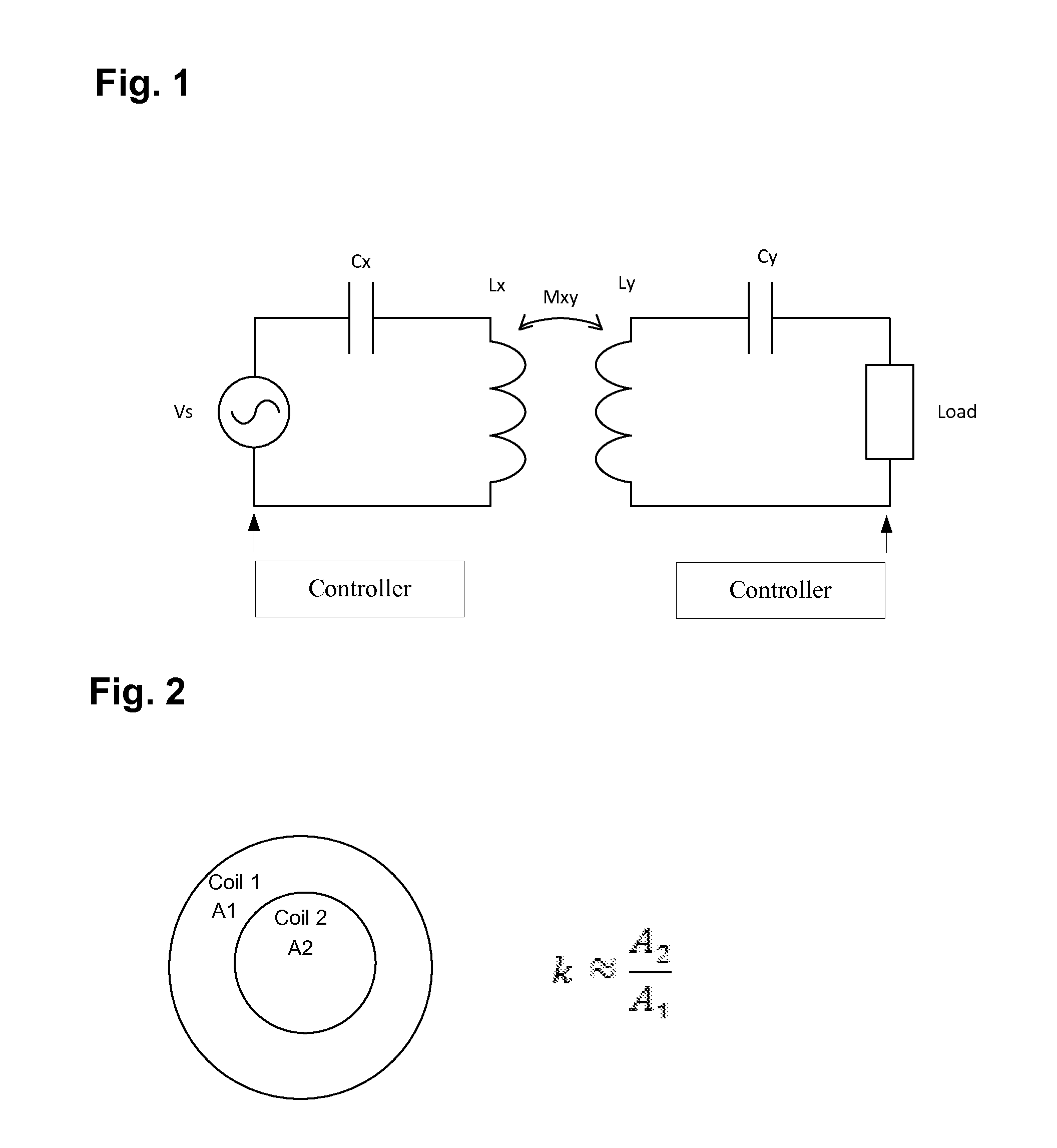
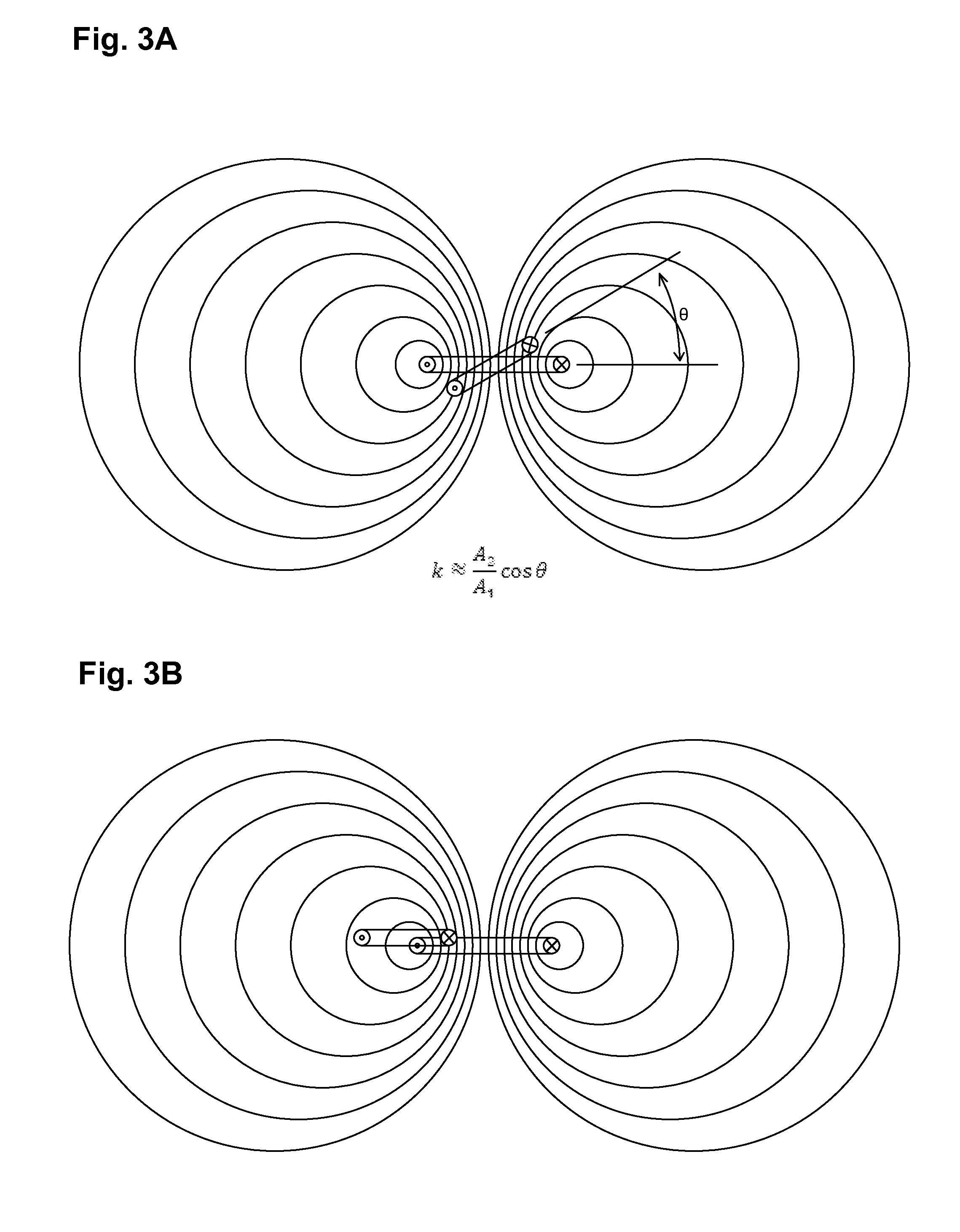
Patents
Literature
12616 results about "Magnetic flux" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, specifically electromagnetism, the magnetic flux (often denoted Φ or ΦB) through a surface is the surface integral of the normal component of the magnetic field B passing through that surface. The SI unit of magnetic flux is the weber (Wb) (in derived units: volt · seconds), and the CGS unit is the maxwell. Magnetic flux is usually measured with a fluxmeter, which contains measuring coils and electronics, that evaluates the change of voltage in the measuring coils to calculate the measurement of magnetic flux.
Planar resonator for wireless power transfer
InactiveUS6960968B2Easy to useEasy wiringMultiple-port networksBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical conductorTransformer
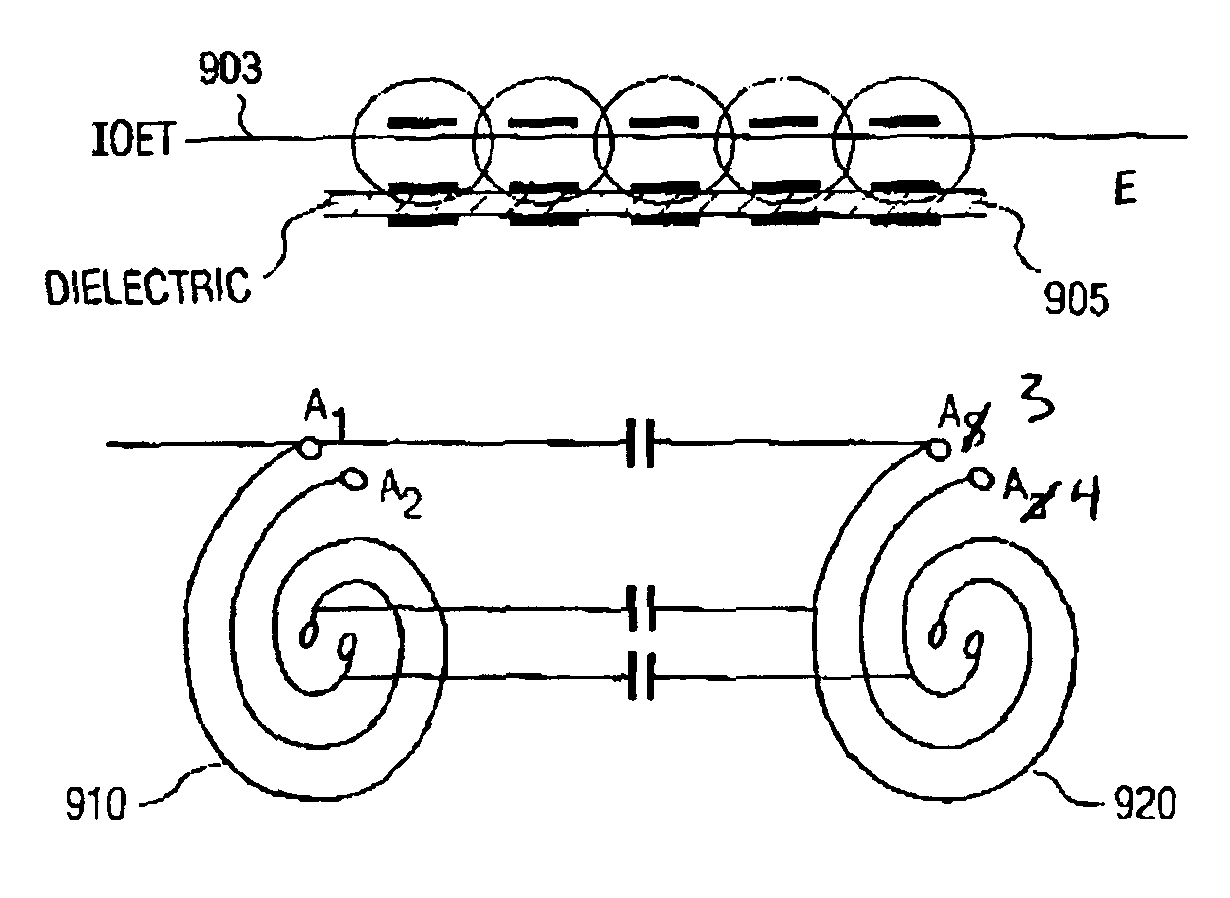
A planar resonator and method of manufacture provides contactless power transfer using at least two electrically isolated axis aligned conductive across the transfer interface in a coupled inductor or transformer configuration. Signal or power transfer is then accomplished by coupling of magnetic flux. The coupling of electric flux is also accomplished across a same interface and driven with the same conductive spiral-wound conductors. An interface of energy transfer(IOET) has a first spiral-shaped conductor arranged on the top surface of said IOET; a second spiral-shaped conductor arranged on the bottom surface of said IOET, has a vertical axis aligned with the first spiral-shaped conductor. The IOET and the first and second spiral-shaped conductors have a predetermined self-resonant frequency. The planar power resonator stores electric energy in the IOET, and at predetermined frequencies, the arrangement of the first and second spiral-shaped conductors and the IOET permits transfers of magnetic flux and electrical energy between the first and second spirals across the IOET. The resonator facilitates contactless battery charging in devices such as cellphones and wearable electronics where the resonator can be woven into fabric or attached to a person's clothes.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Medical instrument with sensor for use in a system and method for electromagnetic navigation
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Magnetic latch mechanism
InactiveUS20080186683A1Unevenness in intensityElectric switchesDetails for portable computersEngineeringElectronic assemblies
A magnetic latch mechanism for latching a first electronic assembly to a second electronic assembly. The magnetic latch mechanism includes a Halbach array captured by the first electronic assembly. The Halbach array is configured to provide a first magnetic flux in a first direction. The magnetic latch mechanism further includes an attraction plate captured by the second electronic assembly. The attraction plate is configured to be coupled with the first magnetic flux when the first electronic assembly is in a closed position with respect to the second electronic assembly such that there is mutual attraction between the attraction plate and the Halbach array in the closed position.
