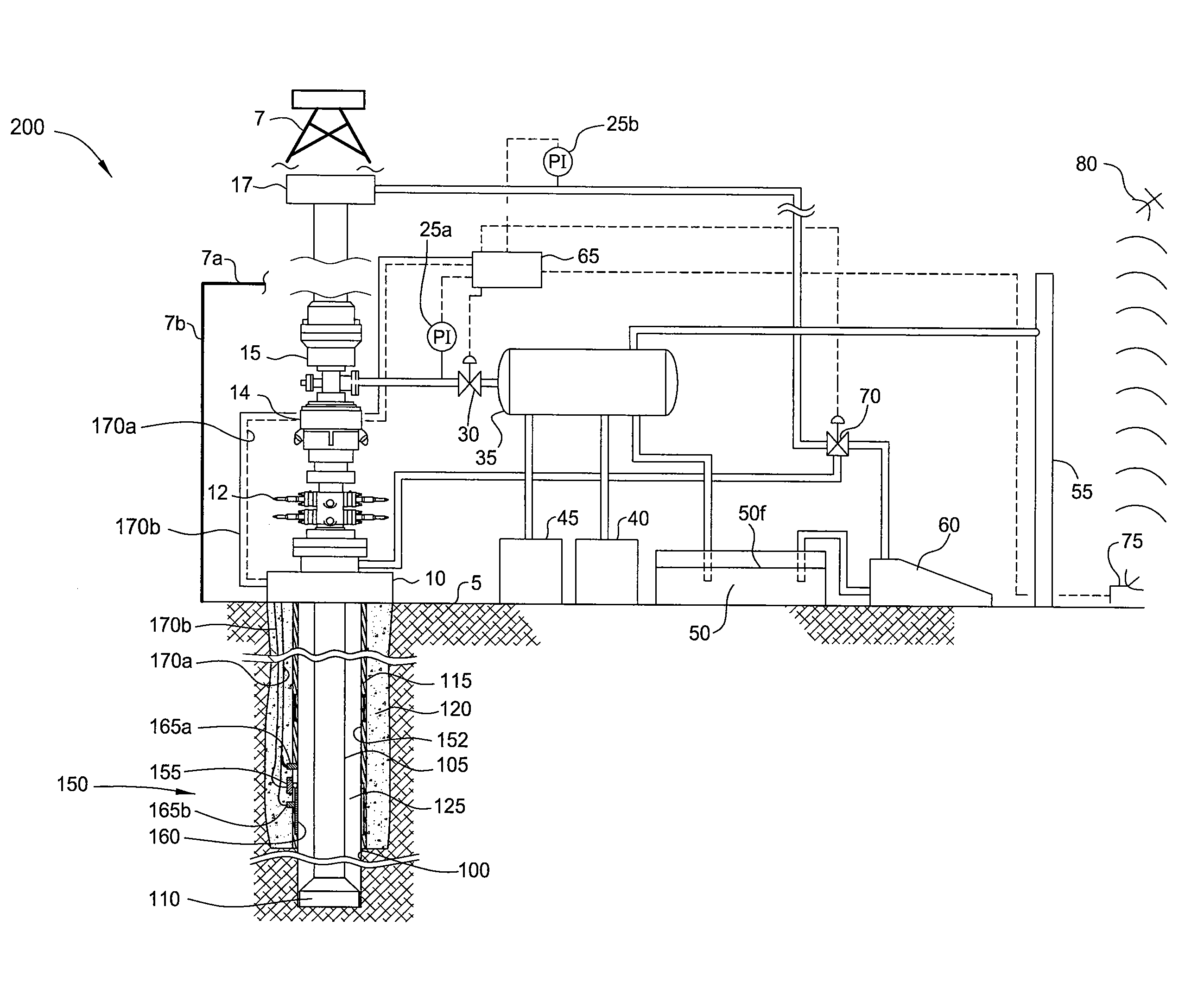
Patents
Literature
4201results about "Borehole drives" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
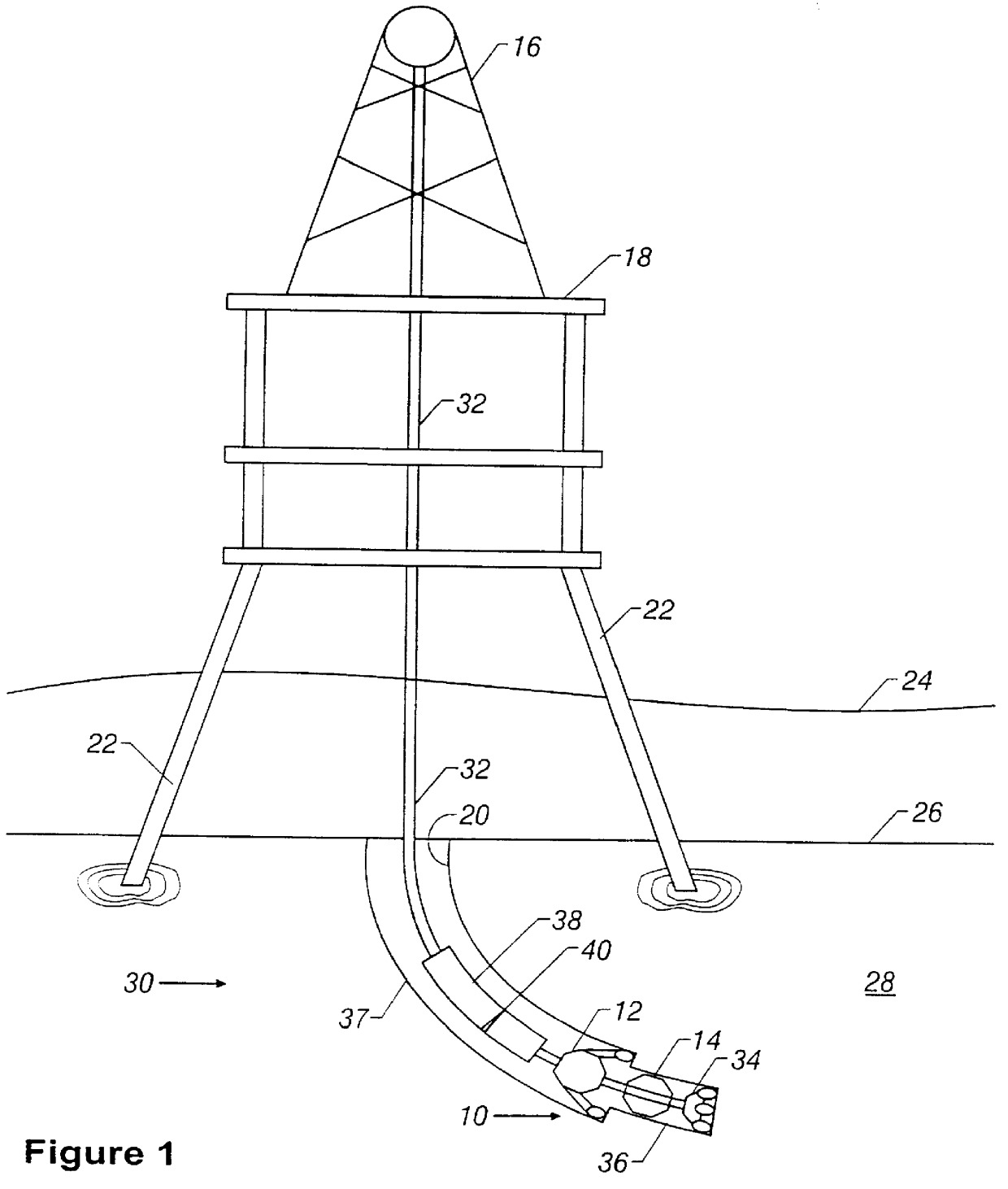
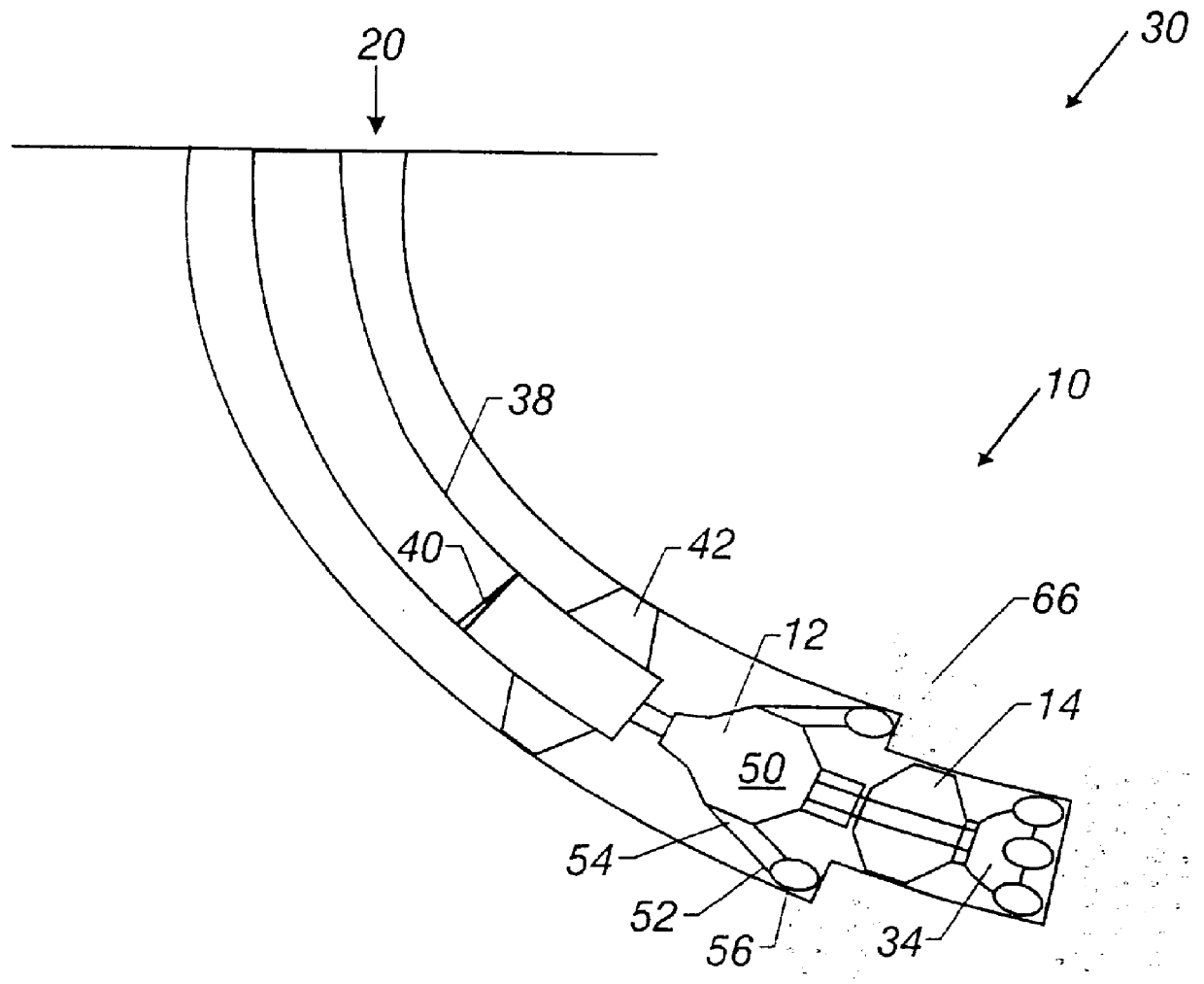
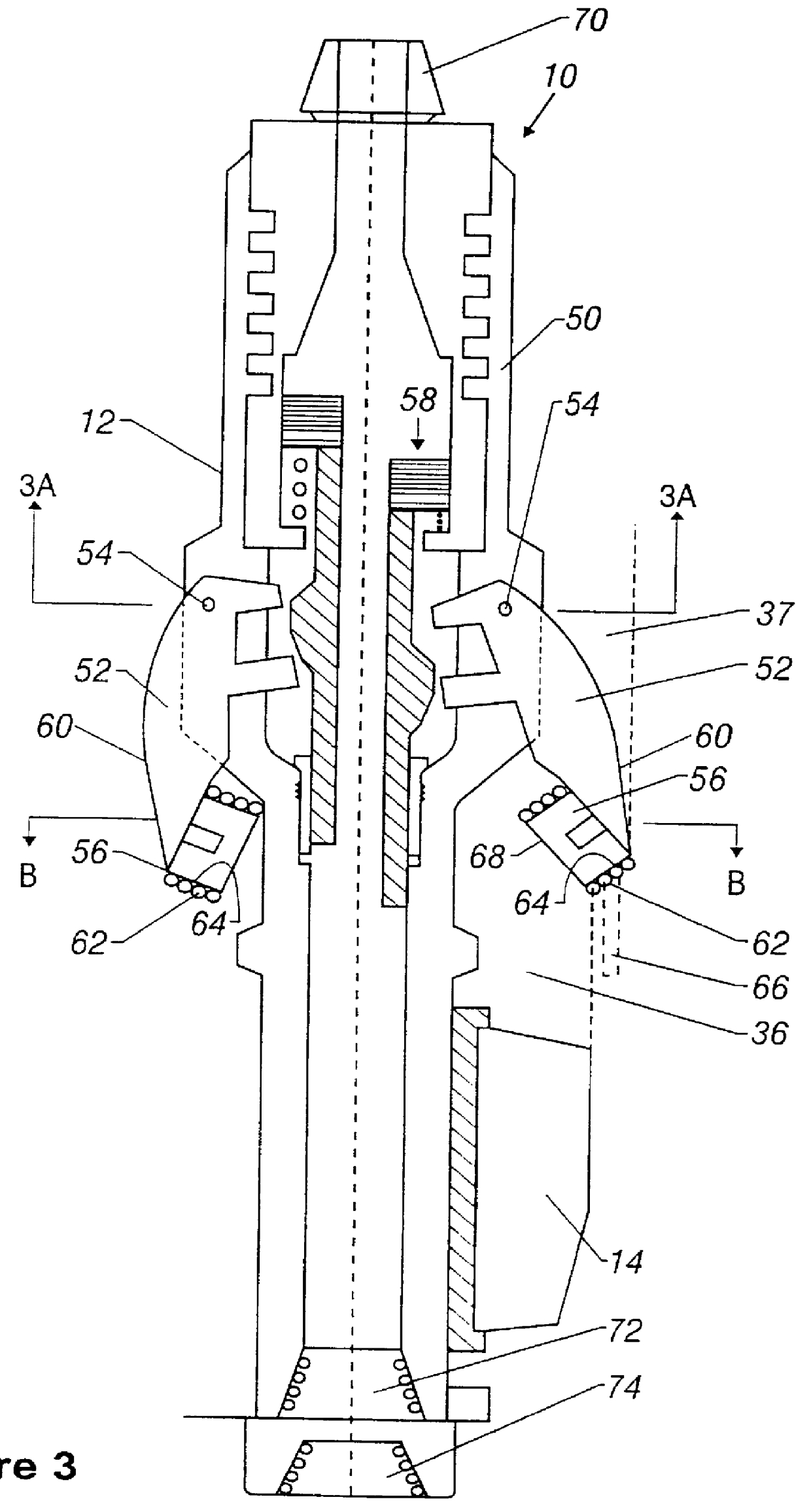
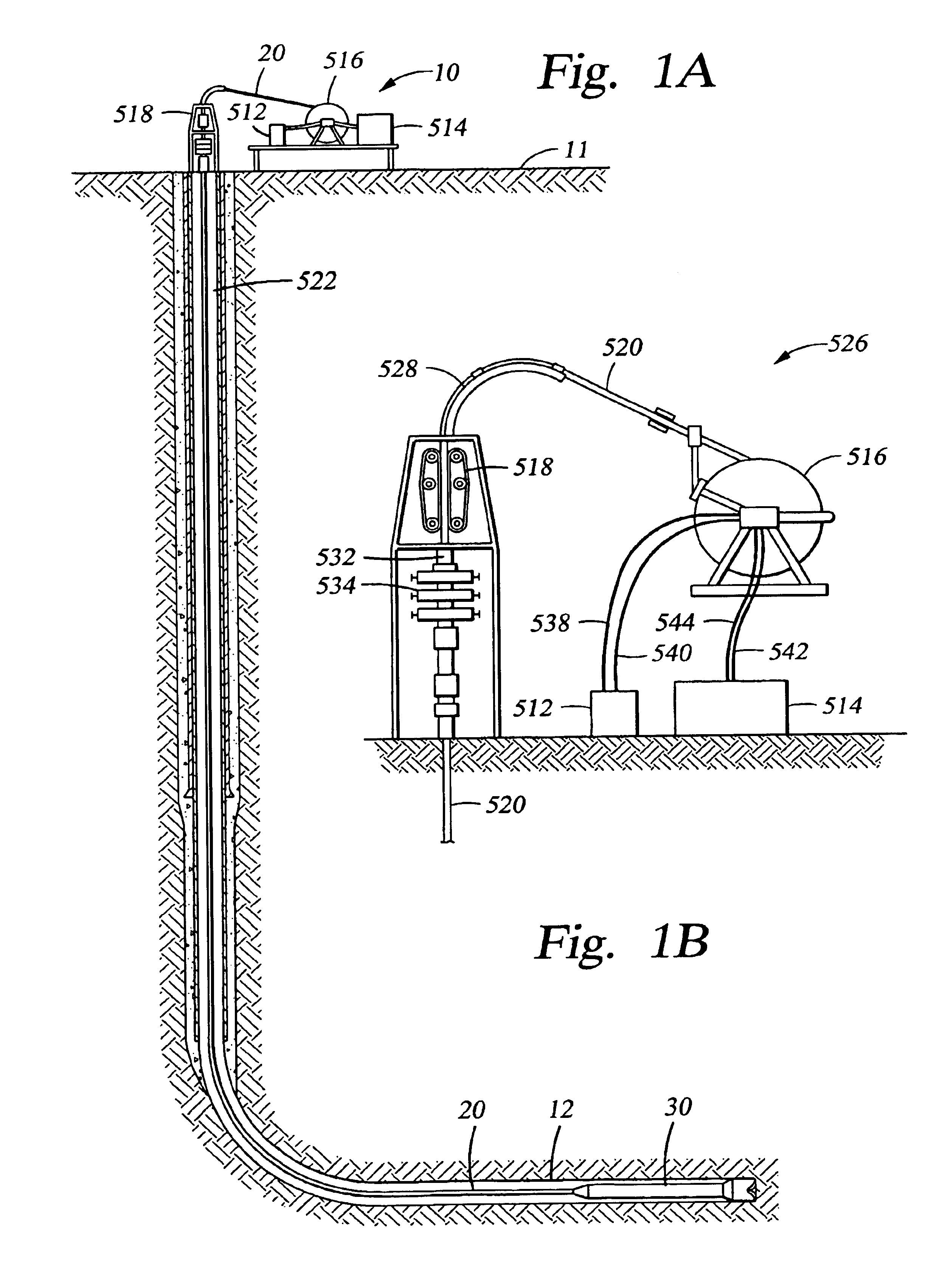
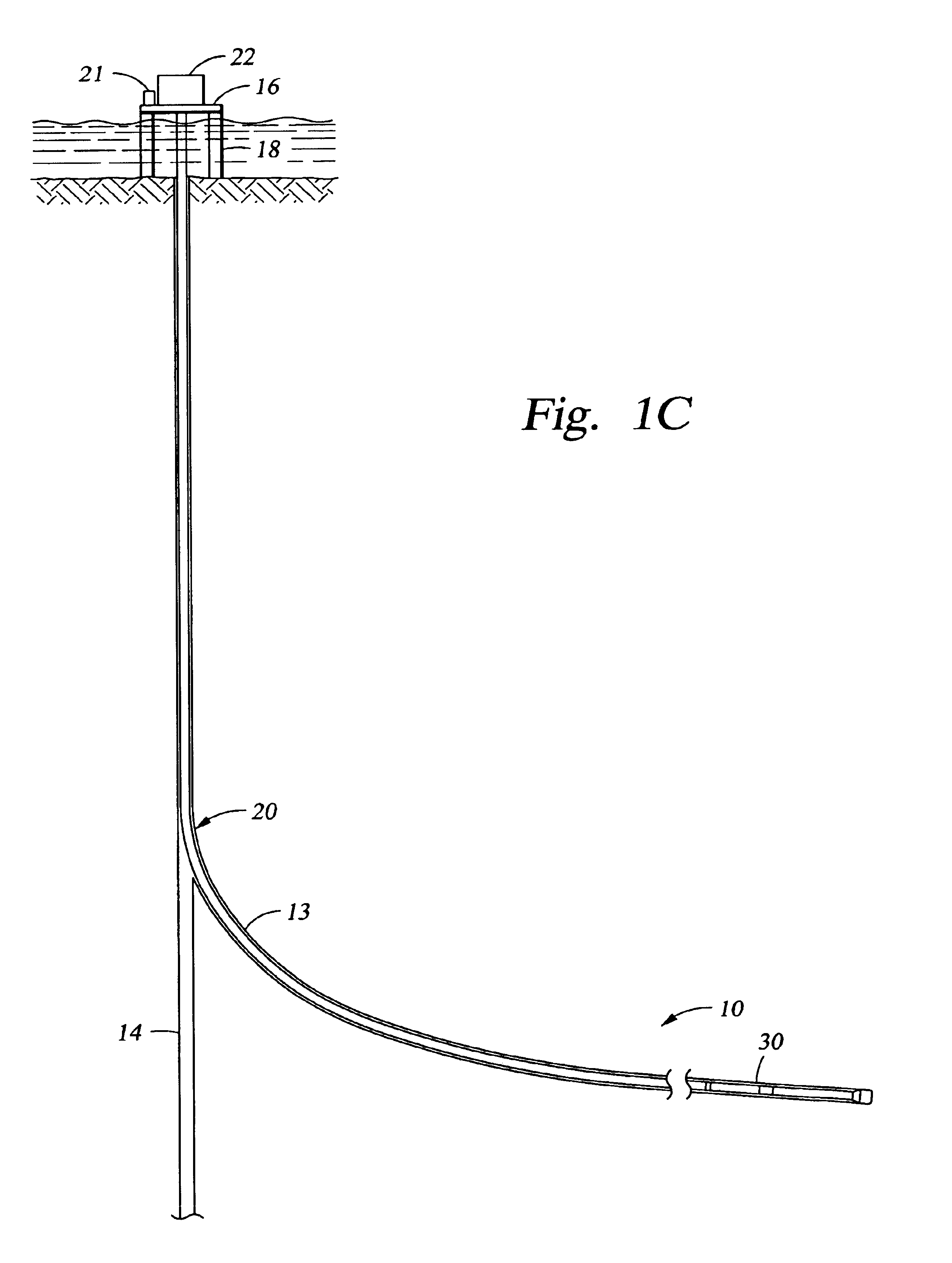
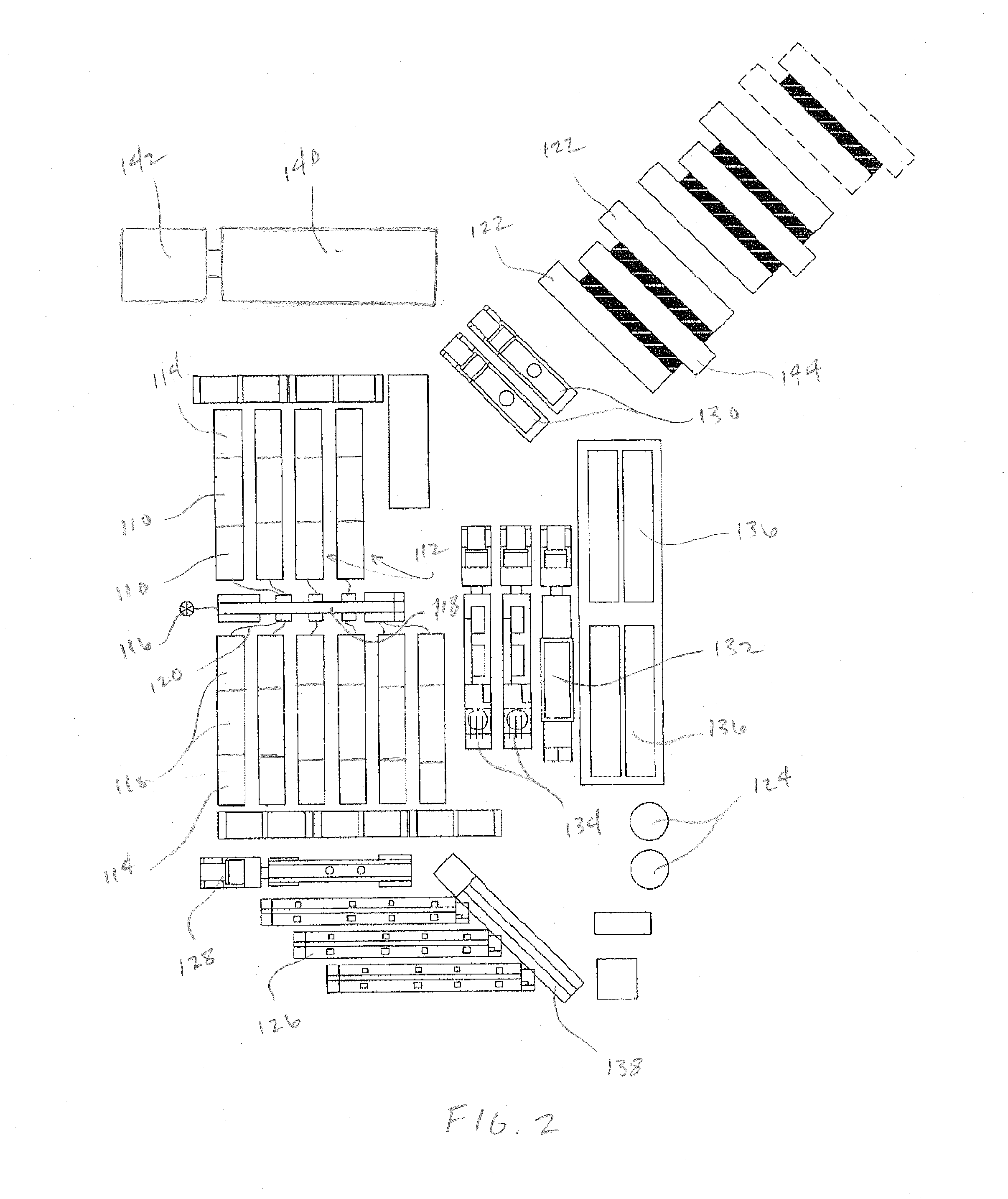
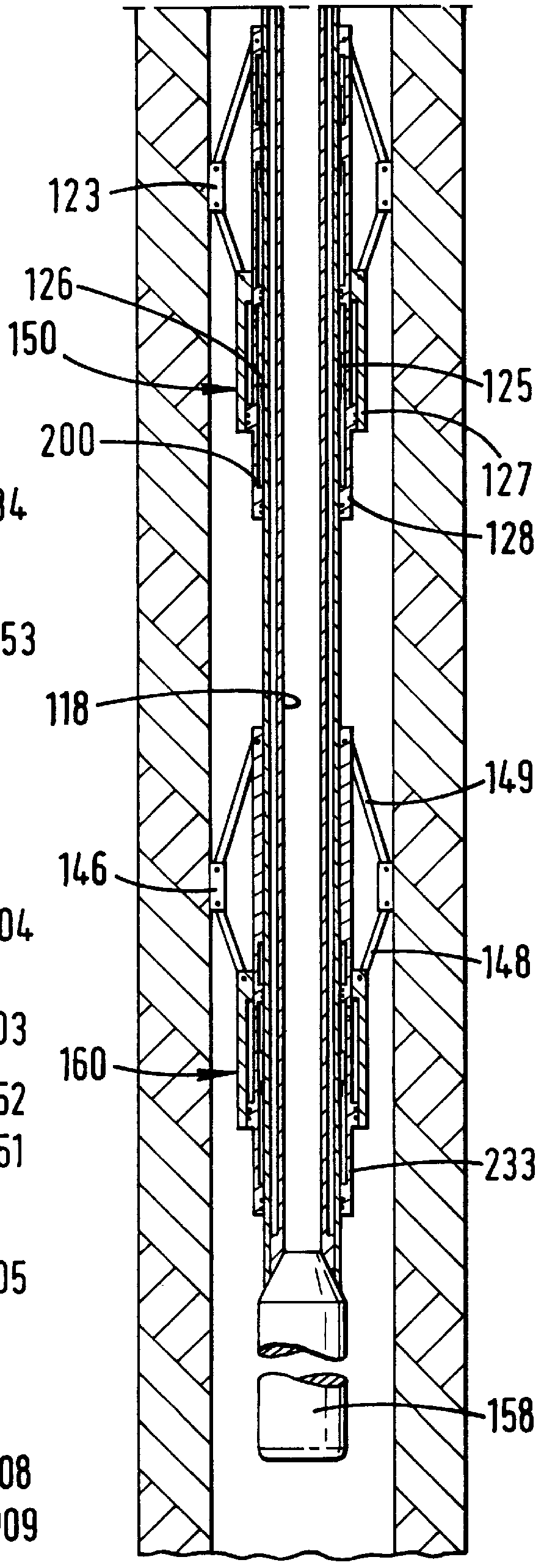
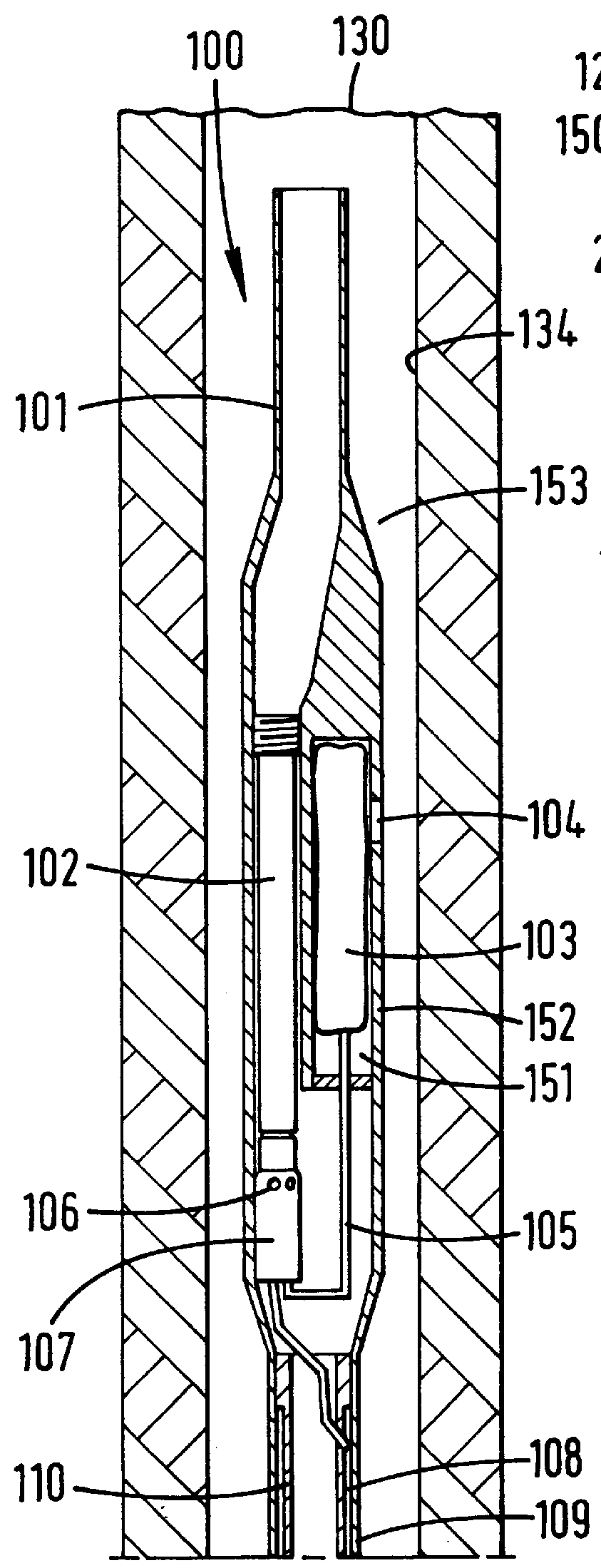
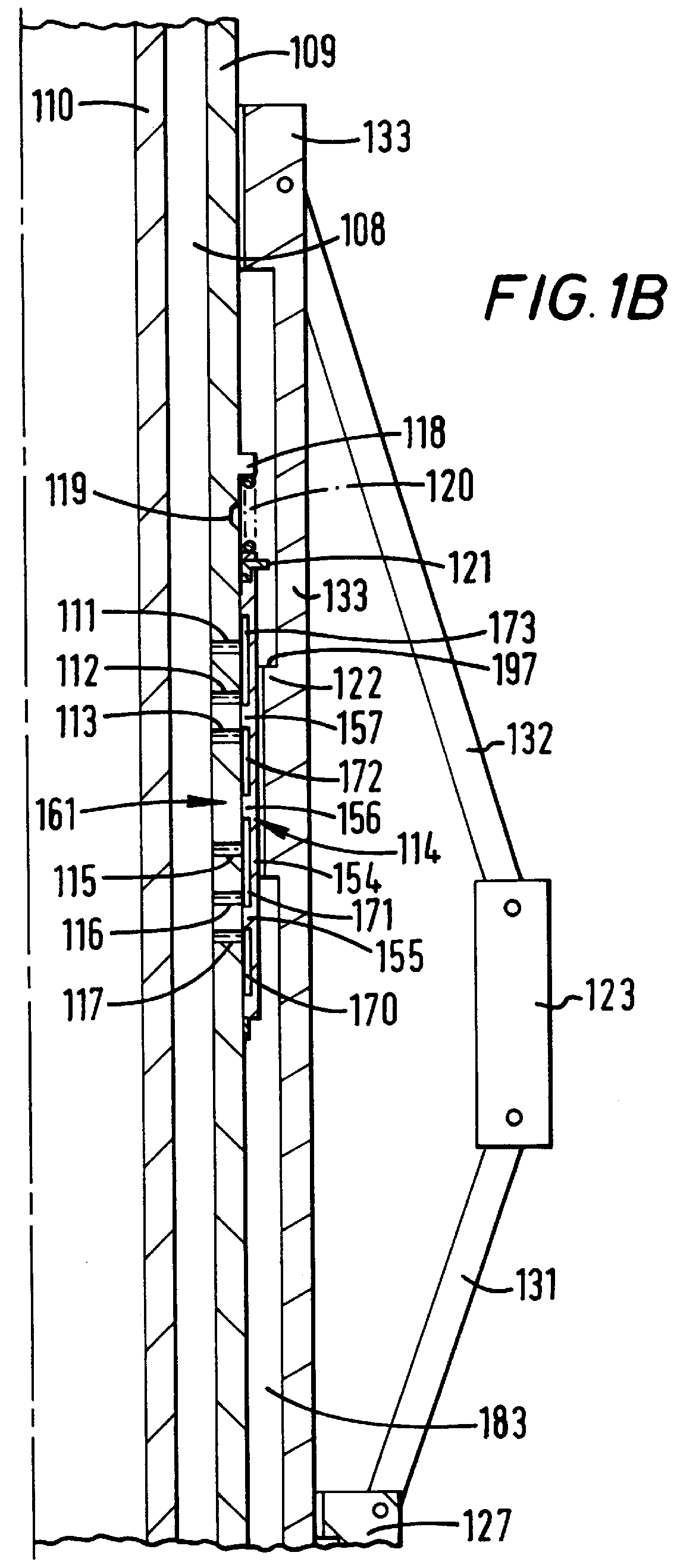
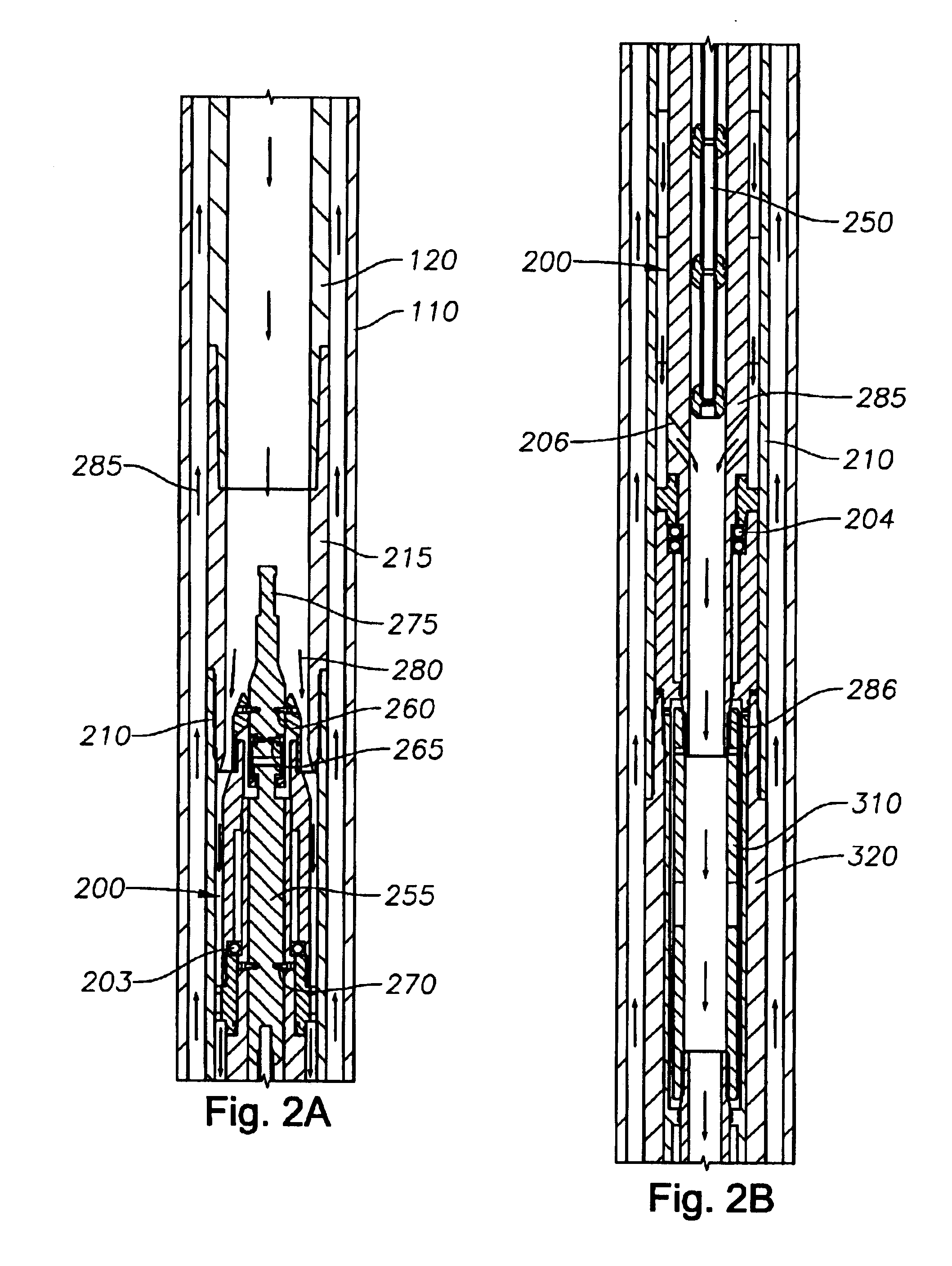
Actively controlled rotary steerable system and method for drilling wells
InactiveUS6092610AEfficient rotary speedPromote productionDrilling rodsConstructionsAccelerometerDirectional drilling
An actively controlled rotary steerable drilling system for directional drilling of wells having a tool collar rotated by a drill string during well drilling. A bit shaft has an upper portion within the tool collar and a lower end extending from the collar and supporting a drill bit. The bit shaft is omni-directionally pivotally supported intermediate its upper and lower ends by a universal joint within the collar and is rotatably driven by the collar. To achieve controlled steering of the rotating drill bit, orientation of the bit shaft relative to the tool collar is sensed and the bit shaft is maintained geostationary and selectively axially inclined relative to the tool collar during drill string rotation by rotating it about the universal joint by an offsetting mandrel that is rotated counter to collar rotation and at the same frequency of rotation. An electric motor provides rotation to the offsetting mandrel with respect to the tool collar and is servo-controlled by signal input from position sensing elements such as magnetometers, gyroscopic sensors, and accelerometers which provide real time position signals to the motor control. In addition, when necessary, a brake is used to maintain the offsetting mandrel and the bit shaft axis geostationary. Alternatively, a turbine is connected to the offsetting mandrel to provide rotation to the offsetting mandrel with respect to the tool collar and a brake is used to servo-control the turbine by signal input from position sensors.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
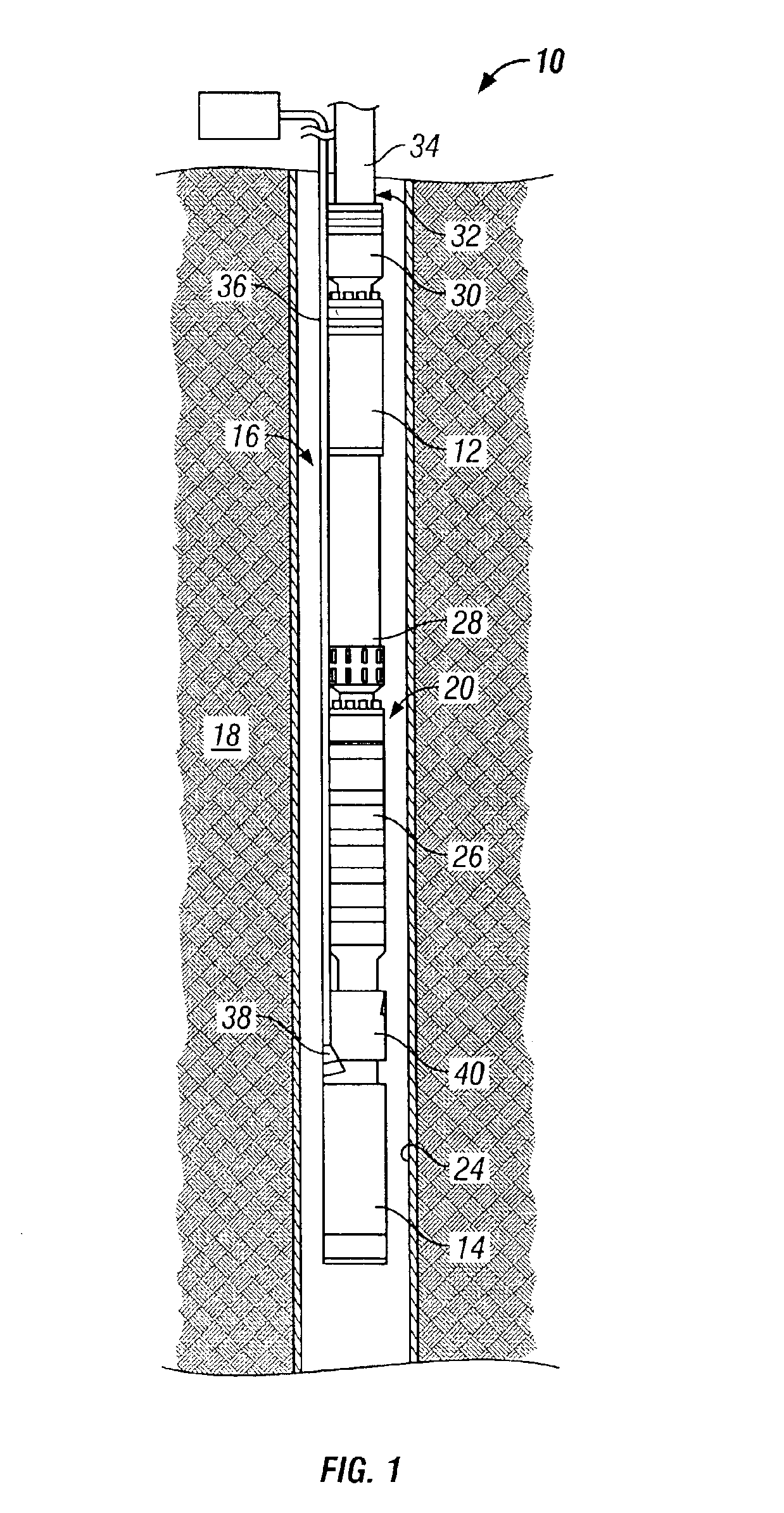
Annulus pressure control drilling systems and methods
