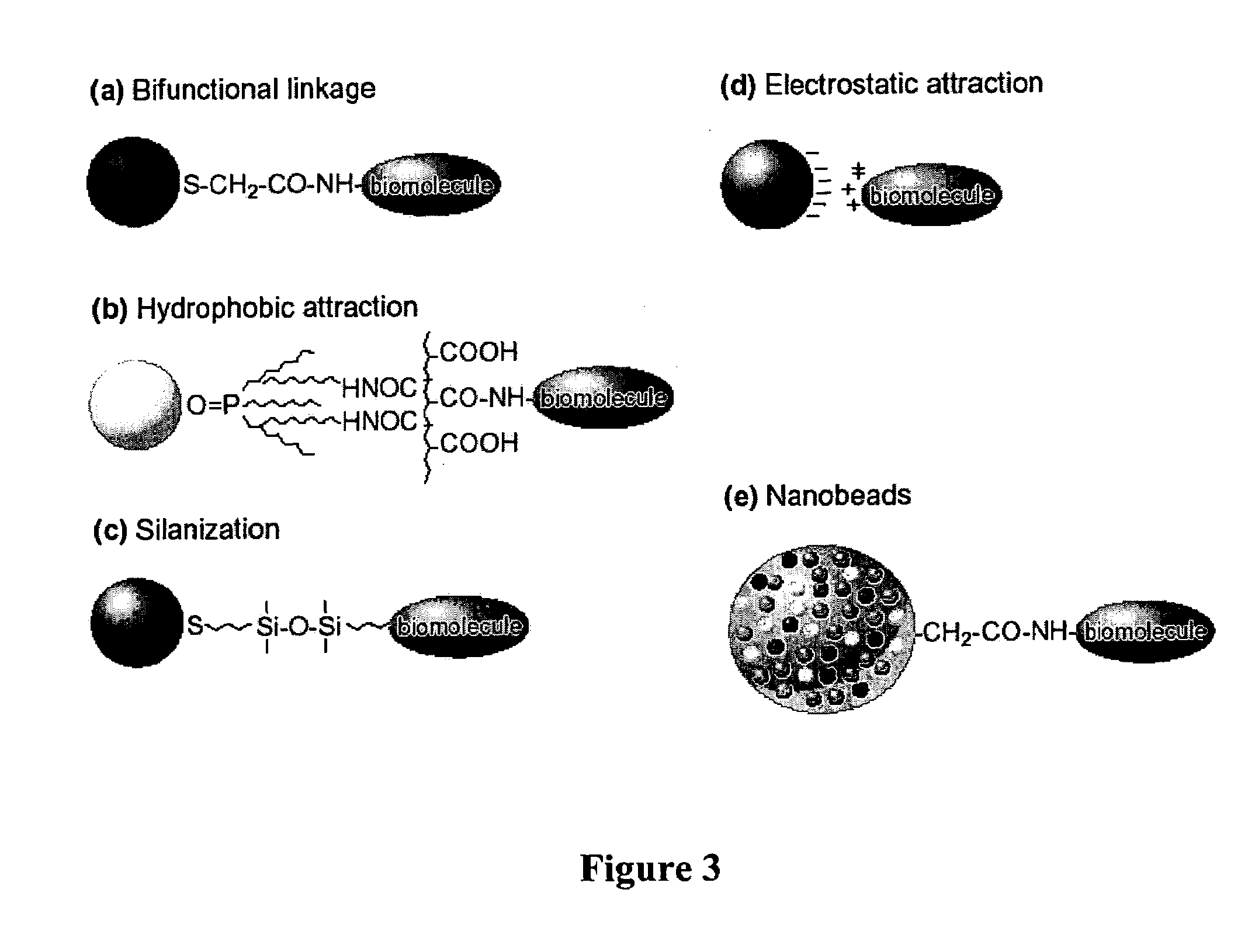
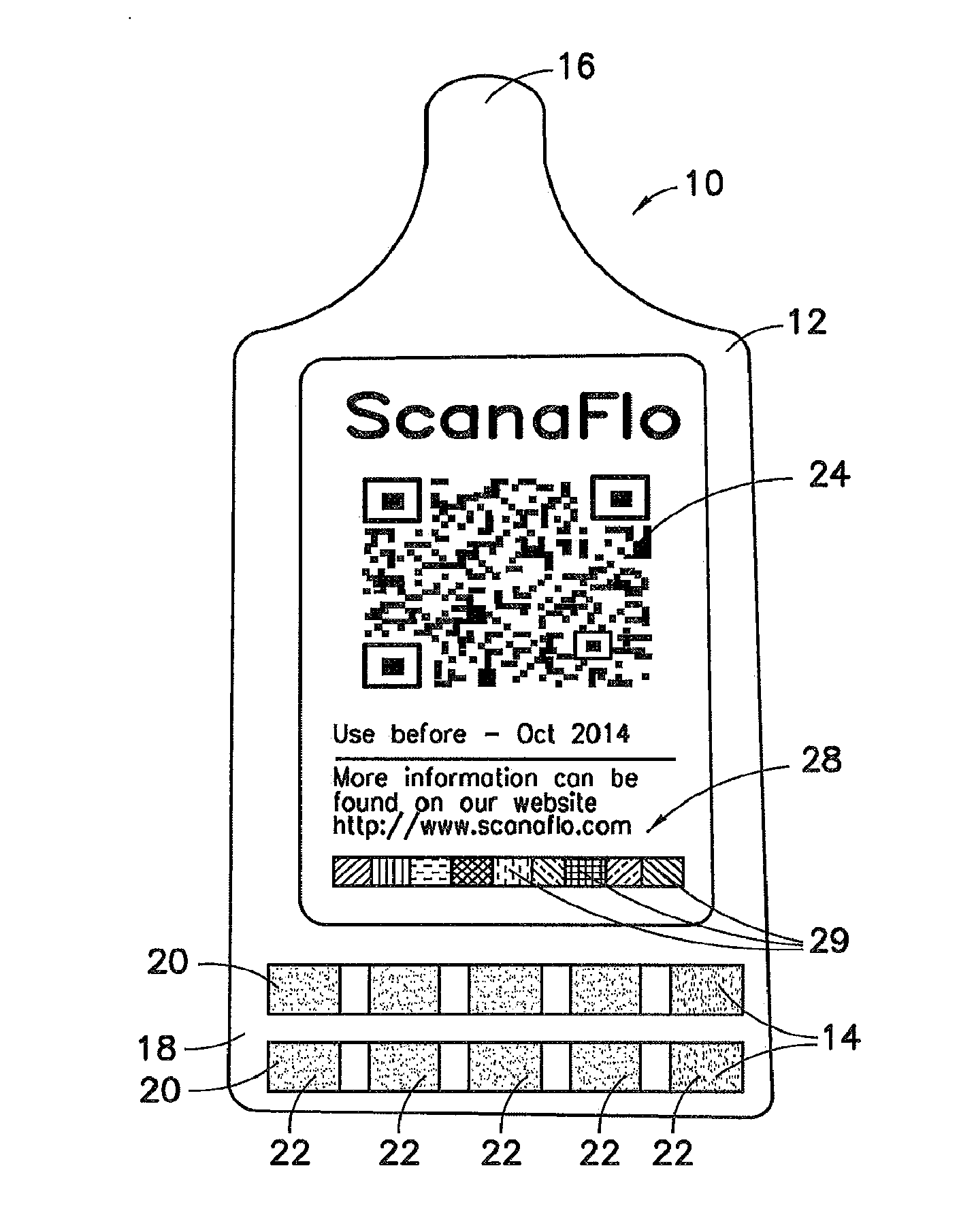
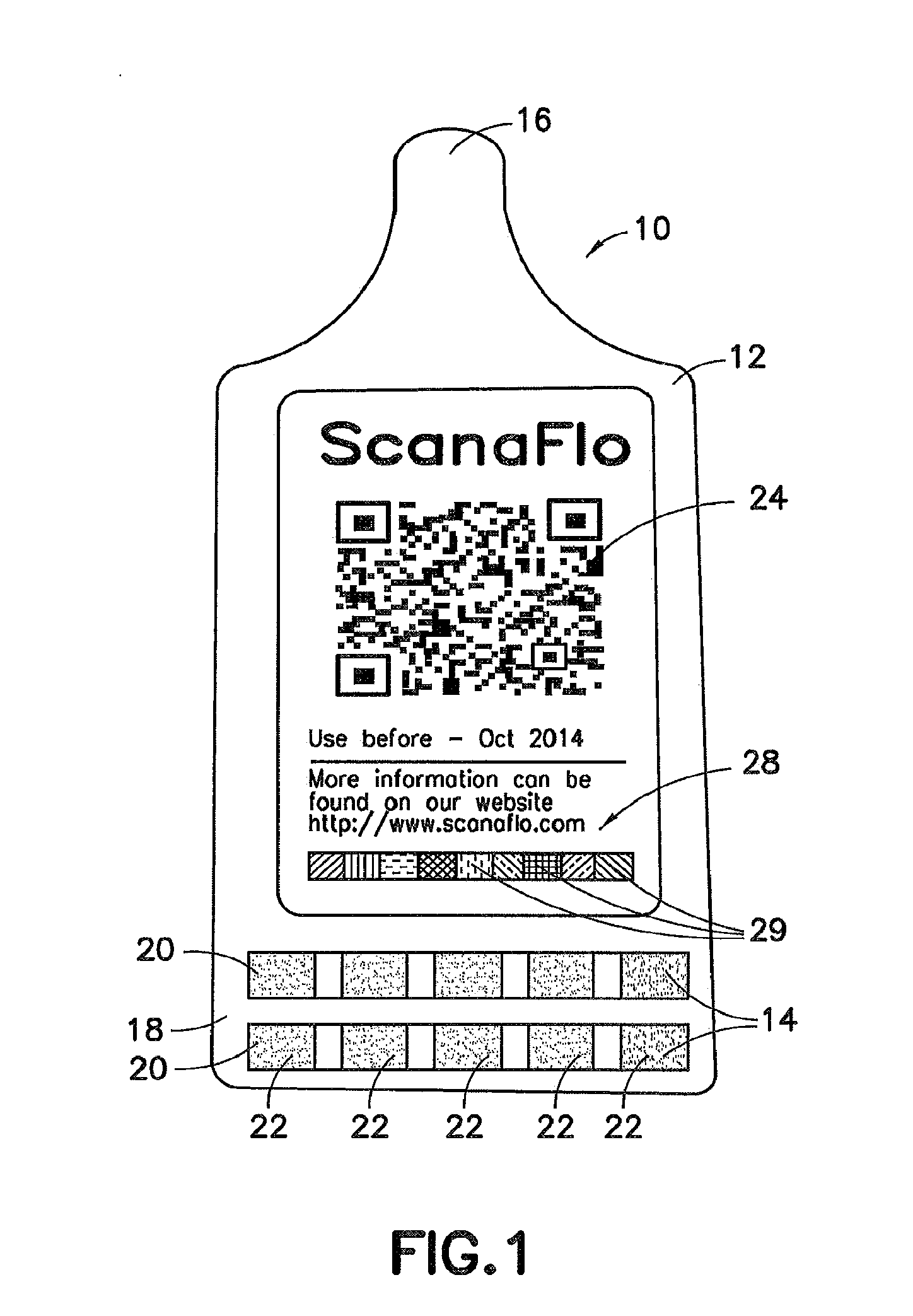
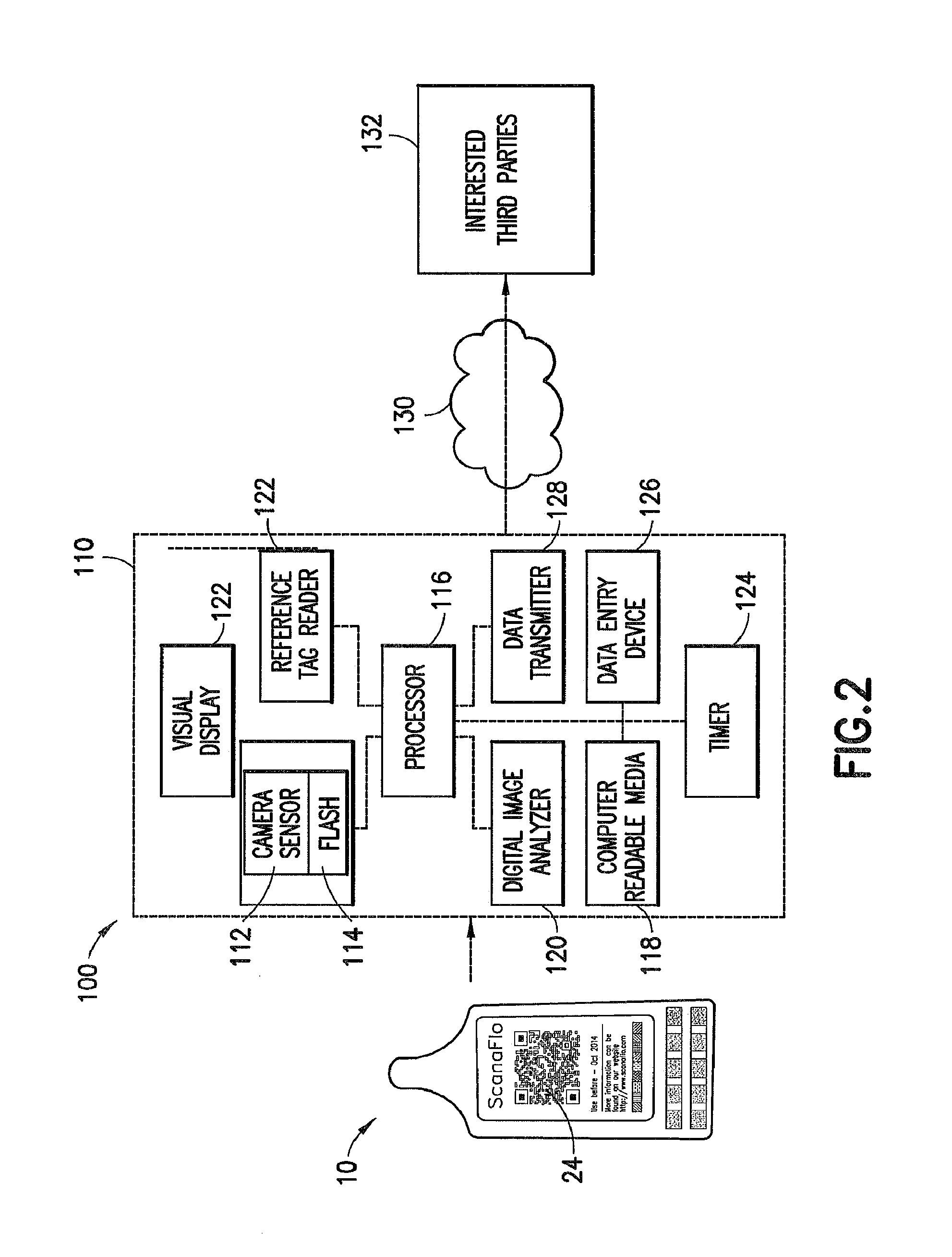
Patents
Literature
604 results about "Bioanalysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bioanalysis is a sub-discipline of analytical chemistry covering the quantitative measurement of xenobiotics (drugs and their metabolites, and biological molecules in unnatural locations or concentrations) and biotics (macromolecules, proteins, DNA, large molecule drugs, metabolites) in biological systems.
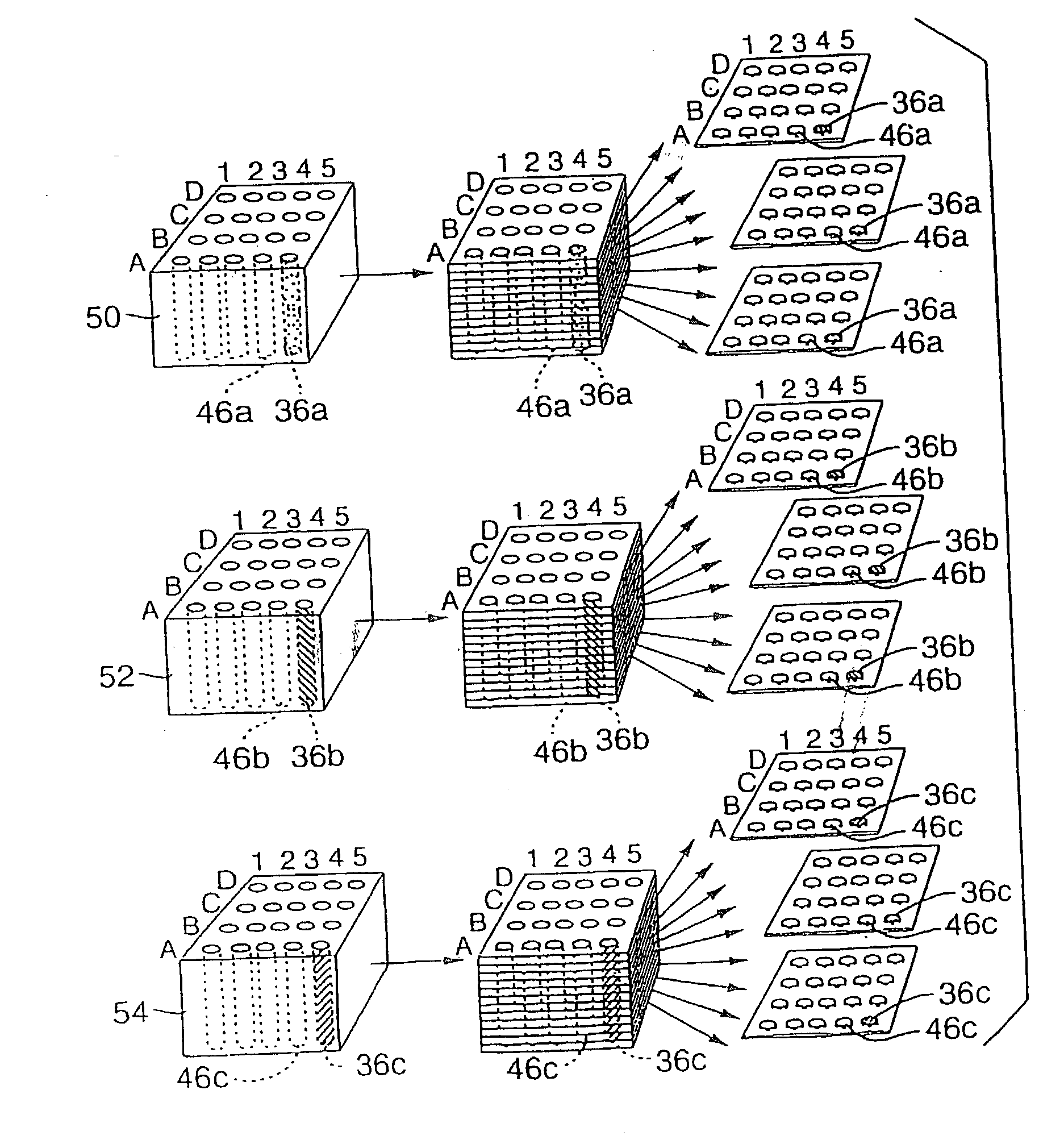
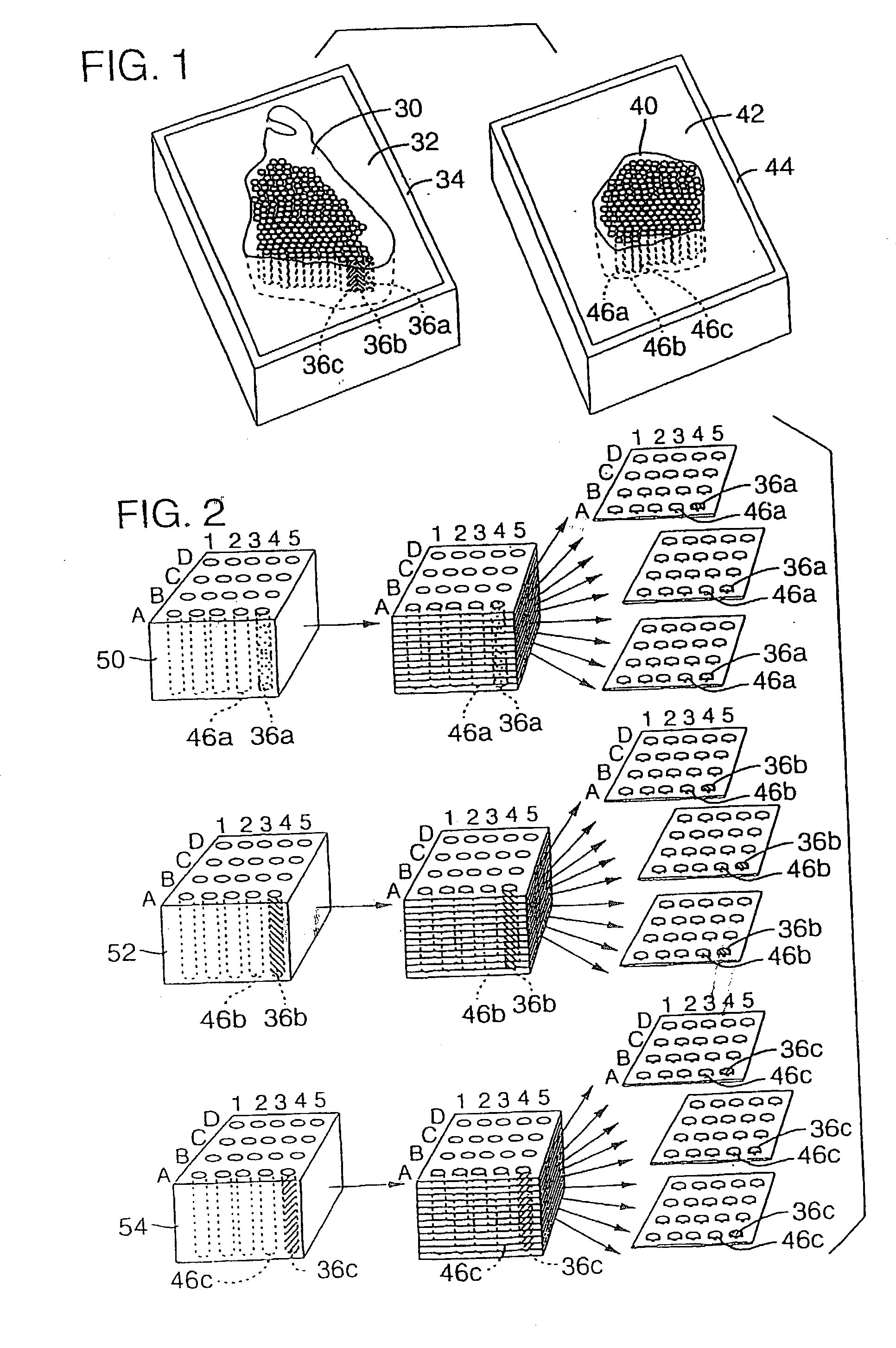
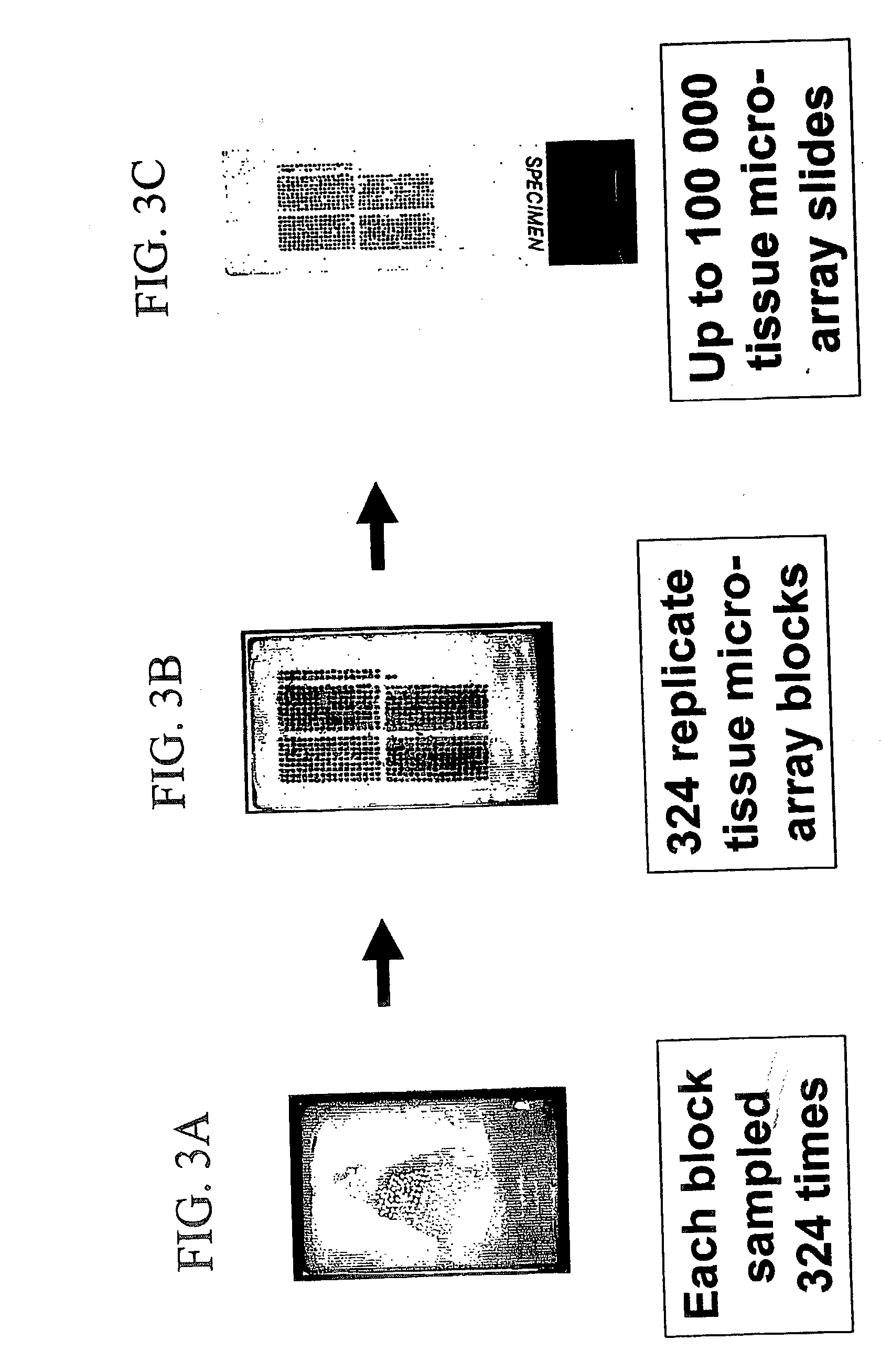
High-throughput tissue microarray technology and applications
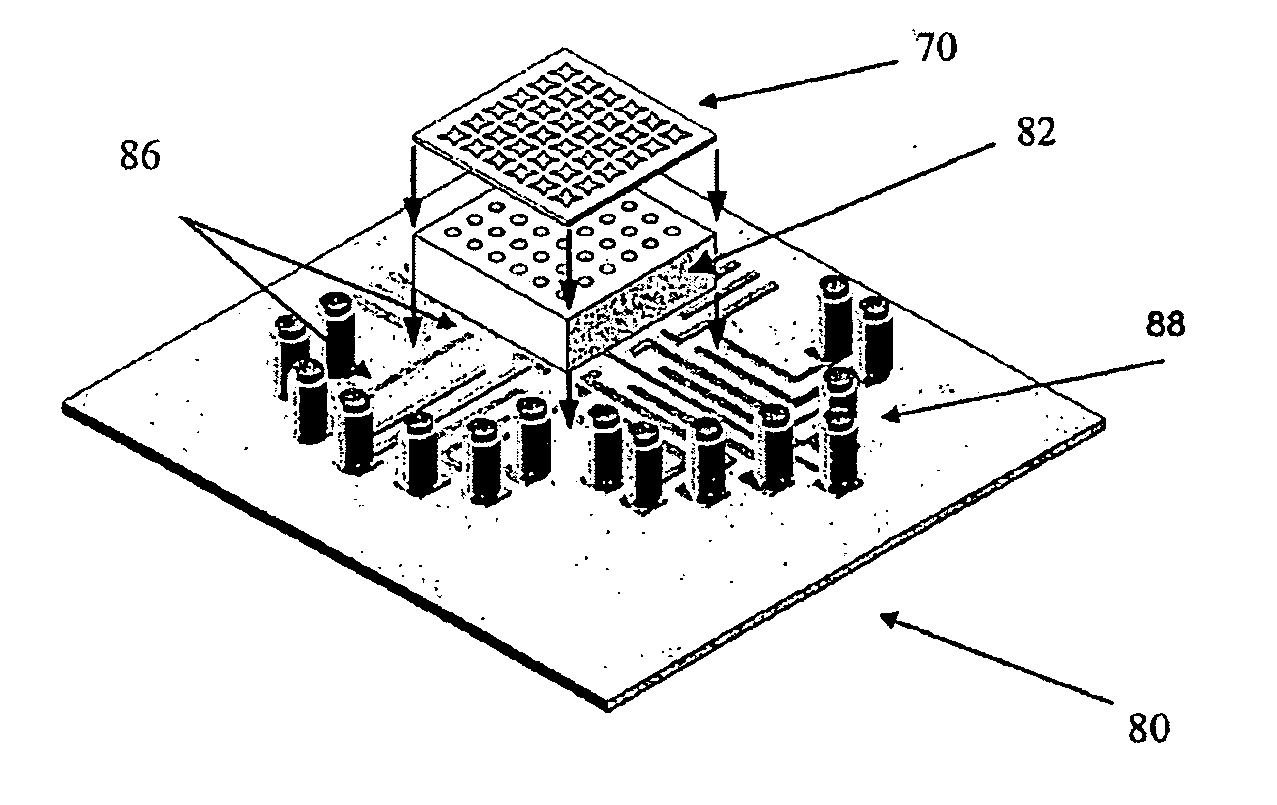
InactiveUS20030215936A1Easy to analyzeGood for comparisonBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClinical informationTissue microarray
A method and apparatus are disclosed for a high-throughput, large-scale molecular profiling of tissue specimens by retrieving a donor tissue specimen from an array of donor specimens, placing a sample of the donor specimen in an assigned location in a recipient array, providing substantial copies of the array, performing a different biological analysis of each copy, and storing the results of the analysis. The results may be compared to determine if there are correlations or discrepancies between the results of different biological analyses at each assigned location, and also compared to clinical information about the human patient from which the tissue was obtained. The results of similar analyses on corresponding sections of the array can be used as quality control devices, for example by subjecting the arrays to a single simultaneous investigative procedure. Uniform interpretation of the arrays can be obtained, and compared to interpretations of different observers.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Compositions and methods for liquid metering in microchannels
InactiveUS7004184B2Easy to assembleIncrease the degree of mixingMaterial nanotechnologyShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersElectrophoresisComputer module
