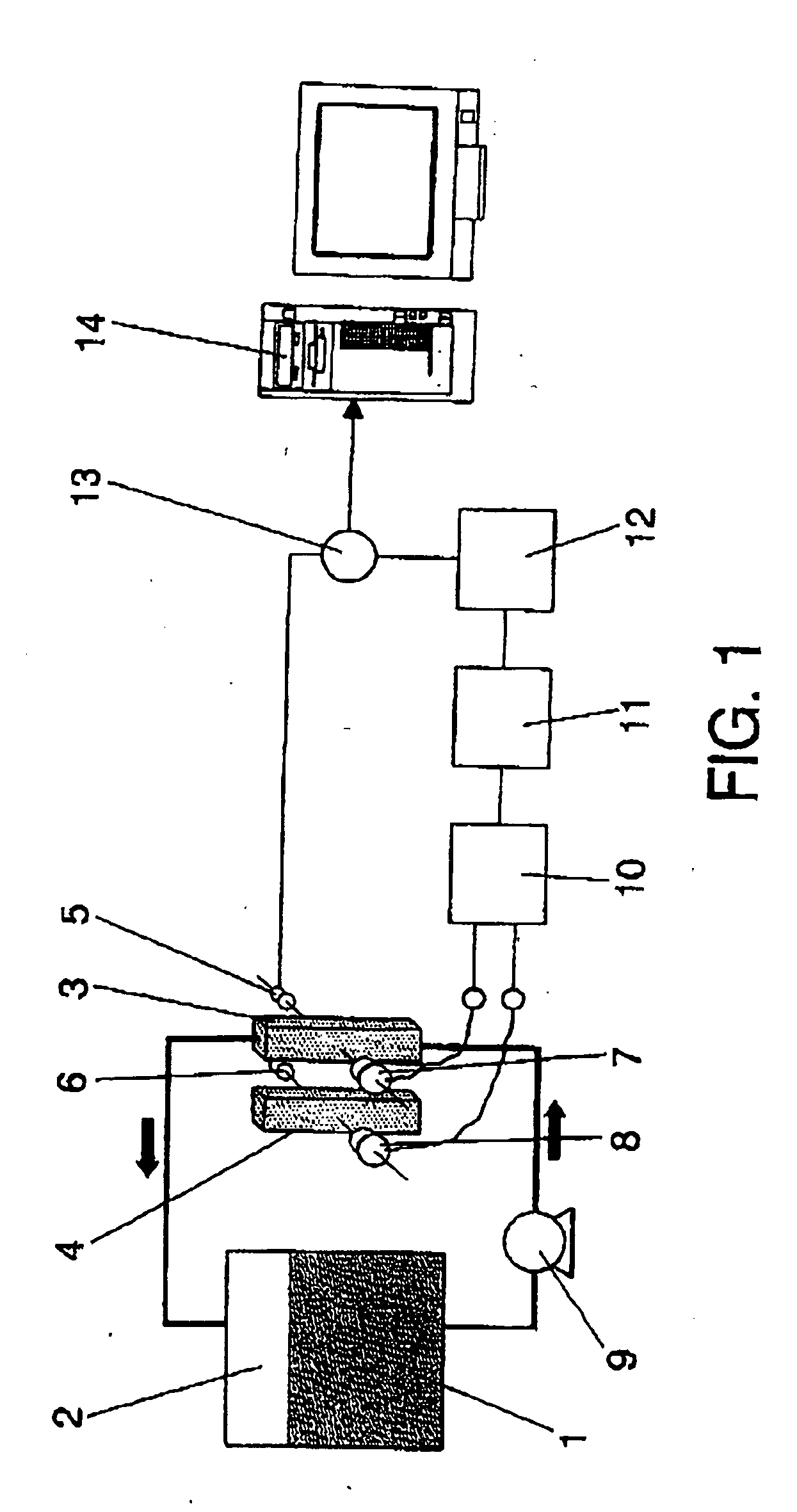
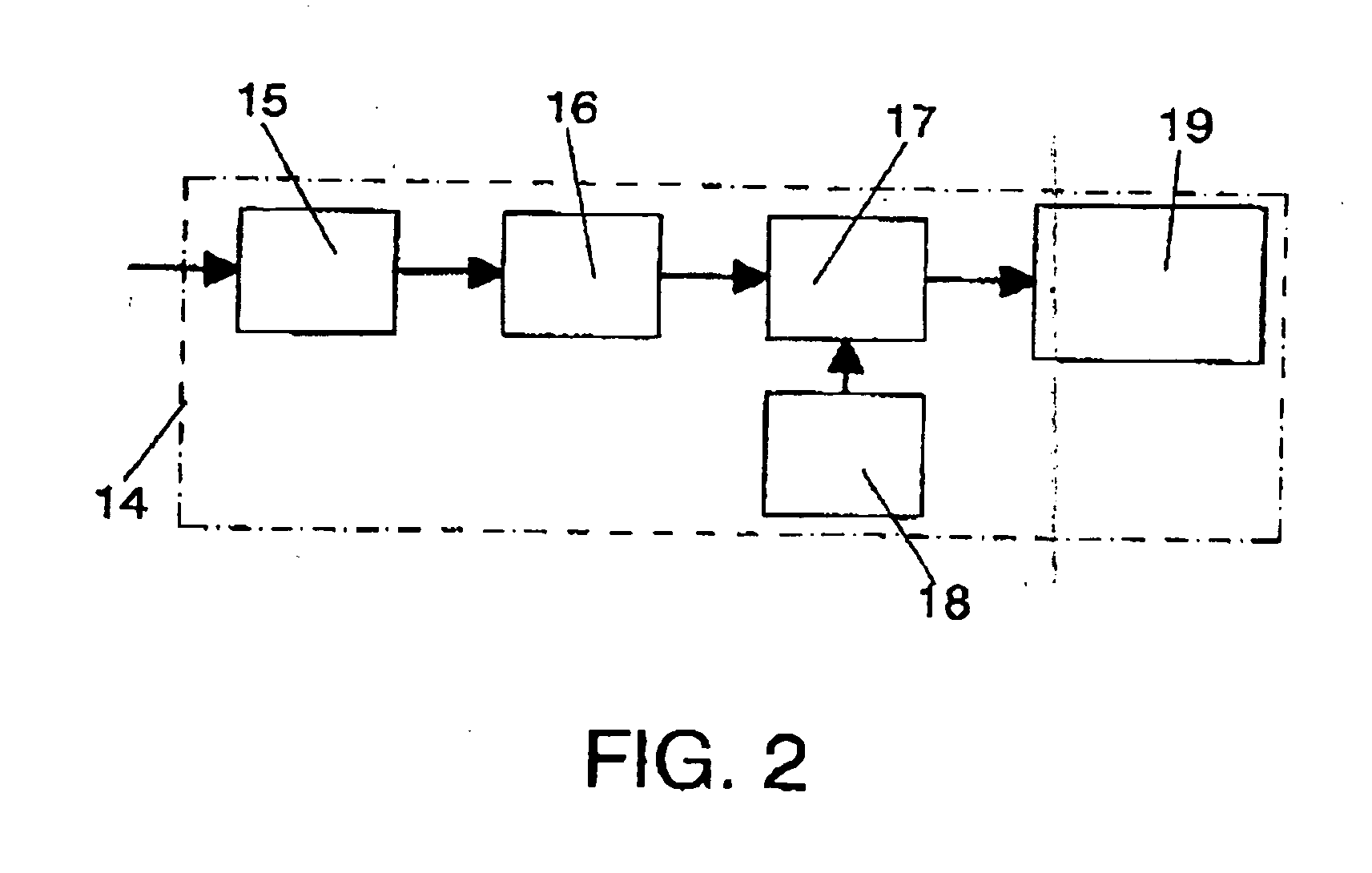
On-line method and equipment for detecting, determining the evolution and quantifying a microbial biomass and other substances that absorb light along the spectrum during the development of biotechnological processes
InactiveUS20040227947A1Microbiological testing/measurementTransmissivity measurementsReference sampleLight beam
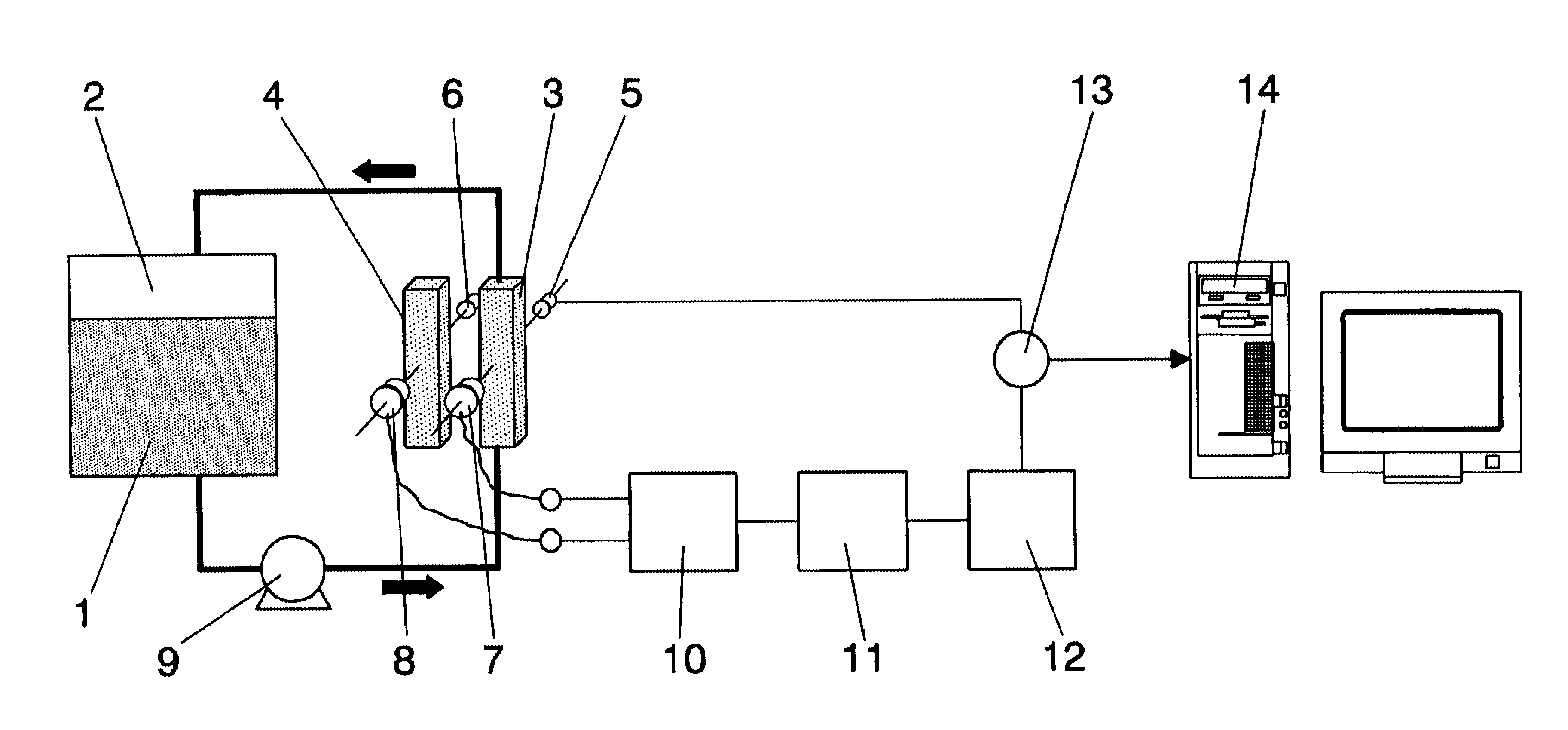
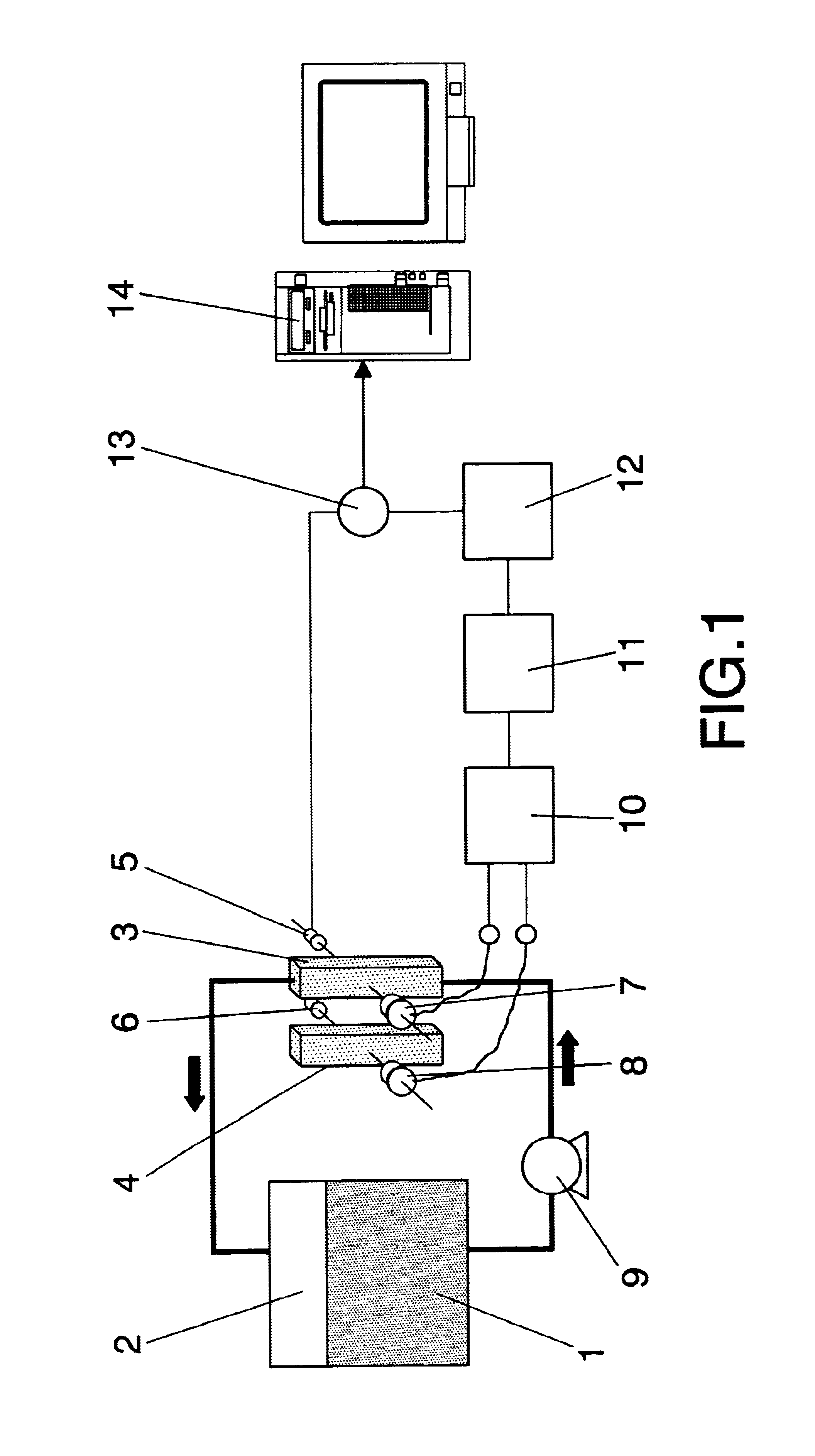
The invention relates to a method comprising passing a first variable intensity light beam across a first test-tube (3) wherein the substance (1) to be controlled is circulating. Subsequently, a second fixed-intensity light beam is passed across a second test-tube (4) with a reference sample. The intensities of both beams are compared once they have crossed over the test tubes and the intensity of the first beam is varied so that said intensities are equal. The parameter of interest in the first test tube is calculated by means of signal processing which causes the first beam to vary.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
Method for determining the quantity of microbiological objects during cultivation thereof
InactiveUS20100047855A1Microbiological testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsMicroorganismLiquid medium
A method for determining the quantity of microbiological objects during the cultivation thereof comprises determining a modification of studied microorganism cells' population, measuring the morphological composition thereof by determining the cells' size distribution in a liquid medium according to intensity changes of the light dispersed thereby. The method comprises probing a liquid flow by monochromatic coherent light, recording signals relating to the interaction between the probing radiation and the cells by measuring amplitudes and durations of impulses of the light dispersed by medium particles, plotting functions, according to measurement results, as two-dimensional distributions of normalized values of the amplitudes and durations in the form of statistic parameters of the dispersed light intensity. According to the functions, the size distribution of the cells and decomposition products of the liquid nutrient medium during the cultivation thereof are obtained. The invention can be applied for medical diagnostics and for control of biotechnological processes.
