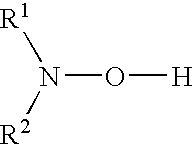
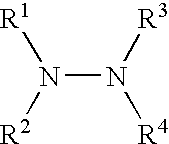
Patents
Literature
2795 results about "Hexavalent chromium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hexavalent chromium (chromium(VI), Cr(VI), chromium 6) is any chemical compound that contains the element chromium in the +6 oxidation state (thus hexavalent). Virtually all chromium ore is processed via hexavalent chromium, specifically the salt sodium dichromate. Approximately 136,000 tonnes (300,000,000 lb) of hexavalent chromium were produced in 1985. Additional hexavalent chromium compounds are chromium trioxide and various salts of chromate and dichromate, among others. Hexavalent chromium is used in textile dyes, wood preservation, anti-corrosion products, chromate conversion coatings, and a variety of niche uses. Industrial uses of hexavalent chromium compounds include chromate pigments in dyes, paints, inks, and plastics; chromates added as anticorrosive agents to paints, primers, and other surface coatings; and chromic acid electroplated onto metal parts to provide a decorative or protective coating. Hexavalent chromium can be formed when performing "hot work" such as welding on stainless steel or melting chromium metal. In these situations the chromium is not originally hexavalent, but the high temperatures involved in the process result in oxidation that converts the chromium to a hexavalent state. Hexavalent chromium can also be found in drinking water and public water systems.
Stabilized curing agent for heavy metal contaminated soil or solid waste treatment and treatment method
ActiveCN104312591AAchieve adsorptionRealize functionContaminated soil reclamationBuilding constructionsTreatment effectDissolution
The invention discloses a stabilized curing agent for heavy metal contaminated soil or solid waste treatment and a treatment method. The stabilized curing agent comprises the following components in parts by weight: 5 to 10 parts of a magnesium-based compound, 1 to 5 parts of a sulfur-based compound and 1 to 3 parts of an activated silicon-based compound. The treatment method comprises the following steps of sampling inspection, experimental determination of adding proportion, mixing, backfill maintenance, sealing up for safekeeping and the like. The stabilized curing agent disclosed by the invention has an efficient long-term stabilizing effect on various heavy metals such as arsenic, mercury, hexavalent chromium, lead, cadmium, nickel, tin and cyanide, the repeated acid and alkali leaching experiments prove that the stabilized and cured harmful heavy metals cannot be dissolved out again, and the defects that in the traditional technology, the treatment effect and treatment agents are greatly affected by the environment, the long-term efficacy of harmless stabilization is poor, the medicament adding amount is difficult to control and the re-dissolution of harmful heavy metals is easily caused by the high alkalinity of cement solidification and the like are overcome.
Owner:GUIZHOU MEIRUITE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
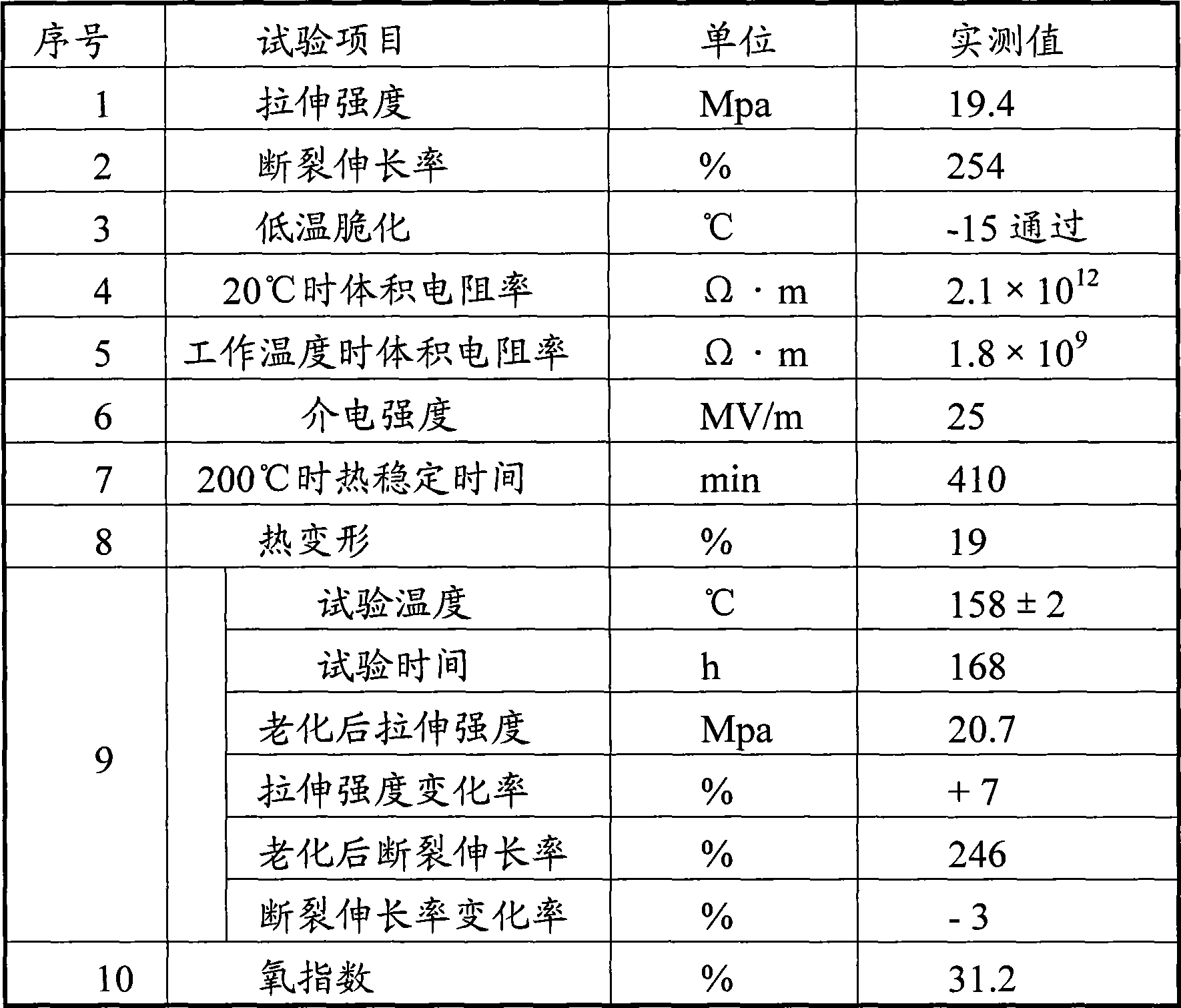
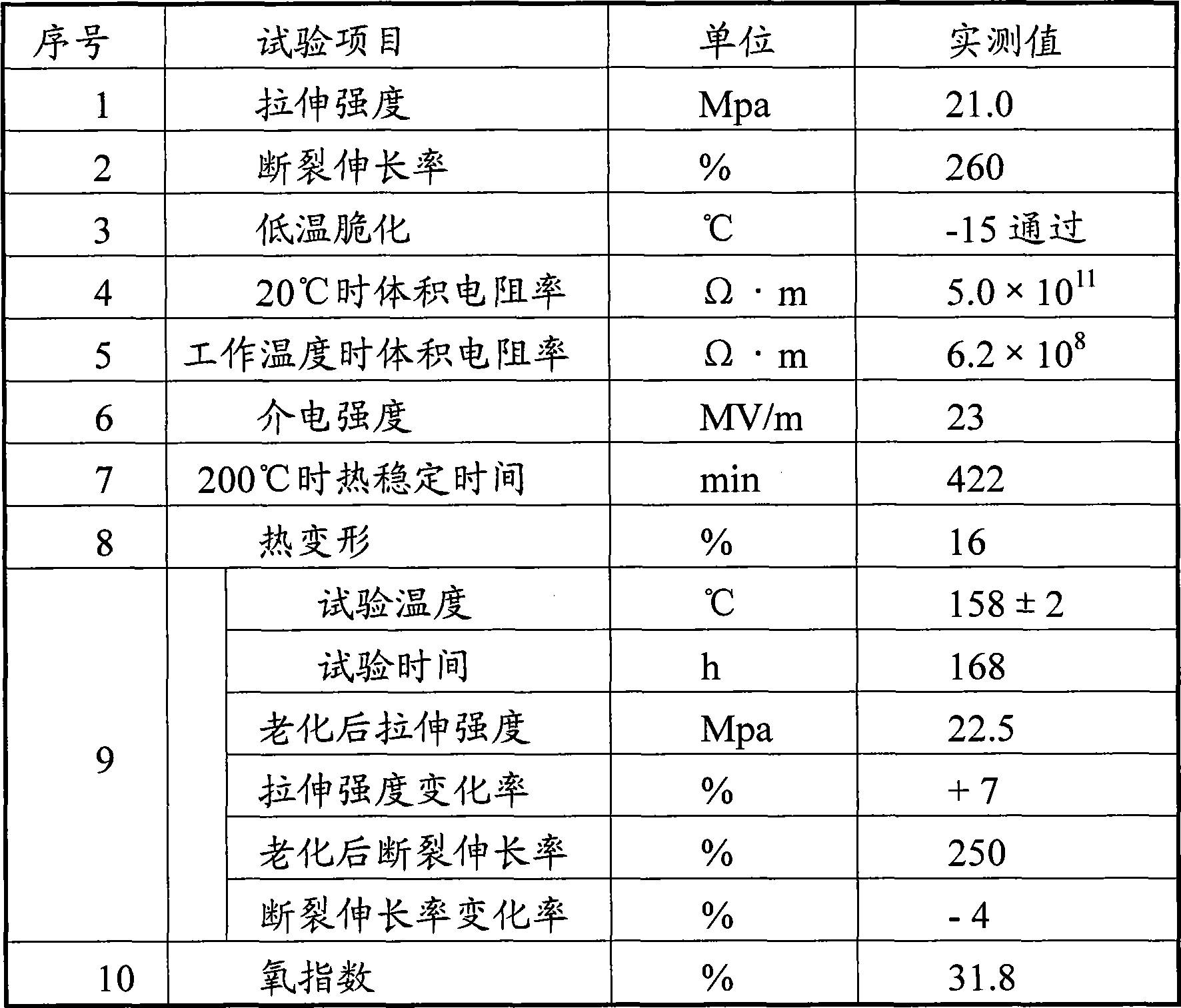
High temperature resistant environment-protective polychloroethylene material for electric wire and cable
InactiveCN101412834AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove insulation performancePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsInsulated cablesPolyesterPolyvinyl chloride
The invention provides a high-temperature resistant environment-friendly polyvinyl chloride material for wires and cables. A raw material formulation mainly comprises the following materials in weight portion: 80 to 120 portions of loose-type polyvinyl chloride resin, 20 to 55 portions of tetraoctyl pyromellitate, 5 to 35 portions of polyester plasticizer and 12 to 18 portions of calcium-zinc stabilizer, wherein the polymerization degree of the loose-type polyvinyl chloride resin is between 2,000 and 3,000; in the calcium-zinc stabilizer, the total content of lead, cadmium, mercury and hexavalent chromium is less than or equal to 10 ppm of the total weight of the calcium-zinc stabilizer; the polyester plasticizer is polypropylene-1, 2-glycol adipate or polypropylene-1, 3-butylene terephthalate; and the molecular weight of the polyester plasticizer is between 3,000 and 4,000. After the material is aged in a hot-air oven for 168 hours at 158 DEG C, the retention rate of tensile strength is up to 106 percent; the retention rate of elongation at break is 97 percent; and the material is good in mechanical physical properties and insulating property. Therefore, the material meets the temperature-resistant requirement on long-term operating temperature at 125 DEG C in UL1581.
Owner:中广核三角洲(江苏)塑化有限公司
Functional fertilizer and repair agents for repairing soil heavy metal
ActiveCN103788960AReduce the content of high-priced heavy metal ionsLow ion contentAgriculture tools and machinesOrganic fertilisersSolubilitySoil heavy metals
The invention discloses functional fertilizer and repair agents for repairing soil heavy metal. Modified attapulgite, chitosan, biochar and sodium thiosulfate are compounded, and on one hand, the absorption performance of the attapulgite and the biochar and the chelation of the chitosan are used for fixing heavy metal ions in soil and preventing the heavy metal ions in the soil from migrating through leaching and runoff. On the other hand, the sodium thiosulfate is used for restoring the high-valence-state heavy metal ions (like hexavalent chromium ions) to low-valence-state ions (like trivalent chromic ions), and therefore virulence and solubleness of the ions are reduced.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Organic coating compositions for aluminizing metal substrates, and related methods and articles
ActiveUS20050031877A1Reduce instabilityGood chemical stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesEpoxyThermal stability
An organic coating composition is described, which can be used to enrich the surface region of a metal-based substrate with aluminum. The composition comprises an aluminum-based powder and at least one organic resin, e.g., alkyds, epoxies, or silicone materials. At least some of the aluminum-based powder is in the form of substantially spherical powder particles. The coating composition is substantially free of hexavalent chromium. It can be applied to the substrate by a variety of techniques, such as spraying. It is then heat-treated, to cause diffusion of aluminum into the surface region of the substrate, e.g., a turbine engine component. The composition exhibits good thermal and chemical stability for extended periods of time. Related articles are also described.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ethylene polymers and method for producing the same
InactiveUS6646069B2Improve impact resistanceImprove balanceOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationChromium CompoundsCrack resistance
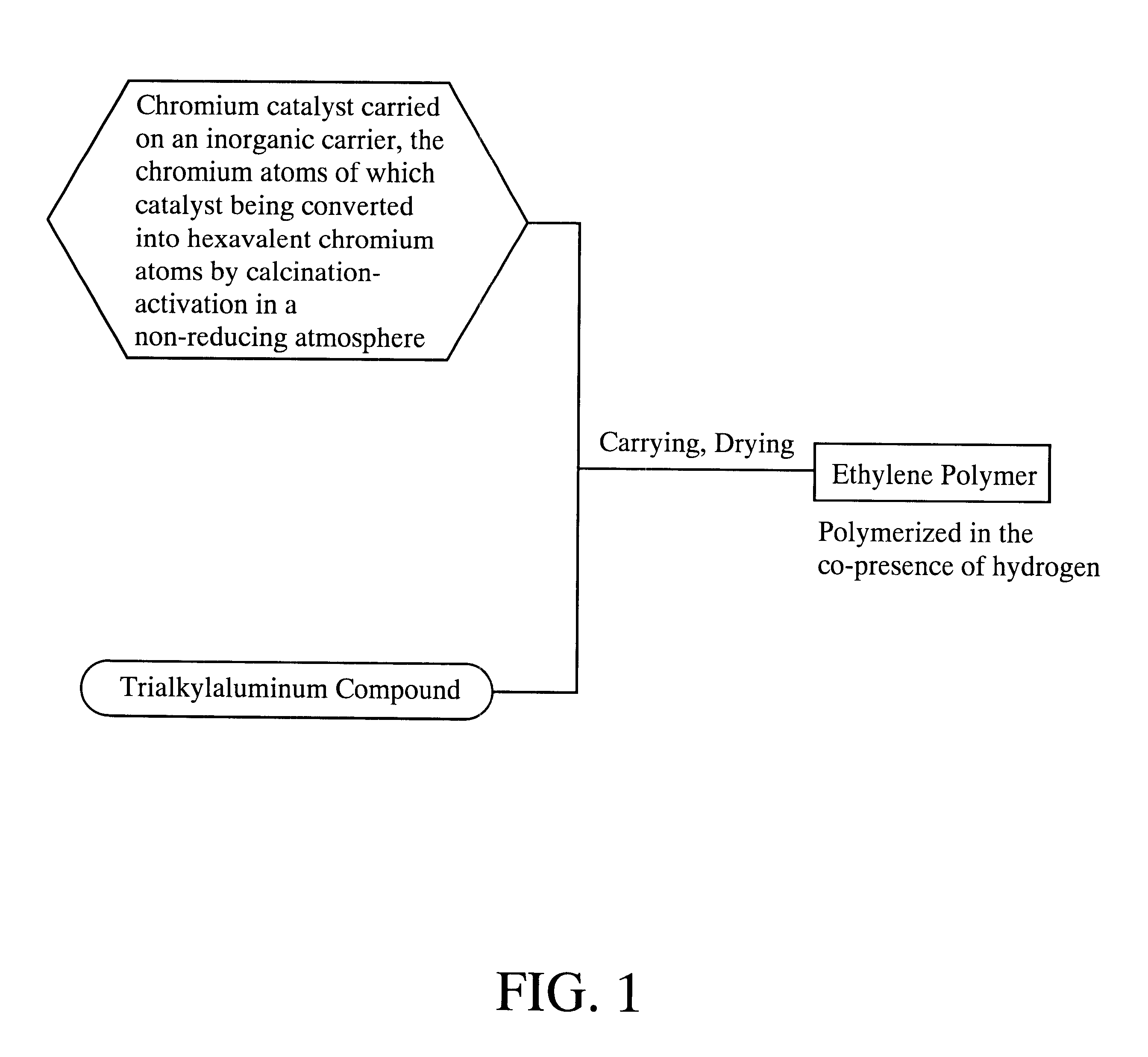
The invention relates to a method for producing an ethylene polymer, comprising performing polymerization of ethylene in co-presence of hydrogen using a trialkylaluminum compound-carried chromium catalyst, wherein the chromium catalyst is obtained by calcination-activating a chromium compound that is carried on an inorganic oxide carrier in a non-reducing atmosphere to convert chromium atoms in the chromium compound into hexavalent chromium atoms for at least a portion thereof, and treating with a trialkylaluminum compound in an inert hydrocarbon solvent to carry thereon and removing to dry the solvent so that the chromium atoms are not over-reduced by the trialkylaluminum compound, and to an ethylene polymer suitable for blow molded articles obtained by the production method. The ethylene polymer of the invention have improved environment stress crack resistance (ESCR) and impact resistance in a good balance and are suitable for molded blow articles, in particular large size blow molded articles.
