Patents
Literature
10978 results about "Geophysics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Geophysics (/ˌdʒiːoʊˈfɪzɪks/) is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.
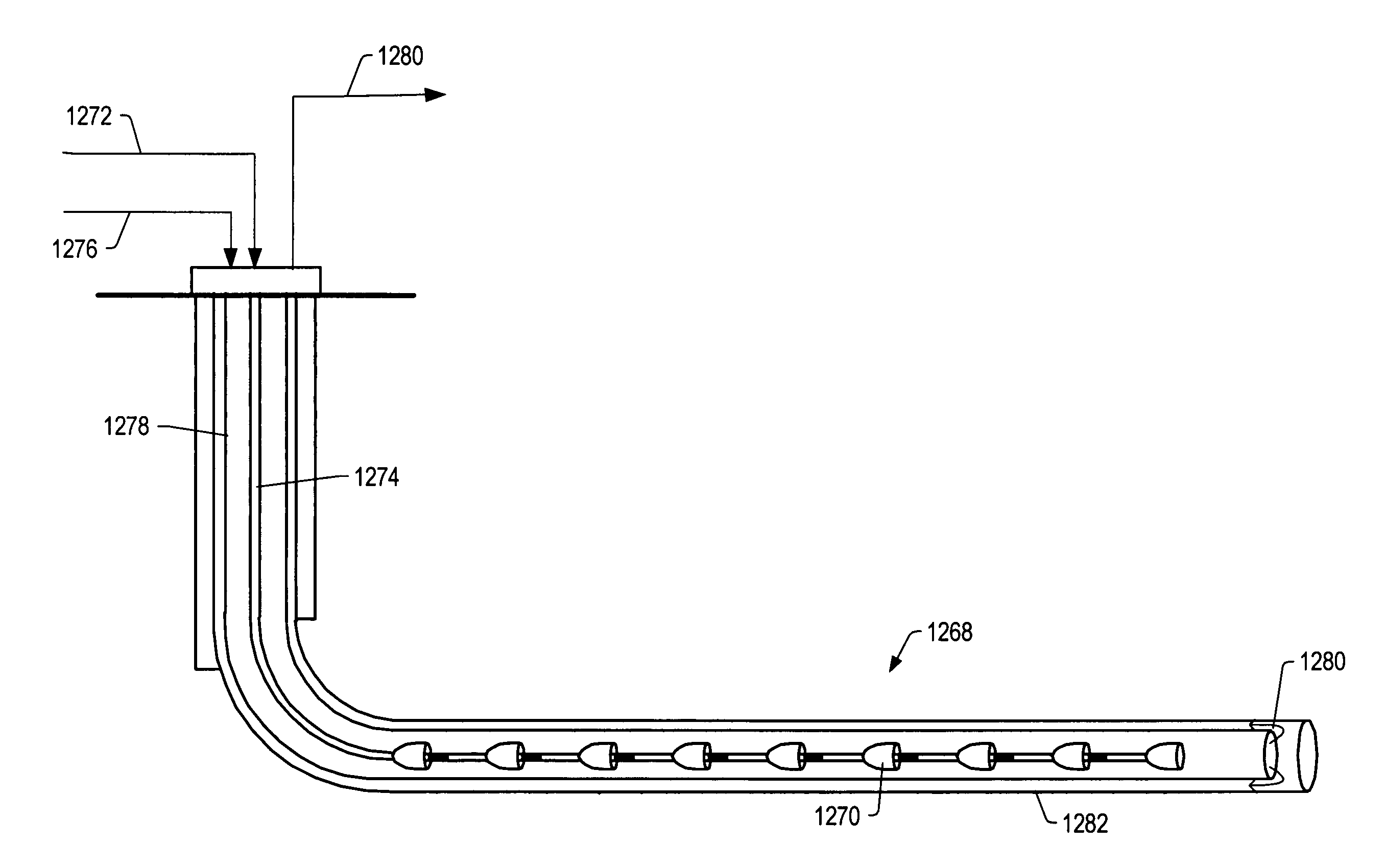
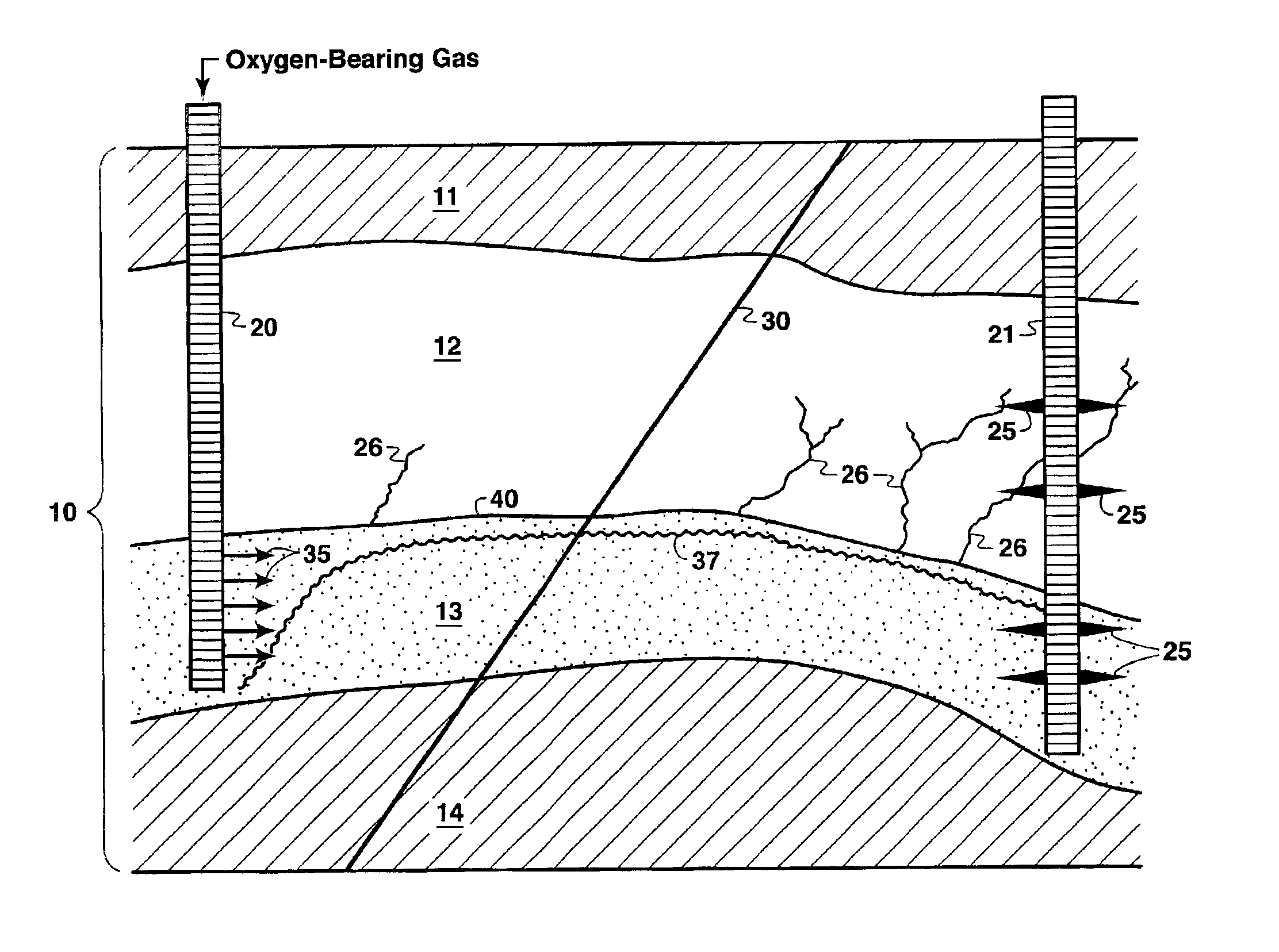
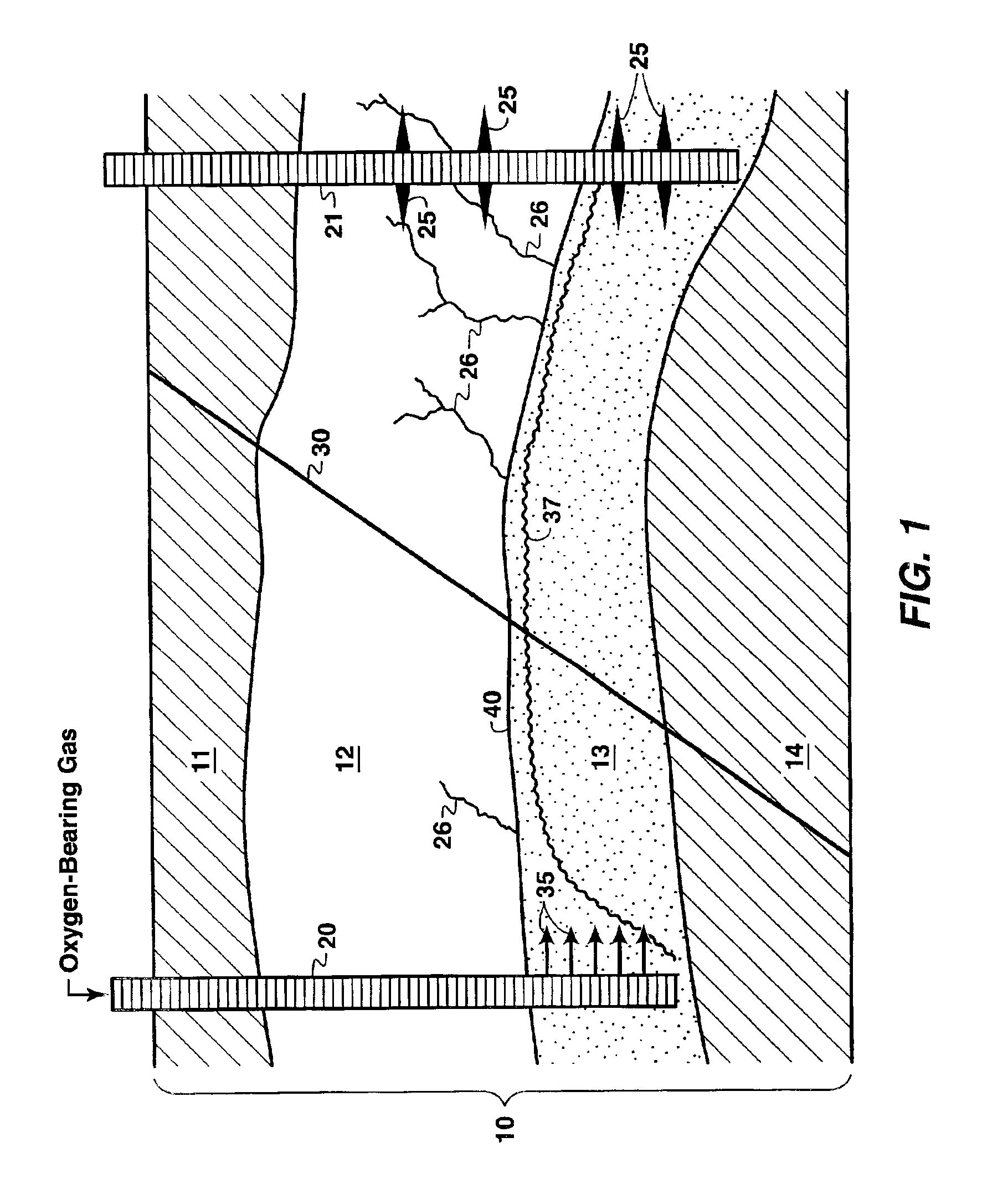
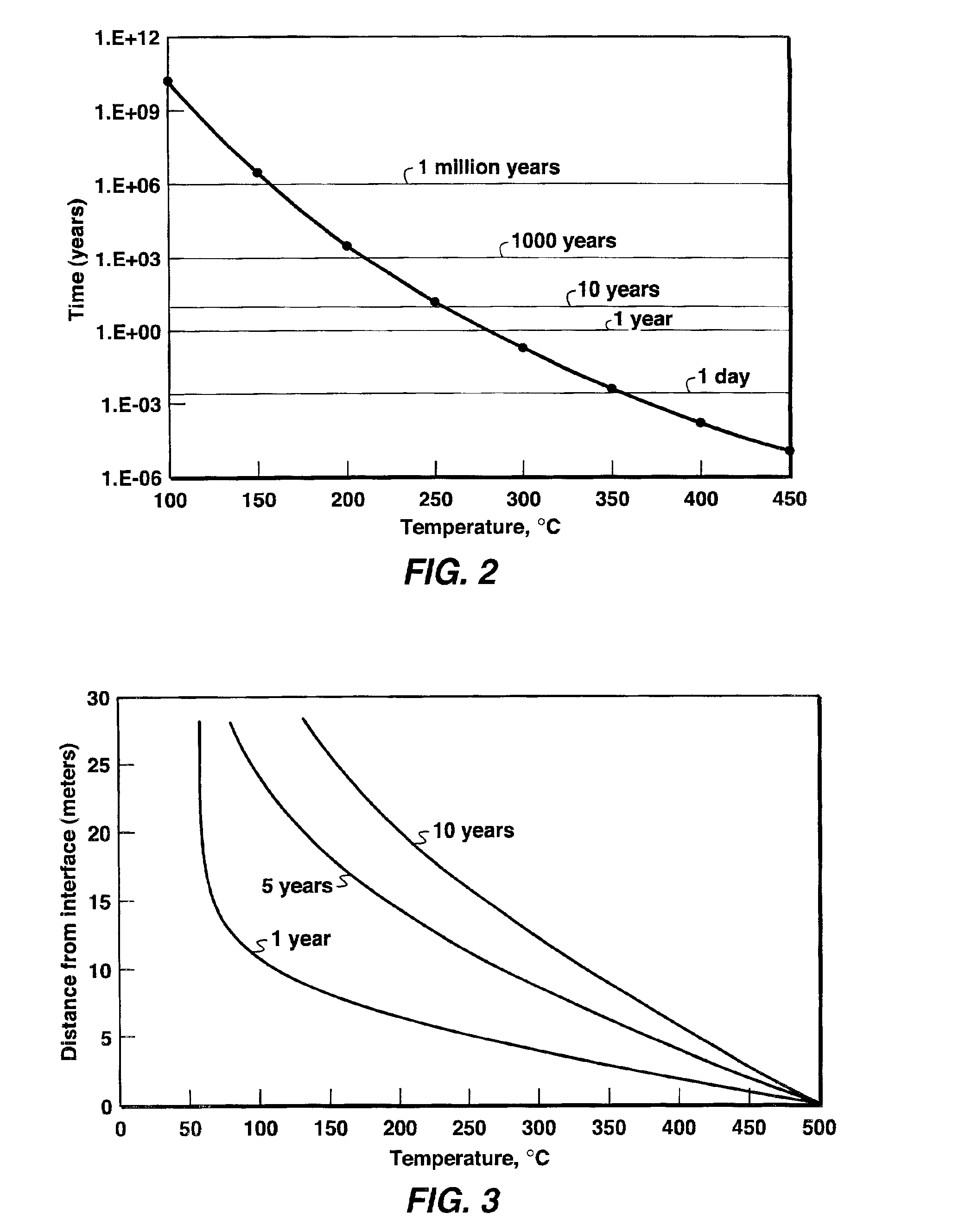
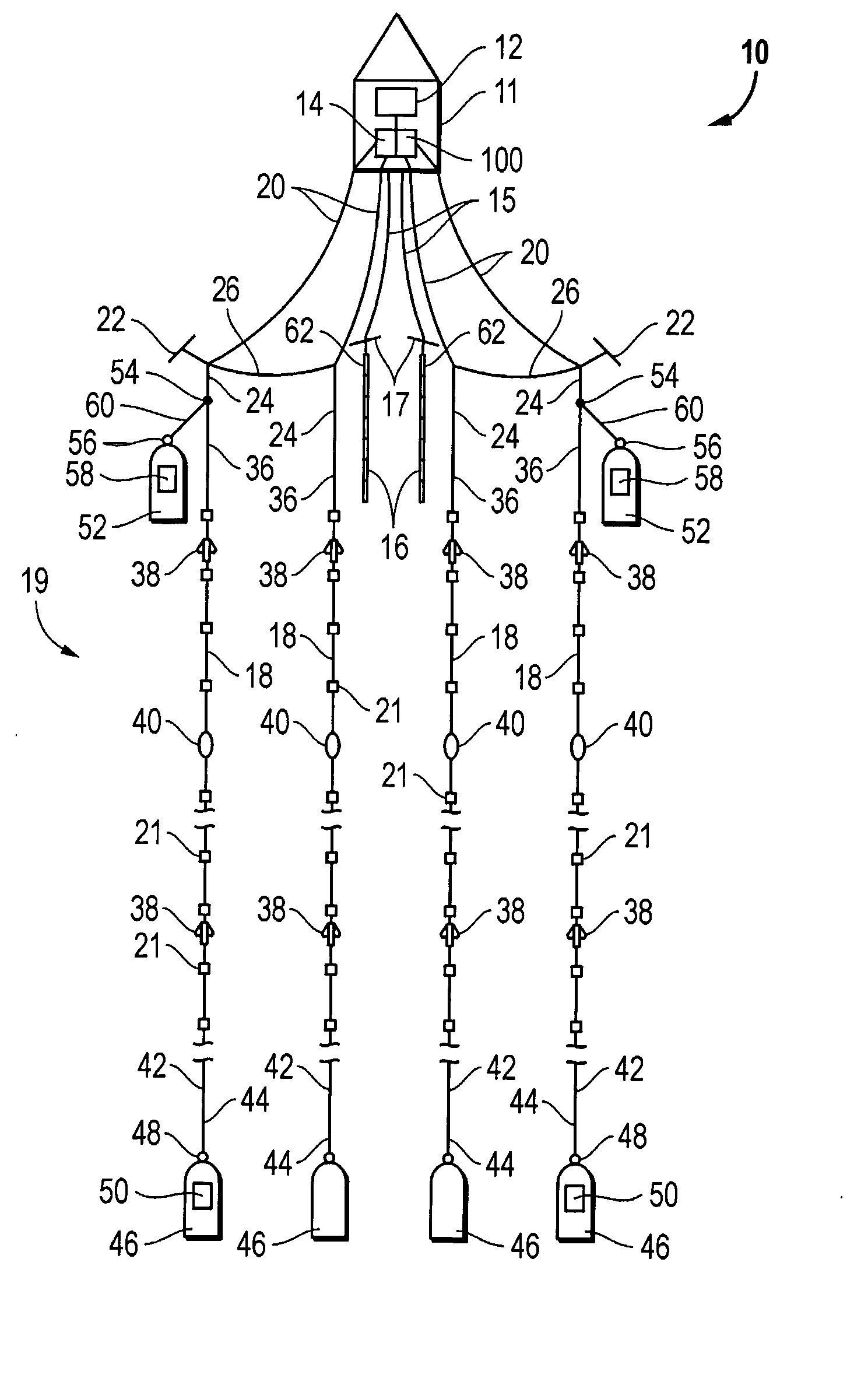
Thermal processes for subsurface formations
A process may include providing heat from one or more heaters to at least a portion of a subsurface formation. Heat may transfer from one or more heaters to a part of a formation. In some embodiments, heat from the one or more heat sources may pyrolyze at least some hydrocarbons in a part of a subsurface formation. Hydrocarbons and / or other products may be produced from a subsurface formation. Certain embodiments describe apparatus, methods, and / or processes used in treating a subsurface or hydrocarbon containing formation.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
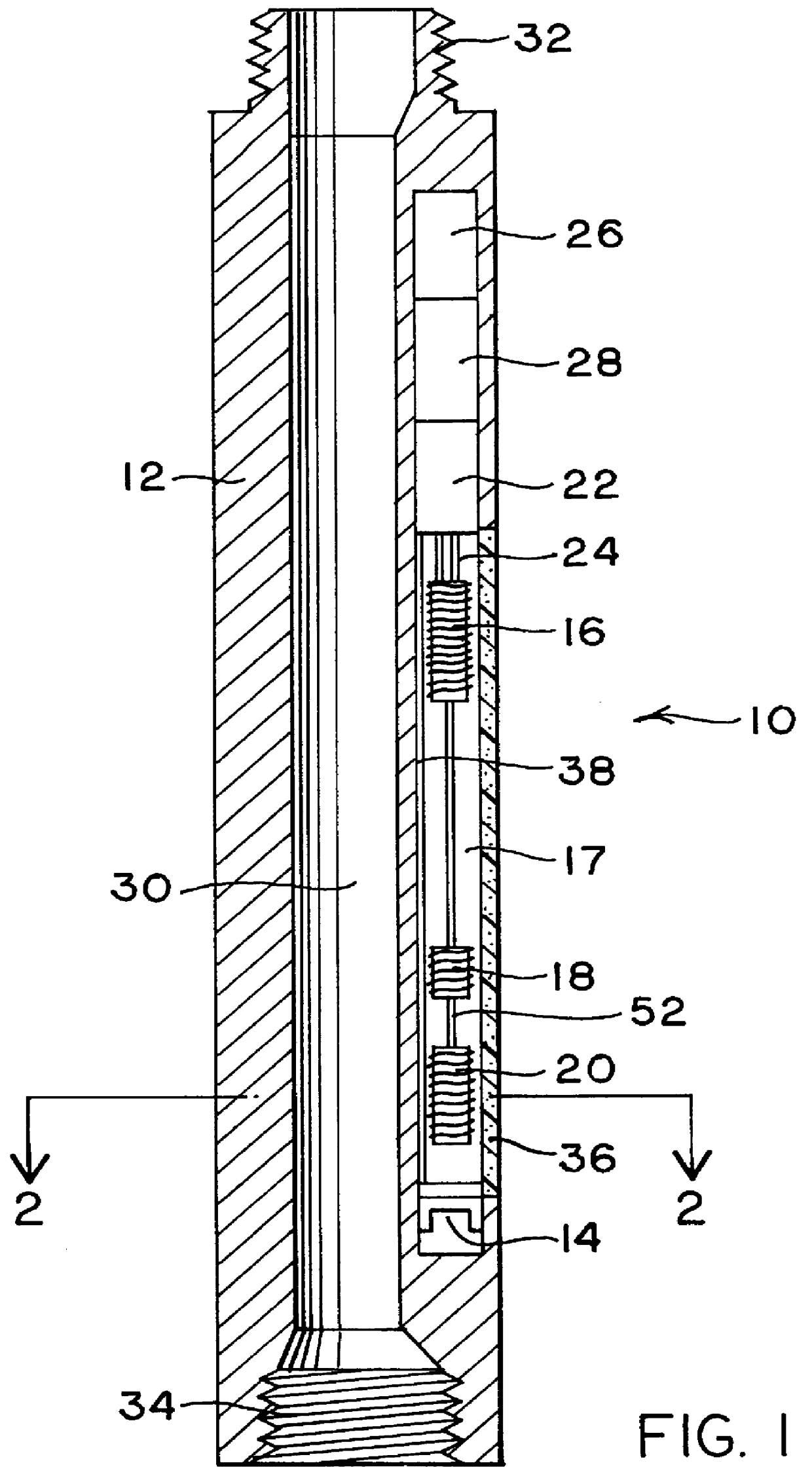
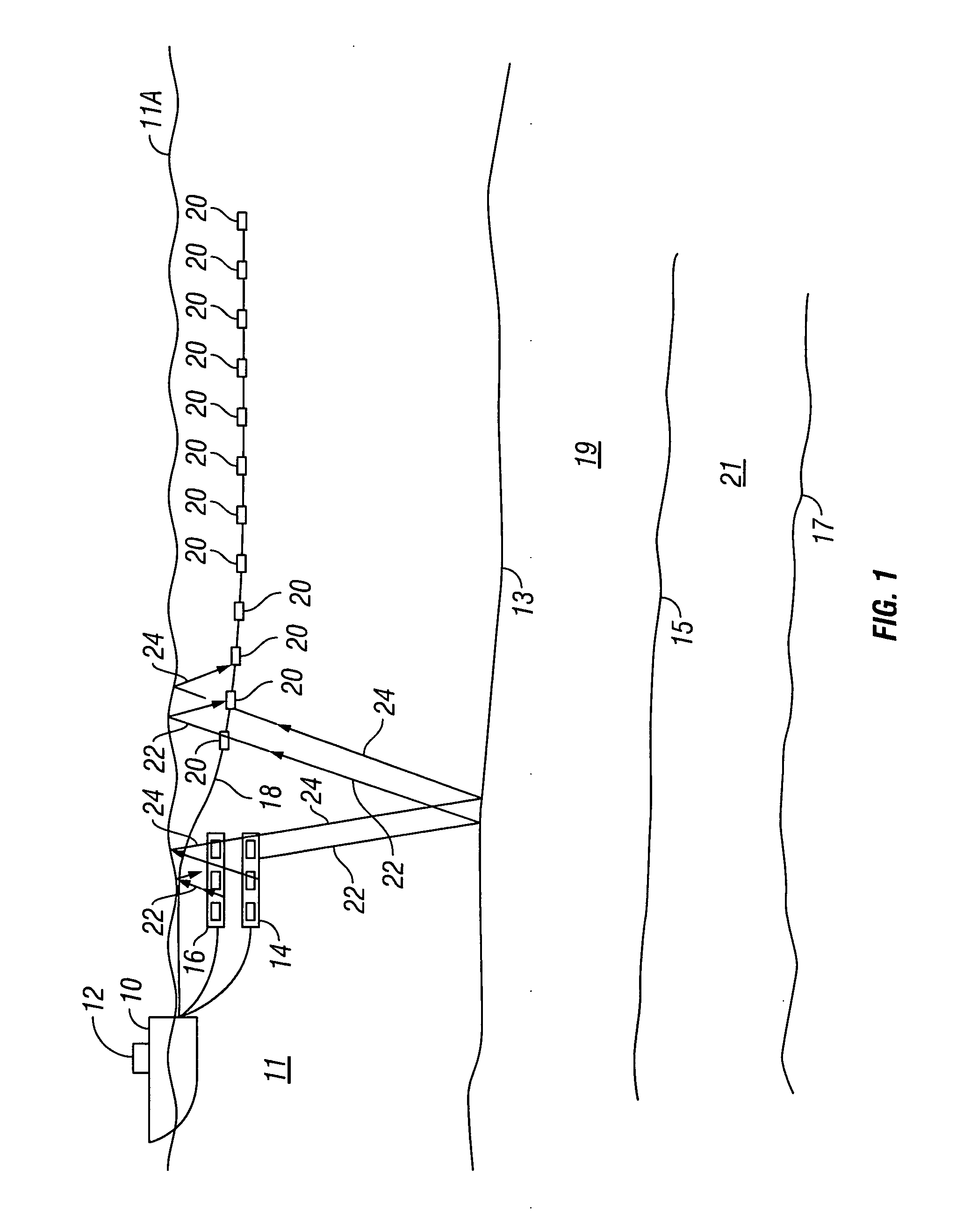
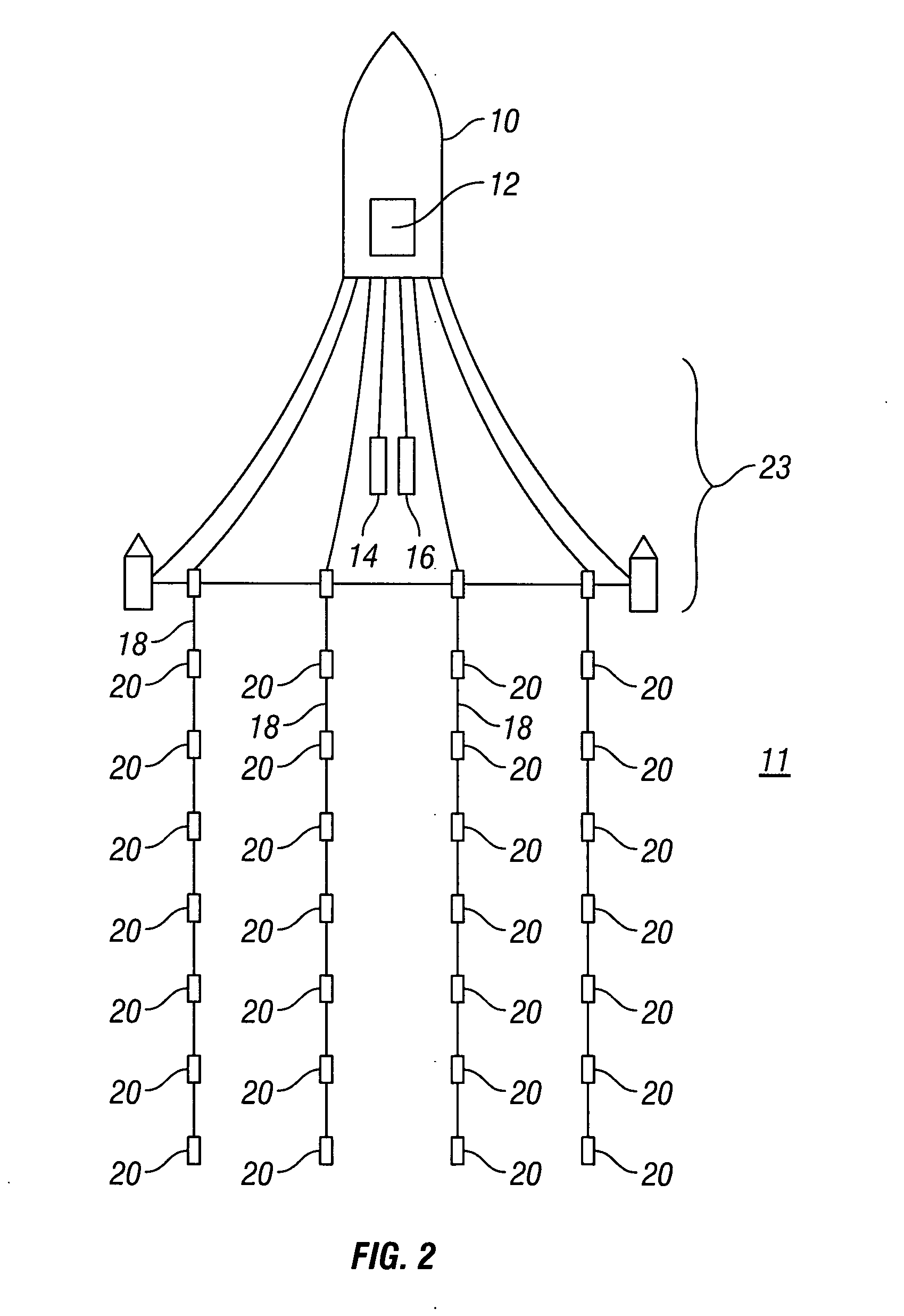
Method and apparatus for directional measurement of subsurface electrical properties
InactiveUS6100696AElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationPhysicsInduction logging
A directional induction logging tool is provided for measurement while drilling. This tool is preferably placed in a side pocket of a drill collar, and it comprises transmitter and receiver coils and an electromagnetic reflector. The reflector, which may be a layer of highly conductive material placed between the coils and the body of the drill collar, serves to focus the electromagnetic fields generated and sensed by the tool in the direction away from the reflector, thus providing a directional response to formation conductivity with a relatively high depth of investigation. In preferred embodiments of the invention, magnetically permeable cores are placed within the coils to concentrate the magnetic fields that pass through them. Circuitry is described for balancing the mutual inductive coupling of the coils by injecting a direct current signal through one or more of the coils, which alters the magnetic permeability of the core material. The magnitude of the direct current required to achieve a balanced condition may be derived from the quadrature phase component of the return signal. Circuitry is also provided for generating a transmitted signal and for processing the return signals, including digital-to-analog conversion circuitry for providing digital data for transmission to the surface. This tool may be employed to provide real-time directional conductivity information that may be used to detect and follow bed boundaries in geosteering operations.
