Patents
Literature
64 results about "Pharmacological chaperone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
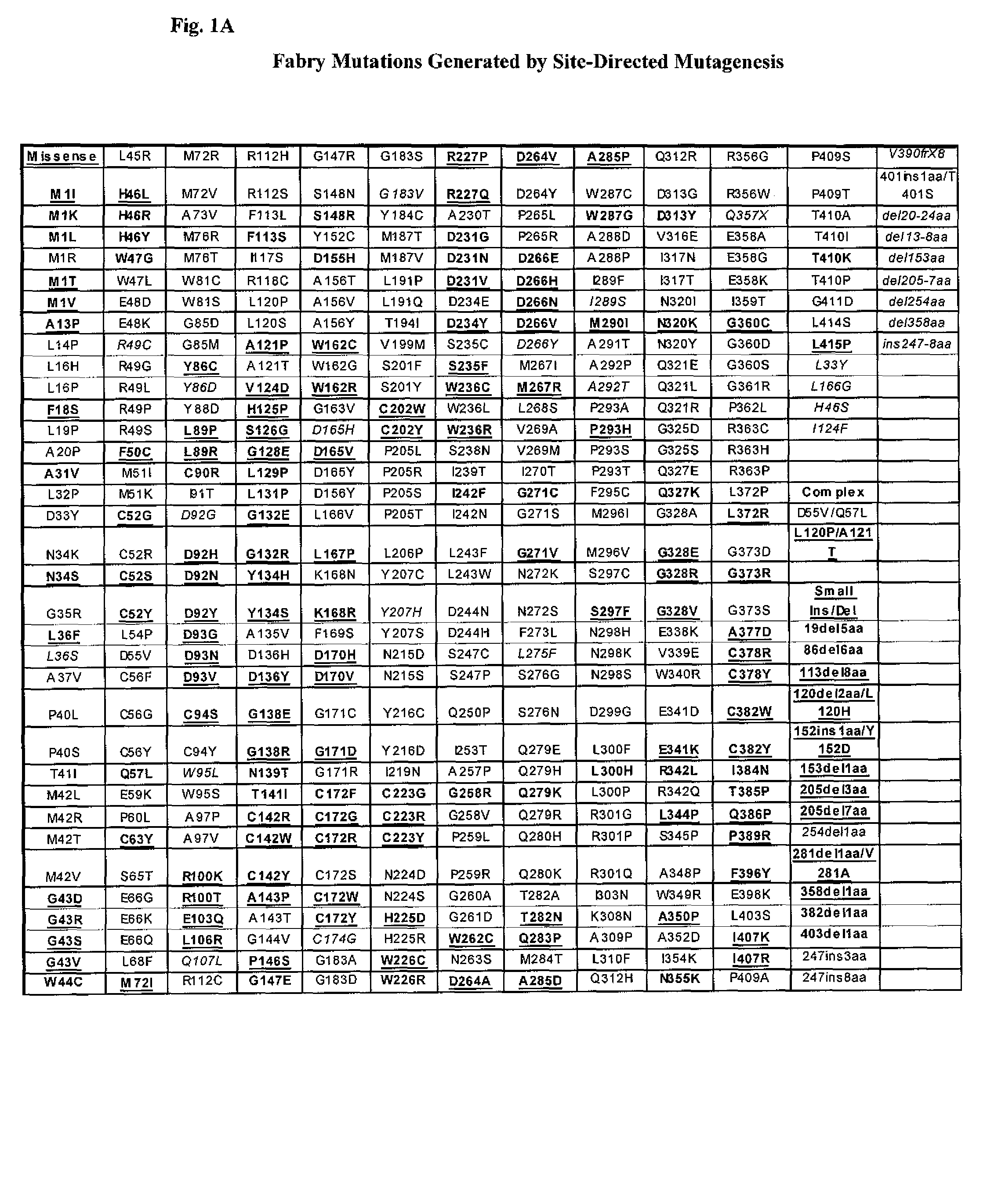
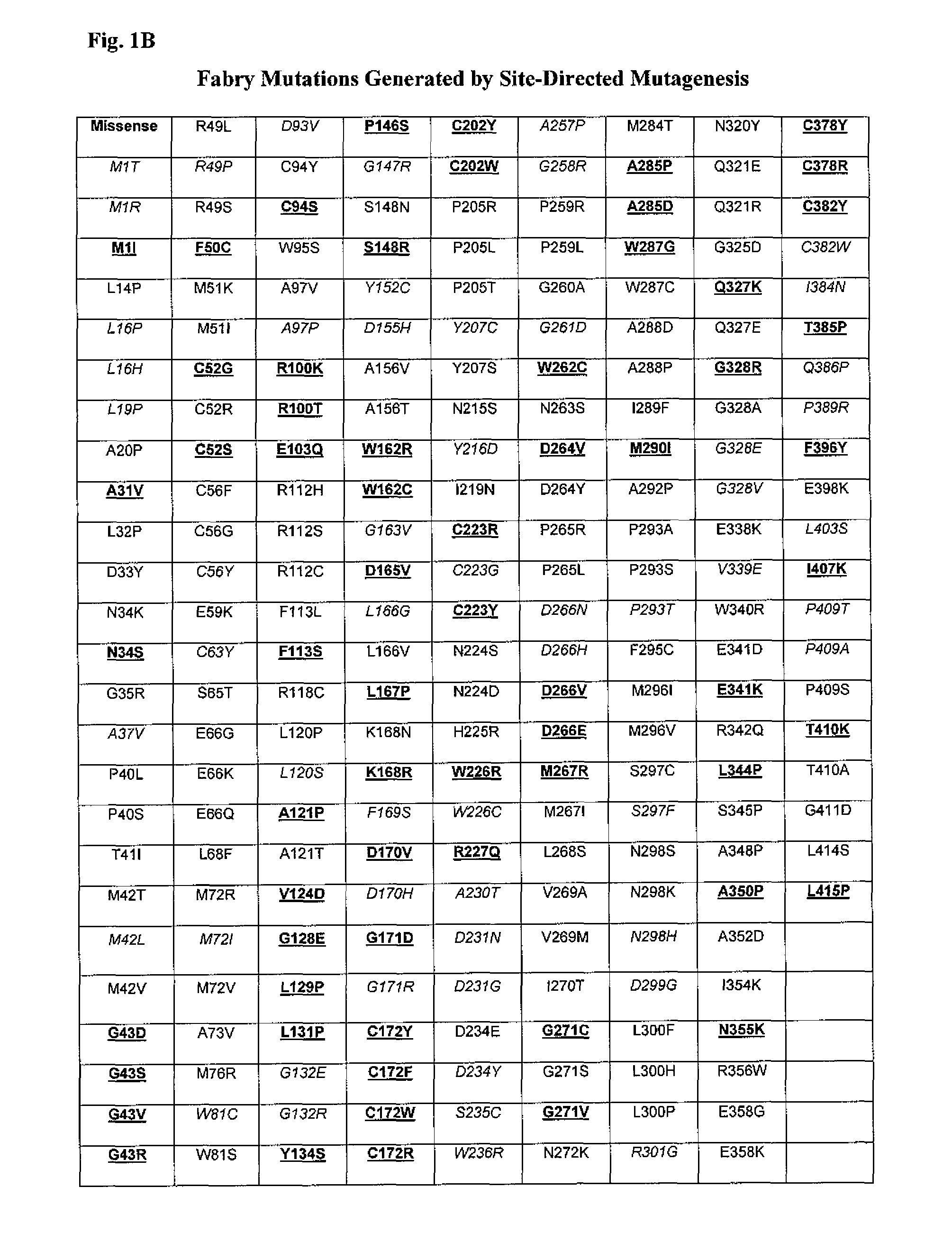
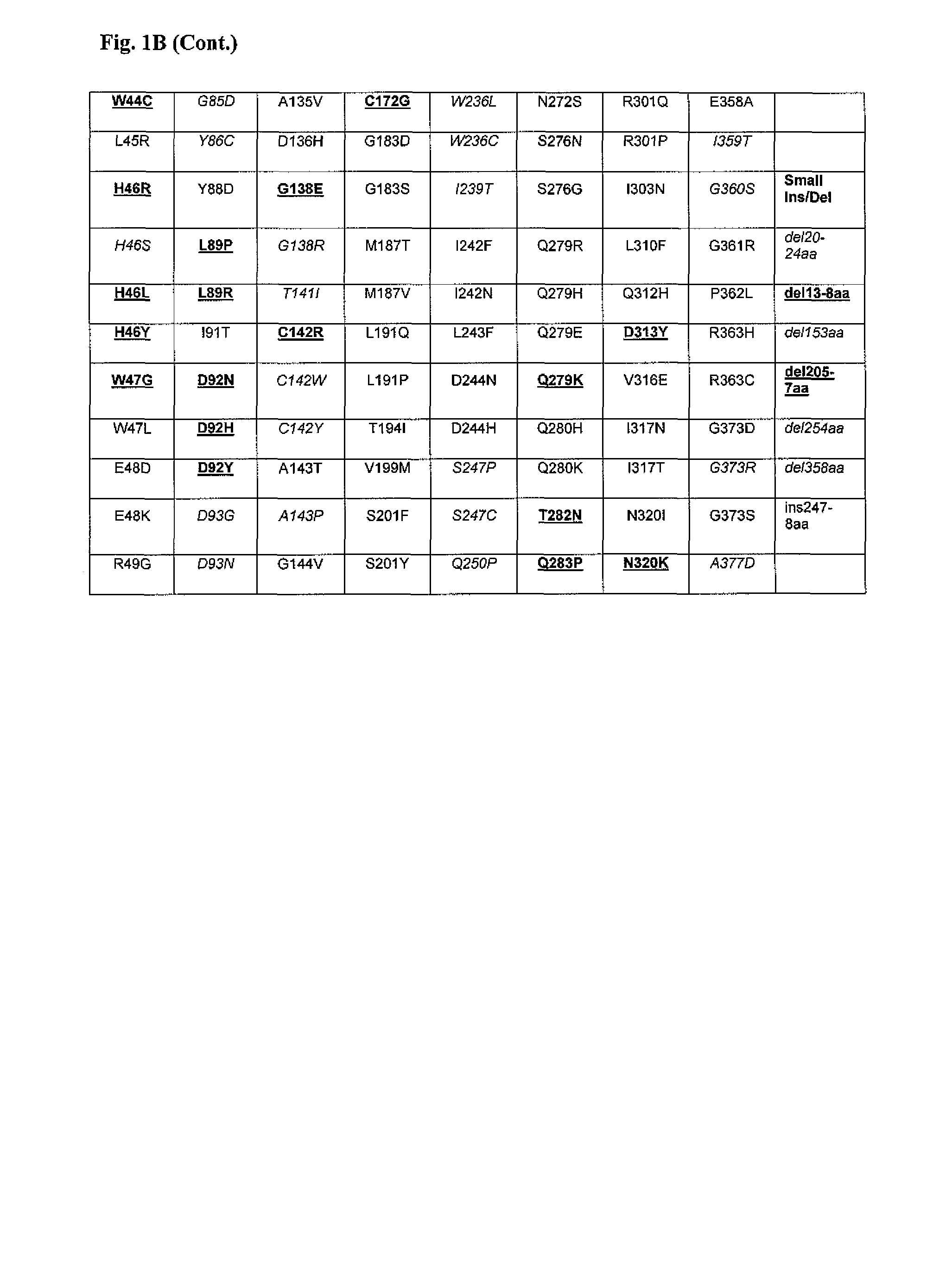
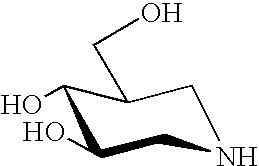
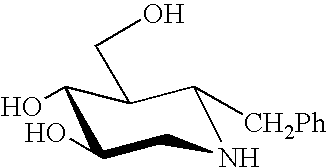
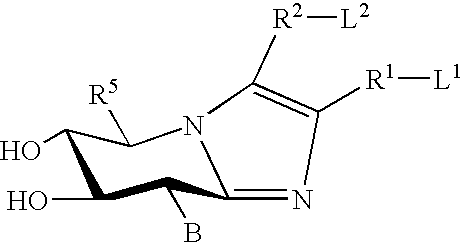
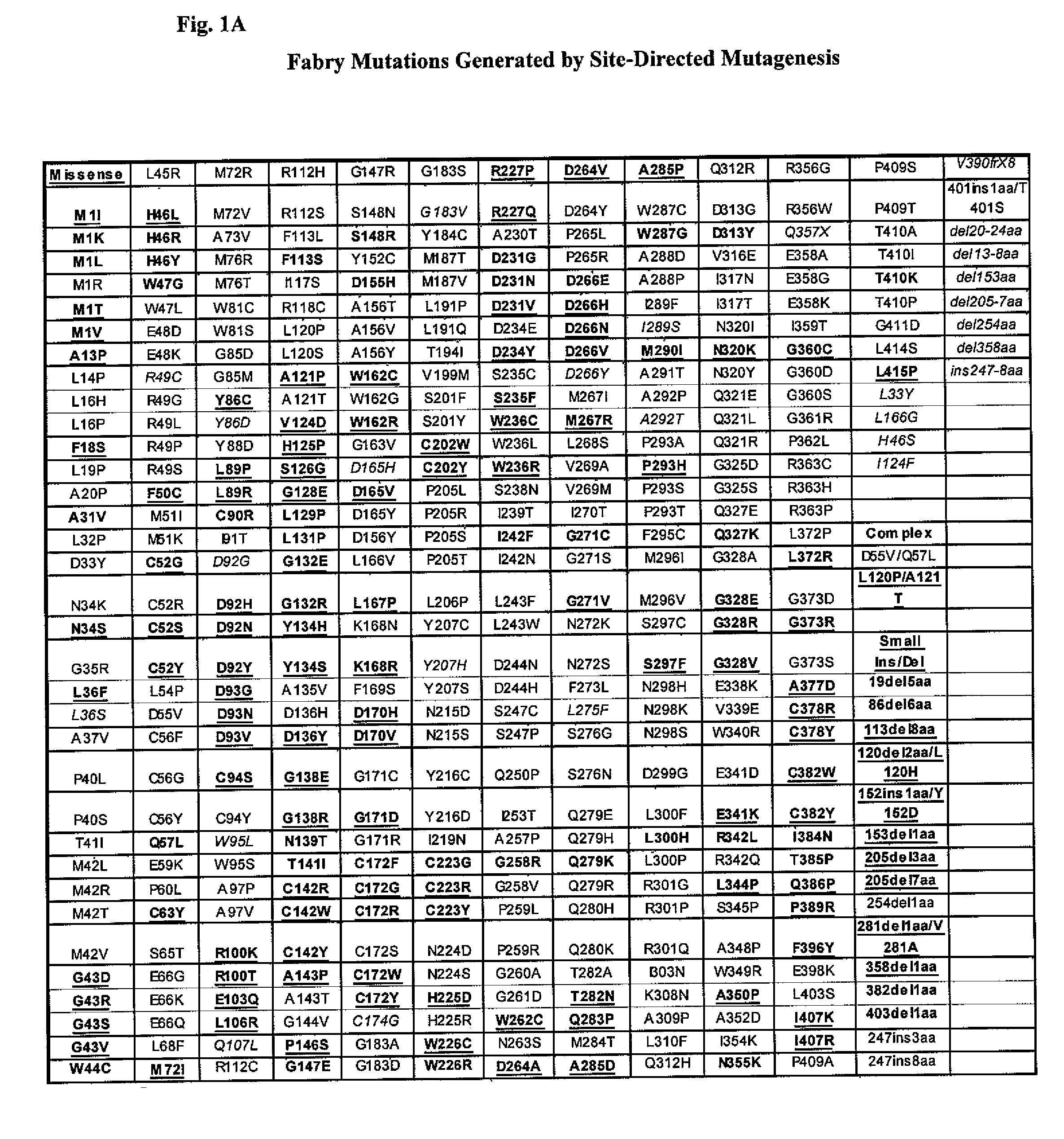
A pharmacological chaperone or pharmacoperone is a drug that acts as a protein chaperone. That is, it contains small molecules that enter cells and serve as a molecular scaffolding in order to cause otherwise-misfolded mutant proteins to fold and route correctly within the cell.
