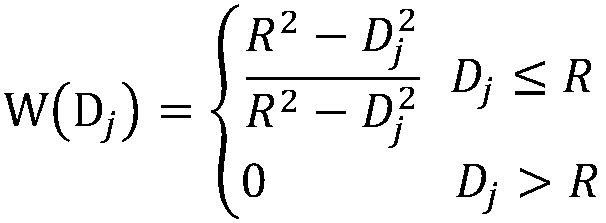Patents
Literature
235 results about "Vertical velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
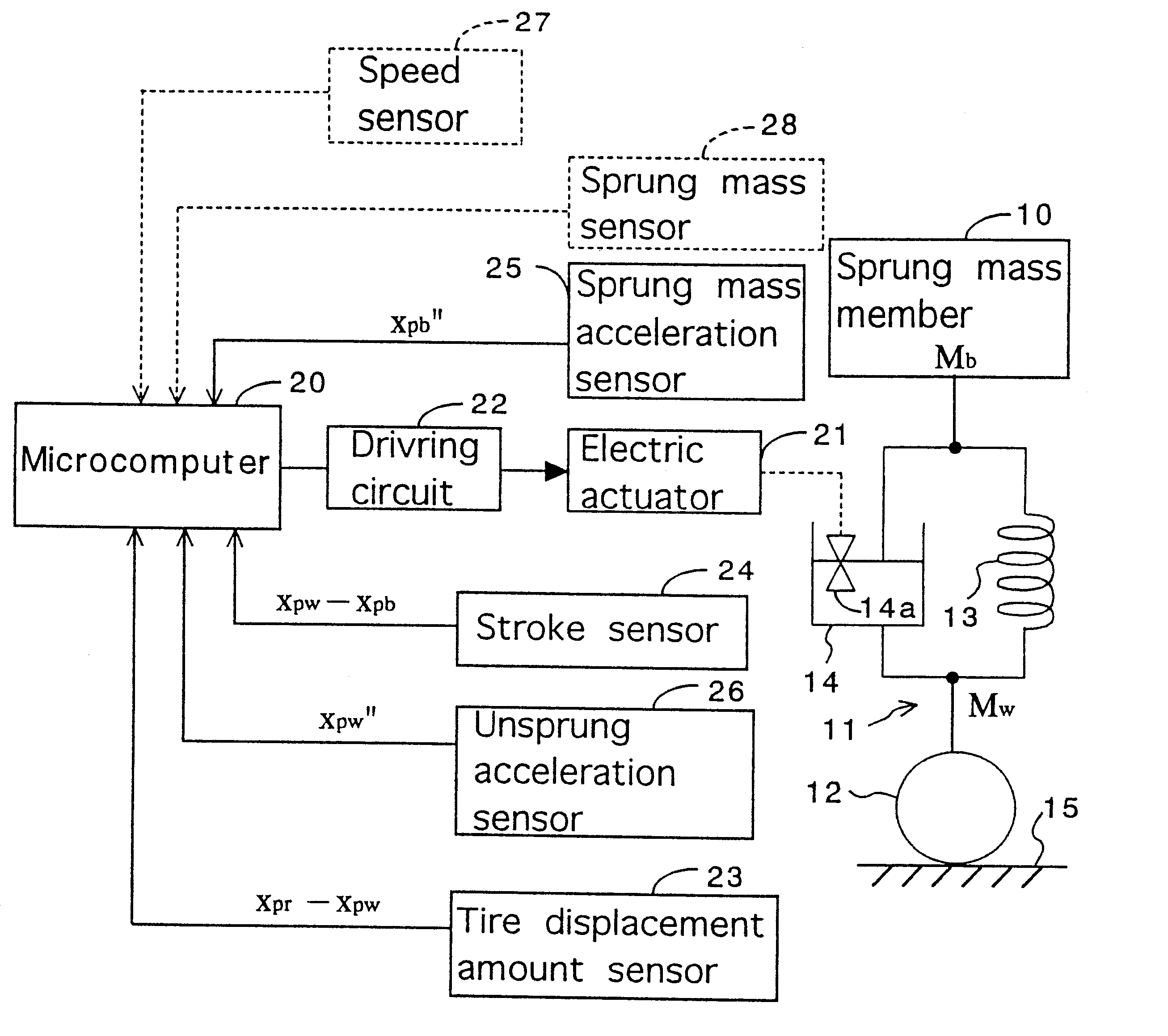
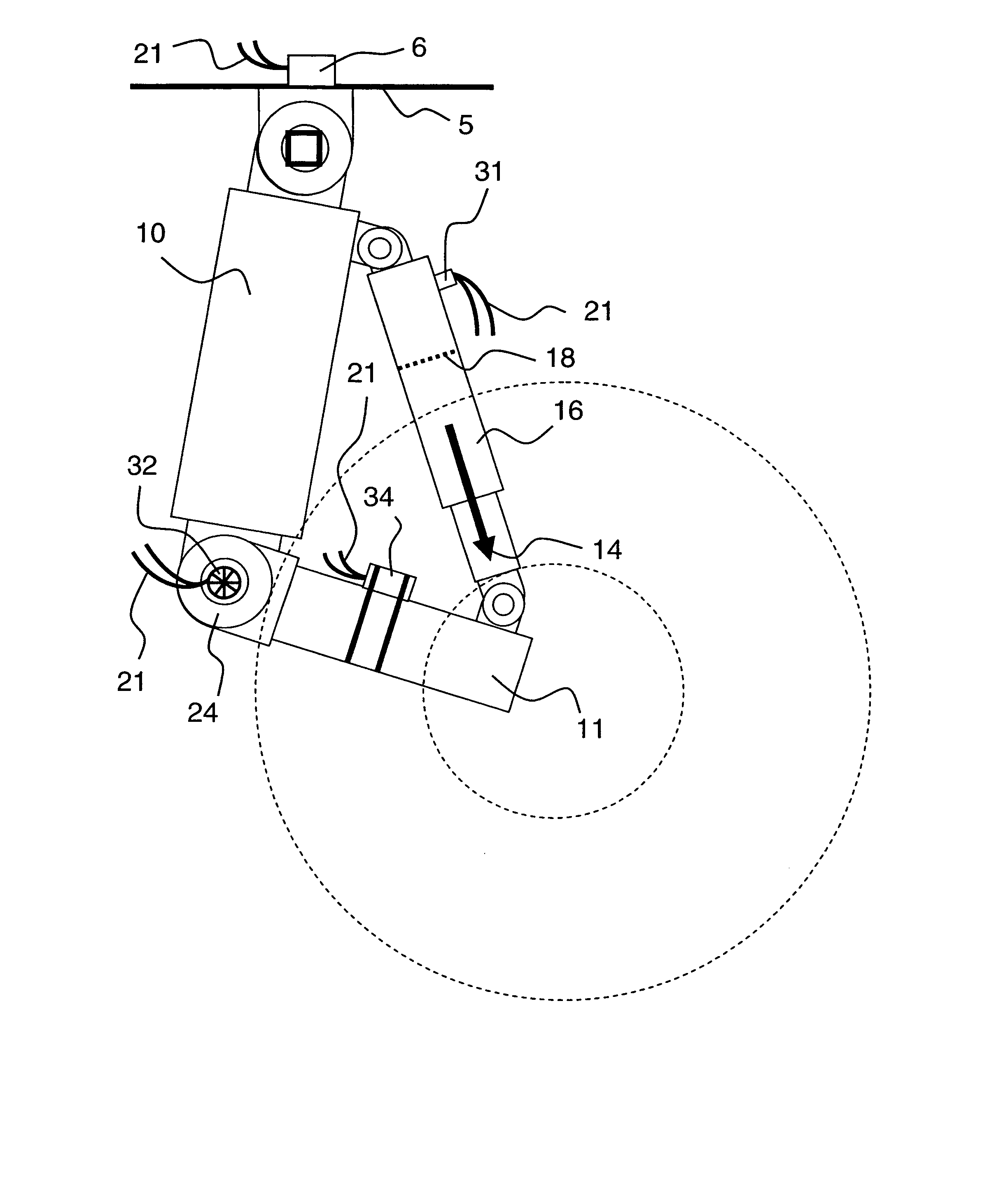
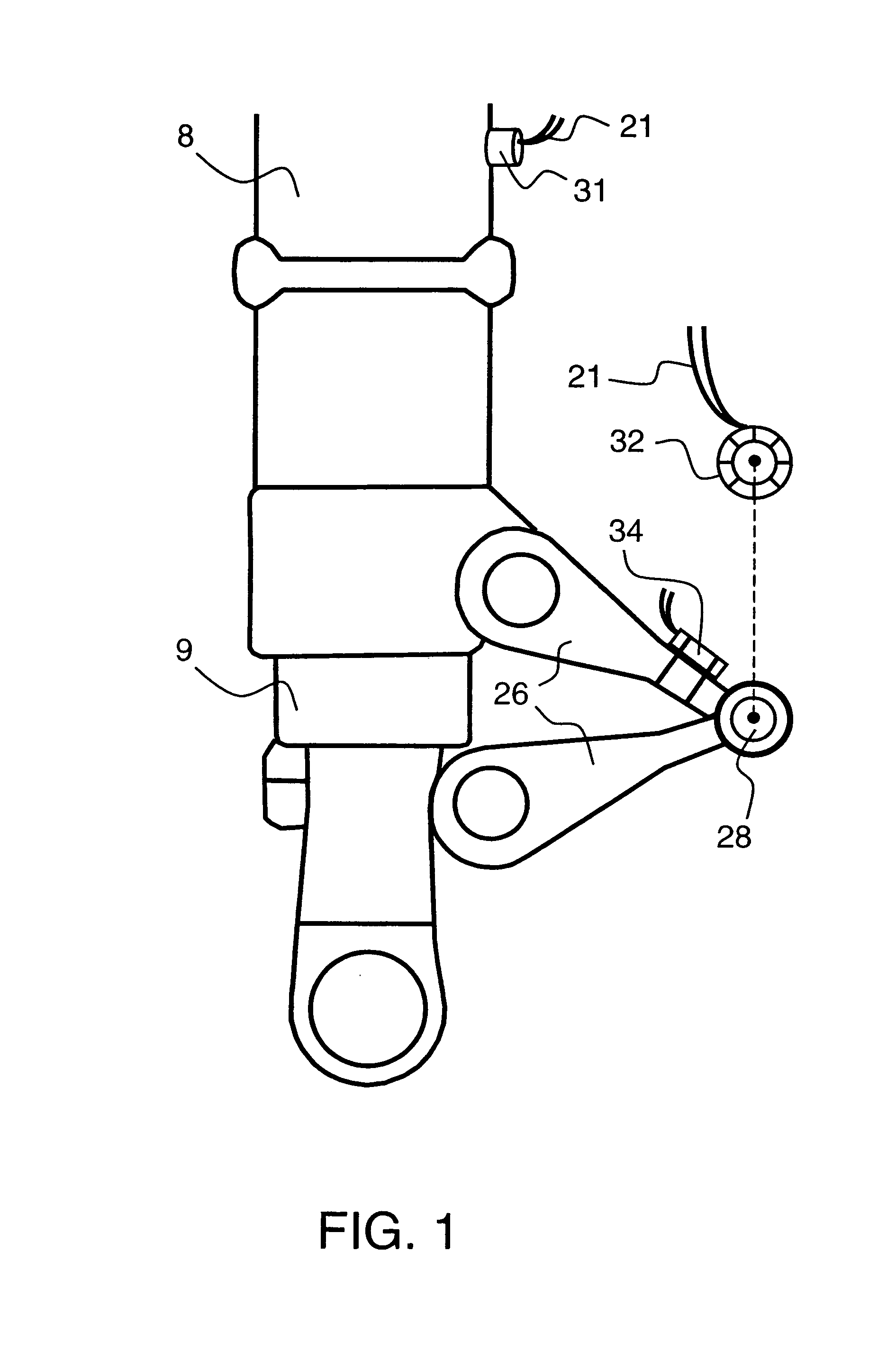
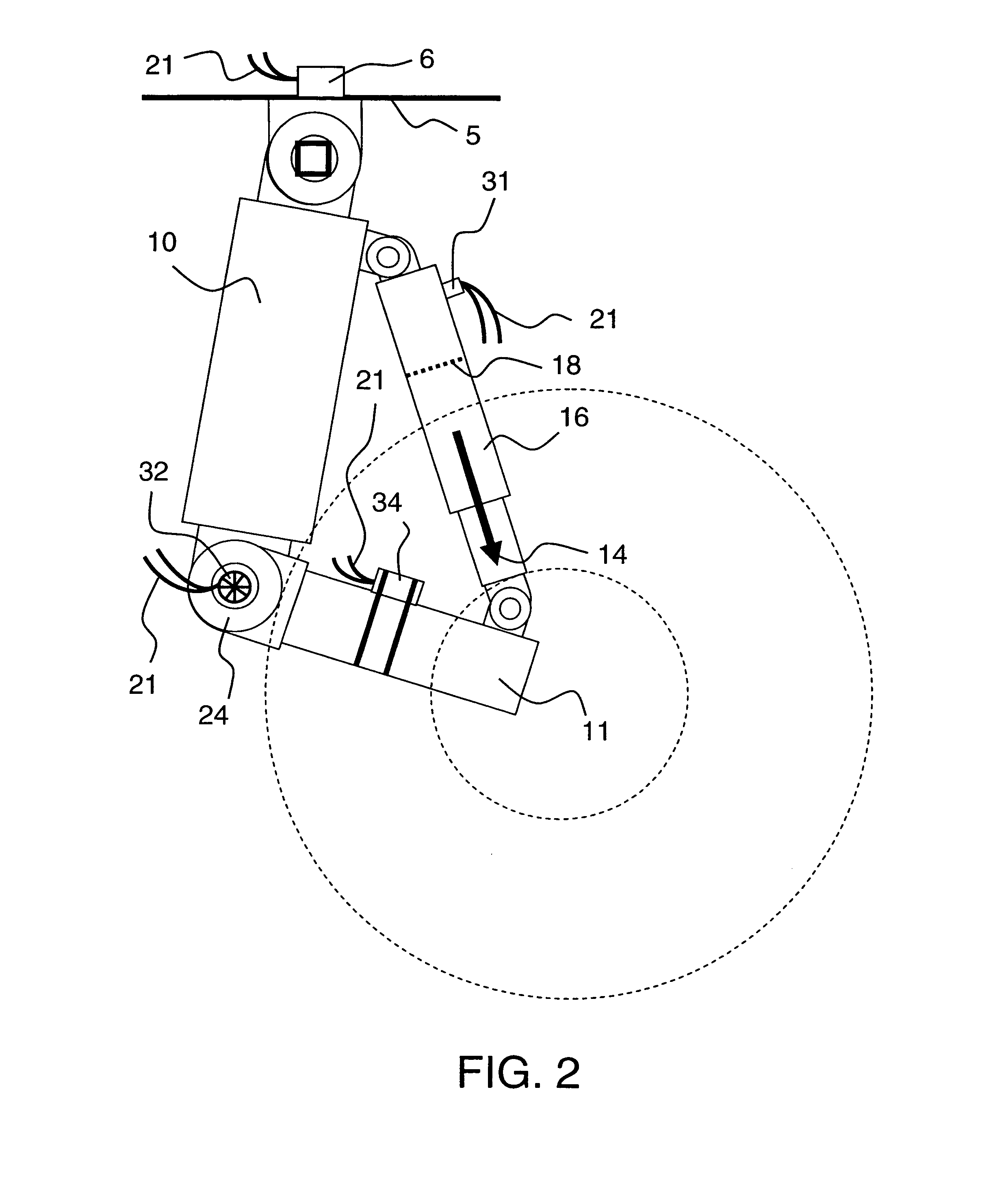
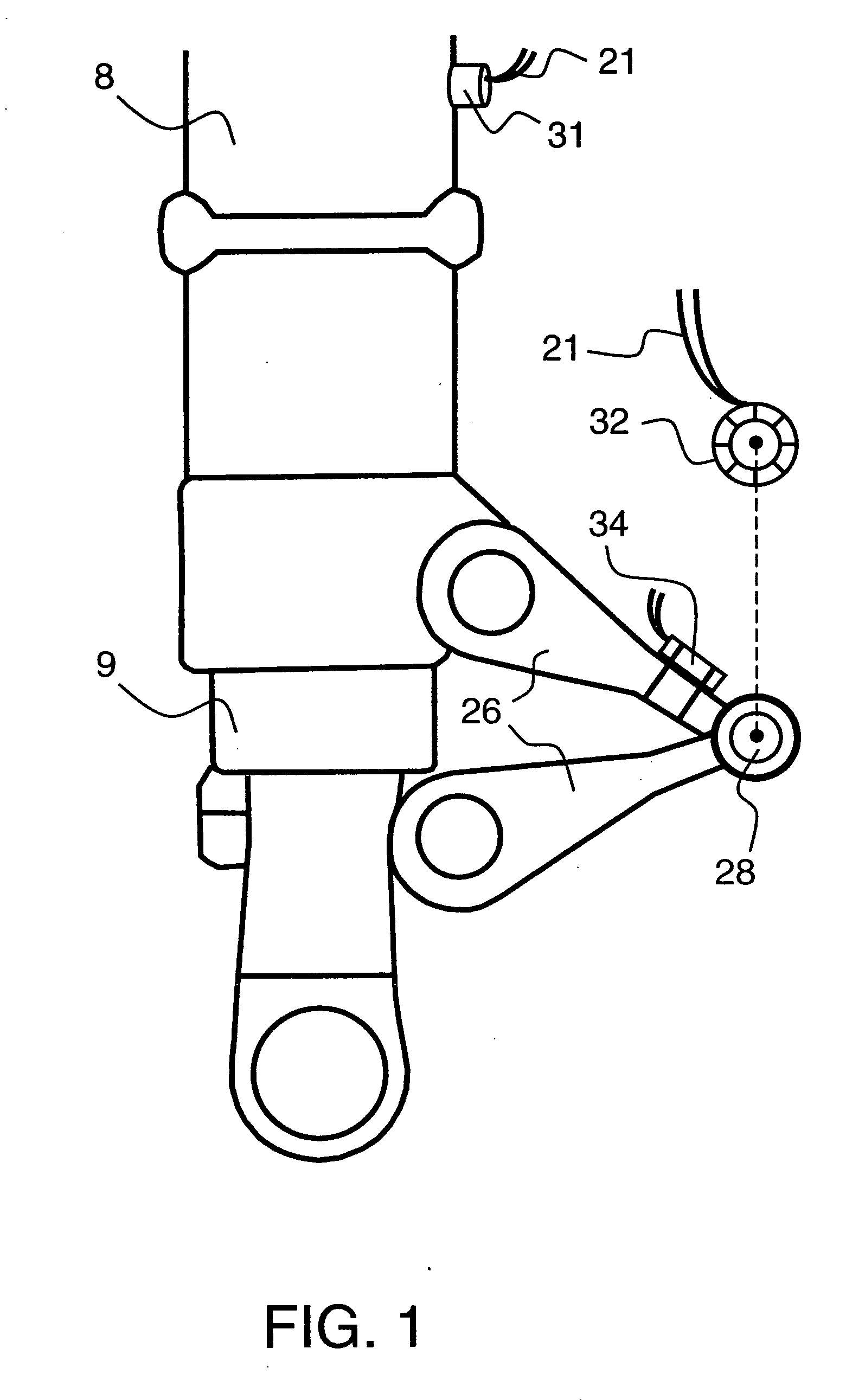
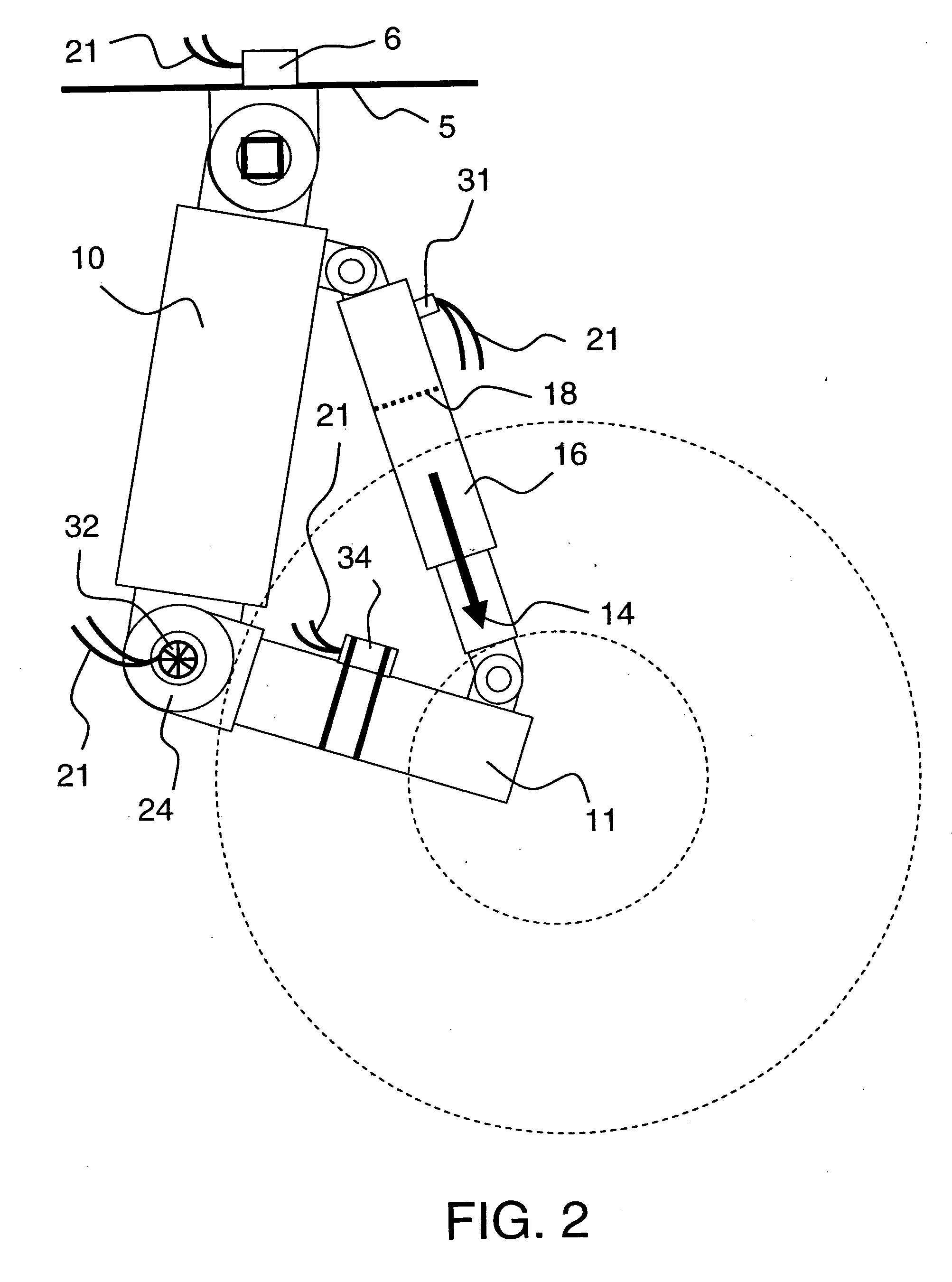
Control system for resilient support mechanism such as vehicle suspension mechanism
InactiveUS6314353B1Continuous changeEnhance running stability and comfortDigital data processing detailsNon-rotating vibration suppressionDamping factorRelative displacement
A control system for a resilient support mechanism such as a suspension mechanism of a wheeled vehicle including a damper disposed between an unsprung mass member and a sprung mass member of the vehicle, wherein a damping coefficient of the damper is divided into a linear portion and a nonlinear portion, and wherein the nonlinear portion of the damping coefficient is defined as a control input u and applied with a frequency weight Wu(s), while a vertical velocity of the sprung mass member, a relative velocity of the sprung mass member to the unsprung mass member and a vertical acceleration of the sprung mass member are defined as an evaluation output zp and applied with a frequency weight Ws(s). In the control system, a nonlinear Hinfin control theory is applied to a generalized plant to obtain a positive definite symmetric solution P and to calculate a target damping force based on the positive definite symmetric solution P and a state amount such as the vertical velocity of the sprung mass member, a relative displacement of the sprung mass member to the unsprung mass member or the like.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
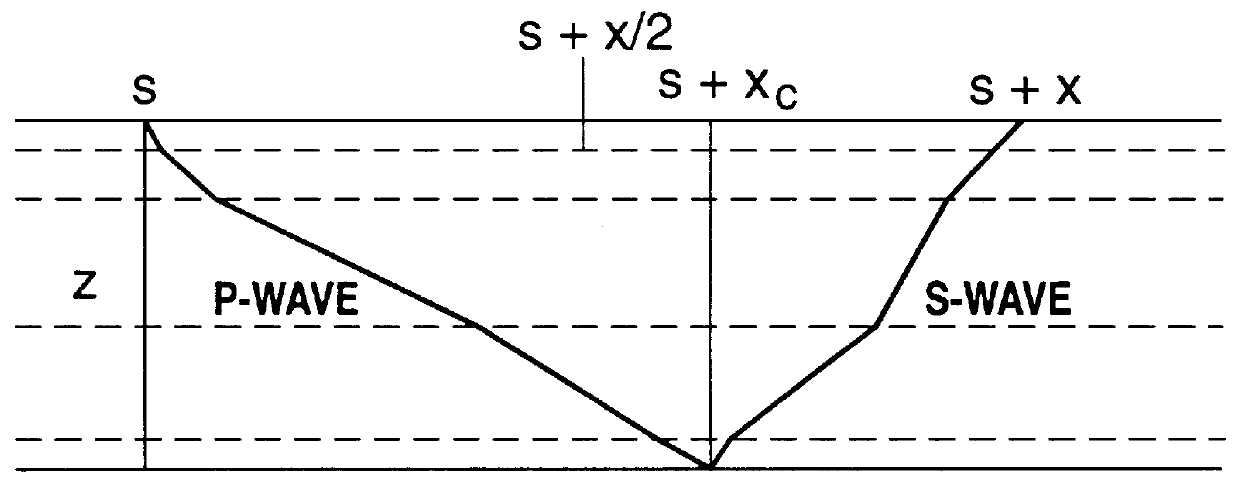
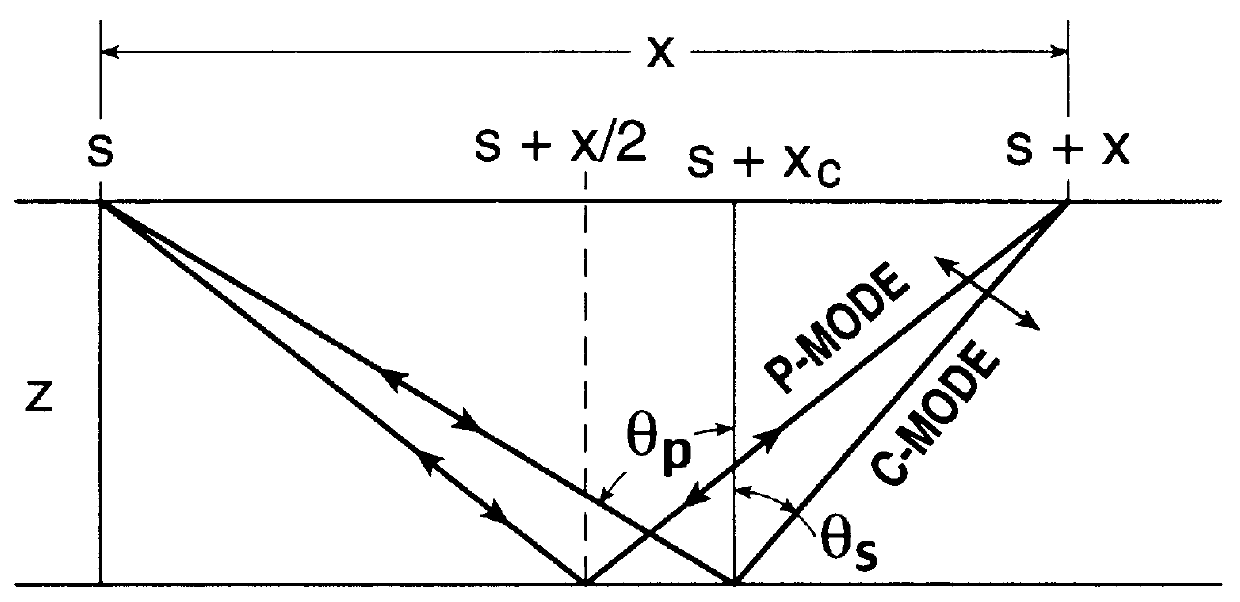
Converted-wave processing in many-layered anisotropic media
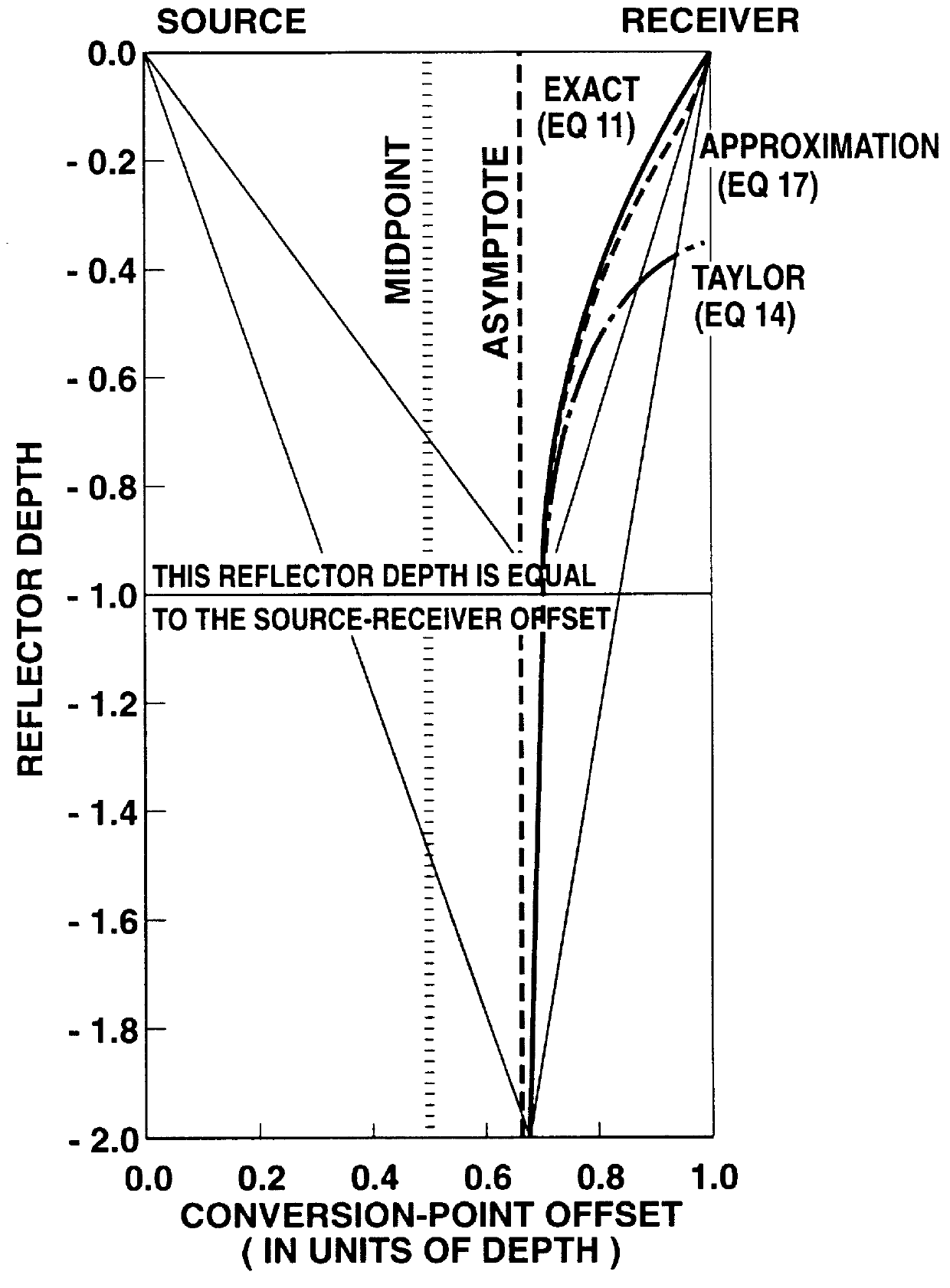
The instant invention provides a method for processing converted-wave data into interpretable images using a compact two-parameter model. The method broadly comprises the steps of: collecting both P-wave and converted-wave seismic data; identifying the arrival times of the P-wave and the converted-wave data; computing the vertical velocity ratio from the arrival time data; computing the moveout velocity ratio from the corresponding moveout velocities; computing the effective velocity ratio from the vertical velocity ratio and the moveout velocity ratio; and computing the conversion point from the short-spread P-wave moveout velocity for each reflector, from the effective velocity ratio, the C-wave moveout velocity ratio, and from the arrival time data.
