Patents
Literature
63 results about "Mud weight" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
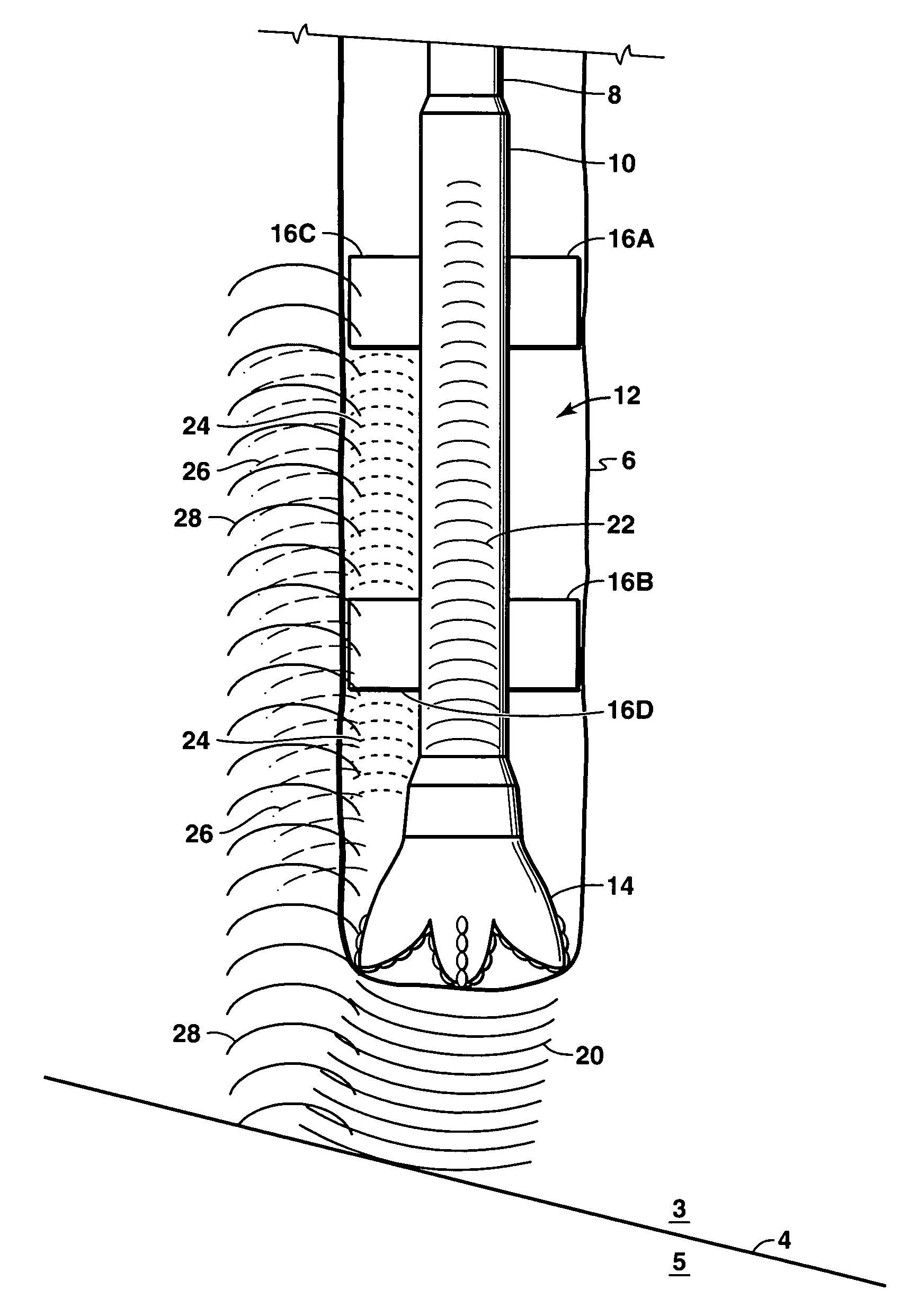
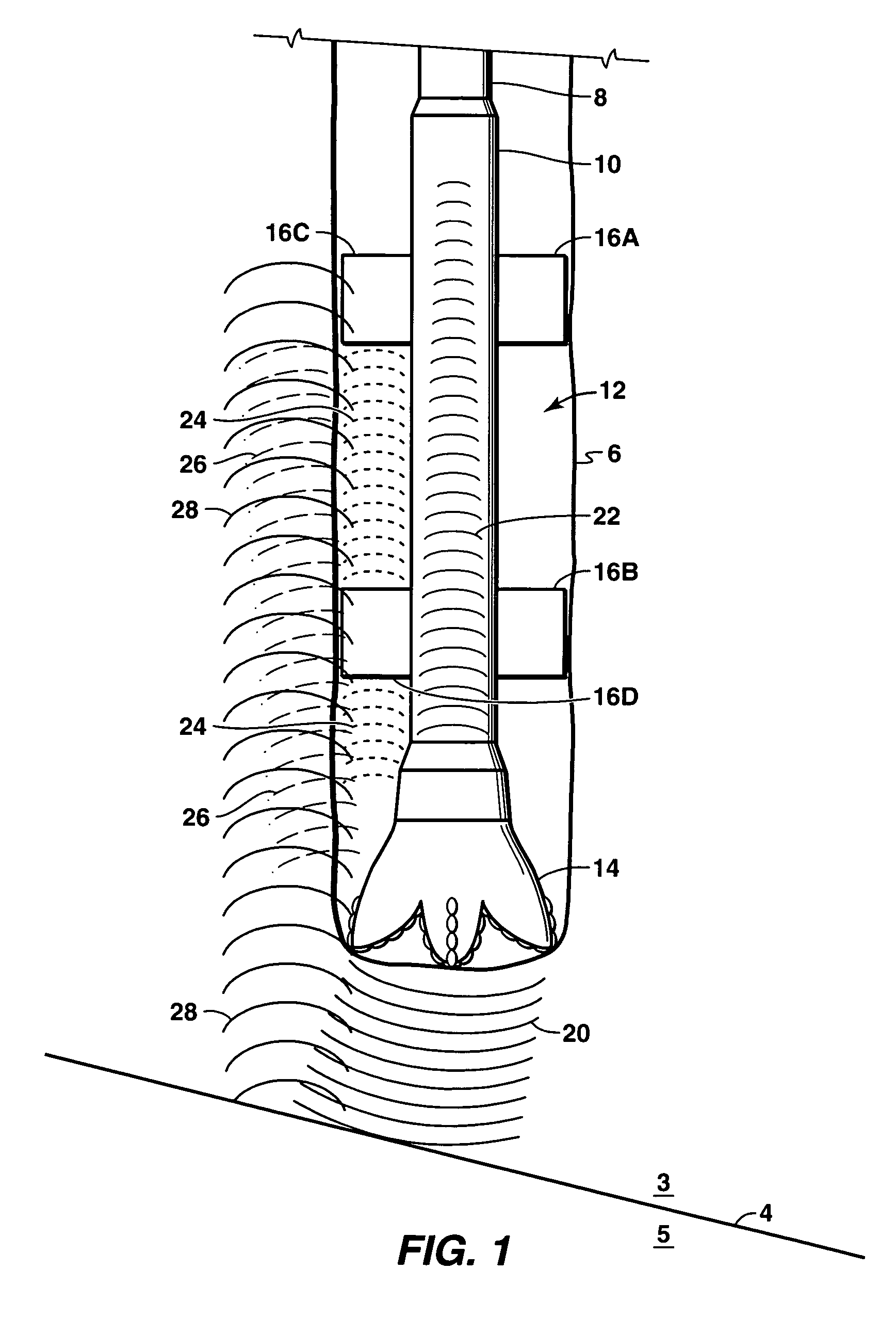
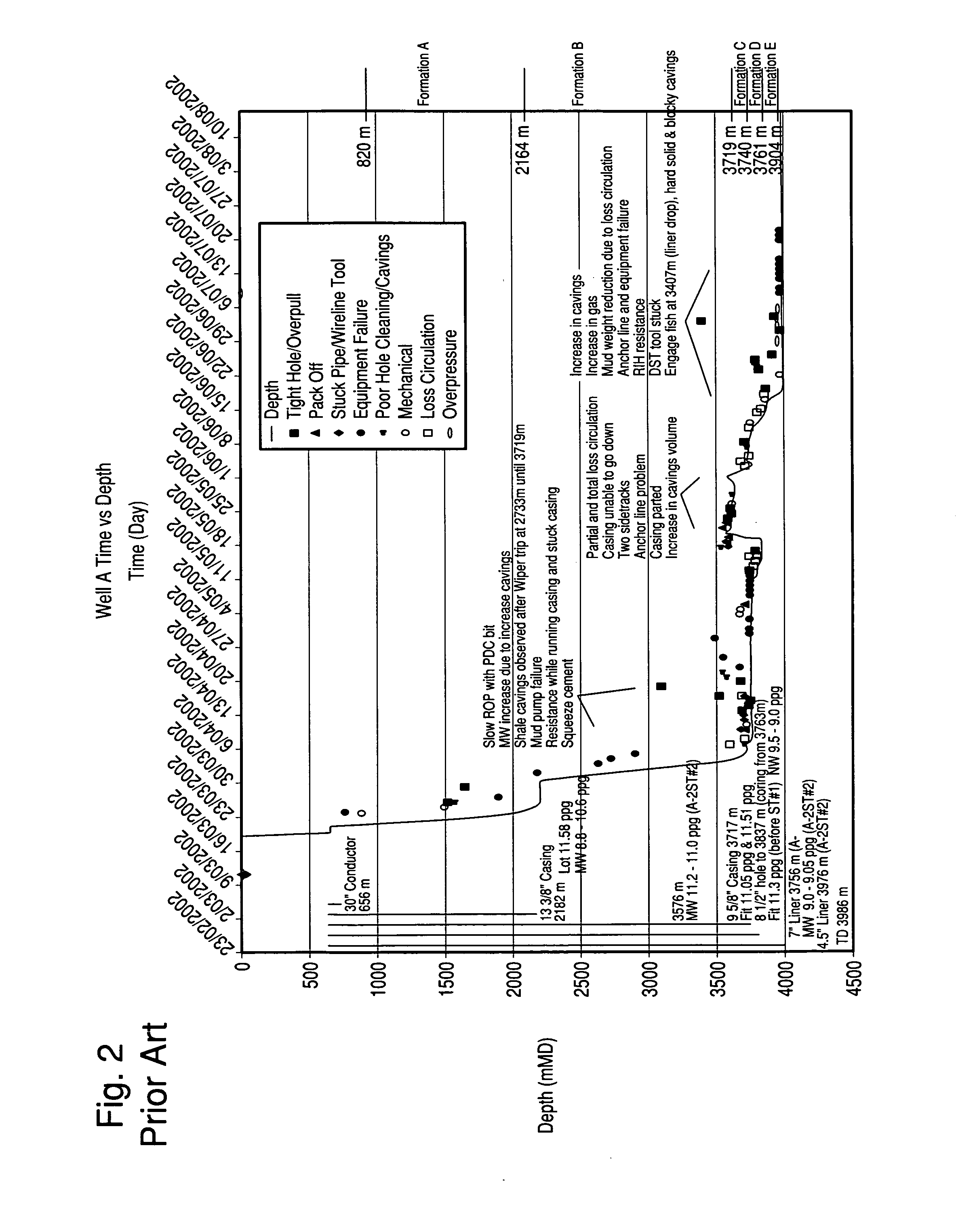
In the oil industry, mud weight is the density of the drilling fluid and is normally measured in pounds per gallon (lb/gal) (ppg) or pound cubic feet (pcf) . In the field it is measured using a mud scale or mud balance. Mud can weigh up to 22 or 23 ppg.
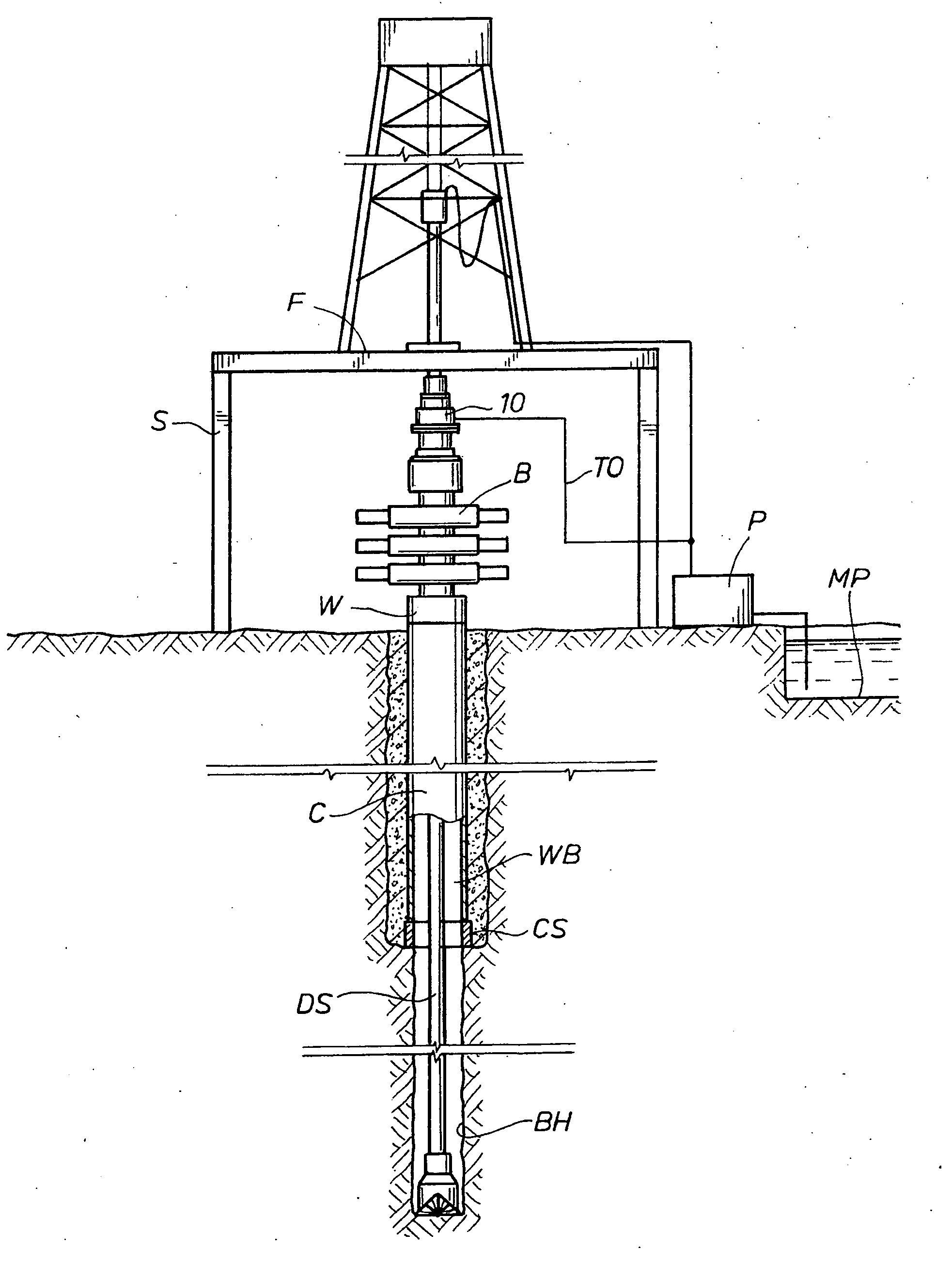
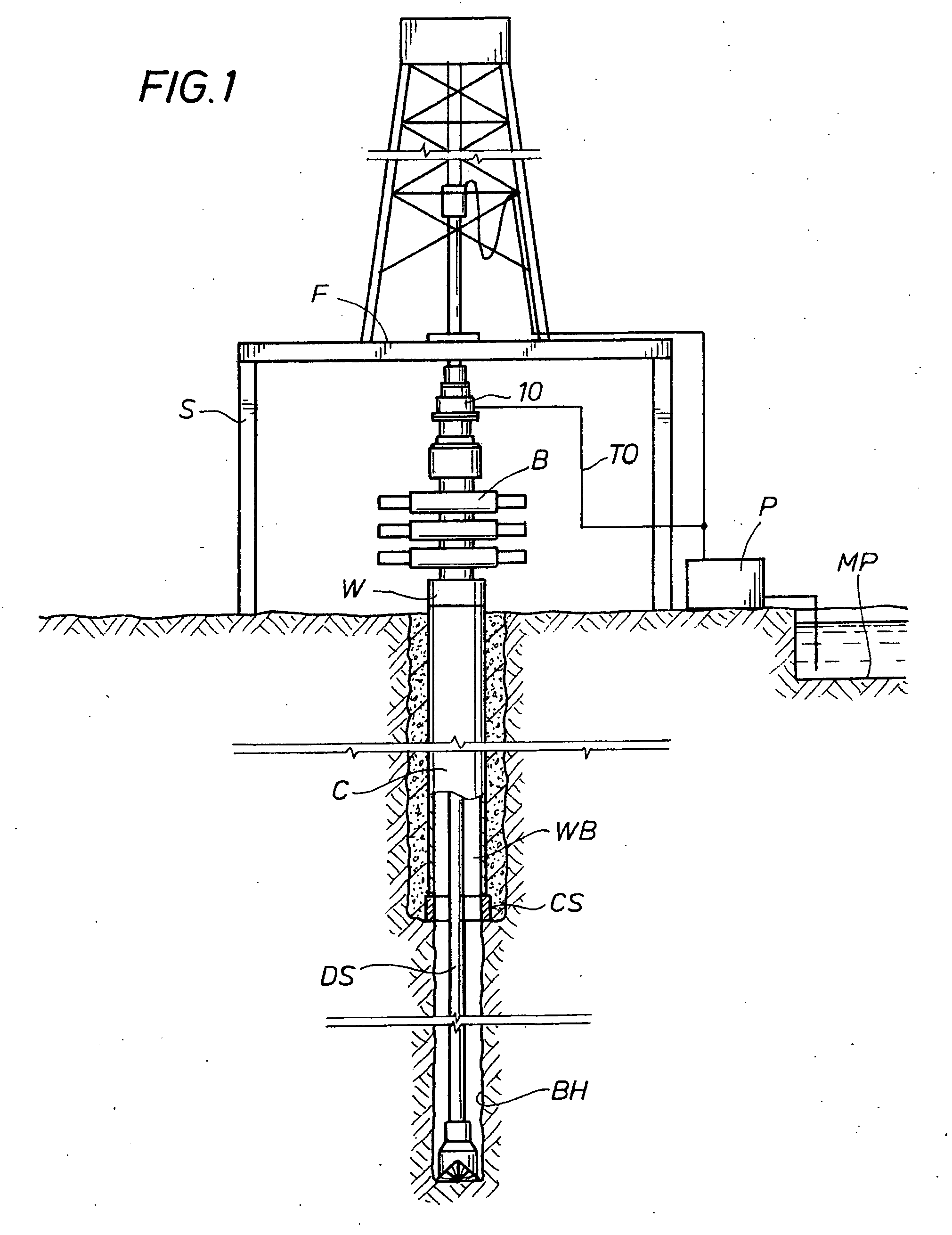
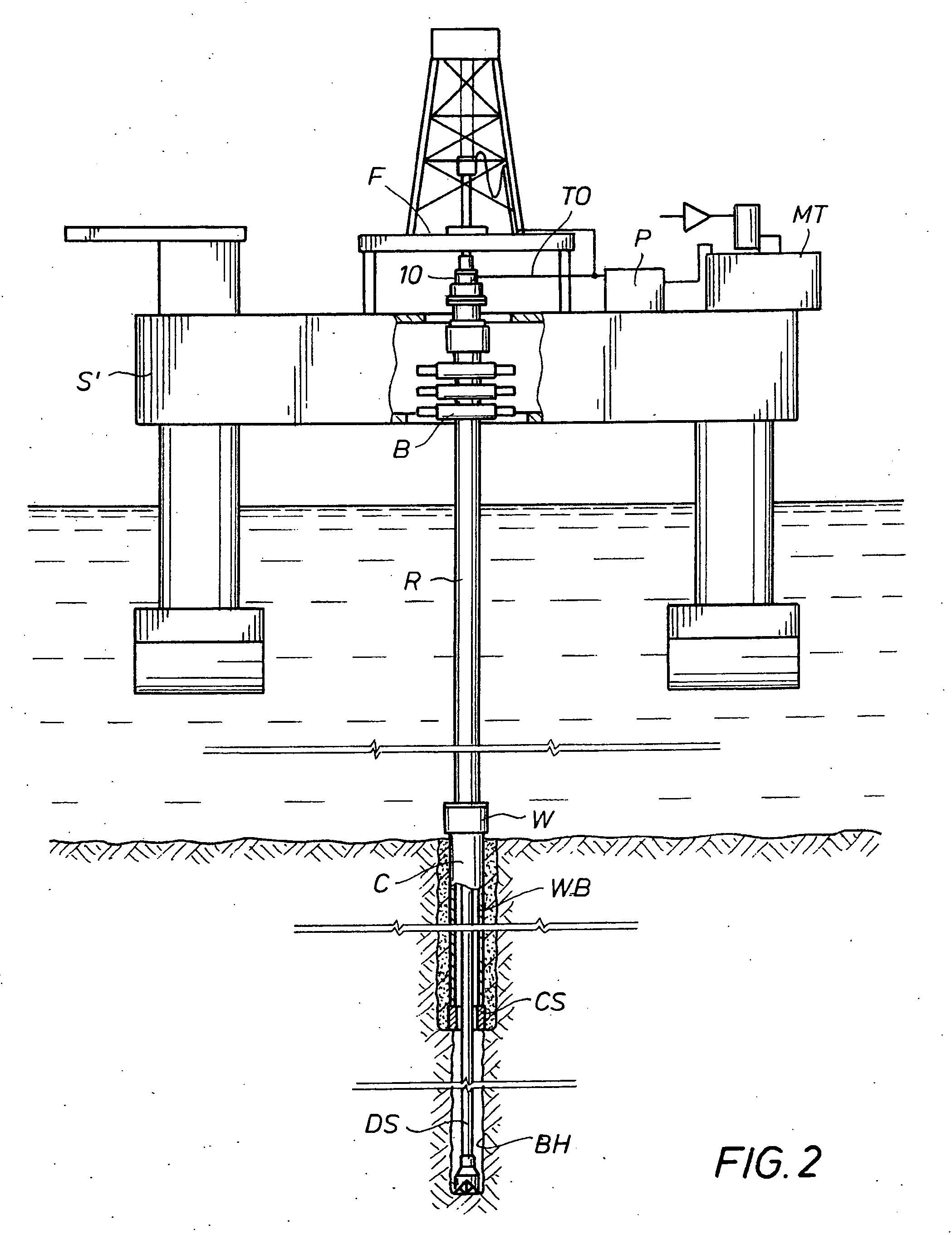
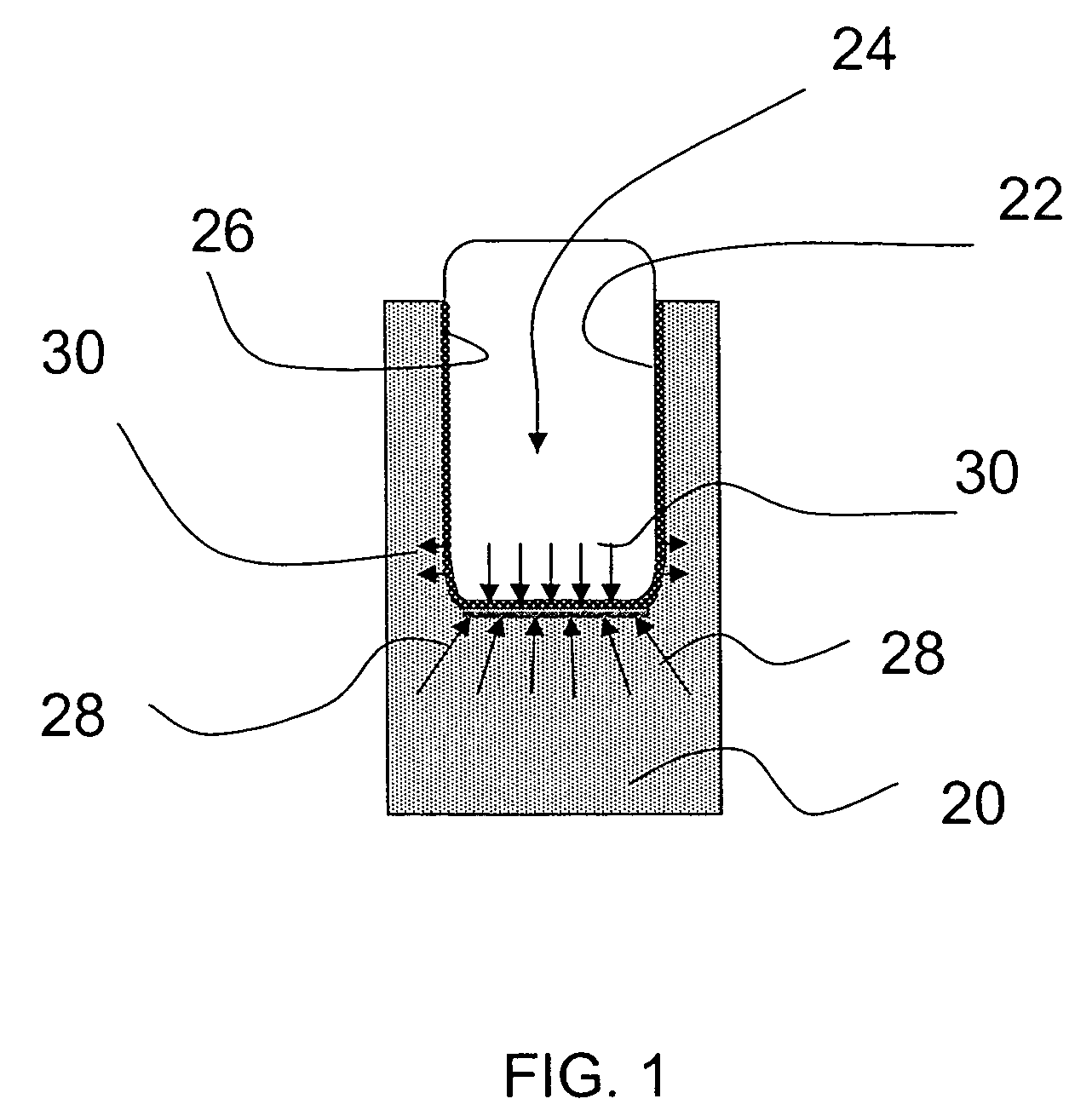
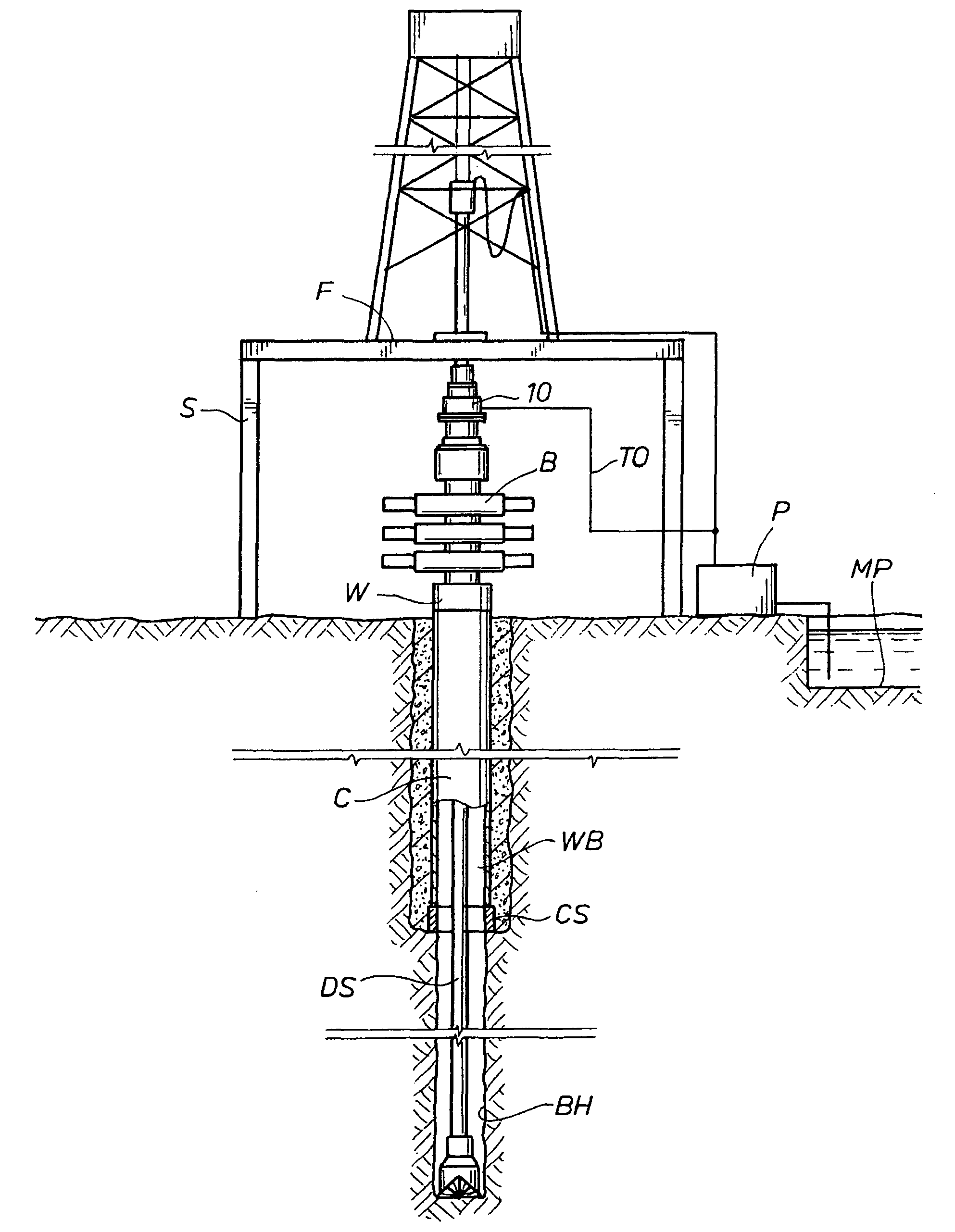
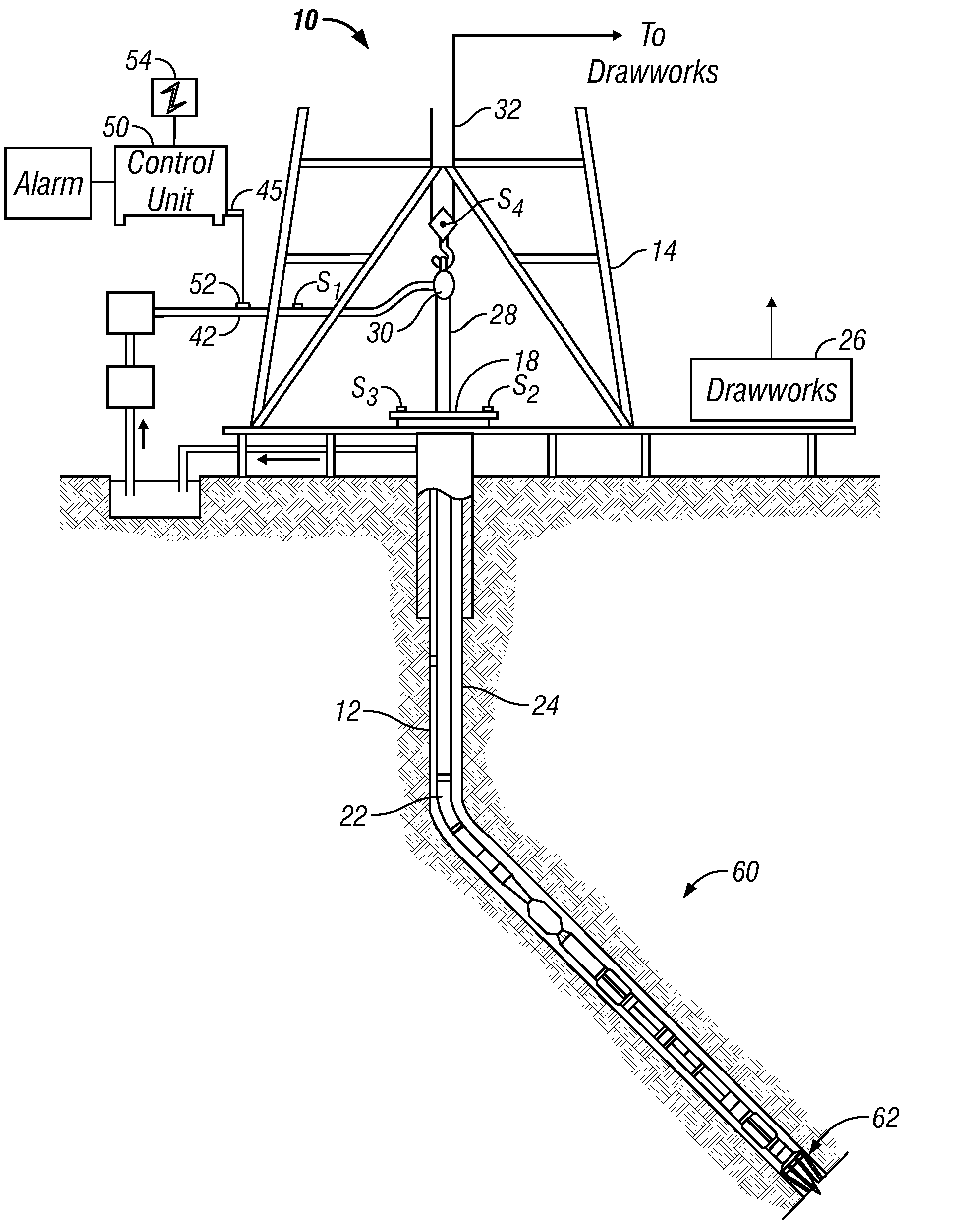
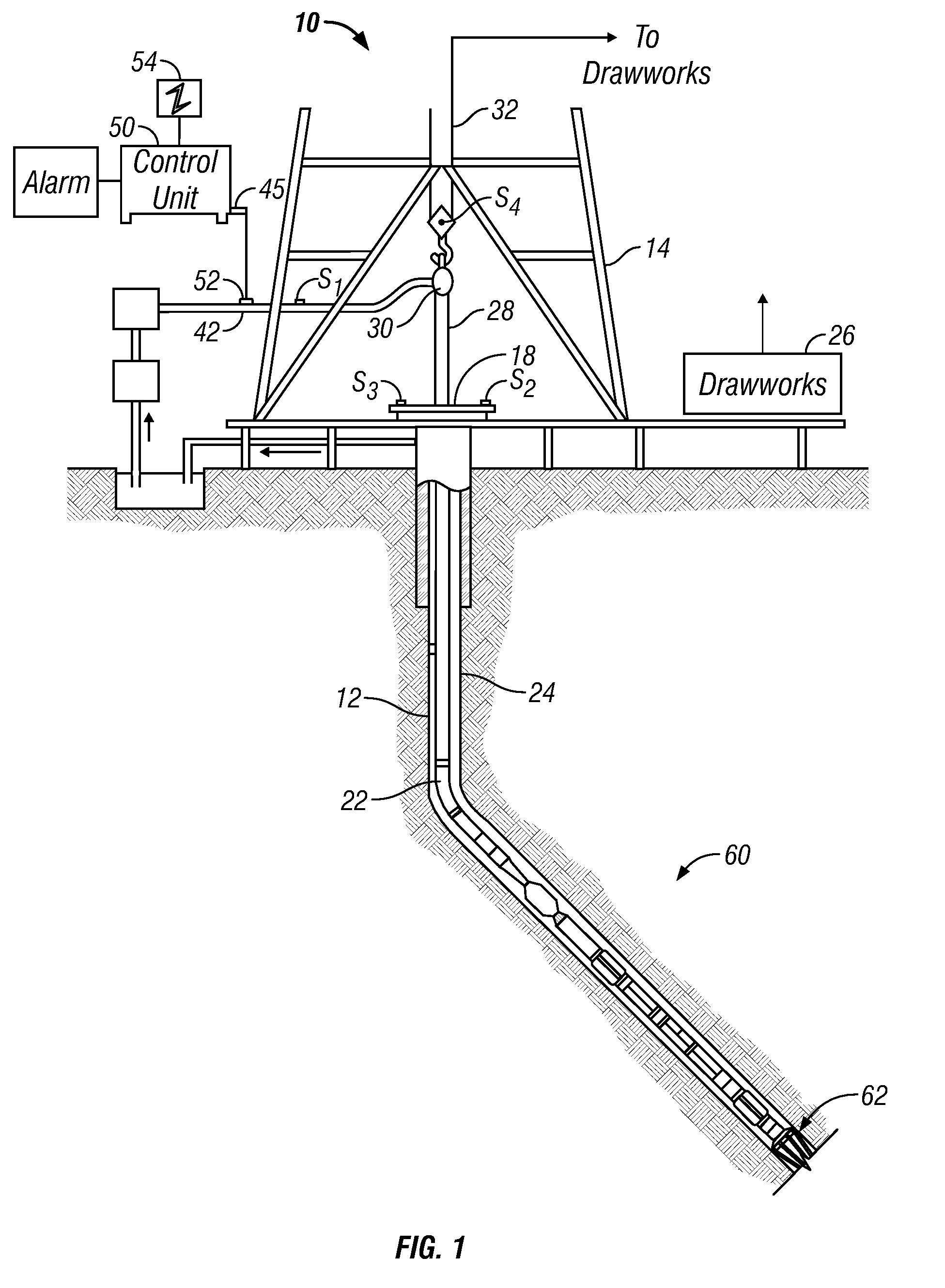
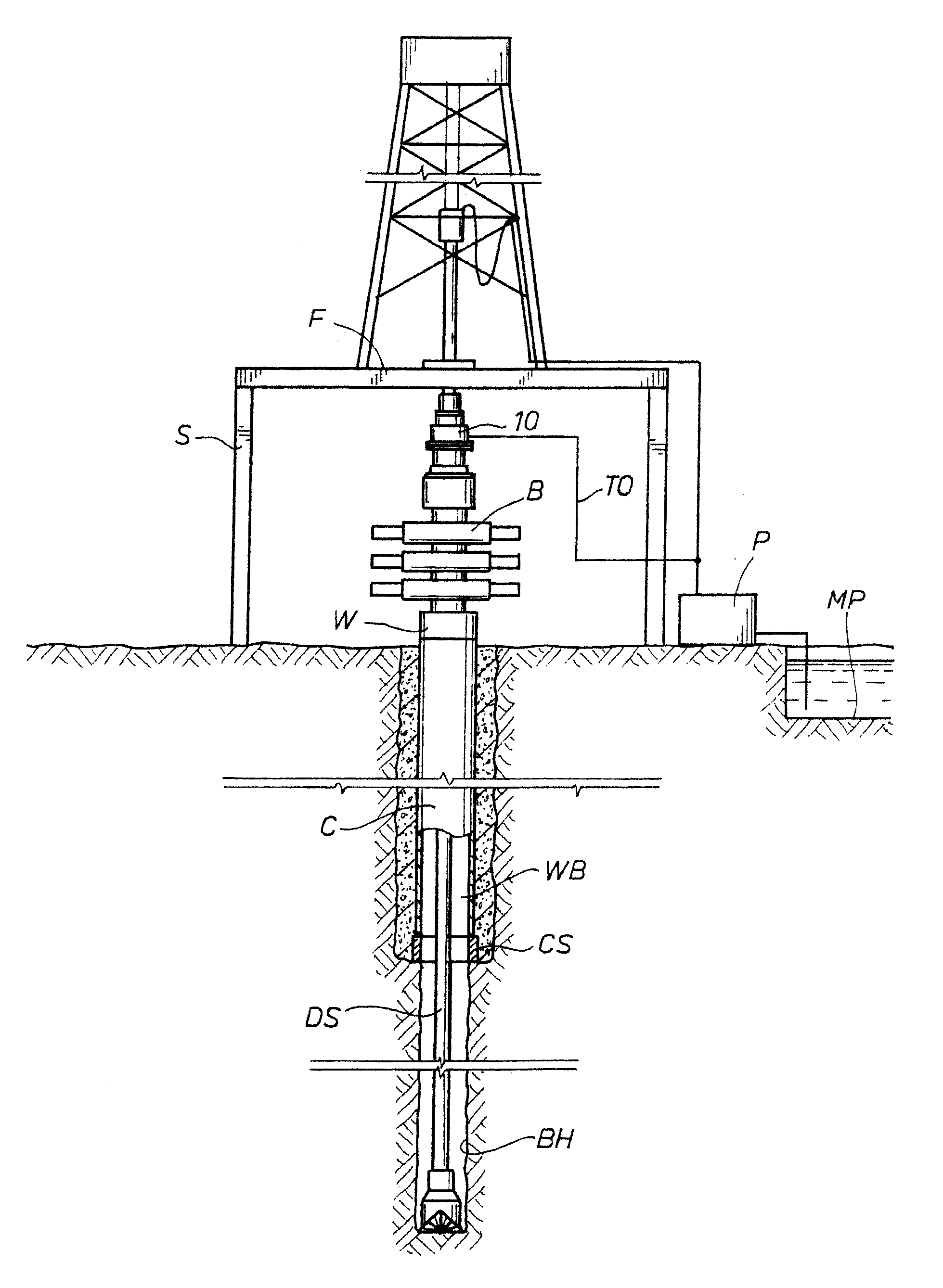
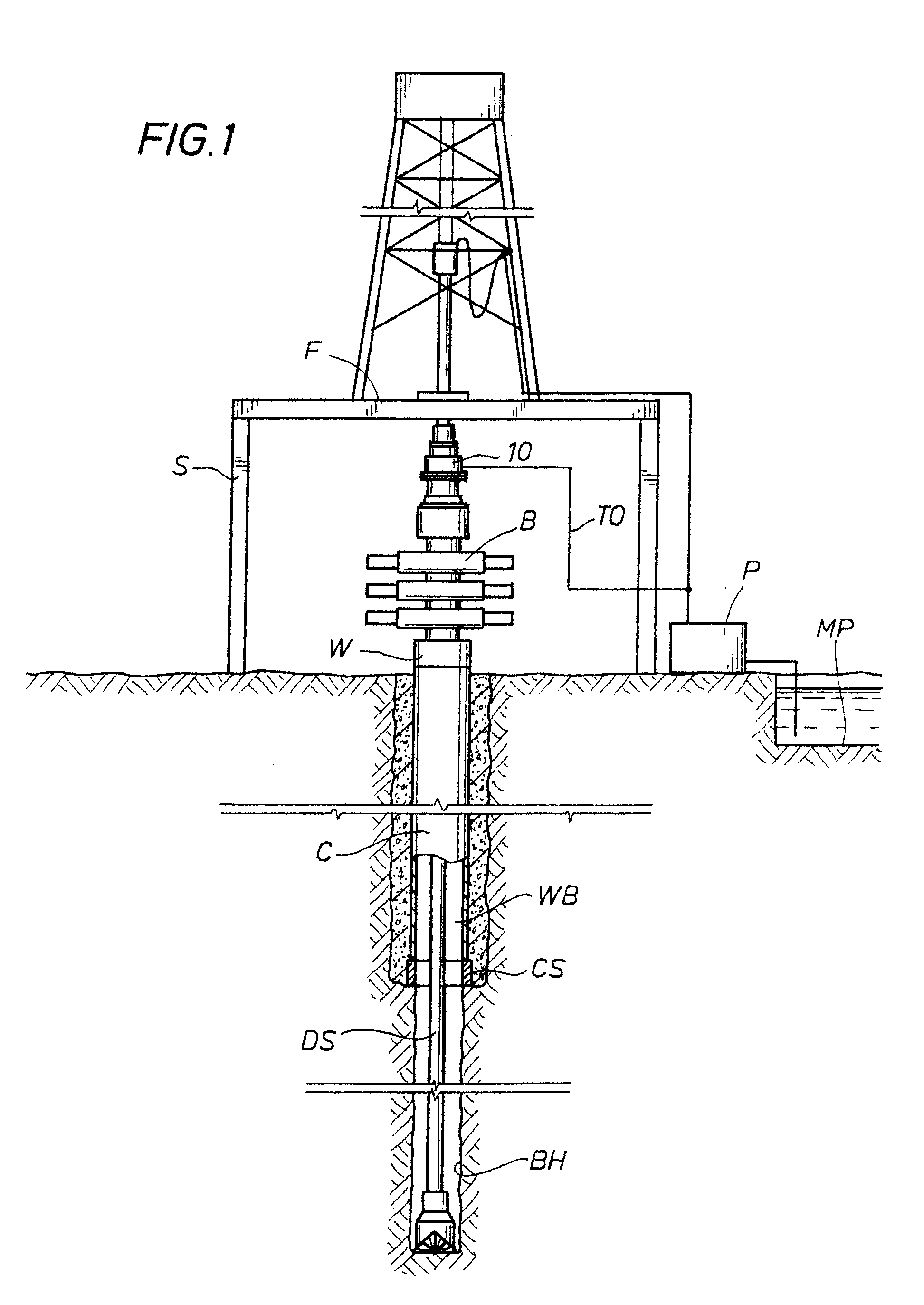
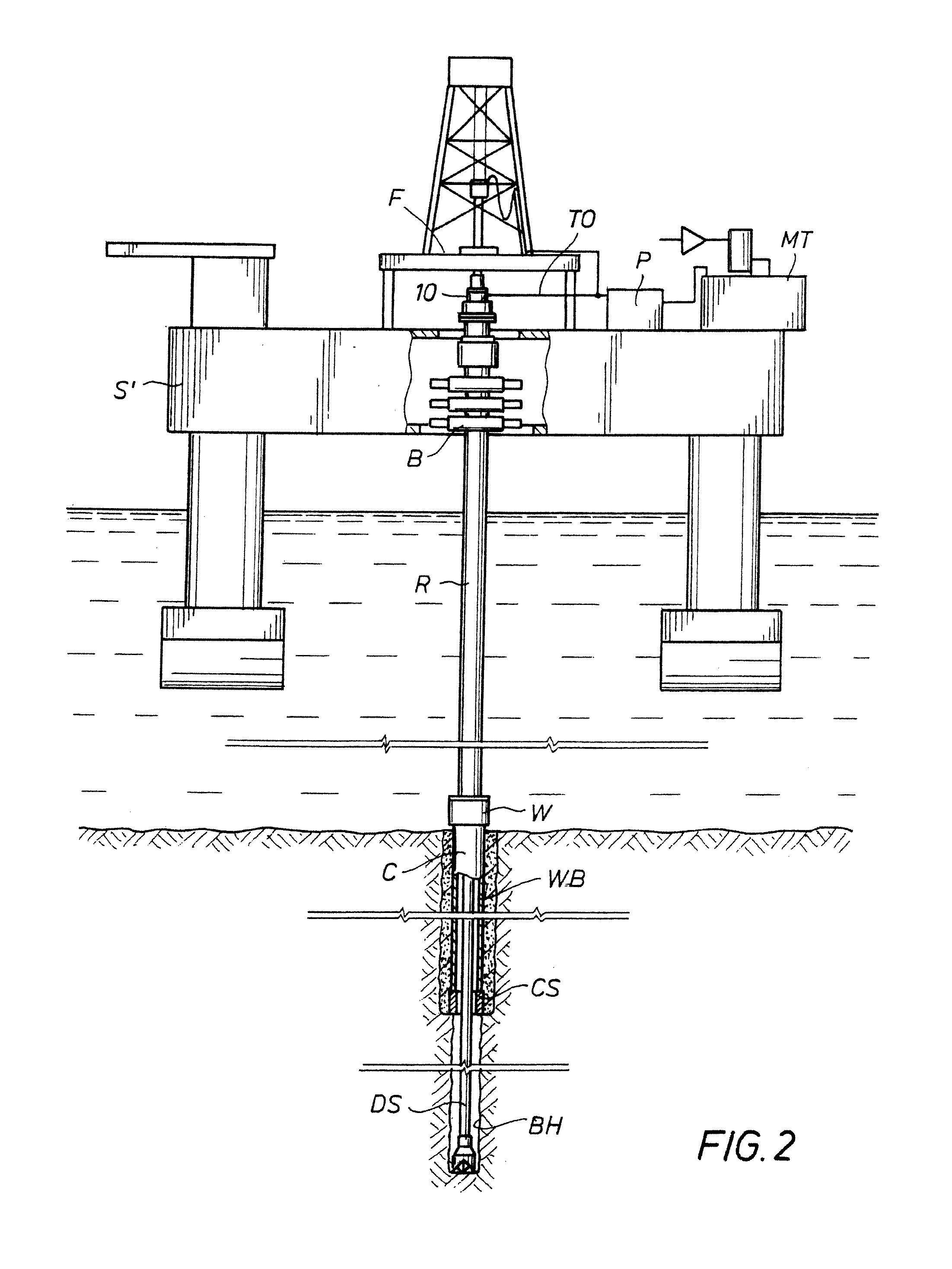
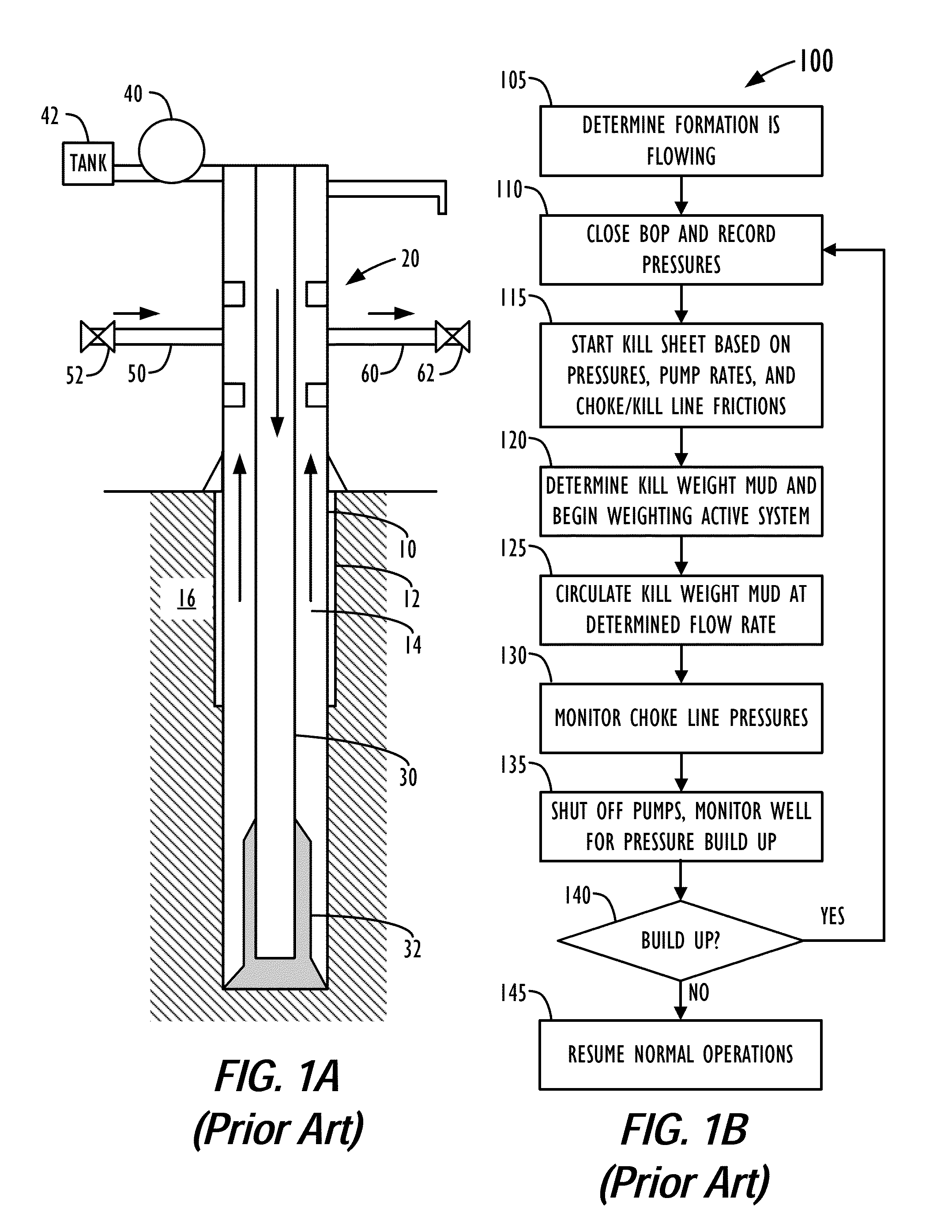
Drilling with a high pressure rotating control device
ActiveUS20110024195A1Operational securityHigh safety factorSurveyDrilling rodsWell drillingControl system
A Drill-To-The-Limit (DTTL) drilling method variant to Managed Pressure Drilling (MPD) applies constant surface backpressure, whether the mud is circulating (choke valve open) or not (choke valve closed). Because of the constant application of surface backpressure, the DTTL method can use lighter mud weight that still has the cutting carrying ability to keep the borehole clean. The DTTL method identifies the weakest component of the pressure containment system, such as the fracture pressure of the formation or the casing shoe leak off test (LOT). With a higher pressure rated RCD, such as 5,000 psi (34,474 kPa) dynamic or working pressure and 10,000 psi (68,948 kPa) static pressure, the limitation will generally be the fracture pressure of the formation or the