In one embodiment, a method for drilling a wellbore includes an act of drilling the wellbore by injecting drilling fluid through a tubular string disposed in the wellbore, the tubular string comprising a drill bit disposed on a bottom thereof. The drilling fluid exits the drill bit and carries cuttings from the drill bit. The drilling fluid and cuttings (returns) flow to a surface of the wellbore via an annulus defined by an outer surface of the tubular string and an inner surface of the wellbore. The method further includes an act performed while drilling the wellbore of measuring a first annulus pressure (FAP) using a pressure sensor attached to a casing string hung from a wellhead of the wellbore. The method further includes an act performed while drilling the wellbore of controlling a second annulus pressure (SAP) exerted on a formation exposed to the annulus.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Downhole tractor
A downhole tractor is provided that includes a housing and a first wheel assembly coupled to the housing that is operable to translate away from the housing in a first direction. The first wheel assembly has a first electric motor, a first wheel, and a first reduction gear assembly coupled between the first electric motor and the first wheel. A second wheel assembly is coupled to the housing and is operable to translate away from the housing in a second direction that is opposite to the first direction. The second wheel assembly has a second electric motor, a second wheel, and a second reduction gear assembly coupled between the second electric motor and the second wheel. A fluid ram is coupled to the first and second wheel assemblies for selectively translating the first and second wheel assemblies toward and away from the housing. A first controller is provided for controlling the flow of current to the first and second electric motors. On-board and surface control systems may be incorporated to permit selective active of the wheels assemblies. In addition, couplings and connectors employing shape-memory materials may be included to secure the tractor to coiled tubing or a wireline.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Fracturing systems and methods for a wellbore
InactiveUS20150114652A1Superior line canceling harmonicReduce the possibilityFluid removalBorehole drivesTransformerPower grid
The disclosure contained herein describes systems, units, and methods usable to stimulate a formation including a pump usable to pressurize fluid, an electric-powered driver in communication with and actuating the pump, and an electrical power source in communication with and powering the electric-powered driver. The electrical power source can include on-site generators and / or grid power sources, and transformers can be used to alter the voltage received to a voltage suitable for powering the electric-powered driver. Air moving devices associated with the electric-powered driver can be used to provide air proximate to the pump to disperse gasses. In combination with fluid supply and / or proppant addition subsystems, the pump can be used to fracture a formation.
