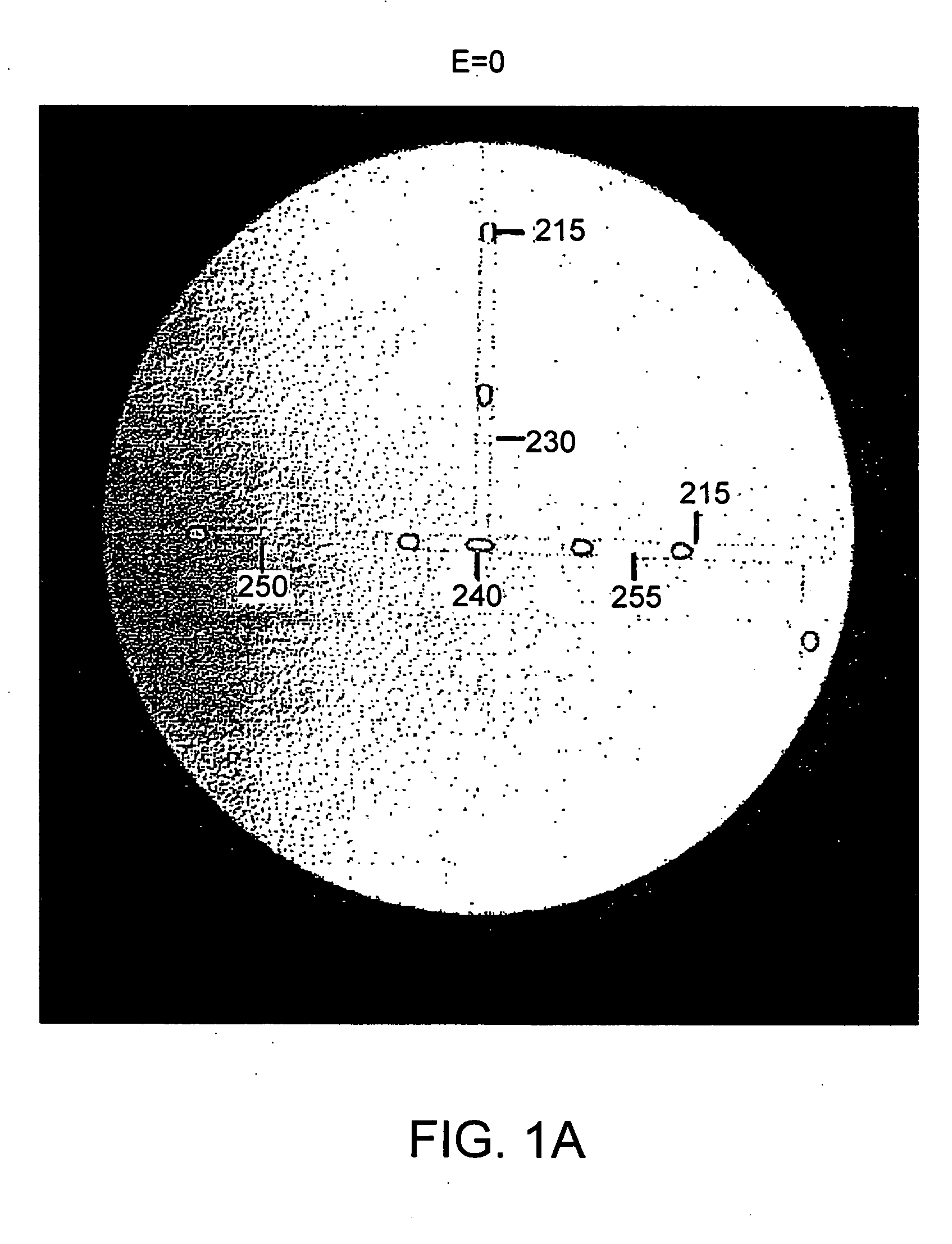
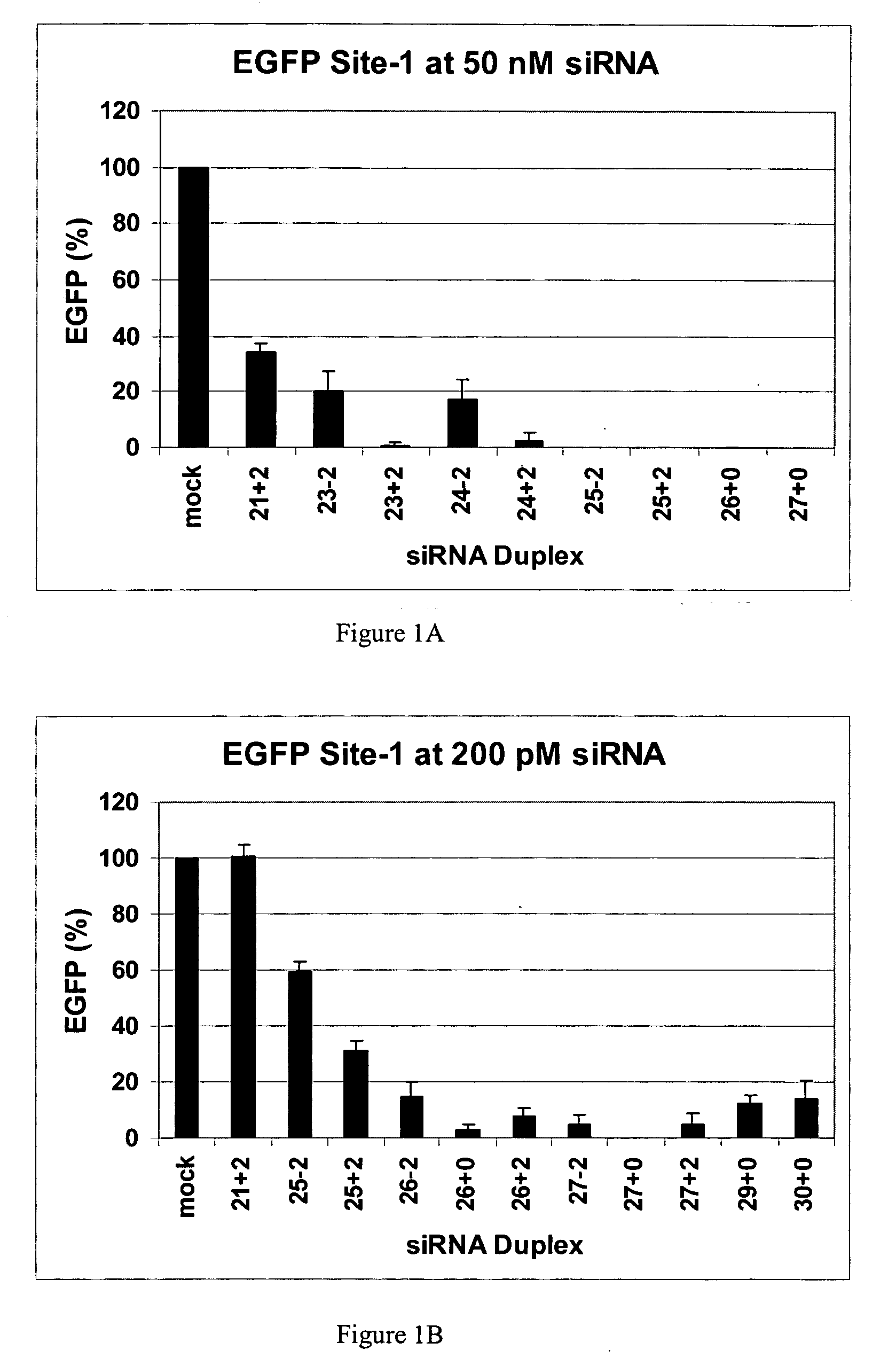
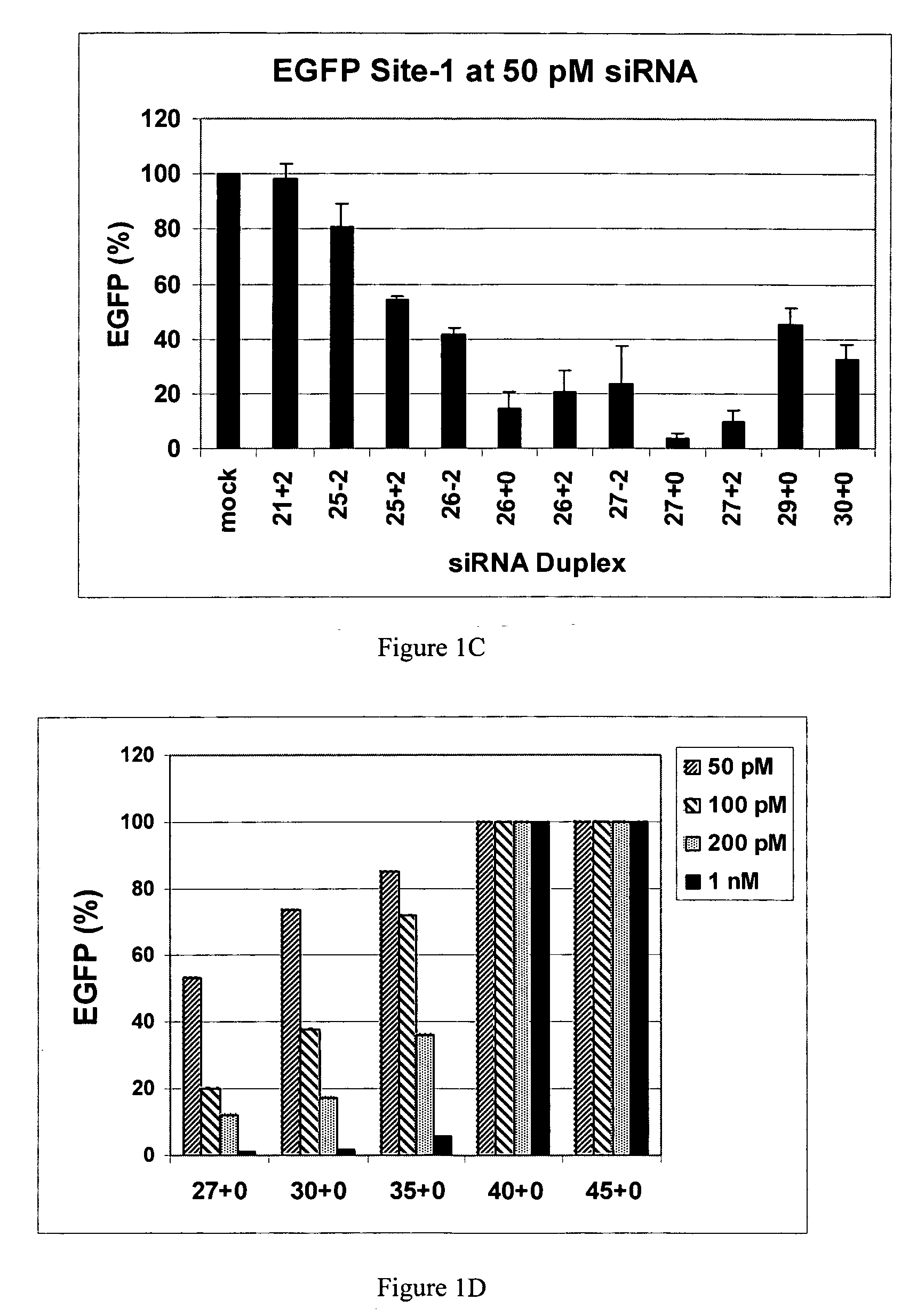
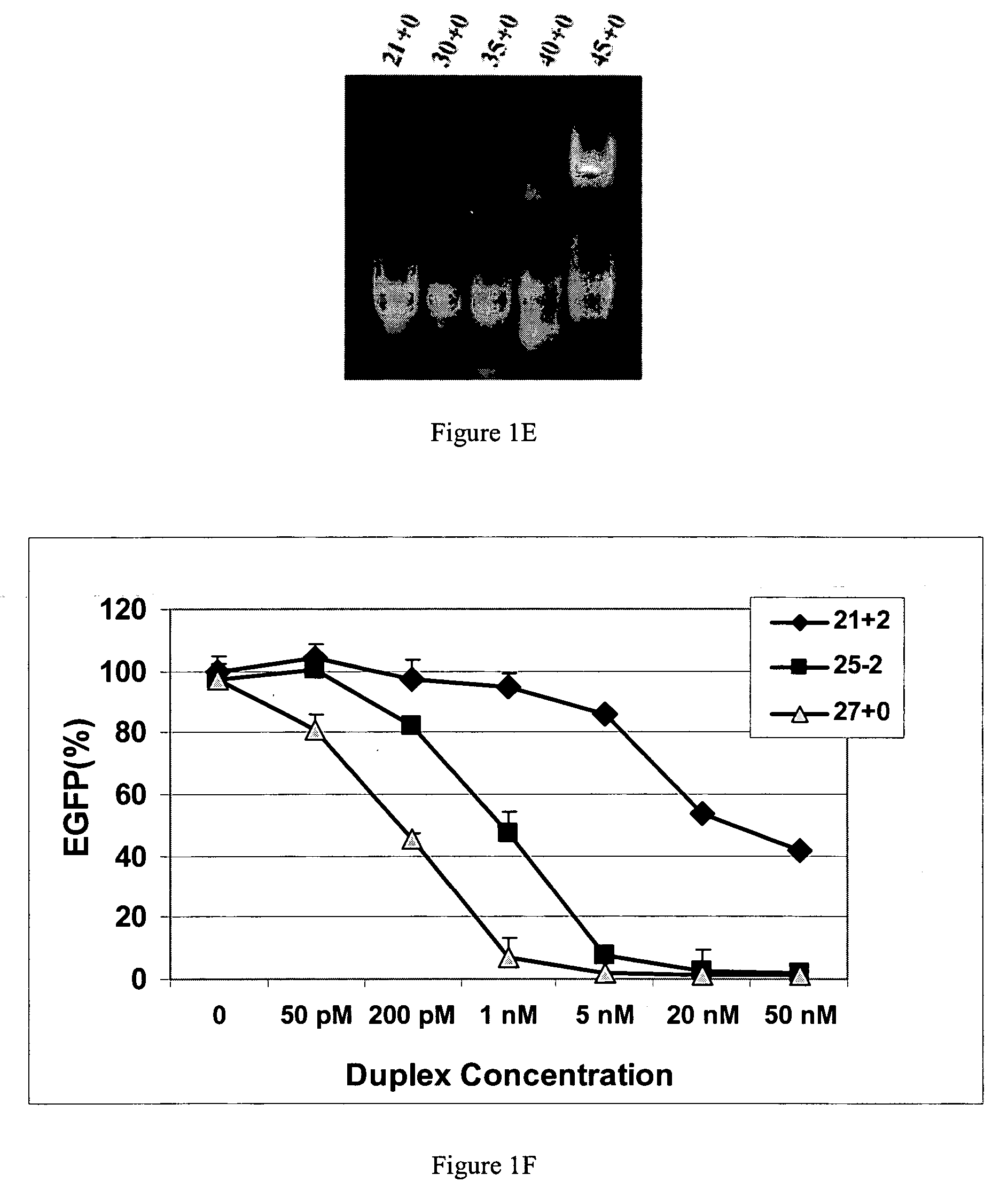
Patents
Literature
1284 results about "Gene product" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A gene product is the biochemical material, either RNA or protein, resulting from expression of a gene. A measurement of the amount of gene product is sometimes used to infer how active a gene is. Abnormal amounts of gene product can be correlated with disease-causing alleles, such as the overactivity of oncogenes which can cause cancer. A gene is defined as "a hereditary unit of DNA that is required to produce a functional product". Regulatory elements include...
Tissue-specific and pathogen-specific toxic agents and ribozymes
InactiveUS6271359B1Rapidly and effectively expressedImprove stabilityVirusesSugar derivativesCancer cellBiology
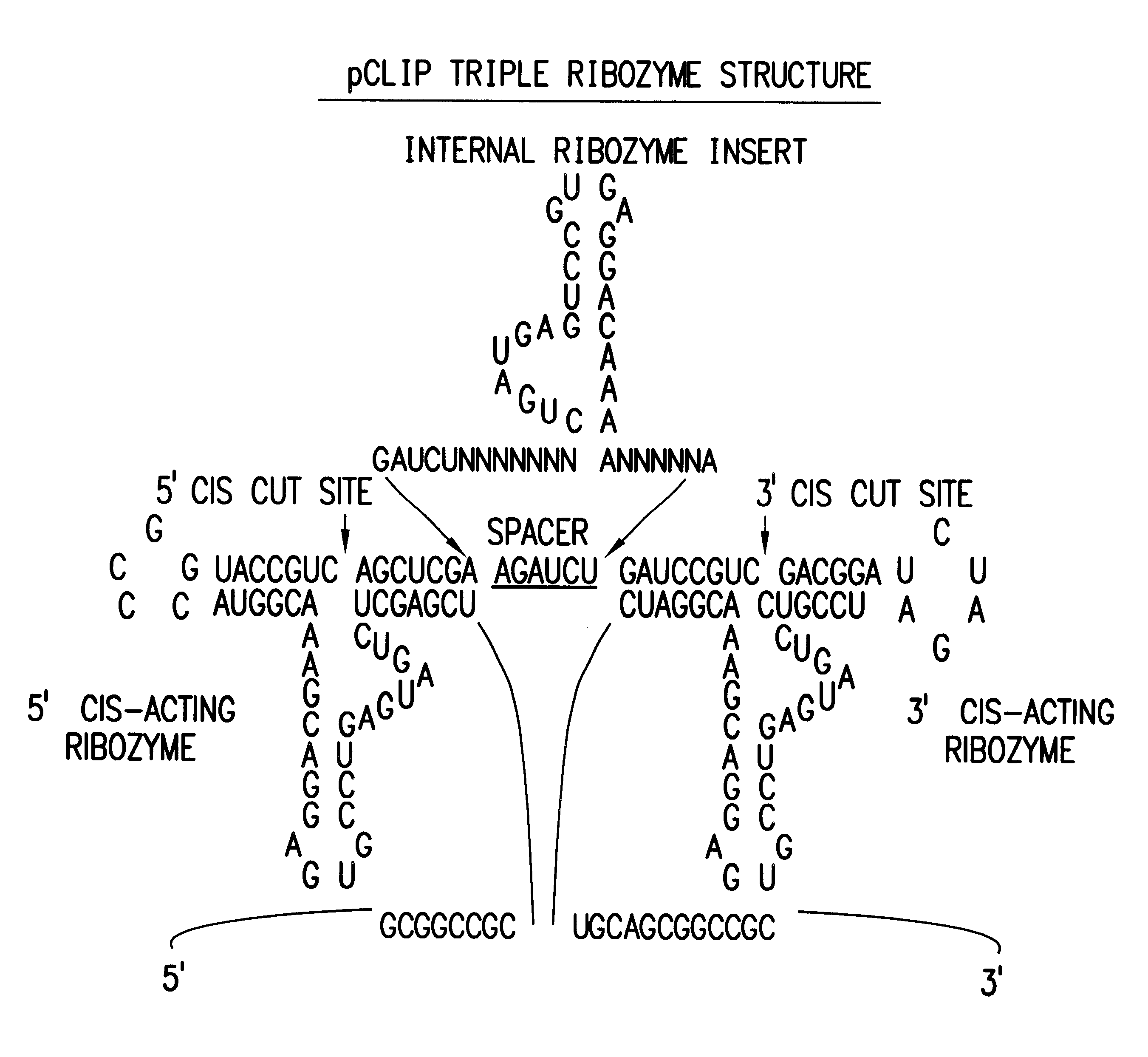
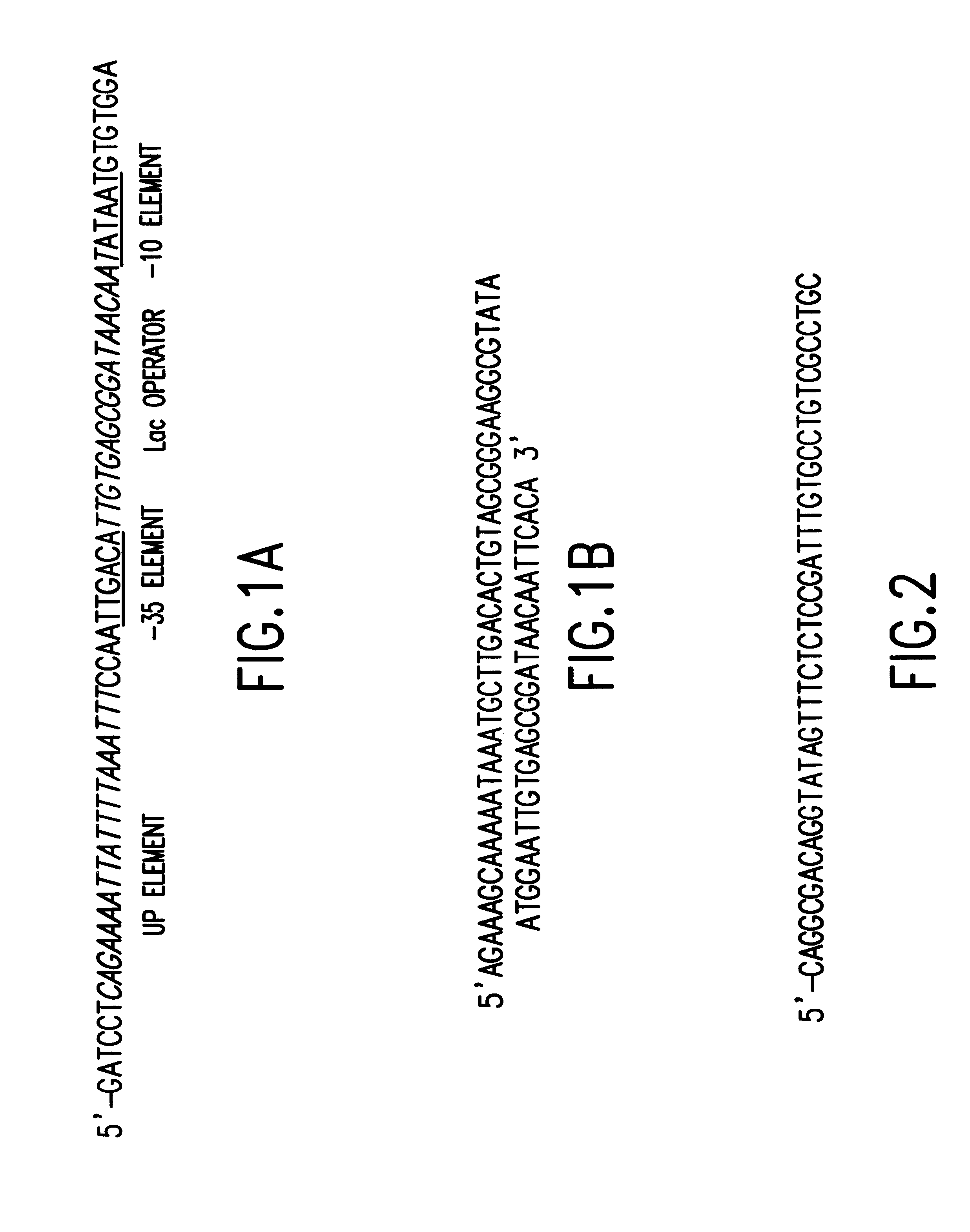
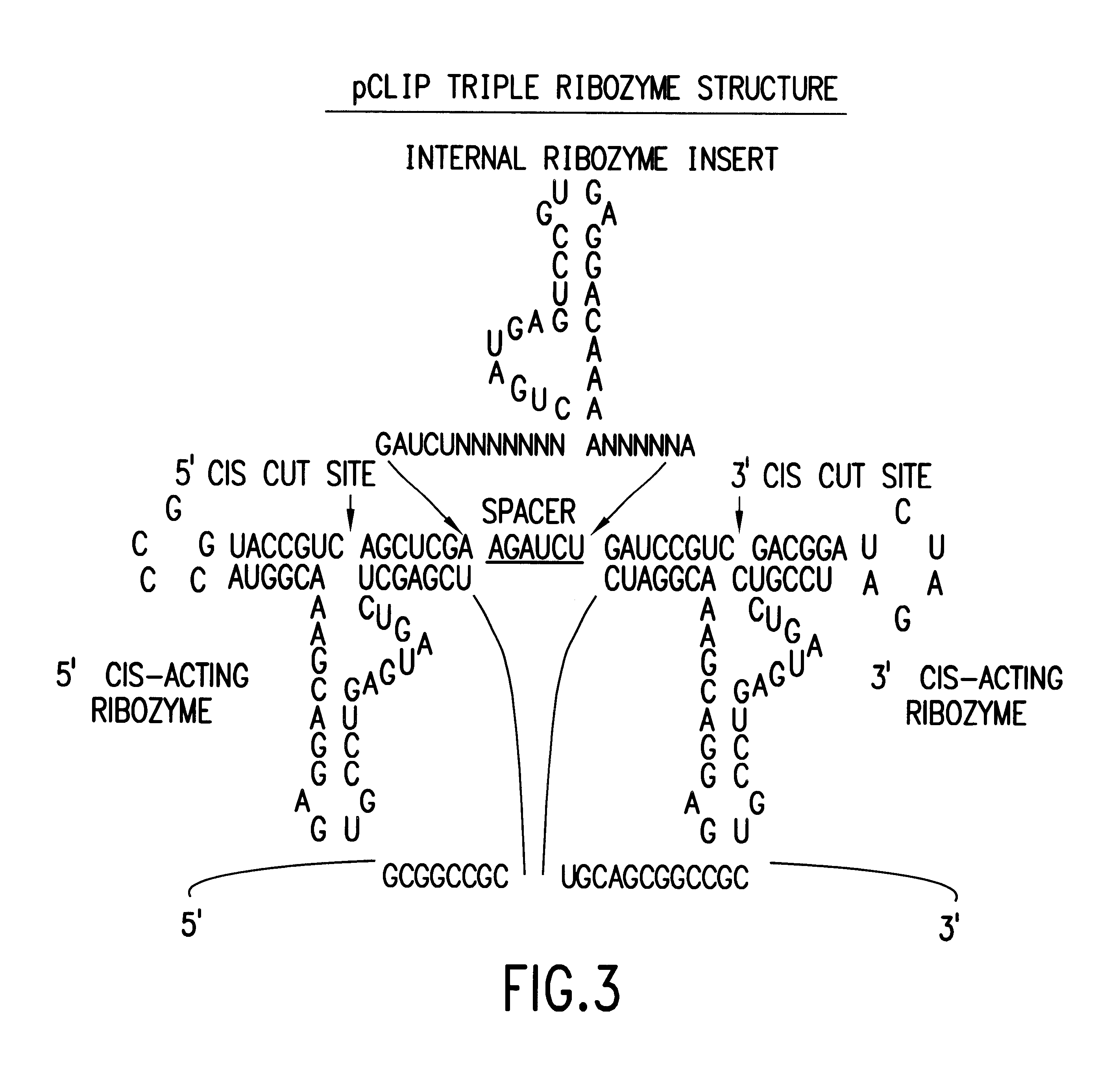
The present invention relates to the discovery, identification and characterization of toxic agents which are lethal to pathogens and methods for targeting such toxic agents to a pathogen or pathogen infected cells in order to treat and / or eradicate the infection. In particular, the present invention relates to toxic agents which target bacteria at different stages of the bacterial life cycle, which are delivered alone or in combination to bacteria or bacteria-infected cells. The invention relates to toxic agents which are lethal to diseased cells and methods for targeting such toxic agents to a diseased cell in order to treat and / or eradicate the disease. The present invention relates to promoter elements which are pathogen-specific or tissue-specific and the use of such promoter elements to achieve pathogen-specific or tissue-specific expression of the toxic agent(s) and / or ribozyme(s) of the present invention. Specifically, the invention relates to the delivery of one or more toxic gene products, antisense RNAs, or ribozymes, or combination thereof. The invention provides a novel system by which multiple pathogenic targets may be simultaneously targeted to cause the death of a pathogen, or cell infected with a pathogen. Further, the invention has important implications in the eradication of drug-resistant bacterium and bacterial pathogens. The invention provides a novel system by which multiple targets may be simultaneously targeted to cause the death of a diseased cell. The invention also has important implications in the eradication of drug-resistant pathogens and drug-resistant diseased cells (such as cancer cells).
