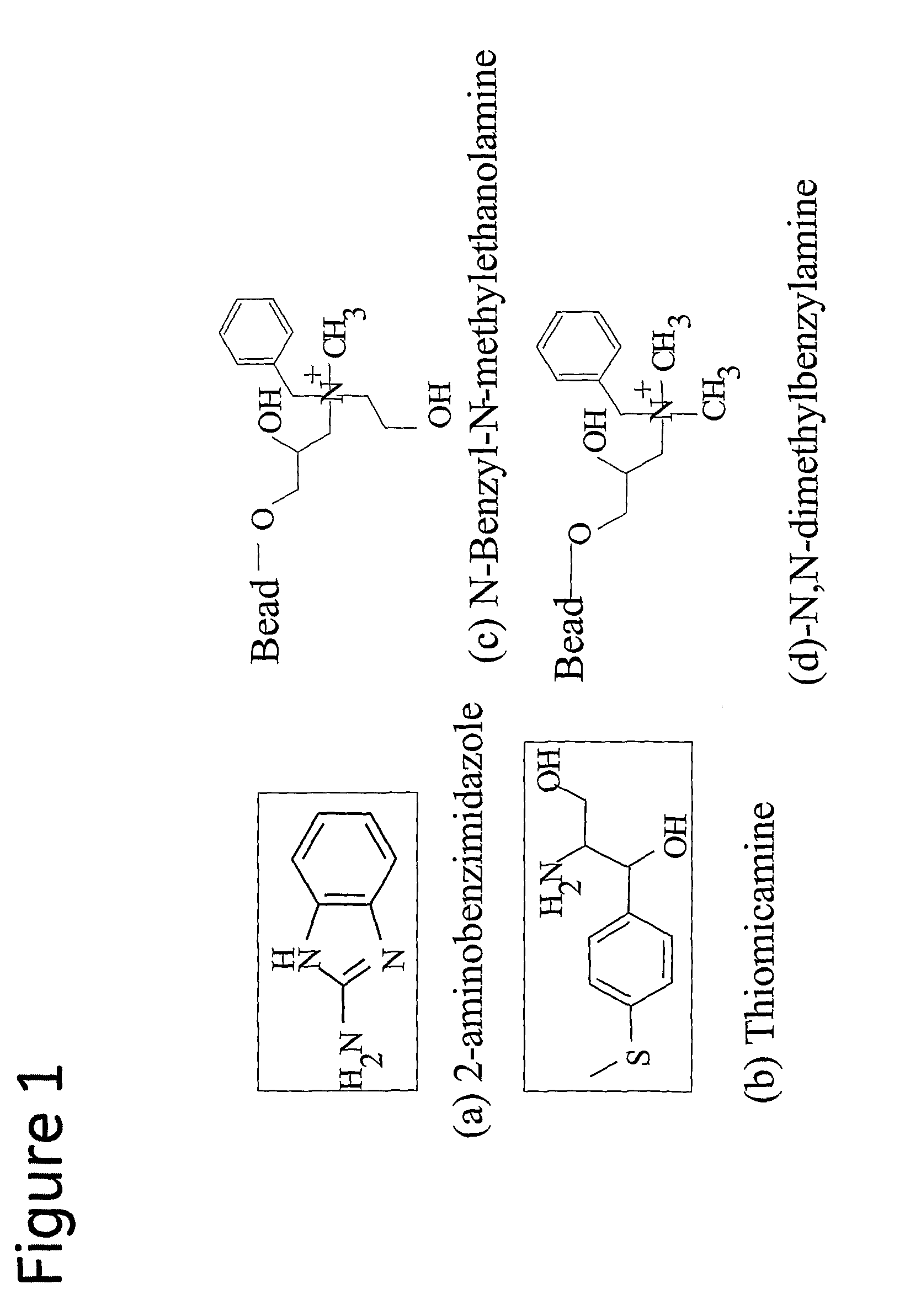
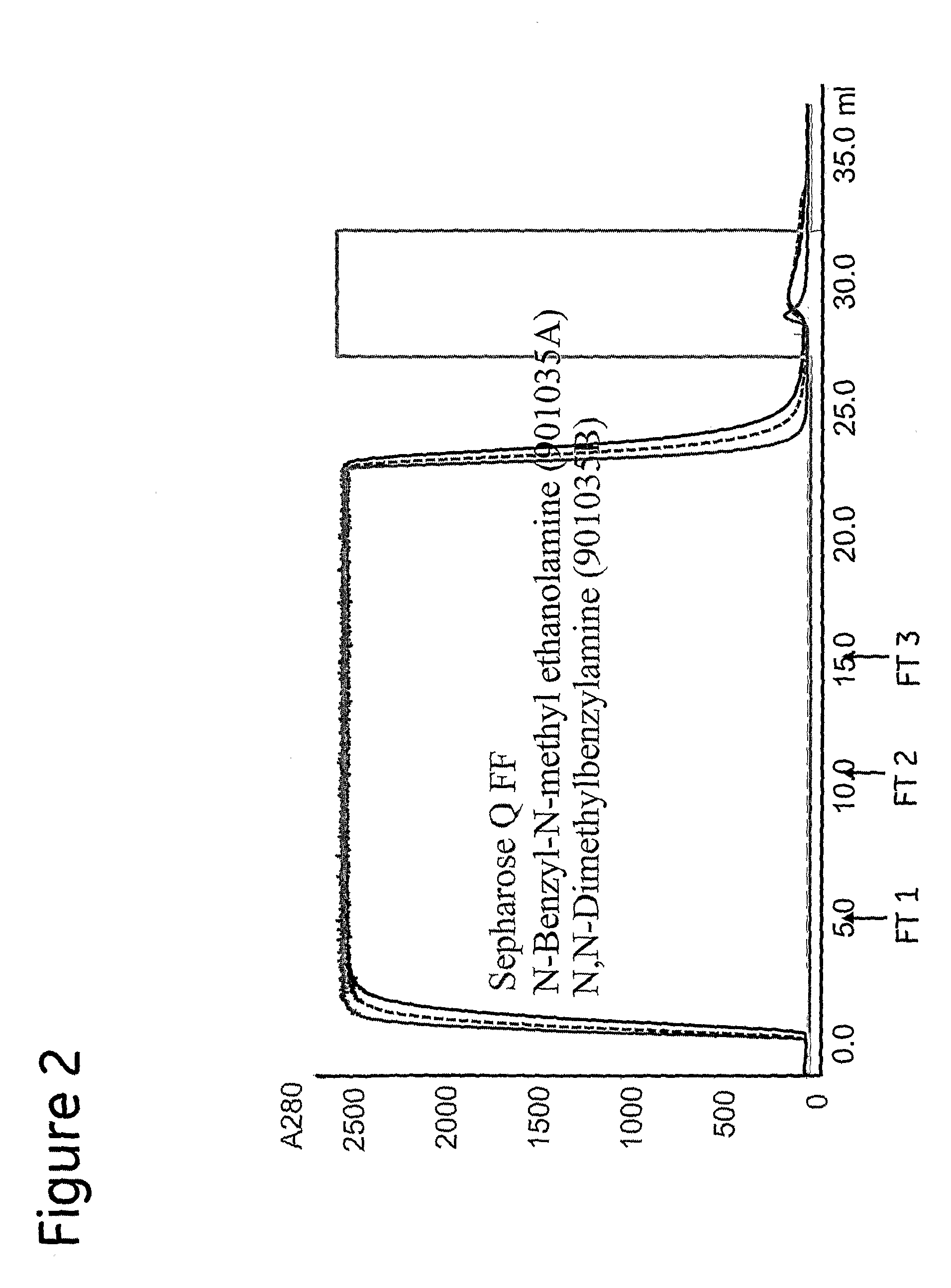
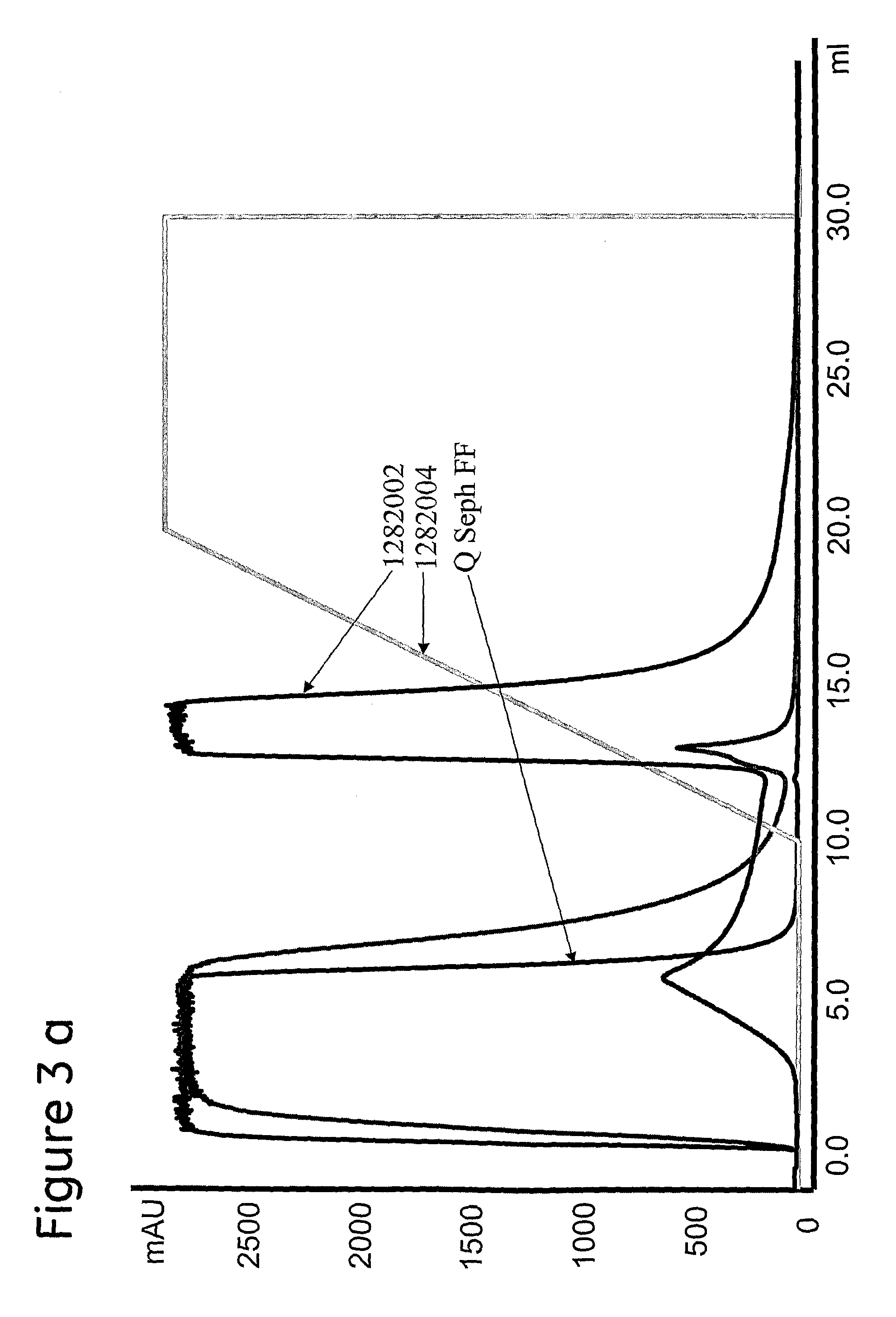
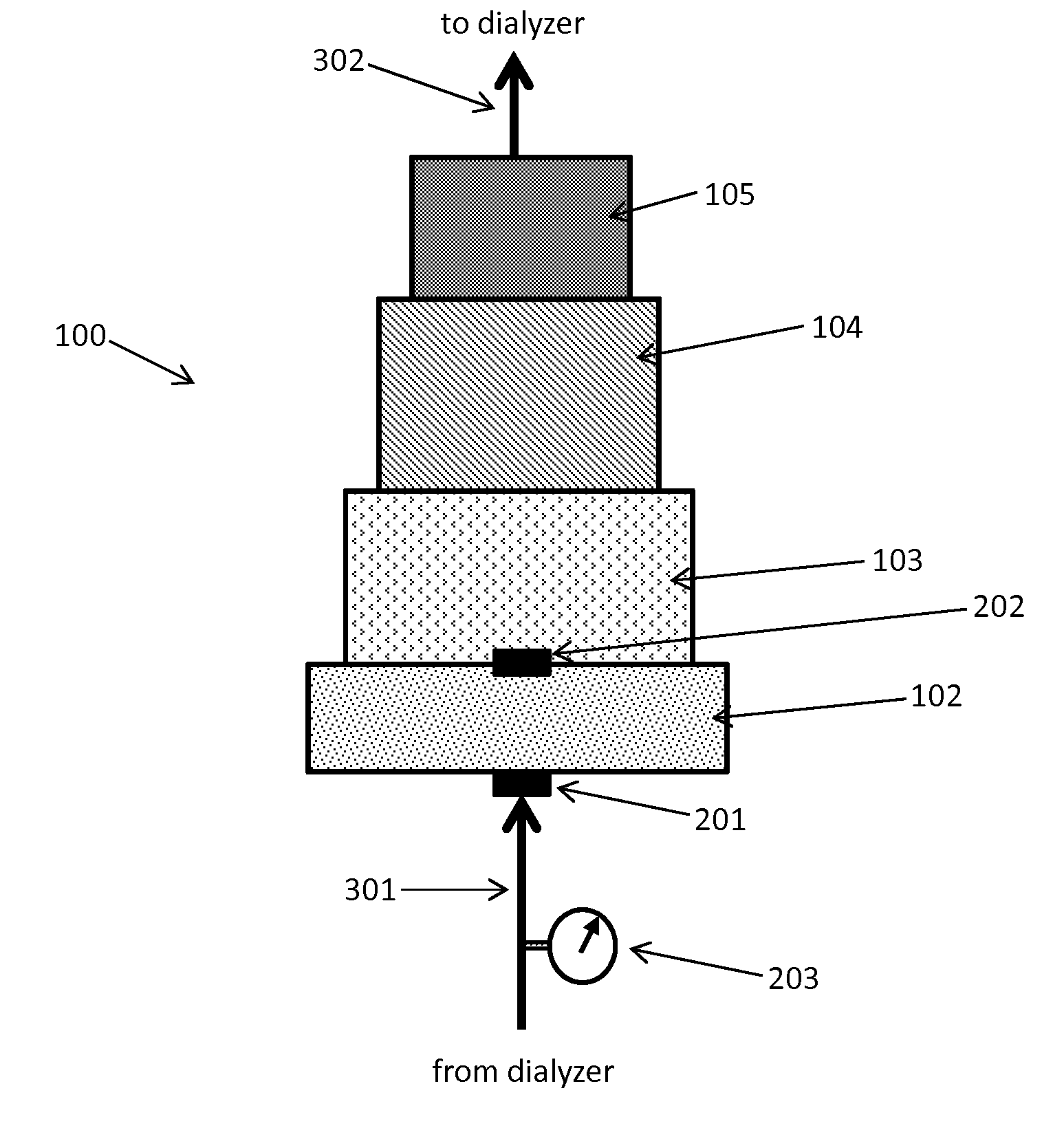
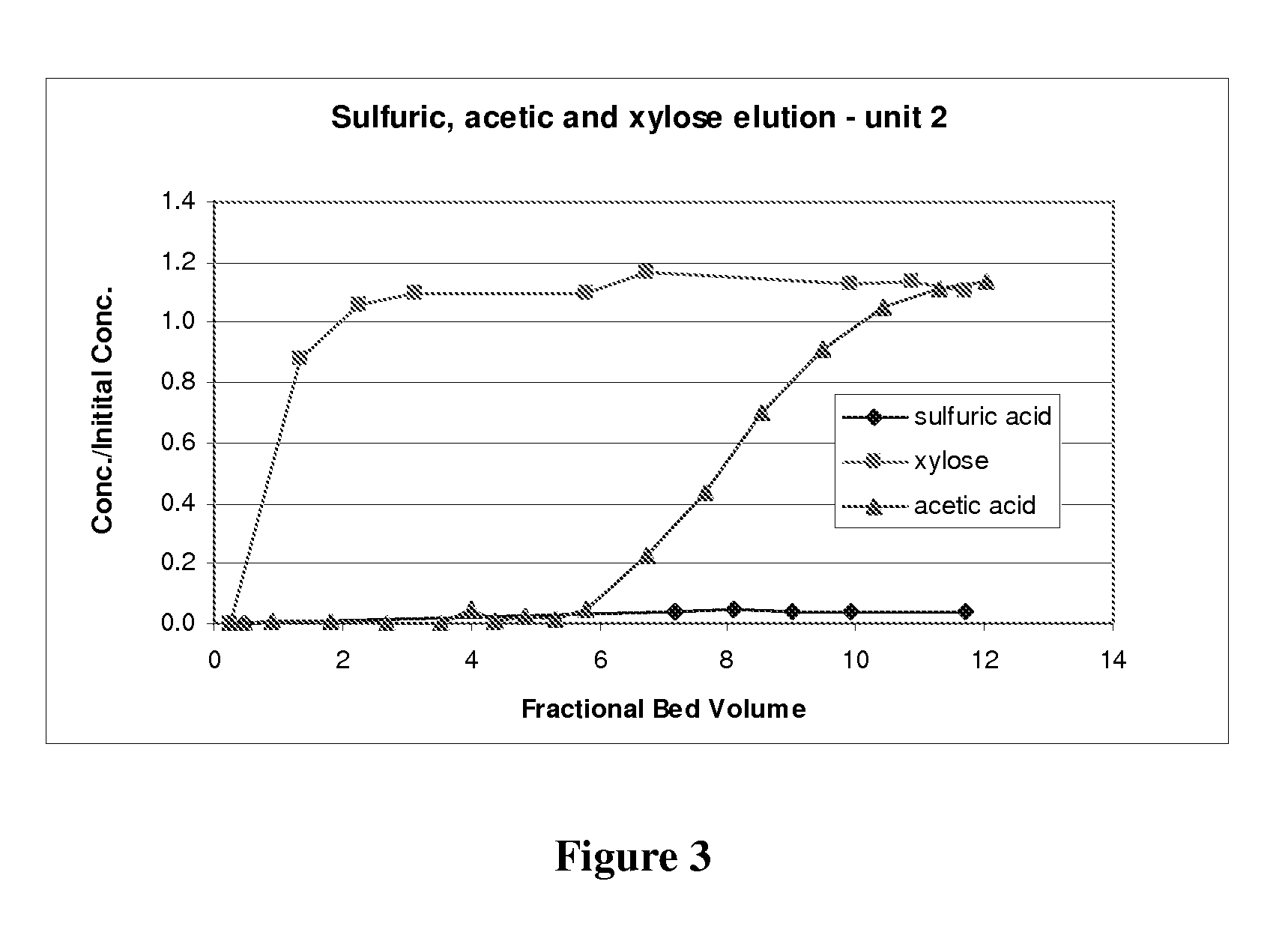
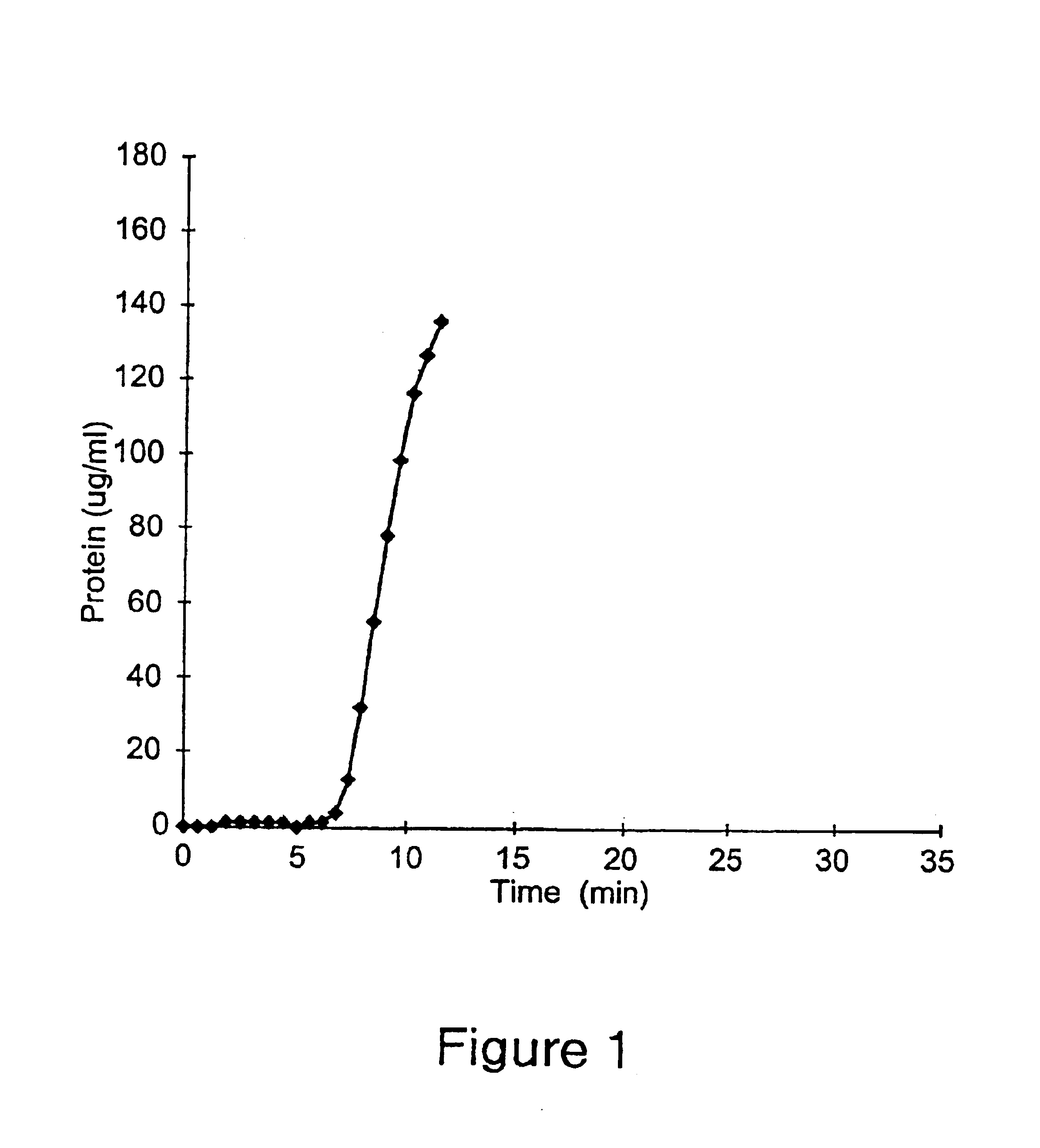
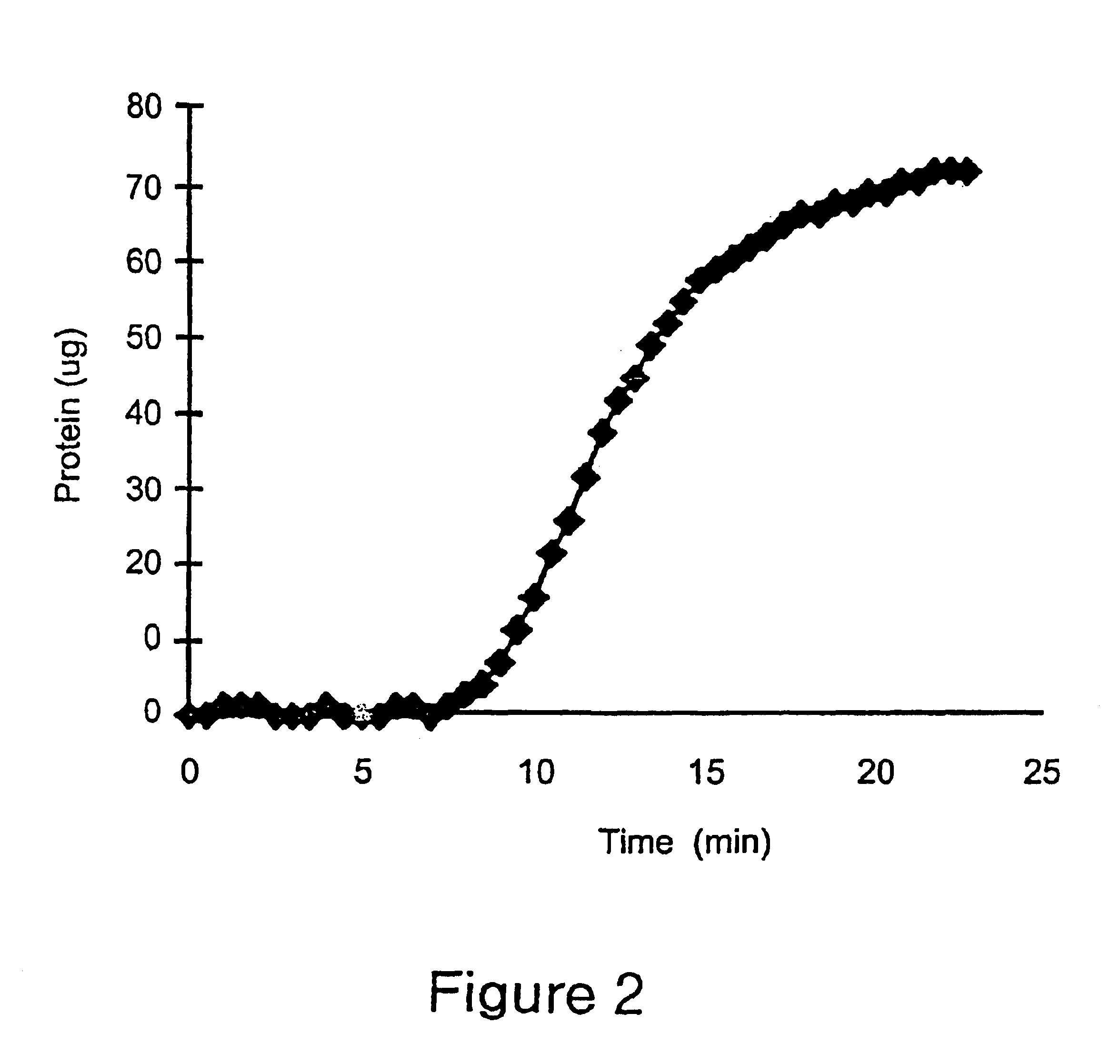
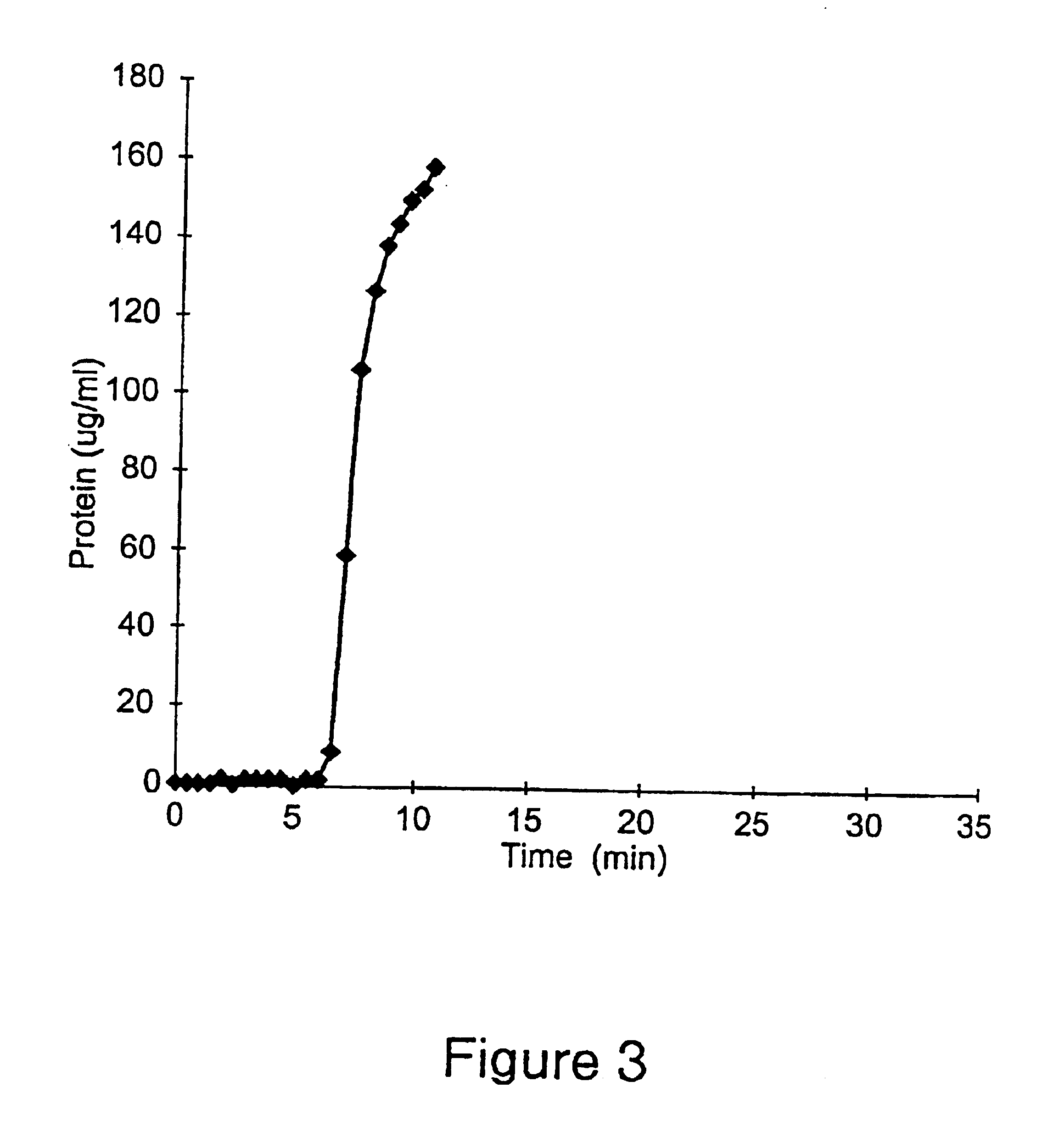
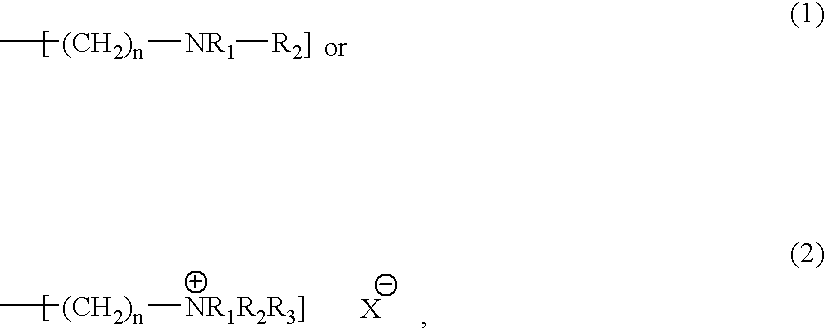Patents
Literature
1496results about "Organic anion exchangers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
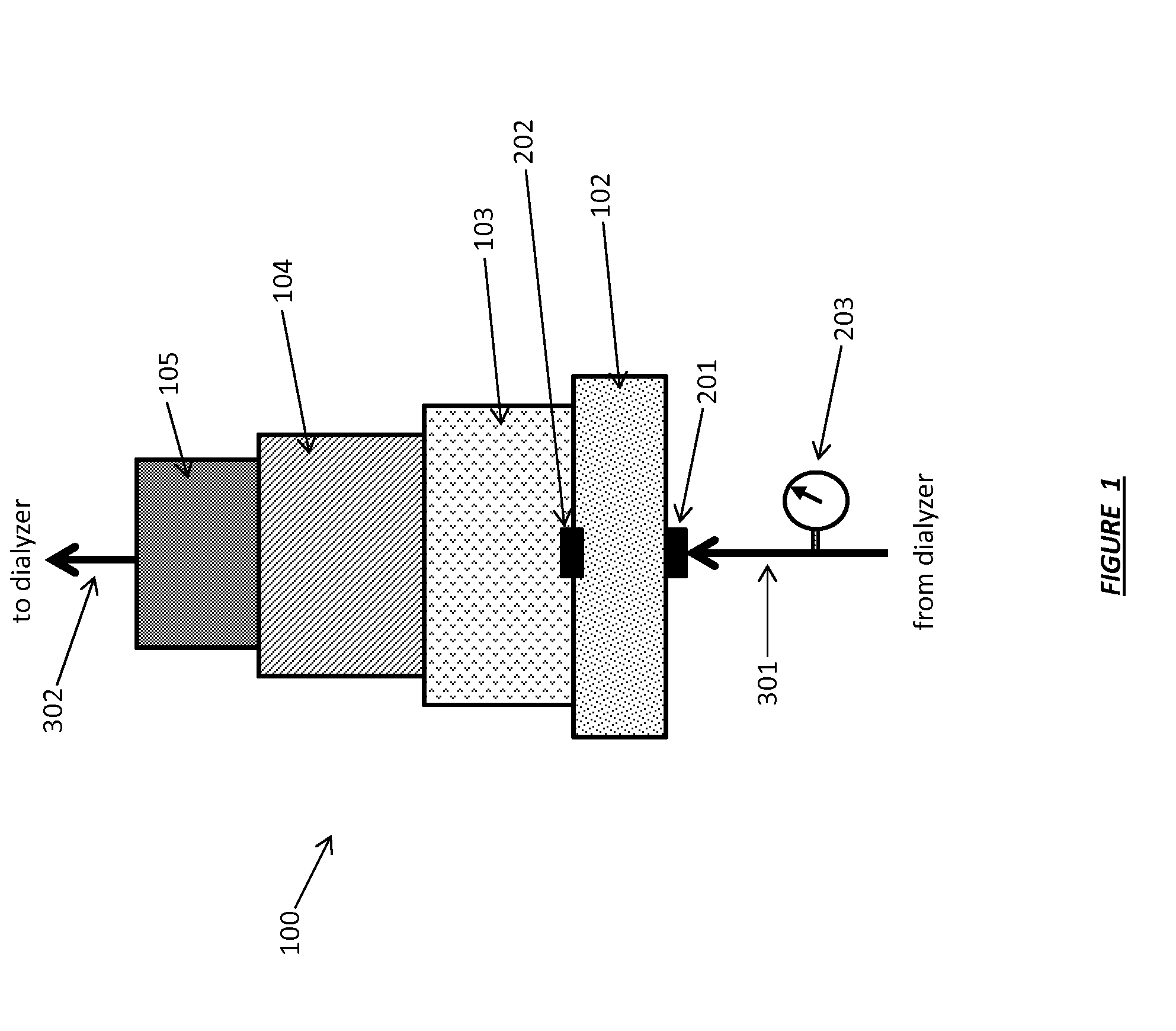
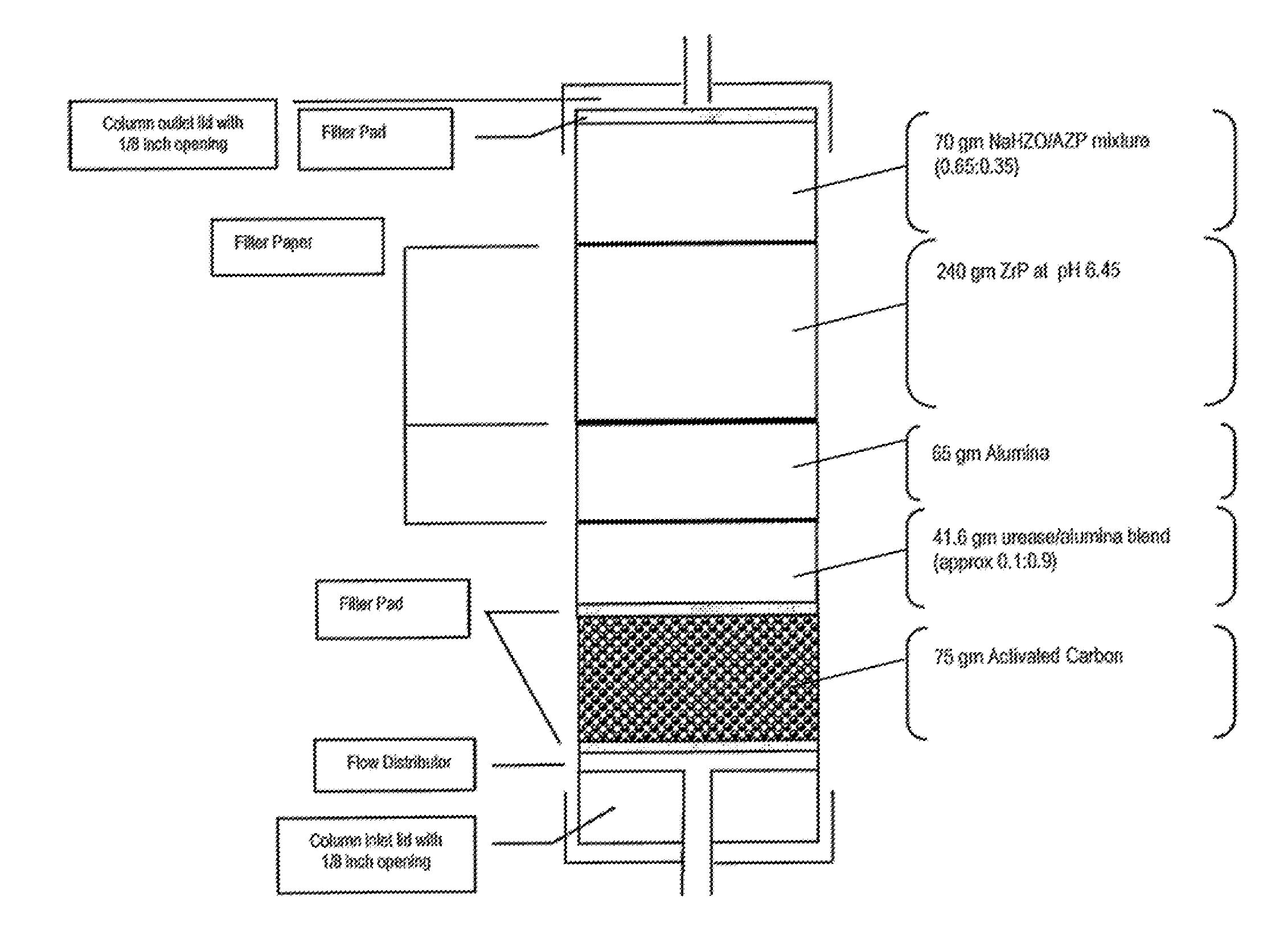
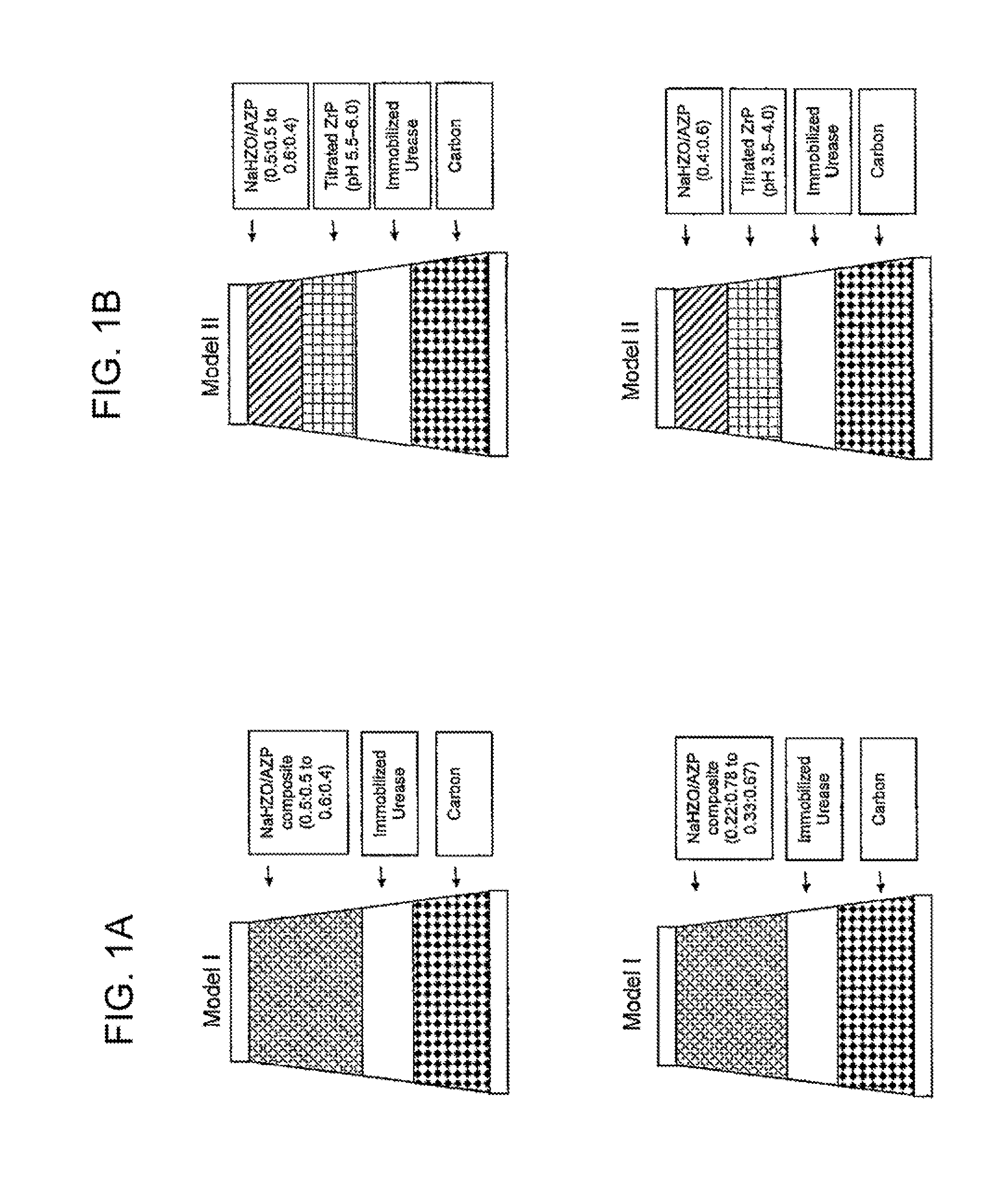
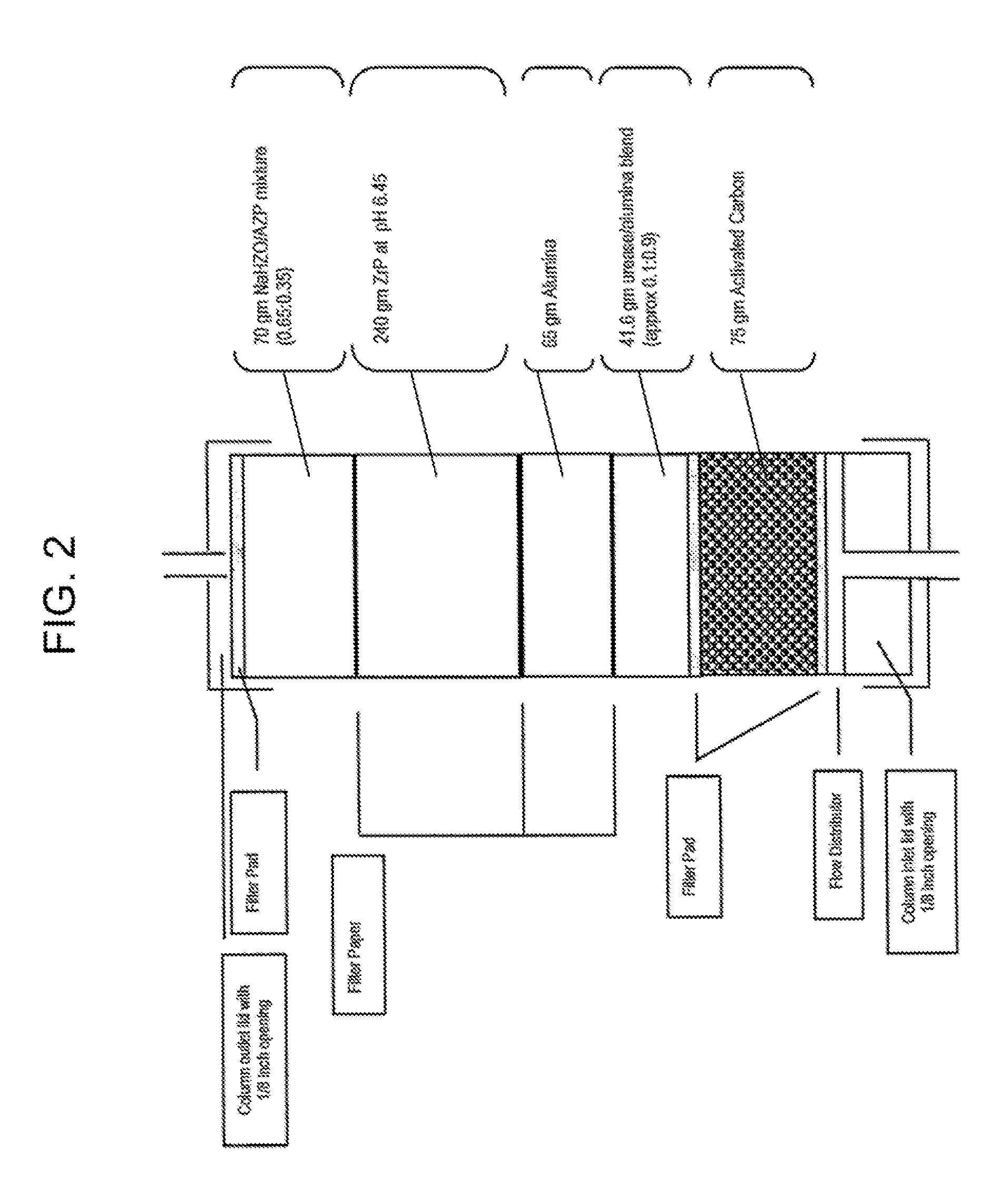
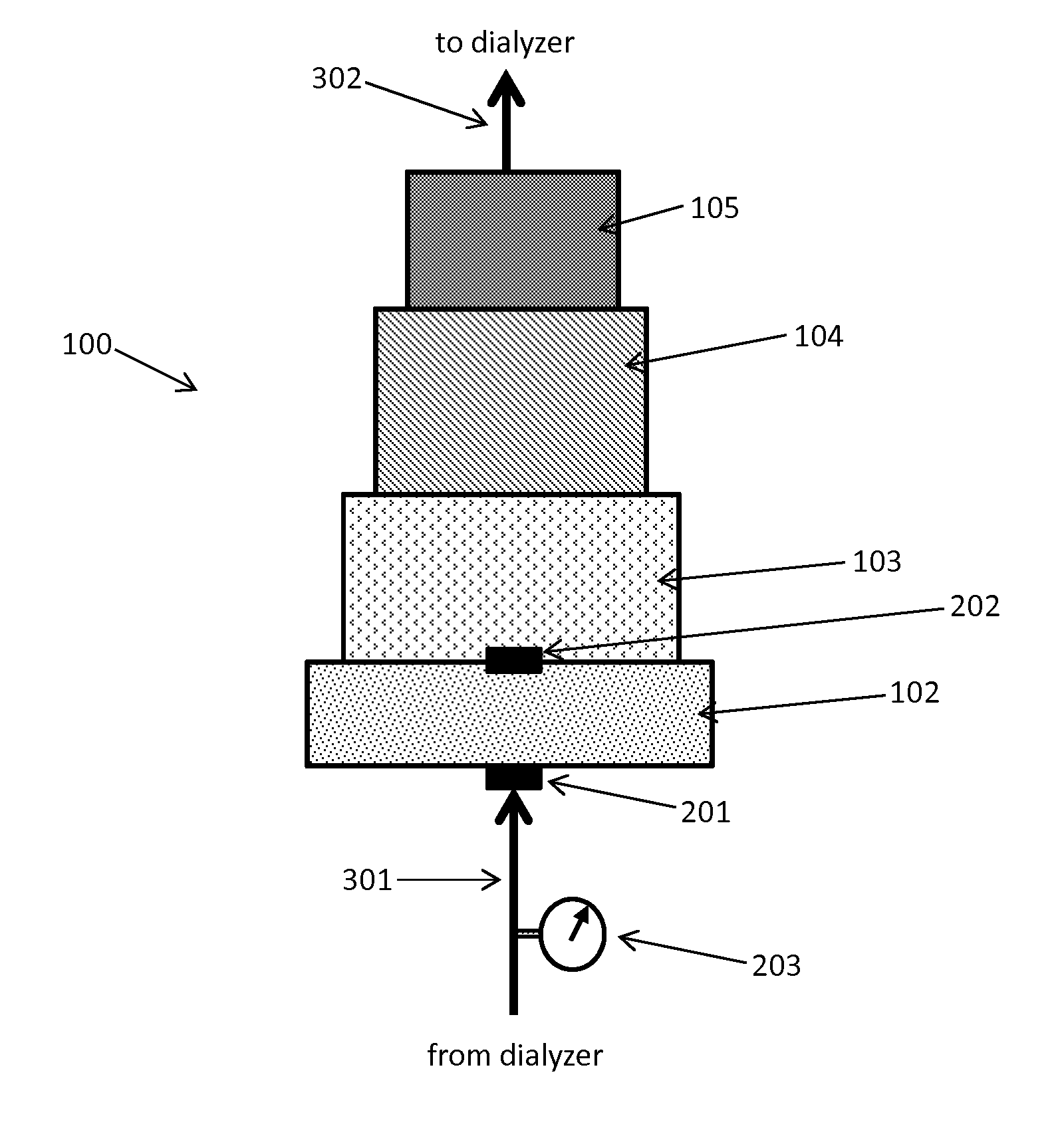
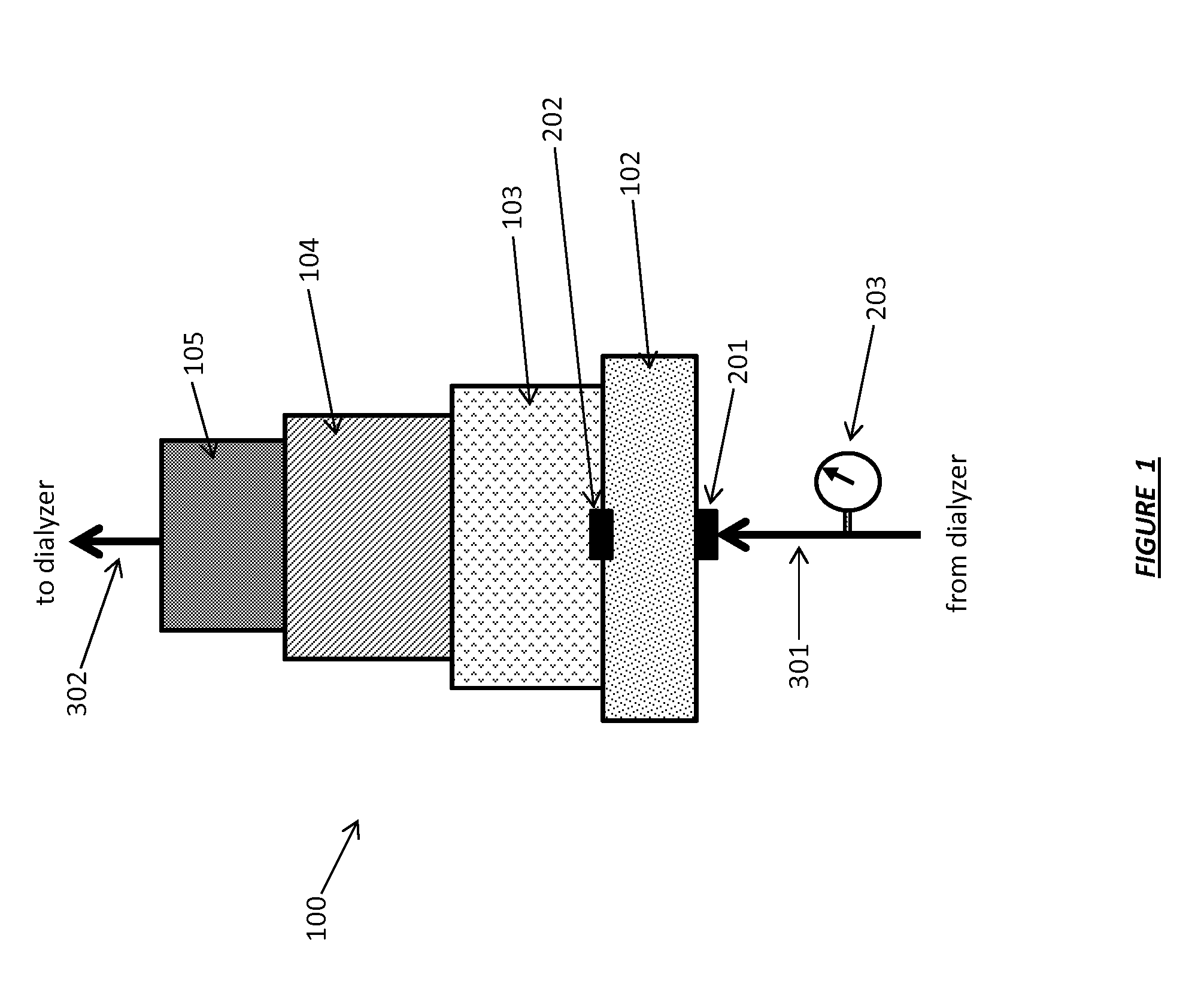
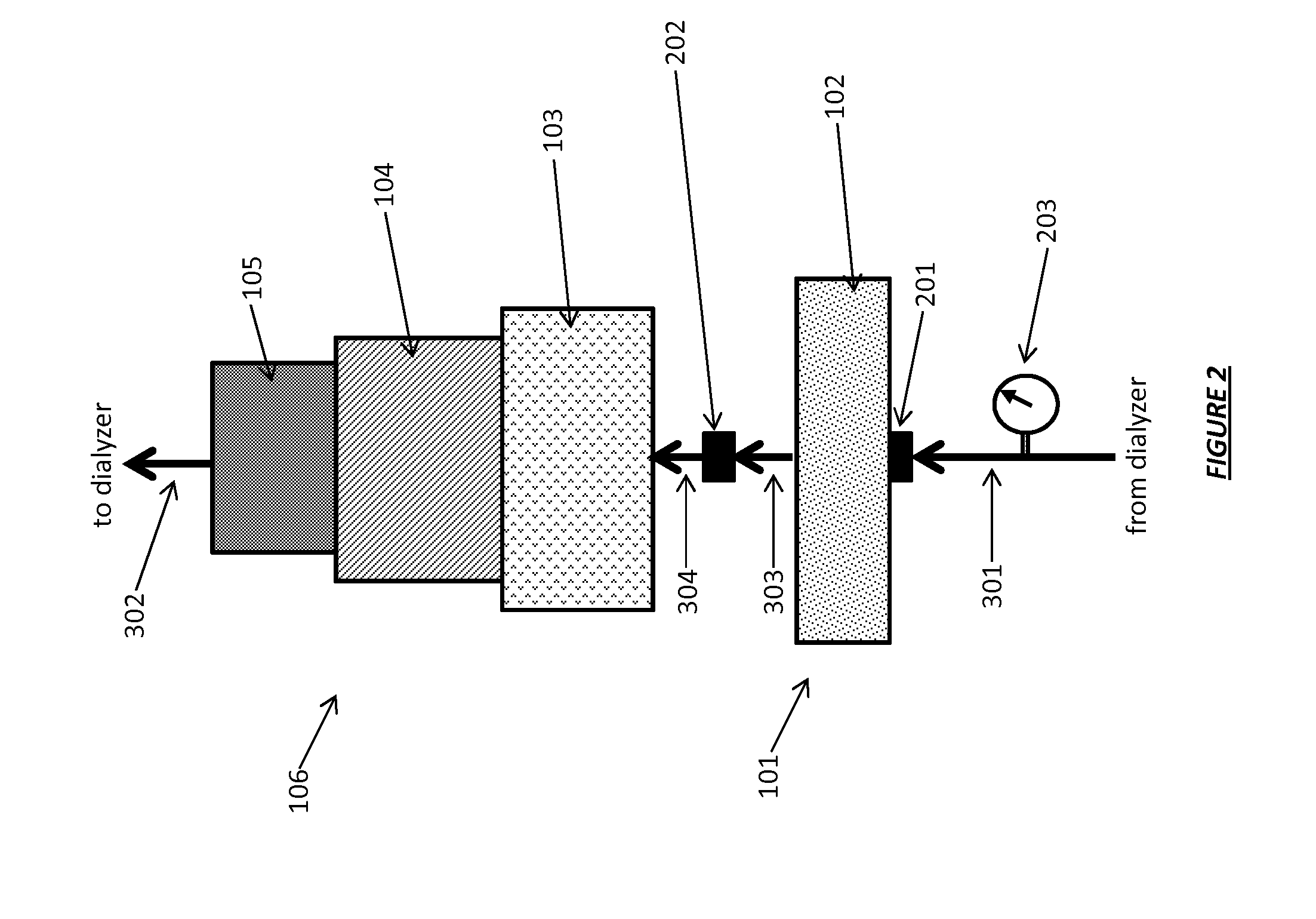
Acid Zirconium Phosphate and Alkaline Hydrous Zirconium Oxide Materials For Sorbent Dialysis
ActiveUS20100078387A1Avoid disadvantagesRestore balanceCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersIon exchangeDialysis fluid
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Positively charged membrane
InactiveUS6780327B1High rateHigh charge densityCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationPorous substrateFiltration
The present invention provides a positively charged microporous membrane having a protein binding capacity about 25 mg / ml or greater comprising a hydrophilic porous substrate and a crosslinked coating that provides a fixed positive charge to the membrane. The present invention further provides a positively charged microporous membrane comprising a porous substrate and a crosslinked coating comprising pendant cationic groups. The membranes of the present invention find use in a variety of applications including ion-exchange chromatography, macromolecular transfer, as well as detection, filtration and purification of biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, endotoxins, and the like.
