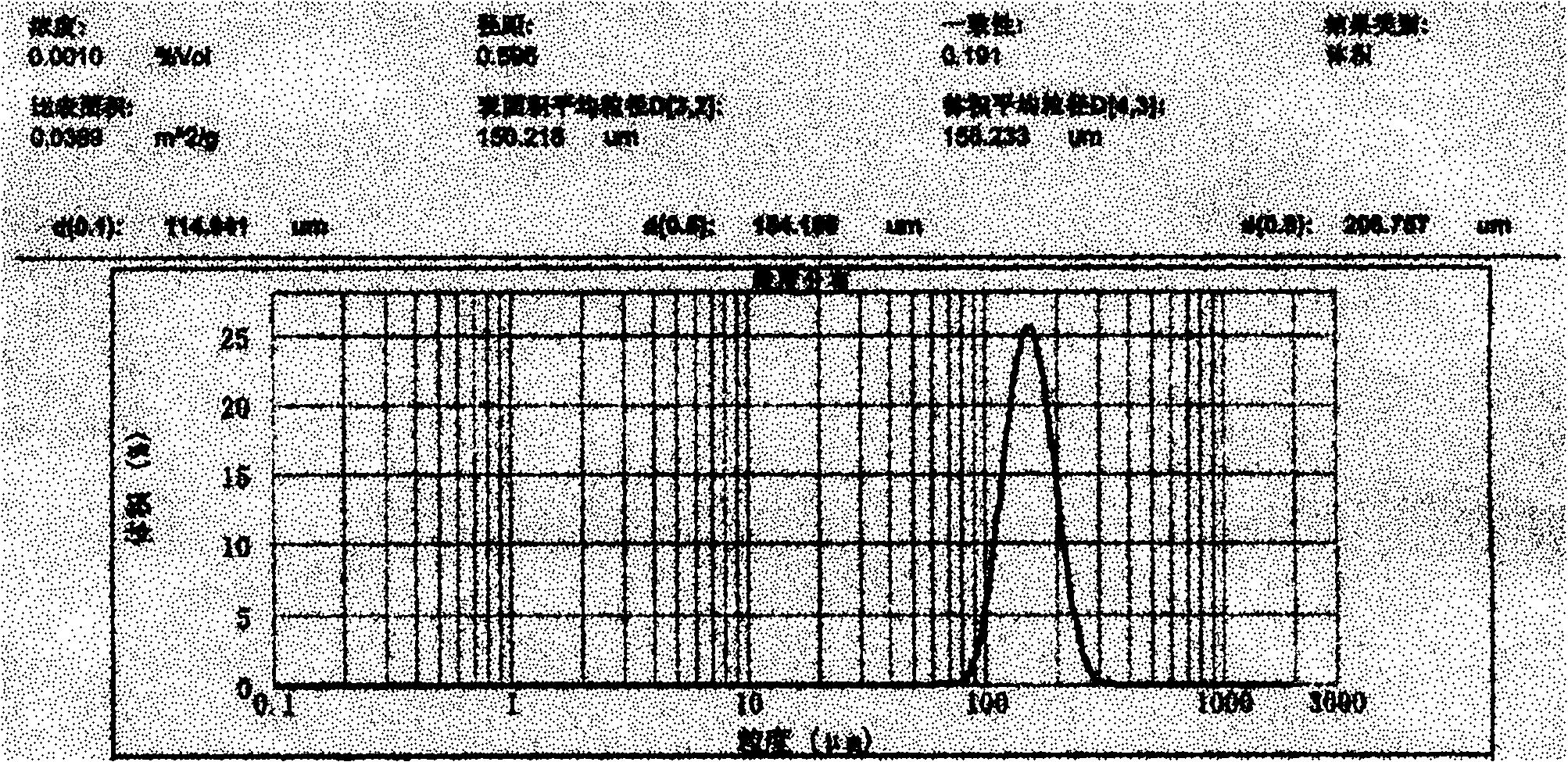
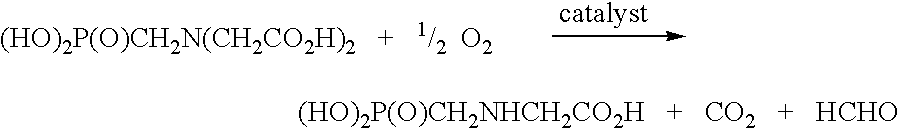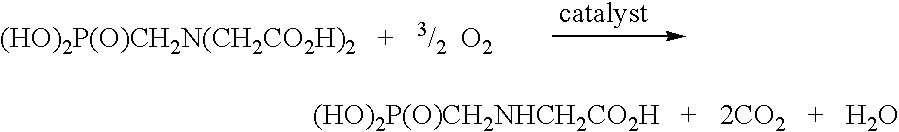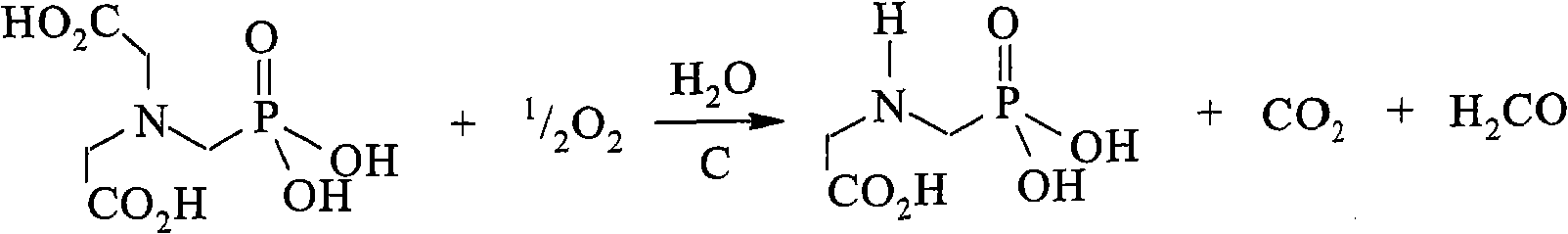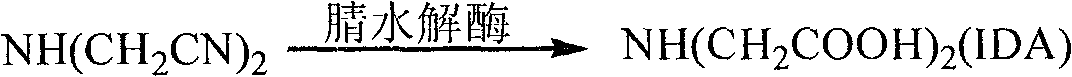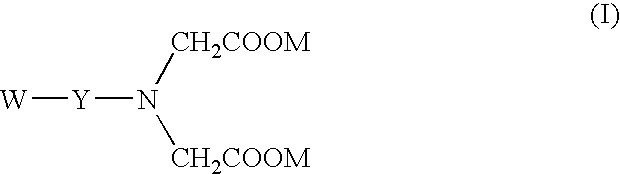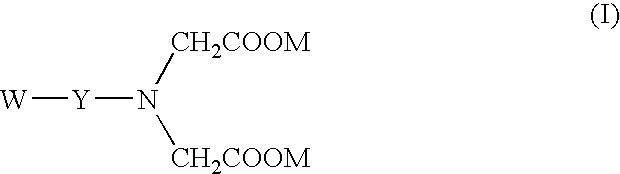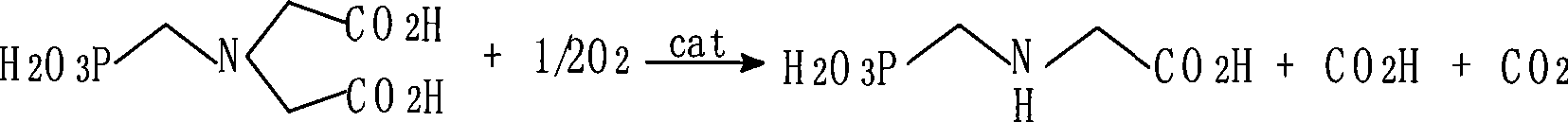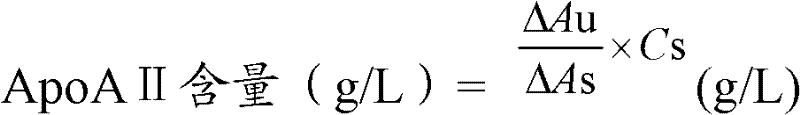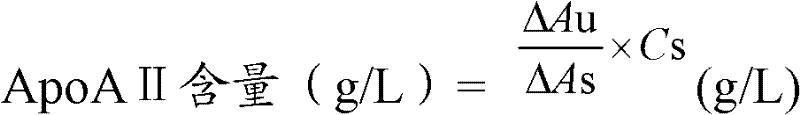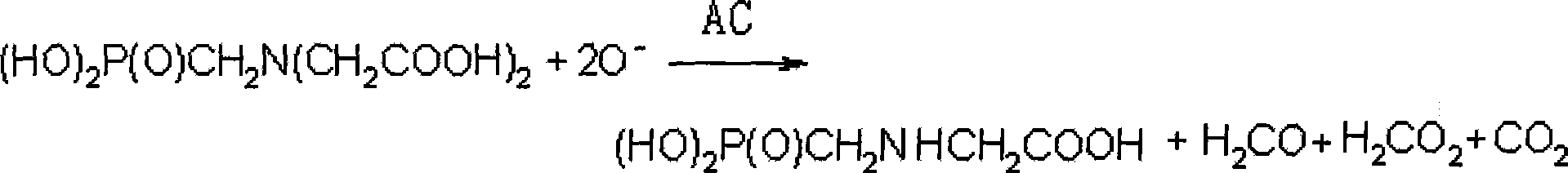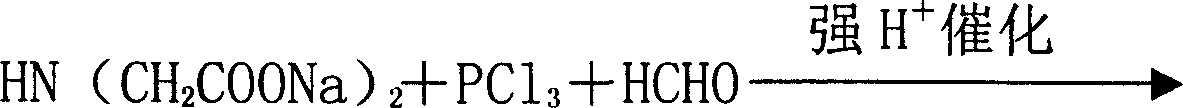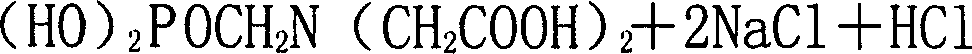Patents
Literature
508 results about "Iminodiacetic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
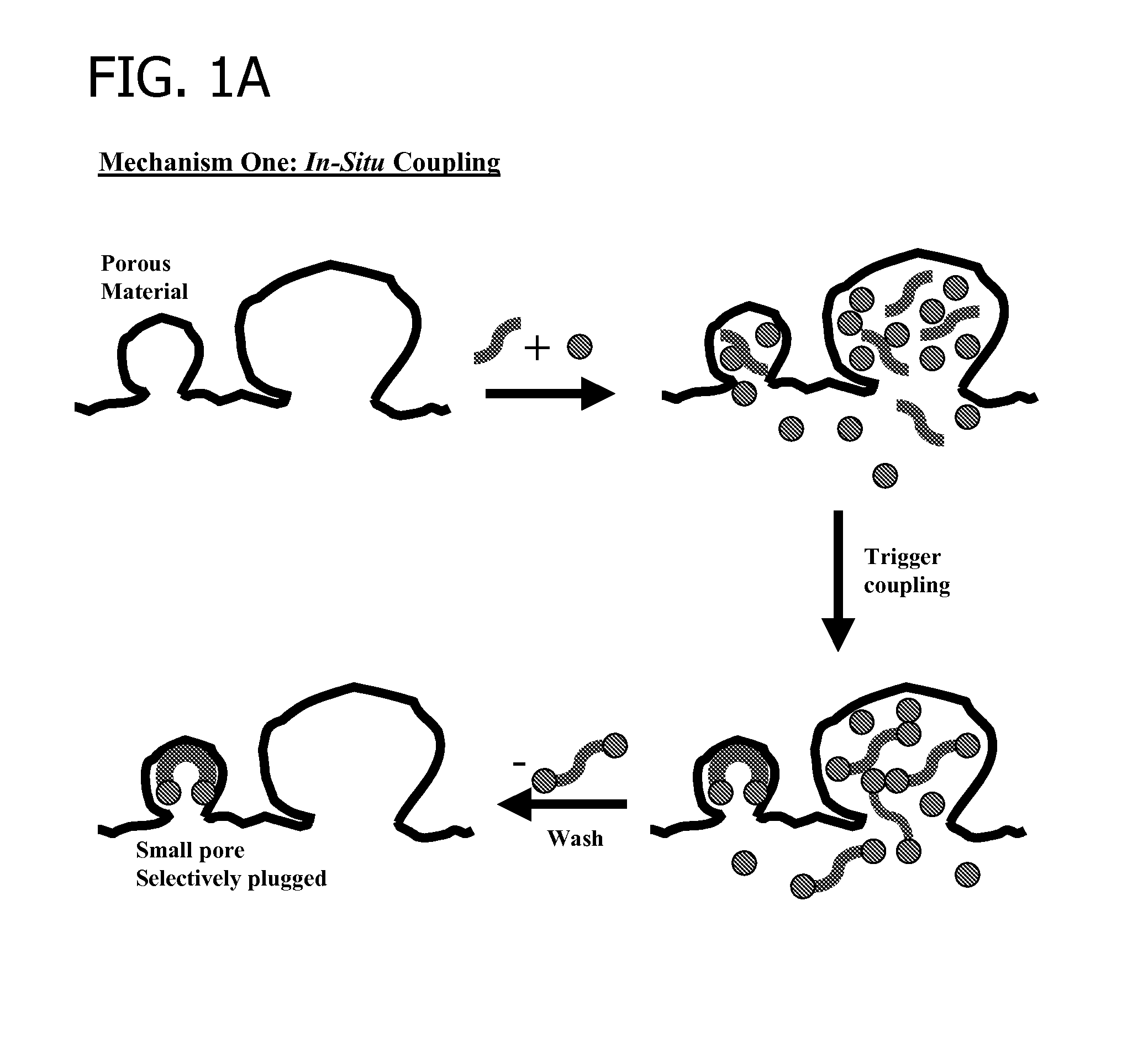
Iminodiacetic acid, HN(CH₂CO₂H)₂, often abbreviated to IDA, is a dicarboxylic acid amine (the nitrogen atom forms a secondary amino group, not an imino group as the name suggests). The iminodiacetate anion can act as a tridentate ligand to form a metal complex with two, fused, five membered chelate rings. The proton on the nitrogen atom can be replaced by a carbon atom of a polymer to create an ion-exchange resin, such as chelex 100.
