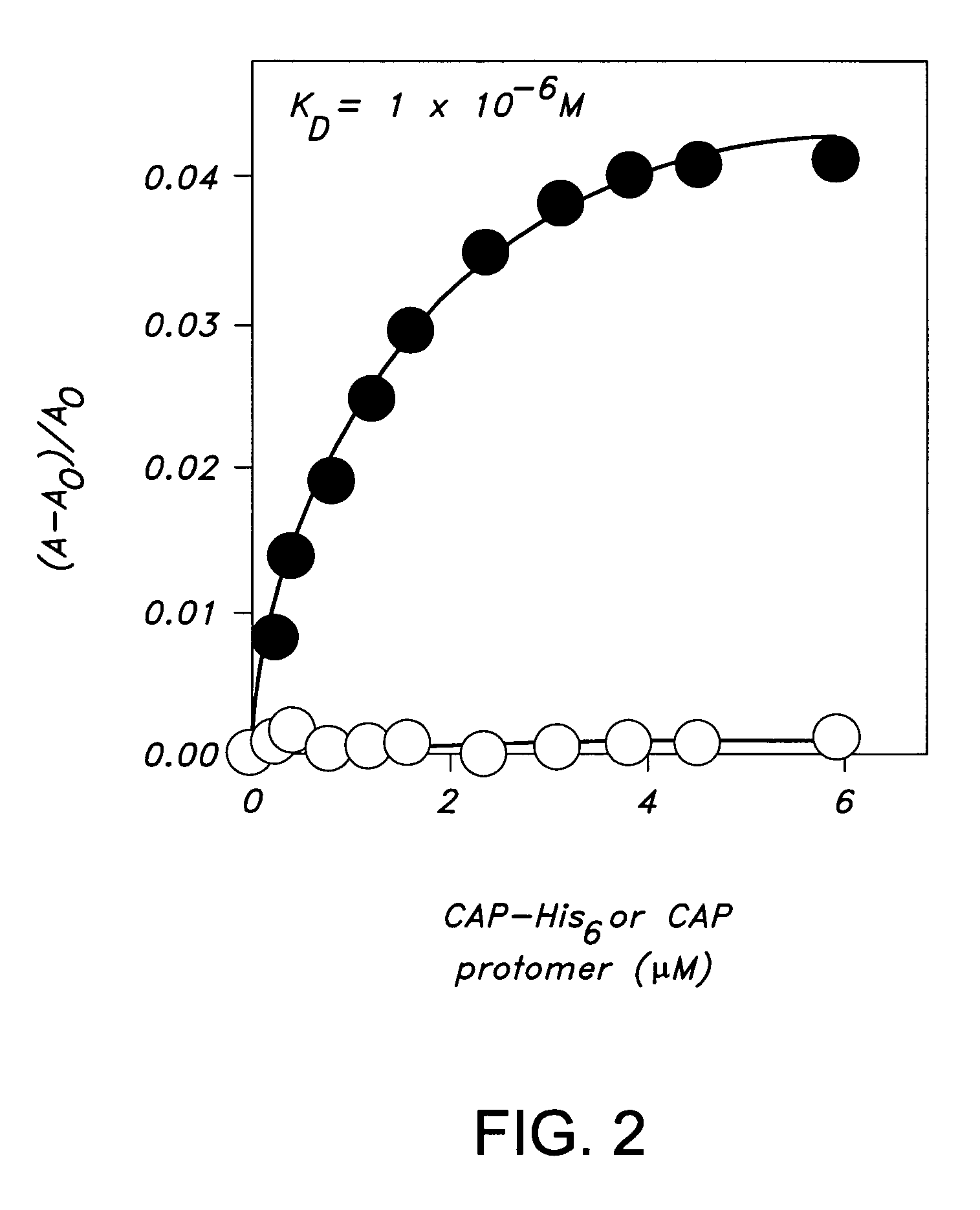
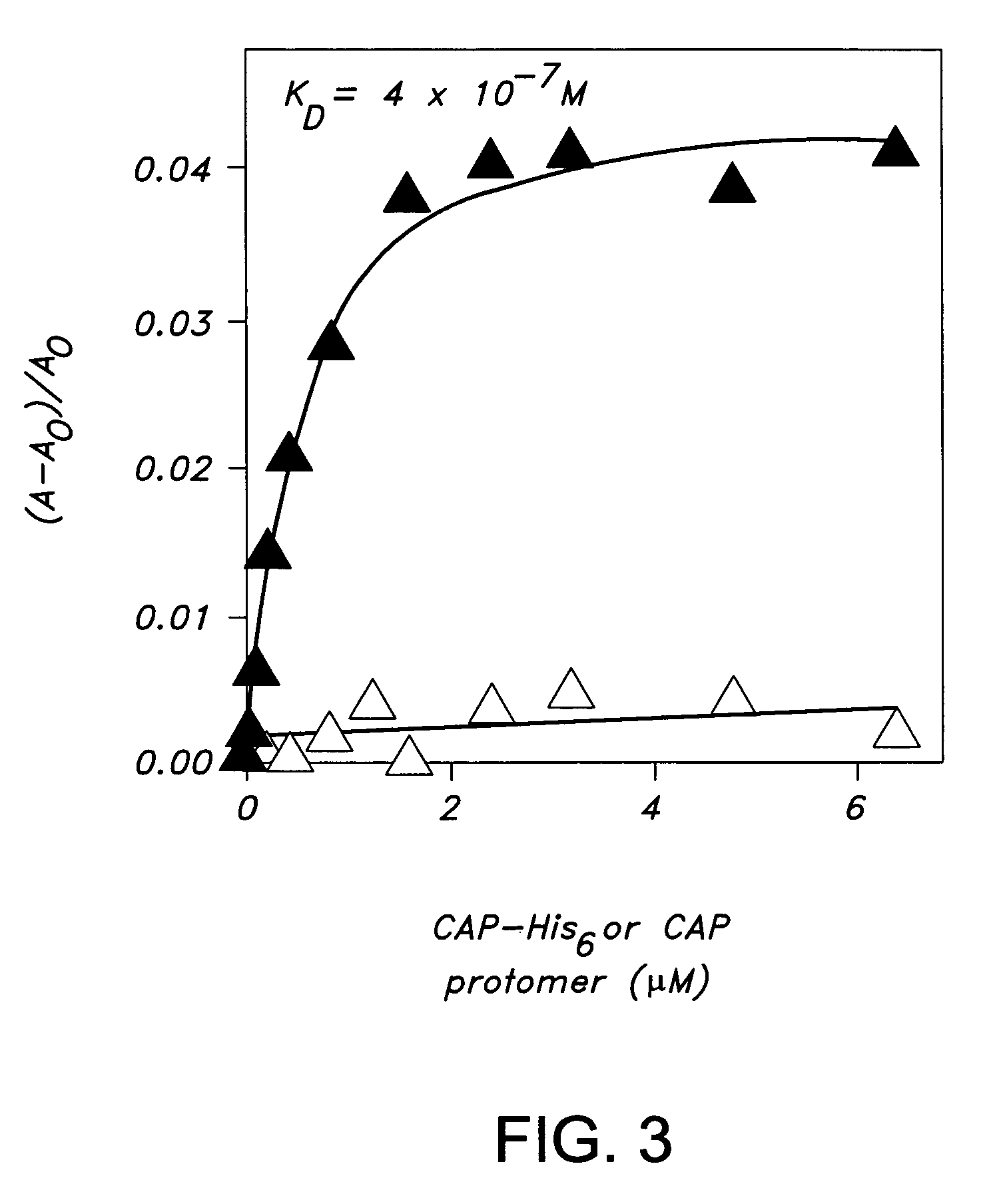
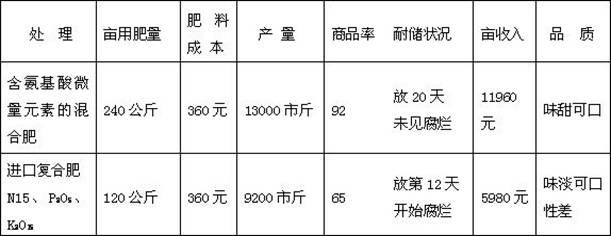
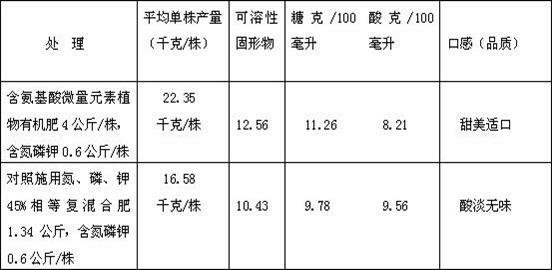
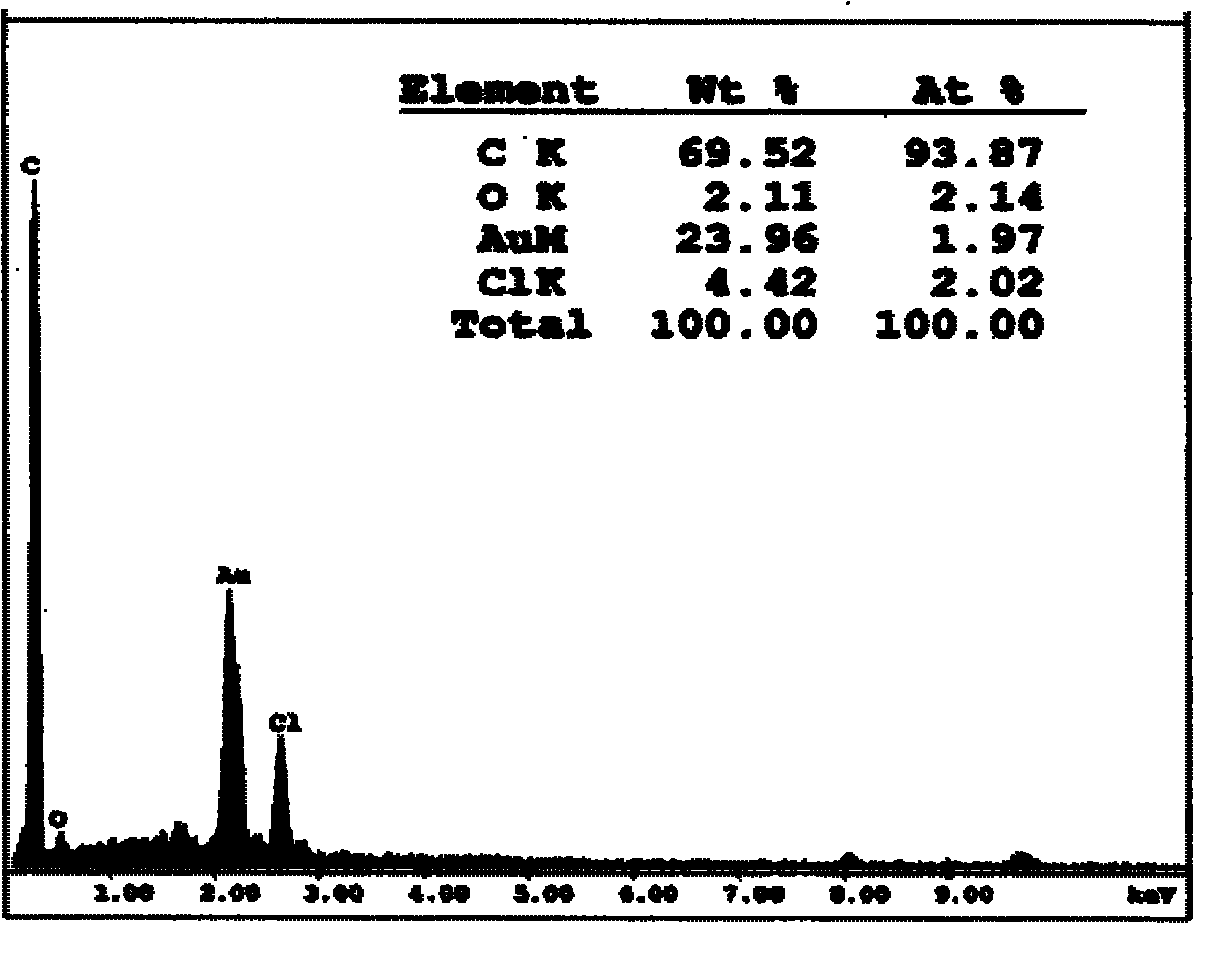
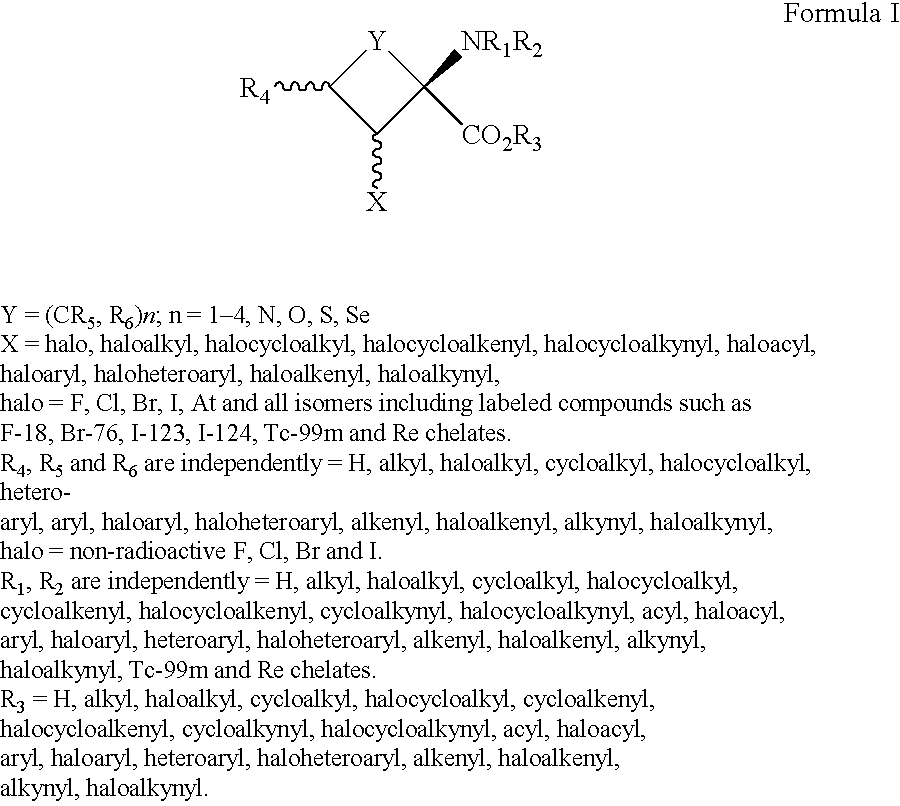
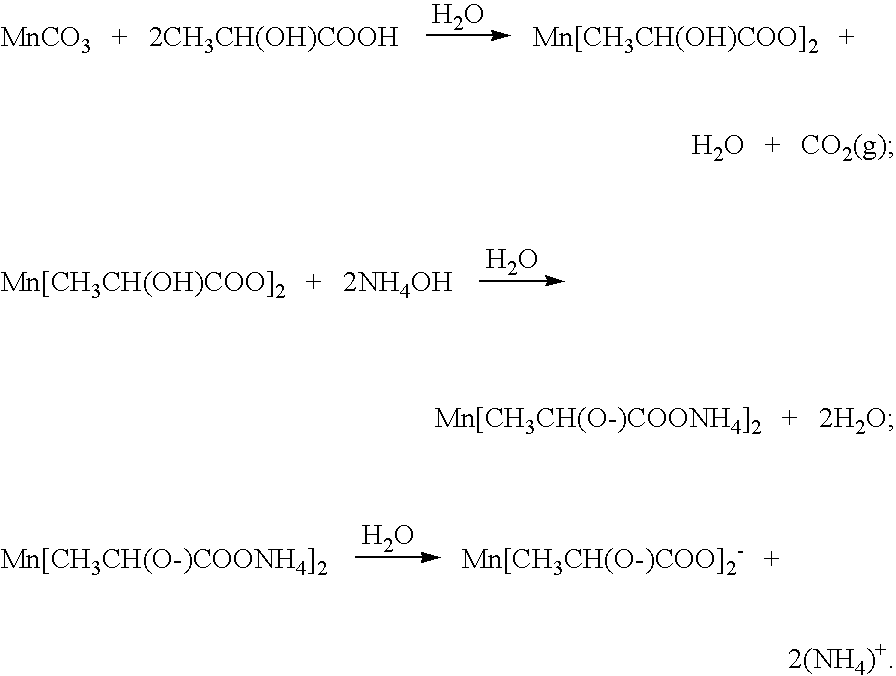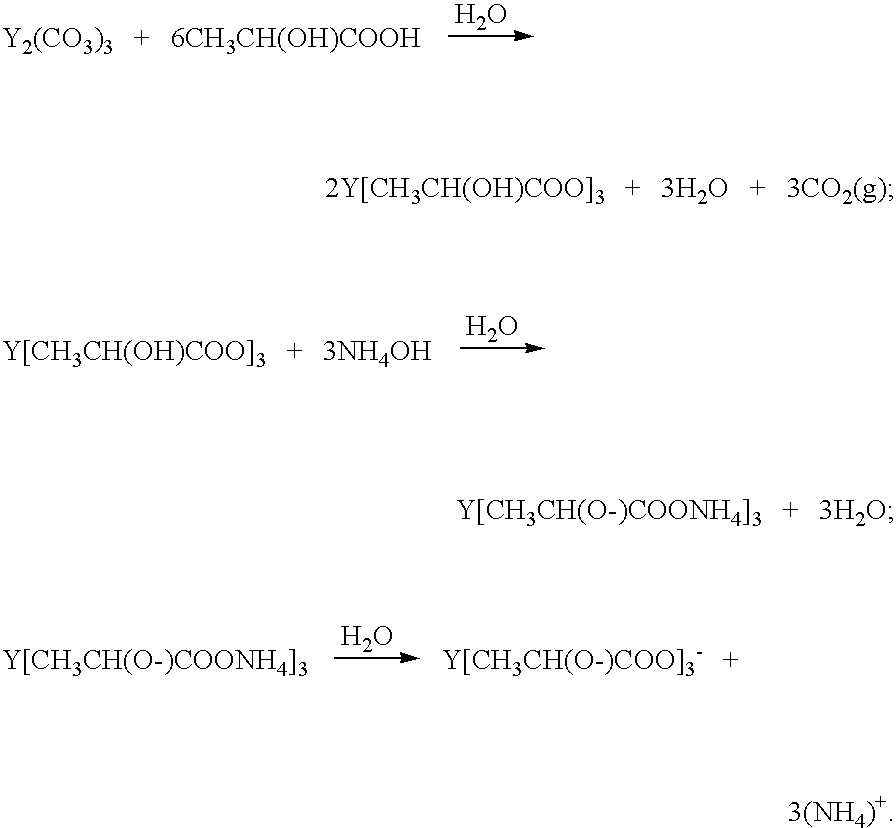Patents
Literature
2980 results about "Chelation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
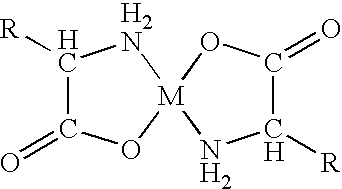
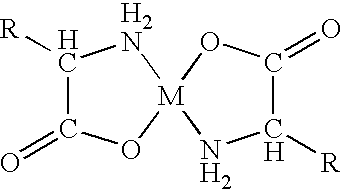
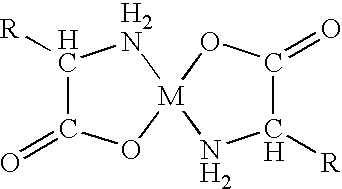
Chelation (US: /kiːˈleɪʃən/, UK: /tʃɪ-/) is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central atom. These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds.