Method to predict response to pharmacological chaperone treatment of diseases
ActiveUS8592362B2Increase activity levelHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocidePharmacological chaperoneΑ galactosidase a
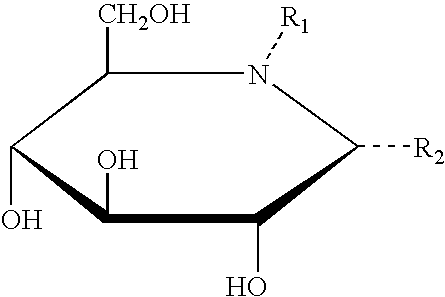
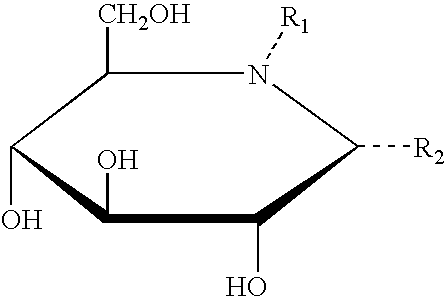
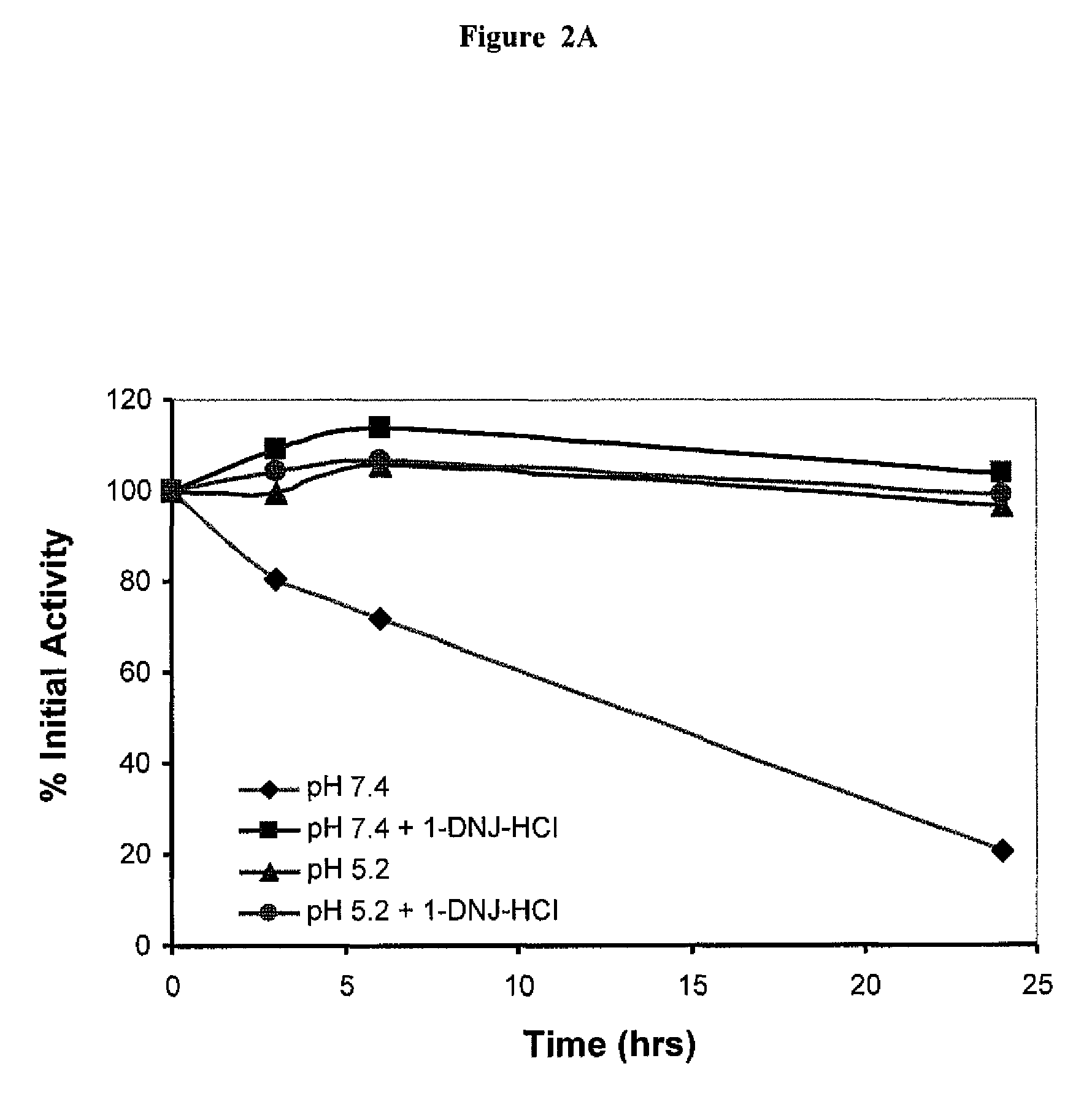
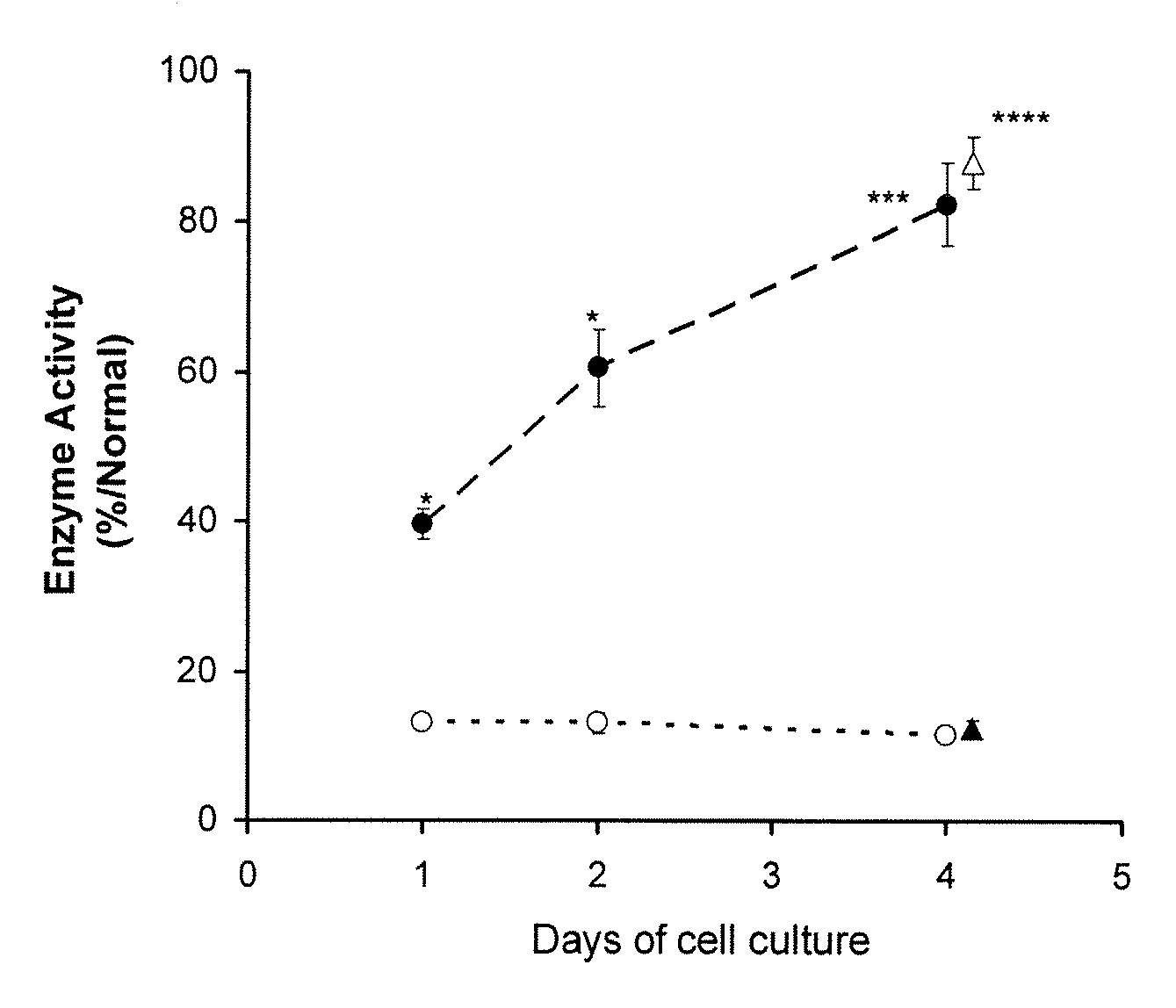
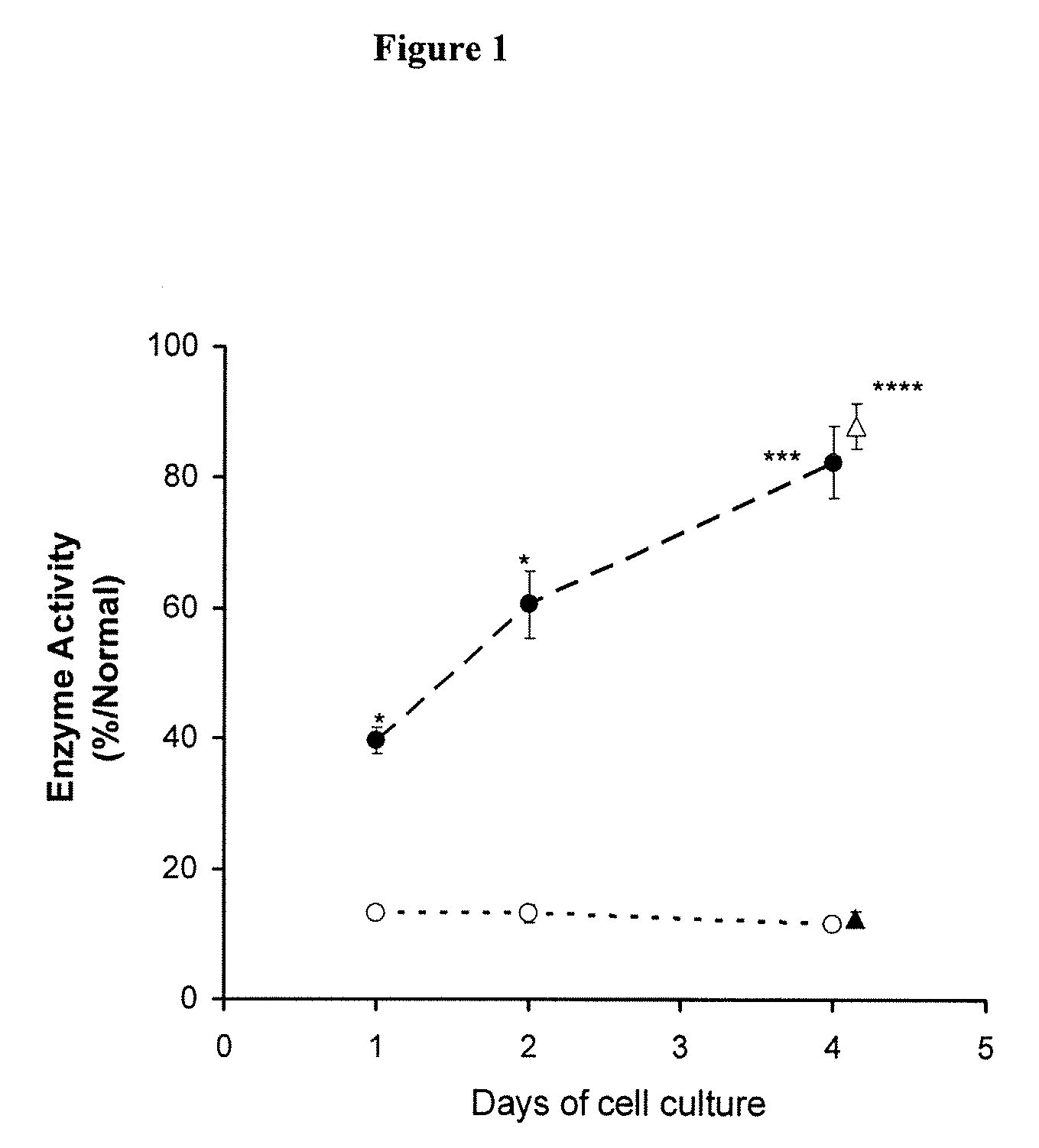
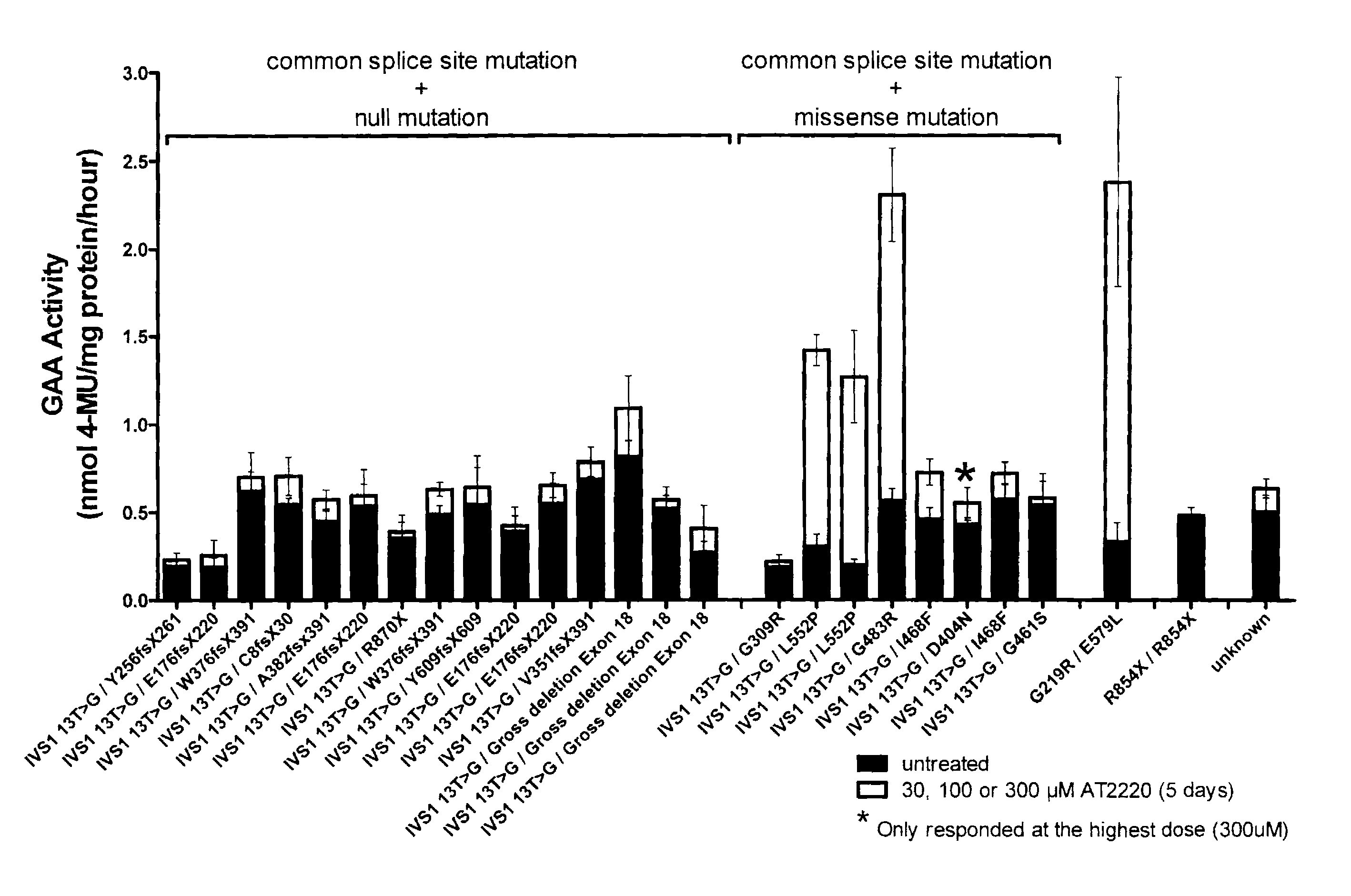
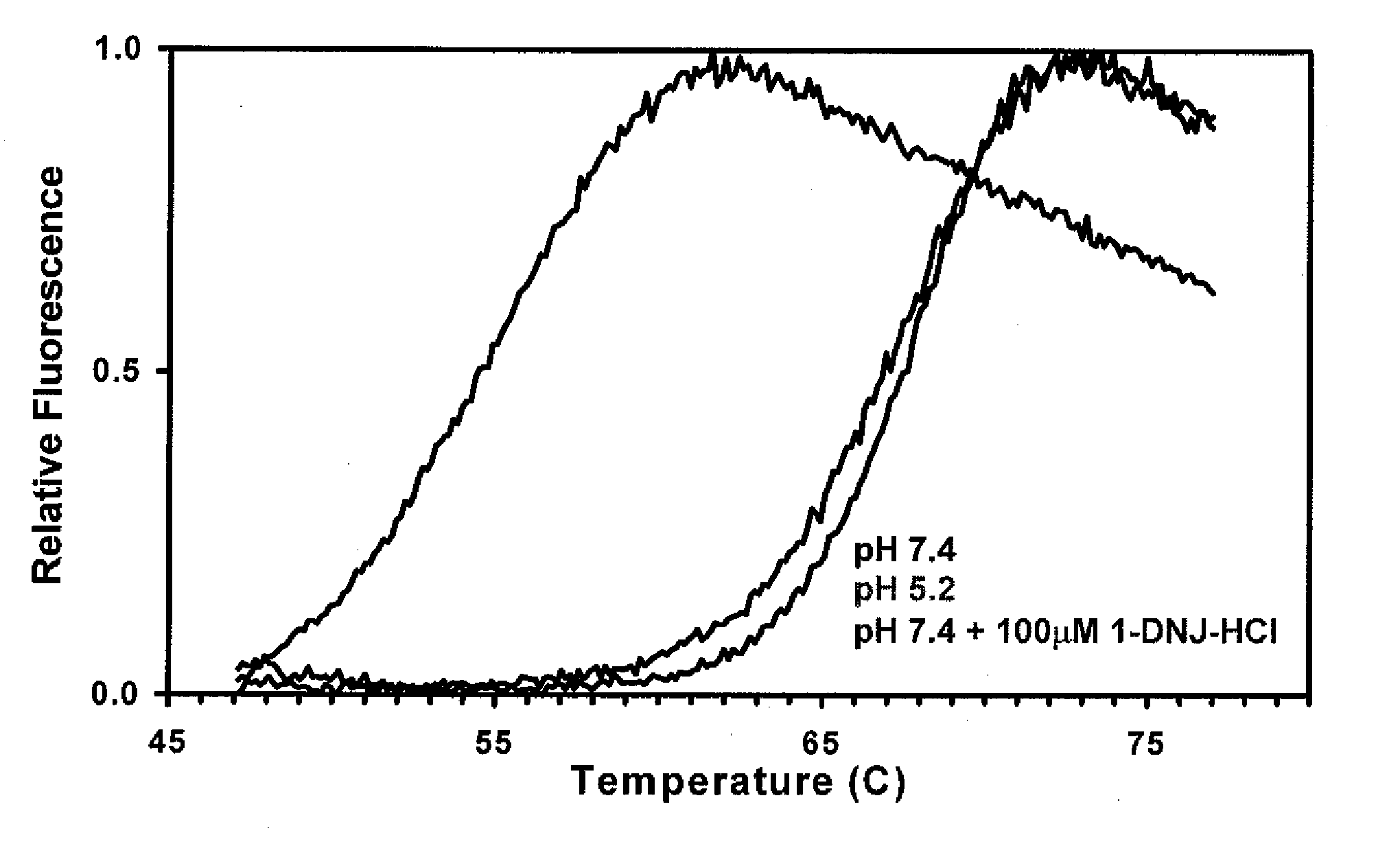
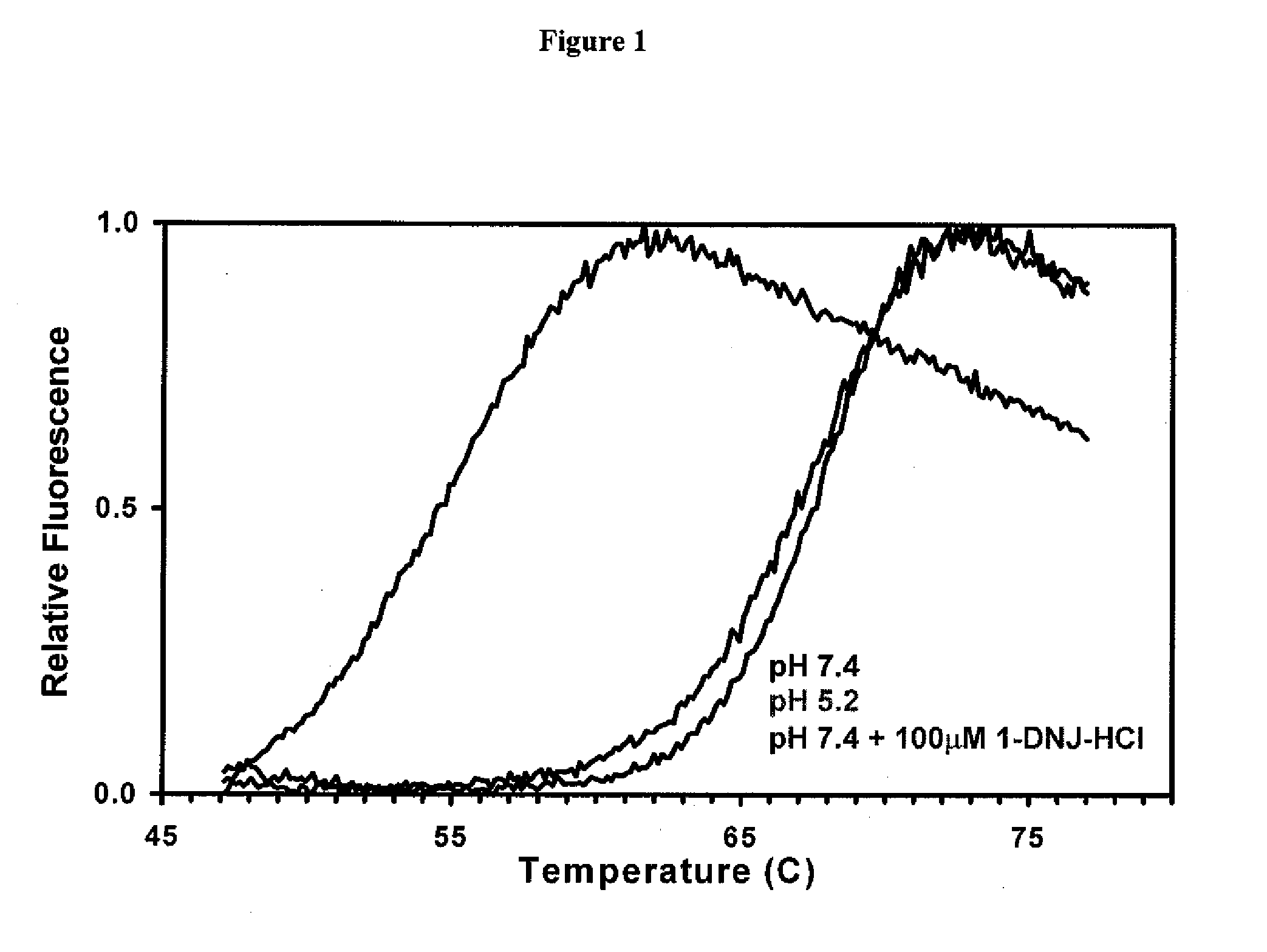
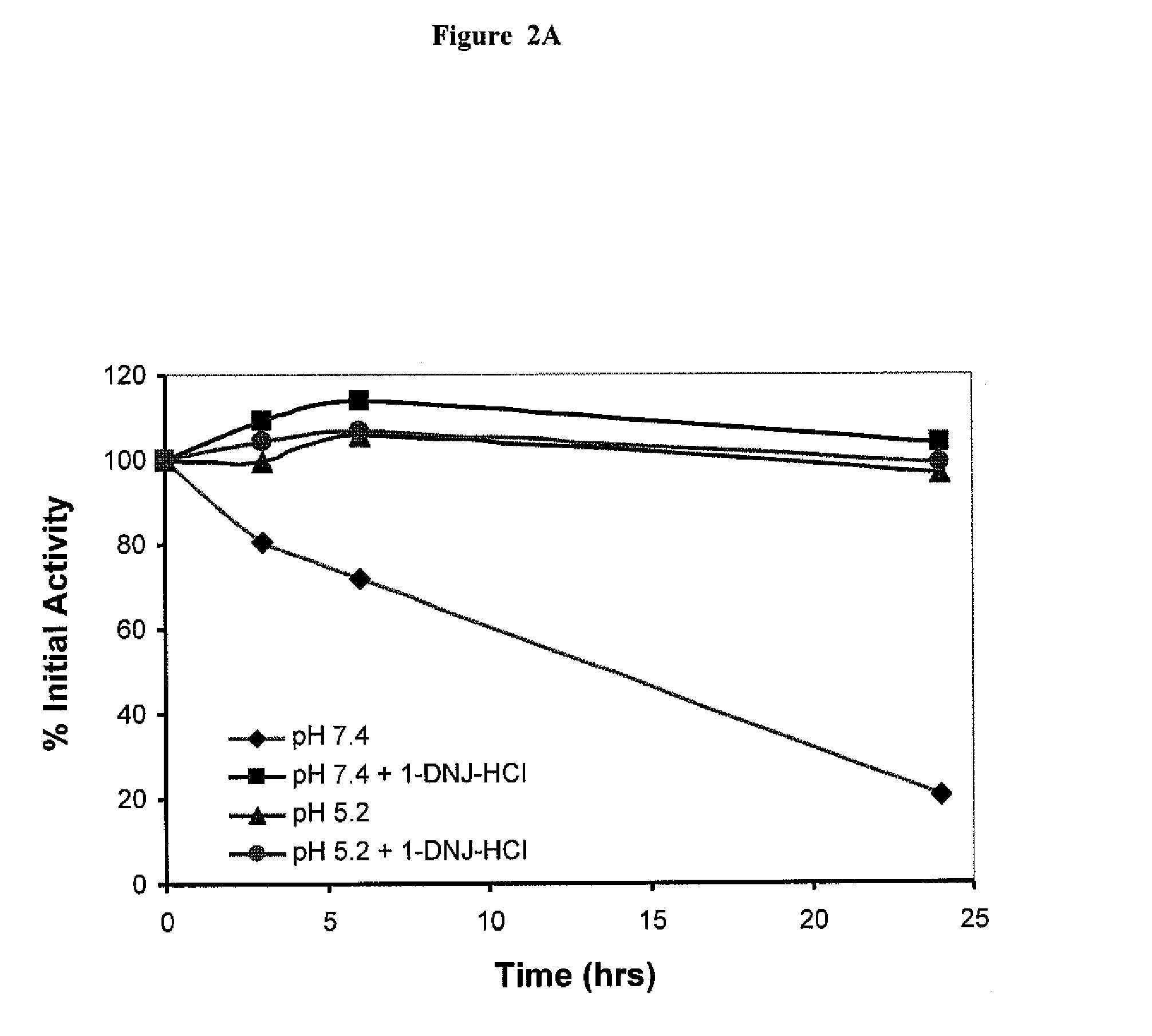
The present invention provides methods to determine whether a patient with a lysosomal storage disorder will benefit from treatment with a specific pharmacological chaperone. The present invention exemplifies an in vitro method for determining α-galactosidase A responsiveness to a pharmacological chaperone such as 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin in a cell line expressing a mutant from of α-galactosidase A. The invention also provides a method for diagnosing Fabry disease in patients suspected of having Fabry disease.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
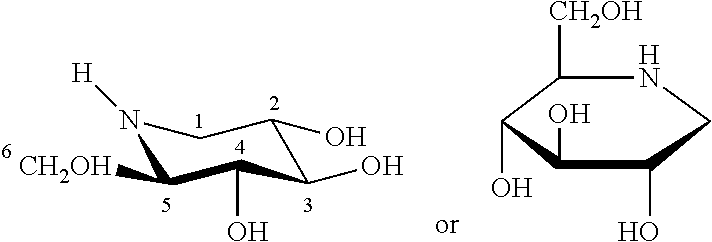
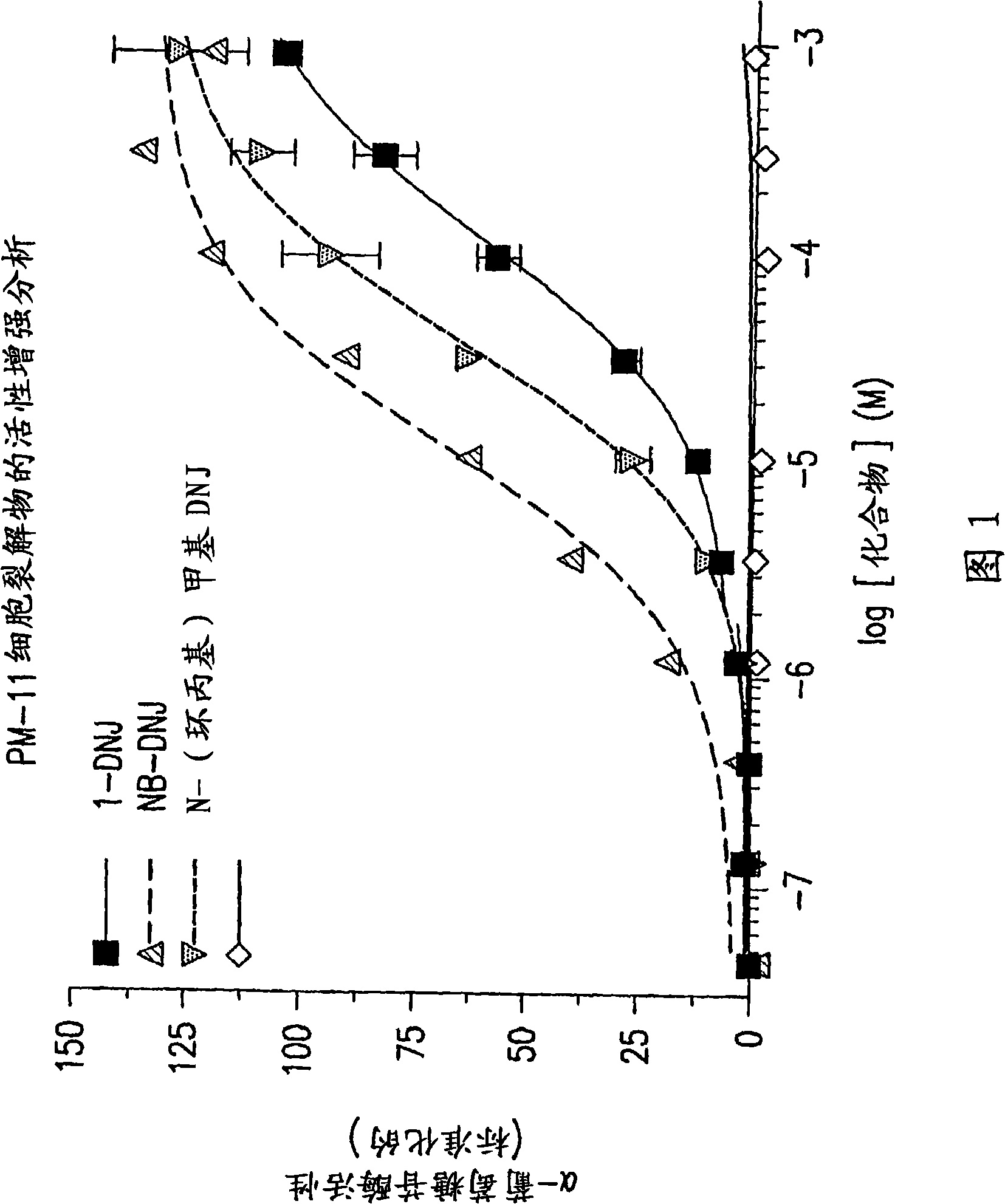
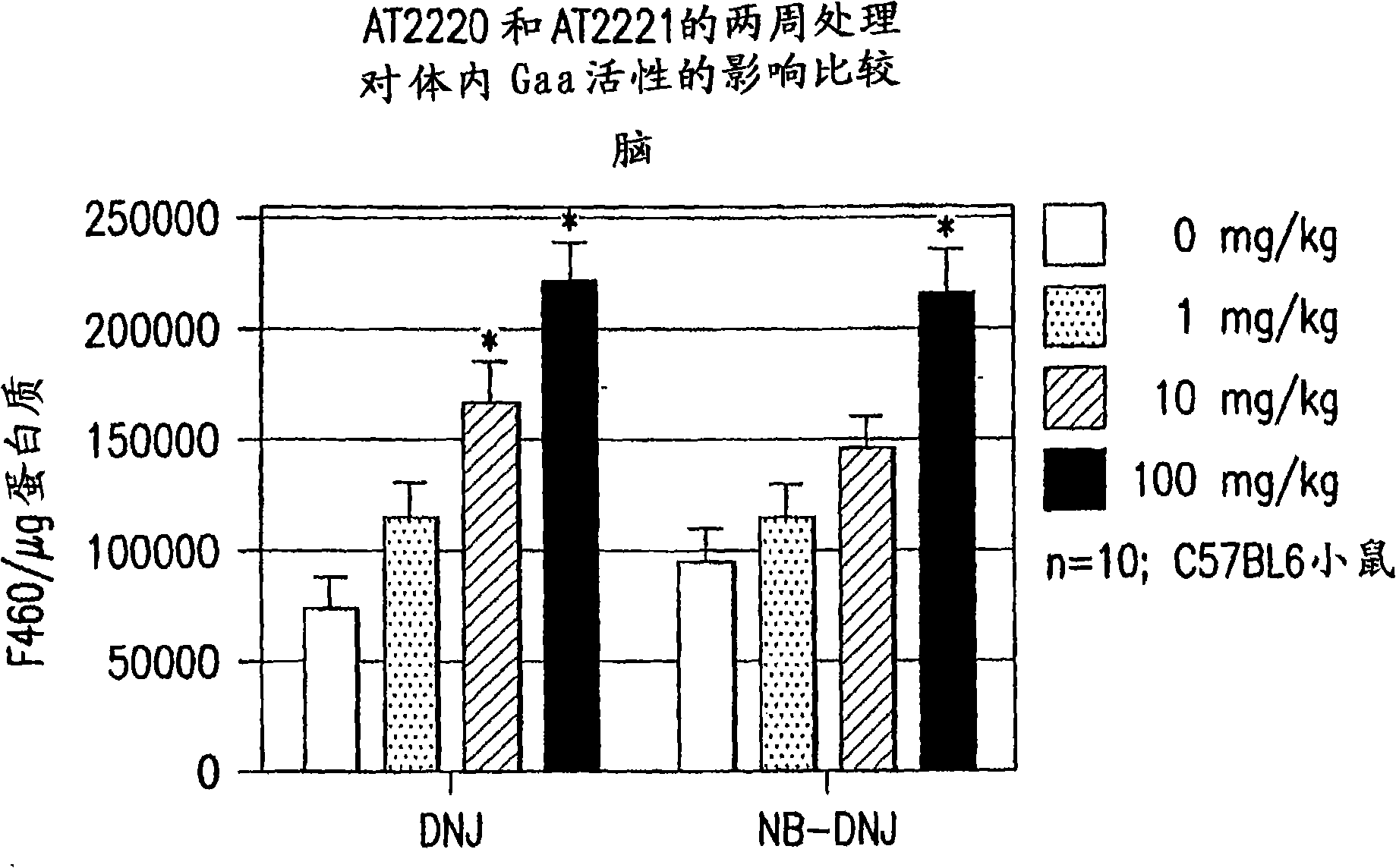
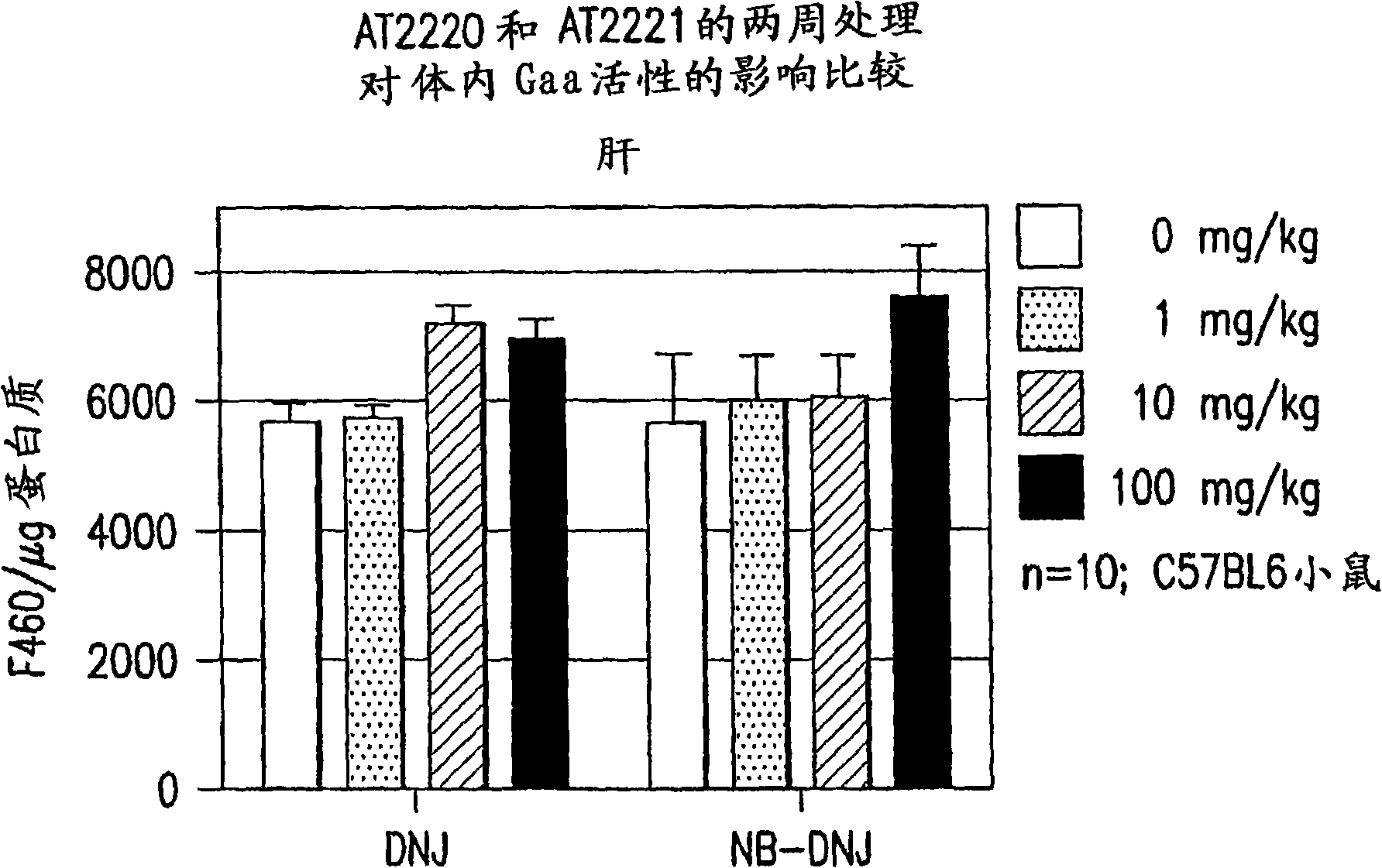
Method for the treatment of Pompe disease using 1-deoxynojirimycin and derivatives
ActiveUS20060264467A1Increased GAA activityRelieve symptomsBiocideNervous disorderDeoxynojirimycineWild type
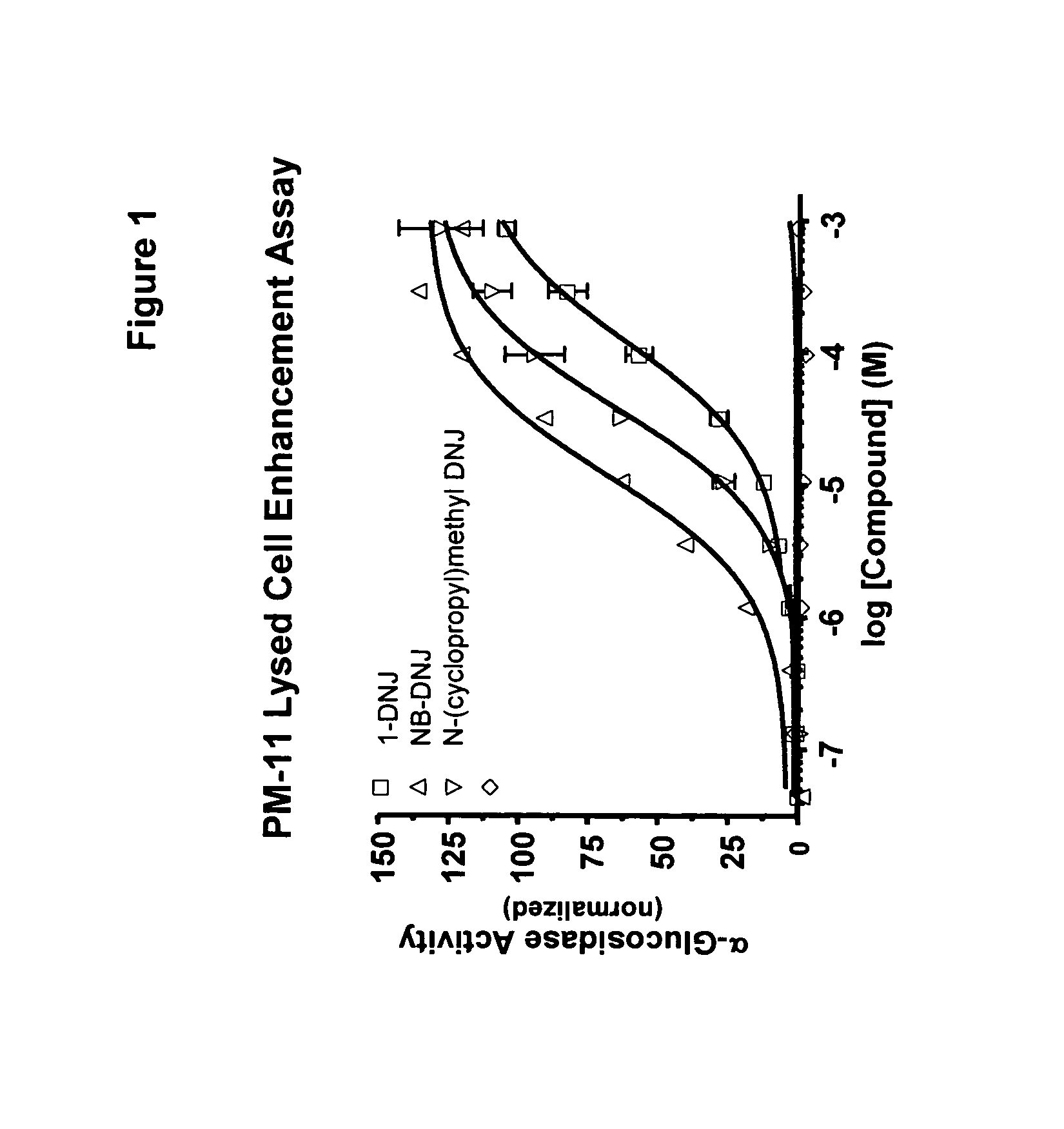
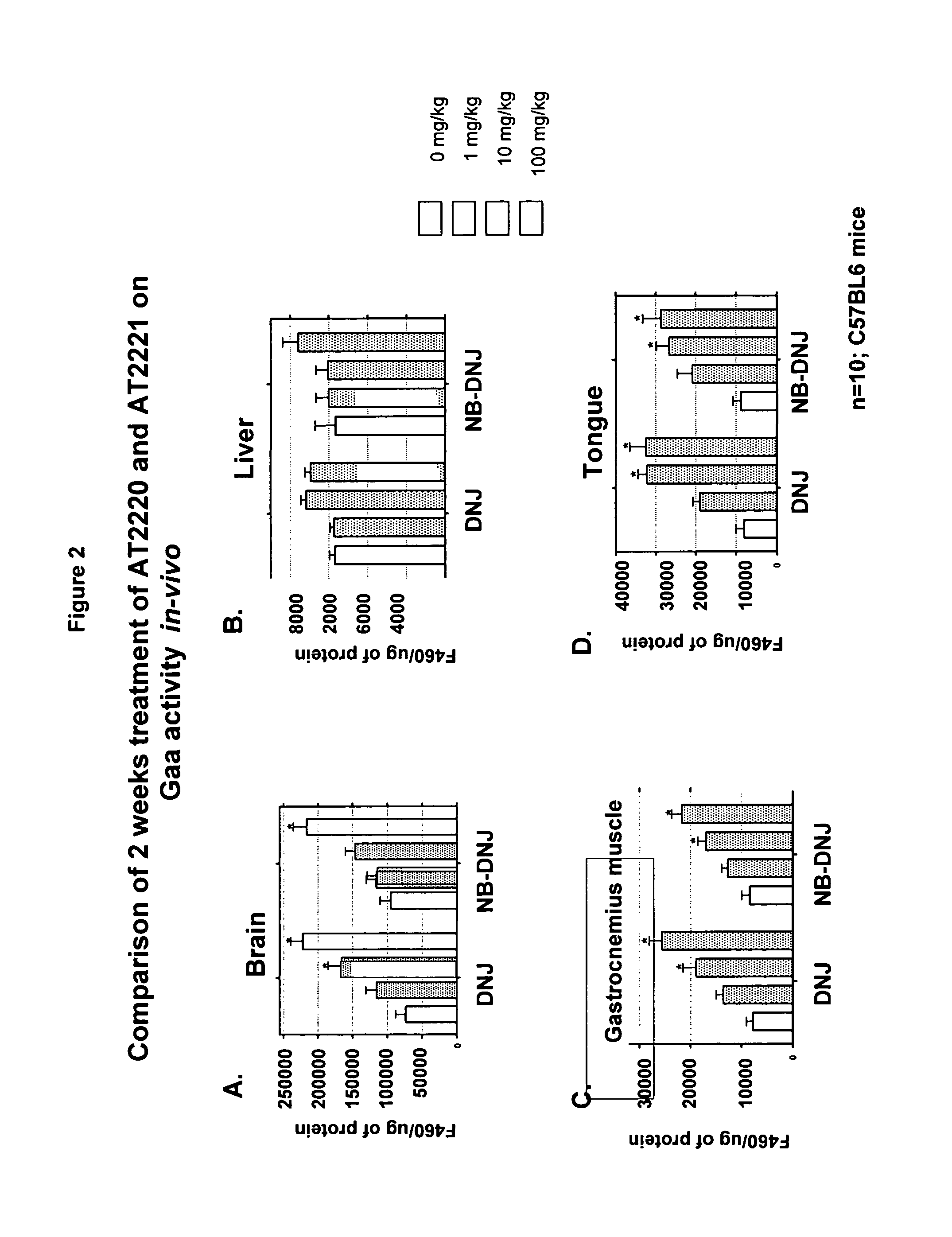
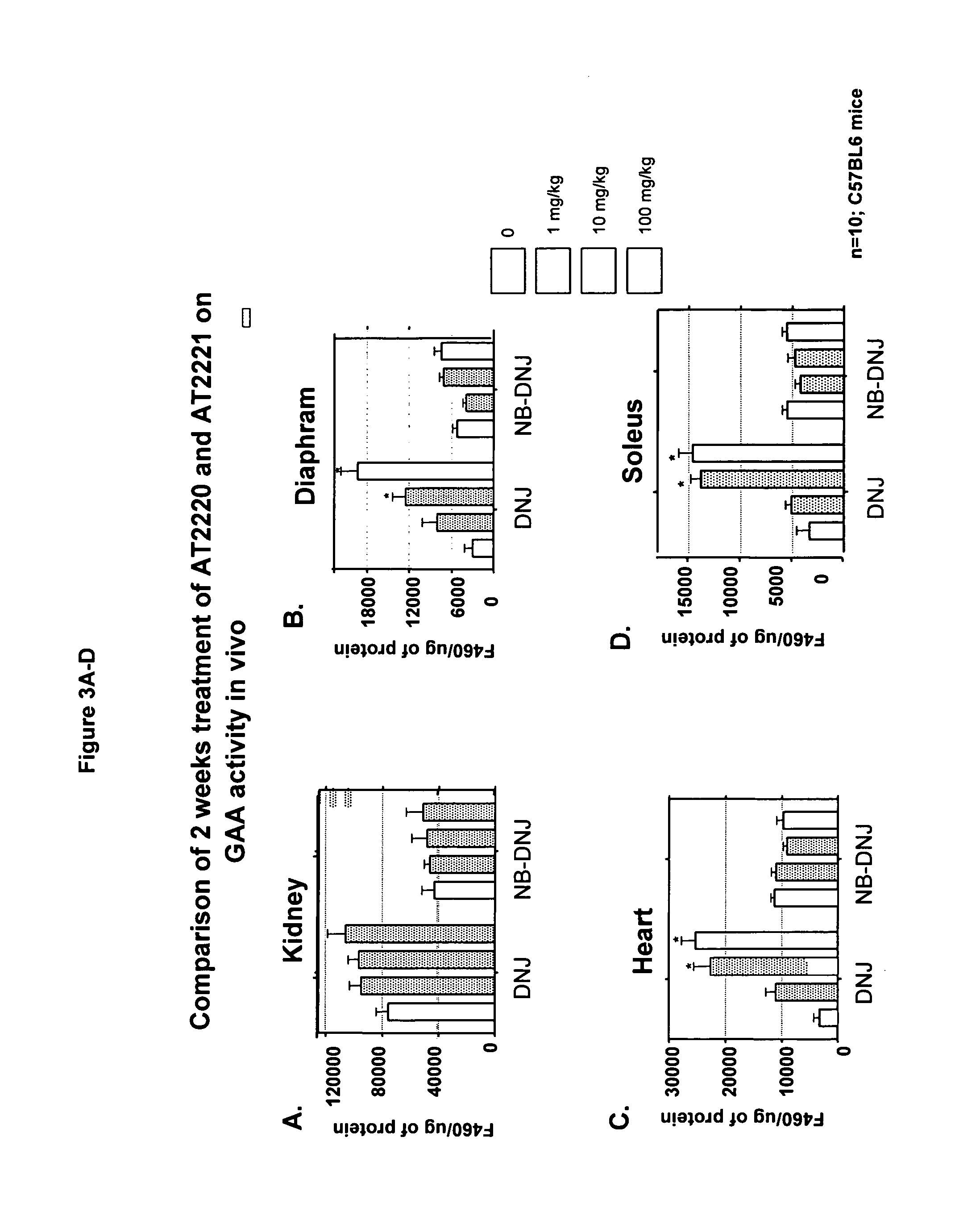
The present invention provides a method for increasing the activity of a mutant or wild-type α-glucosidase enzyme in vitro and in vivo by contacting the enzyme with a specific pharmacological chaperone which is a derivative of 1-deoxynojirimycin. The invention also provides a method for the treatment of Pompe disease by administration of chaperone small molecule compound which is a derivative of 1-deoxynojirimycin. The 1-deoxynojirimycin derivative is substituted at the N or C1 position. Combination therapy with replacement α-glucosidase gene or enzyme is also provided.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS8853260B2Improve abilitiesPromote formationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSuspended particlesWater insoluble
