Patents
Literature
1051 results about "Mutant protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A mutant protein is the protein product encoded by a gene with mutation. Mutated protein can have single amino acid change (minor, but still in many cases significant change leading to disease) or wide-range amino acid changes by e.g. truncation of C-terminus after introducing premature stop codon.
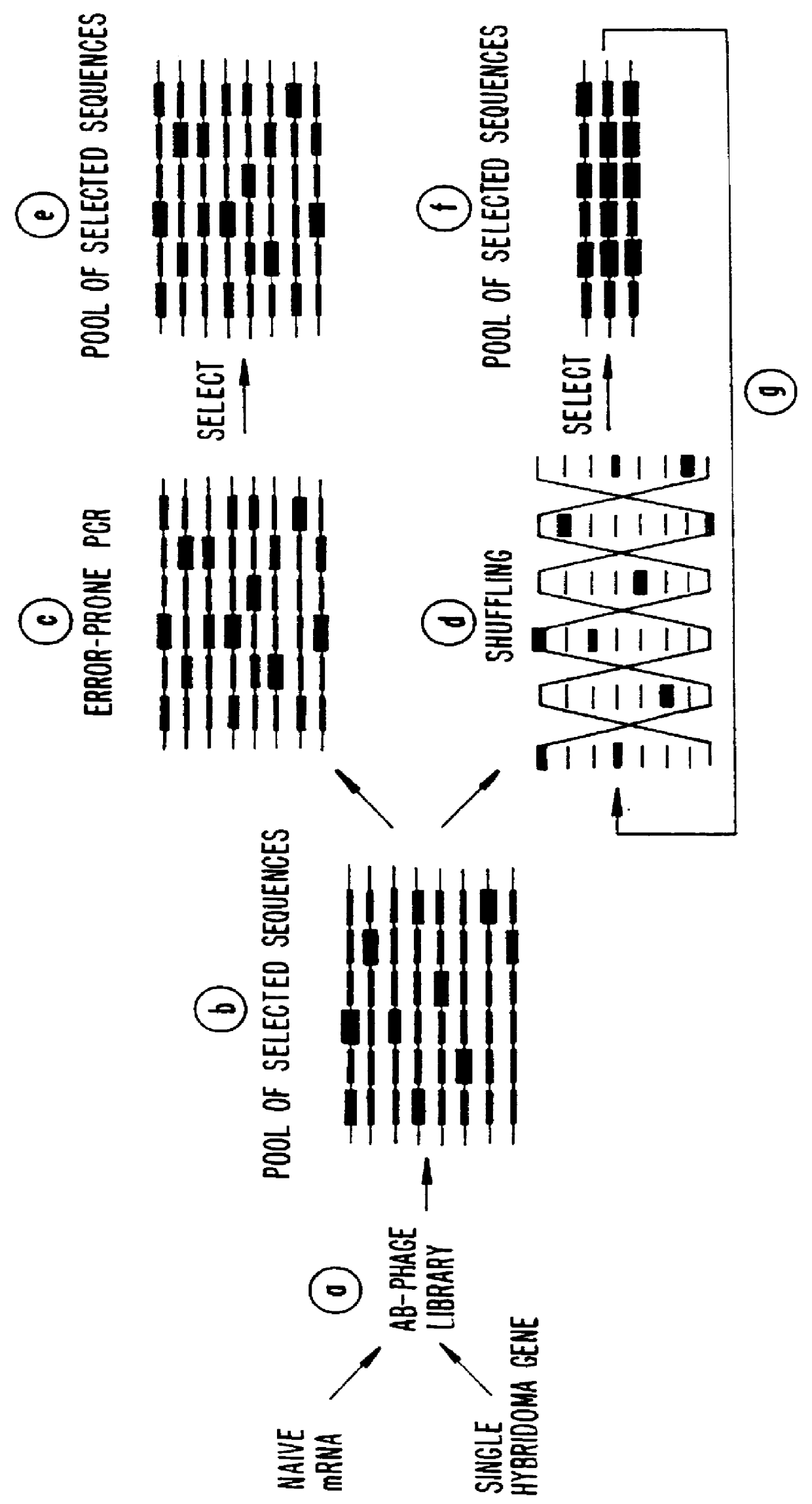
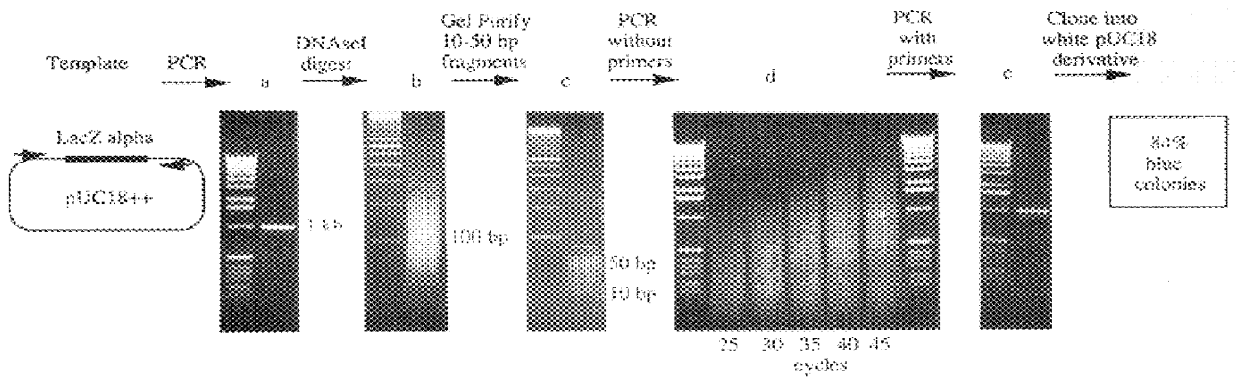
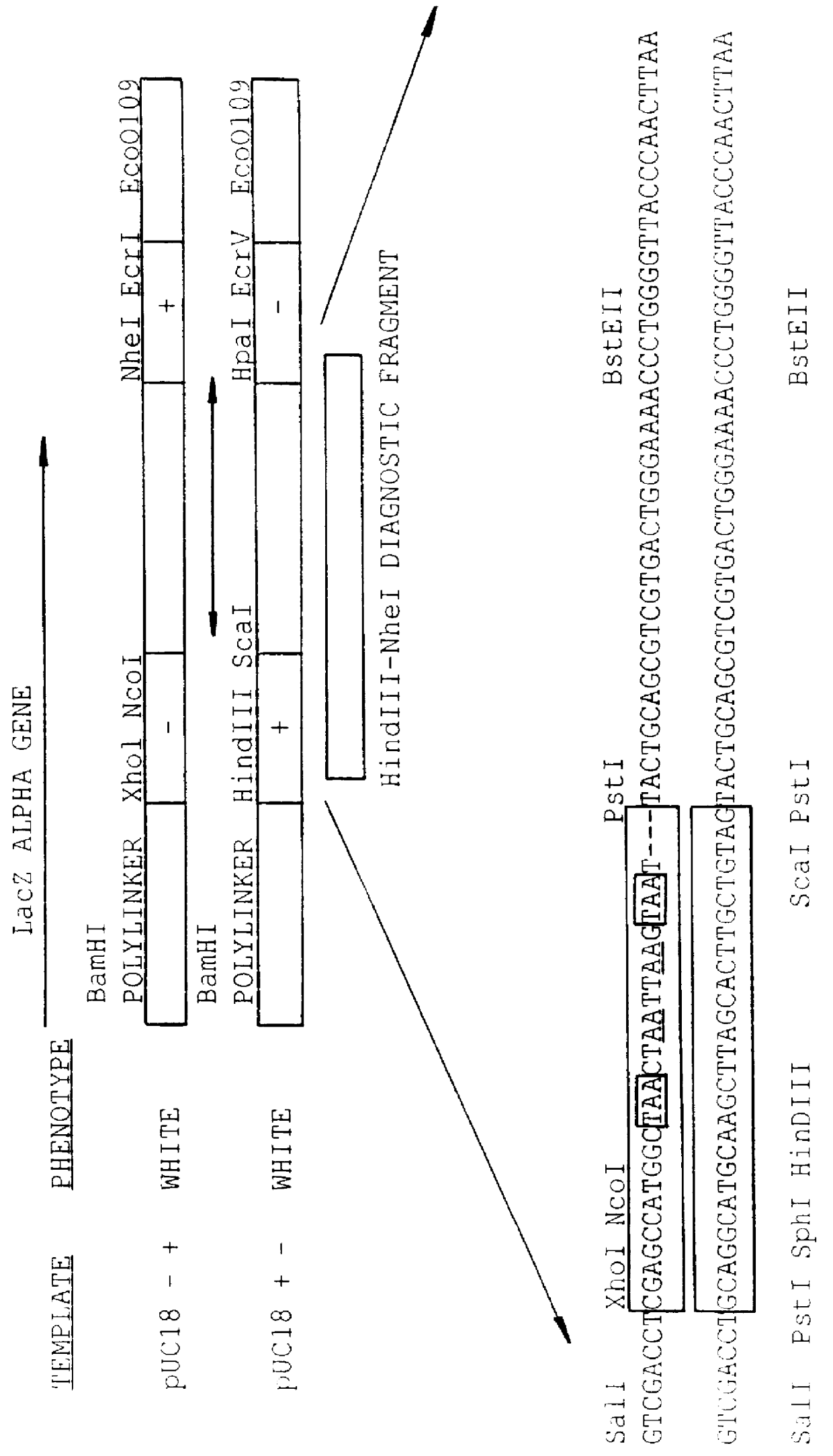
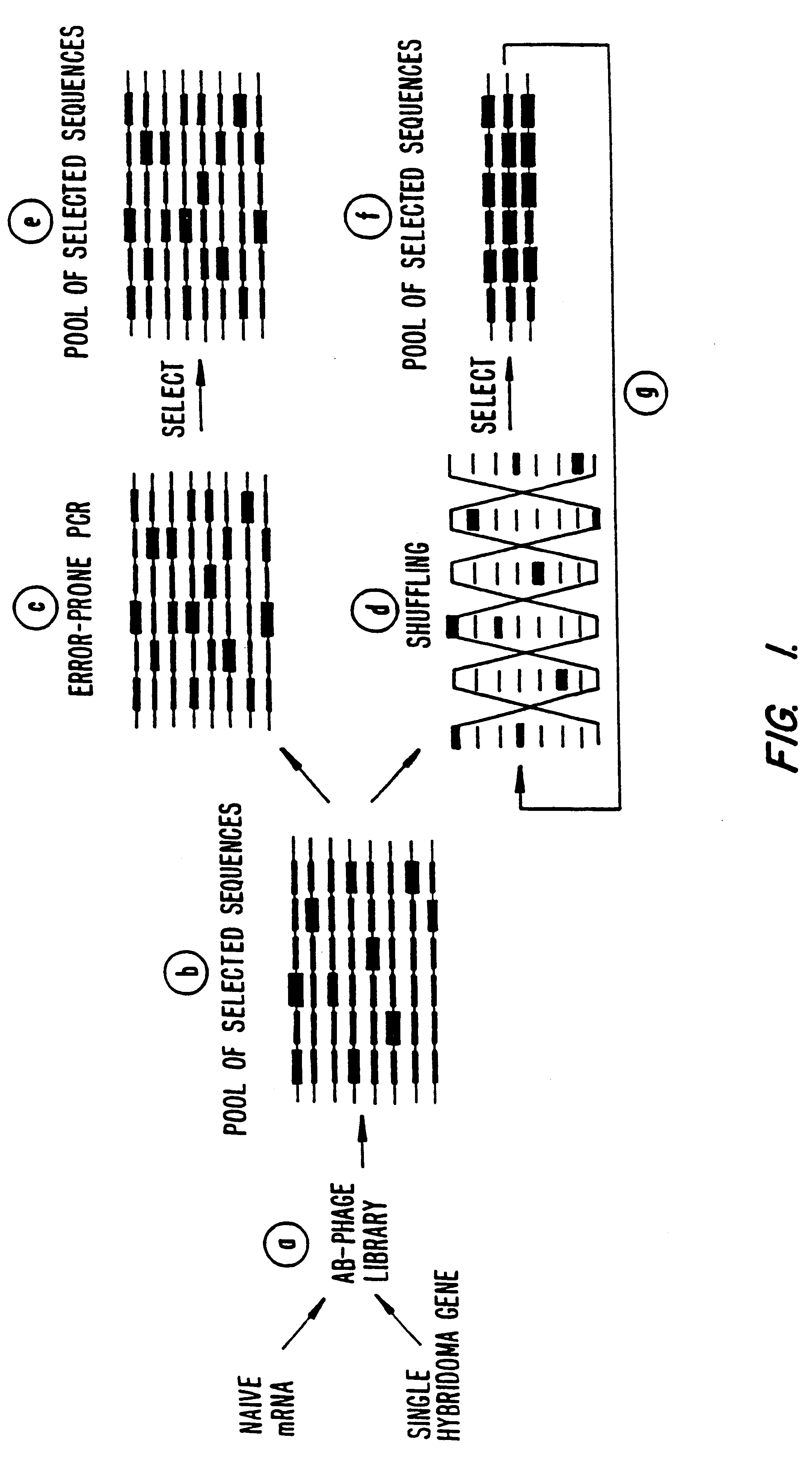
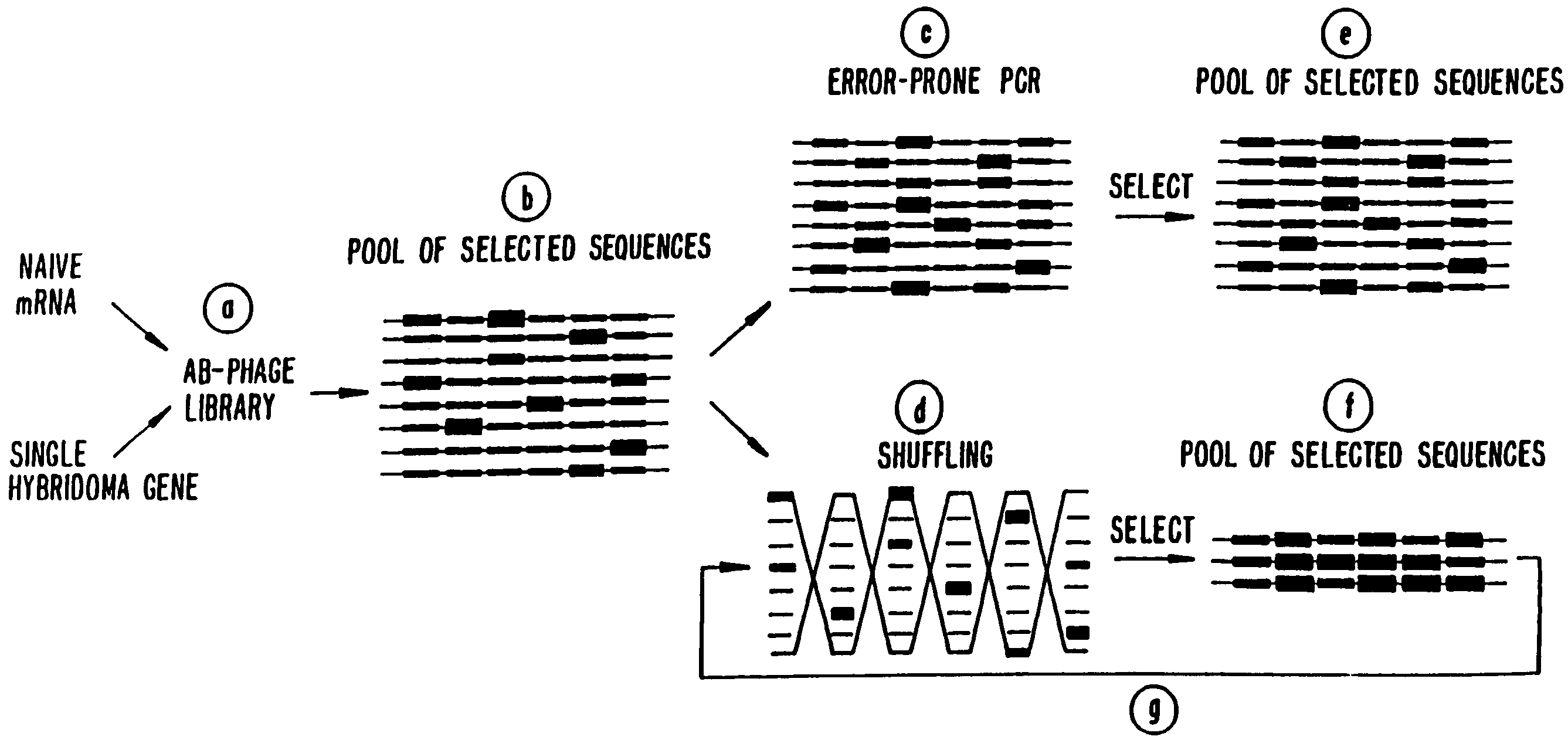
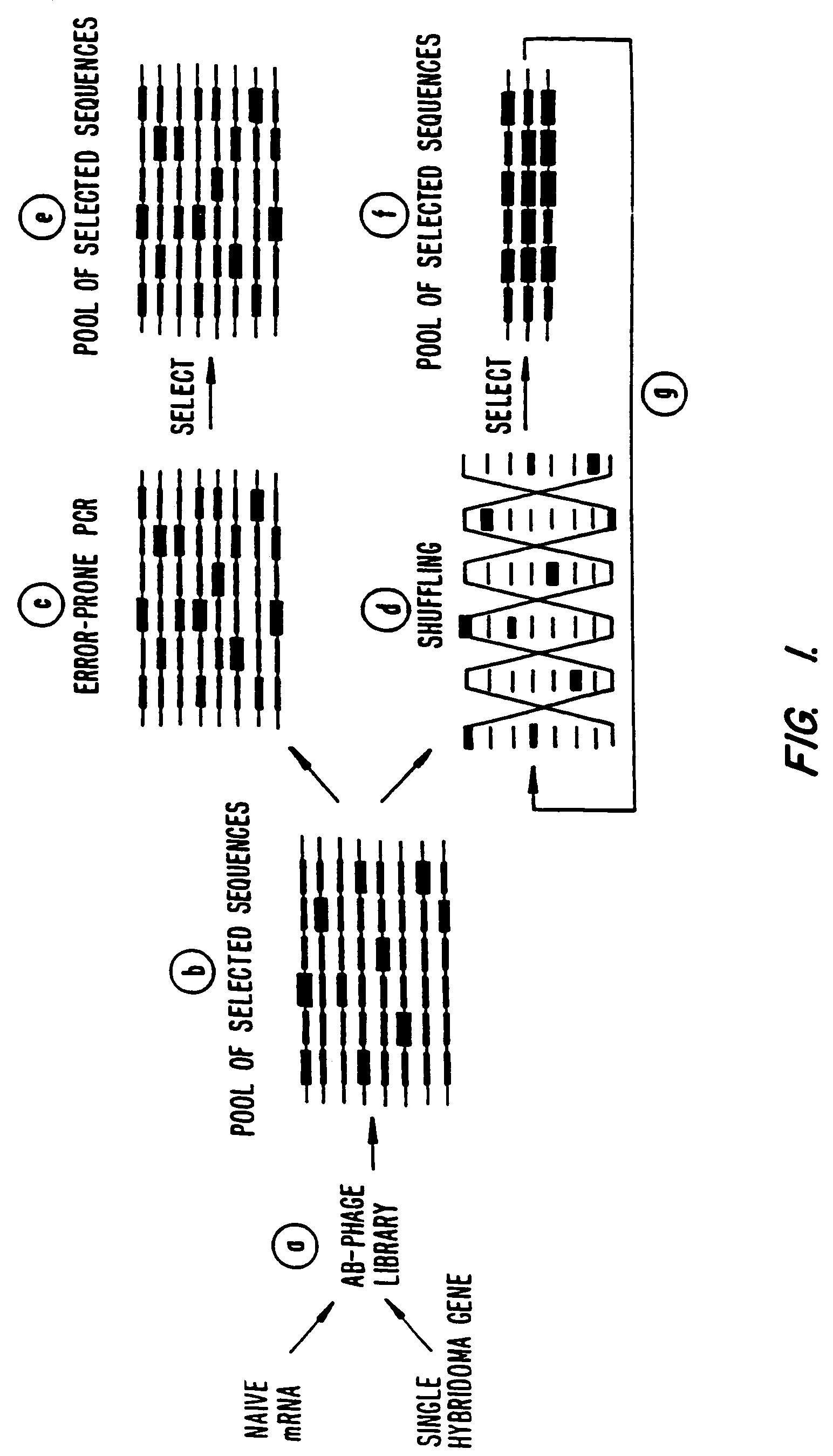
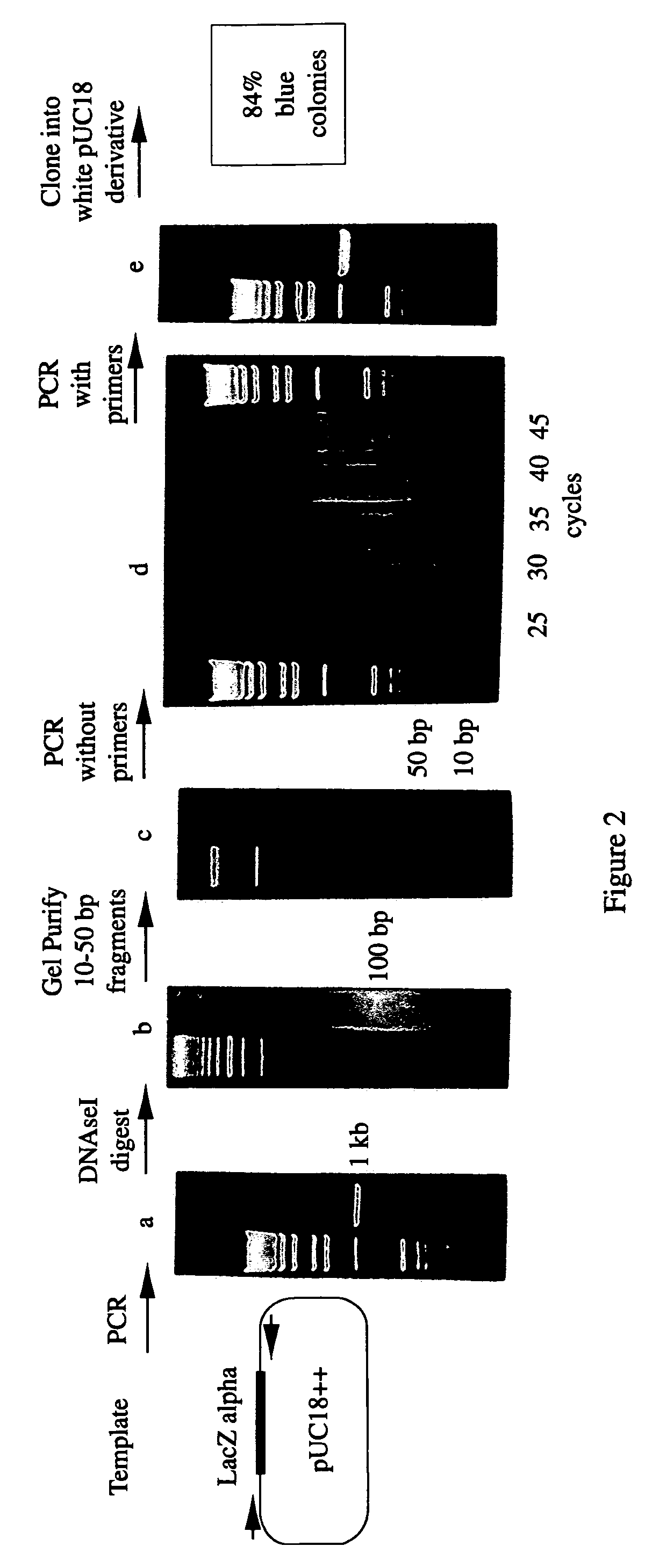
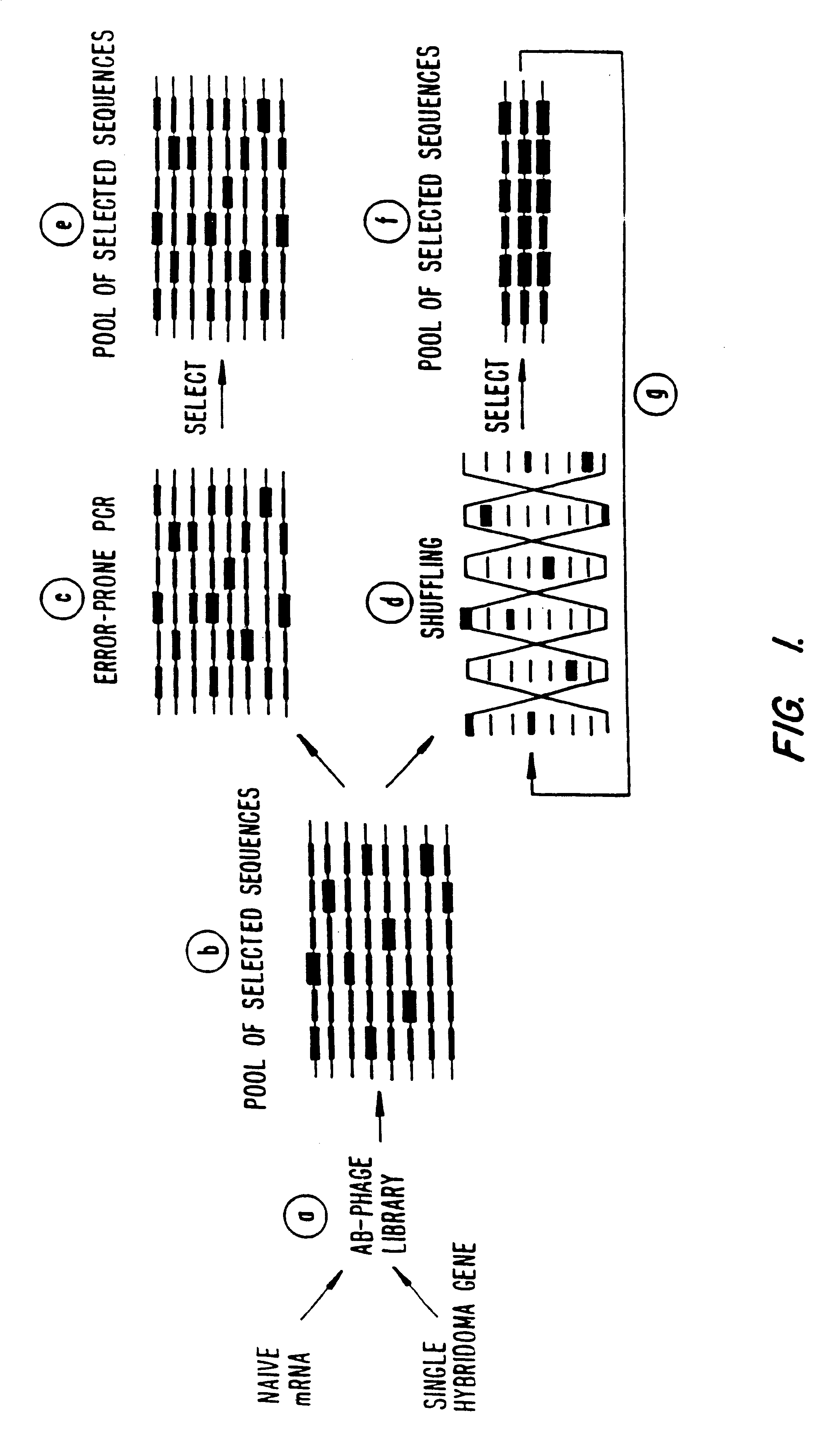
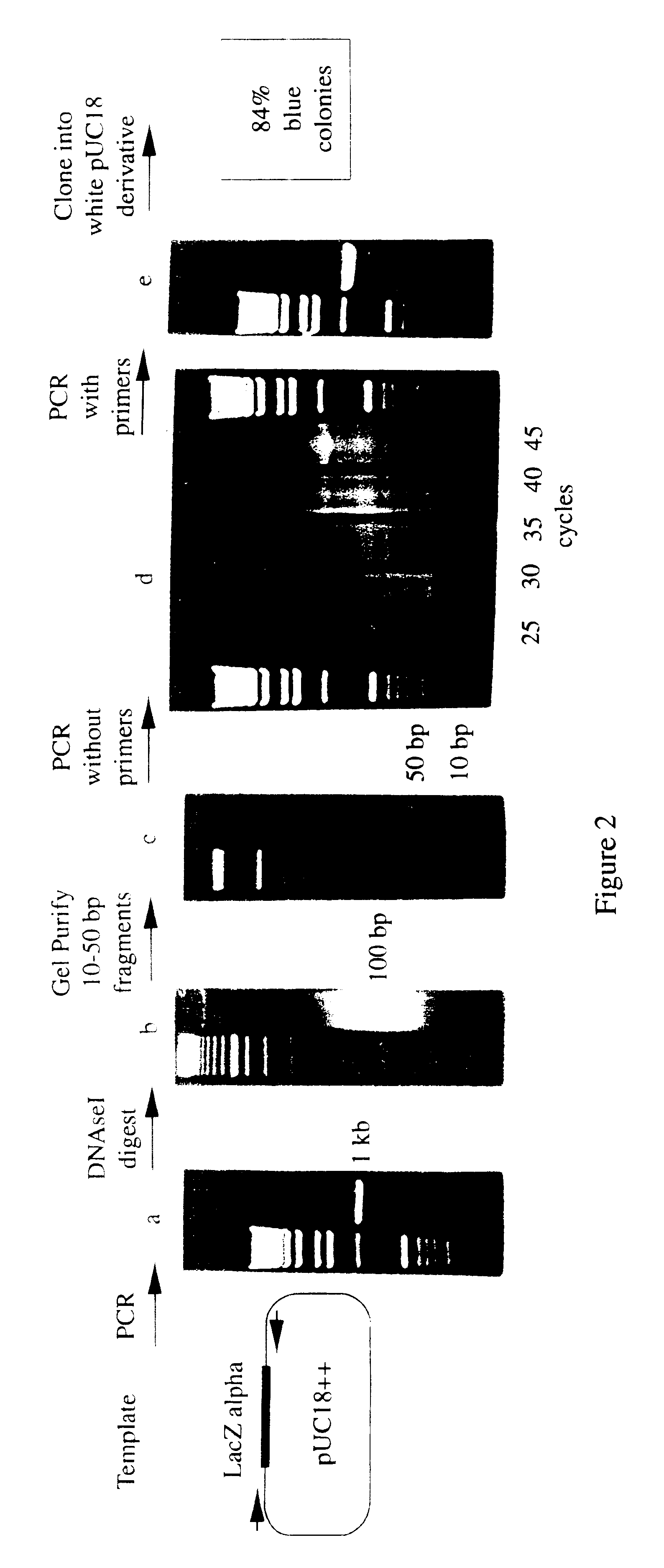
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6117679ALess immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
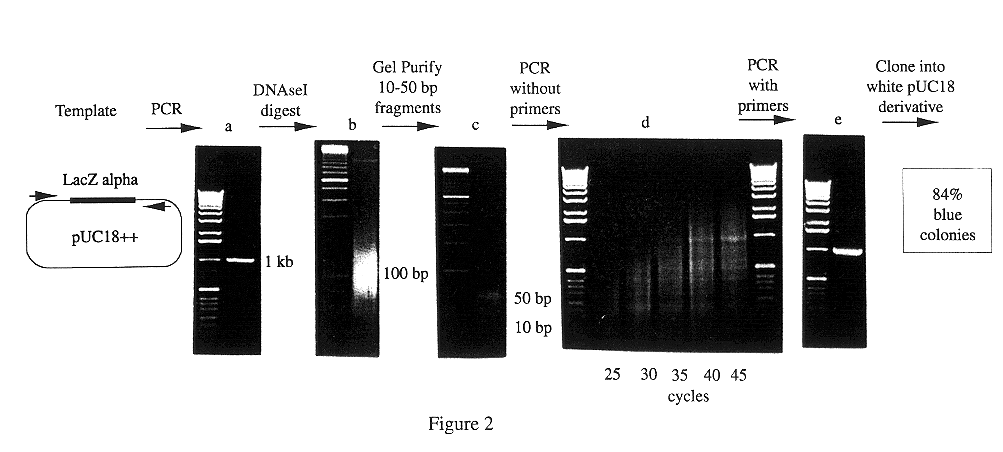
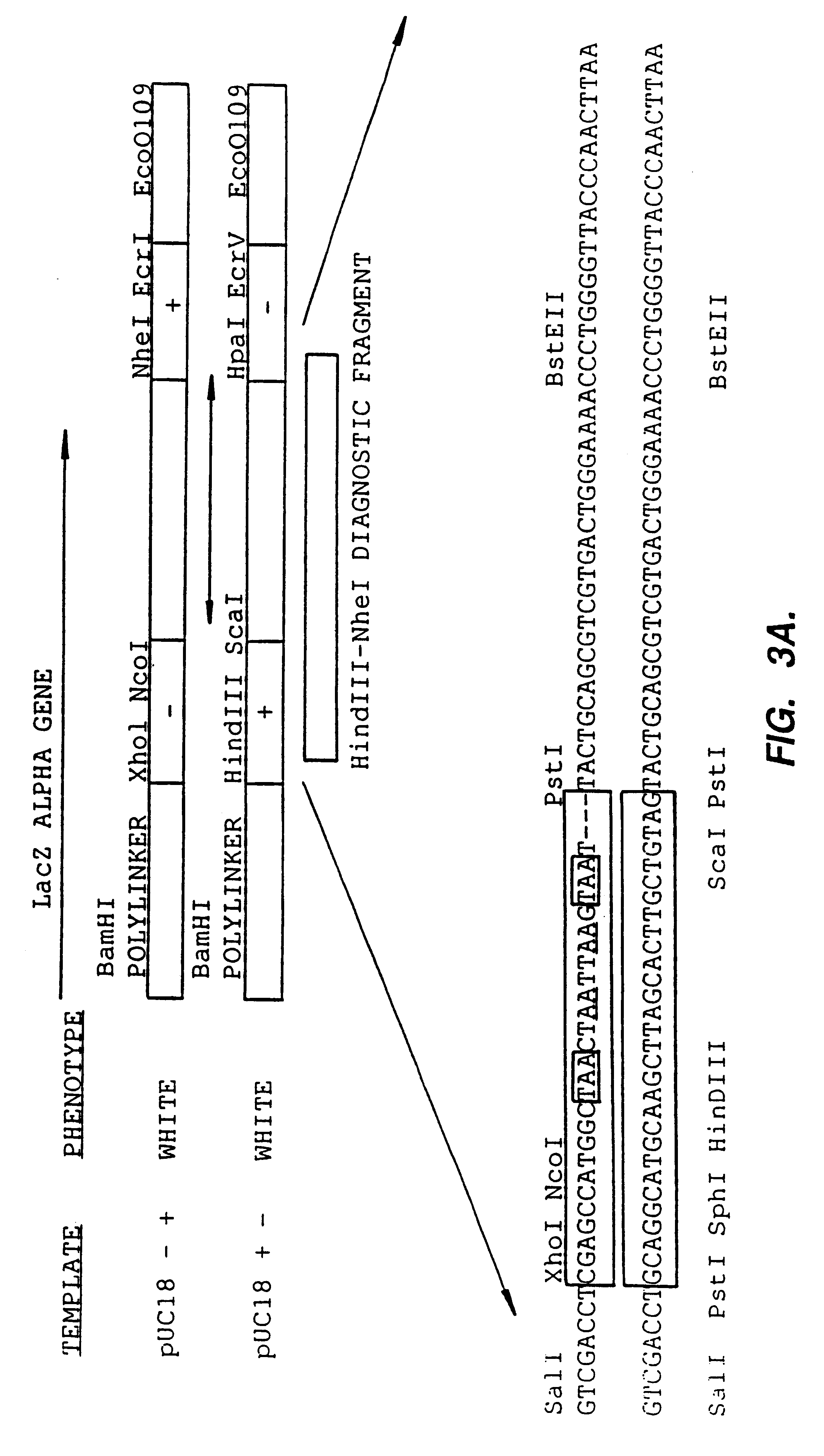
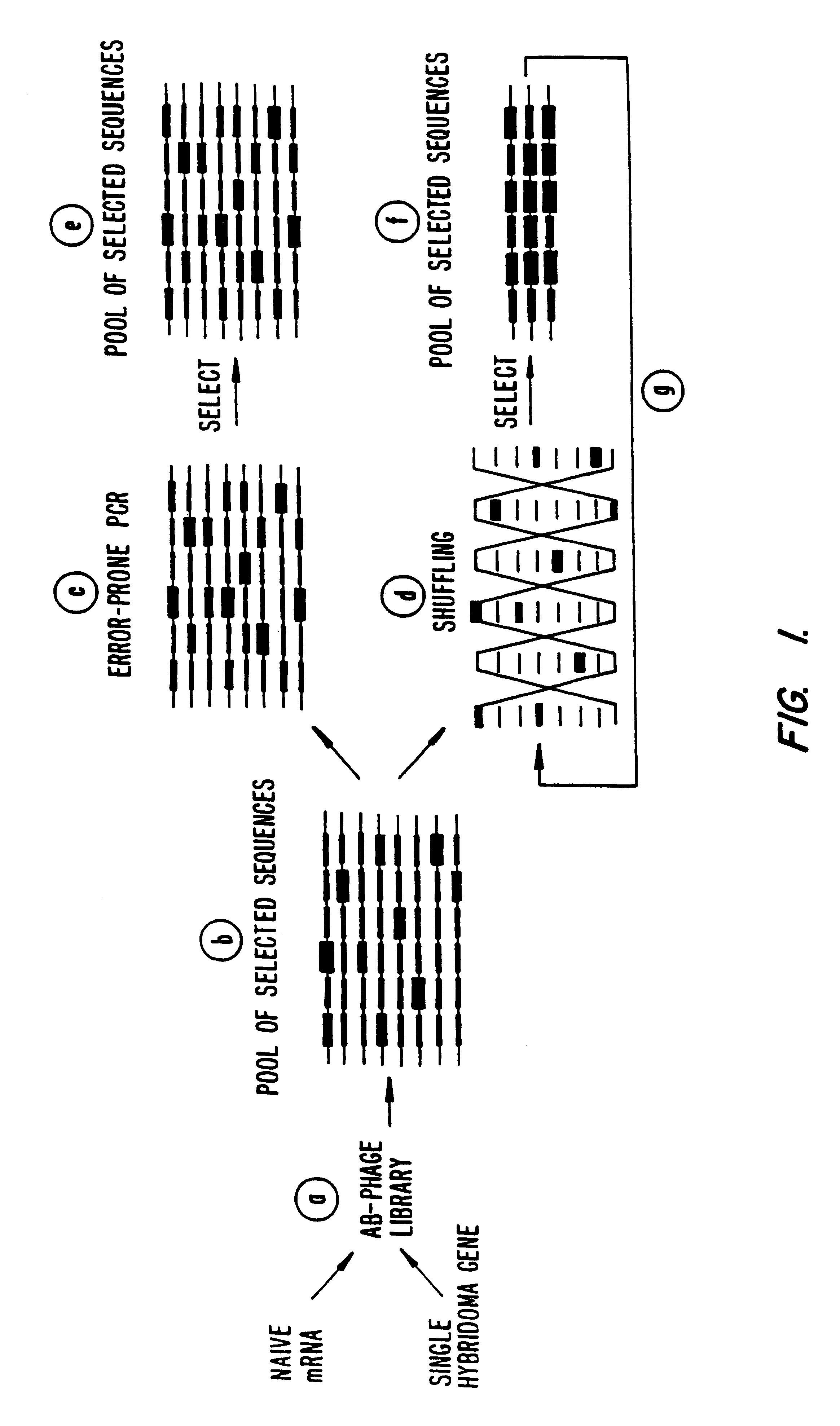
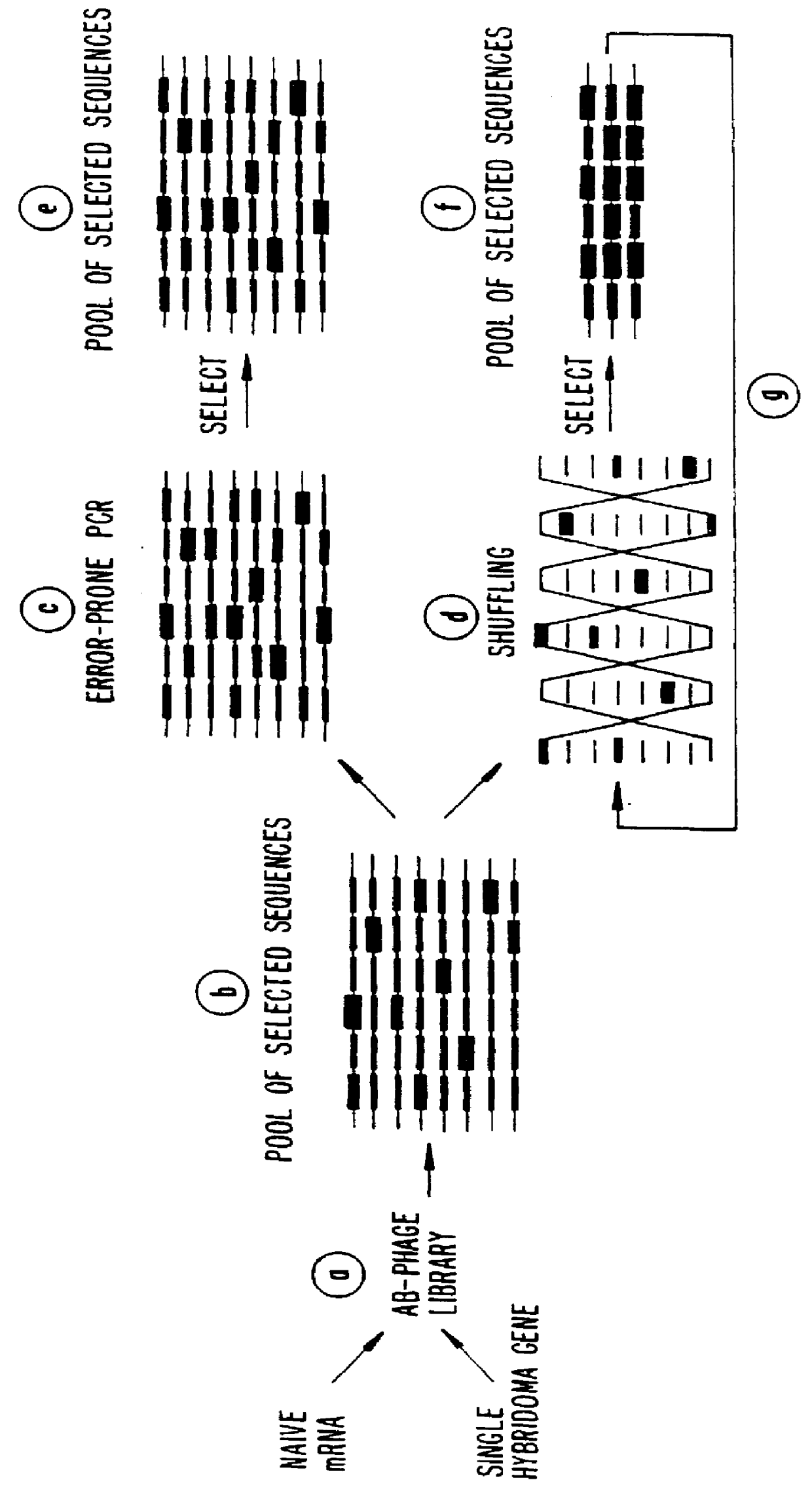