Owner:KUSHNIR IHOR MIKHAJLOVICH +4
A method for industrial production of biocatalysts in the form of enzymes or microorganisms immobilized in polyvinyl alcohol gel, their use and devices for their production
ActiveCN101426472AReduce operating costsReduce unproductive growthBiofuelsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPolyvinyl alcoholHigh pressure
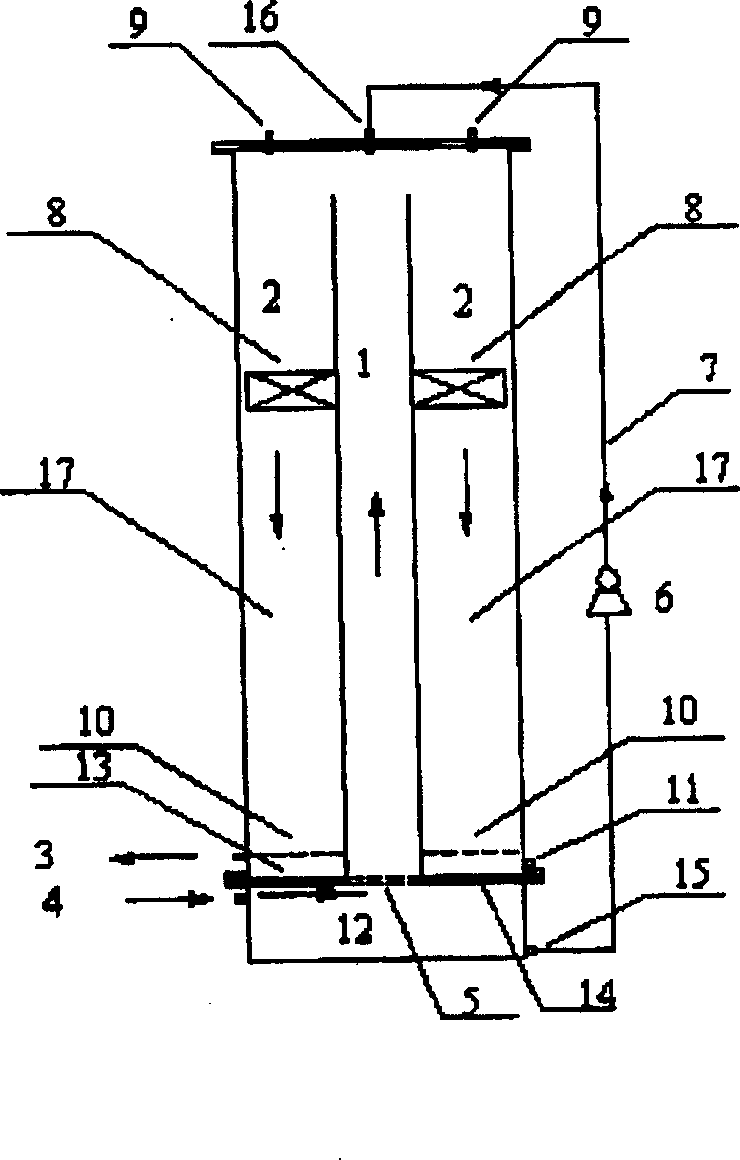
A method for the industrial production of the biocatalysts with biologically active material in the form of immobilized enzymes or microorganisms which are immobilized into the polyvinyl alcohol gel, and their use based on the fact, that the active biological material, formed by the mixture of free native or pretrated (aggregated) enzyme catalyst, or production microorganism, or part of them, and the polyvinyl alcohol gel, is used for their industrial production, the mixture is gelated and shaped in a stream of drying air at the temperature of 800C to 150C, considering the extent of the biologically active material, at the biocatalyst geometrical ratio of the surface to the volume kept larger than 7 mm'1, and consequently thus prepared biocatalysts can be cultivated or stored and then use in biotechnological processes in the conditions,; which ensure given biotechnological process higher productivity, higher production and enzymatic stability, long-term and repeated usage or definable process control with consequence easy separation of the biocatalyst. The industrial production device, providing optimization of the biological carrier volume and surface in dependence on biologically active material extent, consisting of a casting mechanism (17) mounted in front of a drying channel (2), through which a continuous conveyor belt (1) runs, is equipped with at least one casting head (17) with two rows of casting needle injectors connected to a pressure tempered tank (15) and a compressor (16), the conveyor belt (1) and a drying system - the source (4) of a drying air, which is blown by means of ventilator into an air distribution system (6) with incorporated heating elements (5),; which runs into the upper drying channel (2), and further the lower final drying channel (3) and a reswelling tank (7), between which a wiping and collecting device (9) is mounted, designed on the basis of mechanical wiping and high-pressure rinse.
