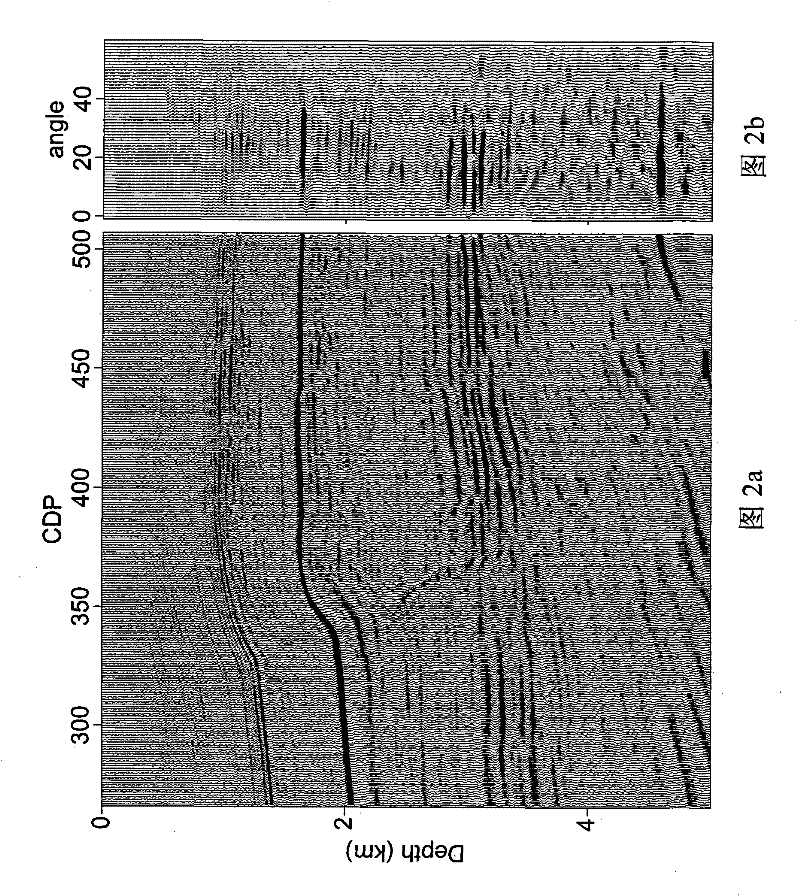
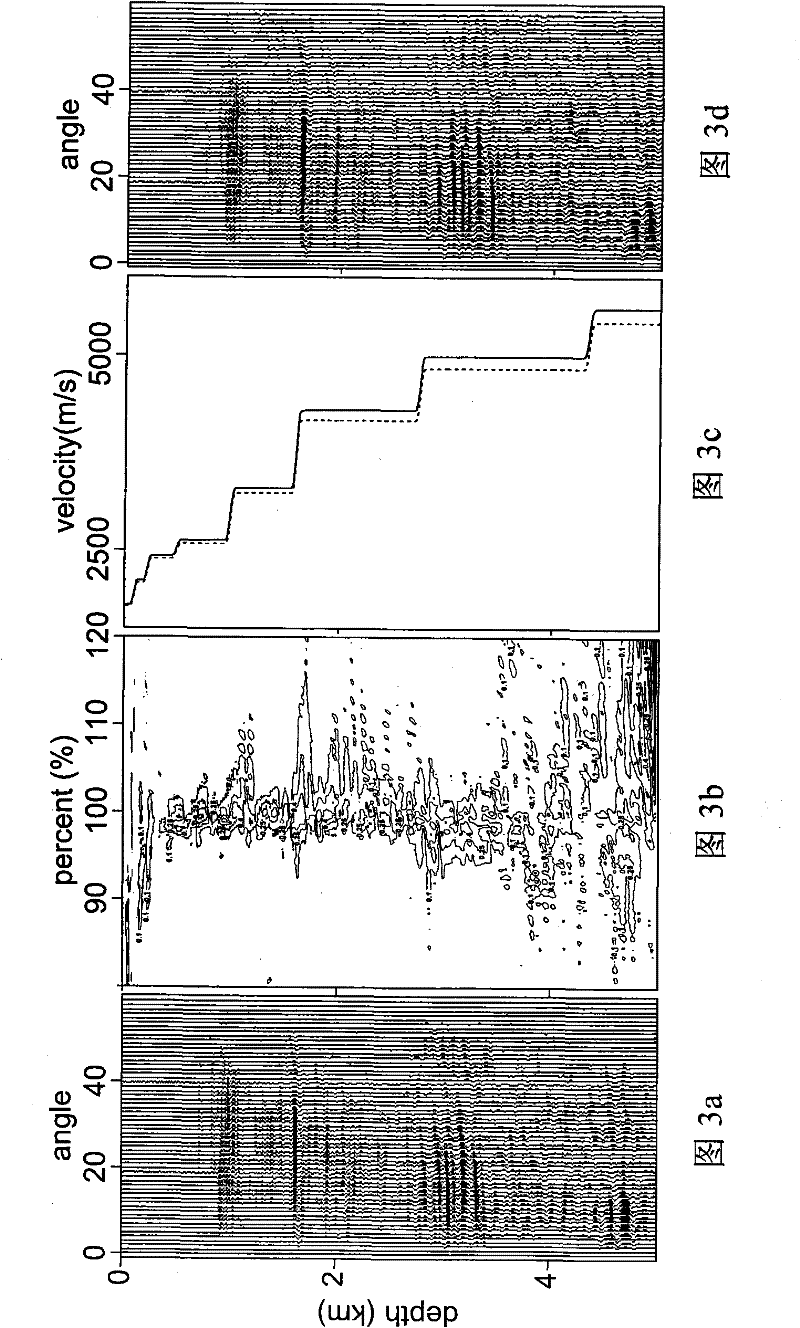
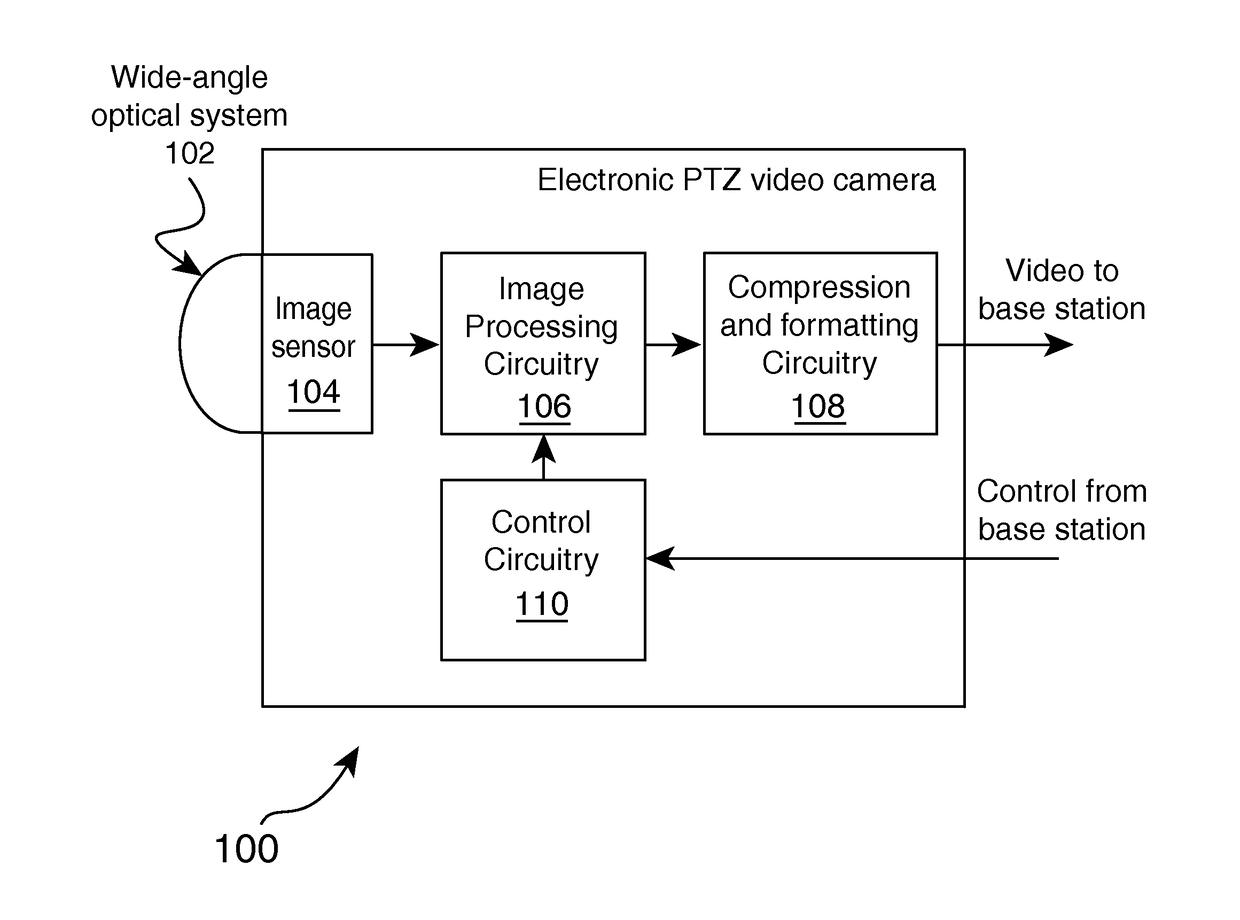
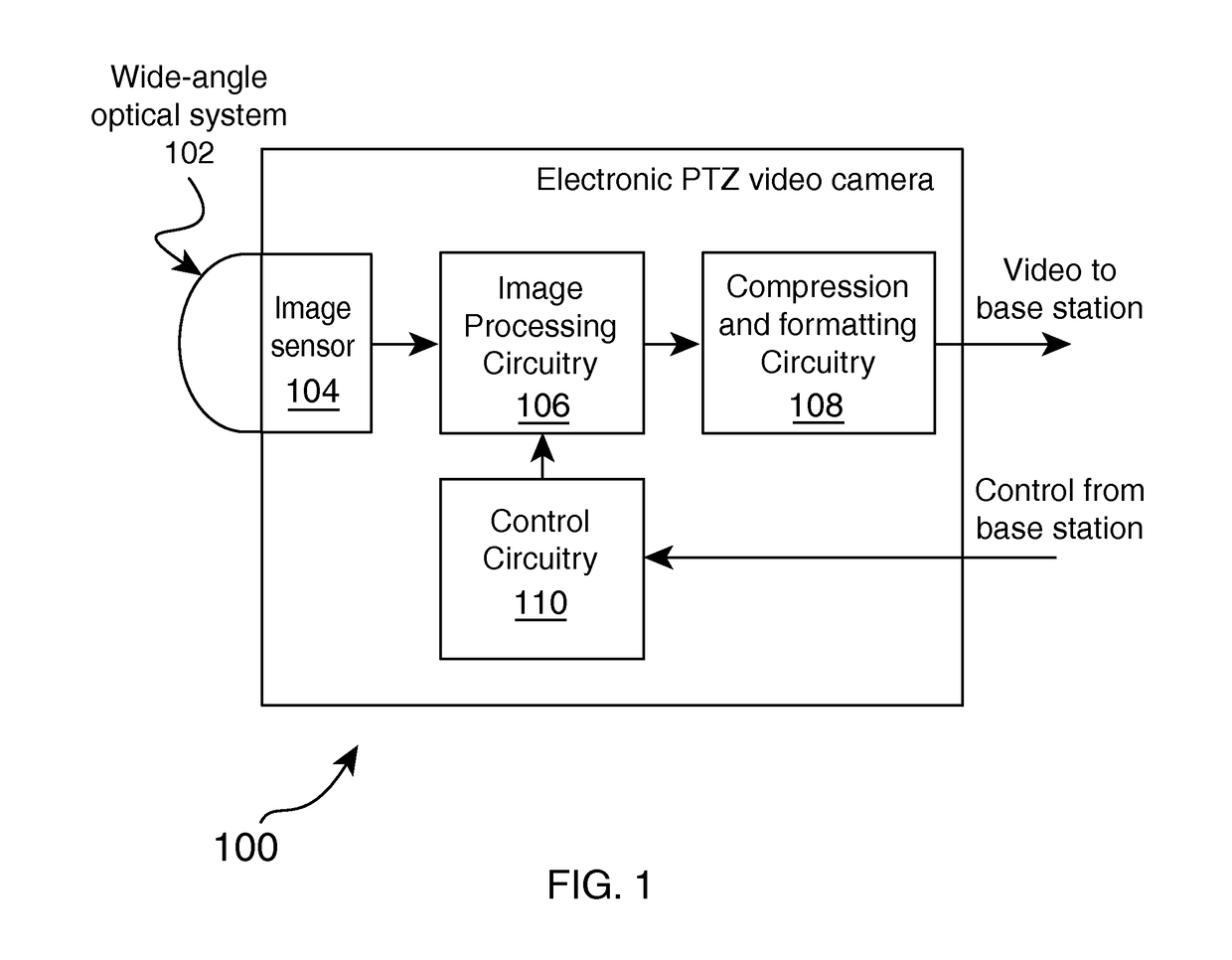
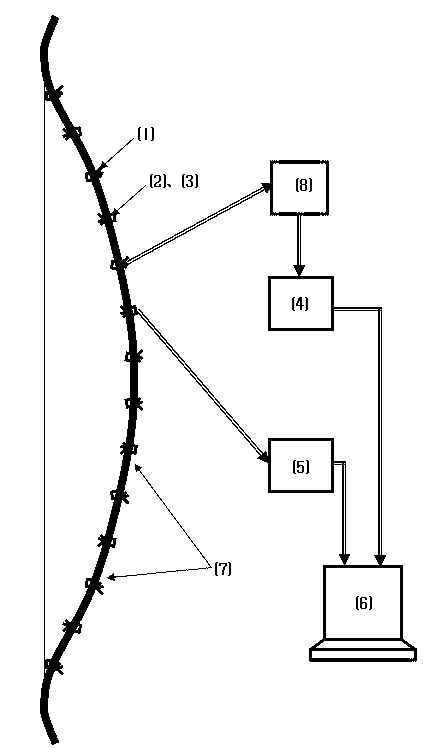
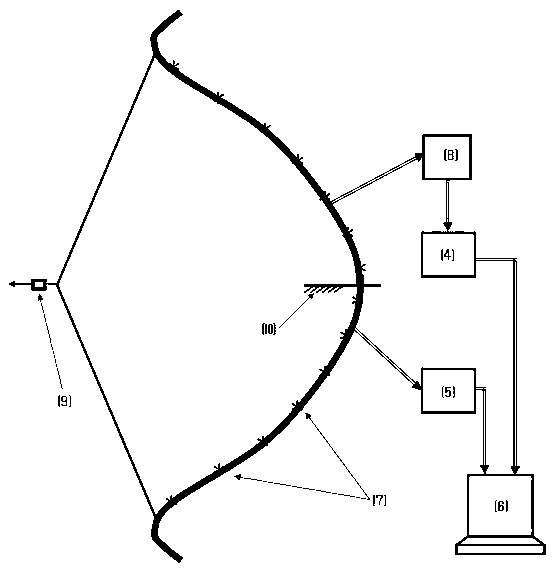
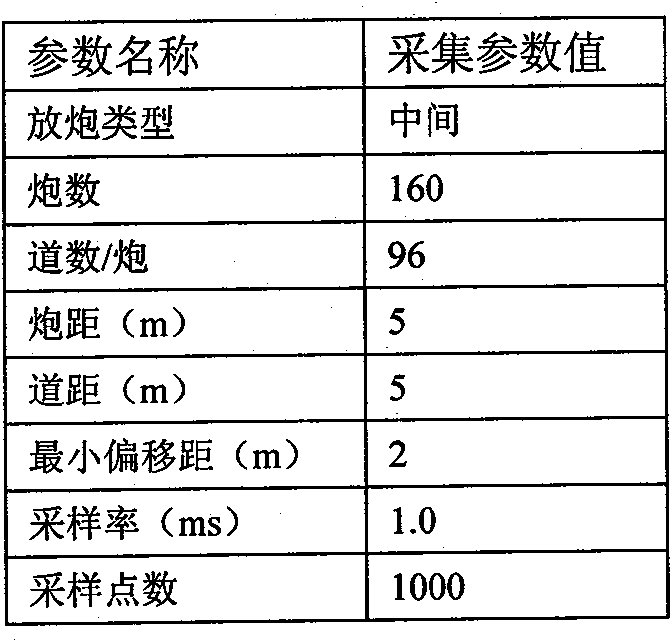
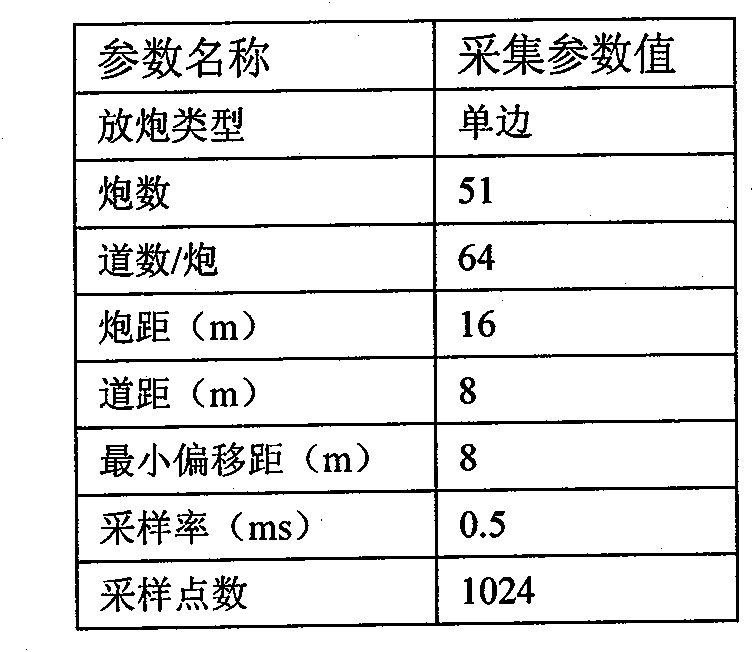
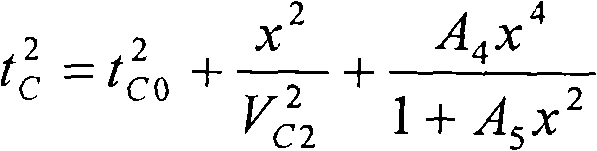Patents
Literature
60 results about "Normal moveout" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
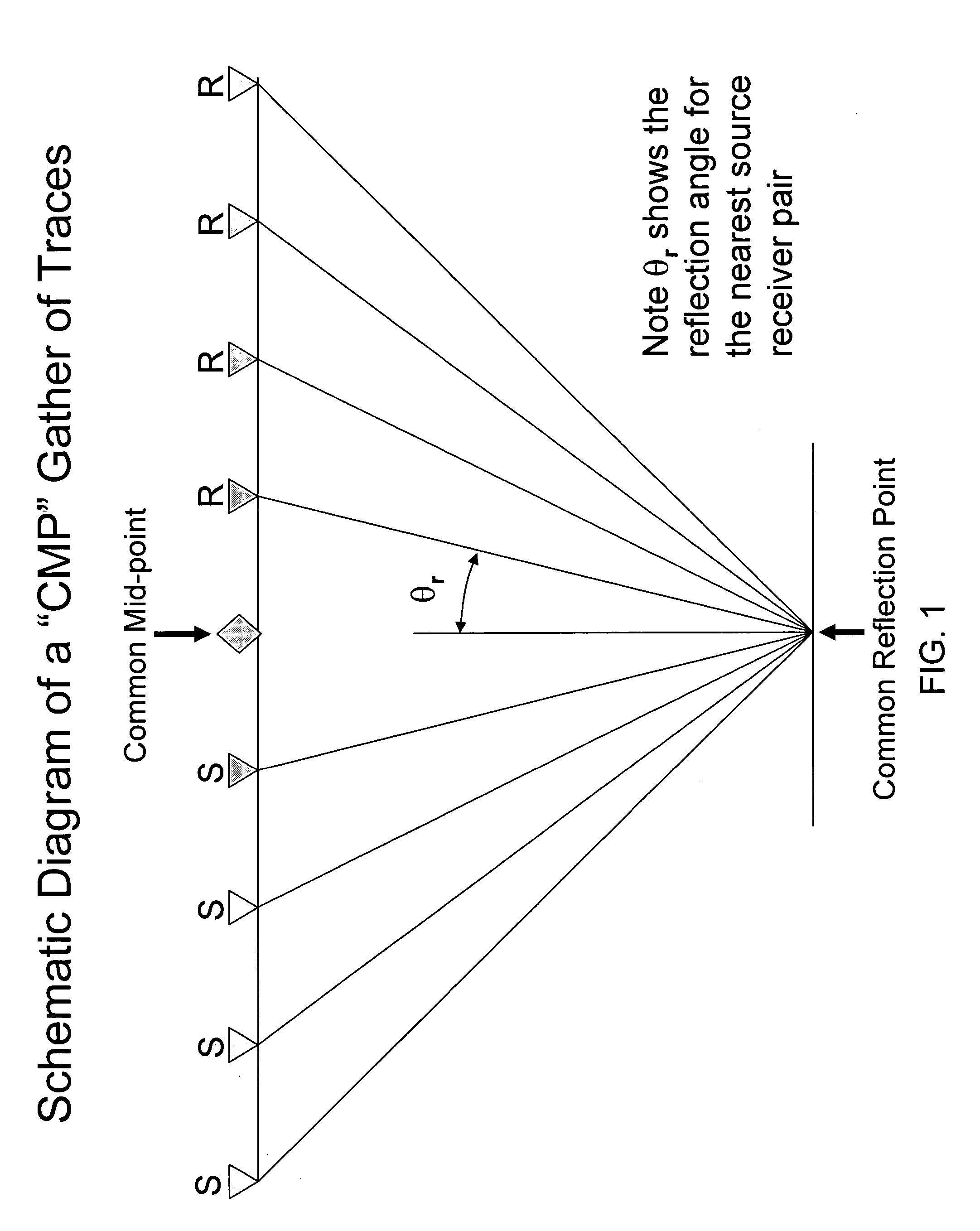
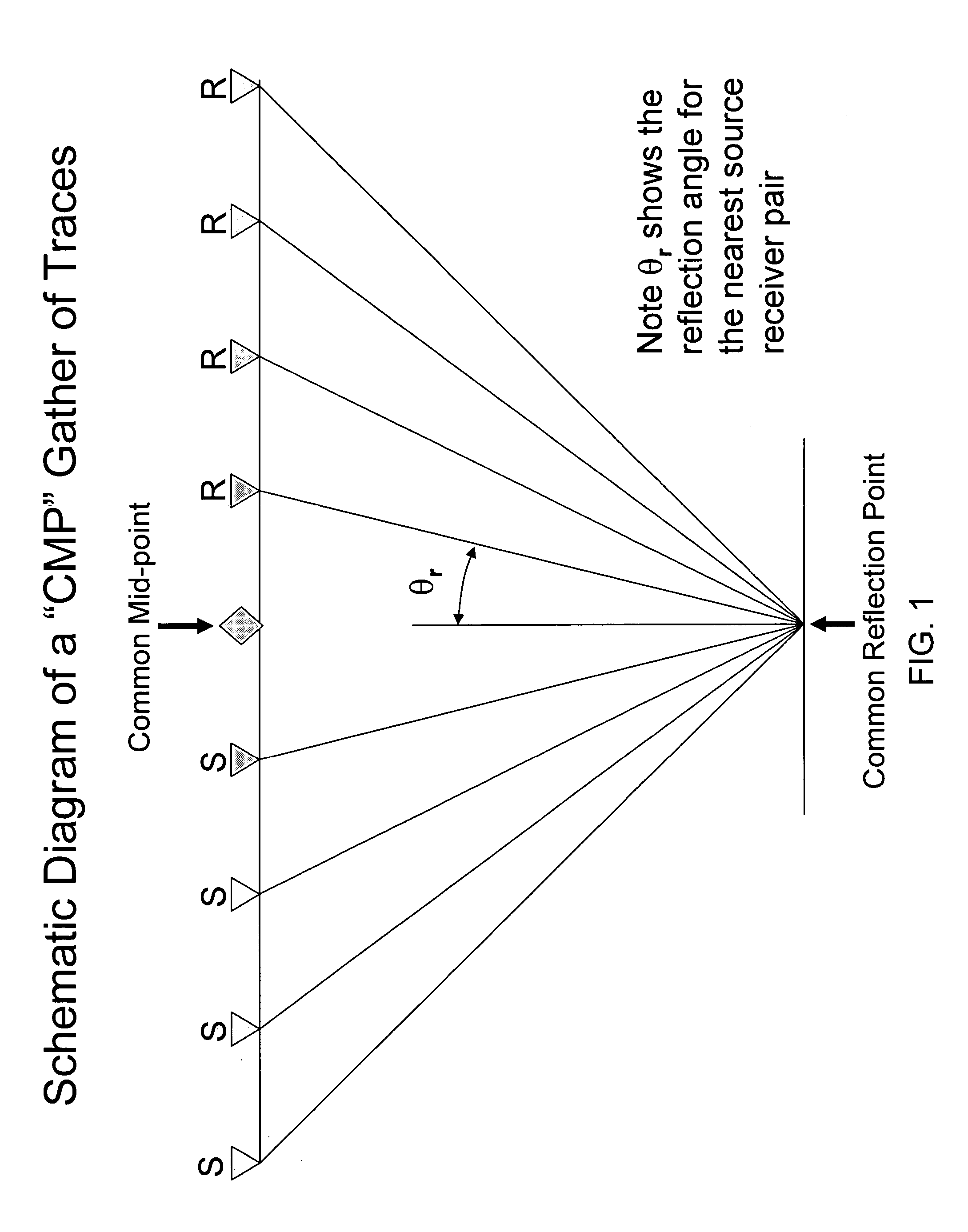
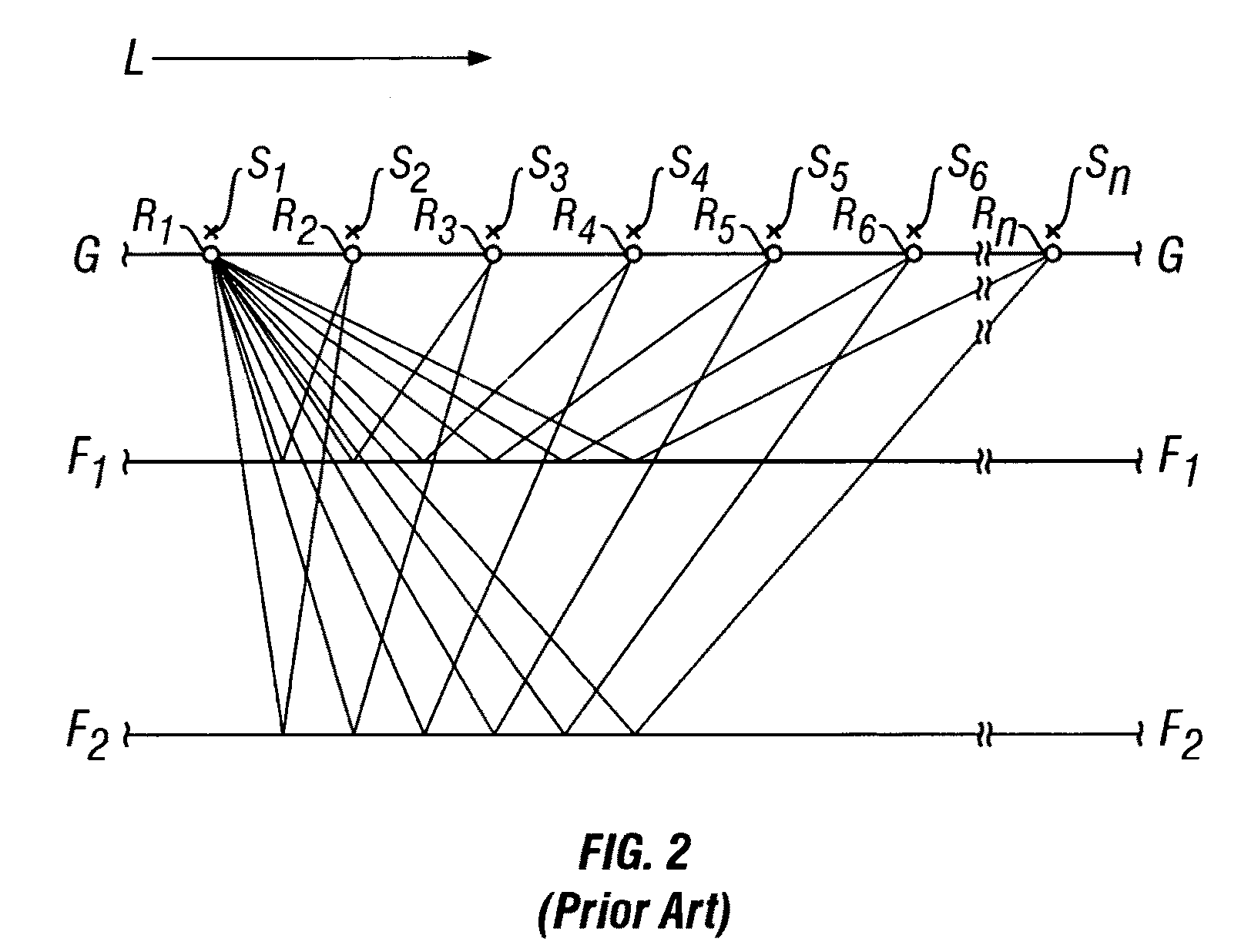
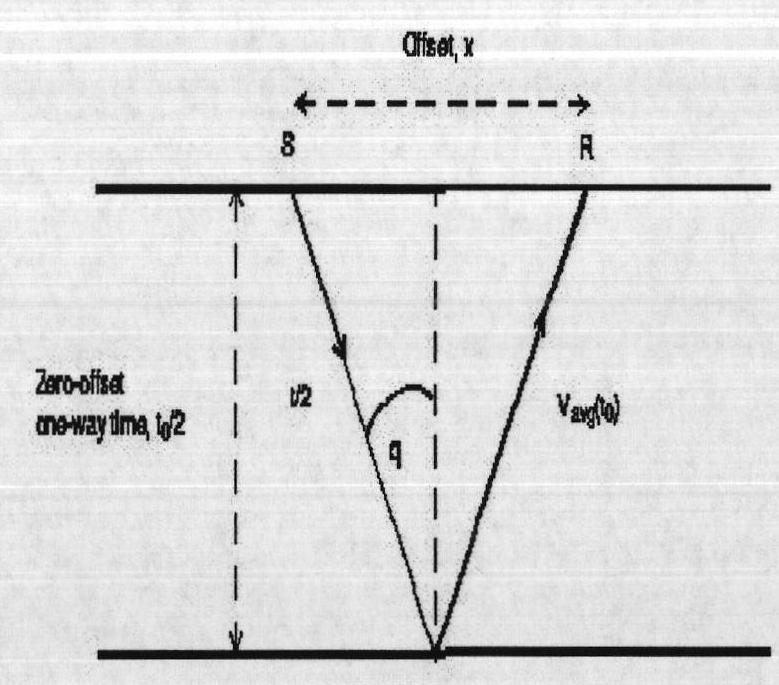
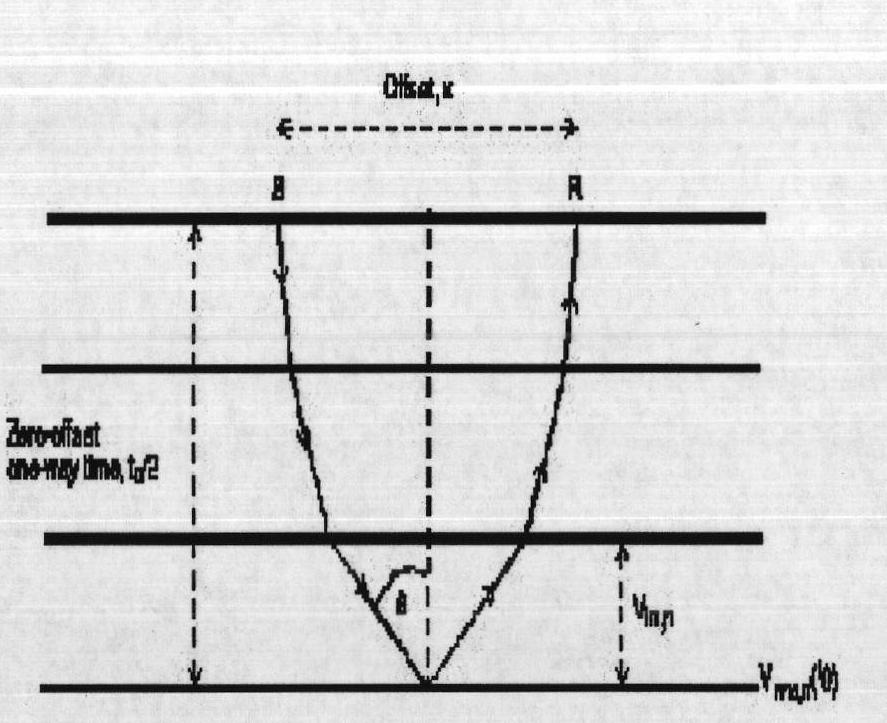
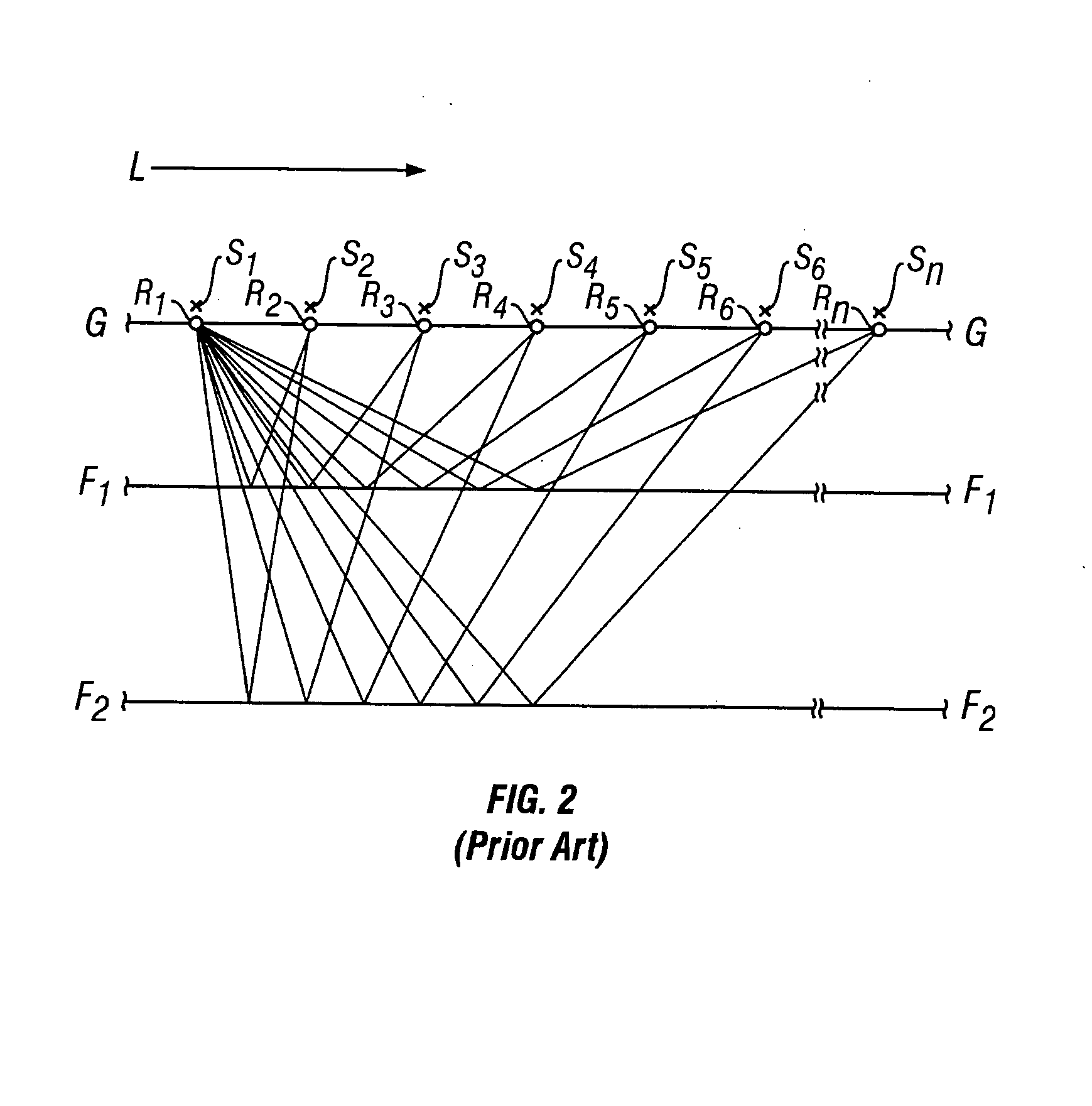
In reflection seismology, normal moveout (NMO) describes the effect that the distance between a seismic source and a receiver (the offset) has on the arrival time of a reflection in the form of an increase of time with offset. The relationship between arrival time and offset is hyperbolic and it is the principal criterion that a geophysicist uses to decide whether an event is a reflection or not. It is distinguished from dip moveout (DMO), the systematic change in arrival time due to a dipping layer.