Owner:JAPAN POLYOLEFINS CO LTD
Laser ablation for the environmentally beneficial removal of surface coatings
ActiveUS20130220982A1Safe disposalMetal working apparatusLaser beam welding apparatusDiamond-like carbonMaterials science
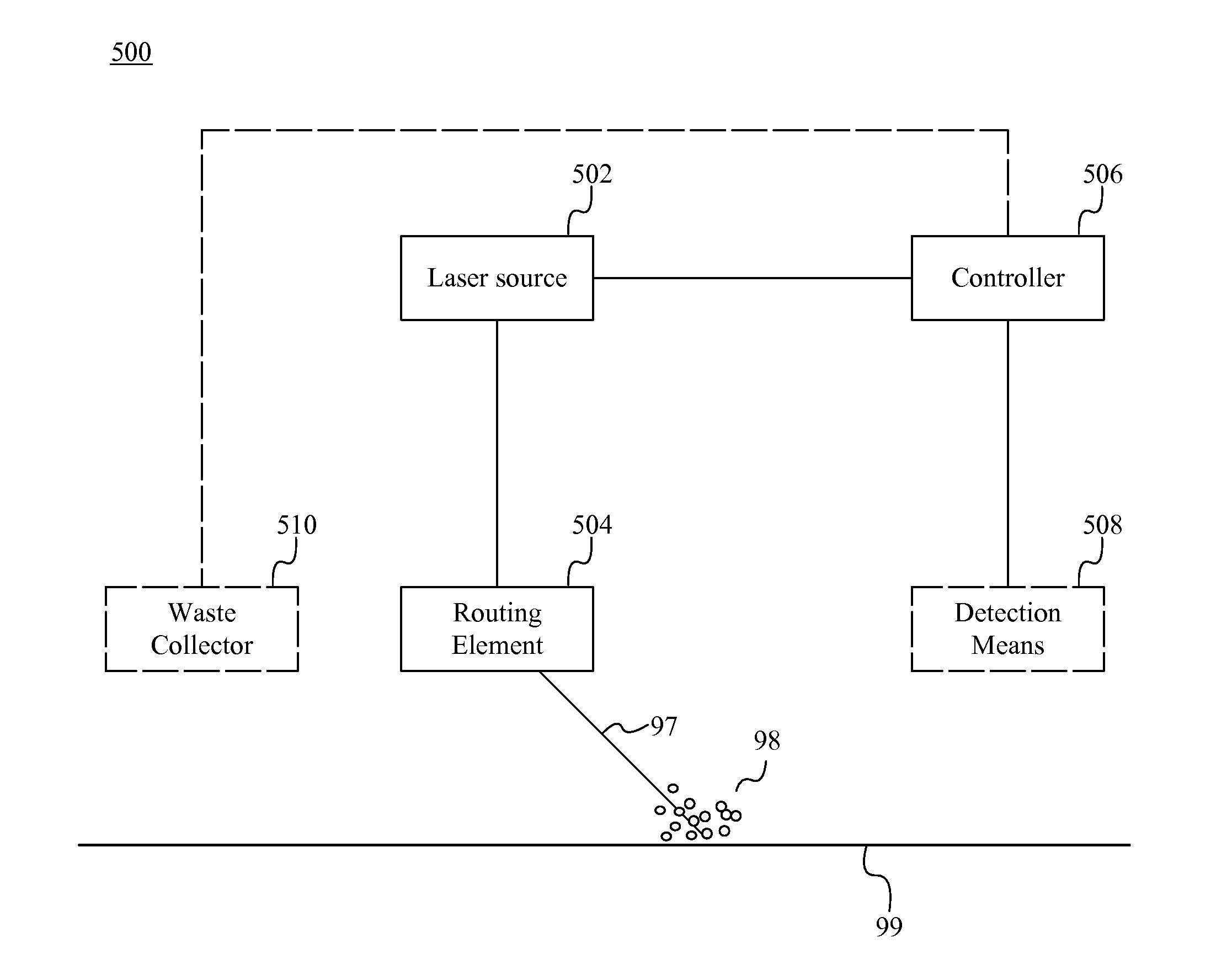
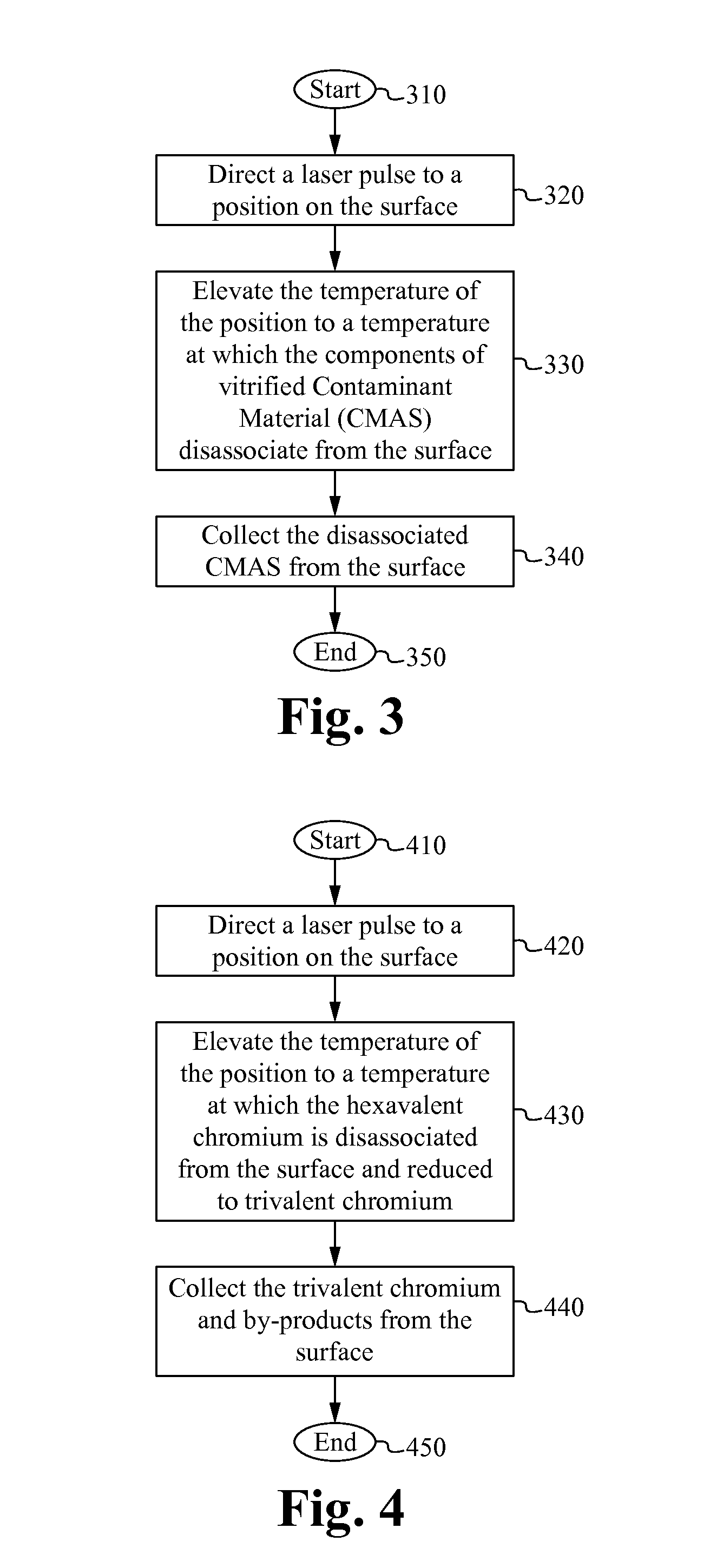
A laser-based method of removing a coating from a surface comprises directing a laser pulse to a first position on the surface, removing the coating from the first position by rapidly elevating a surface temperature of the first position using the laser pulse and thereby disassociating the coating from the surface and collecting the disassociated coating. In some embodiments, the coating comprises an environmentally harmful substance such as Hexavalent Chromium. In some embodiments, the coating comprises Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC), Vitrified Contaminant Material (CMAS). The disassociated coating is collected by a waste collector.
Owner:GEN LASERTRONICS
Film coating process for aluminium alloy wheel hub
InactiveCN101343740AReduce pollutionReduce energy consumptionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPolyesterFilm coating
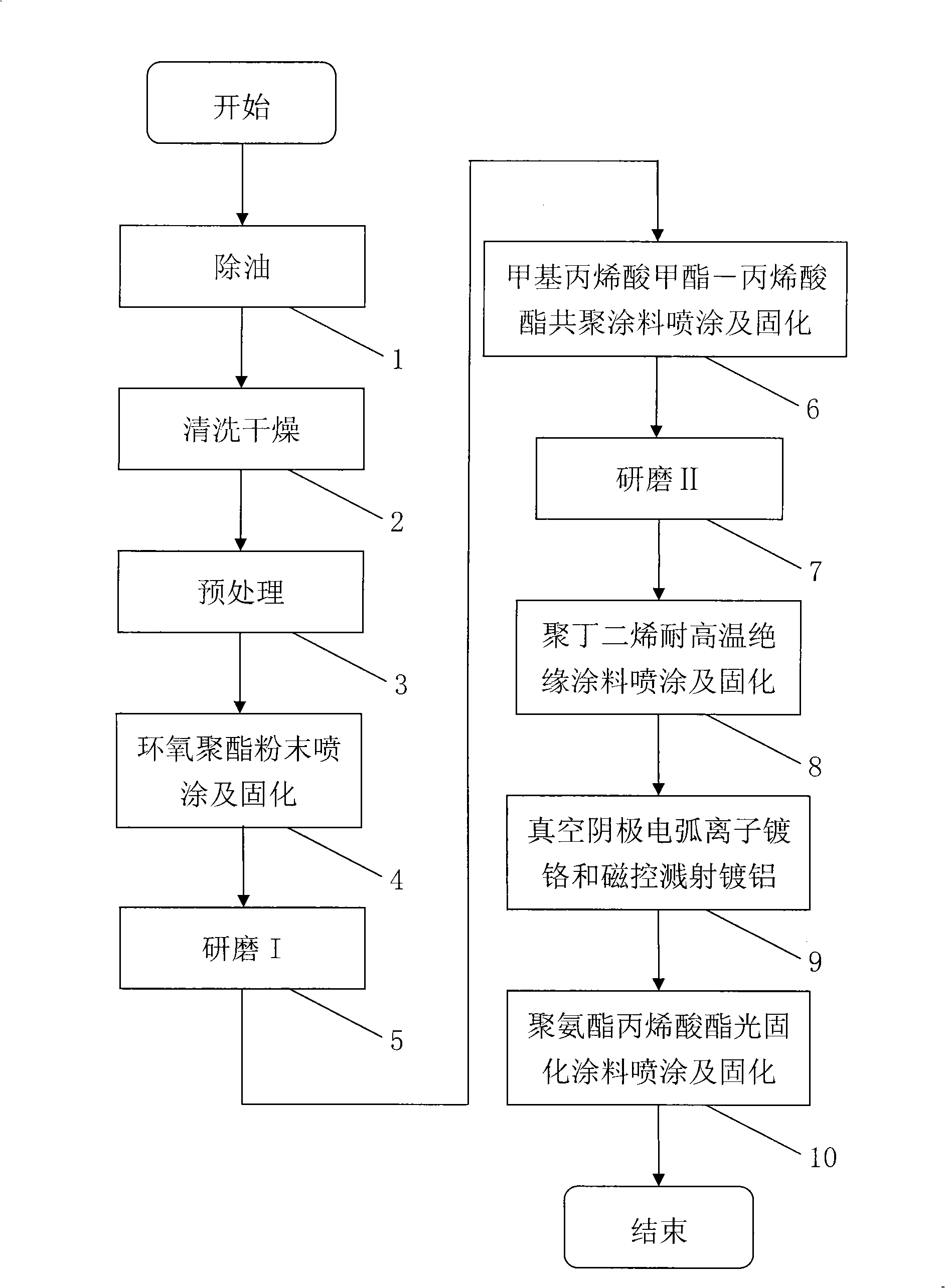
The invention discloses an aluminum alloy wheel hub coating technology. The aluminum alloy wheel hub coating technology comprises the procedures of oil removing, cleaning and drying, pre-treating, epoxy polyester powder spraying and solidifying, grinding I, methyl methacrylate-acrylate copolymer paint spraying and solidifying, grinding II, polybutadiene high temperature resistant insulating coating spraying and solidifying, vacuum cathode arc ion chromium plating and magnetism control sputtering aluminum plating, and polyurethane methacrylate light solidifying paint spraying and solidifying in sequence. The aluminum alloy wheel hub coating technology adopts dry electric plating to replace the traditional wet electric plating, the plating layer surface quality and the physical and chemical properties are approximately equivalent to the wet electric plated aluminum alloy wheel hub, the chromium consumption is reduced to about one fifth of the wet electric plating, the water consumption is reduced to about one seventh of the wet electric plating, precious nickel and copper are not utilized, the poisonous metal substance such as hexavalent chromium is not contained, the pollution to the environment is reduced, the energy, water and precious metal consumption is remarkably reduced, the technological flow is simplified, the production efficiency is enhanced, the heavy polishing working sequence is omitted, the working condition is remarkably improved, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:HUZHOU JINTAI PLATING IND
Nano zero-valent iron with montmorillonite serving as carrier, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102923835AReduce aggregationHigh activityWater/sewage treatment by sorptionWater/sewage treatment by reductionPotassium borohydrideMontmorillonite
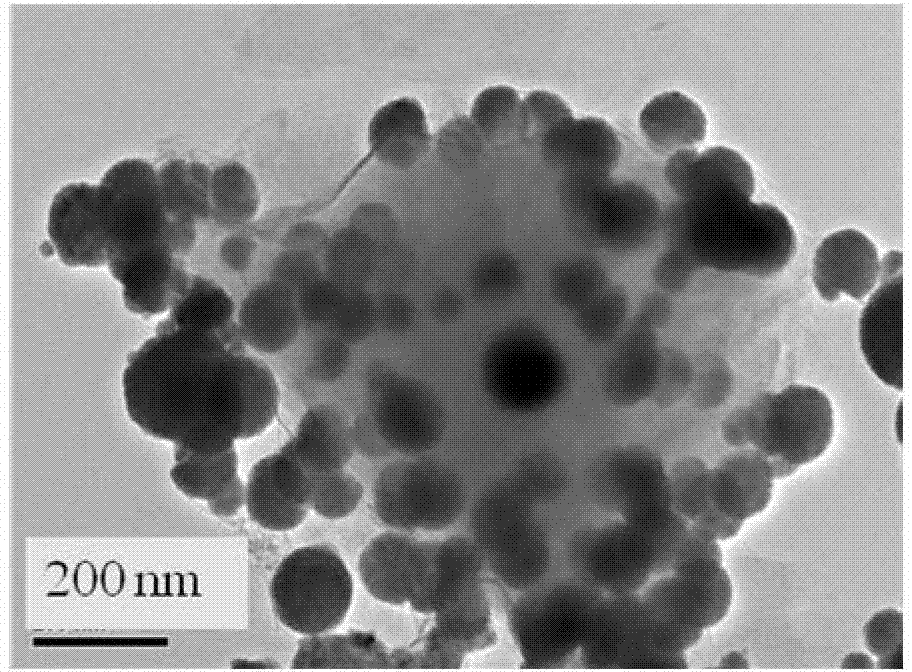
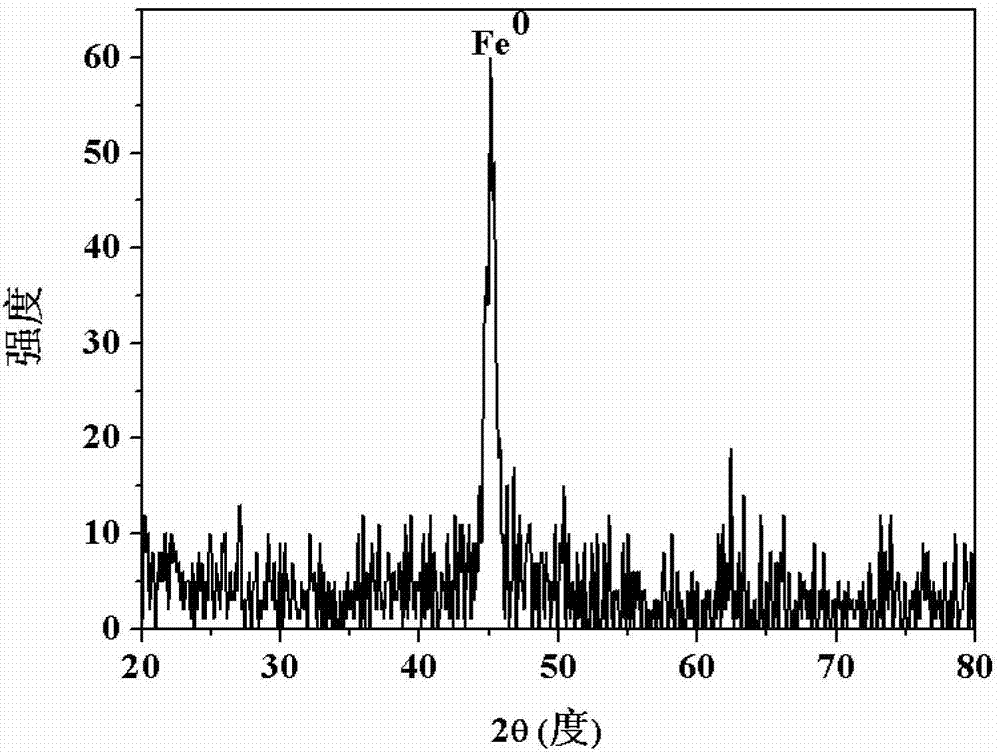
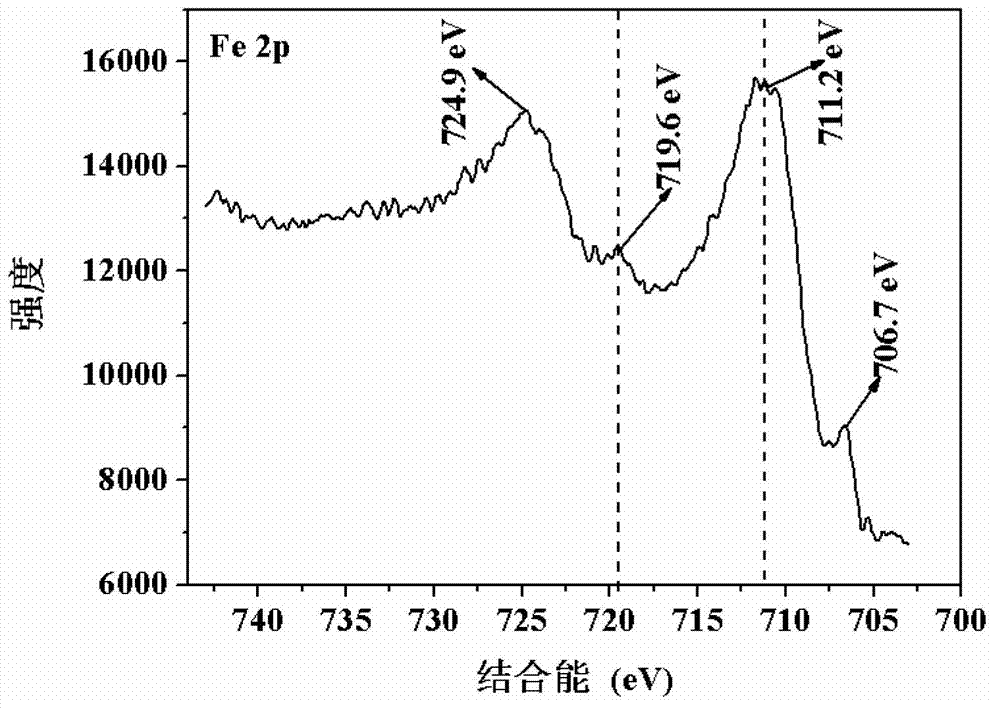
The invention provides nano zero-valent iron with montmorillonite serving as a carrier, and a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the steps of dissolving ferrous sulfate, adding soluble starch and montmorillonite particles into the ferrous sulfate solution in proportion, and obtaining mixed liquid; stirring after performing ultrasound treatment to the obtained mixed liquid, and obtaining precursor solution; adding the obtained precursor solution into sodium borohydride or potassium borohydride solution in proportion under the conditions of continuous stirring, continuing stirring for a period of time, performing solid-liquid separation, and obtaining the solid which is the nano zero-valent iron with montmorillonite serving as the carrier. According to the prepared nano zero-valent iron with montmorillonite serving as the carrier, interlayer and surface spaces of montmorillonite can be fully utilized, the activity and the stability are high, polymerization of the nano zero-valent iron can be reduced, and the nano zero-valent iron has remarkable effect when used for treating waste water containing hexavalent chromium.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Acid-resistant magnetic chitosan microspheres as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104437395AImprove acid resistanceHigh amino contentOther chemical processesWater contaminantsMicrosphereHydrolysis
