Method for separating extracellular vesicles based on metal ion complexing agent
A metal ion and separation method technology, applied in the field of biotechnology and nanomaterials, can solve the problems of expensive antibodies and high separation costs, and achieve the effect of easy-to-obtain raw materials, high purity, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
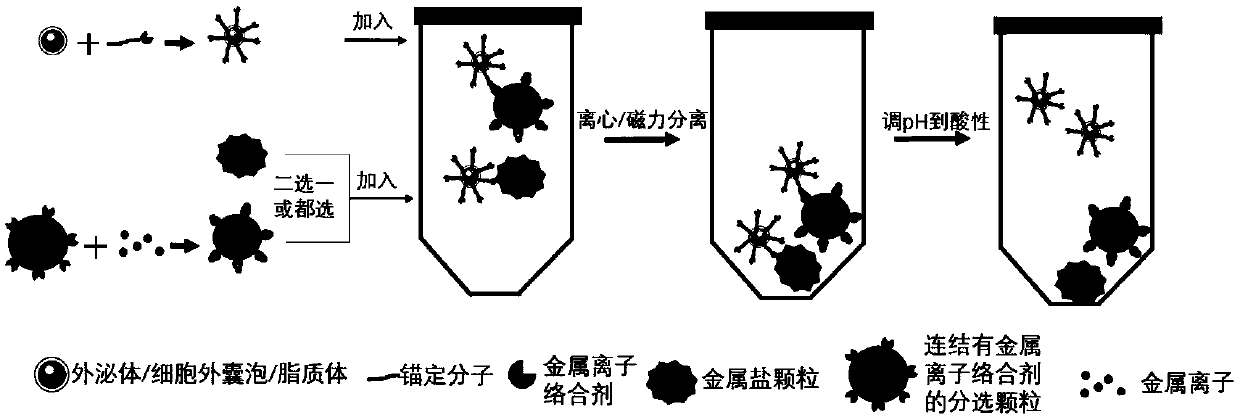
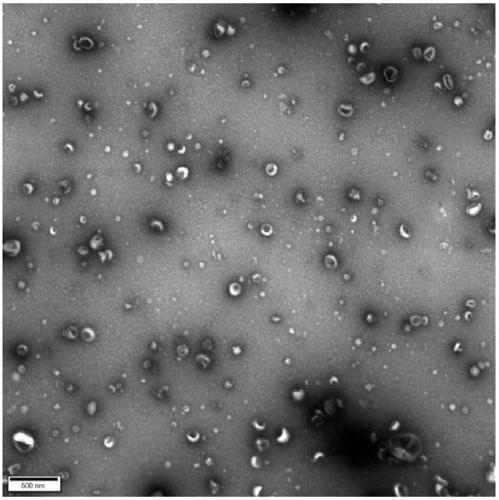
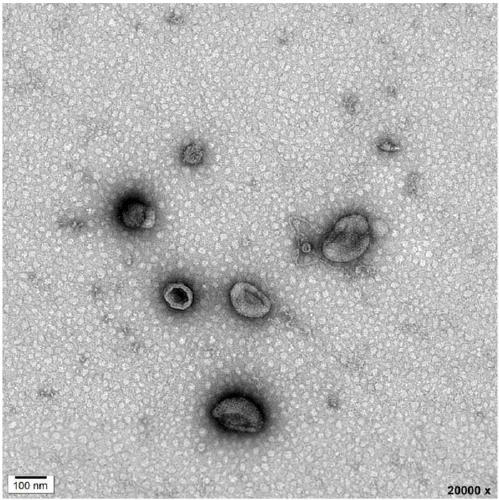
[0045] Separation process such as figure 1 shown. Mix 200 μM oleyl chain molecules modified with amino groups with 200 μM EDTA, react at room temperature for 1 hour, and dilute the reacted mixture to 20 μM. Carry out gradient centrifugation on the cell culture supernatant containing exosomes: centrifuge at 300g for 10min, 2000g for 10min, and 10000g for 30min at 4°C, and take the supernatant after centrifugation. Take the above-mentioned diluted mixed solution and mix it with the supernatant containing the above-mentioned exosomes in equal volumes, and place it at 30°C for 60 minutes of reaction; add the above-mentioned reaction solution into an ultrafiltration tube with a molecular weight cut-off of 100KDa, and centrifuge at a speed of 3000g for 10 minutes. Centrifuge repeatedly 3 times to filter out the oleyl chain molecules and EDTA that are not combined with exosomes. The retained exosomes were resuspended with saline.
Embodiment 2
[0048] Mix 200 μM oleyl chain molecules modified with amino groups with 200 μM EDTA, react at room temperature for 10 hours, and dilute the reacted mixture to 20 μM. Carry out gradient centrifugation on the cell culture supernatant containing exosomes: centrifuge at 300g for 10min, 2000g for 10min, and 10000g for 30min at 4°C, and take the supernatant after centrifugation. Take the above-mentioned diluted mixed solution and mix it with the supernatant containing the above-mentioned exosomes in equal volumes, and place it at 40°C for 10 minutes to react; add the above-mentioned reaction solution to an ultrafiltration tube with a molecular weight cut-off of 80KDa, and centrifuge at a speed of 10,000g for 5 minutes. Centrifuge repeatedly 3 times to filter out the oleyl chain molecules and EDTA that are not combined with exosomes. The retained exosomes were resuspended with saline.
[0049] The magnetic beads coated with iminodiacetic acid (IDA) with a particle size of 100 micron...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Mix 100 μM oleyl chain molecules modified with carboxyl groups with 100 μM glutamic acid diacetic acid (GLDA), react at room temperature for 5 hours, and dilute the reaction mixture to 10 μM. Gradient centrifugation was performed on the urine containing exosomes: centrifuged at 300g for 10min, 2000g for 10min, and 10000g for 30min at 4°C, and the supernatant was taken after centrifugation. Take the above-mentioned diluted mixed solution and mix it with the supernatant containing the above-mentioned exosomes in equal volumes, and place it at 30°C for 60 minutes of reaction; add the above-mentioned reaction solution into an ultrafiltration tube with a molecular weight cut-off of 100KDa, and centrifuge at a speed of 3000g for 10 minutes. Centrifuge repeatedly 3 times to filter out the oleyl chain molecules and GLDA that are not combined with exosomes. The retained exosomes were resuspended with saline.
[0053] Polystyrene microspheres coated with iminodiacetic acid (IDA)...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com