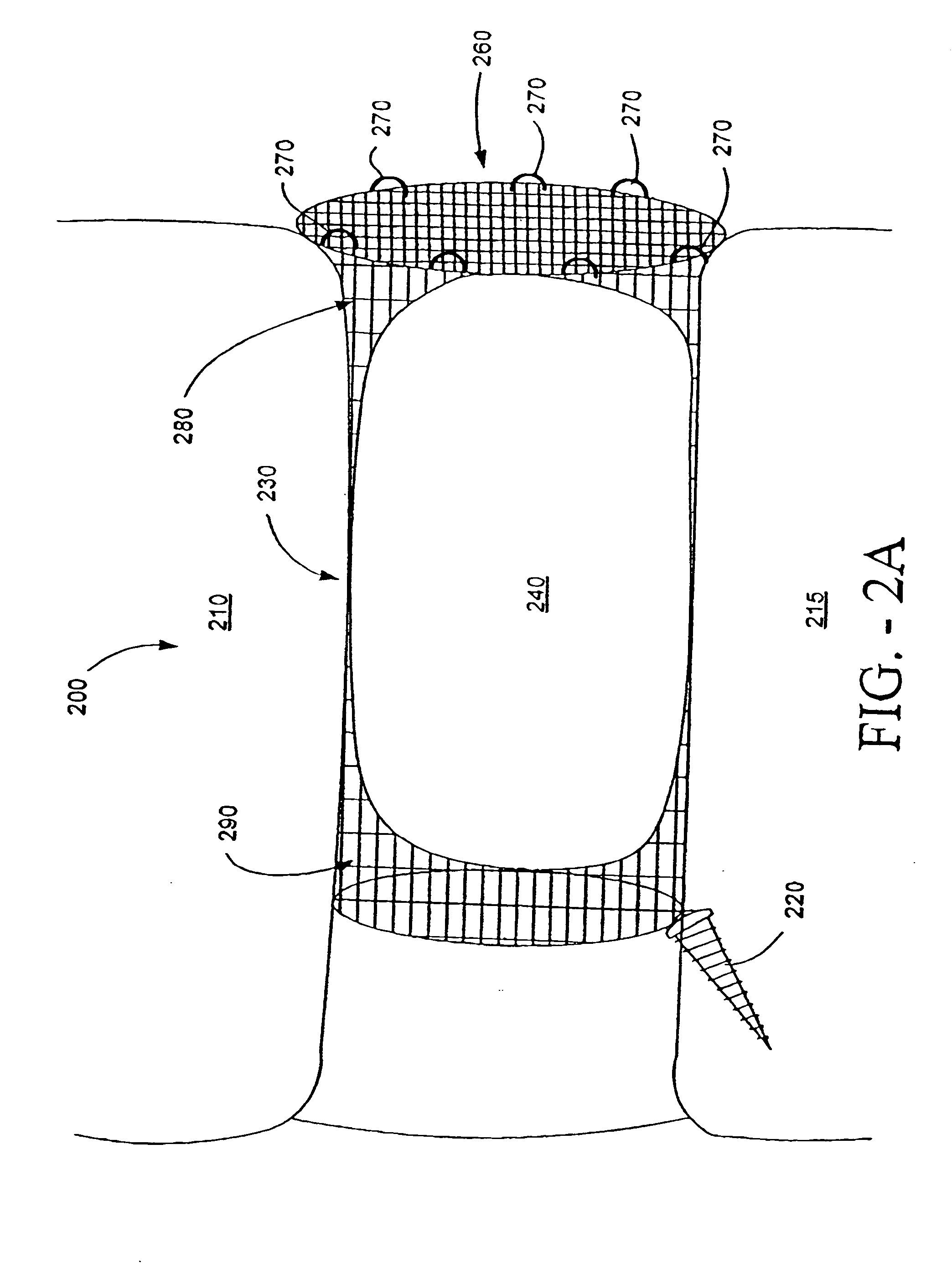
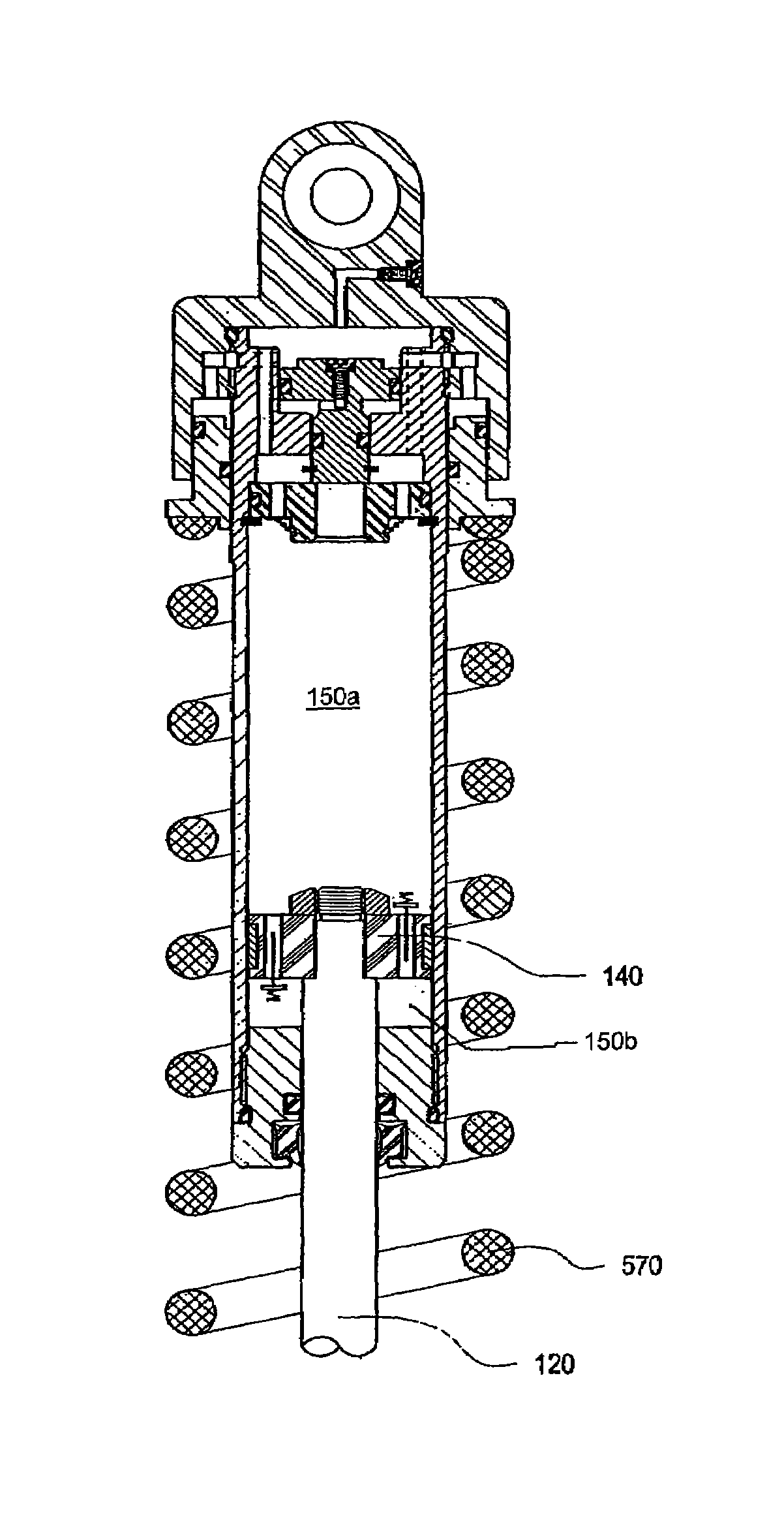
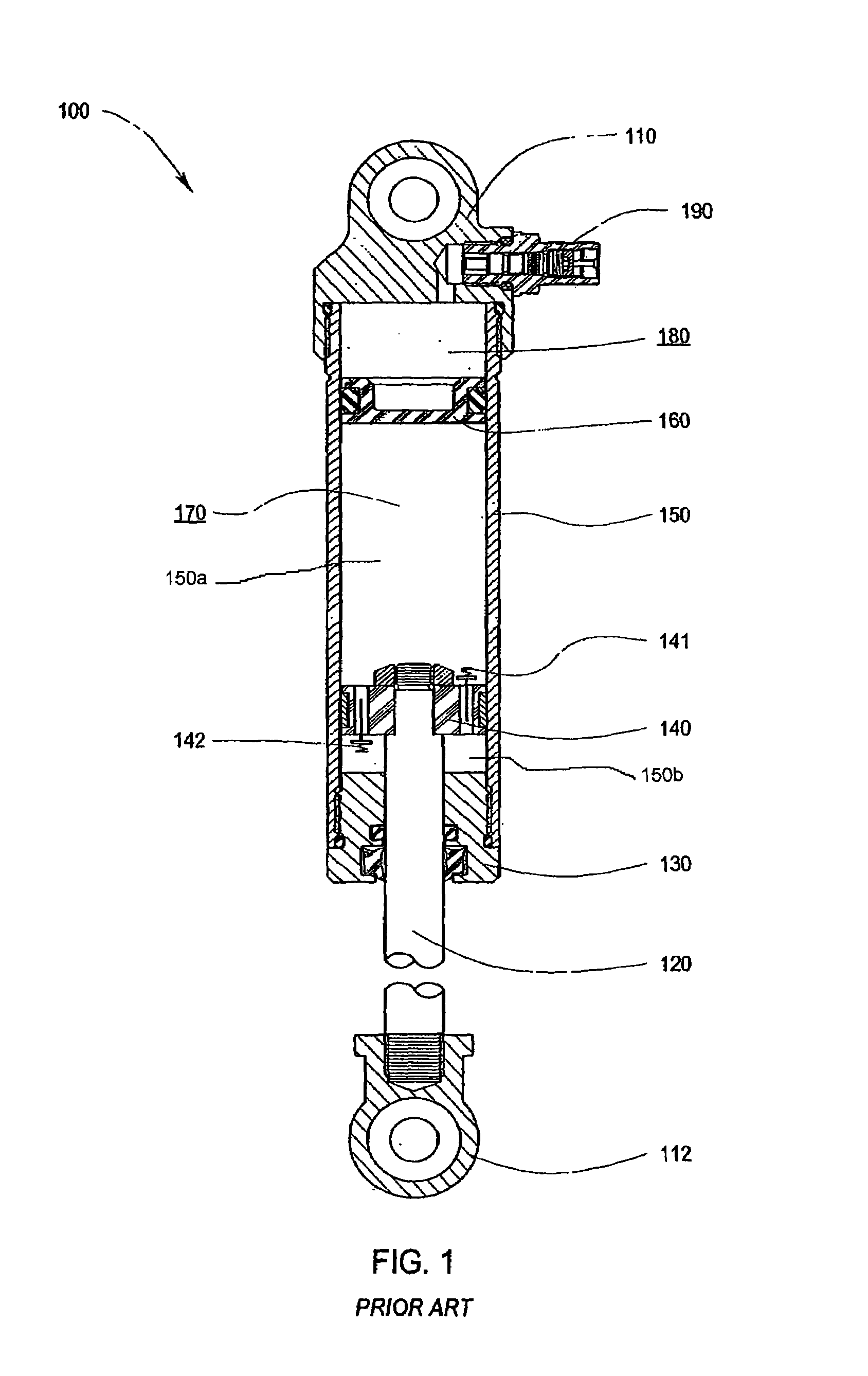
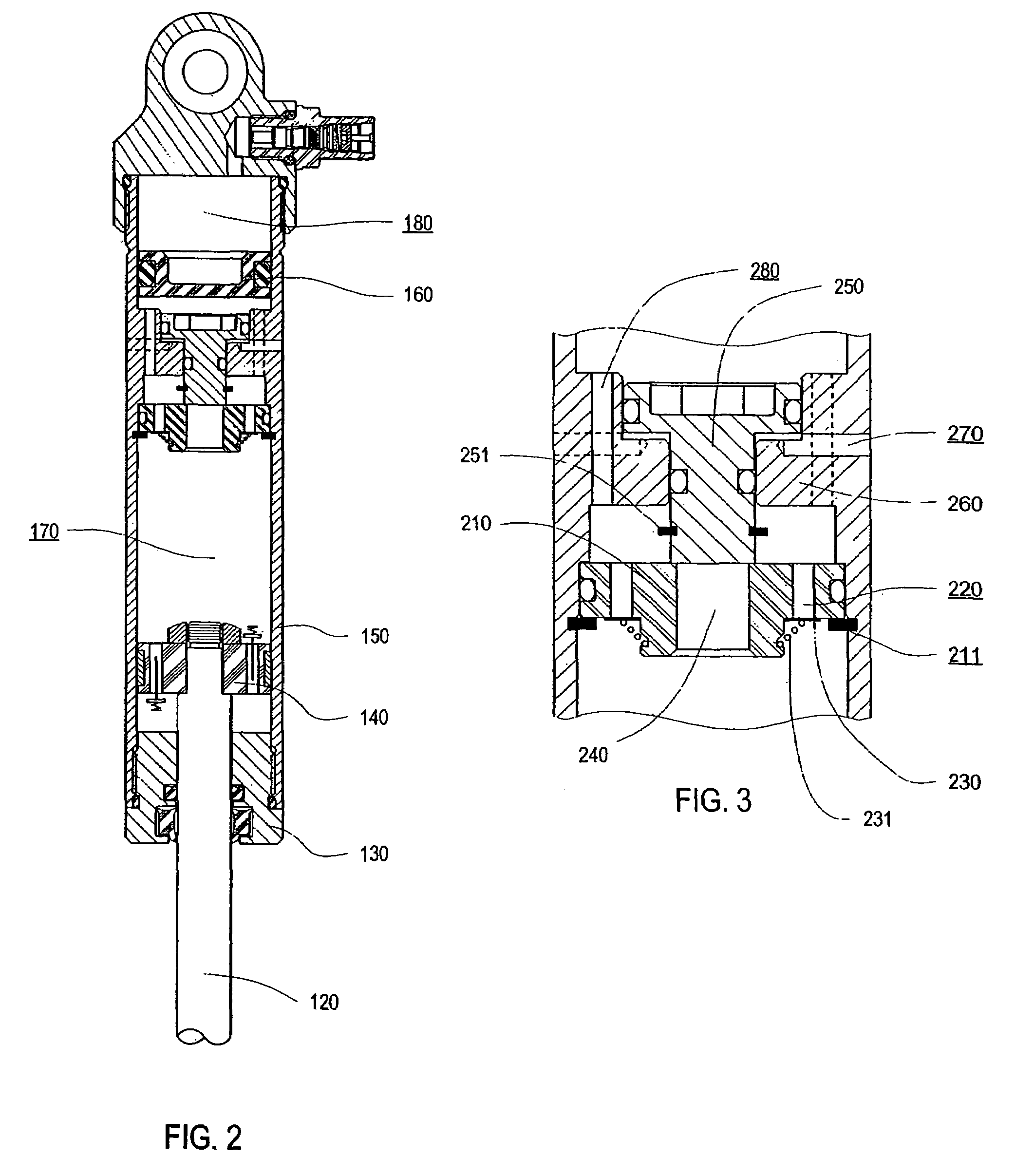
Patents
Literature
24817 results about "Shock absorber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A shock absorber or damper is a mechanical or hydraulic device designed to absorb and damp shock impulses. It does this by converting the kinetic energy of the shock into another form of energy (typically heat) which is then dissipated. Most shock absorbers are a form of dashpot (a damper which resists motion via viscous friction).
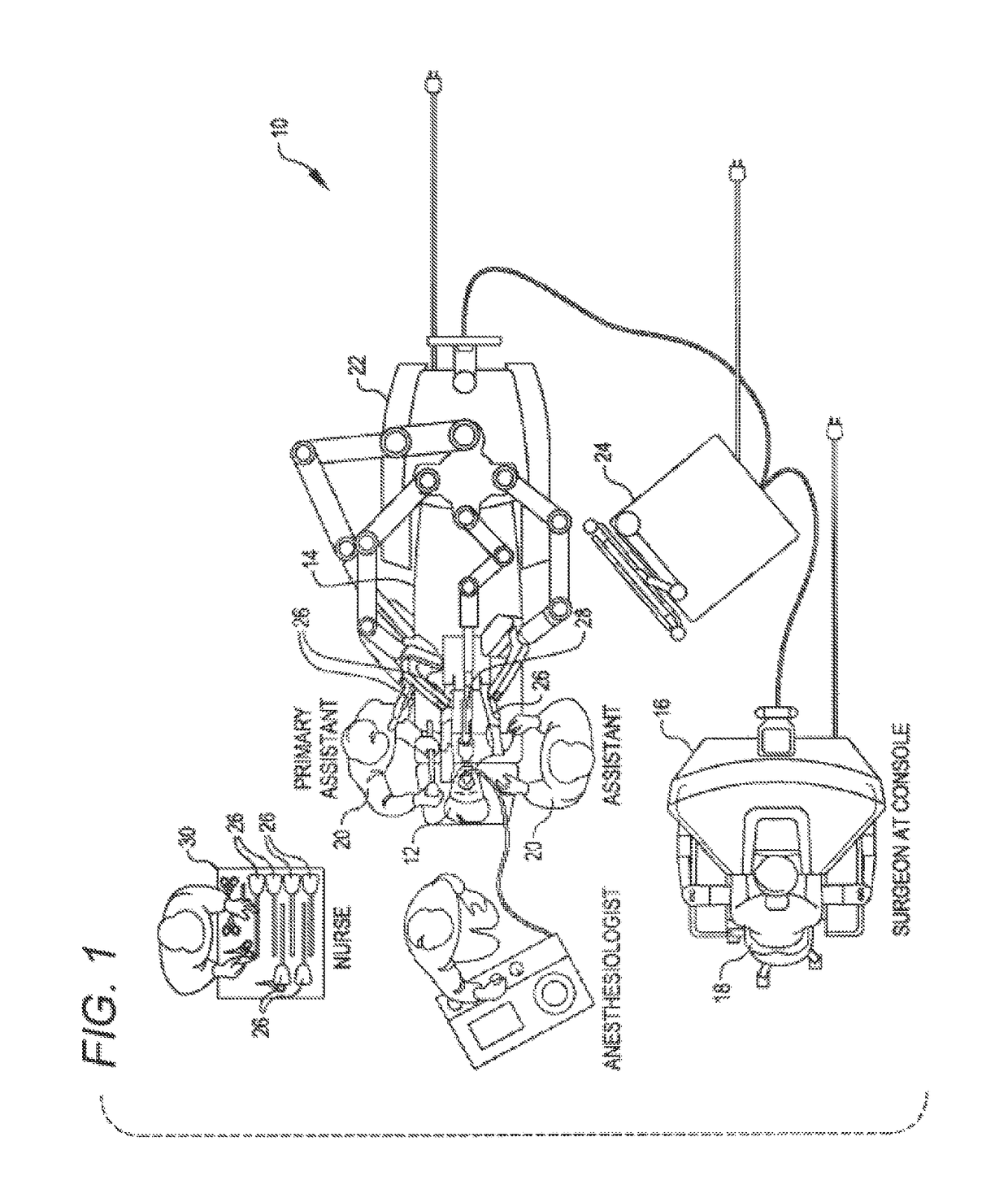
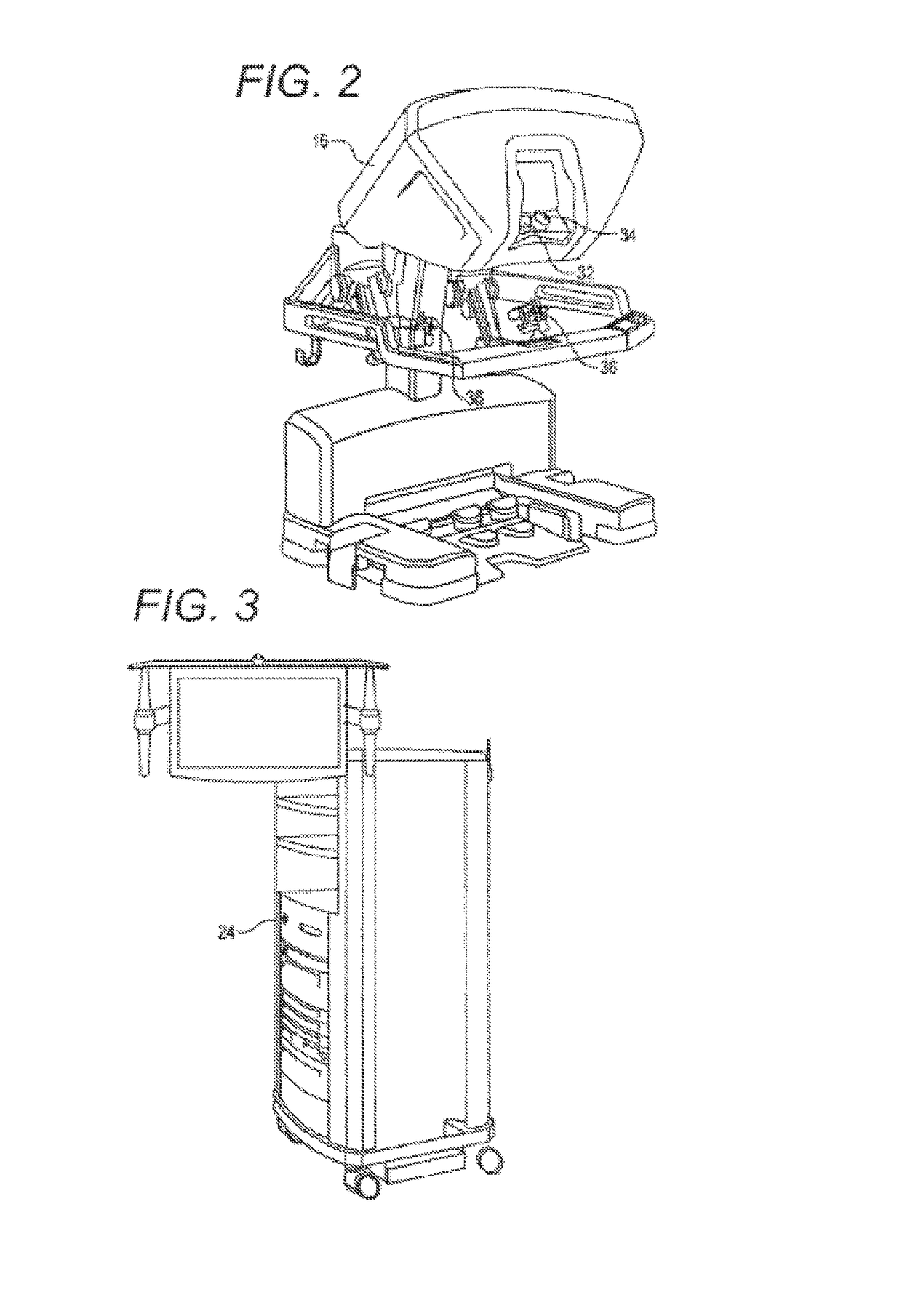
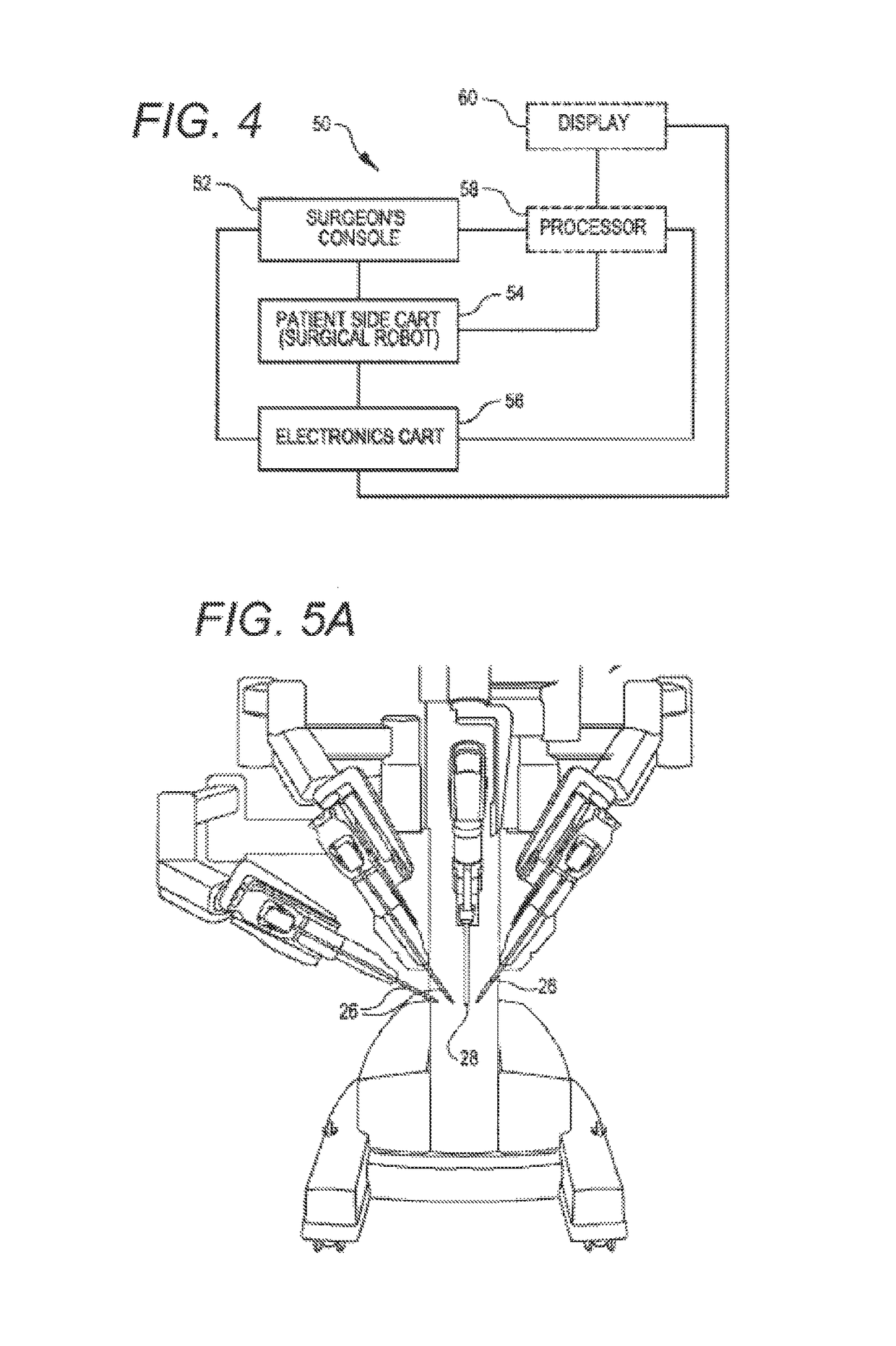
Active and semi-active damping in a telesurgical system
ActiveUS10058395B2Reduce vibrationPrevent movementDiagnosticsSurgical robotsSurgical operationSemi active
Methods and systems for damping vibrations in a surgical system are disclosed herein. The surgical system can include one or several moveable set-up linkages. A damper can be connected with one or several of the set-up linkages. The damper can be a passive, active, or semi-active damper. The damper can mitigate a vibration arising in one of the set-up linkages, and the damper can prevent a vibration arising in one of the linkages from affecting another of the set-up linkages. The active and semi-active dampers can be controlled with a feedback model and a feed-forward model.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Microfluidic devices and methods of use
InactiveUS20020127736A1Lessening oscillation in velocityReduce oscillation amplitudeSludge treatmentFixed microstructural devicesElastomerThin membrane
A microfluidic device comprises pumps, valves, and fluid oscillation dampers. In a device employed for sorting, an entity is flowed by the pump along a flow channel through a detection region to a junction. Based upon an identity of the entity determined in the detection region, a waste or collection valve located on opposite branches of the flow channel at the junction are actuated, thereby routing the entity to either a waste pool or a collection pool. A damper structure may be located between the pump and the junction. The damper reduces the amplitude of oscillation pressure in the flow channel due to operation of the pump, thereby lessening oscillation in velocity of the entity during sorting process. The microfluidic device may be formed in a block of elastomer material, with thin membranes of the elastomer material deflectable into the flow channel to provide pump or valve functionality.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Disk repair structures for positioning disk repair material
The present invention is directed to a device that can be placed between two adjacent vertebrae, and that is used to repair an injury or defect in the anulus of the intervertebral disk. The implant is characterized by having a flexible structure anchored to the vertebral bone, the flexible structure connected with a patch held in place over the injury or defect. The flexible structure has a hollow interior space which can sustain inside it a hydrogel cushion. The hydrogel cushion acts as a shock absorber for the spine, maintains height of the intervertebral disk space, and prevents further disk herniation due to the narrowing of the intervertebral disk space.
