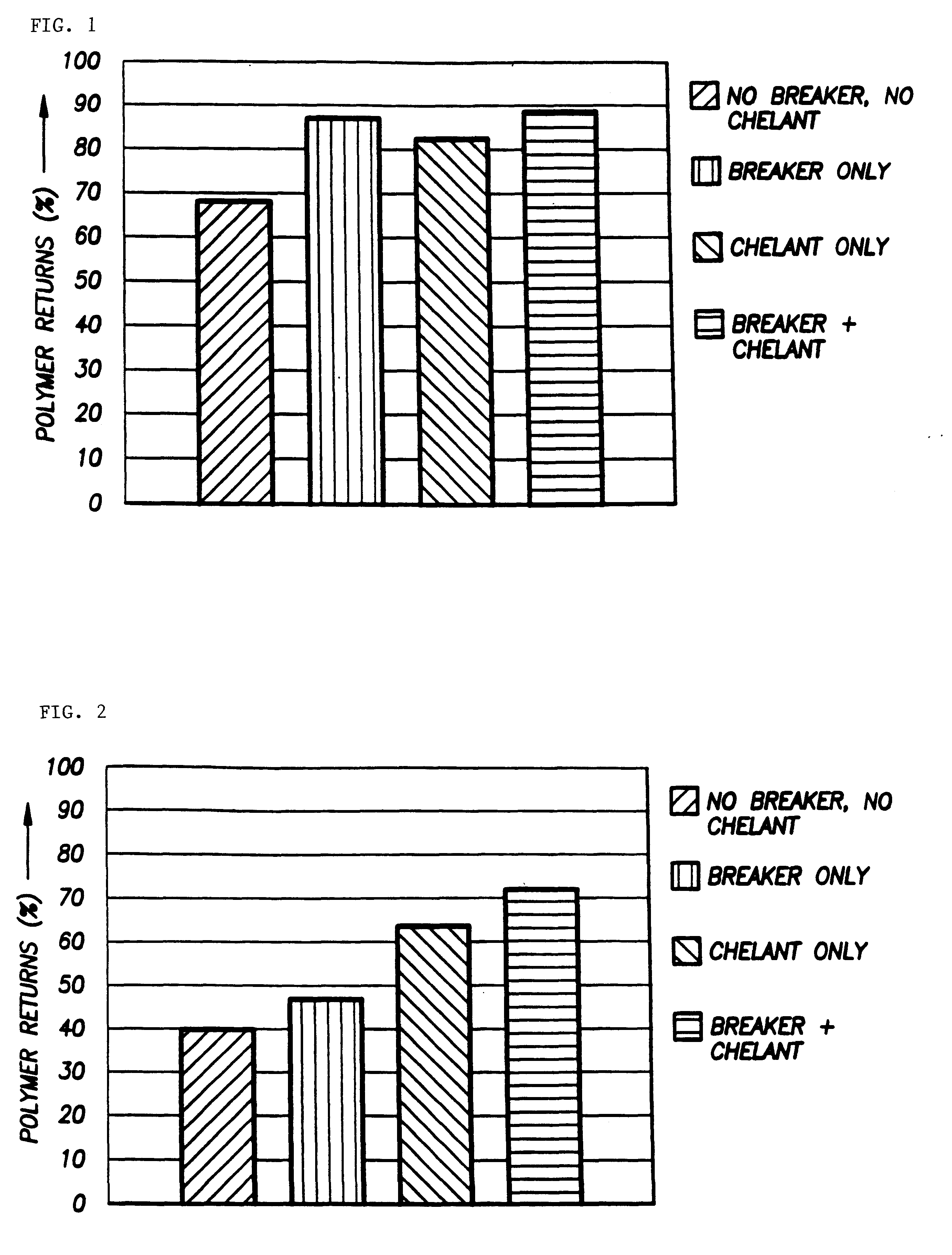
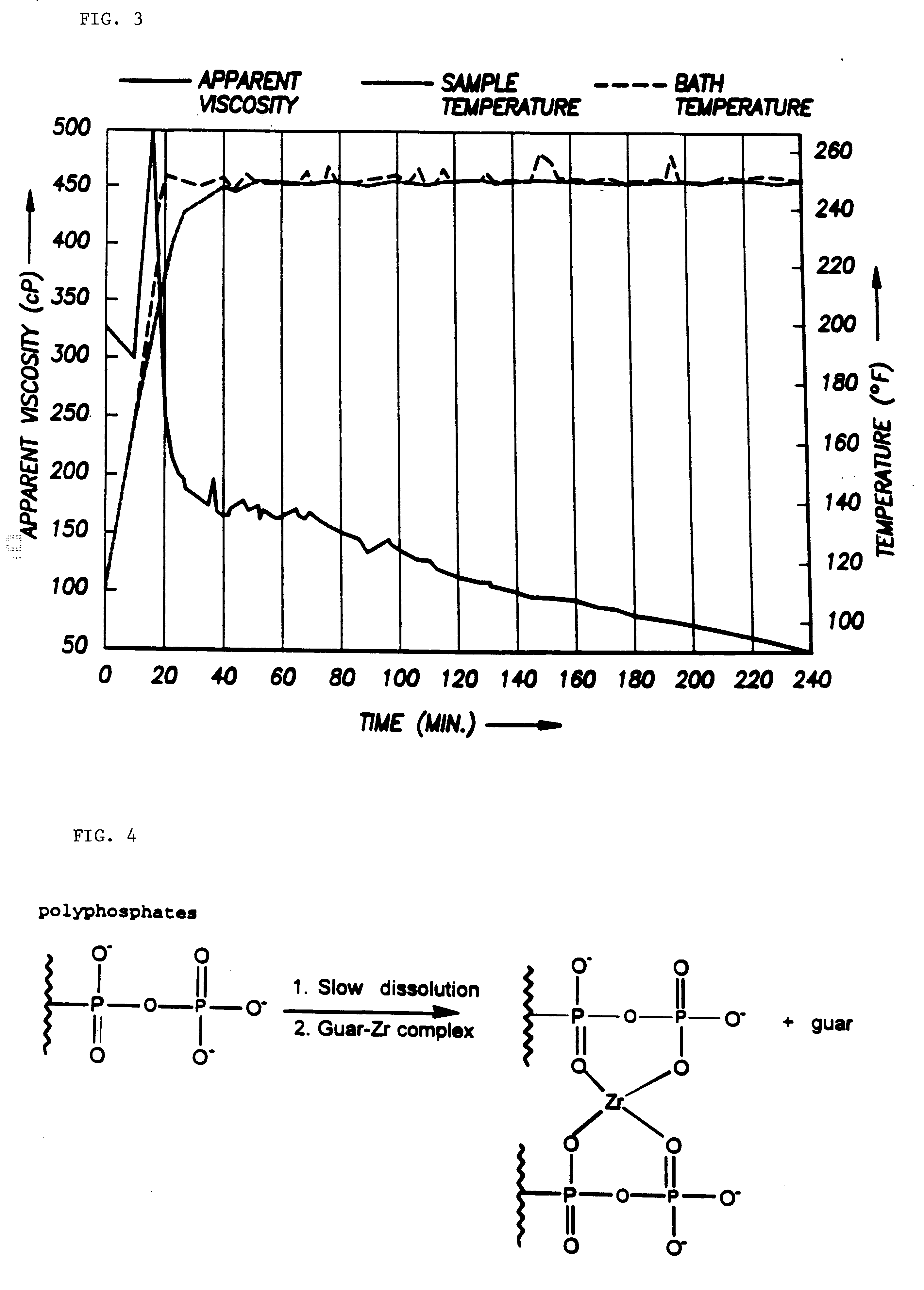
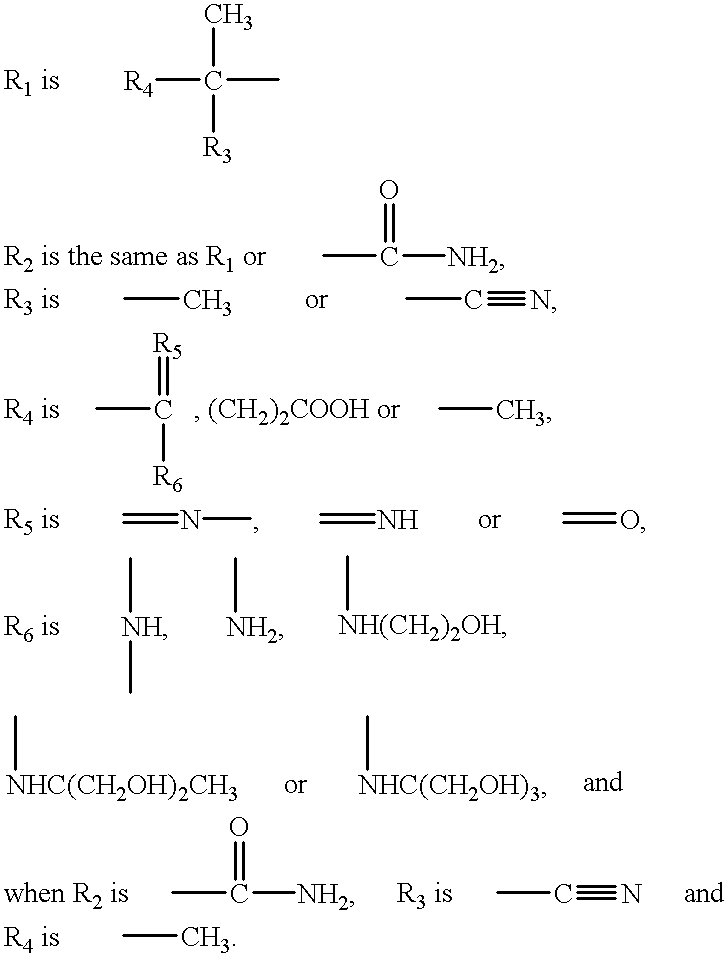
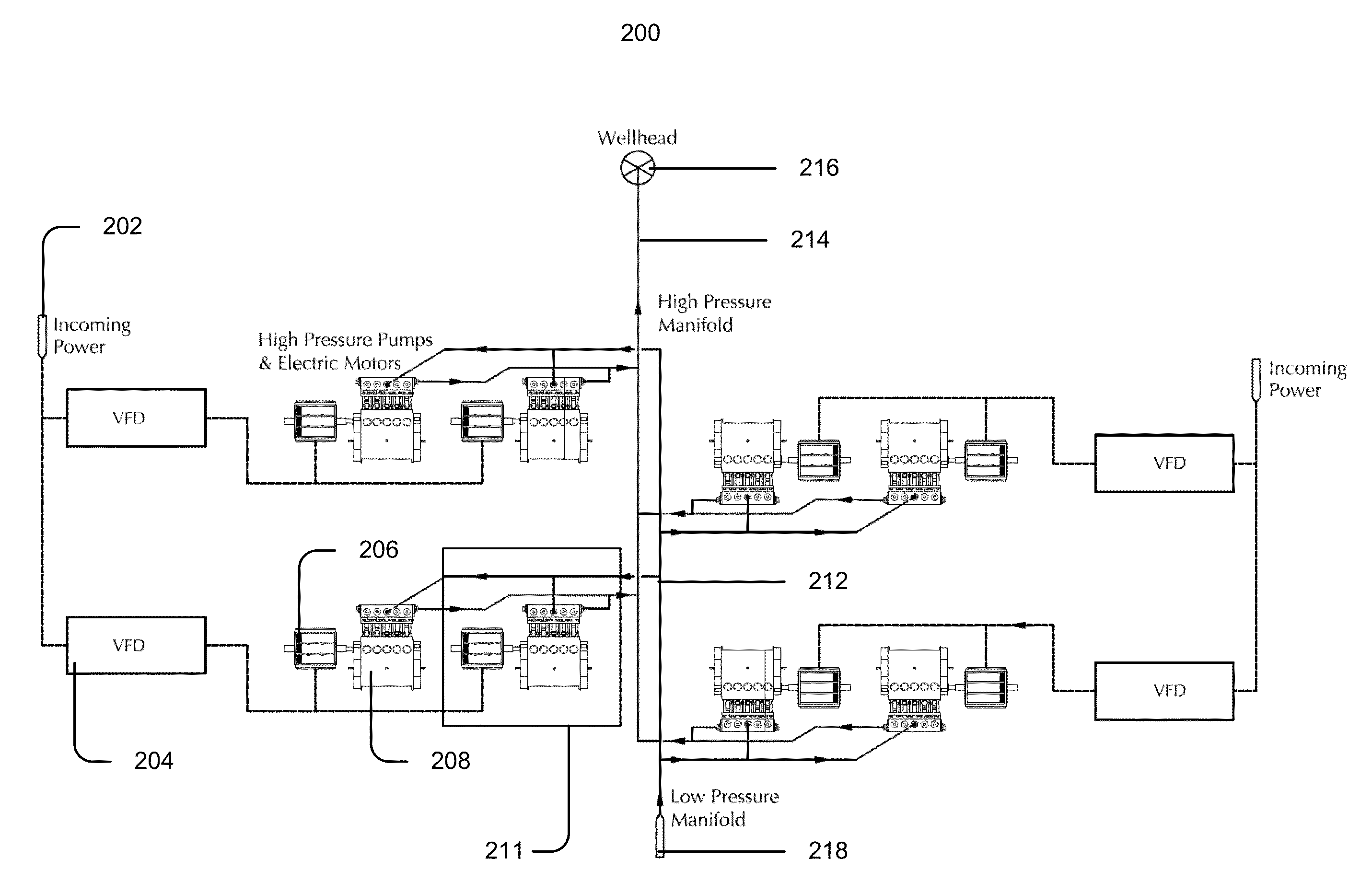
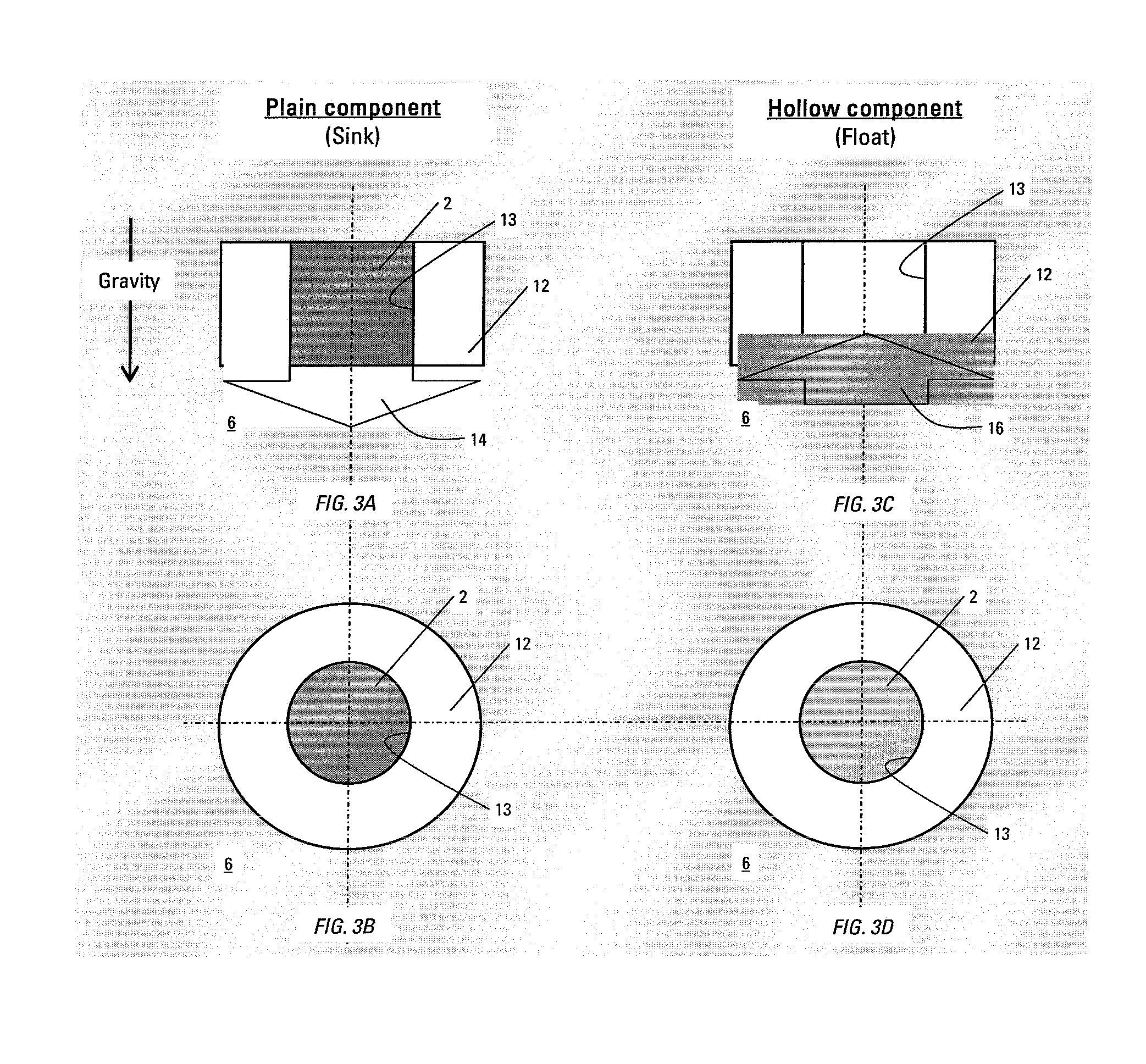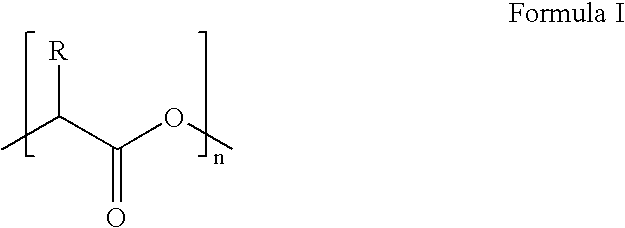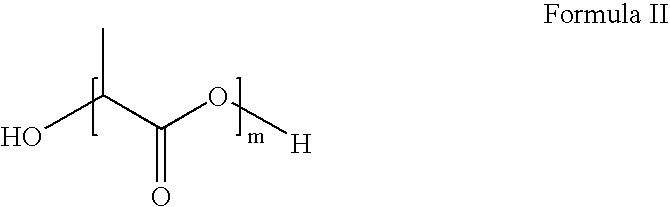Patents
Literature
29989results about "Drilling composition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
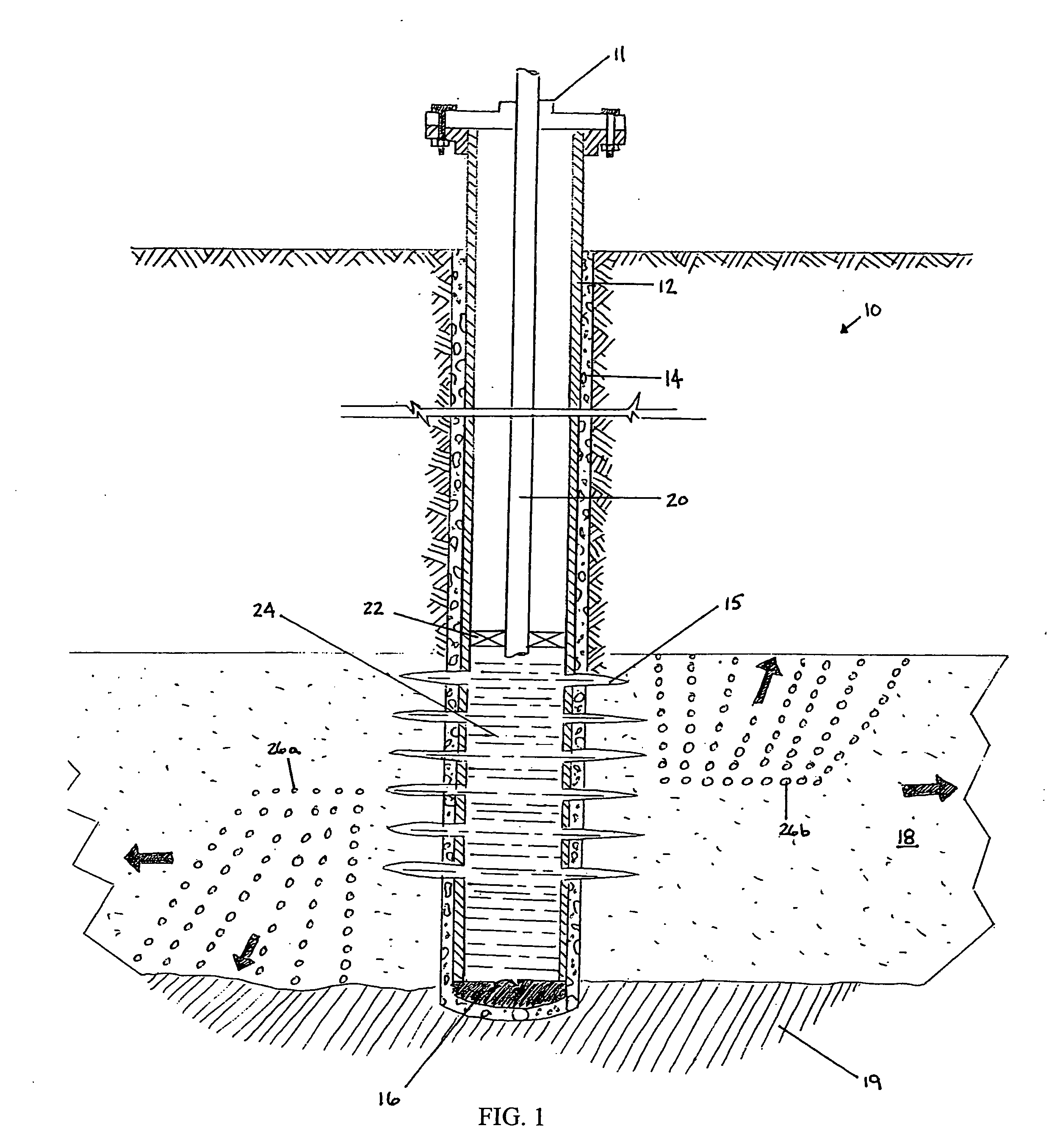
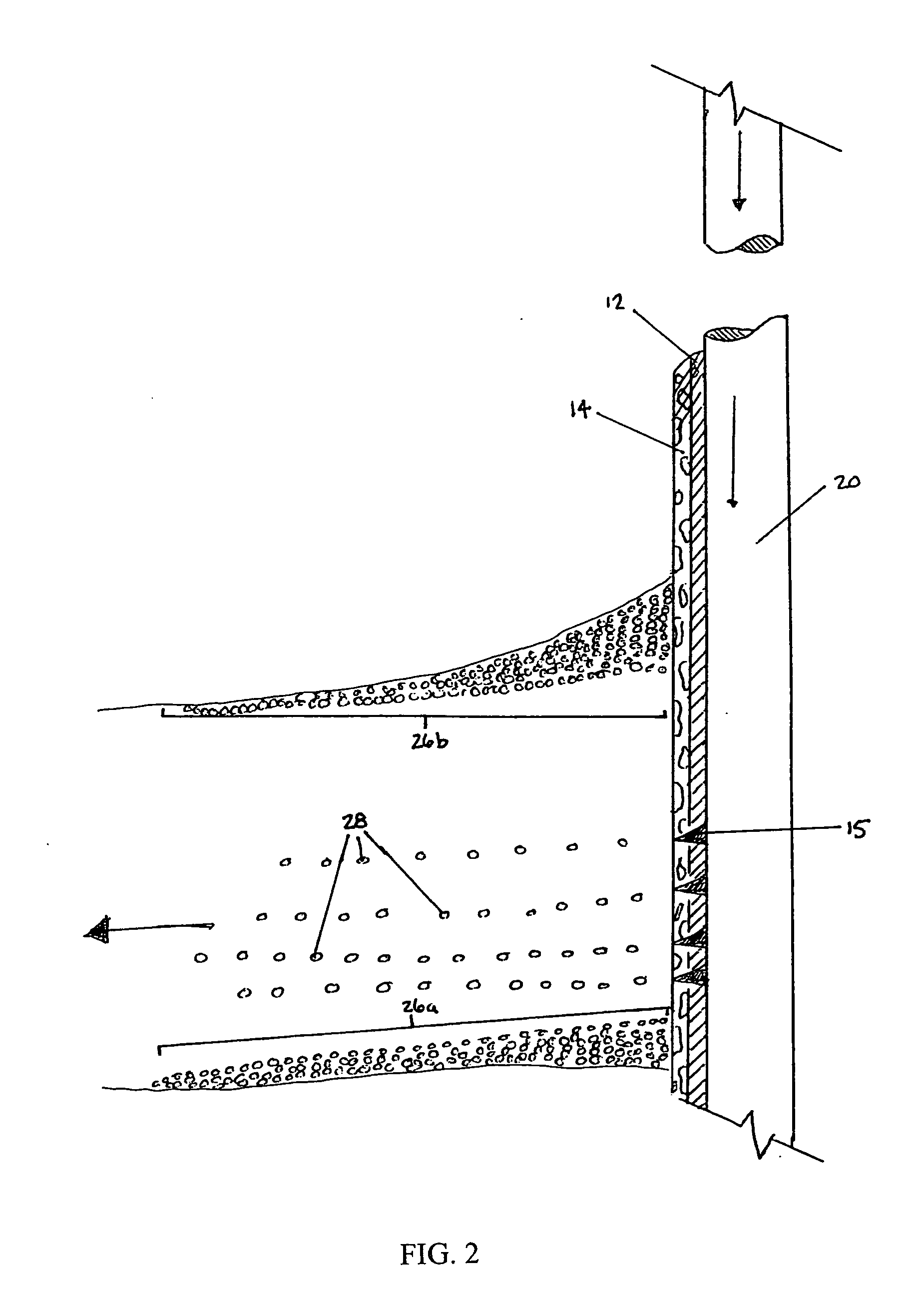
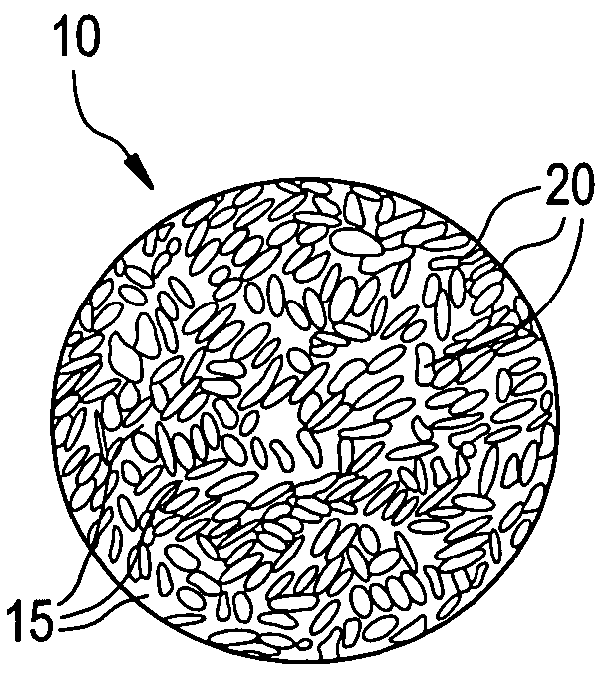
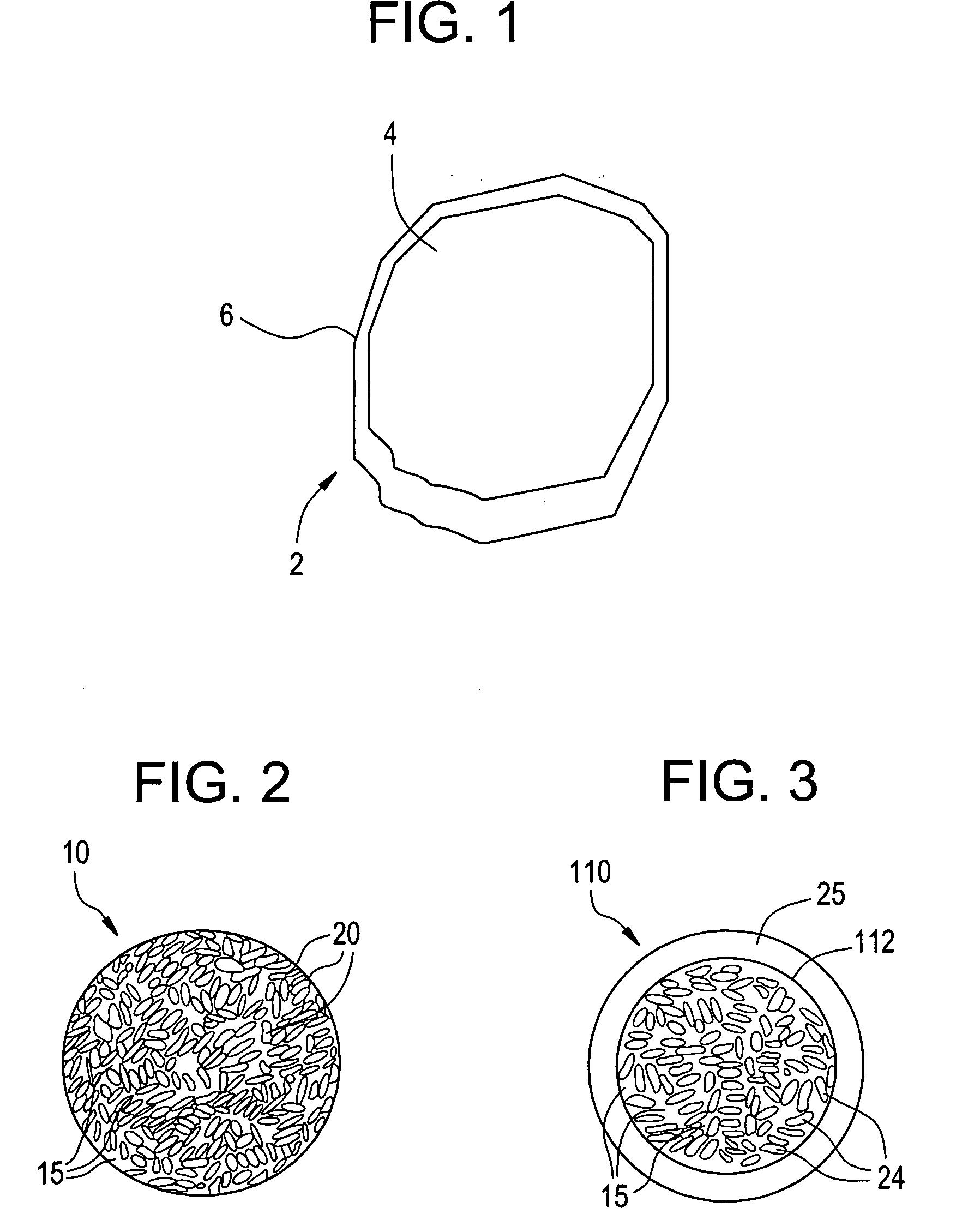
Composite proppant, composite filtration media and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS6632527B1Avoid condensationReduce molecular weightPretreated surfacesGlass/slag layered productsFiberFiltration
Composite particles made of a binder and filler material are provided for use in subterranean formations. The filler is finely divided mineral and optional fiber. The particles are proppants useful to prop open subterranean formation fractures. The particles are also useful for water filtration and artificial turf for sports fields. Methods of making the composite particles are also disclosed.< / PTEXT>
Owner:HEXION INC
Low density composite proppant, filtration media, gravel packing media, and sports field media, and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS6582819B2Low densityEasy to transportGranule coatingPretreated surfacesFiltrationArtificial turf
Low density composite particles made of a binder and filler material are provided for use in subterranean formations. The filler includes low density filler and optionally other filler. The binder includes a polymer and optionally cement. The particles may be employed as proppants useful to prop open subterranean formation fractures. The particles are also useful for gravel packing in subterranean formations, water filtration and artificial turf for sports fields. Methods of making the composite particles are also disclosed.
Owner:HEXION INC
Degradable Compositions, Apparatus Comprising Same, and Method of Use
InactiveUS20070181224A1Improve responseSafe handlingDrilling compositionSealing/packingElemental compositionSubject matter
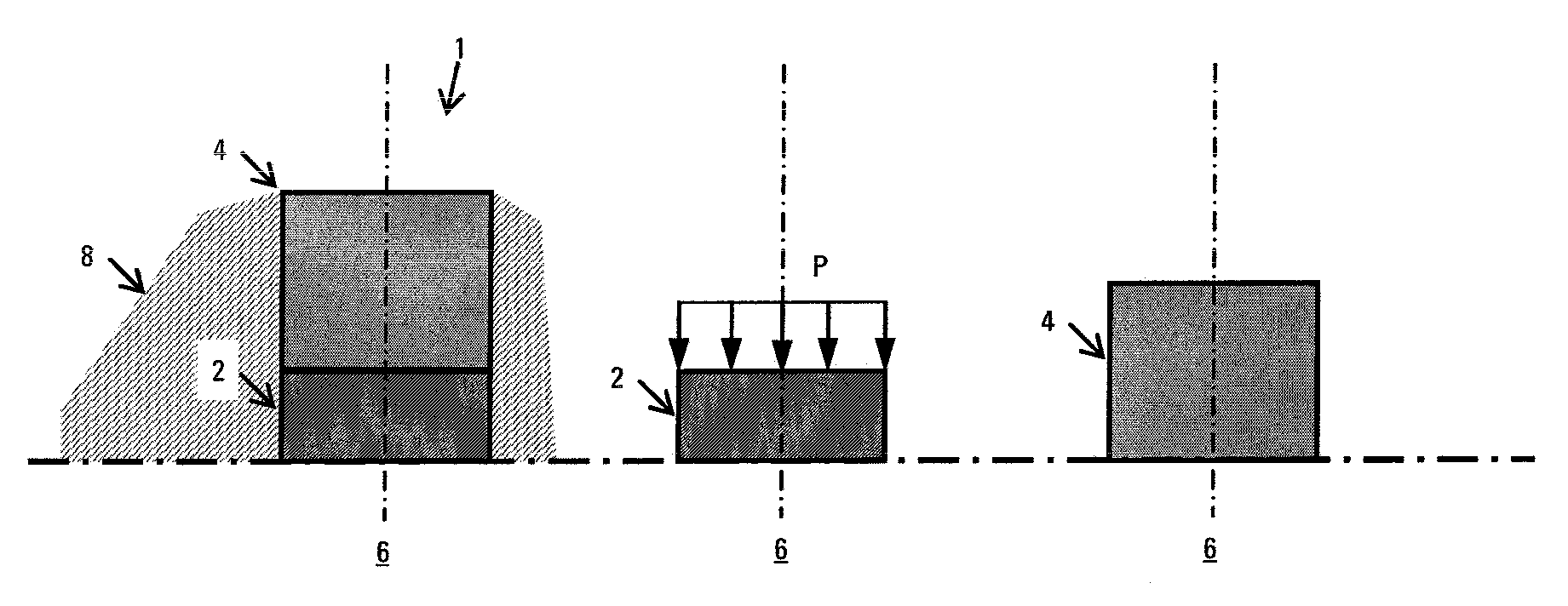
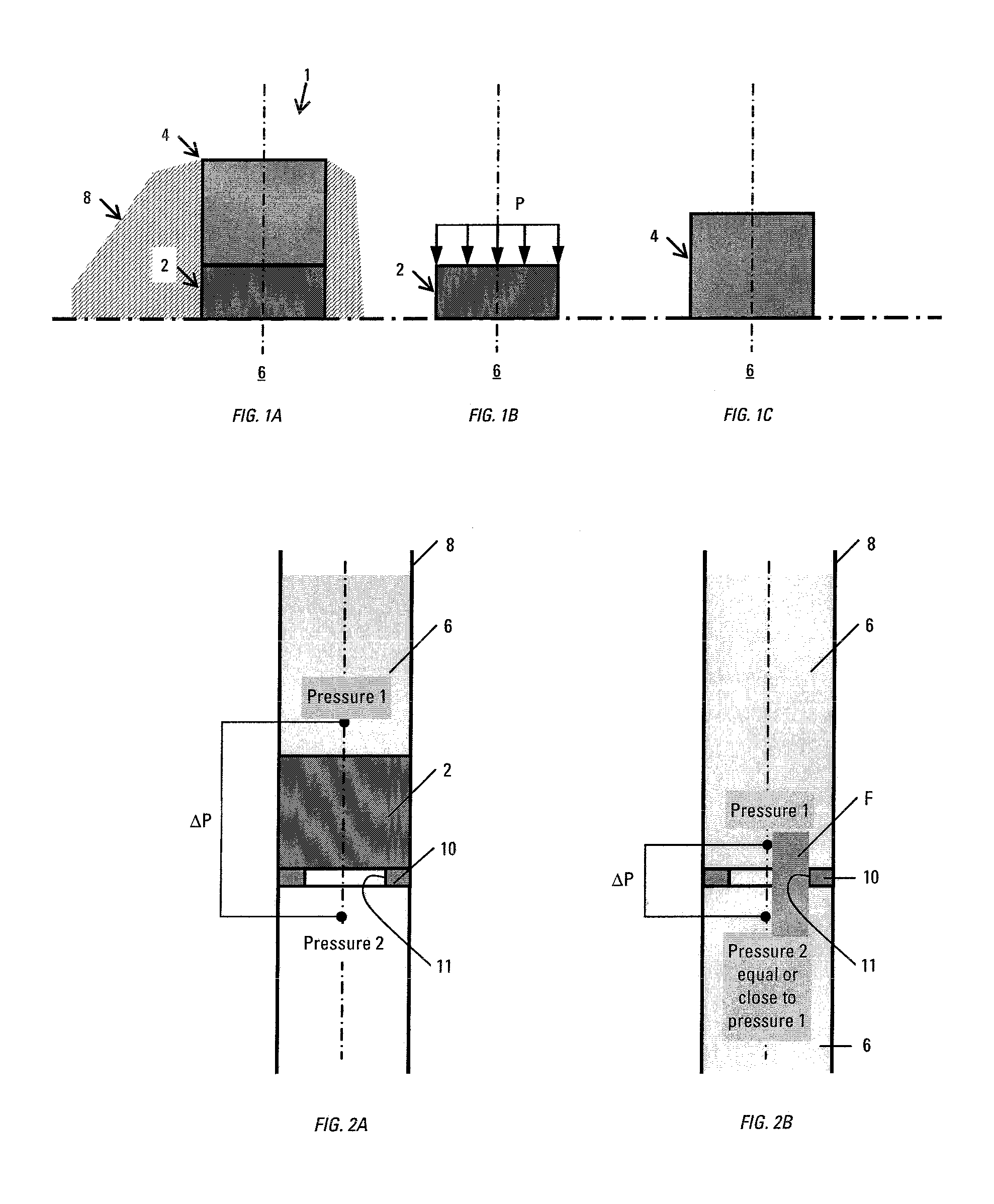
Compositions, apparatus incorporating a composition, and methods of use are described, one composition embodiment consisting essentially of one or more reactive metals in major proportion, and one or more alloying elements in minor proportion, with the provisos that the composition is high-strength, controllably reactive, and degradable under defined conditions. Compositions of the invention may exist in a variety of morphologies, including a reactive metal or degradable alloy processed into an alloy of crystalline, amorphous or mixed structure that may constitute the matrix of other composition, for instance a composite. Methods of using apparatus comprising a composition, particularly in oilfield operations are also described (e.g. flow and displacement control, sensors, actuators). This abstract allows a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure. It will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Generating Acid Downhole in Acid Fracturing
