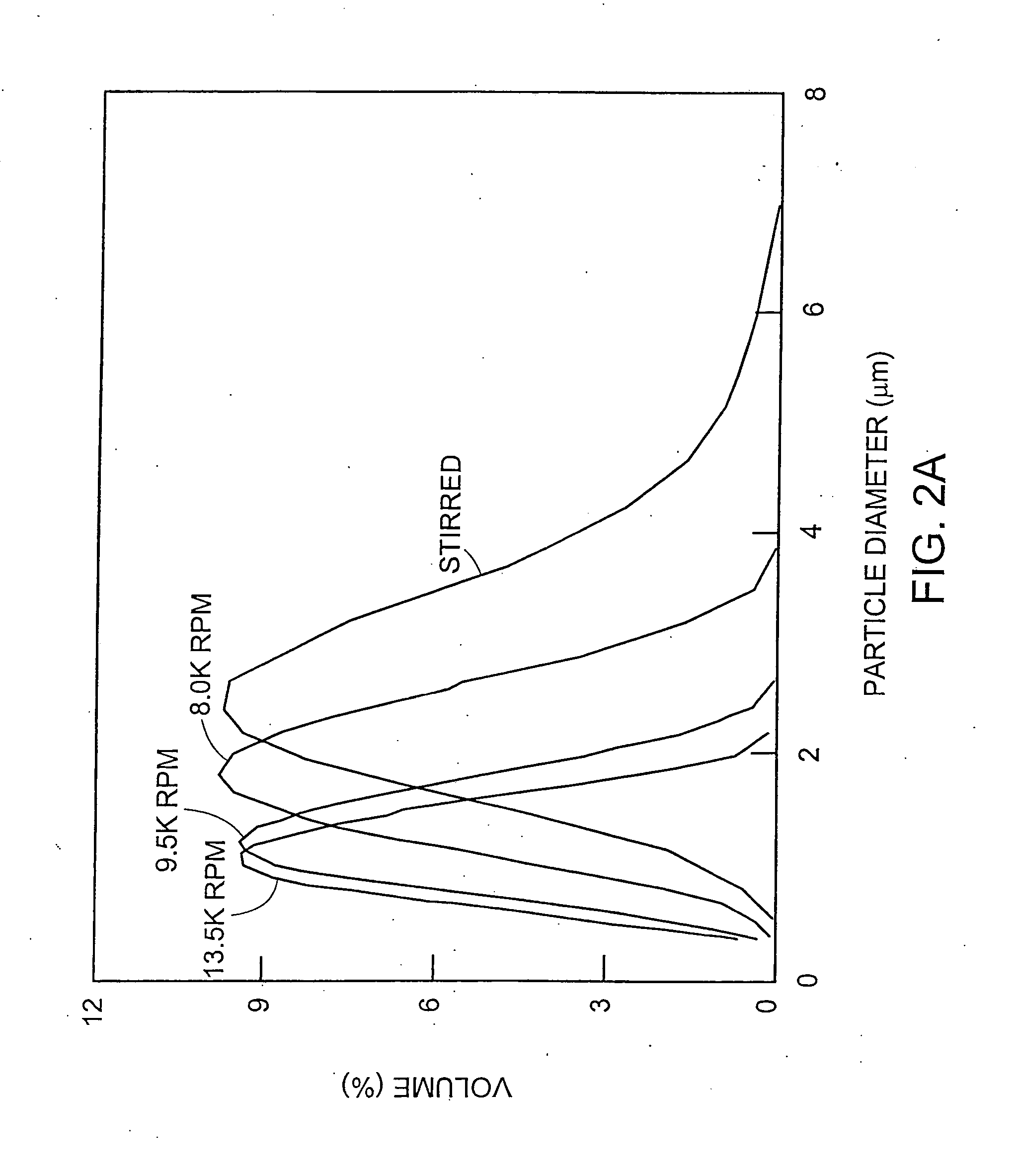
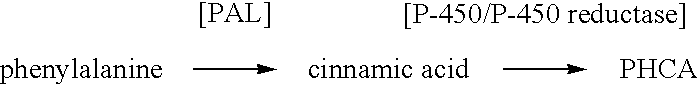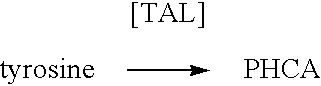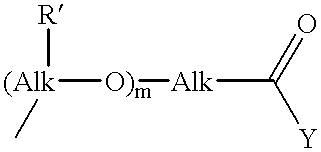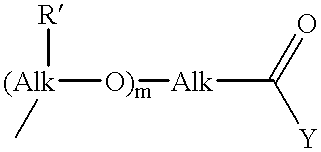Patents
Literature
1118 results about "Mutagenesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mutagenesis /mjuːtəˈdʒɛnɪsɪs/ is a process by which the genetic information of an organism is changed, resulting in a mutation. It may occur spontaneously in nature, or as a result of exposure to mutagens. It can also be achieved experimentally using laboratory procedures. In nature mutagenesis can lead to cancer and various heritable diseases, but it is also a driving force of evolution. Mutagenesis as a science was developed based on work done by Hermann Muller, Charlotte Auerbach and J. M. Robson in the first half of the 20th century.