Owner:KYPHON
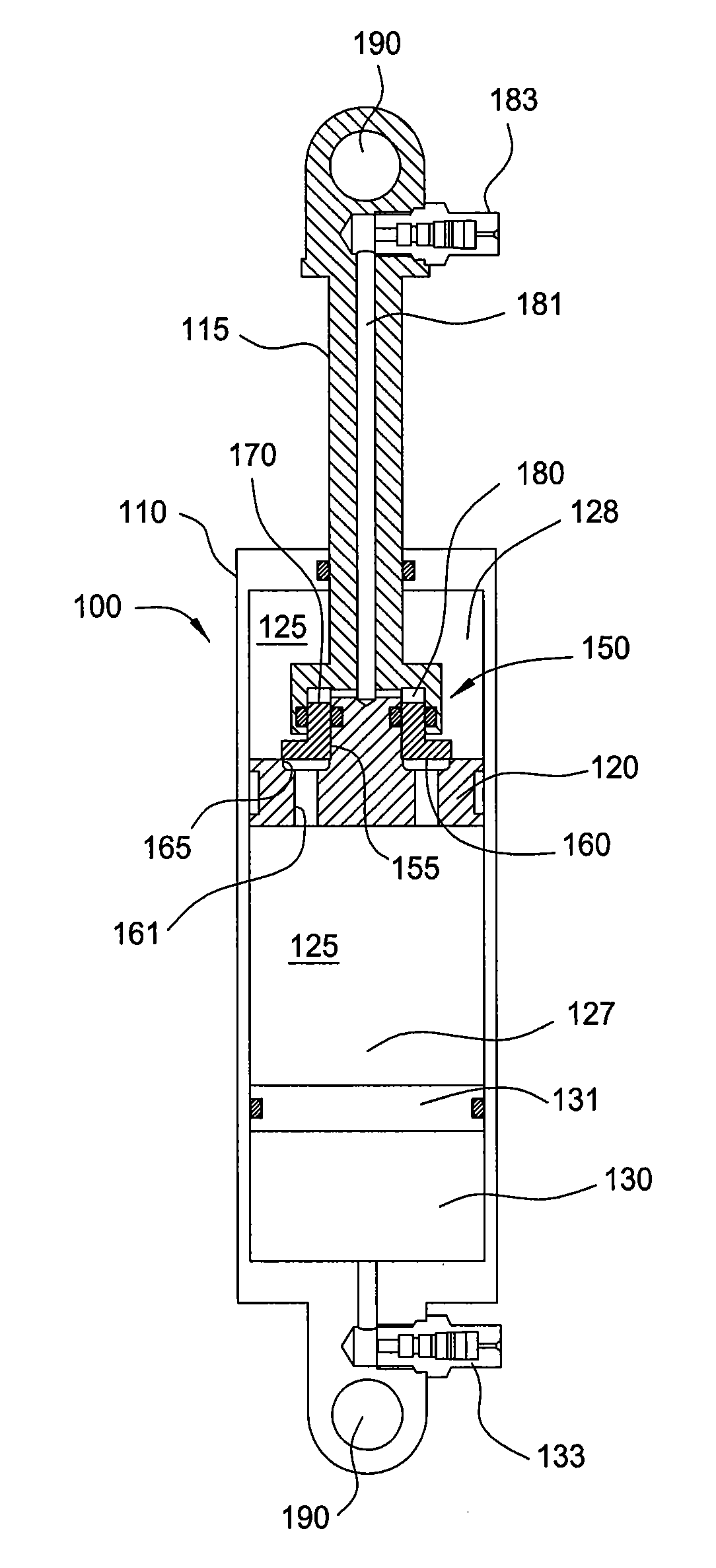
Damper with pressure-sensitive compression damping
A self-pressurized damper, for example, a pressure-sensitive damper is described. At least one suspension spring is used to pressurize the damping fluid, a task typically carried out by a sealed moveable barrier, such as an internal floating piston (IFP) and a pressurized gas. Thus, stroke length may be maximized. Furthermore, the amount of compression damping force produced by the damper may be a function of the force generated by the at least one suspension spring.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
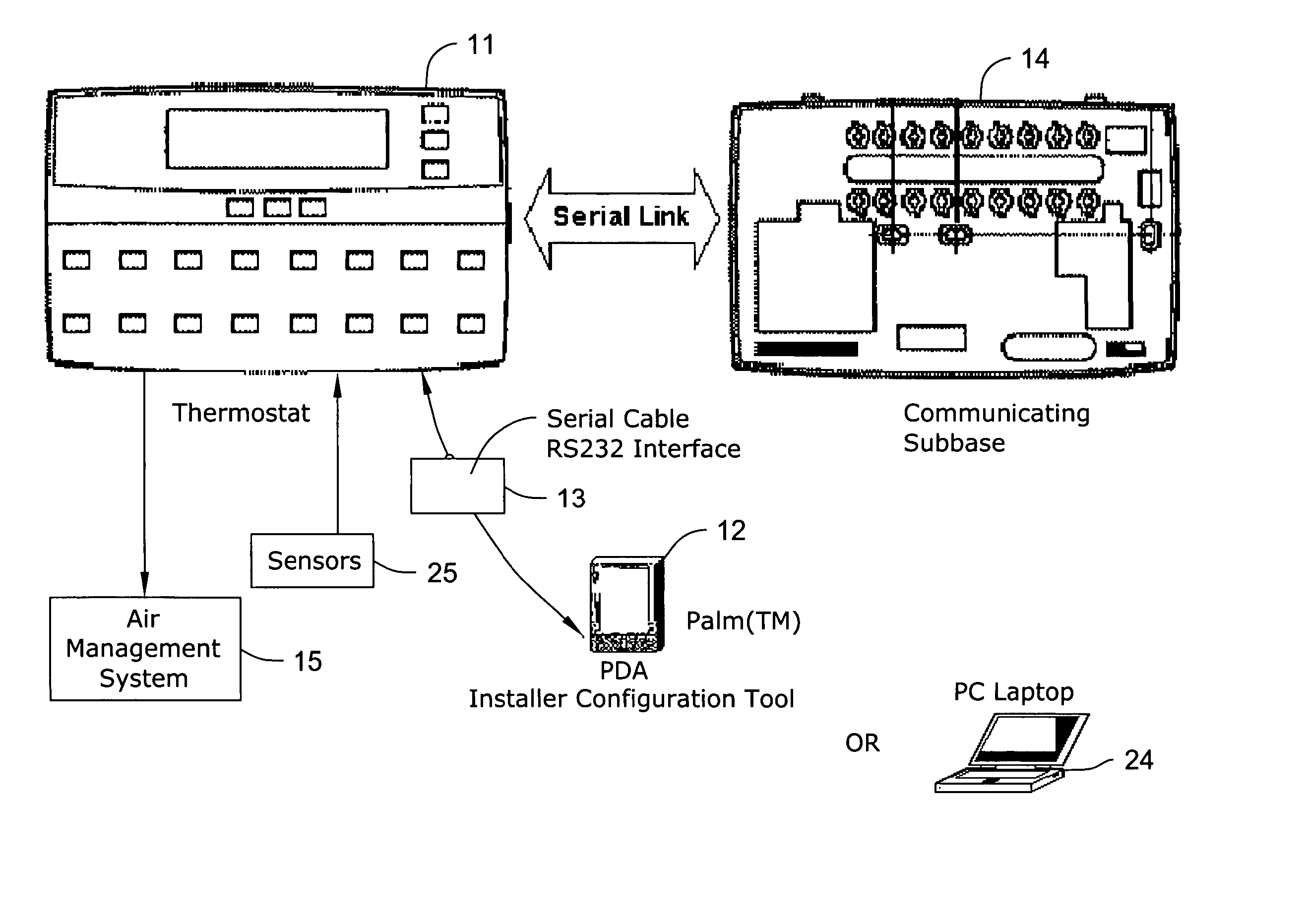
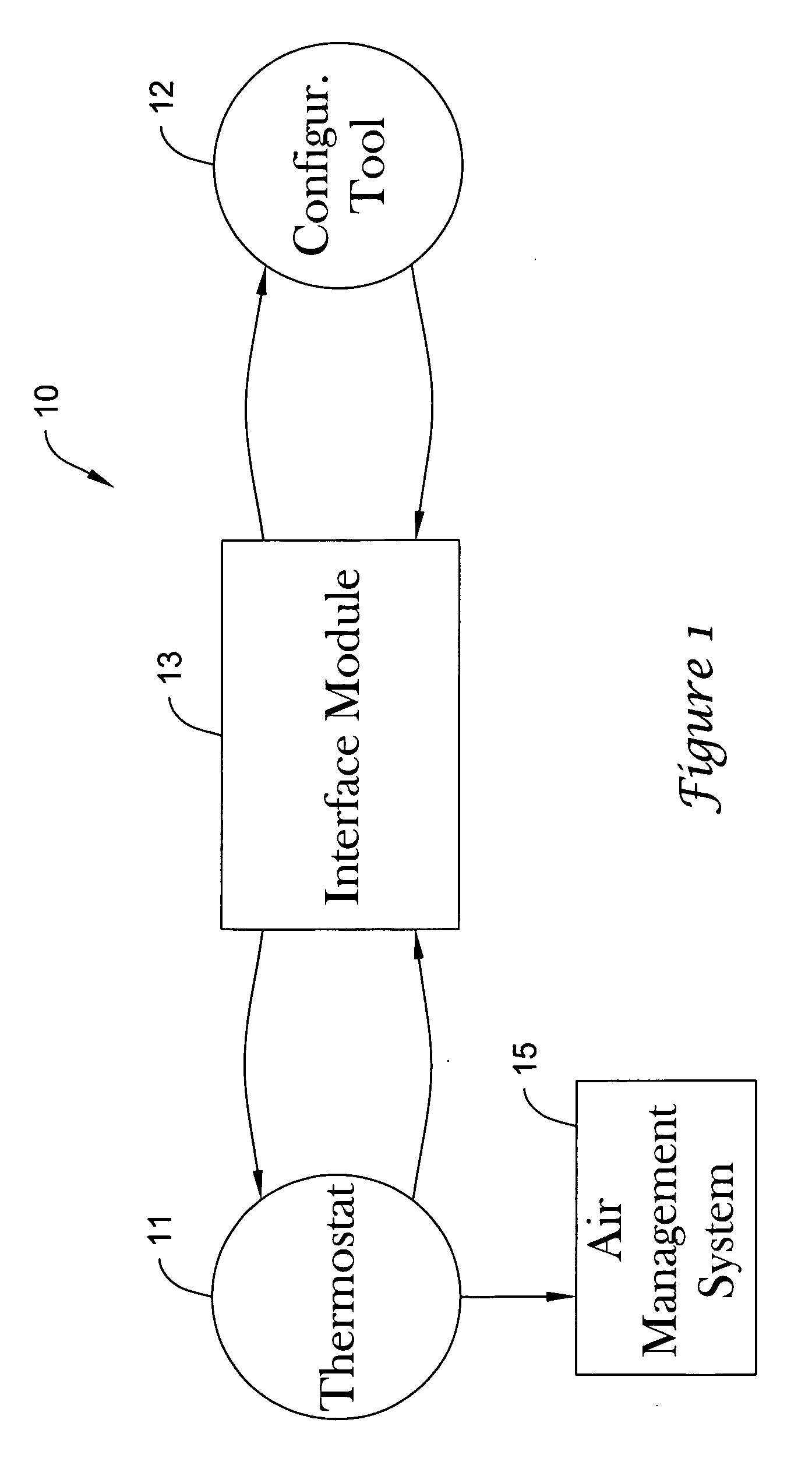
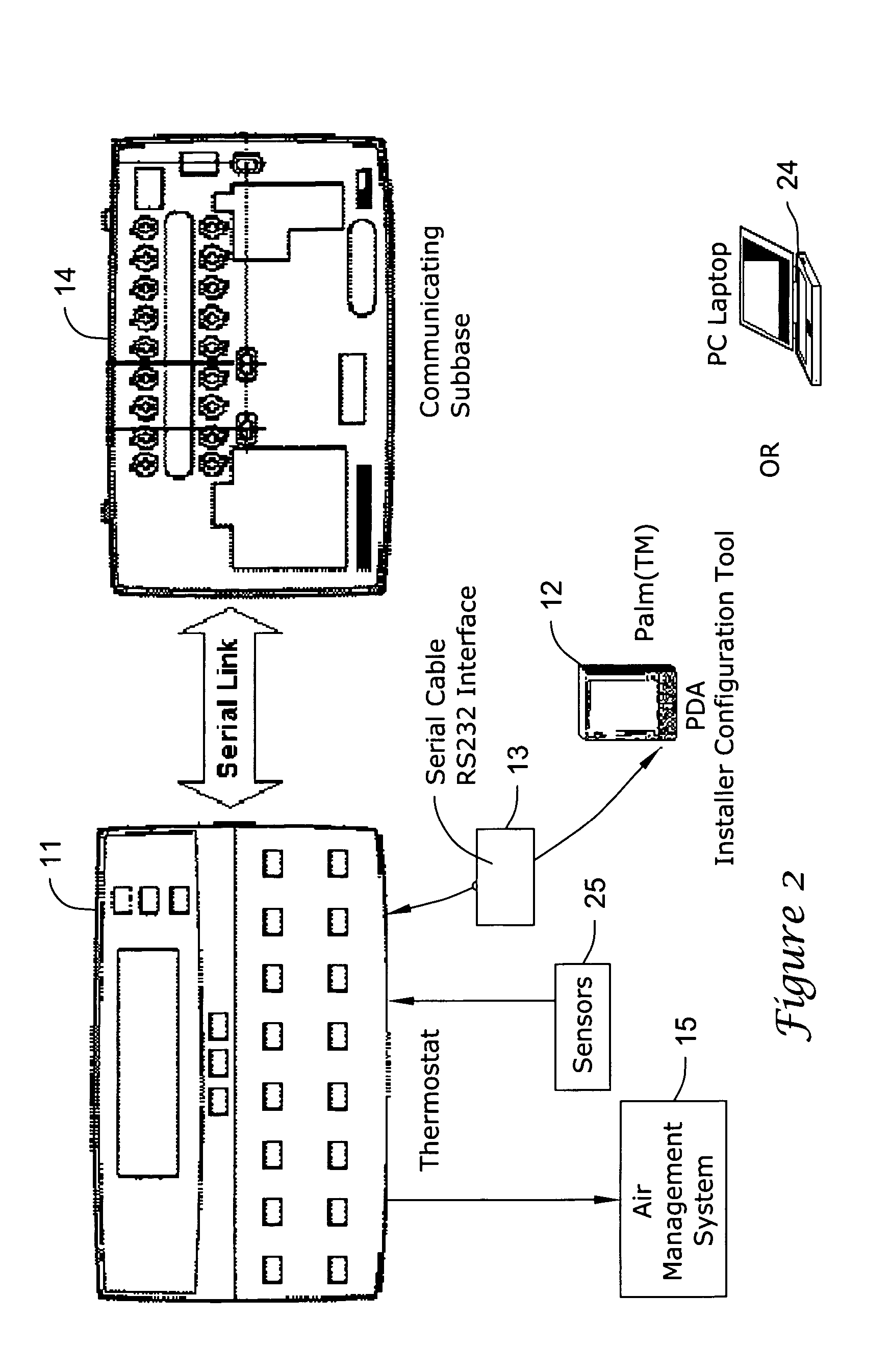
Thermostat having modulated and non-modulated provisions
ActiveUS20050040247A1Quick and efficientEasy to adaptMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsAir managementEngineering
A thermostat providing modulated or analog control of valves or dampers of an air management system. This permits operating a single cooling or heating stage with partially open valves or dampers as needed, since one full stage that is either fully on or off may not be easy to manage for effective air management of a particular type of building, zone or facility. The thermostat may also provide non-modulated control of multi-stage cooling and heating systems. The thermostat may even be used to control a modulated system having more than one stage of cooling or heating.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
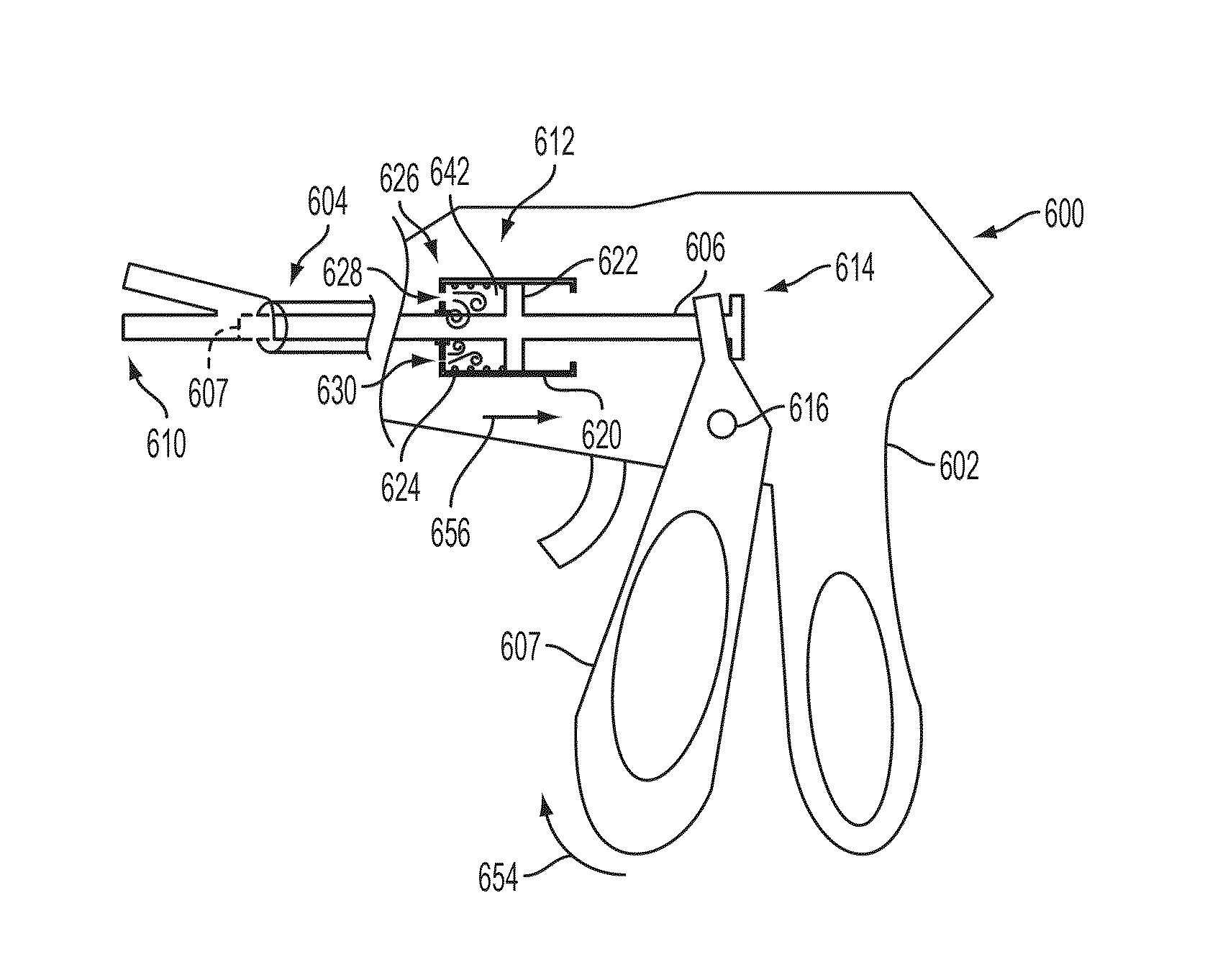
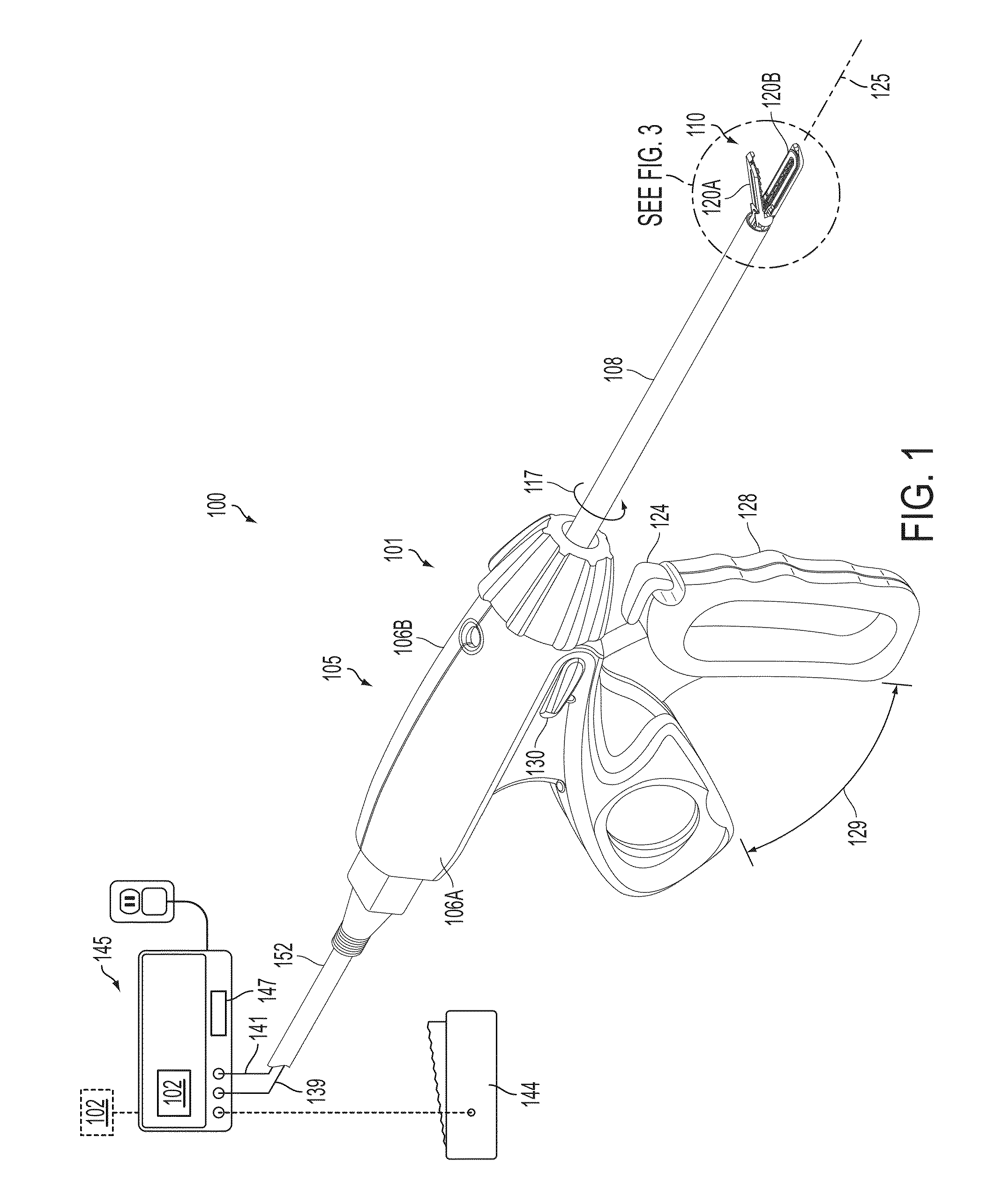
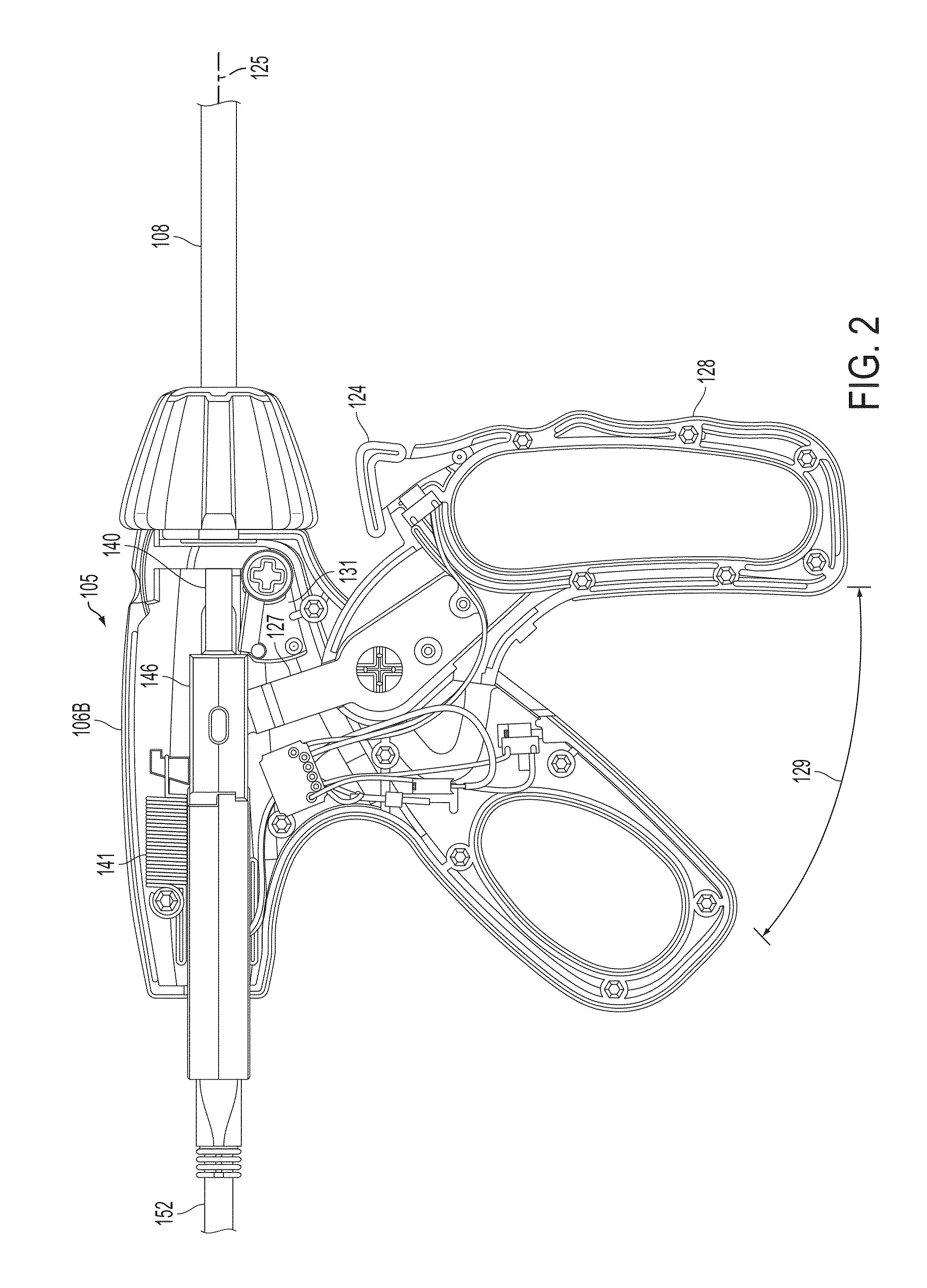
Electrosurgical cutting and sealing instrument
ActiveUS9192431B2Mechanical features of instrumentSurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringSupply energy
A surgical instrument for supplying energy to tissue can comprise a jaw member comprising an electrode, wherein the electrode is configured to supply energy from a power source to captured tissue. The surgical instrument comprises a tissue-cutting element to transect the captured tissue. The rate of distal translation of the tissue-cutting element during the operational stroke may be regulated by a damper. The damper may have barrel and a plunger.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Pusher apparatus for merchandise
InactiveUS20060163272A1Useful driving forceSimple designRacksCoin-freed apparatus detailsCoil springEngineering
A pusher apparatus comprises a track, a pusher mounted on the track for movement along the track; a spring mounted on the pusher for urging the pusher along the track; an axle rotatably mounted on the pusher; and at least one wheel fixed to the axle for positively engaging the track. In one aspect of the invention, two of the said wheels are fixed to the axle to avoid canting of the pusher as it moves along the track. In another aspect of the invention, the spring is a coil spring contained within the pusher unit for driving rotation of the axle. Preferably, a rotary damper regulates the operation of the coil spring.