Detergents having acceptable color
InactiveUS20090176684A1Reduce intensityOrganic detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsBenzeneTitanium
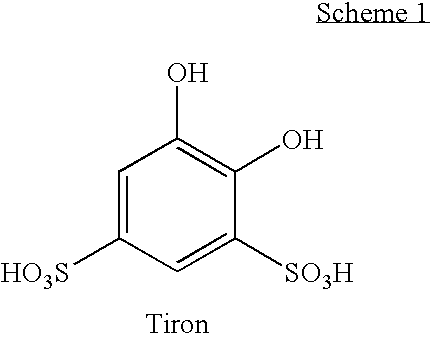
Detergent compositions containing catechols, such as tiron (1,2-dihydroxybenzene-3,5-disulfonic acid), which do not have or do not develop the reddish color associated with the catechol / ferric iron chelate are disclosed. Methods for reducing the intensity of red color in a tiron containing detergent composition are also disclosed.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Dimerized alcohol compositions and biodegradible surfactants made therefrom having cold water detergency
InactiveUS6222077B1Good cold water detergencyOrganic detergent compounding agentsOther chemical processesDouble bondCarboxylic acid
There is provided an alcohol composition obtained by dimerizing an olefin feed comprising C6-C10 linear olefins to obtain C12-C20 olefins, followed by conversion to alcohols, such as by hydroformylation. The composition has an average number of branches ranging from 0.9 to 2.0 per molecule. The linear olefin feed preferably comprises at least 85% of C6-C8-olefins. The primary alcohol compositions are then converted to anionic or nonionic surfactants, preferably sulfated or oxyalkylated or both. The sulfated compositions are biodegradable and possess good cold water detergency. The process for making the dimerized primary alcohol comprises dimerizing, in the presence of a homogeneous dimerization catalyst under dimerization conditions, an olefin feed comprising C6-C10 olefins and preferably at least 85 weight % of linear olefins based on the weight of the olefin feed, to obtain a C12-C20; optionally double bond isomerizing said C12-C20 olefins; and converting the C12-C20 olefins to alcohols, preferably through hydroformylation. The process is preferably a one-step dimerization. The homogenous catalyst comprises a mixture of a nickel carboxylate or a nickel chelate, with an alkyl aluminum halide or an alkyl aluminum alkoxide.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
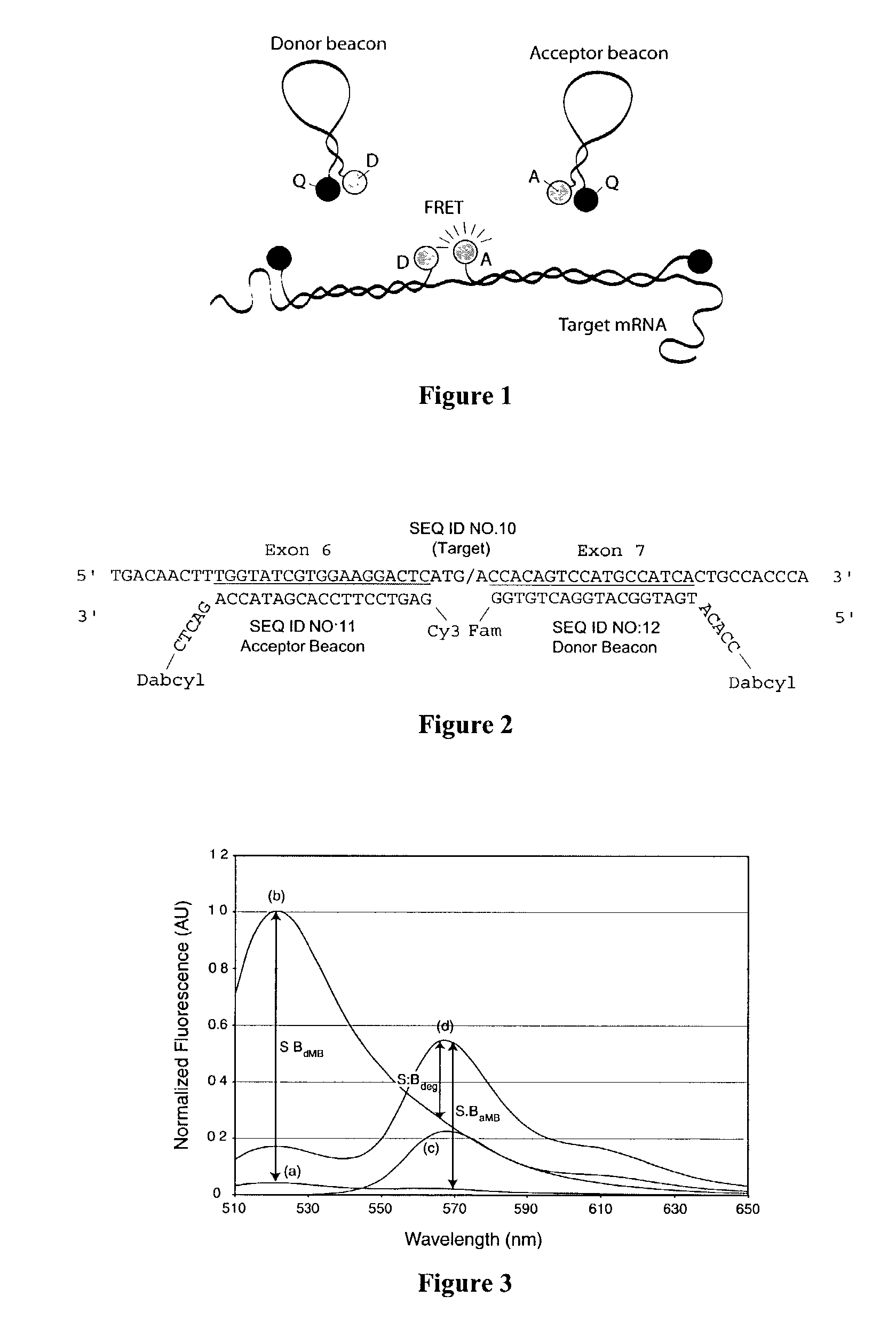
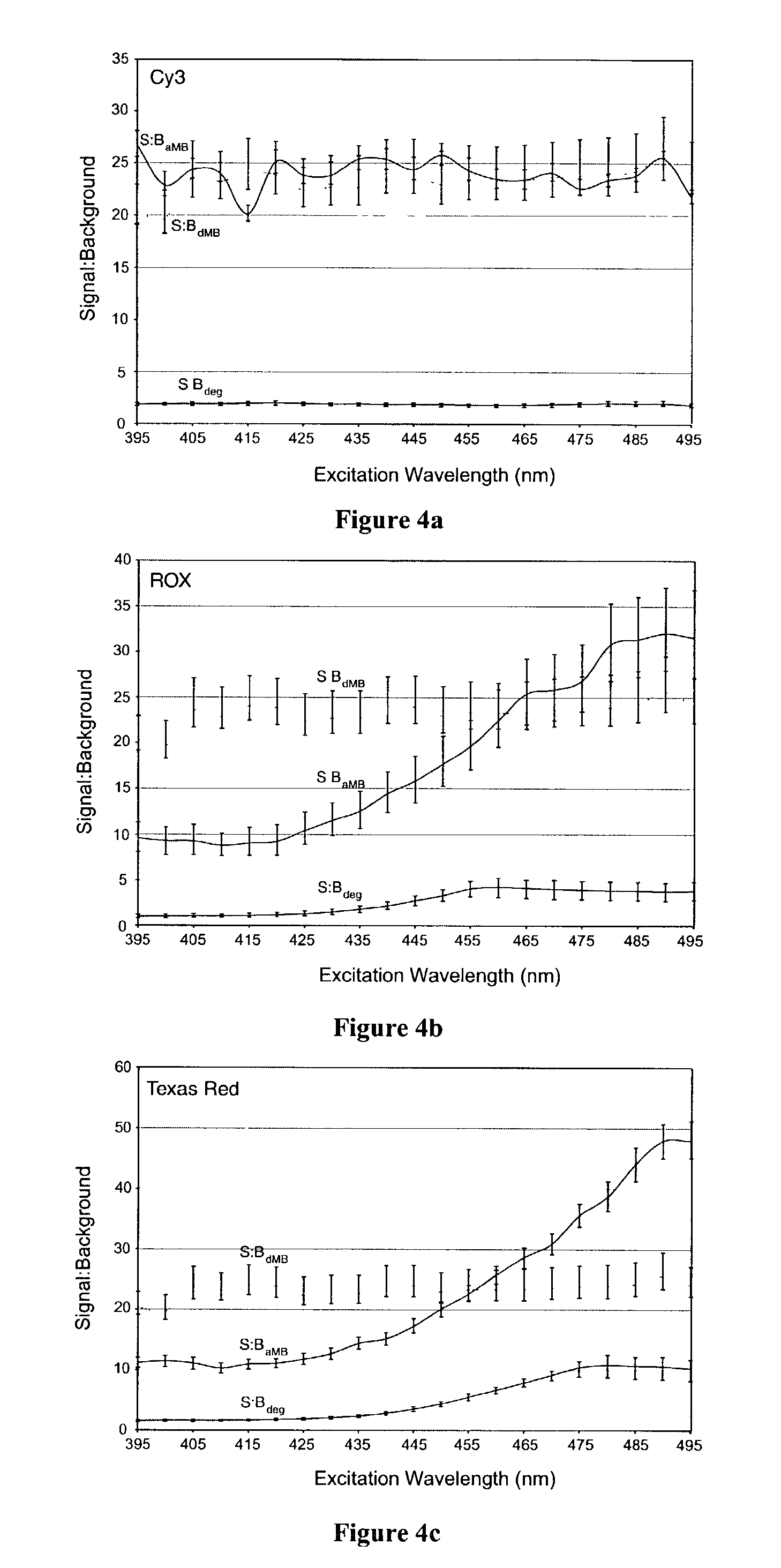
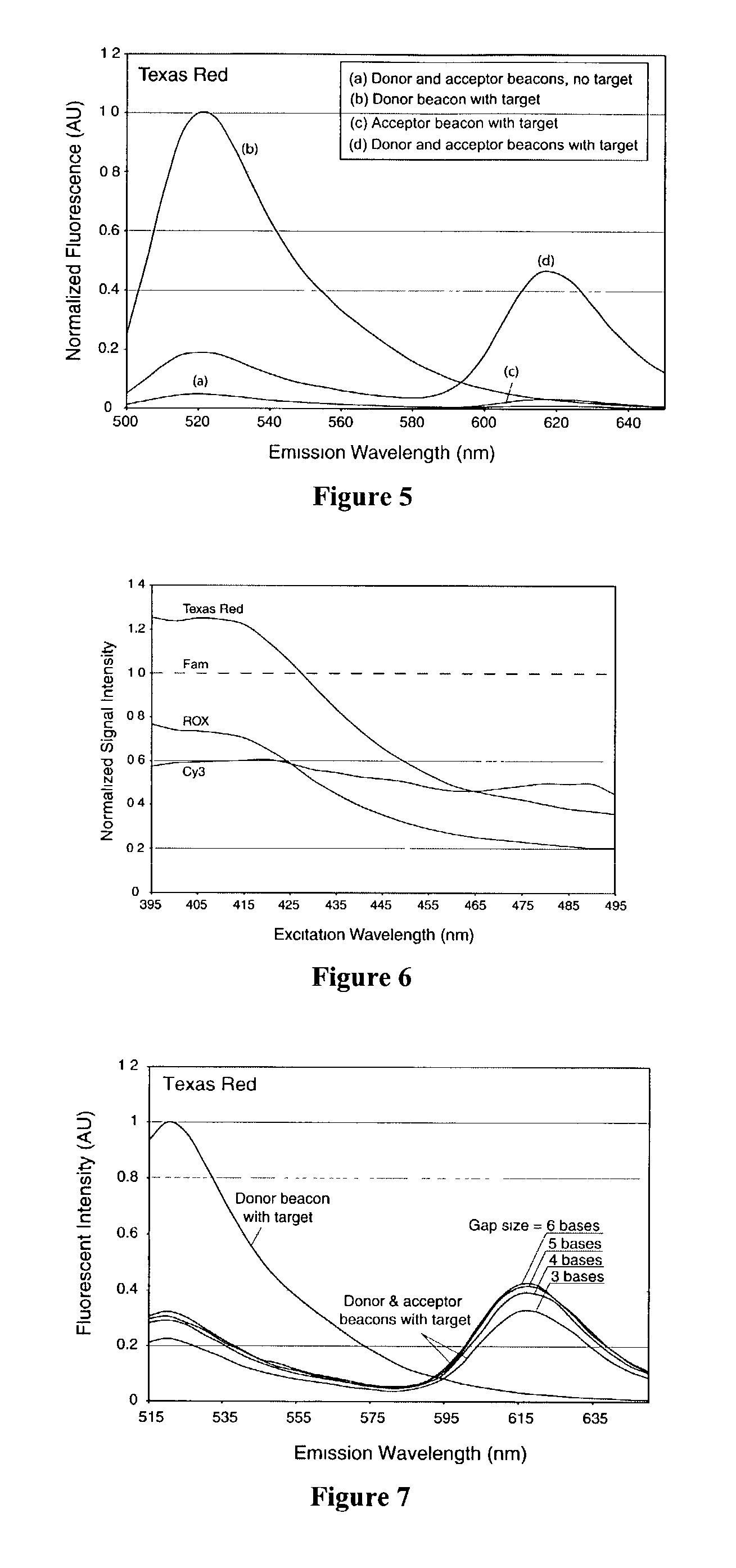
Dual resonance energy transfer nucleic acid probes
InactiveUS7081336B2Quick checkEasy to useSugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDiseaseCell specific
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Atomic layer deposition methods
InactiveUS7077902B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogen sourceNitride
An aluminum-containing material deposition method includes depositing a first precursor on a substrate in the substantial absence of a second precursor. The first precursor can contain a chelate of Al(NR1R2)x(NR3(CH2)zNR4R5)y or Al(NR1R2)x(NR3(CH2)zOR4)y; where x is 0, 1, or 2; y is 3−x; z is an integer 2 to 8; and R1 to R5 are independently selected from among hydrocarbyl groups containing 1 to 10 carbon atoms with silicon optionally substituted for one or more carbon atoms. The method includes depositing the second precursor on the first deposited precursor, the second precursor containing a nitrogen source or an oxidant. A deposition product of the first and second precursors includes at least one of an aluminum nitride or an aluminum oxide. The deposition method can be atomic layer deposition where the first and second precursors are chemisorbed or reacted as monolayers. The first precursor can further be non-pyrophoric.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
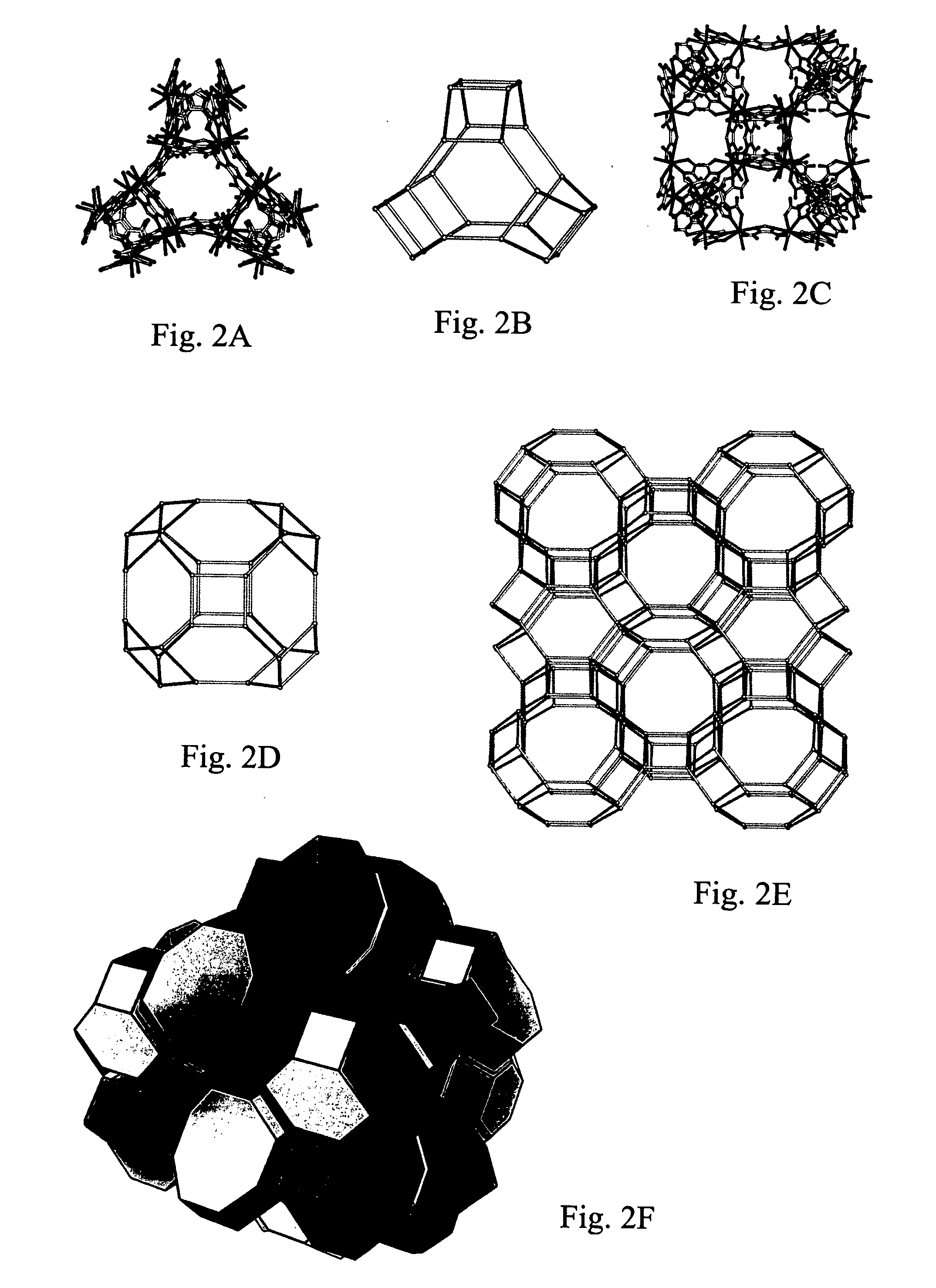