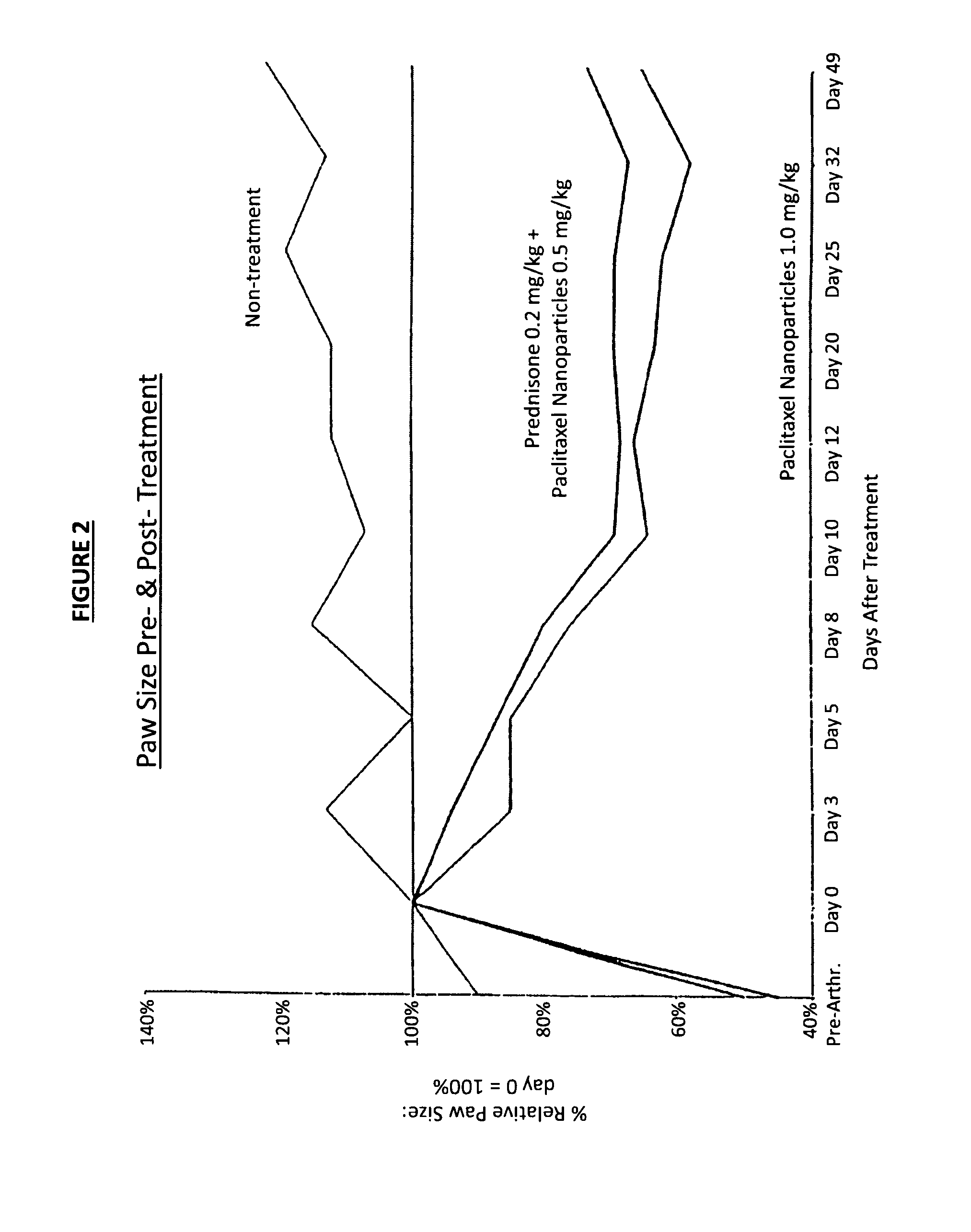
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Treatment of CNS disorders associated with mutations in genes encoding lysosomal enzymes
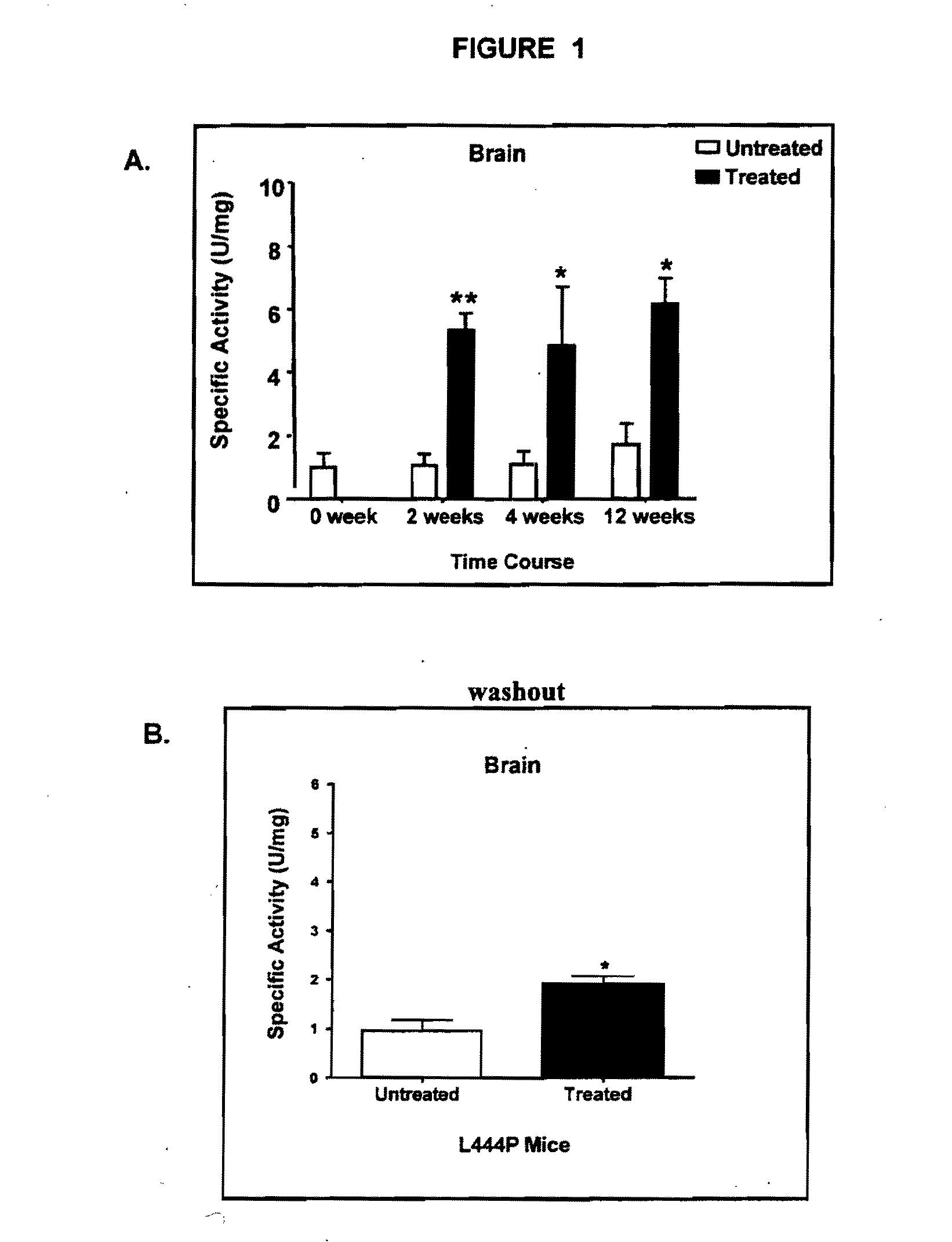
Described is a method for treating an individual having a neurological disorder with an associated mutation or mutations in a gene encoding a lysosomal enzyme. Specifically, the individual is administered a specific pharmacological chaperone for the lysosomal enzyme which increases trafficking of the protein from the ER to the lysosome in neural cells, with or without concomitantly increasing enzyme activity in neural cells. Restoration of trafficking relieves cell stress and other toxicities associated with accumulation of mutant proteins. Restoration of enzyme activity relieves substrate accumulation and pathologies associated with lipid accumulation. In a specific embodiment, the neurological disorder is Parkinson's disease or parkinsonism which is associated with mutations in glucocerebrosidase.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Dosing regimens for the treatment of lysosomal storage diseases using pharmacological chaperones
The present invention provides dosing regimens for administering pharmacological chaperones to a subject in need thereof. The dosing regimens can be used to treat disorders caused by improper protein misfolding, such as lysosomal storage disorders.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Assays for diagnosing and evaluating treatment options for Fabry disease
Provided are in vitro and in vivo methods for determining whether a patient with Fabry disease will respond to treatment with a specific pharmacological chaperone.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Method for the treatment of fabry disease using pharmacological chaperones
InactiveUS20100113517A1High activityHigh protein activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPharmacometricsCytoplasmic staining
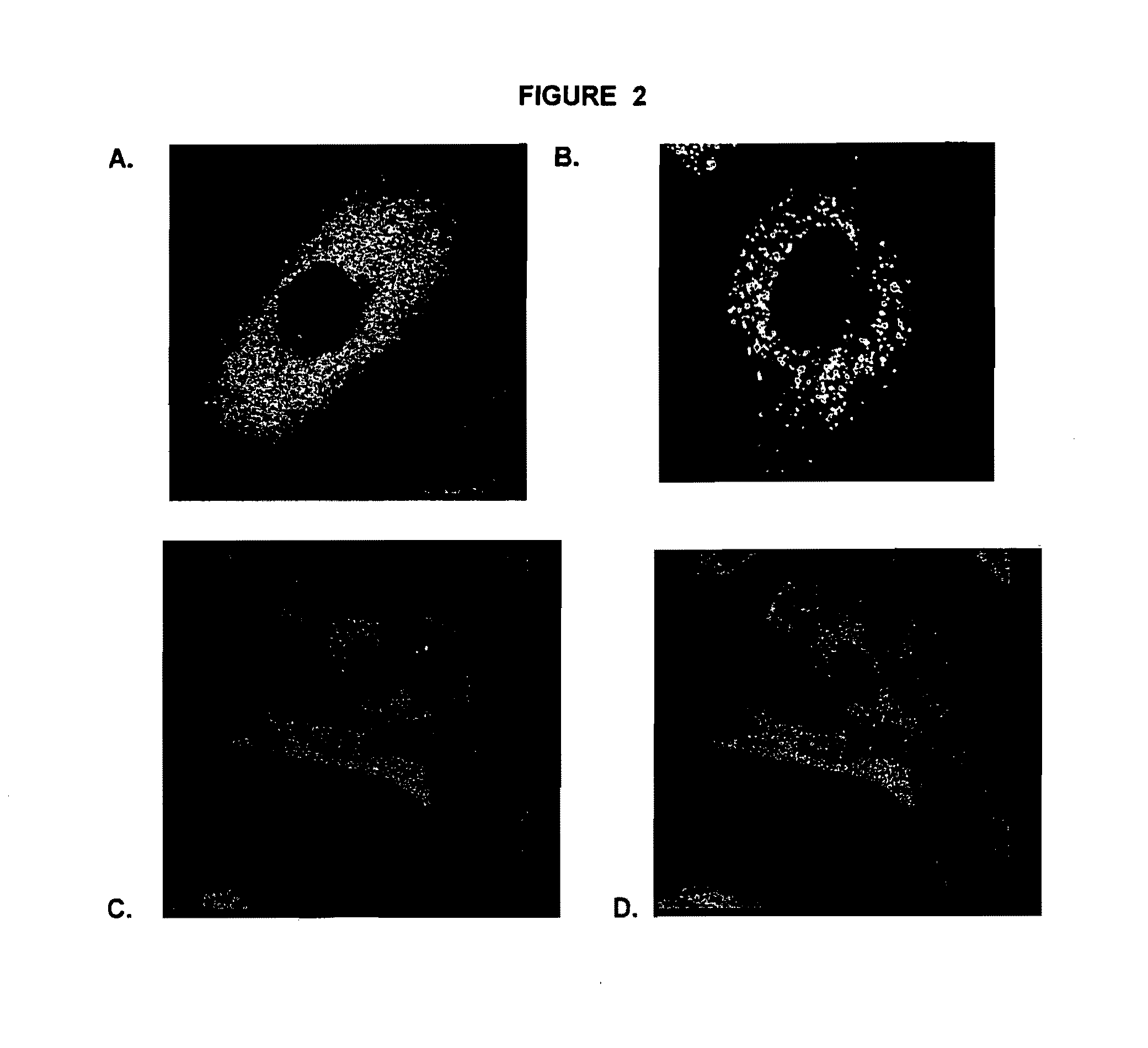