The invention relates to an acid-resistant magnetic chitosan microsphere adsorbent as well as a preparation method and the application thereof, and in particular relates to acid-resistant magnetic chitosan microspheres which have the excellent absorption performance and recycling performance for acid waste water containing hexavalent chromium, a preparation method of the acid-resistant magnetic chitosan microspheres and the application of the acid-resistant magnetic chitosan microspheres. The preparation method of the acid-resistant magnetic chitosan microspheres comprises the following steps: (1) preparing Fe3O4 nano-particles modified by citric acid by using a coprecipitation method; (2) preparing single-coated magnetic SiO2 nano-particles by using a sodium silicate hydrolysis method or a sol-gel method; and (3) preparing the chitosan microspheres coated with magnetic SiO2 by taking chitosan powder as a raw material by adopting an emulsion crosslinking method. Furthermore, in order to further improve the adsorbing capacity of the microspheres, in the method, dendritic polyethylene imine is taken as a functional group for modifying the adsorbent, so that the modified chitosan microspheres can be obtained. The magnetic chitosan microspheres prepared by adopting the method not only have the excellent acid resistance, but also have the good absorption performance on Cr (VI) ions.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chromium-free composite passivator for hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and preparation and application methods of composite passivator
ActiveCN104178757AImprove corrosion resistanceUniform appearanceMetallic material coating processesWater basedChromium free
The invention relates to a chromium-free composite passivator for a hot-dip galvanized steel sheet. The passivator is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 2.20-2.30% of water-base resin, 2.60-2.65% of main salt compound, 0.10-0.15% of organic silane, 0.07-0.09% of sulfate, 0.11-0.13% of inorganic zircon salt, 0.09-0.12% of inorganic acid and the balance of water. A preparation method of the passivator comprises the following steps: firstly, dissolving the organic silane in water; stirring till the organic silane is fully dissolved and adding the main salt compound; after the main salt compound is dissolved, adding the inorganic acid to measure the pH value; then, adding the sulfate and the inorganic zircon salt in the stirring state; after the sulfate and the inorganic zircon salt are fully dissolved, adding the water-base resin; stirring till the water-base resin is fully dissolved; adjusting the pH value to 3-4 by virtue of ammonium water; and standing for later use. An application method of the passivator comprises the following steps: firstly, degreasing the hot-dip galvanized steel sheet by virtue of an alkaline degreaser during use; then, respectively washing by using tap water and deionized water; and after drying, coating the composite passivator on the surface of the hot-dip galvanized steel sheet. The passivator provided by the invention is free from chromium and non-toxic and harmless. The thickness of a passivation film can reach 8-1.0mg / m<2>, and the corrosion resistance is close to that of a hexavalent chromium passivating liquid.
Owner:唐山正元管业有限公司
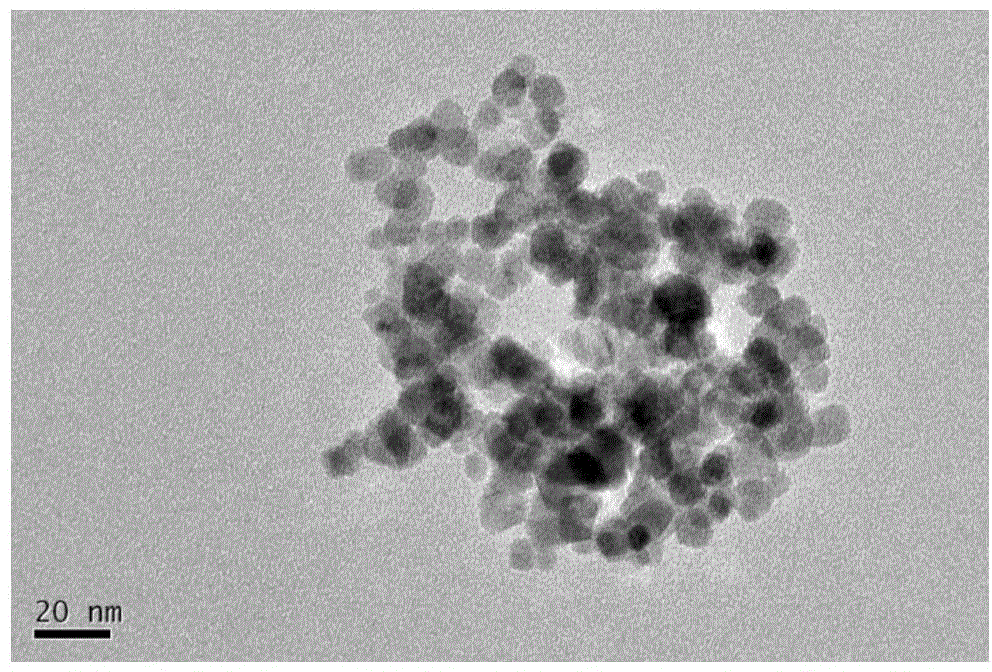
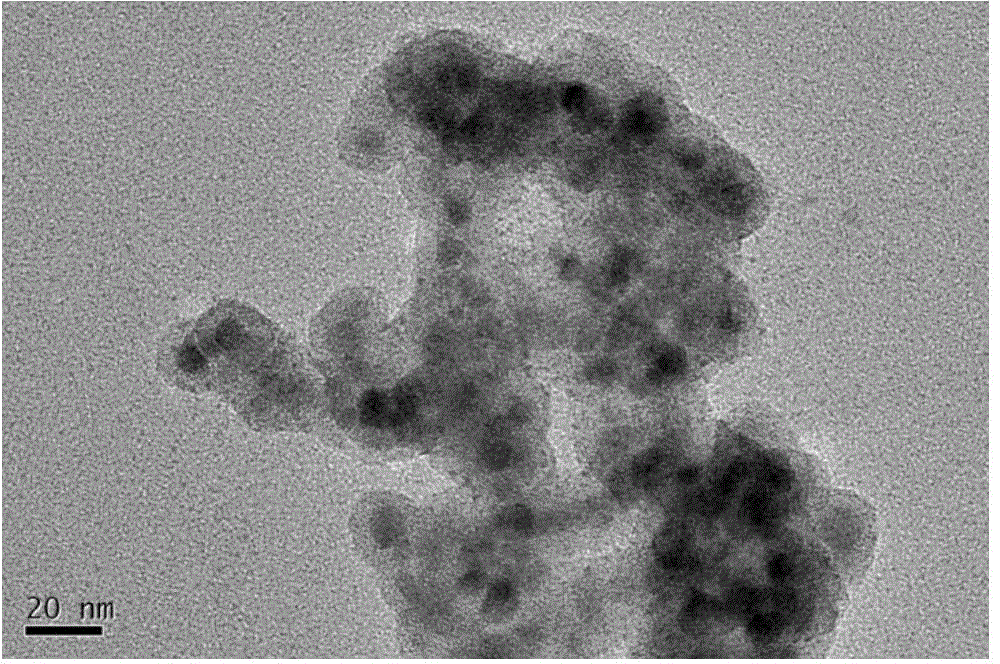
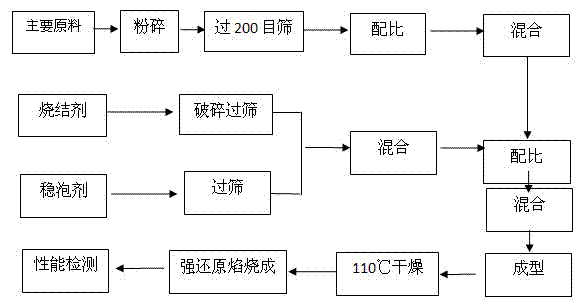
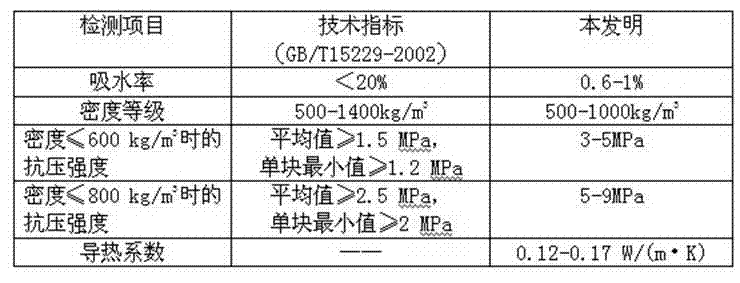
Method for preparing foam ceramic self-insulation wall material by utilizing solid wastes
InactiveCN103396150AReduce manufacturing costRealize comprehensive utilizationSolid waste disposalCeramicwareChromium sesquioxideInsulation layer
The invention relates to a method for preparing a foam ceramic self-insulation wall material by utilizing solid wastes. The wall material comprises a main material and an admixture. The main material is prepared from the following components in proportion: 25% to 35% of chromium slags, 19% to 27% of coal gangue, 20% to 26% of waste ceramic polishing residues, 17% to 25% of albite and 1% to 6% of bentonite. The method comprises the following steps of: adding 16 to 20g of the admixture into every 200g of the main material; evenly mixing and screening the mixture; putting the mixture into a die; molding the mixture in a pressing manner and drying; sintering the mixture under a strong reducing atmosphere at the temperature of 1120-1180 DEG C, thereby obtaining the foam ceramic self-insulation wall material. The carbon in the coal gangue can serve as a foaming agent or a reducing agent, so that hexavalent chromium is reduced into chromium sesquioxide at the high temperature and under the strong reducing atmosphere. Thus, the toxicity of the chromium slags is eliminated. The prepared foam ceramic self-insulation wall material is low in pyroconductivity, small in density and low in water absorption rate; the usage temperature can reach 900 DEG C. In addition, the foam ceramic self-insulation wall material is complete in fire resistance, high in strength and long in service life, and can be used for replacing the existing wall materials and flammable insulation materials. The wall material integrates protection and thermal insulation functions; an exterior wall insulating layer is not required. Thus, the construction cost is lowered.