Zeolite-like metal organic frameworks (ZMOFS): modular approach to the synthesis of organic-inorganic hybrid porous materials having a zeolite like topology
InactiveUS20060287190A1Molecular sieve catalystsOther chemical processesMetal-organic frameworkModularity
The subject invention pertains to metal organic frameworks (MOF) having zeolite-net-like topology, their methods of use, and their modes of synthesis. The ZMOFs are produced by combining predesigned tetrahedral building, generated in situ using heterochelation, with polyfunctional ligands that have the commensurate angle and the required donor groups for the chelation. Each molecular building block is contrasted of a single metal ion and ligands with both heterochelation functionality and bridging functionality. Advantageously, zeolite-net-like MOFs of the subject invention are porous and contain large functional cavities, which is useful for encapsulating large molecules.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Mouth hygienic composition for the treatment of halitosis
InactiveUS6607711B2Pleasant organoleptic qualityUseful in treating and preventing and eliminatingCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsMedicineOral hygiene
Owner:PEDERSEN EJVIND JERSIE
Method of detecting leakage from geologic formations used to sequester CO2
InactiveUS7704746B1Low costLow detection limitDetection of fluid at leakage pointConstructionsGas phaseLeak detection
The invention provides methods for the measurement of carbon dioxide leakage from sequestration reservoirs. Tracer moieties are injected along with carbon dioxide into geological formations. Leakage is monitored by gas chromatographic analyses of absorbents. The invention also provides a process for the early leak detection of possible carbon dioxide leakage from sequestration reservoirs by measuring methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), and / or radon (Rn) leakage rates from the reservoirs. The invention further provides a method for branding sequestered carbon dioxide using perfluorcarbon tracers (PFTs) to show ownership.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Manufacture of composite roofing products with matrix formulated microbiocide
InactiveUS6245381B1Good dispersionEliminate the problemBiocideLiquid surface applicatorsAsphalt shingleBlue green algae
This invention discloses improved residential roofing products with durable active protection against algae discoloration. Versatile organometallic salts and chelates for this purpose are incorporated in manufacture of composite concrete tile and asphalt shingle products via integrated process modifications. These chemically stable non-volatile microbiocides, with exceptional effectiveness against both green and blue green algae, are tailored for specific matrix compatibility. By virtue of their composition and surface activity they serve a dual function in process improvement and product performance. The control of microbiocide activity, long term, significantly advances the state-of-the-art protection against algae and the service life of these products.
Owner:TAMKO BUILDING PRODS
Cereal grains fortified with amino acid chelates and process of making
A composition and method of making a processed cereal piece fortified with a metal amino acid chelate is disclosed and described. A processed cereal piece and one or more metal amino acid chelates may be combined by either 1) admixing the metal amino acid chelate(s) into the dough, flour or other precursor prior to toasting and / or otherwise cooking; and / or 2) coating the processed cereal piece with the metal amino acid chelate(s).
