Patents
Literature
34278results about "Water/sewage treatment by sorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rapid characterization of polymers
InactiveUS6406632B1More separatedHigh sample throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsSamplingFluid phasePhysical chemistry
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
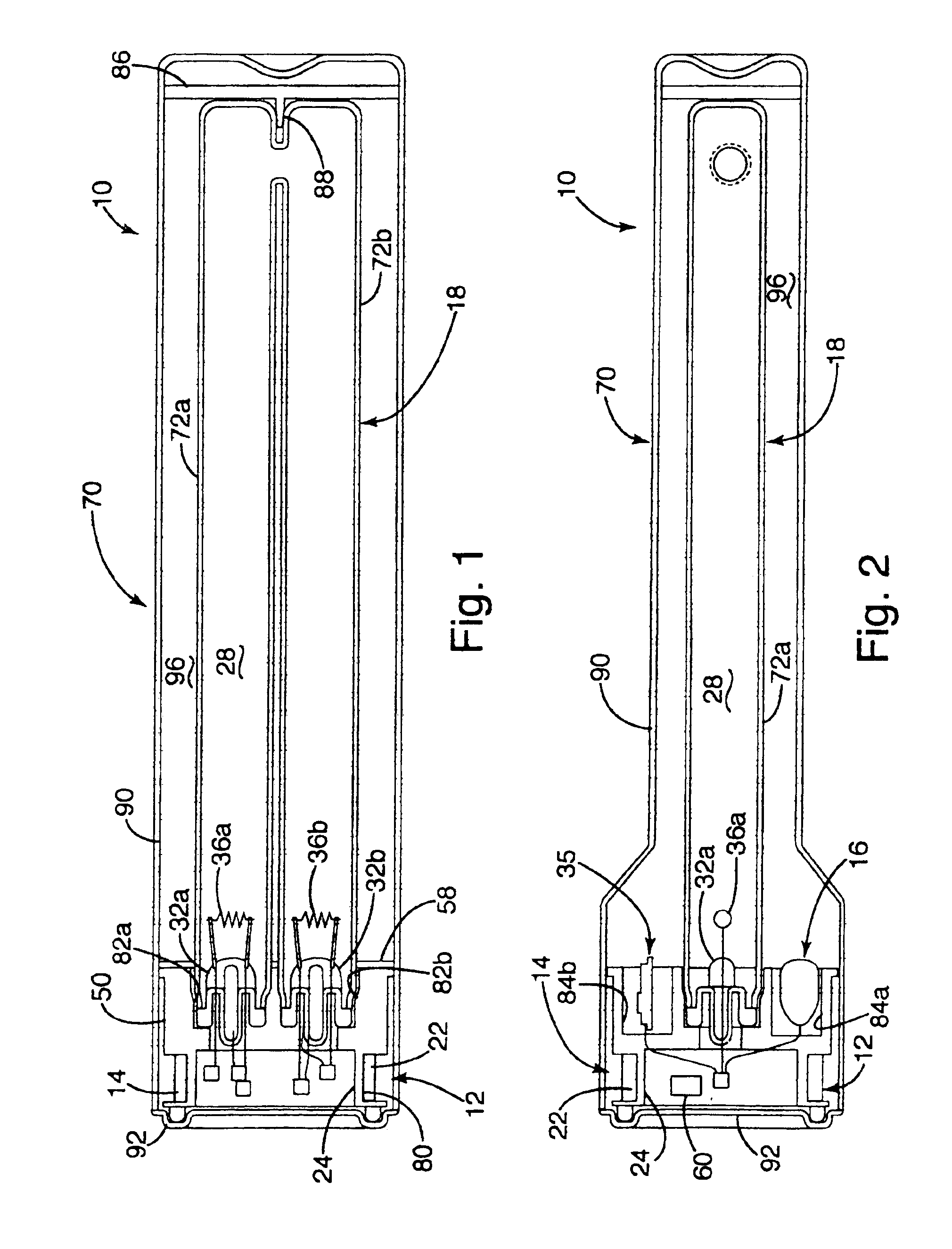
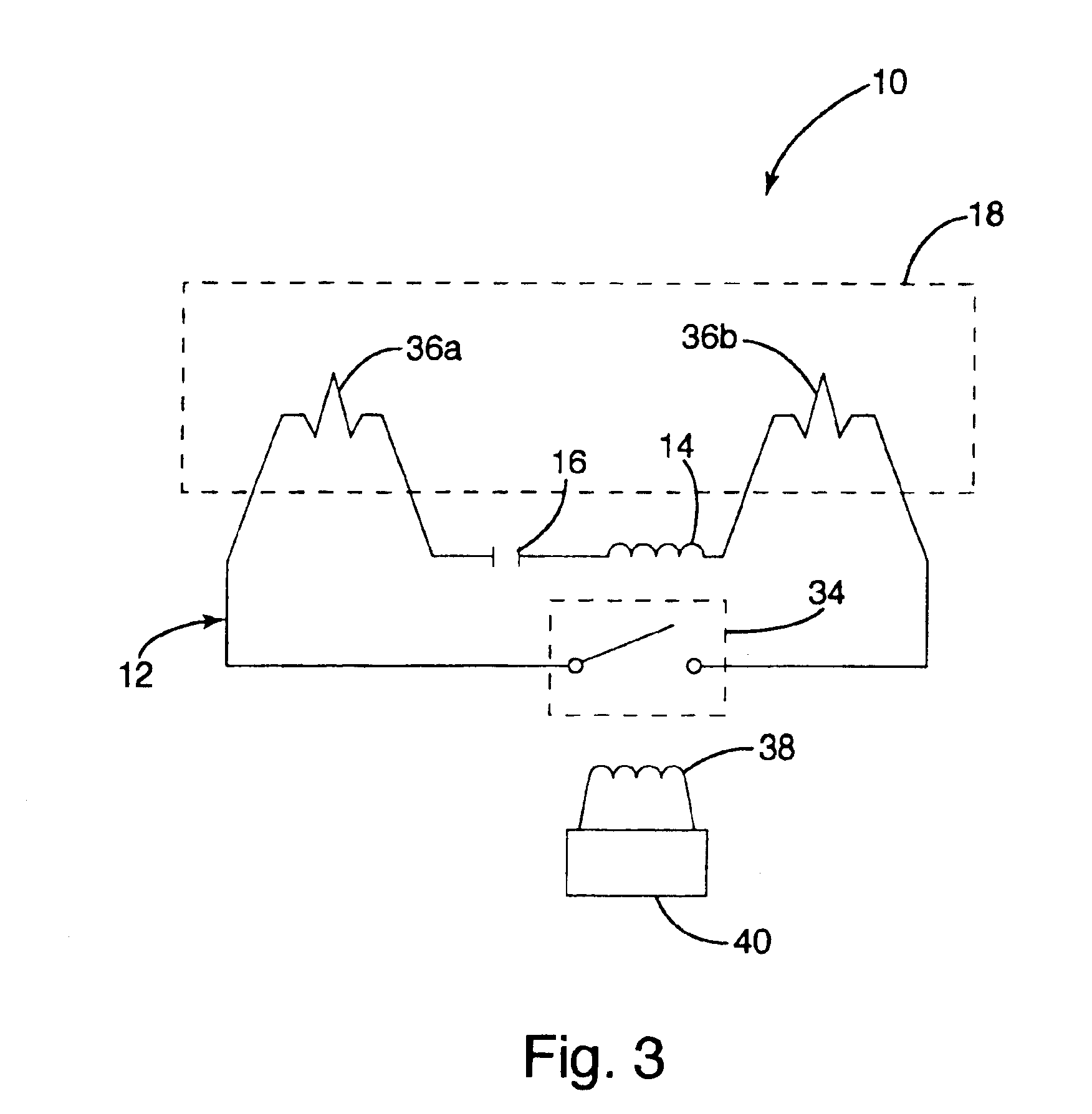
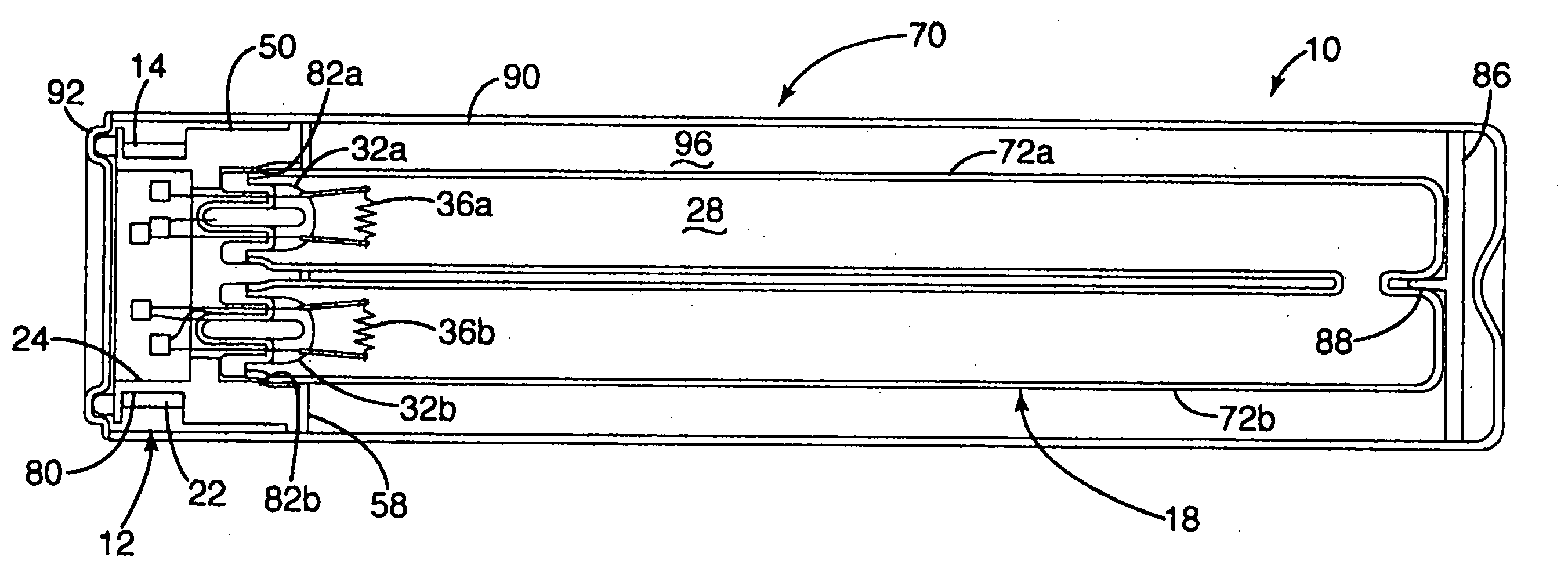
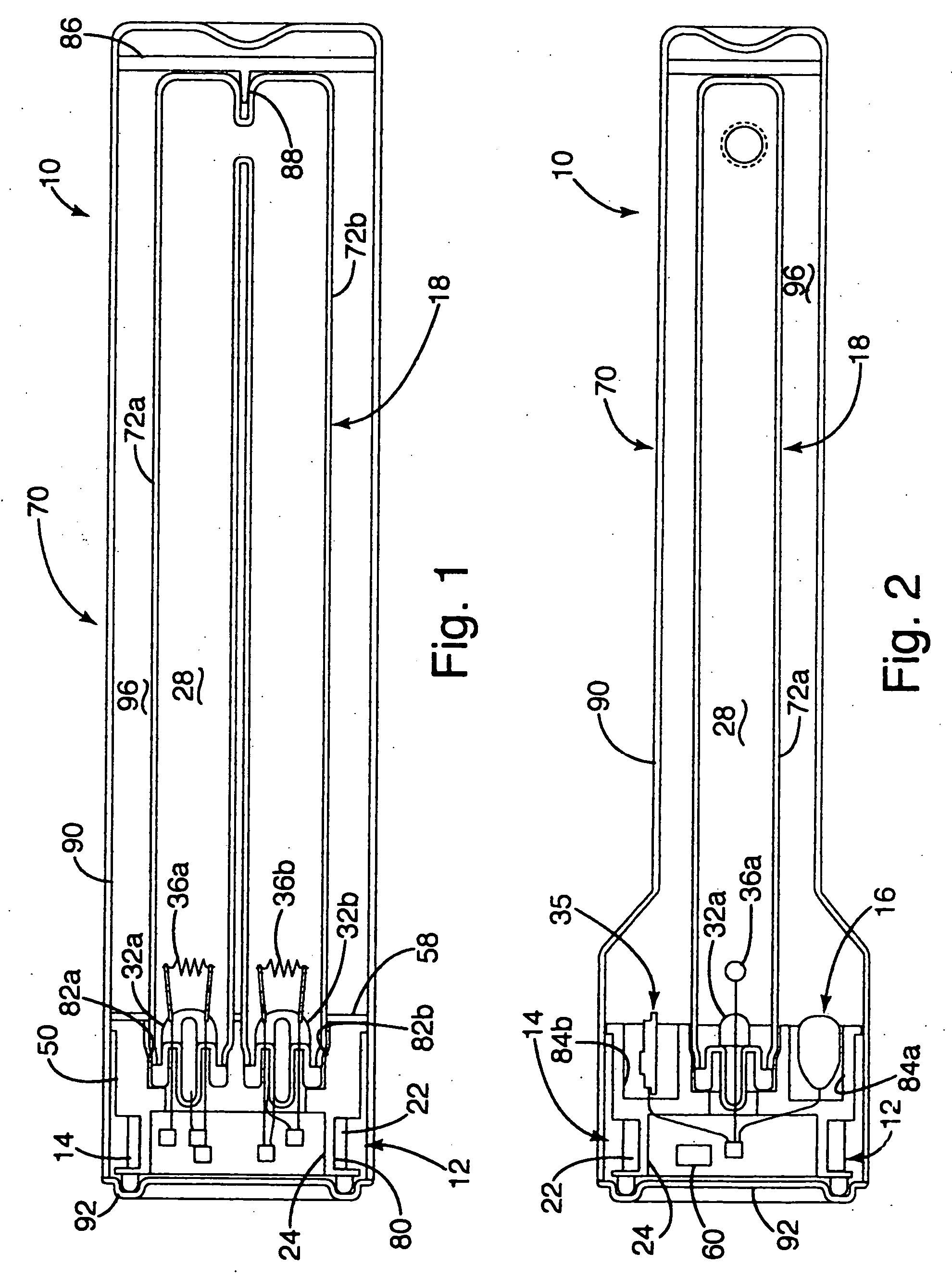
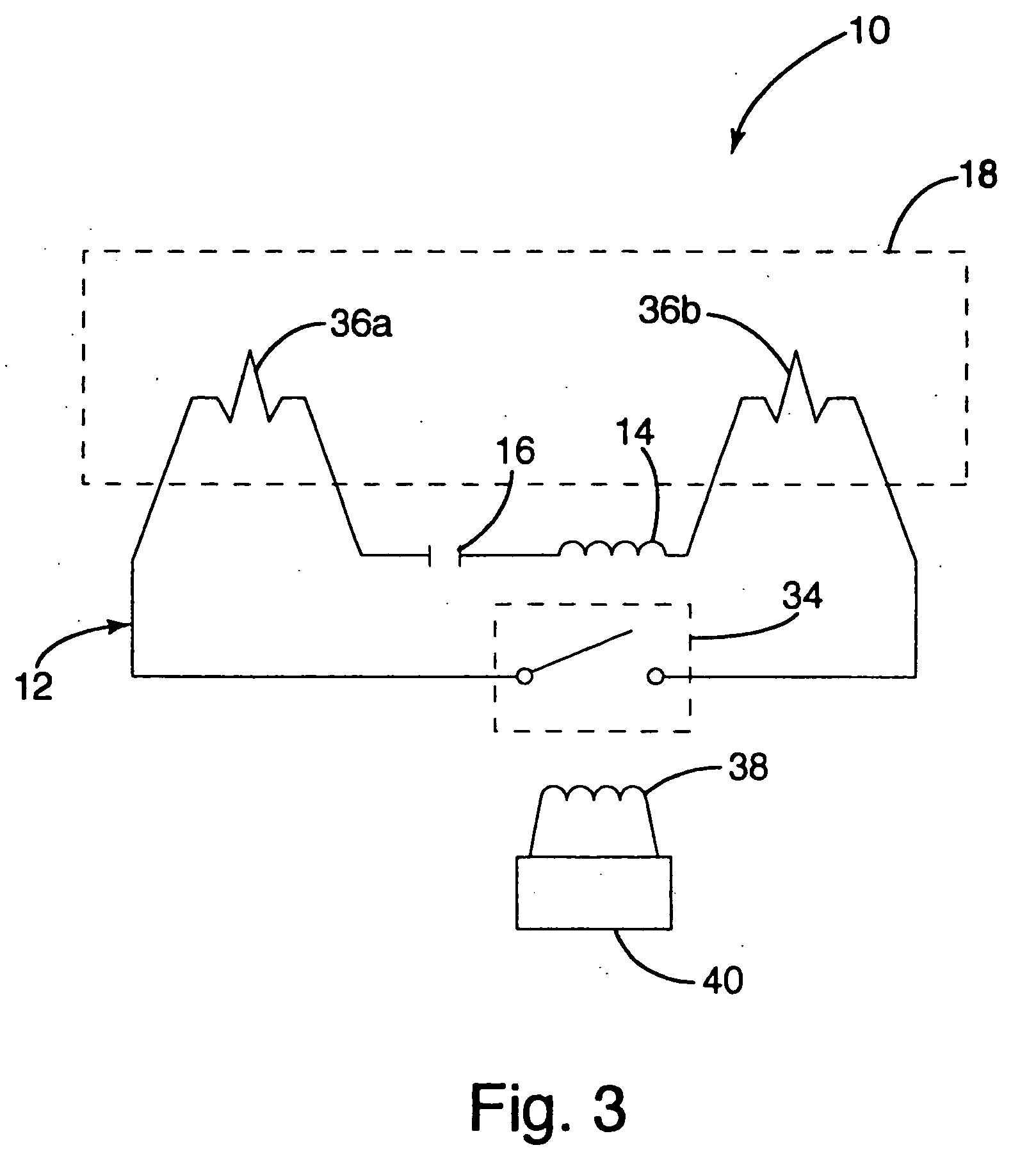
Inductively powered lamp assembly
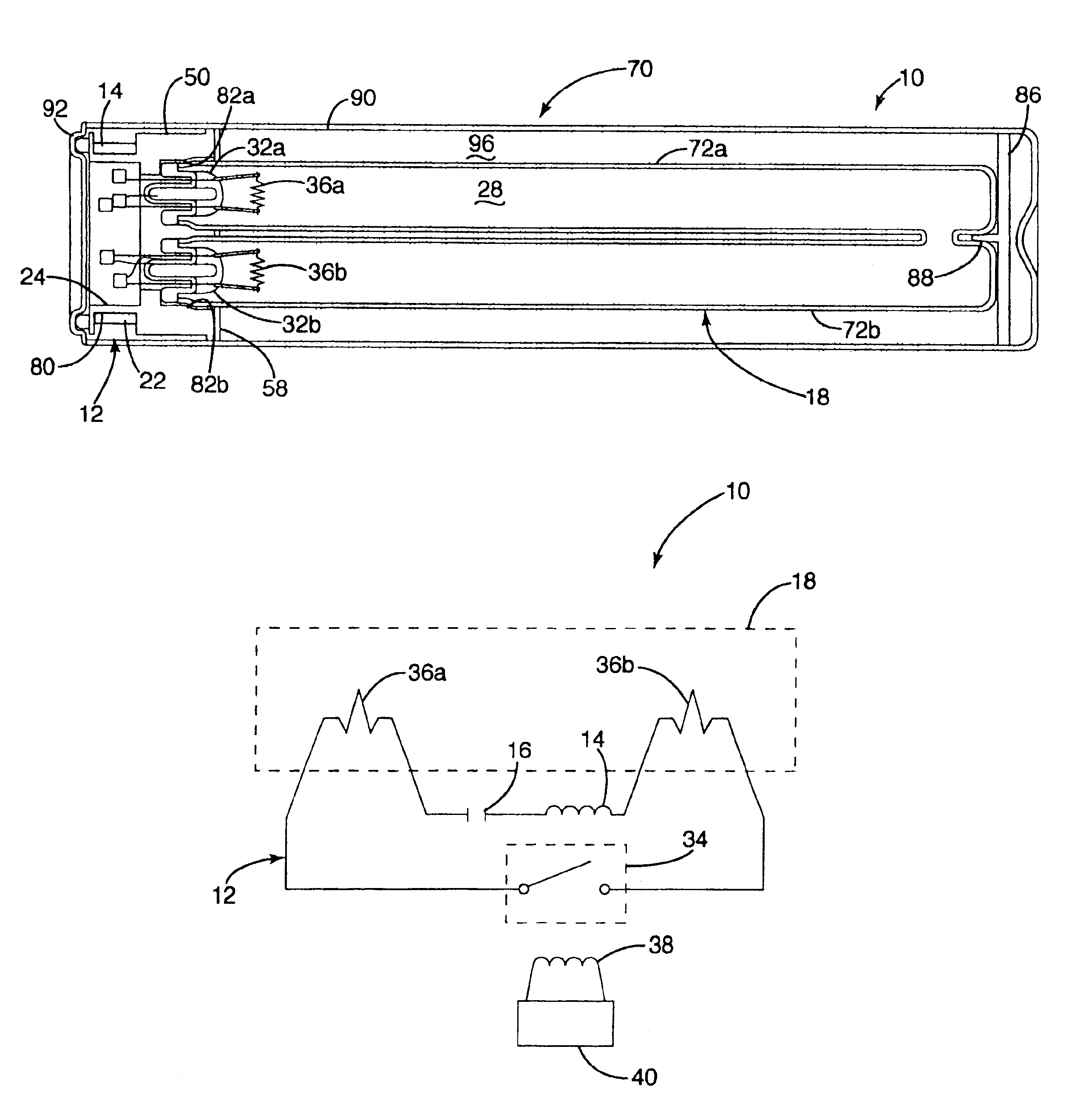
InactiveUS6917163B2Quiet operationLess-precise alignmentPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesResonanceCapacitor
A lamp assembly configured to inductively receive power from a primary coil. The inductively powered lamp assembly includes a lamp circuit including a secondary and a lamp connected in series. In a first aspect, the lamp circuit includes a capacitor connected in series with the lamp and the secondary to tune the circuit to resonance. The capacitor is preferably selected to have a reactance that is substantially equal to or slightly less than the reactance of the secondary and the impedance of the lamp. In a second aspect, the inductively powered lamp assembly includes a sealed transparent sleeve that entirely encloses the lamp circuit so that the transparent sleeve is fully closed and unpenetrated. The transparent sleeve is preferably the lamp sleeve itself, with the secondary, capacitor and any desired starter mechanism disposed within its interior.
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
Parallel high-performance liquid chromatography with post-separation treatment
InactiveUS6436292B1High sample throughputEasy to findIon-exchange process apparatusSamplingChromatographic separationCombinatorial synthesis
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) methods and systems are disclosed that combine parallel chromatographic separation of a plurality of samples with a detection technique that involves post-separation treatment of the plurality of samples to enhance one or more properties of the sample or of a component thereof, followed by detection of the one or more enhanced properties. Selective, tunable detection schemes are achievable, and are particularly advantageous as applied in connection with combinatorial chemistry, combinatorial material science and more particularly, combinatorial synthesis and screening of polymeric materials.
Owner:FREESLATE
Plasma concentrate apparatus and method
ActiveUS6905612B2Effective absorptionPromote absorptionMixing methodsDead animal preservationRed blood cellAbsorption of water
A plasma concentrator for producing plasma concentrate from a plasma from which erythrocytes have been substantially removed. The device comprises a concentrating chamber having an inlet port and an concentrate outlet, the concentrating chamber containing hydrogel beads and at least one inert agitator; and a concentrate chamber having an inlet communicating with the concentrator outlet through a filter, and having an plasma concentrate outlet port. A process for producing plasma concentrate from plasma from which erythrocytes have been substantially removed, comprising the steps of a) moving the plasma into a concentrating chamber containing hydrogel beads and an agitator to form a hydrogel bead-plasma mixture; b) causing the agitator to stir the hydrogel bead-plasma mixture, facilitating absorption of water by the beads from the plasma, until a hydrogel bead-plasma concentrate is formed; and c) separating the plasma concentrate from the hydrogel beads by passing the plasma concentrate through a filter. The concentrator can be one or more syringe devices coupled for multiple concentrations.
Owner:HANUMAN
Method of manufacturing a lamp assembly
InactiveUS20050116650A1Improve power factorReduce power lossPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesElectric forceResonance
A lamp assembly configured to inductively receive power from a primary coil. The lamp assembly includes a lamp circuit including a secondary and a lamp connected in series. In a first aspect, the lamp circuit includes a capacitor connected in series with the lamp and the secondary to tune the circuit to resonance. The capacitor is preferably selected to have a reactance that is substantially equal to or slightly less than the reactance of the secondary and the impedance of the lamp. In a second aspect, the lamp assembly includes a sealed transparent sleeve that entirely encloses the lamp circuit so that the transparent sleeve is fully closed and unpenetrated. The transparent sleeve is preferably the lamp sleeve itself, with the secondary, capacitor and any desired starter mechanism disposed within its interior.
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
Gelatinous cushions with buckling columns
InactiveUS6026527AEliminates pressure peakMaximize surface areaSolesStuffed mattressesCushioningEngineering
A cushioning element that has a number of substantially parallel elongate columns which buckle under an appropriate load. The cushioning element may be formed from a soft, easily deformable elastic or visco-elastic cushioning media. As a force is exerted against the cushioning element generally parallel to a column, the cushioning media may compress, and eventually the walls of the column may buckle. This equalizes pressure across the contact area of the object being cushioned.