The present invention provides a method treating a patient with Fabry disease by determining whether there is an improvement of a surrogate marker that is associated with Fabry disease following administration of a specific pharmacological chaperone of α-galactosidase A. The method includes administering an effective amount of 1-deoxygalactonojirimycn to the individual, wherein the 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin binds to alpha-galactosidase A in an amount effective to increase activity of the alpha-galactosidase A. The present invention also provides a method for monitoring and increasing a therapeutic response of a patient with Fabry disease following administration of a specific pharmacological chaperone of α-galactosidase A by evaluating the effect on the cytoplasmic staining pattern of a cell from the patient, wherein detection of a staining pattern in the cell that is similar to the staining pattern in a cell from a healthy individual indicates that the individual with Fabry disease is a responder.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Dosing regimens for the treatment of lysosomal storage diseases using pharmacological chaperones
The present invention provides dosing regimens for administering pharmacological chaperones to a subject in need thereof. The dosing regimens can be used to treat disorders caused by improper protein misfolding, such as lysosomal storage disorders.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Dosing regimens for the treatment of lysosomal storage diseases using pharmacological chaperones
The present invention provides dosing regimens for administering pharmacological chaperones to a subject in need thereof. The dosing regimens can be used to treat disorders caused by improper protein misfolding, such as lysosomal storage disorders.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
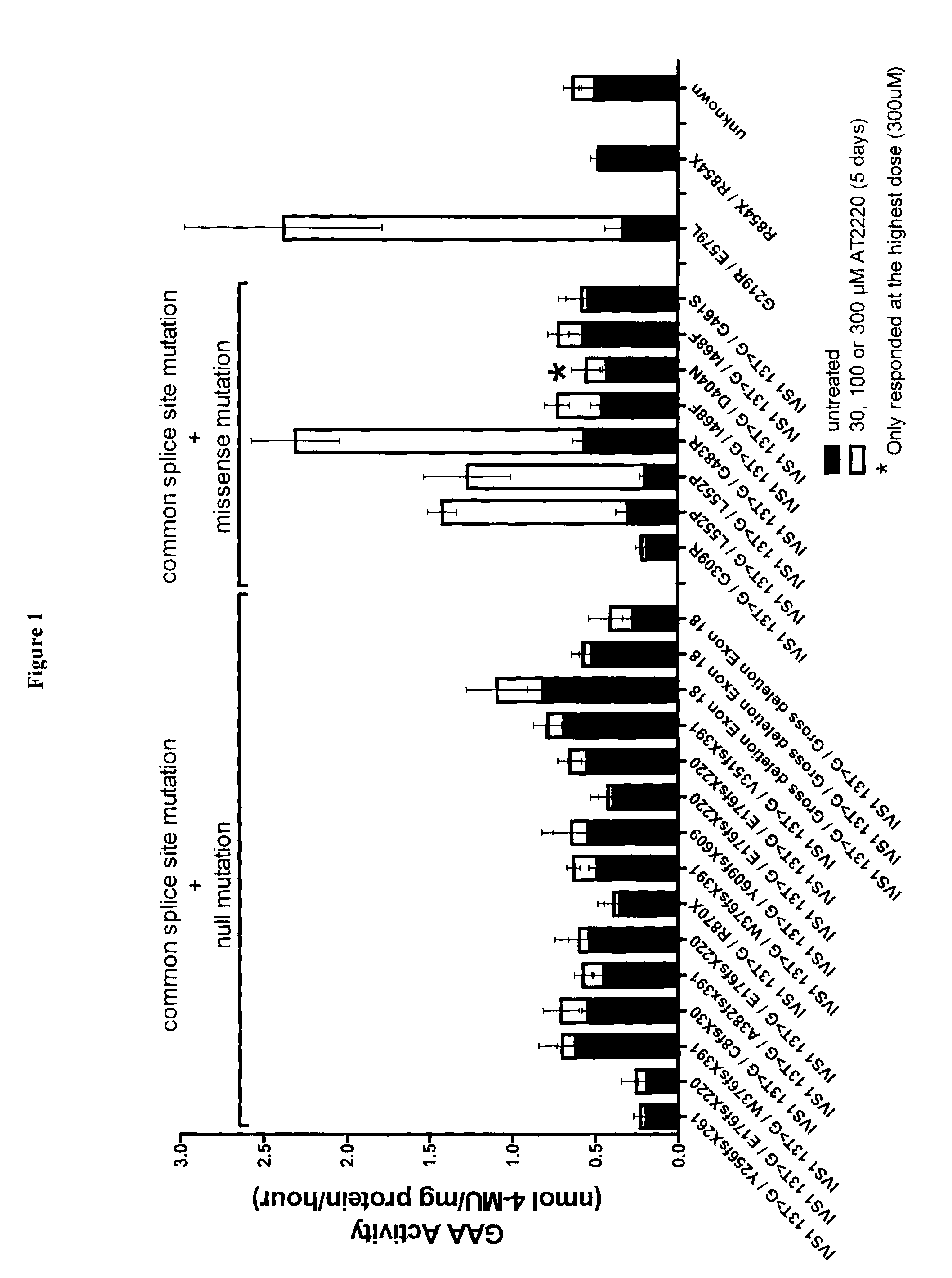
Methods of treating fabry disease in patients having the G9331A mutation in the GLA gene
ActiveUS10537564B2Metabolism disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmacometricsPharmacological chaperone
Provided are methods of treating a patient diagnosed with Fabry disease and methods of enhancing α-galactosidase A in a patient diagnosed with or suspected of having Fabry disease. Certain methods comprise administering to a patient a therapeutically effective dose of a pharmacological chaperone for α-galactosidase A, wherein the patient has a splice site mutation in intron 4 of the nucleic acid sequence encoding α-galactosidase A. Also described are uses of pharmacological chaperones for the treatment of Fabry disease and compositions for use in the treatment of Fabry disease.