Owner:ALBION LAB
Bis-transition-metal-chelate probes
A molecule for labeling a target material is provided including two transition-metal chelates and a detectable group. The molecule has the general structural formula (I):wherein: (a) Y and Y′ are each a transition metal, (b) R1 and R1′ are each independently CH(COO−), CH(COOH), or absent; (c) R2 and R2′ are linkers each having a length of from about 3.0 to about 20 Å; and (d) X is a detectable group. The linkers may be linear or branched, may contain aromatic moieties, and may optionally be further substituted. Methods of using the molecules of the invention as probes in detecting and analyzing target materials as well as kits including the molecule of the invention are also provided.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Compound amino acid organic fertilizer and production method of compound amino acid organic fertilizer
The invention disclose a compound amino acid organic fertilizer, which is characterized in that the compound amino acid organic fertilizer consists of the following ingredients in parts by weight: 5 to 10 of compound amino acid, 0.3 to 0.5 of microbial yeasts, 16 to 29 of inorganic fertilizers, 5 to 10 of humic acid fertilizers and 0.2 to 1 of trace elements. A production method of the compound amino acid organic fertilizer comprises the following steps that: firstly, compound amino acid water solution, the microbial yeasts and the humic acid fertilizers are respectively prepared, then, inorganic compounds containing boron, copper, iron, manganese and zinc are added into the compound amino acid water solution, and the chelation is carried out at a temperature being 80 to 110 DEG C so that the mixture becomes free-state chelated amino acid salt; after the metering, 10 to 50kg of raw materials are added into each ton of farmyard manure to be mixed, then, the mixed materials are placed into a warehouse for natural stacking and curing for 3 to 5 days and can be pelletized and packed to leave factories. The compound amino acid organic fertilizer can be used as a base fertilizer and an additional fertilizer and belongs to a compound organic fertilizer capable of improving the amino acid content of high-quality fragrant rice and fruit and vegetables, improving the fruit and vegetable quality and improving the sugar content of sugarcanes.
Owner:GUANGXI YUXIN BIOLOGICAL TECH
Methods for the preparation and use of ferric pyrophosphate citrate chelate compositions
A highly water soluble ferric pyrophosphate citrate chelate useful for treating iron deficiency contains 2% or less phosphate by weight. These chelate compositions are easily milled and / or processed into dosage forms using conventional techniques, and are expected to exhibit advantageous biocompatibility as compared to conventional soluble ferric pyrophosphates, ferric salts, ferric polysaccharide complexes and ferrous salts.
Owner:ROCKWELL MEDICAL INC
Prefabricated amino chelate mixed feed
InactiveCN1484971AReduce manufacturing costEasy to useAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsManganeseCopper
A premixing feedstuff of amino acid chelate, which is prepared by mixing a chelating complex of amino acid and iron, a chelating complex of amino acid and copper, a chelating complex of amino acid and manganese, a chelating complex of amino acid and zinc and hydrolyzed protein and a carrier. The feedstuff could be added into various foodstuffs, the adding amount could be 1.0í½2.0úÑ relative of the whole feed. The feedstuff could replace fish meat by 1:1, replace soybean cake by 1:1.5.
