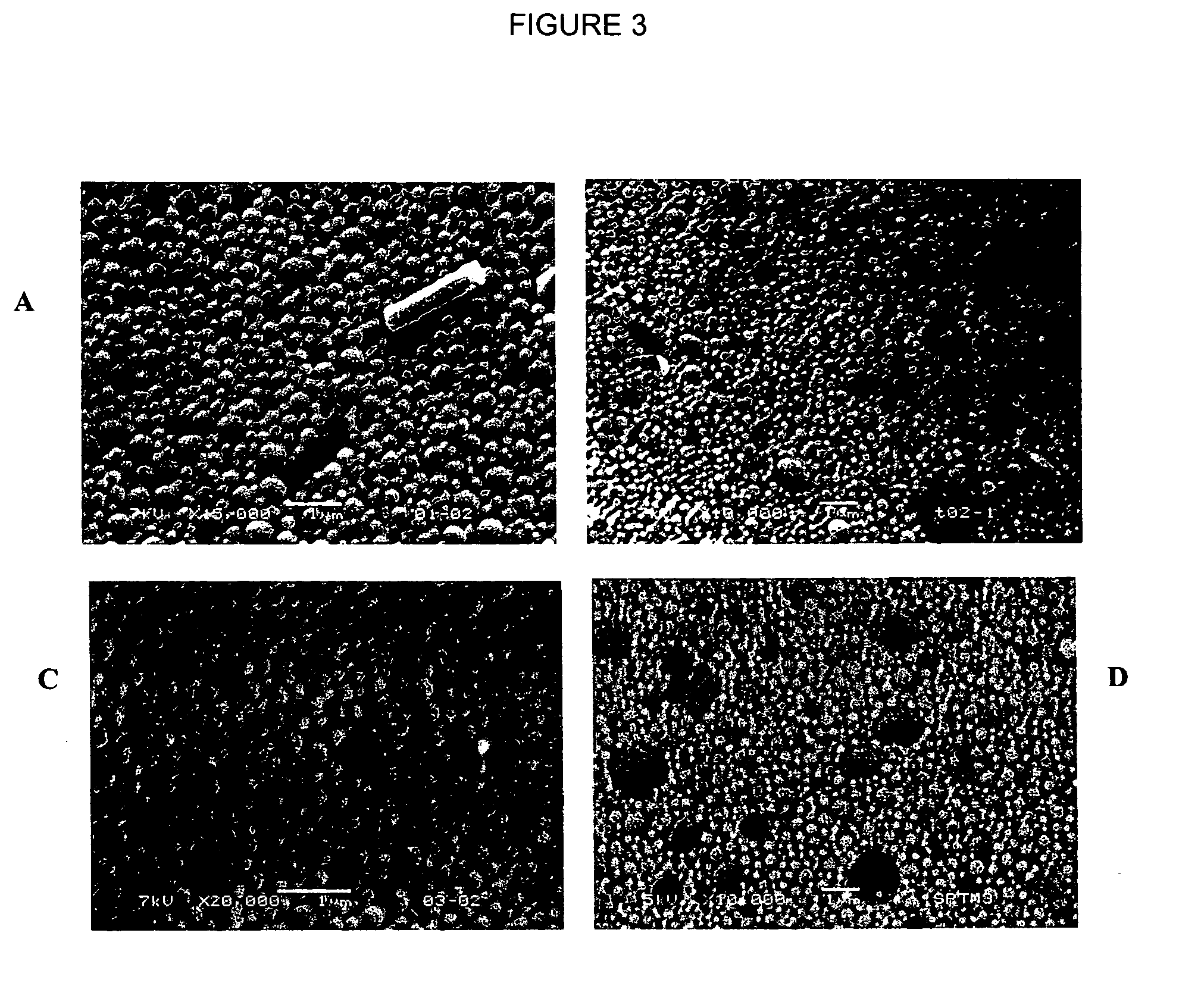
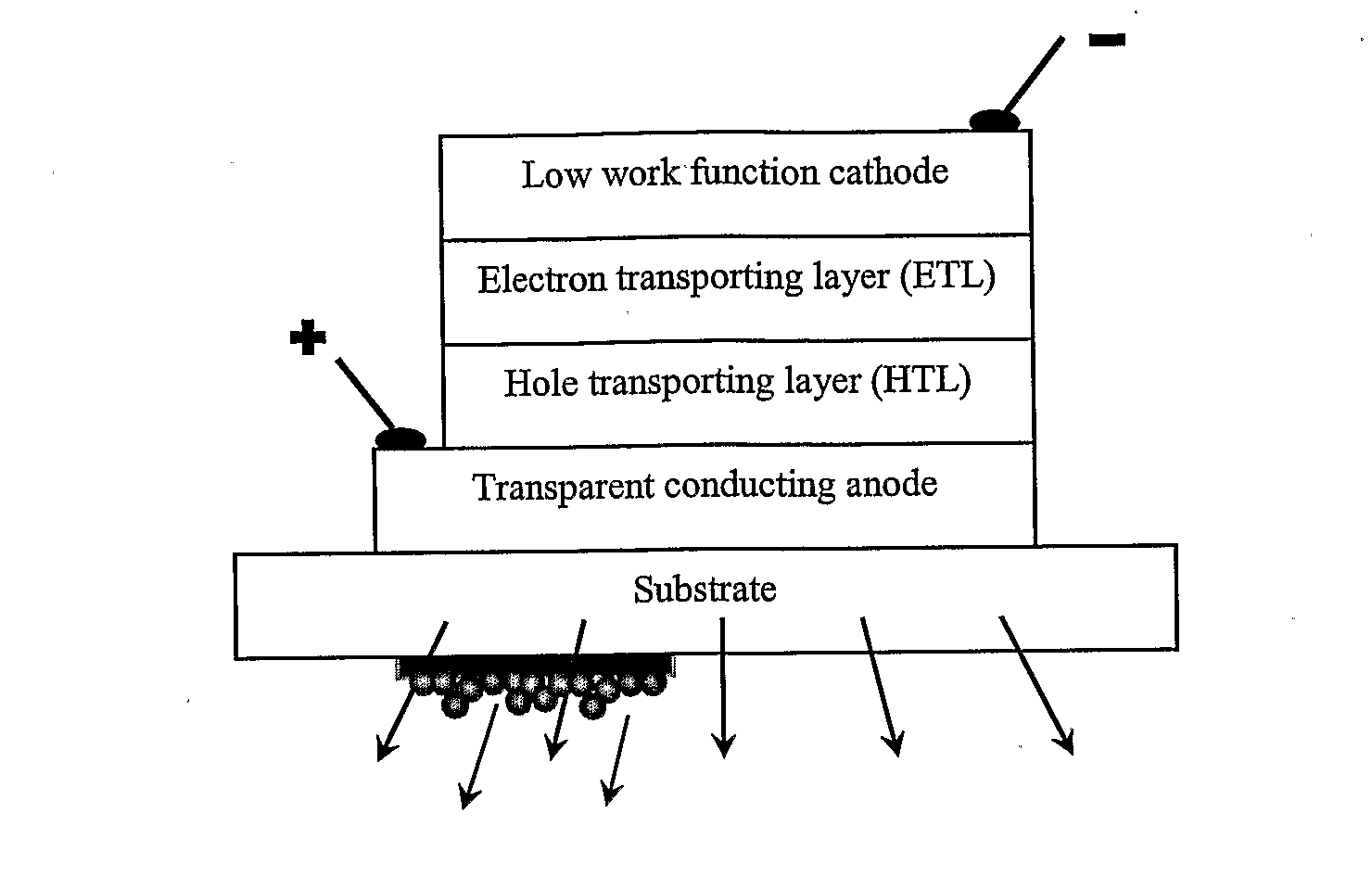
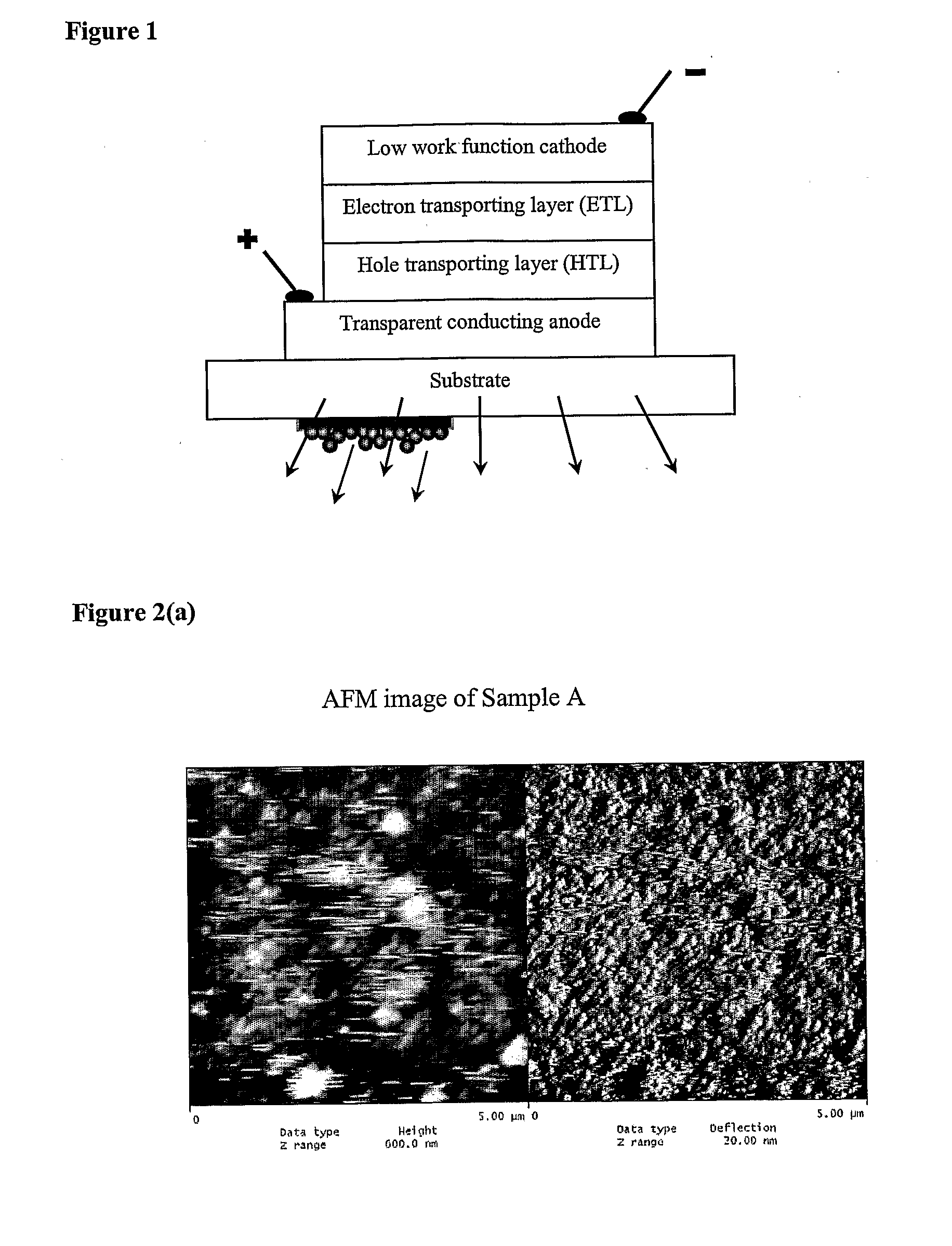
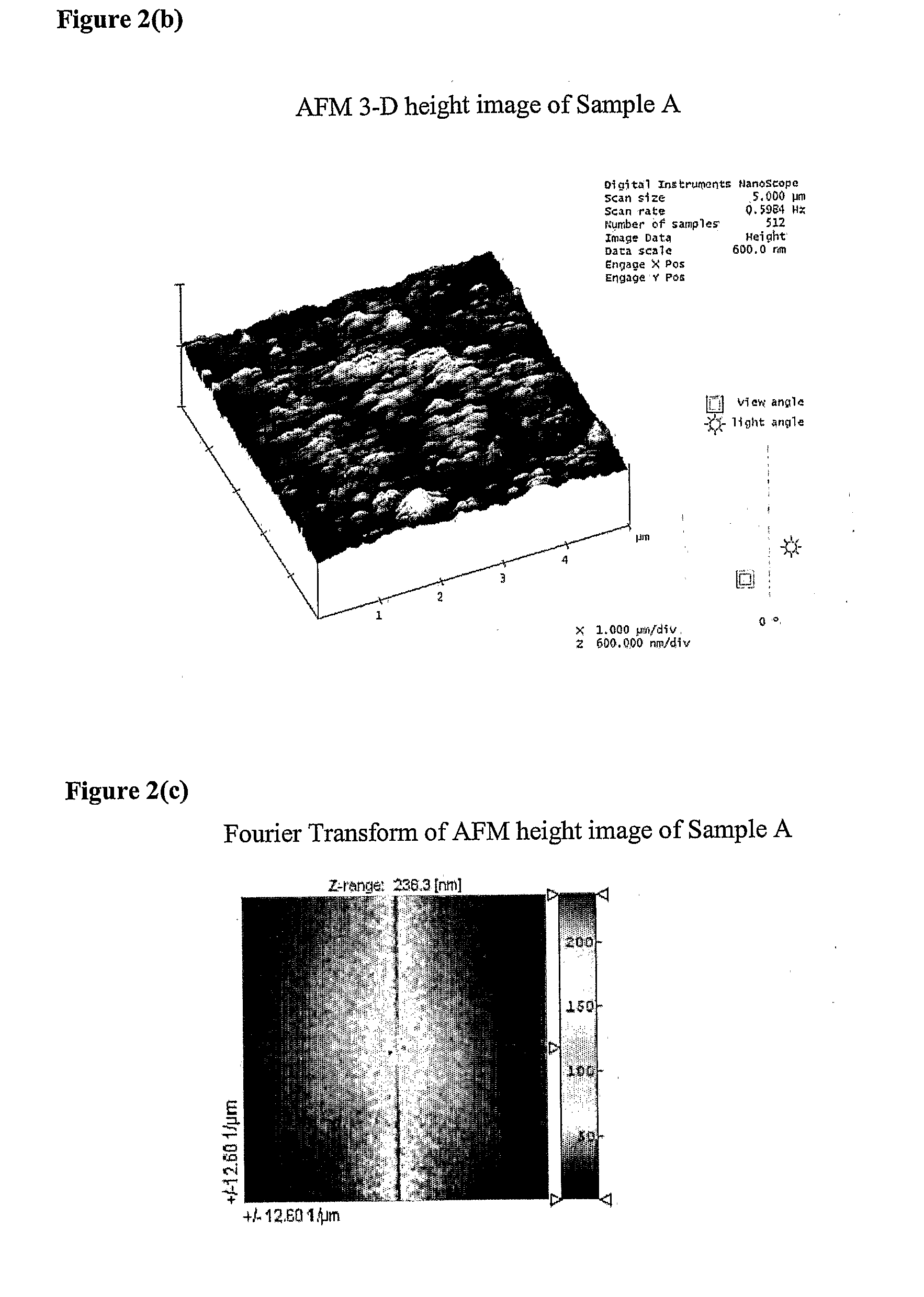
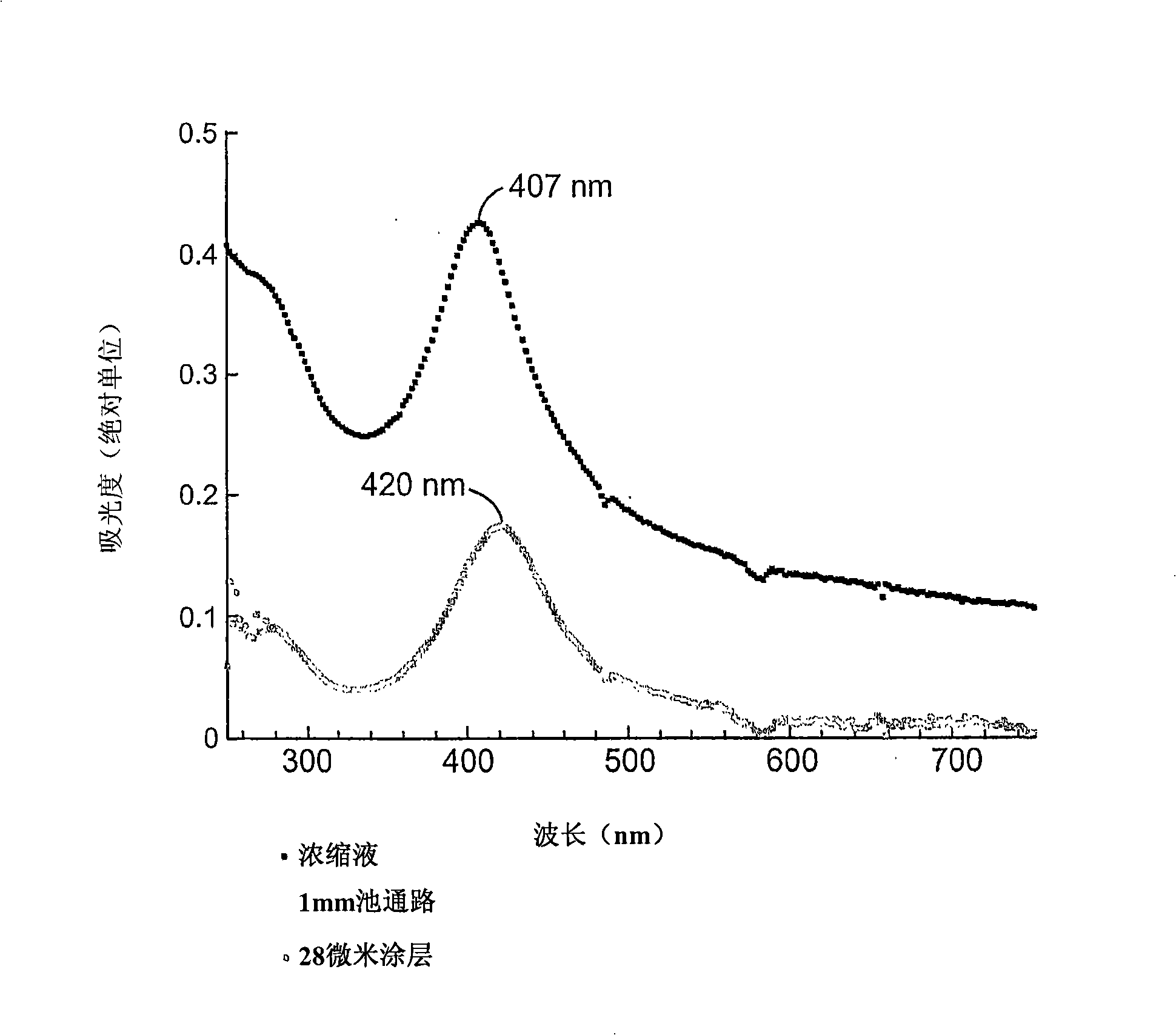
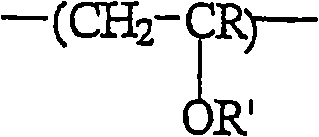
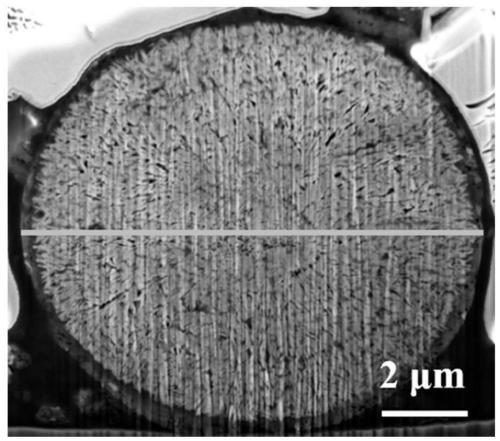
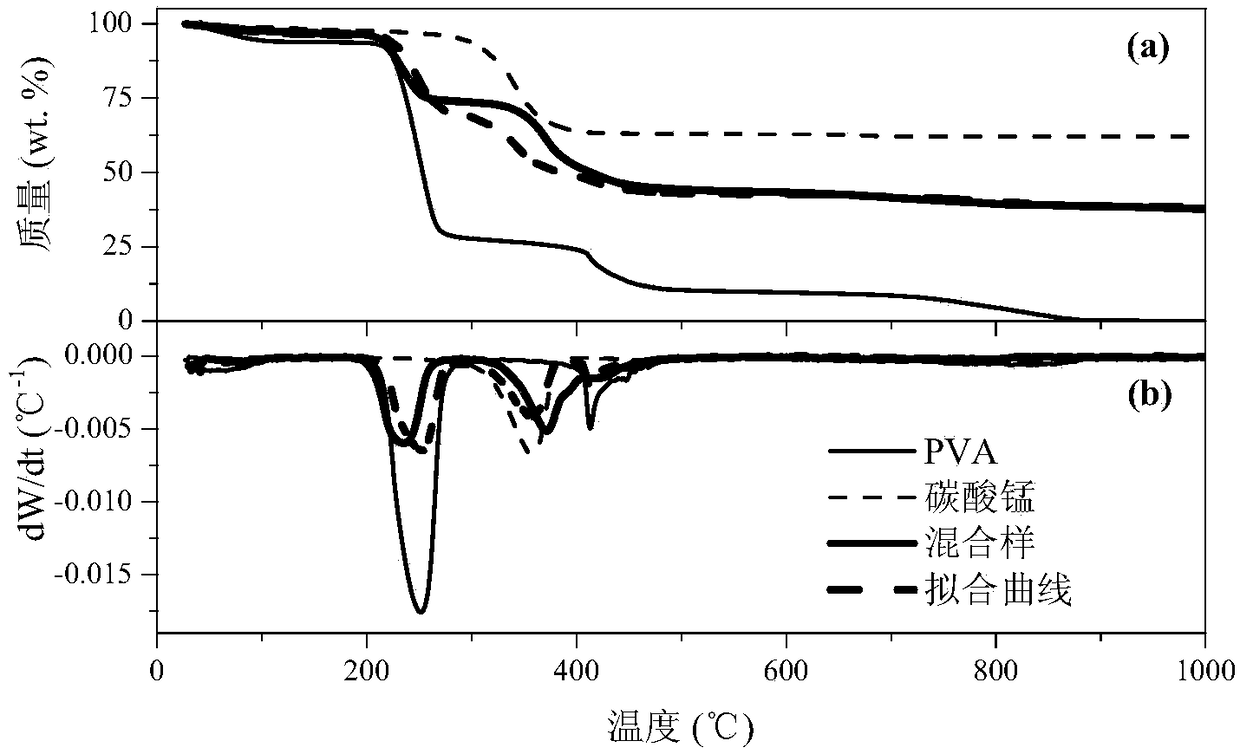
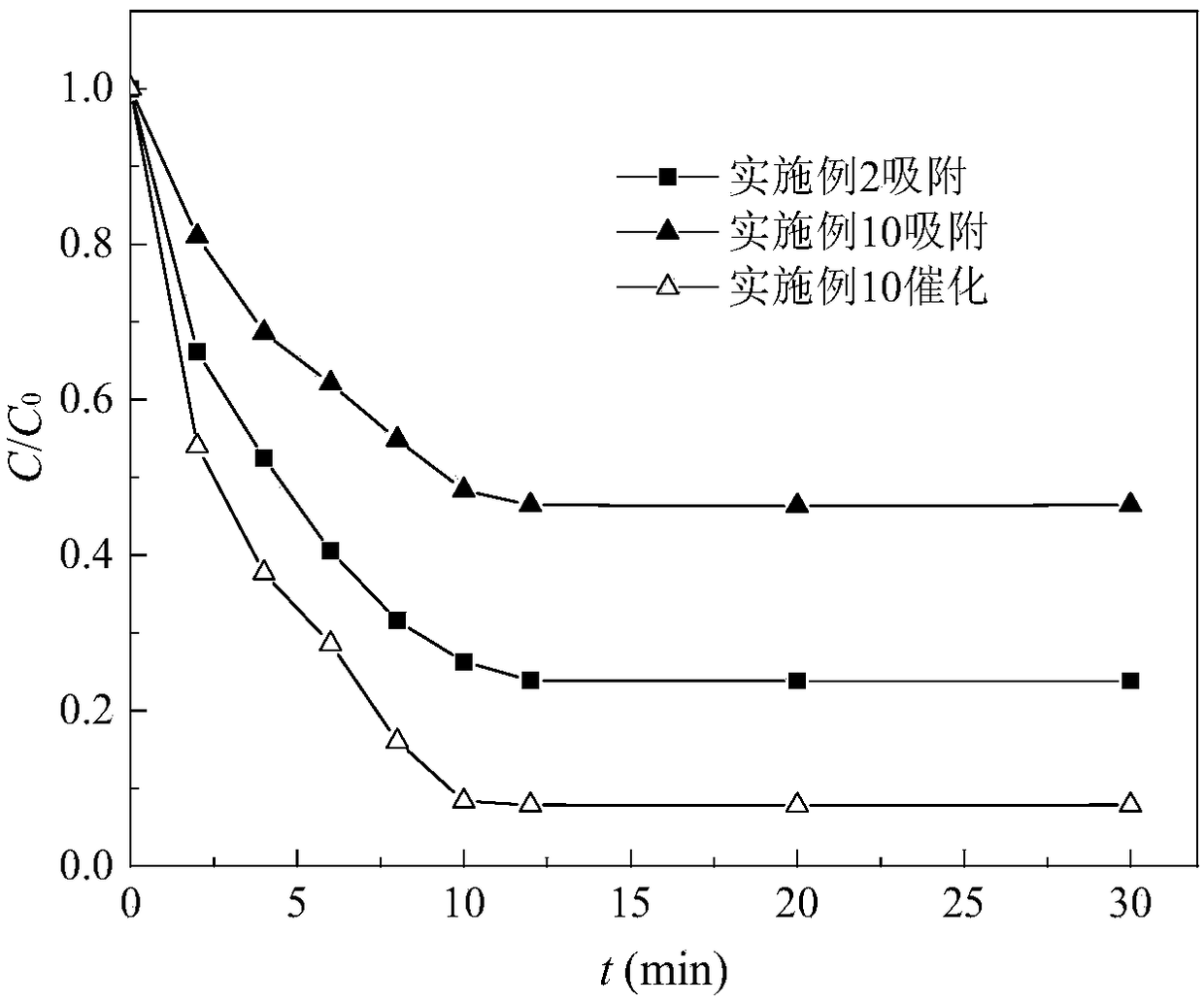
Patents
Literature
100 results about "Nanoparticle coating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical devices having a temporary radiopaque coating
A medical device comprising radiopaque water-dispersible metallic nanoparticles, wherein the nanoparticles are released from the medical device upon implantation of the device. The medical device of the present invention is sufficiently radiopaque for x-ray visualization during implantation, but loses its radiopacity after implantation to allow for subsequent visualization using more sensitive imaging modalities such as CT or MRI.The nanoparticles are formed of a metallic material and have surface modifications that impart water-dispersibility to the nanoparticles. The nanoparticles may be any of the various types of radiopaque water-dispersible metallic nanoparticles that are known in the art. The nanoparticles may be adapted to facilitate clearance through renal filtration or biliary excretion. The nanoparticles may be adapted to reduce tissue accumulation and have reduced toxicity in the human body. The nanoparticles may be applied directly onto the medical device, e.g., as a coating, or be carried on the surface of or within a carrier coating on the medical device, or be dispersed within the pores of a porous layer or porous surface on the medical device. The medical device itself may be biodegradable and may have the nanoparticles embedded within the medical device itself or applied as or within a coating on the biodegradable medical device. The nanoparticles may be released by diffusion through the carrier coating, disruption of hydrogen bonds between the nanoparticles and the carrier coating, degradation of the nanoparticle coating, degradation of the carrier coating, diffusion of the nanoparticles from the medical device, or degradation of the medical device carrying the nanoparticles.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Nanoparticle-based controlled release polymer coatings for medical implants
InactiveUS20050095267A1Improve solubilityFacilitated releaseStentsSurgeryControlled releaseSolubility
Implantable medical devices having a nanoparticle coating applied thereon. The nanoparticle coating comprises nanopulverized antiproliferative compounds. More specifically, the nanoparticulate antiproliferative compounds comprise particles less than 500 nm in size. The nanoparticle size of the compounds improves compounds' solubility. In addition to improving the solubility of otherwise insoluable antiproliferative compounds, the nanoparticle size minimizes the preparation and formulation required to prepare a dose of the antiproliferative compounds.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Nanoparticle coating for drug delivery
InactiveUS20060188543A1Control and reduceReduce controlSurgeryCoatingsNanoparticle coatingImplantation Site
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Nanoparticle coatings for flexible and/or drawable substrates
ActiveUS7438972B2Better able to withstandHigh glossSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationNanoparticle coatingPolyresin
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
System and method for cleaning and/or treating vehicles and the surfaces of other objects
InactiveUS6846512B2Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic anion exchangersHydrophilic coatingNanoparticle coating
The present invention relates to a system and method for cleaning and / or treating a surface, preferably surfaces such as ceramic, steel, plastic, glass and / or painted surfaces such as the exterior surface of a vehicle. In one embodiment, the method forms a transparent, hydrophilic coating on the surface of a vehicle. This embodiment of the method includes the steps of: (a) providing a vehicle having at least some surfaces that are at least one of the following: cured painted surfaces, cured clearcoat surfaces, and glass surfaces; (b) applying a non-photoactive nanoparticle coating composition to such surfaces; and (c) allowing the coating composition to dry on such surfaces before the surfaces are contacted by water.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