Owner:PALL CORP
Adsorption/separation method and a medium for adsorption/separation
InactiveUS6428707B1Increase productionImprove productivityChromatographic cation exchangersCation exchanger materialsChemistrySeparation method
A method for adsorption of a substance from a liquid sample on a fluidized bead or stirred suspension, in which the beads used comprise a base matrix and exhibit a structure having affinity to the substance, characterized in that the structure is covalently bound to the base matrix via an extender. Populations of beads in which the beads contain a filler incorporated in a base matrix and an extender are also described.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIOPROCESS R&D
Process for chromatographic separation of peptides and nucleic acid, and new high affinity ion exchange matrix
InactiveUS6090288ACation exchanger materialsComponent separationChromatographic separationTransferrin
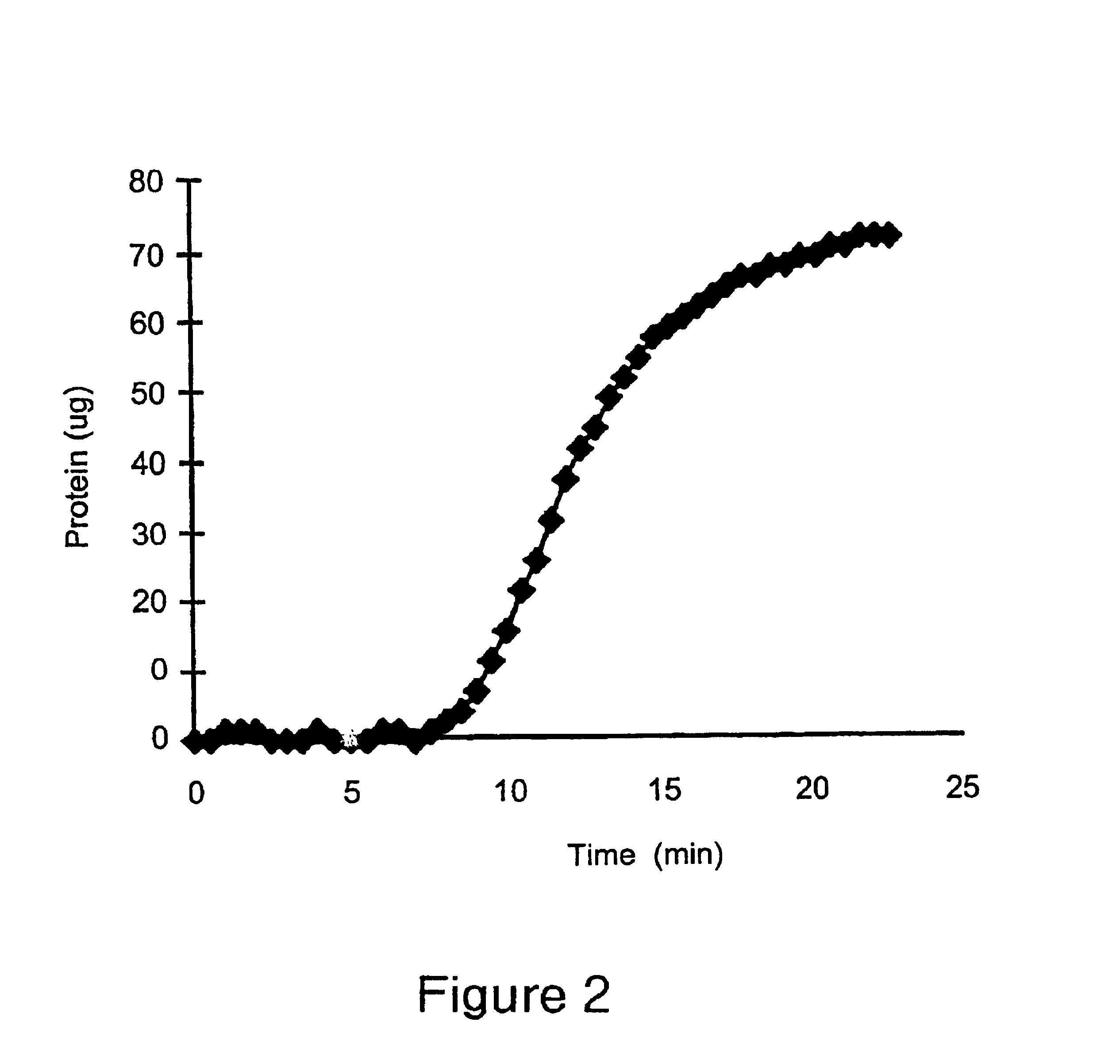
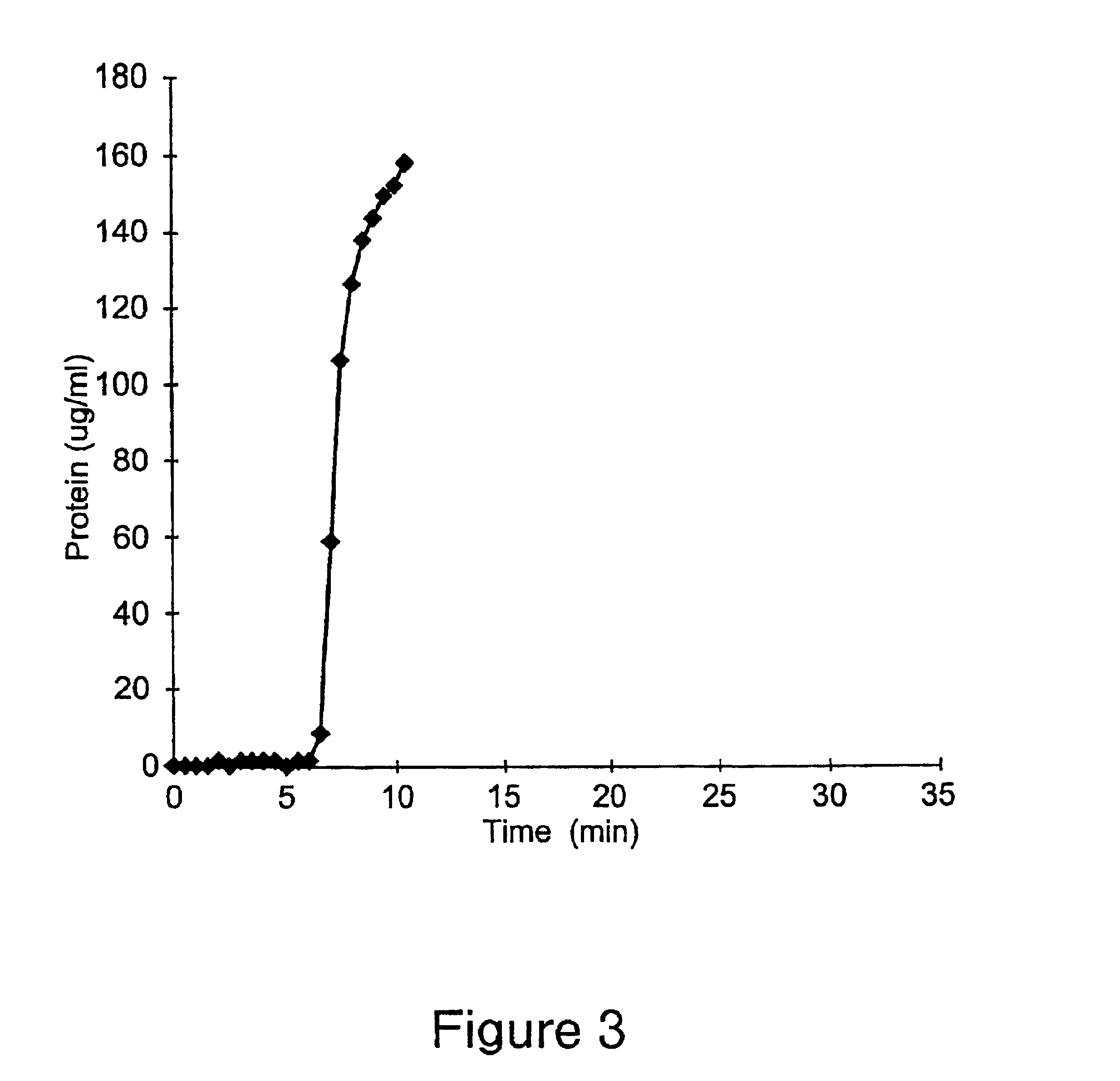
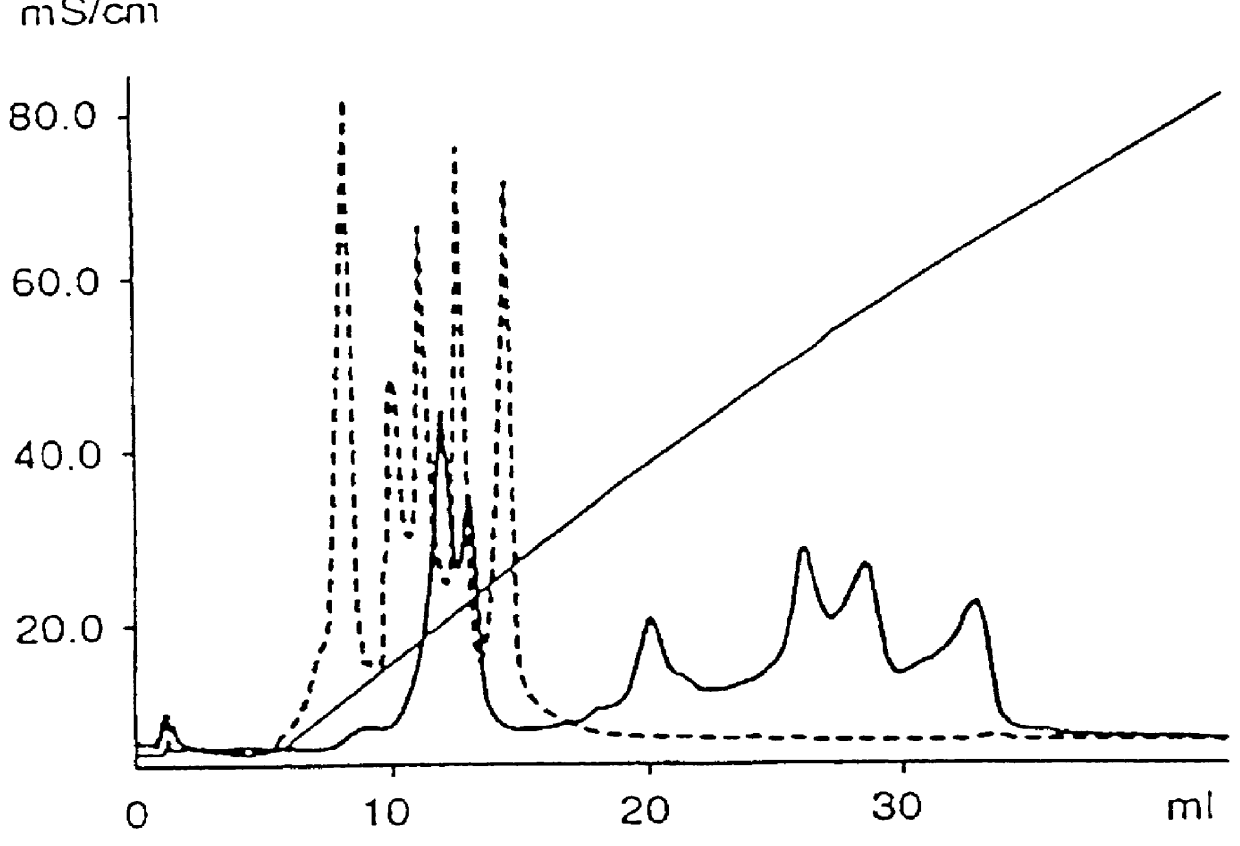
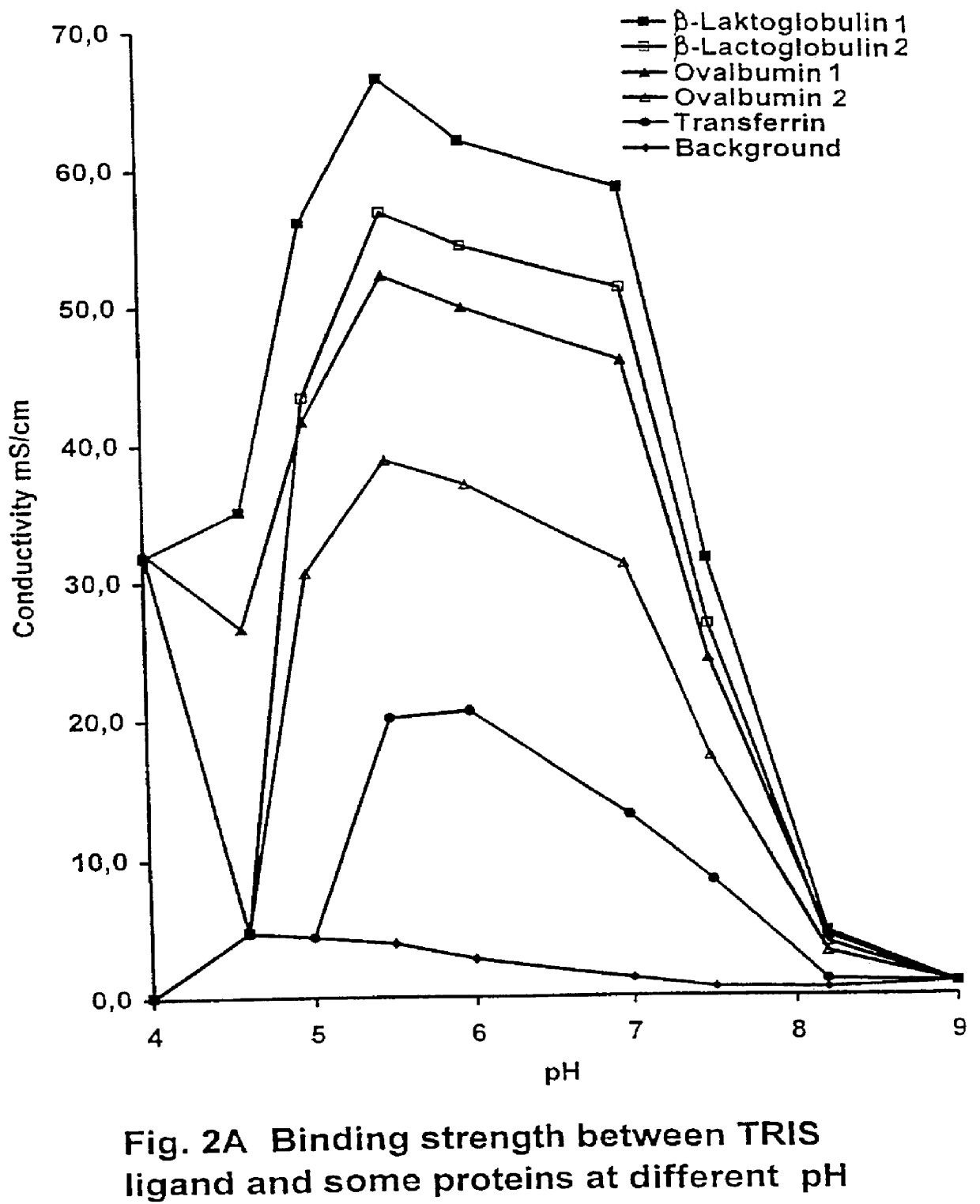
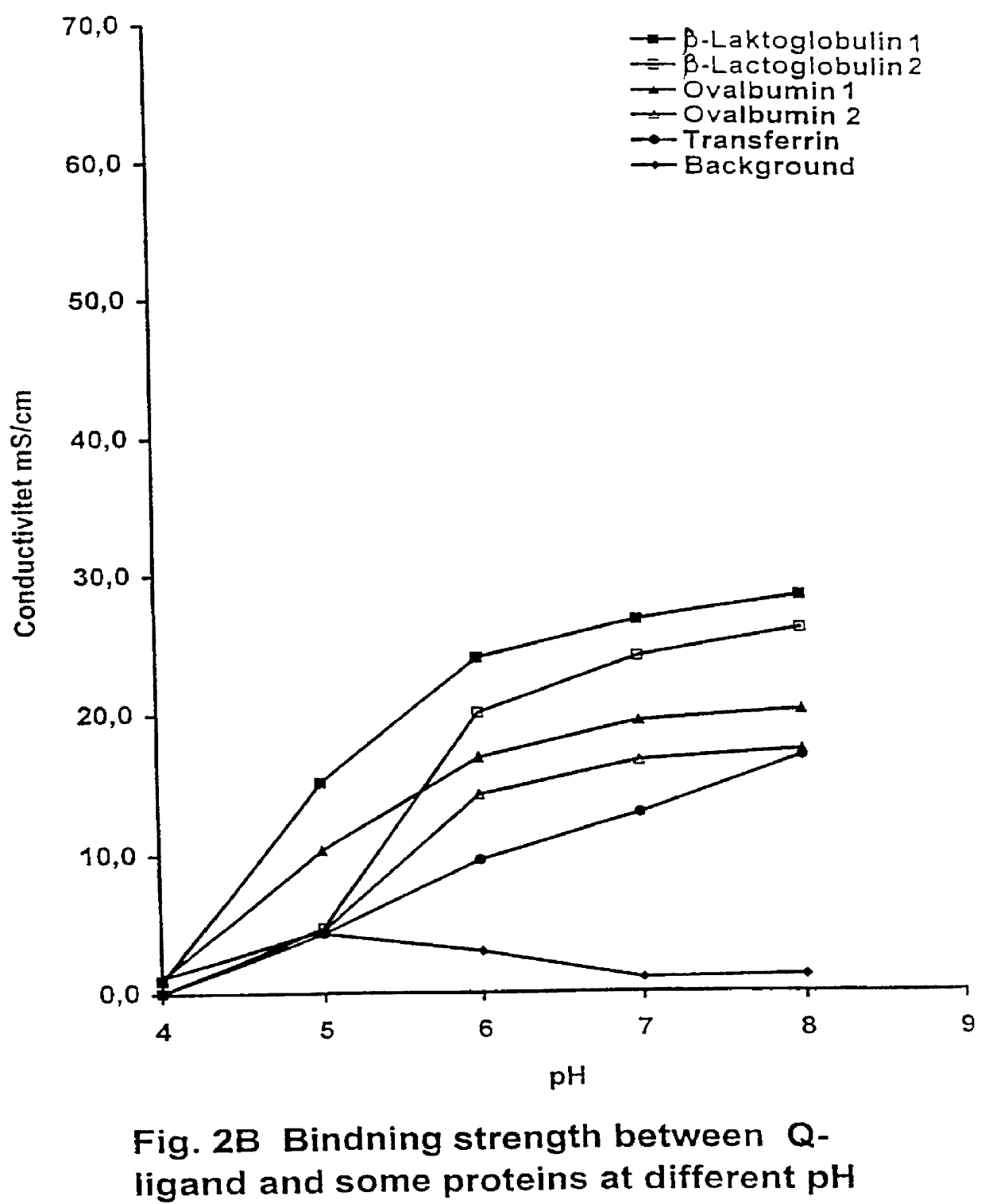
PCT No. PCT / SE97 / 00237 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 29, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 29, 1998 PCT Filed Feb. 14, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 29825 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 21, 1997Process for separating off a peptide or a nucleic acid by an anion exchanger (I) characterized in that a) the anion exchanger (I) exhibits ligands, which (i) contain a primary, secondary or tertiary amino group and (ii) are covalently bound to an organic polymer (matrix), b) there on a carbon atom at a distance of 2 or 3 atoms away from an amino nitrogen in the ligands is a hydroxyl group or a primary, secondary or tertiary amino group, and c) the maximum elution ionic strength in the pH range 2-14 for at least one of the proteins transferrin, ovalbumin 1, ovalbumin 2, beta -lactoglobulin 1 and beta -lactoglobulin 2 on the anion exchanger is higher than the elution ionic strength required for a quaternary comparative ion exchanger.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIOPROCESS R&D
Methods and devices for removal of organic molecules from biological mixtures using anion exchange
InactiveUS7192560B2Improve throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersIon exchangeBiochemistry
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method of antibody purification
ActiveUS7714112B2Few stepsLess timeOrganic anion exchangersChromatographic anion exchangersChromatography columnAntibody
The present invention relates to a method of separating antibodies from other compound(s) in a liquid sample, wherein a mobile phase comprising said sample is contacted with a multi-modal separation matrix to adsorb undesired compounds while the antibodies remain free in the liquid, wherein the multi-modal separation matrix comprises first groups, which are capable of interacting with negatively charged sites of the target compounds, and second groups, which are capable of at least one interaction other than charge-charge interaction with said target compounds. The invention also relates to a chromatography column packed with the above-described multi-modal separation matrix and a filter having such multi-modal groups adsorbed to its surface.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
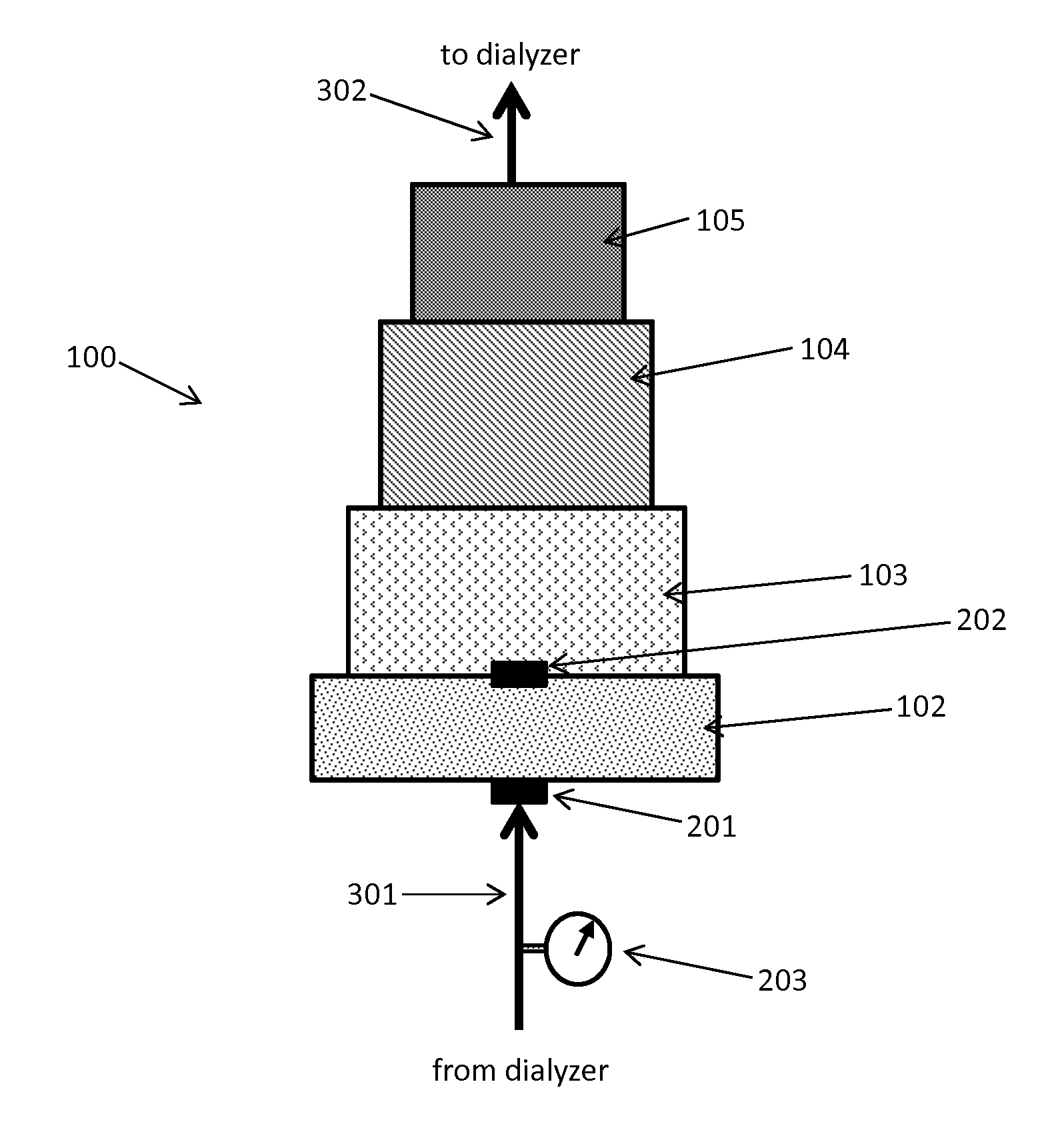
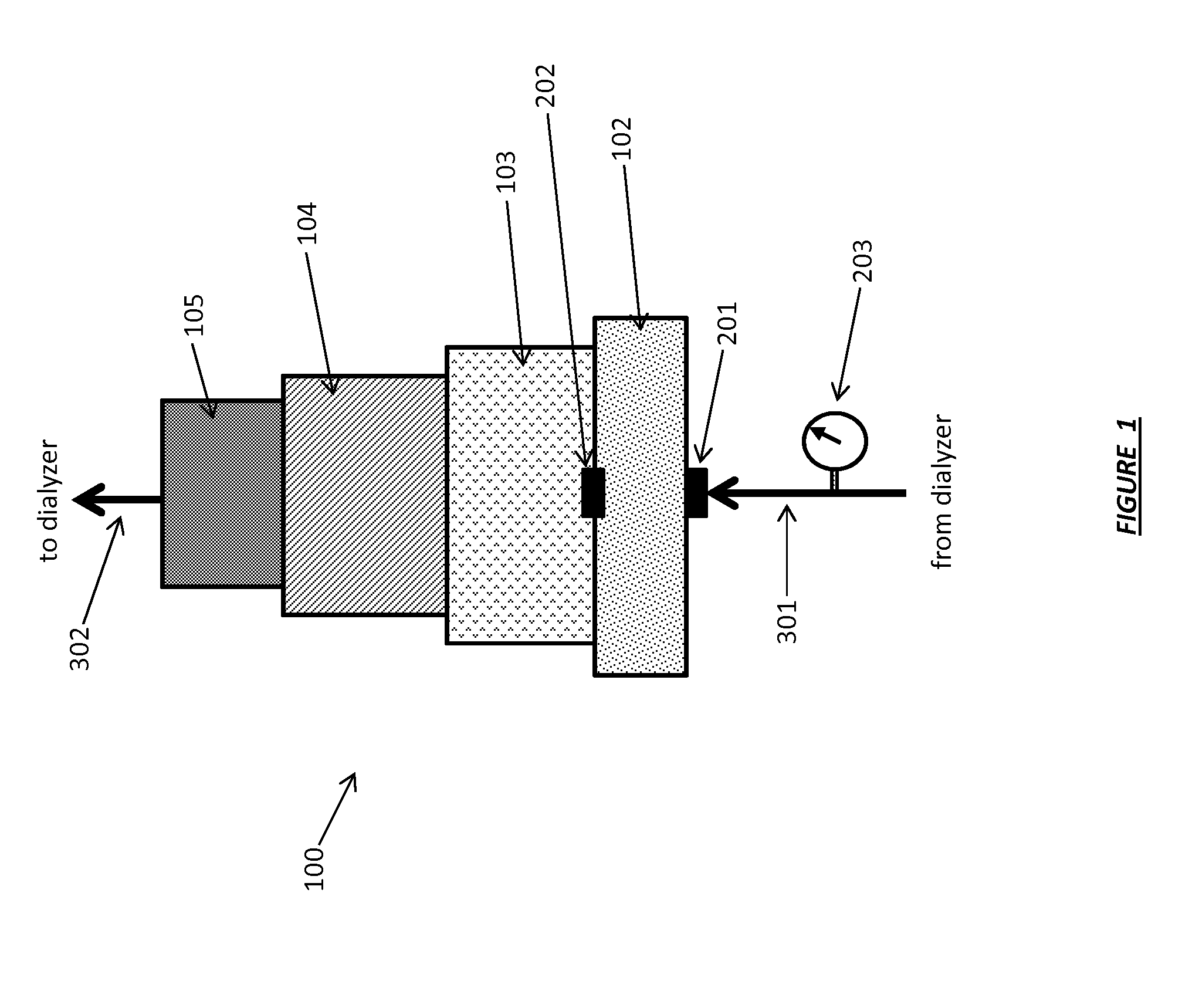
Sorbent cartridge to measure solute concentrations
ActiveUS20140190876A1Detection problemCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersEnvironmental chemistrySorbent