LOT. In the DTTL method, since surface backpressure is constantly applied, the pore pressure limitation of the conventional drilling window can be disregarded in developing the fluid and drilling programs. Using the DTTL method a deeper wellbore can be drilled with larger resulting end tubulars, such as casings and production liners, than had been capable with conventional MPD applications.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
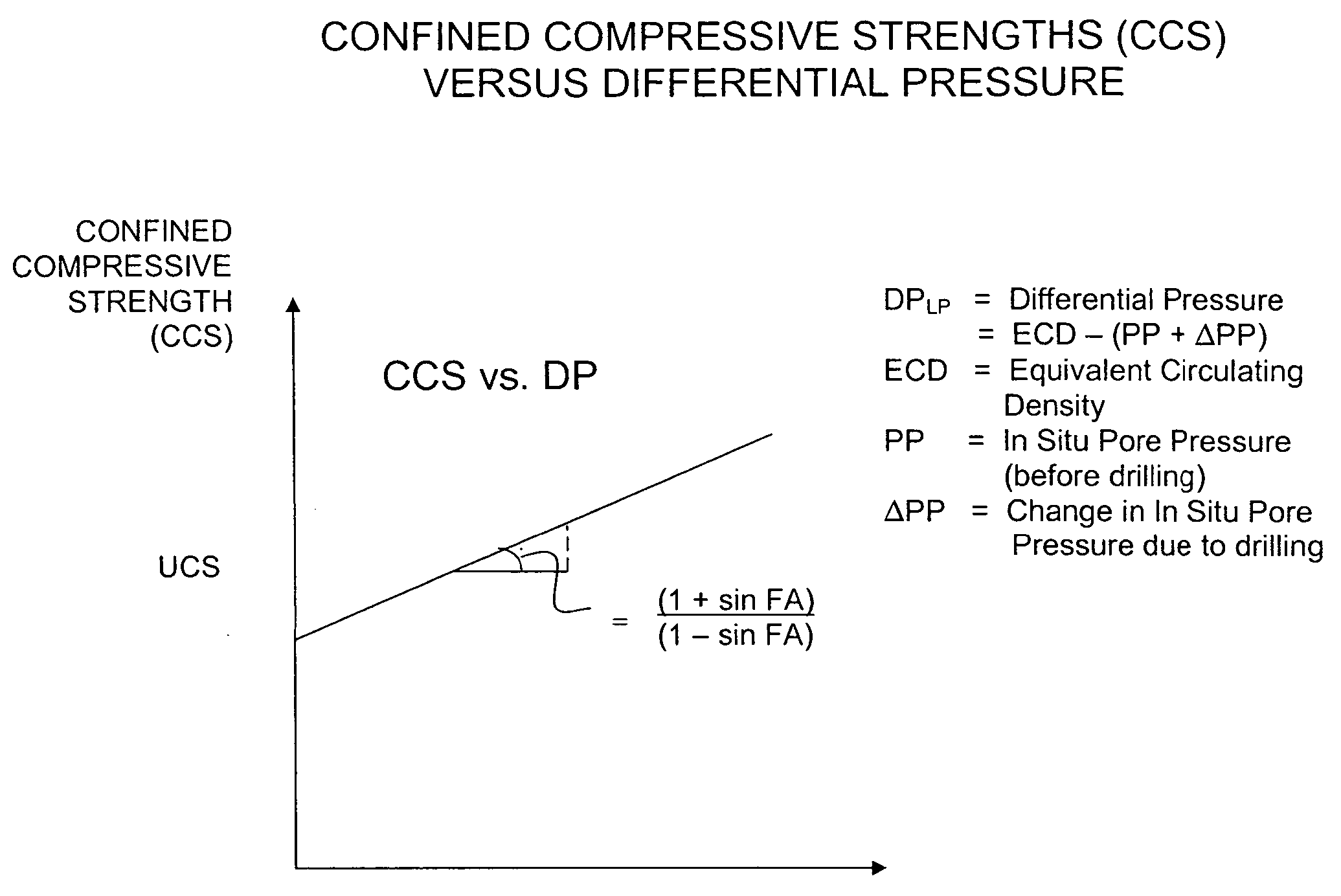
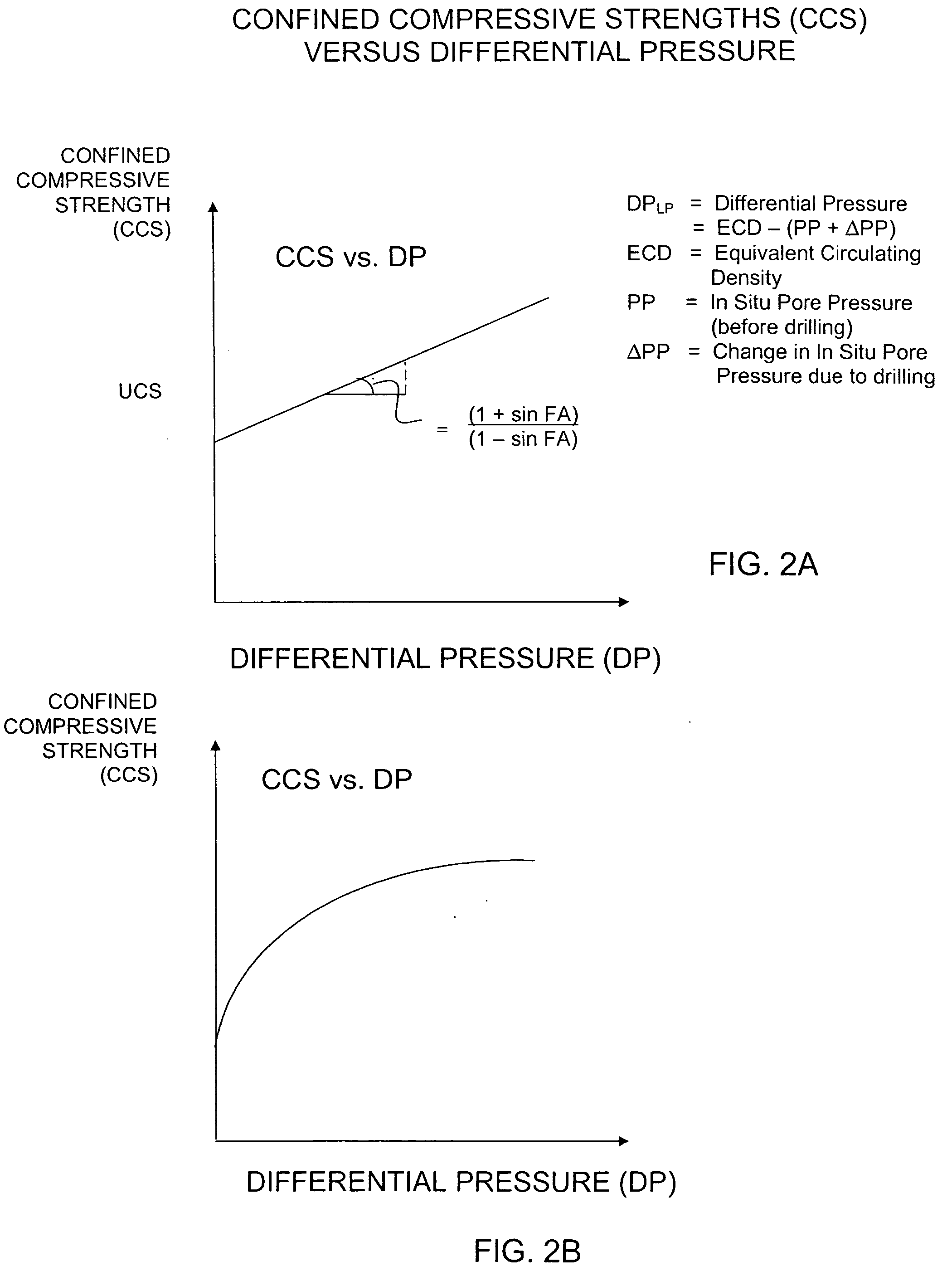
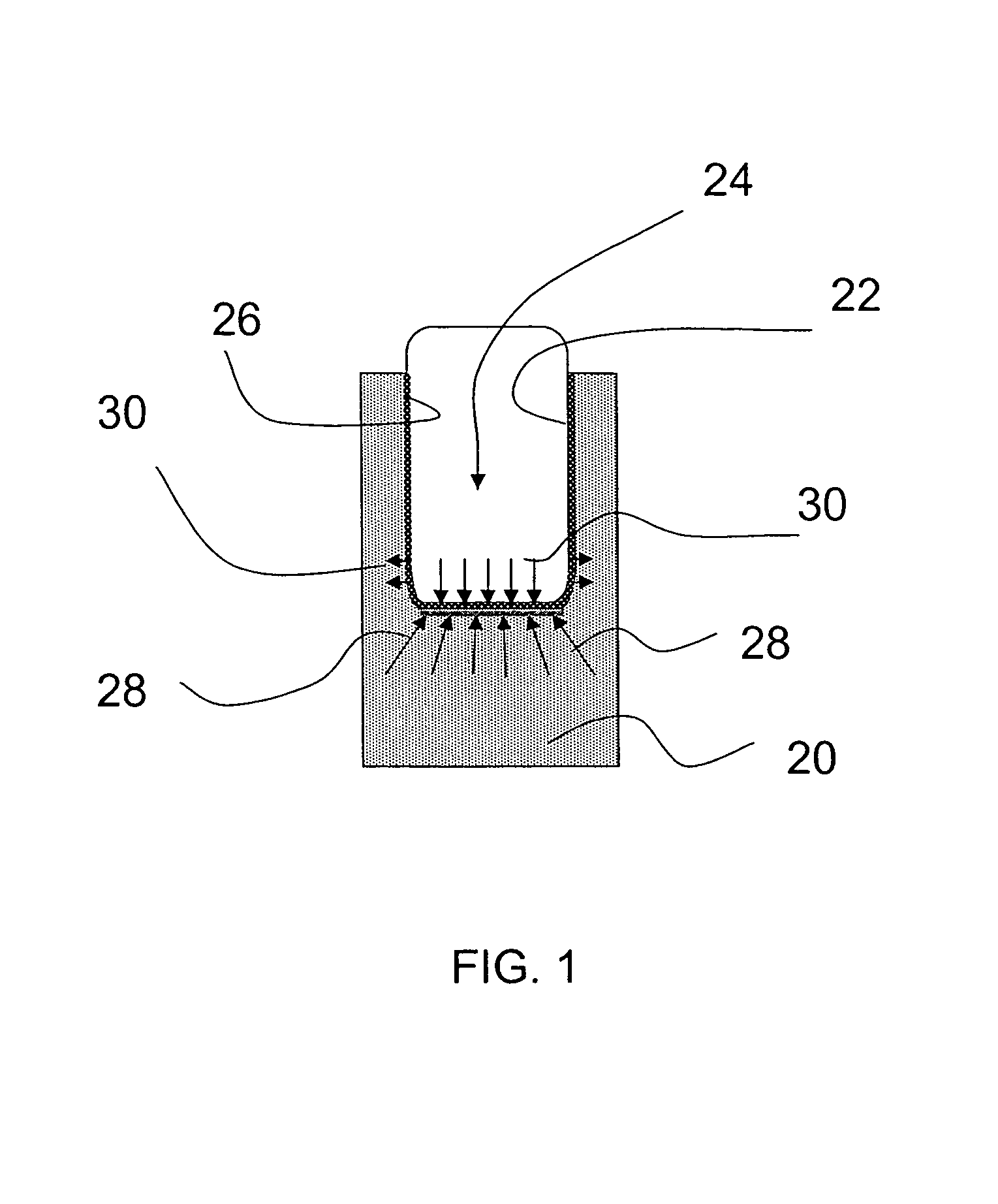
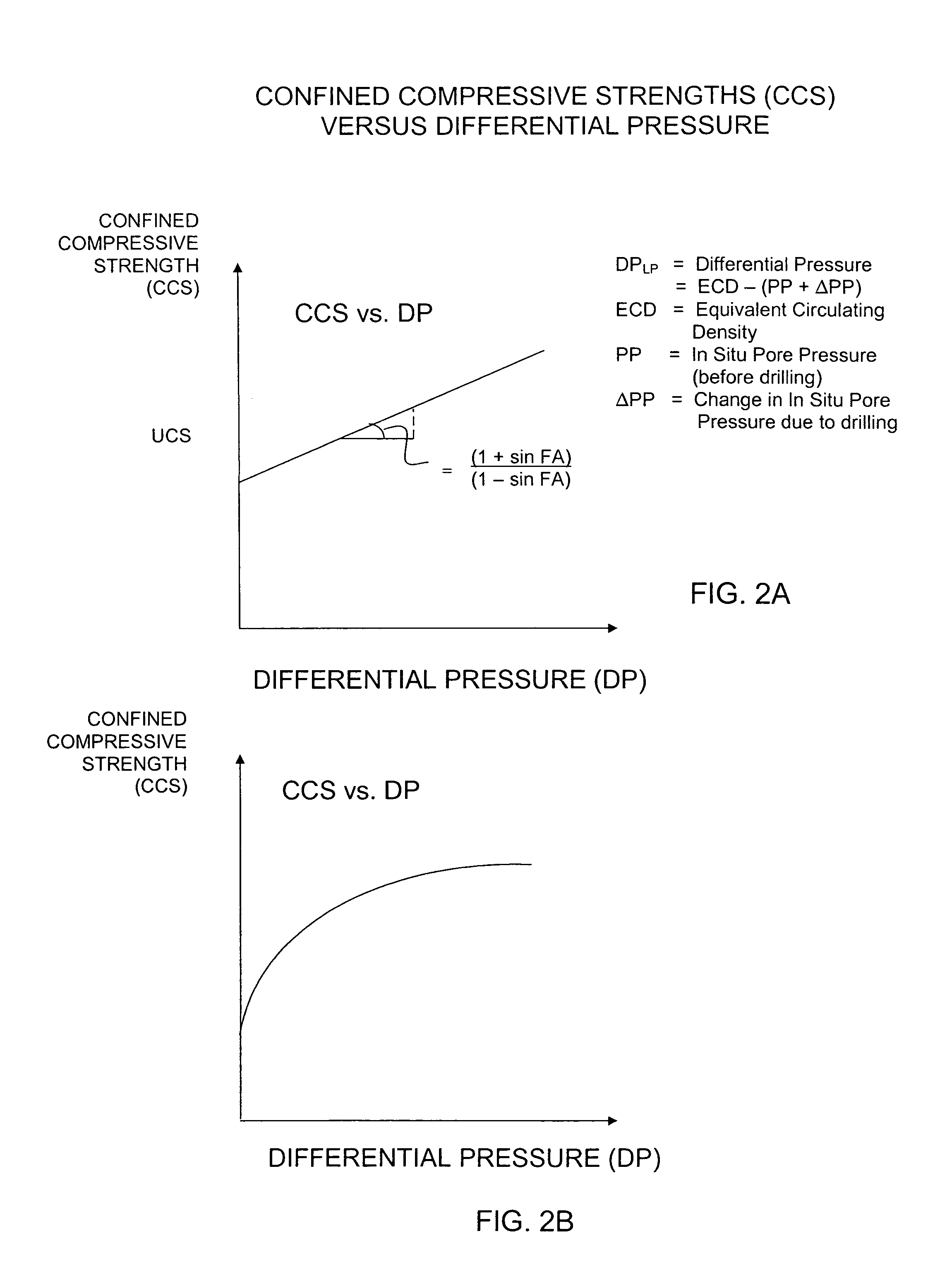
Method for estimating confined compressive strength for rock formations utilizing skempton theory
InactiveUS20060131074A1Improve accuracyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyCompressive strengthUltimate tensile strength
A method for estimating the CCS for a rock in the depth of cut zone of a subterranean formation which is to be drilled using a drilling fluid is disclosed. An UCS is determined for a rock in the depth of cut zone. A change in the strength of the rock due to applied stresses imposed on the rock during drilling is calculated which includes estimating the ΔPP. The CCS for the rock in the depth of cut zone is calculated by adding the estimated change in strength to the UCS. The present invention calculates the ΔPP in accordance with Skempton theory where impermeable rock or soil has a change in pore volume due to applied loads or stresses while fluid flow into and out of the rock or soil is substantially non-existent. CCS may be calculated for deviated wellbores and to account for factors such as wellbore profile, stress raisers, bore diameter, and mud weight utilizing correction factors derived using computer modeling and using a baseline formula for determining an uncorrected value for CCS.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