Owner:EDIZONE LC
Water purifier and method of making and using the same
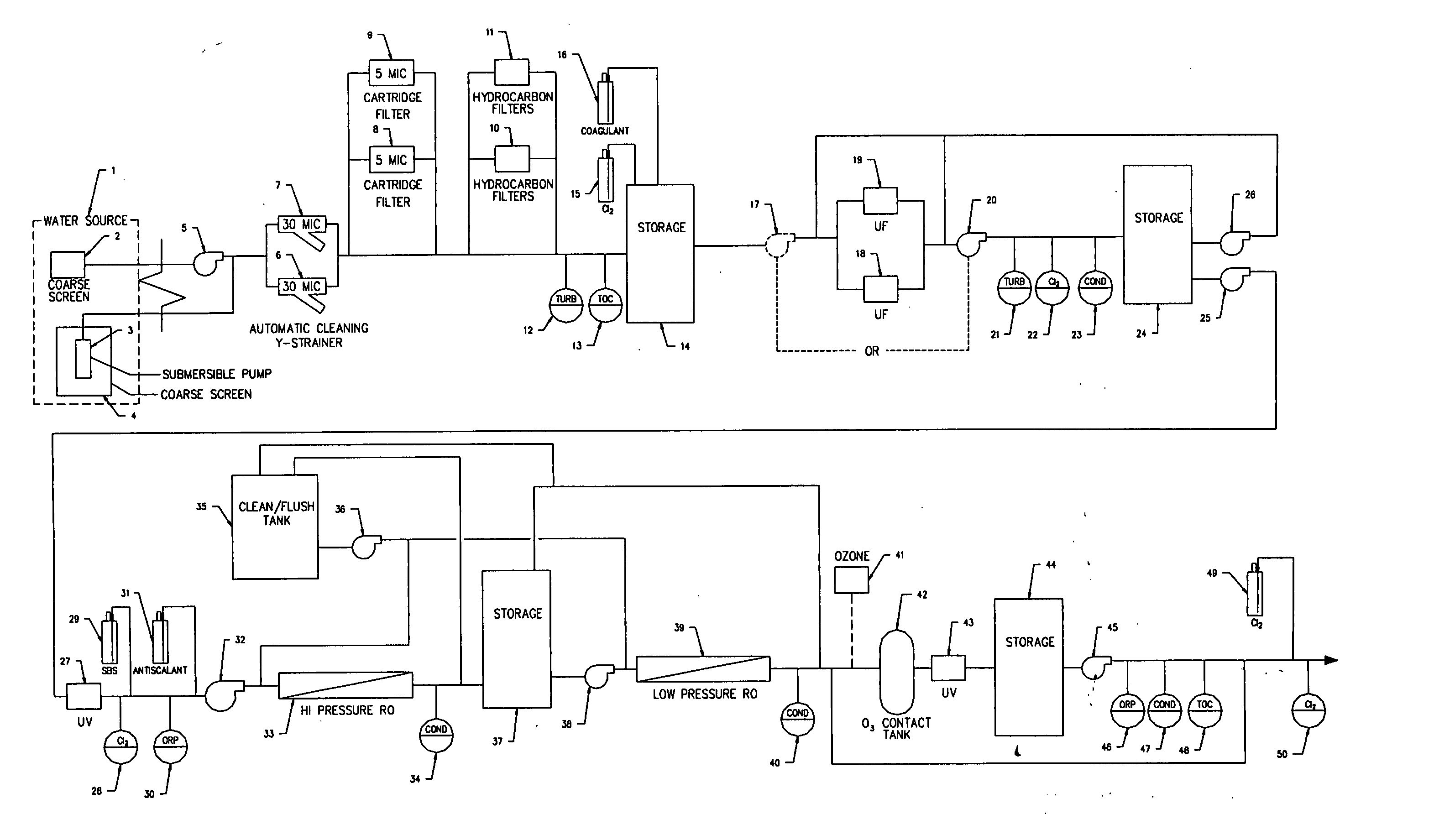
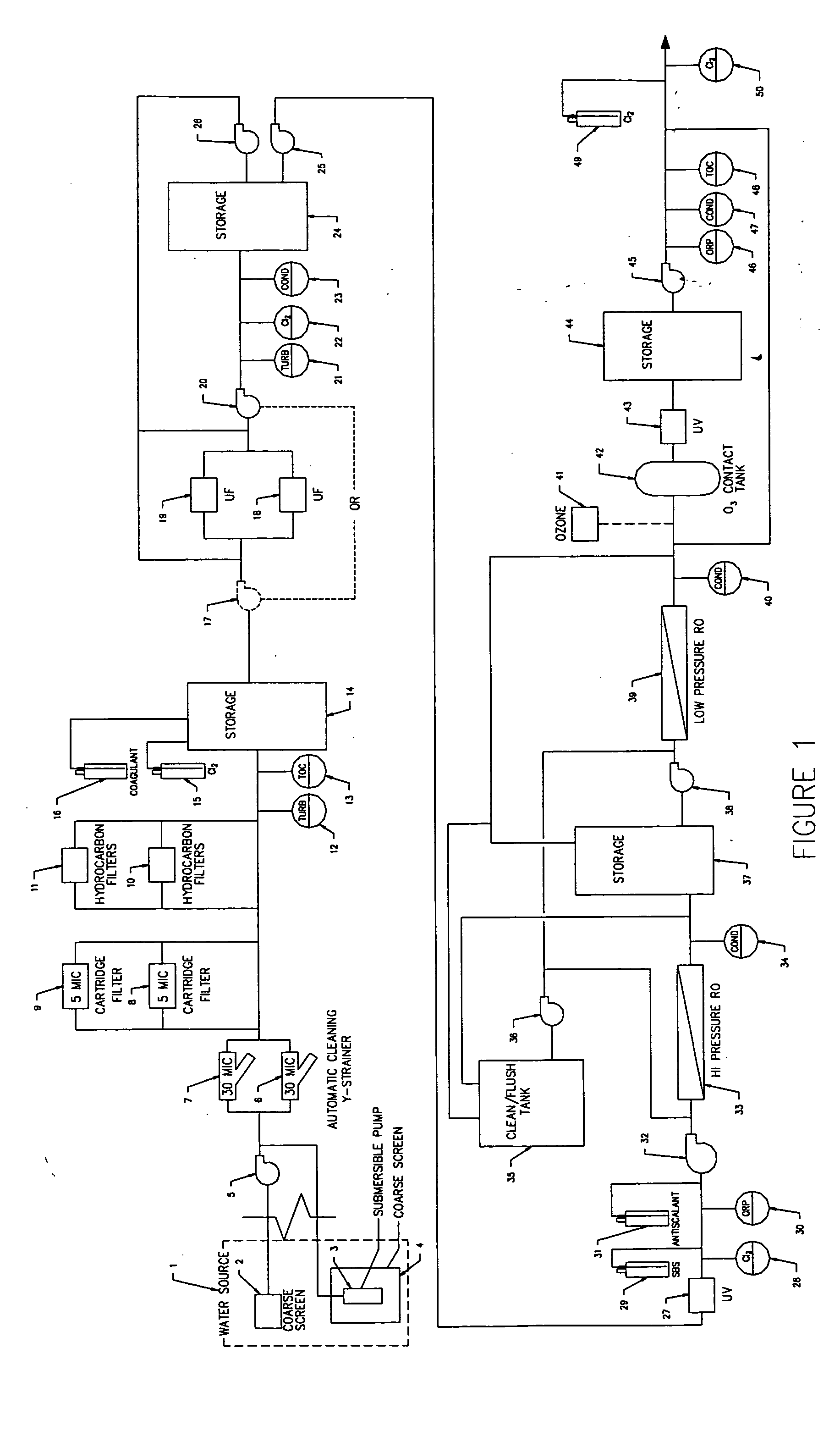
ActiveUS20050139530A1Fully removedGeneral water supply conservationTreatment involving filtrationHigh concentrationPurification methods
A method of producing safe drinking water from virtually any water source utilizing a water purification system is disclosed. The method includes a combination of water purification methods with a control system that evaluates water quality and functional processing parameters, such as pressure and flow. The control system determines what water processing methods to utilize and how most efficiently to operate them. The system is capable of treating highly contaminated water to the necessary degree to produce safe drinking water. Furthermore, the system regulates and cleans itself to maintain functionality despite receiving high concentrations of various contaminants from the feed water source.
Owner:HEISS CHRISTOPHER
Ethanol distillation process
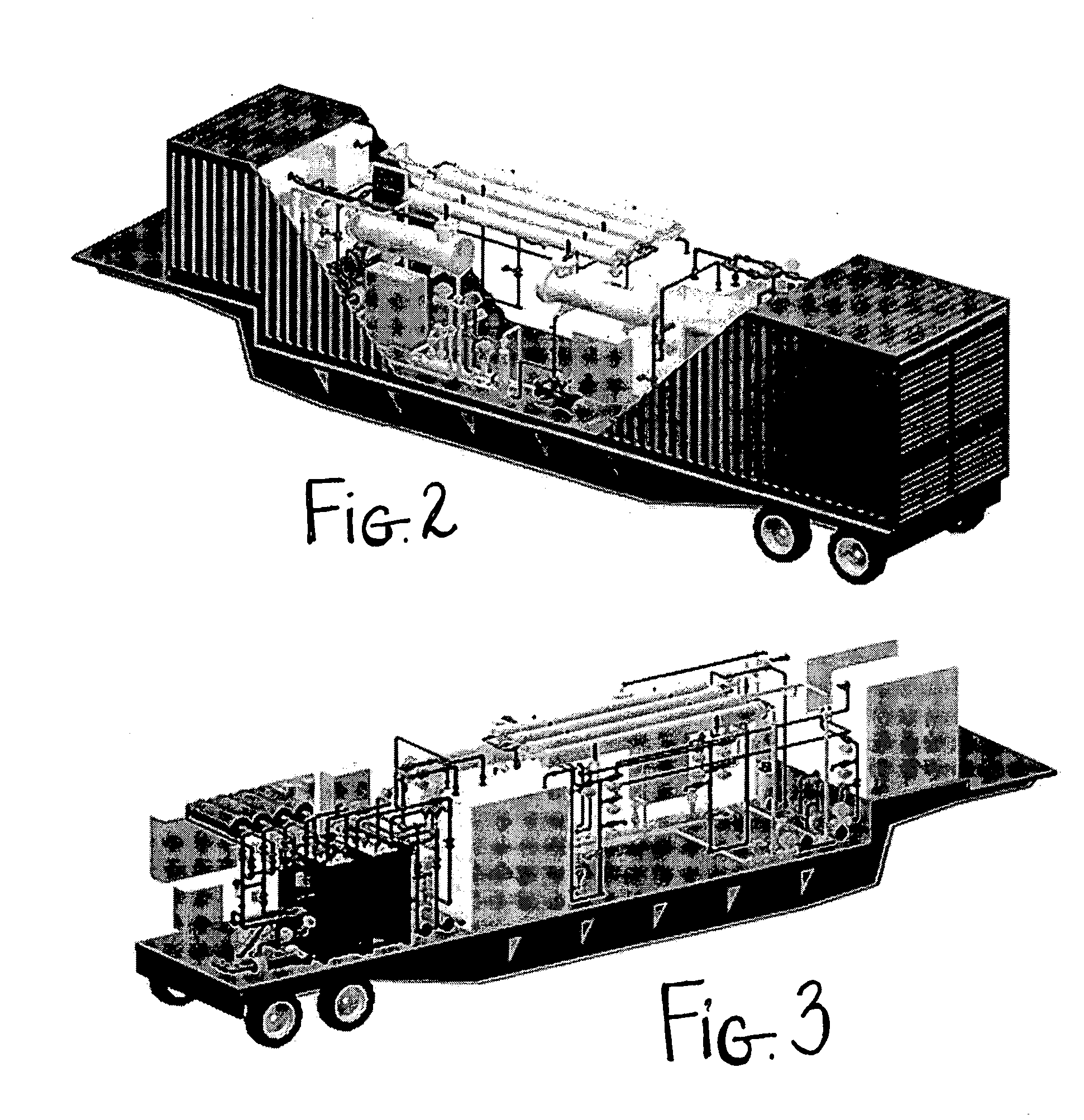
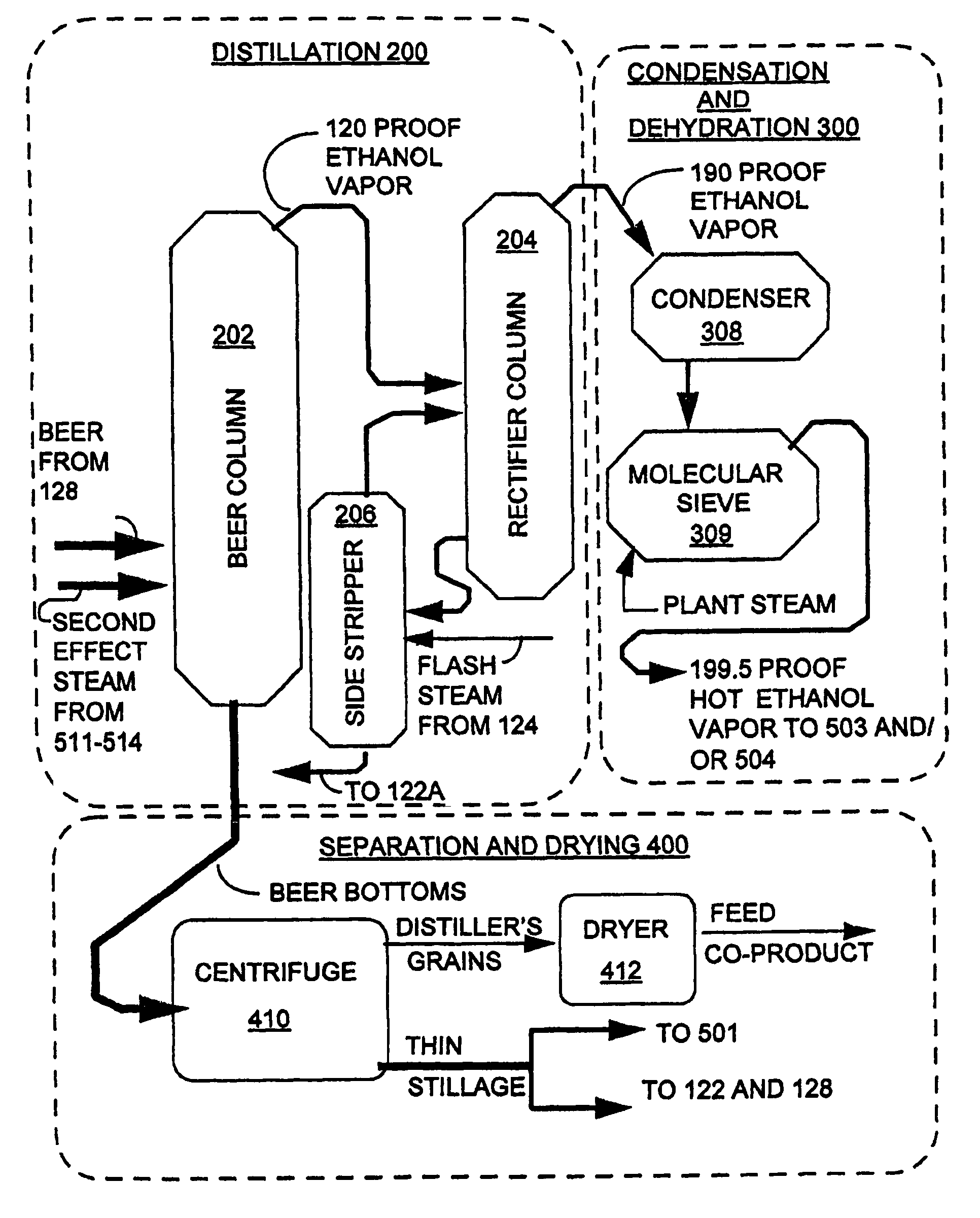
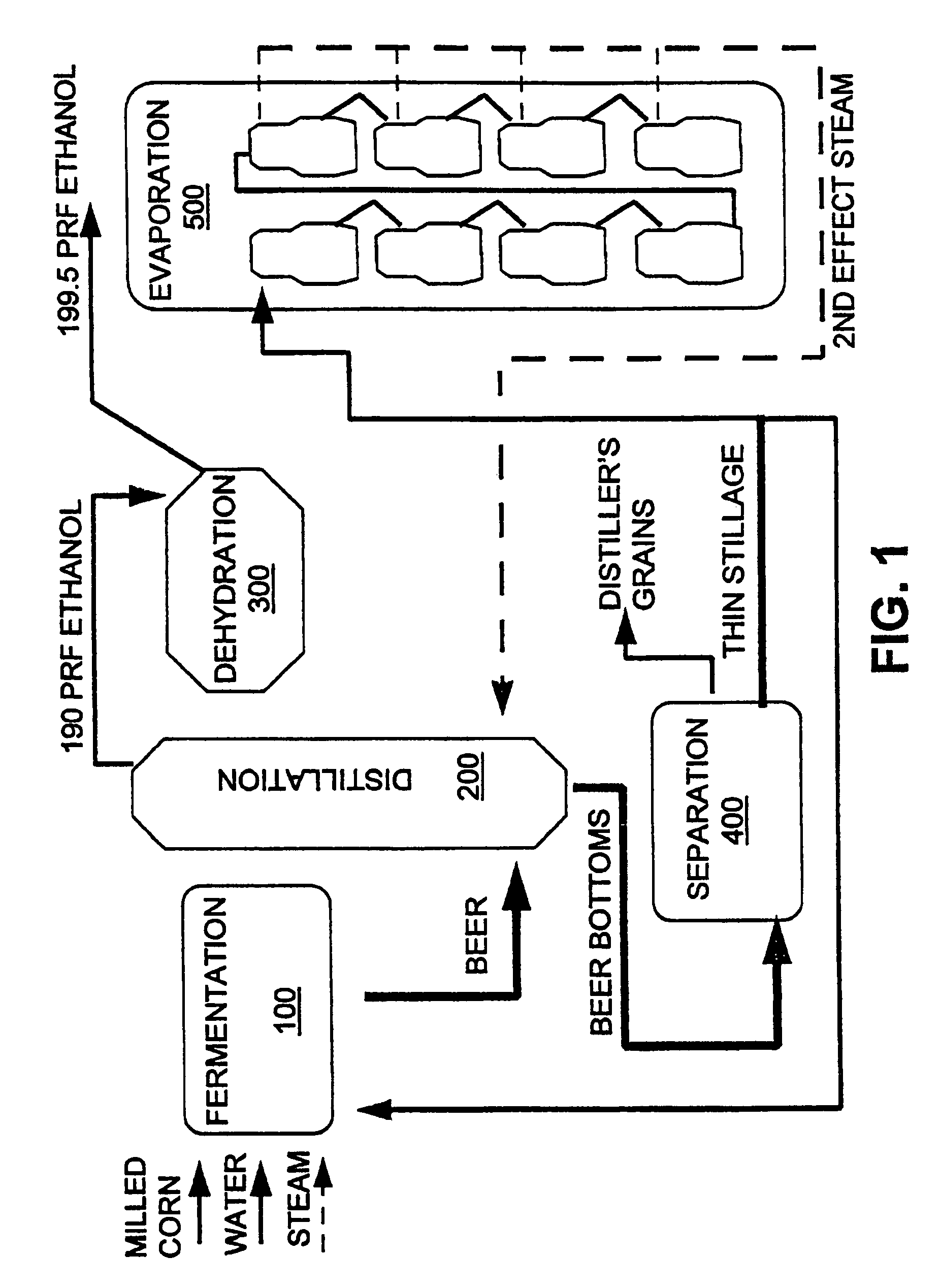
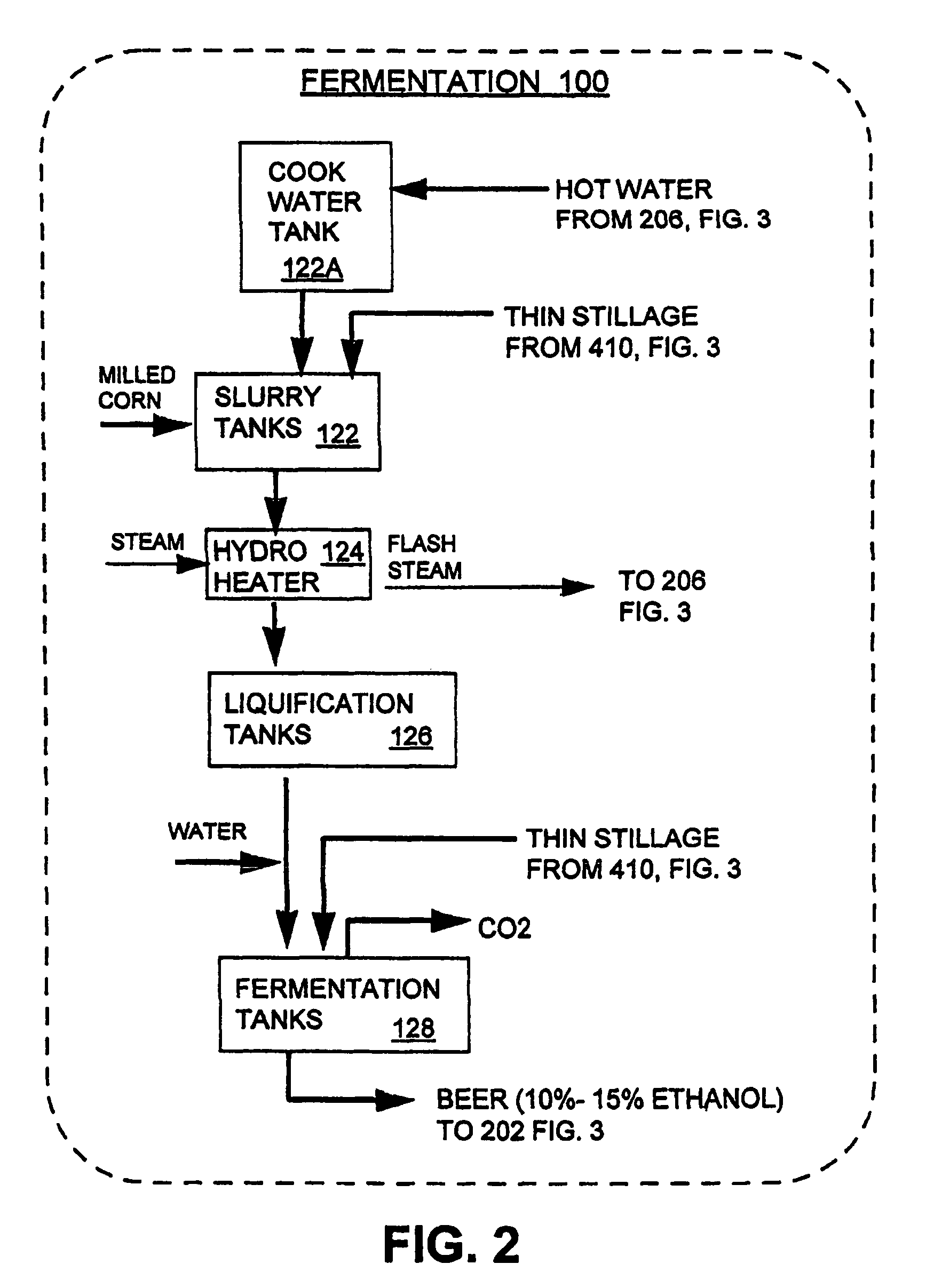
InactiveUS7572353B1Shorten the timeLess rapidlyFermented solutions distillation/rectificationOrganic compound preparationDistillationEvaporation
Owner:ICM
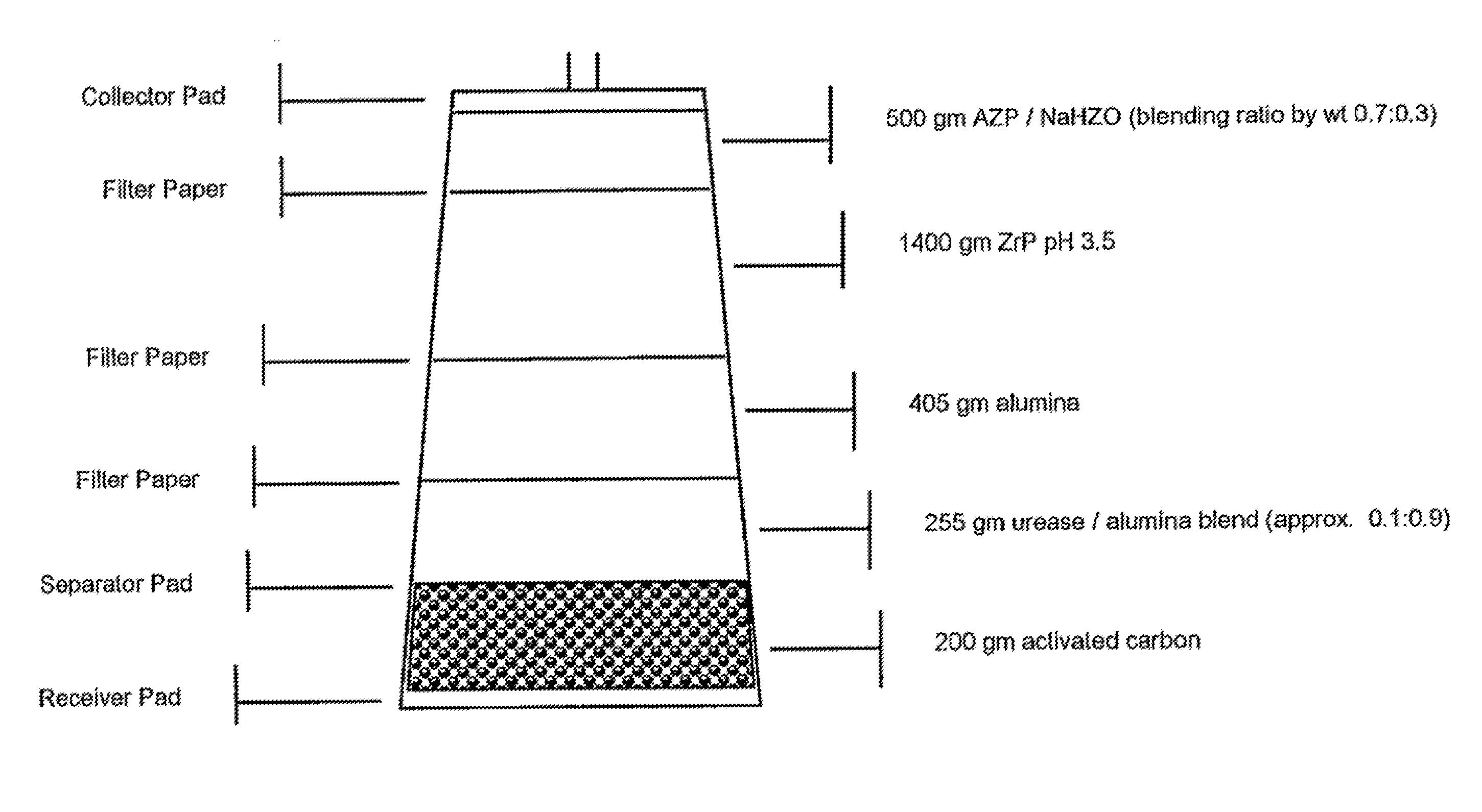
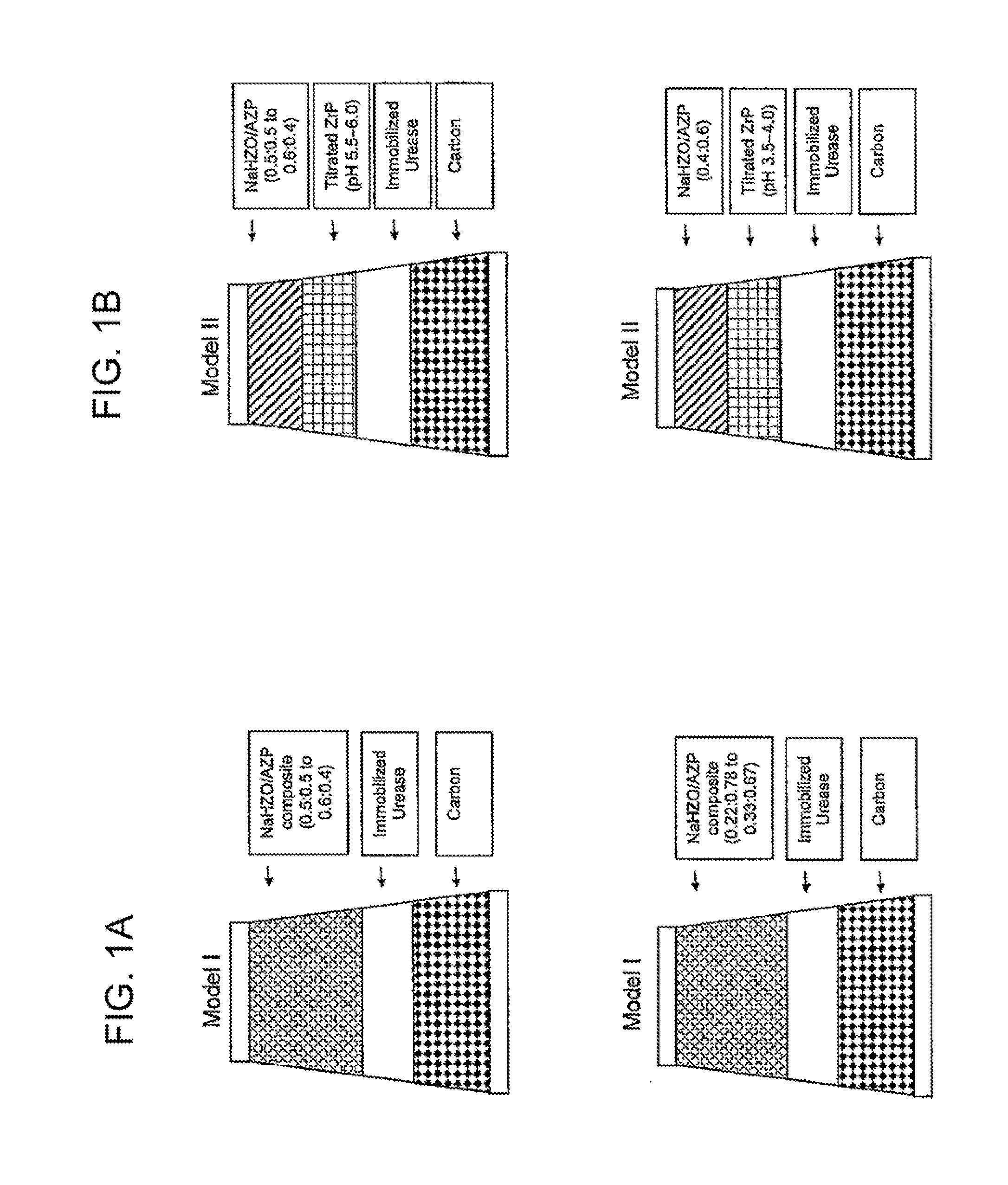
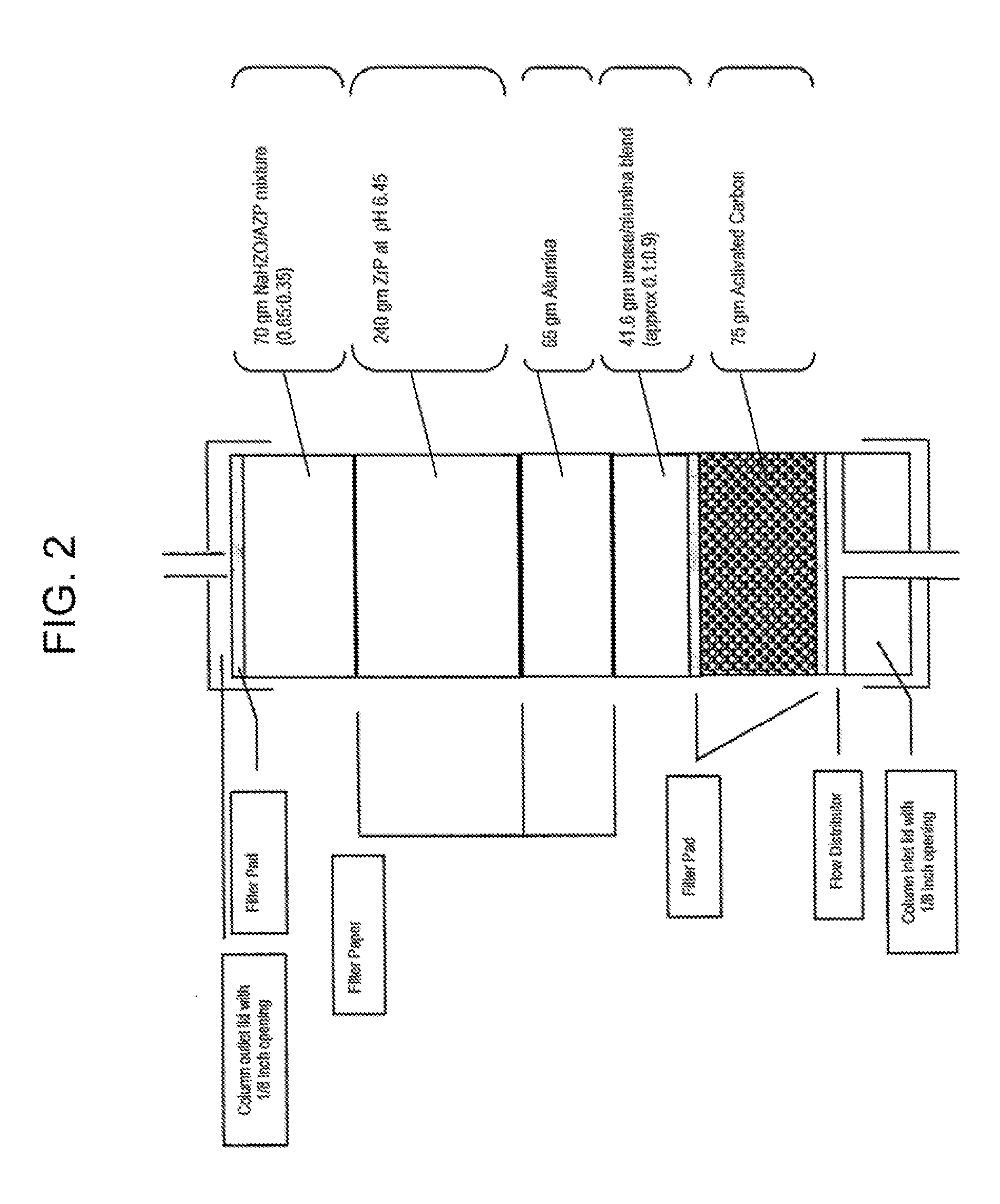
Acid Zirconium Phosphate and Alkaline Hydrous Zirconium Oxide Materials For Sorbent Dialysis
ActiveUS20100078387A1Avoid disadvantagesRestore balanceCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersIon exchangeDialysis fluid
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Microfludic system (EDI)
InactiveUS6717136B2Minimal loss of precious materialCheap and disposableIon-exchange process apparatusMaterial nanotechnologyAnalyteEngineering
A microfluidic device comprising an MS-analyte presentation unit for a EDI-MS apparatus, said unit comprising an essentially planar support plate which on one side has one, two or more ports (MS-ports) comprising an area (EDI area) for presenting the MS-analyte to a mass spectrometer. The EDI area comprises a layer I of conducting material. The characteristic feature of the device is that layer (I) has a conductive connection and / or that there is a calibrator area in the proximity of the MS-port.