Owner:BP AMOCO CORP
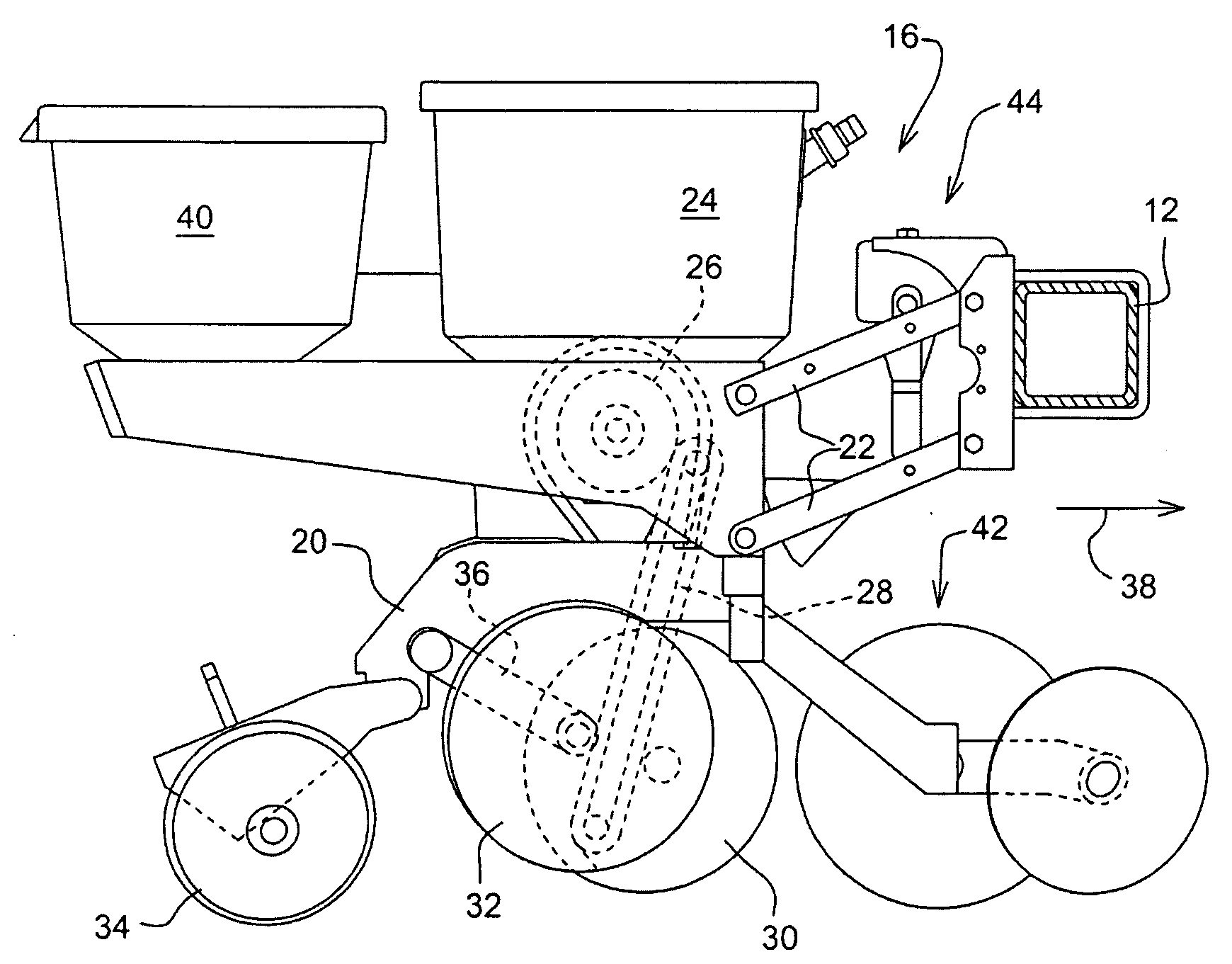
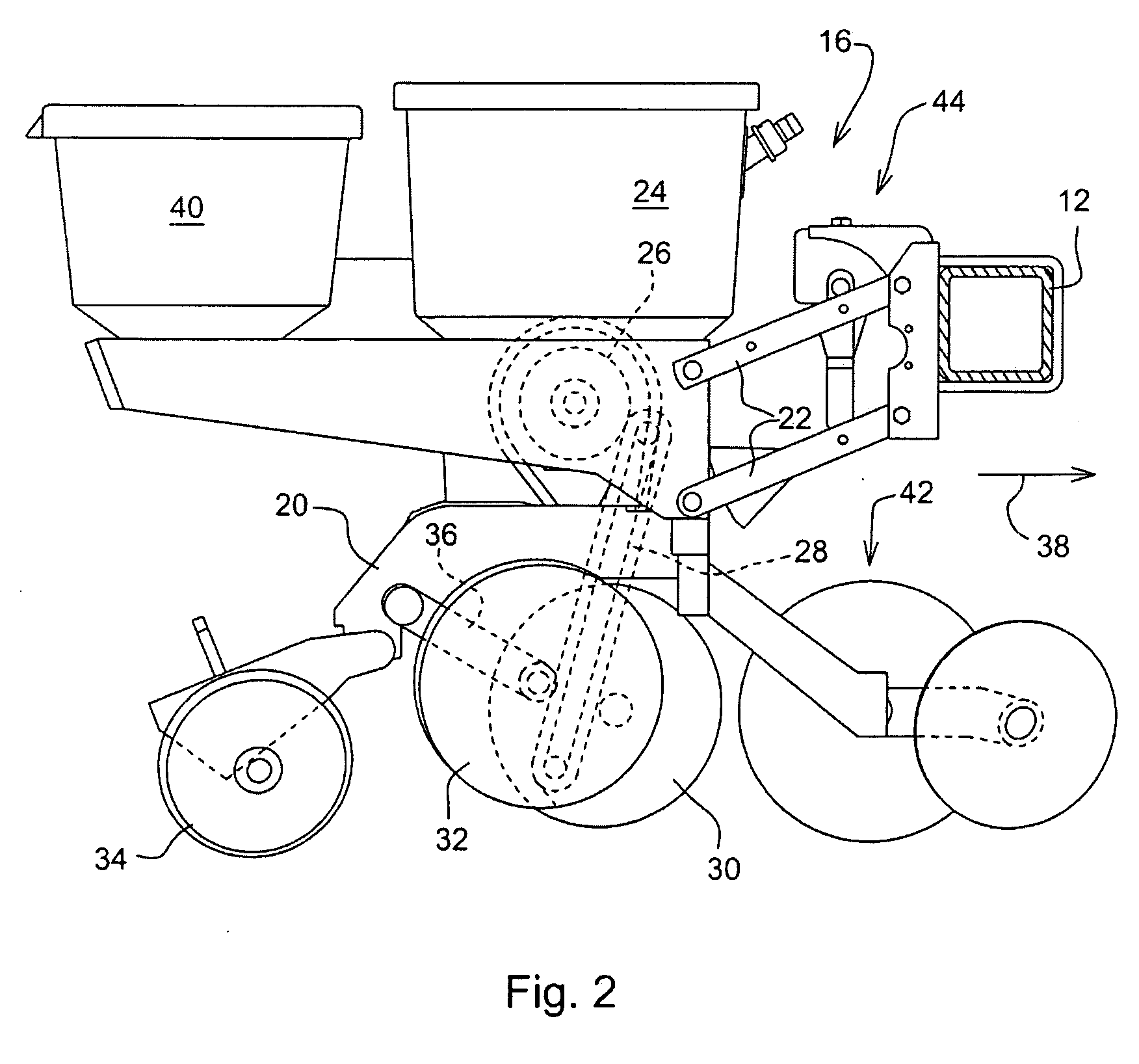
Seeding Machine With Seed Delivery System
ActiveUS20100192819A1Reduces seed spacing variabilityReduce scrollingFertiliser distributersCentrifugal wheel fertilisersEngineeringDelivery system
A seed delivery system for use in a seeding or planting machine that removes the seed from a seed meter by capturing the seed therefrom. The delivery system then moves the seed down to a lower discharge point and accelerates the seed horizontally rearward to a speed approximately equal to the forward travel speed of the seeding machine such that the seed, when discharged has a low or zero horizontal velocity relative to the ground. Rolling of the seed in the trench is thus reduced. Furthermore, as the seed only has a short drop from the outlet to the bottom of the seed trench, the seed has little vertical speed to induce bounce. The delivery system uses a brush belt to capture, move and accelerate the seed. By capturing the seed and moving it from the meter to the discharge, the seed is held in place relative to other seeds and the planter row unit. As a result, the seeds are isolated from row unit dynamics thereby maintaining seed spacing.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Distribution of Targeted Messages and the Serving, Collecting, Managing, and Analyzing and Reporting of Information relating to Mobile and other Electronic Devices
InactiveUS20070262860A1Safely and accurately identify themselves to publicHigh incidenceNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMobile deviceTime of day
The field of invention is computer-implemented methods and systems for distributing targeted messages and the serving, collecting, managing, and analyzing and reporting of information relating to mobile and other electronic devices. Targeting of messages can be improved by employing additional variables to target messages. In the push message process (1000) a message is sent to users of mobile devices based on one or more variables that may include current location as well as temporal variables such as time of day and other spatial or kinetic variables—measured and / or derived—including but not limited horizontal velocity, vertical velocity, heading, orientation, travel distance, travel time, range and / or past points of reference in additional variables such as demographics, user preferences, and / or purchasing behavior. The user may be prompted to take an action in response to the message. In the user request process (2000) a user may make a request for information with or without first receiving a message. The request may be based on one or more variables that may include current location and geographic variables such as altitude as well as temporal variables such as time of day and other spatial or kinetic variables. Information is collected, managed, analyzed, and reported in the collect information process (3000), manage information process (4000), and analysis and report information process (5000), respectively. In addition, such methods and systems can also be used for advertising, marketing, promotions, campaigns, orders, sales, subscriptions, donations, pledges and so on.
Owner:SALINAS ROBERT +1
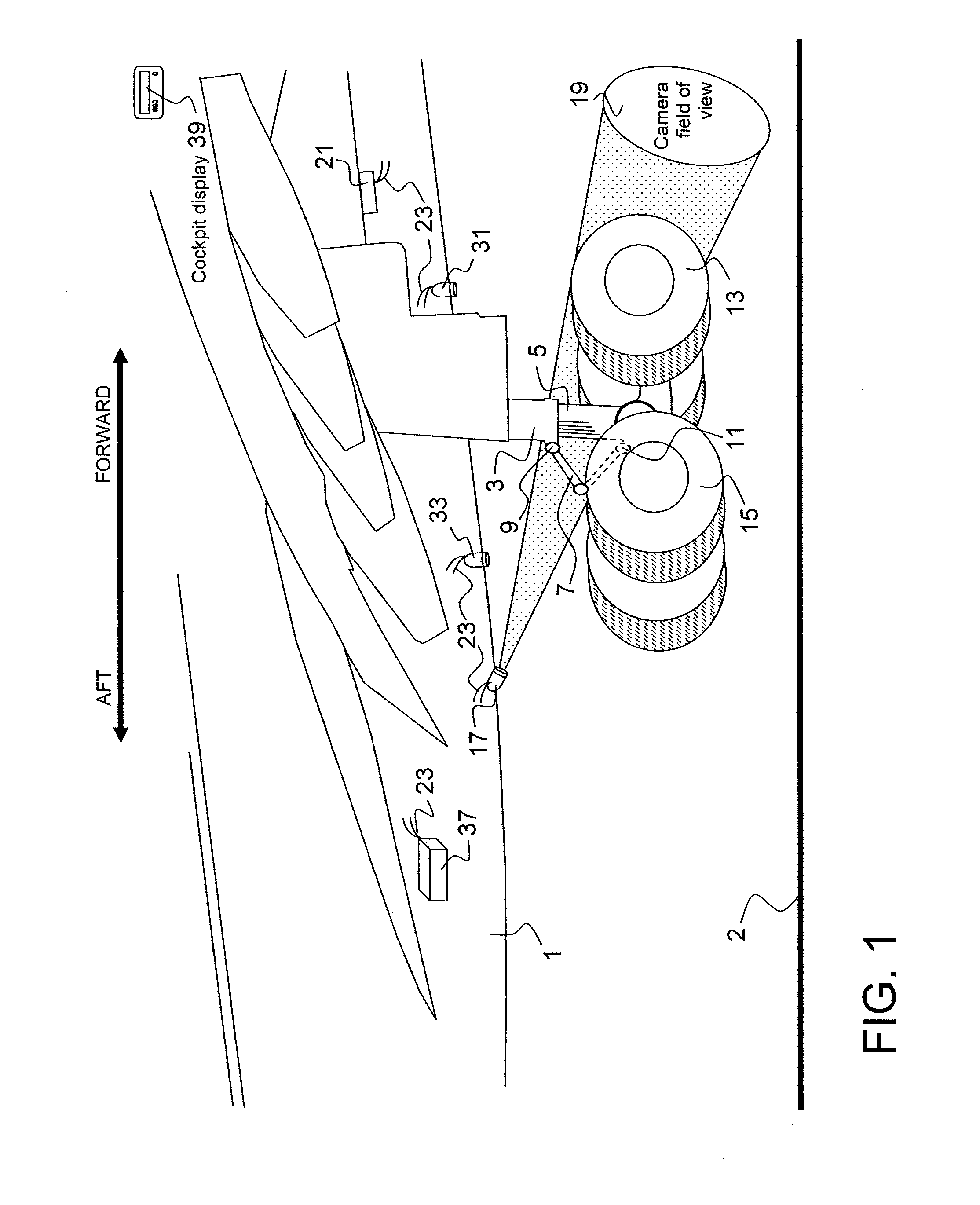
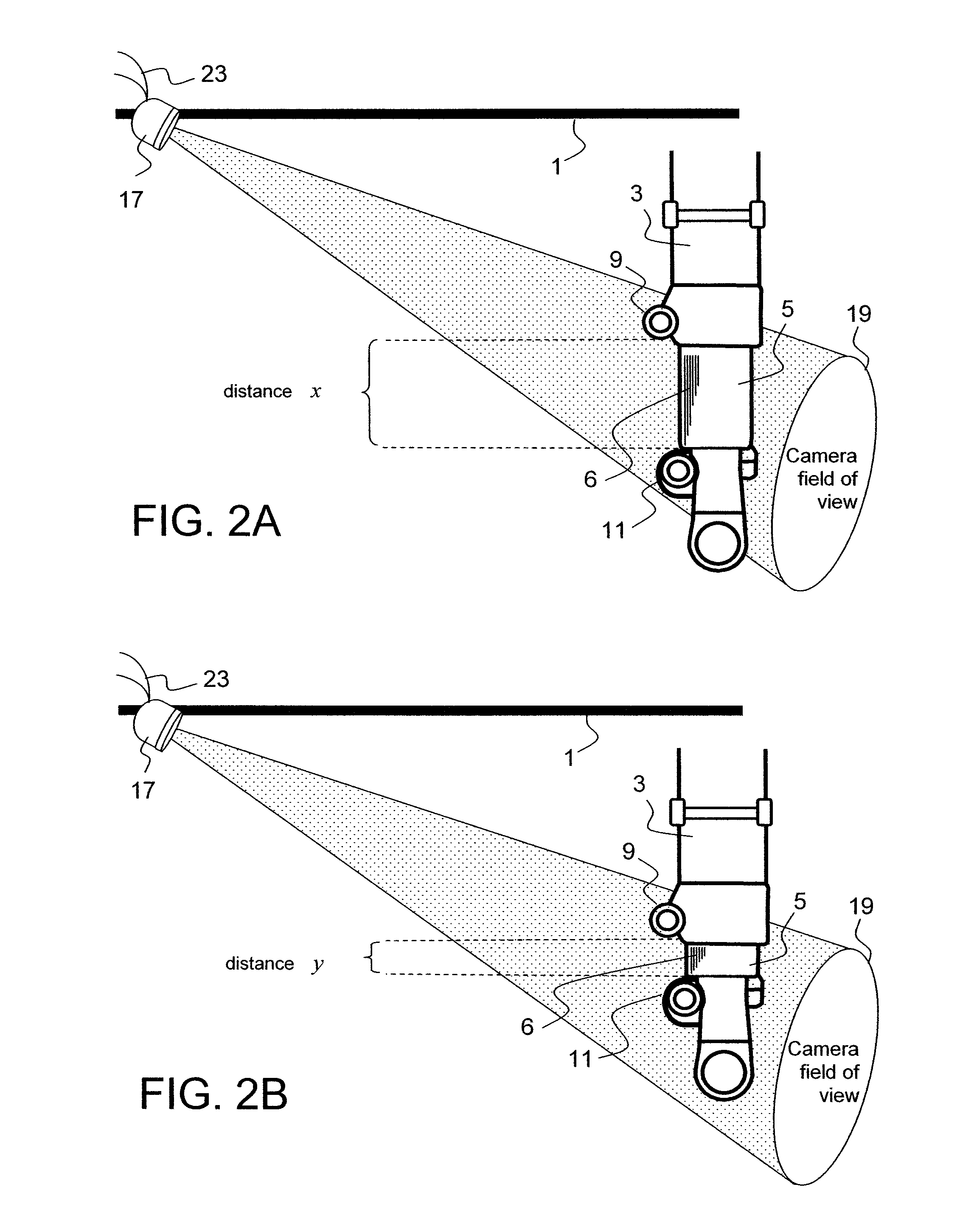
Aircraft landing gear compression rate monitor
ActiveUS8042765B1Aircraft health monitoring devicesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAircraft landingAirplane
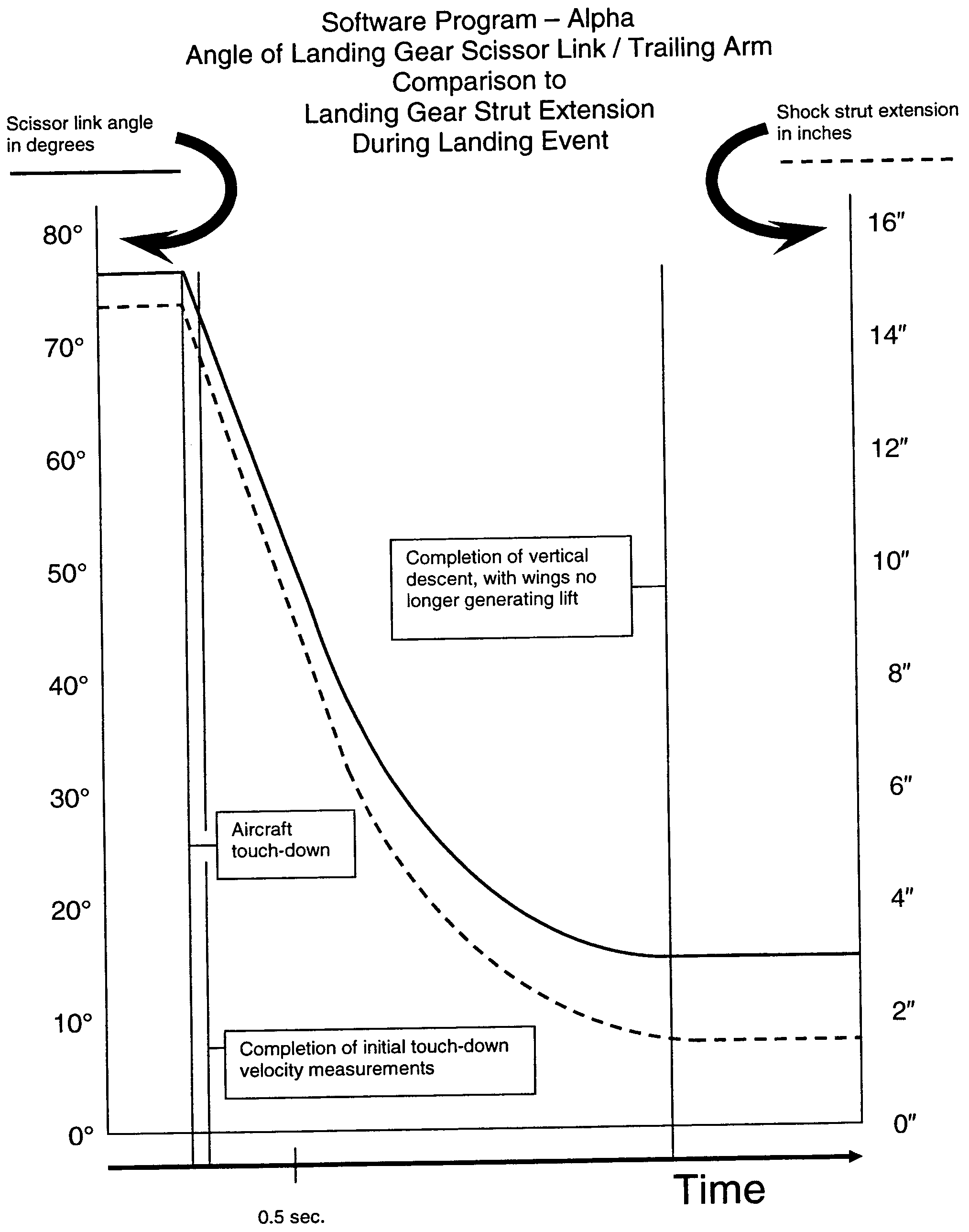
A system for use in monitoring, measuring, computing and displaying the rate of compression of aircraft landing gear struts experienced while aircraft are executing either normal or hard landing events. A high speed computer attached to high speed cameras, or range-finders, mounted in relation to each of the landing gear struts are used to monitor, measure and record the landing gear compression rates and aircraft touch-down vertical velocities experienced by landing gear struts, as the aircraft landing gear initially comes into contact with the ground. The system also determines through landing gear strut compression rates if aircraft landing limitations have been exceeded.