Owner:PROSTIM LABS
Integrated directional under-reamer and stabilizer
The present invention is an apparatus for use in drilling operations. It uses an under-reamer having a plurality of elongated arms with cutting elements at the ends of the arms for enlarging a previously drilled borehole drilled by a drill bit. One or more stabilizers in close proximity to the under-reamer provide stability to the under-reamer and the drill bit. The stabilizer could be rotating or non-rotating; and could be positioned between the under-reamer and the drill bit, or above the under reamer or above a directional device on the drillstring. The cutting arms are selectively operable to perform the enlargement. The stabilizer may be provided with members that closely fit the size of the borehole.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Remotely controlled apparatus for downhole applications and methods of operation
An apparatus for use downhole is disclosed that, in one configuration includes a downhole tool configured to operate in an active position and an inactive position and an actuation device, which may include a control unit. The apparatus includes a telemetry unit that sends a first pattern recognition signal to the control unit to move the tool into the active position and a second pattern recognition signal to move the tool into the inactive position. The apparatus may be used for drilling a subterranean formation and include a tubular body and one or more extendable features, each positionally coupled to a track of the tubular body, and a drilling fluid flow path extending through a bore of the tubular body for conducting drilling fluid therethrough. A push sleeve is disposed within the tubular body and coupled to the one or more features. A valve assembly is disposed within the tubular body and configured to control the flow of the drilling fluid into an annular chamber in communication with the push sleeve; the valve assembly comprising a mechanically operated valve and / or an electronically operated valve. Other embodiments, including methods of operation, are provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES OILFIELD OPERATIONS LLC
Expandable reamer apparatus for enlarging boreholes while drilling and methods of use
ActiveUS7036611B2Reduce capacityReduce the cross-sectional areaSurveyDrill bitsFixed bearingWell drilling
An expandable reamer apparatus and methods for reaming a borehole, wherein a laterally movable blade carried by a tubular body may be selectively positioned at an inward position and an expanded position. The laterally movable blade, held inwardly by blade-biasing elements, may be forced outwardly by drilling fluid selectively allowed to communicate therewith by way of an actuation sleeve disposed within the tubular body. Alternatively, a separation element may transmit force or pressure from the drilling fluid to the movable blade. Further, a chamber in communication with the movable blade may be pressurized by way of a downhole turbine or pump. A ridged seal wiper, compensator, movable bearing pad, fixed bearing pad preceding the movable blade, or an adjustable spacer element to alter expanded blade position may be included within the expandable reamer. In addition, a drilling fluid pressure response indicating an operational characteristic of the expandable reamer may be generated.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES OILFIELD OPERATIONS LLC
Drilling with a high pressure rotating control device
ActiveUS20110024195A1Operational securityHigh safety factorSurveyDrilling rodsWell drillingControl system
A Drill-To-The-Limit (DTTL) drilling method variant to Managed Pressure Drilling (MPD) applies constant surface backpressure, whether the mud is circulating (choke valve open) or not (choke valve closed). Because of the constant application of surface backpressure, the DTTL method can use lighter mud weight that still has the cutting carrying ability to keep the borehole clean. The DTTL method identifies the weakest component of the pressure containment system, such as the fracture pressure of the formation or the casing shoe leak off test (LOT). With a higher pressure rated RCD, such as 5,000 psi (34,474 kPa) dynamic or working pressure and 10,000 psi (68,948 kPa) static pressure, the limitation will generally be the fracture pressure of the formation or the LOT. In the DTTL method, since surface backpressure is constantly applied, the pore pressure limitation of the conventional drilling window can be disregarded in developing the fluid and drilling programs. Using the DTTL method a deeper wellbore can be drilled with larger resulting end tubulars, such as casings and production liners, than had been capable with conventional MPD applications.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Tractor system
A tractor system has been invented which, in certain embodiments, includes a body connected to the item, first setting means on the body for selectively and releasably anchoring the system in a bore, first movement means having a top and a bottom, the first movement means on the body for moving the body and the item, the first movement means having a first power stroke, and the tractor system for moving the item through the bore at a speed of at least 10 feet per minute.
Owner:EXPRO AMERICAS +1
Well system
InactiveUS6923273B2Excessive vibrationLess expensiveElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDrilling rodsElectrical conductorEngineering
The drilling system includes a work string supporting a bottom hole assembly. The work string including lengths of pipe having a non-metallic portion. The work string preferably includes a composite coiled tubing having a fluid impermeable liner, multiple load carrying layers, and a wear layer. Multiple electrical conductors and data transmission conductors may be embedded in the load carrying layers for carrying current or transmitting data between the bottom hole assembly and the surface. The bottom hole assembly includes a bit, a gamma ray and inclinometer instrument package, a steerable assembly, an electronics section, a transmission, and a power section for rotating the bit. It may or may not include a propulsion system. The drilling system may be a gravity based drilling system that does include a propulsion system. Various motive means may be provided such as gravity, to apply weight on the bit.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
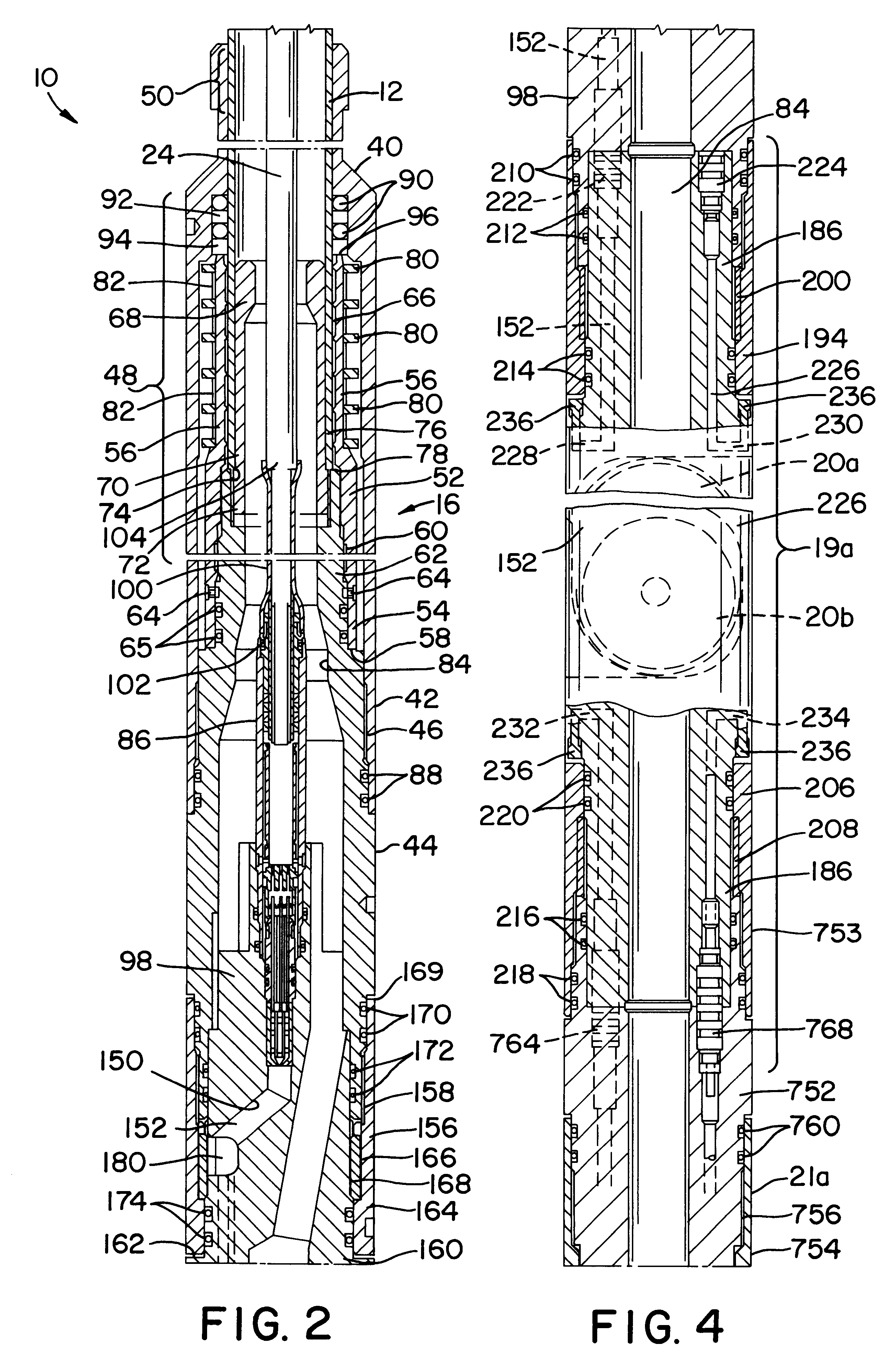
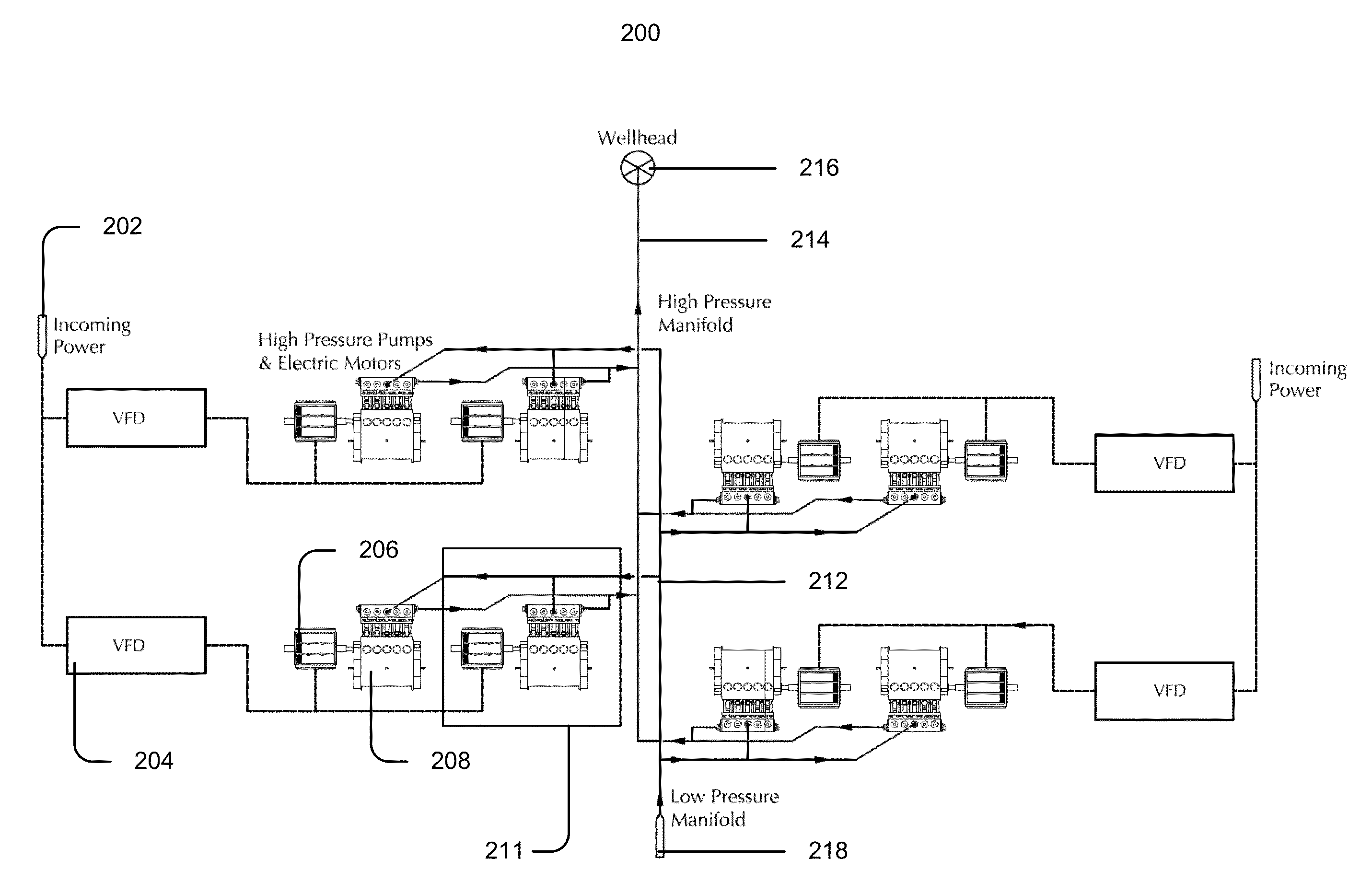
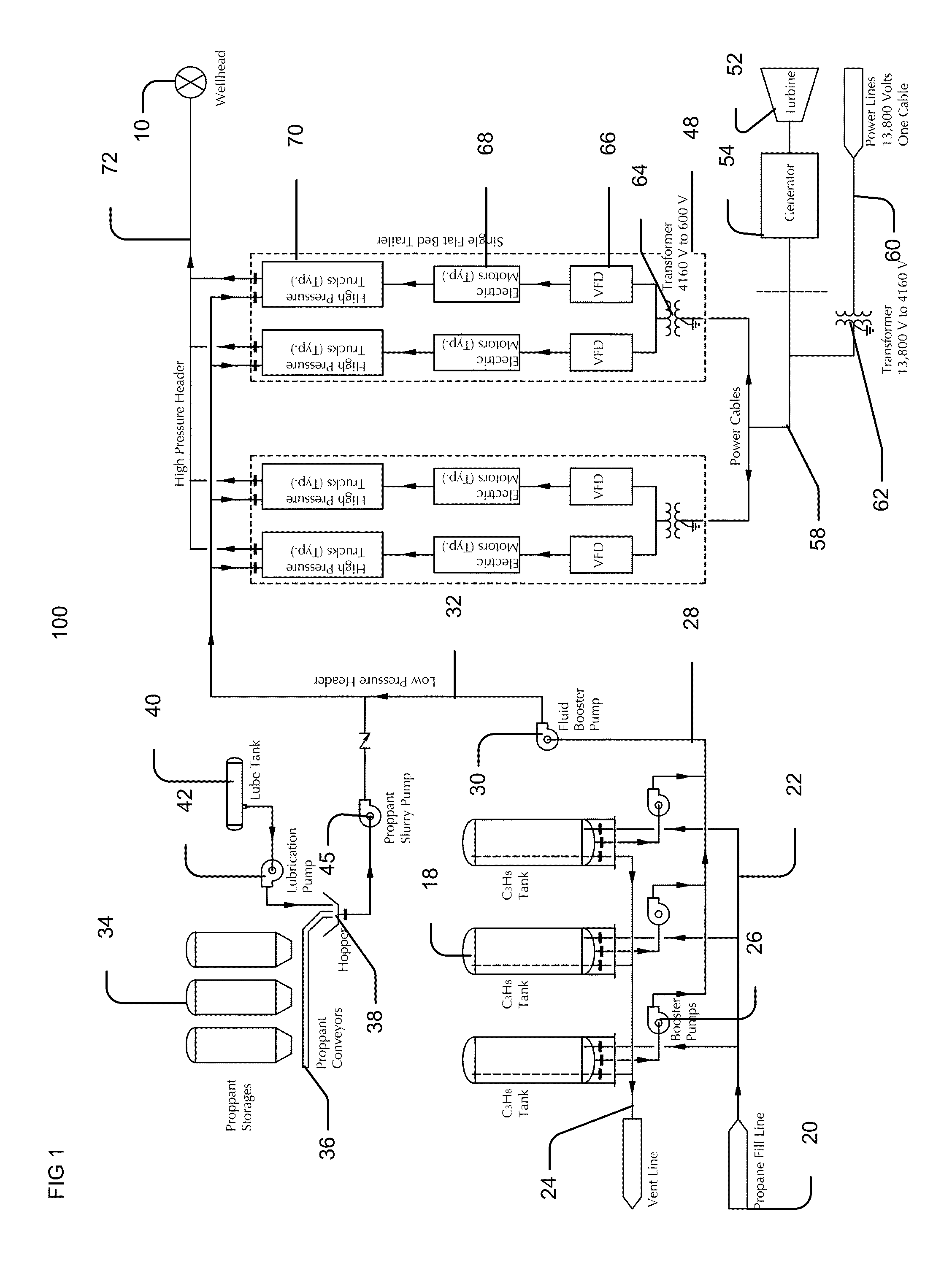
System for Pumping Hydraulic Fracturing Fluid Using Electric Pumps
A system for hydraulically fracturing an underground formation in an oil or gas well to extract oil or gas from the formation, the oil or gas well having a wellbore that permits passage of fluid from the wellbore into the formation. The system includes a plurality of electric pumps fluidly connected to the well, and configured to pump fluid into the wellbore at high pressure so that the fluid passes from the wellbore into the and fractures the formation. The system can also include a plurality of natural gas powered generators electrically connected to the plurality of electric pumps to provide electrical power to the pumps.
Owner:US WELL SERVICS LLC
Bore tractor system
A tractor system for moving an item through a wellbore has been invented with a central mandrel interconnected with the item, first setting means about the central mandrel for selectively and releasably anchoring the system in a wellbore, the central mandrel having a top, and a bottom, and a first power thread therein, the first setting means having a first follower pin for engaging the first power thread to power the first setting means to set the first setting means against an inner wall of the bore. In one aspect, the tractor system is for moving the item through the bore at a speed of at least 10 feet per minute. In one aspect, the tractor system has second setting means on the central mandrel for selectively and releasably anchoring the system in the bore, the second setting means spaced apart from the first setting means, and the central mandrel having a second power thread therein and a second retract thread therein, the second retract thread in communication with the second power thread, and the second setting means having a second follower pin for engaging the second power thread to power the second setting means to set the second setting means against the inner wall of the bore.