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV +1
Emulsion compositions
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
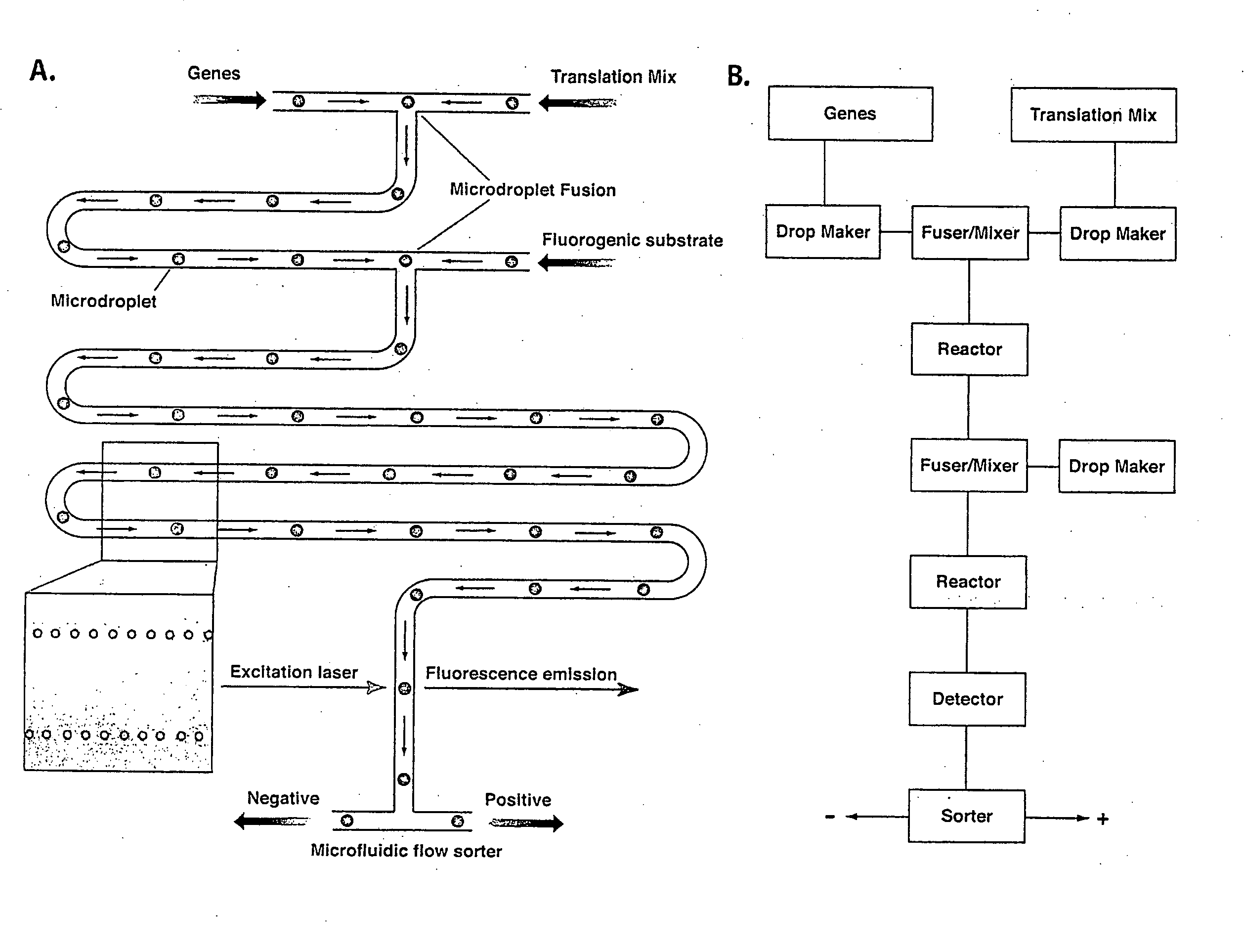
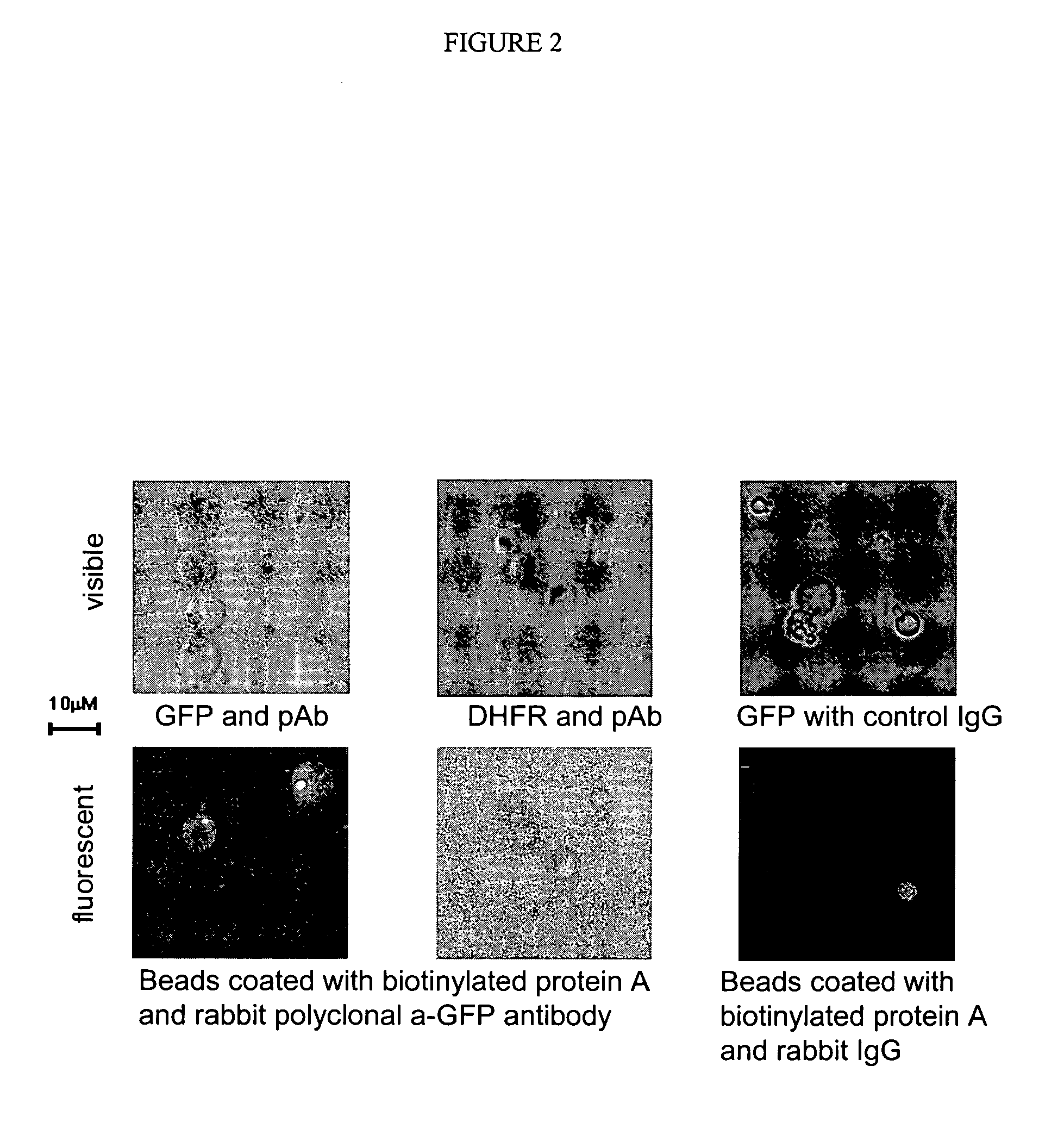
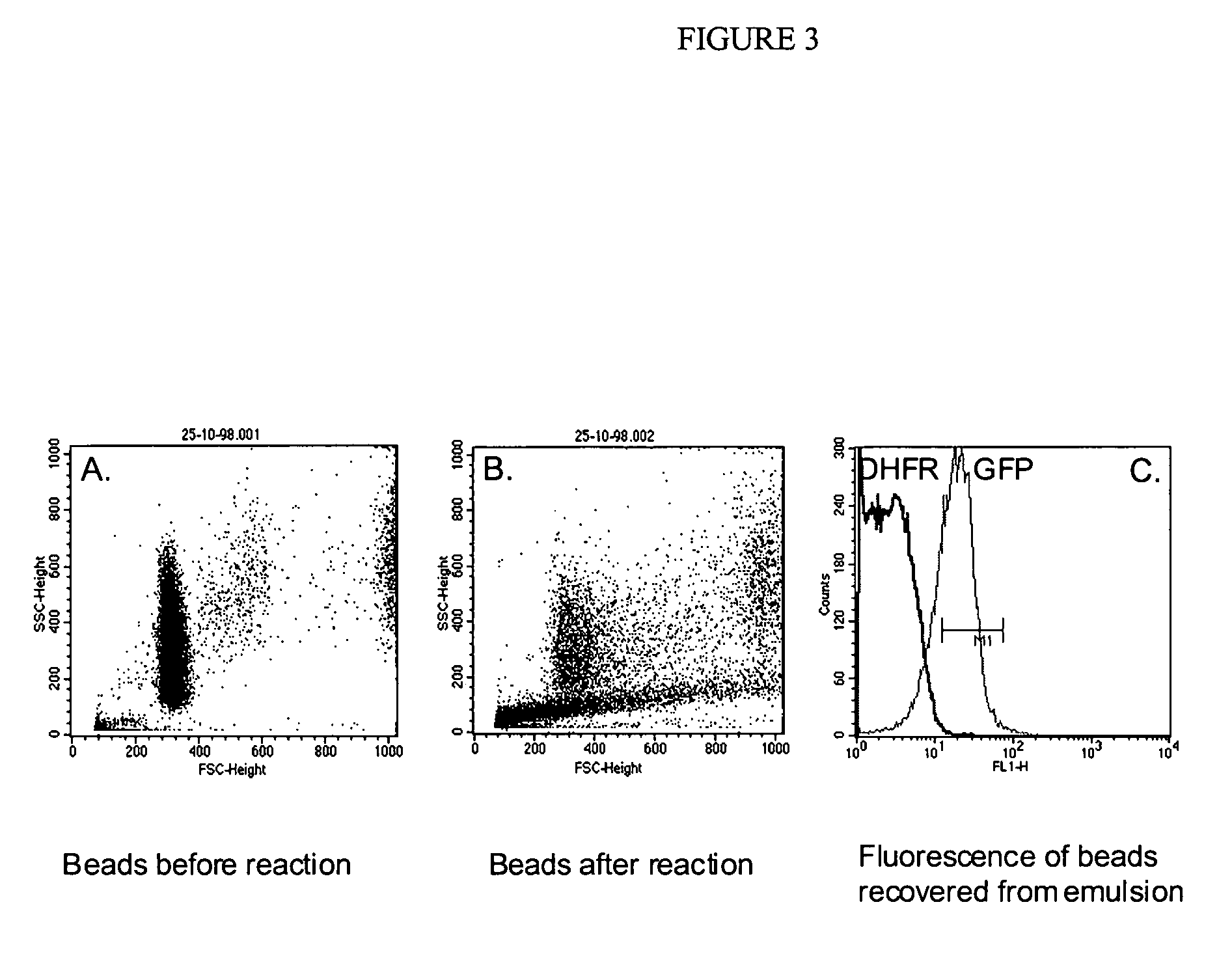
In vitro evolution in microfluidic systems
ActiveUS20060078888A1High activitySpeed up the processSequential/parallel process reactionsFlow mixersGene productGenetic element
The invention describes a method for isolating one or more genetic elements encoding a gene product having a desired activity, comprising the steps of: (a) compartmentalising genetic elements into microcapsules; and (b) sorting the genetic elements which express the gene product having the desired activity; wherein at least one step is under microfluidic control. The invention enables the in vitro evolution of nucleic acids and proteins by repeated mutagenesis and iterative applications of the method of the invention.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Methods and compositions for the specific inhibition of gene expression by double-stranded RNA
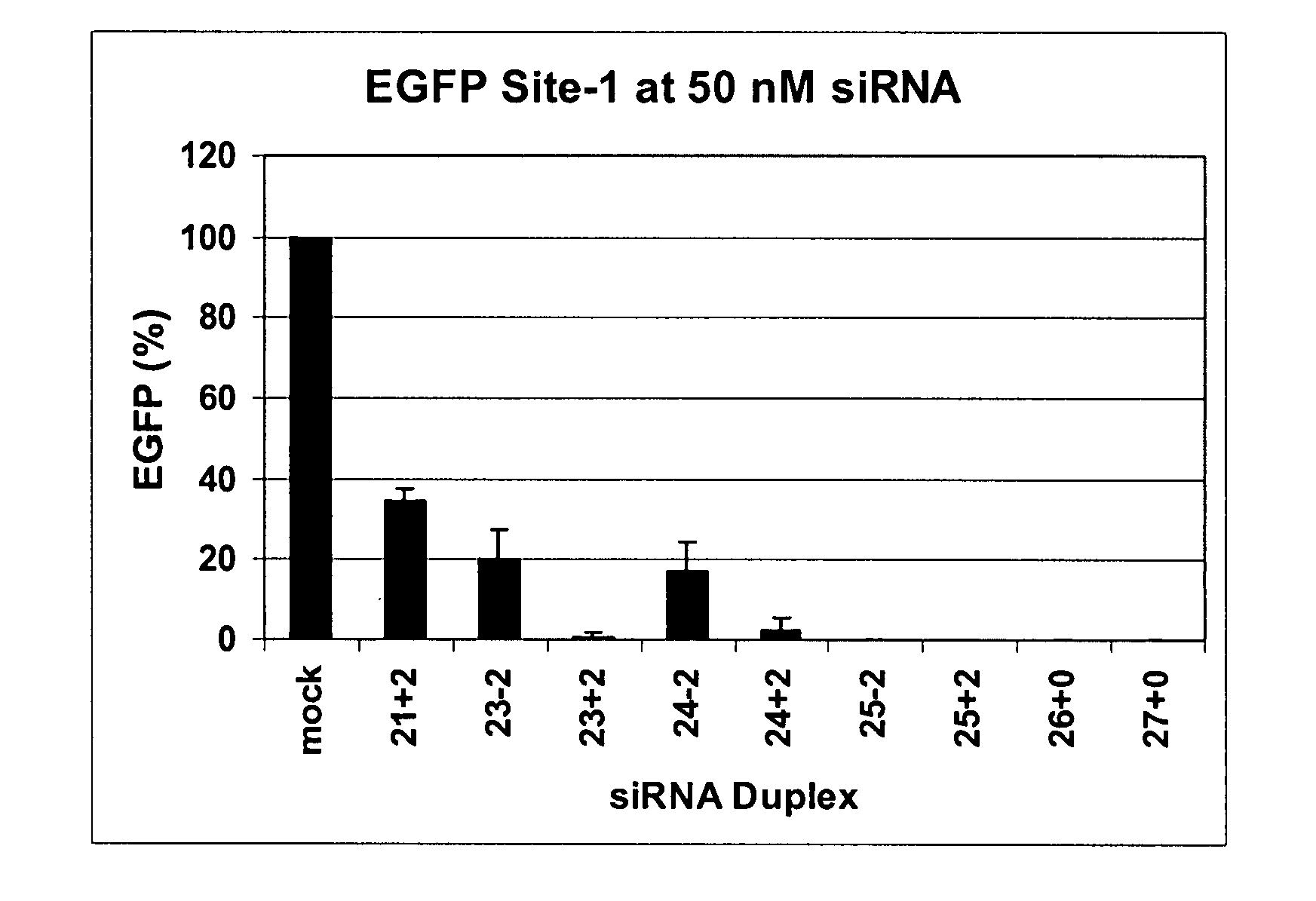
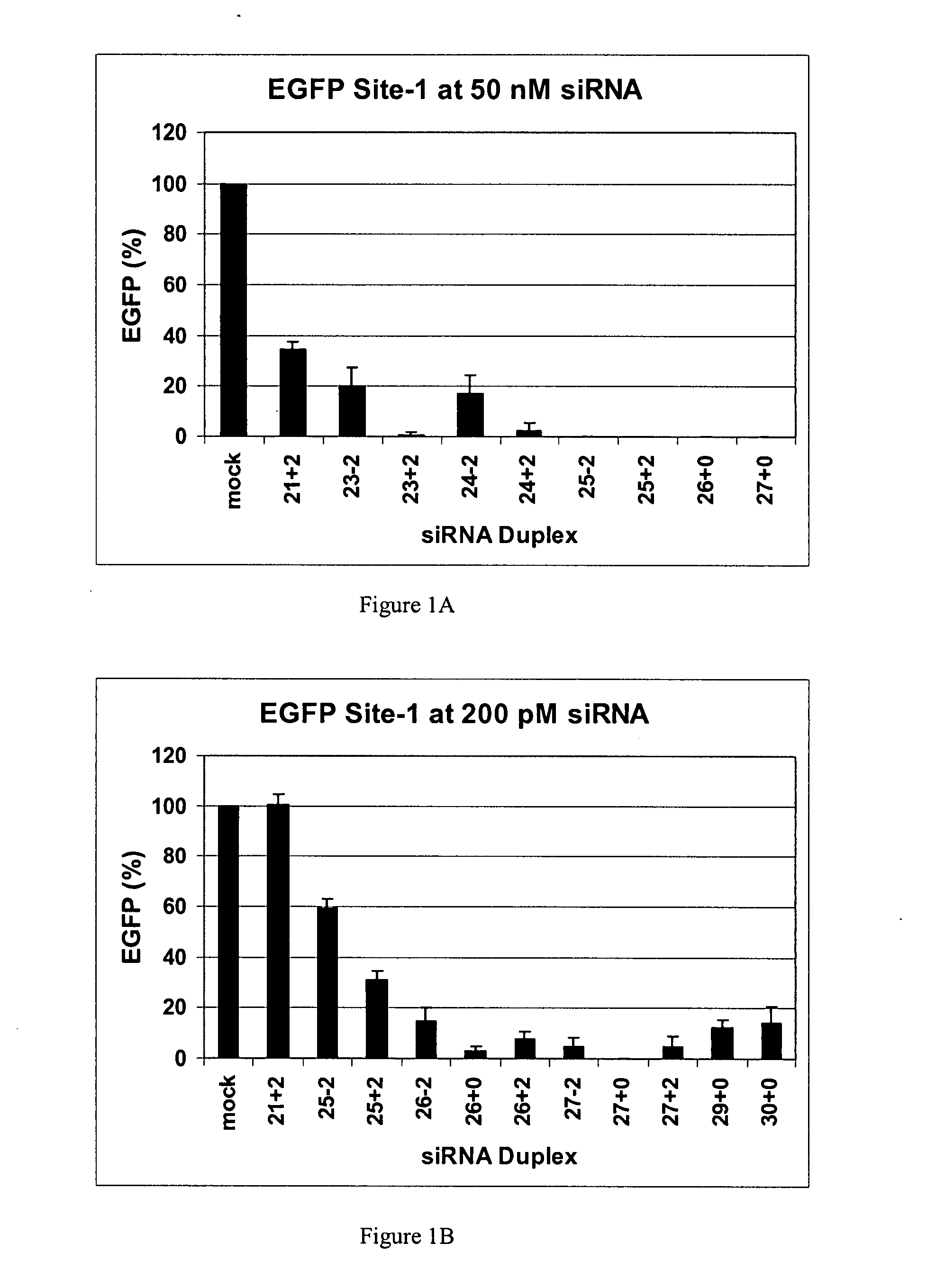
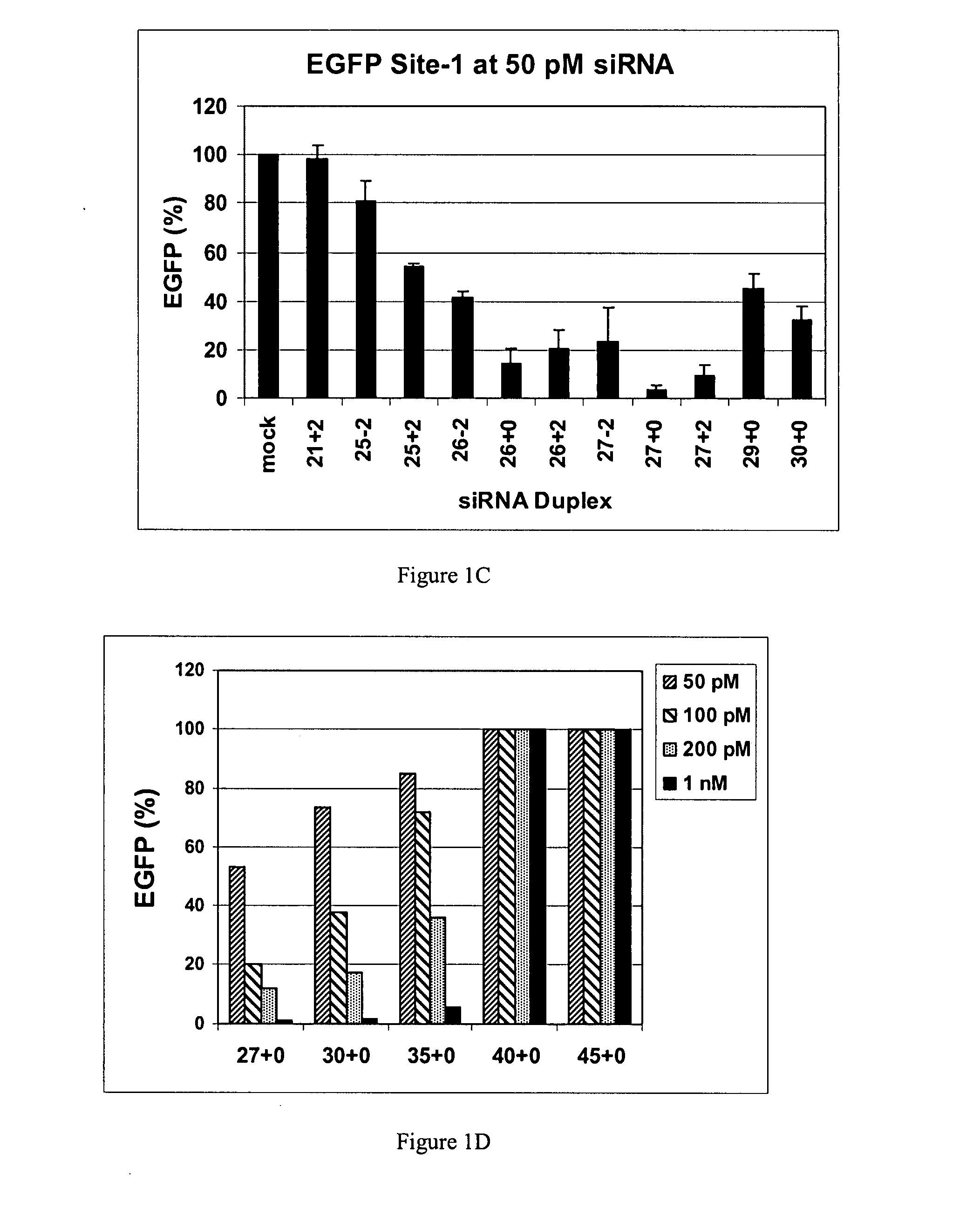
The invention is directed to compositions and methods for selectively reducing the expression of a gene product from a desired target gene in a cell, as well as for treating diseases caused by the expression of the gene. More particularly, the invention is directed to compositions that contain double stranded RNA (“dsRNA”), and methods for preparing them, that are capable of reducing the expression of target genes in eukaryotic cells. The dsRNA has a first oligonucleotide sequence that is between 25 and about 30 nucleotides in length and a second oligonucleotide sequence that anneals to the first sequence under biological conditions. In addition, a region of one of the sequences of the dsRNA having a sequence length of at least 19 nucleotides is sufficiently complementary to a nucleotide sequence of the RNA produced from the target gene to trigger the destruction of the target RNA by the RNAi machinery.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE +1
Methods and compositions for the specific inhibition of gene expression by double-stranded RNA
InactiveUS20070265220A1Improve stabilityConvenience to mergeSenses disorderAntipyreticDouble strandOligonucleotide