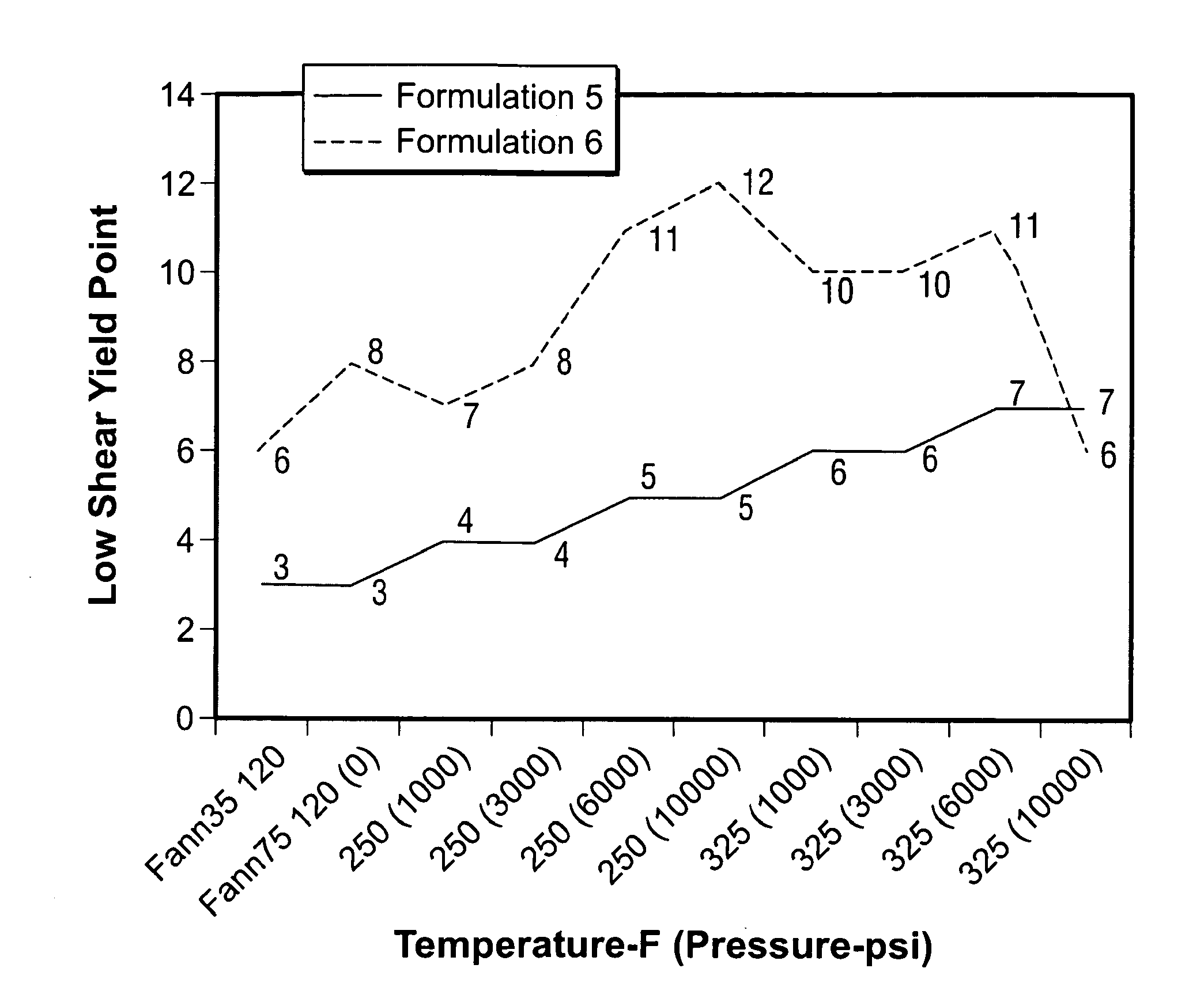
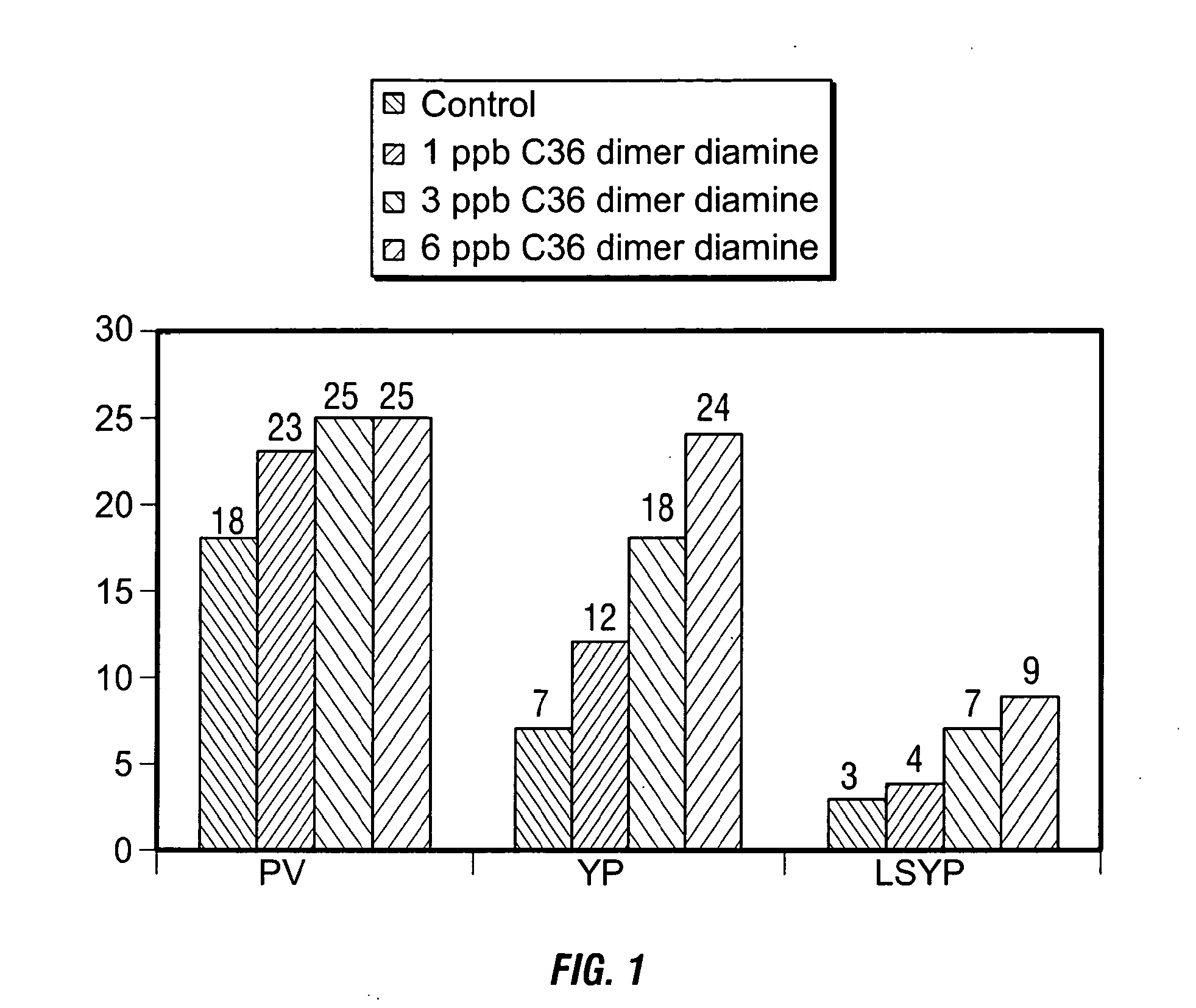
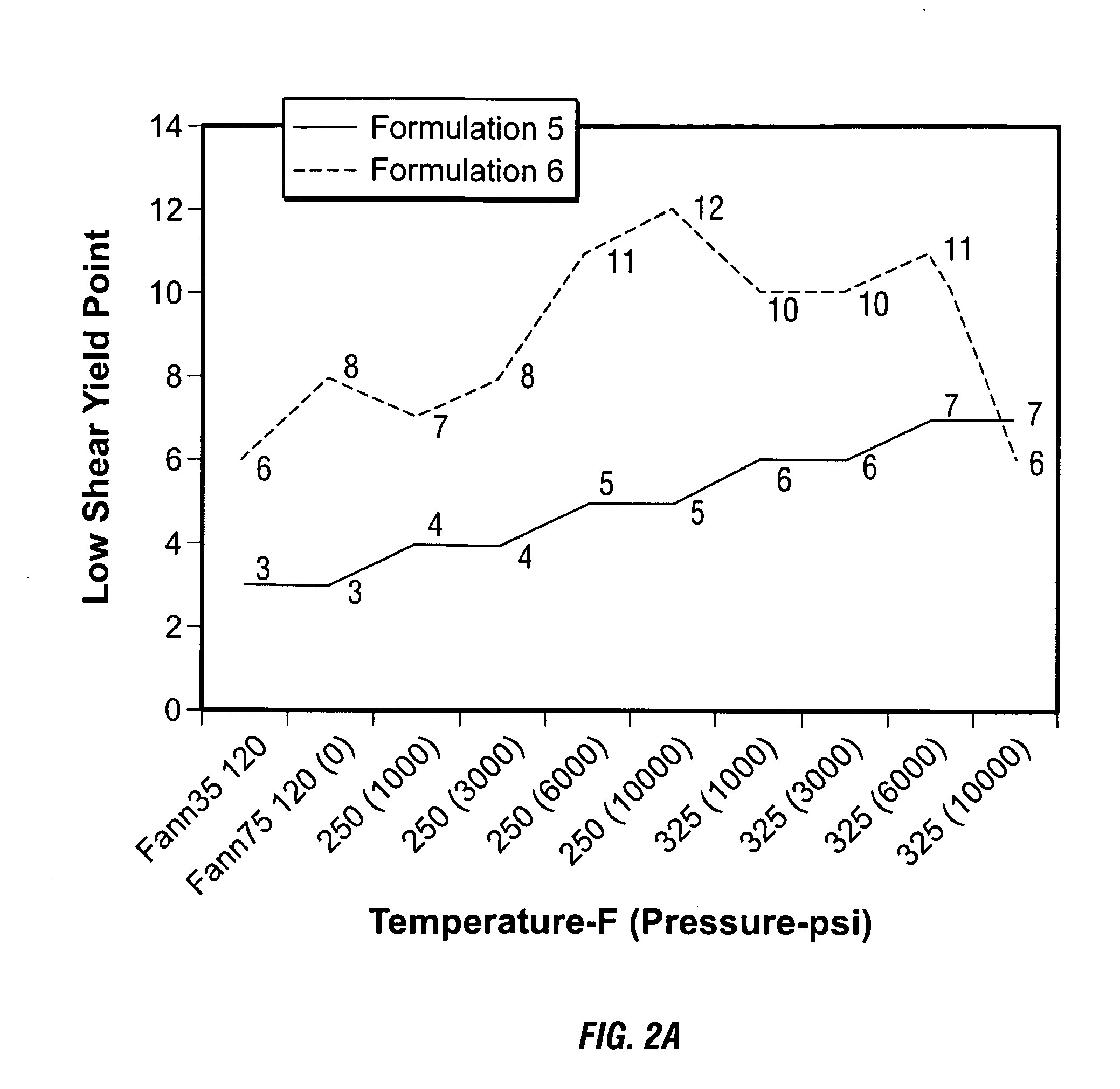
Methods and Materials to Enhance High Temperature Rheology in Invert Emulsions
ActiveUS20130303411A1Quantity minimizationLow pour pointFlushingDrilling compositionOrganic acidEmulsion
An invert emulsion drilling fluid, and a method of drilling with such fluid, having improved rheology at low mud weights and high temperatures. The improved rheology is effected with addition of a rheology additive of the invention comprising fatty dimer diamines or dimer diamines and an organic acid or ester of the acid. A nonlimiting example of such a rheology additive comprises a C36 fatty dimer diamine and adipic acid or dimethyl adipate.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method for borehole measurement of formation properties
InactiveUS7289909B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingWell drillingAcoustic wave
The present invention is a method of estimating formation properties by analyzing acoustic waves that are emitted from and received by a bottom hole assembly. A bottom hole assembly may be deployed in a borehole to estimate formation properties. From the bottom hole assembly, a source signal may be emitted and at least one signal may be received by one or more receivers in the bottom hole assembly. Analysis of the frequency dependent characteristics of the received signal allows the estimation of the formation properties of interest, including pore pressure. The formation properties of interest may be used to monitor a wellbore pressure safety margin and to optimize drilling mud weight.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
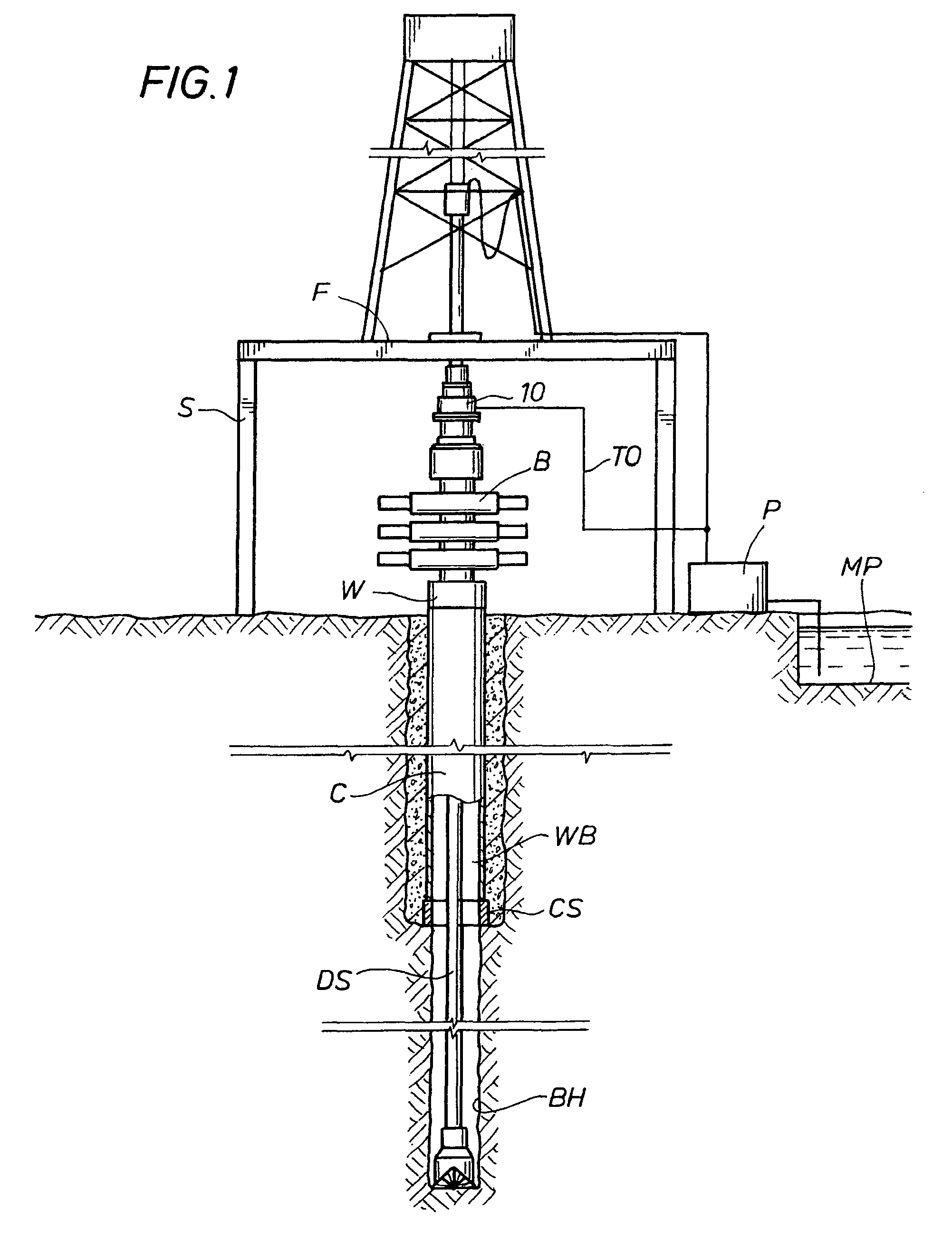
Drilling with a high pressure rotating control device