Owner:BPCR LLP
Dosing Regimens for the Treatment of Lysosomal Storage Diseases Using Pharmacological Chaperones
The present invention provides dosing regimens for administering pharmacological chaperones to a subject in need thereof. The dosing regimens can be used to treat disorders caused by improper protein misfolding, such as lysosomal storage disorders.
Owner:BPCR LLP
Utilization of pharmacological chaperones to improve manufacturing and purification of biologics
ActiveUS9206457B2Increases the export of the proteinReduces proteolytic digestion and chemical damageAnimal cellsPeptide/protein ingredientsReticulum cellPharmacological chaperone
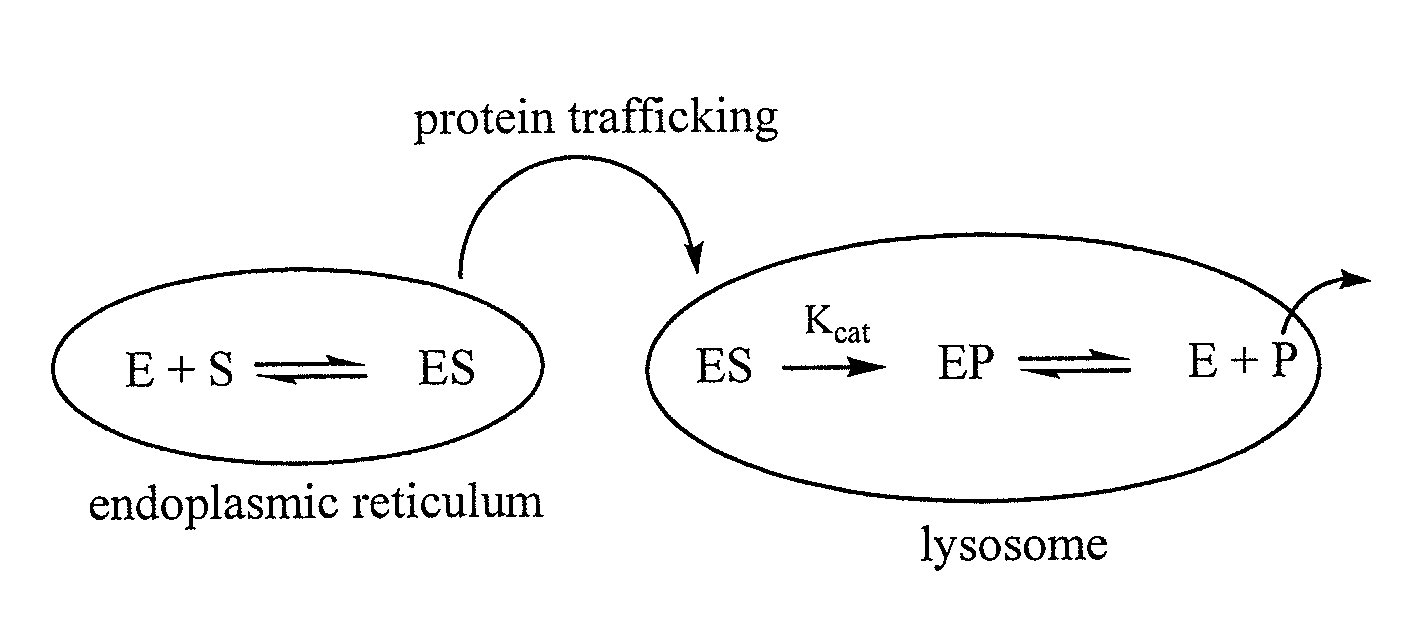
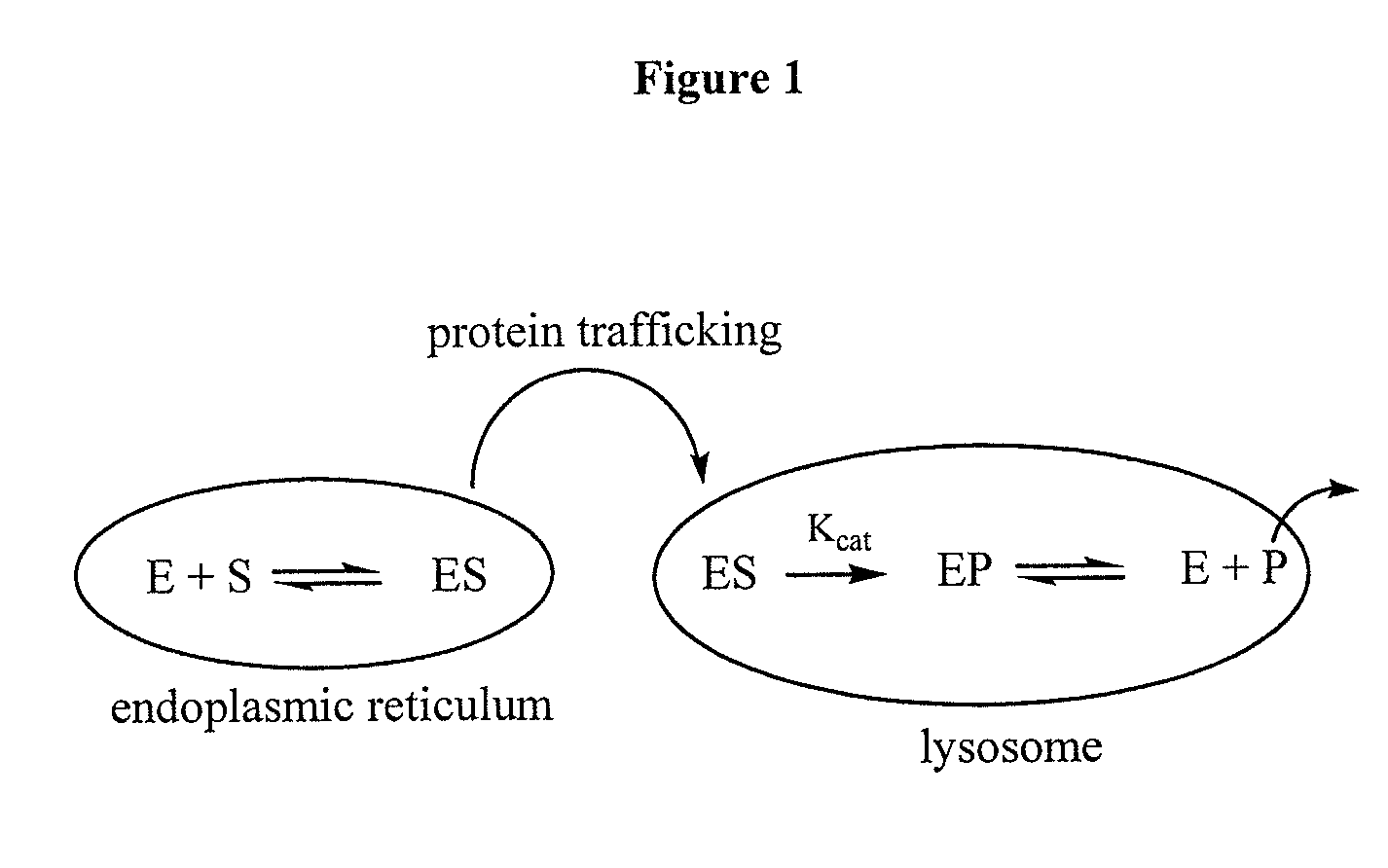
The present invention provides methods for improving the production of recombinant proteins through the use of pharmacological chaperones for the recombinant proteins. As exemplified by the present invention, the binding of a pharmacological chaperone to a recombinant protein expressed by a cell can stabilize the protein and increase export of the protein out of the cell's endoplasmic reticulum, and increase secretion of the protein by the cell.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
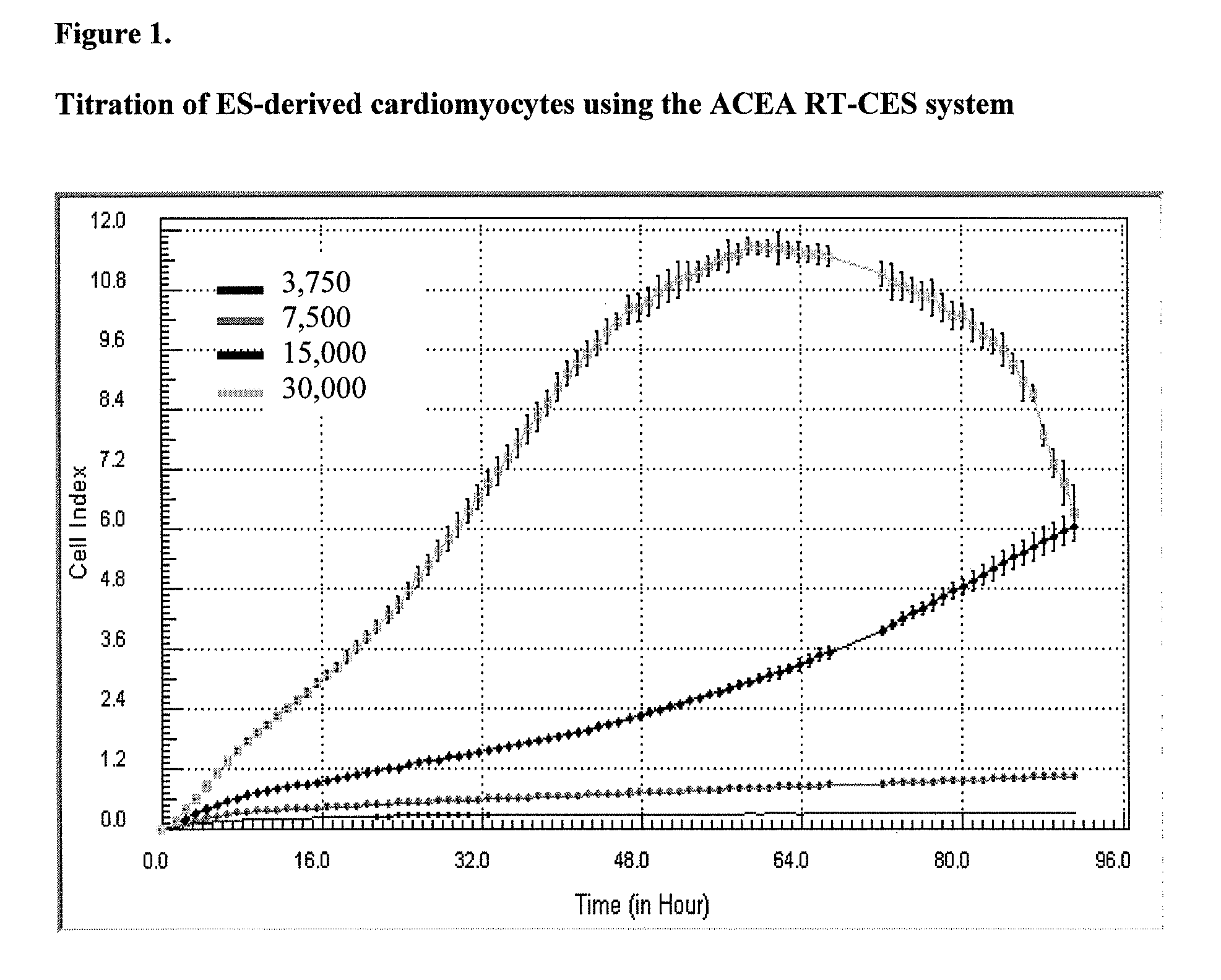
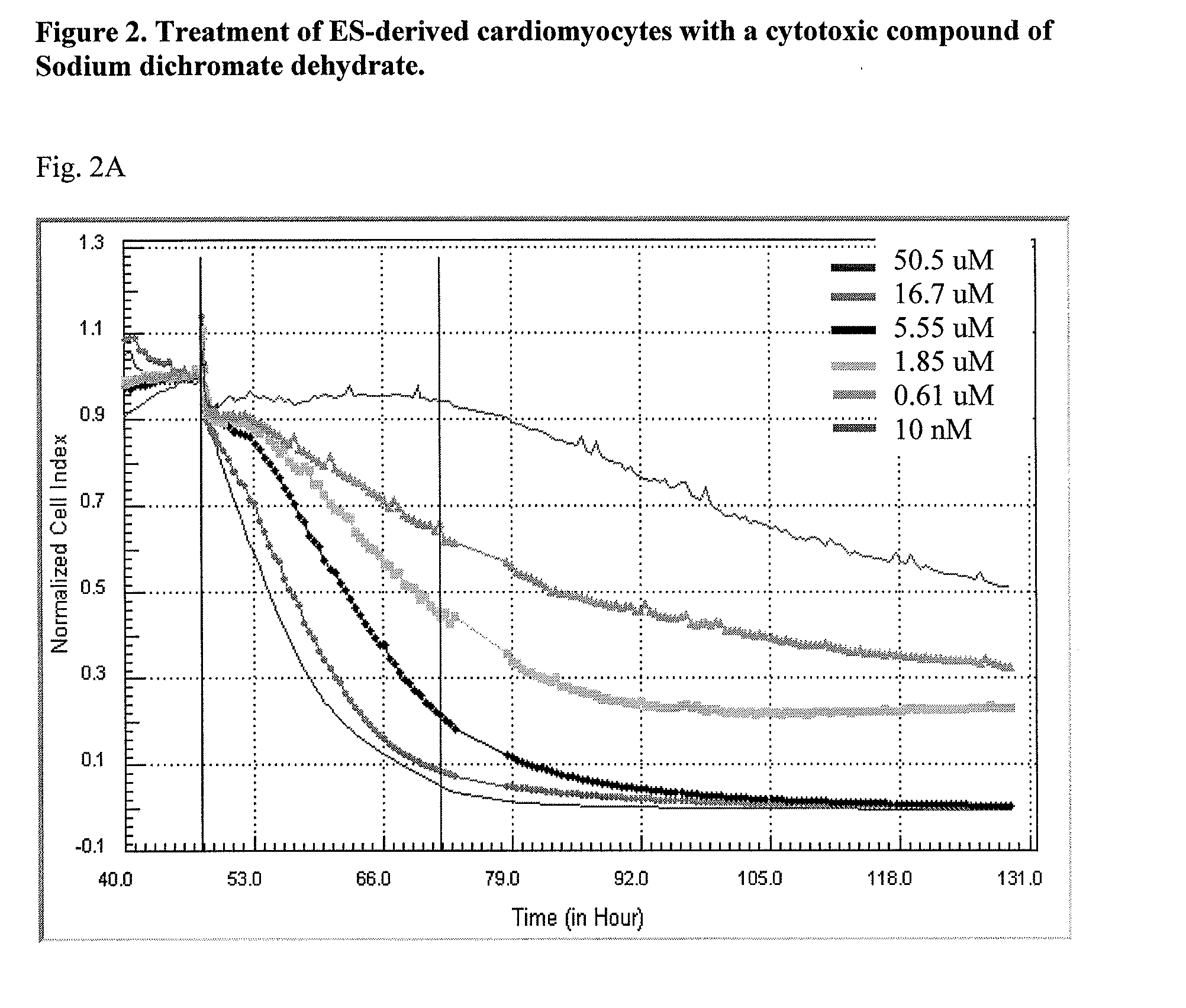
System and method for monitoring cardiomyocyte beating, viability and morphology and for screening for pharmacological agents which may induce cardiotoxicity or modulate cardiomyocyte function
ActiveUS20110039294A1Well representedImprove throughput efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell freePharmacological chaperone
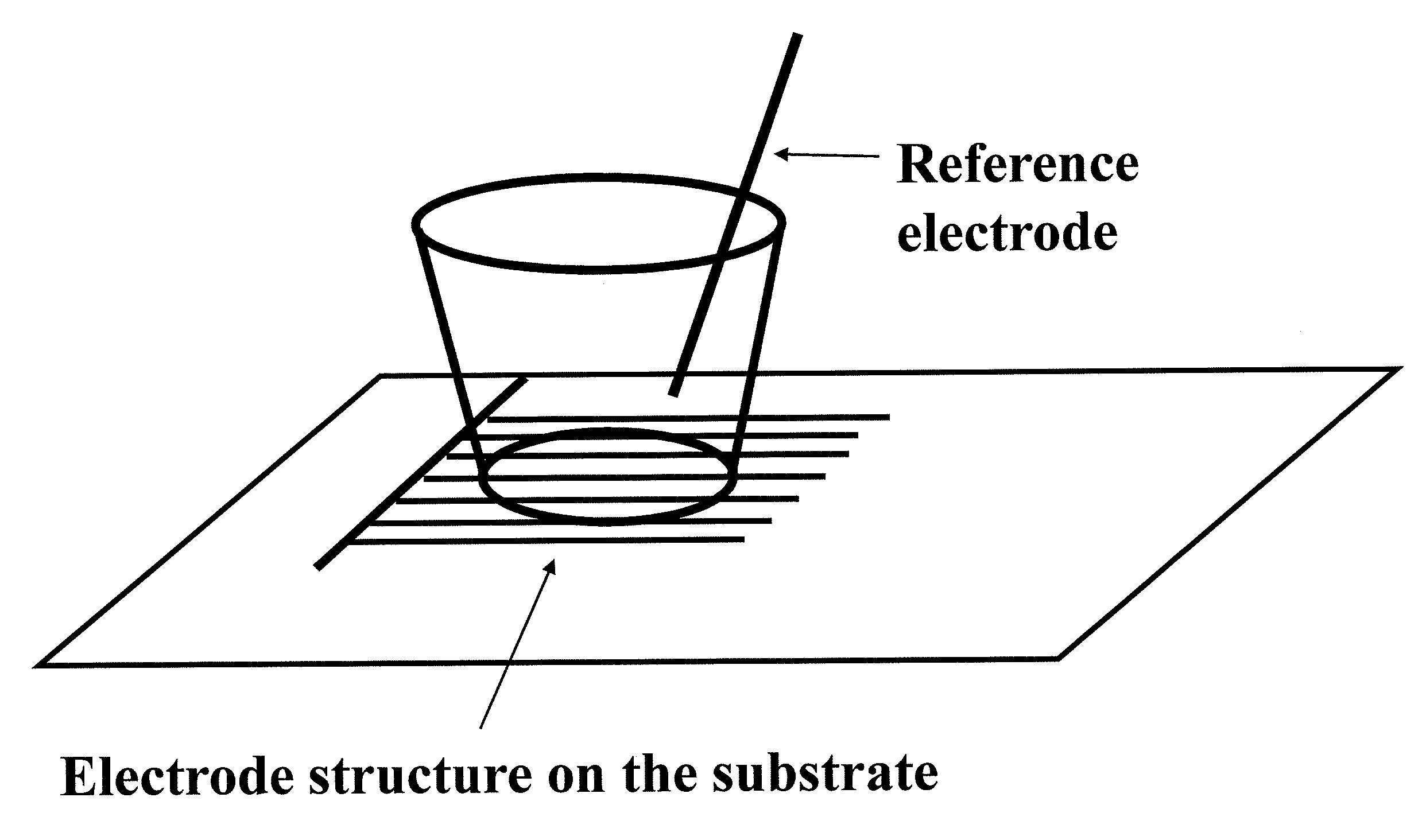
Devices and methods for performing extracellular recording of cells, such as excitable cells, cardiomyocytes, and cardiomyocyte precursor cells is provided. An exemplary device includes a nonconductive substrate forming or provided as a base of one or more wells; a recording electrode positioned on the substrate within the well, wherein the recording electrode is accessible to cells when a cell sample is added to the device; and a reference electrode positioned within the well in a cell-free zone, the cell-free zone characterized as free from contact with cells when the cell sample is added to the device, thereby preventing contact between cells and the reference electrode.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Pharmacologically induced transgene ablation system
InactiveUS20130023033A1Nervous disorderFusion with DNA-binding domainSystems designPharmacological chaperone