The invention is directed to compositions and methods for selectively reducing the expression of a gene product from a desired target gene in a cell, as well as for treating diseases caused by the expression of the gene. More particularly, the invention is directed to compositions that contain double stranded RNA (“dsRNA”), and methods for preparing them, that are capable of reducing the expression of target genes in eukaryotic cells. The dsRNA has a first oligonucleotide sequence that is between 25 and about 30 nucleotides in length and a second oligonucleotide sequence that anneals to the first sequence under biological conditions. In addition, a region of one of the sequences of the dsRNA having a sequence length of at least 19 nucleotides is sufficiently complementary to a nucleotide sequence of the RNA produced from the target gene to trigger the destruction of the target RNA by the RNAi machinery.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE +1
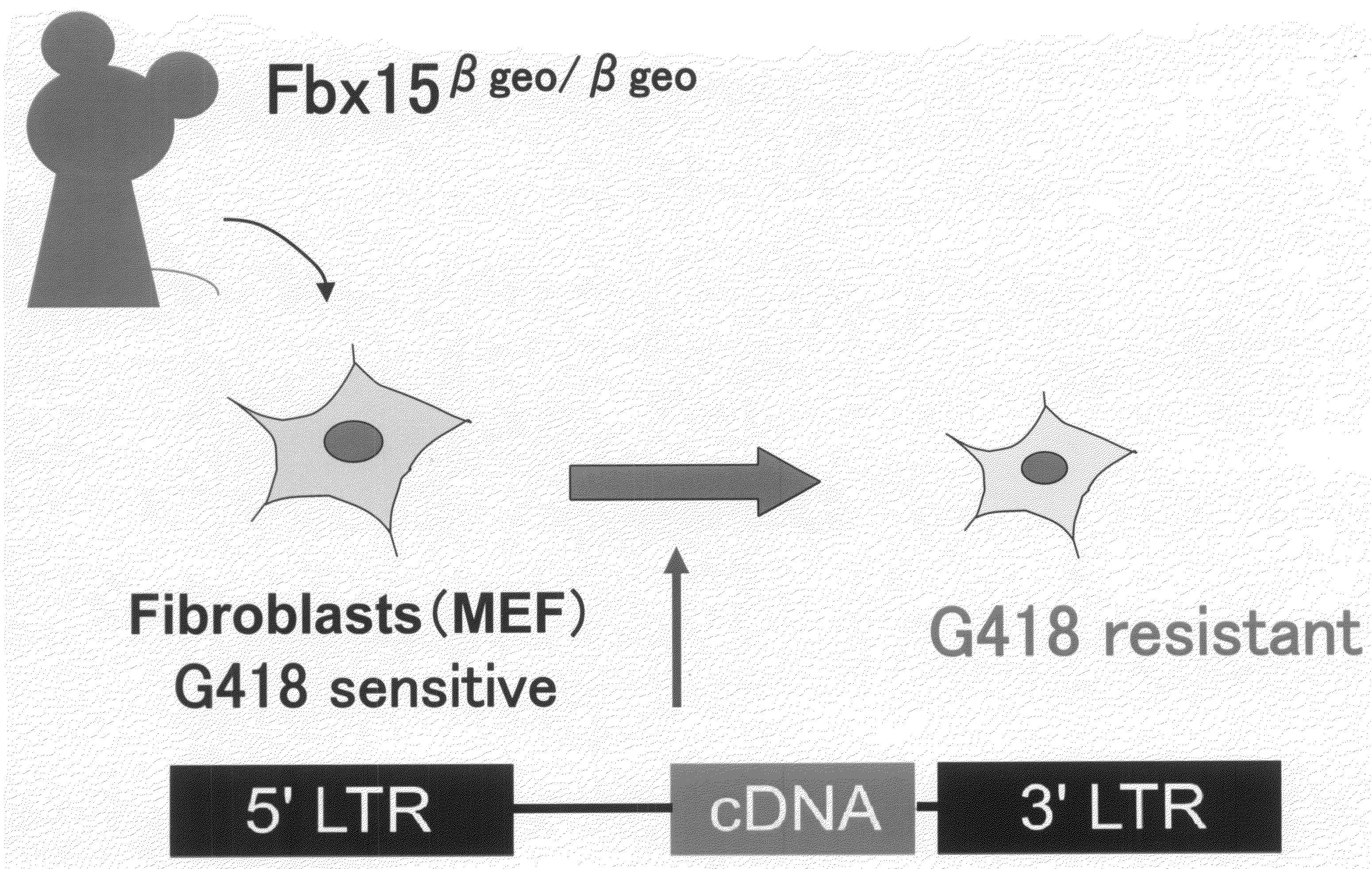
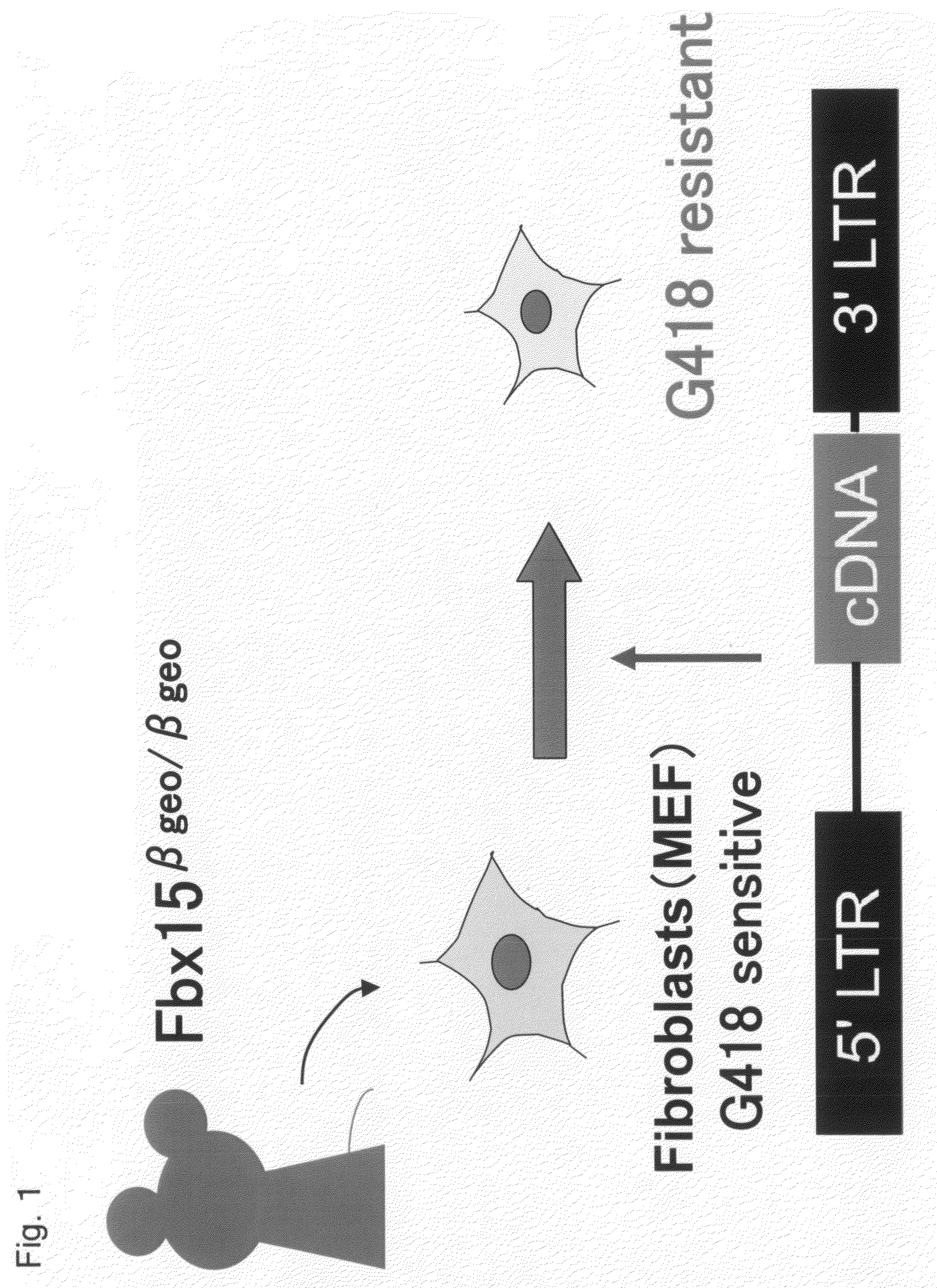
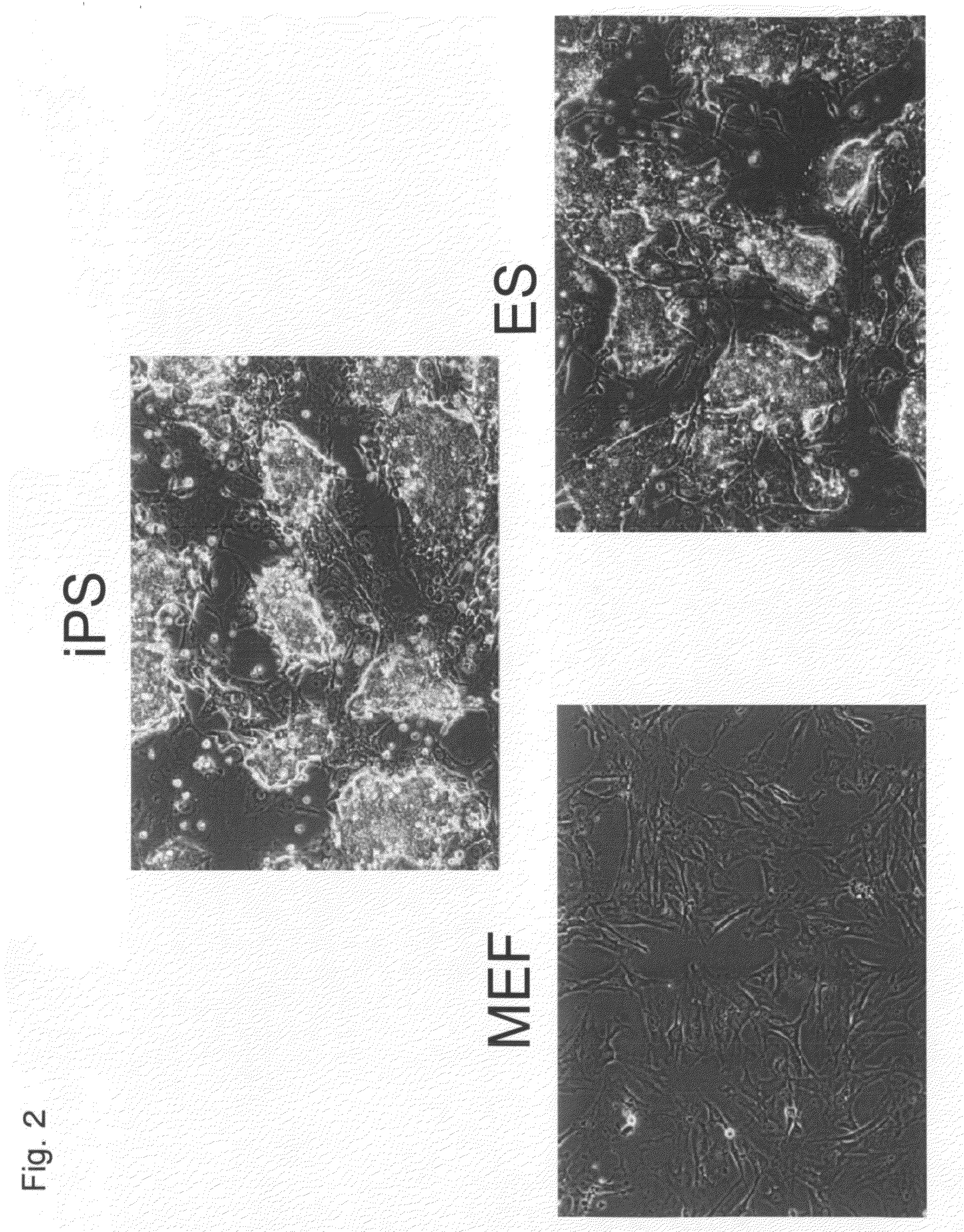
Nuclear Reprogramming Factor
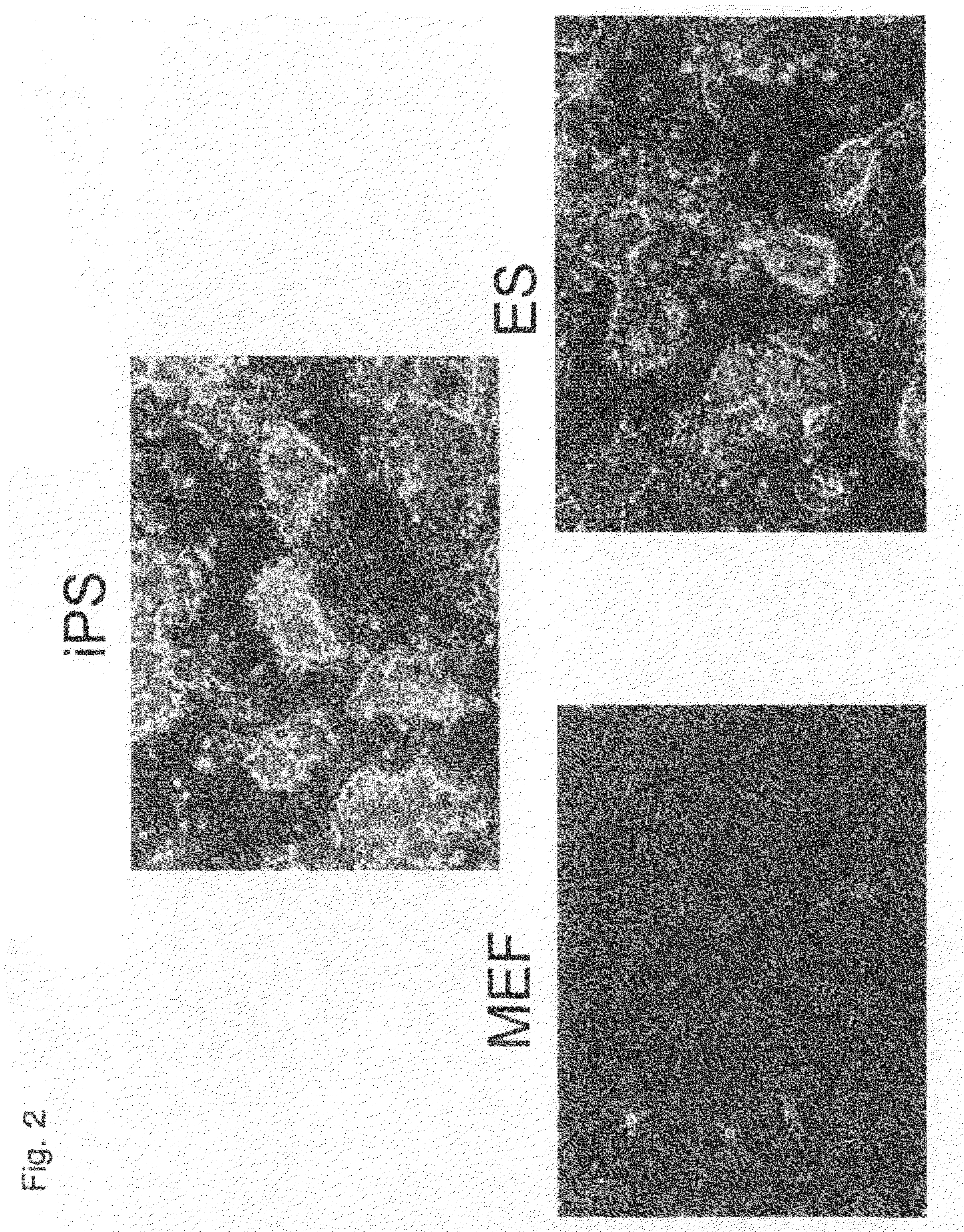
There is provided a nuclear reprogramming factor for a somatic cell, which comprises a gene product of each of the following three kinds of genes: an Oct family gene, a Klf family gene, and a Myc family gene, as a means for inducing reprogramming of a differentiated cell to conveniently and highly reproducibly establish an induced pluripotent stem cell having pluripotency and growth ability similar to those of ES cells without using embryo or ES cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
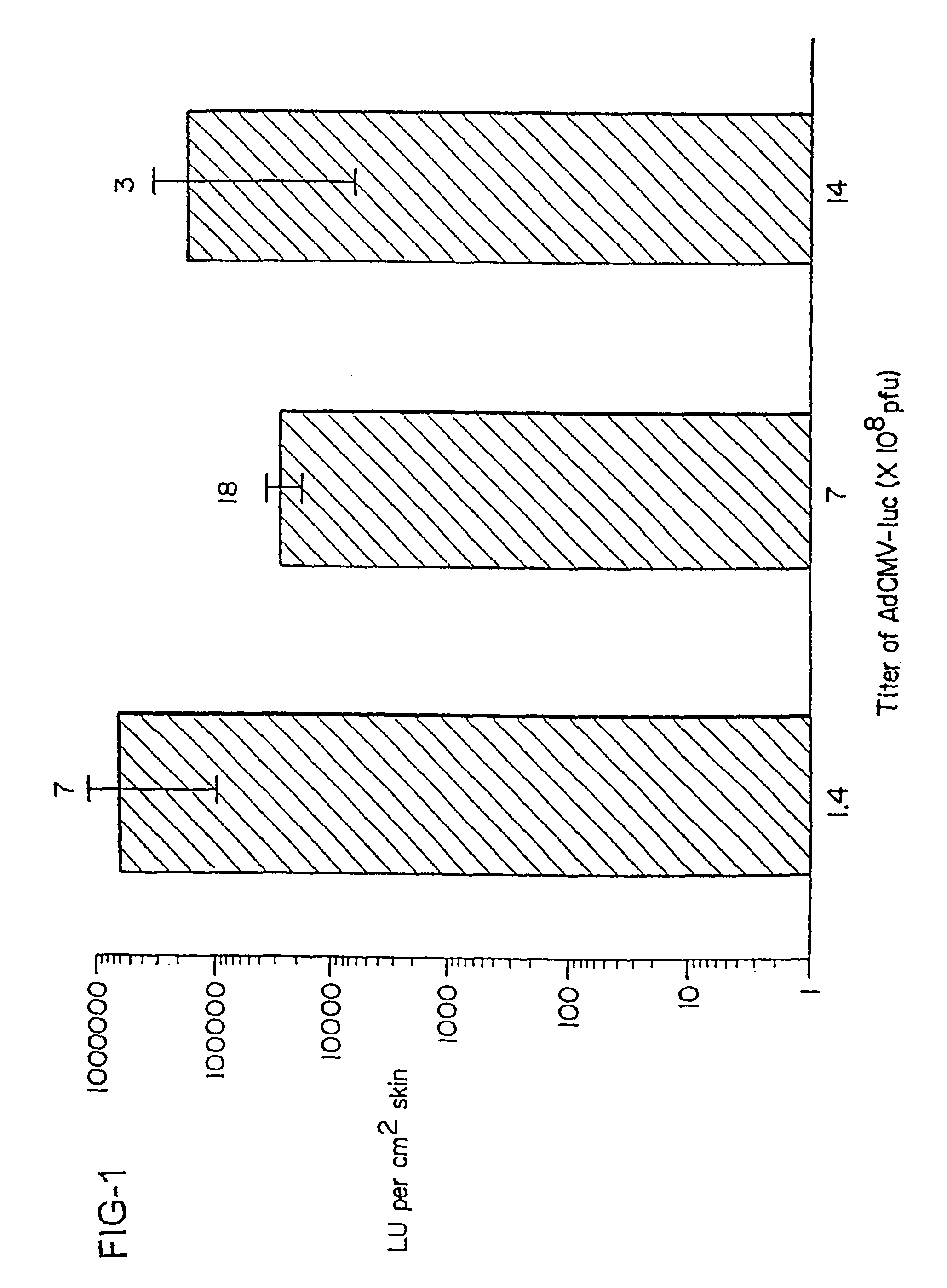
Noninvasive genetic immunization, expression products therefrom and uses thereof
InactiveUS6348450B1Improve vaccination schemeEfficient methodSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideHemagglutininWhole body
Disclosed and claimed are methods of non-invasive genetic immunization in an animal and / or methods of inducing a systemic immune or therapeutic response in an animal, products therefrom and uses for the methods and products therefrom. The methods can include contacting skin of the animal with a vector in an amount effective to induce the systemic immune or therapeutic response in the animal. The vector can