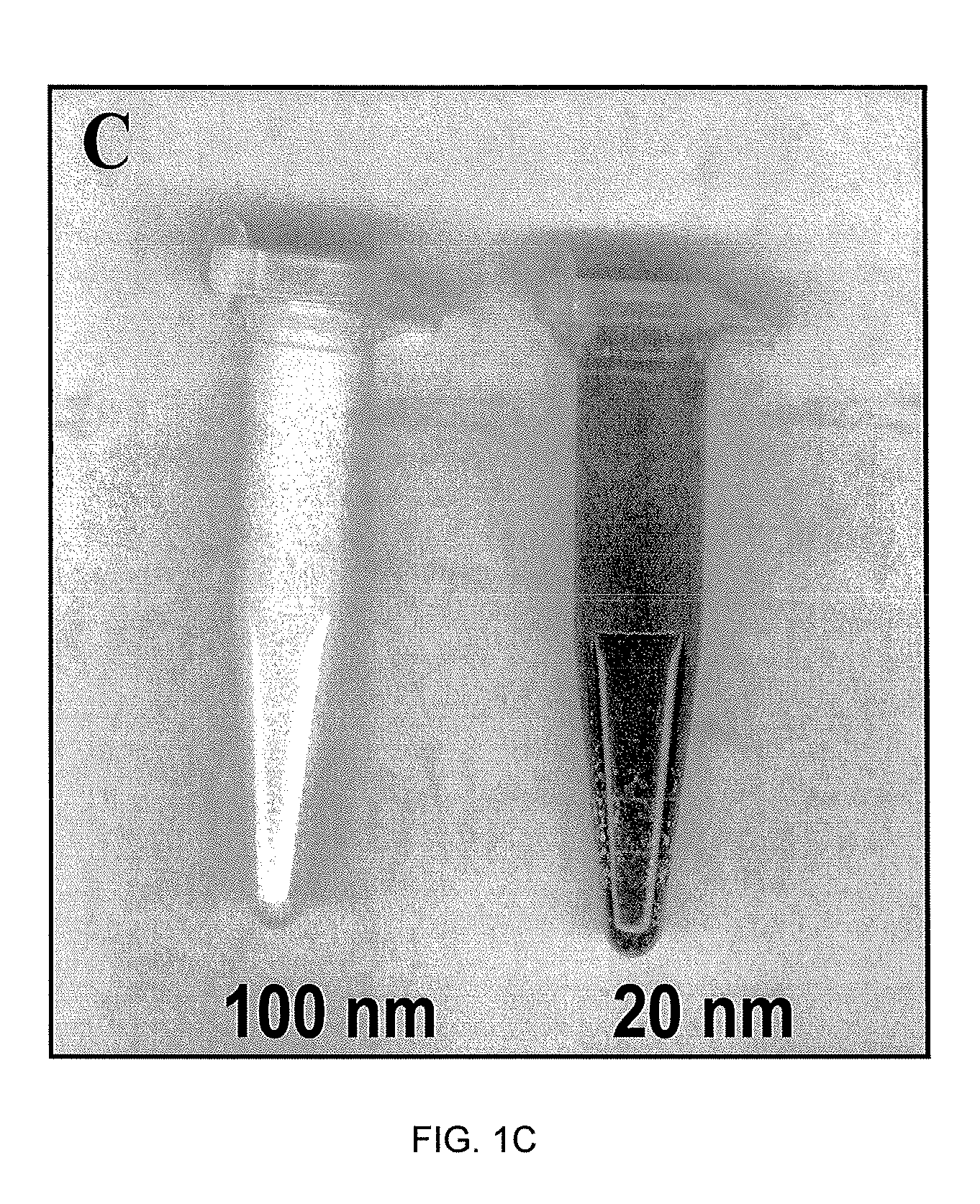
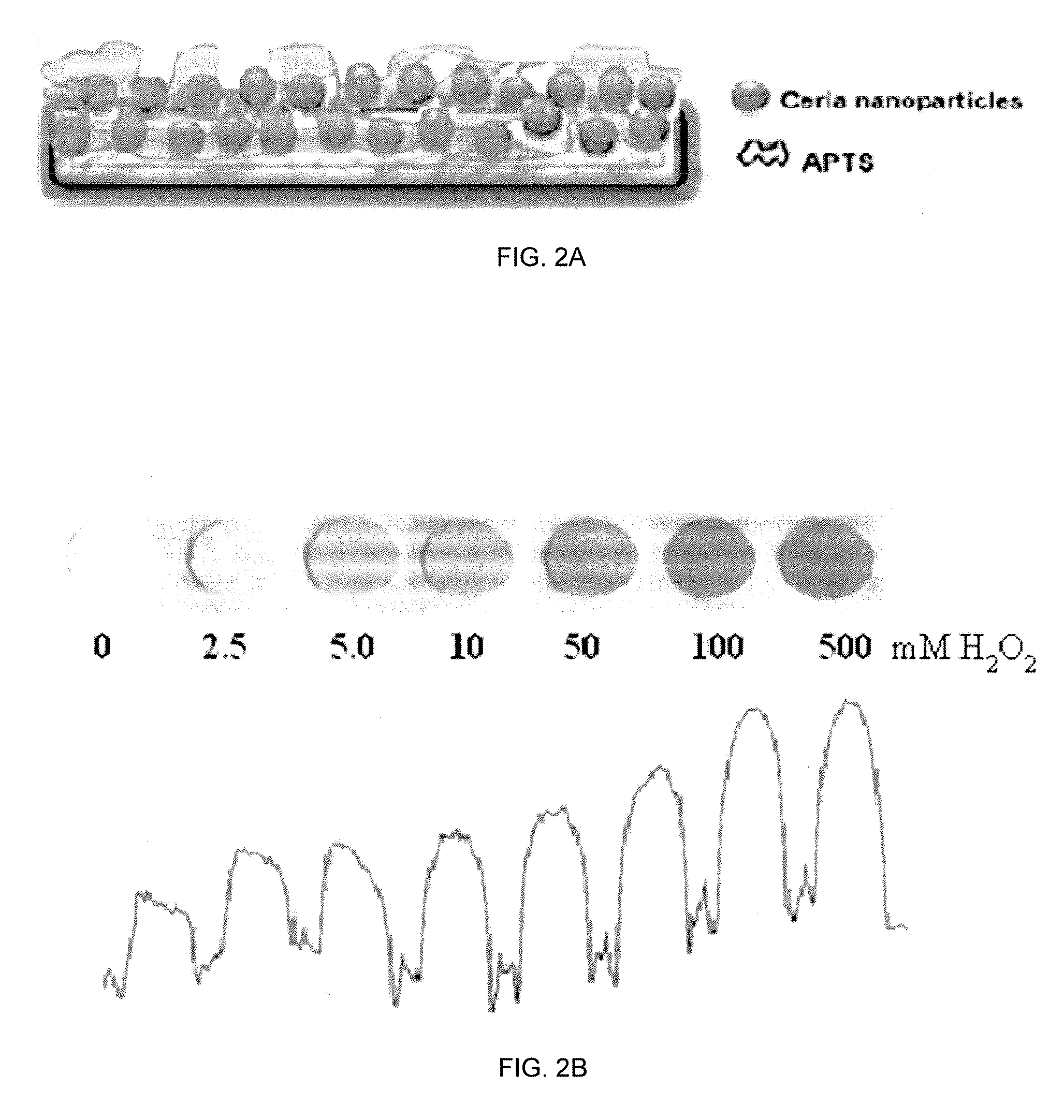
Reagentless Ceria-Based Colorimetric Sensor
ActiveUS20120315659A1Possible to detectIncrease rangeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementDelivery vehicleIn vivo
A colorimetric reagent in the form of nanoparticles, composite nanoparticles, and nanoparticle coatings, including methods of use, methods of preparation, deposition, and assembly of related devices and specific applications. The colorimetric reagent comprises cerium oxide nanoparticles which are used in solution or immobilized on a solid support, either alone or in conjunction with oxidase enzymes, to form an active colorimetric component that reacts with an analyte to form a colored complex. The rate of color change and the intensity of the color are proportional to the amount of analyte present in the sample. Also described is the use of ceria and doped ceria nanoparticles as an oxygen storage / delivery vehicle for oxidase enzymes and applications in biocatalytic processes in anaerobic conditions of interest in biomedicine and bioanalysis. Further described are a variety of related applications of the disclosed technology including clinical diagnosis, in vivo implantable devices, food safety, and fermentation control.
Owner:CLARKSON UNIVERSITY
High-security lithium ion batteries and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106848383AIsolated contact short circuitPrevent precipitationFinal product manufactureElectrolyte accumulators manufactureLithium metalDissolution
The invention discloses high-security lithium ion batteries and a preparation method thereof. A prepared negative pole piece is coated with a chemically inert organic polymer coating, the organic polymer coating is insoluble in water, and the melting point of the organic polymer coating is 90-110 DEG C. when the lithium ion batteries have thermal runaway of battery internal short circuit caused by destructive crash such as overcharge, heavy stuff impact, thermal shock, short circuit, needling, and extrusion, a polyethylene nanoparticle coating is melted and forms a coating of the surface of the negative pole piece, a protective film is formed in the surface of the negative pore piece, the contact short circuit of a positive pore piece and the negative pore piece can be effectively isolated, the inlay and precipitation of lithium metal ions can be effectively prevented, and therefore the further rise of the temperature due to active substance dissolution and the thermal runaway is restrained, and the overall security property of a cell can be improved obviously.
Owner:SPRINGPOWER TECHNOLOGY (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
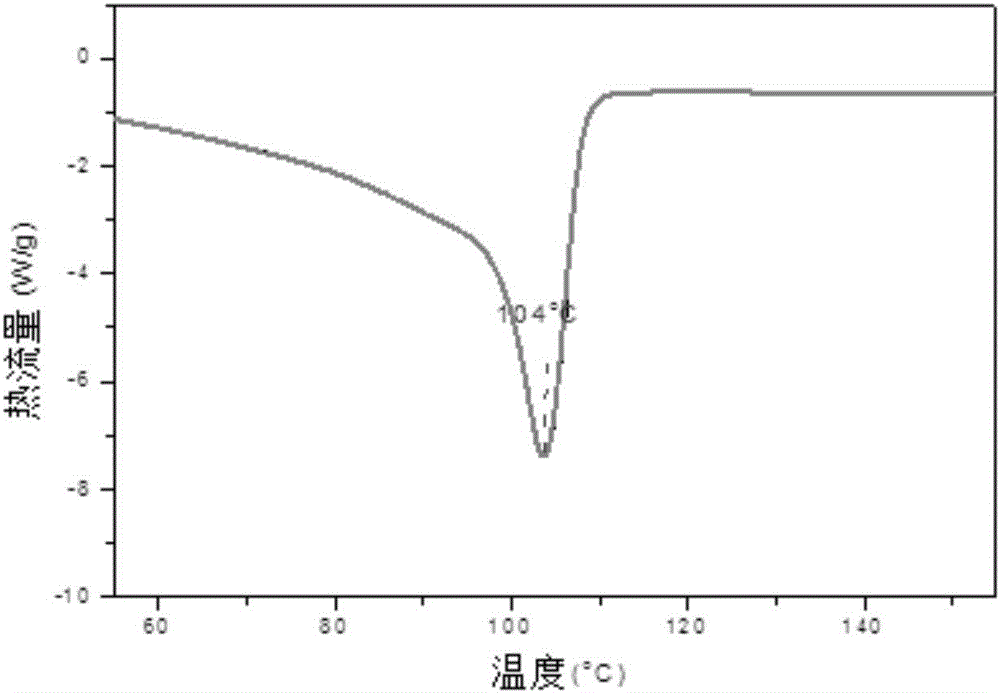
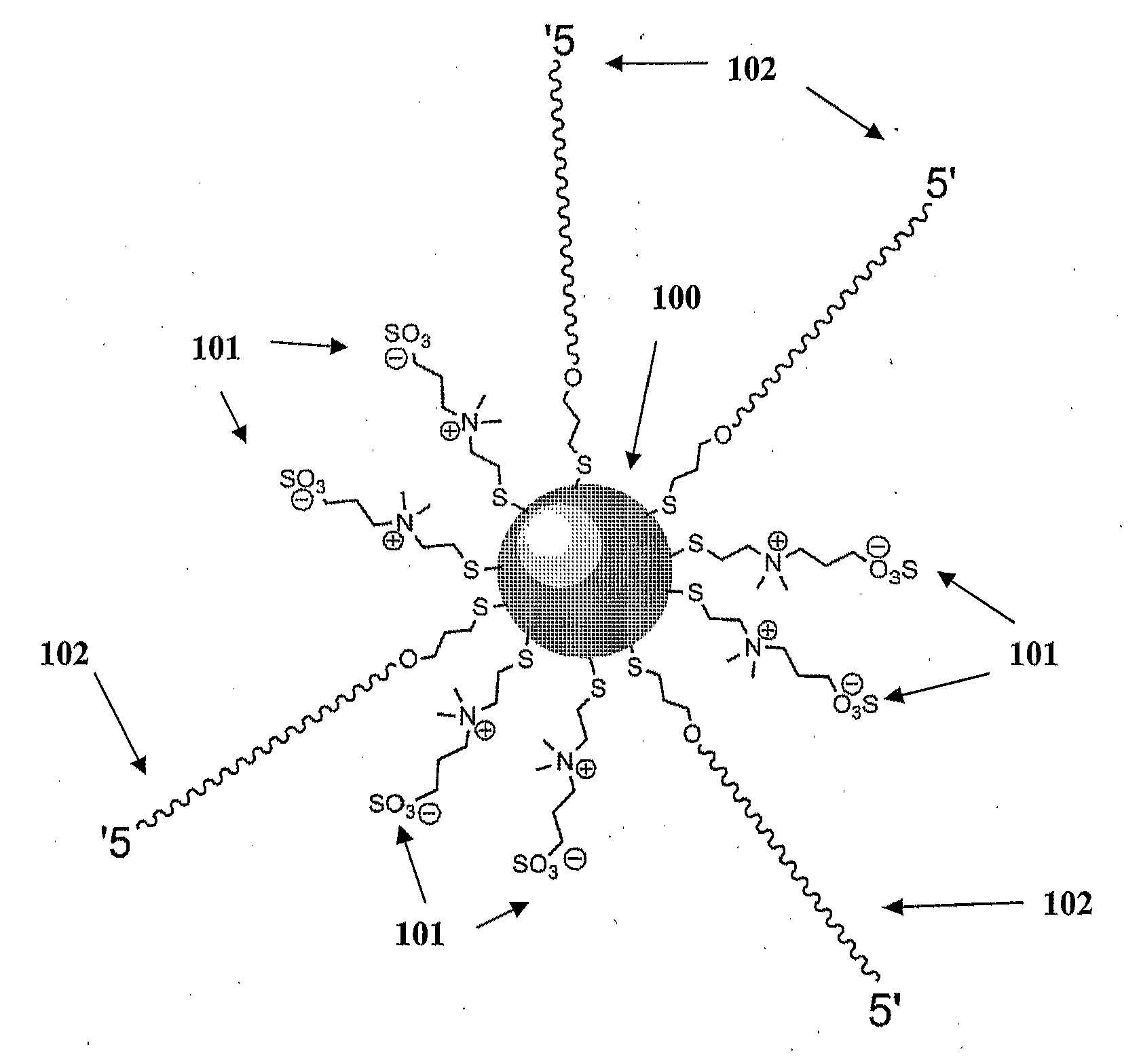
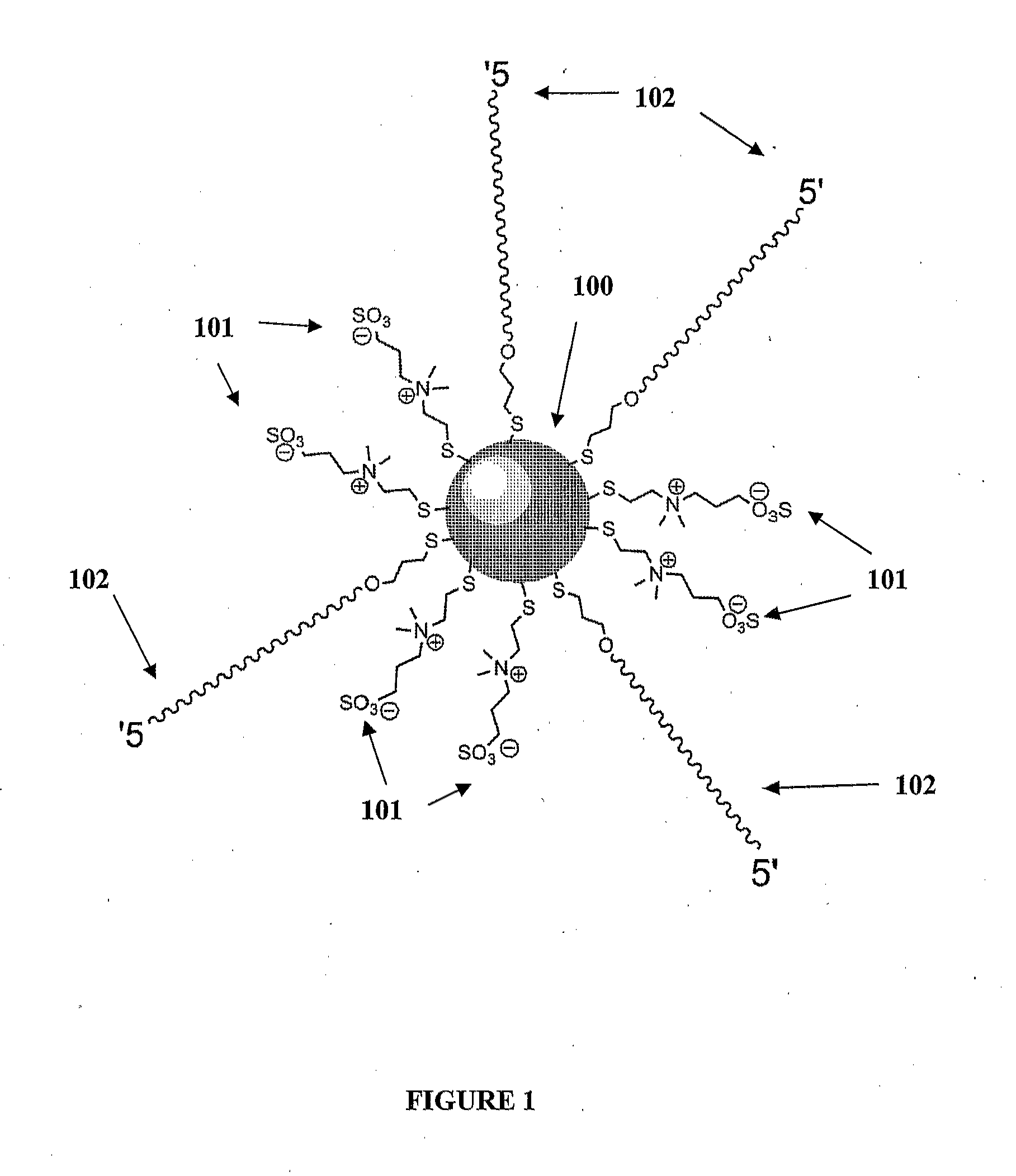
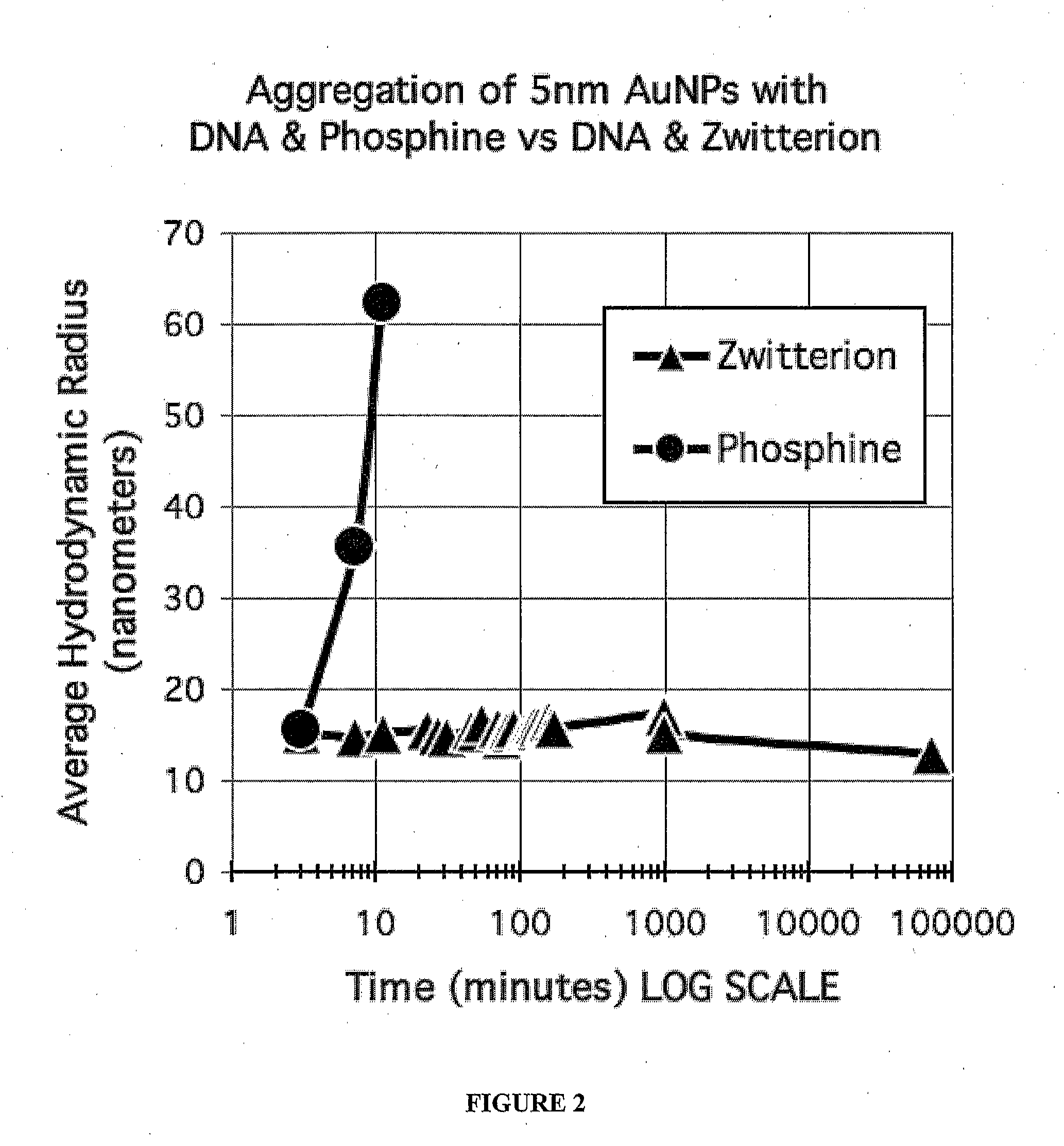
Zwitterion-Linker Coatings for Nano-objects in Solutions of Multivalent Counterions
InactiveUS20120141797A1Facilitates nanostructure assemblyReduce and prevent non-specific spontaneous aggregationMaterial nanotechnologyWater-repelling agents additionNanoparticle coatingCounterion
The disclosure is directed to nanoparticles used in creating nanostructure complexes in the presence of divalent cations. In particular, the disclosure is directed to nanoparticles that are coated with zwitterions and linker portions in a manner that facilitates nanostructure complex assembly while reducing or preventing non-specific spontaneous aggregation of nanoparticle in the presence of divalent cations. The disclosure also provides a method for preparing a nanoparticle coating of the present invention. Furthermore, the disclosure provides a method for assembling nanostructure complexes using coated nanoparticles with a scaffold.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Optical Thin Films with Nano-Corrugated Surface Topologies by a Simple Coating Method
InactiveUS20080157665A1Improve lighting efficiencyLight extraction efficiency of lightMaterial nanotechnologyDischarge tube luminescnet screensStainingNanoparticle coating