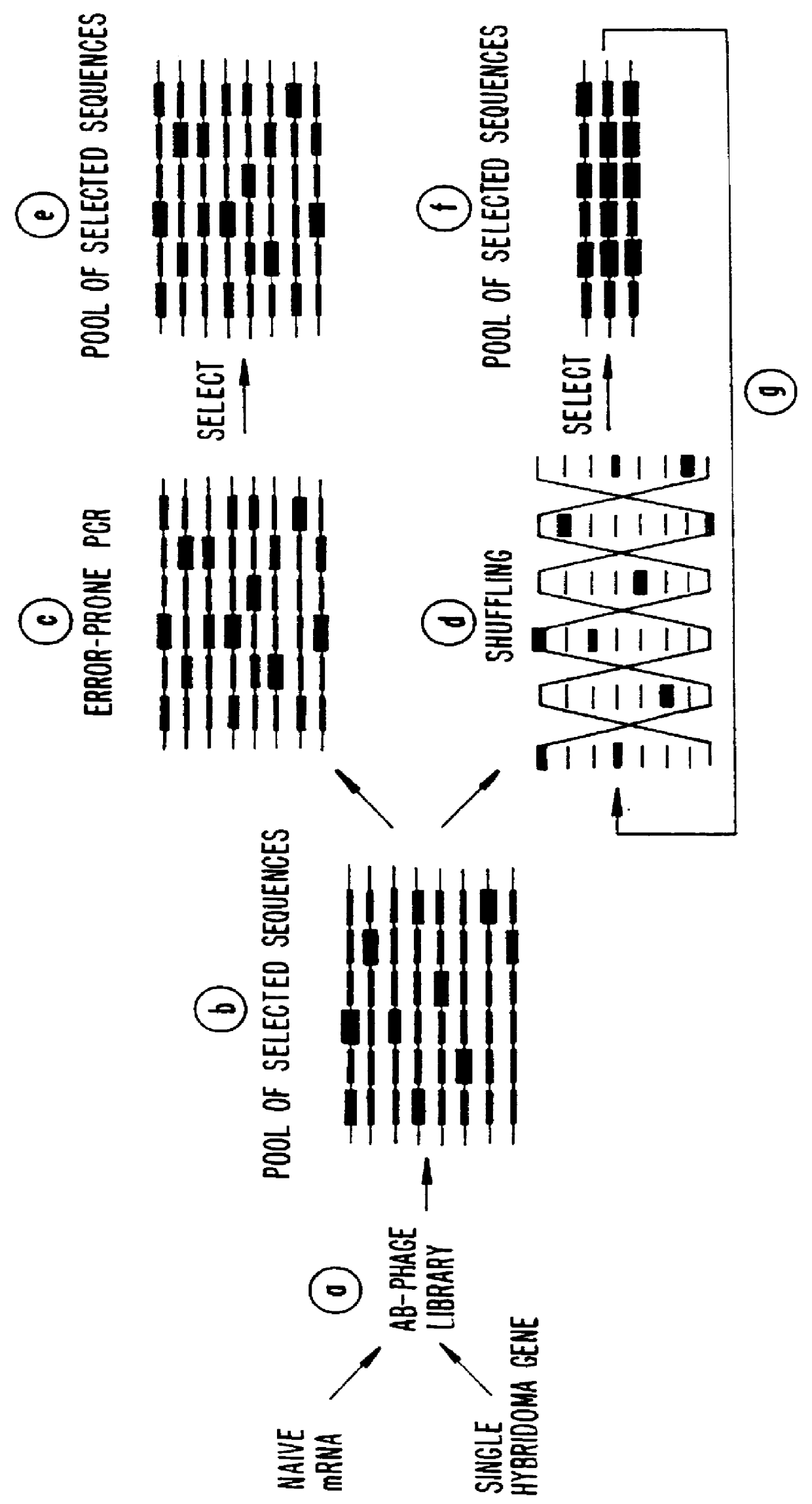
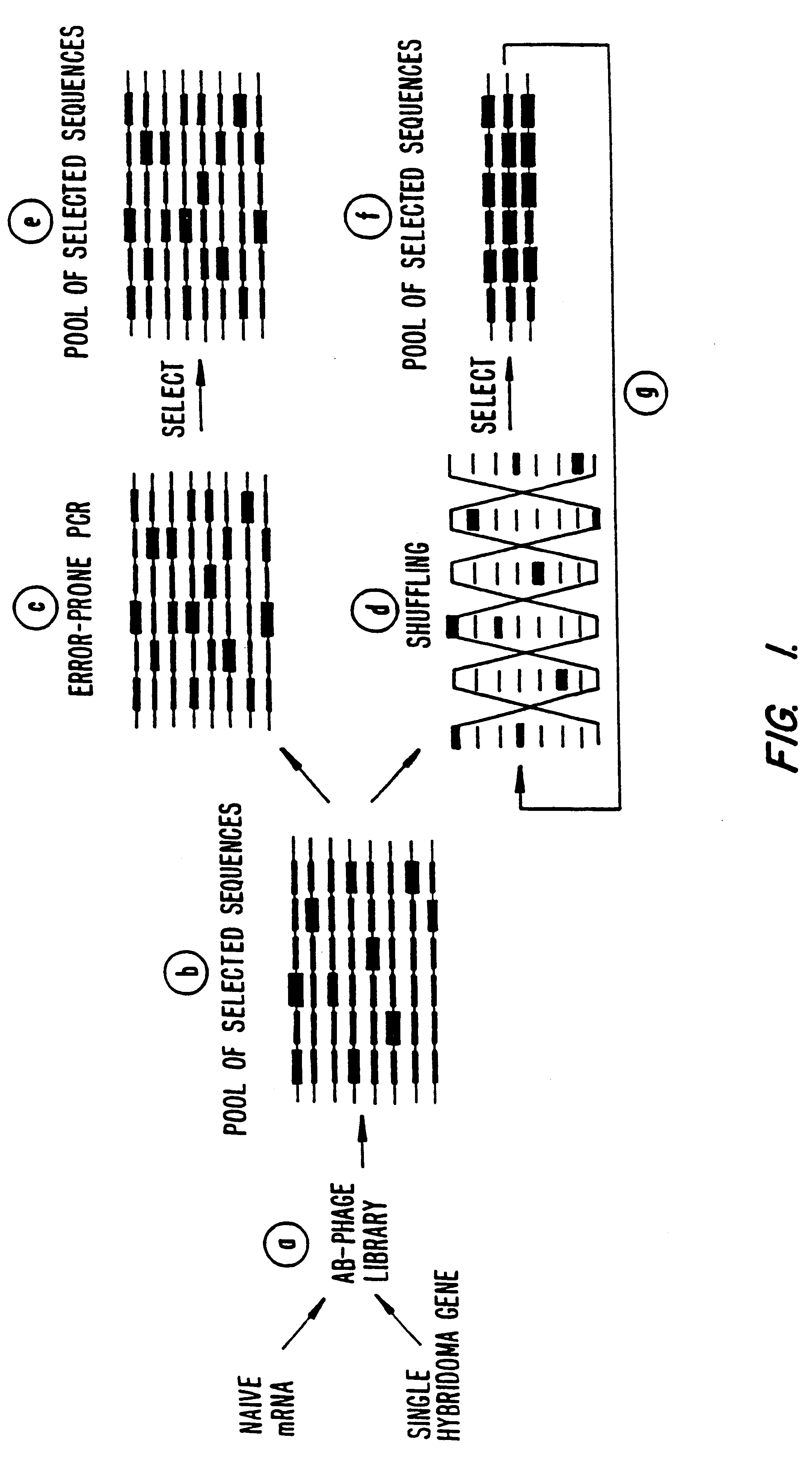
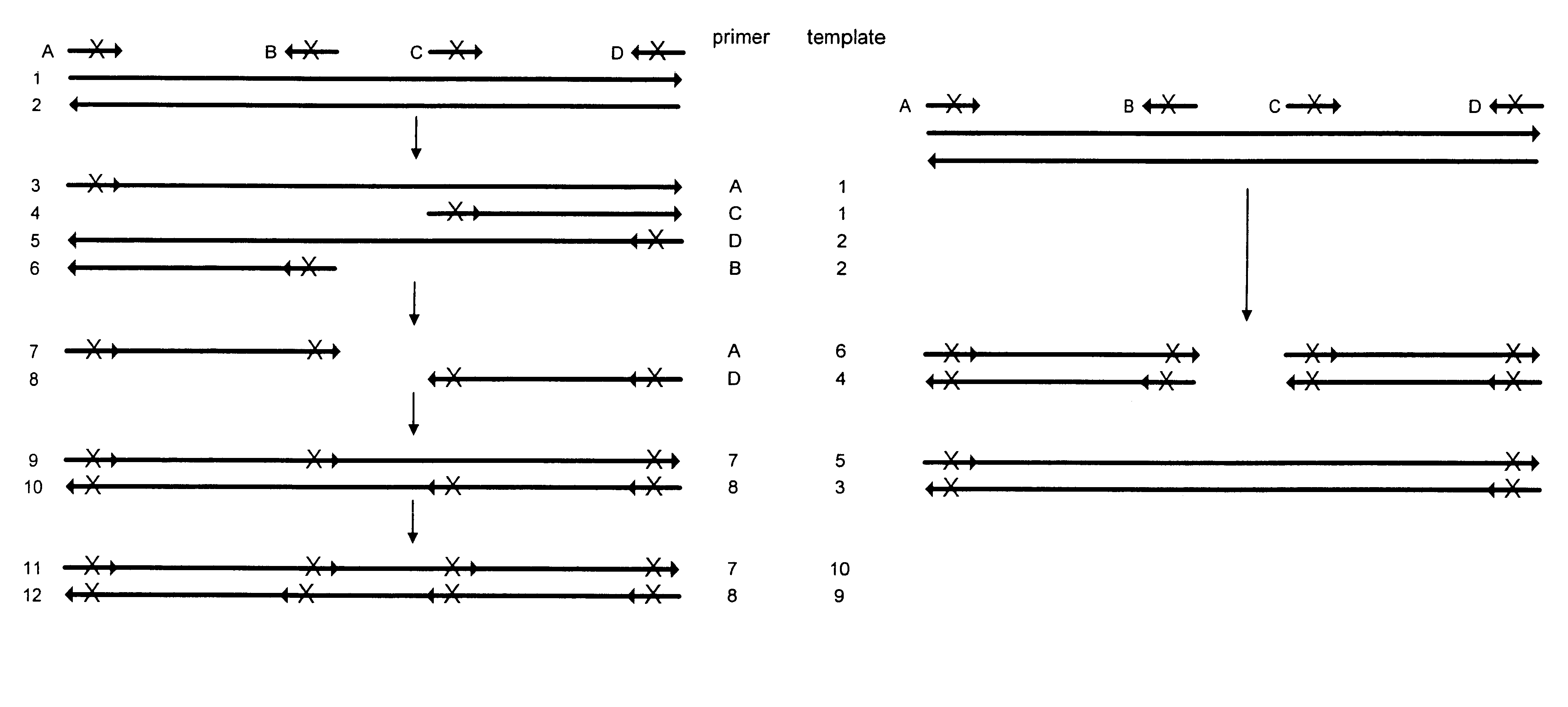
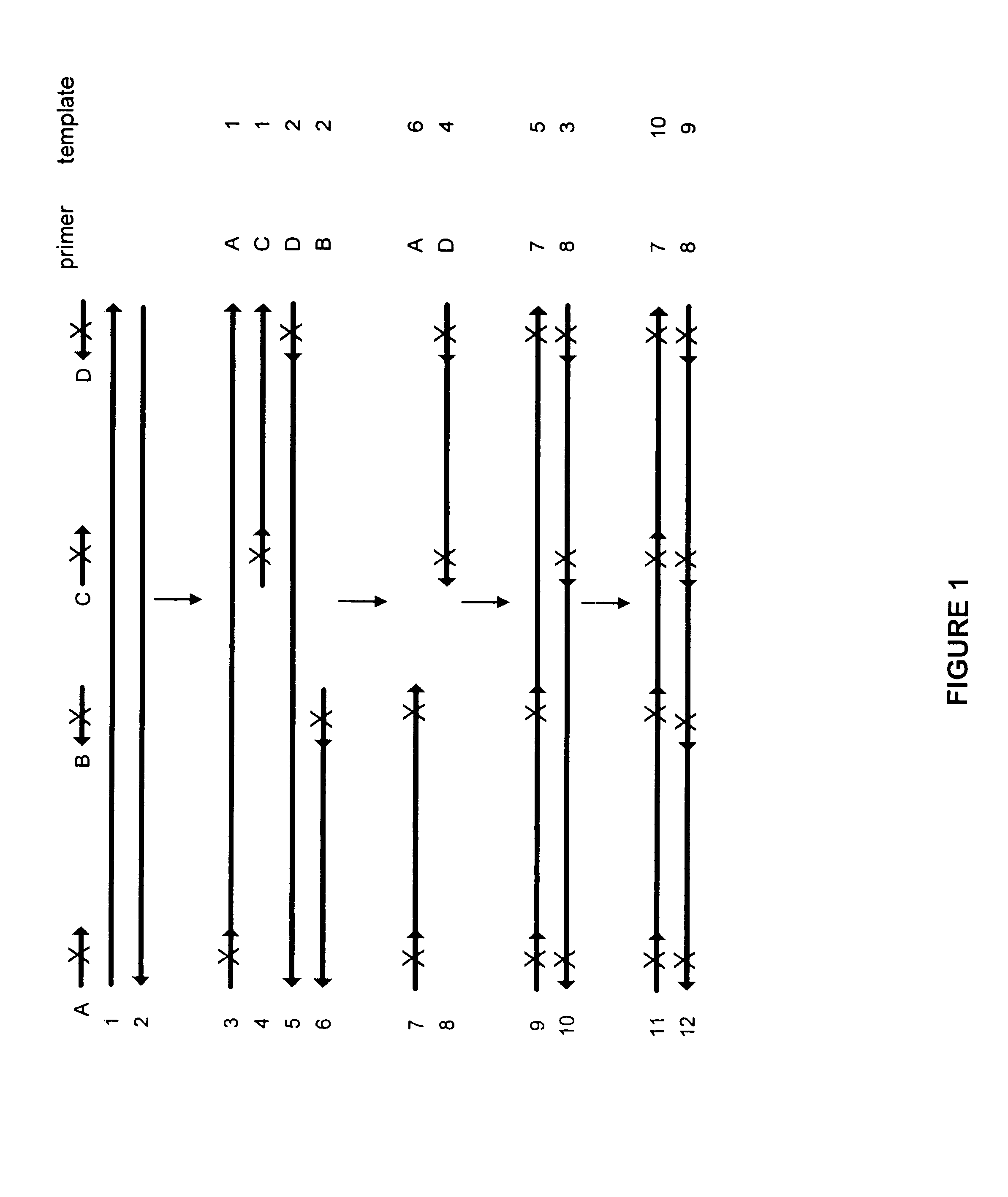
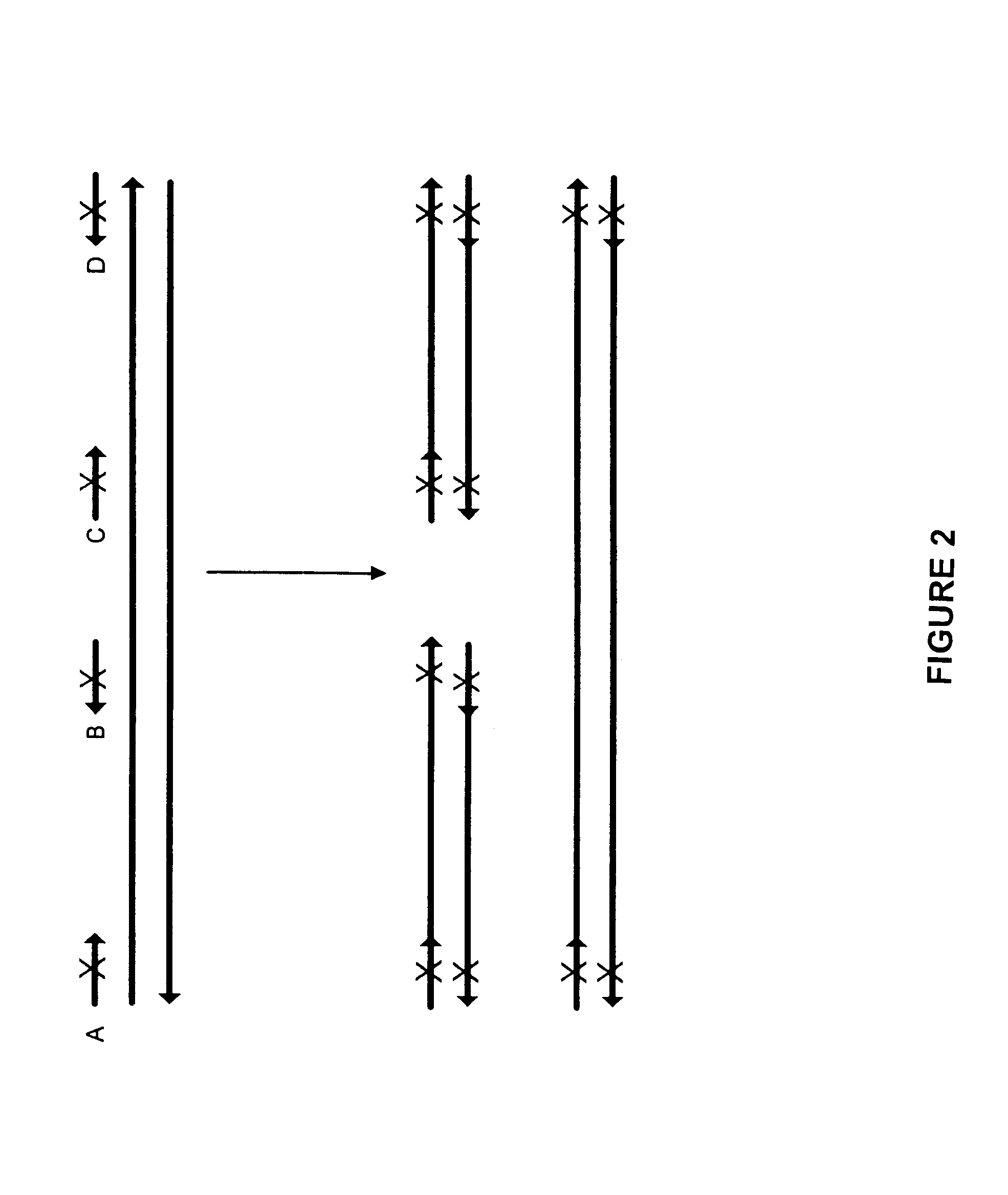
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6117679ALess immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
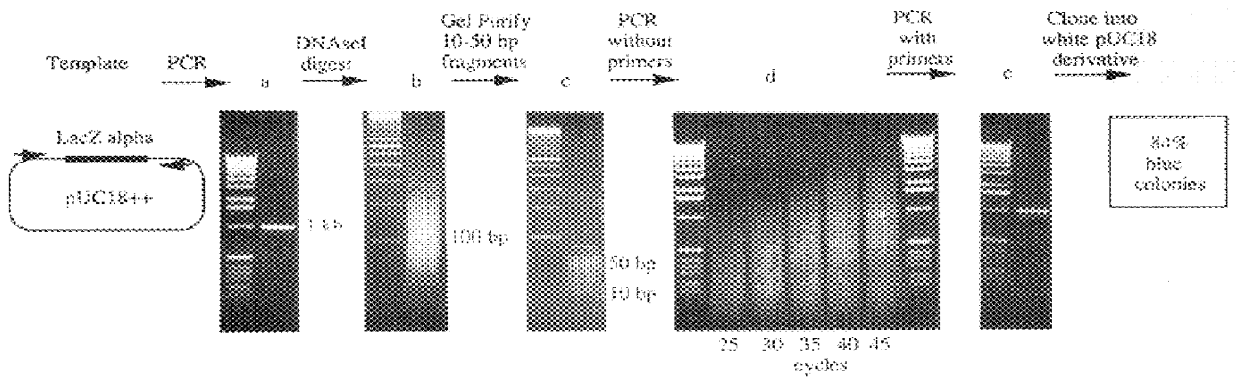
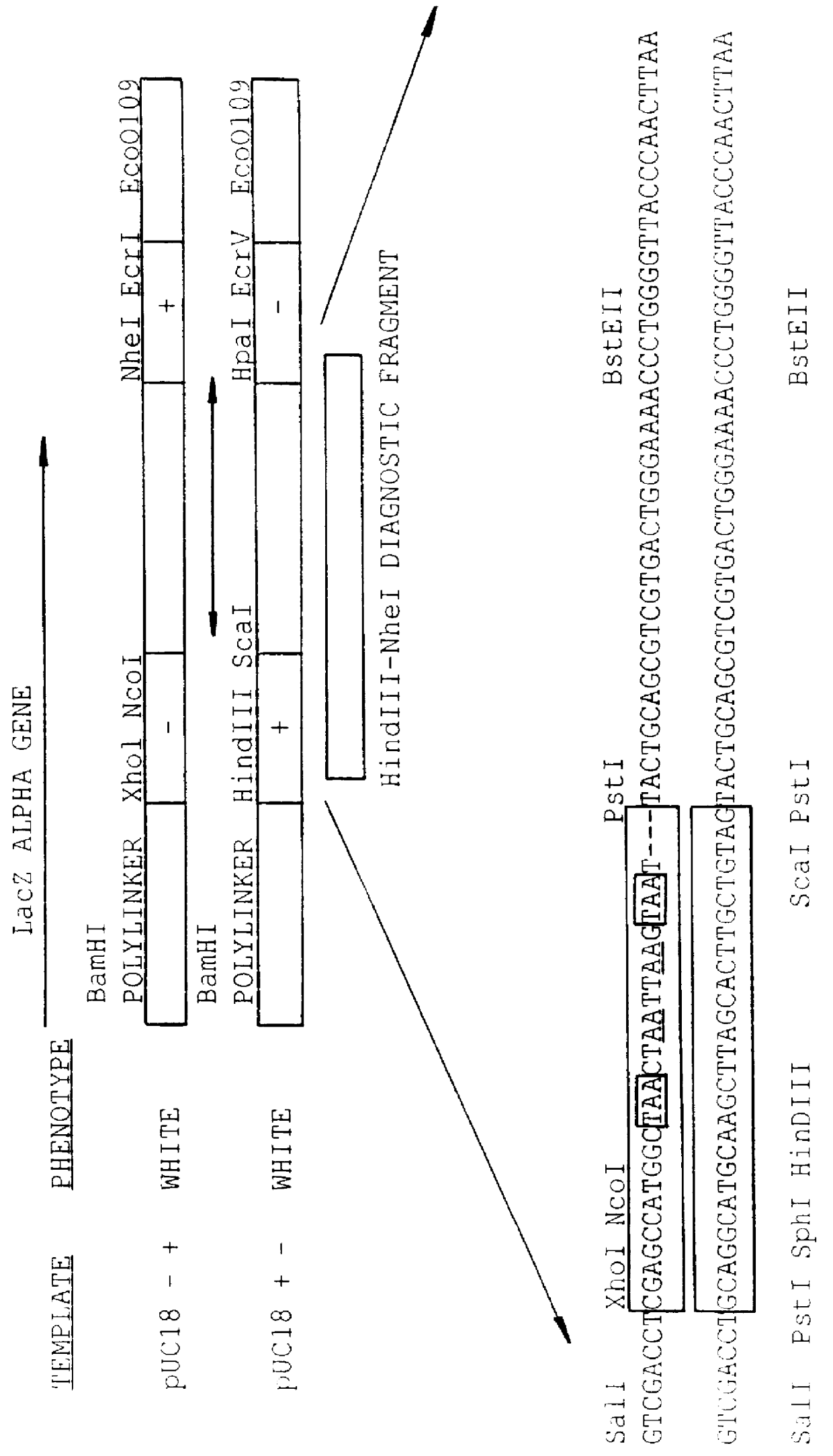
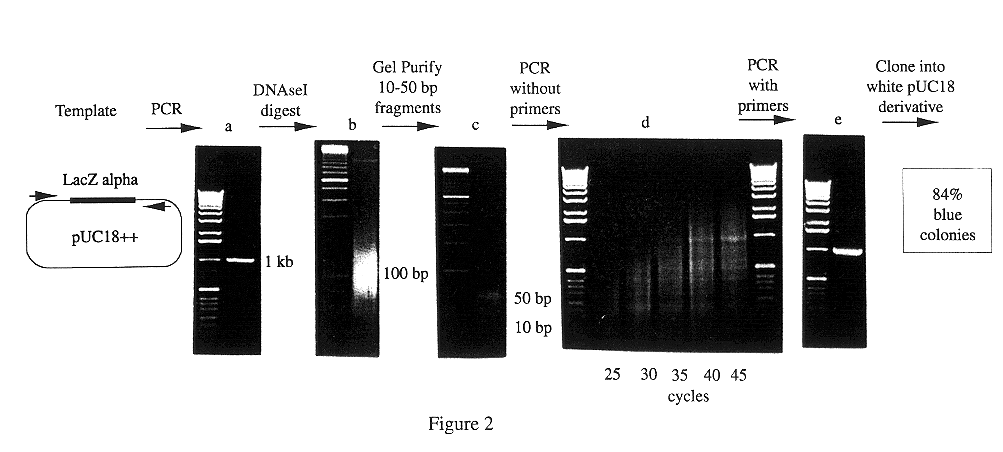
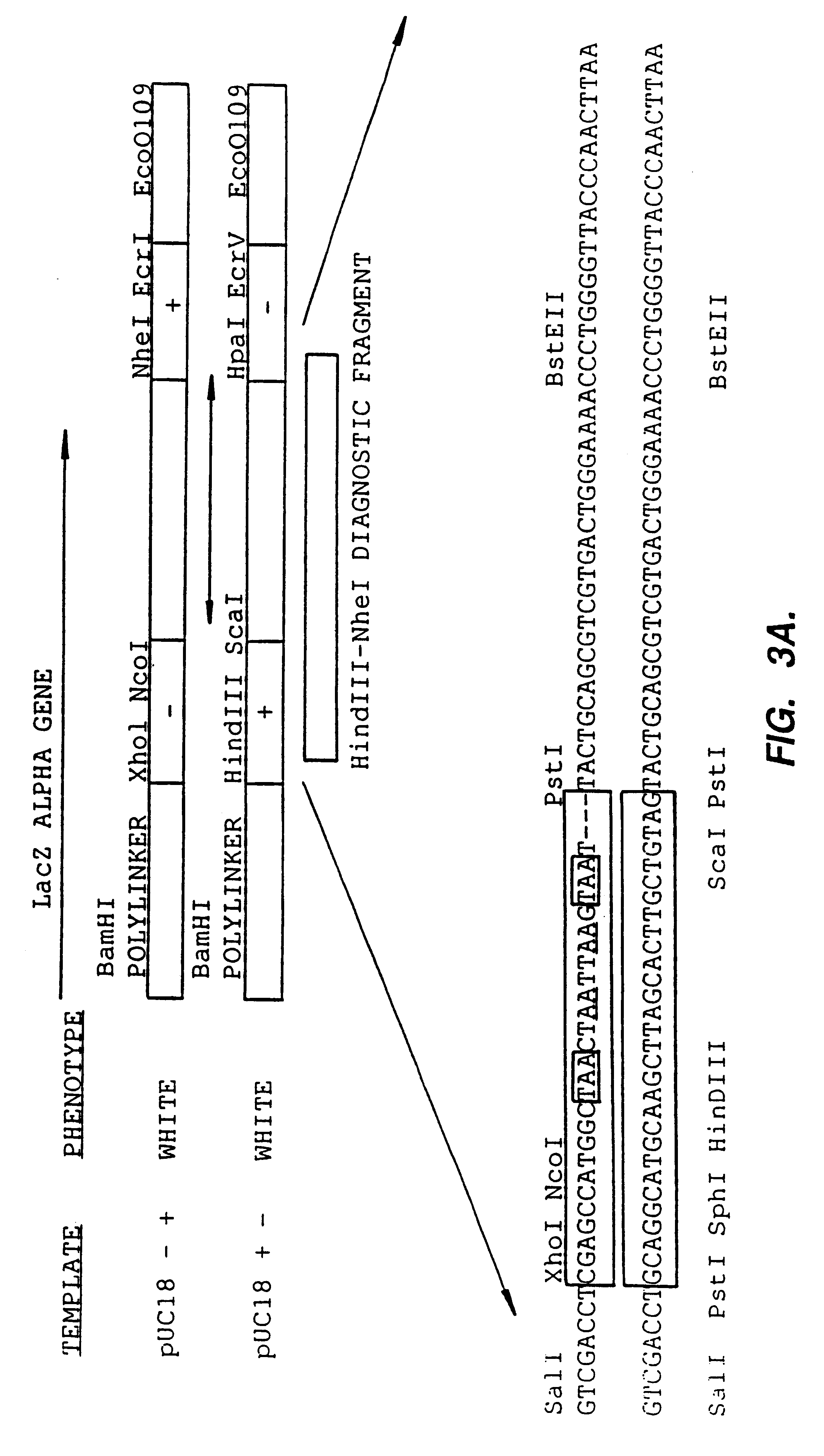
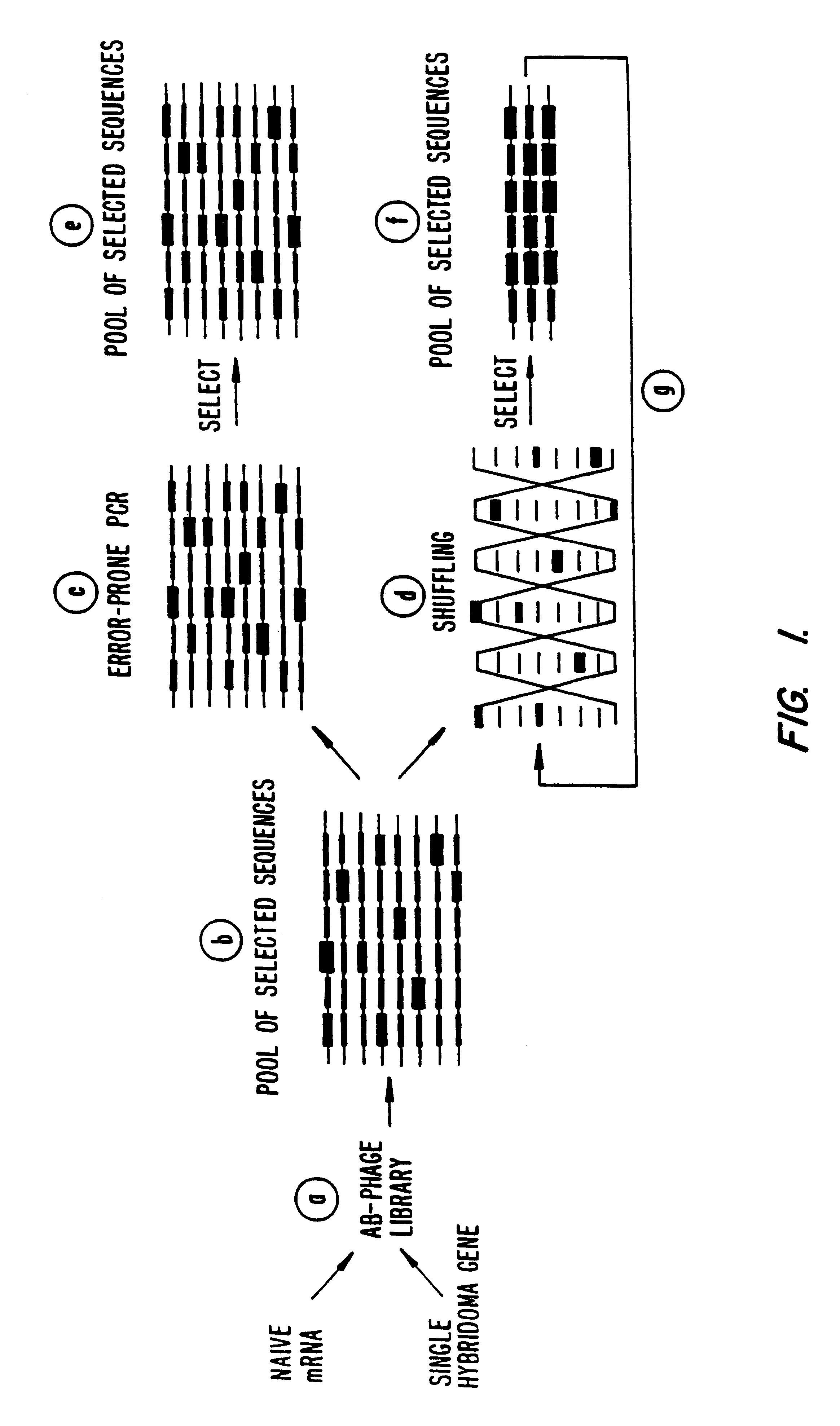
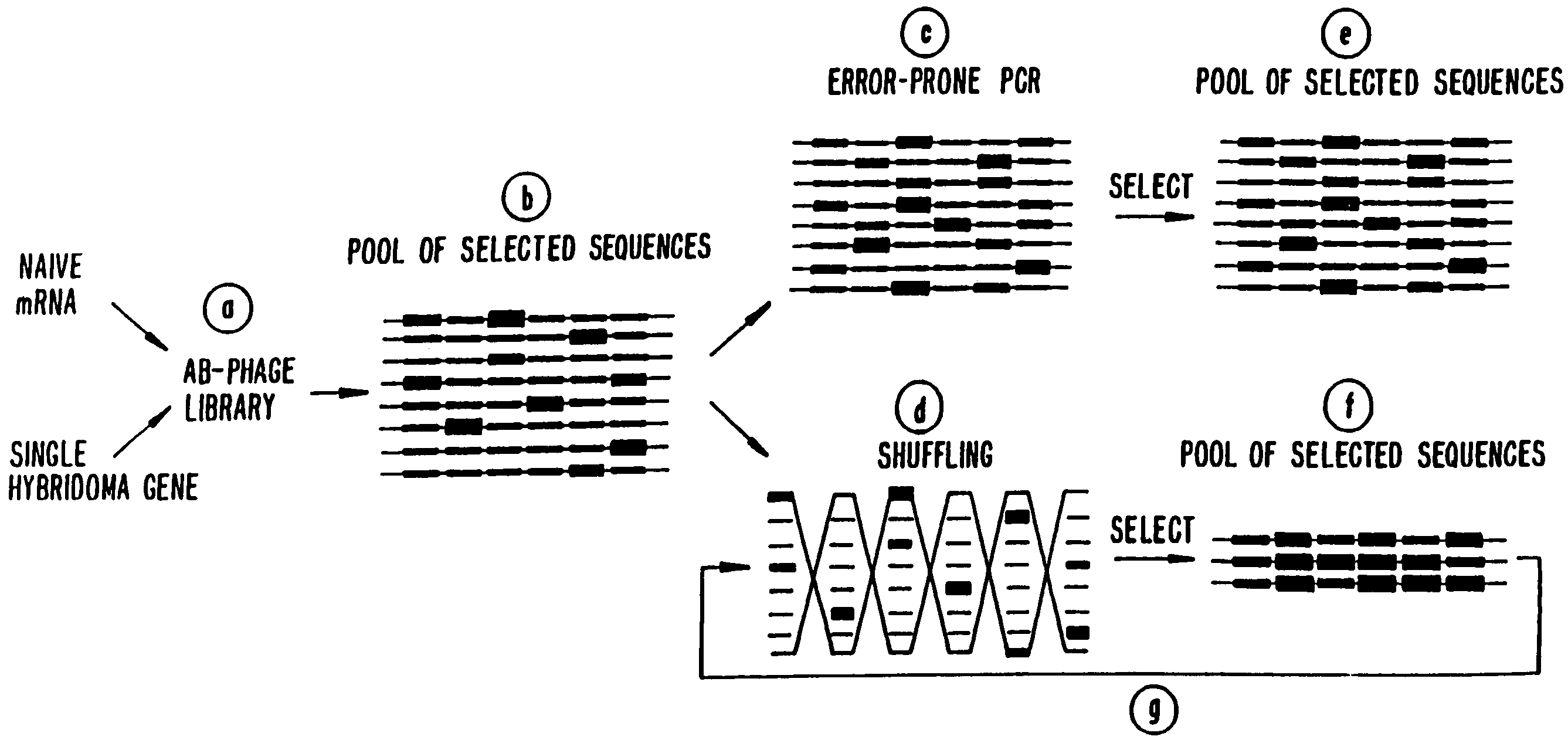
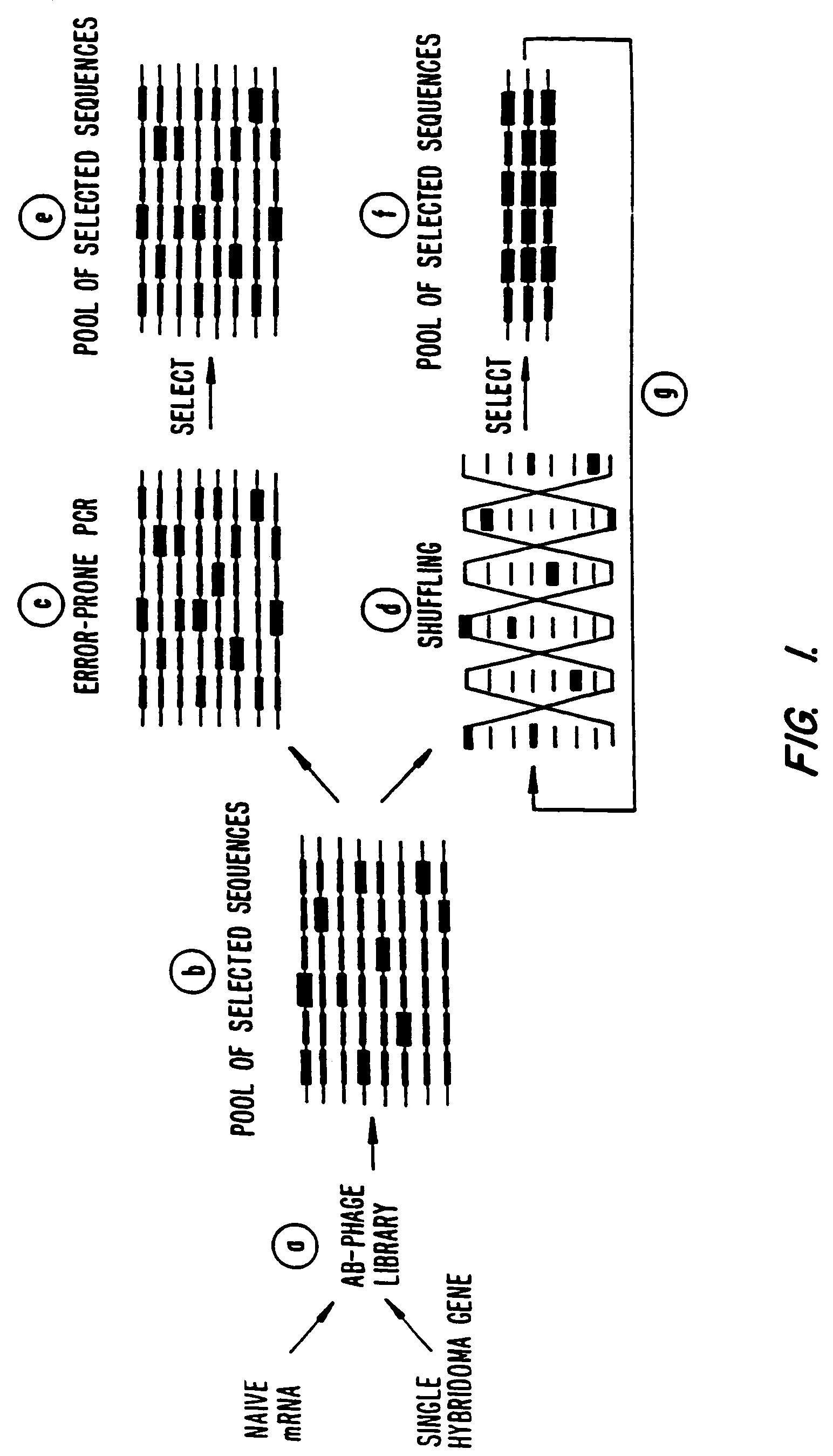
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6180406B1Less immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