Owner:SINCLAIR PAUL L
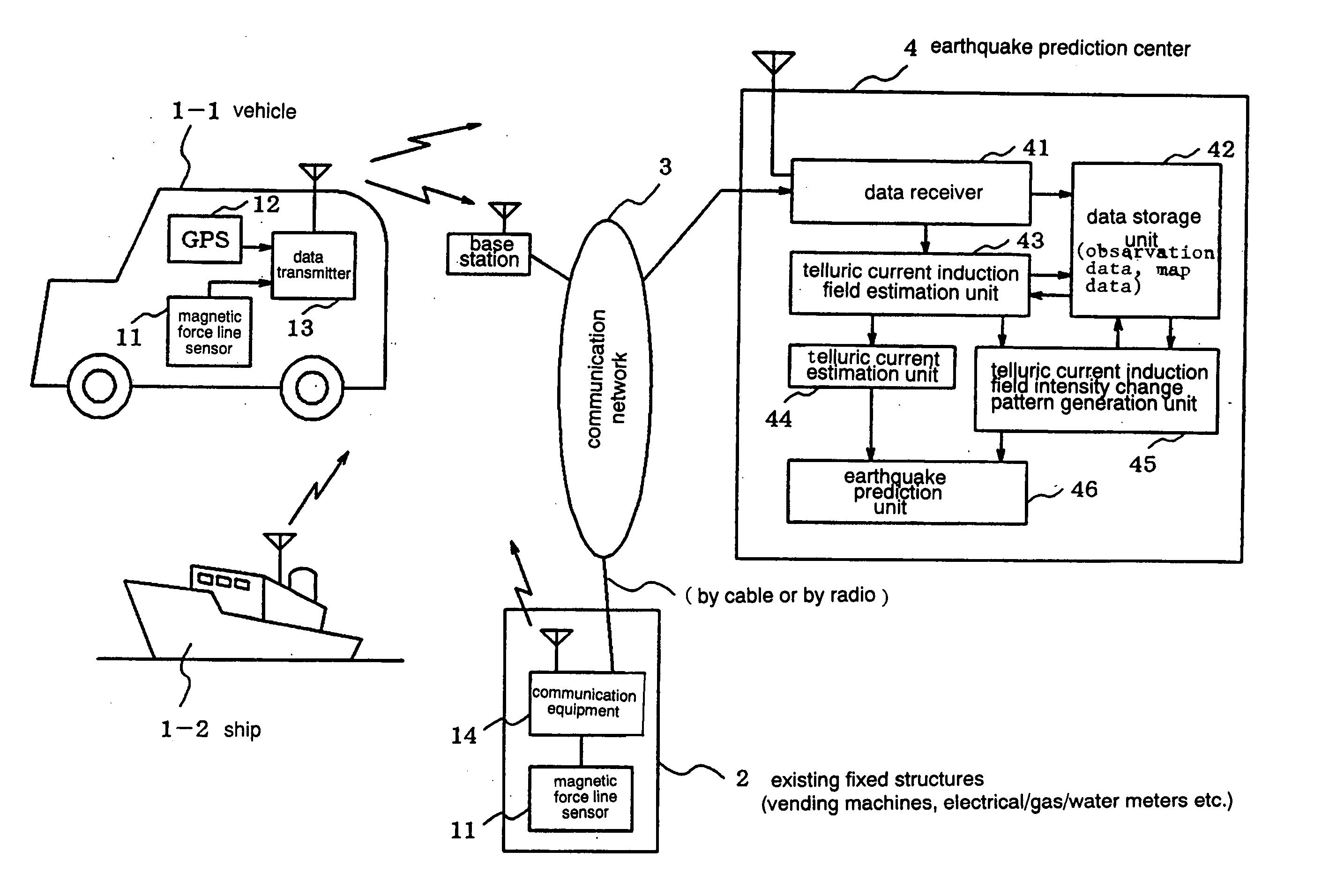
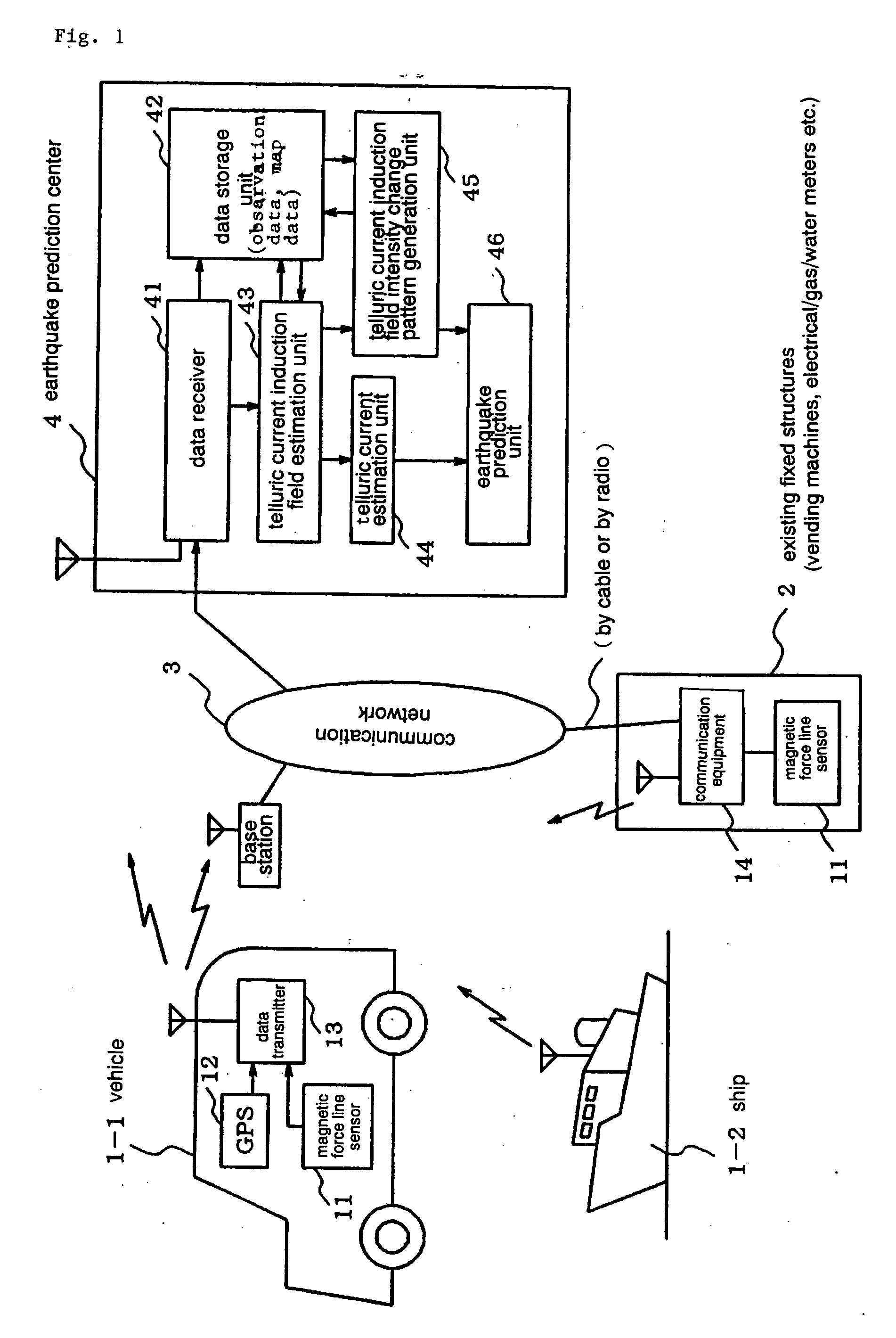
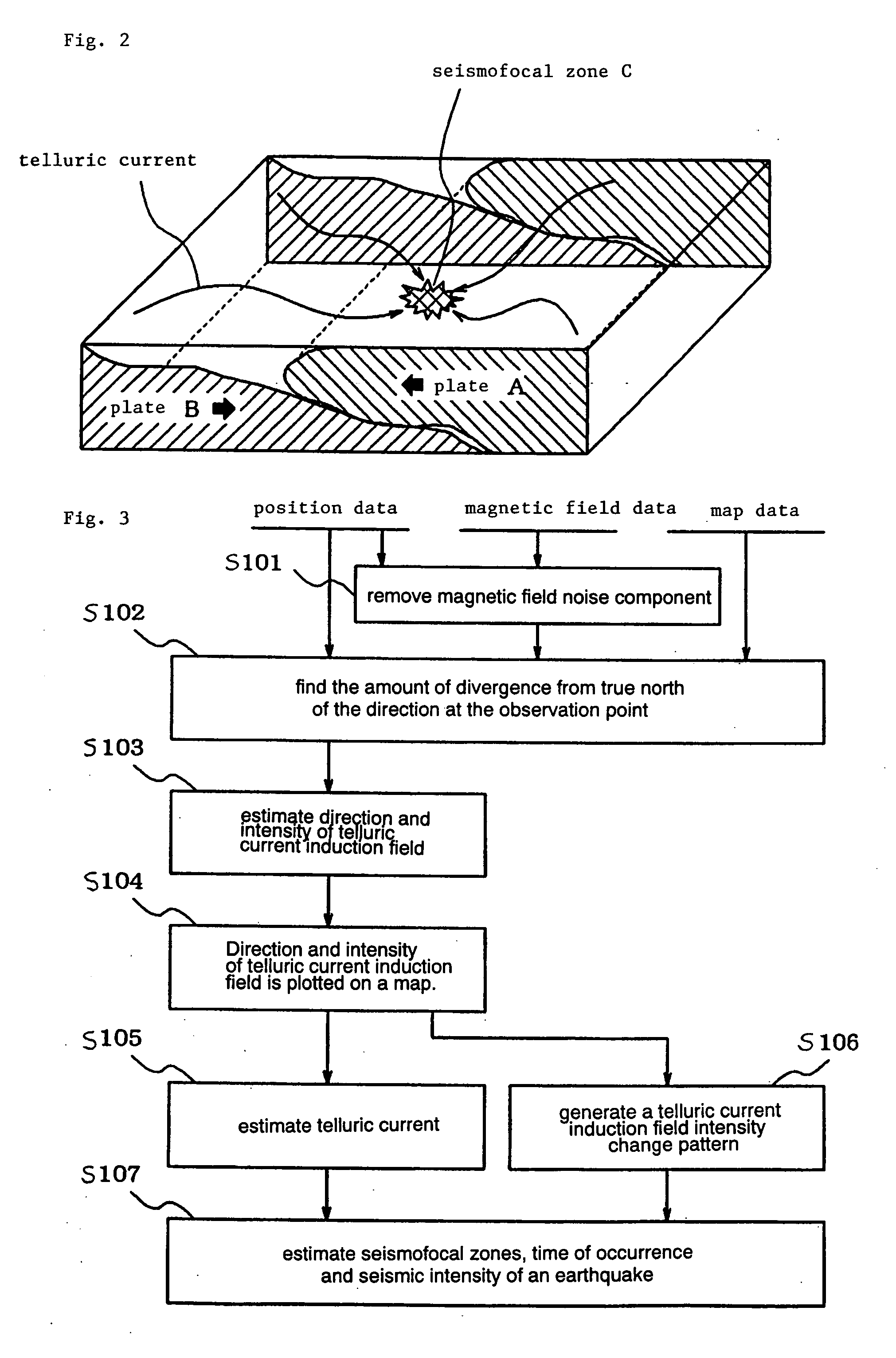
Earthquarke prediction method and system thereof
InactiveUS20050280421A1Low costAccurate predictionEarthquake measurementSeismic signal processingEarthquake predictionTransmitter
Vehicles (1-1) or ships (1-2) each carry a magnetic force line sensor (11), a GPS position detector (12), and a data transmitter (13) and travel within an observation area transmitting magnetic field data and position data of each point to an earthquake prediction center (4). A telluric current induction field estimation unit (43) of the earthquake prediction center (4) estimates telluric current induction fields based on the observation data that it receives and collects. A telluric current estimation unit (44) estimates telluric currents based on the results of estimating the telluric current induction fields. A telluric current induction field intensity change pattern generation unit (45) generates patterns that indicate the change over time of the intensity of telluric current induction fields. An earthquake prediction unit (46) analyzes the state of distribution of the telluric currents and the patterns of change in the intensities of the telluric current induction fields and estimates a seismofocal zone, seismic intensity, and time of occurrence of a seismic event.