Embodiments of the invention relate to functionalized nanoparticle coating compositions. These coating can improve the light extraction efficiency of light emitting devices, including LEDs and OLEDs. In some embodiments, the coating can improve other properties such as anti-staining, abrasion and / or scratch resistance.
Owner:OPTIMAX TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Superhydrophobic self-healing intelligent nano-coating and preparation method thereof
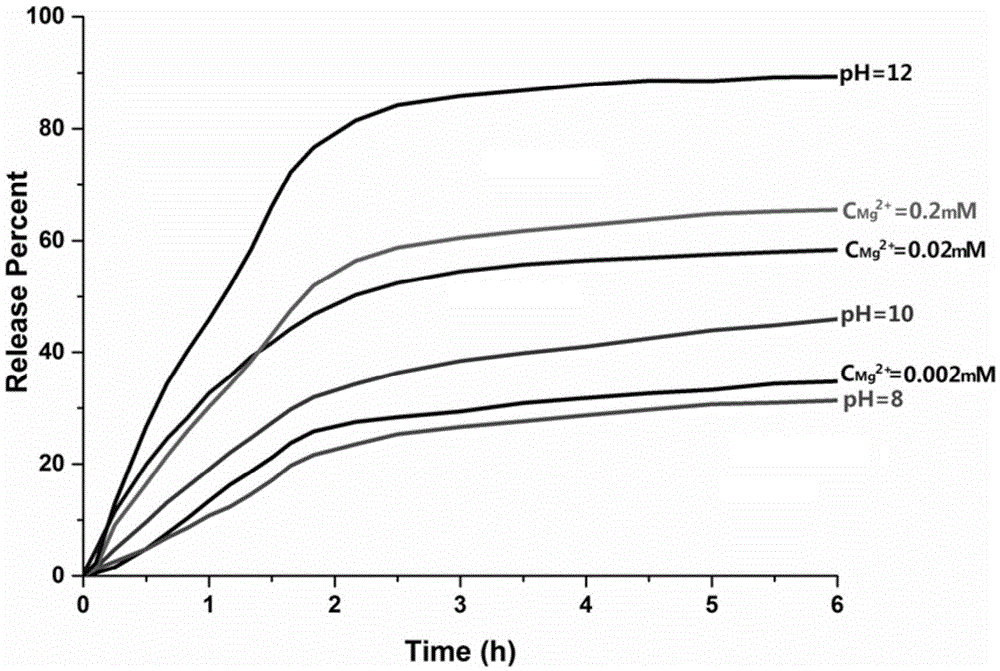
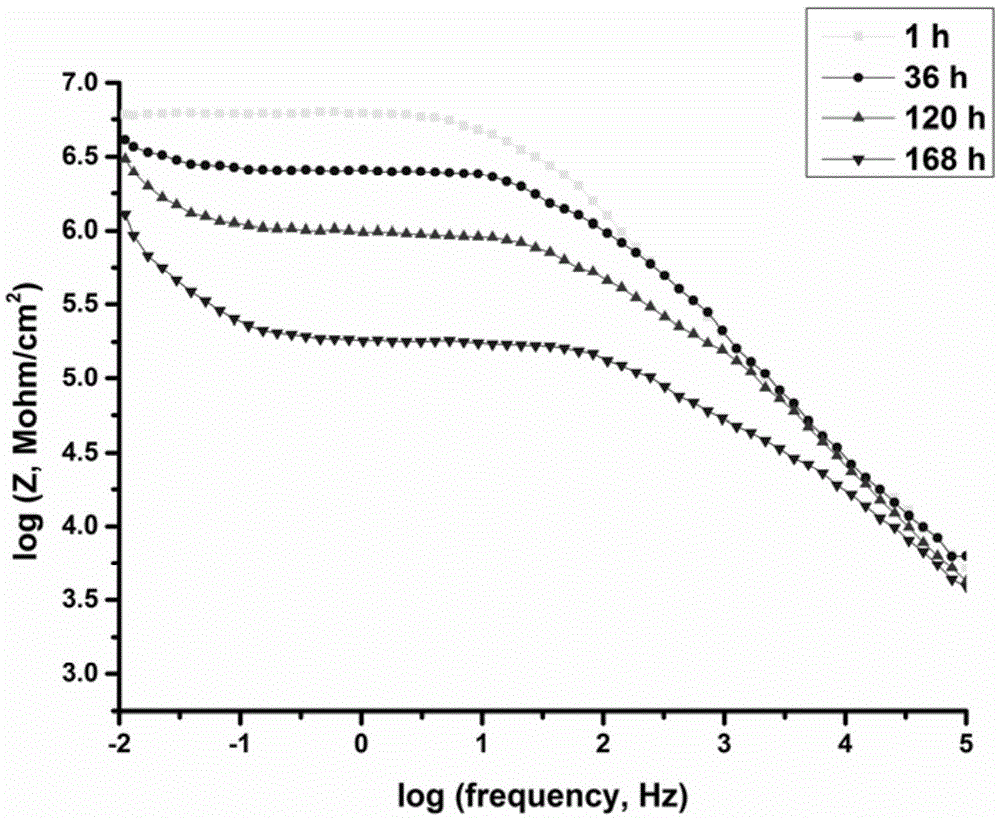
The invention discloses a superhydrophobic self-healing intelligent nano-coating and a preparation method thereof. According to the intelligent nano-coating, a sol-gel self-assembly nanoparticle coating is adopted as a framework; functionalized nano-grade silica particles are doped in the coating; magnesium alloy corrosion inhibitor molecules paeonol are loaded in the functionalized nano-grade silica particles; a superhydrophobic fluorine-containing monomolecular film layer is modified on the surface of the particles. With the superhydrophobic characteristic, the coating has a good waterproof performance, and assists in inhibiting corrosive medium penetration. The intelligent nano-coating layer can sense the pH change and magnesium ion existence when the magnesium alloy micro-area corrosion occurs, and can rapidly release the magnesium alloy corrosion inhibitor paeonol. The paeonol molecules can form a layer of dense film adhering to the damaged magnesium alloy surface and inhibiting corrosion spreading. Therefore, a function of actively protecting the magnesium alloy is realized. Further, the superhydrophobic self-healing intelligent nano-coating is adapted to environment changes. Especially, with the Mg<2+> response characteristic, the nano-coating has a good application prospect in the field of magnesium corrosion inhibition.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Preparation method of coating with bone induction and antibiosis functions on surface of medical metal
InactiveCN103203039AImprove bioavailability in vivoSmall toxicityCoatingsProsthesisAntibiosisNanoparticle coating
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nanoparticle coating with the bone induction and antibiosis functions on the surface of a medical metal. According to the method, nanoparticles with different electric properties as used as a carrier, the nanoparticles are formed by mutual crosslinking of high-molecular polymers, and growth factors and antibiotics are respectively loaded in the process of preparing the nanoparticles with dissimilar electric properties, wherein factors and factor-friendly polyanions are sufficiently mixed to react first and are then immobilized into the nanoparticles through ionic crosslinking; and amino-containing antibiotics are grafted to a polyaldehyde anionic polymer through chemical crosslinking first and are then loaded into the nanoparticles through ionic crosslinking. The two types of nanoparticles are alternately assembled on the surface of the medical metal through electrostatic adsorption, covalent crosslinking is also formed among the particles, and the stability of the coating is enhanced. The coating prepared by using the method has the function of controlling adsorption and release of the growth factors and the antibiotics under the normal physiological environment, the activity of the growth factors are keep well and a strong bone induction function is achieved; and in addition, the antibiotics can be slowly released for a long time, and a good antibiosis effect is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Stent coatings incorporating nanoparticles
Coatings for implantable medical devices including nanoparticles incorporating an active agent, and methods for fabricating the coatings.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
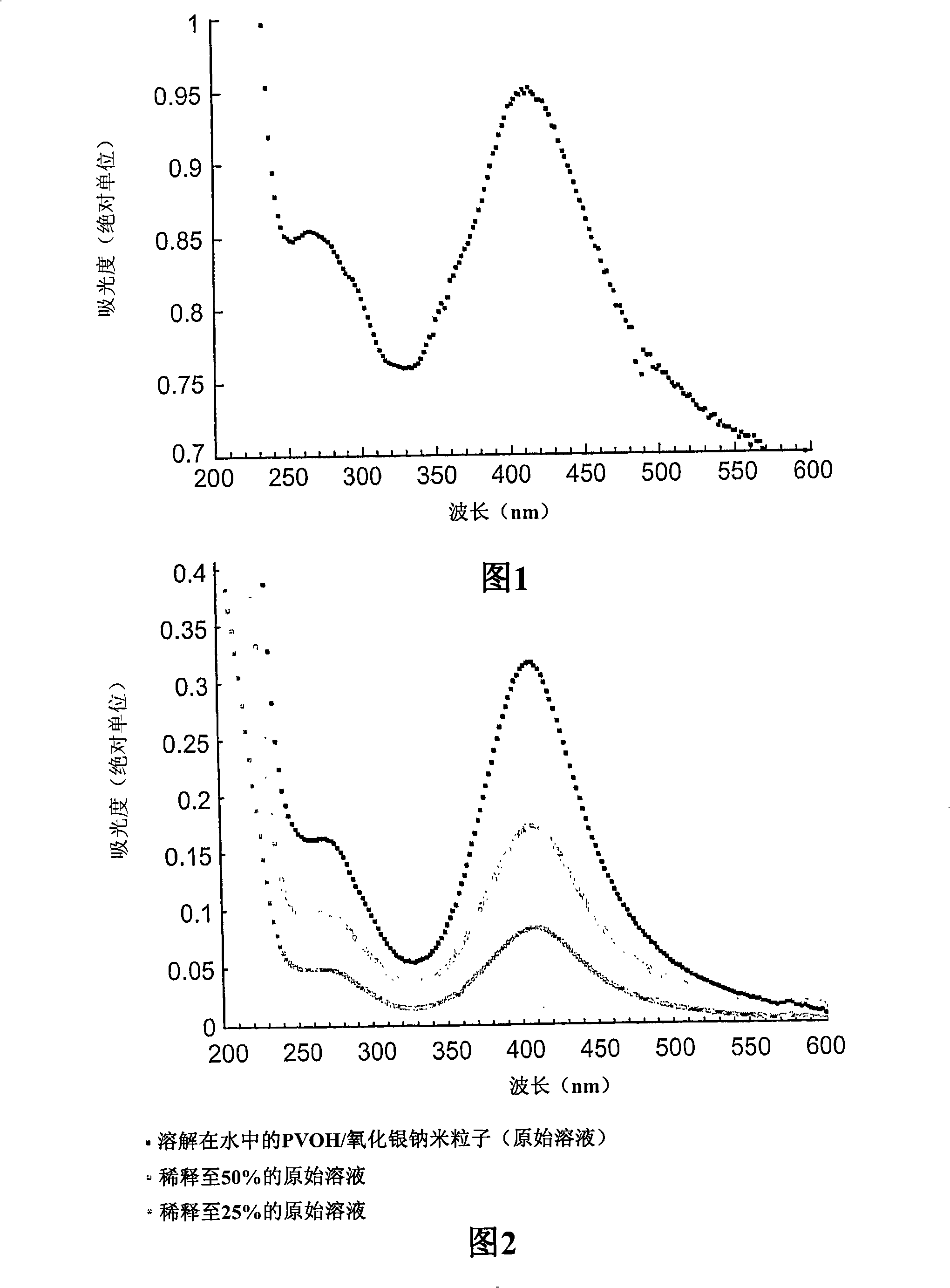
Water-soluble polymer substrate having metallic nanoparticle coating
A metallic nanoparticle coated water-soluble polymeric substrate and the process for preparing and using the same is described.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
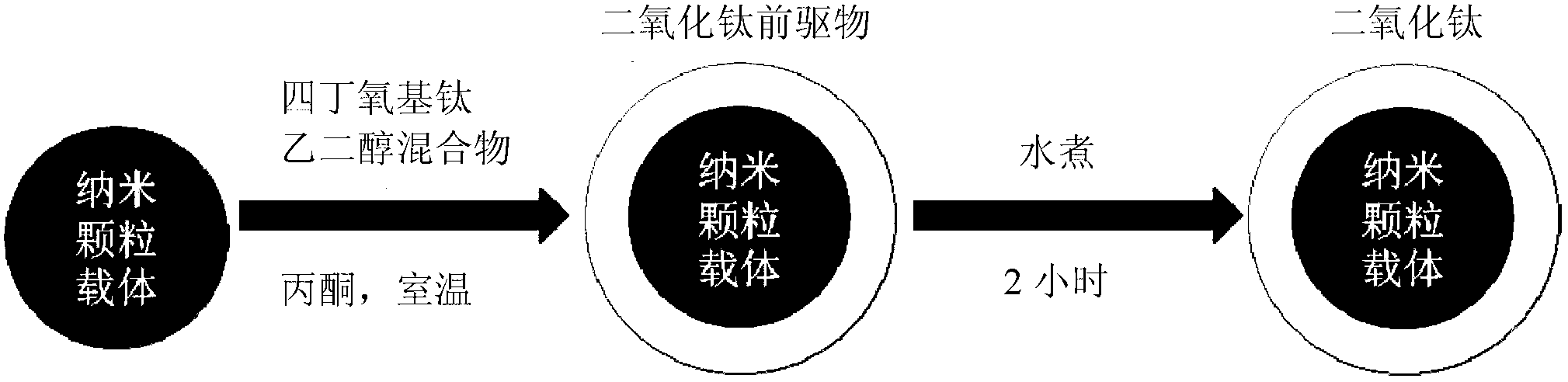
Preparation method of core-shell composite material wrapped in titanium dioxide nanoparticle coating
InactiveCN103192075ALarge specific surface areaImprove stabilityNanotechnologyWater bathsMetal oxide nanoparticles