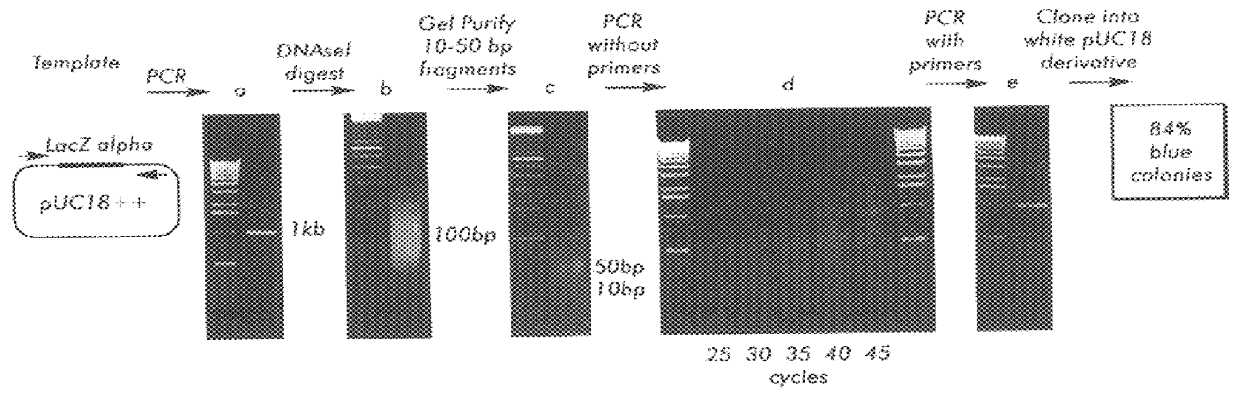
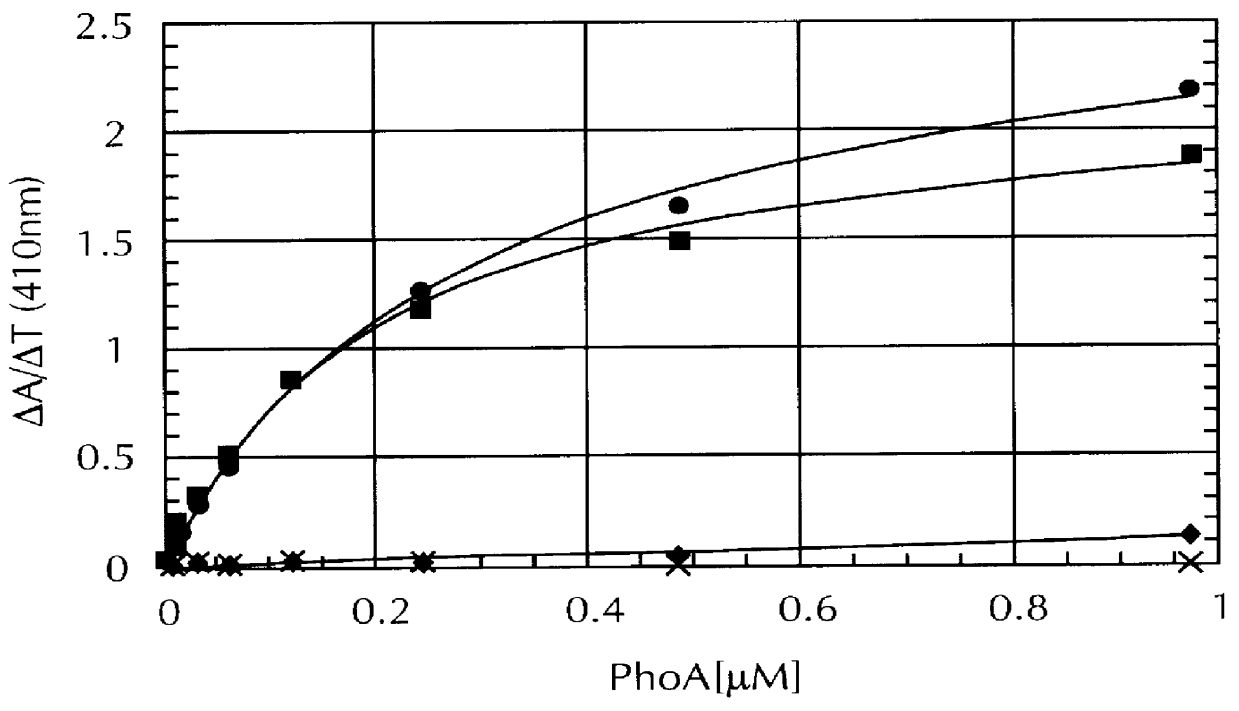
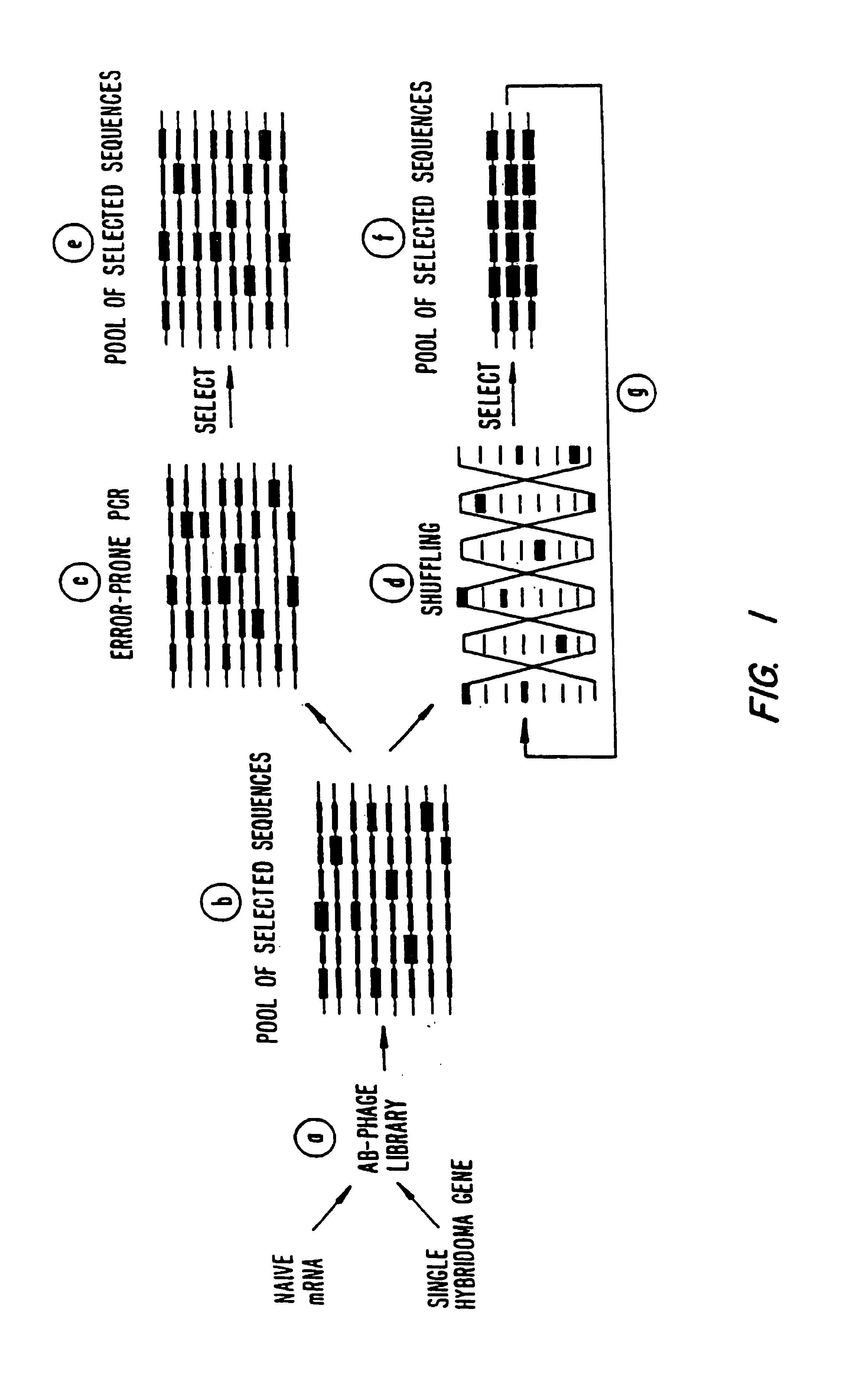
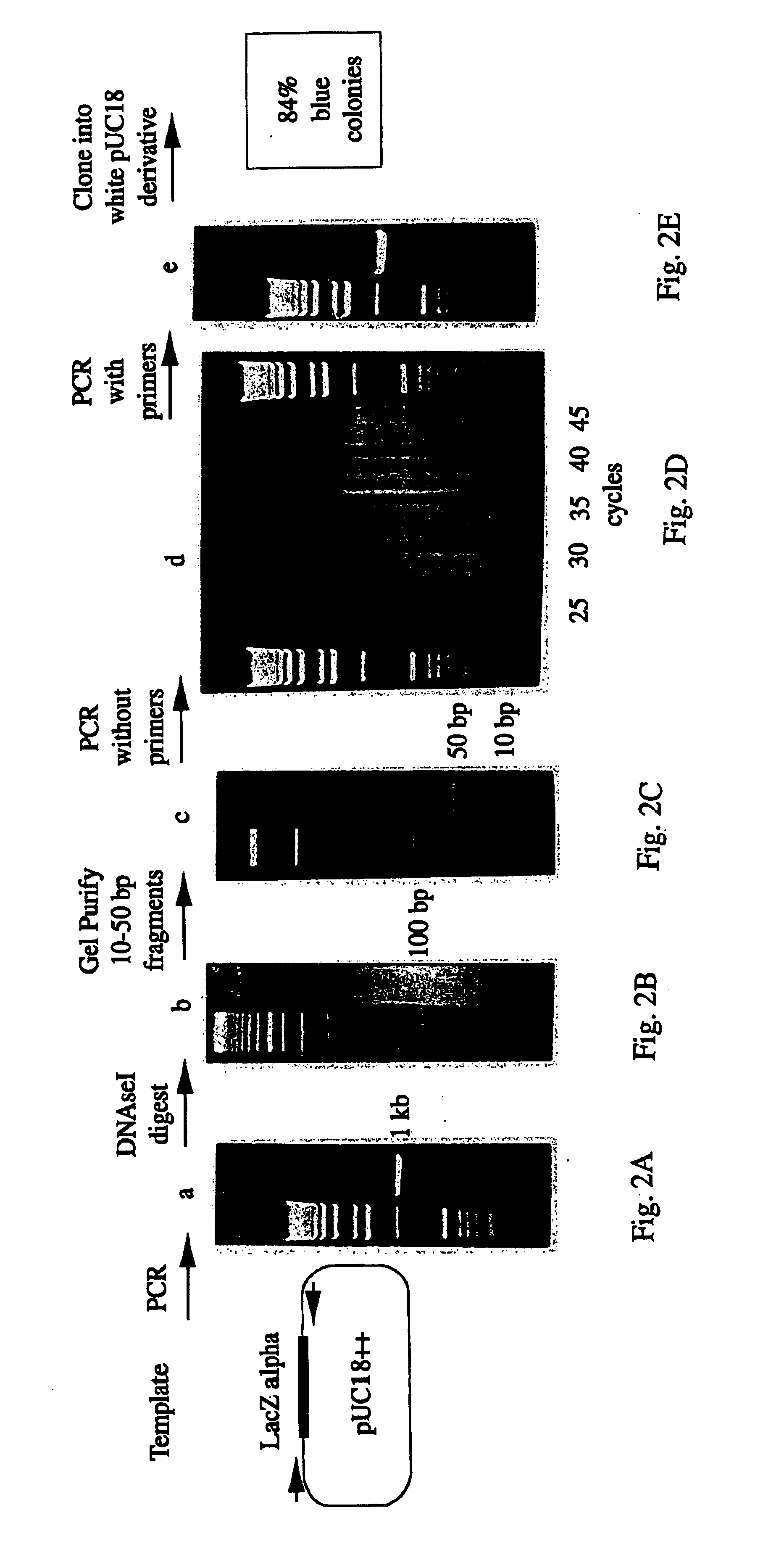
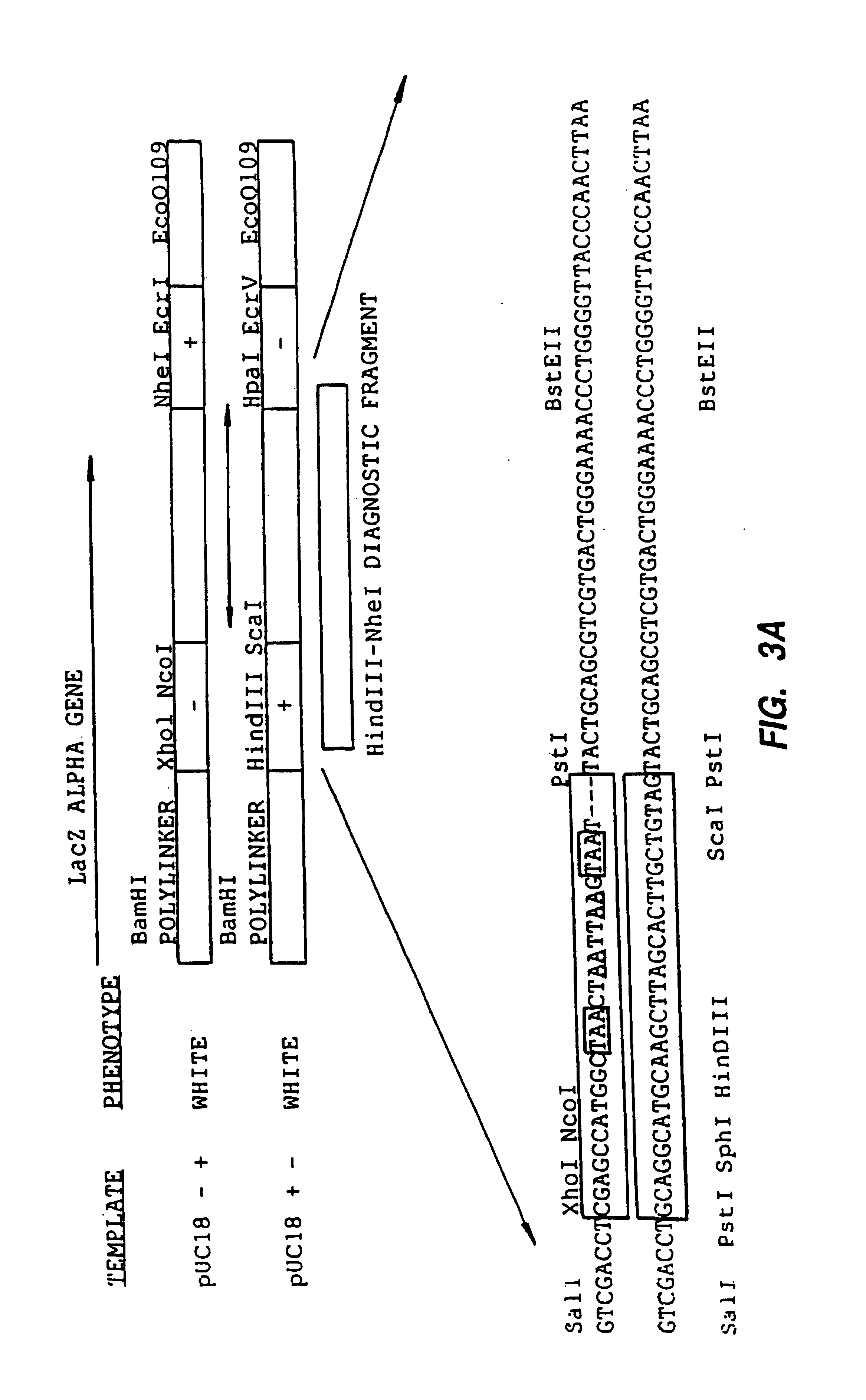
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6180406B1Less immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6165793ALess immunogenicDirected macromolecular evolutionImmunoglobulinsMutated proteinNucleotide
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Streptavidin muteins
InactiveUS6103493AHigh affinityElution can be checked visuallyBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPeptide ligandSubject matter
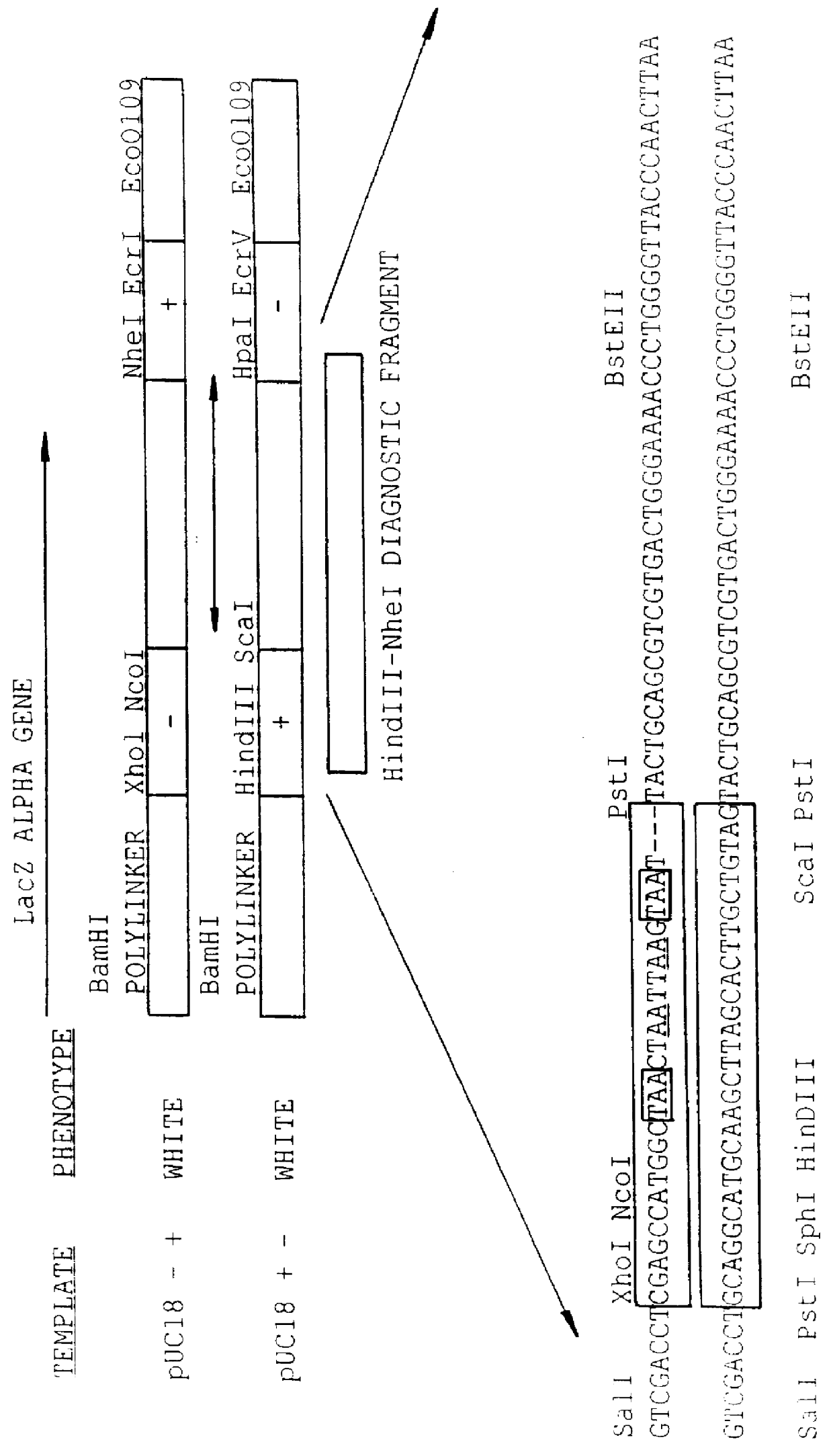
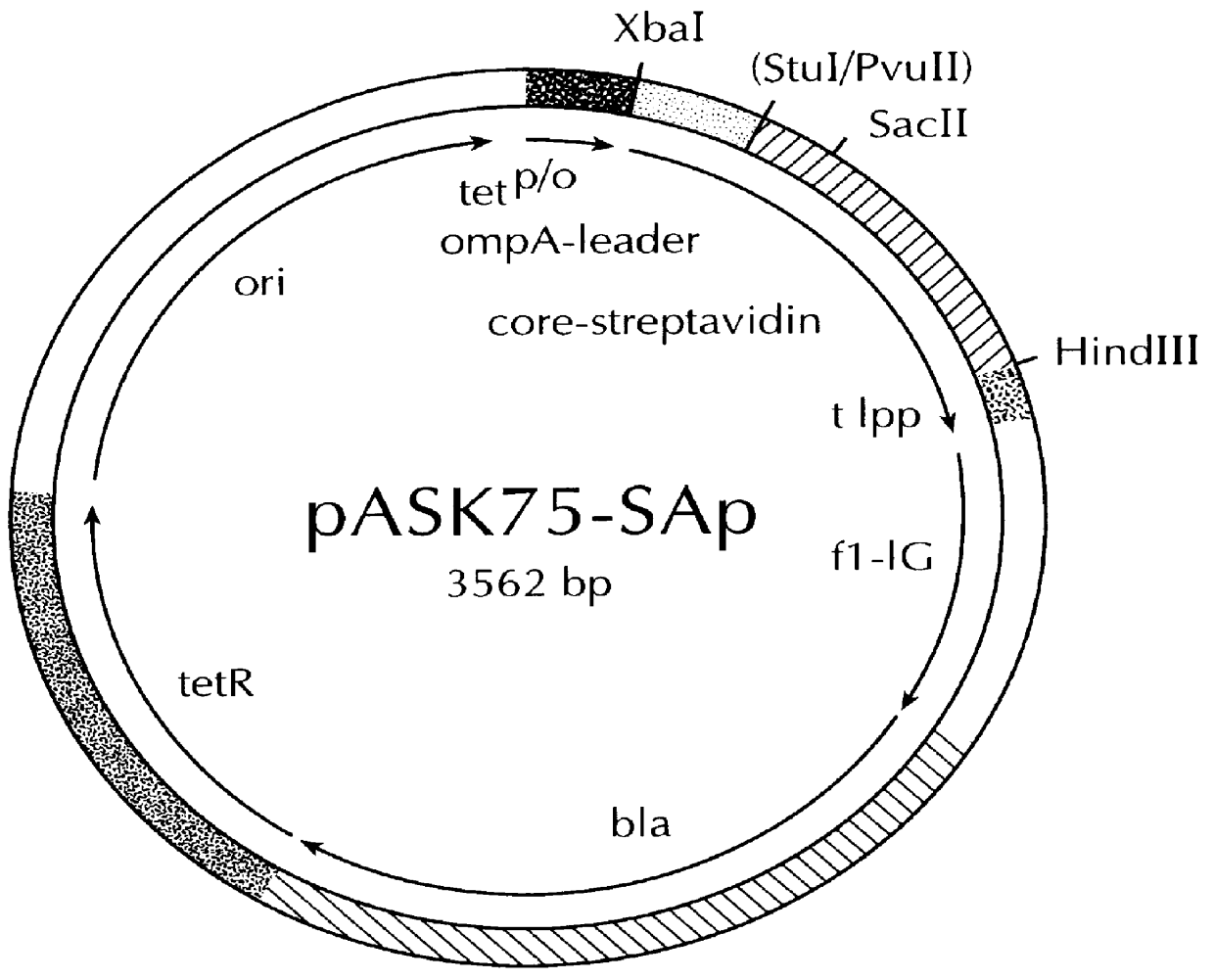
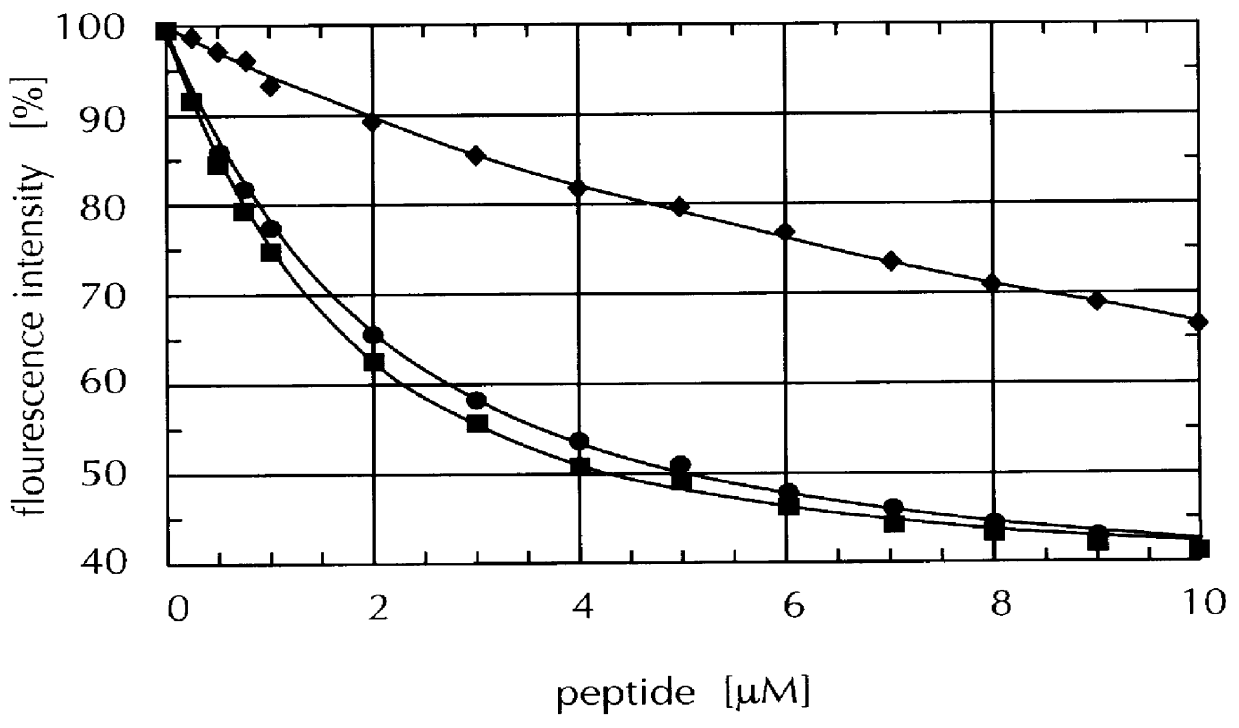
The invention concerns a polypeptide selected from muteins of streptavidin which is characterized in that it (a) contains at least one mutation in the region of the amino acid positions 44 to 53 with reference to wild type-(wt)-streptavidin and (b) has a higher binding affinity than wt-streptavidin for peptide