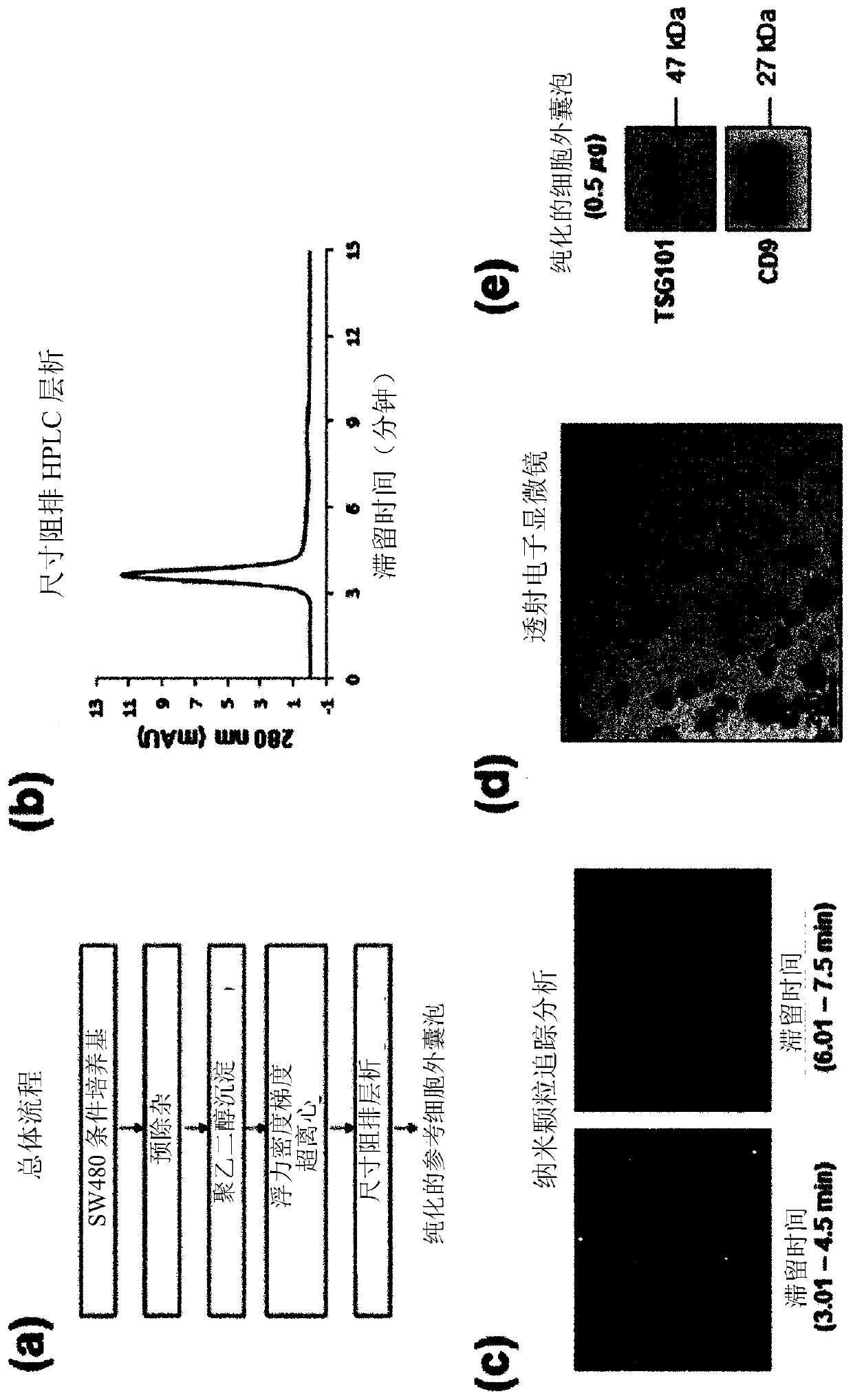
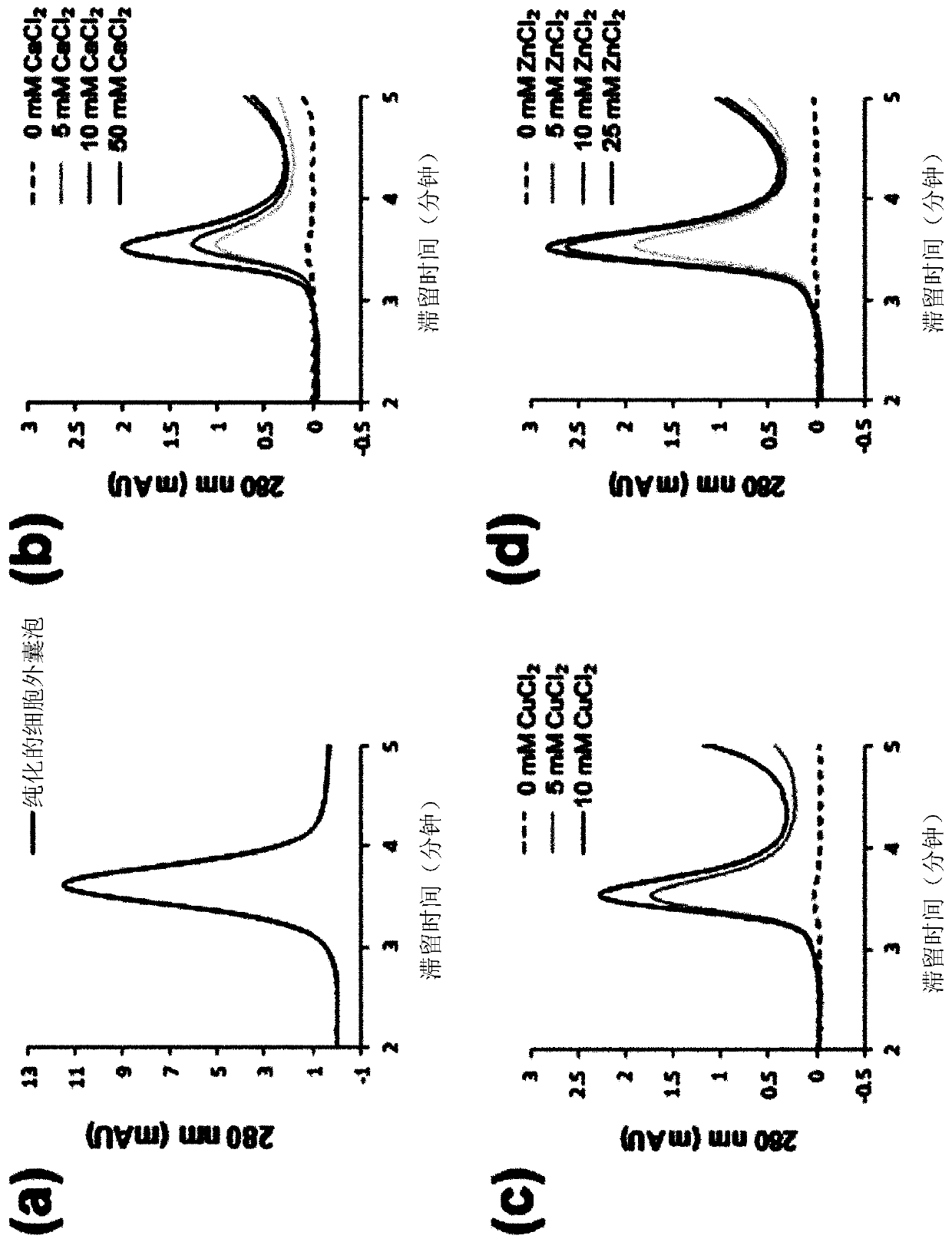
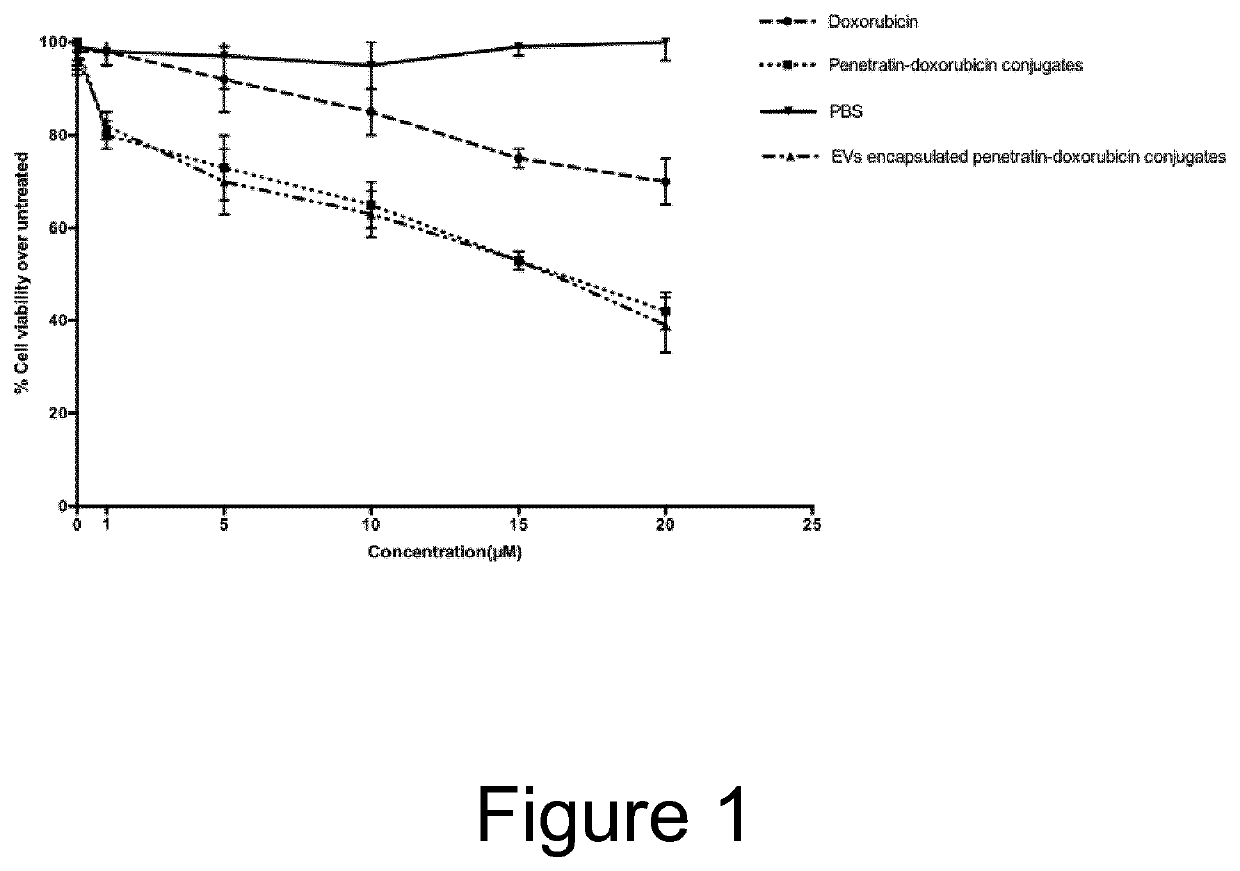
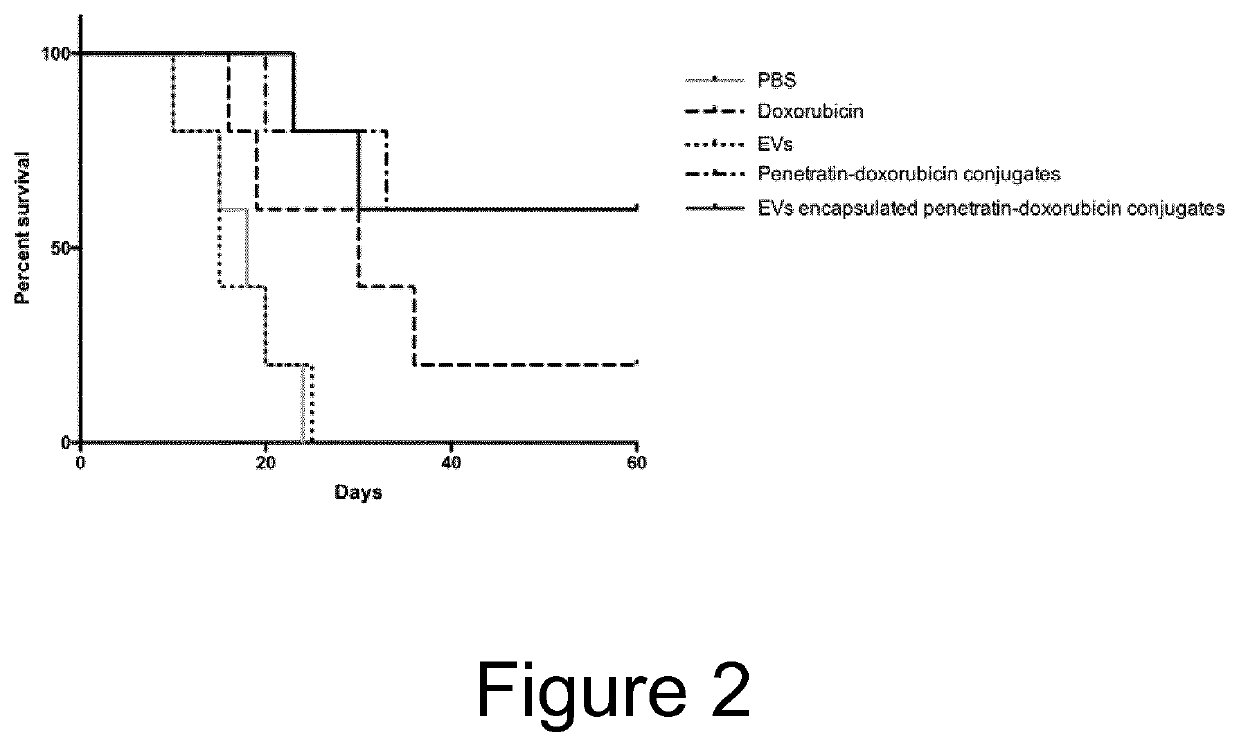
Patents
Literature
501 results about "Extracellular vesicle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
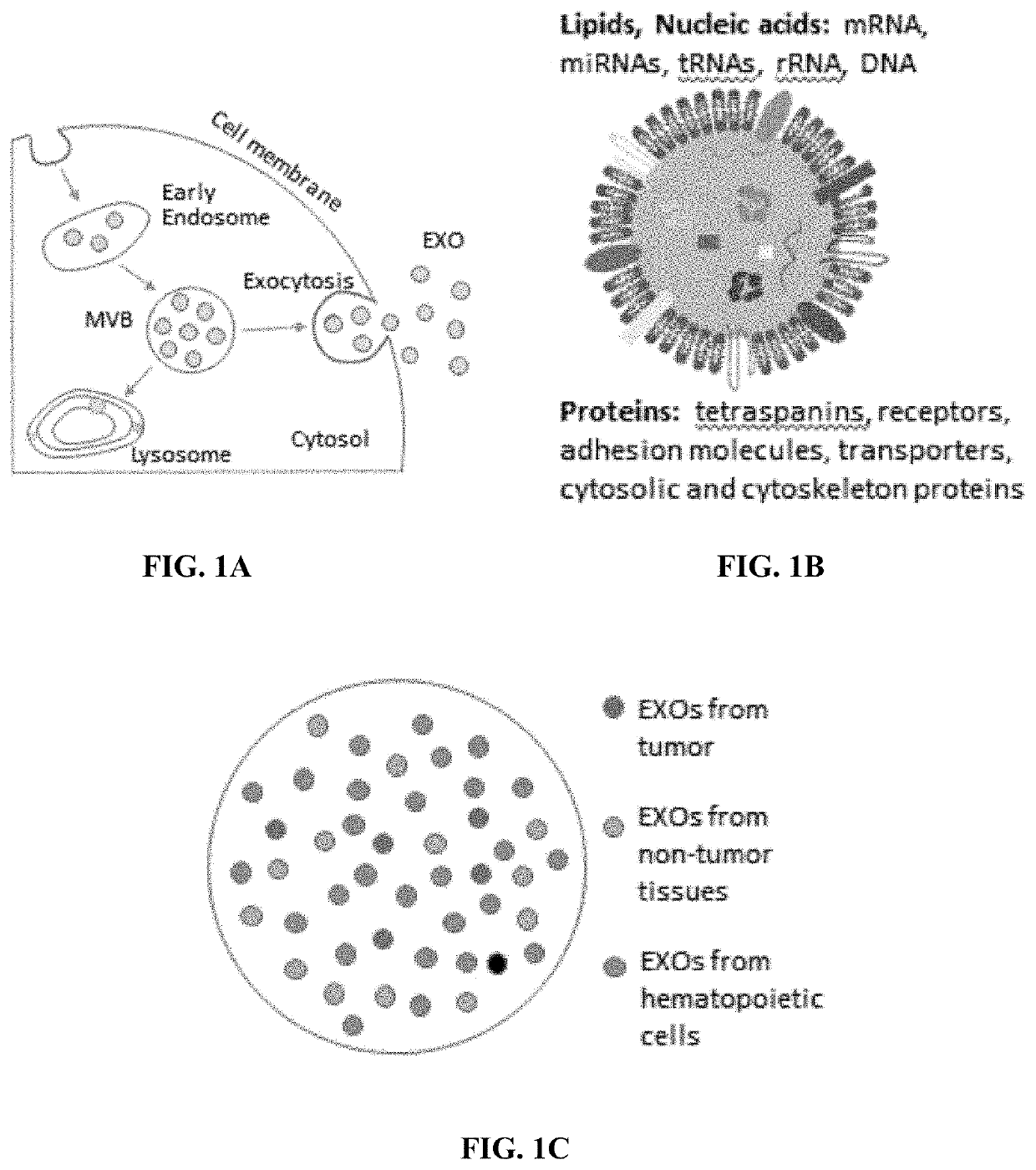
Any vesicle that is part of the extracellular region. [GO_REF:0000064, GOC:pm, GOC:TermGenie, PMID:24769233]
Brain specific exosome based diagnostics and extracorporeal therapies
InactiveUS20170014450A1Reliable and inexpensive and portable and rapid and simple approachMinimally invasive, inexpensive, portable, and reliableCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPsa ncamPhosphorylation
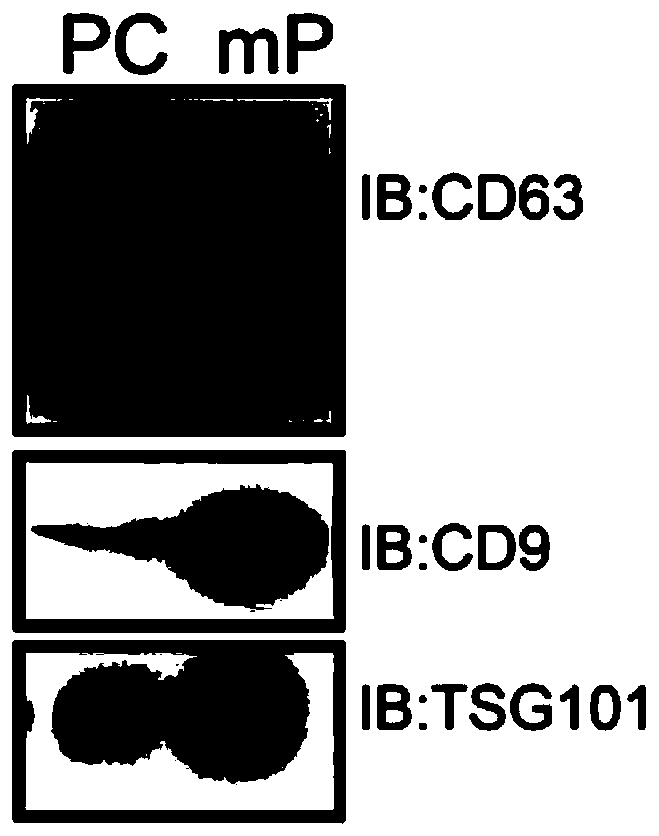
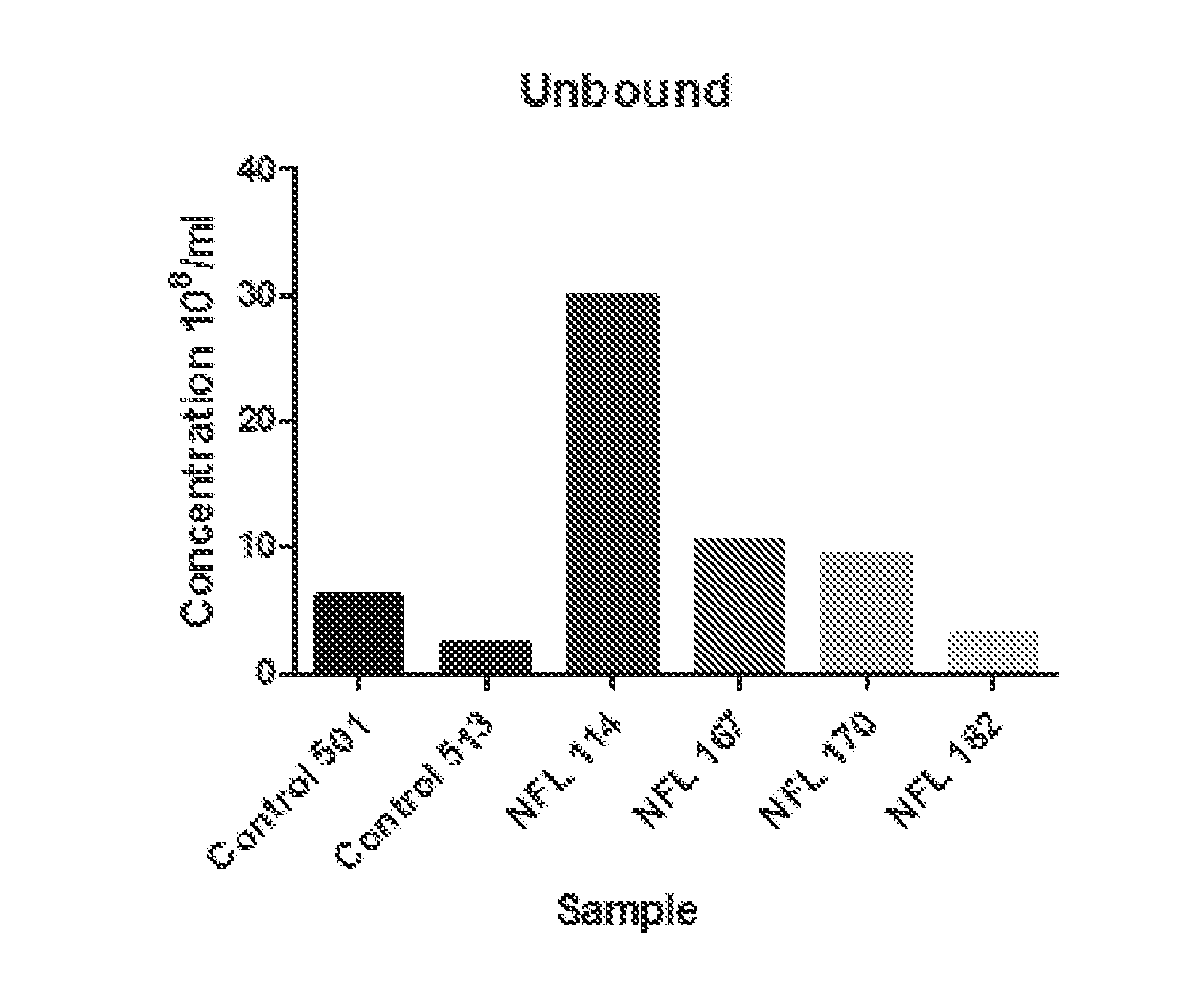
Disclosed are methods, compositions, devices, and kits for the isolation of brain-specific exosomes. Specifically, methods, compositions, devices, and Unbound kits comprising an isolated brain-specific extracellular vesicle or exosome joined to a first binding agent that is specific for tau, β-amyloid, SlOO β, neuron-specific enolase, glycoprotein A2B5, CD133, NQ01, synaptophysin, neuronal nuclei, MAB 1569, polysialic acid-neural cell adhesion molecule (PSA-NCAM), or neurogenic differentiation 1 (NeuroD or Beta2), or glycosylated or phosphorylated forms of these molecules, are provided.