Owner:NEC MOBILING LTD
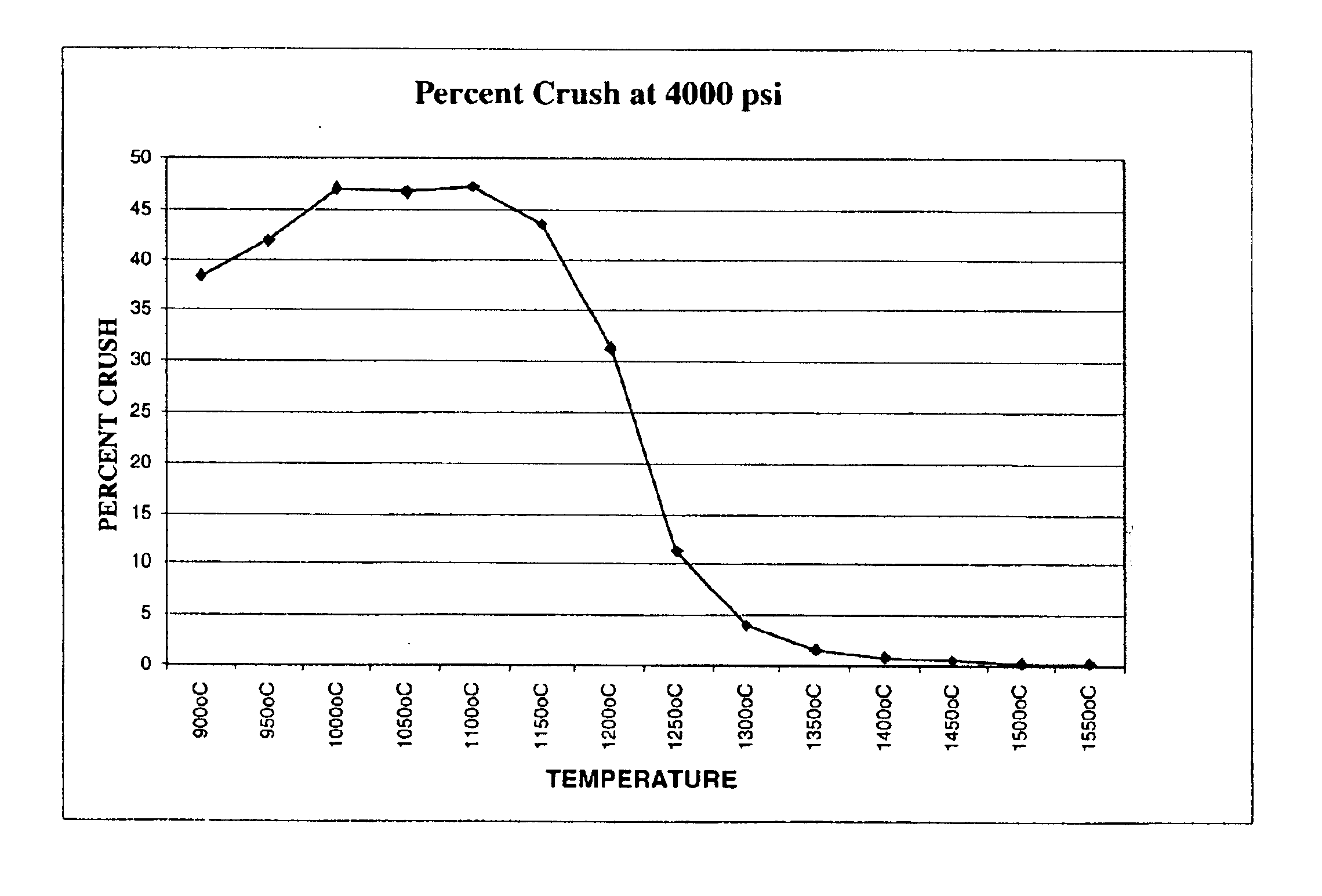
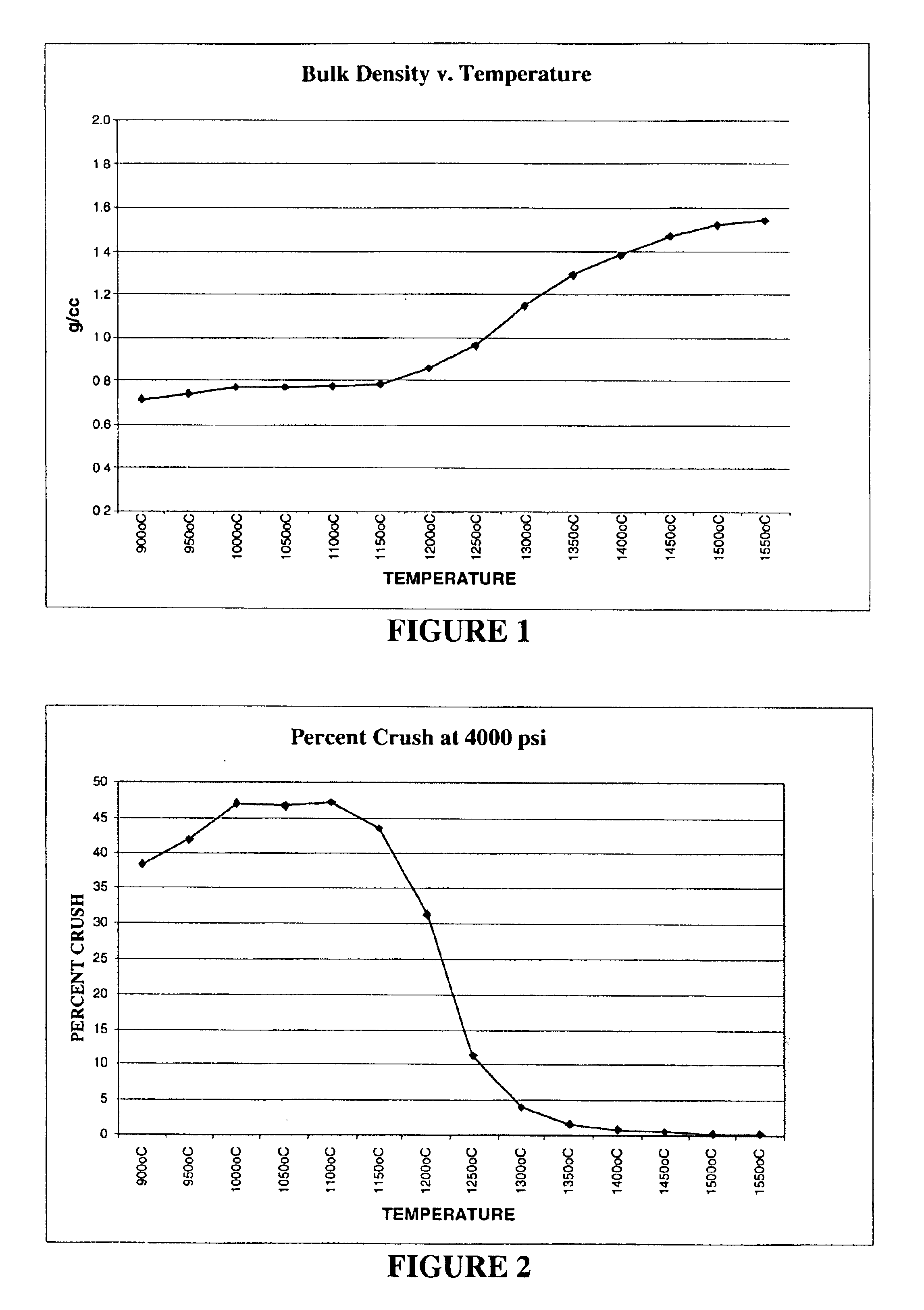
Low density proppant
Owner:CARBO CERAMICS
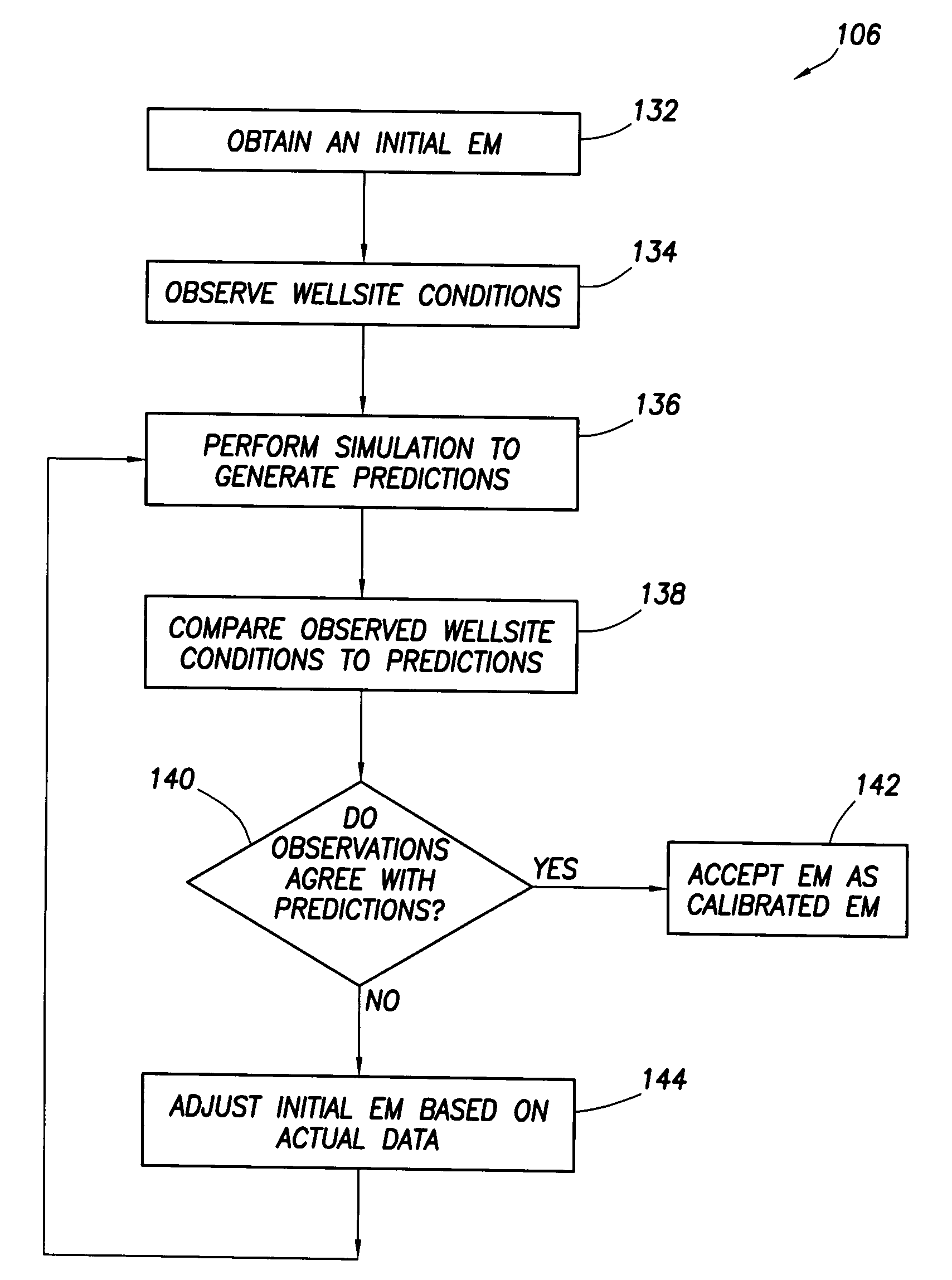
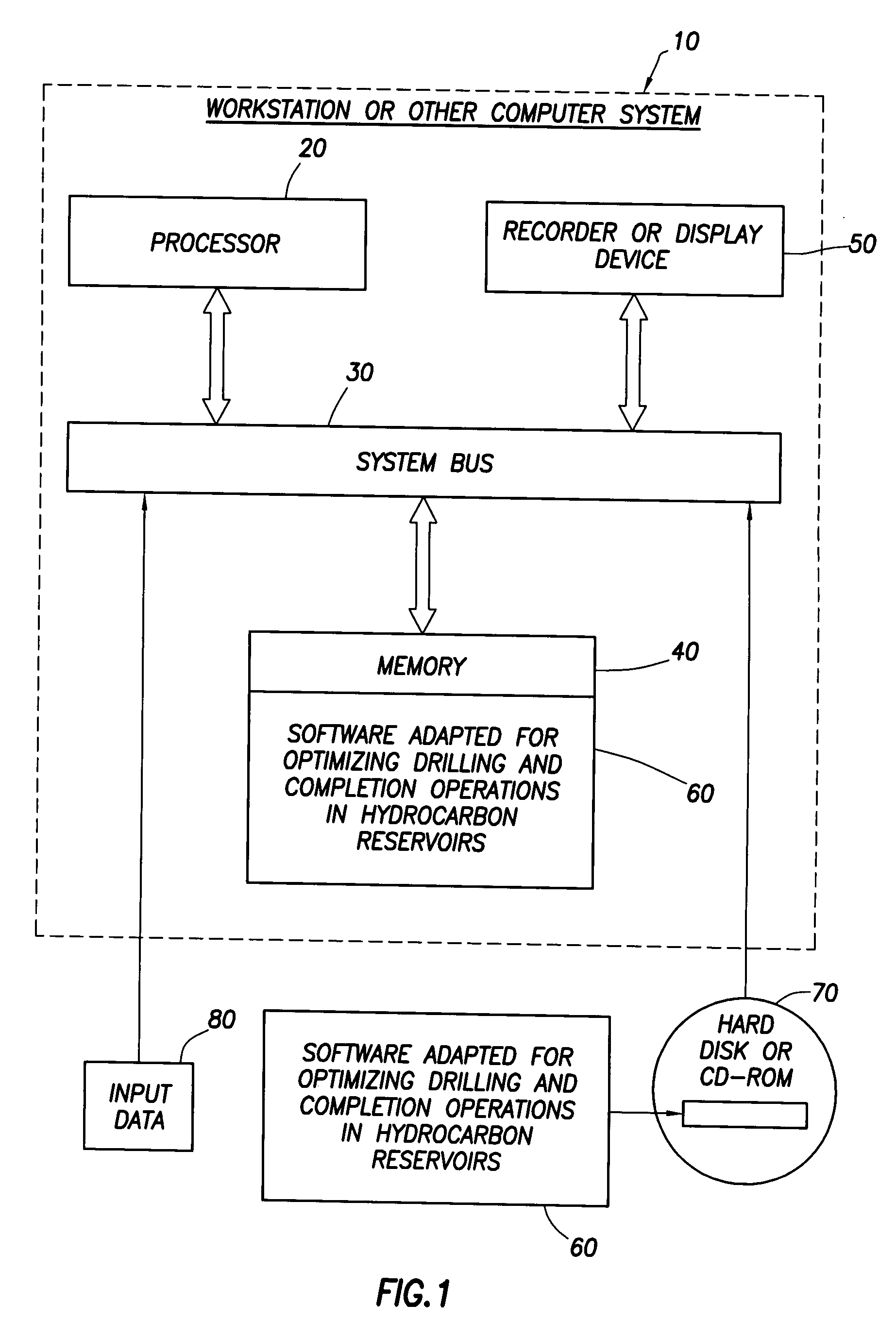
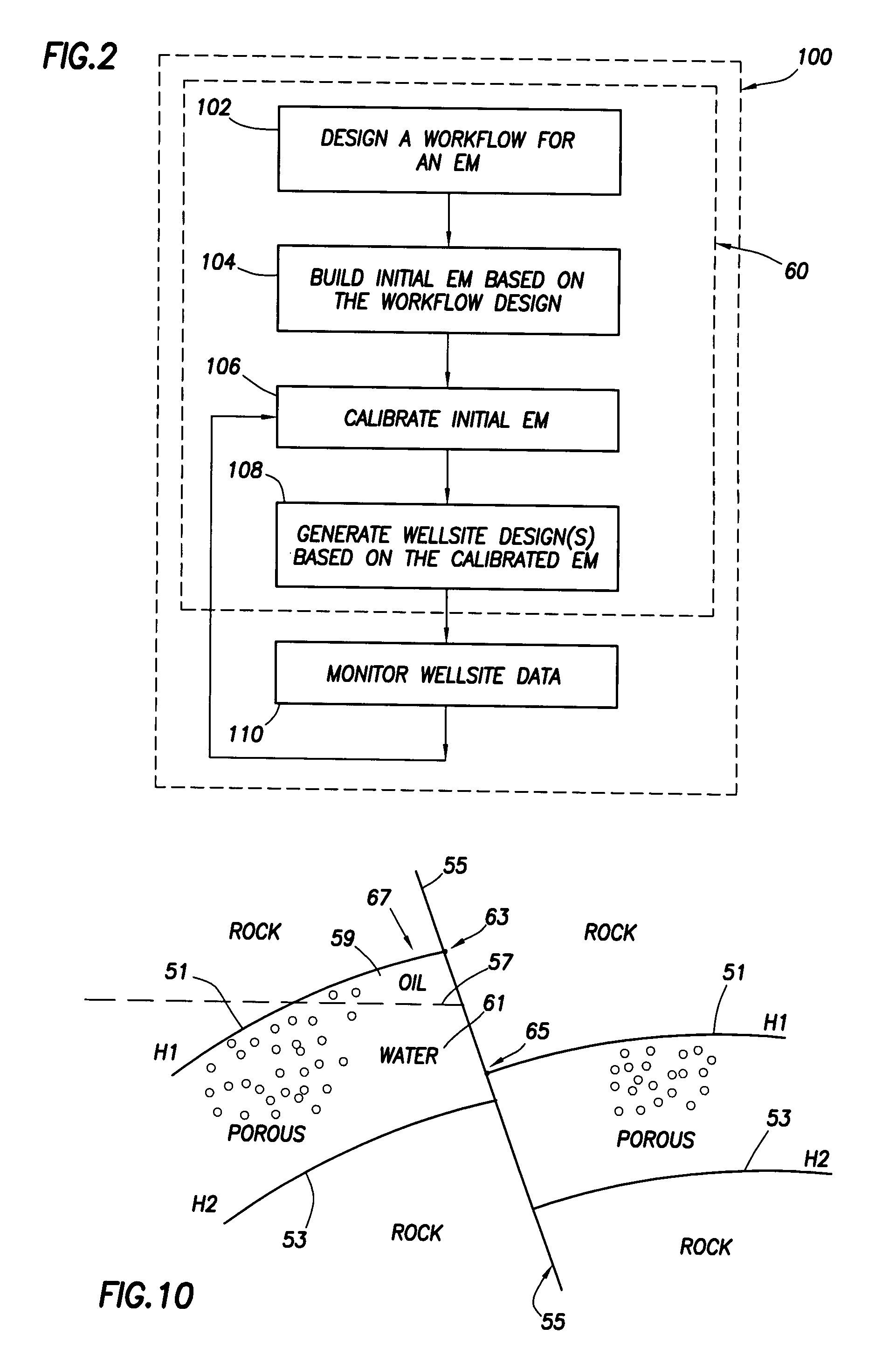
Method for designing and optimizing drilling and completion operations in hydrocarbon reservoirs
ActiveUS20070294034A1Speed maximizationMinimize damageGeometric CADElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWell drillingEarth model
A method is disclosed for generating a wellsite design, comprising: designing a workflow for an Earth Model; building an initial Earth Model based on the workflow adapted for modeling drilling and completions operations in a hydrocarbon reservoir; calibrating the initial Earth Model thereby generating a calibrated Earth Model; and generating the wellsite design using the calibrated Earth Model.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
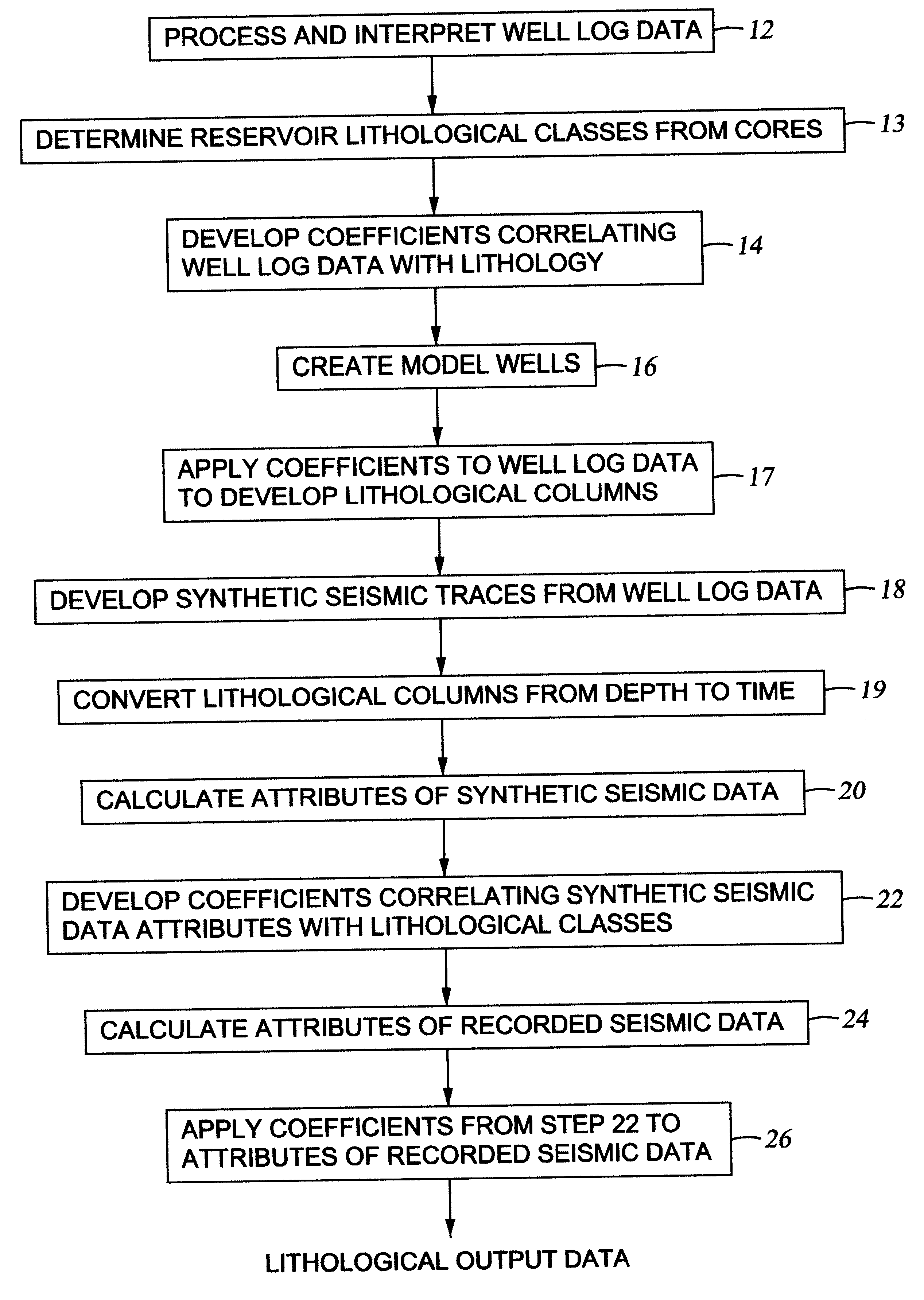
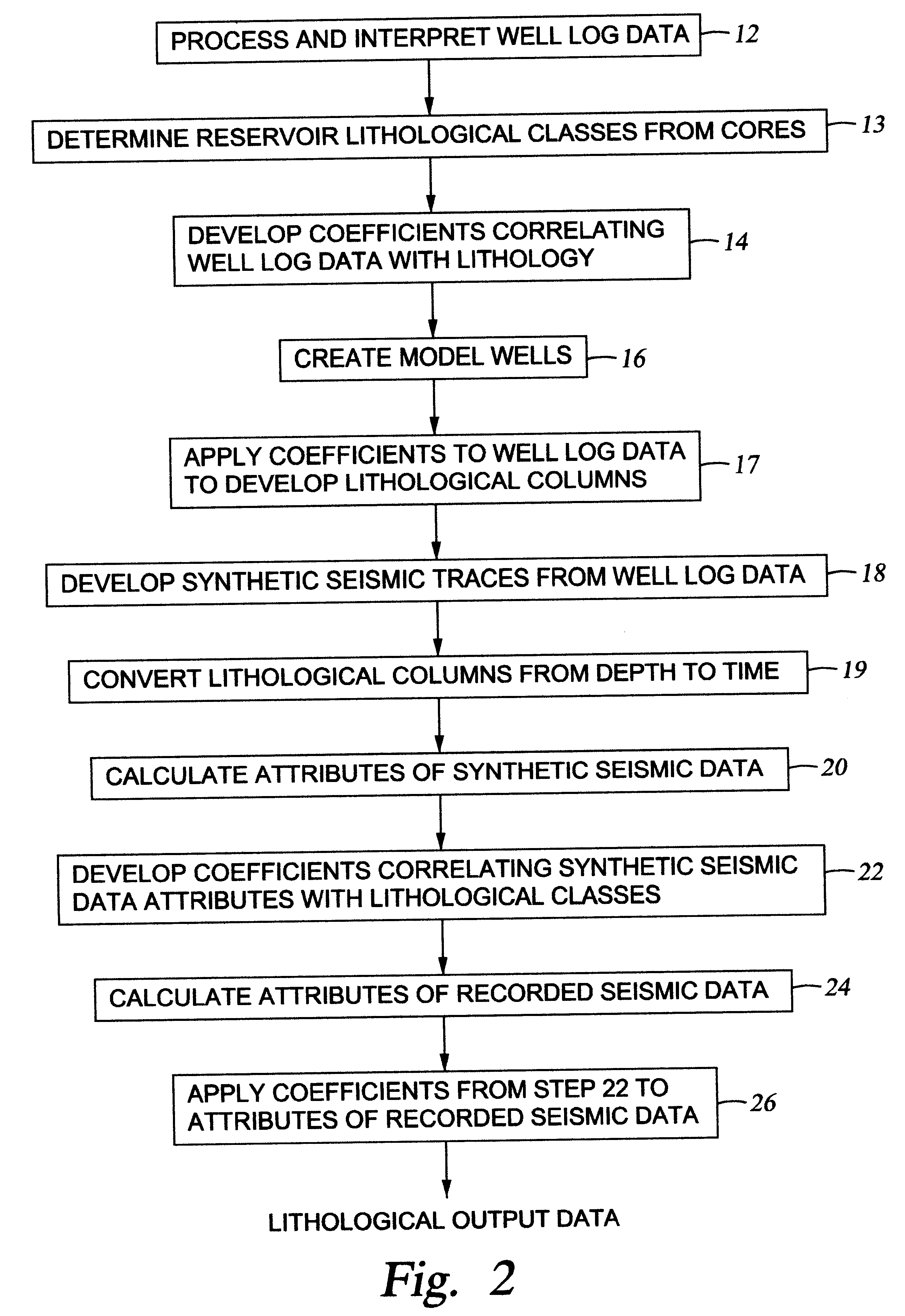
Method for generating an estimate of lithological characteristics of a region of the earth's subsurface
InactiveUS6374185B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingLithologyWellbore
The invention in a first embodiment comprises a system for generating an estimate of lithological characteristics of a region of the earth's subsurface. A correlation is generated between attributes of synthetic seismic data calculated from log data from at least one wellbore penetrating said region and lithological information from said at least one wellbore. The correlation is then applied to recorded seismic data from the region of the earth's subsurface to generate the estimate.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Methods of well stimulation during drilling operations
The present invention relates to subterranean well stimulation. More particularly, the present invention relates to improved methods of stimulating subterranean formations during drilling operations. In some embodiments, the present invention discloses methods of stimulating a section of a subterranean formation comprising (a) forming at least a portion of a well bore that at least penetrates a section of the subterranean formation using a drilling operation; (b) stimulation a section of the subterranean; and (c) continuing the drilling operation. In other embodiments, the present invention discloses methods of stimulation a section of a subterranean formation comprising (a) forming at least a portion of a well bore that at least penetrates a section of the subterranean formation using a drilling operation; (b) stimulating a section of the subterranean formation; and (c) continuing the drilling operation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