Owner:NANCE C KIRK
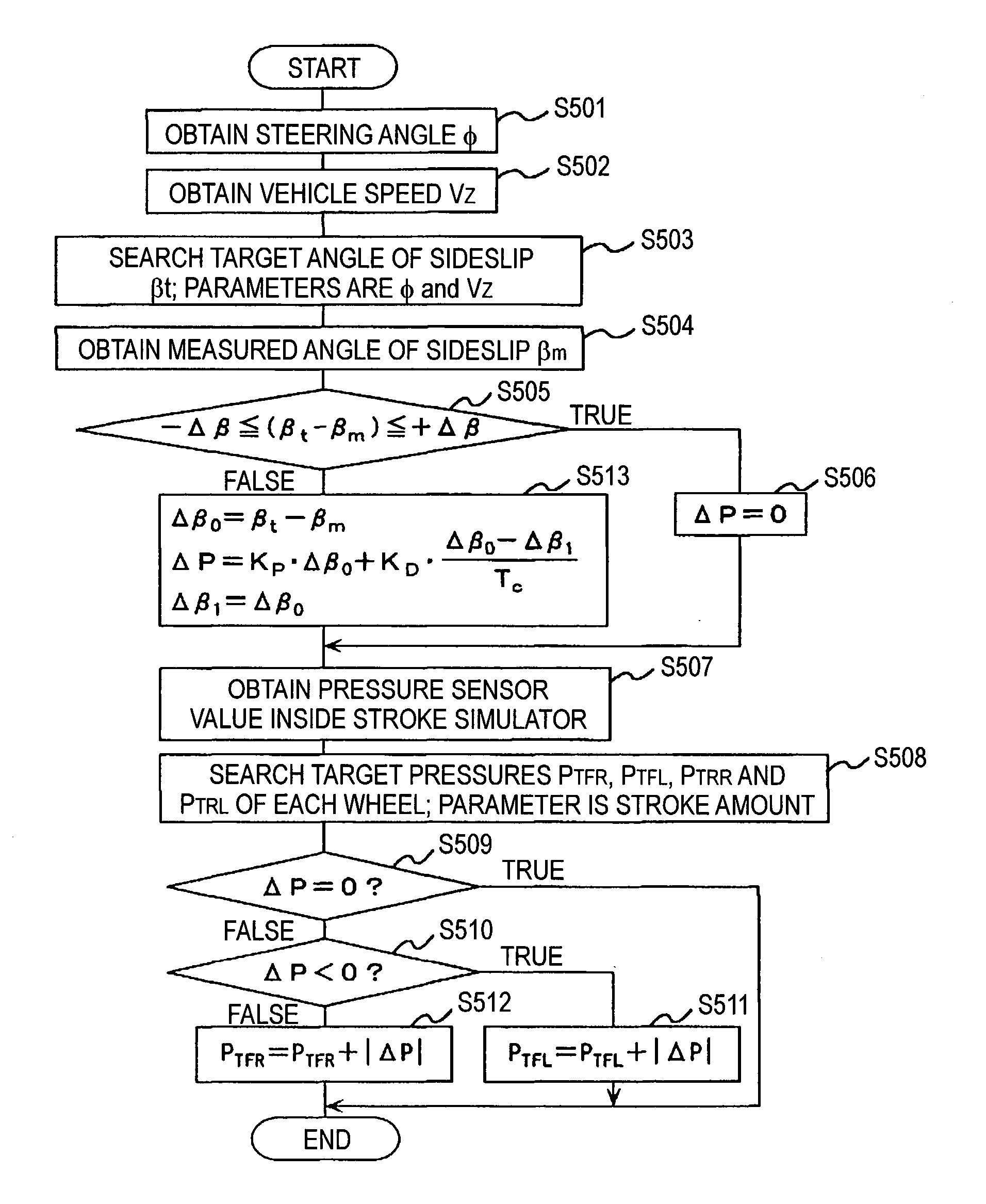
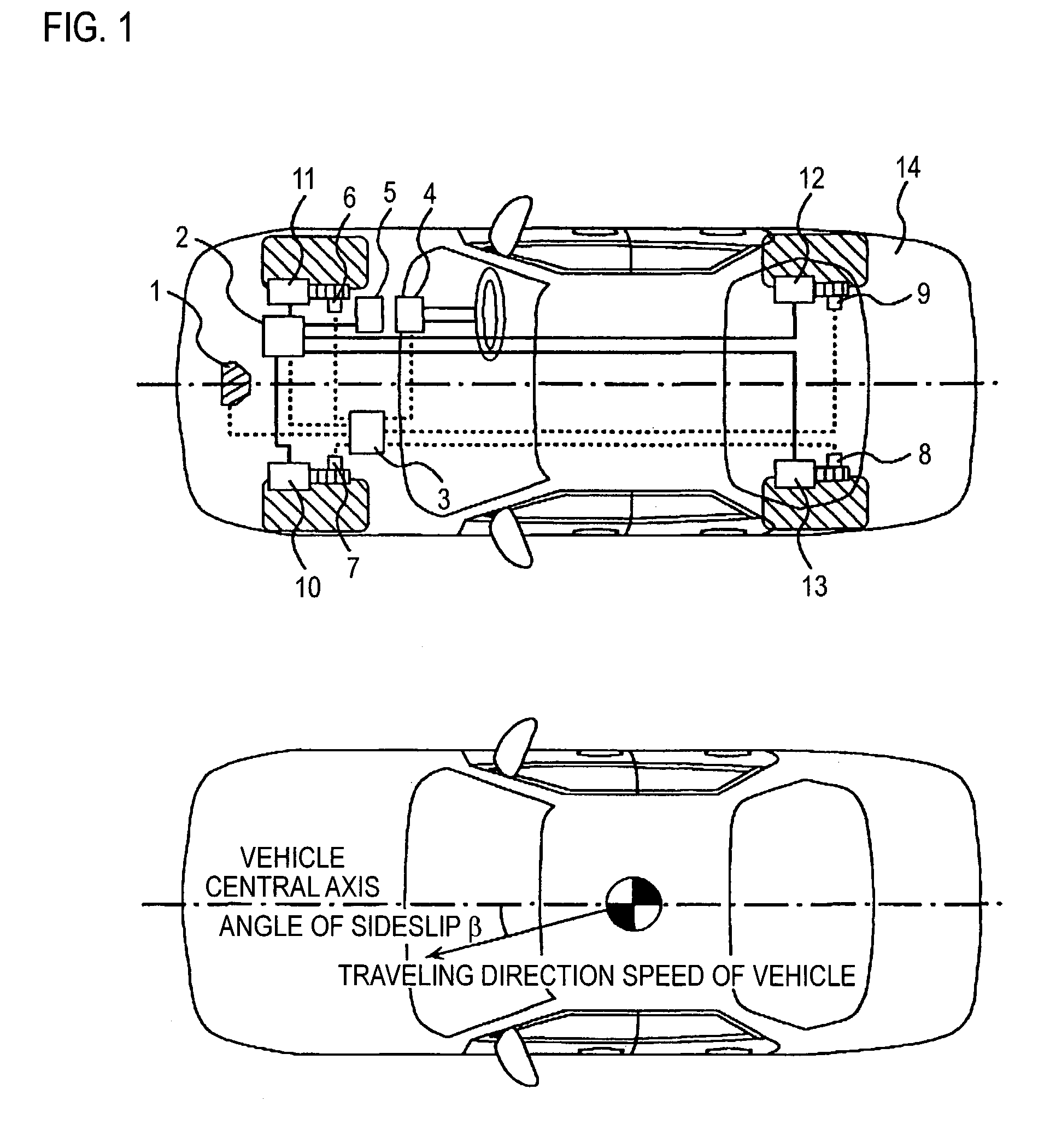
Vehiclar travel control device
InactiveUS20040138802A1Analogue computers for trafficComputations using stochastic pulse trainsDamping factorRadar
In a vehicular control device, it is necessary to measure or calculate six physical quantities-forward-reverse speed, left-right speed, vertical speed, pitch angle, roll angle, and angle of sideslip-representing vehicular movement and to control the braking force of each wheel and / or the damping coefficient of each suspension shock absorber in order to further shorten braking distance particularly at the time of braking and to prevent spin at that time. In this case, it is necessary to furnish sensors to measure speed and angle directly. In the present invention, four radar sensors are used in order to directly measure the forward-reverse speed and the left-right speed. Also, the vertical speed, the pitch angle, the roll angle, and the angle of sideslip are indirectly measured from the output of the radar sensors. By using three or four radar sensors, six physical quantities-the forward speed, the left-right direction speed, the vertical speed, the angle of sideslip, the pitch angle, and the roll angle-can be measured. Also, by using two radar sensors, three physical quantities-the forward speed, the left-right speed, and the angle of sideslip-can be measured.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
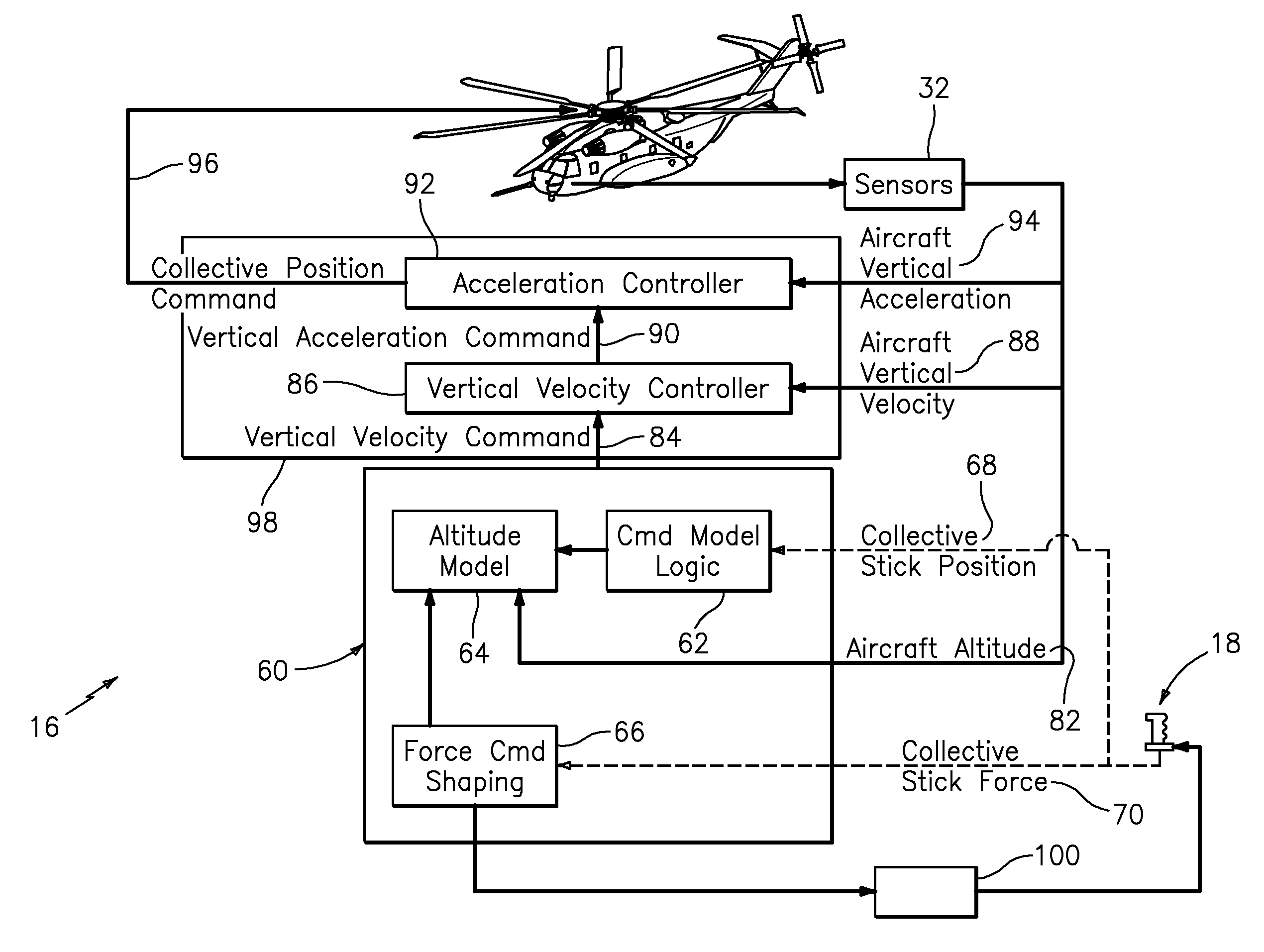
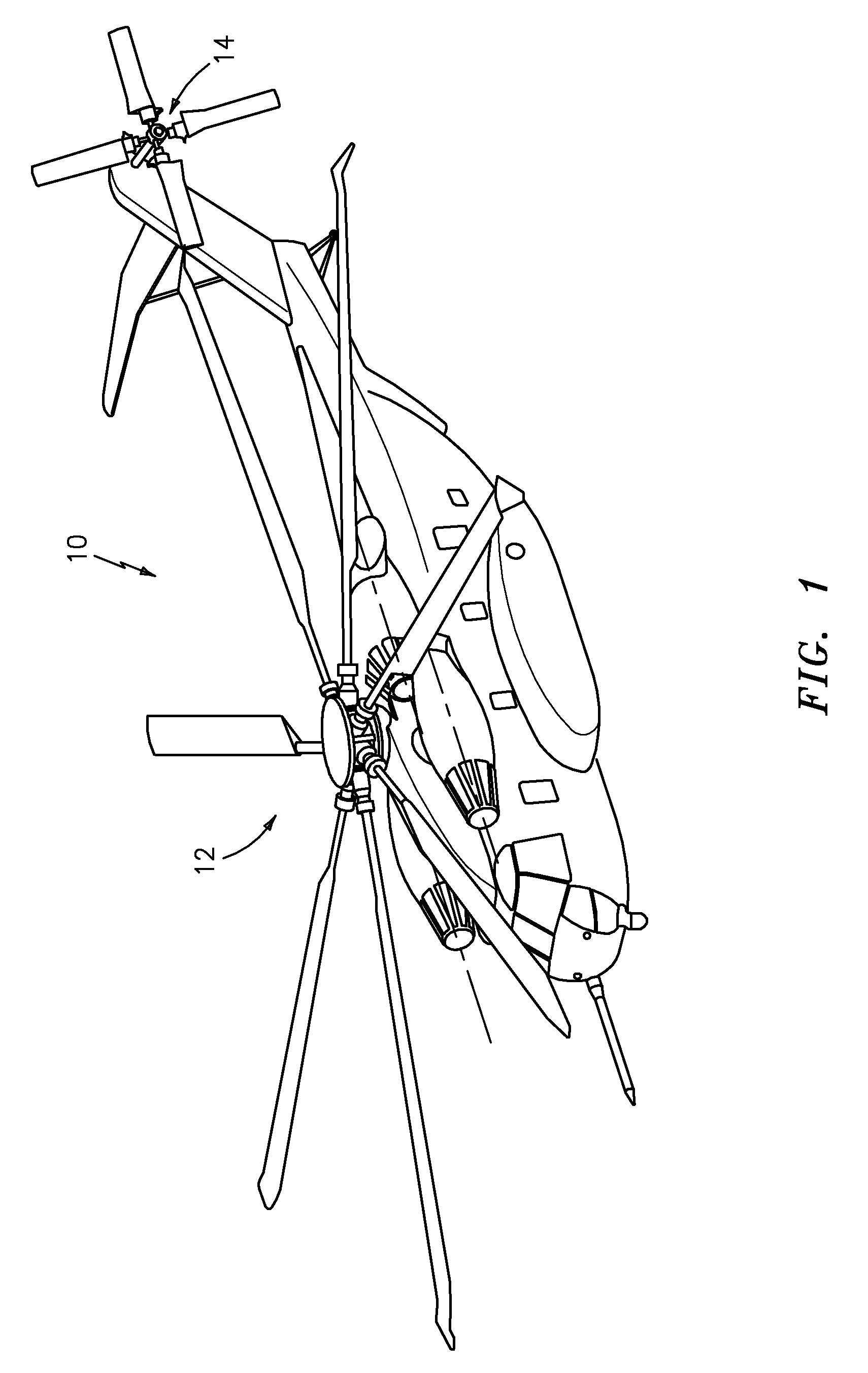
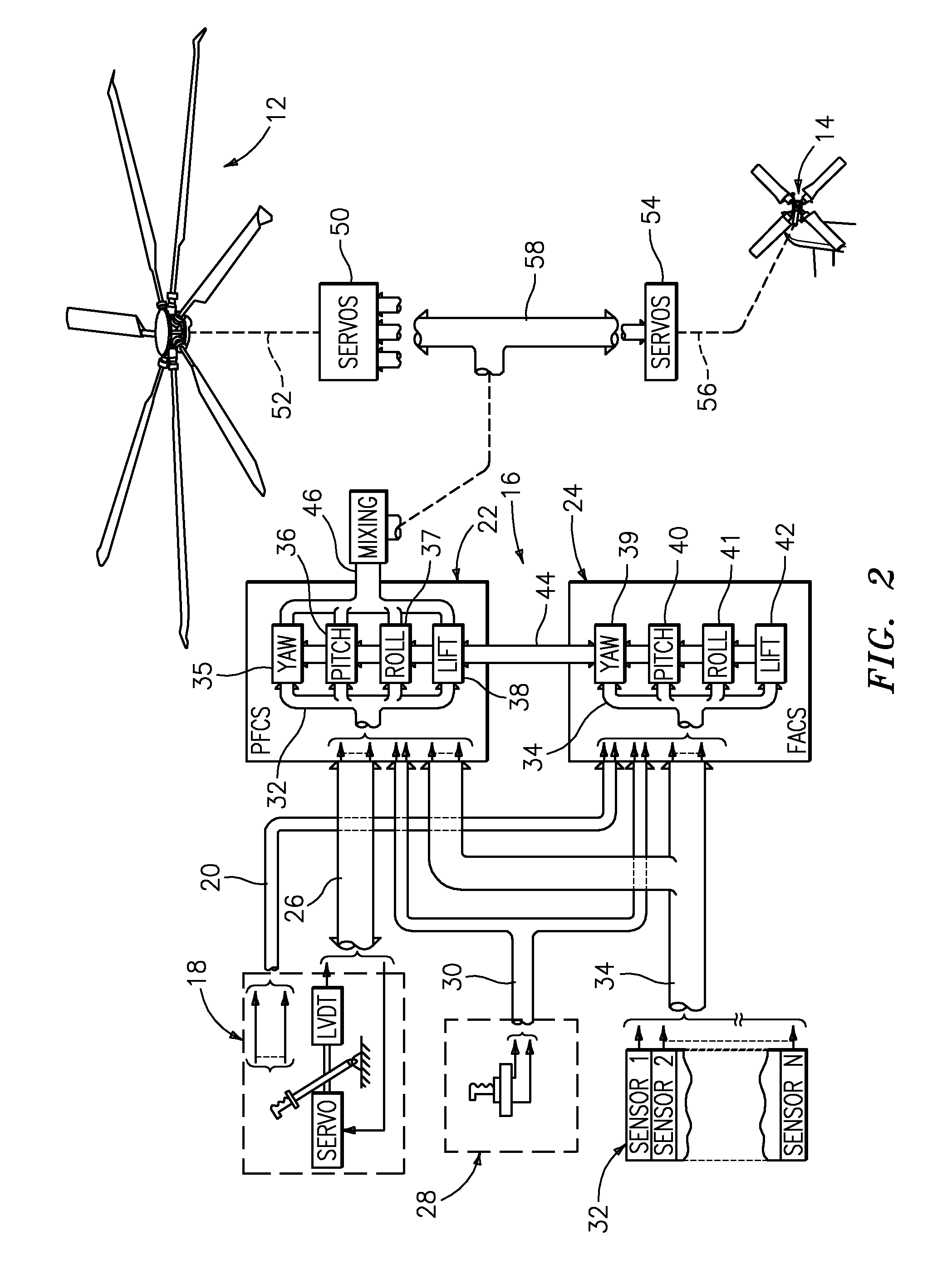
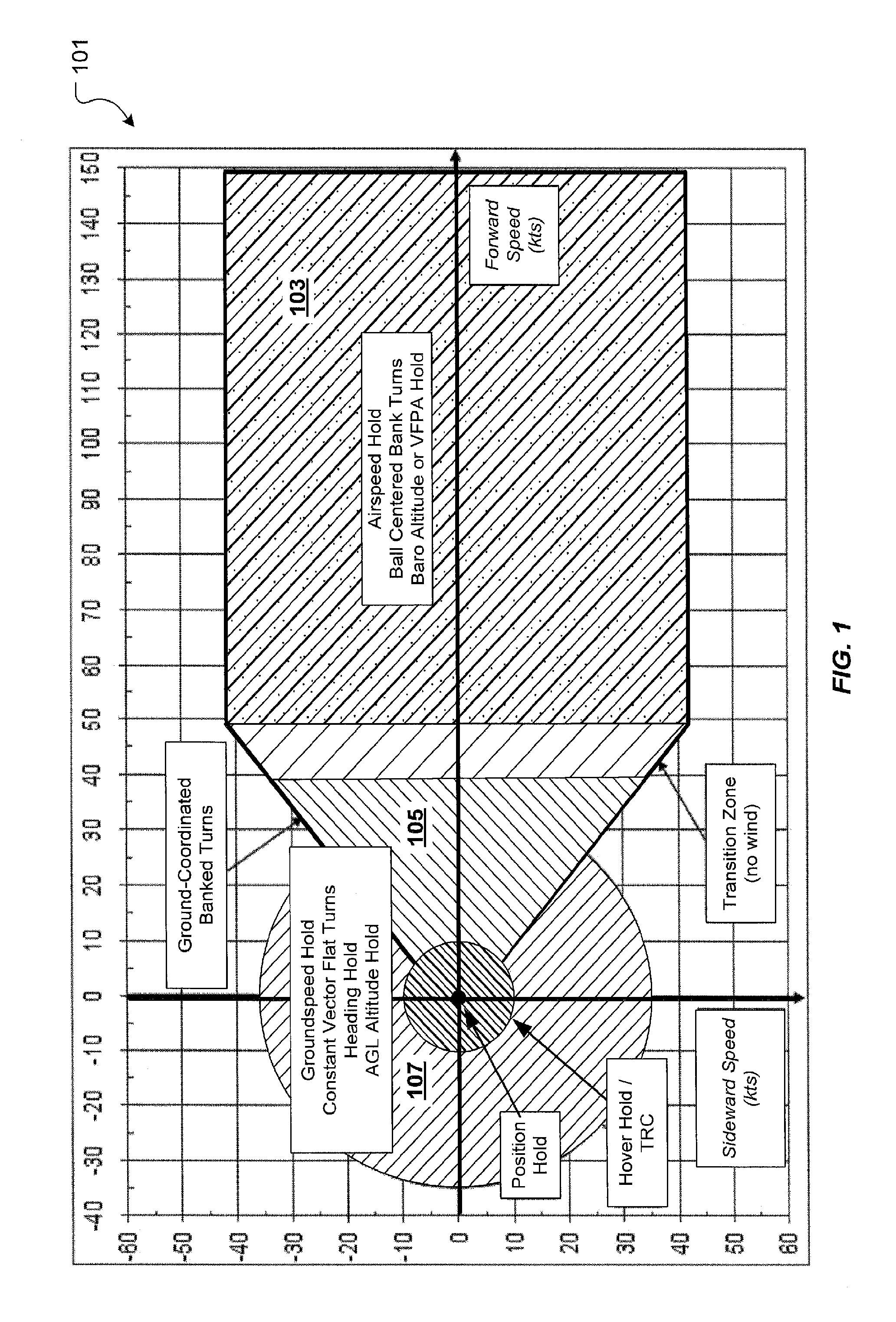
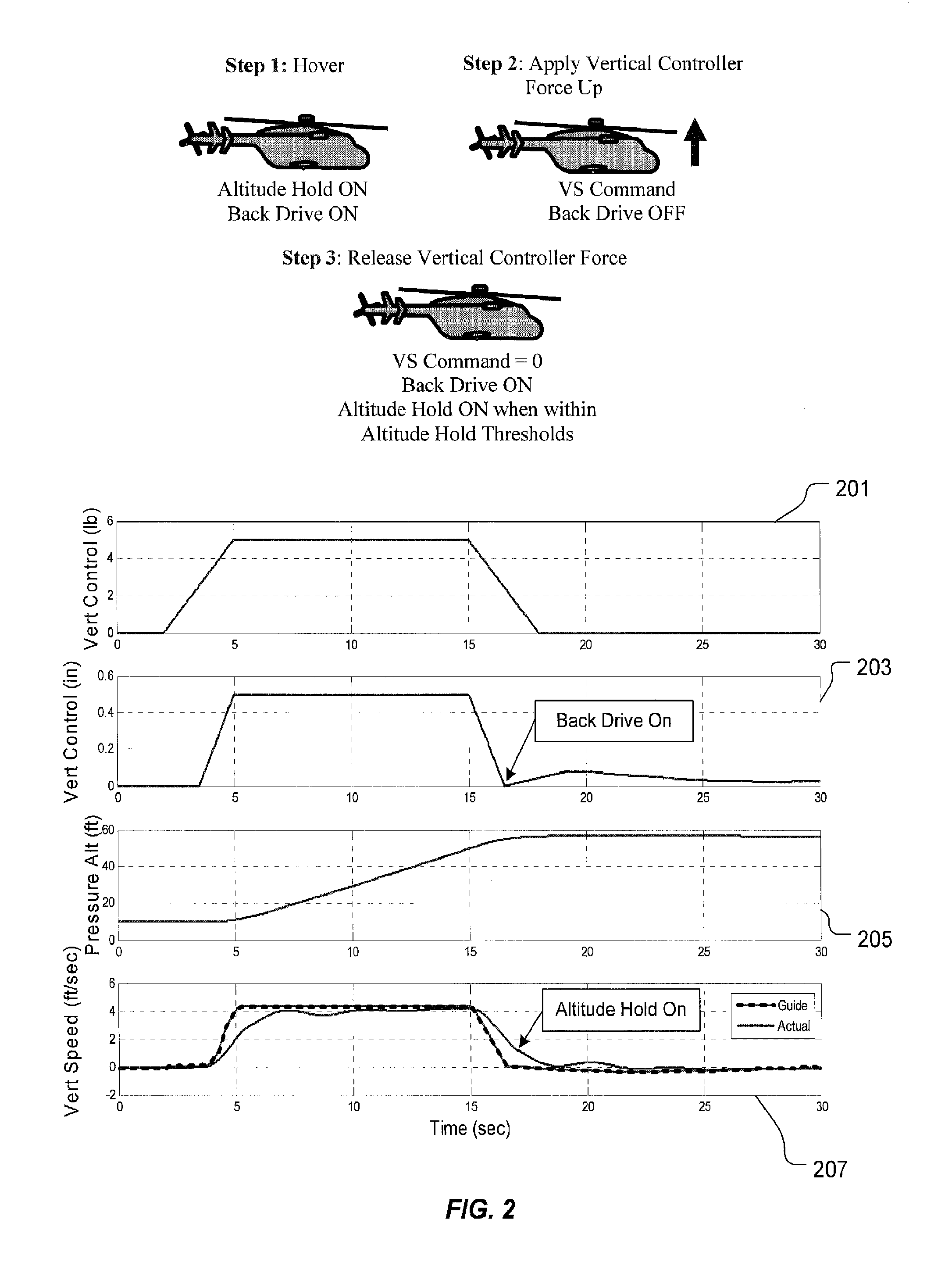
Vertical speed and flight path command algorithm for displacement collective utilizing tactile cueing and tactile feedback
ActiveUS20080234881A1Improve processing qualityEnhanced Situational AwarenessAircraft controlDigital data processing detailsLevel flightDetent
A flight control system includes a collective position command algorithm for a lift axis (collective pitch) which, in combination with an active collective system, provides a force feedback such that a pilot may seamlessly command vertical speed, flight path angle or directly change collective blade pitch. The collective position command algorithm utilizes displacement of the collective controller to command direct collective blade pitch change, while a constant force application to the collective controller within a “level flight” detent commands vertical velocity or flight path angle. The “level flight” detent provides a tactile cue for collective position to reference the aircraft level flight attitude without the pilot having to refer to the instruments and without excessive collective controller movement.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Aircraft landing gear kinetic energy monitor
A system for use in monitoring, measuring, computing and displaying the Kinetic Energy generated and experienced while aircraft are executing either normal, overweight or hard landing events. Pressure sensors and motion sensors are mounted in relation to each of the landing gear struts to monitor, measure and record the impact loads and aircraft touch-down vertical velocities experienced by landing gear struts, as the aircraft landing gear initially comes into contact with the ground. Velocity adjustments are made to correct for errors caused by landing gear per-charge pressure and landing gear strut seal friction. The system also measures the landing loads experienced by each landing gear strut during the landing event and determines if aircraft limitations have been exceeded.