A Drill-To-The-Limit (DTTL) drilling method variant to Managed Pressured Drilling (MPD) applies constant surface backpressure, whether the mud is circulating (choke valve open) or not (choke valve closed). Because of the constant application of surface backpressure, the DTTL method can use lighter mud weight that still has the cutting carrying ability to keep the borehole clean. The DTTL method identifies the weakest component of the pressure containment system, such as the fracture pressure of the formation or the casing shoe leak off test (LOT). With a higher pressure rated RCD, such as 5,000 psi (34,474 kPa) dynamic or working pressure and 10,000 psi (68,948 kPa) static pressure, the limitation will generally be the facture pressure of the formation or the LOT. In the DTTL method, since surface backpressure is constantly applied, the pore pressure limitation of the conventional drilling window can be disregarded in developing the fluid and drilling programs.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
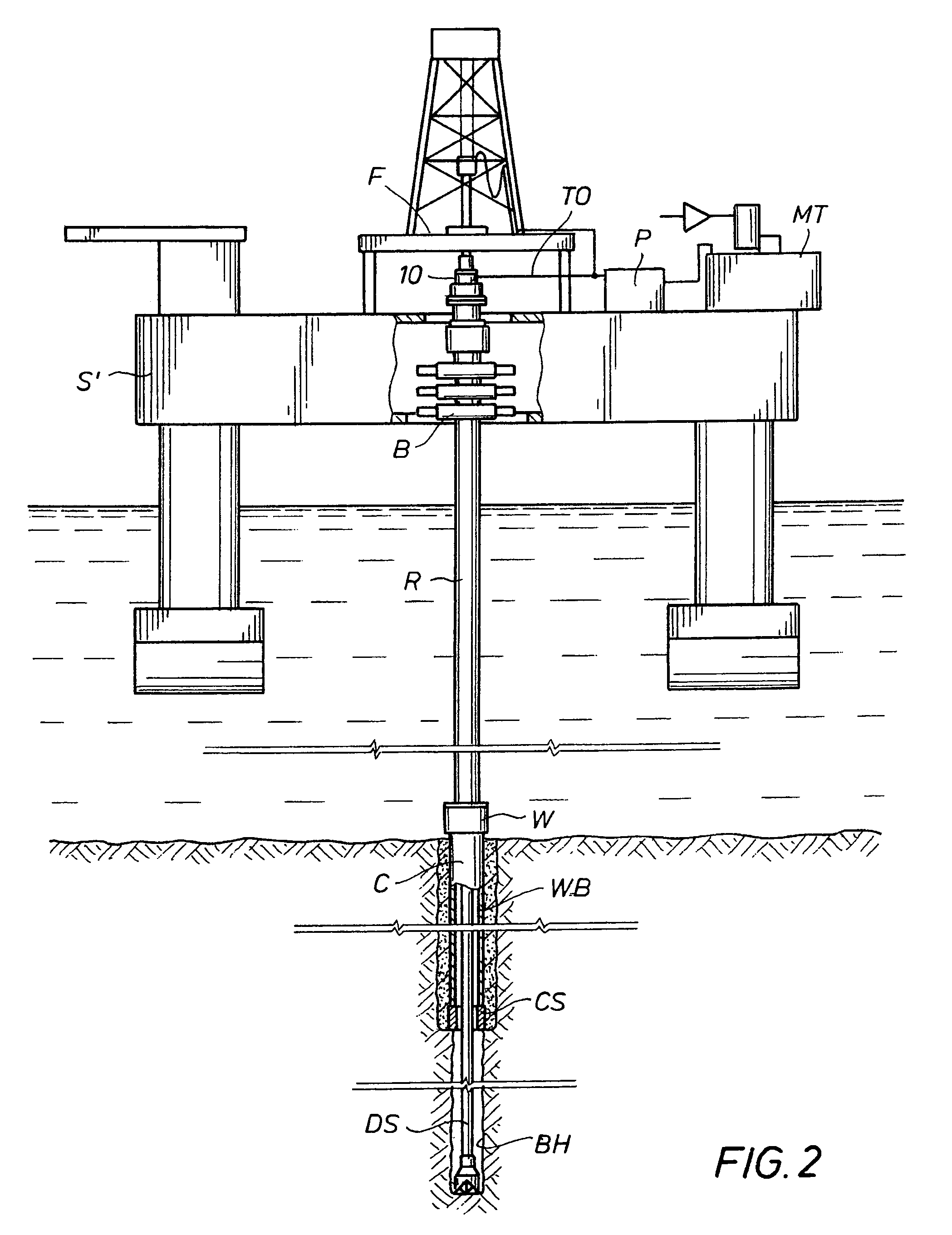
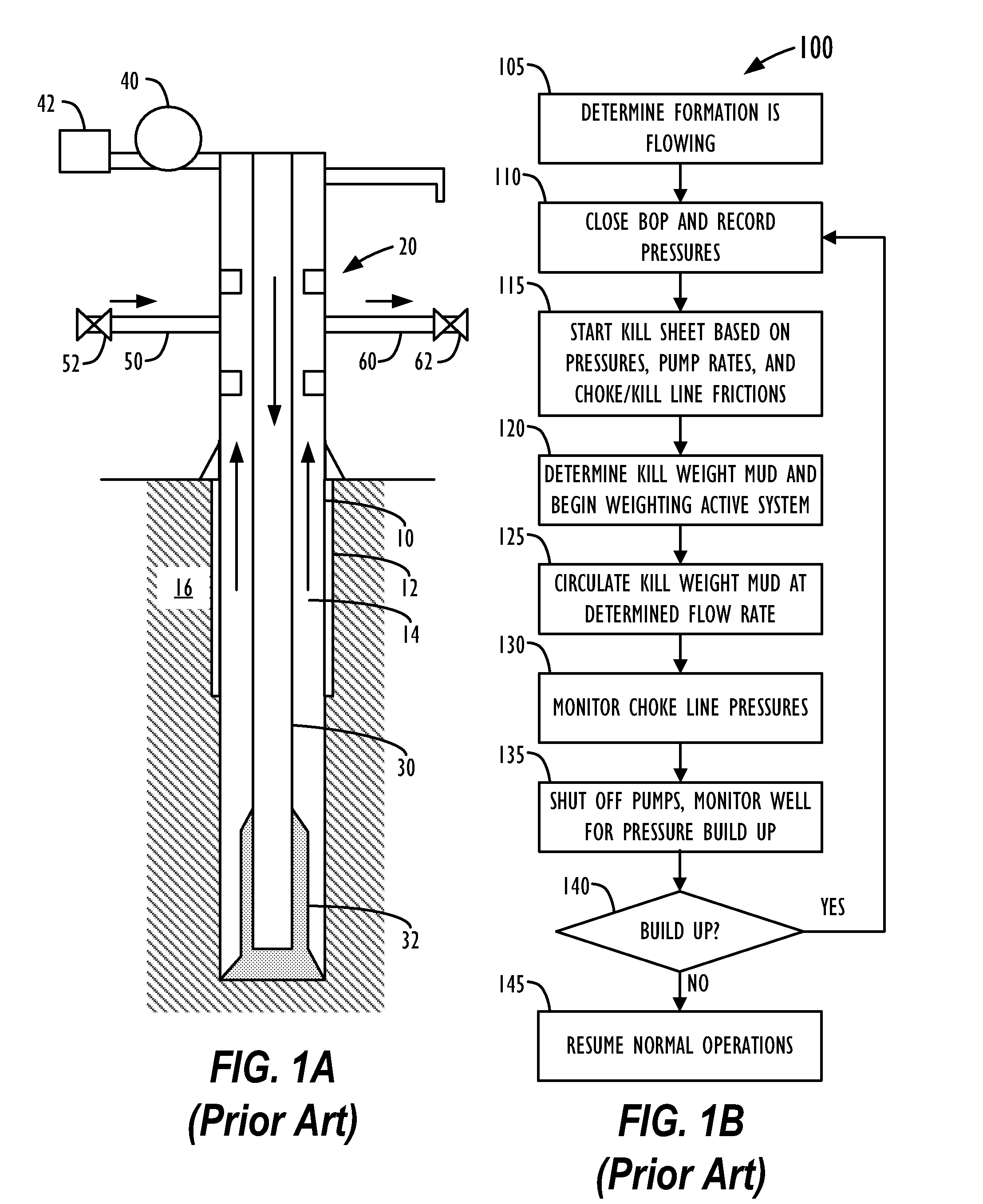
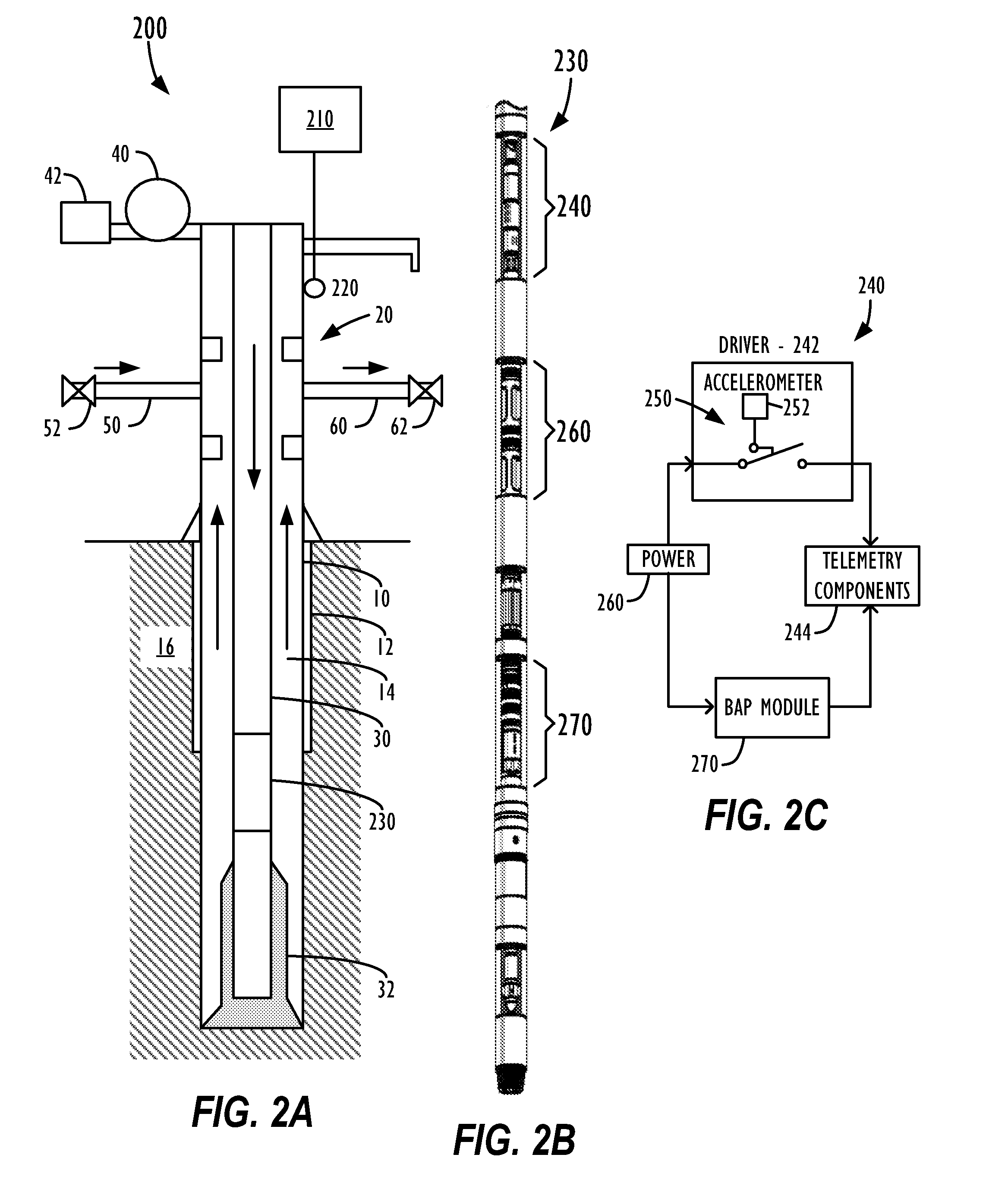
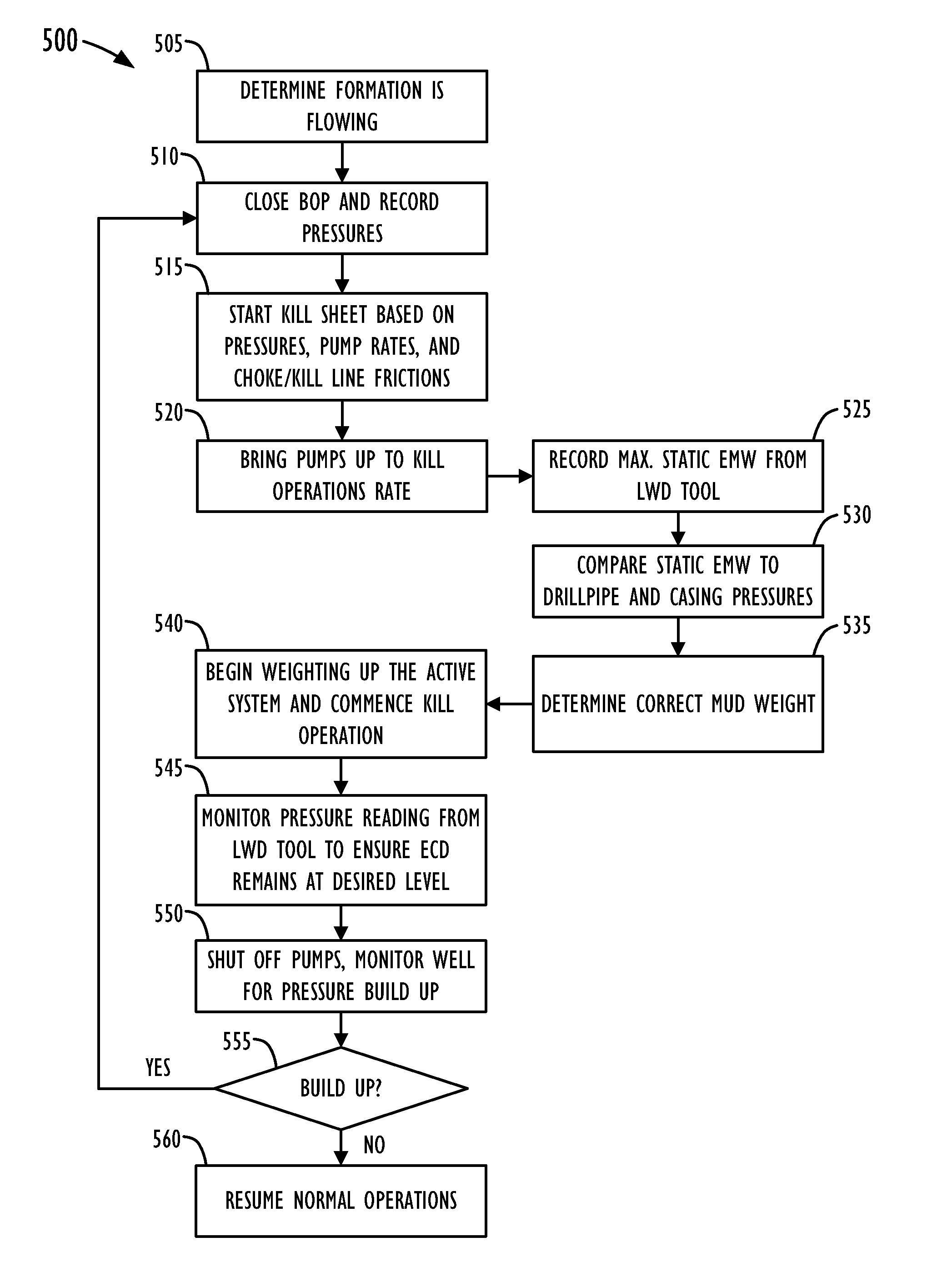
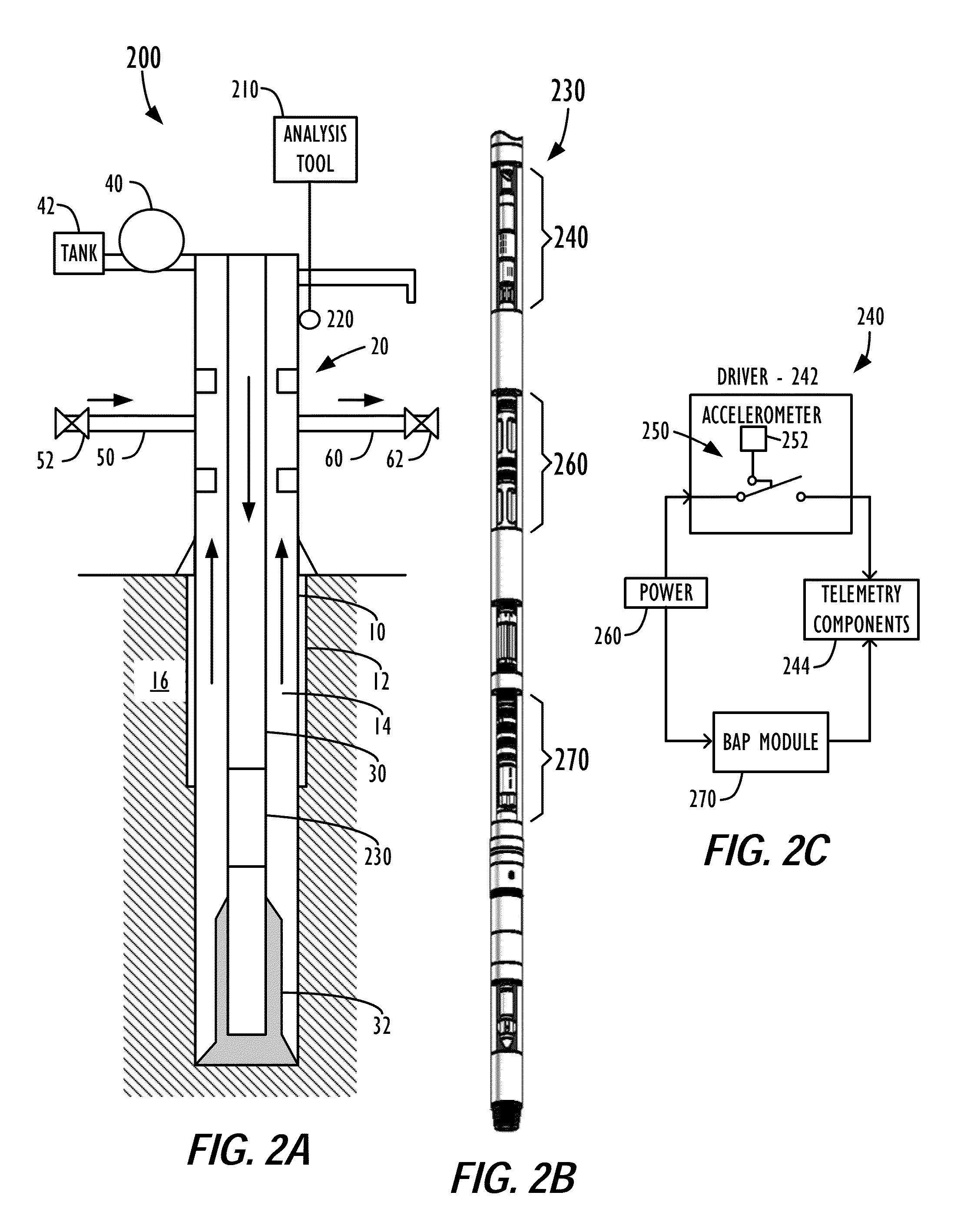
System and Method for Obtaining and Using Downhole Data During Well Control Operations
InactiveUS20090063055A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyPressure dataMechanical engineering
In a well control system and method, a tool driver on a toolstring is configured to activate a telemetry tool in response to a predetermined threshold of accelerometer data measured by an accelerometer. For example, the predetermined accelerometer data threshold preferably corresponds to an acceleration level expected while drilling mud is being pumped at a slow pump rate of a well control operation through the drill pipe of the well. When