The present invention relates to gene therapy systems designed for the delivery of a therapeutic product to a subject using replication-defective virus composition(s) engineered with a built-in safety mechanism for ablating the therapeutic gene product, either permanently or temporarily, in response to a pharmacological agent—preferably an oral formulation, e.g., a pill. The invention is based, in part, on the applicants' development of an integrated approach, referred to herein as “PITA” (Pharmacologically Induced Transgene Ablation), for ablating a transgene or negatively regulating transgene expression. In this approach, replication-deficient viruses are used to deliver a transgene encoding a therapeutic product (an RNA or a protein) so that it is expressed in the subject, but can be reversibly or irreversibly turned off by administering the pharmacological agent; e.g., by administration of a small molecule that induces expression of an ablator specific for the transgene or its RNA transcript.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Treatment of CNS disorders associated with mutations in genes encoding lysosomal enzymes
Described is a method for treating an individual having a neurological disorder with an associated mutation or mutations in a gene encoding a lysosomal enzyme. Specifically, the individual is administered a specific pharmacological chaperone for the lysosomal enzyme which increases trafficking of the protein from the ER to the lysosome in neural cells, with or without concomitantly increasing enzyme activity in neural cells. Restoration of trafficking relieves cell stress and other toxicities associated with accumulation of mutant proteins. Restoration of enzyme activity relieves substrate accumulation and pathologies associated with lipid accumulation. In a specific embodiment, the neurological disorder is Parkinson's disease or parkinsonism which is associated with mutations in glucocerebrosidase.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Assays For Diagnosing And Evaluating Treatment Options For Fabry Disease
Provided are in vitro and in vivo methods for determining whether a patient with Fabry disease will respond to treatment with a specific pharmacological chaperone.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC +1
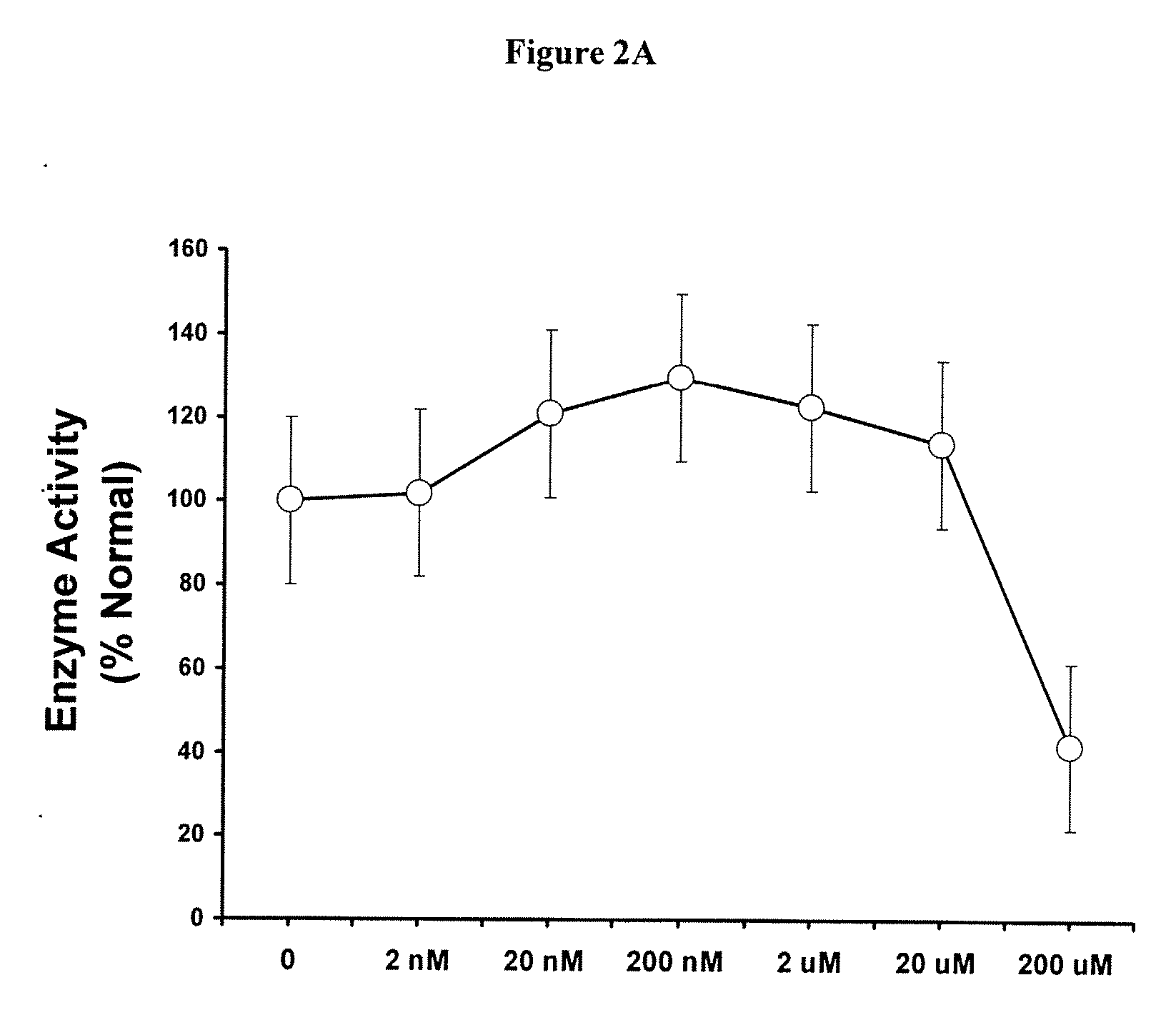
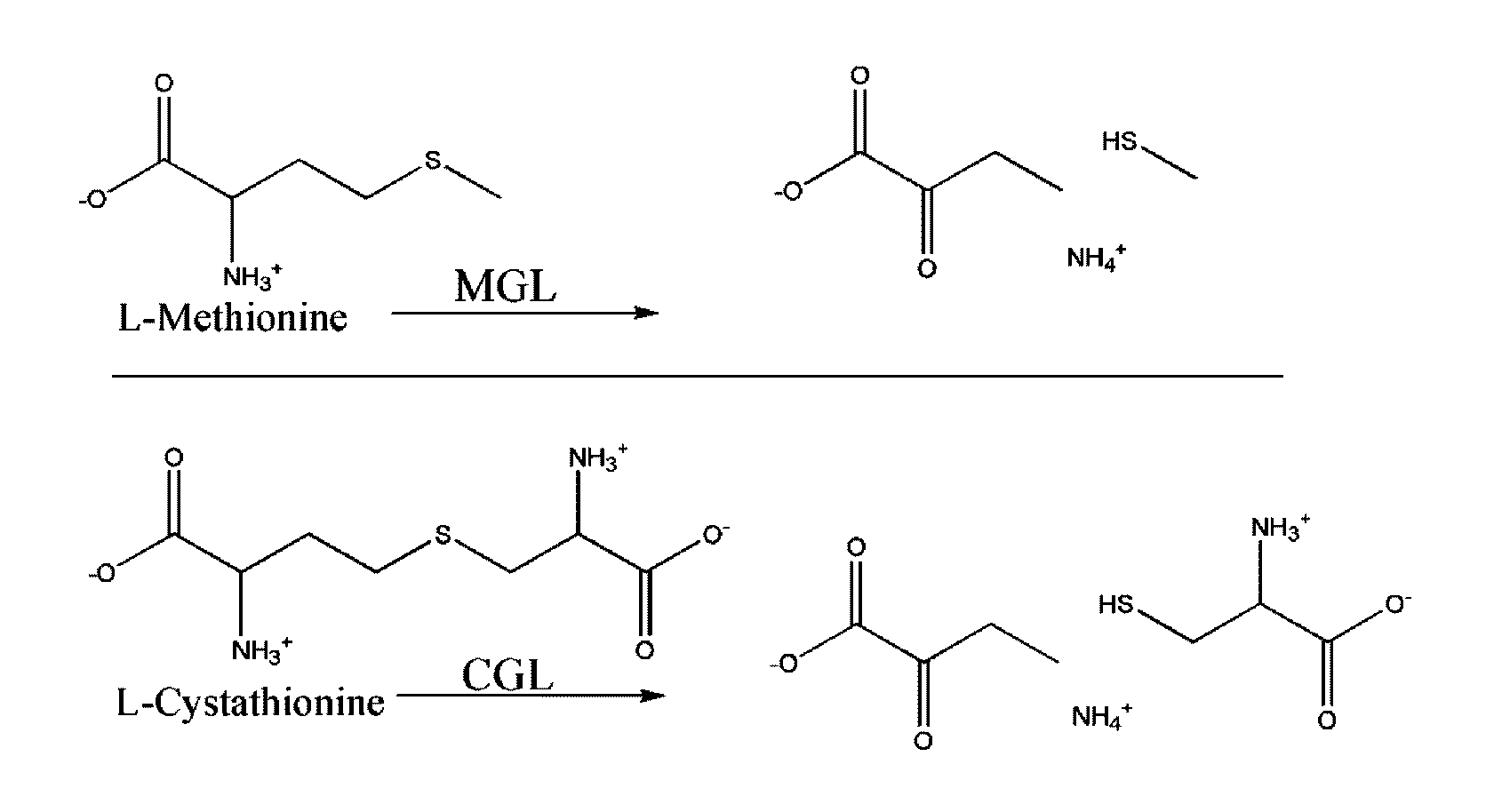
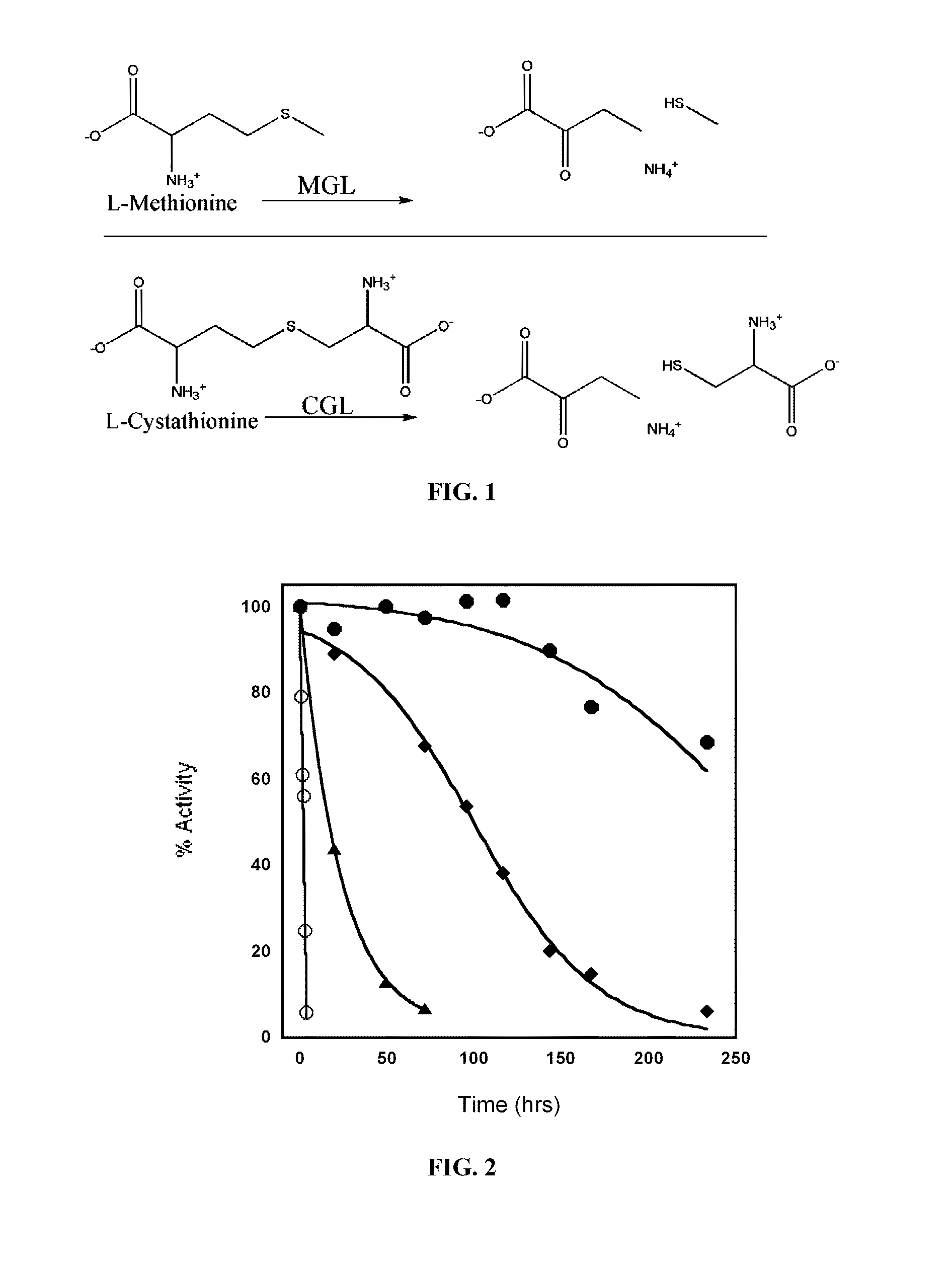
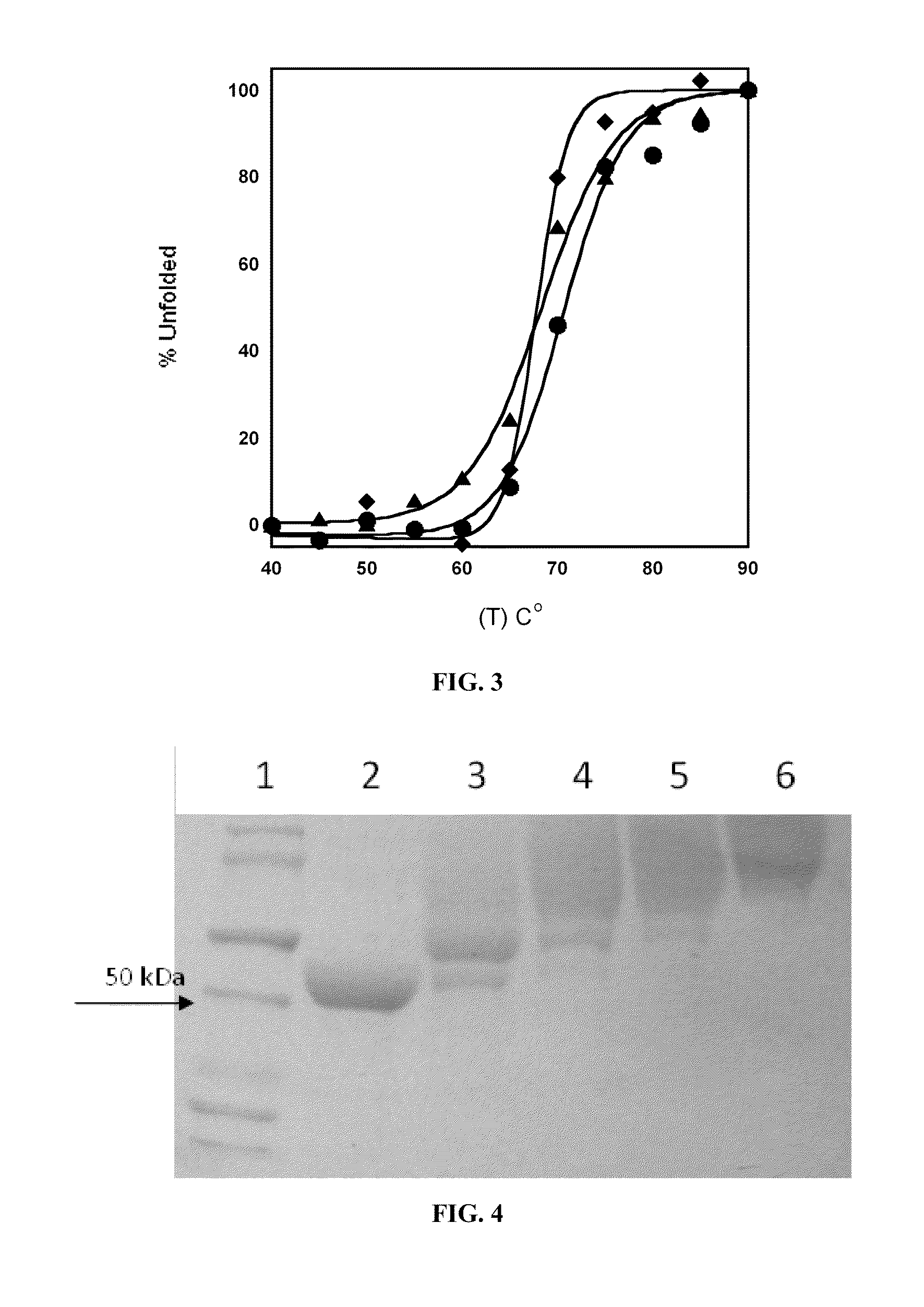
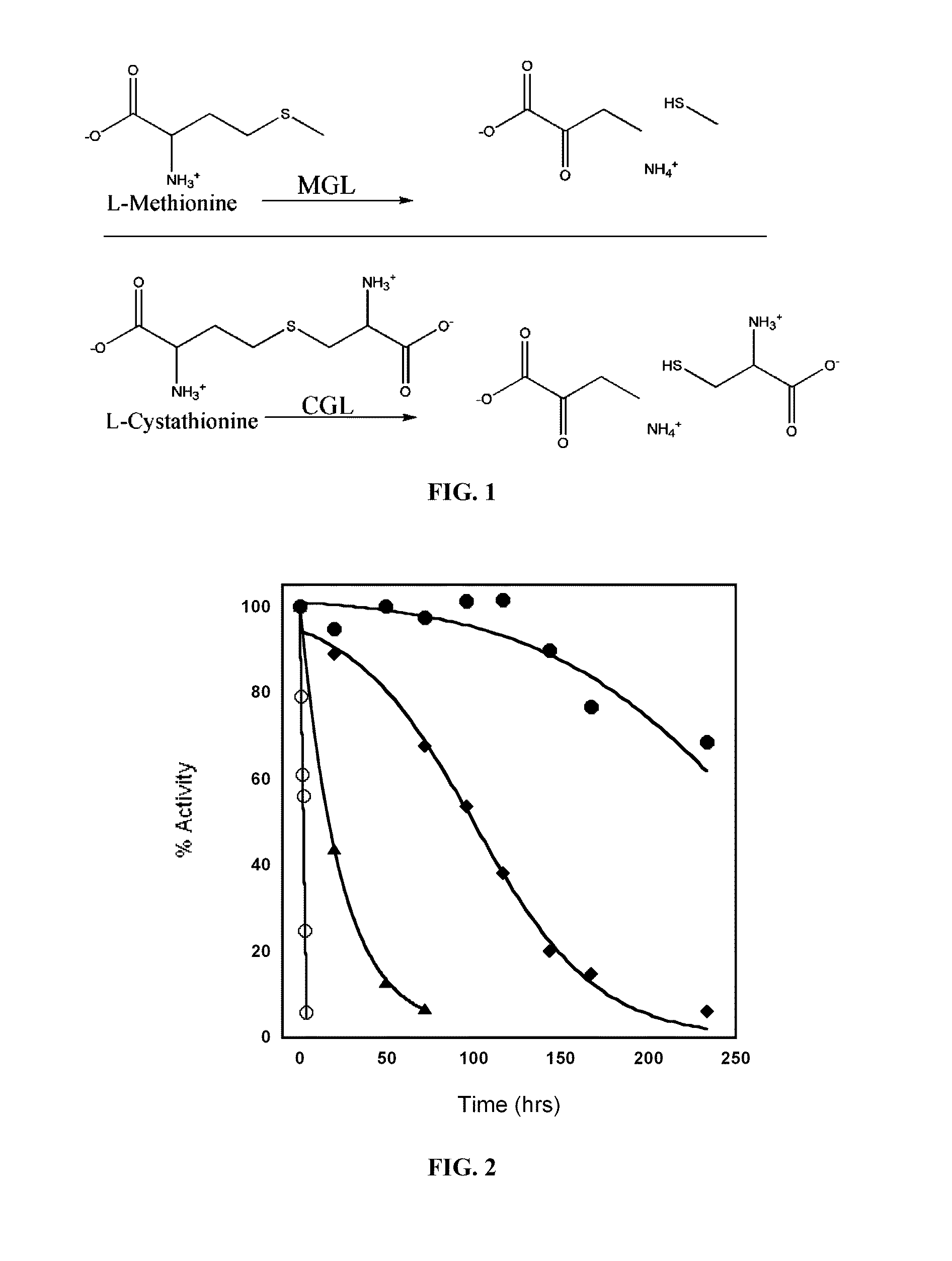
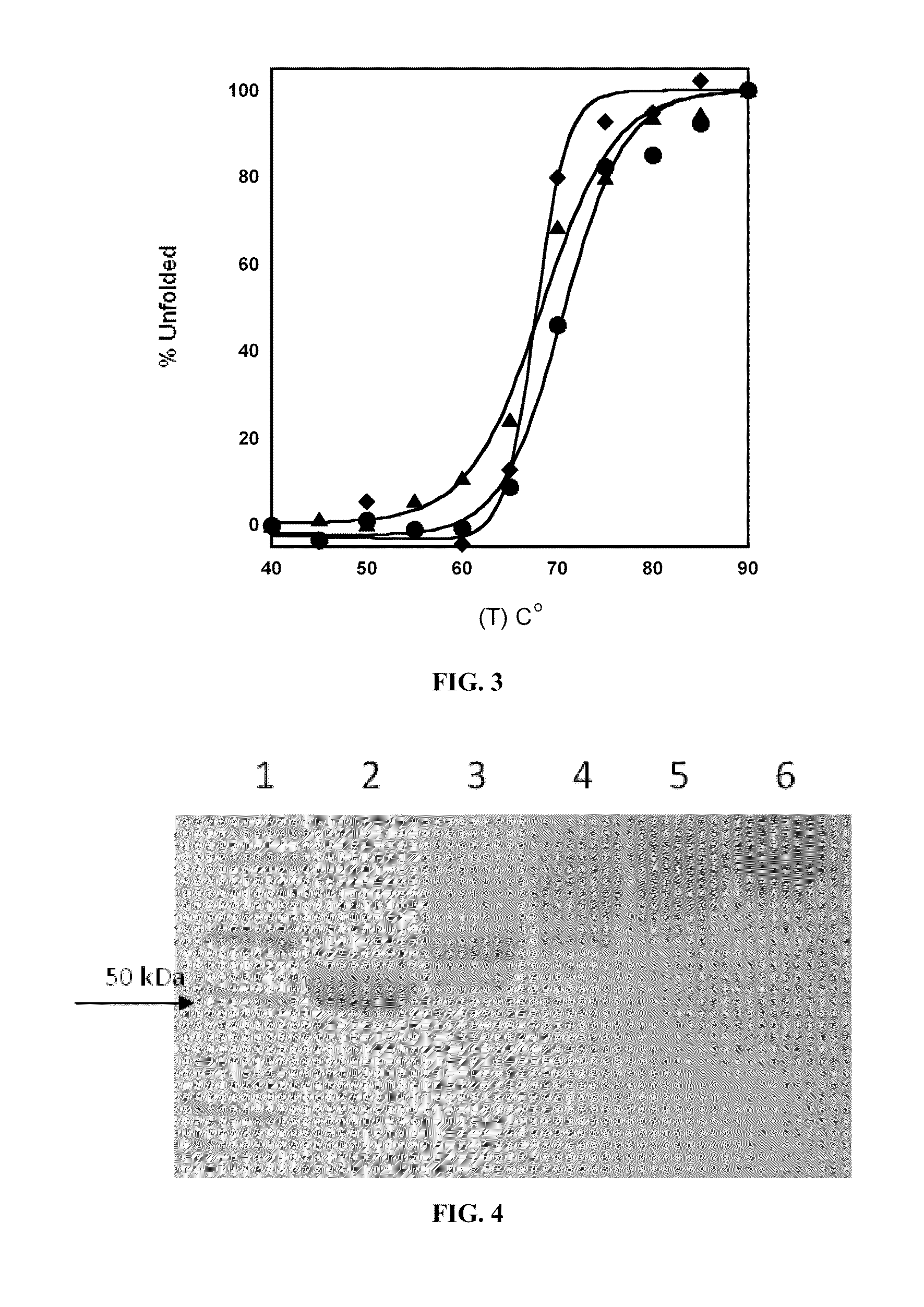
Engineered enzymes with methionine-gamma-lyase enzymes and pharmacological preparations thereof
ActiveUS20110200576A1Low immunogenicityIncrease serum stabilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsAmino acid substitutionLyase
Methods and composition related to the engineering of a novel protein with methionine-γ-lyase enzyme activity are described. For example, in certain aspects there may be disclosed a modified cystathionine-γ-lyase (CGL) comprising one or more amino acid substitutions and capable of degrading methionine. Furthermore, certain aspects of the invention provide compositions and methods for the treatment of cancer with methionine depletion using the disclosed proteins or nucleic acids.