Owner:石家庄市科星动物保健品有限公司
Water-based cleaner
ActiveCN101538512ACause wasteAvoid cleaning costsInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsWater basedSodium metasilicate
A water-based cleaner is prepared by surfactant primary washing part, alkaline auxiliary washing part, solvent part, preservative and water; wherein the surfactant primary washing part is compounded by anion and nonionic surfactant; the alkaline auxiliary agent part selects trolamine, sodium metasilicate pentahydrate which has dispersive action on dirt and EDTA disodium which has chelation on metallic ions, and excludes phosphate accessory aid which pollutes water quality. The solvent part selectes alcohol, glycol ether or natural orange oil extract D-limonene which have good safety performance, strong solvency and little environmental pollution. The preservative selects food grade preservative propylparaben which is safe and nontoxic. The invention adopts concentrate formula, the preparation method is simple, users can dilute the product according to object to be washed and the degree of dirt, and operate with reasonable using concentration, thus avoiding the waste of washing cost due to excessive concentration and the waste of energy. The inventive water-based cleaner reduces package cost and transportation cost, and has no adverse effect on the environment.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIUSHENG IND
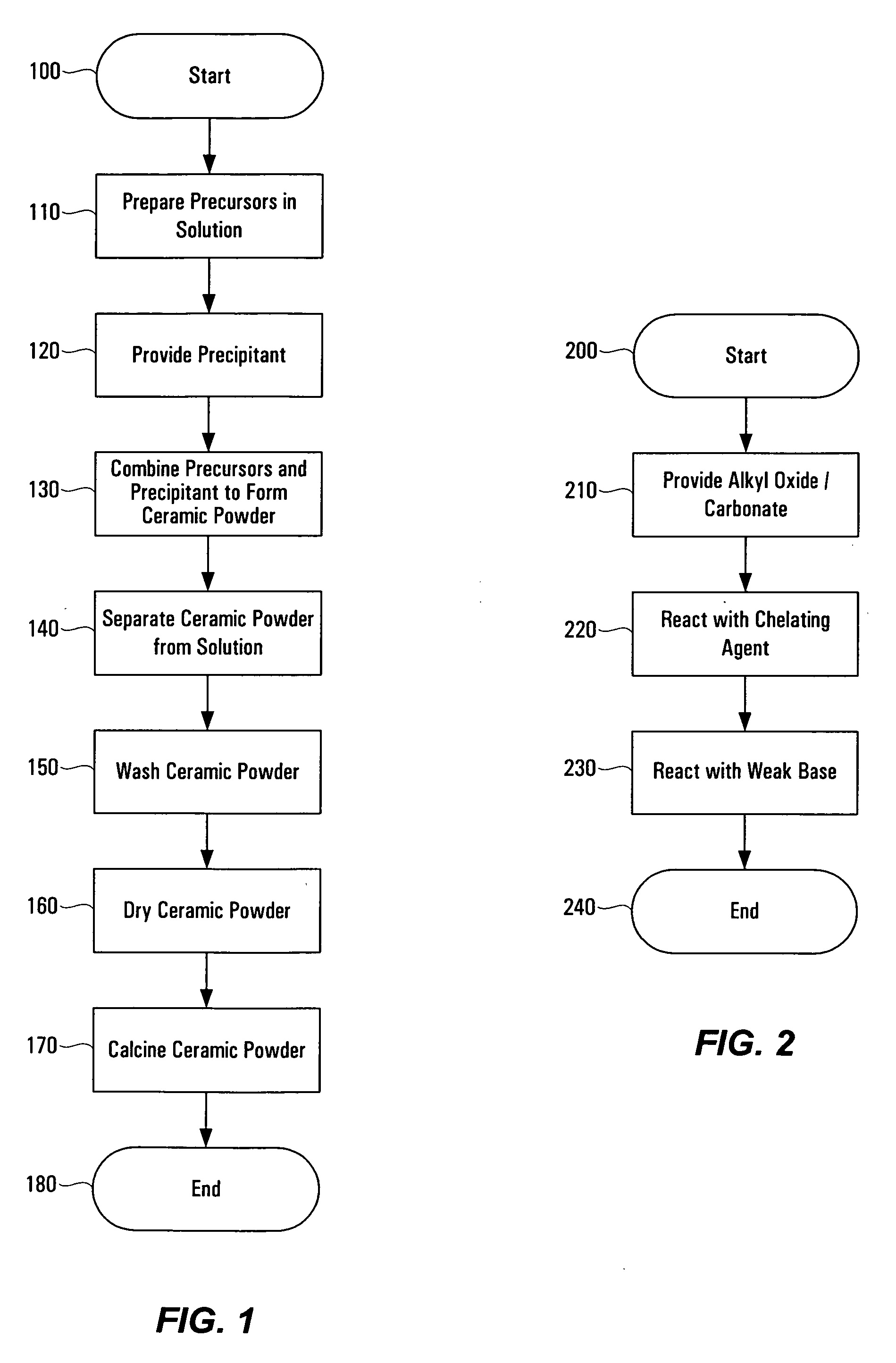
Method of preparing ceramic powders using chelate precursors
InactiveUS20070148065A1Oxide/hydroxide preparationStacked capacitorsBarium titanateAmmonium hydroxide
Wet-chemical methods involving the use of water-soluble hydrolytically stable metal-ion chelate precursors and the use of a nonmetal-ion-containing strong base can be used in a coprecipitation procedure for the preparation of ceramic powders. Examples of the precipitants used include tetraalkylammonium hydroxides. A composition-modified barium titanate is one of the ceramic powders that can be produced. Certain metal-ion chelates can be prepared from 2-hydroxypropanoic acid and ammonium hydroxide.
Owner:EESTOR
Functional fertilizer and repair agents for repairing soil heavy metal
ActiveCN103788960AReduce the content of high-priced heavy metal ionsLow ion contentAgriculture tools and machinesOrganic fertilisersSolubilitySoil heavy metals
The invention discloses functional fertilizer and repair agents for repairing soil heavy metal. Modified attapulgite, chitosan, biochar and sodium thiosulfate are compounded, and on one hand, the absorption performance of the attapulgite and the biochar and the chelation of the chitosan are used for fixing heavy metal ions in soil and preventing the heavy metal ions in the soil from migrating through leaching and runoff. On the other hand, the sodium thiosulfate is used for restoring the high-valence-state heavy metal ions (like hexavalent chromium ions) to low-valence-state ions (like trivalent chromic ions), and therefore virulence and solubleness of the ions are reduced.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Supported catalysts and olefin polymerization processes utilizing same
InactiveUS6197715B1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationGas phaseSlurry
Non-ionic late transition metal chelates of salicylaldimine and pyrrolaldimine can be tethered to an inert support by a covalent bond to provide a catalyst useful in slurry and gas phase polymerization of olefins.
Owner:CRYOVAC INC
Lanthanide Chelates and Use Thereof in Bioanalysis
InactiveUS20110136242A1Improve stabilityGood spectral characteristicsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFluorescenceQuantitative determination
Novel chemical compounds, with application in fluorometric analytical methods, for qualitative and quantitative determination of biomolecules. The aim of the invention is to identify and prove the suitability of such compounds. Said aim is achieved with compounds of formula (1) where R′ is an antenna function, R2 is a chelate forming agent, containing a coordinated lanthanide(III)ion, X is —OH or a group with affinity for the biomolecule, bonded to a carboxylate group of the chelate forming agent by means of an amide bond and Y is —H or a group with affinity for the biomolecule, coupled to the antenna function.