Owner:APPLE INC
Composite magnetic core for switch-mode power converters
ActiveUS6980077B1Avoid Core SaturationLower average currentTransformers/inductances magnetic coresCores/yokesEddy currentConductor Coil
A composite magnetic core formed of a high permeability material and a lower permeability, high saturation flux density material prevents core saturation without an air gap and reduces eddy current losses and loss of inductance. The composite core is configured such that the low permeability, high saturation material is located where the flux accumulates from the high permeability sections. The presence of magnetic material having a relatively high permeability keeps the flux confined within the core thereby preventing fringing flux from spilling out into the winding arrangement. This composite core configuration balances the requirements of preventing core saturation and minimizing eddy current losses without increasing either the height or width of the core or the number of windings.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
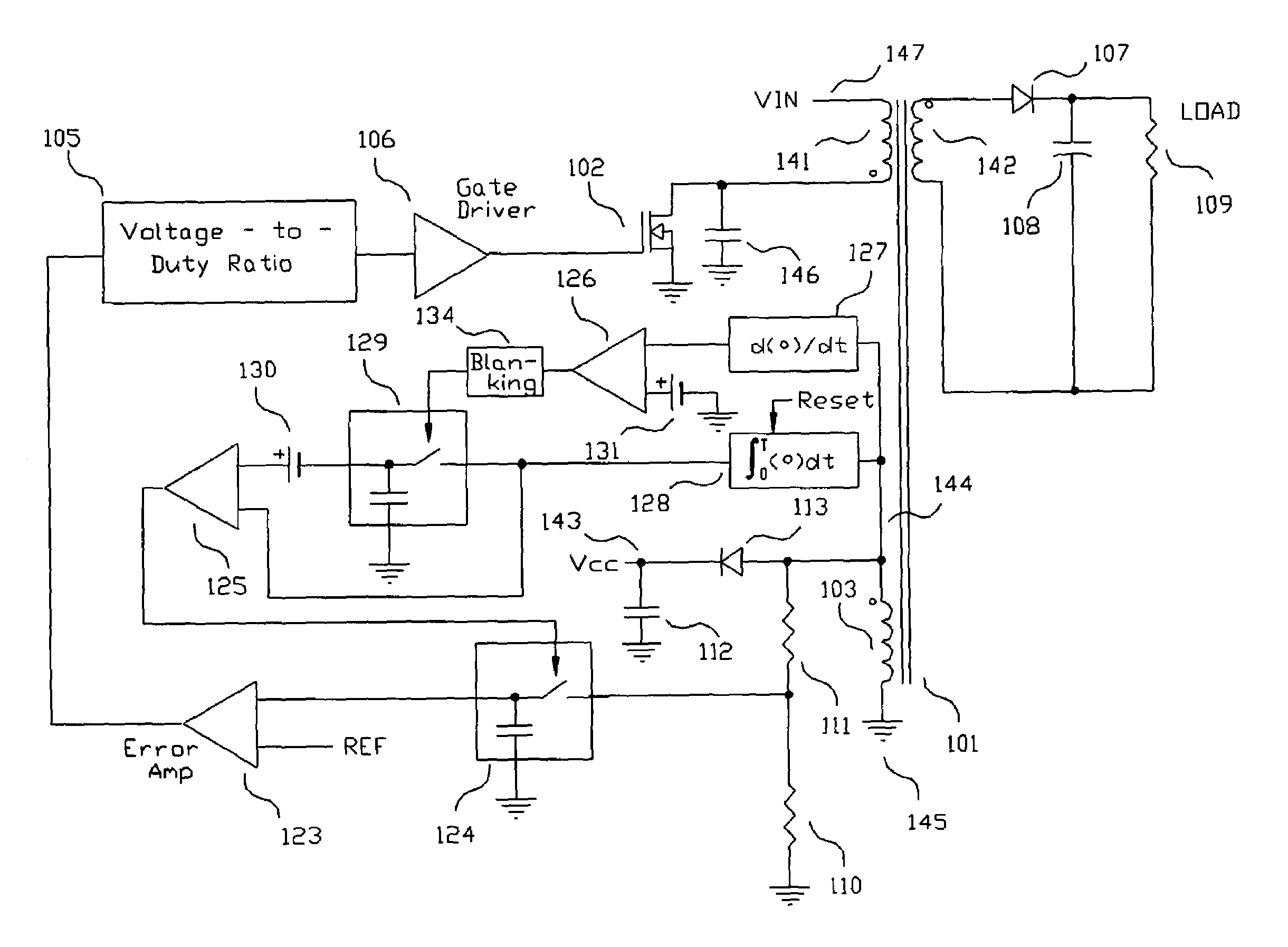
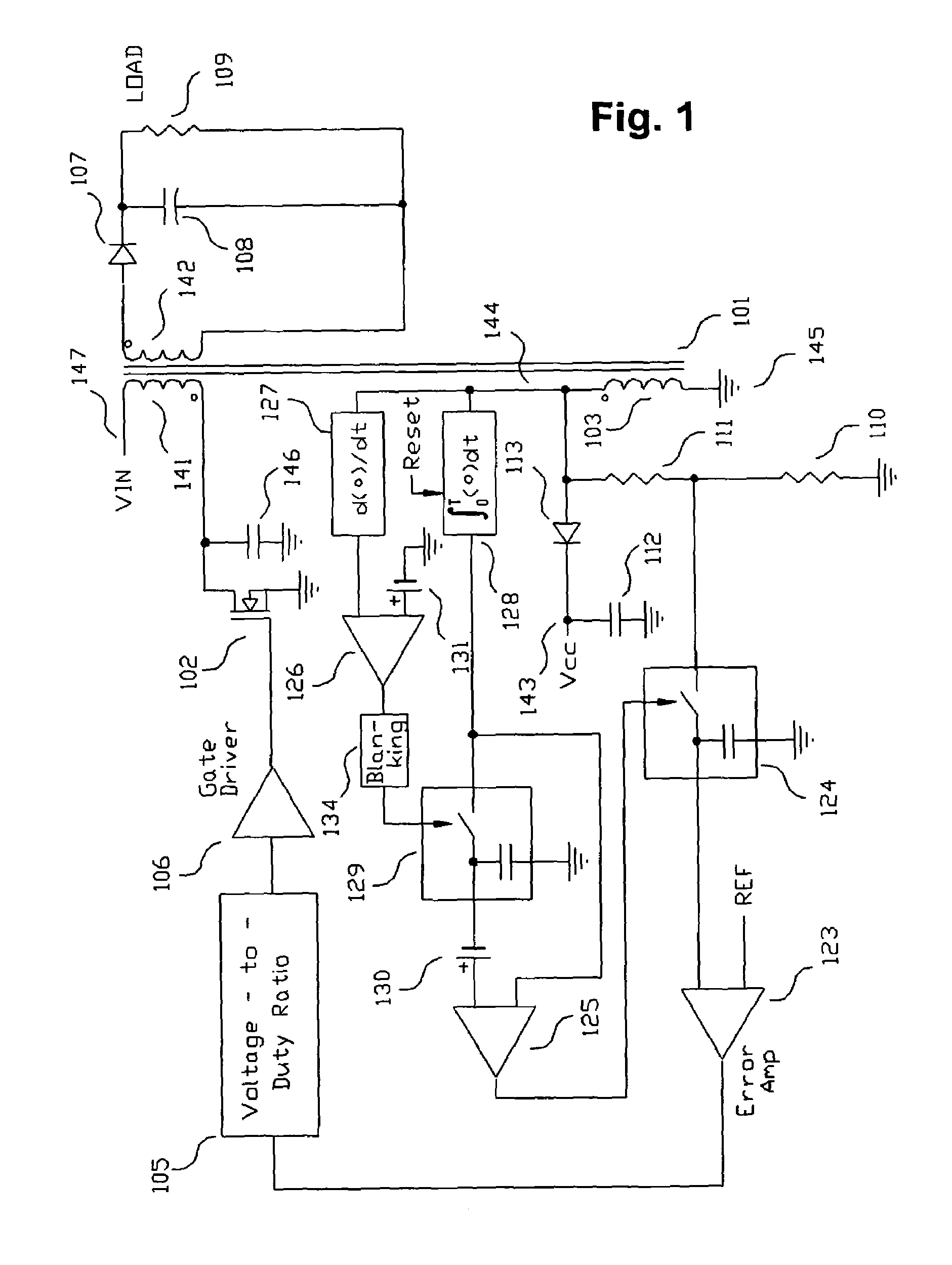
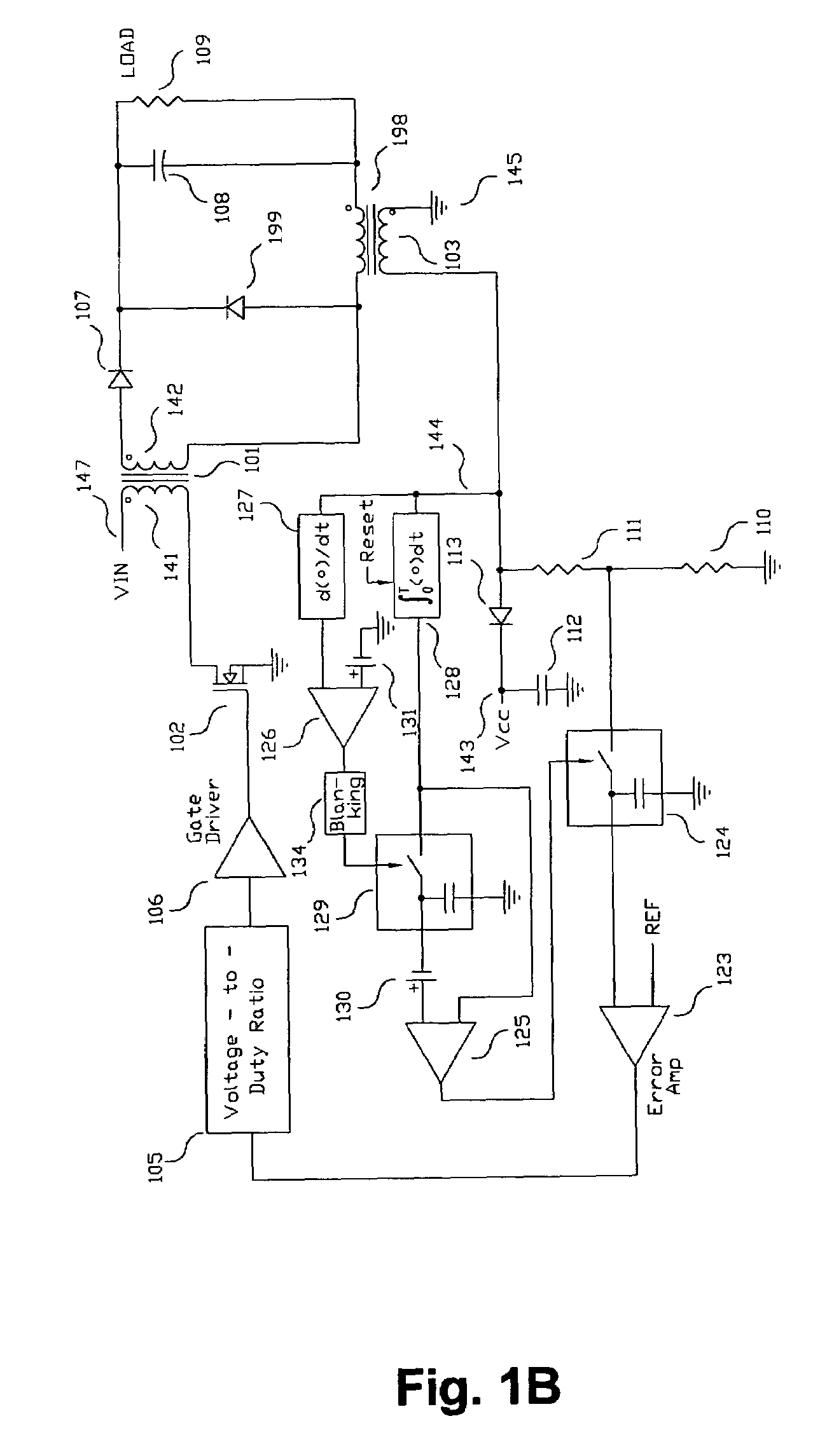
Switching power converter and method of controlling output voltage thereof using predictive sensing of magnetic flux
A switching power converter and method of controlling an output voltage thereof using predictive sensing of magnetic flux provides a low-cost switching power converter via primary-side control using a primary-side winding. An integrator generates a voltage that represents flux within a magnetic element by integrating a primary-side winding voltage. A detection circuit detects the end of a half-cycle of post-conduction resonance that occurs in the power magnetic element subsequent to zero energy level in the power magnetic element. The integrator voltage is stored at the end of the half-cycle and is used to determine a sampling point prior to or equal to the start of post-conduction resonance in a subsequent switching cycle of the power converter. The primary-side winding voltage is then sampled at the sampling point, providing an indication of the output voltage of the power converter by which the output voltage of the converter can be controlled.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Implantable medical device with contactless power transfer housing
InactiveUS20050288743A1Minimizing surgeryMinimizing subsequent treatmentElectrotherapyElectromagnetic wave systemTransmitted powerElectrical battery
A transcutaneous recharging system for providing power to an implantable medical device comprises a primary side circuit for transmitting power in the form of magnetic flux; and a secondary side circuit integral to the implantable medical device for receiving the power transmitted from the primary side circuit and for providing the received power to recharge a battery in the implantable medical device, wherein the primary and secondary side circuits are not physically coupled. A variety of attachment configurations are disclosed for attaching and shielding the secondary circuit directly onto the housing of the implantable medical device, inclusive of flexible printed circuit coils and wire coils recessed into helical notches.