Owner:GYROS
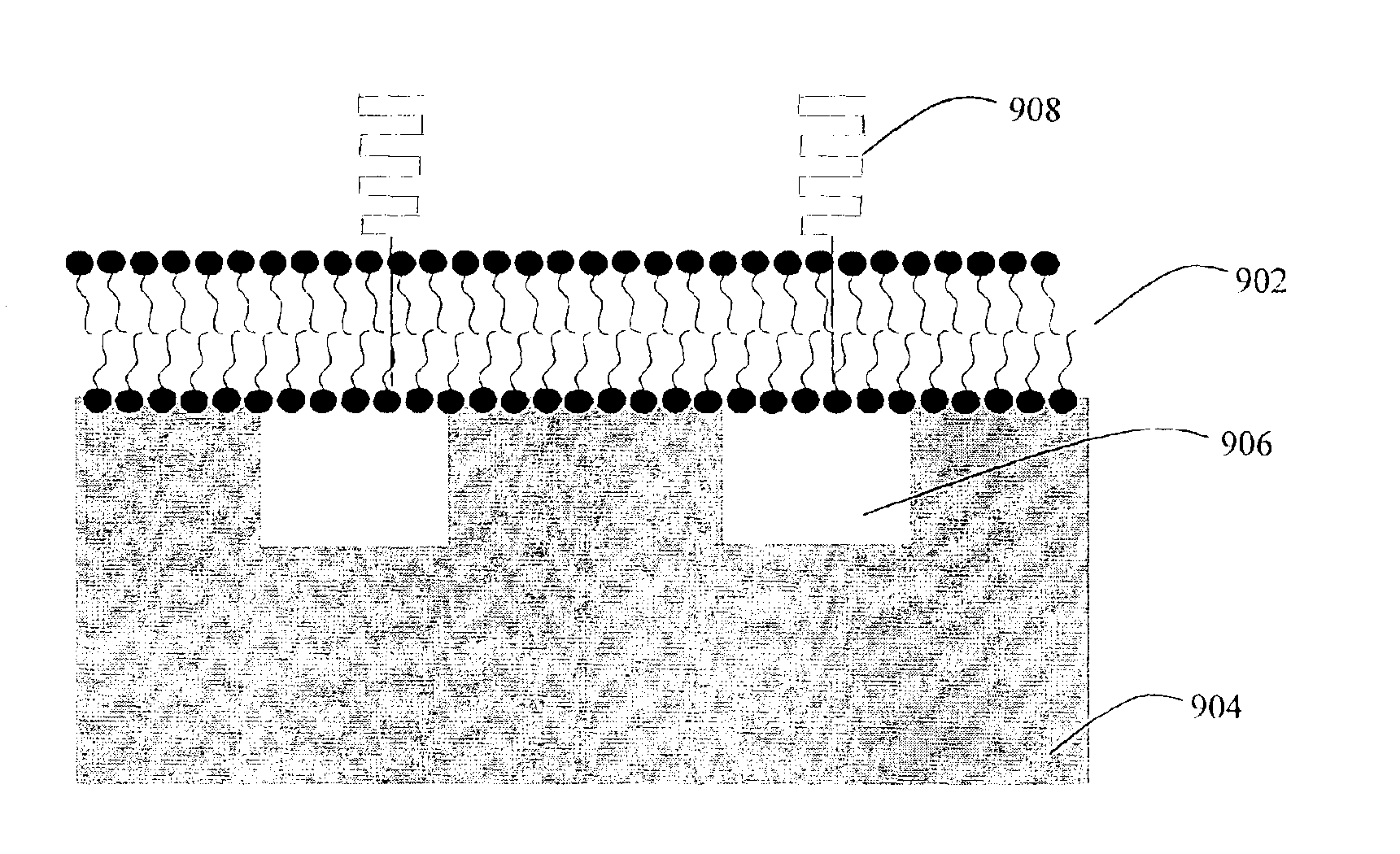
Nanostructured separation and analysis devices for biological membranes
InactiveUS6913697B2Ion-exchanger regenerationVolume/mass flow measurementBiological membraneNanostructure
The present invention provides a nanostructured device comprising a substrate including nanotroughs therein; and a lipid bilayer suspended on or supported in the substrate. A separation method is also provided comprising the steps of supporting or suspending a lipid bilayer on a substrate; wherein the substrate comprises nanostructures and wherein the lipid bilayer comprises at least one membrane associated biomolecule; and applying a driving force to the lipid bilayer to separate the membrane associated biomolecule from the lipid bilayer and to drive the membrane associated biomolecule into the nanostructures.
Owner:STC UNM
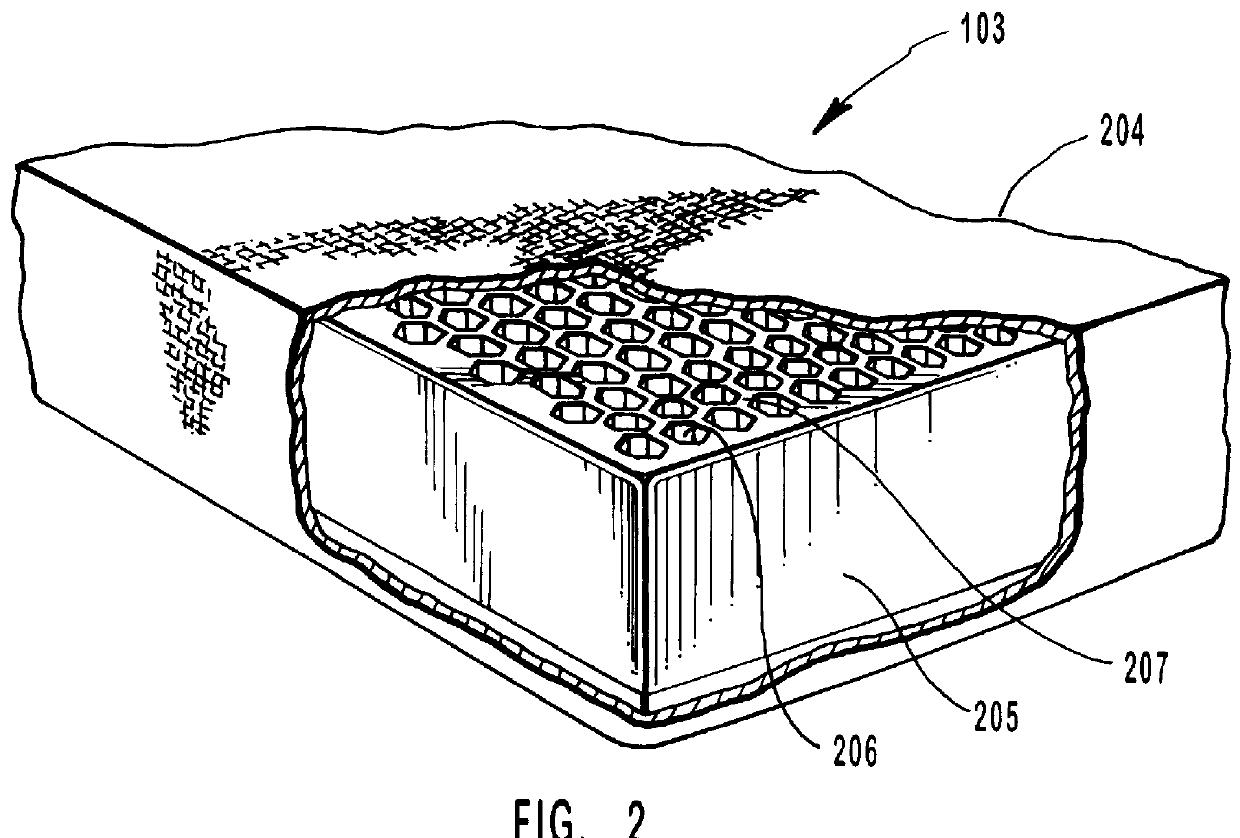
Separation apparatus and separation method
InactiveUS20060000772A1Improve efficiencyHigh activityIon-exchange process apparatusSemi-permeable membranesBuffer solutionAnalytical chemistry
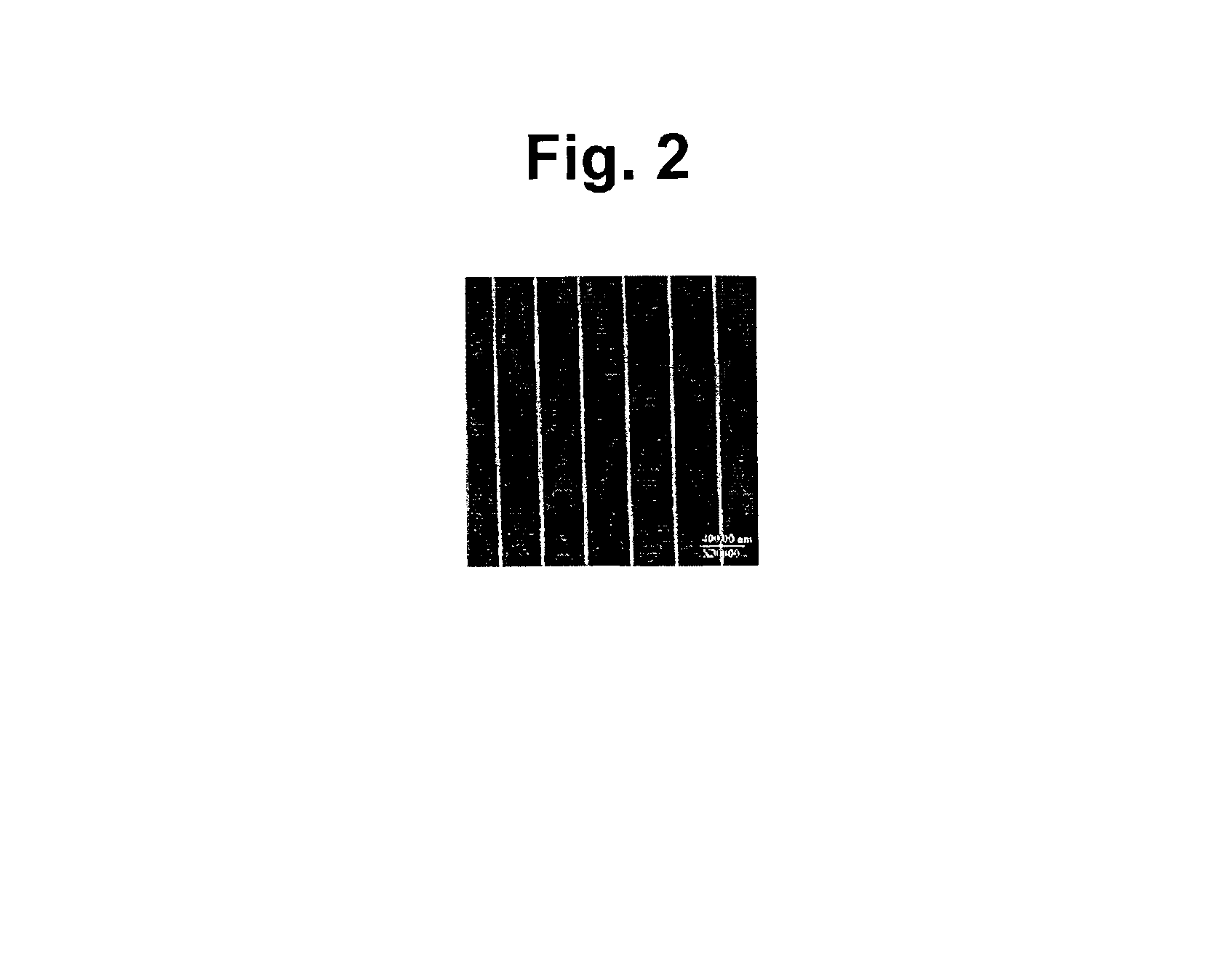
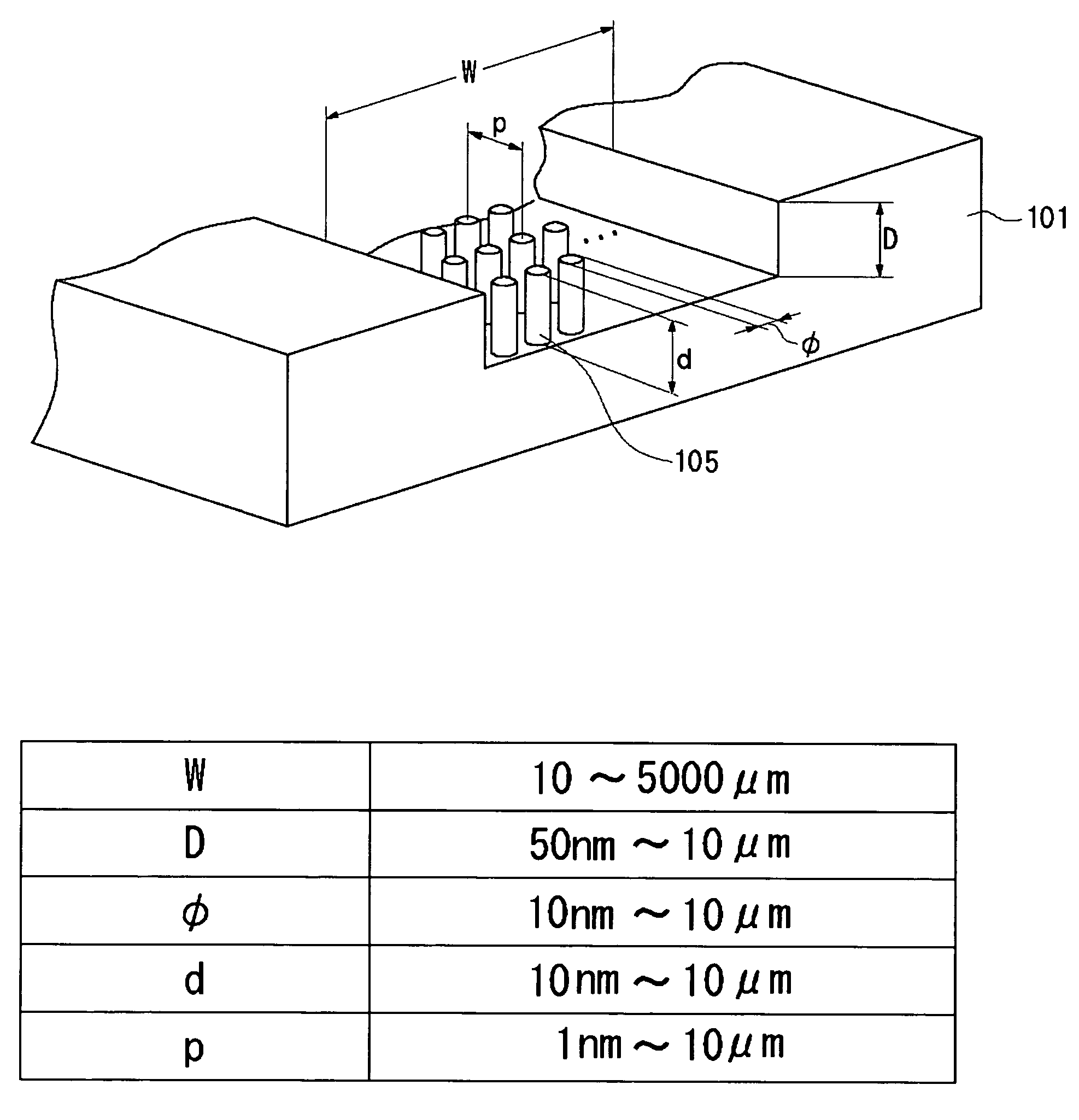
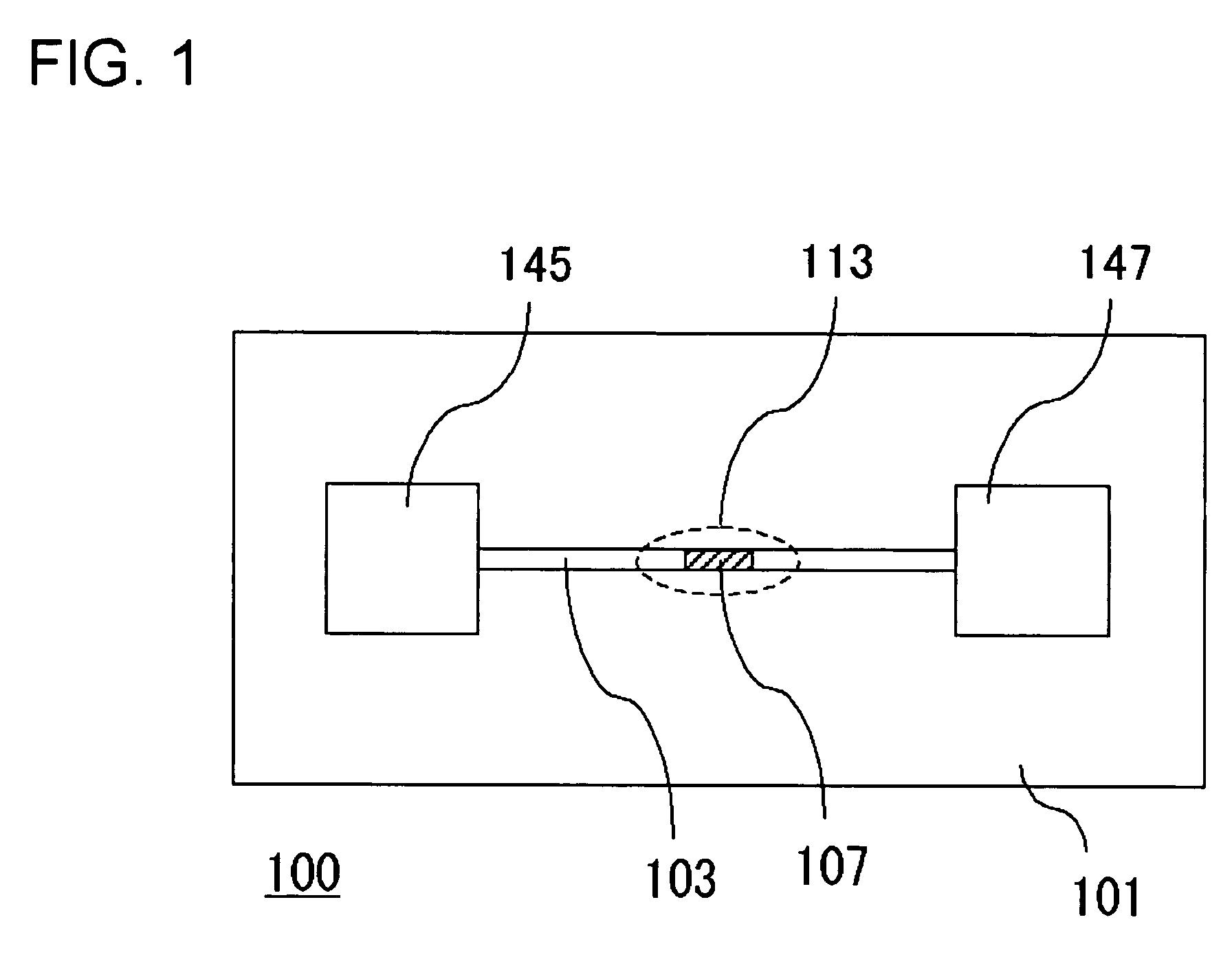
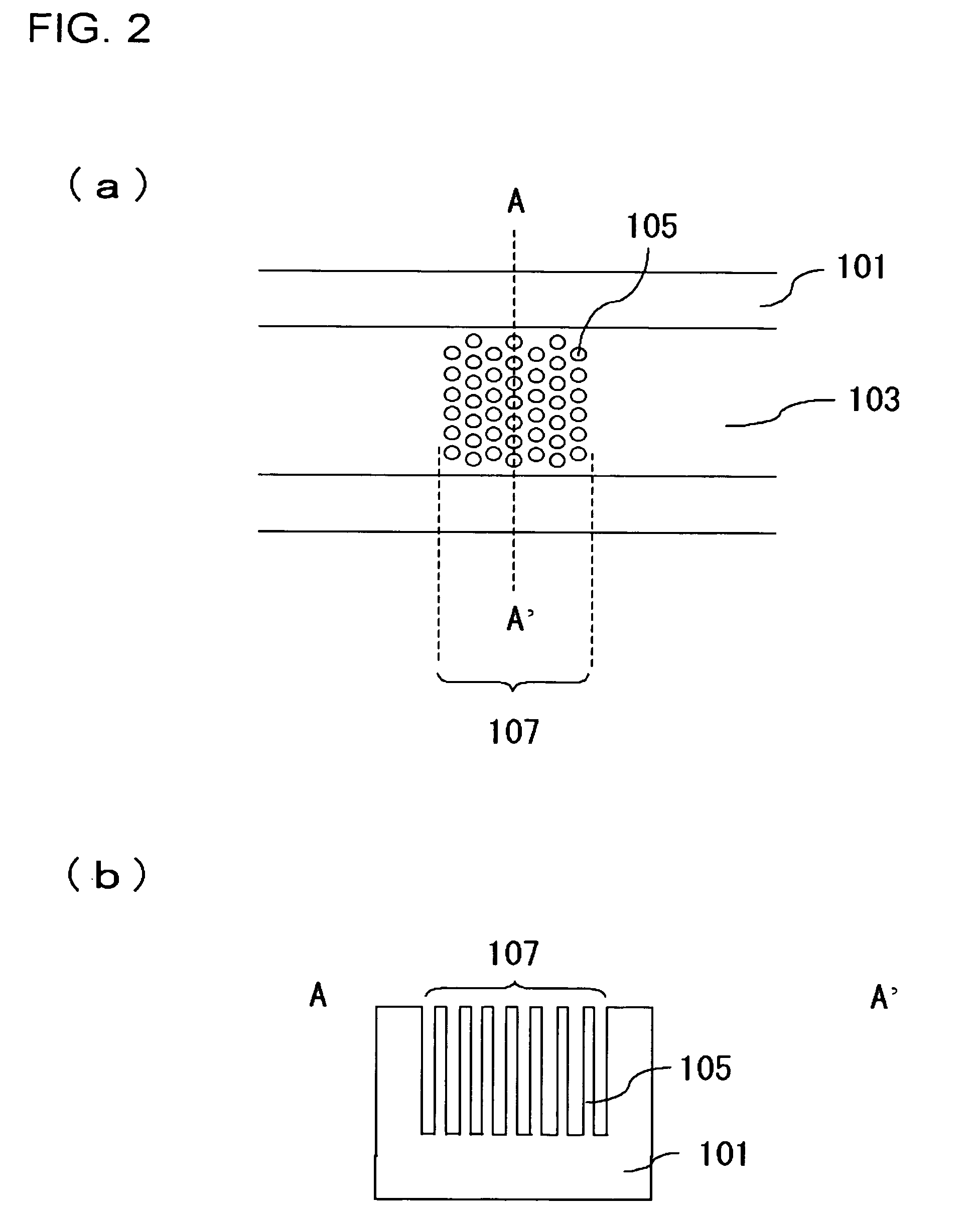
A channel (103) is formed in a substrate (101), and a portion of the channel (103) is provided with a separating portion (107). A number of pillars are formed in the separating portion (107), and an adsorptive substance layer having an adsorptive substance, which exhibits a specific interaction for a specific substance, immobilized on the surface thereof, is formed. Once a sample is introduced into the channel (103), the specific substance is adsorbed on the adsorptive substance layer to be separated from other components. After washing the inside of the channel (103) with a buffer solution, the specific substance is desorbed from the adsorptive substance layer by flowing a eluting solution through the channel (103) and the specific substance is recovered.