Owner:澳源泰科环保科技(北京)有限公司
Fragrant citrus iron chelating reductase gene
InactiveCN1482245AImprove iron nutritionGood for healthDepsipeptidesOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyIron Chelating
The Citrous junos Ferric-chelated Reductase gene CjFR02 is obtained with iron deficiency tolerant Ziyang citron as material and through one series of biotechnological process. The gene has cDNA sequence length of 2403 bp, contains one 2103 bp opened reading frame, encodes 710 amino acids, and has one 64 bp upstream non-coding sequence and 3' end polyA tail. The homology comparison results show that the cloned cDNA sequence has higher homology with reported Ferric-chelated Reductase gene FR02, 49-52 % of same amino acids and 68 % of similar amino acids. The gene engineering of applying the gene and its plant expression carrier in plant can improve the iron deficiency characteristics of grain crop, vegetable and fruit tree to produce high quality agricultural products capable of improving human iron nutrients and raising health level.
Owner:SOUTHWEST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Biotechnological process for neutralizing alkaline beverage industrial waste water
ActiveUS20060141604A1Guaranteed economic efficiencyReduced pHBiocideBacteriaIndustrial waste waterExiguobacterium
The present invention provides a process of neutralizing beverage industrial wastewater by a bacterial strain Exiguobacterium sp. isolated in India, which strain is capable of bring down the pH of wastewater from 12.00 to 7.00 units within 1 to 1.5 hours.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
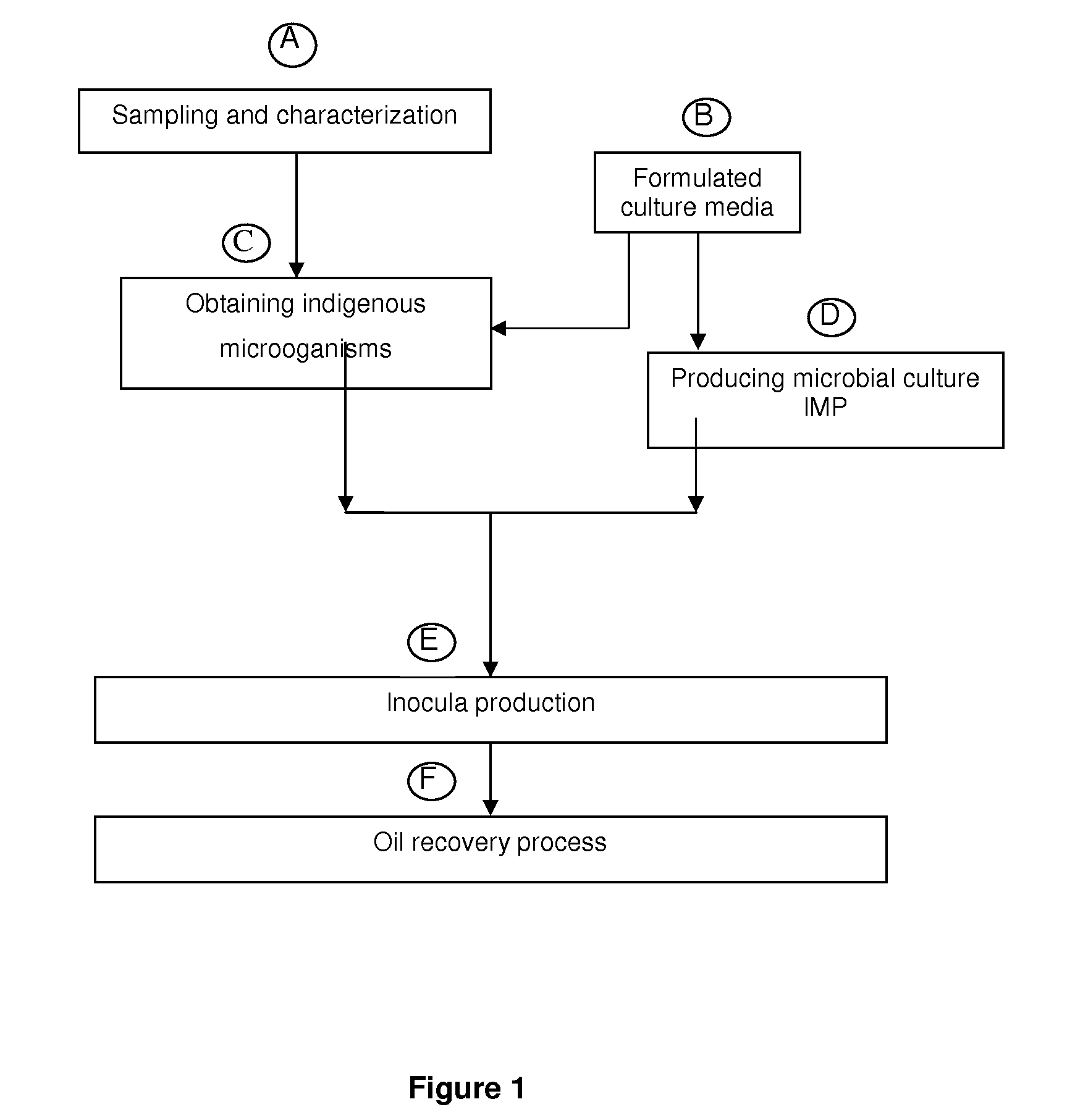
Biotechnological process for hydrocarbon recovery in low permeability porous media
ActiveUS8631865B2Improve mobilityEnhanced overall recoveryMicroorganism based processesFluid removalMetaboliteBiostimulation
A biotechnological process for enhancing oil recovery of 14 to 25° API oil contained in carbonate or sandstone rock systems with low permeability utilizes indigenous extremophile microorganisms (first culture) from the oil well, a second culture containing selected microorganisms and its metabolites (gases, acids, solvents and surfactants), to improve oil mobility. Under anaerobic conditions, such microorganisms are able to grow in temperatures from 60 to 95° C., at pressures from 7 to 154.6 kg / cm2 and NaCl content from 5,000 to 45,000 ppm. Injection of indigenous microorganisms and a second culture for metabolites production into the well improves oil recovery after closing the system for periods from 5 to 10 days. The biotechnical process includes biostimulation (indigenous microorganisms) and bioaugmetation (second culture) to increase oil recovery.