Owner:AHN IN +2
Electromagnetic linear generator and shock absorber
InactiveUS6952060B2Maximizing magnetic flux densityMaximize power generationNon-rotating vibration suppressionMechanical energy handlingElectromagnetic generatorFuel efficiency
An electromagnetic linear generator and regenerative electromagnetic shock absorber is disclosed which converts variable frequency, repetitive intermittent linear displacement motion to useful electrical power. The innovative device provides for superposition of radial components of the magnetic flux density from a plurality of adjacent magnets to produce a maximum average radial magnetic flux density within a coil winding array. Due to the vector superposition of the magnetic fields and magnetic flux from a plurality of magnets, a nearly four-fold increase in magnetic flux density is achieved over conventional electromagnetic generator designs with a potential sixteen-fold increase in power generating capacity. As a regenerative shock absorber, the disclosed device is capable of converting parasitic displacement motion and vibrations encountered under normal urban driving conditions to a useful electrical energy for powering vehicles and accessories or charging batteries in electric and fossil fuel powered vehicles. The disclosed device is capable of high power generation capacity and energy conversion efficiency with minimal weight penalty for improved fuel efficiency.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
Apparatus and process for reducing the susceptability of active implantable medical devices to medical procedures such as magnetic resonance imaging
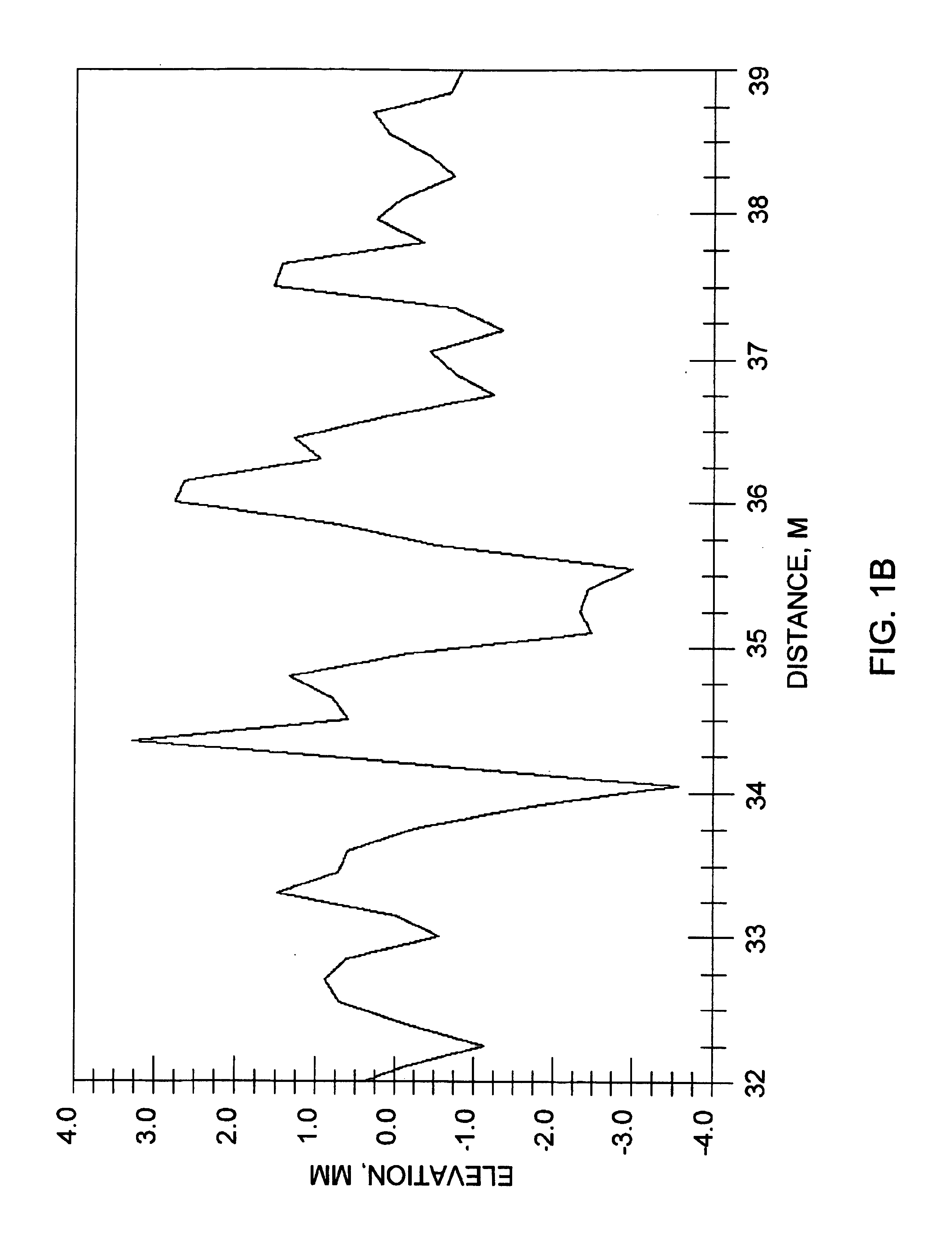
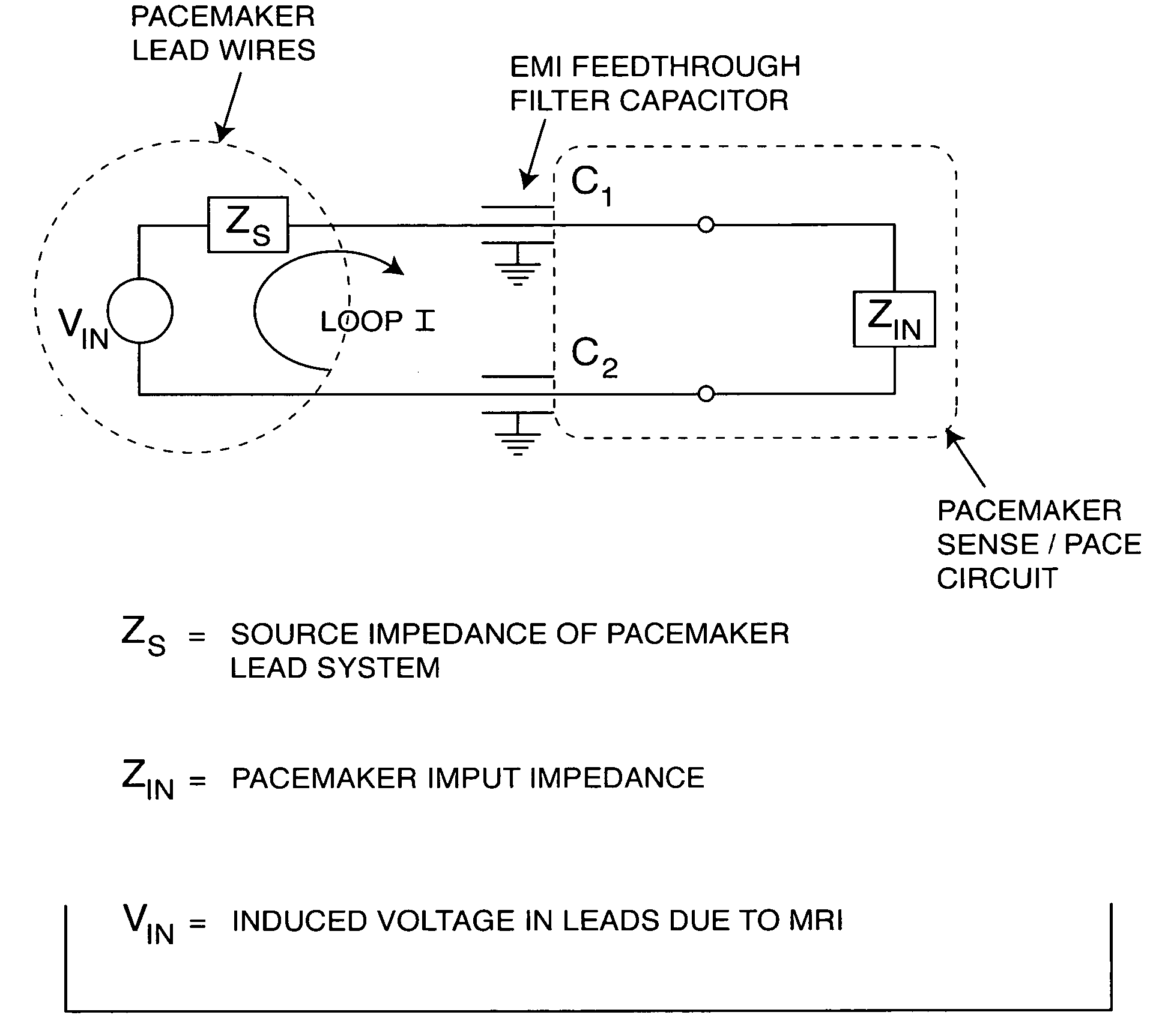
InactiveUS20050197677A1Improving impedanceReducing magnetic flux core saturationAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyPhase cancellationElectromagnetic field
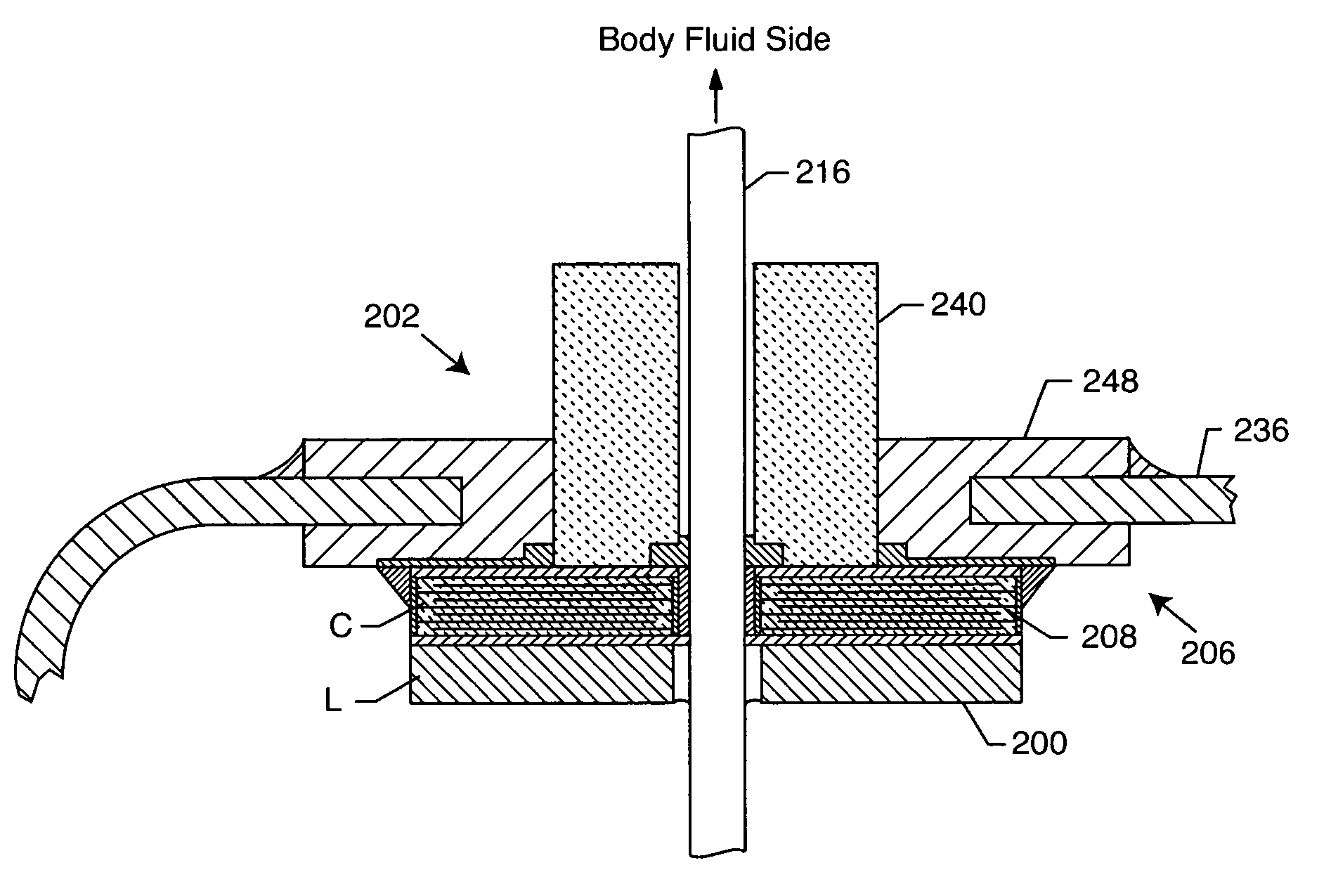
A feedthrough terminal assembly for an active implantable medical device (AIMD) includes a plurality of leadwires extending from electronic circuitry of the AIMD, and a lossy ferrite inductor through which the leadwires extend in non-conductive relation for increasing the impedance of the leadwires at selected RF frequencies and reducing magnetic flux core saturation of the lossy ferrite inductor through phase cancellation of signals carried by the leadwires. A process is also provided for filtering electromagnetic interference (EMI) in an implanted leadwire extending from an AIMD into body fluids or tissue, wherein the leadwire is subjected to occasional high-power electromagnetic fields such as those produced by medical diagnostic equipment including magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:GREATBATCH SIERRA INC
Apparatus and method for a communication device
InactiveUS6927738B2Improve permeabilityAvoid attenuationLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringConductive materials
This invention aims to provide a communication device, installation structure for the communication device, a method of manufacturing the communication device, and a method of communication with the communication device in which the communication device is able to exceedingly restain a conductive material from attenuating magnetic flux and to expand communication distance even when the communication device is attached to a conductive member e.g., metal, in a closely contacting manner.This invention has a sheet-like amorphous magnetic material being arranged in a manner extending from a magnetic flux generating portion of a concentric disk-shaped antenna coil of an RFID tag serving as the communication device to an outer area of the antenna coil.
Owner:HANEX CO LTD
System and method for selective communication with RFID transponders
InactiveUS6848616B2Minimizing creationSmall sizeMemory record carrier reading problemsCo-operative working arrangementsTransceiverCoupling
A system having an RFID transceiver is adapted to communicate exclusively with a single RFID transponder located in a predetermined confined transponder target area. The system includes a magnetic coupling device comprising a magnetic flux generator responsive to a radio frequency input signal and a magnetic field pattern former. The pattern former is configured to collect flux produced by the flux generator and to form a field pattern in the location of the transponder target area. The system establishes, at predetermined transceiver power levels, a mutual magnetic coupling which is selective exclusively for a single transponder located in the transponder target area.
Owner:ZEBRA INVESTMENT HLDG CORP +1
Wind turbine
InactiveUS7042109B2Improve efficiencyCost per unit power generationWindingsWind motor controlRotational energyAir core
A wind turbine for generating electrical power from wind energy includes a turbine rotor mounted for rotation in wind, and having multiple blades for converting energy in the wind into rotational energy. A generator is coupled with said turbine rotor such that said turbine rotor drives said generator. The generator has a stationary air core armature that is located in a magnetic airgap between two generator rotor portions. The generator rotor portions have circumferential arrays of multiple alternating polarity permanent magnets attached to ferromagnetic back irons such that the permanent magnets drive magnetic flux back and forth between each rotor portion and through the stationary air core armature. The stationary air core armature has multiple phase windings of multiple individually insulated strand conductor wire that is wound with two separate portions including an active length portion and an end turn portion. The end turn portion is located outside the magnetic airgap and traverses predominately circumferentially, and the active length portion is located in the magnetic airgap and traverses predominately non-circumferentially and perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic airgap. The end turn portion has a thickness that is greater than the thickness of said active length portion in the direction of said magnetic airgap. AC voltage is induced in the multiple phase windings as the turbine rotor rotates.