Owner:HENAN COAL CHEM IND GROUP INST +1
Transformation liquid for preparation of corrosion-resistant oxidation film on aluminium alloy surface and method of use thereof
InactiveCN101139708AImprove corrosion resistanceGood adhesionMetallic material coating processesHigh resistancePersulfate
The invention discloses a transforming solution for preparing anti-corrosion compound oxidation film on an aluminum alloy surface and a using method for the oxidation film. The invention is characterized in that, the transforming solution is a film-forming promoter containing rare-earth salt (nitrate or sulfate and compound salt of cerium, praseodymium, and neodymium), such compound oxidant as radical of permanganate, nitrate and perchlorate, etc., film-forming promoter of vanadium salt and strontium salt, etc.; the transforming solution contains no sexavalent chromium, is environmental friendly; the reaction speed is improved by the compound oxidant and the film-forming promoter, no heating is needed for the chemical transforming, the treating time is 1-5 min. The invention can rapidly prepare under room temperature compound oxidation film comprising compound rare-earth oxide, alumina and manganese oxide with good resistance to corrosion on aluminum alloy surface. The treating solution from the invention is of rapid film-forming speed, simple process, even film layer, high resistance to corrosion, and low environmental pollution, etc.
Owner:陈东初 +2
Heavy metal treating agent and heavy metal pollutants treating method
ActiveCN101947381AGood storage stabilityInhibitionSludge treatmentWater contaminantsHigh concentrationSludge
Provided is a heavy metal treating agent and a heavy metal pollutants treating method. The invention provides a medicament and a treating method thereof. The medicament is used for treating heavy metal pollutants, like burning ash and fly ash discharged from a garbage burning field, soil polluted by heavy metal, sludge generated from waste water treatment, and heavy metal contained in the waste water discharged by factories. Heavy metal treating agent comprising piperazine dithiocarboxylic acids salt and reductible composition is used. In terms of reductible composition, water soluble bivalent iron compound and aliphatics Alpha - hydroxycarboxylic acid and / or salt, or sulfurated bi-alkali metal salt are preferably used. With the heavy metal treating agent, harmful cation species heavy metal like lead, zincum, cadmium, mercury, arsenic, selenium, and hexavalent chromium can be treated by encapsulation in a high concentration, and harmful anion species heavy metal like hexavalent chromium, arsenic and selenium can be treated by encapsulation in a high concentration.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
Liquid additive for intergrinding cement
InactiveUS20060169177A1Reducing hexavalent chromium (CrVI)Reduced dose rateOxygen scavengerHexavalent chromium
Exemplary compositions and methods for reducing hexavalent chromium in cementitious compositions involve the use of a liquid additive composition, comprising stannous chloride. Along with the stannous chloride may be used at least one co-additive comprising an antioxidant, oxygen scavenger, or mixture thereof, and / or at least one agent comprising a cement grinding aid, cement quality improver, or mixture thereof.
Owner:GCP APPL TECH INC
Biomass-derived grinding aids
Compositions and methods for increasing grinding efficiency of cement, cement clinker, raw materials for cement, and other inorganic particles. Use of biomass-derived polyols such as diols, triols, or mixtures thereof, optionally with a conventional grinding aid, cement quality improver, and / or hexavalent chromium reducer, are believed to provide less risk of sludging when compared to glycerides obtained from fossil fuel sources.
Owner:GCP APPL TECH INC
Preparation method and electroplating method of normal-temperature environment-friendly sulfate trivalent chromium electroplating liquid
The invention provides a preparation method and an electroplating method of normal-temperature environment-friendly sulfate trivalent chromium electroplating liquid, which relates to electroplating liquid and electroplating technology. The invention solves the problems of poor stability of the traditional trivalent chromium electroplating liquid, low precipitating and depositing rate of harmful gas in an electroplating process, more components of the electroplating liquid, sensitivity for impurities, poor corrosion resistance of an electroplating layer, and the like. The normal-temperature environment-friendly sulfate trivalent chromium electroplating liquid mainly comprises the following components of main salt, a complexation stabilizing agent, a combined additive, a buffering agent and a conducting salt. The electroplating liquid can work at normal temperature, thereby saving energy resources and having simple technology and high deposition rate, wherein the deposition rate can reach above 0.22micron.min<-1> under 6A / dm<2>. An anode of the invention is a Ti-based rare-metal tantalum-iridium-titanium anode, the anode oxygen-evolution overpotential is low, and harmful hexavalent chrome can not be generated. The normal-temperature environment-friendly sulfate trivalent chromium electroplating liquid has good corrosion resistance and high stability.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
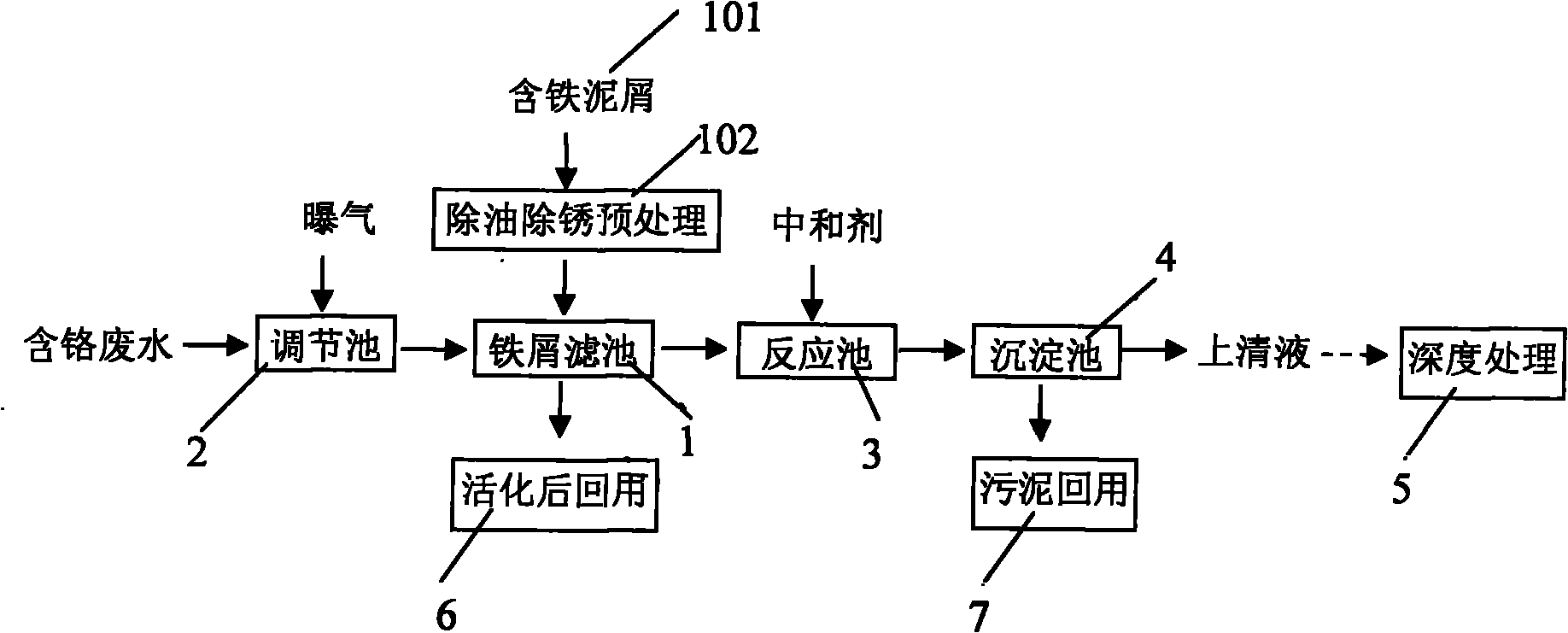
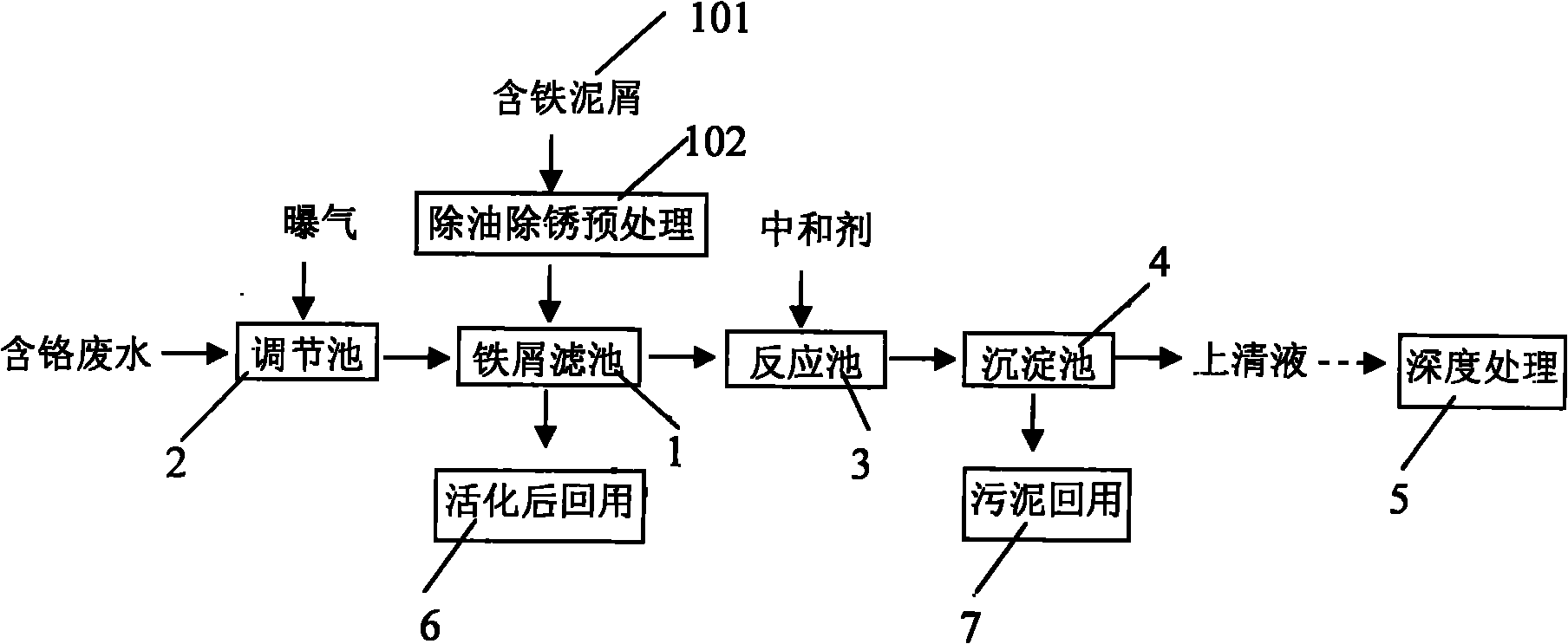
Pretreatment process of chromium-containing wastewater
InactiveCN101811793AIncrease productionDrive up processing costsWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentElectrolysisResource utilization