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO
On-line method and equipment for detecting, determining the evolution and quantifying a microbial biomass and other substances that absorb light along the spectrum during the development of biotechnological processes
InactiveUS6975403B2Microbiological testing/measurementTransmissivity measurementsReference sampleLight beam
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
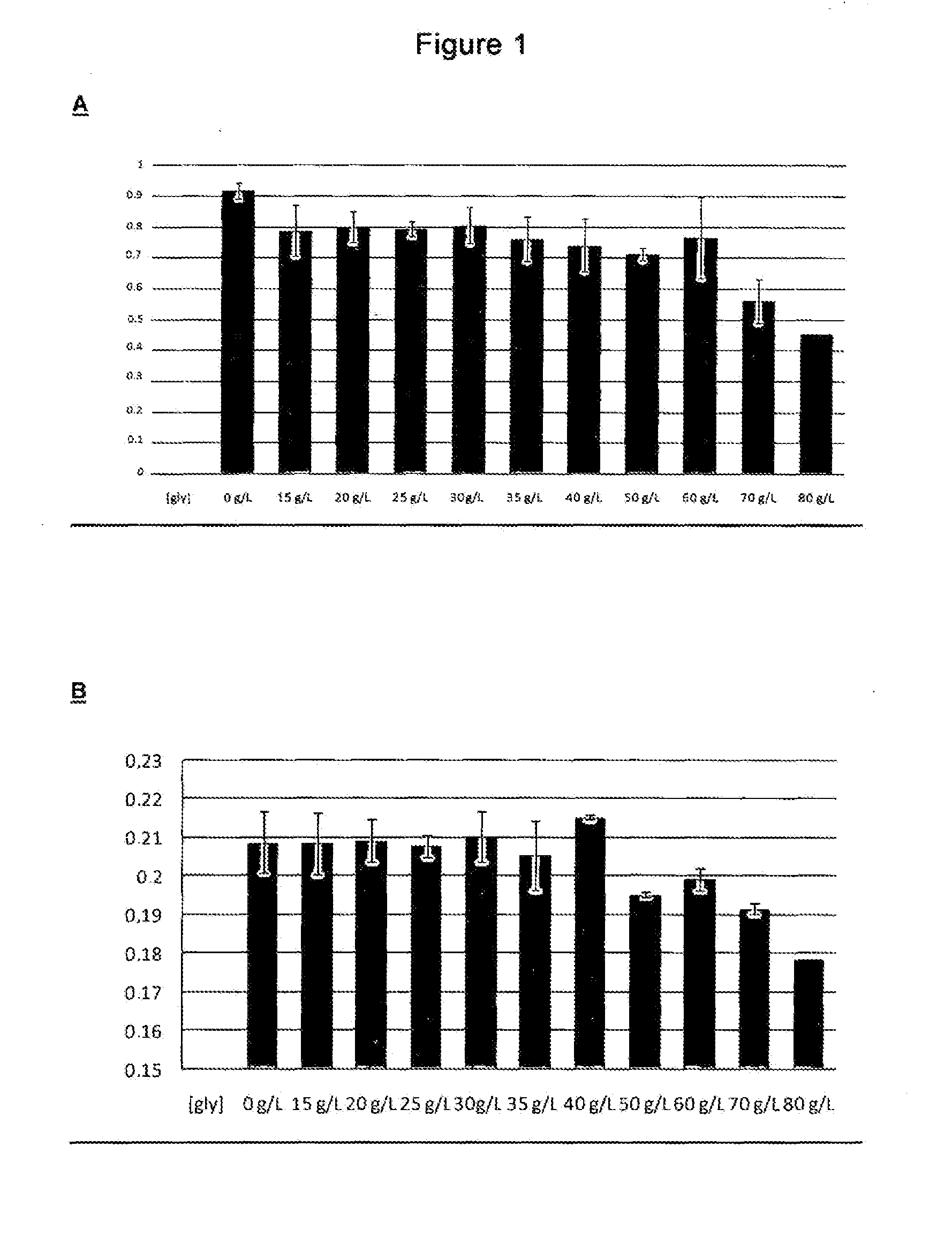
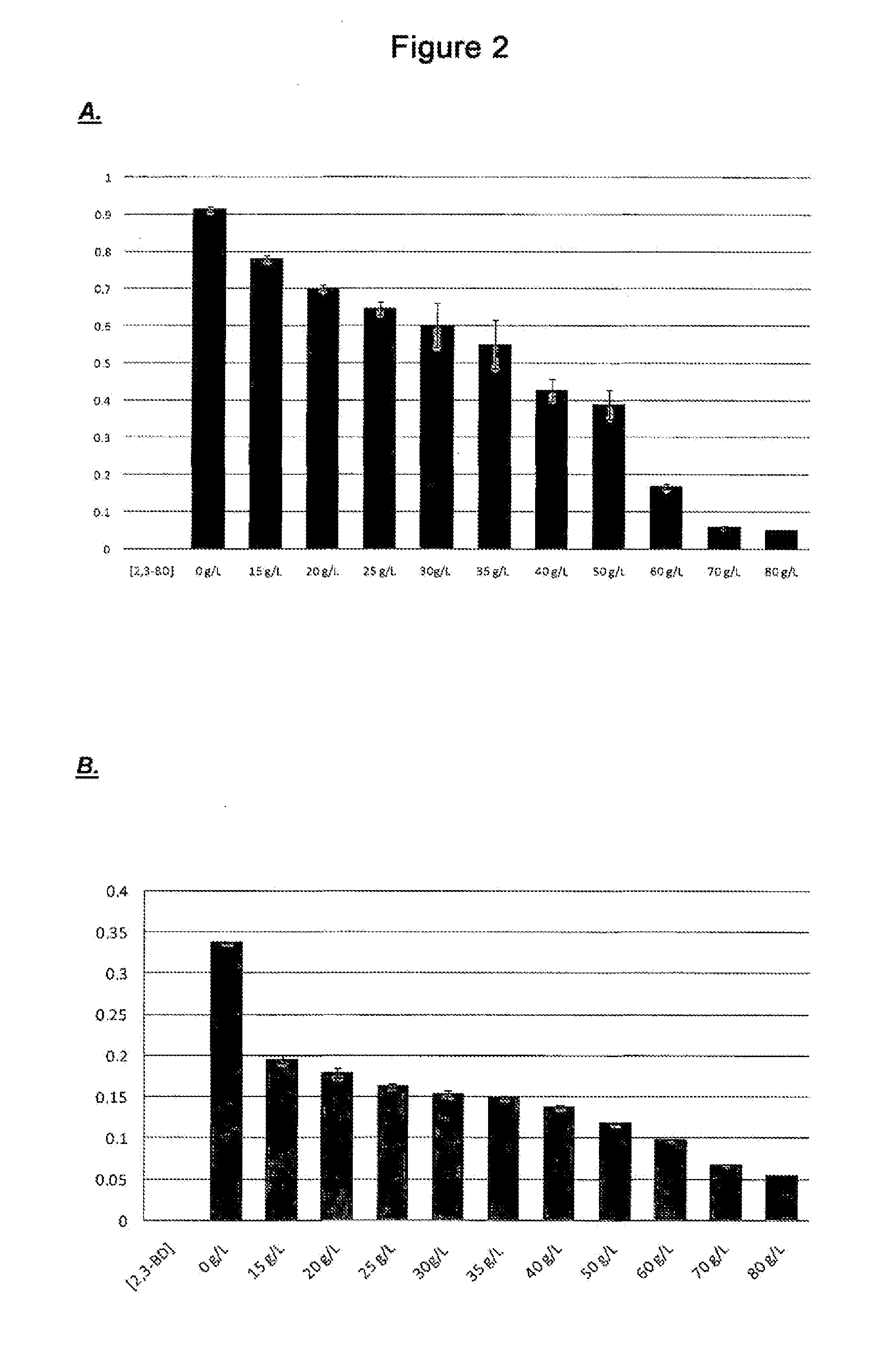
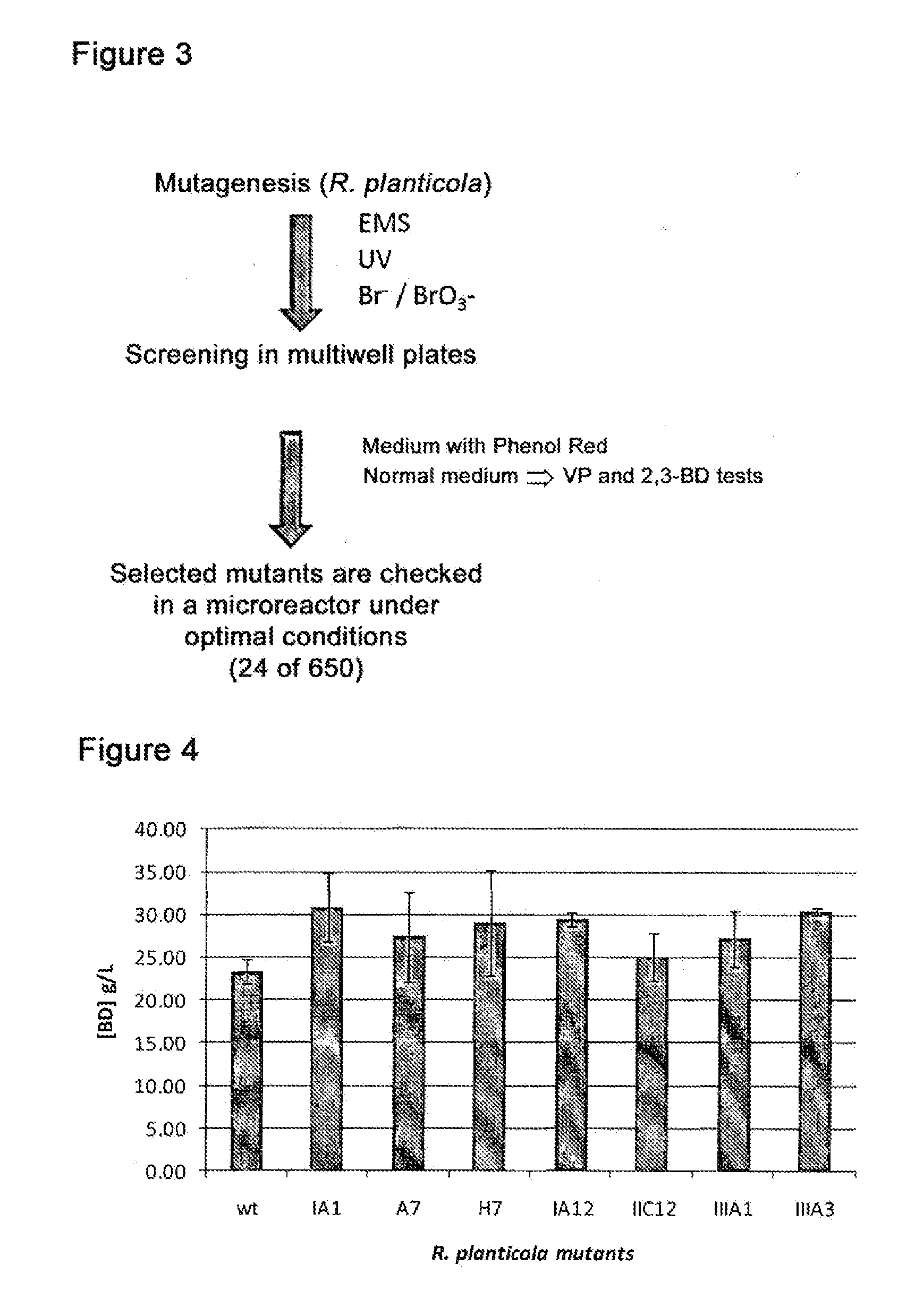
Method for producing 2,3-butanediol using improved strains of raoultella planticola
The invention relates to a method for producing 2,3-butanediol using improved strains of Raoultella planticola, and to novel mutant strains obtained by random mutagenesis from the bacterial species Raoultella planticola CECT843, that can be used in the industrial production of 2,3-butanediol from glycerol. The invention preferably relates to the Raoultella planticola strains designated IA1 and IIIA3 and deposited in the Spanish Type Culture Collection (CECT) under deposit number CECT8158 (corresponding to the strain designated IA1) and deposit number CECT8159 (corresponding to the strain designated IIIA3). The invention also relates to a method for producing 2,3-butanediol from glycerol by means of a biotechnological process using the novel strains of the invention.