Owner:MARIAH POWER
Transcutaneous energy transfer primary coil with a high aspect ferrite core
InactiveUS20050288742A1Enhanced couplingElectrotherapyCoilsLaparoscopic adjustable gastric bandingFerrite core
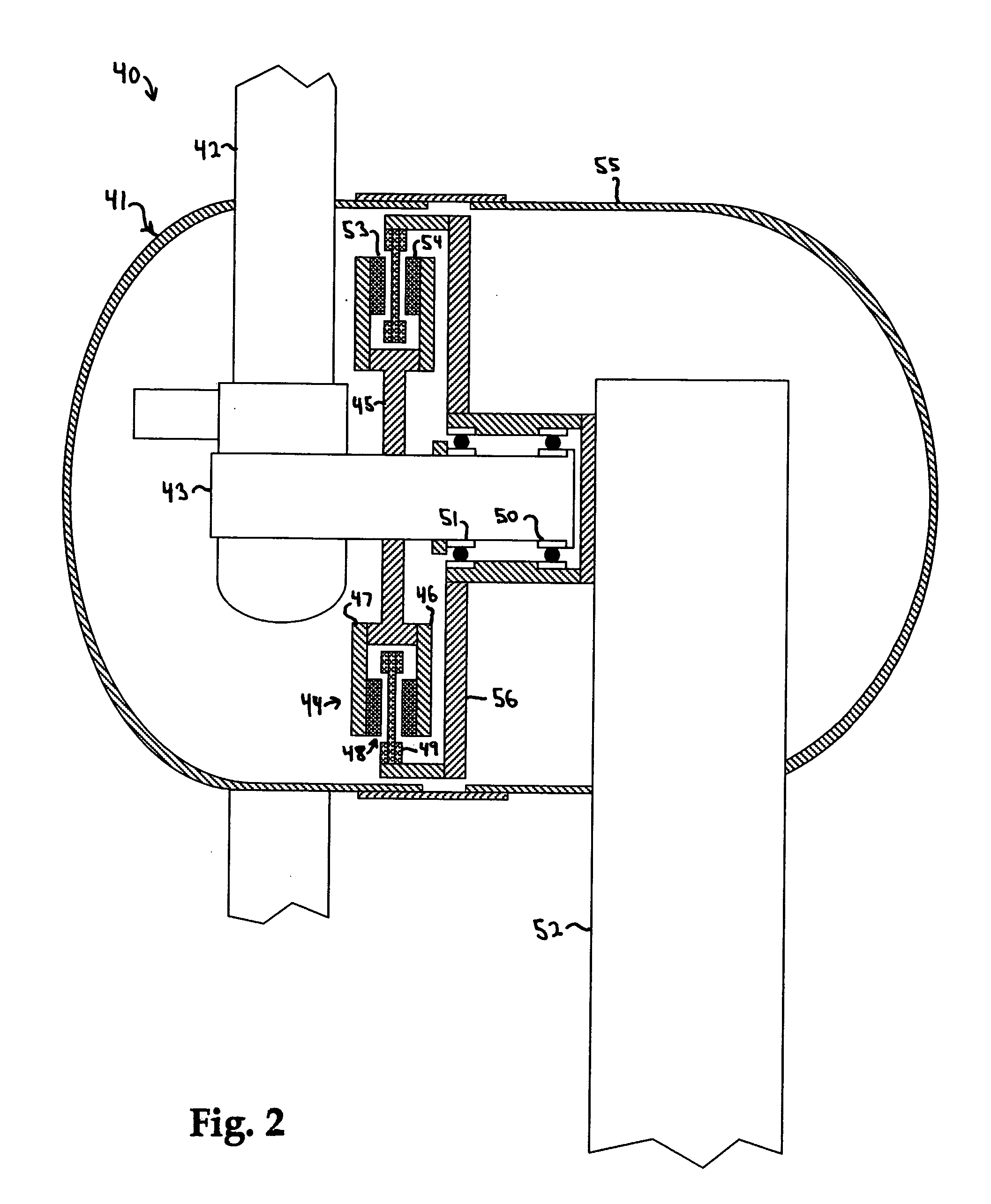
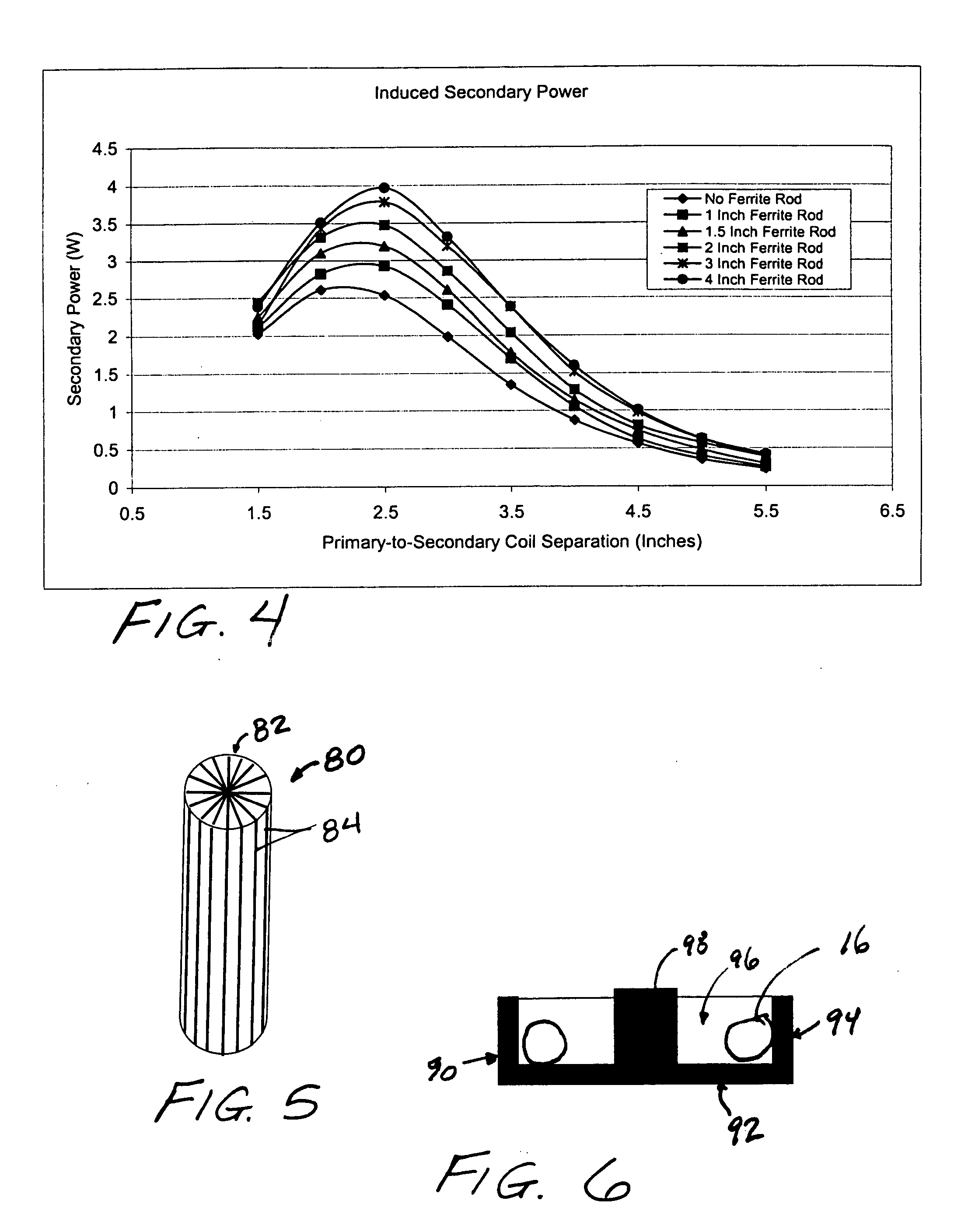
Adjustable gastric band implants contain a hollow elastomeric balloon with fixed end points encircling a patient's stomach just inferior to the esophago-gastric junction. These balloons can expand and contract through the introduction of saline solution into the balloon. In current bands, this saline solution must be injected into a subcutaneous port with a needle to reach the port located below the skin surface. The port communicates hydraulically with the band via a catheter. As an alternative to using a percutaneously accessed injection port, a system for regulating the flow of saline that is totally implanted may rely upon bi-directionally pumping fluid from an implant device. This system instead transfers AC magnetic flux energy from an external primary coil to a secondary coil that powers the pump in the implanted reservoir. A magnetically permeable rod centered within the primary coil increases power coupled to the secondary coil.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Multifaceted balanced magnetic proximity sensor
An apparatus and method of proximity switch / sensor based generally on a balanceable magnetic pole array. The magnetic pole array contains at least four poles with optional ferromagnetic shunt(s). The proximity of a shunt to a magnetic pole array determines whether the array is balanced or unbalanced. A balanced array is one with a zone where the vector sum of magnetic fields emanating from the array's poles can be made to approach zero. A sensor such as a reed switch is placed in the balanced zone. When the balance of the array is disturbed by the application of one or multiple shunts, the resulting finite magnetic field vector along with the resulting magnetic flux, activates the sensor. This approach can be implemented in a variety of array structures that offer implementation of a variety of logical functions. Multiple shunts and their proximity to the array are used as the logical function's inputs and the sensor's state as the logical function's output.
Owner:OSTERWEIL JOSEF
Self-powered leadless pacemaker
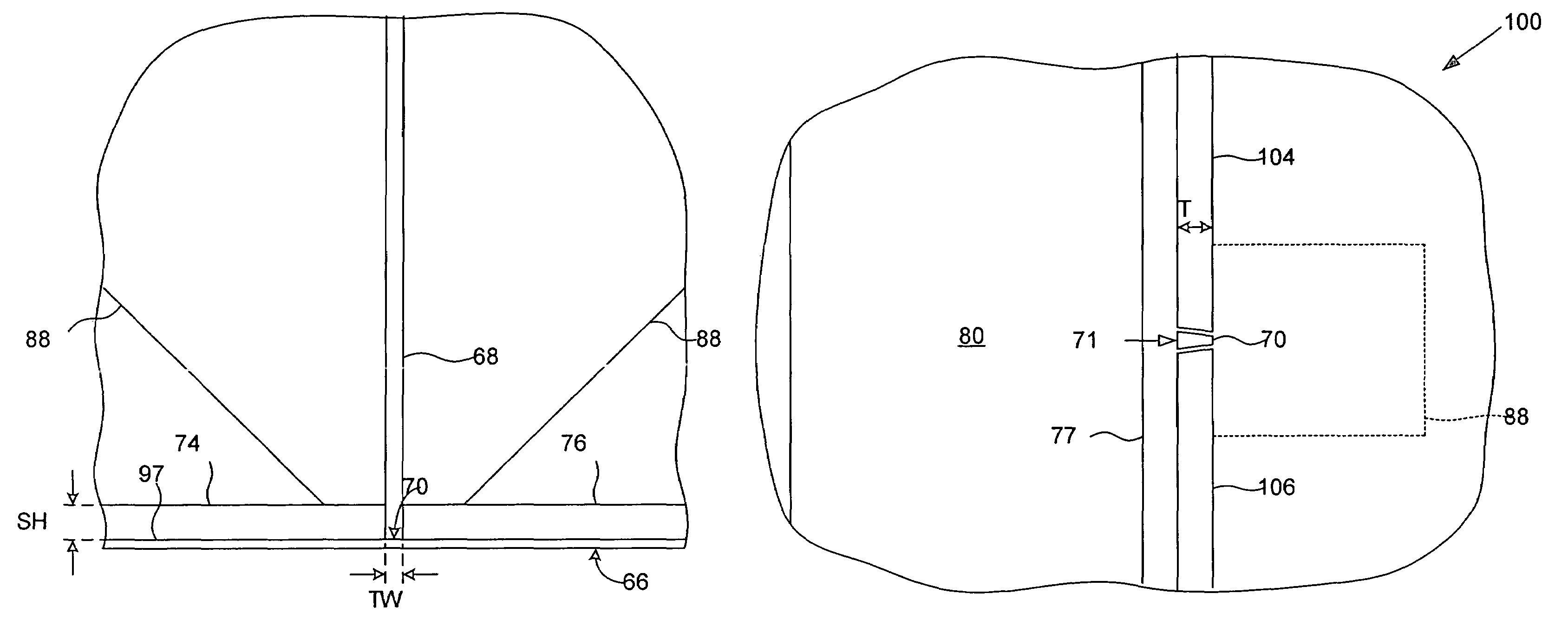
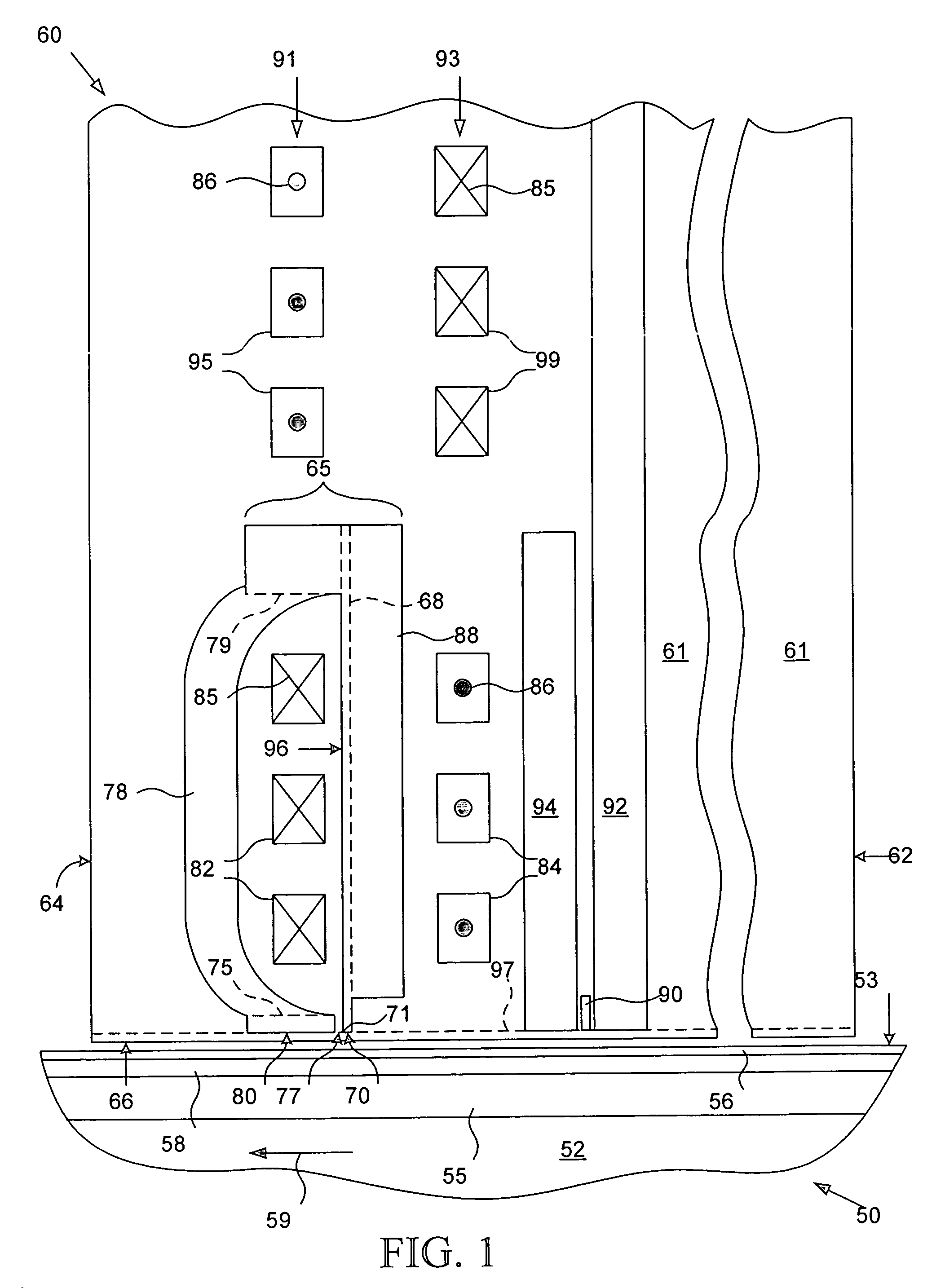
InactiveUS20070276444A1Minimize interferenceImprove compression performanceElectrotherapyCardiac pacemaker electrodeEngineering
A self-powered pacemaker uses the variations of blood pressure inside the heart or a major artery to create a periodic change in the magnetic flux inside a coil. The pressure variations compress a bellows carrying a magnet moving inside a coil. The inside of the bellows is evacuated to a partial or full vacuum, and a spring restores the bellows to the desired equilibrium point, acting against the blood pressure. The current pulses are stored in a capacitor. Eliminating the battery allows dramatic miniaturization of the pacemaker to the point it can be implanted at the point of desired stimulation via a catheter. The invention includes means of compensating for atmospheric pressure changes.