The invention relates to a pretreatment process of chromium-containing wastewater, which comprises the following steps that: 1) scrap iron filter tank is established, iron-containing spare is mixed with carbon-containing particles and porous filler to form a scrap iron filter tank after being washed by alkali so as to remove the oil and being washed by acid to remove the rust and to be activated; 2) chromium-containing wastewater is introduced into the scrap iron filter tank to be undertaken the micro electrolysis reaction after being aerated by an adjusting tank, and pH value and the oxidation reduction potential level ORP value are adjusted by acid liquid, so major hexavalent chrome is reduced to trivalent chromium; 3) the water which is discharged from the filter tank is guided to a reaction tank, neutralizing agent is added, heavy metal complex-precipitation happens, and discharged water is guided into a sedimentation tank; 4) after the majority of heavy metal pollutant inside the sedimentation tank is removed, the upper clean liquid is undertaken the advanced treatment and is discharged after reaching the standard. The pretreatment process not only realizes the resource utilization of waste scrap iron and waste acid liquid, but also greatly reduces the cost of the medicine, reduces the quantity of the following mud, and is easier to realize the resource utilization of the produced mud.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method for separating and recovering chromium from waste residue containing hexavalent chromium
ActiveCN101209873ASolve the problem of difficult leachingLow in chromiumSolid waste disposalWater/sewage treatmentSodium bicarbonateSocial benefits
The invention discloses a method for separating and recycling chromium from the waste residue containing hexavalent chromium. The waste residue containing hexavalent chromium which has fine particles and is difficult to subside is added with mineralizer and then is subject to hydrothermal method or heating treatment to generate the waste residue which can subside, the upper clear liquid is separated from the waste residue and then the waste residue is cleaned and dried. Sodium bicarbonate or salt-mixture of sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate is adopted as mineralizer. The invention has simple process, low cost, quick results, large throughput, complete detoxification and no secondary pollution and can make use of all the residue, thereby bringing comparatively high social benefit and economic benefit.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
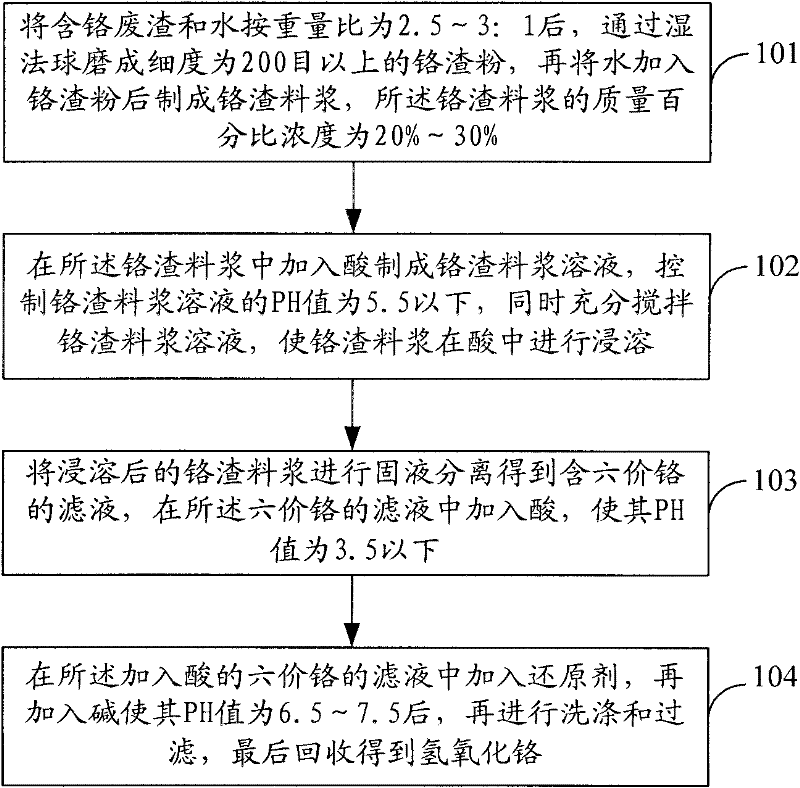
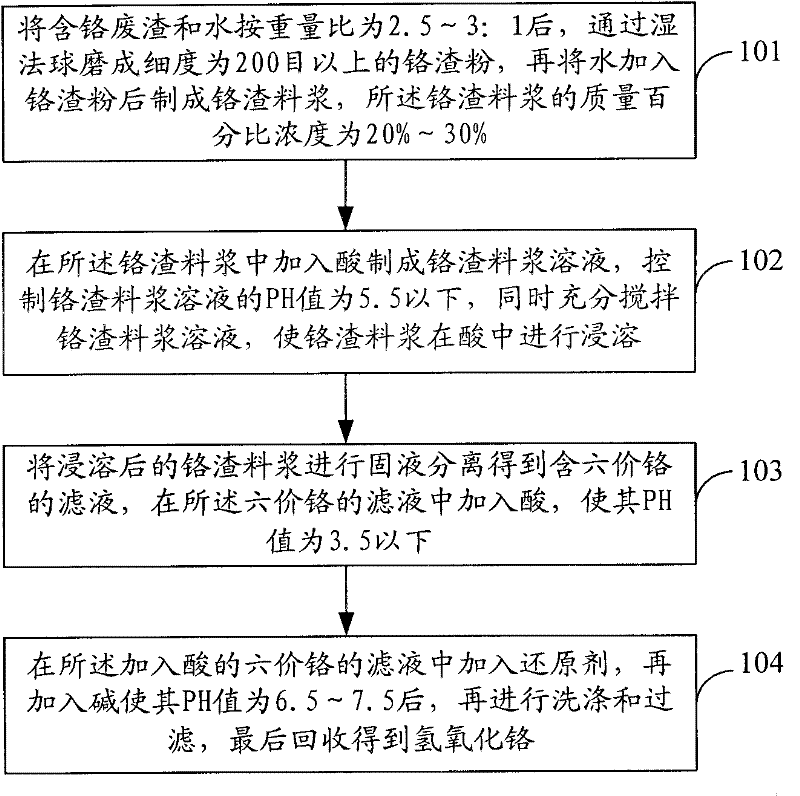
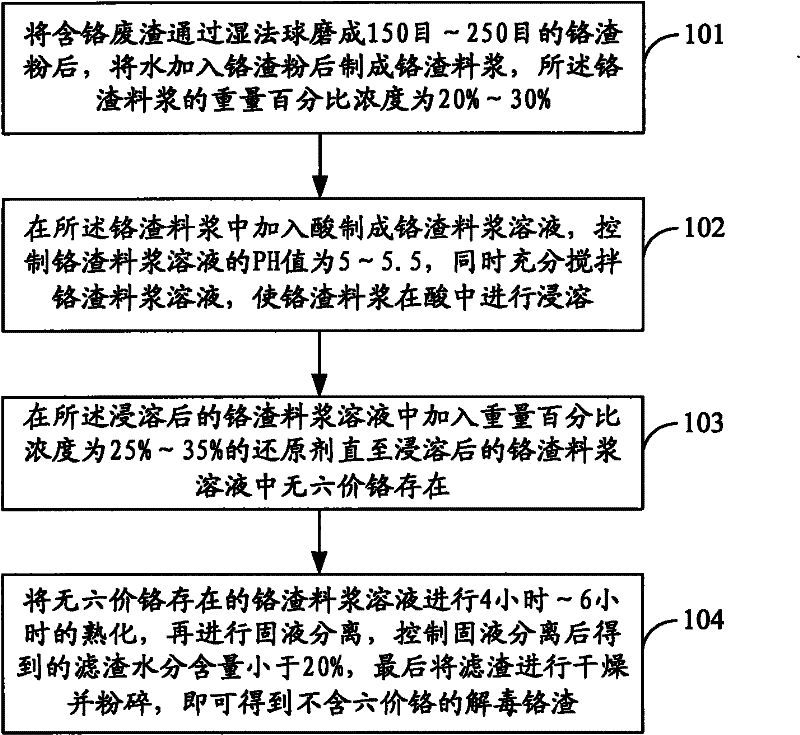
Method for recovering hexavalent chromium resources from chromium slag
The invention relates to a method for recovering hexavalent chromium resources from chromium slag. The method comprises the following steps of: subjecting chromium-containing slag to wet-process ball milling to obtain chromium slag powder, and adding water into the chromium slag powder to prepare chromium slag slurry; adding acid into the chromium slag slurry to prepare a chromium slag slurry solution, and simultaneously stirring the chromium slag slurry solution sufficiently to ensure that the chromium slag slurry is leached in the acid; subjecting the leached chromium slag slurry to solid-liquid separation to obtain hexavalent-chromium-containing filtrate, and adding acid into the hexavalent-chromium-containing filtrate; and adding a reducing agent into the hexavalent-chromium-containing filtrate added with the acid, adding base, washing and filtering to finally recover chromium hydroxide. By adopting the method for recovering the hexavalent chromium resources from the chromium slag, 60-80% of the hexavalent chromium resources can be recovered from the chromium slag, the total chromium residual amount in the chromium slag can be greatly reduced, and the residual amount of hexavalent chromium in the filtrate subjected to separation of the chromium hydroxide is below 0.5mg / L.
Owner:刘杰
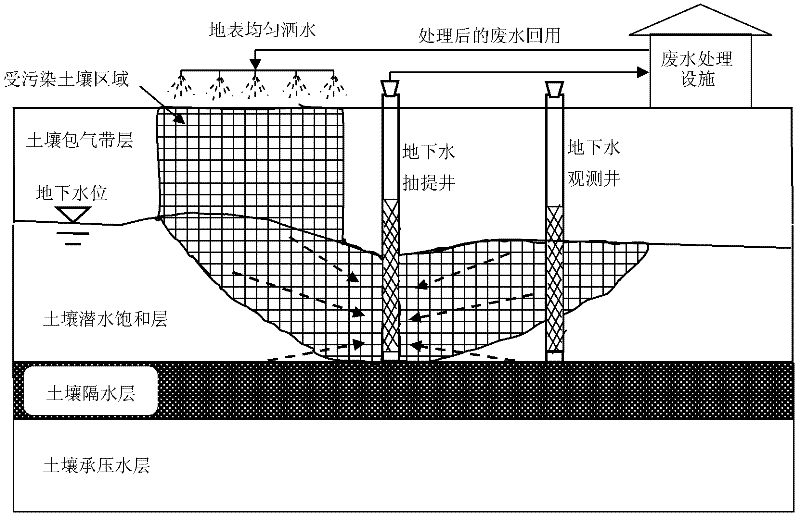
Chromium pollution soil in-situ leaching treatment method
InactiveCN102652956AReduce power consumptionReduce processing costsContaminated soil reclamationPollution soilEarth surface
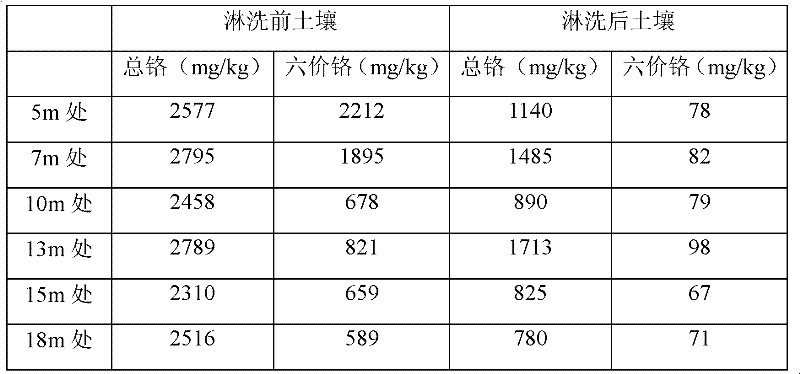
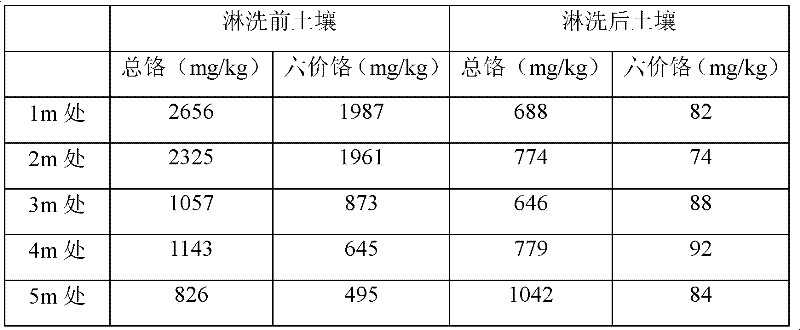
The invention relates to a chromium pollution soil in-situ leaching treatment method which is implemented in a way that: the periphery of the soil region in need of leaching treatment is provided with a plurality of groundwater extraction wells; water is sprayed on the ground to leach the polluted soil; the hexavalent-chromium-containing leaching water enters the groundwater; and under the control of a groundwater flow field, the hexavalent-chromium-containing leaching water is sucked to the ground surface; and the water is treated and recycled for ground spraying leaching. The hexavalent chromium content of the soil treated by the method can be reduced from 1000mg / kg to less than 100mg / kg.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Water-based surface-treating agent for metallic material
InactiveUS6447620B1Raise the ratioIncreased insolubilityOther chemical processesSolid state diffusion coatingWater basedMetallic materials
A water-based surface-treating agent for metallic materials which gives a film highly satisfactory in corrosion resistance, blackening resistance, wet secondary adhesion to topcoatings, low-pollution characteristics (amount of fixed chromium), chemical resistance (especially acid resistance and alkali resistance), etc., while retaining the intact practical liquid stability of conventional chromate-containing resinous coating agents. The water-based surface-treating agent comprises a synthetic resin emulsion and hexavalent chromium ions and has a pH of 5 or lower, the synthetic resin emulsion being one obtained by emulsion-polymerizing the following ingredients using a nonionic polymerizable emulsifier and a nonionic nonpolymerizable emulsifier: (1) an ethylenic carboxylic acid, (2) a functional acrylic monomer having at least one of N-((un)substituted methylol)carbamoyl, phosphonate, alkoxy, cyano, and carbamoyl groups, and (3) a third monomer which is different from the ingredients (1) and (2) and forms the skeleton of the copolymer to be obtained.