Owner:COILED TUBING ENG SERVICES
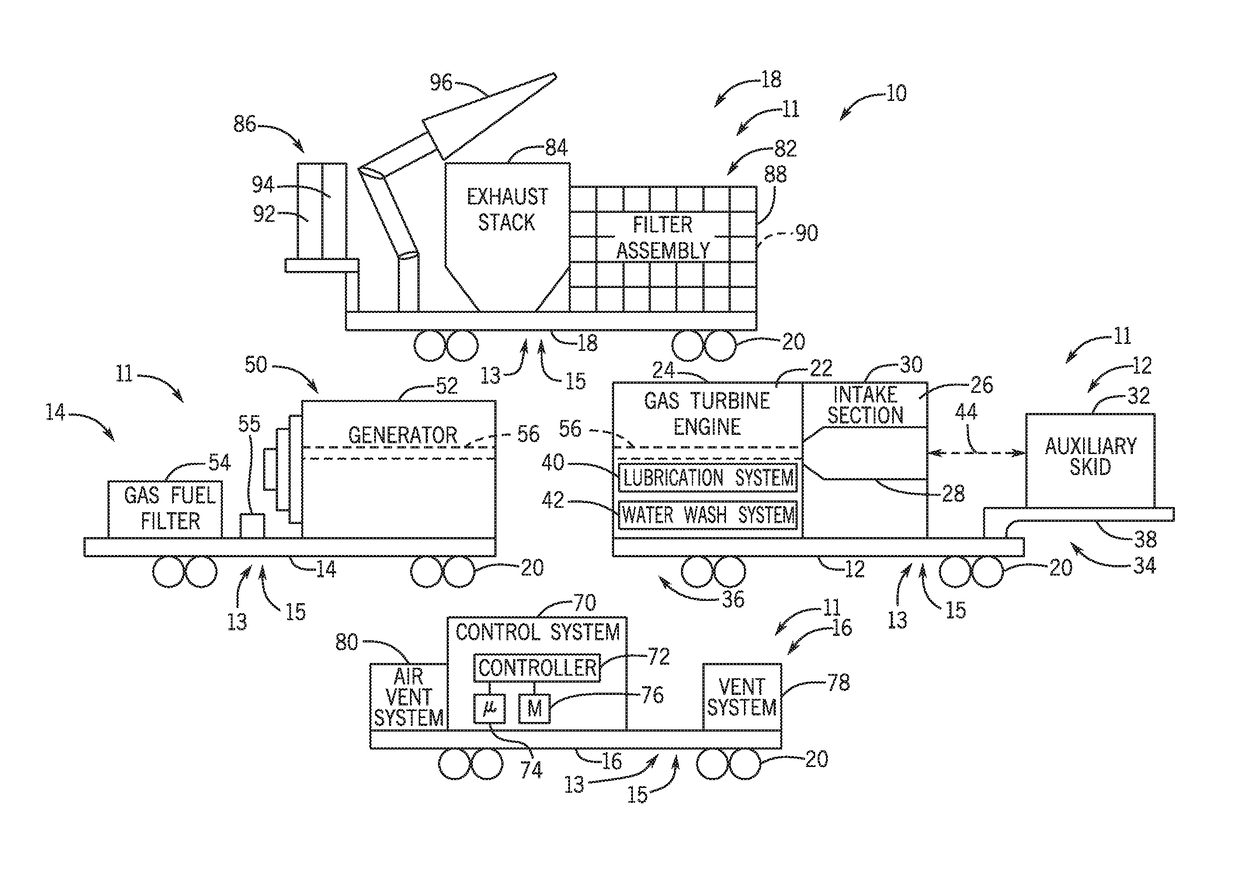
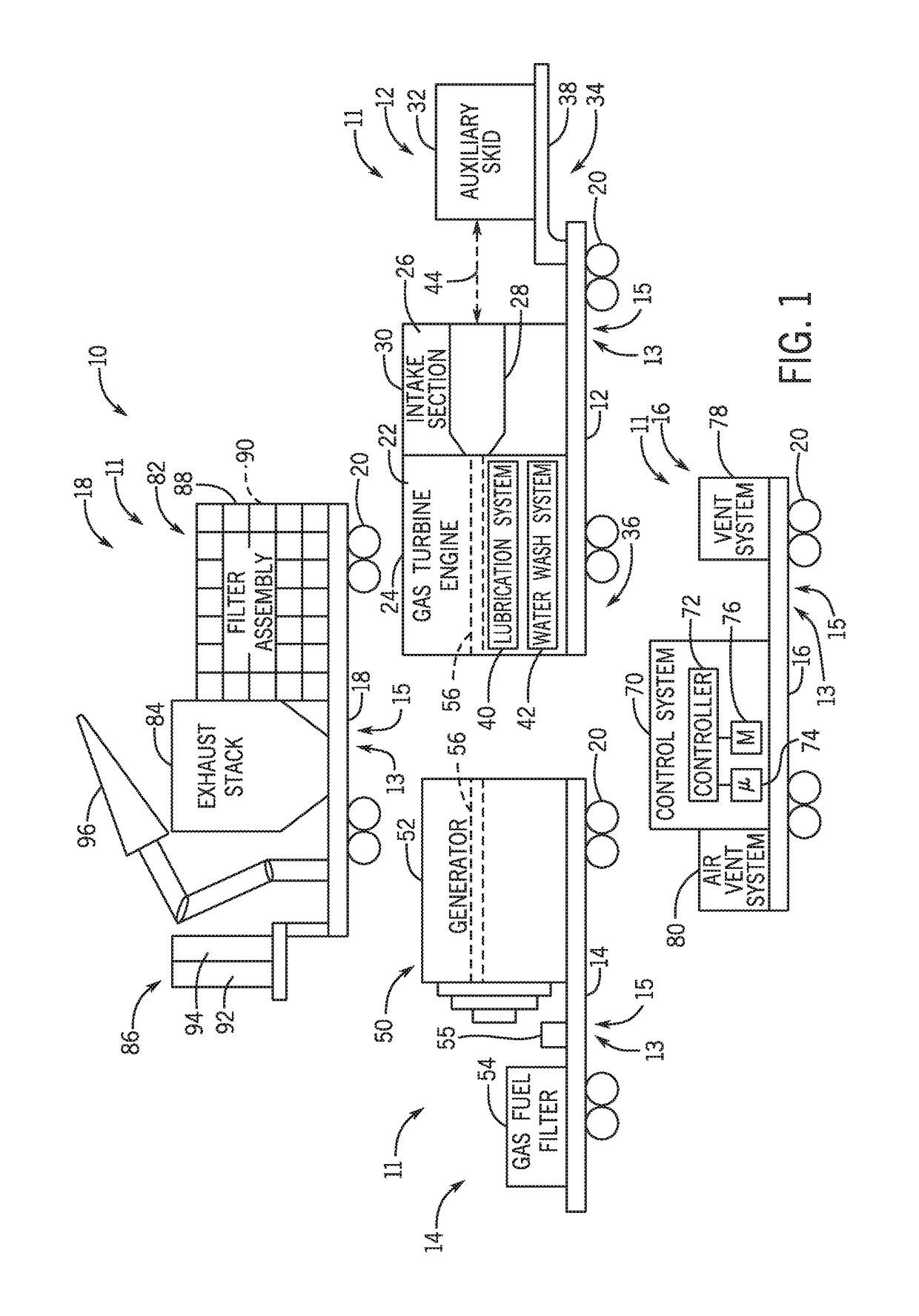
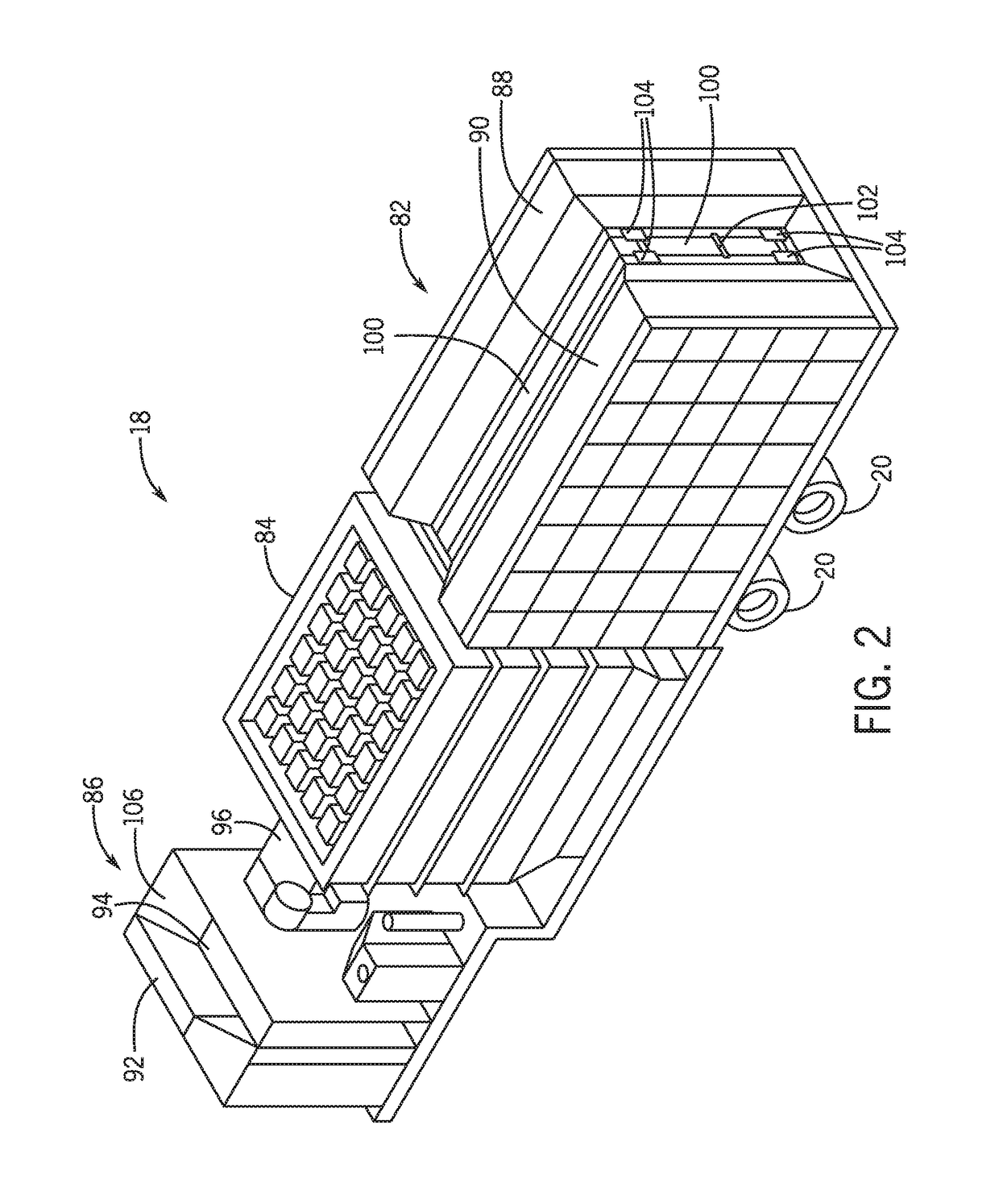
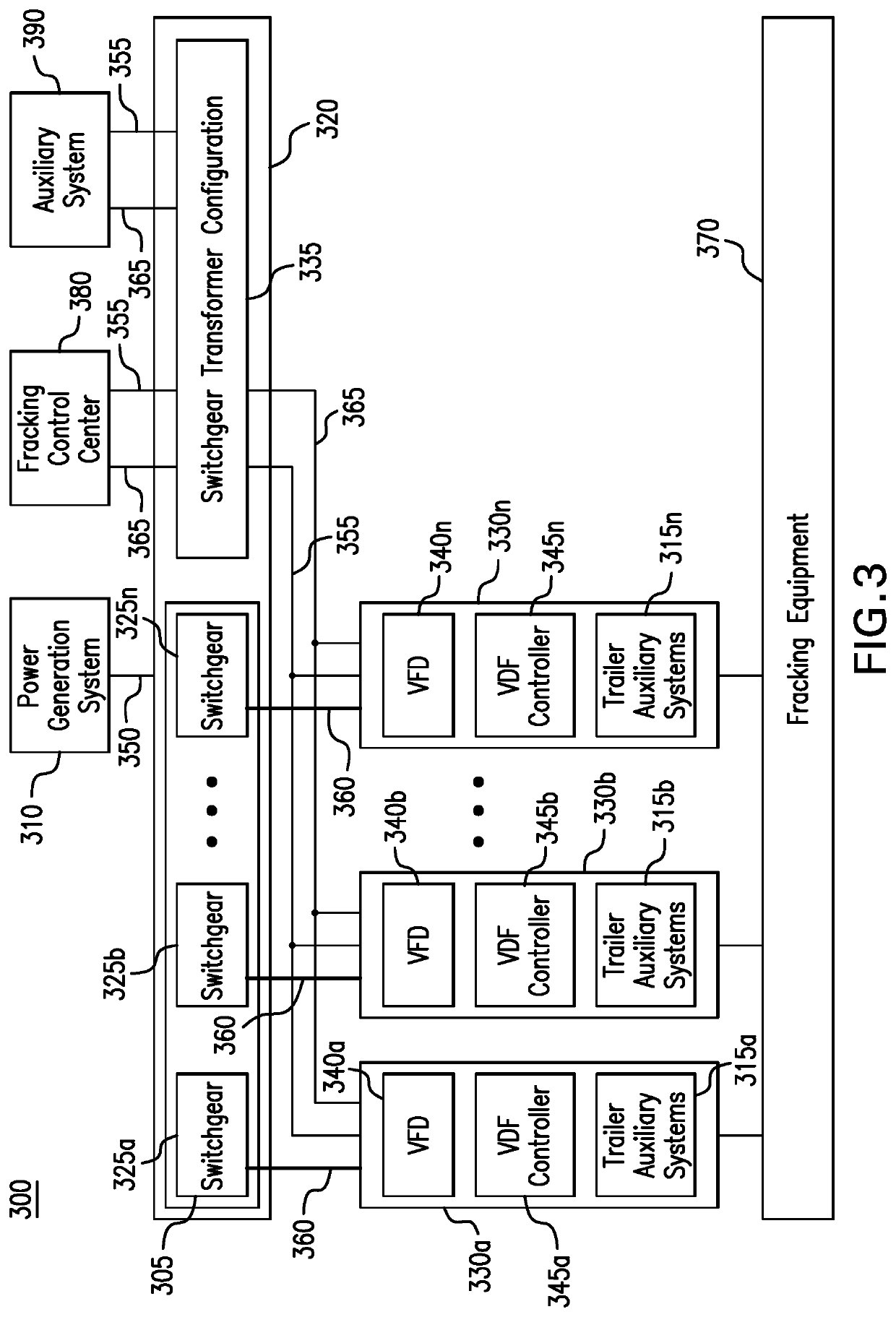
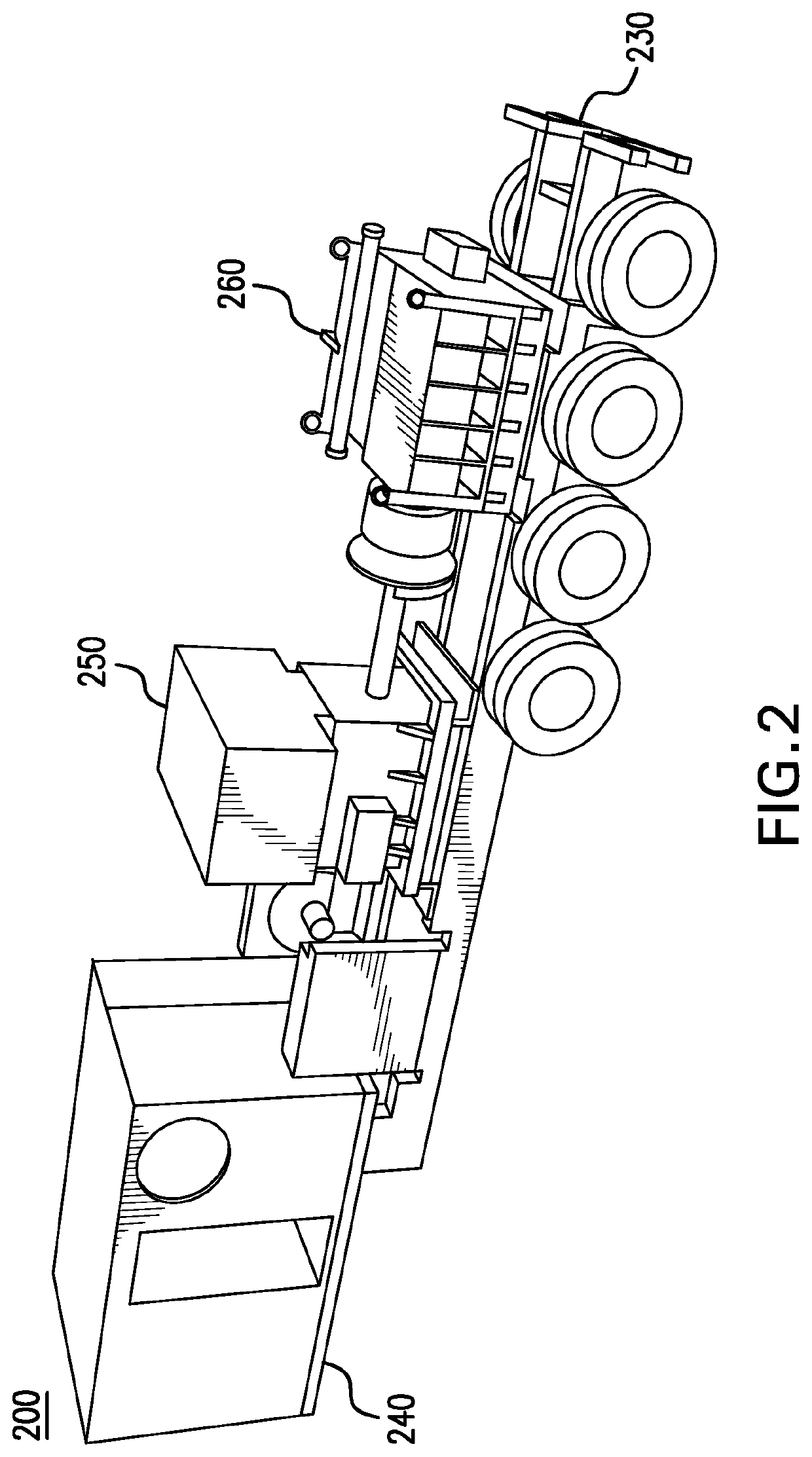
Systems and methods for a mobile power plant with improved mobility and reduced trailer count
A system a first mobile body configured to support a turbine engine and an auxiliary skid communicatively and fluidly coupled to the turbine engine. The auxiliary skid includes one or more interconnects configured to support a turbine engine component. The system also includes a second mobile body configured to support a generator. The first and second mobile bodies are configured to align a removable coupling between the turbine engine and the generator.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Composite coating with nanoparticles for improved wear and lubricity in down hole tools
Owner:SMITH INT INC
Apparatus and method to reduce fluid pressure in a wellbore
The present invention generally provides apparatus and methods for reducing the pressure of a circulating fluid in a wellbore. In one aspect of the invention an ECD (equivalent circulation density) reduction tool provides a means for drilling extended reach deep (ERD) wells with heavyweight drilling fluids by minimizing the effect of friction head on bottomhole pressure so that circulating density of the fluid is close to its actual density. With an ECD reduction tool located in the upper section of the well, the friction head is substantially reduced, which substantially reduces chances of fracturing a formation.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
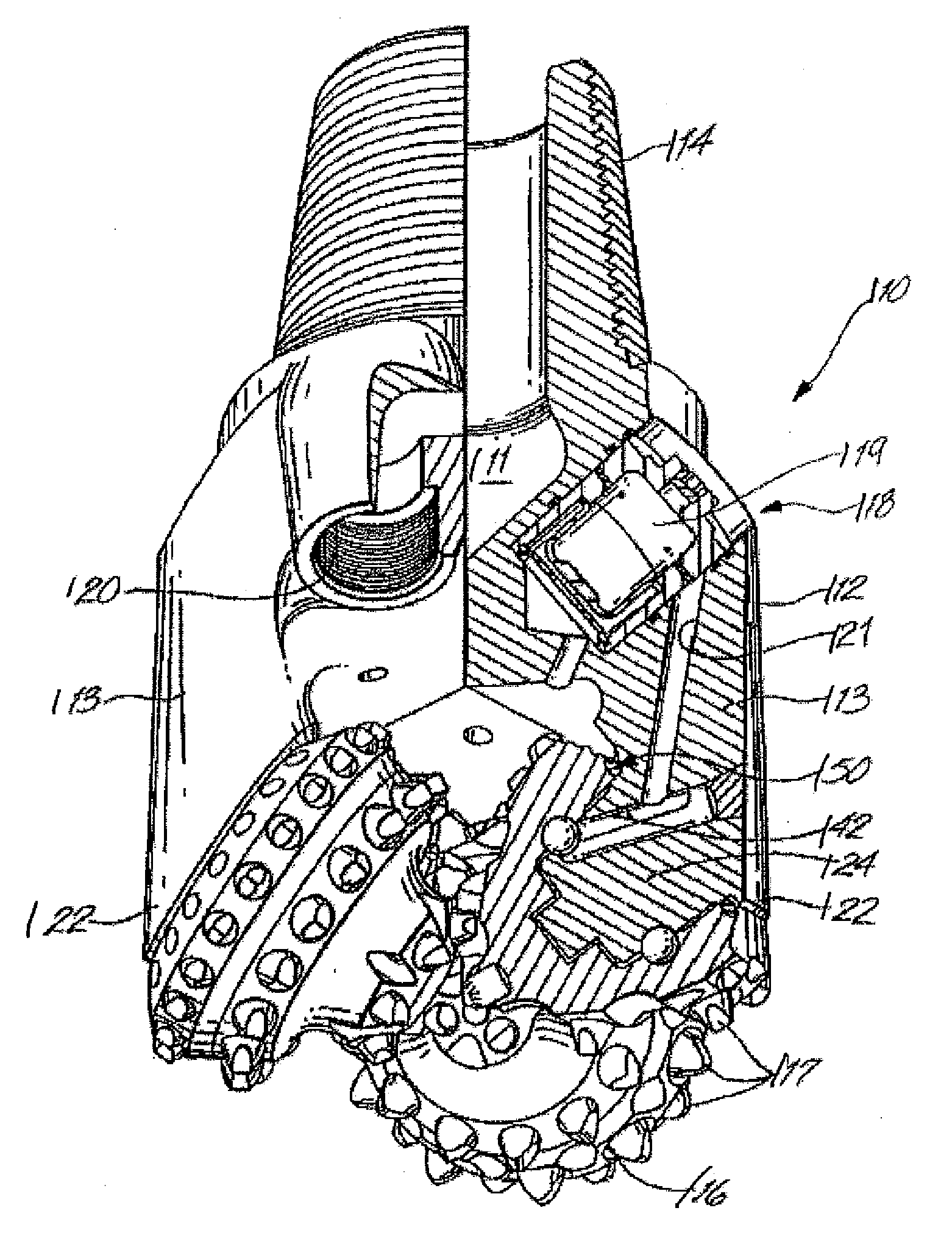
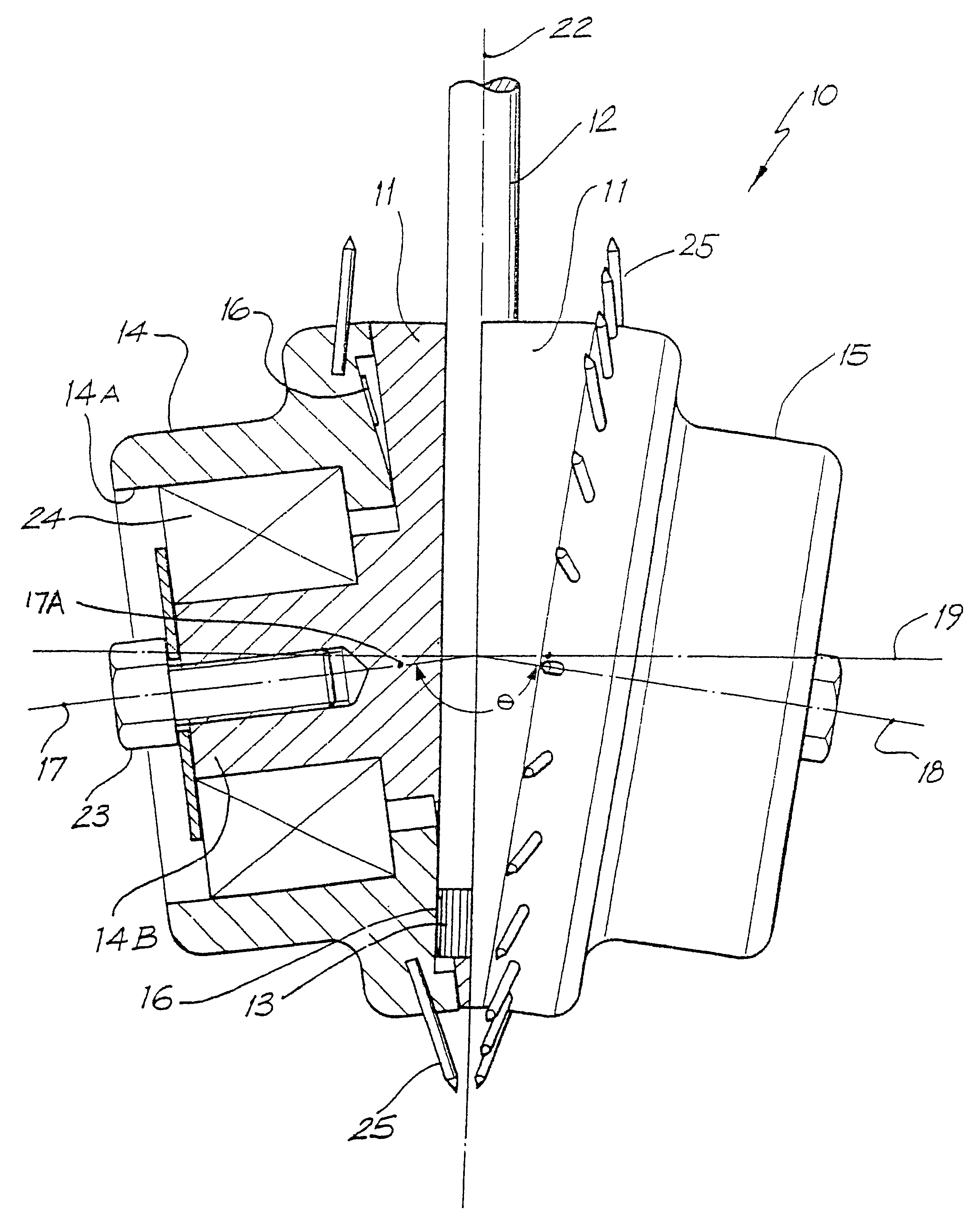
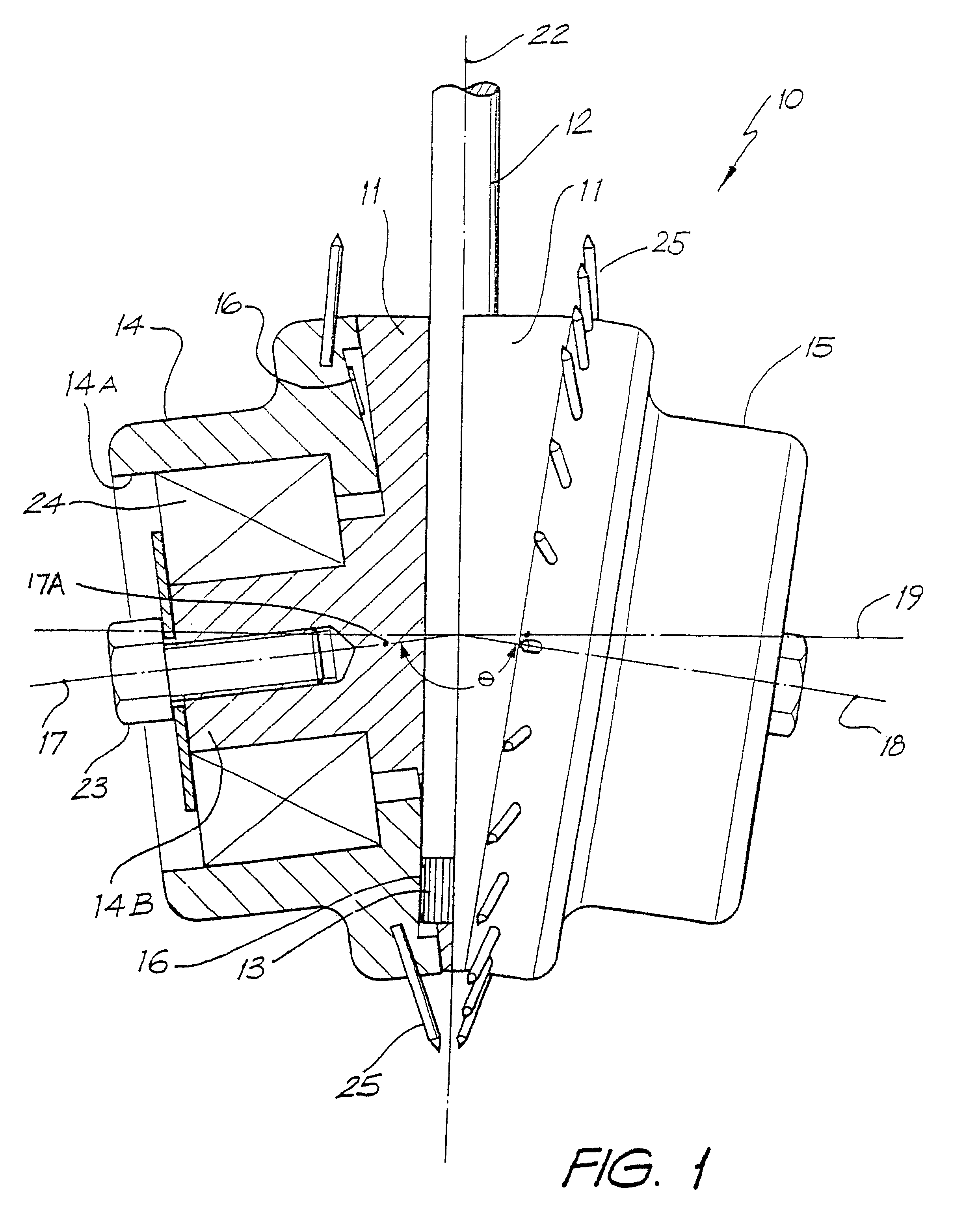
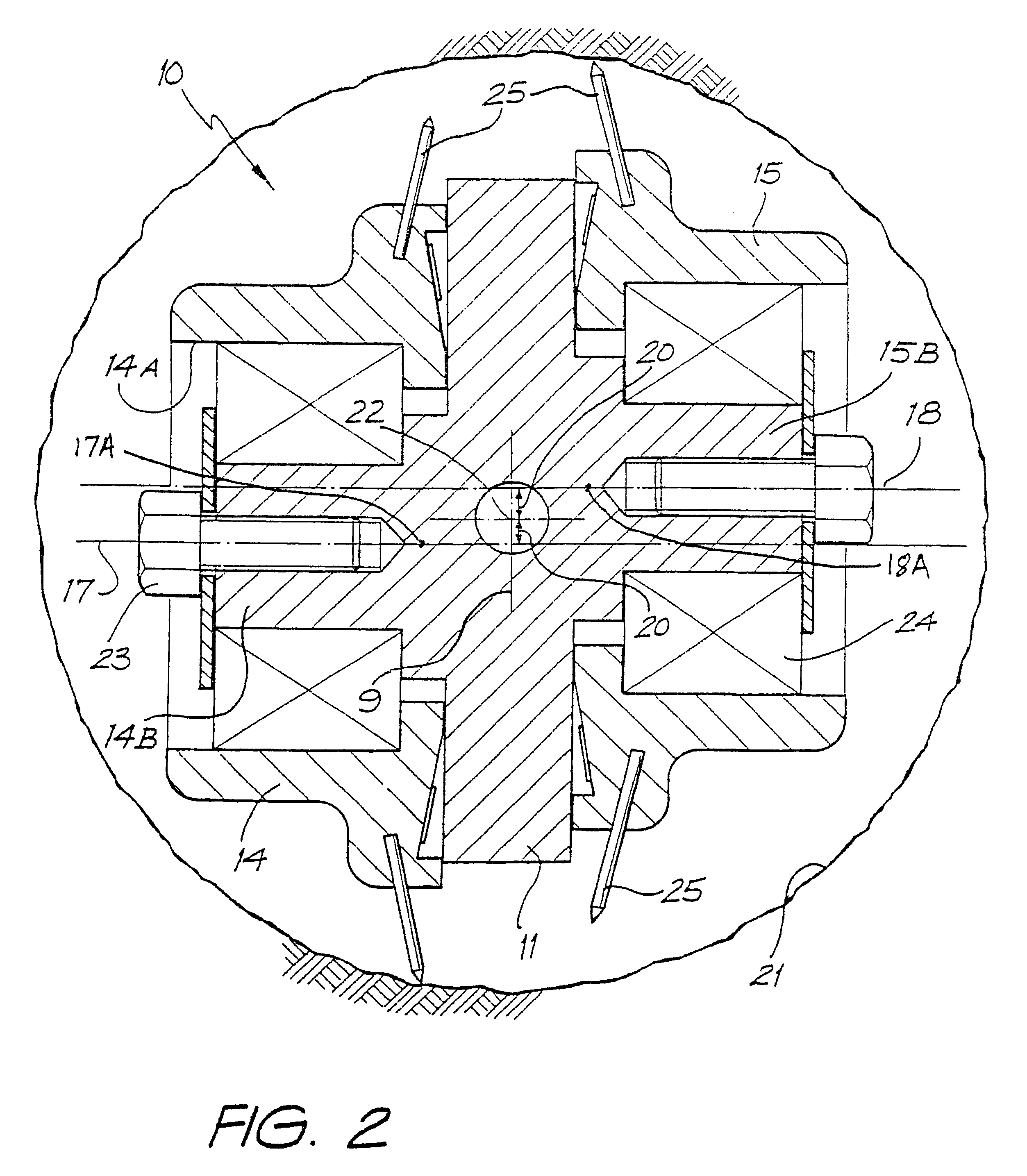
Excavation bit for a drilling apparatus