The movement and mixing of microdroplets through microchannels is described employing microscale devices, comprising microdroplet transport channels, reaction regions, electrophoresis modules, and radiation detectors. Microdroplets are metered into defined volumes and are subsequently incorporated into a variety of biological assays. Electronic components are fabricated on the same substrate material, allowing sensors and controlling circuitry to be incorporated in the same device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Self-contained biological analysis
ActiveUS8394608B2Rapid and sensitiveMinimize contaminationHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementImmuno pcrBiological organism
Owner:BIOFIRE DIAGNOSTICS LLC
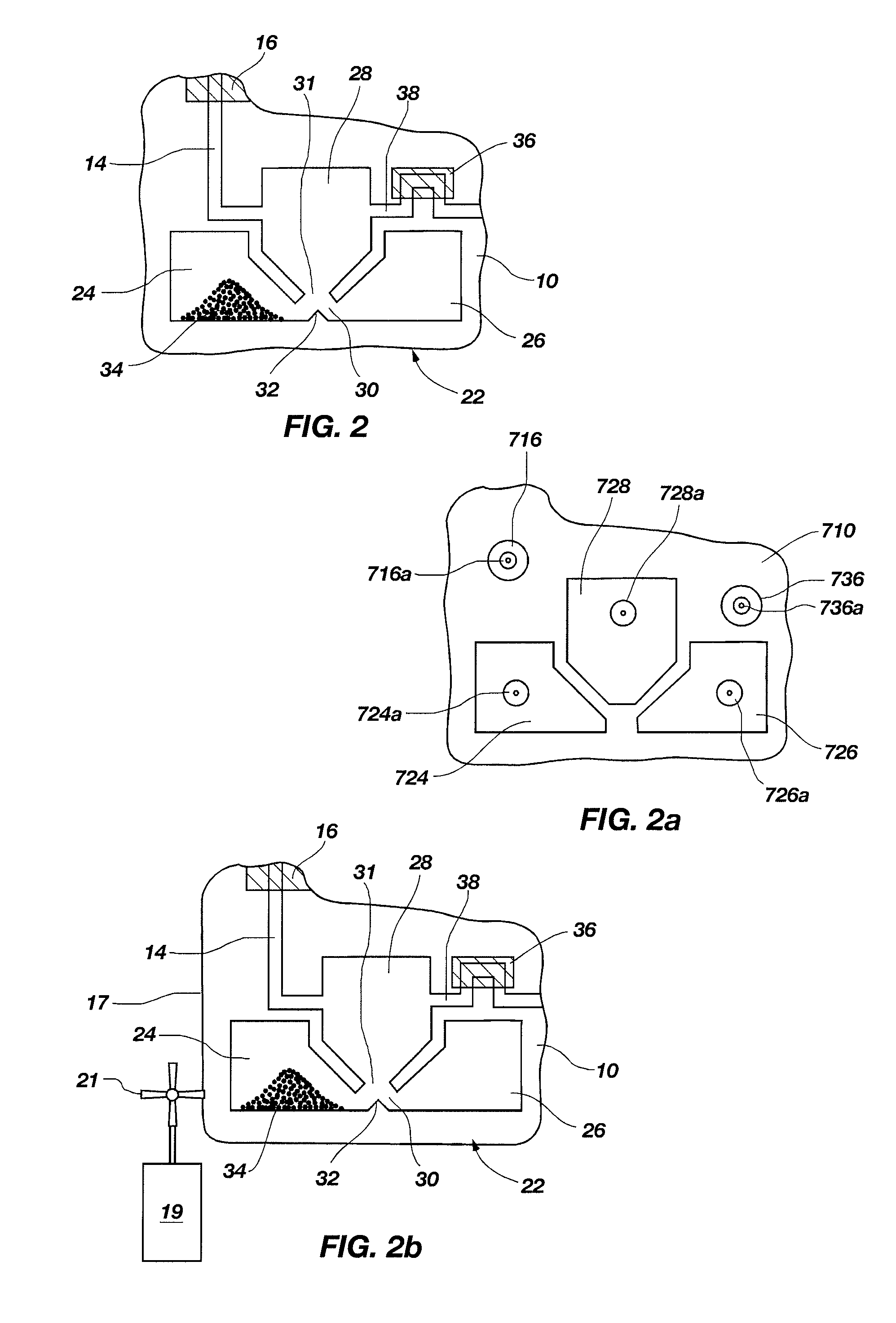
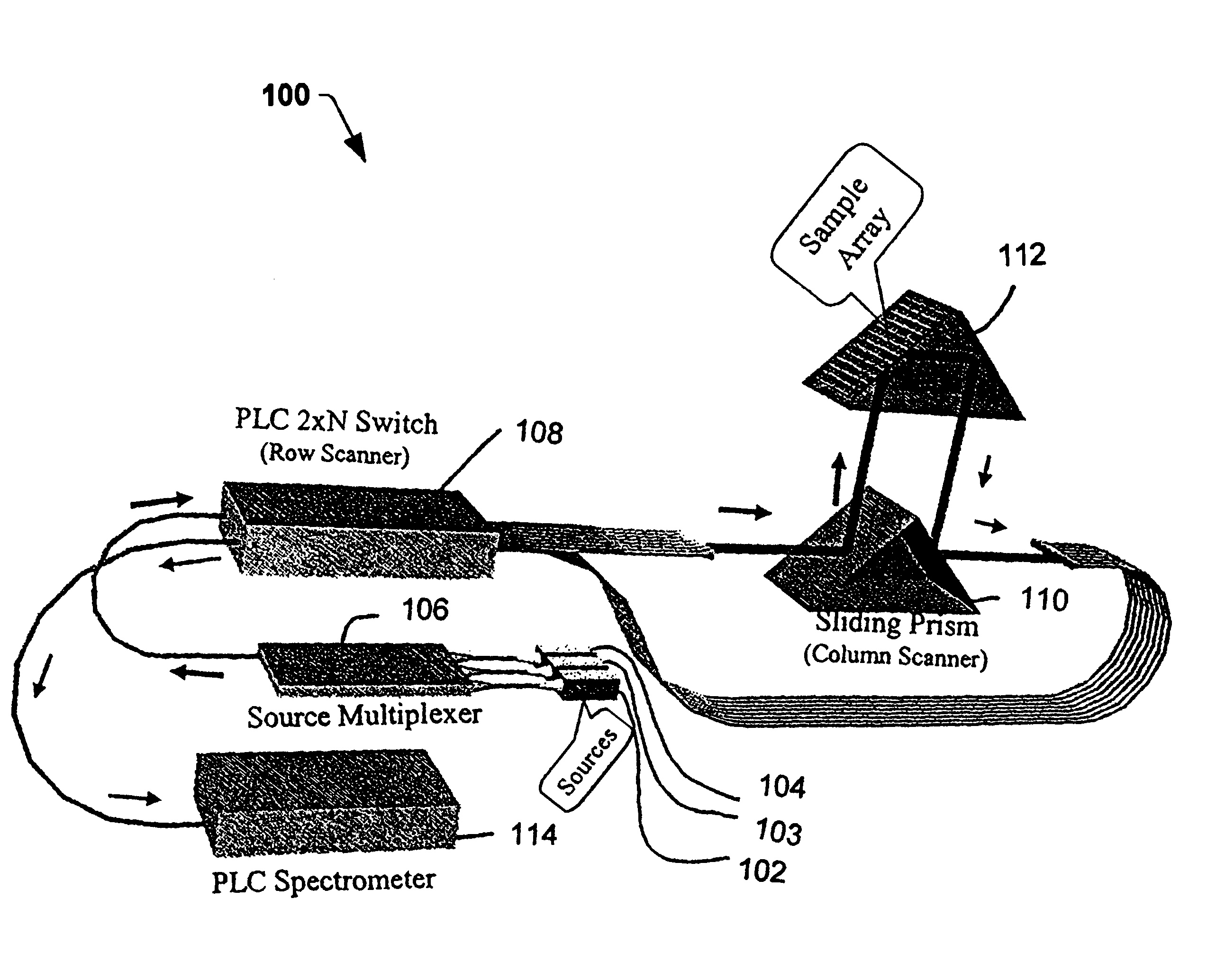
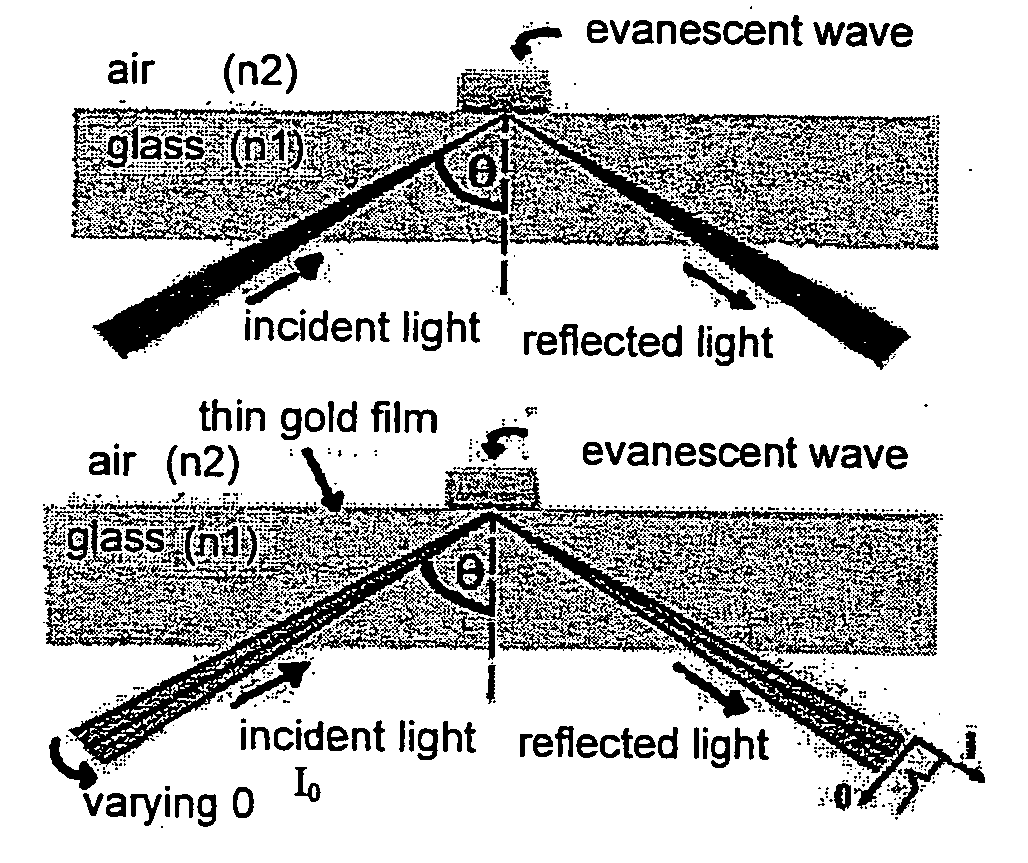
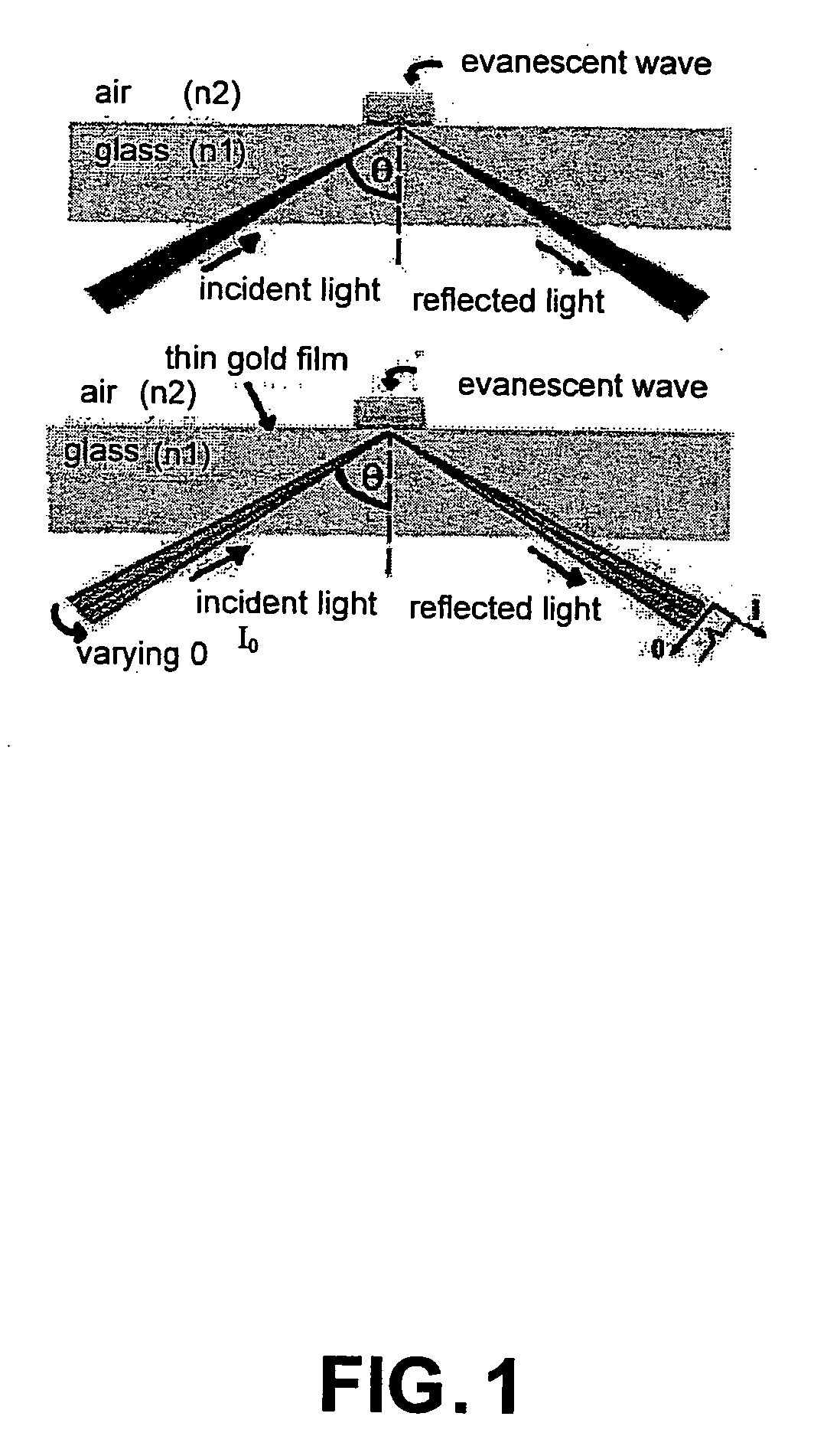
Bioanalysis systems including optical integrated circuit
InactiveUS6956651B2Reduce decreaseImprove throughputScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsMicrowell PlateReduced size
Optical Integrated Circuits (OIC) in Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Analysis Systems combined with micorarray or microwell plates to provide enhanced sensitivity, stability, speed of analysis and reduced size are disclosed. Using the OIC with other optical analysis methods to provide enhance analysis systems is also disclosed.
Owner:LIGHTWAVE BIOAPPL
Hydrodynamic focusing for analyzing rectangular microbeads
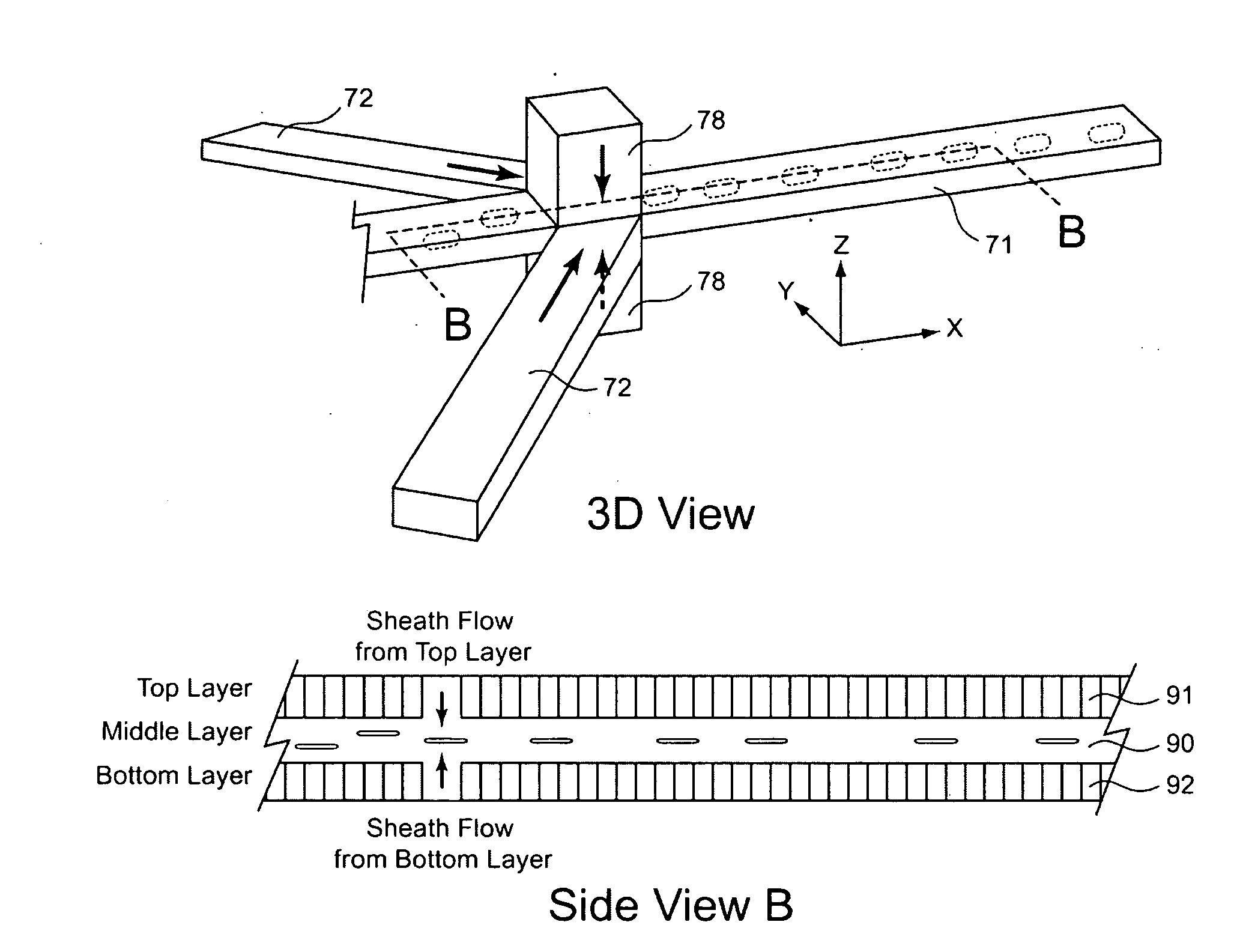
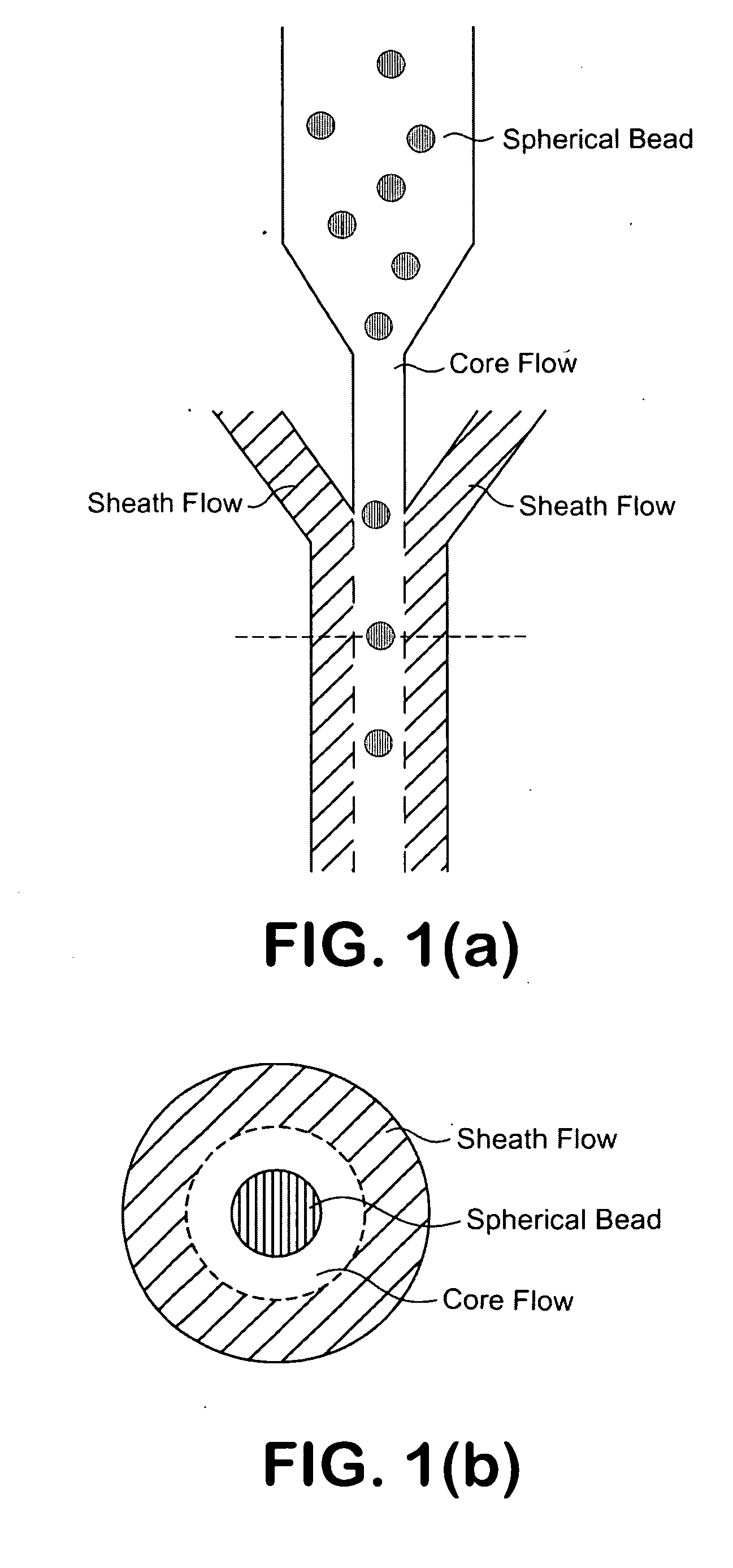
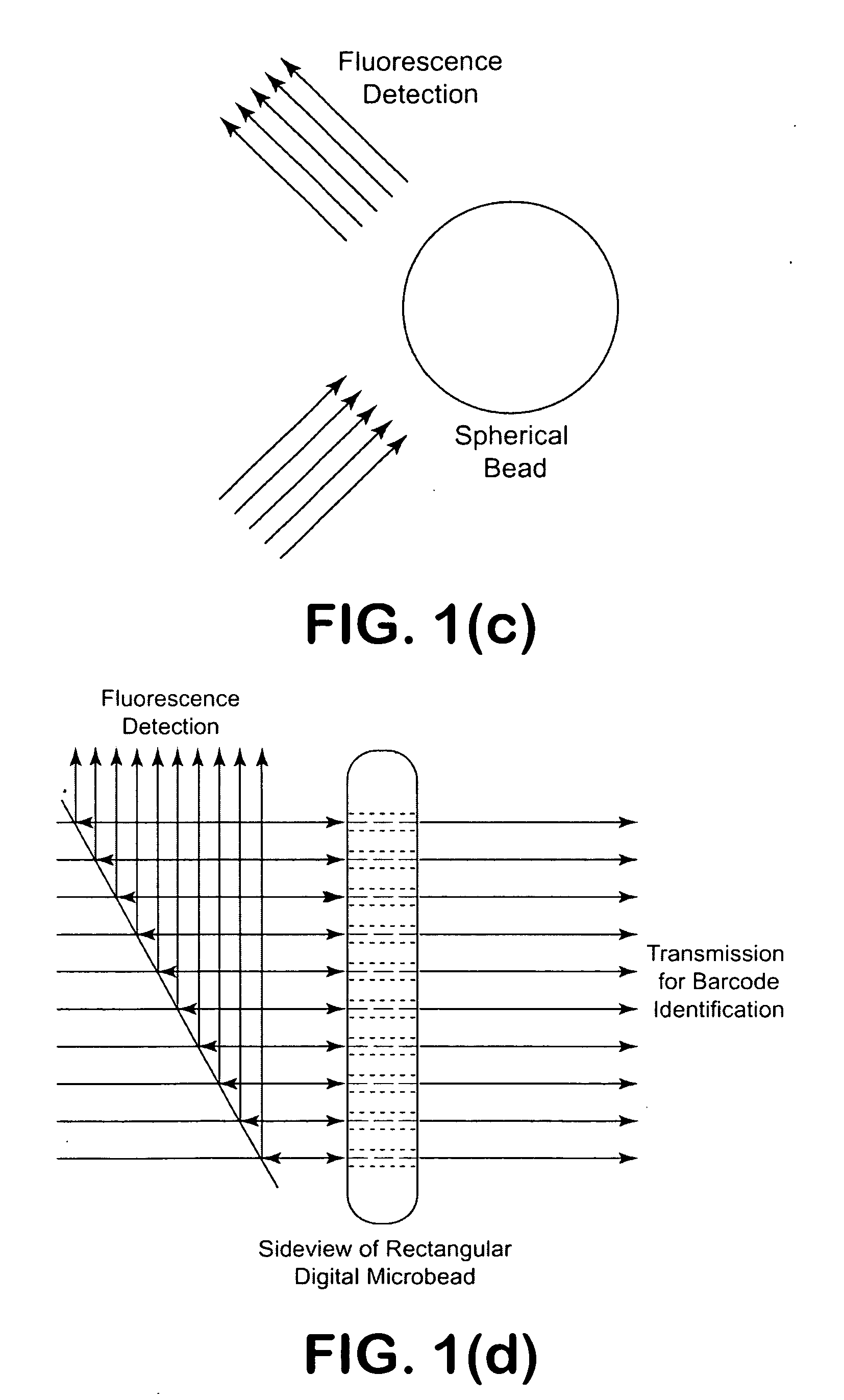
InactiveUS20090201504A1Improve liquidityNo cloggingVolume/mass flow measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansBarcodeEngineering
A microfluidic apparatus having a one-dimensional or two-dimensional hydrodynamic flow system to control stable and proper digitally coded bead orientation through the optical detection area of a bioanalysis system. The hydrodynamic system include one core flow, which carries the rectangular barcode beads, and sheath flows, on the sides of or about or around the outer periphery of the core flow, pull the core flow into a proper orientation. The sheath flows, at much higher flow speed but lower volume flow rate, can be pushed or pulled by vacuum, gravity, or pressure. By this method, the coded bead will align themselves in line and flow reliably, without wobbling or flipping, in the core flow channel through the detection zone. By adjusting the relative flow rate of core flow and sheath flows, the coded beads flow reliably in the flow system, thus it can be decoded and detected by an optical system accurately.