Owner:LG RES PARTNERSHIP
Medical Devices, Apparatuses, Systems, and Methods With Configurations for Shaping Magnetic-Fields and Interactions
Embodiments of apparatuses and / or medical devices, and systems and methods including apparatuses and / or medical devices, comprising one or more elements configured to define a U-shaped magnetic flux path and / or magnetic field.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Variable magnetic flux electric rotary machine
InactiveUS20100164422A1Easy to operateWide operating speed rangeDC motor speed/torque controlRailway vehiclesElectrical polarityEngineering
An electric rotary machine is disclosed which can adjust relative angles of sub-rotors continuously and regardless of torque direction without generating an attractive force between the field magnets of the sub-rotors. The electric rotary machine includes: a stator having a winding; a dual rotor which is rotatably disposed with a gap from the stator and divided axially along a shaft into a first rotor and a second rotor each having field magnets with different polarities arranged alternately in a rotation direction; a mechanism for varying the axial position of the second rotor relative to the first rotor continuously; and a non-magnetic member located between the first rotor and the second rotor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and system for a static magnetic read/write head
ActiveUS7591427B2Simplify complexityReduce complexitySensing record carriersDigital marking by magnetic meansLinear motionDriving current
The present invention enables reading from and writing onto a magnetic stripe medium with a static read / write head that does not require relative linear motion between the magnetic stripe medium and the head while reading or writing takes place. The reading and writing is accomplished using a stationary uni-dimensional, bi-dimensional, or multi-dimensional conductor array addressing and driving current through an individual conductor element. Reading from magnetic stripe is accomplished by using magnetic flux sensing method such as a fluxgate.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
Rotation-angle-detecting apparatus, rotating machine, and rotation-angle-detecting method
ActiveUS20090206827A1High resolutionAccurate measurementUsing electrical meansConverting sensor outputMagnetic polesSpin valve
A rotation-angle-detecting apparatus comprising a magnet rotor having 4 or more magnetic poles on the surface, and sensor device for detecting magnetic flux from the magnet rotor, and an electronic circuit for outputting a signal representing the rotation angle of the magnet rotor using pluralities of signals obtained from the sensor device, the sensor device having pluralities of spin-valve, giant-magnetoresistive devices for outputting two or more different phase signals from a rotating magnetic field near the rotating magnet, each spin-valve, giant-magnetoresistive device having a pinned layer and a free layer, the magnetization direction of the pinned layer being fixed, and the magnetization direction of the free layer rotating depending on a magnetic field direction, pluralities of the spin-valve, giant-magnetoresistive devices comprising a first spin-valve, giant-magnetoresistive device having a reference magnetic-field-sensing direction, and a second spin-valve, giant-magnetoresistive device having a magnetic-field-sensing direction different from that of the first spin-valve, giant-magnetoresistive device.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Magnetic tunnel junction memory device