A preparation method of core-shell composite material wrapped in a titanium dioxide nanoparticle coating includes: firstly, acquiring nanoparticle carrier; and secondly, wrapping the surface of the metal or metal oxide nanoparticle carrier with a titanium dioxide nanoparticle coating. The second step includes dissolving titanium isobutoxide in glycol, mixing at room temperature for 4-8 hours to obtain titanium dioxide precursor mixed solution A, dispersing the nanoparticle carrier in acetone, mixing well to obtain even mixed solution B, adding the titanium dioxide precursor mixed solution A into the mixed solution B, allowing for obtained solution to stand at room temperature to form precipitate mixed solution, and subjecting the precipitate mixed solution to centrifugal separation, and heating in water bath at 80-100 DEG C. The preparation method of the core-shell composite material wrapped in the titanium dioxide nanoparticle coating allows for increasing of photocatalysis efficiency and is low in cost.
Owner:杨晓红
Modification method of high-nickel ternary anode material of lithium ion battery
InactiveCN111477867ACoating method is simpleReduce difficultySecondary cellsPositive electrodesManganeseLithium-ion battery
The invention discloses a modification method of a high-nickel ternary anode material of a lithium ion battery. The method comprises the following steps: a, mixing an original precursor of the high-nickel ternary material with a lithium source, and presintering to prepare a lithiated precursor; b, preparing manganese / aluminum oxide nanoparticles by using a sol-gel method; c, uniformly coating thesurface of the lithiation precursor of the high-nickel ternary material with manganese / aluminum oxide nanoparticles; and d, preparing the manganese / aluminum element doped high-nickel ternary materialthrough high-temperature calcination. According to the lithiation precursor route provided by the invention, the breakage of the precursor in the nanoparticle coating process can be greatly reduced, and the uniform coating of the manganese / aluminum oxide nanoparticles on the lithiation precursor is realized. By regulating and controlling the crystal microstructure of the manganese / aluminum doped high-nickel ternary material, cracks of the ternary material microspheres in the charge-discharge cycle process of the battery can be greatly reduced, so that the high-nickel ternary material shows excellent cycle stability.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Three-dimensional graphene-based combined electrode with MnO2 and Au nanoparticle-coating surface, and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN103840179ASimple preparation processReduce energy consumptionFuel and secondary cellsCell electrodesNanoparticle coatingLithium–air battery
The invention discloses a three-dimensional graphene-based combined electrode with a MnO2 and Au nanoparticle-coating surface. By taking three-dimensional porous foam nickel as a matrix, graphene directly grows on the matrix, and flower-shaped delta-MnO2 directly grows on the graphene and loaded with Au nanoparticles. The invention further discloses a preparation method and applications of the three-dimensional graphene-based combined electrode with the MnO2 and Au nanoparticle-coating surface. The preparation method has the advantages of being simple in preparation technology, low in cost, short in period, low in energy consumption and the like, and is suitable for industrial mass production; the prepared three-dimensional graphene-based combined electrode does not contain any conductive agent and binder, and due to the synergistic catalytic action of a special three-dimensional porous structure and the flower-shaped delta-MnO2, Au nanoparticles and graphene, the three-dimensional graphene-based combined electrode shows low polarization and better cycling stability when being used as a lithium-air battery cathode.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
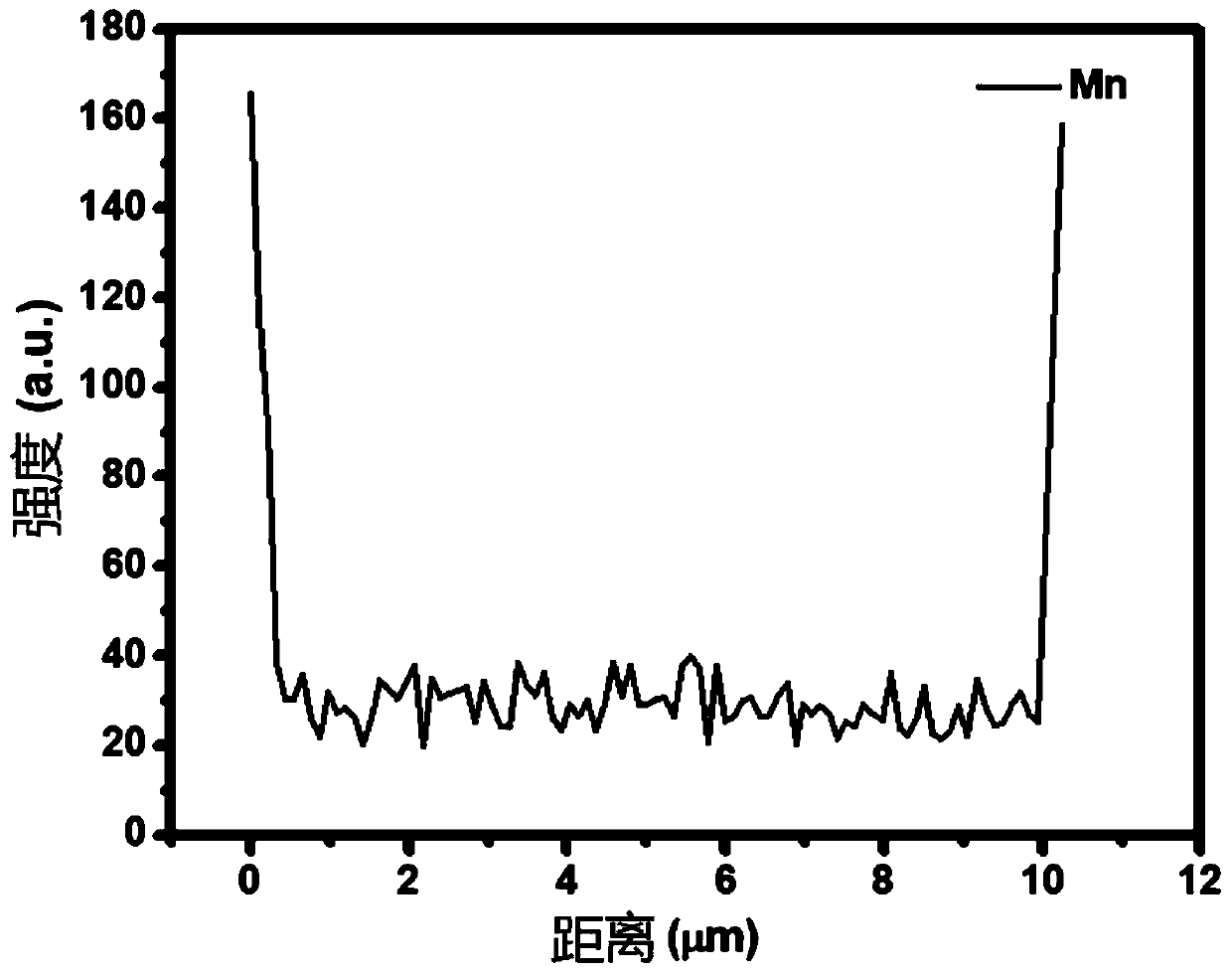
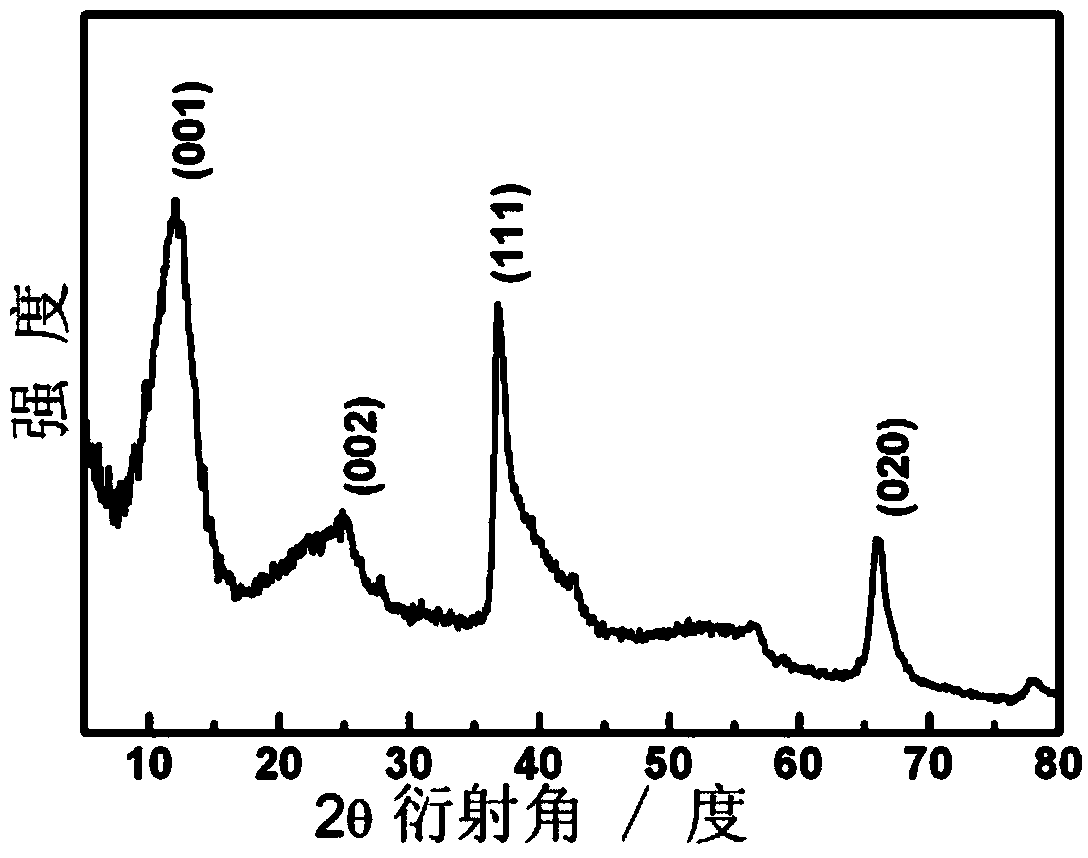
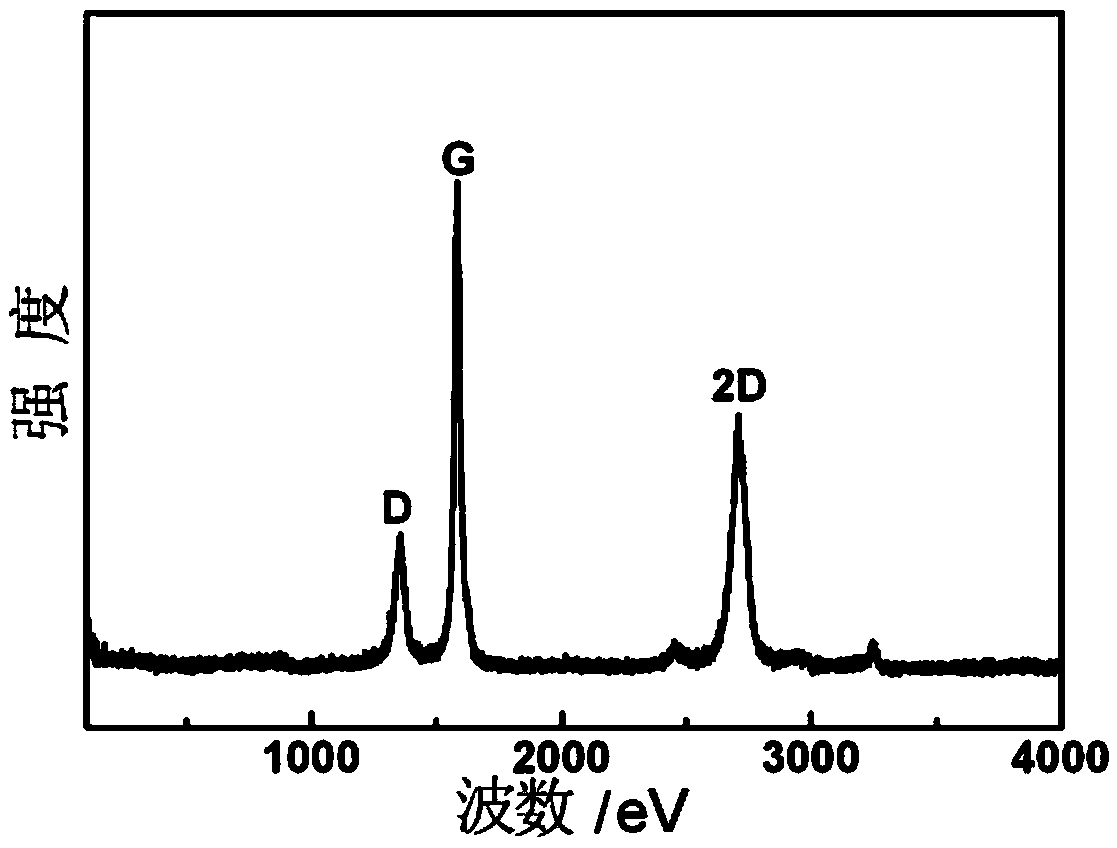
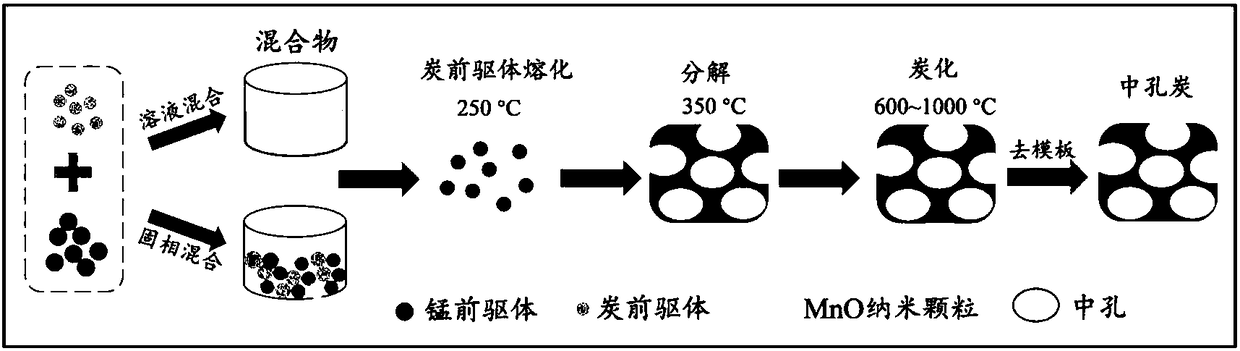
Mesoporous carbon prepared by using manganese compound, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109110742AAchieve recyclingLarge specific surface areaMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst carriersNanoparticle coatingChemical compound