Owner:EXOSOME SCI
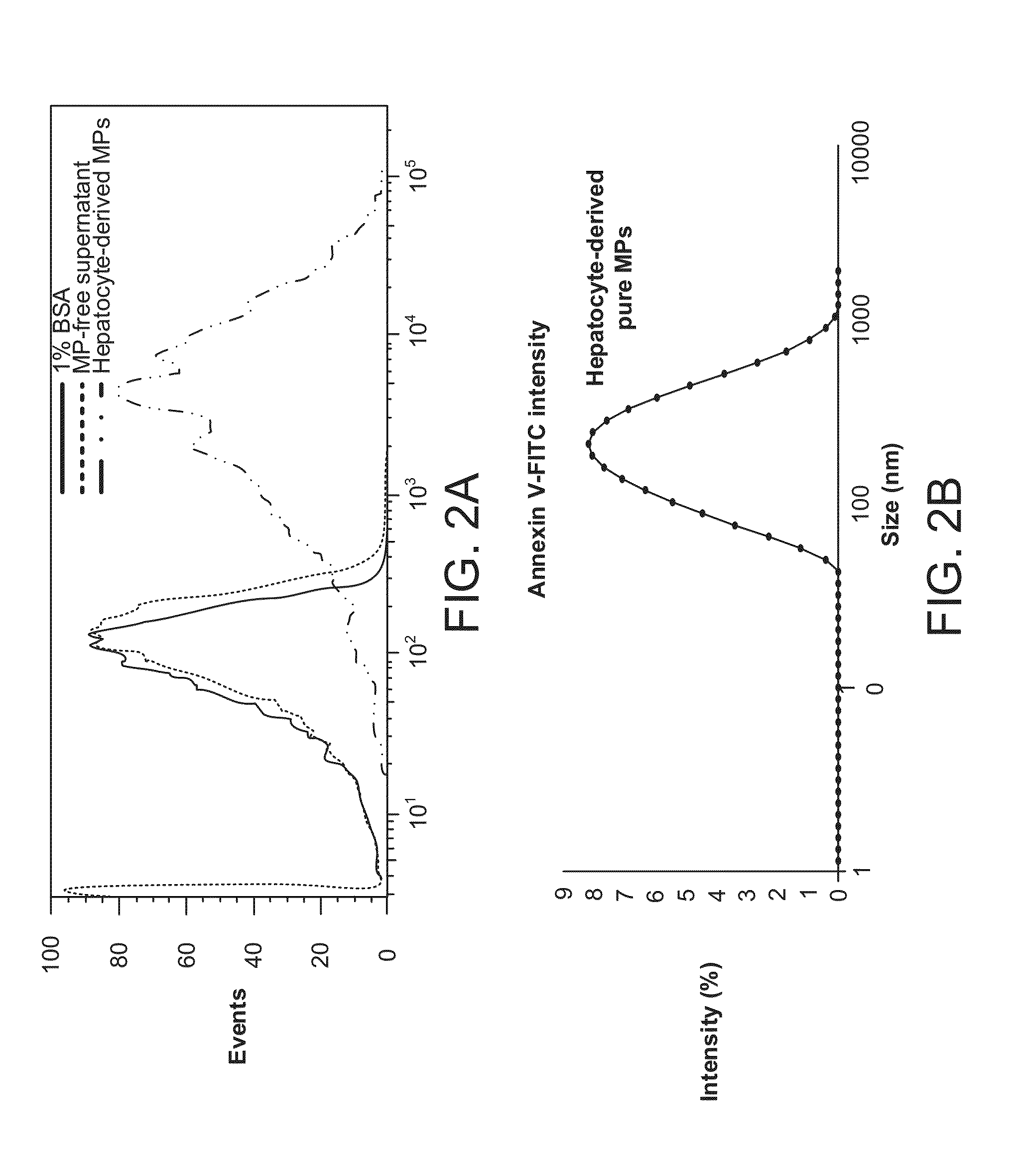
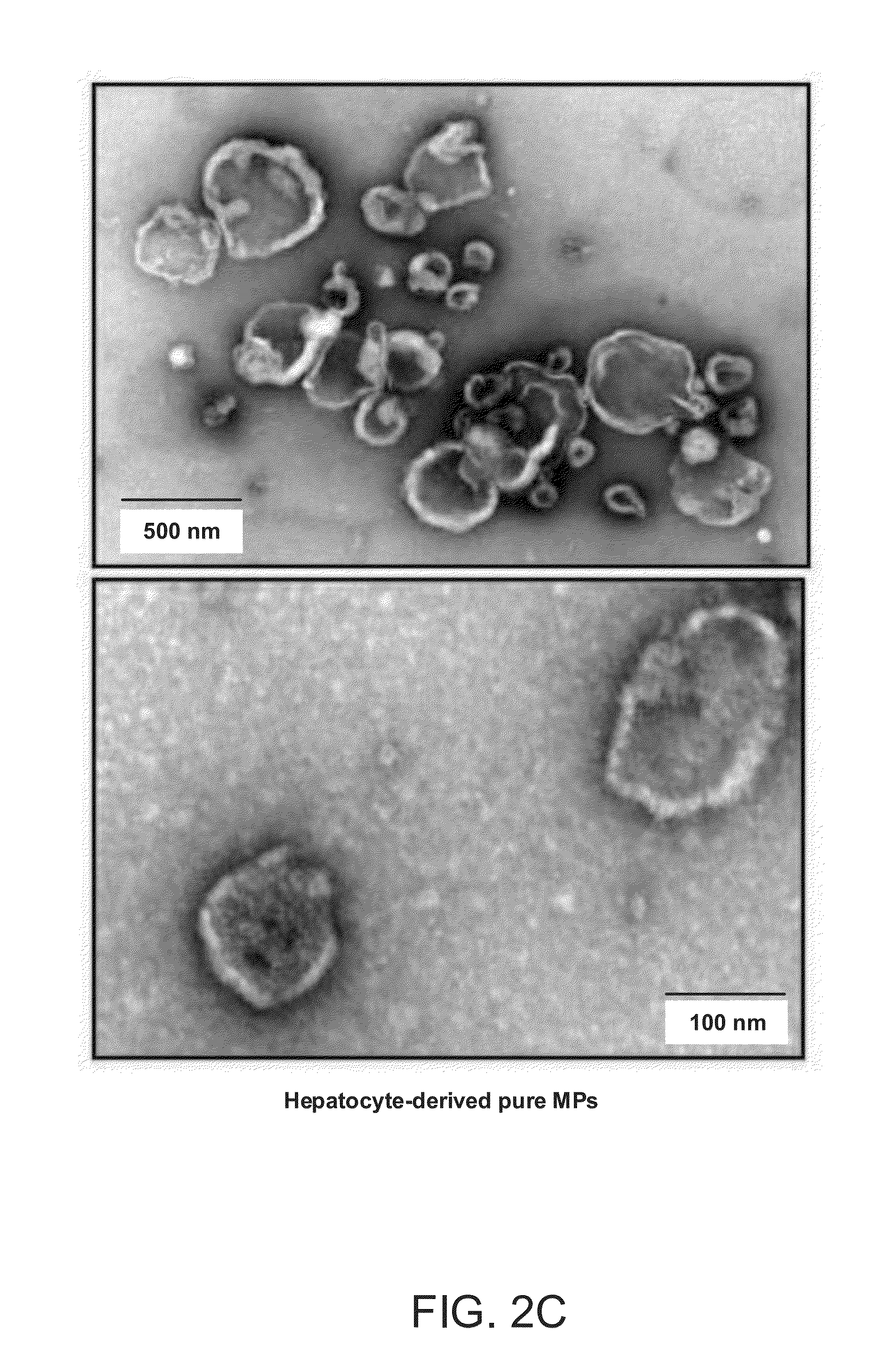
Detecting and Treating Liver Damage
InactiveUS20150247149A1Reducing blocking internalizationShorten the progressAntibody ingredientsDisease diagnosisMicroparticleLiver fibrosis
The invention provides a method of detecting, monitoring, assessing and treating non-alcoholic fatty acid liver disease (NAFLD) and associated liver damage in a subject comprising measuring the amount of hepatocyte-derived circulating extracellular vesicles (EVs) and / or microparticle (MPs) in the bodily sample, or the expression level or activity of at least one biomarker expressed or detected in the EVs and / or MPs. The increased amount of EVs or MPs in the bodily sample and / or the increased expression or detection level of the biomarker of interest correlate with the degree or severity of NAFLD, NASH, liver fibrosis, or other associated liver damage, which can be associated with angiogenesis. Prevention and treatment of NAFLD, NASH, liver fibrosis or associated liver damage by reducing EVs or MPs, or targeting the biomarkers expressed in the EVs or MPs are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
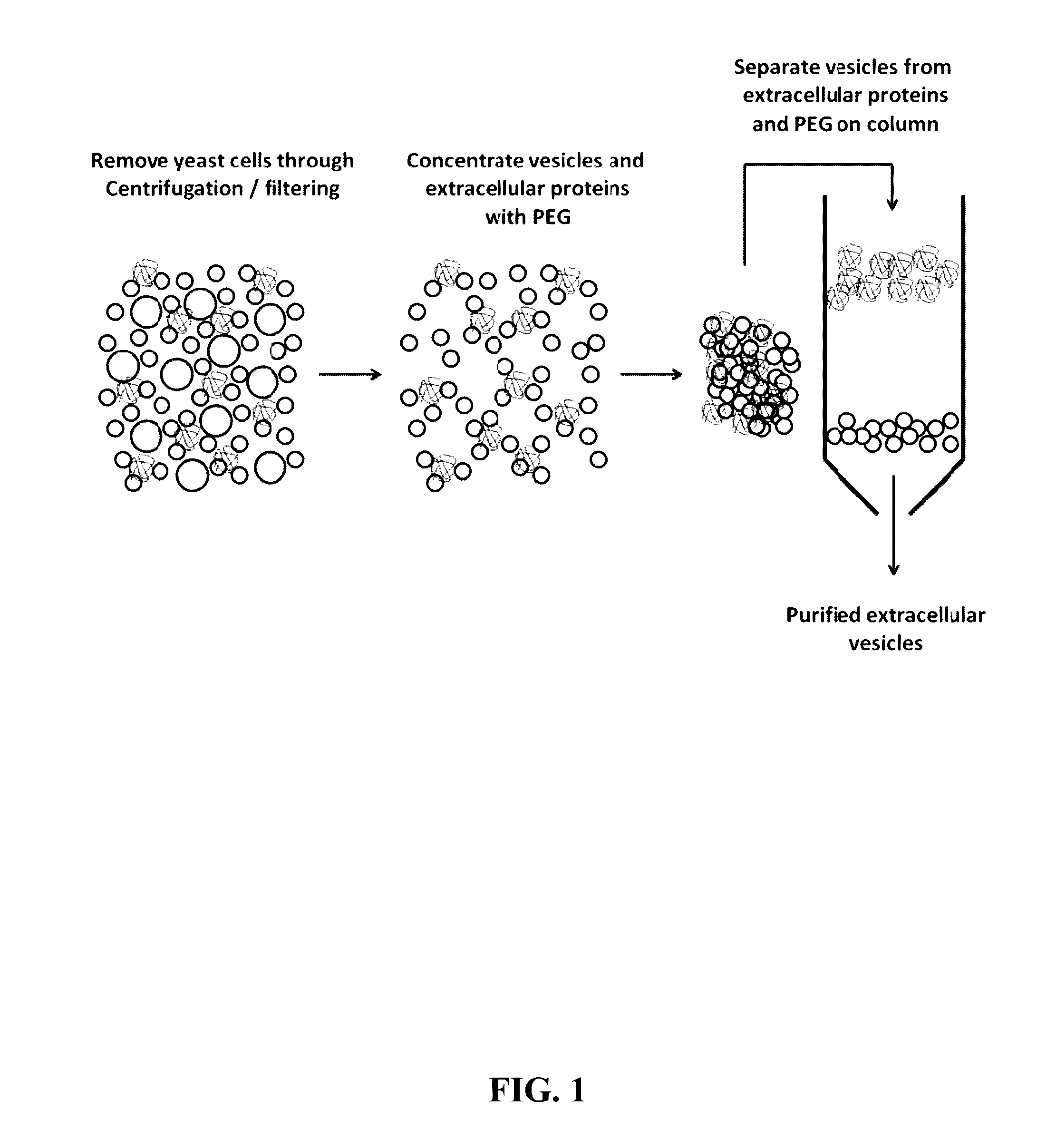
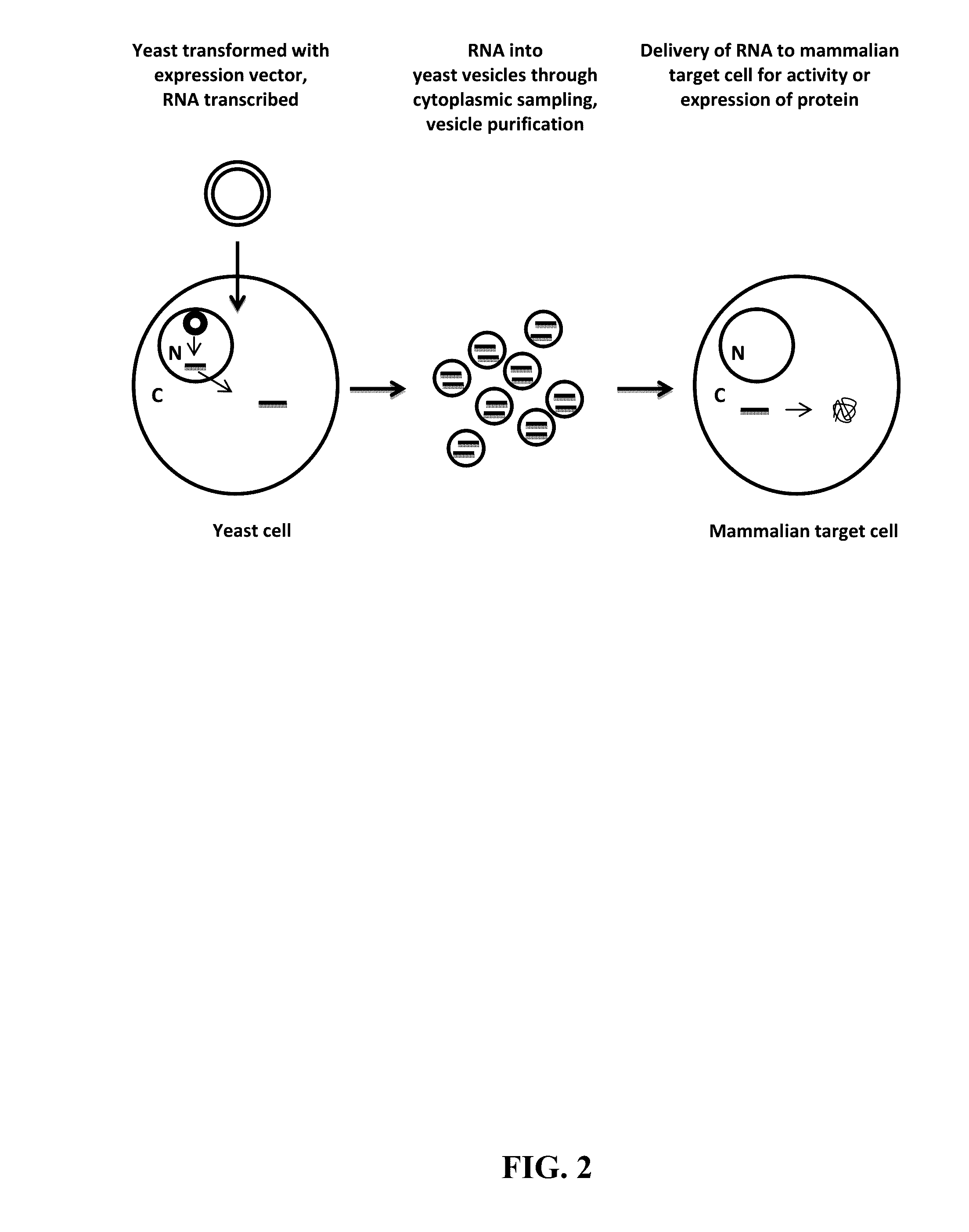
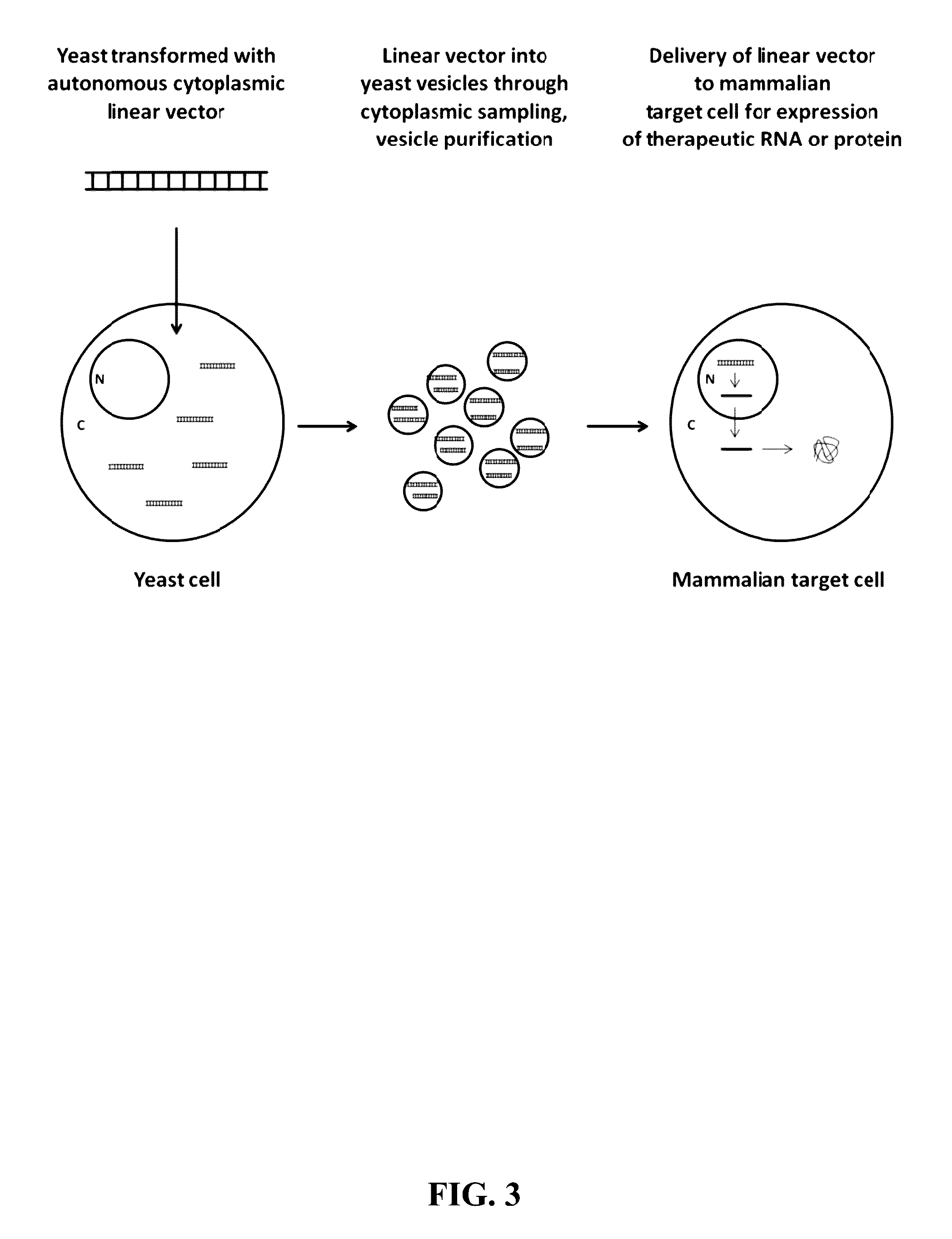
Compositions and Methods for Yeast Extracellular Vesicles as Delivery Systems
InactiveUS20160331686A1Less availableGreat range of targetSpecial deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseA-DNA
The present invention provides compositions of yeast extracellular vesicles comprising biologically active molecules, methods for making the same, and methods for the use of the yeast extracellular vesicles to deliver biologically active molecules to target cells. In addition, the invention provides cells and compositions comprising the biologically active molecules and vesicles, which can be used as transfection reagents. The invention further provides methods for producing said compositions of biologically active molecules with vesicles as well as the cells that produce those compositions. Compositions and methods for delivering biologically active molecules, such as a small molecule, a DNA expression plasmid, an RNA molecule, a peptide, or a protein, to cells and / or tissues are provided. The compositions and cells are useful, for example, in delivering biologically active RNA molecules to cells to modulate target gene expression in the diagnosis, prevention, amelioration, and / or treatment of diseases, disorders, or conditions in a subject or organism.