A sorbent based monitoring system for measuring the solute concentration of at least one component of a fluid. The system has a sorbent regeneration system for regeneration of the fluid and has a sorbent cartridge that has at least one material layer. The fluid is conveyed through the sorbent cartridge and contacts at least one sensor after having contacted at least one material layer.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
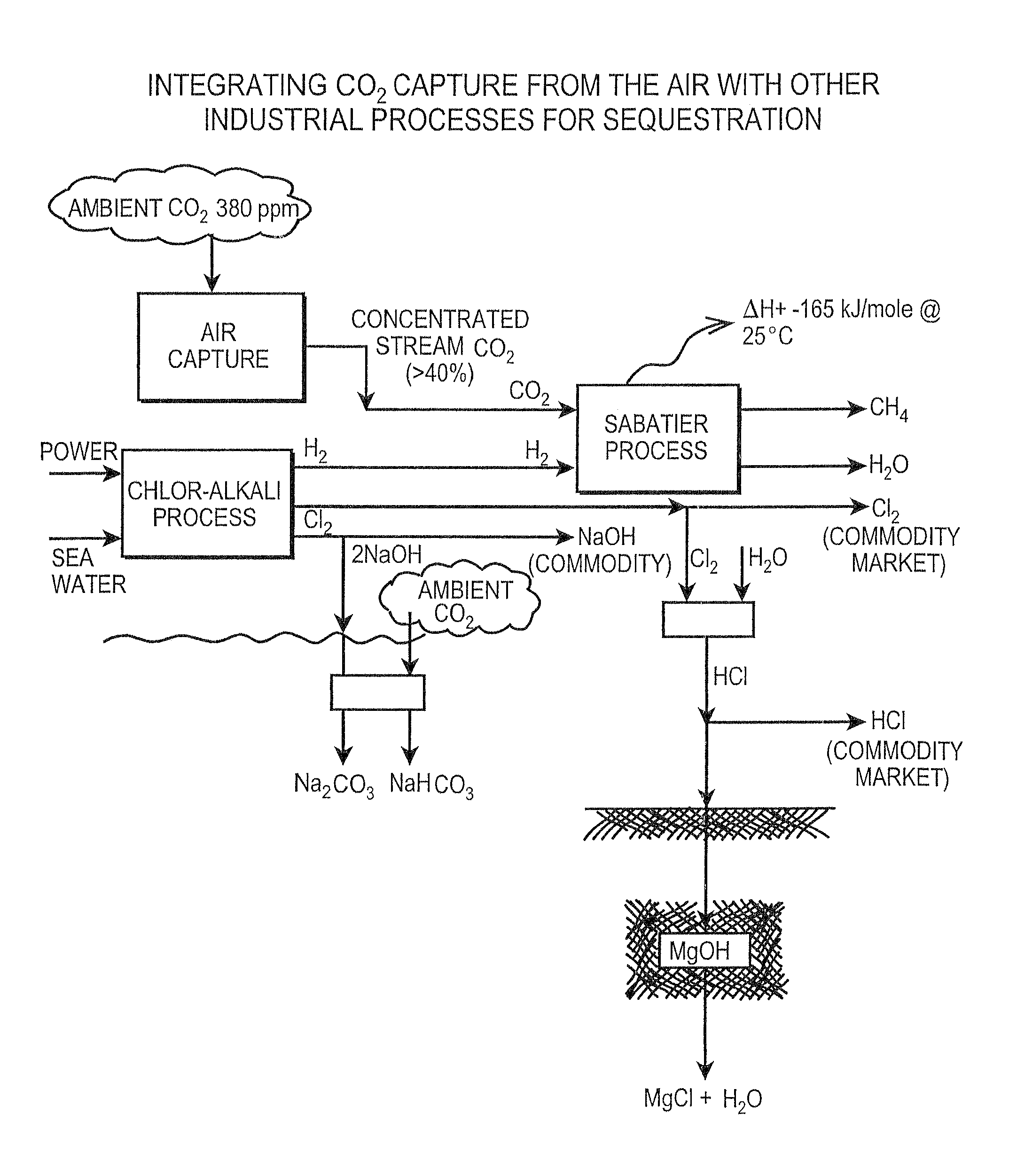
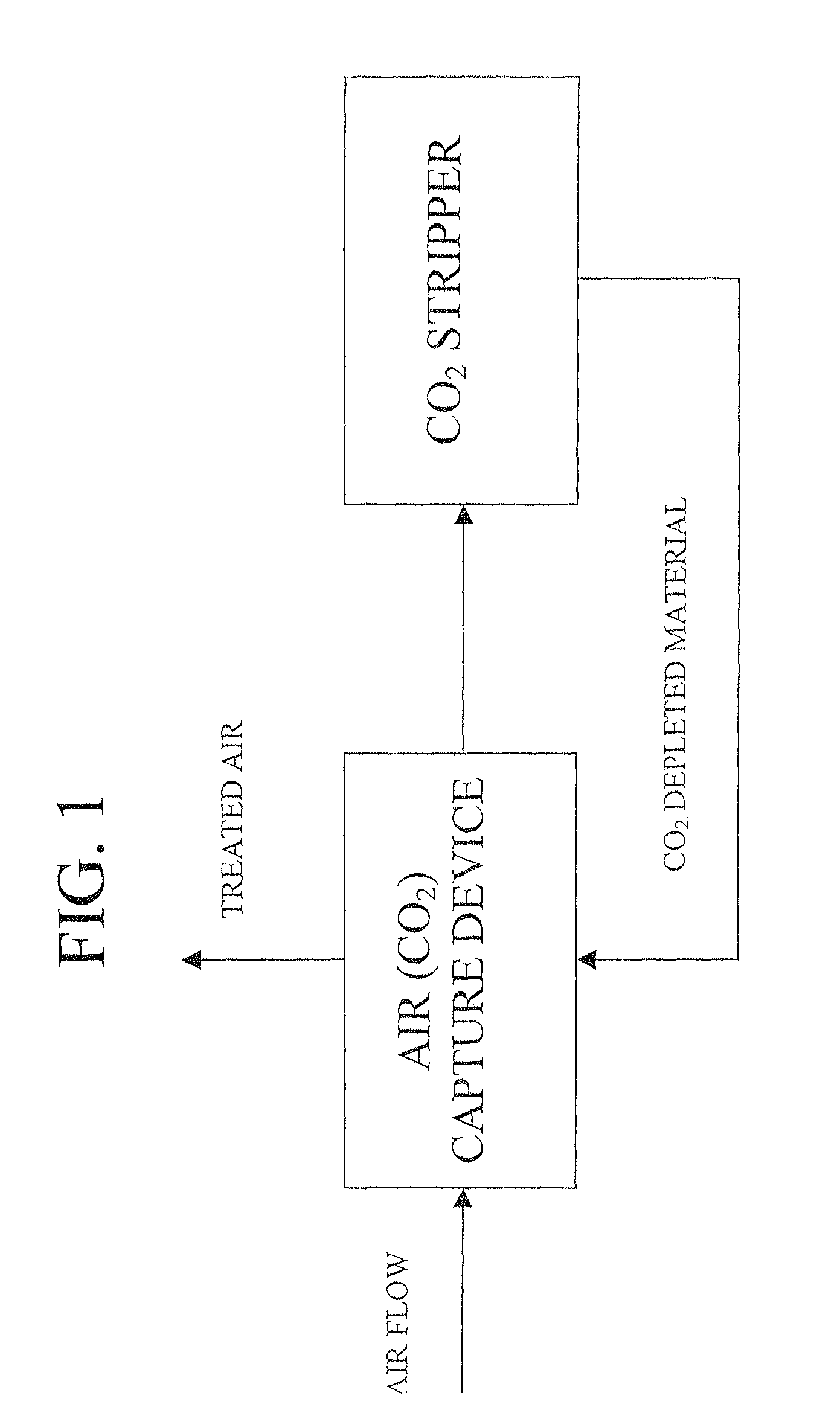
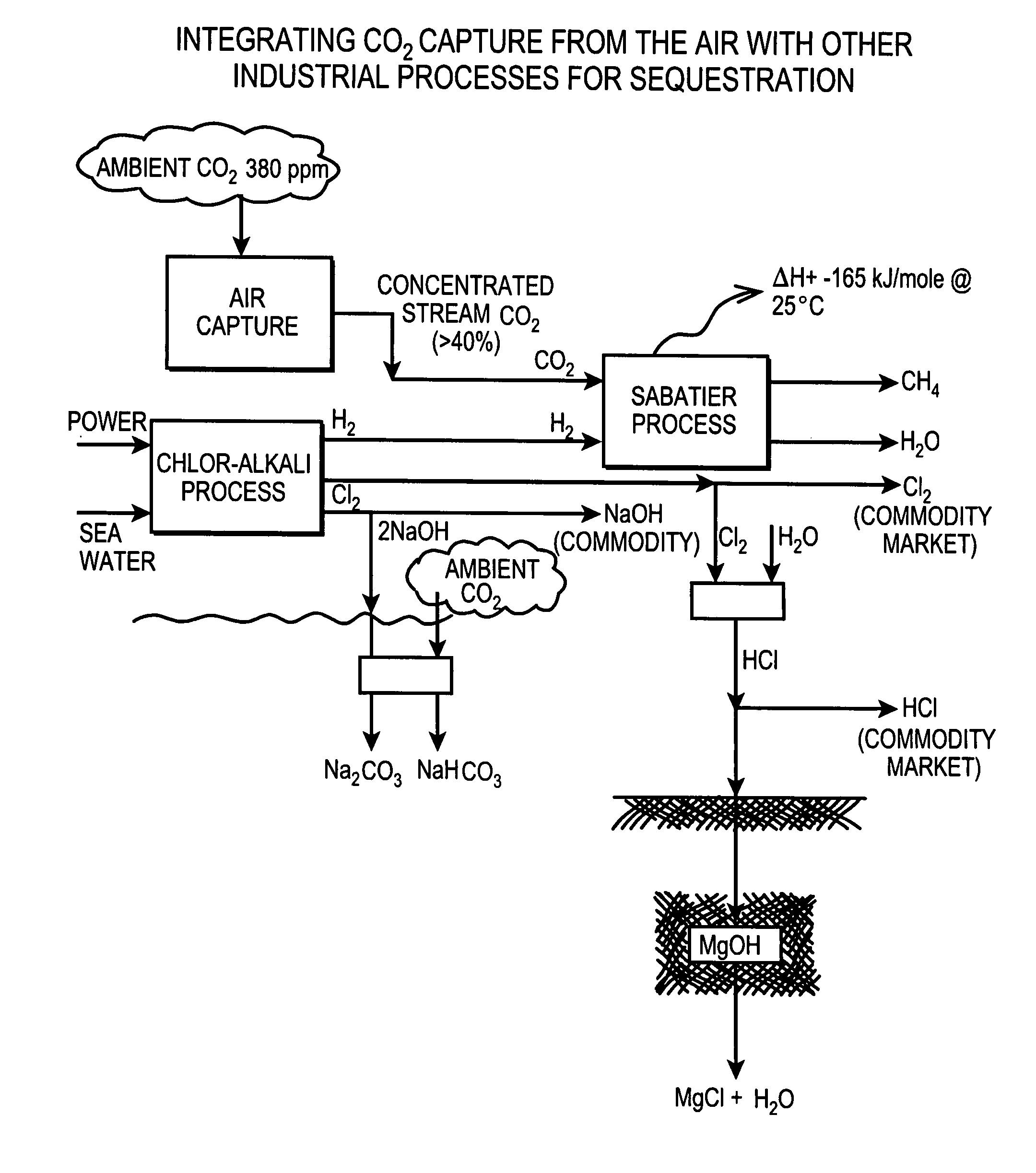
Air collector with functionalized ion exchange membrane for capturing ambient CO2
ActiveUS7993432B2Lower energy requirementsRepeatable air capture performanceMechanical apparatusElectrolysis componentsIon-exchange membranesAtmosphere
An apparatus for capture of CO2 from the atmosphere comprising an anion exchange material formed in a matrix exposed to a flow of the air.
Owner:CARBON SINK
Method of separating anionic fluorochemical surfactant
InactiveUS20040010156A1Short elution timeHigh recovery rateFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteIon-exchanger regenerationOrganic solventIon-exchange resin
Separation of an anionic fluorochemical surfactant from an aqueous solution containing the anionic fluorochemical surfactant is carried out by i) contacting the aqueous solution with a basic anion-exchange resin so that the anionic fluorochemical surfactant is adsorbed on the resin, and ii) eluting the anionic fluorochemical surfactant adsorbed on the resin with an eluent which is an alkaline solution containing water and an organic solvent.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Method for anion-exchange adsorption and anion-exchangers
InactiveUS6702943B1Reduced ligand contentSolve insufficient capacityIon-exchanger regenerationOrganic anion exchangersHydrogenDesorption
A method for the removal of a substance carrying a negative charge and being present in an aqueous liquid (I). The method comprises the steps of: (i) contacting the liquid with a matrix carrying a plurality of ligands comprising a positively charged structure and a hydrophobic structure, and (ii) desorbing the substance. The characterizing feature is that (I) each of said ligands together with a spacer has the formula: -SP-[Ar-R1-N<+>(R2R3R4)] where (A) [Ar-R1-N<+>(R2R3R4)] represents a ligand a) Ar is an aromatic ring, b) R1 is [(L)nR'1]m where n and m are integers selected amongst zero or 1; L is amino nitrogen, ether oxygen or thioether sulphur; R'1 is a linker selected among 1) hydrocarbon groups; 2) -C(=NH)-; c) R2-4 are selected among hydrogen and alkyls; (B) SP is a spacer providing a carbon or a heteroatom directly attached to Ar-R1-N<+>(R2R3R4); (C)-represents that SP replaces a hydrogen in (Ar-R1-N<+>(R2R3R4); (D)-represents binding to the matrix; and (II) desorption. There is also described (a) anion-exchangers having high breakthrough capacities, (b) a screening method and (c) a desalting protocol.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Iodinated matrices for disinfecting biological fluids
InactiveUS6096216ALarge capacityEfficient workAntibacterial agentsBiocideIon exchangeDrug biological activity
The present invention provides media for inactivating pathogens found within protein-containing biological fluids. The media of the present invention preserve the structural integrity and biological activity of labile proteins while simultaneously exhibiting potent disinfectant activity. The media of the present invention comprise iodinated chromatographic media, particularly ion exchange media. The invention further provides methods for disinfecting biological fluids.
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
Air collector with functionalized ion exchange membrane for capturing ambient co2
ActiveUS20070217982A1Lower energy requirementsRepeatable air capture performanceMechanical apparatusElectrolysis componentsIon-exchange membranesAtmosphere
An apparatus for capture of CO2 from the atmosphere comprising an anion exchange material formed in a matrix exposed to a flow of the air.