Owner:GAMBLE NIGEL FRANCIS
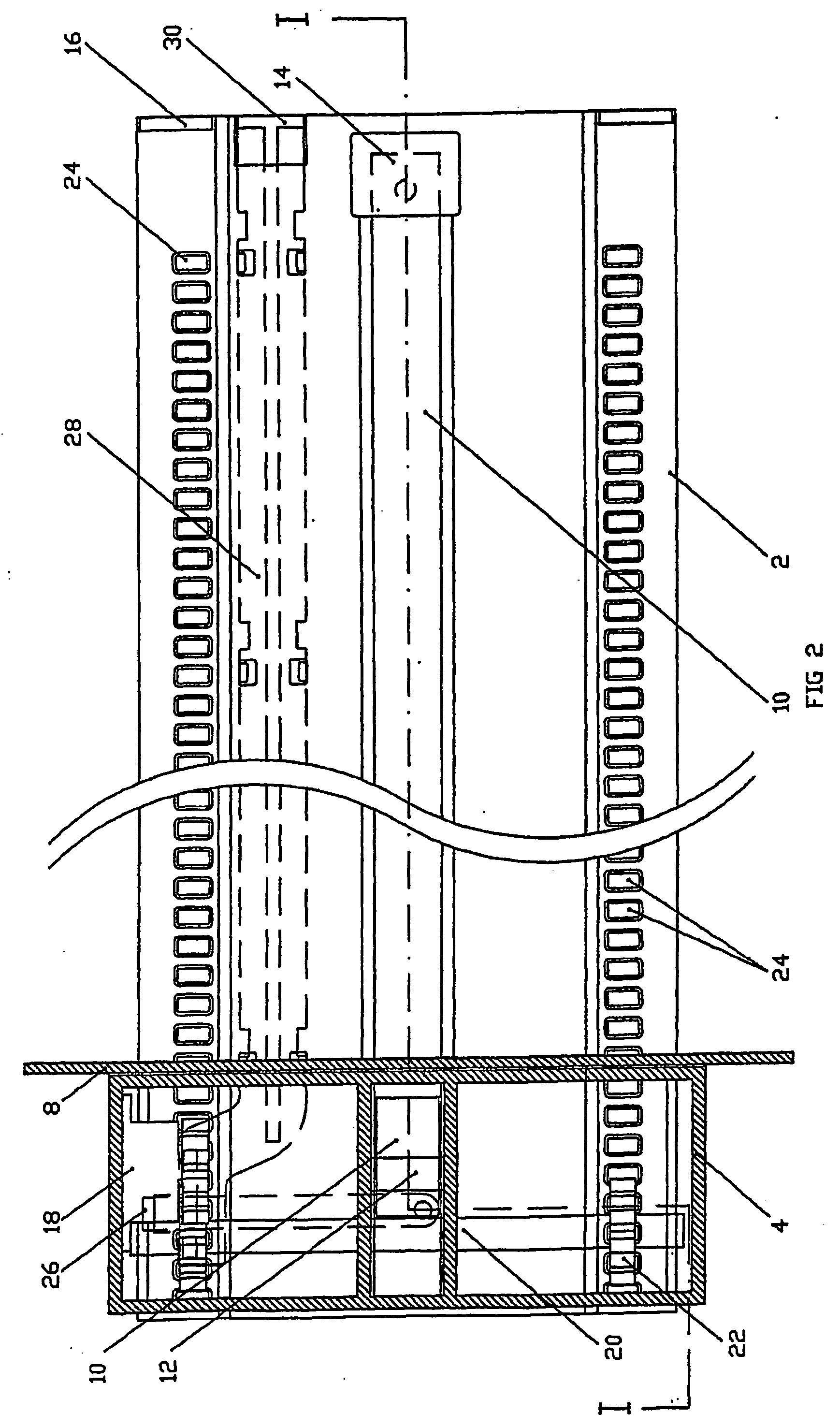
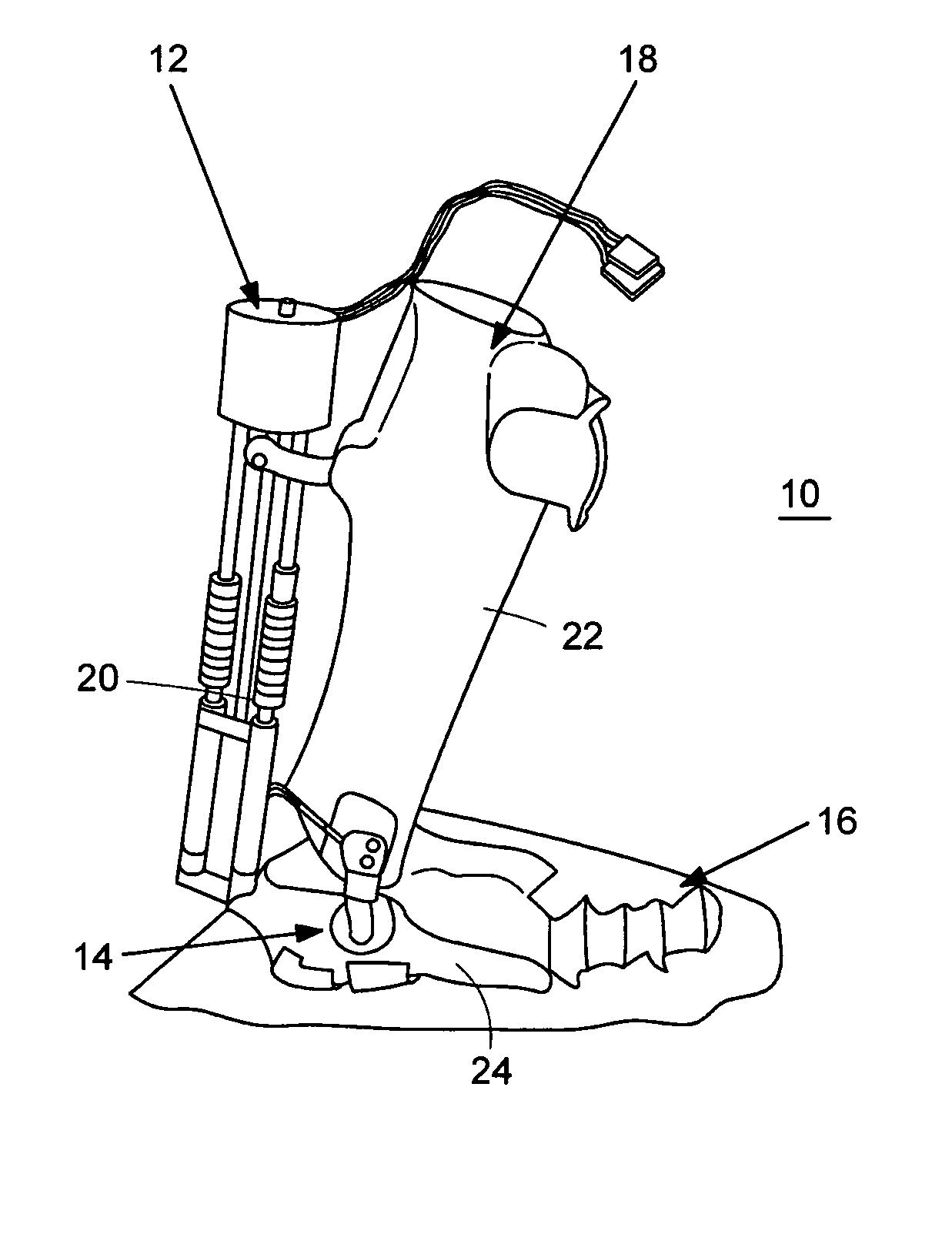
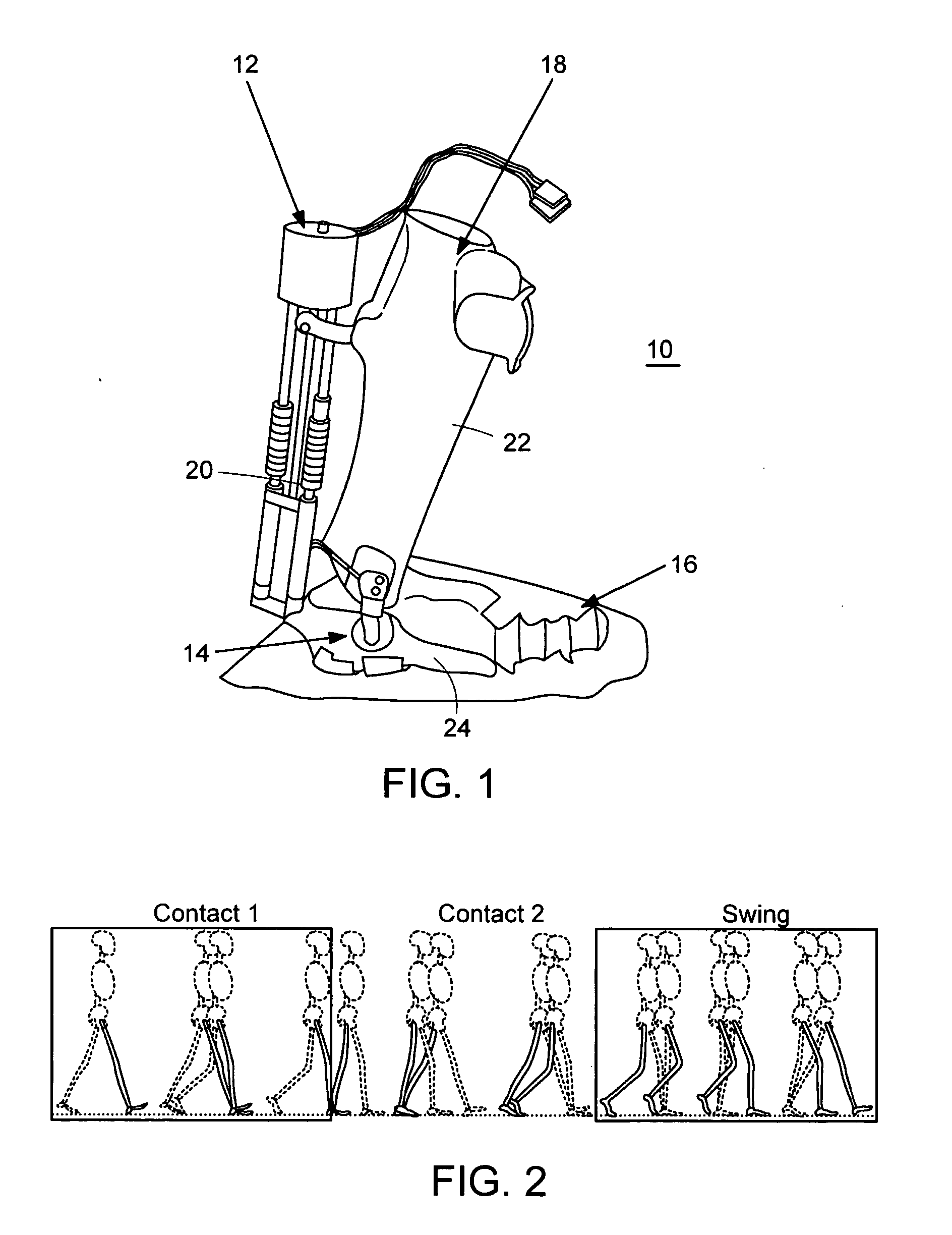
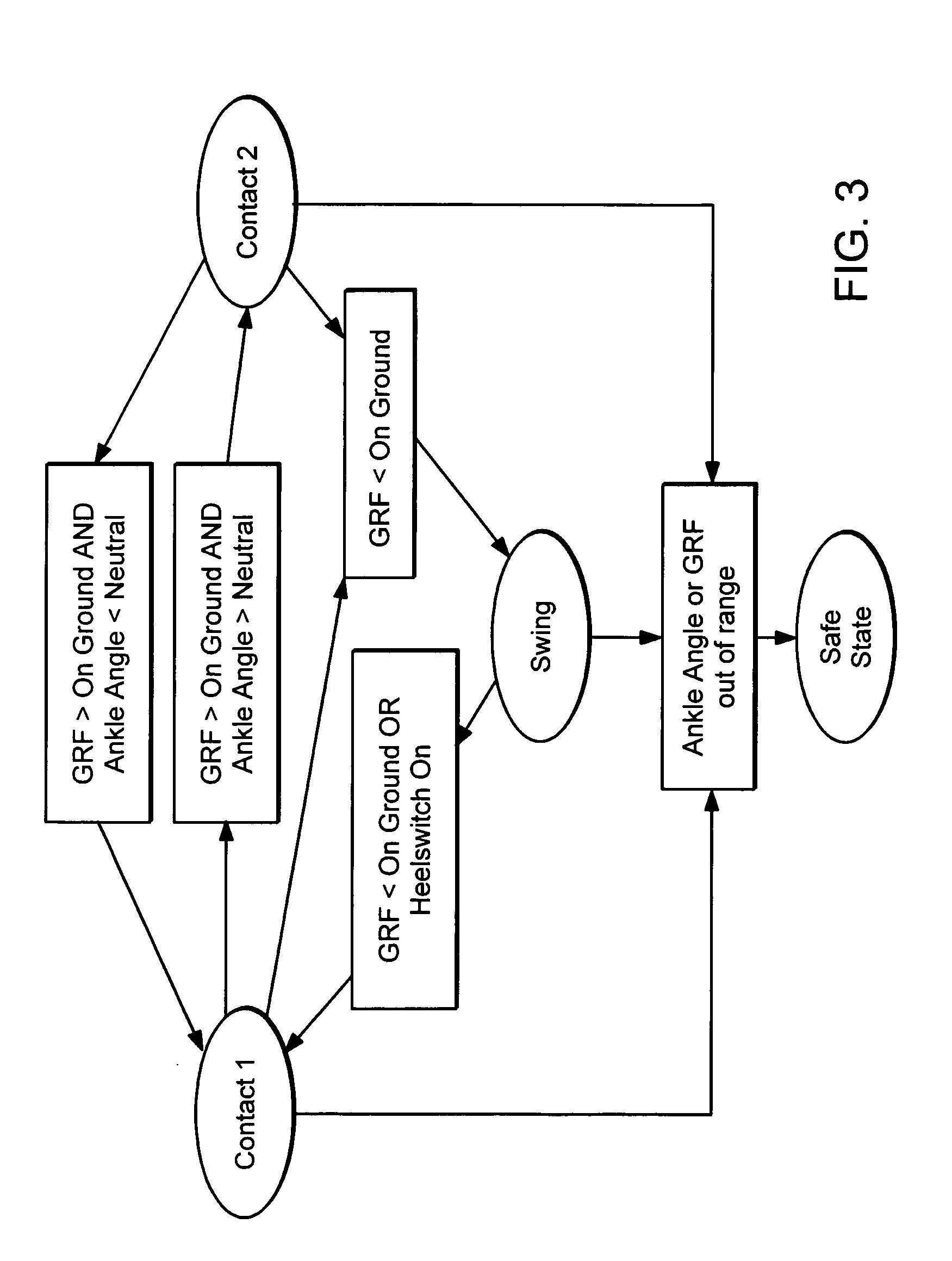
Active Ankle Foot Orthosis
ActiveUS20050070834A1Less kinematic differenceIncrease independenceWalking aidsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesWalking cyclePathology diagnosis
An Active Ankle Foot Orthosis (AAFO) is provided where the impedance of an orthotic joint is modulated throughout the walking cycle to treat ankle foot gait pathology, such as drop foot gait. During controlled plantar flexion, a biomimetic torsional spring control is applied where orthotic joint stiffness is actively adjusted to minimize forefoot collisions with the ground. Throughout late stance, joint impedance is minimized so as not to impede powered plantar flexion movements, and during the swing phase, a torsional spring-damper (PD) control lifts the foot to provide toe clearance. To assess the clinical effects of variable-impedance control, kinetic and kinematic gait data were collected on two drop foot participants wearing the AAFO. It has been found that actively adjusting joint impedance reduces the occurrence of slap foot, allows greater powered plantar flexion, and provides for less kinematic difference during swing when compared to normals.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
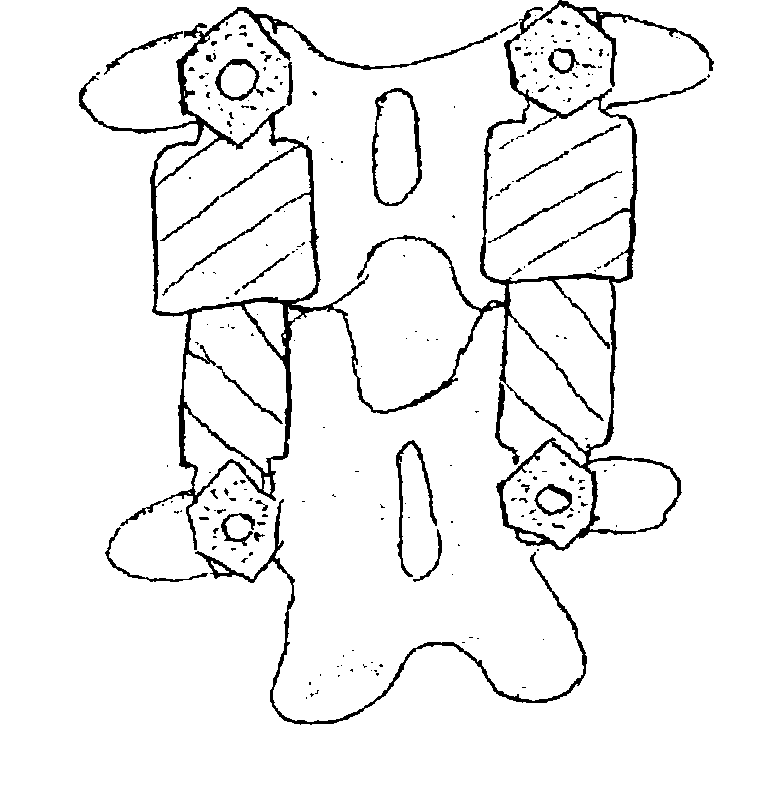
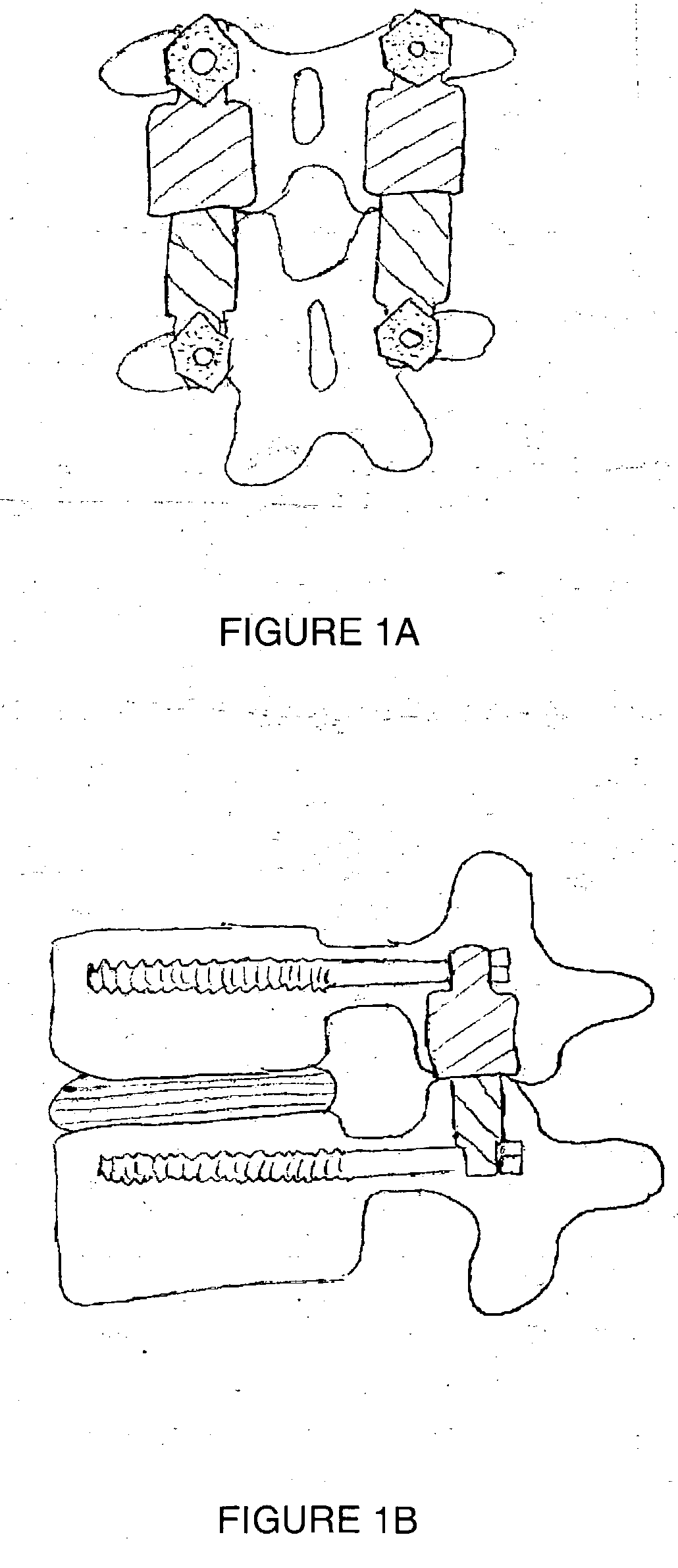
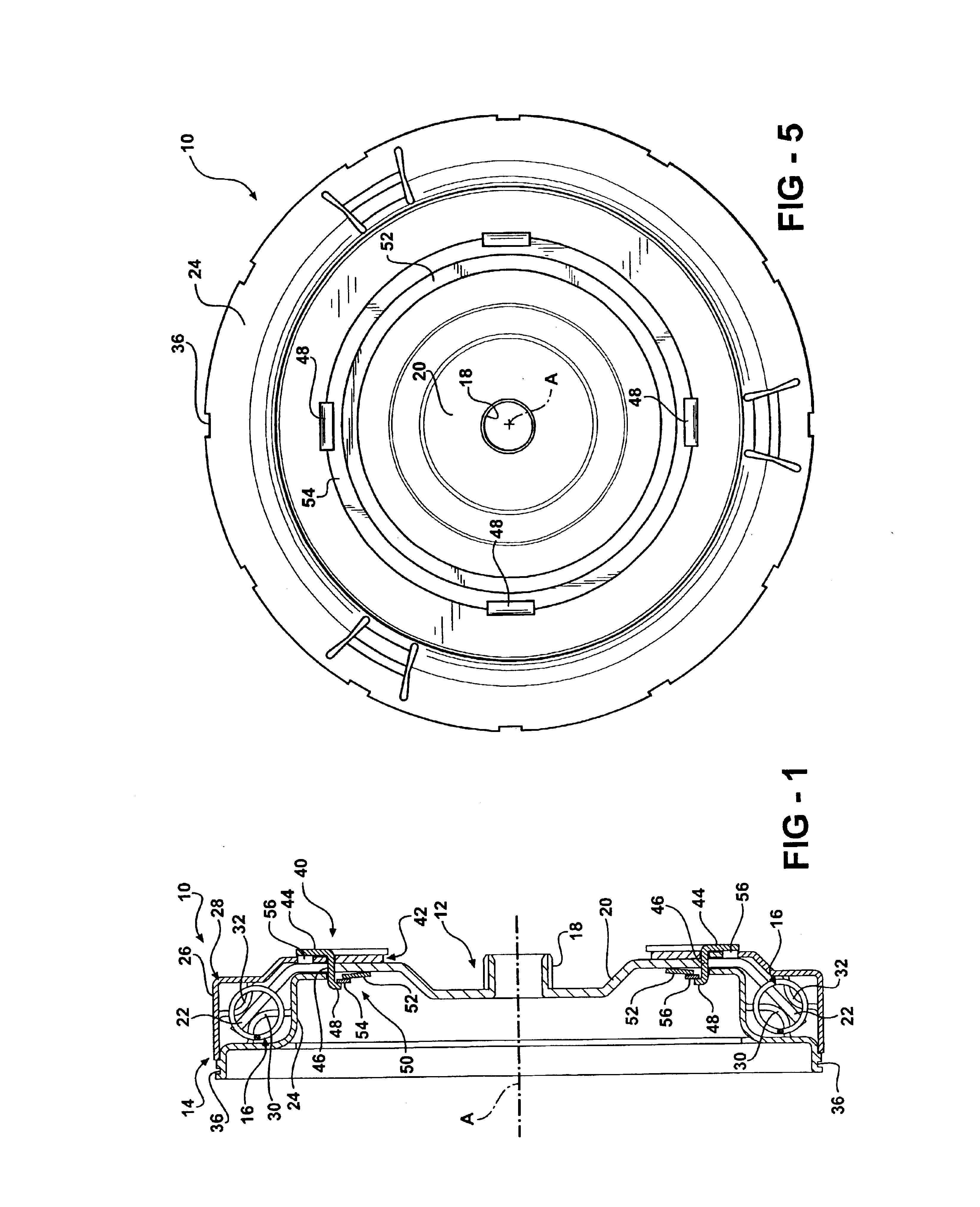
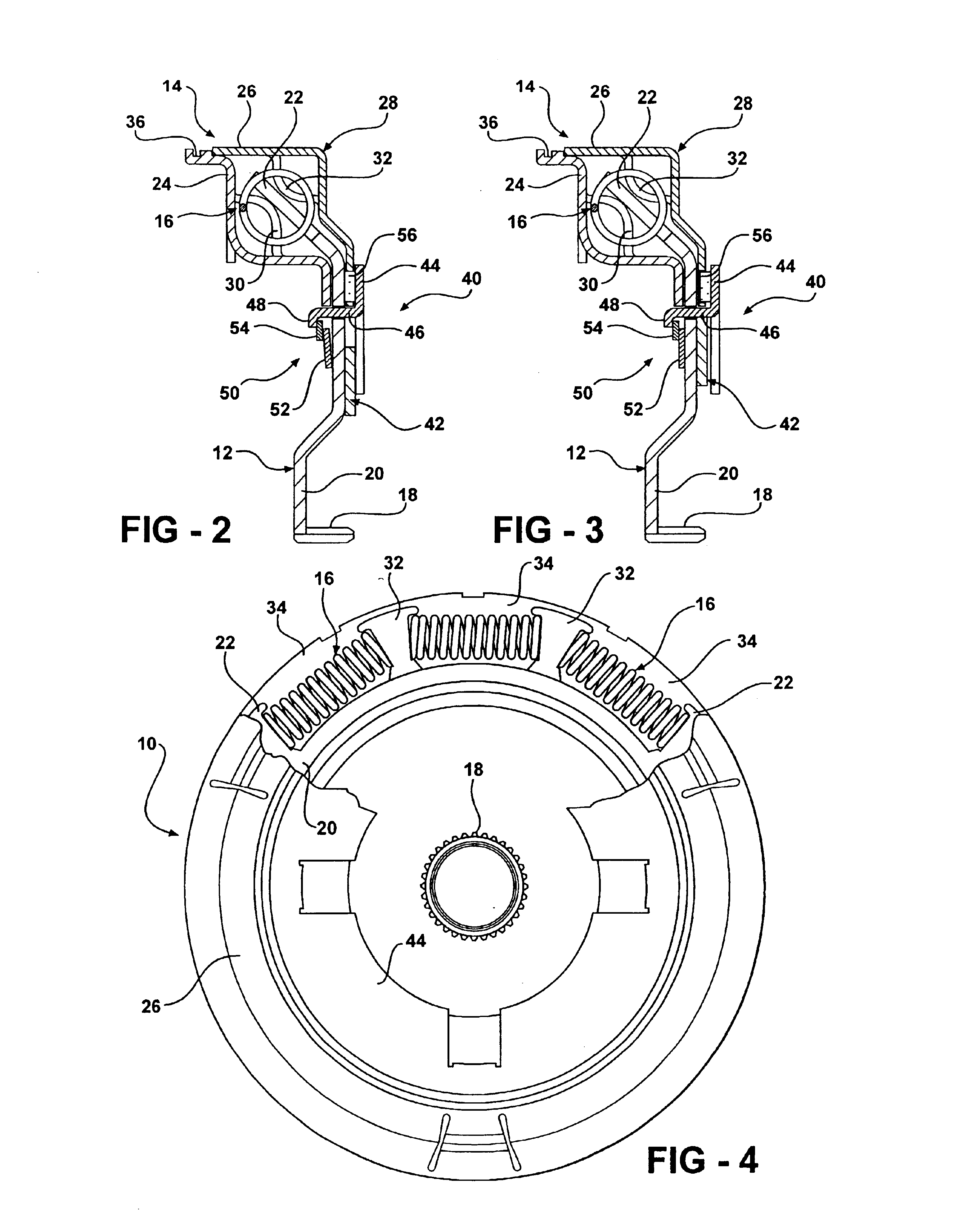
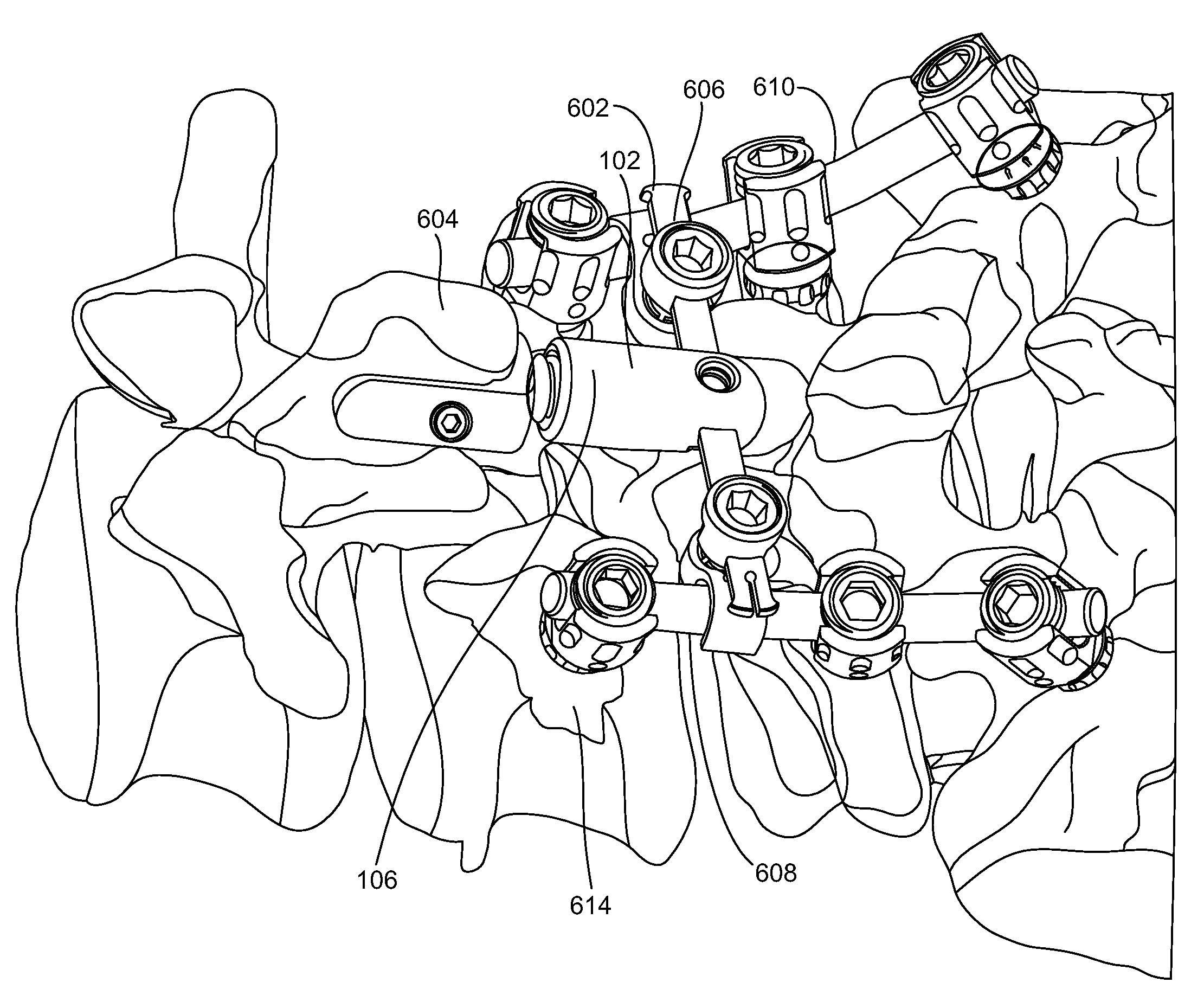
Vertebral shock absorbers
InactiveUS20050261682A1Extended range of motionFacilitate lateral applicationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsElastic componentLamina terminalis
A vertebral shock absorber in the form of an elongated compressible member having two ends, one fastened to an upper vertebra, and the other fastened to a lower vertebra. The elongated member may be fastened using pedicle screws or by way of ball-and-socket joints for enhanced range of motion. In the preferred embodiment, the elongated compressible member is constructed using telescoping sleeves to create a cavity wherein there is disposed a compressible, resilient component such as a spring, elastomeric material, liquid, gel, hydrogel, or other suitable substance. The shock absorber may be combined with an intradiscal component and / or one or more plates that extends at least partially onto a vertebral endplate to facilitate lateral application.