Owner:NEC CORP
Point-of-use water purification system with a cascade ion exchange option
InactiveUS6080313AHigh purityEasy to install and replaceSolid sorbent liquid separationLoose filtering material filtersFiltrationIon exchange
A modular water treatment and purification system, suitable for home use, is connected to a water supply and contains a closed fluid treatment circuit extending to a water outlet. The closed fluid circuit flows through a plurality of replaceable water treatment modules each having a specific water treatment function, such as the removal of a particular material from the water by the use of filtration, carbon adsorption, ion exchange or the addition of a chemical to balance the desired water conditions. Preferably the circuit also includes traversing a radiation device, for example an ultra violet light, for the purpose of sanitizing the water.
Owner:KELADA MAHER I
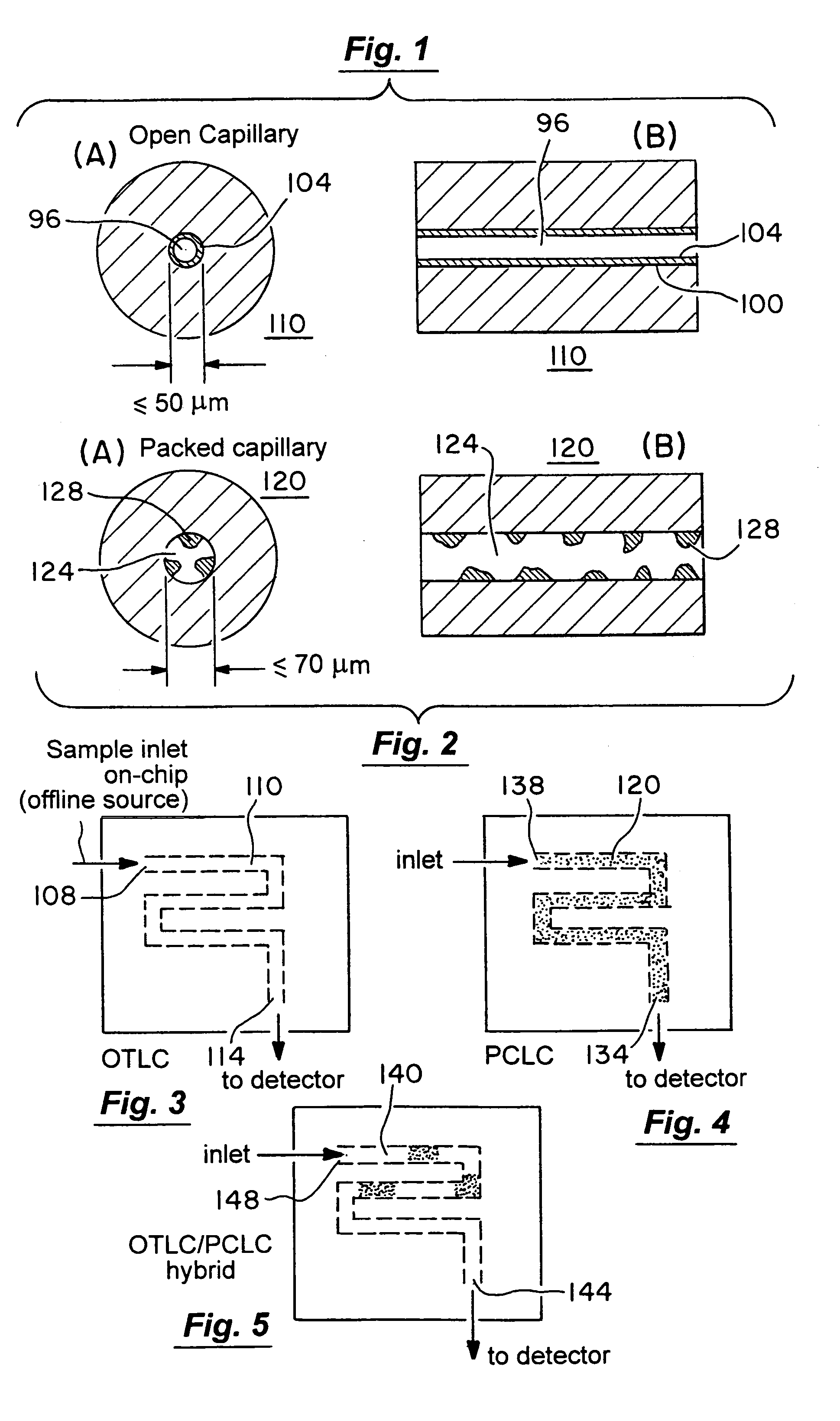
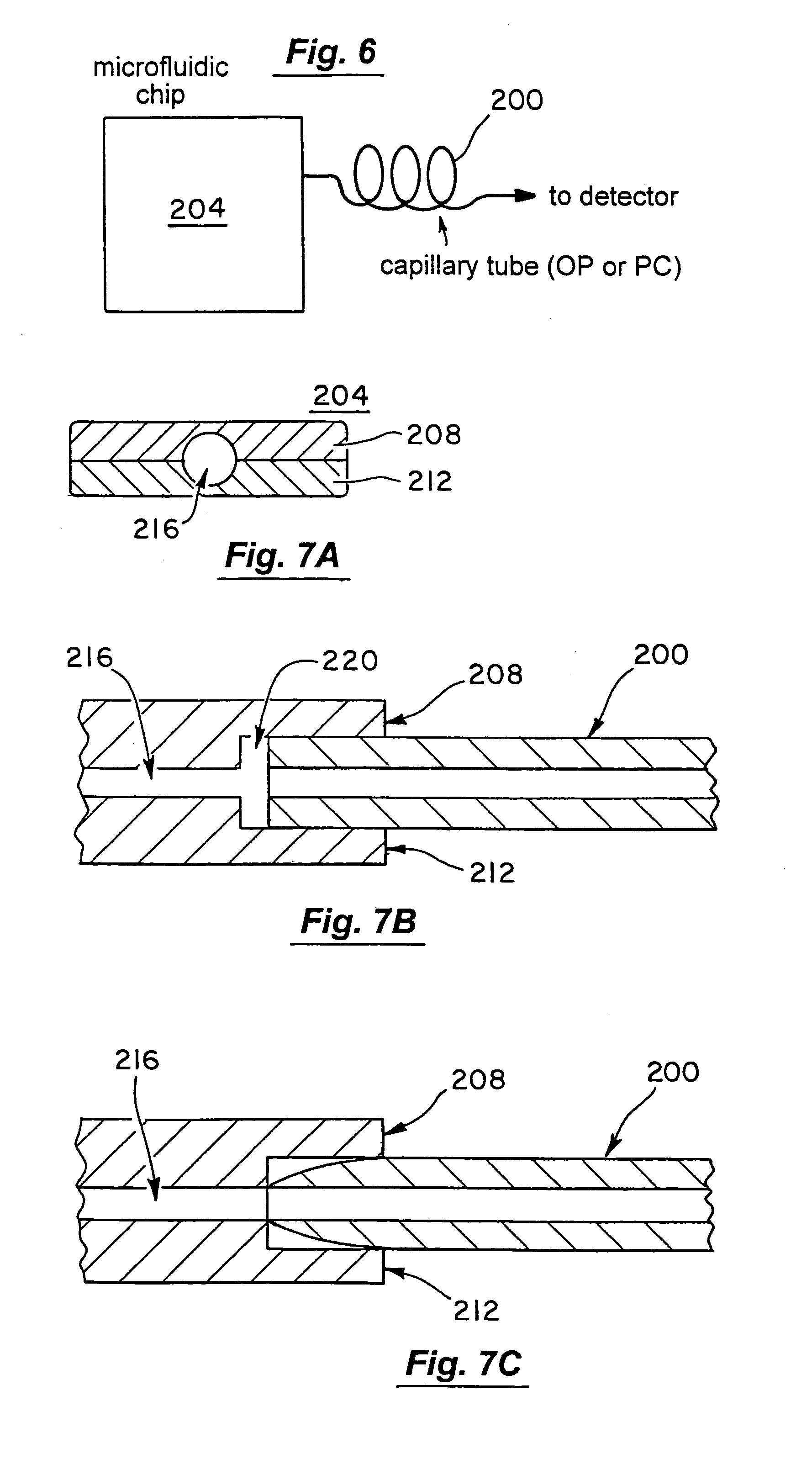
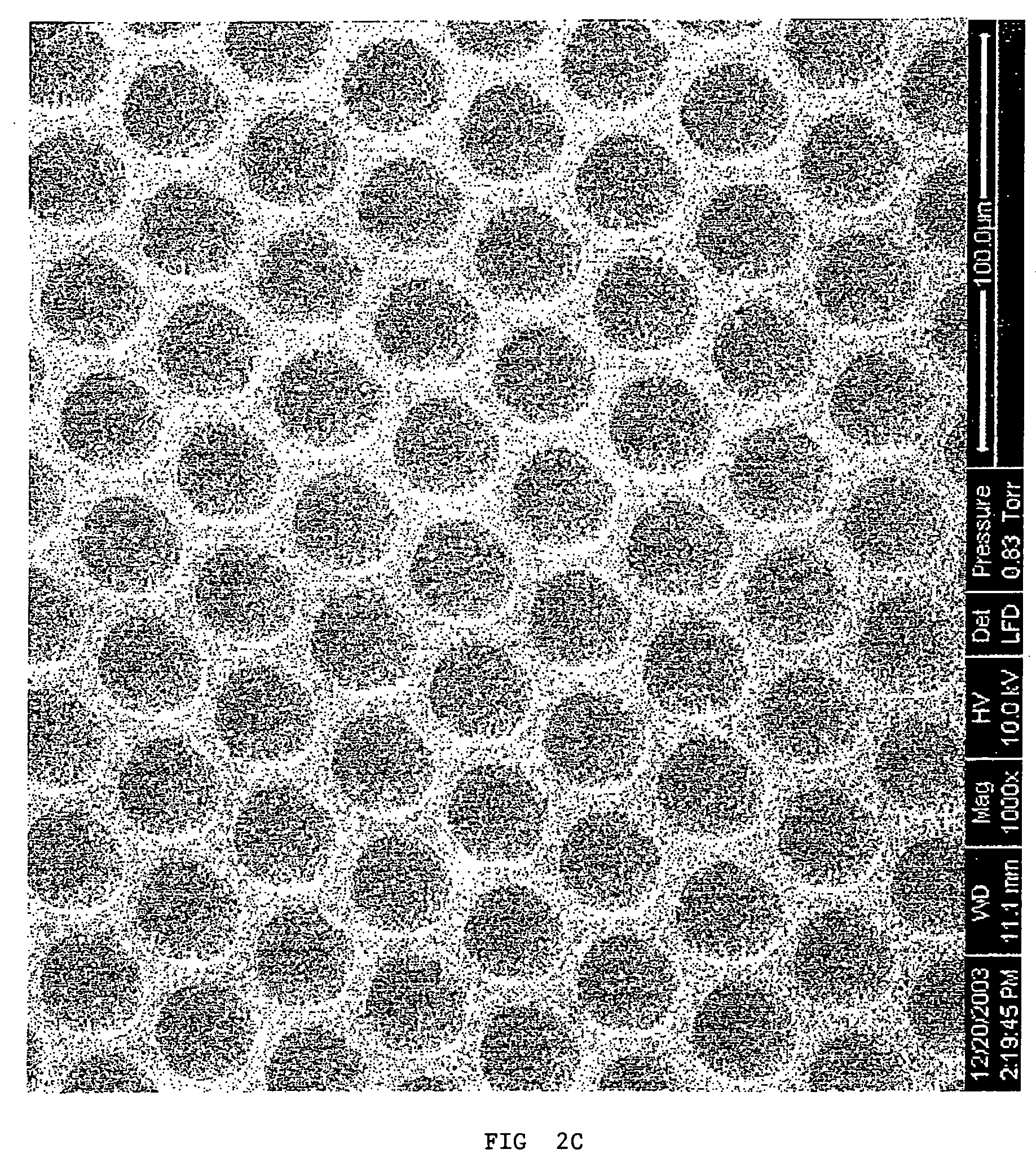
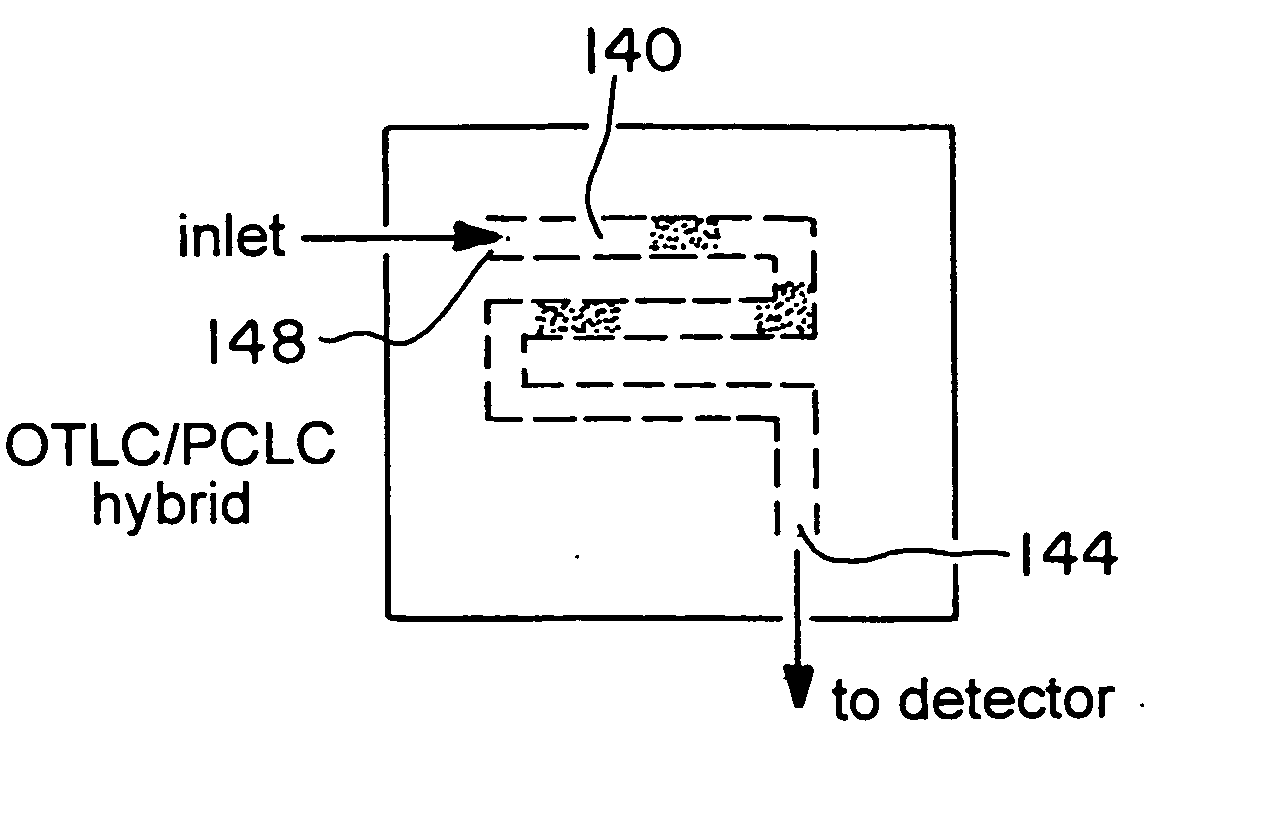
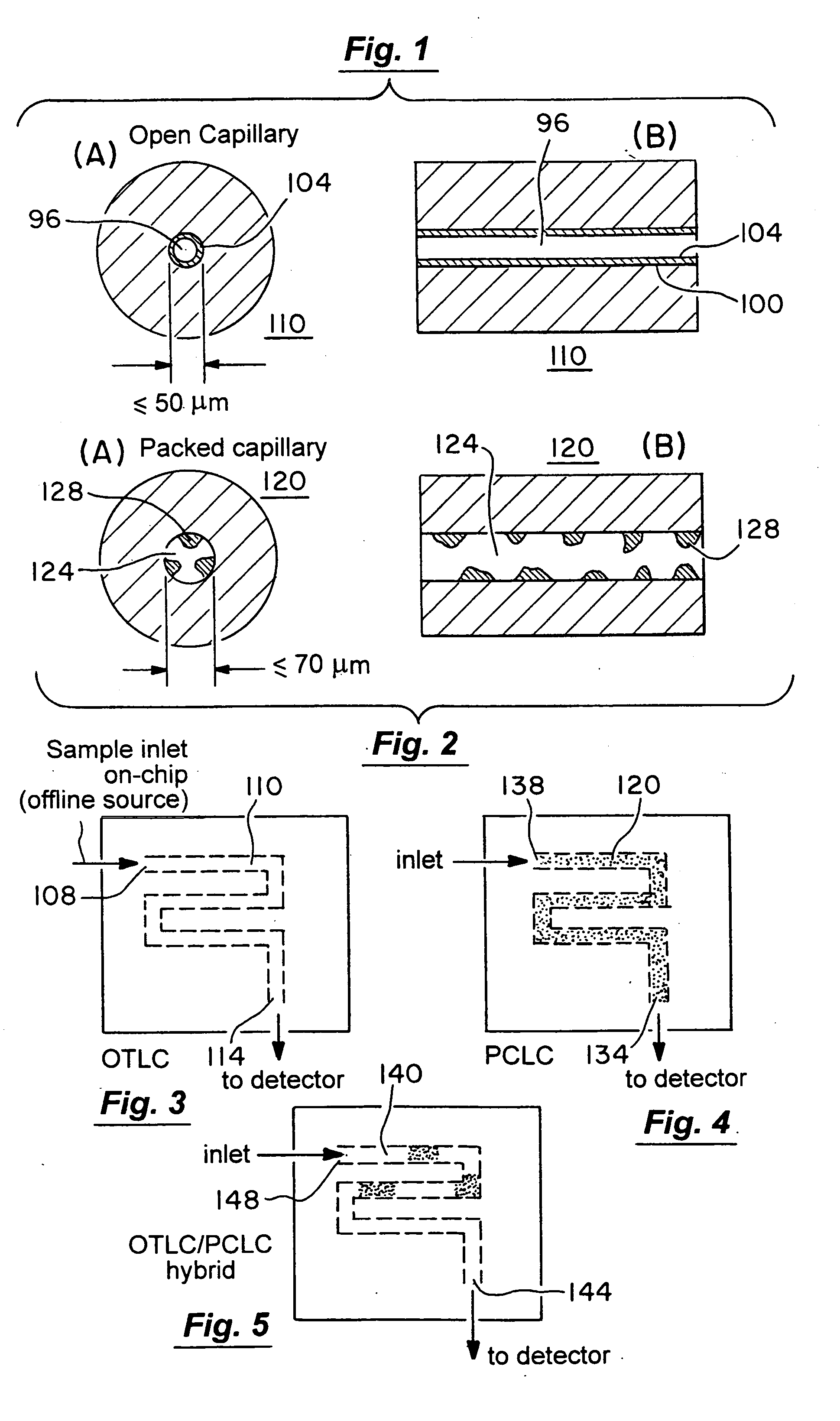
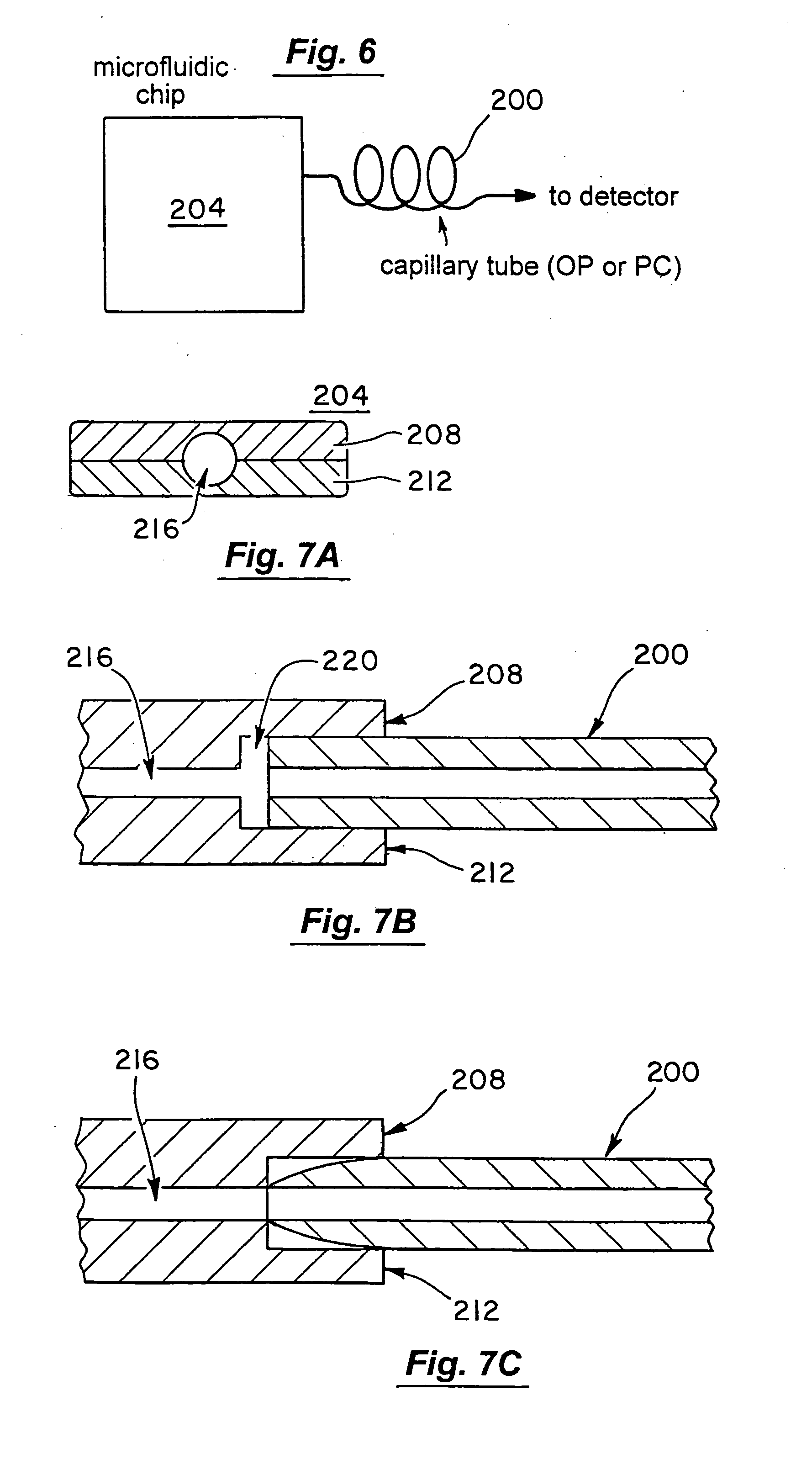
Microfluidic chromatography
InactiveUS7217367B2Ion-exchange process apparatusComponent separationChromatography columnDelivery system
The present invention is directed to a microfluidic chromatography apparatus comprising a microfabricated fluid delivery system and a chromatography column which is in fluid communication with the fluid delivery system, and a method for producing and using the same. Preferably, the chromatography column comprises an OTLC, PCLC, or combinations thereof.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Nanosize electropositive fibrous adsorbent
InactiveUS6838005B2Improve the immunityEfficient precipitationIon-exchanger regenerationLoose filtering material filtersFiberParticulates
Aluminum hydroxide fibers approximately 2 nanometers in diameter and with surface areas ranging from 200 to 650 m2 / g have been fount to be highly electropositive. When dispersed in water they are able to attach to and retain electronegative particles. When combined into a composite filter with other fibers or particles they can filter bacteria and nano size particulates such as viruses and colloidal particles at high flux through the filter. Such filters can be used for purification and sterilization of water, biological, medical and pharmaceutical fluids, and as a collector / concentrator for detection and assay of mirobes and viruses. The alumina fibers are also capable of filtering sub-micron inorganic and metallic particles to produce ultra pure water. The fibers are suitable as a substrate for growth of cells. Macromolicules such as proteins may be separated from each other based on their electronegative charges.