Owner:HENKEL CORP
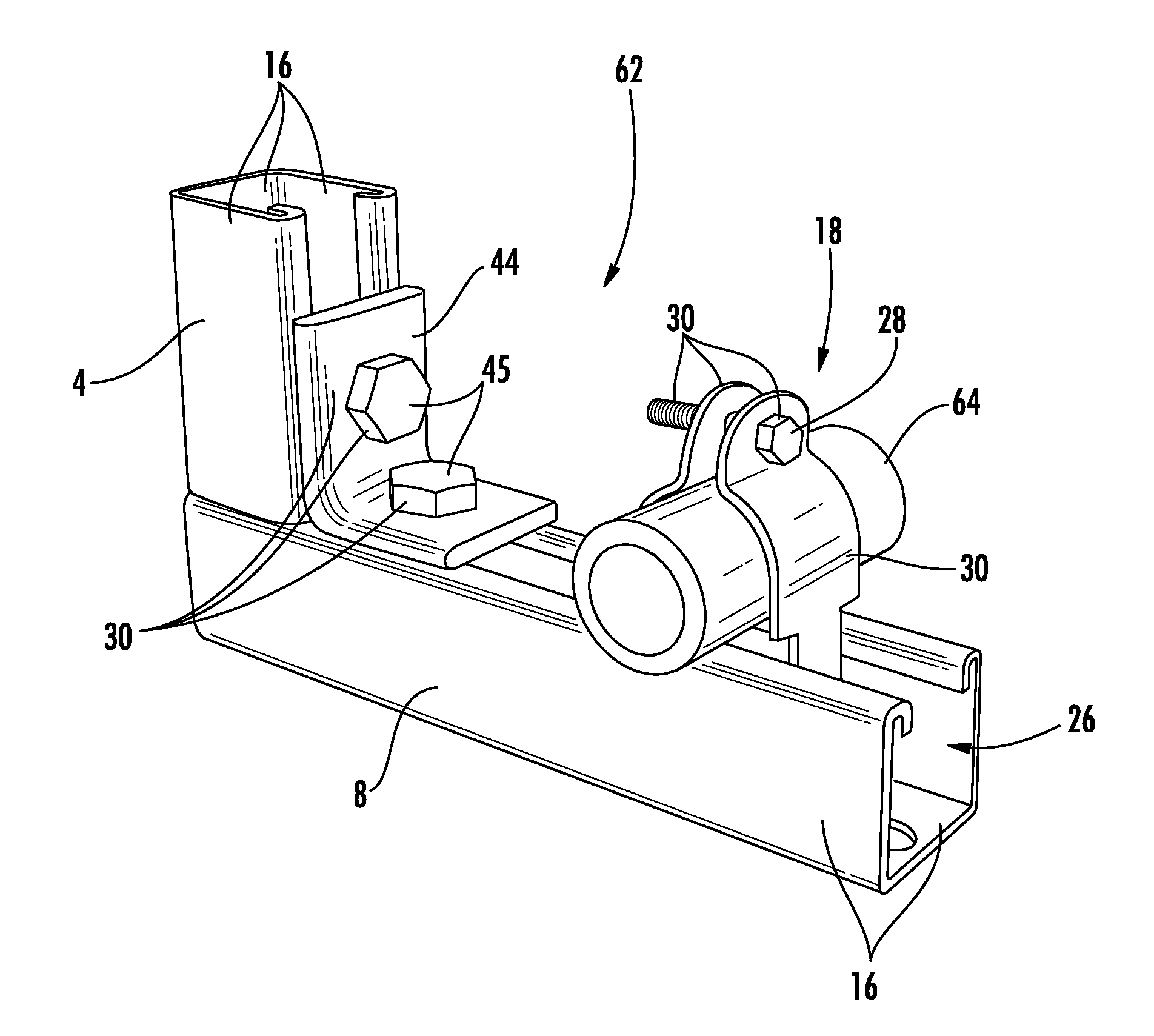
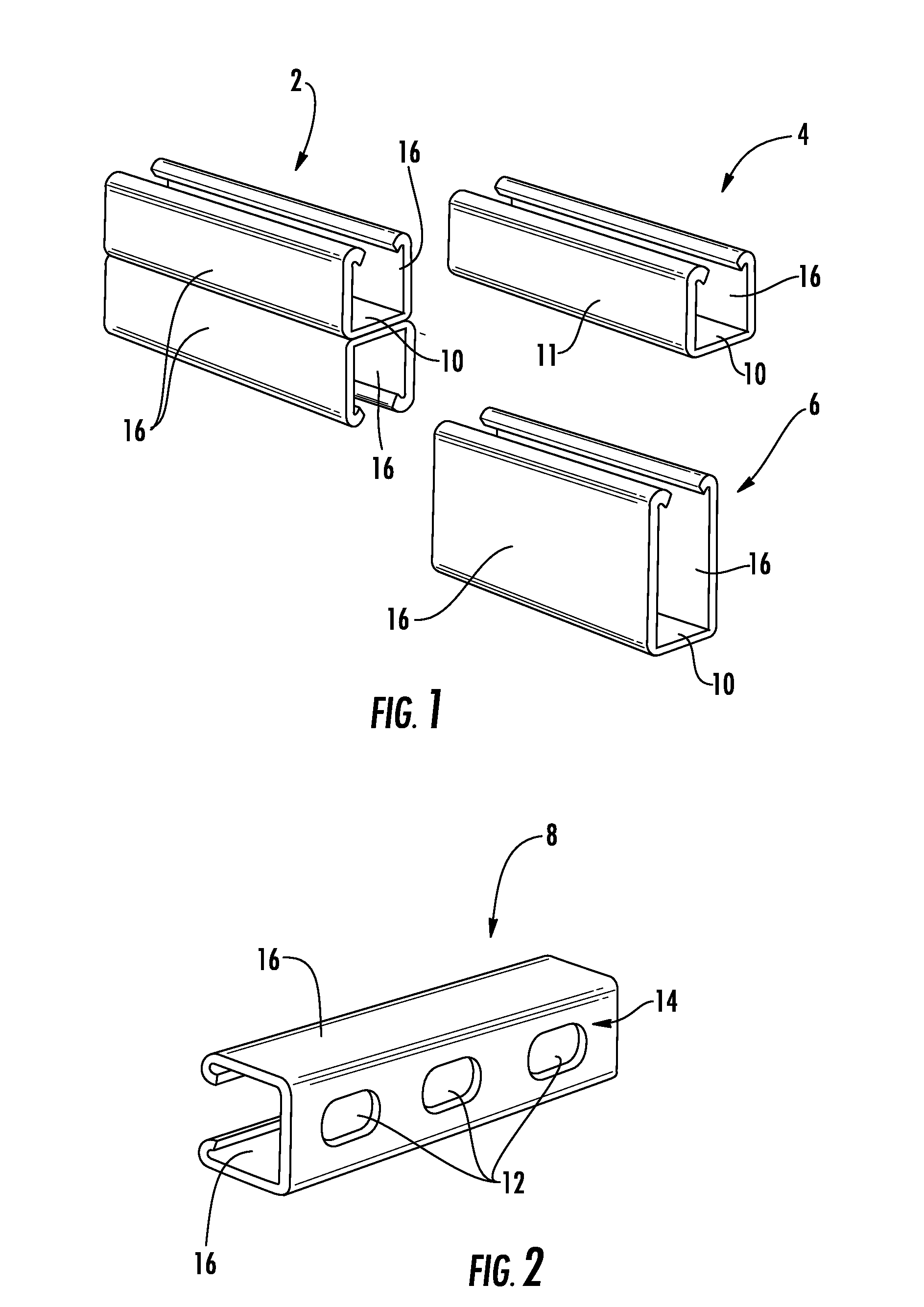
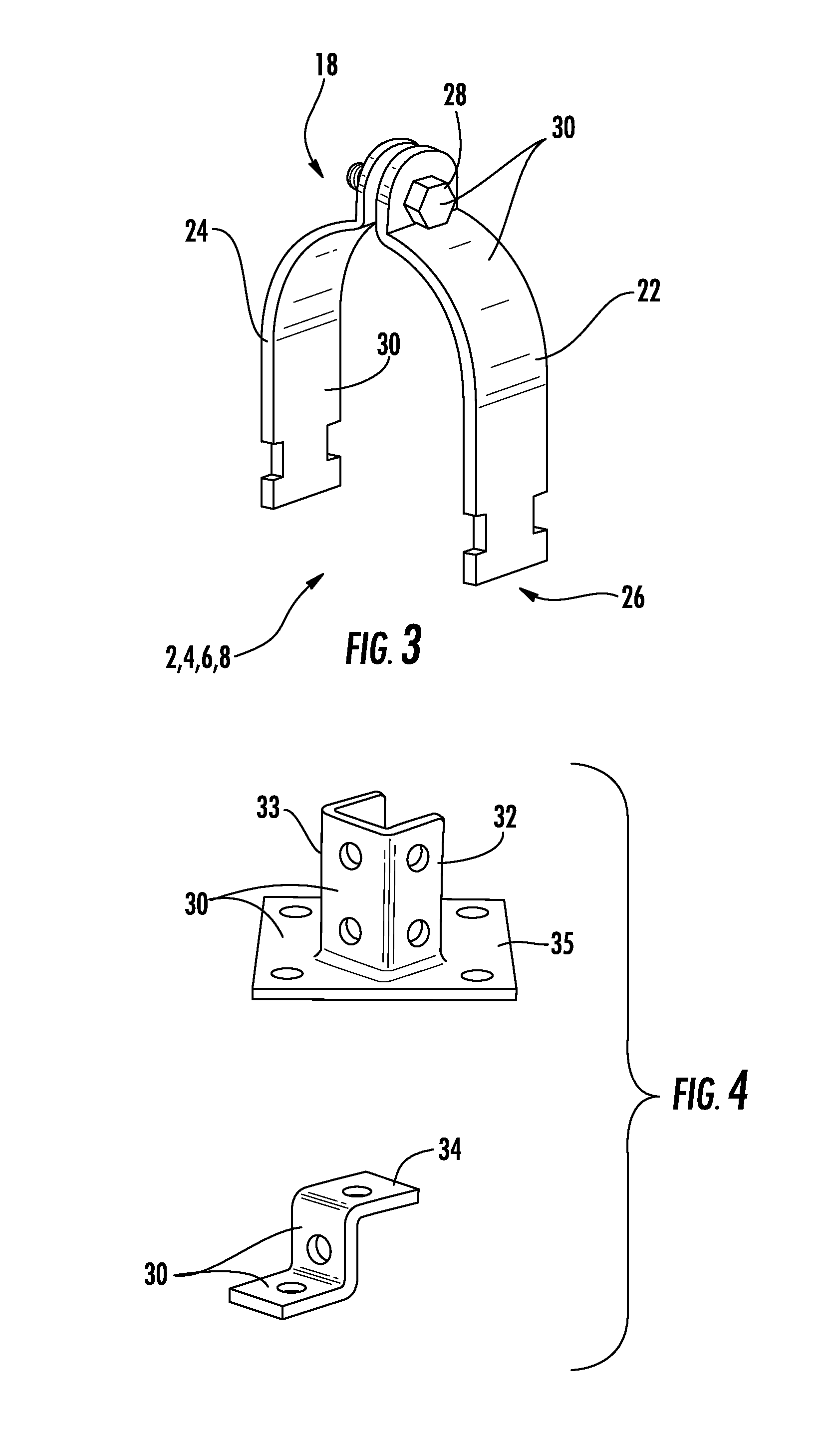
Enhanced corrosion resistant channels, fittings and fasteners
A corrosion resistant support system includes a first channel member having a first corrosion resistant coating. The first corrosion resistant coating is a zinc-aluminum-magnesium coating. A fitting is engageable with said channel member and a first mechanical fastener to couple the fitting to the channel member, the fitting and the first mechanical fastener having a second corrosion resistant coating. The second corrosion resistant coating is a thermal diffusion galvanized coating or a zinc-aluminum-magnesium coating. The first channel member and the first mechanical fastener may also have a third corrosion resistant coating disposed over the first and second corrosion resistant coatings, respectively. The third corrosion resistant coating can be a Perma-Green™ coating, a powder coating, an electrocoating (E-coat or Electrophoretic deposition coating), a paint coating, an epoxy coating, a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) coating, a trivalent chromium coating, a hexavalent chromium coating, a zinc coating, and / or a copper coating.
Owner:UNISTRUT INT CORP
Treatment method of chromium-polluted soil
InactiveCN102228901AReduce leaching concentrationEasy to operateContaminated soil reclamationHigh concentrationIron salts
The invention discloses a treatment method of chromium-polluted soil, which comprises the following steps of: 1, adding a ferrous iron salt solution in the chromium-polluted soil, uniformly stirring to ensure that a ferrous iron salt reacts with hexavalent chromium in the soil, and reducing the hexavalent chromium in the soil into trivalent chromium; and 2, adding a lime solution in the soil obtained from the step 1, and uniformly stirring to ensure that the trivalent chromium in the soil is converted into chromium hydroxide. The high-concentration chromium-polluted soil is treated by using an in situ curing / stabilizing method, thus the treatment method is rapid and efficient, is simple in operation, and is especially suitable for in situ emergence treatment of chromium pollution accidents caused by paroxysmal heavy environmental contamination events. The curing / stabilizing rate reaches above 99 percent.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Treating fluid and method for preparing vanadium-zirconium composite conversion coatings with self-repairing performance on aluminum alloy surfaces through same
ActiveCN102766862AImprove corrosion resistanceGuaranteed stabilityMetallic material coating processesMetallic bondingSodium fluoride
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical materials, and relates to a treating fluid and a method for preparing vanadium-zirconium composite conversion coatings with self-repairing performance on aluminum alloy surfaces through the same. The method includes the steps of firstly preparing the treating fluid containing fluorozirconate, metavanadate, sodium fluoride, nitrate, an accelerate and an additive; then putting an aluminum alloy after surface pretreatment into a working fluid made of the diluted treating fluid for 2min-10min; and finally subjecting the aluminum alloy to washing, drying and cooling to obtain the vanadium-zirconium composite conversion coatings. The preparation process is simple, heavy metals such as hexavalent chromium and nickel are not contained, the environment is friendly, the conversion coatings of the aluminum alloy after a conversion coating treatment are dense and high in binding force, metal ions in the conversion coatings can bond with base metal under a corrosion environment and provided with a certain self-repairing performance, and the treating technology of vanadium-zirconium conversion coatings can effectively replace chromate treatment on aluminum alloy surfaces.
Owner:湖南松井先进表面处理与功能涂层研究院有限公司
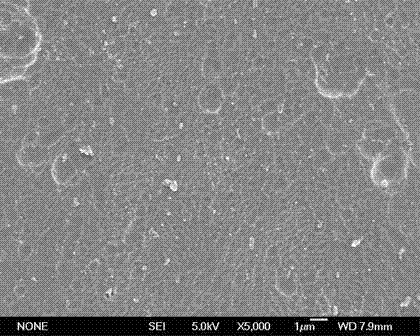
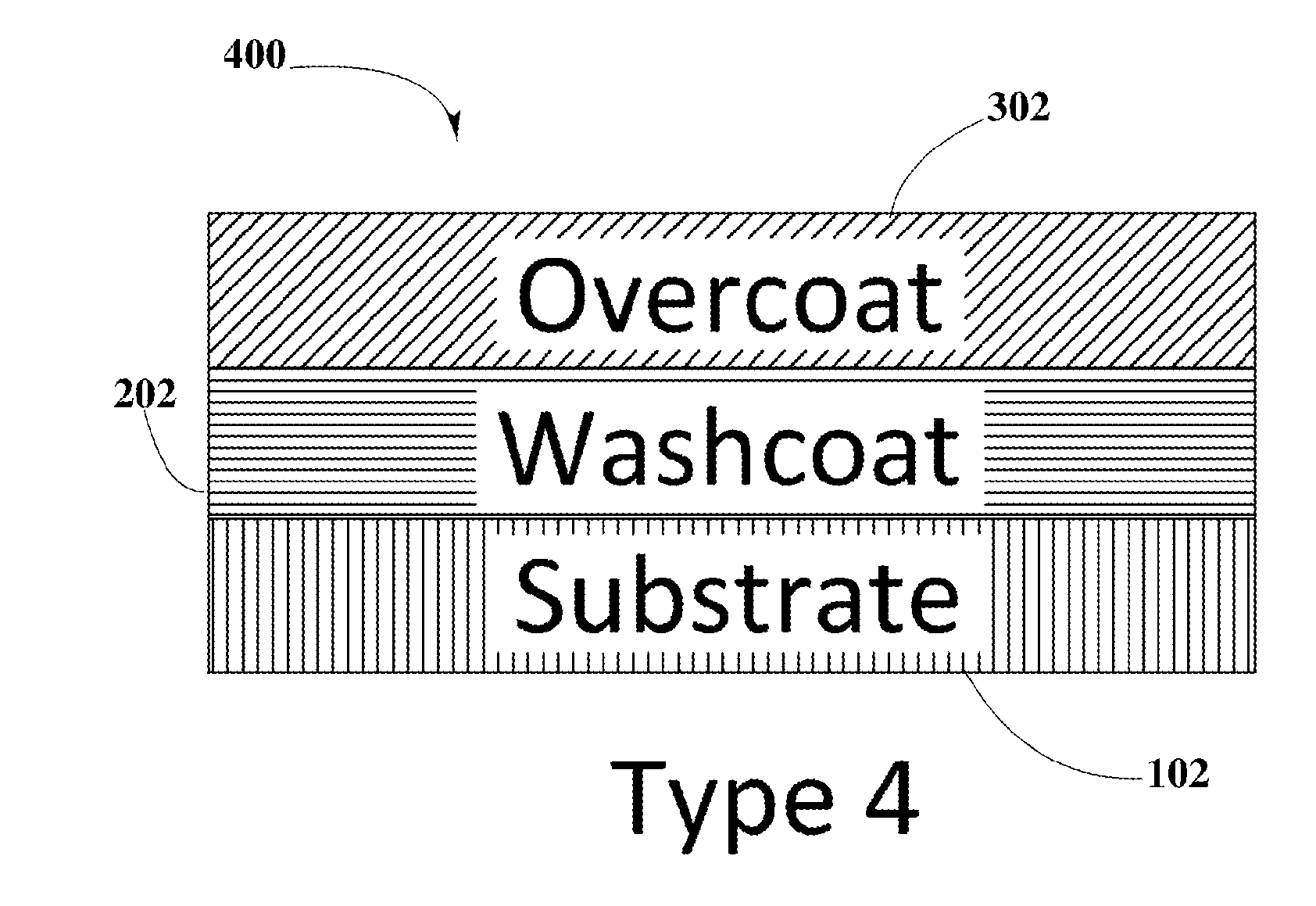
Methods for Identification of Materials Causing Corrosion on Metallic Substrates within ZPGM Catalyst Systems
InactiveUS20150004709A1Improve catalytic performanceChemical analysis using catalysisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHigh concentrationMetal catalyst
The present disclosure provides an identification process which may employ various identification techniques on Zero platinum group metal (ZPGM) catalyst systems, in order to identify responsible materials for the formation of corrosion material, such as hexavalent chromium compounds. Identification analysis, such as X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) may be performed on various thermally treated ZPGM catalyst systems, such as in bare substrate, substrate with one type of ZPGM in washcoat, a substrate with one type of ZPGM in overcoat and substrate combination of ZPGM metals in both washcoat and overcoat. Results of identification analysis may show that regardless of metal catalyst (for example Ag, Cu, Ce), hexavalent chromium (Cr6+) may be formed on aged catalysts systems, which may be due to the high concentration of chromium in substrate. Therefore, corrosion and production of hexavalent chromium may initiate from elements found in the substrate and not from elements within the ZPGM metal catalysts.