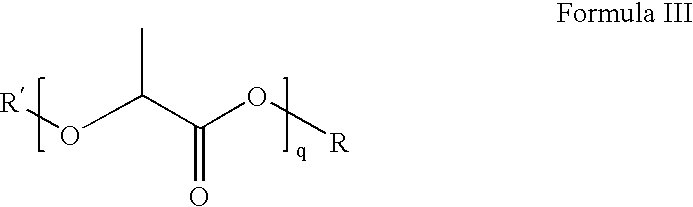
An acid fracturing method is provided in which the acid is generated in the fracture by hydrolysis of a solid acid-precursor selected from one or more than one of lactide, glycolide, polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid, a copolymer of polylactic acid and polyglycolic acid, a copolymer of glycolic acid with other hydroxy-, carboxylic acid-, or hydroxycarboxylic acid-containing moieties, and a copolymer of lactic acid with other hydroxy-, carboxylic acid or hydroxycarboxylic acid-containing moieties. The solid acid-precursor may be mixed with a solid acid-reactive material to accelerate the hydrolysis and / or coated to slow the hydrolysis. Water-soluble liquid compounds are also given that accelerate the hydrolysis. The method ensures that the acid contacts fracture faces far from the wellbore.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Reduced-density proppants and methods of using reduced-density proppants to enhance their transport in well bores and fractures
InactiveUS20050006095A1Easy to transportImprove conductivitySynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsParticulatesMaterials science
The present invention provides reduced-density coated particulates and methods for enhancing the transport of such particulates into well bores and fractures, and for enhancing the conductivity and permeability of subterranean formations using such particulates, and for sand control treatments using such particulates. The reduced-density, coated particulates of the present invention generally comprise particulate having a surface and a coating wherein the surface comprises a porous or partially hollow geometry and coating is capable of trapping a fluid between the particulate's surface and the coating.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Proppants with fiber reinforced resin coatings
InactiveUS6528157B1High compressive strengthWithstanding stressCeramic layered productsDrilling compositionParticulatesResin coating
Coated particles made of particulate substrates having a coating of resin and fibrous material are provided for use in subterranean formations. The coated substrate particles are proppants useful to prop open subterranean formation fractures. The coated substrate particles are also useful for sand control, that is, acting as a filter or screen to prevent backwards flow of sand, other proppants or subterranean formation particles. Methods of making the coated particles are also disclosed.