Owner:ARGONIDE CORP
Purification of fluids with nanomaterials
ActiveUS7211320B1Low costSimple processMaterial nanotechnologyRecord information storageNanostructured materialsNanometre
Disclosed herein is a nanostructured material comprising defective carbon nanotubes chosen from impregnated, functionalized, doped, charged, coated, and irradiated nanotubes, and combinations thereof. The defective carbon nanotubes contain a defect which is a lattice distortion in at least one carbon ring. Also disclosed is a method of purifying fluids, such as liquids, including water, as well as gases, including the air using, this nanostructured material.
Owner:MULTIPURE INT
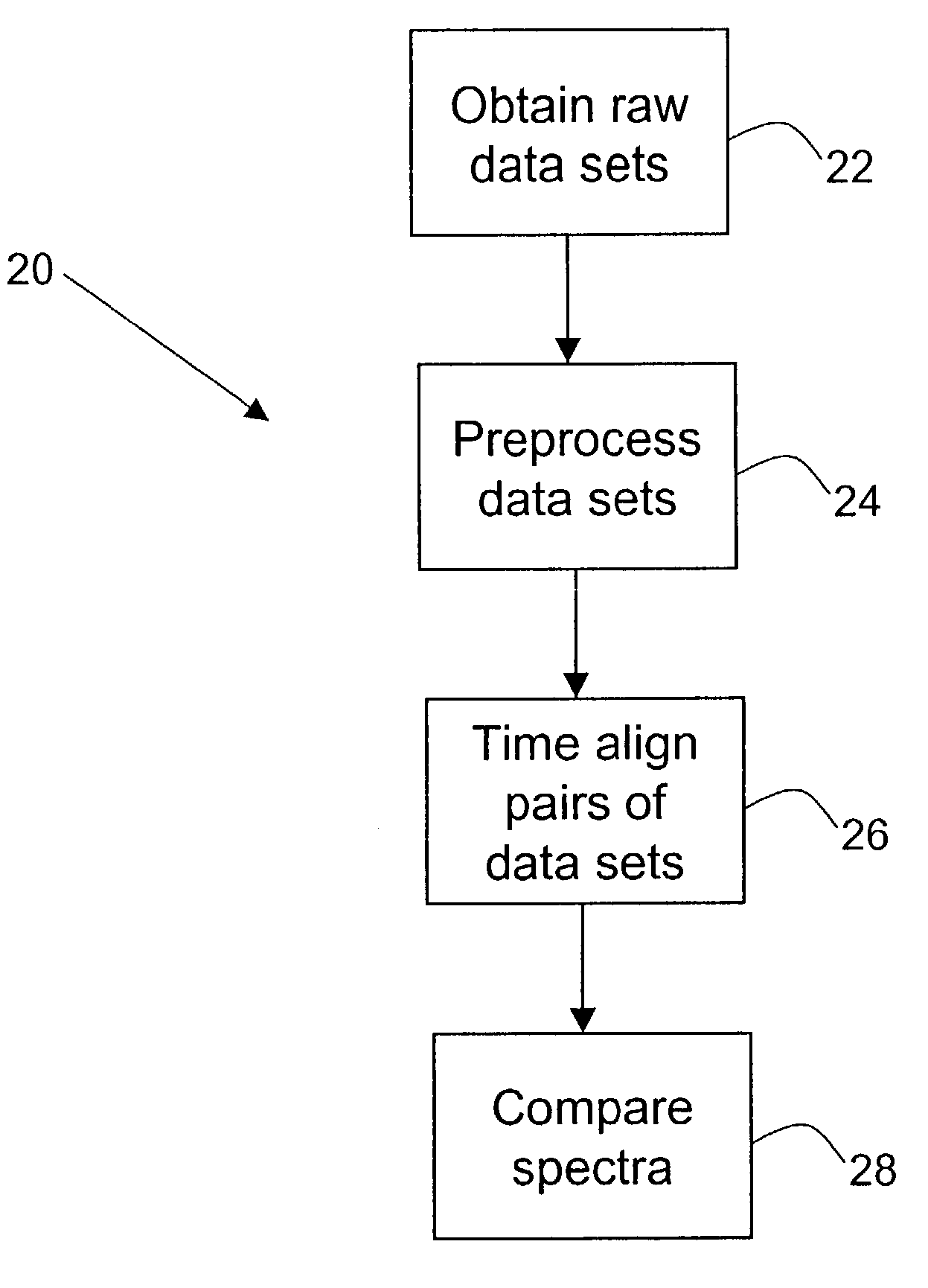
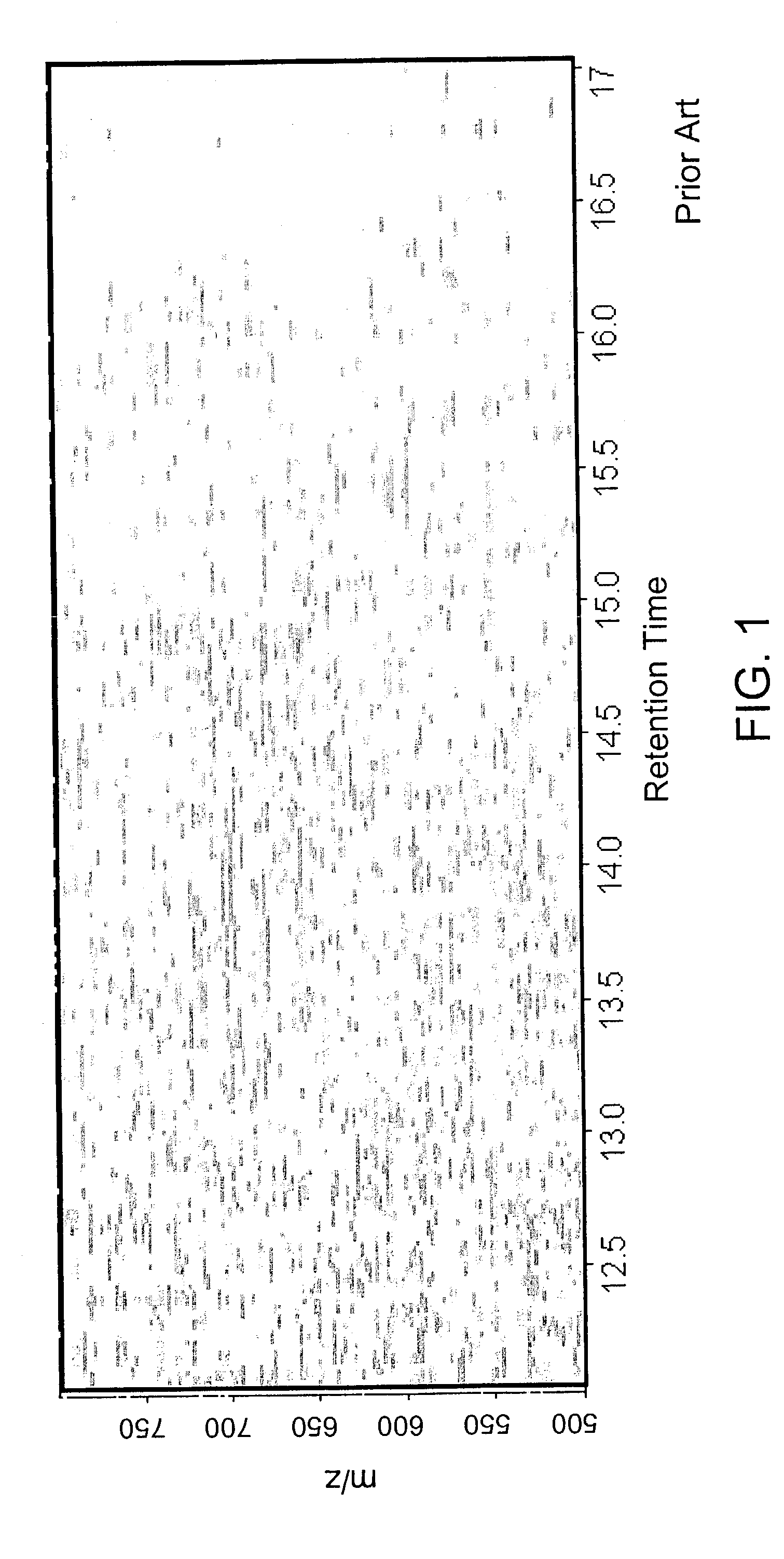
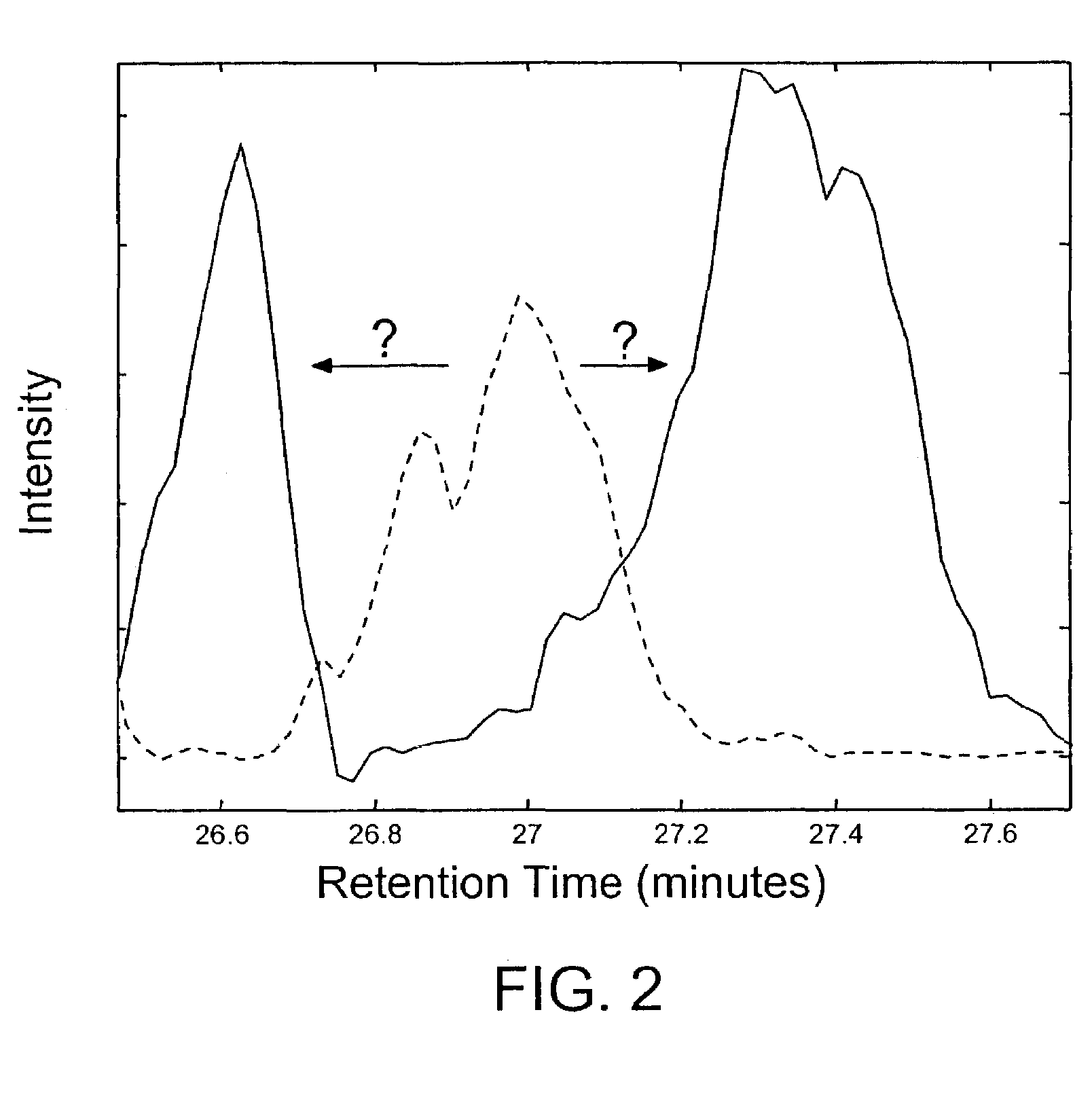
Methods for time-alignment of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry data
Nonlinear retention time variations in chromatography-mass spectrometry data sets are adjusted by time-alignment methods, enabling automated comparison of spectra for differential phenotyping and other applications.
Owner:CAPRION PROTEOMICS INC
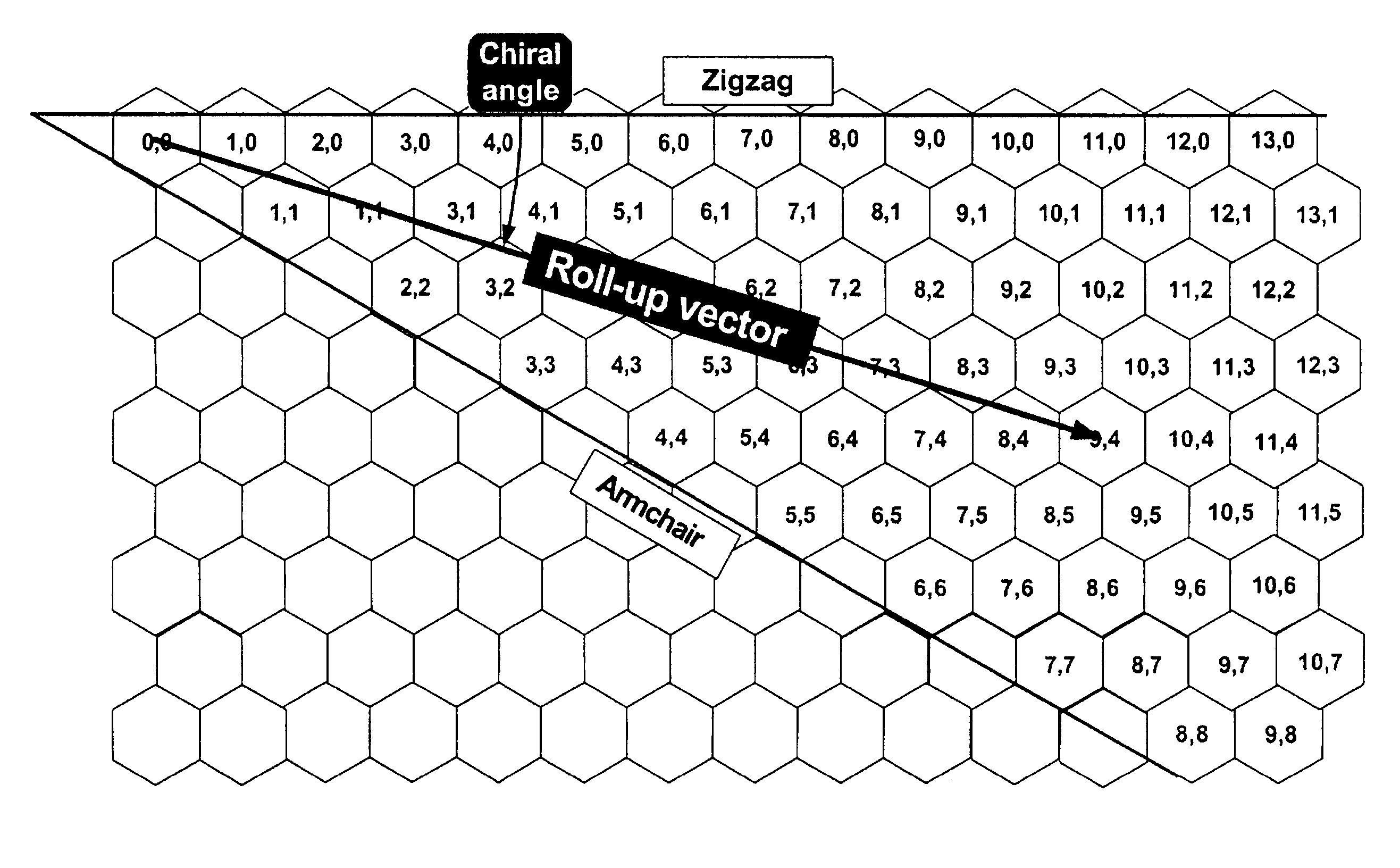
Method for separating single-wall carbon nanotubes and compositions thereof
The invention relates to a process for sorting and separating a mixture of (n, m) type single-wall carbon nanotubes according to (n, m) type. A mixture of (n, m) type single-wall carbon nanotubes is suspended such that the single-wall carbon nanotubes are individually dispersed. The nanotube suspension can be done in a surfactant-water solution and the surfactant surrounding the nanotubes keeps the nanotube isolated and from aggregating with other nanotubes. The nanotube suspension is acidified to protonate a fraction of the nanotubes. An electric field is applied and the protonated nanotubes migrate in the electric fields at different rates dependent on their (n, m) type. Fractions of nanotubes are collected at different fractionation times. The process of protonation, applying an electric field, and fractionation is repeated at increasingly higher pH to separated the (n, m) nanotube mixture into individual (n, m) nanotube fractions. The separation enables new electronic devices requiring selected (n, m) nanotube types.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Wastewater treatment system and method
ActiveUS20070209999A1Treatment using aerobic processesTreatment involving filtrationActivated carbonWater treatment system
The invention is directed to a method and apparatus for treating wastewater. The wastewater treatment system includes a bioreactor including activated carbon and a first biological population. The wastewater treatment system may also include a membrane bioreactor and / or a wet oxidation unit.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Membrane based fluid treatment systems
InactiveUS7186344B2Readily availableImprove the level ofLiquid separation auxillary apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationMembrane foulingTreatment system