Owner:MAXWELL SENSORS
Use of particulate labels in bioanalyte detection methods
InactiveUS7413868B2Maintain their viabilitySimple methodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParticulatesCellular component
New applications for the use of distinguishable particulate labels available in a variety of hues and sized in the submicron range are described. These applications include profiling of cellular components, obtaining secretion patterns, identifying a multiplicity of components in chromatographic or electrophoretic techniques and identification of desired immunoglobulin secreting cells.
Owner:TRELLIS BIOSCIENCE LLC
Method and apparatus for performing and quantifying color changes induced by specific concentrations of biological analytes in an automatically calibrated environment
ActiveUS20150211987A1Accurate and precise and cost-effective measurementMinimizing user interactionImage enhancementRadiation pyrometryColor changesColor calibration
Methods and electronic devices for performing color-based reaction testing of biological materials. The method includes capturing and interpreting digital images of an unexposed and later exposed paddle at various delay times within an automatically calibrated environment. The test paddle includes a unique identification mechanism (UID), a Reference Color Bar (RCB) providing samples of standardized colors for image color calibration, compensation and corrections, and several test-specific sequences of Chemical Test Pads (CTP). The method further includes locating the paddle in the image, extracting the UID and validating the paddle, extracting the RCB and locating the plurality of CTP in each image. The method further reduces image noise in the CTP and calibrates the image automatically according to lighting measurements performed on the RCB. To determine test results, the method further determines several distances between the CTP and its possible trajectory in the color space described by the Manufacturer Interpretation Color Chart.
Owner:HEALTHY IO LTD
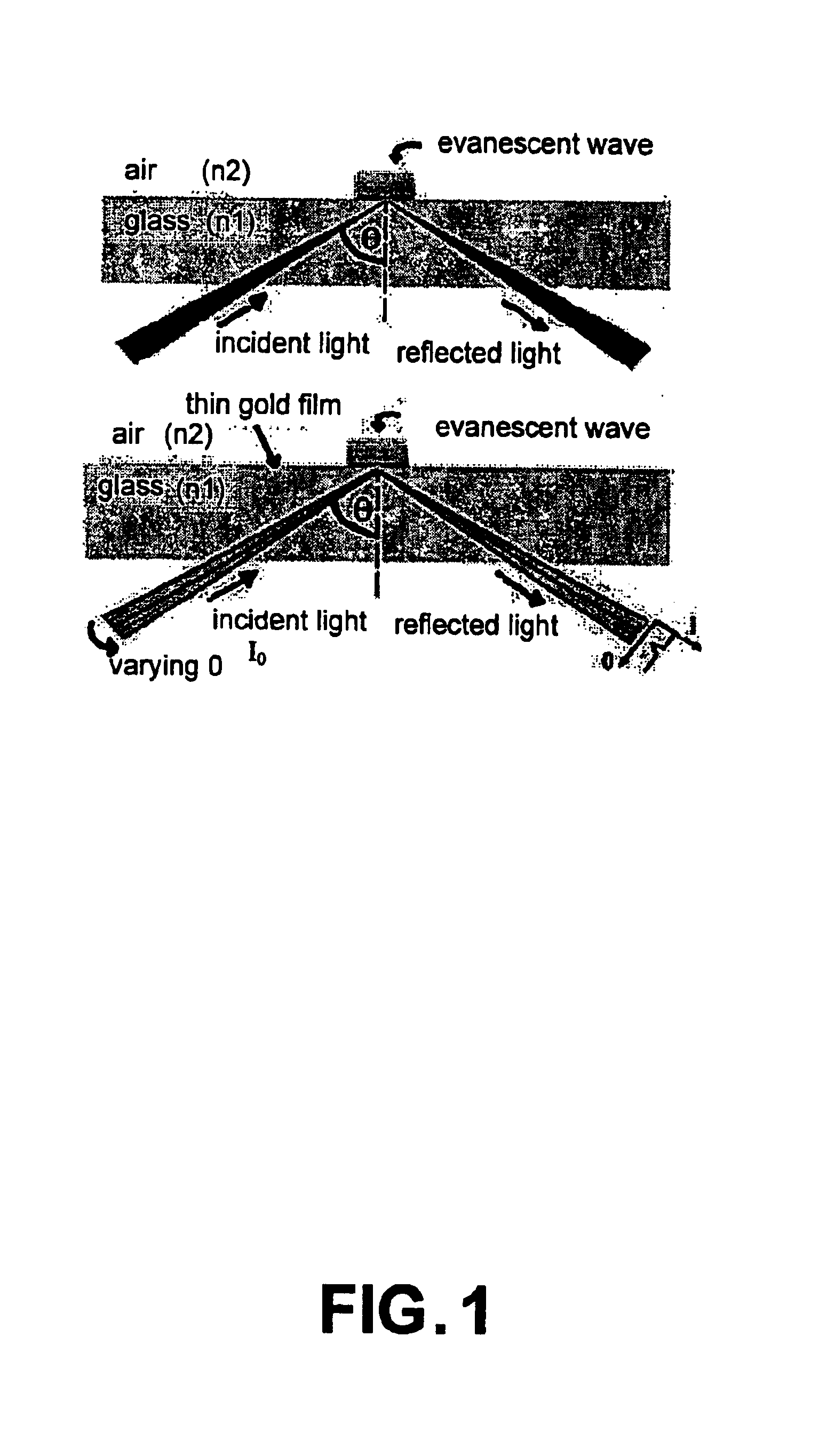
Metal nanoshells for biosensing applications
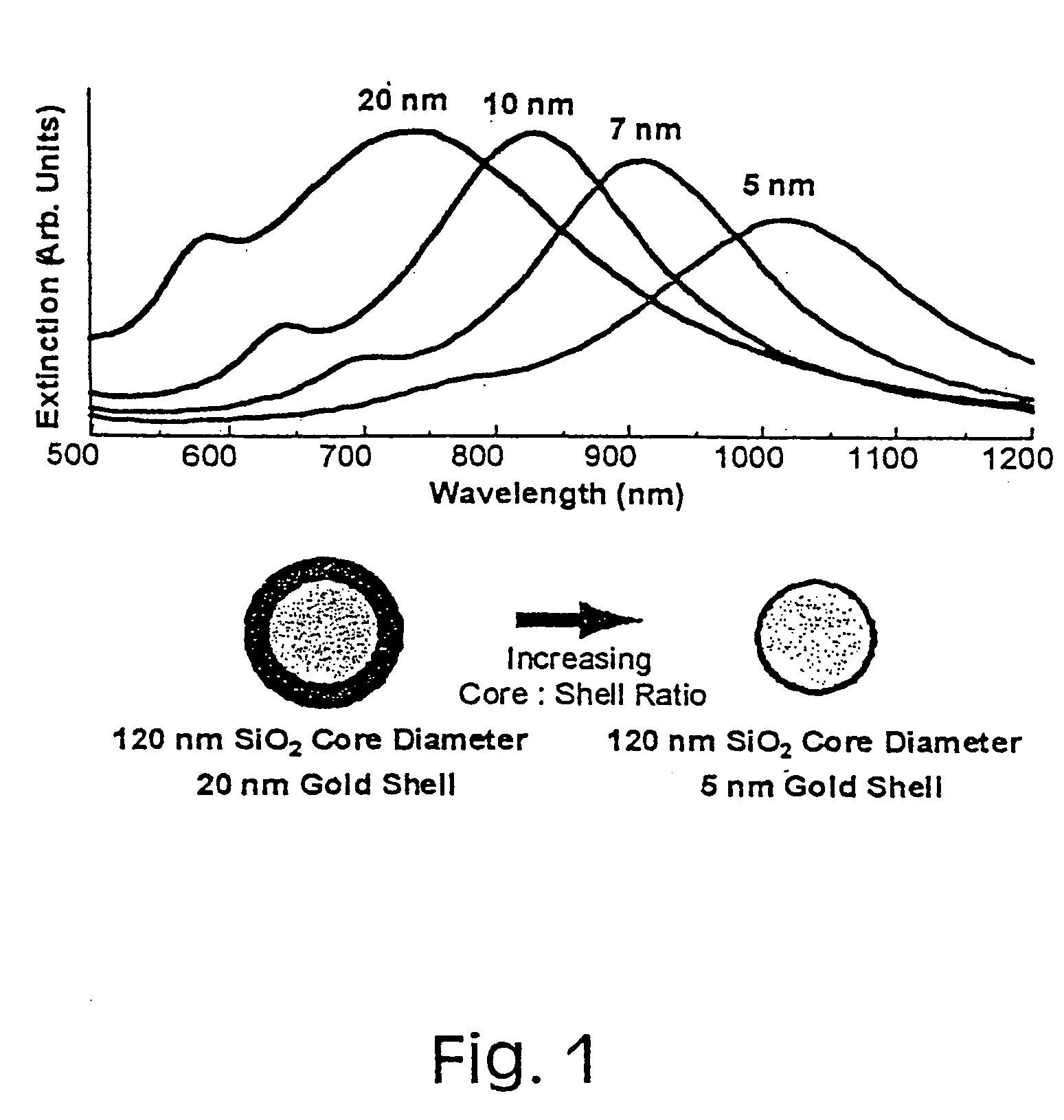
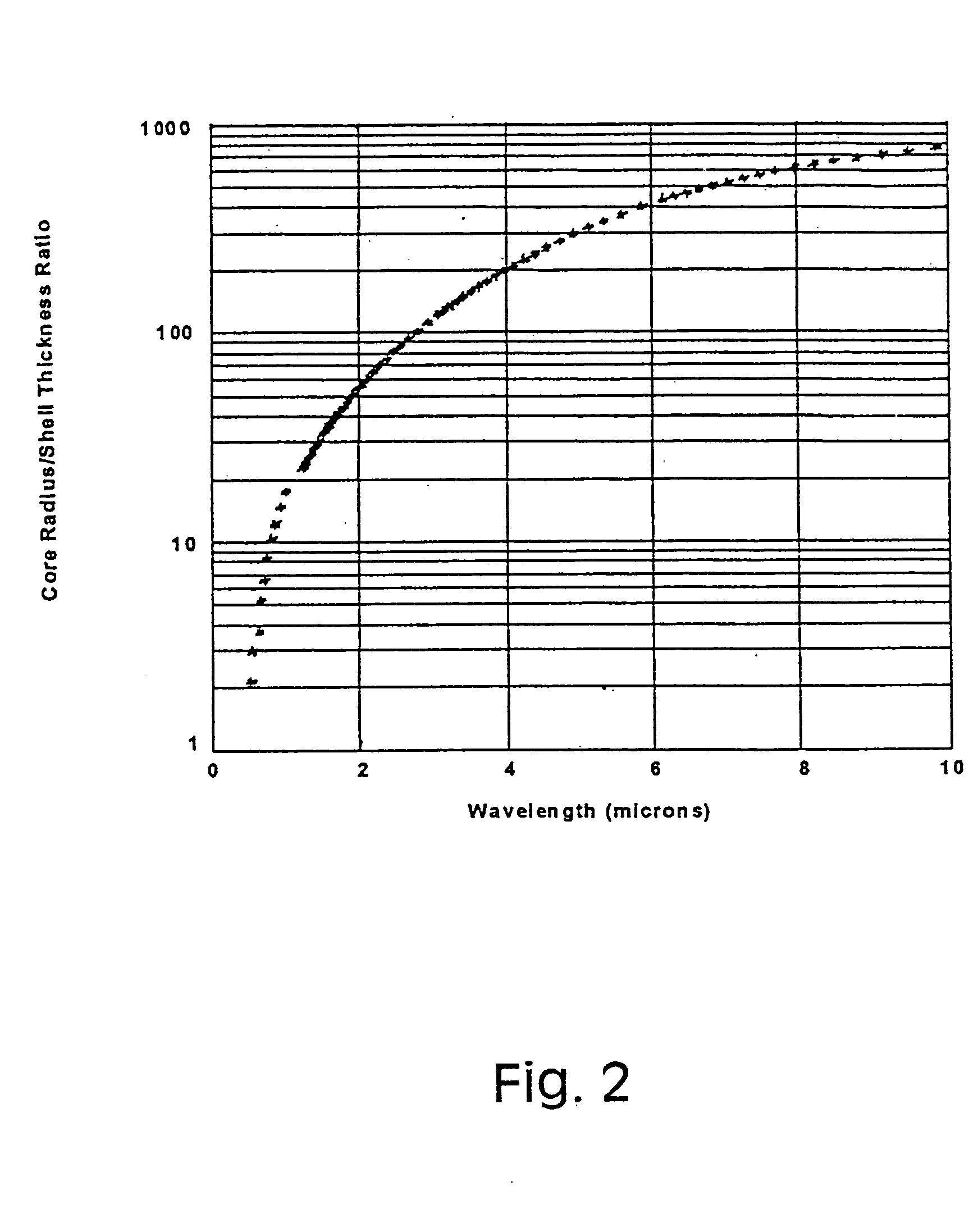
InactiveUS20050130324A1Eliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPigmenting treatmentUltravioletIn vivo
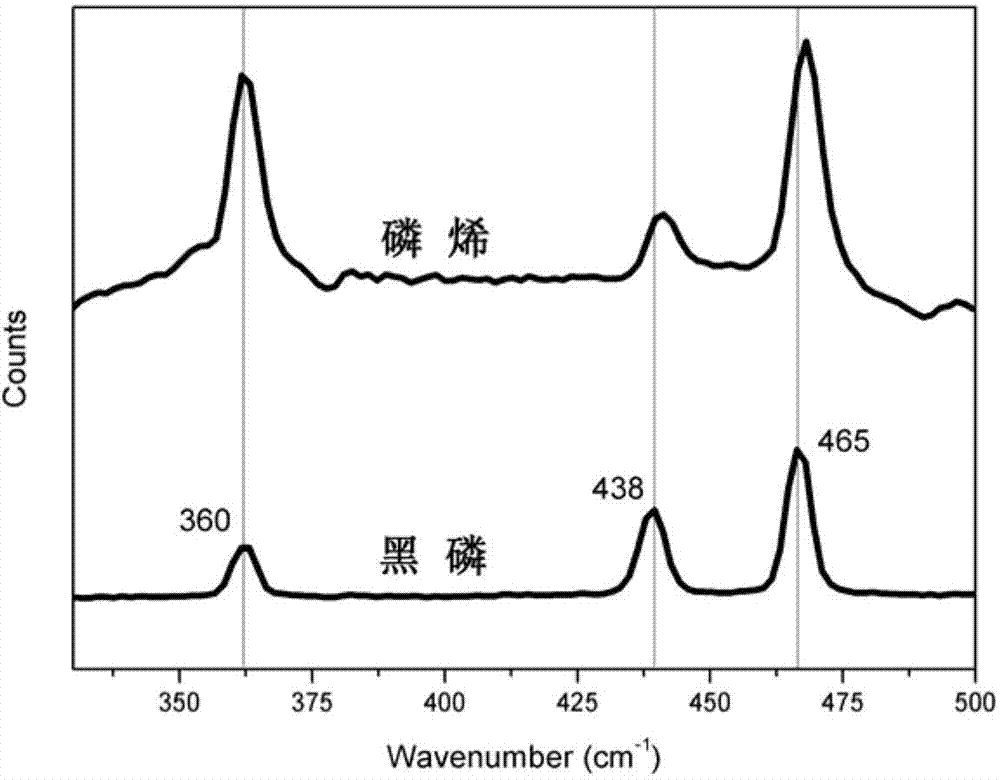
The present invention provides nanoshell particles (“nanoshells”) for use in biosensing applications, along with their manner of making and methods of using the nanoshells for in vitro and in vivo detection of chemical and biological analytes, preferably by surface enhanced Raman light scattering. The preferred particles have a non-conducting core and a metal shell surrounding the core. For given core and shell materials, the ratio of the thickness (i.e., radius) of the core to the thickness of the metal shell is determinative of the wavelength of maximum absorbance of the particle. By controlling the relative core and shell thicknesses, biosensing metal nanoshells are fabricated which absorb light at any desired wavelength across the ultraviolet to infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum. The surface of the particles are capable of inducing an enhanced SERS signal that is characteristic of an analyte of interest. In certain embodiments a biomolecule is conjugated to the metal shell and the SERS signal of a conformational change or a reaction product is detected.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Method of electrically detecting a biological analyte molecule
InactiveUS20100194409A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceMicrobiological testing/measurementElectricityNanoparticle
The invention provides a method of electrically detecting a biological analyte molecule by means of a pair of electrodes. The electrodes are arranged at a distance from one another within a sensing zone. A capture molecule, which has an affinity to the analyte molecule and which is capable of forming a complex with the analyte molecule, is immobilised on an immobilisation unit. The immobilisation unit is contacted with a solution suspected to comprise the analyte molecule. The analyte molecule is allowed to form a complex with the capture molecule. The invention also provides a probe defined by a nanoparticulate tag that comprises or consists of electrically conducting matter that is capable of chemically interacting with the analyte molecule. In the method of the invention the electrically conducting nanoparticulate tag is added. Thereby the electrically conducting nanoparticulate tag is allowed to associate to the complex formed between the capture molecule and the analyte molecule. The presence of the analyte molecule is determined based on an electrical characteristic, influenced by the electrically conducting nanoparticulate tag, of a region in the sensing zone.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
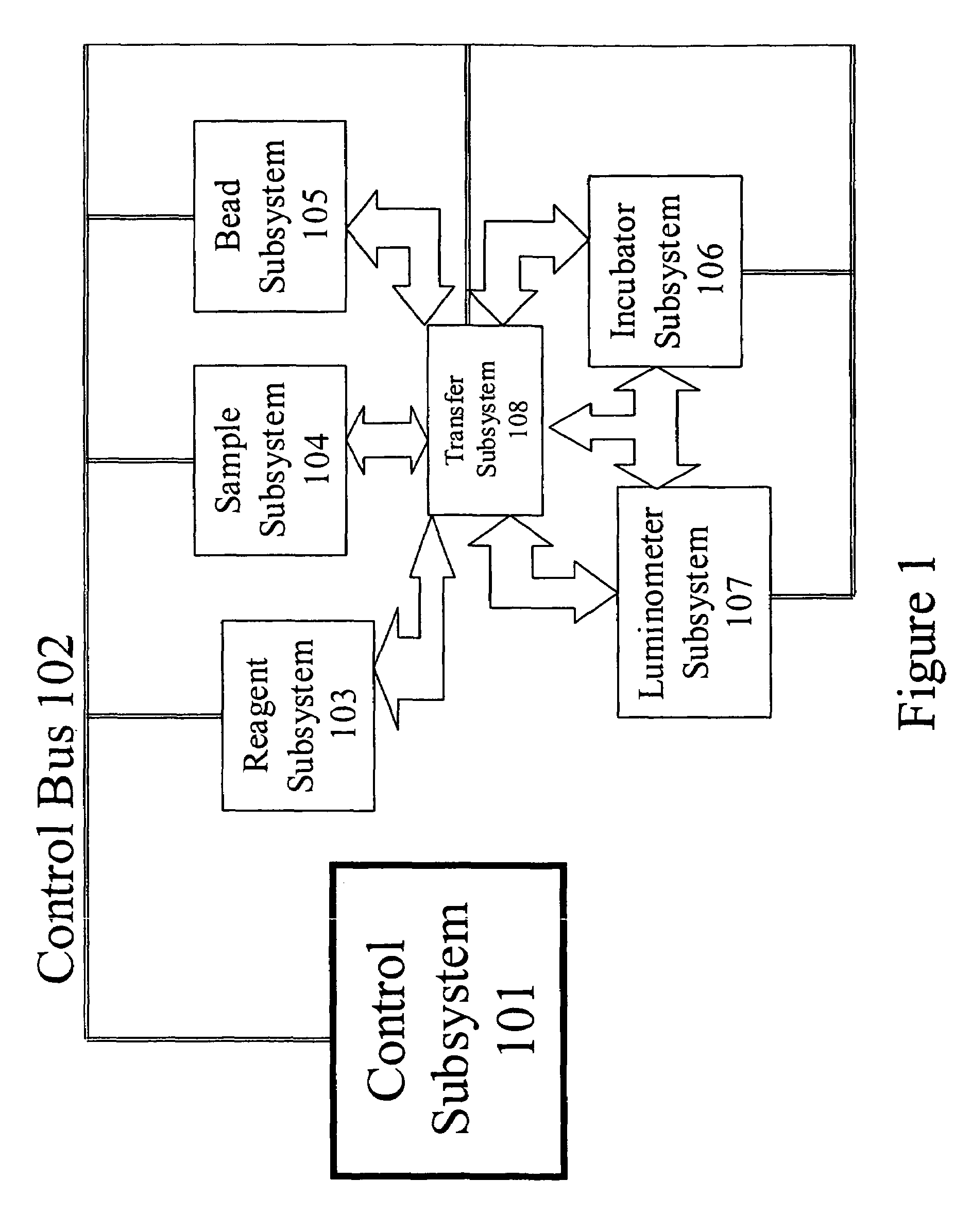
Bioanalytical instrumentation using a light source subsystem
ActiveUS20070281322A1Low heat generationStrong specificityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRadiation pyrometryChemical MoietyFluorescence
The invention relates to a light source for irradiating molecules present in a detection volume with one or more selected wavelengths of light and directing the fluorescence, absorbance, transmittance, scattering onto one or more detectors. Molecular interactions with the light allow for the identification and quantitation of participating chemical moieties in reactions utilizing physical or chemical tags, most typically fluorescent and chromophore labels. The invention can also use the light source to separately and simultaneously irradiate a plurality of capillaries or other flow confining structures with one or more selected wavelengths of light and separately and simultaneously detect fluorescence produced within the capillaries or other flow confining structures. In various embodiments, the flow confining structures can allow separation or transportation of molecules and include capillary, micro bore and milli bore flow systems. The capillaries are used to separate molecules that are chemically tagged with appropriate fluorescent or chromophore groups.