Owner:CLSN LAB
Extracellular vesicles derived from gram-positive bacteria, and use thereof
The present invention relates to extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from gram-positive bacteria. In detail, the present invention provides animal models of disease using extracellular vesicles derived from gram-positive bacteria, provides a method for screening an active candidate substance which is capable of preventing or treating diseases through the animal models of disease, provides vaccines for preventing or treating diseases caused by extracellular vesicles derived from gram-positive bacteria, and provides a method for diagnosing the causative factors of diseases caused by gram-positive bacteria using extracellular vesicles.
Owner:AEON MEDIX
Methods for attenuating viral infection and for treating lung injury
PendingUS20200384034A1Reduce developmentReduce expressionPowder deliverySpray deliveryViral antibodyAntiendomysial antibodies
The described invention provides compositions and methods for treating a susceptible subject at risk of pulmonary complications of an acute lung injury caused by a severe infection with a respiratory virus and for restoring lung function to donor lungs. The methods include administering a therapeutic amount of a pharmaceutical composition comprising extracellular vesicles (EVs) comprising one or more miRNAs and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The population of EVs can be derived from a patient who has recovered from an infection with the respiratory virus or has been exposed to anti-viral antibodies through treatment, can be derived from MSCs of a normal healthy individual, can be modified by a viral vector, or can be synthetic.
Owner:SPIRITUS THERAPEUTICS INC
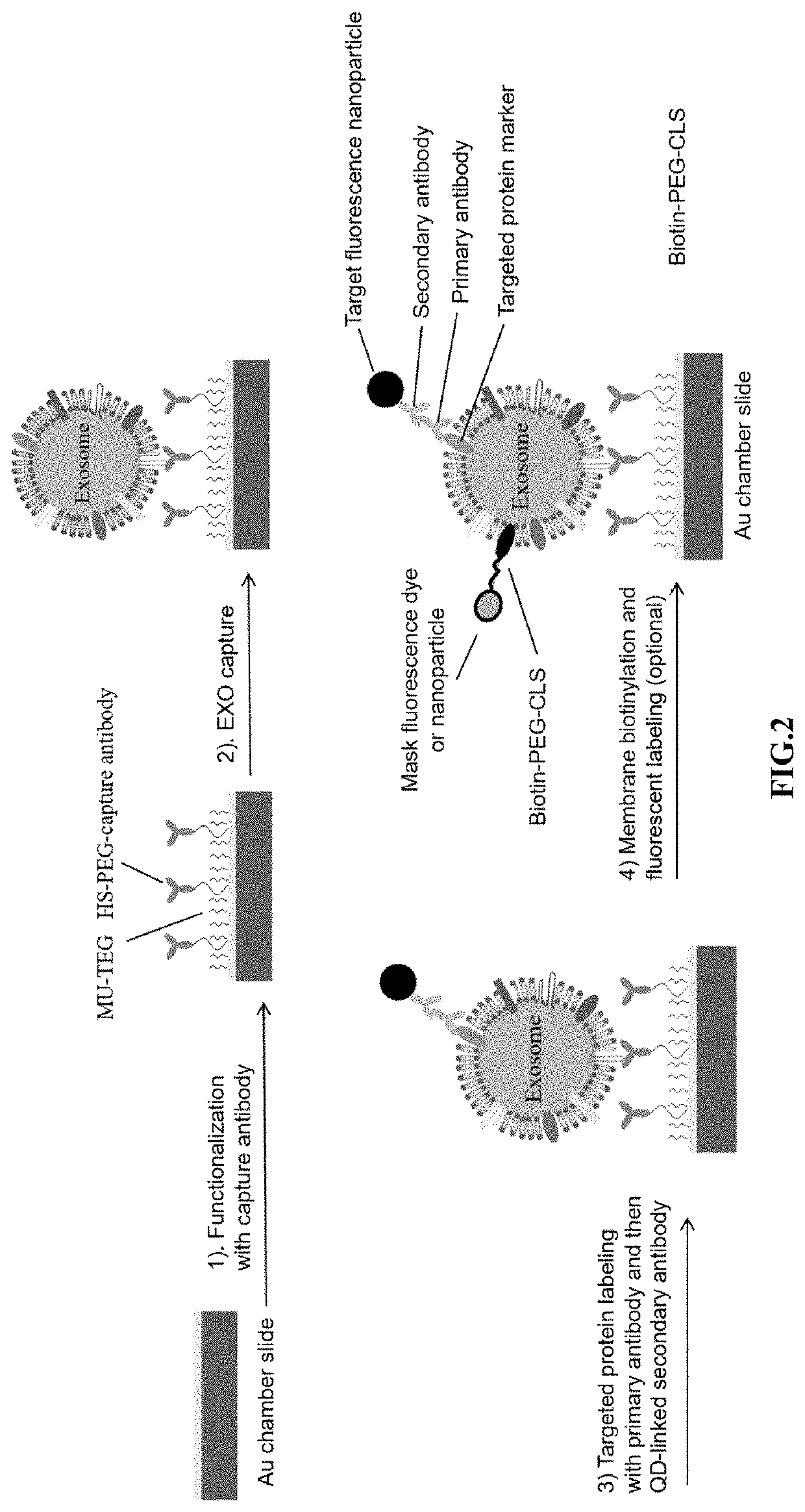
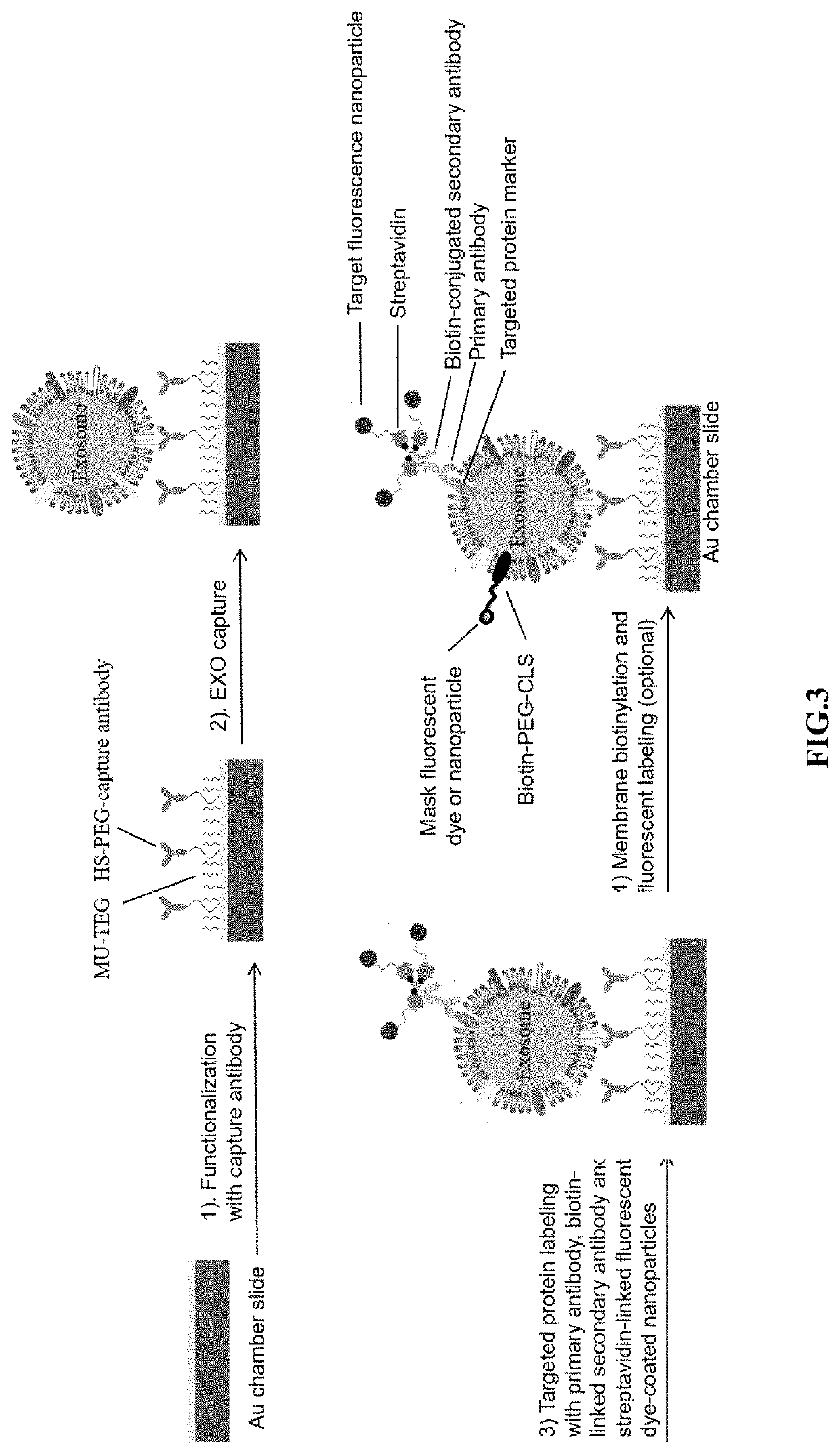
ImmunoLipoplex Nanoparticle Biochip Containing Molecular Probes for Capture and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles
ActiveUS20160202248A1Eliminate stepsDetect directlyLibrary screeningLibrary creationDiseaseExtracellular vesicle
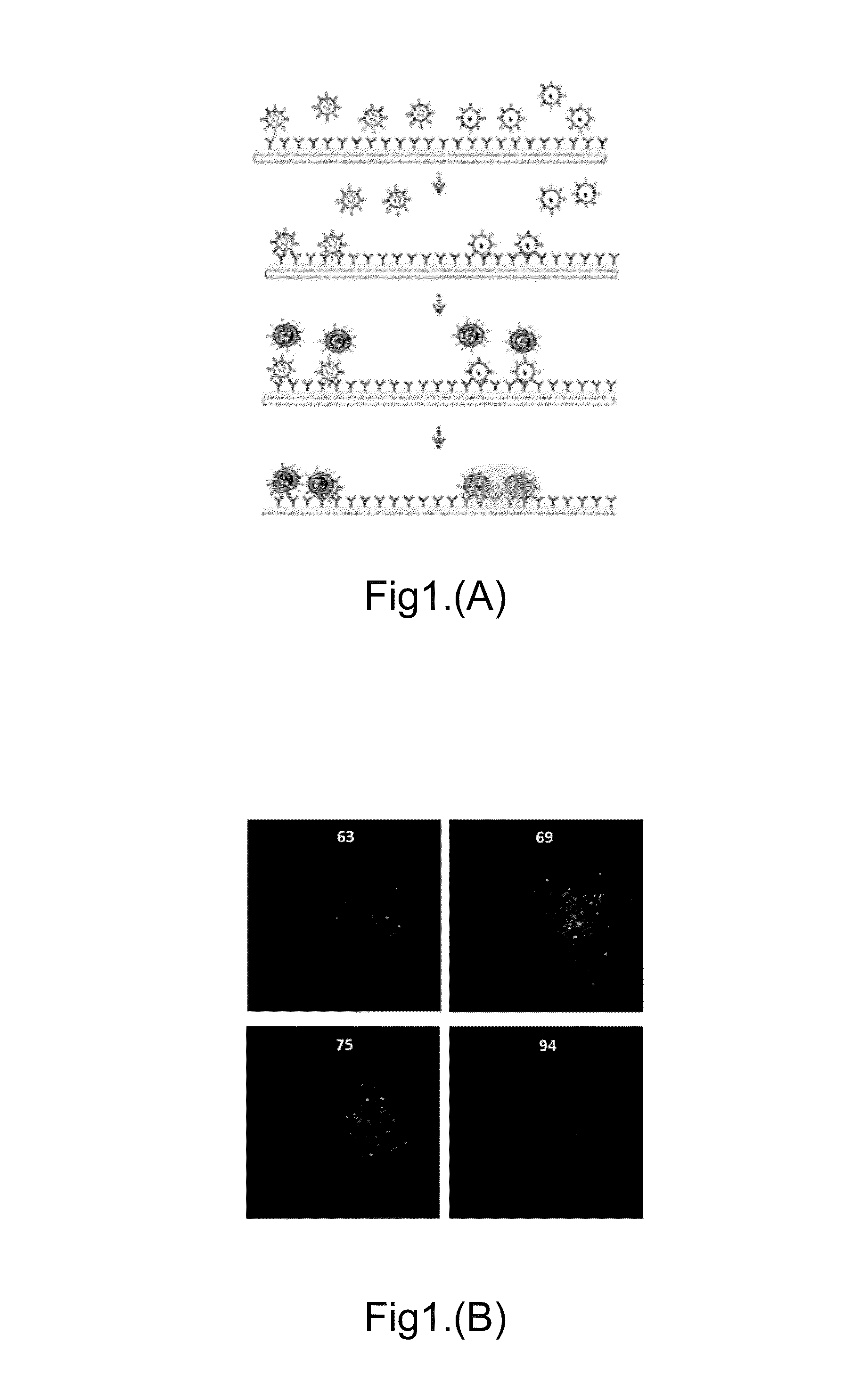
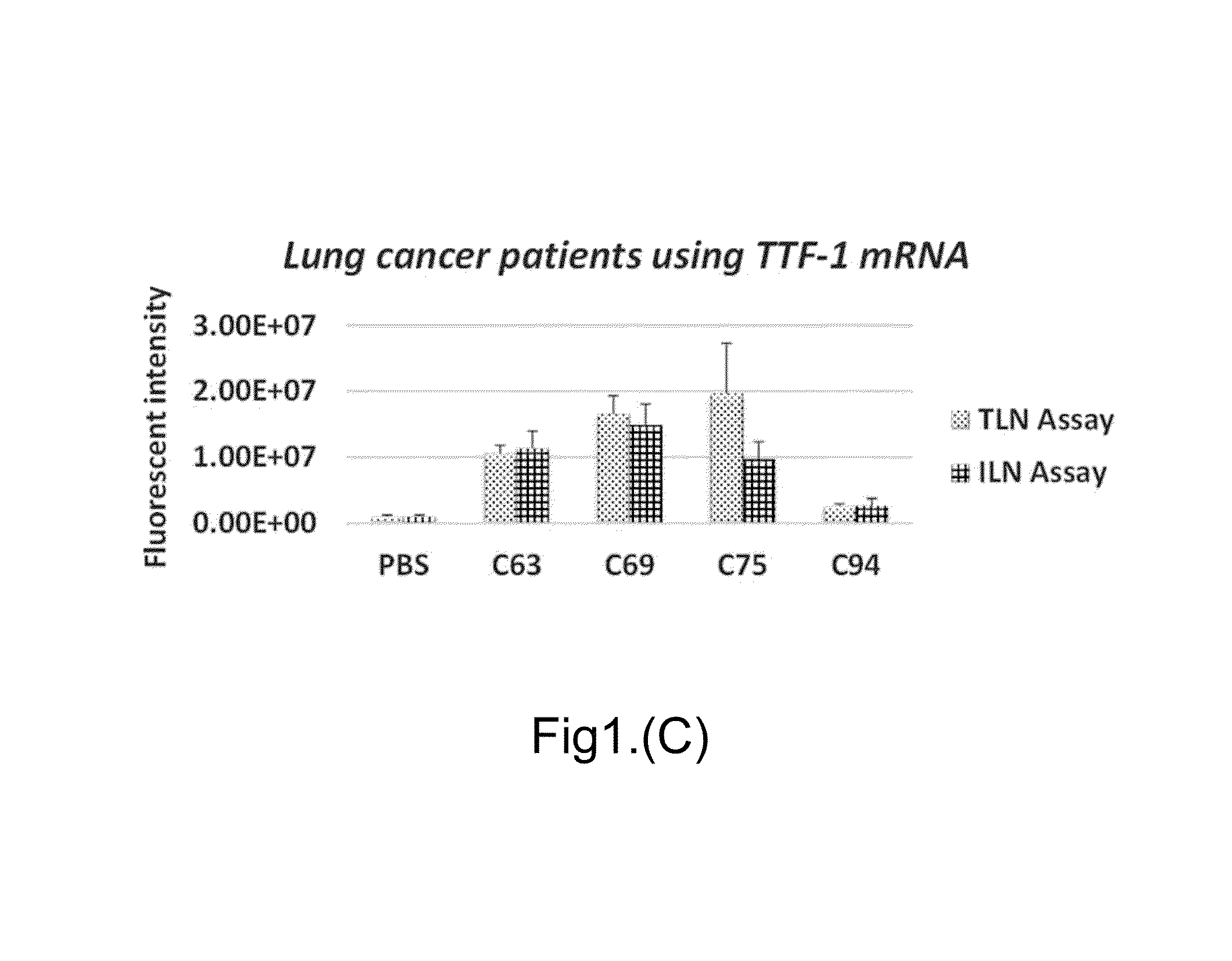
The present invention disclosed a method of fabricating an antibody immunolipoplex nanoparticle (Ab-ILN) biochip and antibody tethered lipoplex nanoparticle (Ab-TLN) biochip. The aforementioned antibody-based lipoplex nanoparticle biochip or the related array contains molecular probes and is applied for detecting the presence of a disease or condition in a subject obtaining a body fluid sample by capturing and identifying both membrane protein and intra-vesicular DNA / RNA / proteins of extracellular vesicles (EVs).
Owner:SPOT BIOSYST LTD
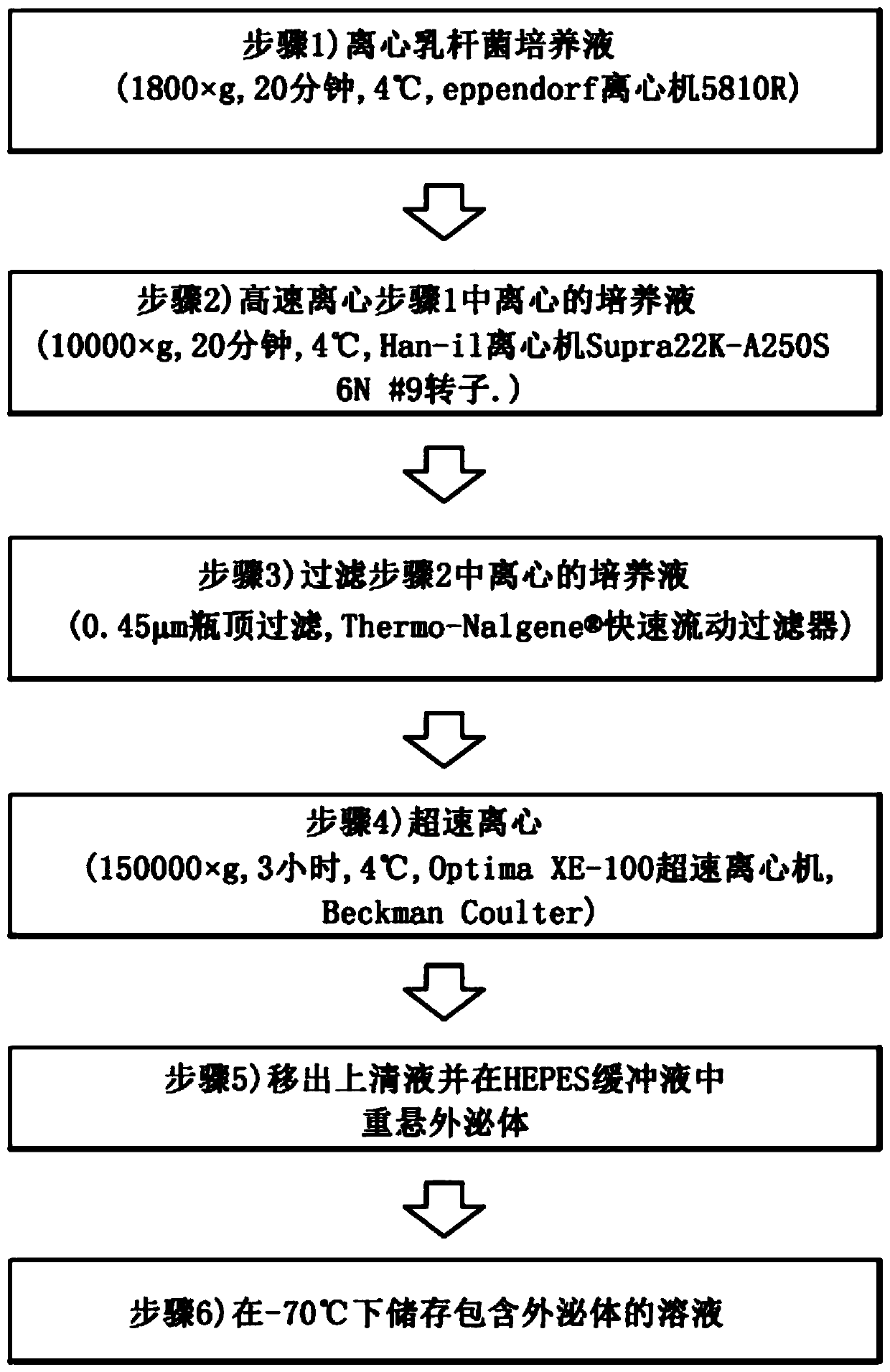
Extracting method of extracellular vesicles and kit
PendingCN109825472ALow costIncrease throughputBacteriaMicroorganism based processesExtracellular vesicleBasic research
The invention relates to the technical field of biological separation and extraction, in particular to an extracting method of extracellular vesicles. The method comprises the steps that a biologicalsample is provided; the biological sample is in contact with a capturing surface at least twice on the condition that impurities in the biological sample are partially or wholly reserved on the capturing surface, wherein the impurities are partial or whole other substances except the extracellular vesicles in the biological sample, and the capturing surface comprises an inner surface and / or outersurface of a spherical-particle porous material; when the impurities are partially or wholly reserved on the surface of a capture, breakthrough liquid is extracted liquid containing the extracellularvesicles; or the breakthrough liquid is further concentrated. By means of the method, the epicyte vesicles can be quickly separated and purified, the separation operation is simple, the single use cost is low, the separated sample in high in purity, the bioactivity of the sample is kept good, and the extracting method is applied to fundamental research in the aspects of biomarker discovery, biotherapy and the like and industrial production.