The invention discloses mesoporous carbon prepared by using a manganese compound, and a preparation method thereof. According to the method, manganese oxide crystal nanoparticles formed by decomposinga manganese compound during pyrolysis carbonization of a carbon precursor have mesoporous size characteristic, the manganese compound can catalyze the carbon precursor to form carbon, and the manganese compound is used as a template agent precursor so as to prepare mesoporous carbon. The method specifically comprises: 1, uniformly mixing a thermoplastic carbon precursor and a manganese compound through solid phase powder or a liquid phase solution; 2, carrying out high-temperature carbonizing on the mixture in an inert atmosphere to obtain a MnO-nanoparticle-coating carbide; and 3, uniformlymixing the carbide and a dilute acid solution, and removing MnO to obtain mesoporous carbon. According to the present invention, the prepared mesoporous carbon has characteristics of high specific surface area, high mesoporosity, large mesopore volume, easily-controlled pore structure and easily-controlled pore size distribution, can greatly reduce the carbonization temperature of the carbon precursor, and can be widely used in the fields of adsorption, catalysis and separation.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
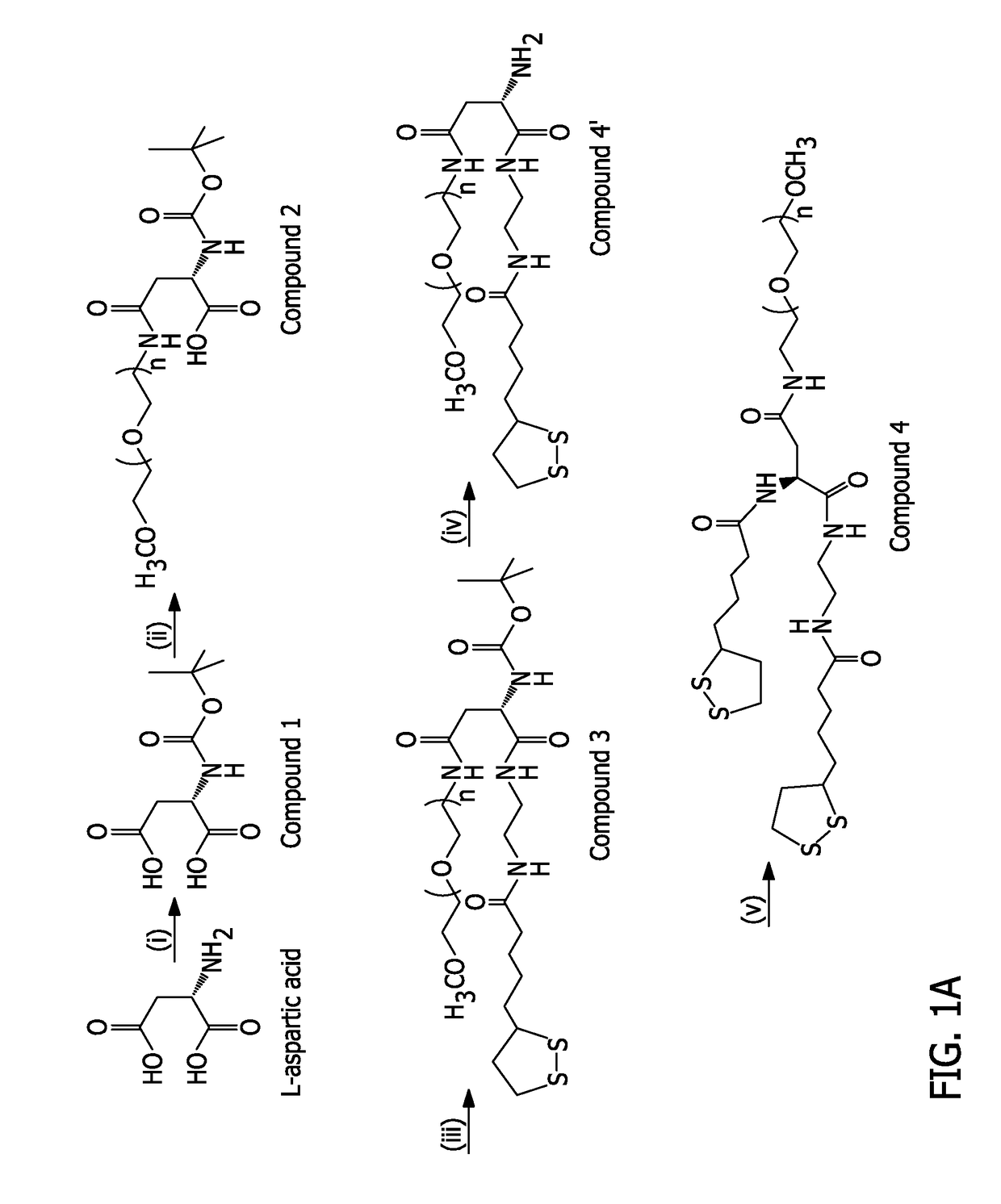
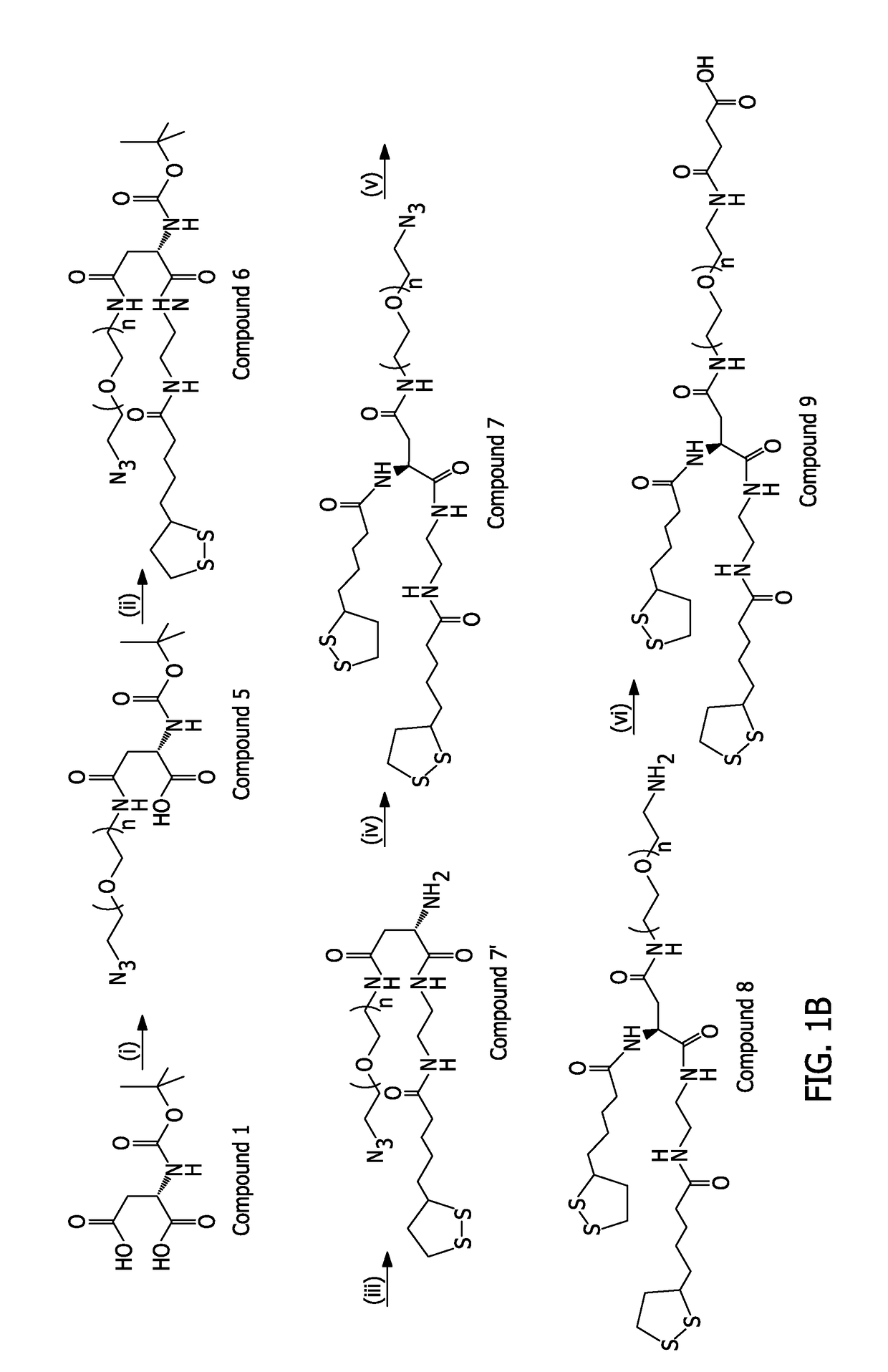
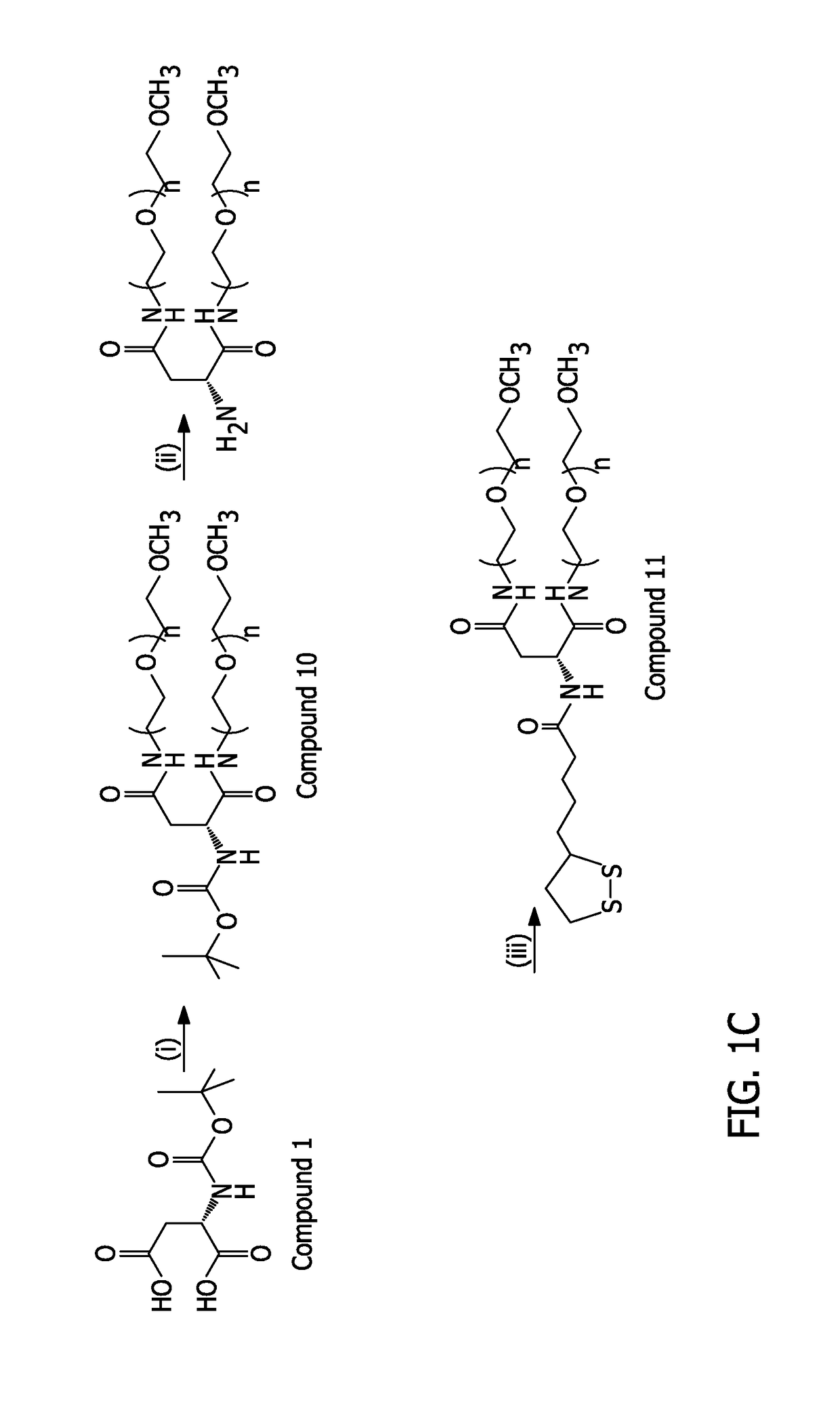
Controlling the architecture, coordination, and reactivity of nanoparticle coating utilizing an amino acid central scaffold
ActiveUS20170168042A1Improve stabilityImprove the immunityOrganic chemistryBiological testingNanoparticle coatingL-Aspartate
A series of multicoordinating and multifunctional ligands optimized for the surface-functionalization of luminescent quantum dots (QDs) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) alike is disclosed. An L-aspartic acid precursor is modified with functionality, through simple peptide coupling chemistry, one or two lipoic acid (LA) groups and poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) moieties in the same ligand. These ligands were combined with a new photoligation strategy to yield hydrophilic and reactive QDs that are colloidally stable over a broad range of conditions, including storage at nanomolar concentration and under ambient conditions.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Method for constructing nano coating on surface of micro-nano structure and application of nano coating on antireflection
ActiveCN108373610AStable chargingUniform thicknessCoatingsSemiconductor devicesMicro nanoElectricity
The invention discloses a method for constructing a nano coating on the surface of a micro-nano structure and application of the nano coating on antireflection. In the method, a nano-particle coatingis adopted and comprises a solution a and a solution b; the solution a comprises a silane coupling agent and a solvent; the solution b comprises nano-particle dispersion liquid and a solvent; the solution a is dropwise added in the solution b to obtain the nano-particle coating; and the silane coupling agent in the solution a has positive electricity, and nano-particles in the solution b has negative electricity or is improved by substances which have negative electricity. By the method, the conformal nano coating with the uniform thickness is constructed on the surface with an irregular micro-nano structure, and furthermore, the thickness of the coating can be regulated and controlled according to time of immersion in the nano-particle coating. In addition, the method for constructing thenano coating is applied to antireflection, and thus, a transmittance value of a substrate is increased to a certain extent on the original.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Stent coatings incorporating nanoparticles
Coatings for implantable medical devices including nanoparticles incorporating an active agent, and methods for fabricating the coatings.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Nanoparticle photocatalysis board, its preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102513074AReduce manufacturing costGood effectInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsLaminationNanoparticle coatingDesorption