Owner:CLEAN DIESEL TECHNOLOGIES
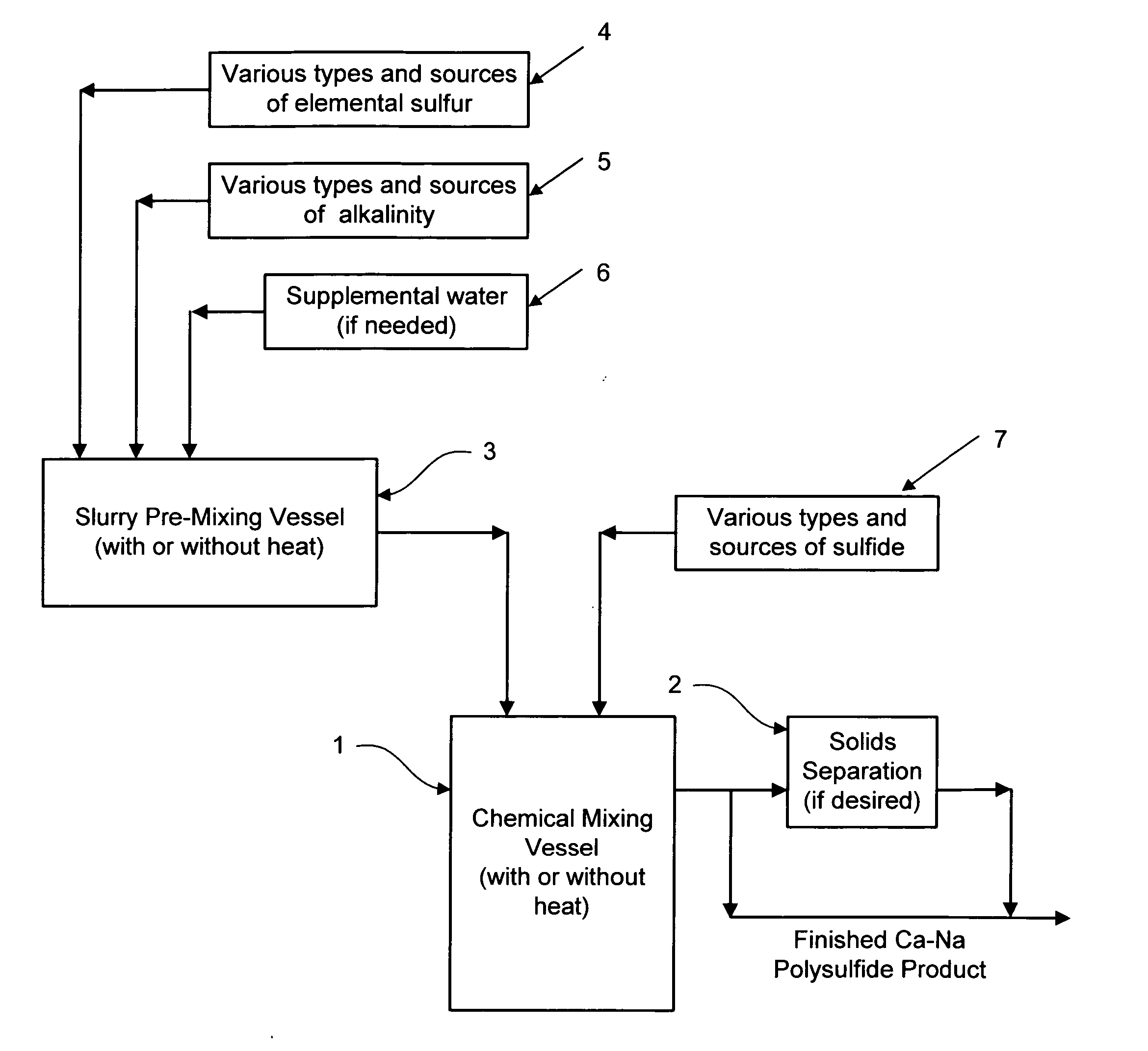
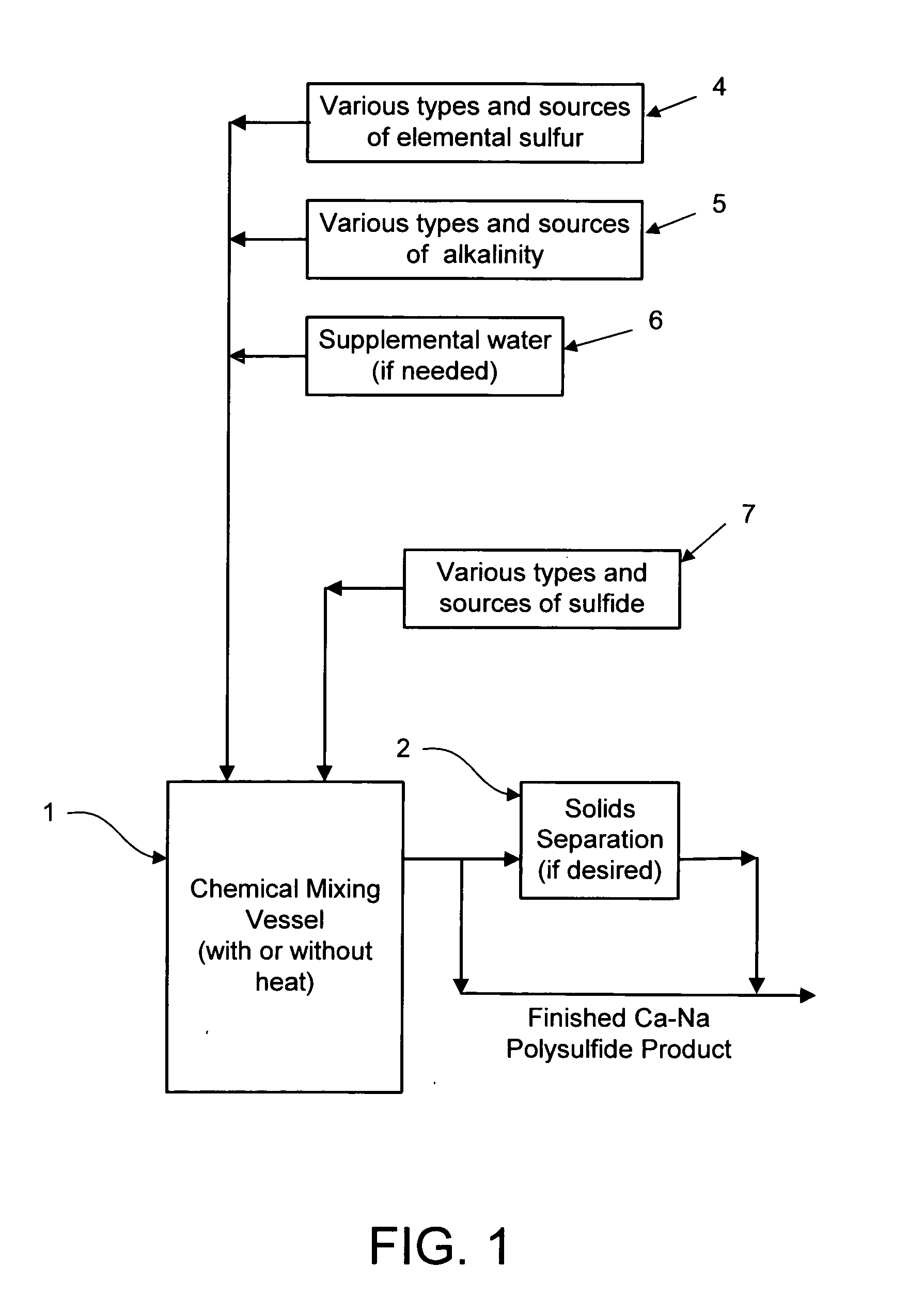
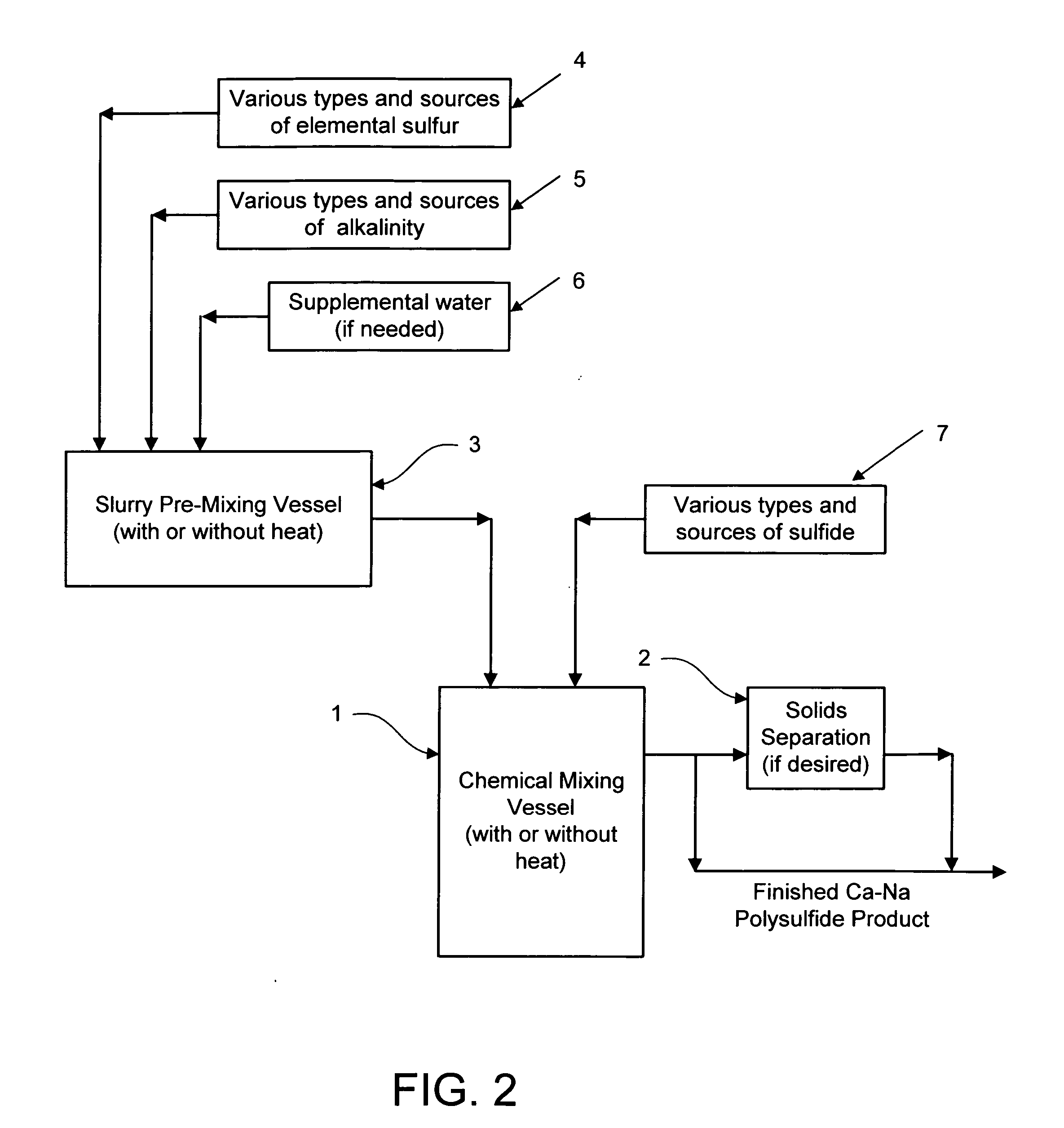
Calcium-sodium polysulfide chemical reagent and production methods
Owner:REDOX TECH GRP
Aluminium alloy chromium-free chemical converting liquid and its using method
The present invention relates to surface treatment of aluminum alloy, and especially a kind of chromium-free chemical aluminum alloy converting solution capable of endowing aluminum alloy surface with excellent corrosion resistance and its usage. The chromium-free chemical aluminum alloy converting solution consists of silicate, titanium salt, peroxide, fluoride, and water solution of sulfuric acid. The solution is used in 50-99 deg.c and pH 4-9 and has aluminum alloy contacting time of 2-20 min. The solution contains no hexavalent chromium and potassium ferricyanate, and has less environmental pollution, low cost, easy filming and high corrosion resistance.
Owner:郭瑞光
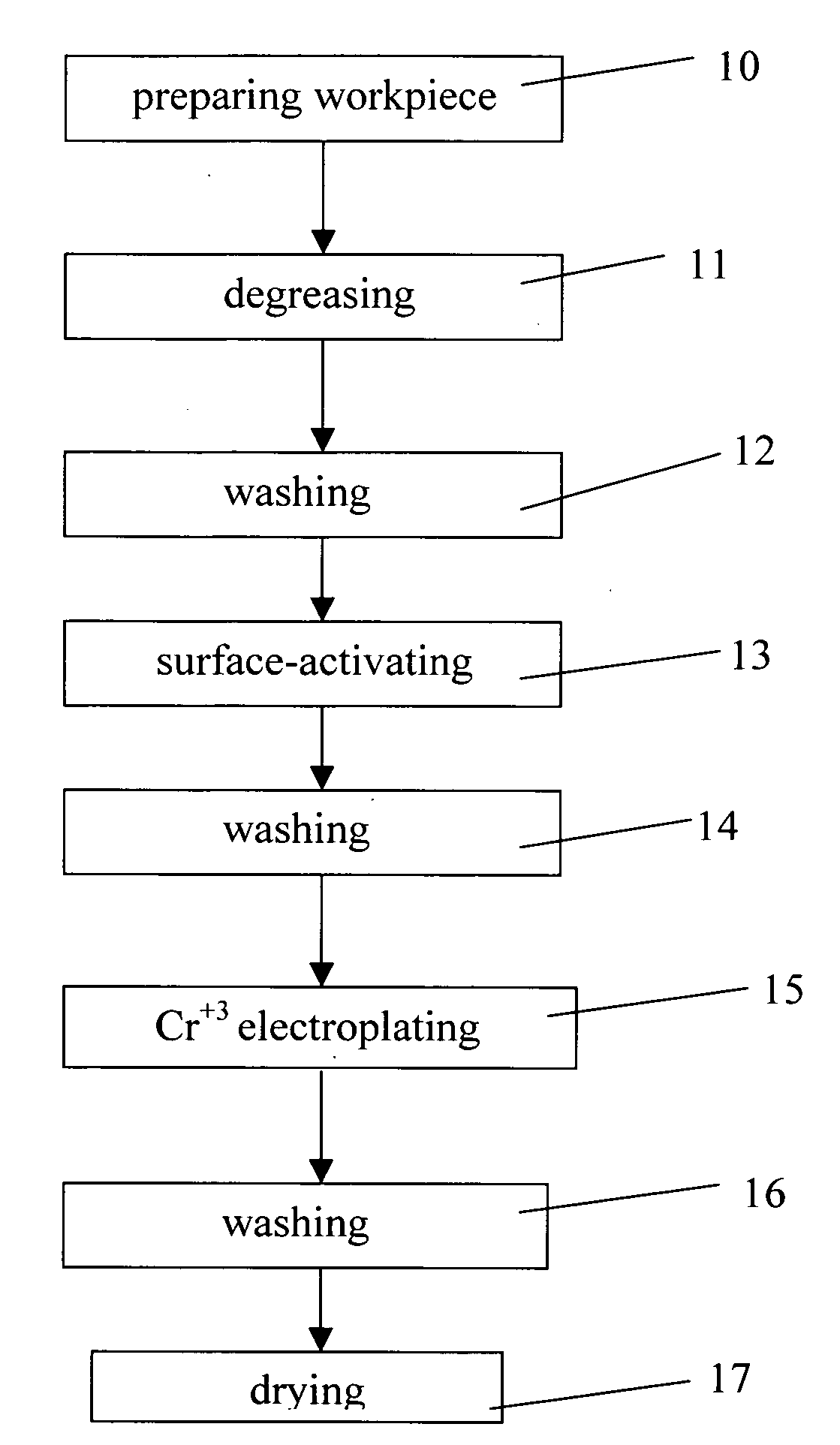
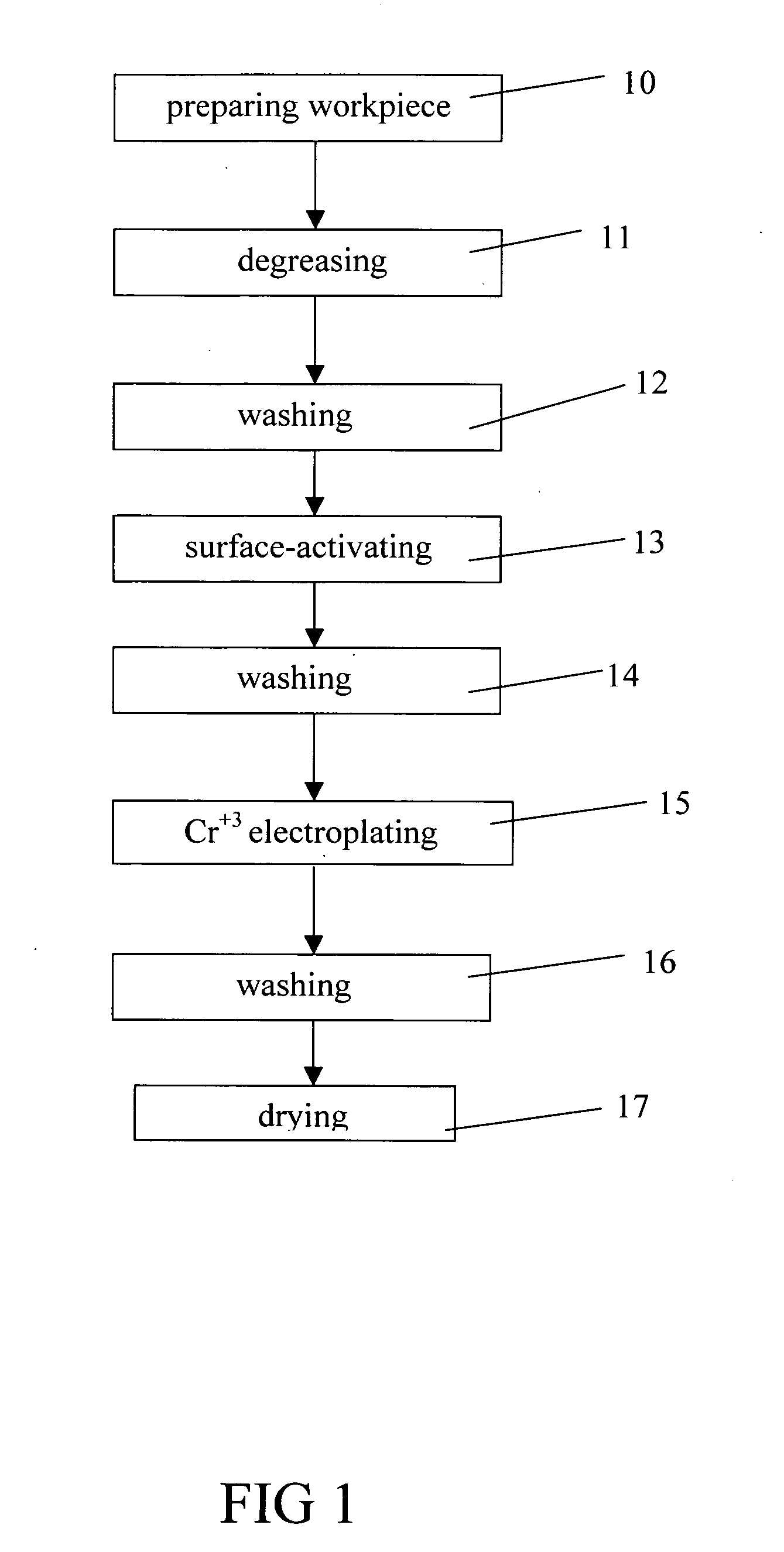
Trivalent chromium electroplating solution and an electroplating process with the solution
A trivalent chromium electroplating solution in accordance with the present invention contains at least one trivalent chromium salt for electroplating a chromium coating layer on a workpiece. By using the low toxic trivalent chromium to substitute highly toxic hexavalent chromium, an electroplating process of the present trivalent chromium electroplating solution has less pollution.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
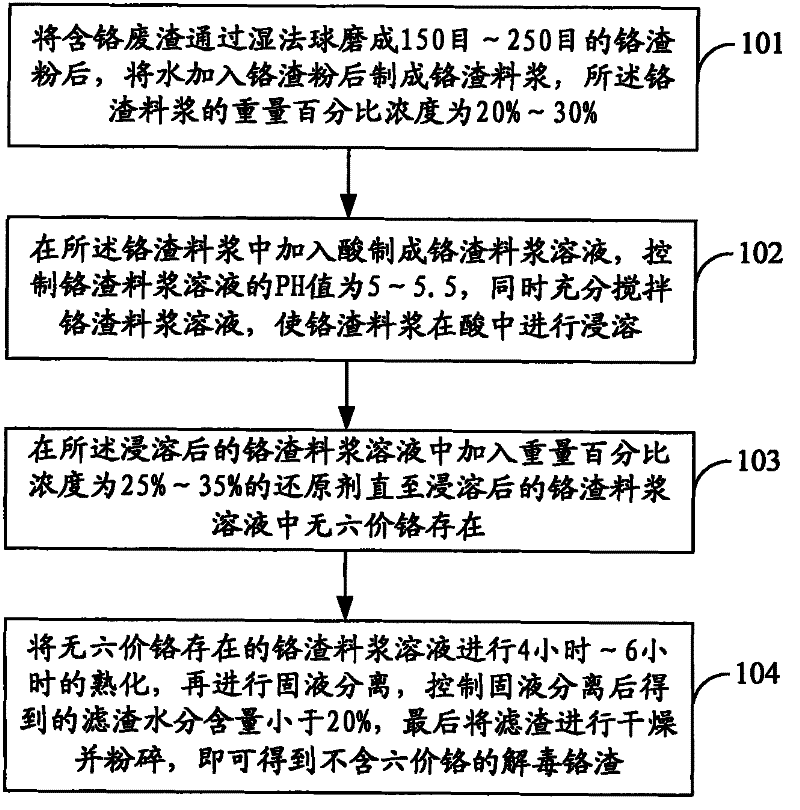
Method for detoxicating chromium residues and comprehensive utilization of detoxicated chromium residues
InactiveCN102189093ASave land resourcesSolid waste managementSolid waste disposalSlurryChromium Hexavalent Compound
The invention relates to a method for detoxicating chromium residues and the comprehensive utilization of the detoxicated chromium residues. The method for detoxicating the chromium residues comprises the following steps of: performing wet ball milling on chromium-containing waste residues to obtain chromium residue powder; adding water into the chromium residue powder to prepare chromium residue slurry; adding acid into the chromium residue slurry to prepare chromium residue slurry solution, and fully stirring the chromium residue slurry solution simultaneously to make the chromium residue