3-D prestack/poststack multiple prediction
InactiveUS6735527B1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsNormal moveoutCommon depth point
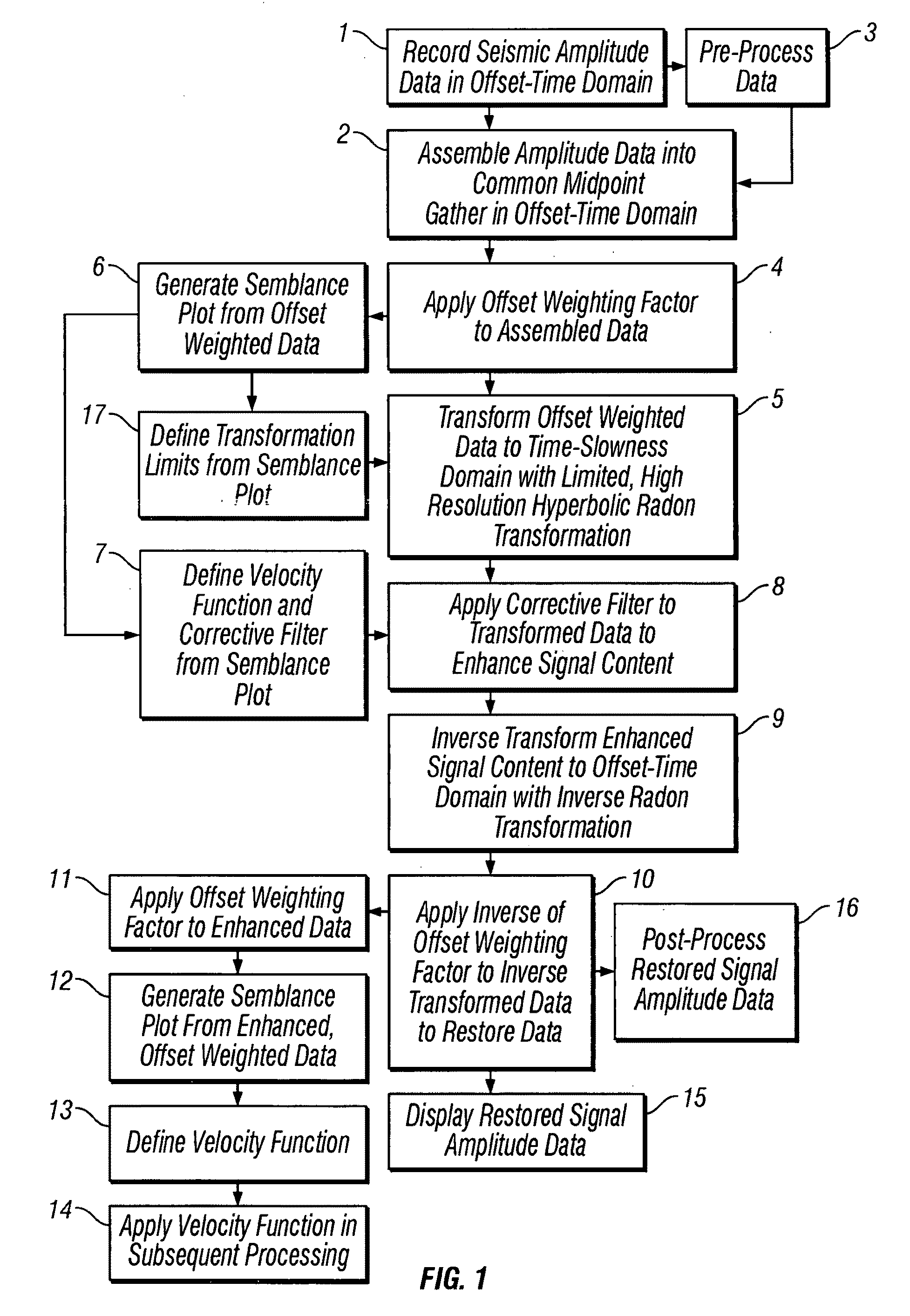
System and method for analyzing seismic data from a formation. Stacked seismic data are provided, including a plurality of stack traces, e.g., by collecting seismic data from source and receiver locations and stacking the collected seismic data to produce the stacked seismic data. 3-dimensional (3-D) prestack traces are generated from the plurality of stack traces, e.g., by performing inverse moveout of stack traces, e.g., in a specified neighborhood, at common-depth-points, e.g., by inverse normal moveout, ray tracing, spike synthesis, etc. The inverse moveout corrected traces are convolved to compute predicted multiples which are useable in analyzing the formation. The multiples may be adaptively subtracted from the stacked seismic data, or optionally, from prestack data, to generate processed seismic data useable in analyzing the formation, e.g., for petroleum production potential. Dip moveout (DMO) corrected seismic data may be used, where DMO velocities are adjusted by dividing by cosine of the dip angle.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS
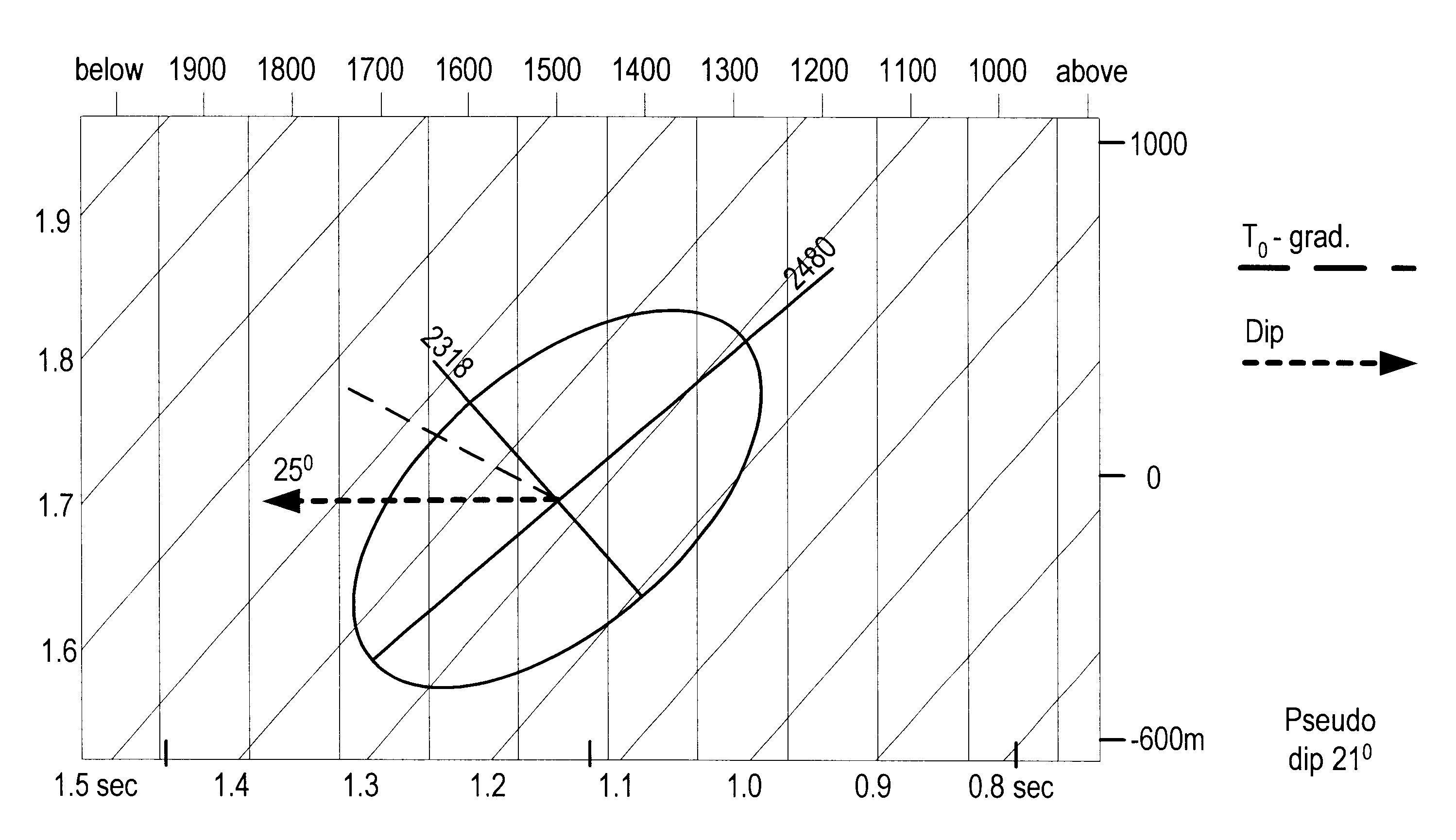
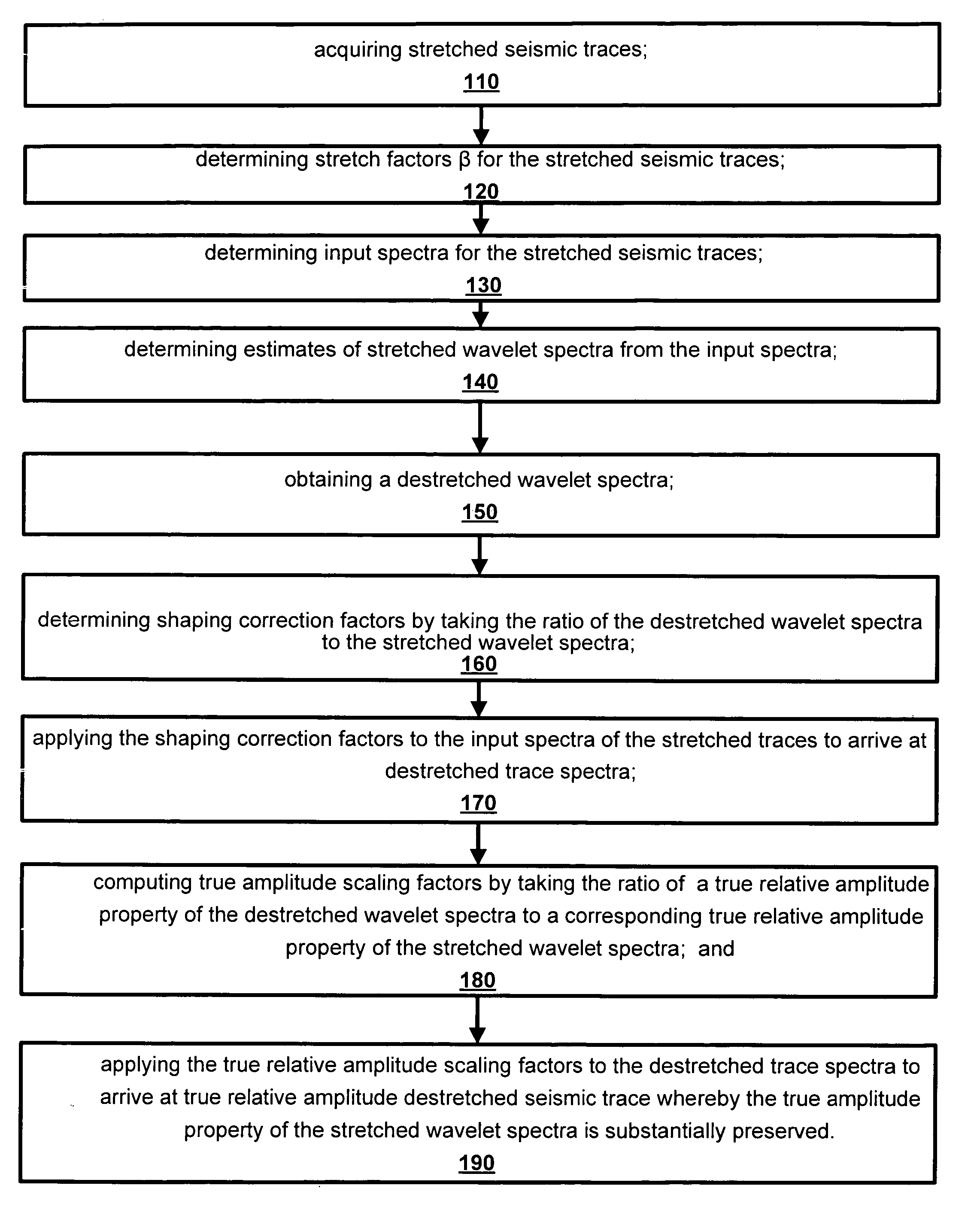
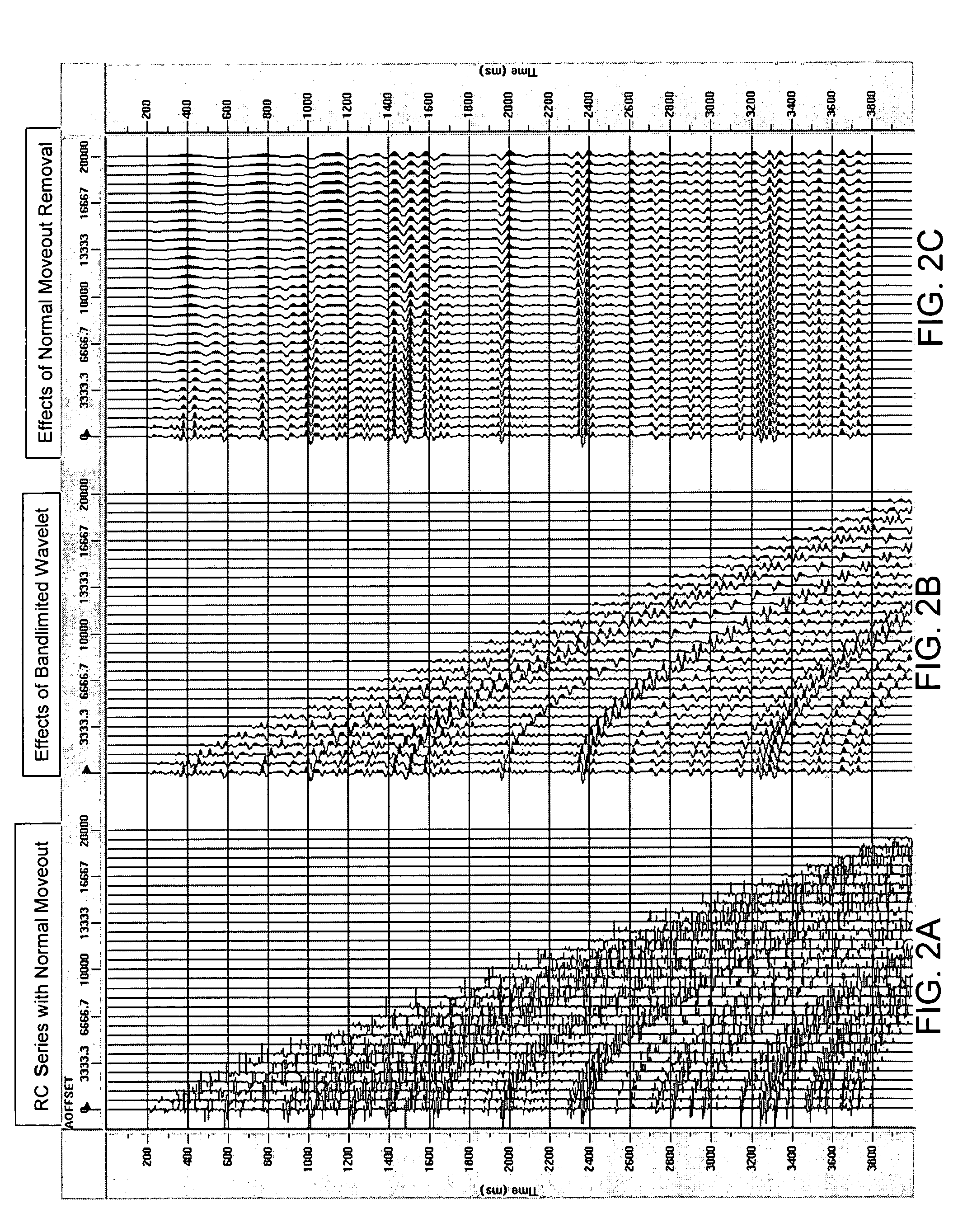
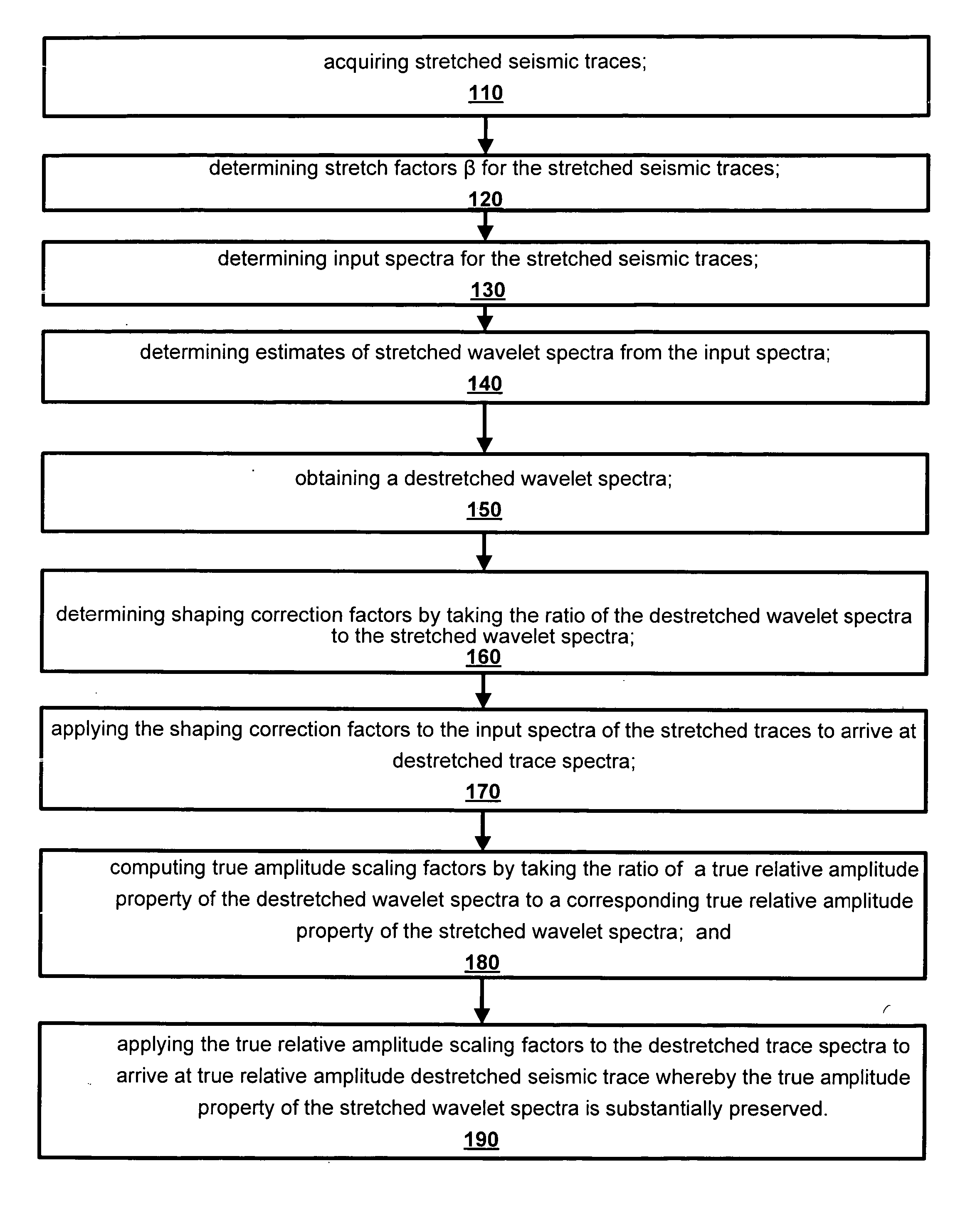
Method and apparatus for true relative amplitude correction of seismic data for normal moveout stretch effects
InactiveUS7230879B2Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsRelative magnitudeVibration amplitude
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for arriving at true relative amplitude destretched seismic traces from stretched seismic traces. The method compensates for offset varying reflection interference effects due to normal moveout. Stretch factors β and also input spectra are determined for NMOR stretched seismic traces. Estimates are then made of stretched wavelet spectra from the input spectra. A destretched wavelet spectra is then obtained. Shaping correction factors are determined by taking the ratio of the destretched wavelet spectra to the stretched wavelet spectra and are applied