Owner:HEXION INC
Degradable Material Assisted Diversion
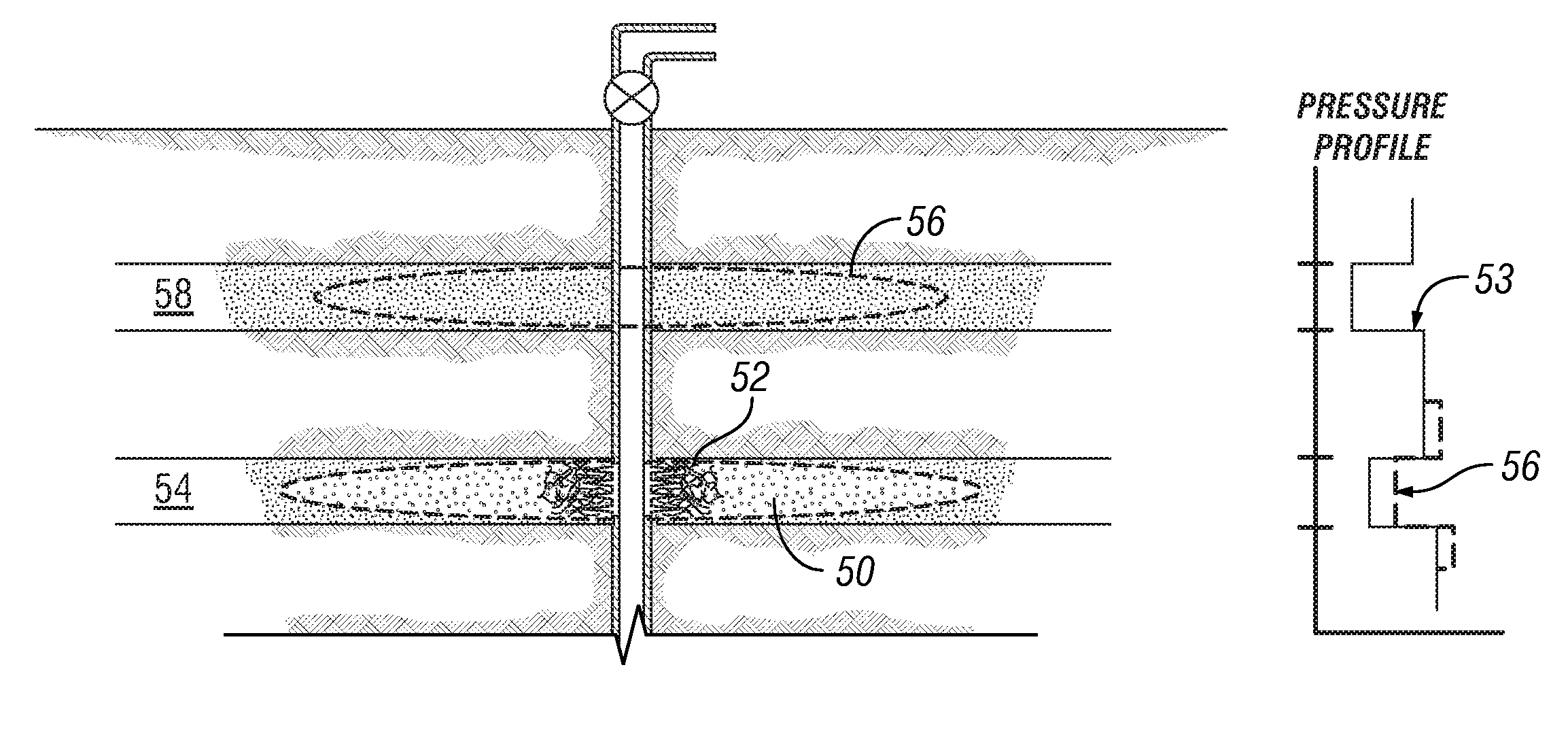
Degradable material assisted diversion (DMAD) methods for well treatment, DMAD treatment fluids, and removable plugs for DMAD in downhole operations. A slurry of solid degradable material is injected into the well, a plug of the degradable material is formed, a downhole operation is performed around the plug diverter, and the plug is then degraded for removal. Degradation triggers can be temperature or chemical reactants, with optional accelerators or retarders to provide the desired timing for plug removal. In multilayer formation DMAD fracturing, the plug isolates a completed fracture while additional layers are sequentially fractured and plugged, and then the plugs are removed for flowback from the fractured layers. In DMAD fluids, an aqueous slurry can have a solids phase including a degradable material and a fluid phase including a viscoelastic surfactant. The solids phase can be a mixture of fibers and a particulate material.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Low density composite proppant, filtration media, gravel packing media, and sports field media, and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS20020048676A1Point becomes highImprove interfacial organic-inorganic adhesionPigmenting treatmentDead plant preservationFiltrationArtificial turf
Low density composite particles made of a binder and filler material are provided for use in subterranean formations. The filler includes low density filler and optionally other filler. The binder includes a polymer and optionally cement. The particles may be employed as proppants useful to prop open subterranean formation fractures. The particles are also useful for gravel packing in subterranean formations, water filtration and artificial turf for sports fields. Methods of making the composite particles are also disclosed.
Owner:HEXION INC
Oilfield Elements Having Controlled Solubility and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20070107908A1Ease of the element traversingFluid removalDrilling compositionPolyamideSubject matter
Oilfield elements are described, one embodiment comprising a combination of a normally insoluble metal with an element selected from a second metal, a semi-metallic material, and non-metallic materials; and one or more solubility-modified high strength and / or high-toughness polymeric materials selected from polyamides, polyethers, and liquid crystal polymers. Methods of using the oilfield elements in oilfield operations are also described. This abstract allows a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure. It will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
In situ thermal processing of a hydrocarbon containing formation using a controlled heating rate
InactiveUS6745837B2High calorific valueImprove the heating effectSurveyCombustion processFormation fluidHeat energy
A hydrocarbon containing formation may be treated using an in situ thermal process. A mixture of hydrocarbons, H.sub.2, and / or other formation fluids may be produced from the formation. Heat may be applied to the formation to raise a temperature of a portion of the formation to a pyrolysis temperature. A heating rate to a selected volume of the formation may be controlled by altering an amount of heating energy per day that is provided to the selected volume.
Owner:SALAMANDER SOLUTIONS INC
Alkaline surfactant polymer flooding composition and process
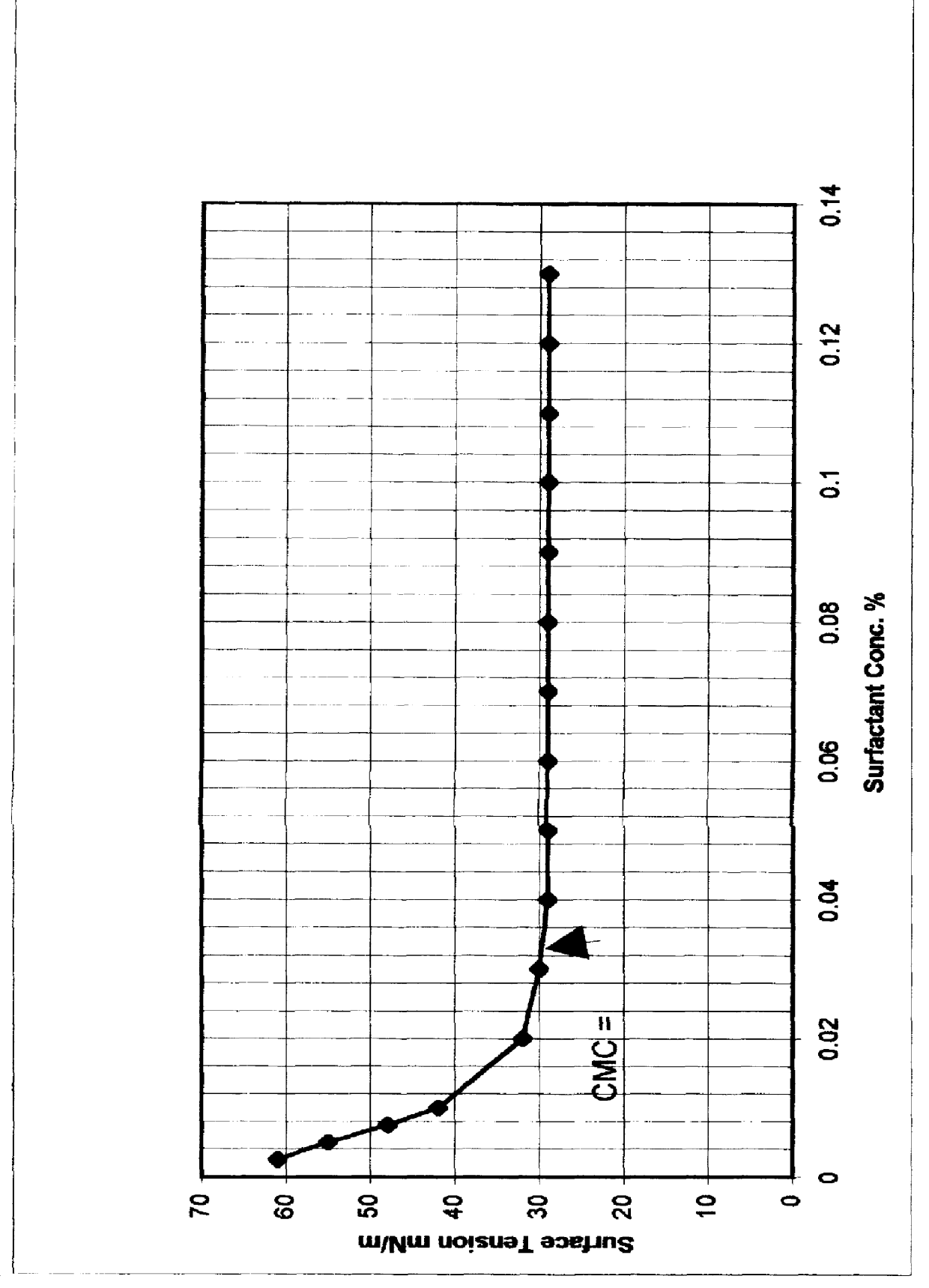
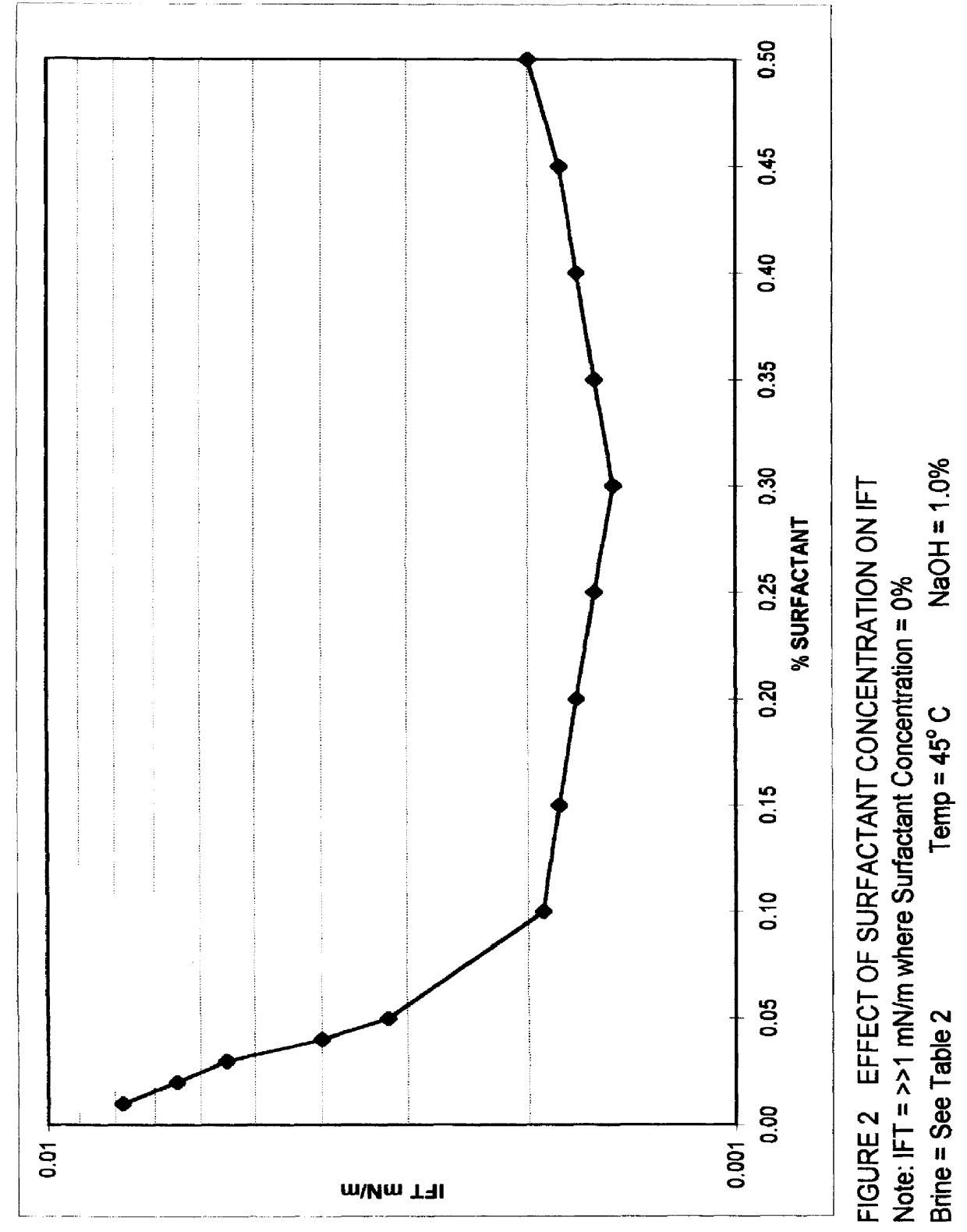
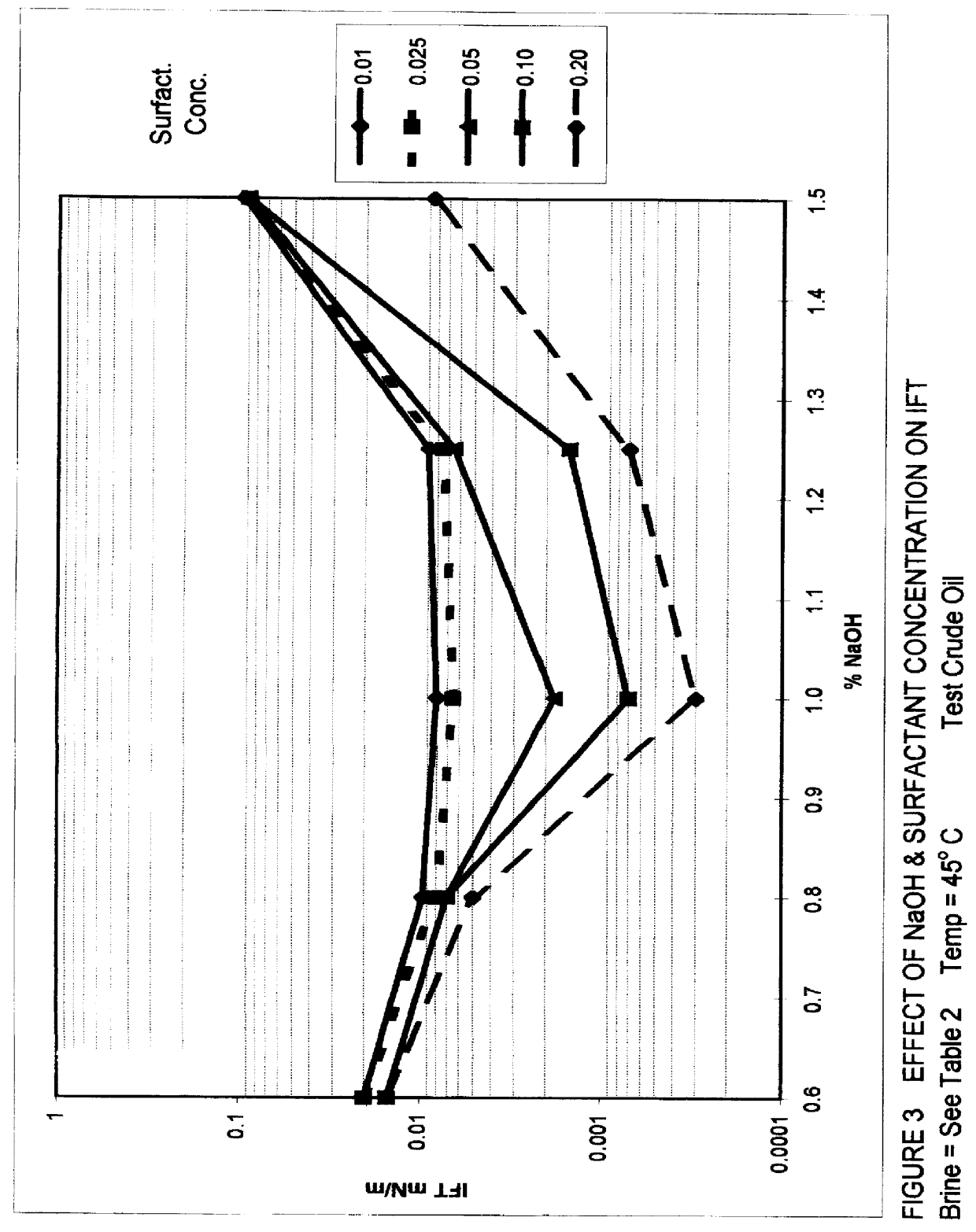
An improved concentrated surfactant formulation and process for the recovery of residual oil from subterranean petroleum reservoirs, and more particularly an improved alkali surfactant flooding process which results in ultra-low interfacial tensions between the injected material and the residual oil, wherein the concentrated surfactant formulation is supplied at a concentration above, at, or, below its CMC, also providing in situ formation of surface active material formed from the reaction of naturally occurring organic acidic components with the injected alkali material which serves to increase the efficiency of oil recovery.