Owner:NANCE C KIRK
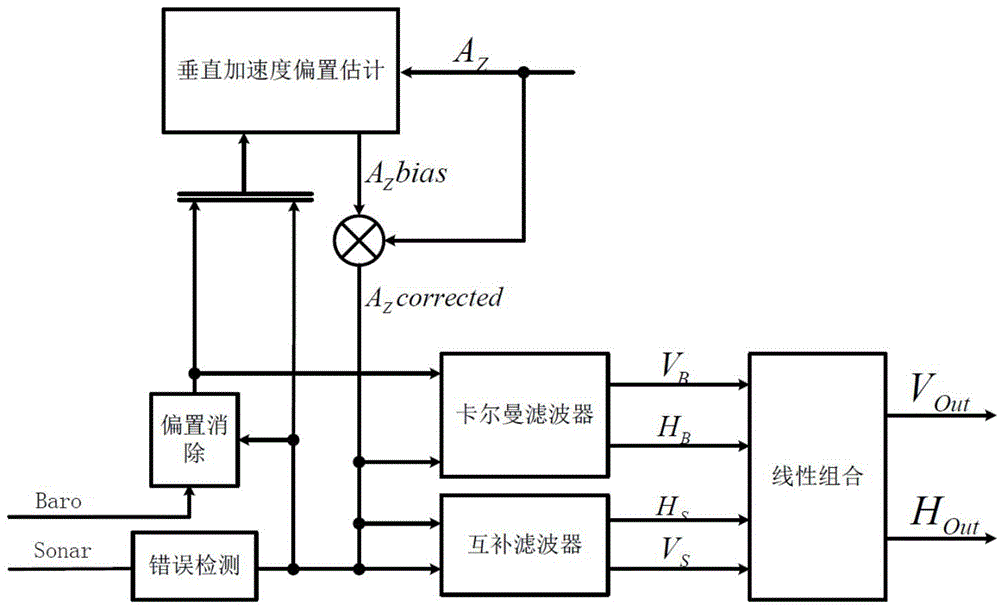
Multi-sensor information fusion-based method for measuring height of small unmanned gyroplane
ActiveCN104567799AImprove reliabilityHigh precisionHeight/levelling measurementAccelerometerMulti sensor
The invention belongs to the field of small unmanned gyroplane autonomous flight control research, provides a multi-sensor information fusion-based method for measuring the height of a small unmanned gyroplane, and aims at providing real-time, precise and reliable height information for the small unmanned gyroplane. The adopted technical scheme is as follows: a sonar arranged at the bottom of the unmanned gyroplane is used for acquiring the distance from the sonar to the ground, and the distance is used as a sonar measurement height; an accelerometer is utilized for acquiring the triaxial accelerated speed of the unmanned gyroplane under an object coordinate system, thereby acquiring the vertical acceleration in a geodetic reference system; a barometer is used for measuring barometric pressure information of the unmanned gyroplane at certain height, comparing the barometric pressure information of the unmanned gyroplane at certain height with ground barometric pressure information, substituting a comparing result into a standard atmosphere model to obtain the height measurement information based on the barometric pressure measurement; and the multi-sensor information fusion height measurement method is adopted for obtaining the high-frequency real-time height and vertical velocity information by use of the inputs. The method is mainly applied to the unmanned gyroplane autonomous flight control.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Self-evolution ANFIS and UKF combined GPS/MEMS-INS integrated positioning error dynamic forecasting method
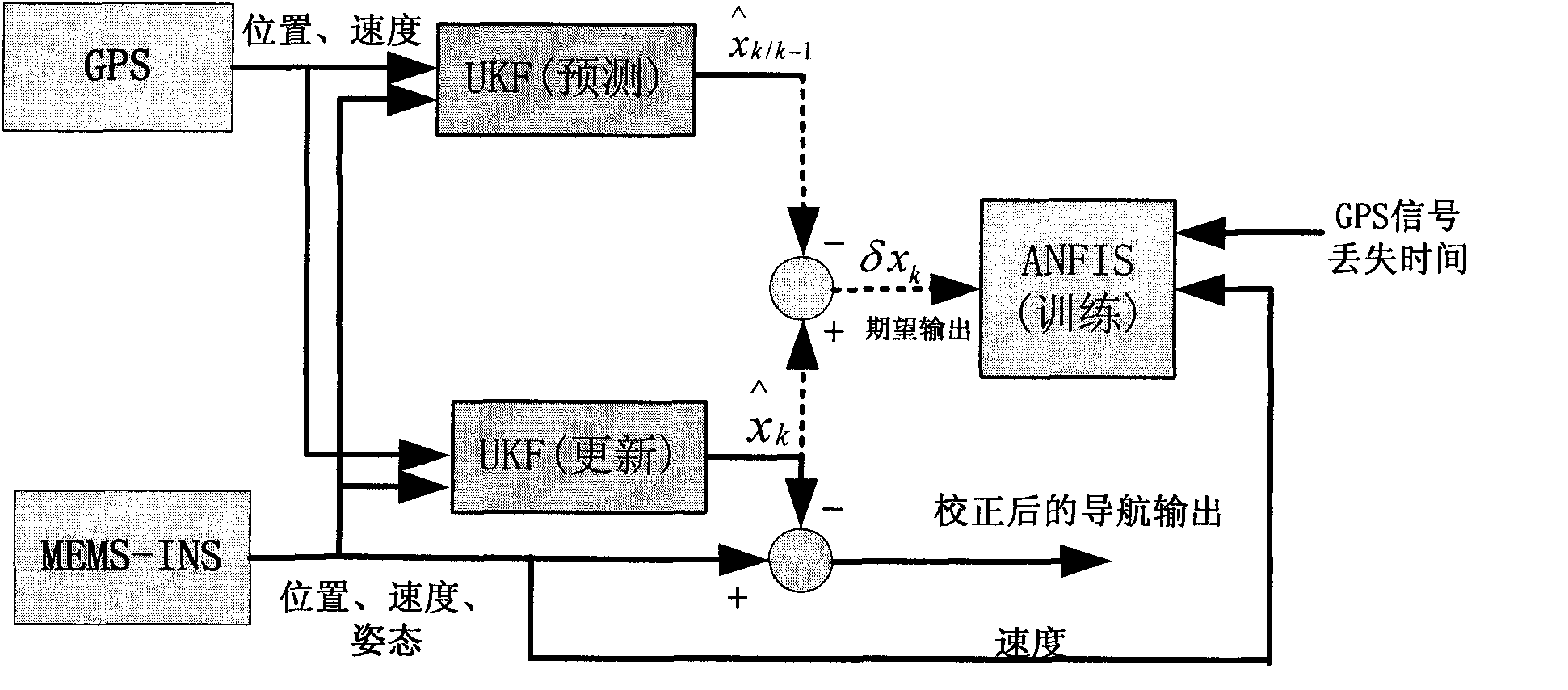
InactiveCN101819041ARealize self-evolving real-time updateGuaranteed real-timeInternal combustion piston enginesNavigational calculation instrumentsBusiness forecastingNavigation system
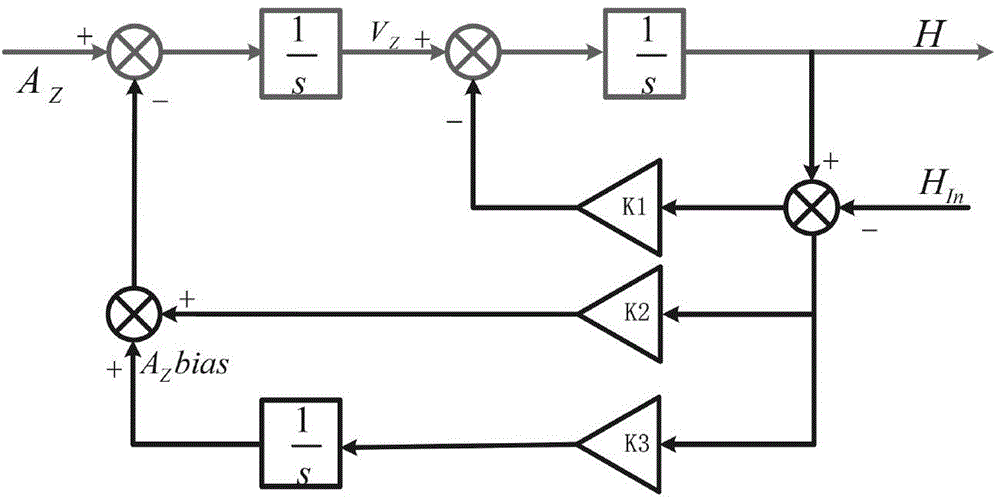
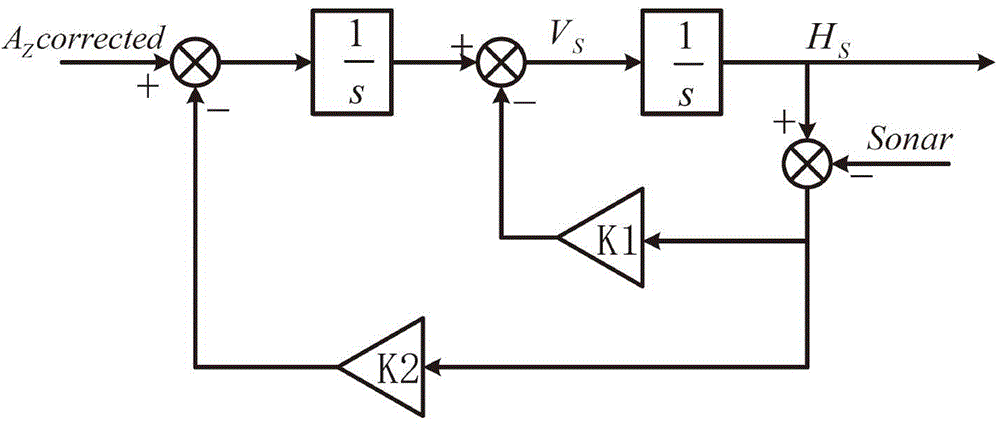
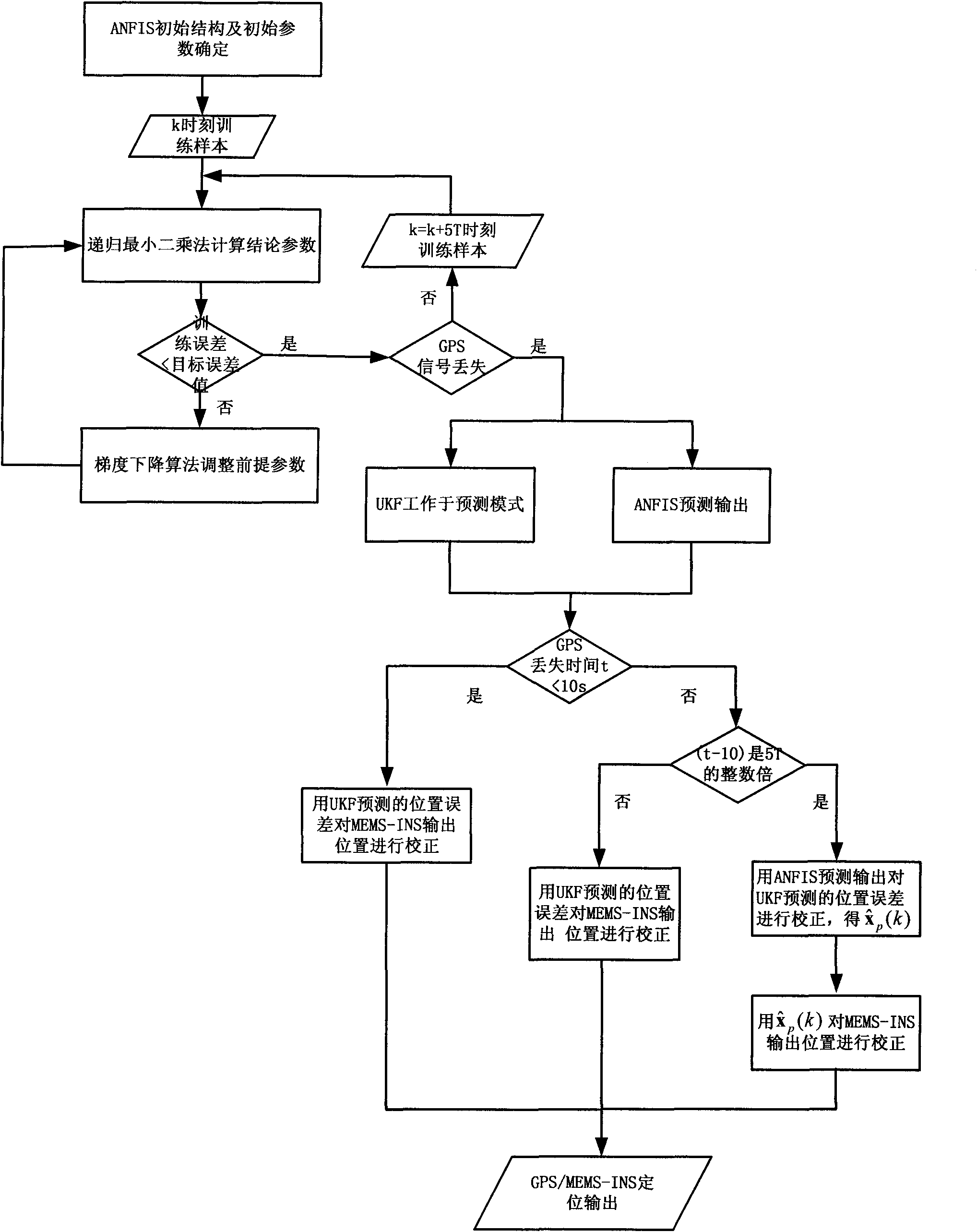
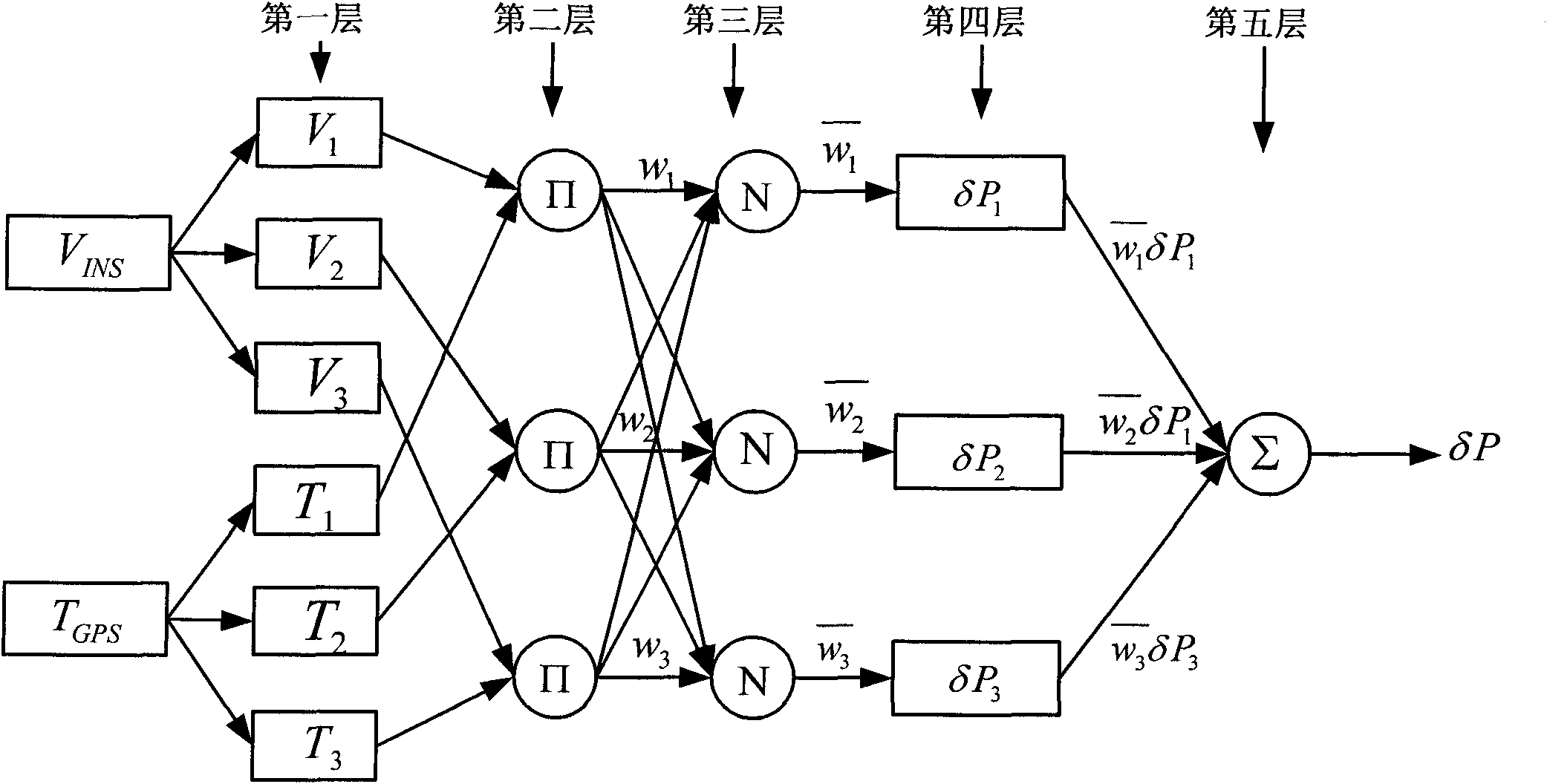
The invention relates to a self-evolution ANFIS and UKF combined GPS / MEMS-INS integrated positioning error dynamic forecasting method. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) off-line confirming an ANFIS structure and an initial premise parameter according to a mass of experimental data comprising different motion characteristics of a carrier; (2) performing the self-evolution real-time updating of an ANFIS model by using an east, north and vertical velocity and GPS signal loss time outputted by the corresponding MEMS-INS under a UKF forecasting mode as input of the ANFIS and using an error value of a position error outputted under two modes of the UKF is used as expected output of the ANFIS, wherein the UKF comprises two concurrent working modes, namely, a forecasting mode and an updating mode, when a GPS / MEMS-INS integrated navigation system starts to work and the GPS signal is in good condition; and (3) forecasting the position error and correcting by a method of dynamically combining the ANFIS mode prediction with the UKF prediction when the GPS signal is lost and the ANFIS mode and the UKF work in a forecasting mode, and outputting the corrected integrated navigation system result. The method enhances the dynamic property and the adaptive ability of the ANFIS mode, and improves the position performance of the integrated navigation system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Legged robot
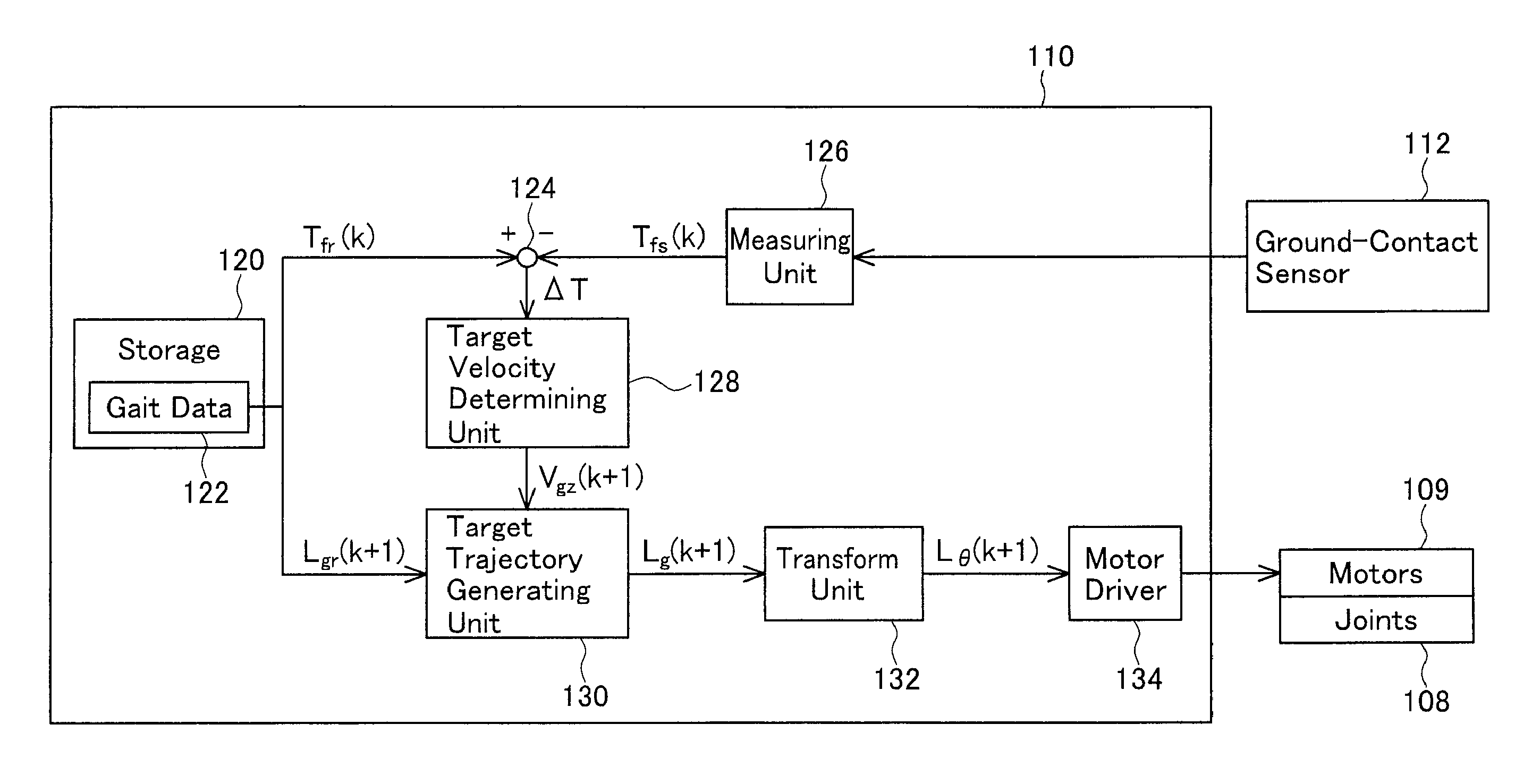
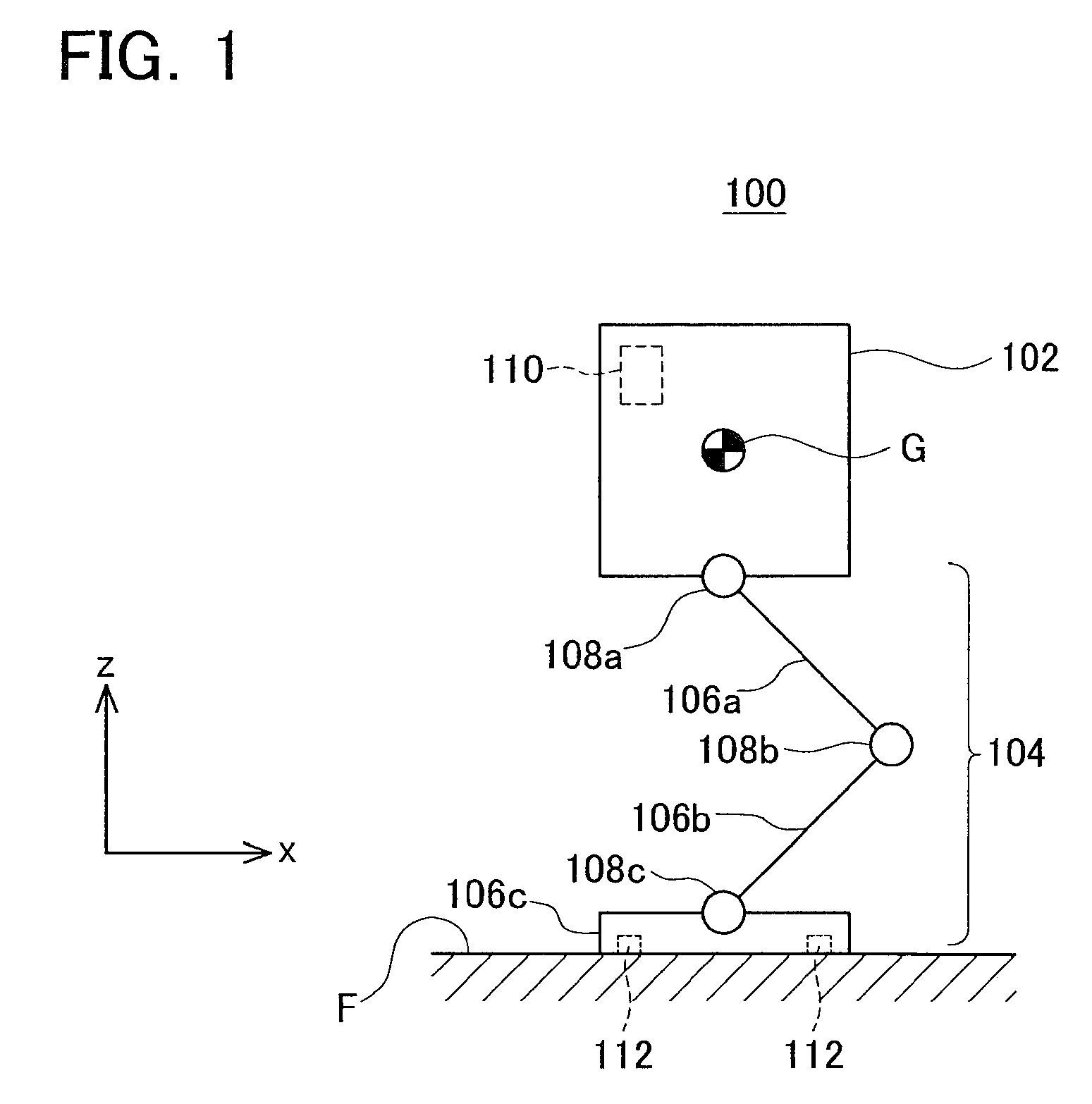
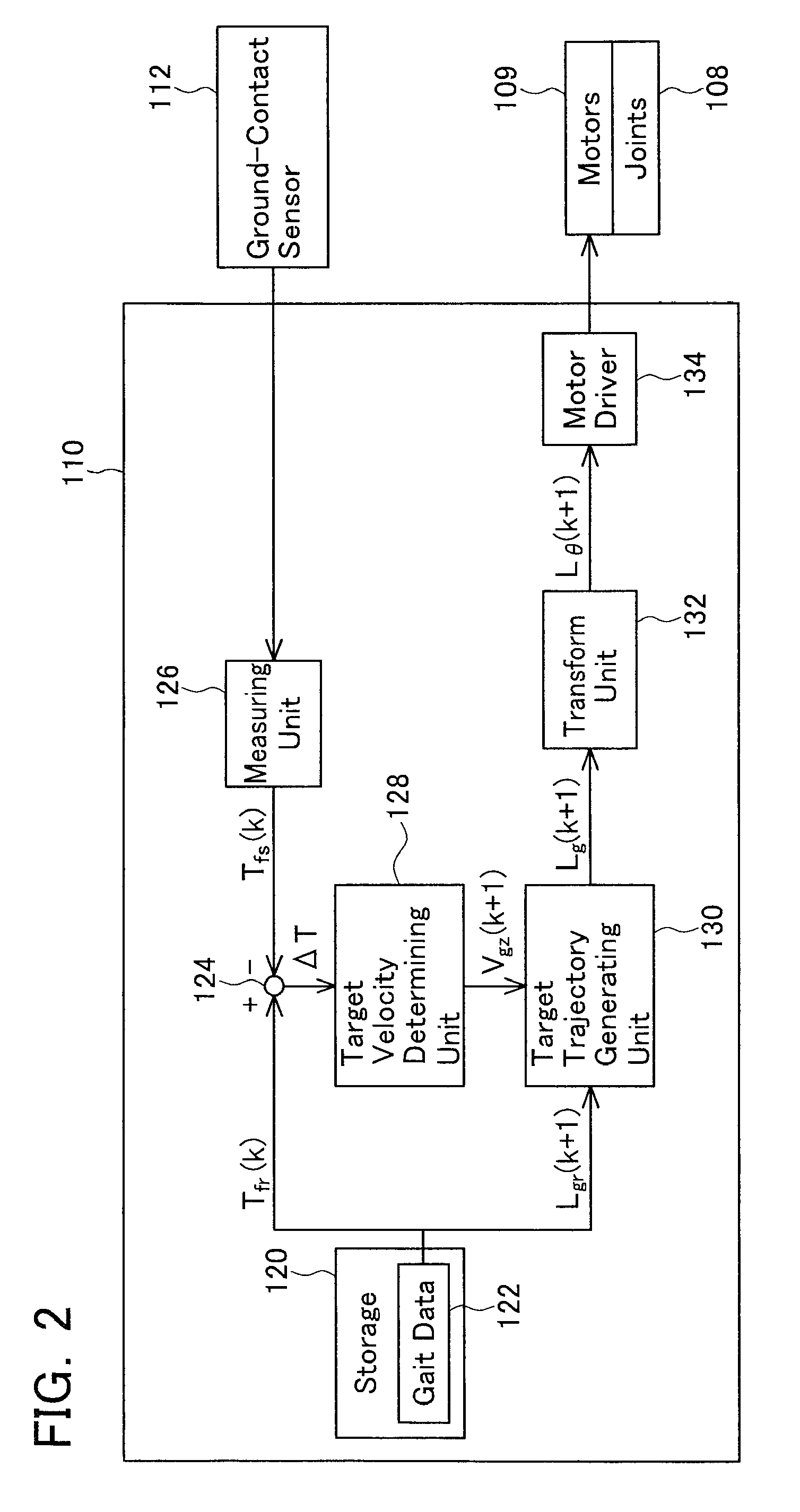
InactiveUS20100017028A1Exclude influenceGuaranteed uptimeComputer controlSimulator controlGround contactProgram planning
A legged robot that runs while repeating a jump cycle including a ground-contact phase from a landing to a takeoff and an aerial phase from a takeoff to a landing is provided. The legged robot adjusts the landing timing after a jump in accordance with a planned timing, thereby attaining a smooth landing. A measuring unit of the legged robot measures an actual aerial phase period in a k-th jump cycle. A subtractor calculates a time difference between a target aerial phase period and the actual aerial phase period in the k-th jump cycle. A target velocity determining unit calculates a target vertical velocity of a center of gravity on a takeoff timing in a (k+1)-th jump cycle so as to eliminate the time difference. Motors in respective joints are controlled so as to realize the calculated target vertical velocity in the (k+1)-th jump cycle. As a result, the time difference generated in the k-th jump cycle in the (k+1)-th jump cycle can be compensated, thereby adjusting the landing timing with the planned landing timing, resulting in the jump motion with smooth landing.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