a fluid influx occurs during drilling, the well is shut-in so that the tool driver turns off the telemetry tool. The drill pipe and casing pressures of the shut-in well are obtained. Then, drilling mud having a first weight is pumped into the drill pipe at a slow mud pump rate. Because the tool driver is set to activate the telemetry tool in response to accelerometer data at the slow pump rate, the telemetry tool begins sending downhole pressure data to the surface. In this way, rig operations can change the mud weight and adjust the choke line during the kill operation based on an analysis of the downhole pressure data obtained during the well control operation.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Plaster multi-step treatment device for underground engineering construction
InactiveCN101177325AReduce sand contentLight weightWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationSludge treatmentSlurryMud weight
The invention discloses a multilevel treatment equipment for slurry in underground construction, which comprises a prescreening device, a desander and a desilter; wherein, through a pipeline the dredge pump is connected with the prescreening device the prescreening device is connected with the desander through a pipeline; the outlet of the middle storage tank of the desander is respectively connected with a slurry-storing tank and a slurry-adjusting pool of the desilter through a conversion valve and a pipeline; the middle storage tank of the desilter is connected with the slurry-adjusting pool. The invention can process the slurry in complex strata stage by stage, meeting the requirements of processing slurry under different construction condition. The invention has the advantages of strong adaptability for strata, high precision of solid phase separation, low mud weight ratio for processed clean mud and low sand content rate.