include and express an exogenous nucleic acid molecule encoding an epitope or gene product of interest. The systemic immune response can be to or from the epitope or gene product. The nucleic acid molecule can encode an epitope of interest and / or an antigen of interest and / or a nucleic acid molecule that stimulates and / or modulates an immunological response and / or stimulates and / or modulates expression, e.g., transcription and / or translation, such as transcription and / or translation of an endogenous and / or exogenous nucleic acid molecule; e.g., one or more of influenza hemagglutinin, influenza nuclear protein, tetanus toxin C-fragment, anthrax protective antigen, HIV gp 120, human carcinoembryonic antigen, and / or a therapeutic, an immunomodulatory gene, such as co-stimulatory gene and / or a cytokine gene. The immune response can be induced by the vector expressing the nucleic acid molecule in the animal's cells. The immune response can be against a pathogen or a neoplasm. A prophylactic vaccine or a therapeutic vaccine or an immunological composition can include the vector.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
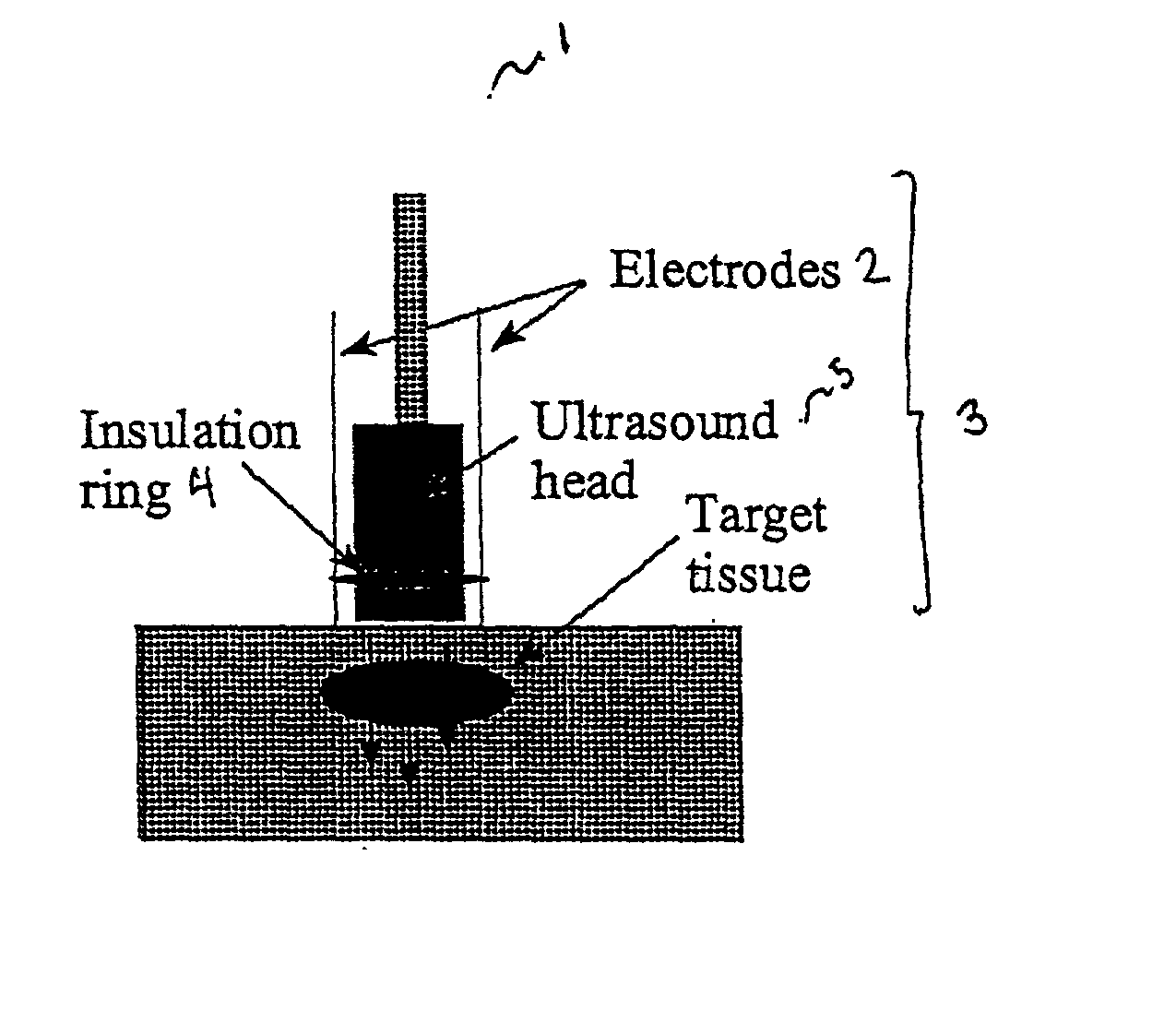
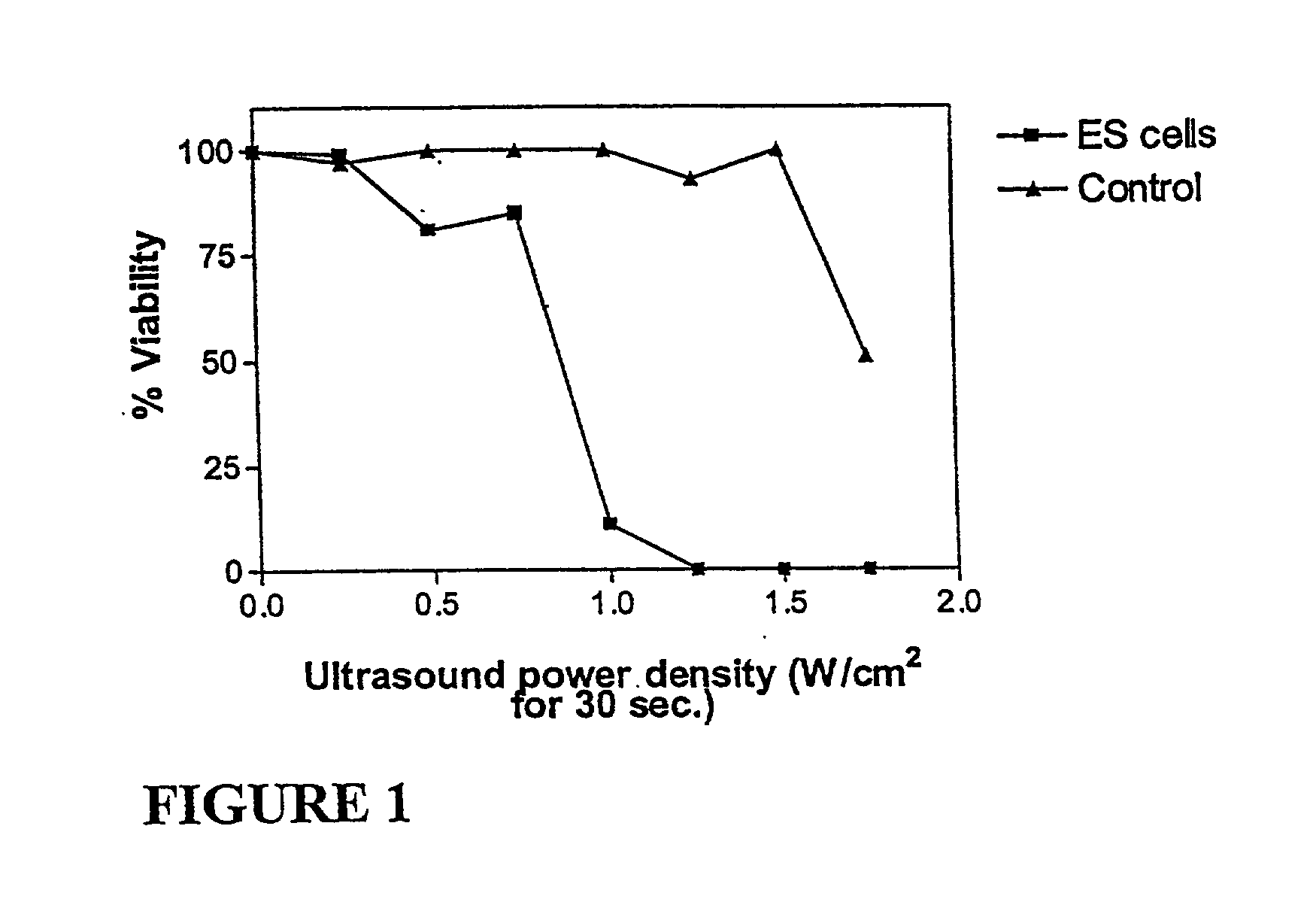
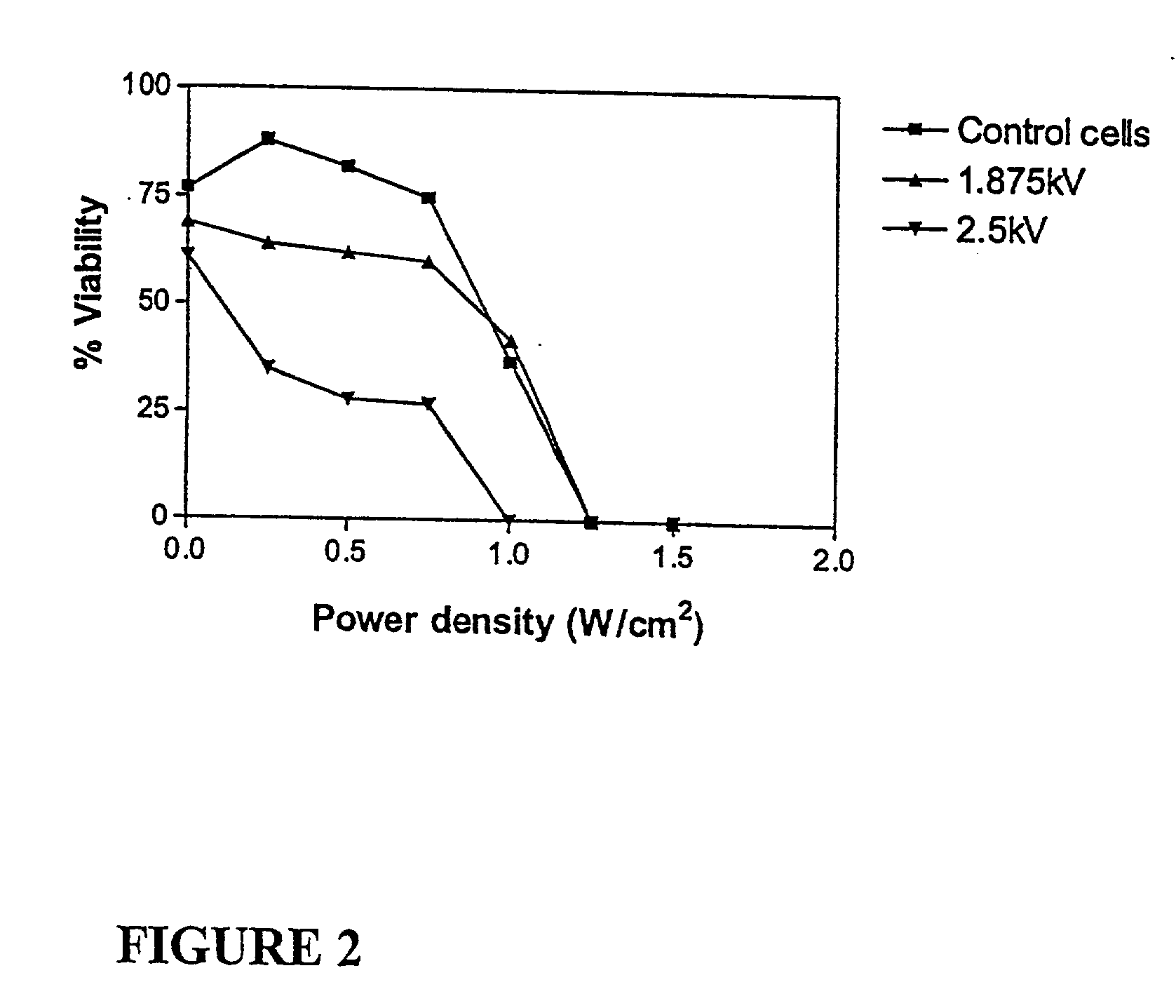
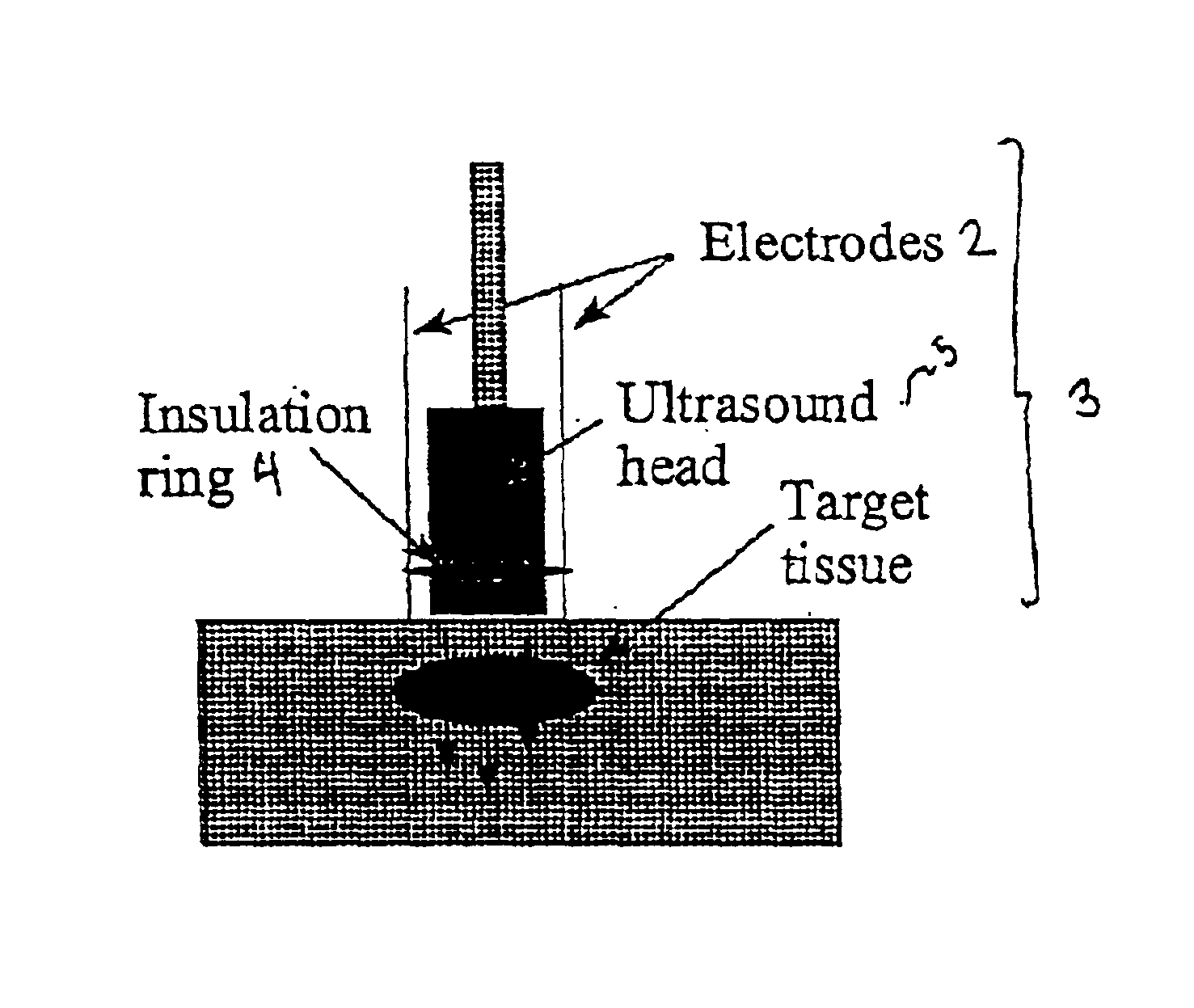
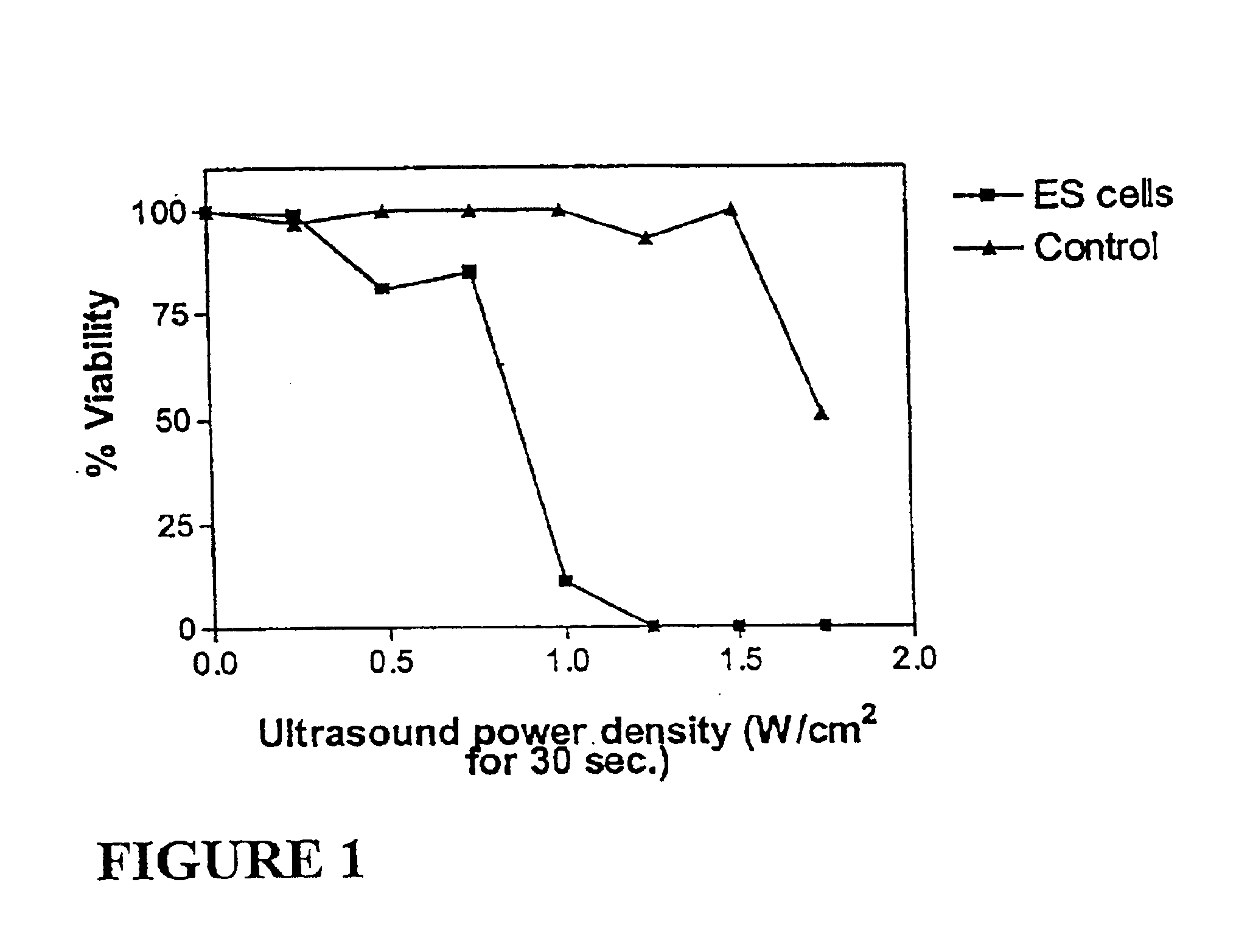
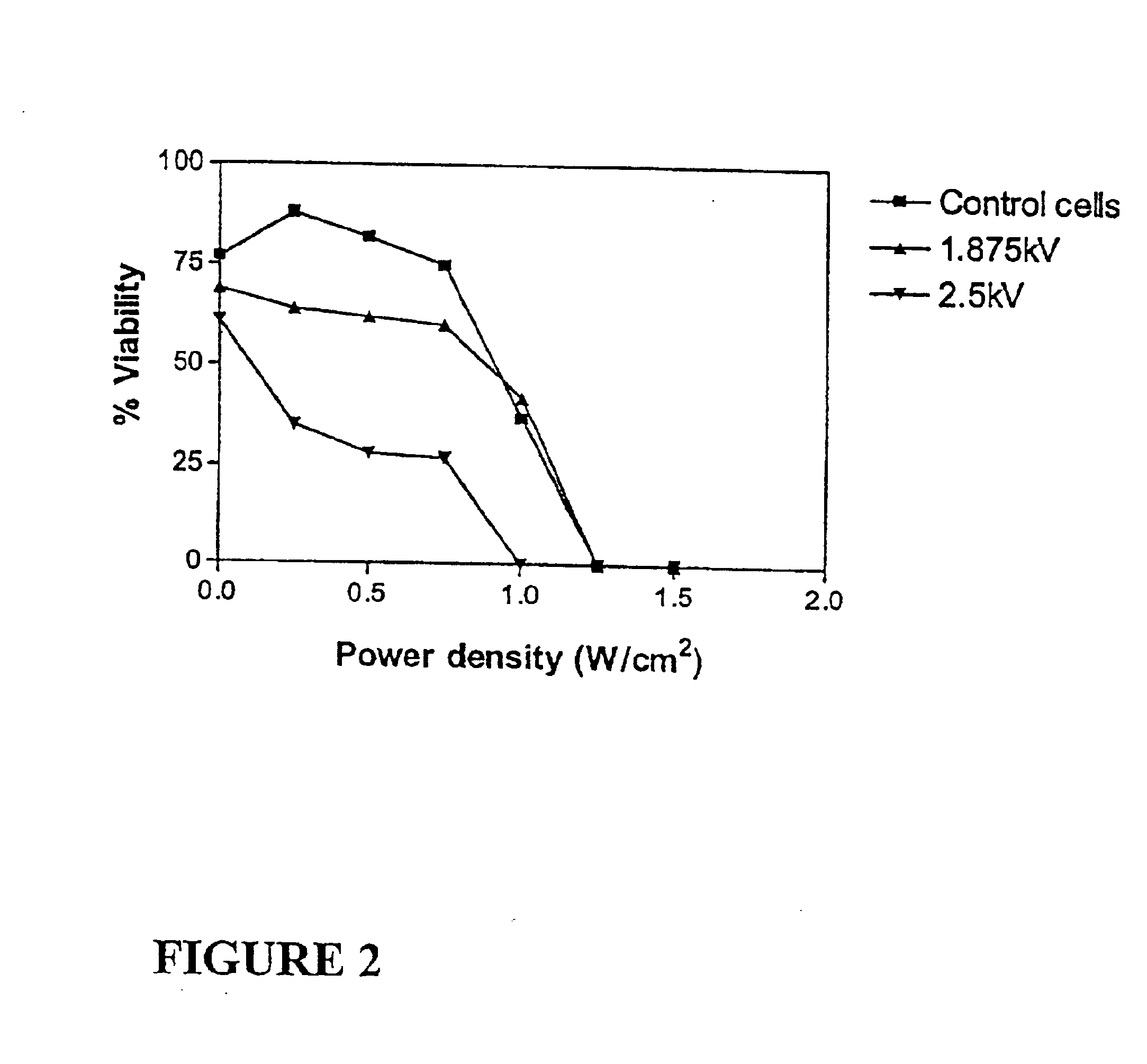
Ultrasound therapy for selective cell ablation
InactiveUS20020193784A1Ultrasound therapyElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentApoptosisGene product
The invention provides a method of sensitising target cells to ultrasound energy using a stimulus such as an electric field. This "electrosensitisation" enables target cells to be disrupted by ultrasound at frequencies and energies of ultrasound which do not cause disruption of non-sensitised (i.e., non-target) cells. As a consequence, the method increases the selectivity of ultrasound therapy, providing a way to ablate undesired cells, such as diseased cells (e.g., tumor cells) while minimising harm to neighboring cells. In another aspect, however, ultrasound can be used to sensitise cells while the electrical field is used to disrupt cells. The invention also provides an apparatus for performing the method and assays for identifying gene products and other molecules involved in apoptosis.