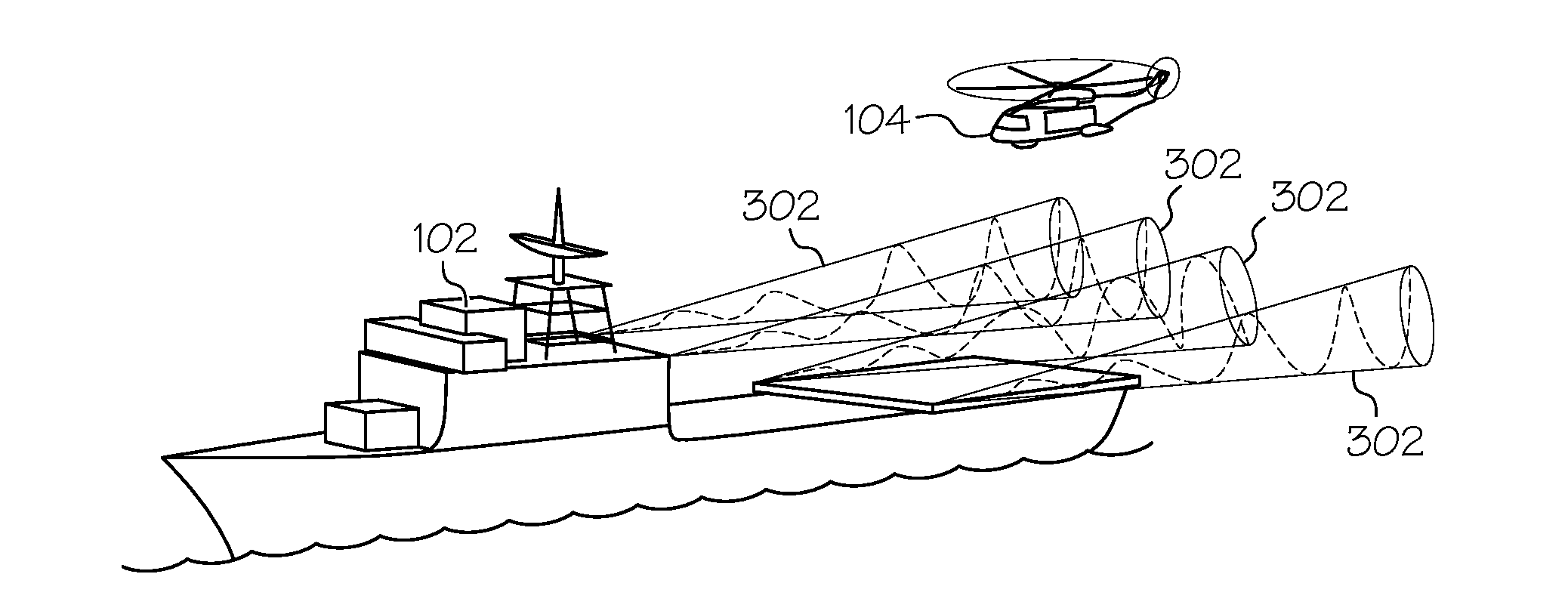
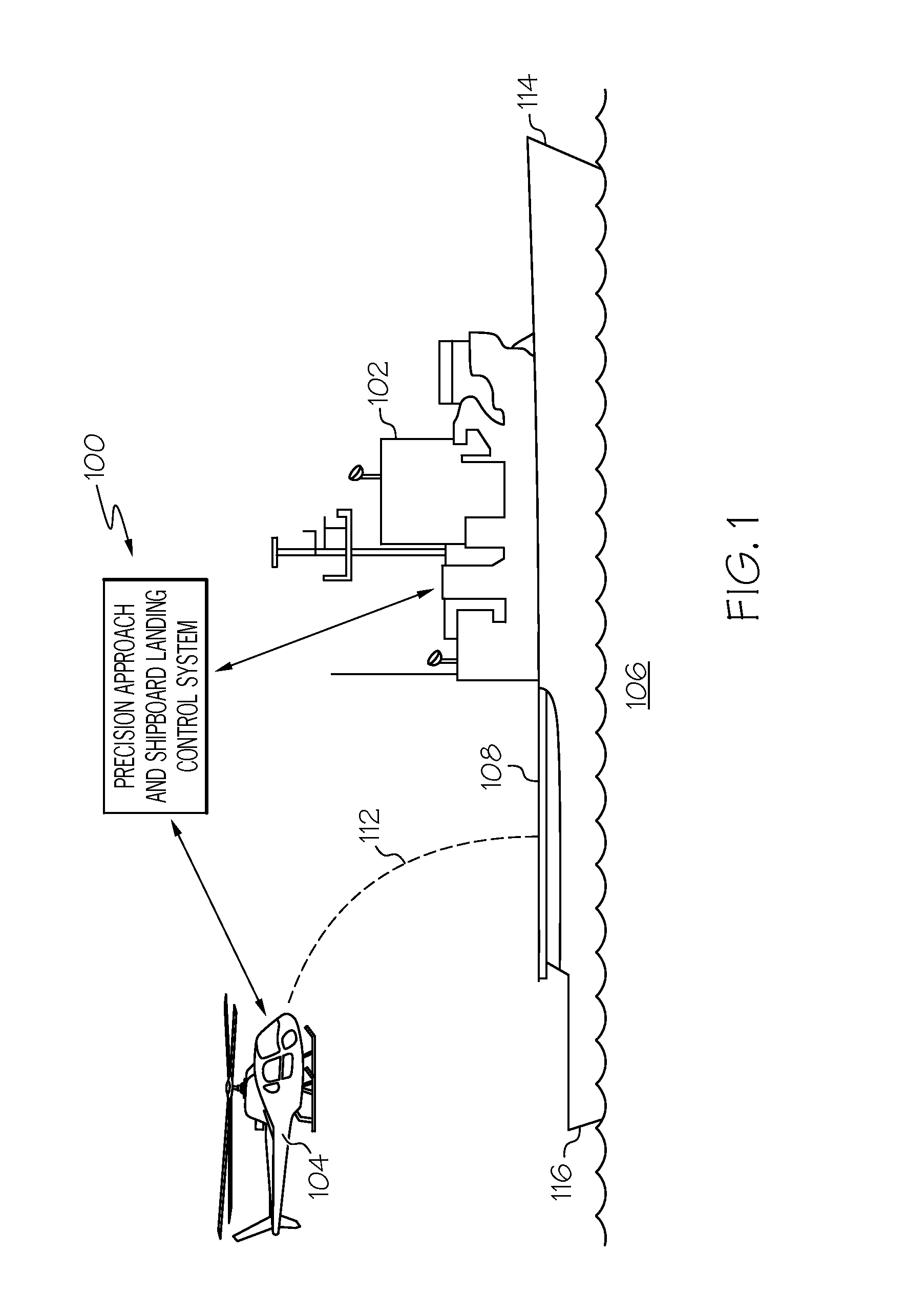
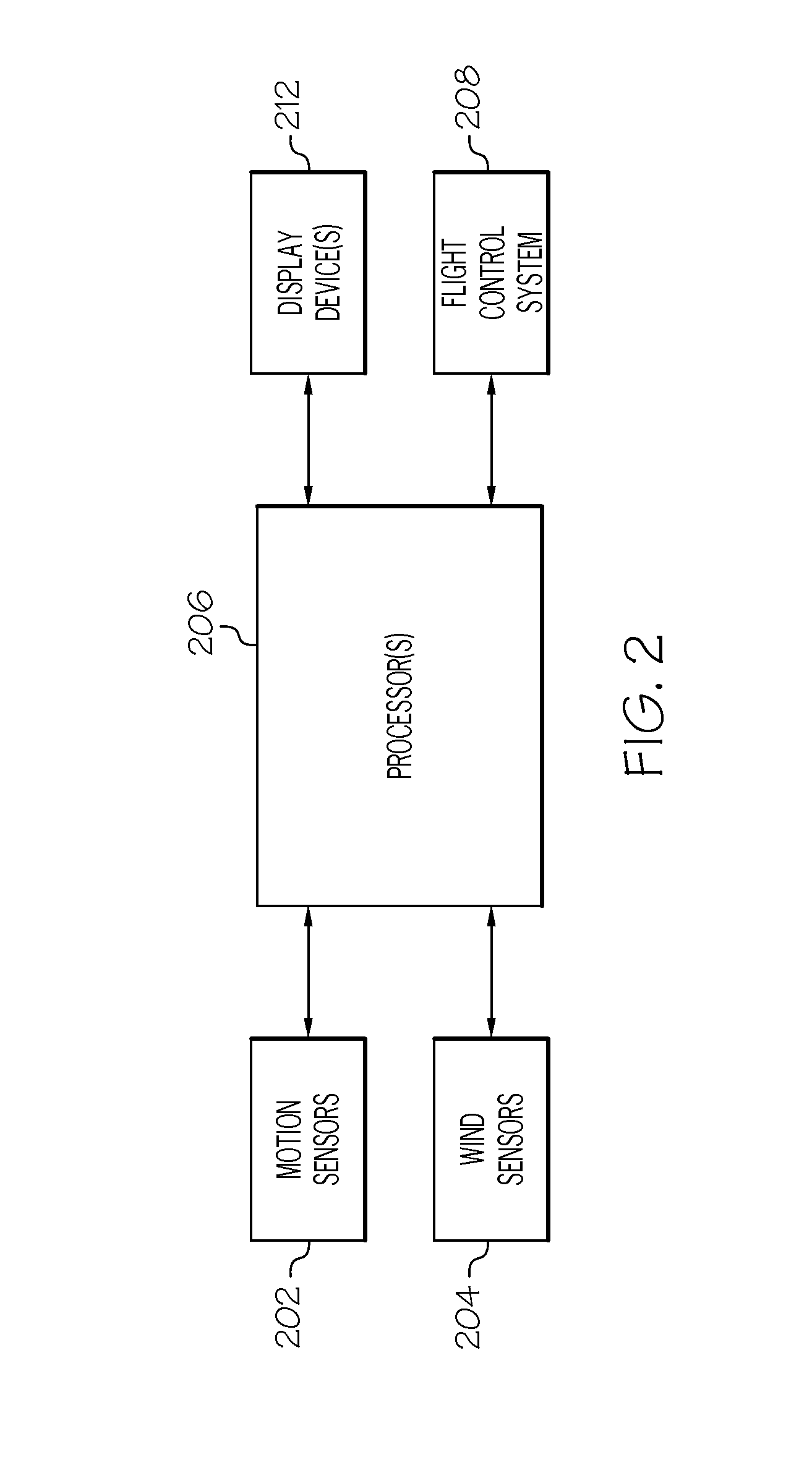
Aircraft precision approach and shipboard landing control system and method
ActiveUS20140350754A1Analogue computers for vehiclesActuated automaticallyAir velocityControl system
A system and method of generating a landing trajectory for use in landing an aircraft onto a deck of a waterborne ship includes sensing motion of the ship, and sensing wind speed and wind direction. The sensed motion of the ship is processed to generate estimates of ship attitude and vertical speed, and the sensed wind speed and wind direction are processed to generate estimates of air-wake disturbances ahead of the aircraft. The landing trajectory is generated based on the estimates of ship attitude and vertical speed and the estimates of air-wake disturbances. The system and method implement model predictive control to calculate the control maneuvers multiple steps ahead, which provides the capability to smoothly control the timing of the aircraft touchdown phase.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Vertical speed and flight path command module for displacement collective utilizing tactile cueing and tactile feedback
ActiveUS7930074B2MoreImprove handling qualityAircraft controlDigital data processing detailsLevel flightConstant force
A flight control system includes a collective position command module for a lift axis (collective pitch) which, in combination with an active collective system, provides a force feedback such that a pilot may seamlessly command vertical speed, flight path angle or directly change collective blade pitch. The collective position command module utilizes displacement of the collective controller to command direct collective blade pitch change, while a constant force application to the collective controller within a “level flight” detent commands vertical velocity or flight path angle. The “level flight” detent provides a tactile cue for collective position to reference the aircraft level flight attitude without the pilot having to refer to the instruments and without excessive collective controller movement.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
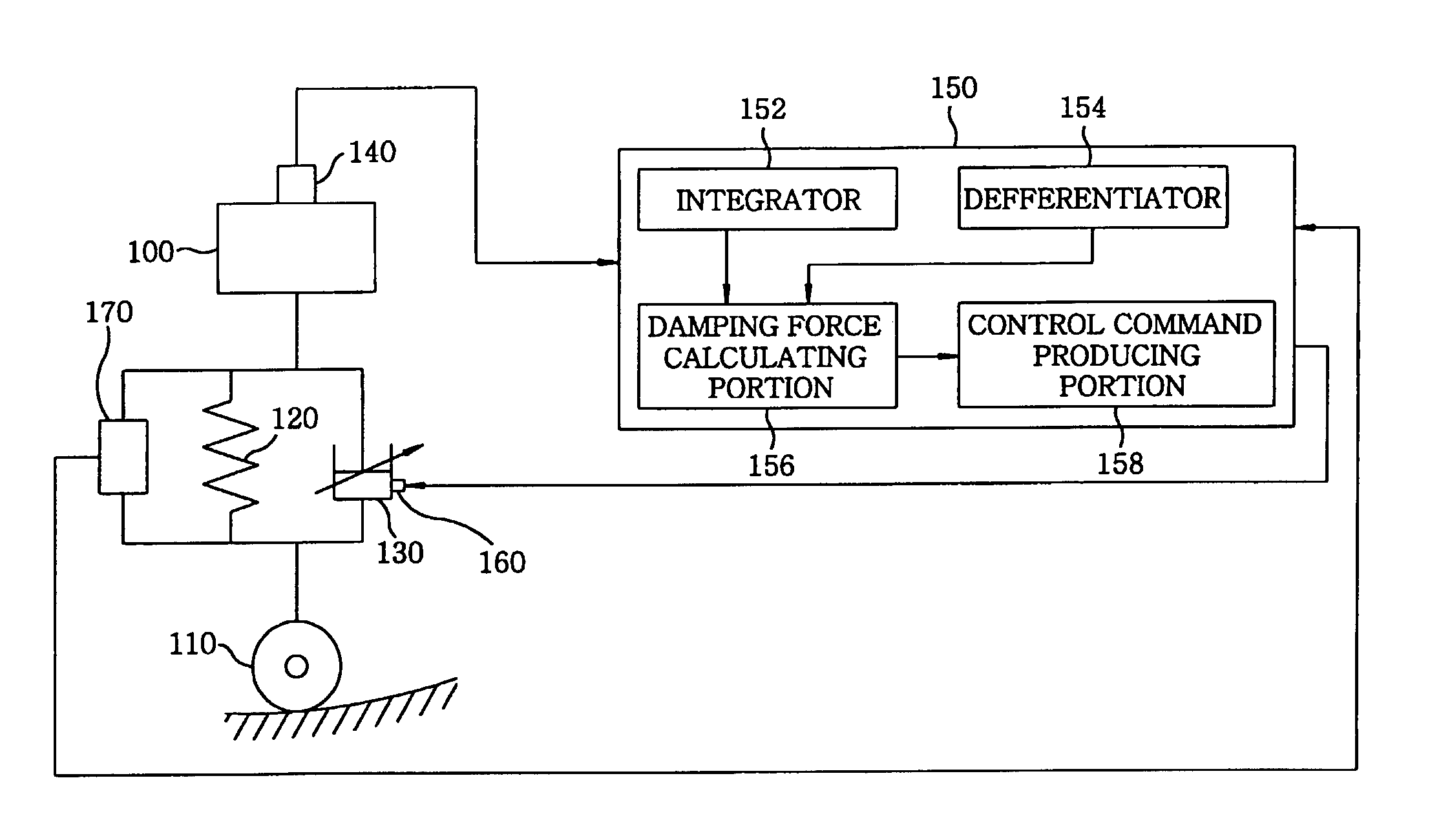
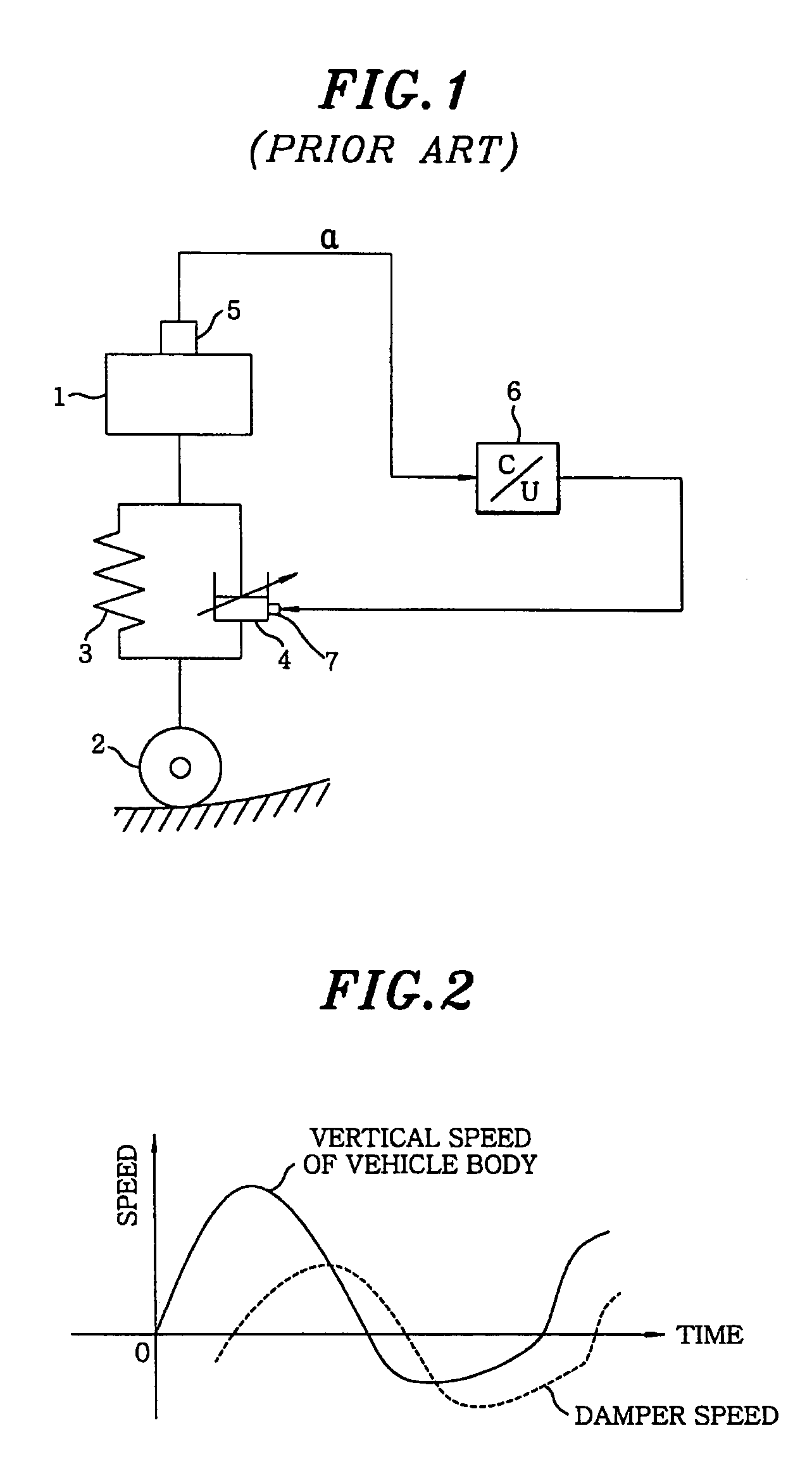
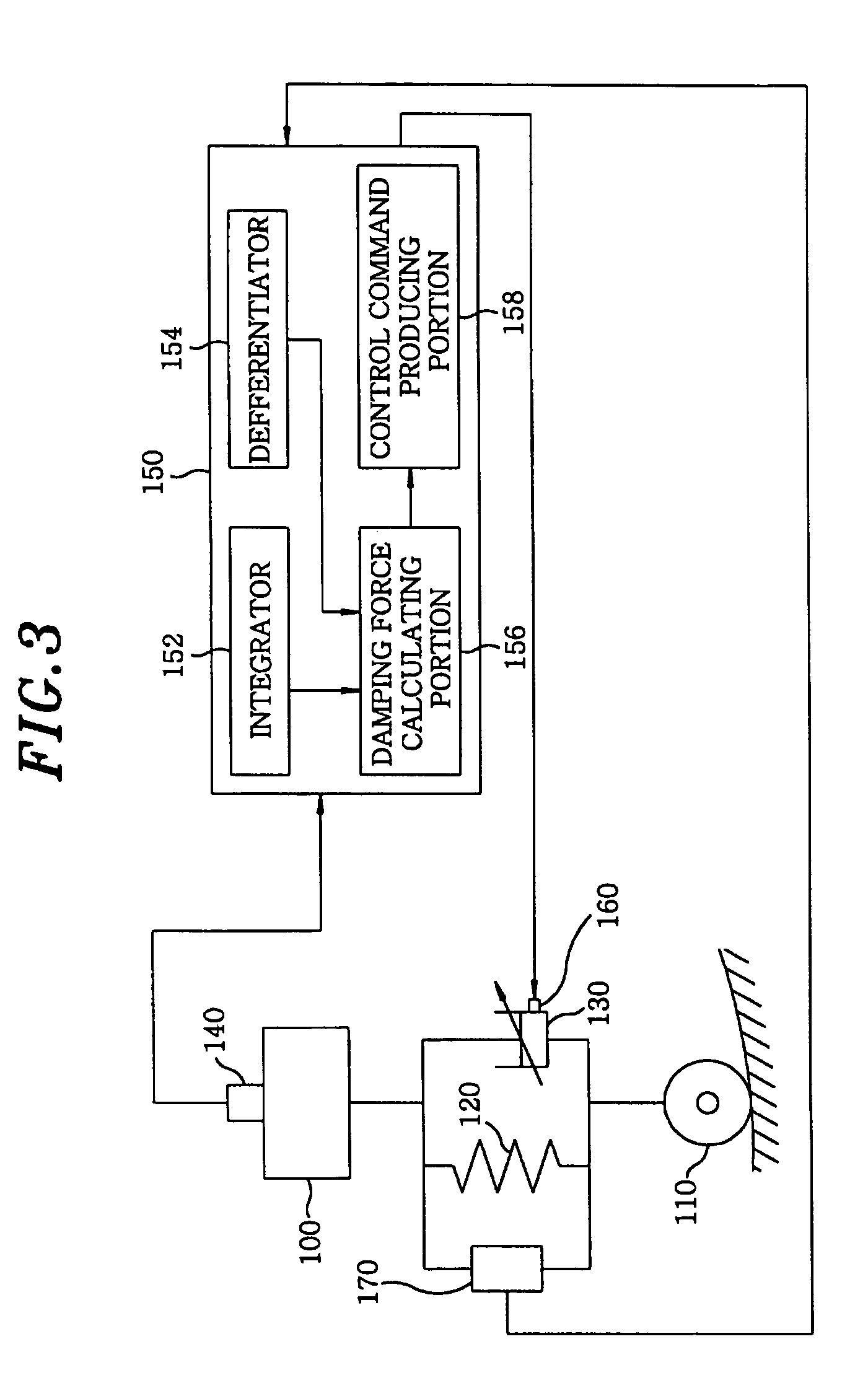
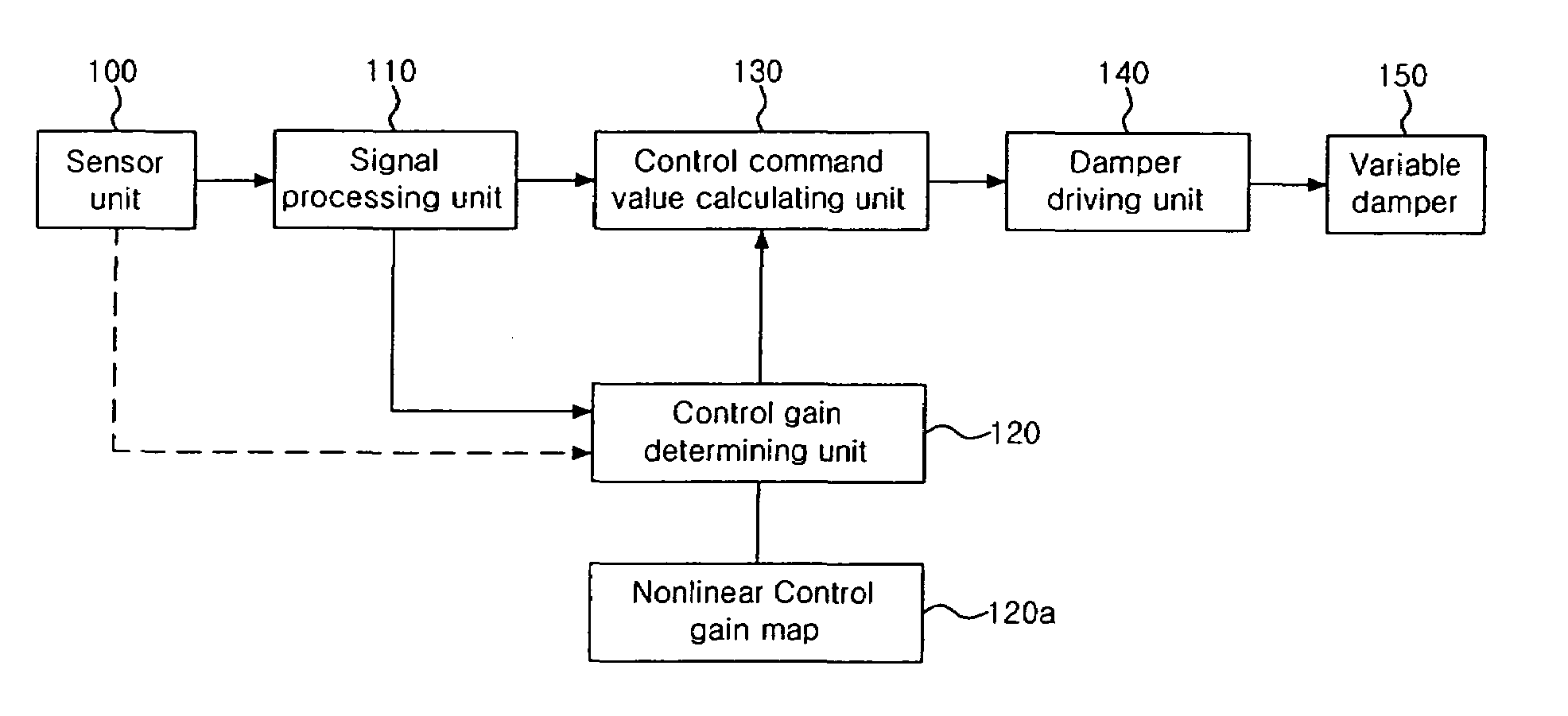
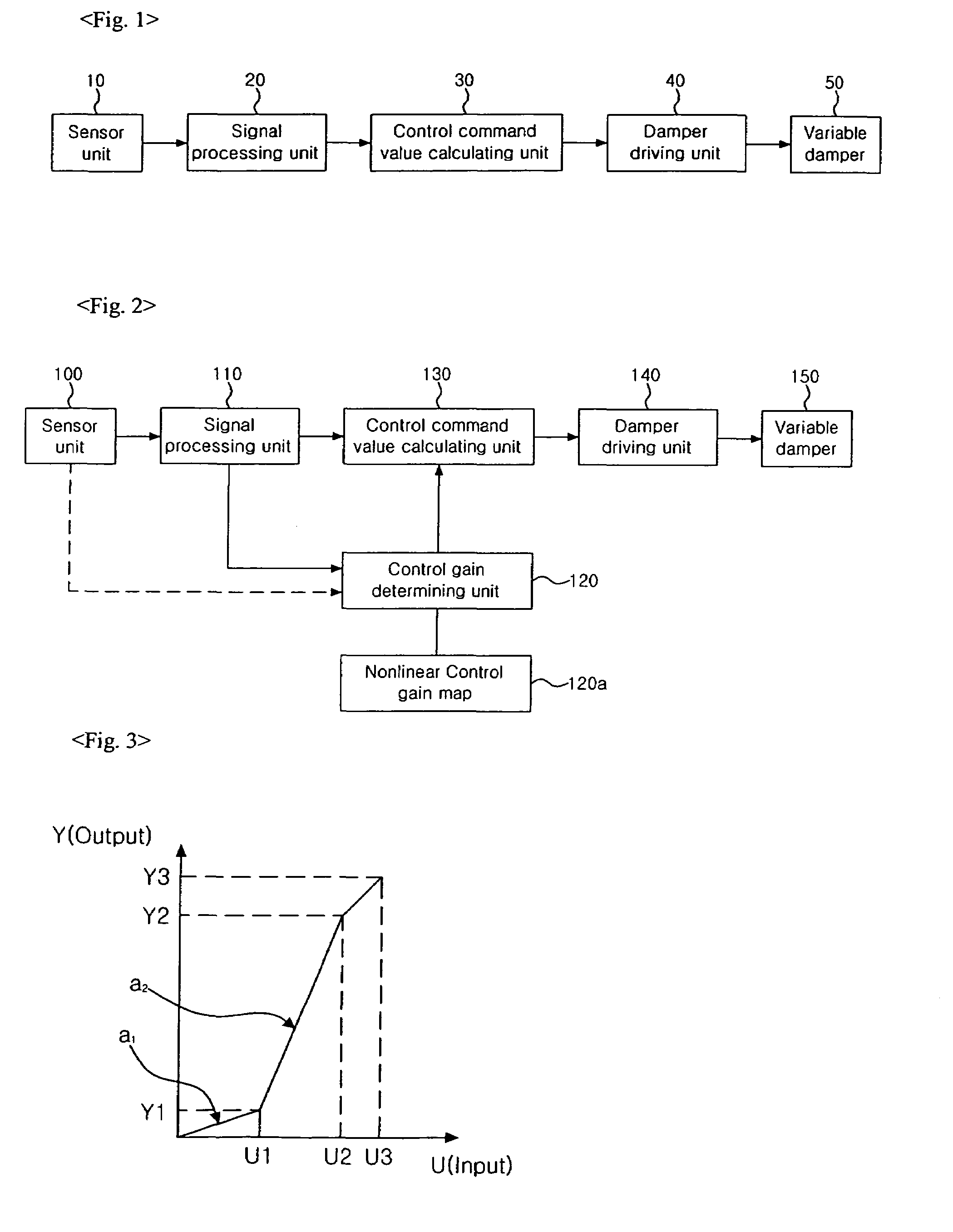
Electronically-controlled suspension apparatus and damping force control method
InactiveUS20050113997A1Improve vehicle stabilityDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesActuatorElectric control
An electronically-controlled suspension apparatus includes a first sensing device for detecting a vertical acceleration of a vehicle body; a second sensing device for detecting vertical movements of a vehicle body relative to a wheel axle; and a controller for obtaining a vertical speed of the vehicle body by using the vertical acceleration detected by the first sensing device, obtaining a damper speed of a variable damper by using the vertical movements detected by the second sensing device, calculating a target damping force by using the vertical speed of the vehicle body and the damper speed, and determining a control command value by using the target damping force. The control command value is transmitted from the controller to the actuator of the variable damper to change damping force characteristics of the variable damper.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
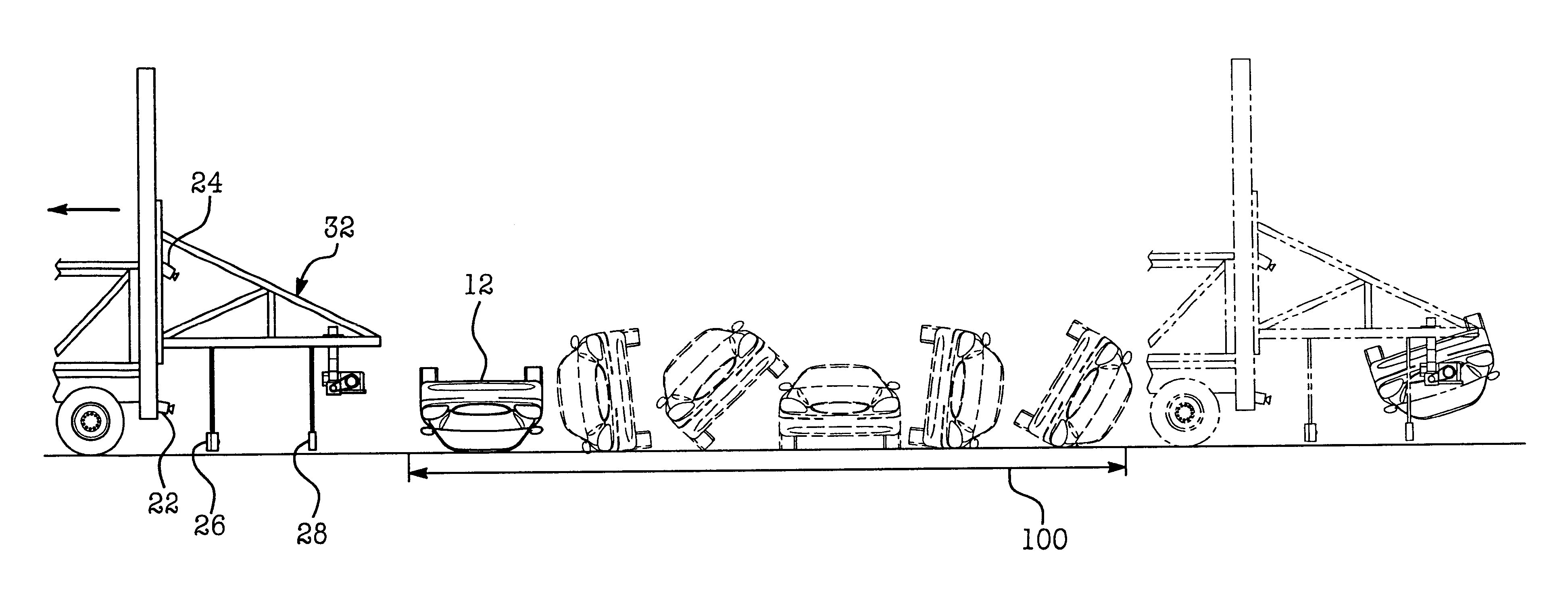
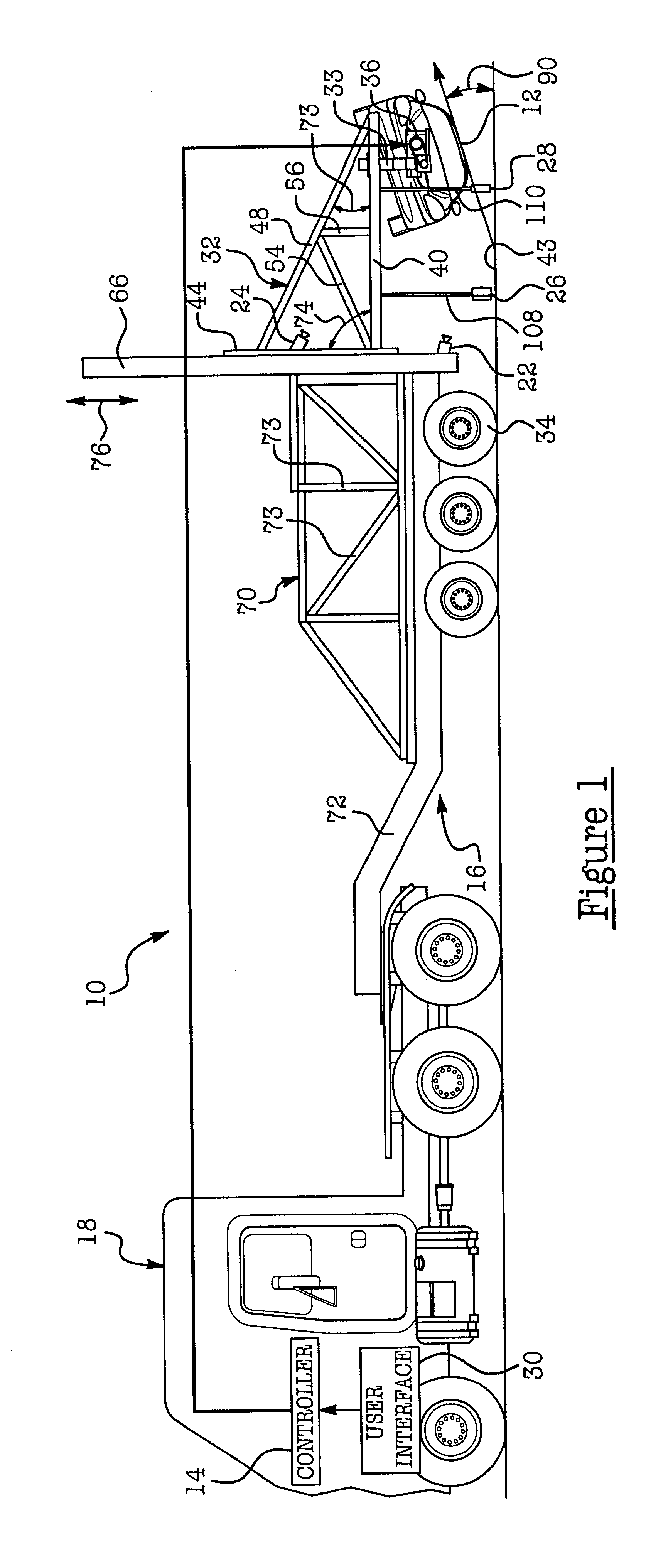
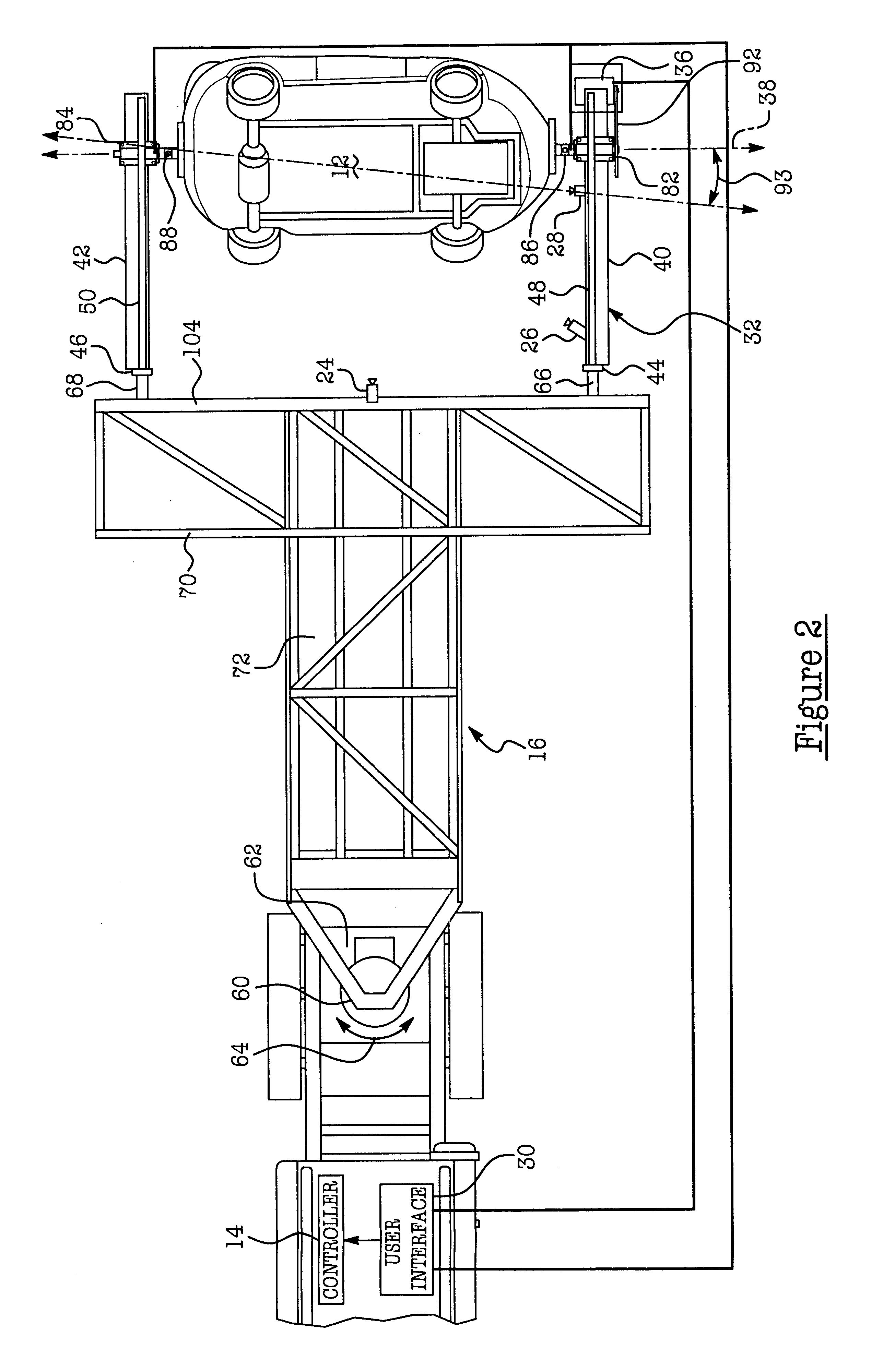
Apparatus and method for vehicle rollover crash testing
An apparatus 10 for measuring and / or analyzing the rollover characteristics of a vehicle 12. Apparatus 10 includes a controller 14, a selectively movable test fixture assembly 16, a truck or towing vehicle 18 which is coupled to trailer assembly 16 and which selectively tows or drives assembly 16, several cameras 22, 24, 26 and 28, and a user interface 30. Vehicle 12 is attached to test fixture 16, and user interface 30 is used to activate motor assembly 36 which selectively rotates vehicle 12 to a desired roll angle 90 relative to the ground surface 43. Once vehicle 12 is correctly positioned, an operator drives truck 18 at a predetermined and desired speed. Controller 14 generates release signals to exploding bolts 86, 88, which simultaneously explode, thereby releasing vehicle 12 from frame 32. In this manner, apparatus 10 allows the drop height and the translational and vertical velocity of a vehicle to be selectively controlled, adjusted and repeated from test to test, and provides controllable and predictable roof-to-ground impacts.