The invention provides an excavation bit, which is constructed from either a single or double carrier. If two carriers are present the carriers are contra-rotating. By the off setting of the axes of rotation of single or dual carriers from a longitudinal axis of the bit, and by driving to carriers to rotate, a ground engaging thrust is produced, as well as the rotation of the excavation bit in the ground as a consequence of the rotation of the carriers, and not vice versa as is the case with prior art. By the invention, there can result sufficient thrust on the bit, by the rotation of the carriers, so that the need to apply thrust down the bore via the drill rod is reduced or eliminated. As a result of the invention the number and or size of the ground engaging tools are not a function of the bore diameter to be drilled. Thus as the excavation bit is scaled up for larger diameter bores more ground engaging tools and or an increase in their size is not required. By the invention, thrust applied (either via the drill rod or from the rotation of the carriers) is thought to be, through a quasi lever system, multiplied at some of the ground engaging tools in the radial direction. That is the total thrust in the longitudinal axis direction (whether externally applied or resultant from the contra-rotation of the carriers), is multiplied so that the outward forces exerted (by the cutters onto the rock surface in the region approaching perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the bore) is thought to be significantly higher than the magnitude of the total thrust.
Owner:MOLLOY ANTHONY
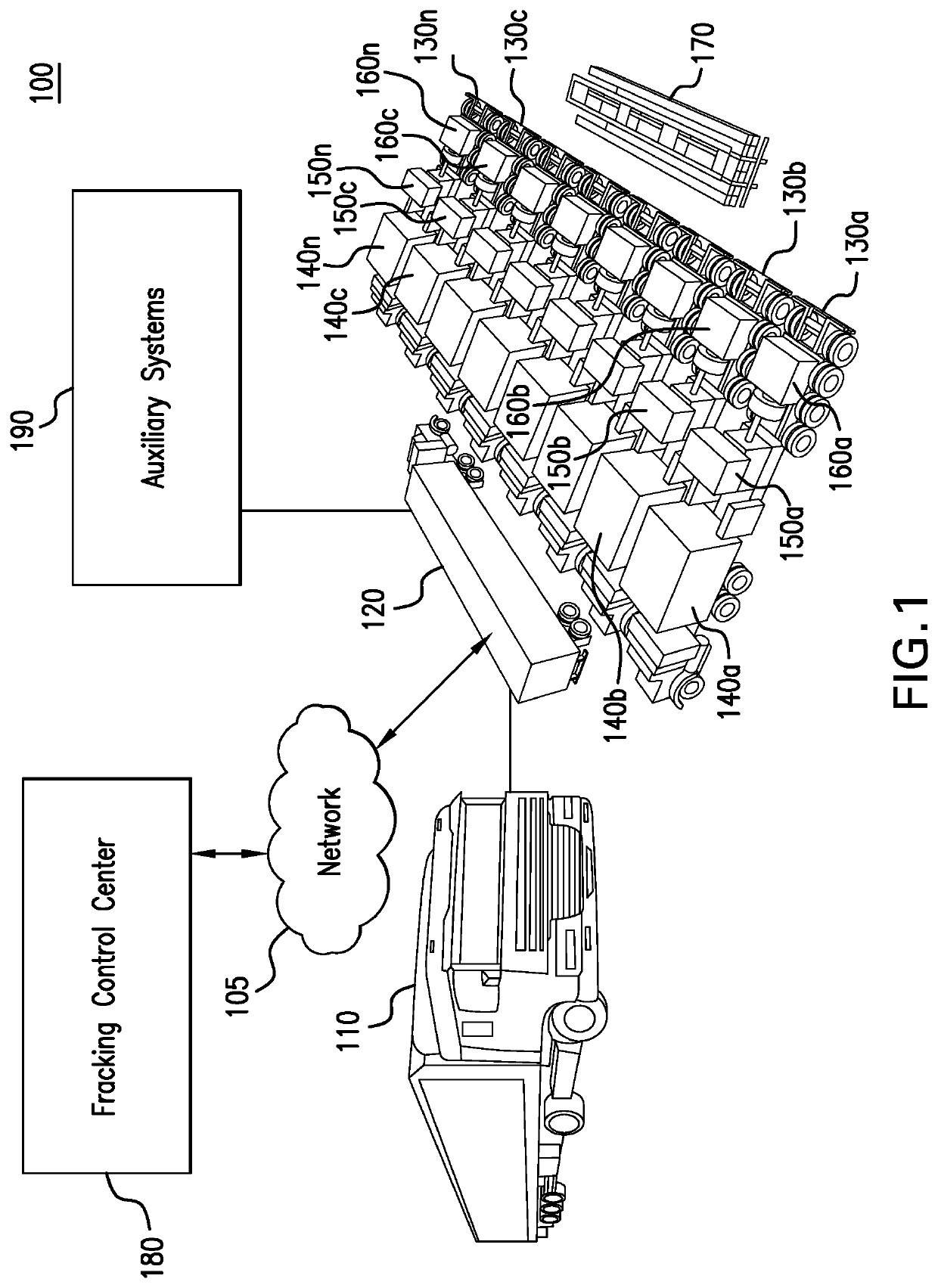
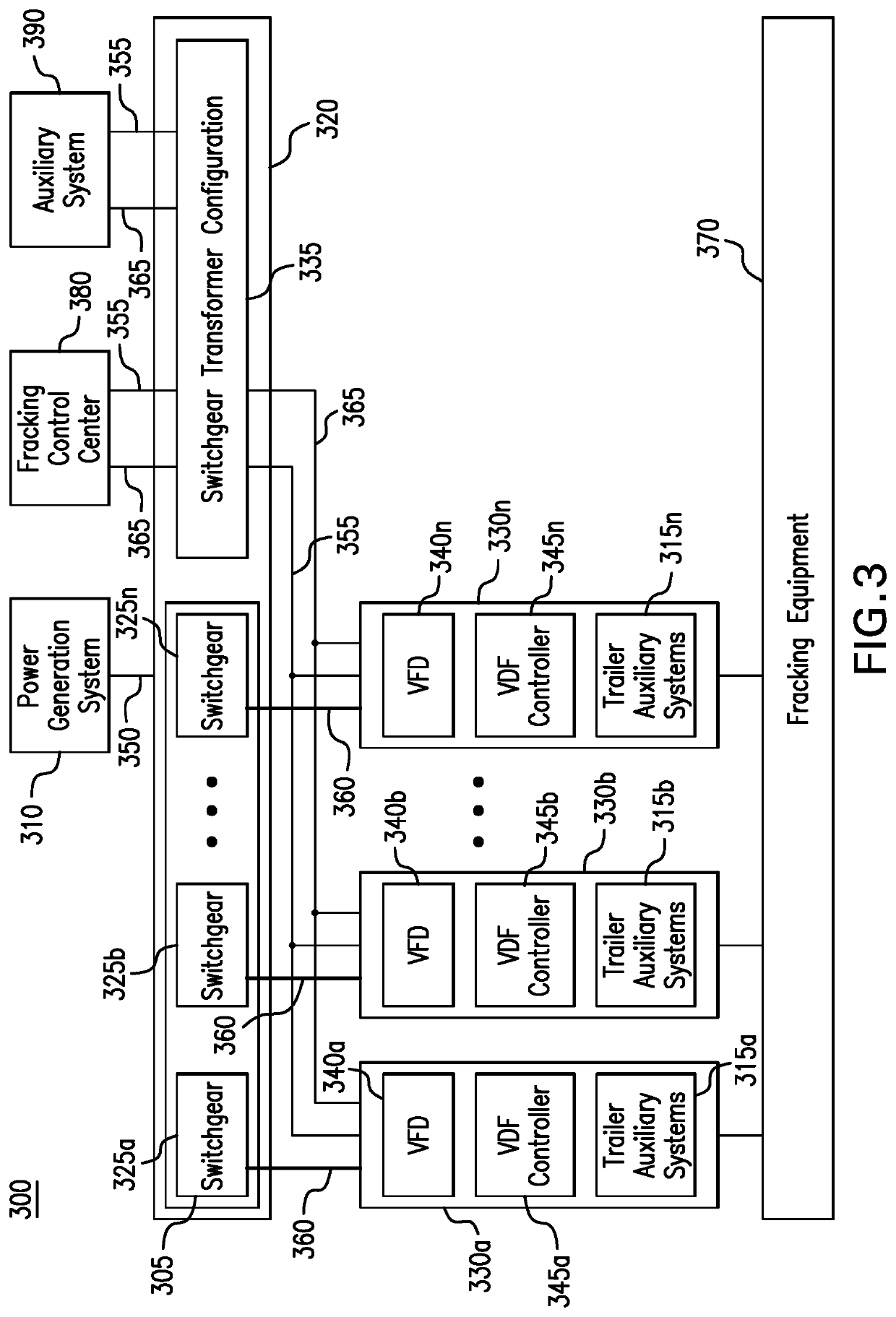
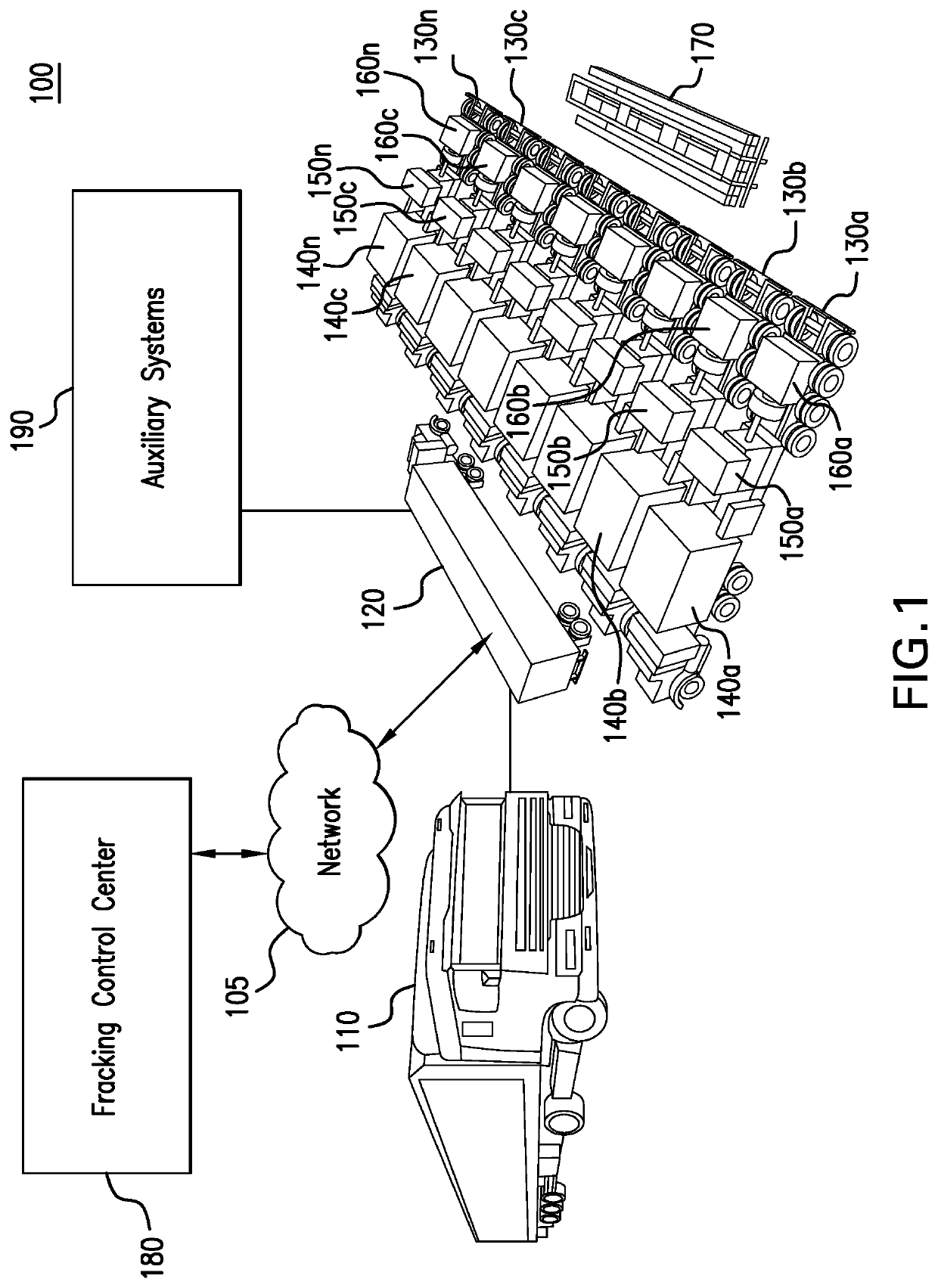
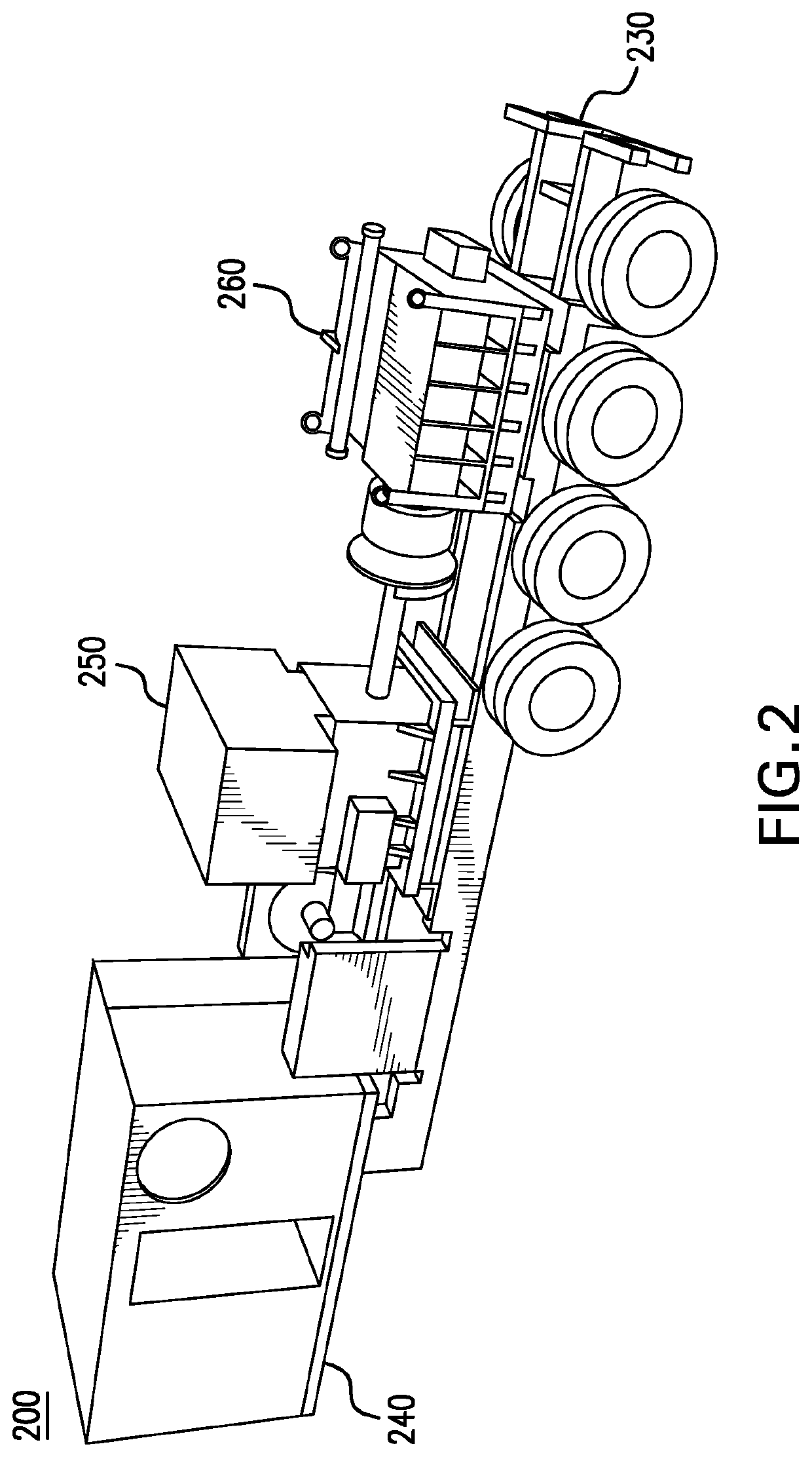
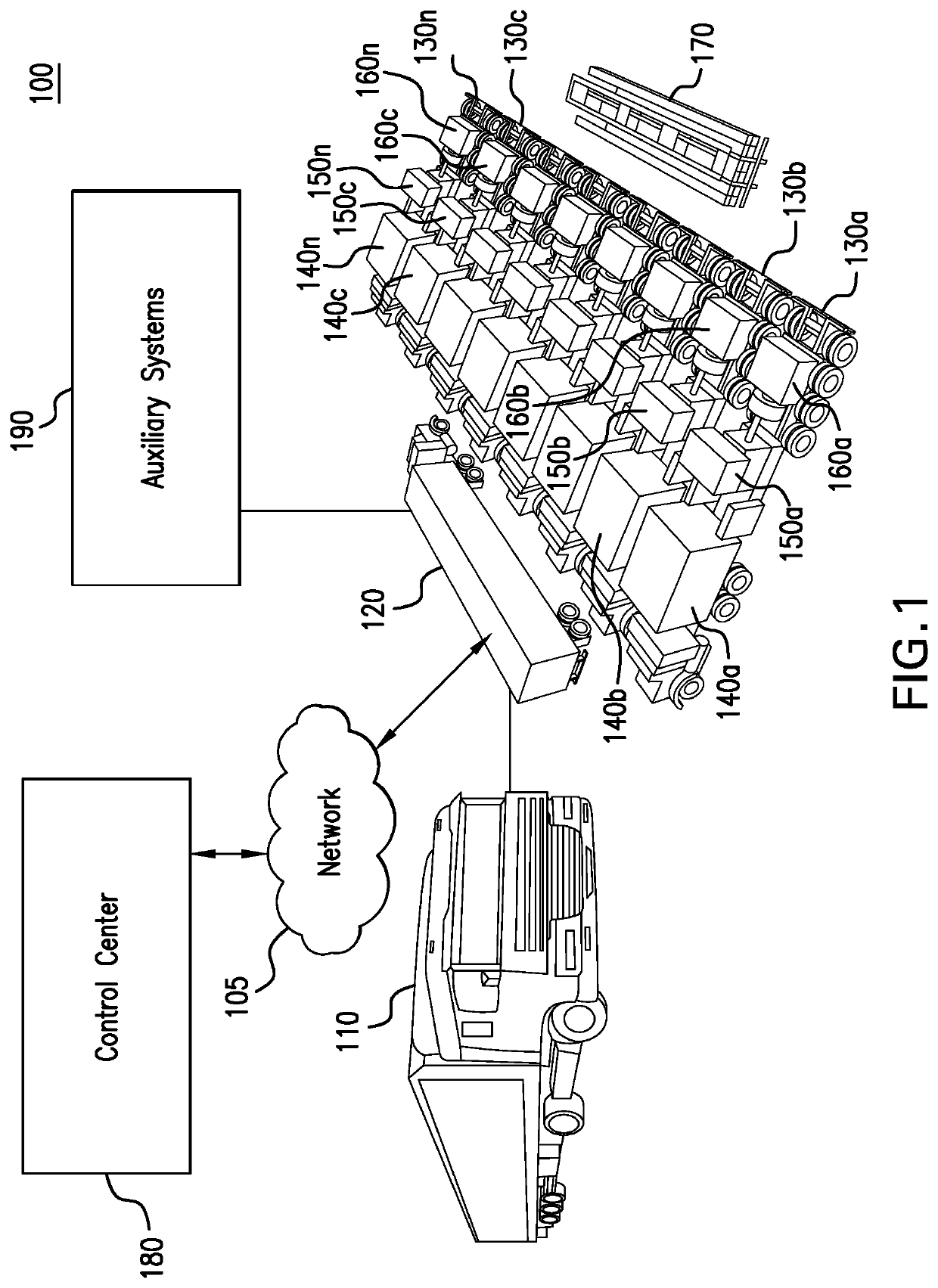
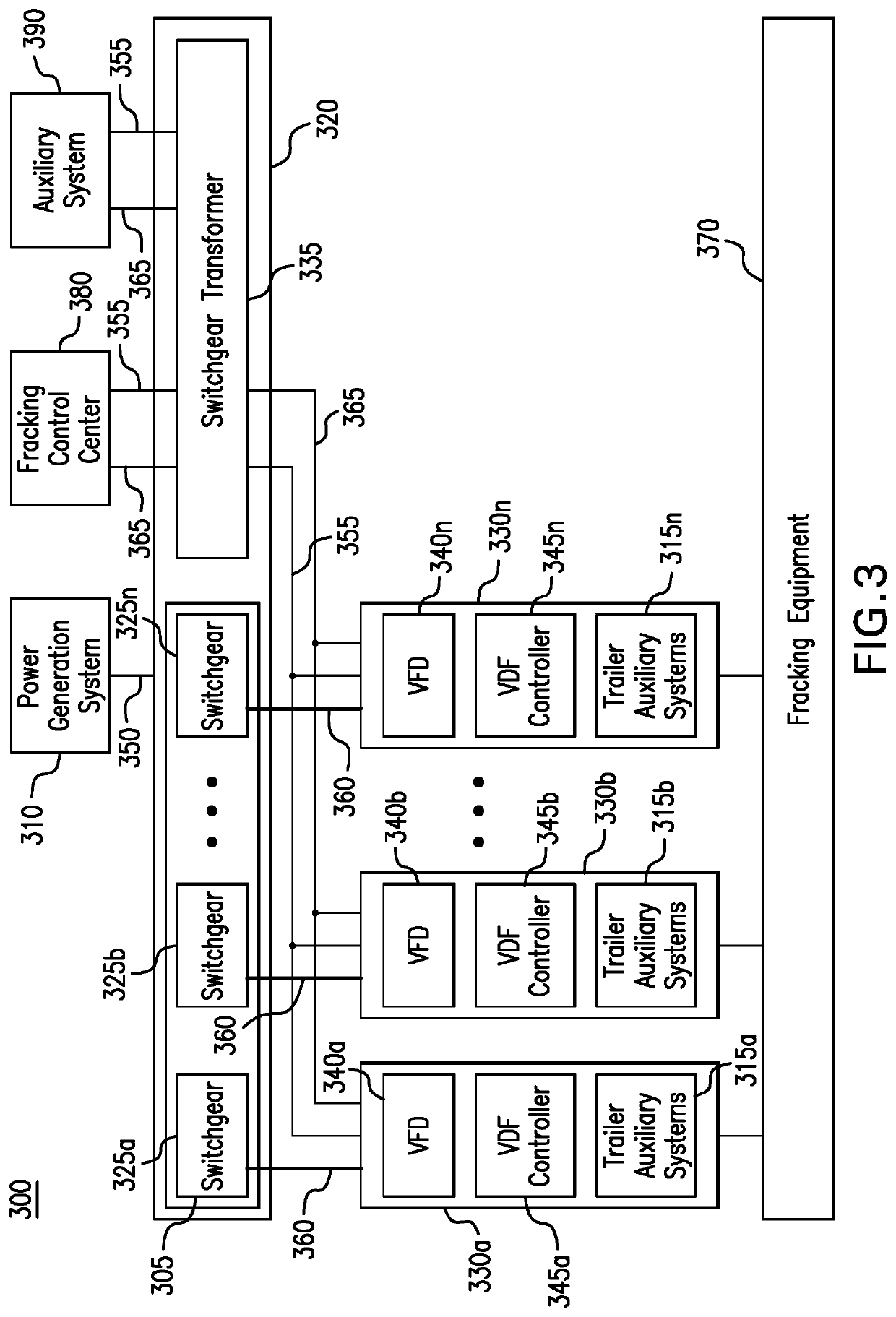
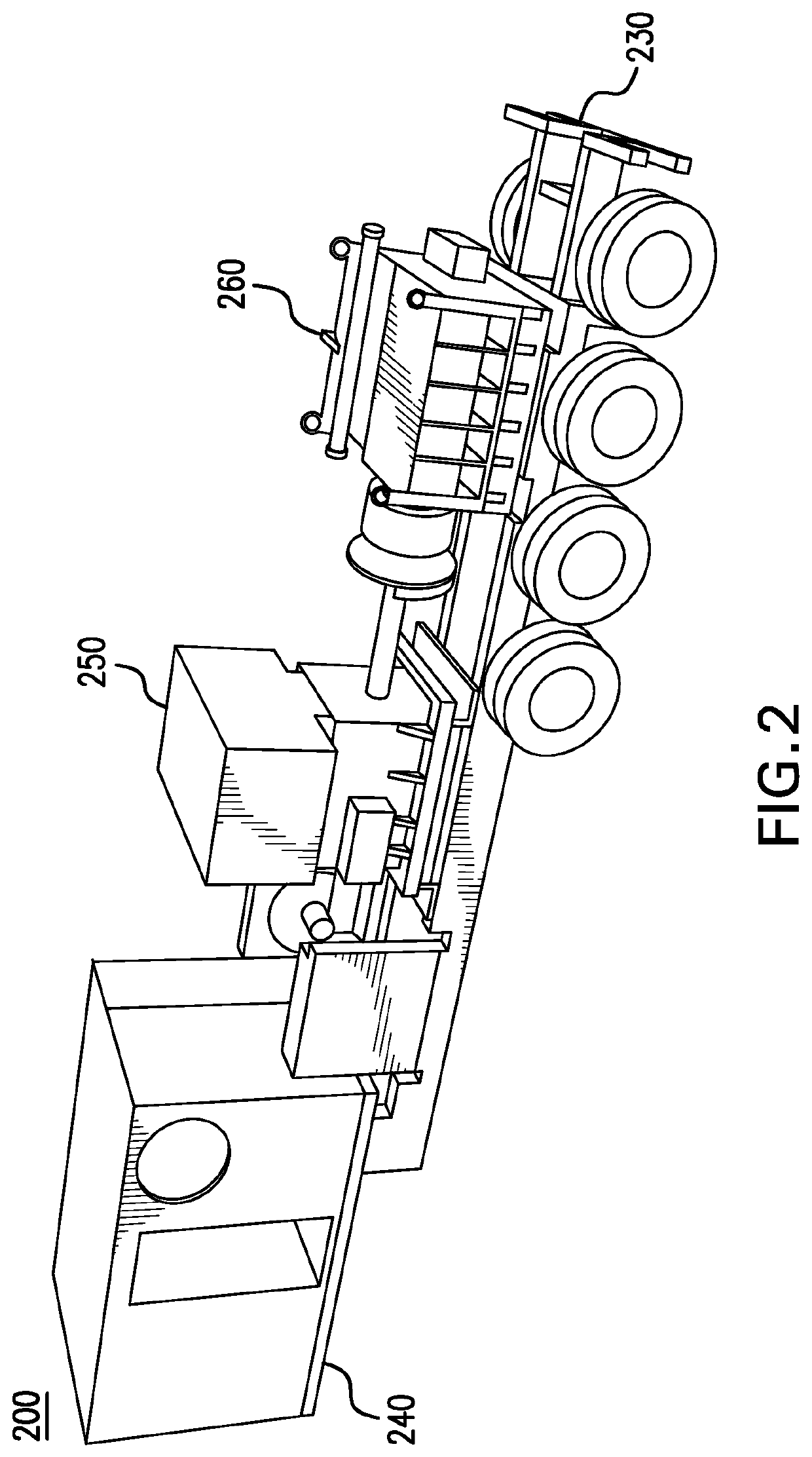
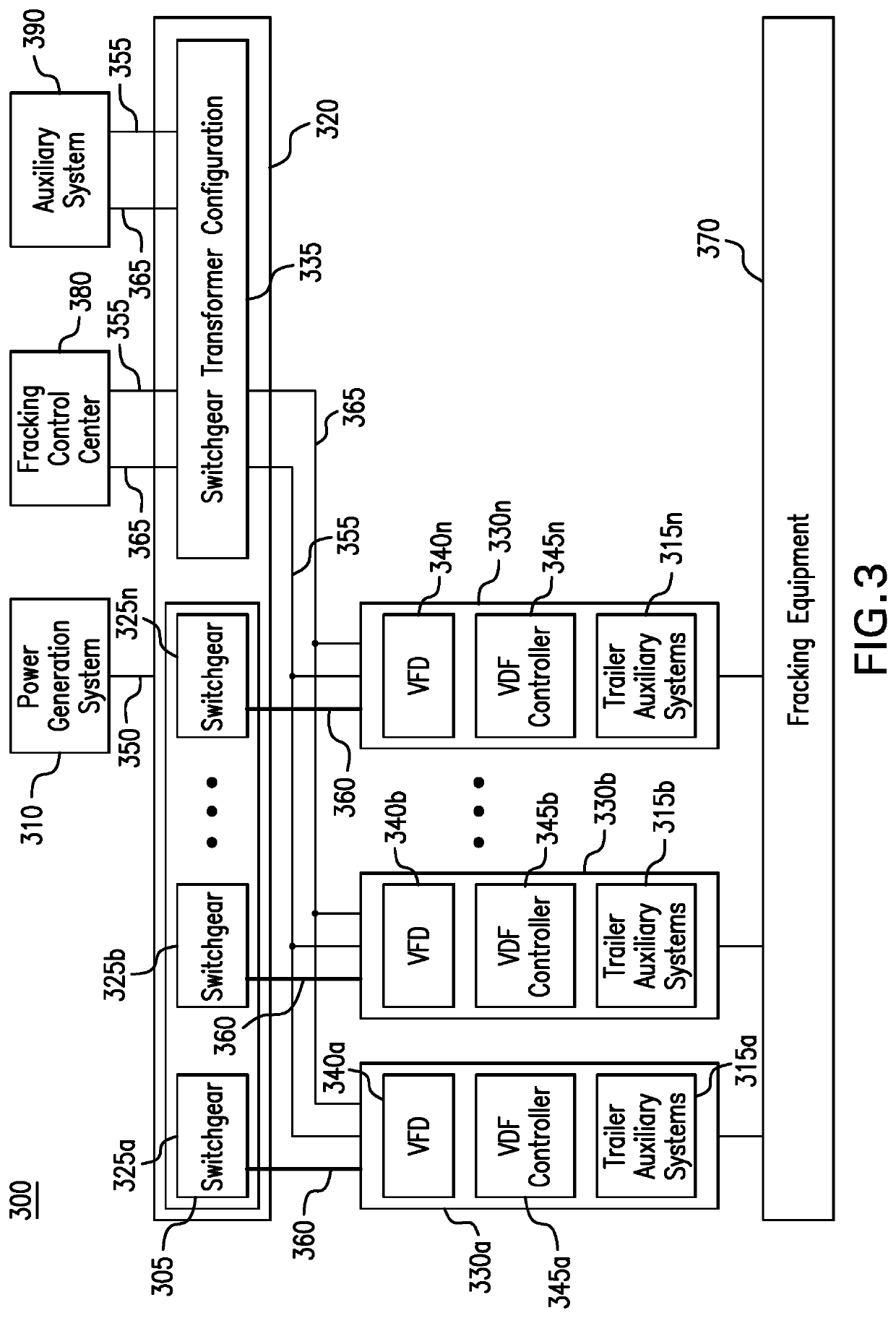
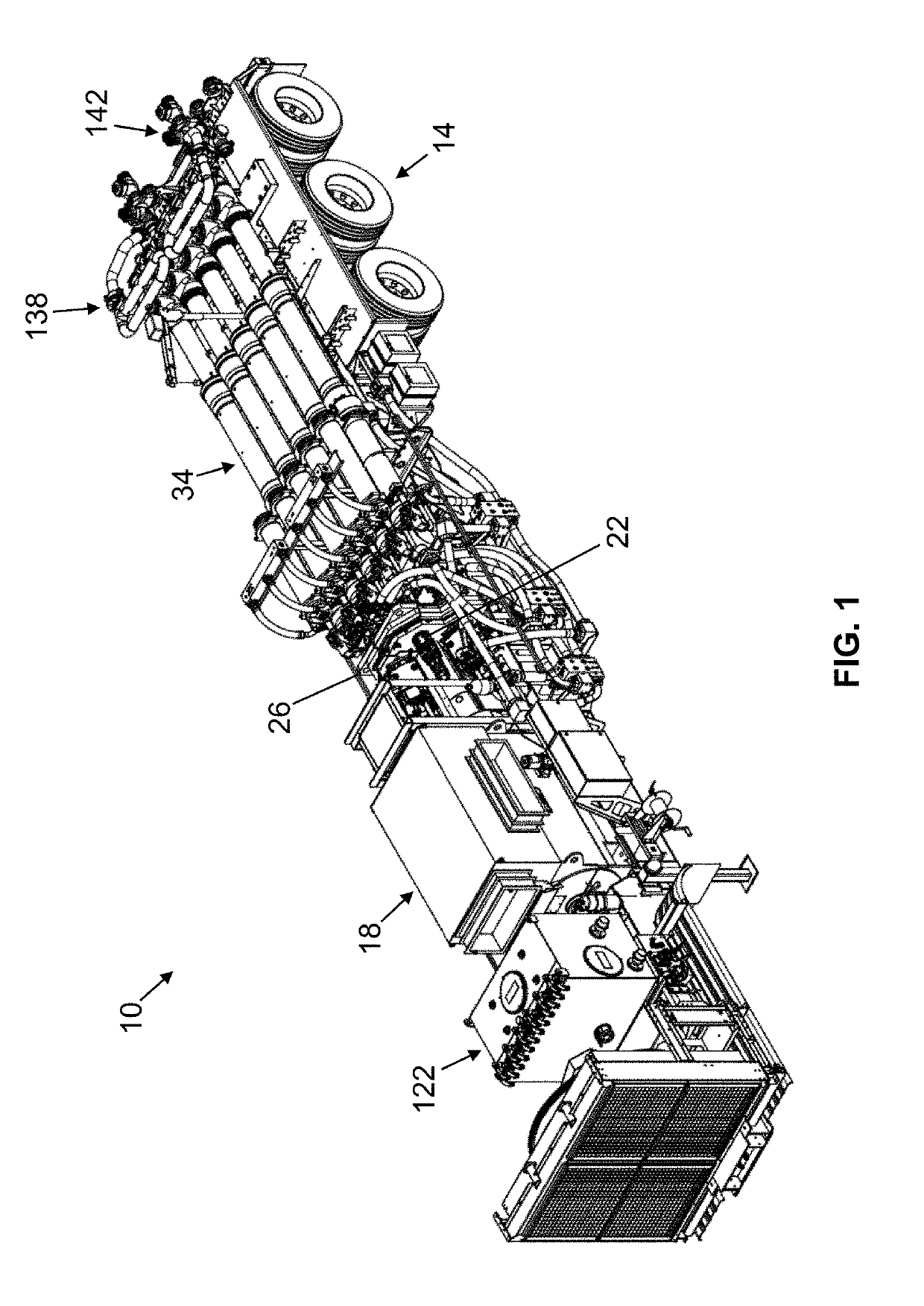
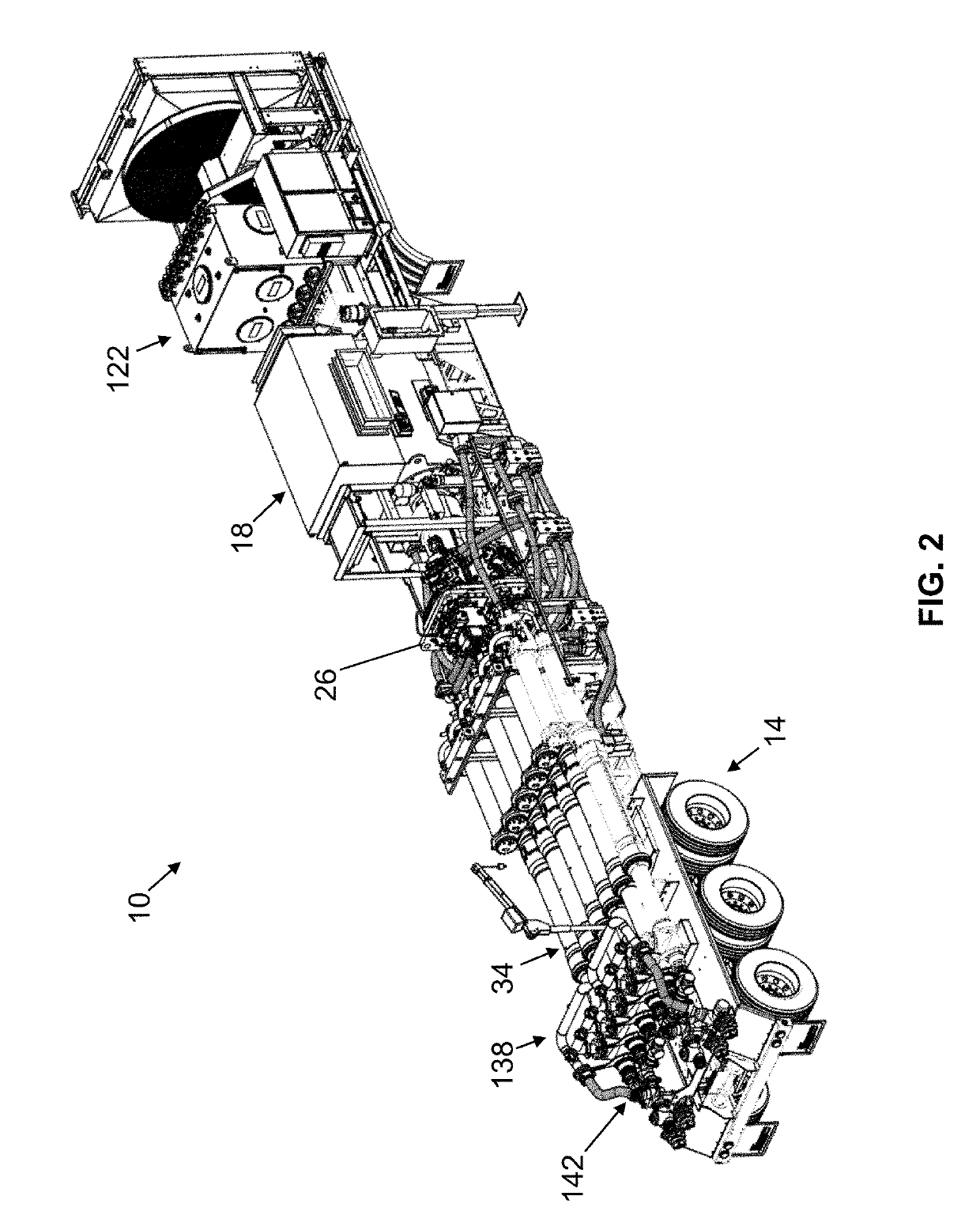
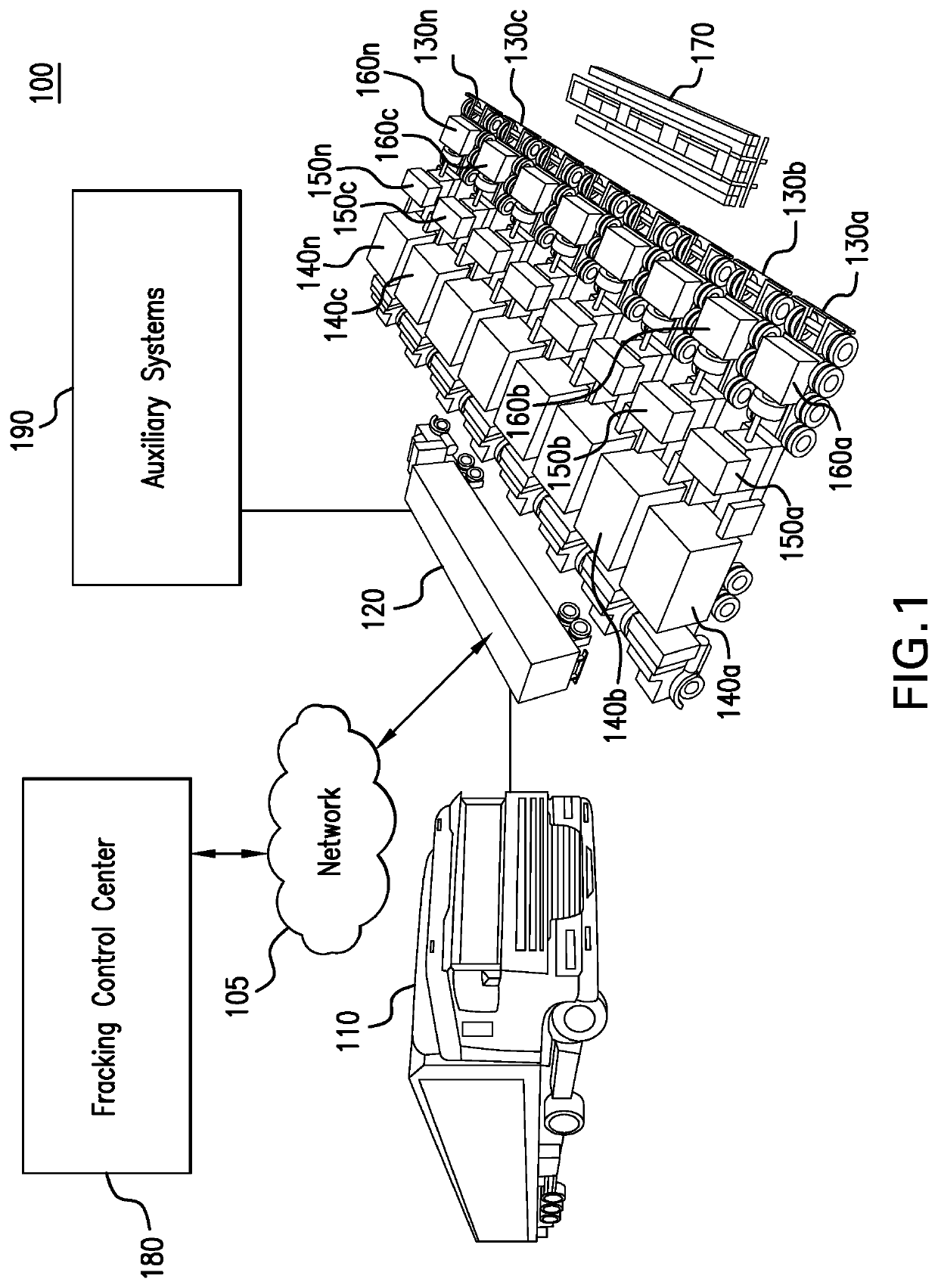
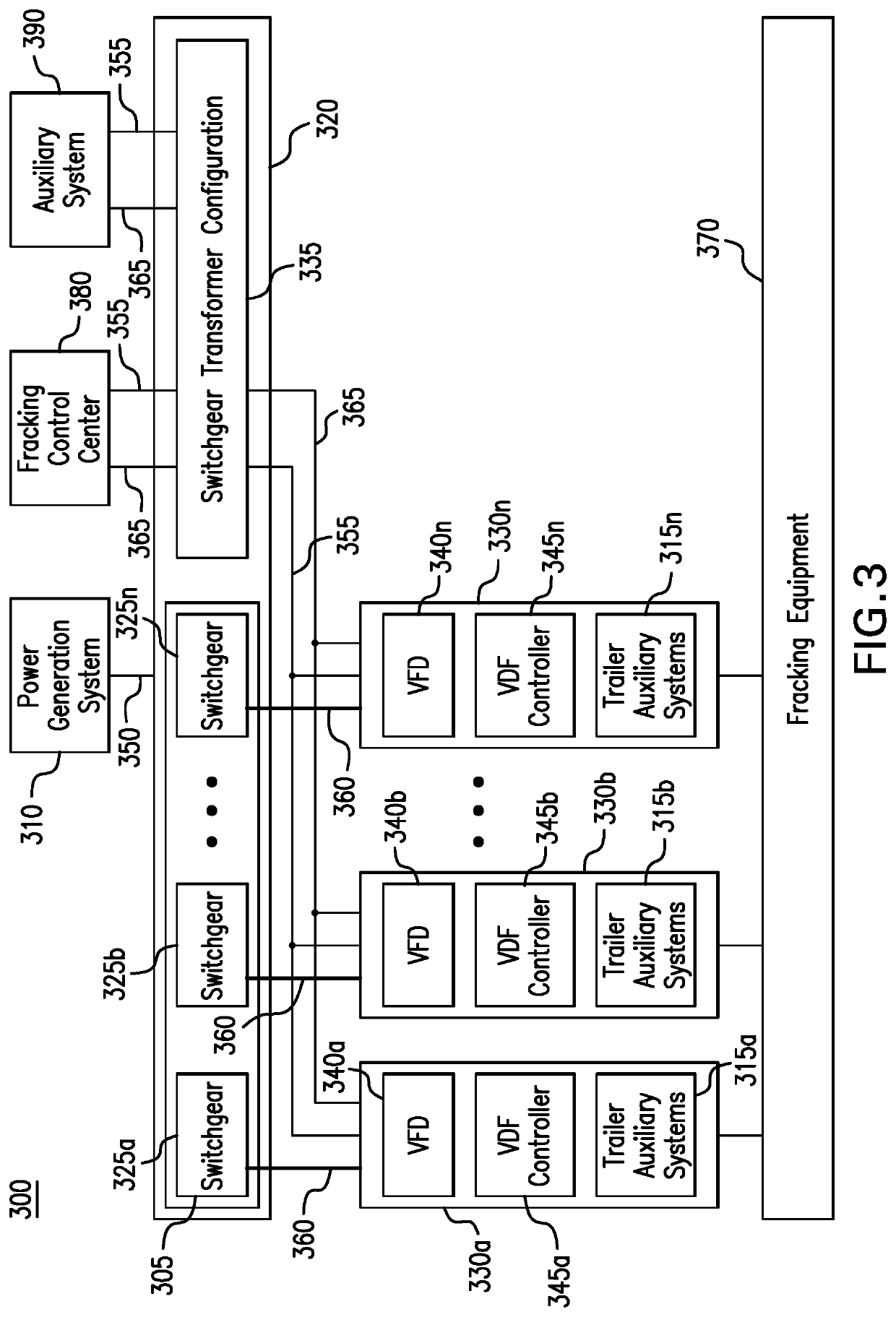
Parameter monitoring and control for an electric driven hydraulic fracking system