Owner:FERREE BRET A
Inertia valve shock absorber
InactiveUS7128192B2Reducing and eliminating delayBlock fluid flowSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionEngineeringTimer
A damper including a valve movable between an open position and a closed position to selectively alter the compression damping rate of the shock absorber. The valve may include a self-centering feature that operates to keep the valve body centered about the valve shaft. The damper may also include a timer feature, which retains the valve in an open position for a predetermined period of time after it is initially opened.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
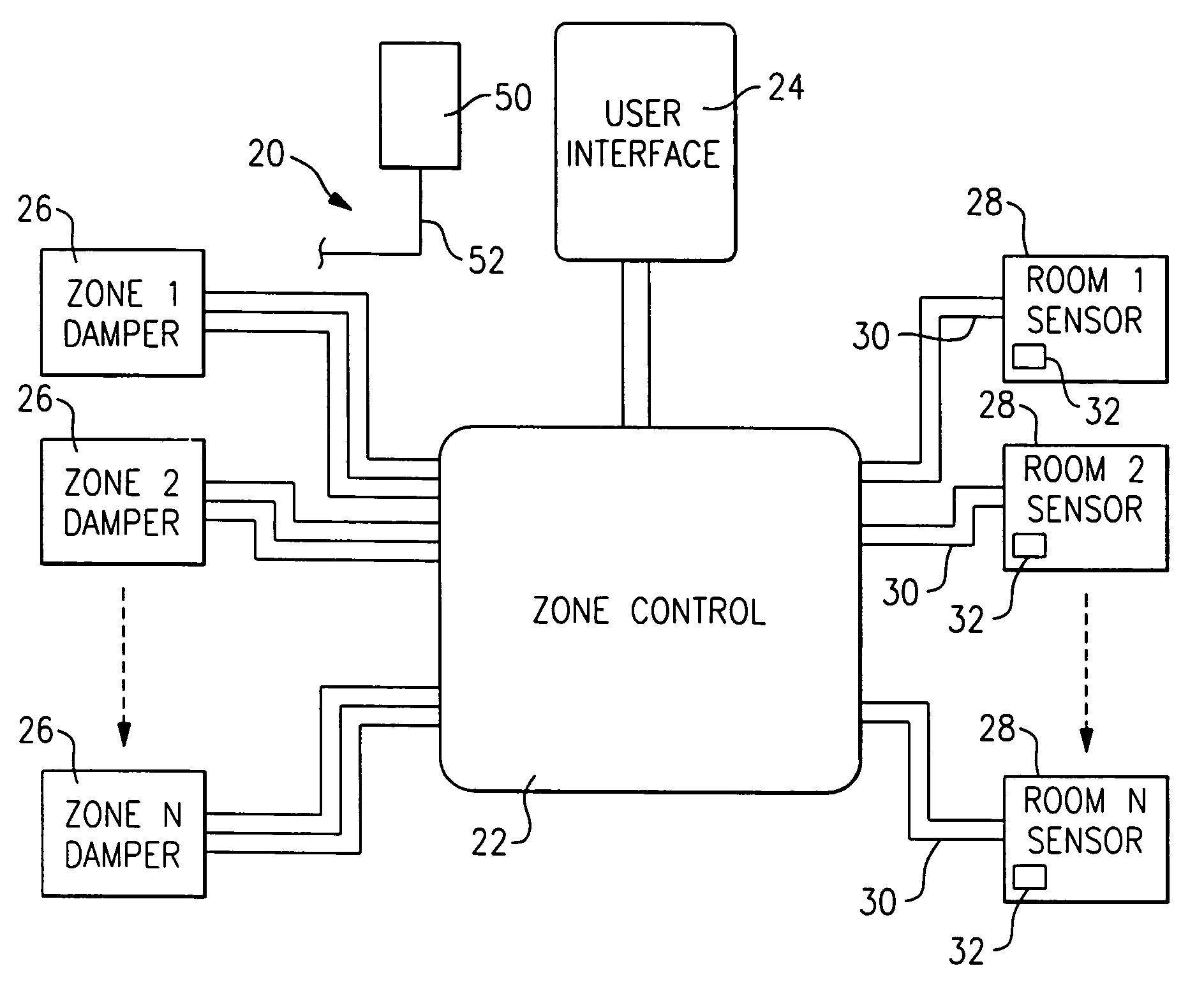
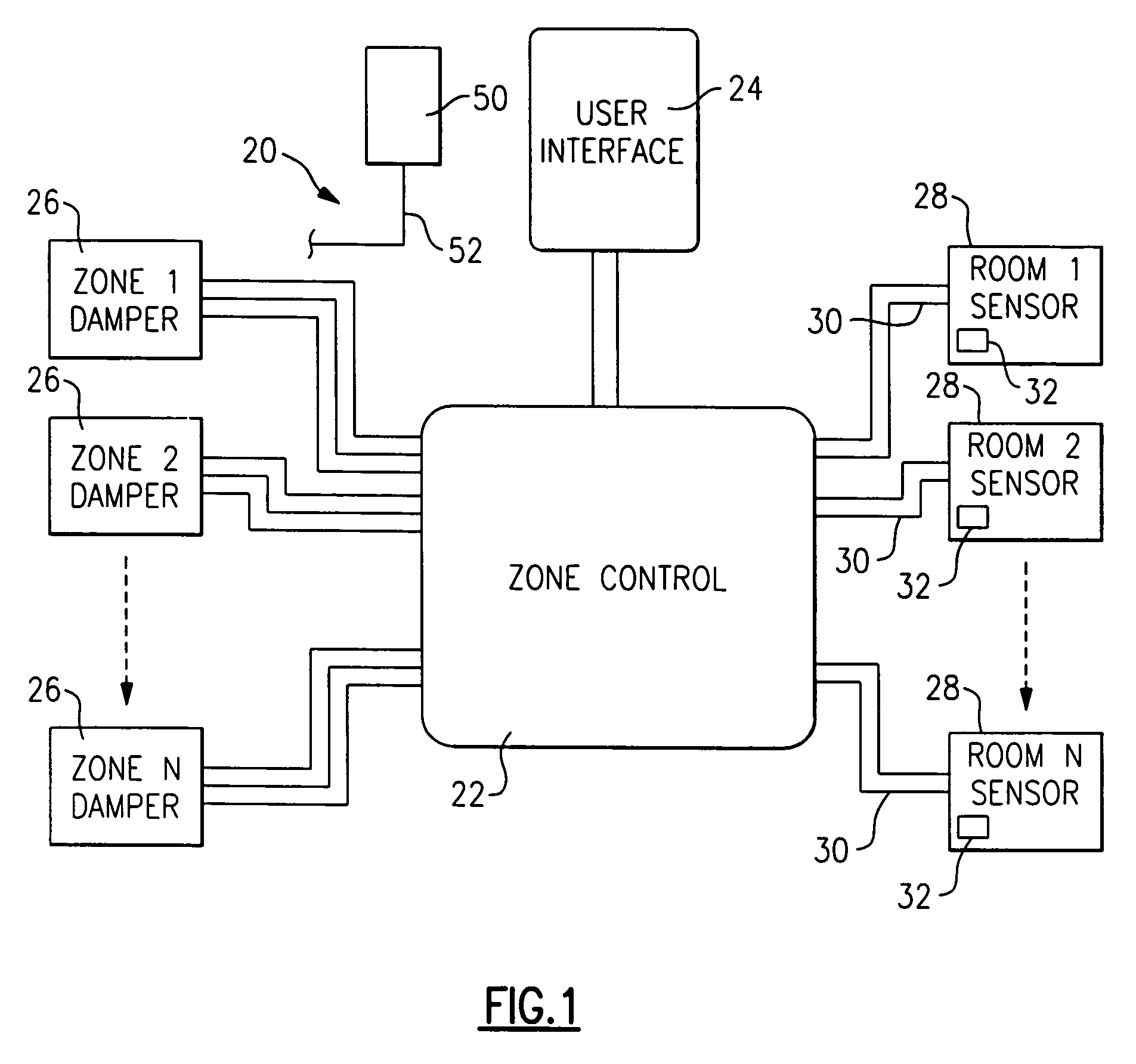
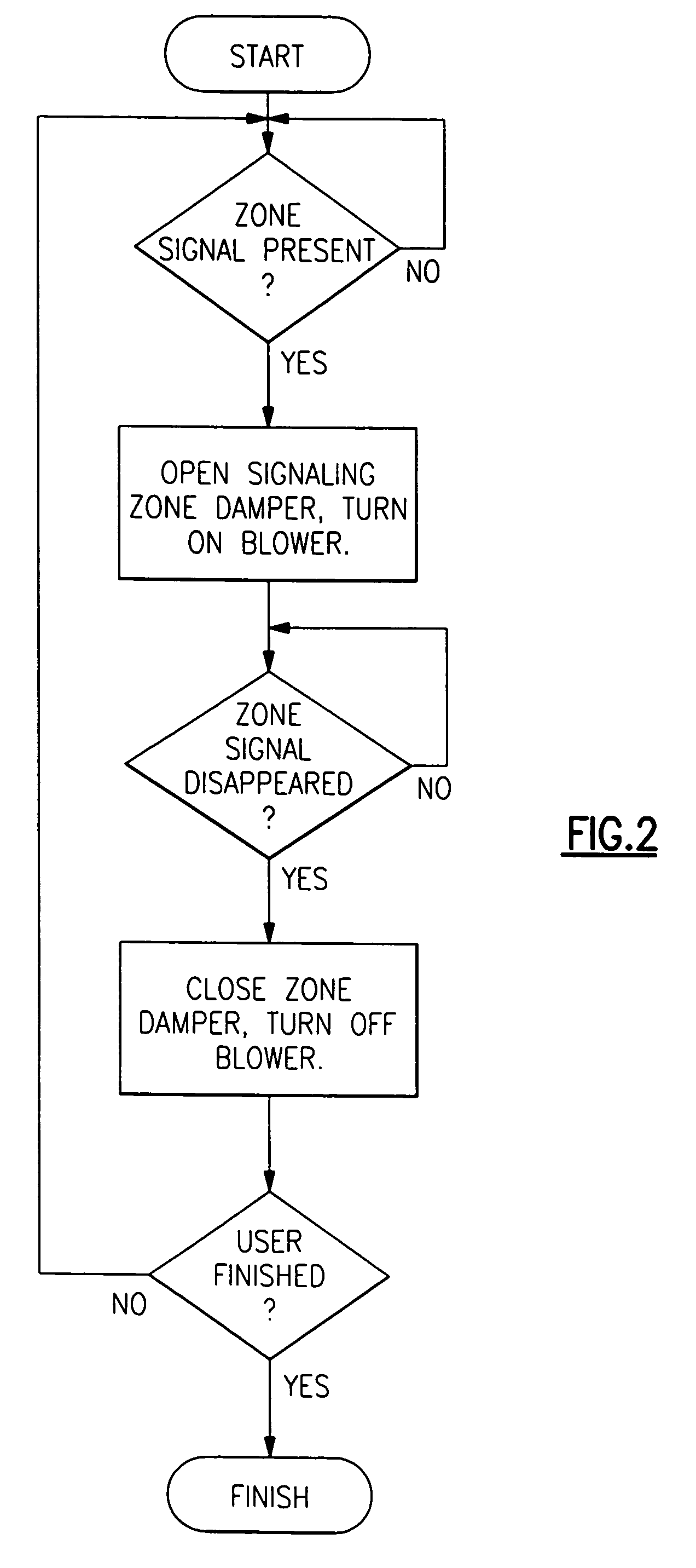
Method of verifying proper installation of a zoned HVAC system
A method and control is provided wherein the sensors in a plurality of zones are properly associated with the dampers associated for each of the zones after installation. A technician goes to each zone and sends a signal from the sensor, and the control then makes a change at the associated damper. The technician can then ensure the two are properly associated within the control.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Endoscopic ultrasonic surgical aspirator for use in fluid filled cavities
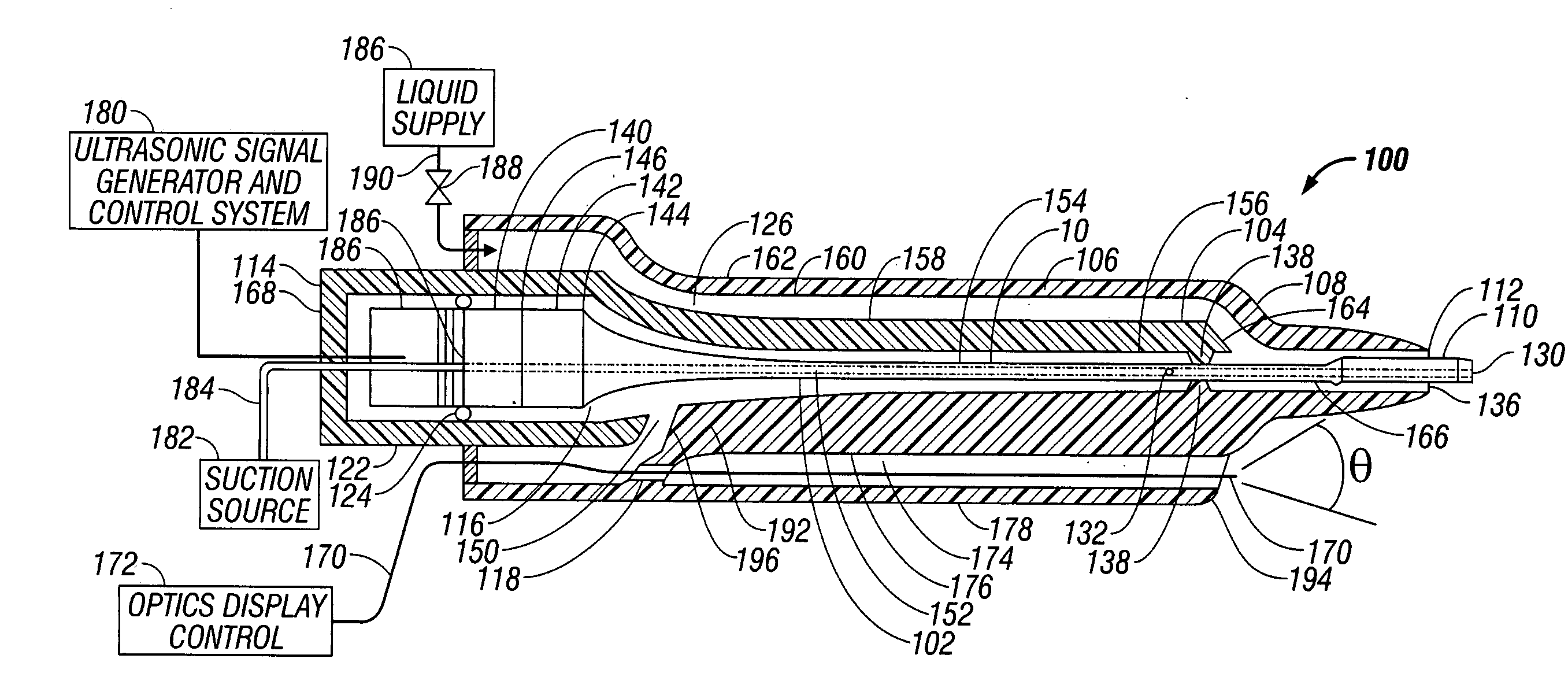
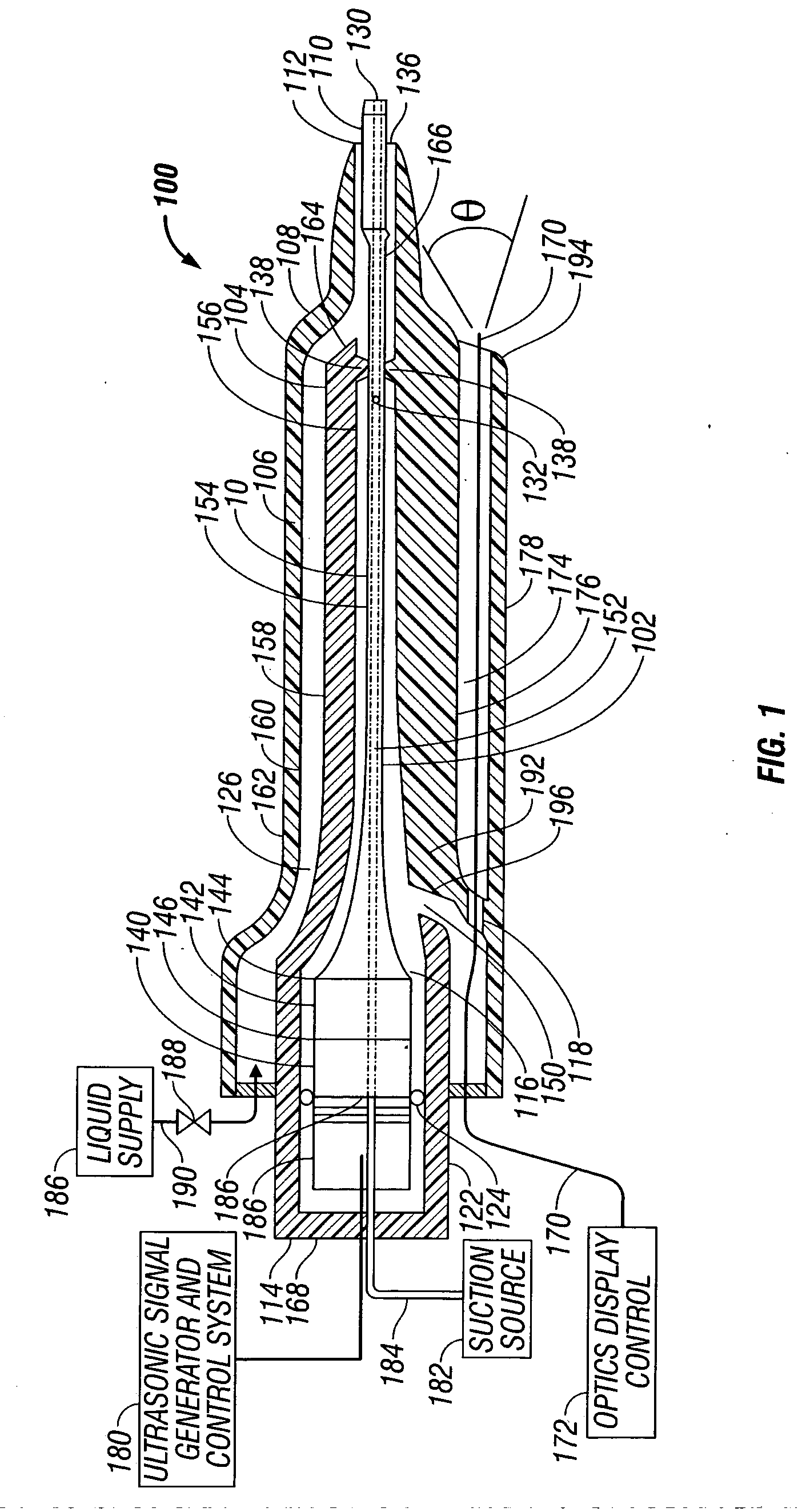
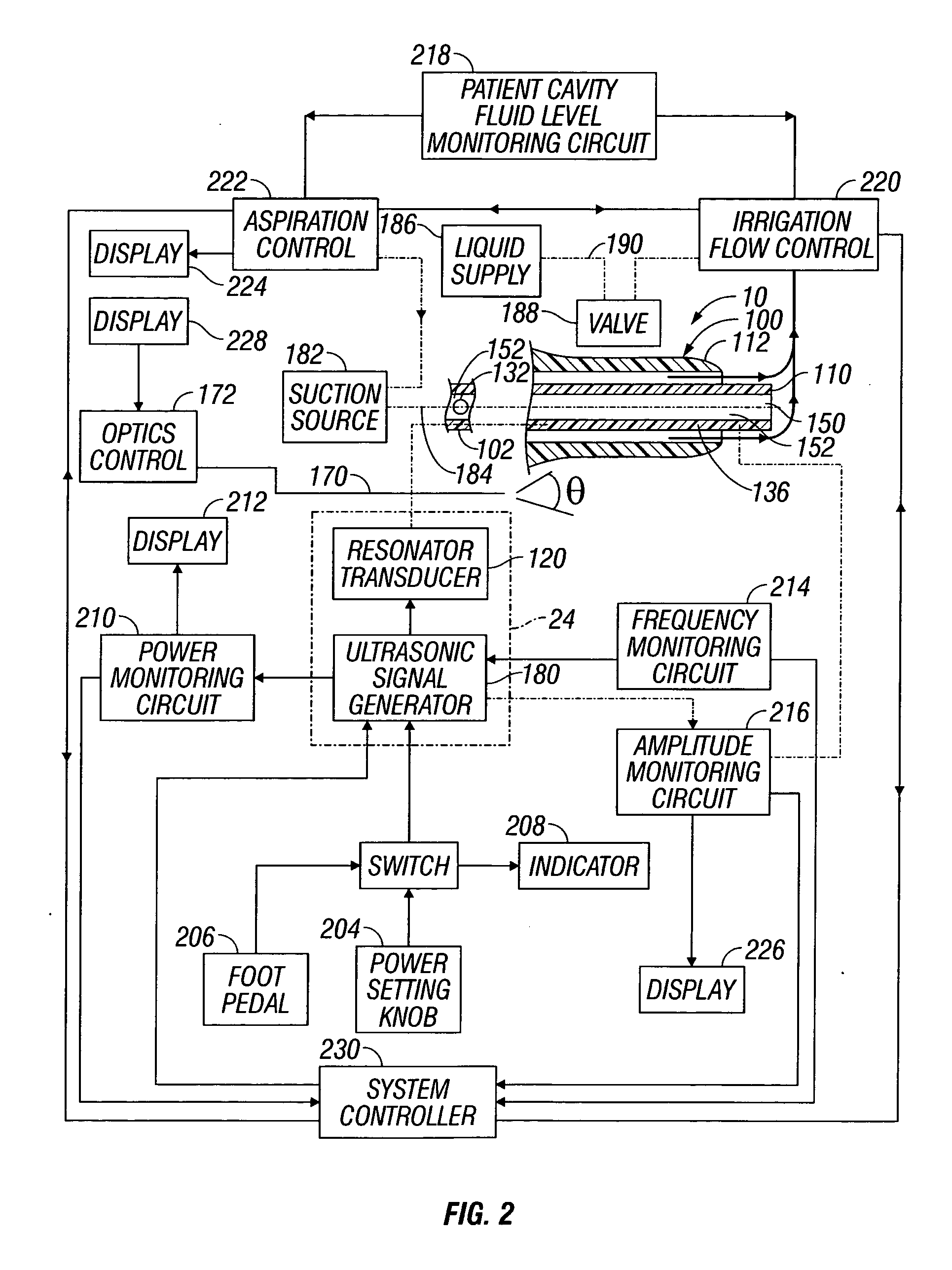
ActiveUS20070162050A1Minimize damping vibrationVibration minimizationDiagnosticsSurgeryControl powerMedicine
An ultrasonic horn assembly is configured so that irrigating fluid can be supplied only to a vibrating tip portion of the ultrasonic horn and so that suction aspiration can occur through a portion of the ultrasonic horn not in contact with the irrigating fluid. Controllers supplying irrigation fluid during a surgical procedure and controlling suction aspiration via monitoring of fluid level in the patient cavity are operatively coupled one to another to coordinate control of the fluid level