Owner:OIL CHEM TECH
Method Of Manufacture And The Use Of A Functional Proppant For Determination Of Subterranean Fracture Geometries
ActiveUS20090288820A1Accurate imagingPromote recoveryMaterial nanotechnologyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingElectricityGeophone
Proppants having added functional properties are provided, as are methods that use the proppants to track and trace the characteristics of a fracture in a geologic formation. Information obtained by the methods can be used to design a fracturing job, to increase conductivity in the fracture, and to enhance oil and gas recovery from the geologic formation. The functionalized proppants can be detected by a variety of methods utilizing, for example, an airborne magnetometer survey, ground penetrating radar, a high resolution accelerometer, a geophone, nuclear magnetic resonance, ultra-sound, impedance measurements, piezoelectric activity, radioactivity, and the like. Methods of mapping a subterranean formation are also provided and use the functionalized proppants to detect characteristics of the formation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Soluble deverting agents
Methods and compositions for stimulating single and multiple intervals in subterranean wells by diverting well treatment fluids into a particular direction or into multiple intervals using water soluble coated diverting agents are described. The water soluble coating of the diverting material is preferably a collagen, poly(alkylene) oxide, poly(lactic acid), polyvinylacetate, polyvinylalcohol, polyvinylacetate / polyvinylalcohol polymer or a mixture thereof applied as a coating on any number of proppants. The method allows for the diverting of the flow of fluids in a downhole formation during a well treatment, such as during a fracturing process. Following completion of a treatment such as a hydraulic stimulation, the soluble diverting agent can be dissolved and removed by the water component of the well production.
Owner:FAIRMOUNT SANTROL
Compositions and methods for controlling the release of chemicals placed on particulates
InactiveUS20050028976A1Simple methodSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsParticulatesCompound (substance)
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for creating and using particulate materials having treating agents absorbed thereon and coated with a degradable coating material. One embodiment of a method of the present invention provides a method treating to a subterranean formation comprising placing a coated, treated particulate into a subterranean formation wherein the coated, treated particulate comprises a particulate material having a treating agent placed thereon and a substantially complete layer of a degradable coating material coated placed thereon over the treating agent.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
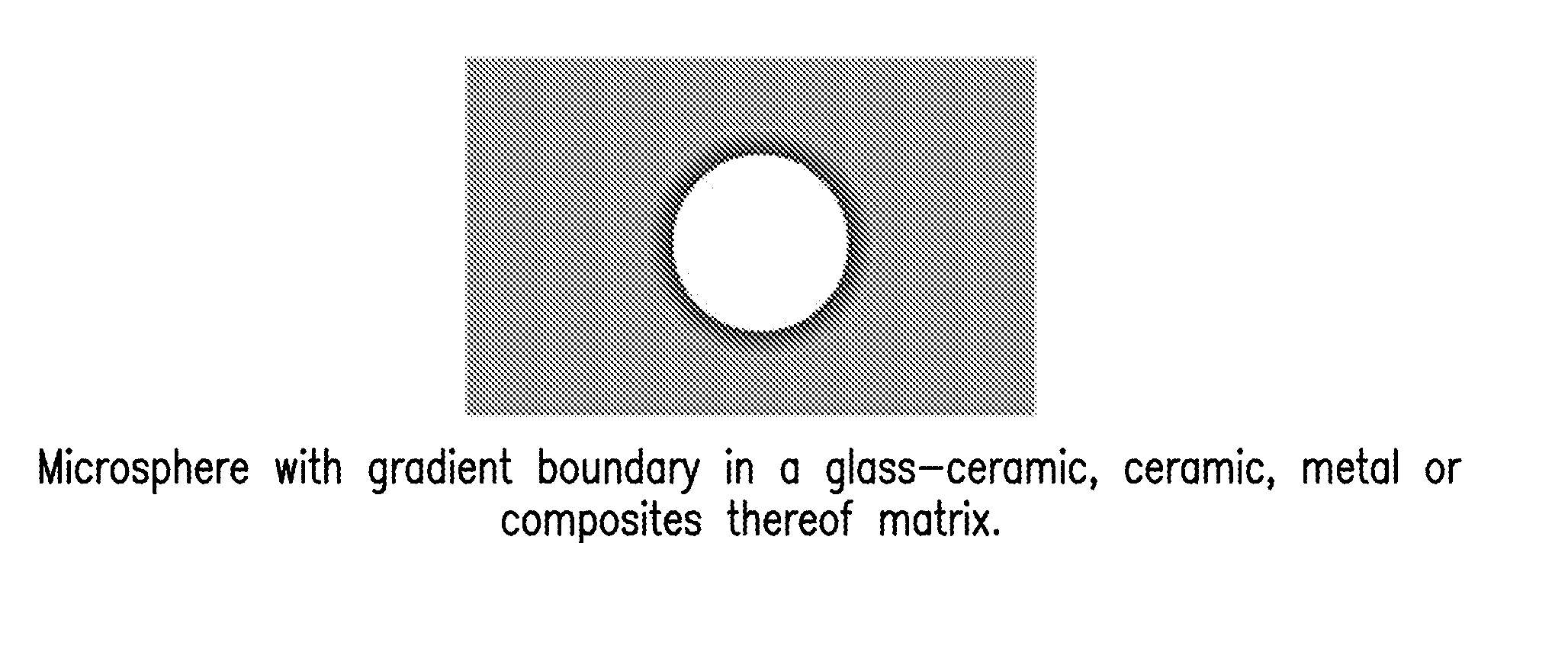
Ceramic Particles With Controlled Pore and/or Microsphere Placement and/or Size and Method Of Making Same
InactiveUS20110160104A1Improve balanceFluid removalCeramic shaping apparatusMicrosphereHigh intensity
The present invention relates to lightweight high strength microsphere containing ceramic particles having controlled microsphere placement and / or size and microsphere morphology, which produces an improved balance of specific gravity and crush strength such that they can be used in applications such as proppants to prop open subterranean formation fractions. Proppant formulations are further disclosed which use one or more microsphere containing ceramic particles of the present invention. Methods to prop open subterranean formation fractions are further disclosed. In addition, other uses for the microsphere containing ceramic particles of the present invention are further disclosed, as well as methods of making the microsphere containing ceramic particles.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
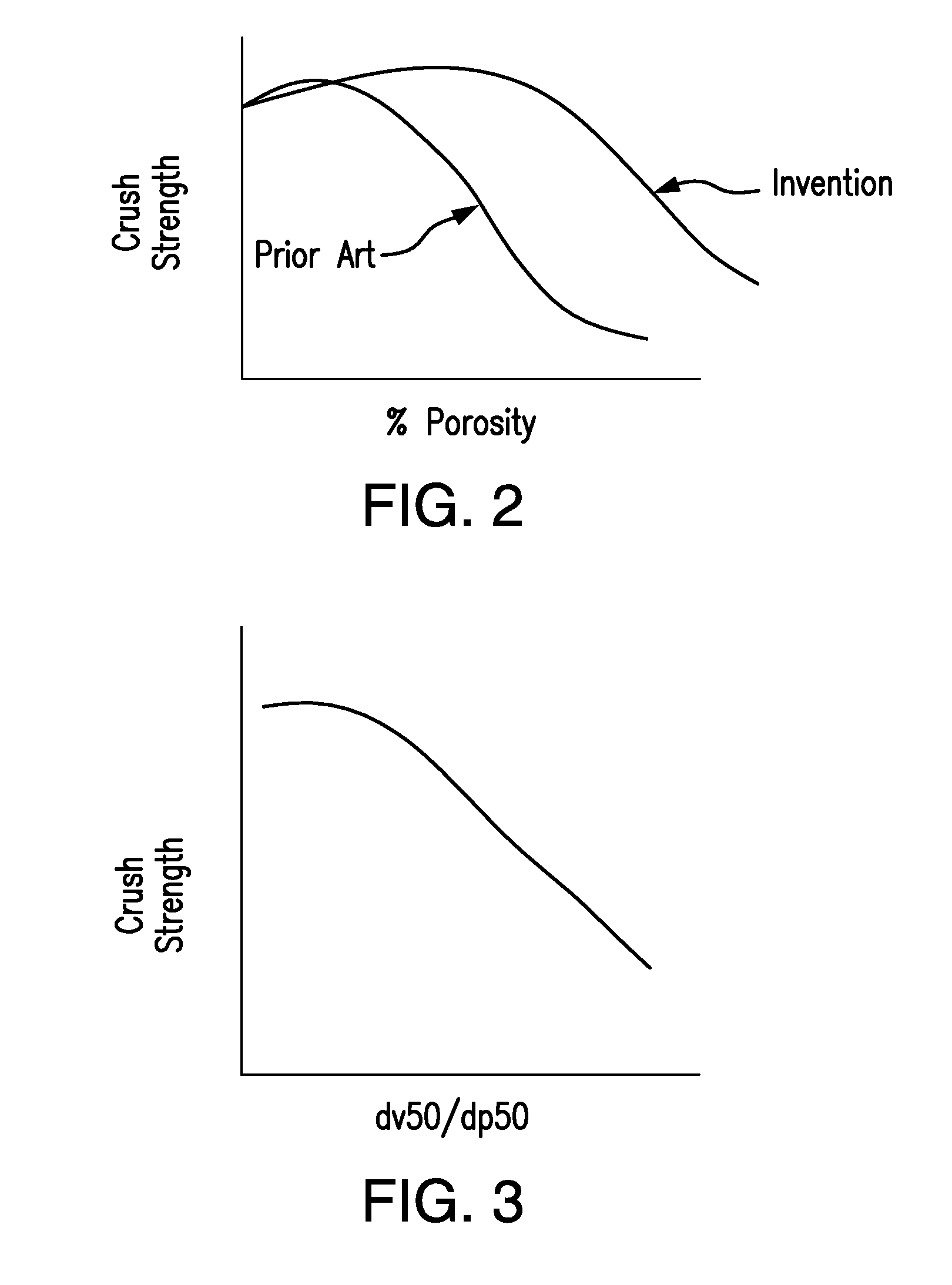
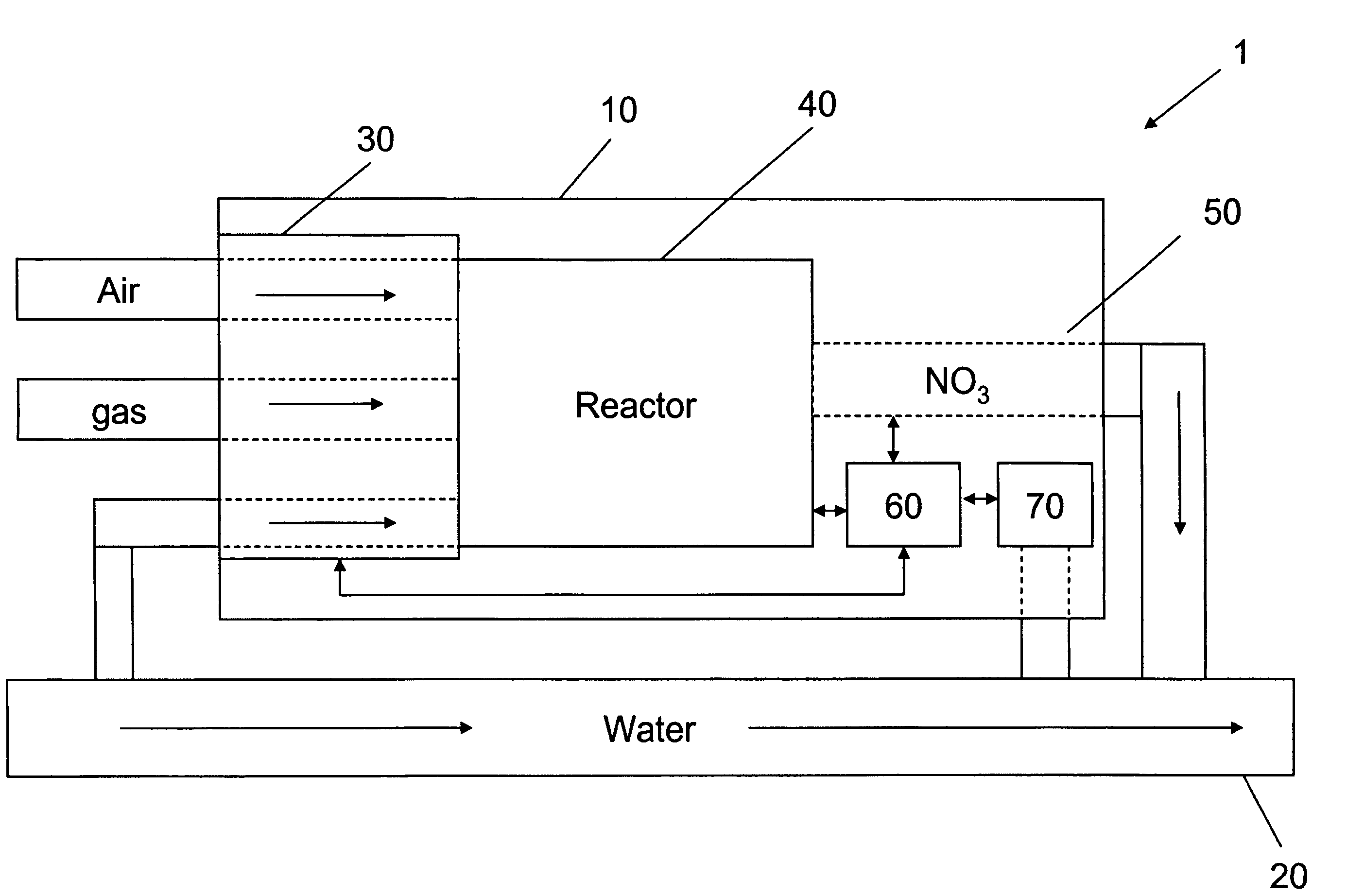
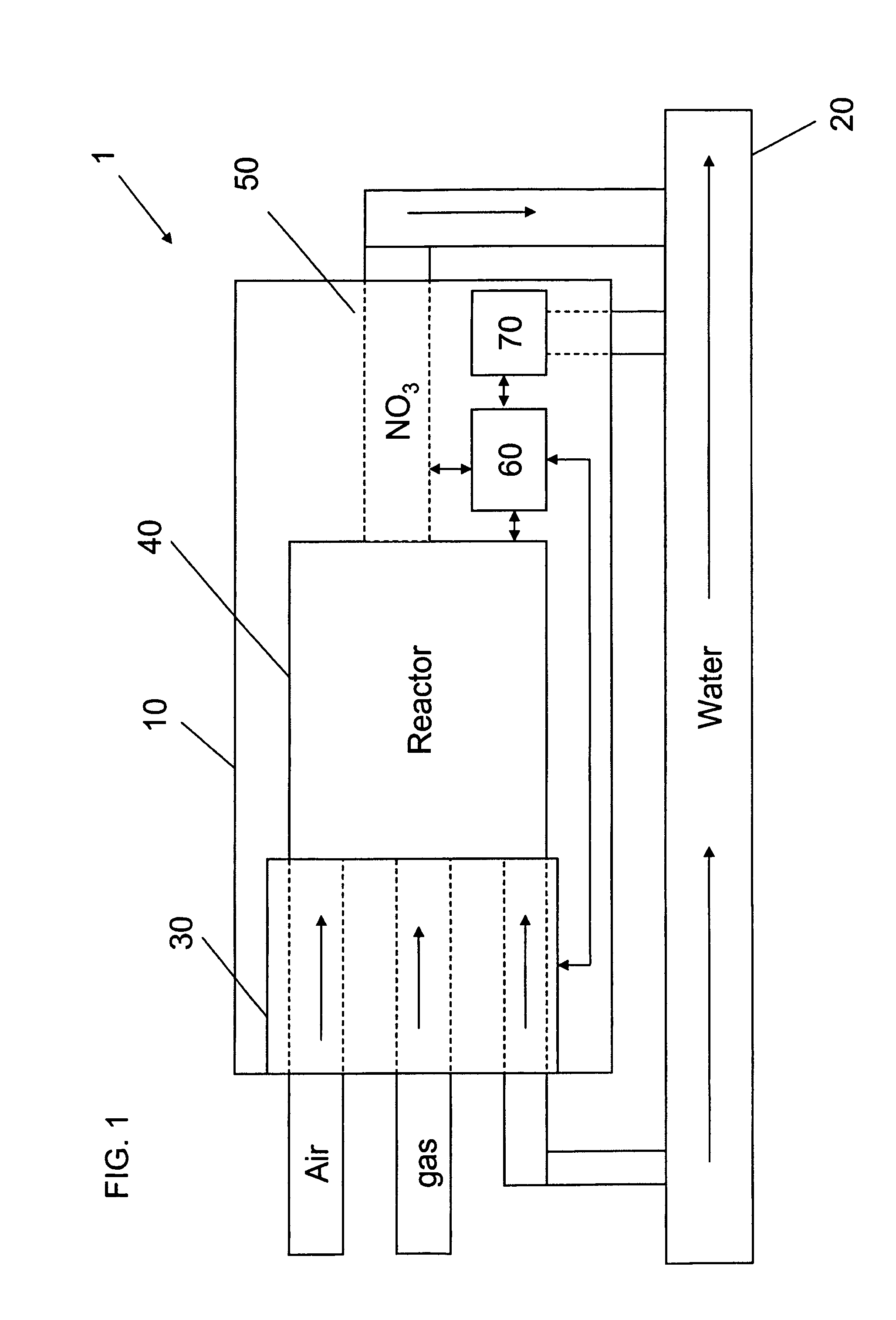
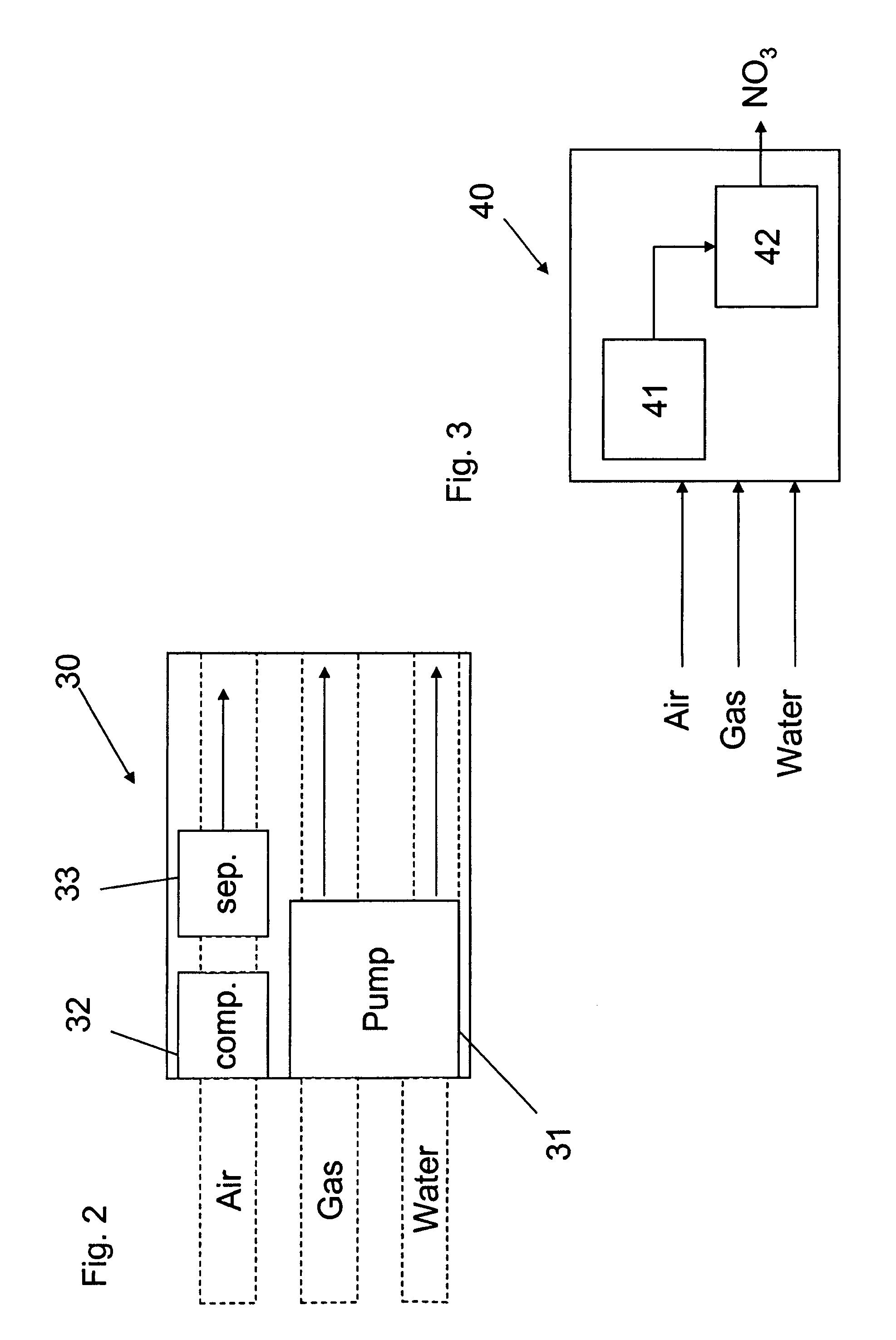
Apparatus for on-site production of nitrate ions
InactiveUS7514058B1Enhanced overall recoveryWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsMicrobial enhanced oil recoverySulfate-reducing bacteria
An apparatus and method produces nitrate ions on-site from water, natural gas and air extracted in proximity to the apparatus. The apparatus generates nitrate ions and brings the nitrate ions into contact with an aqueous system. Hydrogen sulfide present in the aqueous system is removed and the production of hydrogen sulfide by sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) is eliminated by introducing into the system nitrate ions, whereby denitrifying microorganisms, using nitrate, outcompete the sulfate-reducing bacteria for the available carbon nutrients, thus preventing the SRB from producing hydrogen sulfide. Nitrate ions generated by the apparatus and added to the aqueous system which contains the denitrifying microorganisms can enhance oil recovery by means of microbial enhanced oil recovery mechanisms.