Cleaning Composition
ActiveUS20090281017A1Improve abilitiesGood removal effectOrganic detergent compounding agentsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsIminodiacetic acidGlycine
The invention relates to compositions and methods for cleaning integrated circuit substrates. The compositions are in the form of an aqueous solution and include a quaternary ammonium hydroxide compound and a chelating compound. The chelating compound includes either boric acid or at least one N-substituted aminocarboxylate selected from the group consisting of N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine(bicine), N-tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl glycine (tricine) and mixtures thereof, and can optionally include glycine, Iminodiacetic acid (IDA), Nitrilo trizacetic acid (NTA), Ethylenediammine Tetraacetic acid (EDTA), or mixtures thereof.
Owner:EKC TECH
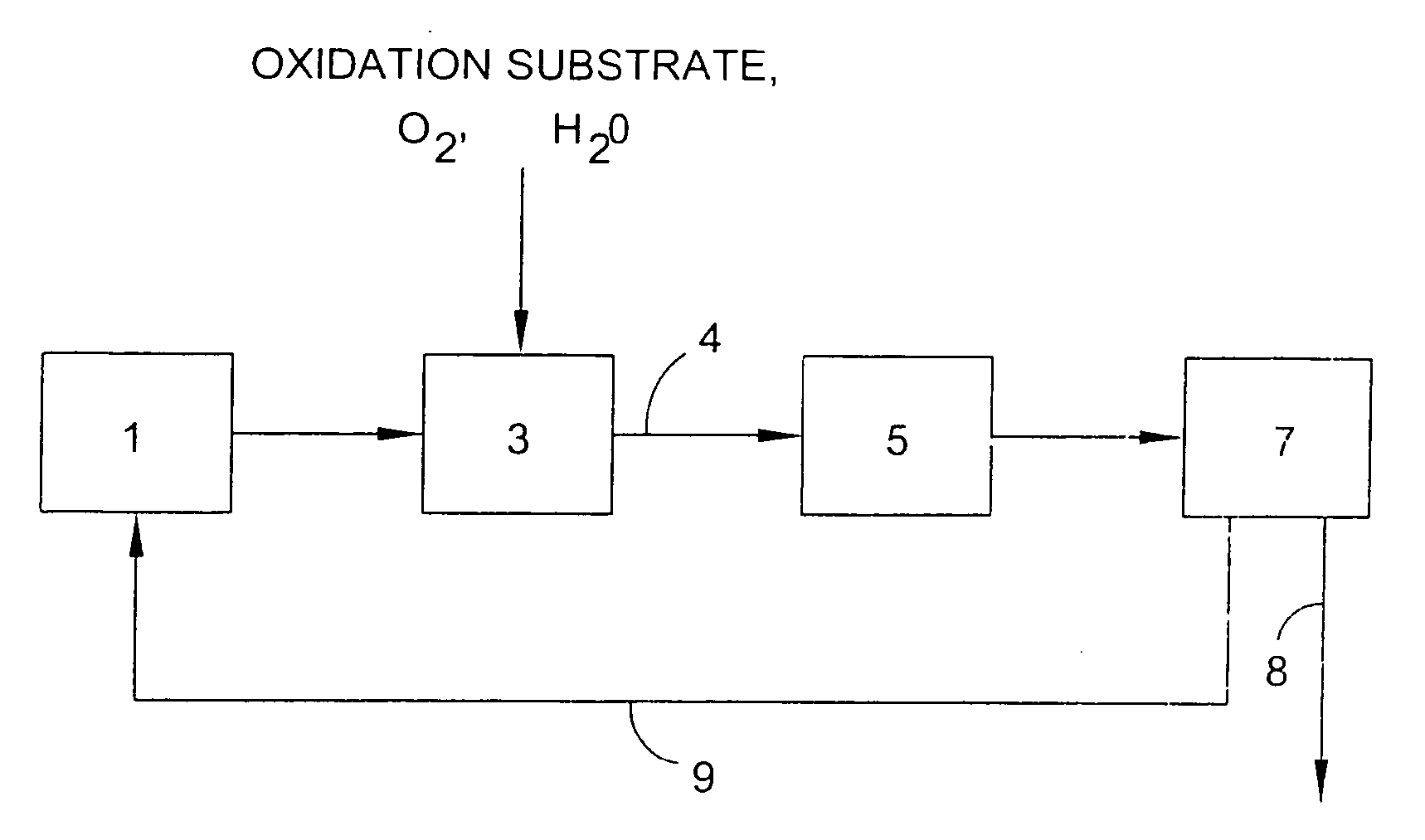
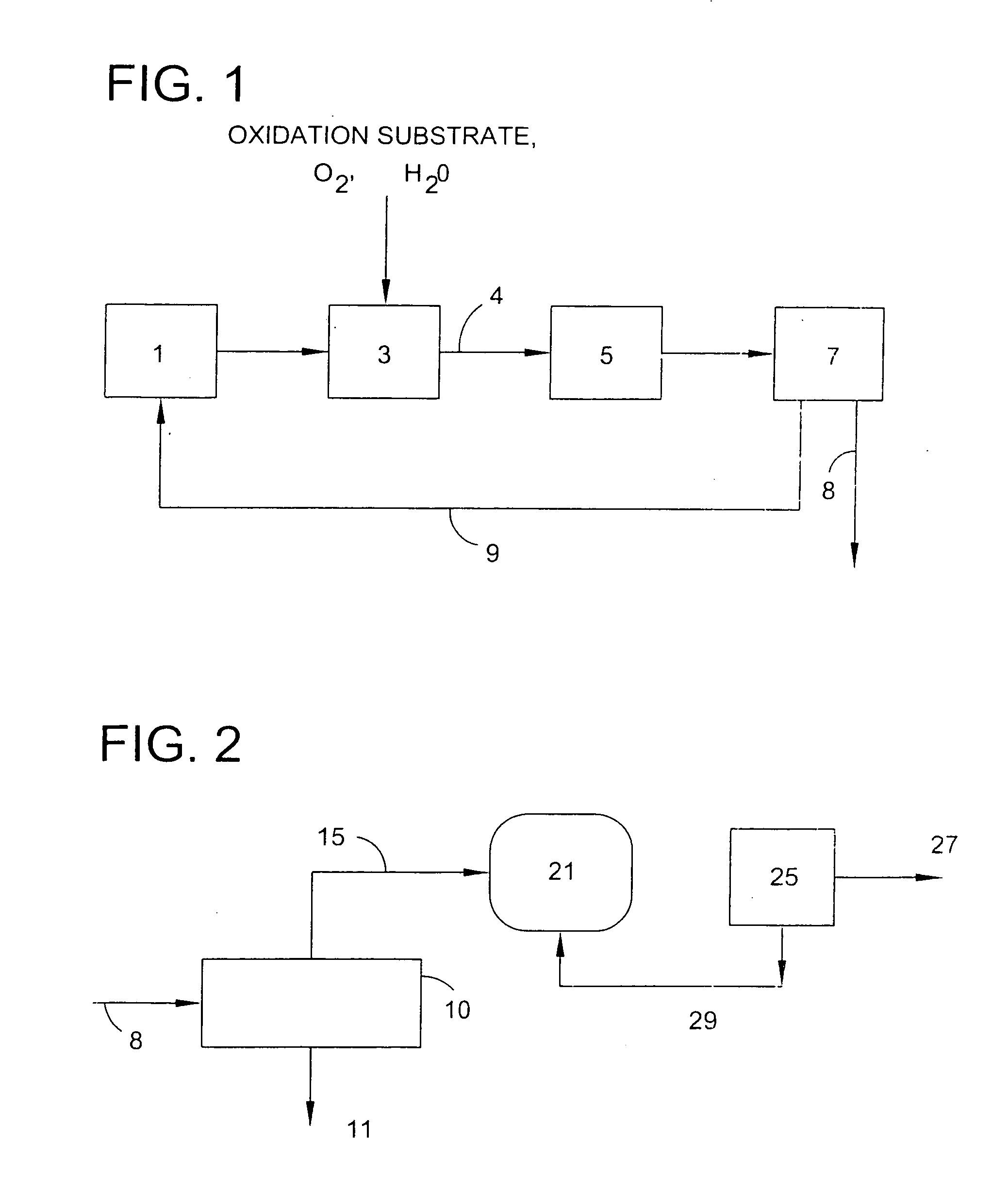
Use of tellurium in carbon-supported, noble metal-containing catalysts for liquid phase oxidation reactions
InactiveUS6956005B2High activityHigh selectivityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsCatalyst activation/preparationIminodiacetic acidTe element
An improved catalyst comprising a noble metal and tellurium at the surface of a carbon support is provided. Also provided are novel methods for preparing such catalysts and novel processes for the use of such catalysts in liquid phase oxidation reactions, particularly the oxidation of N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid or a salt thereof.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Metal utilization in supported, metal-containing catalysts
ActiveUS20090326262A1Reduce riskGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPorous substratePlatinum
Generally, the present invention relates to improvements in metal utilization in supported, metal-containing catalysts. For example, the present invention relates to methods for directing and / or controlling metal deposition onto surfaces of porous substrates. The present invention also relates to methods for preparing catalysts in which a first metal is deposited onto a support (e.g., a porous carbon support) to provide one or more regions of a first metal at the surface of the support, and a second metal is deposited at the surface of the one or more regions of the first metal. Generally, the electropositivity of the first metal (e.g., copper or iron) is greater than the electropositivity of the second metal (e.g., a noble metal such as platinum) and the second metal is deposited at the surface of the one or more regions of the first metal by displacement of the first metal. The present invention further relates to treated substrates, catalyst precursor structures and catalysts prepared by these methods. The invention further relates to use of catalysts prepared as detailed herein in catalytic oxidation reactions, such as oxidation of a substrate selected from the group consisting of N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid or a salt thereof, formaldehyde, and / or formic acid.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Activated carbon and use therefor
ActiveUS20130023405A1High catalytic activityEfficient decompositionPhysical/chemical process catalystsCarbon compoundsChloramine BActivated carbon