in the patient cavity. Circuitry controlling power, frequency and amplitude of the tip of the ultrasonic horn occurring as a result of operation of a source of ultrasonic signal generating power controls either or both the supply of irrigation fluid and the suction aspiration so as to minimize damping of vibration of the tip of the ultrasonic horn. An optical viewing element is provided to view the tip of the ultrasonic horn.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI IRELAND
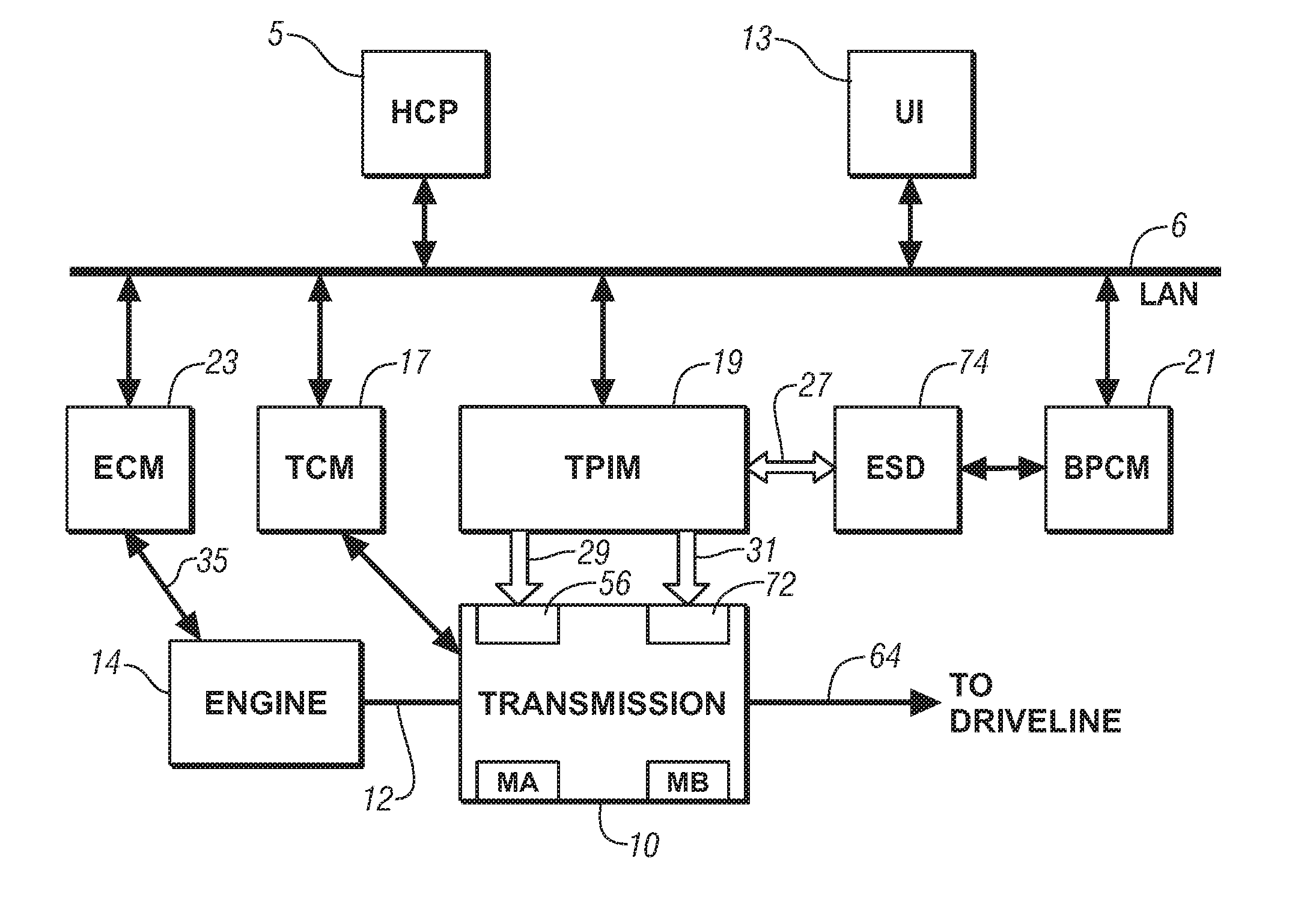
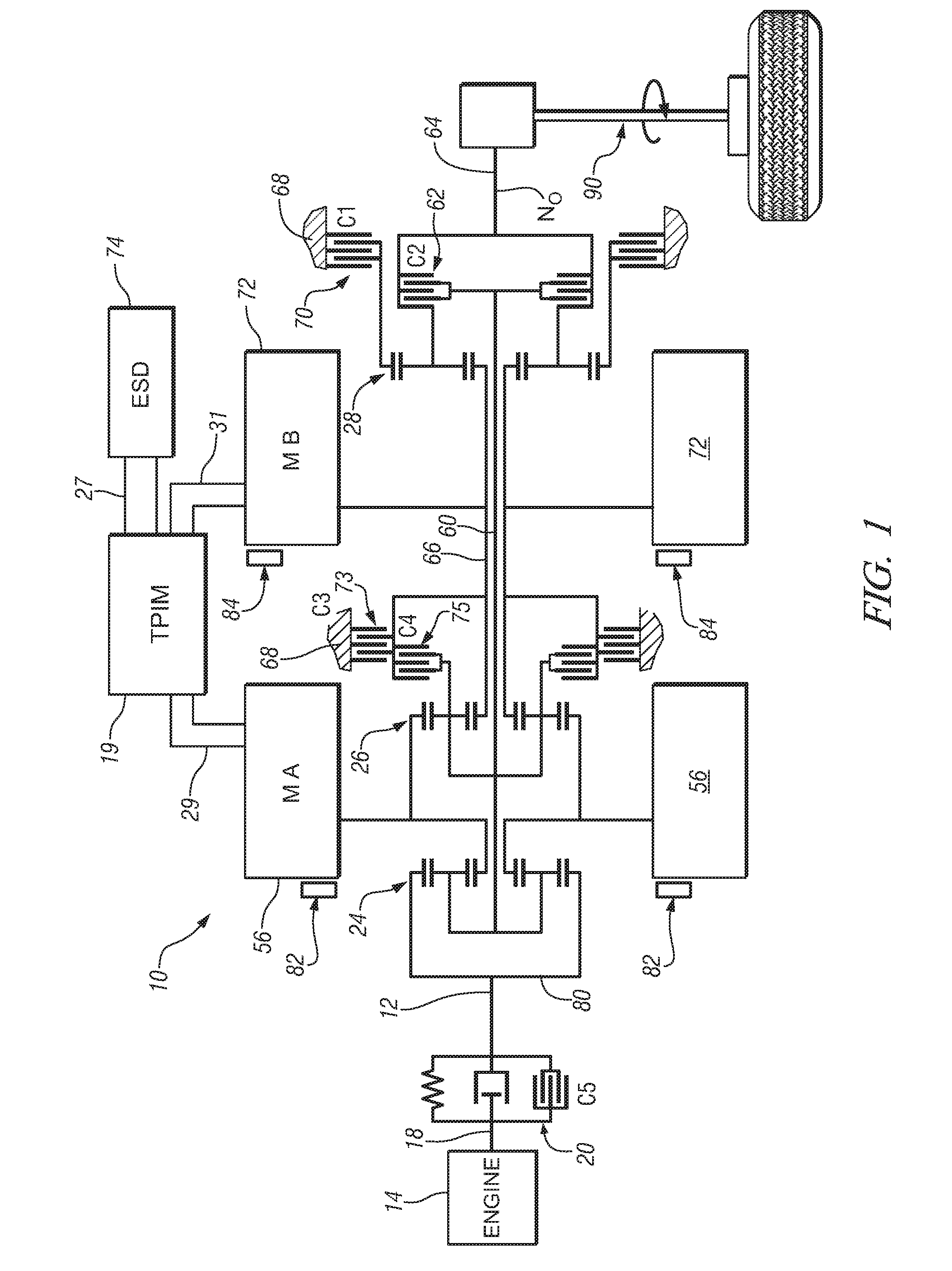
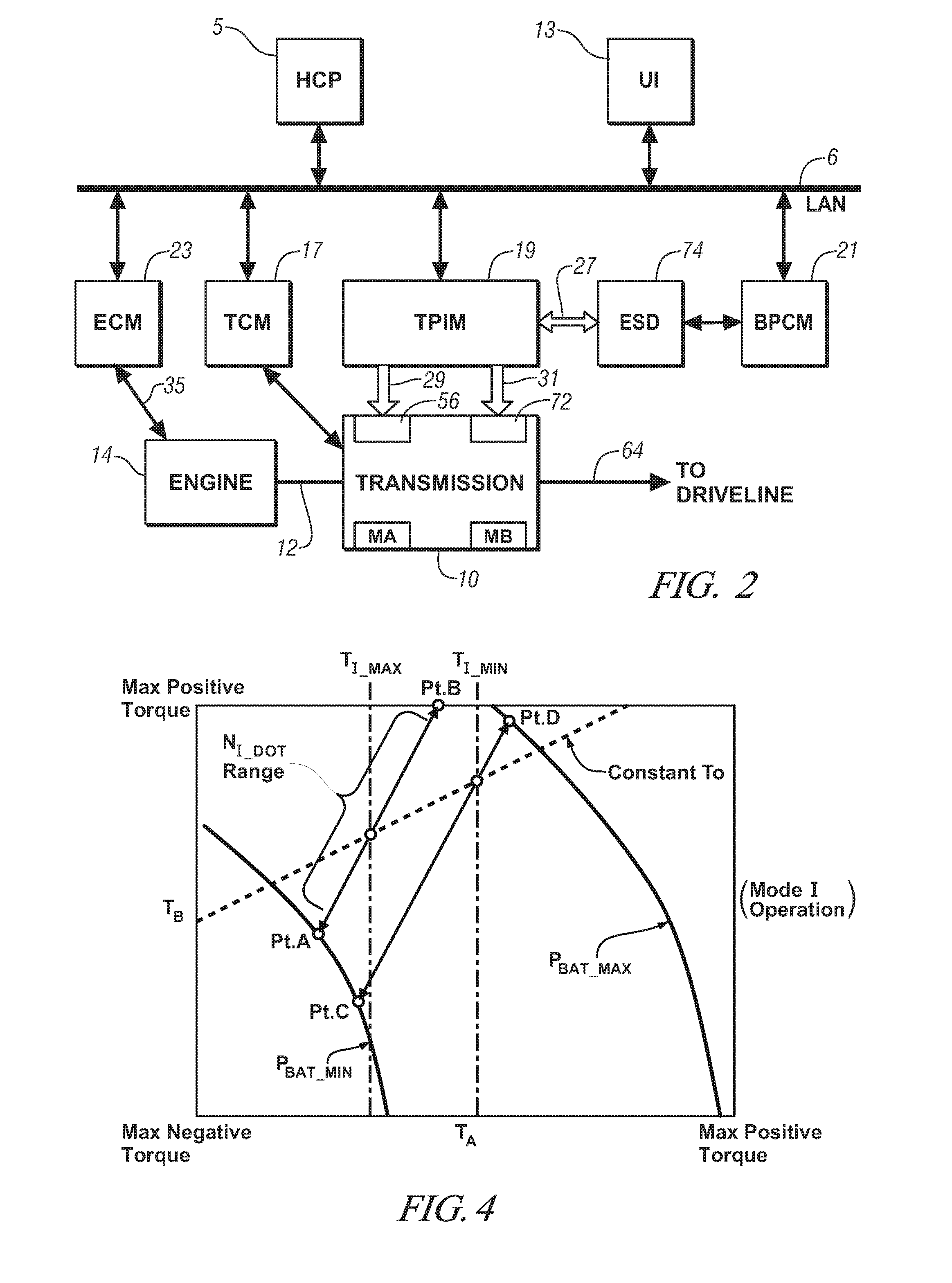
Method and apparatus to control engine stop for a hybrid powertrain system
ActiveUS20080275625A1Accurately determineAccurate pressureHybrid vehiclesAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectric machineSnubber
A control scheme is provided for stopping an internal combustion engine of a hybrid powertrain during ongoing vehicle operation. The method, executed as program code in an article of manufacture comprises the following steps in the sequence set forth. First, engine operation is controlled to stop firing the engine. A damper clutch is controlled to lock rotation of the engine and the electro-mechanical transmission. Torque outputs from the first and second electrical machines are then selectively controlled to reduce engine speed. Torque outputs from the first and second electrical machines are then selectively controlled to stop rotation of the engine substantially near a predetermined crank position.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
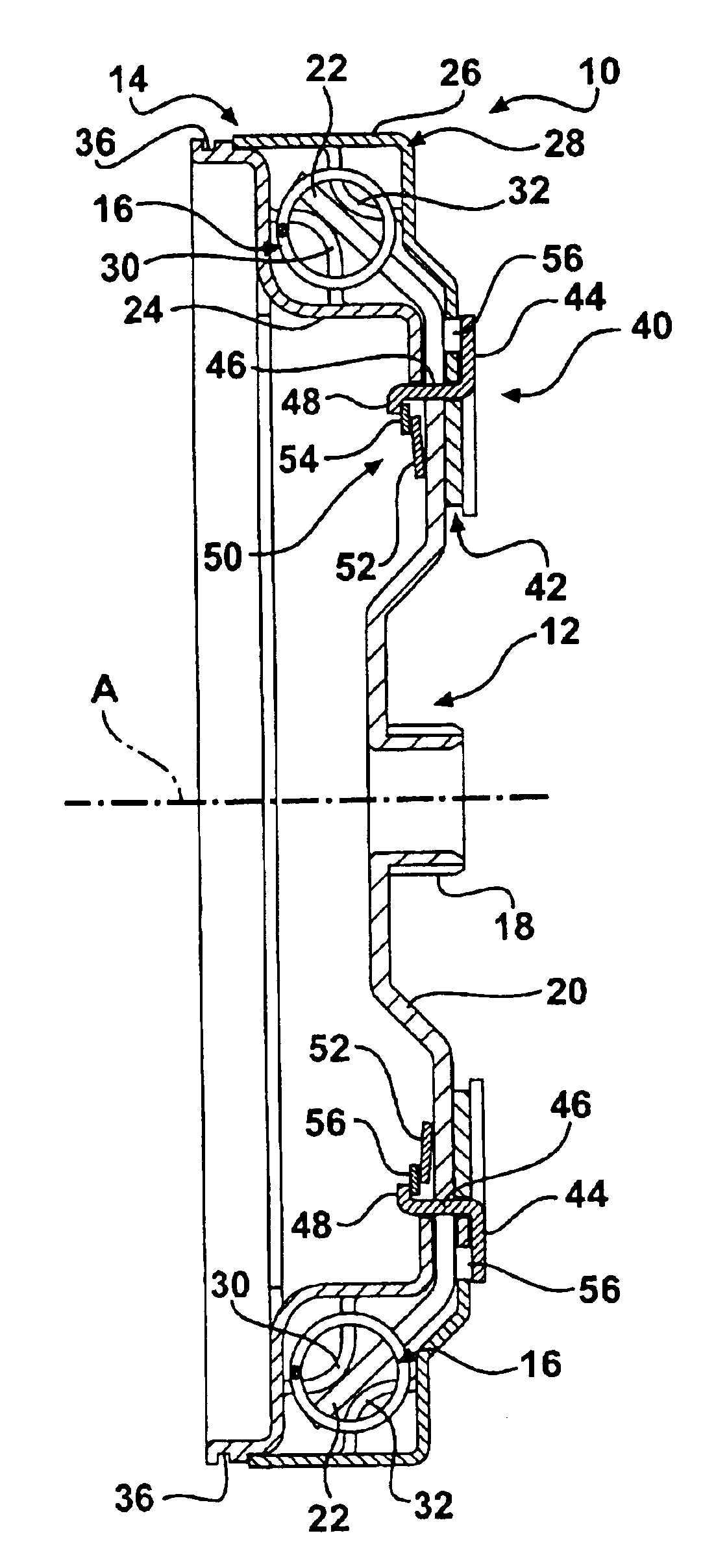
Torsional damper having variable bypass clutch with centrifugal release mechanism
InactiveUS6854580B2Restraint torsionReduce torqueYielding couplingRotary clutchesCentrifugal forceControl theory