InactiveUS6845038B1Improve permeabilityLow resistivityDigital storageBit linePerpendicular magnetization
A memory cell for magnetic random access memory devices based on a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) memory element with a perpendicular orientation of magnetization in pinned and free magnetic layers, and a tunnel barrier layer sandwiched between the pinned and free layers. The memory cell can include the MTJ memory element, a magnetic flux guide in series with selection devices, such as a bit line, a word line, and a transistor. The magnetic flux guide can have two electrically conductive magnetic portions with the MTJ memory element positioned between the magnetic portions. The MTJ memory element is magnetically isolated from the magnetic flux guide by thin non-magnetic conductive spacers. The MTJ memory element is arranged in a vertical space between the intersecting bit and word lines at their intersection region. The memory cell also includes write and excitation lines. The write line is parallel to the bit line and the excitation line is parallel to the word line. The write and excitation lines also intersect each other and define a corner. The MTJ memory element is positioned in the corner of the intercepting write and excitation lines.
Owner:SHUKH ALLA MIKHAILOVNA
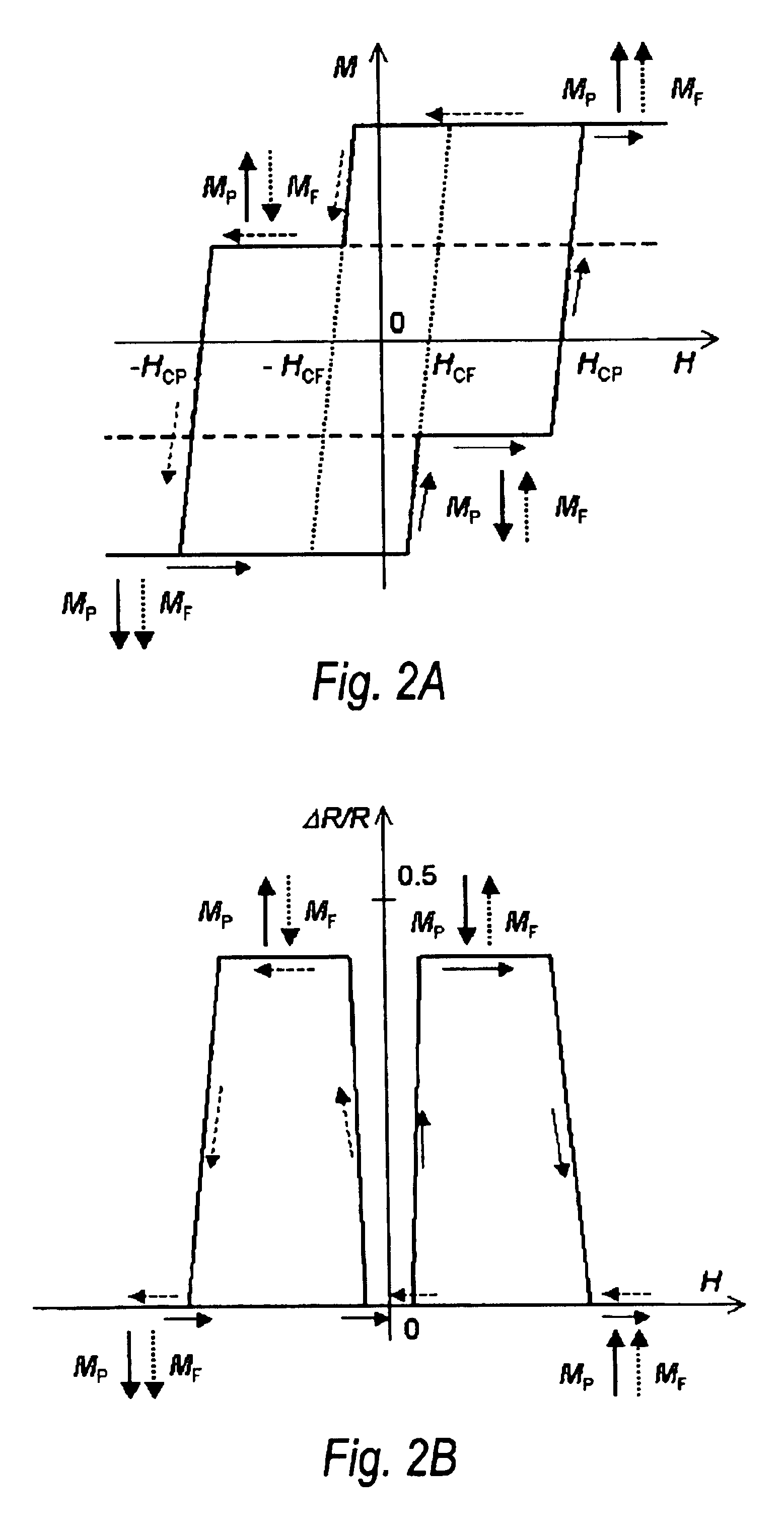
Thermal controlling method, magnetic field generator and MRI apparatus
InactiveUS20080048656A1Permanent magnetsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic polesRoom temperature
With a view toward implementing a thermal controlling method for making reversible a temperature characteristic of a magnetic field generator using permanent magnets small in Hcj, a magnetic field generator whose temperature characteristic is reversible, using permanent magnets small in Hcj, and an MRI apparatus provided with such a magnetic field generator, there is provided a method for controlling the temperature of a magnetic field generator having a pair of disc-shaped permanent magnets whose magnetic poles opposite in polarity to each other are opposed to each other with spacing defined therebetween, and a yoke that forms return passes for magnetic fluxes of the permanent magnets, comprising the steps of raising the temperature from room temperature to a temperature higher than the room temperature, maintaining the temperature higher than the room temperature, and lowering the temperature from the temperature higher than the room temperature to the room temperature, whereby the temperature characteristics of the permanent magnets are made reversible.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Housing structure for RFID tag, installation structure for RFID tag, and communication using such RFID tag
InactiveUS7088249B2Effective protectionLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreAntenna supports/mountingsConductive materialsUltimate tensile strength
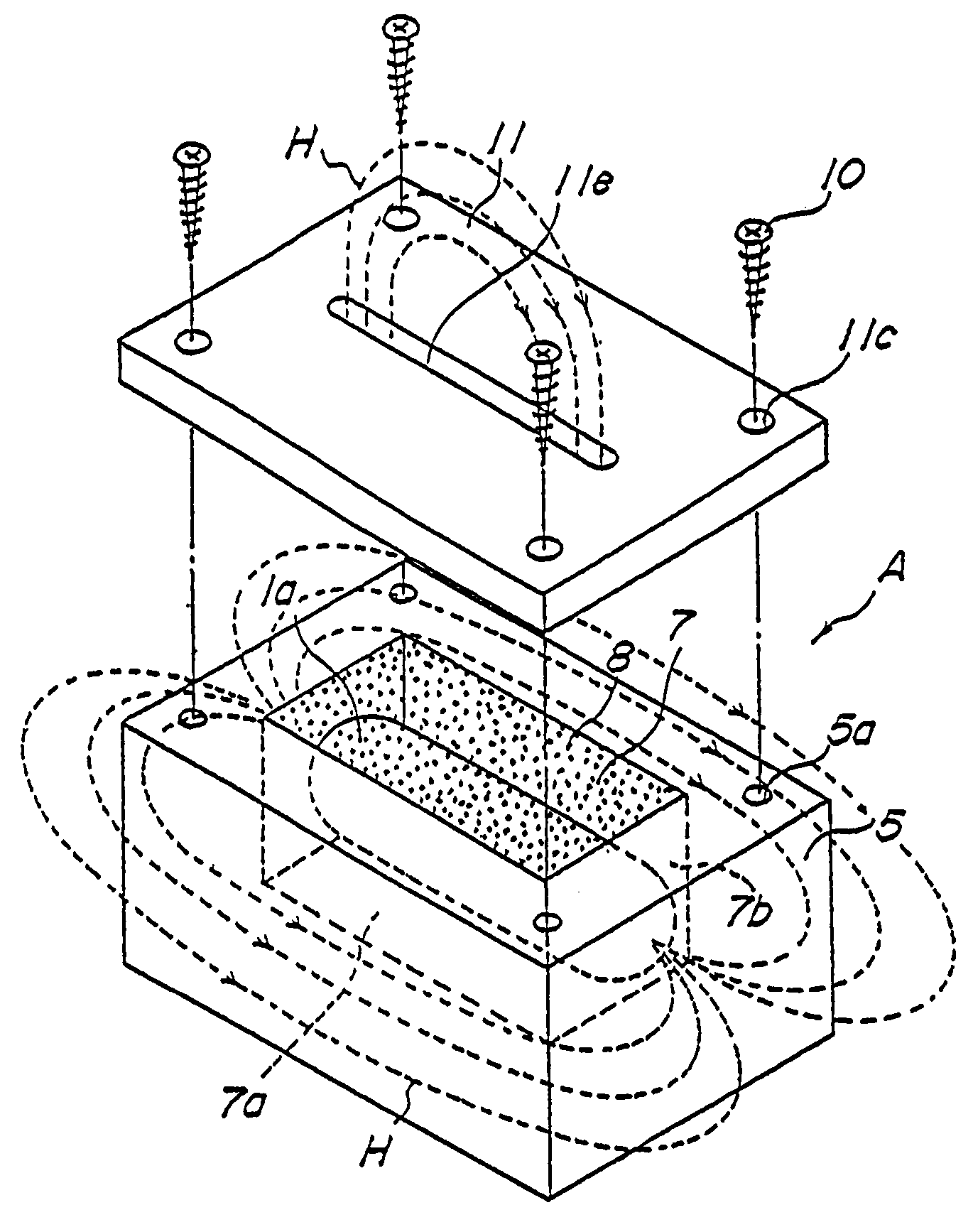
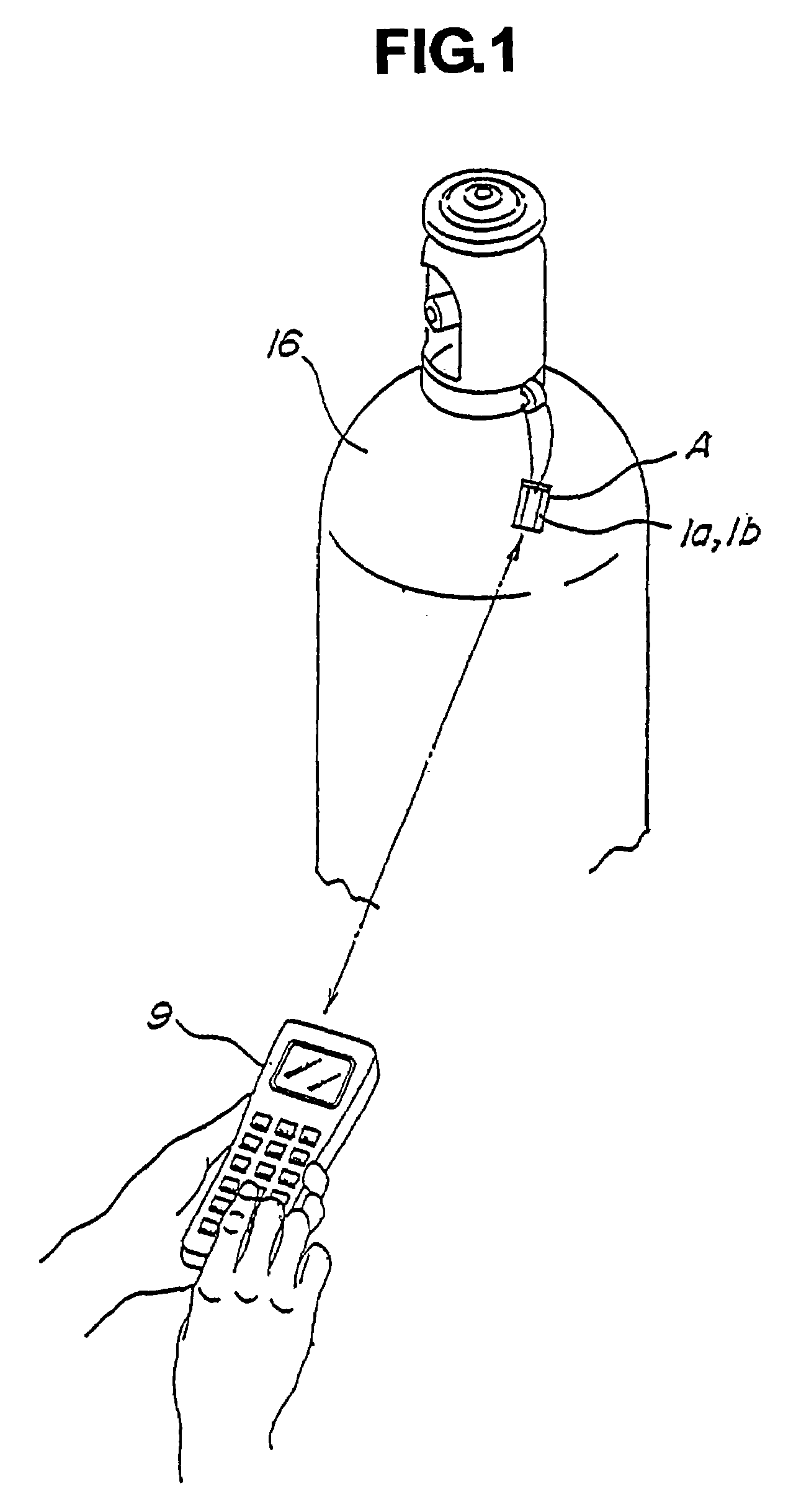
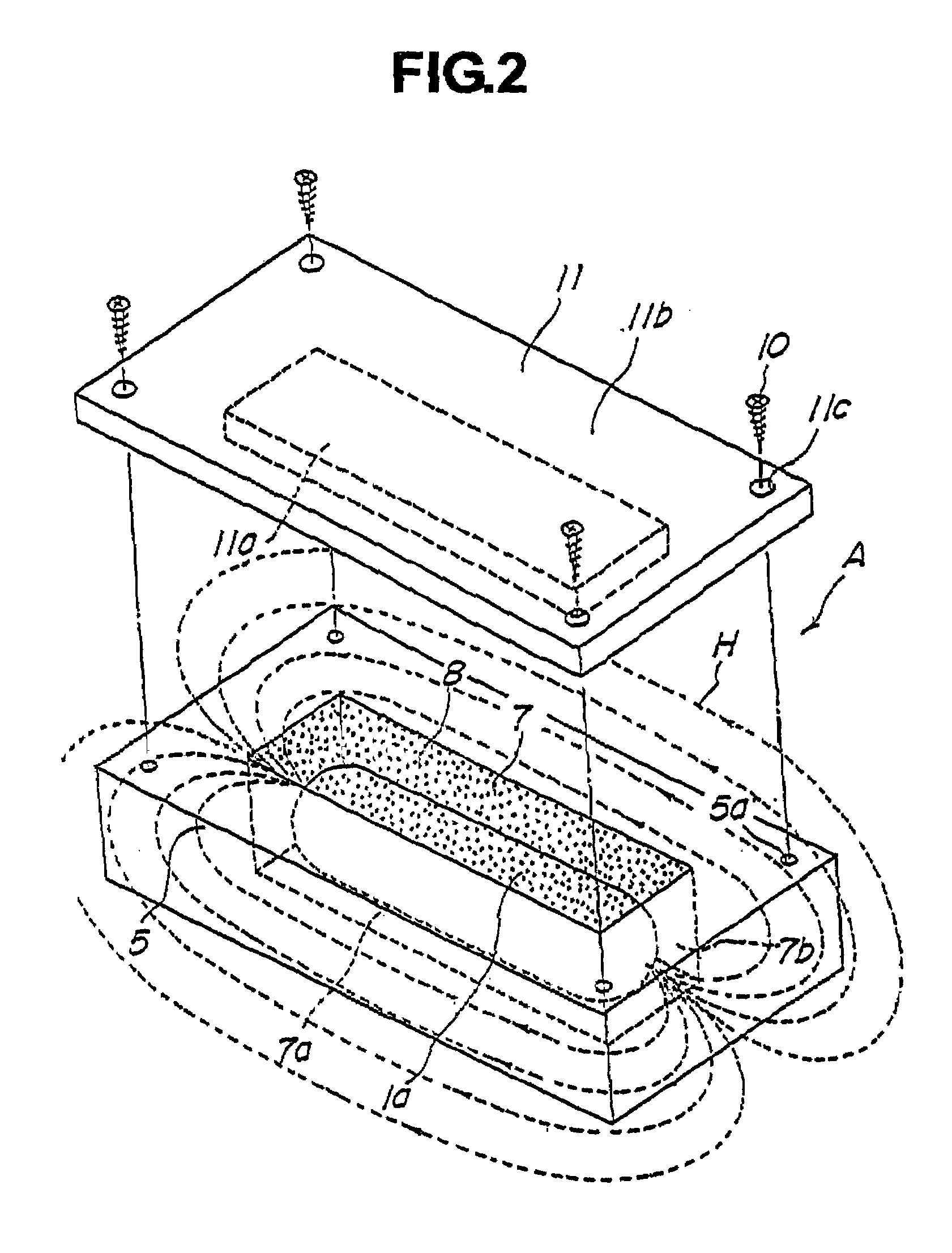