ligands comprising the amino acid sequence Trp-X-His-Pro-Gln-Phe-Y-Z in which X represents an arbitrary amino acid and Y and Z either both denote Gly or Y denotes Glu and Z denotes Arg or Lys. In addition nucleic acids coding for the polypeptide, a vector containing this nucleic acid, a cell transfected with the vector as well as the use of a polypeptide in a method for the isolation, purification or determination of proteins are disclosed. Yet a further subject matter is a reagent kit containing the polypeptide.
Owner:INST FUR BIOANALYTIC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6995017B1Enhance rate of recombinationEnhancing recombinationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMutated proteinNucleotide
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Method and device for detecting mutated proteins
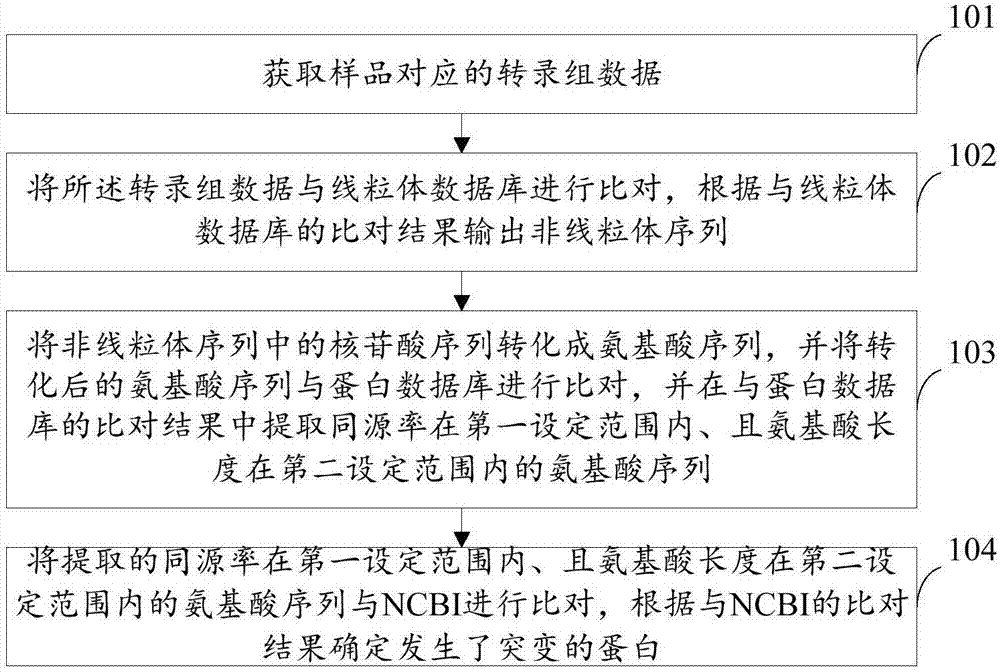
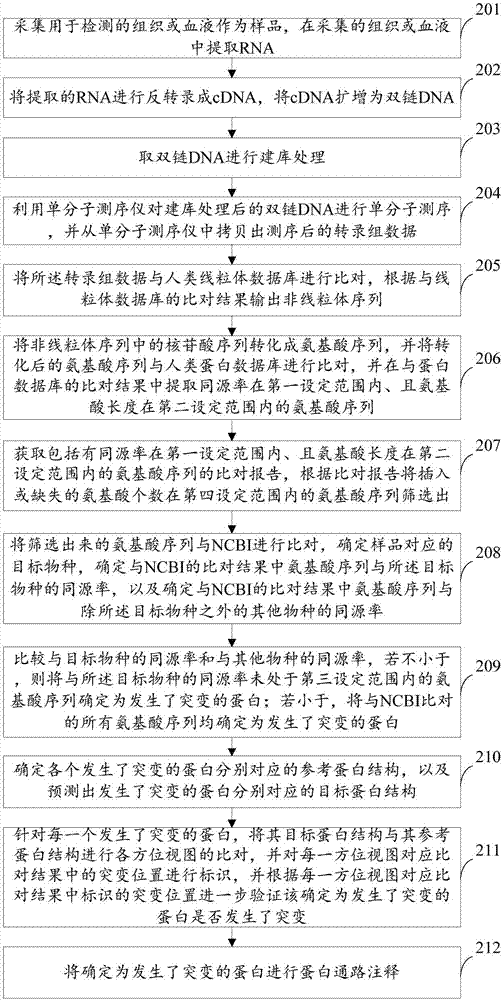
The invention provides a method and a device for detecting mutated proteins. The method includes acquiring transcriptome data corresponding to samples; comparing the transcriptome data to mitochondrion databases and outputting non-mitochondrion sequences according to comparison results of the transcriptome data and the mitochondrion databases; transforming nucleotide sequences in the non-mitochondrion sequences into amino acid sequences, comparing the transformed amino acid sequences to protein databases and extracting amino acid sequences with homogenous rates in first set ranges and amino acid lengths in second set ranges from comparison results of the transformed amino acid sequences and the protein databases; comparing the extracted amino acid sequences with the homogenous rates in the first set ranges and the amino acid lengths in the second set ranges to NCBI (national center of biotechnology information) and determining the mutated proteins according to comparison results of the extracted amino acid sequences and the NCBI. According to the scheme, the method and the device have the advantage that the mutated proteins in the samples can be detected by the aid of the method and the device.