Owner:BIOPOLIS
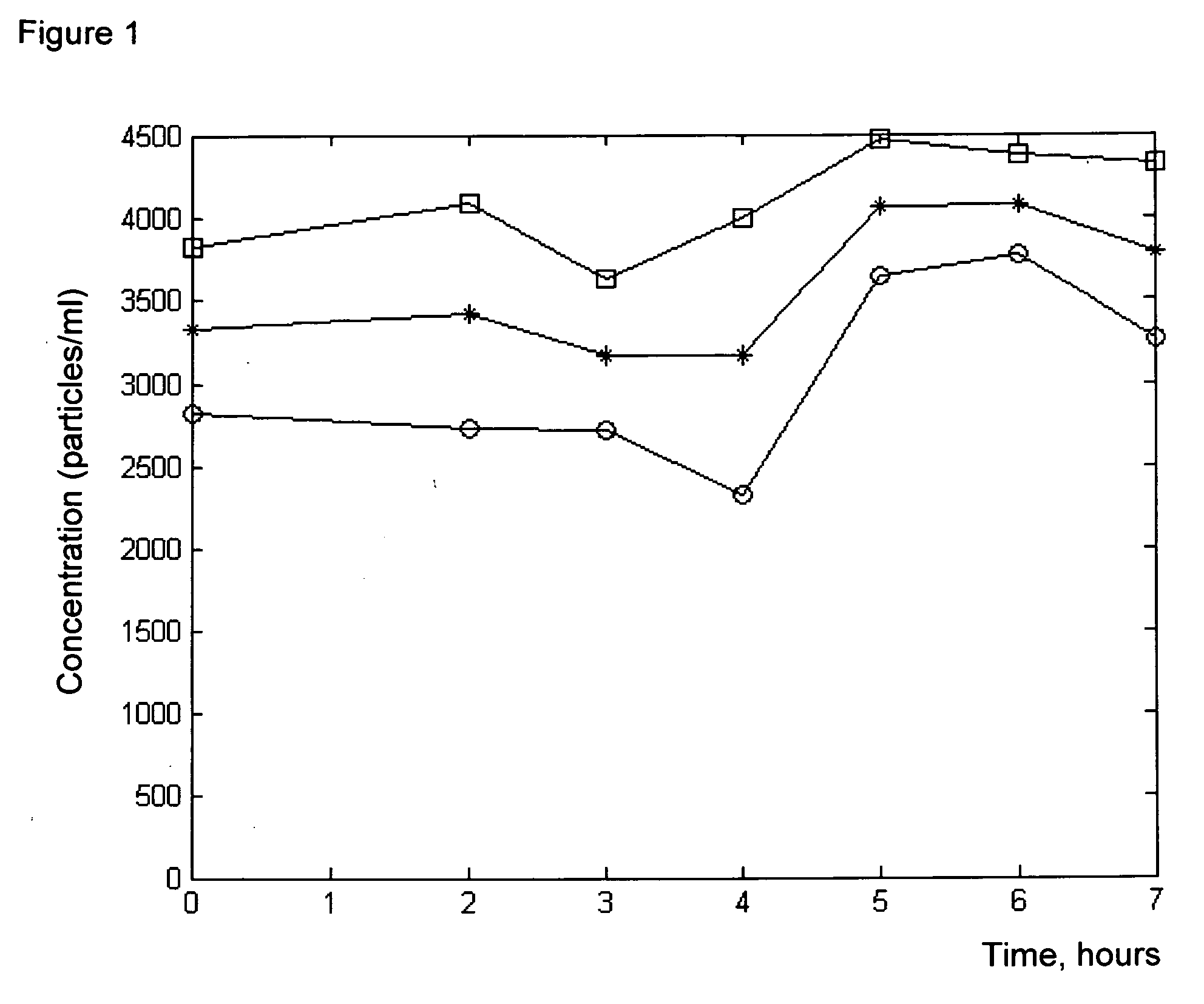
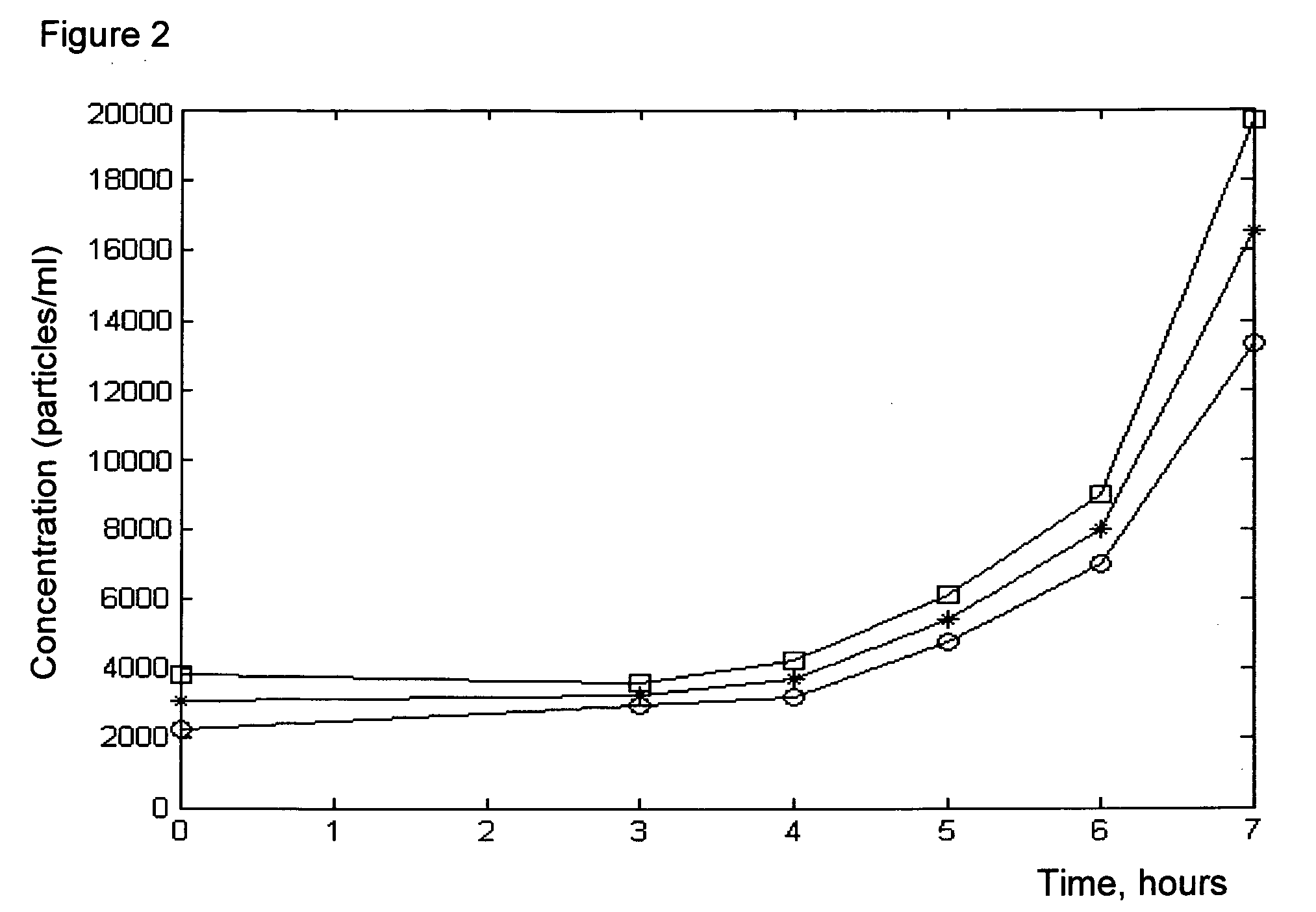
Container with sensor arrangement
ActiveCN106902900AGood for moist storageMeasurement apparatus componentsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansInterior spaceHandling system
The invention relates to a container with a sensor arrangement. A container for use as a single-use component in a processing system for performing a biological, biochemical, or biotechnological process includes a wall surrounding a container interior space with a sensor arrangement integrated into the wall, where the sensor arrangement includes at least one sensor and one housing, and where the housing includes a housing wall, which surrounds a housing interior space containing the sensor and separates the housing interior space from the container interior space, characterized in that the housing wall comprises a wall region, which is designed as a predetermined breaking point.