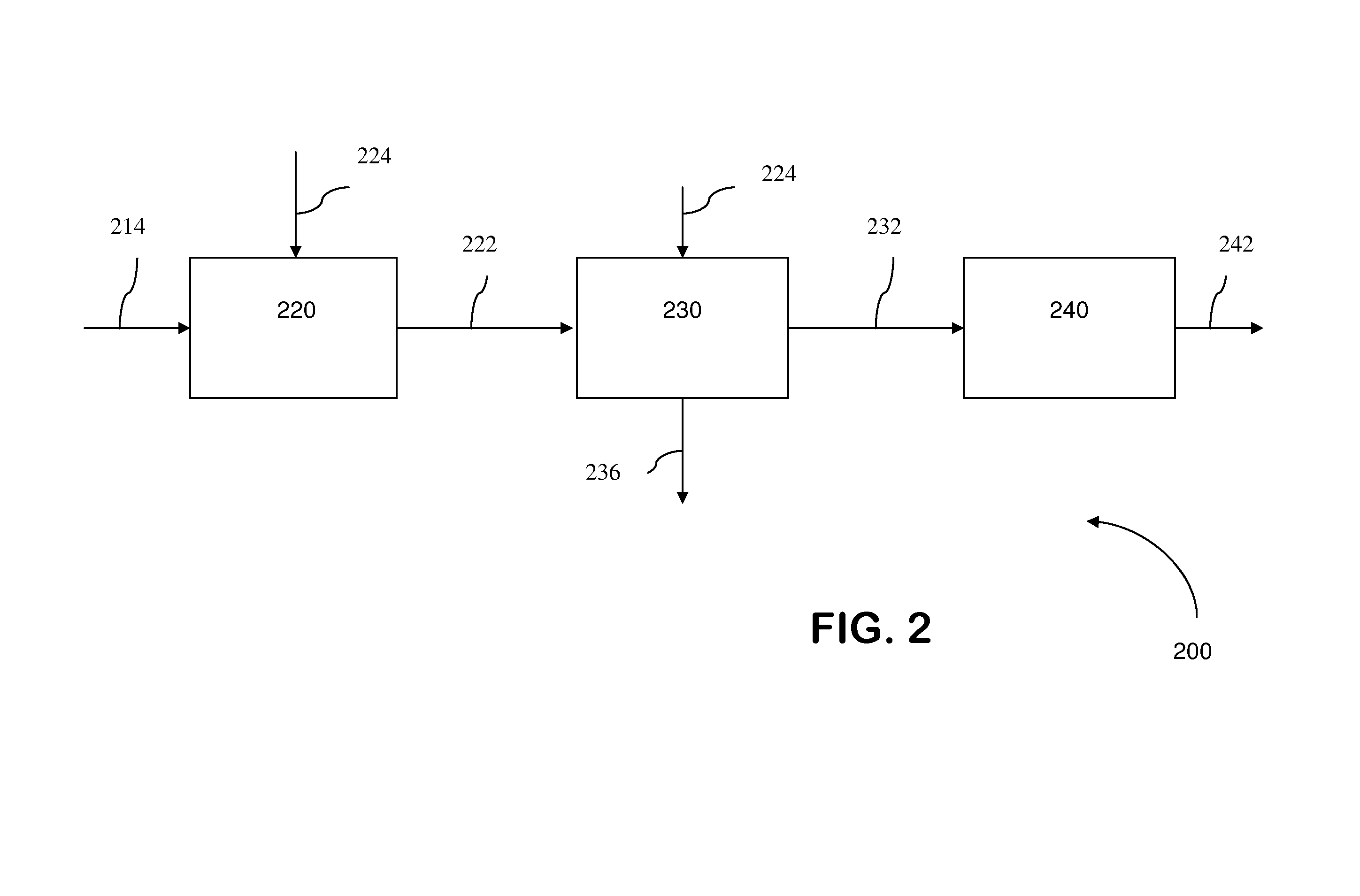
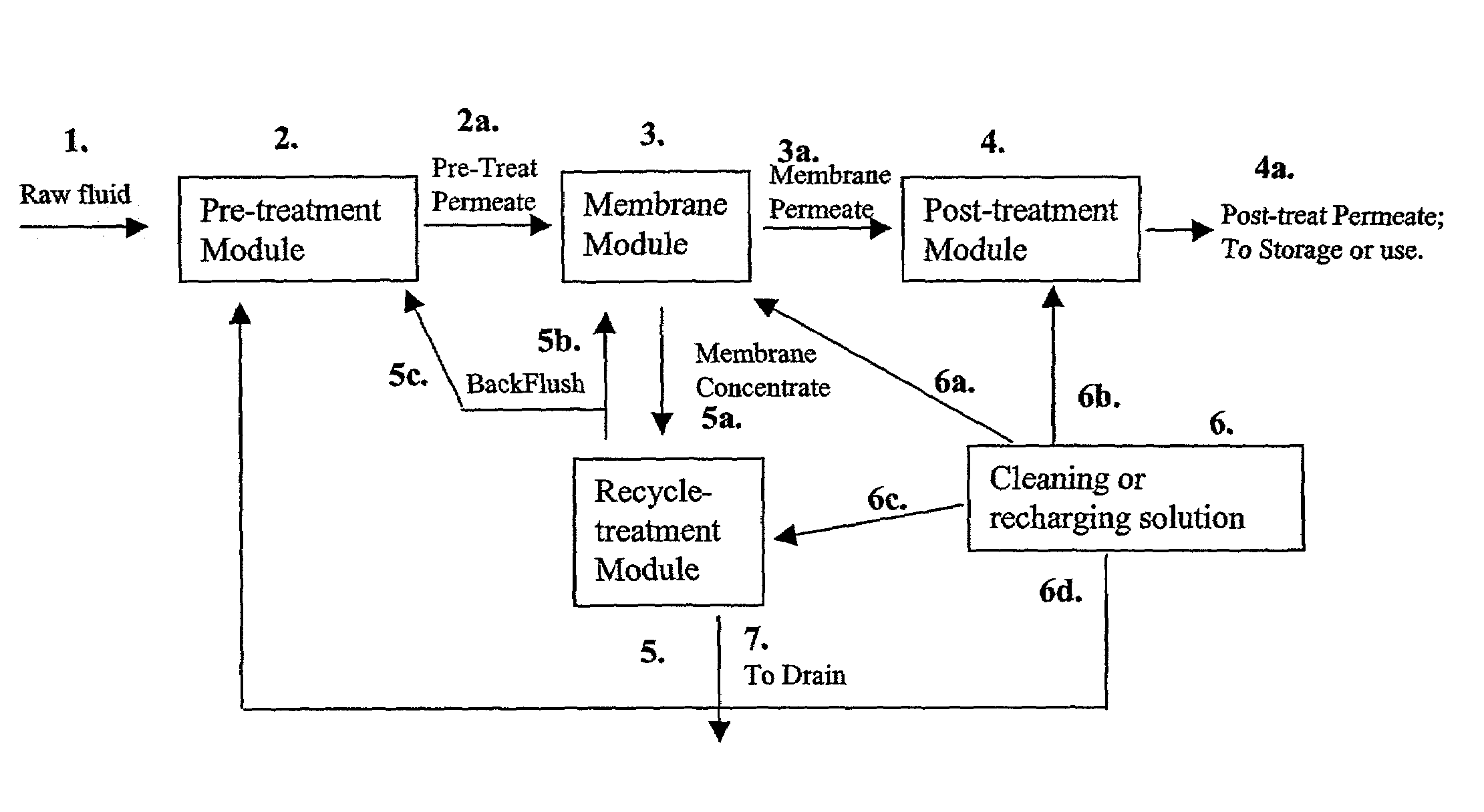
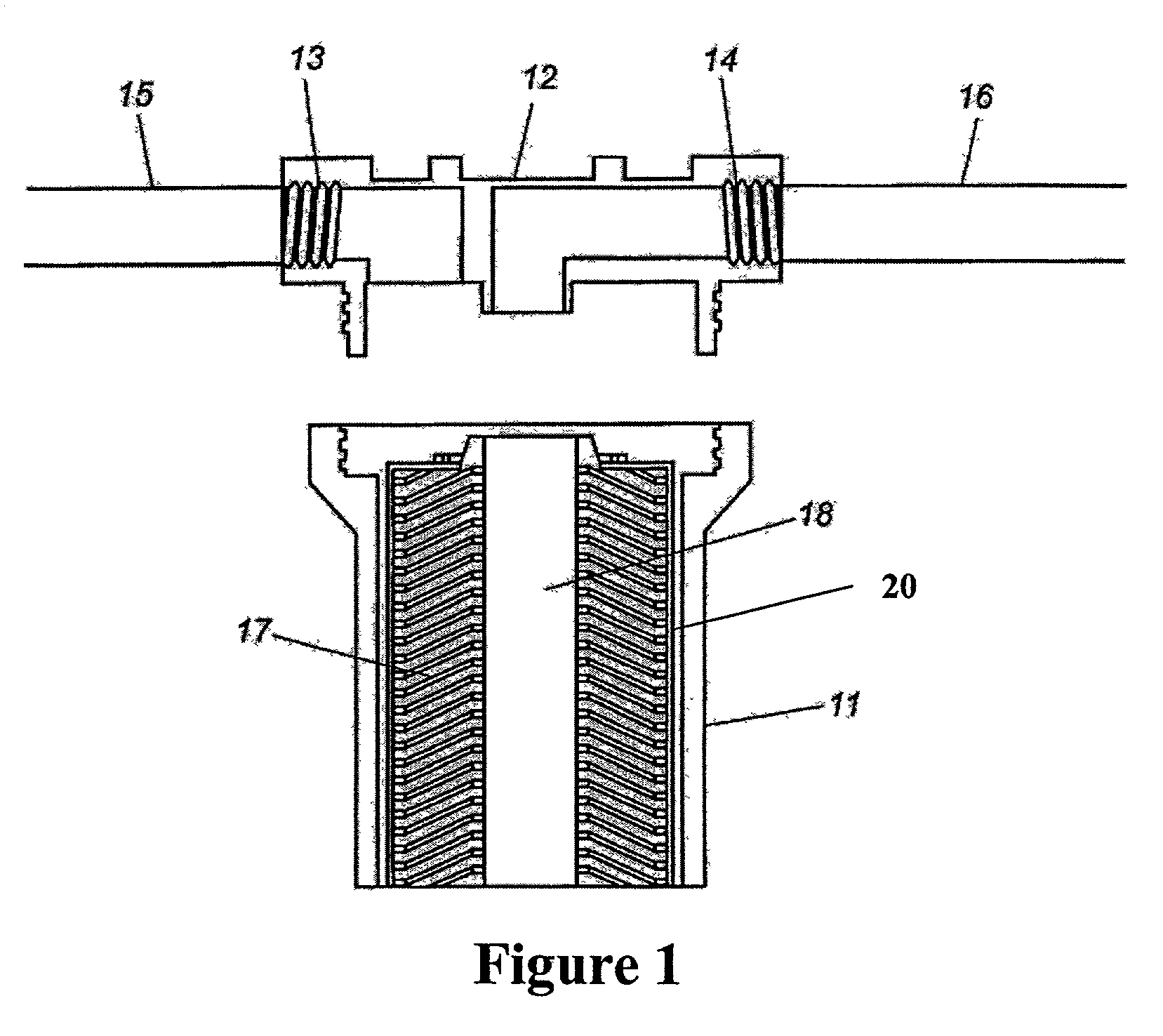
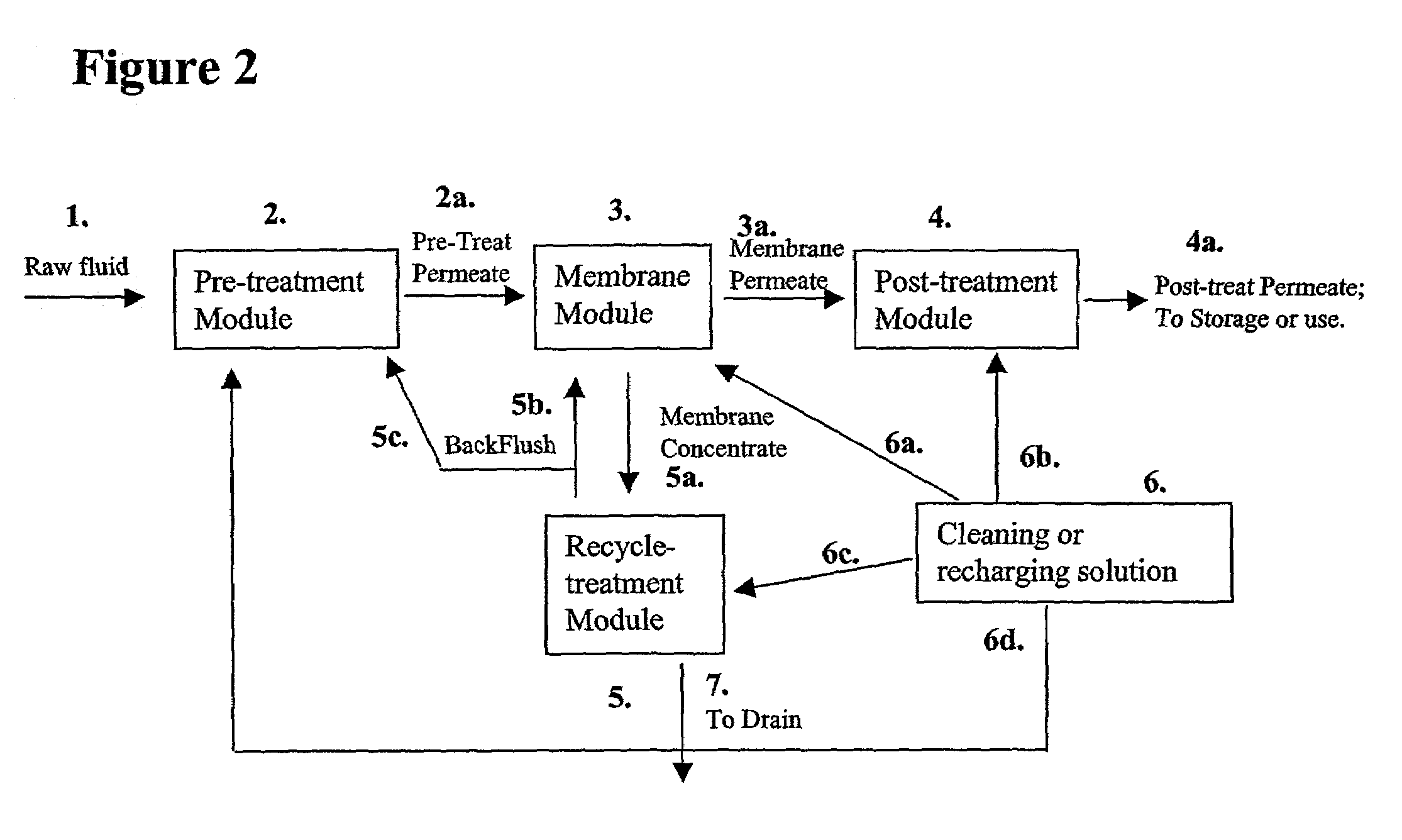
A process for removing soluble and insoluble inorganic, organic, and microbiological contaminants from a fluid stream employing a pretreatment module, a post-treatment module, a recycle stream module or any combination thereof, and a membrane module, is provided. The process provided reduces the problems associated with membrane fouling and increases contaminant removal capacity.
Owner:WATERVISIONS INT
Water treatment system and method
InactiveUS20050103717A1Water treatment parameter controlWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsElectricityWater treatment system
A water treatment system provides treated water to a point of use by removing at least a portion of any hardness-causing species contained in water from a water source, such as municipal water, well water, brackish water and water containing foulants. The water treatment system typically receives water from the water source or a point of entry and purifies the water containing at least some undesirable species before delivering the treated water to a point of use. The water treatment system has a pressurized reservoir system in line with an electrochemical device such as an electrodeionization device. The water treatment system can have a controller for adjusting or regulating at least one operating parameter of the treatment system or a component of the water treatment system.
Owner:SIEMENS WATER TECH HLDG CORP
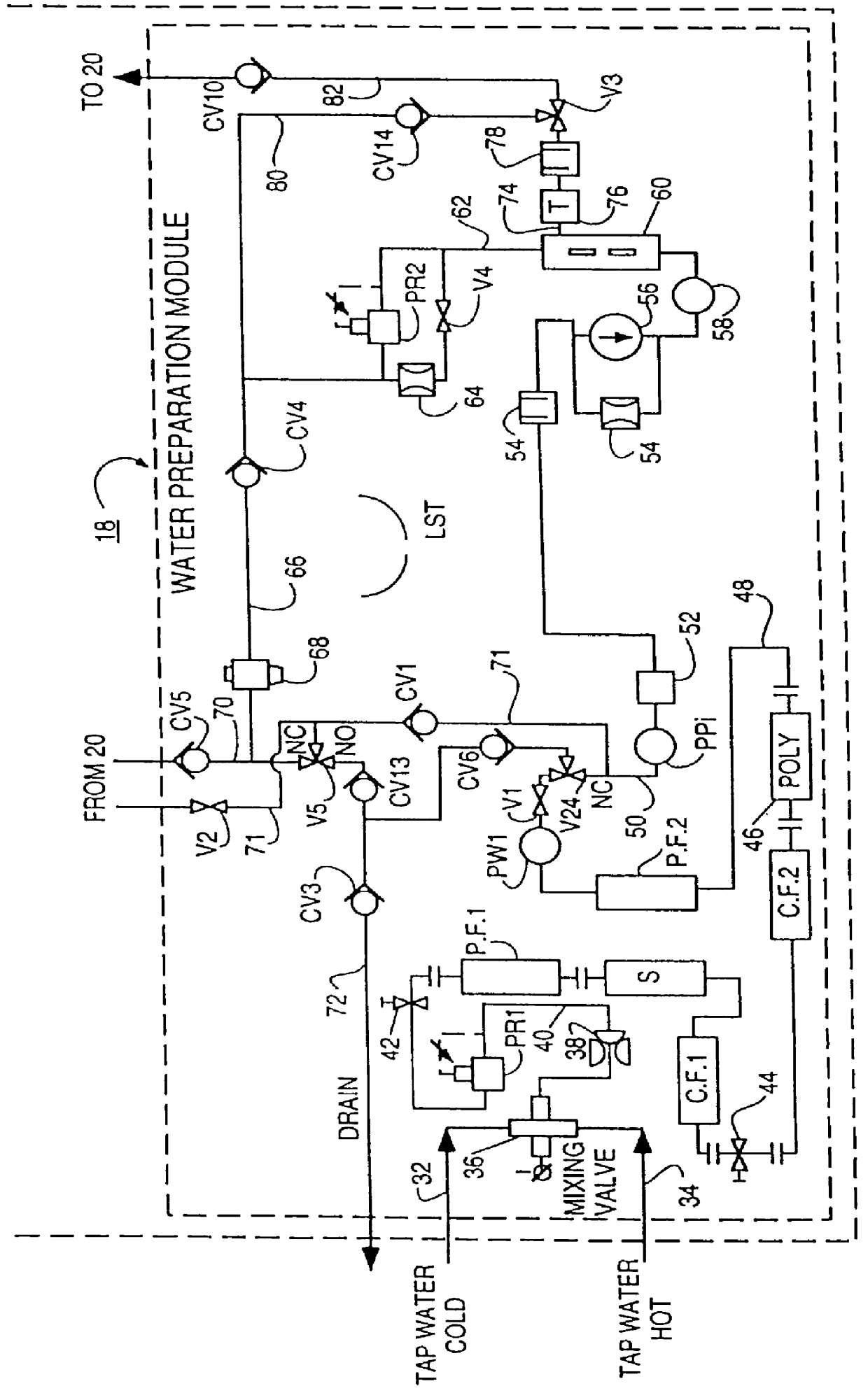
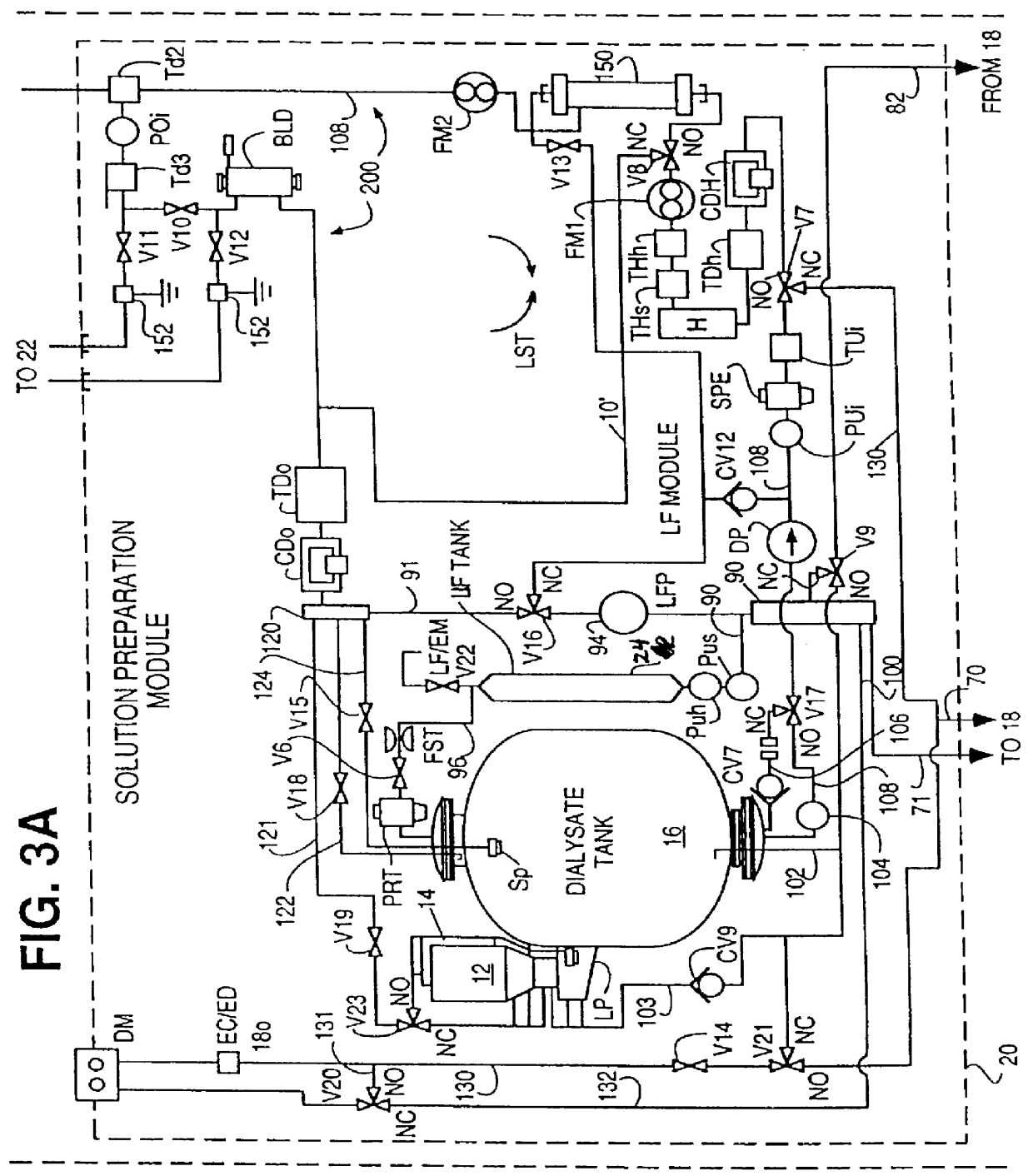
Method of preparation of batch of physiologic solution
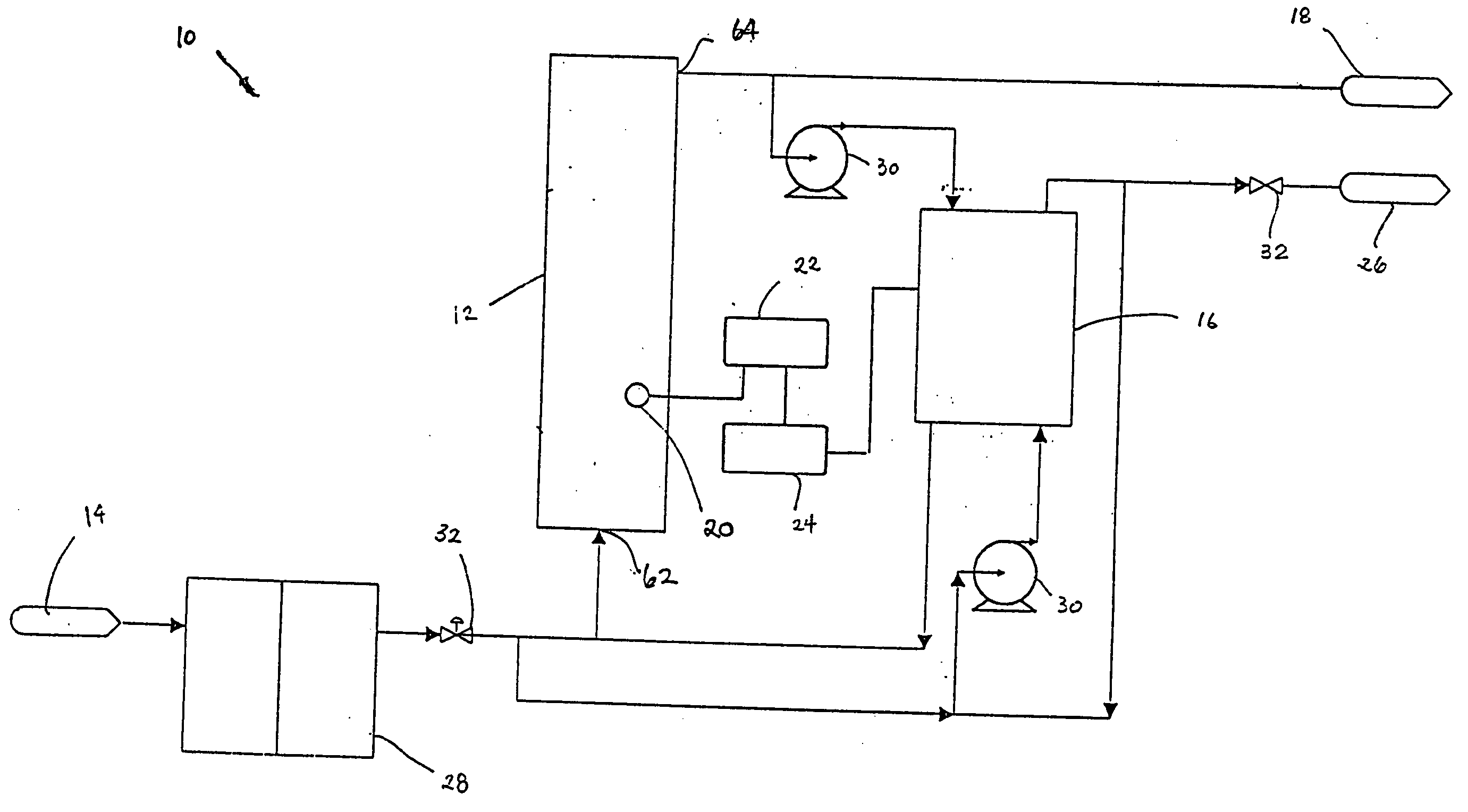
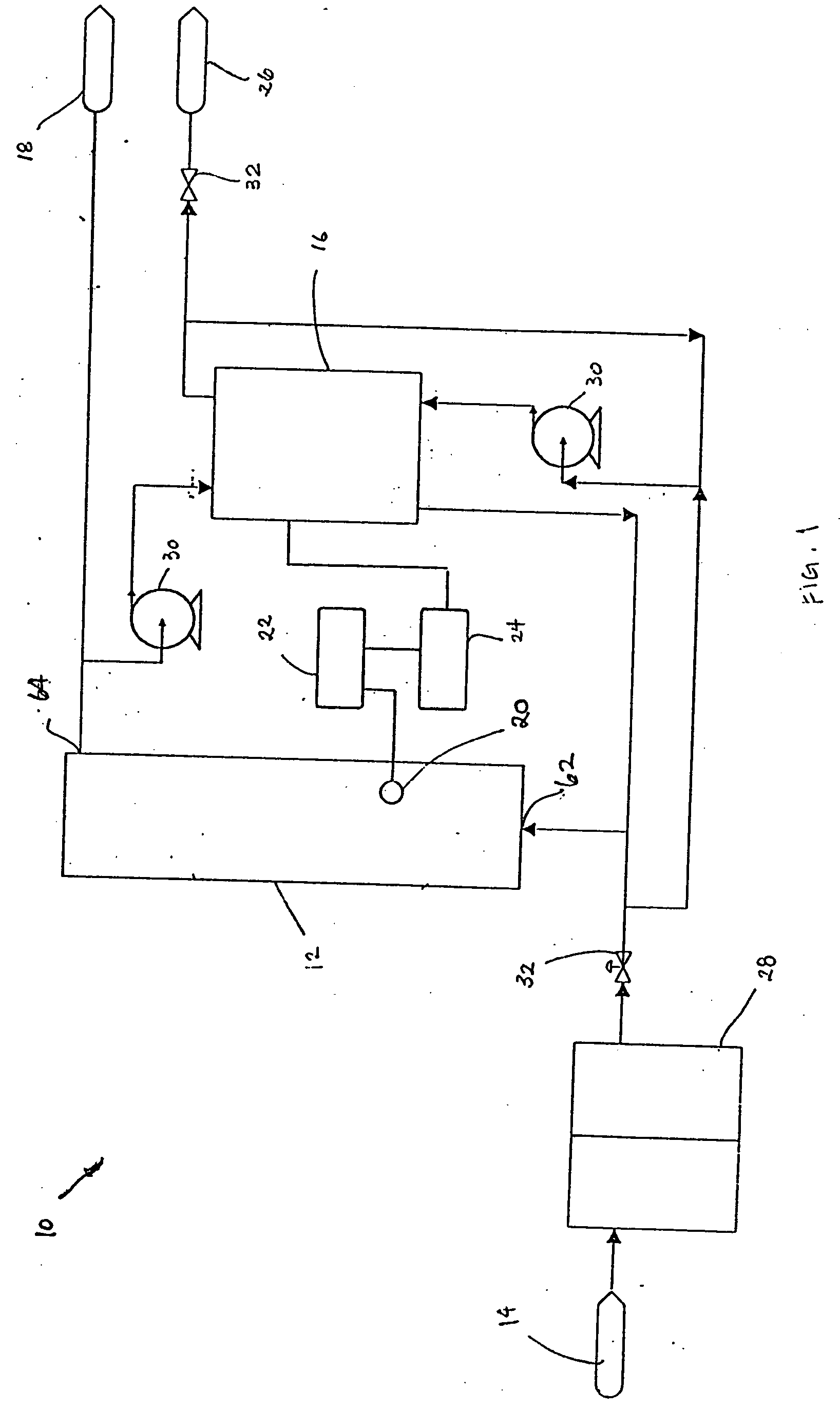
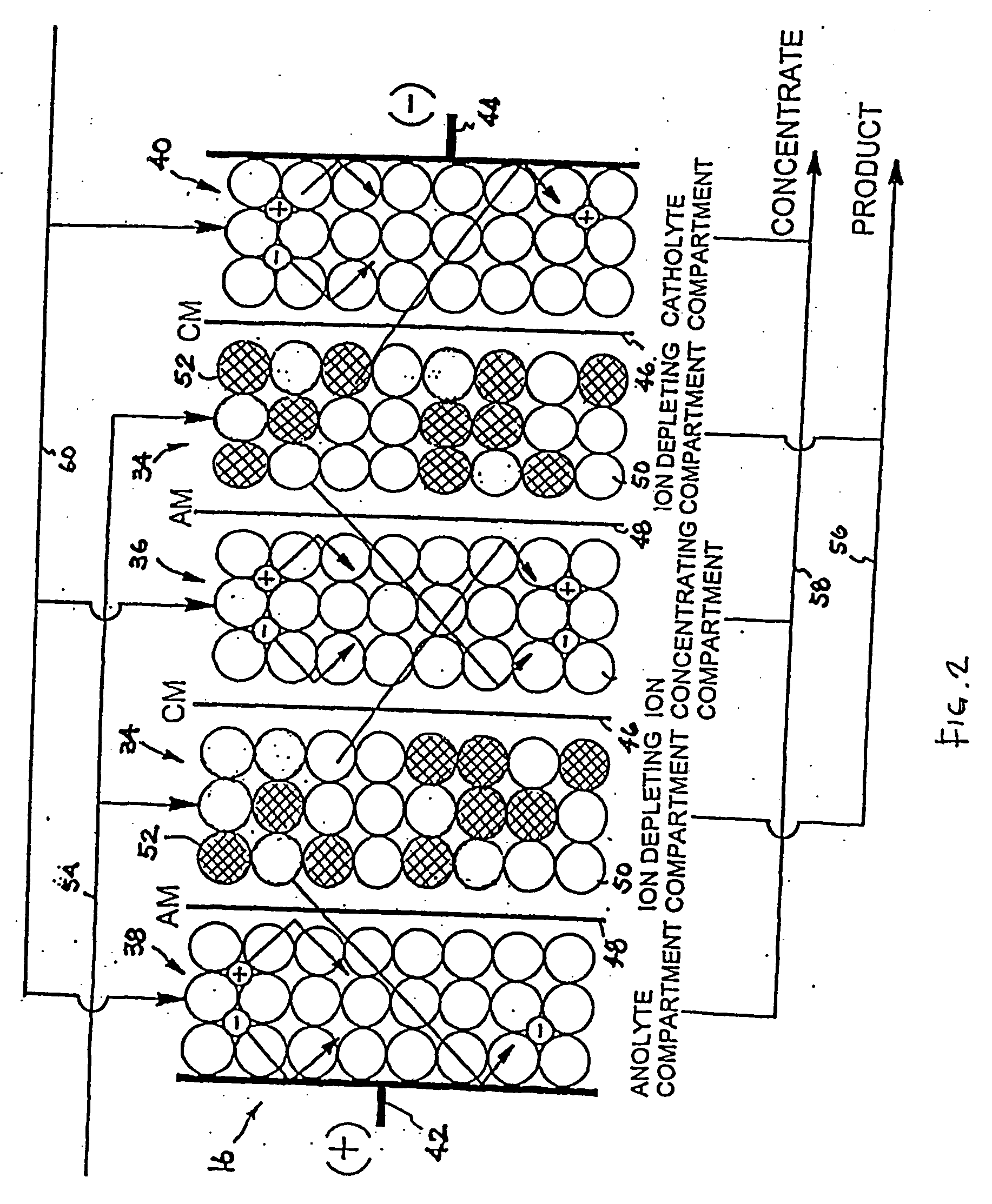
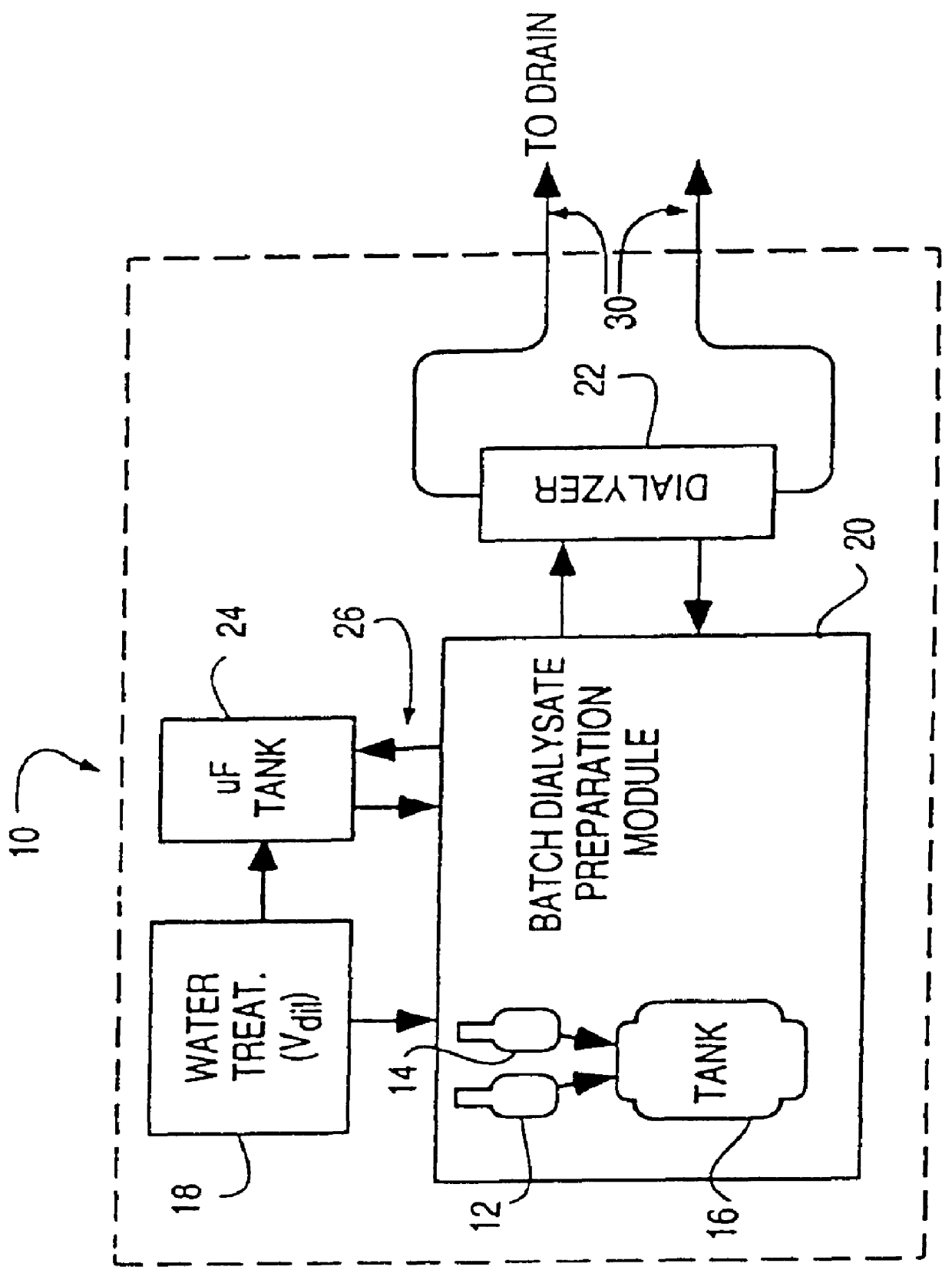
A batch of dialysate solution is made from a mixture of bicarbonate formulation and a liquid acid formulation. The liquid acid formulation is introduced into a dialysate tank and then removed from the tank and stored elsewhere, such as in an ultrafiltration tank, where it is diluted with a few litres of water. The dialysate tank is then filled with water and the bicarbonate formulation is added to the dialysate tank. The bicarbonate formulation is mixed and dissolved by circulation in a closed loop, with the liquid acid formulation kept separate. When the bicarbonate solution has been prepared, the liquid acid solution and the bicarbonate solution are mixed together and stored in the dialysate preparation tank. An additional quantity of dilution water is introduced into the dialysate system to bring the final conductivity down to the desired range. The excess dialysate solution can be used for several purposes, such as an endotoxin flush of the blood tubing set or a dialyzer clearance test.