Owner:易春 +2
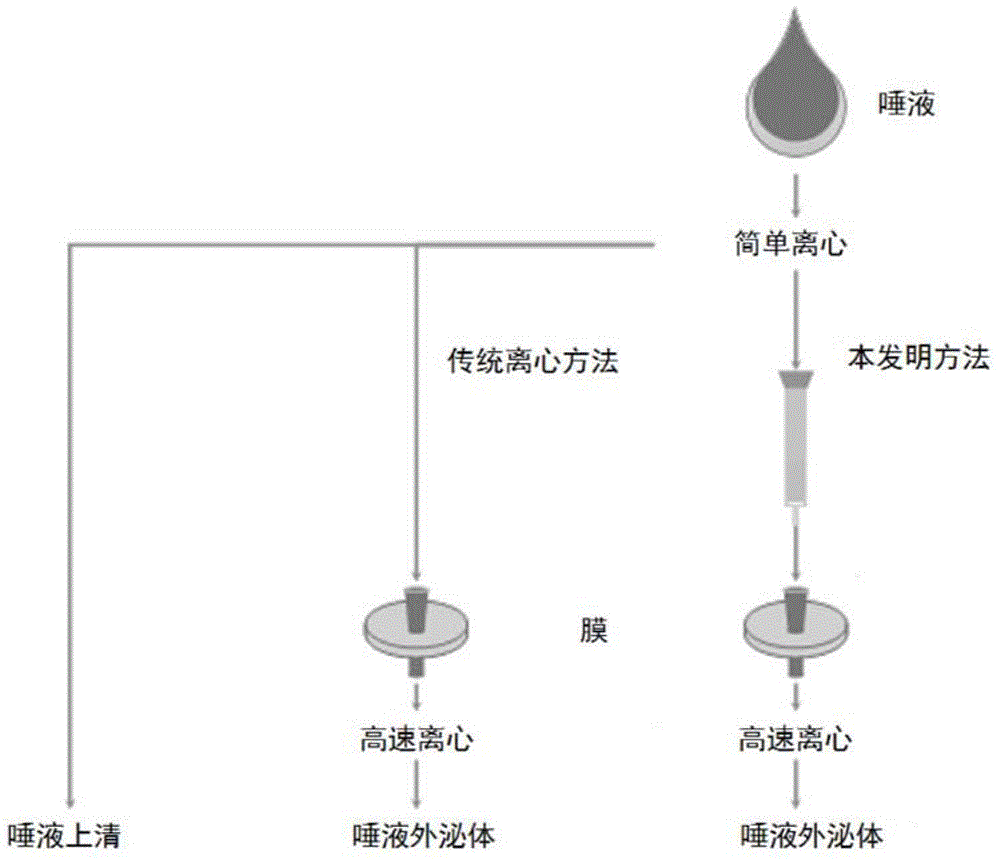
Preparation method of saliva extracellular vesicles and application of saliva extracellular vesicles to molecular diagnosis
ActiveCN105675774AEasy to operateHigh recovery rateComponent separationSaliva sampleBiomarker discovery
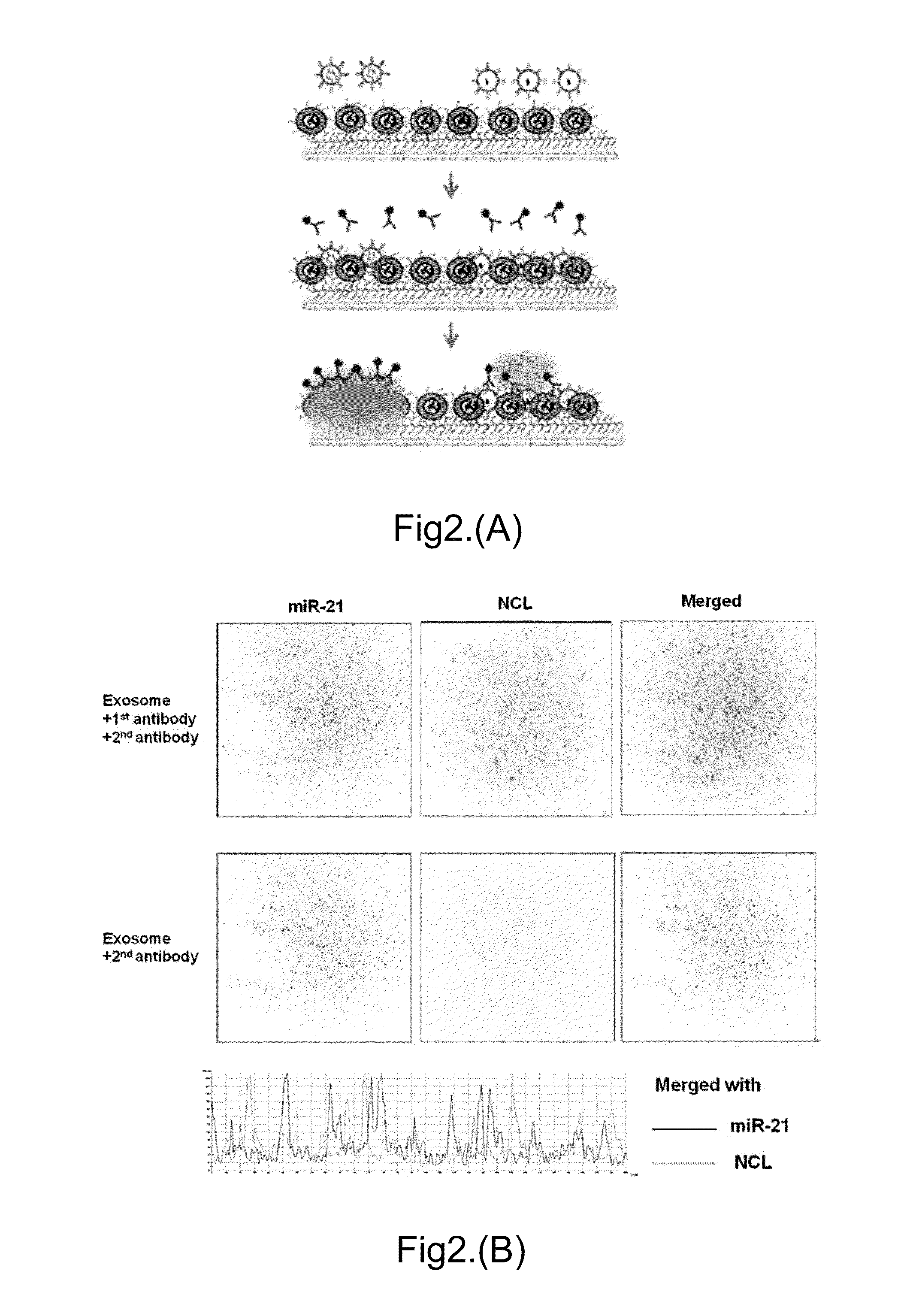
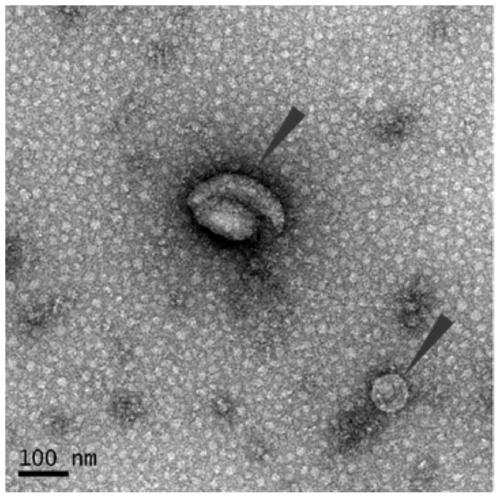
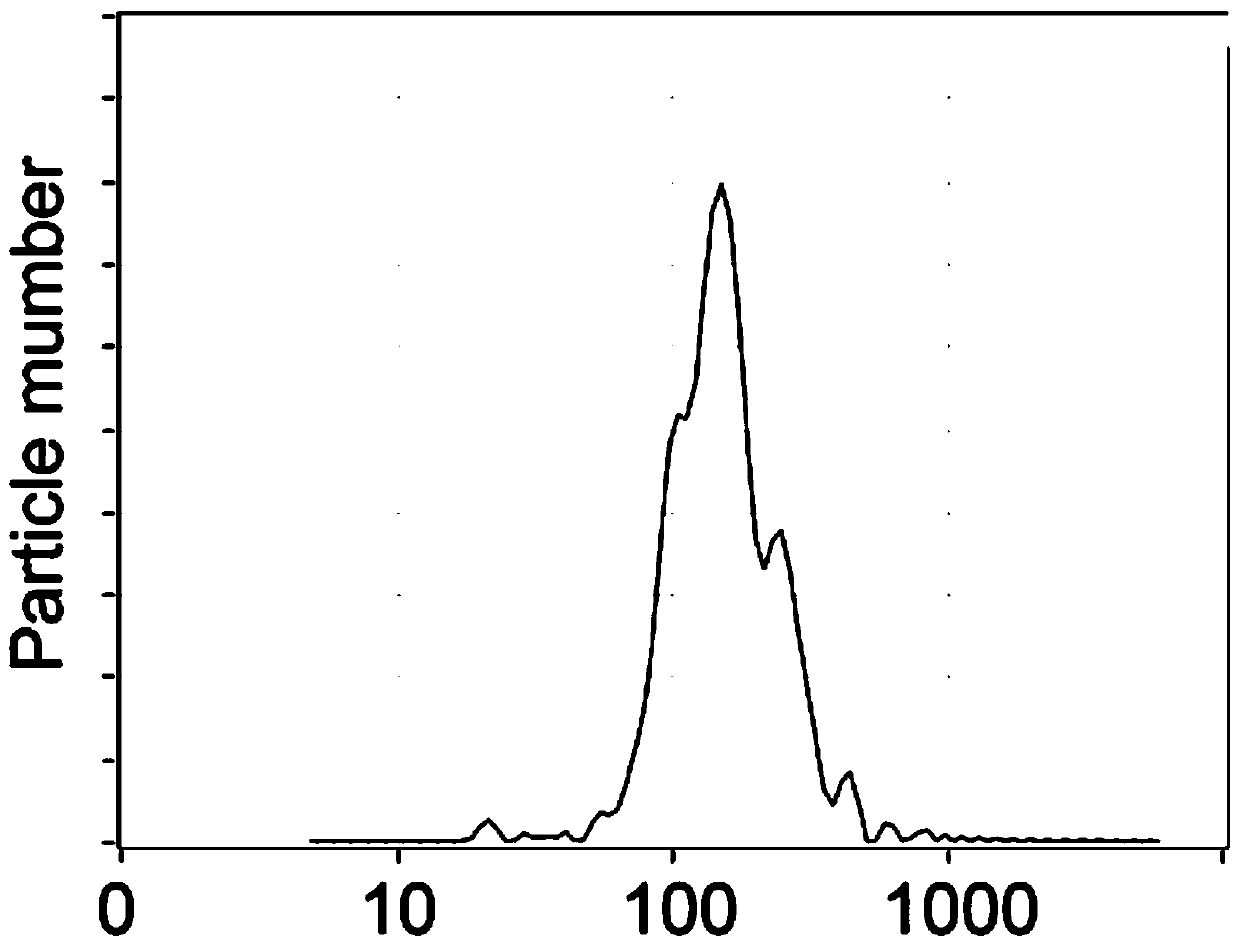
The invention discloses a preparation method of saliva extracellular vesicles and application of the saliva extracellular vesicles to molecular diagnosis.The preparation method includes the steps of removing high-abundance proteins from saliva samples, filtering out mucoproteins, separating and extracting the extracellular vesicles, characterizing the obtained extracellular vesicles, extracting extracellular vesicle proteins, identifying the extracellular vesicle proteins and applying the extracellular vesicle proteins to lung cancer biomarker discovery.Currently, a normalized saliva extracellular vesicle preparation technology is absent, and high-abundance protein interference and background impurity interference, existing in existing preparation technologies, result in shortcomings of low extracellular vesicle recovery rate, fewer identified proteins and the like, so that true extracellular vesicle proteomics information can be reflected difficultly.The preparation method of the saliva extracellular vesicles and application of the saliva extracellular vesicles to molecular diagnosis have the advantages that saliva of healthy adult volunteers and lung cancer patients is taken as the samples, and an affinity chromatography and membrane separation combined technology is adopted, so that after the high-abundance proteins and the mucoproteins of the saliva are removed, the extracellular vesicles in the saliva are extracted centrifugally, proteomes of the extracellular vesicles are analyzed and more extracellular vesicle proteins are identified.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for adsorbing and separating extracellular vesicles including exosomes secreted to medium by cells based on anion exchange resin
ActiveCN107858324ALow costReduce the difficulty of operationAntipyreticAnalgesicsExtracellular vesicleUltracentrifuge
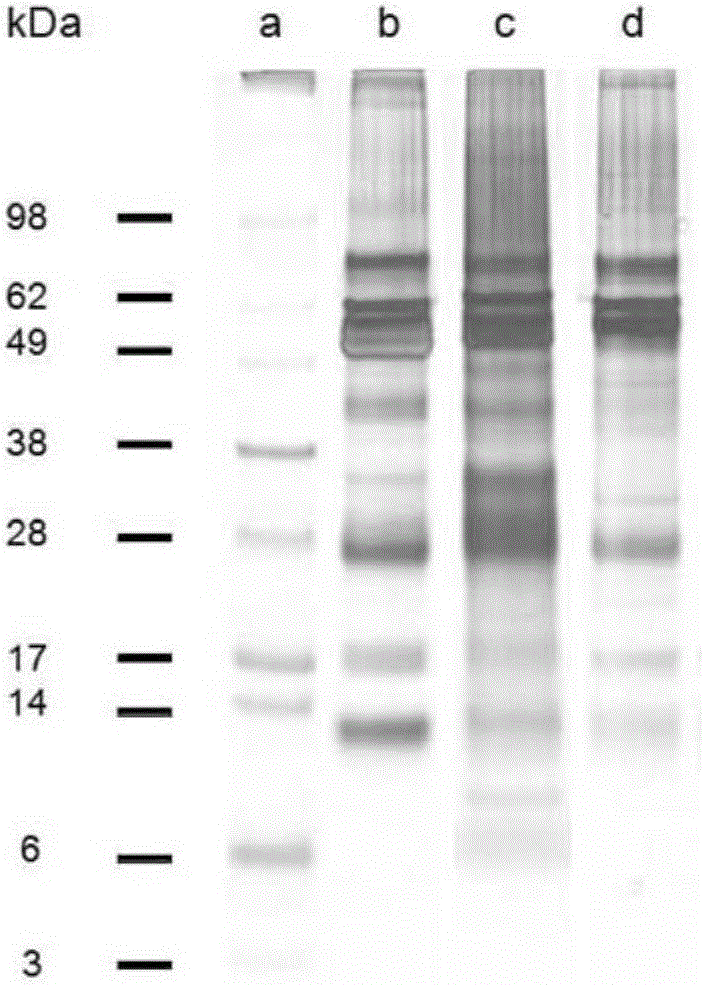
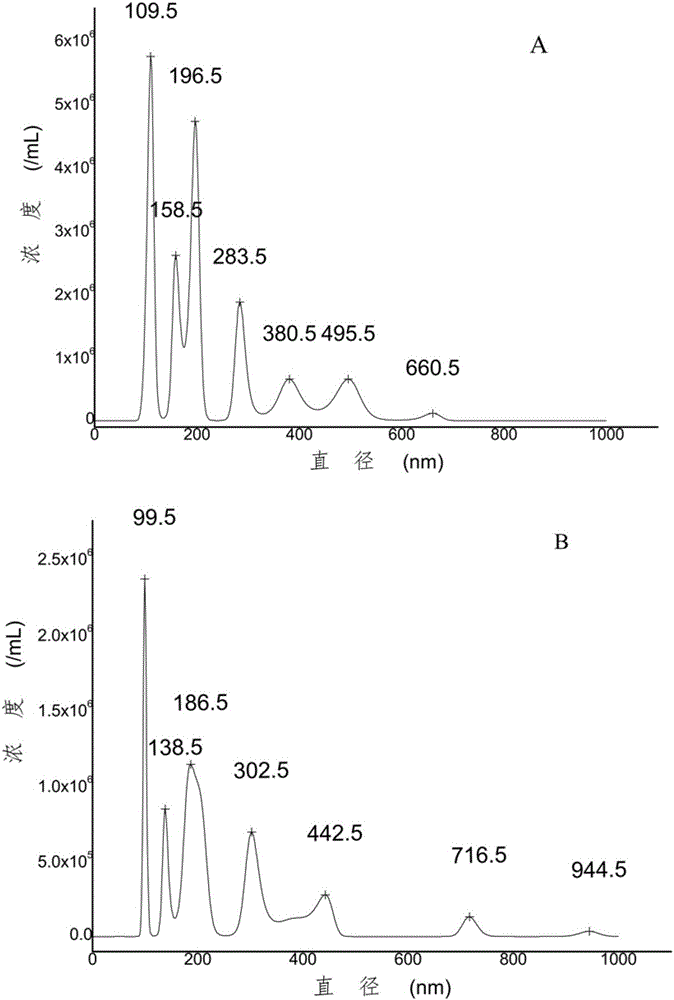
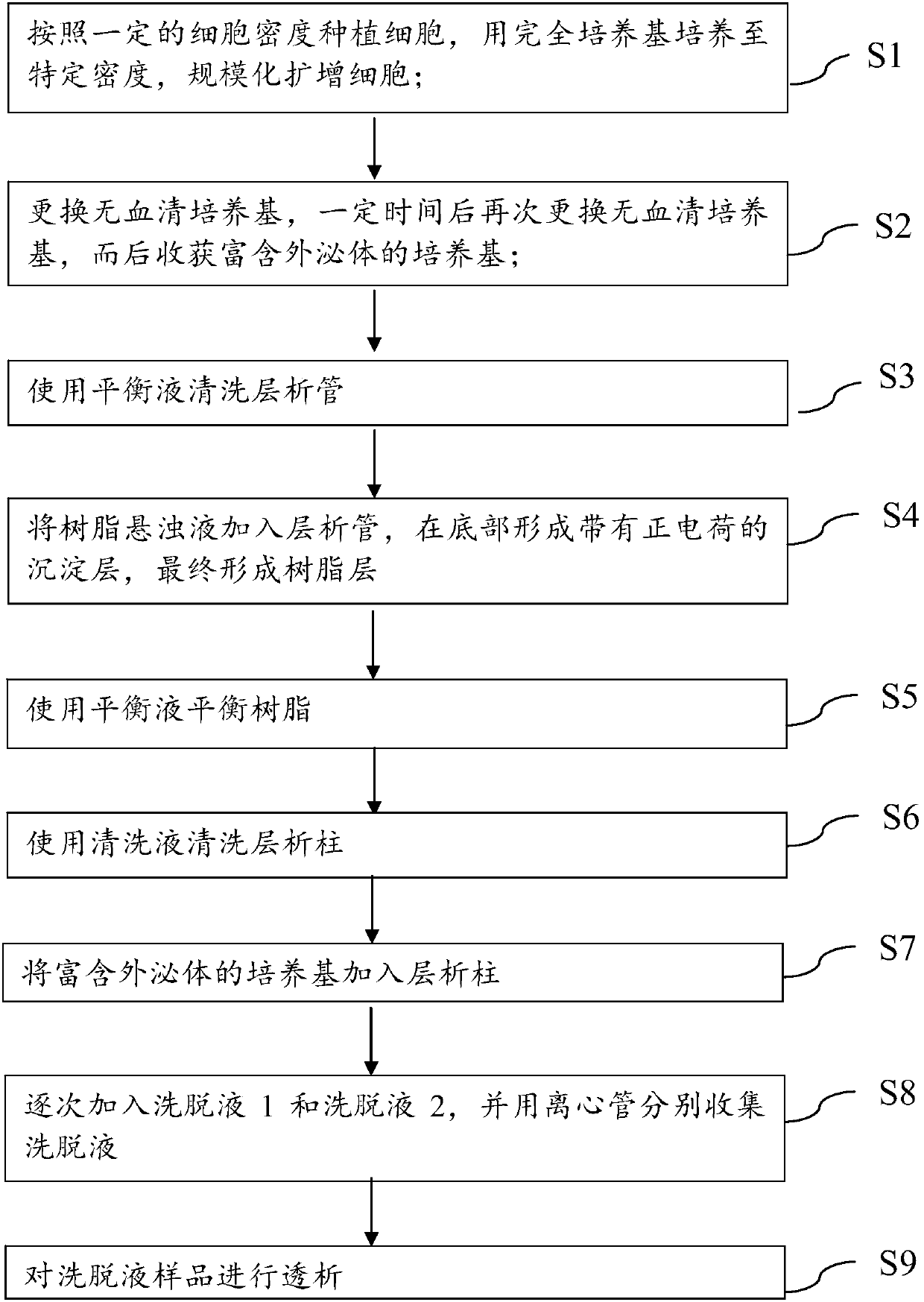
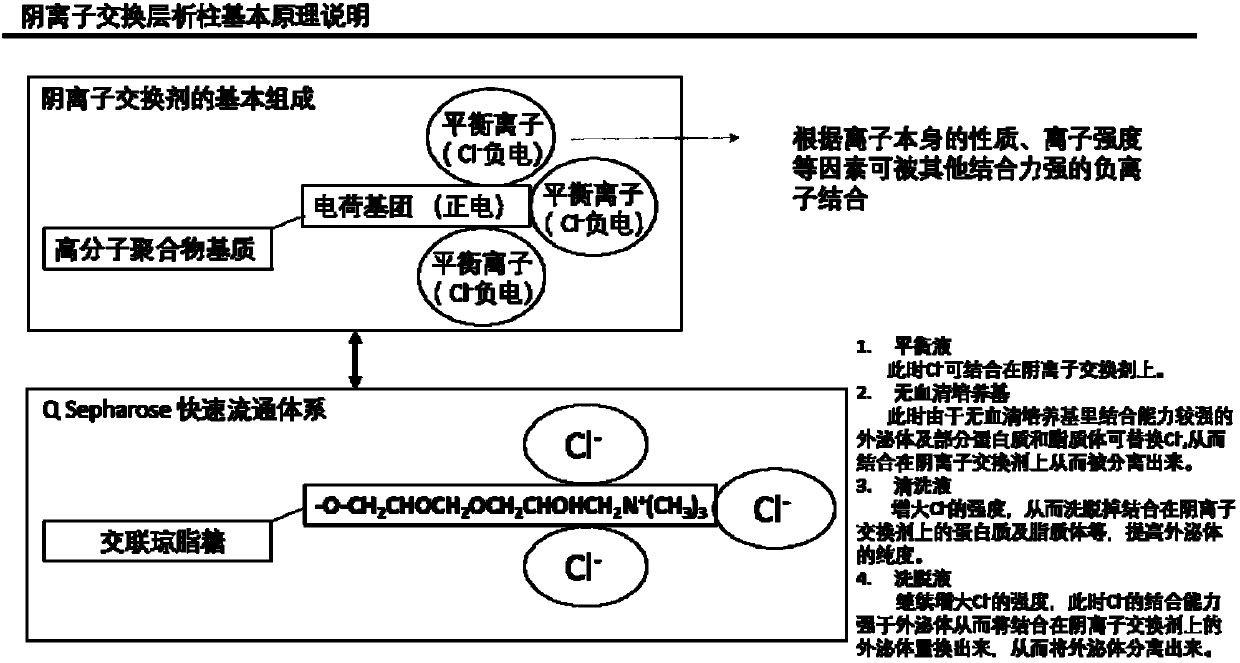
The invention discloses a method for adsorbing and separating extracellular vesicles including exosomes secreted to a medium by cells based on an anion exchange resin, the extracellular vesicles including exosomes produced by the method, and application thereof. The method provided by the invention is simple and convenient to operate and only needs to use chromatographic tubes / columns and pipetteguns and other common laboratory consumables, does not require use of ultra centrifuges, saves cost and time; the obtained extracellular vesicles has high purity and large concentration, can be produced in a large scale, and is easy to be further applied clinically.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for isolating extracellular vesicles using aqueous two-phase system
ActiveUS20180164197A1Improve efficiencySimple processSolvent extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseExtracellular vesicle
Disclosed is a method of isolating extracellular vesicles using an aqueous two-phase system (ATPS), including (a) preparing an ATPS by mixing a first material and a second material, which are immiscible with each other, with a body fluid or an aqueous solution containing extracellular vesicles and (b) isolating extracellular vesicles concentrated in the second material of the ATPS. This method can exhibit very high isolation efficiency, a simple isolation manner, and a very short isolation time. The isolation of extracellular vesicles using the ATPS requires no ultracentrifuge and achieves almost 100% isolation efficiency within a short time of about 10˜20 min, and thus the method of the invention is practical, is economical due to low costs thereof, can increase the purity of extracellular vesicles contaminated with protein, enables the diagnosis of disease using the isolated extracellular vesicles, and can be applied to various fields using extracellular vesicles.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
Compositions and methods for the detection and molecular profiling of membrane bound vesicles
The present disclosure features compositions and methods related to the detection and molecular profiling of extracellular vesicles using fluorescent probes. These compositions and methods leverage the unique optoelectrical properties of quantum dots and fluorescently labeled nanoparticles, which allows reliable, real-time detection of extracellular vesicles and vesicle surface bound or lumenal molecules.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MEMPHIS RESEARCH FOUNDATION
Anti-aging composition comprising lactic acid bacteria-derived extracellular vesicle
Disclosed in the specification is an anti-aging composition comprising, as an effective ingredient, extracellular vesicles that are complex physiologically active substances derived from lactic acid bacteria. The extracellular vesicles may be exosome-like vesicles with a diameter of 20 to 200 nm and the composition inhibits the expression of MMP-1 protein, thereby providing the effects of reducingskin wrinkles, improving skin elasticity, suppressing collagen reduction, and preventing ultraviolet light-induced skin damage.