Owner:GENDEL
Methods for the treatment and diagnosis of cardiovascular disease
InactiveUS6156500AImprove throughputBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsClinical trialPercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment and diagnosis of cardiovascular disease, including, but not limited to, atherosclerosis, ischemia / reperfusion, hypertension, restenosis, and arterial inflammation. Specifically, the present invention identifies and describes genes which are differentially expressed in cardiovascular disease states, relative to their expression in normal, or non-cardiovascular disease states, and / or in response to manipulations relevant to cardiovascular disease. Further, the present invention identifies and describes genes via the ability of their gene products to interact with gene products involved in cardiovascular disease. Still further, the present invention provides methods for the identification and therapeutic use of compounds as treatments of cardiovascular disease. Moreover, the present invention provides methods for the diagnostic monitoring of patients undergoing clinical evaluation for the treatment of cardiovascular disease, and for monitoring the efficacy of compounds in clinical trials. Additionally, the present invention describes methods for the diagnostic evaluation and prognosis of various cardiovascular diseases, and for the identification of subjects exhibiting a predisposition to such conditions.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Methods and compositions for the specific inhibition of gene expression by double-stranded RNA
Owner:CITY OF HOPE +1
Compositions and methods for helper-free production of recombinant adeno-associated viruses
InactiveUS6953690B1Efficient productionIncrease the number ofBiocideGenetic therapy composition manufactureMammalWild type
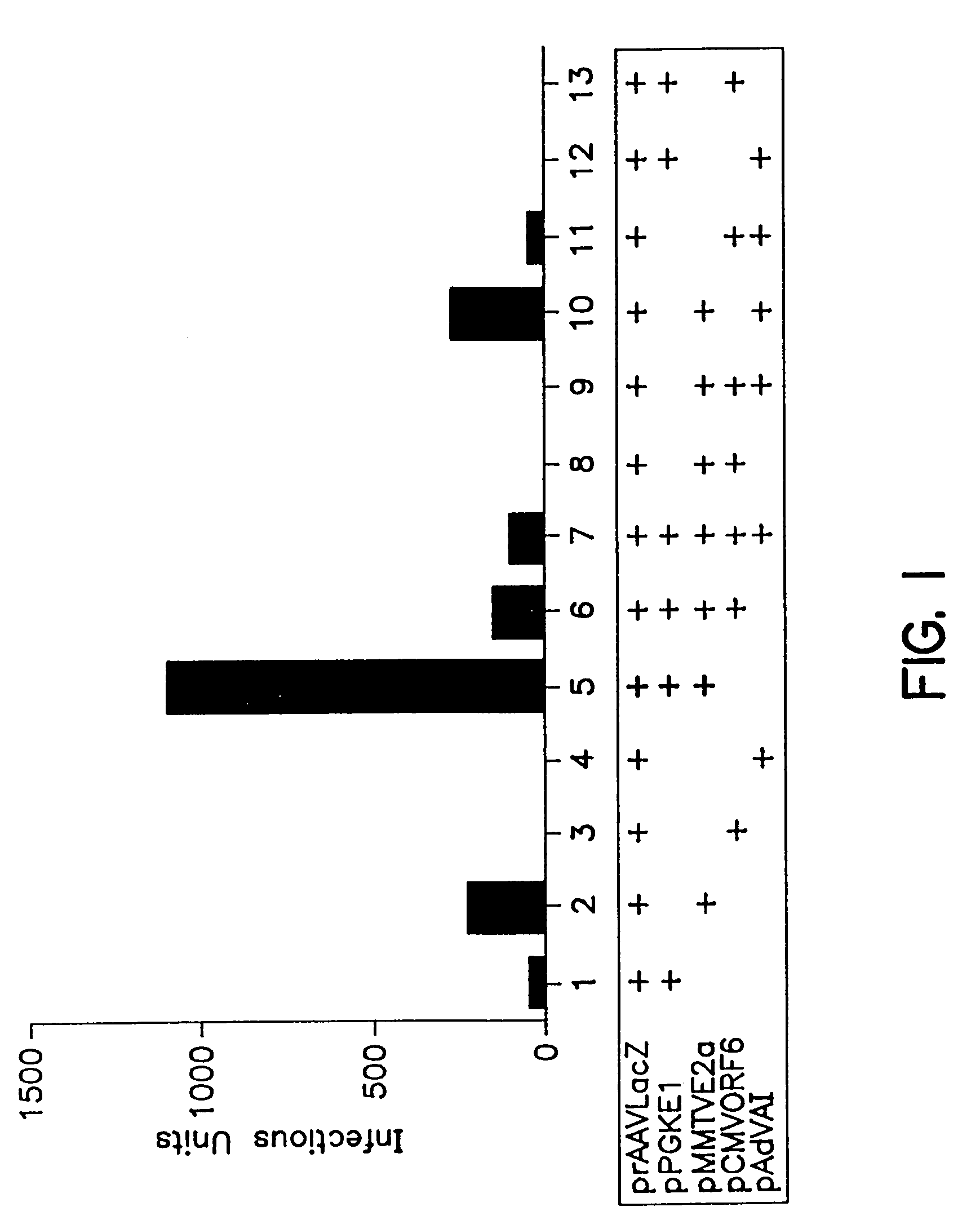
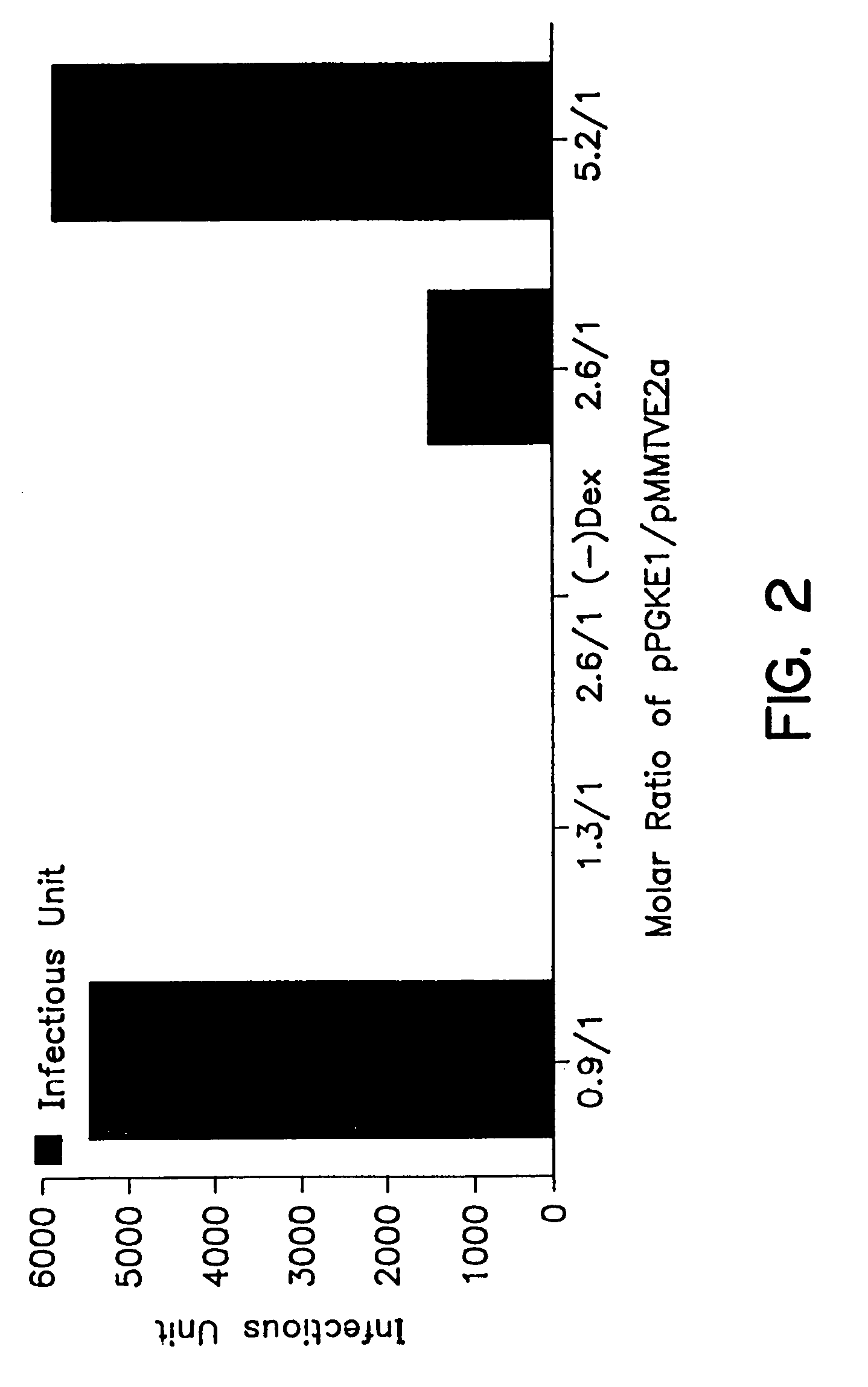
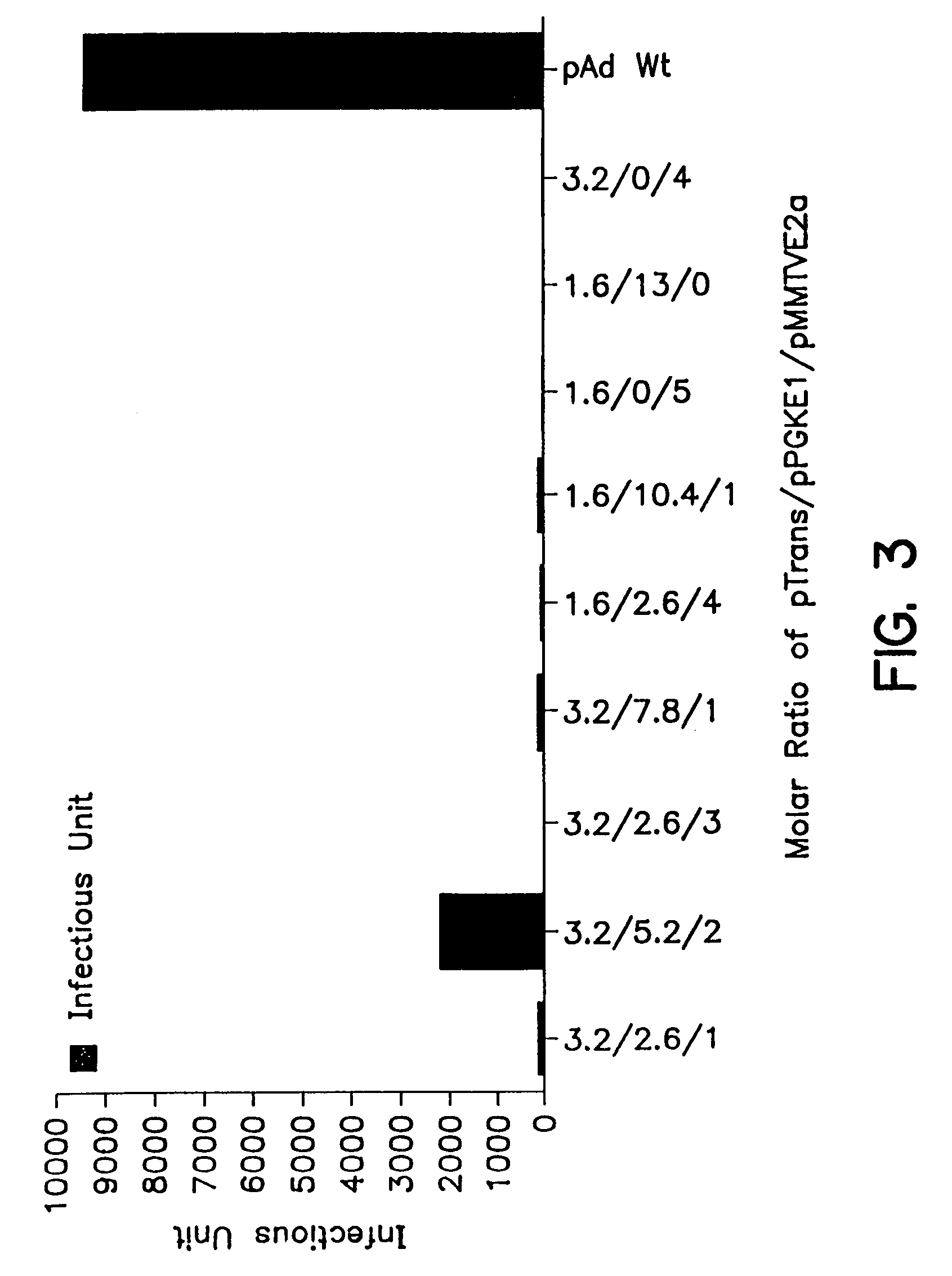
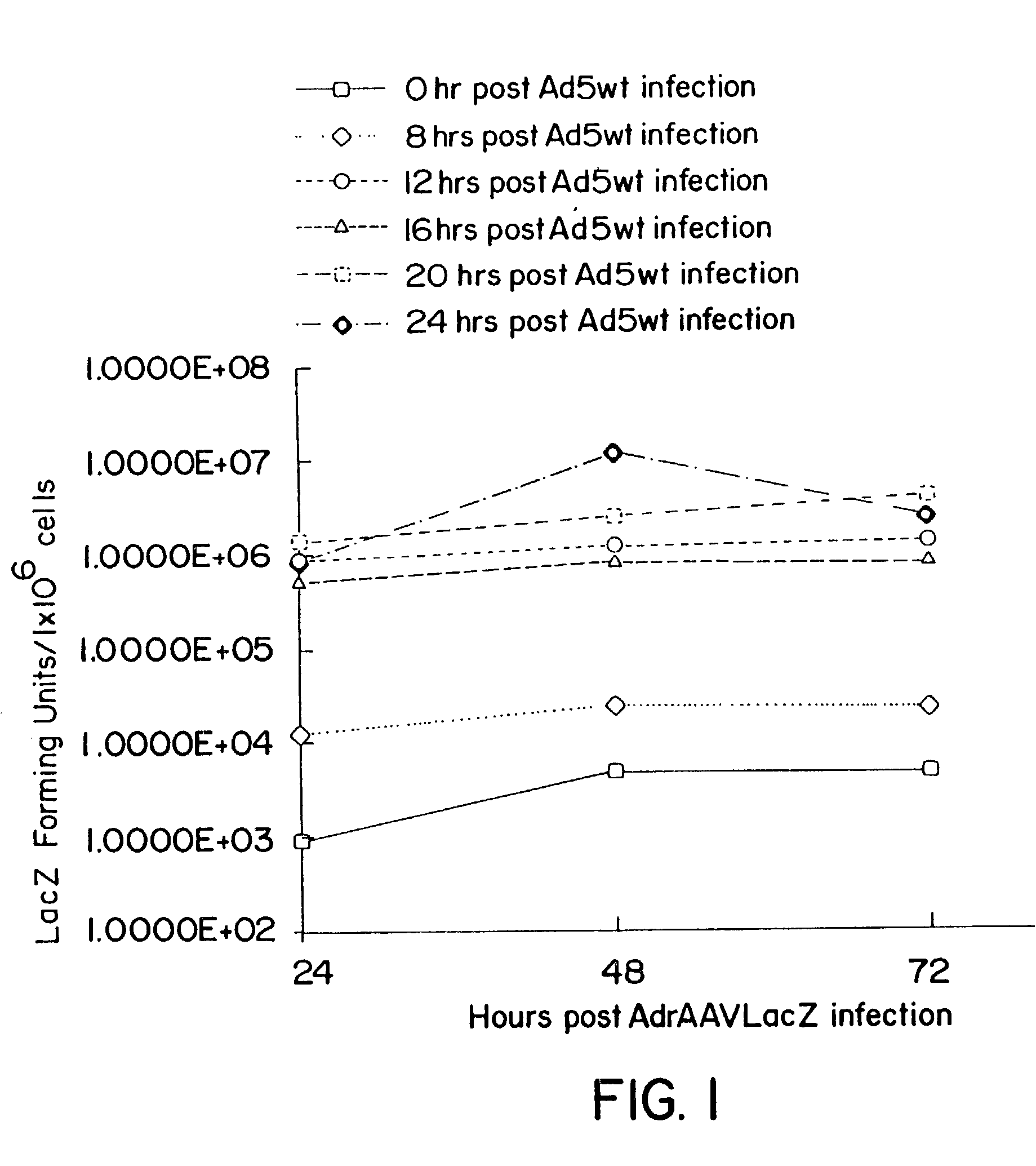
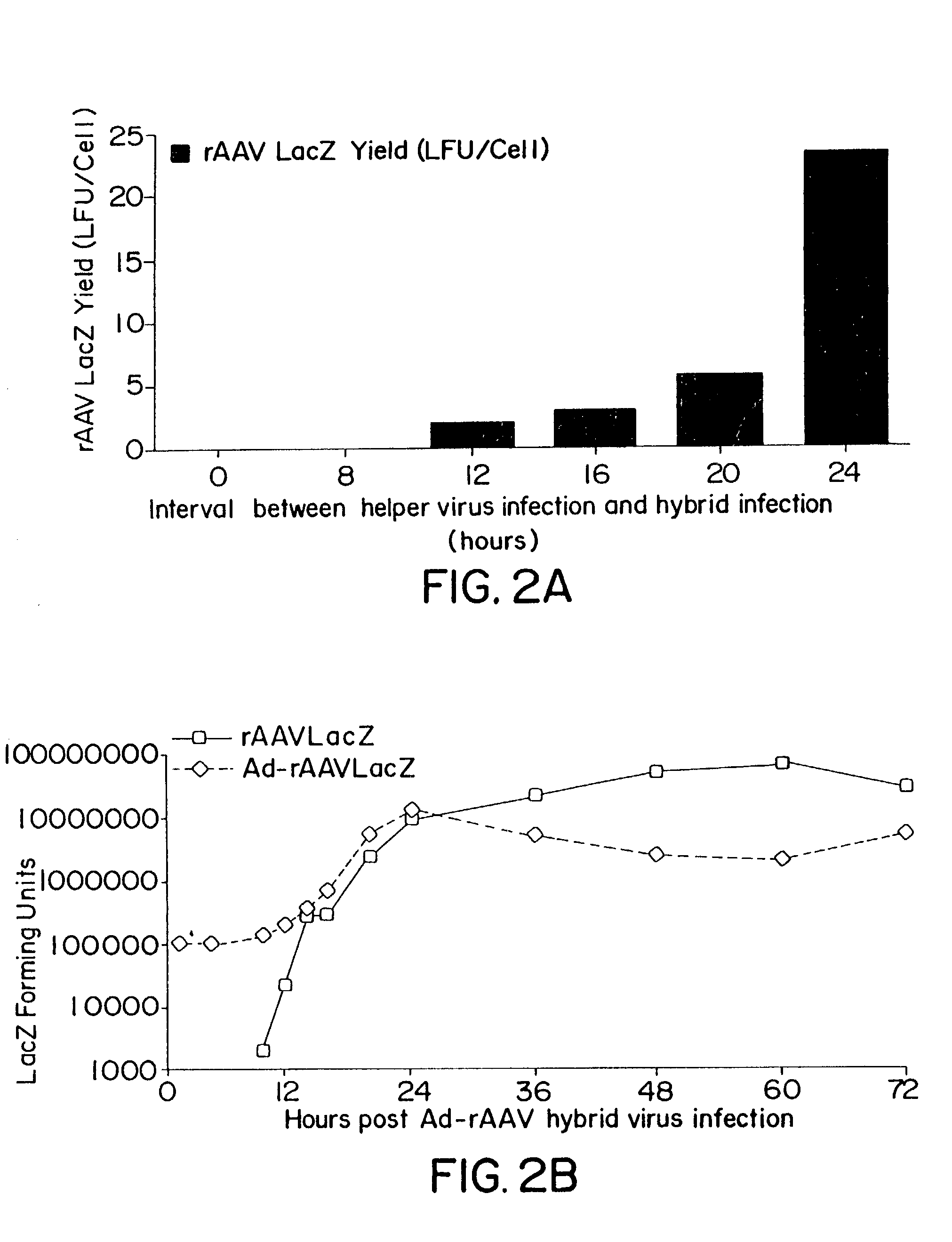
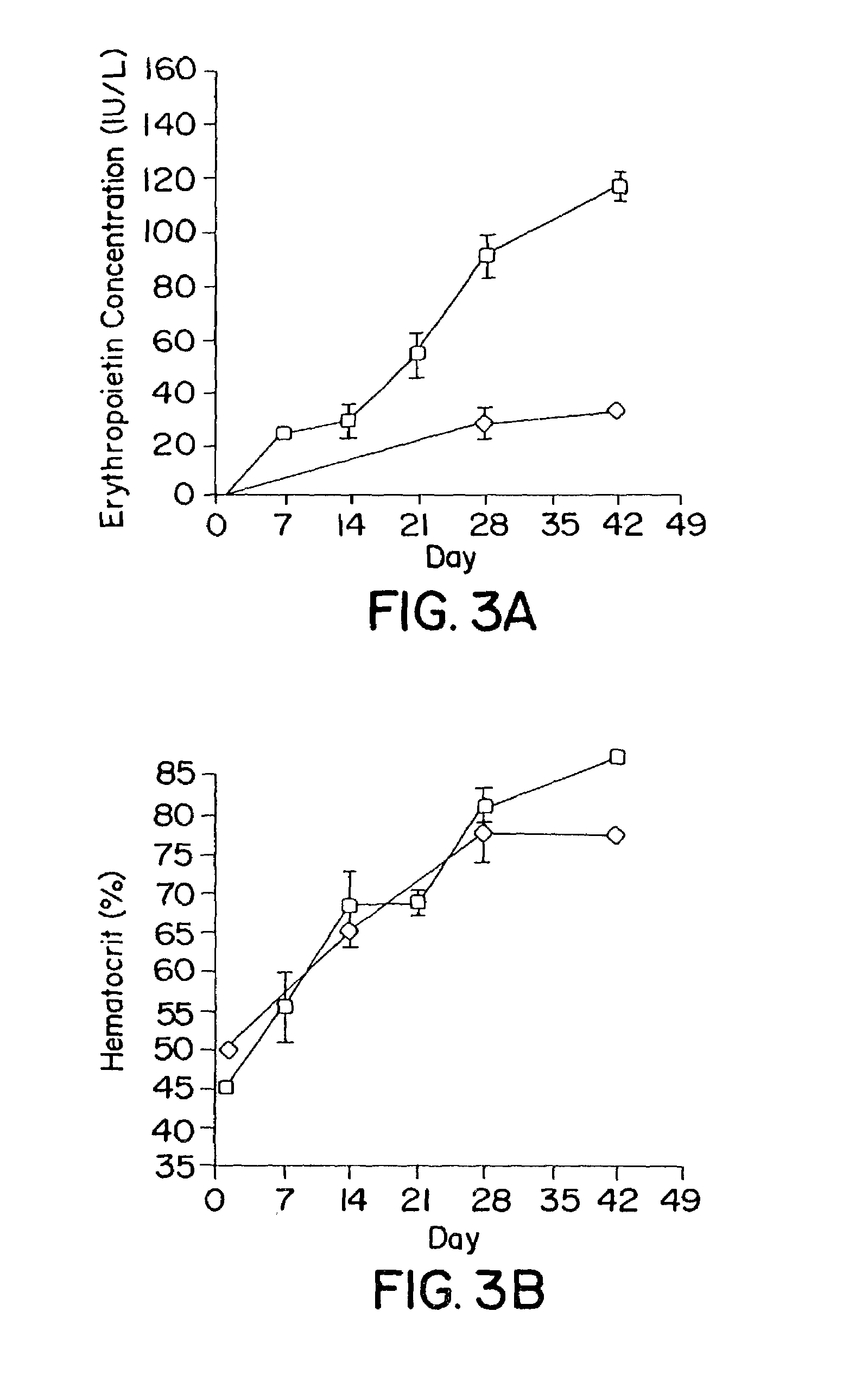
A method for producing recombinant adeno-associated virus in the absence of contaminating helper virus or wild-type virus involves culturing a mammalian host cell containing a transgene flanked by adeno-associated virus (AAV) inverse terminal repeats and under the control of regulatory sequences directing expression thereof, an AAV rep sequence and an AAV cap sequence under the control of regulatory sequences directing expression thereof, and the minimum adenovirus DNA required to express an E1a gene product, an E1b gene product and an E2a gene product, and isolating therefrom a recombinant AAV which expresses the transgene in the absence of contaminating helper virus or wildtype AAV. This method obviates a subsequent purification step to purify rAAV from contaminating virus. Also provided are various embodiments of the host cell.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods and cell line useful for production of recombinant adeno-associated viruses
InactiveUS7238526B2High yieldInduce expressionGenetically modified cellsGenetic material ingredientsPlasmid VectorAdeno associate virus
Methods for efficient production of recombinant AAV employ a host cell which comprising AAV rep and cap genes stably integrated within the cell's chromosomes, wherein the AAV rep and cap genes are each operatively linked to regulatory sequences capable of directing the expression of the rep and cap gene products upon infection of the cell with a helper virus, a helper gene, and a helper gene product. A method for producing recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) involves infecting such a host cell with a helper virus, gene or gene product and infecting the infected host cell with a recombinant hybrid virus or plasmid vector containing adenovirus cis-elements necessary for replication and virion encapsidation, AAV sequences comprising the 5′ and 3′ ITRs of an AAV, and a selected gene operatively linked to regulatory sequences directing its expression, which is flanked by the above-mentioned AAV sequences.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Pox virus containing DNA encoding a cytokine and/or a tumor associated antigen
InactiveUS6265189B1Improve securityImprove security levelVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman tumorWild type
Attenuated recombinant viruses containing DNA coding for a cytokine and / or a tumor associated antigen, as well as methods and compositions employing the viruses, are disclosed and claimed. The recombinant viruses can be NYVAC or ALVAC recombinant viruses. The DNA can code for at least on of: human tumor necrosis factor; nuclear phosphoprotein p53, wildtype or mutant; human melanoma-associated antigen; IL-2; IFNgamma; IL-4; GNCSF; IL-12; B7; erb-B-2 and carcinoembryonic antigen. The recombinant viruses and gene products therefrom are useful for cancer therapy.