Owner:LUMENCOR
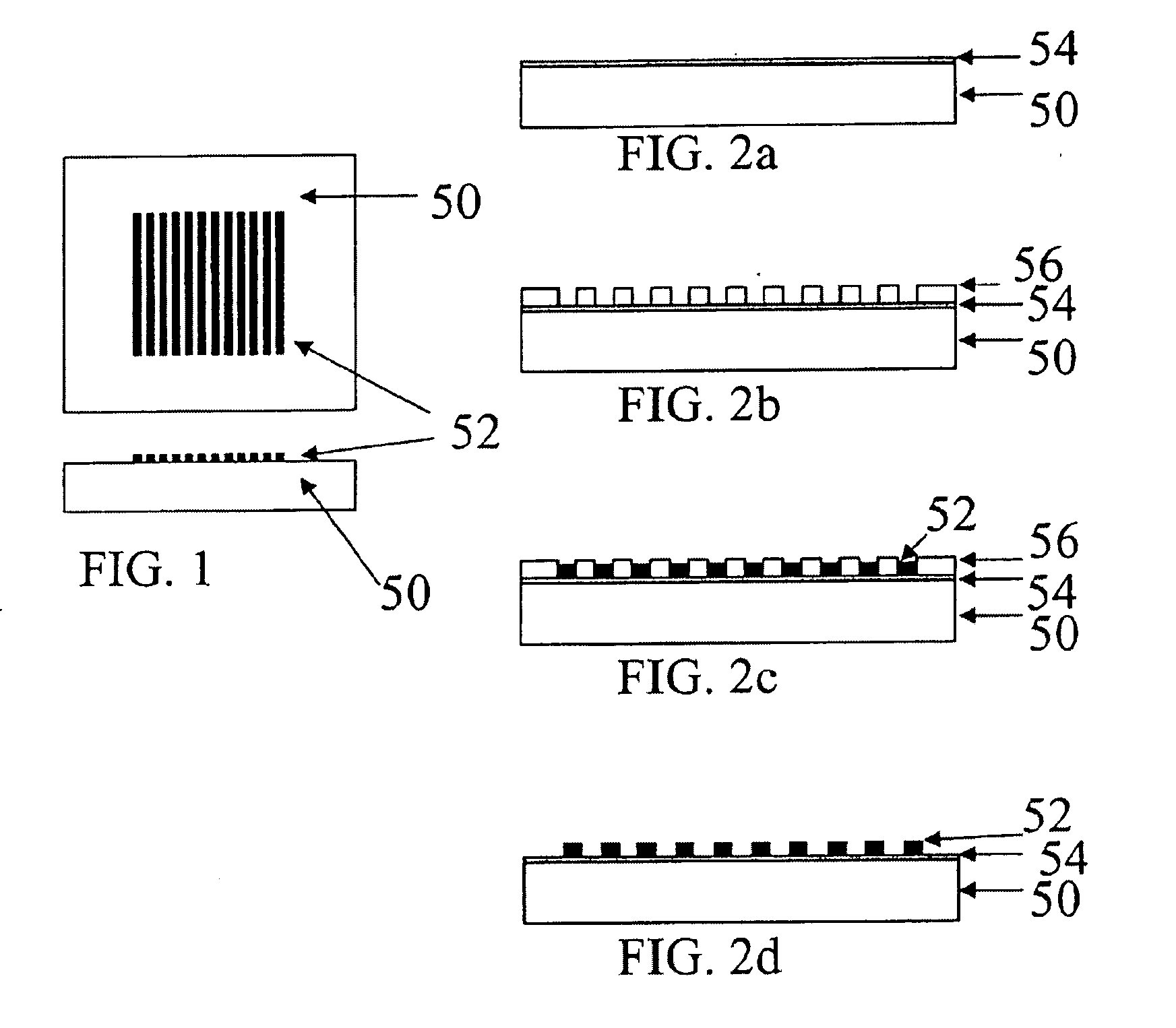
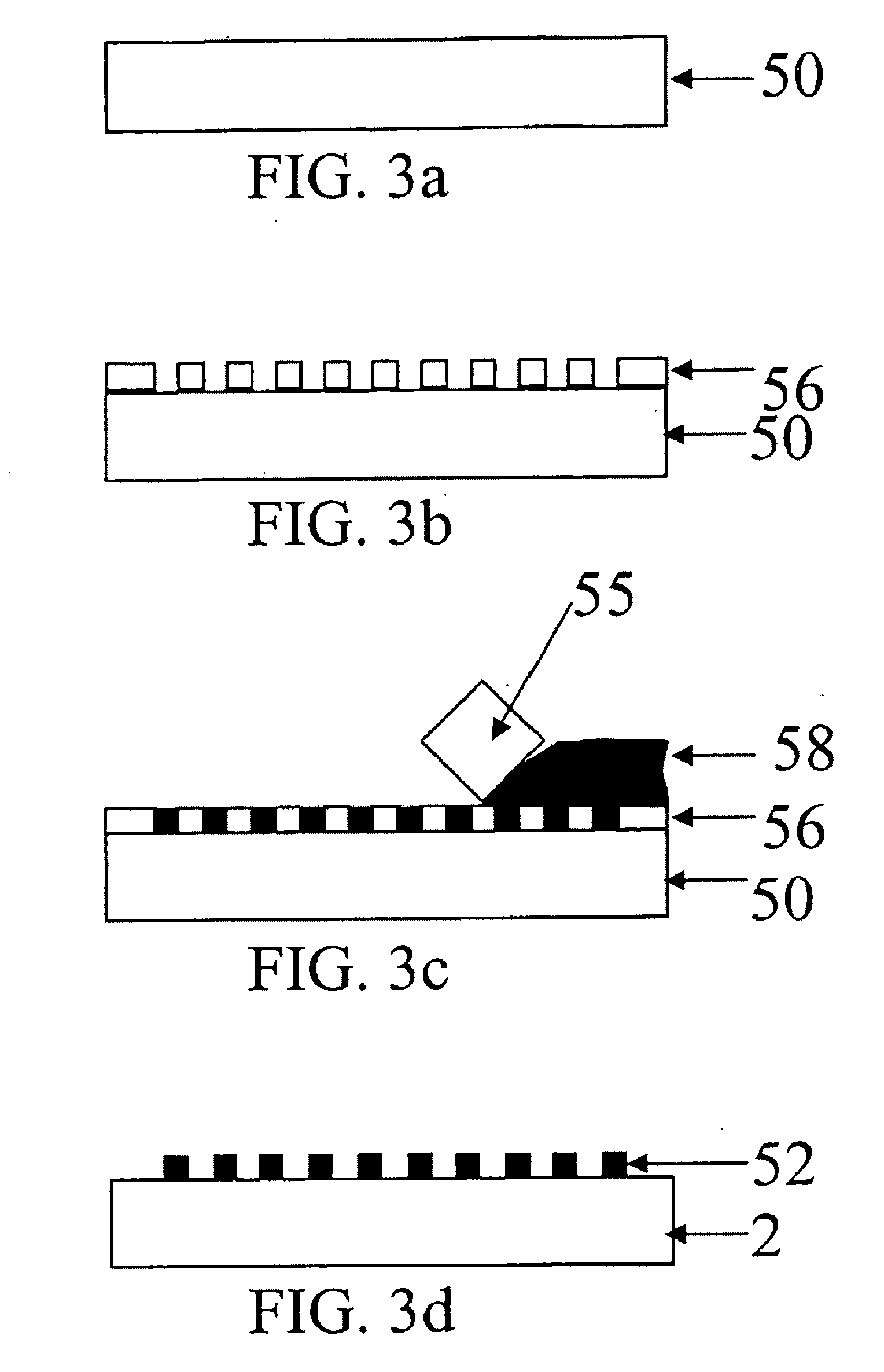
Waveguide plate and process for its production and microtitre plate
InactiveUS6961490B2Raise capacityHigh precisionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorScattering properties measurementsMicrotitre plateMethods of production
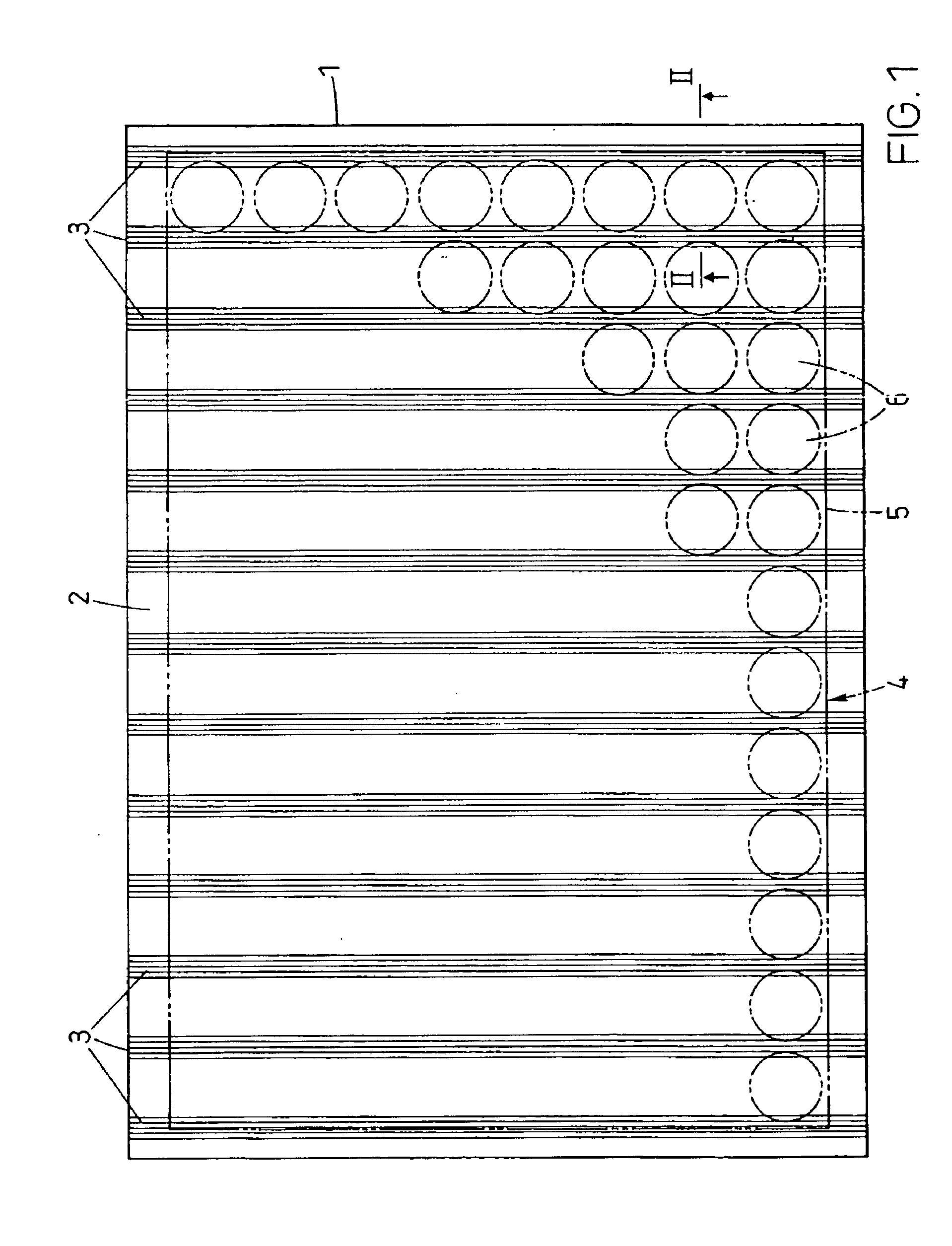
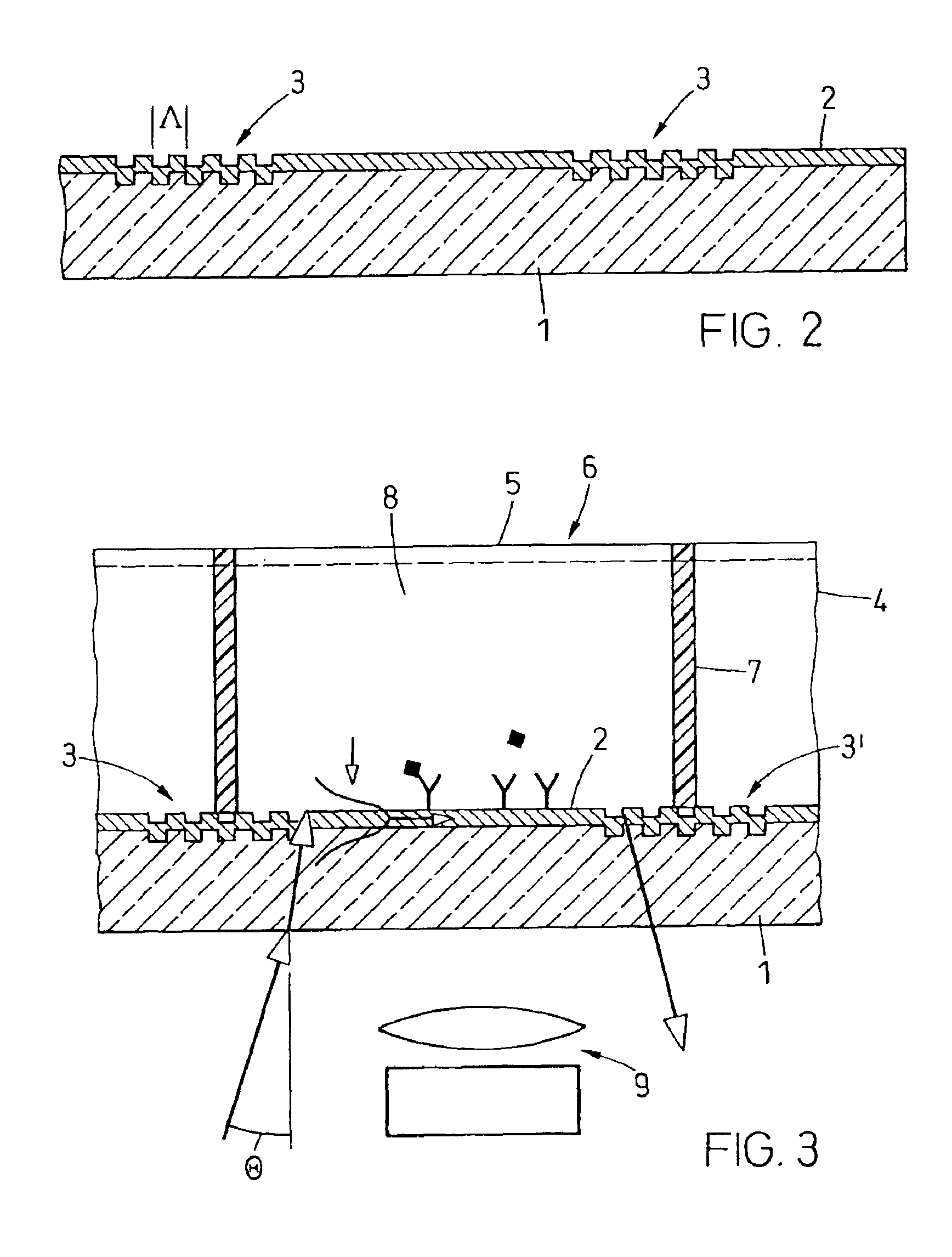
A waveguide plate and a process for making the waveguide plate with a plate-like glass substrate (1), carrying a waveguiding layer (2), with at least one coupling grating on the surface carrying said waveguiding layer (2), which coupling grating is formed as a grating of lines with a period between 150 nm and 1000 nm, the extension of said grating being at least 5 cm with lines parallel to one another, wherein the coupling angle () varies by not more than 0.1_ / cm along a line of said grating and wherein the absolute value of the deviation of the coupling angle () on said waveguide plate, from a predefined desired value, does not exceed 0.5_. The deviation from the average value of the coupling angle does not exceed 0.3_, preferably not 0.15_ on the whole waveguide plate. The waveguide plate is suitable as part of a sensor platform and of an arrangement of sample compartments for chemo-and bioanalytical investigations in order to produce a coupling grating formed as a line grating with a grating period between 100 nm and 2500 nm
Owner:ZEPTOSENS +1
Light transmitted assay beads
ActiveUS20070037195A1Increase contrastImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechBarcodeTransmitted light
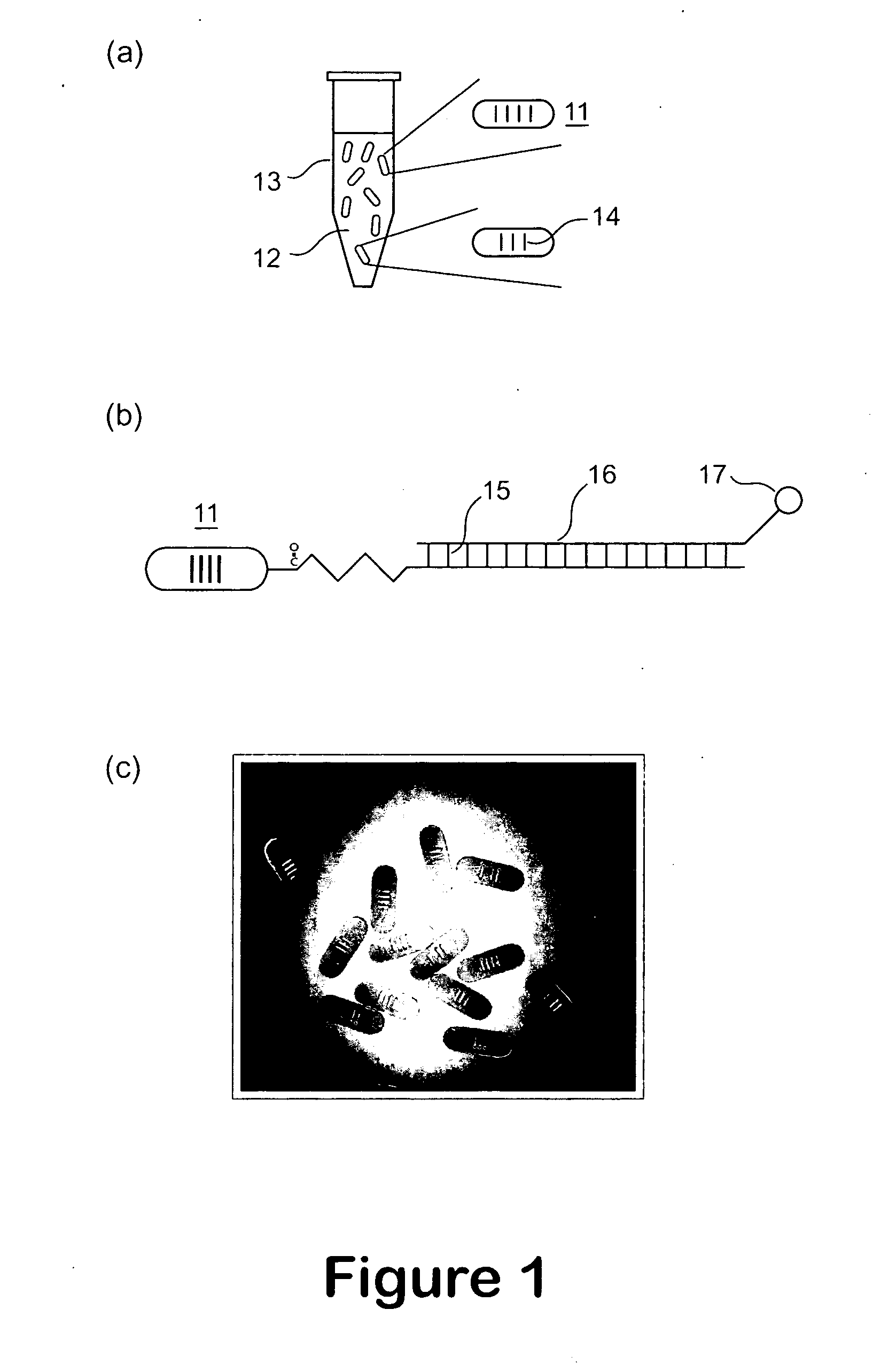
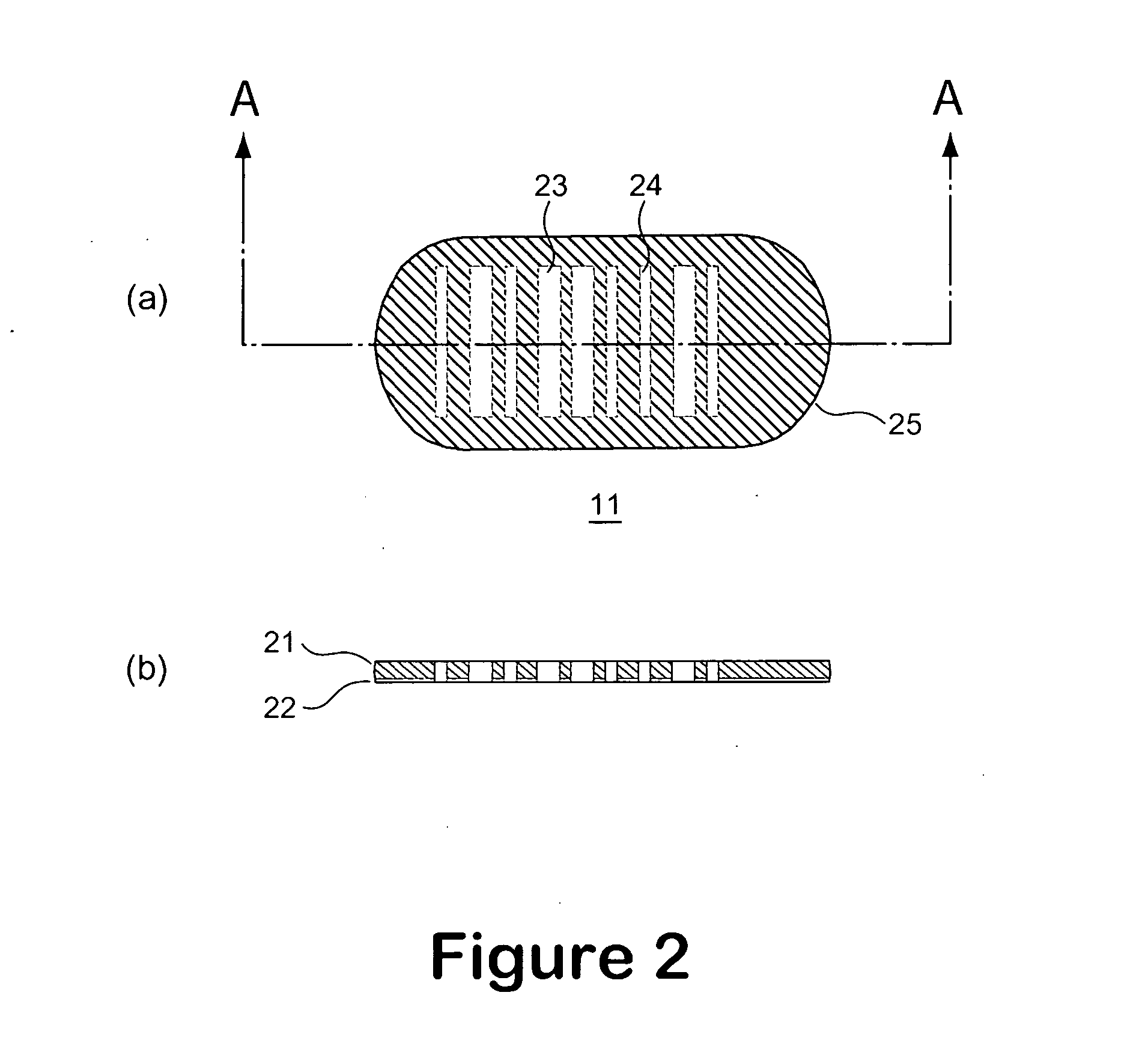
A micro bead having a digitally coded structure that is partially transmissive and opaque to light. The pattern of transmitted light is determined by to decode the bead. The coded bead may be structured a series of alternating light transmissive and opaque sections, with relative positions, widths and spacing resembling a 1D or 2D bar code image. To decode the image, the alternating transmissive and opaque sections of the body are scanned in analogous fashion to bar code scanning. The coded bead may be coated or immobilized with a capture or probe to effect a desired bioassay. The coded bead may include a paramagnetic material. A bioanalysis system conducts high throughput bioanalysis using the coded bead, including a reaction detection zone and a decoding zone.