Owner:AMOREPACIFIC CORP
Method of detecting membrane protein of extracellular vesicles
The invention relates to the field of biological detection, in particular to a method for detecting membrane protein of extracellular vesicles. The method comprises the following steps: a) co-incubating a composition containing extracellular vesicles (EVs) with a solid phase carrier; wherein the solid phase carrier is coated with a first antibody group of anti-EVs membrane protein; b) washing offnon-specifically bound EVs and other impurities, and c) adding a second antibody group for detection to carry out signal detection, the second antibody group being an antibody of a biomarker of EVs and coupled with a marker for displaying signal intensity. The method is simple and convenient to operate, the detection flux can be flexibly adjusted according to conditions, and the sensitivity is high.
Owner:北京益微生物科技有限公司
Method for isolating extracellular vesicles using cations
PendingCN111148828AEfficient separationKeep shapeCell dissociation methodsCation exchanger materialsExtracellular vesicleDisease
The present invention relates to a method for isolating extracellular vesicles using cations, and more particularly, to a method for isolating extracellular vesicles from various samples by using theaffinity between the extracellular vesicles and cations. A method for isolating extracellular vesicles according to the present invention does not require expensive equipment, can be applied irrespective of sample amount, and has the advantage of being capable of efficiently isolating the extracellular vesicles while preserving the shape or characteristics thereof. Moreover, the method according to the present invention can be combined with existing isolation methods to maximize extracellular vesicle isolation efficiency, and can be applied to disease diagnosis, disease treatment, and multi-omics research using isolated extracellular vesicles, as well as to research on the properties of extracellular vesicles.
Owner:ROSETTA EXOSOME CO LTD
Cell penetrating peptide (CPP)-mediated ev loading
ActiveUS20190388347A1Increase doseAnimal cellsMicroencapsulation basedExtracellular vesiclePharmacological chaperone
The present invention relates to methods for loading extracellular vesicles (EVs) with a pharmacological agent. The invention discloses the use of cell-penetrating peptides as carriers into EVs, using either a non-covalent or covalent loading approach. Furthermore, the present invention pertains to medical uses and compositions comprising such pharmacological agent-loaded EVs.
Owner:EVOX THERAPEUTICS LTD
Exosomes comprising therapeutic polypeptides
ActiveUS20190167810A1Efficient deliveryExtensive medical potentialAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDrugMedicine
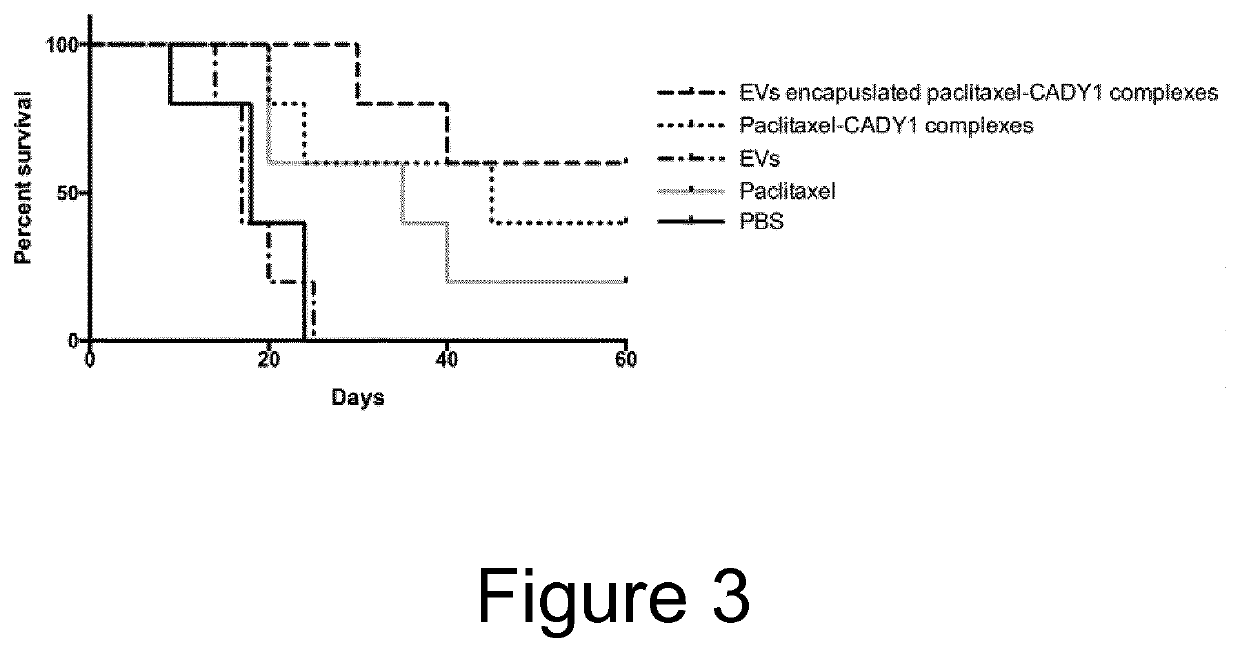
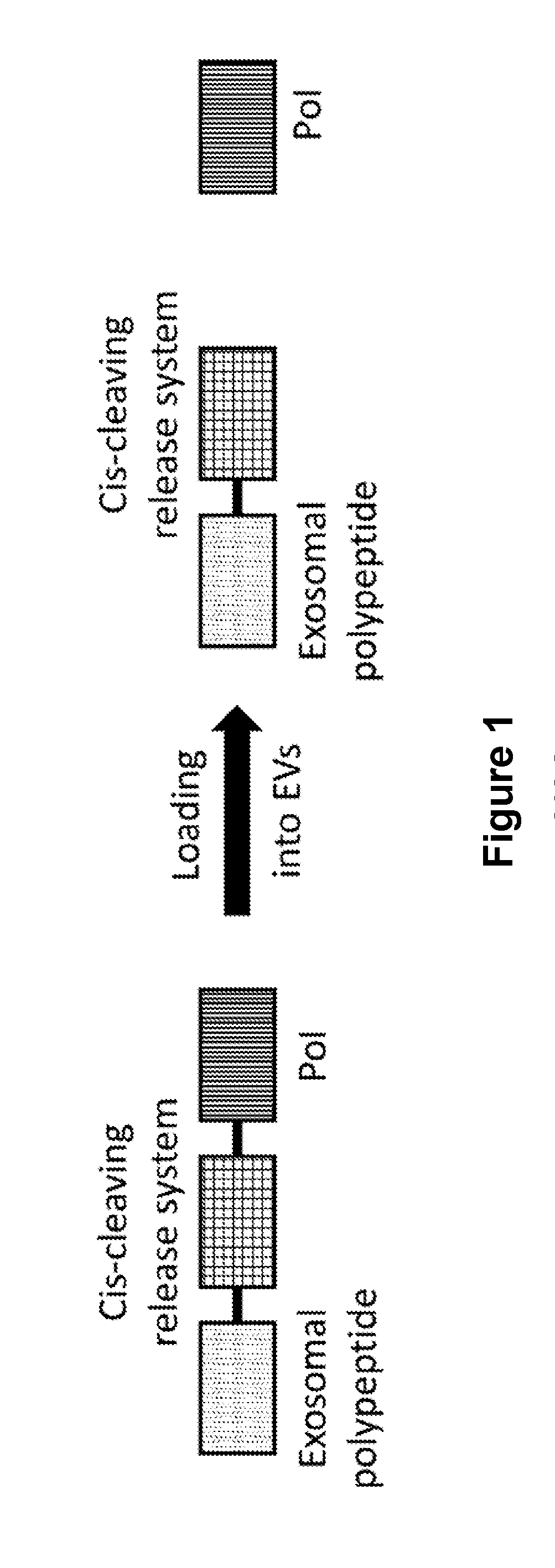
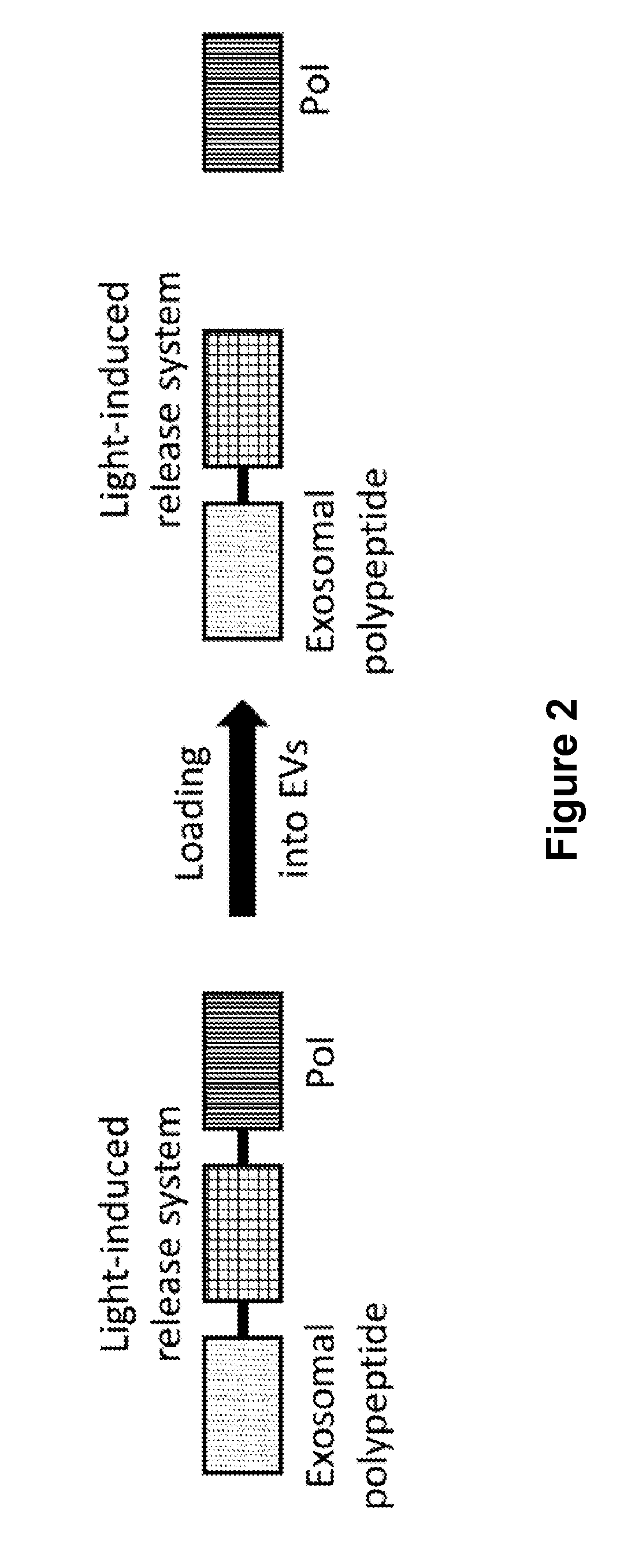
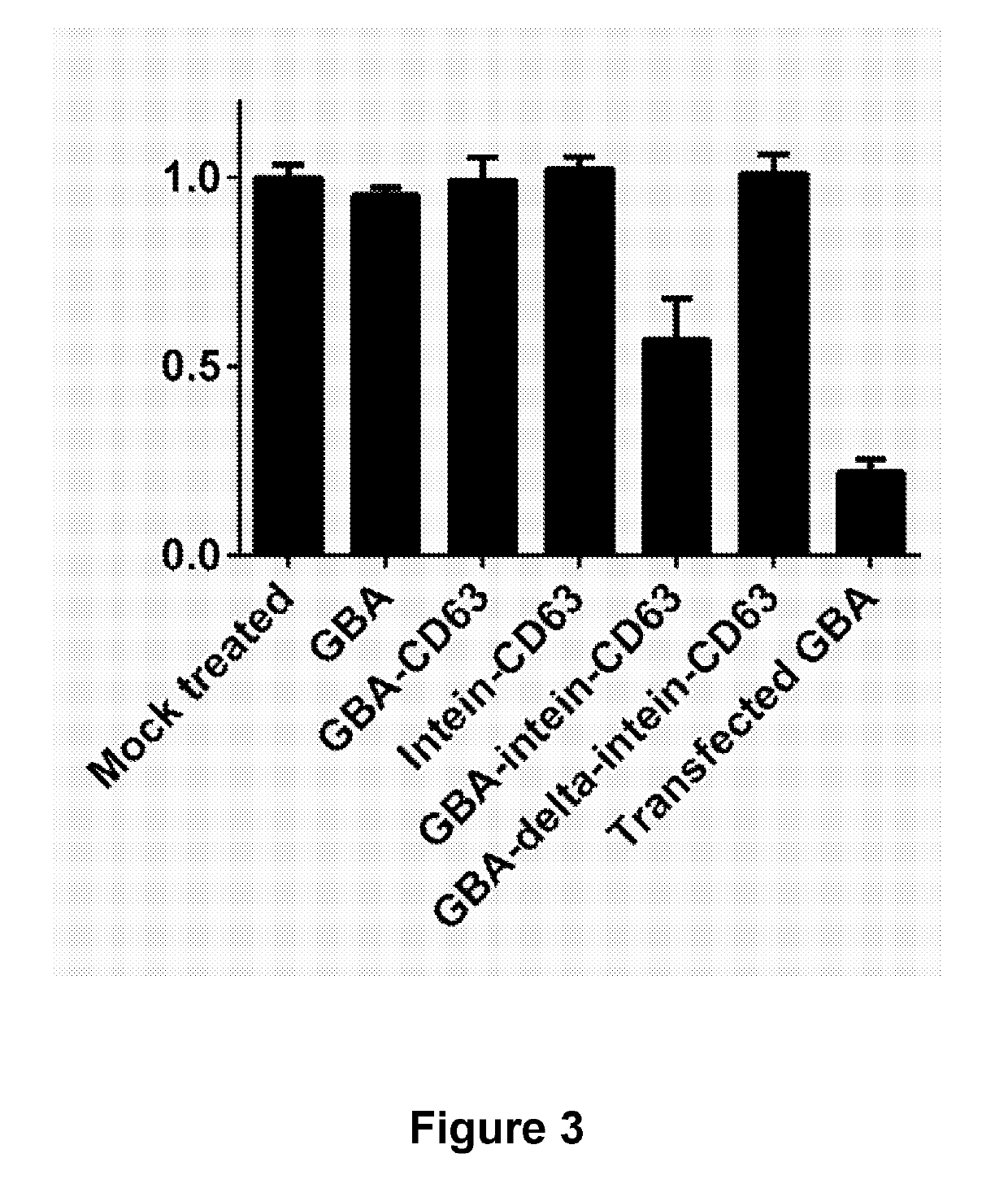
The present invention pertains to an inventive release mechanism for extracellular vesicle (EV)-mediated intracellular and intramembrane delivery of therapeutic polypeptides. More specifically, the invention relates to EVs comprising polypeptide constructs which comprise a therapeutic polypeptide releasably attached to an exosomal polypeptide. Furthermore, the present invention pertains to manufacturing methods, pharmaceutical compositions, medical uses and applications, and various other embodiments related to the inventive EVs.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD +1
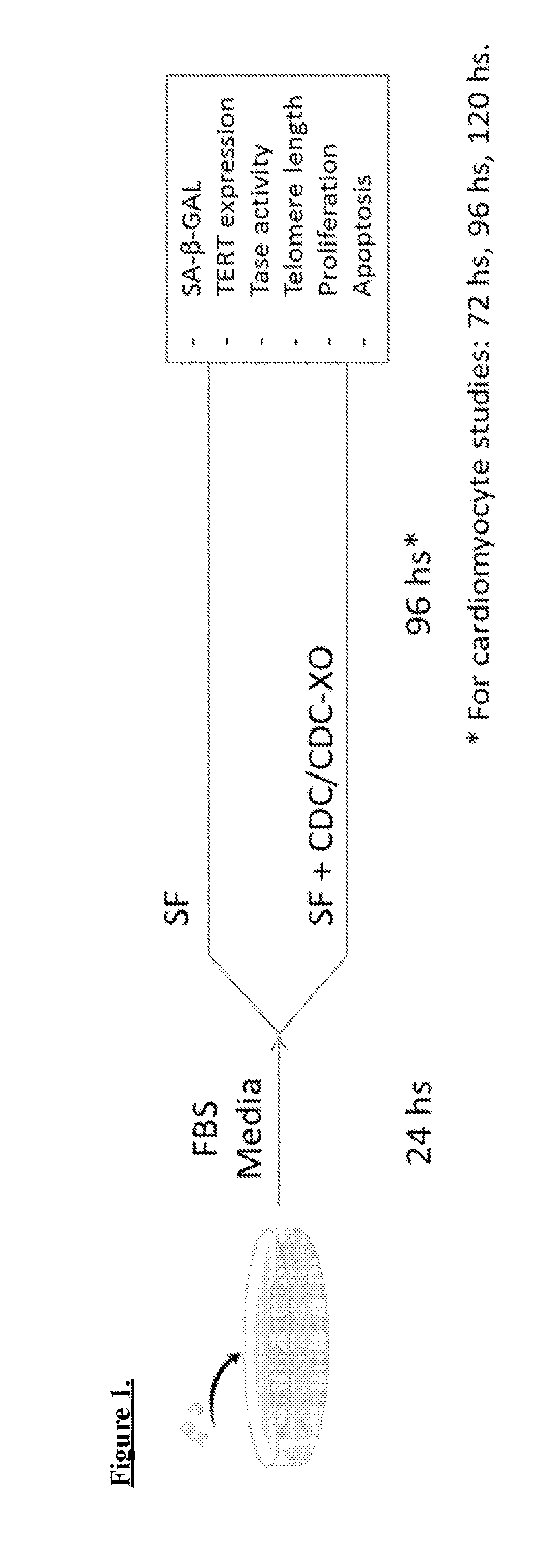
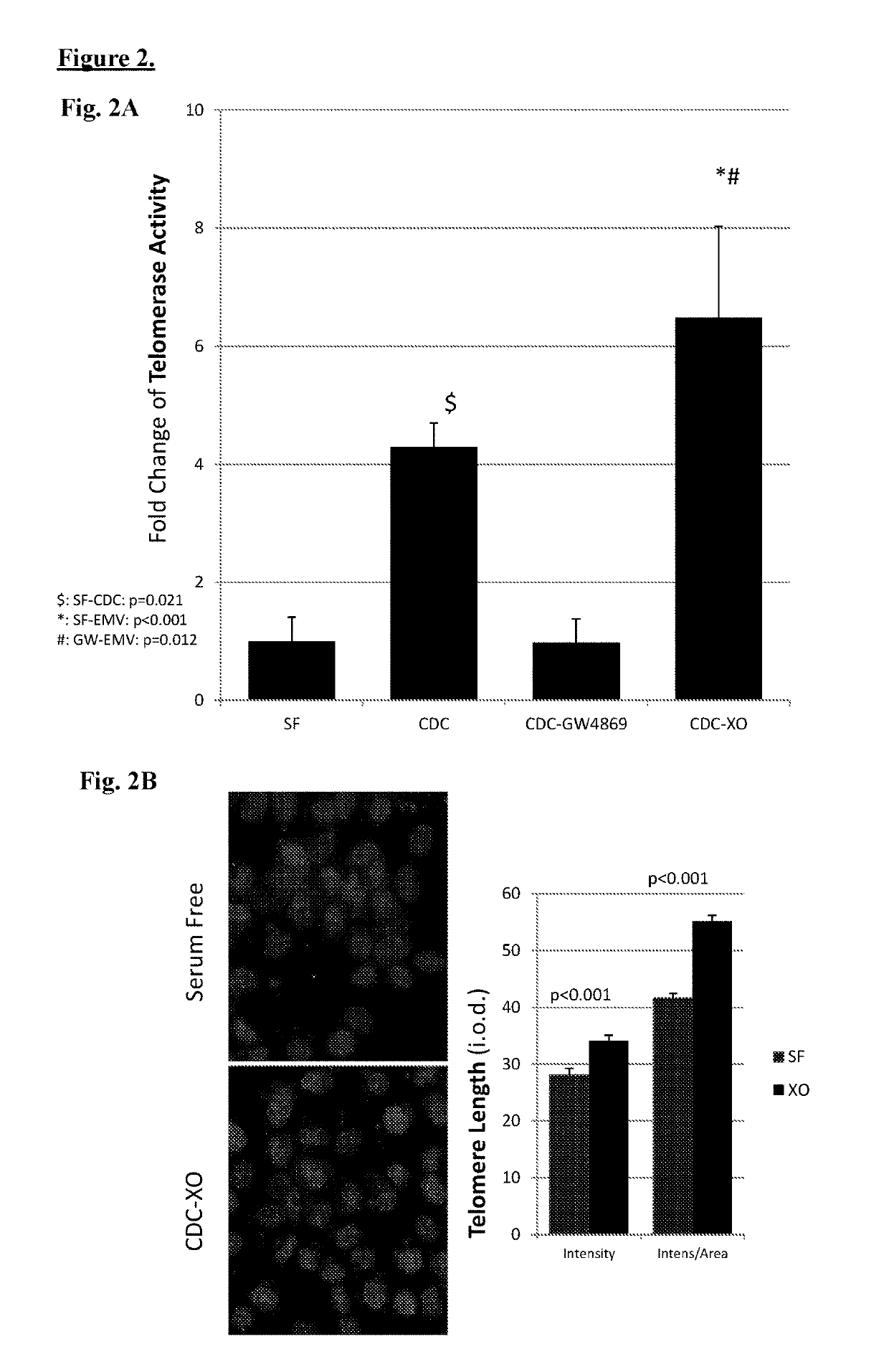
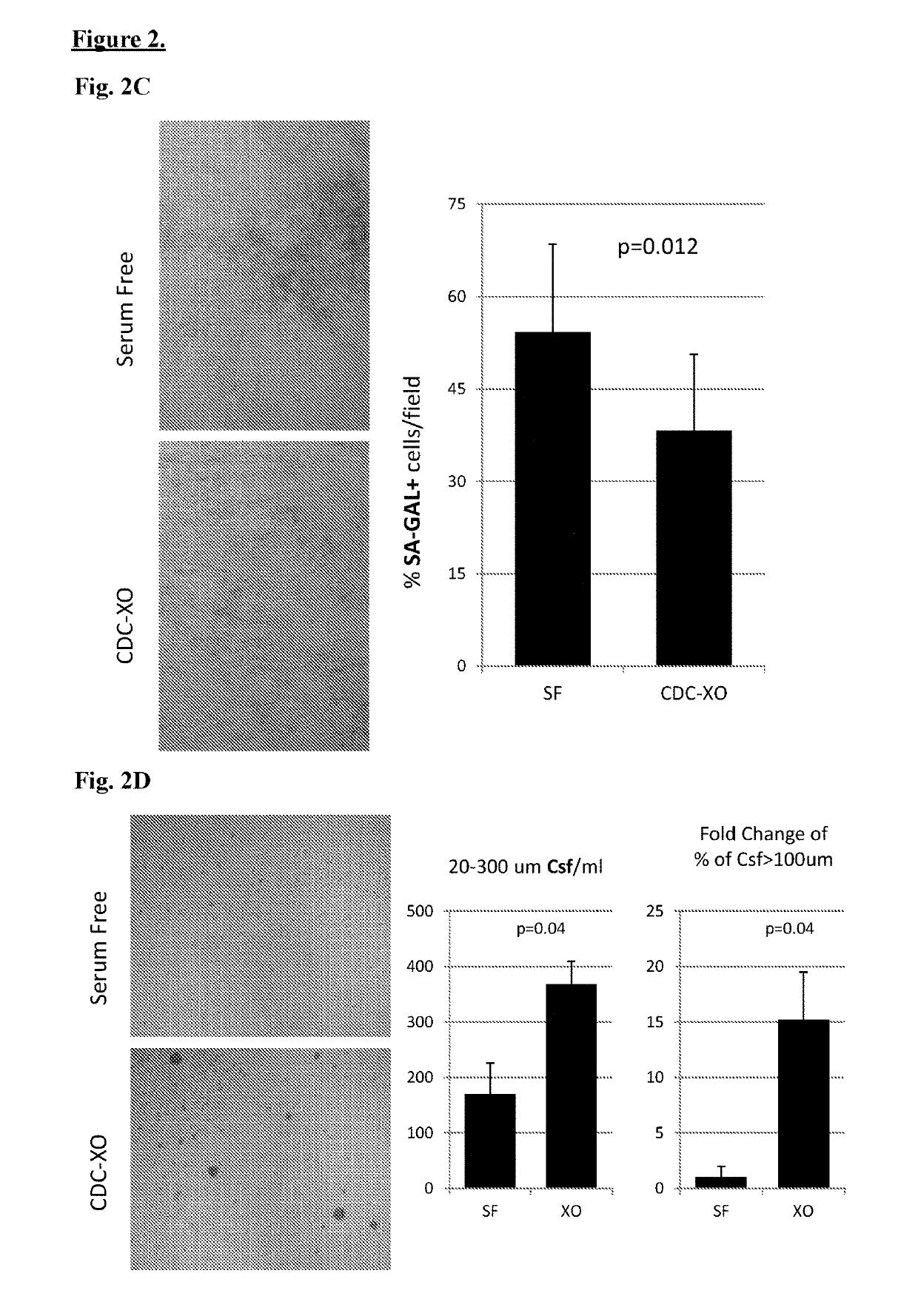
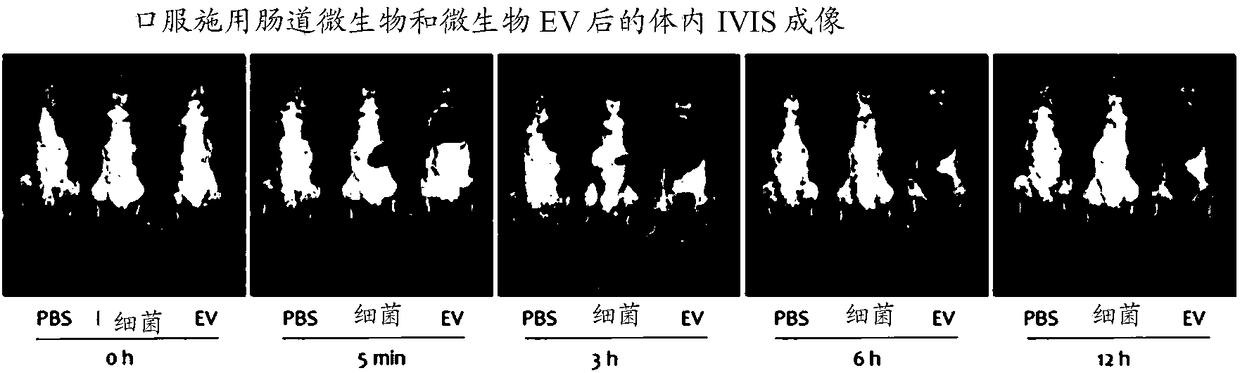
Cardiosphere-derived cells and their extracellular vesicles to retard or reverse aging and age-related disorders
Described herein are compositions and methods related to use of cardiosphere-derived cells and their extracellular vesicles, such as exosomes and microvesicles, for achieving anti-aging and rejuvenation. This includes discoveries for effects on heart structure, function, gene expression, and systemic parameters. For animal studies, intra-cardiac injections of neonatal rat CDCs was compared to in old and young rats including evaluation of blood, echocardiographic, haemodynamic and treadmill stress tests. For in vitro studies, human heart progenitors from older donors, or cardiomyocytes from aged rats were exposed to human CDCs or cardiosphere derived cell (CDC) derived exosomes (CDC-XO) from pediatric donors. CDCs and CDC-XOs were capable of effectuating youthful patterns of gene expression in the hearts of old, along with a variant of physiological and function benefits, including elongation of telomere length. Together, these results indicate capacity of CDCs and CDC-XO to ward off the effects of aging through rejuvenation.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Kit and method for diagnosis of gastric cancer using analysis of bacteria meta-genome
The present invention relates to a kit and method for diagnosis of gastric cancer using analysis of bacteria meta-genome. Provided are a kit and method for providing information on the diagnosis of gastric cancer through a bacterial meta-genome analysis. More specifically, the bacterial meta-genome analysis is executed on the genomes present in the vesicles isolated from a sample derived from an inspection target to analyze the increase or decrease in the content of the extracellular vesicles derived from specific bacteria, thereby diagnosing gastric cancer and predicting the risk of the gastric cancer. According to the present invention, the meta-genomes of EVs derived from bacteria present in the human-derived sample are analyzed to predict the risk of gastric cancer, thereby predictingand diagnosing the risk groups of gastric cancer to prevent or delay the incidence of gastric cancer through appropriate management. The present invention also enables early prediction even after theincidence to lower the incidence rate of gastric cancer and enhance the treatment effects.
Owner:MD HEALTHCARE INC
Kit and method for diagnosis of lung cancer in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients through meta-genome analysis
InactiveCN108239670AMicrobiological testing/measurementObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesTherapeutic effect