Owner:天津市湖滨盘古基因科学发展有限公司
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS7288375B2Less immunogenicPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsMutated proteinNucleotide
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6518065B1Less immunogenicImmunoglobulinsLibrary member identificationMutated proteinNucleotide
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
IL-2 selective agonists and antagonists
InactiveUS6955807B1Great therapeutic useToxic reductionBacteriaSugar derivativesNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsNucleotide
The invention is directed to a polypeptide comprising a human IL-2 mutein numbered in accordance with wild-type IL-2 wherein said human IL-2 is substituted at at least one of positions 20, 88 or 126, whereby said mutein preferentially activates T cells over NK cells. D20H and I, N88G, I, and R, in particular have a relative T cell-differential activity much greater than native IL-2, with predicted associated reduced in vivo toxicity. The invention also includes polynucleotides coding for the muteins of the invention, vectors containing the polynucleotides, transformed host cells, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the muteins, and therapeutic methods of treatment.
Owner:AICURIS GMBH & CO KG
Homogeneous preparations of IL-28 and IL-29
ActiveUS7157559B2Improve expression levelIncrease productionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticMutated proteinPolynucleotide
Homogeneous preparations of IL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29 have been produced by mutating one or more of the cysteine residues in the polynucleotide sequences encoding the mature proteins. The cysteine mutant proteins can be shown to either bind to their cognate receptor or exhibit biological activity. One type of biological activity that is shown is an antiviral activity.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
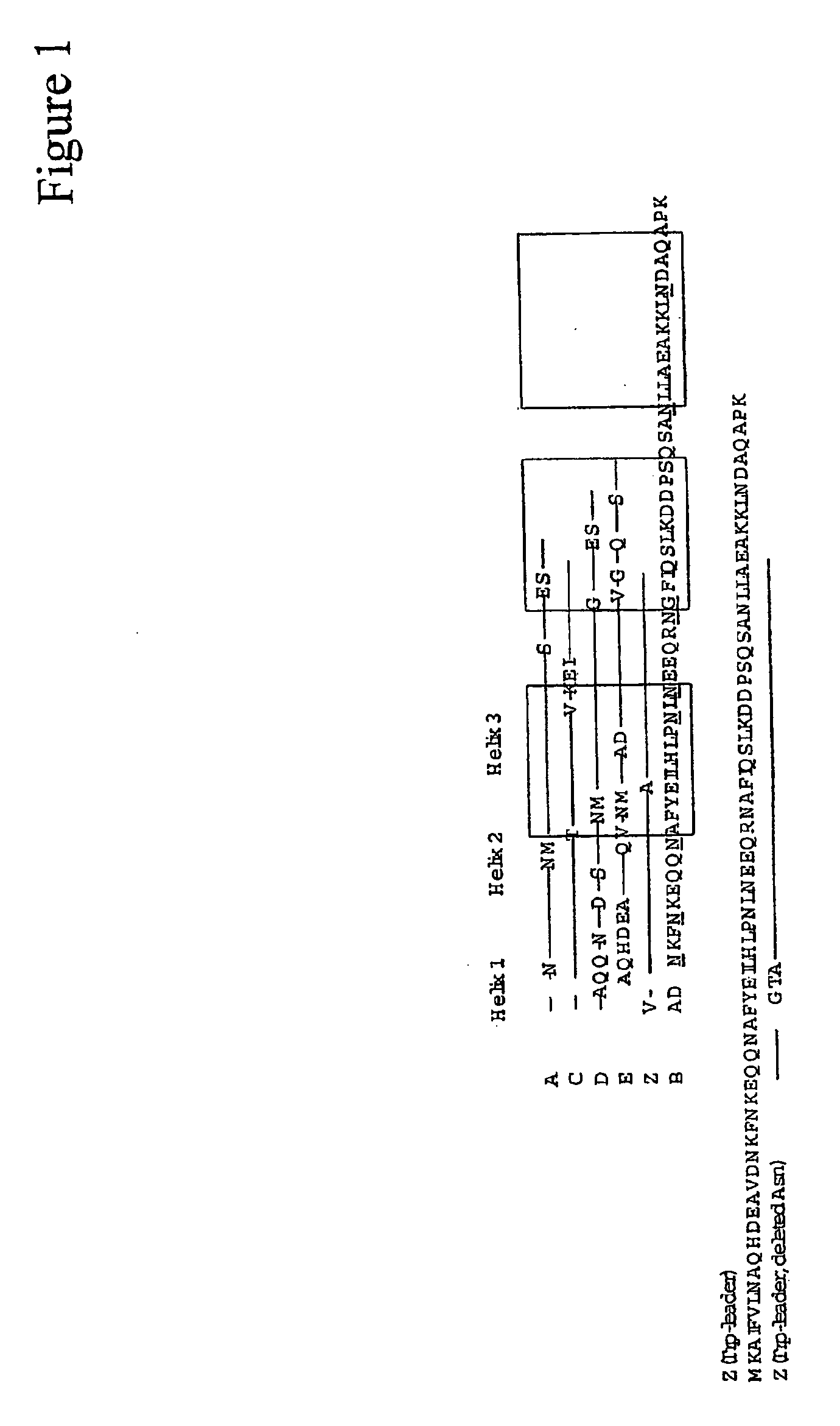
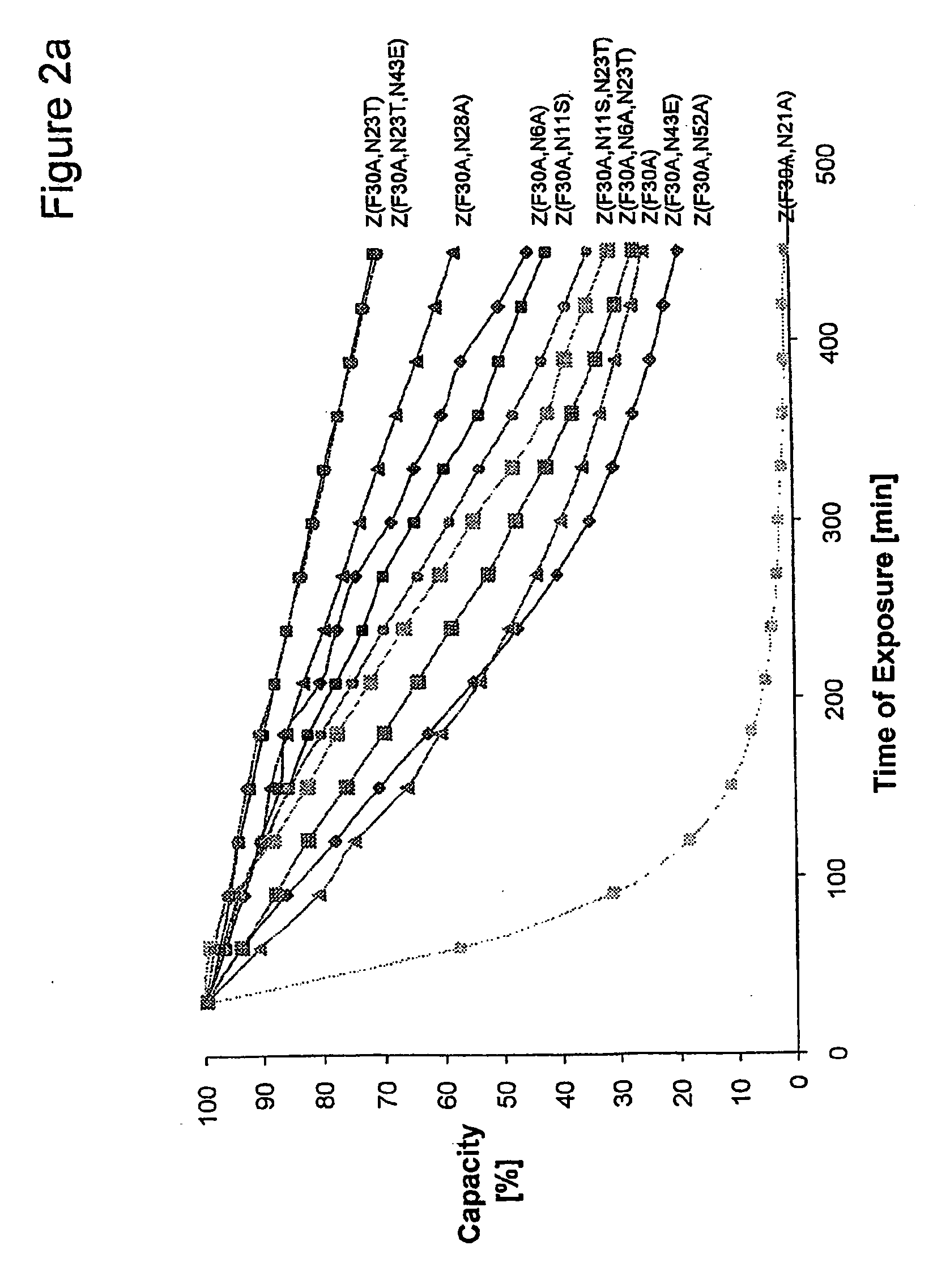
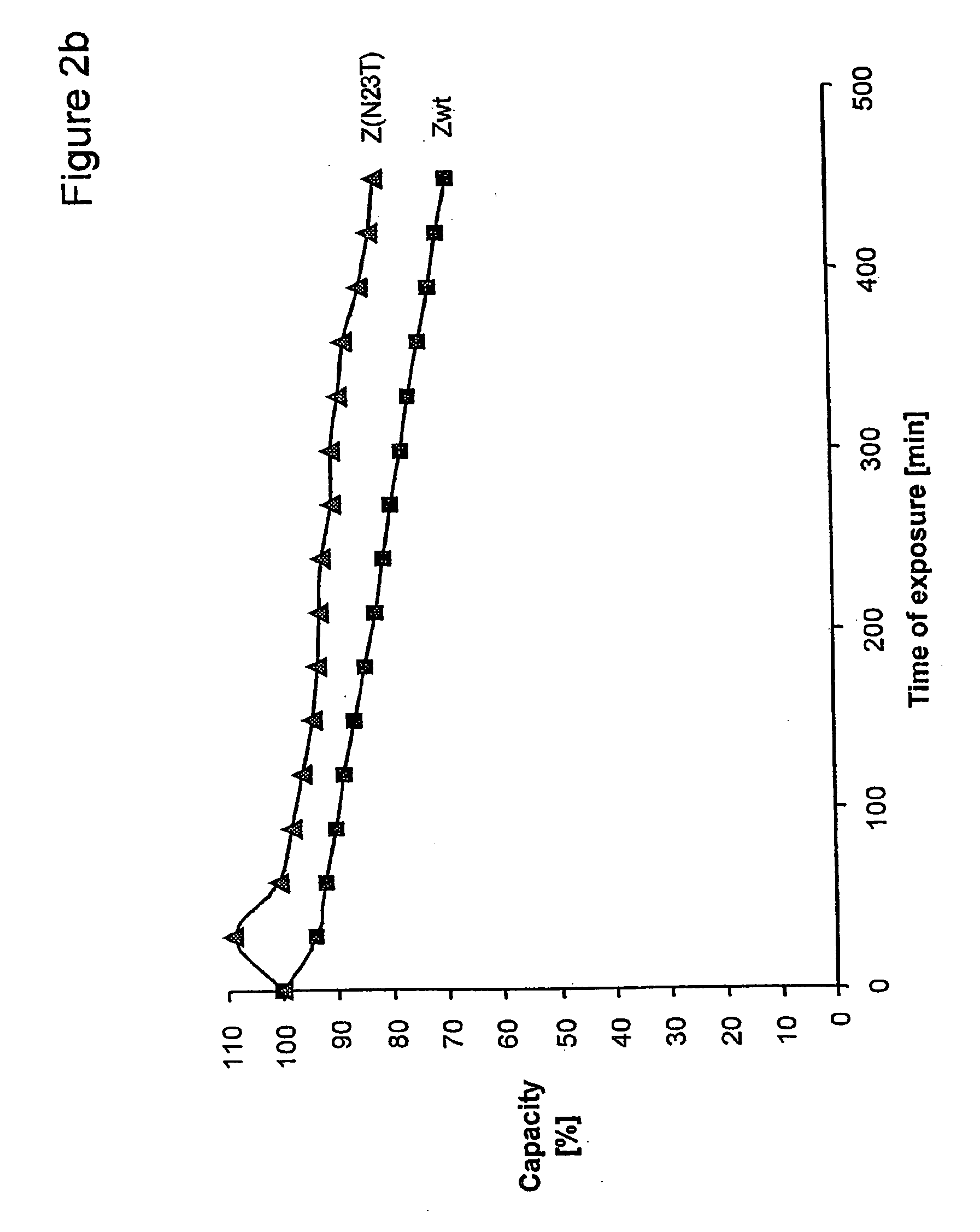
Mutant protein
InactiveUS20060194950A1Improve stabilityIncreased pH-valuesBacteriaSerum immunoglobulinsMutated proteinComplementarity determining region
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Muteins of fibroblast growth factor 21
The present invention relates to novel muteins of human fibroblast growth factor 21 with improved pharmaceutical properties. Both protein and the respective encoding nucleic acid species are disclosed. The invention also embodies vectors and host cells for the propagation of said nucleic acid sequences and the production of said muteins. Also disclosed are methods for treating type 2 diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and in reducing the mortality and morbidity of critically ill patients.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
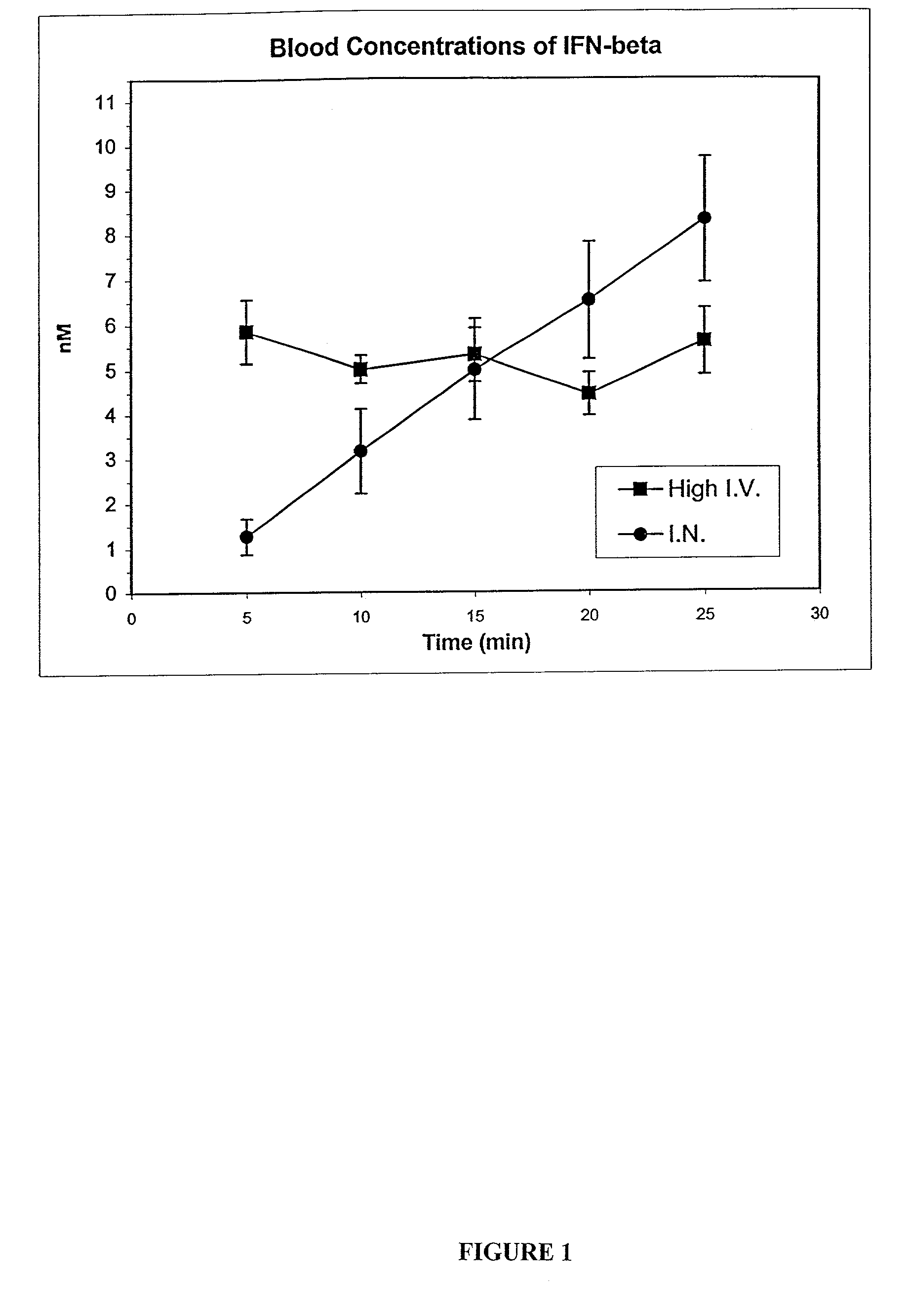
Method for administering a cytokine to the central nervous system and the lymphatic system
InactiveUS6991785B2Provide effectModulate immune and inflammatory responseBiocideNervous disorderImmunologic disordersInterferon alpha