Owner:SENSIENT IMAGING TECH GMBH
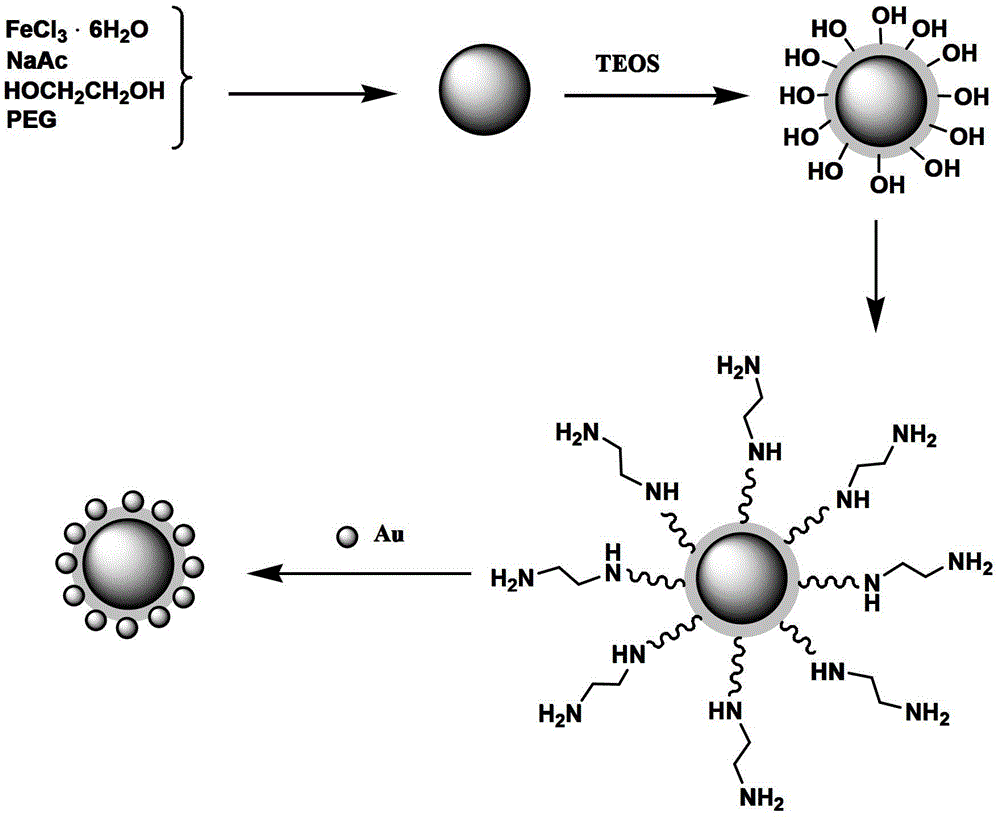
Magnetic gold nanoparticle composite material, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102974314AEasy to controlGood reproducibilityOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesMicrosphereMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention discloses a magnetic gold nanoparticle composite material, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: synthesizing ferroferric oxide magnetic microspheres, adding tetraethoxyl silicon to implement hydrolysis and polymerization on the magnetic microsphere surfaces, adding N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane to obtain surface-modified double-amino-group Fe3O4 / SiO2 magnetic microspheres, and compounding the surface-modified double-amino-group magnetic microspheres with gold nanoparticles. The chelation action of the double amino groups is utilized to adsorb the gold nanoparticles more firmly; and the material combines the surface selectivity of the gold nanoparticles and the superparamagnetism of the magnetic nanoparticles, can extract benzopyrene in water, and can implement quick and efficient separation.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method of chelate coating with copper ions capable of controllably catalyzing release of nitrogen monoxide and polyphenol complex
ActiveCN104194460ALong-term antibacterialImprove antibacterial propertiesAntifouling/underwater paintsSurgeryBiocompatibility TestingPhenol
The invention discloses a preparation method of a chelate coating with copper ions capable of controllably catalyzing release nitrogen monoxide and a polyphenol complex. The preparation method comprises the following steps: soaking a target modified material or an instrument in a mixed aqueous solution consisting of soluble metal salt, soluble copper salt and a compound having an o-phenol structure; and depositing a layer of chelate coating with copper ions with a function of catalyzing nitrogen monoxide and the polyphenol complex on the surface. The chelate coating with the copper ions and the polyphenol complex, which is obtained by the preparation method disclosed by the invention, not only has excellent biocompatibility and bacterial resistance, but also has a function of inducing catalysis of endogenous nitrogen monoxide to release in a blood environment. In addition, the coating is nearly applicable to surface modification of materials of all textures, complex geometrical shapes and different topological structures.
Owner:GUANGZHOU NANCHUANG EVEREST MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
High molecular weight poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene ether) and process therefor
ActiveUS20090211967A1Mitigate such drawbackSemi-permeable membranesGreenhouse cultivationEtherChelation
A poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene ether) having a high molecular weight and a reduced content of low molecular weight species can be prepared by a method that includes specific conditions for the oxidative polymerization, chelation, and isolation steps. The poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene ether) is particularly useful for the fabrication of fluid separation membranes.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Method of production of transition metal nanoparticles
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Preparation method and application of magnetic fluorescent nanoparticle with shell-core structure
ActiveCN102500291AHigh fluorescence quantum efficiencyExcitation spectral bandwidthMagnetic materialsMicroballoon preparationMicrospherePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application of a magnetic fluorescent nanoparticle with a shell-core structure. Firstly, a silica magnetic microsphere with a shell-core structure is prepared by using one or more than one of nanoparticles of Fe3O4, gamma-Fe2O3, MeFe2O4 (Me=Co, Mn, Ni), metal Ni, Co, Fe, and alloy Fe-Co, Ni-Fe as the inner core, and coating a silica shell, and then a fluorescent material (a chelate of Eu3+, Sm3+, Dy3+, Tb3+ and the like) is absorbed on the silica shell. Then, a layer of silica is coated on the surface to improve the stability of the fluorescent magnetic microsphere, and to prevent agglomeration and fluorescent material leakage. A lot of rare earth fluorescent materials are wrapped in the shell layer, so the fluorescence intensity signal of a prepared sample is greatly increased. The nanoparticle has dual functions of enrichment and marking, and has wider application prospects in the biomedical field.
Owner:SHENZHEN BIOEASY BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
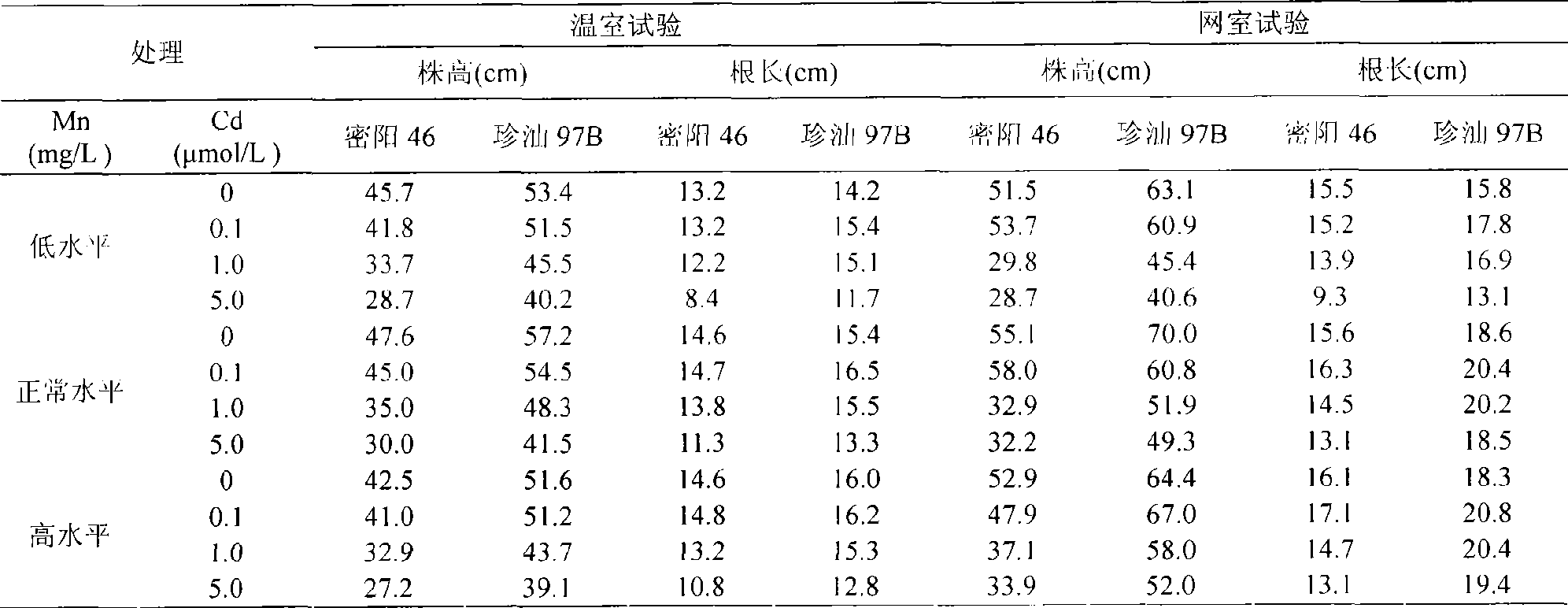
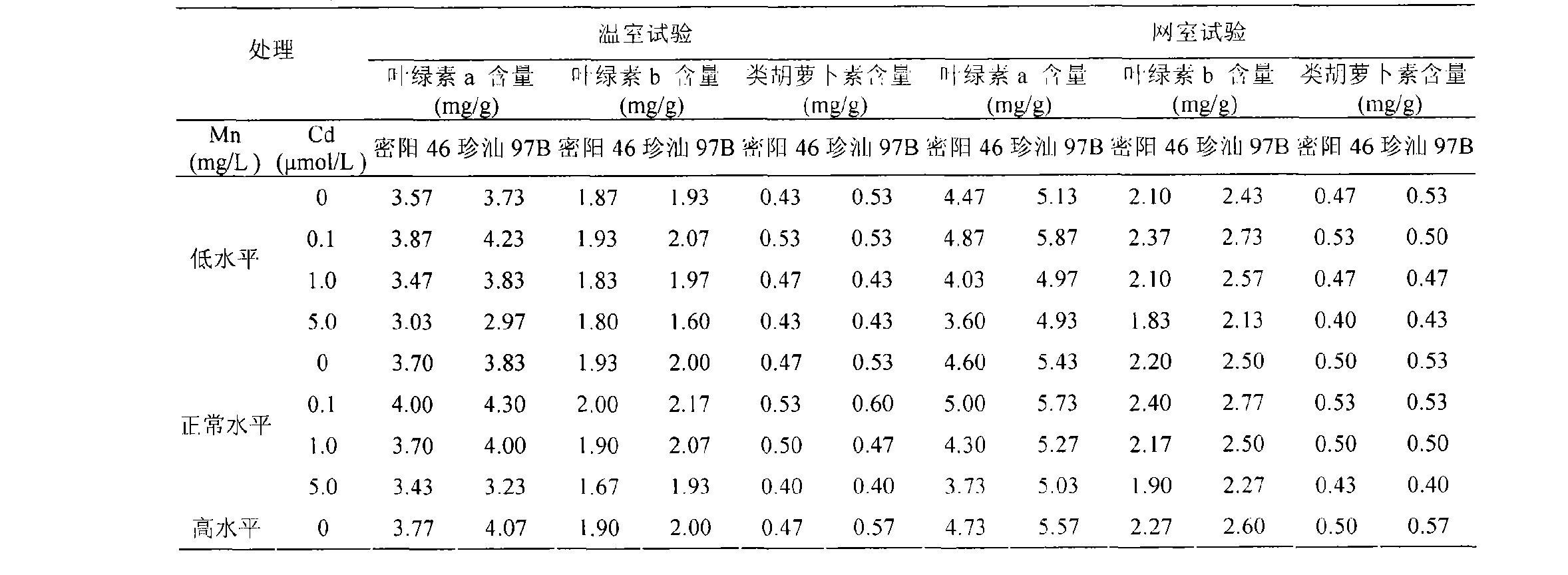
Method of controlling heavy metal cadmium accumulation of paddy
InactiveCN101507400AWide variety of sourcesReduce usageFertilising methodsHorticulture methodsManganeseCadmium Cation
The invention discloses a method for controlling the accumulation of heavy metal cadmium in rice, and belongs to the technical field of rice planting. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) before the land preparation for seedling transplanting, applying a divalent manganese chelate in soil and uniformly mixing the divalent manganese chelate and the soil; (2) during a period from 15 to 20 days after seedling transplanting to 35 to 45 days after the seedling transplanting, spraying aqueous solution of a divalent manganese fertilizer once every other 7 to 10 days; (3) spreading the divalent manganese chelate in the early booting stage and the grouting stage of the rice respectively; (4) irrigating the paddy land within 3 to 5 days after the soil application of the divalent manganese chelate; (5) from the earing period of the rice to the ripening period of the rice, spraying the aqueous solution of the divalent manganese fertilizer once every other 7 to 10 days; and (6) after the soil application of the divalent manganese chelate, applying the divalent manganese chelate in the same way each year, but with an application rate which is reduced by half or three quarters. The method adopts soil application and leaf surface spraying application of the divalent manganese fertilizer and is more effective. The method is wider in application range, more economic and effective and is capable of improving the mineral nutrient element content of the rice and overcoming the adverse effects of the prior art.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Phosphorus-free corrosion and scale inhibitor
InactiveCN101607763AReduce dosagePlay a role in corrosion inhibitionTreatment using complexing/solubilising chemicalsChelationPrecipitation types