A first object of the present invention resides in providing a novel installation structure for an RFID tag, which effectively protects the RFID tag from external stress or impact during the storage, transportation and usage, and allows communication with the external.A second object of the present invention resides in that providing a novel installation structure for an RFID tag, which enables communication with the external even if the RFID tag is installed on a conductive member such as a metal member, and the surface thereof is covered with a protective member typically made of a metal which has an excellent strength and durability.A third object of the present invention is to provide a communication method using an RFID tag as being surrounded by a conductive member typically made of a metal.Even if an RFID tag 1a is housed in a container A typically made of a conductive material such as a metal having a large mechanical strength, the RFID tag 1a can communicate with an external read / write terminal 9 as mediated by leakage magnetic flux if only a flux leakage path 12 composed for example of a gap is formed in such container A.
Owner:HANEX CO LTD
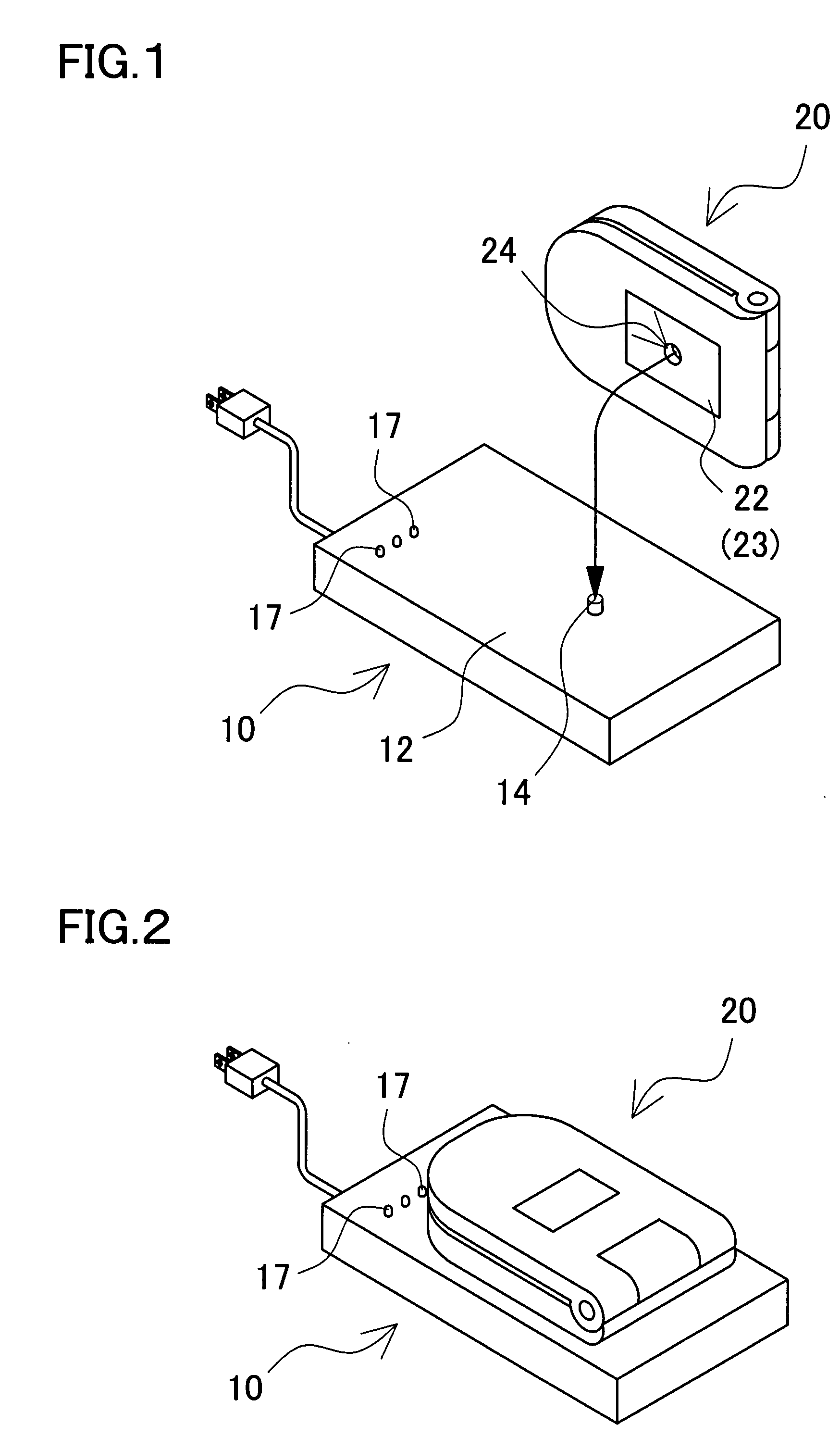
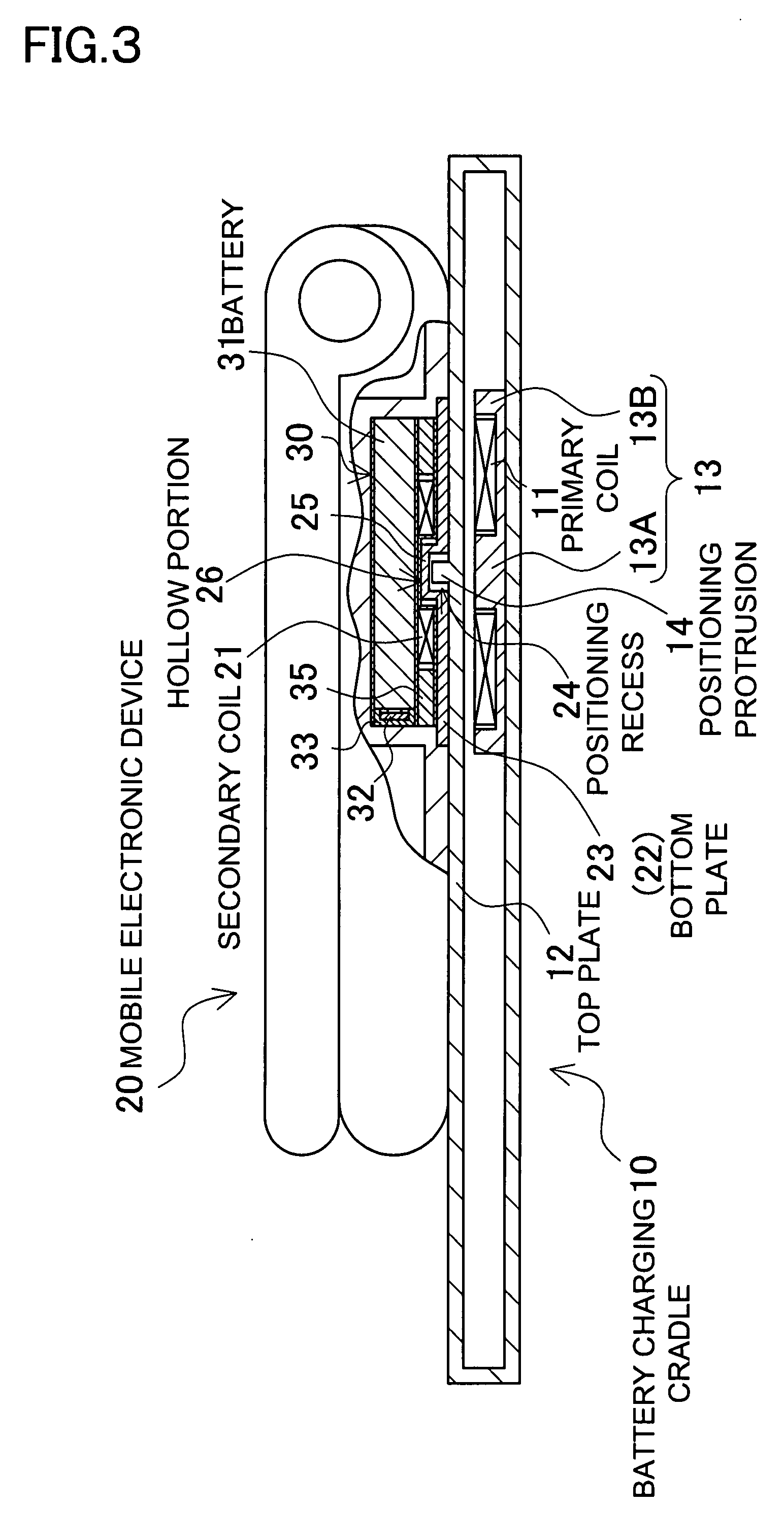
Battery charging cradle and mobile electronic device
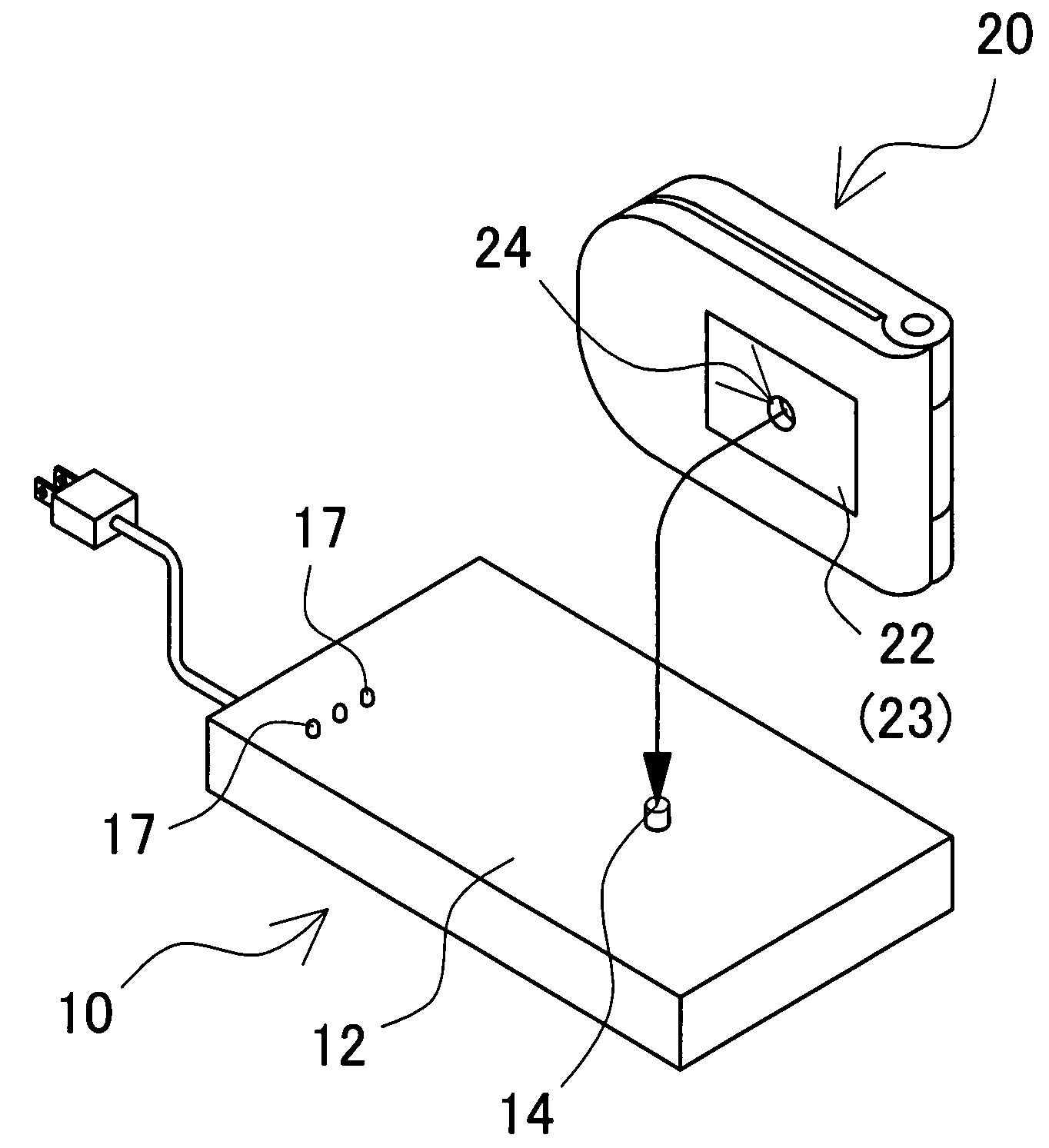
InactiveUS20080111518A1Relative misalignment can be avoidedPrecise positioningBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerElectromagnetic couplingElectricity
A battery charging cradle and mobile electronic device include a battery charging cradle incorporating a primary coil which induces an AC magnetic flux to a specific portion of a planar, top plate of the cradle, and a rechargeable battery incorporated inside a bottom plate and charged by electric power which is induced to a secondary coil being electromagnetically coupled to the primary coil. The battery charging cradle has a positioning portion, so that the mobile electronic device is placed in a predetermined position by means of the positioning portion, the primary coil is electromagnetically coupled to the secondary coil, and thus the rechargeable battery incorporated in the mobile electronic device is charged.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
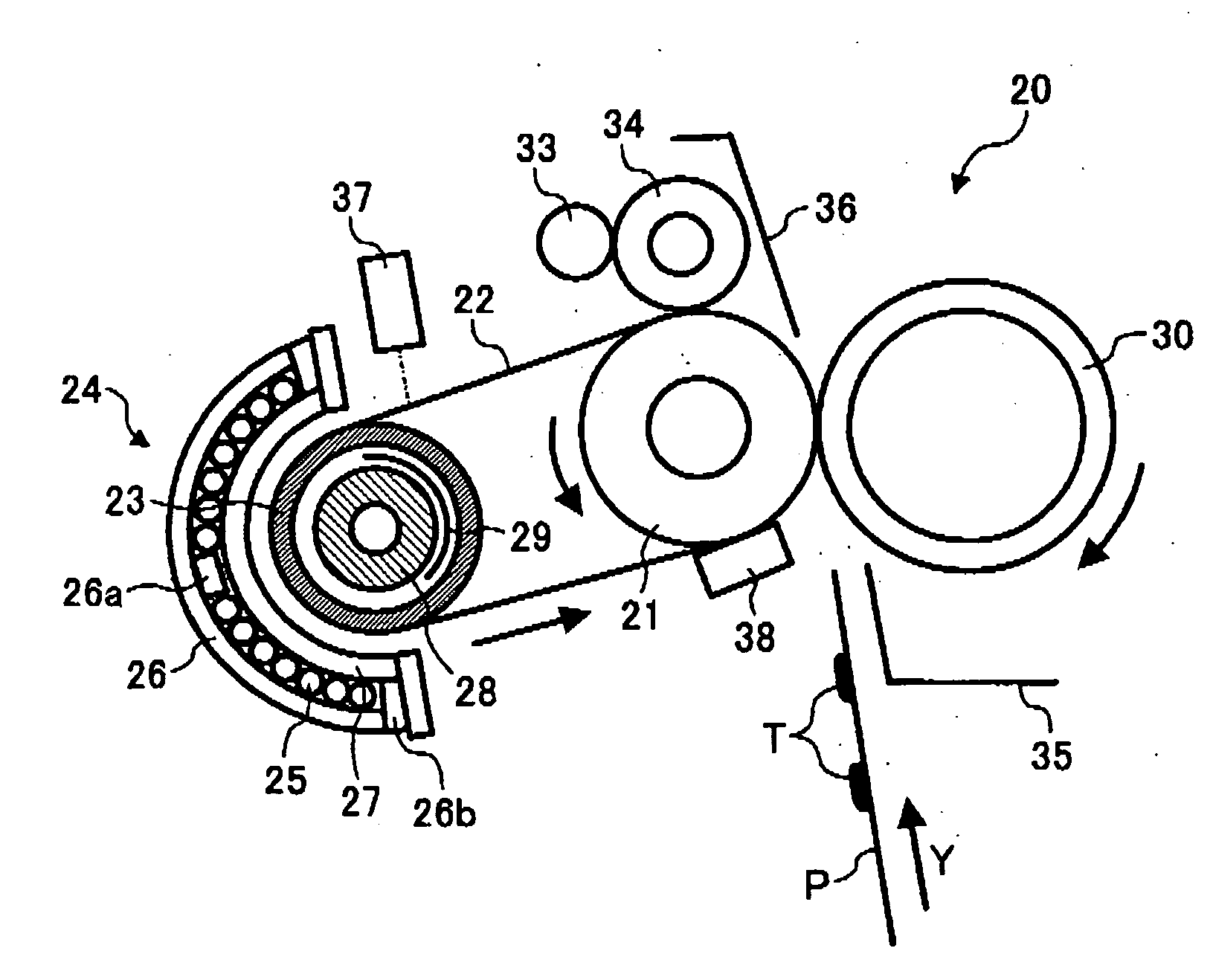
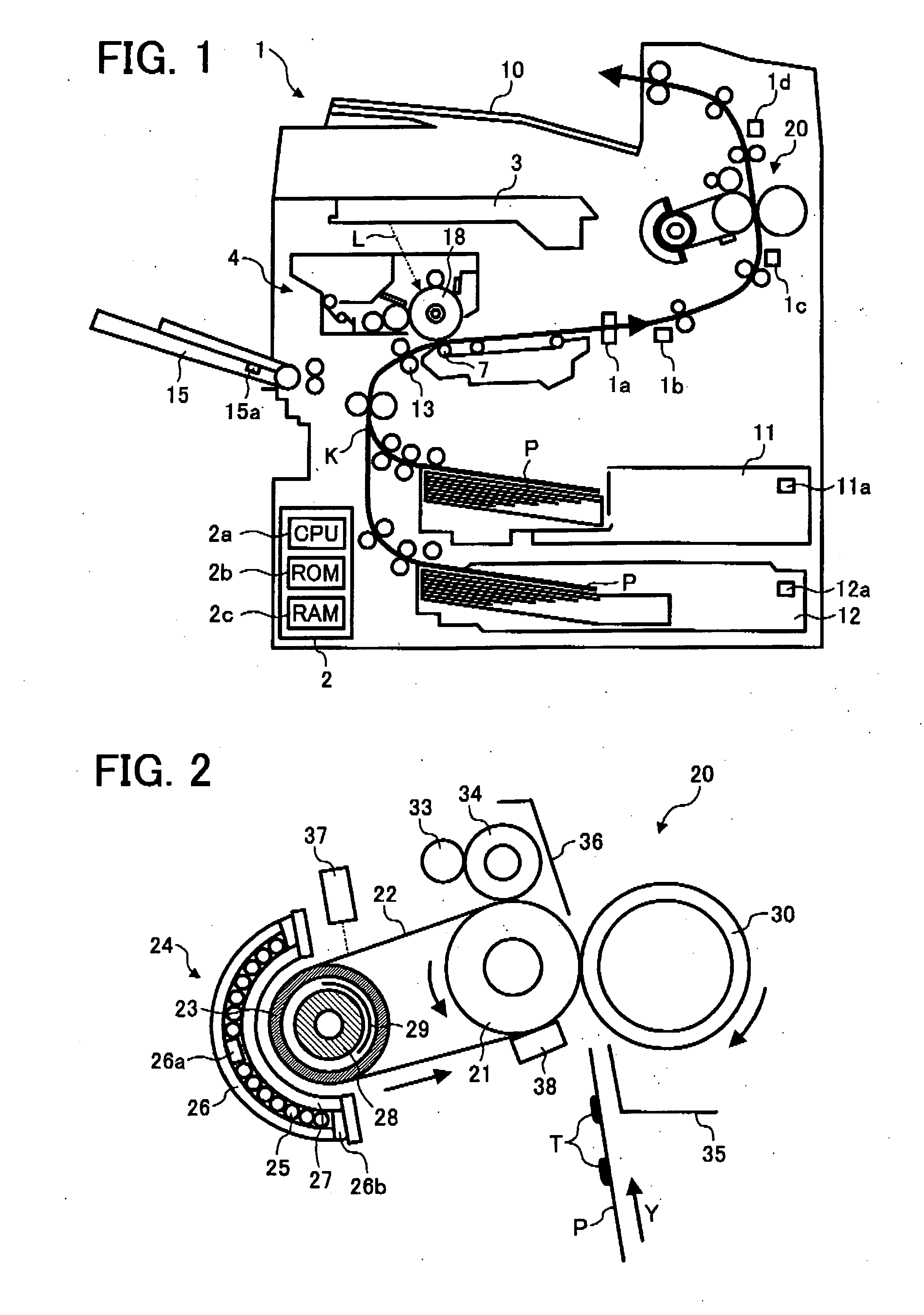
Image fixing apparatus stably controlling a fixing temperature, and image forming apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20060029411A1Electrographic process apparatusInduction heating apparatusImage formationEngineering
An image forming apparatus includes an image forming mechanism and an image fixing unit. The image forming mechanism forms a toner image on a recording sheet. The image fixing unit fixes the toner image onto the recording sheet. The image fixing unit includes a magnetic flux generator, a heat member, a magnetic flux adjuster, and a controlling member. The magnetic flux generator generates a magnetic flux. The heat member is heated inductively by the magnetic flux generated by the magnetic flux generator. The magnetic flux adjuster reduces the magnetic flux active on the heat member to form a heat reduction area in an outer circumferential surface of the heat member in a width direction thereof. The controlling member moves the magnetic flux adjuster to change the heat reduction area.