to the input spectra of the stretched traces to arrive at a destretched trace spectra. True relative amplitude scaling factors are computed by taking the ratio of a true relative amplitude property of the destretched wavelet spectra to a corresponding true relative amplitude property of the stretched wavelet spectra. Finally, the true relative amplitude scaling factors are applied to the destretched trace spectra to arrive at true relative amplitude destretched seismic traces.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
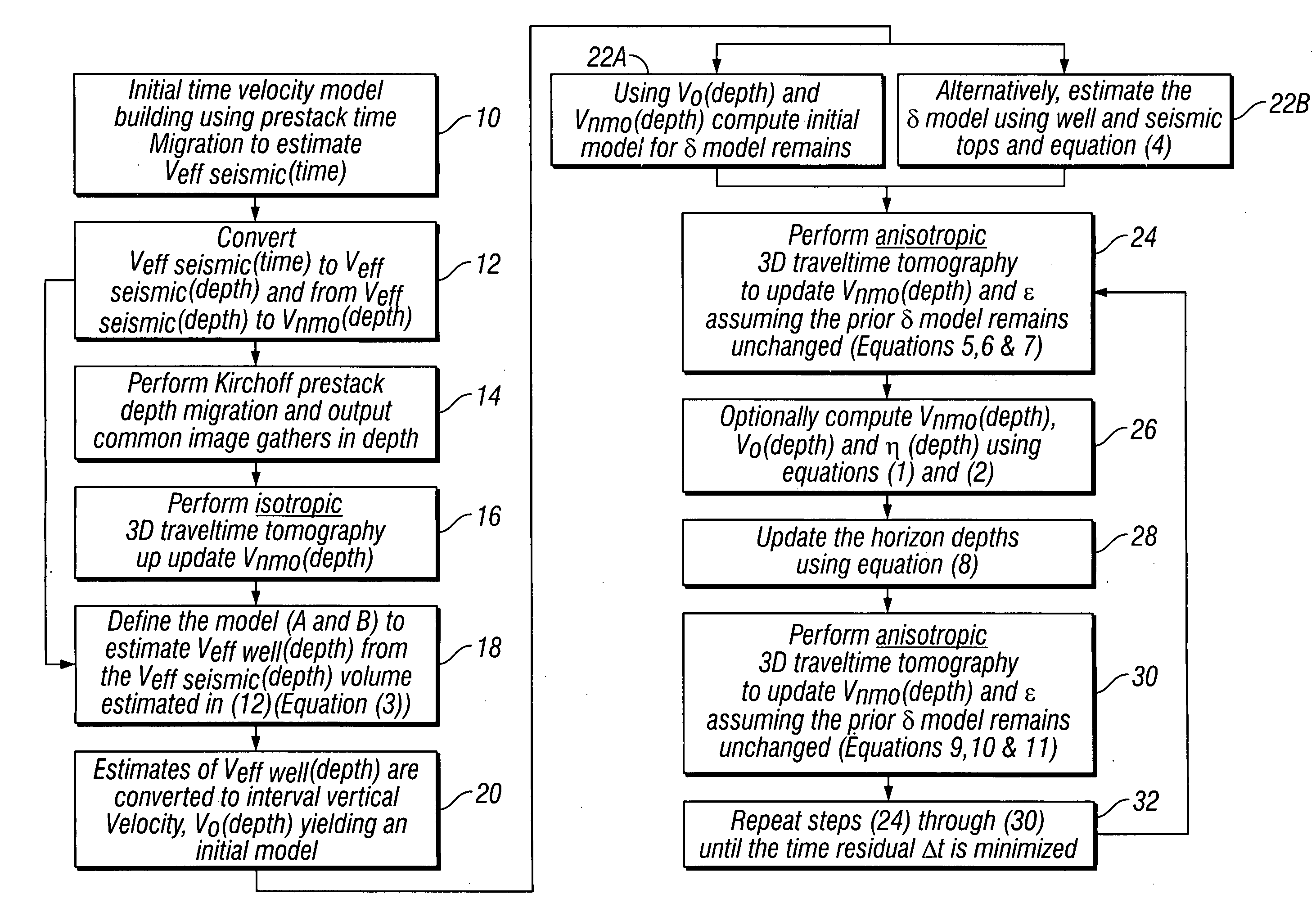
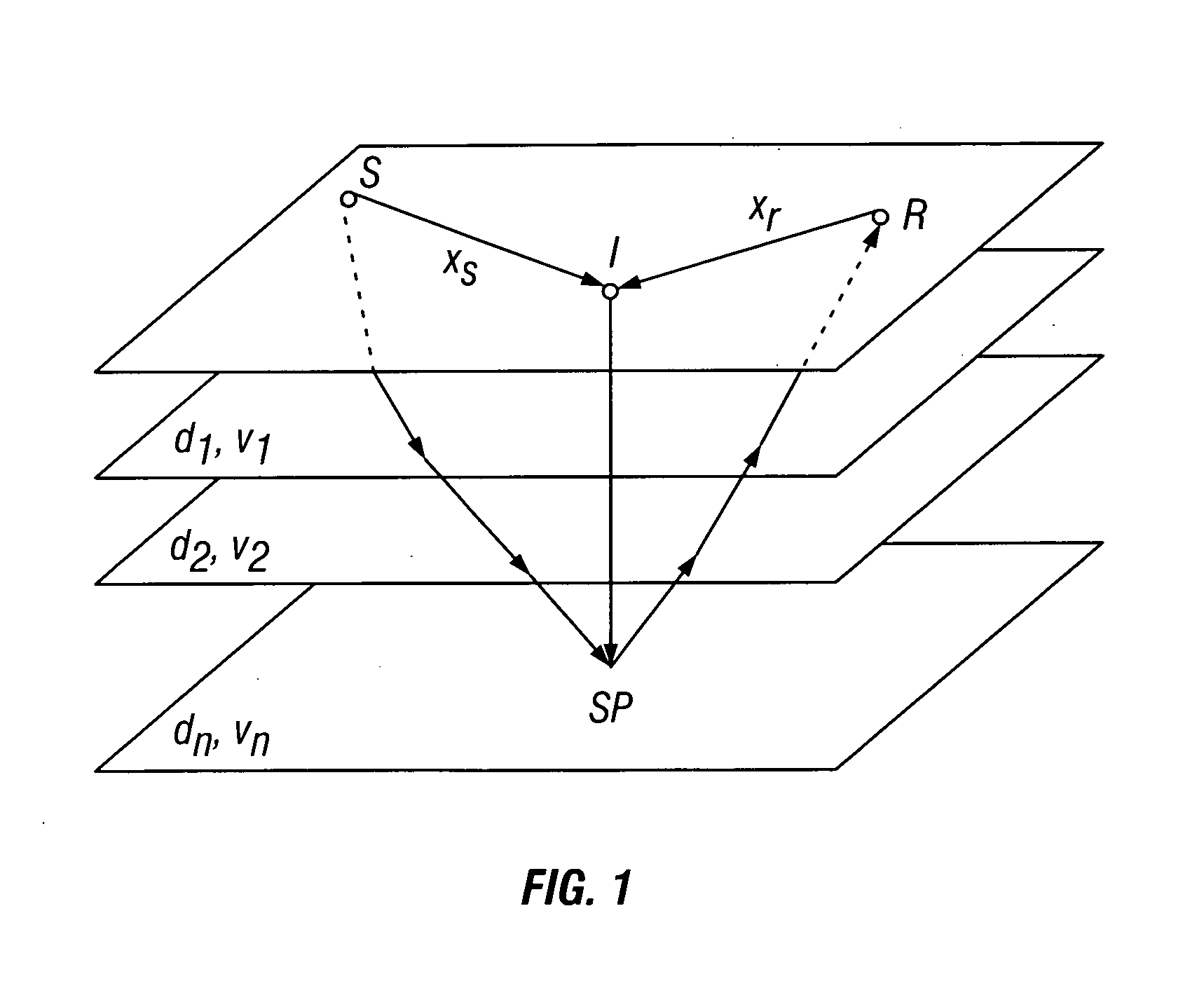
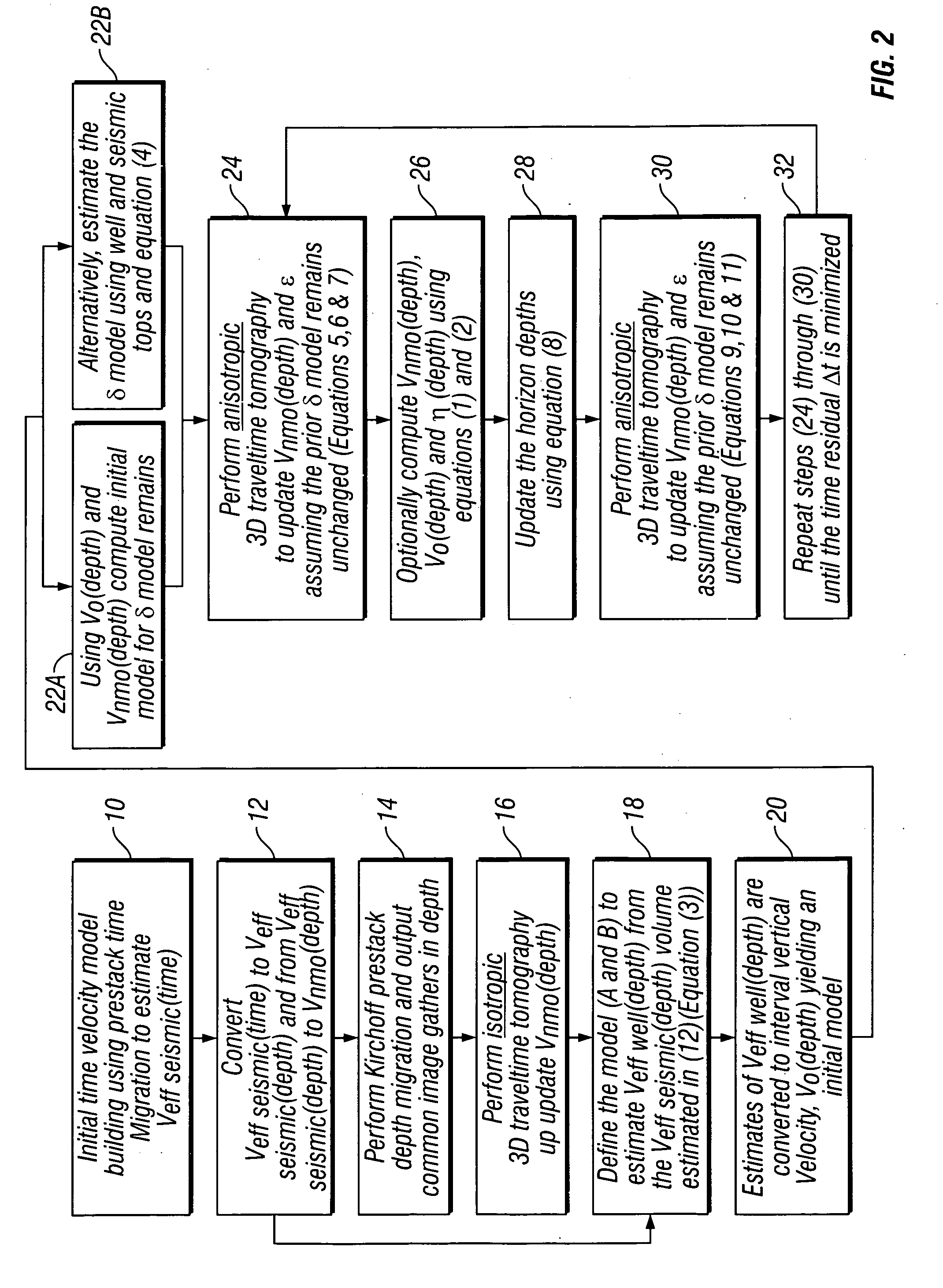
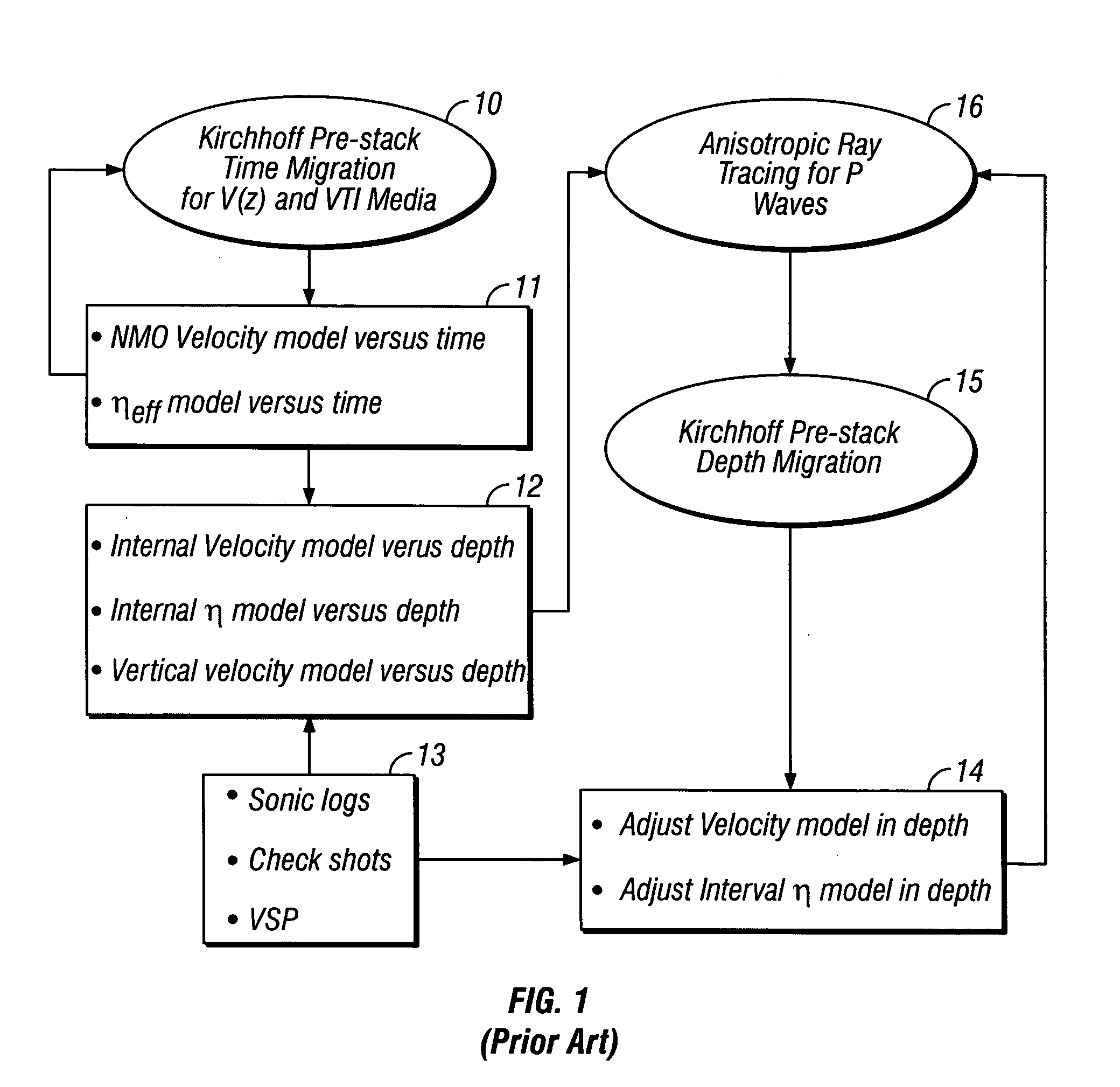
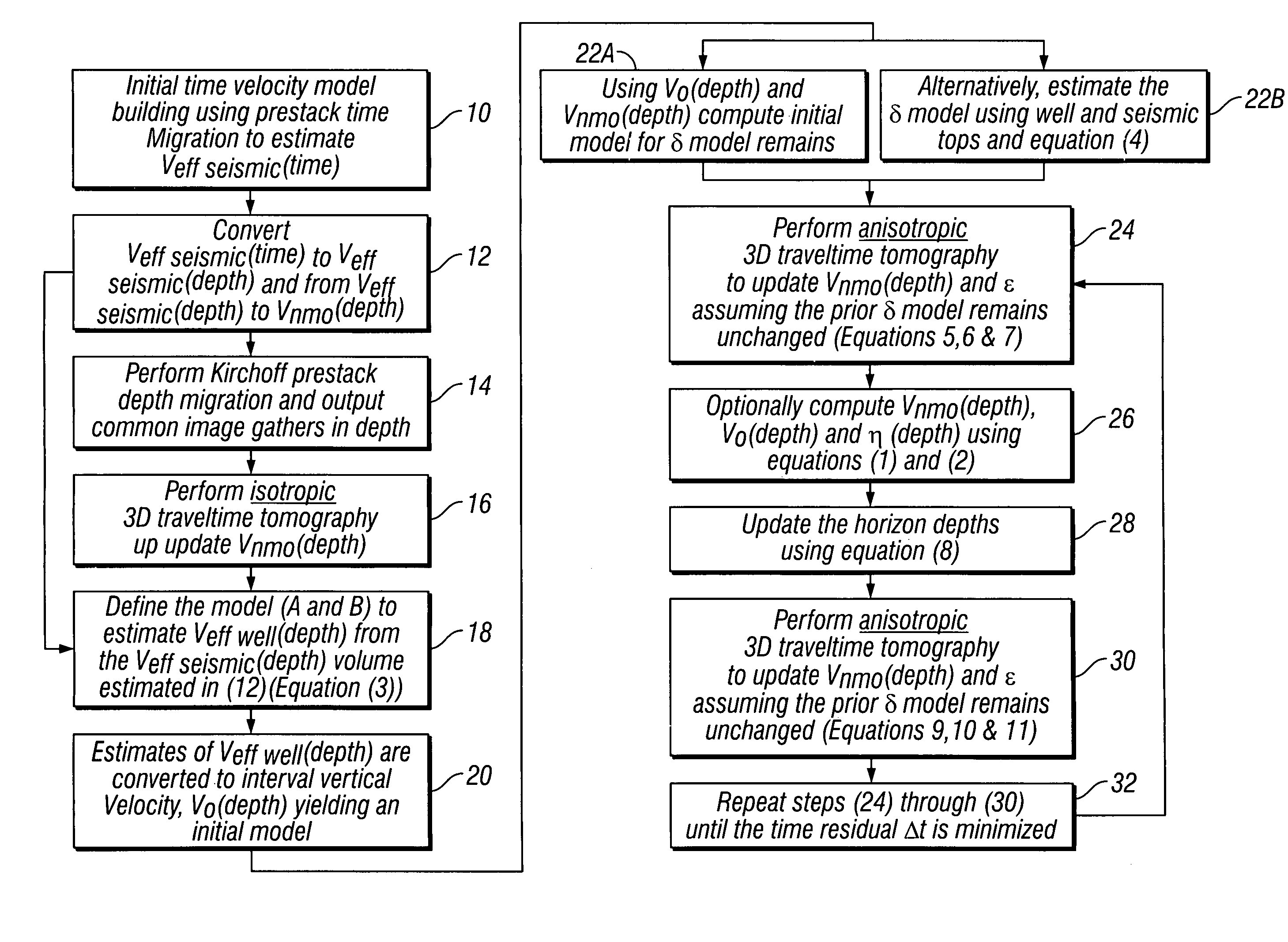
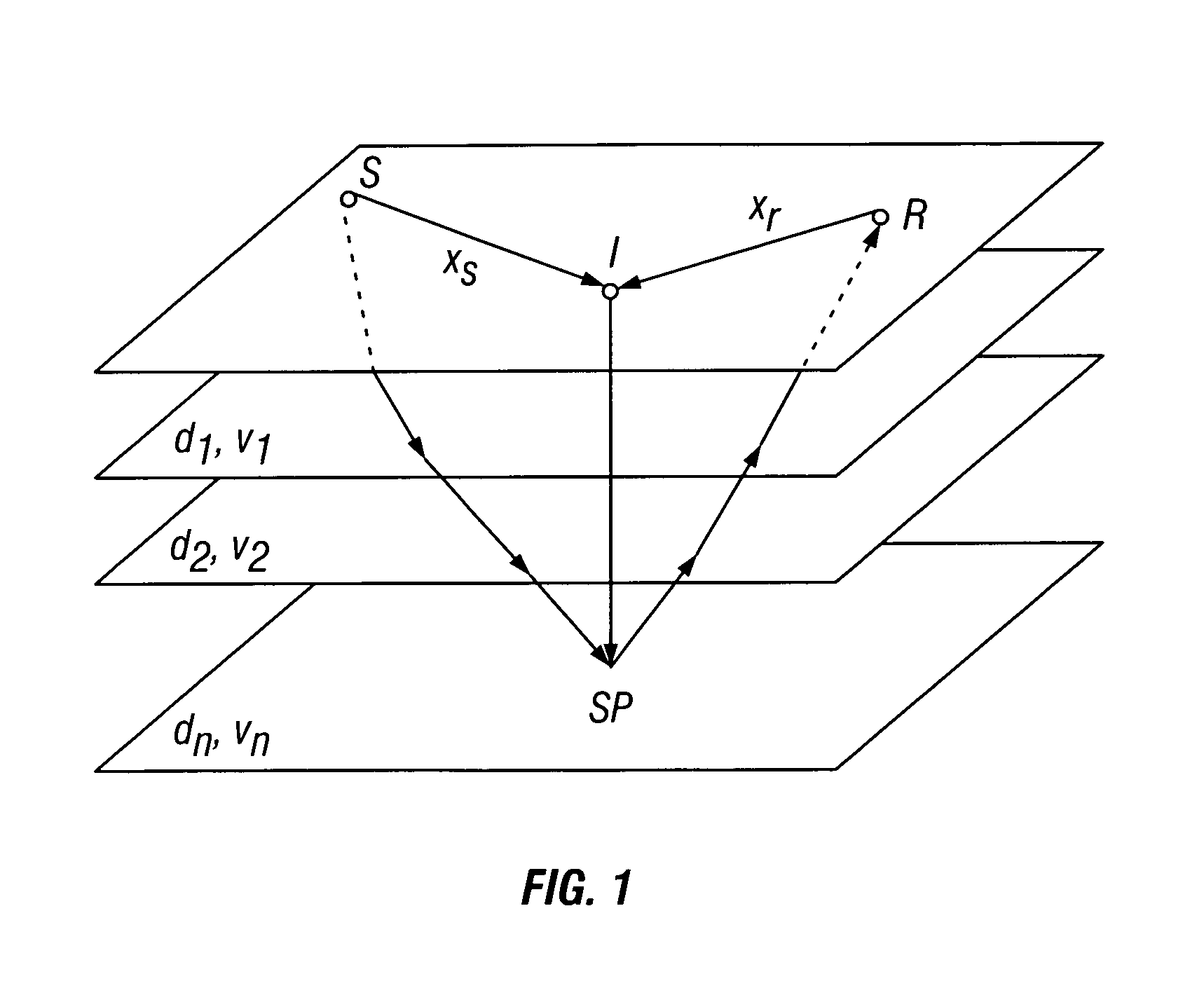
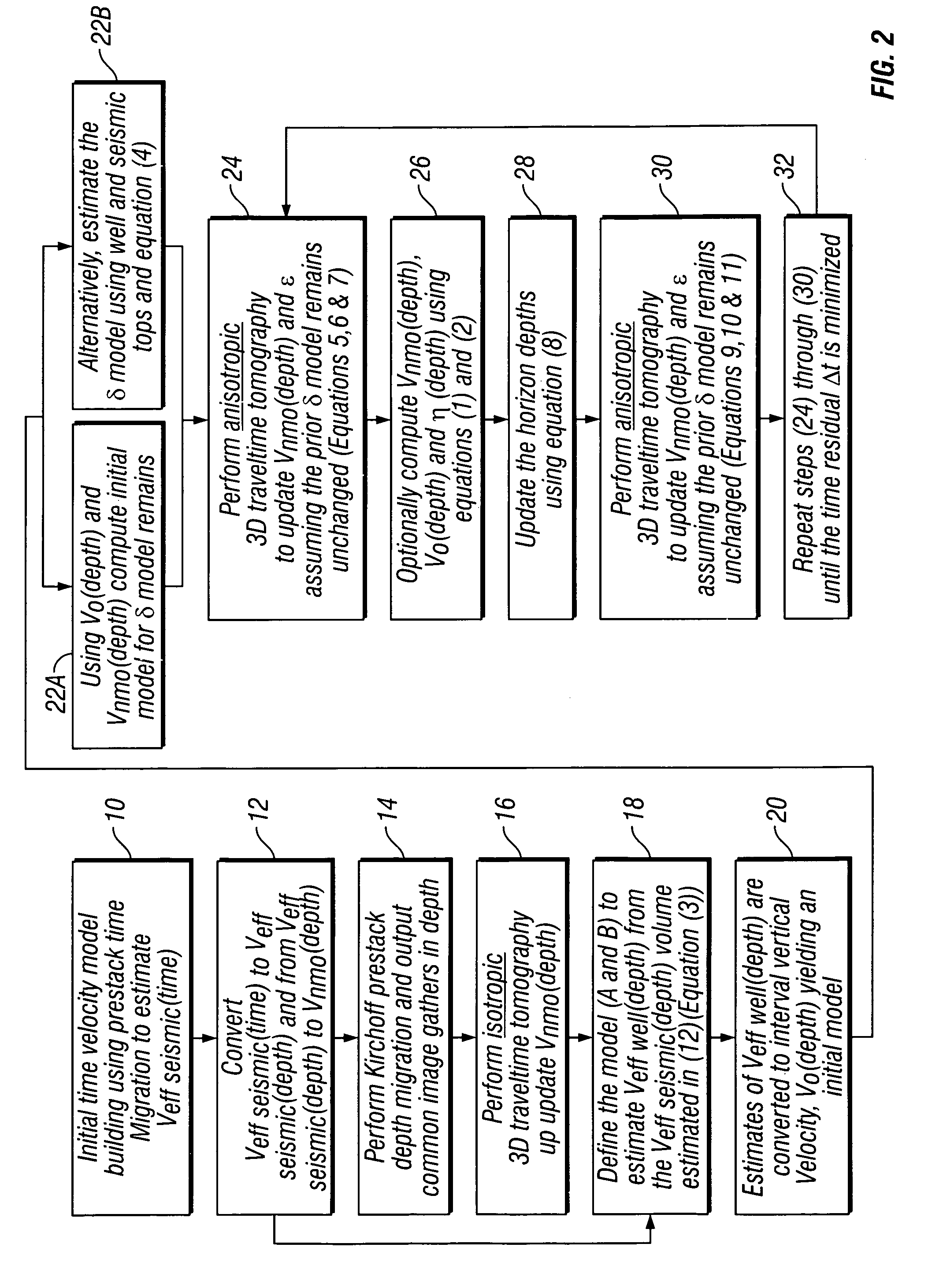
Method for three dimensional seismic travel time tomography in transversely isotropic media
A method for estimating seismic velocities in vertically transversely isotropic media includes generating an initial estimate of vertical interval velocity and interval normal moveout velocity with respect to depth from seismic data. An initial estimate is generated of a first anisotropy parameter with respect to depth. The first anisotropy parameter is related to the interval normal moveout velocity and the interval vertical velocity. An initial estimate is generated with respect to depth of a second anisotropy parameter. The second anisotropy parameter is related to the first anisotropy parameter and an interval anelliptic parameter. A first tomographic inversion is performed with respect to the interval normal moveout velocity and the second anisotropy parameter at a constant value of the first anisotropy parameter until travel time differentials reach minimum values. Layer depths are adjusted with the initial estimate of vertical interval velocity. Using values of the second anisotropy parameter determined in the first tomographic inversion, a second tomographic inversion is performed of interval normal moveout velocity and the first anisotropy parameter with respect to depth. The adjusted layer depths, interval normal moveout velocities and interval vertical velocities are again adjusted and interval anelliptic parameters are calculated from the second tomographic inversion.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