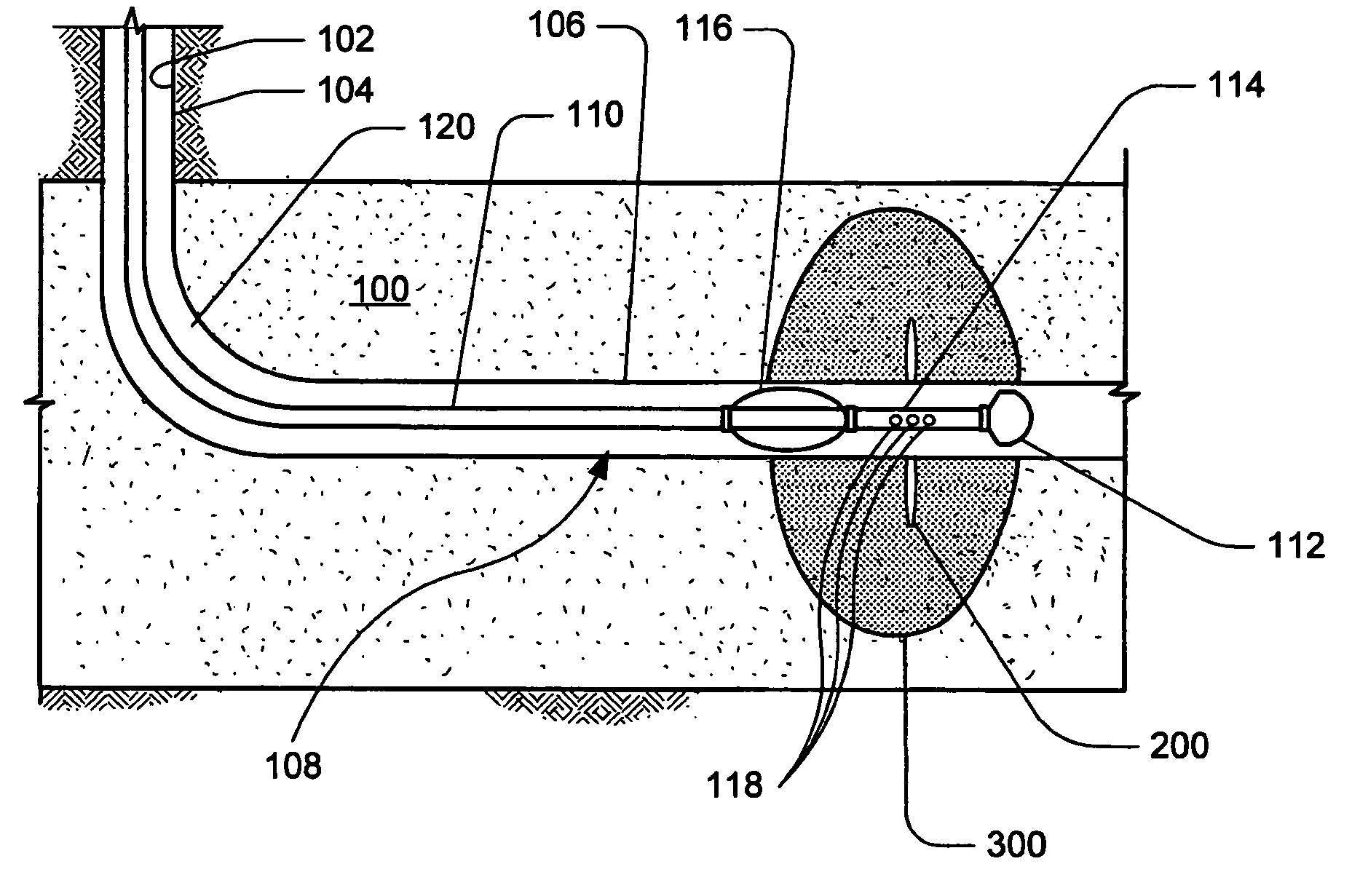
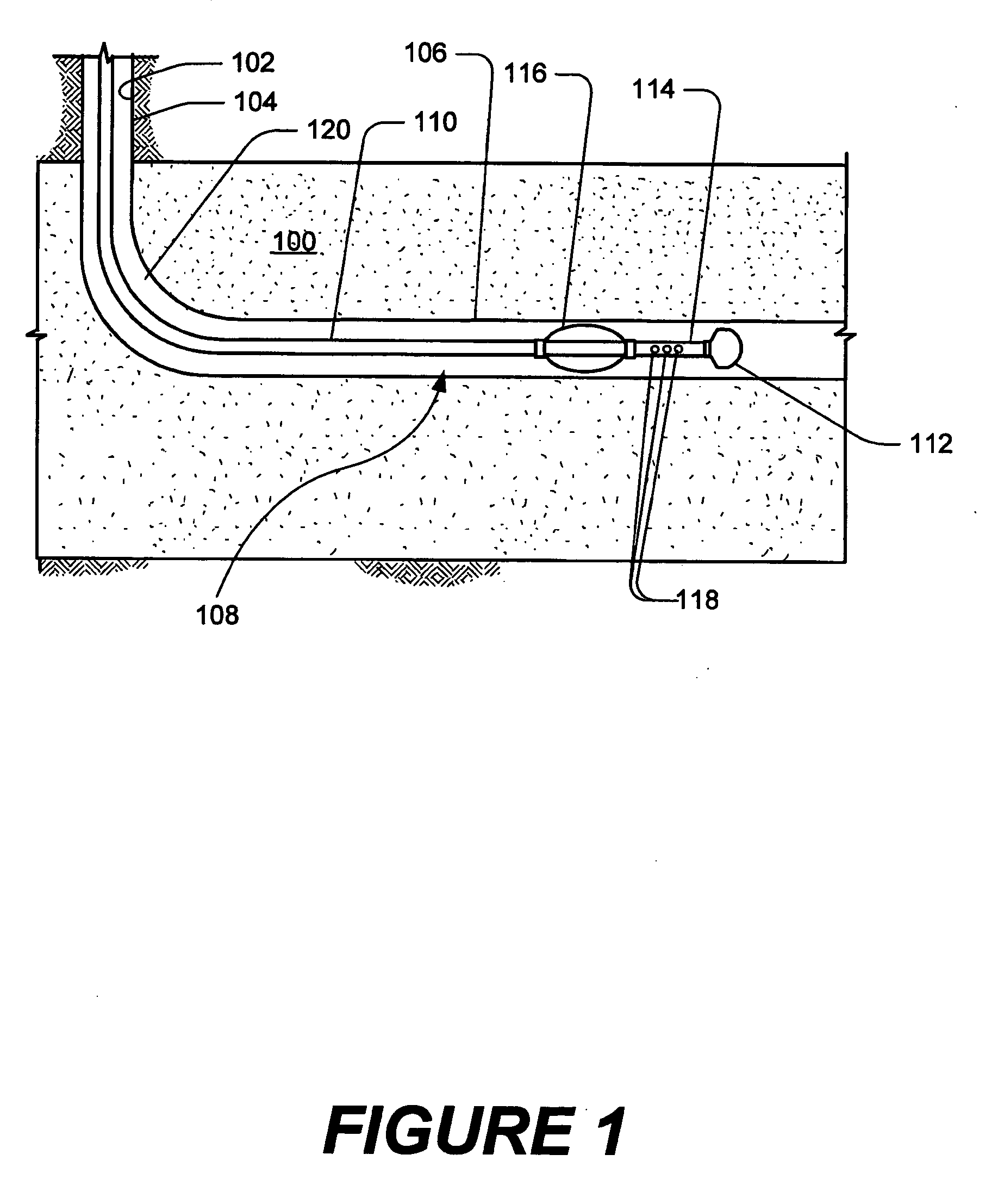
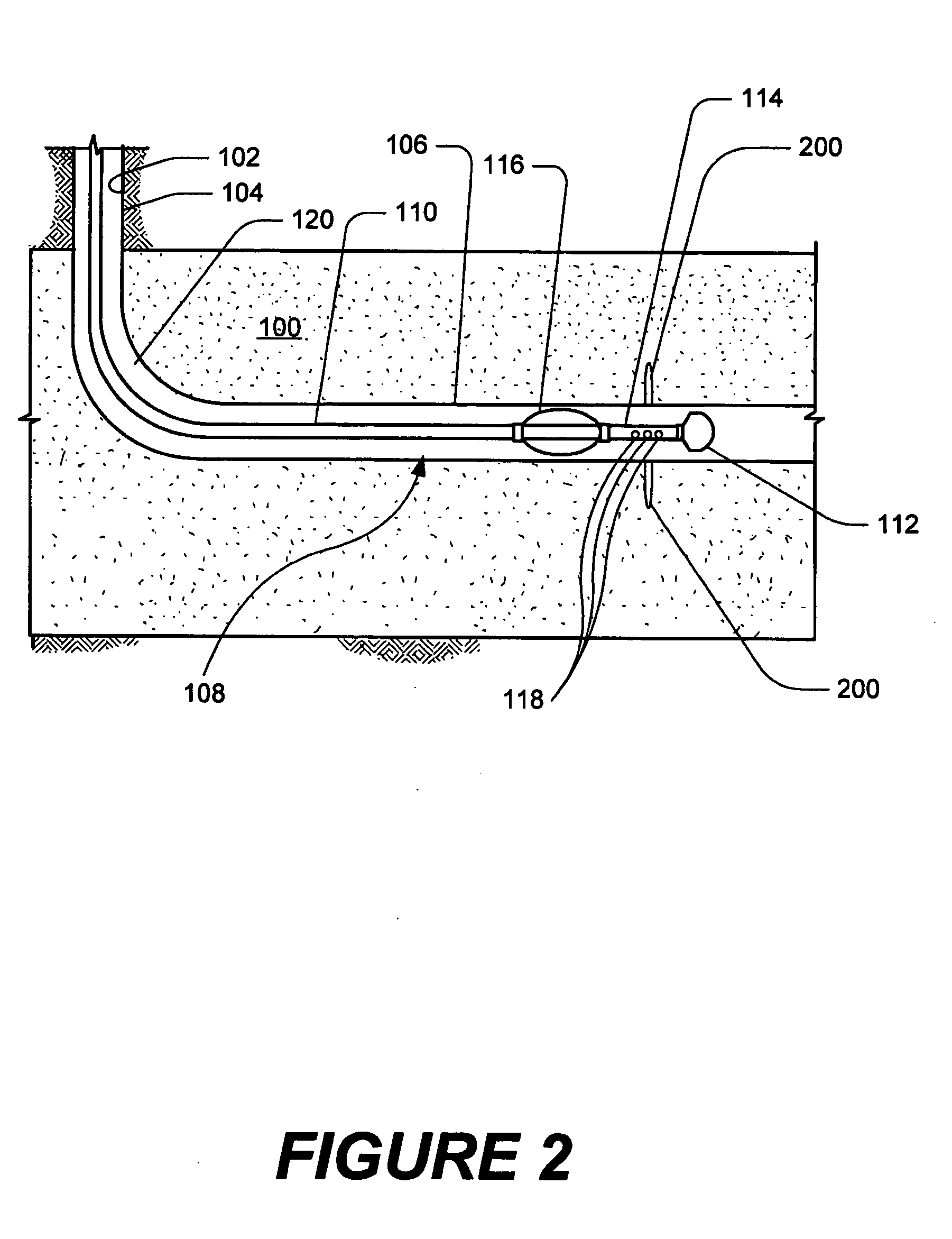
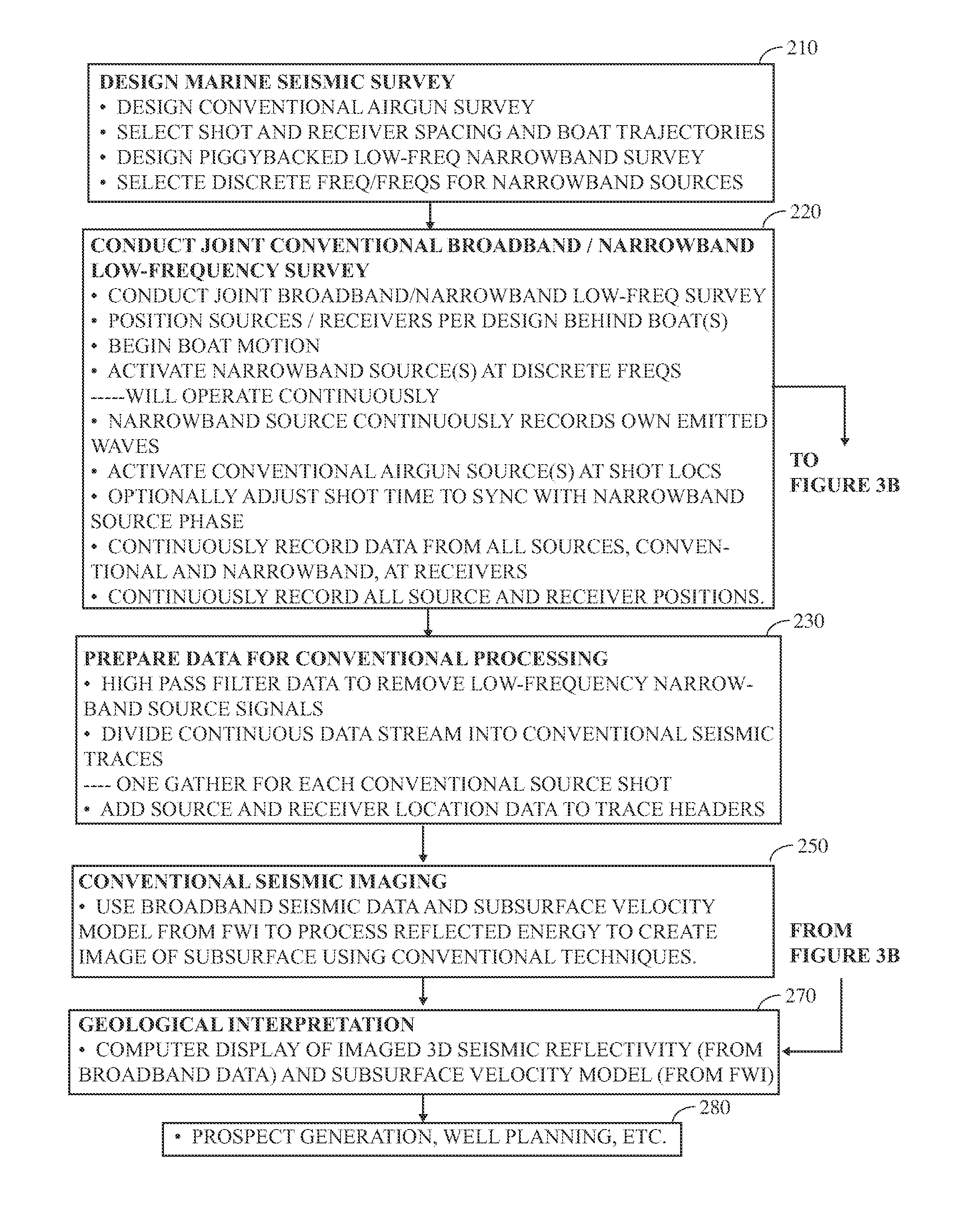
Seismic acquisition using narrowband seismic sources
ActiveUS20120155217A1Reduce crosstalkSpeed up the processSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingMonochromatic colorFull waveform
There is provided herein a system and method of seismic data collection for land and marine data that utilizes narrowband to monochromatic low-frequency non-impulsive sources designed to optimize the ability of migration / inversion algorithms to image the subsurface of the Earth, in particular, full-waveform inversion.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Thermal processes for subsurface formations
InactiveUS20050051327A1Reduce heatMaintaining separation distanceSurveyConstructionsGeophysicsHydrocarbon
A process may include providing heat from one or more heaters to at least a portion of a subsurface formation. Heat may transfer from one or more heaters to a part of a formation. In some embodiments, heat from the one or more heat sources may pyrolyze at least some hydrocarbons in a part of a subsurface formation. Hydrocarbons and / or other products may be produced from a subsurface formation. Certain embodiments describe apparatus, methods, and / or processes used in treating a subsurface or hydrocarbon containing formation.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
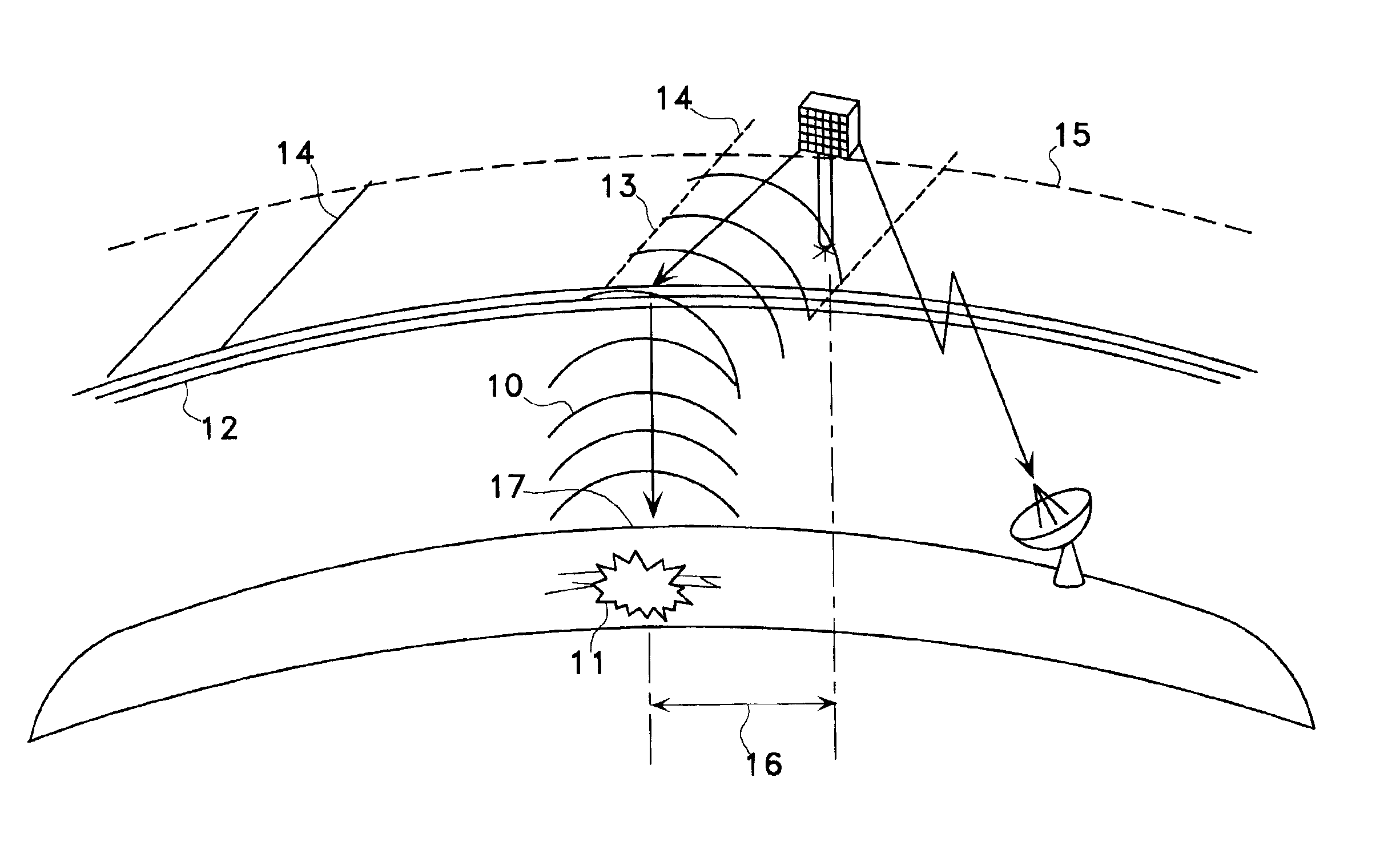
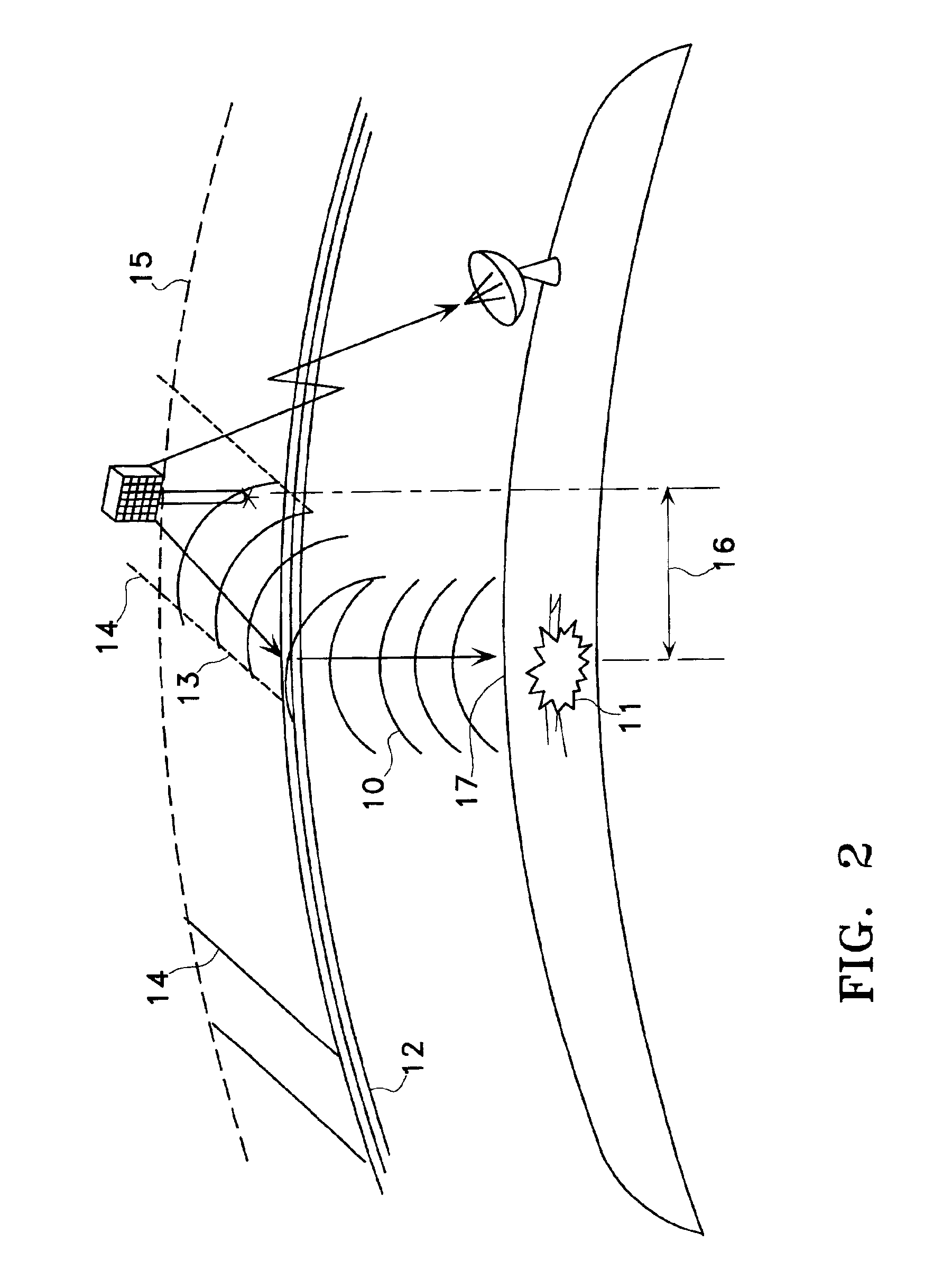
Satellite and ground system for detection and forecasting of earthquakes
InactiveUS6873265B2Low costSignificant comprehensive benefitsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementEarthquake measurementNatural satelliteWide area
The present invention describes the use of a space-based Extremely Low Frequency (ELF) magnetic field detector in conjunction with ground-based network of ELF magnetic field detectors. In particular, a space based ELF detection system can be used to perform a wide area search and find precursor earthquake signals in both known and unknown earthquake zones, and a ground-based network of ELF detectors can be used to verify that the signals are indeed earthquake generated signals. The use of this invention will minimize cost and manpower necessary to effectuate an accurate and reliable earthquake detection system.