The present invention is directed to a method for delivering cytokines to the central nervous system and the lymphatic system by way of a tissue innervated by the trigeminal nerve and / or olfactory nerve. Cytokines include tumor necrosis factors, interleukins, interferons, particularly interferon-β and its muteins such as IFN-βser17. Such a method of delivery can be useful in the treatment of central nervous system disorders, brain disorders, proliferative, viral, and / or autoimmune disorders such as Sjogren's disorder.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
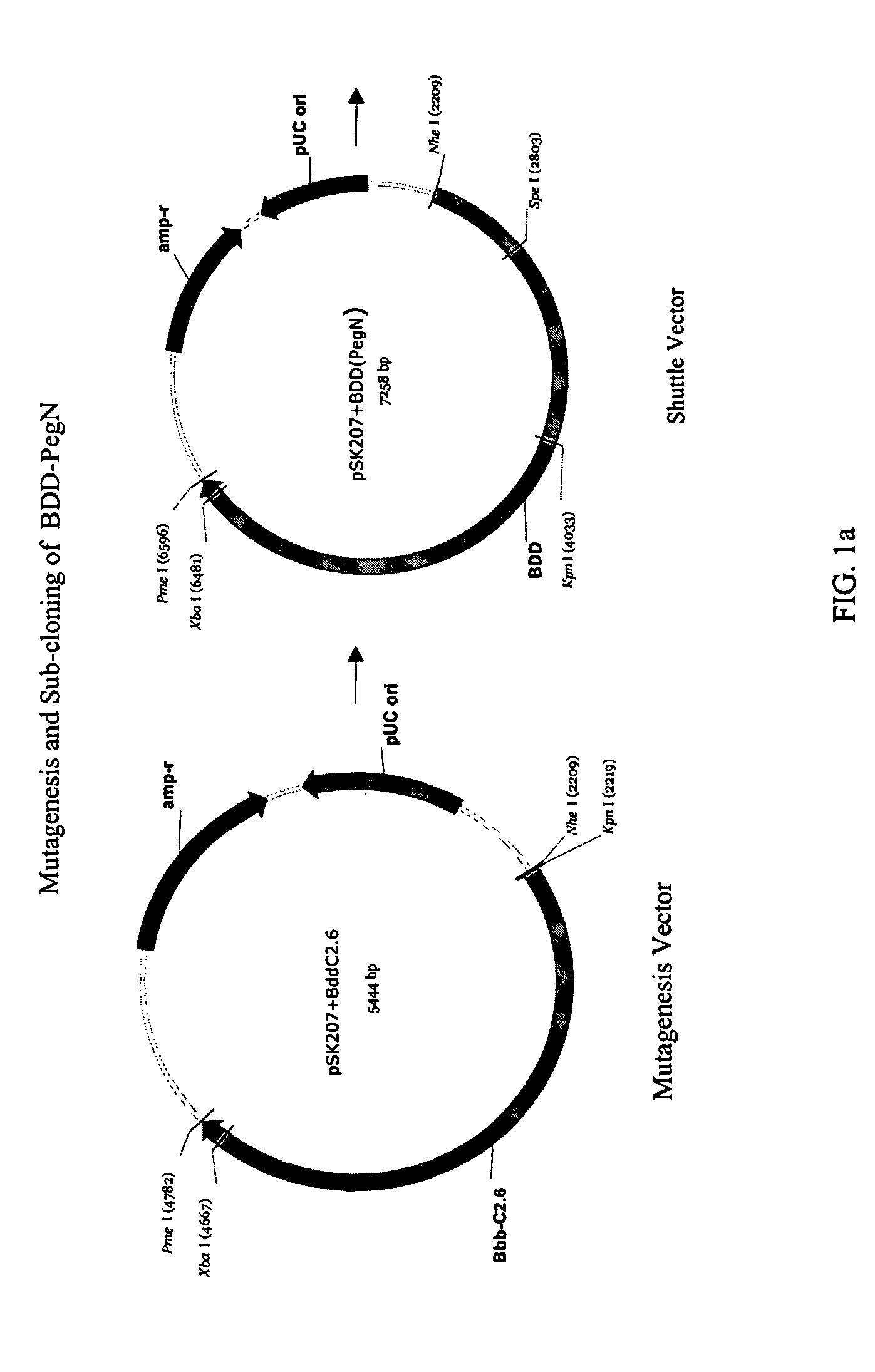
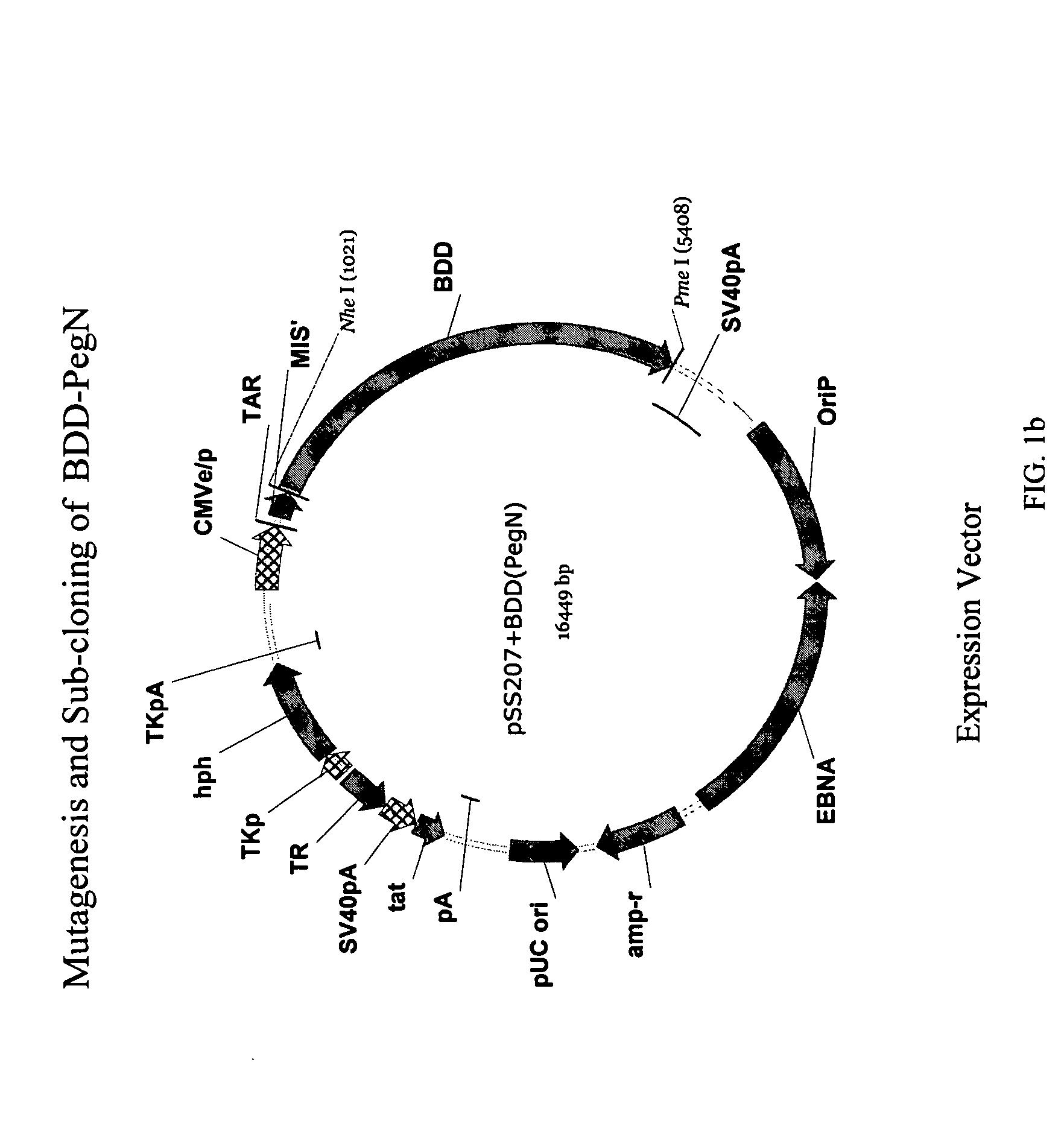
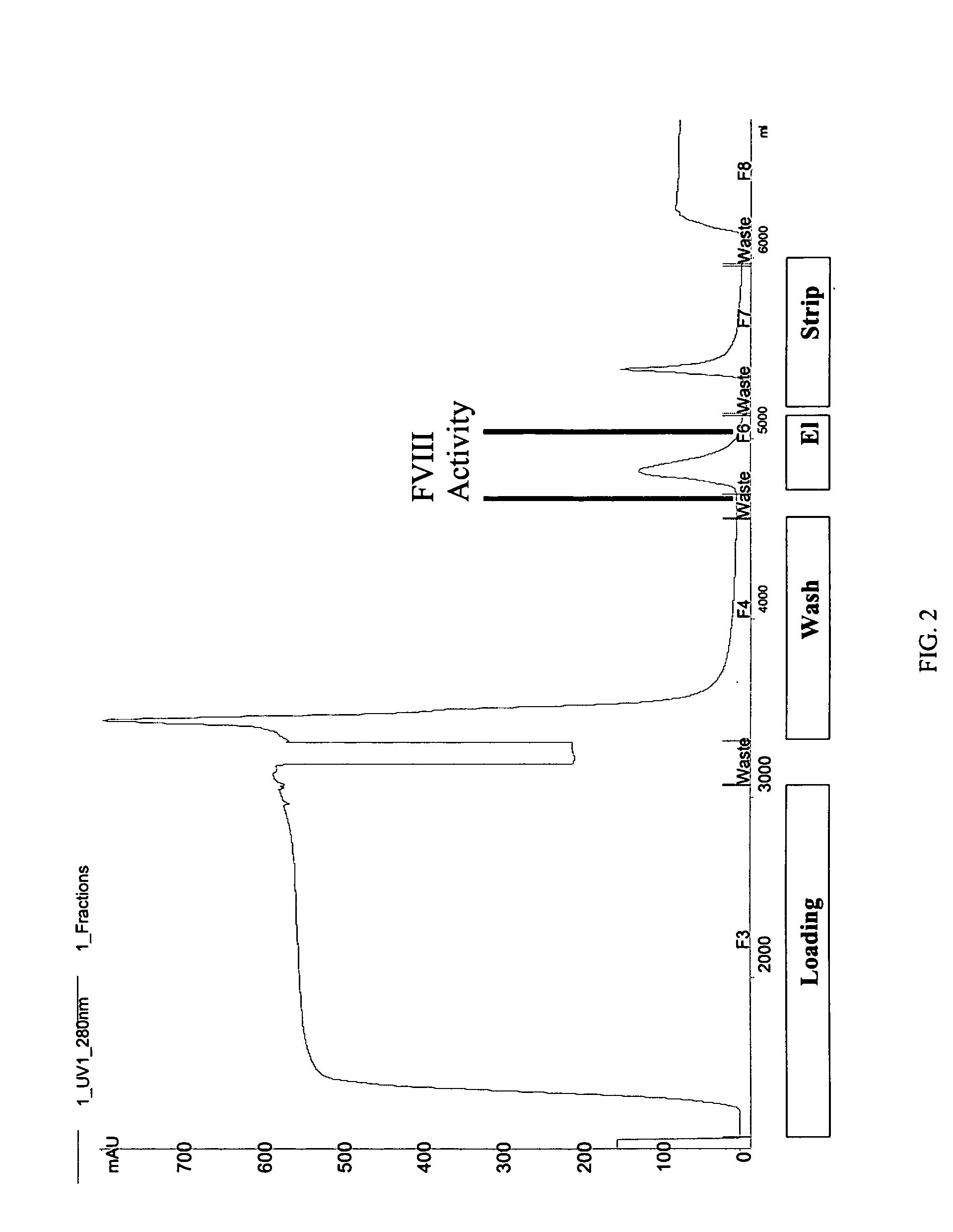
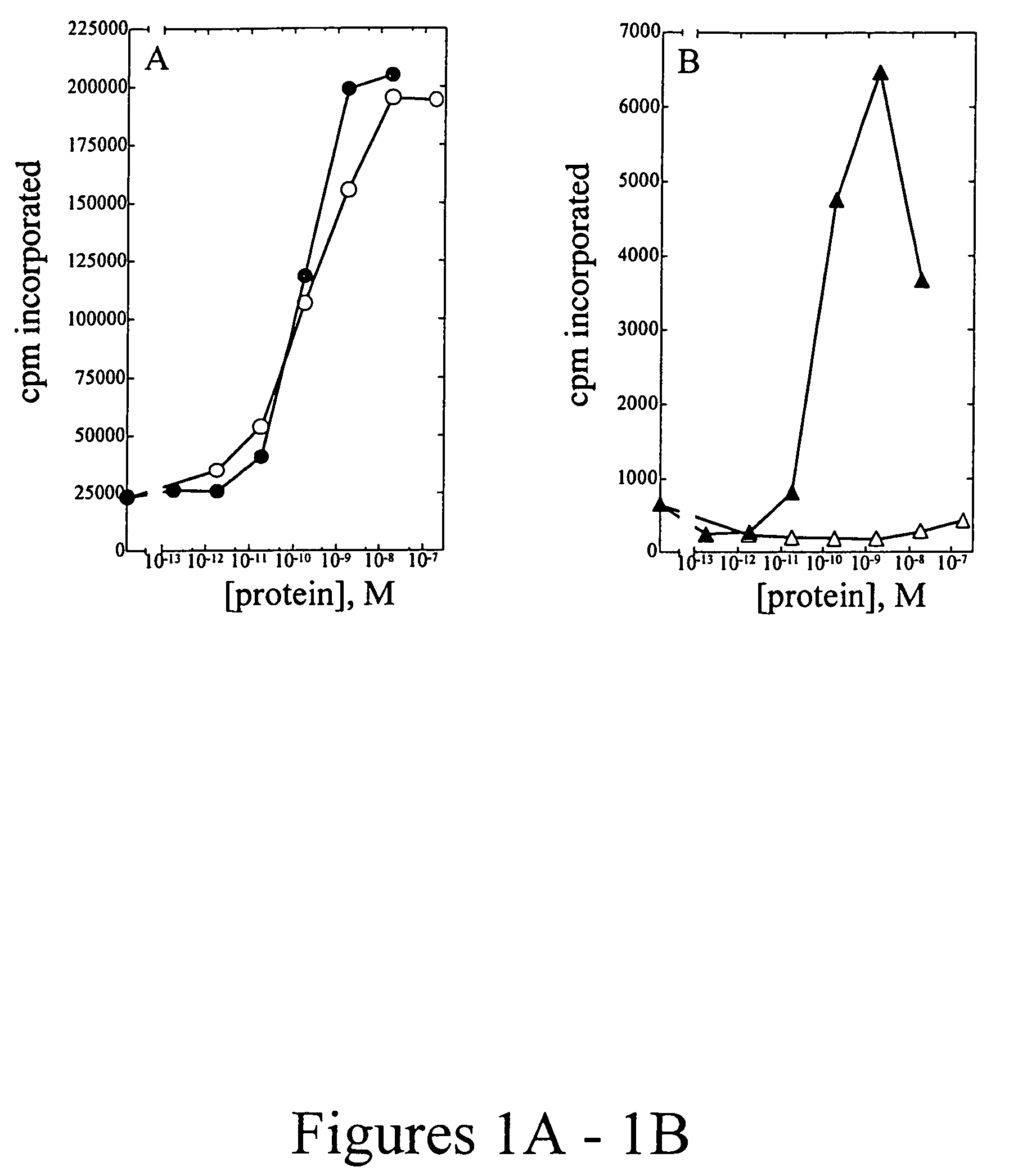
Site-directed modification of FVIII
ActiveUS20060115876A1Improve featuresImproved pharmacokinetic propertiesFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsPolyethylene glycolMutant protein
This invention relates to Factor VIII muteins that are covalently bound, at a predefined site that is not an N-terminal amine, to one or more biocompatible polymers such as polyethylene glycol. The mutein conjugates retain FVIII procoagulant activity and have improved pharmacokinetic properties.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Muteins of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21
InactiveUS20070293430A1Reduced deamidationReduce capacityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderWild typeNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to novel muteins of human fibroblast growth factor 21 with reduced deamidation compared to wild-type human FGF-21. Both protein and the respective encoding nucleic acid species are disclosed. The invention also embodies vectors and host cells for the propagation of said nucleic acid sequences and the production of said muteins. Also disclosed are methods for treating type 2 diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Homogeneous preparations of IL-31
Homogeneous preparations of human and murine IL-31 have been produced by mutating one or more of the cysteine residues in the polynucleotide sequences encoding the mature proteins. The cysteine mutant proteins can be shown to either bind to their cognate receptor or exhibit biological activity.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
IL-2 selective agonists and antagonists
The invention is directed to a polypeptide comprising a human IL-2 mutein numbered in accordance with wild-type IL-2 wherein said human IL-2 is substituted at at least one of positions 20, 88 or 126, whereby said mutein preferentially activates T cells over NK cells. D20H and I, N88G, I, and R, in particular have a relative T cell-differential activity much greater than native IL-2, with predicted associated reduced in vivo toxicity. The invention also includes polynucleotides coding for the muteins of the invention, vectors containing the polynucleotides, transformed host cells, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the muteins, and therapeutic methods of treatment.