Owner:AEMASE
Method for the treatment of pompe disease using 1-deoxynojirimycin and derivatives
The present invention provides a method for increasing the activity of a mutant or wild-type α-glucosidase enzyme in vitro and in vivo by contacting the enzyme with a specific pharmacological chaperone which is a derivative of 1-deoxynojirimycin. The invention also provides a method for the treatment of Pompe disease by administration of chaperone small molecule compound which is a derivative of 1-deoxynojirimycin. The 1-deoxynojirimycin derivative is substituted at the N or C1 position. Combination therapy with replacement α-glucosidase gene or enzyme is also provided.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Assays for diagnosing and evaluating treatment options for pompe disease
InactiveUS20110136151A1Accurate measurementDisease diagnosisBiological testingDiseaseTreatment options
Provided are in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo methods for determining whether a patient with Pompe disease will respond to treatment with a specific pharmacological chaperone.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Engineered enzymes with methionine-gamma-lyase enzymes and pharmacological preparations thereof
ActiveUS8709407B2Low immunogenicityIncrease serum stabilityCarbon-sulfur lyasesSugar derivativesAmino acid substitutionLyase
Owner:AEMASE
TREATMENT OF POMPE DISEASE WITH SPECIFIC PHARMACOLOGICAL CHAPERONES AND MONITORING TREATMENT USING SURROGATE MARkERS
InactiveUS20110189710A1Reduced activityImprove the level ofMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisWhole bodyPharmacological chaperone
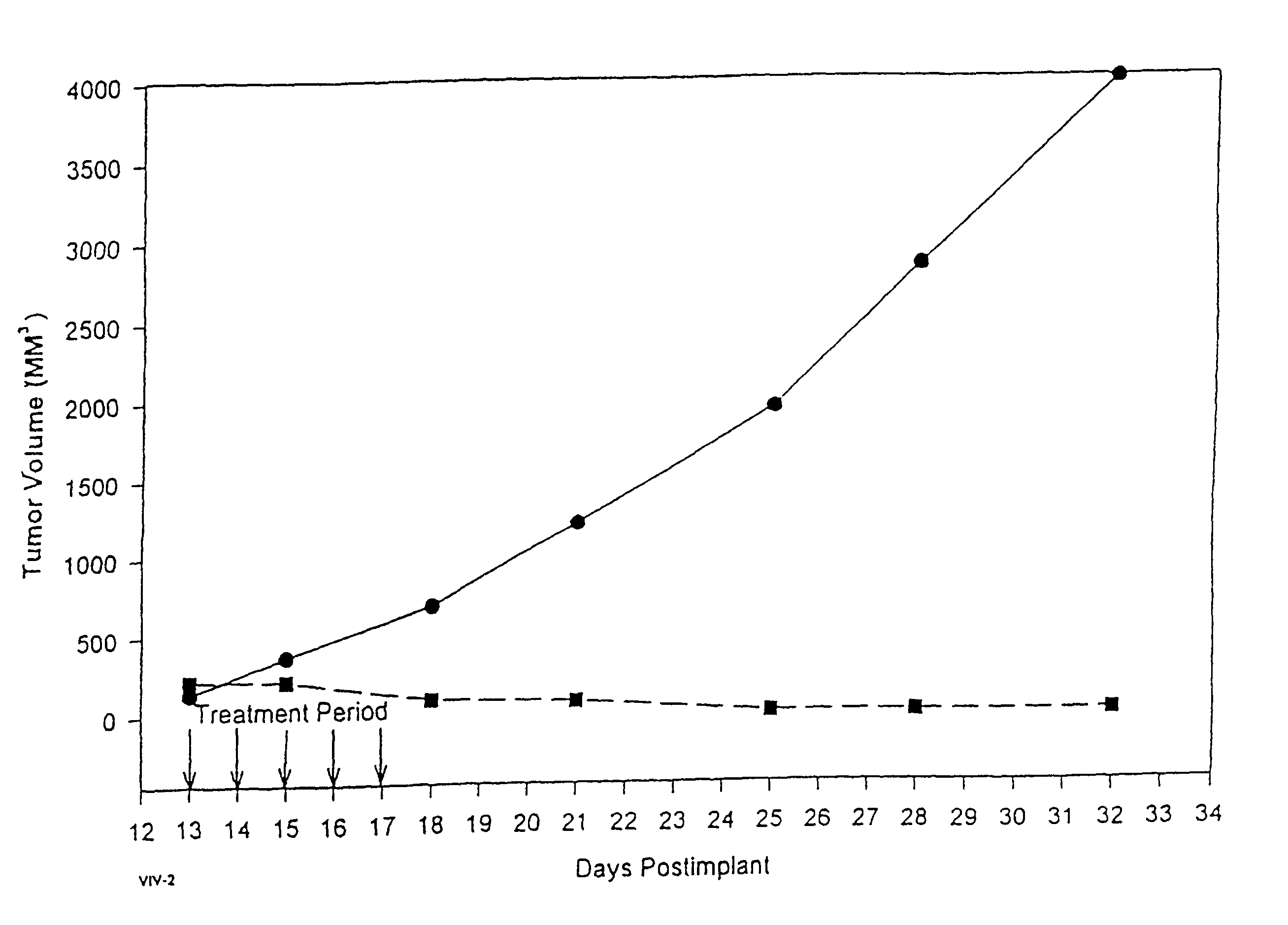
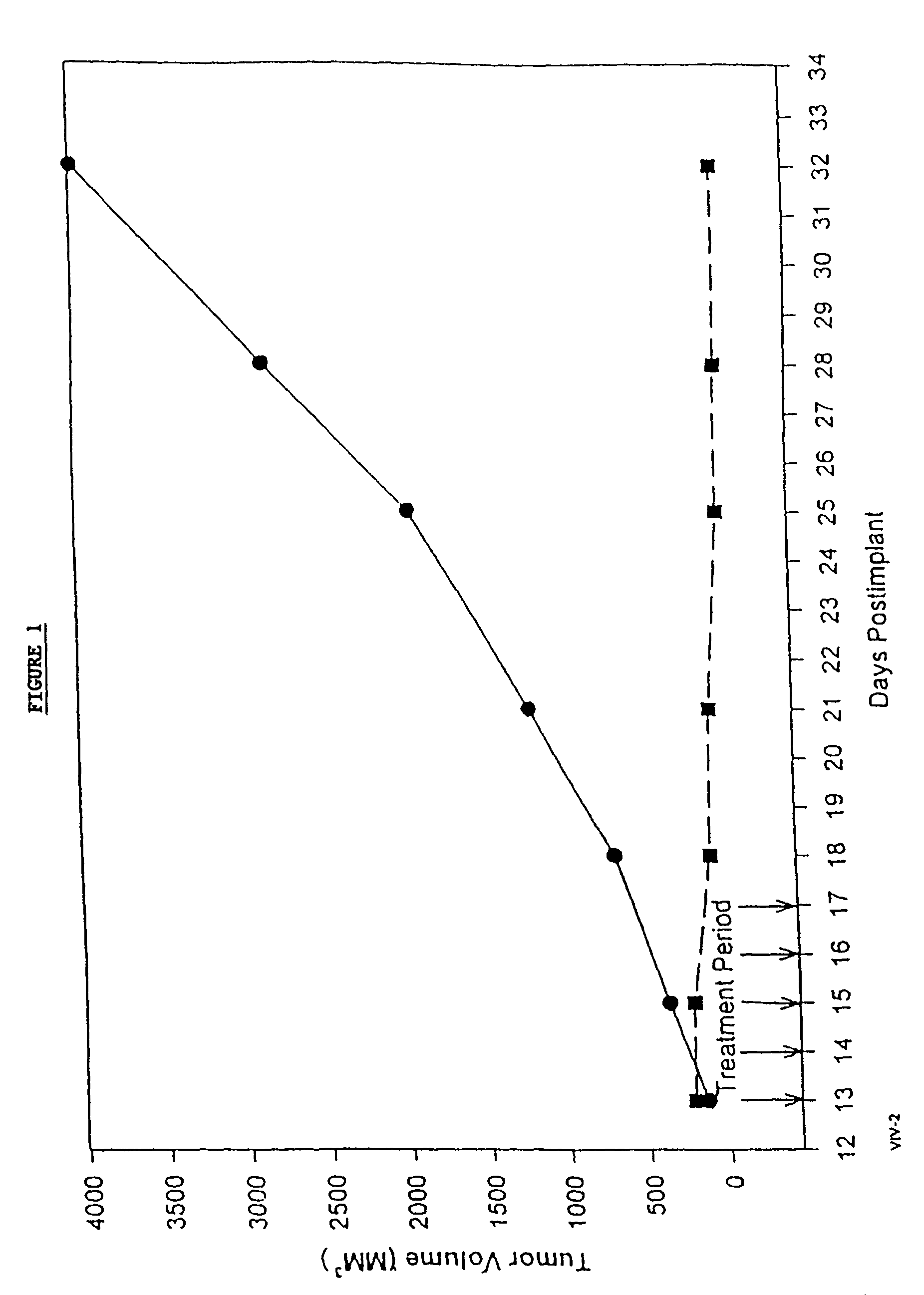
Provided is a method of monitoring the treatment of Pompe disease with specific pharmacological chaperones using systemic and / or cellular surrogate markers.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Method to predict response to pharmacological chaperone treatment of diseases
InactiveUS20110152319A1Increase activity levelHigh activityBiocideMetabolism disorderPharmacological chaperoneΑ galactosidase a
The present invention provides methods to determine whether a patient with a lysosomal storage disorder will benefit from treatment with a specific pharmacological chaperone. The present invention exemplifies an in vitro method for determining α-galactosidase A responsiveness to a pharmacological chaperone such as 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin in a cell line expressing a mutant from of α-galactosidase A. The invention also provides a method for diagnosing Fabry disease in patients suspected of having Fabry disease.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Dosing Regimens for the Treatment of Lysosomal Storage Diseases Using Pharmacological Chaperones
ActiveUS20160324839A1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsRegimenPharmacological chaperone
The present invention provides dosing regimens for administering pharmacological chaperones to a subject in need thereof. The dosing regimens can be used to treat disorders caused by improper protein misfolding, such as lysosomal storage disorders.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Compositions and methods for high throughput screening of pharmacological chaperones
Assays are provided for the screening and classification of biologically active agents that alter the conformation of conformationally defective proteins. The methods of the invention find use in the identification and classification of agents with chaperone activity, particularly the identification and classification of small molecule chemical and pharmacological chaperones. The agents thus identified find use altering the conformation of otherwise conformationally defective proteins.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
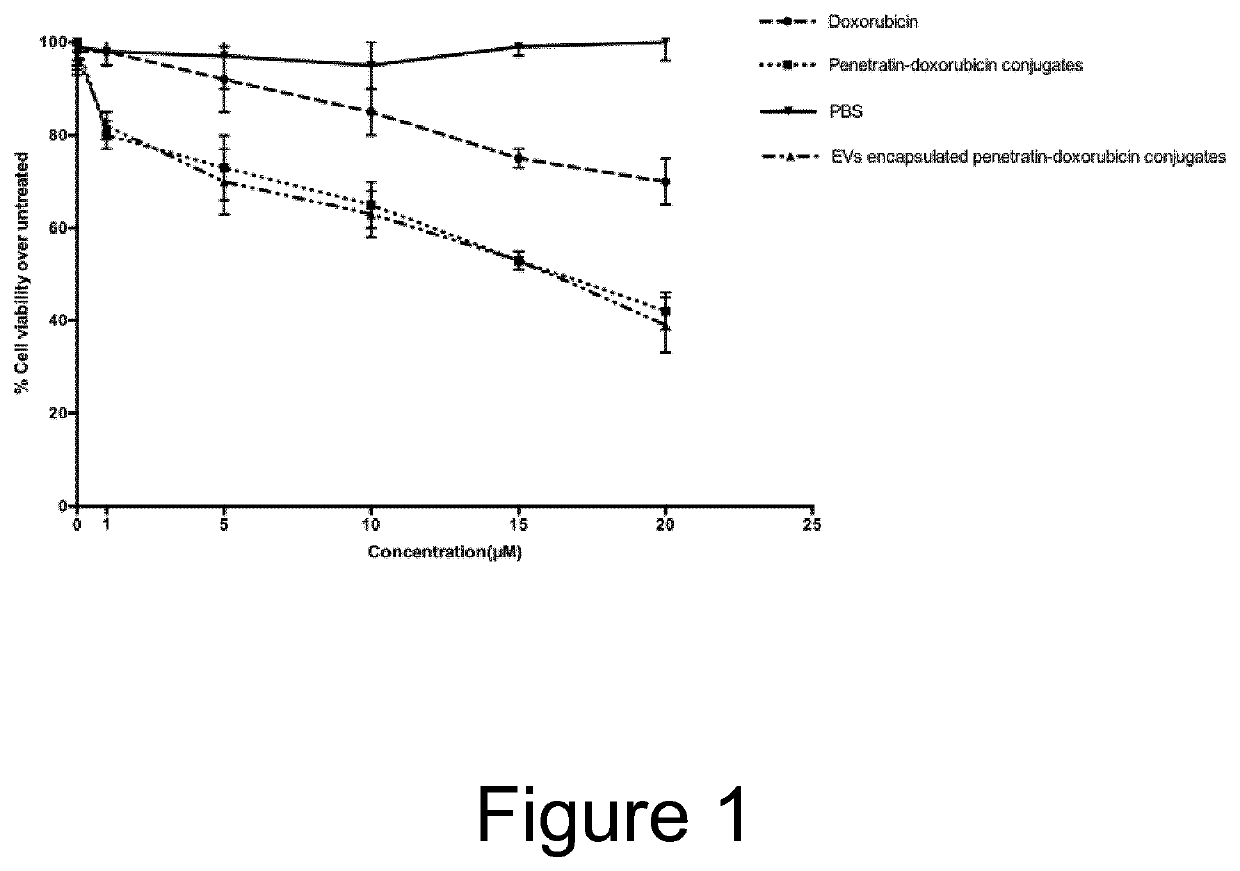
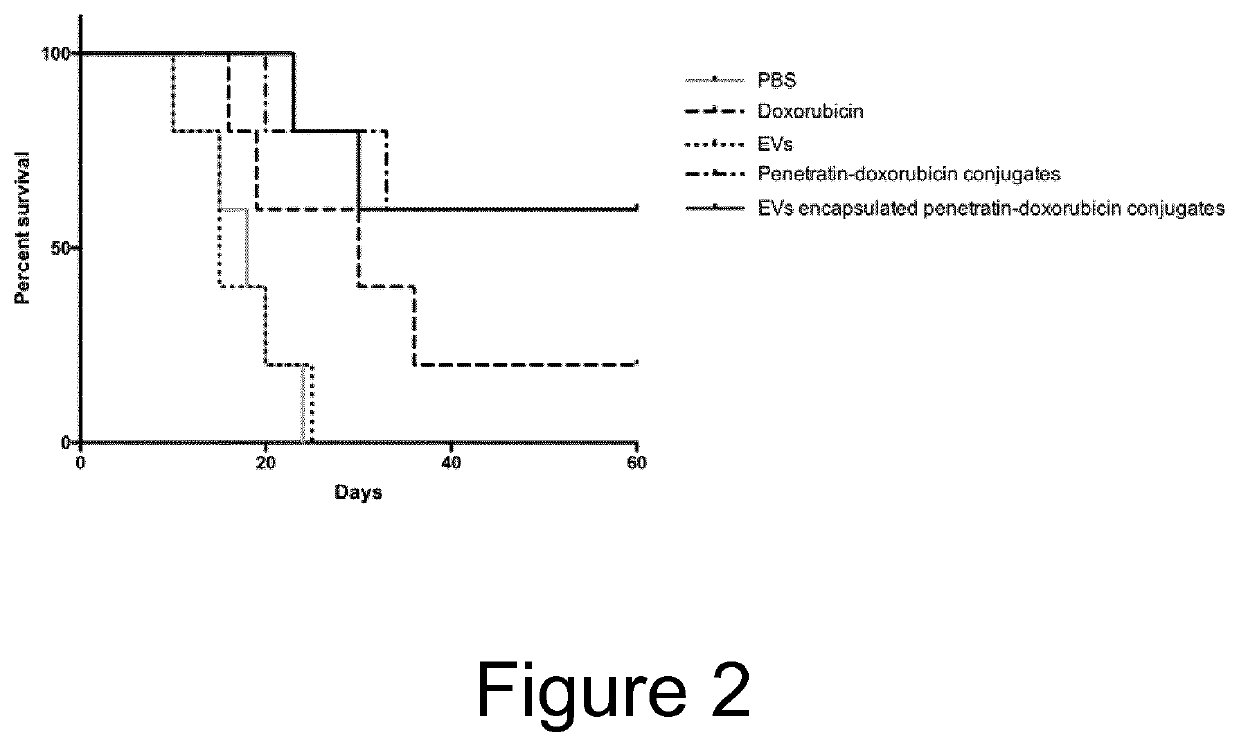
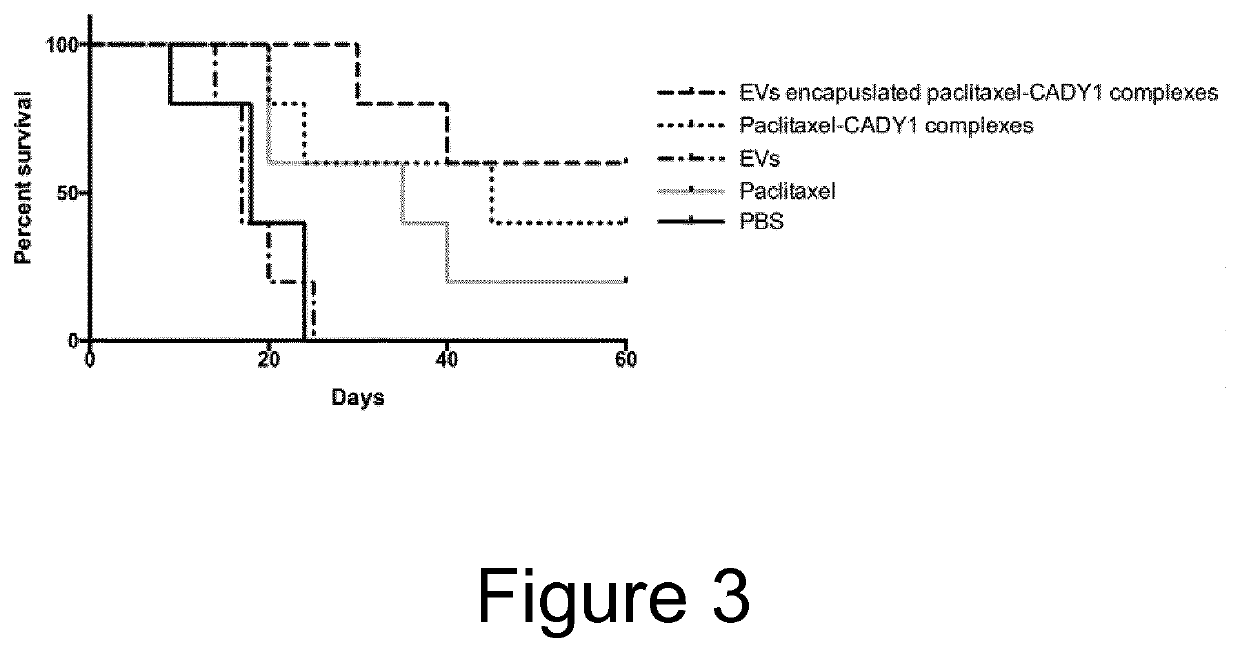
Cell penetrating peptide (CPP)-mediated ev loading
ActiveUS20190388347A1Increase doseAnimal cellsMicroencapsulation basedExtracellular vesiclePharmacological chaperone
The present invention relates to methods for loading extracellular vesicles (EVs) with a pharmacological agent. The invention discloses the use of cell-penetrating peptides as carriers into EVs, using either a non-covalent or covalent loading approach. Furthermore, the present invention pertains to medical uses and compositions comprising such pharmacological agent-loaded EVs.