An activated carbon having a high catalytic activity as an oxidation catalyst or a decomposition catalyst, and use therefor are provided.The activated carbon has (a) an oxygen content in a range from 1.40 to 4.30% by mass, (b) a nitrogen content in a range from 0.90 to 2.30% by mass, (c) a sulfur content in a range from 0.50 to 1.20% by mass, and (d) a hydrogen content in a range from 0.40 to 0.65% by mass. The activated carbon may have at least one characteristic of (e) an amount of an acidic surface functional group of 0.10 to 0.36 meq / g, (f) an amount of a basic surface functional group of 0.50 to 1.30 meq / g, and (g) a benzene adsorption capacity of 25 to 50%. The activated carbon catalyzes an oxidation reaction of N-(phosphonomethyl) iminodiacetic acid with a peroxide (e.g., hydrogen peroxide) and achieves an efficient production of N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine even after repetitive use. The activated carbon also efficiently decomposes a chloramine.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
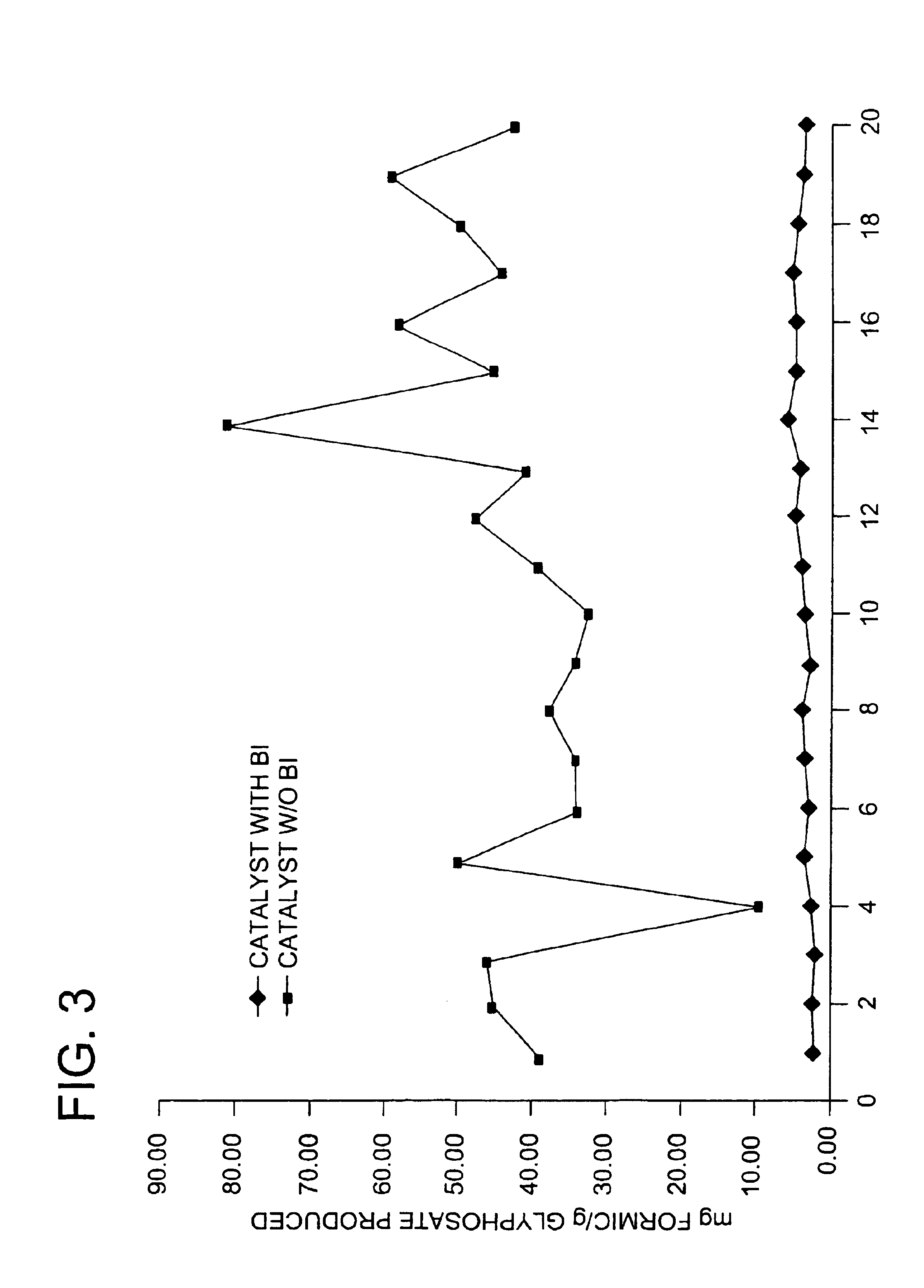
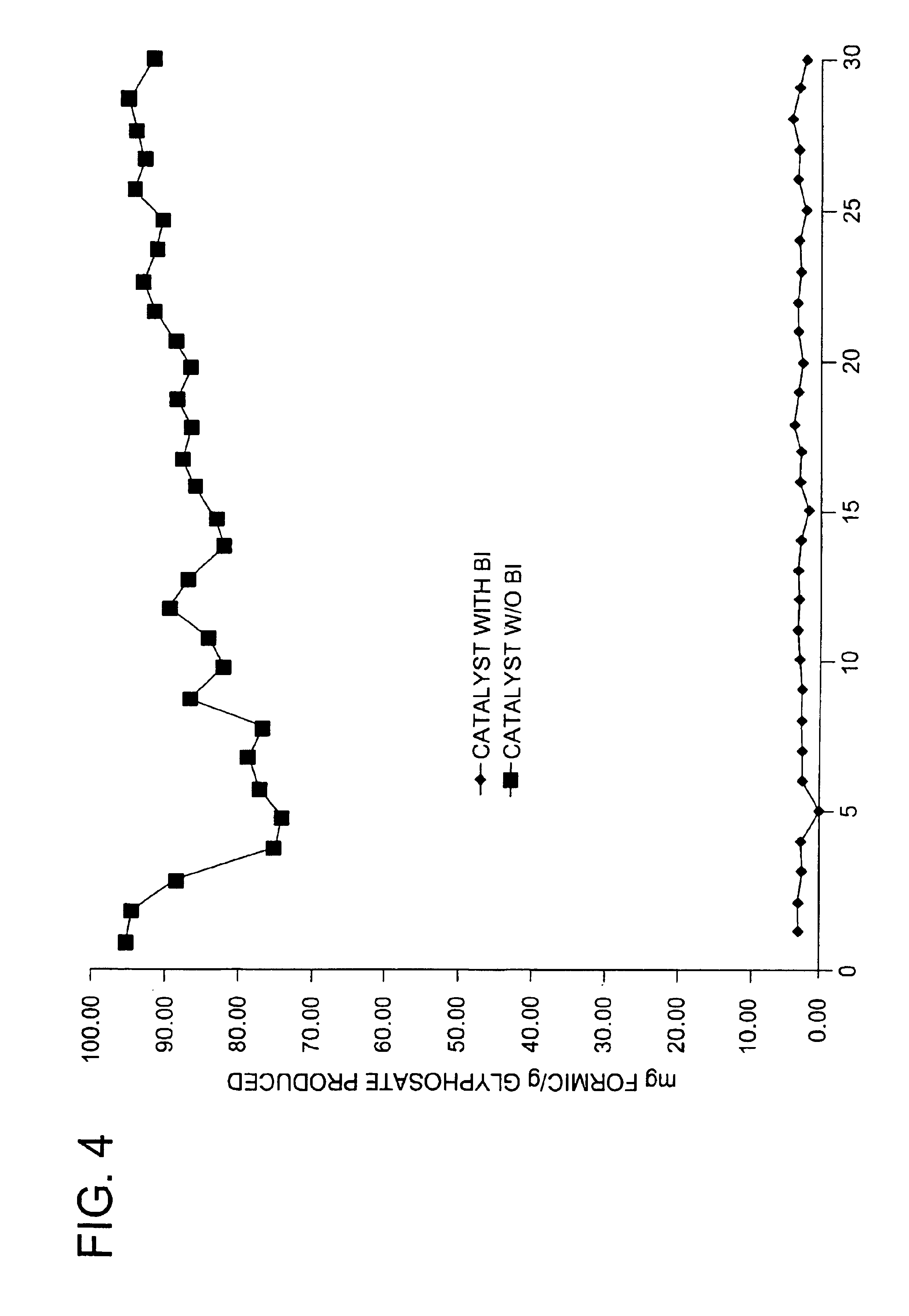
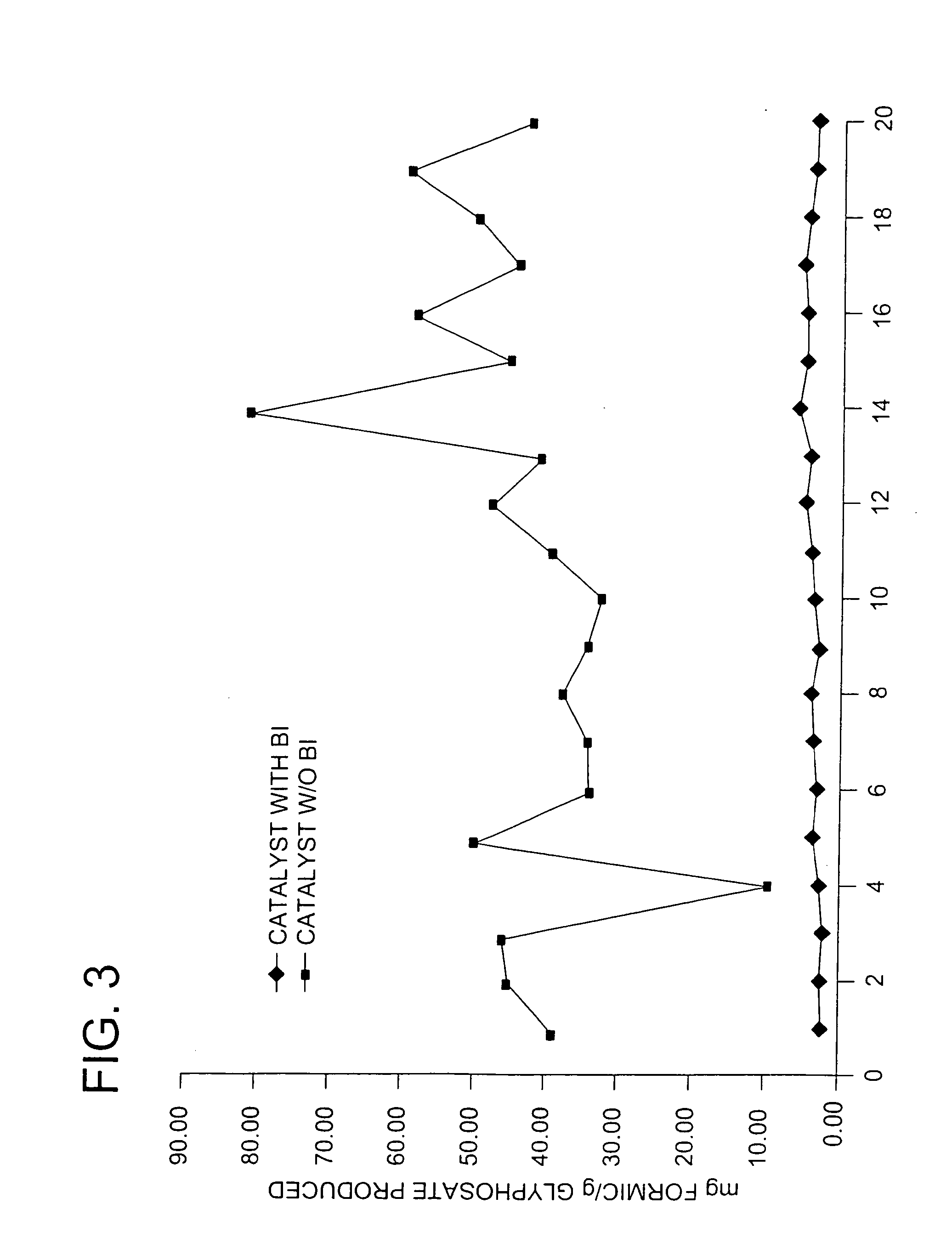
Use of a supplemental promoter in conjunction with a carbon-supported noble-metal-containing catalyst in liquid phase oxidation reactions
InactiveUS6963009B2Promote oxidationHigh activityBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsTe elementMethyl group
This invention relates to the use of a supplemental promoter in conjunction with a noble-metal-containing catalyst comprising a carbon support in catalyzing liquid phase oxidation reactions.In a particularly preferred embodiment, a supplemental promoter (most preferably bismuth or tellurium) is used in conjunction with a noble-metal-containing catalyst comprising a carbon support in a liquid phase oxidation process wherein N-(phosphonomethyl) iminodiacetic acid (i.e., “PMIDA”) or a salt thereof is oxidized to form N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine (i.e., “glyphosate”) or a salt thereof. The benefits of such a process include oxidation of the formaldehyde and formic acid by-products, and, consequently, decreased final concentrations of those by-products as well as other undesirable by-products, most notably N-methyl-N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine (i.e., “NMG”).
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Use of a supplemental promoter in conjunction with a carbon-supported, noble-metal-containing catalyst in liquid phase oxidation reactions
InactiveUS20060020143A1High activityPromote oxidationBiocideOrganic chemistry methodsTe elementChemistry
This invention relates to the use of a supplemental promoter in conjunction with a noble-metal-containing catalyst comprising a carbon support in catalyzing liquid phase oxidation reactions, a process for making of an improved catalyst comprising such a supplemental promoter, and an improved catalyst comprising such a supplemental promoter. In a particularly preferred embodiment, a supplemental promoter (most preferably bismuth or tellurium) is used in conjunction with a noble-metal-containing catalyst comprising a carbon support in a liquid phase oxidation process wherein N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid (i.e., “PMIDA”) or a salt thereof is oxidized to form N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine (i.e., “glyphosate”) or a salt thereof. The benefits of such a process include increased oxidation of the formaldehyde and formic acid by-products, and, consequently, decreased final concentrations of those by-products as well as other undesirable by-products, most notably N-methyl-N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine (i.e., “NMG”).