Owner:NITRA GEN LLC
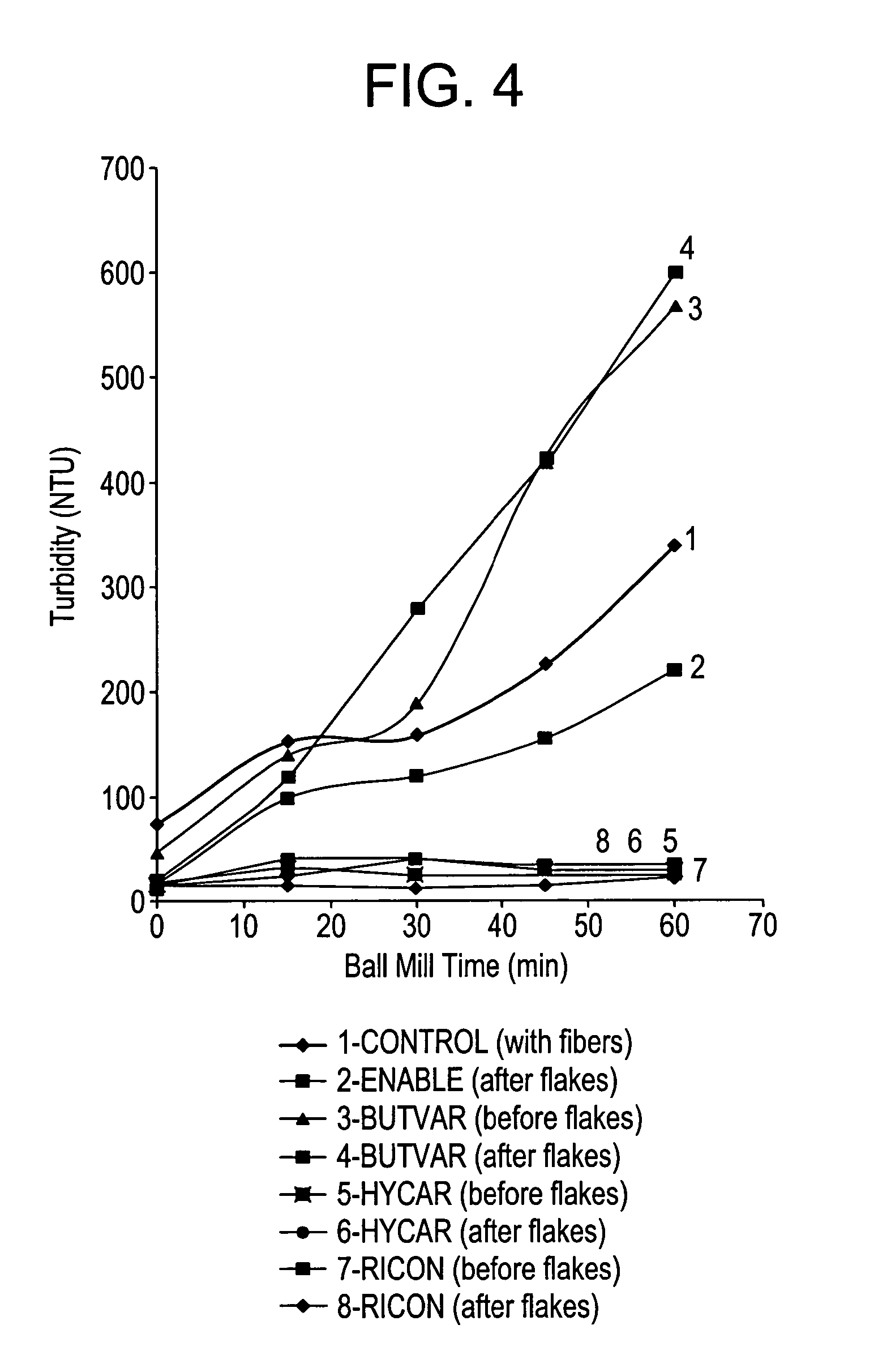
Particulate material containing thermoplastics and methods for making and using the same
ActiveUS20050019574A1Retain and enhance proppant propertyReducing dust formationPretreated surfacesDrilling compositionThermoplasticPolymer chemistry
Disclosed herein is a particle comprising a particulate substrate; and a thermoplastic elastomer present on or in the substrate as an amount sufficient to improve the dust suppression of the particle above that which would occur if the thermoplastic elastomer was absent. Disclosed herein is a particle comprising a particulate substrate; and a thermoplastic elastomer, wherein the particle has a compressive strength retention of greater than about 50% as measured by a UCS test and a turbidity of about 10 to 200 NTU after a one hour ball mill test.
Owner:HEXION INC
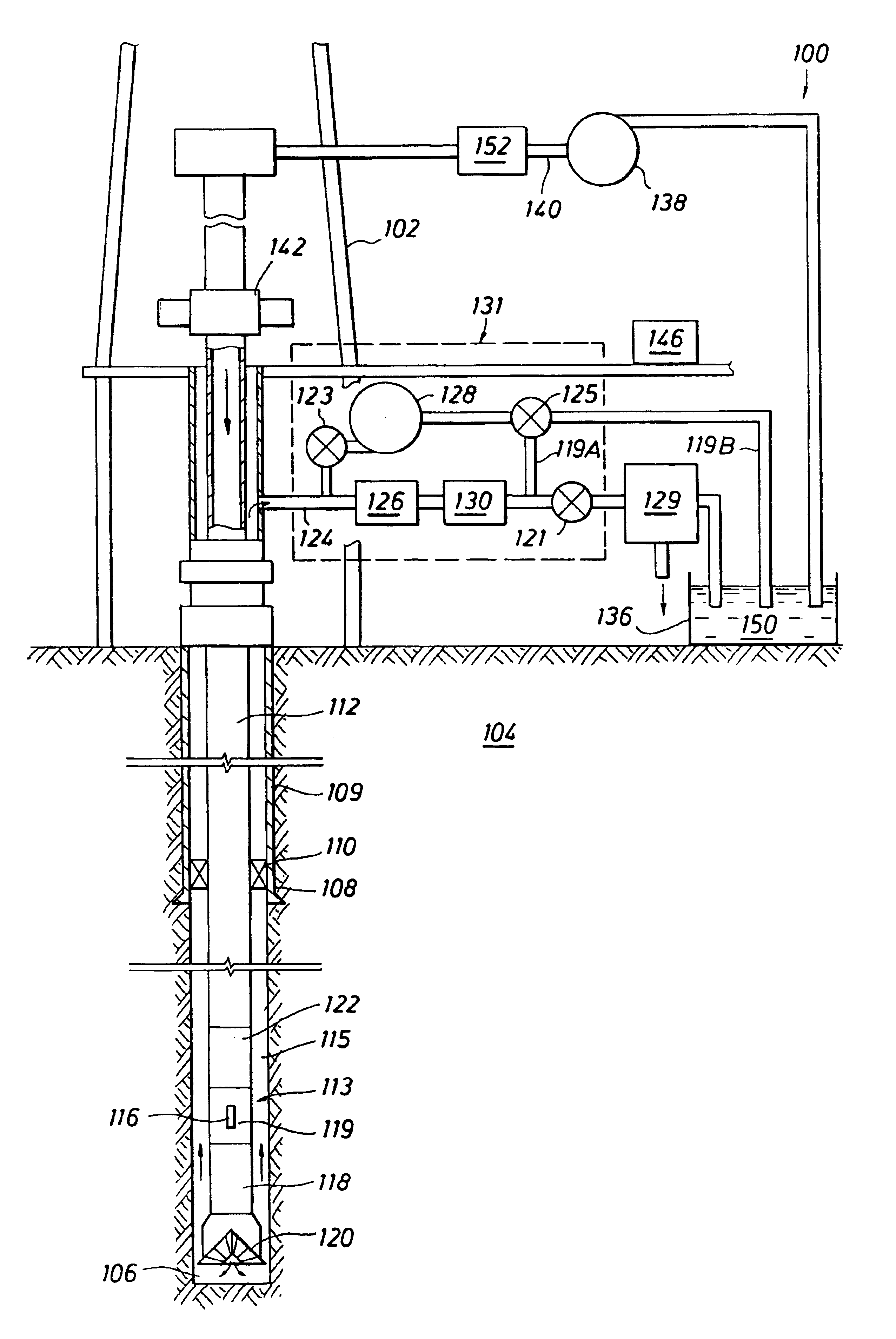
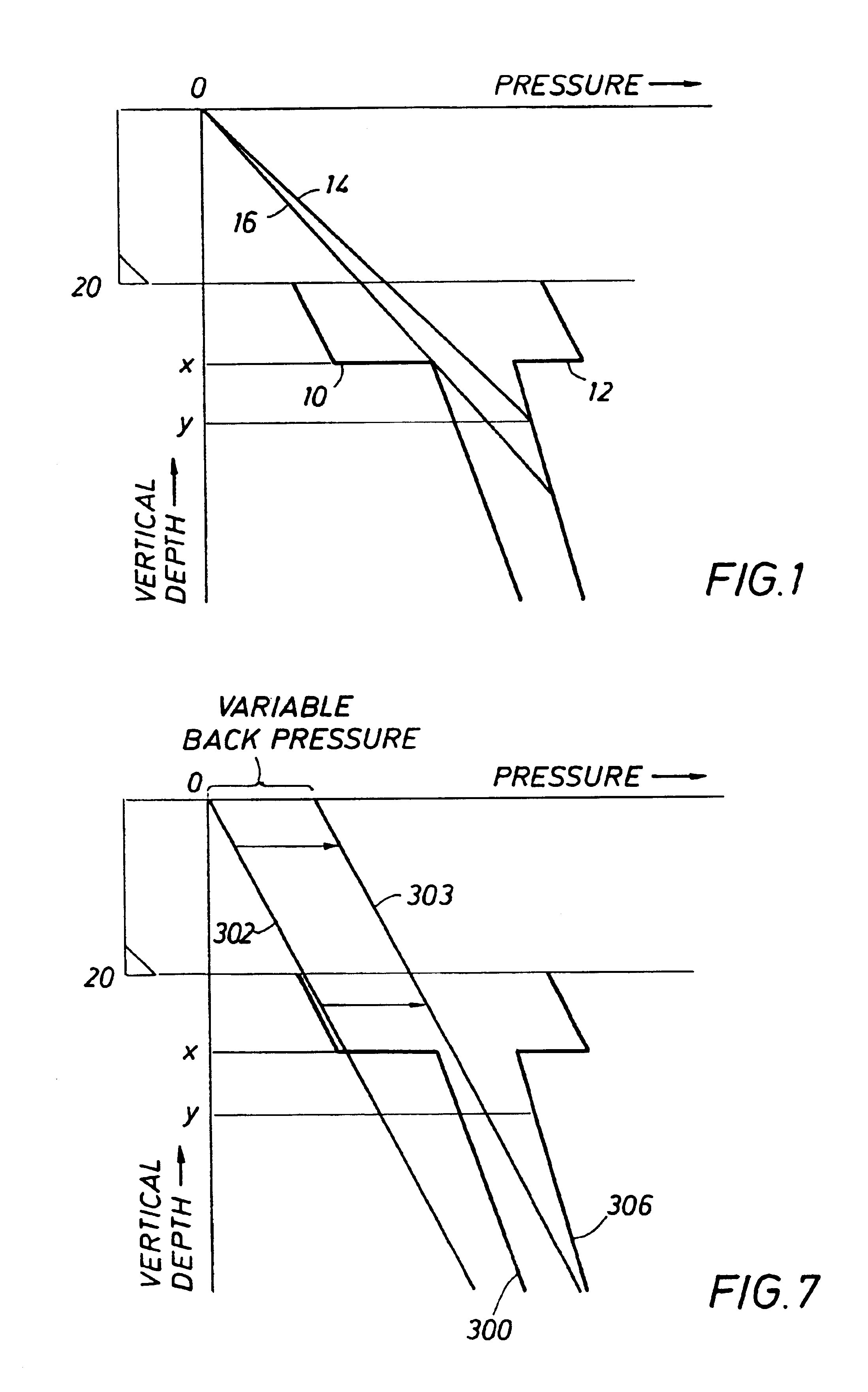
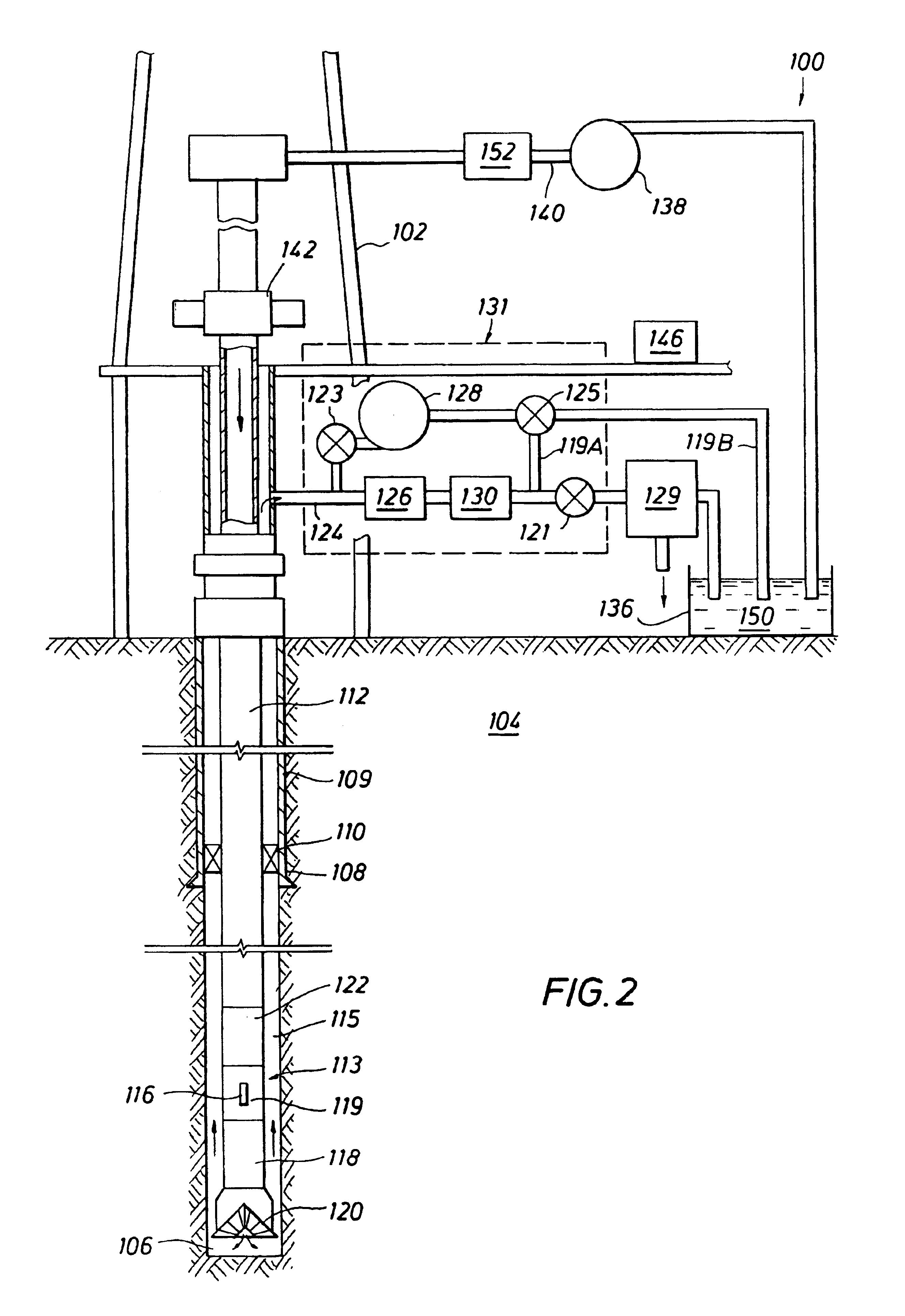
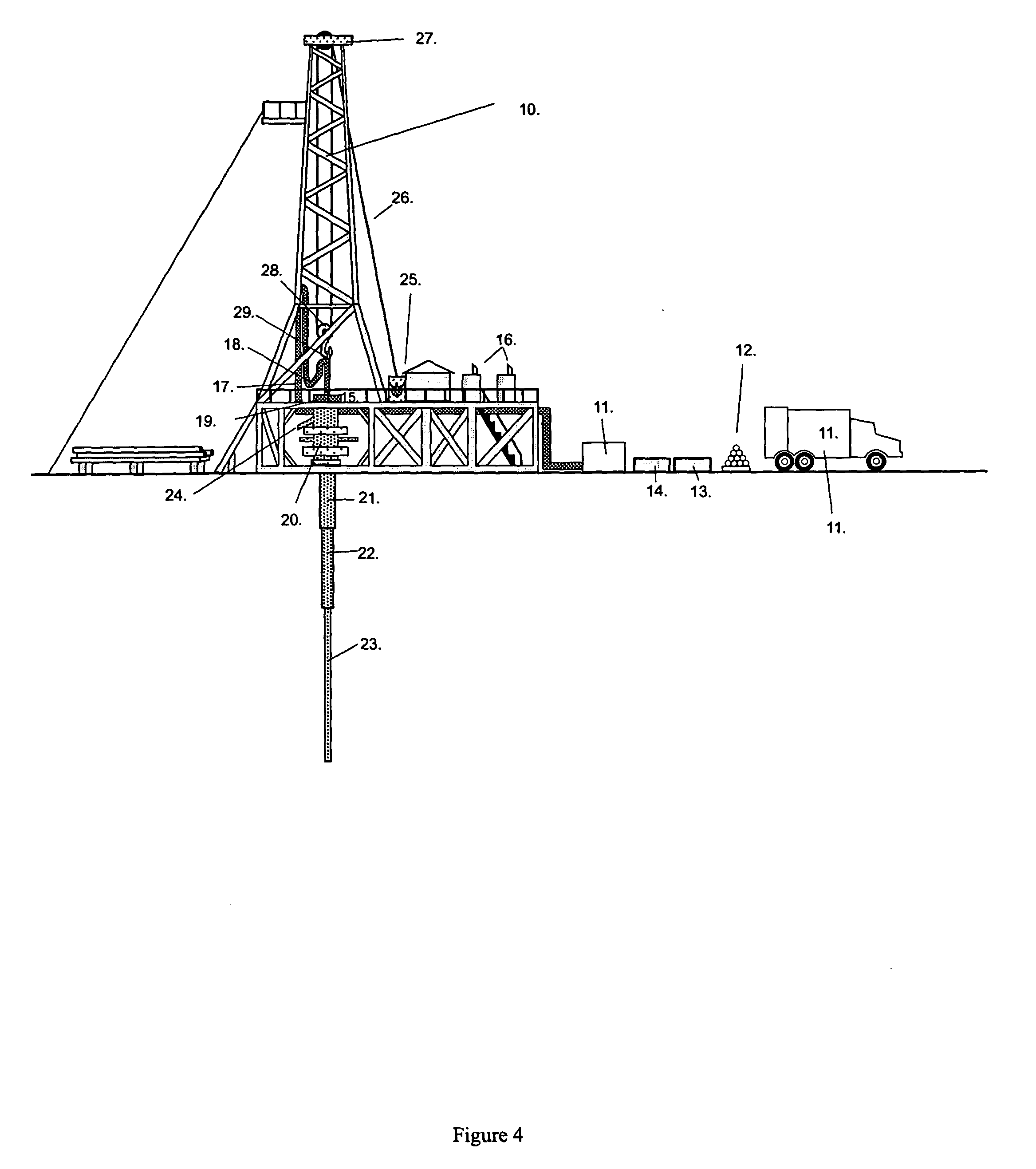
Dynamic annular pressure control apparatus and method
InactiveUS6904981B2Increased annular pressureBuildFluid removalFlushingPressure controlled ventilationPressure control
A system and method for controlling formation pressures during drilling of a subterranean formation utilizing a selectively fluid backpressure system in which fluid is pumped down the drilling fluid return system in response to detected borehole pressures. A pressure monitoring system is further provided to monitor detected borehole pressures, model expected borehole pressures for further drilling and control the fluid backpressure system.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Well pressure control system
The present invention contemplates a choke control system that provides for local and off-site monitoring and control of the annulus flow pressure of a well. The choke control system includes a choke manifold connected to at least one choke and its associated actuator; a variety of instrumental drilling sensors, pump stroke counter switches, and choke position indicators; a local choke and hydraulic pressure control console; and a programmable controller in communication with the local choke and hydraulic pressure control console. The programmable controller handles the logical operations of the choke control system, including processing instrument measurements and operator input data to produce control signals for operating the choke, the choke actuator and the various valves associated with the choke manifold. The programmable controller is typically either an electronic digital computer and / or a programmable logic controller (PLC). The present invention further contemplates the two-way communication between the choke control system and the Internet via a satellite linkage.