Owner:CARBON SINK
Long lasting coatings for modifying hard surfaces and processes for applying the same
InactiveUS6955834B2Improve smoothnessImprovement in wetting and sheetingInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic anion exchangersMetallurgyDefect repair
Materials for coating, coating compositions, methods and articles of manufacture comprising a nanoparticle system or employing the same to impart surface modifying benefits for all types of inanimate hard surfaces are disclosed. In some embodiments, dispersement of nanoparticles in a suitable carrier medium allows for the creation of coating compositions, methods and articles of manufacture that create multi-use benefits to modified hard surfaces. These surface modifications can produce long lasting or semi-permanent multi-use benefits that include at least one of the following improved surface properties: wetting and sheeting, quick drying, uniform drying, soil removal, self-cleaning, anti-spotting, anti-soil deposition, cleaner appearance, enhanced gloss, enhanced color, minor surface defect repair, smoothness, anti-hazing, modification of surface friction, release of actives and transparency, relative to hard surfaces unmodified with such nanoparticle systems. Actively curing the coating composition on the hard surfaces, including, but not limited to by radiative heating the air surrounding the hard surface with the coating thereon can be used to increase the durability of the hard surface coating.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
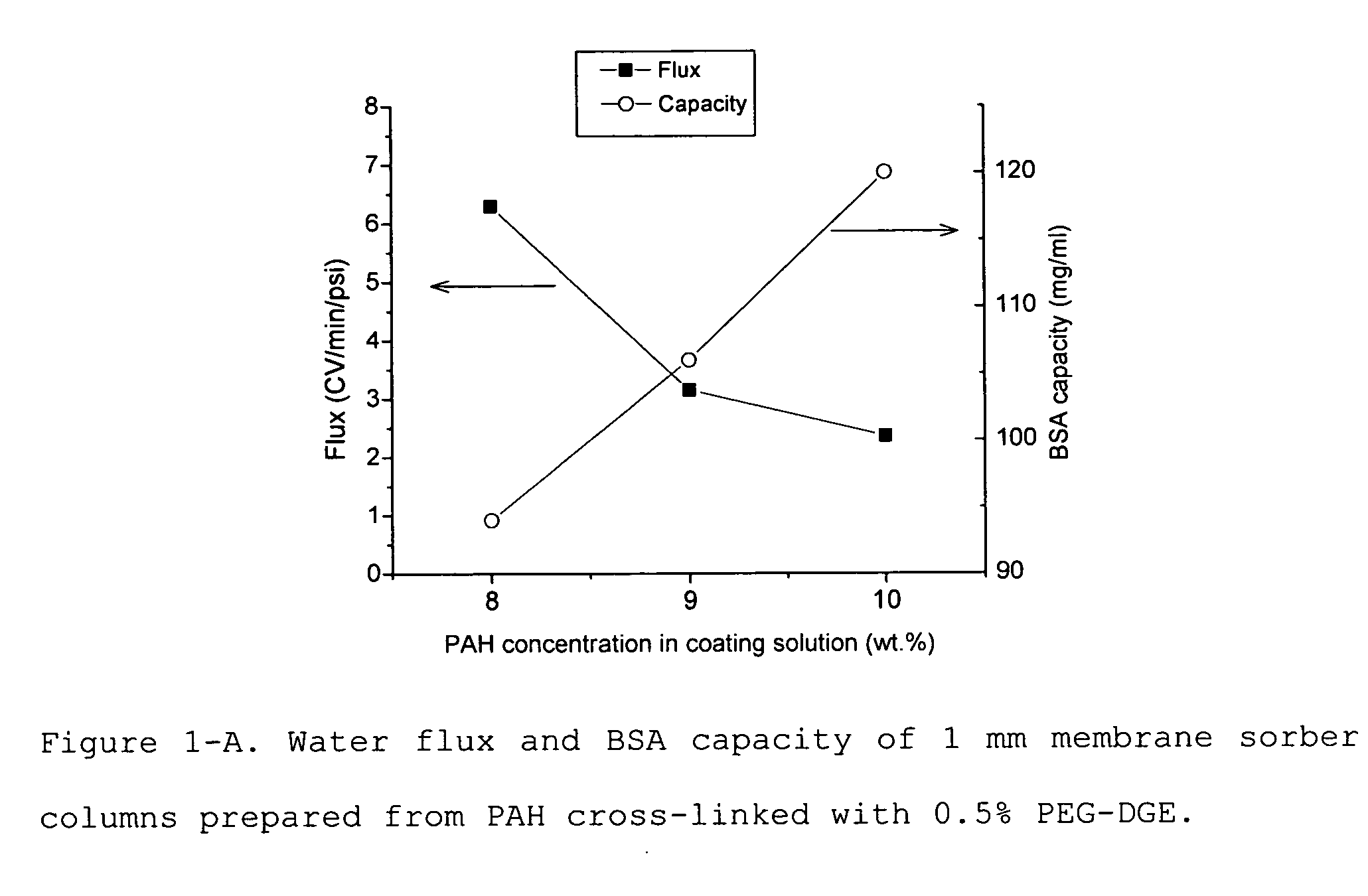
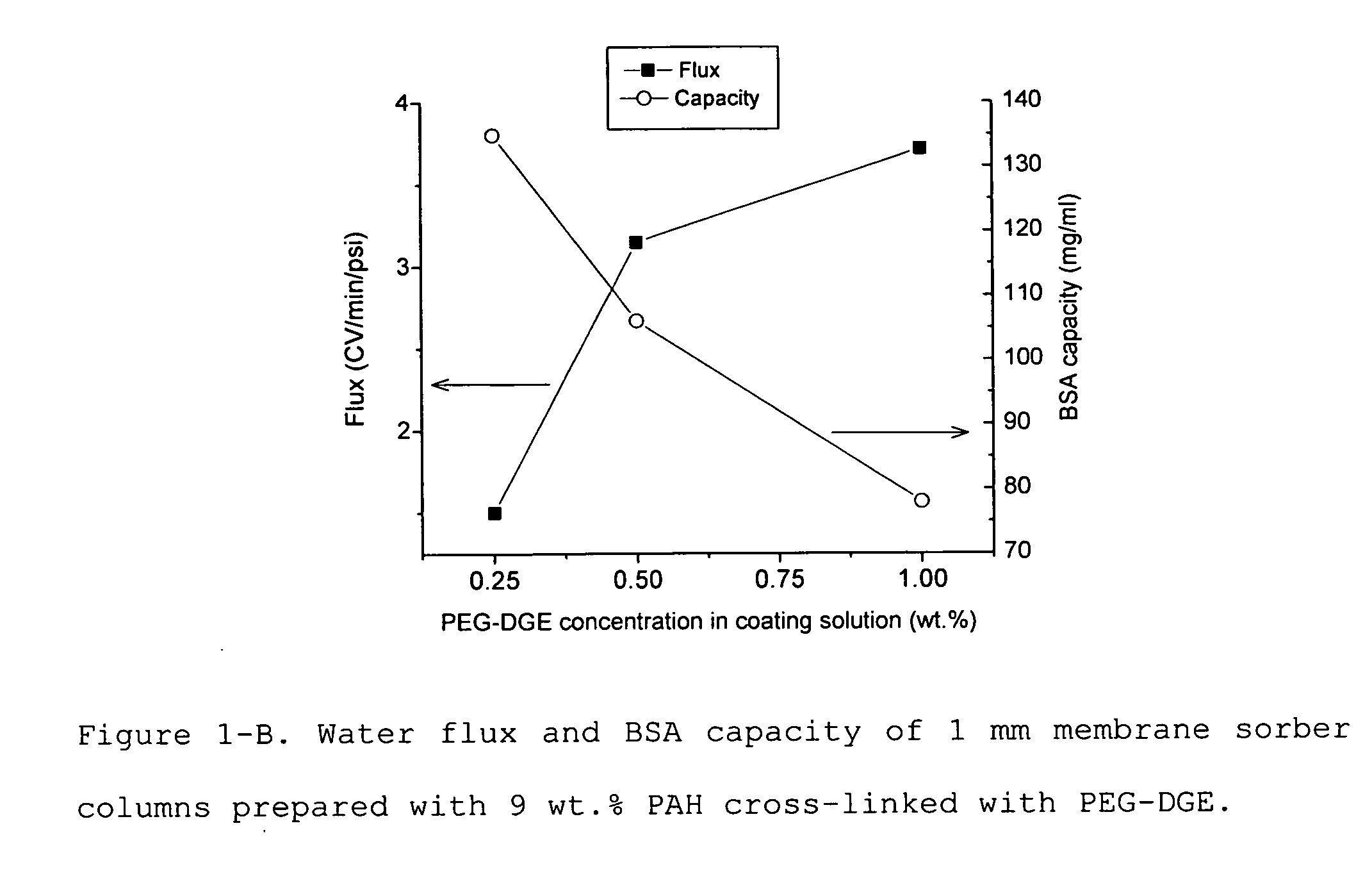
Media for membrane ion exchange chromatography based on polymeric primary amines, sorption device containing that media, and chromatography scheme and purification method using the same
ActiveUS20090050566A1Improve bindingGood removal effectCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationPurification methodsSorbent
Media and devices, such as anion exchangers including such media, wherein the media is a membrane having a surface coated with a polymer such as a polyallylamine. The resulting membrane offers stronger binding of protein impurities and superior removal of host cell proteins from biological samples than conventional ligands based on quaternary ammonium salts, including trimethylammonium ligands. Also described is a chromatography scheme and method for purifying monoclonal antibodies, wherein the anion exchange sorber is placed downstream of an affinity column (such as Protein A or Protein G affinity column) and optionally one or more polishing devices such as cationic exchange columns. Little or no dilution of the cation exchanger pool (or affinity column exchange pool where no cation exchanger is used) is necessary to lower the conductivity of the sample. The sorber functions well to strongly bind host cell proteins and other impurities in biological samples even at high conductivities and pH.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
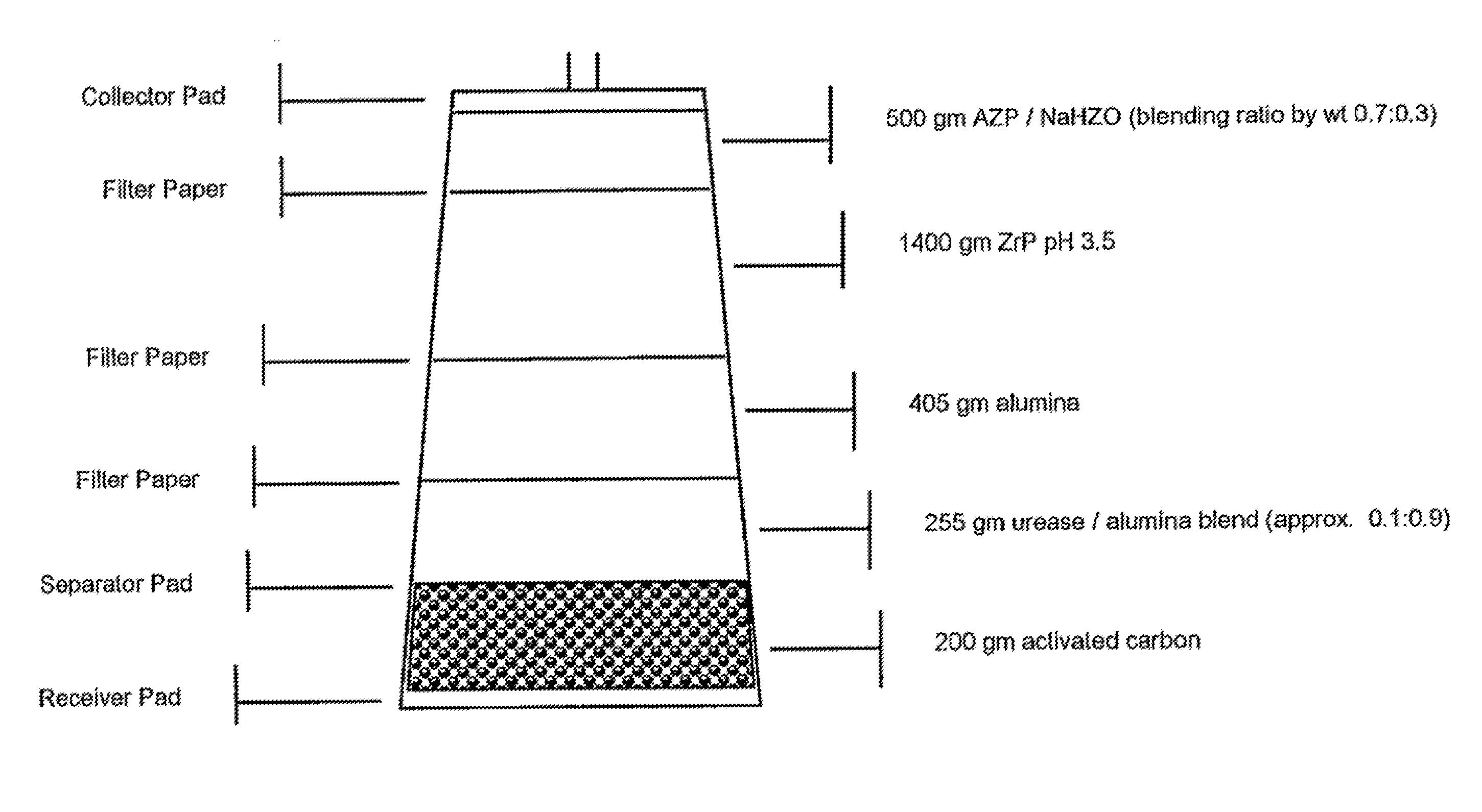
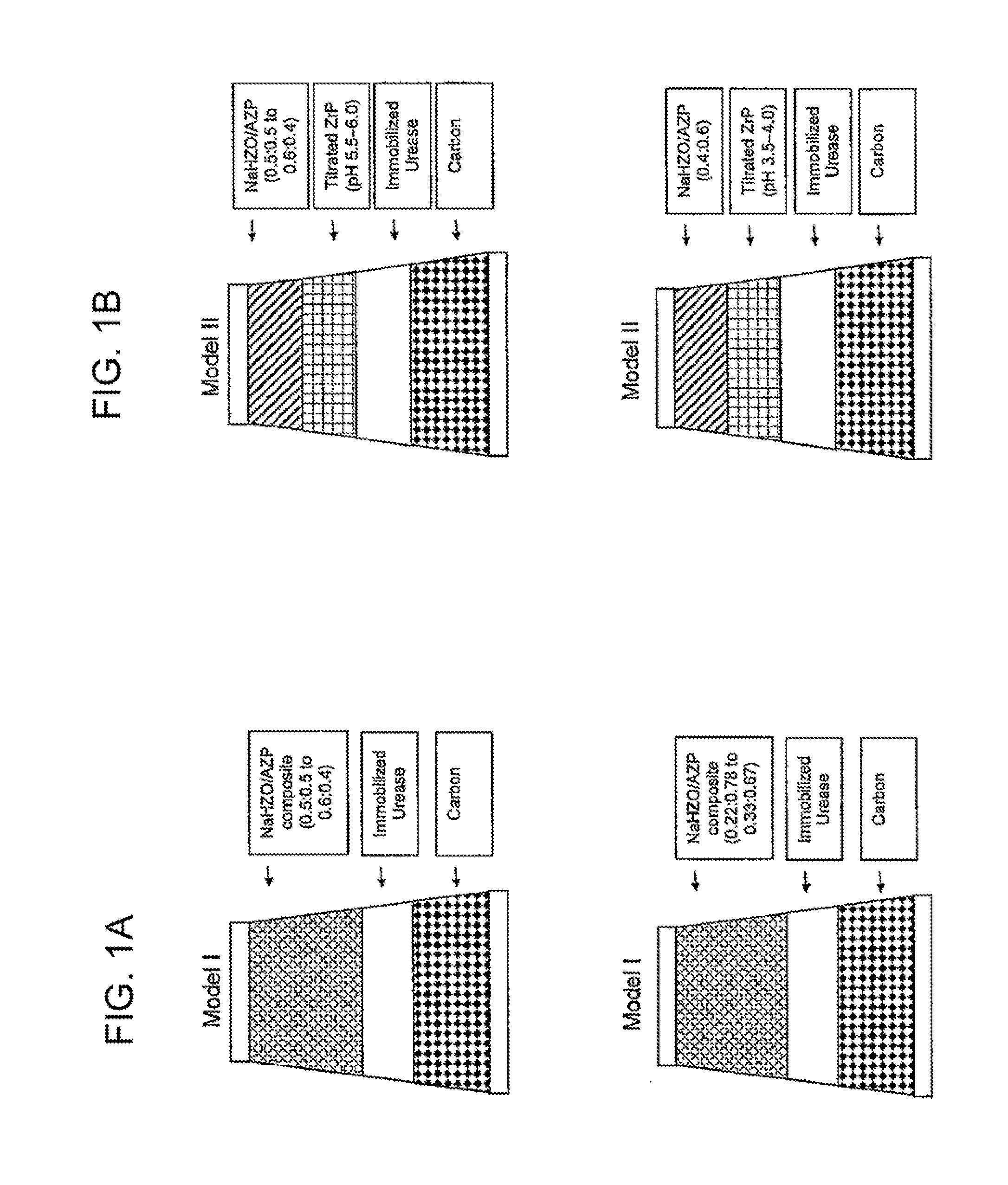
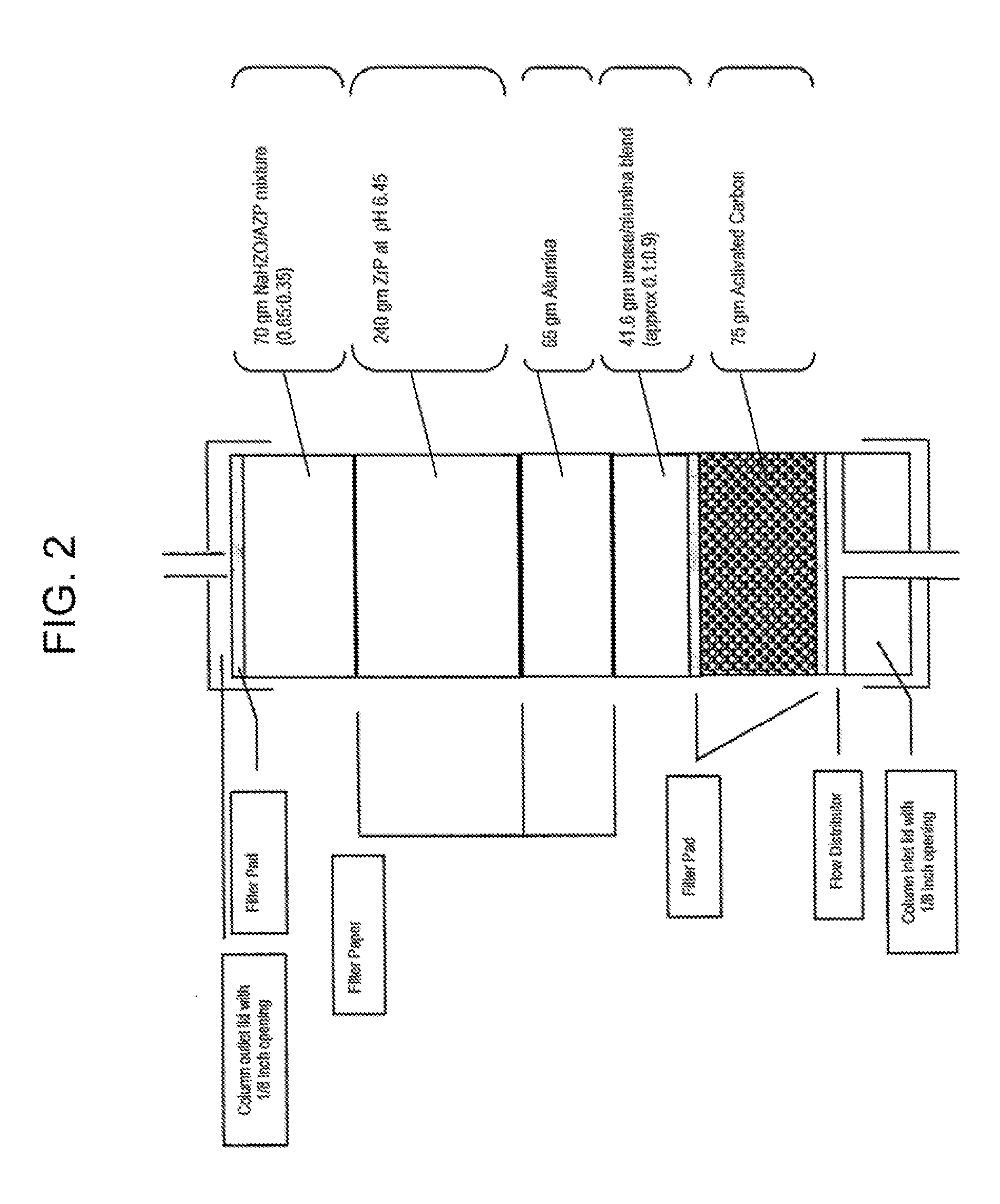
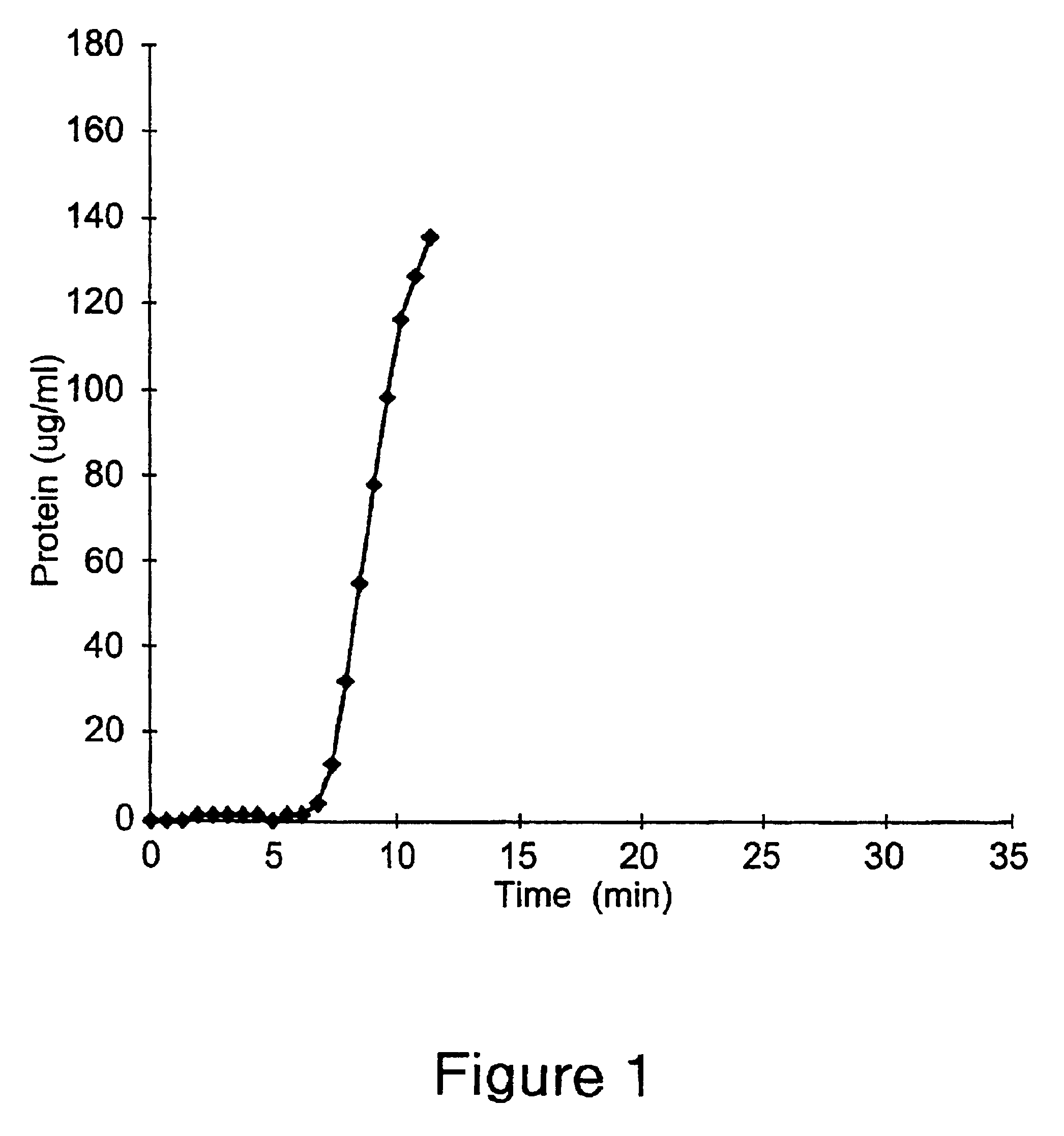
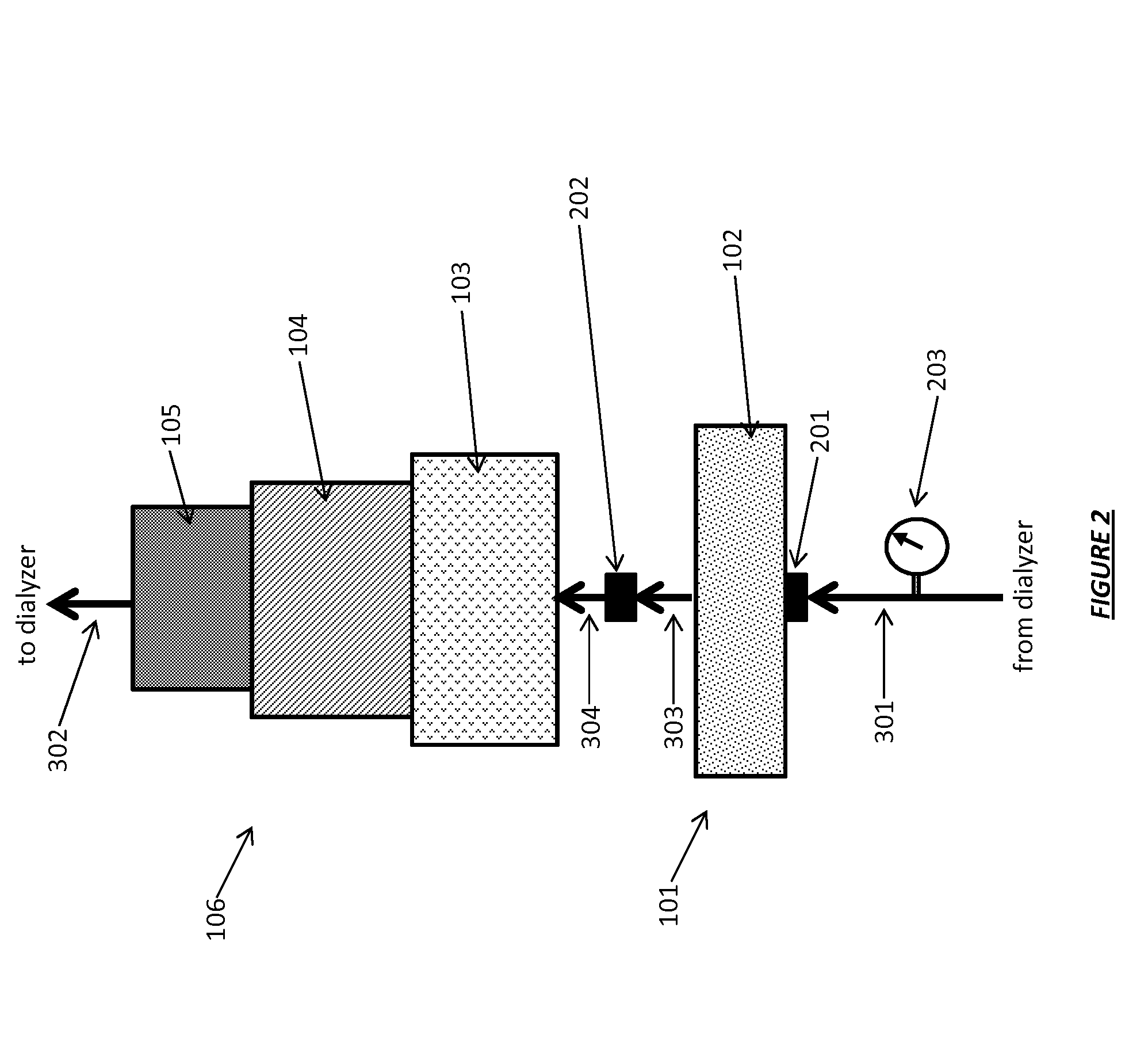
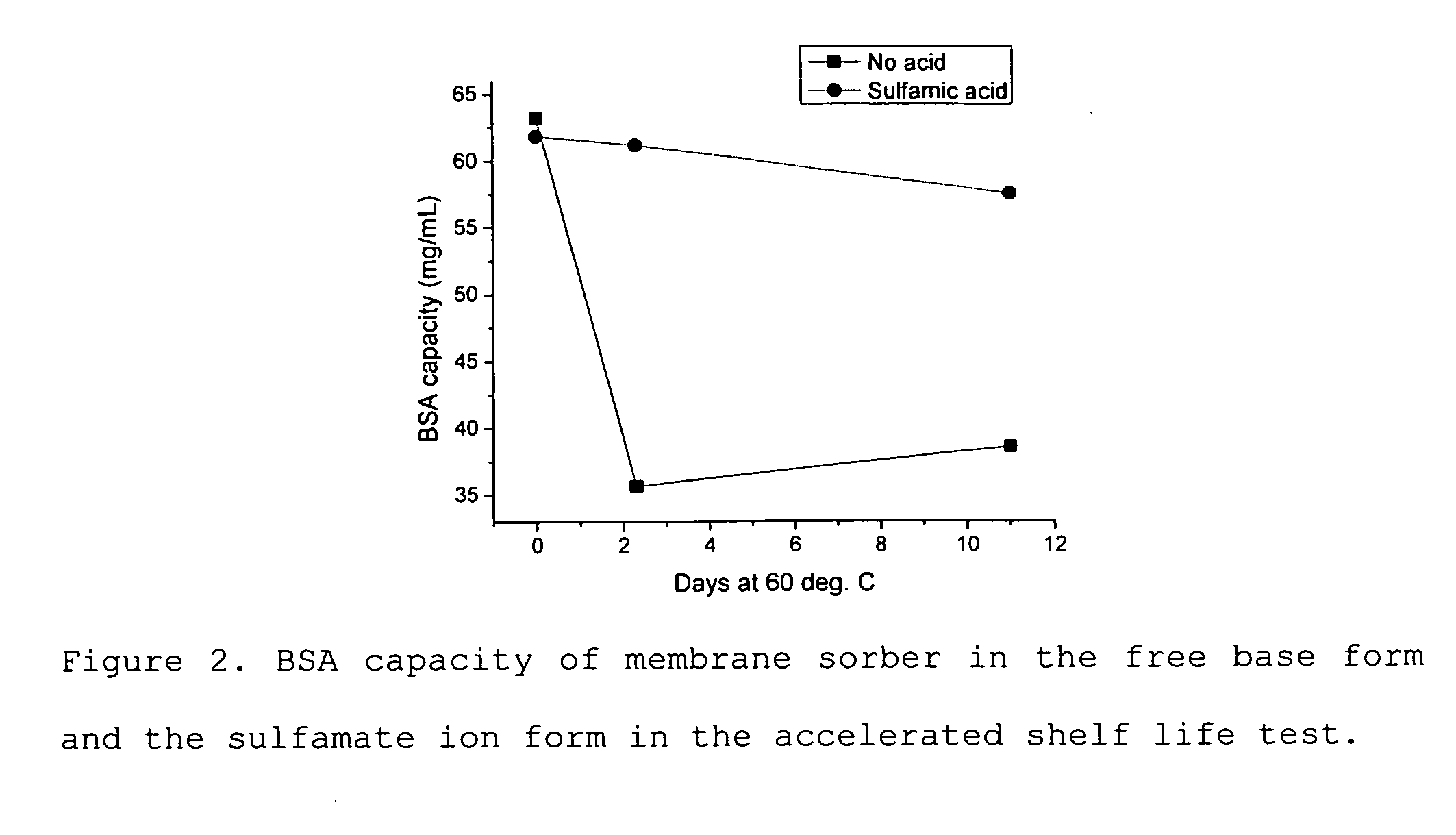
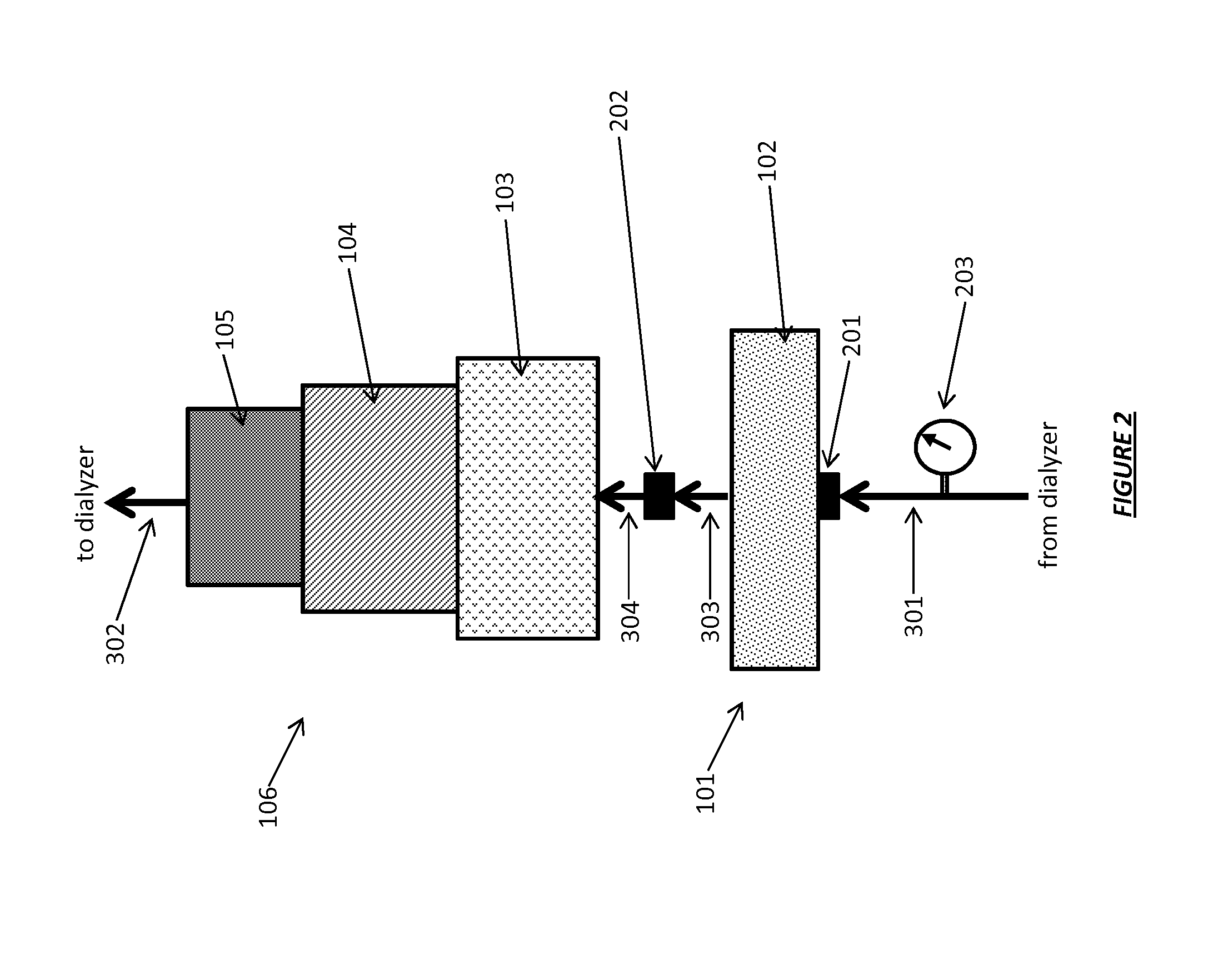
Acid zirconium phosphate and alkaline hydrous zirconium oxide materials for sorbent dialysis
ActiveUS8409444B2Avoid disadvantagesRestore balanceCation exchanger materialsSolvent extractionIon exchangeDialysis fluid
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
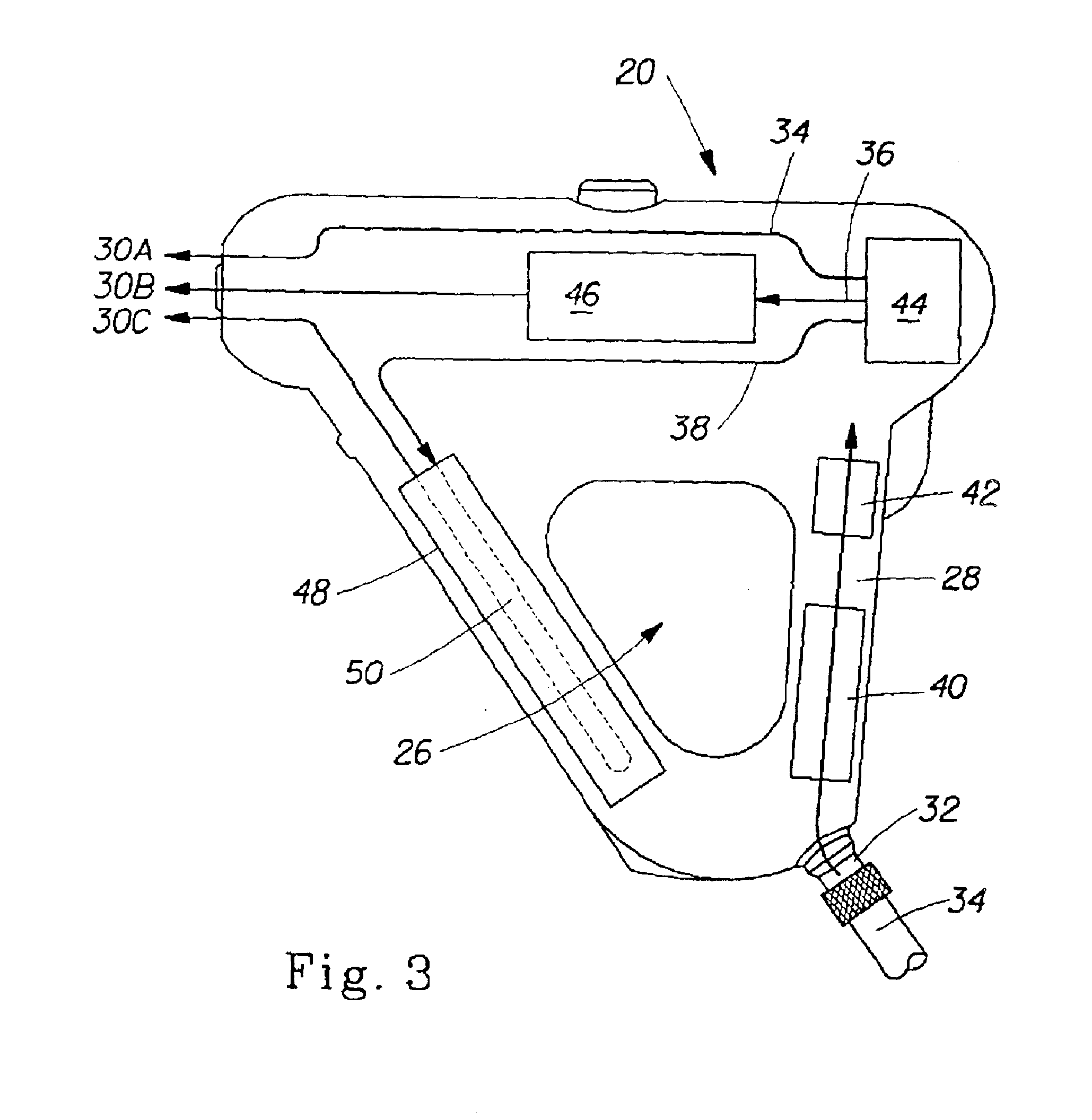
Recirculating dialysate fluid circuit for blood measurement
ActiveUS20140190886A1Short balance timeIncreasing dialysateCation exchanger materialsSolvent extractionMonitoring systemBiomedical engineering