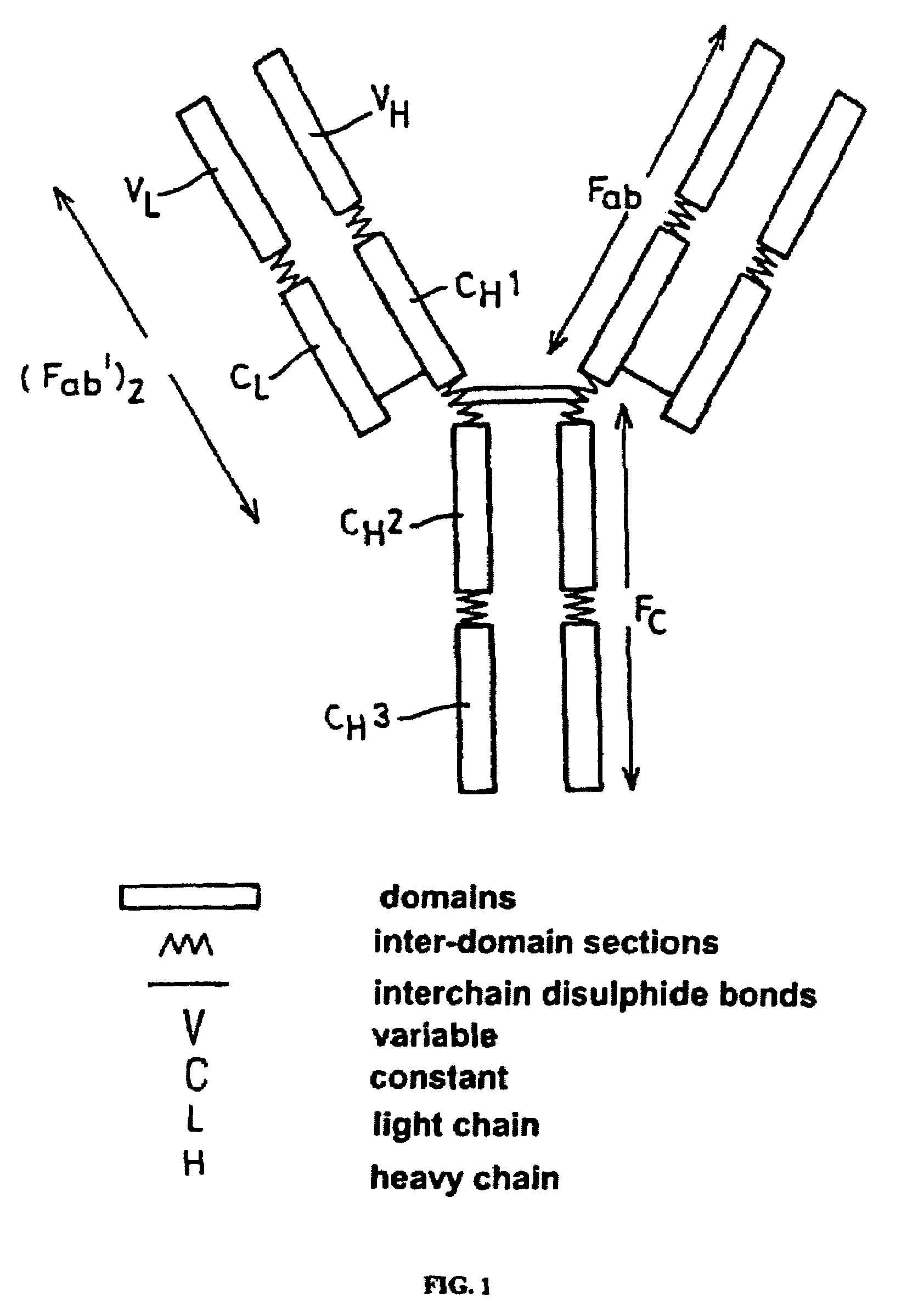
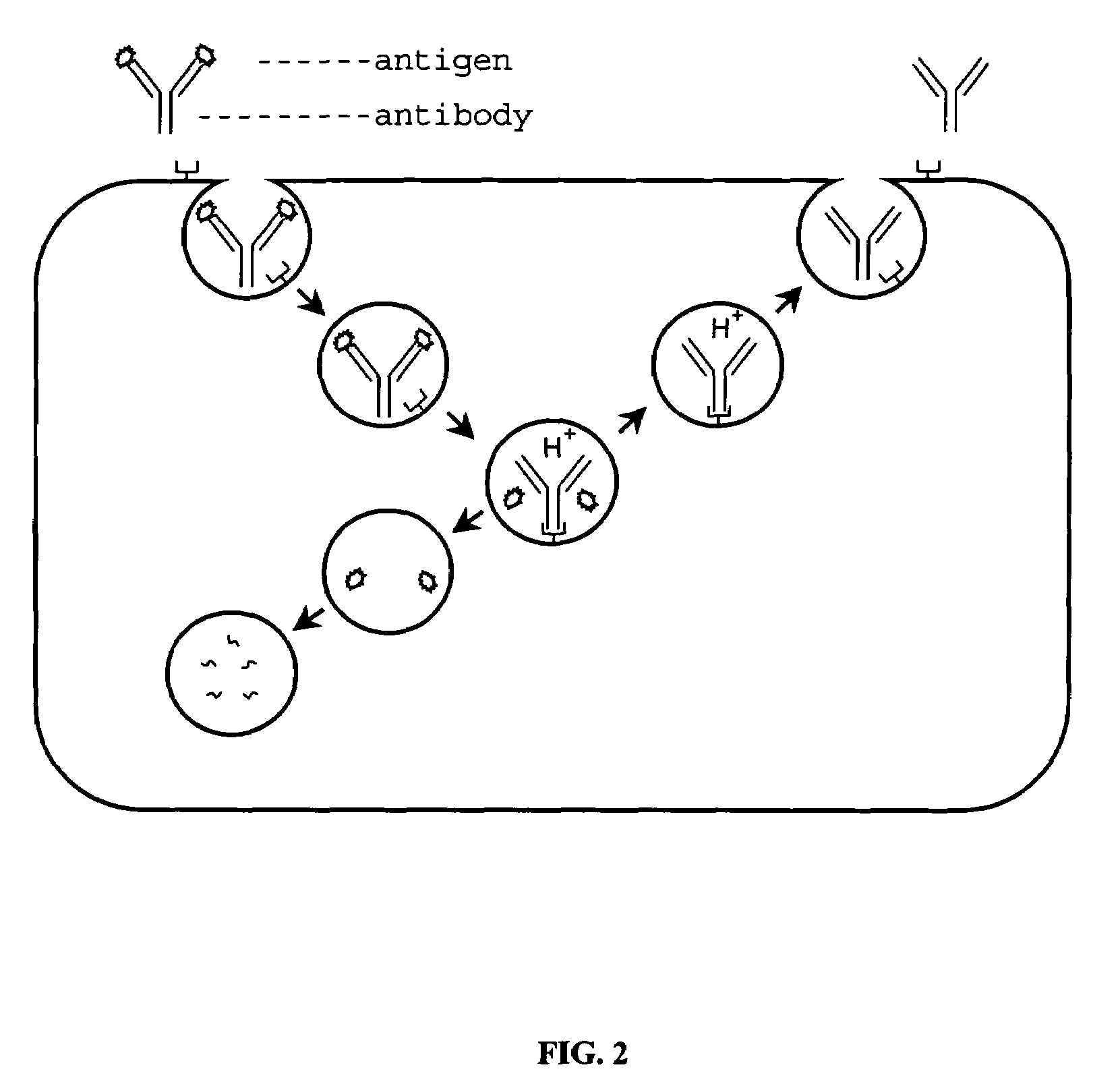
Alteration of FcRn binding affinities or serum half-lives of antibodies by mutagenesis
ActiveUS7217797B2Function increaseExtended half-lifeAnimal cellsSugar derivativesAntiendomysial antibodiesBiochemistry
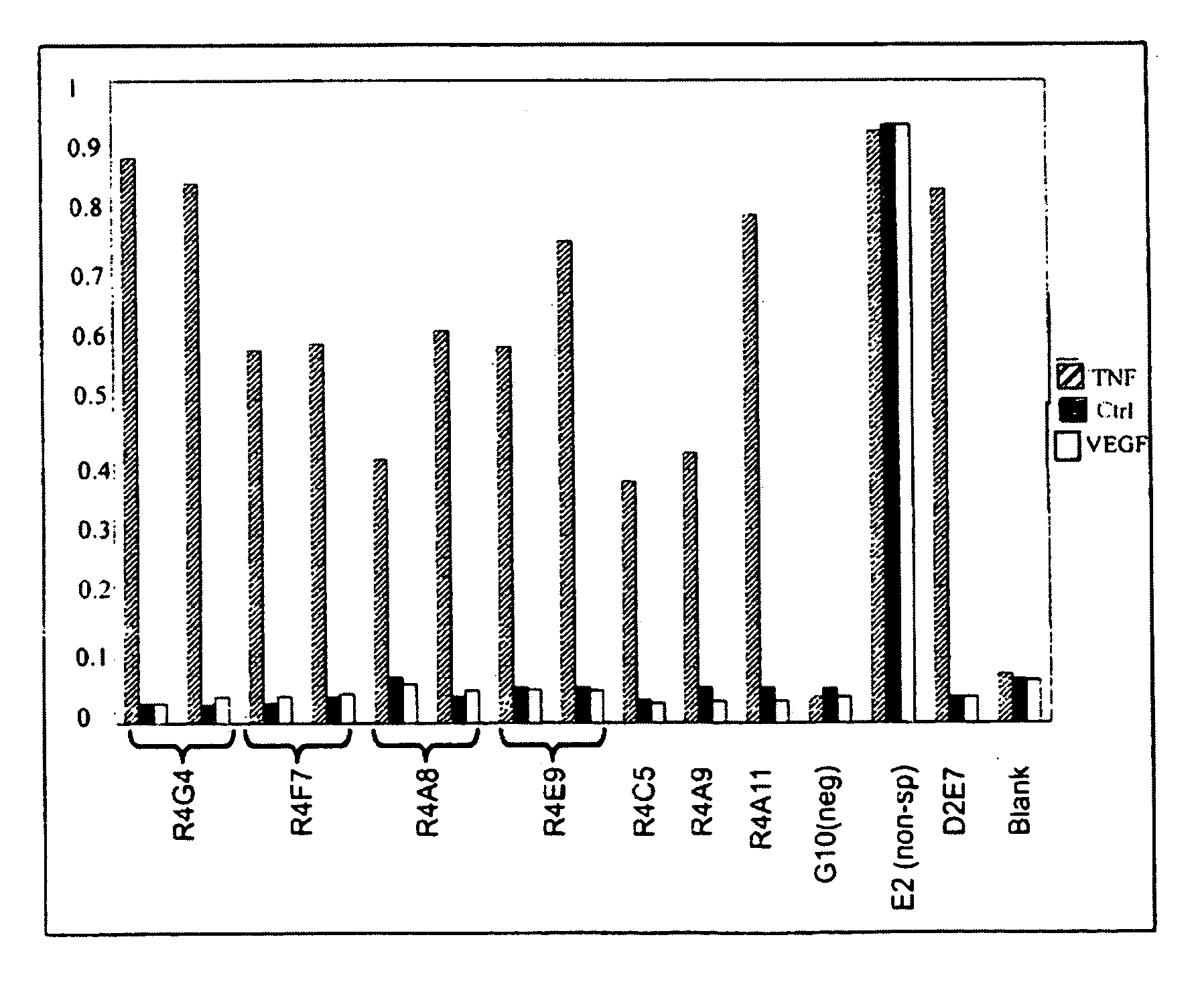
The present invention provides for a modified antibody of class IgG, in which at least one amino acid from the heavy chain constant region selected from the group consisting of amino acid residues 250, 314, and 428 is substituted with another amino acid which is different from that present in the unmodified antibody, thereby altering the binding affinity for FcRn and / or the serum half-life in comparison to the unmodified antibody.