Owner:HHD LLC A DELAWARE LLC +2
Multicapillary device for sample preparation
InactiveUS20070017870A1Large specific surface areaLoad largeIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationStationary phaseMICRO PIPETTE
A multicapillary sample preparation device, especially useful for handling biological samples, comprising a plurality of uniform capillary tubes coated with a stationary phase, and arranged in a monolithic element. The multicapillary device is suitable for attachment to a pipette, micropipette, syringe, or other analytical or sample preparation instrument.
Owner:BIOEDGE
Microfluidic chromatography
InactiveUS20050000900A1Ion-exchange process apparatusComponent separationChromatography columnDelivery system
The present invention is directed to a microfluidic chromatography apparatus comprising a microfabricated fluid delivery system and a chromatography column which is in fluid communication with the fluid delivery system, and a method for producing and using the same. Preferably, the chromatography column comprises an OTLC, PCLC, or combinations thereof.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
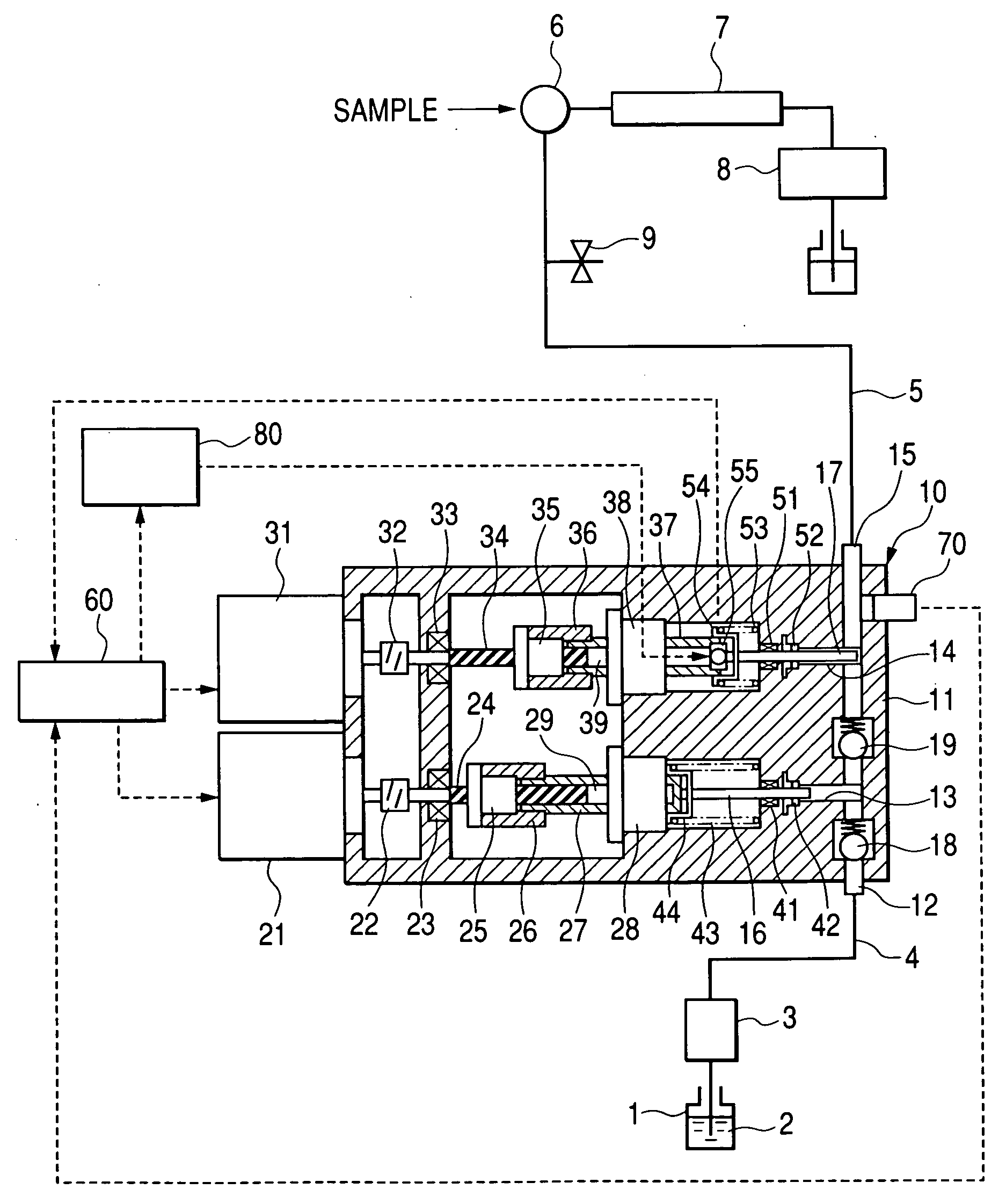
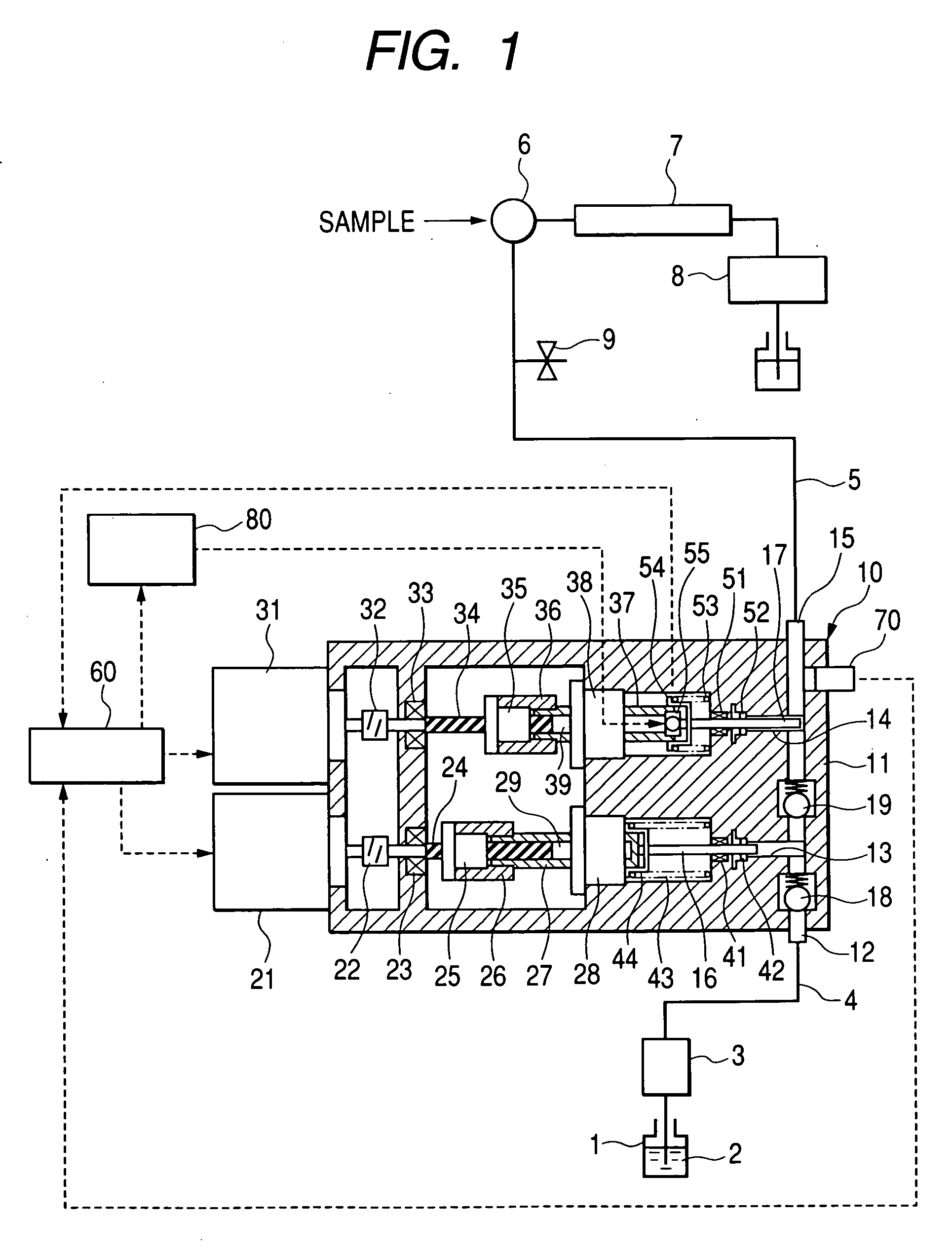
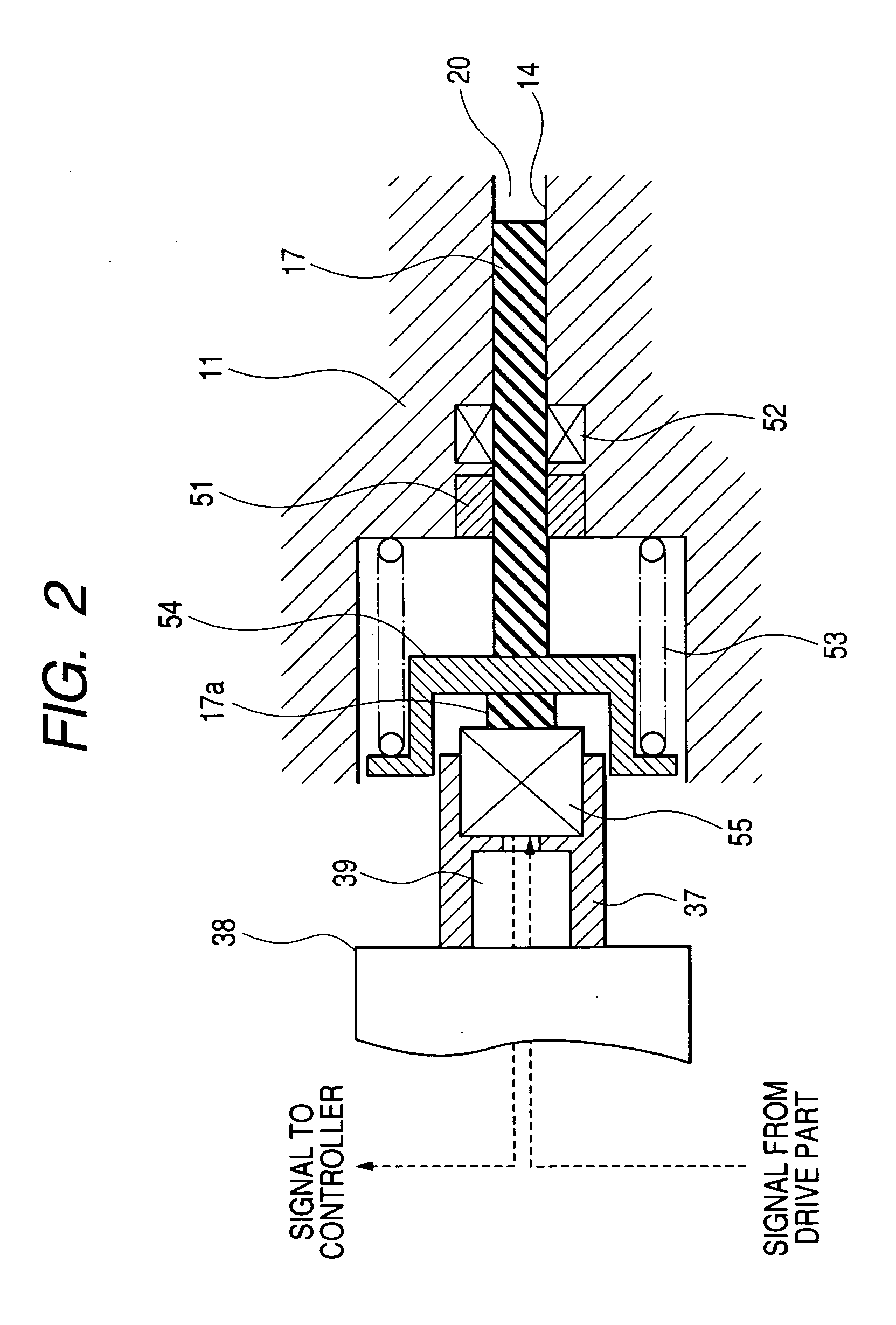
Pump, pump for liquid chromatography, and liquid chromatography apparatus
The invention provides a pump for liquid chromatography excellent in feeding liquid stably at an extremely low flow rate and in discharging bubbles at startup. In a pump for liquid chromatography including a cylinder and a plunger that reciprocates in the cylinder to suck and discharge fluid, the pump further includes a large-flow-rate pump that feeds liquid by the plunger, a small-flow-rate pump that feeds the liquid by the plunger, motion conversion means that converts the rotational motion of a motor to a reciprocating motion, an actuator that directly drives the plunger, and a drive part that drives the actuator, and selectively switches means for driving the plunger.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Removal of fluorinated surfactants from waste water
The present invention provides a method of removing a fluorinated surfactant from waste water comprising fluoropolymer particles. The method comprises (i) adding a non-fluorinated surfactant to the waste water (ii) contacting the thus obtained waste water with adsorbent particles to adsorb at least a portion of the fluorinated surfactant to the adsorbent particles and (iii) separating the waste water and the adsorbent particles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Adsorption/separation method and a medium for adsorption/separation
InactiveUS6428707B1Increase productionImprove productivityChromatographic cation exchangersCation exchanger materialsChemistrySeparation method
A method for adsorption of a substance from a liquid sample on a fluidized bead or stirred suspension, in which the beads used comprise a base matrix and exhibit a structure having affinity to the substance, characterized in that the structure is covalently bound to the base matrix via an extender. Populations of beads in which the beads contain a filler incorporated in a base matrix and an extender are also described.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIOPROCESS R&D
Filtering water bottle
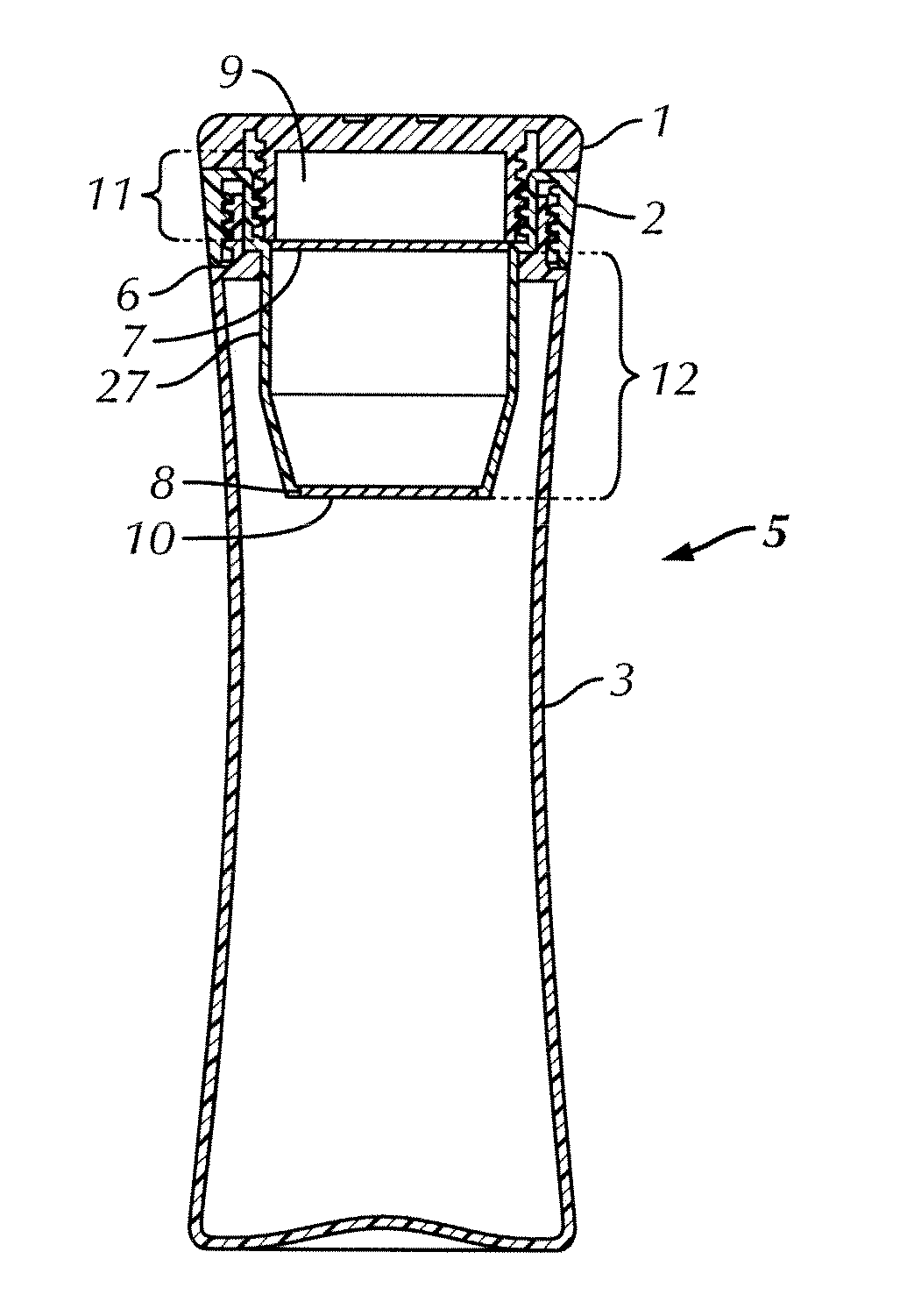
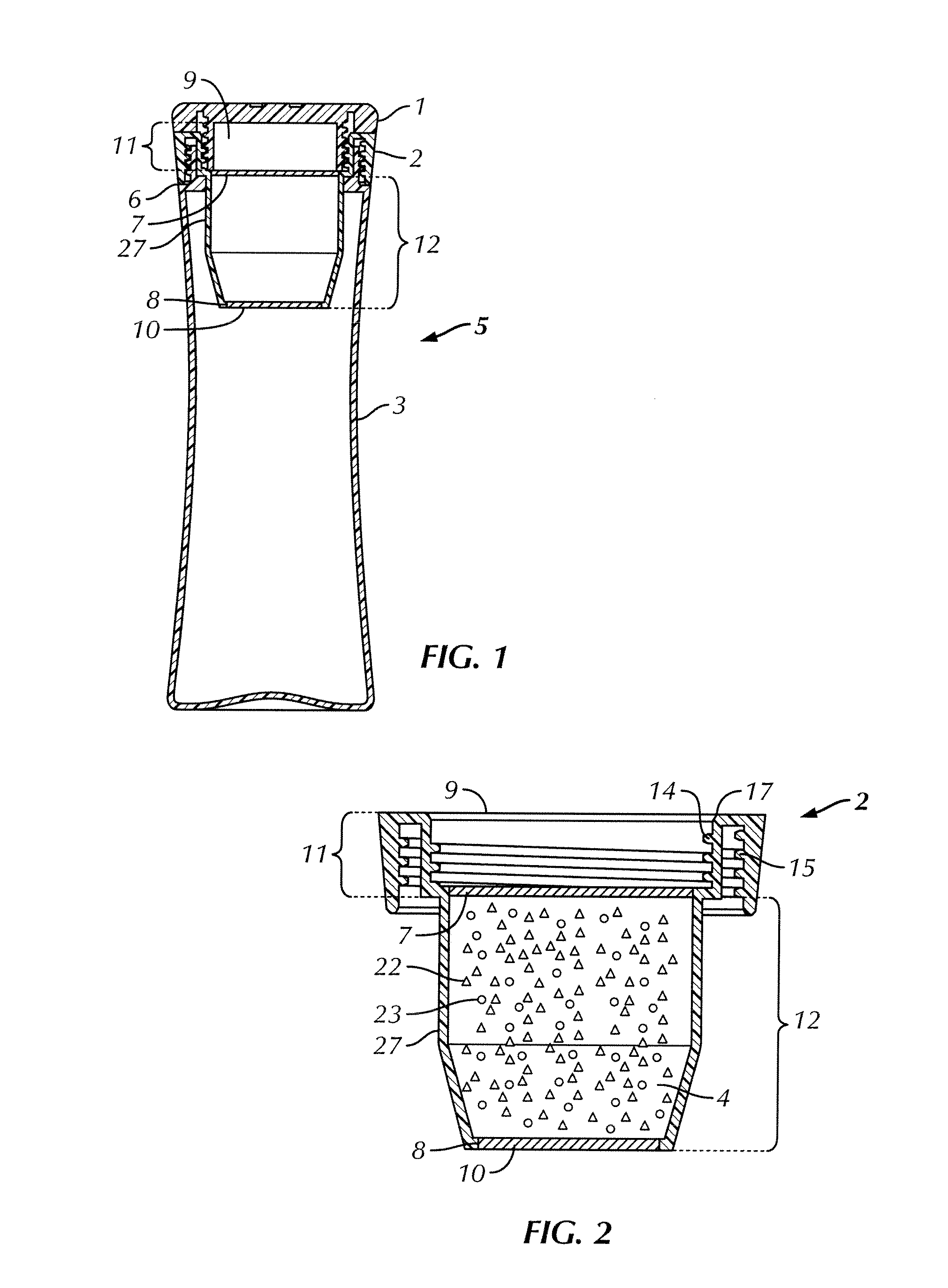
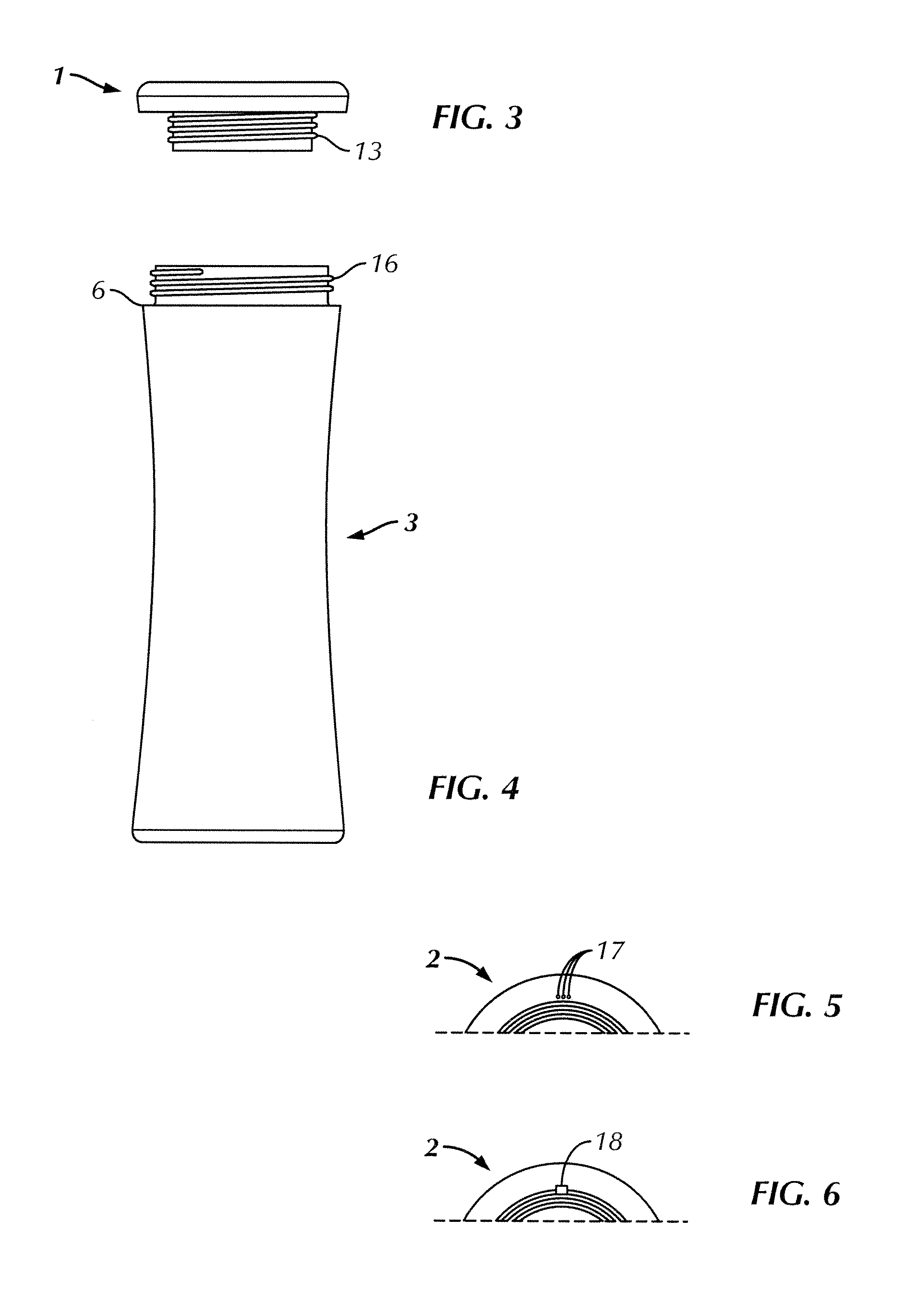
ActiveUS20120055862A1Improve filtering effectIncrease ratingsGeneral water supply conservationTreatment involving filtrationFiltrationGravity flow
A portable, personal apparatus for treating drinking water comprises a generally tubular or cylindrical filter housing containing filtration media and water-permeable screen or mesh or felt or membrane or netting layer at the top and bottom ends of the filter. The design of the apparatus involves the bottle exterior and interior contouring to the filter and enables the efficient and rapid gravity flow of water in through the filter. The apparatus may be configured such that water is first passed through a top reservoir designed to receive water, followed by a porous mesh, followed by granular filtration and antimicrobial media agitated by turbulent motion of influent water, followed by a porous mesh before reaching a durable and reusable water containment vessel.