A torsional damper (10) rotatably supported for translating torque between a prime mover and the input of a transmission including a torque input member (12) that is operatively connected for rotation with the power take-off of a prime mover, an output member (14) operatively connected for rotation with the input to a transmission and a plurality of damping elements (16) interposed between the input member and the output member. The damping members (16) act to translate torque between the input and output members and to dampen torsional forces generated between the prime mover and the transmission. A bypass clutch (40) acts to translate torque directly between the input and output members thereby providing a path for partial torque translation that bypasses the damping elements at low rotational speeds of the input and output members. In addition, the torsional damper (10) includes a clutch release mechanism (42) that is responsive to centrifugal forces acting on the torsional damper to disengage the bypass clutch (40) to reduce the torque translated directly between the input and output members at high rotational speeds.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
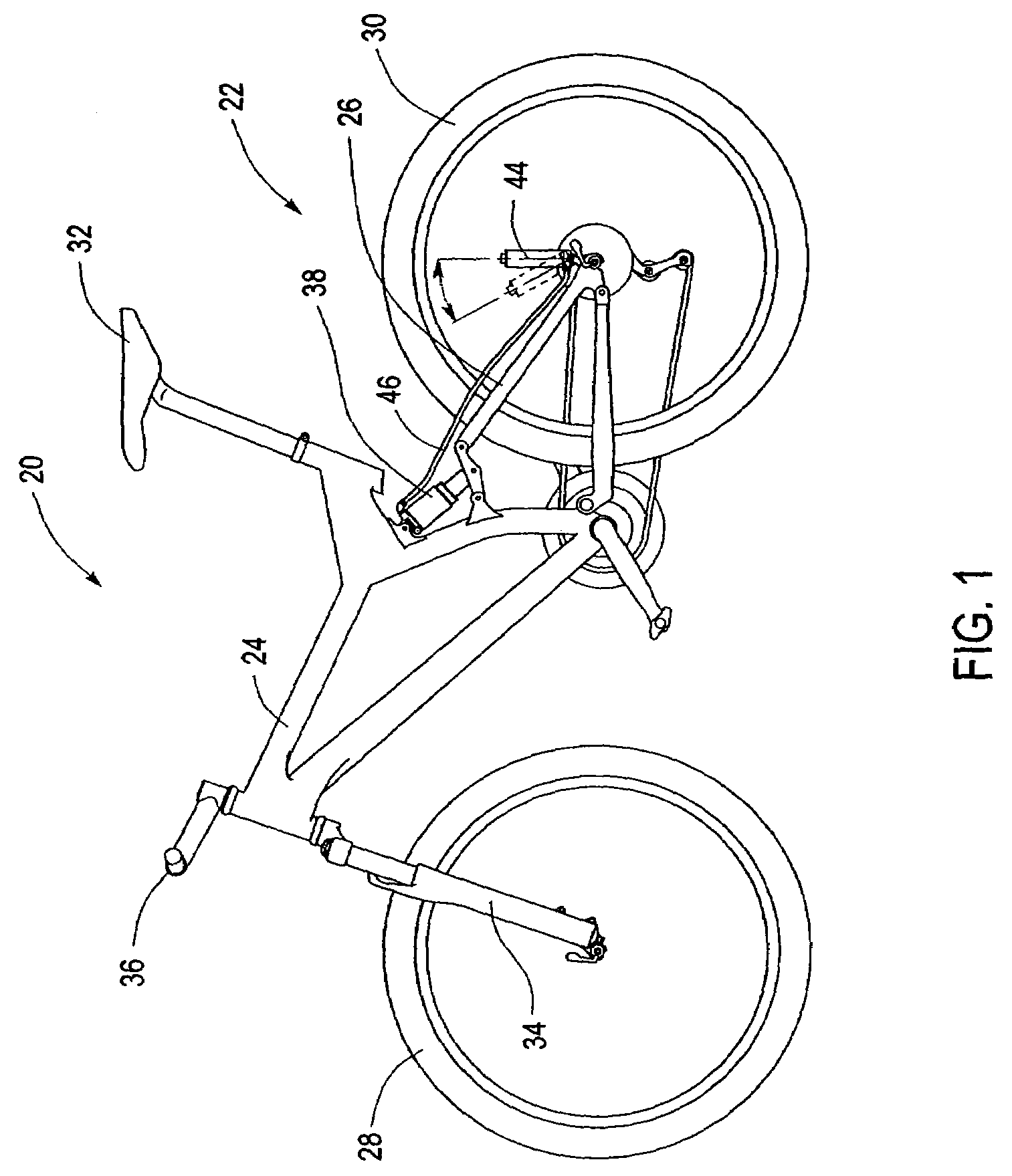
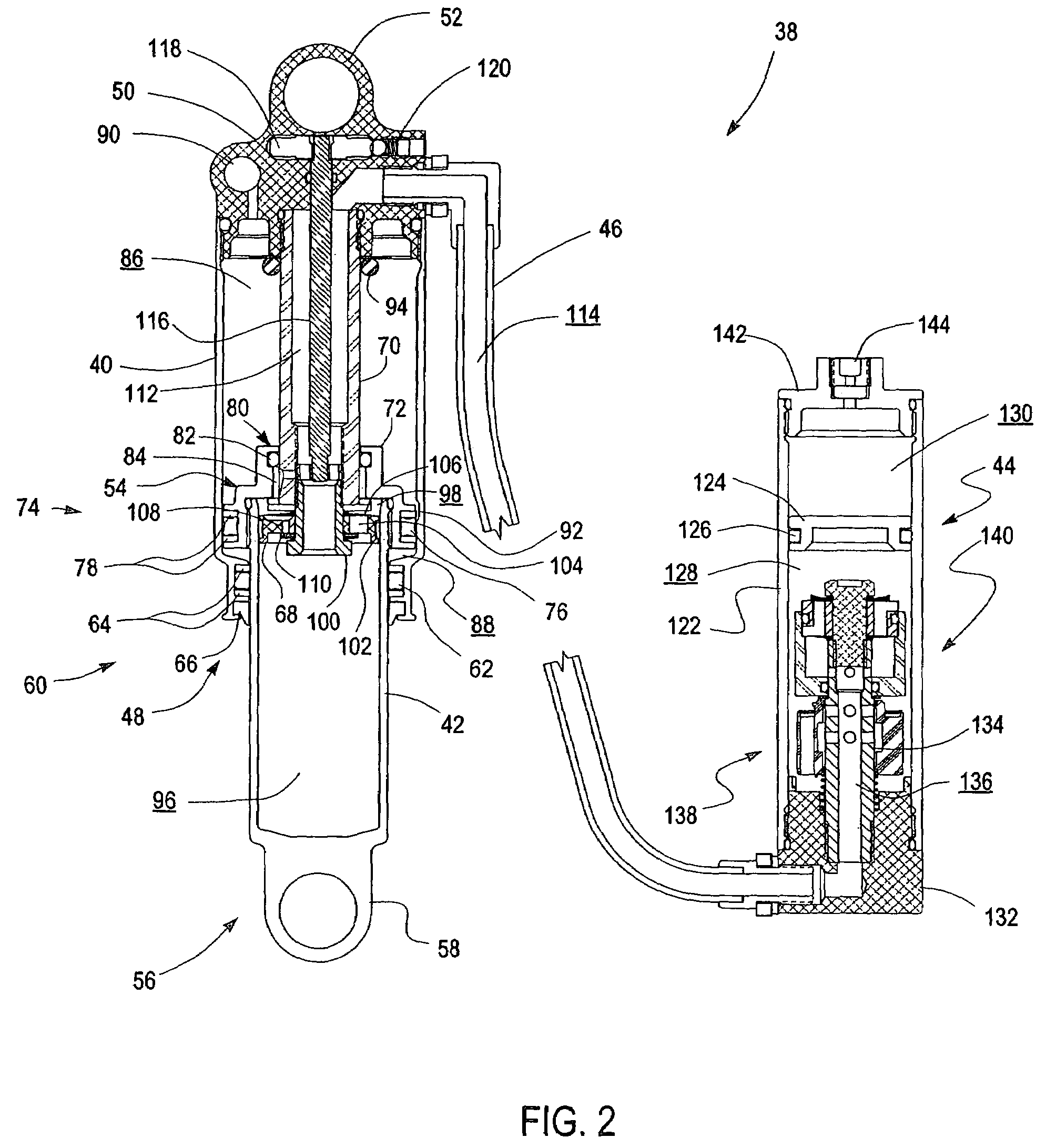
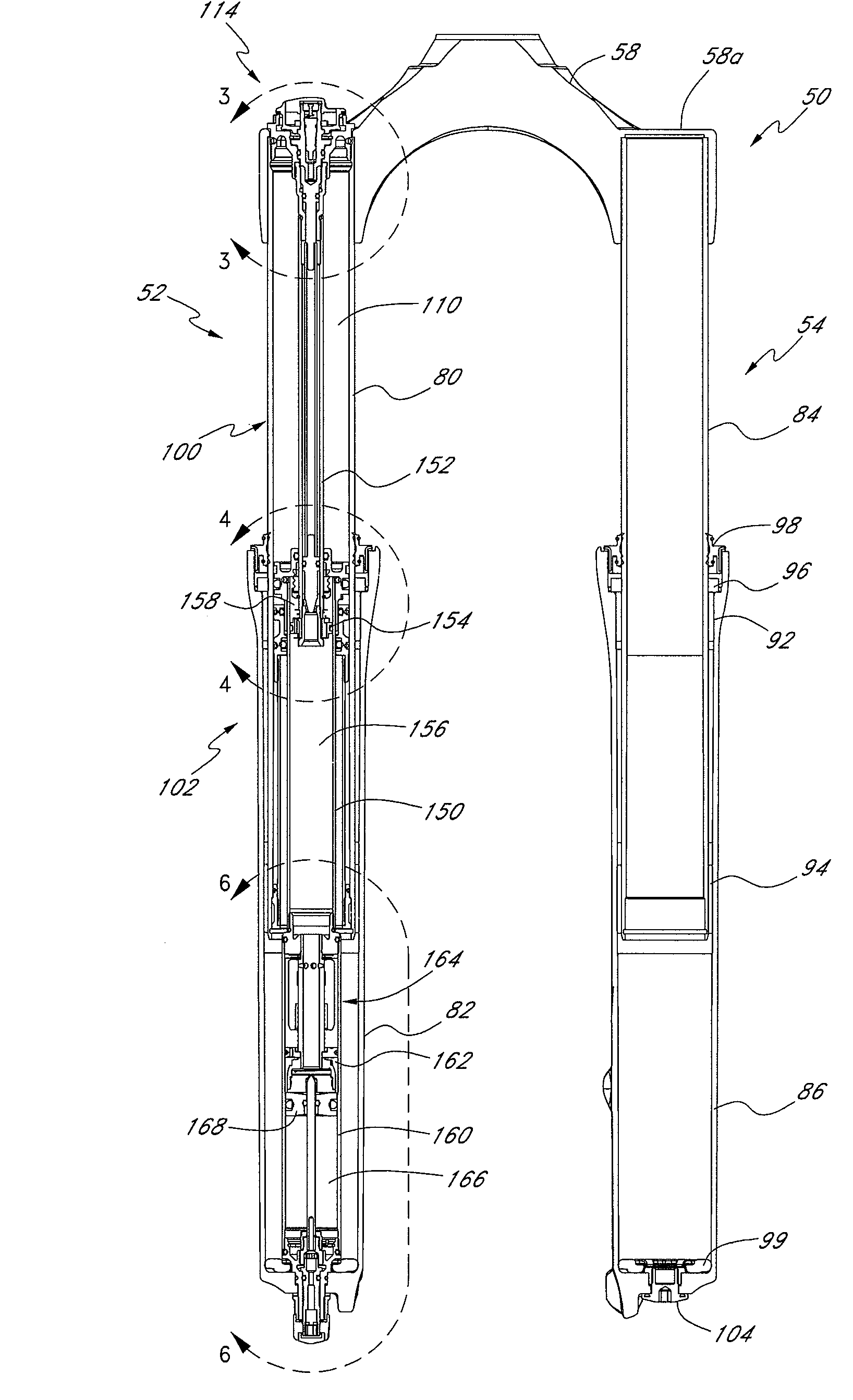
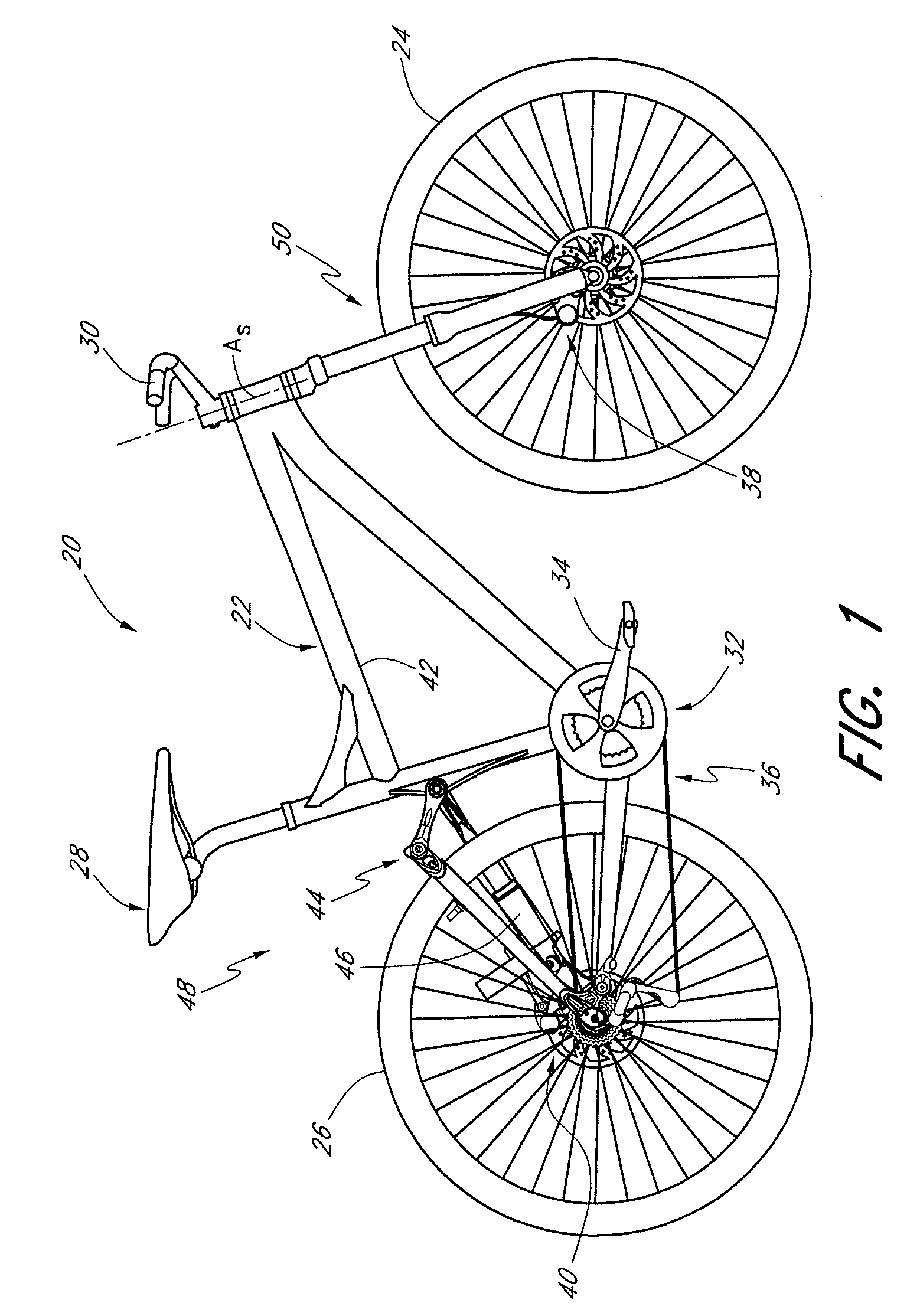
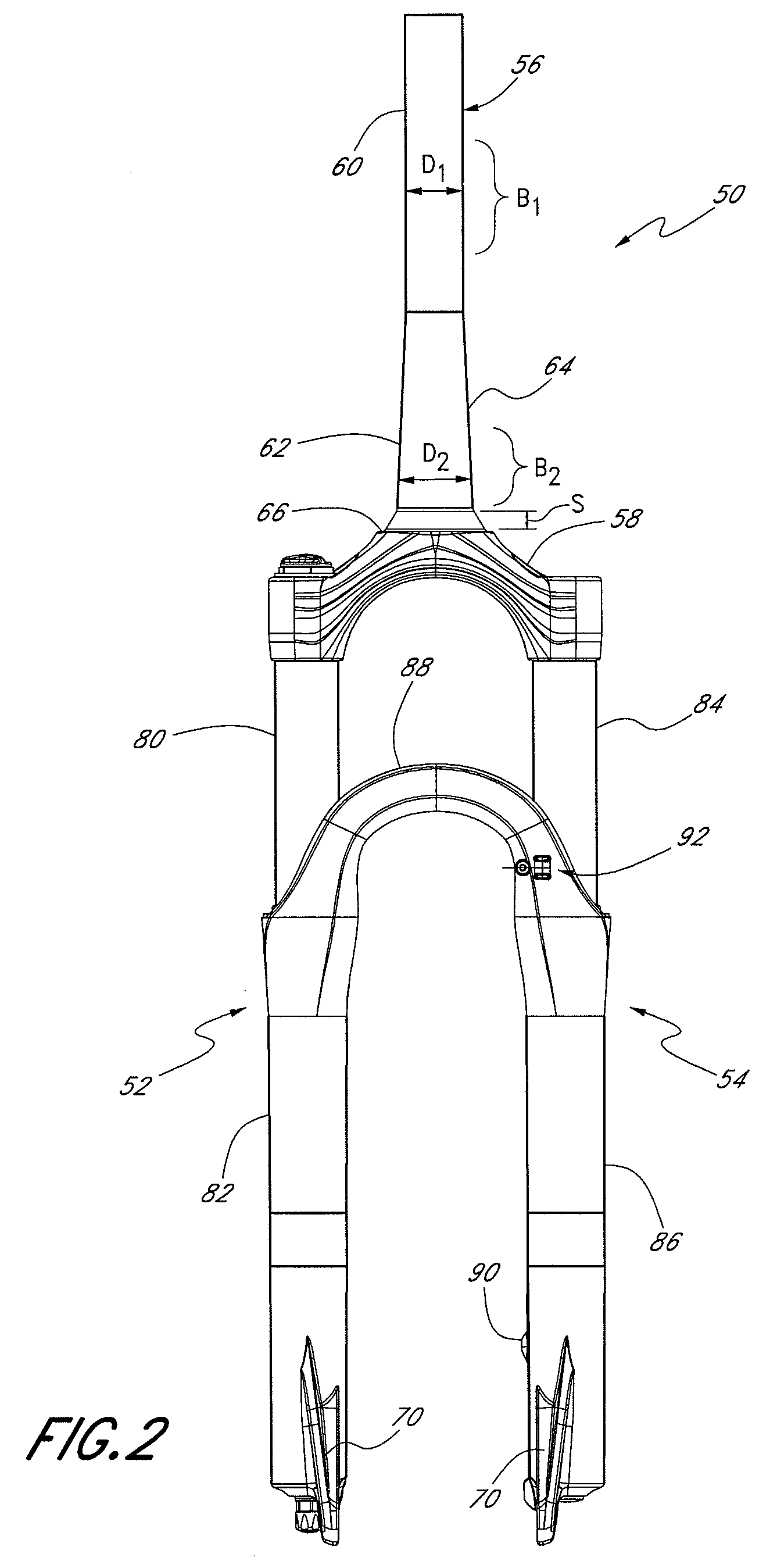
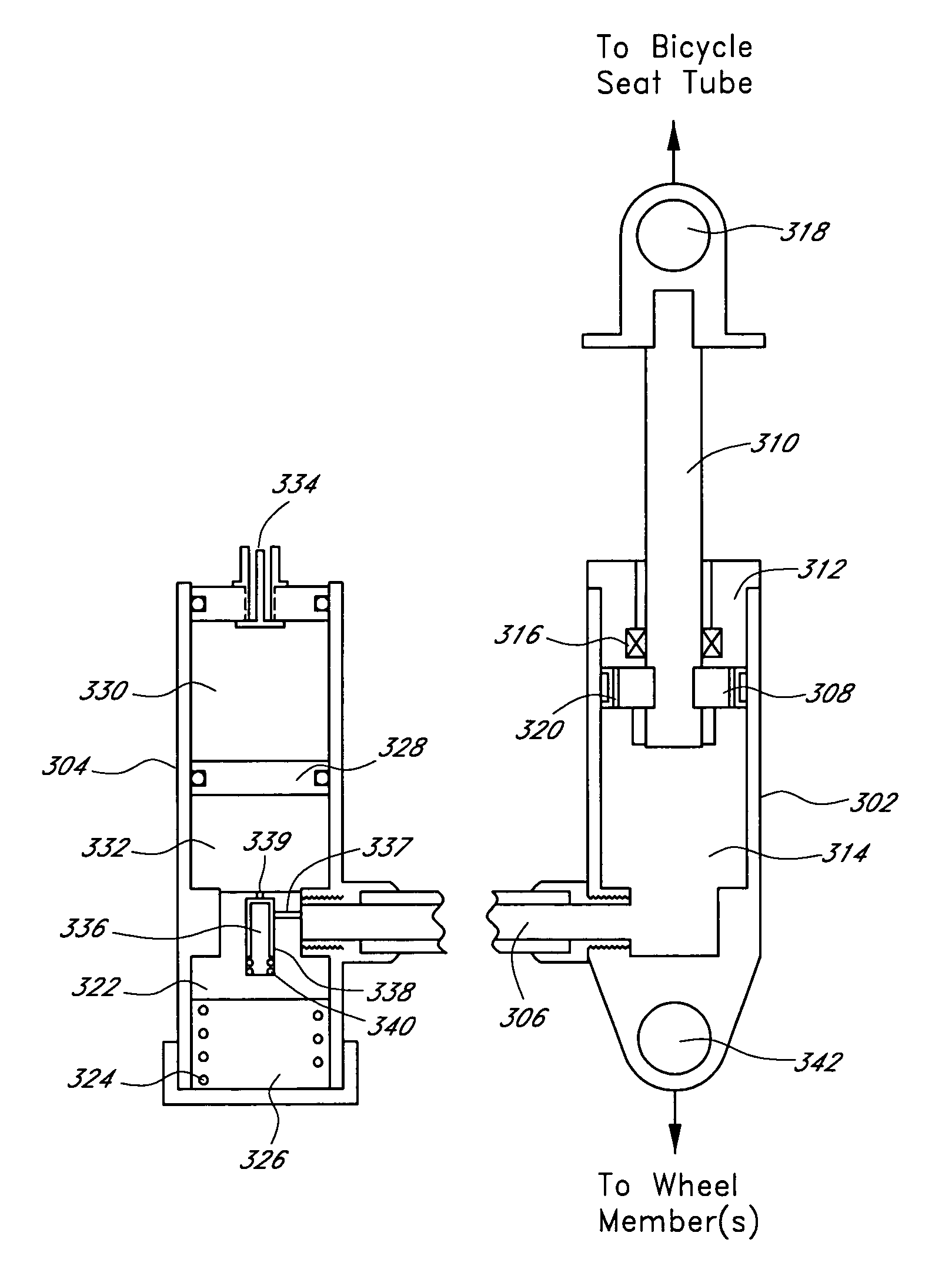
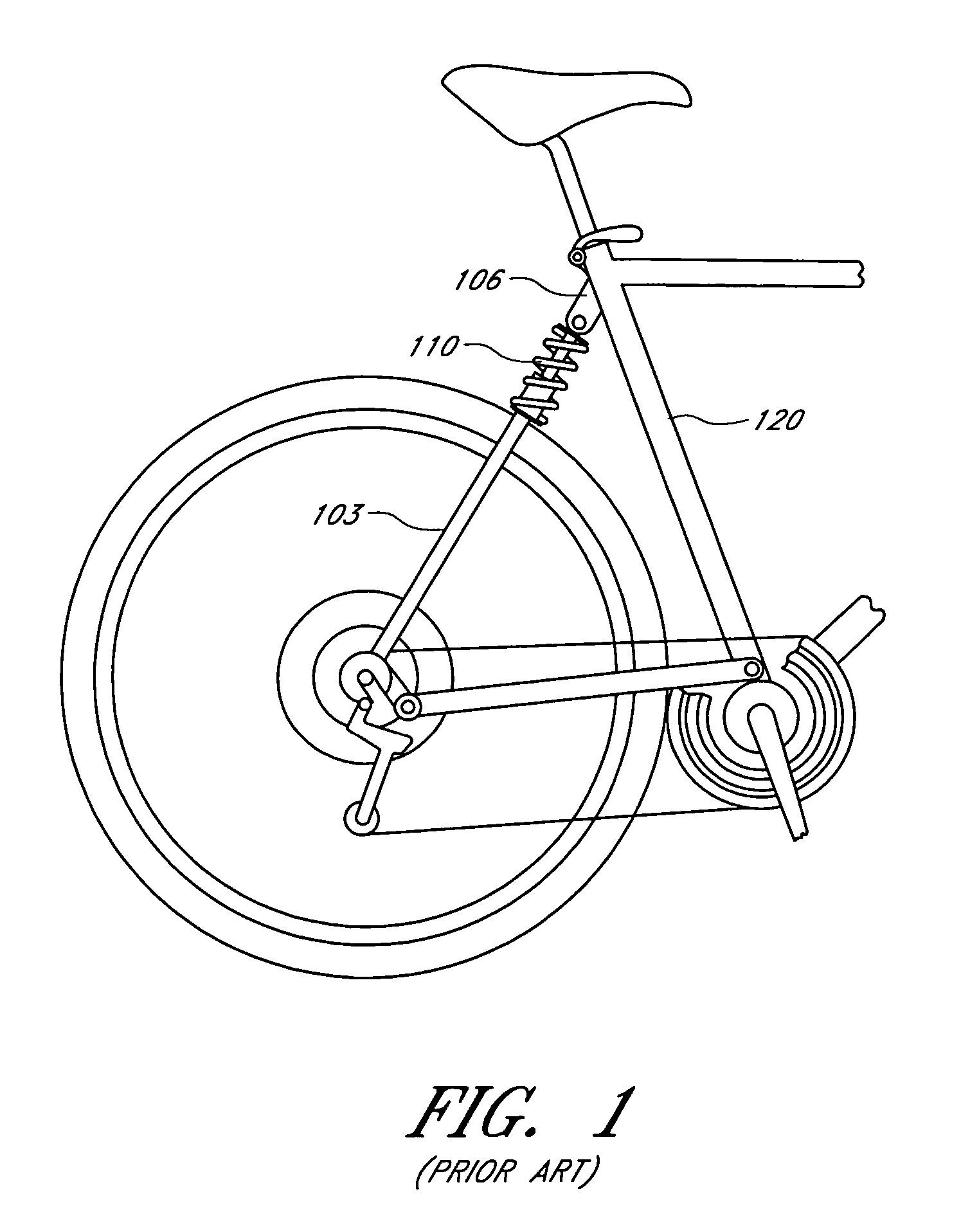
Bicycle suspension assembly
InactiveUS20090001684A1Wheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionDual stageGas spring
A bicycle suspension assembly may be in the form of a bicycle front suspension fork. The suspension fork may include a pair of telescoping fork legs. In one arrangement, a suspension spring and a damper are provided in only one of the pair of fork legs. The suspension spring assembly may include a negative spring. In one arrangement, the negative spring is a dual stage negative gas spring in which a negative spring gas chamber includes a first chamber section and a second chamber section. The first chamber section and the second chamber section are uncoupled in a first position of the suspension spring and the first chamber section and the second chamber section are coupled in a second position of the suspension spring.