An electric driven hydraulic fracking system is disclosed. A pump configuration includes the single VFD, the single shaft electric motor, and the single hydraulic pump mounted on the single pump trailer. A controller associated with the single VFD and is mounted on the single pump trailer. The controller monitors operation parameters associated with an operation of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system as each component of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system operates to determine whether the operation parameters deviate beyond a corresponding operation parameter threshold. Each of the operation parameters provides an indicator as to an operation status of a corresponding component of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system. The controller initiates corrected actions when each operation parameter deviates beyond the corresponding operation threshold. Initiating the corrected actions when each operation parameter deviates beyond the corresponding operation threshold maintains the operation of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Parameter monitoring and control for an electric driven hydraulic fracking system
An electric driven hydraulic fracking system is disclosed. A pump configuration includes the single VFD, the single shaft electric motor, and the single hydraulic pump mounted on the single pump trailer. A controller associated with the single VFD and is mounted on the single pump trailer. The controller monitors operation parameters associated with an operation of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system as each component of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system operates to determine whether the operation parameters deviate beyond a corresponding operation parameter threshold. Each of the operation parameters provides an indicator as to an operation status of a corresponding component of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system. The controller initiates corrected actions when each operation parameter deviates beyond the corresponding operation threshold. Initiating the corrected actions when each operation parameter deviates beyond the corresponding operation threshold maintains the operation of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system.
Owner:NAT SERVICE ALLIANCE HOUSTON LLC