Owner:VIROGENETICS
Vitro evolution in microfluidic systems
ActiveUS20090197248A1High activitySpeed up the processSequential/parallel process reactionsSugar derivativesGene productGenetic element
The invention describes a method for isolating one or more genetic elements encoding a gene product having a desired activity, comprising the steps of: (a) compartmentalising genetic elements into microcapsules; and (b) sorting the genetic elements which express the gene product having the desired activity; wherein at least one step is under microfluidic control. The invention enables the in vitro evolution of nucleic acids and proteins by repeated mutagenesis and iterative applications of the method of the invention.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Mutant adeno-associated virus virions and methods of use thereof
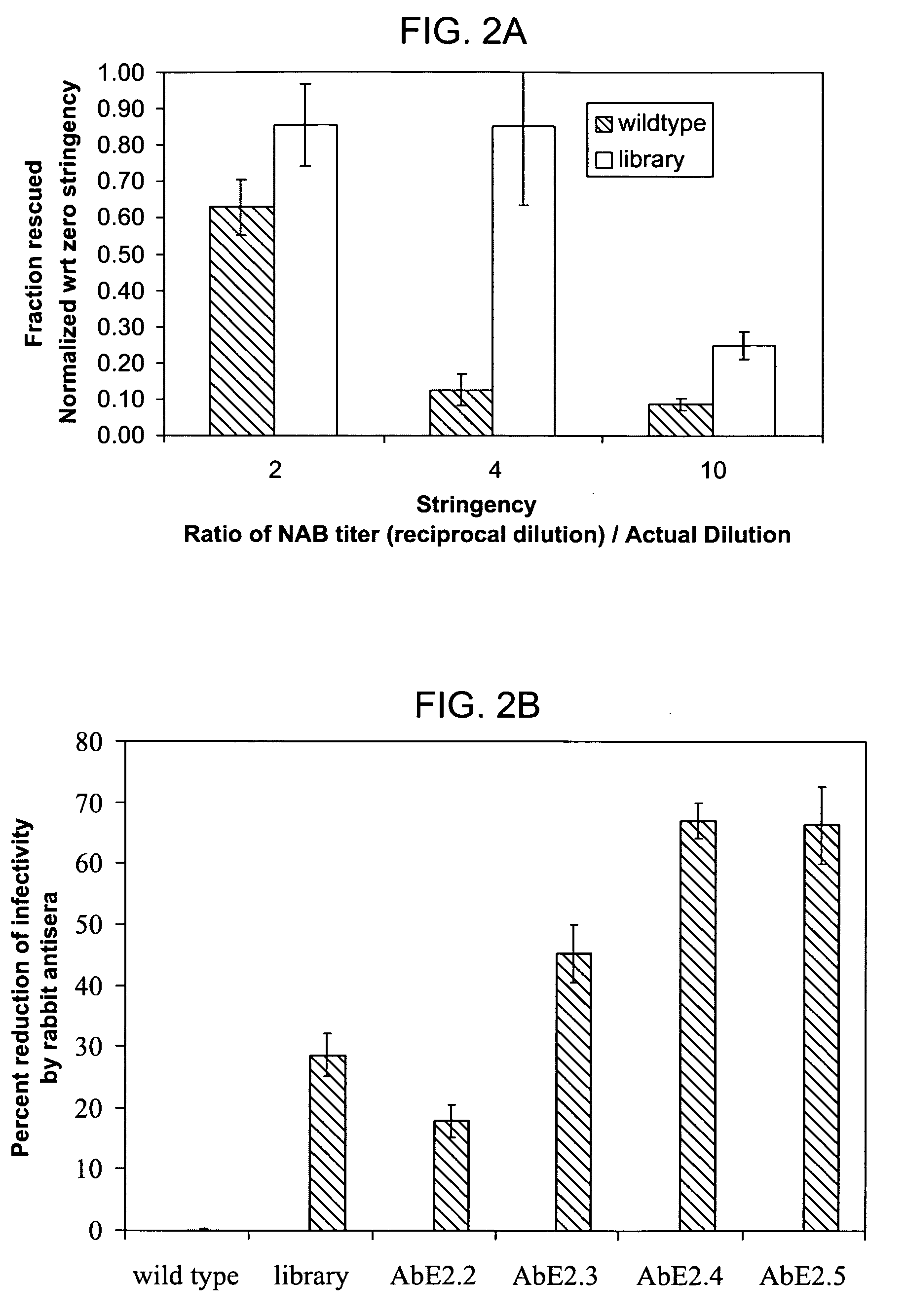
ActiveUS20090202490A1Reduce the binding forceAltered infectivityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCell type specificNeutralizing antibody
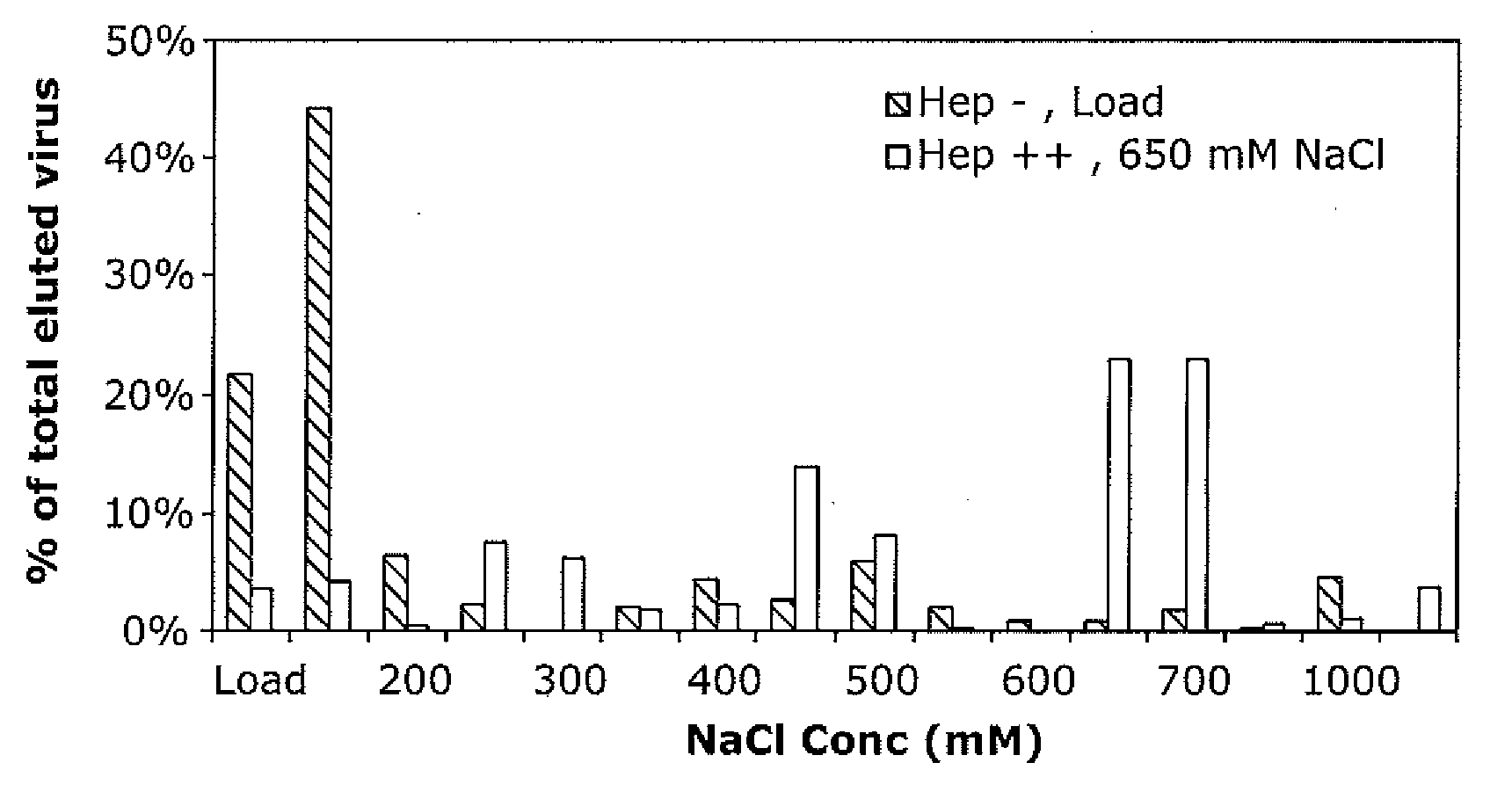
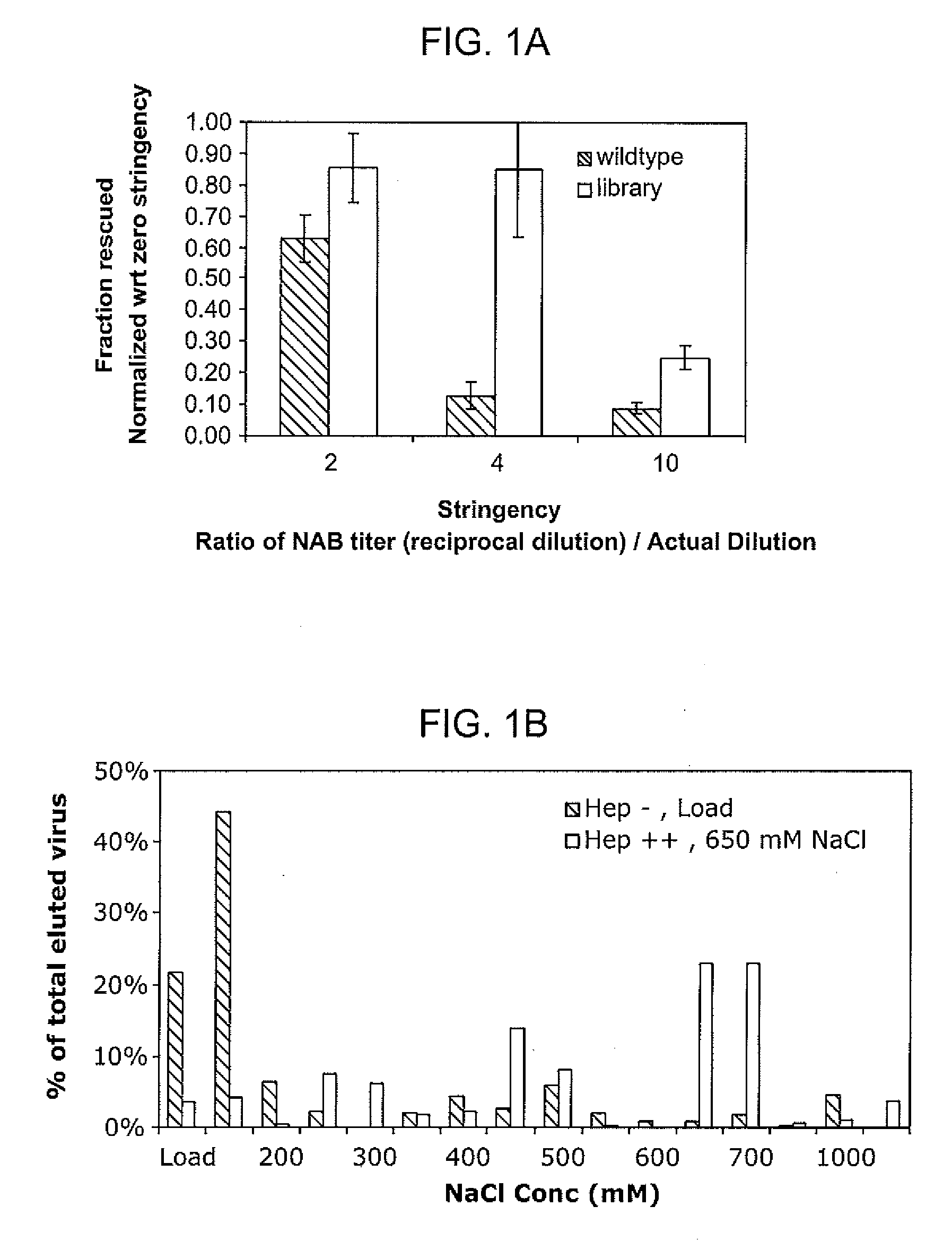
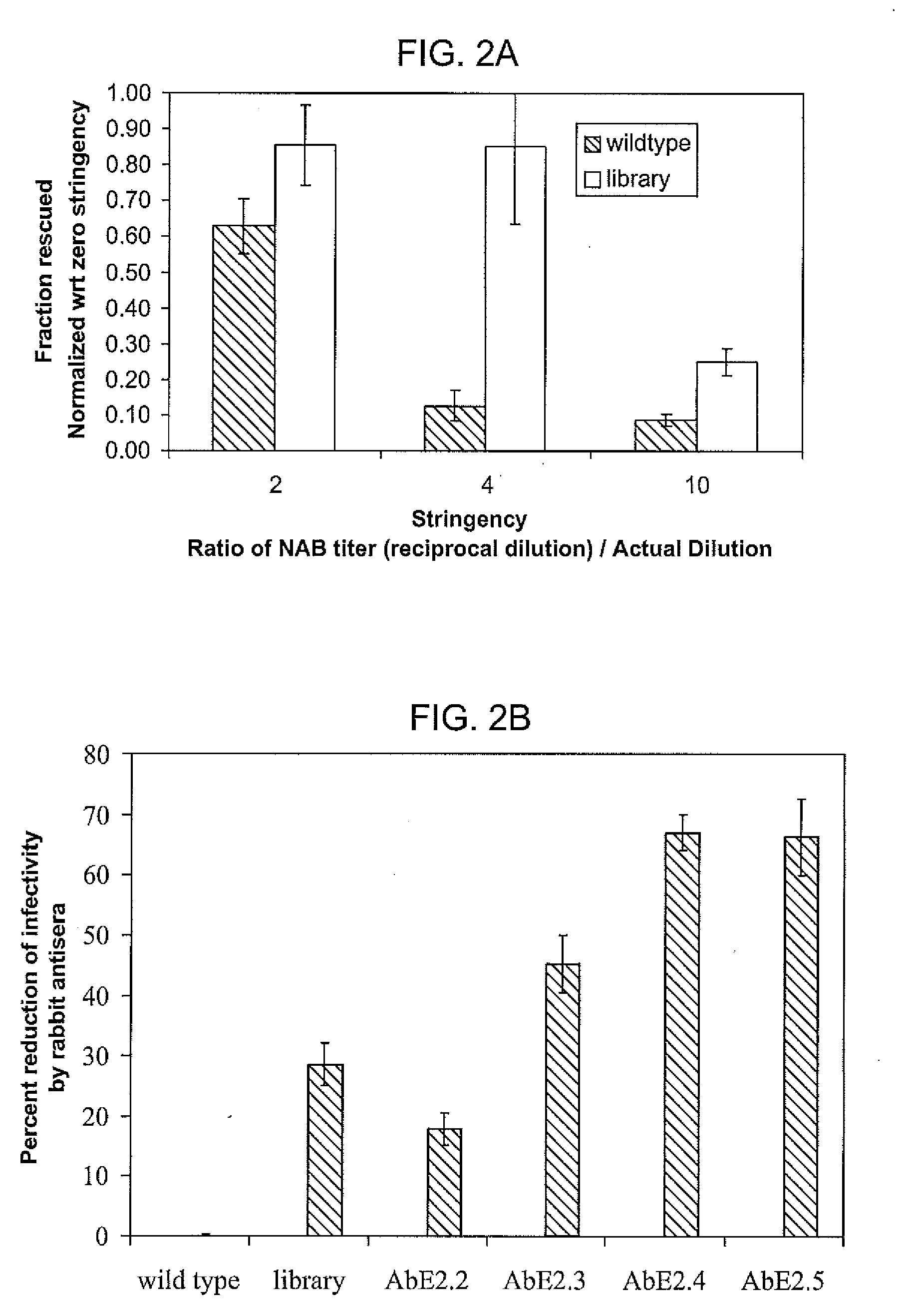
The present invention provides mutant adeno-associated virus (AAV) that exhibit altered capsid properties, e.g., reduced binding to neutralizing antibodies in serum and / or altered heparin binding and / or altered infectivity of particular cell types. The present invention further provides libraries of mutant AAV comprising one or more mutations in a capsid gene. The present invention further provides methods of generating the mutant AAV and mutant AAV libraries, and compositions comprising the mutant AAV. The present invention further provides recombinant AAV (rAAV) virions that comprise a mutant capsid protein. The present invention further provides nucleic acids comprising nucleotide sequences that encode mutant capsid proteins, and host cells comprising the nucleic acids. The present invention further provides methods of delivering a gene product to an individual, the methods generally involving administering an effective amount of a subject rAAV virion to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Nuclear reprogramming factor
ActiveUS8048999B2Improve abilitiesPromote growthNervous disorderVirusesGene productNuclear reprogramming
There is provided a nuclear reprogramming factor for a somatic cell, which comprises a gene product of each of the following three kinds of genes: an Oct family gene, a Klf family gene, and a Myc family gene, as a means for inducing reprogramming of a differentiated cell to conveniently and highly reproducibly establish an induced pluripotent stem cell having pluripotency and growth ability similar to those of ES cells without using embryo or ES cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Ultrasound therapy for selective cell ablation
InactiveUS6821274B2Ultrasound therapyElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentSensitized cellApoptosis
The invention provides a method of sensitizing target cells to ultrasound energy using a stimulus such as an electric field. This "electrosensitisation" enables target cells to be disrupted by ultrasound at frequencies and energies of ultrasound which do not cause disruption of non-sensitized (i.e., non-target) cells. As a consequence, the method increases the selectivity of ultrasound therapy, providing a way to ablate undesired cells, such as diseased cells (e.g., tumor cells) while minimizing harm to neighboring cells. In another aspect, however, ultrasound can be used to sensitize cells while the electrical field is used to disrupt cells. The invention also provides an apparatus for performing the method and assays for identifying gene products and other molecules involved in apoptosis.
Owner:GENDEL
Mutant adeno-associated virus virions and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20050053922A1Reduce the binding forceAltered infectivityAntibacterial agentsVirusesReassortant VirusesNeutralizing antibody
The present invention provides mutant adeno-associated virus (AAV) that exhibit altered capsid properties, e.g., reduced binding to neutralizing antibodies in serum and / or altered heparin binding and / or altered infectivity of particular cell types. The present invention further provides libraries of mutant AAV comprising one or more mutations in a capsid gene. The present invention further provides methods of generating the mutant AAV and mutant AAV libraries, and compositions comprising the mutant AAV. The present invention further provides recombinant AAV (rAAV) virions that comprise a mutant capsid protein. The present invention further provides nucleic acids comprising nucleotide sequences that encode mutant capsid proteins, and host cells comprising the nucleic acids. The present invention further provides methods of delivering a gene product to an individual, the methods generally involving administering an effective amount of a subject rAAV virion to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:INTEGRATIVE GENE THERAPEUTICS +1
Methods for treating restenosis with p21
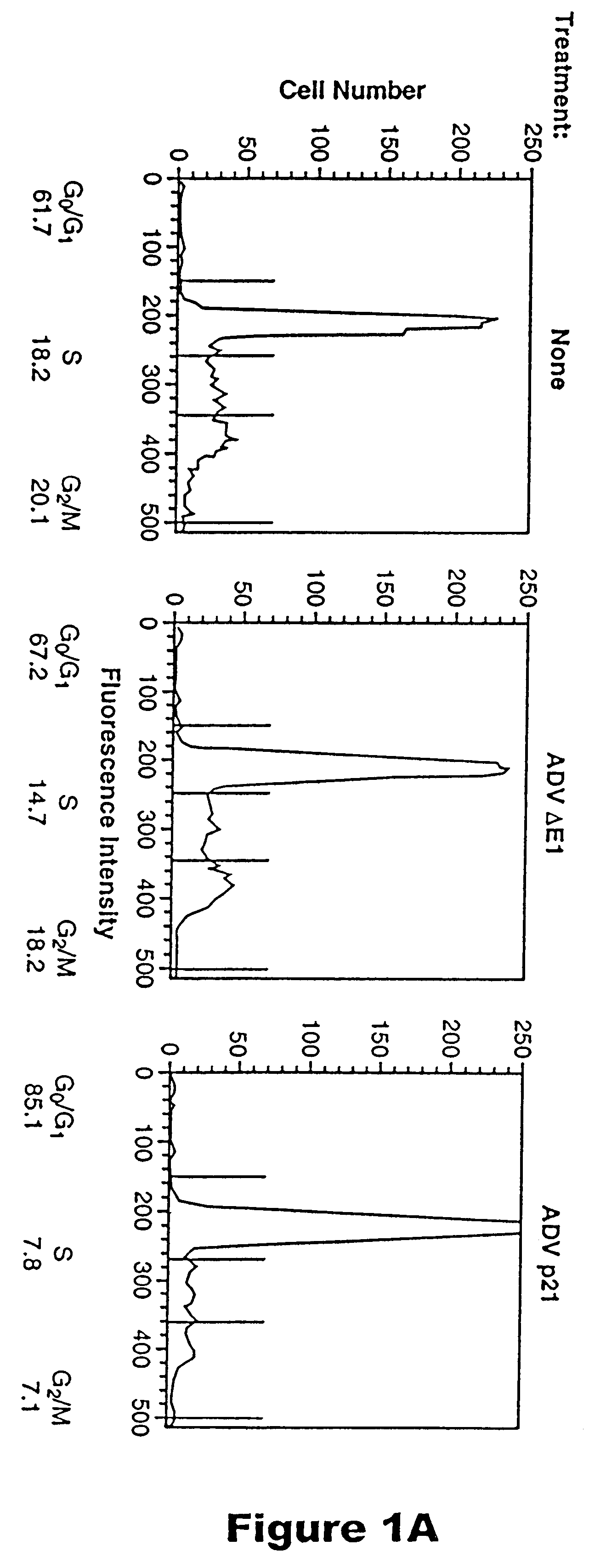
InactiveUS6218372B1Treating and preventing restenosis in vivoFacilitate immune recognitionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPercent Diameter StenosisGene product
The p21 gene encodes a cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor which affects cell cycle progression, but the role of this gene product in altering tumor growth has not been established. The present inventors have now discovered that the growth of malignant cells in vivo is inhibited by expression of p21. Expression of p21 resulted in an accumulation of cells in G0 / G1, alteration in morphology, and cell differentiation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
IN vitro sorting method
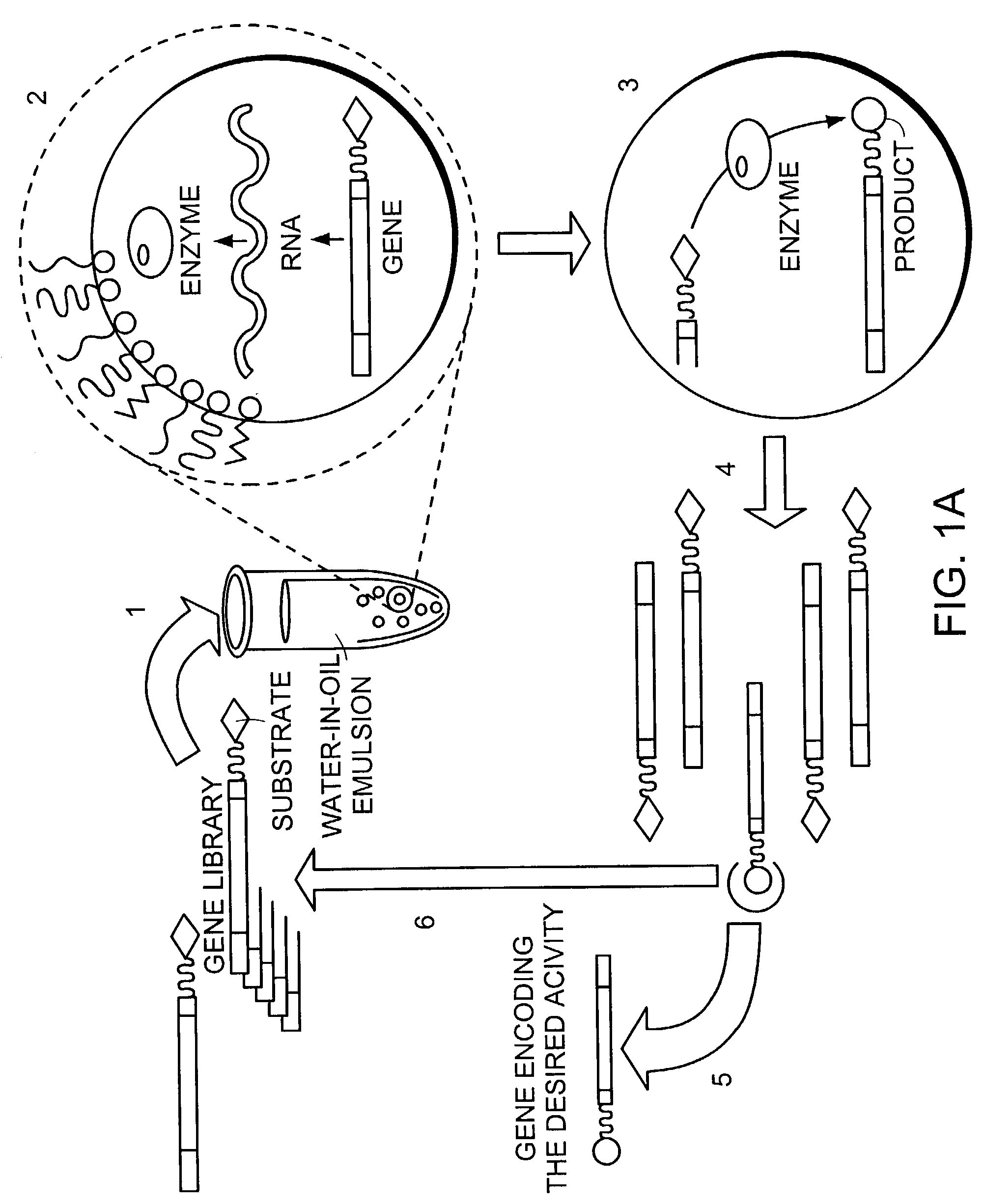