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
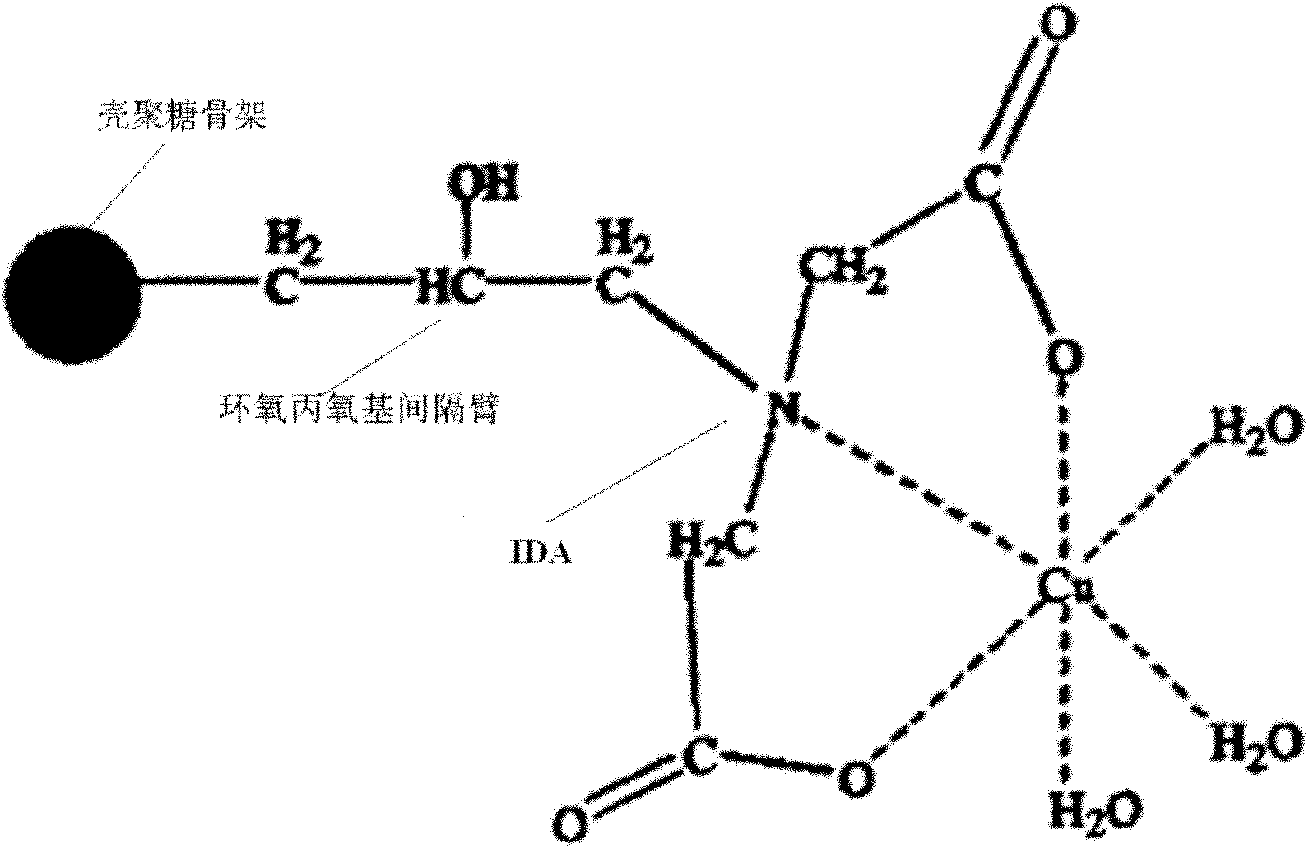
Method for preparing chitosan separation medium suitable for protein purification
ActiveCN102068965AEasy to operateGood particle size uniformityOther chemical processesPeptide preparation methodsCross-linkEpoxy
The invention relates to a method for preparing a chitosan separation medium suitable for protein purification, which comprises the following steps of: (1) dispersing acetic acid solution of chitosan into liquid paraffin with stirring to form chitosan particles in the presence of cyclohexane serving as a porogen and a small amount of span80, and further cross-linking the chitosan particles to form a chitosan skeleton under the action of glutaraldehyde serving as a cross-linking agent; (2) swelling the chitosan skeleton, and reacting a hydroxyl group on the chitosan skeleton with epoxy chloropropane in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) / NaOH mixed solution to introduce an epoxy group into the chitosan skeleton so as to obtain a grafted chitosan skeleton; and (3) adding iminodiacetic acid (IDA) / NaOHmixed solution into the grafted chitosan skeleton, reacting at the temperature of between 20 and 80 DEG C for 1 to 10 hours, and performing suction-filtration to obtain the chitosan separation medium. The chitosan separation medium solves the leakage problem of metal ions to a large extent, has the advantages of process stability, high repeatability and the like, and is suitable for mass production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Comprehensive treatment method for glyphosate mother liquid
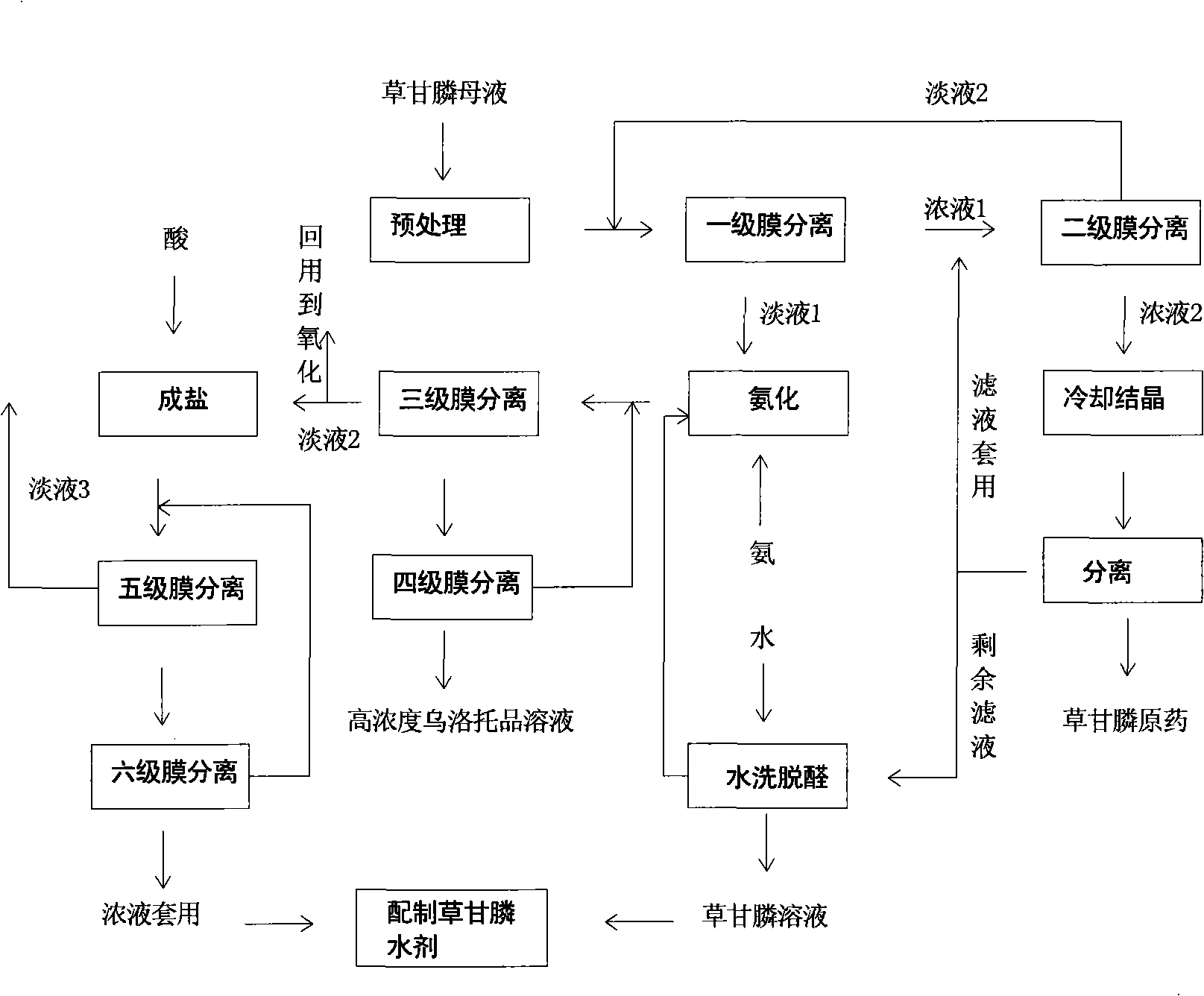
The invention relates to a comprehensive treatment method for mother liquid synthesized by oxidizing glyphosate by N-(Phosphonomethyl) iminodiacetic acid with an IDA (Iminodiacetic Acid) method. The mother liquid is treated by a condensed system to obtain condensed liquid and thin liquid, wherein the condensed liquid subjected to formaldehyde removal is used for preparing a gyphosate solution with high content or carrying out oxidation treatment, the treated thin liquid can be used for gyphosate production or biochemical treatment. The comprehensive treatment method not only recovers gyphosate, but also reduces the pollution to the environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XINAN CHEM INDAL GROUP
Oligonucleotide labeling reactants and their use
InactiveUS6949639B1Highly simplifiedSimple methodSugar derivativesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAlkyl transferIminodiacetic acid
Owner:WALLAC
Method for treating glyphosate mother liquor by oxidation method
ActiveCN101757761AReduce pollutionReduce compactionChemical protectionPhosphate ionInorganic compound
The invention provides a method for treating glyphosate mother liquor by an oxidation method, which comprises the following steps: firstly, using regulating agents for regulating the pH value of the glyphosate mother liquor with organic phosphor or glyphosate or nitrogenous compounds or salt to 0.1 to 14; then, carrying out the pressurized oxidation reaction with strong oxidizing gas under the condition of the existence of catalysts; oxidizing phosphorus-containing impurities such as glyphosate, glyphosine, orthophosphorous acid, methyl glyphosate, aminomethyl phosphonic acid, N-(Phosphonomethyl) iminodiacetic acid and the like into phosphate radical ions; oxidizing nitrogenous organic impurities such as glycin, triethylene ammonia, diethanolameine, aminomethyl phosphonic acid, hydroxyethyl glycine and the like into ammonia radical ions; and then, carrying out concentration and separation to obtain phosphate and amine salt inorganic compounds for recovery and reuse. The invention can effectively oxidize the complicated organic phosphor and the nitrogenous compounds in the glyphosate mother liquor into single phosphate radicals and amine salt inorganic compounds for convenient recovery and reuse, and can simultaneously reduce the environment pollution and the soil hardening caused by the mother liquor. Thereby, the total conversion rate of the phosphorus-containing compounds reaches 60 to 90 percent, the conversion rate of the nitrogenous compounds reaches more than 90 percent, in addition, the removal rate of the glyphosate reaches 95 to 99 percent, a large amount of produced phosphate and amine salt can be used for agricultural fertilizers, and the goal of changing waste materials into valuable materials is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XINAN CHEM INDAL GROUP
Battery separator and nonaqueous lithium ion secondary battery having the same
InactiveUS20100239900A1Little deteriorated in capacityAvoid depositionSolid electrolytesFinal product manufactureIminodiacetic acidHydrogen atom
The invention provides a battery separator comprising a porous resin film and a crosslinked polymer supported thereon and having iminodiacetic acid groups in side chains of the polymer chains. The iminodiacetic acid group is preferably represented by the formulawherein M1 and M2 are each independently a hydrogen atom, a lithium atom, a potassium atom, a sodium atom, or triethylamine. It is preferred that the layer of the crosslinked polymer is substantially nonporous or solid, and ion conductive, and that the crosslinked polymer has in the molecule oxetanyl groups which are capable of cation polymerization.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Method for preparing supported nano copper nickel catalyst and application thereof in oxidative dehydrogenation reaction of alkylol amine
InactiveCN1827218AHigh yieldHigh reuse rateCatalyst carriersCatalyst activation/preparationNickel saltDehydrogenation
The invention discloses a method for preparing the carrier catalyst which can be used in aminoethyl alcohol dehydrogenation reaction to prepare the iminodiacetic acid, and relative usage. It comprises following steps: using the copper salt and nickel salt as main raw material, via dipping, drying, high-temperature baking and programmed increasing temperature, to from said catalyst nanometer copper nickel composite catalyst, then using said catalyst in aminoethyl alcohol dehydrogenation reaction to prepare the iminodiacetic acid. Said inventive catalyst has higher reaction activity. And the raw materials are easily to be attained, the producing cost is lower, and it has better application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
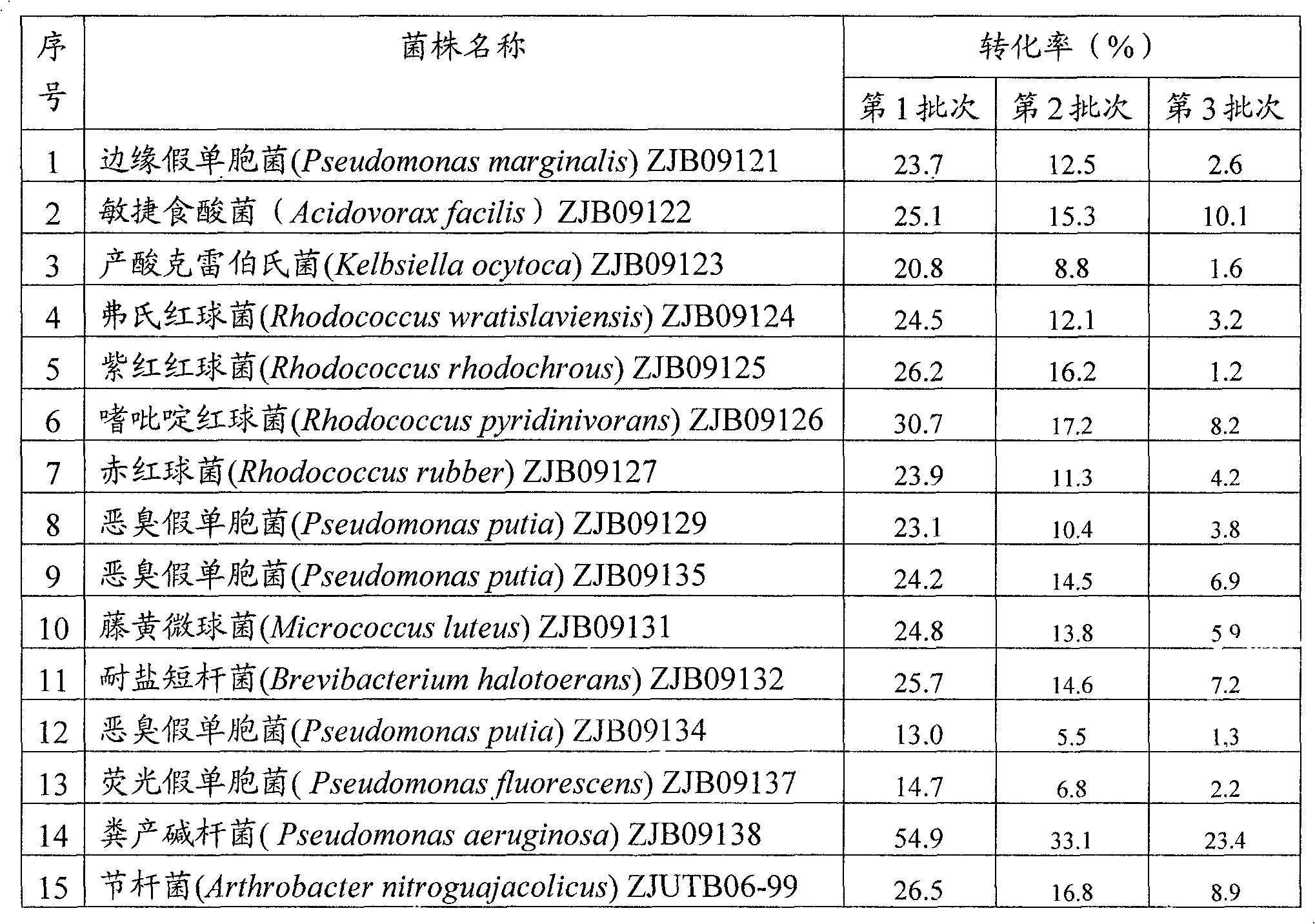
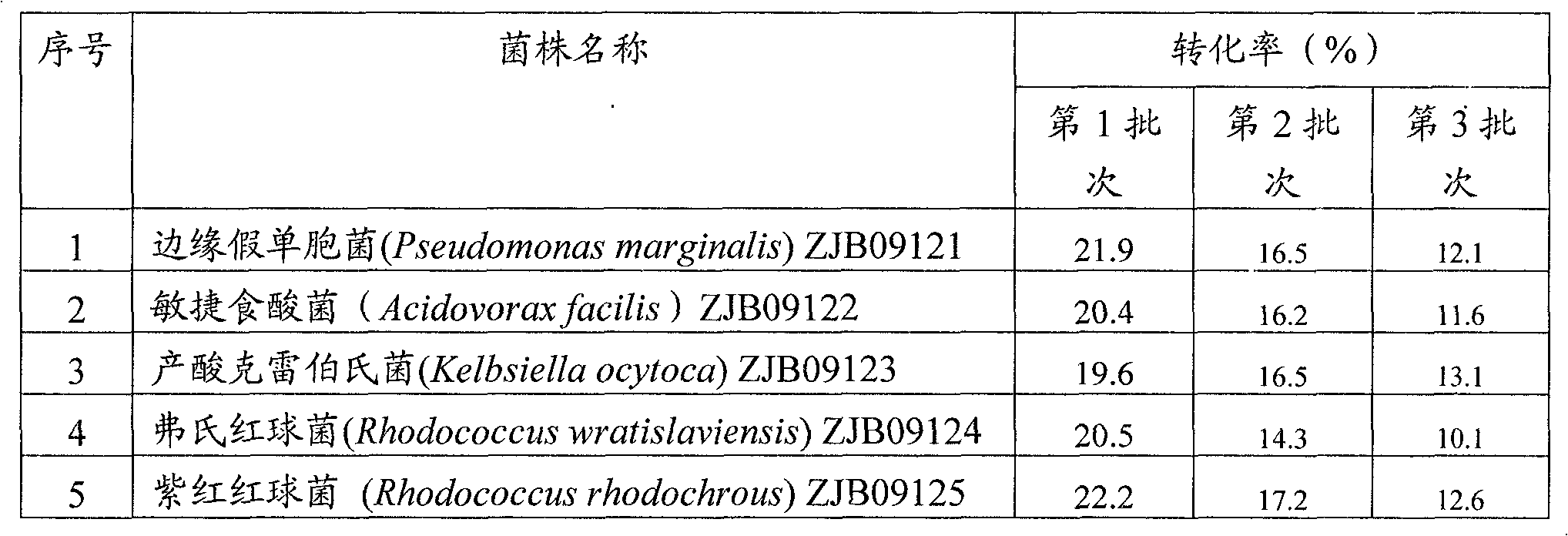
Method for preparing iminodiacetic acid by catalyzing iminodiacetonitrile with microbes
ActiveCN101629192AEfficient productionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismIminodiacetic acid
The invention provides a method for preparing iminodiacetic acid by catalyzing iminodiacetonitrile with microbes, which comprises the following steps: using bacterial strains which produce nitrilase to obtain the nitrilase through enzyme production cultivation; and taking the nitrilase as a biological catalyst to biologically catalyze the iminodiacetonitrile to prepare the iminodiacetic acid. The invention also relates to a screening method of the microbes which produce the nitrilase and the bacterial strains with nitrilase activity obtained by the screening method. The invention provides the basis for producing the iminodiacetic acid by biologically catalyzing the iminodiacetonitrile, thereby having important application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Gravel-packing carrier fluid with internal breaker
A method of gravel packing a hole in a subterranean formation having a filter cake coated on the surface thereof that includes injecting into the hole a gravel pack composition comprising gravel and a carrier fluid comprising a base fluid and at least one iminodiacetic acid or salt thereof is disclosed.