Owner:INNOVA DYNAMICS +1
Multifunctional composite absorbing material for purifying water and preparation method thereof
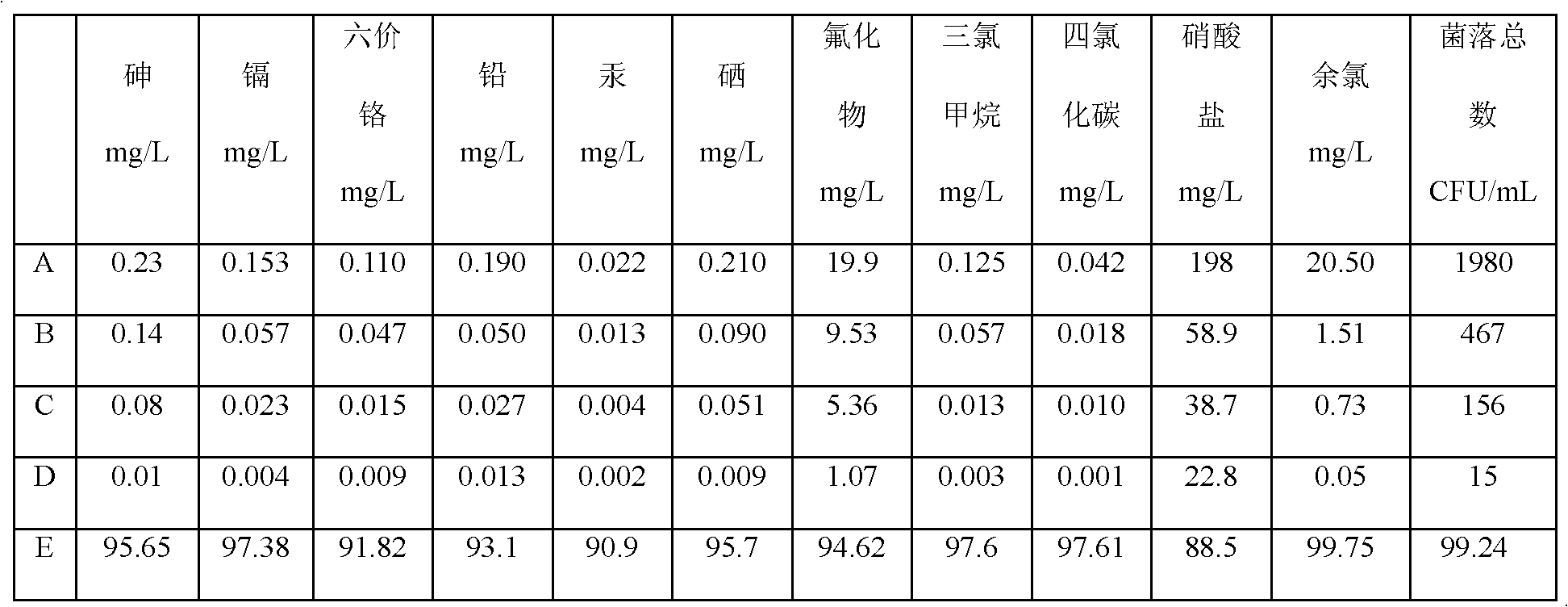
ActiveCN102350298AReduce wasteEfficient removalOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisAcrylic resinCerium
The invention provides a multifunctional composite absorbing material for purifying water and a preparation method thereof, relating to an absorbing material. The invention provides the multifunctional composite absorbing material for purifying water, which can be used for effectively removing a plurality of harmful substances in the water and has higher removal efficiency and lower production cost, and the preparation method thereof. The absorbing material is selected from at least one of absorbing materials A, B and C; the absorbing material A takes a mesoporous adsorption ceramic material as a carrier to load nano metals including nano silver, nano zinc, nano iron and nano cerium; the absorbing material B takes the mesoporous adsorption ceramic material as the carrier to load nano metal oxides including nano titanium dioxide, nano zinc oxide, nano ferric oxide and nano cerium dioxide; and the absorbing material C is prepared from the following raw materials according to the mass ratio: 100-200 parts of active carbon powder, 20-30 parts of polyethylene powder, 10-30 parts of calcium sulfite powder, 10-30 parts of natural zeolite powder, 20-40 parts of macroporous acrylic resin and 10-20 parts of attapulgite powder.
Owner:XIAMEN BAILIN WATER PURIFICATION TECH CO LTD
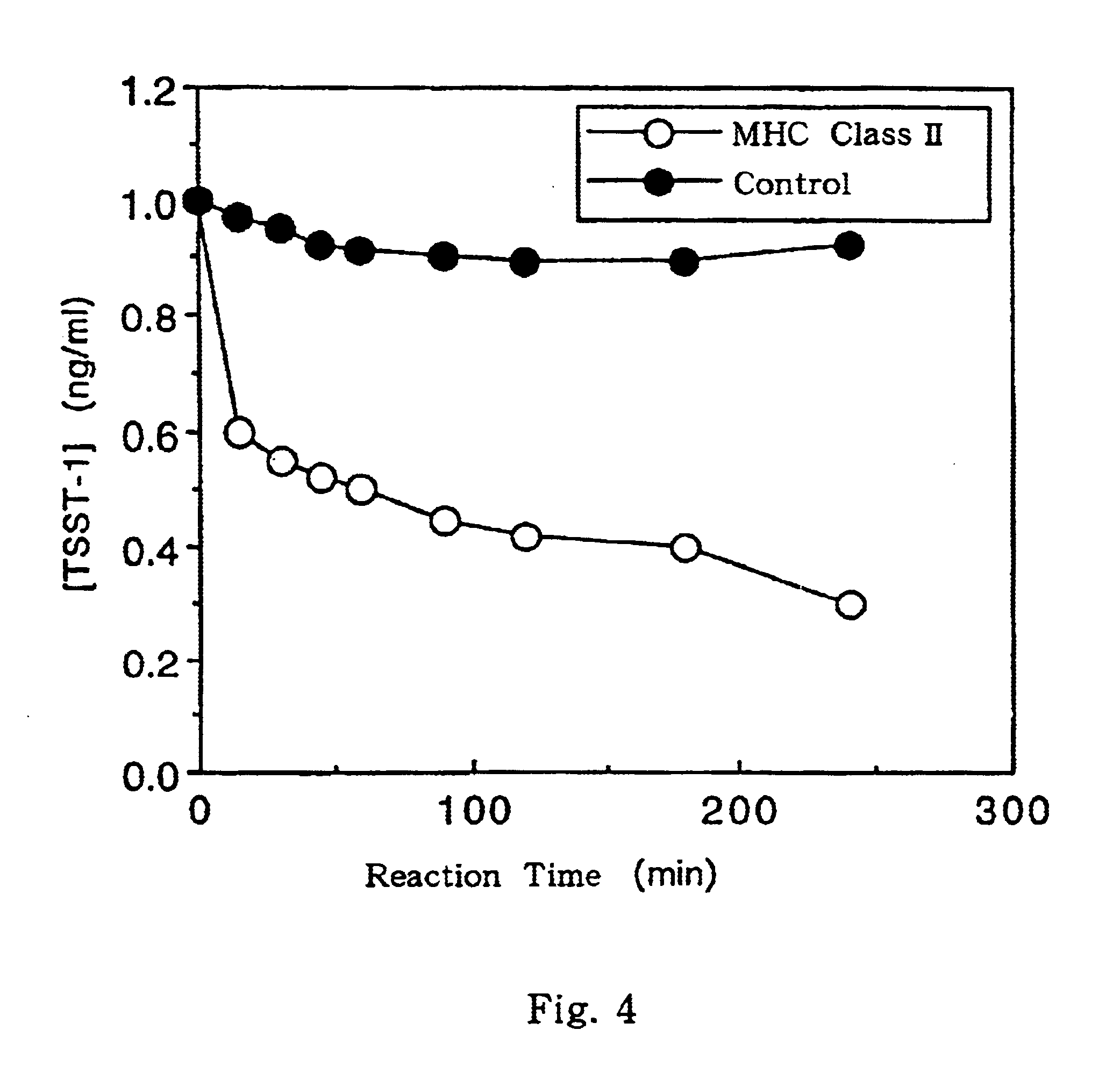
Process for preparing major histocompatibility antigen class II protein and materials in which the same is bound
InactiveUS6630315B1Produce significantIon-exchanger regenerationMicroorganism based processesFiberMajor histocompatibility
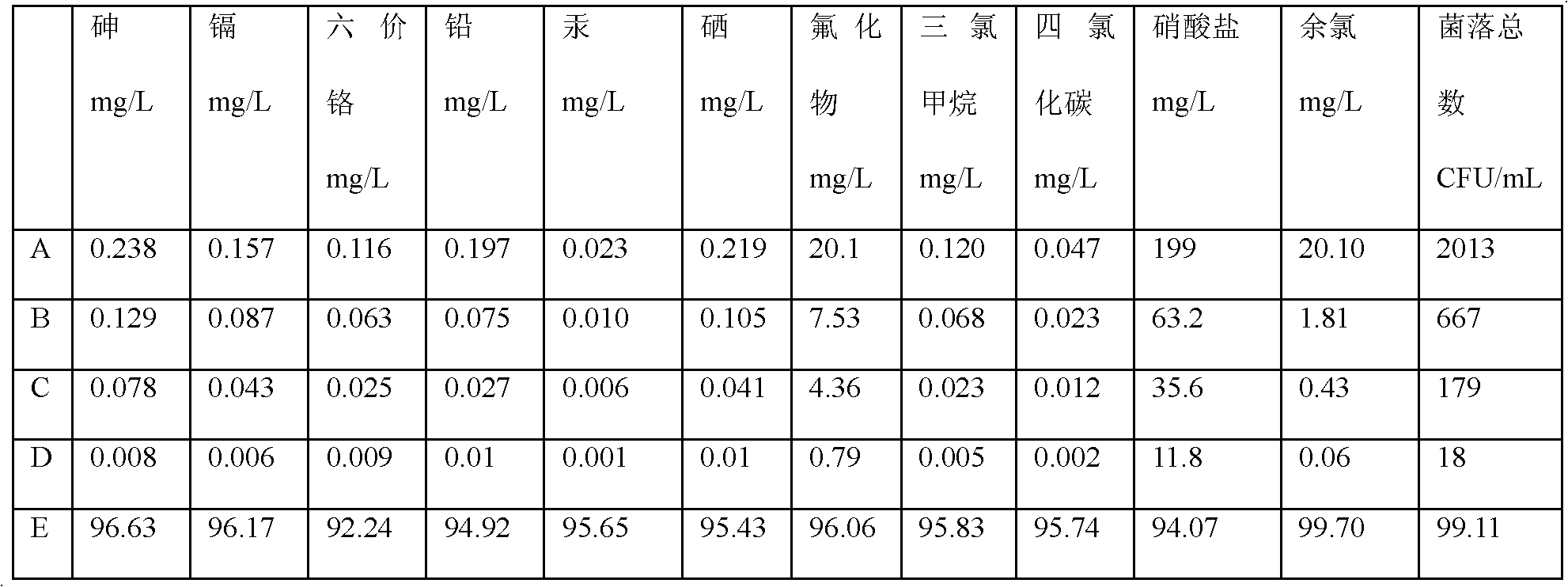
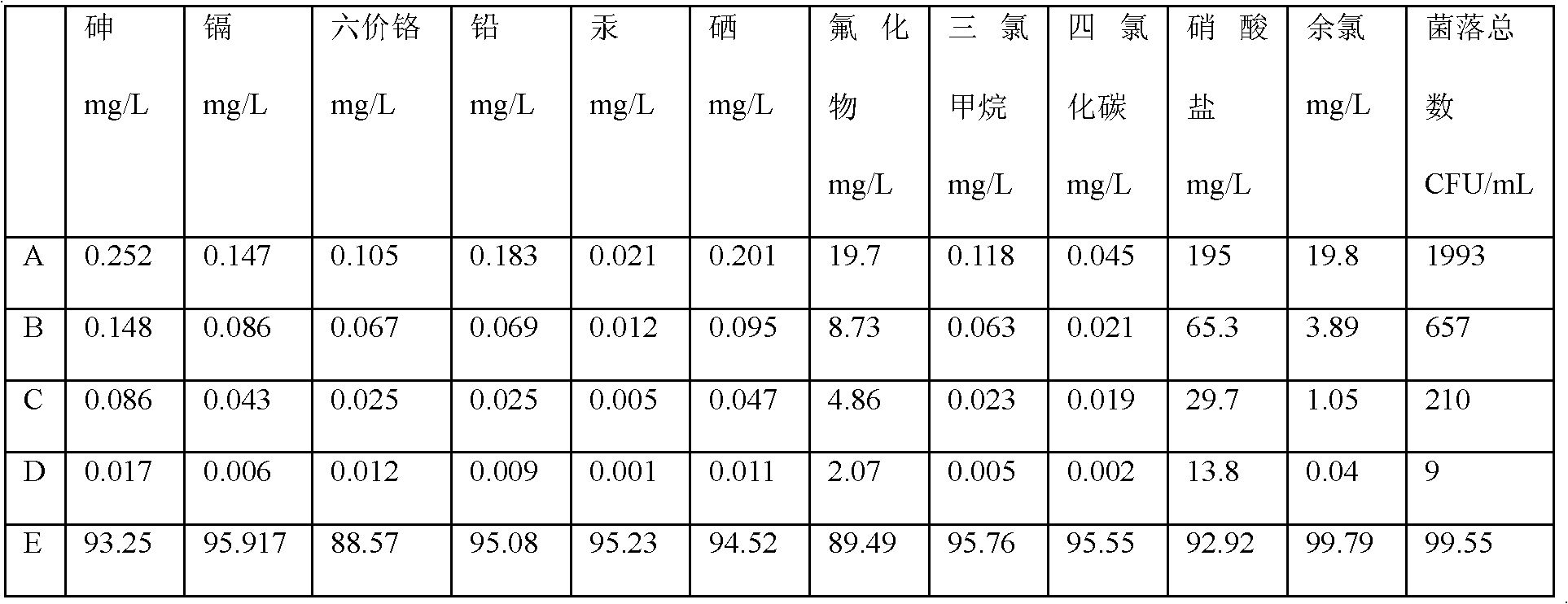
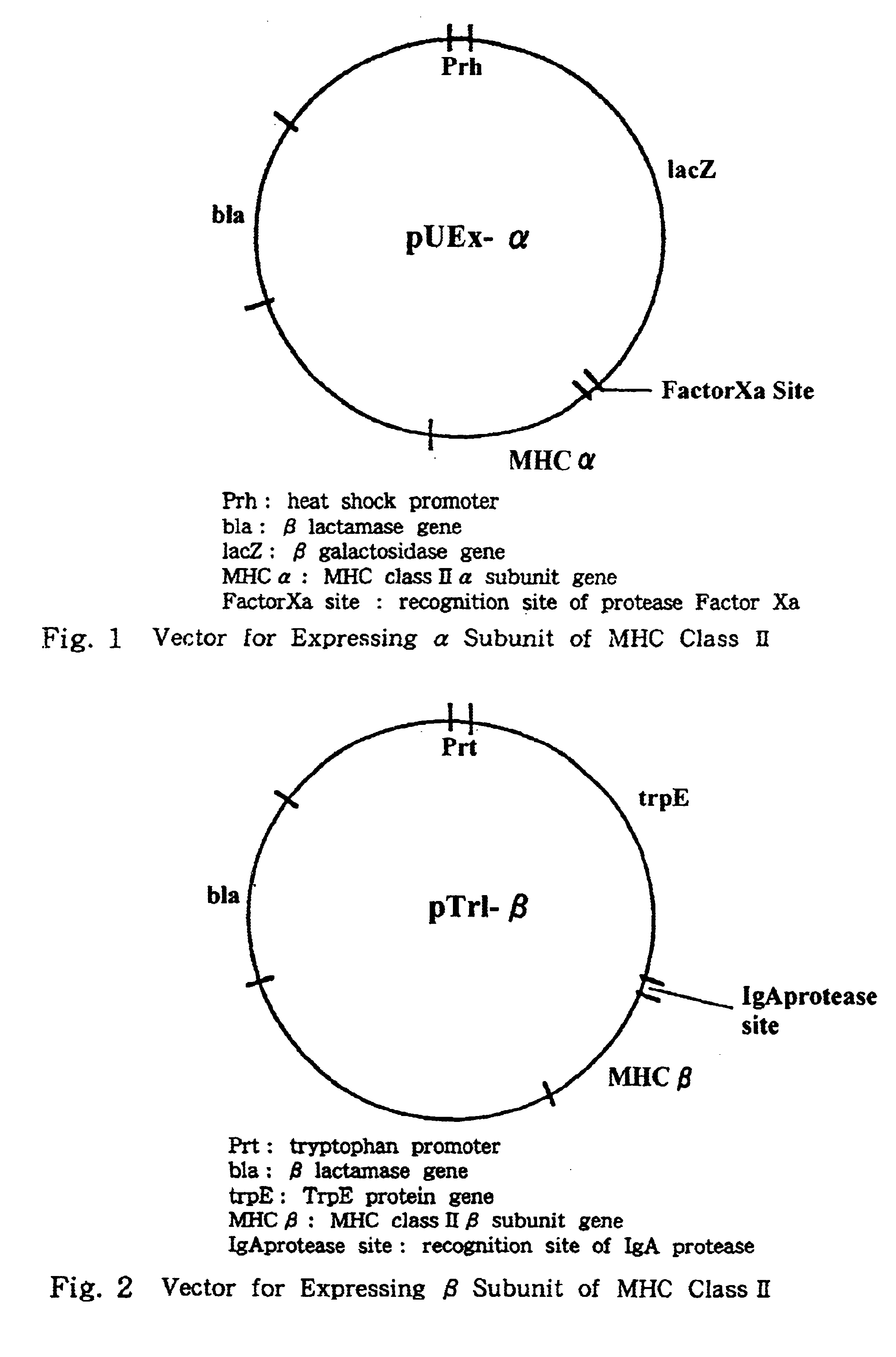
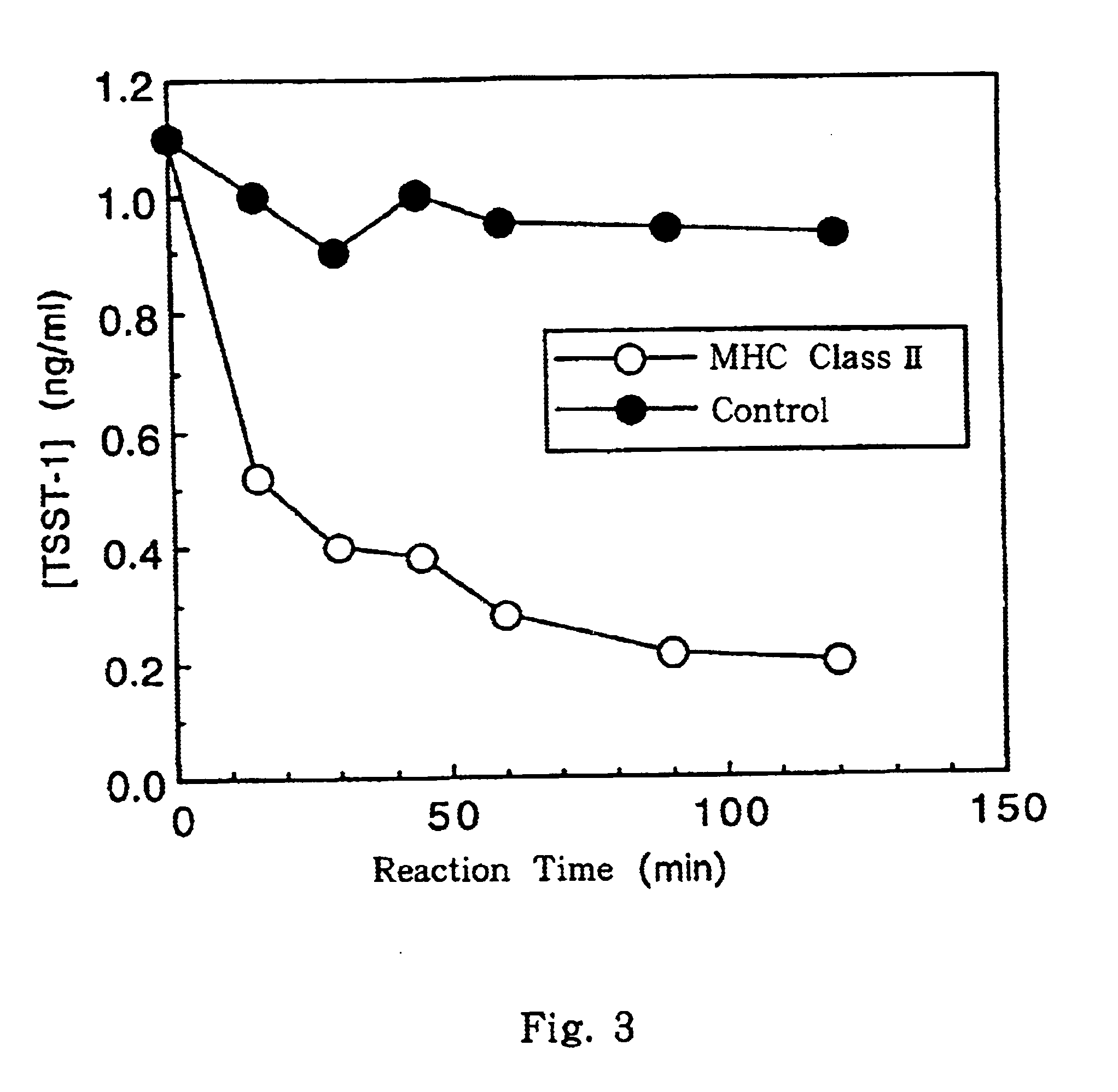
This invention provides a process for producing major histocompatibility antigen class II protein (hereinafter referred to as "MHC class II" for short) which occurs on the surfaces of antigen-presenting cells and the like, and MHC class II-bound materials in which MHC class II, alpha and / or beta subunit of MHC class II, or a part thereof is bound to a carrier such as beads, fibers and hollow fibers via covalent bond, as well as a module for removing superantigen using the same. This invention also provides a method for detecting or quantifying superantigens using MHC class II or a part thereof having an affinity to the superantigens, as well as an assay kit therefor.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com