Owner:EXPRO AMERICAS
Methods and fluid compositions designed to cause tip screenouts
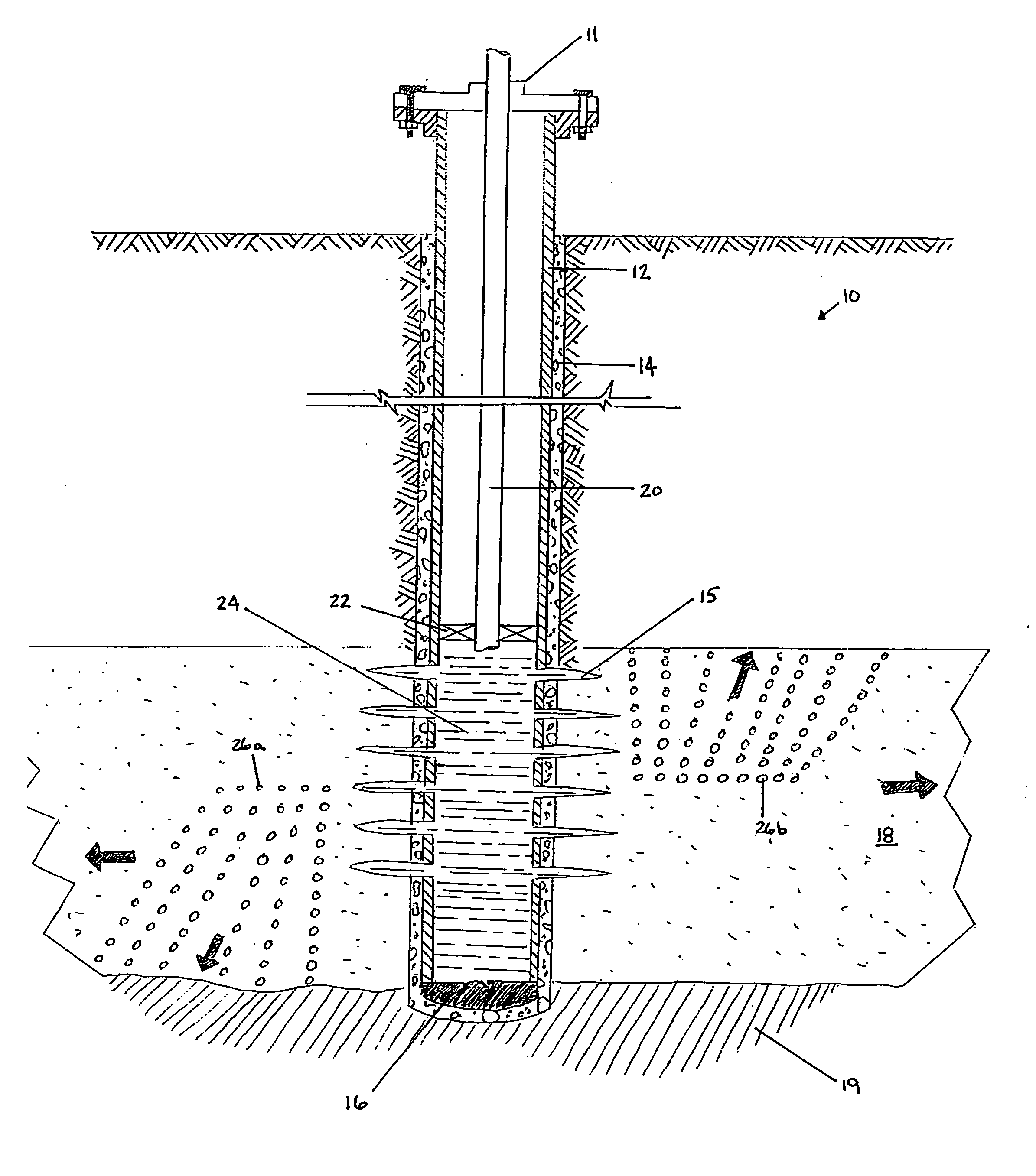
InactiveUS6837309B2Increase probabilityTreatment is limitedFluid removalDrilling compositionHigh concentrationFiber
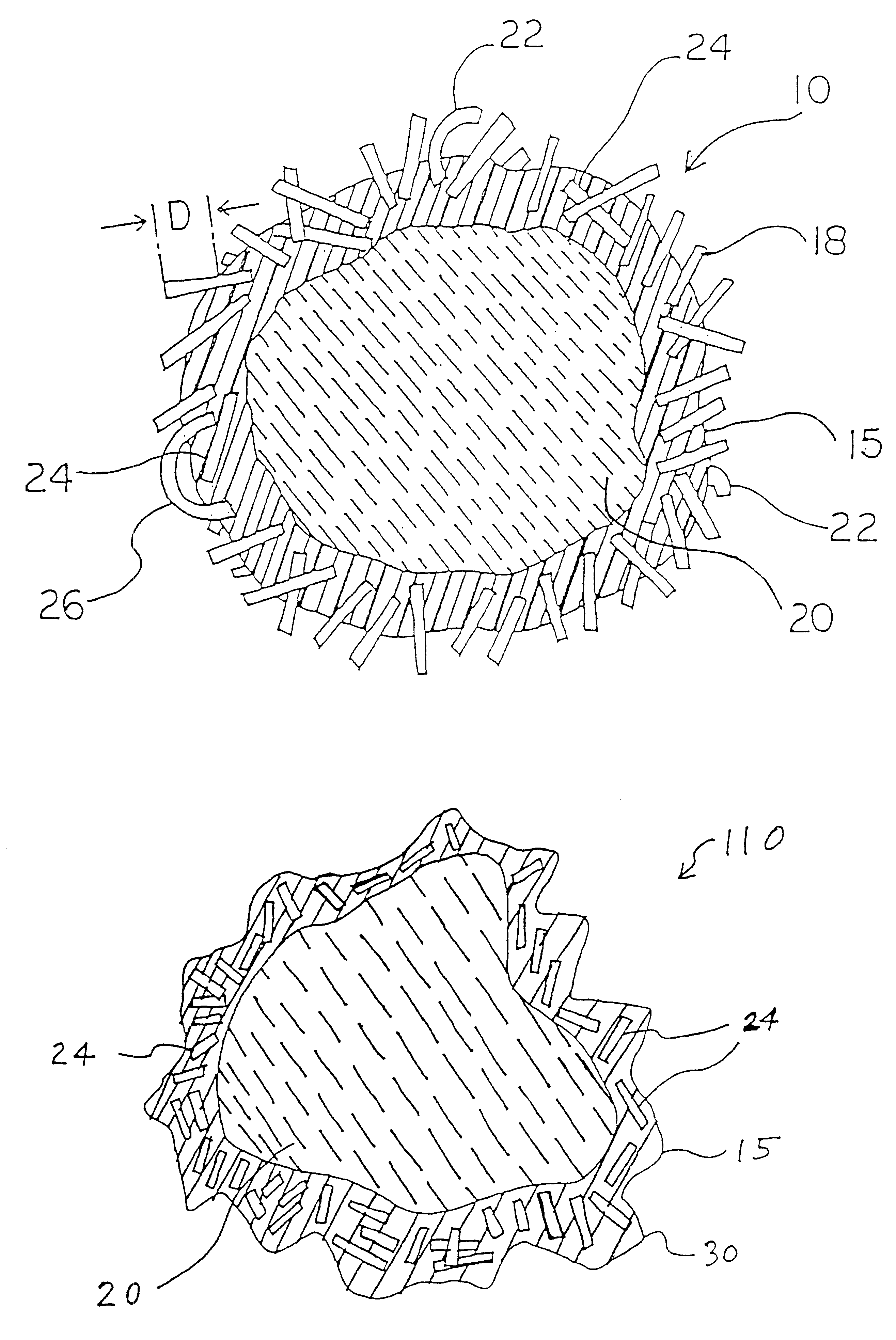
In stimulation treatments to increase the production of hydrocarbons from subterranean formations, especially in treatments including hydraulic fracturing followed by gravel packing, desirable short wide fractures are created and filled with proppant by deliberately including in the first fluid / proppant slurry pumped a sufficiently high concentration of a bridging-promoting material, such as fibers, that reduces the mobility of the slurry when it dewaters so that screenout at or near the tip occurs.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Degradable material assisted diversion or isolation
A method for well treatment by forming a temporary plug in a fracture, a perforation, a wellbore, or more than one of these locations, in a well penetrating a subterranean formation is provided, in which the method of well treatment includes: injecting a slurry comprising a degradable material, allowing the degradable material to form a plug in a perforation, a fracture, or a wellbore in a well penetrating a formation; performing a downhole operation; and allowing the degradable material to degrade after a selected time such that the plug disappears.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method of generating and recovering gas from subsurface formations of coal, carbonaceous shale and organic-rich shales
InactiveUS20040033557A1Maximizes bacterial degradationStable and economically favorable and environmentally cleanMicrobiological testing/measurementGas production bioreactorsOrganic compoundCoal
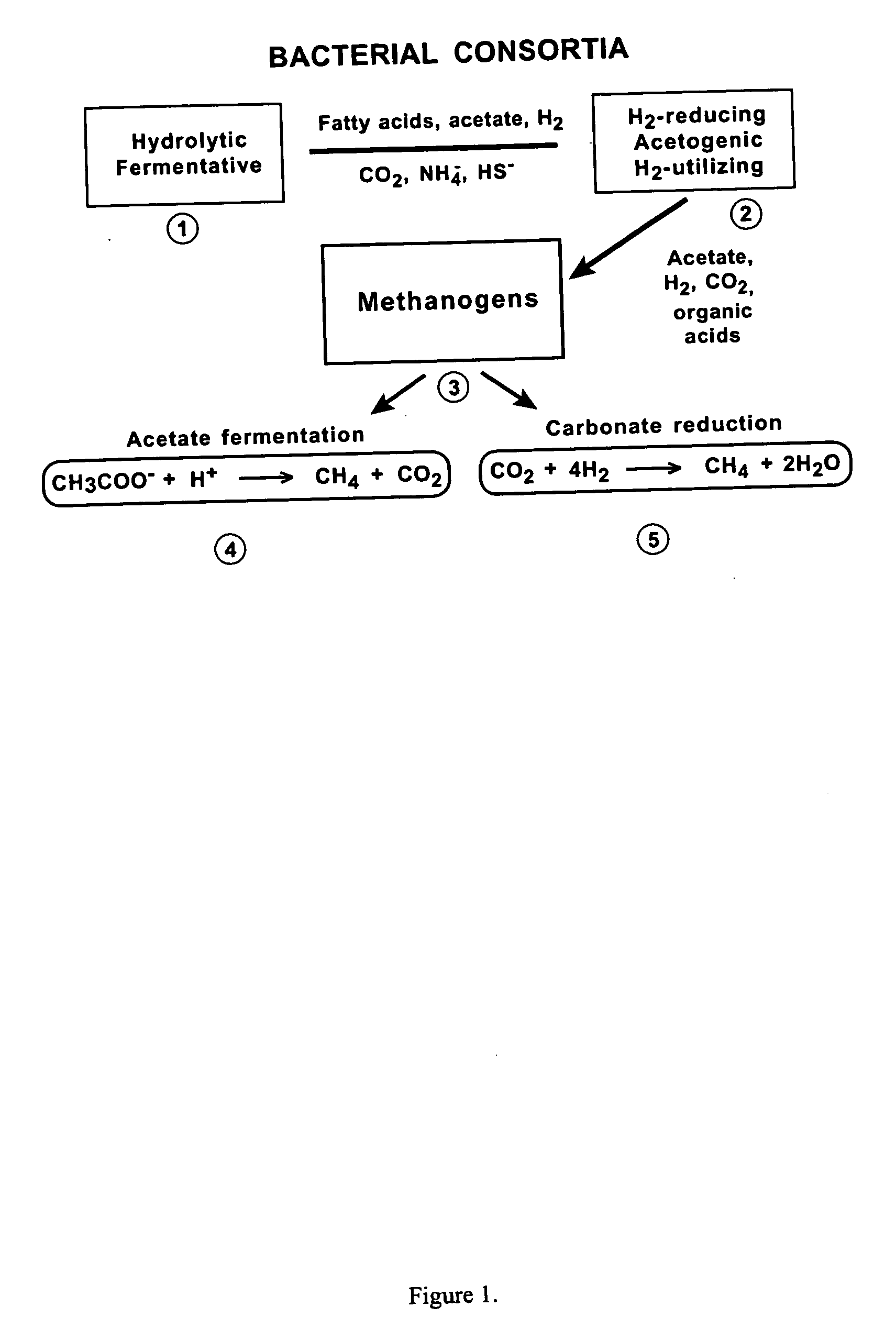
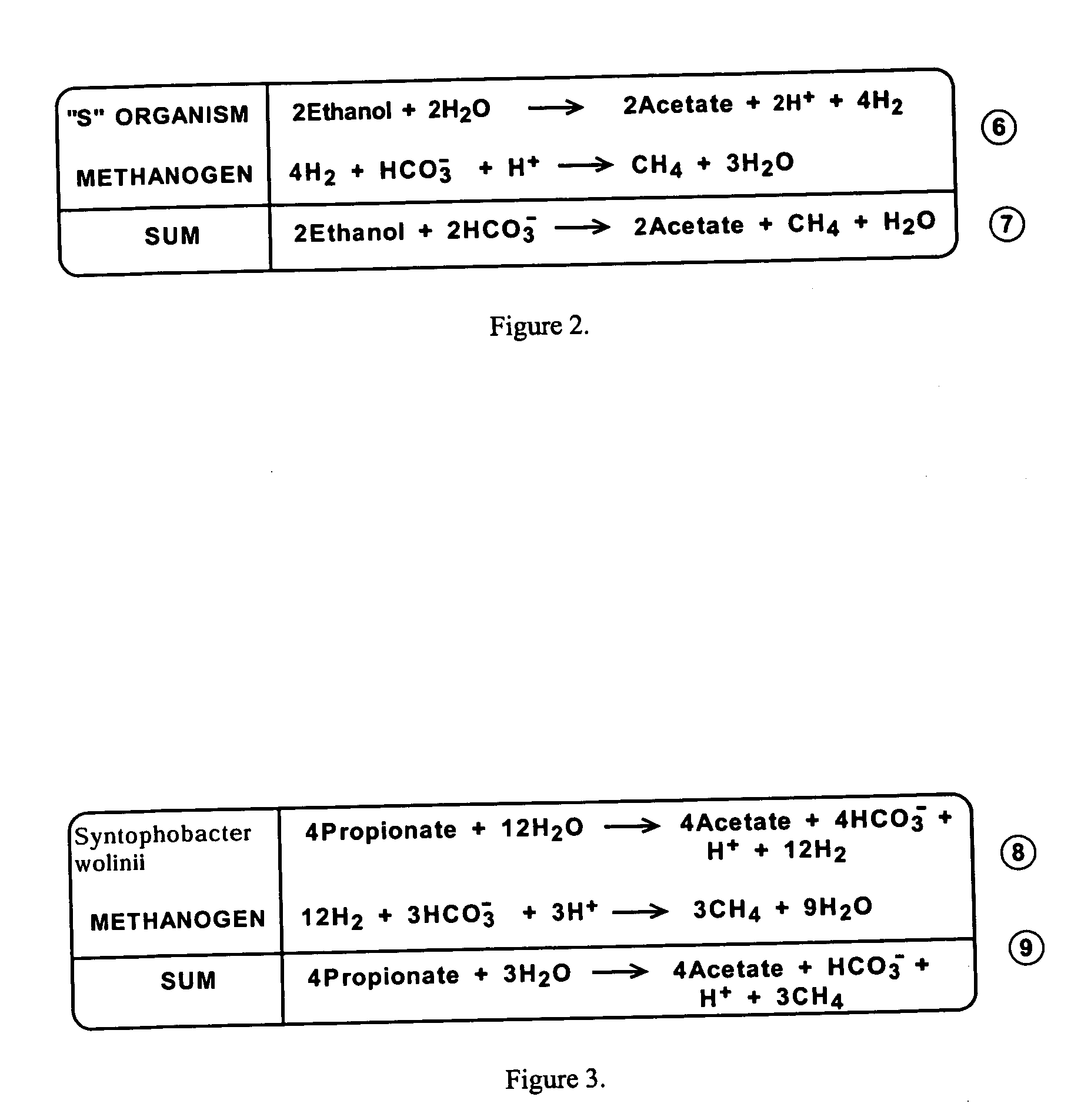
A method of generating and recovering gas from naturally existing subsurface formations Of coal, carbonaceous shale or organic-rich shales comprising the steps Of: injecting into fracture of the subsurface formation, under substantially anaerobic conditions, a consortia of selected anaerobic, biological microorganisms for in situ conversion of organic compounds in said formation into methane and other compounds; and producing methane through at least one well extending from said subsurface formation to the surfaces.