Owner:APPLIED BIOCODE
Systems and methods for analyzing pathologies utilizing quantitative imaging
ActiveUS20180330477A1Improving Imaging AccuracyImprove analysisImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionAnalyte
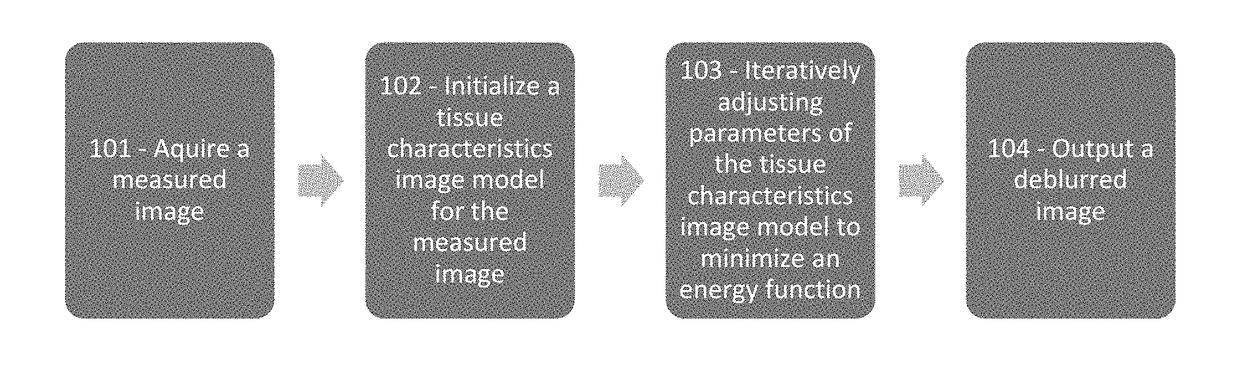
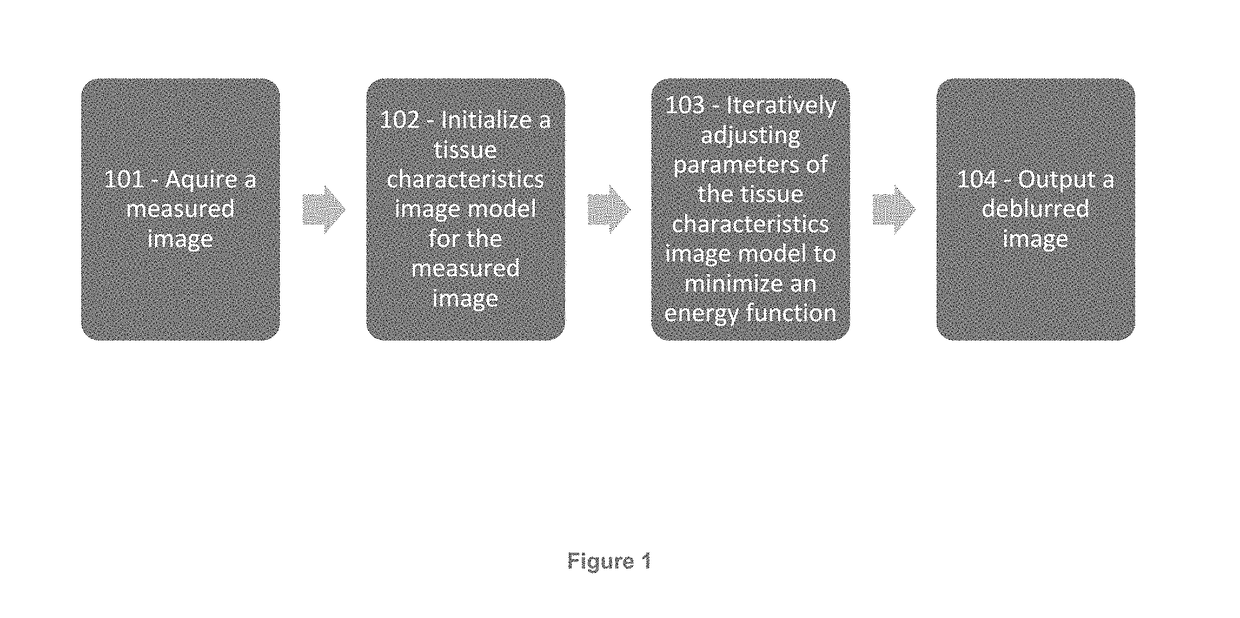
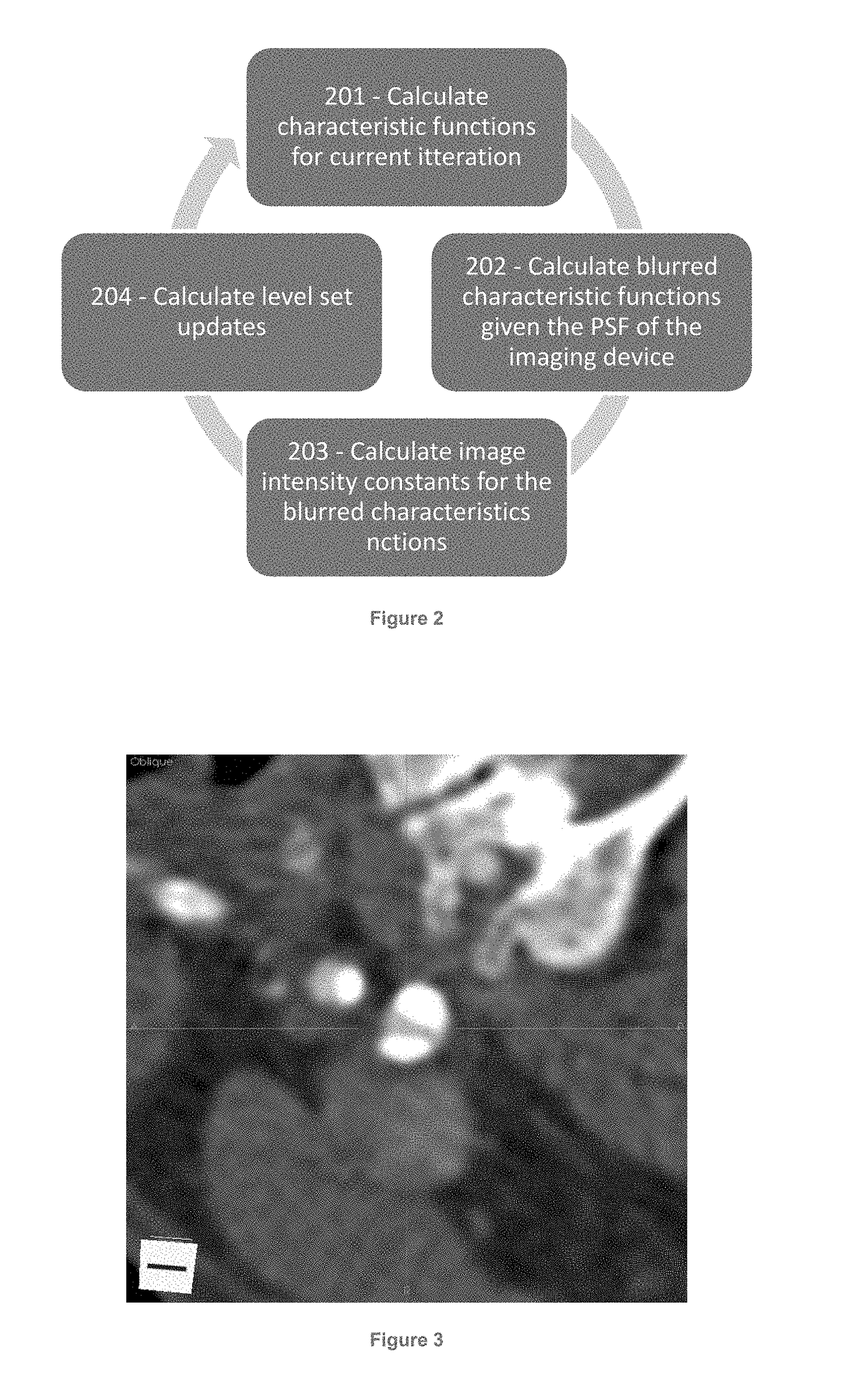
The present disclosure provides for improved image analysis via novel deblurring and segmentation techniques of image data. These techniques advantageously account for and incorporate segmentation of biological analytes into a deblurring process for an image. Thus, the deblurring of the image may advantageously be optimized for enabling identification and quantitative analysis of one or more biological analytes based on underlying biological models for those analytes. The techniques described herein provide for significant improvements in the image deblurring and segmentation process which reduces signal noise and improves the accuracy of the image. In particular, the system and methods described herein advantageously utilize unique optimization and tissue characteristics image models which are informed by the underlying biology being analyzed, (for example by a biological model for the analytes). This provides for targeted deblurring and segmentation which is optimized for the applied image analytics.
Owner:ELUCID BIOIMAGING INC
Carousel system for automated chemical or biological analyzers employing linear racks
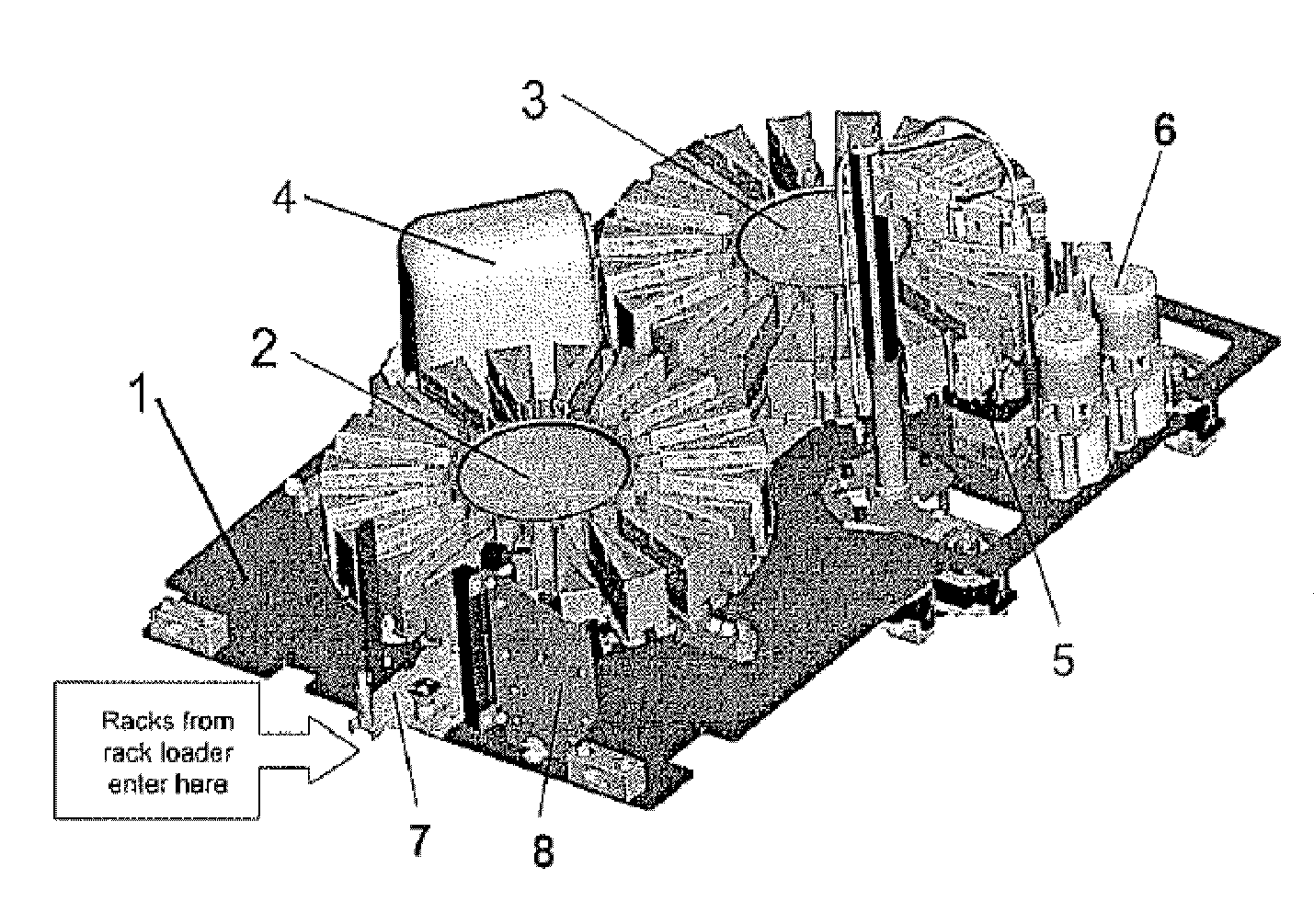
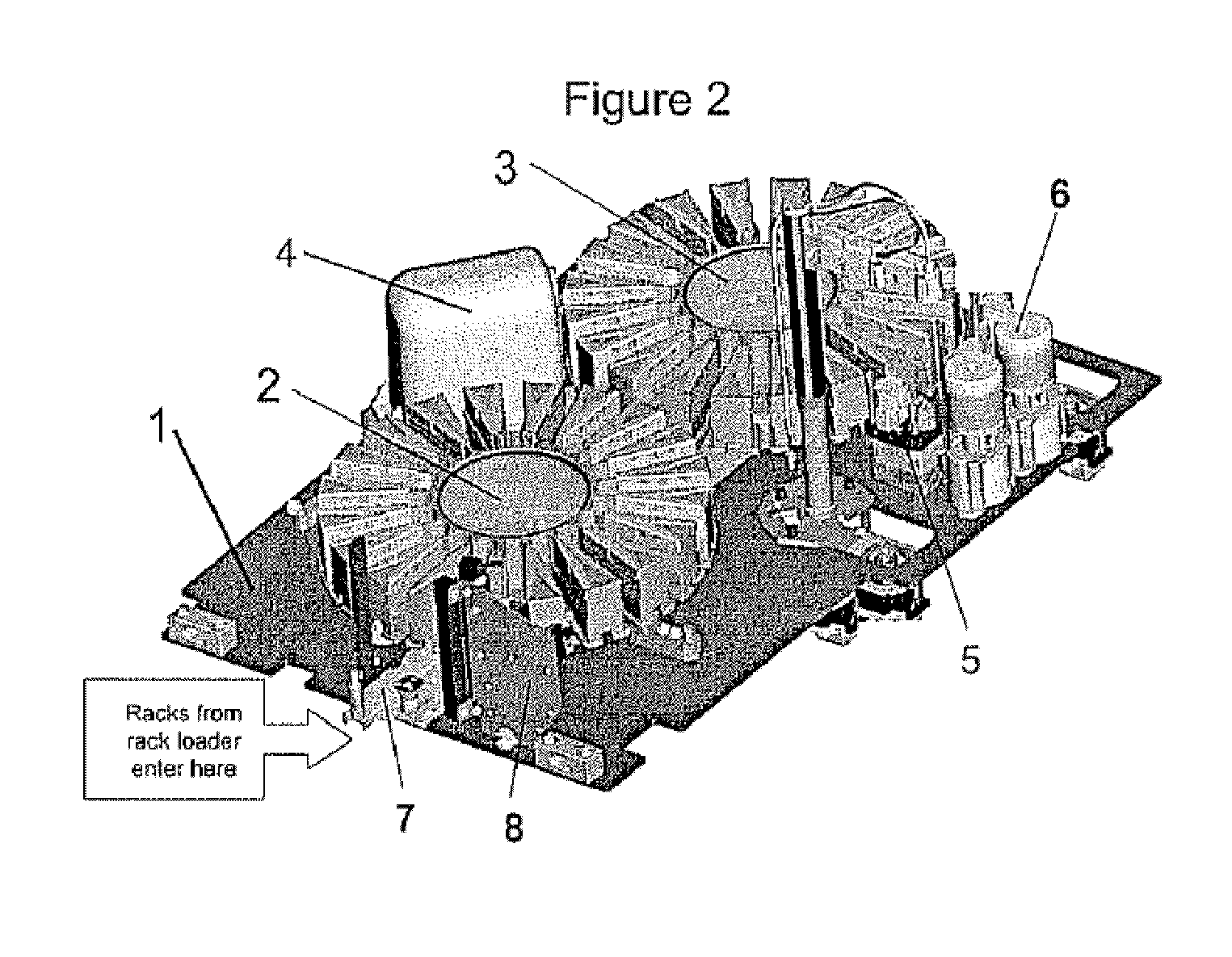
ActiveUS7670553B2Minimize and eliminate involvementMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological testingLinear motionEngineering
An automated chemical or biological sample analyzer includes a plurality of linear sample carrying racks that are moved to a processing station for conducting an analysis using one or more carousel devices. Under computer control, rotational movements of the carousel or carousels, linear movements of the transfer or shuttle mechanisms, and operation of a pipetting station are performed in a coordinated fashion so as to handle the processing of a large number of samples simultaneously in an optimized fashion that allows random ordering of samples for processing.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
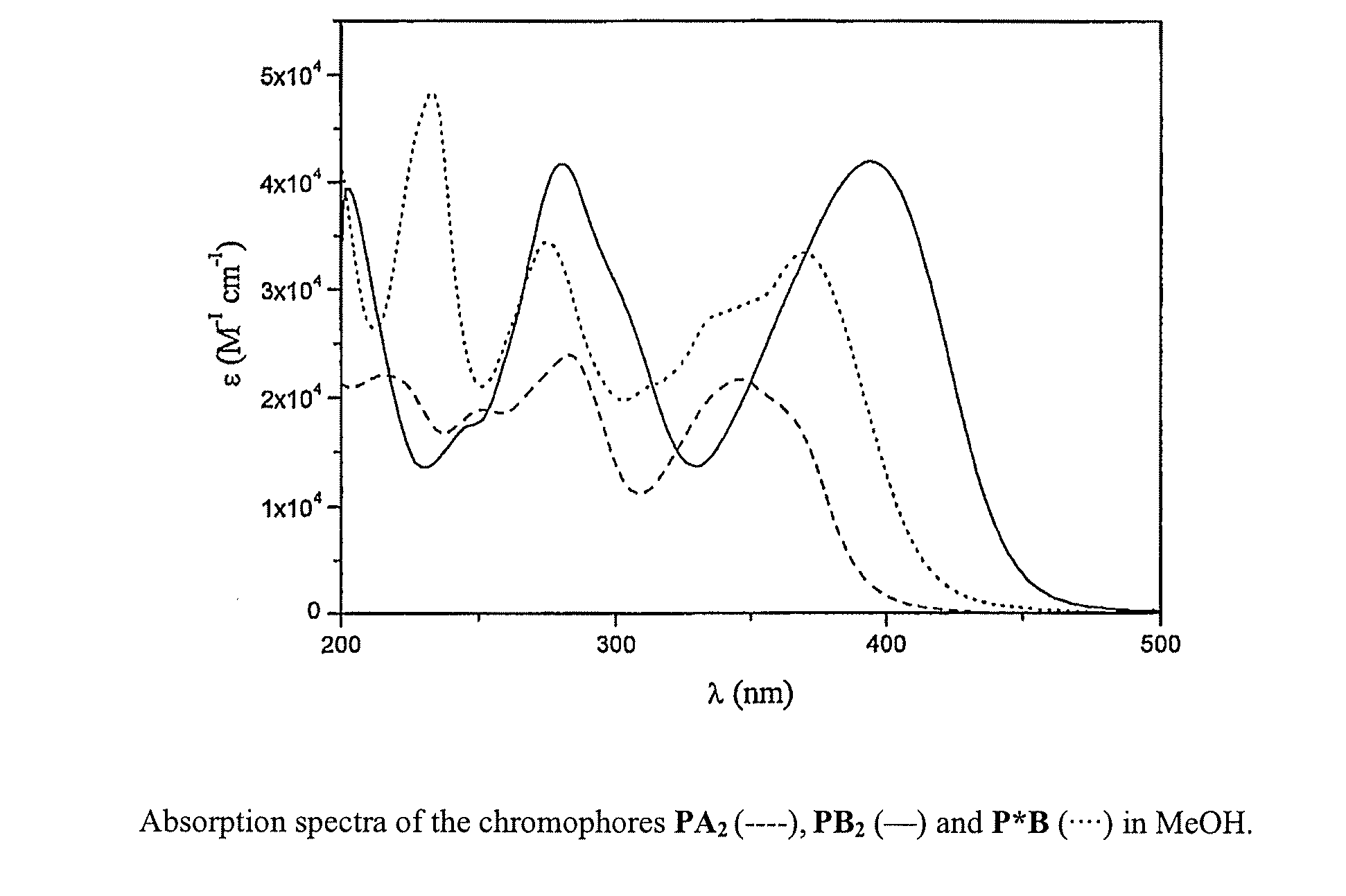
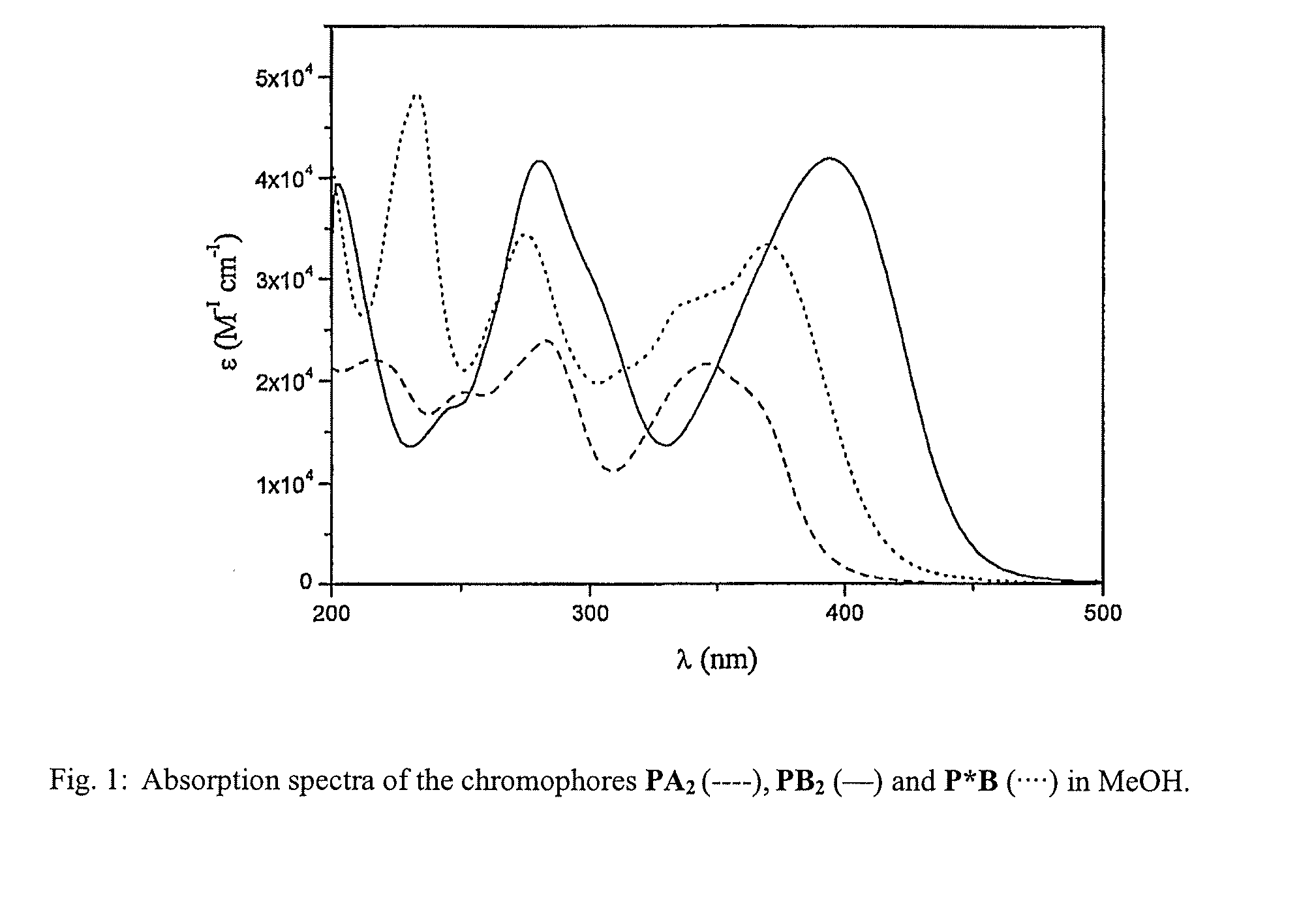
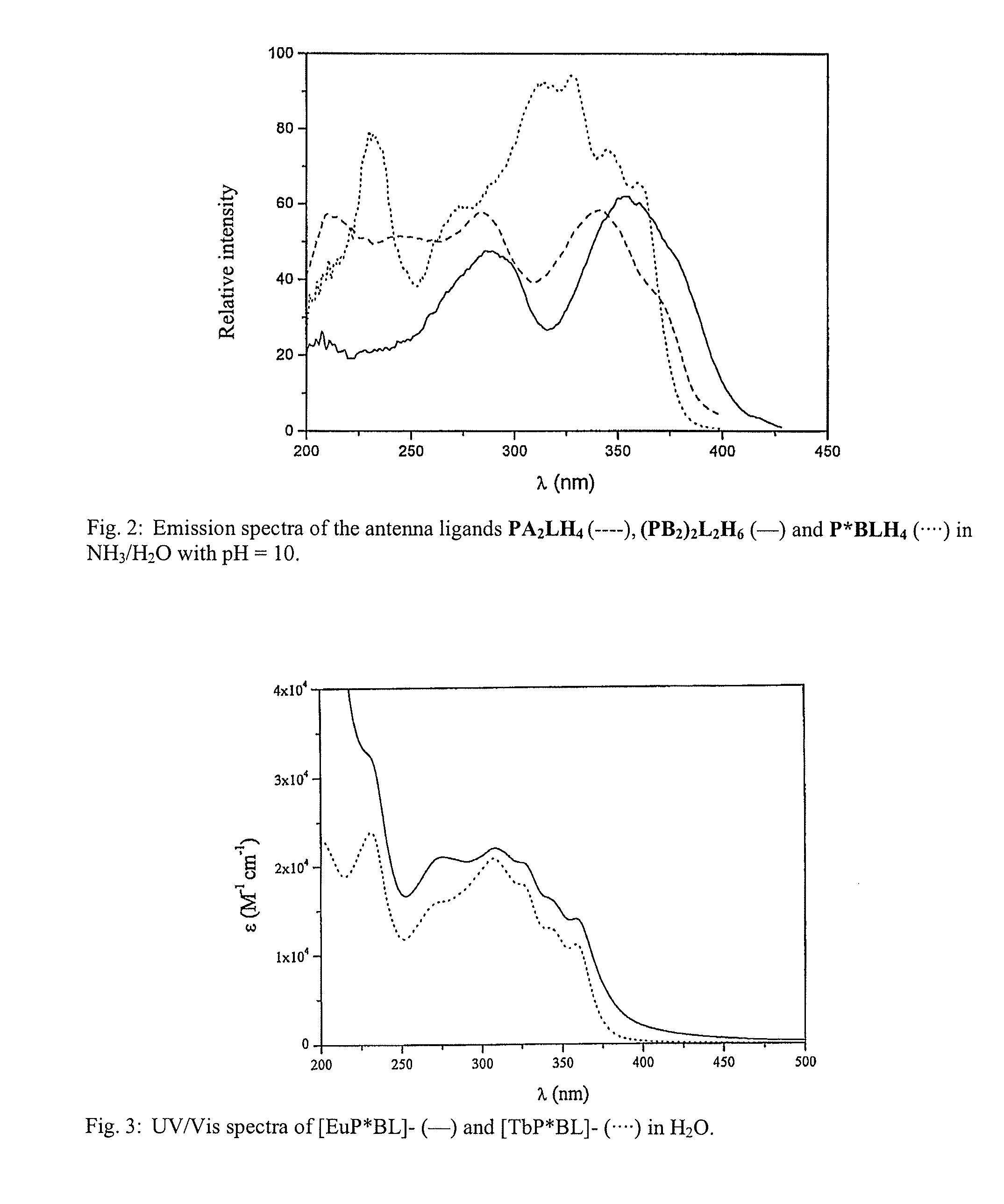
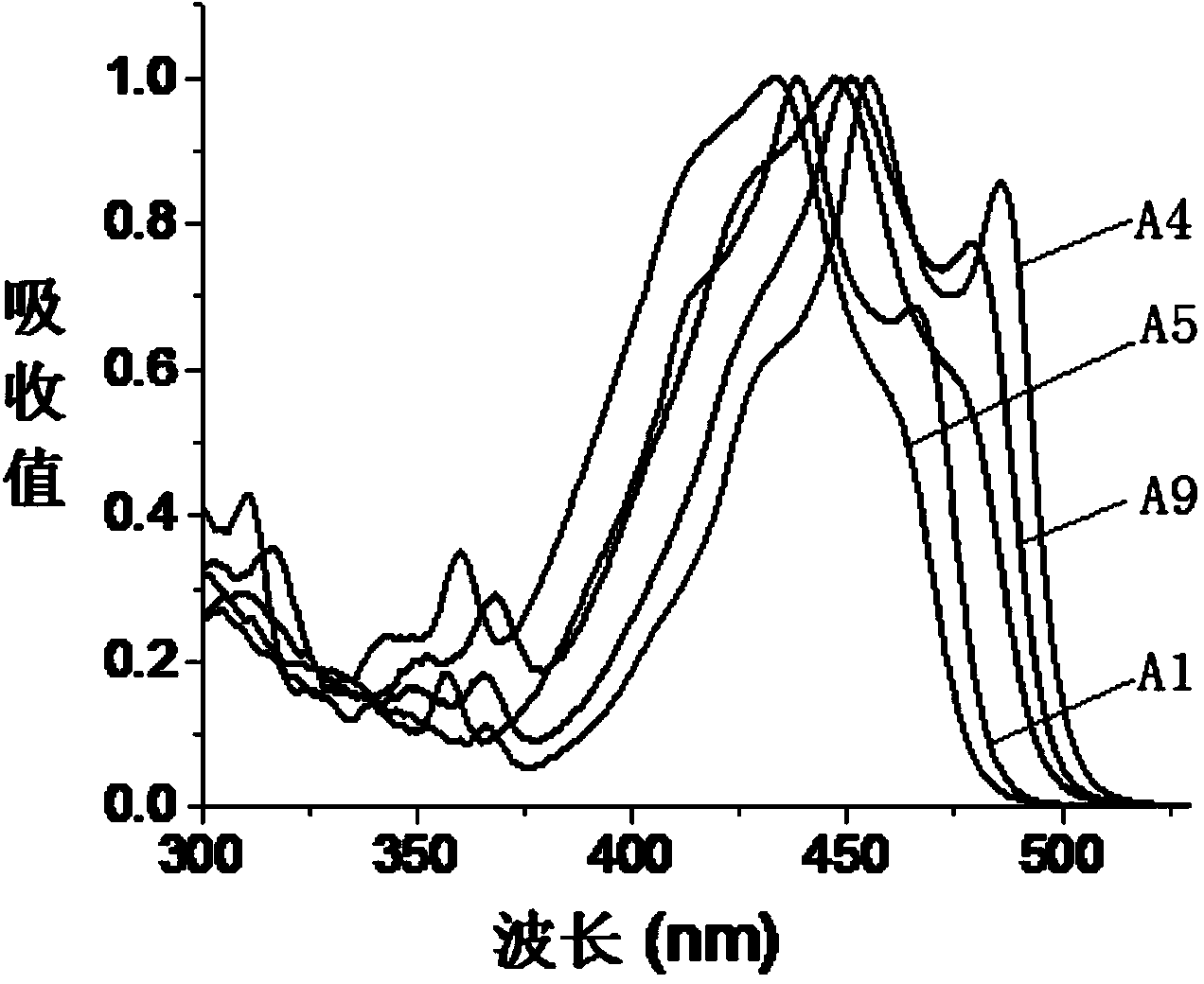
Lanthanide Chelates and Use Thereof in Bioanalysis
InactiveUS20110136242A1Improve stabilityGood spectral characteristicsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFluorescenceQuantitative determination
Novel chemical compounds, with application in fluorometric analytical methods, for qualitative and quantitative determination of biomolecules. The aim of the invention is to identify and prove the suitability of such compounds. Said aim is achieved with compounds of formula (1) where R′ is an antenna function, R2 is a chelate forming agent, containing a coordinated lanthanide(III)ion, X is —OH or a group with affinity for the biomolecule, bonded to a carboxylate group of the chelate forming agent by means of an amide bond and Y is —H or a group with affinity for the biomolecule, coupled to the antenna function.