A blood based solute monitoring system for measuring at least one blood solute species that has a first recirculation flow path in fluid communication with a dialyzer. The first recirculation flow path is configured to allow a fluid to recirculate through a dialyzer such that the concentration of at least one solute species in the fluid becomes equilibrated to the solute species concentration of the blood in a blood compartment of the dialyzer. The blood solute monitoring system has at least one sensor to measure a fluid characteristic.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
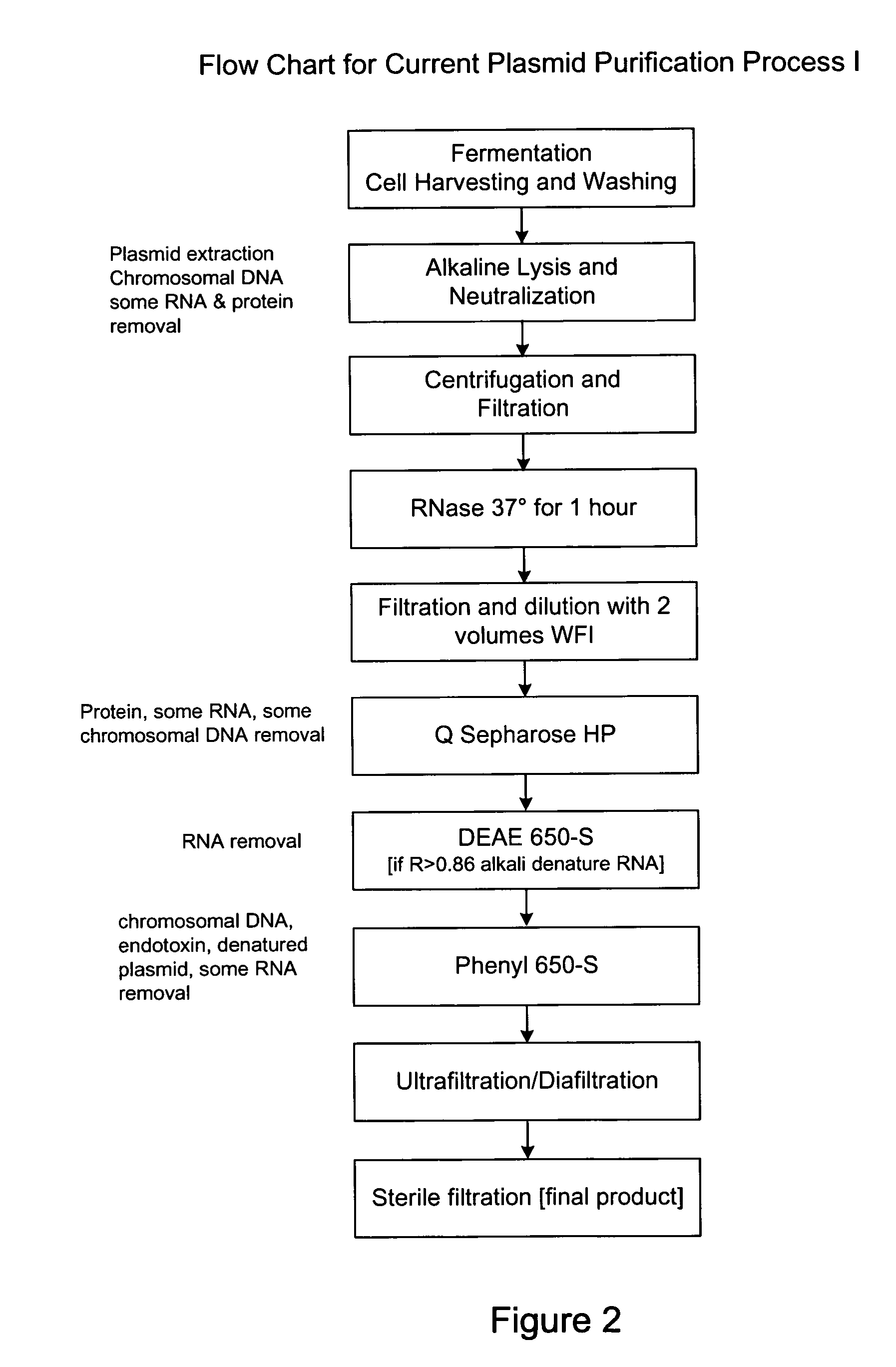
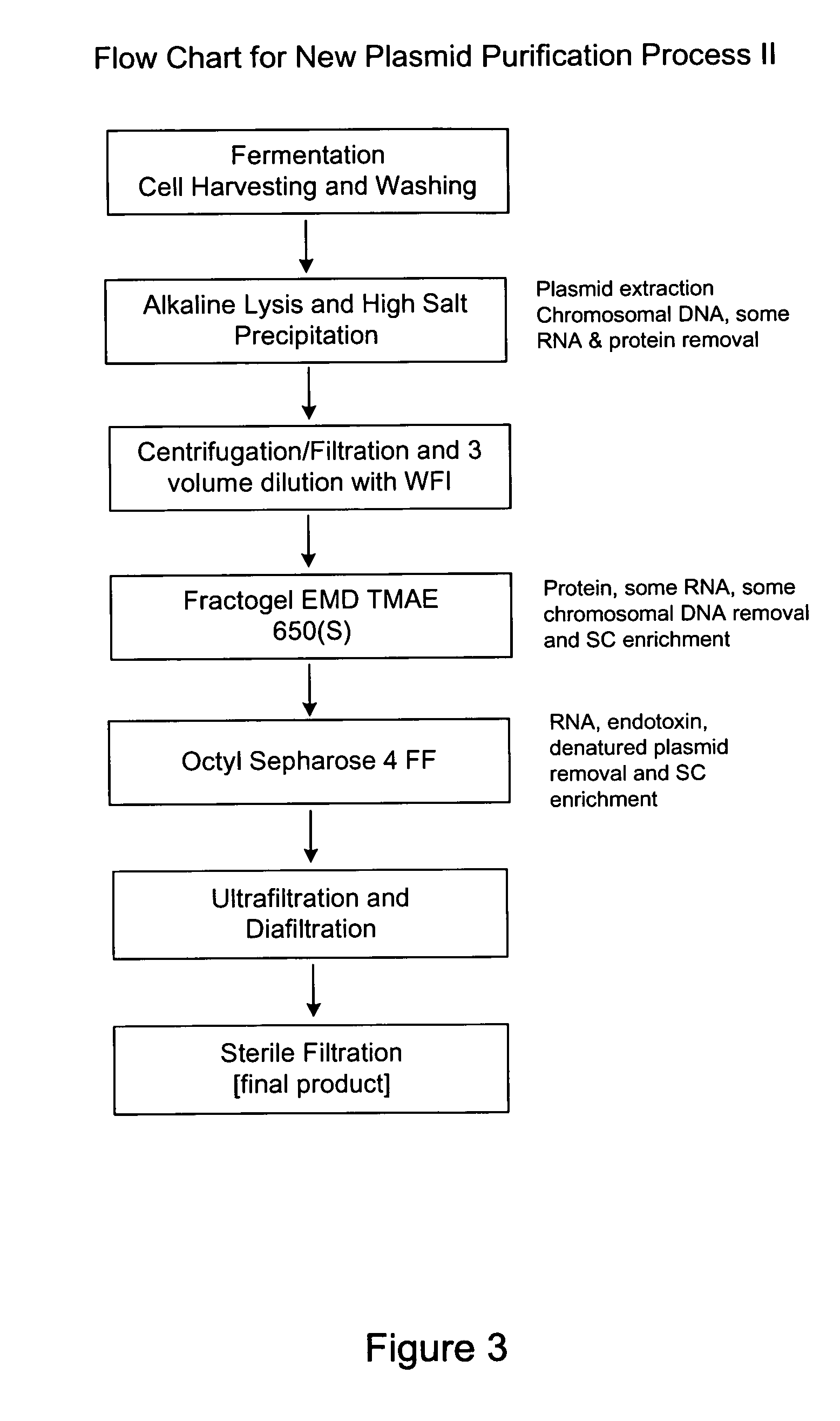
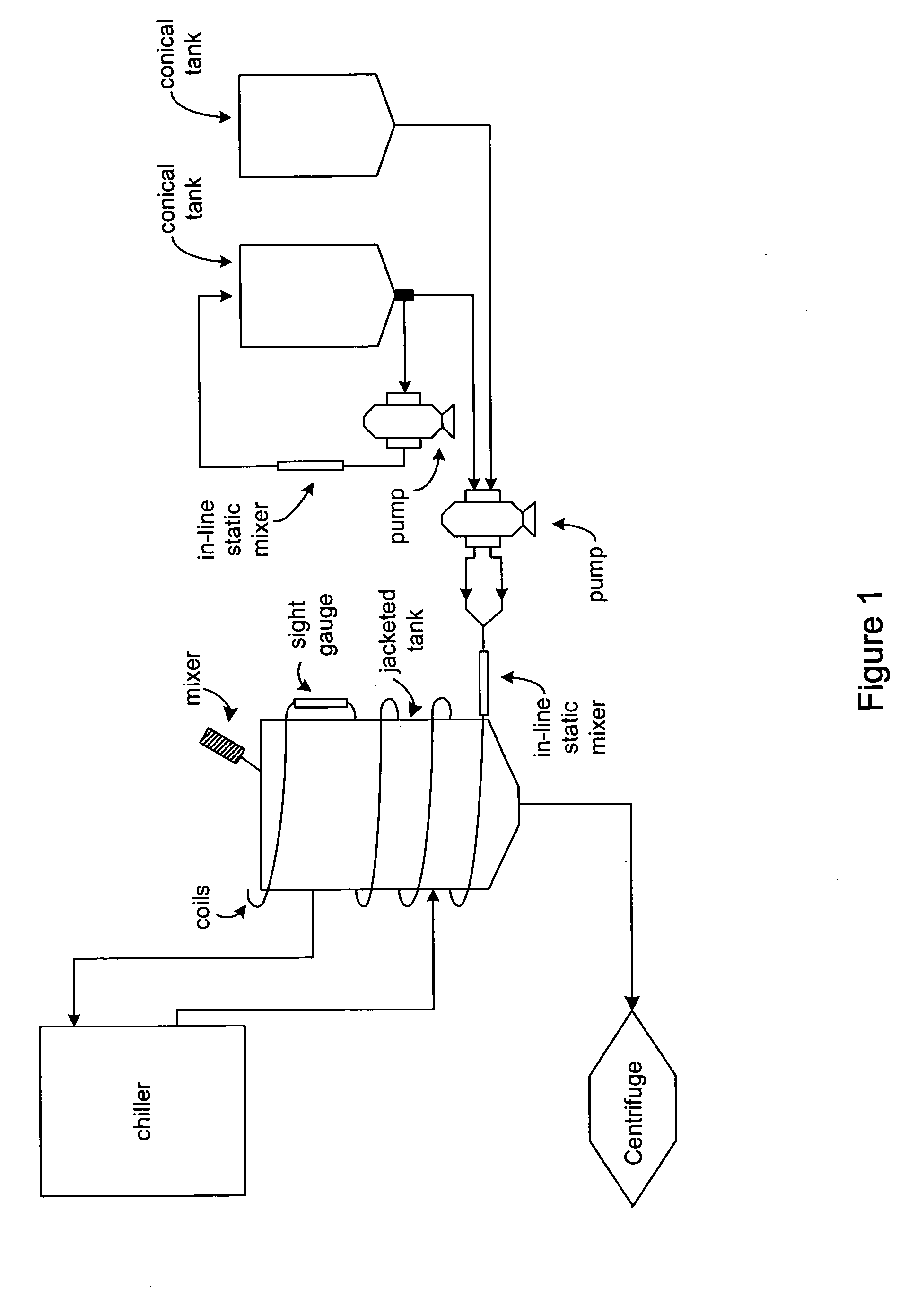
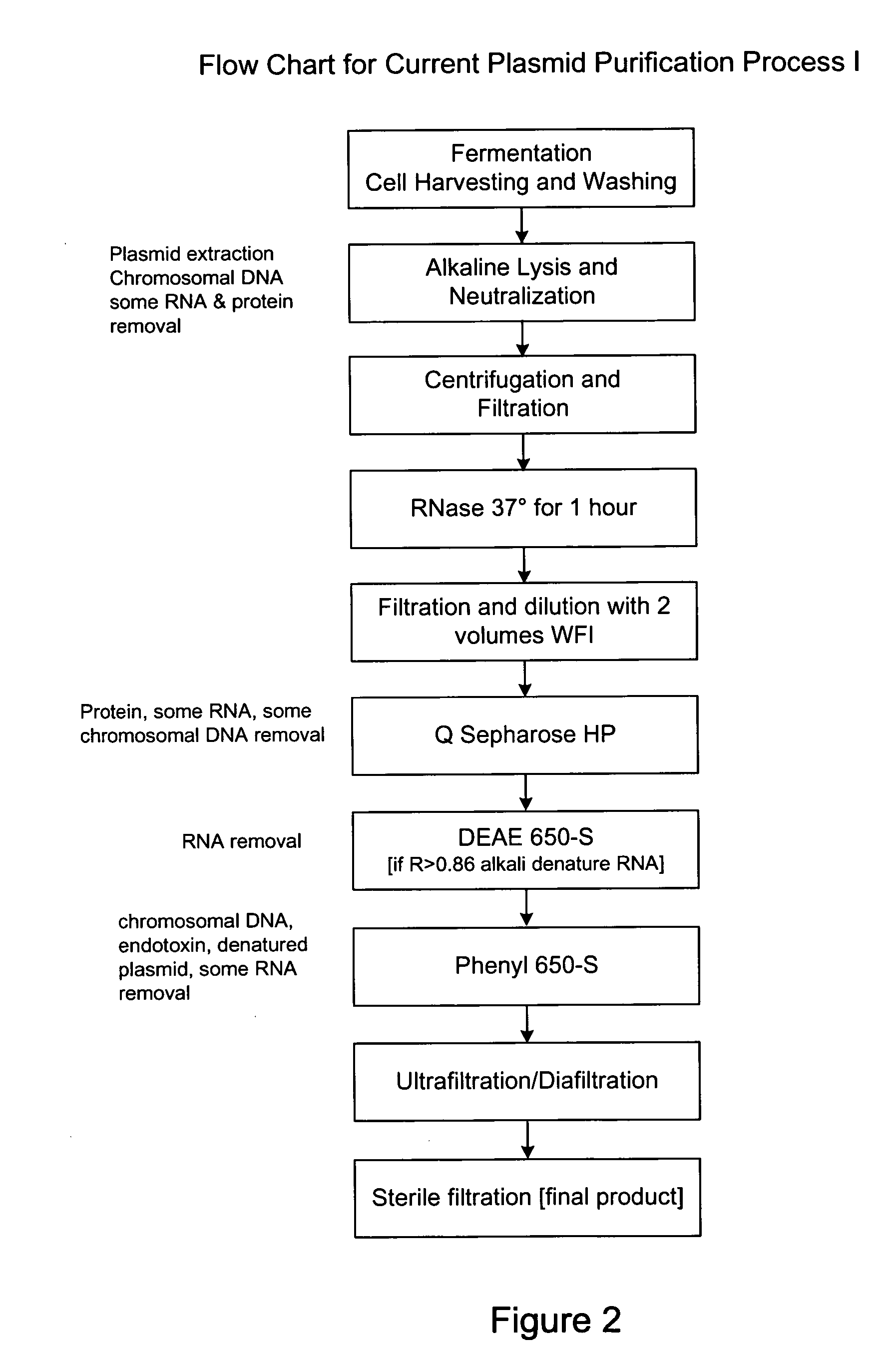
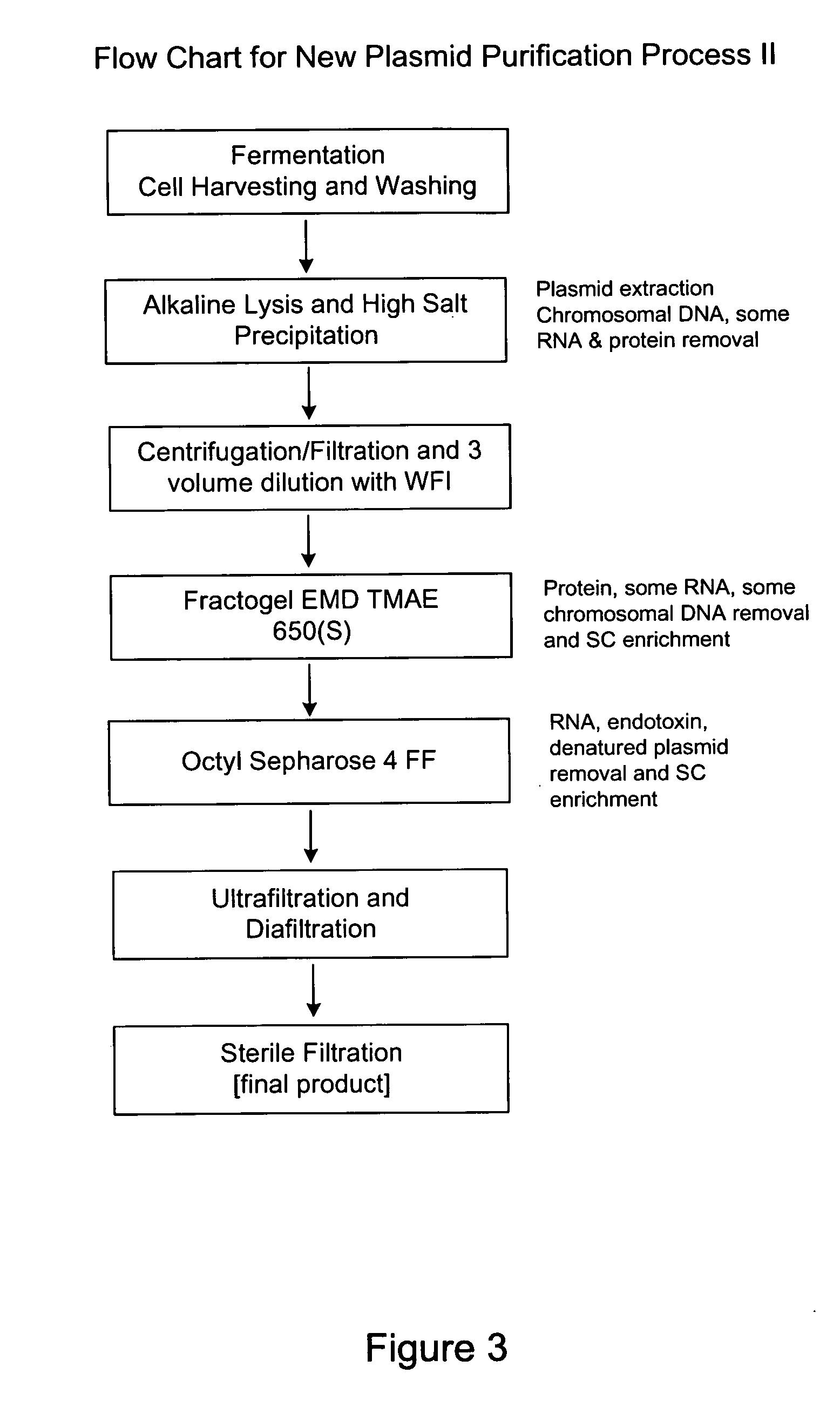
Process and equipment for plasmid purification
InactiveUS8236495B2Easy to operateConsistent levelCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersEscherichia coliLysis
A scalable alkaline lysis process, including procedures and devices for the isolation of large quantities (grams and kilograms) of plasmid DNA from recombinant E. coli cells. Effective, controllable, and economical operation, and consistent low level of host chromosomal DNA in the final plasmid product. Involves a series of new unit operations and devices for cell resuspension, cell lysis, and neutralization.
Owner:URIGEN PHARMA INC
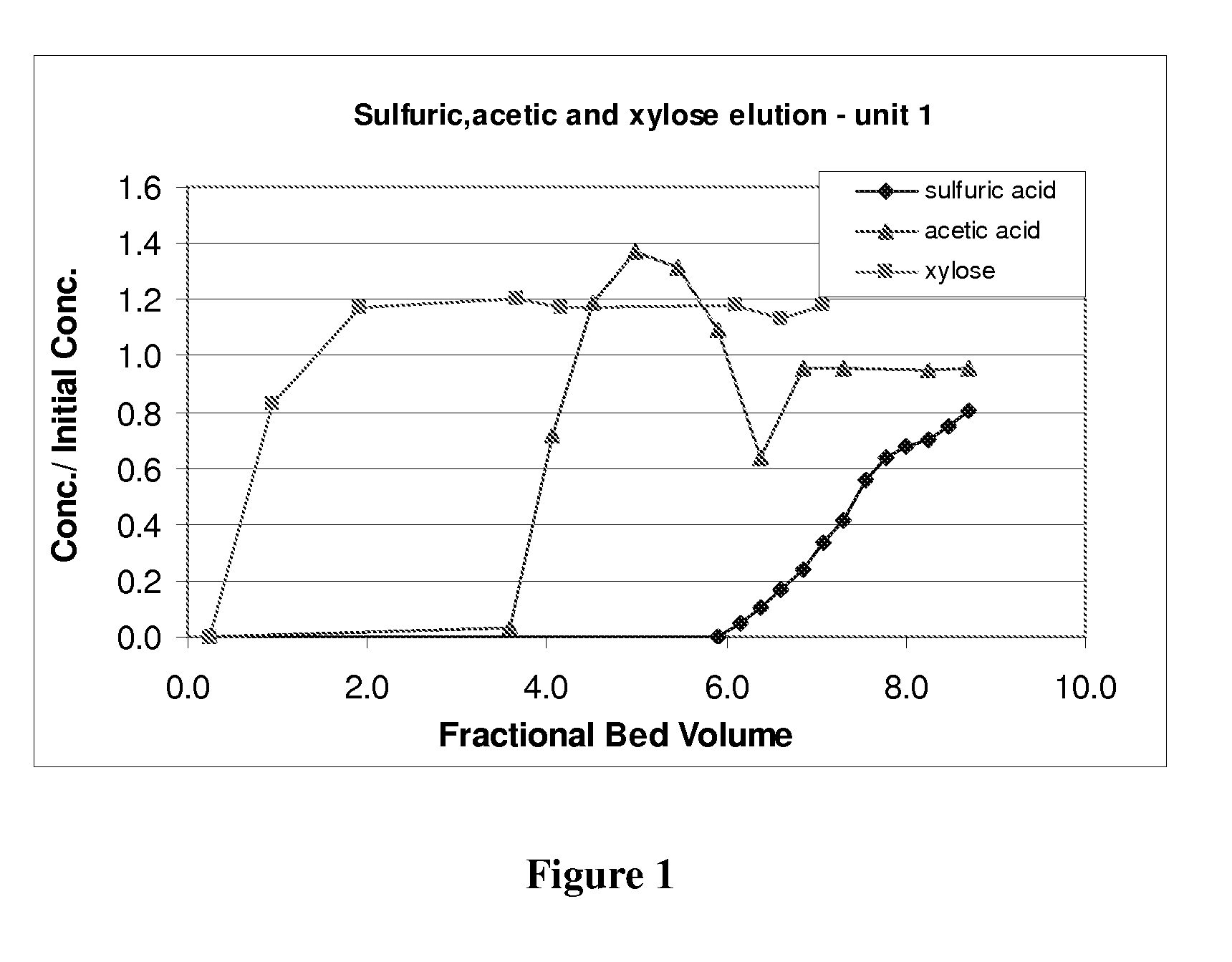
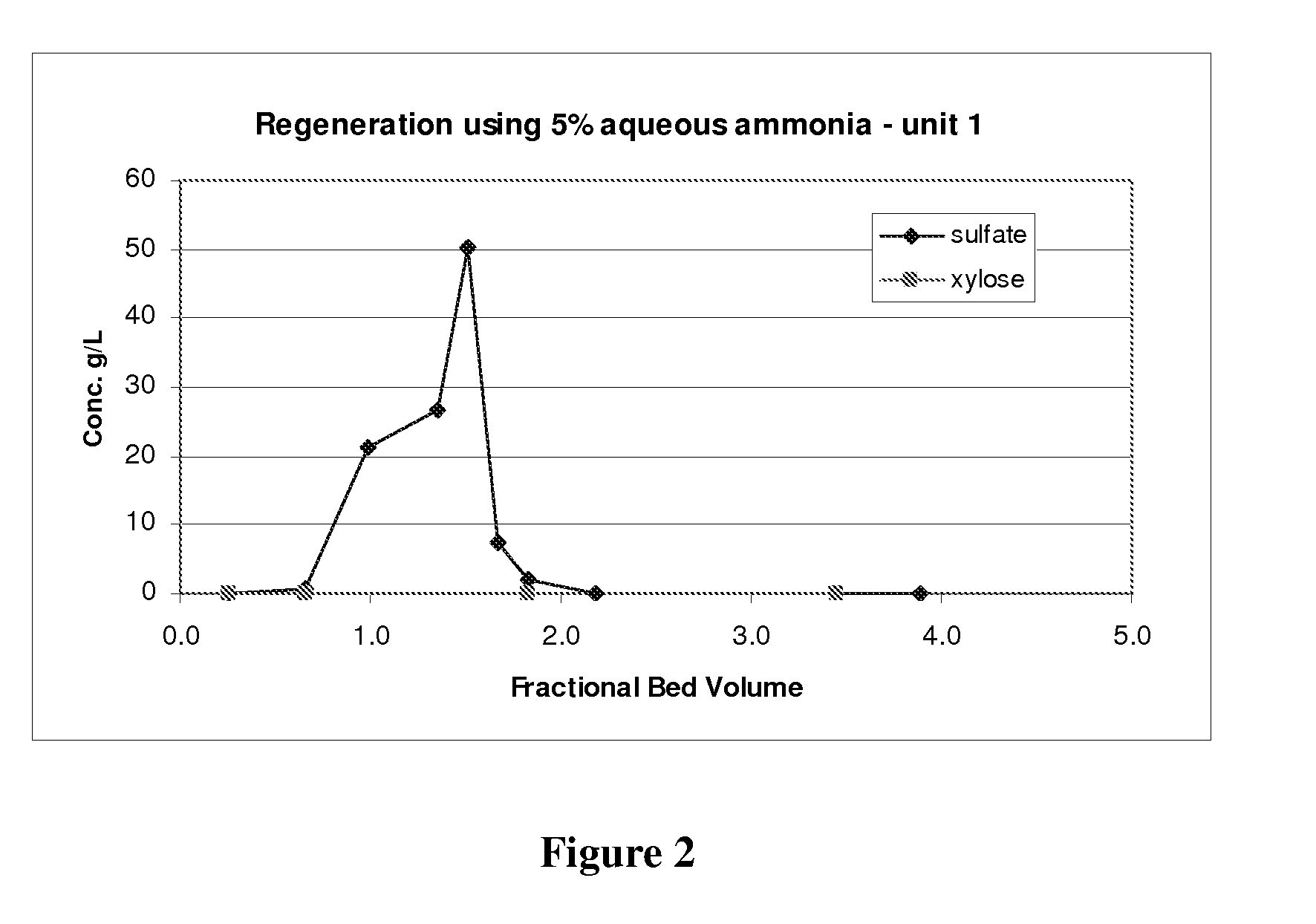
Method of obtaining an organic salt or acid from an aqueous sugar stream
InactiveUS20080041366A1Low costPromote recoverySugar derivativesComponent separationOrganic acidOrganic Ester
A process for obtaining one or more than one salt of an organic acid(s), or organic acid(s), from an aqueous sugar stream comprising one or more than one mineral acid and the organic acid(s) is provided. The process comprises introducing the aqueous sugar stream to a separation system comprising one or more beds of anion exchange resin and obtaining a stream therefrom comprising the sugar. The one or more beds of anion exchange resin are then regenerated in one or more stages to produce at least one product stream comprising the organic acid, a salt of the organic acid, or a combination thereof, and a separate outlet stream comprising the mineral acid, a salt of the mineral acid, or a combination thereof. The product stream is then recovered. The separation may be conducted with two separation units, or using a single anion exchange unit.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
Positively charged membrane
The present invention provides a positively charged microporous membrane having a protein binding capacity of about 25 mg / ml or greater comprising a hydrophilic porous substrate and a crosslinked coating that provides a fixed positive charge to the membrane. The present invention further provides a positively charged microporous membrane comprising a porous substrate and a crosslinked coating comprising pendant cationic groups. The membranes of the present invention find use in a variety of applications including ion-exchange chromatography, macromolecular transfer, as well as detection, filtration and purification of biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, endotoxins, and the like.
Owner:PALL CORP
Process and equipment for plasmid purfication
InactiveUS20060106208A1Easy to operateConsistent levelCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationLysisGram
A scalable alkaline lysis process, including procedures and devices for the isolation of large quantities (grams and kilograms) of plasmid DNA from recombinant E. coli cells. Effective, controllable, and economical operation, and consistent low level of host chromosomal DNA in the final plasmid product. Involves a series of new unit operations and devices for cell resuspension, cell lysis, and neutralization.