Owner:MD HEALTHCARE INC
Mesenchymal stem cells populations, their products, and use thereof
PendingUS20190269739A1Improve survivalImpact can be more specific and efficientNervous disorderMetabolism disorderDiseaseExtracellular vesicle
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising a mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) population, extracellular vesicles secreted from said MSC population, and a combination thereof, and methods of use thereof in treatment of a disease or disorder.
Owner:EXOSTEM BIOTEC LTD
Exosomes comprising RNA therapeutics
ActiveCN111629760AAdverse immune responseFusion with RNA-binding domainOrganic active ingredientsExtracellular vesicleEngineering protein
The present invention pertains to extracellular vesicle (EV) therapeutics, wherein the EVs comprise nucleic acid (NA)-based therapeutics such as m RNAs, circular RNAs, mi RNAs, sh RNAs, circular RNA and / or DNA molecules. The NA therapeutics are loaded into EVs using inventive engineering protein and NA engineering strategies to enhance loading into EVs and to facilitate release of the NA cargo molecules inside target cells.
Owner:EVOX THERAPEUTICS LTD
Extracellular vesicle separation and enrichment method based on exclusion chromatography and ultrafiltration technology
ActiveCN110511902ASolve the problem of low concentrationPrecise positioningCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsEnrichment methodsUltrafiltration
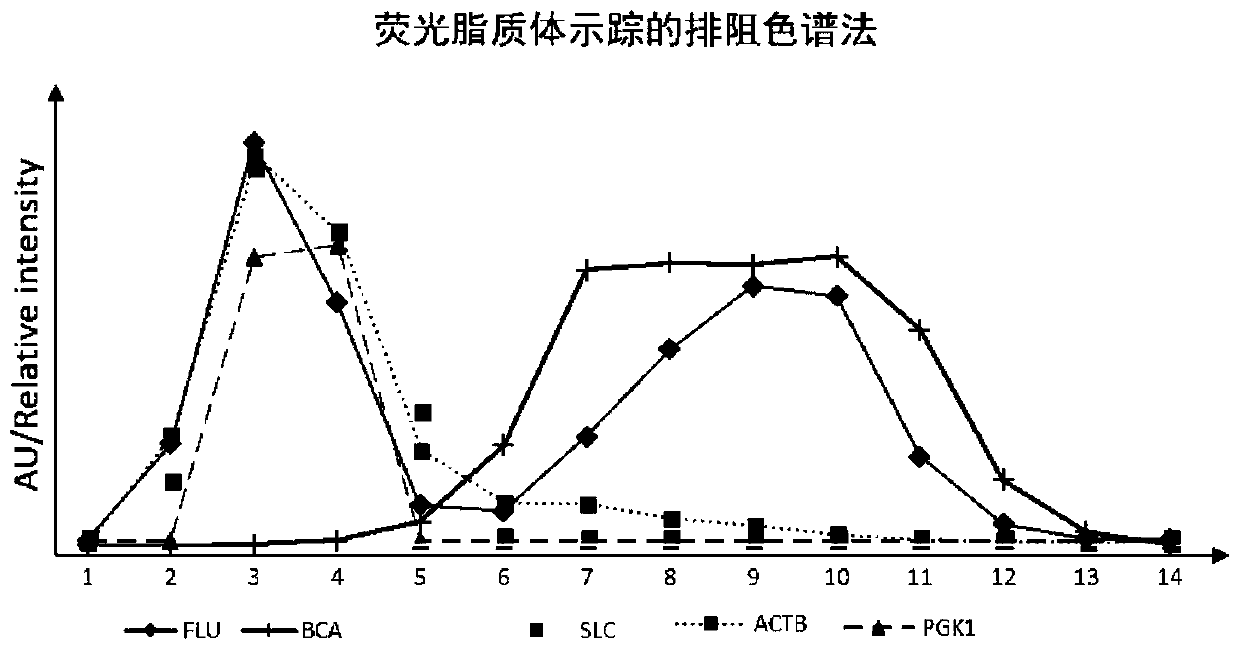
The invention provides an extracellular vesicle separation and enrichment method based on exclusion chromatography and an ultrafiltration technology. The extracellular vesicle separation and enrichment method comprises the following steps: mixing a fluorescent dye with a body fluid, adding a sample to an exclusion chromatographic column, collecting fractions according to fluorescence intensity, combining the fractions, sequentially treating the combined fractions with protease K and RNase A, and finally carrying out ultrafiltration concentration. The exclusion chromatography and the ultrafiltration method are combined to solve the problem of low product concentration of the exclusion chromatography, and the fluorescent dye is introduced as a tracing external reference, so that the fractionof EVs can be accurately positioned, and the EVs loss caused by damage of a filter membrane can be eliminated before entering the next operation. The invention also provides a kit capable of separating and enriching high-purity extracellular vesicles from body fluid. According to the method, the high-purity EVs can be separated from the body fluid without ultracentrifugation, and meanwhile, in cooperation with protease K and RNase A treatment, nucleic acid pollution from non-vesicle sources in the body fluid can be effectively eliminated, so that the nucleic acid purity of the extracellular vesicles is greatly improved.
Owner:北京恩泽康泰生物科技有限公司
Biological ink for 3D (Three Dimensional) printing and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108310463AMaintain microstructureMaintain biological activityAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationExtracellular vesicleBiological macromolecule
The invention discloses biological ink for 3D (Three Dimensional) printing and a preparation method thereof. The biological ink for the 3D printing is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 10 to 30 percent of an extracellular vesicle mixed suspension solution, 5 to 15 percent of a biological macromolecular material, 0.1 to 1 percent of dissolution promoter and the balance of water. The biological ink disclosed by the invention can be used for simulating extracellular matrix component, structure and biological activity characteristics better by utilizing advantages ofextracellular vesicles and characteristics of the biological macromolecular material and hydrogel.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
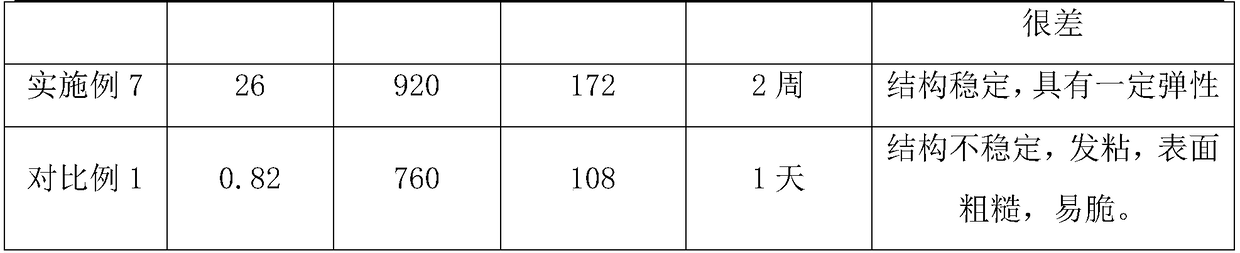
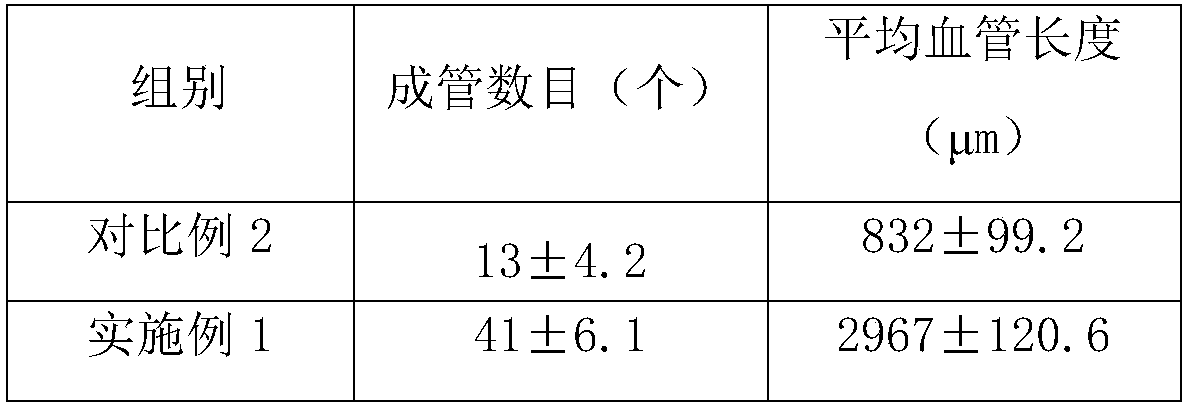
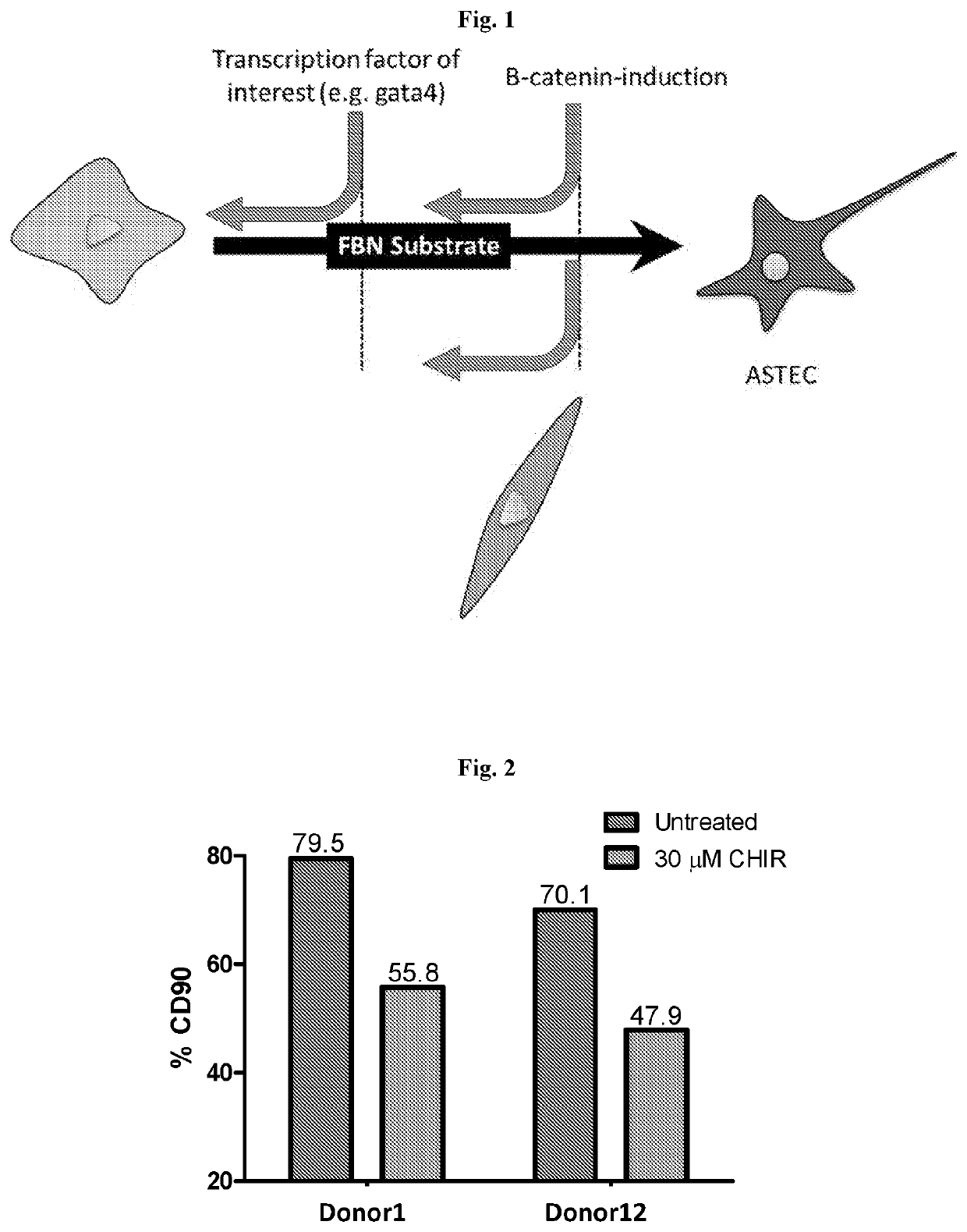
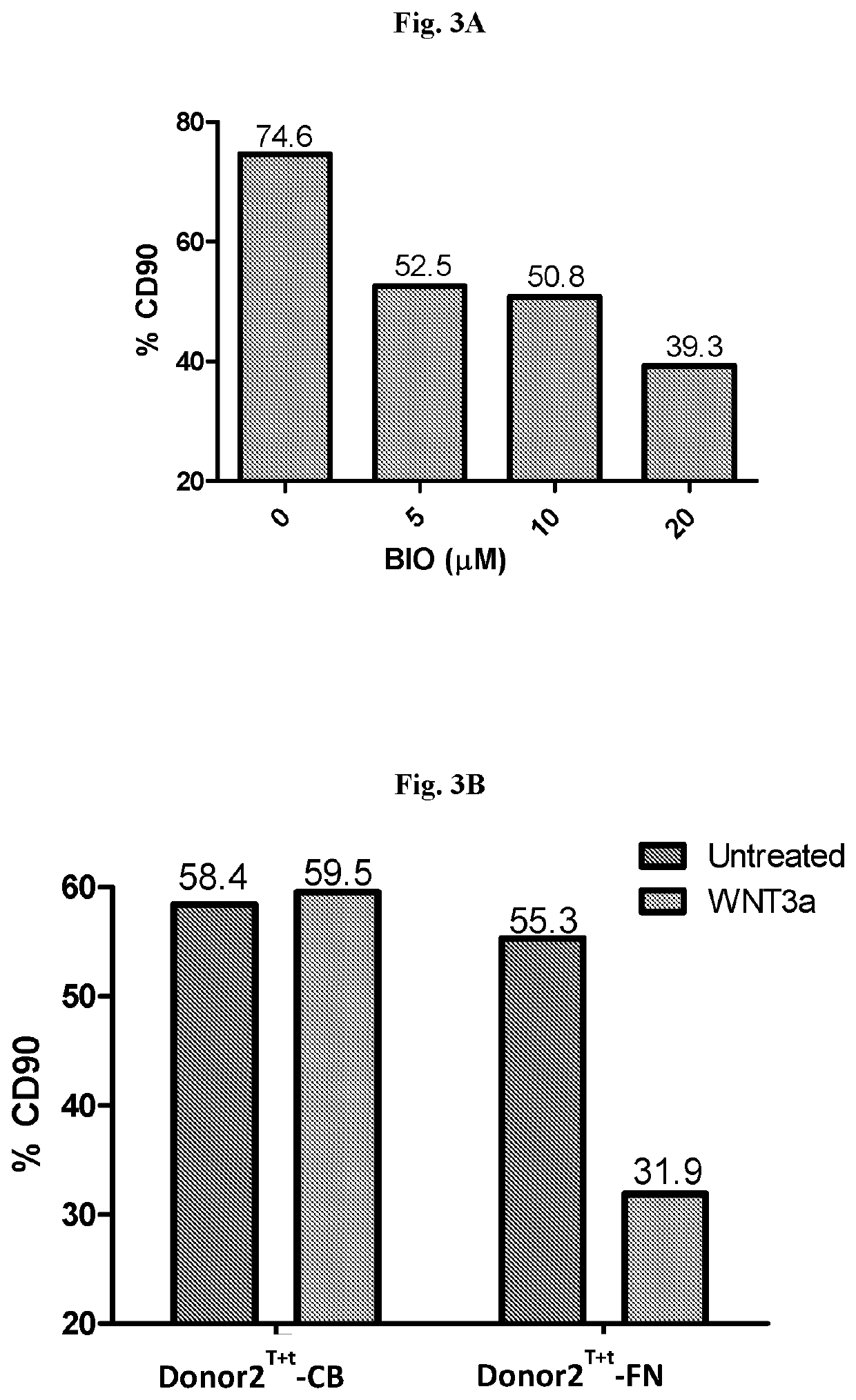
Activation-induced tissue-effector cells suitable for cell therapy and extracelluar vesicles derived therefrom
PendingUS20210032598A1Improving disease stateIncrease ventricular ejection fractionAntipyreticGenetically modified cellsExtracellular vesicleEffector cell
The present invention provides a method of inducing activation of a non-potent or insufficiently potent cell to convert the cell into a tissue-effector cell, thereby producing an activation-induced tissue-effector cell suitable for use in cell therapy—e.g., an activated specialized tissue-effector cell (ASTEC) suitable for cell therapy for a particular tissue type. The present invention further provides activation-induced tissue-effector cells produced thereby, as well as extracellular vesicles, e.g., exosomes, derived therefrom (e.g., ASTEX). The present invention further provides a method of improving the efficacy of a cell therapy by converting non-potent or insufficiently potent cells into activation-induced tissue-effector cells having increased potency suitable for cell therapy. The present invention further provides a method for treating a disease or condition amenable to cell therapy in a subject in need thereof, the method comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of activation-induced tissue-effector cells or extracellular vesicles derived therefrom.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT +1
Methods of diagnosing diseases by extracellular vesicles and uses thereof
InactiveUS20200072843A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisExtracellular vesicleBiochemistry
Disclosed herein is a method of treating a cancer, a degenerative disease, an infectious disease, or aging in a subject. According to certain embodiments of the present disclosure, the method comprises, (a) obtaining a biological sample from the subject; (b) isolating a plurality of extracellular vesicles (EVs) from the biological sample; (c) determining the expression level of a target molecule of the plurality of EVs; and (d) treating the cancer, the degenerative disease, the infectious disease, or the aging based on the expression level of the target molecule determined in step (c).