Owner:ABBOTT BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
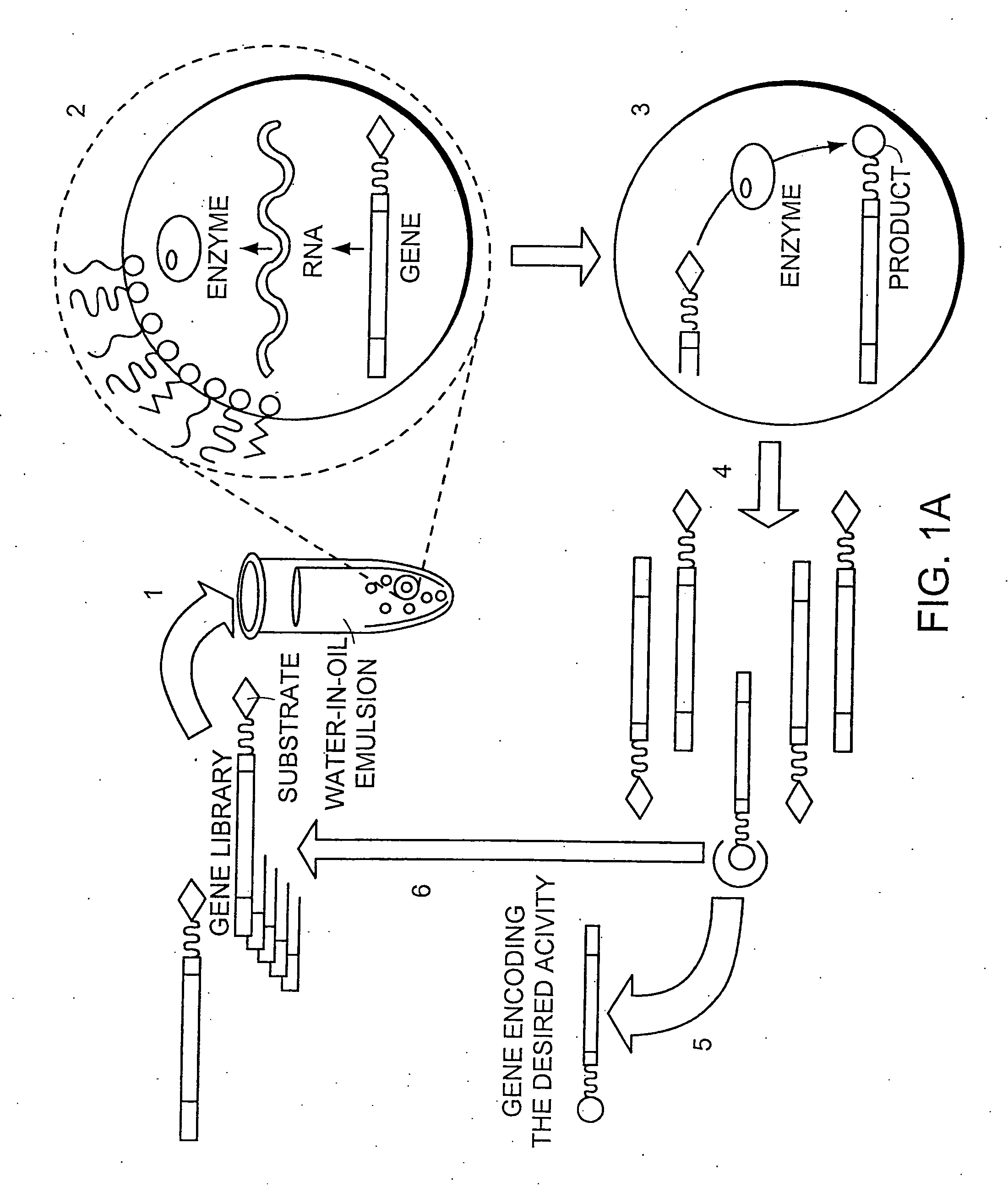
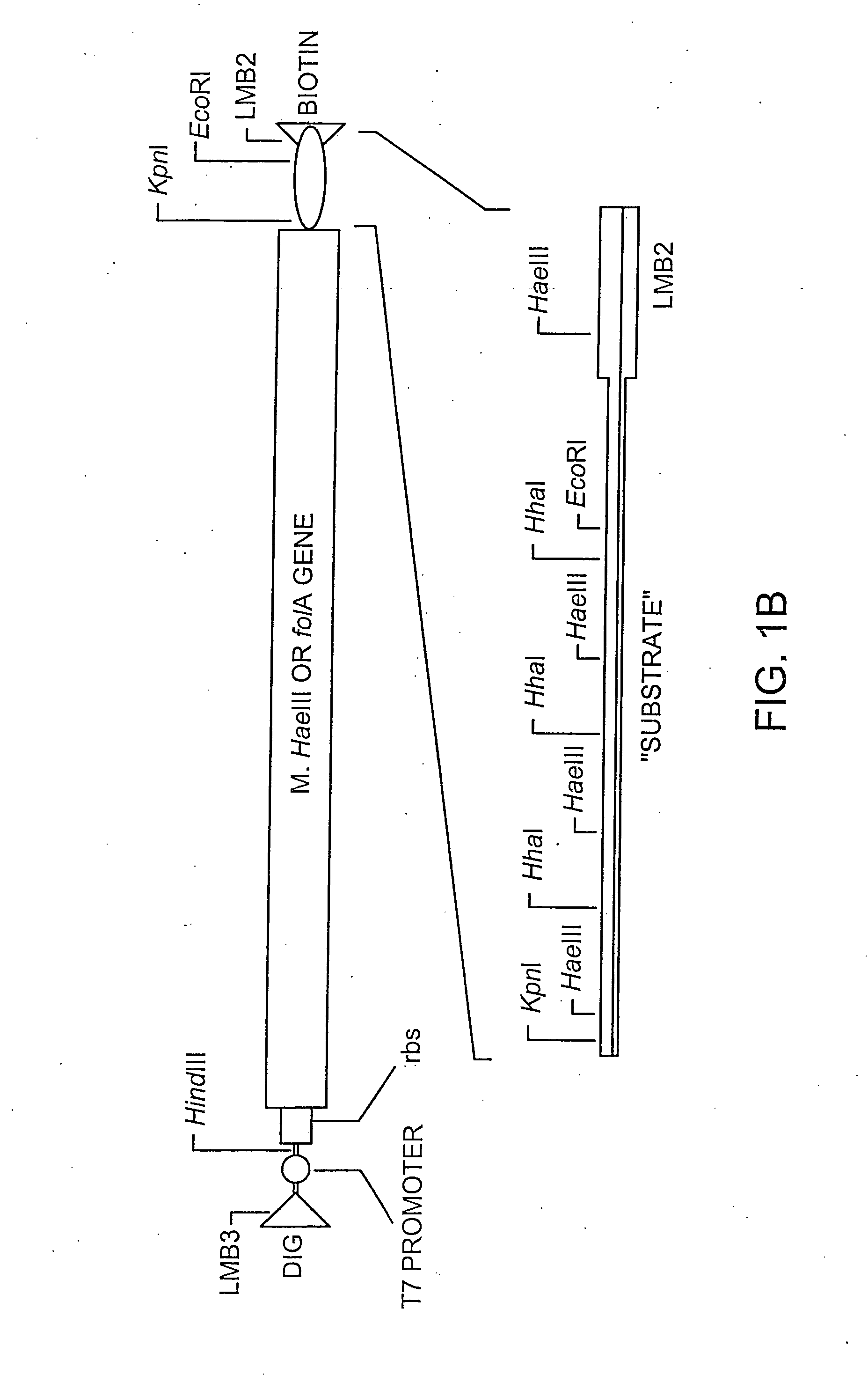
In vitro evolution in microfluidic systems
ActiveUS20060078888A1High activitySpeed up the processSequential/parallel process reactionsFlow mixersGene productGenetic element
The invention describes a method for isolating one or more genetic elements encoding a gene product having a desired activity, comprising the steps of: (a) compartmentalising genetic elements into microcapsules; and (b) sorting the genetic elements which express the gene product having the desired activity; wherein at least one step is under microfluidic control. The invention enables the in vitro evolution of nucleic acids and proteins by repeated mutagenesis and iterative applications of the method of the invention.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Method for generating a library of oligonucleotides comprising a controlled distribution of mutations
InactiveUS6582914B1Microbiological testing/measurementOrganic chemistry methodsOligonucleotideComputational biology
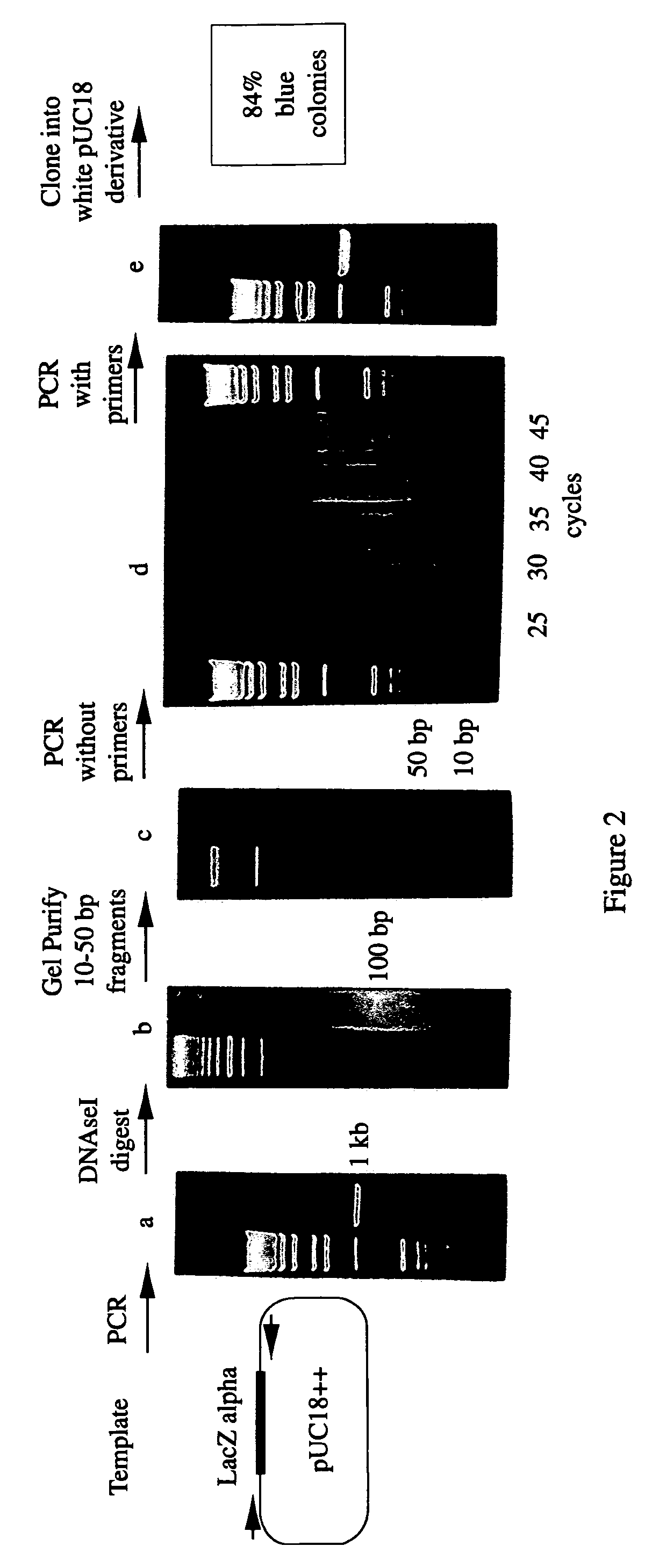
Methods are disclosed for producing libraries of nucleic acid molecules which libraries are derived from a nucleic acid template. The libraries comprise variant nucleic acids which are produced from a mutagenesis strategy using, e.g., a plurality of defined mutagenic and / or non-mutagenic primers and specific reaction conditions which favor the production of varied combinatorial mutants.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Procedure for the production of ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass using a new heat-tolerant yeast
InactiveUS20050069998A1Low conversion rateReduce yieldFungiBiological substance pretreatmentsFiltrationSolid fraction
It includes the stages of grinding the lignocellulosic biomass to a size of 15-30 mm, subjecting the product obtained to steam explosion pre-treatment at a temperature of 190-230° C. for between 1 and 10 minutes in a reactor (2), collecting the pre-treated material in a cyclone (3) and separating the liquid and solid fractions by filtration in a filter press (9), introducing the solid fraction in a fermentation deposit (10), adding a cellulase at a concentration of 15 UFP per gram of cellulose and 12.6 International Units of β-glucosidase enzyme dissolved in citrate buffer pH 4.8, inoculating the fermentation deposit (10) with a culture of the heat-tolerant bacteria Kluyveromyces marxianus CECT 10875, obtained by chemical mutagenesis from strain DER-26 of Kluyveromyces marxianus and shaking the mixture for 72 hours at 42° C.
Owner:CENT DE INVESTIGACIONES ENERGETICAS MEDIO AMBIENTALLES Y TECNOLOGICAS (C I E M A T)
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS7288375B2Less immunogenicPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsMutated proteinNucleotide
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
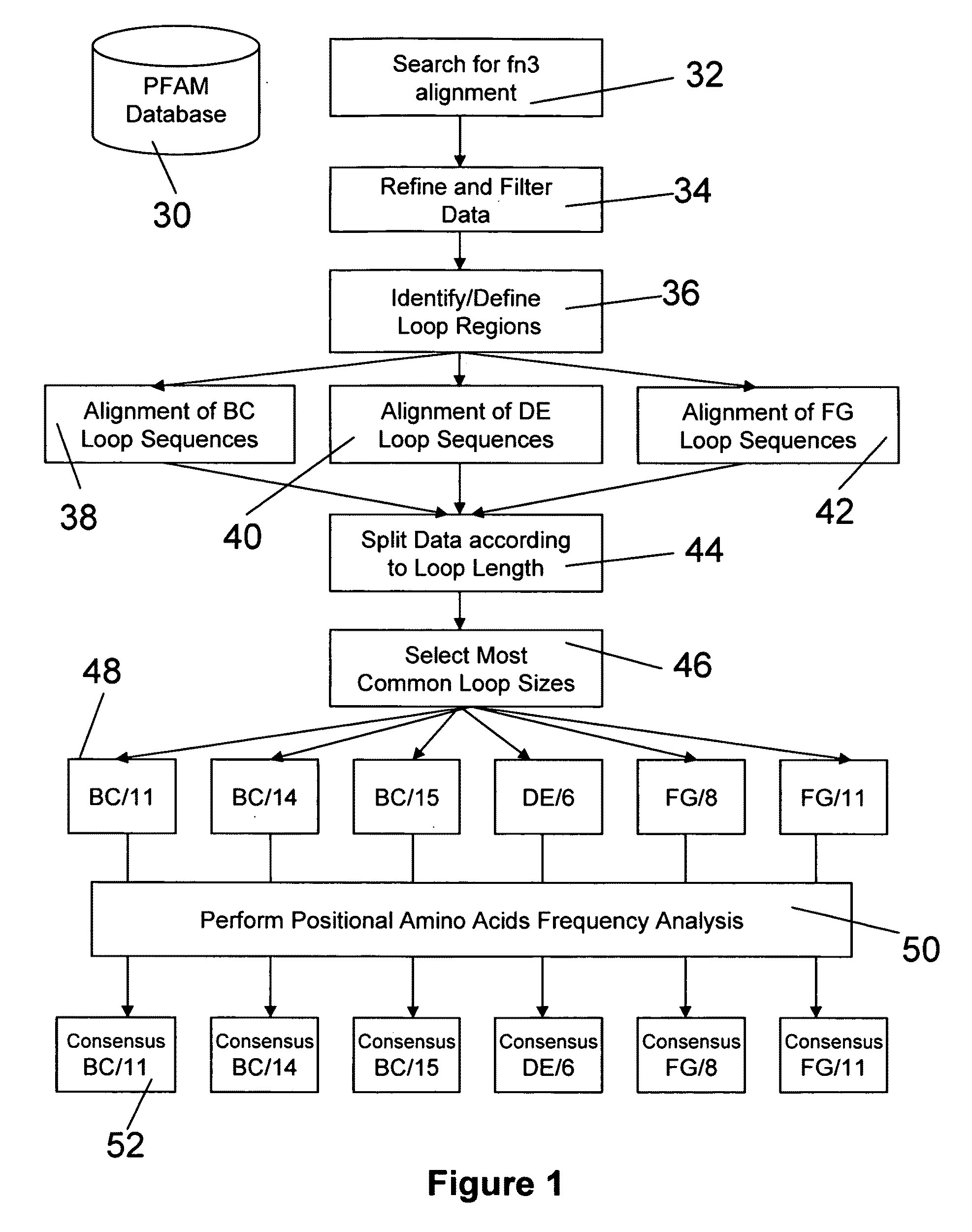
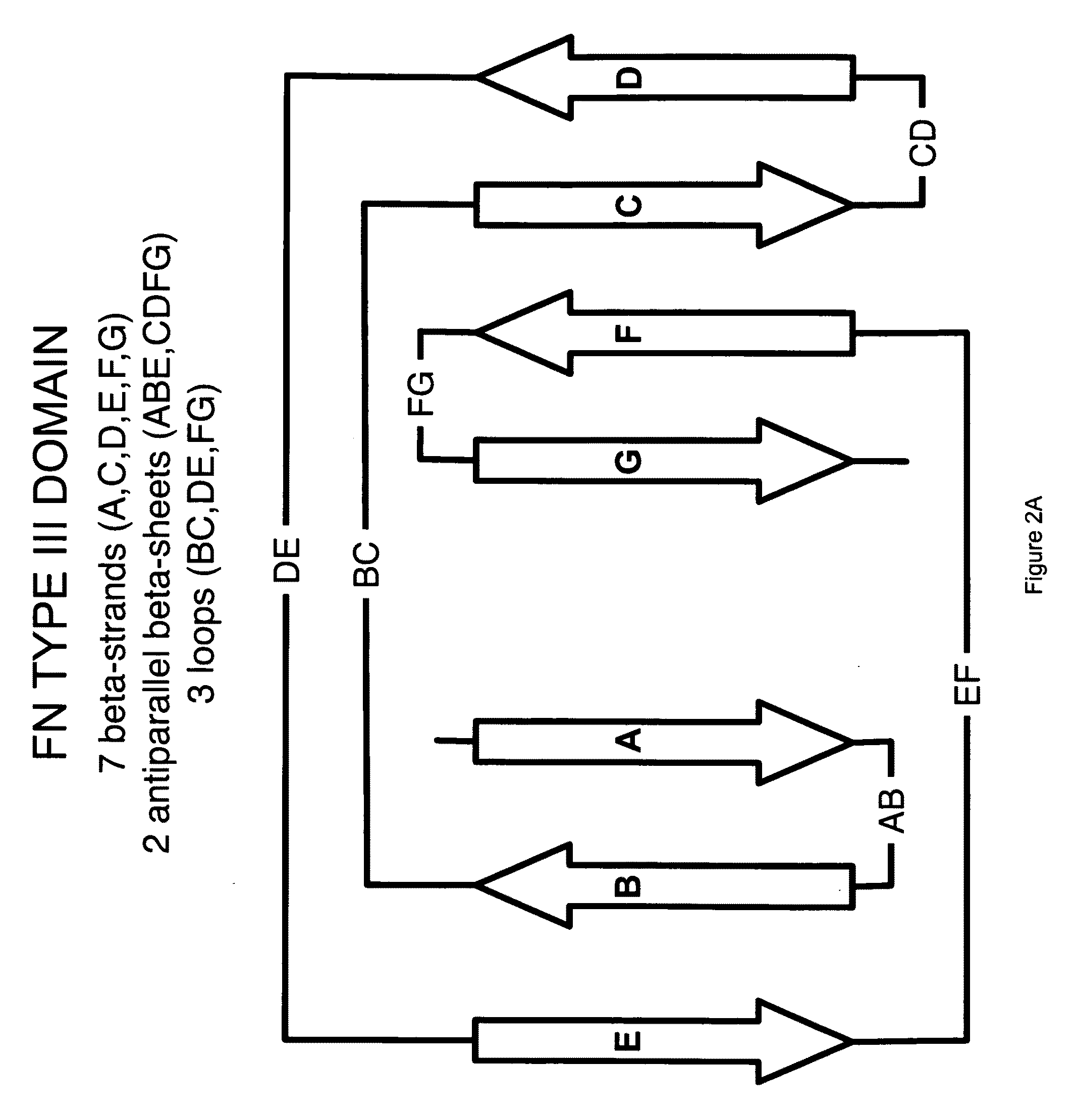
Universal fibronectin type III binding-domain libraries
Walk-through mutagenesis and natural-variant combinatorial fibronectin Type III (FN3) polypeptide libraries are described, along with their method of construction and use. Also disclosed are a number of high binding affinity polypeptides selected by screening the libraries against a variety of selected antigens.