Owner:SPECIALIZED BICYCLE COMPONENTS INC
Force transmission device in particular for power transmission between a drive engine and an output
ActiveUS8161739B2Reduce variationEliminate variationRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingTuned mass damperSelf adaptive
A force transmission device, in particular or power transmission between a drive engine and an output, comprising a damper assembly with at least two dampers, which can be connected in series, and a rotational speed adaptive absorber, wherein the rotational speed adaptive tuned mass damper is disposed between the dampers at least in one force flow direction through the force transmission device.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Electrostrictive polymer as a combined haptic-seal actuator
ActiveUS7342573B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringActuator
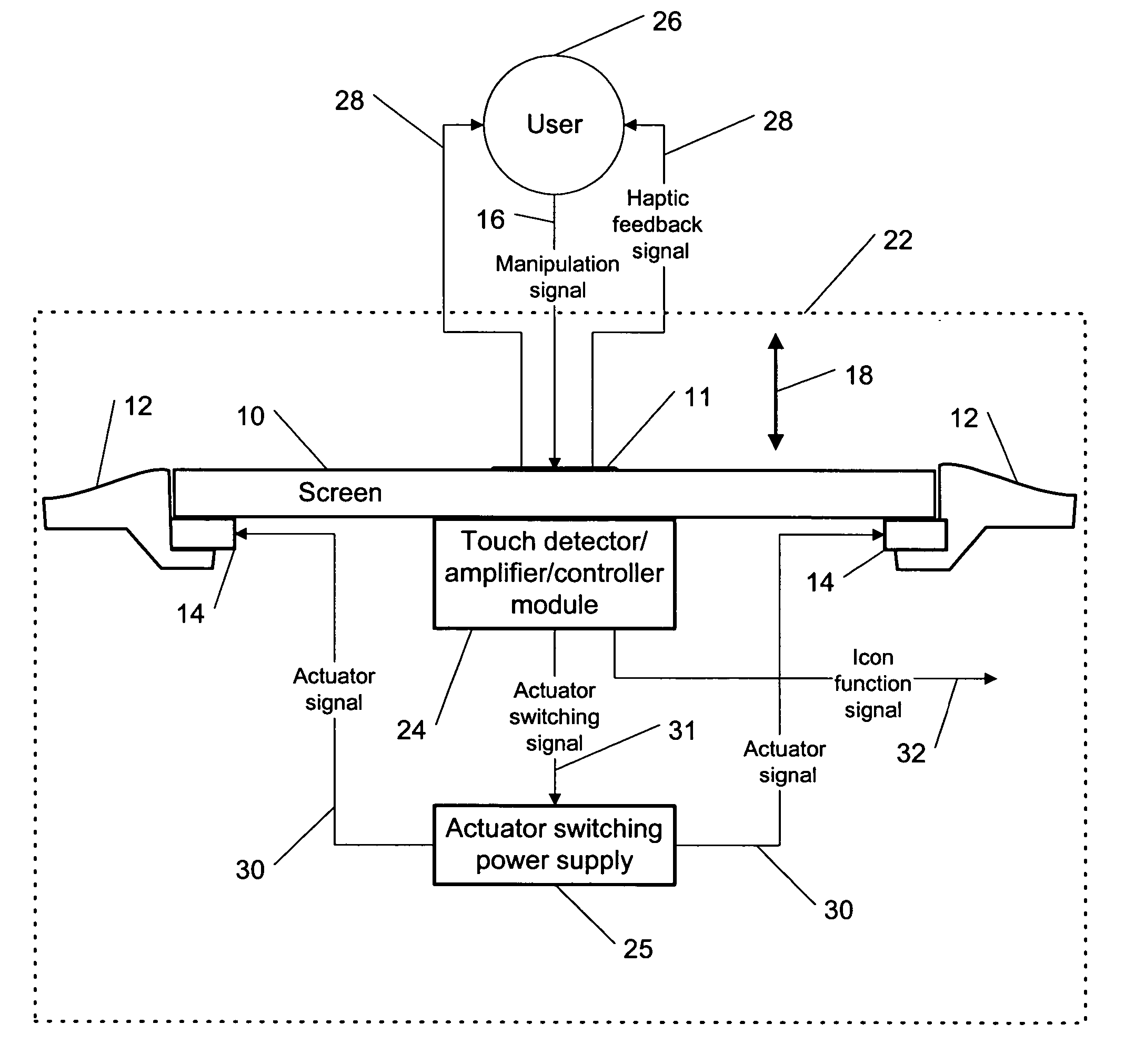
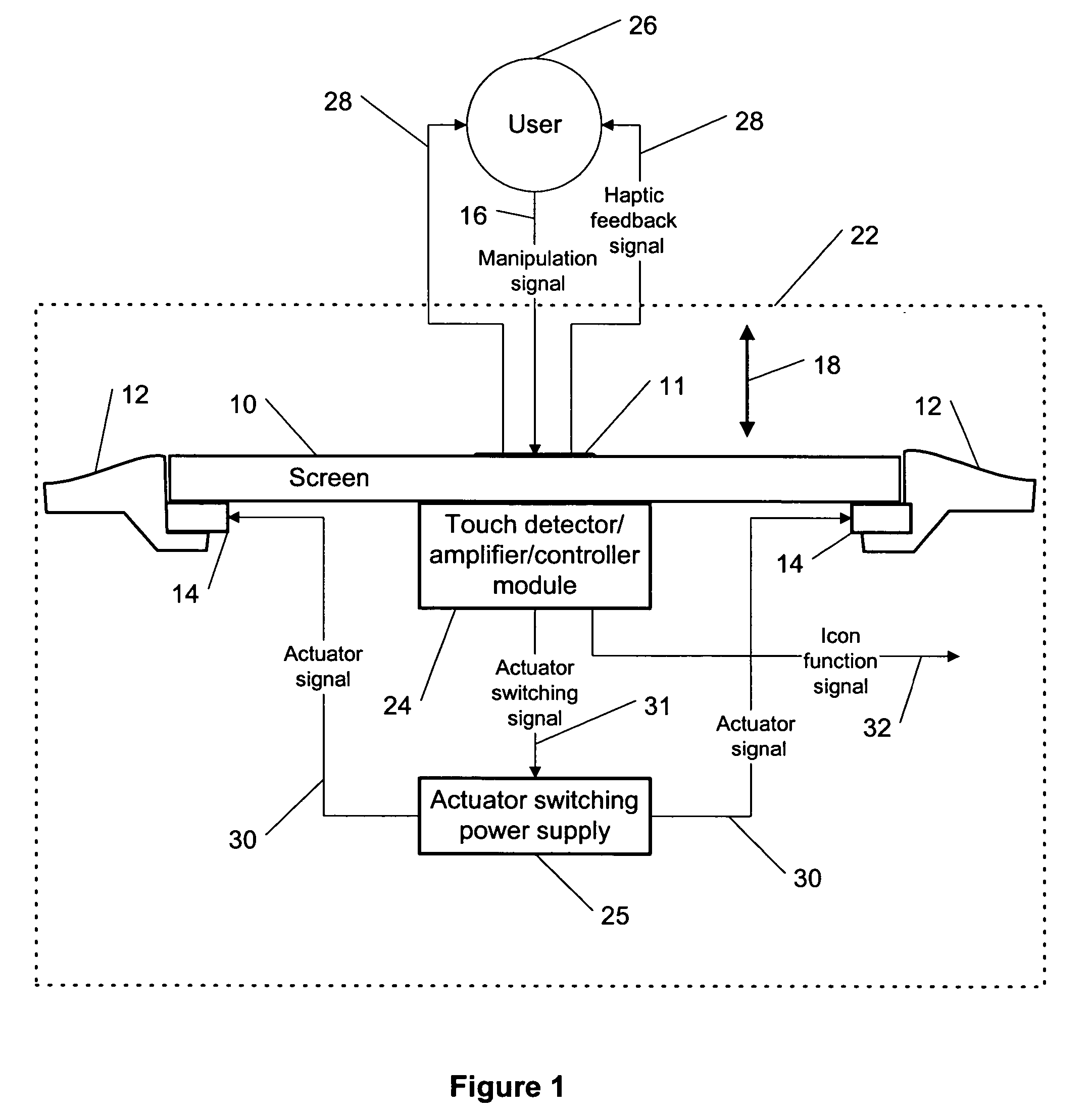
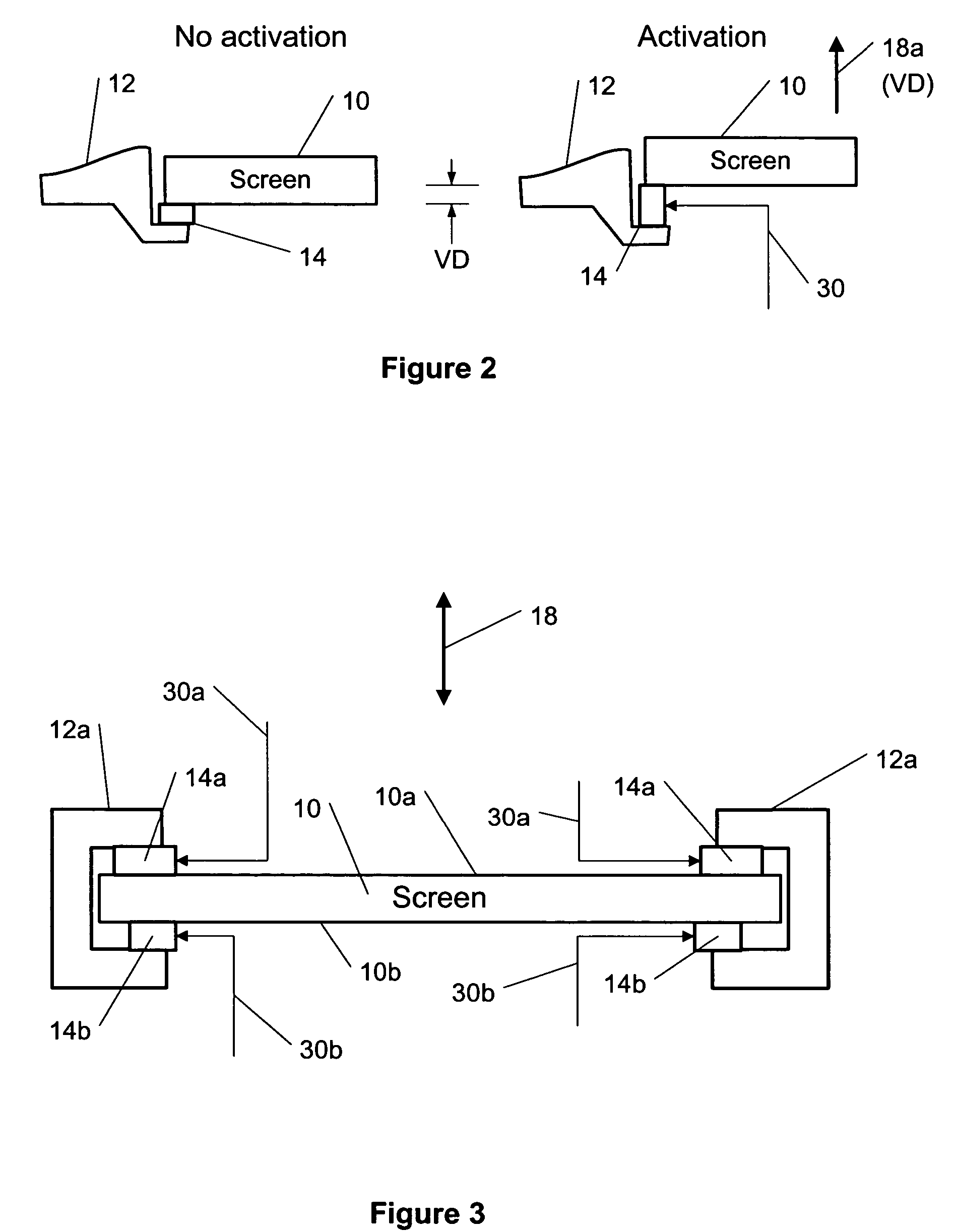
This invention describes a method for a haptic (tactile) feedback to a user of an electronic device having a touch display (screen) by utilizing an electrostrictive polymer as a combined haptic-seal actuator attached to the touch screen. In addition, the combined seal-actuator also makes a shock absorber. The electrostrictive polymer is a suitable material for haptic-seal-shock absorbing actuator because of its robustness and large stroke.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
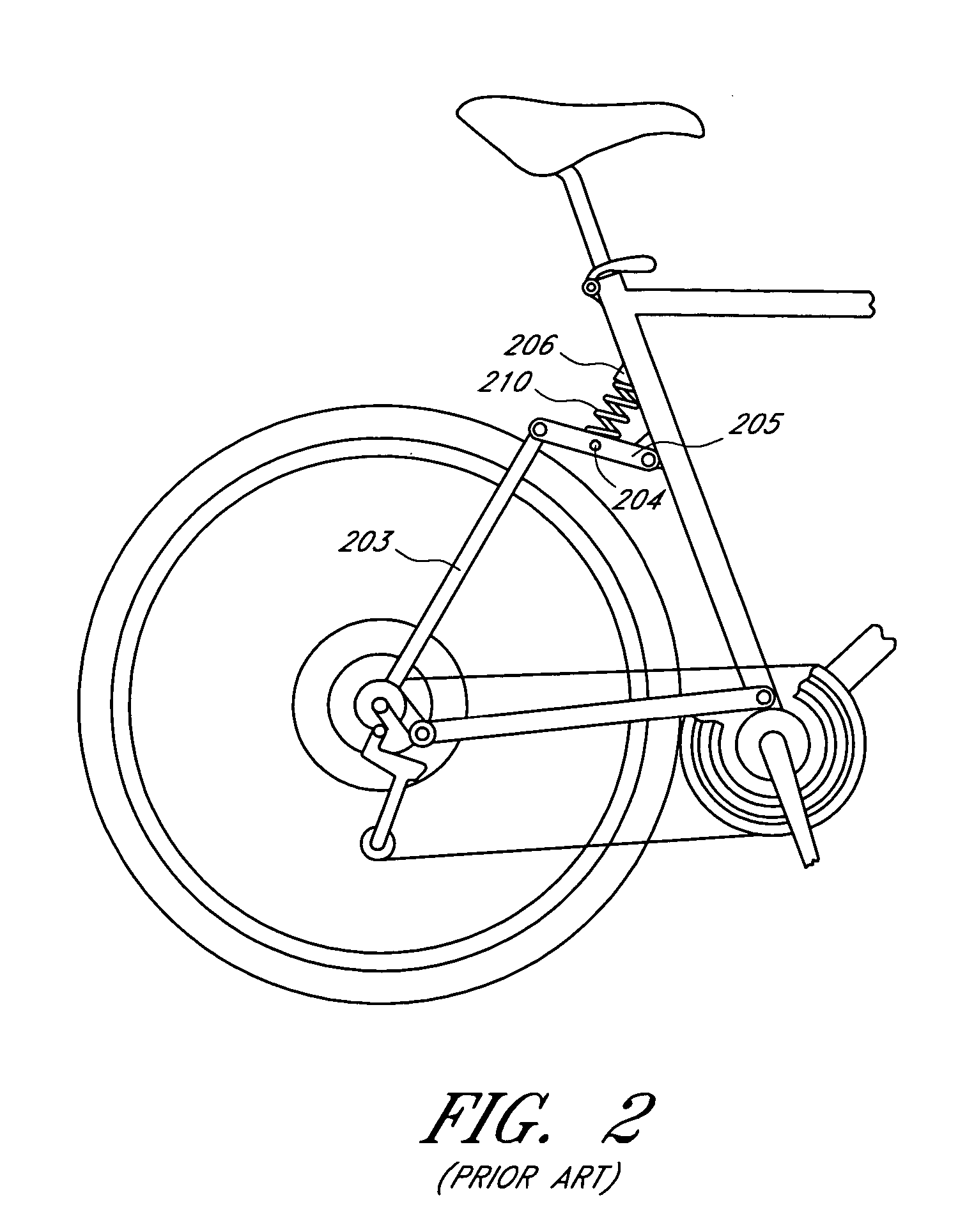
Bicycle damping enhancement system
A bicycle shock absorber for differentiating between rider-induced forces and terrain-induced forces includes a first fluid chamber having fluid contained therein, a piston for compressing the fluid within the fluid chamber, a second fluid chamber coupled to the first fluid chamber by a fluid communication hose, and an inertial valve disposed within the second fluid chamber. The inertial valve opens in response to terrain-induced forces and provides communication of fluid compressed by the piston from the first fluid chamber to the second fluid chamber. The inertial valve does not open in response to rider-induced forces and prevents communication of the fluid compressed by the piston from the first fluid chamber to the second fluid chamber.
Owner:SPECIALIZED BICYCLE COMPONENTS INC
Lockup clutch with a compensation flywheel mass at the torsional vibration damper
A lockup clutch at a hydrodynamic torque converter is constructed with a torsional vibration damper which has a drive-side transmission element and a driven-side transmission element which is rotatable relative to the latter. Both of the transmission elements are provided with driving devices for driving elastic elements of a damping device. A carrier for a compensation flywheel mass is associated with the driven-side transmission element, wherein the carrier is connected with the turbine wheel on the one hand and with the driven-side driving device of the elastic elements on the other hand so as to be fixed with respect to rotation relative thereto and is provided at least with a cutout for receiving the compensation flywheel mass. The cutout has a guide path at least in its area of contact with the compensation flywheel mass, which guide path allows a movement of the compensation flywheel mass with at least one component perpendicular to the radial direction at the carrier.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Vertically integrated 3-axis MEMS accelerometer with electronics
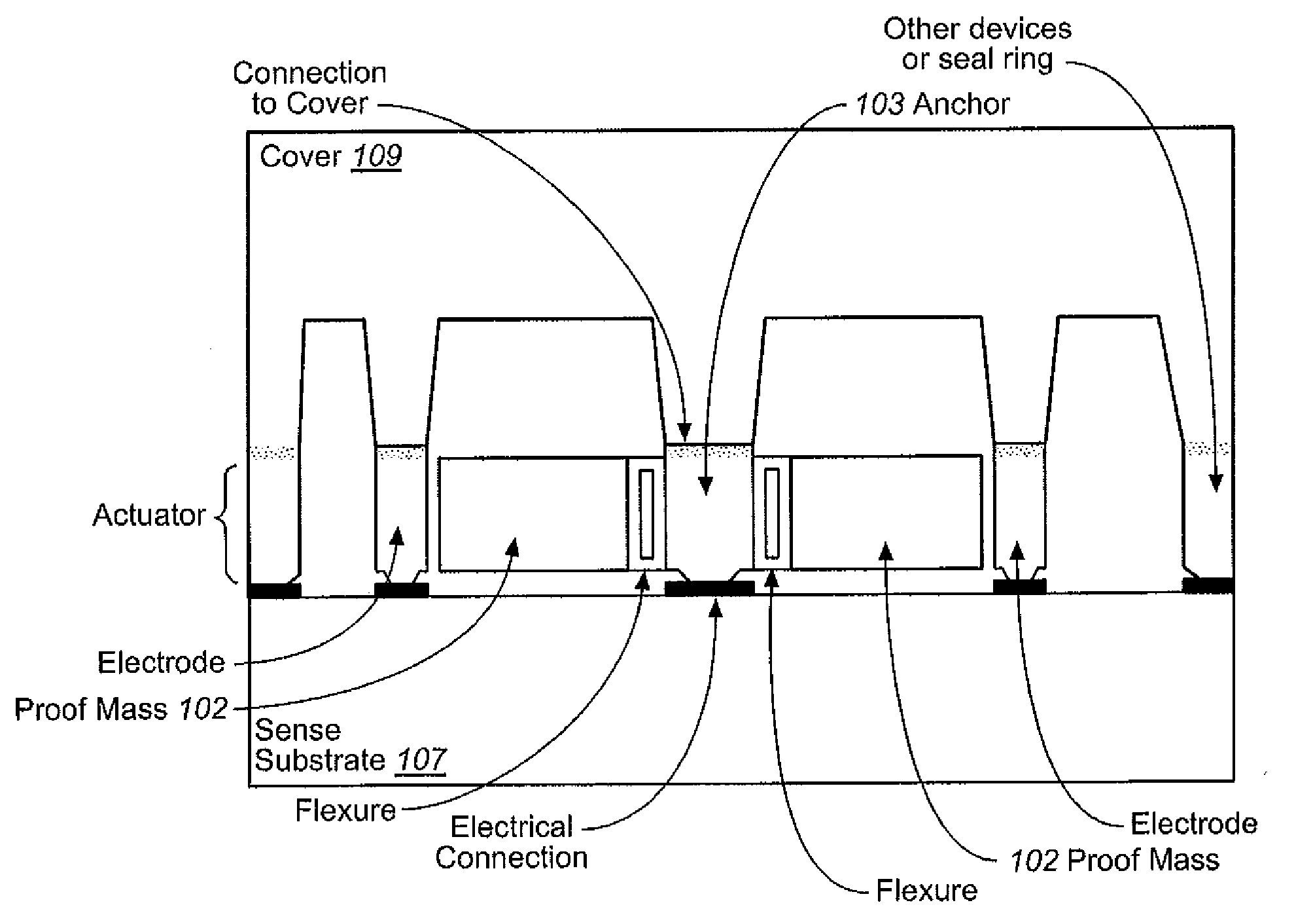
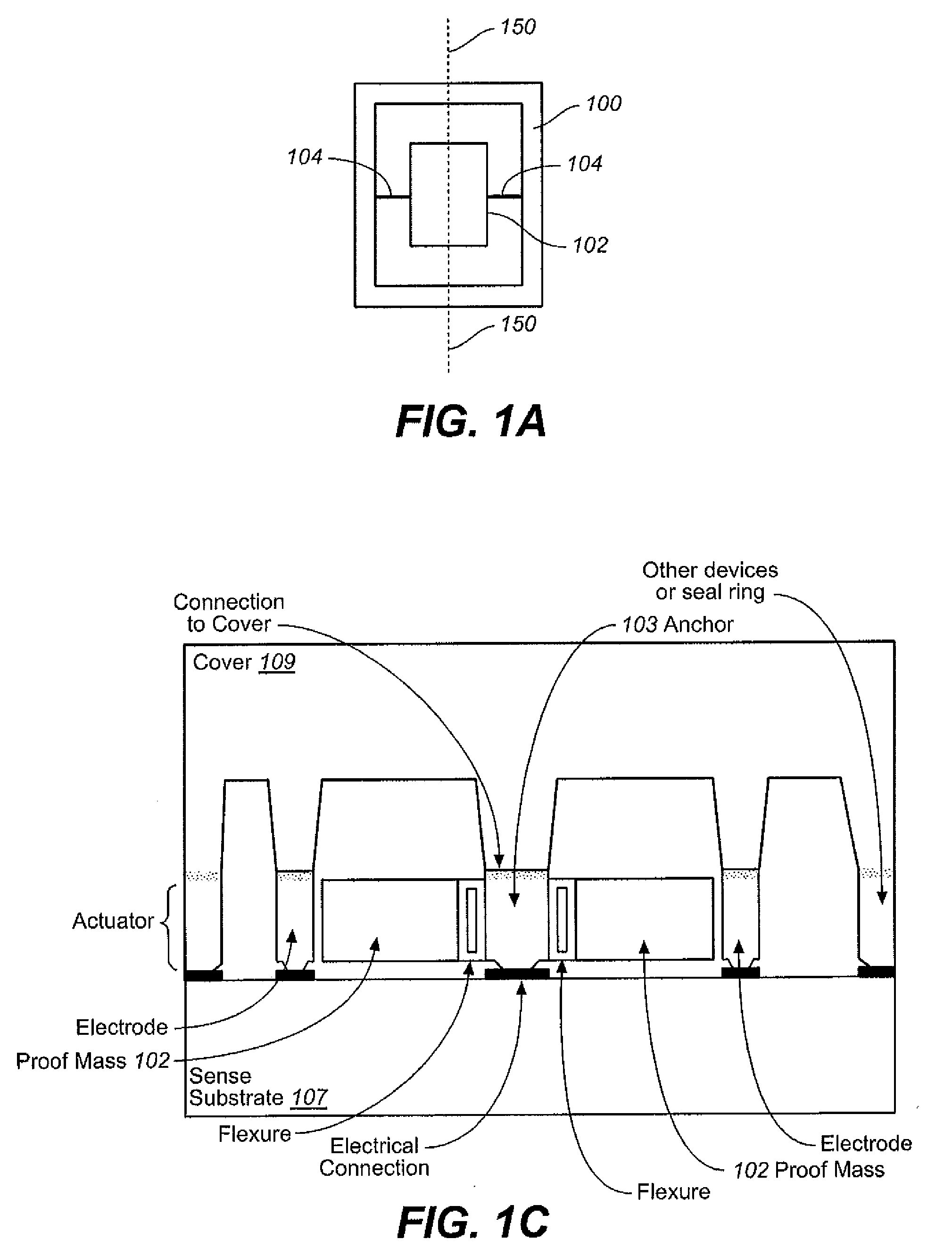
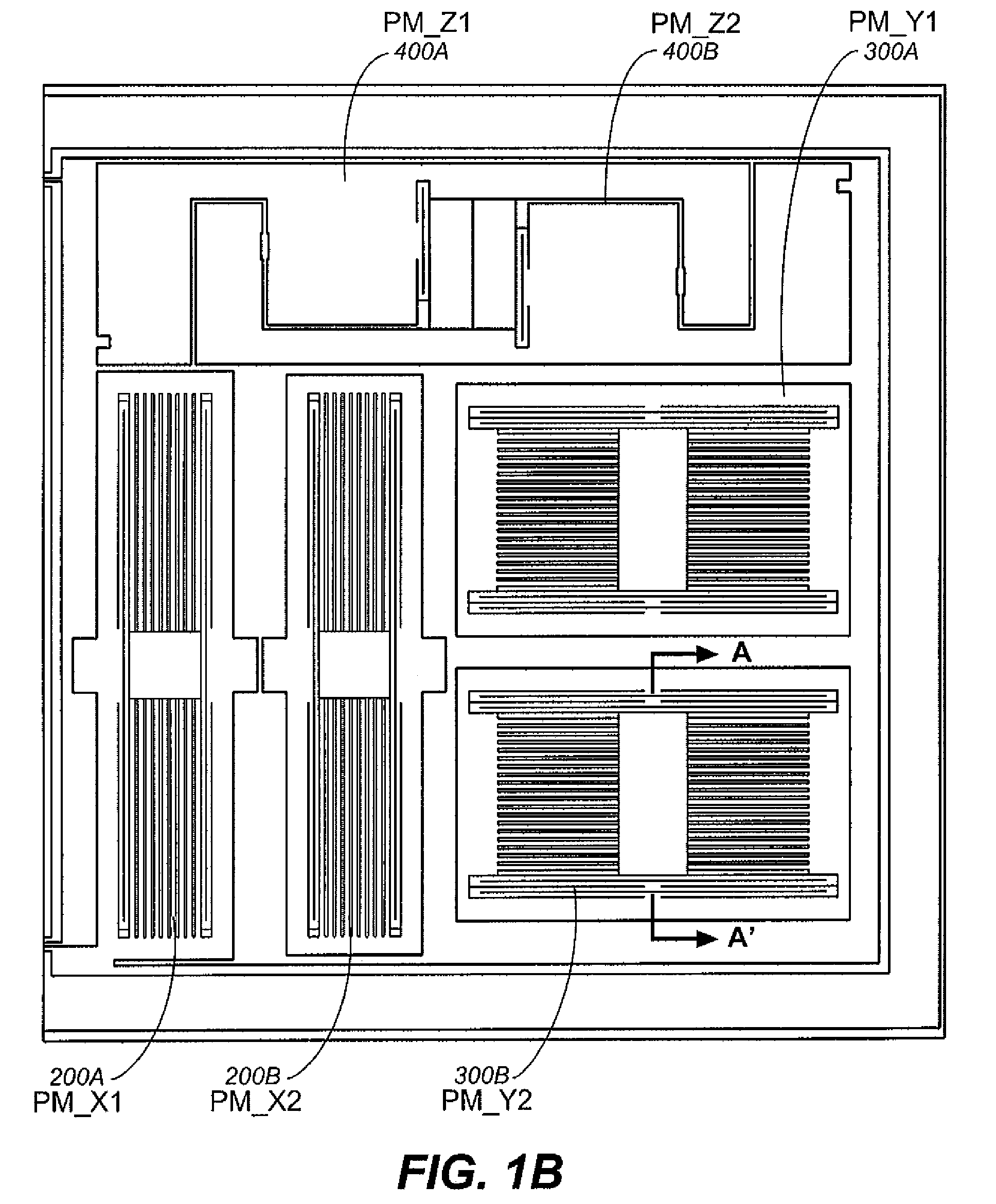
ActiveUS20080314147A1Reduce sensitivityReduce temperature changesDevices characerised by mechanical meansAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsFull bridgeResonance
A system and method in accordance with the present invention provides for a low cost, bulk micromachined accelerometer integrated with electronics. The accelerometer can also be integrated with rate sensors that operate in a vacuum environment. The quality factor of the resonances is suppressed by adding dampers. Acceleration sensing in each axis is achieved by separate structures where the motion of the proof mass affects the value of sense capacitors differentially. Two structures are used per axis to enable full bridge measurements to further reduce the mechanical noise, immunity to power supply changes and cross axis coupling. To reduce the sensitivity to packaging and temperature changes, each mechanical structure is anchored to a single anchor pillar bonded to the top cover.