Owner:STELLAR SOLUTIONS
Method for production of hydrocarbons from organic-rich rock
A method for accelerating the conversion of kerogen to hydrocarbons in a subterranean formation containing organic-rich rock that is located in the vicinity of reservoir-quality strata. Sufficient heat is generated in the reservoir-quality strata such that it heats the organic-rich rock in the subterranean formation and accelerates the conversion of kerogen to hydrocarbons in the formation.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Marine seismic survey method and system
ActiveUS20090141587A1Reduce non-productive timeSeismic signal recordingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyEnvironmental data
An inventive method provides for control of a seismic survey spread while conducting a seismic survey, the spread having a vessel, a plurality of spread control elements, a plurality of navigation nodes, and a plurality of sources and receivers. The method includes the step of collecting input data, including navigation data for the navigation nodes, operating states from sensors associated with the spread control elements, environmental data for the survey, and survey design data. The positions of the sources and receivers are estimated using the navigation data, the operating states, and the environmental data. Optimum tracks for the sources and receivers are determined using the position estimates and a portion of the input data that includes at least the survey design data. Drive commands are calculated for at least two of the spread control elements using the determined optimum tracks. The inventive method is complemented by an inventive system.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
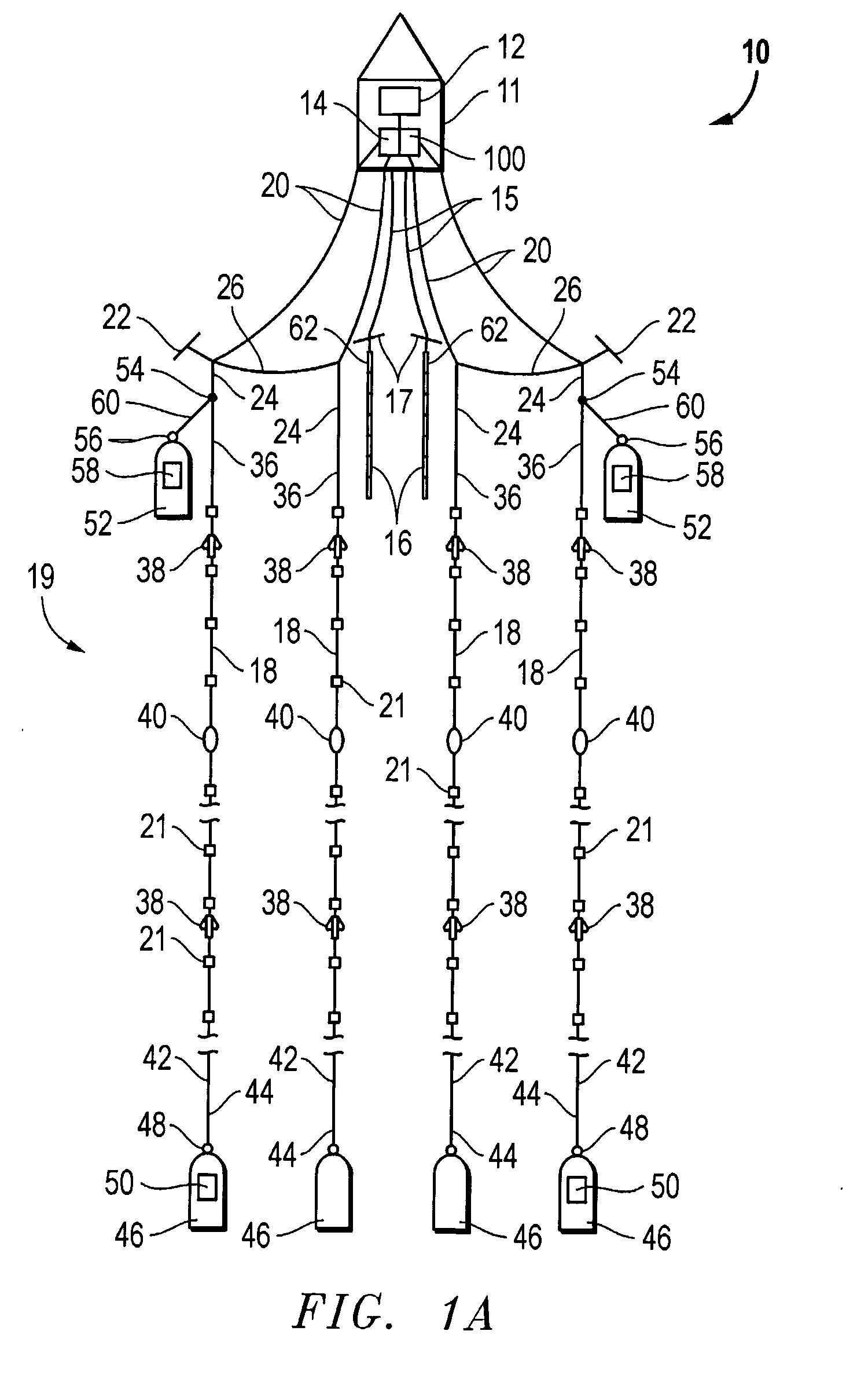
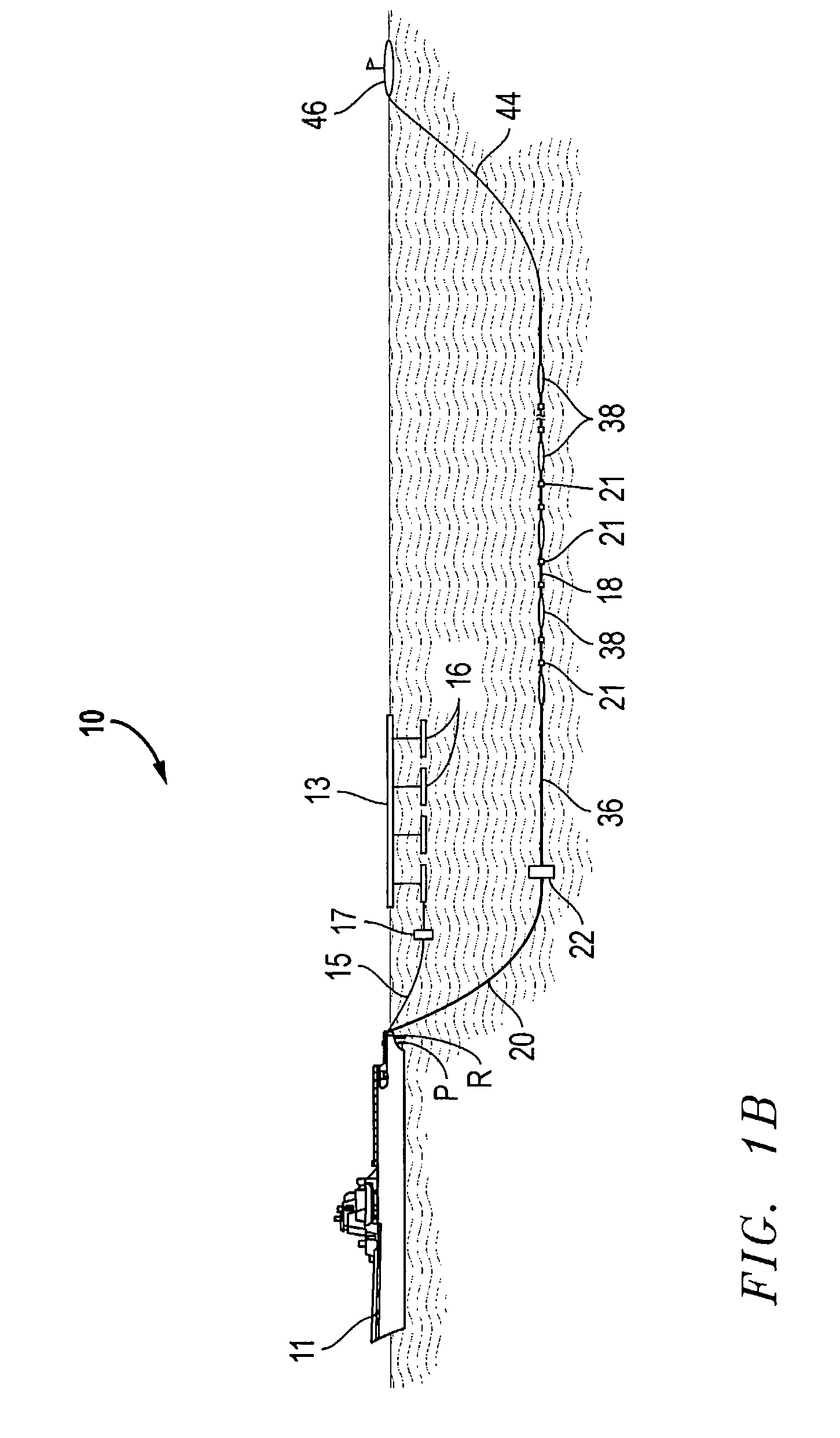
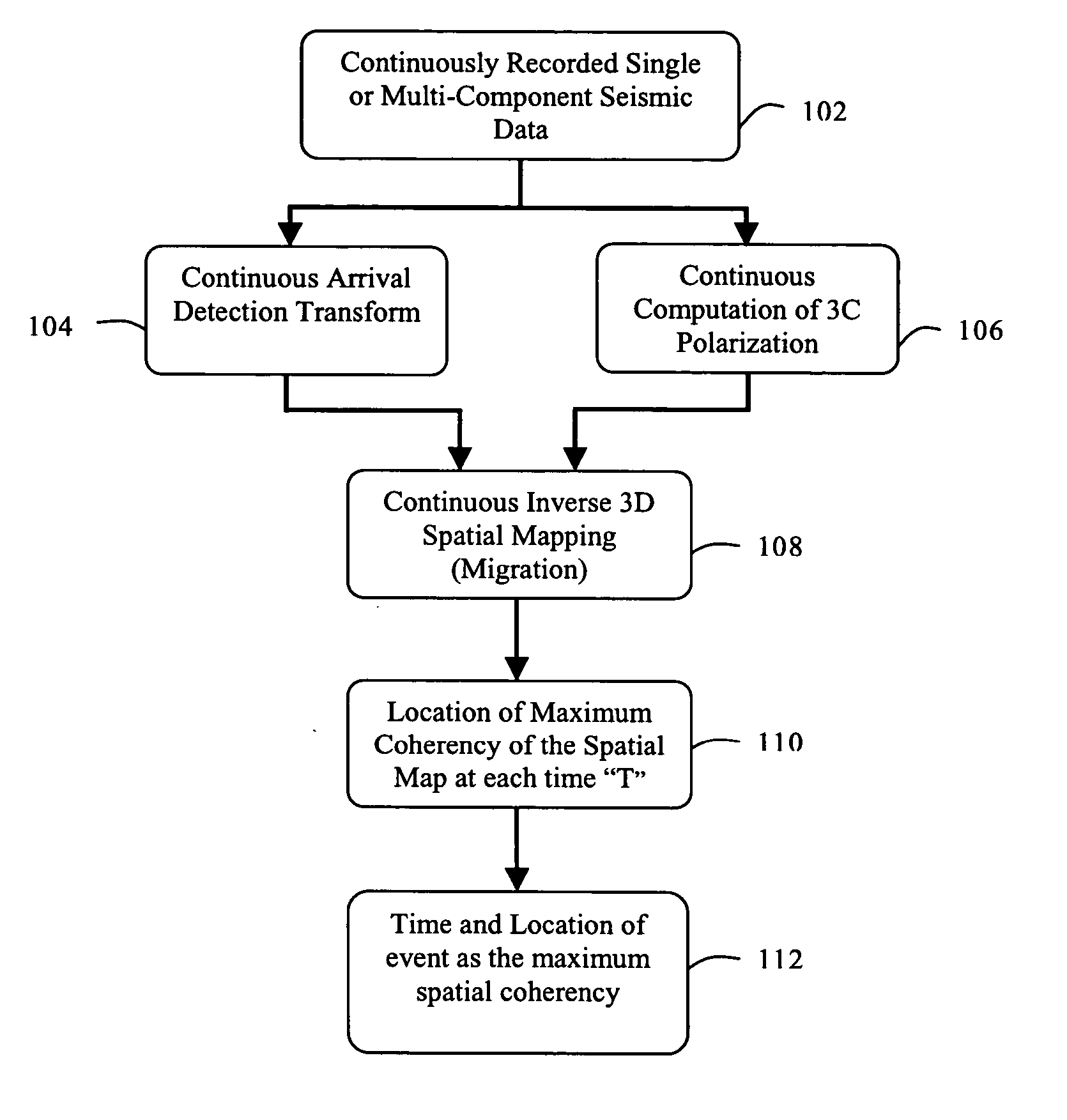
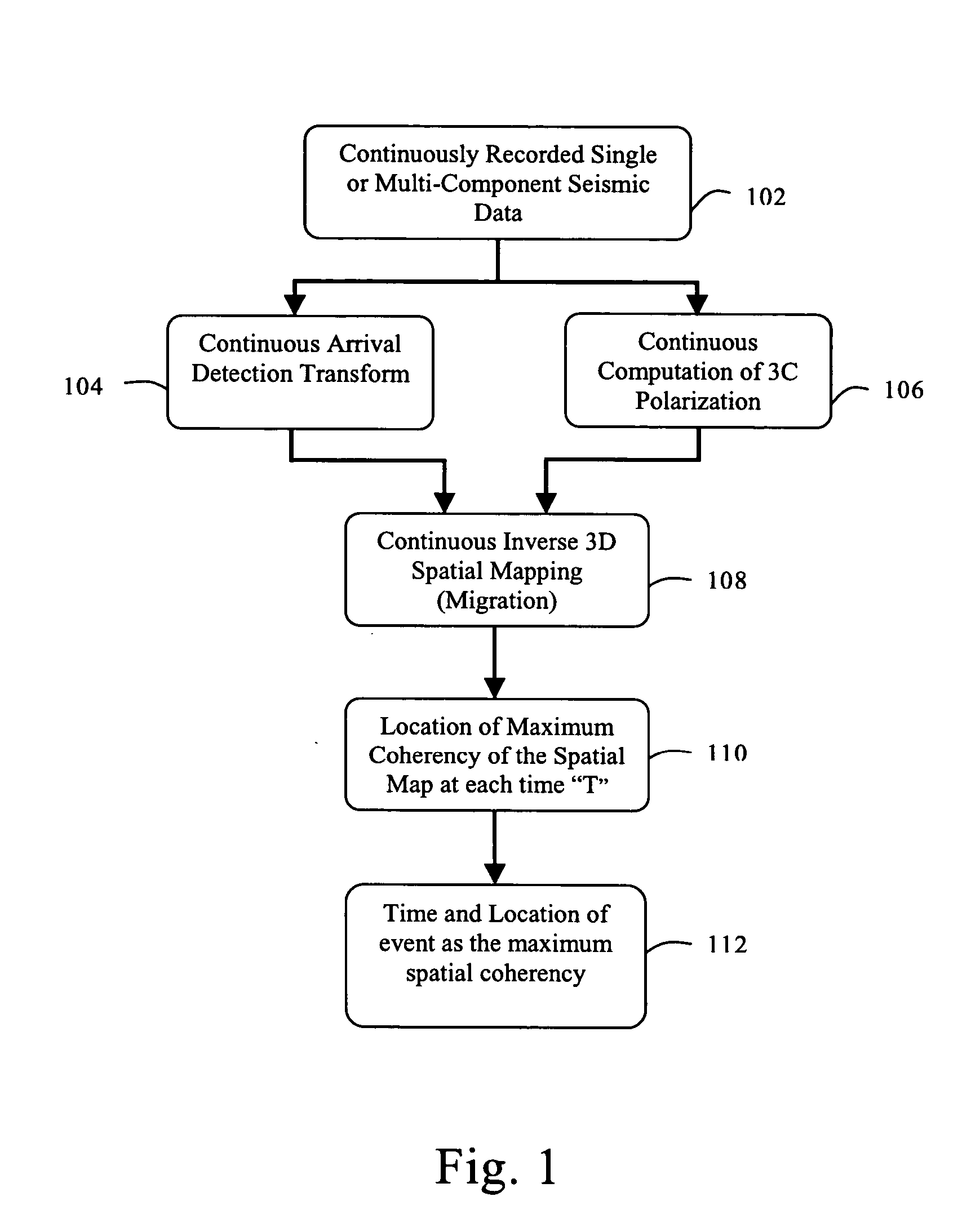
Microseismic event detection and location by continuous map migration
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and system for acquiring marine seismic data using multiple seismic sources
InactiveUS6906981B2Easy to foldIncrease the lengthSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationSeismic surveySurveyor
A method for seismic surveying is disclosed which includes towing a first seismic energy source and at least one seismic sensor system. A second seismic energy source is towed at a selected distance from the first source. The first seismic energy source and the second seismic energy source are actuated in a plurality of firing sequences. Each of the firing sequences includes firing of the first source, waiting a selected time firing the second source and recording signals generated by the seismic sensor system. The selected time between firing the first source and the second source is varied between successive ones of the firing sequences. The firing times of the first and second source are indexed so as to enable separate identification of seismic events originating from the first source and seismic events originating from the second source in detected seismic signals.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Method for separating seismic signals from two or more distinct sources
InactiveUS6882938B2Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSpatial directionSeismic energy
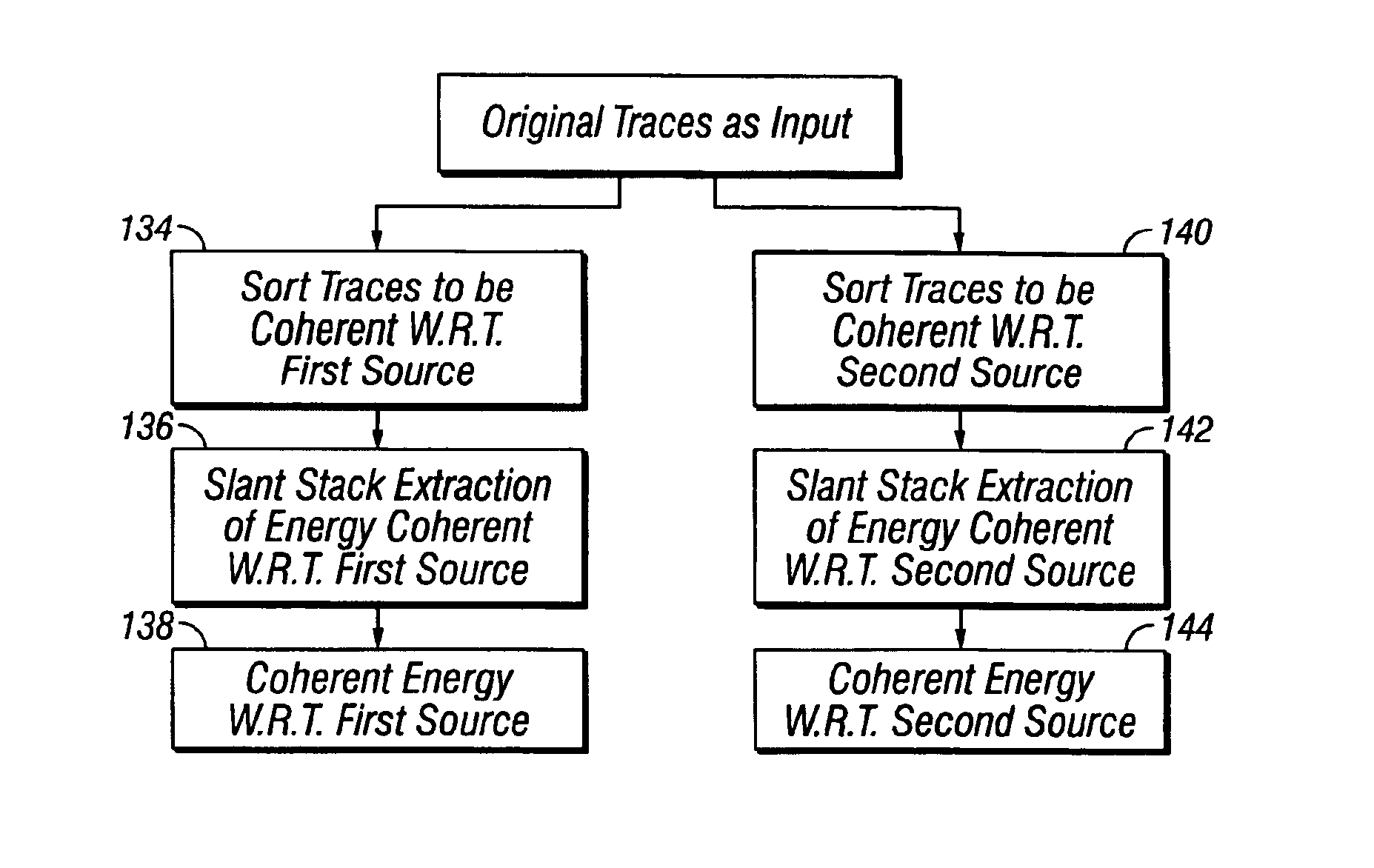
A method is disclosed for separating energy resulting from actuating at least two different seismic energy sources from seismic signals. The sources are actuated to provide a variable time delay between successive actuations of a first one and a second one of the sources. The method includes sorting the seismic signals such that events therein resulting from actuations of the first source are substantially coherent in all spatial directions, coherency filtering the first source coherency sorted signals, sorting the seismic signals such that events therein resulting from actuations of the second source are substantially coherent in all spatial directions, and coherency filtering the second source coherency sorted signals.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
Stability monitoring method for cold high-altitude steep slope
ActiveCN107067333AComprehensive monitoringComprehensive judgmentAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesData processing applicationsSlope stability analysisInstability