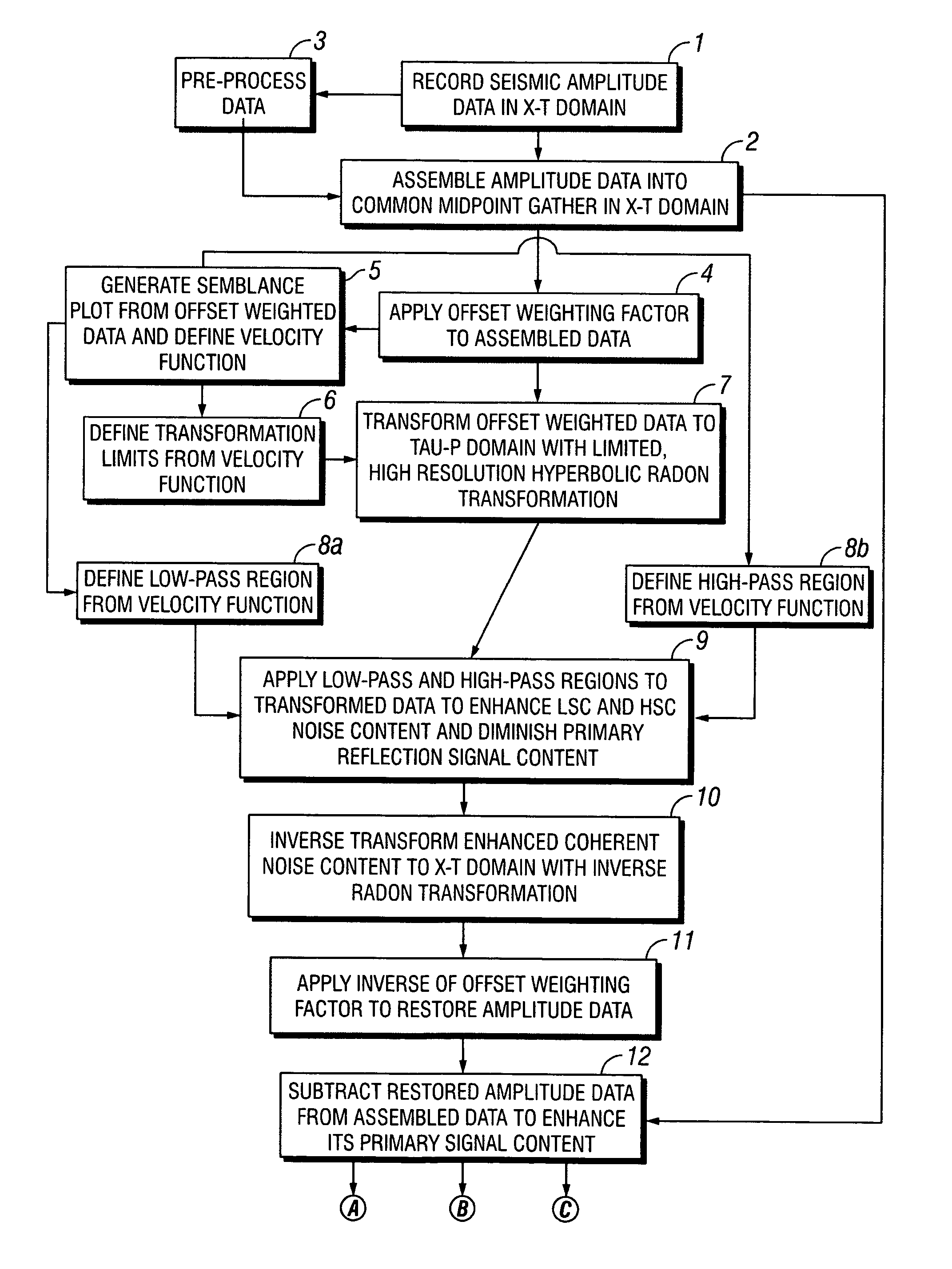
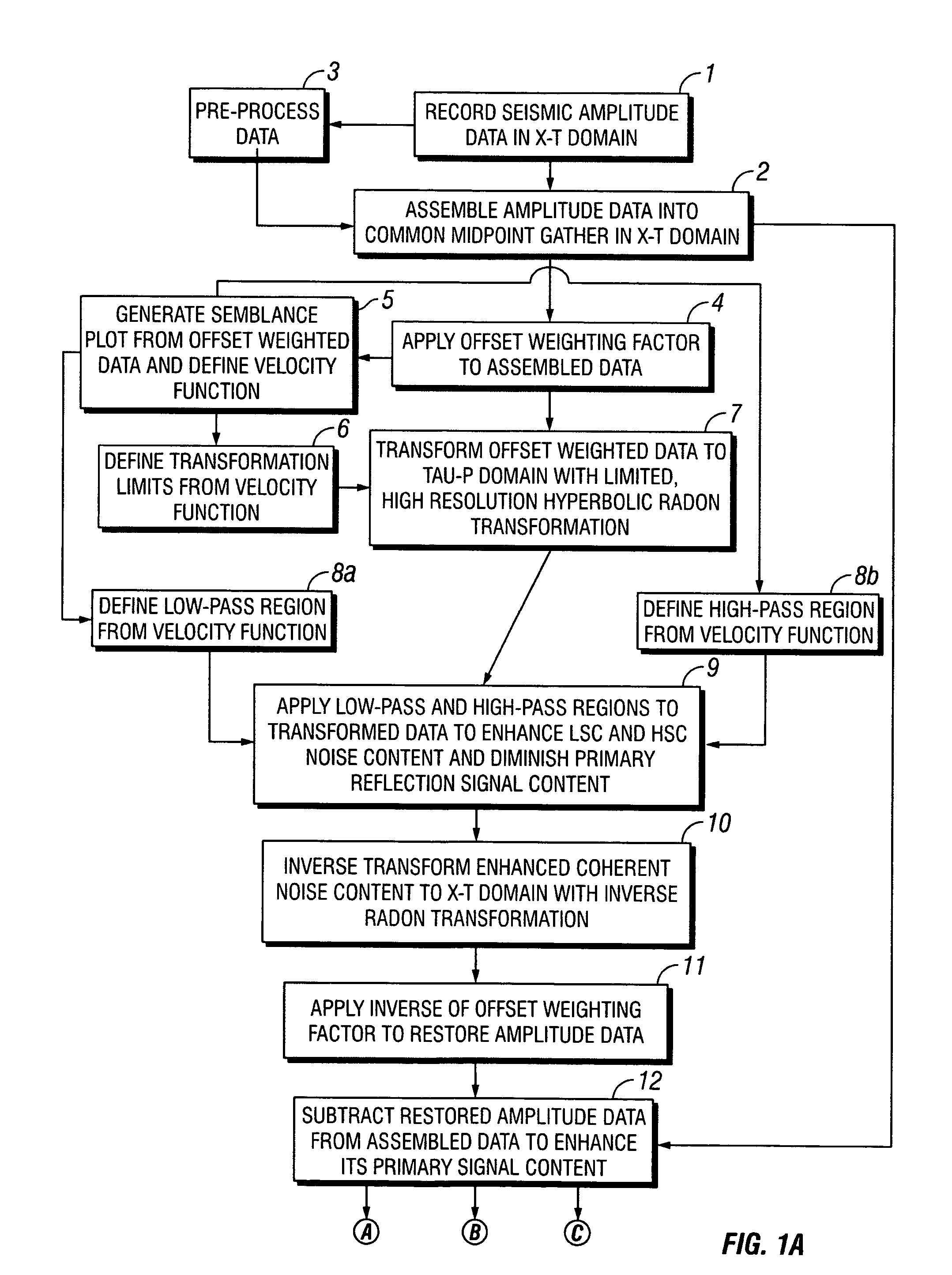
Removal of noise from seismic data using radon transformations
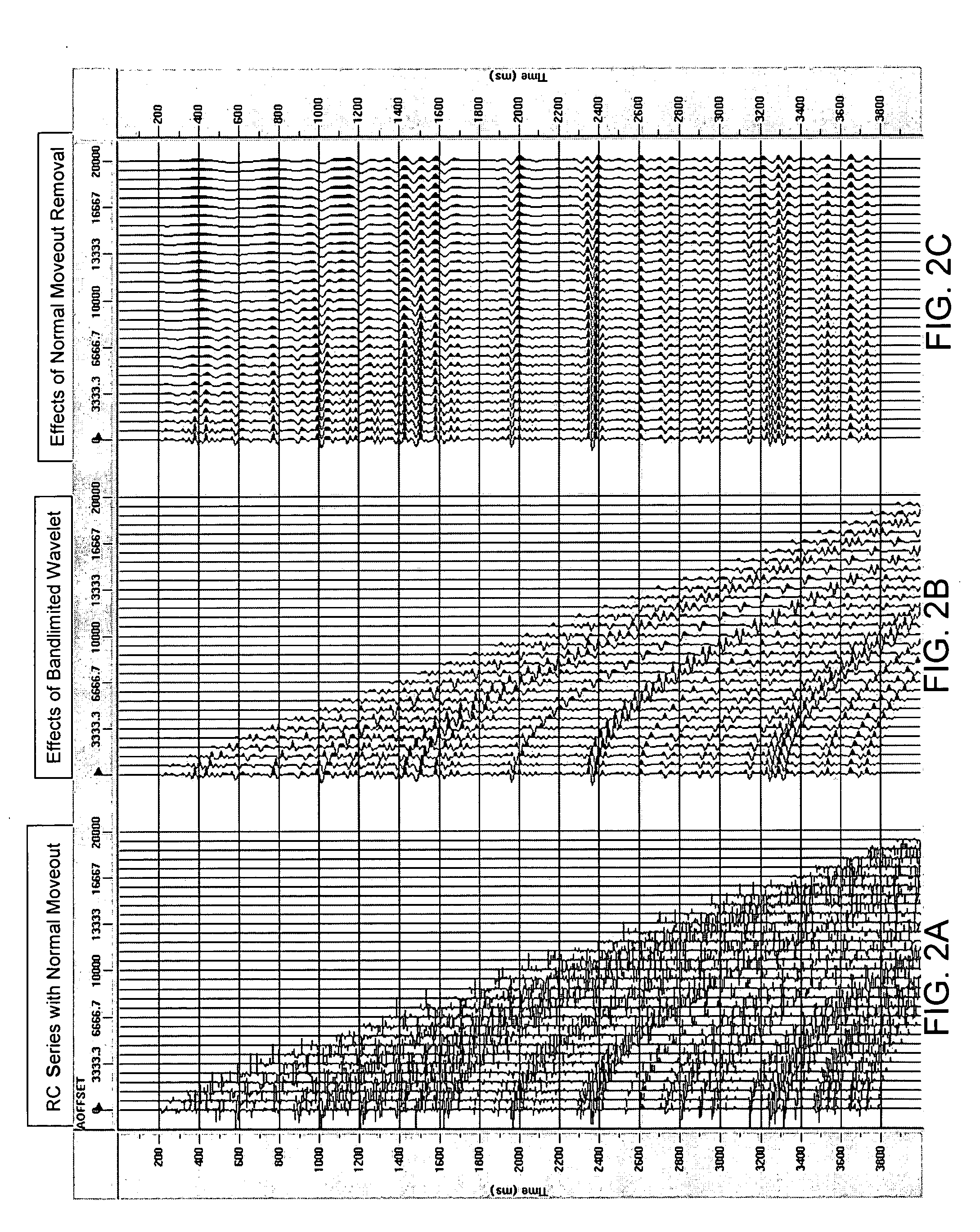
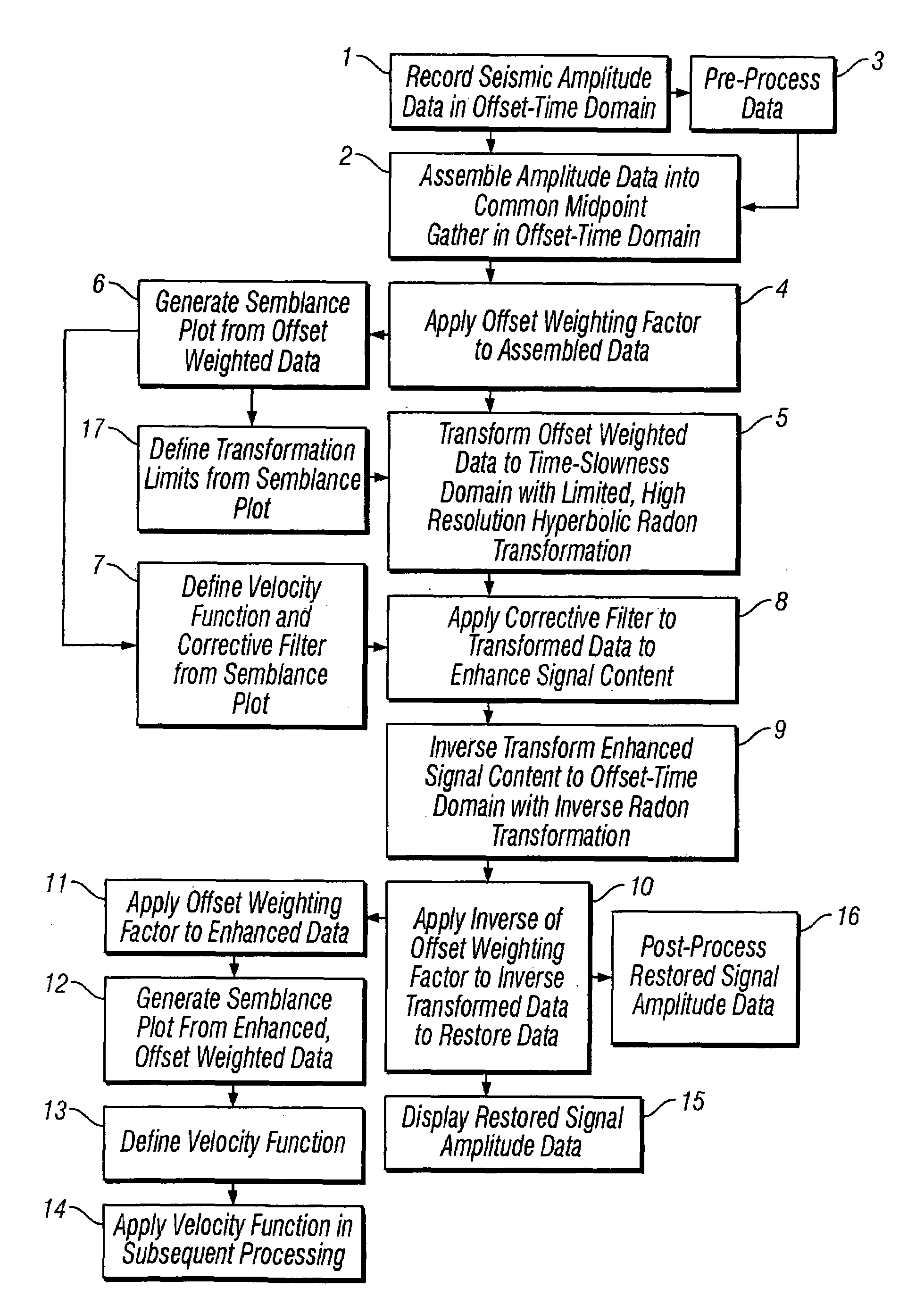
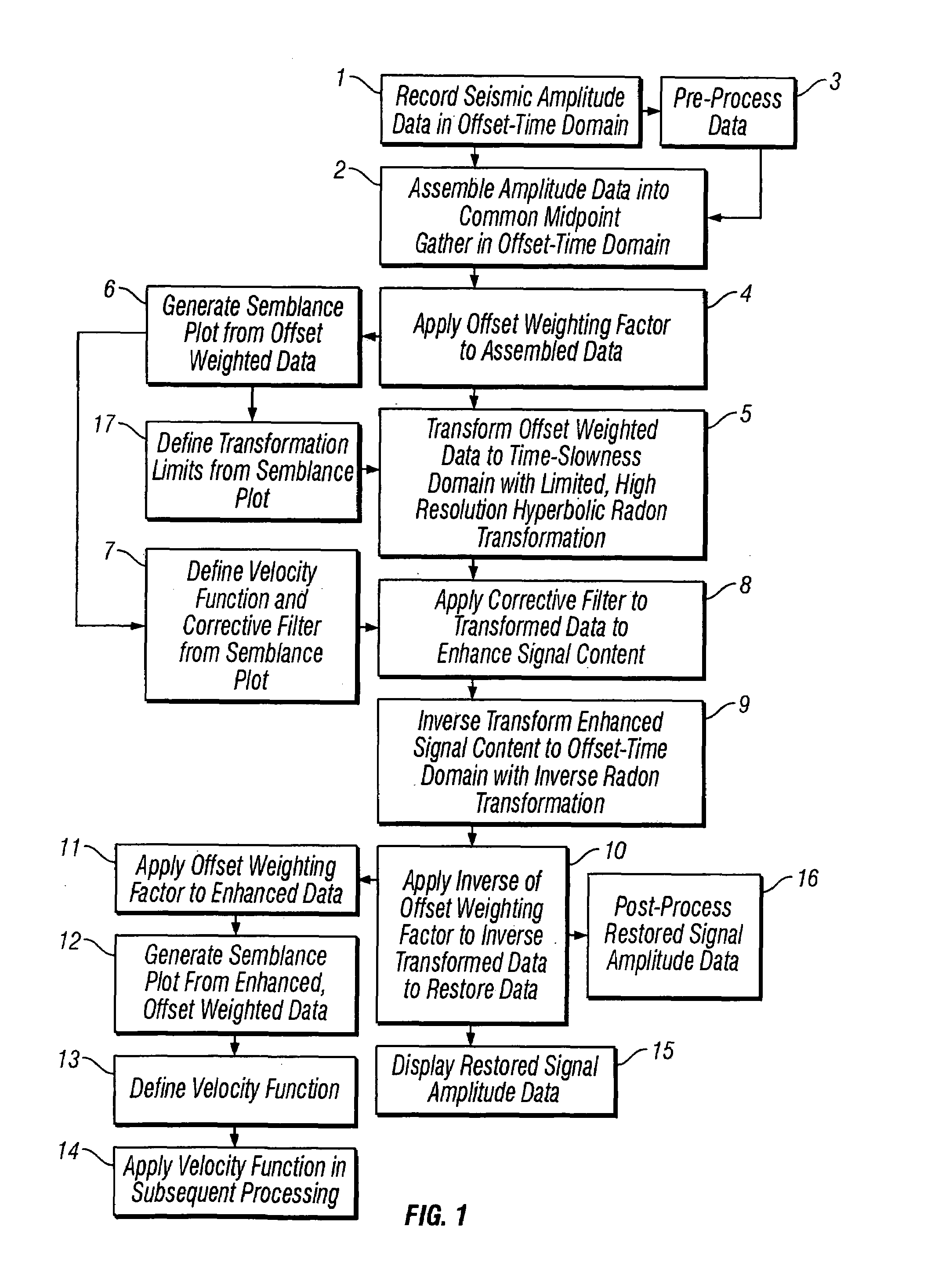
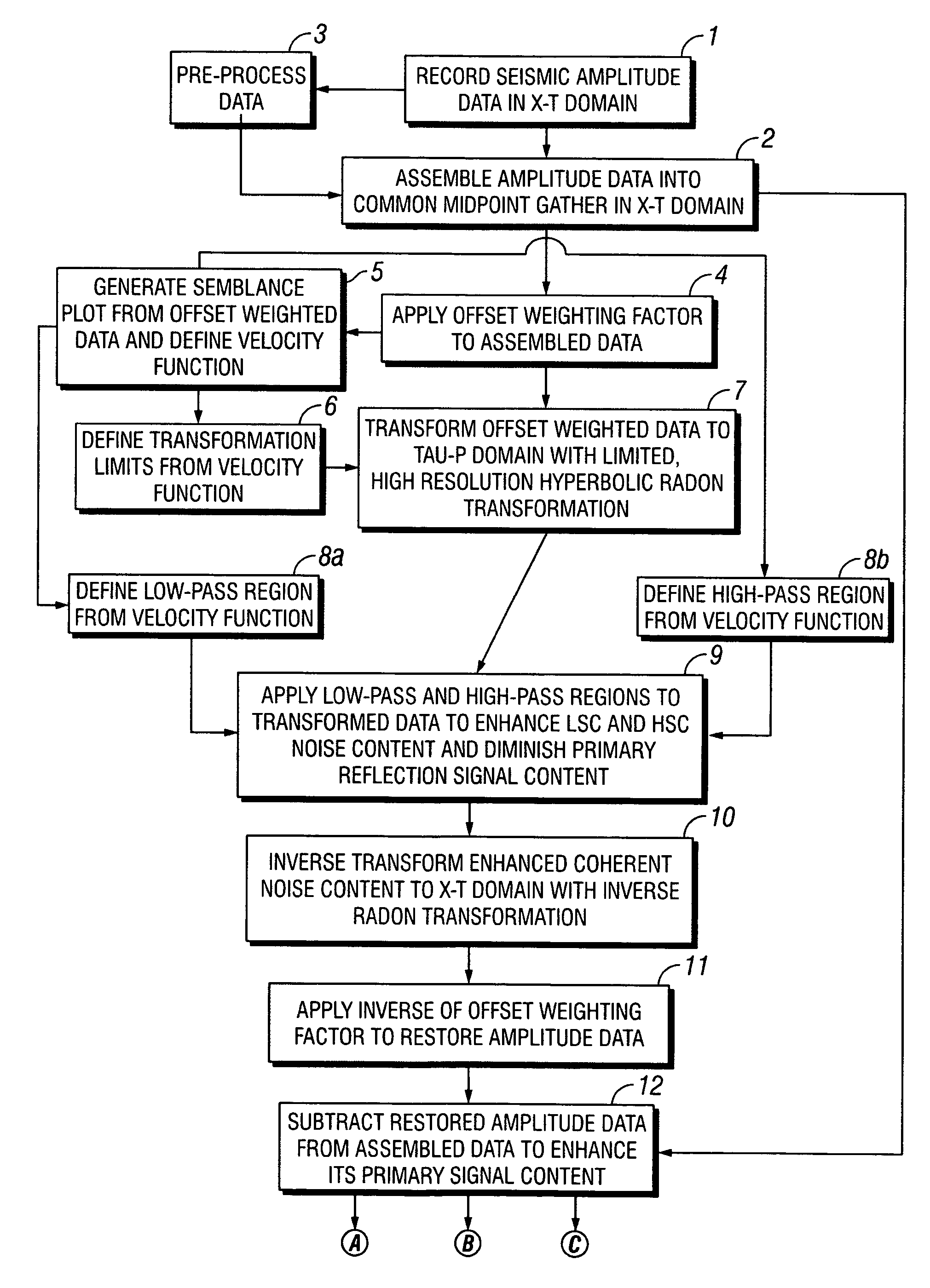
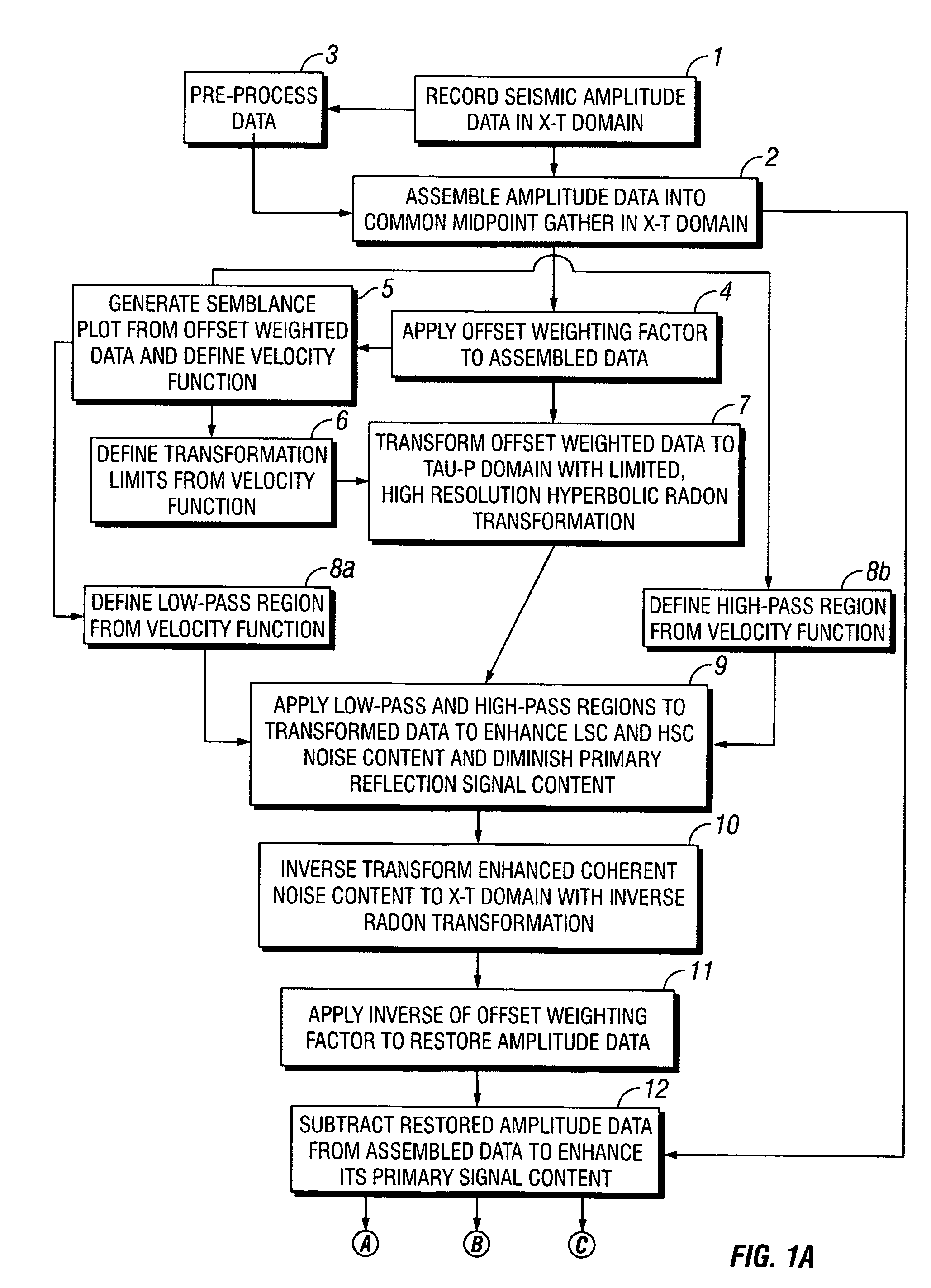
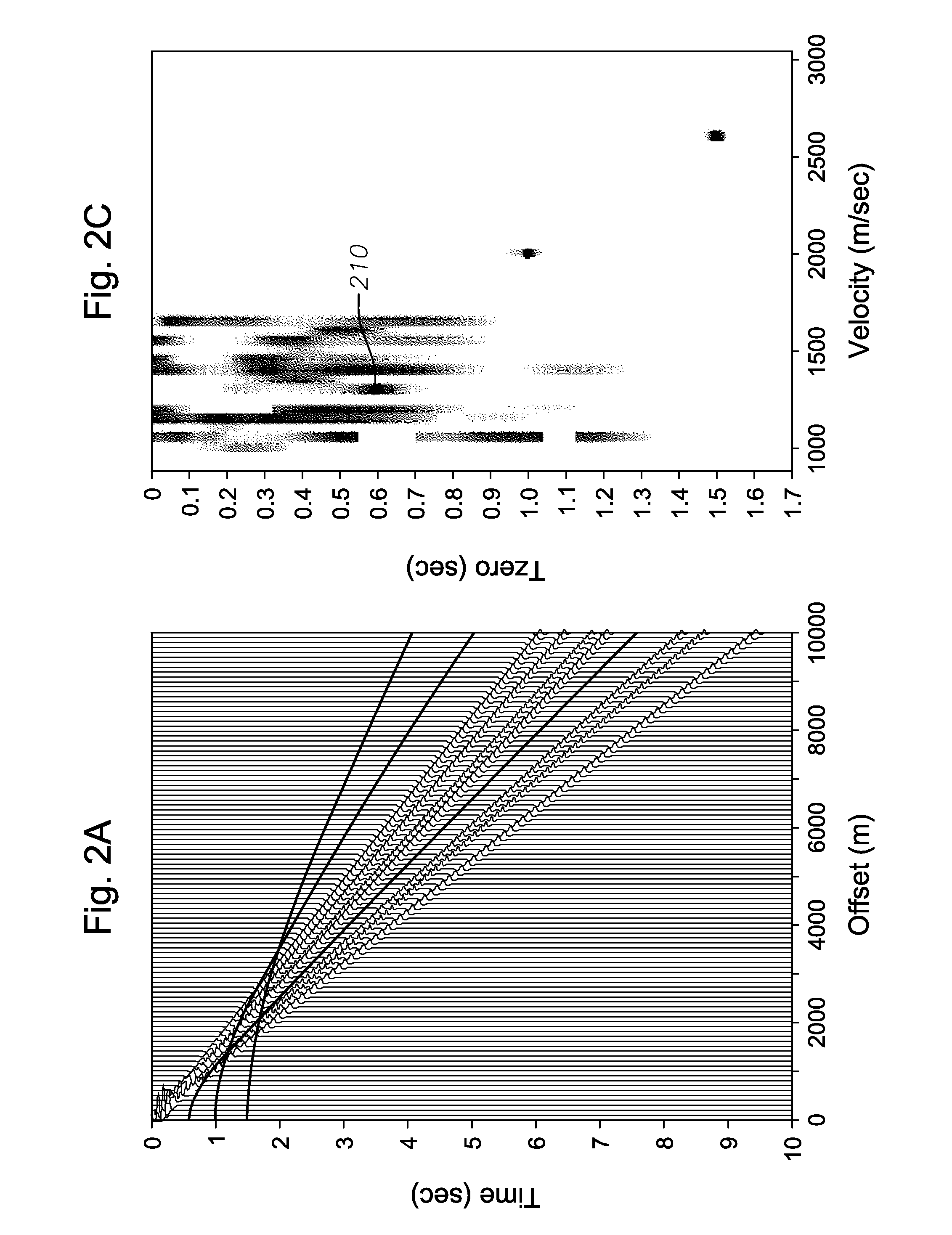
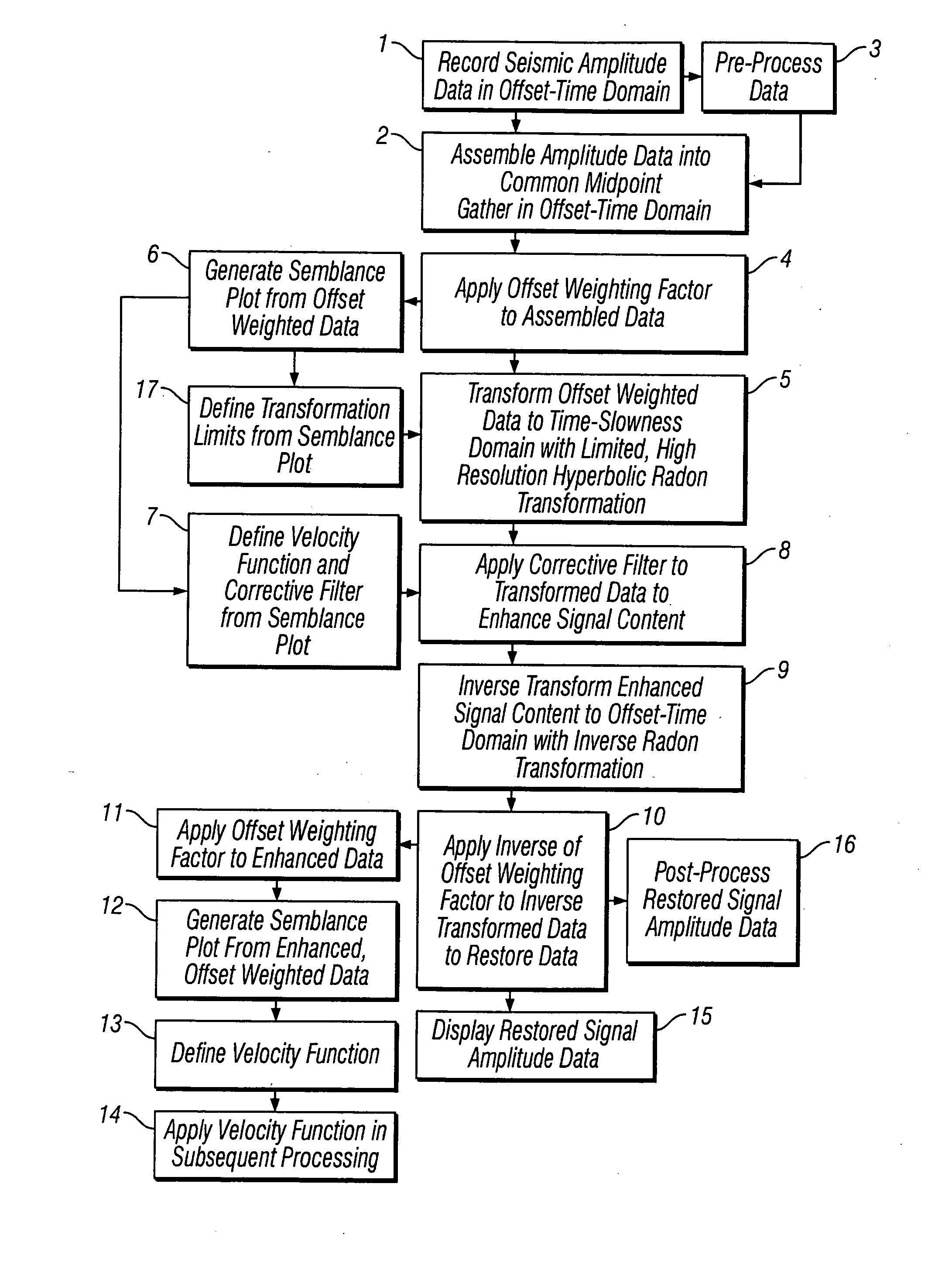
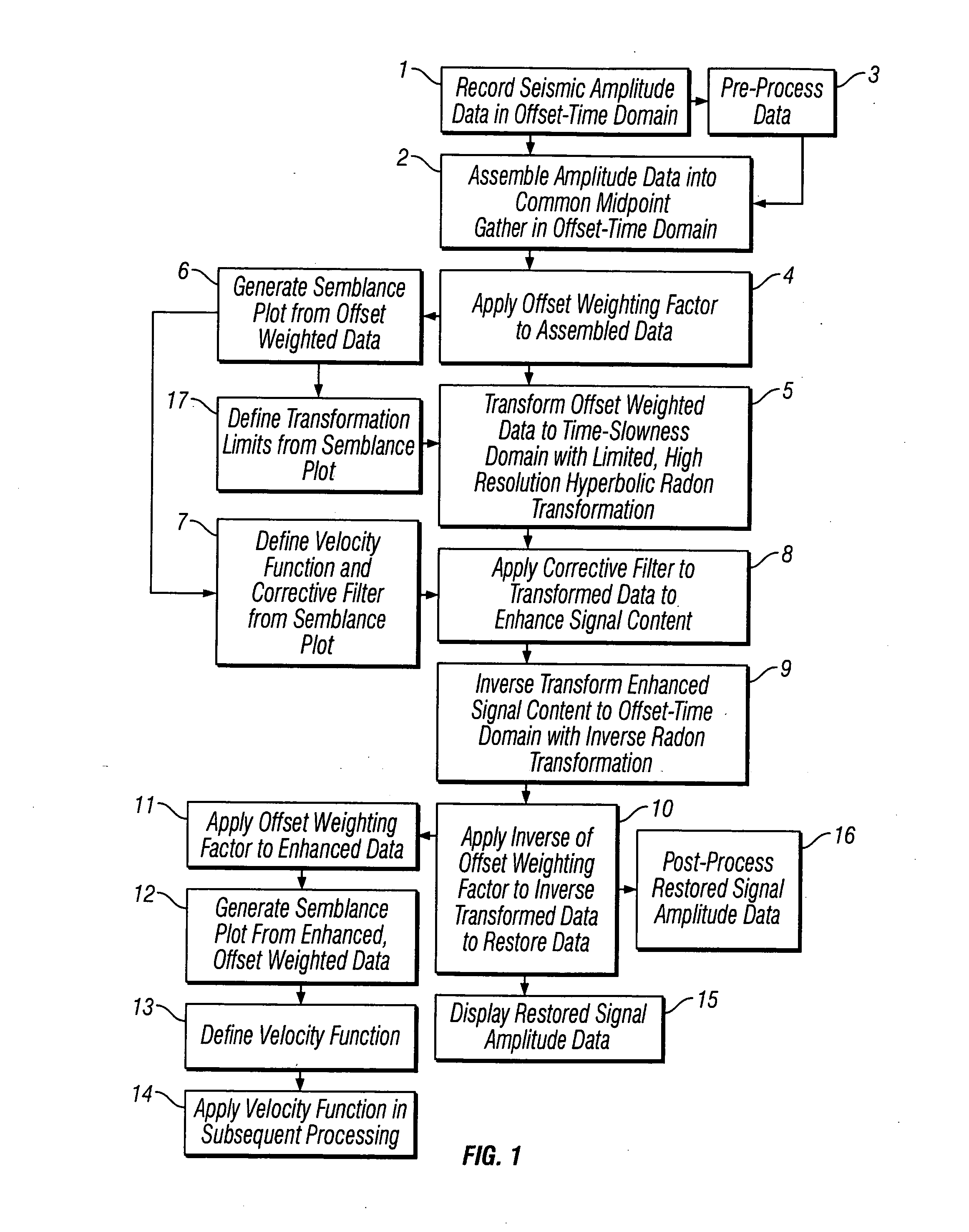
ActiveUS20050180262A1Diminish primary reflection signal contentImprove noiseSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainNormal moveout
Methods of processing seismic data to remove unwanted noise from meaningful reflection signals are provided for. The methods comprise the steps of assembling seismic data into common midpoint geometry gathers in an offset-time domain without correcting the data for normal moveout. The amplitude data are then transformed from the offset-time domain to the time-slowness domain using a Radon transformation. At least of subset of the transformed data is filtered to enhance its coherent noise content and to diminish its primary reflection signal content by defining a slowness high-pass region and, preferably, a slowness low-pass region. The low-pass region is defined to enhance the low slowness coherent noise content and to diminish the primary reflection signal content thereof, thereby generating a first subset of said transformed data having enhanced low slowness coherent noise content. The high-pass region is defined to enhance the high slowness coherent noise content and to diminish the primary reflection signal content thereof, thereby generating a second subset of said transformed data having enhanced high slowness coherent noise content. After filtering, the first and second subsets of transformed data are inverse transformed from the time-slowness domain back to the offset-time domain using an inverse Radon transformation to restore the data. The restored signal amplitude data of the first and second subsets of data are then subtracted from the assembled data, thereby enhancing its primary reflection signal content.