Owner:SCOTT ANDREW R +1
Cleanup additive
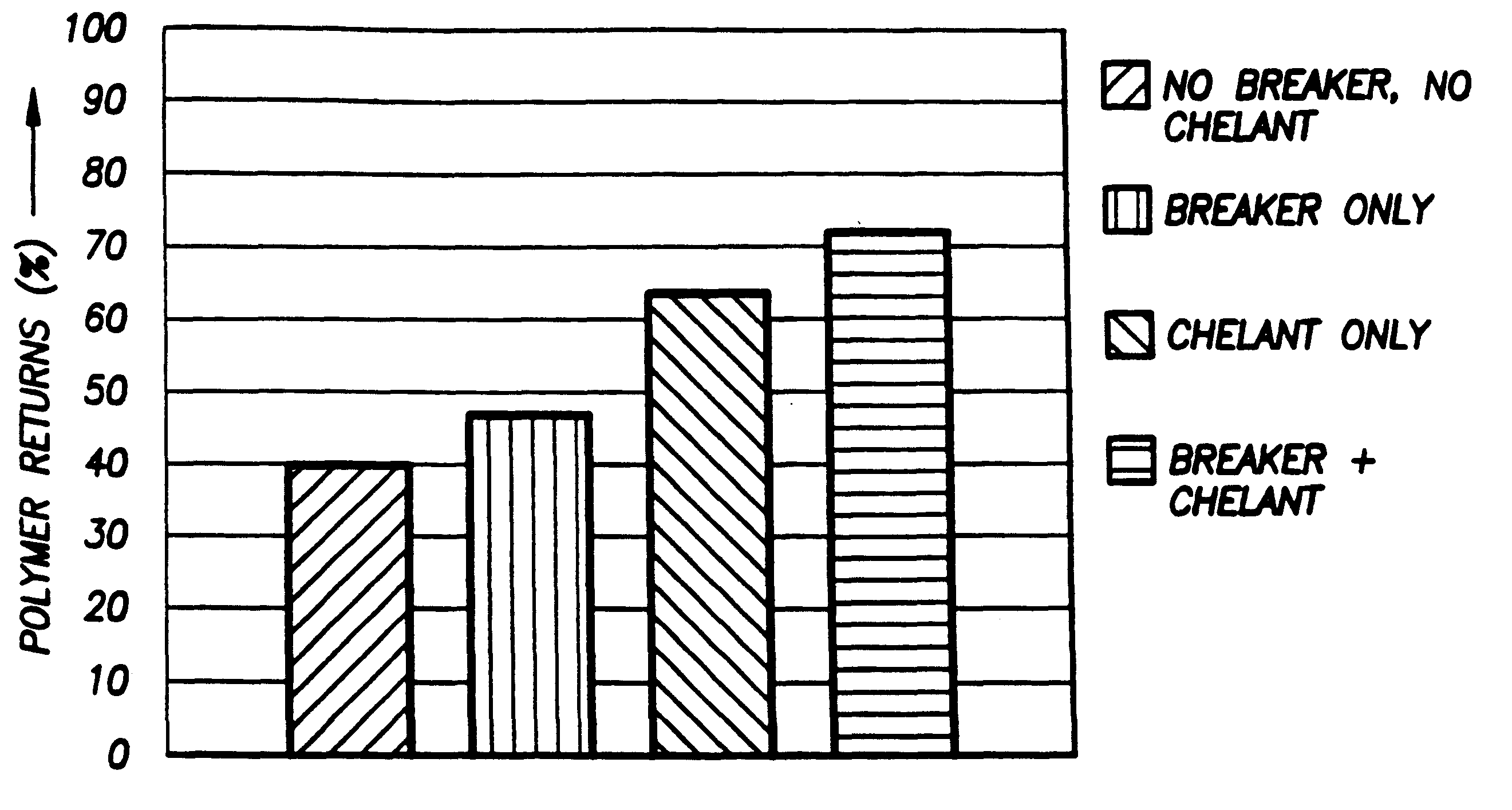
InactiveUS6242390B1Low viscosityEasy to disassembleOther chemical processesFluid removalSolubilityHydraulic fracturing
According to the present invention, a composition and method for hydraulically fracturing a subterranean formation is provided. The composition comprises an aqueous mixture of a hydrated polysaccharide, preferably a galactomannan gum, the hydrated polysaccharide having a plurality of bonding sites; a crosslinking agent for crosslinking the hydrated polysaccharide at the bonding sites at the conditions of the subterranean formation with a polyvalent metal ion to form a polyvalent metal crosslink, thereby increasing the viscosity of the hydrated polysaccharide; and a controlled solubility compound for releasing a chelating agent for controllably breaking the polyvalent metal crosslink and bonding with the polyvalent metal ion released by breaking the crosslink, thereby decreasing the viscosity of the hydrated polysaccharide. The method comprises the steps of injecting the above-described composition into the subterranean formation at fracturing pressures; allowing the controlled solubility compound to begin breaking the polyvalent metal crosslink, thereby reducing the viscosity of the hydrated polysaccharide and yielding a lower viscosity fluid; and removing the lower viscosity fluid from the subterranean formation.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Methods of sealing compositions and methods
InactiveUS6187839B1Shorten the timeShorten the overall cycleDrilling compositionSealing/packingHigh densitySalt solution
The present invention provides methods of sealing subterranean zones using high density sealing compositions. The methods are basically comprised of introducing a sealing composition into the subterranean zone comprised of a high density aqueous salt solution, a polymerizable monomer and a polymerizable initiator and allowing said sealing composition to form a sealing gel in said zone.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Fracturing systems and methods for a wellbore
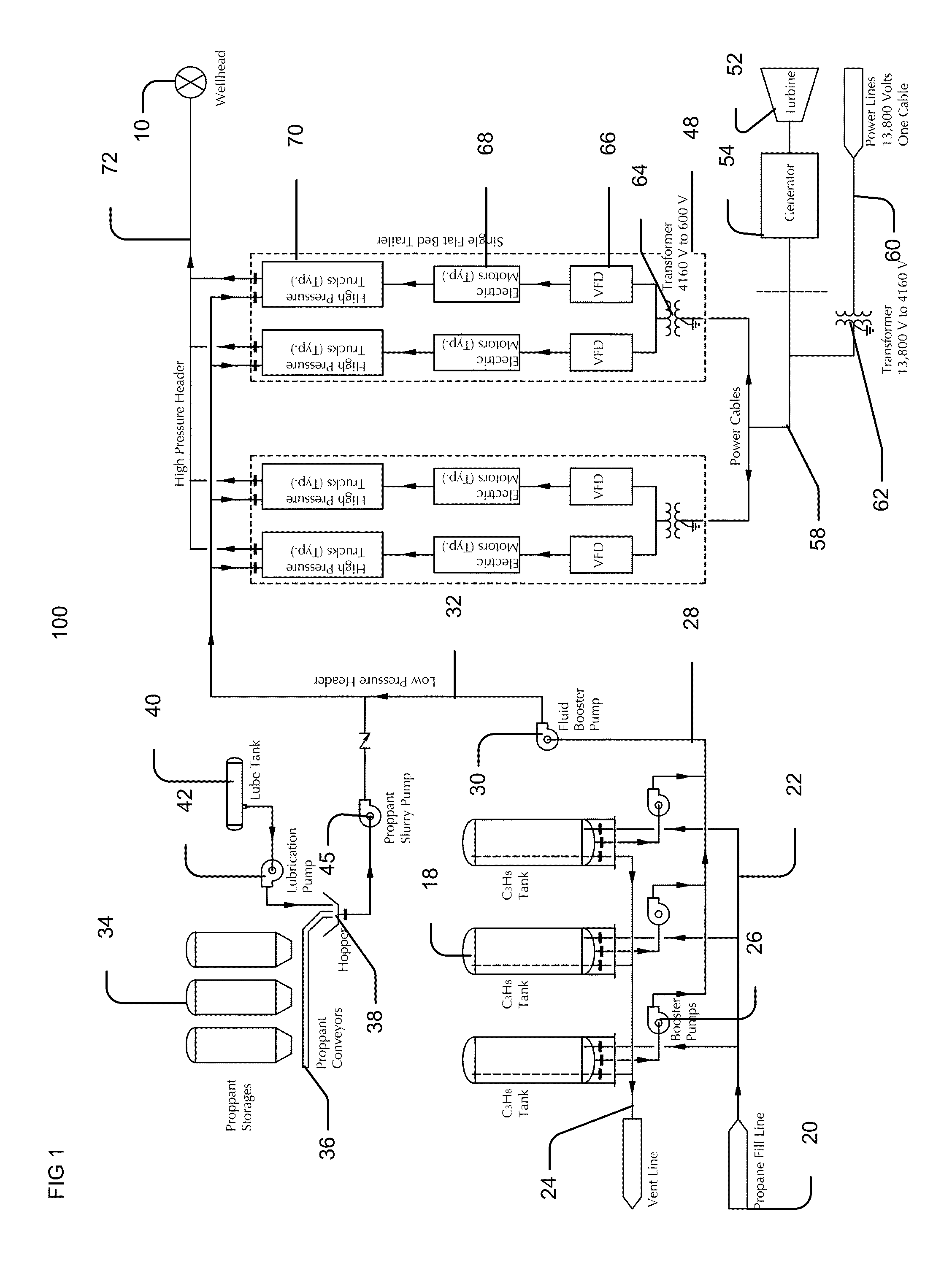
InactiveUS20150114652A1Superior line canceling harmonicReduce the possibilityFluid removalBorehole drivesTransformerPower grid
The disclosure contained herein describes systems, units, and methods usable to stimulate a formation including a pump usable to pressurize fluid, an electric-powered driver in communication with and actuating the pump, and an electrical power source in communication with and powering the electric-powered driver. The electrical power source can include on-site generators and / or grid power sources, and transformers can be used to alter the voltage received to a voltage suitable for powering the electric-powered driver. Air moving devices associated with the electric-powered driver can be used to provide air proximate to the pump to disperse gasses. In combination with fluid supply and / or proppant addition subsystems, the pump can be used to fracture a formation.
Owner:PROSTIM LABS
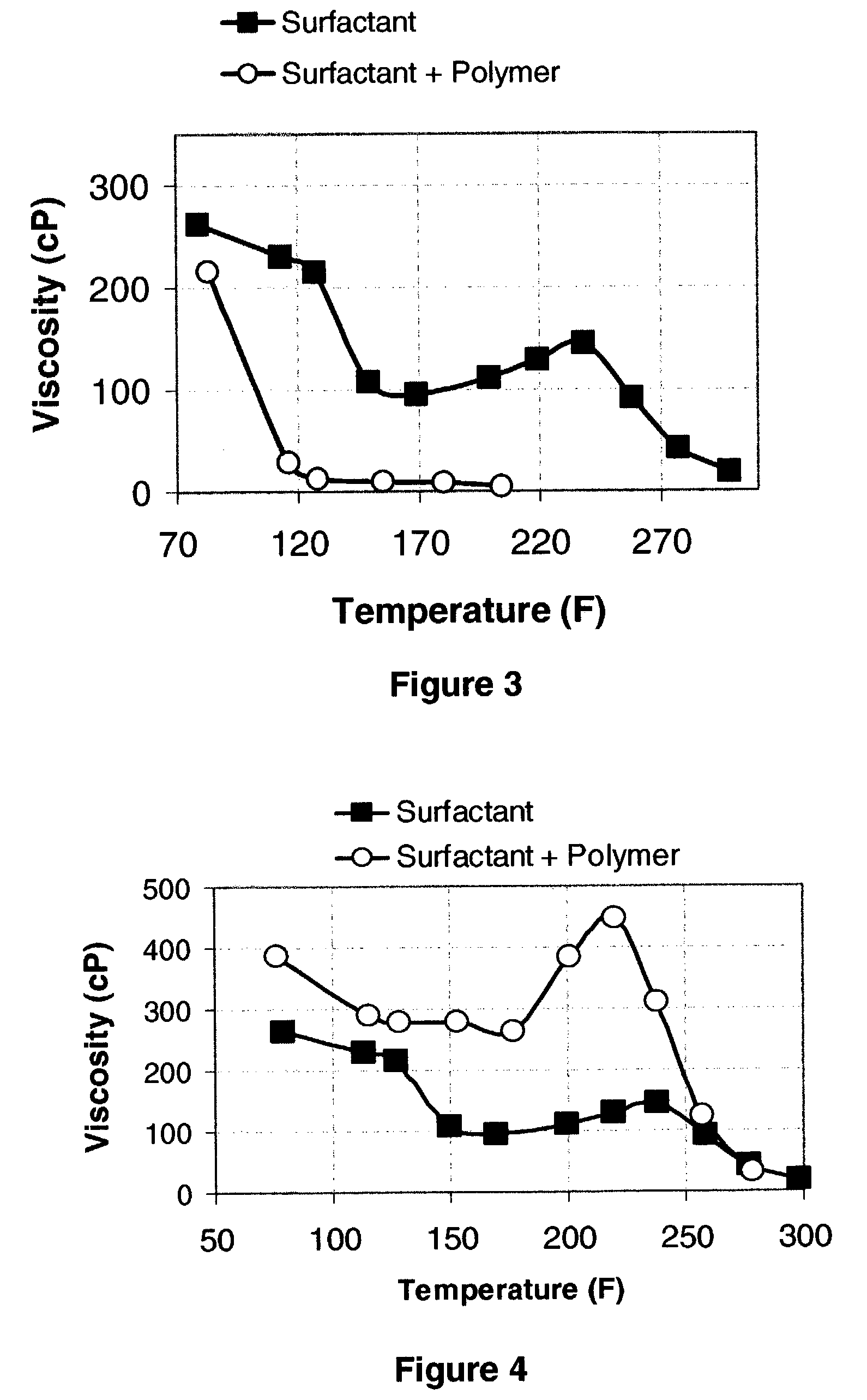
Methods for controlling the rheological properties of viscoelastic surfactants based fluids
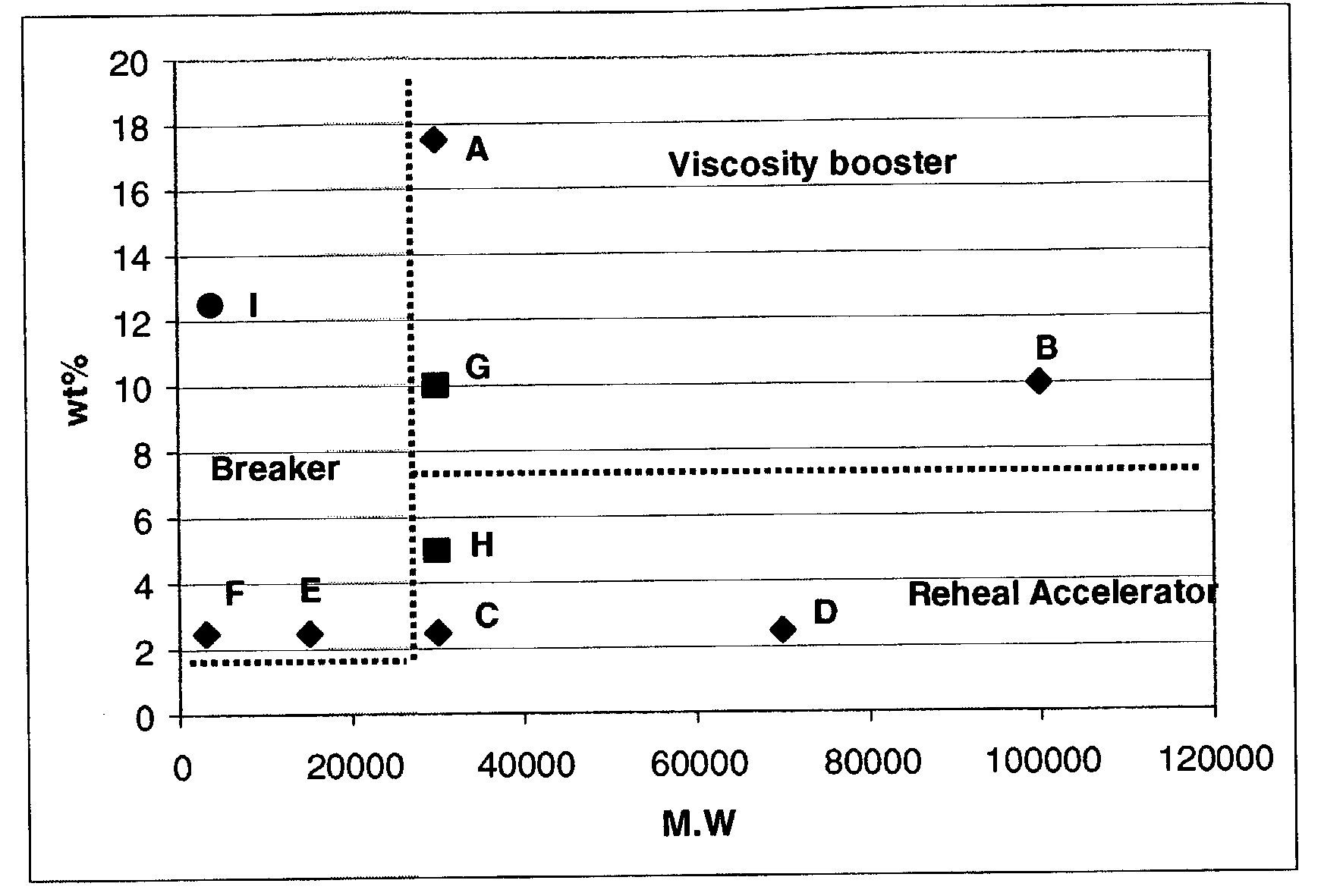
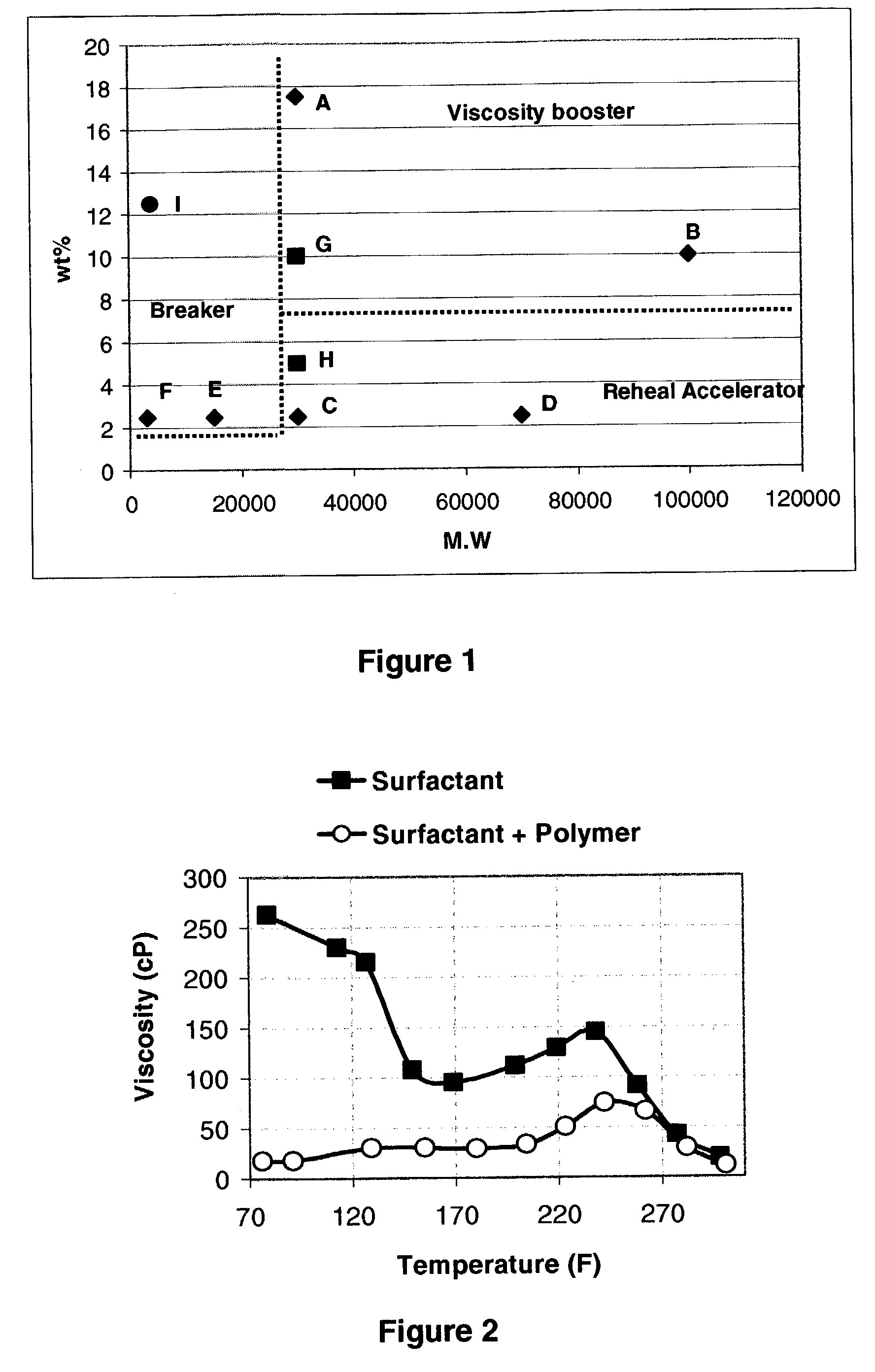