Owner:PROTELIX
Wheat variety W020757F1
ActiveUS8809654B1Increased seed yieldImprove granulation qualityBiocideDough treatmentTriticeaeTriticum turgidum
A wheat variety designated W020757F1, the plants and seeds of wheat variety W020757F1, methods for producing a wheat plant produced by crossing the variety W020757F1 with another wheat plant, and hybrid wheat seeds and plants produced by crossing the variety W020757F1 with another wheat line or plant, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of variety W020757F1. This invention also relates to methods for producing other wheat varieties or breeding lines derived from wheat variety W020757F1 and to wheat varieties or breeding lines produced by those methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
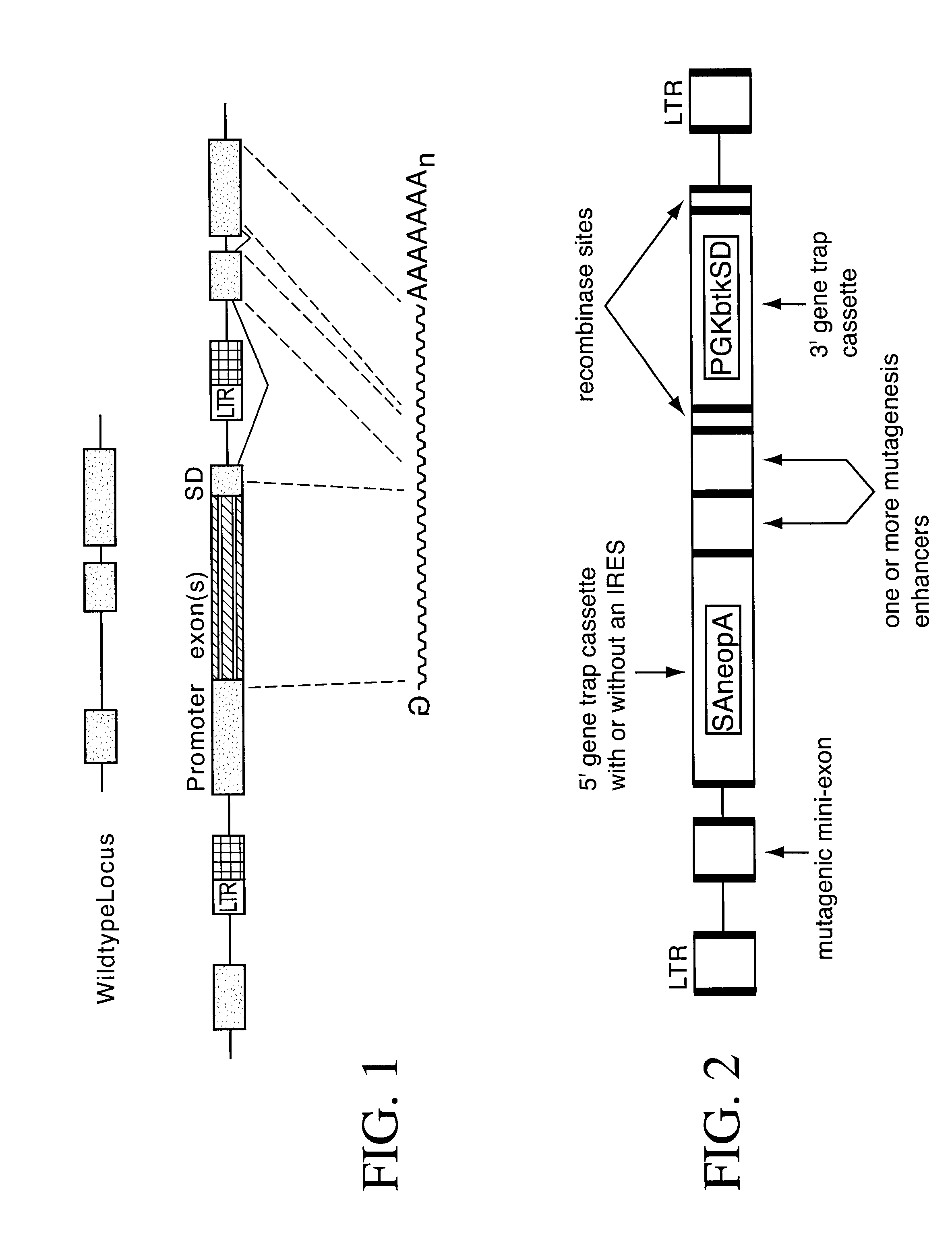
Vectors for gene mutagenesis and gene discovery
InactiveUS6436707B1Quick identificationLimit exploitationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsGene mutationGene trapping
Novel vectors are described that incorporate, inter alia, a novel 3' gene trap cassette which can be used to efficiently trap and identify previously unknown cellular genes. Vectors incorporating the described 3' gene trap cassette find particular application in gene discovery and in the production of mutated cells and animals.
Owner:LEXICON PHARM INC
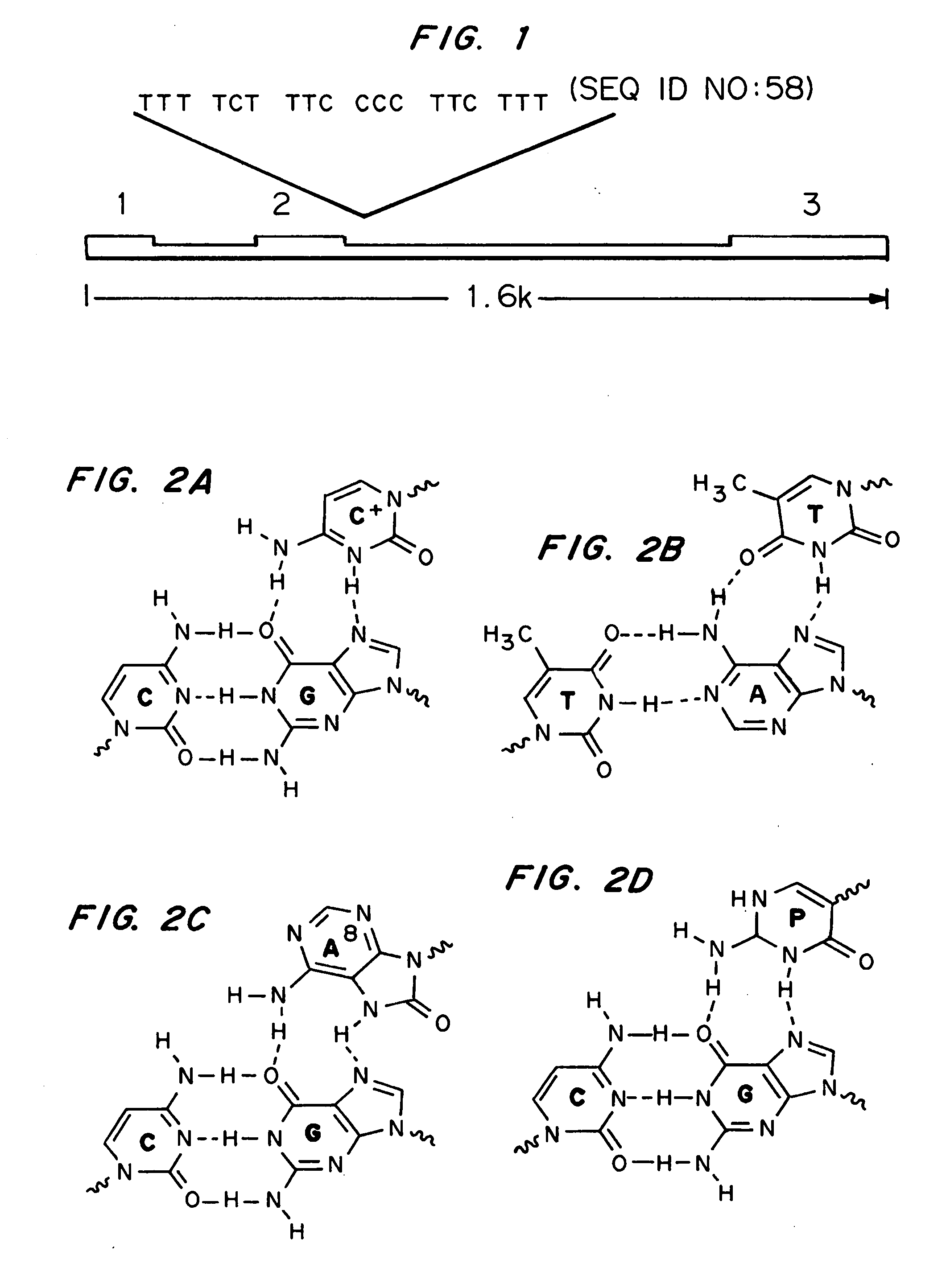
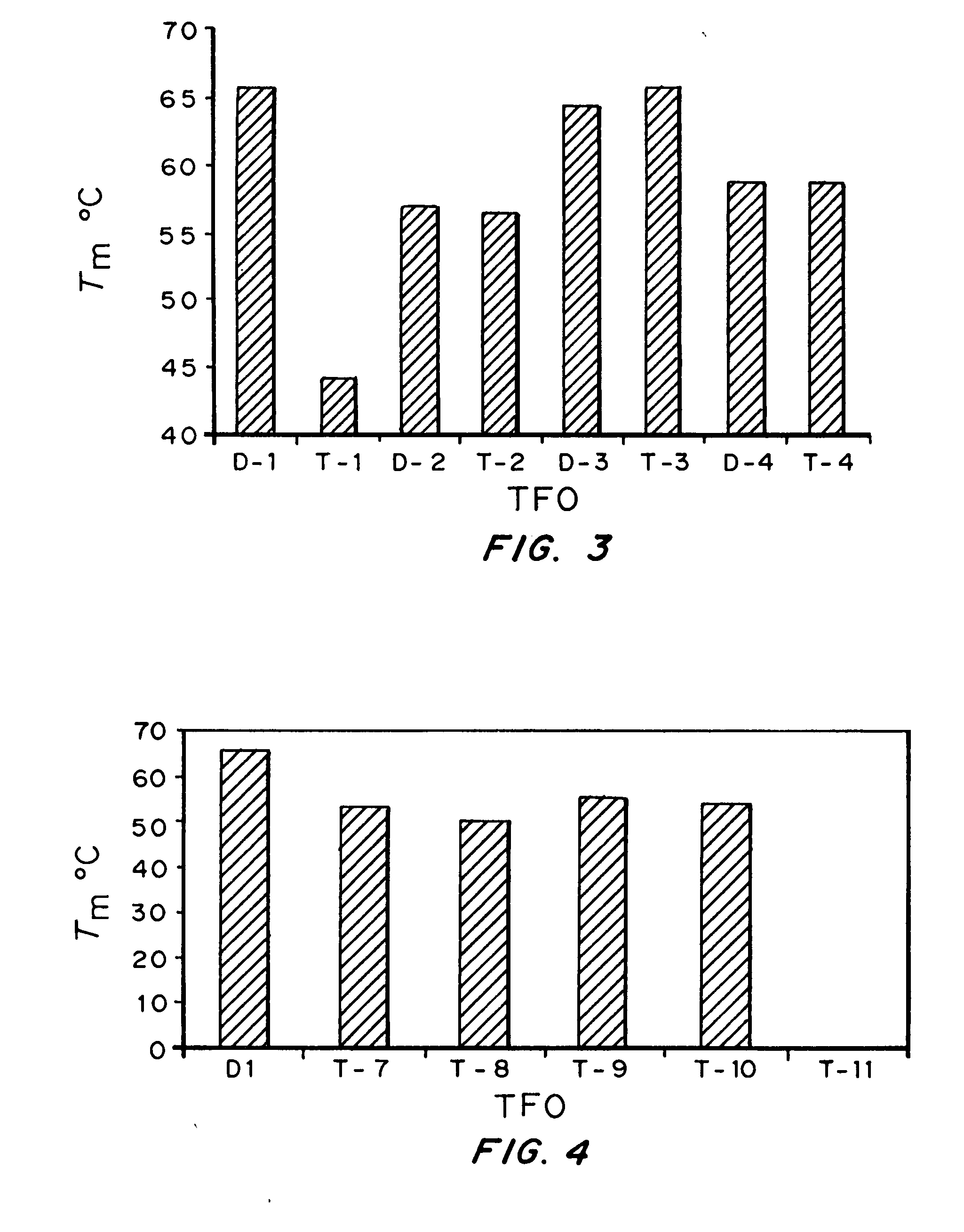
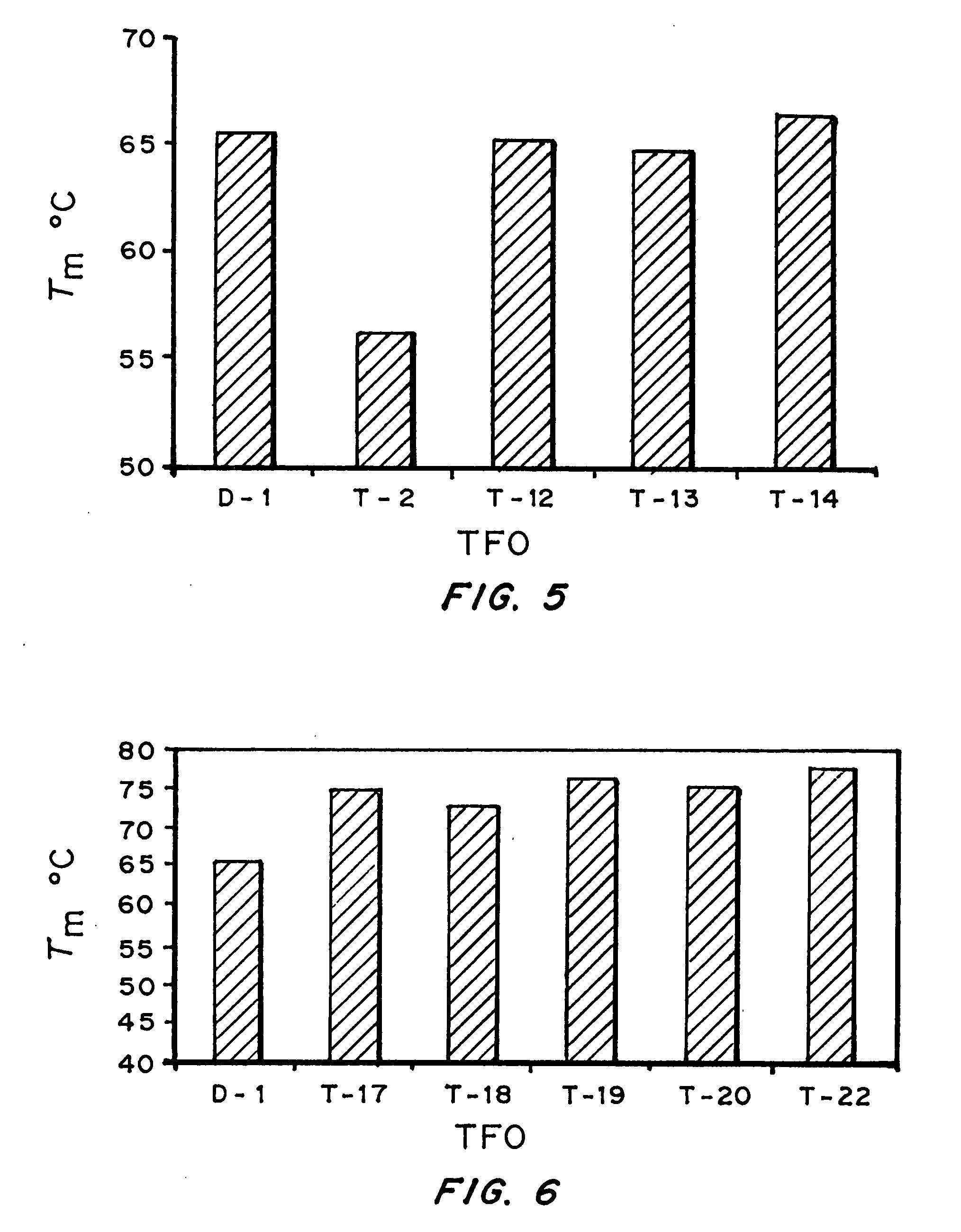
Modified triple-helix forming oligonucleotides for targeted mutagenesis
ActiveUS20070219122A1Enhance stabilityImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsMutagenic ProcessChemistry
High affinity, chemically modified triplex-forming oligonucleotides (TFOs) and methods for use thereof are disclosed. TFOs are defined as triplex-forming oligonucleotides which bind as third strands to duplex DNA in a sequence specific manner. Triplex-forming oligonucleotides may be comprised of any possible combination of nucleotides and modified nucleotides. Modified nucleotides may contain chemical modifications of the heterocyclic base, sugar moiety or phosphate moiety. A high affinity oligonucleotide (Kd≦2×10−8) which forms a triple strand with a specific DNA segment of a target gene DNA is generated. It is preferable that the Kd for the high affinity oligonucleotide is below 2×10−10. The nucleotide binds or hybridizes to a target sequence within a target gene or target region of a chromosome, forming a triplex region. The binding of the oligonucleotide to the target region stimulates mutations within or adjacent to the target region using cellular DNA synthesis, recombination, and repair mechanisms. The mutation generated activates, inactivates, or alters the activity and function of the target gene.