Owner:MI
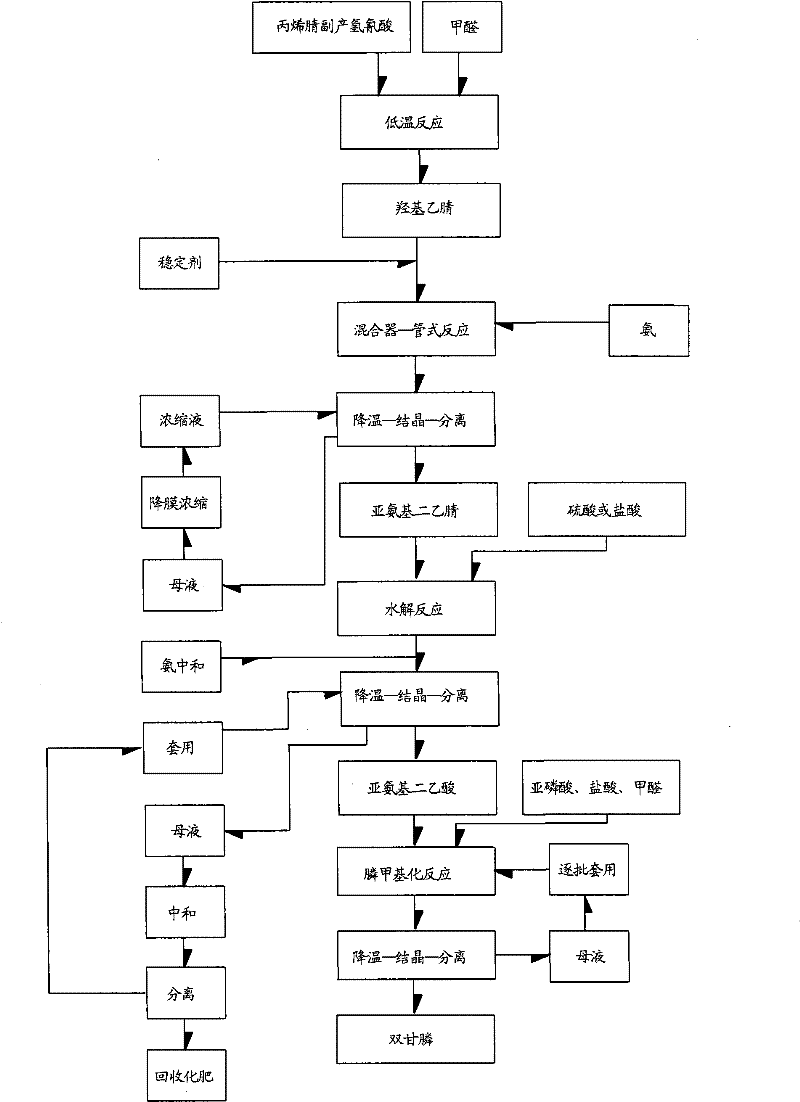
Environmental-friendly new method for preparing N-phosphonomethyl iminodiacetic acid by utilizing acrylonitrile byproduct hydrocyanic acid
InactiveCN101747369AQuality improvementHigh yieldGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsIminodiacetic acidControl system
The invention relates to an environmental-friendly new method for preparing N-phosphonomethyl iminodiacetic acid by utilizing acrylonitrile byproduct hydrocyanic acid, belonging to the comprehensive utilization of acrylonitrile device byproduct hydrocyanic acid in industrial scale. The method includes that: step first, acrylonitrile byproduct hydrocyanic acid is used for preparing hydroxyl acetonitrile, and then iminodiacetonitrile is prepared; step two, the obtained iminodiacetonitrile is used for preparing iminodiacetic acid by acid hydrolysis method; and step three, the obtained iminodiacetic acid is used for preparing N-phosphonomethyl iminodiacetic acid. No report of preparing PMIDA by utilizing acrylonitrile byproduct hydrocyanic acid in industrial scale is seen, and the inventor uses local materials, utilizes the advantages of being adjacent to Qilu petrochemical and having resource of hydrocyanic acid (4000 ton / year) transmitted by pipeline and initially provides the method for preparing PMIDA by utilizing acrylonitrile byproduct hydrocyanic acid in industrial scale. The invention solves the problem of region restriction of product production caused by inconvenient transportation of hydrocyanic acid. A gas and liquor mixer is applied to iminodiacetonitrile reaction, and by virtue of DCS control system, quality and yield of iminodiacetonitrile are improved.
Owner:YINGKOU YINGXIN CHEM TECH CO LTD
Oxidation catalyst and process
InactiveUS7129373B2Promote lowerImprove productivityAmino preparation from aminesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIminodiacetic acidOxidative cleavage
An oxidation catalyst is prepared by pyrolyzing a source of iron and a source of nitrogen on a carbon support. Preferably, a noble metal is deposited over the modified support which comprises iron and nitrogen bound to the carbon support. The catalyst is effective for oxidation reactions such as the oxidative cleavage of tertiary amines to produce secondary amines, especially the oxidation of N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid to N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Glyphosate waste water low-discharging and mother liquor recycling method
InactiveCN101648755AAchieve recyclingLess impuritiesBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsIminodiacetic acidHexamethylenetetramine
The invention relates to a glyphosate waste water low-discharging and mother liquor recycling method comprising the following steps: (1) taking mother liquor left after an original glyphosate medicineis crystallized, precipitated and separated in the process of preparing glyphosate by an iminodiacetic acid method as glyphosate mother liquor; (2) carrying out hyperfiltration processing for the mother liquor so that the pollution index of the mother liquor is less than or equal to 5; (3) separating the mother liquor by a first-stage membrane to obtain a concentrated solution (1) with the glyphosate concentration of 2-7 percent and a dilute solution (1) with the glyphosate concentration of 0-0.1 percent, respectively collecting the concentrated solution (1) and the dilute solution (1) into astorage tank, separating the concentrated solution (1) by a second-stage membrane to obtain a concentrated solution (2) with the glyphosate concentration of 5-15 percent and a dilute solution (2) with the glyphosate concentration of 0.1-2 percent and respectively collecting the concentrated solution (2) and the dilute solution (2) into the storage tank; (4) reducing the temperature of the concentrated solution (2) to -10-25 DEG C to be crystallized, separating the concentrated solution (2) to obtain the original glyphosate medicine and filter liquor, mechanically using the filter liquor for 1-20 times, returning the dilute solution (2) to the first-stage membrane to be separated; (5) adding ammonia into the dilute solution (1) of the step (3) till the pH value of the dilute solution (1) is equal to 8-11 so as to generate methenamine.
Owner:HANGZHOU TIAN CHUANG ENVIRONMENTAL TECH +1
Method for preparing glyphosate
ActiveCN101531677AReduce manufacturing costEliminate generationBiocidePhysical/chemical process catalystsHigh concentrationIminodiacetic acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing glyphosate. N- (Phosphonomethyl) iminodiacetic acid is in the oxygenation reaction with oxygen in the water medium in the presence of catalyzer such as activated carbon, the solid-liquid separation is performed after the reaction to obtain the crystal with glyphosate and the filter cake with activated carbon, the reaction mother liquor is in the later process; the filter cake is added in the glyphosate saturated solution, after heating and dissolving the activated carbon is separated from the glyphosate solution, the glyphosate solution is cooled and crystallized, after separation the solid glyphosate product and the filter solution are obtained, the filter cake is made into the glyphosate saturated solution; the reaction mother liquor passes through a barrier separation device, the glyphosate in the mother liquor is separated from the by-product such as formaldehyde, the glyphosate mother liquor is recycled in the oxygenation reaction, or used as the glyphosate saturated solution. The invention provides the low-cost method for preparing glyphosate by the catalytic oxidation of high-concentration N- (Phosphonomethyl) iminodiacetic acid by the cyclic utilization of the reaction mother liquor, improving the yield of solid glyphosate and solving the environmental protection problem caused by the byproduct such as formaldehyde.
Owner:捷马化工股份有限公司
Polishing composition and polishing method
A polishing composition includes fumed alumina, alumina other than fumed alumina, colloidal silica, a first organic acid, a second organic acid, an oxidizing agent, and water. When the second organic acid is citric acid, the first organic acid is preferably malic acid, while when the second organic acid is malic acid, the first organic acid is preferably citric acid. When the second organic acid is succinic acid, iminodiacetic acid, itaconic acid, maleic acid, malonic acid, crotonic acid, gluconic acid, glycolic acid, lactic acid, or mandelic acid, the first organic acid is preferably either citric acid or malic acid. The polishing composition can be suitably used for polishing the surface of a substrate for a magnetic disk.