Owner:SENSIENT IMAGING TECH GMBH
Preparation method of water-soluble material in core-shell or core-corona-shell structure
ActiveCN102146288AHigh yieldGood water solubilityLuminescent compositionsChemical reactionWater soluble
The invention discloses a preparation method of a water-soluble material in a core-shell or core-corona-shell structure, which comprises the following steps: (1) using a water-soluble material or a water-soluble material modified by a modifying material as a core material; (2) carrying out physical reaction or chemical reaction on the core material and a chemical reagent A to obtain a core material modified by the chemical reagent A; (3) reacting the core material modified by the chemical reagent A in the step (2) with a metal-cation-containing water solution or reaction reagent B to obtain awater-soluble material in a core-shell structure; and (4) repeating the step (2) and the step (3) by using the material in a core-shell structure in the step (3) as a core material to obtain the water-soluble material in a core-corona-shell structure. The method has the advantages of simple technique and high core-shell yield, and is applicable to the fields of bioanalysis, medical diagnosis and imaging, environmental science, analytic science and the like.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
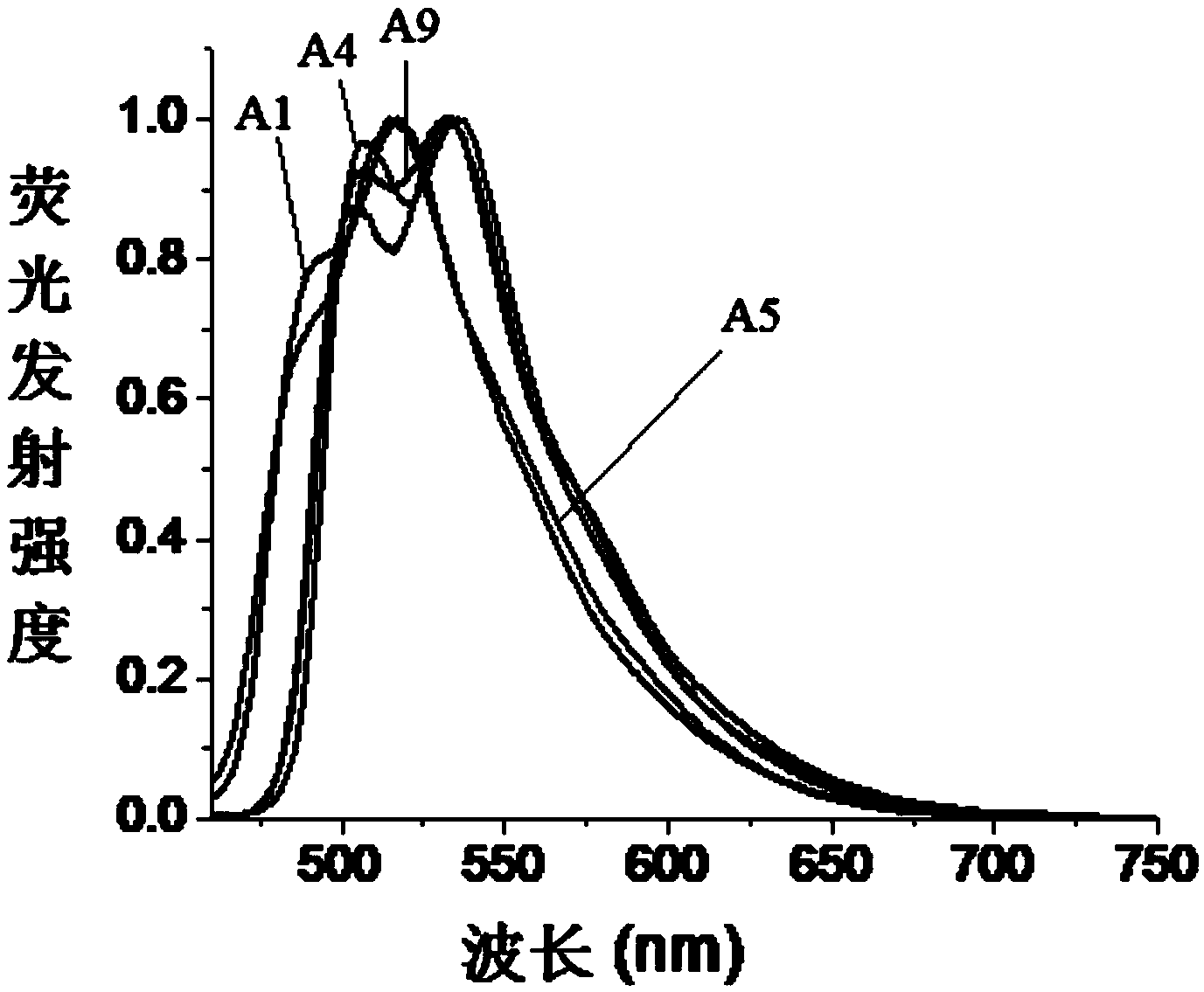
Fluorine-boron fluorescent dye as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103865290ANarrow absorbencyNarrow emission peakAzo dyesGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsQuantum yieldHalogen
The invention discloses a fluorine-boron fluorescent dye as well as a preparation method and application thereof, wherein the structure of the fluorine-boron fluorescent dye is shown as a formula (I) or a formula (II), in the formula (I) and the formula (II), R1 is H or halogen; R2 is CN; R3, R4, R5 and R6 are independently selected from H, halogen, C1-C6 alkyl or C1-C6 alkoxy; V, W, X, Y and Z are independently CH or N, and when V, W, X, Y or Z is N, N has no substituent group. According to the fluorine-boron fluorescent dye and the preparation method thereof, the maximal fluorescence emission wavelength of the fluorine-boron fluorescent dye is 518-600nm, and the fluorine-boron fluorescent dye also has excellent fluorescence quantum yield and Stokes shift, which shows that the fluorine-boron fluorescent dye has good application prospect in the bioanalysis fields of fluorescence labeling, bioimaging and so on; meanwhile, the preparation method is simple in steps, and raw materials can be obtained easily.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
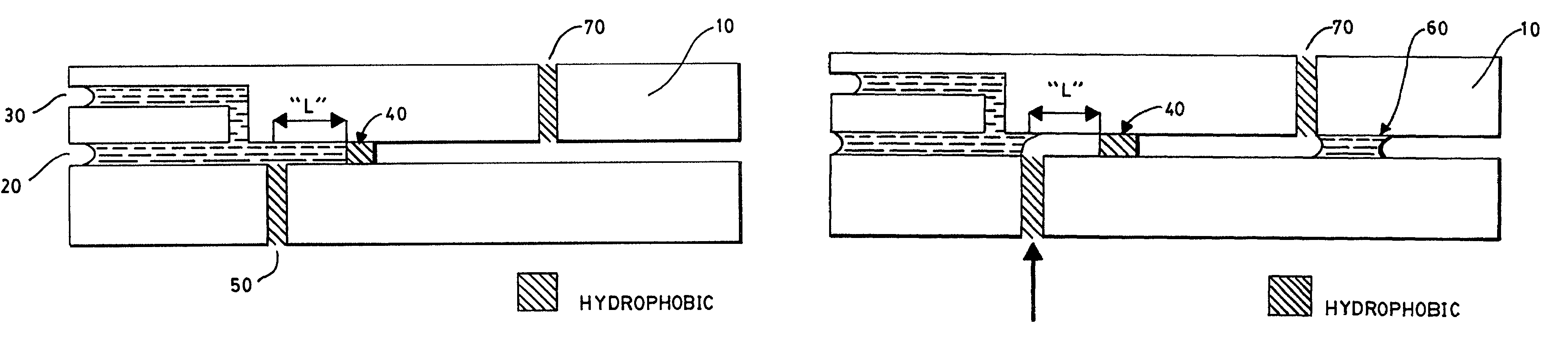
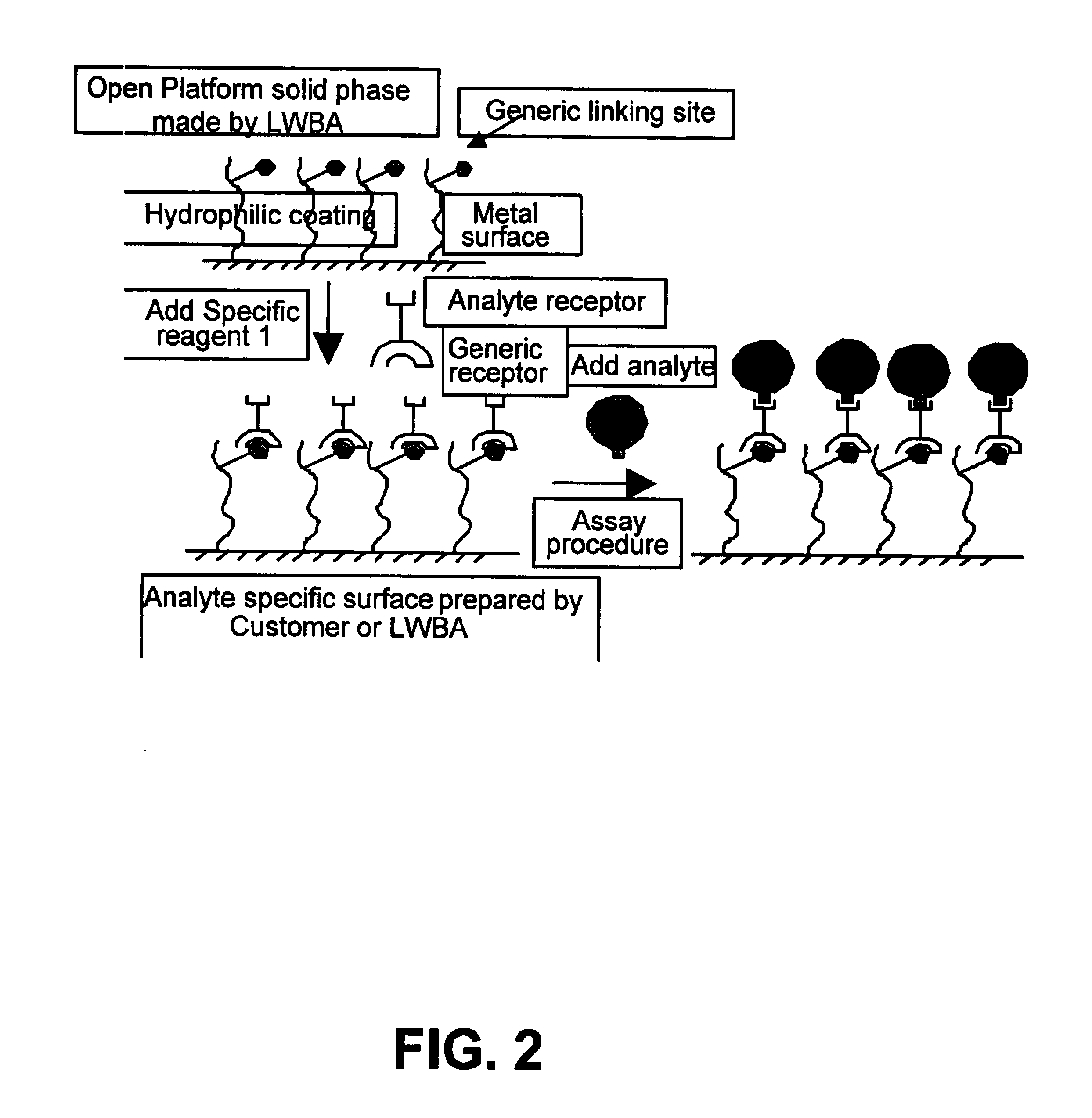
Device comprising a plurality of analysis sites on a support
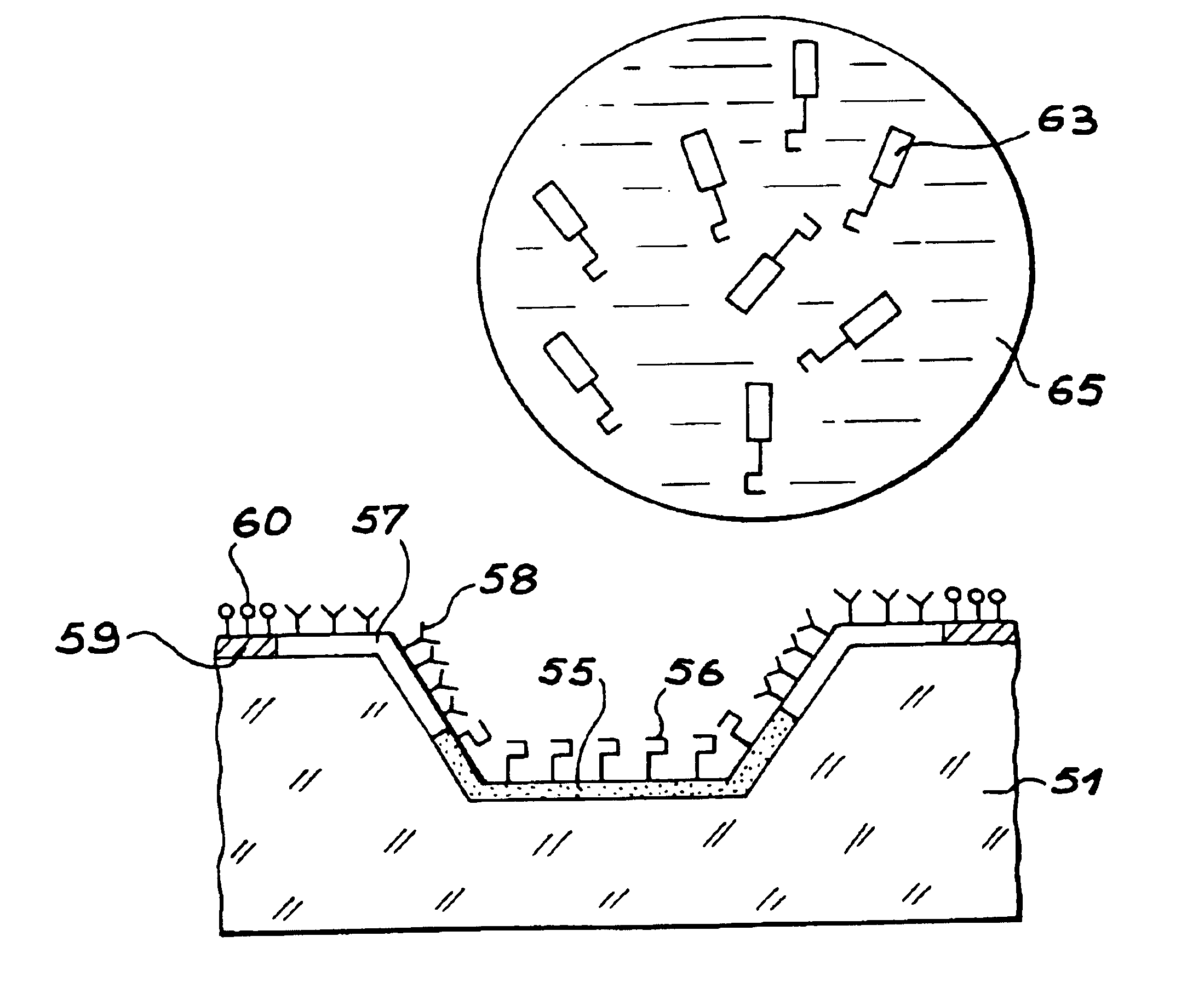
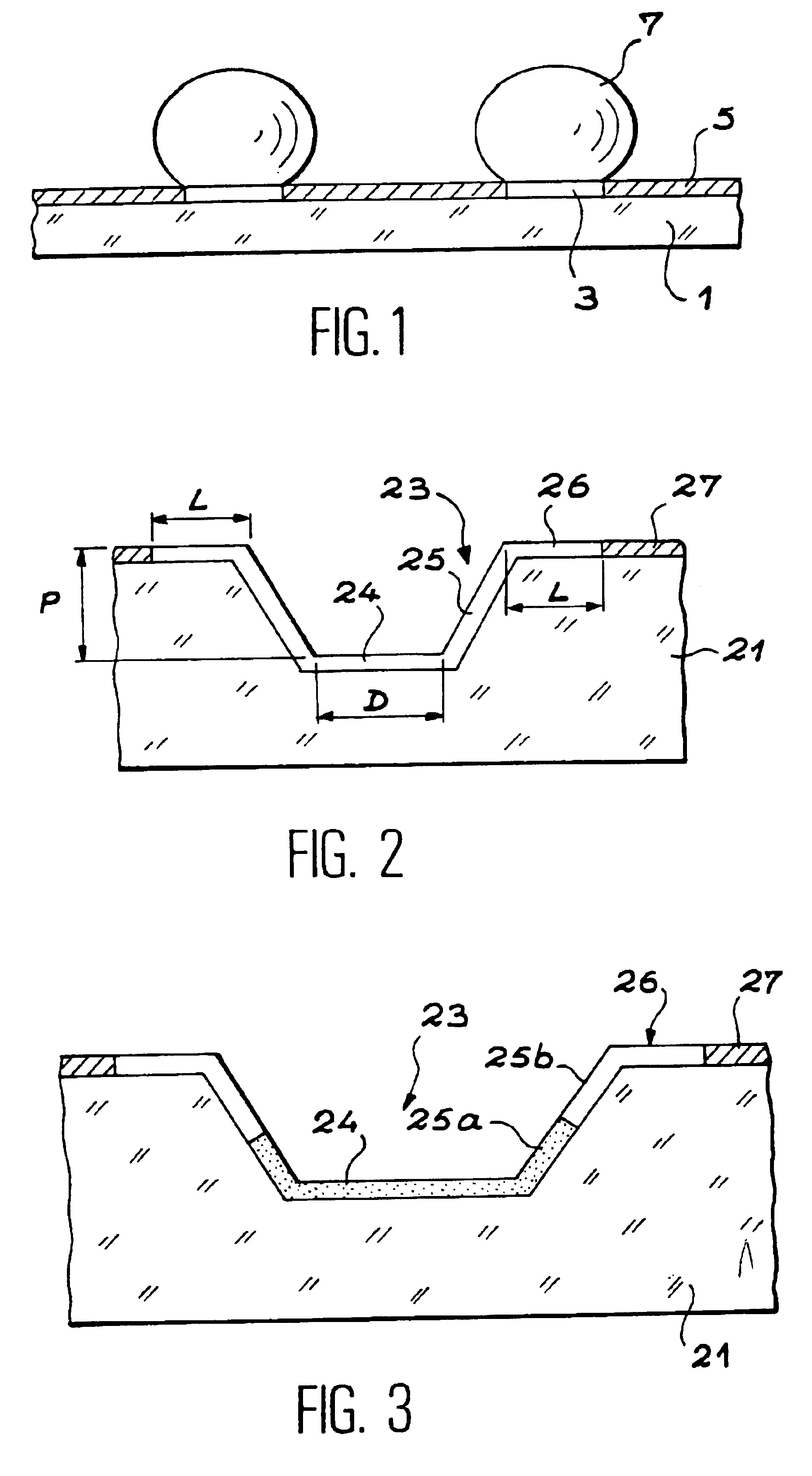
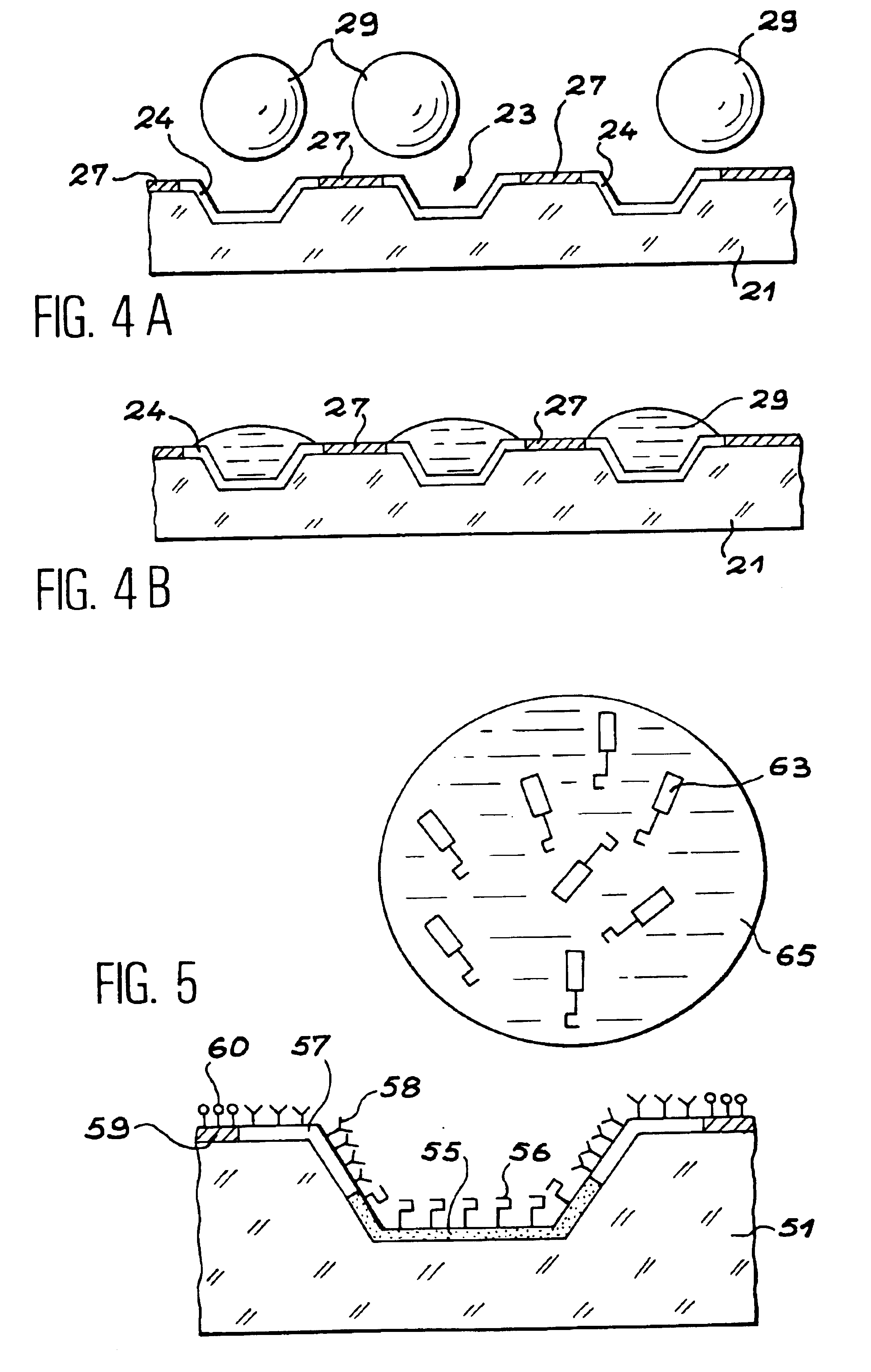
InactiveUS6902705B1Large diameterIncrease concentrationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
The subject of the invention is a device for chemical or biological analysis comprising a carrier (21) containing a plurality of analysis sites able to fix a chemical or biological reagent, in which the analysis sites are formed of microdishes (23) hollowed out of the carrier, the side walls and the bottom of the microdishes and the areas of the carrier surface surrounding each microdish, called microdish edges, being made in at least one hydrophilic material (24), and the planar areas of the carrier arranged between the areas surrounding the microdishes being made in a hydrophobic material (27).Drops (29) of reagent are therefore guided into the microdishes (23) on account of the hydrophobic areas (27). It is therefore possible to increase the density of analysis sites on the carrier.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Bioanalysis systems including optical integrated circuit
InactiveUS20060205092A1Reduce decreaseFaster and simpler discoveryScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsMicrowell PlateReduced size
Optical Integrated Circuits (OIC) in Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Analysis Systems combined with micorarray or microwell plates to provide enhanced sensitivity, stability, speed of analysis and reduced size are disclosed. Using the OIC with other optical analysis methods to provide enhance analysis systems is also disclosed.