Owner:CONCORD +2
In vitro sorting method
InactiveUS20070077579A1High activityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGene productGene
The invention describes a method for isolating one or more genetic elements encoding a gene product having a desired activity, comprising of the steps of: (a) compartmentalising genetic elements into microcapsules; (b) expressing the genetic elements to produce their respective gene products within the microcapsules; (c) sorting the genetic elements which produce the gene product having a desired activity. The invention enables the in vitro evolution of nucleic acids by repeated mutagenesis and iterative applications of the method of the invention.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
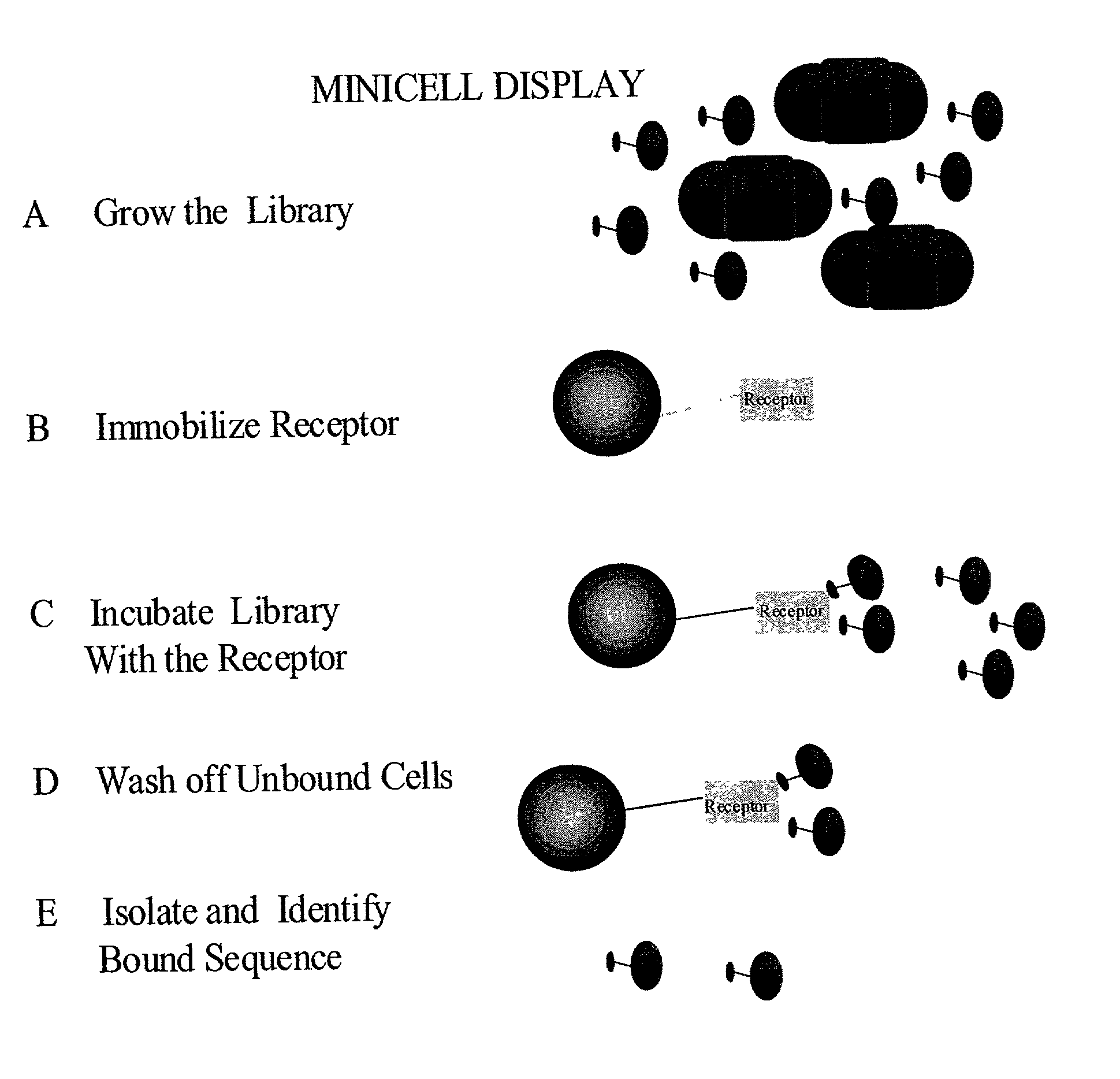
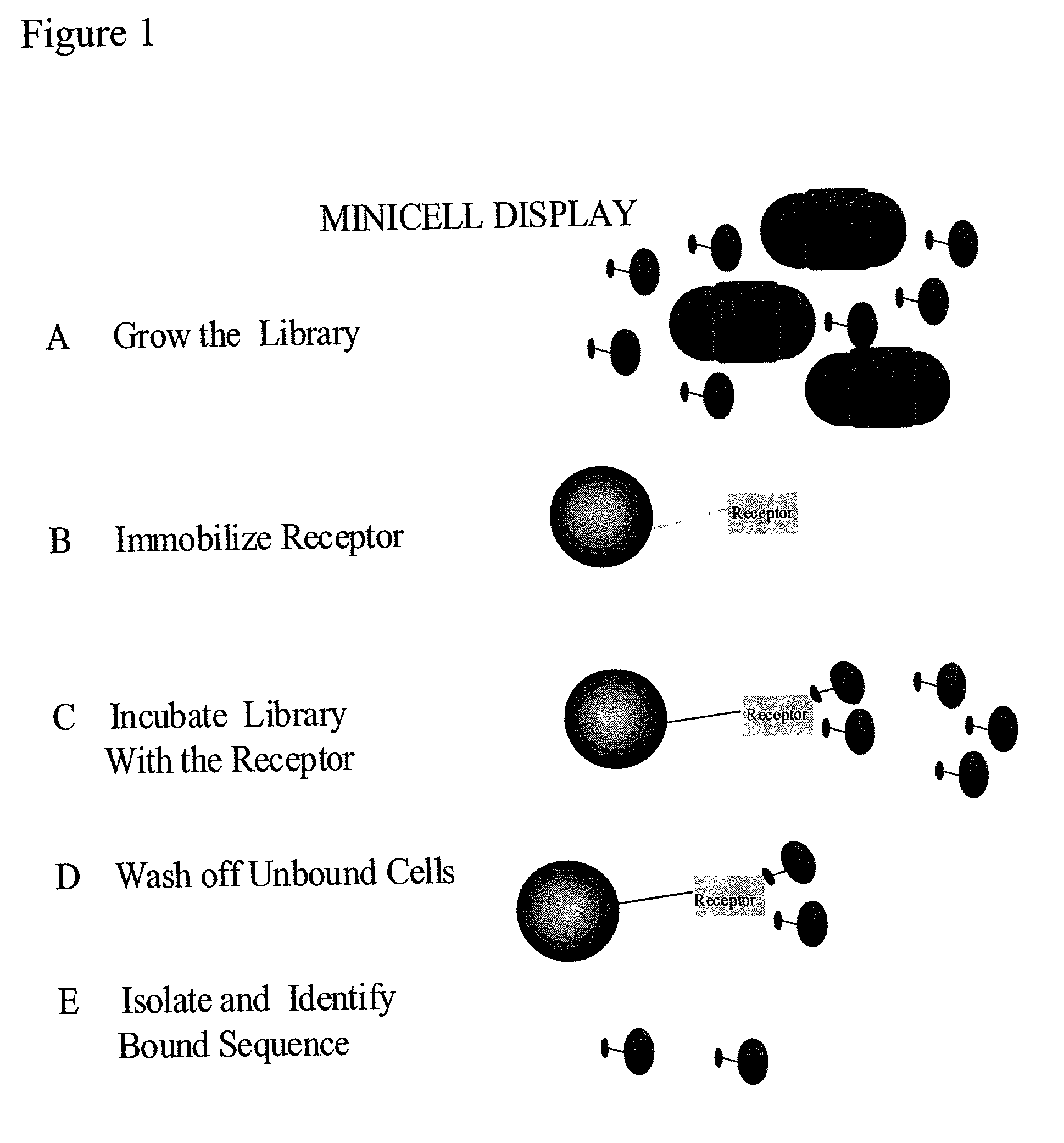
Methods to screen peptide libraries using minicell display
InactiveUS7125679B2Easy to eluteIncrease mutation frequencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesIn vivoMutagenesis
A minicell display method has been developed which has significant advantages for screening peptide libraries for candidates that can bind and effectively modulate a particular biological process. The method, based on the small, anucleate minicell, has increased versatility in generating unique sequences to screen as well as increasing the size of the peptides to be screened. In vivo mutagenesis, at the level of protein synthesis, as well as DNA replication, increases diversification of the library to be screened and therefore substantially increases the number of potential peptides that can modulate a particular biological response or mechanism.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
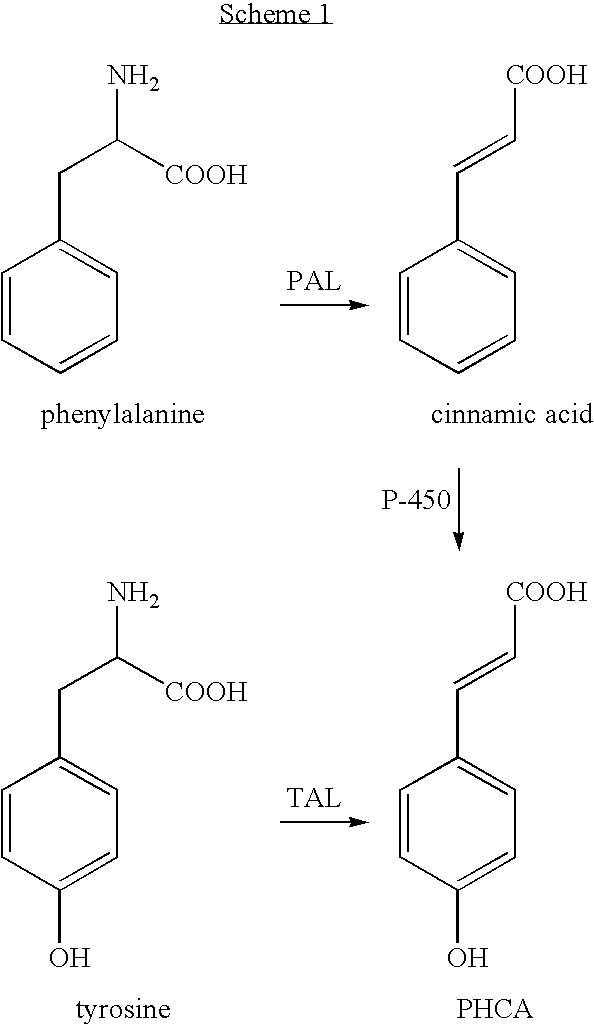
Bioproduction of para-hydroxycinnamic acid
The present invention provides several methods for biological production of para-hydroxycinnamic acid (PHCA). The invention is also directed to the discovery of new fungi and bacteria that possess the ability to convert cinnamate to PHCA. The invention relates to developing of a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wild type PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis into E. coli underlining the ability of the wildtype PAL to convert tyrosine to PHCA. The invention is also directed to developing a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wildtype PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis plus the plant cytochrome P-450 and the cytochrome P-450 reductase into E. coli. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides for the developing of a new biocatalyst through mutagenesis of the wild type yeast PAL which possesses enhanced tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) activity.
Owner:GATENBY ANTHONY A +4
Canola cultivar dn040845
ActiveUS20080263717A1Improve nutritional qualityPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyCultivar
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola cultivar, designated DN040845. Also included are seeds of canola cultivar DN040845, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola DN040845 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola DN040845 with itself or another canola cultivar, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola DN040845.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
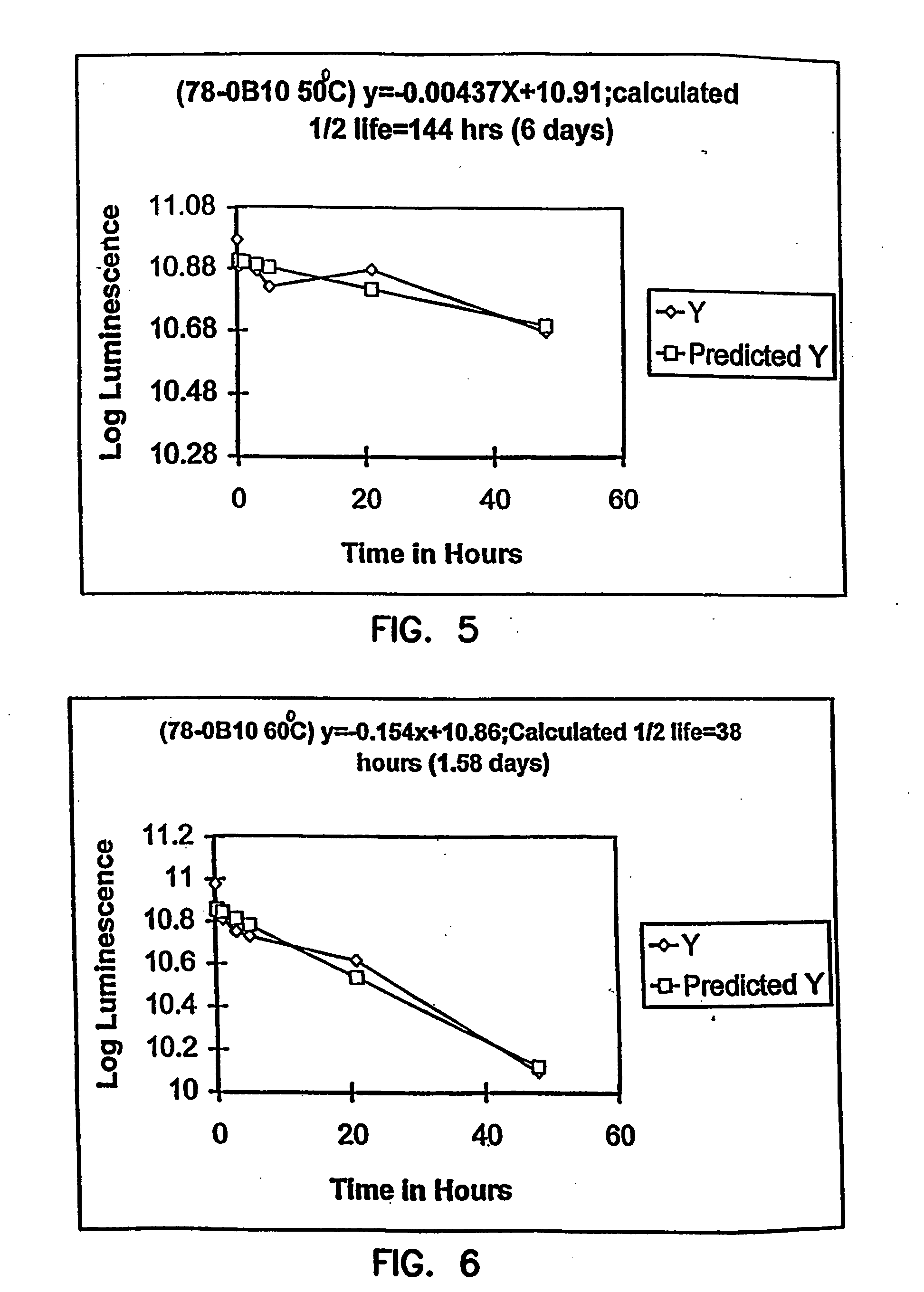
Thermostable luciferases and methods of production
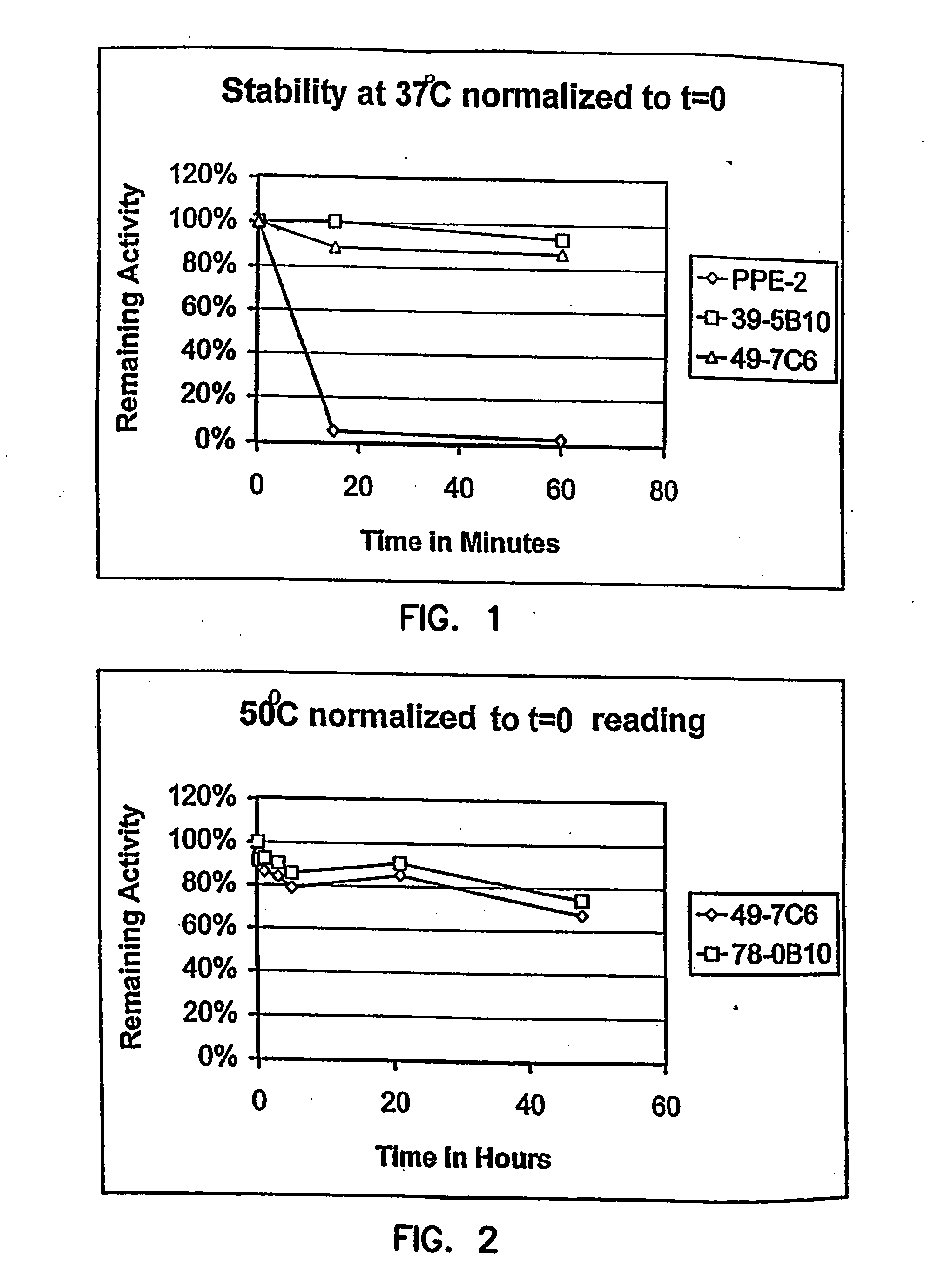
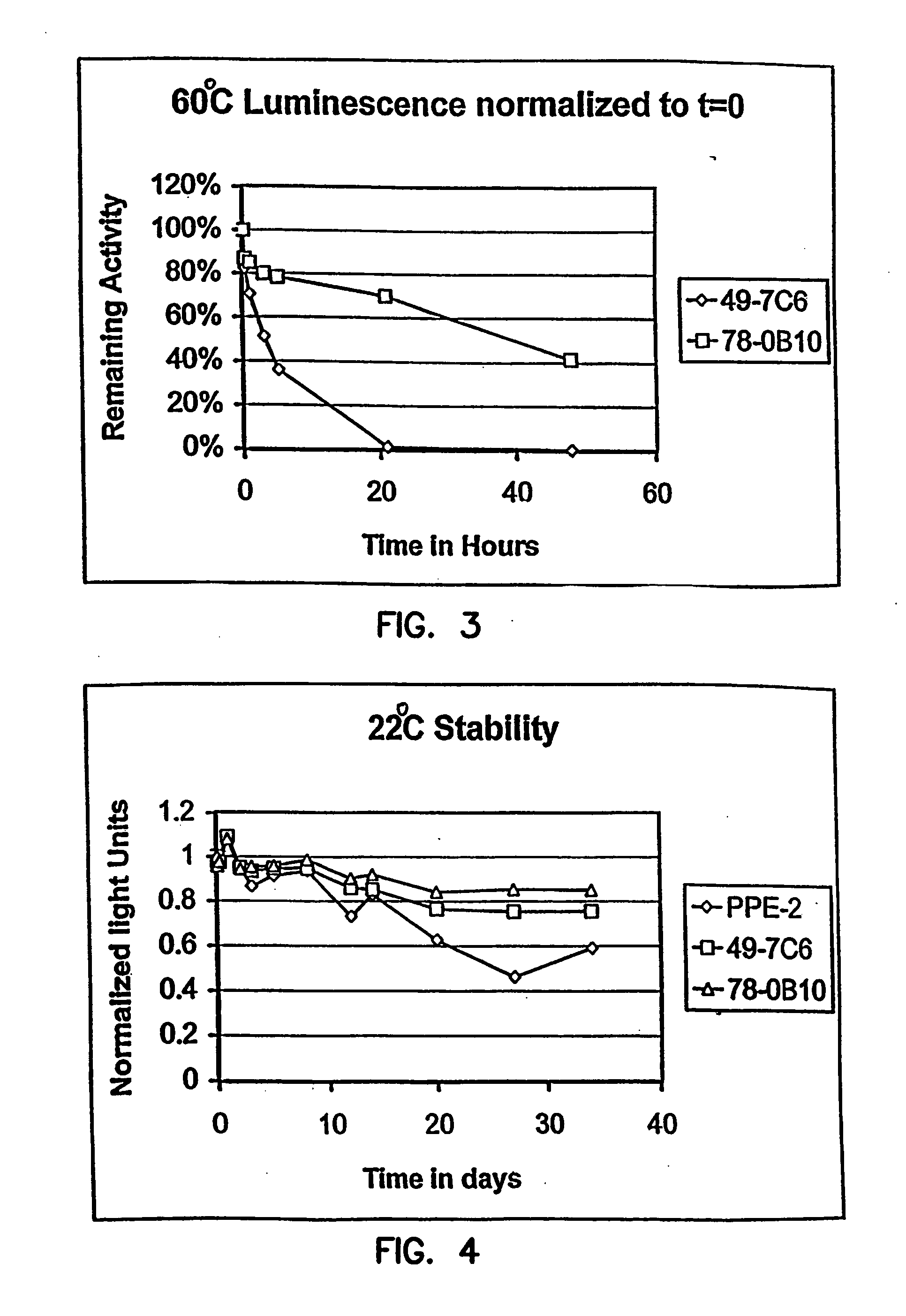
InactiveUS20060183212A1High luminous intensityLost less than 5% luminescence activityFungiNanotechBiotechnologyLuciferase Gene
Luciferase enzymes with greatly increased thermostability, e.g., at least half lives of 2 hours at 50° C., cDNAs encoding the novel luciferases, and hosts transformed to express the luciferases, are disclosed. Methods of producing the luciferases include recursive mutagenesis. The luciferases are used in conventional methods, some employing kits.