Owner:EVOX THERAPEUTICS LTD
Method for the treatment of pompe disease using 1-deoxynojirimycin and derivatives
The present invention provides a method for increasing the activity of a mutant or wild-type a-glucosidase enzyme in vitro and in vivo by contacting the enzyme with a specific pharmacological chaperone which is a derivative of 1- deoxynojirimycin. The invention also provides a method for the treatment of Pompe disease by administration of chaperone small molecule compound which is a derivative of 1-deoxynojirimycin. The 1-deoxynojirimycin derivative is substituted at the N or Cl position. Combination therapy with replacement a-glucosidase gene or enzyme is also provided.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
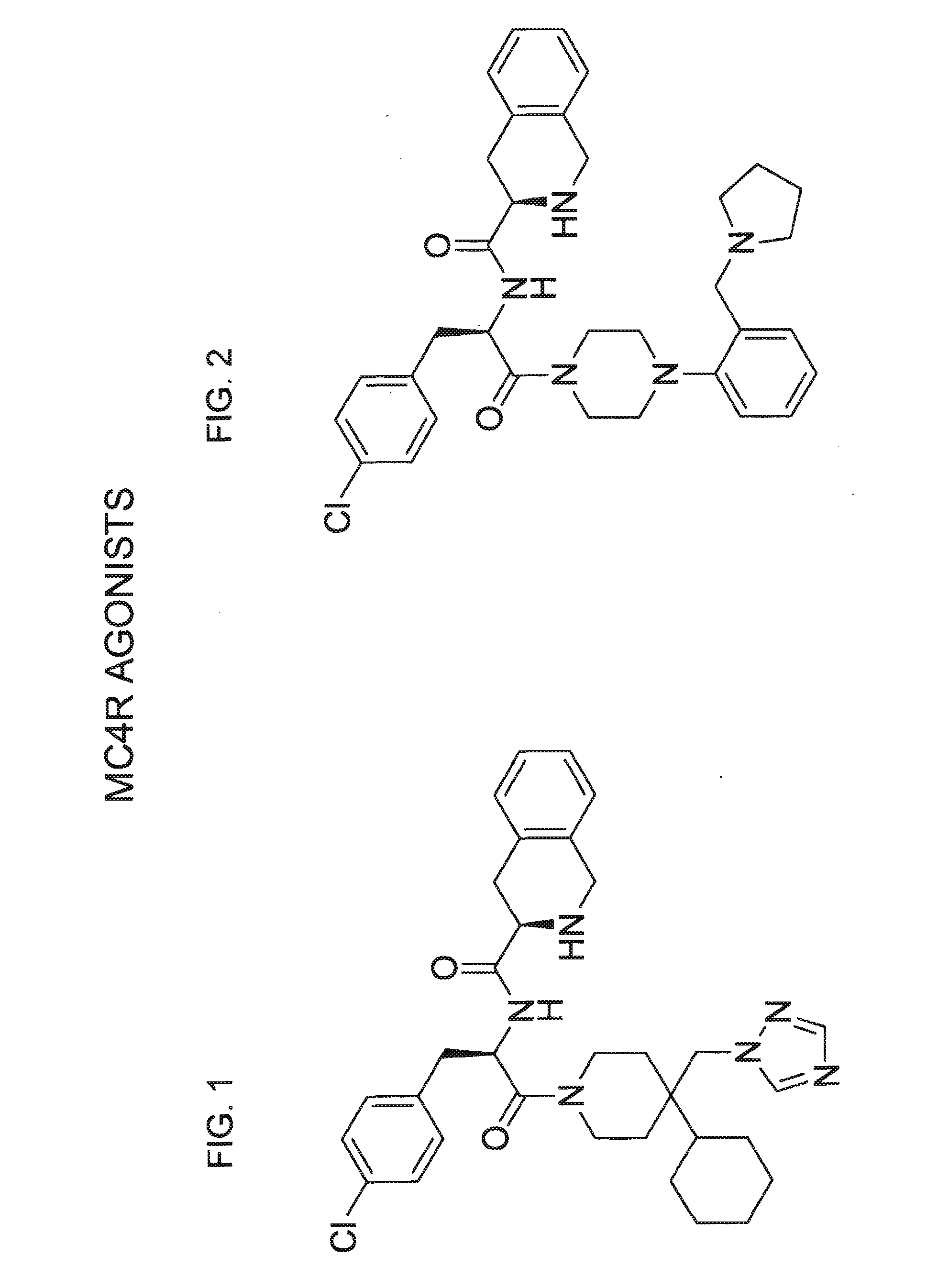
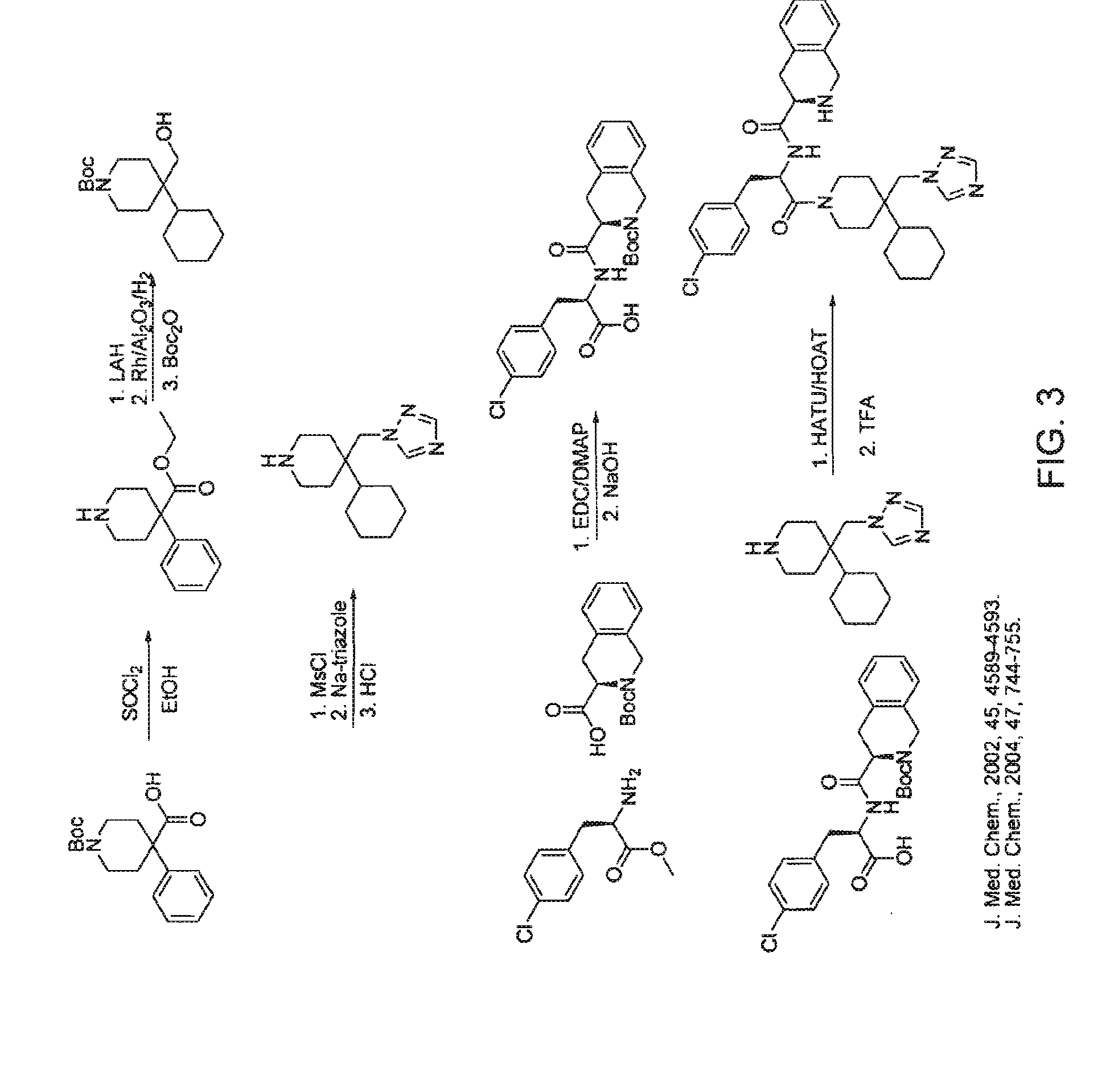
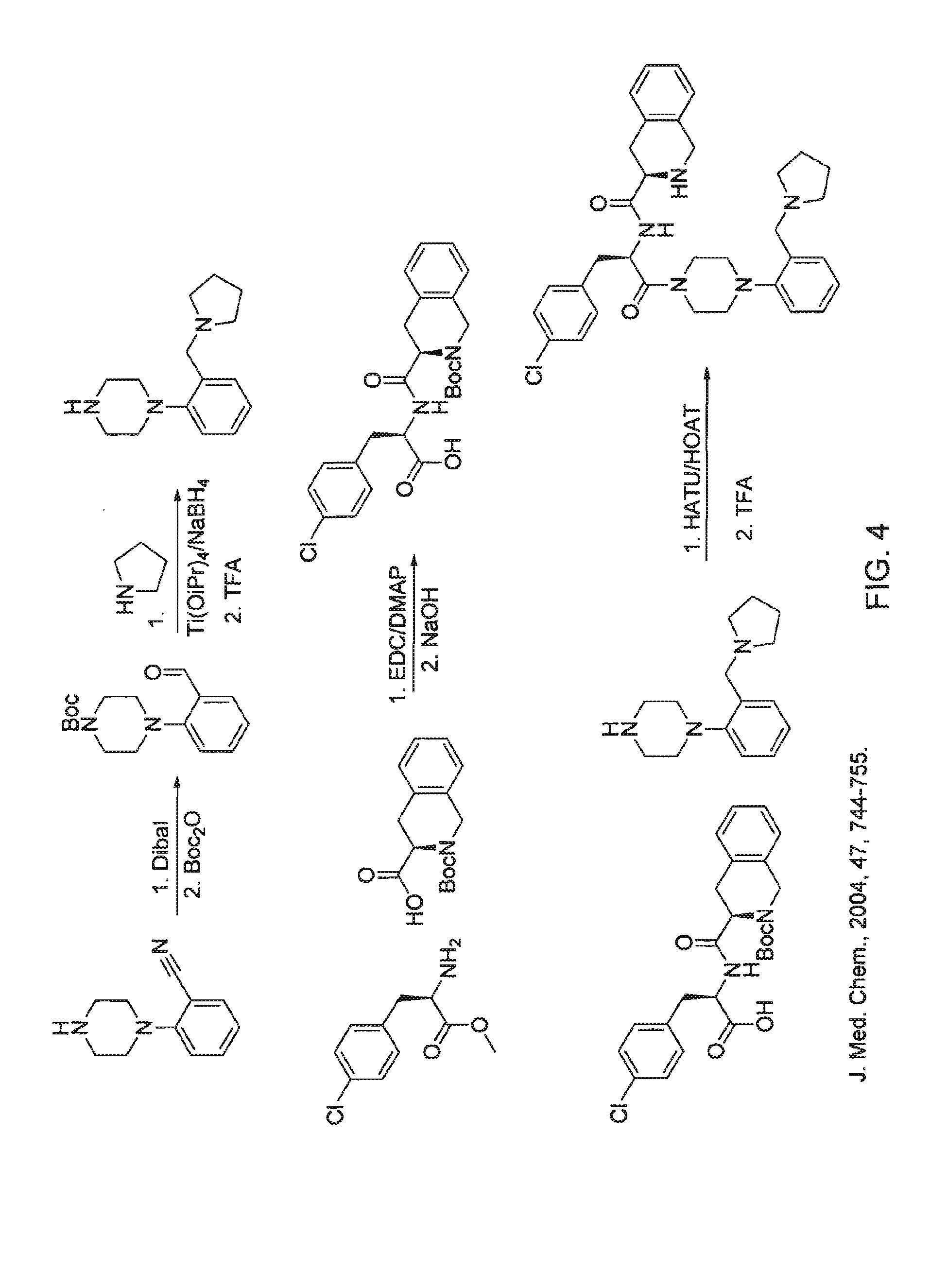
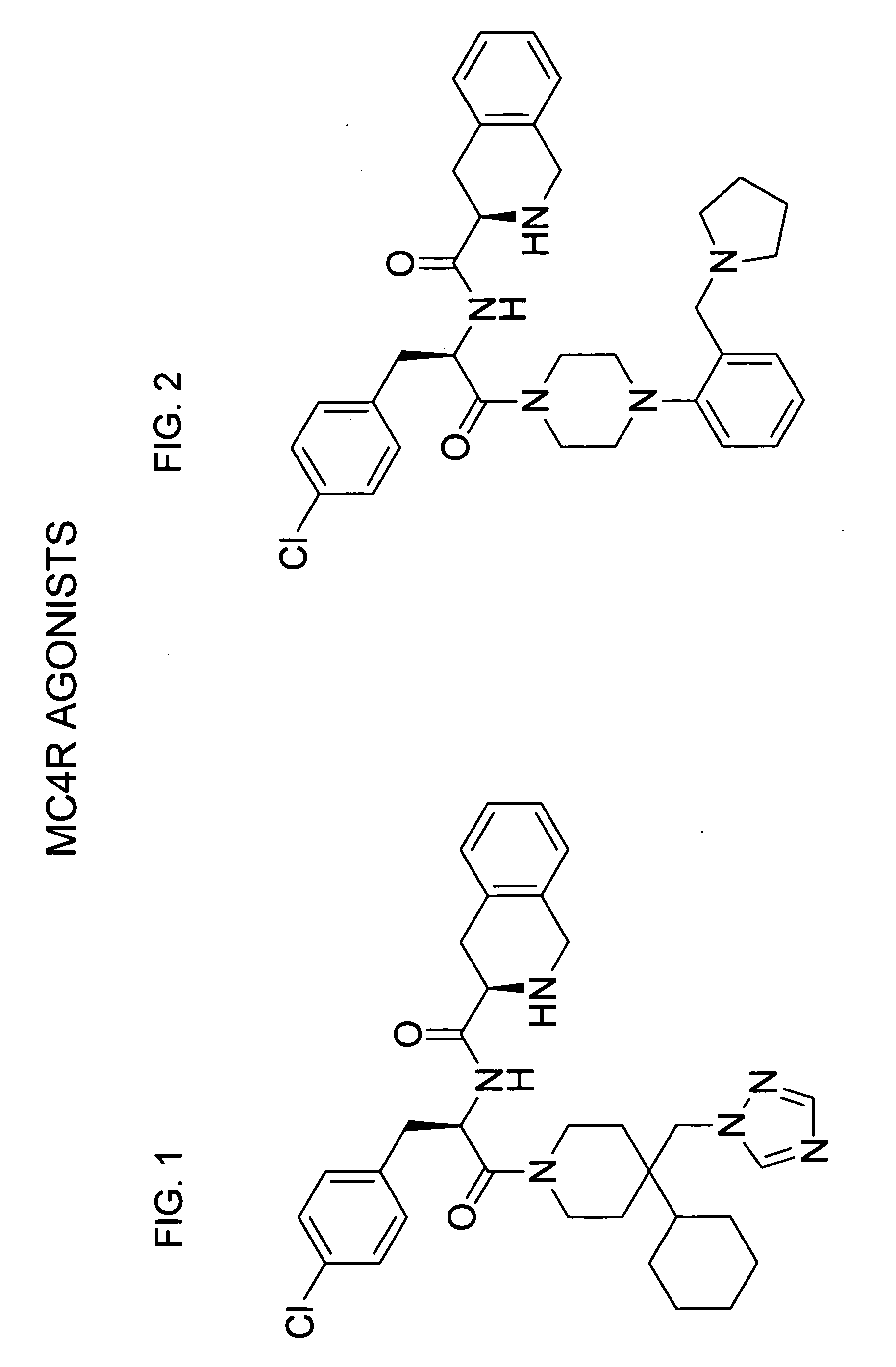
Pharmacological chaperones for treating obesity
ActiveUS20090312345A1High activityImprove scalabilityBiocideMetabolism disorderReticulum cellMedicine
The invention relates to methods of enhancing normal melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) activity, and to enhancing activity of an MC4R having a mutation which affects protein folding and / or processing of the MC4R. The invention provides a method of treating an individual having a condition in which increased activity of an MC4R at the cell surface would be beneficial, for example in obesity, by administering an effective amount of a pharmacological chaperone for the MC4R. The invention provides MC4R pharmacological chaperones which enhance the activity of MC4R. The invention further provides a method of screening to identify pharmacological chaperones which enhance folding of an MC4R in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), in order to enhance the activity of the MC4R at the cell surface.
Owner:UNIV DE MONTREAL
Utilization of Pharmacological Chaperones to Improve Manufacturing and Purification of Biologics
ActiveUS20110143419A1Increase productionProduction of recombinant proteinPeptide preparation methodsFermentationReticulum cellADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides methods for improving the production of recombinant proteins through the use of pharmacological chaperones for the recombinant proteins. As exemplified by the present invention, the binding of a pharmacological chaperone to a recombinant protein expressed by a cell can stabilize the protein and increase export of the protein out of the cell's endoplasmic reticulum, and increase secretion of the protein by the cell.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Use of substrates as pharmacological chaperones
InactiveUS20100197018A1High activityOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesLysosomePharmacological chaperone
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Pharmacological chaperones for treating obesity
InactiveUS20070021433A1High activityImprove scalabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideReticulum cellPharmacological chaperone
The invention relates to methods of enhancing normal melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) activity, and to enhancing activity of an MC4R having a mutation which affects protein folding and / or processing of the MC4R. The invention provides a method of treating an individual having a condition in which increased activity of an MC4R at the cell surface would be beneficial, for example in obesity, by administering an effective amount of a pharmacological chaperone for the MC4R. The invention provides MC4R pharmacological chaperones which enhance the activity of MC4R. The invention further provides a method of screening to identify pharmacological chaperones which enhance folding of an MC4R in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), in order to enhance the activity of the MC4R at the cell surface.
Owner:UNIV DE MONTREAL +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com