Owner:LACKRITZ HILARY S +3
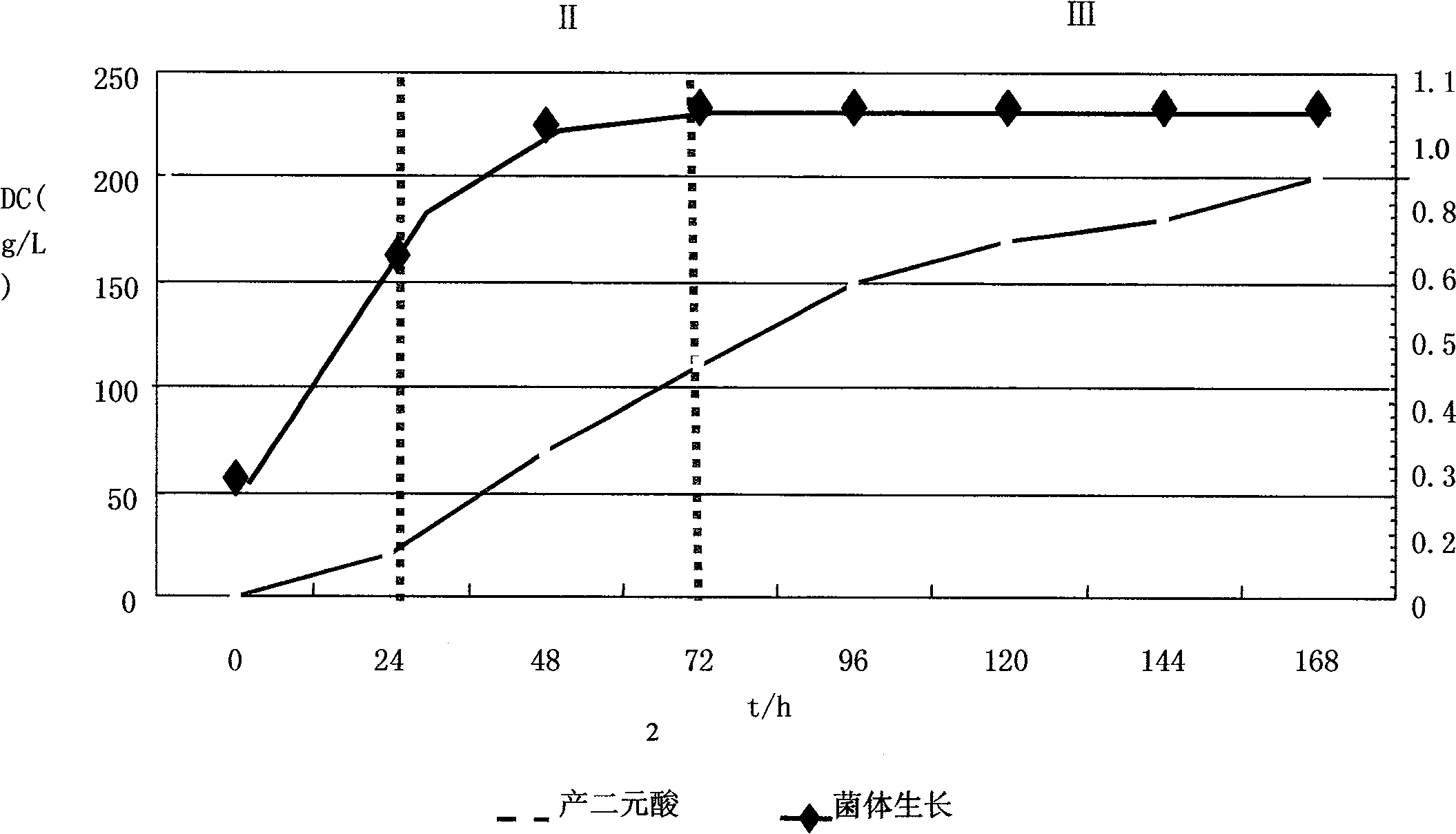
Preparation method of long carbon chain dibasic acid
The invention relates to a preparation method of a long carbon chain dibasic acid. C11 and upper alkane is used as a substrate to produce a corresponding long carbon chain dibasic acid product through the conversion of the substrate into the long carbon chain dibasic acid by using a microbial fermentation method as well as the extraction and the separation of fermentation liquid and the refining processes of a crude product of dibasic acid. Through technological innovation and process innovation, the invention researches a new preparation method of the long carbon chain dibasic acid, greatly decreases the production cost of the long carbon chain dibasic acid, improves the yield and the product quality of the long carbon chain dibasic acid, can produce C11 and upper long carbon chain dibasic acid, finally solve the bottleneck problem restricting the rapid development of the long carbon chain dibasic acid, and form the industrialized scale and the technological predominance. The long carbon chain dibasic acid produced by using the bioanalysis provided by the invention has the advantages of high acid generation level, low production cost, good product quality, complete variety, and the like, the prepared long carbon chain dibasic acid product has high single acid content, good light transmission and high thermal stability, can meet the requirements of different clients, and can be used for producing high-grade spices, high-performance engineering plastics, high-temperature dielectric medium, high-grade hot-melt adhesive, coldness-resistant plasticizer, high-grade lubricating oil, high-grade paint, coating, and the like. The invention greatly widens the development space of the downstream products of the long carbon chain dibasic acid.
Owner:CATHAY R&D CENT CO LTD +2
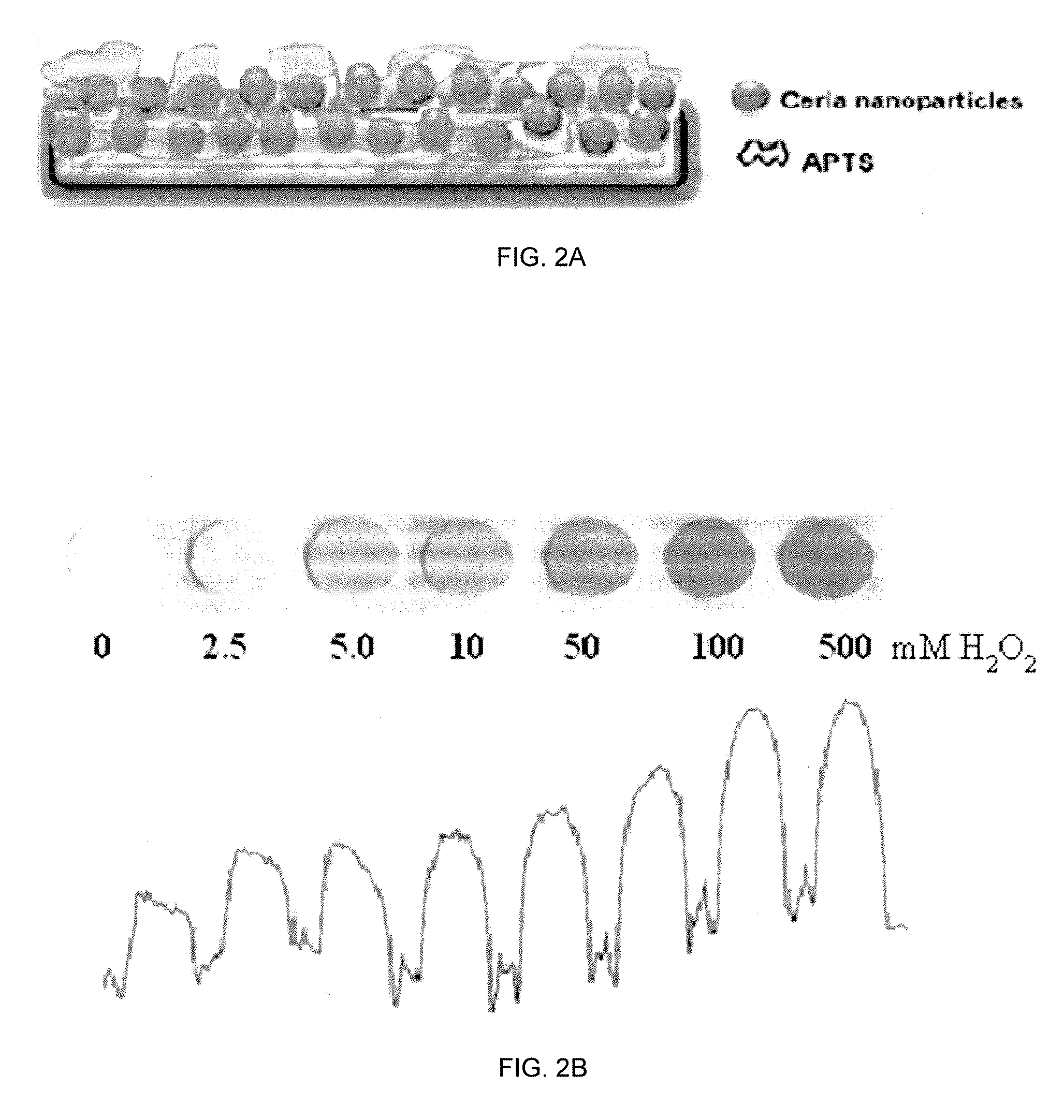
Reagentless Ceria-Based Colorimetric Sensor
ActiveUS20120315659A1Possible to detectIncrease rangeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementDelivery vehicleIn vivo
A colorimetric reagent in the form of nanoparticles, composite nanoparticles, and nanoparticle coatings, including methods of use, methods of preparation, deposition, and assembly of related devices and specific applications. The colorimetric reagent comprises cerium oxide nanoparticles which are used in solution or immobilized on a solid support, either alone or in conjunction with oxidase enzymes, to form an active colorimetric component that reacts with an analyte to form a colored complex. The rate of color change and the intensity of the color are proportional to the amount of analyte present in the sample. Also described is the use of ceria and doped ceria nanoparticles as an oxygen storage / delivery vehicle for oxidase enzymes and applications in biocatalytic processes in anaerobic conditions of interest in biomedicine and bioanalysis. Further described are a variety of related applications of the disclosed technology including clinical diagnosis, in vivo implantable devices, food safety, and fermentation control.
Owner:CLARKSON UNIVERSITY
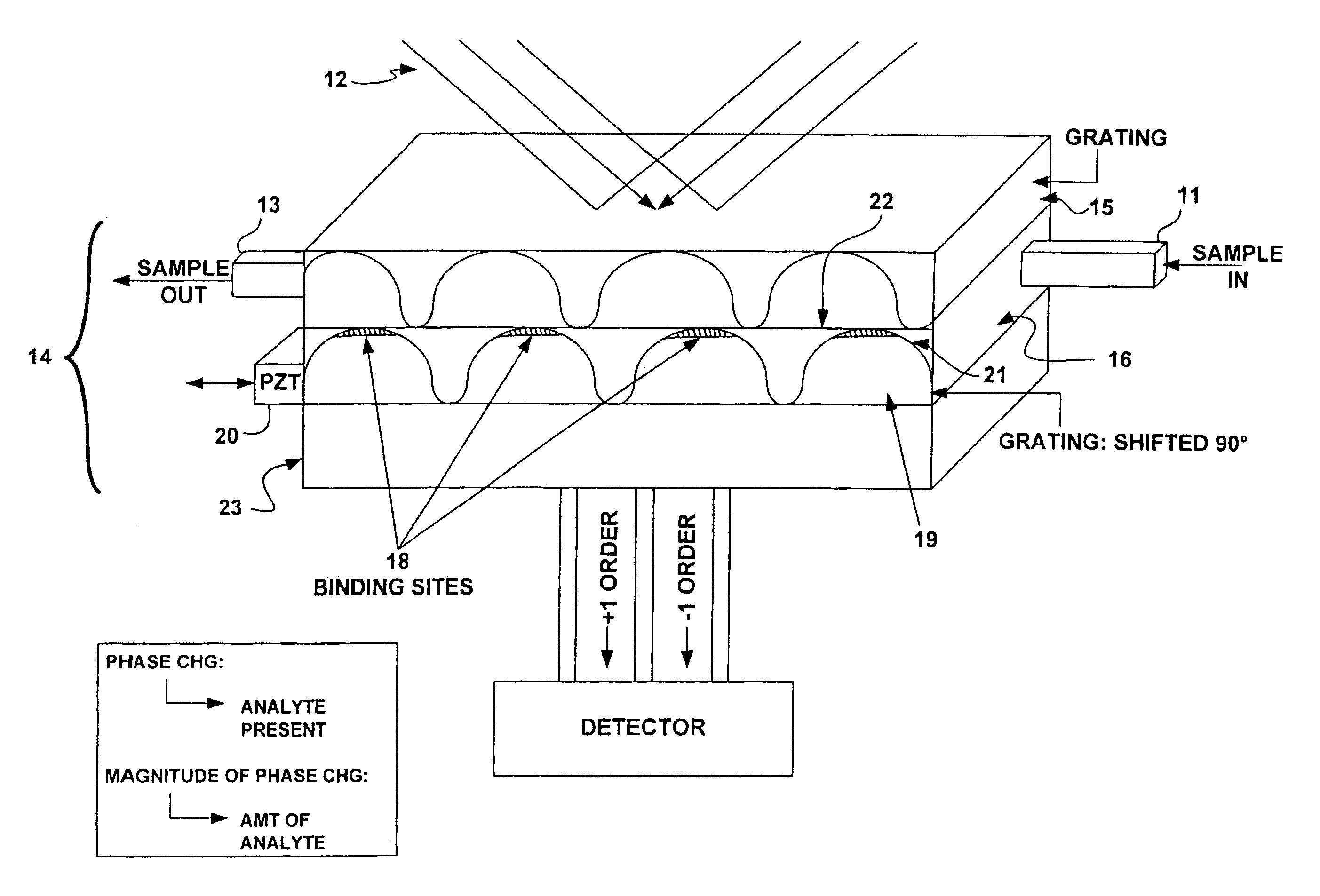
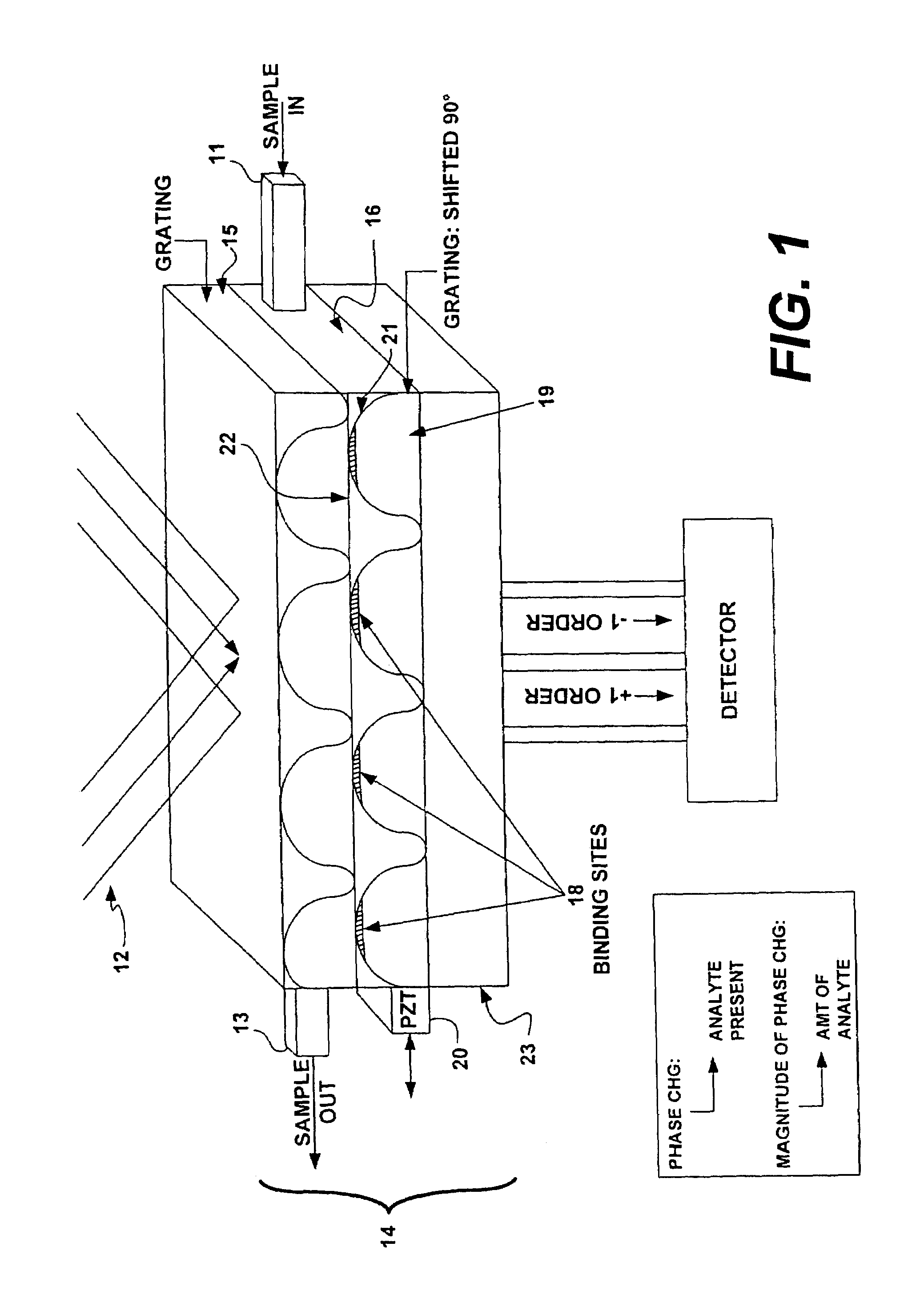
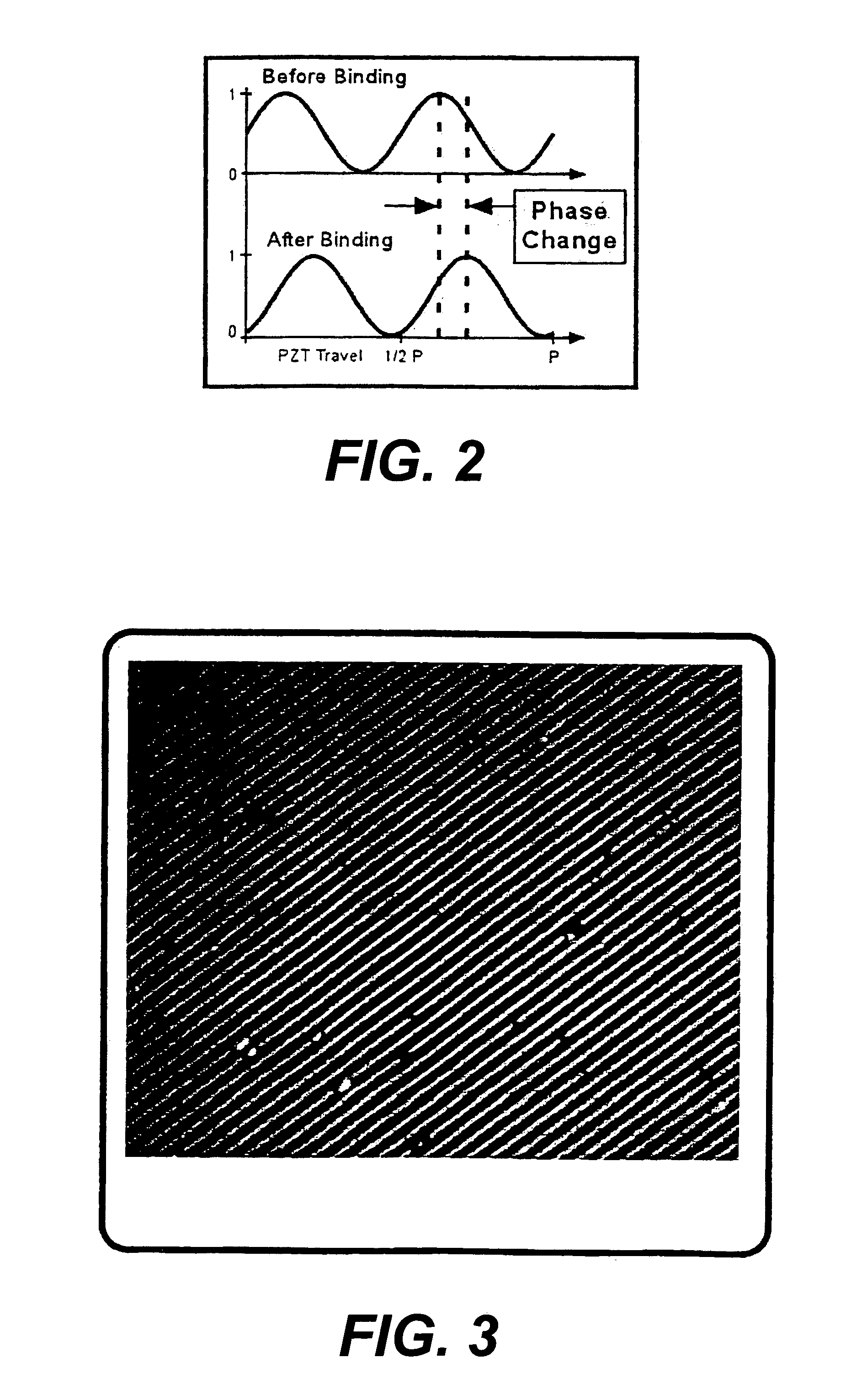
Grating sensor
A fast, accurate and reliable sensor applicable to chemical and biological analytes resides in an optical grating-based sensor, sensing system, and method of use. The sensor, configured for use with an illumination source and a signal detector in the system embodiment, includes first and second periodic diffraction gratings superimposed and shifted laterally relative to each other by a distance of less than one period, such that the illumination from the source is affected by both gratings before reaching the detector. An analyte recognition material disposed on a surface of the second diffraction grating. In operation, the output of the detector is first used to establish a baseline optical phase signal. The analyte recognition material is exposed to a sample, and the output of the detector is used to to determine a second optical phase signal. The baseline optical phase signal is compared to the second optical phase signal to detect the presence of the analyte, if any, in the sample. The analyte recognition material may be an antibody, nucleic acid, lectin or other substance. The sample may obtained from a mammal, including a human, plant, or the environment.
Owner:VERIDIAN SYST
Magnetic bead-based arrays
InactiveUS20080187472A1Easy to separateEasy to replaceSequential/parallel process reactionsFlow mixersFluorescenceMagnetic bead
The present invention relates to magnetic particle separators using micromachined magnetic arrays and more particularly, to magnetic particle separators or manipulators using controlled magnetization on micromachined magnetic arrays for the separation of cells and other biological materials. The present invention also pertains to using such devices for the separation and analysis of biological materials for immunoassays, DNA sequencing, protein analysis, and biochemical detection applications. The present invention can also be viewed as a novel method for fabricating fully integrated permanent magnet components within any microelectromechanical system (“MEMS”) structures. The present invention also provides a magnetic particle separation and manipulation system for rapid separation and accurate manipulation of magnetic particles in two-dimensional electromagnetic arrays, which utilize high throughput biological analyses. A disposable cartridge can be produced in low cost using a low cost substrate such as plastic or other polymer, glass, or metal. Magnetic flux is generated by conventional or micromachined electromagnets a platform system consisting of magnetic flux sources, magnetic flux guidance, and a microprocessor control interface. By controlling direction of electric currents into inductors on the platform system, arbitrary magnetic poles can be generated on Permalloy structures of the cartridge to separate and manipulate magnetic particles. The magnetic particle separator and manipulator in the present invention can be easily combined with automated detection systems such as a fluorescent monitoring system.