InactiveUS7084095B2High viscosityPromote recoveryFlushingDrilling compositionOrganic chemistrySURFACTANT BLEND
It was found that the addition of polymers to viscoelastic surfactant base system allows to adjust the rheological properties of the base fluid. Depending in particular on one side of the ratio of the concentration of added polymer and the concentration of viscoelastic surfactant and on the other side of the molecular weight of the added polymer, the same polymer—or the same type of polymer—may perform different functions such as viscosity enhancer, viscosity breaker or viscosity-recovery enhancer.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Process for incremental coating of proppants for hydraulic fracturing and proppants produced therefrom
A high strength composite particle comprised of a series of incrementally applied resin microlayer coatings such that each of the microlayer partial coatings are interleaved with each other is described. Methods of making the composite particles, as well as methods of using such particles as a proppant in oil and gas well hydraulic fracturing are also described.
Owner:FAIRMOUNT SANTROL
Acid coated sand for gravel pack and filter cake clean-up
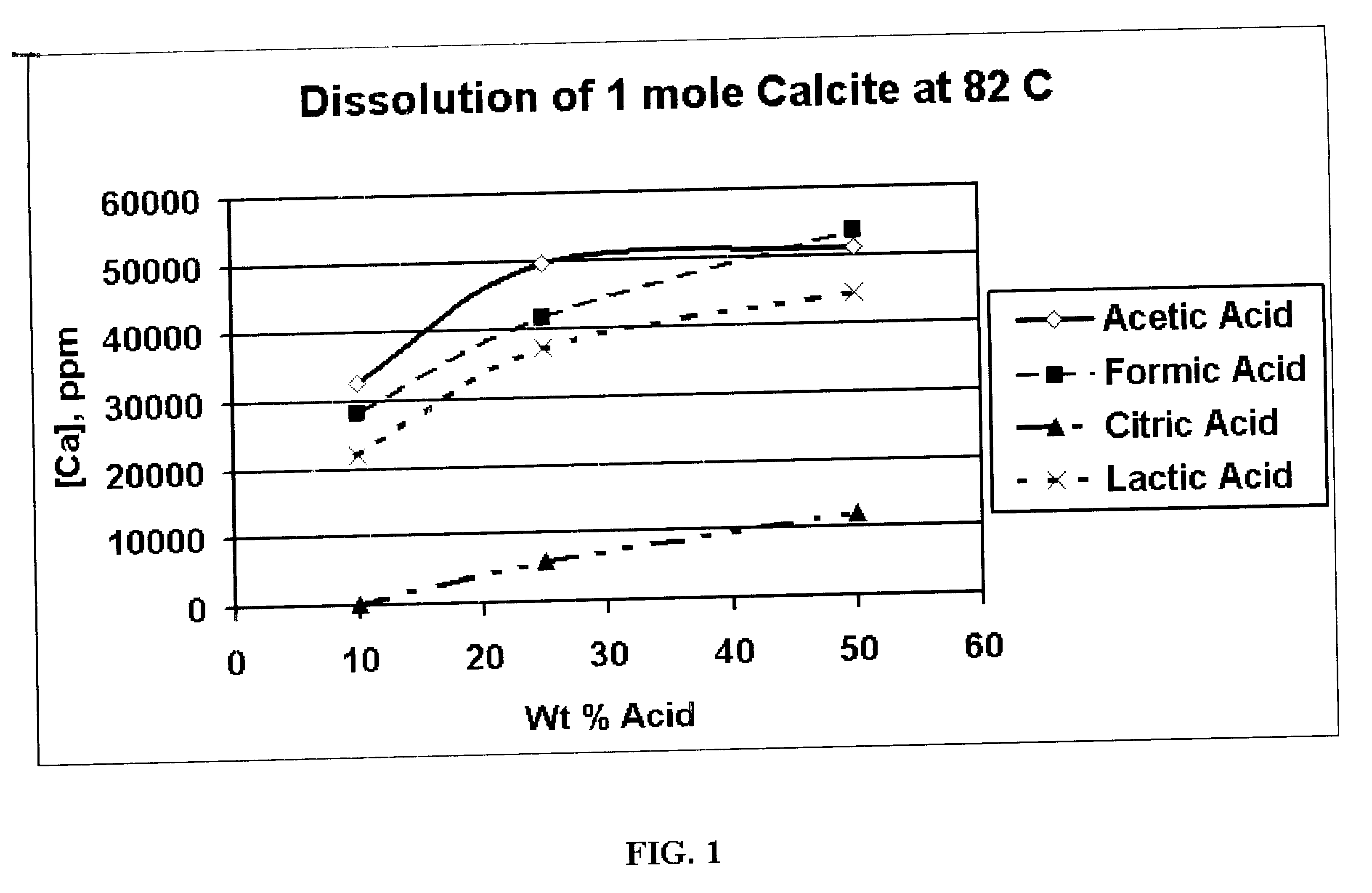
InactiveUS20040055747A1Enhances filter cake removalSpeed up the flowCleaning apparatusFluid removalCarboxylic acidGlycollic acid
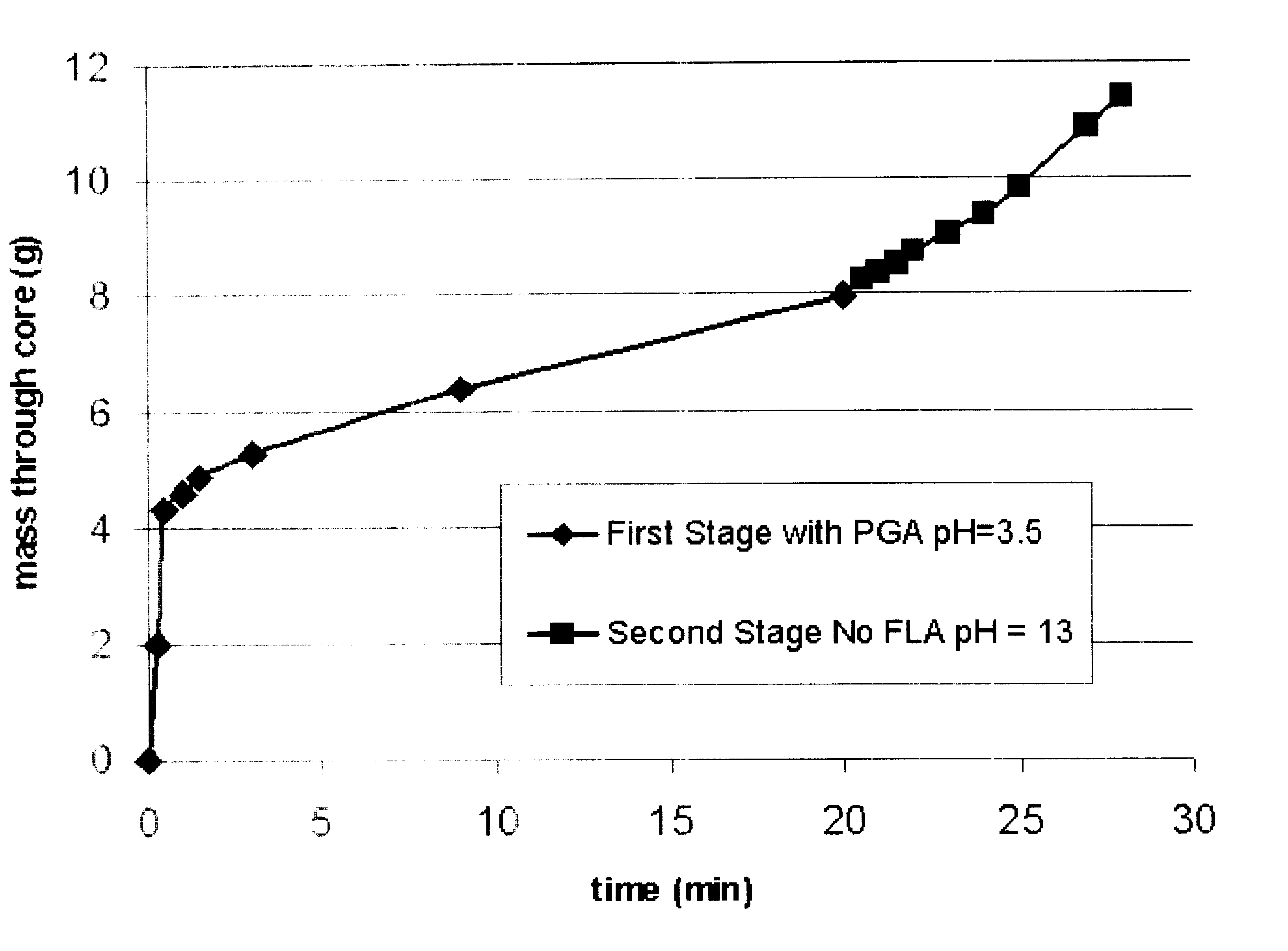
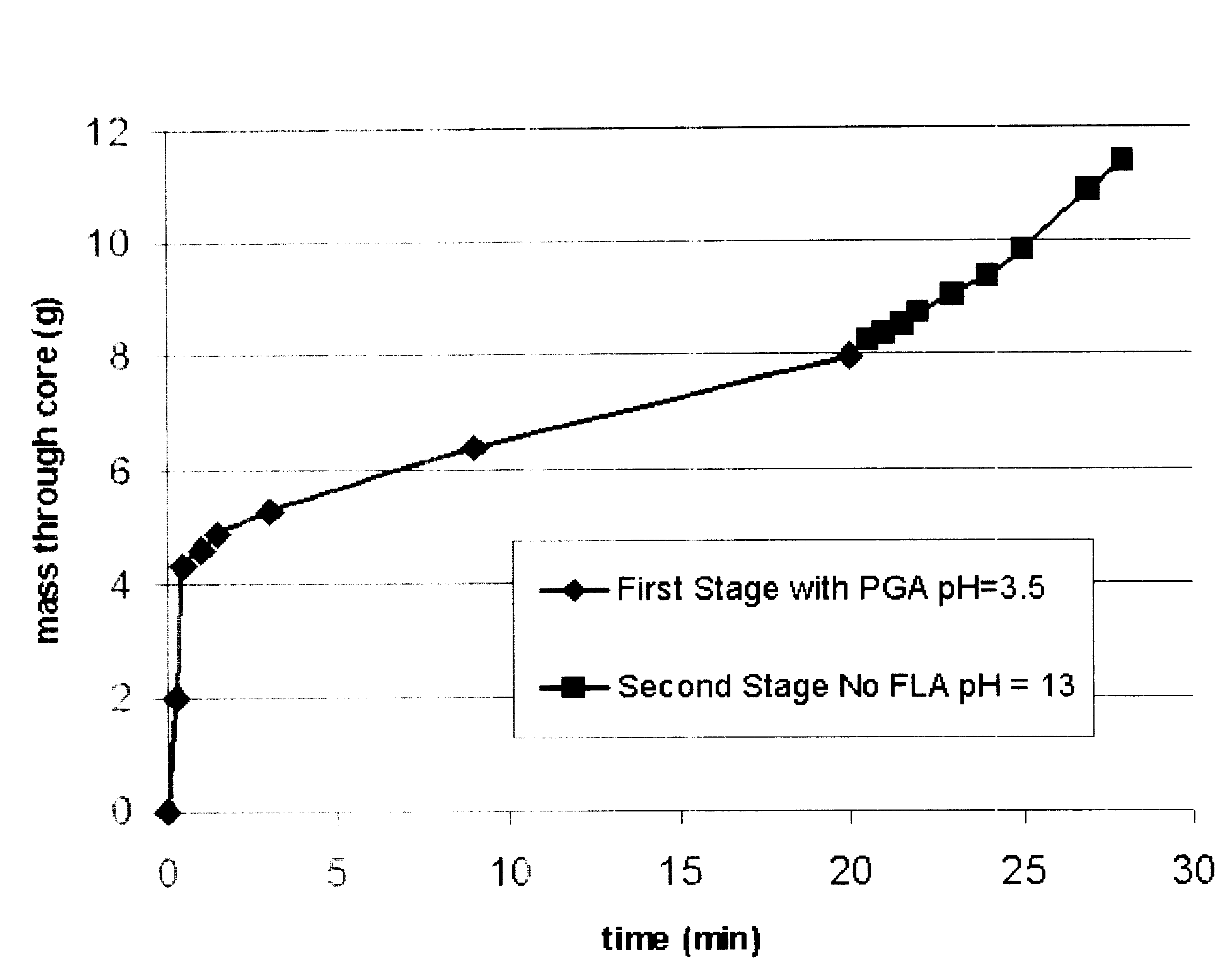
A method of the preparation and utilization of polymerized alpha-hydroxycarboxylic-acid-coated proppants for gravel pack and removal of filter cake that was deposited by reservoir drilling fluid. In a preferred example, polyglycolic-acid-coated sand is used to replace conventional gravel pack sand typically used for gravel packing. Under downhole conditions, the acidic by-product generated from the hydration of polyglycolic-acid-coated sand can break down acid-soluble and / or acid-breakable components embedded in the filter cake. This reaction enhances the filter cake removal and the flow of hydrocarbon from the producing formation. The polyglycolic-acid-coated sand may be produced by polymerizing a glycolic acid with a natural or synthetic proppant like 20-40 mesh commercial sand, at temperatures of about 210° F. or higher.
Owner:MI
Dissolving Filter Cake
InactiveUS20040094300A1Needed propertyWider fractureCleaning apparatusFluid removalSolid baseCarrier fluid
Methods are presented to induce a screenout during a subterranean formation fracturing or combined fracturing and gravel packing treatment having a viscoelastic surfactant-based carrier fluid by laying down a filter cake at least a portion of which is a base-soluble material, injecting proppant slurry, and causing hydrolysis and dissolution of the solid base-soluble material by adding base so that leak-off increases, the concentration of proppant in the fracture increases, and the proppant screens out. A method of gravel packing with a viscoelastic surfactant-based carrier fluid by laying down a filter cake at least a portion of which is a base-soluble material, injecting gravel, and causing hydrolysis and dissolution of the solid base-soluble material by adding base. Methods of slowing or accelerating the hydrolysis and dissolution are given, and addition of bridging-promoting materials is included.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com