Owner:EXPONENT
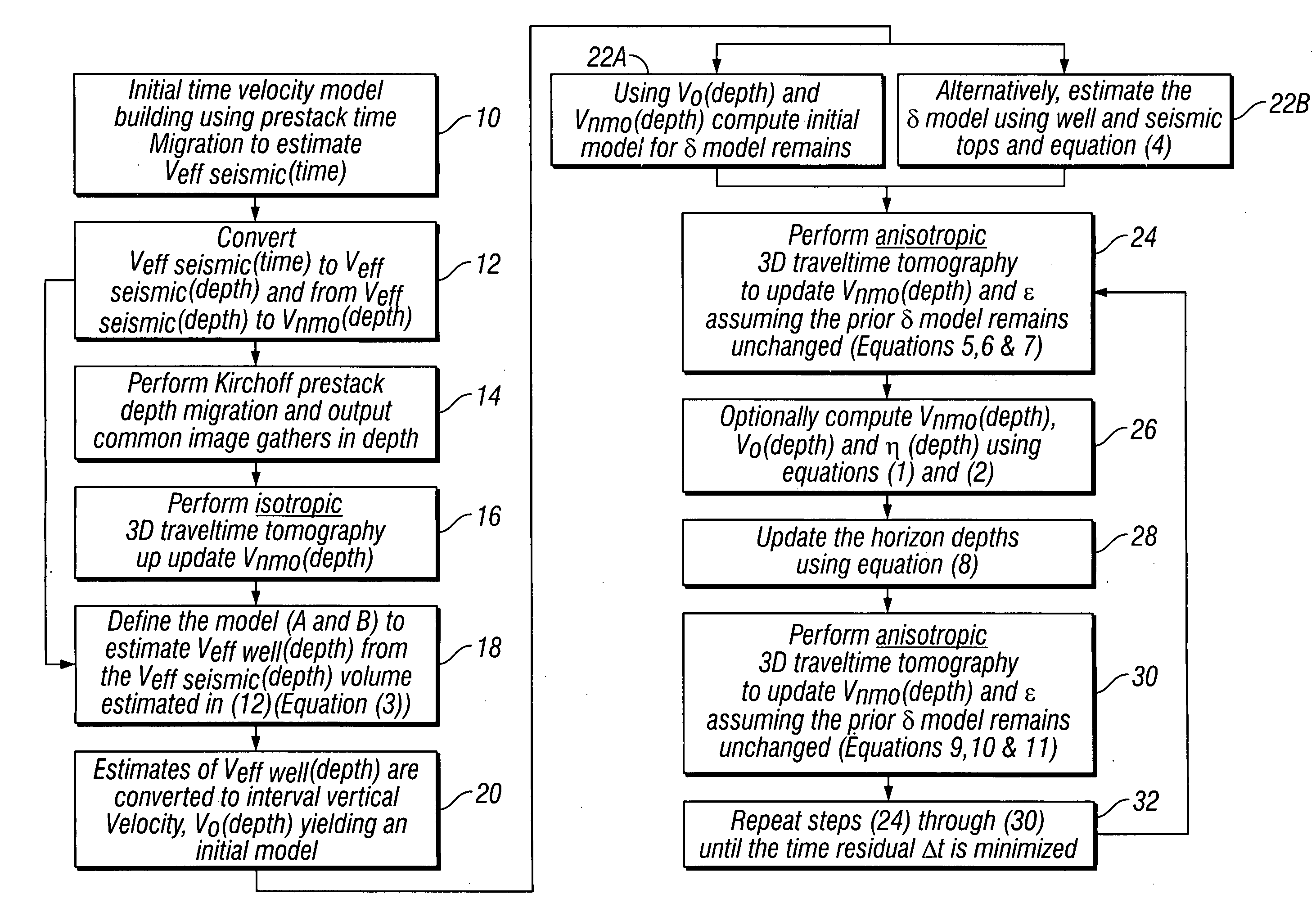
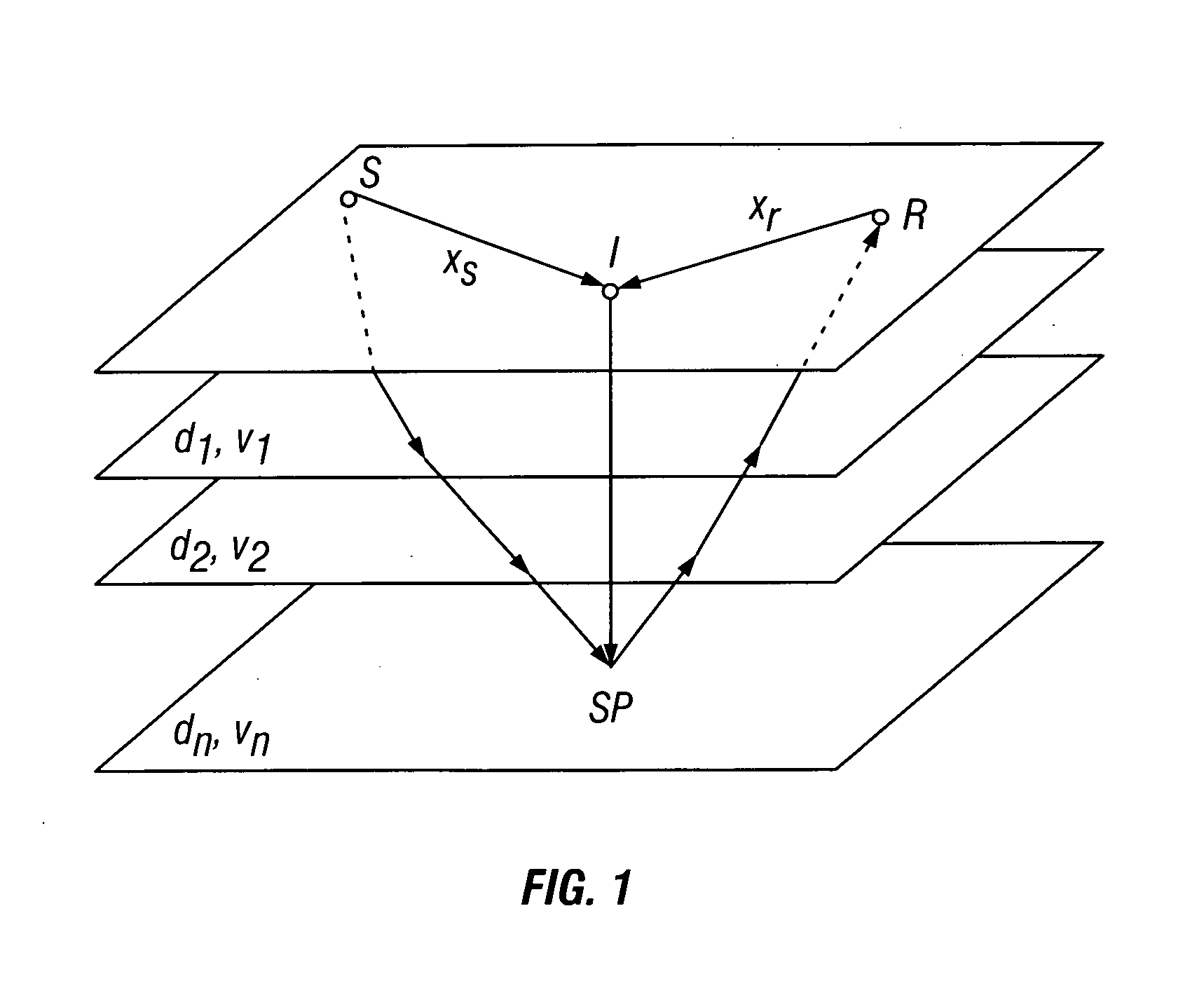
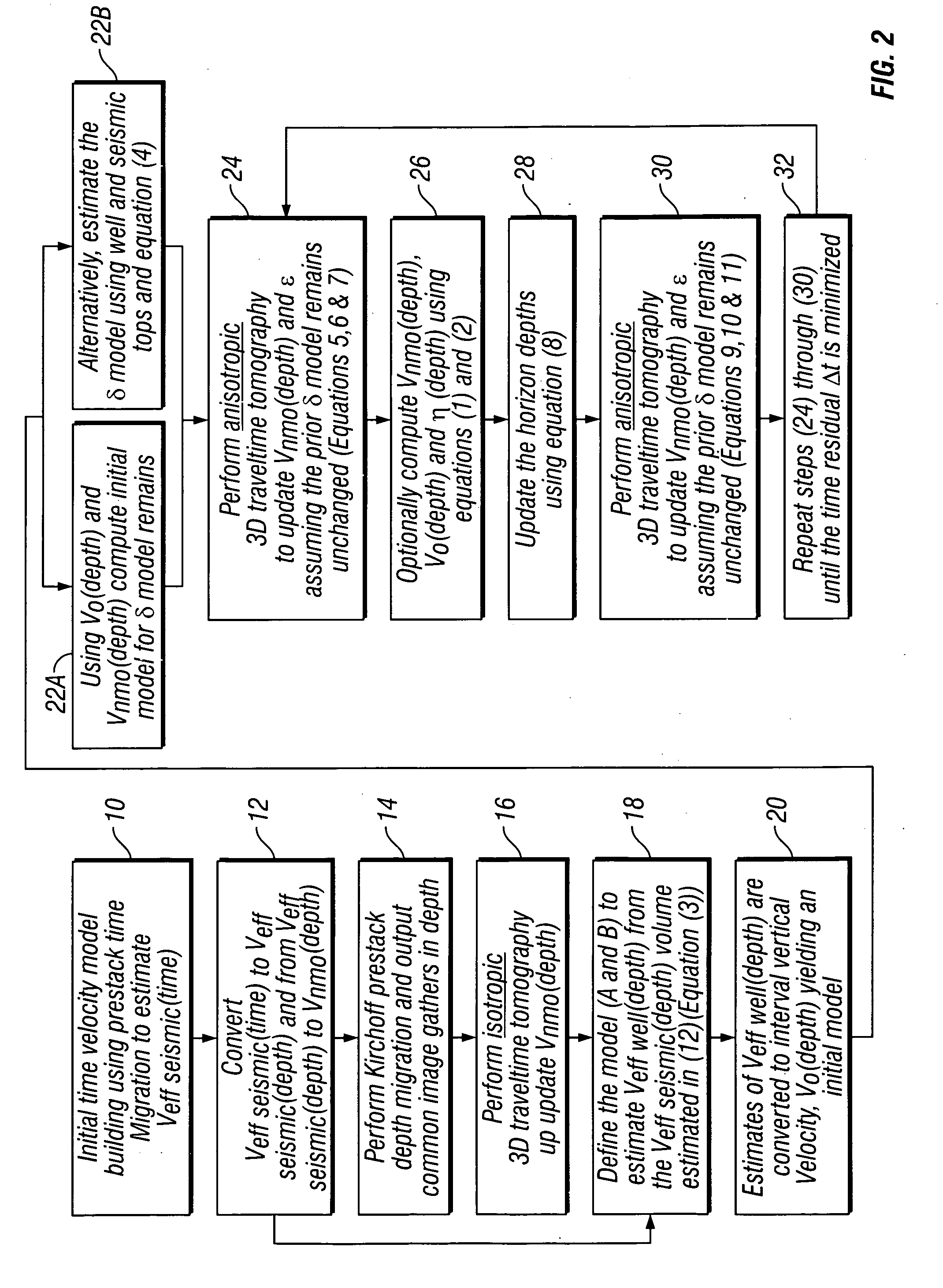
Method for three dimensional seismic travel time tomography in transversely isotropic media
A method for estimating seismic velocities in vertically transversely isotropic media includes generating an initial estimate of vertical interval velocity and interval normal moveout velocity with respect to depth from seismic data. An initial estimate is generated of a first anisotropy parameter with respect to depth. The first anisotropy parameter is related to the interval normal moveout velocity and the interval vertical velocity. An initial estimate is generated with respect to depth of a second anisotropy parameter. The second anisotropy parameter is related to the first anisotropy parameter and an interval anelliptic parameter. A first tomographic inversion is performed with respect to the interval normal moveout velocity and the second anisotropy parameter at a constant value of the first anisotropy parameter until travel time differentials reach minimum values. Layer depths are adjusted with the initial estimate of vertical interval velocity. Using values of the second anisotropy parameter determined in the first tomographic inversion, a second tomographic inversion is performed of interval normal moveout velocity and the first anisotropy parameter with respect to depth. The adjusted layer depths, interval normal moveout velocities and interval vertical velocities are again adjusted and interval anelliptic parameters are calculated from the second tomographic inversion.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
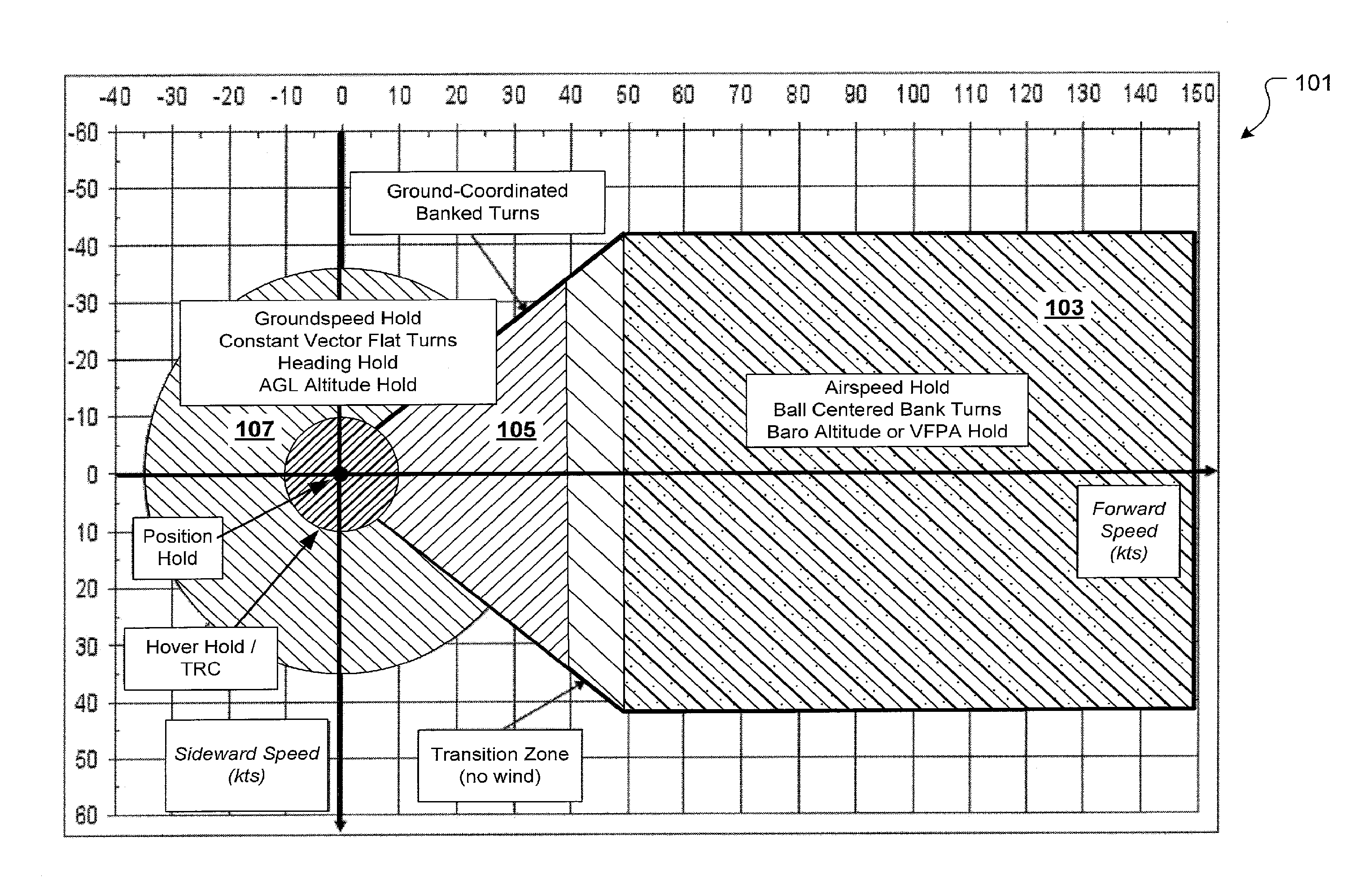
Flight Control Laws for Vertical Flight Path
ActiveUS20130060406A1Aircraft controlDigital data processing detailsFlight vehicleFlight control modes
A flight control system and method for controlling the vertical flight path of an aircraft, the flight control system includes a stable decoupled model having a decoupled lateral equation of motion and a decoupled longitudinal equation of motion and a feedback command loop operably associated with the stable decoupled model. The feedback command loop includes a vertical flight path angle control law; an altitude control law; and a vertical speed control law.
Owner:TEXTRON INNOVATIONS
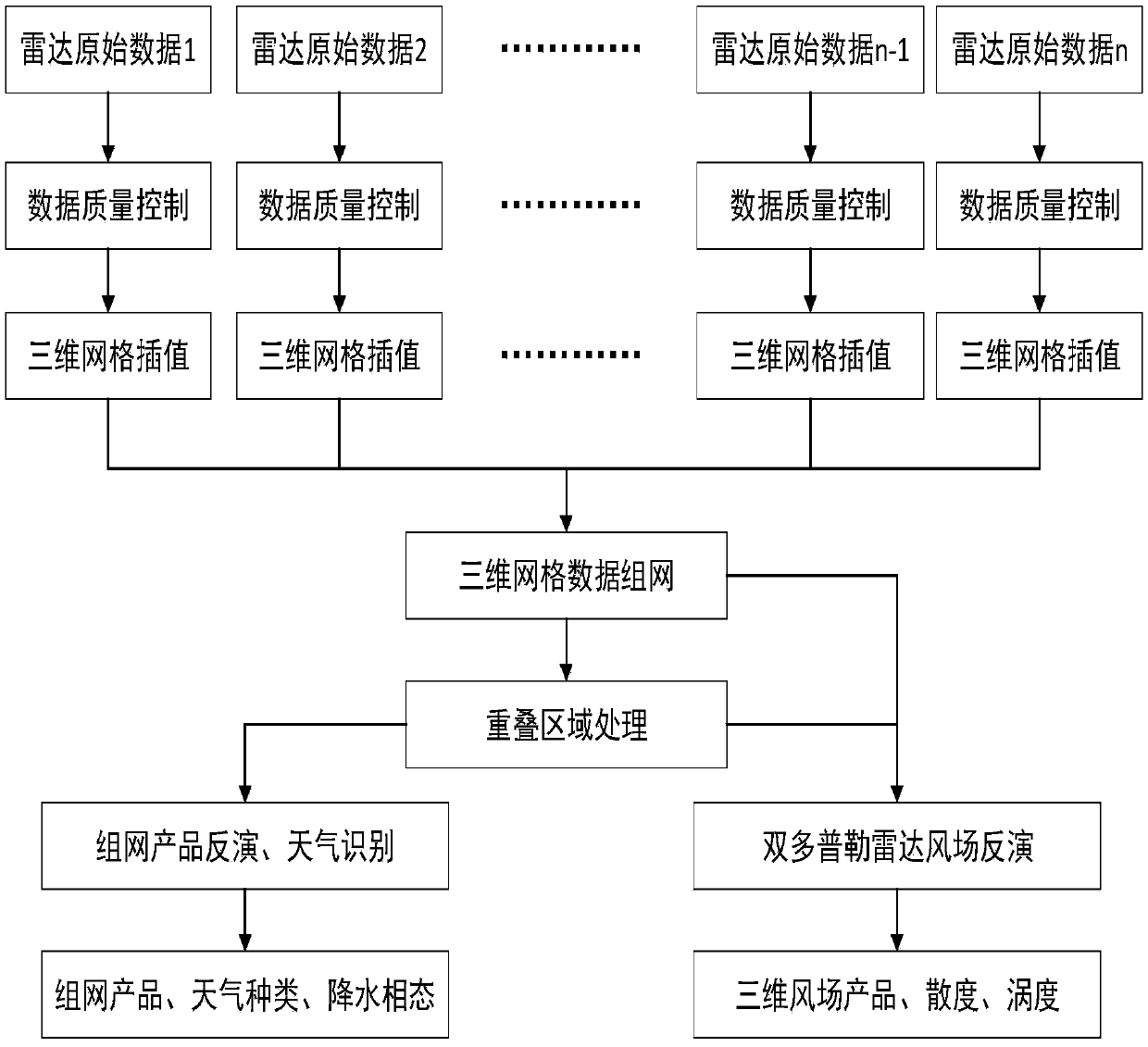
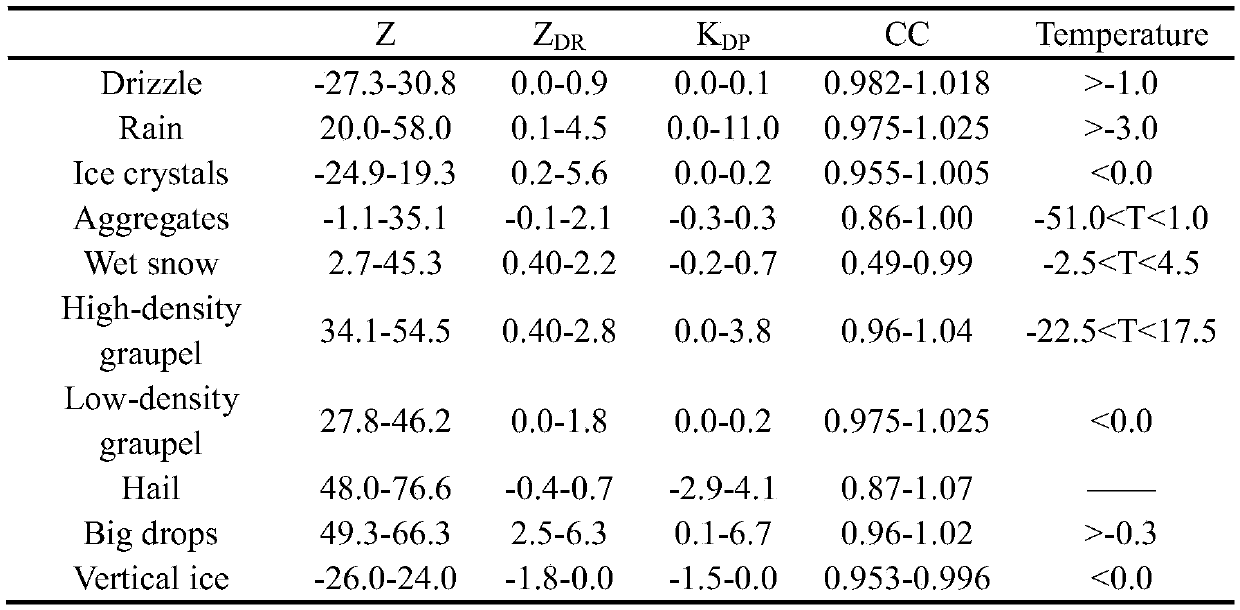
NRIET X-band radar cooperative networking analysis method
InactiveCN108693534AImprove spatial resolutionImprove time resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationClassification methodsRain intensity
The invention discloses a NRIET X-band radar cooperative networking analysis method. The method comprises the steps that data are collected; the data quality is controlled; a distance weight interpolation technology is used, and a three-dimensional cressman interpolation method is used to perform lattice interpolation on radar echo, radial wind and each polarization; three-dimensional data networking is carried out; for a three-dimensional wind field inversed by a dual Doppler radar, the inversed wind field is constrained by a mass continuous equation, and the three-dimensional wind field is acquired by repeatedly iteratively solving the equation; the vertical velocity w is acquired by the mass continuous equation, and a trace boundary condition is used to adjust a vertical motion field, wherein the upper boundary of the mass continuous equation is set to integrate down; based on a radar product reflectivity algorithm, a combined reflectivity puzzle product and an echo top puzzle product are generated; through Z-R relationship, quantitative precipitation is estimated to acquire a rain intensity product; a texture classification method is used to identify a precipitation stratus convection region; and a fuzzy logic algorithm is used to recognize the phase state of precipitation particles in each region at different stages of a precipitation process.