Owner:E S & A ROBINSON
Method for determining fluid by utilizing seismic fluid impedance
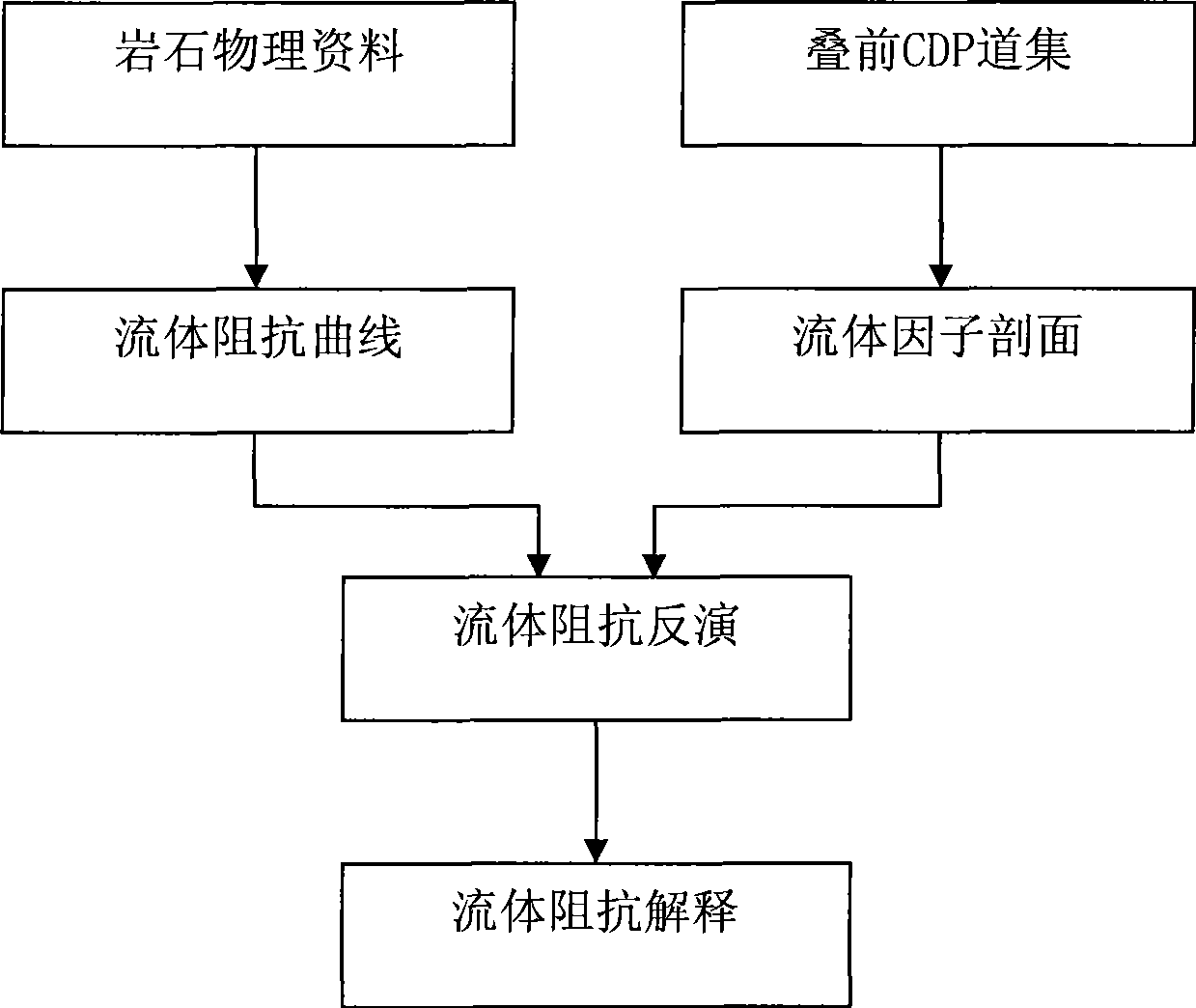
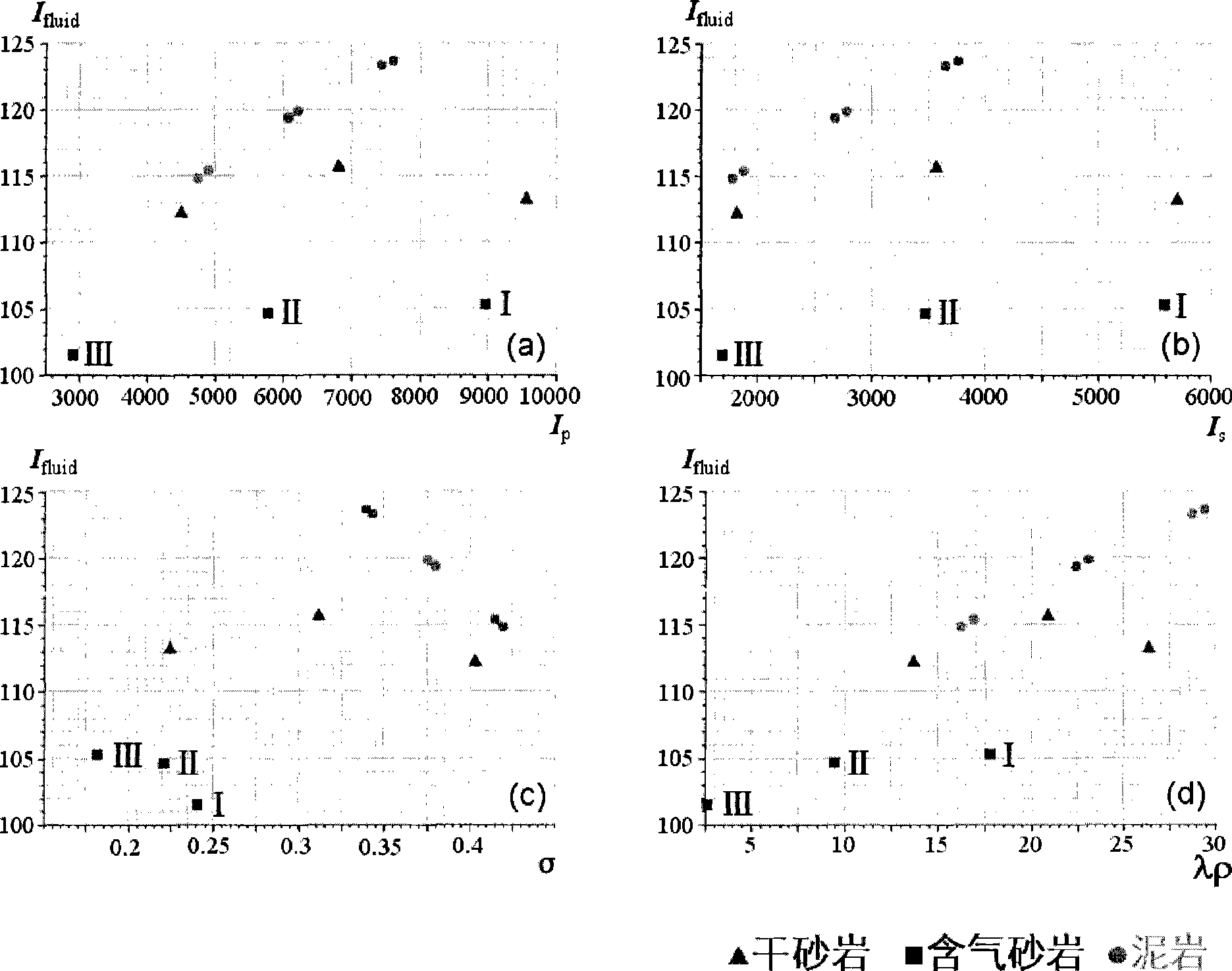
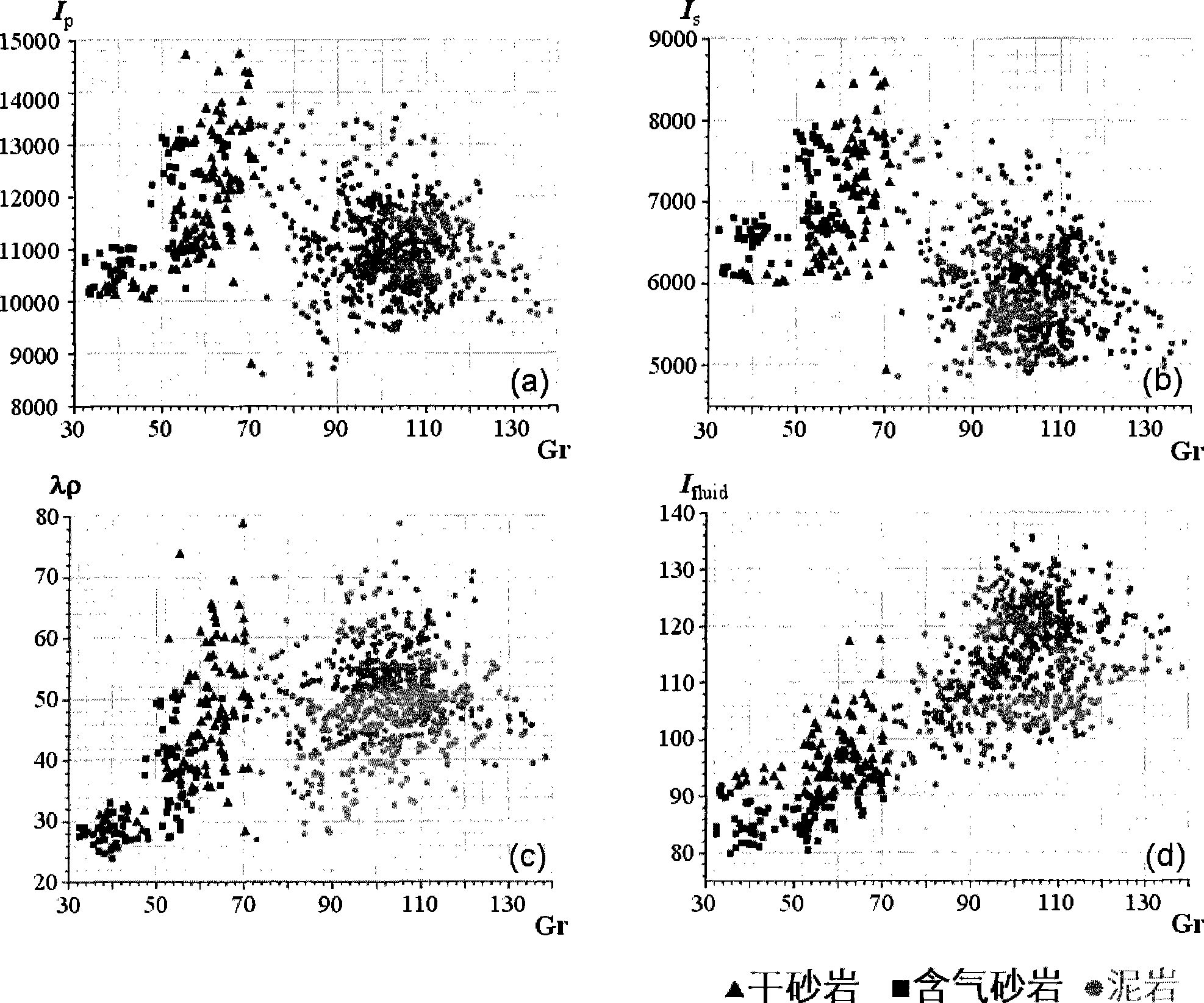
ActiveCN101446645AGuaranteed accuracyReduce interpretation ambiguitySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingNormal moveoutLongitudinal wave
The invention discloses a method for determining a fluid by utilizing seismic fluid impedance. The method comprises the following steps: exciting and recording a seismic wave to obtain an angle gather; eliminating signal frequency distortion caused by a normal moveout correction stretching effect; extracting longitudinal wave reflectivity attributes and weighted transverse wave reflectivity attributes from the compensated angle gather; computing improved fluid factors; obtaining logging data to obtain a fluid impedance curve; performing iterative inversion to obtain a section of the fluid impedance; qualitatively analyzing fluid anomalies in pores by the fluid factors, and describing spatial distribution of the fluid by the fluid impedance. The method helps accurately extract the fluid factors and directly identify components of the fluid in the pores without an assumption of a velocity ratio of the longitudinal wave to the transverse wave as well as the relation between density and the longitudinal wave velocity, which reduces ambiguity of gas layer identification, realizes direct conversion from the fluid factors to the fluid impedance and improves the precision of gas reservoir identification.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method and apparatus for true relative amplitude correction of seismic data for normal moveout stretch effects
InactiveUS20060193205A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsRelative magnitudeNormal moveout
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for arriving at true relative amplitude destretched seismic traces from stretched seismic traces. The method compensates for offset varying reflection interference effects due to normal moveout. Stretch factors β and also input spectra are determined for NMOR stretched seismic traces. Estimates are then made of stretched wavelet spectra from the input spectra. A destretched wavelet spectra is then obtained. Shaping correction factors are determined by taking the ratio of the destretched wavelet spectra to the stretched wavelet spectra and are applied to the input spectra of the stretched traces to arrive at a destretched trace spectra. True relative amplitude scaling factors are computed by taking the ratio of a true relative amplitude property of the destretched wavelet spectra to a corresponding true relative amplitude property of the stretched wavelet spectra. Finally, the true relative amplitude scaling factors are applied to the destretched trace spectra to arrive at true relative amplitude destretched seismic traces.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Tau-P filters for removal of noise from seismic data
InactiveUS7366054B1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencySeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainNormal moveout
Methods of processing seismic data to remove unwanted noise from meaningful reflection signals are provided for. The methods comprise the steps of assembling seismic data into common geometry gathers in an offset-time domain without correcting the data for normal moveout. The amplitude data are then transformed from the offset-time domain to the time-slowness domain using a Radon transformation. A corrective filter is then applied to enhance the primary reflection signal content of the data and to eliminate unwanted noise events. The corrective filter has a pass region with a lower pass limit and a higher pass limit. The higher pass limit is set within 15% above the slowness of the primary reflection signals and, preferably, it is more closely set to the slowness of the primary reflection signals. The lower pass limit is also preferably set within 15% below the slowness of the primary reflection signals. The tau-P filter preferably is defined by reference to the velocity function of the primary reflection signals, and preferably is expressed as:1vs(1+r2)≤p≤1vs(1-r1)where r1 and r2 are percentages expressed as decimals. After filtering, the enhanced signal content is inverse transformed from the time-slowness domain back to the offset-time domain using an inverse Radon transformation.
Owner:ROBINSON JOHN M
Method for stable estimation of anisotropic parameters for P-wave prestack imaging
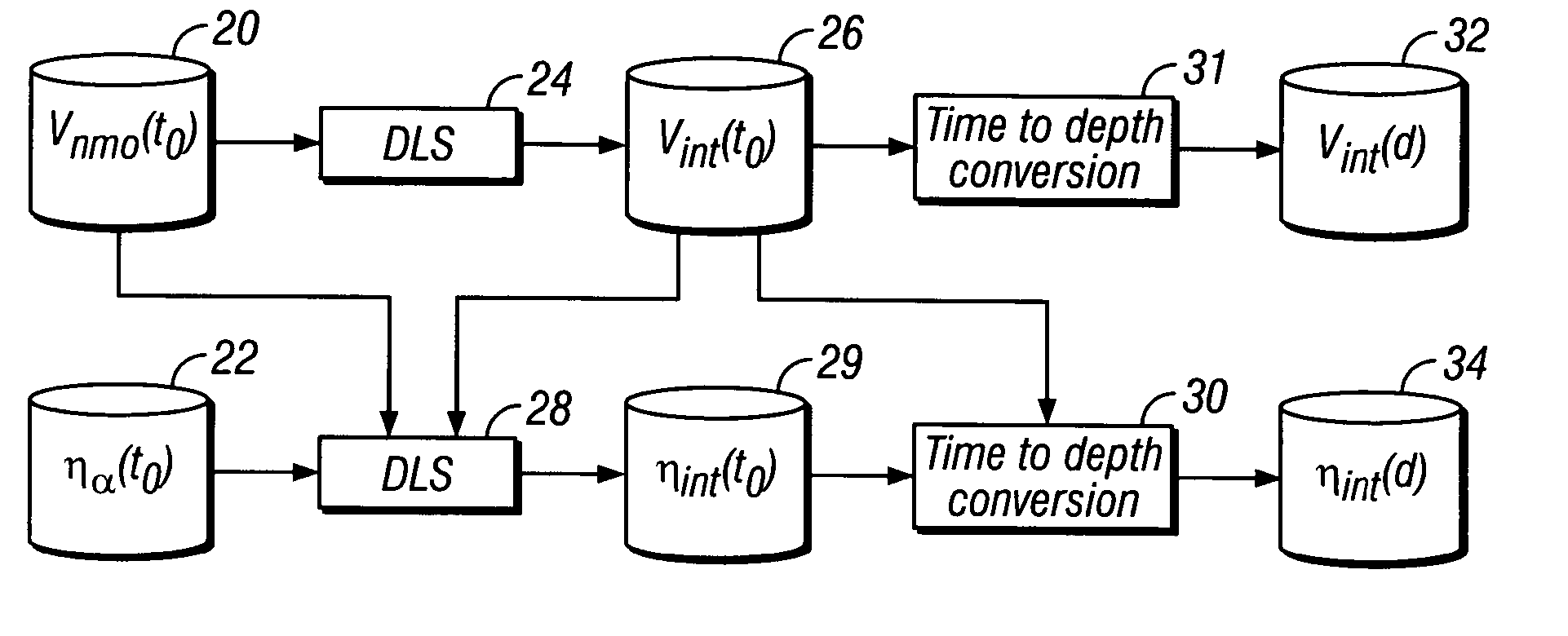
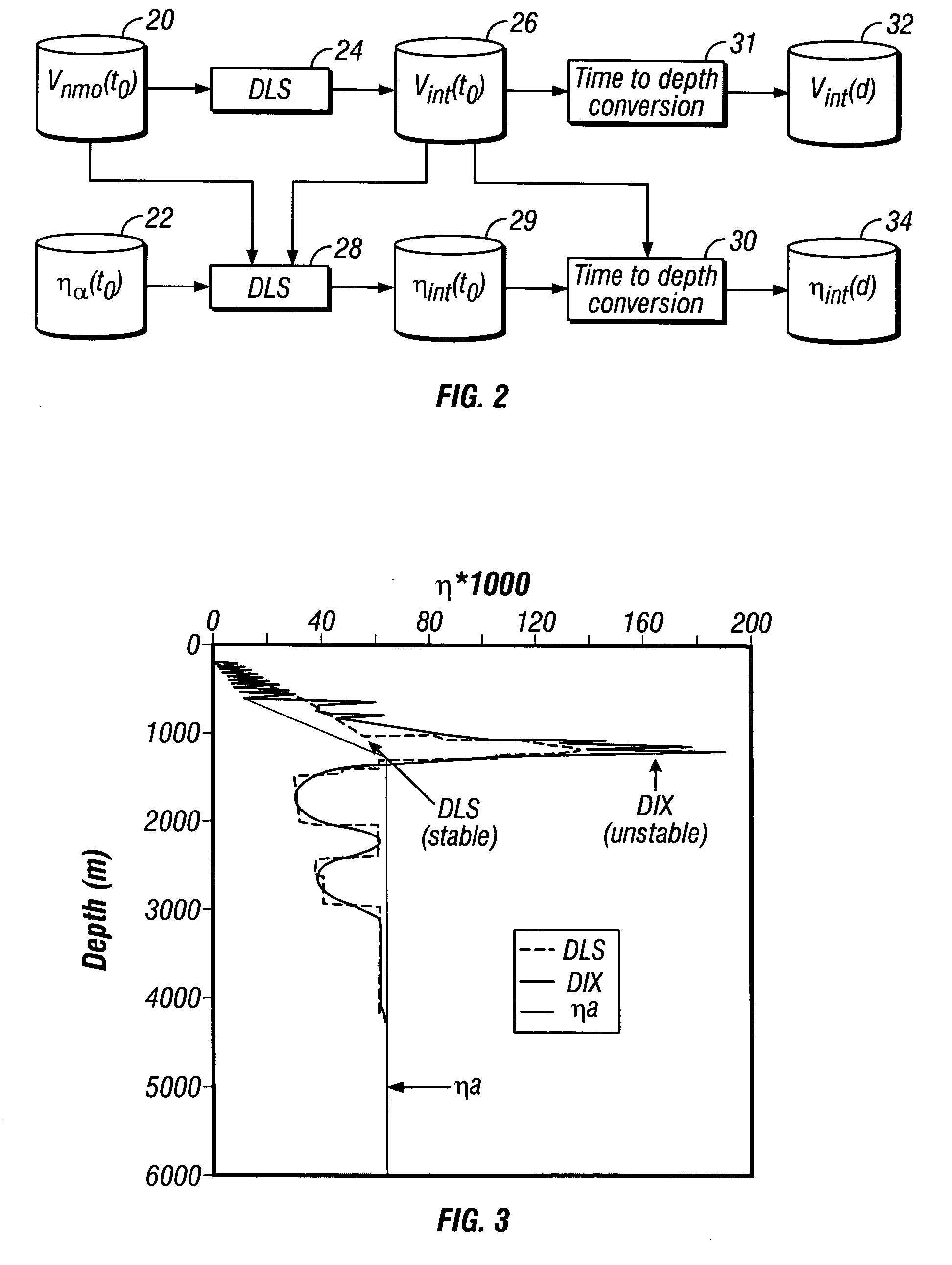
A method is disclosed for determining interval anisotropic parameters. The method includes determining normal moveout (NMO) velocities and effective anelliptical parameters from seismic data traces. The NMO velocities are processed to obtain interval NMO velocities. The NMO velocities, effective anelliptical parameters and interval NMO velocities are inverted to obtain the interval anisotropic parameters. In one embodiment, the inversion includes damped least squares. In one embodiment, the inversion is preconditioned.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
Anisotropic Parameter Determination
InactiveUS20100128562A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingKinematicsNormal moveout
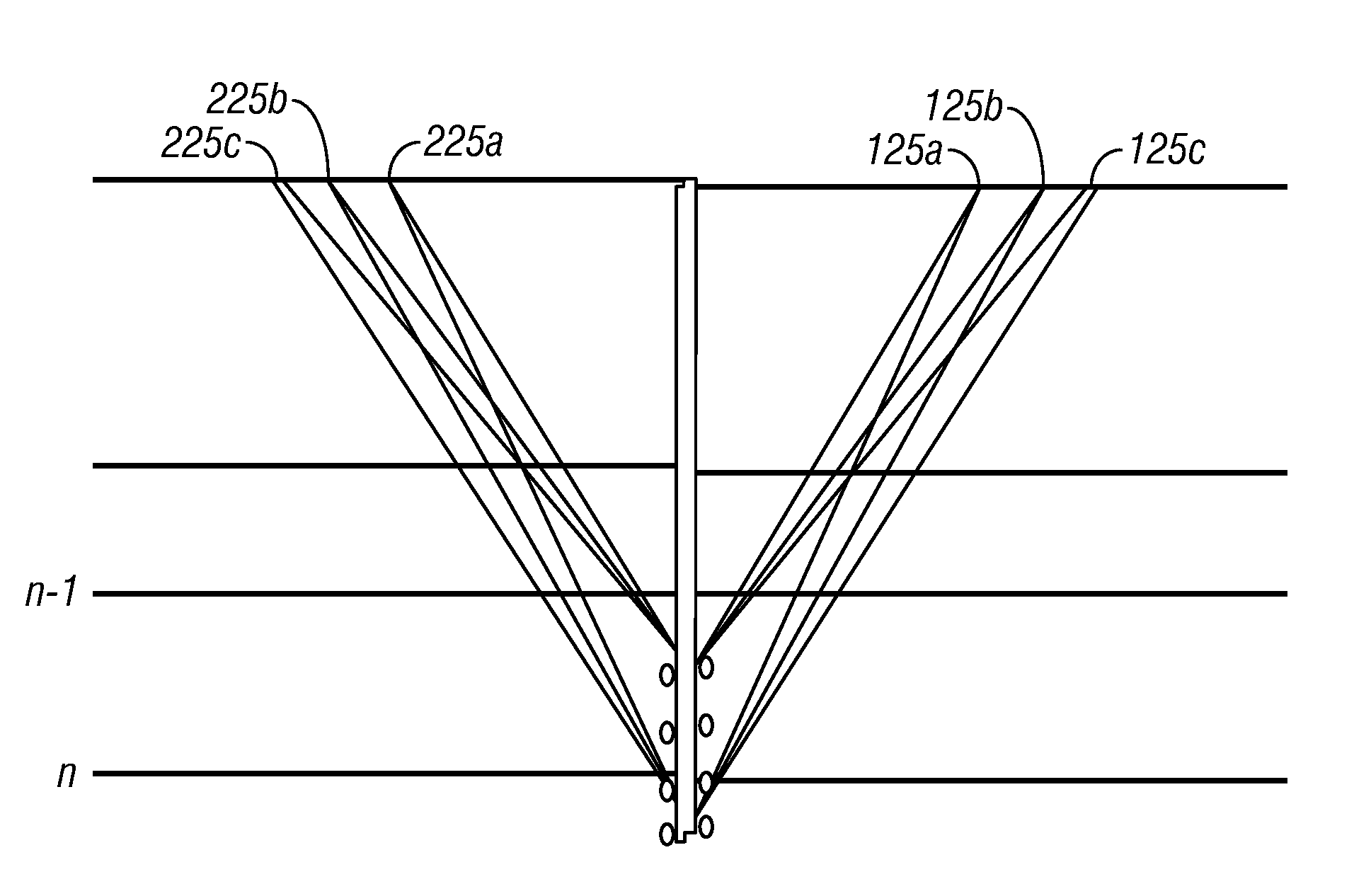
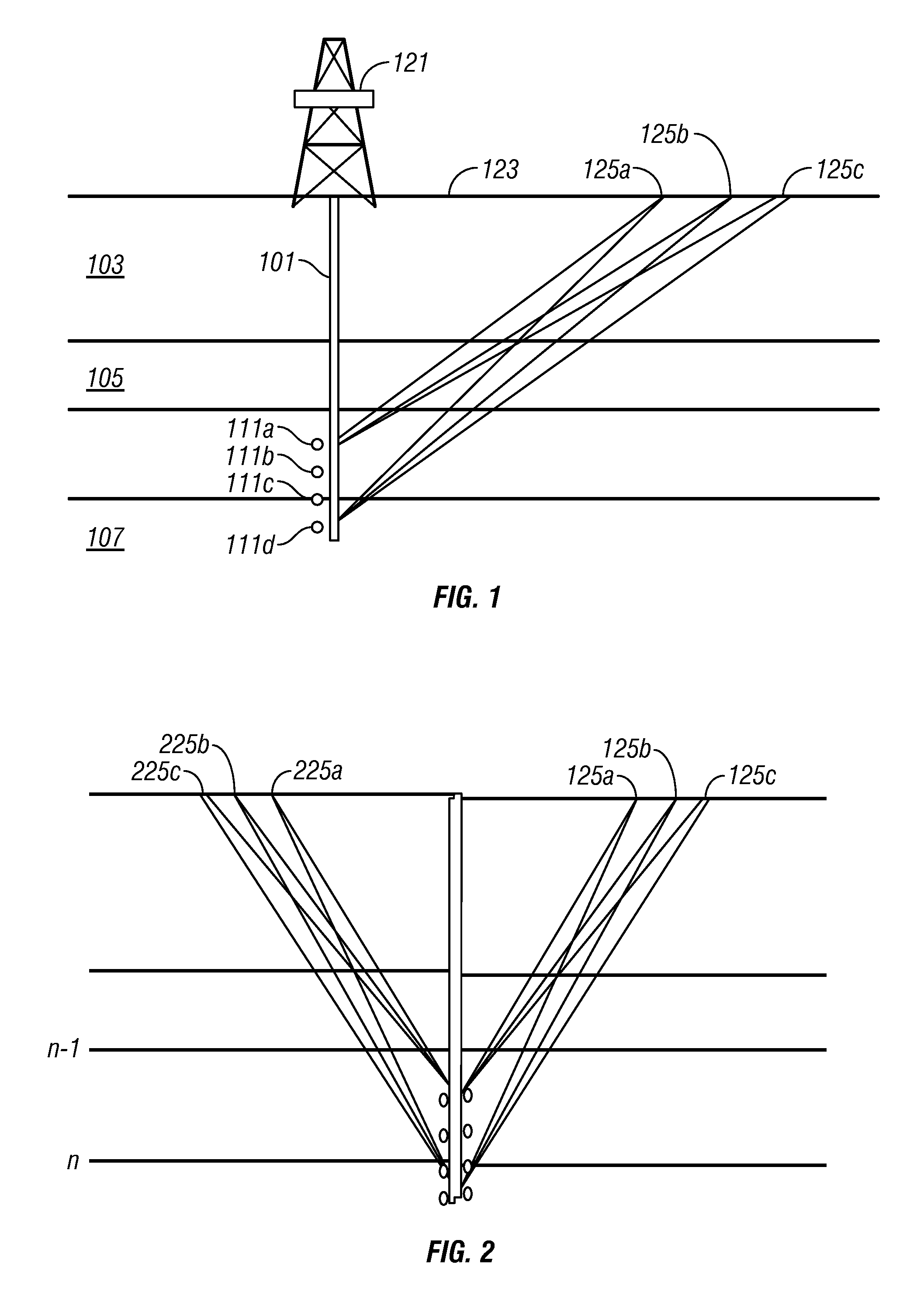
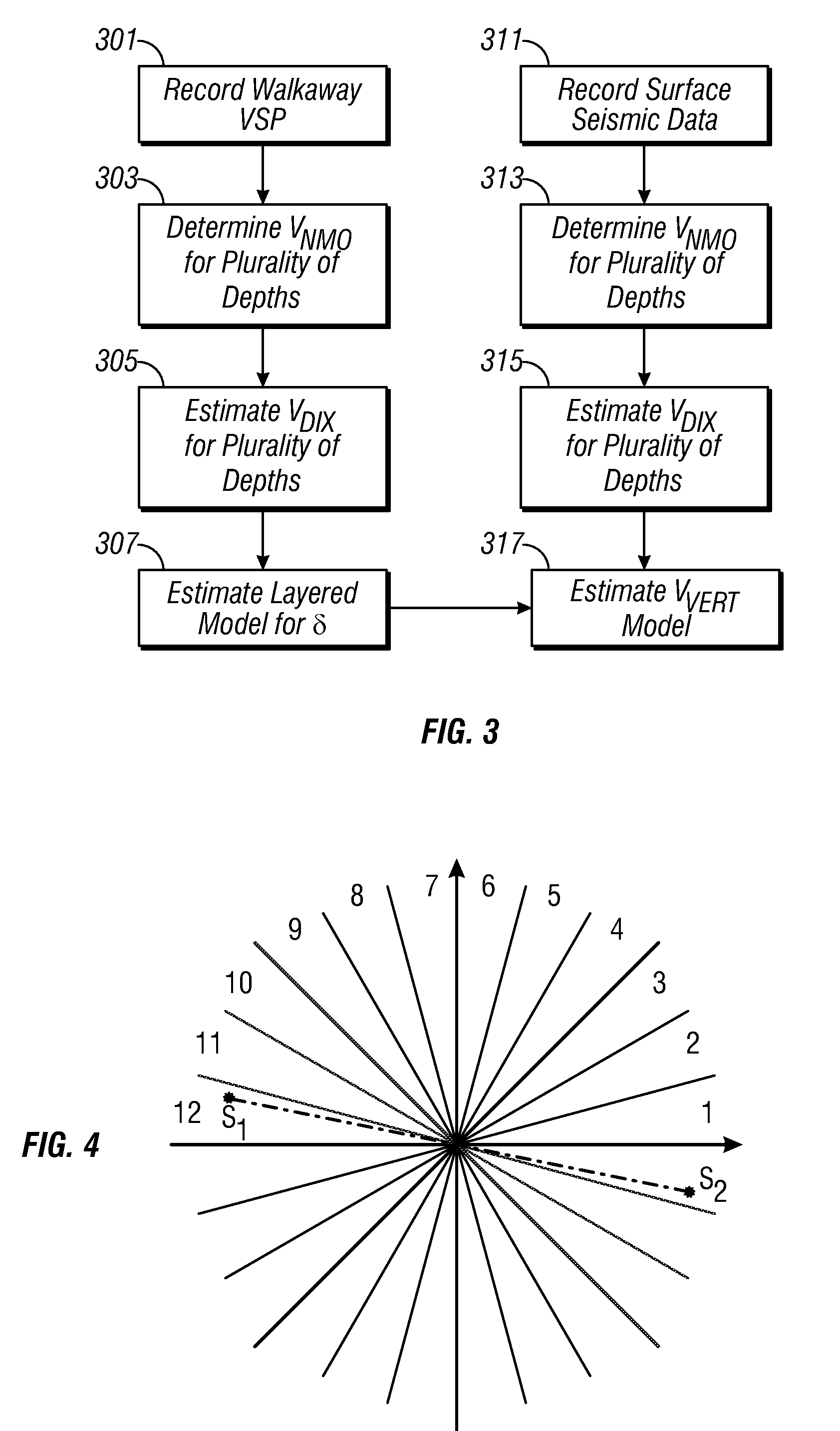
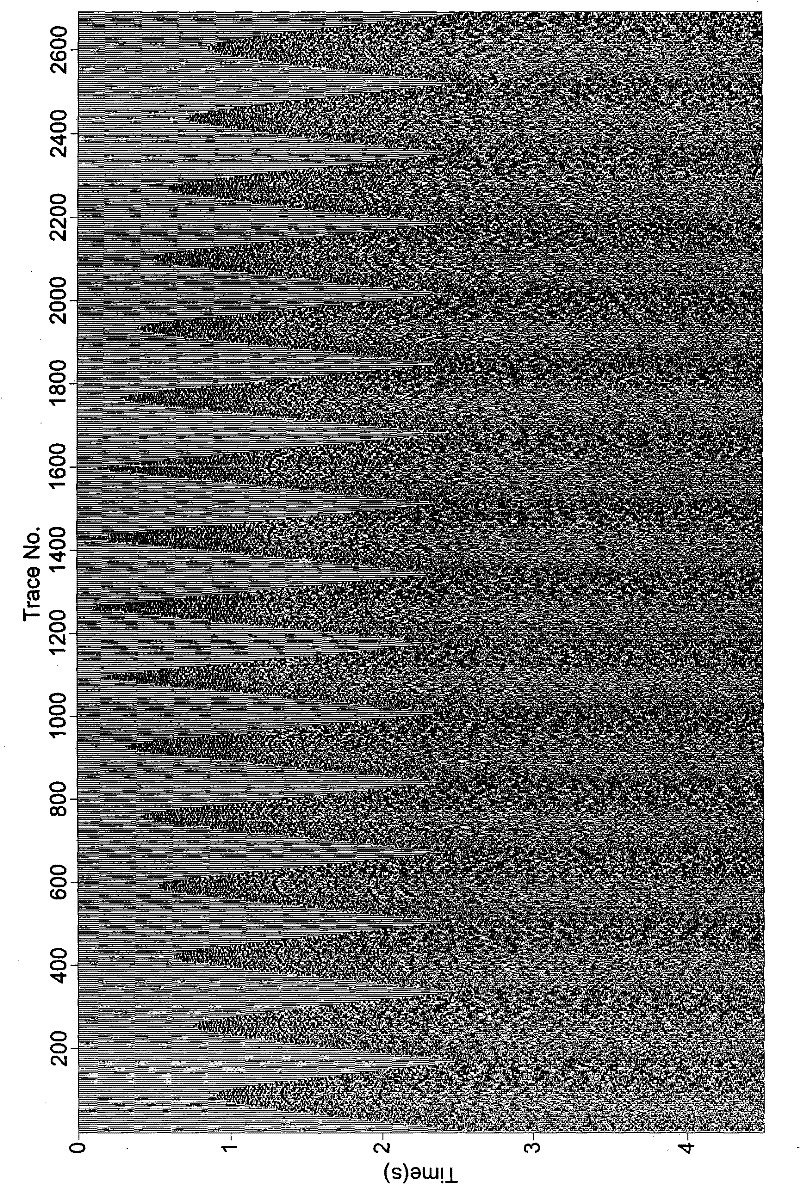
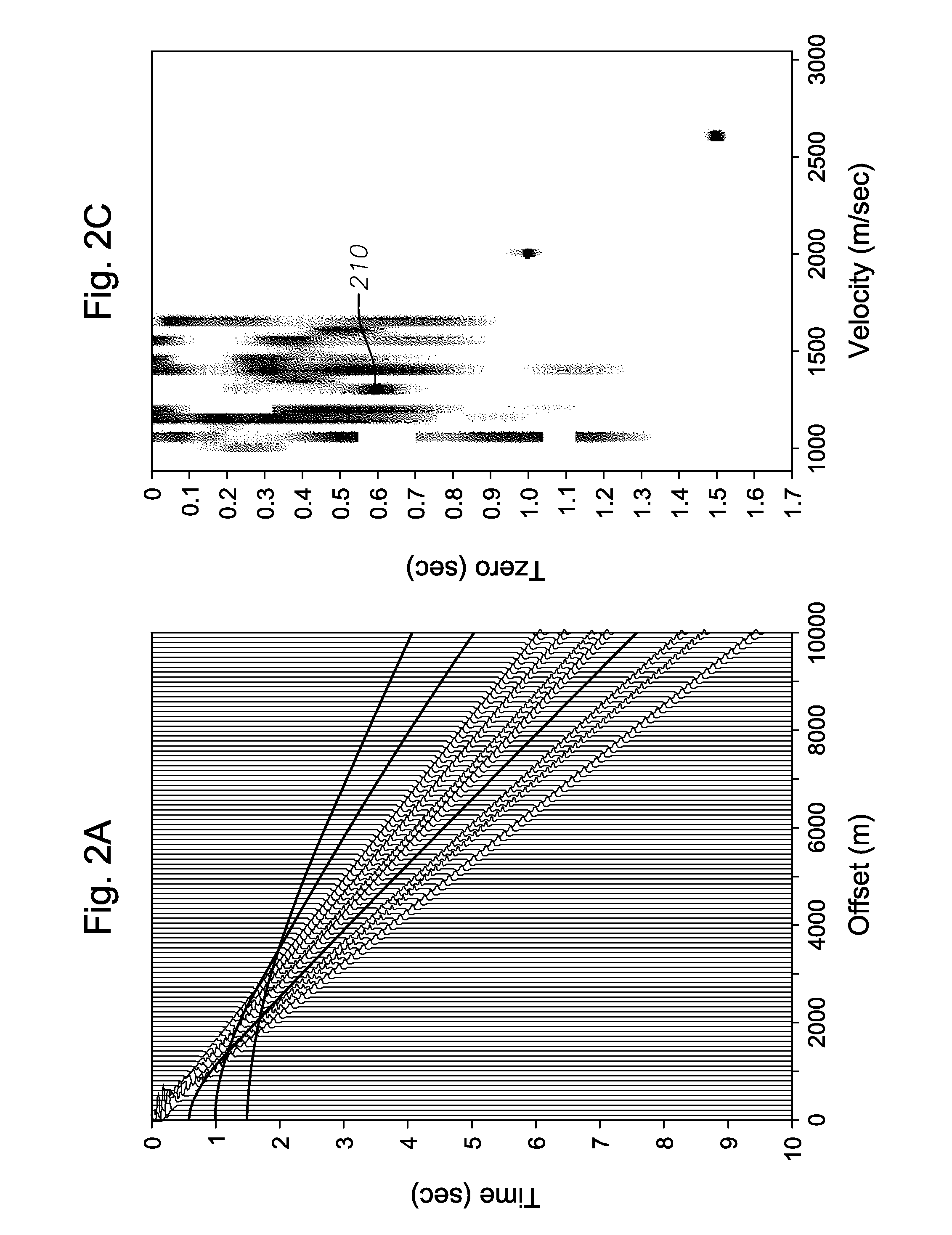
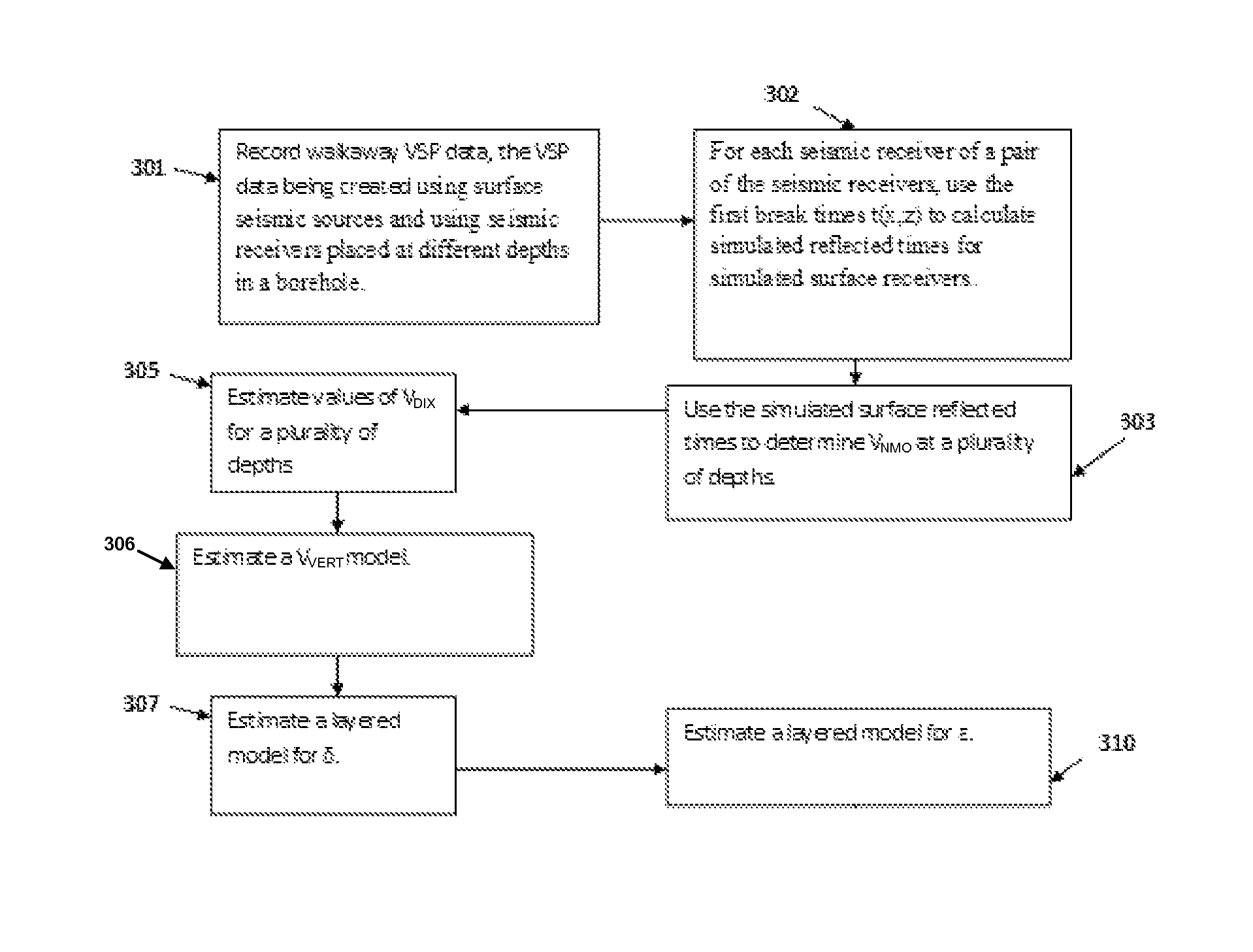
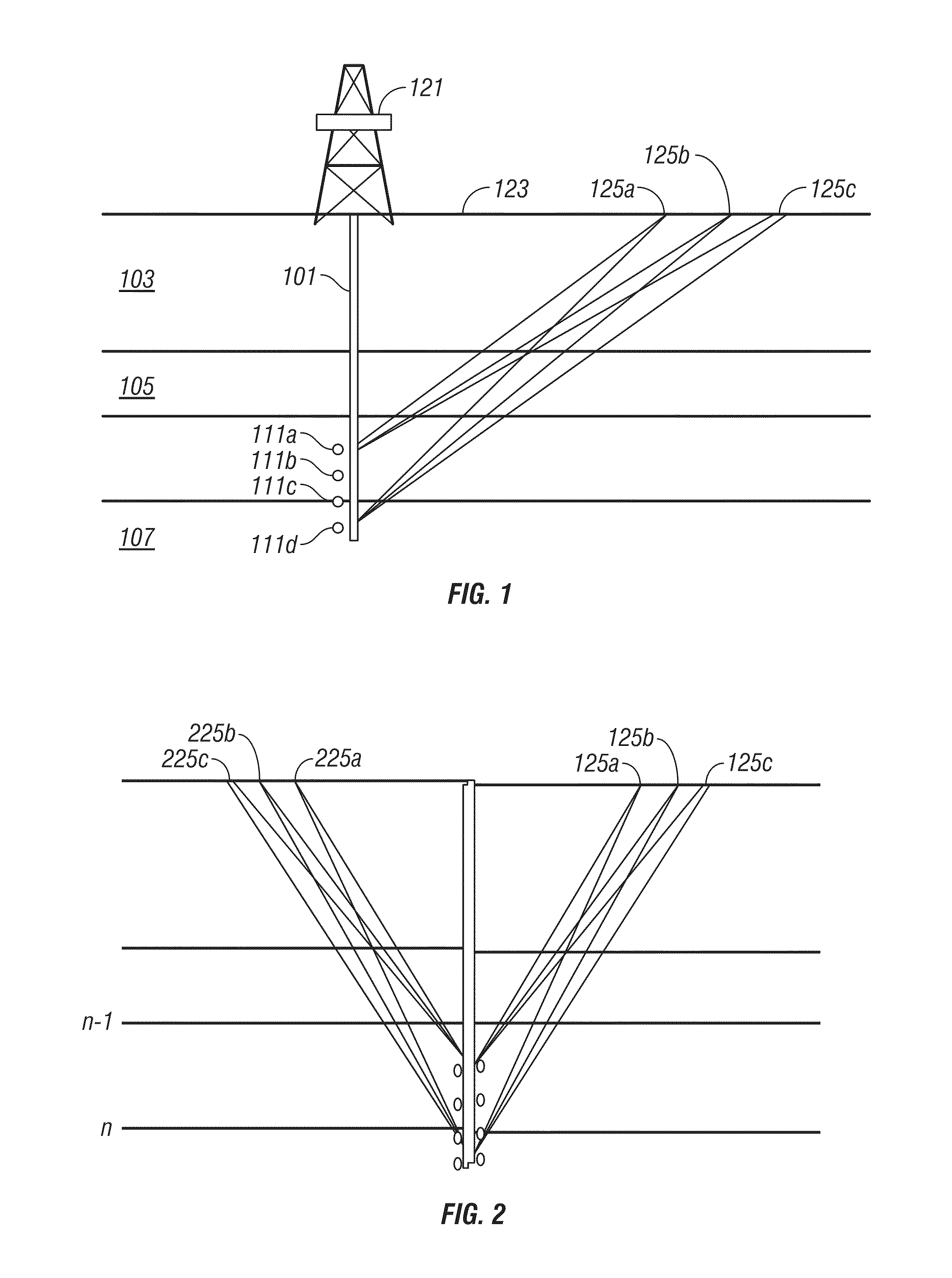
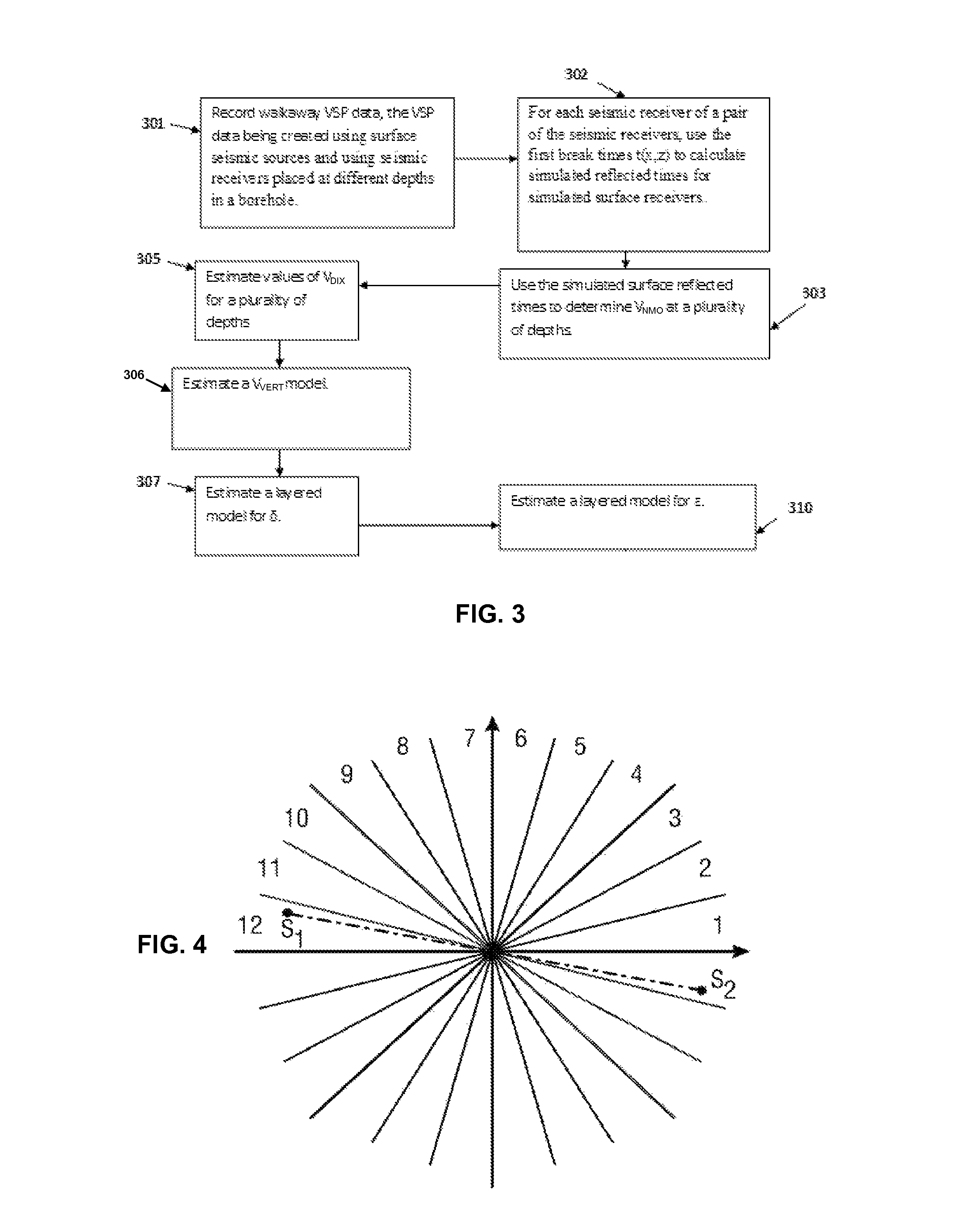
A walkaway VSP survey is carried out using a receiver array. First arrivals to a plurality of receivers are picked and used to estimate a normal-moveout (NMO) velocity. Using the NMO velocity and vertical velocities estimated from the VSP data, two anisotropy parameters are estimated for each of the layers. The anisotropy parameters may then be used to process surface seismic data to give a stacked image in true depth and for the interpretation purposes. For multi-azimuthal walkaway or 3D VSP data, we determine two VTI parameters ε and δ for multi-azimuth vertical planes. Then we determine five anisotropic interval parameters that describe P-wave kinematics for orthorhombic layers. These orthorhombic parameters may then be used to process surface seismic data to give a stacked image in true depth and for the interpretation purposes.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method for improving imaging effect of wave equation prestack depth migration