Owner:AHN CHONG H +2
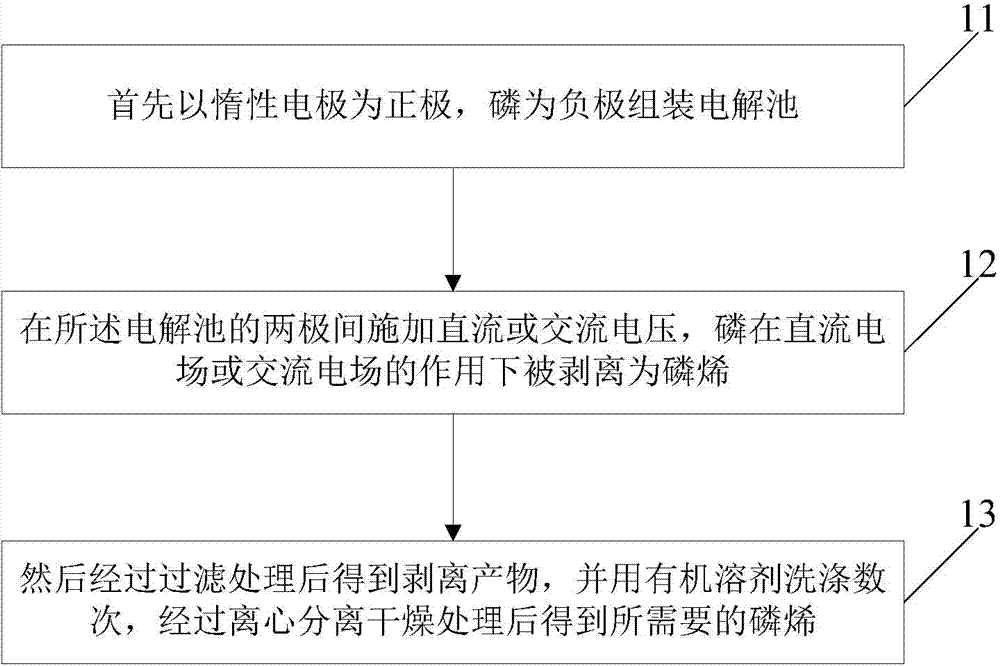
Method for preparing phosphaalkene by utilizing electrochemistry
ActiveCN104779380AImprove product qualityHigh yieldElectrolysis componentsHybrid capacitor electrodesFiltrationAqueous electrolyte
The invention discloses a method for preparing phosphaalkene by utilizing electrochemistry. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, assembling an electrolytic cell by using an inert electrode as a positive electrode and phosphorus as a negative electrode, wherein in the electrolytic cell, the electrolyte solution is one or several of an aqueous electrolyte solution, an organic electrolyte solution and an ionic liquid electrolyte solution containing the electrolyte; applying direct current or alternating current voltage between the two electrodes of the electrolytic cell and stripping the phosphorus into phosphaalkene under a function of a direct current electric field or an alternating current electric field; and performing filtration treatment to obtain a stripped product, washing the stripped product for a plurality of times by using an organic solvent, centrifugally separating and drying to obtain the required phosphaalkene. According to the method, a phosphaalkene material with good quality, high yield and low cost can be conveniently, quickly and securely produced in an environment-friendly form, and can be applied to multiple fields of secondary ion batteries, supercapacitors, solar batteries, fuel batteries, electro-catalysis, electronic elements, bioanalysis, biological sensors and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Methods and apparatus for SERS assay of biological analytes
InactiveUS20060147941A1Material nanotechnologyRadiation pyrometryHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsPolynucleotide
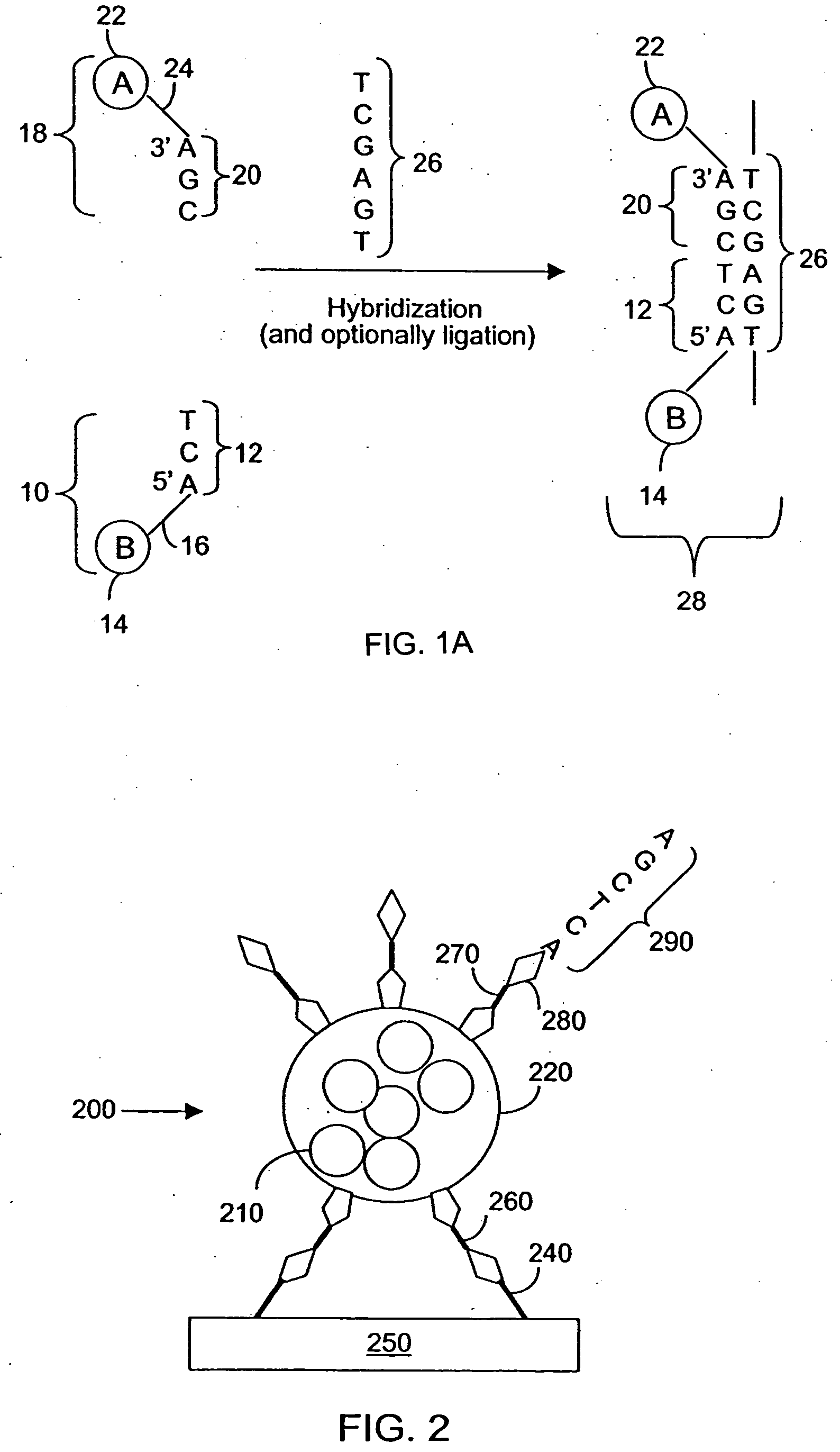
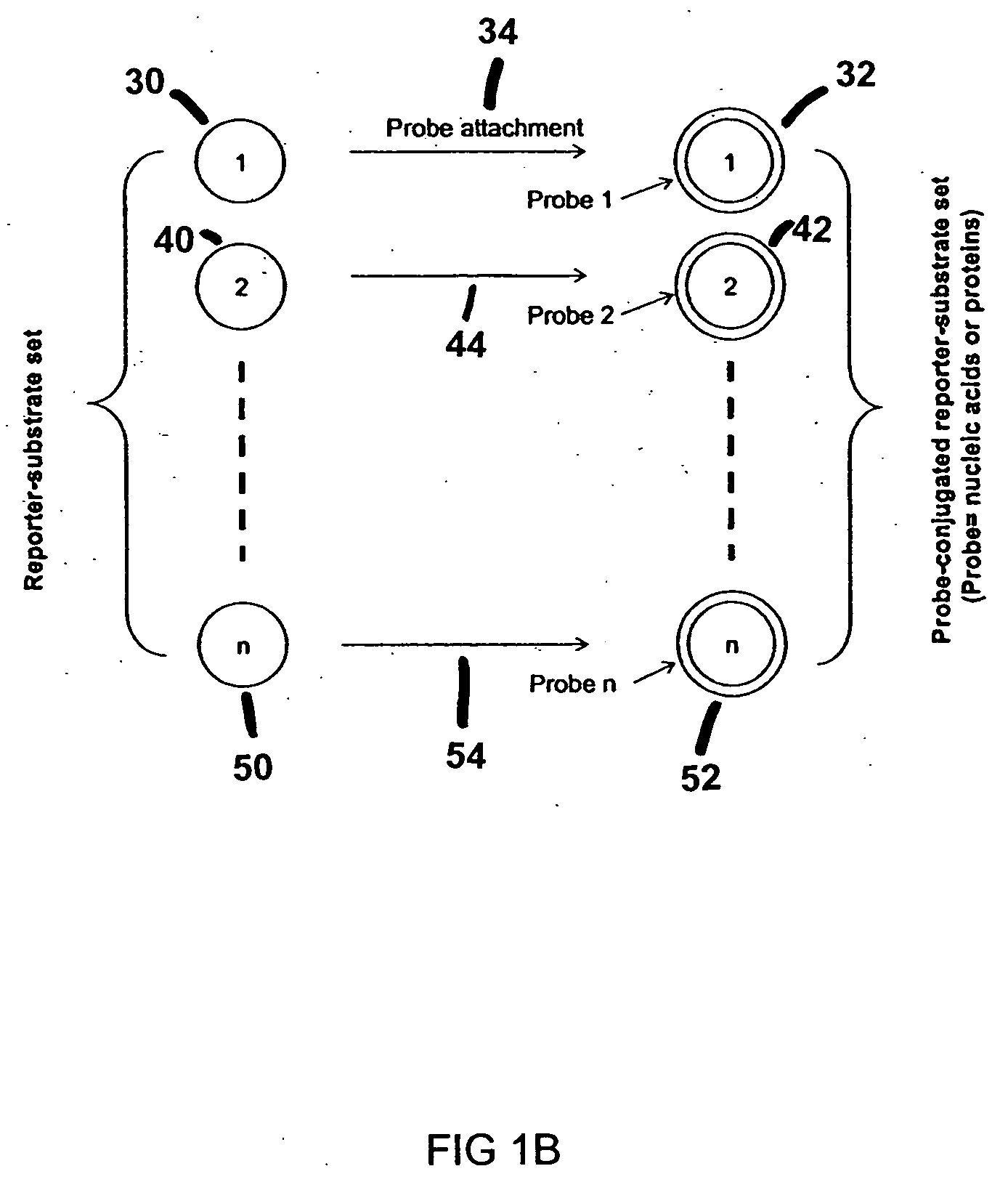
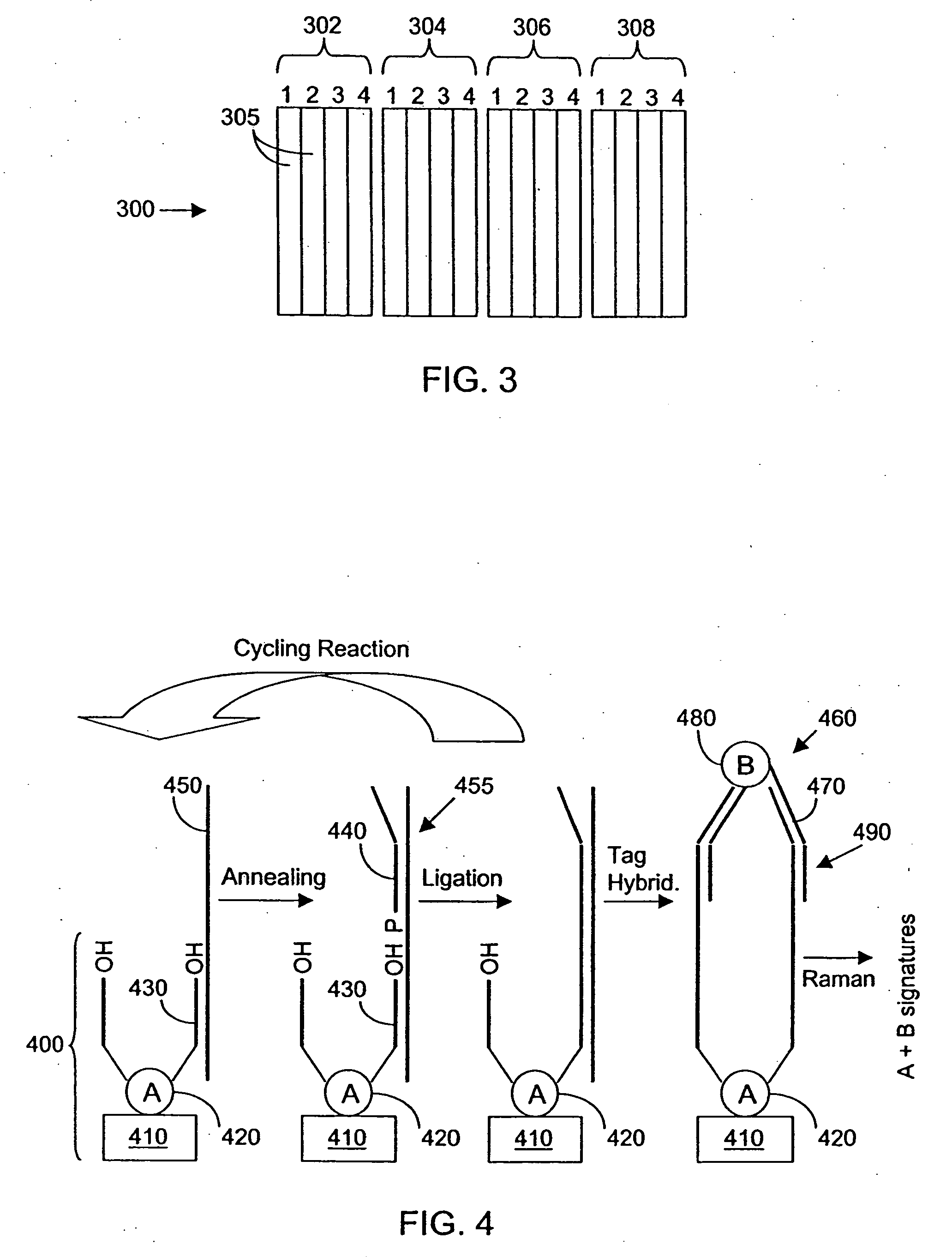
SERS technology is used for high throughput screening of biological analytes and samples. For polynucleotide sequencing, sets of oligonucleotide probes are labeled with composite organic-inorganic nanoparticles (COIN) that produce distinguishable SERS signals when excited by a laser. Detection of a hybridization complex containing members of two such COIN-labeled probe sets will reveal a 12 nucleotide sequence segment of the target polynucleotide. Also provided are surface-modified arrays and chips with multiple arrays to which sets of probe-conjugated COIN or other reporter substrates are immobilized. Analytes are detected by contacting a sample, such as a bodily fluid, with the array-anchored probes. Captured analytes are tagged with an additional target-specific Raman-active tag. Two or more Raman signatures emanating from the detection complexes reveal the identity of the captured analytes.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Use of particulate labels in bioanalyte detection methods
InactiveUS20050106641A1Avoid turbulenceMaintain their viabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParticulatesCellular component
New applications for the use of distinguishable particulate labels available in a variety of hues and sized in the submicron range are described. These applications include profiling of cellular components, obtaining secretion patterns, identifying a multiplicity of components in chromatographic or electrophoretic techniques and identification of desired immunoglobulin secreting cells.
Owner:TRELLIS BIOSCIENCE LLC
Systems and methods for genetic and biological analysis
ActiveUS20140235457A1Reduction tendencyReduce errorsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBio moleculesSingle-Use Device
The invention relate to systems and methods for sequencing polynucleotides, as well as detecting reactions and binding events involving other biological molecules. The systems and methods may employ chamber-free devices and nanosensors to detect or characterize such reactions in high-throughput. Because the system in many embodiments is reusable, the system can be subject to more sophisticated and improved engineering, as compared to single use devices.
Owner:SEQUENCING HEALTH INC
Method for preparing composite microspheres with surface functional group and controllable function
InactiveCN101053811ASimple methodImprove efficiencyMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationPolyelectrolyteMicrosphere
The invention relates to a preparation method of microsphere with surface functional group and controllable functionality, and to the field of nano-technology. The invention firstly uses the microsphere with the surface having ionic functional group as a starting shuttering to coat layer of layer the nano-particle with certain functionality or polyelectrolyte by the power of static electrification to obtain the composite microsphere with surface functional group and controllable functionality. The microsphere with surface functional group and controllable functionality prepared by the invention, of which the size is controllable, has single functionality or multiple functionality, can respond to the circumstance of magnetism, light and pH value, and the response intensity is controllable. Furthermore, the surface can have different functional groups. The invention can get an extensive use in the fields of biology medical carrier, bioanalysis and intelligent material, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Fluorescent probes for labelling and/or detecting lipid droplets in cells as well as preparation and applications of fluorescent probes
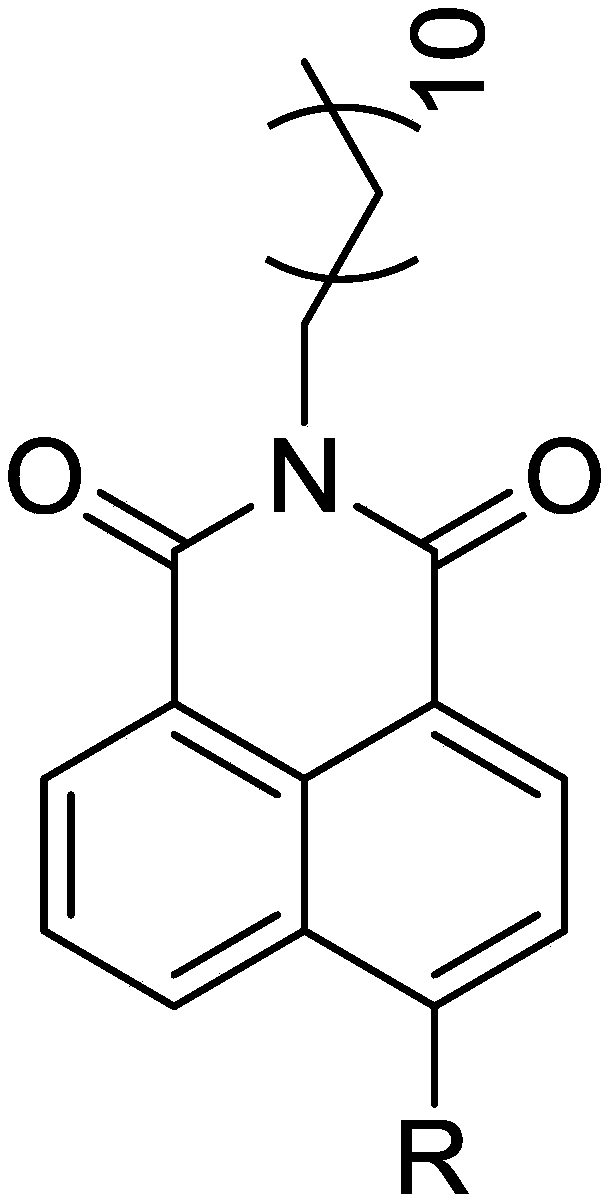
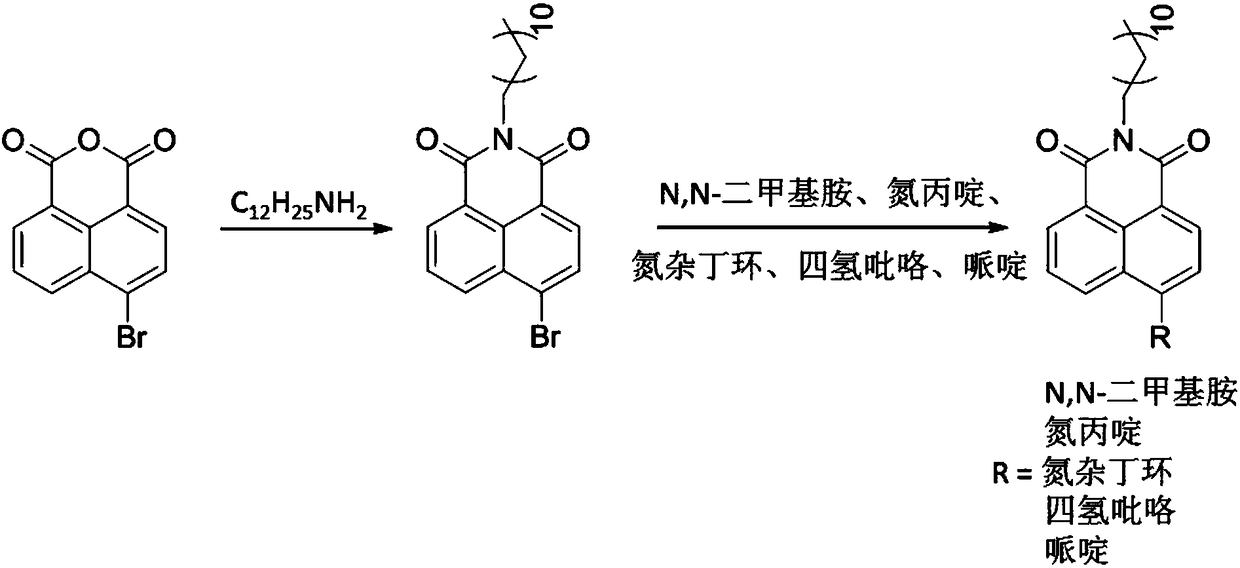
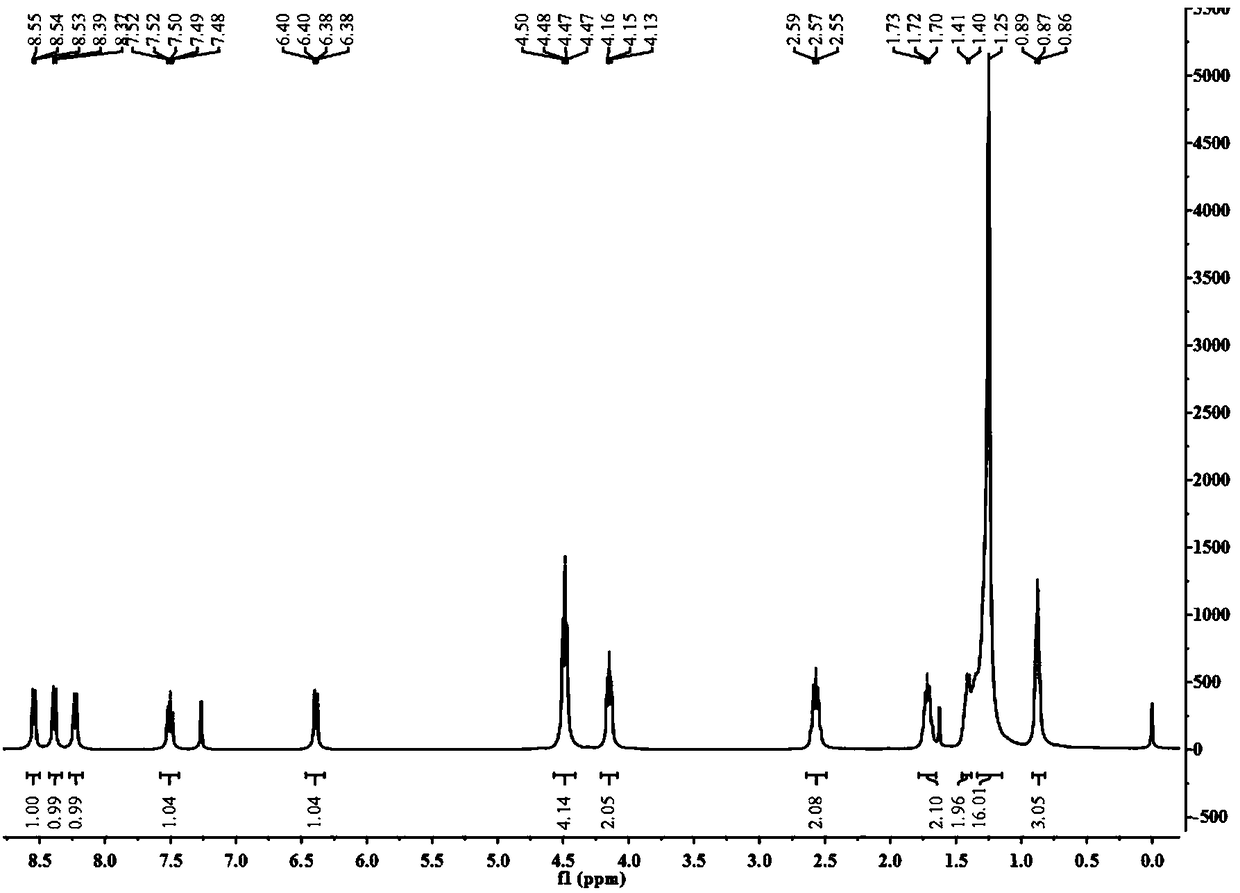
InactiveCN108069902ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getSpecific recognition abilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorophoreLipid Body
The invention belongs to the field of biological analysis and detection and relates to fluorescent probes for labelling and / or detecting lipid droplets in cells as well as preparation and applicationsof the fluorescent probes. The probes are synthesized with 4-bromo-1,8-naphthalic anhydride as an initial material and take 1,8-naphthalimide as a fluorophore, a C12 alkyl long chain as a specific lipid droplet positioning group and an N-containing group on the 4th site of a naphthalene ring as a fluorescence enhanced and stabilized group. The probes are simple to prepare and have high yield. Compared with existing Nile red and boron dipyrromethene lipid droplet fluorescent probes, the probes have high light stability and large stokes shift and are more suitable for fluorescence imaging. Theprobes have very important application value in cell labelling fluorescent imaging and biomedical fields.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Phenylboronic-acid-functionalized graphene oxide composite nano material and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN106475068AEasy to manufactureMild conditionsOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesPhenylboronic acidOxide composite
The present invention relates to a new phenylboronic-acid-functionalized graphene oxide composite nano material and preparation and application thereof. The material is prepared by immobilization of polydopamine-packed magnetic nanoparticles onto polyethyleneimine-modified graphene oxide and further introduction of phenylboronic acid monomers with carboxyl by amino of polyethyleneimine, and finally the material is used for enrichment of glycoproteins. The specific process is as follows: firstly, Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles are prepared by a solvothermal method, and auto polymerization of polydopamine can be performed on surface of the Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles under alkaline conditions; the magnetic graphene oxide composite nano material can be prepared by hydrogen bond and PI-PI interaction between the polydopamine and graphene oxide, then the positively charged polyethyleneimine is immobilized onto the surface of the negatively charged magnetic graphene oxide by electrostatic self-assembly; and finally the phenylboronic-acid-functionalized magnetic graphene oxide composite nano material can be prepared by introduction of the phenylboronic acid monomers by amidation reaction, and the phenylboronic-acid-functionalized magnetic graphene oxide composite nano material is successively used in the enrichment of the glycoproteins in bioanalysis.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com