Owner:NANJING NRIET IND CORP
Vehicle carried road slope angle measuring system and vehicle carried road slope angle measuring method
ActiveCN1800780APedestrian/occupant safety arrangementIncline measurementElectricityMeasuring instrument
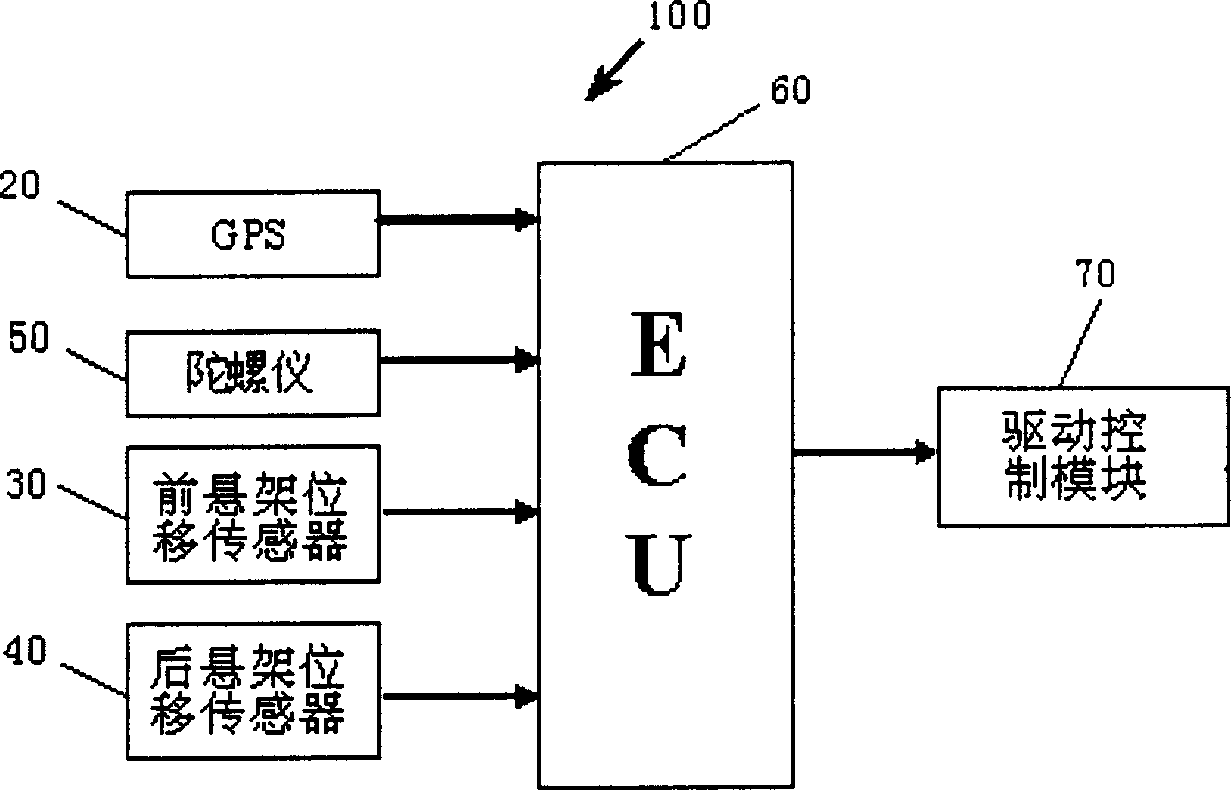
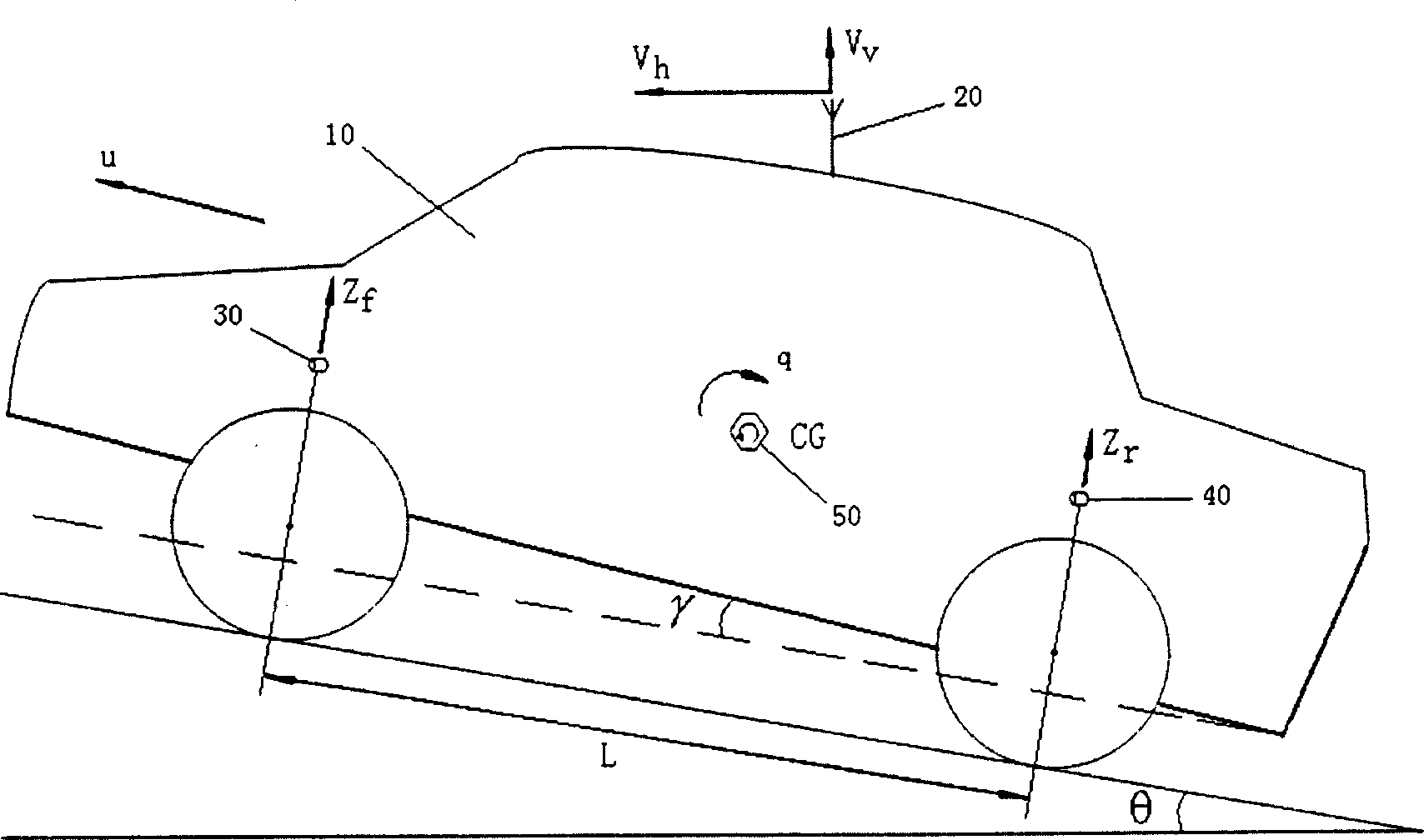
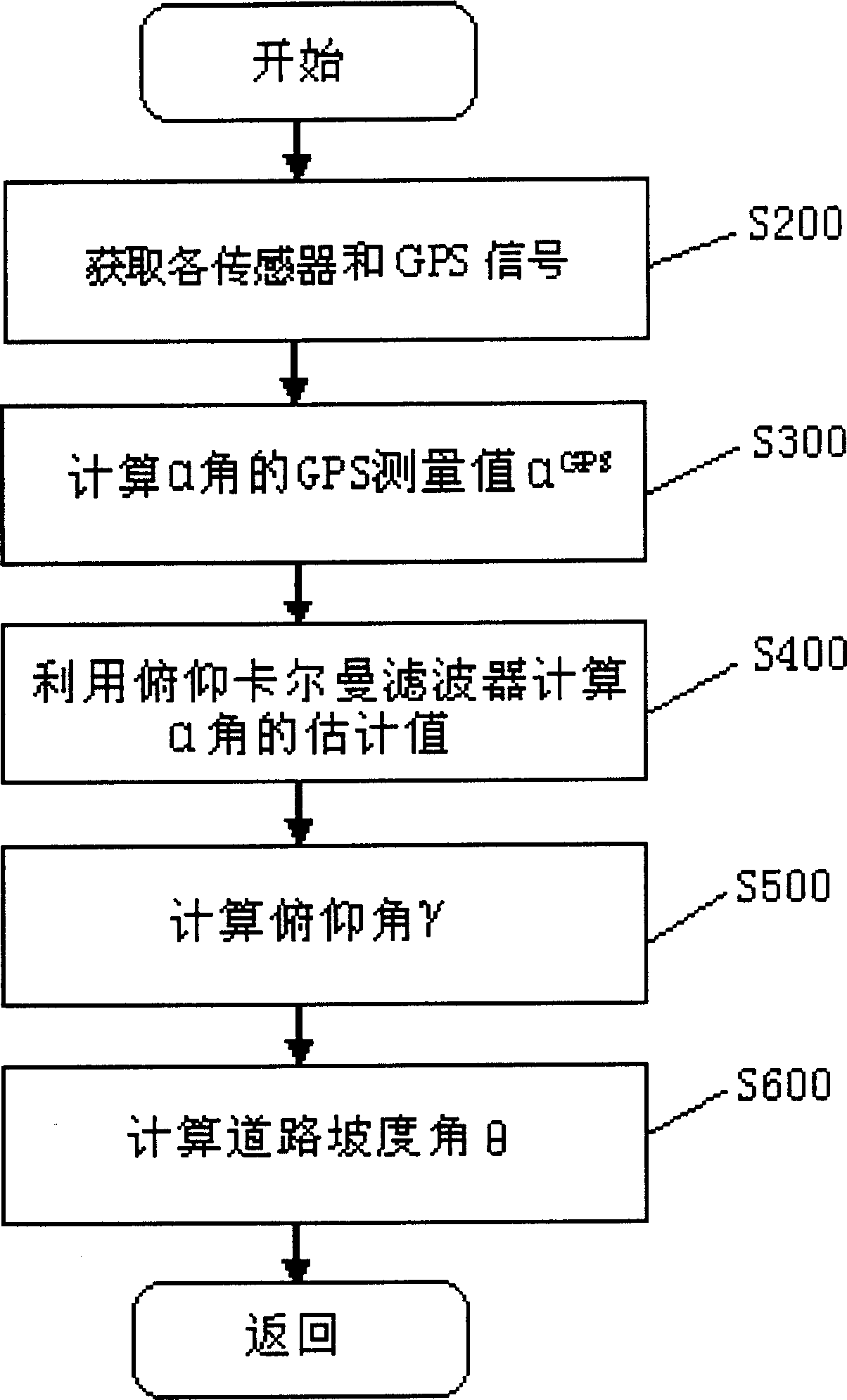
This invention provides a vehicle path grade angle measuring system and its measuring method. The measuring system includes: GPS speed measuring instrument, which is used to measure the flashy vertical velocity Vv and horizontal velocity Vh of the vehicles; the front suspension position sensing device installed at the front suspension of the vehicle, which is used to measure the related flashy displacement Zf of the body at the front suspension that is perpendicular to the path; the back suspension position sensing installed at the back suspension, which is used to measure the related flashy displacement Zf of the body at the back suspension that is perpendicular to the path; the electric control cell, which connects with the CPS speed measuring instrument, the front suspension position sensing device and the back suspension position sensing device to obtain the value of VvíóVhíóZfíóZr, and it computes the path grade angel ª according to the formula (1)íó(2) and (3). ªGPSú¢arctan(Vv / Vh) (1)ú ªú¢arctan((Zf-Zr) / L) (2)ú ªú¢ªGPS-ª (3).
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Dynamic Adjustment of Wing Surfaces for Variable Camber
ActiveUS20080255713A1Increase the burdenRaise the ratioAircraft controlDigital data processing detailsFlaperonFlight control surfaces
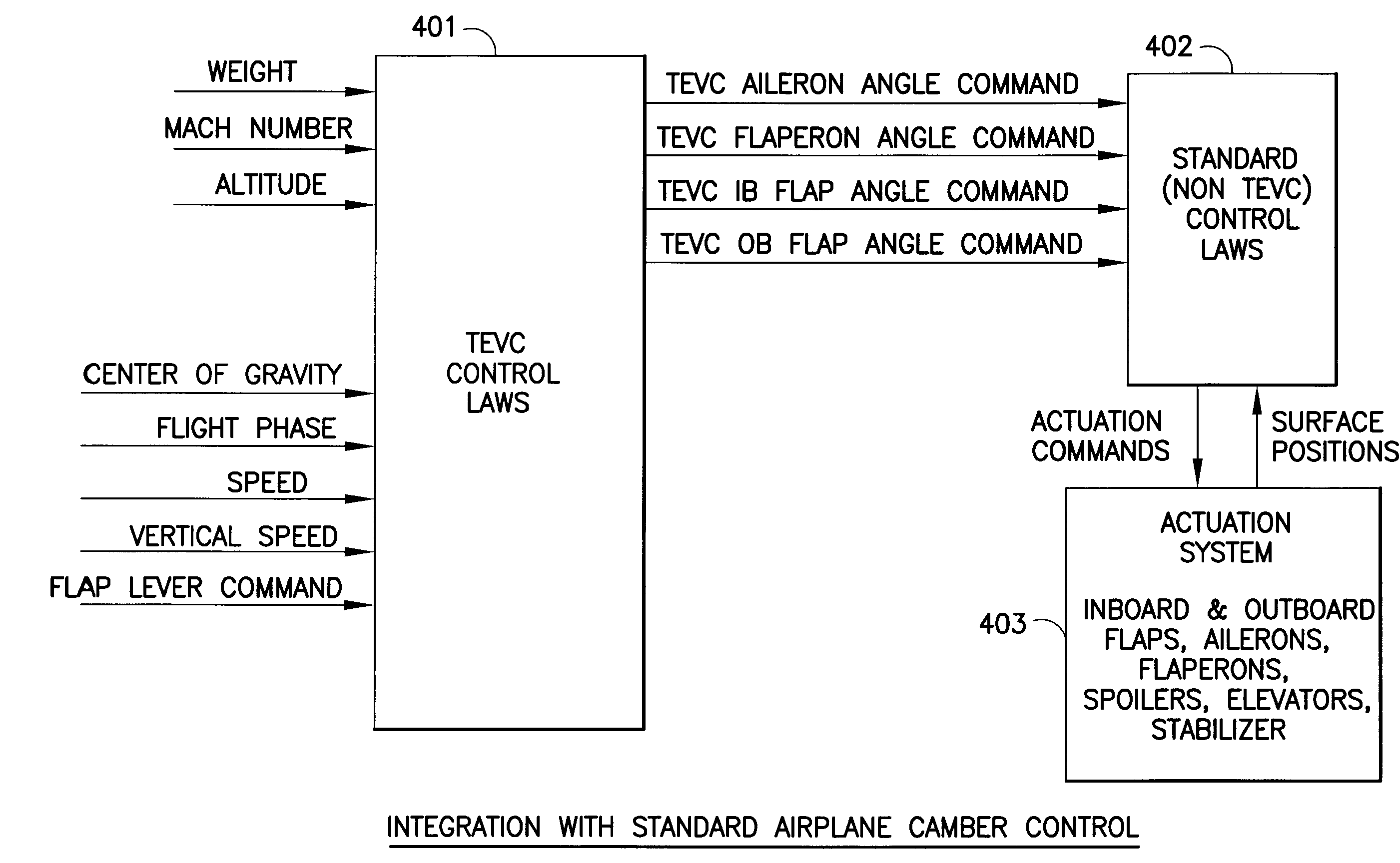
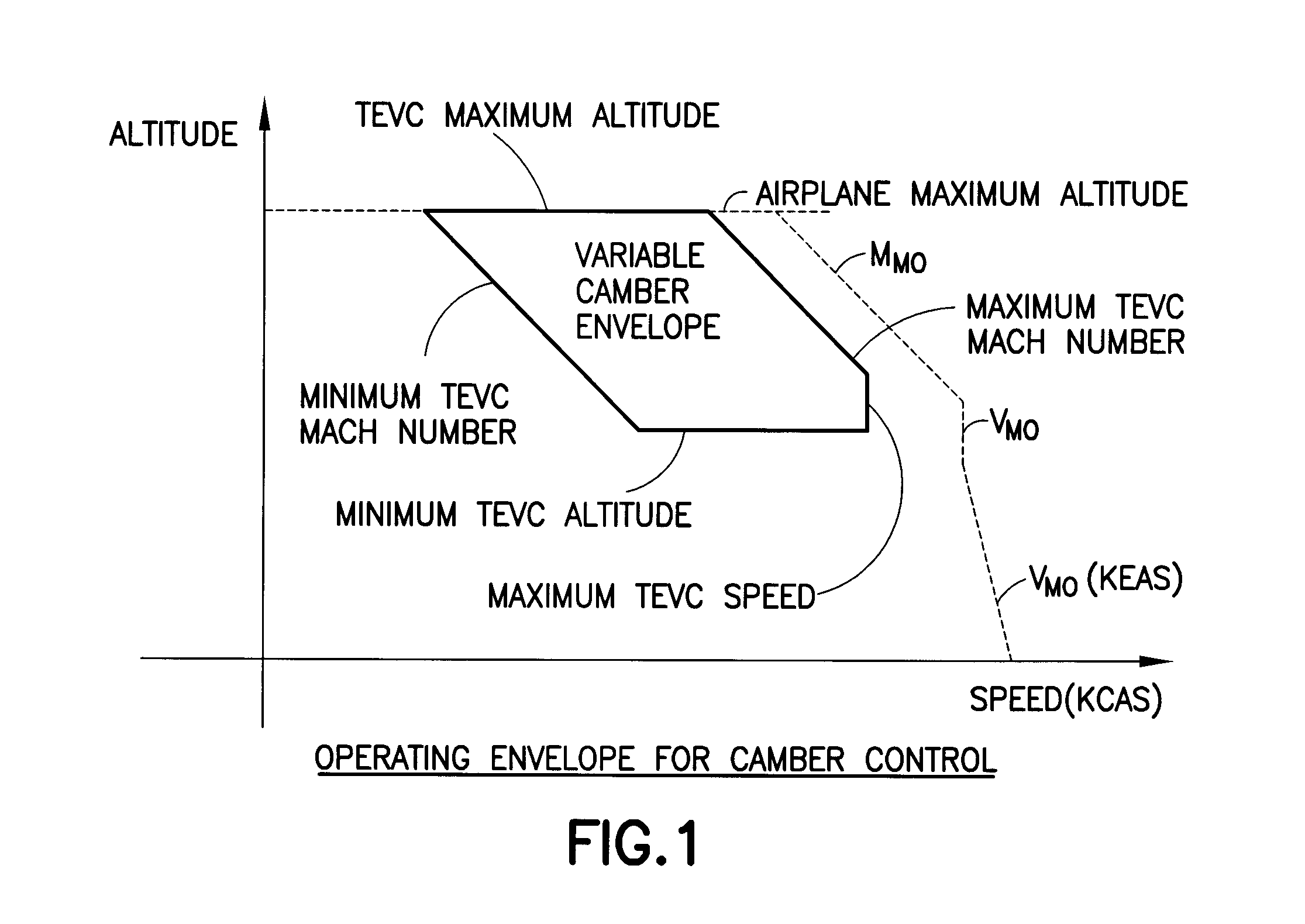
The movable surfaces affecting the camber of a wing are dynamically adjusted to optimize wing camber for optimum lift / drag ratios under changing conditions during a given flight phase. In a preferred embodiment, an add-on dynamic adjustment control module provides command signals for optimum positioning of trailing edge movable surfaces, i.e., inboard flaps, outboard flaps, ailerons, and flaperons, which are used in place of the predetermined positions of the standard flight control system. The dynamic adjustment control module utilizes inputs of changing aircraft conditions such as altitude, Mach number, weight, center of gravity, vertical speed and flight phase. The dynamic adjustment control module's commands for repositioning the movable surfaces of the wing are transmitted through the standard flight control system to actuators for moving the flight control surfaces.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Aircraft landing gear initial touch-down velocity monitor
A system for use in monitoring, measuring, computing and displaying the initial touch-down descent velocity experienced while aircraft are executing either normal, overweight or hard landing events. Pressure sensors and motion sensors are mounted in relation to each of the landing gear struts to monitor, measure and record the impact loads and aircraft touch-down vertical velocities experienced by landing gear struts, as the aircraft landing gear initially comes into contact with the ground. Velocity adjustments are made to correct for errors caused by landing gear per-charge pressure and landing gear strut seal friction. The system also measures the landing loads experienced by each landing gear strut during the landing event and determines if aircraft limitations have been exceeded.
Owner:NANCE C KIRK
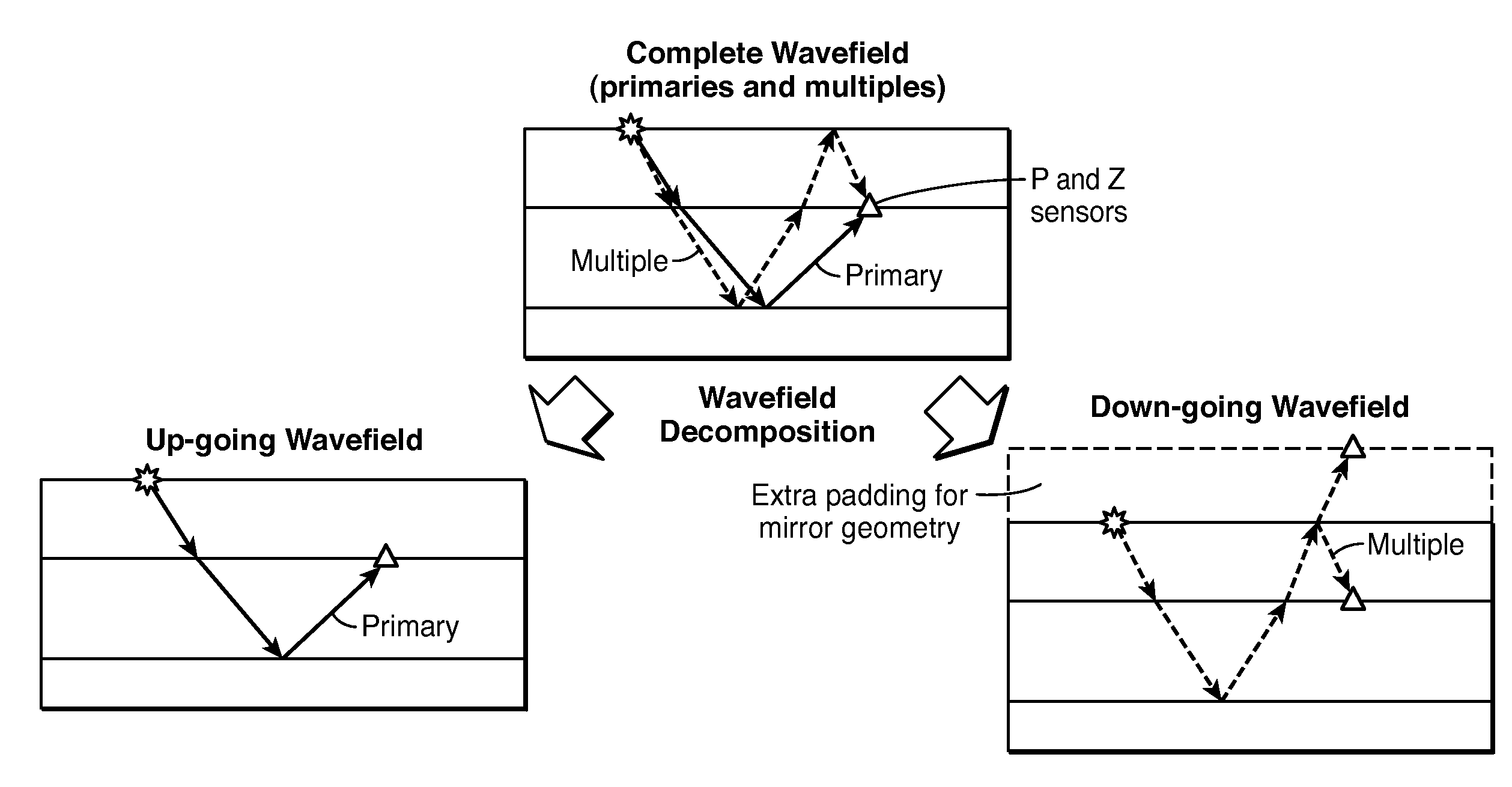
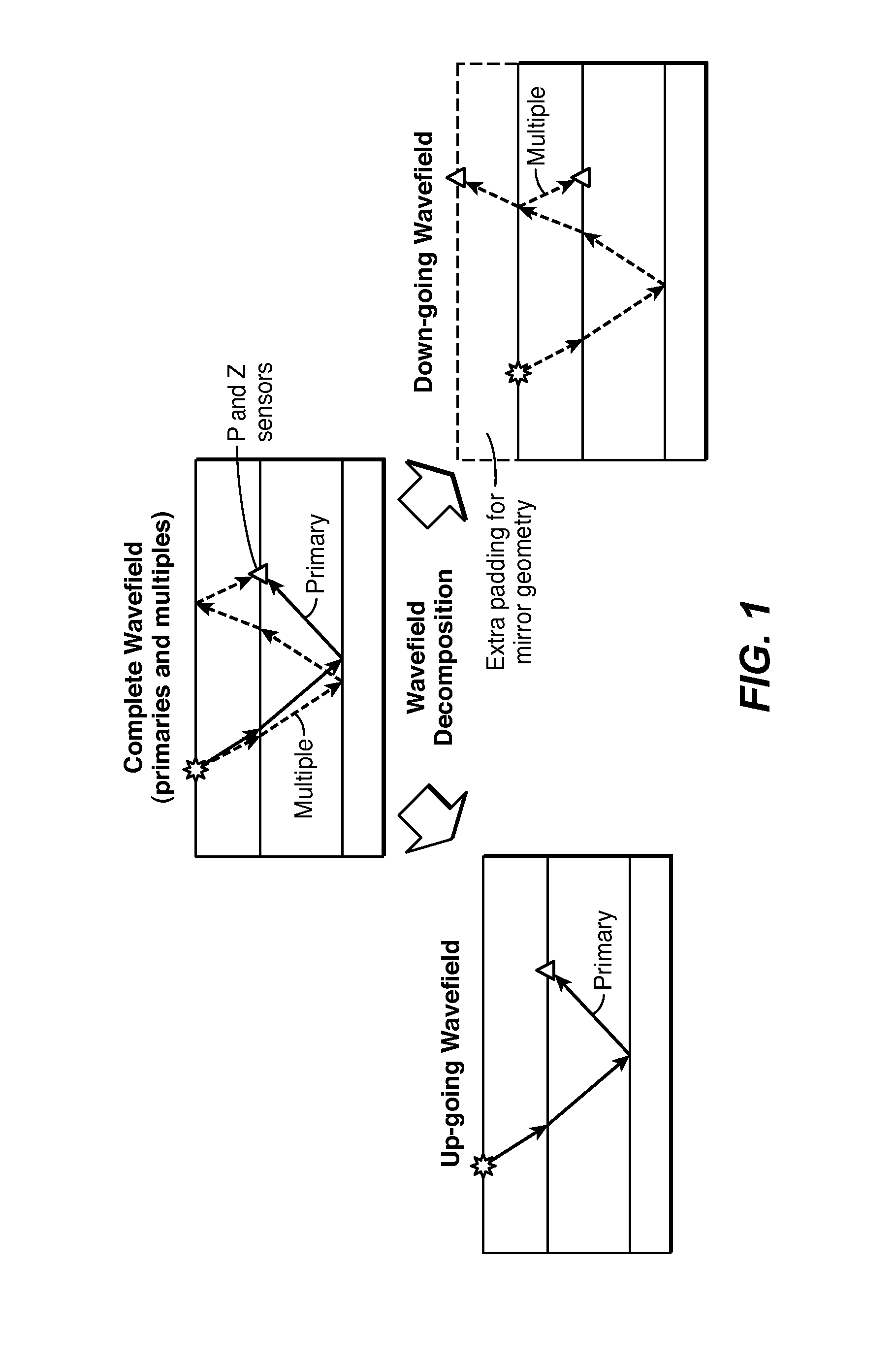
Full-Wavefield Inversion of Primaries and Multiples in Marine Environment
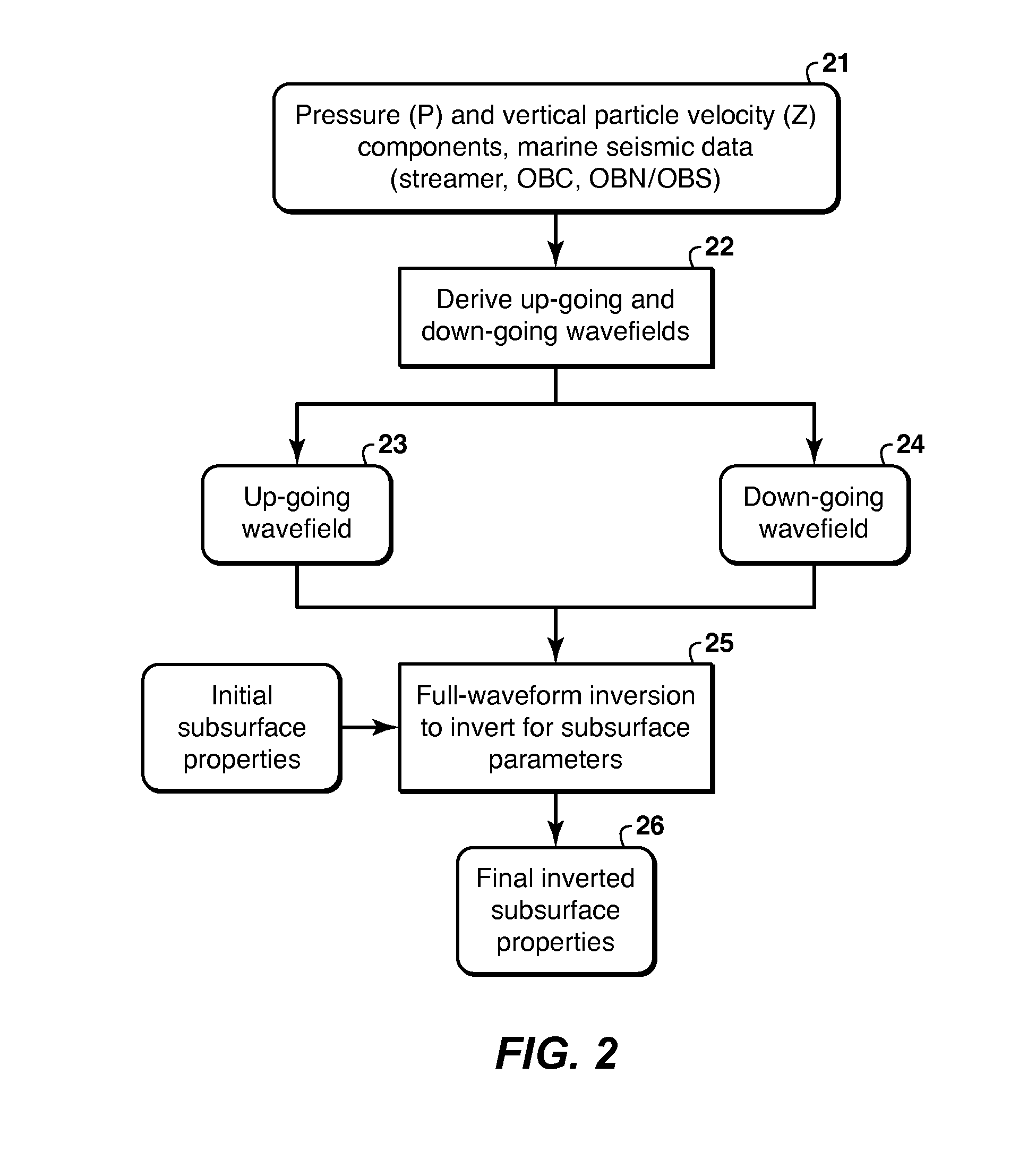
ActiveUS20150012221A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsPhysical propertySpeed of sound
Method for using the full wavefield (primaries, internal multiples and free-surface multiples) in inversion of marine seismic data, including both pressure and vertical velocity data (21), to infer a subsurface model of acoustic velocity or other physical property. The marine seismic data are separated (22) into up-going (23) and down-going (24) wavefields, and both wavefields are inverted in a joint manner, in which the final model is impacted by both wavefields. This may be achieved by inverting both wavefields simultaneously (25), or one after the other, i.e. in a cascaded approach (35→37, or 45→47), for the subsurface properties (26, 38, 48).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Aircraft landing gear initial touch-down velocity monitor
A system for use in monitoring, measuring, computing and displaying the initial touch-down descent velocity experienced while aircraft are executing either normal, overweight or hard landing events. Pressure sensors and motion sensors are mounted in relation to each of the landing gear struts to monitor, measure and record the impact loads and aircraft touch-down vertical velocities experienced by landing gear struts, as the aircraft landing gear initially comes into contact with the ground. Velocity adjustments are made to correct for errors caused by landing gear per-charge pressure and landing gear strut seal friction. The system also measures the landing loads experienced by each landing gear strut during the landing event and determines if aircraft limitations have been exceeded.