Owner:AICURIS GMBH & CO KG
Muteins of fibroblast growth factor 21
ActiveUS7622445B2Reduce sensitivityReduced O-glycosylationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMutated proteinNucleic acid sequence
The present invention relates to novel muteins of human fibroblast growth factor-21 with reduced susceptibility for proteolytic degradation when expressed in yeast. Both protein and the respective encoding nucleic acid species are disclosed. The invention also embodies vectors and host cells for the propagation of said nucleic acid sequences and the production of said muteins. Also disclosed are methods for treating type 2 diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Muteins of fibroblast growth factor 21
The present invention relates to novel muteins of human fibroblast growth factor 21 with reduced capacity of O-glycosylation when expressed in yeast compared to wild-type human FGF-21. Both protein and the respective encoding nucleic acid species are disclosed. The invention also embodies vectors and host cells for the propagation of said nucleic acid sequences and the production of said muteins. Also disclosed are methods for treating type 2 diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Muteins of fibroblast growth factor 21
InactiveUS7655627B2Reduced deamidationReduce capacityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderADAMTS ProteinsWild type
The present invention relates to novel muteins of human fibroblast growth factor 21 with reduced deamidation compared to wild-type human FGF-21. Both protein and the respective encoding nucleic acid species are disclosed. The invention also embodies vectors and host cells for the propagation of said nucleic acid sequences and the production of said muteins. Also disclosed are methods for treating type 2 diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
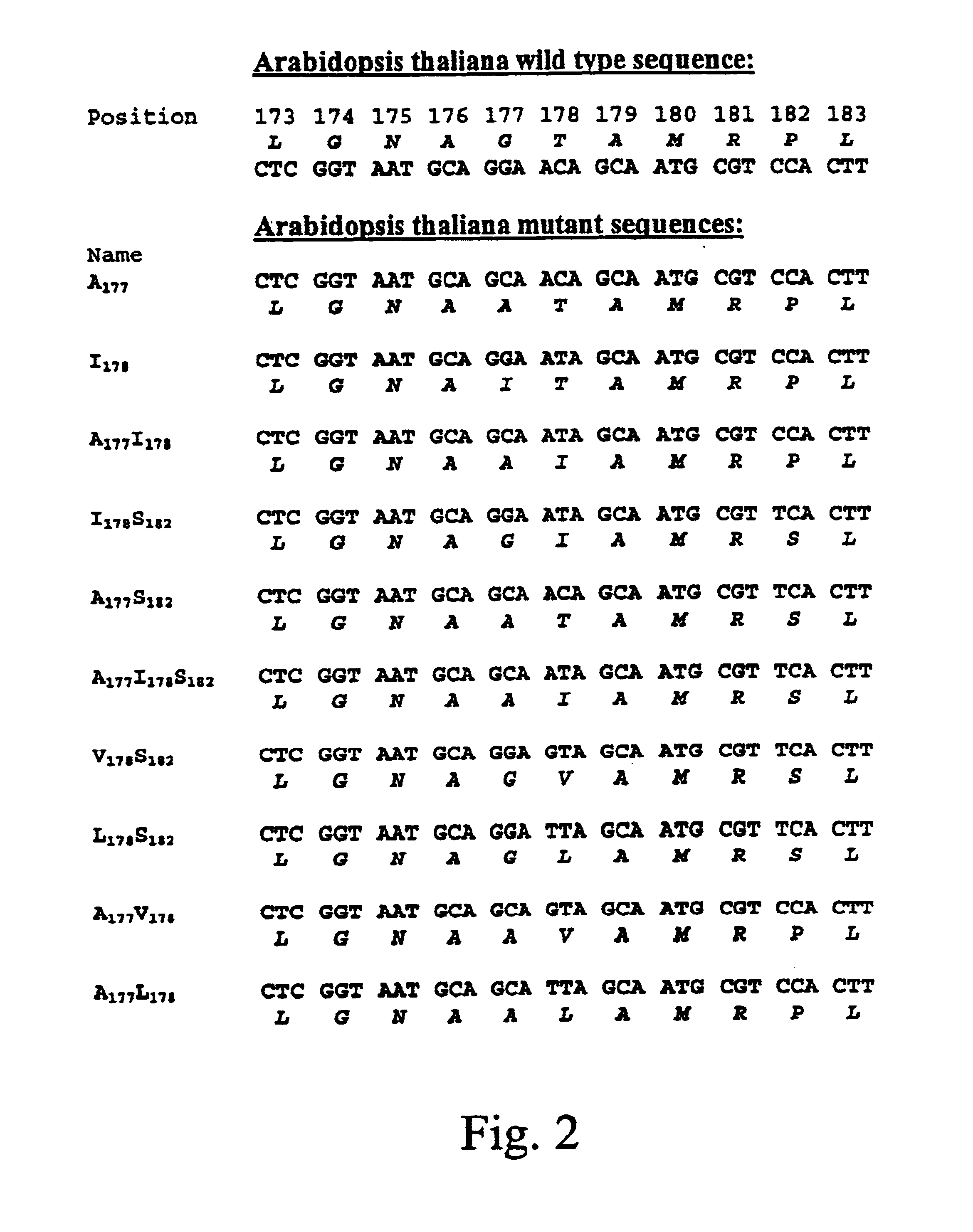
Methods of making non-transgenic herbicide resistant plants
The present invention relates to the production of a non-transgenic plant resistant or tolerant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, e.g., glyphosate. The present invention also relates to the use of a recombinagenic oligonucleobase to make a desired mutation in the chromosomal or episomal sequences of a plant in the gene encoding for 5-enol pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). The mutated protein, which substantially maintains the catalytic activity of the wild-type protein, allows for increased resistance or tolerance of the plant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, and allows for the substantially normal growth or development of the plant, its organs, tissues or cells as compared to the wild-type plant irrespective of the presence or absence of the herbicide.
Owner:CIBUS
Muteins OF Fibroblast Growth Factor 21
ActiveUS20070299007A1Reduced O-glycosylationImprove drug stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderYeastNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to novel muteins of human fibroblast growth factor-21 with reduced susceptibility for proteolytic degradation when expressed in yeast. Both protein and the respective encoding nucleic acid species are disclosed. The invention also embodies vectors and host cells for the propagation of said nucleic acid sequences and the production of said muteins. Also disclosed are methods for treating type 2 diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome. X-16816
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Muteins of fibroblast growth factor 21
The present invention relates to novel muteins of human fibroblast growth factor 21 with improved pharmaceutical properties. Both protein and the respective encoding nucleic acid species are disclosed. The invention also embodies vectors and host cells for the propagation of said nucleic acid sequences and the production of said muteins. Also disclosed are methods for treating type 2 diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and in reducing the mortality and morbidity of critically ill patients.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Forms of soluble pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase
InactiveUS7132270B2Increased substrate specificityImprove propertiesFungiBacteriaMutated proteinGlucose polymers
The present invention relates to improved variants of soluble pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ)-dependent glucose dehydrogenases (s-GDH), to genes encoding mutated s-GDH, to mutant proteins of s-GDH with improved substrate specificity for glucose, and to different applications of these s-GDH variants, particularly for determining concentrations of sugar, especially of glucose in a sample.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Mutant adeno-associated virus virions and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS9441244B2Altered capsid propertiesReduce the binding forceAntibacterial agentsVirusesNucleotideCell type specific