InactiveCN102176053AResolve mismatchAvoid multiple offset calculationsSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Normal moveout
The invention provides a method for improving the imaging effect of wave equation prestack depth migration, wherein the method is used for processing seismic reflection data in seismic exploration so as to improve the application effect of the wave equation prestack depth migration. The method can be used for improving the imaging effect of the wave equation prestack depth migration by constructing the relationship of residual normal moveout between a depth domain and an angle domain and an interval velocity inversion method to directly update a migration velocity model of the wave equation prestack depth migration based on the residual normal moveout of an angle gather. Based on the relationship of residual normal moveout between the depth domain and the angle domain, the method can be used for removing the residual normal moveout, noise and stretching of a migration gather of the wave equation prestack depth migration, thereby improving the signal-to-noise ratio and resolution of a migration stack profile and improving the quality of the angle gather applied to the prestack inversion. Accordingly, the method can be used for well achieving the direct recognition of underground oil, gas or water, can be used for 2D (two-dimensional) and 3D (three-dimensional) wave equation prestack depth migration of the seismic reflection data, and has important application value for exploration of oil-gas and mineral resources.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Unusual Event Detection in Wide-Angle Video (Based on Moving Object Trajectories)
InactiveUS20170161563A1Correct optical distortionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsNormal moveoutImage capture
Owner:GRANDEYE
Seismic receiver motion compensation
InactiveUS20020126576A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyNormal moveout
A method of compensating for seismic receiver motion in a marine seismic survey wherein at least one receiver is towed behind a moving seismic vessel comprises producing an acoustic energy wave at a seismic source, and recording the reflection arrival time t.sub.2 of the acoustic energy wave at the one receiver. The offset x between the source and the one receiver is determined. The normal moveout velocity V for the acoustic energy, and the velocity V.sub.B of the seismic vessel, are also estimated. A corrected reflection arrival time t.sub.1 of the acoustic energy wave is then determined by applying a time correction to the recorded reflection arrival time t.sub.2. The time correction is a function of the offset x, the normal moveout velocity V, and the velocity V.sub.B of the seismic vessel. The method is applicable to a plurality of receivers, whether the receivers are arranged in a single sensor acquisition system or hardwired to form receiver groups.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Method for stable estimation of anisotropic parameters for P-wave prestack imaging
ActiveUS20050088914A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsNormal moveoutVelocity inversion
A method is disclosed for determining interval anelliptical parameters. The method includes determining normal moveout velocities and effective anelliptical parameters from seismic data traces. The normal moveout velocities are processed to obtain interval velocities. The normal moveout velocities, effective anelliptical parameters and interval velocities are inverted to obtain the interval anelliptical parameters. In one embodiment, the inversion includes damped least squares. In one embodiment, the inversion is preconditioned.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
Removal of noise from seismic data using radon transformations
ActiveUS7239578B2Diminish primary reflection signal contentEnhanced low slowness coherent noise contentSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainNormal moveout
Methods of processing seismic data to remove unwanted noise from meaningful reflection signals are provided for. The methods comprise the steps of assembling seismic data into common geometry gathers in an offset-time domain without correcting the data for normal moveout. The amplitude data are then transformed from the offset-time domain to the time-slowness domain using a Radon transformation. At least of subset of the transformed data is filtered to enhance its coherent noise content and to diminish its primary reflection signal content by defining a slowness high-pass region and, a slowness low-pass region. The low-pass region is defined to enhance the low slowness coherent noise content and to diminish the primary reflection signal content thereof, thereby generating a first subset of said transformed data having enhanced low slowness coherent noise content. The high-pass region is defined to enhance the high slowness coherent noise content and to diminish the primary reflection signal content thereof, thereby generating a second subset of said transformed data having enhanced high slowness coherent noise content. After filtering, the first and second subsets of transformed data are inverse transformed from the time-slowness domain back to the offset-time domain using an inverse Radon transformation to restore the data. The restored signal amplitude data of the first and second subsets of data are then subtracted from the assembled data, thereby enhancing its primary reflection signal content.
Owner:E S & A ROBINSON
Horizontal streamer broadband marine seismic acquisition configuration and processing
InactiveUS20140064027A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasNormal moveoutBroadband
A method for de-ghosting marine seismic trace data is described. A reference seismic trace and a candidate seismic trace are selected from acquired seismic data. The acquired seismic data is gathered using a configuration wherein either a first streamer and a second streamer are disposed at different depths relative to one another and are laterally offset relative to one another, or using a configuration wherein a first source and a second source are disposed at different depths relative to one another and are laterally offset from one another. The reference seismic trace and the candidate seismic trace are processed, e.g., to perform normal moveout correction and / or vertical datum shifting, and the processed reference seismic trace is de-ghosted using the processed, candidate seismic trace.