Owner:三川德青工程机械有限公司
Method for estimating confined compressive strength for rock formations utilizing skempton theory
InactiveUS7555414B2Improve accuracyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyStress concentrationWell drilling
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Rotor type aircraft water landing model test method
ActiveCN106525388AEffectively evaluate ditching performanceAccurate and effective measurementHydrodynamic testingData acquisitionBottom pressure
The invention provides a rotor type aircraft water landing model test method. Firstly, a test device is installed, and electrical signal connection and test are completed. Then, a hydrodynamic high speed test trailer moves in an orbit and drives a model to move, when the speed of the model reaches the running speed required by the test and is stable, data acquisition equipment is started, after the normal working of the data acquisition equipment is determined, a model connection component is controlled to loosen the model, and the model freely separates and goes into water to slide. After the model goes into the water, the hydrodynamic high speed test trailer brakes and slows down until parking. After the test process is ended, the effectiveness of collected test data is analyzed, valid test parameters are recorded, and the valid test parameters comprises model weight, center of gravity, forward speed and sinking speed at the instant of going into water, a pitch angle, a roll angle and a yaw angle in a model initial state, and a pitch angle, a roll angle and a yaw angle, overload of center of gravity, cockpit overload, bottom pressure of the model after the model goes into the water. According to the method, a reliable basis is provided for effectively evaluating the water landing performance of a rotor type aircraft.