Variable frequency drive configuration for electric driven hydraulic fracking system
ActiveUS10753153B1Non-enclosed substationsSubstation/switching arrangement detailsHydraulic pumpElectric drive
An electric driven hydraulic fracking system is disclosed. A pump configuration that includes the single VFD, the single shaft electric motor, and the single hydraulic pump that is mounted on the single pump trailer. A pump configuration includes a single VFD configuration, the single shaft electric motor, and the single shaft hydraulic pump mounted on the single pump trailer. The single VFD configuration converts the electric power at the power generation voltage level distributed from the power distribution trailer to a VFD voltage level and drives the single shaft electric motor to control the operation of the single shaft electric motor and the single hydraulic pump. The VFD voltage level is a voltage level that is required to drive the single shaft electric motor. The VFD configuration also controls operation of the auxiliary systems based on the electric power at the auxiliary voltage level.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Electric driven hydraulic fracking system
ActiveUS10738580B1Non-enclosed substationsSubstation/switching arrangement detailsHydraulic pumpElectro hydraulic
An electric driven hydraulic fracking system is disclosed. A pump configuration that includes the single VFD, the single shaft electric motor, and the single hydraulic pump that is mounted on the single pump trailer. The single VFD converts the electric power of at least 13.8 kV to a VFD rated voltage level of at least 4160V and drives the single shaft electric motor at the VFD voltage level of up to 4160V to control the operation of the single shaft electric motor and the single hydraulic pump. The single shaft electric motor drives the single hydraulic pump with the rotation at the rated RPM level of at least 750 RPM. The single hydraulic pump continuously pumps the fracking media into the well at the HP level of at least 5000 HP. The single hydraulic pump operates on a continuous duty cycle to continuously pump the fracking media at the HP level of at least 5000 HP.