The invention relates to the technical field of mining safe engineering, and particularly to a stability monitoring method for a cold high-altitude steep slope. According to the stability monitoring method, through field engineering geology, hydrogeology survey, engineering geological rock quality evaluation and rock mechanical parameter determining, the lithologic condition, the rock structure, the hydrogeology condition, the slope shape, earthquake parameters, explosion parameters and the like of the slope are determined. Slope stability analysis and a treatment strategy measure are performed. Furthermore a comprehensive monitoring system and a slope instability criterion are established.
Owner:CHINA MINMETALS CHANGSHA MINING RES INST
Sand monitoring within wells using acoustic arrays
ActiveUS6837098B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcoustic arrayData point
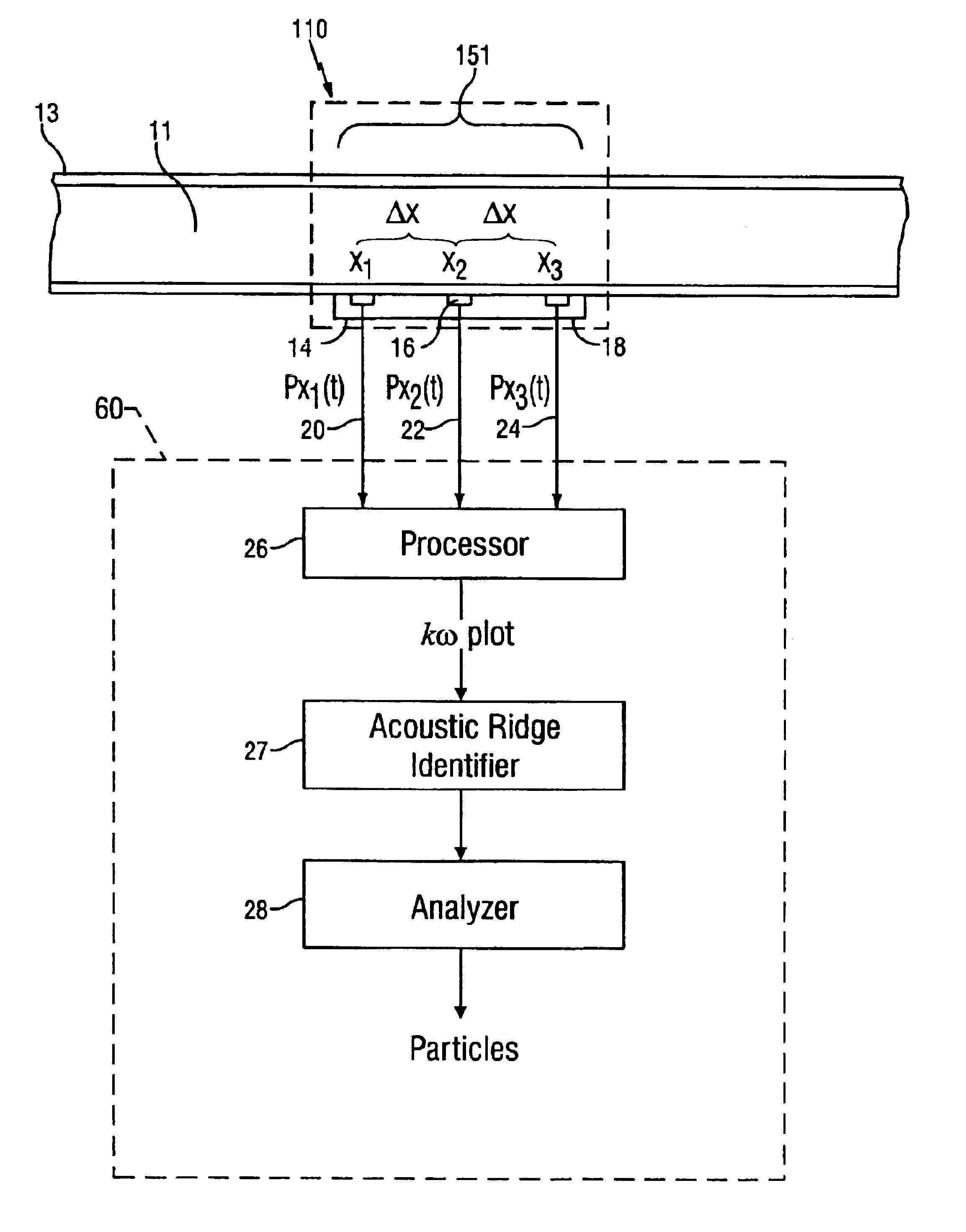
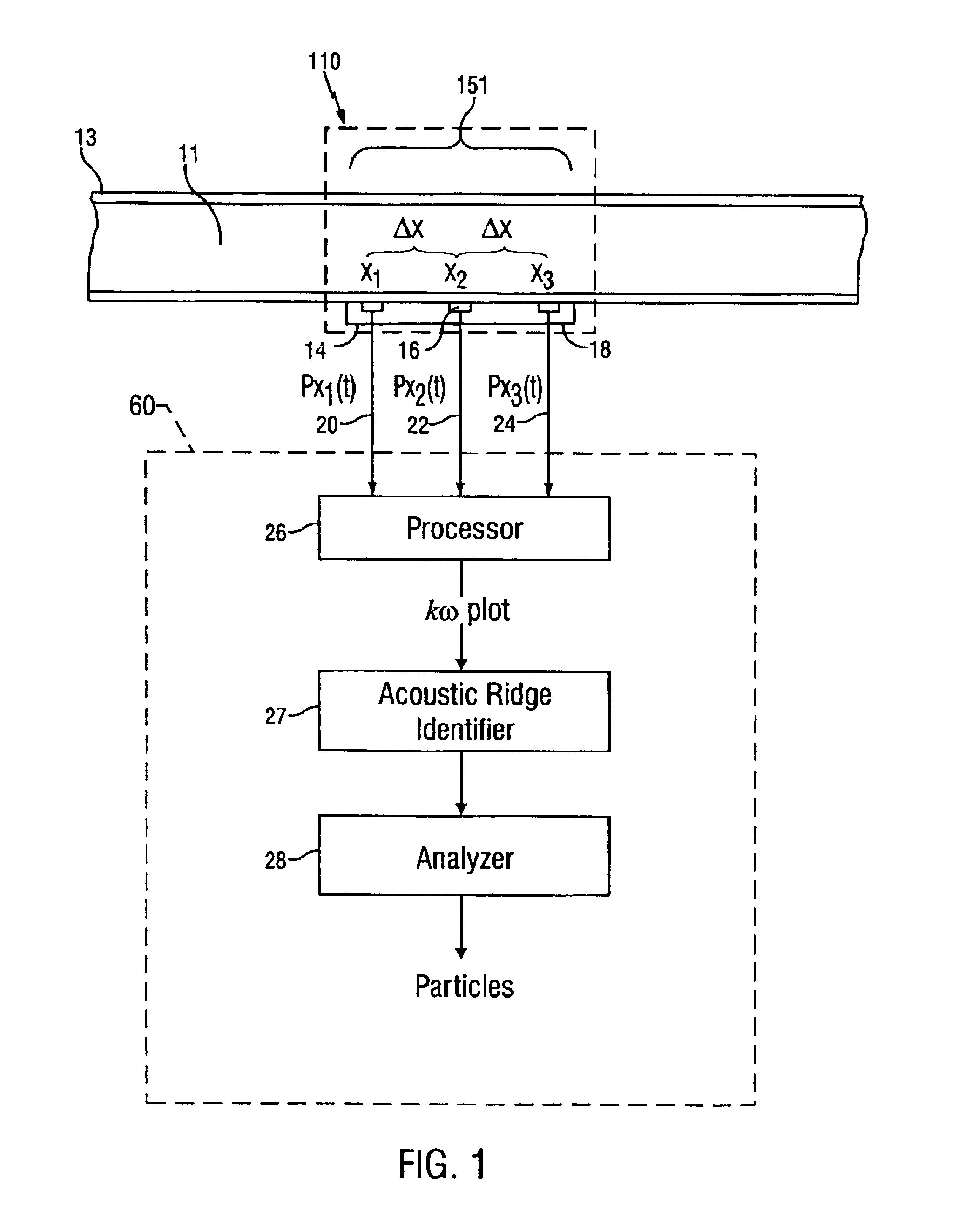
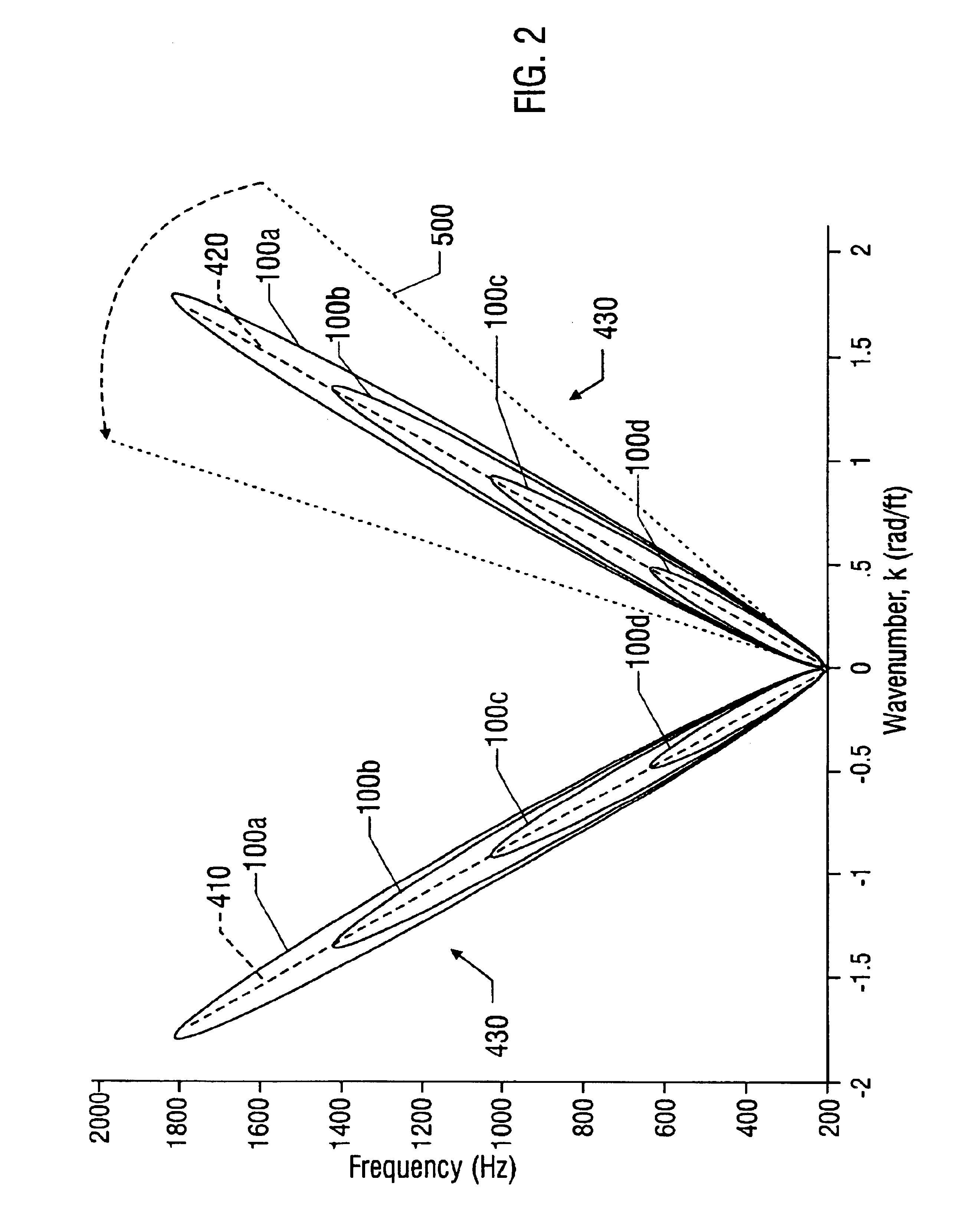
A method for detecting the presence of particles, such as sand, flowing within a fluid in a conduit is disclosed. At least two optical sensors measure pressure variations propagating through the fluid. These pressure variations are caused by acoustic noise generated by typical background noises of the well production environment and from sand particles flowing within the fluid. If the acoustics are sufficiently energetic with respect to other disturbances, the signals provided by the sensors will form an acoustic ridge on a kω plot, where each data point represents the power of the acoustic wave corresponding to that particular wave number and temporal frequency. A sand metric then compares the average power of the data points forming the acoustic ridge to the average power of the data points falling outside of the acoustic ridge. The result of this comparison allows one to determine whether particles are present within the fluid. Furthermore, the present invention can also determine whether the generated acoustic noise is occurring upstream or downstream of the sensors, thus giving an indication of the location of the particles in the fluid relative to the sensors.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for subterranean formation flow imaging
InactiveUS6856132B2Accurate measurementAccurately determineElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceMri imageGeophysics
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for measuring a property relating to fluid flow in an earth formation, more specifically to directly measuring formation permeability and other fluid characteristics. The present invention provides a method for determining the permeability of a hydrocarbon bearing earth formation, which method comprises the steps of: locating a tool at a selected position in a borehole penetrating the earth formation; inducing a flow of fluid within the earth formation to said tool; creating at least two MRI images of said fluid while flowing within the earth formation to said tool, said at least two images being created at different times; determining displacement of said fluid within the earth formation between said different times, using the at least two MRI images.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
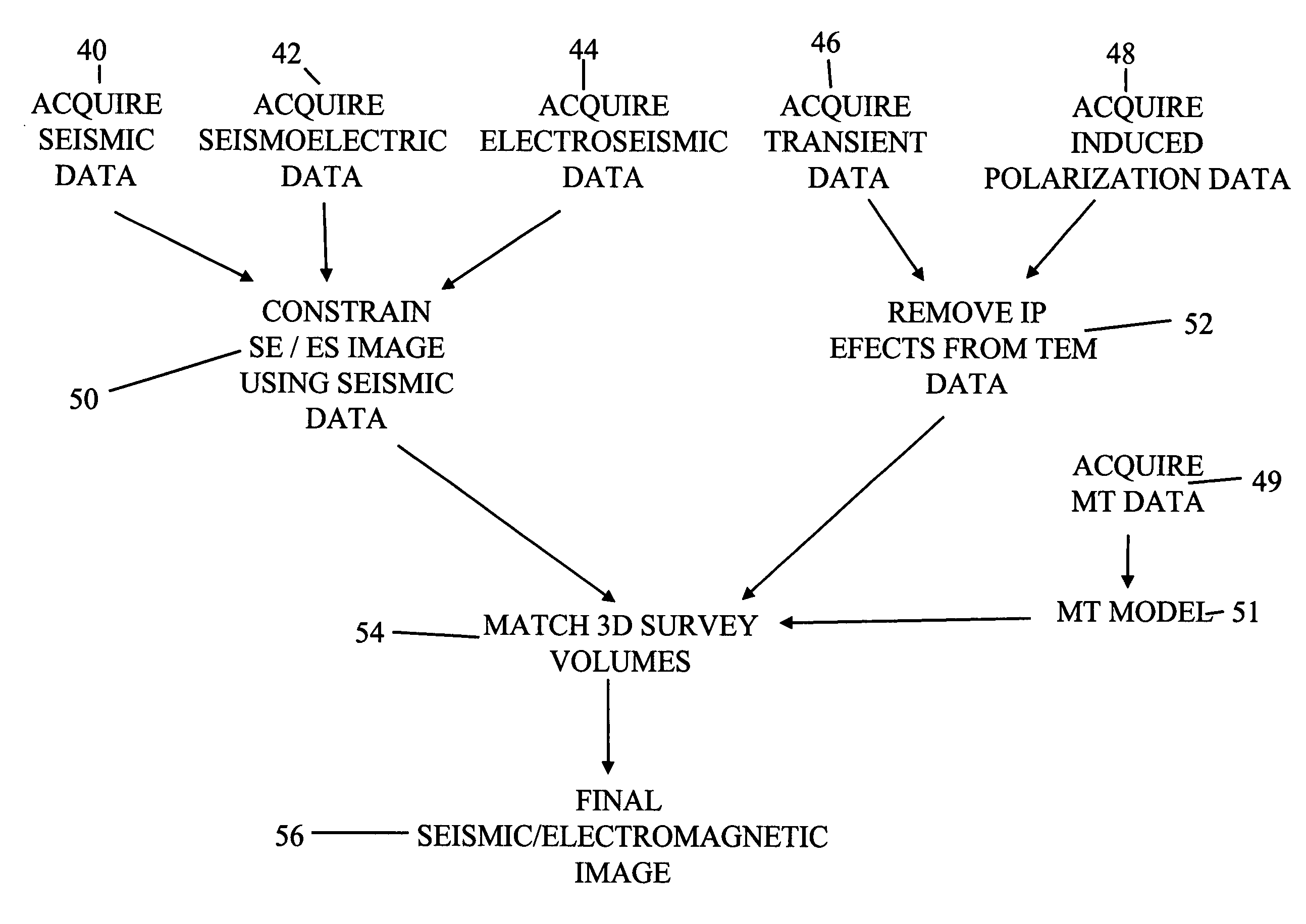
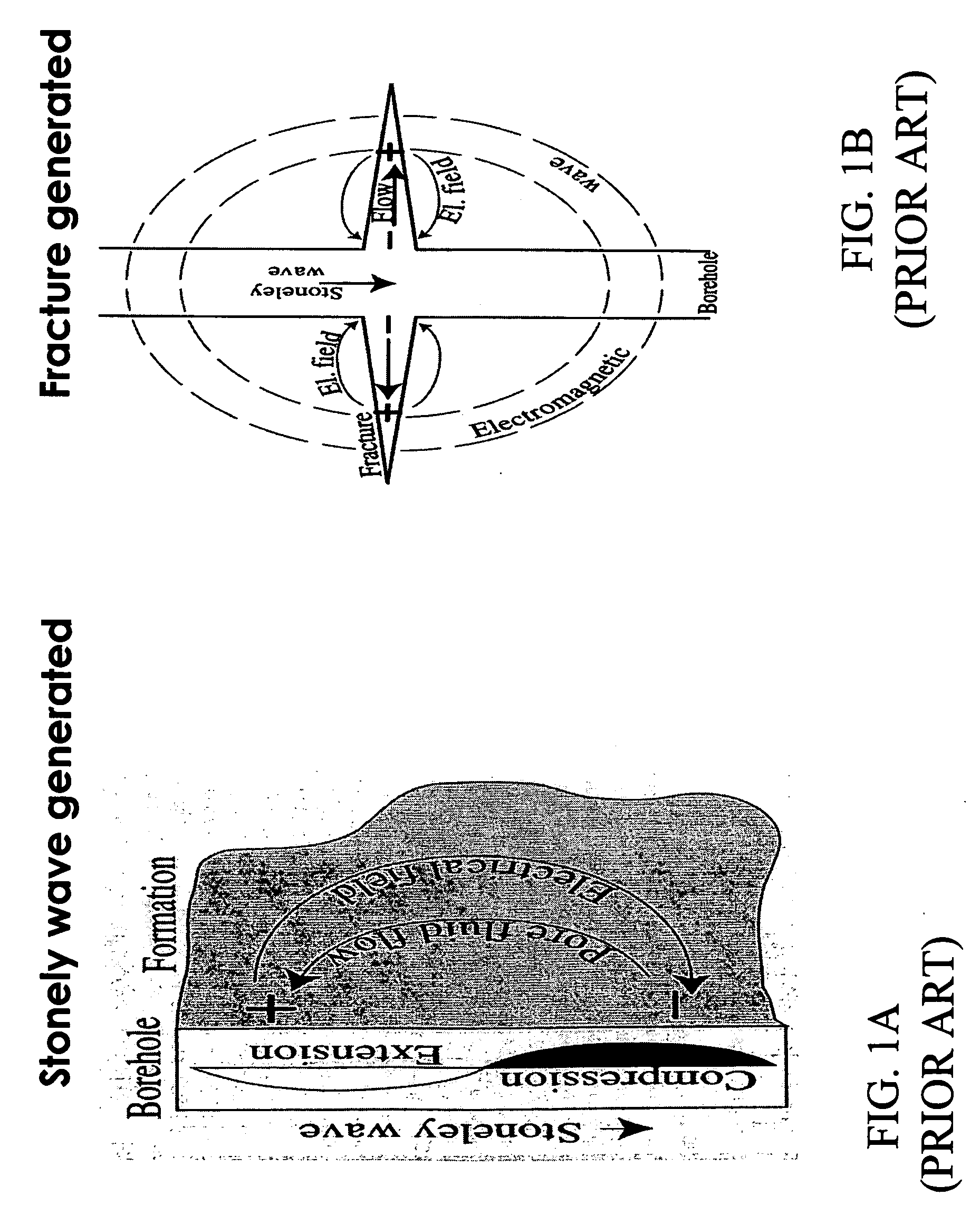
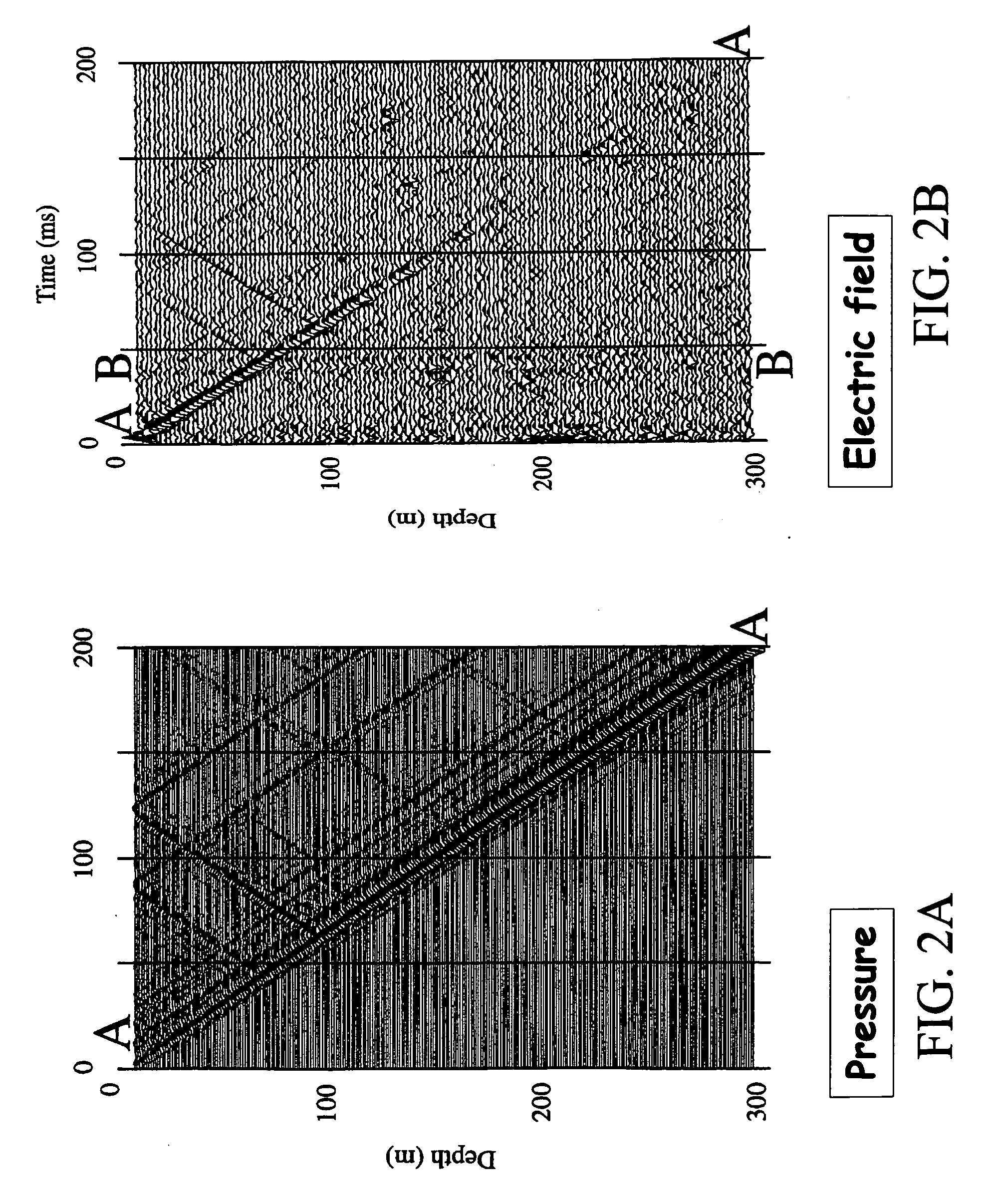
Method for acquiring and interpreting seismoelectric and eletroseismic data
InactiveUS20070294036A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsGeophysics
Owner:KJT ENTPR
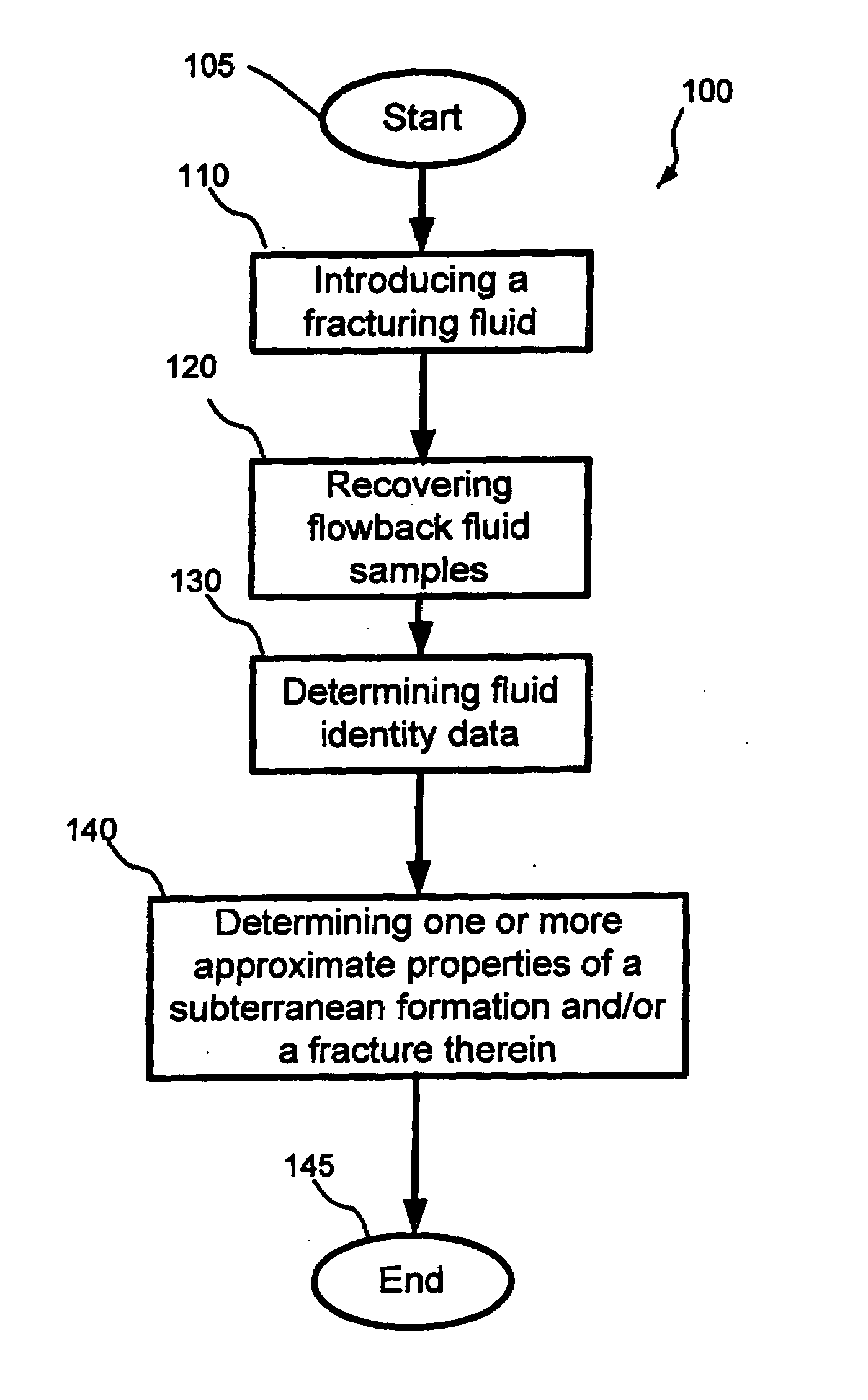
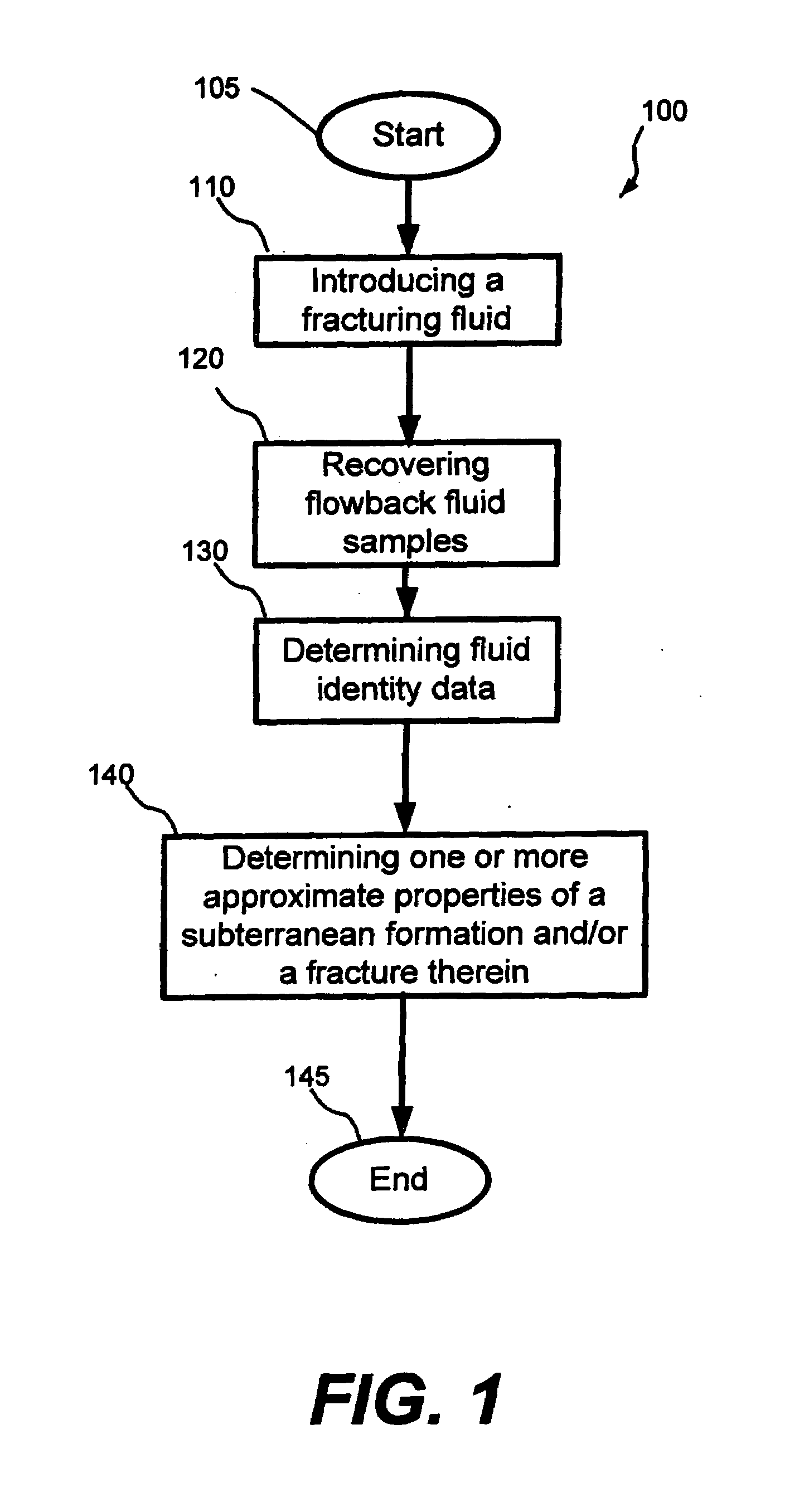
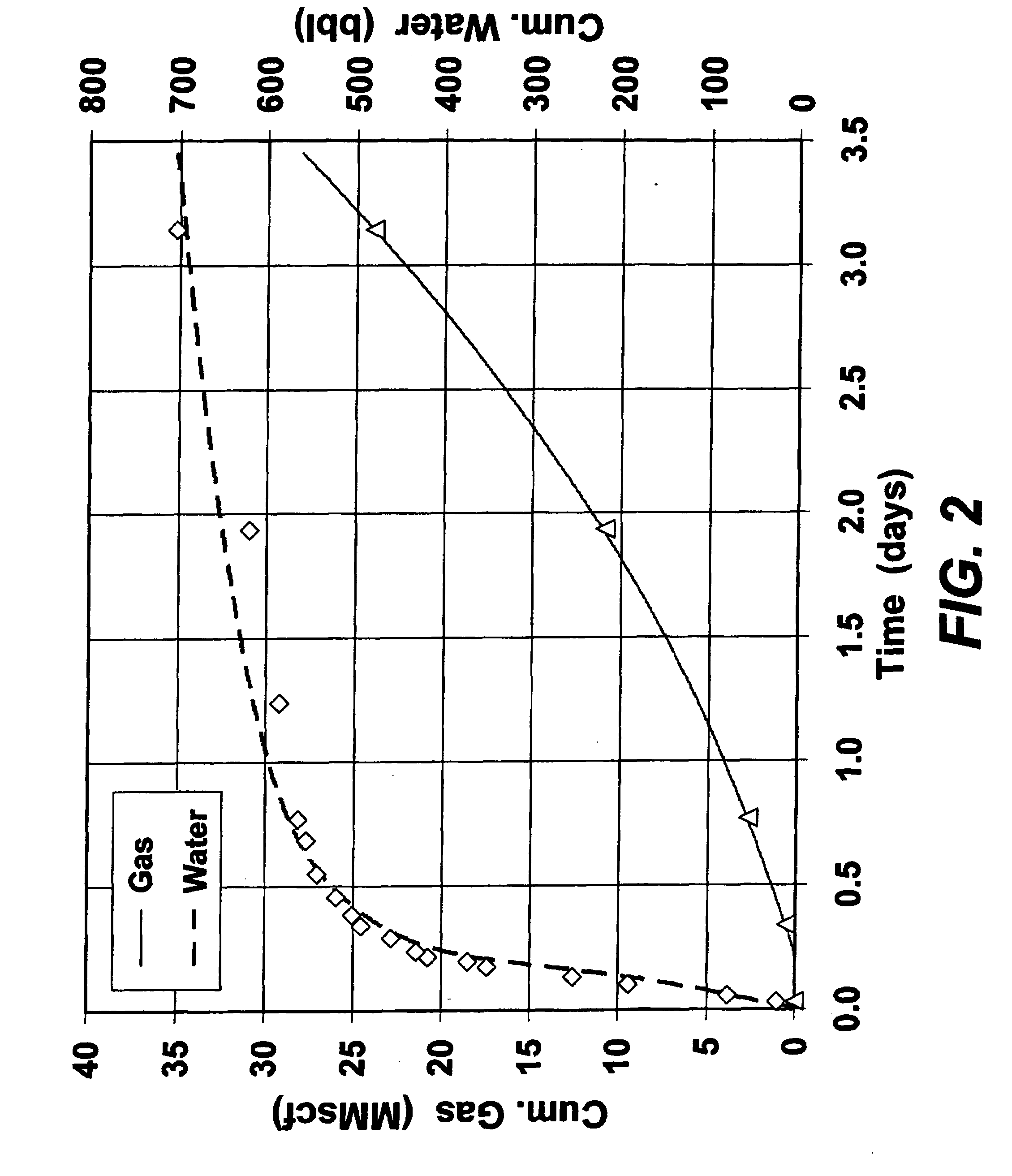
Methods for estimating properties of a subterranean formation and/or a fracture therein
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
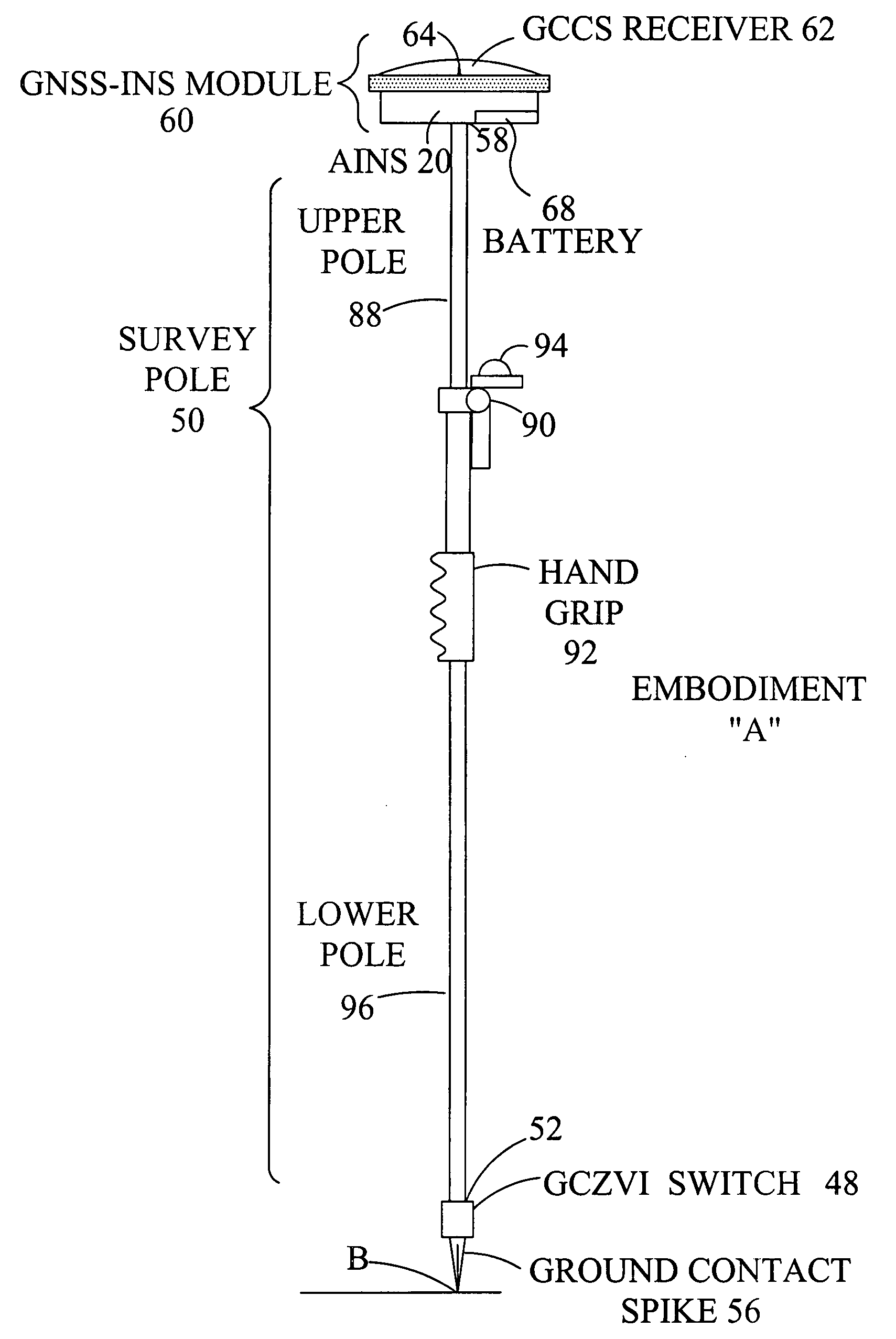
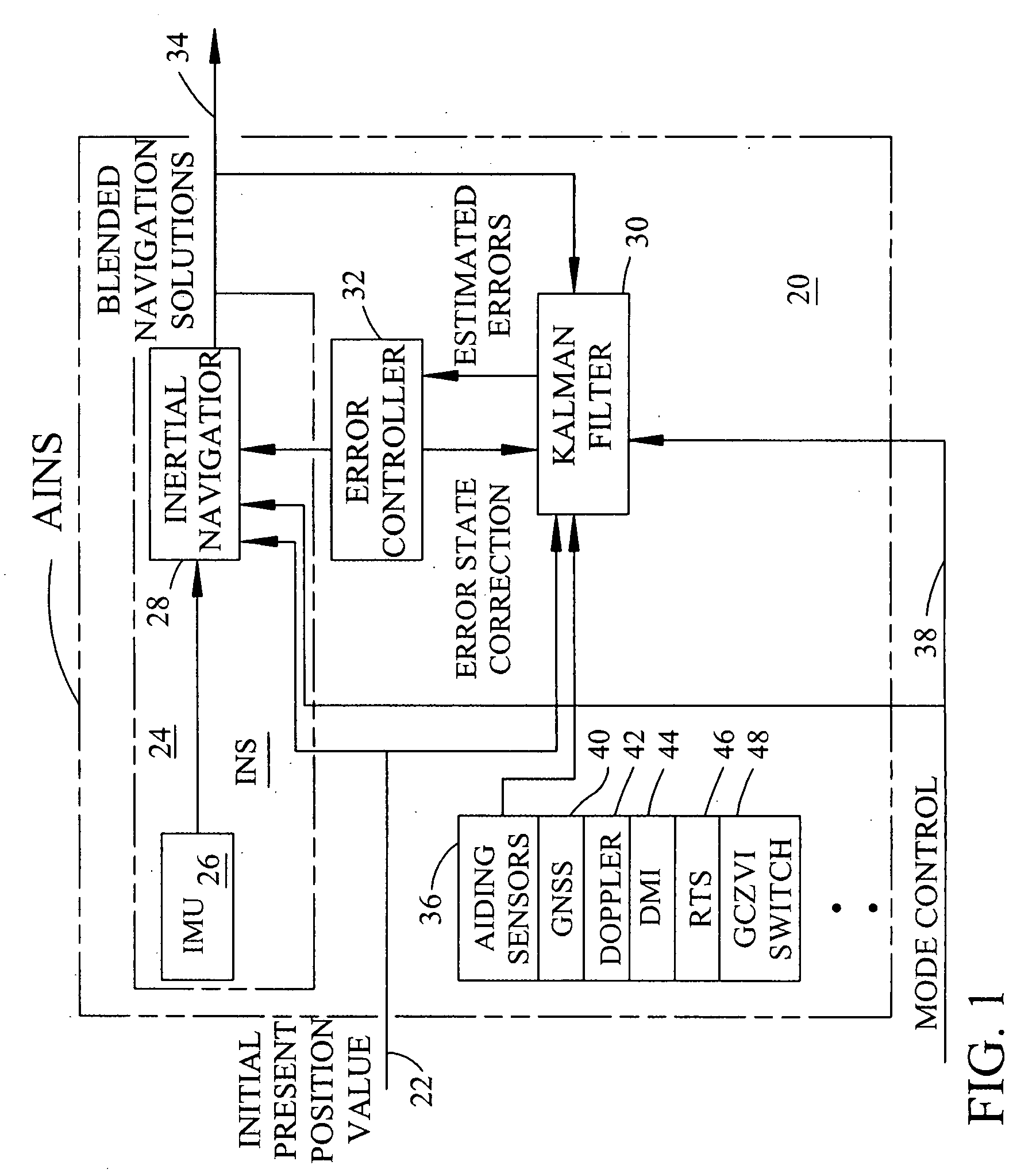
AINS enhanced survey instrument
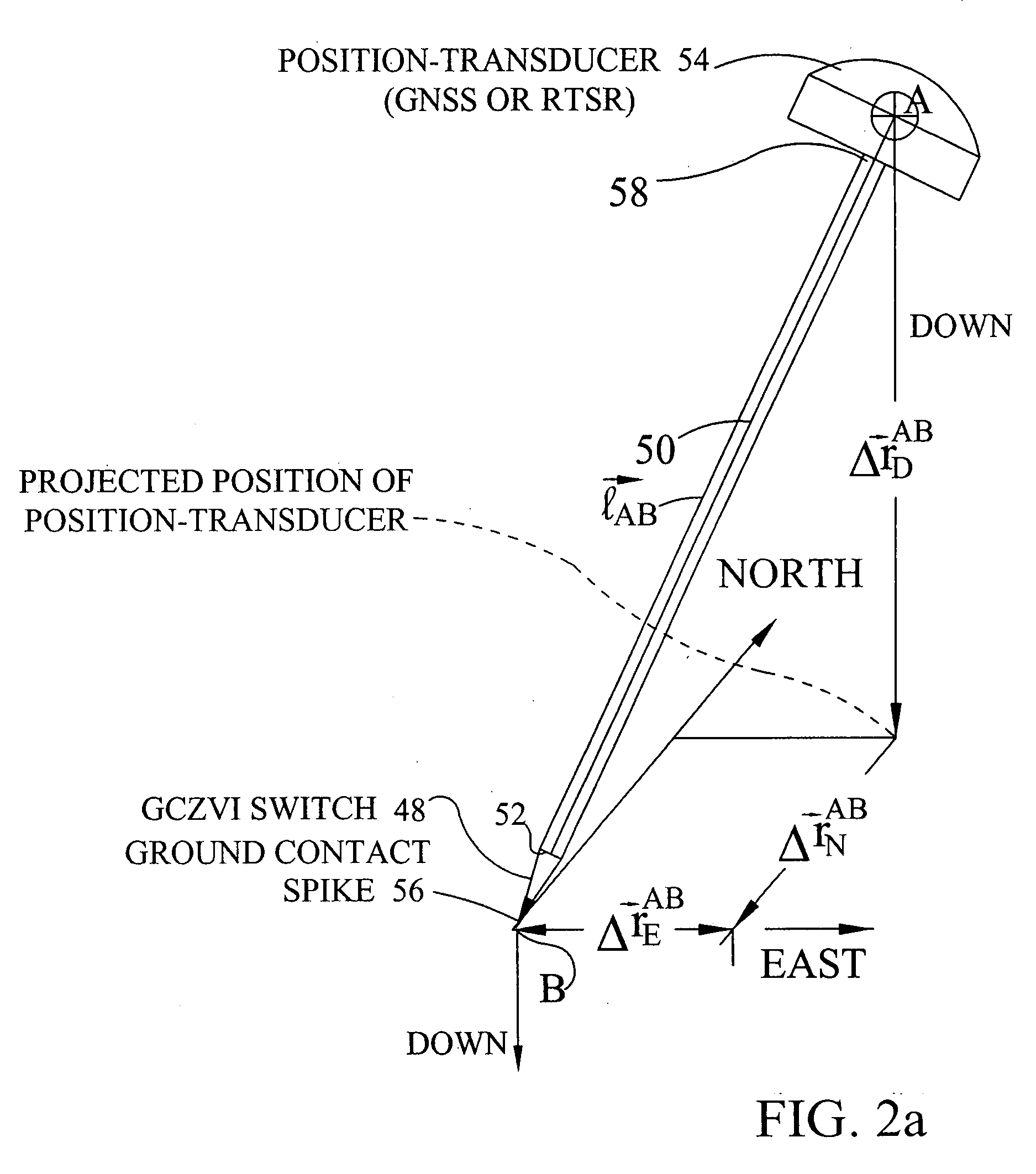
The invention comprises a survey pole having a survey pole bottom end, with a position-transducer coupled to a survey pole top end. A ground contact spike is on the bottom end. The survey pole uses an AINS as a combined tilt and heading sensor. The AINS provides heading and Euler angle outputs characterizing the tilt of the survey pole. The heading and Euler angle outputs are used by a computer and program to perform position transfers from a position-transducer at the pole top end to the GCZVI switch or spike on the ground using a set of position offset or transfer equations. The position-transducer is either a GNSS or an RTS serving as a position-transducer. The transfer of the position data from the position of the position-transducer provides the earth referenced or grid referenced position of the spike at the survey pole survey bottom end.
Owner:APPLANIX
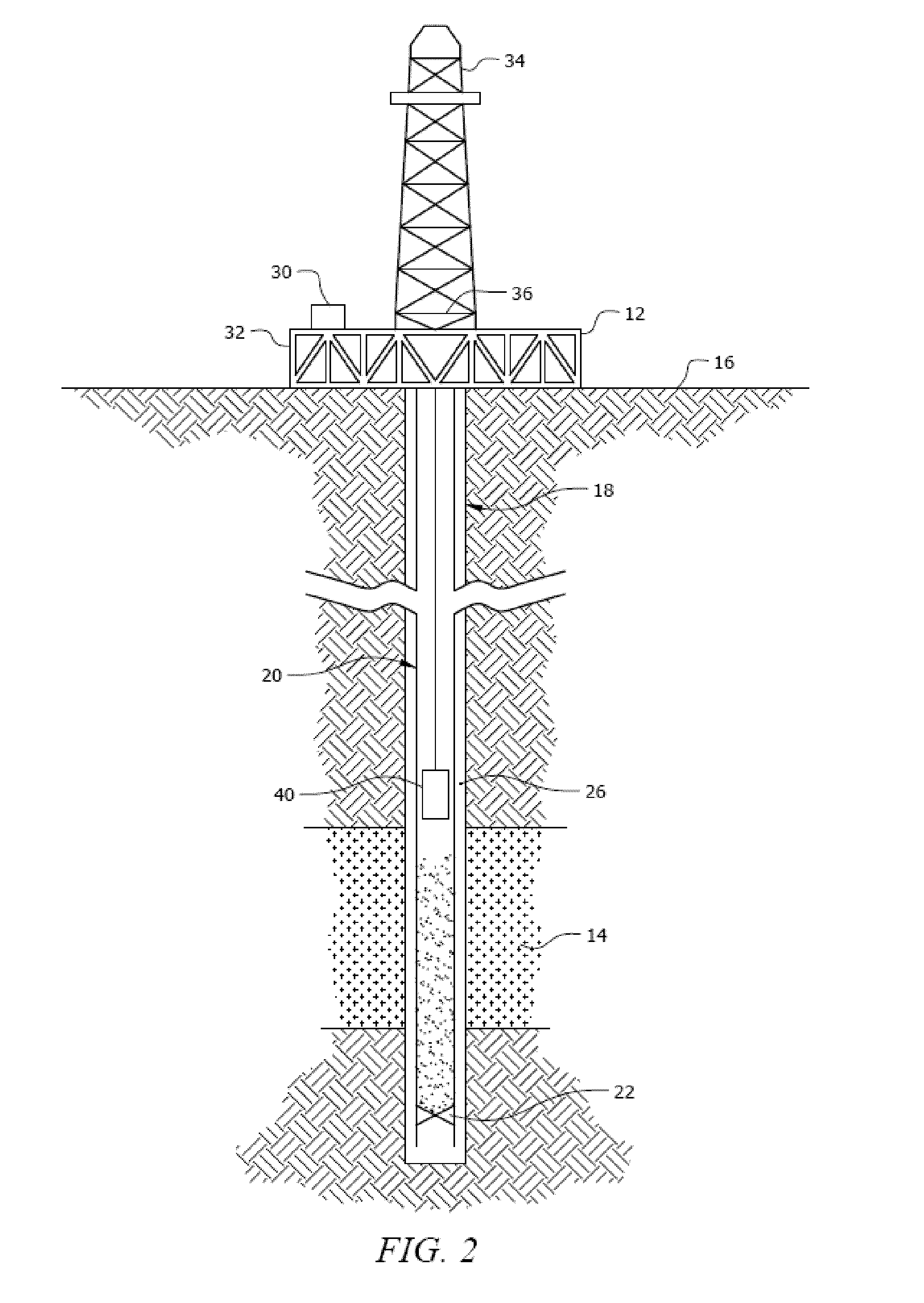
Use of Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) in Well Treatments