Owner:ENDRESSHAUSER CONDUCTA GMBHCO
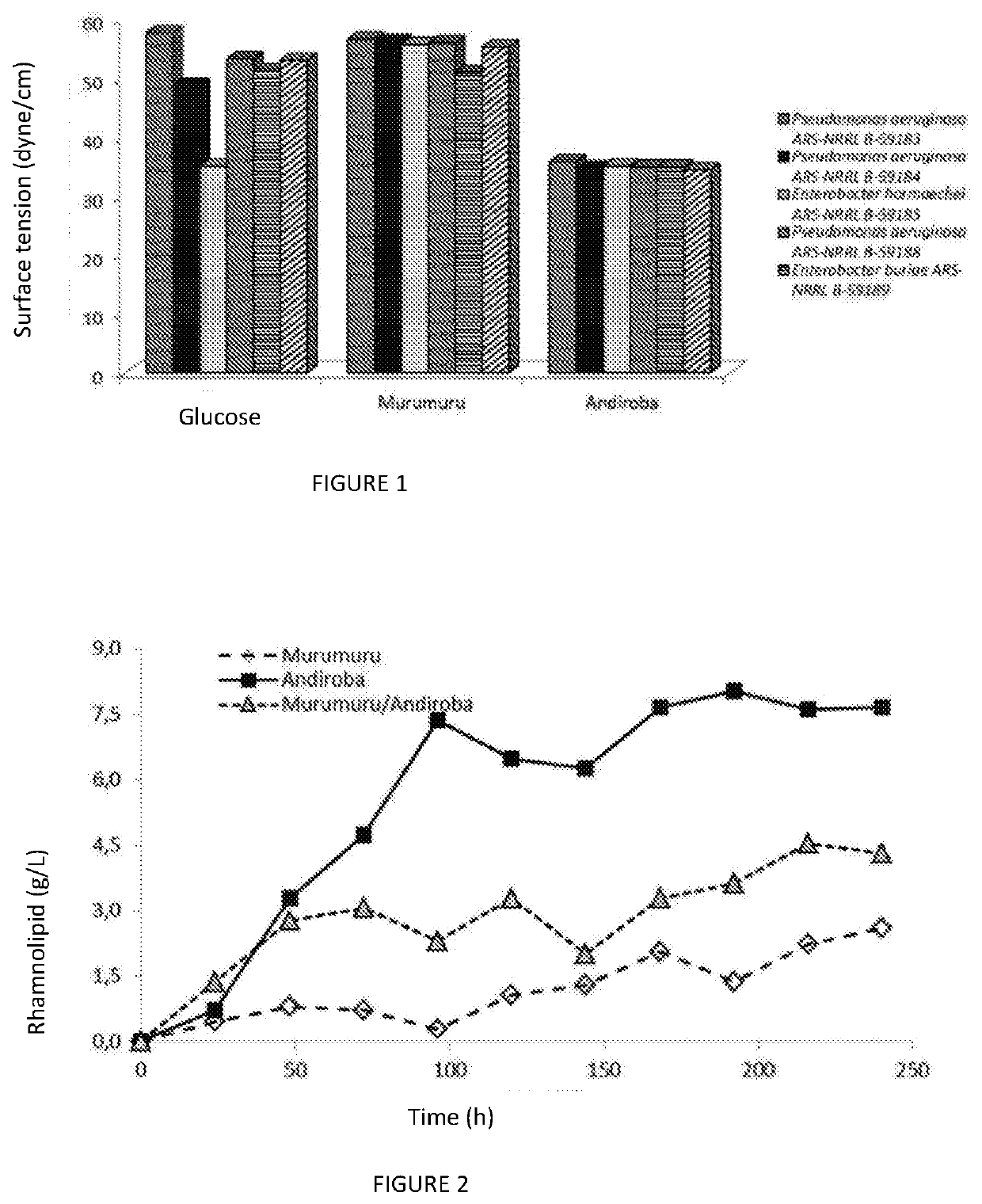
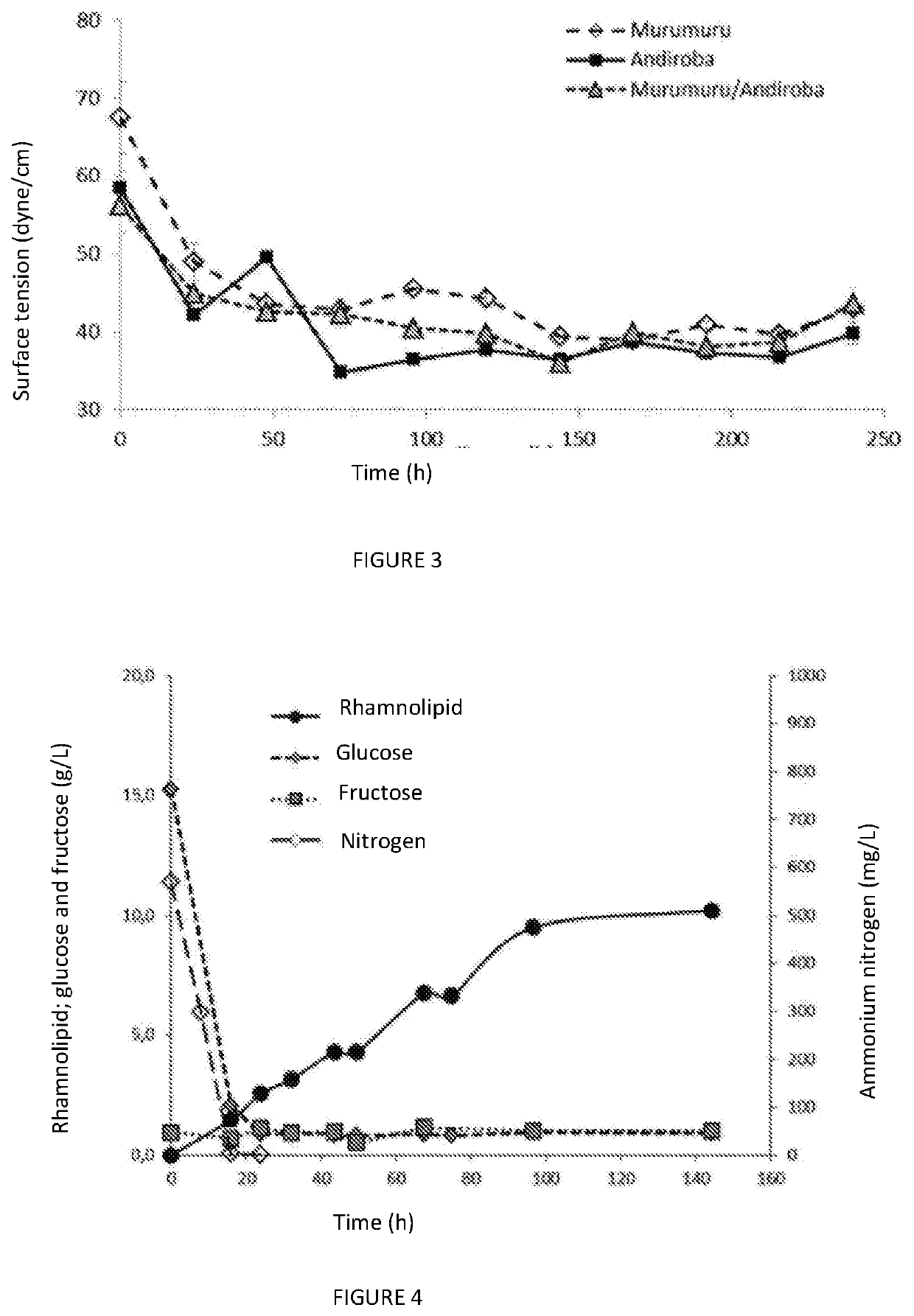
Process for producing a rhamnolipid produced by pseudomonas or enterobacter using andiroba or murumuru seed waste
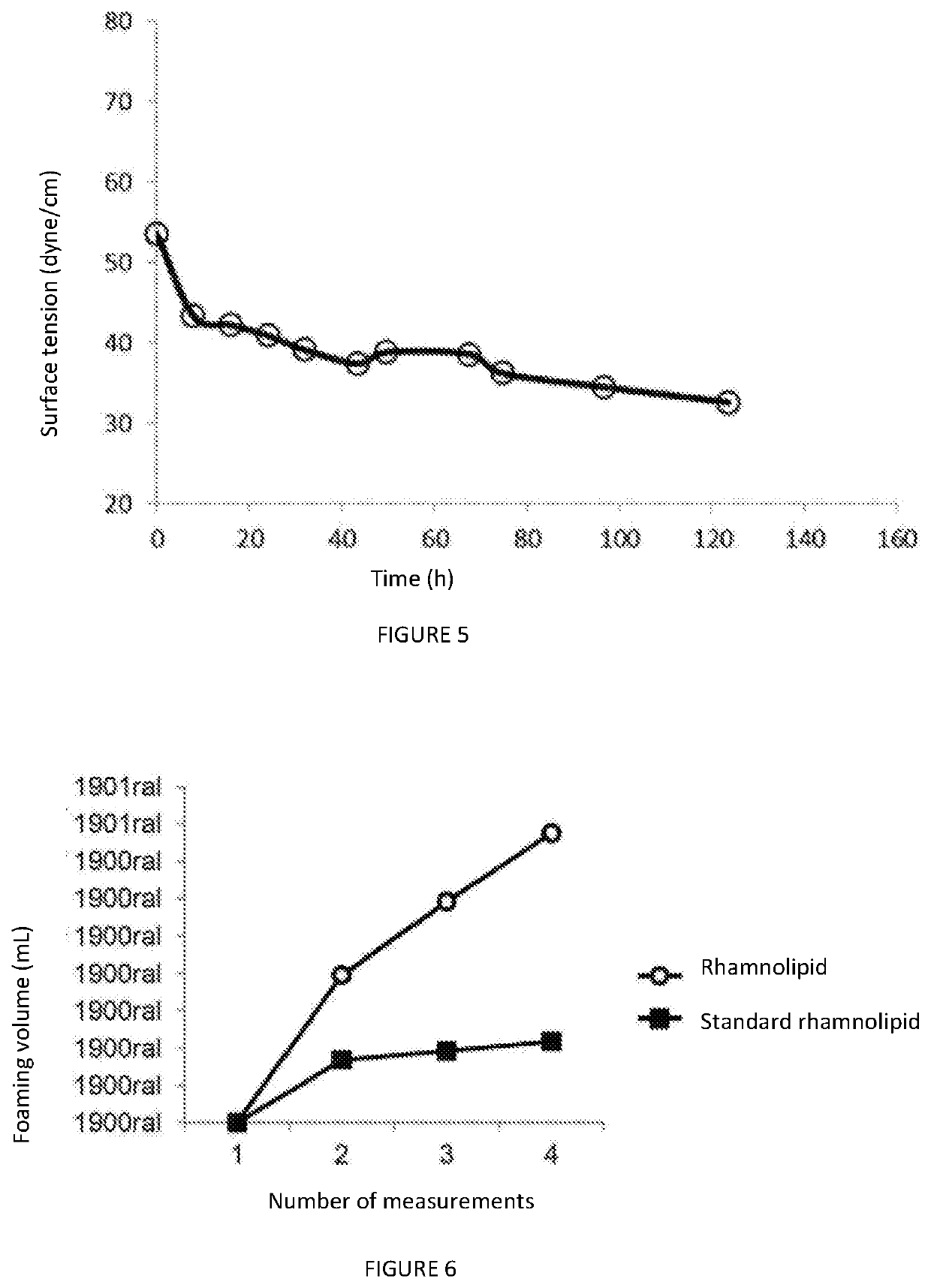
Process for producing a rhamnolipid produced by Pseudomonas or Enterobacter using andiroba or murumuru seed waste, pertaining to the sector of compounds containing monosaccharide radicals, consists of producing rhamnolipids by a biotechnological process using andiroba or murumuru seed waste, following oil extraction, as a substrate for a Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter hormaechei or Enterobacter buriae line cultivated in a bioreactor with a non-dispersive aeration system for reducing foam, producing a rhamnolipid content of 10.5 g / L for Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria, in bioreactors carried out in a stirred tank with non-dispersive aeration using microporous membranes, particularly of silicone tubes, which allow oxygen to be supplied by diffusion. This type of aeration allows for various configurations, and in the embodiment of the invention, the porous membrane / tube was internally located in the liquid in the bioreactor in the form of a serpentine, under the following process conditions: pure oxygen with suitable pressure and flow rate to maintain O2 pressure in the bioreactor at 20% during the first 24 hours of the assay and stirring varying from 300 to 700 rpm, using 2 radial impellers and manual adjustment according to the decrease in the concentration of dissolved oxygen. The product produced has features that can be used primarily in the cosmetic industry due to its emulsifying, stability and non toxicity capacities.