Owner:FUJIMI INCORPORATED
Method for treating glyphosate mother solution by using oxidization method
ActiveCN101830580AReduce pollutionReduce compactionMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationPhosphorous acidPhosphate ion
The invention relates to a method for treating a glyphosate mother solution by using an oxidization method, comprising the following steps of: regulating the PH value of the glyphosate mother solution containing organophosphorus or glyphosate or the glyphosate mother solution containing nitrogen-containing compounds or salts to 0.1-14, slowly dropwise adding hydrogen peroxide, raising temperature and then introducing strong-oxidization gas, wherein the reaction temperature is 0-100 DEG C, and the molar ratio of the added hydrogen peroxide to the strong-oxidization gas is 1:0.1-20; and carrying out oxidization reaction at normal pressure or under the condition of pressurization, oxidizing nitrogen-containing impurities, such as glyphosate, glyphosine, phosphorous acid, methyl glyphosate, aminomethyl phosphoric acid, N-(phosphonomethyl) iminodiacetic acid and the like, into phosphate radical irons, oxidizing nitrogen-containing organic impurities, such as glycine, triethyl ammonia, diethanol amine, aminomethyl phosphoric acid, ethoxyl glycine and the like, into ammonium radical ions, and then concentrating and separating to obtain a phosphate and amine salt inorganic compound for recycling. The invention can effectively oxidize the complex organophosphorus and the nitrogen-containing compounds in the glyphosate mother solution into a single phosphate radical and amine salt inorganic compound for convenient separation and recycling and simultaneously reduces the environmental pollution and the soil hardening of the mother solution; the total conversion rate of phosphorus-containing compounds reaches 60%-90%, the conversion rate of the nitrogen-containing compounds reaches above 90%, and the removing rate of the glyphosate reaches 95%-99% so that a great deal of generated phosphate and amine salt can be used for agricultural fertilizers, thereby achieving the purpose of turning wastes into valuable.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XINAN CHEM INDAL GROUP
Method and kit for determining apolipoprotein A2 by using immunity transmission turbidimetric method
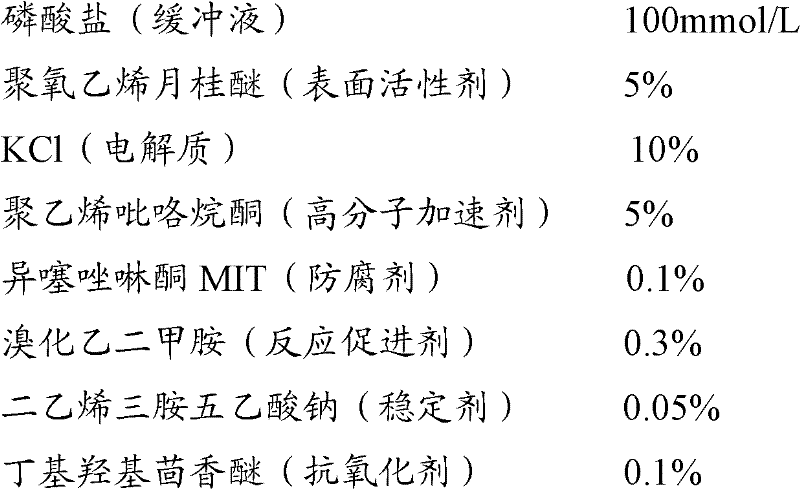
InactiveCN102507957AImprove anti-interference abilityEasy to operateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingHemolysisHigh fat
The invention provides a method for determining apolipoprotein A2 by using an immunity transmission turbidimetric method, and a kit composed of applied reagents. The reagents applied by the method comprises one or more stabilizing agent selected from substances of: glycol(alpha-amino ethyl)ether tetraacetic acid, iminodiacetic acid, sodium polyoxyethylene fatty alcohol ether sulfate (AES), 1,2-cylohexanediol diglycidol, sodium diethylene triamine pentacetate, and hexapolyglycerol dioleates; and one or more high-molecular accelerating agents selected from substances of: fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether, polyvinylpyrrolidone, glycol polyoxylethylene ether, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, carboxymethyl cellulose, and sodium polyacrylate. The method provided by the invention can be used in batch detection and analysis. The method and the kit have high anti-interference capabilities against high fat, jaundice and hemolysis samples.
Owner:BEIJING LEADMAN BIOCHEM
Secondary battery negative electrode material
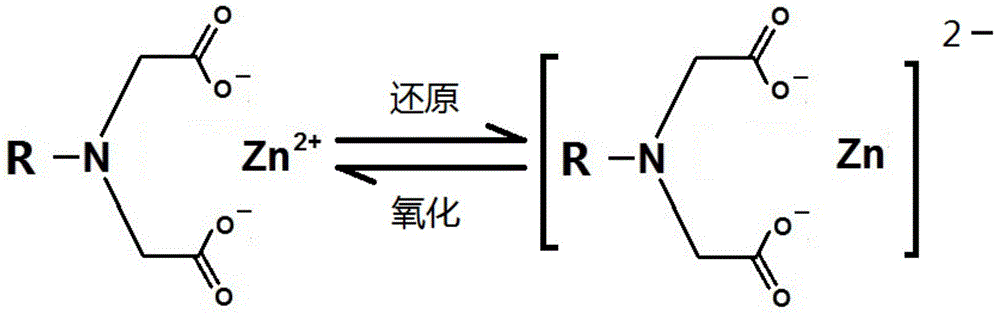
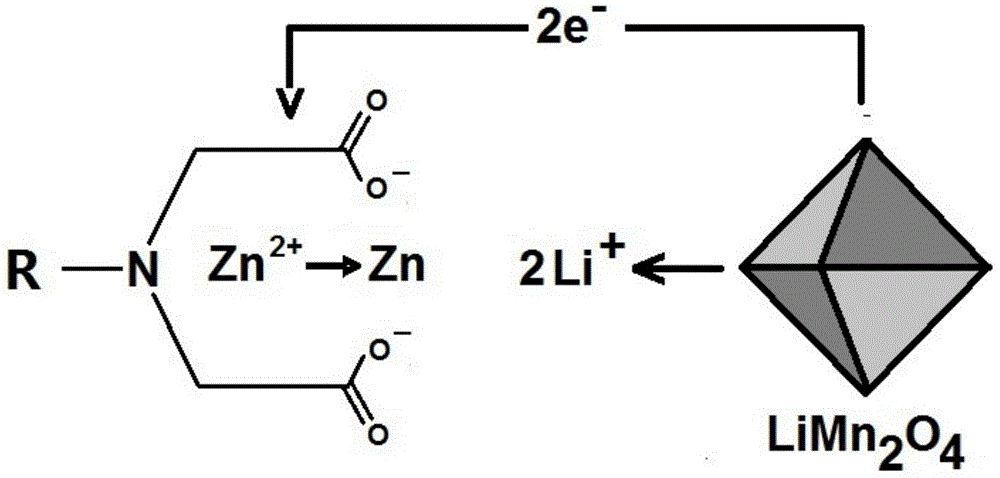
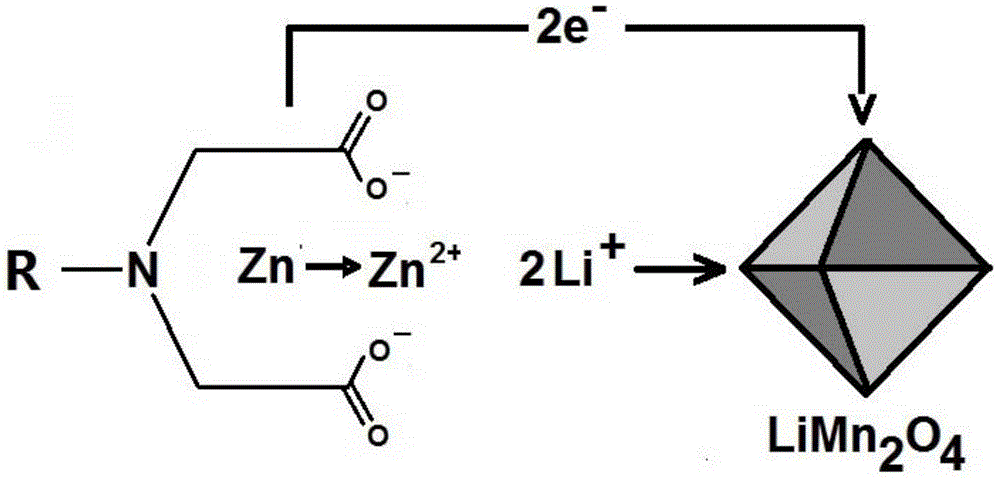
ActiveCN104659342AImprove performanceSolving intractable dendrite problemsCell electrodesElectrochemical responseIminodiacetic acid
The invention discloses a secondary battery negative electrode material which comprises a framework, a chelation / adsorption radical and an active substance, wherein the framework does not participate in electrochemical reaction, and only provides a carrier for the chelation / adsorption radical; the chelation / adsorption radical comprises outer electrodes of atoms of N, S, P, O and the like, and can form a chelated / chemical adsorption bond (represented by an iminodiacetic acid chelated radical in figure) with two-valent and polyvalent metals; the active substance can be two-valent and polyvalent metal ions which can be reduced into relatively low valent. During charging, the metal ions which are taken as the active substance is reduced into a relatively-low-valent state or a metal elemental state; during discharging, the metal ions are reversely generated and form chelated / chemical adsorption bonds with the chelation / adsorption radical. The negative electrode material can be matched with a plurality of positive electrode materials to form a battery. The battery negative electrode disclosed by the invention is novel in principle and structure, expected to be applied to electric vehicles and large-scale energy storage projects due to low price and reliability.
Owner:浙江精研深蓝新能源科技有限公司
Refining process method of by-product salt on production line of glyphosate
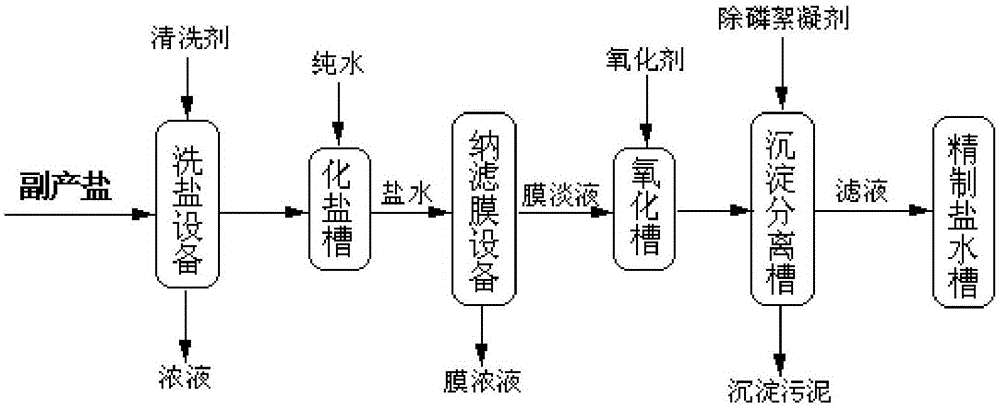
ActiveCN105036155ARealize resource utilizationTo achieve the purpose of purifying solid saltAlkali metal halide purificationResource utilizationToxic industrial waste
The invention belongs to the technical field of environment protection and relates to a refining process method of by-product salt on a production line of glyphosate. The method is specifically applied to the treatment of waste water of glycine glyphosate mother liquor and treatment of by-product salt in the industries of PMIDA mother liquor, iminodiacetic acid mother liquor, trimethyl phosphate mother liquor and chlor-alkali; due to the fact that the solid waste salt on the production process line of glyphosate contains a large amount of organic matters, the solid waste salt can not be applied but serve as industrial waste salt. By means of the process method, most organic matters in the solid salt can be removed, the purpose of purifying the solid salt is achieved, the purified solid salt or refined saline water can be used for other industries such as chlor-alkali production and caustic soda production, the resource utilization of the waste is achieved, and great economic benefit and social benefit are achieved.
Owner:HANGZHOU TIAN CHUANG ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Treatment process of glyphosate mother liquor
ActiveCN101525351AAchieve recyclingLess impuritiesBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsFiltrationHexamethylenetetramine
The invention relates to a treatment process of glyphosate mother liquor, comprising the following steps: step 1. glyphosate mother liquor is the remaining mother liquor extracted after the glyphosate technical is crystallized and separated out in the process of preparing glyphosate by iminodiacetic acid method; step 2. the mother liquor is pretreated by ultra-filtration to cause the pollution index of the mother liquor to be less than or equal to 5; step 3. strong liquor (1) with concentration of 2%-7% and light liquor (1) with concentration of 0%-0.1% are obtained from the mother liquor by a first order membrane separation and are respectively collected in storage tanks, strong liquor (2) with concentration of 5%-15% and light liquor (2) with concentration of 0.1%-0.2% are obtained fromthe strong liquor (1) by a second order membrane separation and are respectively collected in storage tanks; step 4. the strong liquor (2) is cooled to negative 10 DEG C to 25 DEG C for crystallizingand separating to obtain glyphosate bulk drug and filtrate, the filtrate is used indiscriminately for 1-20 times, the light liquor (2) returns to the first order membrane for separation; step 5. the light liquor (1) in step 3 is fed with ammonia until pH is equal to 8-11 and generates urotropine, urotropine solution with the mass percentage of 5%-40% and light liquor (2) with the pH of 7-11 are obtained after a third order and a fourth order membrane separation; and step 6. after the filtrate in the step (4) is used indiscriminately for 1-20 times, the remaining filtrate is added with water according to the proportion of 1:0.5-5 to remove formaldehyde, glyphosate filtrate with the content of formaldehyde less than or equal to 0.30% is obtained and is used for preparing gyphosate solution.