InactiveUS7138233B2High activityMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesGene productGenetic element
The invention describes a method for isolating one or more genetic elements encoding a gene product having a desired activity, comprising of the steps of: (a) compartmentalising genetic elements into microcapsules; (b) expressing the genetic elements to produce their respective gene products within the microcapsules; (c) sorting the genetic elements which produce the gene product having a desired activity.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
Noninvasive genetic immunization, expression products therefrom, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6716823B1Improve vaccination schemeEfficient methodSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideMalariaNon invasive
Disclosed and claimed are methods of non-invasive genetic immunization in an animal and / or methods of inducing a systemic immune or therapeutic response in an animal, products therefrom and uses for the methods and products therefrom. The methods can include contacting skin of the animal with a vector in an amount effective to induce the systemic immune or therapeutic response in the animal. The vector can include and express an exogenous nucleic acid molecule encoding an epitope or gene product of interest. The systemic immune response can be to or from the epitope or gene product. The nucleic acid molecule can encode an epitope of interest and / or an antigen of interest and / or a nucleic acid molecule that stimulates and / or modulates an immunological response and / or stimulates and / or modulates expression, e.g., transcription and / or translation, such as transcription and / or translation of an endogenous and / or exogenous nucleic acid molecule; e.g., one or more of influenza hemagglutinin, influenza nuclear protein, influenza M2, tetanus toxin C-fragment, anthrax protective antigen, anthrax lethal factor, rabies glycoprotein, HBV surface antigen, HIV gp 120, HIV gp 160, human carcinoembryonic antigen, malaria CSP, malaria SSP, malaria MSP, malaria pfg, and mycobacterium tuberculosis HSP; and / or a therapeutic, an immunomodulatory gene, such as co-stimulatory gene and / or a cytokine gene. The immune response can be induced by the vector expressing the nucleic acid molecule in the animal's cells. The animal's cells can be epidermal cells. The immune response can be against a pathogen or a neoplasm. A prophylactic vaccine or a therapeutic vaccine or an immunological composition can include the vector. The animal can be a vertebrate, e.g., a mammal, such as human, a cow, a horse, a dog, a cat, a goat, a sheep or a pig; or fowl such as turkey, chicken or duck. The vector can be one or more of a viral vector, including viral coat, e.g., with some or all viral genes deleted therefrom, bacterial, protozoan, transposon, retrotransposon, and DNA vector, e.g., a recombinant vector; for instance, an adenovirus, such as an adenovirus defective in its E1 and / or E3 and / or E4 region(s). The method can encompass applying a delivery device including the vector to the skin of the animal, as well as such a method further including disposing the vector in and / or on the delivery device. The vector can have all viral genes deleted therefrom. The vector can induce a therapeutic and / or an anti-tumor effect in the animal, e.g., by expressing an oncogene, a tumor-suppressor gene, or a tumor-associated gene. Immunological products generated by the expression, e.g., antibodies, cells from the methods, and the expression products, are likewise useful in in vitro and ex vivo applications, and such immunological and expression products and cells and applications are disclosed and claimed. Methods for expressing a gene product in vivo and products therefor and therefrom including mucosal and / or intranasal administration of an adenovirus, advantageously an E1 and / or E3 and / or E4 defective or deleted adenovirus, such as a human adenovirus or canine adenovirus, are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Emulsion compositions
An emulsion is useful in allowing a wide variety of gene products to be expressed via eukaryotic in vitro expression. The emulsion comprises a silicone based surfactant, a hydrophobic phase and a hydrophilic phase; wherein the hydrophilic phase comprises a plurality of compartments containing a functional in vitro eukaryotic expression system.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
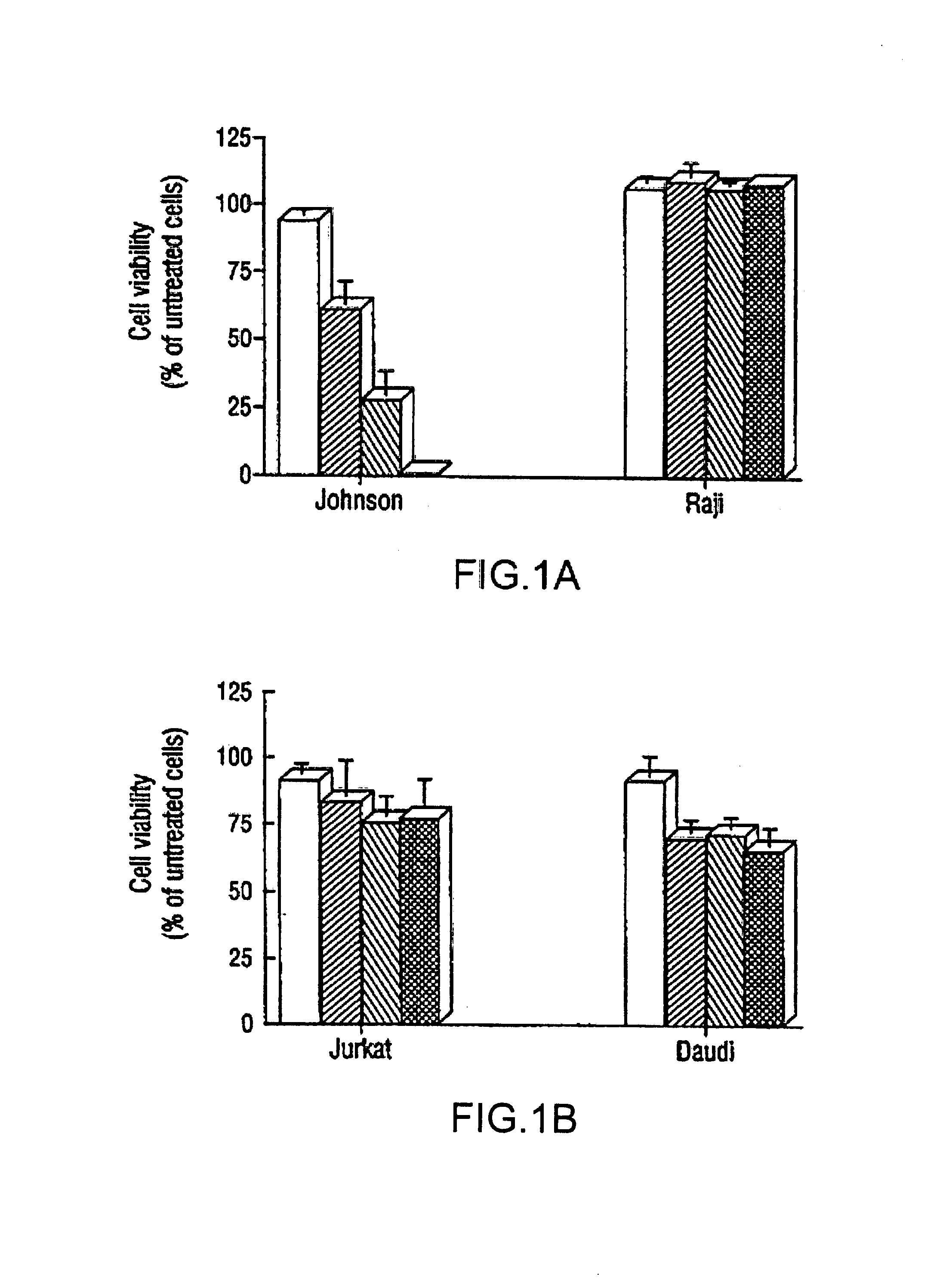
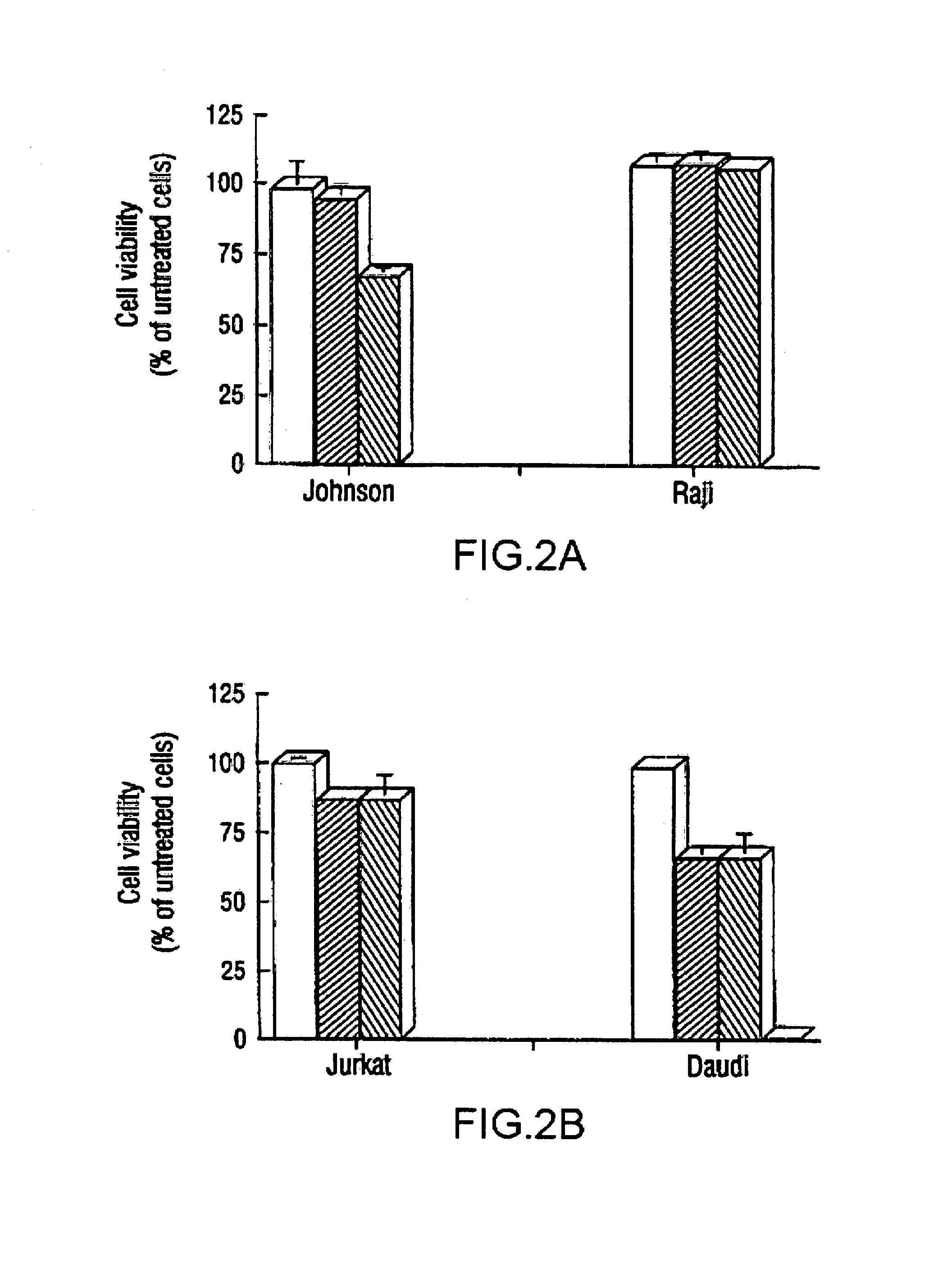
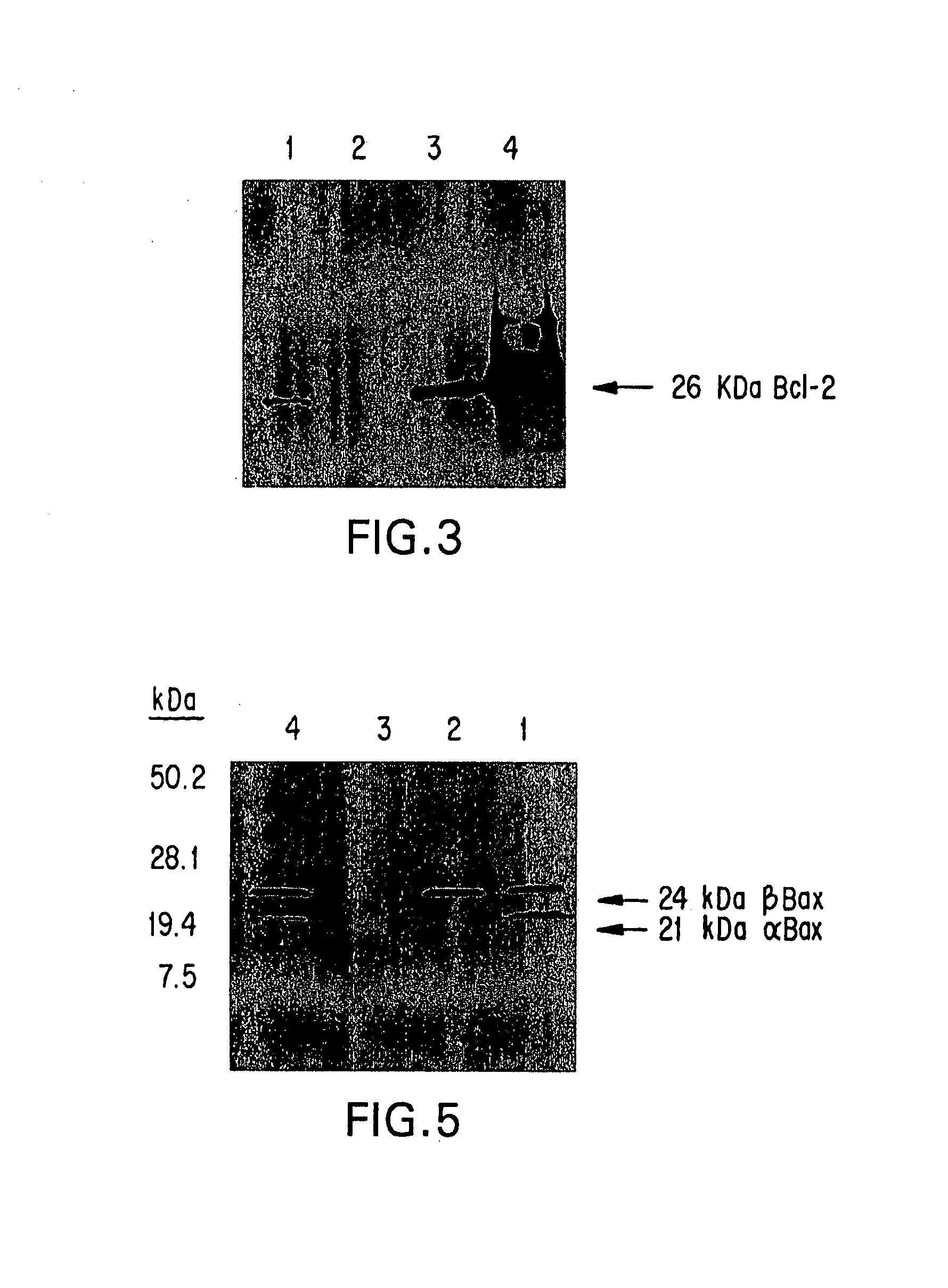
Inhibition of Bcl-2 protein expression by liposomal antisense oligodeoxynucleotides
InactiveUS7285288B1Lower the volumeIncrease the effective concentrationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseCancer cell
The present invention provides novel compositions and methods for use in the treatment of Bcl-2-associated diseases like cancer, specifically, in the treatment of follicular lymphoma (FL). The compositions contain antisense oligonucleotides that hybridize to Bcl-2 nucleic acids, the gene products of which are known to interact with the tumorigenic protein Bcl-2. Used alone, or in conjunction with other antisense oligonucleotides, these compositions inhibit the proliferation of FL cancer cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Optical sorting method
InactiveUS20050037392A1High activityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementOptical propertyGene product