Owner:CGG SERVICES SA
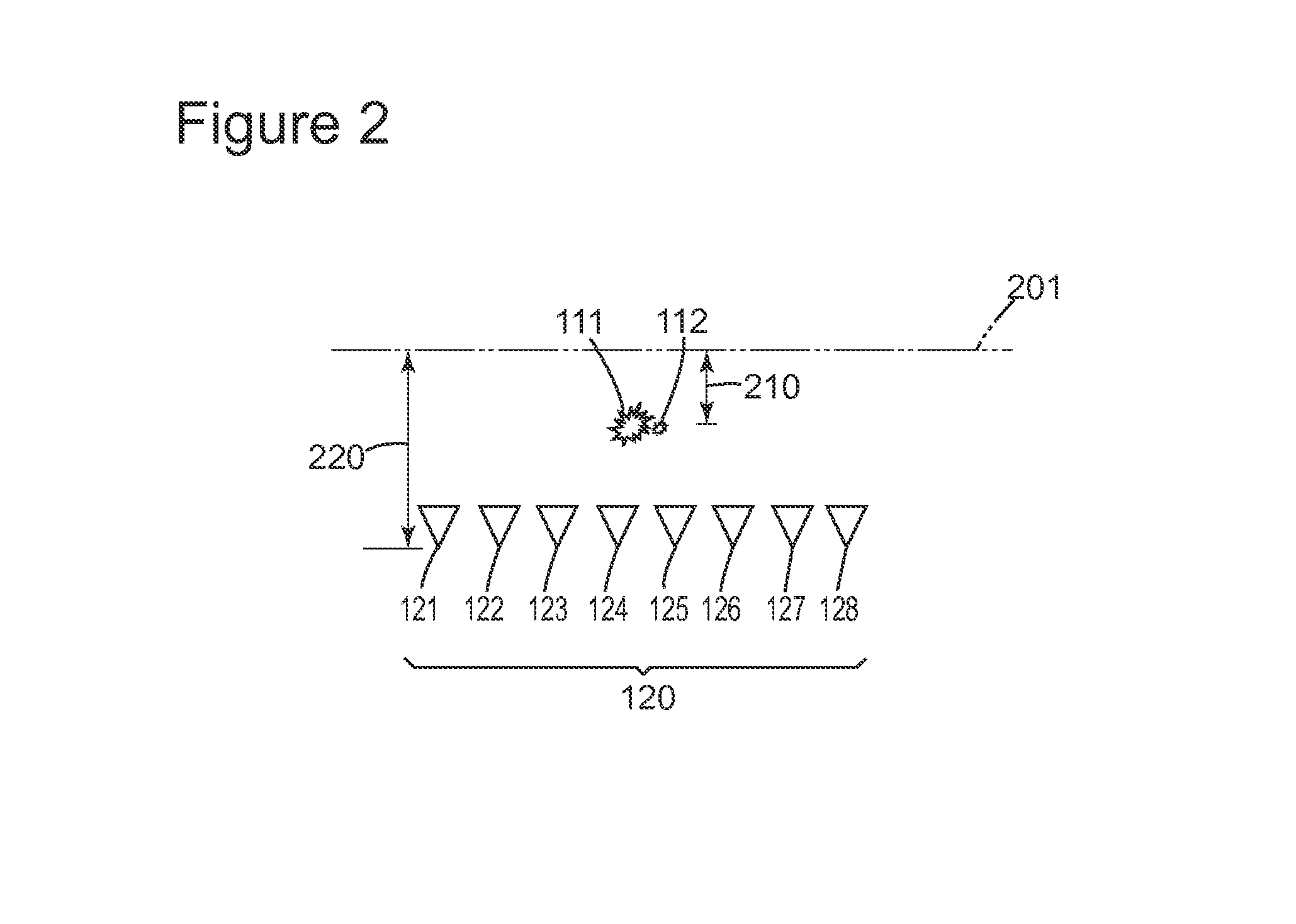
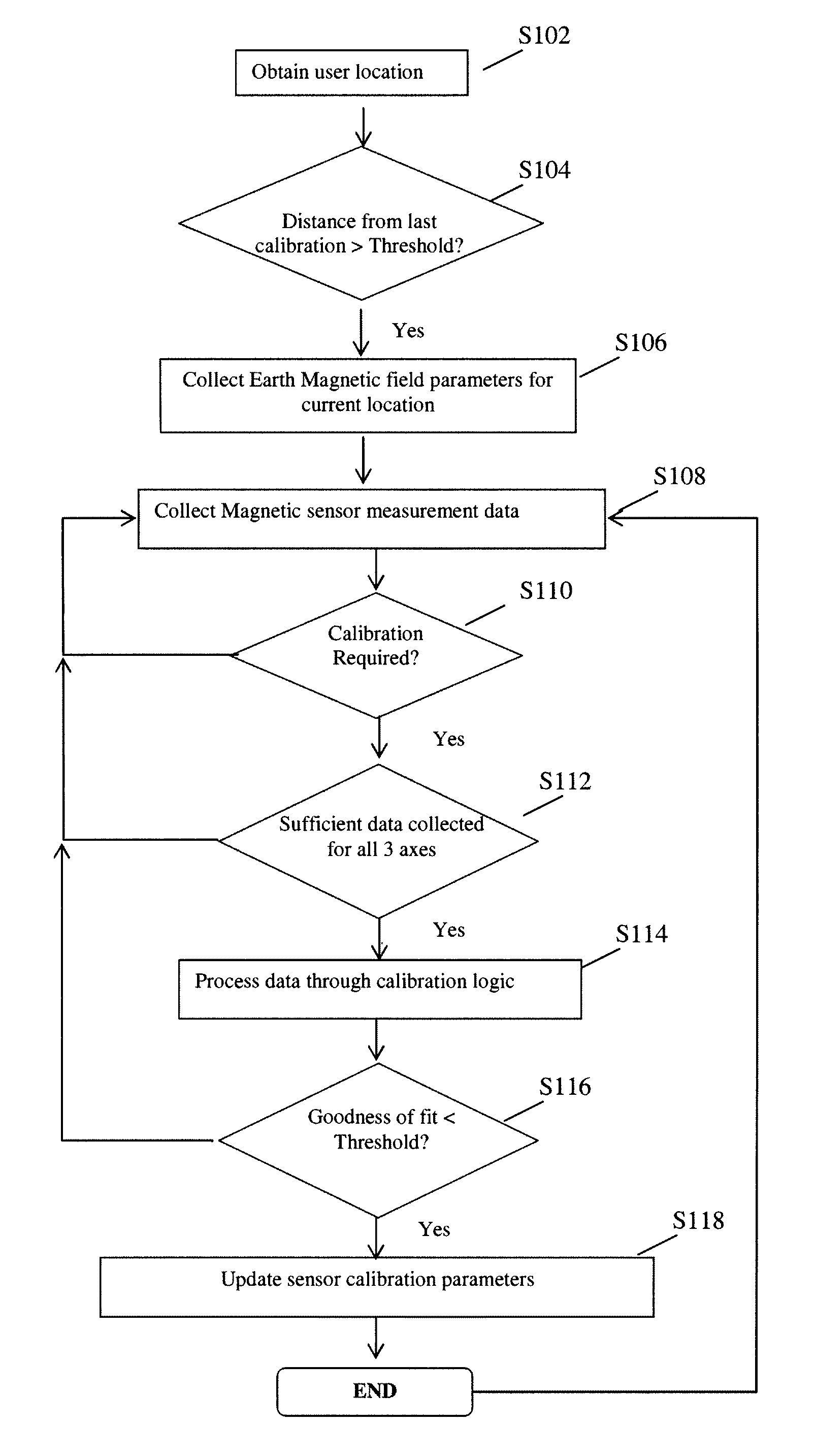
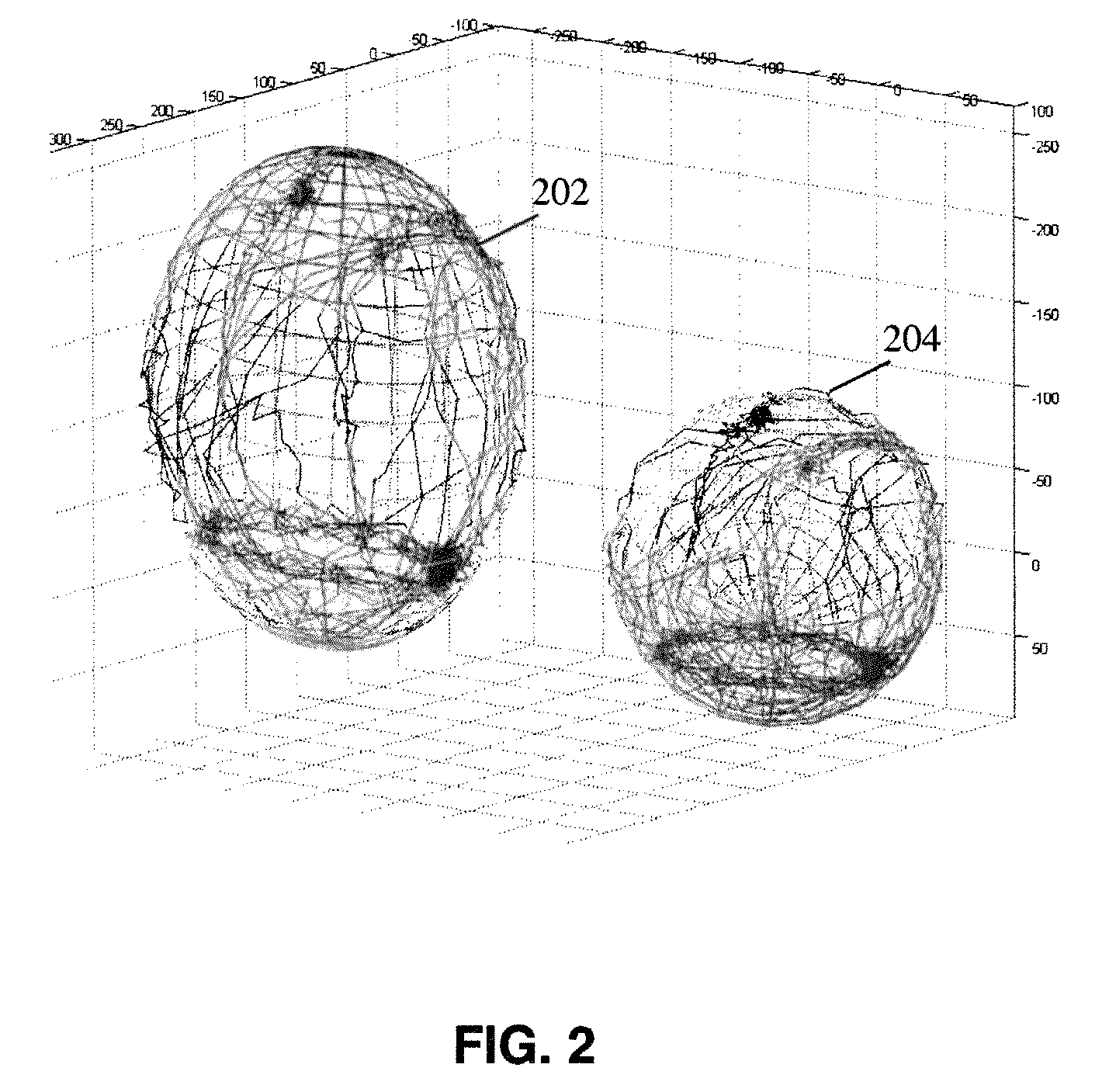
Method and apparatus for calibrating a magnetic sensor
In general, the invention relates to an algorithm and process for automated and / or continuous calibration of magnetic sensor, for example such as a sensor installed in a mobile positioning system handset. According to certain aspects, the calibration process can use the normal motion of the handset such that all measurement data from the three orthogonal axes of sensor when exposed to Earth's magnetic field is collected. According to still further aspects, the process includes fitting measurement data to an ellipsoid that characterizes the actual magnetic field measurements from a magnetic sensor, so that anomalies such as hard iron effect, soft iron effect and scale factors can be extracted and / or corrected by comparison to a sphere represented by magnetic field data from a model at the sensor's location.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
Method for improving velocity spectrum resolution by using phase information
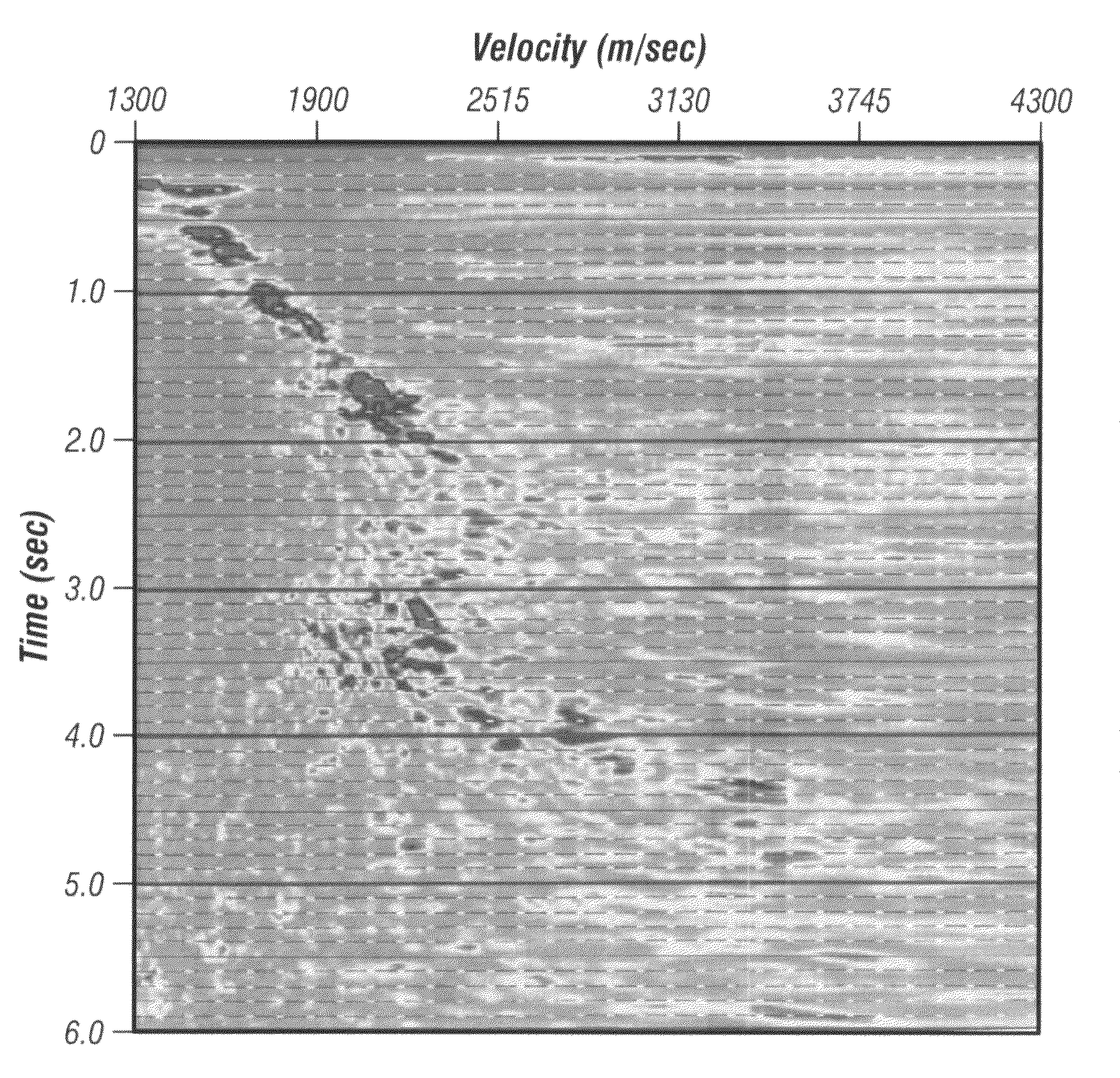
ActiveCN102073064AHigh-resolutionAvoid Velocity Analysis EffectsSeismic signal processingNormal moveoutVelocity spectrum
The invention relates to a technique for processing petroleum geophysical prospecting seismic data, which is a method for improving the velocity spectrum resolution by using phase information. The method comprises the following steps of: stimulating and recording seismic waves to obtain a common midpoint gather; performing a first-order derivative operation along a time direction, and performing Hilbert transform to obtain a complex seismic trace; superimposing P(t) traces to obtain the optimal velocity of normal moveout correction (NMO); calculating a velocity spectrum by using a conventional velocity analysis method; and performing side lobe suppression on the selected common midpoint (CMP) for velocity analysis and each time sample vector in SPS to finally obtain the velocity spectrum. By the method, influences on the velocity analysis due to amplitude changes can be avoided, the distribution of noises is converted into the distribution with gauss distribution characteristics, so that influences on the velocity analysis due to abnormal noises can be effectively inhibited, and the resolution of the velocity spectrum and the accuracy of the velocity analysis are improved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Correction for Errors Caused by Variation in Water Conditions
InactiveUS20080255762A1Well formedTesting/calibration apparatusFluid pressure measurementNormal moveoutWater velocity
Method for processing seismic data to correct for errors caused by variation in water conditions. In one implementation, the method may include (a) applying a dip correction to a plurality of observed water bottom reflection times using a model water velocity and an estimate of geologic dip; (b) applying a normal moveout (NMO) correction to the dip corrected observed water bottom reflection times using the model water velocity; (c) applying a common mid point (“CMP”) bin centering correction to the NMO corrected, dip corrected observed water bottom reflection times using the model water velocity and the estimate of geologic dip; (d) solving for Δsi, which is an estimate of the difference in slowness between the observed water bottom reflection times and the water bottom reflection times that would have been observed had the water velocity been the same as the model water velocity; (e) solving for an estimate of observed water velocity based on sobs,i=sm+Δsi, where sobs,i is an estimate of observed slowness and sm is defined as the model slowness; (f) layer replacing the observed water bottom reflection times using the estimate of the observed water velocity and the model water velocity; and (g) repeating steps (a) to (f) using the layer replaced observed water bottom reflection times until the changes in the estimate of observed water velocity approach zero.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Method for three dimensional seismic travel time tomography in transversely isotropic media
A method for estimating seismic velocities in vertically transversely isotropic media includes generating an initial estimate of vertical interval velocity and interval normal moveout velocity with respect to depth from seismic data. An initial estimate is generated of a first anisotropy parameter with respect to depth. The first anisotropy parameter is related to the interval normal moveout velocity and the interval vertical velocity. An initial estimate is generated with respect to depth of a second anisotropy parameter. The second anisotropy parameter is related to the first anisotropy parameter and an interval anelliptic parameter. A first tomographic inversion is performed with respect to the interval normal moveout velocity and the second anisotropy parameter at a constant value of the first anisotropy parameter until travel time differentials reach minimum values. Layer depths are adjusted with the initial estimate of vertical interval velocity. Using values of the second anisotropy parameter determined in the first tomographic inversion, a second tomographic inversion is performed of interval normal moveout velocity and the first anisotropy parameter with respect to depth. The adjusted layer depths, interval normal moveout velocities and interval vertical velocities are again adjusted and interval anelliptic parameters are calculated from the second tomographic inversion.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
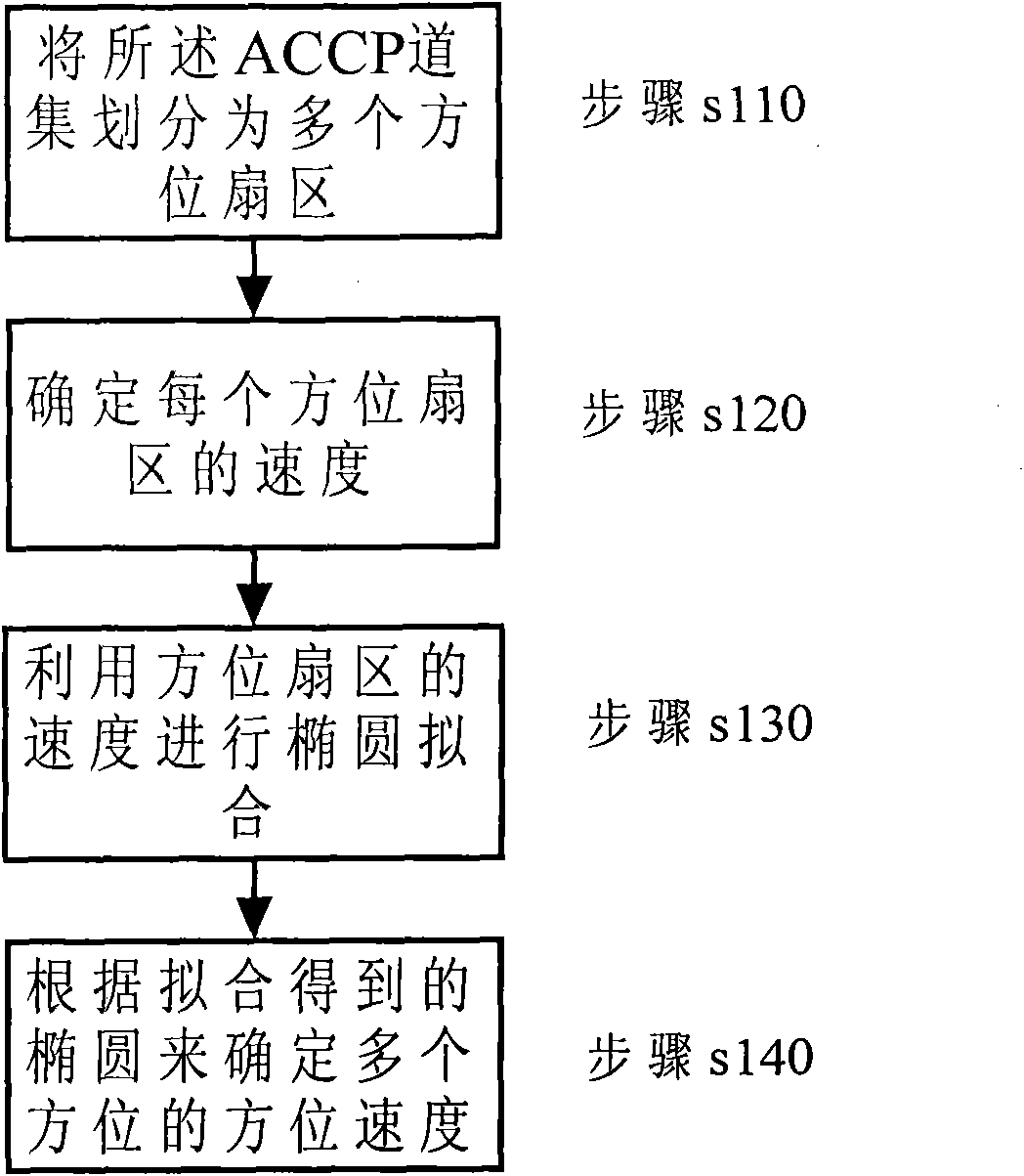
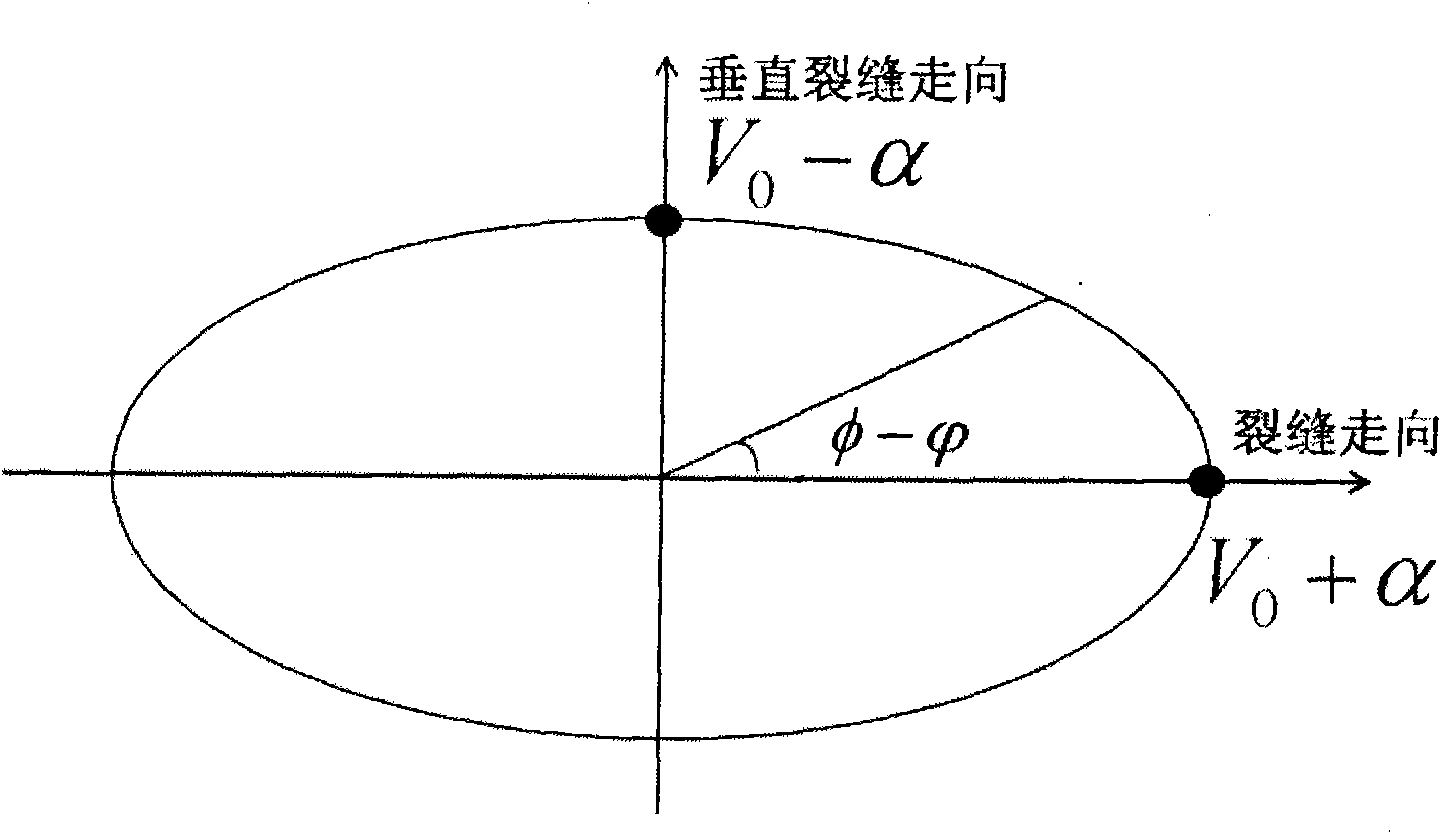
Method for acquiring azimuth velocity of seismic converted wave and method for processing seismic data
The invention provides a method for acquiring the azimuth velocity of a seismic P-SV converted wave and a method for processing the data of the seismic converted wave according to the acquired azimuth velocity. The method for acquiring the azimuth velocity of the seismic P-SV converted wave comprises the following steps: in the asymptotic common conversion point (ACCP) gather of wide azimuth converted wave seismic data, the ACCP gather is divided into a plurality of azimuth sectors based on the difference between azimuth angles, and the seismic data in each azimuth sector comprises a plurality of channels in the ACCP gather; on the basis of the seismic data of the plurality of channels in each azimuth sector, the velocity of the azimuth sector is determined; ellipse fitting is performed on the velocity of each azimuth sector; and the azimuth velocity of each azimuth is determined based on the fitted ellipse, and the velocity is applied to the normal-moveout correction of each azimuth seismic data and other processes.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
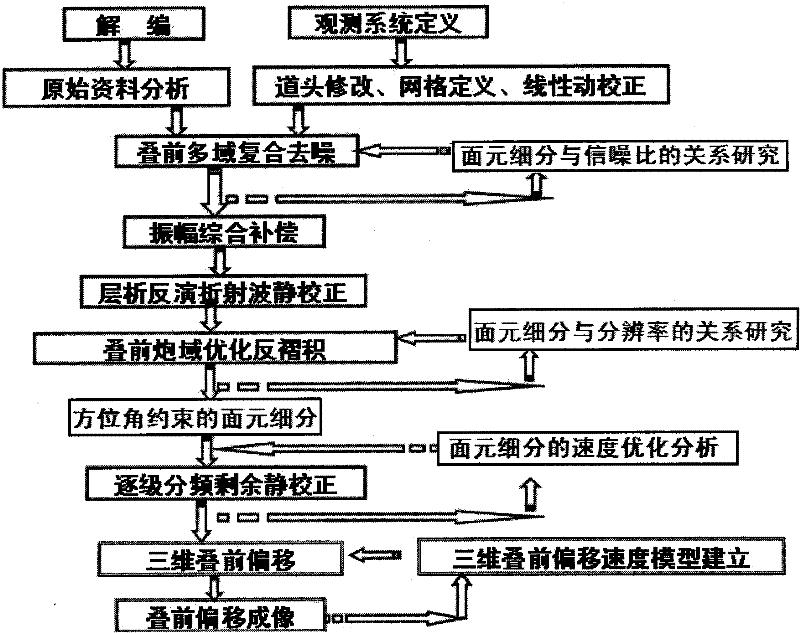
Three-dimensional high-precision bin fractionation processing and evaluation technology for seismic data
InactiveCN102230974AImprove exploration accuracyIncrease reachSeismic signal processingVibration amplitudeNormal moveout
The invention provides a three-dimensional high-precision bin fractionation processing and evaluation technology for seismic data, and the method comprises the following steps: analyzing original data, and carrying out trace header modification, grid definition and linear normal moveout correction on data acquired by an observation system, thus acquiring a prestack multi-domain composite denoised image; based on the relationship between bin fractionation and the signal-to-noise ratio as well as the relationship between bin fractionation and the multiplicity during forward modeling, comprehensively compensating for the vibration amplitude, thus acquiring a tomographic inversion refracted wave static correction image; analyzing the quantitative relationship between bin fractionation and the longitudinal resolution and lateral resolution, carrying out prestack shot-domain optimized deconvolution, and carrying out azimuth restrained bin fractionation and speed optimized analysis, thus acquiring a progressive frequency-divided residual correction image; and carrying out multiple three-dimensional prestack migrations, and establishing a three-dimensional prestack migration speed model, thus acquiring a prestack migration image. Thus, the method provided by the invention provides a reliable guarantee for improving the exploration development precision and upgrading a seismic exploration technology.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Processing seismic data using interferometry techniques
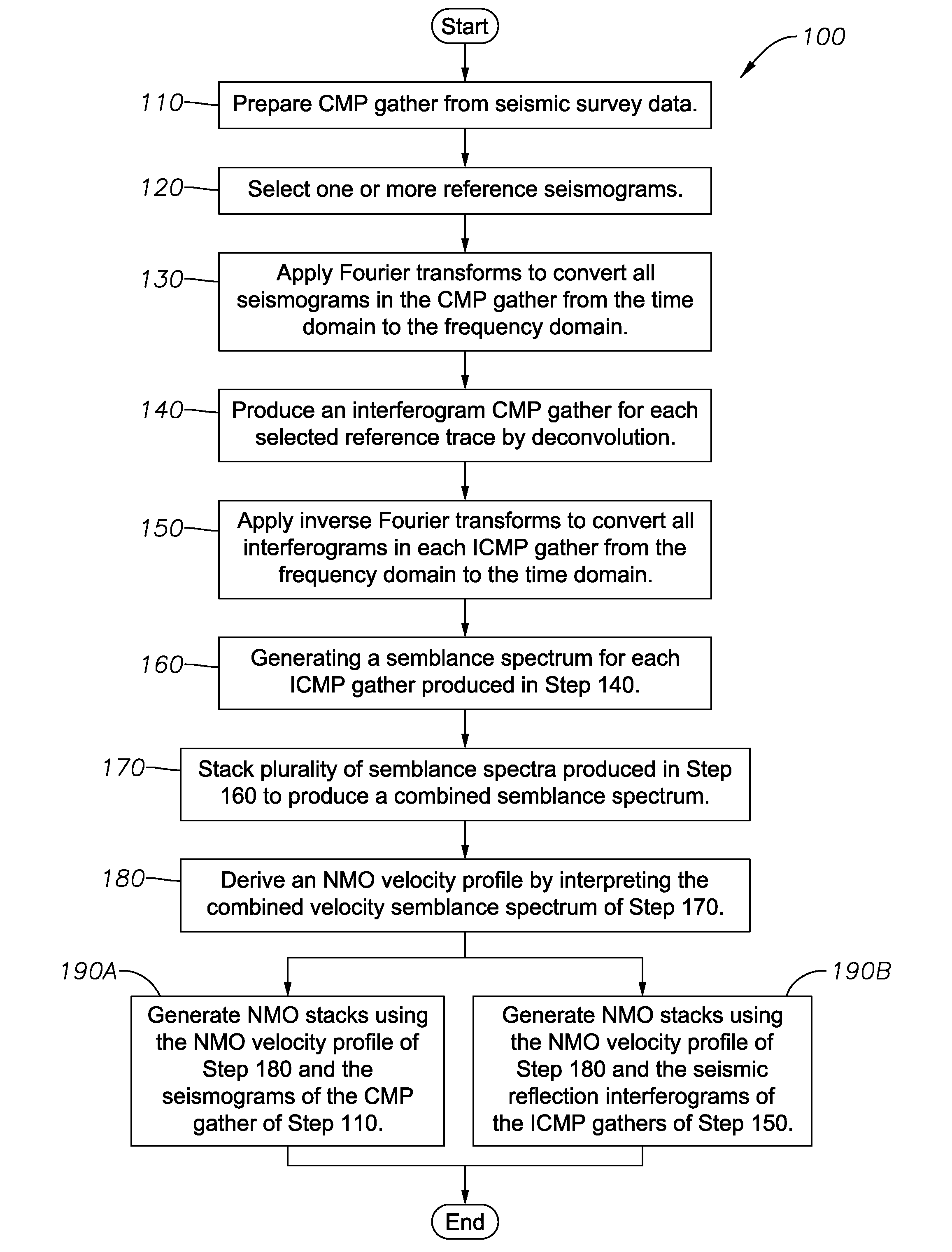
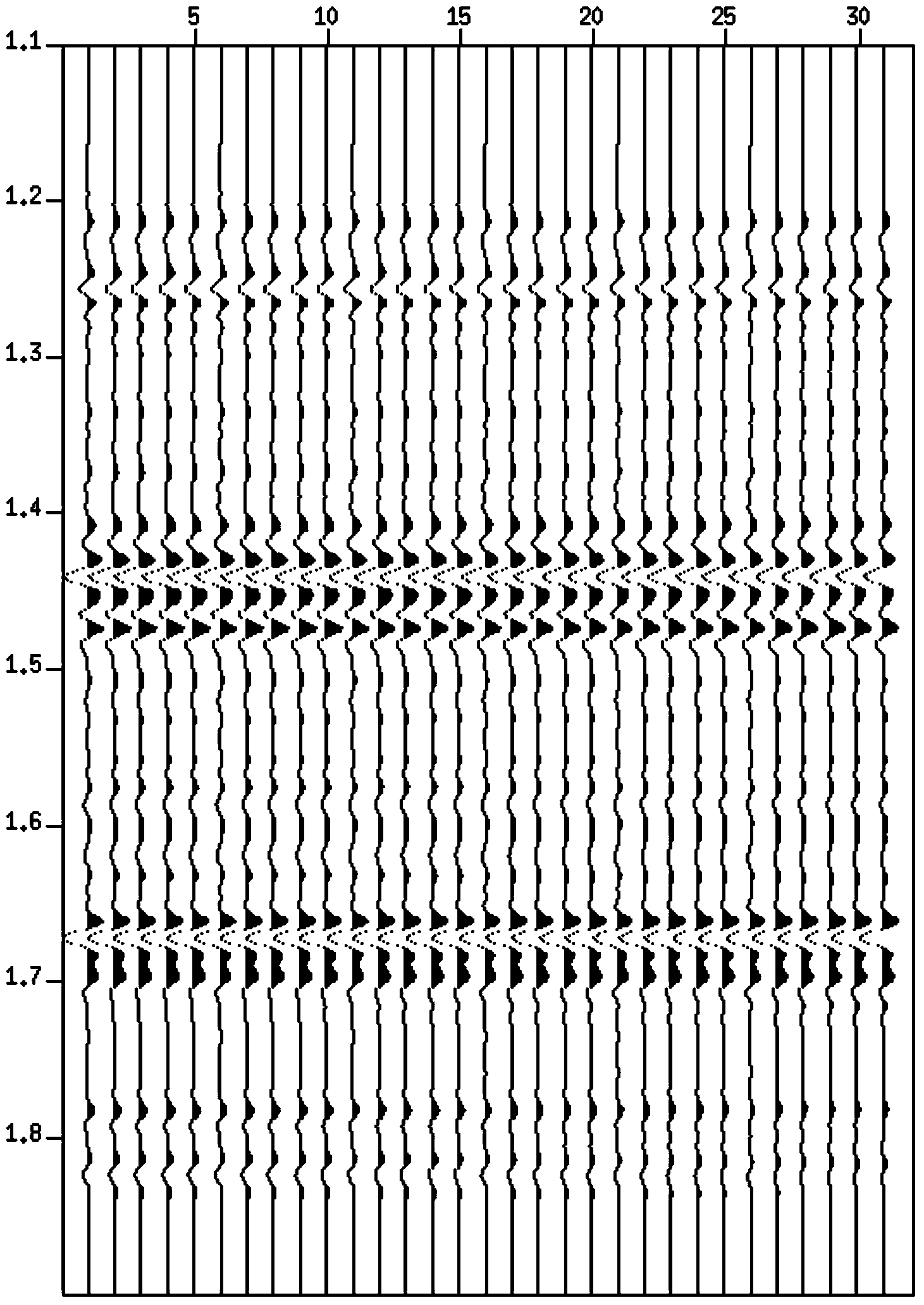
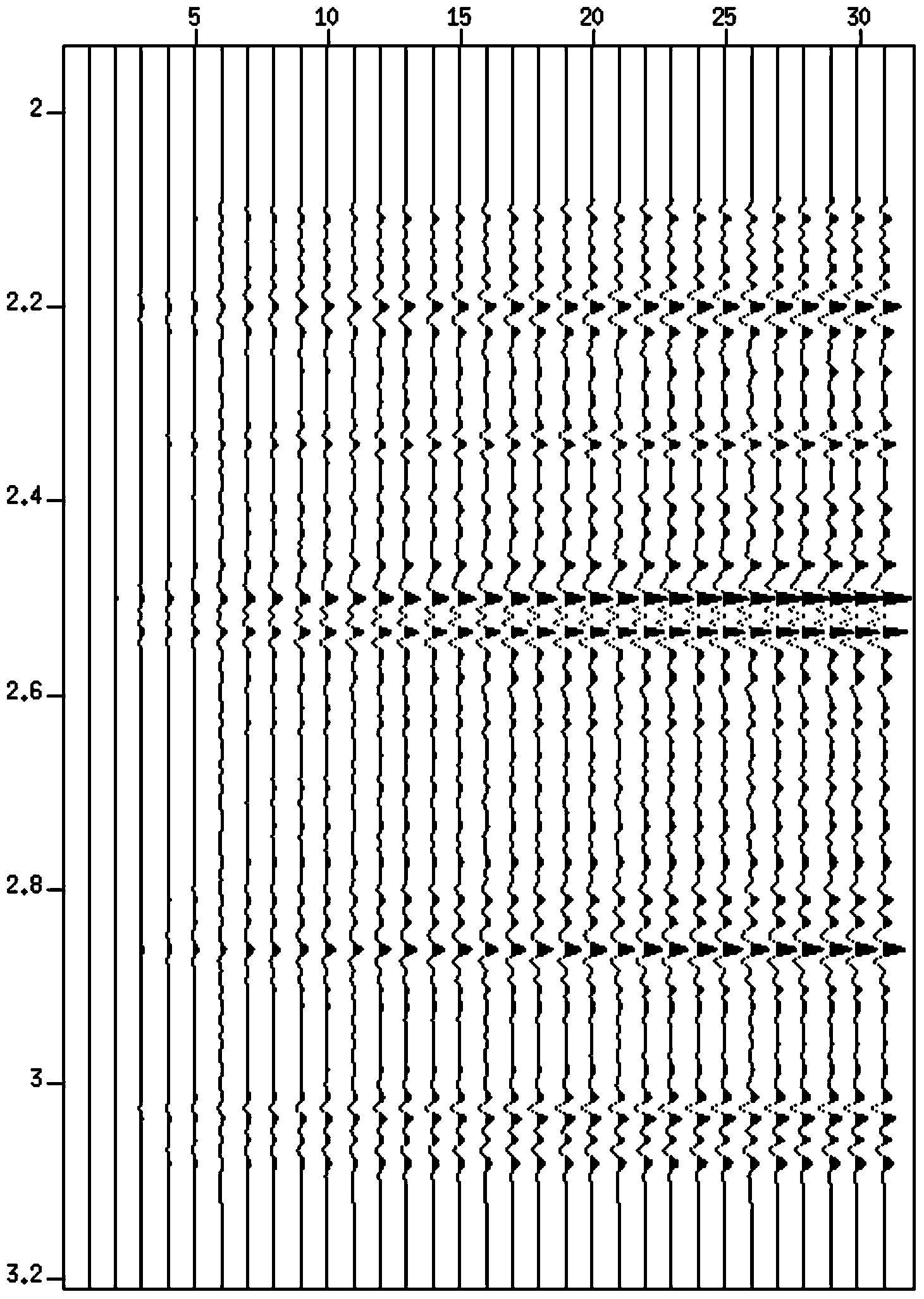
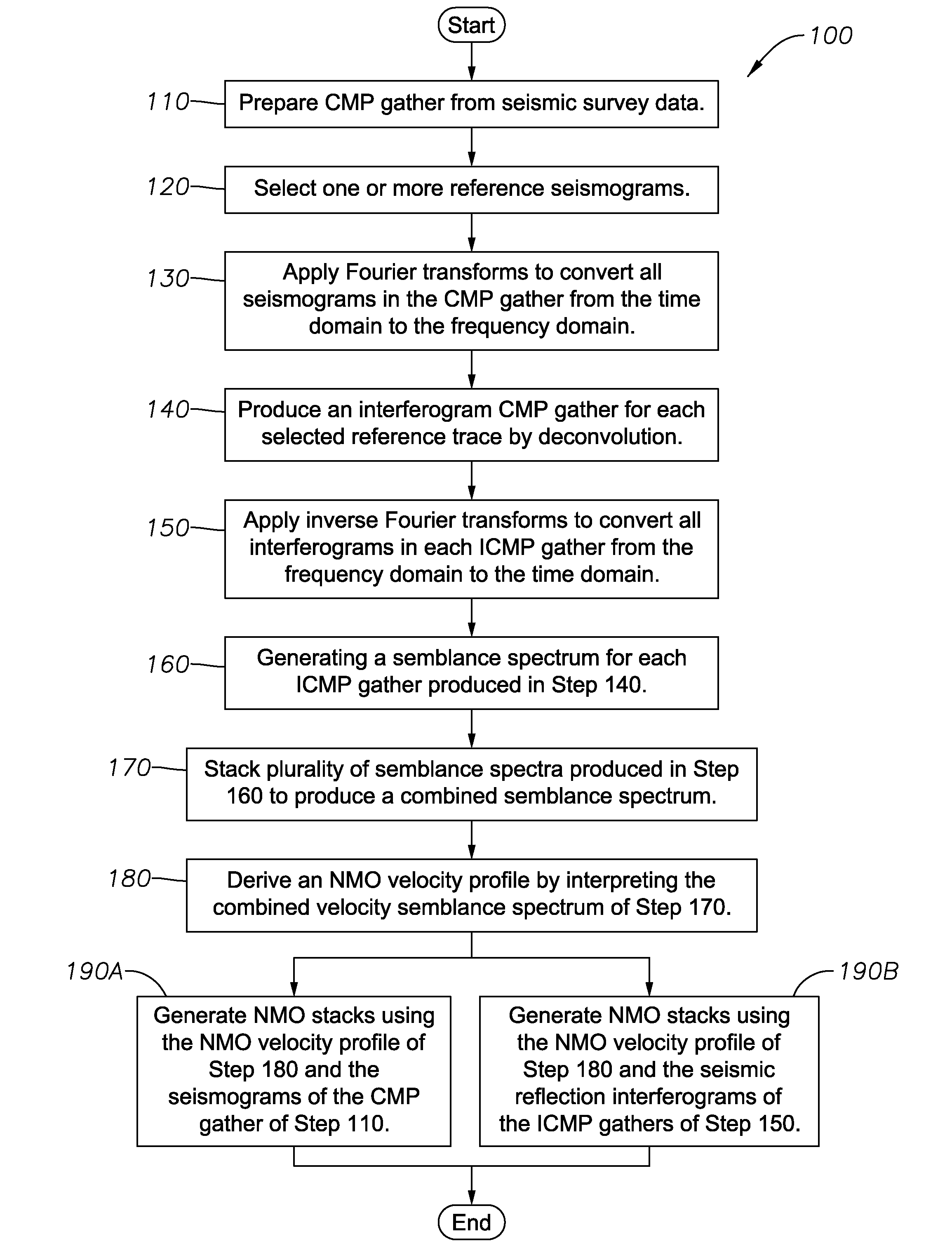
InactiveUS20080133140A1Well formedSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsNormal moveoutComputer science
Method for processing seismic data. In one implementation, the method includes converting a common midpoint (CMP) gather of seismograms into one or more interferogram common midpoint (ICMP) gathers, generating a semblance spectrum for each ICMP gather, stacking the semblance spectrum from each ICMP gather to generate a combined semblance spectrum and deriving a normal moveout (NMO) velocity profile from the combined semblance spectrum.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Limited radon transformations for removal of noise from seismic data
InactiveUS20090005999A1Enhance primary reflection signal contentRemove noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionSeismic signal processingPattern recognitionTime domain
Methods of processing seismic data to remove unwanted noise from meaningful reflection signals are provided for. The methods comprise the steps of assembling seismic data into common geometry gathers in an offset-time domain without correcting the data for normal moveout. The amplitude data are then transformed from the offset-time domain to the time-slowness domain using a limited Radon transformation. That is, the Radon transformation is applied within defined slowness limits pmin and pmax, where pmin is a predetermined minimum slowness and pmax is a predetermined maximum slowness. A corrective filter is then applied to the transformed data enhance the primary reflection signal content of the data and to eliminate unwanted noise events. After filtering, the enhanced signal content is inverse transformed from the time-slowness domain back to the offset-time domain using an inverse Radon transformation.