Owner:CHINA SPECIAL TYPE FLIER RES INST
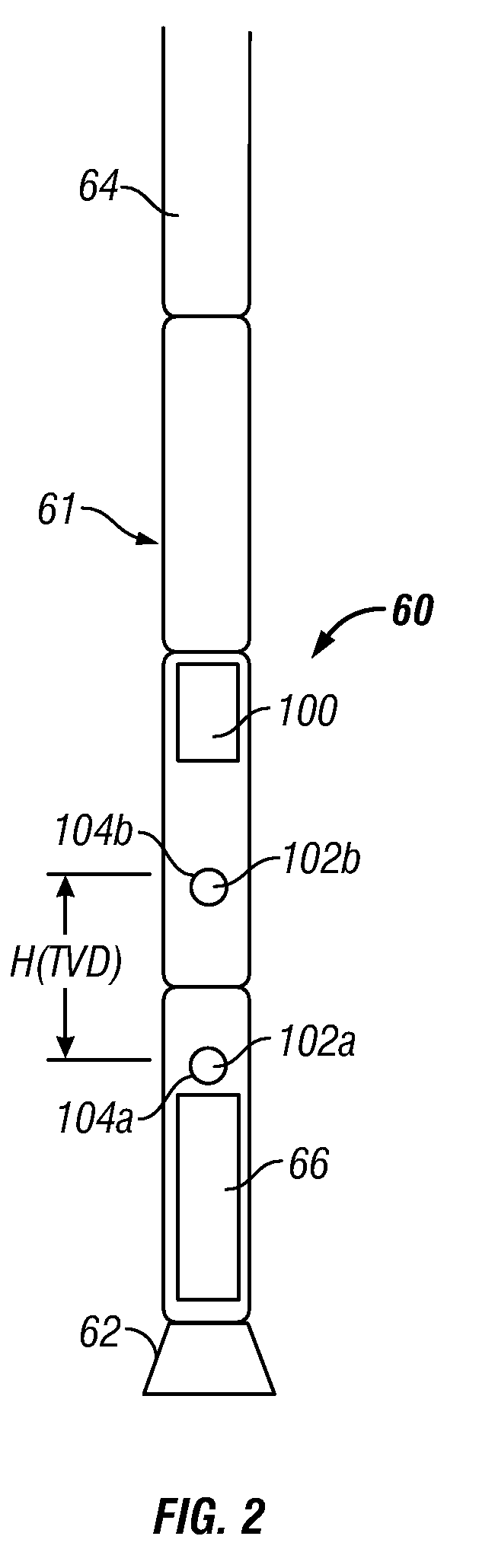
Downhole Local Mud Weight Measurement Near Bit
ActiveUS20090205822A1Reduce offsetElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyVolumetric Mass DensityPressure difference
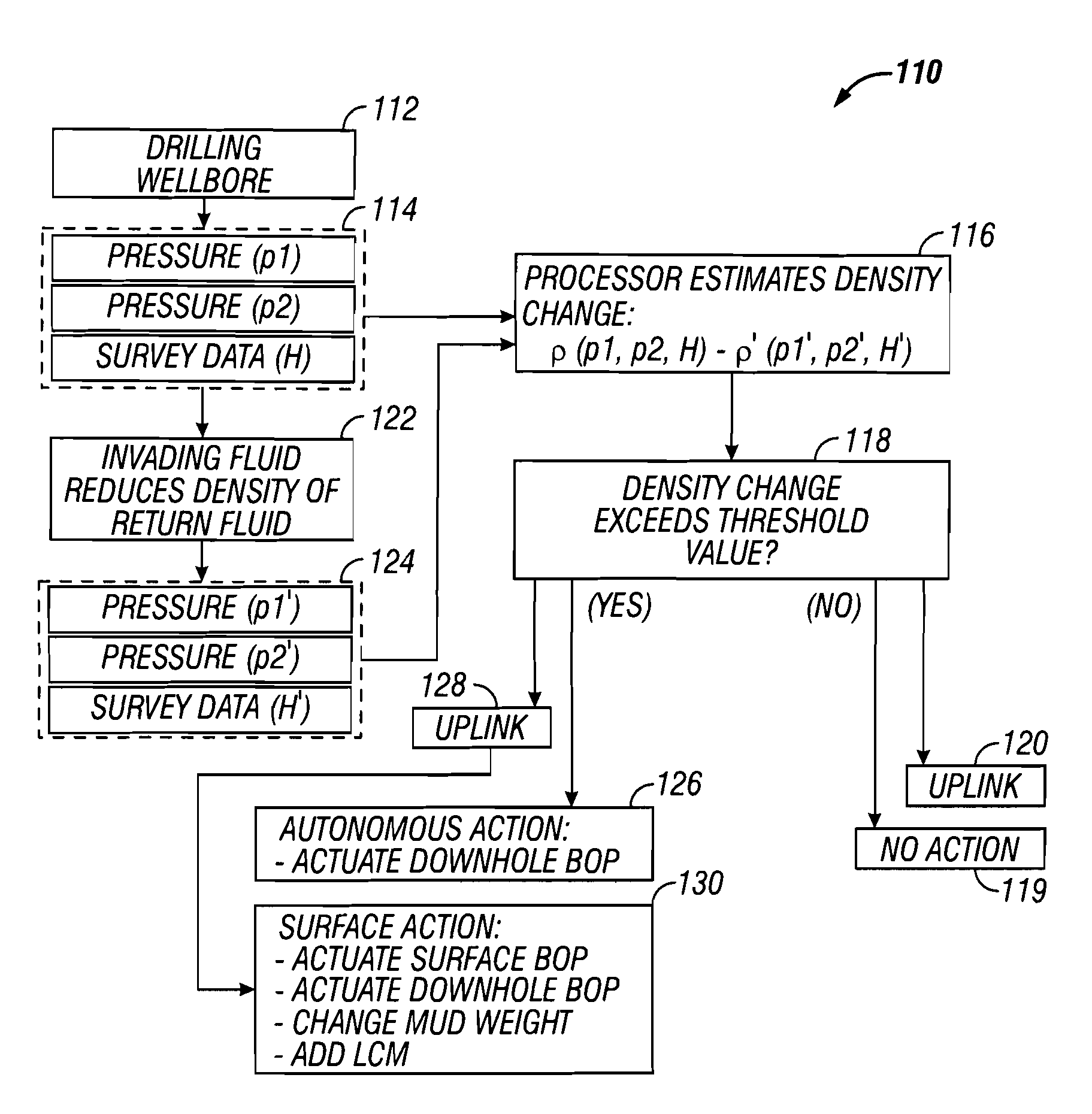
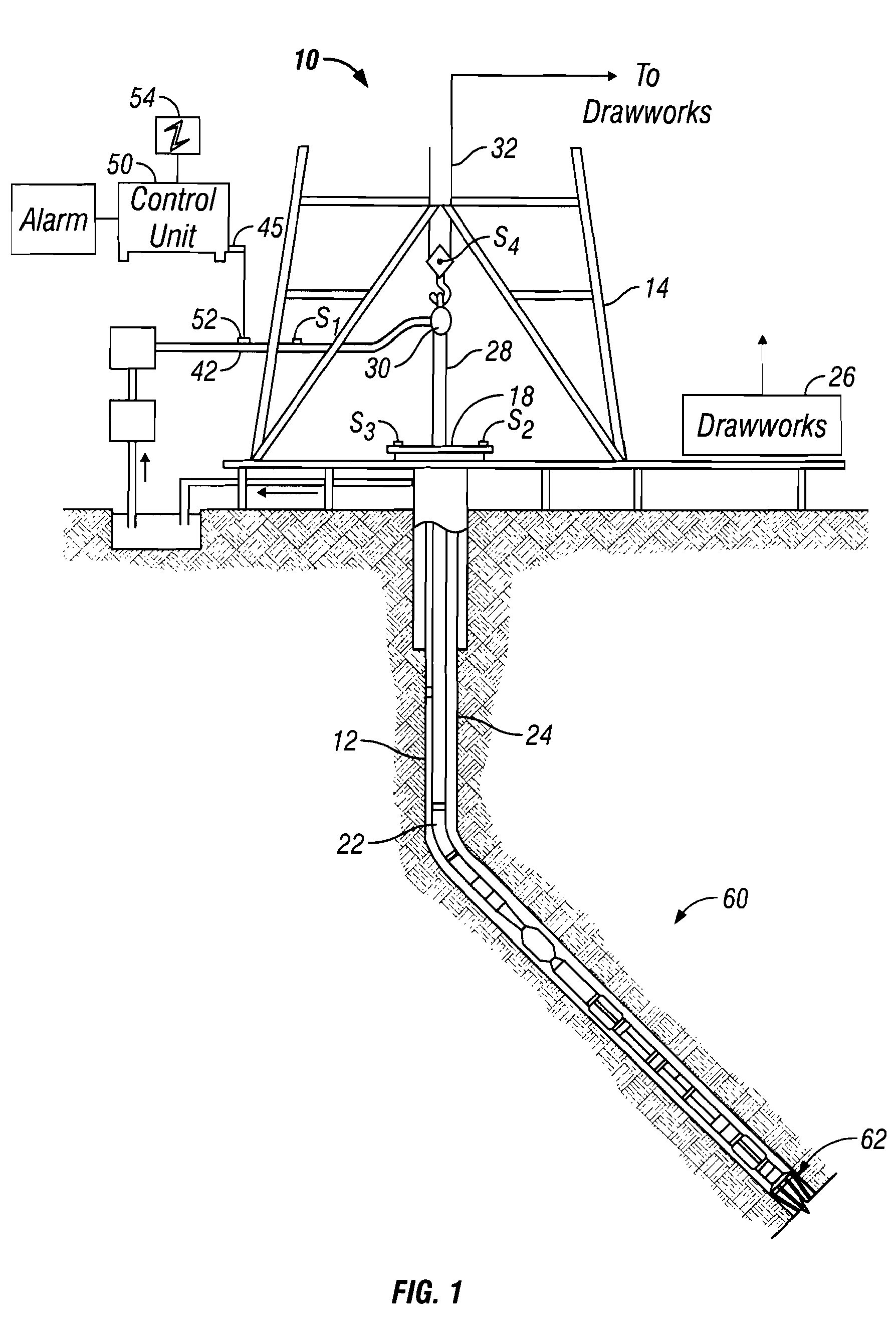
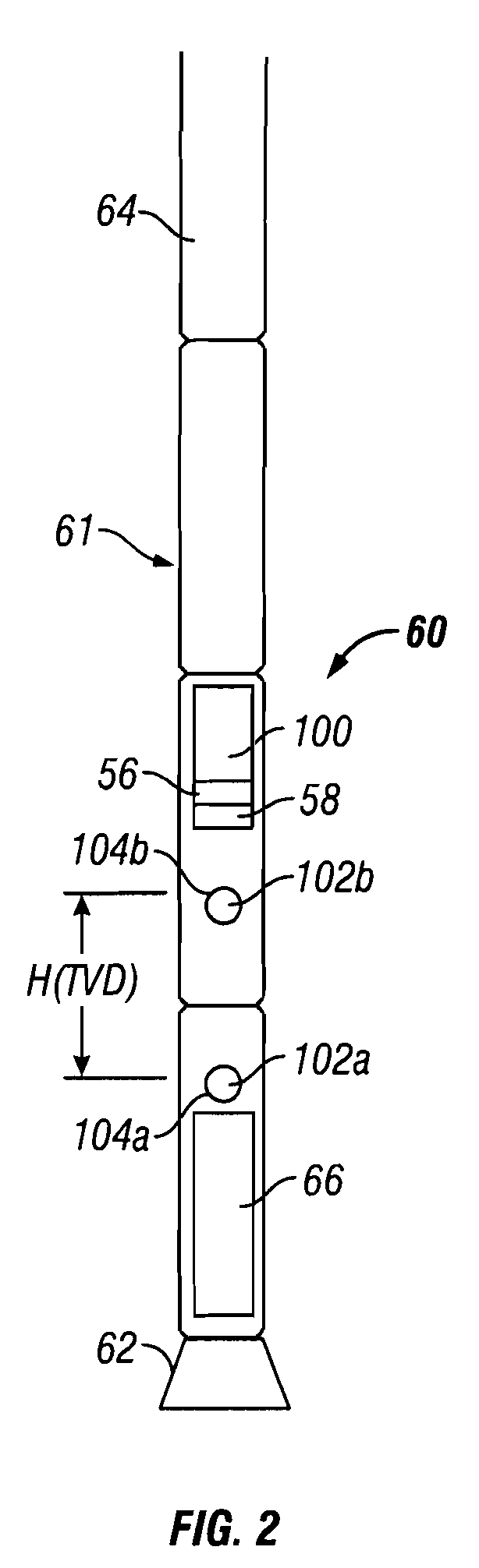
A method for detecting a change in a wellbore fluid includes estimating at least two pressure differences in the wellbore fluid and estimating a change in a density of the fluid using the at least two pressure differences. The density change may be estimated by the equation, Δρ=(ΔPbefore<sub2>—< / sub2>influx−ΔPafter<sub2>—< / sub2>influx) / (g×ΔTVD), wherein ΔP is a fluid pressure difference between two points along the wellbore, ρ is a mean value of density of the fluid between the two points, g is gravity and ΔTVD is a vertical distance between the two points. The method may include estimating a density change using an estimated inclination of the wellbore. An apparatus for estimating density changes includes at least two axially spaced apart pressure sensors. The sensor positions may be switched to estimate a correction term to reduce a relative offset between the two pressure sensors.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Downhole local mud weight measurement near bit
ActiveUS7950472B2Reduce offsetSurveySpecific gravity by measuring pressure differencesVolumetric Mass DensityPressure difference
A method for detecting a change in a wellbore fluid includes estimating at least two pressure differences in the wellbore fluid and estimating a change in a density of the fluid using the at least two pressure differences. The density change may be estimated by the equation, Δρ=(ΔPbefore<sub2>—< / sub2>influx−ΔPafter<sub2>—< / sub2>influx) / (g×ΔTVD), wherein ΔP is a fluid pressure difference between two points along the wellbore, ρ is a mean value of density of the fluid between the two points, g is gravity and ΔTVD is a vertical distance between the two points. The method may include estimating a density change using an estimated inclination of the wellbore. An apparatus for estimating density changes includes at least two axially spaced apart pressure sensors. The sensor positions may be switched to estimate a correction term to reduce a relative offset between the two pressure sensors.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
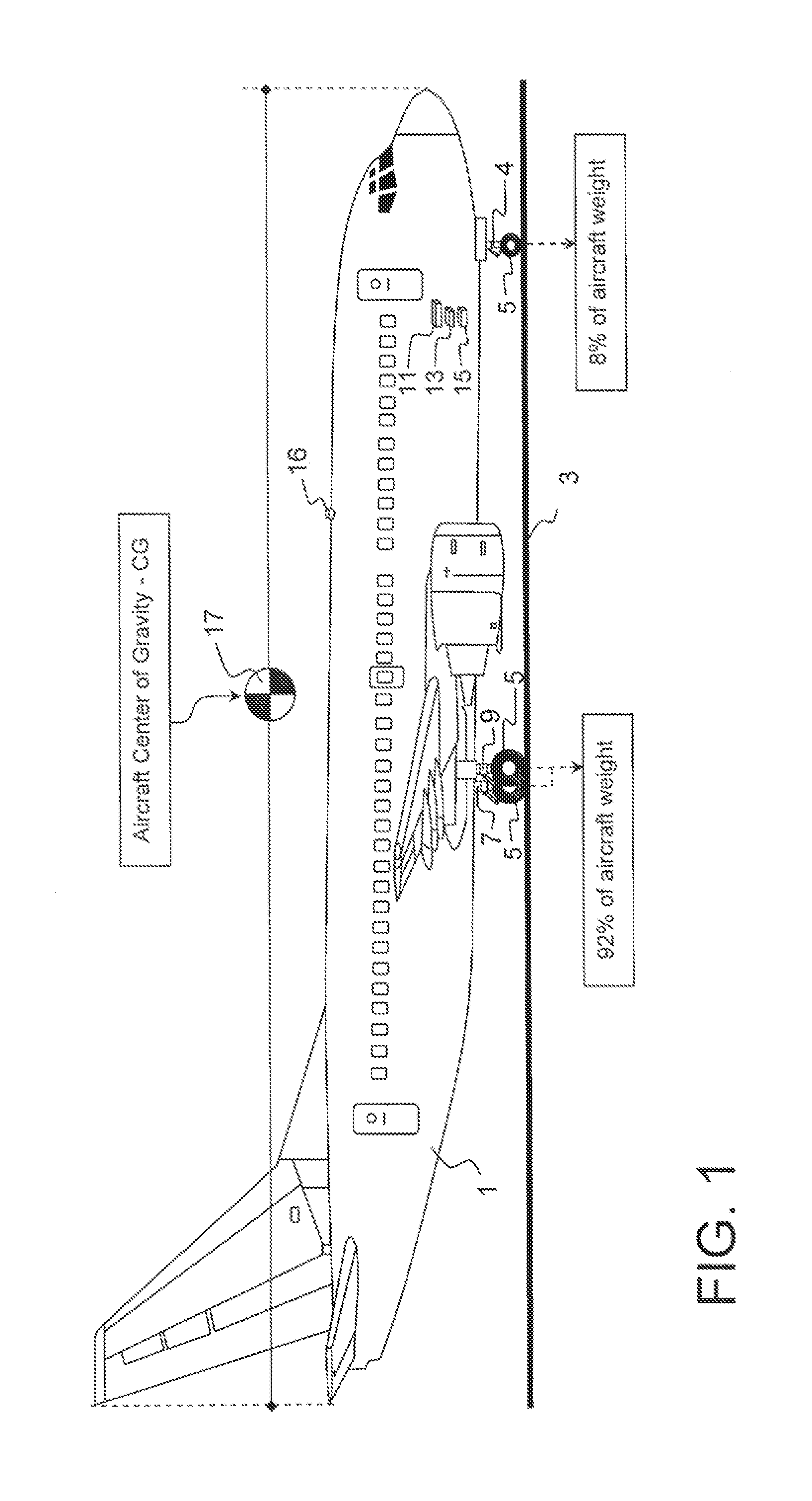
Method for determining aircraft center of gravity independent of measuring aircraft total weight
InactiveUS20160195447A1Static/dynamic balance measurementFreight handlingCenter of gravity of an aircraftMud weight
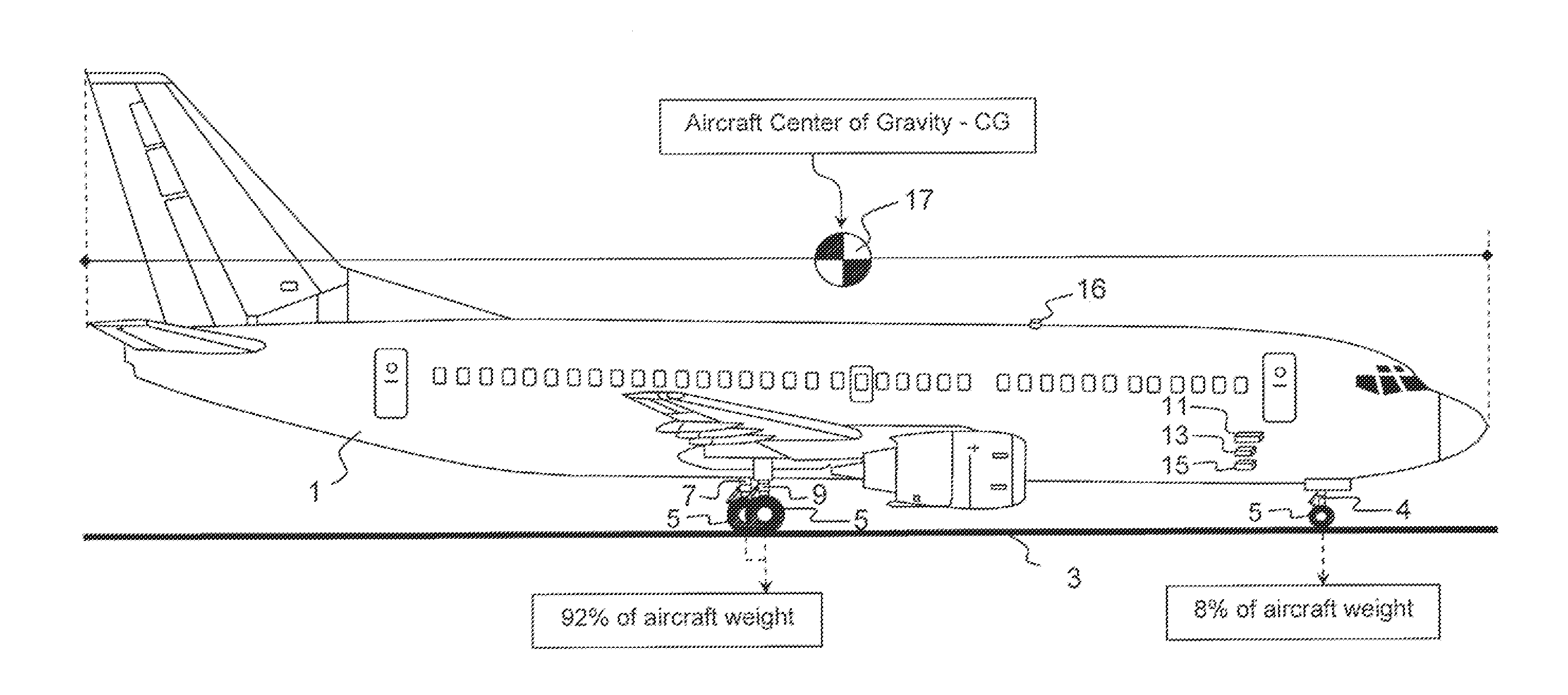
A method for determining a Center of Gravity of an aircraft, which is independent of measuring the aircraft weight. The total aircraft weight is determined by a method independent of measuring the weight supported by the main landing gear struts. The weight supported by the nose landing gear strut is subsequently measured. The measured weight associated with nose landing gear is subtracted from the independently determined total aircraft weight, to determine a calculated weight supported by the combined main landing gear struts. The resulting determined weight supported by the combined main landing gear is compared to the independently determined total aircraft weight, and allows for determination of the aircraft Center of Gravity. Inversely the measured nose strut weight is compared to the total aircraft weight, and allows for determination of the aircraft Center of Gravity. Aircraft Center of Gravity is determined without the total aircraft weight being measured.