slurry immersed in the acid; adding a reducing agent into the immersed chromium residue slurry solution until hexavalent chromium does not exist in the immersed chromium residue slurry solution; curing the chromium residue slurry solution without the hexavalent chromium, and performing solid-liquid separation; and drying and grinding filter residues to obtain the detoxicated chromium residues without the hexavalent chromium. By the method for detoxicating the chromium residues, various hexavalent chromium compounds contained in the chromium residues can be systematically and completely detoxicated and removed, the hexavalent chromium in various produced building material products is comprehensively utilized, and the content of extract is less than 0.1mg / L.
Owner:刘杰
Method for processing chrome wastewater
InactiveCN101269871AChange pHReduce dosageWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentSorbentWastewater
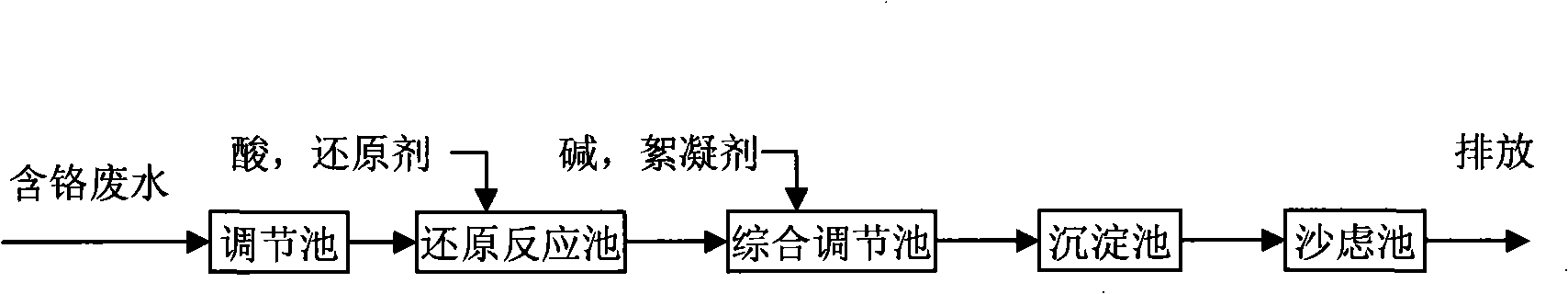
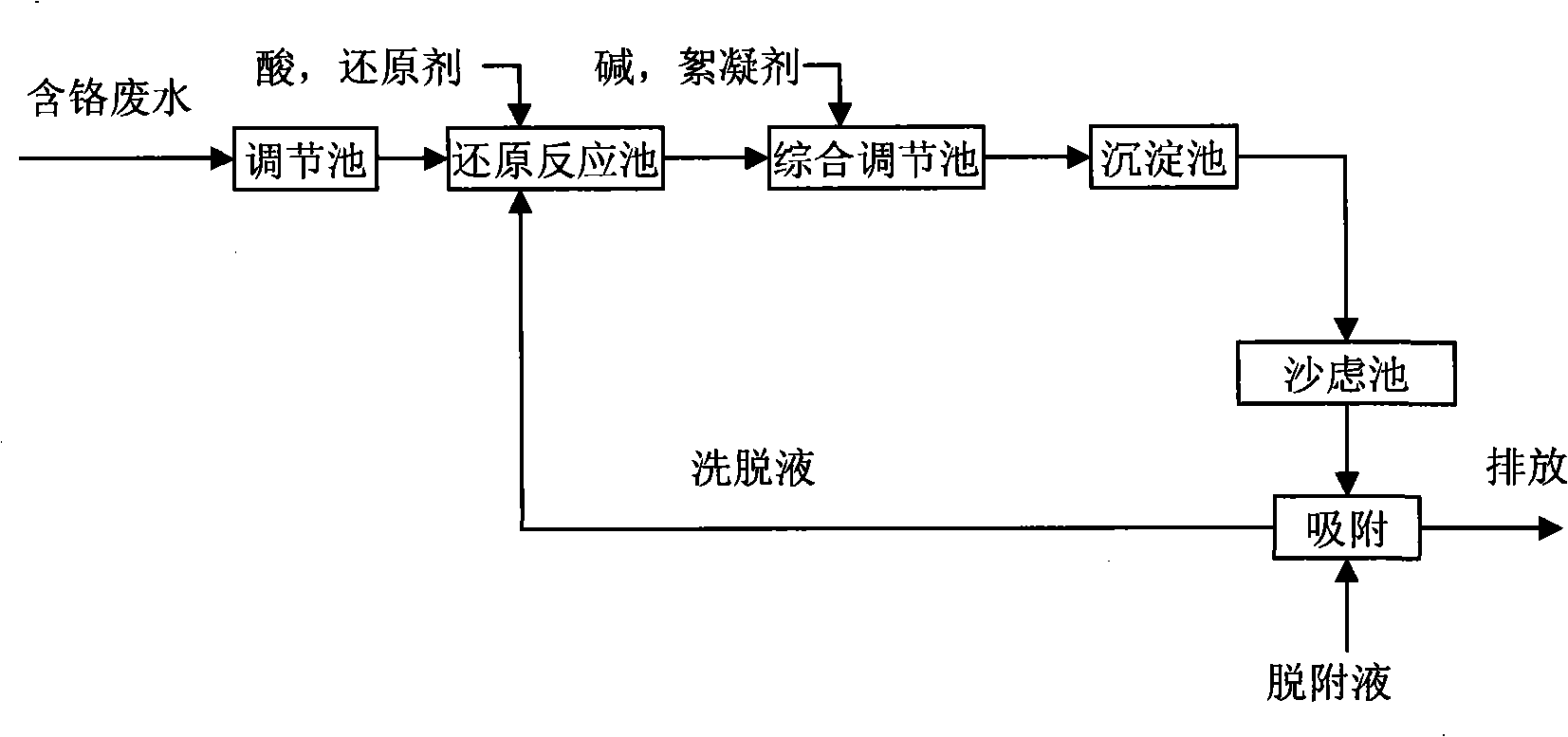
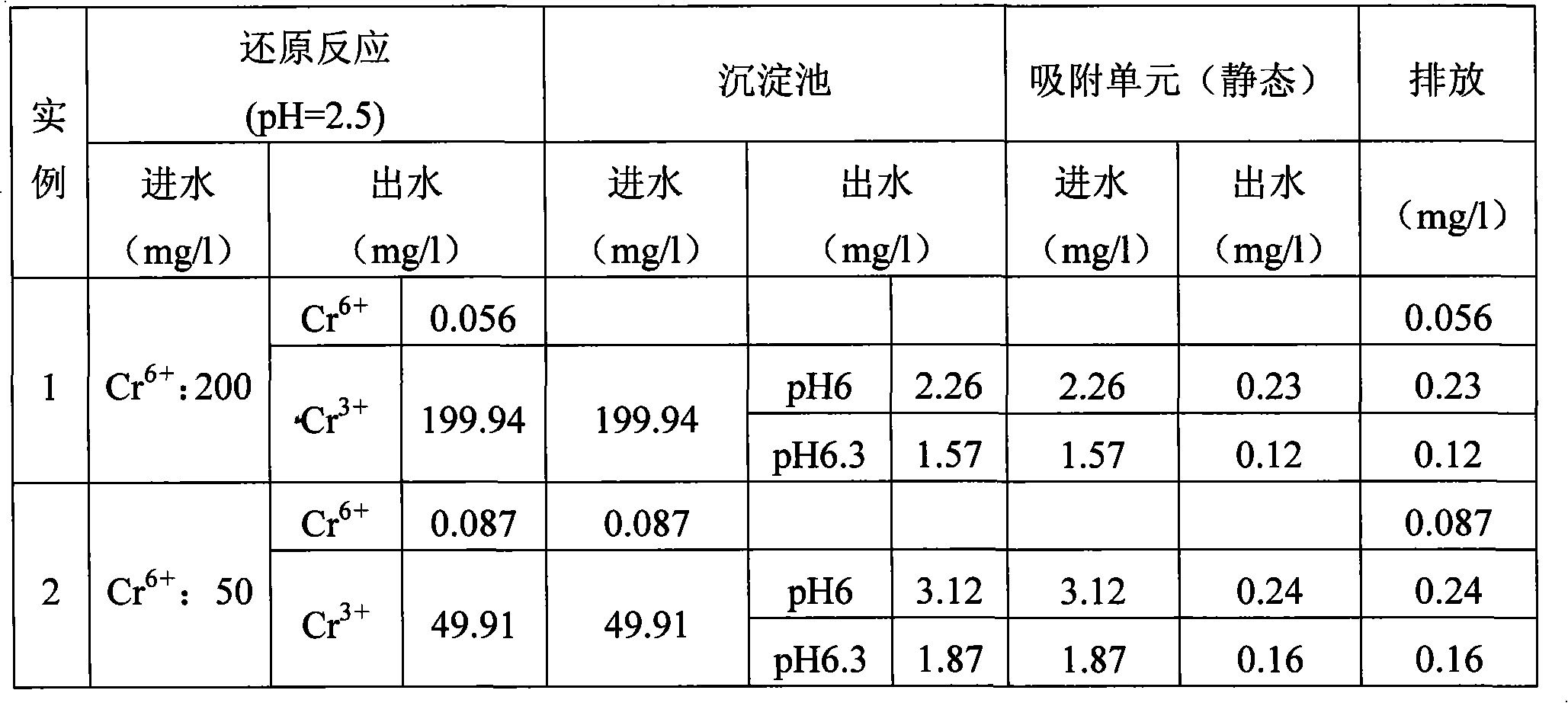
The invention improves the reduction-precipitation process of traditional hexavalent chrome wastewater, changes the pH value of the trivalent chromium ion precipitation in the original process, and avoids the problem that the treated yielding water does not reach the mark caused by that the trivalent chromium precipitation is oxidized newly to generate the hexavalent chrome when performing the settlement and the filtering under the alkalescence condition. When avoiding the trivalent chromium is easily oxidized under the alkalescence condition, the adding quantity of reducing agent can be effectively reduced when reducing the hexavalent chrome. During the settlement procedure of the trivalent chromium ion in the process, the originally required precipitation pH value range 8.5-9.5 is changed, and the pH value range is adjusted to 6.0-6.3. After the settlement and the filtering, an adsorption unit is added. Treated earthnut shells are adopted to be used as a sorbent, so the trivalent chromium ion left in the solution after the adsorption and the filtering can be effectively adsorbed to lead the discharging of the yielding water to reach the mark. The sorbent containing the adsorption adopts acid solution with the pH value being 2-3 for the elution, and eluant can enter into a reduction reactor for adjusting the pH value of raw water.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com