The invention provides a nanoparticle photocatalysis board, its preparation method and application thereof. The nanoparticle photocatalysis board comprises a substrate and a photosensitive nanoparticle coating that is cured on the substrate. The preparation method consists of: subjecting the substrate to ultrasonic cleaning and drying it in the air, and applying a light curing adhesive uniformly in a darkroom environment, then conducting drying treatment so as to obtain a light curing rubber board; spraying the photosensitive nanoparticles on the light curing rubber board uniformly, then placing it in an ultraviolet light environment for curing, thus obtaining the nanoparticle photocatalysis board, which can be applied in removing residual washing agents in washed clothes. The photocatalysis board provided in the invention has the advantages of low preparation cost, low particle desorption rate, current scour resistance, and no loss of the activity of the nanoparticles. The method of the invention is simple and operated at normal temperature, and it reduces the cost as well as improves production efficiency.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
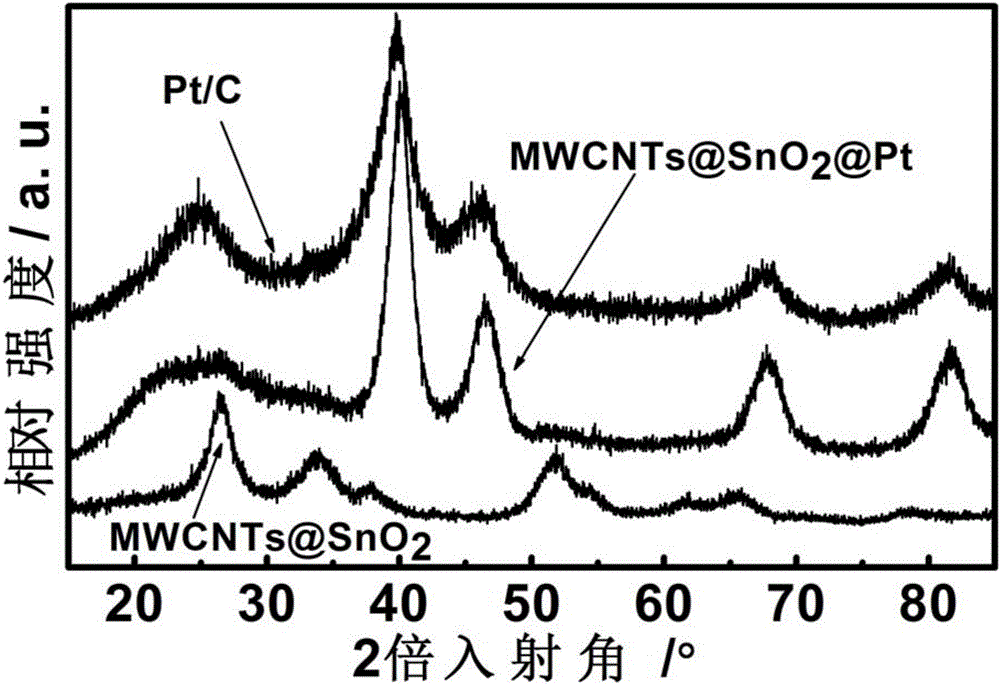
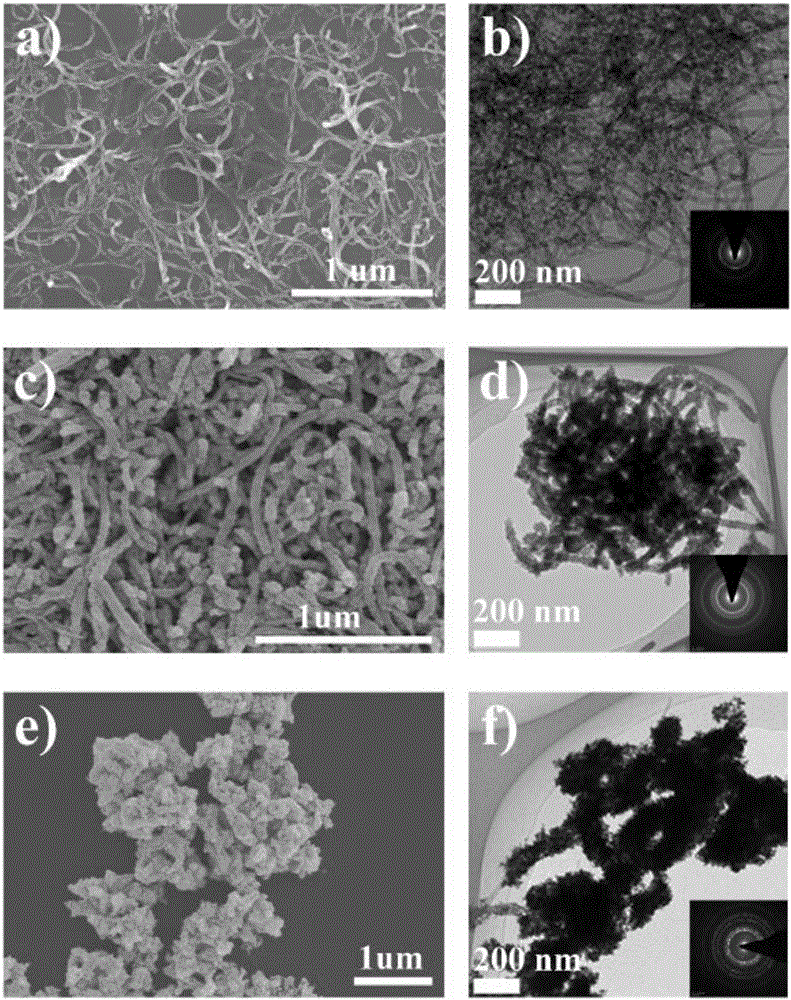
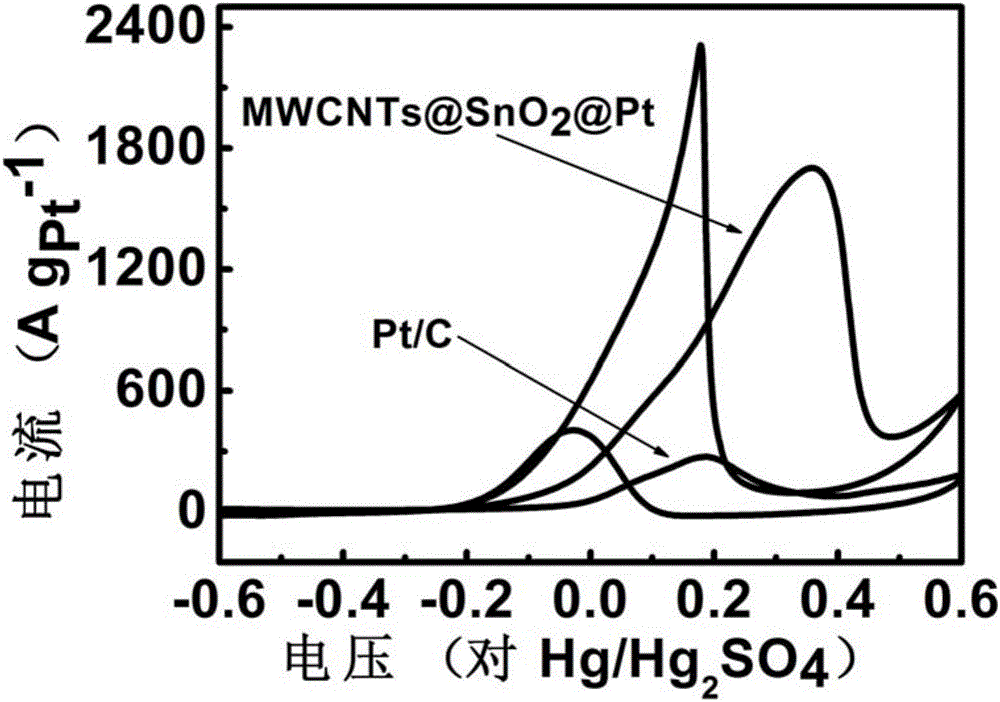
Platinum-based nanoparticle coating and tin dioxide covering carbon nanotube and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106784900AImprove the quality of catalytic activityImprove catalytic stabilityCell electrodesTin dioxideCatalytic oxidation
The invention relates to a platinum-based nanoparticle coating and tin dioxide covering carbon nanotube and a preparation method thereof, wherein the carbon nanometer tube is a multi-wall carbon nanotube; a layer of tin dioxide is loaded on the carbon nanotube; a layer of platinum-based metal is loaded on the tin dioxide layer; the platinum-based metal exists in a nanometer particle form, and is connected into a network structure. The catalyst provided by the invention has the advantages that the noble metal utilization rate is high; the catalytic activity and the carbon monoxide poisoning resistance performance of the catalyst are high; the service life of the catalyst is long; the methanol catalytic oxidation activity is more than 6.2 times of the commercial Pt / C catalyst; the oxygen reduction mass activity at the hydrogen scale potential being 0.9V is 9.6 times of that of the commercial Pt / C catalyst; the granularity is preferably between 1.0 to 10.0nm, and is also preferably between 2.0 to 4.0nm.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dynamic thermal infrared invisible composite material based on dual phase change and preparation method
ActiveCN109181650AGive full play to the temperature control abilityActive and quick responsePretreated surfacesCamouflage devicesSupport matrixNanoparticle coating
The invention discloses a dynamic thermal infrared invisible composite material based on dual phase change and a preparation method and especially relates to a VO2 / mica based phase change heat-accumulation thin layer composite material and a preparation method, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of infrared invisible materials. The VO2 / mica based phase change heat-accumulation thinlayer composite material is composed of a VO2 nanoparticle coating and a mica based phase change heat-accumulation thin layer, wherein the mica based phase change heat-accumulation thin layer is composed of stearic acid and a vanadium-extracted mica matrix according to the mass ratio of (3 to 5) to (5 to 7). The preparation method comprises the following step: preparing VO2 nanoparticles from vanadium-extracted mica by adopting a roasting and acid leaching technology; taking the vanadium-extracted mica as a supporting matrix and embedding to a phase change functional body to prepare the mica based phase change heat-accumulation thin layer; and coating the mica based phase change heat-accumulation thin layer with the VO2 nanoparticles to obtain a dual phase change composite material. The dynamic thermal infrared invisible composite material based on the dual phase change, provided by the invention, can be used for cooperatively strengthening the thermal infrared invisible performance and can be applied to a thermal infrared invisible technology.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