The invention describes a method for isolating one or more genetic elements encoding a gene product having a desired activity, comprising the steps of: (a) compartmentalising genetic elements into microcapsules; (b) expressing the genetic elements to produce their respective gene products within the microcapsules; (c) sorting the genetic elements which produce the gene product having the desired activity using a change in the optical properties of the genetic elements. The invention enables the in vitro evolution of nucleic acids and proteins by repeated mutagenesis and iterative applications of the method of the invention.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Transgenic mouse model of alzheimer's disease and cerebral amyloid angiopathy
InactiveUS6175057B1Lower Level RequirementsConvenient treatmentVectorsIn-vivo testing preparationsOrganismTgf beta1
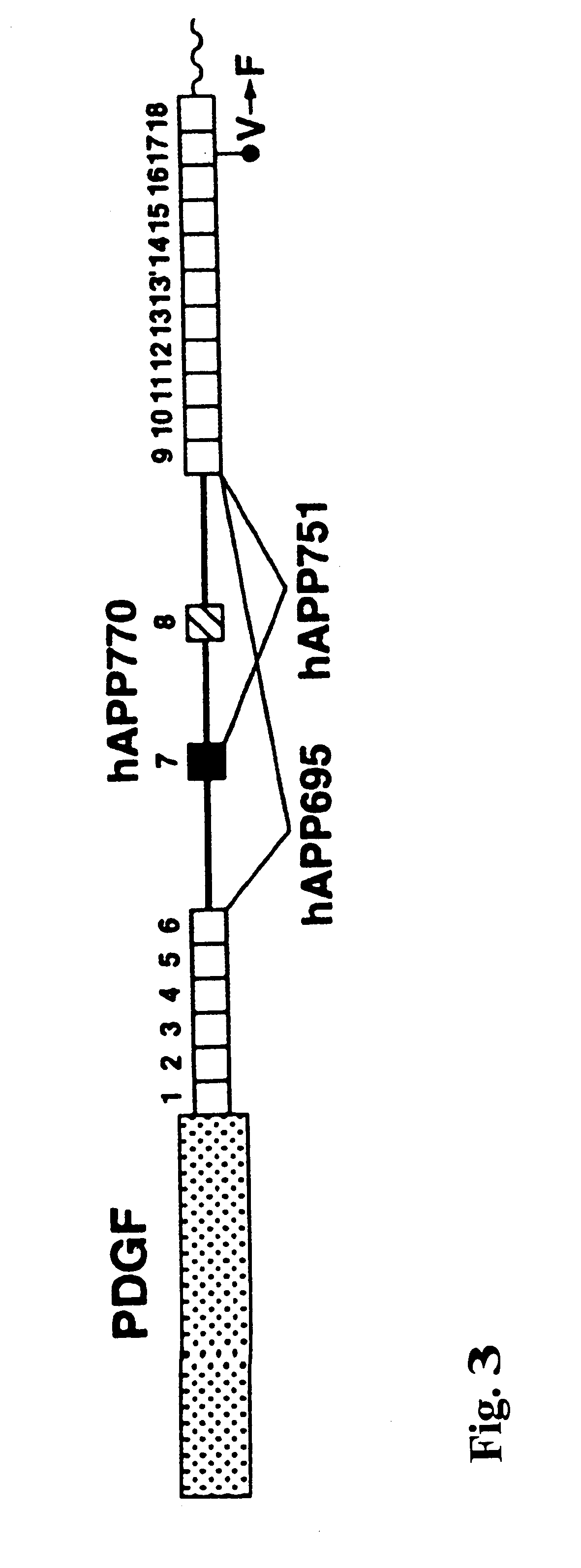
The present invention features non-human transgenic animal models for Alzheimer's disease (AD) and CAA, wherein the transgenic animal is characterized by 1) overexpression of bioactive transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) or 2) both overexpression of bioactive TGF-beta1 and expression of a human amyloid beta precursor protein (APP) gene product. The transgenic animals may be either homozygous or heterozygous for these alterations. Bigenic animals are further characterized by development of AD-associated and / or CAA-associated pathology within about two to three months of age.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Recombinant negative strand RNA virus expression systems and vaccines
Owner:MEDIMMUNE VACCINES
Bio-synthetic photostimulators and methods of use
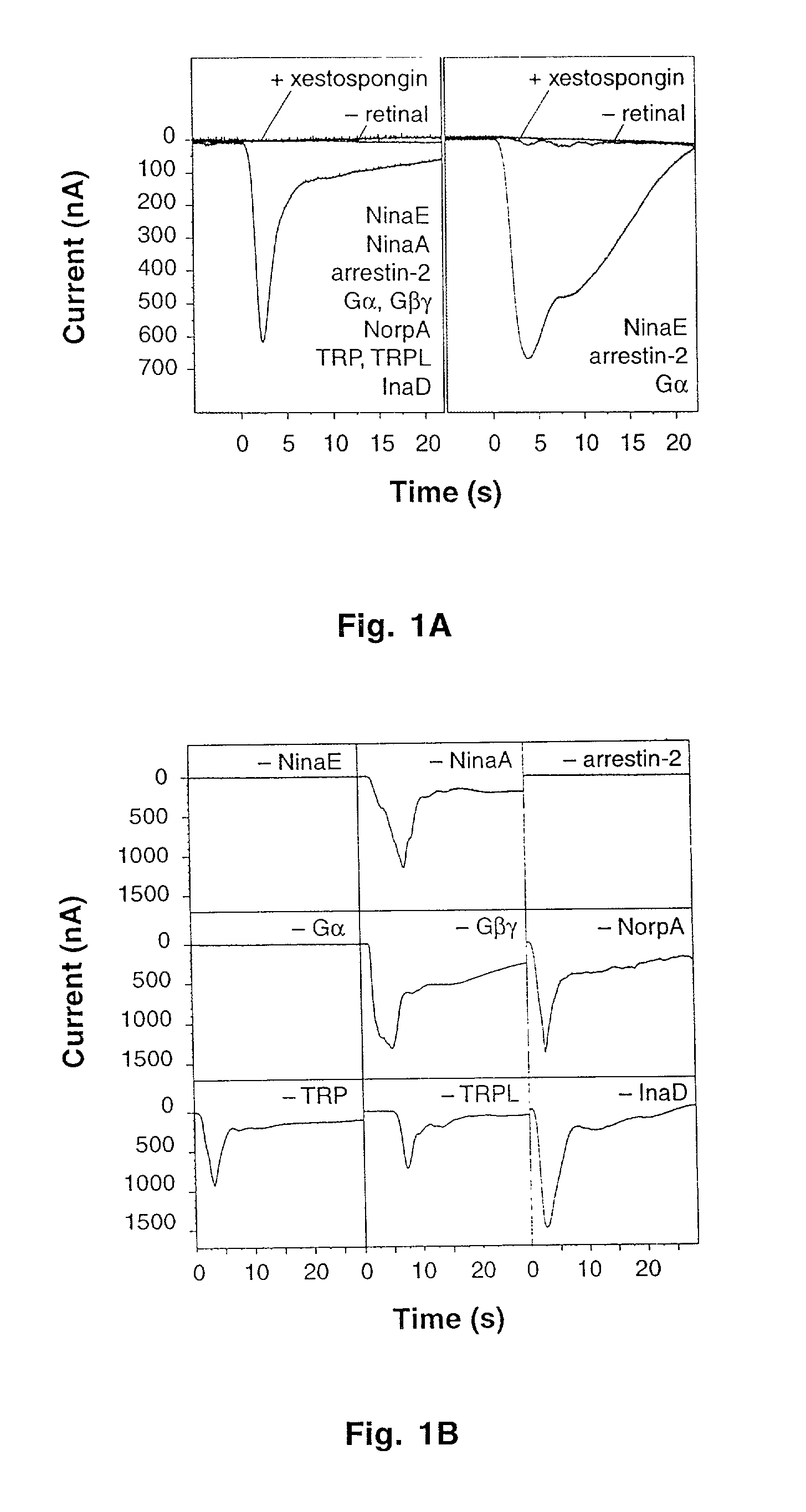
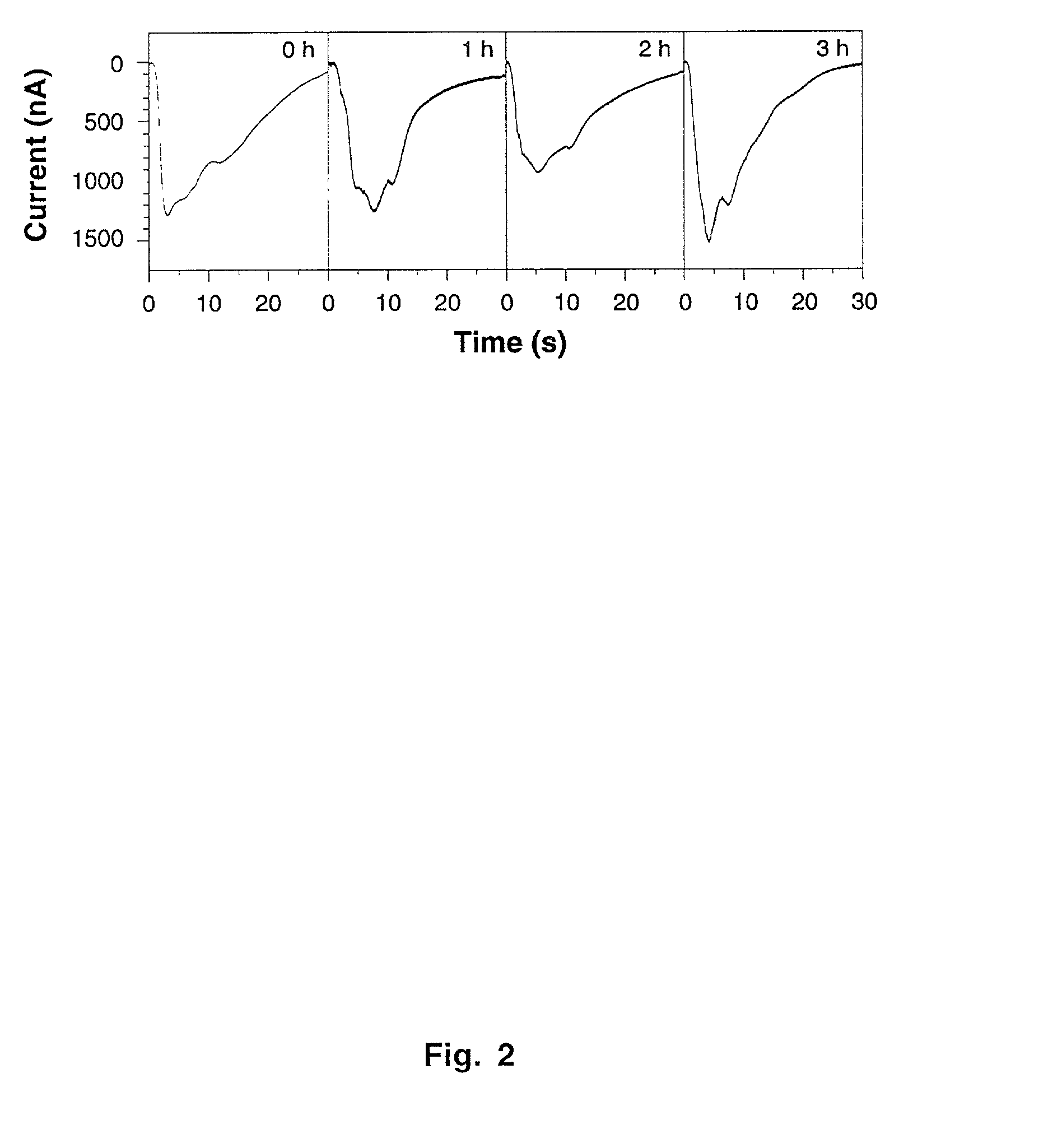
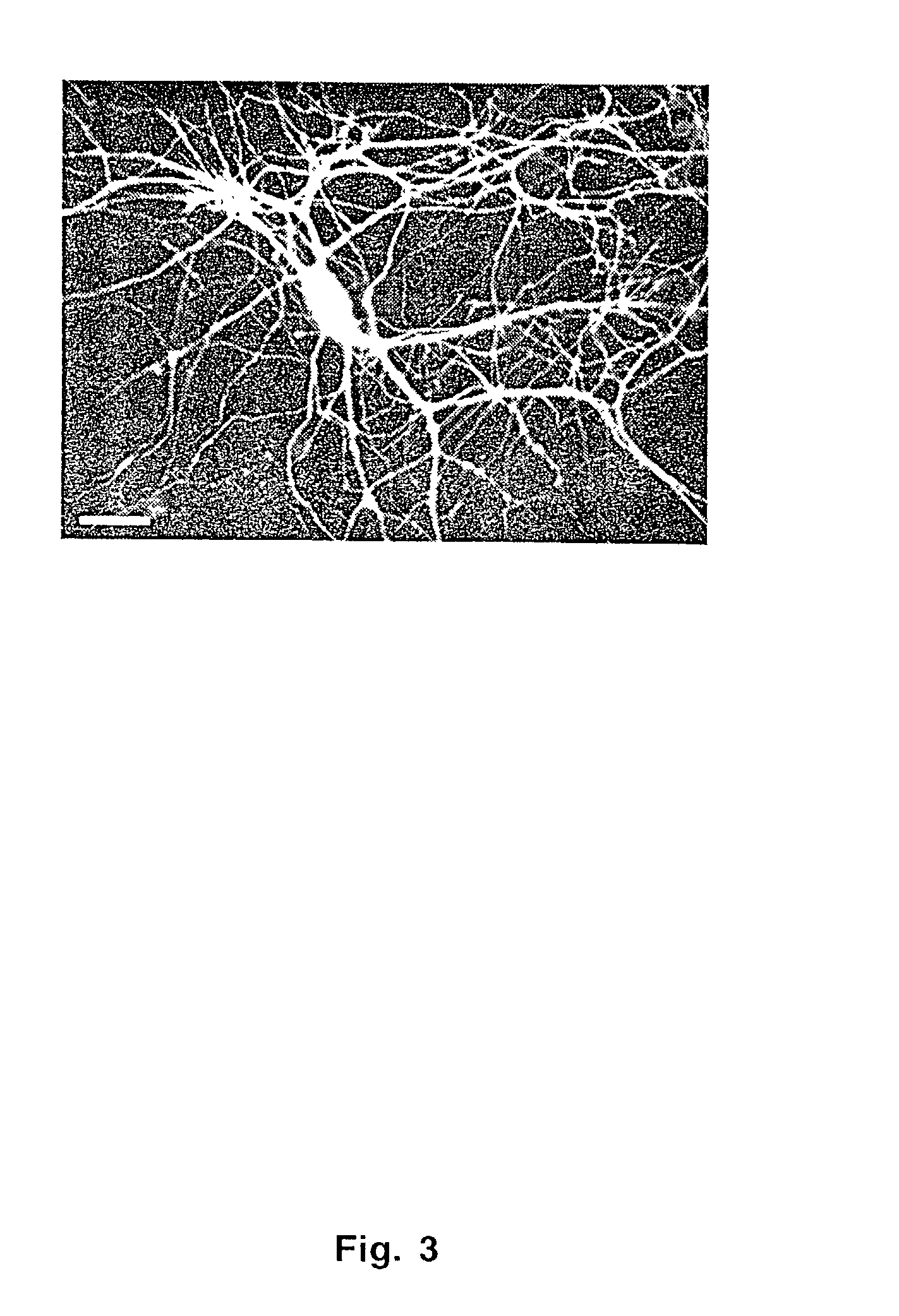
Cells are rendered sensitive to stimulation by introducing into a non-photoreceptor cell nucleic acid sequences encoding at least an opsin gene product, an arrestin gene product, and the alpha subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein of the Gq family. The introduced sequences are expressed by the cell to yield at least the opsin gene product, the arrestin gene product, and the alpha subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein of the Gq family. Retinal or a derivative thereof capable of bonding with the opsin gene product to form a rhodopsin is provided to the cell. The cell is then irradiated with light having a wavelength capable of converting the rhodopsin to metarhodopsin. The conversion of rhodopsin to metarhodopsin triggers a cascade of intracellular responses within the cell resulting in an increased intracellular concentration of IP3 and calcium ions.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
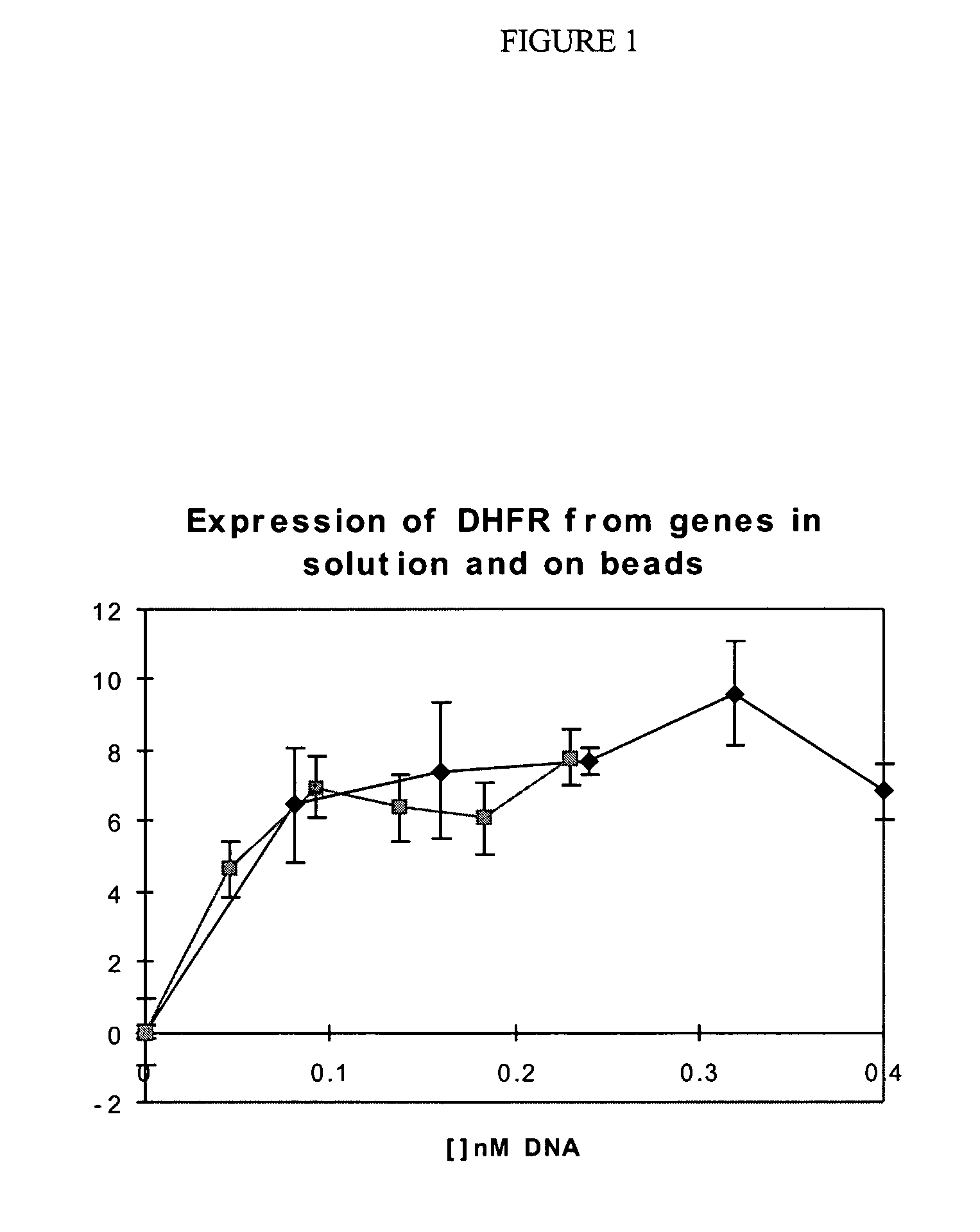
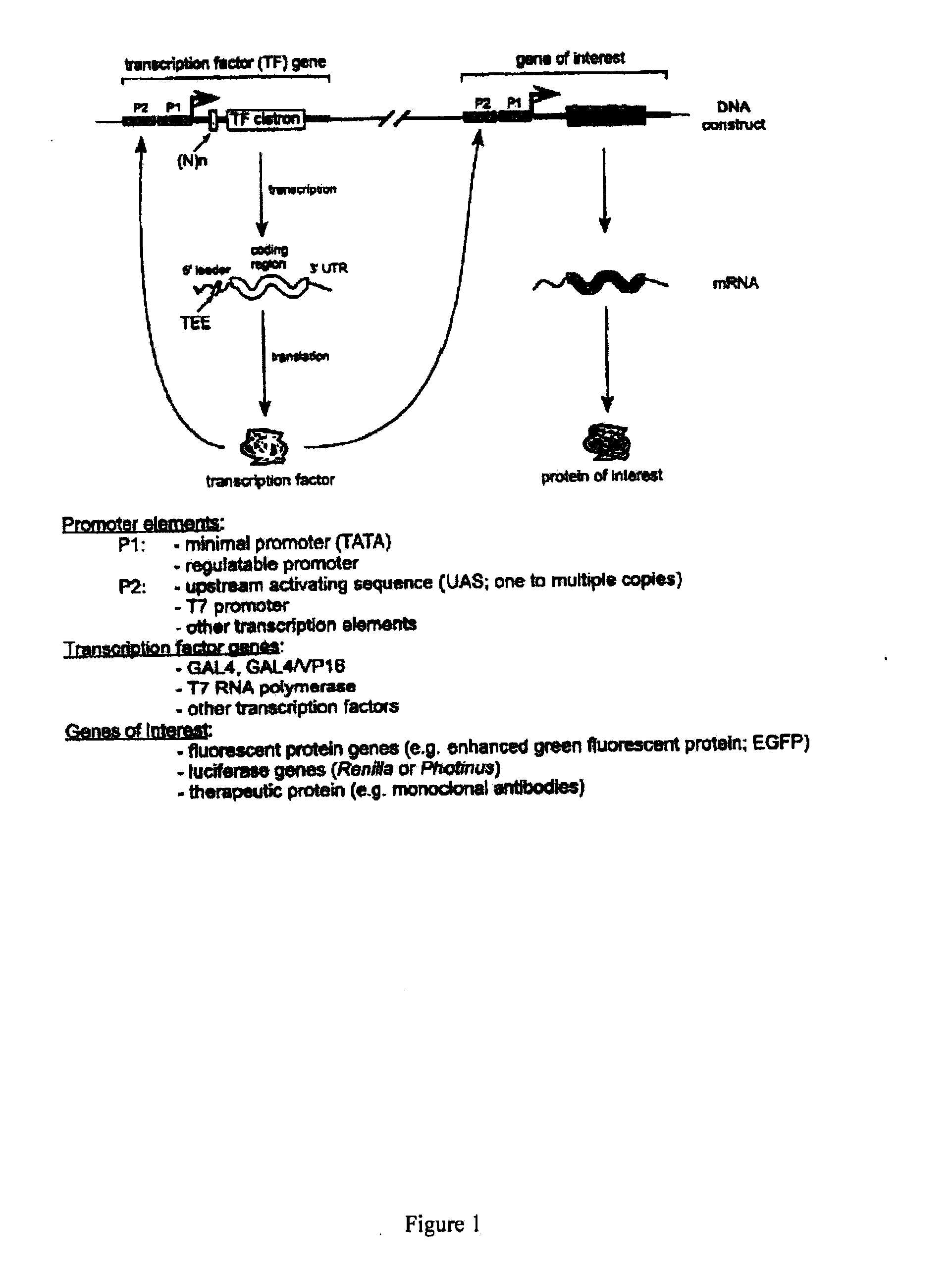
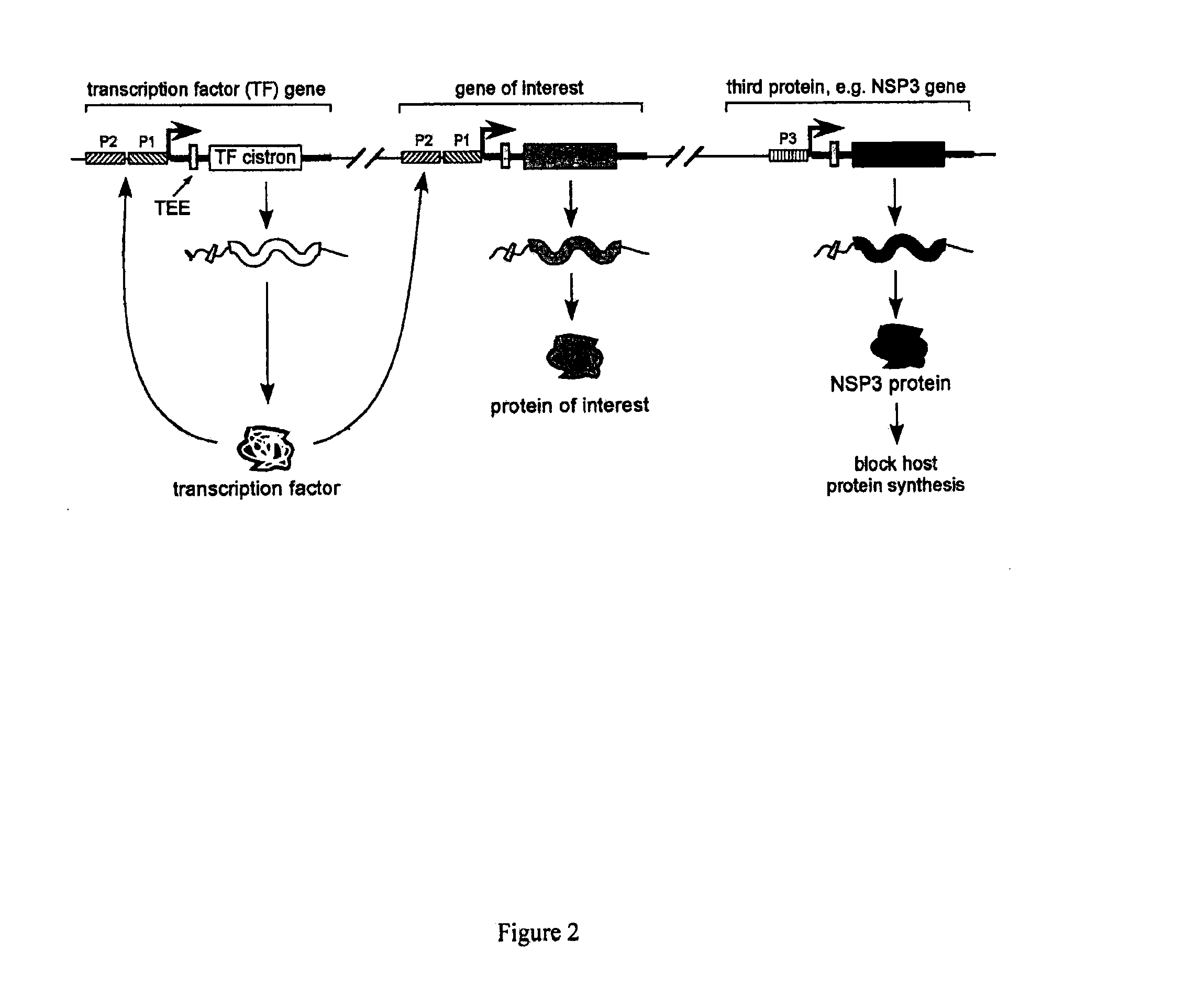
Translation enhancer-element dependent vector systems
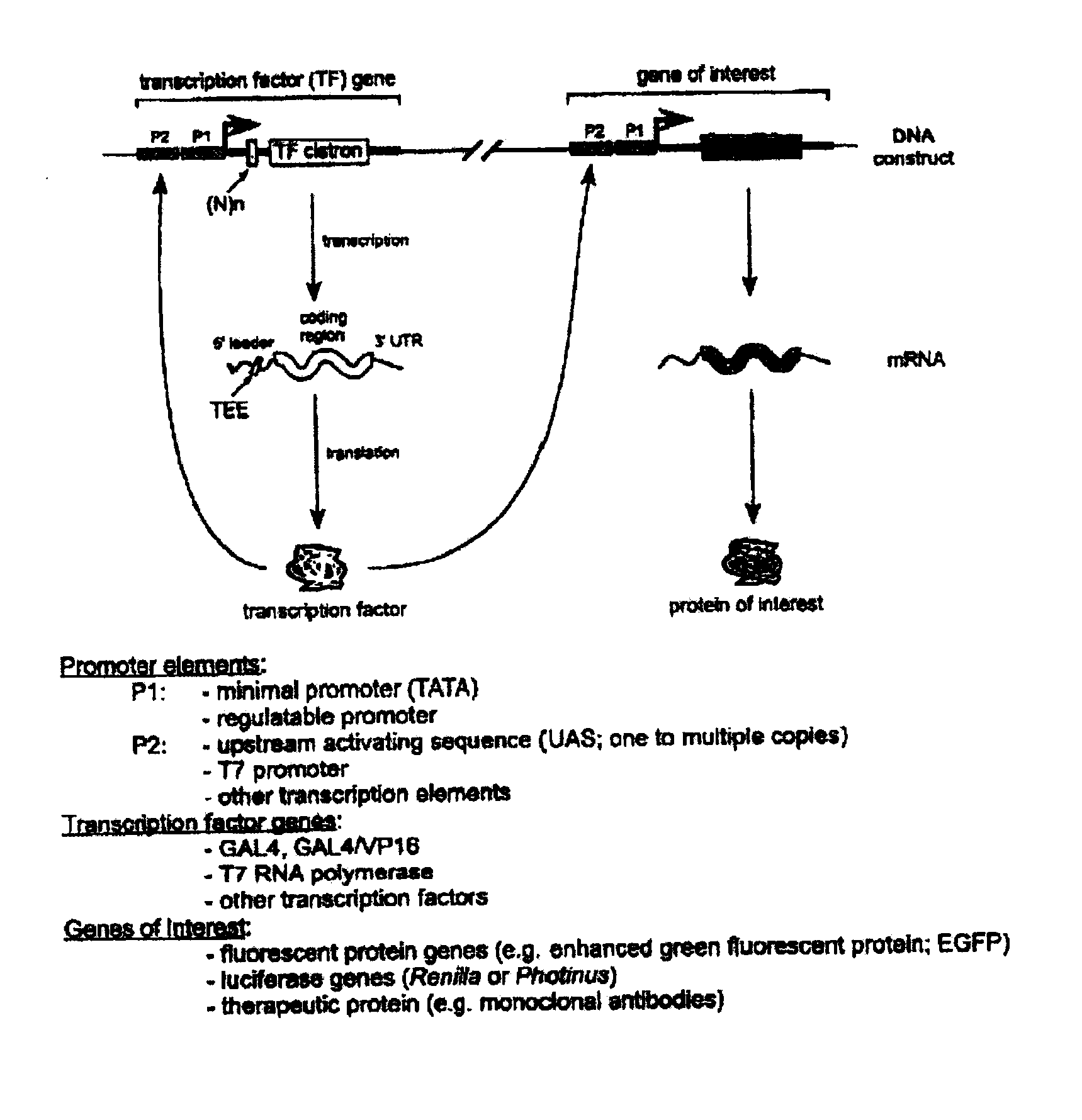
InactiveUS20110124100A1High in proteinLevel of gene product expressed from the second constructNucleic acid vectorFermentationVector systemNucleotide
A translation enhancer-driven positive feedback vector system is disclosed which is designed to facilitate identification of a Translational Enhancer Element (TEE) and to provide a means for overexpression of gene products. The system exploits both transcriptional and translational approaches to control the expression levels of genes and / or gene products. Methods are also disclosed for screening libraries of random nucleotide sequences to identify translational elements and for overproduction of proteins, which have uses in both research and industrial environments.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Immunodeficiency recombinant poxvirus
InactiveUS6596279B1SsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseFeline immunodeficiency virusCtl epitope
Attenuated recombinant viruses containing DNA encoding an immunodeficiency virus and / or CTL antigen, as well as methods and compositions employing the viruses, expression products therefrom, and antibodies generated from the viruses or expression products, are disclosed and claimed. The recombinant viruses can be NYVAC or ALVAC recombinant viruses. The DNA can code for at least one of: HIV1gag(+pro)(IIIB), gp120(MN)(+transmembrane), nef(BRU)CTL, pol(IIIB)CTL, ELDKWA or LDKW epitopes, preferably HIV1gag(+pro)(IIIB), gp120(MN) (+transmembrane), two (2) nef(BRU)CTL and three (3) pol(IIIB)CTL etpitopes; or two ELDKWA in gp120 V3 or another region or in gp160. The two (2) nef(BRU)CTL and three (3) pol(IIIB)CTL epitopes are preferably CTL1, CTL2, pol1, pol2 and pol3. The recombinant viruses and gene products therefrom and antibodies generated by the viruses and gene products have several preventive, therapeutic and diagnostic uses. DNA from the recombinant viruses are useful as probes or, for generating PCR primers or for immunization. Also disclosed and claimed are HIV immunogens and modified gp160 and gp120.
Owner:VIROGENETICS
Poxvirus-canine distemper virus (CDV) or measles virus recombinants and compositions and methods employing the recombinants
InactiveUS6309647B1Improve securityImprove security levelSsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseHemagglutininCanine distemper virus Antigen
Attenuated recombinant viruses containing DNA coding for a canine distemper virus antigen or measles M or N antigen, as well as methods and compositions employing the viruses, are disclosed and claimed. The recombinant viruses can be NYVAC or ALVAC recombinant viruses. The DNA can code for at least one of: canine distemper virus fusion protein, canine distemper virus hemagglutinin glycoprotein, canine distemper nucleocaspid protein, canine distemper matrix protein, measles virus nucleocaspid protein, and measles virus matrix protein. The recombinant viruses and gene products therefrom are useful for eliciting protection against canine distemper virus and / or measles virus, and, the gene products and antibodies elicited thereby are useful in assays. Additionally, DNA from the recombinants is used for probes or for generating PCR primers.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com