Owner:RICOH KK
Apparatus and process for reducing the susceptability of active implantable medical devices to medical procedures such as magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS7765005B2Improving impedanceReducing magnetic flux core saturationAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyPhase cancellationElectromagnetic interference
A feedthrough terminal assembly for an active implantable medical device (AIMD) includes a plurality of leadwires extending from electronic circuitry of the AIMD, and a lossy ferrite inductor through which the leadwires extend in non-conductive relation for increasing the impedance of the leadwires at selected RF frequencies and reducing magnetic flux core saturation of the lossy ferrite inductor through phase cancellation of signals carried by the leadwires. A process is also provided for filtering electromagnetic interference (EMI) in an implanted leadwire extending from an AIMD into body fluids or tissue, wherein the leadwire is subjected to occasional high-power electromagnetic fields such as those produced by medical diagnostic equipment including magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:GREATBATCH SIERRA INC
Speaker device and mobile phone
InactiveUS20070147651A1High sensitivityImprove efficiencyTransducer detailsSound producing devicesLoudspeakerVoice coil
A speaker device includes: a magnetic circuit which includes two magnetic gaps; a diaphragm which is arranged at a position passing through at least the two magnetic gaps and includes a recessed part extending in a direction substantially orthogonal with respect to an extending direction of a magnetic flux in the magnetic gaps; and a voice coil, formed into an annular shape, which includes a first parallel part extending in one direction and a second parallel part extending in a direction in parallel with the first parallel part and opposite to the first parallel part with a constant space. Particularly, the first parallel part and the second parallel part are arranged in a direction in parallel with an extending direction of the recessed part, respectively, and the first parallel part and the second parallel part are arranged in the recessed part to be positioned in the two magnetic gaps, respectively.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
Coupling system
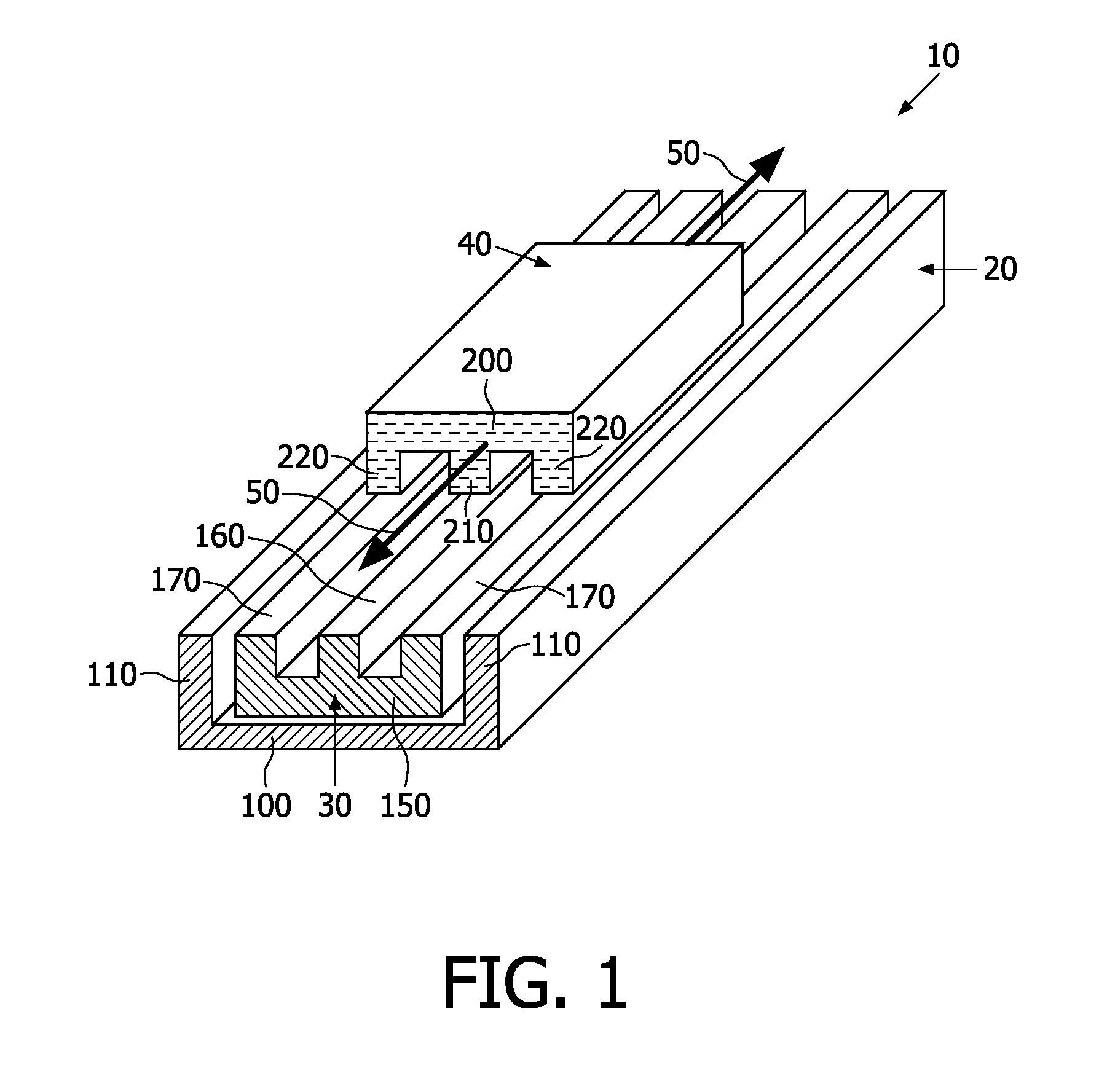
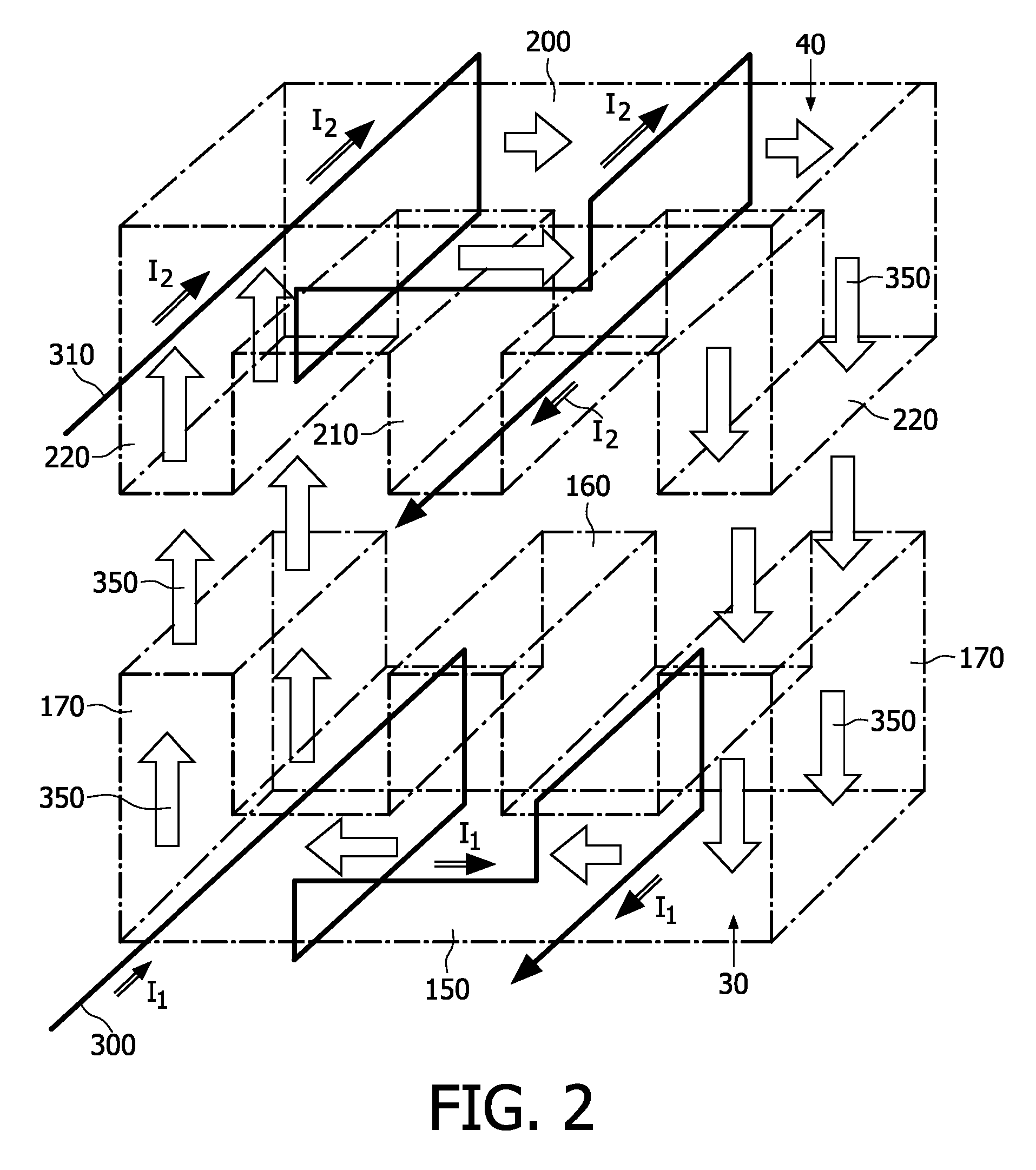
There is elucidated a device (10) comprising first and second magnetic cores (30, 40; 30a, 30b, 30c, 40a, 40b, 40c) forming a magnetic circuit. The circuit includes a first set of electrical windings (300, 310) for magnetically coupling a first electrical signal through the device (10) via a first magnetic path (350) in the circuit. The circuit includes a second set of electrical windings (400, 410) for magnetically coupling a second electrical signal through the device (10) via a second magnetic path (450) in the circuit. The paths (350, 450) are partially spatially intersecting. The sets of windings (300, 310, 400, 410) are configured so that: (a) the first set of windings (300, 310) is sensitive to magnetic flux in the first magnetic path (350), and insensitive to magnetic flux in the second magnetic path (450); and (b) the second set of windings (400, 410) is sensitive to magnetic flux in the second magnetic path (450), and insensitive to magnetic flux in the first magnetic path (350). The first and second cores (30, 40; 30a, 30b, 30c, 40a, 40b, 40c) enable relative motion (50) there between whilst coupling the signals through the circuit. The device (10) is beneficially employed in a medical system (800).
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Magnetic head for perpendicular recording with hard bias structure for write pole tip
A magnetic head for writing information on a relatively-moving medium is disclosed, the head having a leading end, a trailing end and a medium-facing surface, the head comprising: a soft magnetic write pole that terminates in a pole tip that is disposed adjacent to the medium-facing surface; at least one coil section that is disposed adjacent to the write pole to induce a magnetic flux in the write pole; and a hard magnetic bias structure disposed within one micron of the pole tip to magnetically bias the pole tip.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Low resistance coil structure for high speed writer
InactiveUS6333830B2Lower coil resistanceReduce dissipationConstruction of head windingsHeads using thin filmsElectrical conductorLower pole
The present invention provides a thin film write head having an upper and lower pole structures and conductor turns forming a winding for generating magnetic flux. The conductor is formed with a non-planar top surface. The winding of the present invention may be formed of lower and upper turns. The upper turns may be formed with a non-planar top surface, a non-planar bottom surface, or both. It is preferred that the bottom surface of the upper conductor turns be coherent with the non-planar top surface of the lower conductor turns. The non-planar top surface may be formed by removing corners formed during deposition between a generally planar top surface and abutting side walls. The corners may be removed by ion milling to form the non-planar top surface. The conductor may be copper with the non-planar top surface having sloping facets. The thin film write head of the present invention may be utilized to provide an improved data storage and retrieval apparatus. The preferred embodiment provides reduced coil resistance thereby reducing Johnson Thermal Noise and power dissipation. It also allows for reduced yoke length and reduced stack height while providing low apex angles to expand and improve yoke material deposition thereby improving head response and operational frequency.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Wireless charger decreased in variation of charging efficiency
InactiveUS20090102419A1Reduce variationBatteries circuit arrangementsTransformersConductor CoilMagnetic flux
A wireless charger charges a storage battery of a portable electronic device in a wireless manner (non-contacting or contact-less) so that a variation of charging efficiency is not serious though the storage battery is placed any position of the wireless charger. The wireless charger is provided with a primary coil for generating a magnetic field so as to charge a subject, which is provided with a secondary coil, by means of inductive coupling with the secondary coil. The primary coil includes an outer coil arranged with a predetermined winding number and a predetermined size; and at least one inner coil arranged to be included inside the outer coil. The outer coil and the inner coil are arranged so that, when a primary current is applied to the outer coil and the inner coil, magnetic fluxes generated in the outer coil and the inner coil are formed in the same direction.
Owner:LG CABLE LTD (KR)
Magnetic power transmission utilizing phased transmitter coil arrays and phased receiver coil arrays
ActiveUS20140028111A1Maximize power transferPower maximizationElectrotherapyTransformersTransmitter coilWireless transmission
An improved wireless transmission system for transferring power over a distance. The system includes a transmitter generating a magnetic field and a receiver for inducing a voltage in response to the magnetic field. In some embodiments, the transmitter can include a plurality of transmitter resonators configured to transmit wireless power to the receiver. The transmitter resonators can be disposed on a flexible substrate adapted to conform to a patient. In one embodiment, the polarities of magnetic flux received by the receiver can be measured and communicated to the transmitter, which can adjust polarities of the transmitter resonators to optimize power transfer. Methods of use are also provided.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com