Owner:NANCE C KIRK
Anisotropic Parameter Determination
InactiveUS20100128562A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingKinematicsNormal moveout
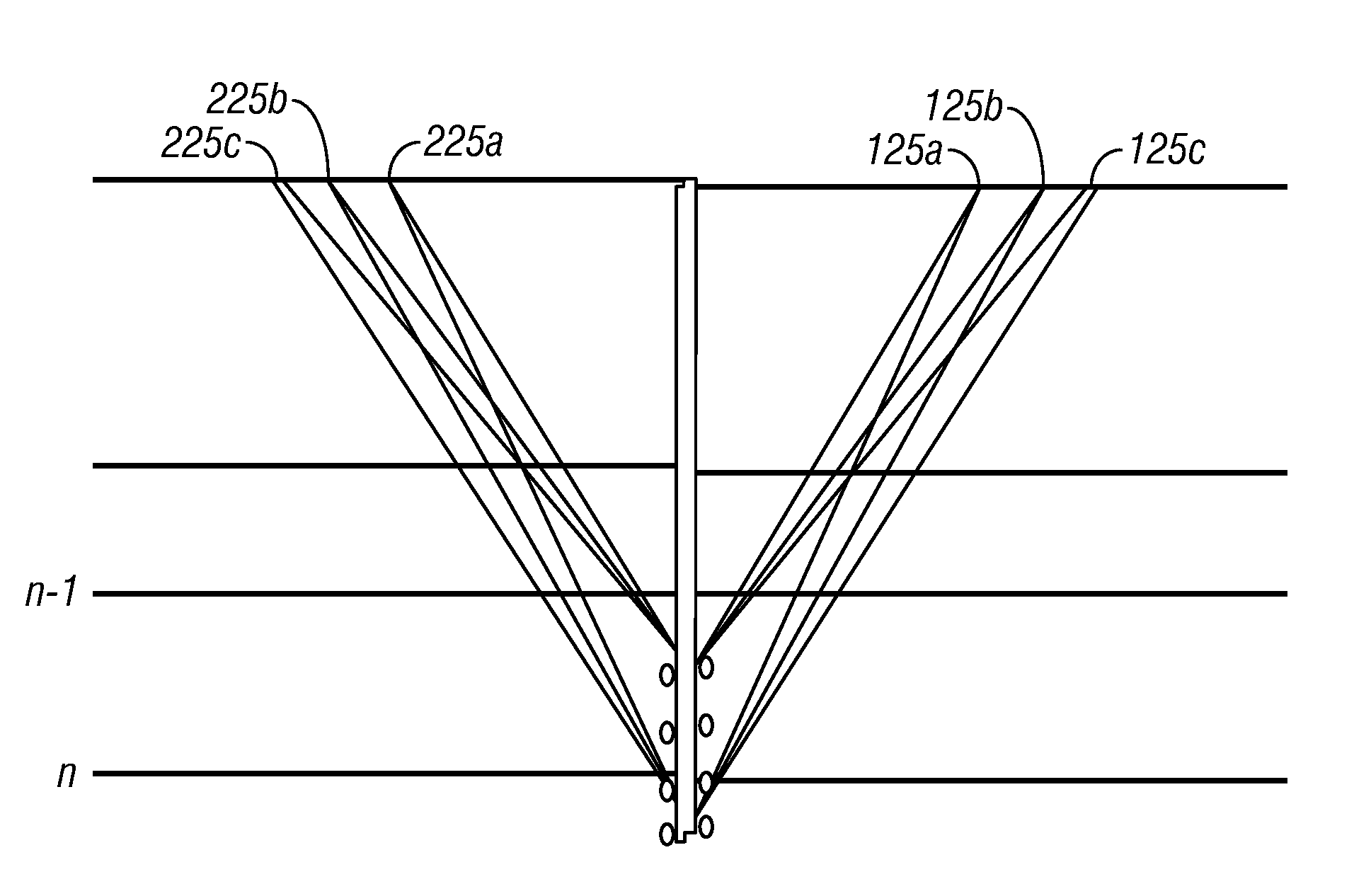
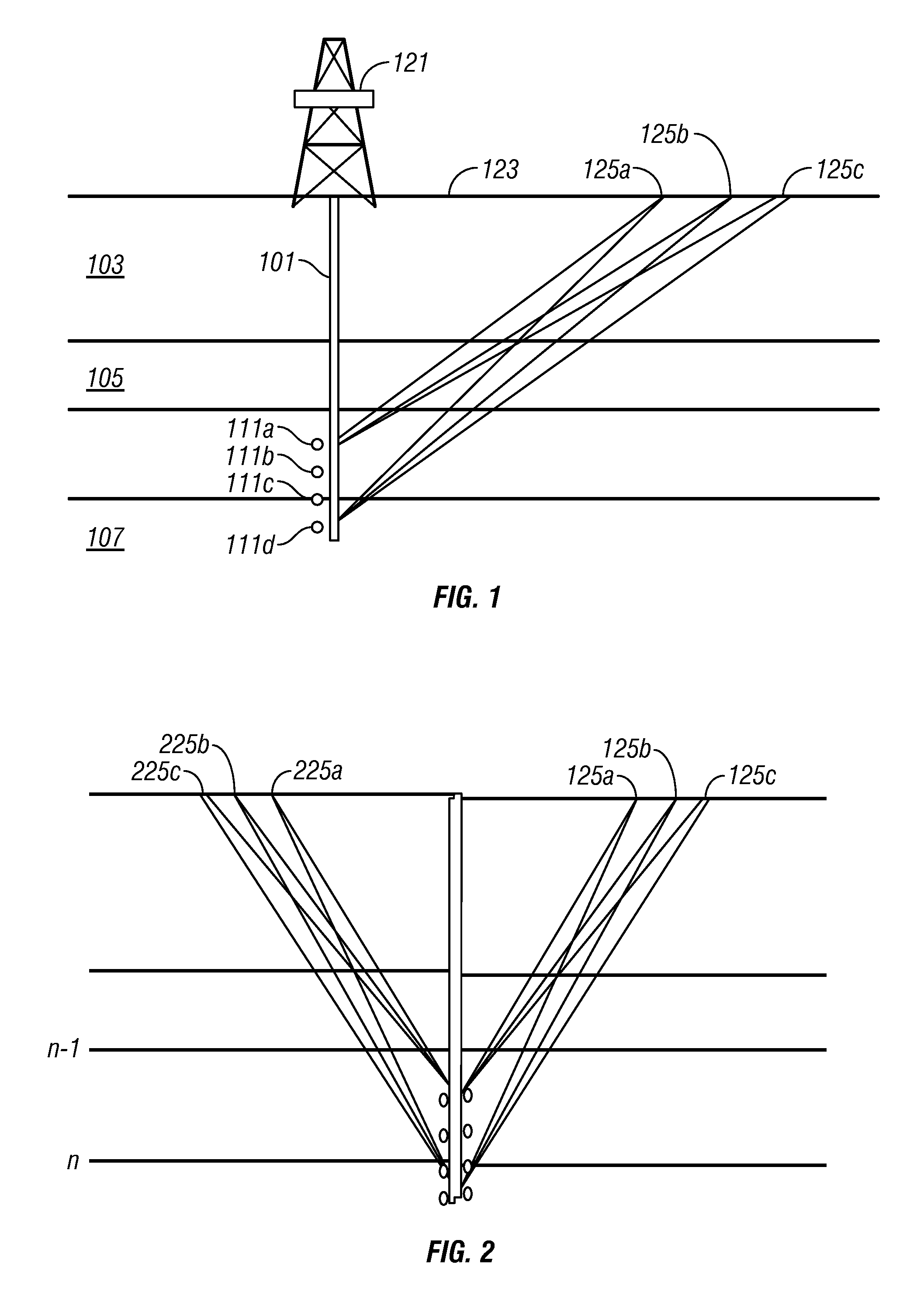
A walkaway VSP survey is carried out using a receiver array. First arrivals to a plurality of receivers are picked and used to estimate a normal-moveout (NMO) velocity. Using the NMO velocity and vertical velocities estimated from the VSP data, two anisotropy parameters are estimated for each of the layers. The anisotropy parameters may then be used to process surface seismic data to give a stacked image in true depth and for the interpretation purposes. For multi-azimuthal walkaway or 3D VSP data, we determine two VTI parameters ε and δ for multi-azimuth vertical planes. Then we determine five anisotropic interval parameters that describe P-wave kinematics for orthorhombic layers. These orthorhombic parameters may then be used to process surface seismic data to give a stacked image in true depth and for the interpretation purposes.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Converted wave anisotropy velocity analysis method and device
ActiveCN104155691AImprove accuracyReduce processing costsSeismic signal processingLongitudinal waveClassical mechanics
The invention provides a converted wave anisotropy velocity analysis method and device. The method includes the steps that the vertical velocity ratio, the effective velocity ratio and equivalent anisotropy parameters of converted waves are worked out according to the stacked section of longitudinal waves, the stacked section of the converted waves, the velocity of the longitudinal waves, the velocity of the converted waves and anisotropy parameters of the converted waves; with the speed of the converted waves, the vertical velocity ratio, the effective velocity ratio and the equivalent anisotropy parameters of the converted waves which are obtained as the initial parameters of pre-stack time migration of seismic data of the converted waves, the velocity parameter of pre-stack time migration of the converted waves is worked out, the first time of pre-stack time migration is performed, and a common imaging point gather is acquired; by analyzing the velocity of the converted waves corrected by residual moveout and the anisotropy parameters of the converted waves in the common imaging point gather, the common imaging point gather is acquired, and the velocity of the converted waves and the anisotropy parameters of the converted waves continue to be corrected till the acquired common imaging point gather is in even alignment in window. Through the converted wave anisotropy velocity analysis method and device, the accuracy of the converted wave anisotropy velocity analysis result is improved, and the processing cost is reduced.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
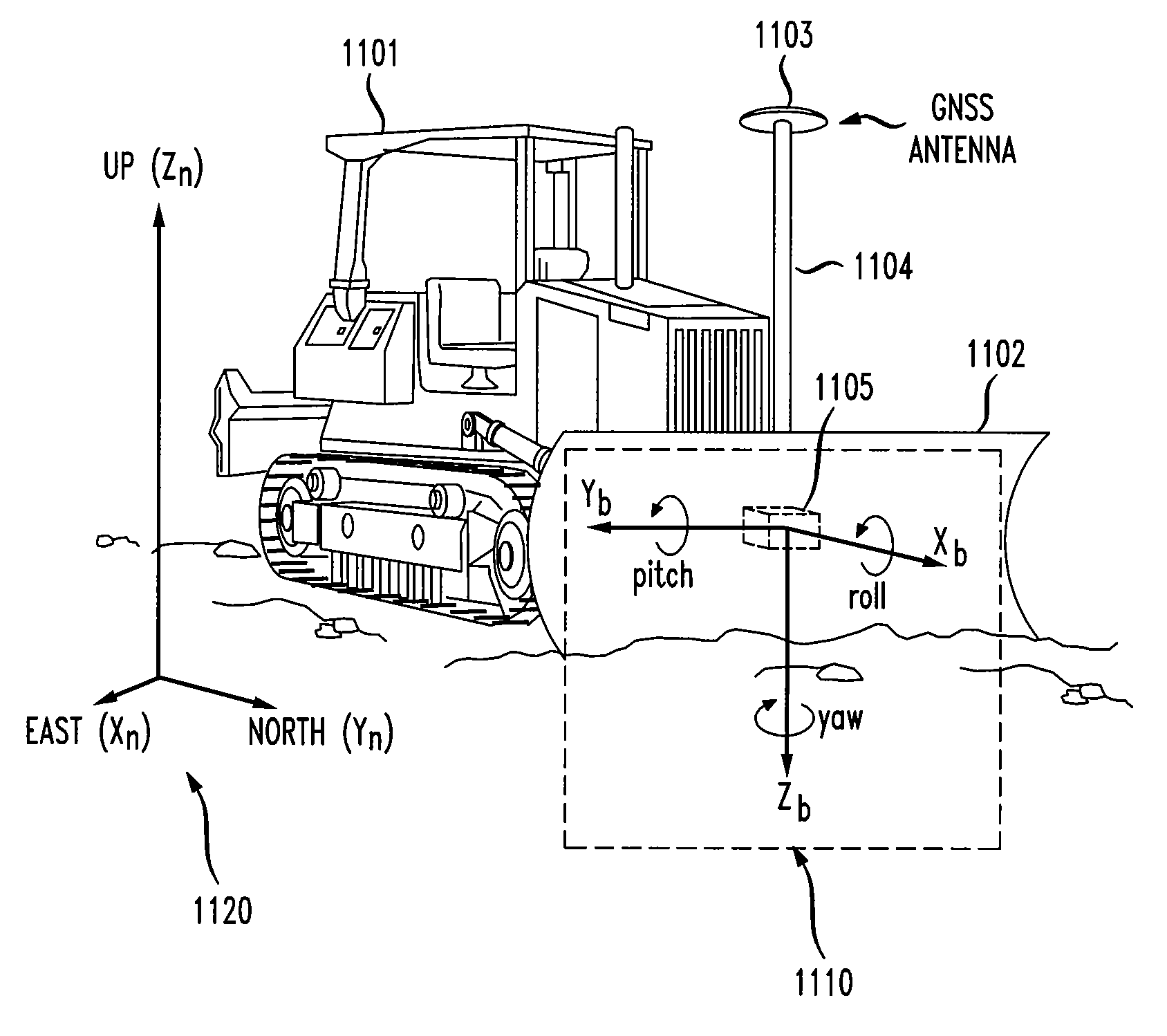
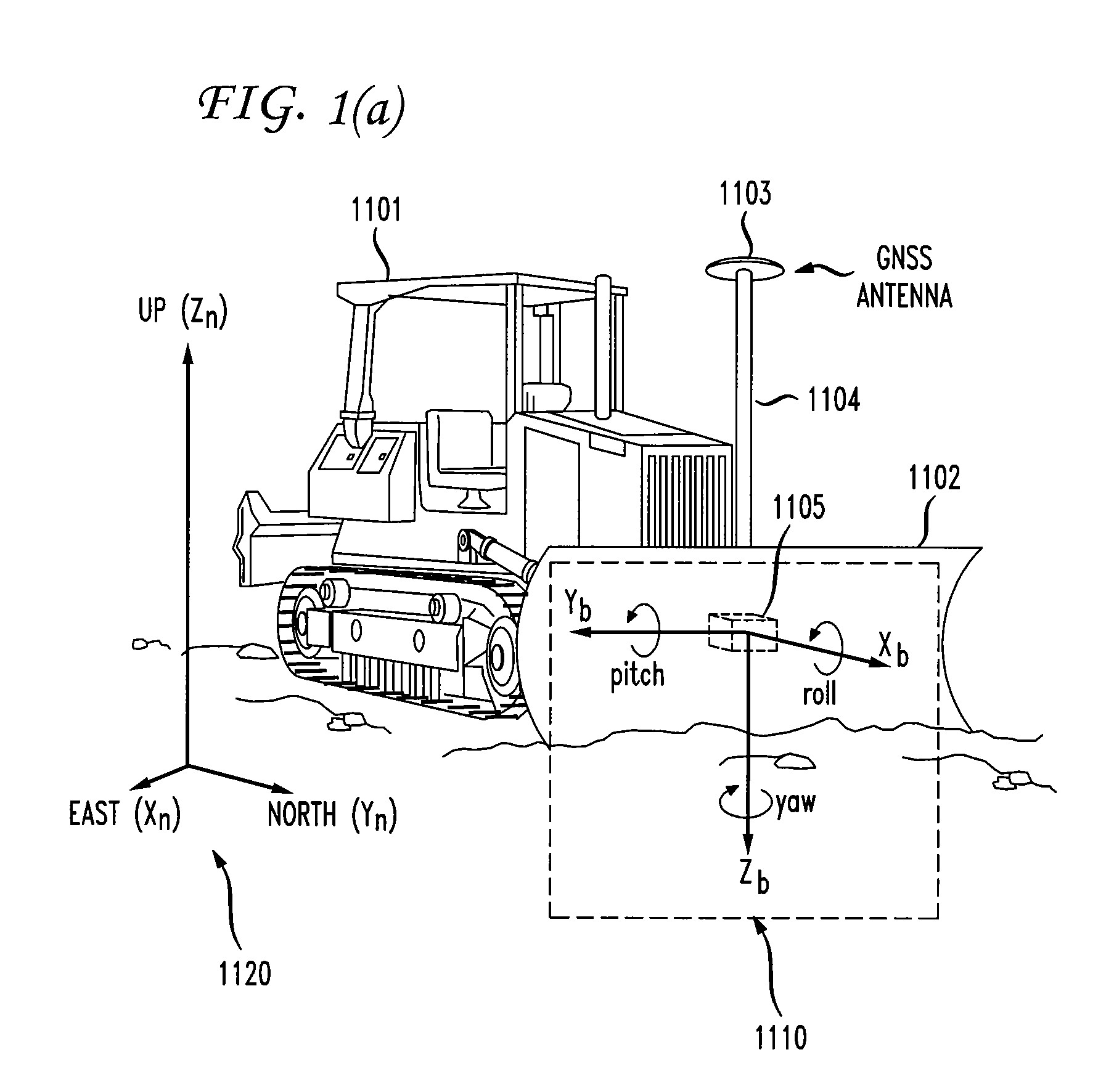
Automatic blade control system with integrated global navigation satellite system and inertial sensors
ActiveUS8145391B2Analogue computers for trafficMechanical machines/dredgersAccelerometerAutomatic control
Disclosed are method and apparatus for controlling the blade elevation and blade slope angle of a dozer blade. Elevation and slope angle measurements are calculated from measurements received from a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) antenna and an inertial measurement unit mounted on the dozer blade. The inertial measurement unit includes three orthogonally placed accelerometers and three orthogonally placed rate gyros. The measurements are processed by algorithms to calculate estimates of the blade elevation, blade vertical velocity, blade slope angle, and blade slope angular velocity. These estimates are then provided as inputs to a control algorithm which provides control signals to control a dozer hydraulic system which controls the blade elevation and blade slope angle.
Owner:TOPCON POSITIONING SYST INC
Electrically controlled suspension system
ActiveUS7526665B2Secure control stabilityDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesEngineeringElectric control
An electronically controlled suspension system according to the present invention comprises a sensor unit for extracting and providing a vertical acceleration component of a vehicle body of a vehicle; a signal processing unit for calculating a vertical velocity of the vehicle body using the vertical acceleration component provided by the sensor unit; a control gain determining unit having a control gain set according to the amplitude of the vertical acceleration component, and detecting the amplitude of the vertical acceleration component provided by the sensor unit and extracting a control gain corresponding to the detected amplitude; a control command value calculating unit for calculating a control command value using the control gain provided by the control gain determining unit and the vertical velocity of the vehicle body provided by the signal processing unit; and a damper driving unit for driving the variable damper based in the control command value.According to the present invention described above, a control command value for use in controlling a damping force of a damper is calculated using a nonlinear control gain according to a signal outputted from a speed or vertical acceleration sensor, thereby securing ride comfort and control stability.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Water surface aircraft water load full-aircraft power-free model pool test method
ActiveCN103832598APractical methodMethod is feasibleAircraft components testingFlight vehicleClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a water surface aircraft water load full-aircraft power-free model pool test method. A test includes the following steps that firstly, full-aircraft power-free model test installation is performed; secondly, a full-aircraft power-free model pool test is performed, an electric cylinder (2) is started, an electromagnetic throwing device (3) is turned on, a full-aircraft power-free model (9) is thrown on the water surface at a constant vertical speed, the trailer speed, the water touching angle of the model, the overload and the pressure value are recorded at the same time, the water touching conditions of the model are recorded, and the loaded conditions of the model after the model touches the water are analyzed according to the model postures, the overloads and the pressure values of different test states. The water surface aircraft water load full-aircraft power-free model pool test method has the advantages of being practical, feasible, easy to operate, reliable in test result and wide in application range.
Owner:CHINA SPECIAL TYPE FLIER RES INST
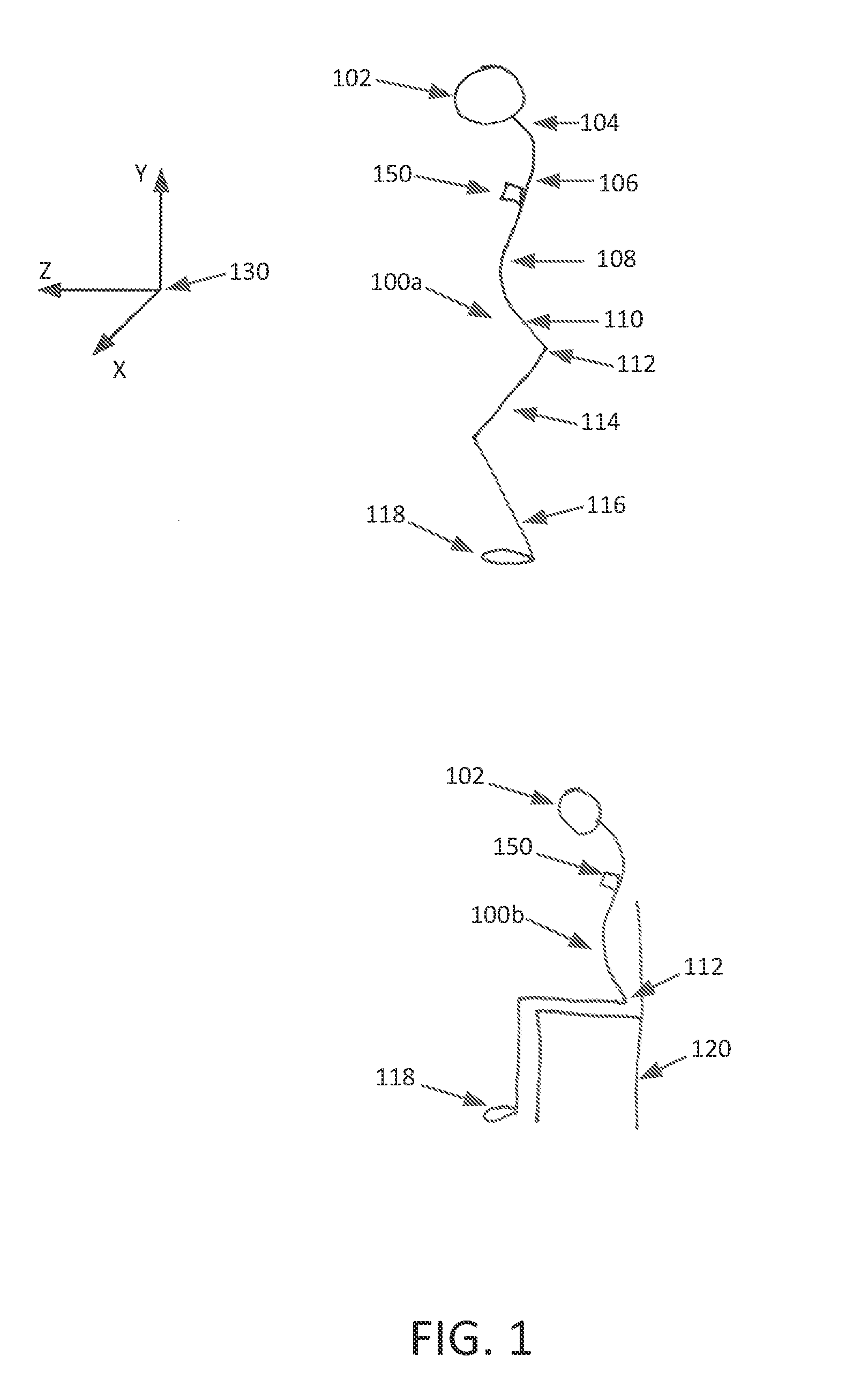
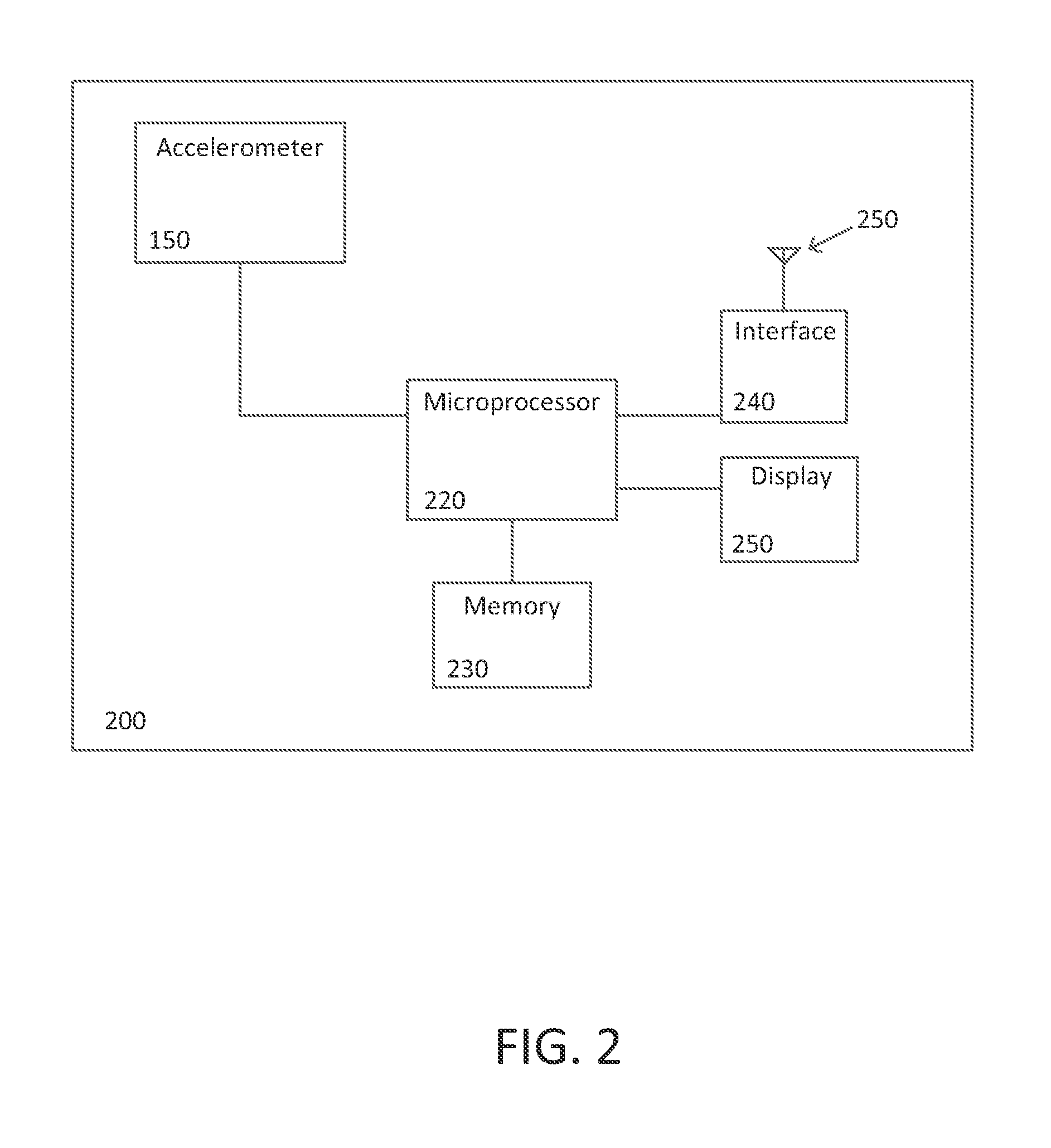
System and method for detecting transitions between sitting and standing states
A system and method are described herein for detecting a user's transition between sitting and standing postures. Transitions between sitting and standing states are reliably detected using an accelerometer attached to the user. By modeling error introduced by the accelerometer, and correcting for this error, transitions between sitting and standing states are reliably detected. A microprocessor coupled to the accelerometer converts the captured accelerometer data to approximate vertical acceleration. Vertical velocity, which includes accelerometer error, is determined from the approximate vertical acceleration. The vertical velocity is corrected, and the corrected vertical velocity used to determine vertical displacement. Transitions between sitting and standing states are determined from the vertical displacement.
Owner:SEISMIC HLDG INC
Fall detectors and a method of detecting falls
There is provided a fall detector for detecting falls of a user or an object to which the fall detector is attached, characterized in that the fall detector comprises an air flow sensor for providing measurements indicative of vertical velocity and / or changes in altitude of the fall detector.
Owner:LIFELINE SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com