Owner:INVENSENSE
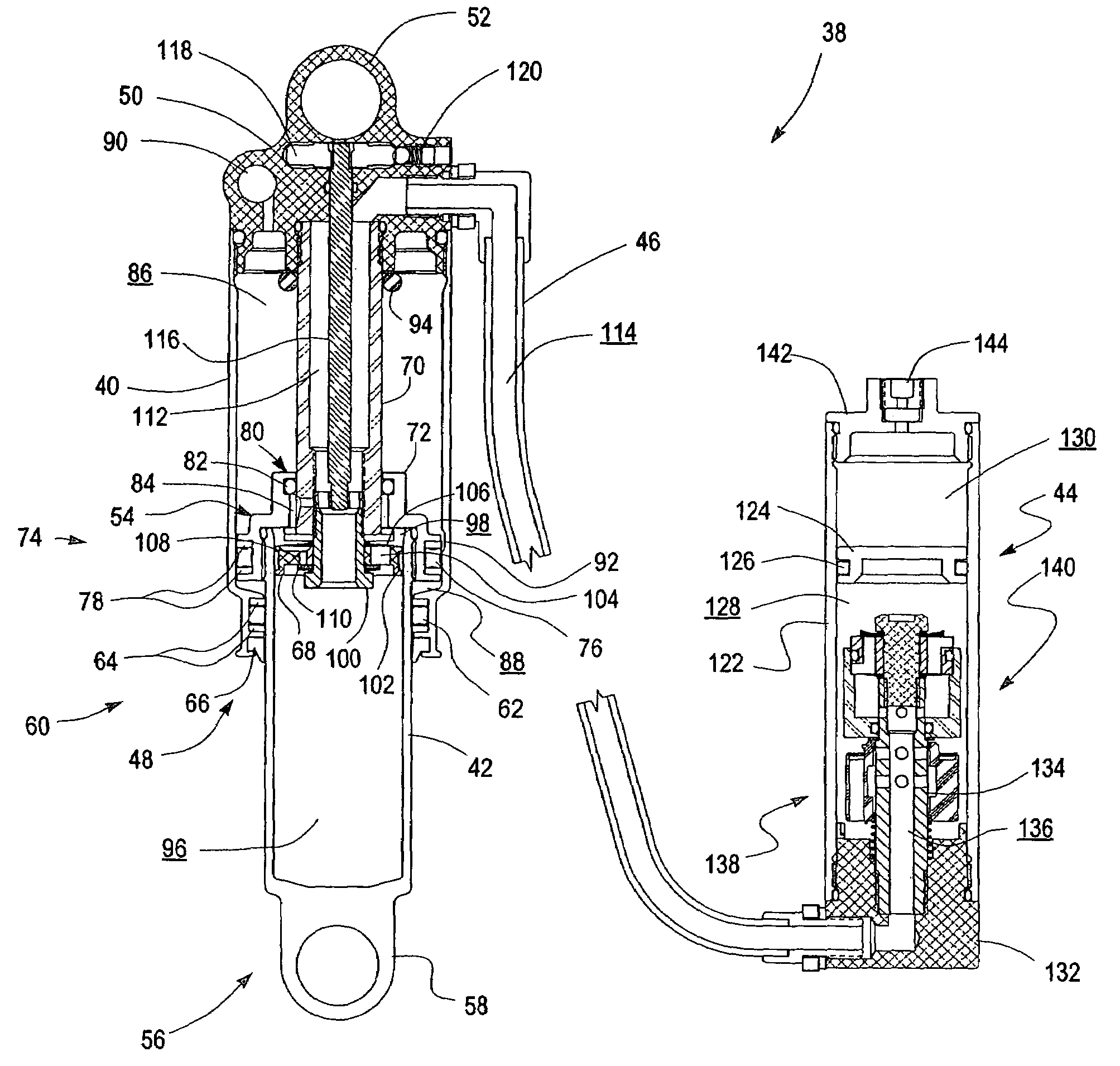
Methods and apparatus for combined variable damping and variable spring rate suspension
Pressure-sensitive vales are incorporated within a dampening system to permit user-adjustable tuning of a shock absorber. In one embodiment, a pressure-sensitive valve includes an isolated gas chamber having a pressure therein that is settable by a user.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
Pump drivetrain damper system and control systems and methods for same
ActiveUS10316832B2Reduce vibrationLiquid resistance brakesPositive displacement pump componentsControl signalDrivetrain
Owner:SPM OIL & GAS INC
Damper with pressure-sensitive compression damping
InactiveUS20060289258A1Quickly and easily tunedQuickly and easily and adjustedSpringsShock absorbersElectrical resistance and conductanceSpring force
A damper includes a piston rod, a damping piston, at least one cylinder containing a damping liquid, a fixed partition member for partitioning the interior of the damper into two liquid chambers, a pressure source, and a valve in communication with the pressure source which reacts as a function of the pressure. The valve can also be in communication with additional forces, such as mechanical spring forces, which can be adjustable. The valve can include a pressure intensifier. The valve generates fluid flow resistance during flow of liquid in a first direction through the partition member. The fluid flow resistance in the first direction varies according to the amount of force communicated to the valve by the pressure source and any additional forces. The partition member can include means for providing low-resistance return flow of liquid in a second direction.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
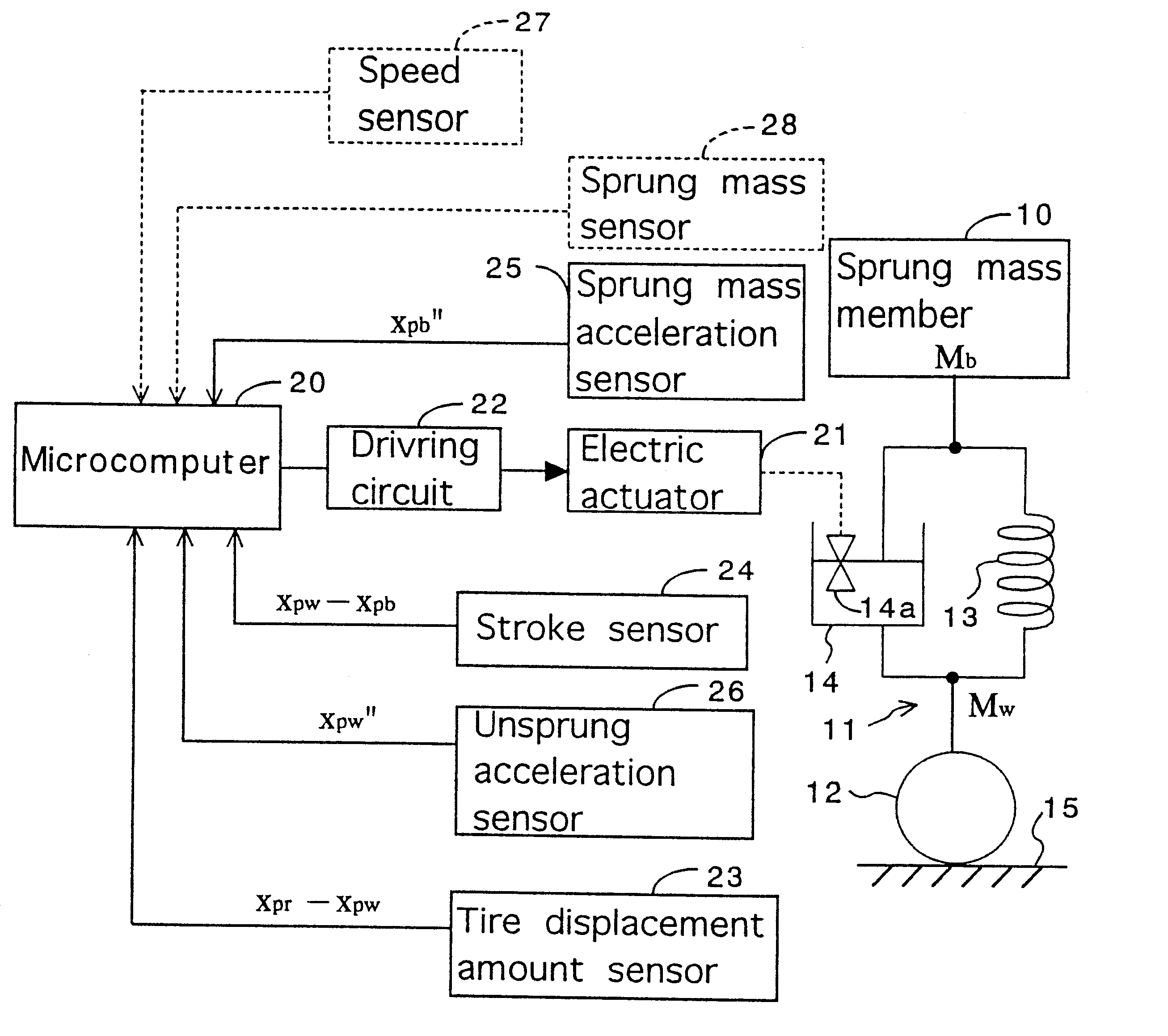
Control system for resilient support mechanism such as vehicle suspension mechanism
InactiveUS6314353B1Continuous changeEnhance running stability and comfortDigital data processing detailsNon-rotating vibration suppressionDamping factorRelative displacement
A control system for a resilient support mechanism such as a suspension mechanism of a wheeled vehicle including a damper disposed between an unsprung mass member and a sprung mass member of the vehicle, wherein a damping coefficient of the damper is divided into a linear portion and a nonlinear portion, and wherein the nonlinear portion of the damping coefficient is defined as a control input u and applied with a frequency weight Wu(s), while a vertical velocity of the sprung mass member, a relative velocity of the sprung mass member to the unsprung mass member and a vertical acceleration of the sprung mass member are defined as an evaluation output zp and applied with a frequency weight Ws(s). In the control system, a nonlinear Hinfin control theory is applied to a generalized plant to obtain a positive definite symmetric solution P and to calculate a target damping force based on the positive definite symmetric solution P and a state amount such as the vertical velocity of the sprung mass member, a relative displacement of the sprung mass member to the unsprung mass member or the like.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Stack damper
InactiveUS20090124191A1Mechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsSnubberActuator
A damper comprising a duct defining an air flow path, opposing damper blades pivotally mounted within the duct, each damper blade having an end that is pivotally mounted in cantilevered fashion in the duct so that an opposing end is free to move within the duct, wherein each damper blade is planar in shape, cooperating flow straightening members disposed centrally in the air flow path, an air flow sensor for generating a signal cooperatively disposed between the flow straightening members, and an actuator for pivoting each damper blade within the duct in response to the signal from the air flow sensor to vary the damper blade position and thereby maintain a desired velocity of air exiting the damper.
Owner:RUSKIN COMPANY
Hydronic rooftop cooling systems
InactiveUS20050056042A1Improve RTU efficiencyEnhanced evaporative cooling effectEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingHeat recovery systemsAir filterEngineering
A roof top cooling unit has an evaporative cooling section that includes at least one evaporative module that pre-cools ventilation air and water; a condenser; a water reservoir and pump that captures and re-circulates water within the evaporative modules; a fan that exhausts air from the building and the evaporative modules and systems that refill and drain the water reservoir. The cooling unit also has a refrigerant section that includes a compressor, an expansion device, evaporator and condenser heat exchangers, and connecting refrigerant piping. Supply air components include a blower, an air filter, a cooling and / or heating coil to condition air for supply to the building, and optional dampers that, in designs that supply less than 100% outdoor air to the building, control the mixture of return and ventilation air.
Owner:DAVIS ENERGY GROUP
Outlet silencer and heat recovery structures for gas turbine
InactiveUS6851514B2Reduce sound levelPrevent escapeSilencing apparatusGas turbine plantsTurbineMuffler
A sound attenuating duct unit suitable for connection to an outlet of a gas turbine and an improved heat recovery apparatus for use with such a turbine are disclosed. The former unit includes a duct housing having exterior sides, an air inlet at one end and first and second air outlets. Interior walls define a main airflow passageway extending from the air inlet to both of the outlets. Sound absorbing and heat insulation material is arranged between these walls and the exterior sides. Sound attenuating members are mounted in the passageway and a diverter damper is mounted in the housing and is able to direct air flow to either one of the air outlets. The sound attenuating members are mounted between the diverter damper and the air inlet. The heat recovery apparatus includes a series of aerodynamic diffusers mounted in a housing adjacent an air flow inlet connectable to the gas turbine.
Owner:M & I POWER TECH
Methods and apparatus for selective spring pre-load adjustment
ActiveUS20100252972A1Springs/dampers functional characteristicsResilient suspensionsEngineeringPiston
A method and apparatus for a suspension comprising a spring having a threaded member at a first end for providing axial movement to the spring as the spring is rotated and the threaded member moves relative to a second component. In one embodiment, the system includes a damper for metering fluid through a piston and a rotatable spring member coaxially disposed around the damper and rotatable relative to the damper.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
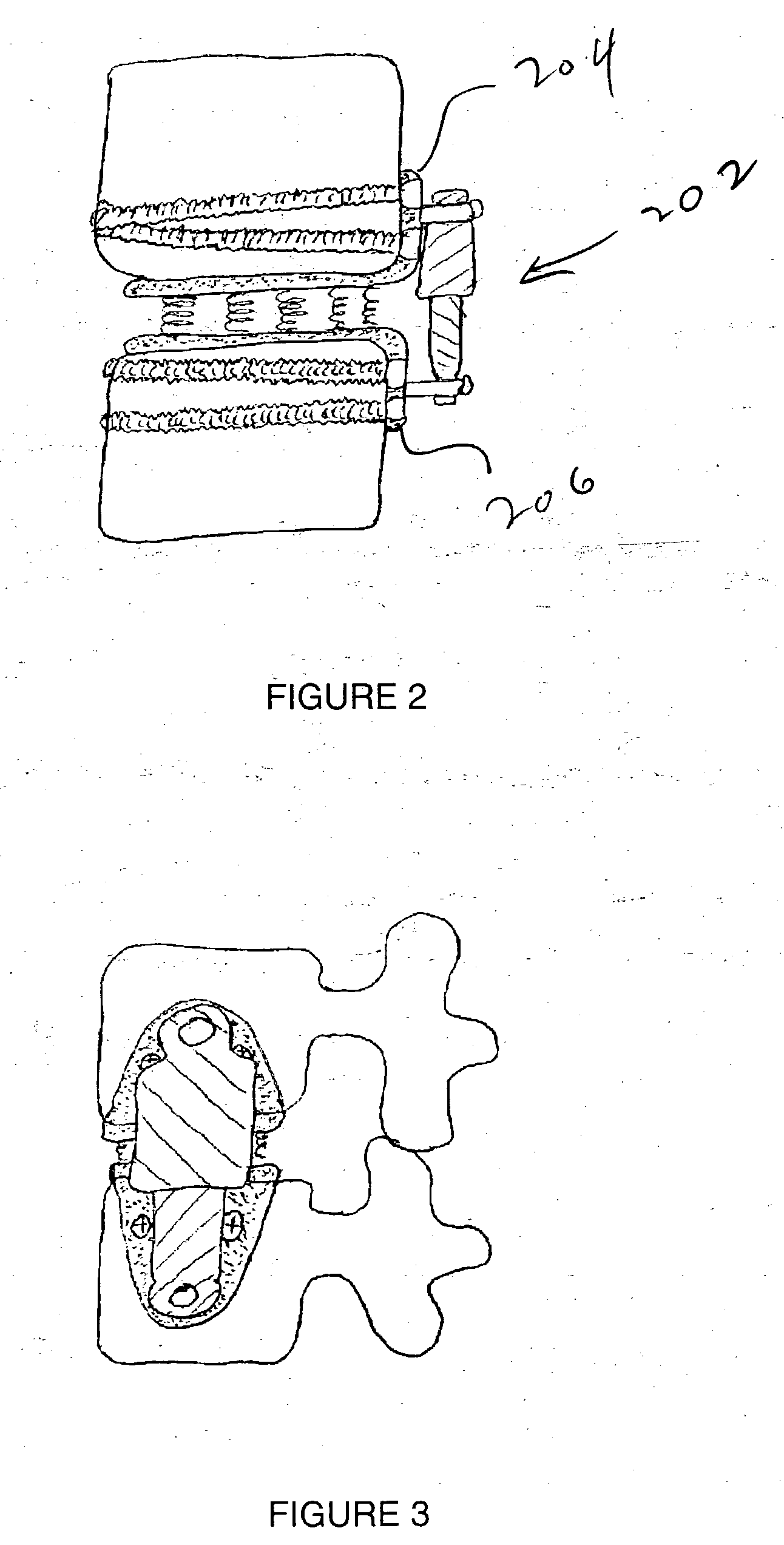
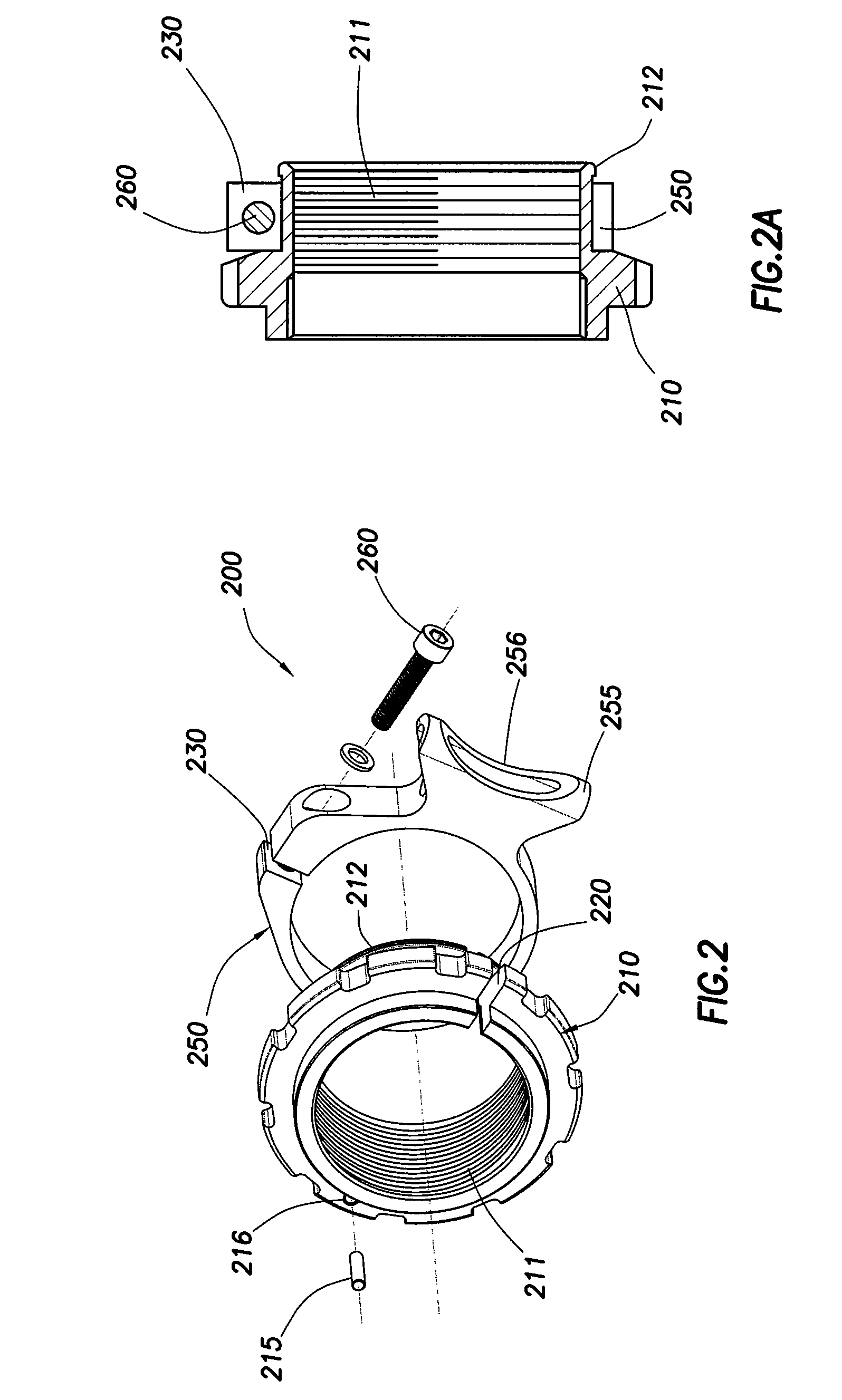
Spinal flexion and extension motion damper
ActiveUS20090149885A1Limited degreeSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisStretch exerciseEngineering
An orthopedic damper system and method to control the degree of flexion and / or extension motion of the mobile vertebral segment while providing additional stability to the spine. The damper system includes an anchor having a spring hitch, a spring coupled to the spring hitch, and a cap coupled to the spring. The anchor is adapted to connect to a spinous process. The spring includes an inner hollow area adapted to accommodate the spring hitch. The cap includes an opening connected to an inner cavity that is adapted to accommodate the spring and the spring hitch.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
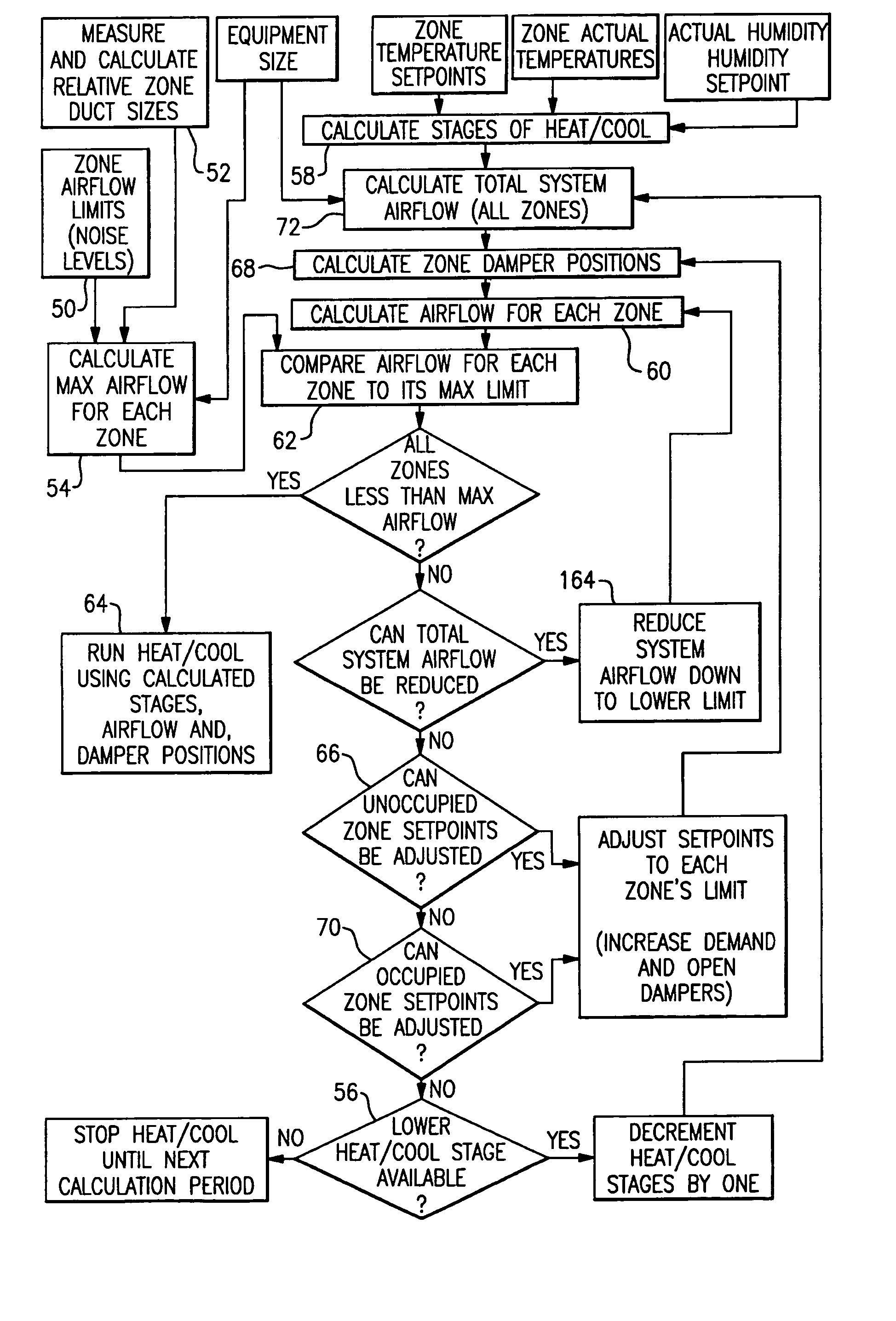
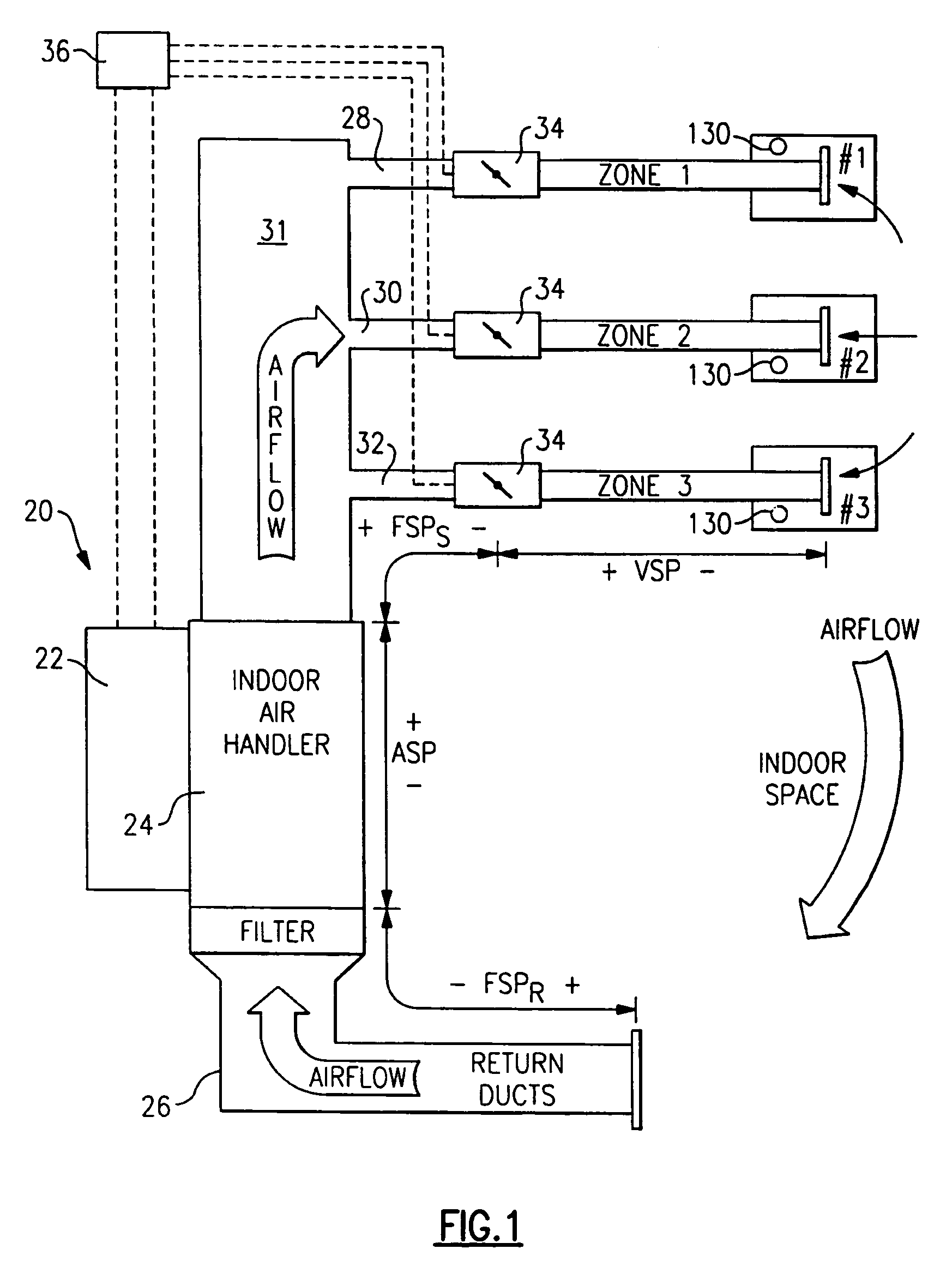
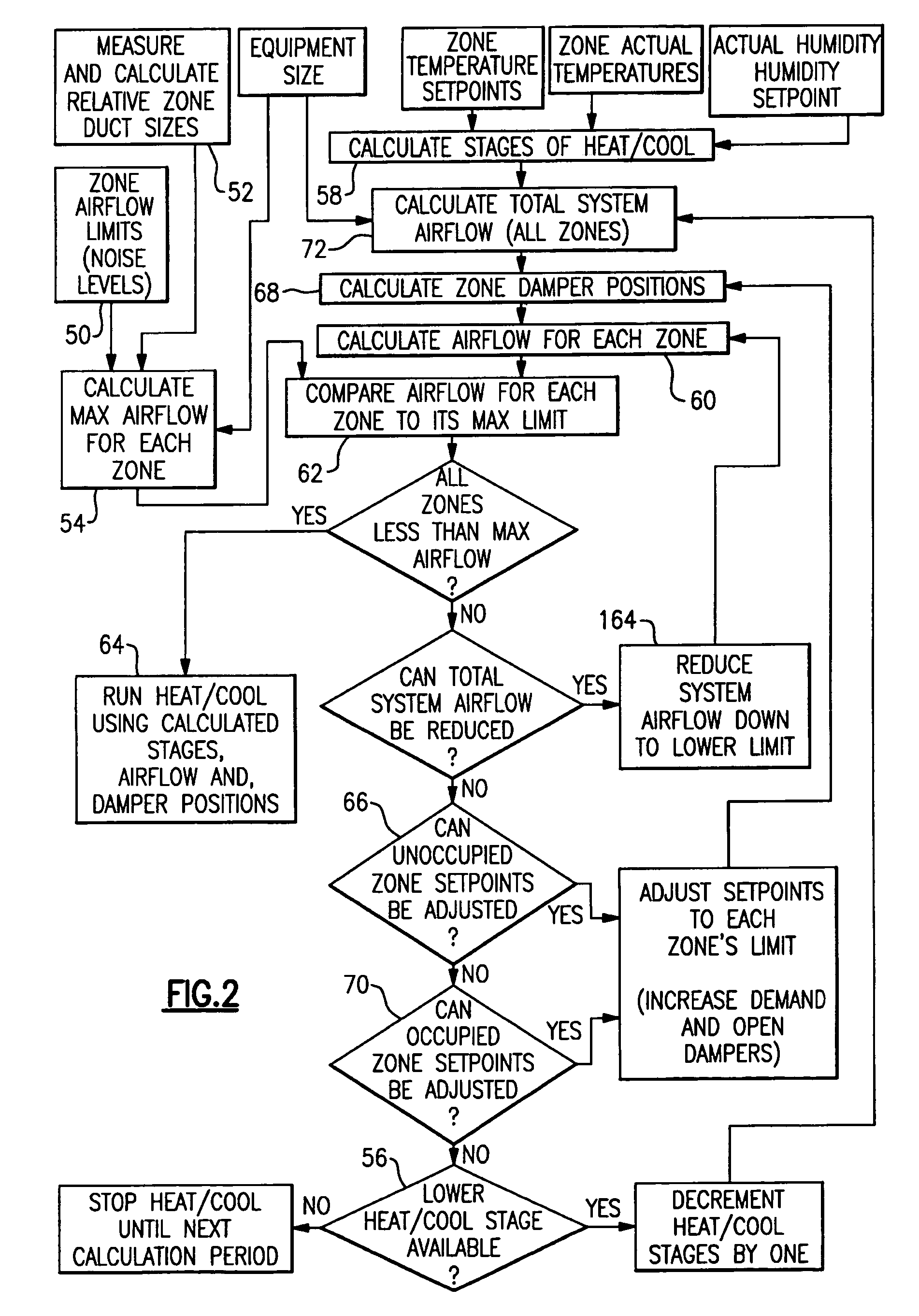
Method and system for automatically optimizing zone duct damper positions
A control is functional to perform a method of determining a maximum desired airflow for each of a plurality of zones in a multi-zone HVAC system, and an expected airflow to those zones. In part, these determinations are based upon an algorithm that calculates the relative size of the ducts leading to each of the zones. The expected and maximum airflows are compared for each of the zones, and if any zone has an expected airflow that exceeds its maximum airflow, certain steps are taken to reduce airflow to that zone.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com