Owner:NATURA COSMETICOS SA +1
Method for improving expression quantity of pichia pastoris foreign protein by using mercaptan peroxidase
ActiveCN103898142AContributes to correct conformational formationPromote secretionVector-based foreign material introductionPichia pastorisBiotechnology
The invention discloses a method for improving the expression quantity of a pichia pastoris foreign recombinant protein by using mercaptan peroxidase as a cofactor aiming at improving the preparation capability of the pichia pastoris foreign recombinant protein, belonging to the field of biochemical engineering. The method comprises the steps of connecting a mercaptan peroxidase gene with an inducible promoter or a constitutive promoter from pichia pastoris or saccharomyces cerevisiae to construct a gene expression vector, and transferring the gene expression vector to a methanol induced pichia pastoris strain for expressing the foreign recombinant protein to perform co-expression or over-expression, wherein the mercaptan peroxidase gene serving as a global control gene of oxidation reduction stress response improves the expression quantity of the foreign recombinant protein in the methanol induced pichia pastoris under the control effects of the promoter of different strengths and the transcriptional level of a gene copy number. The invention provides a new method for improving the capability of producing recombinant protein by cells and the bio-reaction efficiency, which has an important value for strengthening a biotechnology process.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Biological neutralization of highly alkaline textile industrial wastewater
ActiveUS7179633B2Guaranteed economic efficiencyReduced pHBacteriaSolid waste disposalBiotechnologyIndustrial effluent
The present invention provides a novel process of neutralizing textile industrial wastewater by a bacterial strain isolated in India. The isolated bacterial strain is capable to bring down the pH of wastewater from 12.00 to 7.00 units within two hours. The neutralization of alkaline textile industrial wastewater by such biotechnological process is highly effective and economical as compared to conventional neutralization by chemical means. This biotechnological process may find wide commercial application in textile industries emanating alkaline wastewater.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
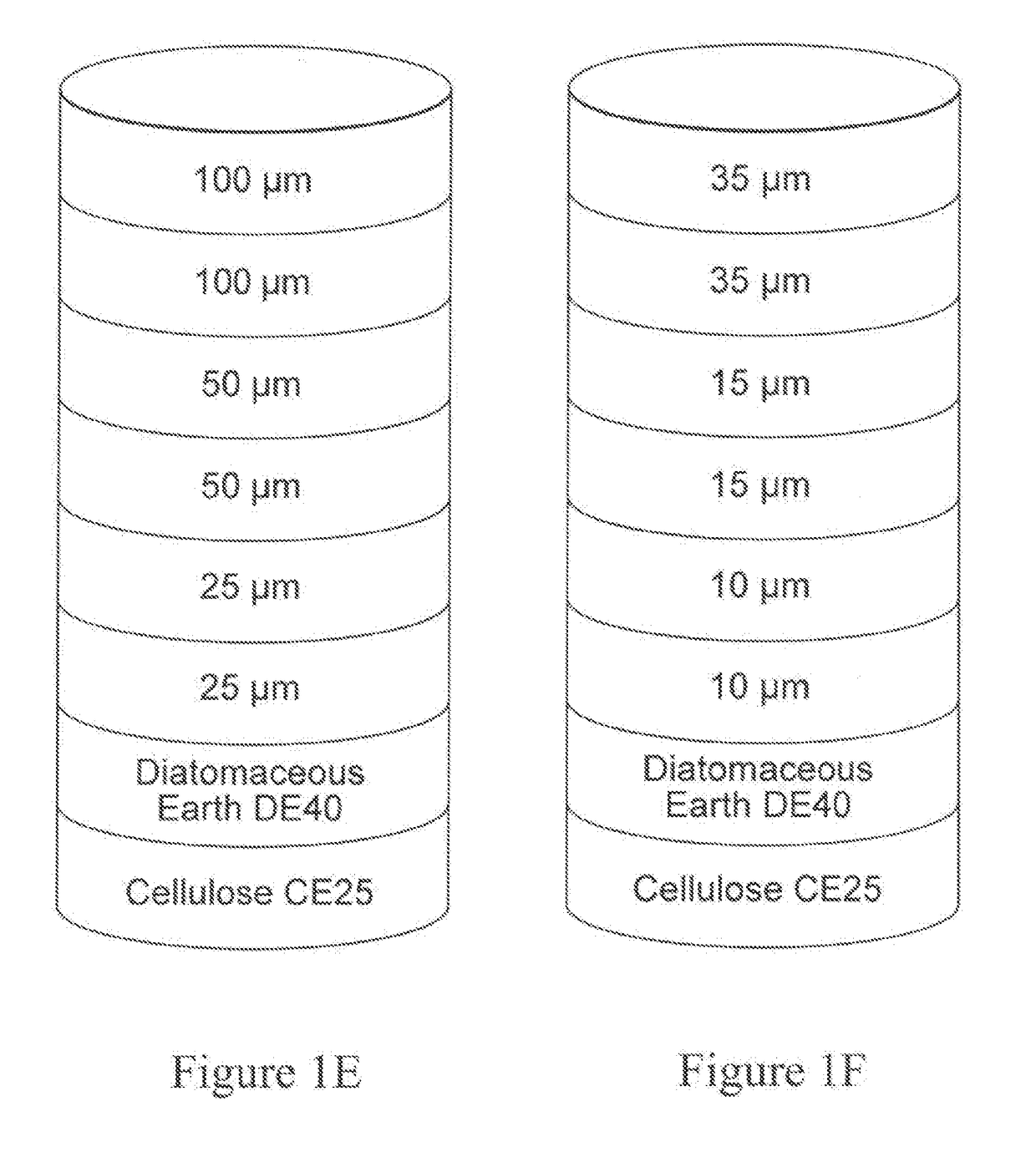
Depth Filters For Disposable Biotechnological Processes
ActiveUS20180345173A1Efficient separationImprove throughputSemi-permeable membranesTreatment involving filtrationCellular DebrisPorous layer
A process for the primary clarification of feeds, including chemically treated flocculated feeds, containing the target biomolecules of interest such as mAbs, mammalian cell cultures, or bacterial cell cultures, using a primary clarification depth filtration device without the use of a primary clarification centrifugation step or a primary clarification tangential flow microfiltration step. The primary clarification depth filtration device contains a porous depth filter having graded porous layers of varying pore ratings. The primary clarification depth filtration device filters fluid feeds, including chemically treated flocculated feeds containing flocculated cellular debris and colloidal particulates having a particle size distribution of approximately about 0.5 μm to 200 μm, at a flow rate of about 10 litres / m2 / hr to about 100 litres / m2 / hr. Kits and methods of using and making the same are also provided.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Process for producing lipids suitable for biofuels
ActiveUS9441252B2Increase temperatureHigh pHFatty acid esterificationUnicellular algaeBiofuelBioreactor
The present invention provides a cost effective biotechnological process for production of bio-fuels from isolated and characterized microalgae. The algal strains used in the present invention having higher biomass, higher lipid productivity, higher pH and temperature tolerance are selected from the group consisting of Chlorella vulgaris iOC-1, Chlorella vulgaris iOC-2, Chlorella kessleri, Botrococcus bruni, Dunaliella salina and Nannochloris oculat or a combination thereof having 95-100% similarity with 18s ribosomal nucleic acids nucleotide sequences (rDNA) given for Seq. ID I, Seq. ID 2, Seq. ID 3, Seq. ID 4, Seq. ID 5 and Seq. ID 6. The present process of bio-fuel production comprises the steps of producing lipid from green algae in bioreactors by various novel steps and extracting oil from dried algal cells and ultimately producing biodiesel by transesterification of the said extracted oil.