A method comprising placing a Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) sensor in a subterranean formation, placing a wellbore composition in the subterranean formation, and using the MEMS sensor to detect a location of the wellbore composition. A method comprising placing a Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) sensor in a subterranean formation, placing a wellbore composition in the subterranean formation, and using the MEMS sensor to monitor a condition of the wellbore composition. A method comprising placing one or more Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) sensors in a subterranean formation, placing a wellbore composition in the subterranean formation, using the one or more MEMS sensors to detect a location of at least a portion of the wellbore composition, and using the one or more MEMS sensors to monitor at least a portion of the wellbore composition. A method comprising placing one or more Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) sensors in a subterranean formation using a wellbore composition, and monitoring a condition using the one or more MEMS sensors.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
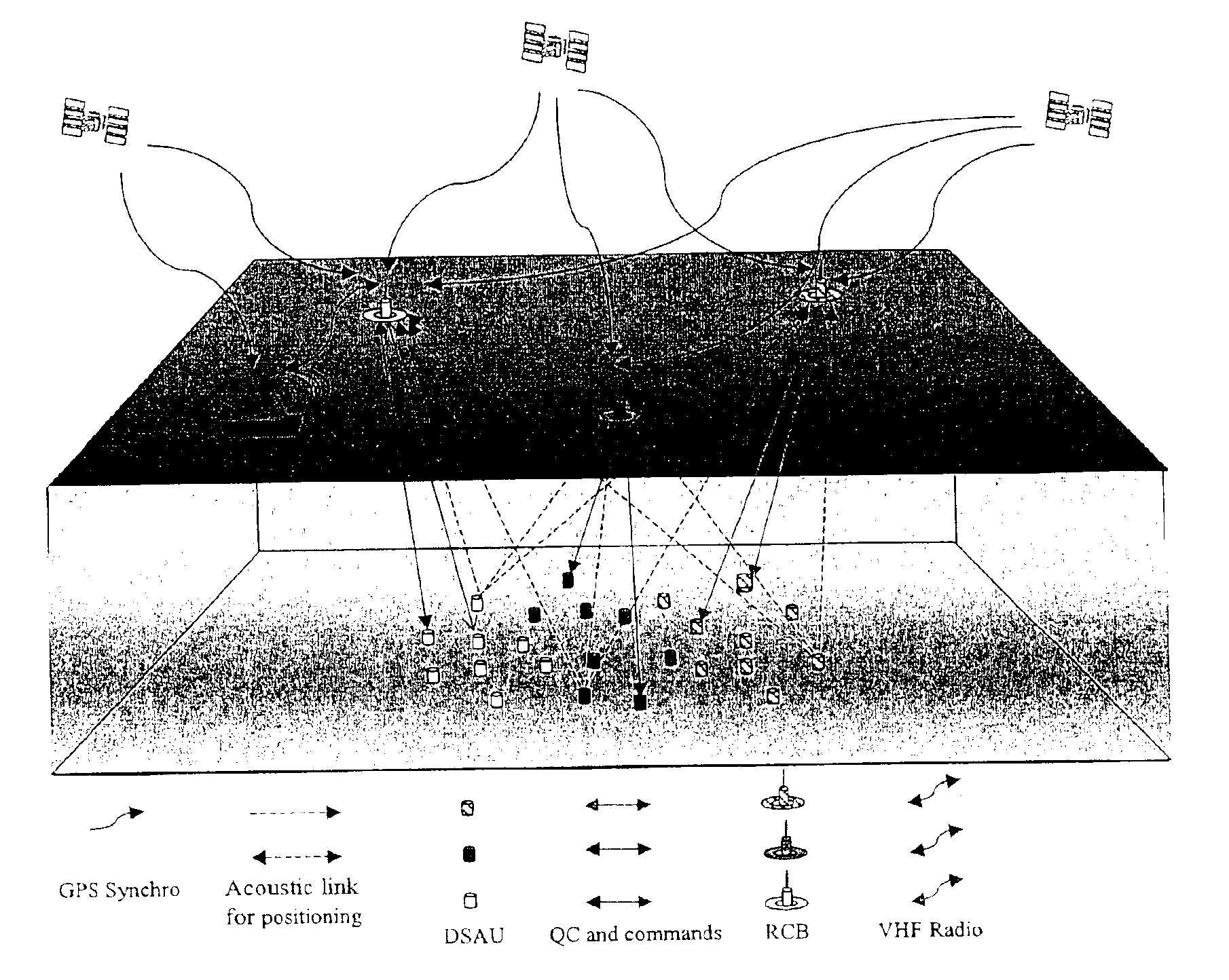
Seismic data acquisition system using acquisition stations set on the sea bottom
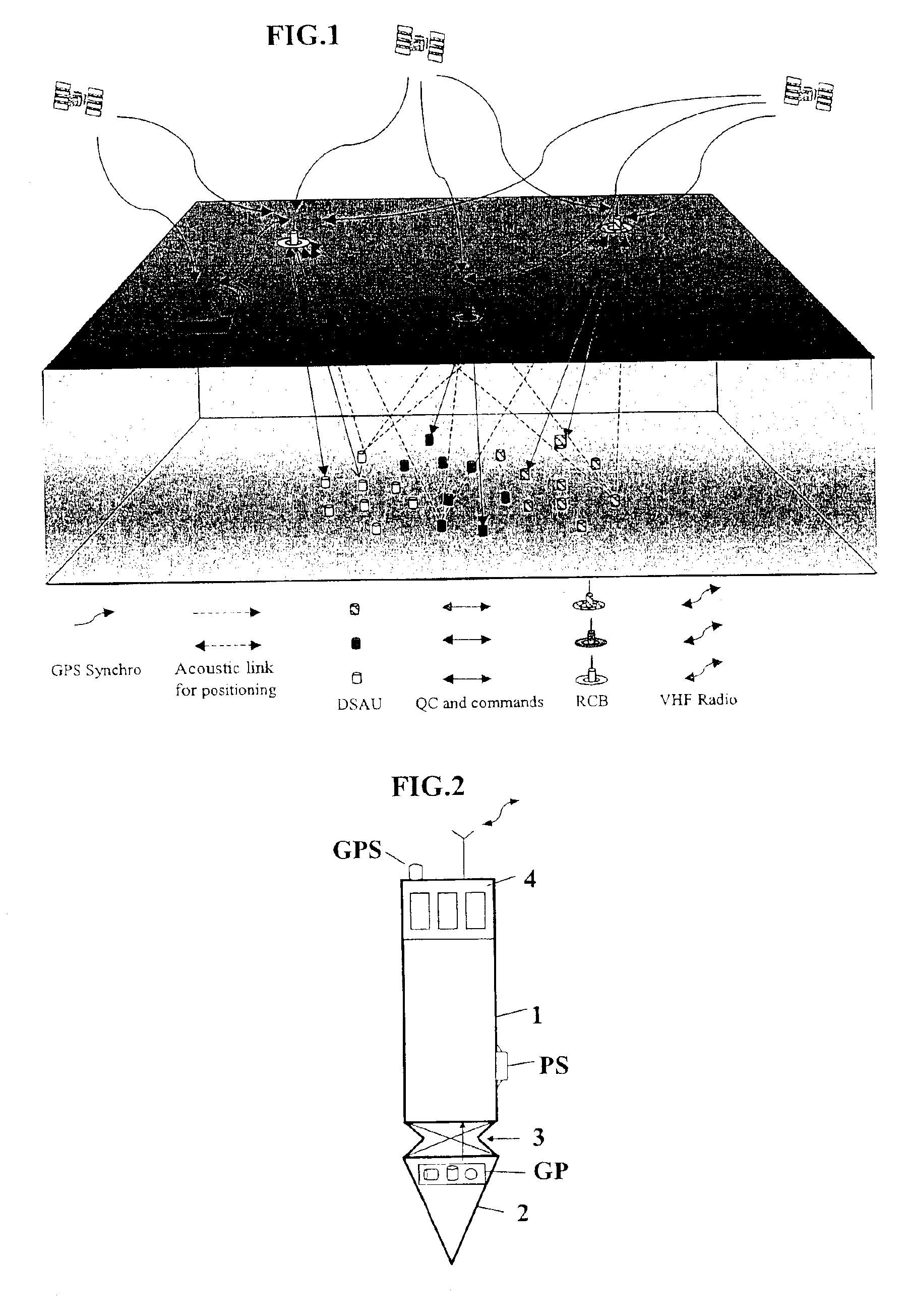
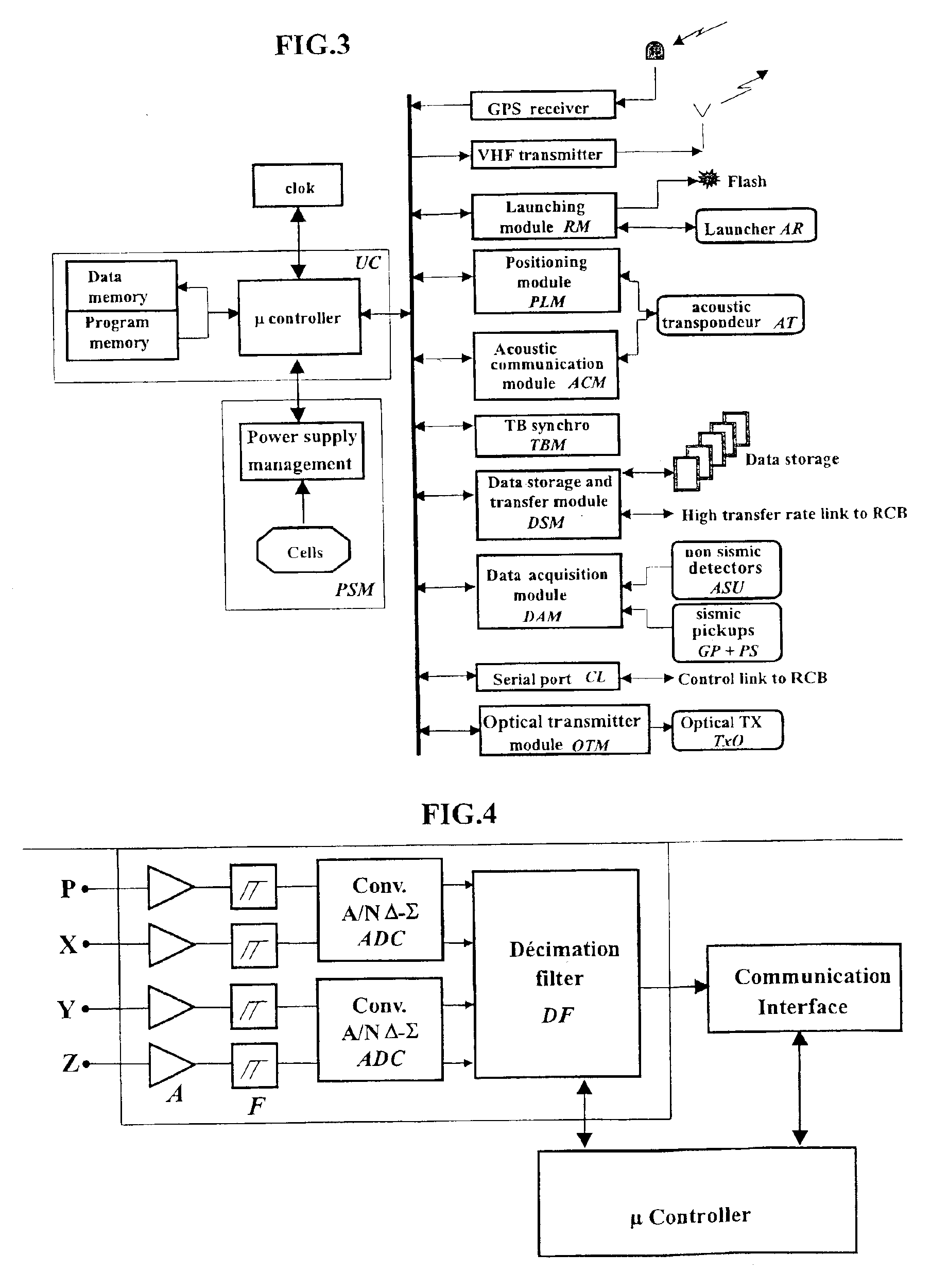
InactiveUS7016260B2Good synchronizationTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsTransmission systemsSystems designData acquisition
The invention is a system designed for acquisition of seismic data by means of acquisition stations set on water bottom of a water body. The system comprises acquisition stations (DSAU) combining a streamlined boom suited to penetrate the bottom and thus couple seismic receivers with the underlying formation, a sealed body for electronic data acquisition and communication modules. These acquisition stations (DSAU) are placed in the water and drop to the bottom under the effect of gravity. Relay buoys (RCB) are positioned at the surface, each with a GPS positioning module, a radio link with a central station (CCRU), on a ship for example, and modules providing acoustic communication with bottom acquisition stations (DSAU), which are used to determine the position of the stations in relation to the relay buoys and to exchange control data and seismic data (good running order data or possibly seismic traces acquired if the conditions lend themselves thereto) to provide seismic prospecting or monitoring of an underground formation.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Coding and Decoding: Seismic Data Modeling, Acquisition and Processing
InactiveUS20070274155A1Seismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingSource encodingData modeling
A method for coding and decoding seismic data acquired, based on the concept of multishooting, is disclosed. In this concept, waves generated simultaneously from several locations at the surface of the earth, near the sea surface, at the sea floor, or inside a borehole propagate in the subsurface before being recorded at sensor locations as mixtures of various signals. The coding and decoding method for seismic data described here works with both instantaneous mixtures and convolutive mixtures. Furthermore, the mixtures can be underdetemined [i.e., the number of mixtures (K) is smaller than the number of seismic sources (I) associated with a multishot] or determined [i.e., the number of mixtures is equal to or greater than the number of sources). When mixtures are determined, we can reorganize our seismic data as zero-mean random variables and use the independent component analysis (ICA) or, alternatively, the principal component analysis (PCA) to decode. We can also alternatively take advantage of the sparsity of seismic data in our decoding process. When mixtures are underdetermined and the number of mixtures is at least two, we utilize higher-order statistics to overcome the underdeterminacy. Alternatively, we can use the constraint that seismic data are sparse to overcome the underdeterminacy. When mixtures are underdetermined and limited to single mixtures, we use a priori knowledge about seismic acquisition to computationally generate additional mixtures from the actual recorded mixtures. Then we organize our data as zero-mean random variables and use ICA or PCA to decode the data. The a priori knowledge includes source encoding, seismic acquisition geometries, and reference data collected for the purpose of aiding the decoding processing.The coding and decoding processes described can be used to acquire and process real seismic data in the field or in laboratories, and to model and process synthetic data.