Owner:MACKAY MEMORIAL HOSPITAL
3D biology-printed hydrogel ink and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110393823AKeep aliveGuaranteed in vitro living environmentPharmaceutical delivery mechanismProsthesisAcellular matrixSolvent
The invention discloses 3D biology-printed hydrogel ink and a preparation method thereof. The 3D biology-printed hydrogel ink is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 1-10% of a solidifiable polymer, 1-10% of acellular matrix hydrogel, 1-10% of an extracellular vesicle suspension, 5-15% of a biomacromolecule material, 1-5% of a bioactive molecule, 0.1-0.5% of a solvent accelerating agent and the balance of water, and the total mass is 100%. According to the solidifiable polymer, water-soluble natural polysaccharide and natural high-polymer materials are adopted, and compatibility of the solidifiable polymer with cells is solved. In order to further improve the solidifiable polymer to provide establishment of a 3D model, the biomacromolecule material is added in biological ink, the solidifiable polymer can be assisted to further improve the ink viscosity, so that the mechanical strength of a final 3D model is better; and secondly, the biomacromolecule materialcan further provide substances required by part cells growing, and activity of the cells is guaranteed.
Owner:苏州苏新瑞可医疗科技有限公司
Methods of measuring exosomes using intrinsic fluorescence
InactiveUS20200025685A1Chemiluminescene/bioluminescenceFluorescence/phosphorescenceExtracellular vesicleExosome
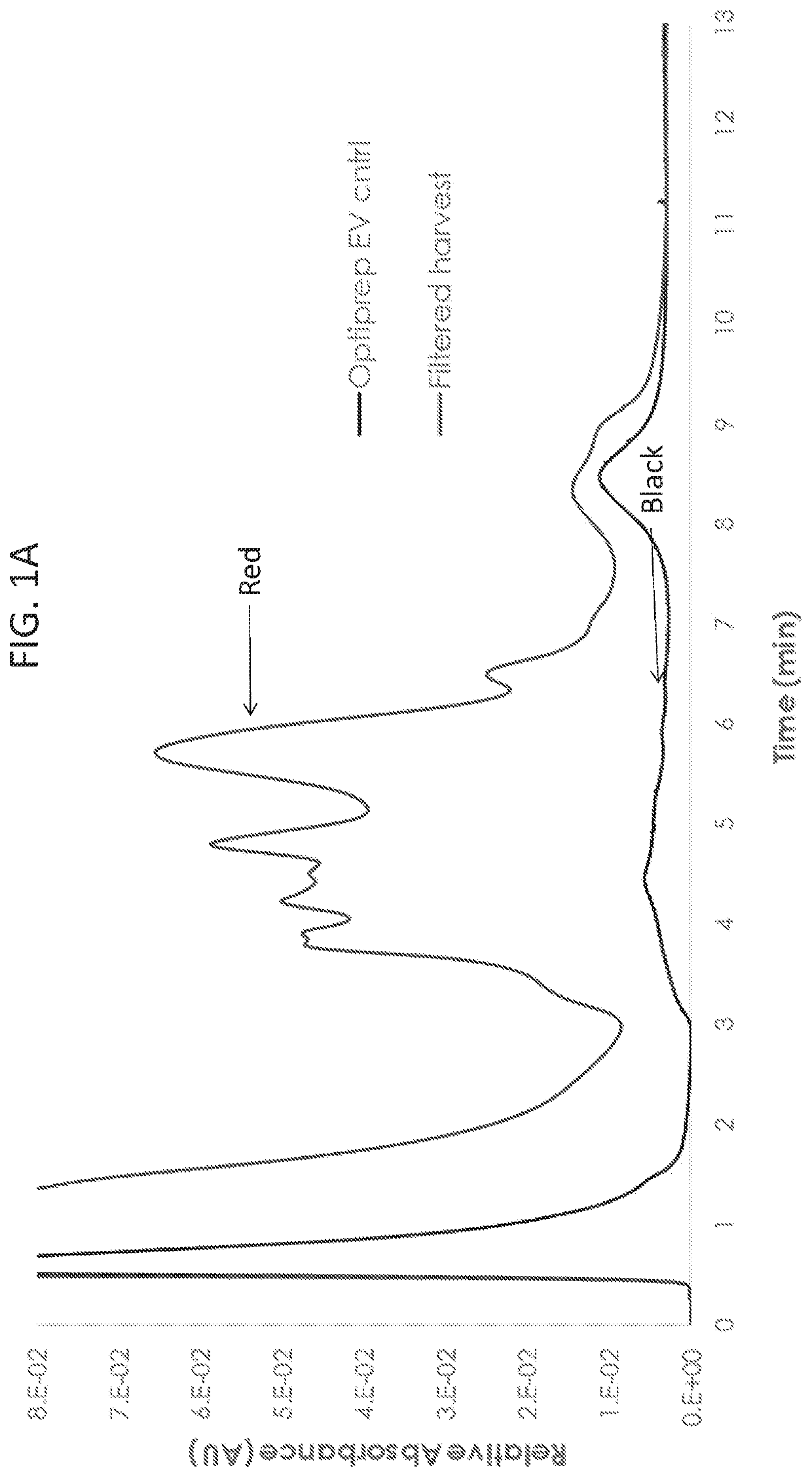
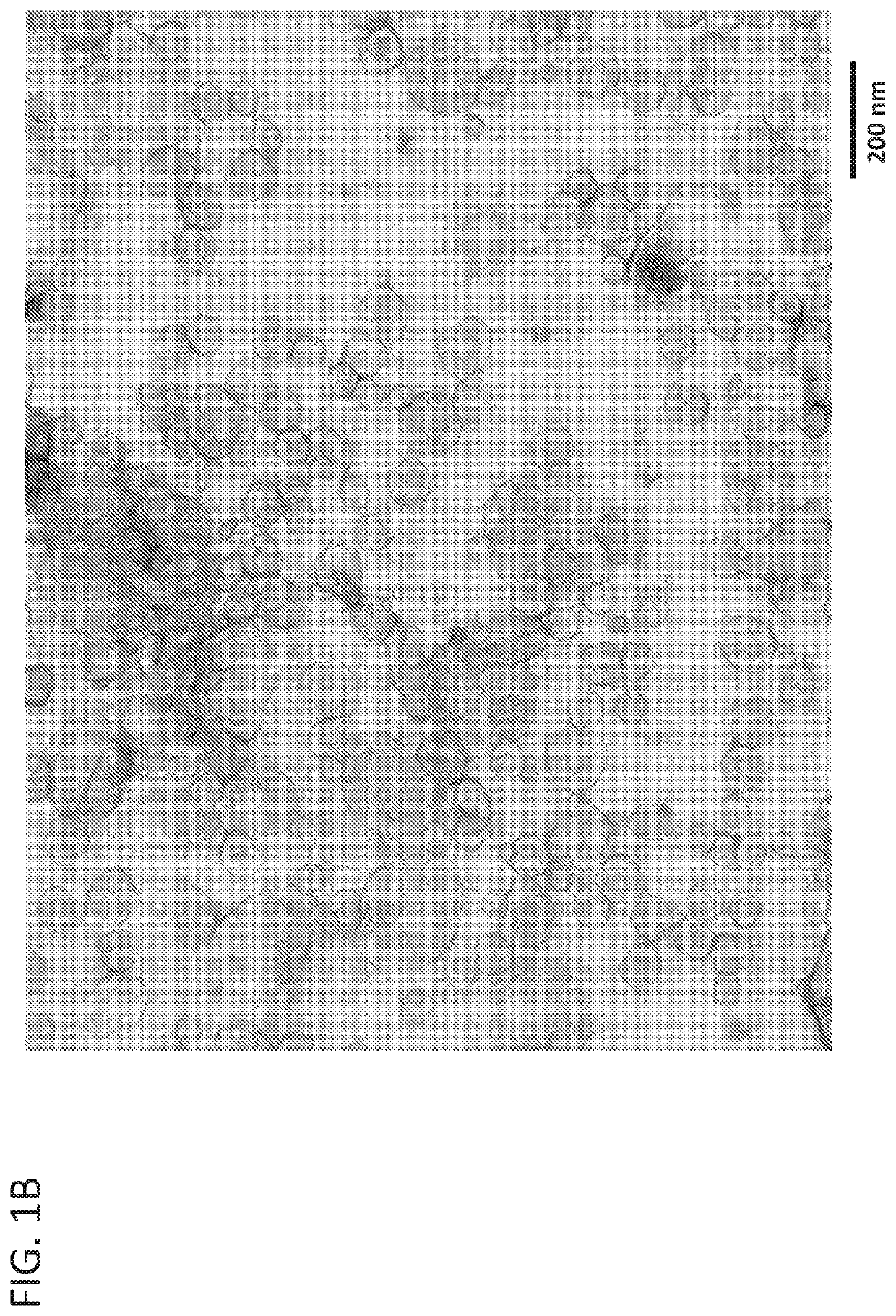
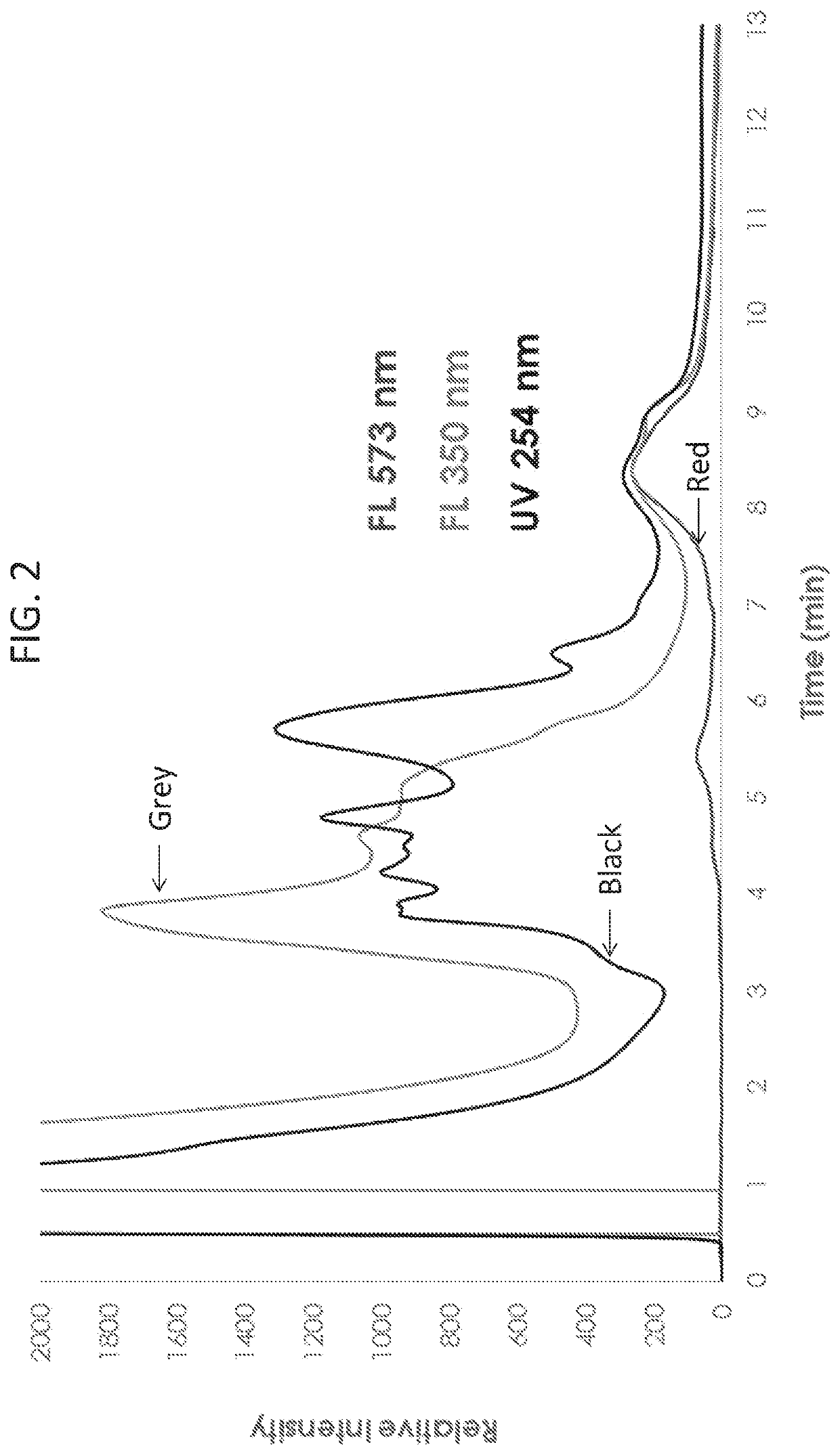
Described herein are novel rapid and reliable methods of detection of extracellular vesicles and quantifying extracellular vesicle concentrations and absolute number from various sources, including raw cell harvest. The methods described herein comprise detection of intrinsic fluorescence of extracellular vesicles in biological samples. Extracellular vesicles analyzed by the methods of this application have a stereotypical elution profile distinct from known contaminants. The methods described herein are a significant improvement over the state of the art and fulfills an unmet need in the field of extracellular vesicle manufacturing and quality control.
Owner:LONZA SALES AG
Molecular Imaging Biomarkers
ActiveUS20180286044A1Increase photodamage riskEnhanced local invasionImage enhancementImage analysisExtracellular vesicleMolecular imaging
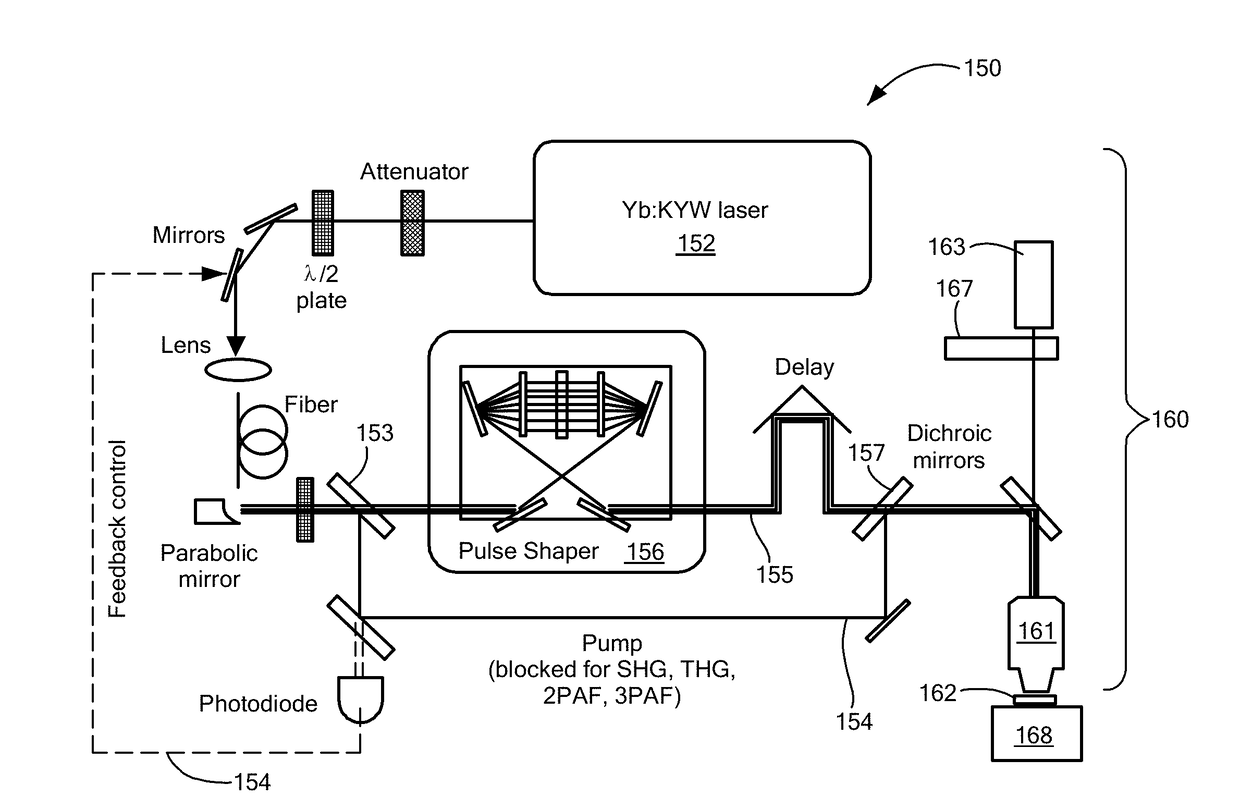
Methods for label-free characterization of untagged molecules within a biological sample in-situ. The untagged molecules may be constituent of extracellular vesicles, and are excited in the biological sample with at least one wavelength band of light derived from a single stream of optical pulses. Light emitted by the untagged molecules by SHG, THG, 2PAF and 3PAF processes is detected. Separate measures of the biological sample corresponding to light emitted by the untagged molecules in each of the SHG, THG, 2PAF and 3PAF processes are derived. On that basis, normal extracellular vesicles may be differentiated from extracellular vesicles associated with a tumor on the basis of a specified signature of characteristics of images of SHG, THG, 2PAF and 3PAF processes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Ev-mediated delivery of binding protein-small molecule conjugates
InactiveCN109689109AOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderExtracellular vesiclePharmaceutical drug
The present invention relates to extracellular vesicles (EVs) comprising a binding protein which may be used for delivery of protein-drug conjugates comprising the binding protein and a small moleculeagent, typically a small molecule drug. The present invention also relates to methods for producing such EVs as well as pharmaceutical compositions and medical uses of such EVs.