Owner:URIGEN PHARMA INC
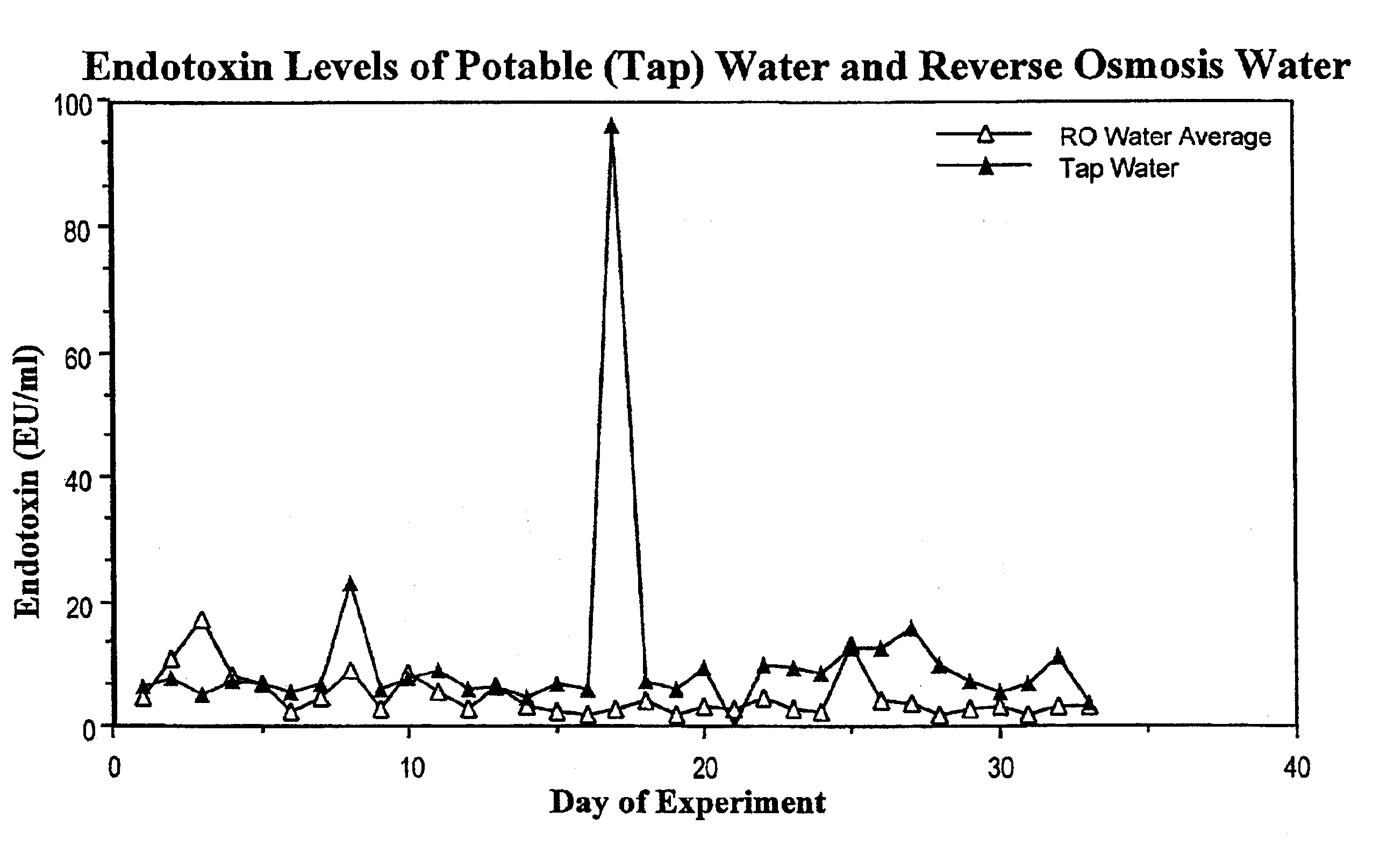
Methods for the on-line, on-demand preparation of sterile, water-for-injection grade water
InactiveUS6745903B2Low costLower Level RequirementsOrganic anion exchangersDialysis systemsSpecific adsorptionFiltration
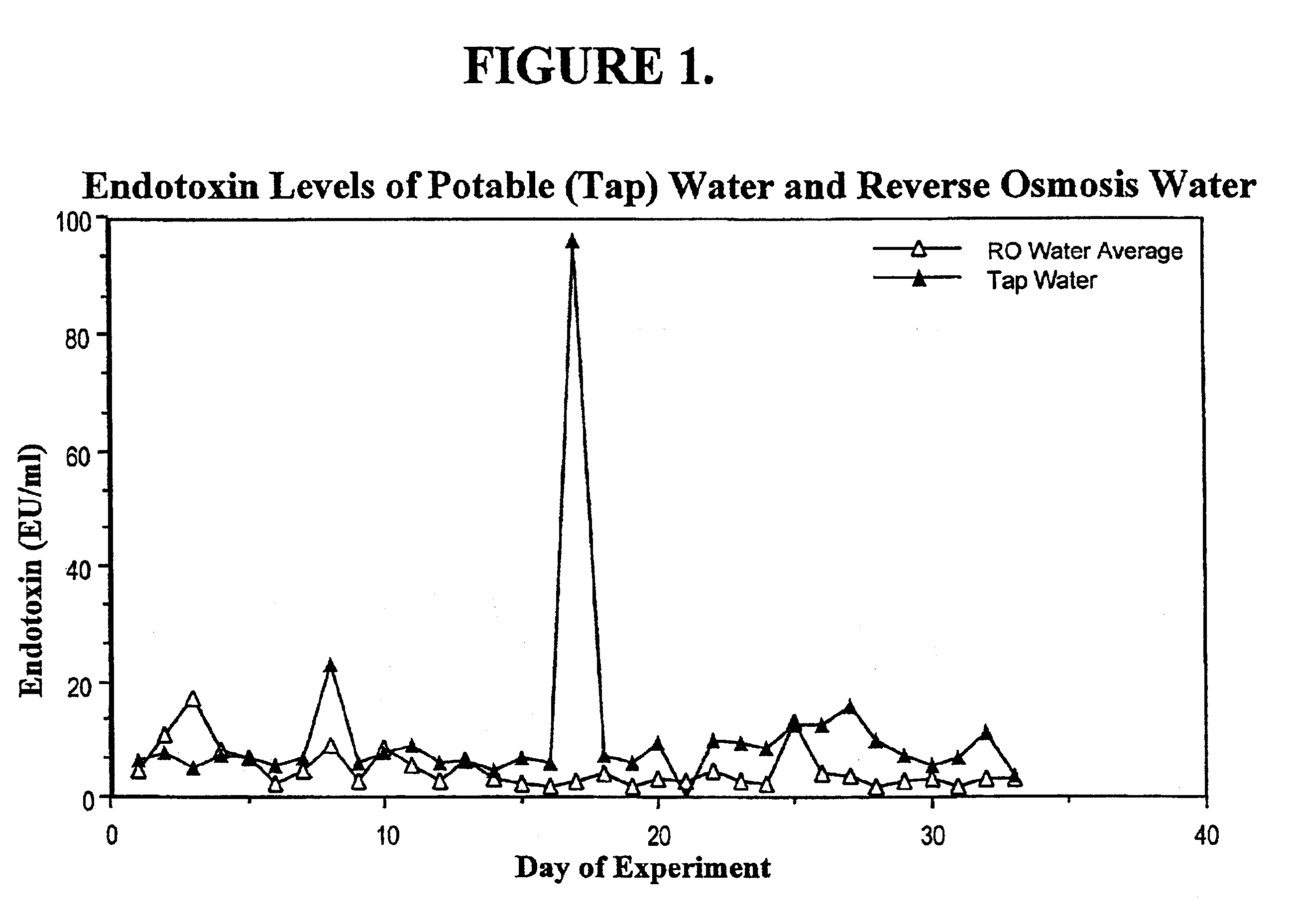
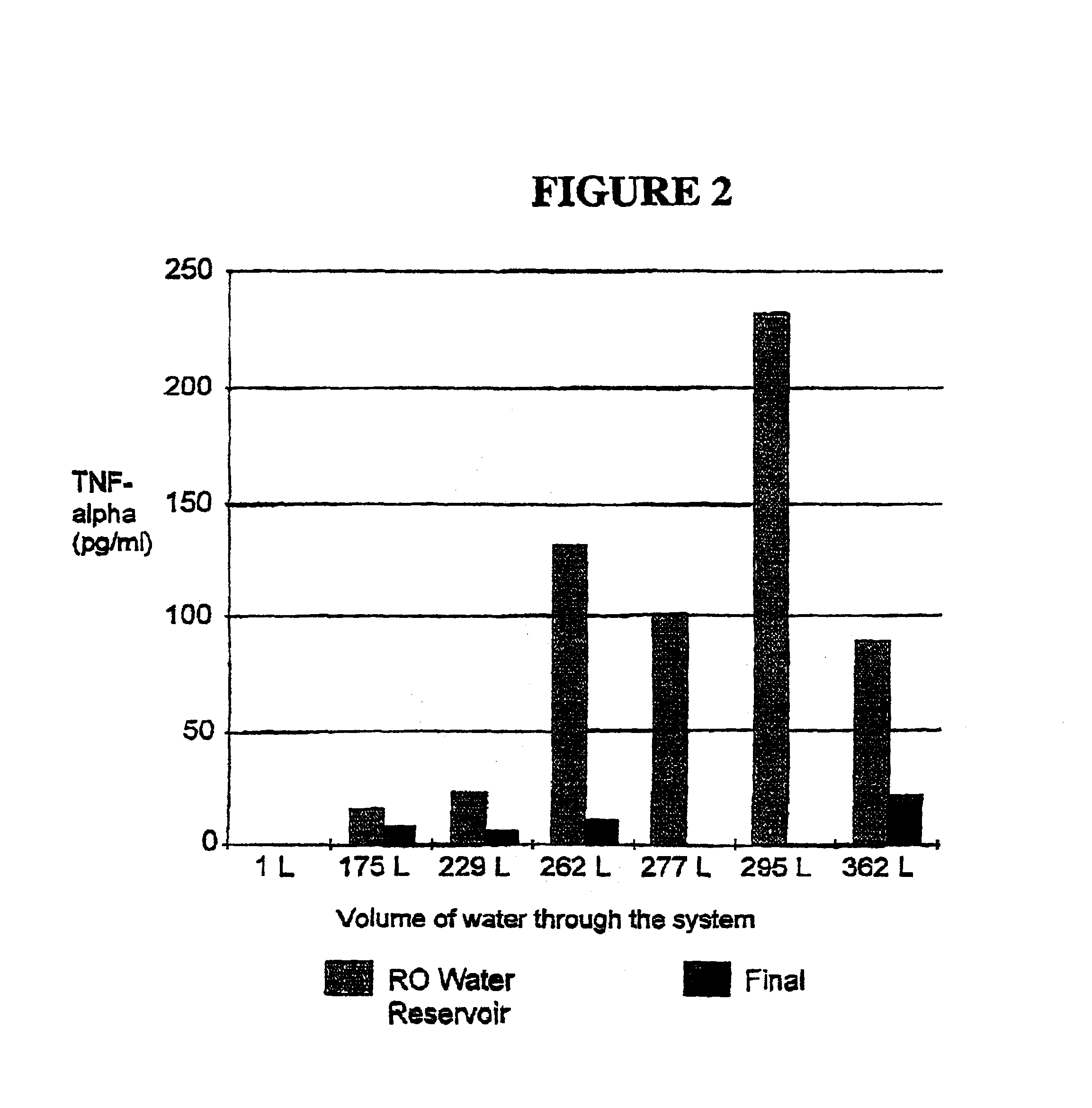
A new method is described to produce large volumes of low cost sterile, Water-for-Injection (WFI) grade water on-line, on-demand from potable water in order to meet the needs of dialysis therapies and other biological applications for sterile, injectable grade water. The source water is processed by a combination of membrane and column chromatographic methods including reverse osmosis, chemical sterilization, reduction of iodine sterilant to iodide, deionization, endotoxin-specific adsorption and polishing filtration in order to reduce contaminant levels below those specified by the US Pharmacopoeia.
Owner:GRANDICS PETER
System and method for cleaning and/or treating vehicles and the surfaces of other objects
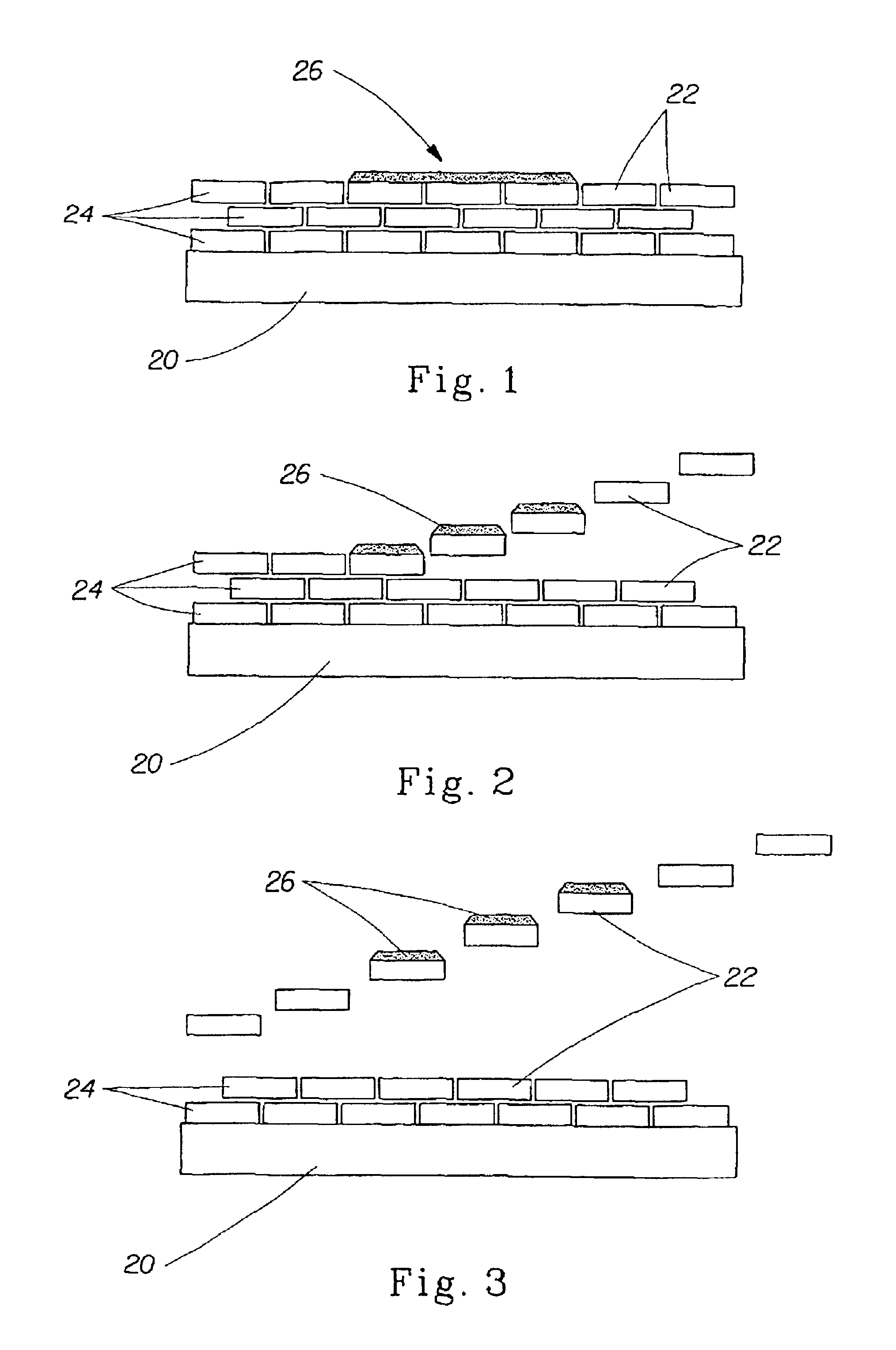
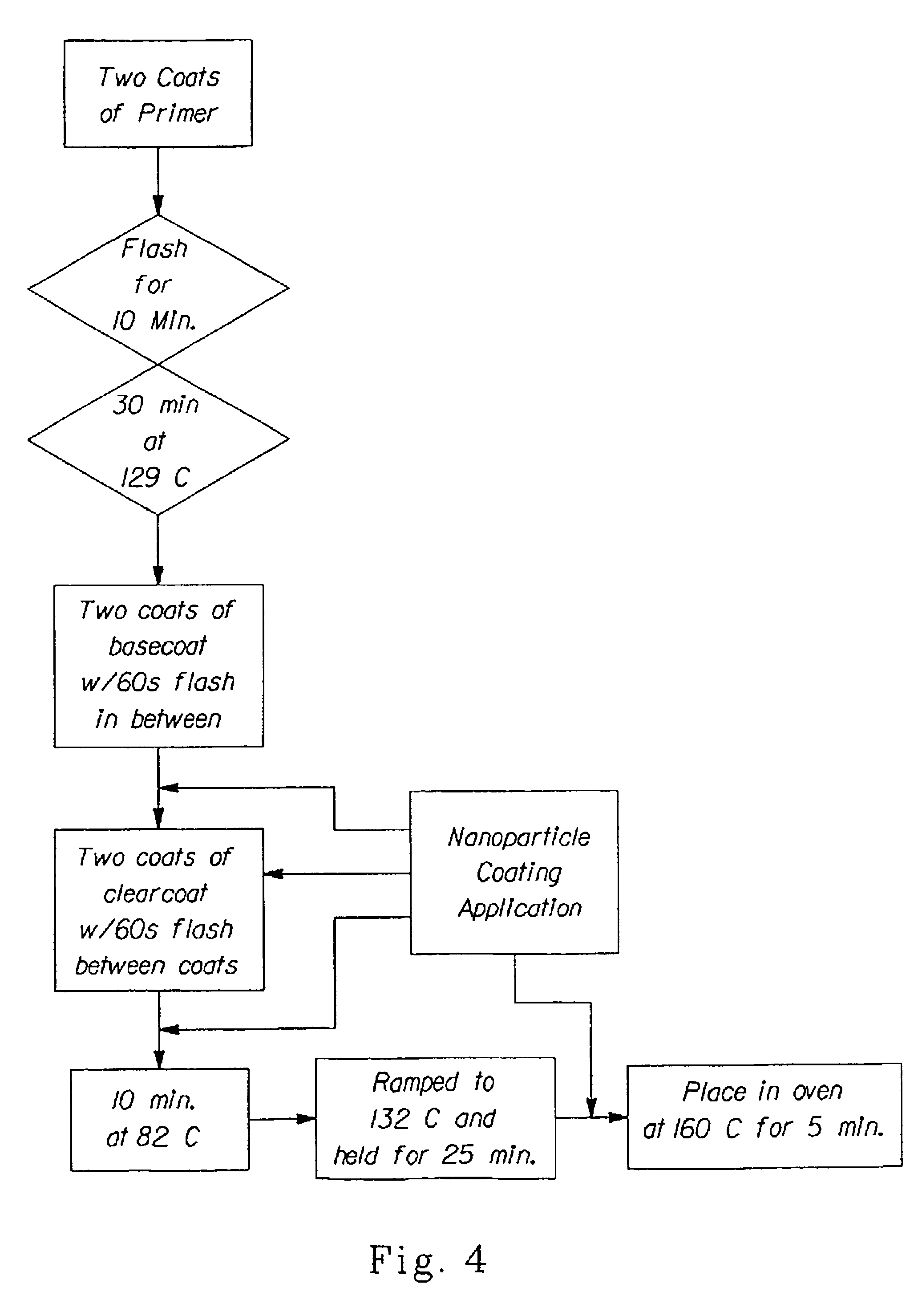
InactiveUS6846512B2Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic anion exchangersHydrophilic coatingNanoparticle coating
The present invention relates to a system and method for cleaning and / or treating a surface, preferably surfaces such as ceramic, steel, plastic, glass and / or painted surfaces such as the exterior surface of a vehicle. In one embodiment, the method forms a transparent, hydrophilic coating on the surface of a vehicle. This embodiment of the method includes the steps of: (a) providing a vehicle having at least some surfaces that are at least one of the following: cured painted surfaces, cured clearcoat surfaces, and glass surfaces; (b) applying a non-photoactive nanoparticle coating composition to such surfaces; and (c) allowing the coating composition to dry on such surfaces before the surfaces are contacted by water.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
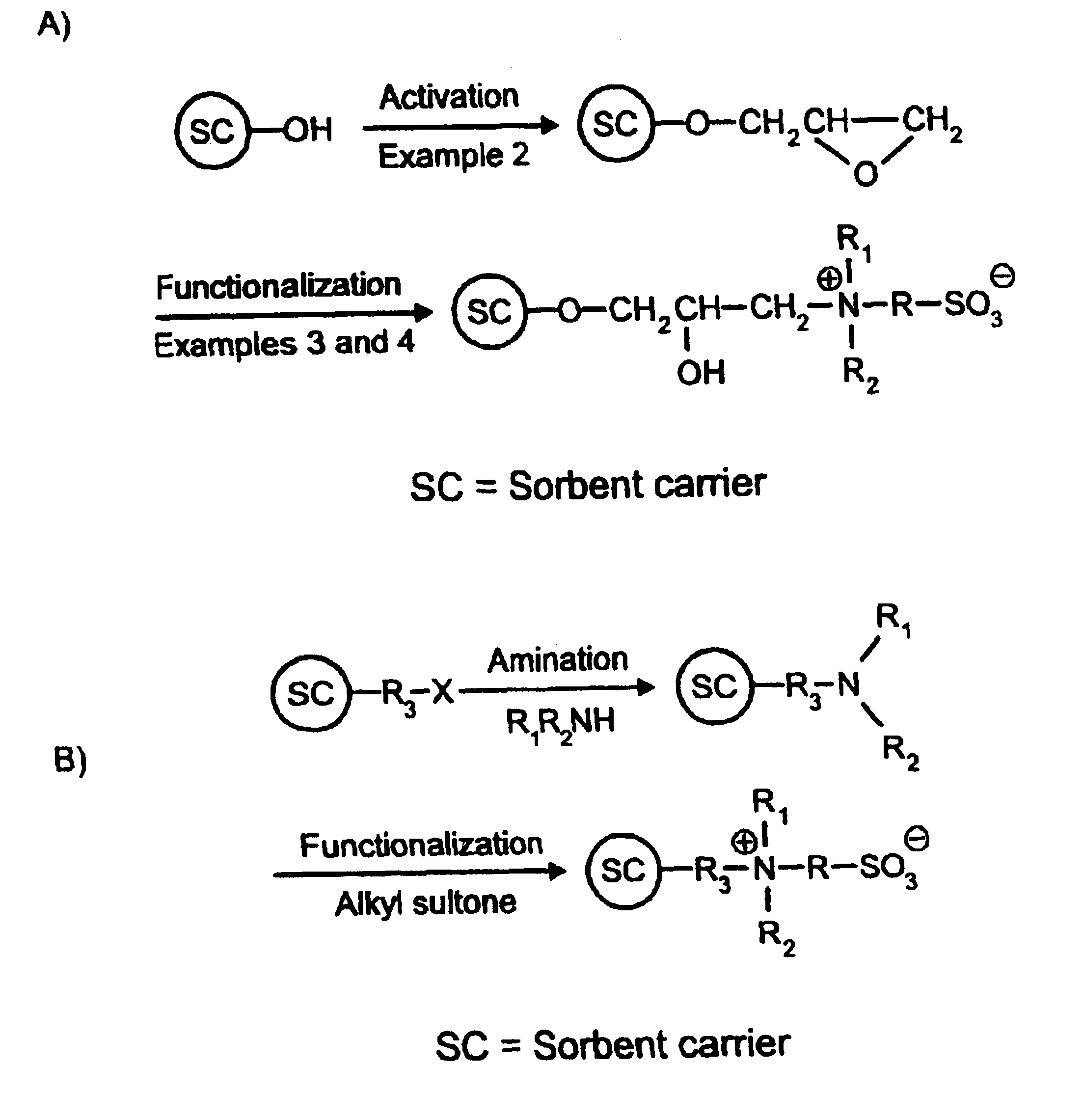
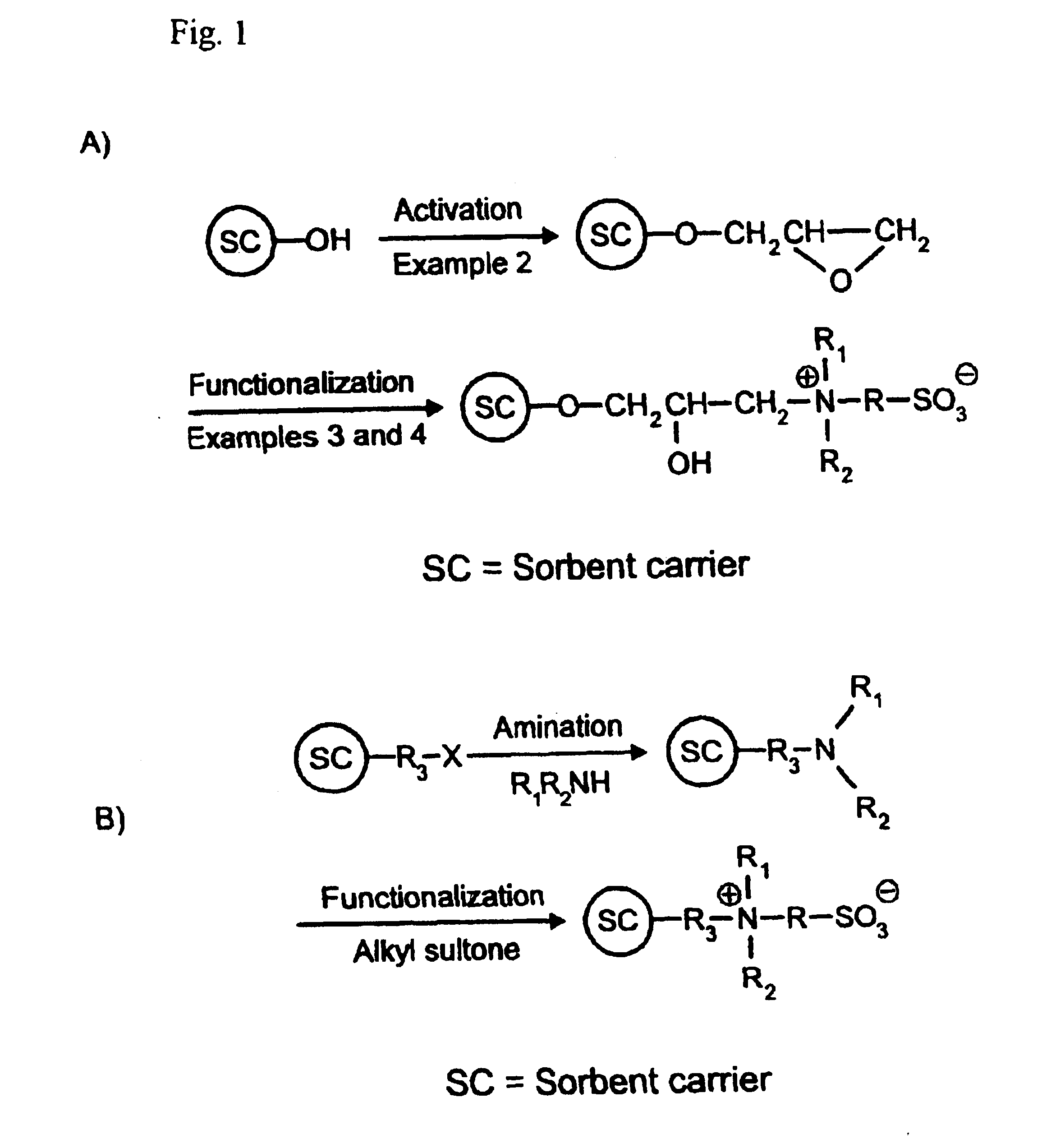
Process for preparing monodisperse anion exchangers
The present invention relates to a process for preparing novel, monodisperse anion exchangers by(a) reacting monomer droplets made from monovinylaromatic compounds and polyvinylaromatic compounds, and optional porogens and / or initiators,(b) amidomethylating the resultant monodisperse, crosslinked bead polymers with phthalimide derivatives,(c) converting the amidomethylated bead polymers to aminomethylated bead polymers, and(d) alkylating the aminomethylated bead polymers.