Owner:HANGZHOU TIAN CHUANG ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
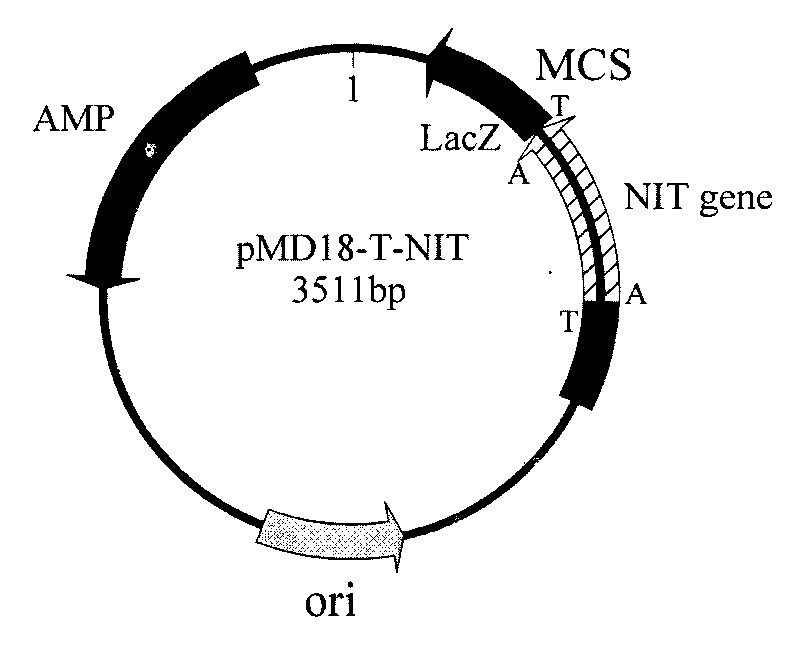
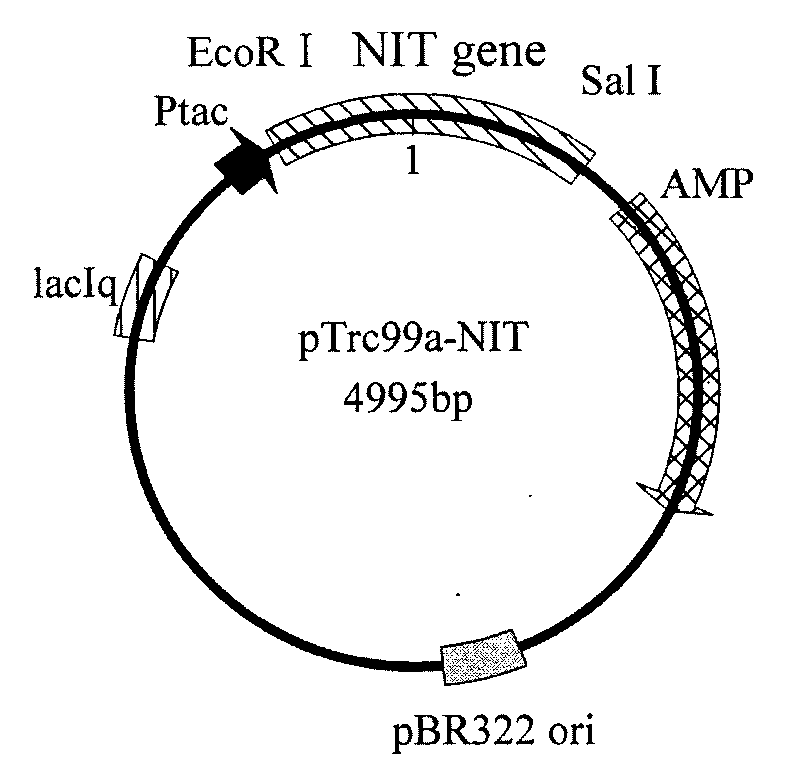
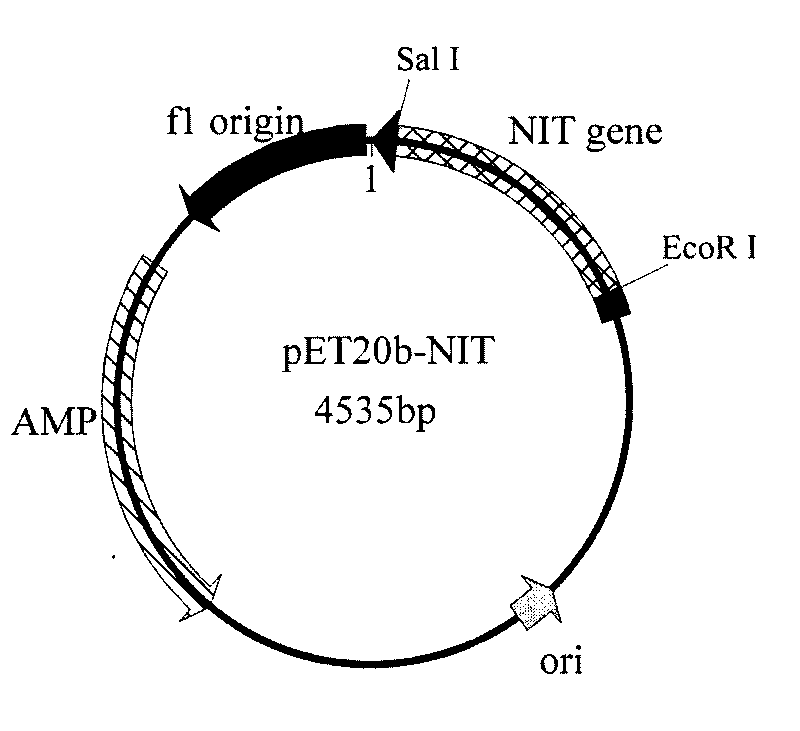
Nitrilase gene, vector, engineering bacteria and application thereof
The invention provides a nitrilase gene coding nitrilase, a recombinant vector containing the gene, a recombinant gene engineering bacteria obtained by converting the recombinant vector and application thereof in preparing recombinant nitrilase. The nitrilase gene can be connected with an expression vector for construction to obtain endoenzyme expression recombinant plasmid containing the gene or secretion expression recombinant plasmid, and then the endoenzyme expression recombinant plasmid containing the gene or the secretion expression recombinant plasmid is respectively and correspondingly converted to a colibacillus bacterial strain to obtain recombinant colibacillus; the recombinant colibacillus contains recombinant nitrilase and can recombine colibacillus into an enzyme resource for biological catalysis and conversion. The recombinant nitrilase serves as the enzyme for conversion, and racemisation mandelonitrile, acrylonitrile, iminodiacetonitrile or 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane carbonitrile and the like serve as a substrate for converting to react and prepare corresponding R-mandelic acid, crylic acid, iminodiacetic acid or chiral 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane formic acid and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for treating N-Phosphonomethyl iminodiacetic acid (PMIDA) mother liquid
ActiveCN102874983AAchieving zero emissionsSolve processing problemsMultistage water/sewage treatmentNature of treatment waterInorganic saltsIminodiacetic acid
The invention relates to a method for treating an N-Phosphonomethyl iminodiacetic acid (PMIDA) mother liquid which is obtained by producing glyphosate by an iminodiacetic acid method. The method includes adding alkaline substances into the PMIDA mother liquid, adjusting potential of hydrogen (pH) of the mother liquid to be in a range from 9 to 12, subjecting the mother liquid to multiple-effect evaporation and concentration, filtering to obtain a filter cake and a filter liquid, washing the filter cake to remove organic matters to obtain inorganic salt, and burning the filter liquid to obtain pyrophosphate. The method for treating the PMIDA mother liquid has the advantages that chlorine containing substances and phosphorus containing substances in the mother liquid can be recycled in a high yield coefficient mode, the process is simple, the environment-friendly benefit is remarkable, and the method is suitable for popularization and usage in industrial mass production.
Owner:SHANDONG WEIFANG RAINBOW CHEM
Core-shell type magnetic composite microsphere for separation and purification of recombinant proteins and preparation method thereof
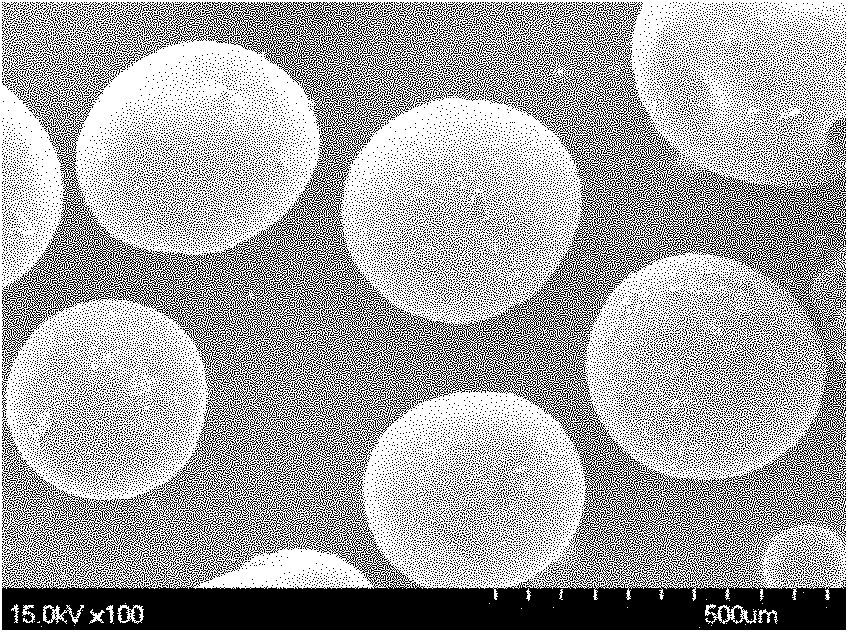
InactiveCN103665278AUniform particle size distributionRegular structureInorganic material magnetismPeptide preparation methodsPolymer networkHistidine
The invention belongs to the technical field of nano functional materials, and particularly relates to a core-shell type magnetic composite microsphere for the separation and purification of recombinant proteins and a preparation method thereof. A core of the core-shell type magnetic composite microsphere disclosed by the invention is a magnetic ferroferric oxide nano particle cluster, and a shell of the core-shell type magnetic composite microsphere is a crosslinked polymer network containing epoxy groups. The core-shell type magnetic composite microsphere is prepared through the following method implemented through the steps that: a magnetic nano particle cluster with stable sodium citrate is prepared firstly; then, by using a sol gel method, an active vinyl functional group is modified on the surface of the magnetic cluster; a high-magnetic-responsiveness monodispersed core-shell type magnetic composite microsphere of which the surface is rich in epoxy groups is prepared through distilling-precipitation polymerization; an iminodiacetic acid is adopted for carrying out ring-opening reaction with the epoxy groups and complexing nickel ions; finally, histidine marked proteins are separated and purified. The preparation method of the core-shell type magnetic composite microsphere is simple, controllable in process, and high in efficiency of separation and purification of recombinant proteins. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the thickness and crosslinking degree of a polymer shell layer and the density of surface functional groups can be precisely controlled, therefore, the method has a good application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI YAOKE BIOTECH DEV