The invention relates to a phosphorus-free corrosion and scale inhibitor, which is prepared from sodium molybdate, zinc salt, citrate, triethanolamine, benzotriazole (BTA), polyaspartic acid (PASP), polyepoxysuccinic acid (PESA), AA / AMPS terpolymer, solid alkali and water. The phosphorus-free corrosion and scale inhibitor inhibits corrosion of metals by forming oxidization type and precipitation type films on the surfaces of the metals, has the effect of inhibiting scale through chelation and dispersive action on salts causing scale in cooling water, is non-toxic and phosphorus-free, has easily biodegradable major organic compositions, does not cause environmental pollution and is not limited by phosphorus in emission.
Owner:SHANGHAI WEILAI ENTERPRISE
Method for remedying organic compound pollution in soil and/or water
ActiveCN103752601AReduce consumptionWater contaminantsContaminated soil reclamationHydrogenPersulfate
The invention discloses a method for remedying the organic compound pollution in soil and / or water. The method comprises the following steps: adding persulfates into the soil which is dispersed in the water and subjected to the organic compound pollution, or adding the persulfates into the water subjected to the organic compound pollution; adjusting the pH (Potential of Hydrogen) value to 3-12; adding hydrogen peroxide; and finally adding an activating agent, wherein the activating agent is a chelate chelated by metal salts and a chelate agent; the metal salt is selected from one or any combination of two of Fe salts or Mn salts. In the condition that the same amount of the organic compound is oxidized, the method provided by the invention can be used for greatly saving the consumption of hyperoxides.
Owner:BEIJING GEOENVIRON ENG & TECH
Polymer microsphere and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101798372AHigh mechanical strengthImprove stress resistanceMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationMicrosphereAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
The invention discloses a polymer microsphere and preparation method thereof. The microsphere comprises a core and surface graft; wherein the core is monodispersed polystyrene-divinyl benzene microsphere with crosslinking degree of 60-90% and grain diameter of 2-20 microns, and the surface graft is polyglycidyl methacrylate or derivate thereof. Friedel-Crafts acylation is utilized, alpha-halogenacyllhalide is taken as acylation agent, initiator molecule is bonded on the surface of the microsphere; conventional atom transfer radical polymerization method is utilized to initiate monomers glycidyl methacrylate to condense; then different nucleopilic reagent is utilized for opening ring, and amino, hydroxyl, hydrazine, carboxyl and sulfydryl groups are introduced onto the surface of the microsphere. The polymer microsphere can be used as separation material for different chromatographs for high efficiency ion exchange, chelation and high efficiency affiliation, also can be used as carrier for fixing enzyme and catalyst and is an excellent functional microsphere.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +2
Conductor composition and method for production thereof
InactiveUS20040245507A1Conductive materialNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialOrganic acidElectrical conductor
The present invention provides a conductor composition that can be formed into a film conductor having a resistance to soldering heat of a sufficient level in practical use without using a large amount of expensive precious metals such as Pd and without performing a Ni plating treatment or other treatments separately. This conductor composition is provided in the form of paste or ink having metal powder as the main component. This metal powder is constituted substantially by particulates of Ag or an Ag based alloy whose surface is coated with an organic metal compound. The organic metal compound is preferably an organic acid metal salt, metal alkoxide or a chelate compound having as a main constituent metal element any one selected from the group consisting of Al, Zr, Ti, Y, Ca, Mg and Zn.
Owner:NORITAKE CO LTD
Imaging Agents
InactiveUS20070082879A1High yieldExcessive reactionBiocideIn-vivo radioactive preparationsRheniumAbnormal tissue growth
The present invention provides novel amino acid compounds useful in detecting and evaluating brain and body tumors. These compounds have the advantageous properties of rapid uptake and prolonged retention in tumors and can be labeled with halogen isotopes such as fluorine-18, iodine-123, iodine-124, iodine-125, iodine-131, bromine-75, bromine-76, bromine-77, bromine-82, astatine-210, astatine-211, and other astatine isotopes. These compounds can also be labeled with technetium and rhenium isotopes using known chelation complexes. The compounds disclosed herein bind tumor tissues in vivo with high specificity and selectivity when administered to a subject. Preferred compounds show a target to non-target ratio of at least 2:1, are stable in vivo and substantially localized to target within 1 hour after administration. Preferred compounds include 1-amino-2-[18F]fluorocyclobutyl-1-carboxylic acid (2-[18F]FACBC) and 1-amino-2-[18F]fluoromethylcyclobutyl-1-carboxylic acid (2-[18F]FMACBC). The labeled amino acid compounds of the invention are useful as imaging agents in detecting and / or monitoring tumors in a subject by PET or SPECT.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for enhancing mineral levels in animals with reduced environmental impact
InactiveUS20070269495A1Increase the amount of metalReduce amountBiocideAnimal feeding stuffFecesNitrate
A method of enhancing a mineral level in an animal with reduced environmental impact can comprise orally administering a metal amino acid chelate to an animal, wherein the amino acid to metal molar ratio of the metal amino acid chelate is from about 1:1 to 4:1. The metal can contribute to a mineral level within the blood and tissues of the animal that is effective for stimulating growth of the animal to a greater degree than would be realized by administering the same amount of metal in the form of an inorganic metal salt. Additionally, the amount of the metal excreted in the feces of the animal can be less than would be present when administering the same amount of metal in the form of the inorganic metal salt. The metal amino acid chelate can also serve as a source highly bioavailable amino acids, so that the excretion of nitrates by the animal may be reduced while still promoting efficient growth.
Owner:NOVUS INTERNATIONAL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com