Owner:NAT SERVICE ALLIANCE HOUSTON LLC
Drilling components and systems to dynamically control drilling dysfunctions and methods of drilling a well with same
Drilling tools that may detect and dynamically adjust drilling parameters to enhance the drilling performance of a drilling system used to drill a well. The tools may include sensors, such as RPM, axial force for measuring the weight on a drill bit, torque, vibration, and other sensors known in the art. A processor may compare the data measured by the sensors against various drilling models to determine whether a drilling dysfunction is occurring and what remedial actions, if any, ought to be taken. The processor may command various tools within the bottom hole assembly (BHA), including a bypass valve assembly and / or a hydraulic thruster to take actions that may eliminate drilling dysfunctions or improve overall drilling performance. The processor may communicate with a measurement while drilling (MWD) assembly, which may transmit the data measured by the sensors, the present status of the tools, and any remedial actions taken to the surface.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Managed pressure drilling
Embodiments of the present invention include methods and apparatus for dynamically controlling pressure within a wellbore while forming the wellbore. In one aspect, one or more pressure control apparatus are used to maintain desired pressure within the wellbore while drilling the wellbore. In another aspect, pressure is dynamically controlled while drilling using foam to maintain a substantially homogenous foam flow regime within the wellbore annulus for carrying cuttings from the wellbore.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
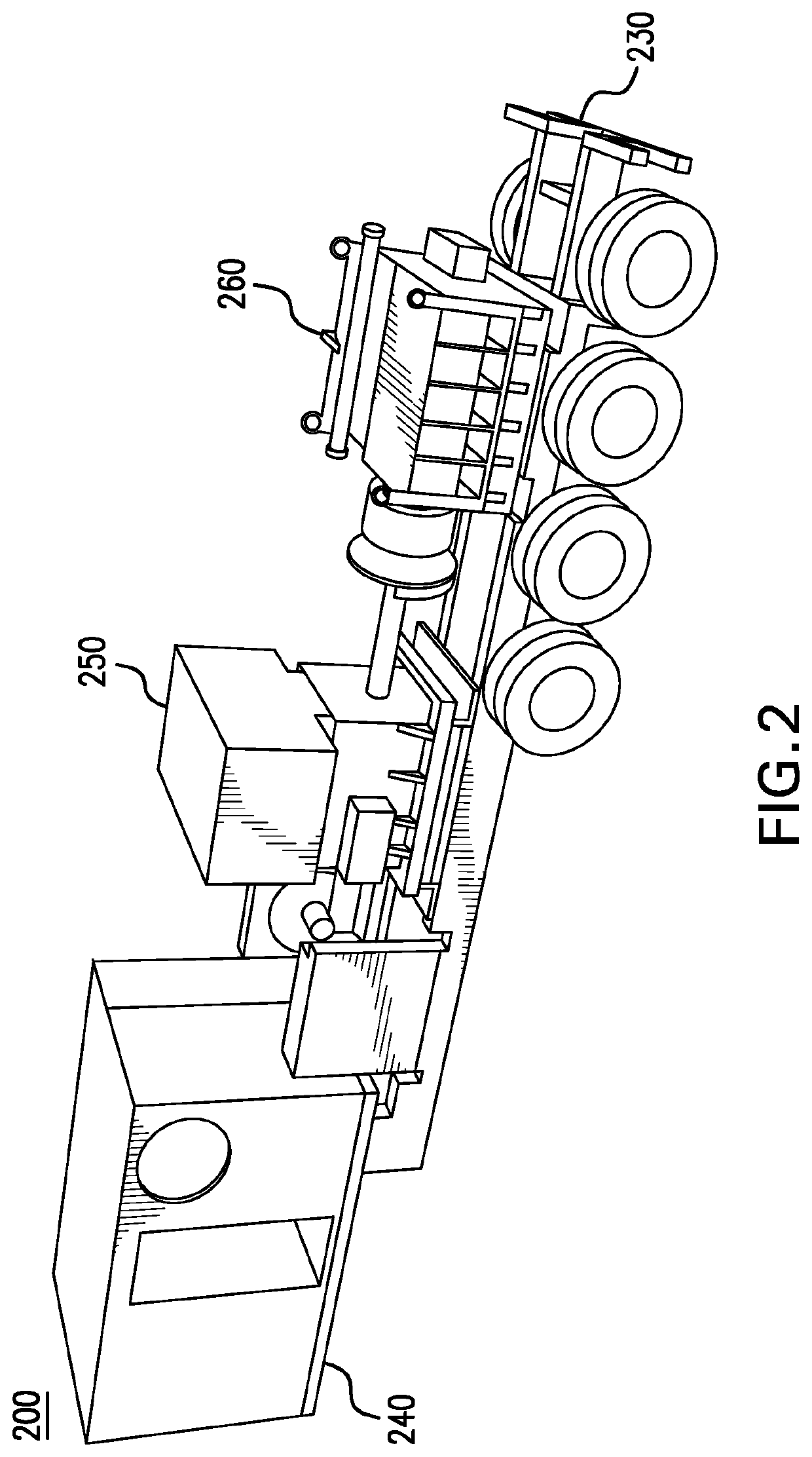
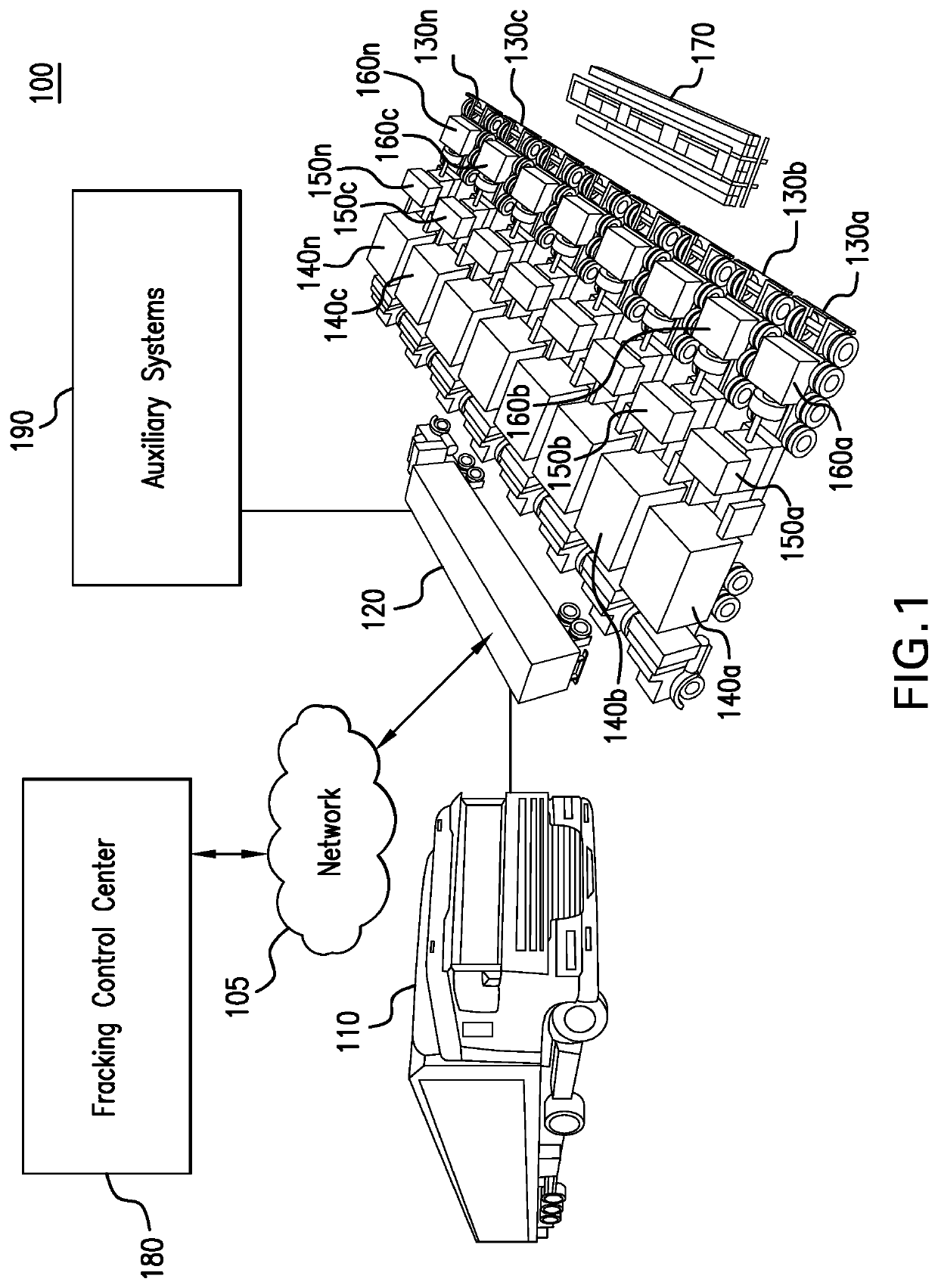
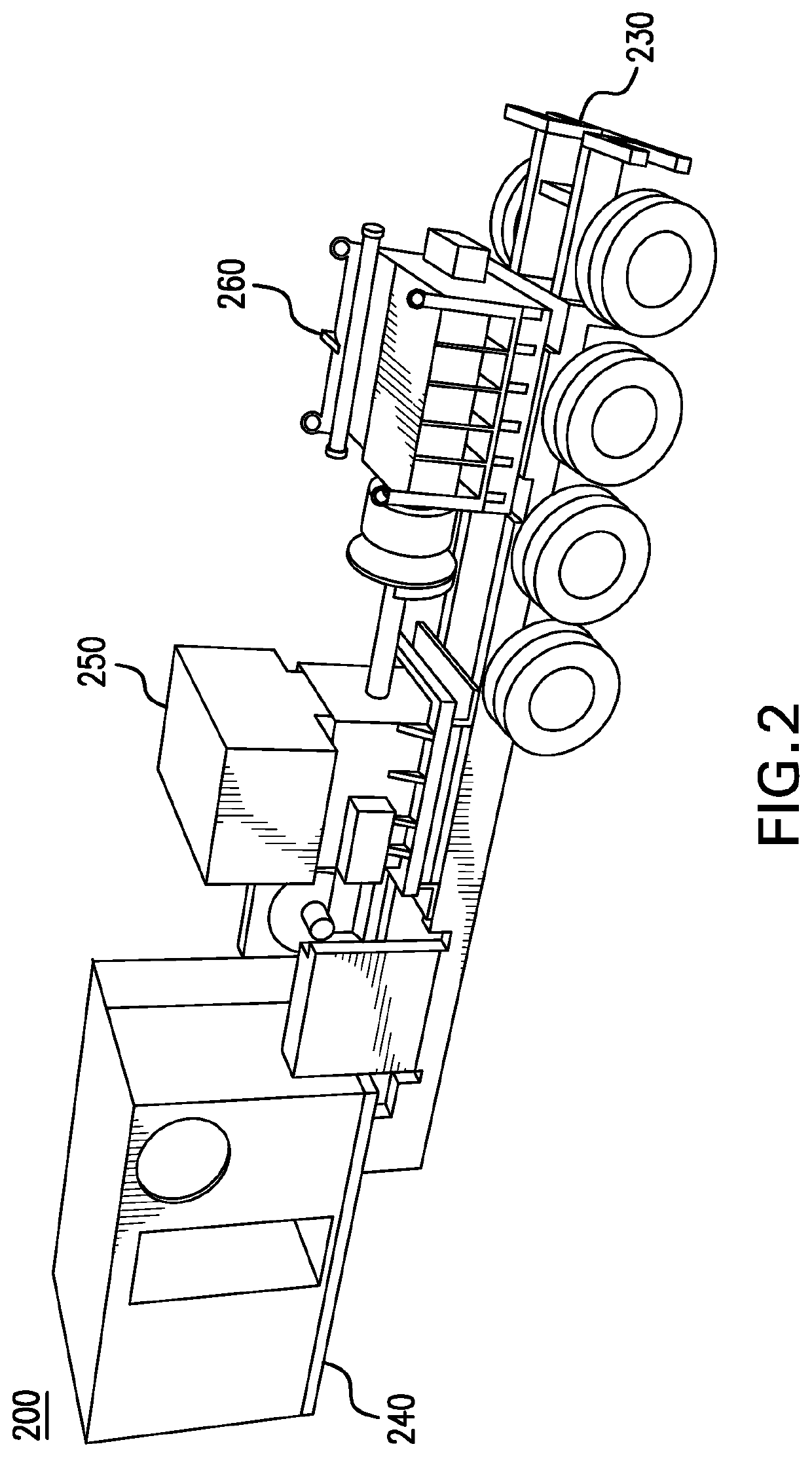
Well service pump systems and related methods
A well service pump system supplies high pressure working fluid to a well. The pump system includes a closed-loop hydraulic circuit for actuating a plurality of working pump assemblies. The pump system is powered by a motor, which transfers mechanical energy to a plurality of pumps, which, in turn, provide hydraulic fluid to operate hydraulic ram cylinders, and thereby operate the working pump assemblies. Each of the polished rods of the hydraulic ram cylinders is connected axially to a plunger rod end of the working fluid end cylinder to operate the working pump assembly.
Owner:AMERIFORGE GRP
Methods and apparatus to control downhole tools
The present invention generally provides a downhole tool with an improved means of transmitting data to and from the tool through the use of wired pipe capable of transmitting a signal and / or power between the surface of the well and any components in a drill string. In one aspect, a downhole tool includes a body, and a mandrel disposed in the body and movable in relation to the body. A conducive wire runs the length of the body and permits signals and / or power to be transmitted though the body as the tool changes its length.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Electric driven hydraulic fracking system
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Well service pump power system and methods
A well service pump system supplies high pressure working fluid to a well. The pump system is a linear design which incorporates an electric motor, a variable frequency drive (VFD), a pump drive, closed loop variable flow rate hydraulic pumps, hydraulic ram cylinders, working fluid end cylinders, and a coupling to connect the hydraulic ram cylinders and the working fluid end cylinders. The electric motor powers the hydraulic system which, in turn, provides hydraulic fluid to operate the hydraulic ram cylinders. The VFD is connected to a single one of the hydraulic pumps at a time and applies power to the connected pump, via the pump drive, to drive the connected pump from a cold start to an operating speed. The VFD is connected sequentially, one pump at a time, to each of the hydraulic pumps and disconnected from each pump once the pump reaches the operating speed. Once the pump reaches operating speed, the pump is connected to receive power directly to the electric motor.
Owner:AMERIFORGE GRP
Annulus pressure control drilling systems and methods
In one embodiment, a method for drilling a wellbore includes an act of drilling the wellbore by injecting drilling fluid through a tubular string disposed in the wellbore, the tubular string comprising a drill bit disposed on a bottom thereof. The drilling fluid exits the drill bit and carries cuttings from the drill bit. The drilling fluid and cuttings (returns) flow to a surface of the wellbore via an annulus defined by an outer surface of the tubular string and an inner surface of the wellbore. The method further includes an act performed while drilling the wellbore of measuring a first annulus pressure (FAP) using a pressure sensor attached to a casing string hung from a wellhead of the wellbore. The method further includes an act performed while drilling the wellbore of controlling a second annulus pressure (SAP) exerted on a formation exposed to the annulus.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
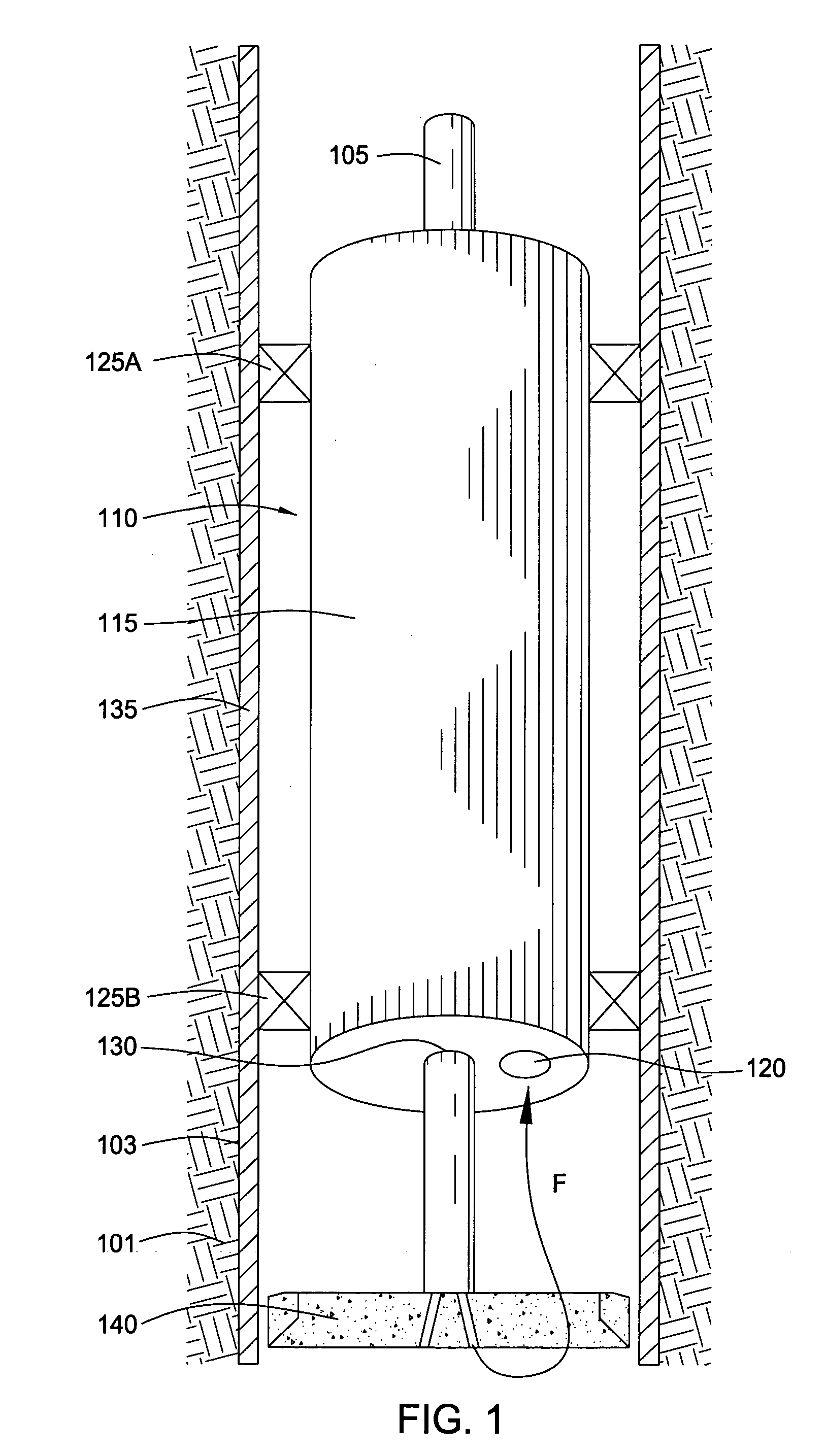
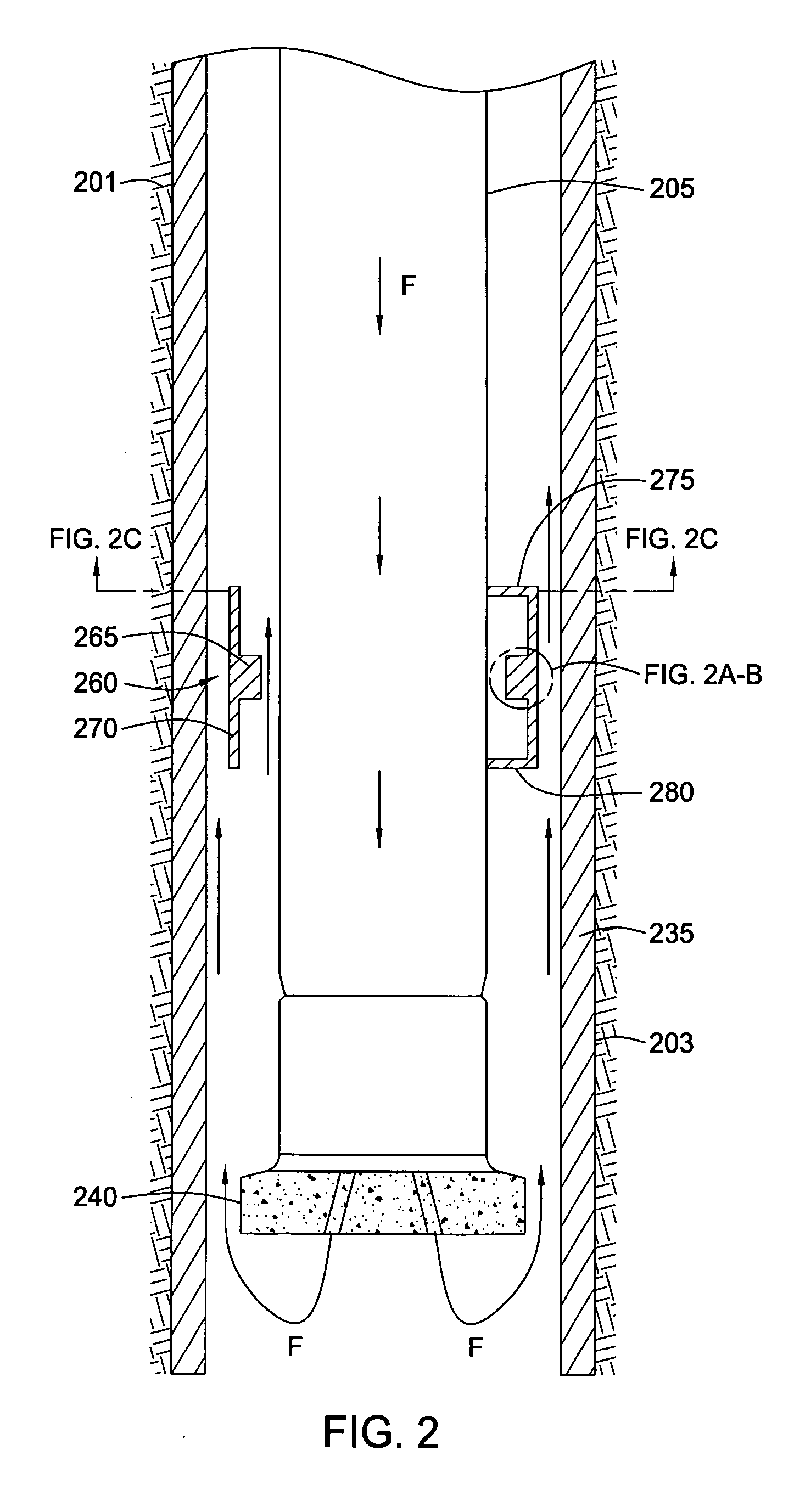
Overburden drilling apparatus having a down-the-hole hammer separatable from an outer casing/drill bit unit
Overburden drilling equipment for drilling a hole includes a down-the-hole hammer formed by a cylinder and a piston reciprocating in the cylinder due to pressurized water being directed alternately to the upper and lower ends of the piston. Each downward stroke inflicts an impact blow upon an anvil portion of a drill bit extending upwardly within the lower portion of the cylinder. A drill chuck is mounted at a lower end of the cylinder to receive the drill bit. A generally cylindrical casing shoe is attached to a casing and is rotatably connected to the drill bit to be longitudinally advanced thereby during drilling operation. The drill chuck includes at least one key which defines the largest radius of the drill chuck. The casing includes a diametrically reduced portion which has at least one keyway therein. The key and the diametrically reduced portion retain the hammer longitudinally in relation to the drill bit.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
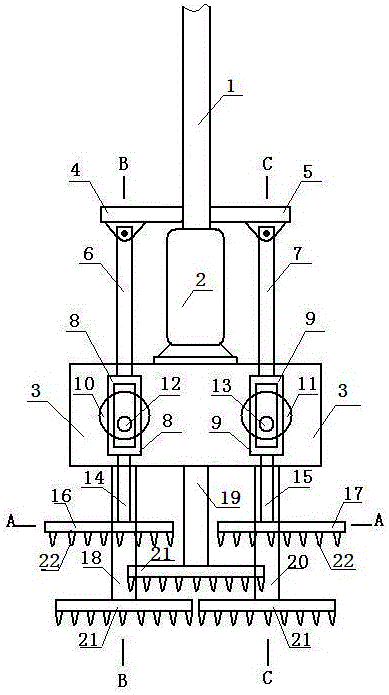
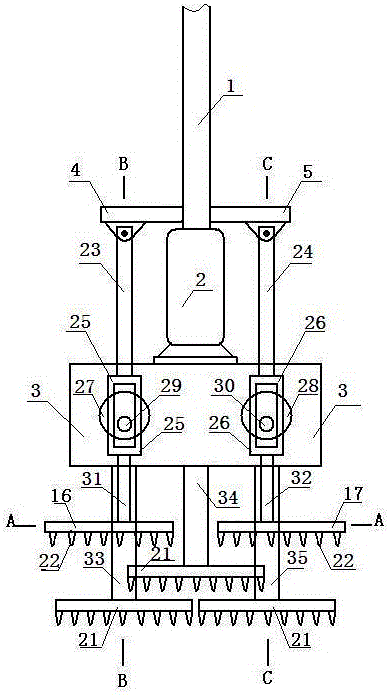
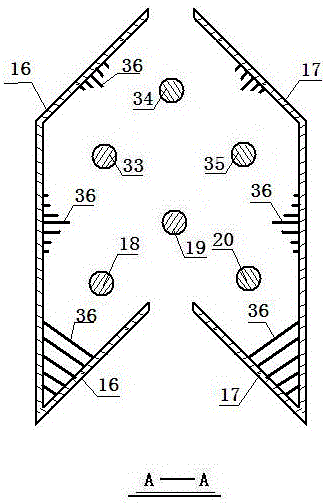
Socket pile molding device
Disclosed is a socket pile molding device. A left half socket frame and a right half socket frame are opposite to form a fish-spindle frame; the front end of the fish-spindle frame is in a concave-fold line shape, and the rear end of the fish-spindle frame is in a convex-fold line shape; and the concave-fold line at the front end and the convex-fold line at the rear end are matched; multiple first stirring teeth are arranged at the lower end of the left half socket frame, and multiple second stirring teeth are arranged inside the left half socket frame; and multiple first stirring teeth are arranged at the lower end of the right half socket frame, and multiple second stirring teeth are arranged inside the right half socket frame.
Owner:靖江汇恒新材料有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com