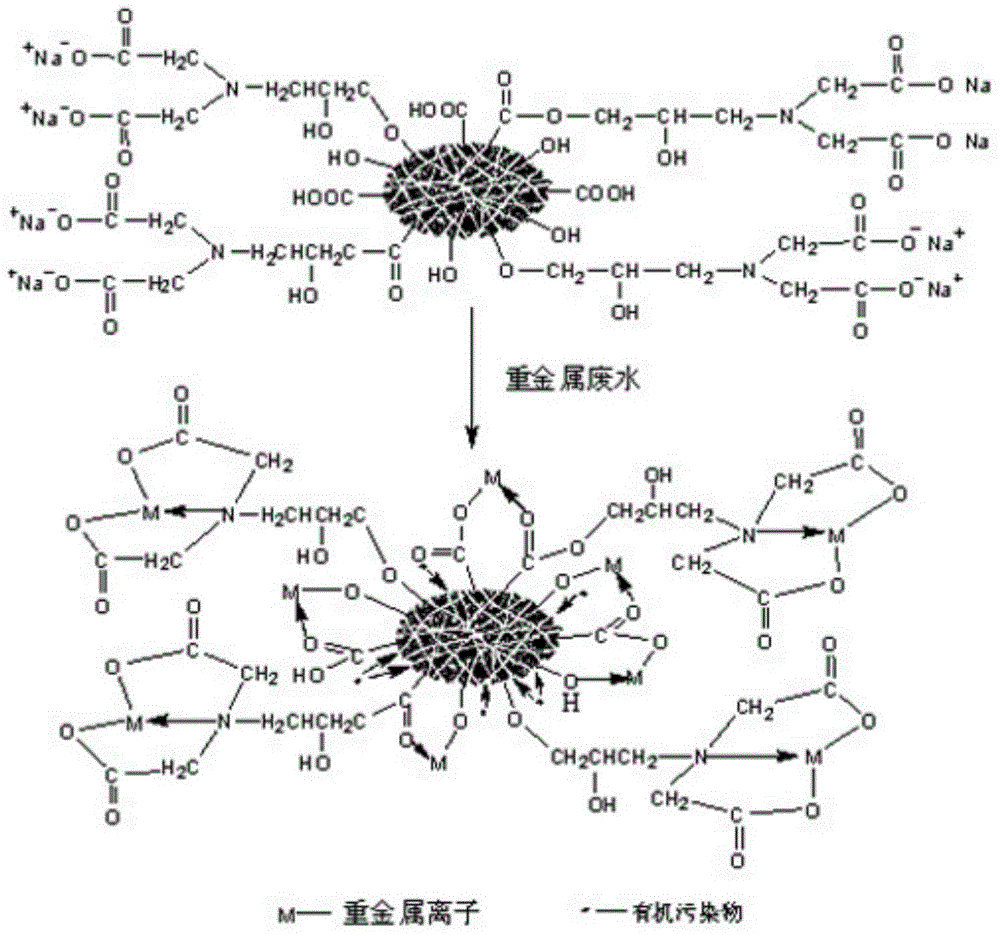
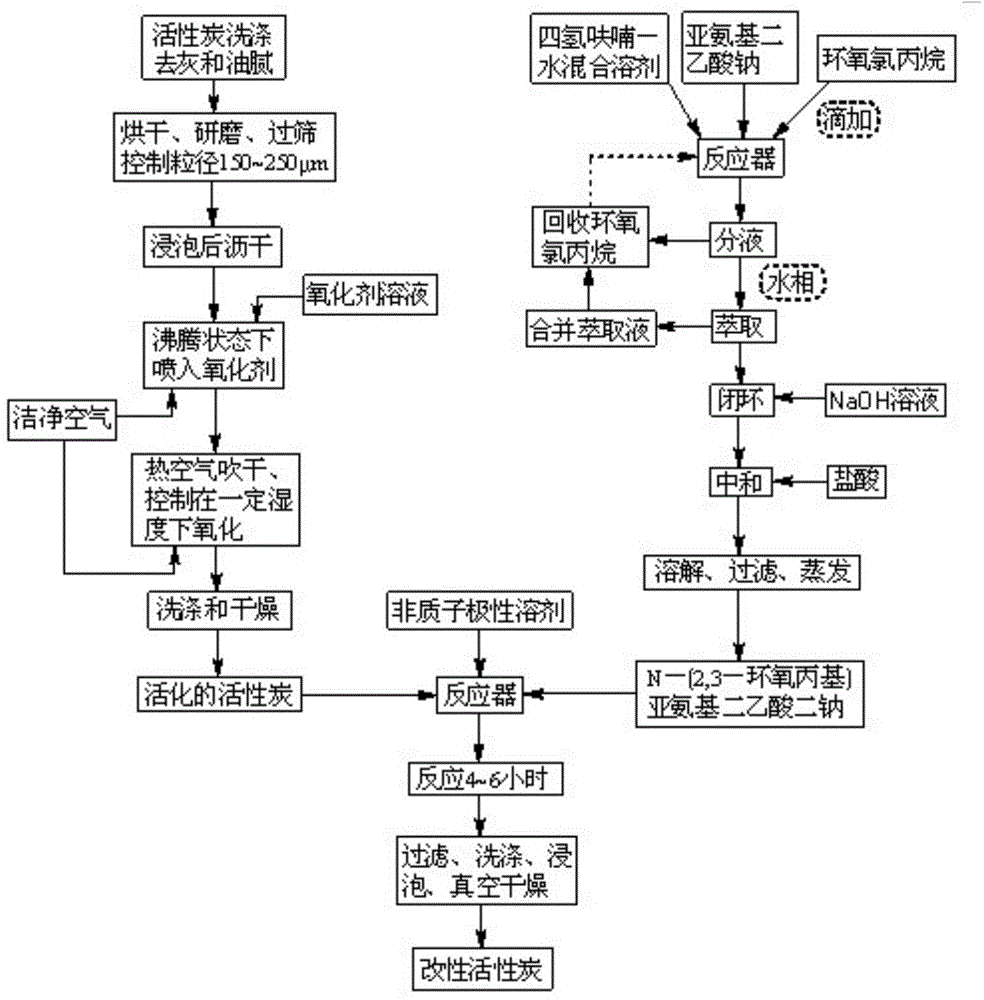
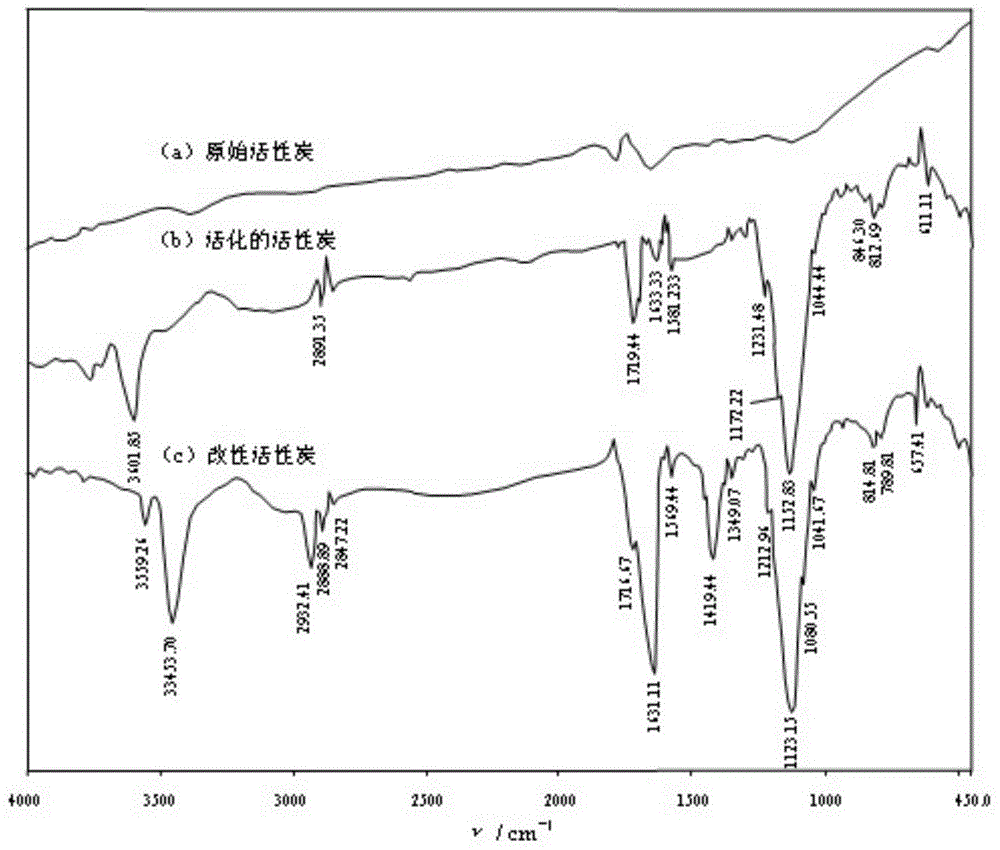
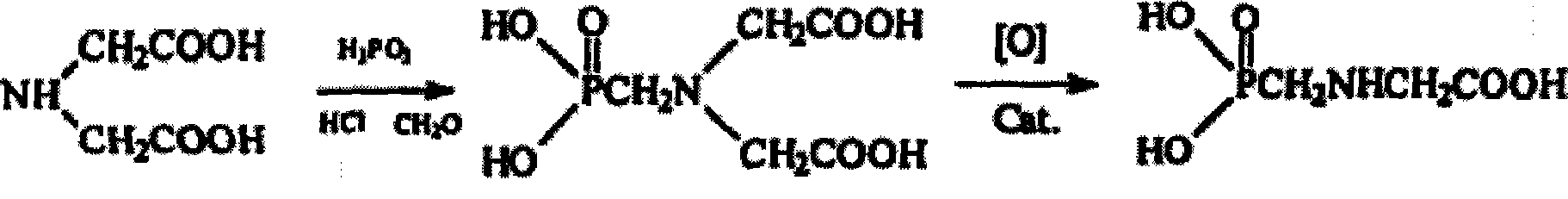
Preparation method of modified activated carbon used for heavy metal wastewater treatment
ActiveCN104525129AReduce oxidationMaintain structural propertiesOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesActivated carbonEpoxy
The invention discloses a preparation method of modified activated carbon used for heavy metal wastewater treatment. The preparation method comprises the steps that firstly, activated carbon is washed, dried, ground, sieved and soaked, so that pores of the activated carbon are filled with water; secondly, clean air is blown so that the activated carbon can be in a boiling state, and an oxidizing agent is sprayed for controllable oxidation; thirdly, N-(2,3-glycidyl) iminodiacetic acid disodium allows iminodiacetic acid disodium to be connected to the surface of the activated carbon through epoxy group ring opening. According to the prepared modified activated carbon, hydroxyls, carboxyls and iminodiacetic acid groups having a strong effect on heavy metal ions are introduced only on the surface, the original hole channel structure feature of the activated carbon is maintained, the capacities of strong heavy metal adsorption and organic pollutant removal are both achieved, and the dual purposes of removing heavy metal and organic pollution can be achieved by one step through adsorption via activated carbon. Meanwhile, the adsorbed heavy metal is easy to recycle, the activated carbon is easy to regenerate, the cycle service life of the activated carbon is long, no secondary pollution will occur, and therefore the preparation method has good application and popularization prospects.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing glyphosate by oxidizing N-(Phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid with active carbon as catalyst oxygen
ActiveCN101508701AExtensive sources of raw materialsWide variety of sourcesBiocidePhysical/chemical process catalystsIminodiacetic acidOxygen
The invention discloses a method for preparing glyphosate by taking active carbon as a catalyst and oxidizing N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid with oxygen. The method comprises the following steps: taking the active carbon which is made from coal, coconut shell and wood and has specific surface area of 800-1200m / g as the catalyst; oxidizing the N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid in the presence of the oxygen to prepare the glyphosate with reaction selectivity of 98% and 99% conversion of the N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid and solid glyphosate yield of 98.61-97.12% while producing a small amount of formaldehyde gas during the reaction; filtering after the reaction is over and then recovering the active carbon catalyst for indiscriminate use; supplementing 5% of the active carbon for each batch, wherein, the activity of the catalyst does not reduce after the oxidization reaction is repeated for 20 batches. The recovered catalyst and water can be repetitively used indiscriminately and recovered after the reaction without waste gas, waste water and waste residue. The method has the advantages of low material cost and convenient use.
Owner:SHANGHAI TAIHE INT TRADE CO LTD
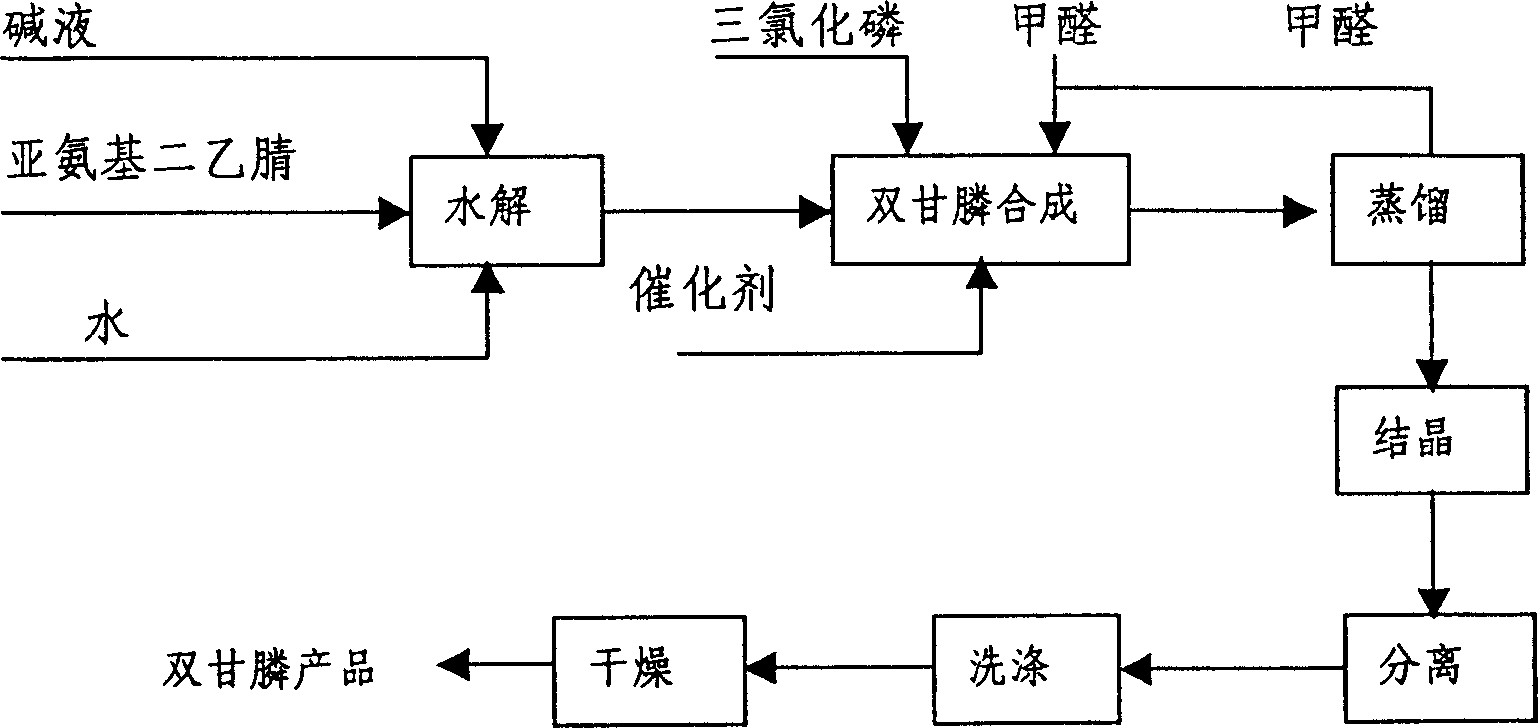
Method for preparing Phosphonomethyl iminodiacetic acid (PMIDA) through hydrolysis of imino diacetonitrile
InactiveCN1916005AShort process routeSave investmentGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSaline waterIminodiacetic acid
This invention discloses a method for preparing N-phosphonomethyl iminodiacetic acid (PMIDA) by iminodiacetonitrile hydrolysis. The method comprises: (1) hydrolyzing iminodiacetonitrile (greater than or equal to 95 wt.%) in an alkali solution under stirring at 20-100 deg.C and -(0.01-0.04) MPa to obtain iminodiacetate solution; (2) dropping phosphorous trichloride (1.0-1.5 mol times of iminodiacetonitrile) to the iminodiacetate solution at 20-100 deg.C and -(0.01-0.04) MPa with an acidic catalyst added before or after the phosphorous trichloride addition; (3) adding formaldehyde at a temperature not lower than 80 deg.C; (4) reacting at 100-120 deg.C for 1-7 h to obtain PMIDA suspension; (5) vacuum-distilling to recover formaldehyde; (6) crystallizing, separating, washing and drying to obtain PMIDA with a purity higher than 98%. The method has such advantages as simple process, low cost and high yield.
Owner:SICHUAN BEIER CHEM GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com