Owner:IKELLE LUC T
3-D prestack/poststack multiple prediction
InactiveUS6735527B1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsNormal moveoutCommon depth point
System and method for analyzing seismic data from a formation. Stacked seismic data are provided, including a plurality of stack traces, e.g., by collecting seismic data from source and receiver locations and stacking the collected seismic data to produce the stacked seismic data. 3-dimensional (3-D) prestack traces are generated from the plurality of stack traces, e.g., by performing inverse moveout of stack traces, e.g., in a specified neighborhood, at common-depth-points, e.g., by inverse normal moveout, ray tracing, spike synthesis, etc. The inverse moveout corrected traces are convolved to compute predicted multiples which are useable in analyzing the formation. The multiples may be adaptively subtracted from the stacked seismic data, or optionally, from prestack data, to generate processed seismic data useable in analyzing the formation, e.g., for petroleum production potential. Dip moveout (DMO) corrected seismic data may be used, where DMO velocities are adjusted by dividing by cosine of the dip angle.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS
Method and apparatus for determining the shape of an earth borehole and the motion of a tool within the borehole
A method and apparatus are provided for estimating the cross-sectional shape and orientation of an earth borehole and the motion of a tool therein. The method and apparatus involve measuring the distance from the tool to the borehole wall at a plurality of locations around the periphery of the tool and fitting those measured distances to a predetermined shape function using a nonlinear parameter estimation technique to minimize the error between the estimated shape of the borehole and the measured distances. The method and apparatus may be used to estimate elliptical and higher order borehole shapes. Additionally, the method and apparatus may be used while drilling the borehole.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
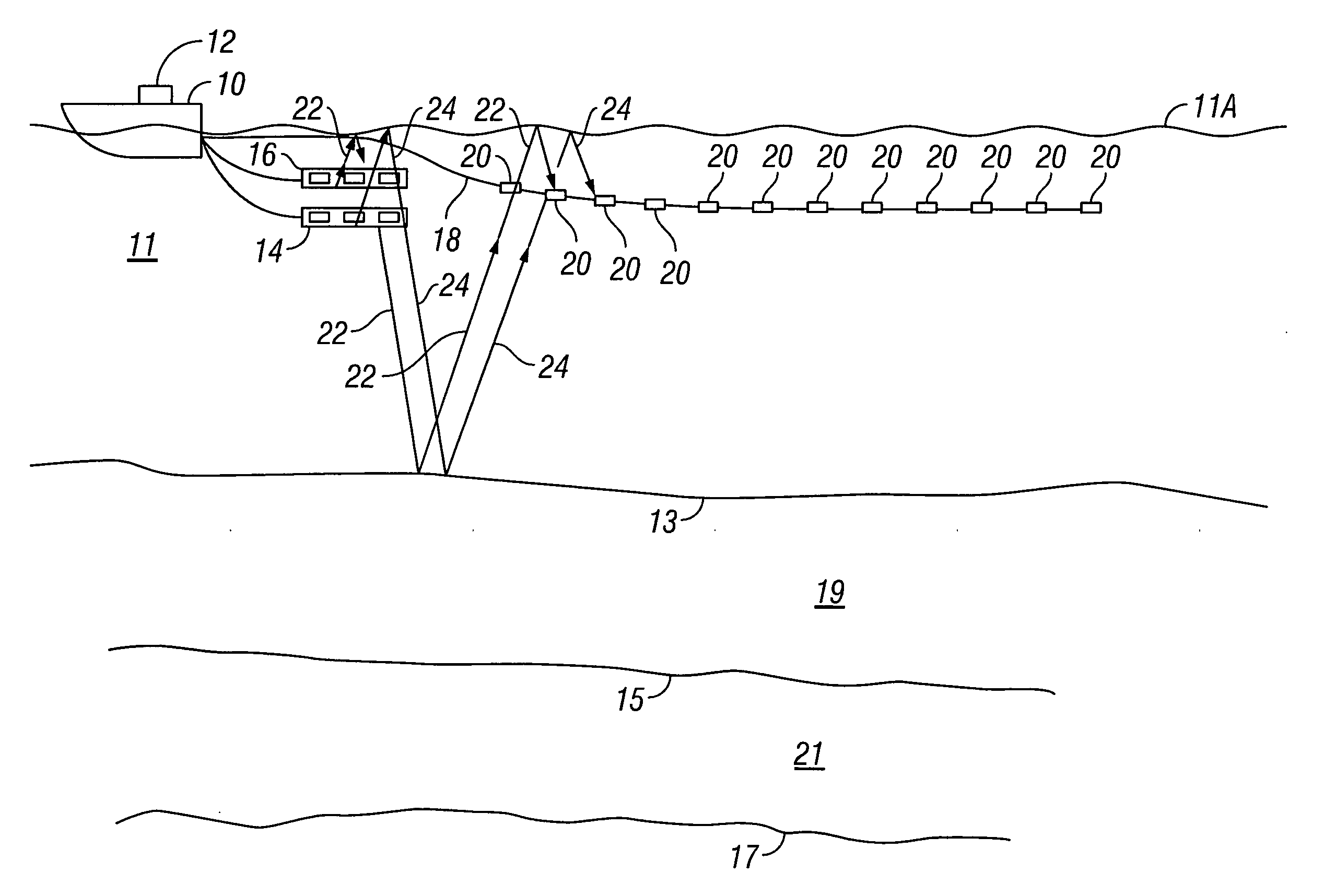
Marine seismic acquisition system and method
InactiveUS6684160B1Reduce contentReduce noiseSeismic signal receiversSeismic signal processingHydrophoneSeismic survey
A method and system for performing a marine seismic survey is described, including towing at least one seismic streamer comprising a plurality of hydrophones distributed at average intervals of not more than 625 cm therealong in the water over the area to be surveyed; directing acoustic signals down through the water and into the earth beneath; receiving with the hydrophones seismic signals reflected from strata in the earth beneath the water; digitizing the output of each hydrophone separately; and filtering the output to reduce the noise present in the output and to generate a signal with a reduced noise content wherein the filtering process uses as further input the digitized output of at least one nearby hydrophone. The filtering is applied to single sensor recording prior to group-forming and thus able to detect and reduce coherent noise with a coherency length of 20 meters or less. It reduces noise such as streamer or bulge noise.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Electromagnetic surveying for hydrocarbon reservoirs
InactiveUS7126338B2Water resource assessmentDetection using electromagnetic wavesOcean bottomUltrasound attenuation
An electromagnetic survey method for surveying an area previously identified as potentially containing a subsea hydrocarbon reservoir, comprising obtaining first and second survey data sets with an electromagnetic source aligned end-on and broadside relative to the same or different receivers. The invention also relates to planning a survey using this method, and to analysis of survey data taken in combination allow the galvanic contribution to the signals collected at the receiver to be contrasted with the inductive effects, and the effects of signal attenuation, which are highly dependent on local properties of the rock formation, overlying water and air at the survey area. This is very important to the success of using electromagnetic surveying for identifying hydrocarbon reserves and distinguishing them from other classes of structure.
Owner:STATOIL ASA PETRO SA (NO)
System and method for extraction of hydrocarbons by in-situ radio frequency heating of carbon bearing geological formations
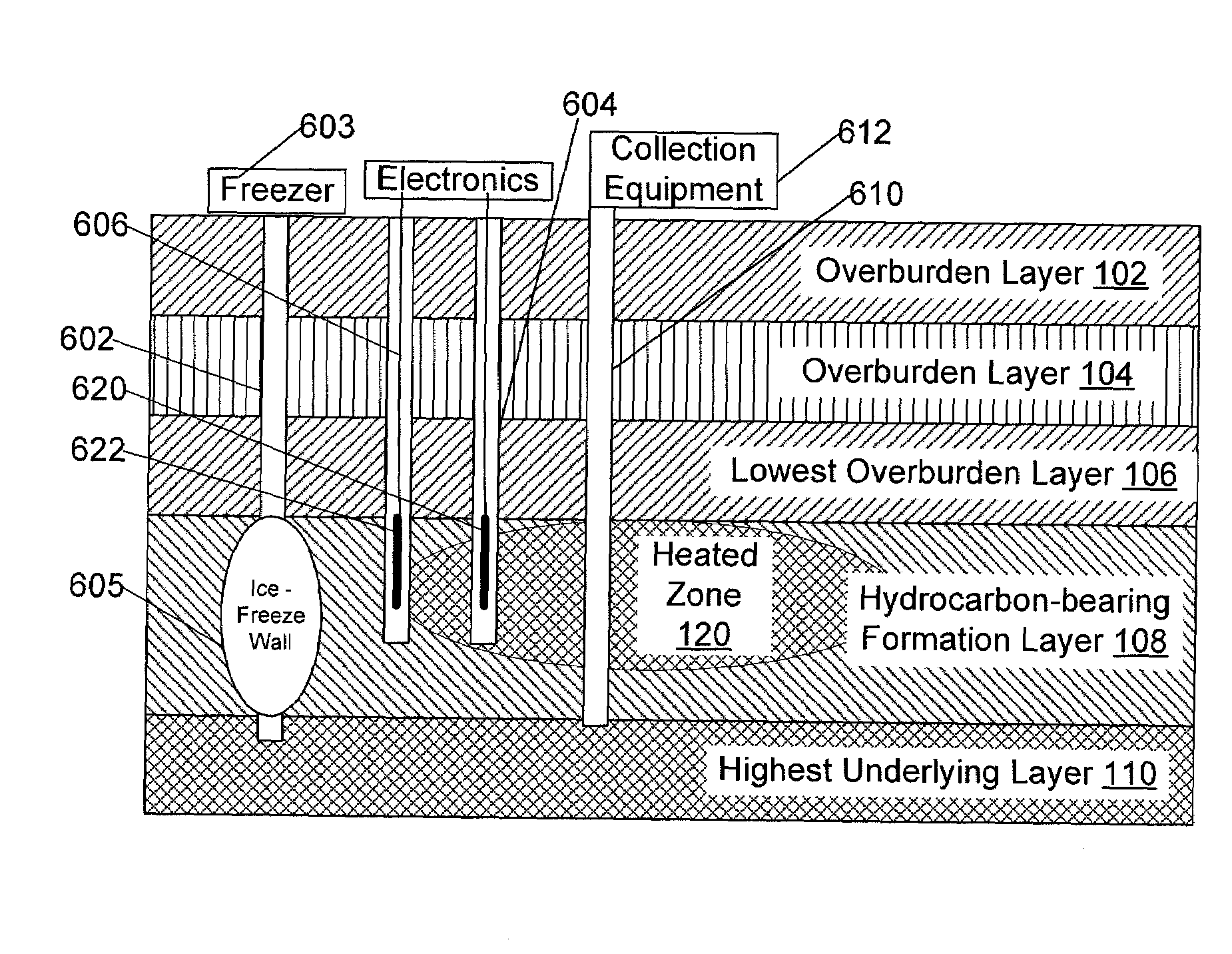
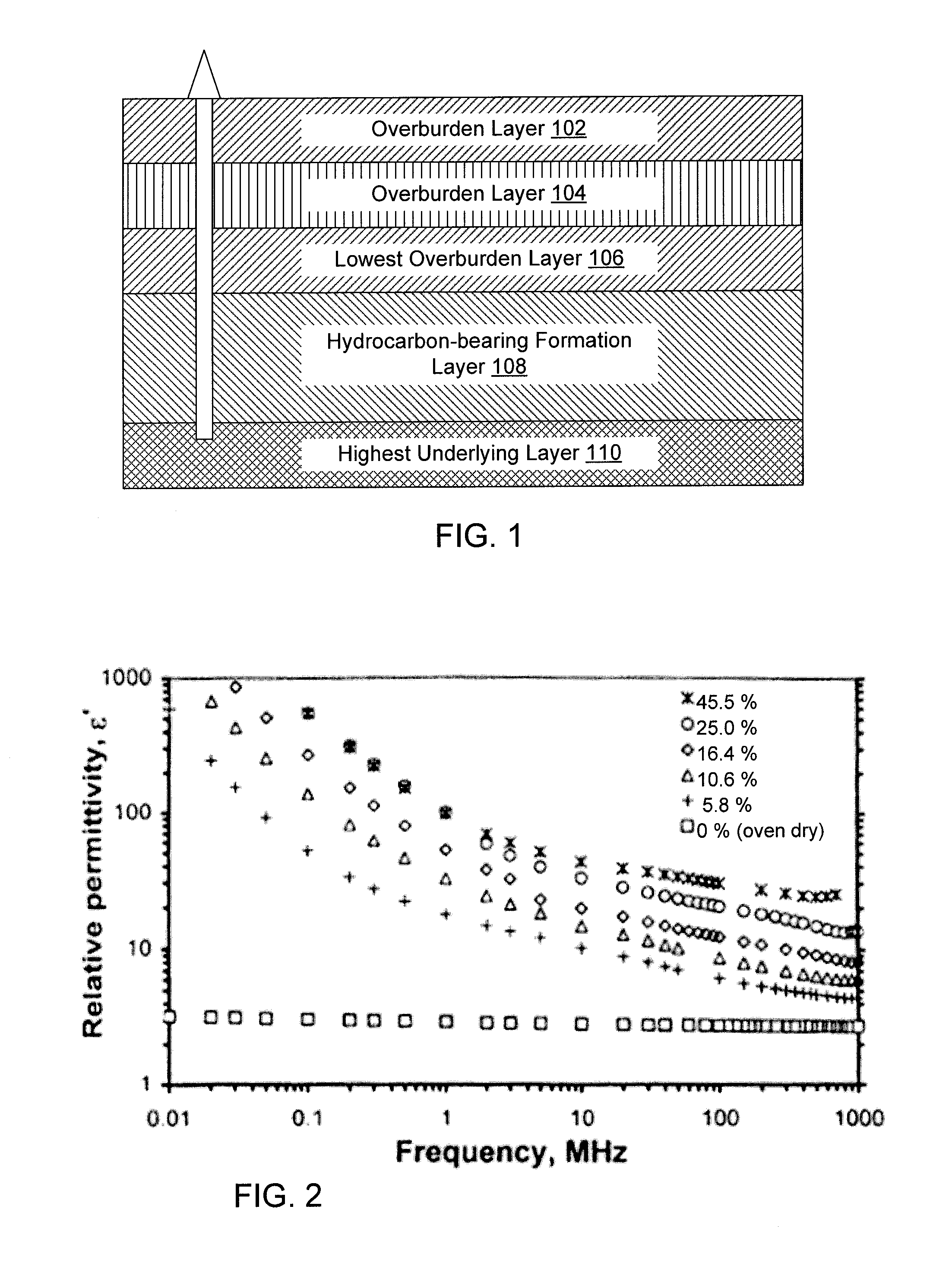
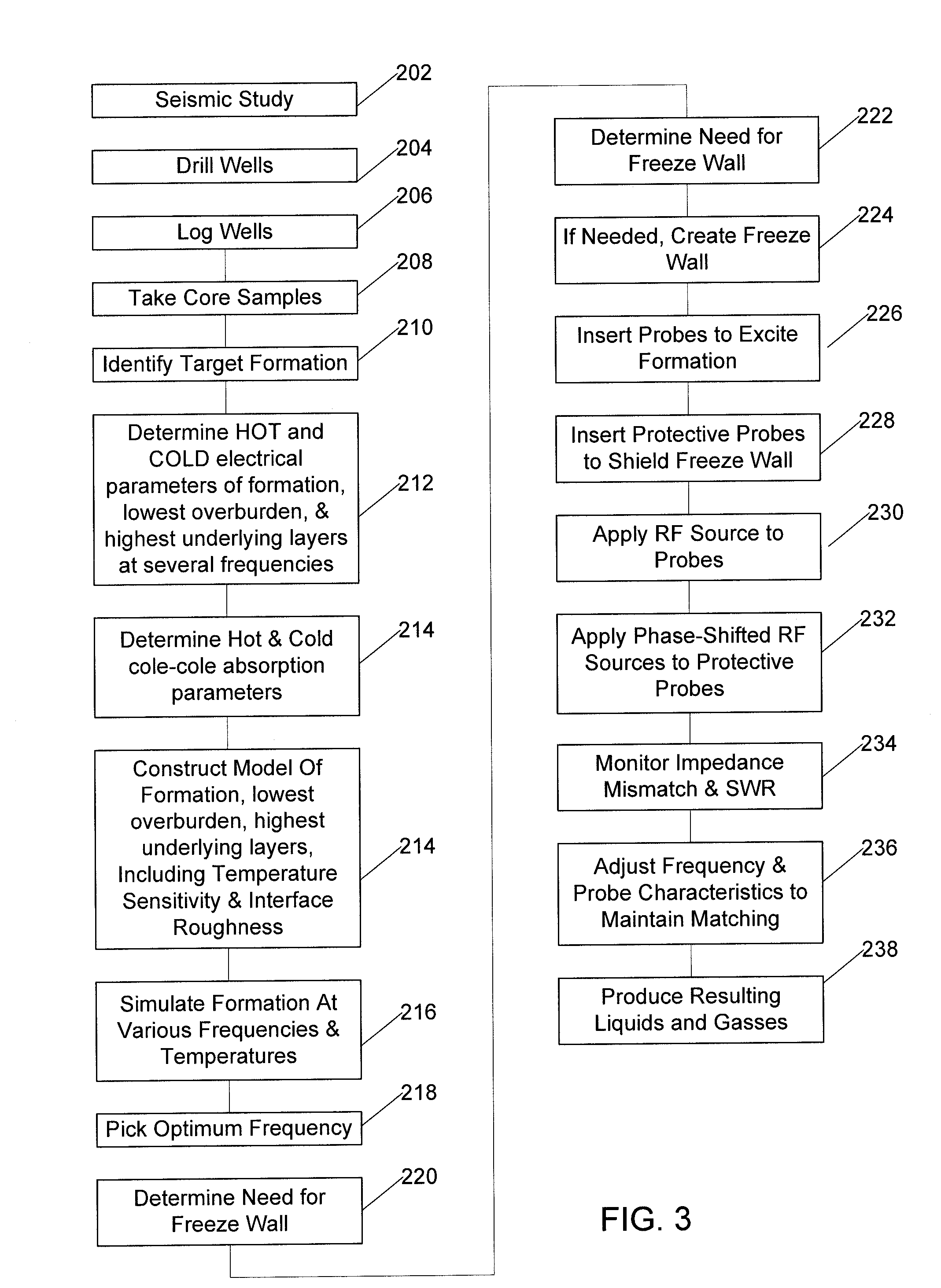
A method of producing liquid hydrocarbons from a hydrocarbon-bearing rock in situ in a geological formation begins with exploring the formation by drilling a plurality of boreholes into the formation and taking core samples of the hydrocarbon-bearing rock and at least one overburden layer. Electrical parameters of the hydrocarbon-bearing rock and the overburden layer are determined, as well as a roughness of a boundary between the hydrocarbon-bearing rock and the at least one overburden layer. These electrical parameters are used to construct a computer model of a portion of the hydrocarbon-bearing rock and at least one overburden layer, the computer model based upon modeling the formation as a rough-walled waveguide. This computer model is used to simulate propagation of radio frequency energy within the hydrocarbon-bearing rock, including simulation of radio frequency wave confinement within the hydrocarbon-bearing rock, at several frequencies and temperatures. A frequency for retorting is selected based upon simulation results. Radio frequency couplers are installed into at least one borehole in the hydrocarbon-bearing rock and driven with radio frequency energy to heat the hydrocarbon-bearing rock. As the rock heats, it releases carbon compounds and these are collected.
Owner:PAO HSUEH YUAN
Method for aquiring and processing marine seismic data to extract and constructively use the up-going and down-going wave-fields emitted by the source(s)
InactiveUS20100008184A1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesSeismic signal processingSurface oceanPhase shifted
A method for acquisition and processing of marine seismic signals to extract up-going and down- going wave-fields from a seismic energy source includes deploying at least two marine seismic energy sources at different depths in a body of water. These seismic energy sources are actuated with known time delays that are varied from shot record to shot record. Seismic signals from sources deployed at different depths are recorded simultaneously. Seismic energy corresponding to each of the sources is extracted from the recorded seismic signals. Up-going and down-going wave-fields are extracted from the sources deployed at different depths using the extracted seismic energy therefrom. A method includes the separated up-going and down-going wave-fields are propagated to a water surface or a common reference, the up-going or the down-going wave-field is 180 degree phase shifted, and the signals from these modified up-going and down-going wave-fields are summed.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com