Owner:LANXESS DEUTDCHLAND GMBH
Fluid circuits for sorbent cartridge with sensors
ActiveUS20140190885A1Cation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersSorbentMechanical engineering
A system for measuring at least one fluid characteristic at various stages within a sorbent system that has a sorbent cartridge that has at least one material layer and at least one fluid passageway in at least one location in the sorbent system to provide a diverted sample stream from the various stages. At least one fluid characteristic of the diverted sample stream is measured.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
Chromatography method and a column material useful in said method
InactiveUS6884345B1Chromatographic cation exchangersCation exchanger materialsNatural sourceStationary phase
A novel sorbent suitable for use as a stationary phase in a chromatography column, the core of which consists of an organic polymer of synthetic or natural origin. Further, the carrier exhibits a plurality of covalently bonded non-aromatic zwitterionic groups on its surface. Additionally, the invention also relates to a method for purifying a particular biological macromolecule, such as a protein or a nucleic acid, by zwitterionic ion exchange chromatography as well as an ion exchange column suitable for use in the zwitterionic ion exchange chromatography.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Use of Ionic Liquids
InactiveUS20080191170A1Increase polarityImprove hydrophilicityOrganic compound preparationOrganic anion exchangersIonic liquidIon
Owner:CAMBRIDGE UNIV TECH SERVICES LTD
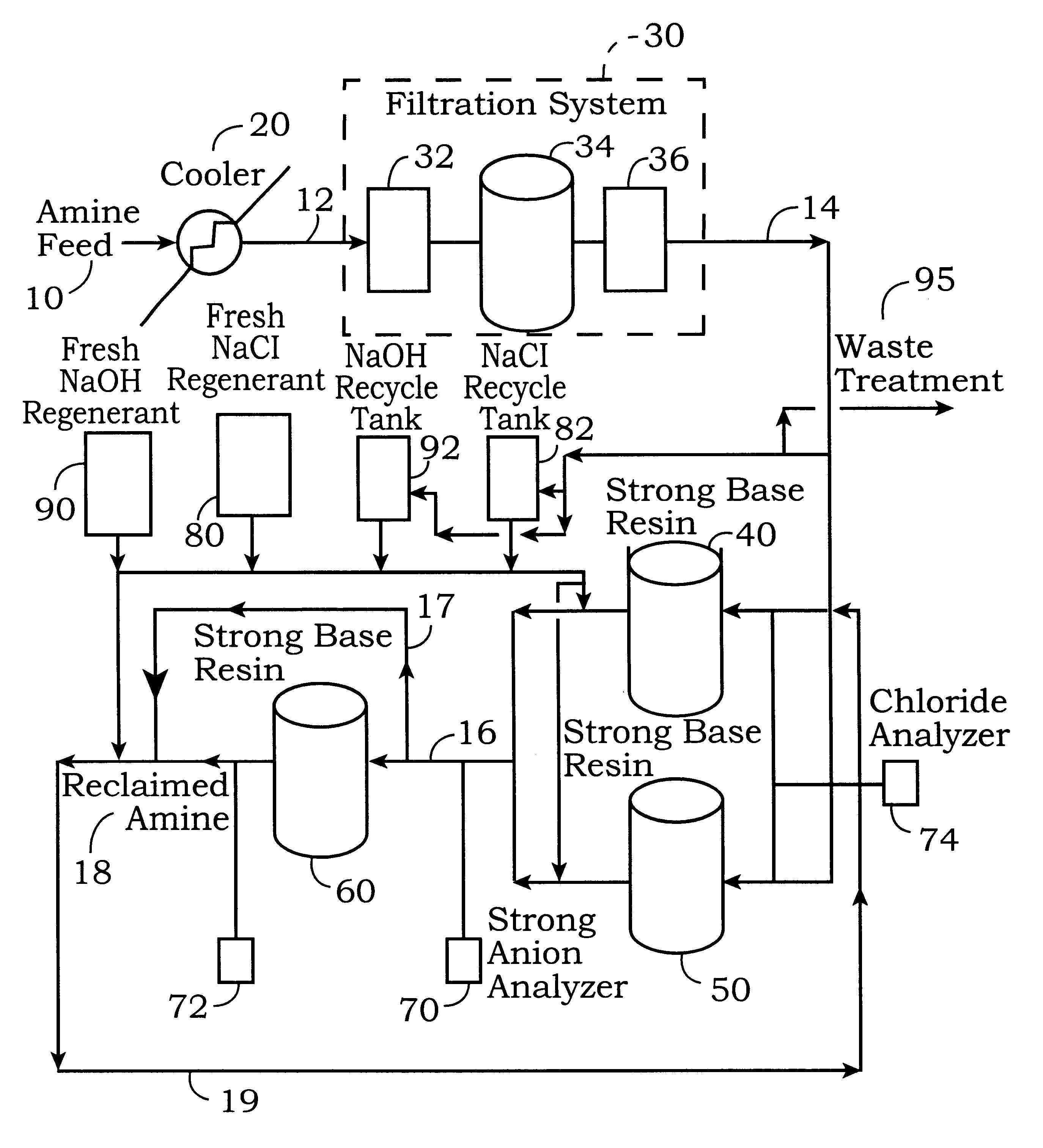
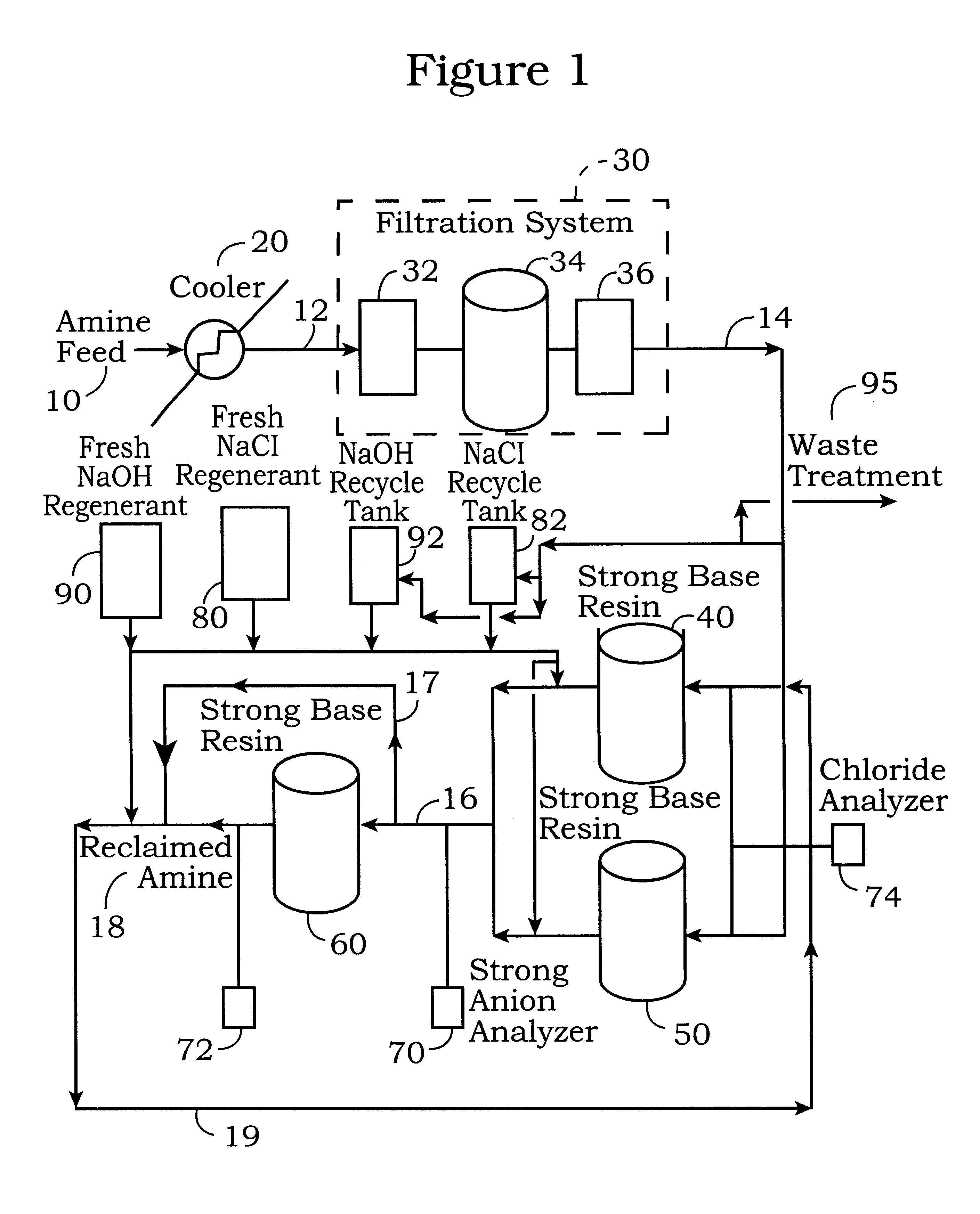
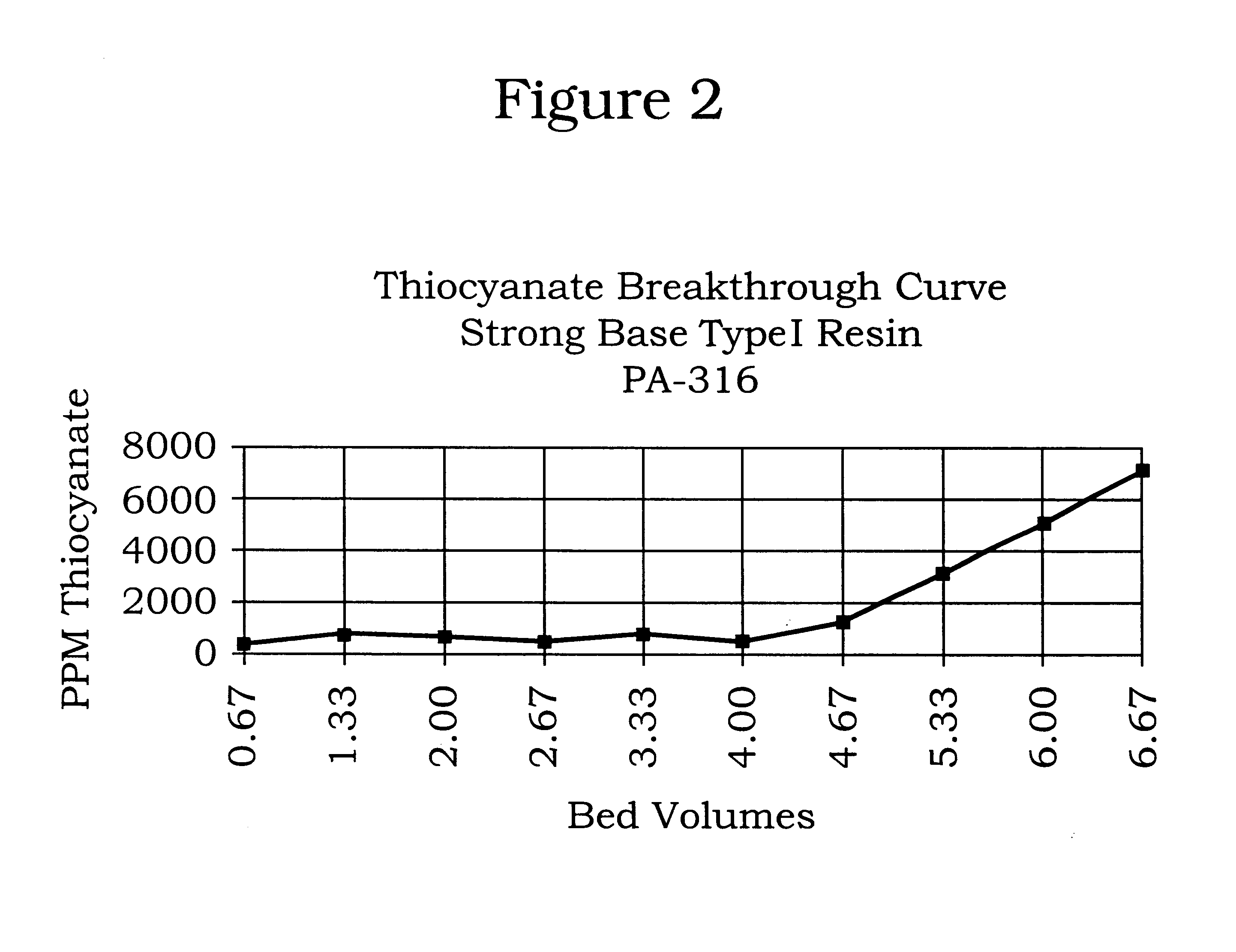
Process for the reclamation of spent alkanolamine solution
InactiveUS6245128B1Raise the potentialReduces efficiency of systemLiquid degasificationIon-exchange column/bed processesHigh concentrationNitrogen gas
A process for the reclamation of spent aqueous alkanolamine solutions by contacting a spent aqueous alkanolamine solution with a strong base ion exchange resin for time sufficient to sorb from the aqueous alkanolamine solution at least a portion of the accumulated ions and after a high concentration of ions accumulate on the resin, regenerating the strong base ion exchange resin by: a) purging the resin with water or nitrogen, b) contacting the strong base ion exchange resin with a sodium chloride solution for a time sufficient to remove the ions, c) purging the resin to remove the sodium chloride solution, d) contacting the resin with an alkali metal hydroxide solution, preferably sodium hydroxide, for a time sufficient to convert the resin to a substantially hydroxide form; and e) purging the resin, wherein the ion sorption capacity of the resin is maintained at a substantially constant value.
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP
Rinse aid surface coating compositions for modifying dishware surfaces
InactiveUS7087662B2Increased durabilityInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsStainingNanoparticle
Rinse aid materials for coating, coating compositions, methods and articles of manufacture for use in automatic dishwashing appliances comprising a nanoparticle system or employing the same to impart surface modifying benefits for all types of dishware surfaces are disclosed. In some embodiments, dispersement of nanoparticles in a suitable carrier medium allows for the creation of rinse aid surface coating compositions, methods and articles of manufacture that create multi-use benefits to modified dishware surfaces. These surface modifications can produce long lasting or semi-permanent multi-use benefits that include at least one of the following improved surface properties: wetting and sheeting, uniform drying, anti-spotting, anti-staining, anti-filming, self cleaning, and durability benefits, relative to dishware surfaces unmodified with such nanoparticle systems. In some embodiments, actively curing the rinse aid surface coating composition on the dishware surfaces, including, but not limited to by radiative heating the air surrounding the dishware surface with the coating thereon can be used to increase the durability of the dishware surface coating.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
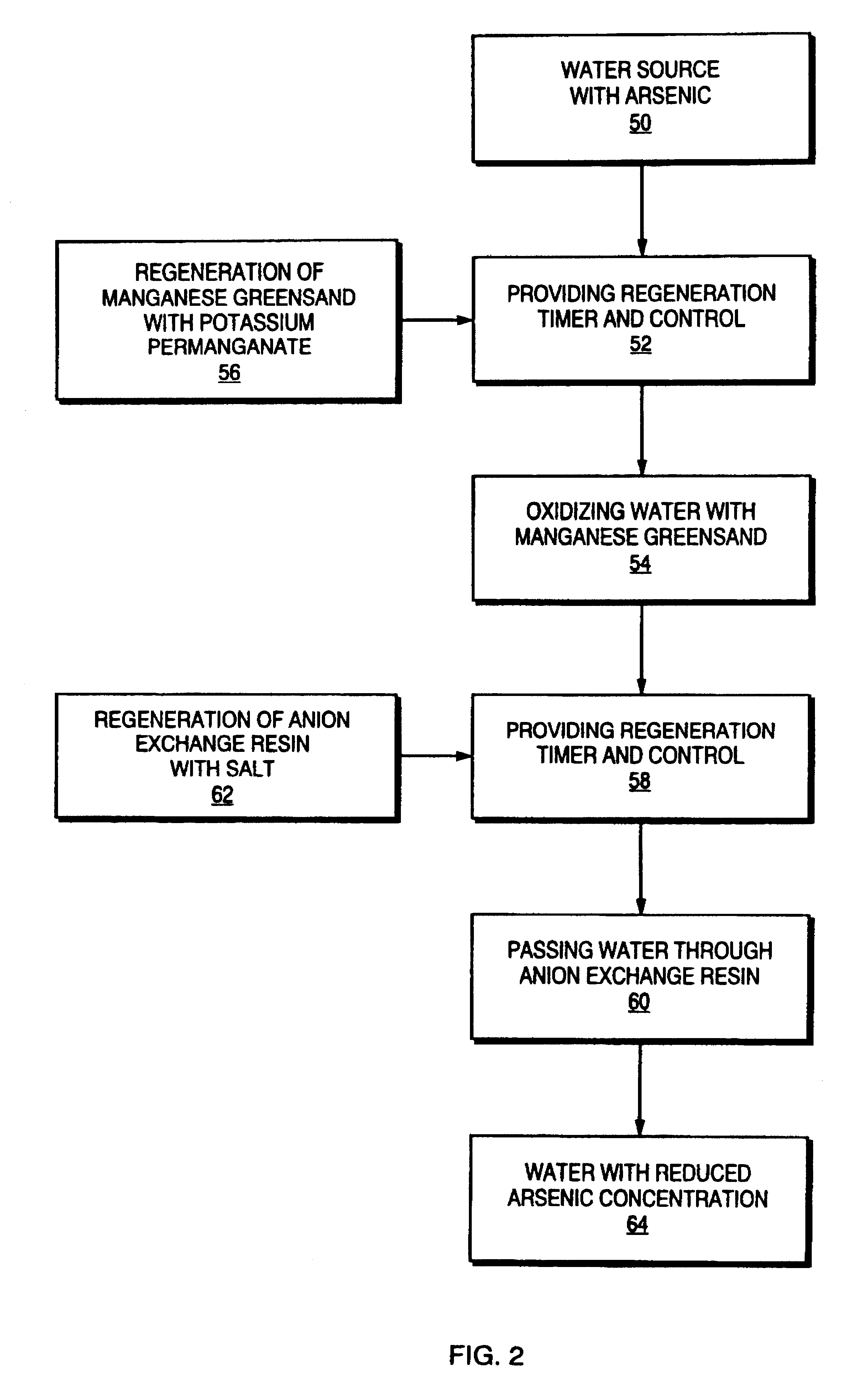
Method and apparatus for the removal of arsenic from water
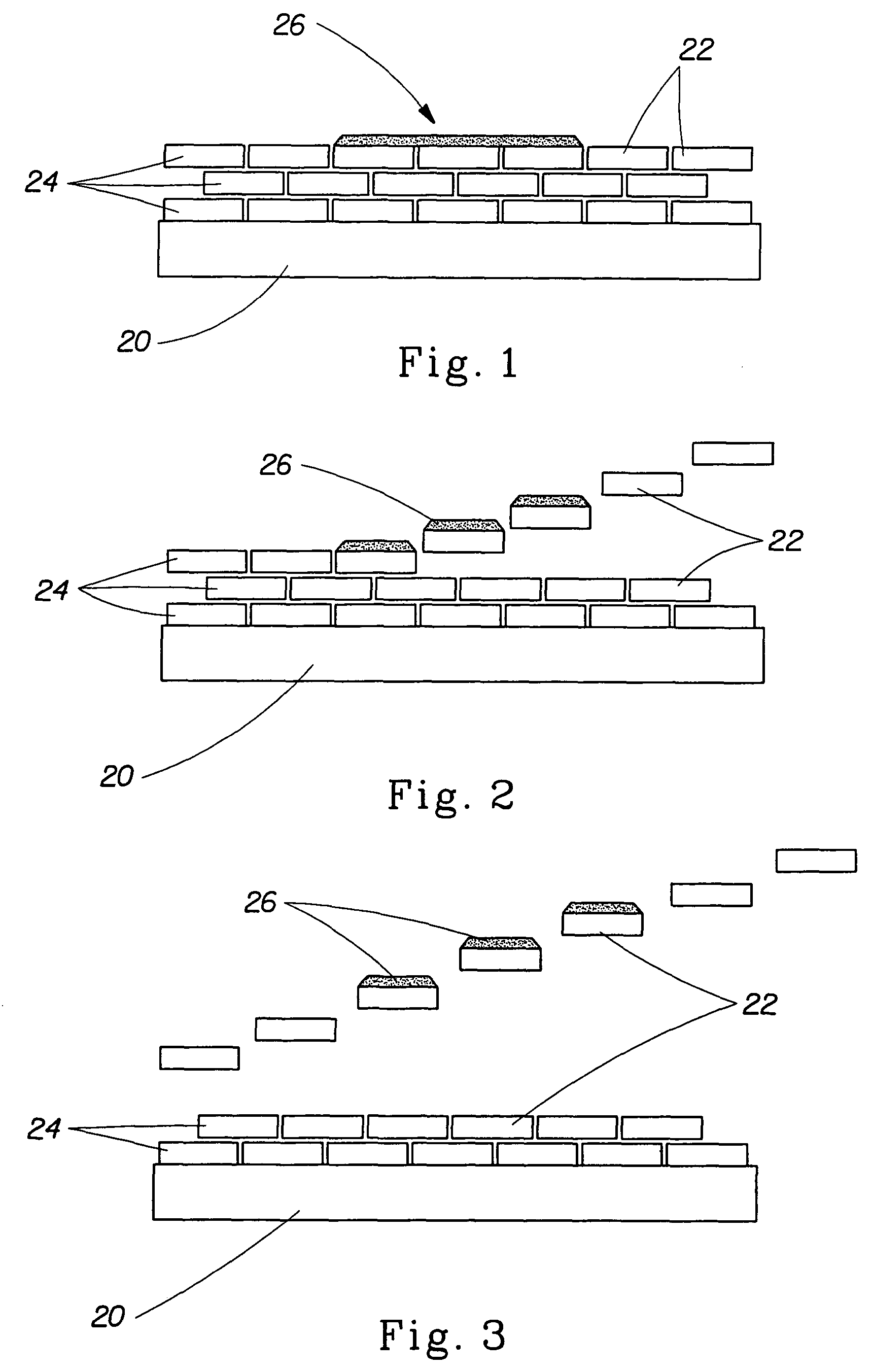
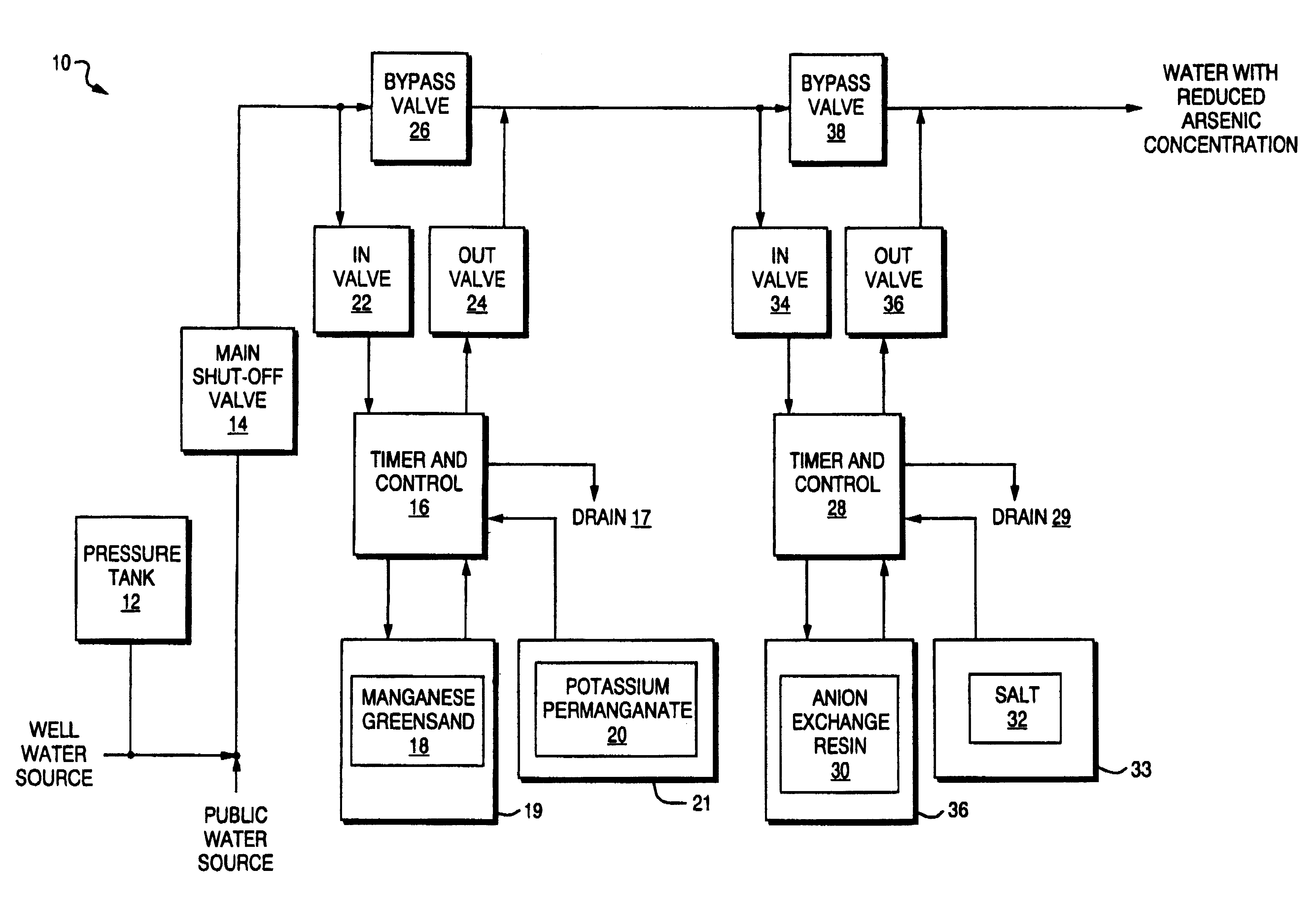
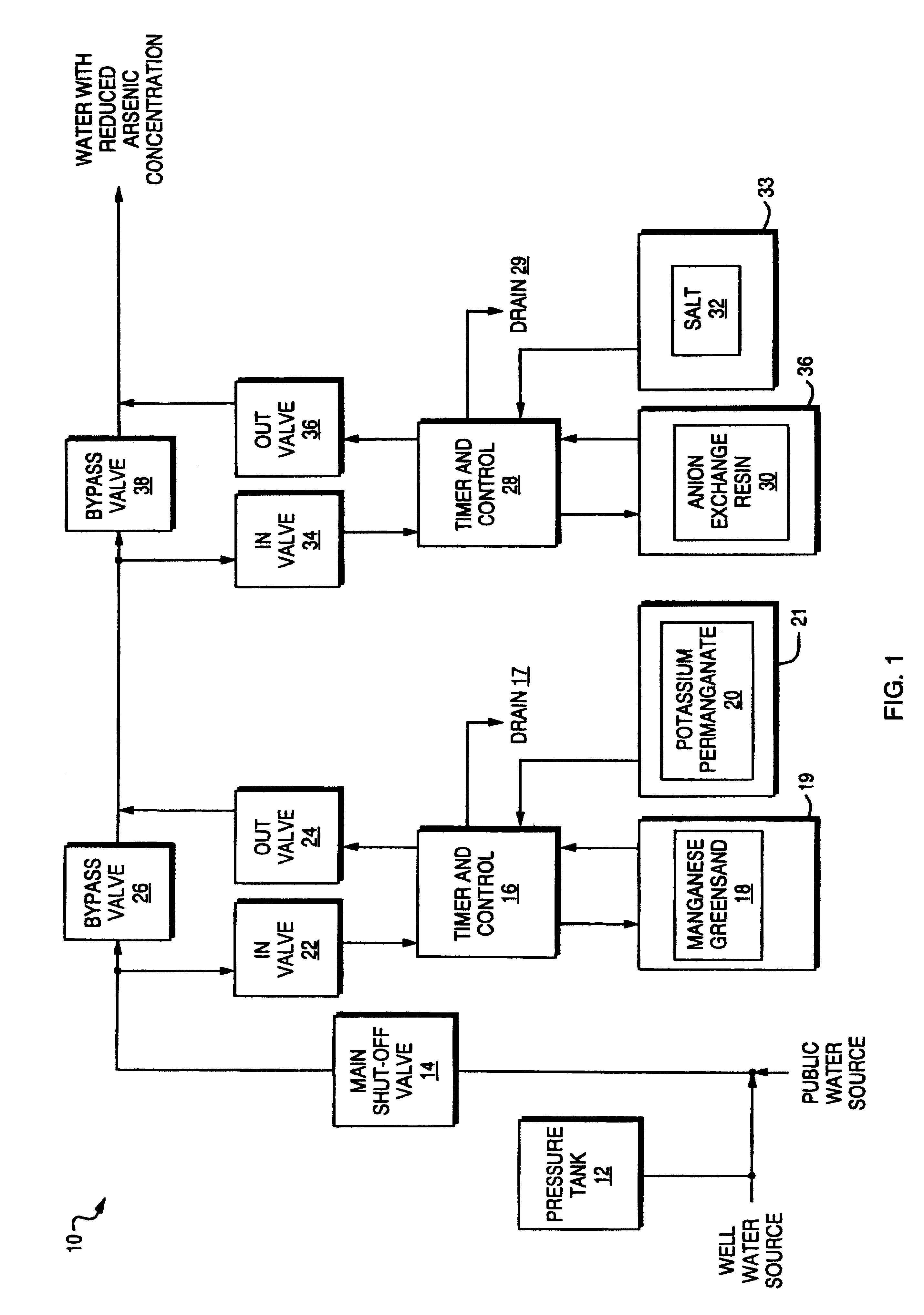
InactiveUS6368510B2Suitable in cost and space required and efficiencyOrganic anion exchangersIon-exchanger regenerationArsenateManganese
A method and apparatus for removing arsenic from water at point of entry or point of use particularly for residential application. The point of entry system comprises a first stage having a manganese greensand oxidizer to convert arsenite (As+3) present in the water to arsenate (As+5) and a second stage for passing the water through an anion exchange resin. Each stage includes a control head for automatic regeneration at a predetermined frequency. The manganese greensand is regenerated with a solution of potassium permanganate and the anion exchange resin is regenerated with a salt solution. An alternate embodiment for point of use application comprises a manganese greensand oxidizer cartridge to convert arsenite (As+3) to arsenate (As+5) followed by removal of the arsenate (As+5) with a reverse osmosis system.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO +1
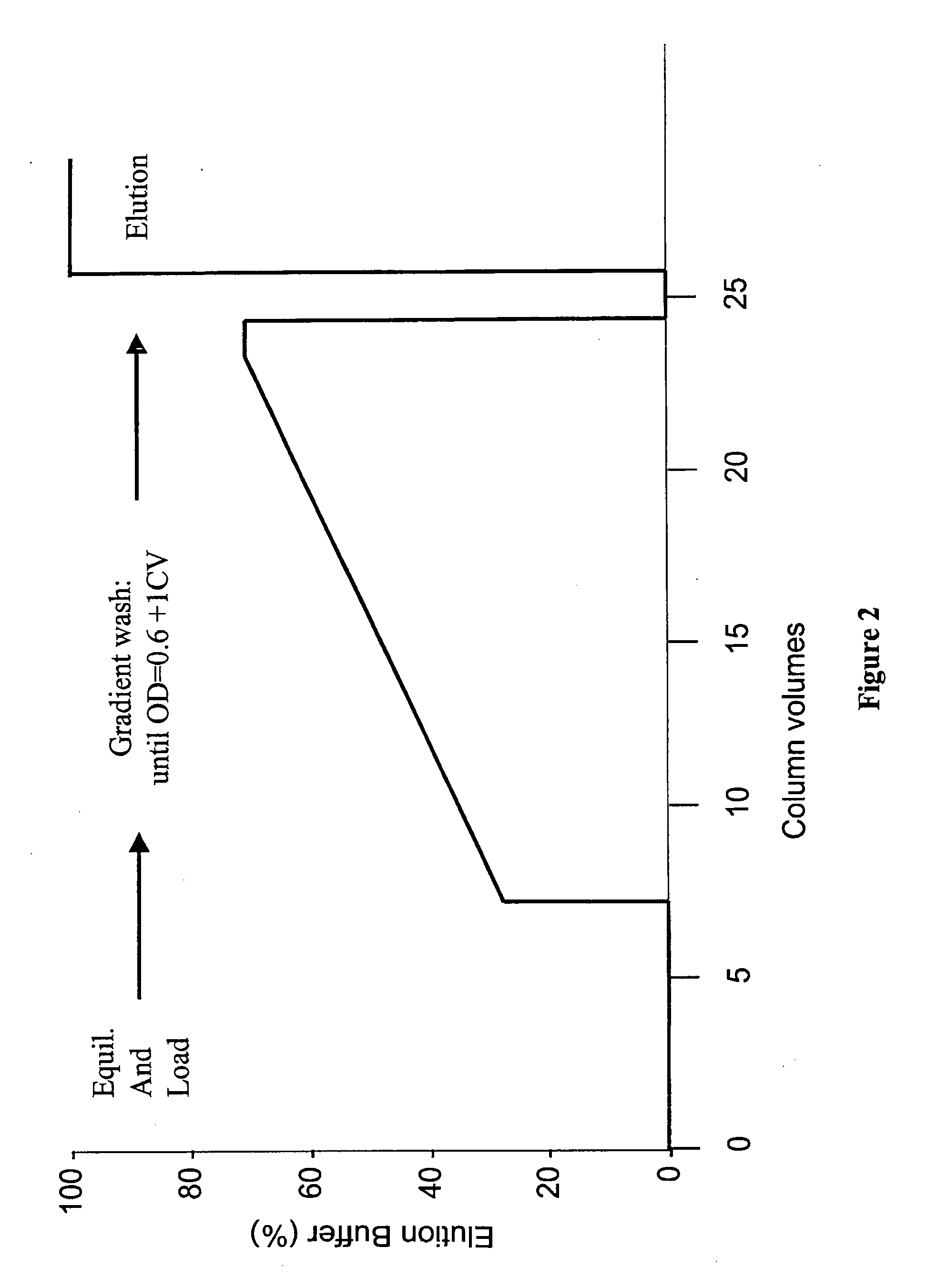
Protein purification
InactiveUS20120065381A1Improve conductivityCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersIon chromatographyMulti pollutant
A method for purifying a polypeptide by ion exchange chromatography is described in which a gradient wash is used to resolve a polypeptide of interest from one or more contaminants.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com