Owner:EVOX THERAPEUTICS LTD
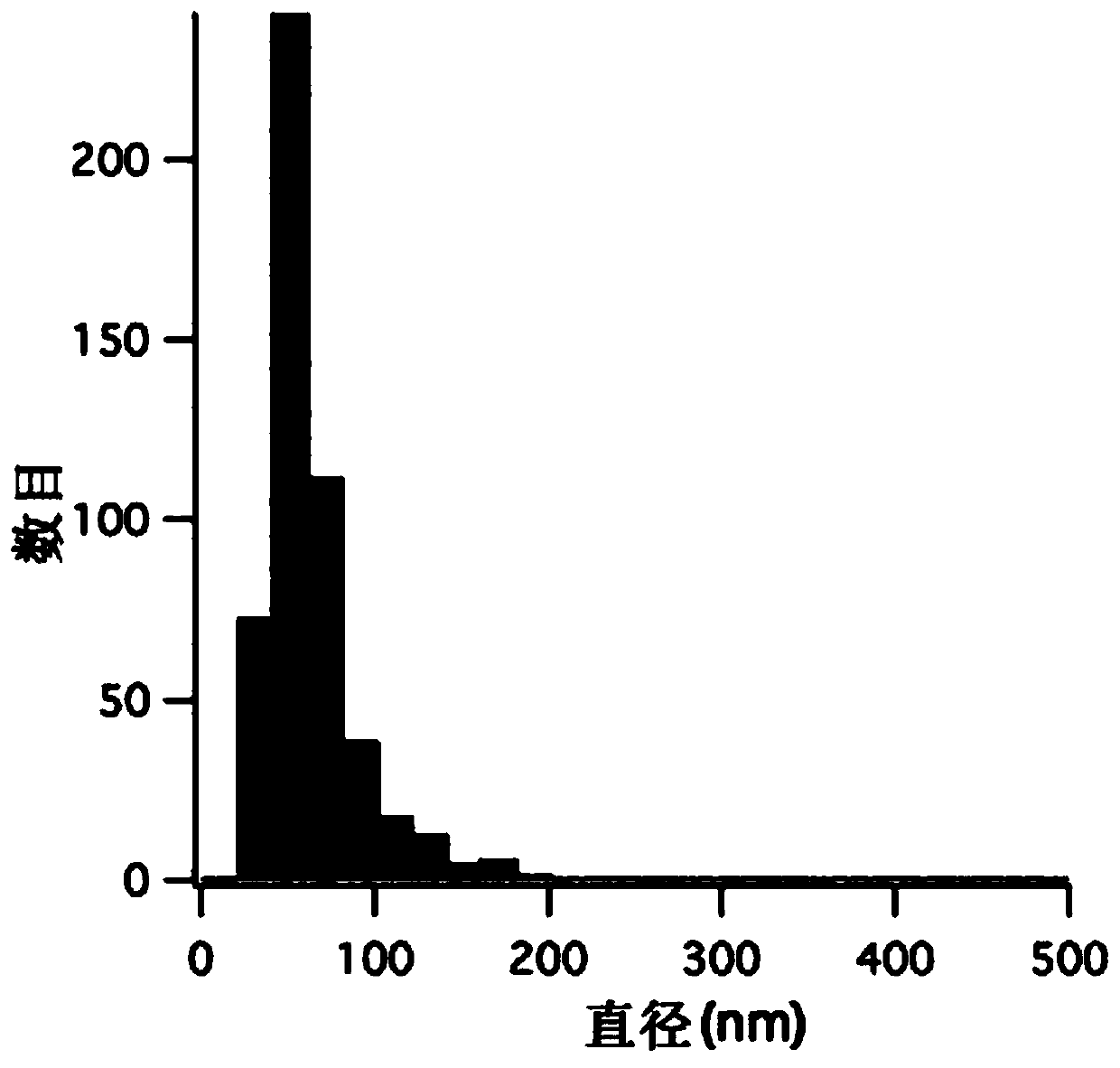
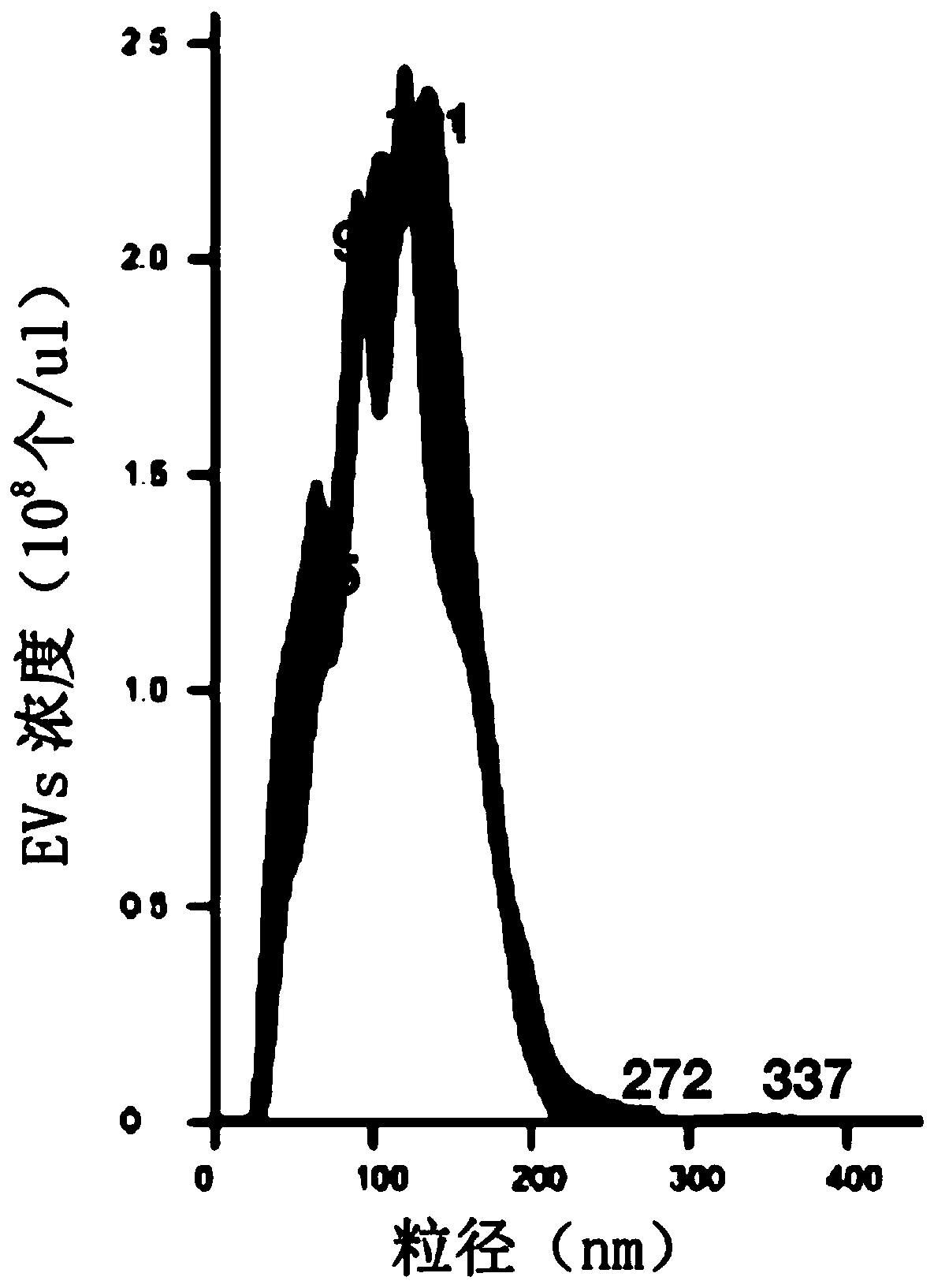
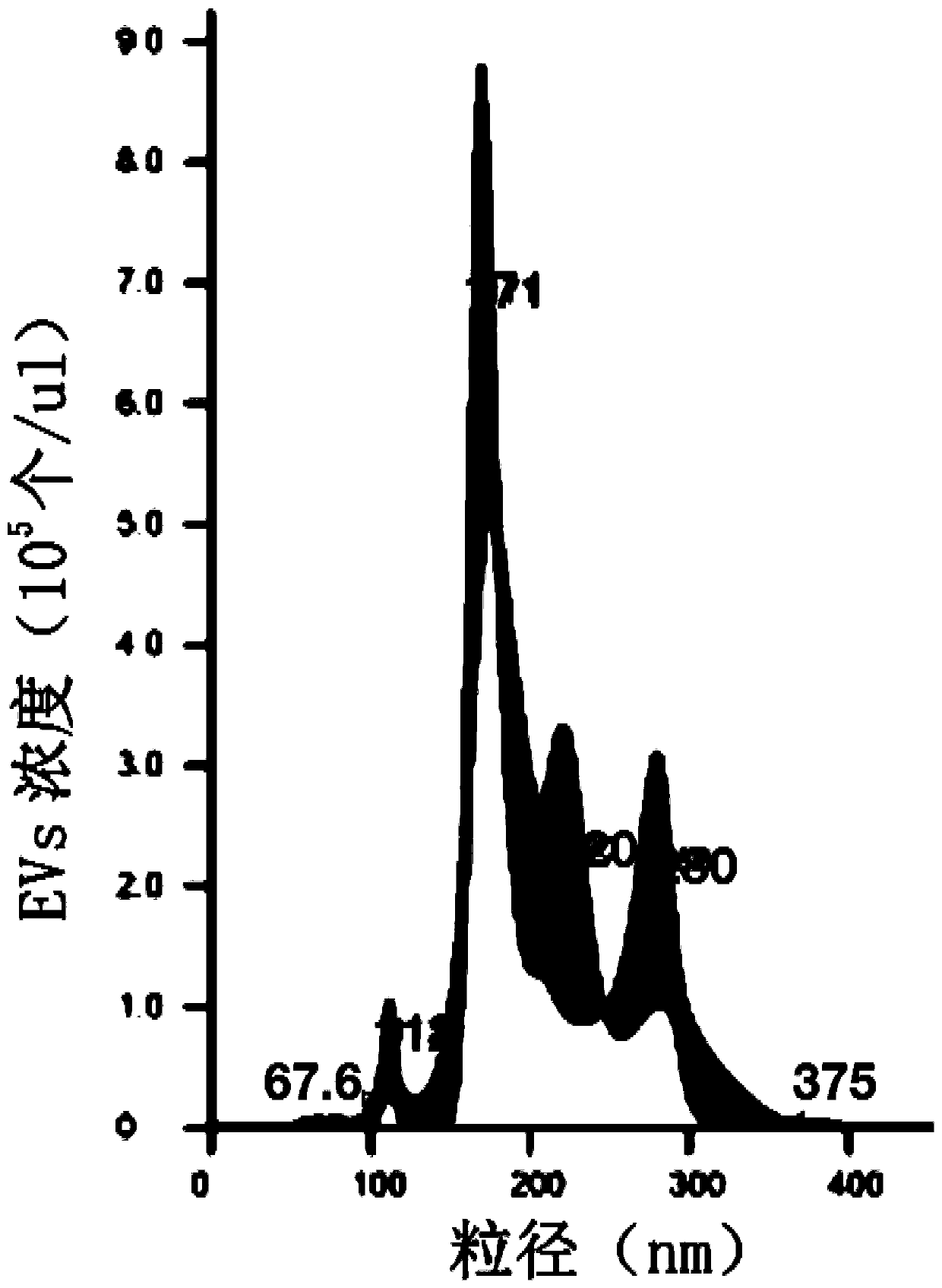
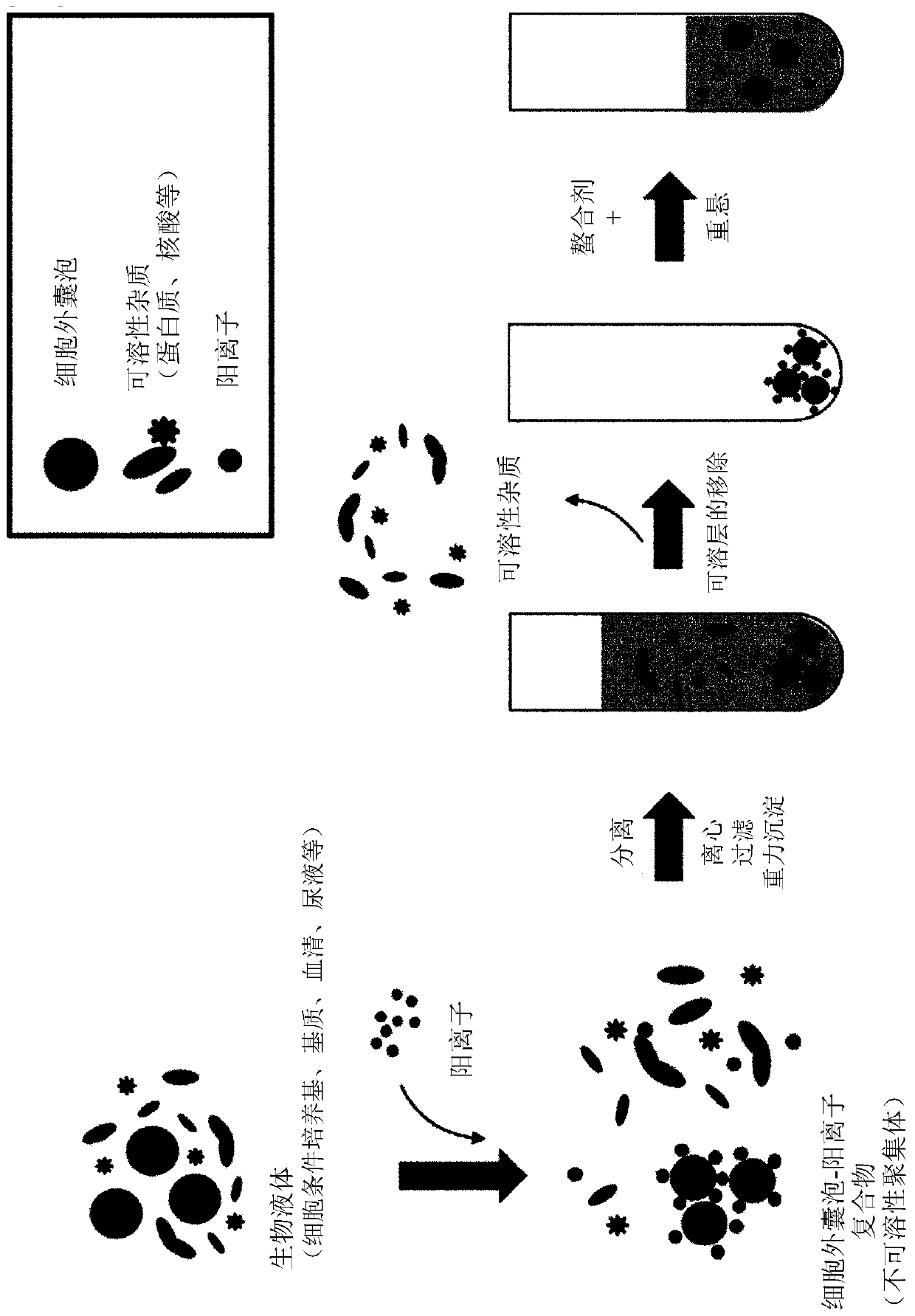
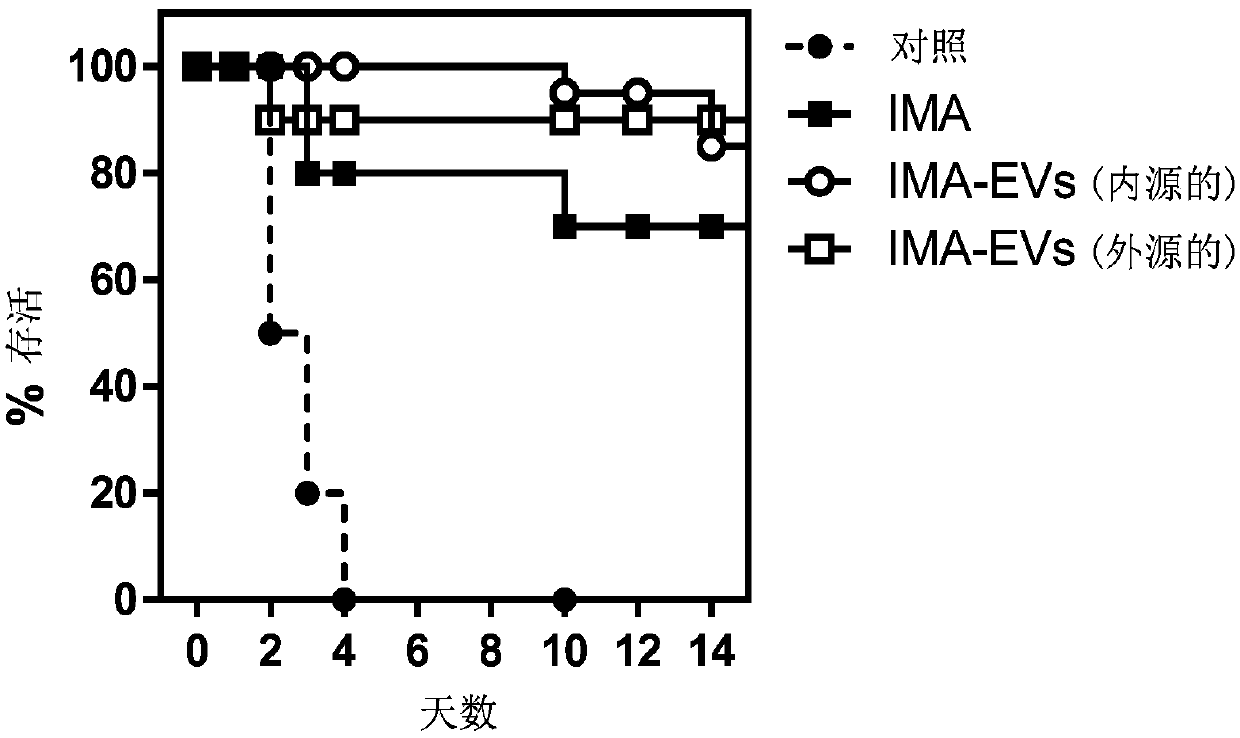
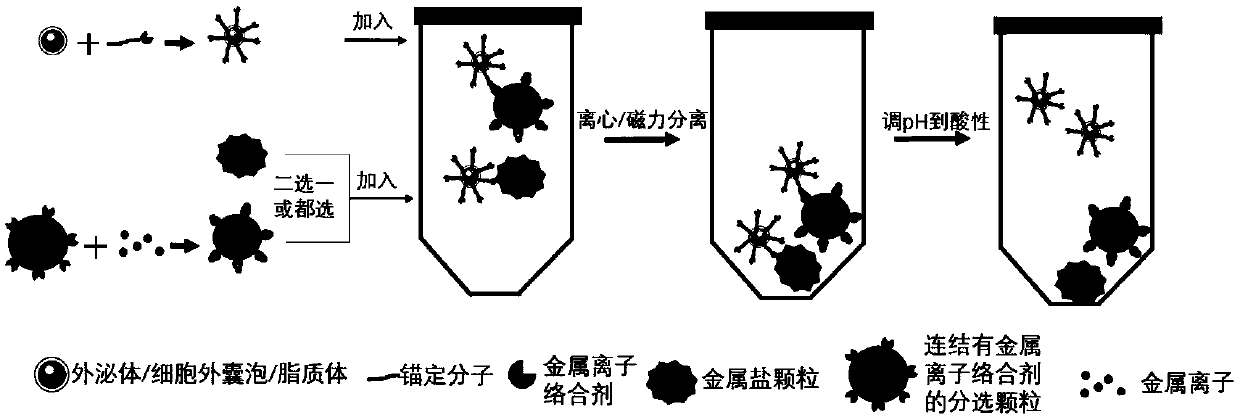
Method for separating extracellular vesicles based on metal ion complexing agent
InactiveCN109576207AEfficient separationEasy to operateCell dissociation methodsExtracellular vesicleChemical physics
The invention discloses a method for separating extracellular vesicles based on a metal ion complexing agent. The method comprises the steps of performing co-incubation by using an anchoring molecule-metal ion complexing agent molecular complex and liquid which is to be separated and contains the extracellular vesicles, and anchoring the molecular complex onto the extracellular vesicles; mixing sorted particles or salt particles of metal ions with the extracellular vesicles linked with the molecular complex, and incubating to enable the extracellular vesicles to be linked with the sorted particles (or the salt particles); separating, re-suspending a separated product, and adding an eluent to separate the extracellular vesicles from the sorted particles (or the salt particles); and separating out the sorted particles (or the salt particles) to obtain the separated extracellular vesicles remaining in a remaining solution. The method can realize the efficient separation of the extracellular vesicles, does not have special requirements for equipment, and is low in cost and wide in application scope; and exosome obtained by separation is high in purity, and a reagent added in a separating step does not affect the subsequent analysis or application.
Owner:贺川江
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com