Owner:INDIAN OIL CORPORATION
Apparatus, methods and compositions for biotechnical separations
InactiveUS20060141521A1Improve performanceSeparationMicrobiological testing/measurementMessenger RNAEukaryotic plasmids
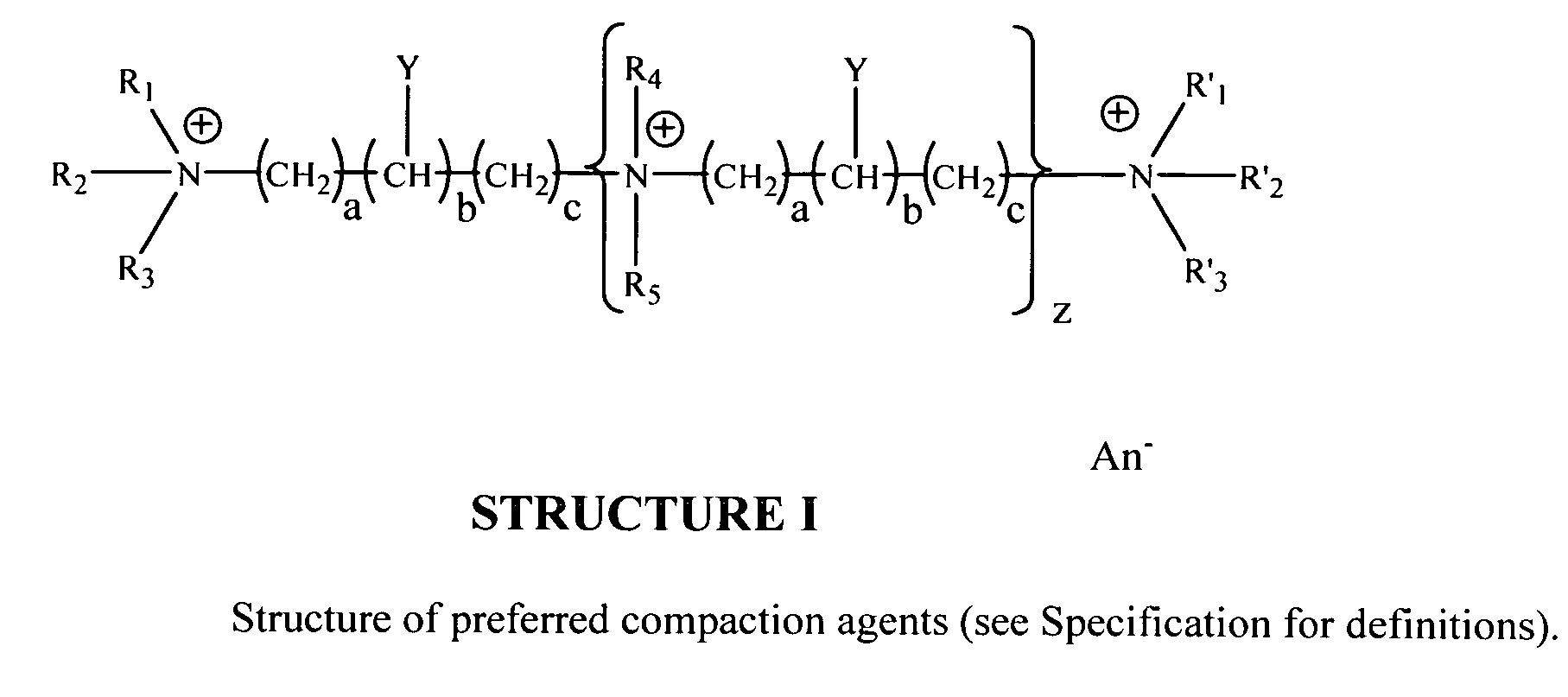
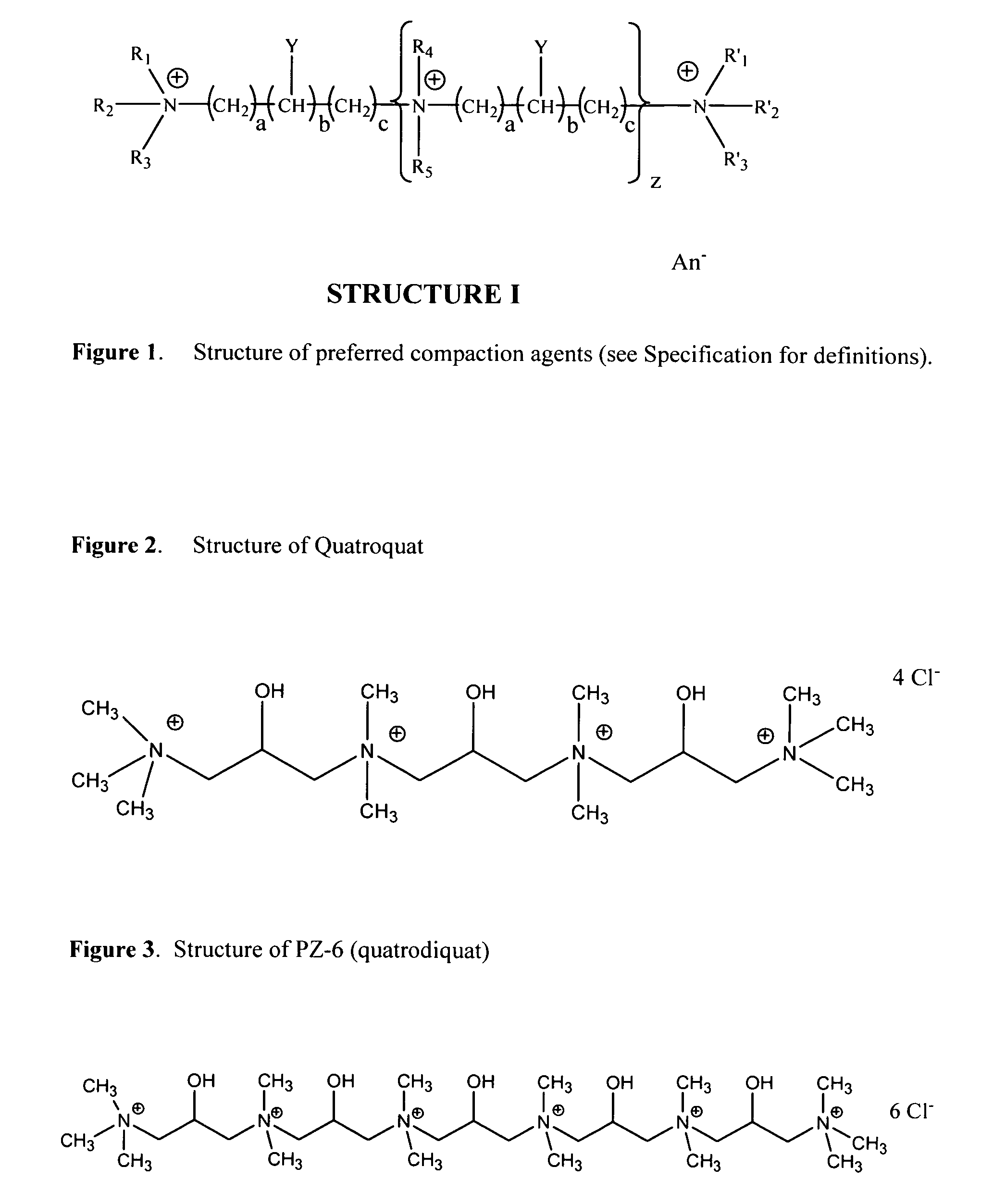
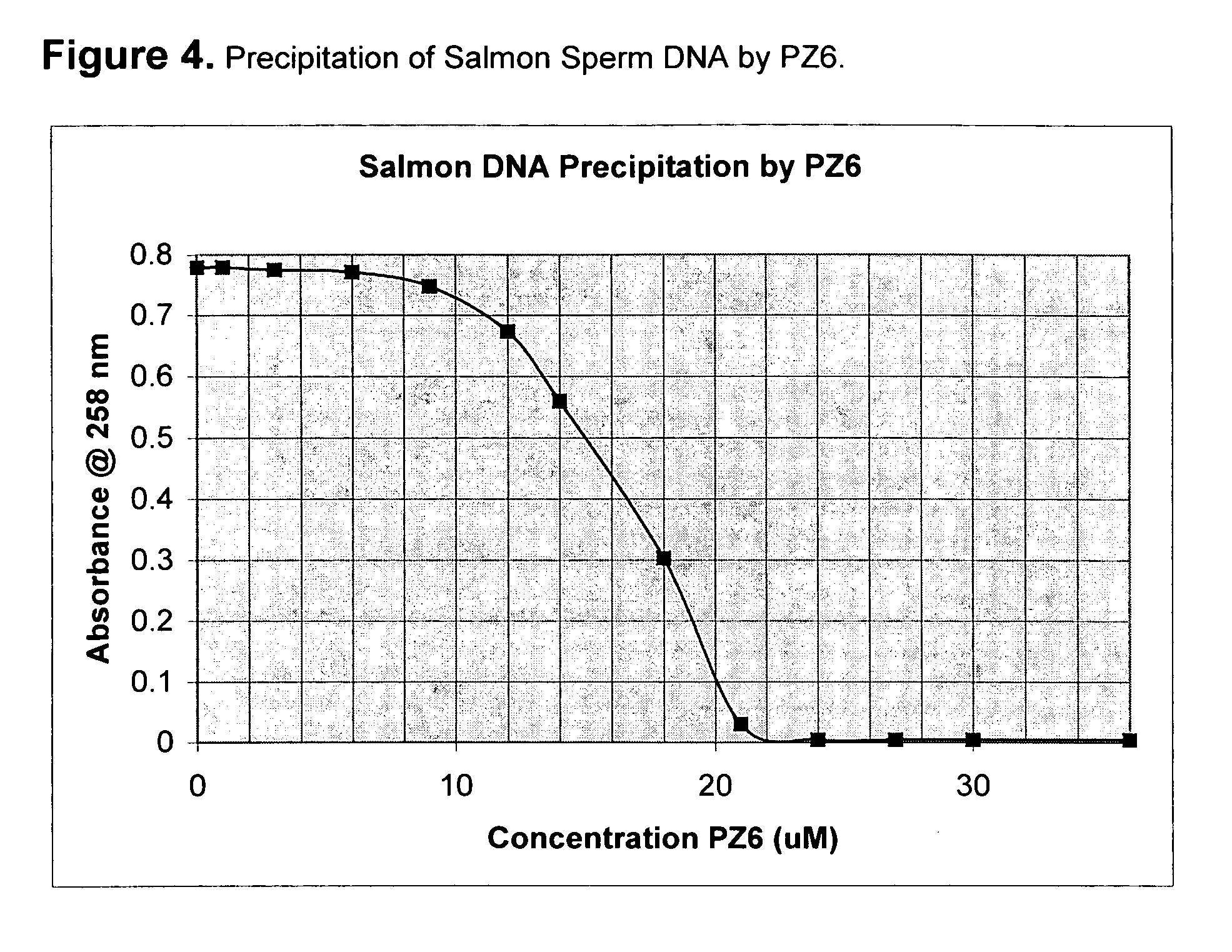
RNA, preferably messenger RNA, is purified by use of selective precipitation, preferably by addition of compaction agents. Also included is a scaleable method for the liquid-phase separation of DNA from RNA. RNA may also be recovered by fractional precipitation according to the invention. We have discovered that specific classes of compounds are unexpectedly potent in causing selective precipitation of DNA away from RNA, at low concentrations and in the presence of relatively elevated ionic strength. Modification of the selective removal of DNA can also remove both RNA and DNA, leaving behind a mixture which is advantageous for the further purification of, e.g., proteins. Additional aspects of the invention include mini-preps, preferably of RNA or of plasmid and chromosomal DNA to obtain sequenceable and restriction digestible DNA in high yields in multiple simultaneous procedures. Still further aspects disclose enhanced stripping of the compaction agent by a stripping method comprising high salt addition and pH shift, and combinations of these techniques. RNA Abstract Additionally, a new approach to the isolation of RNA from bacterial lysates employs selective precipitation by compaction agents. The above techniques can be enhanced by use of phase transfer catalysts (PTCs), most preferably selected polyamines of U.S. Pat. No. 6,617,108 polyamines which are quaternary compounds. (The use of PTCs in biotechnical processes is not evident in the literature, see e.g. www. / ptorganics.com as of 27 Jan. 2005.)
Owner:TECH LICENSING CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com