Owner:E S & A ROBINSON
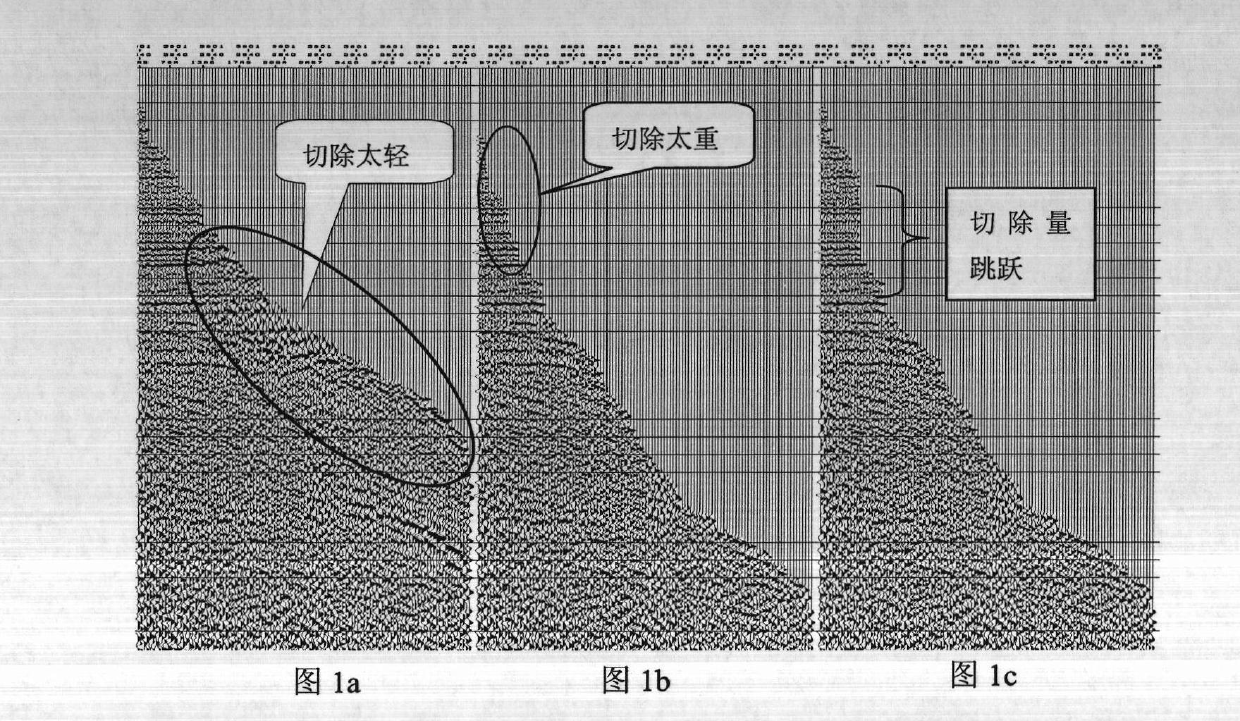
Normal moveout stretch cutting method for processing geophysical exploitation seismic data
ActiveCN102636813AHigh resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioSeismic signal processingGeophoneNormal moveout
The invention provides a normal moveout stretch cutting method for processing geophysical exploitation seismic data. According to the method, a stacking velocity field is utilized, average speed is calculated, or interval velocity is calculated after smoothing the average speed. Further, by using the velocity and shot-geophone distance information, approximate calculation of an incident angle is performed according to the theory of ray (straight ray or curved ray) propagated by seismic wave, and a 1D or 3D space varying incident angle threshold value reference is used as a standard of measurement to determine the cut of each seismic channel. Thus, more accurate automatic cutting of the normal moveout stretch is realized, the interference caused by net normal moveout stretch can be cut, effective wave amplitude can also be protected to the greatest extent, and finally, the resolution and the signal-noise ratio of a stacked section are improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for matching longitudinal wave and converted wave data through dynamic time adjustment
The invention provides a method for matching longitudinal wave and converted wave data through dynamic time adjustment. The method includes the steps that acquired seismic waves are processed through normal moveout correction and the like to generate a longitudinal wave gather with amplitude changing along with offset and a converted wave gather with amplitude changing along with offset; inversion of changes of amplitude along with offset is performed on the longitudinal wave gather and the converted wave gather respectively, and an attribute set of changes of amplitude along with offset of longitudinal waves and an attribute set of changes of amplitude along with offset of converted waves are obtained; the attribute set of changes of amplitude along with offset of longitudinal waves and the attribute set of changes of amplitude along with offset of converted waves are calculated based on dynamic time adjustment, and the time shift quantity sequence between the longitudinal waves and the converted waves is obtained; time shift is performed on the converted wave gather according to the time shift quantity sequence, and a converted wave data set is obtained after the converted wave gather is matched in the time domain of longitudinal waves. Through the method, the time shift quantity of each sampling point can be obtained so that the method is adaptive to intense changes of the time shift quantities and free of influences of relevant time windows and thresholds, and a good result can also be obtained on the basis of data with a low signal-to-noise ratio and resolution ratio.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Processing seismic data using interferometry techniques
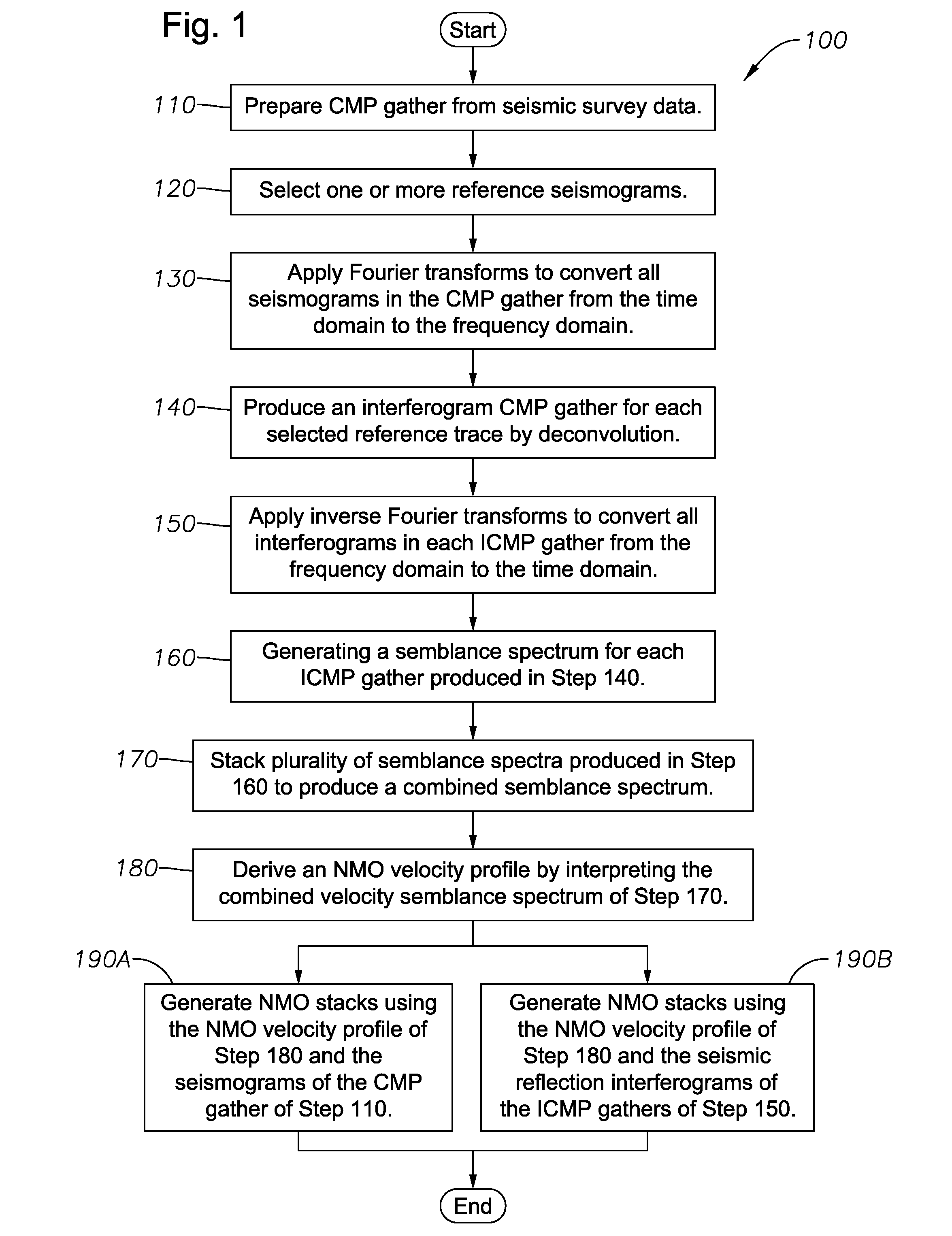
InactiveUS7447115B2Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsNormal moveoutComputer science
Method for processing seismic data. In one implementation, the method includes converting a common midpoint (CMP) gather of seismograms into one or more interferogram common midpoint (ICMP) gathers, generating a semblance spectrum for each ICMP gather, stacking the semblance spectrum from each ICMP gather to generate a combined semblance spectrum and deriving a normal moveout (NMO) velocity profile from the combined semblance spectrum.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Anisotropic parameter determination
InactiveUS8750074B2Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingVertical planeNormal moveout
A walkaway VSP survey is carried out using a receiver array. First arrivals to a plurality of receivers are picked and used to estimate a normal-moveout (NMO) velocity. Using the NMO velocity and vertical velocities estimated from the VSP data, two anisotropy parameters are estimated for each of the layers. The anisotropy parameters may then be used to process surface seismic data to give a stacked image in true depth and for the interpretation purposes. For multi-azimuthal walkaway or 3D VSP data, we determine two VTI parameters ε and δ for multi-azimuth vertical planes. Then we determine five anisotropic interval parameters that describe P-wave kinematics for orthorhombic layers. These orthorhombic parameters may then be used to process surface seismic data to give a stacked image in true depth and for the interpretation purposes.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Recurve bow response on-line detection system
InactiveCN102706270AGood effectAcceleration measurement using interia forcesForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceNormal moveout
The invention discloses a recurve bow response on-line detection system. Resistance strain testing, vibration testing and a control virtual-type signal analyzing soft and hardware technology are adopted; the static and dynamic strain and acceleration response of selected testing points on a recurve bow and mechanical dynamic parameters of the recurve bow are detected in real time on line, and objective experiment data are provided for the training of sportsmen and the development of a novel recurve bow. The particular implementation is that a small-type three-shaft resistance strain rosettes and a micro-piezoelectric-type acceleration transducer are bonded on the selected testing points of the recurve bow; response signals are transmitted to a strain meter and a vibration testing meter by leads; and after being converted and amplified, the response signals are transmitted to a control virtual-type signal analyzing meter for real-time analyzing treatment, thus the corresponding data curve diagrams and animation display and the like are obtained. The detection system can not influence the using performance of the recurve bow and the normal motion of users, not only can be used for the training of contestants, but also can be used for the detection analysis of stress and response of the recurve bow and prevents from adopting and installing each type of shock absorbers blindly, and is an effective means for archery coaches, sportsmen and the recurve bow researchers.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
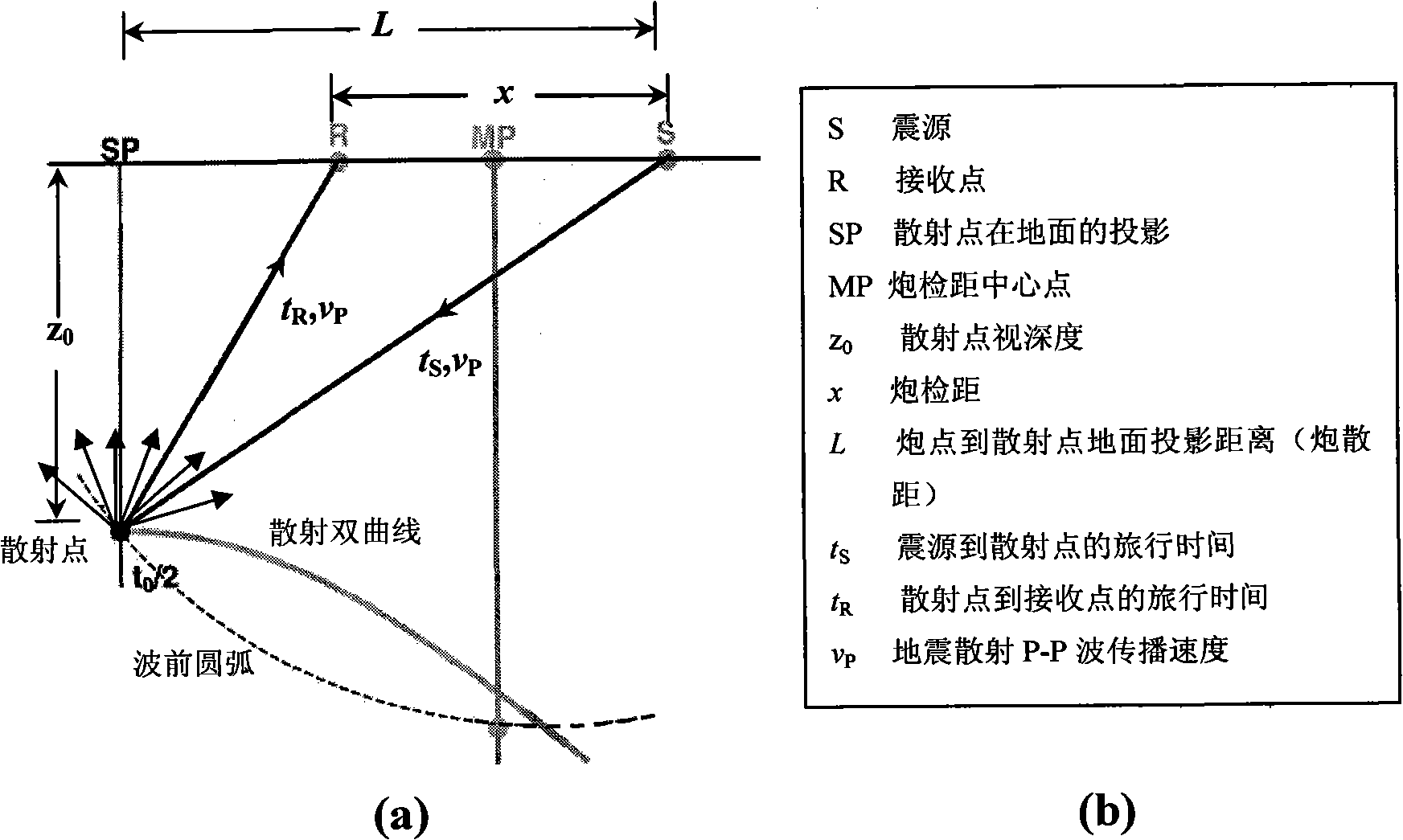
Seismic scattering P-P wave imaging method
InactiveCN101900830ATake advantage ofIncrease the number of stacksSeismic signal processingGeophoneNormal moveout
The invention relates to a seismic scattering P-P wave imaging method which comprises the following steps: step 1: reading the seismic data into a two-dimensional array F, simultaneously loading observation system parameters into an original seismic data header, and calculating positions and coordinates of scattering points according to an observation system and acquisition parameters; step 2: according to the time-distance hyperbolic equation of scattering waves, under the condition of fixing t0i on a shot set, determining the scattering hyperbolic trace through the imaging speed, and then, calculating the seismic scattering P-P wave normal moveout; step 3: subtracting the seismic scattering P-P wave normal moveout from the seismic wave traveltime; step 4: calculating the weighted sum of the scattering amplitude of the hyperbolic trace from which the seismic scattering P-P wave normal moveout is subtracted on each shot-geophone distance, thereby realizing the seismic scattering P-P wave imaging; and step 5: outputting the imaging data in the seismic format. The invention has the characteristics of improving the stacking times of the horizontal stacking imaging technique and effectively improving the signal-to-noise ratio and the imaging precision.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
Methods of enhancing separation of primary reflection signals and noise in seismic data using radon transformations
InactiveUS20050135188A1Precise processingImprove accuracySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasTime domainNormal moveout
Improved methods of processing seismic data which comprise amplitude data assembled in the offset-time domain in which primary reflection signals and noise overlap are provided for. The methods include the step of enhancing the separation between primary reflection signals and coherent noise by transforming the assembled data from the offset-time domain to the time-slowness domain. More specifically, the assembled amplitude data are transformed from the offset-time domain to the time-slowness domain using a Radon transformation according to an index j of the slowness set and a sampling variable Δp; wherein j=pmax-pmin+1 μ sec / mΔ p,Δp is from about 0.5 to about 4.0 μsec / m, pmax is a predetermined maximum slowness, and pmin is a predetermined minimum slowness. Alternately, an offset weighting factor xn is applied to the assembled amplitude data, wherein 0<n<1, and the amplitude data are transformed with a Radon transformation. The assembled amplitude data also may be transformed with a Radon transformation applied within defined slowness limits pmin and pmax, where pmin is a predetermined minimum slowness and pmax is a predetermined maximum slowness, with a hyperbolic Radon transformation, or, as applied to data which have been uncorrected for normal moveout, with a hyperbolic or parabolic Radon transformation. Thus, the primary reflection signals and coherent noise transform into different regions of the time-slowness domain to enhance the separation therebetween.
Owner:ROBINSON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com