Owner:PROMEGA CORP
DNA polymerase blends and uses thereof
ActiveUS7960157B2Improve efficiencyImprove performanceHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementLong pcrGenomic DNA
The present invention discloses novel blends of chimeric and non-chimeric thermostable DNA polymerases for use in PCR, DNA sequencing and mutagenesis protocols. The invention allows for PCR reactions with shorter extension times that will facilitate PCR amplification of genomic DNA templates and improve the efficacy of long PCR.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
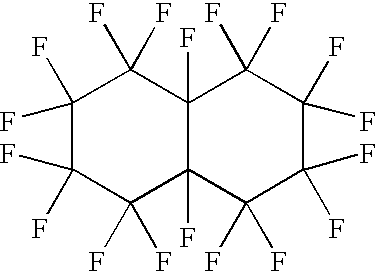
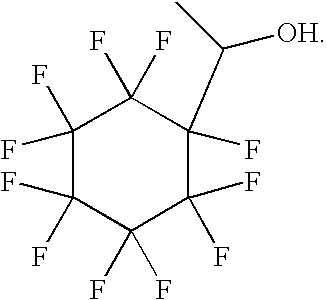
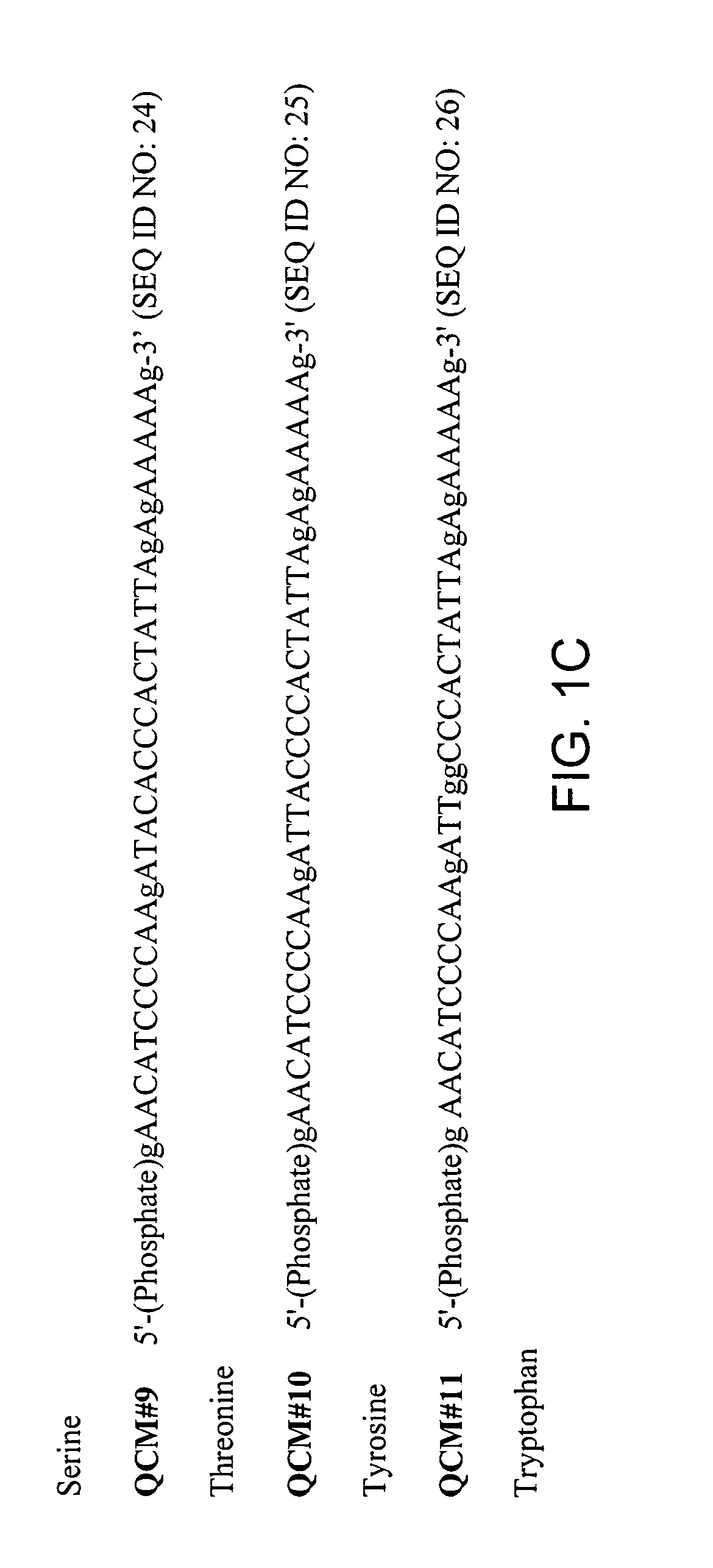
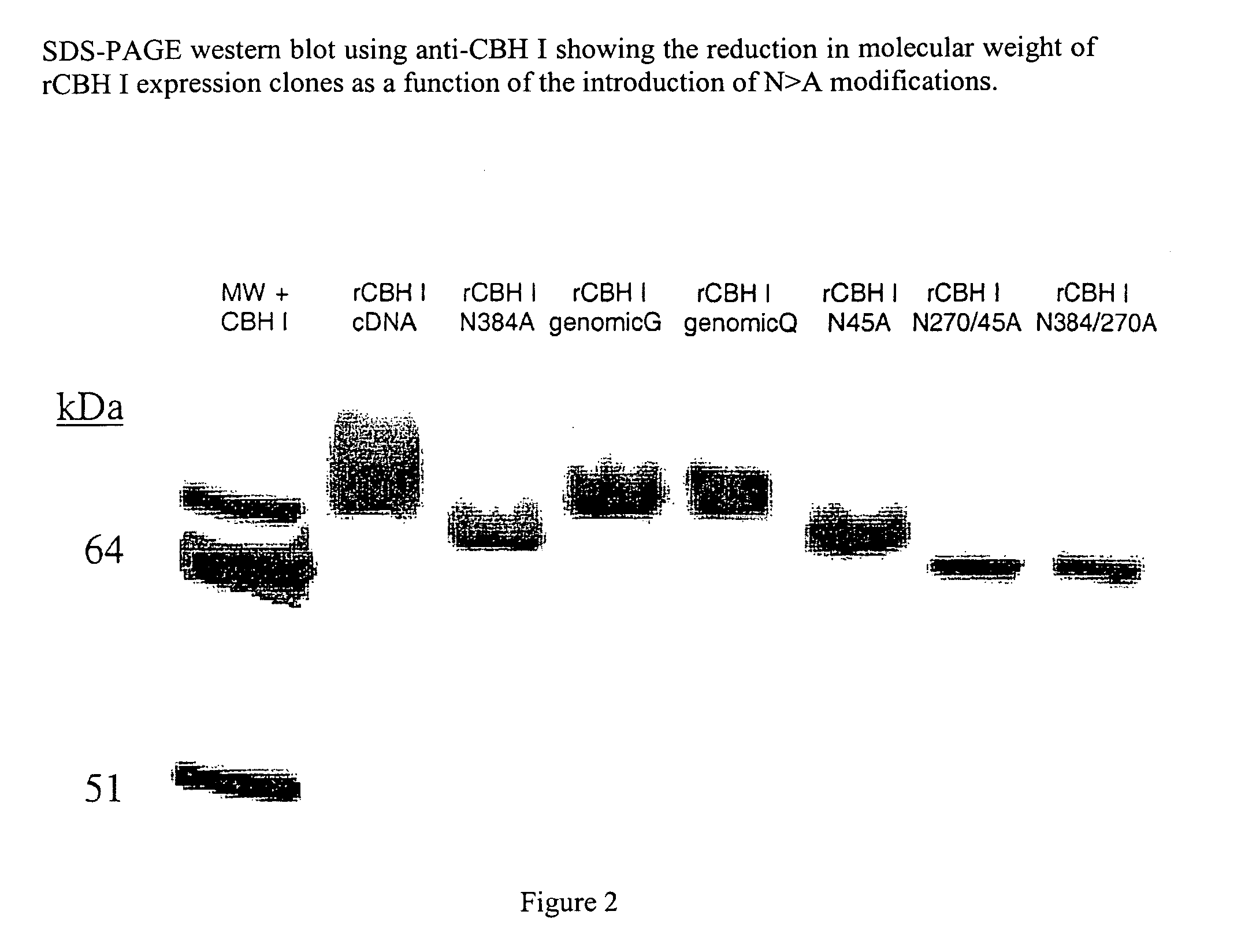
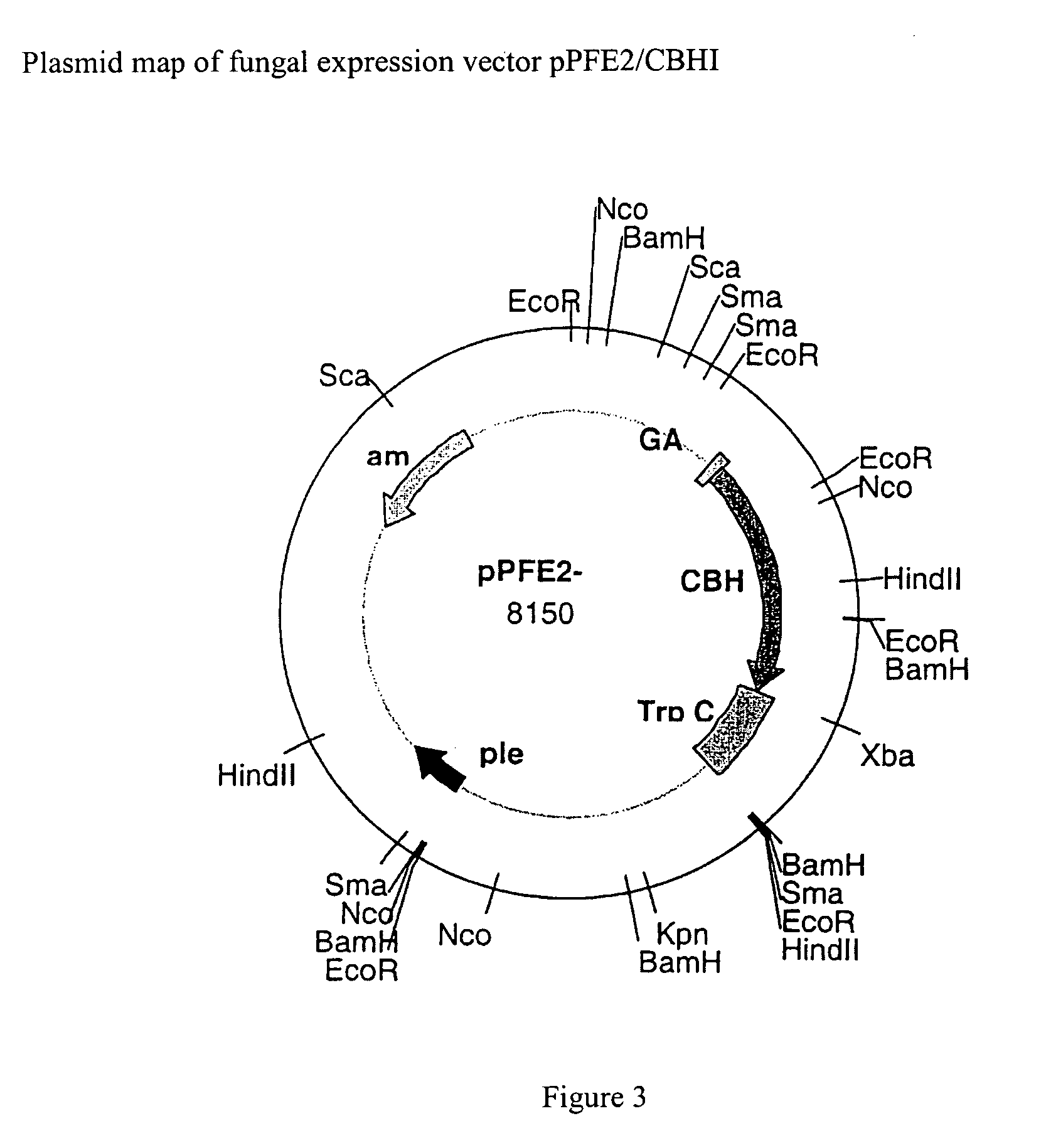
Cellobiohydrolase I gene and improved variants
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
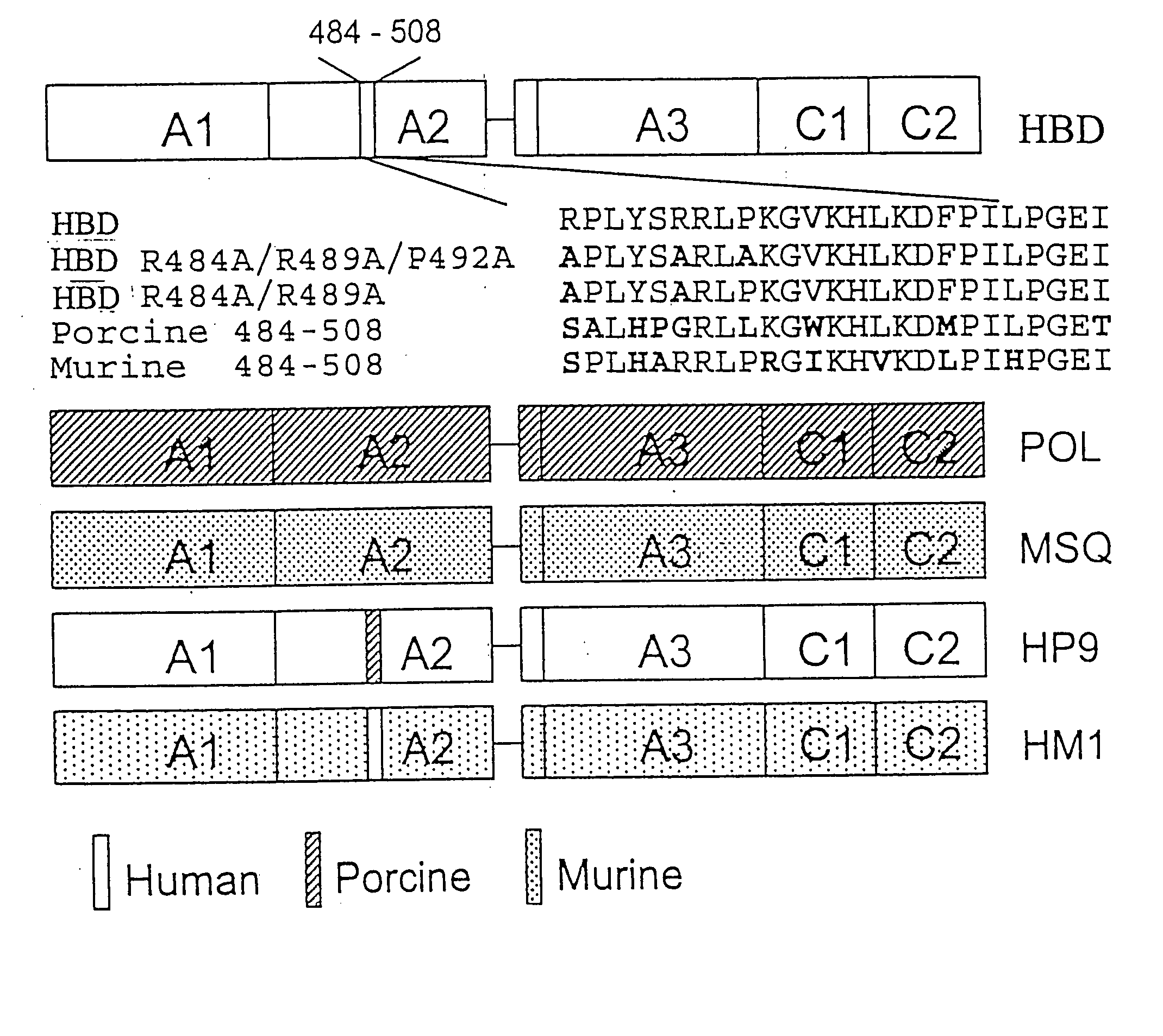
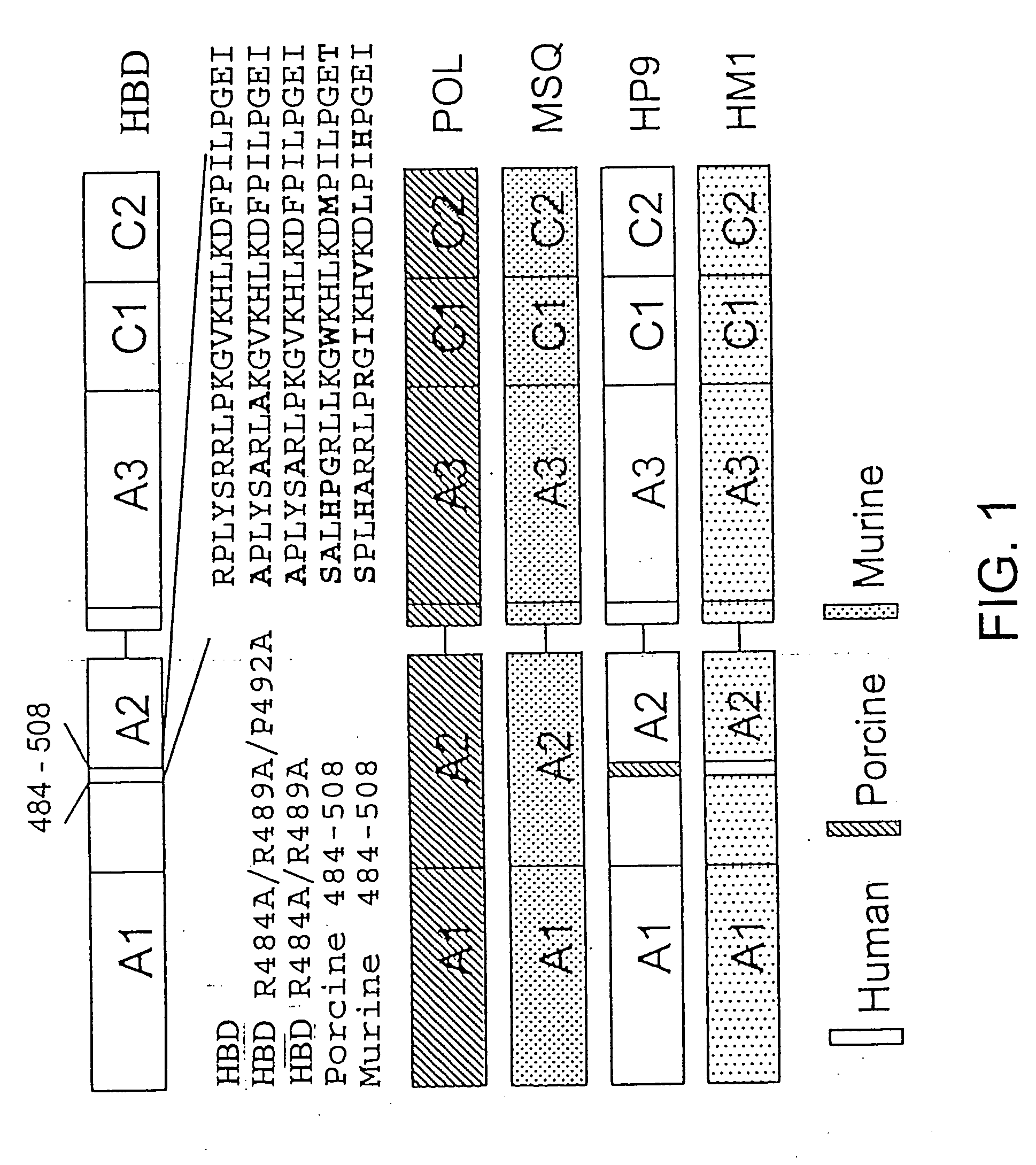
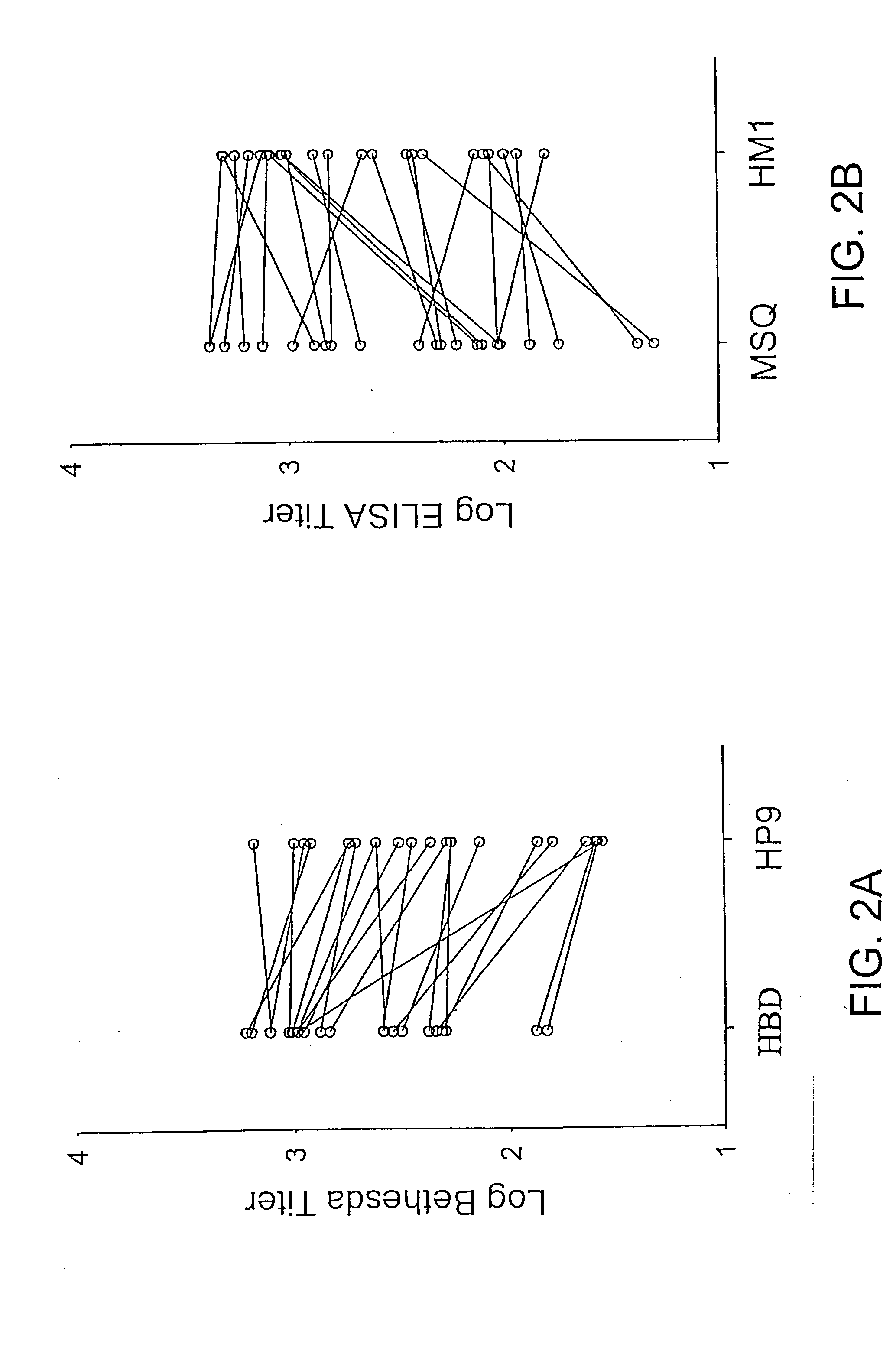
Modified fVIII having reduced immunogenicity through mutagenesis of A2 and C2 epitopes
InactiveUS20050123997A1Low immunogenicityImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsFactor VIIEpitopeVaccine Immunogenicity
Specific amino acid loci of human fVIII interact with inhibitory antibodies of hemophilia patients after being treated with fVIII. Modified fVIII is disclosed in which the amino acid sequence is changed by multiple substitutions in human fVIII A2 and C2 domains. The modified fVIII is useful for hemophiliacs, either to avoid or prevent the action of inhibitory antibodies.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
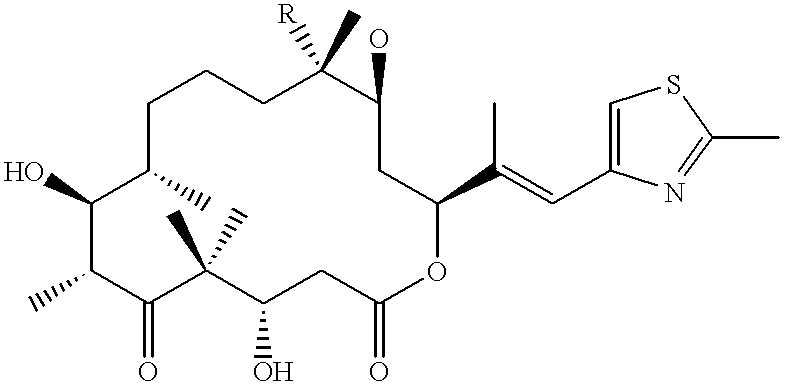
Fermentative preparation process for and crystal forms of cytostatics
The invention relates to a new process for concentrating epothilones in culture media, a new process for the production of epothilones, a new process for separating epothilones A and B and a new strain obtained by mutagenesis for the production of epothilones, as well as aspects related thereto. New crystal forms of epothilone B are also described.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Novel canola cultivars having high yield and stabilized fatty acid profiles
ActiveUS20120174266A1Improve nutritional qualityFruit and vegetables preservationOrganic chemistryΑ-linolenic acidOleic Acid Triglyceride
According to the invention, there are provided novel canola cultivars, seeds of canola cultivars, to the plants, or plant parts, of novel canola cultivars and to methods for producing a canola plants produced by crossing the novel canola cultivars with themselves or another canola cultivar, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of the canola cultivars. The novel canola cultivar(s) include canola plants having a desired trait that includes an oleic acid value of about 70% and a yield greater than about 2100 kg / ha, and oils canola seeds having an oleic acid content of greater than about 70% and an α-linolenic acid value of less than about 3%.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Canola hybrid cultivar G152936H
ActiveUS8664477B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGenetics
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola, designated G152936H. Also included are seeds of canola G152936H, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola G152936H and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola G152936H with itself or another canola genotype, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola G152936H.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Canola cultivar G2X0023