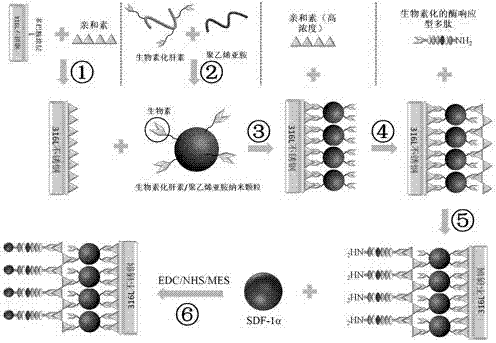
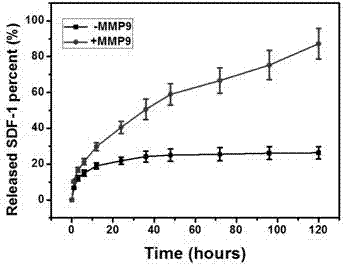
Construction method of enzyme-reponsive multifunctional nano-coating
ActiveCN107376036AOrderly assemblySustained and stable surface biological functionSurgeryCoatingsEndothelial regenerationHigh concentration
The invention discloses a construction method of an enzyme-reponsive multifunctional nano-coating. The construction method comprises the following steps: firstly, immobilizing avidin molecules to the surface of dopamine-coated stainless steel; then, on the basis of specific recognition and binding effects between avidin and biotin, immobilizing biotinylated heparin / PEI nanoparticles to the surface of a material, and further binding high-concentration avidin molecules to residual biotin on the surface of a nanoparticle coating, so that a novel biotin binding site is introduced; then, continuing to assemble biotinylated enzyme-responsive polypeptide to the surfaces of the nanoparticles on the basis of an interaction between the biotin and the avidin; and finally, by virtue of an EDC / NHS / MES coupling agent, immobilizing SDF-1[alpha] to an amino terminal of the polypeptide in a covalent mode, so that the multifunctional nano-coating, which has a matrix metalloproteinase 9 responsive characteristic, is constructed. According to the construction method provided by the invention, by constructing a multifunctional layer, which has anti-coagulating and endothelial regeneration inducing capacities, on a titanium surface, blood compatibility and a damaged endothelial repair capacity of the material can be obviously improved.
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Sinter-resistant low-cost catalysts manufactured by solution-based nanoparticle coating processes
InactiveCN107020153ACatalyst protectionCatalyst activation/preparationNanoparticle coatingOxide coating
Catalysts that are resistant to high-temperature sintering and methods for preparing such catalysts that are resistant to sintering at high temperatures are provided. The catalysts include a metal nanoparticle bound to a metal oxide support, where the metal nanoparticle and support are coated with a porous metal oxide coating layer. The catalyst is prepared by contacting a metal nanoparticle bound to a metal oxide support with a solution of metal salts, drying the solution of metal salts, and calcining the metal salts to generate a porous metal oxide coating on the metal nanoparticle and metal oxide support.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Preparation method of seawater electrolytic reaction anode IrO2-RuO2-SnO2-TiO2 nanoparticle coating
InactiveCN102251252ASmall sizeImprove electrocatalytic activitySolid/suspension decomposition chemical coatingElectrodesElectrolysisNanoparticle coating
The invention relates to a preparation method of a seawater electrolytic reaction anode IrO2-RuO2-SnO2-TiO2 nanoparticle coating. The seawater electrolytic reaction anode IrO2-RuO2-SnO2-TiO2 nanoparticle coating is prepared by the following improved thermal decomposition method: mixing soluble SnIV, RuIII and IrIV salt solution and titanium dioxide, adding high molecular polymer, and stirring or carrying out supersonic oscillation to form a suspension, thereby obtaining the anode coating liquid; and brushing the suspension on a Ti matrix, drying, calcining, cooling, and repeating many times until the coating reaches the required thickness. The anode coating prepared by the method provided by the invention has the advantages of uniform metallic oxide particle distribution, small microcrystal particle size, large specific area, increased electrode conductivity, excellent electrocatalytic activity and high stability, and has a mud crack appearance on the surface. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple, and suitable for industrial large-scale production.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Latex paint with antibacterial function and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107189574AEvenly dispersedHas antibacterial functionAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesFiberEmulsion
Relating to the technical field of latex paint, the invention discloses a latex paint with antibacterial function and a preparation method thereof. The latex paint comprises the following raw materials: 55-65 parts of a vinyl acetate-acrylic emulsion, 45-55 parts of a nanoparticle coating component, 35-40 parts of bamboo vinegar, 30-33 parts of nanometer polymer hollow microspheres, 25-27 parts of diatom mud, 20-23 parts of plant dehydrated fiber, 20-22 parts of lavender essential oil, 15-20 parts of assistant and 65-75 parts of deionized water. The latex paint provided by the invention has good antibacterial and bacteriostatic effect, is environment-friendly and safe, combines with wall stably, does not generate paint surface peeling, bursting or other phenomena easily, and greatly improves weather resistance.
Owner:合肥市淑芹美装饰工程有限公司
Perovskite photovoltaic cell passivated with Au@CdS nanoparticles
ActiveCN110289353AStrong resonance absorptionWide absorption spectrum rangeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHole transport layerElectron
The present invention discloses a perovskite photovoltaic cell passivated with Au@CdS nanoparticles. An interface passivation layer is disposed between an electron transport layer and a perovskite photosensitive active layer, or the interface passivation layer is disposed between the perovskite photosensitive active layer and a hole transport layer, or the interface passivation layer is disposed among the electron transport layer, the perovskite photosensitive active layer and the hole transport layer. The interface passivation layer is an Au@CdS nanoparticle coating having a core-shell structure. The perovskite photovoltaic cell suppress its diffusion (to reduce electric leakage) in a device, reduces the interface barrier, achieves effective energy level matching between the hole / electron transport layer and the perovskite photosensitive layer, and balances the respective current carrier extraction rates of the hole transport layer and the electron transport layer so as to achieve a purpose of increasing the short-circuit current and the fill factor of a battery.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
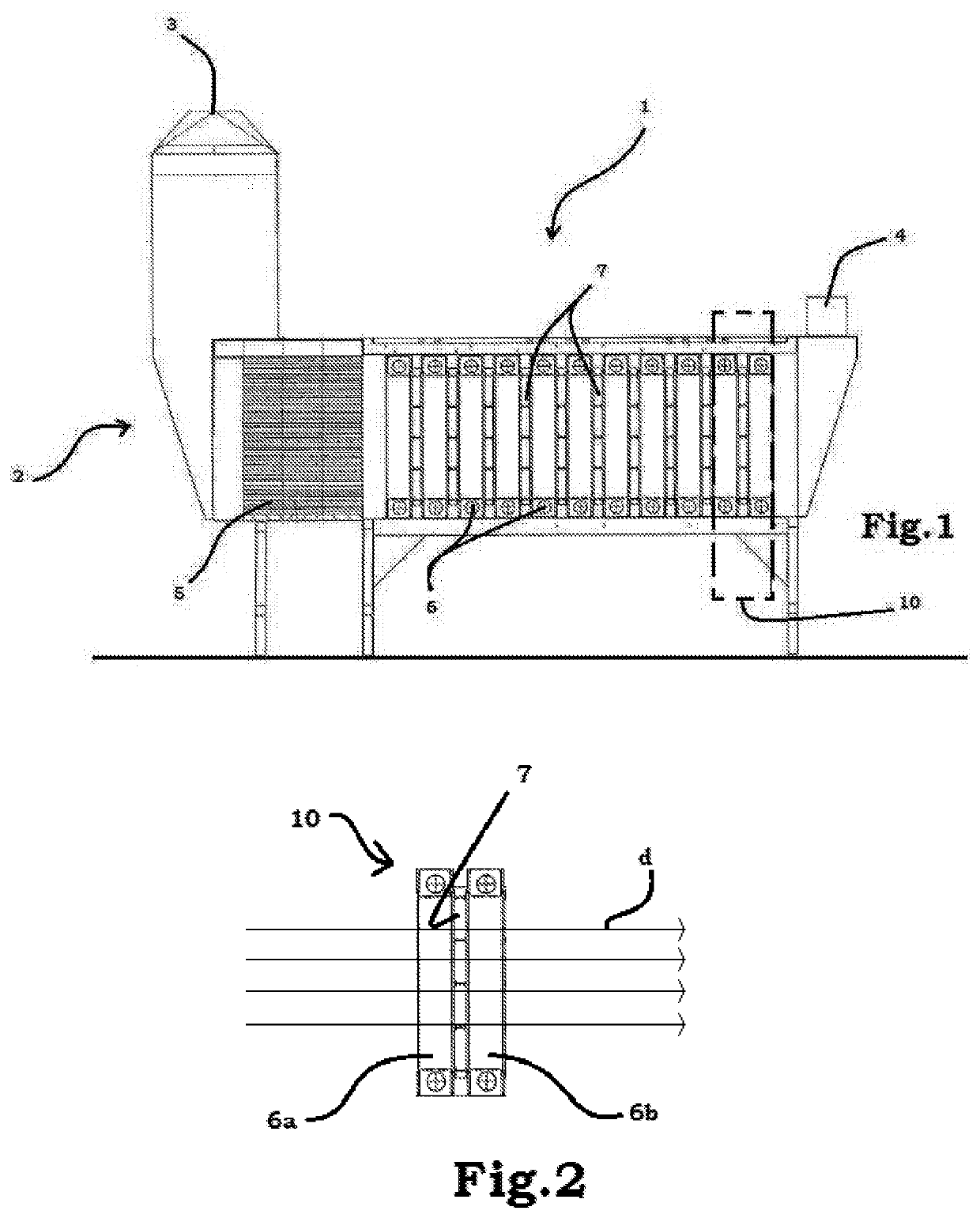
Device for reducing pollutants in a gaseous mixture
ActiveUS20200282097A1Improve efficiencyInexpensive and reliable in daily useGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesFirst lightPhotochemistry
Described is a device (1) for reducing pollutants in a gaseous mixture comprising: •a containment body (2) having an inlet portion (3) for the gaseous mixture and an outlet portion (4) for the gaseous mixture, the containment body (2) imposing on the gaseous mixture a fixed direction of flow (D), •at least one filtering unit (10) comprising a photocatalytic filter (7) interposed, along the fixed direction of flow (D), between a first light source (6a) and a second light source (6b), both having a wavelength in the visible spectrum (400-700 nm), the photocatalytic filter (7) comprising a photocatalytic nanoparticle coating and the nanoparticle coating comprising titanium dioxide doped with a nitrogen doping agent. •a unit (5) for straightening the flow before the filtering unit (10).
Owner:CONSORZIO COLTECH
Dynamic thermal infrared stealth composite material based on dual phase change and preparation method thereof
PendingUS20210324254A1Reduce surface temperatureReduce radiant energyPretreated surfacesCamouflage devicesRoscoeliteNanoparticle coating
A dynamic thermal infrared stealth composite material based on dual phase change is a VO2 / mica-based phase change thermal storage thin layer composite material composed of a VO2 nanoparticle coating and a mica-based phase change thermal storage thin layer, wherein the mica-based phase change thermal storage thin layer consists of stearic acid and a vanadium-extracted mica substrate in a mass ratio of 3-5:5-7. The composite material based on dual phase change is prepared by extracting vanadium from vanadium mica using a roasting and acid leaching process to prepare VO2 nanoparticles and a vanadium-extracted mica, embedding a phase change functional body into the vanadium-extracted mica as a support substrate to prepare a mica-based phase change thermal storage thin layer, and coating the VO2 nanoparticles on the mica-based phase change thermal storage thin layer. The dynamic thermal infrared stealth composite material can synergistically reinforce thermal infrared stealth performance.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com