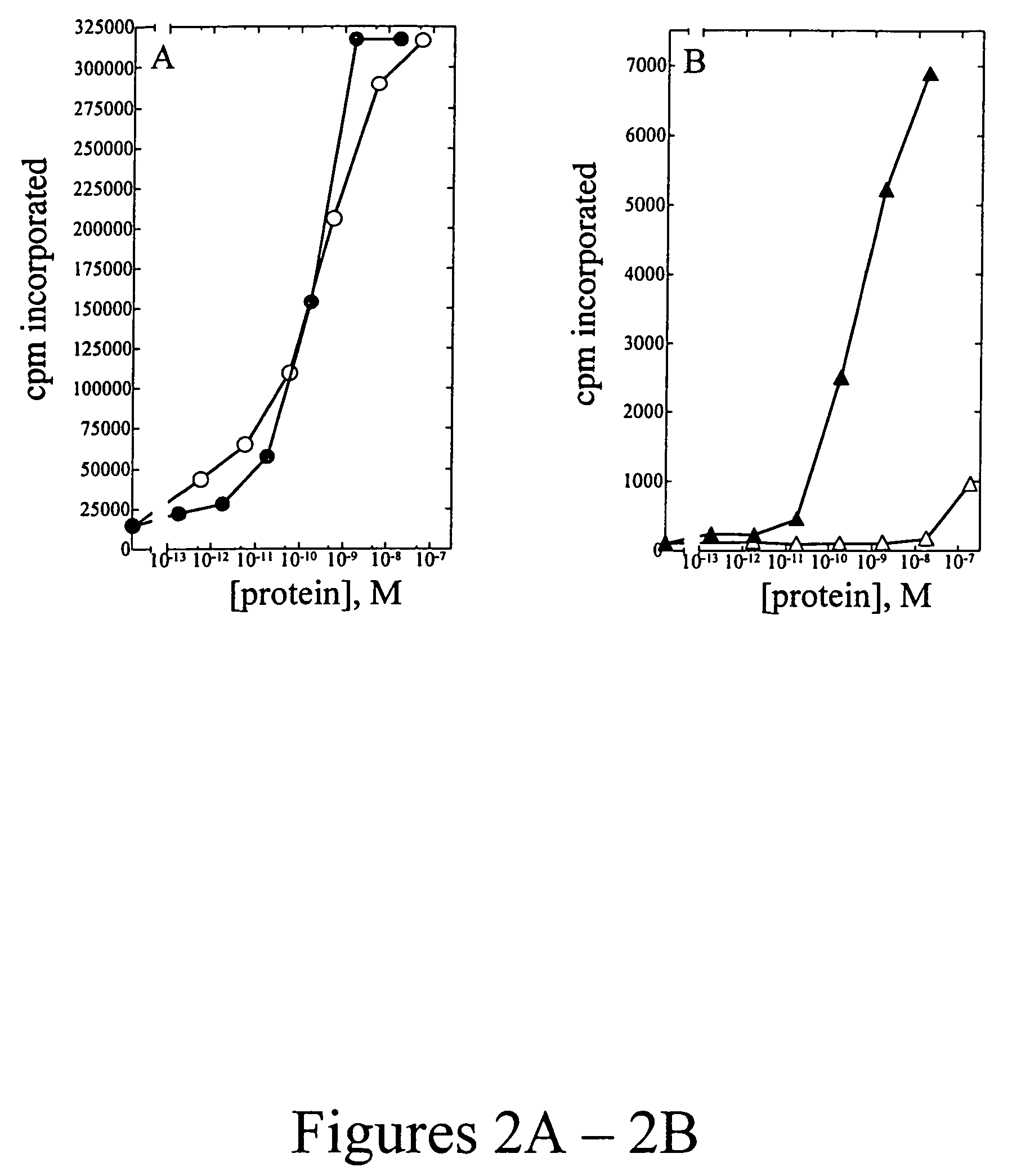
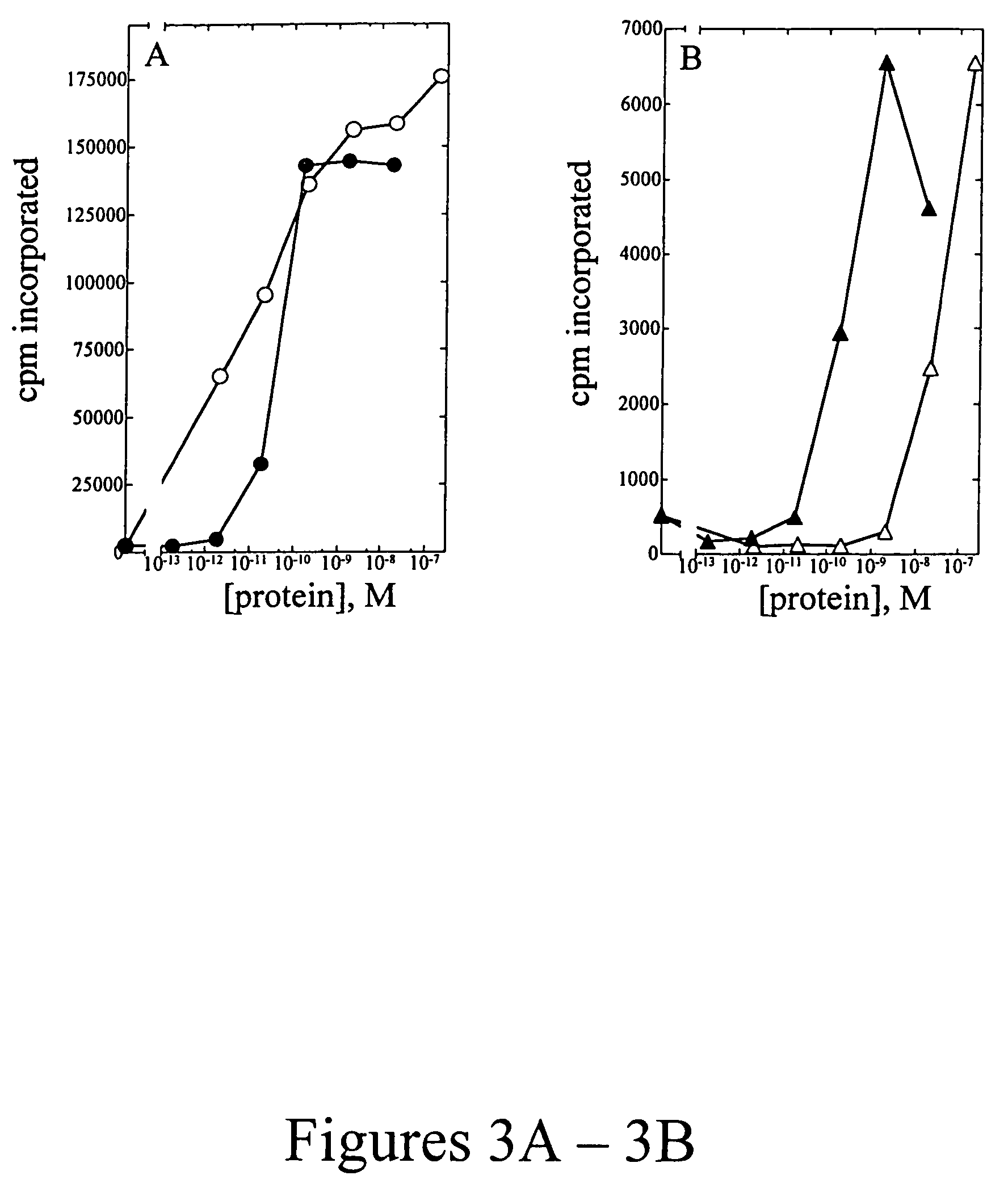
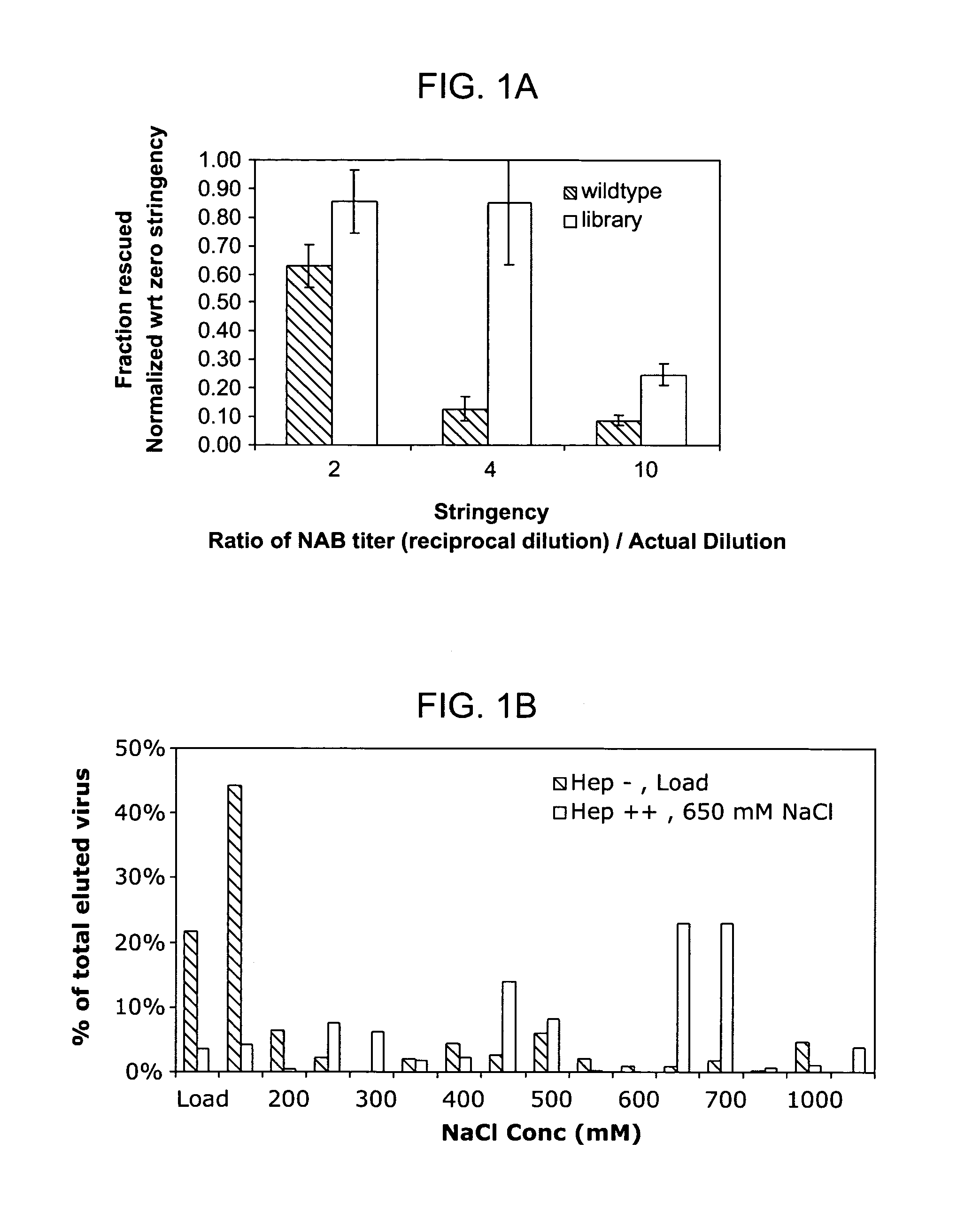
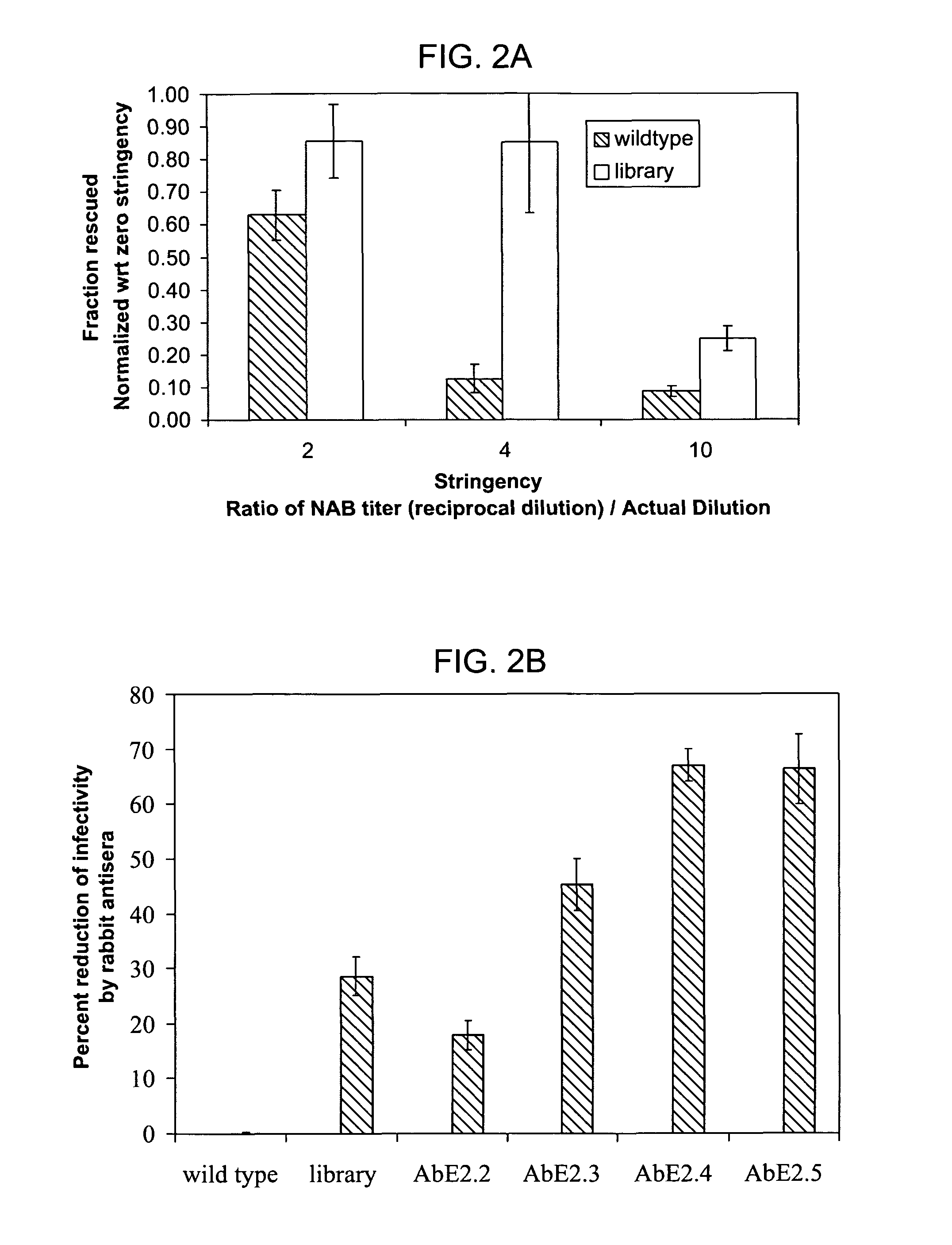
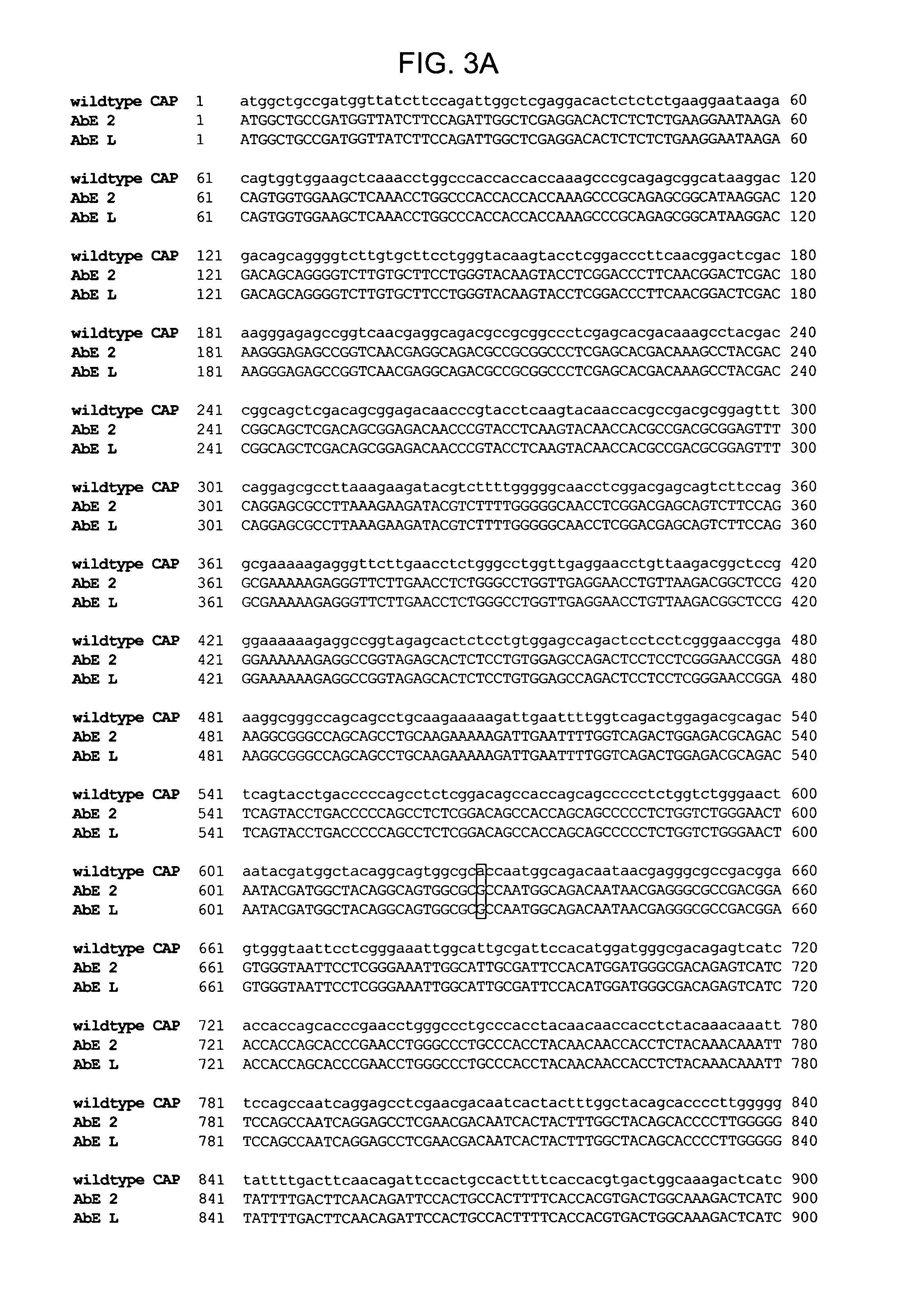
The present invention provides mutant adeno-associated virus (AAV) that exhibit altered capsid properties, e.g., reduced binding to neutralizing antibodies in serum and / or altered heparin binding and / or altered infectivity of particular cell types. The present invention further provides libraries of mutant AAV comprising one or more mutations in a capsid gene. The present invention further provides methods of generating the mutant AAV and mutant AAV libraries, and compositions comprising the mutant AAV. The present invention further provides recombinant AAV (rAAV) virions that comprise a mutant capsid protein. The present invention further provides nucleic acids comprising nucleotide sequences that encode mutant capsid proteins, and host cells comprising the nucleic acids. The present invention further provides methods of delivering a gene product to an individual, the methods generally involving administering an effective amount of a subject rAAV virion to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:INTEGRATIVE GENE THERAPEUTICS +1
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mutants
The present invention has an object to provide a tumor necrosis factor mutant protein, particularly, a tumor necrosis factor mutant protein specific to TNF-R1 or TNF-R2; tumor necrosis factor inhibitor; or tumor necrosis factor preparation containing it as an effective ingredient, and the object is solved by providing a tumor necrosis factor mutant protein where one or more amino acid residues selected from the group consisting of 29th, 31st, 32nd, 145th, 146th and 147th, or the group consisting of 84th to 89th from the N-terminal of the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 is / are replaced with other amino acid residue(s); a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor; and a tumor necrosis factor preparation containing it as an effective ingredient.
Owner:MAYUMI TADANORI +3
Treatment of CNS disorders associated with mutations in genes encoding lysosomal enzymes
Described is a method for treating an individual having a neurological disorder with an associated mutation or mutations in a gene encoding a lysosomal enzyme. Specifically, the individual is administered a specific pharmacological chaperone for the lysosomal enzyme which increases trafficking of the protein from the ER to the lysosome in neural cells, with or without concomitantly increasing enzyme activity in neural cells. Restoration of trafficking relieves cell stress and other toxicities associated with accumulation of mutant proteins. Restoration of enzyme activity relieves substrate accumulation and pathologies associated with lipid accumulation. In a specific embodiment, the neurological disorder is Parkinson's disease or parkinsonism which is associated with mutations in glucocerebrosidase.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Muteins of fibroblast growth factor 21
InactiveUS20090118190A1Antibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCritically illNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to novel muteins of human fibroblast growth factor 21 with improved pharmaceutical properties. Both protein and the respective encoding nucleic acid species are disclosed. The invention also embodies vectors and host cells for the propagation of said nucleic acid sequences and the production of said muteins. Also disclosed are methods for treating type 2 diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and in reducing the mortality and morbidity of critically ill patients.
Owner:BEALS JOHN MICHAEL +7
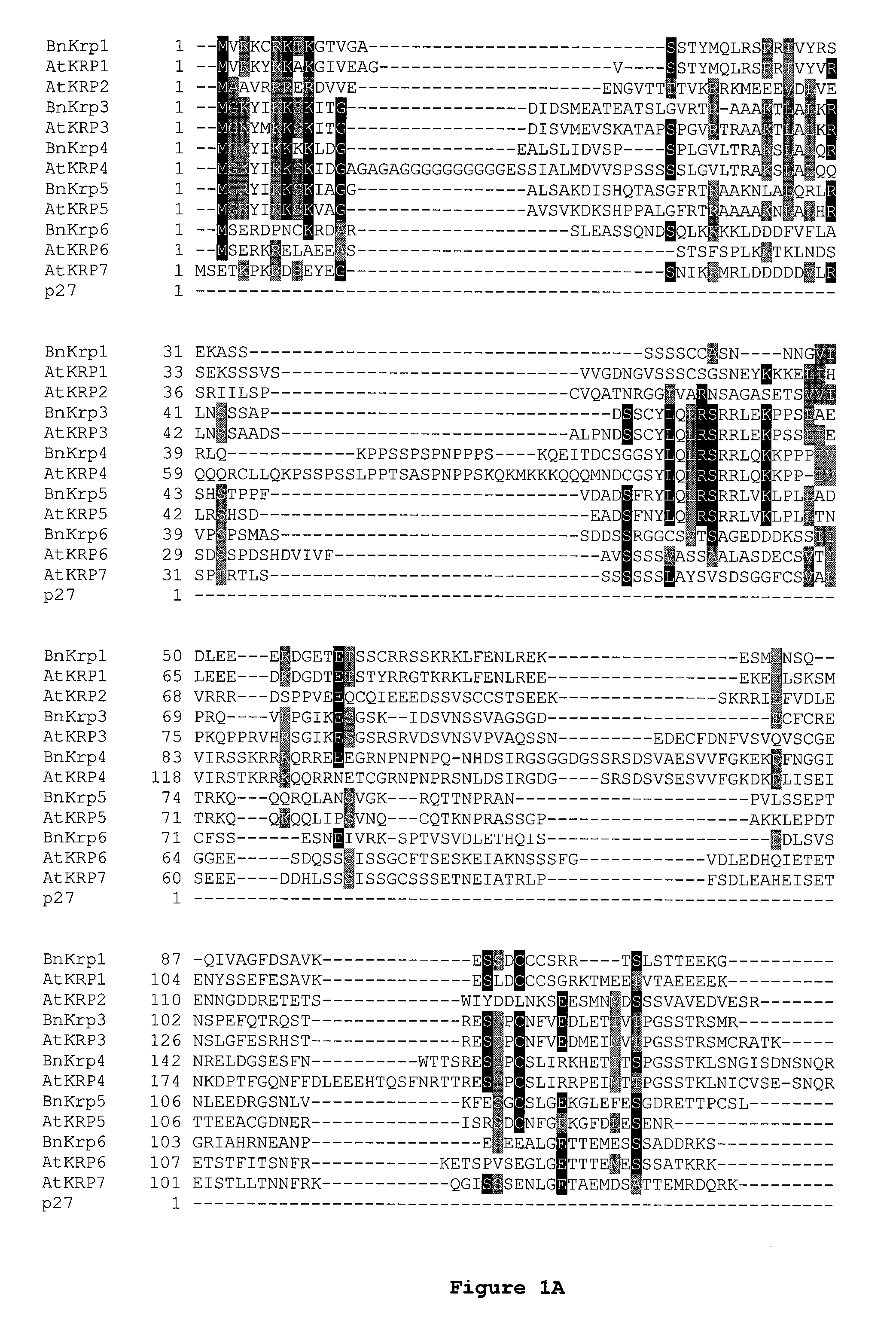
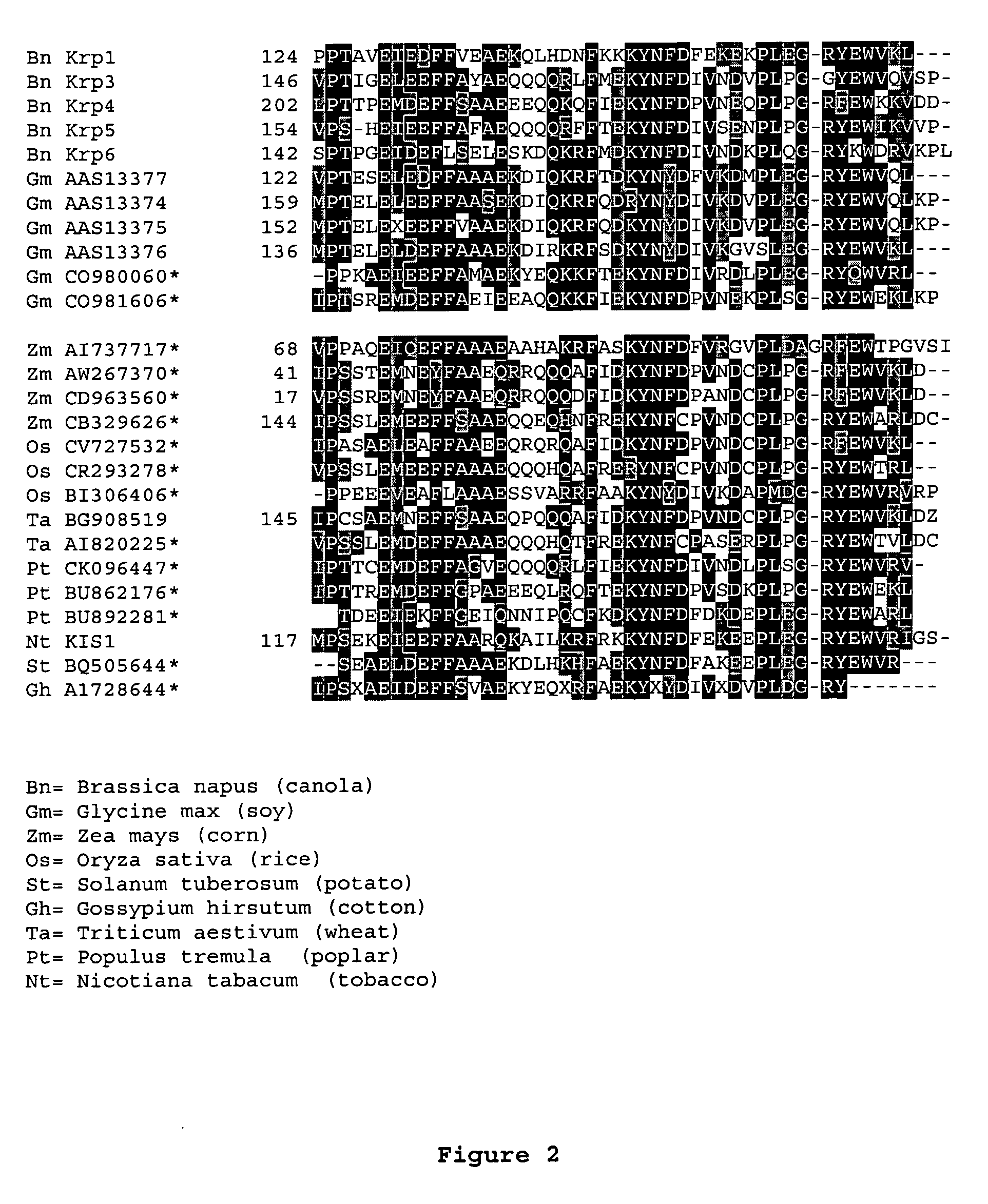
Dominant negative mutant krp protein protection of active cyclin-cdk complex inhibition by wild-type krp
InactiveUS20070056058A1Speed upIncreasing cell proliferationBacteriaSugar derivativesMutated proteinPlant cell
Disclosed are mutant CDK inhibitor (CKI) polypeptides having dominant negative antagonist activity against wild-type CKI proteins, as well as related compositions, including nucleic acids and vectors encoding the mutant CKI polypeptides and transformed host cells and transgenic plants comprising such nucleic acids and vectors. Also disclosed are related methods for using the mutant proteins to modulate cell division in cells, particularly plant cells.
Owner:TARGETED GROWTH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com