ActiveUS8304611B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionCultivarCanola
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola cultivar, designated G2X0023. Also included are seeds of canola cultivar G2X0023, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola G2X0023 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola G2X0023 with itself or another canola cultivar, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola G2X0023.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Canola cultivar G31064
ActiveUS8558065B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyRapeseed
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola cultivar, designated G31064. Also included are seeds of canola cultivar G31064, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola G 31064 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola G31064 with itself or another canola cultivar, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola G31064.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Canola cultivar G030994
ActiveUS8530726B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyCultivar
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola cultivar, designated G030994. Also included are seeds of canola cultivar G030994, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola G030994 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola G030994 with itself or another canola cultivar, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola G030994.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
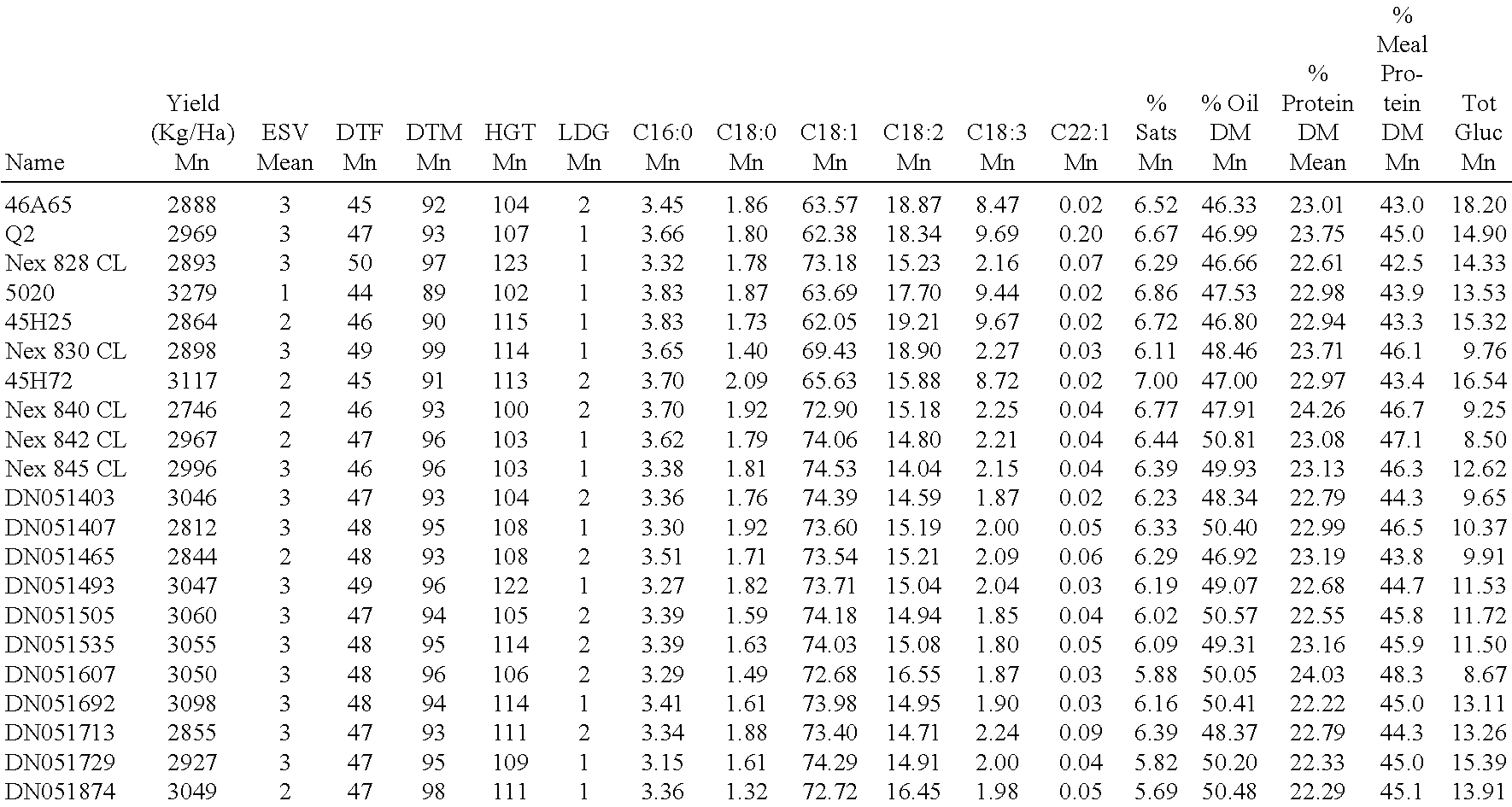
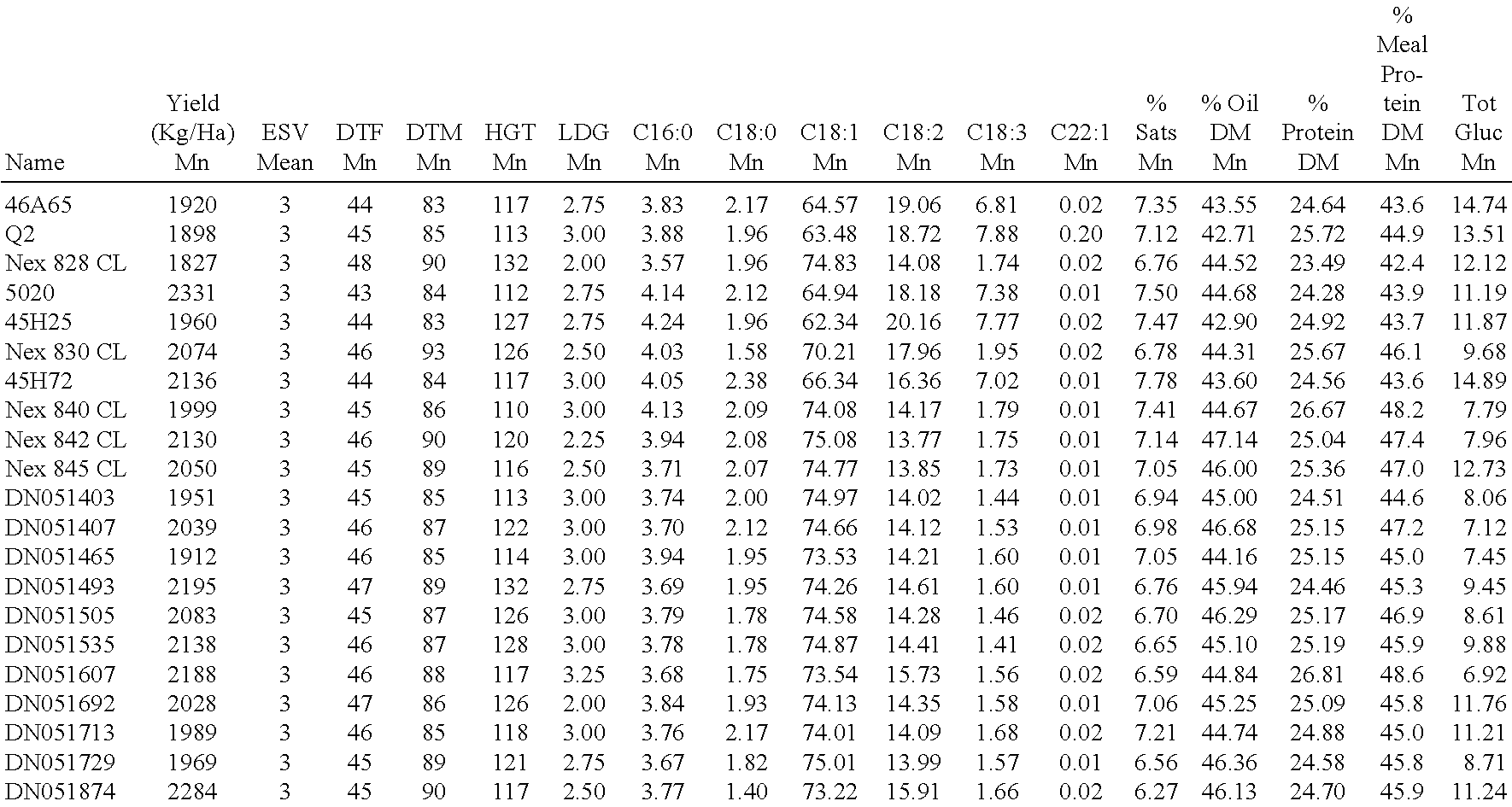
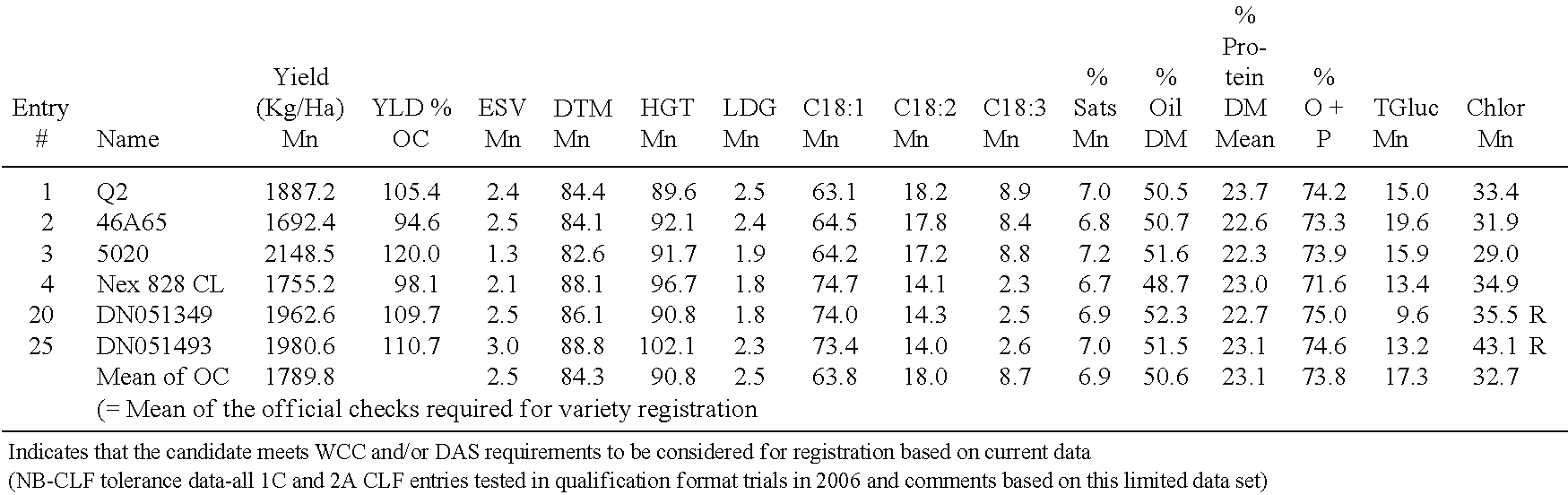
Canola cultivar DN051493
ActiveUS8378177B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyCultivar
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Canola cultivar DN051465
ActiveUS8541656B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGenotype
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola, designated DN051465. Also included are seeds of canola DN051465, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola DN051465 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola DN051465 with itself or another canola genotype, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola DN051465.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Canola cultivar G2X0039
ActiveUS8324459B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyRapeseed
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola cultivar, designated G2X0039. Also included are seeds of canola cultivar G2X0039, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola G2X0039 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola G2X0039 with itself or another canola cultivar, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola G2X0039.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Canola cultivar CL31613
ActiveUS8558064B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyCultivar
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola cultivar, designated CL31613. Also included are seeds of canola cultivar CL31613, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola CL31613 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola CL31613 with itself or another canola cultivar, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola CL31613.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com