Owner:NANCE C KIRK
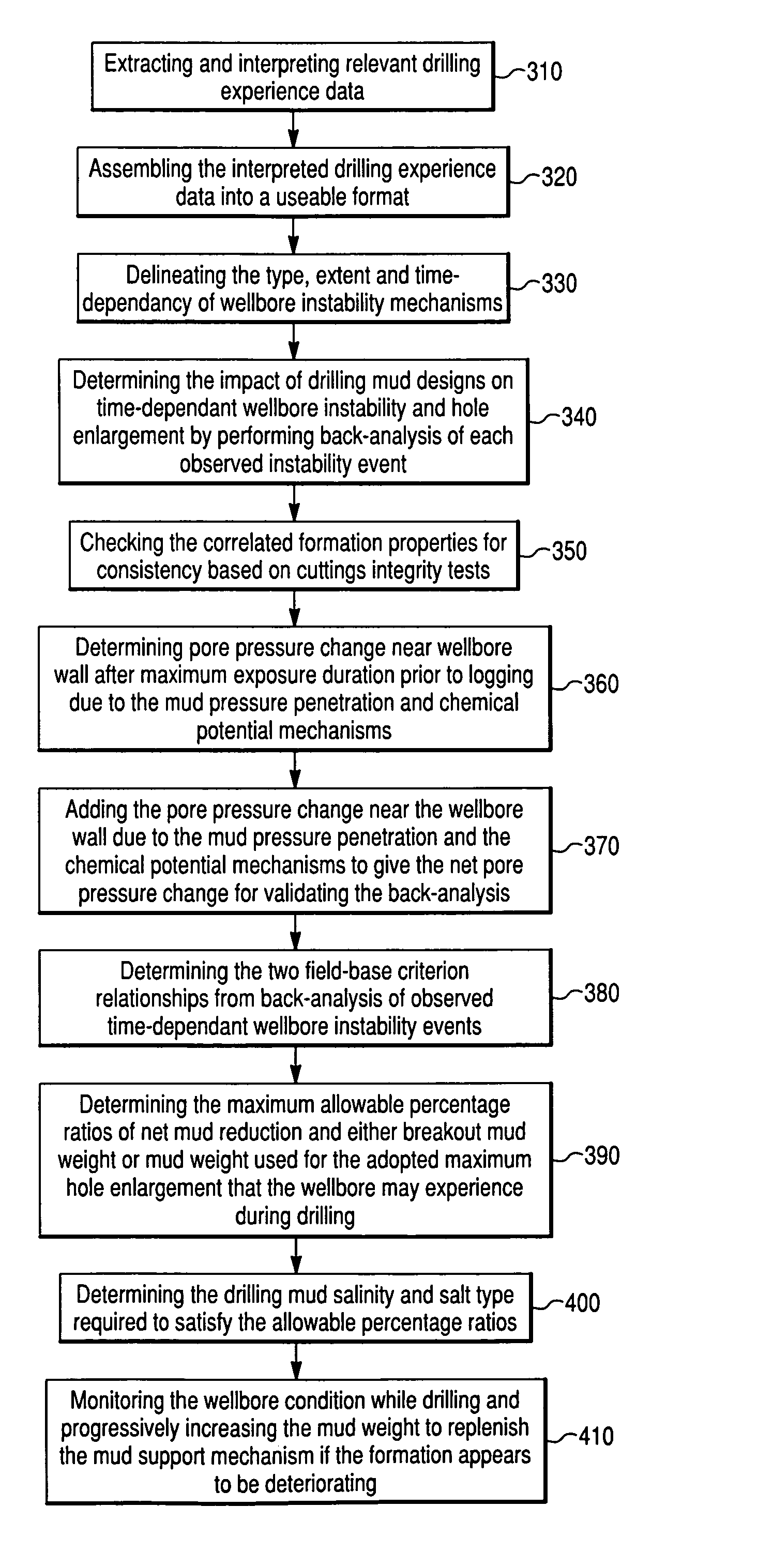
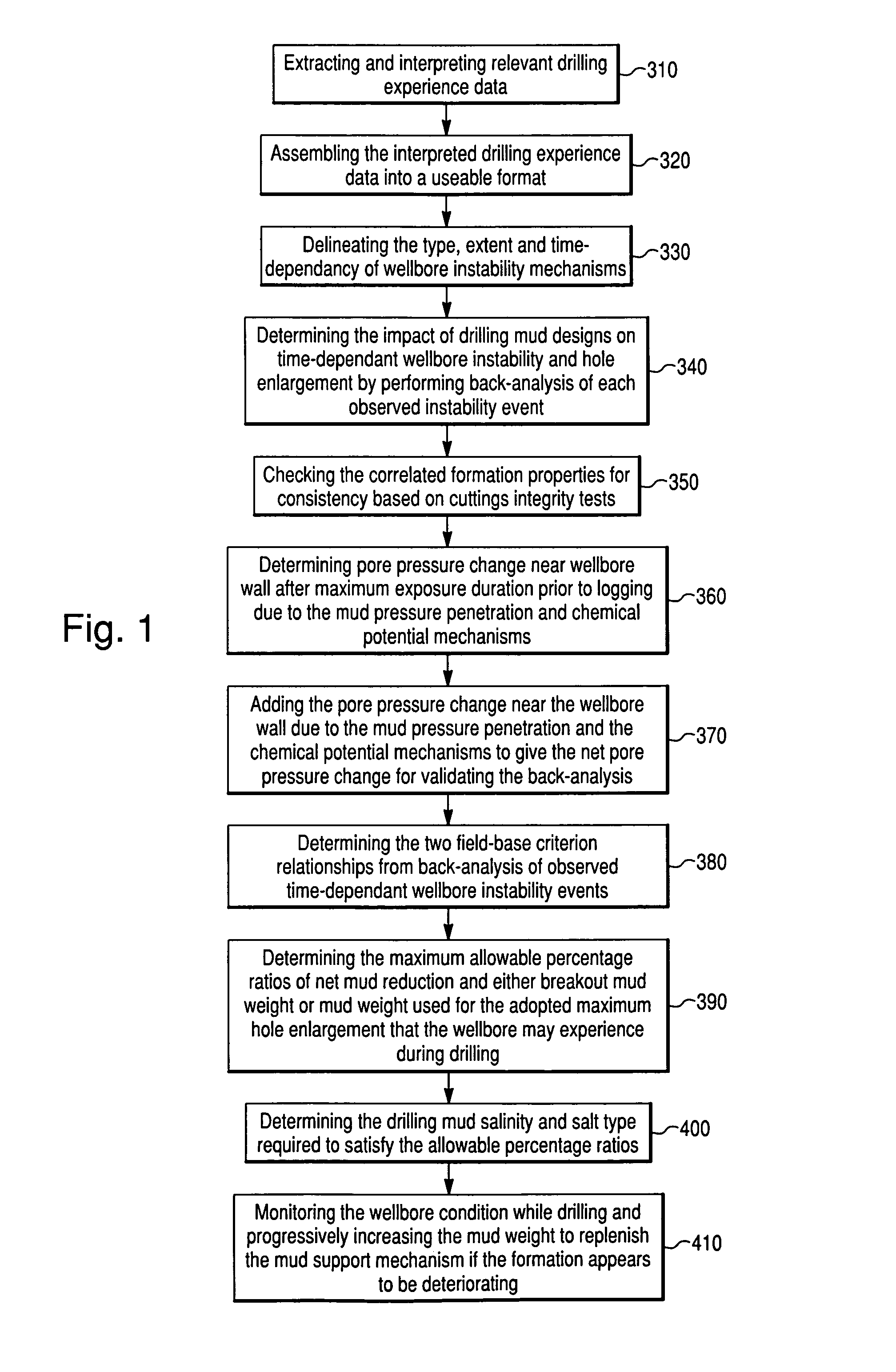
Method and computer program product for drilling mud design optimization to maintain time-dependent stability of argillaceous formations
InactiveUS20080190190A1Increase pressureElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyWell drillingInstability
A method and computer program product of either preventing or minimizing pore pressure increase near the wellbore wall within argillaceous formations through which a borehole has been drilled. By interpreting relevant drilling experience data, the type, extent and time-dependency of wellbore instability mechanisms are determined. The impact of drilling mud designs on the time-dependent wellbore instability and hole enlargement is determined by back-analyzing observed drilling events. At least one field-based criterion relationship between net mud weight reduction percentage ratio and hole enlargement is determined. A maximum allowable percentage ratio(s) of net mud weight reduction and either breakout mud weight or mud weight used for the adopted maximum hole enlargement that the wellbore may experience during drilling is determined. Drilling mud salinity value and salt type to satisfy maximum allowable percentage ratio(s) is then determined.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
High efficiency solidifying processing agent for waste sludge in oil area and its solidifying treating process
InactiveCN1821129AShort setting and hardening timeGood water stabilitySludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningGypsumSludge
The present invention relates to environment protecting technology, and is especially waste drilling slurry solidifying and treating agent and solidifying and treating process. The efficient waste drilling slurry solidifying and treating agent consists of two parts, including the first part comprising ionic precipitant 1-3 wt%, cracking agent 1-2 wt%, adsorbent 2-8 wt%, and the second part comprising hardening agent of aluminosulfate 5-20 wt%, loosener 2-4 wt% and gypsum powder 2-8 wt%. The waste drilling slurry solidifying and treating process with the efficient waste drilling slurry solidifying and treating agent includes: mixing waste drilling slurry with ionic precipitant and cracking agent through stirring, stilling for 1-3 hr, adding adsorbent to separate solid, mixing the deposited solid with hardening agent, loosener and gypsum powder, and stilling for 3-7 days. The present invention has high water stability, and can obtain solidified matter capable of being used in planting.
Owner:俞然刚
Invert Drilling Fluids Having Enhanced Rheology and Methods of Drilling Boreholes
An invert emulsion drilling fluid, and a method of drilling with such fluid, having improved rheology at low mud weights and high temperatures. The improved rheology is effected with addition of hydrophobic amines, most preferably dimer diamines.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Rotating Control System and Method for Providing a Differential Pressure
A Drill-To-The-Limit (DTTL) drilling method variant to Managed Pressure Drilling (MPD) applies constant surface backpressure, whether the mud is circulating (choke valve open) or not (choke valve closed). Because of the constant application of surface backpressure, the DTTL method can use lighter mud weight that still has the cutting carrying ability to keep the borehole clean. The DTTL method identifies the weakest component of the pressure containment system, such as the fracture pressure of the formation or the casing shoe leak off test (LOT). With a higher pressure rated RCD, such as 5,000 psi (34,474 kPa) dynamic or working pressure and 10,000 psi (68,948 kPa) static pressure, the limitation will generally be the fracture pressure of the formation or the LOT. In the DTTL method, since surface backpressure is constantly applied, the pore pressure limitation of the conventional drilling window can be disregarded in developing the fluid and drilling programs. Using the DTTL method a deeper wellbore can be drilled with larger resulting end tubulars, such as casings and production liners, than had been capable with conventional MPD applications.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
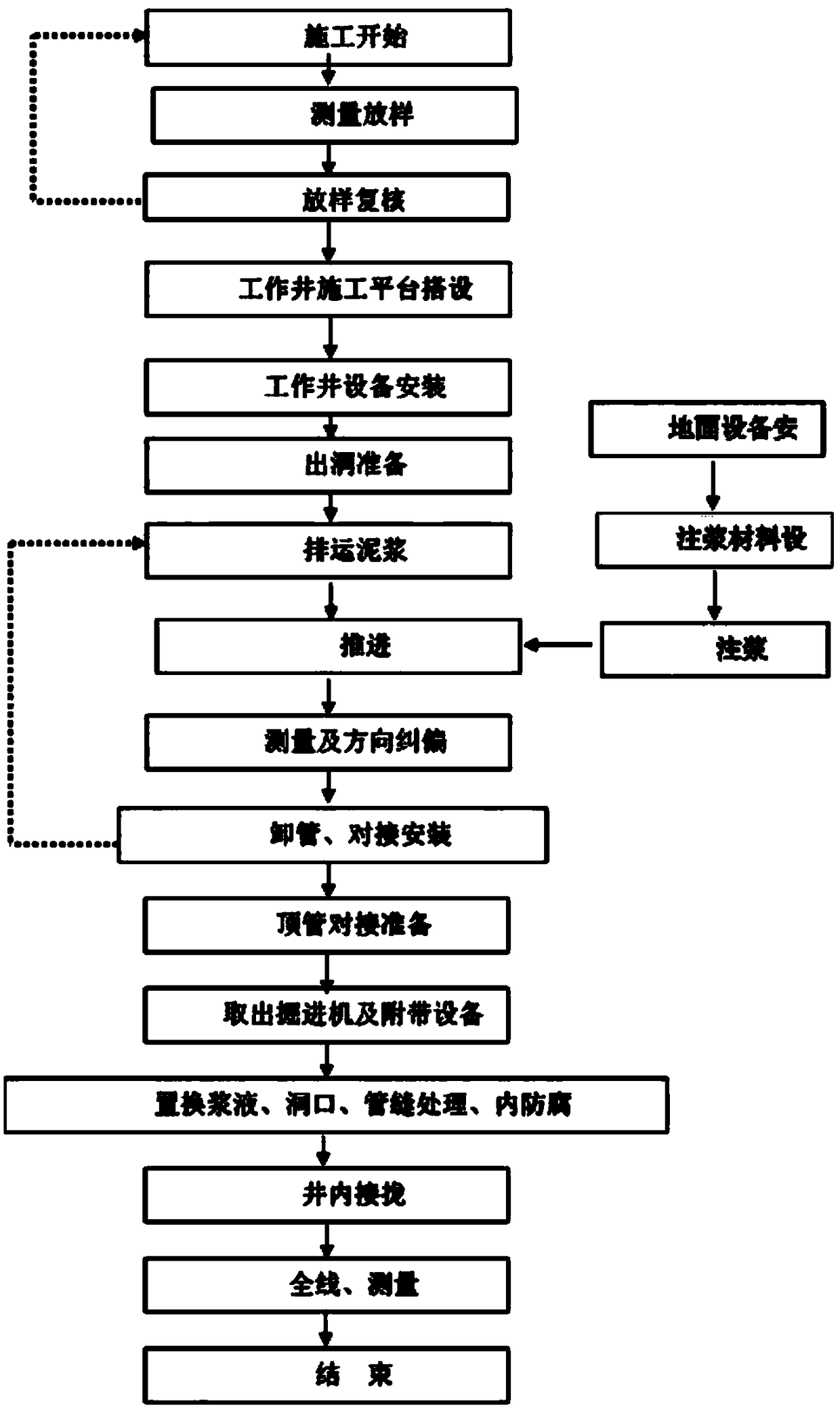
Pipe jacking construction method in complex terrain environment
InactiveCN109372532AReduce disturbanceReduce extrusion stressBuilding constructionsOrganic fertilisersTerrainEarth pressure balance
The invention discloses a pipe jacking construction method in a complex terrain environment. A panel type 3.5m large cutter head earth pressure balance pipe jacking heading machine is adopted; cut soil enters a muddy water cabin from gaps of a main cutting edge; soil in the muddy water cabin is broken into mud under the joint action of a stirring bar behind a cutter head and muddy water; and the water and earth pressure of excavation surfaces is balanced by controlling the mud and water pressure and the mud weight of the muddy water cabin, so that the excavation surfaces are always in a stablestate. As for sections with poor soil quality and a large buried depth of pipelines, or sections located in a prosperous region with buildings (structures) or traffic trunks above and strict restrictions on displacement and groundwater by surrounding environments, the large-diameter earth pressure balance pipe jacking method is easy and safety in construction, high in quality, low in investment and short in construction period, extrusion of surrounding pipelines and settlement of the ground are effectively controlled, and smooth operation of ground transportation is ensured while important underground pipelines are protected during construction.
Owner:CHINA CONSTR 4TH ENG BUREAU 6TH
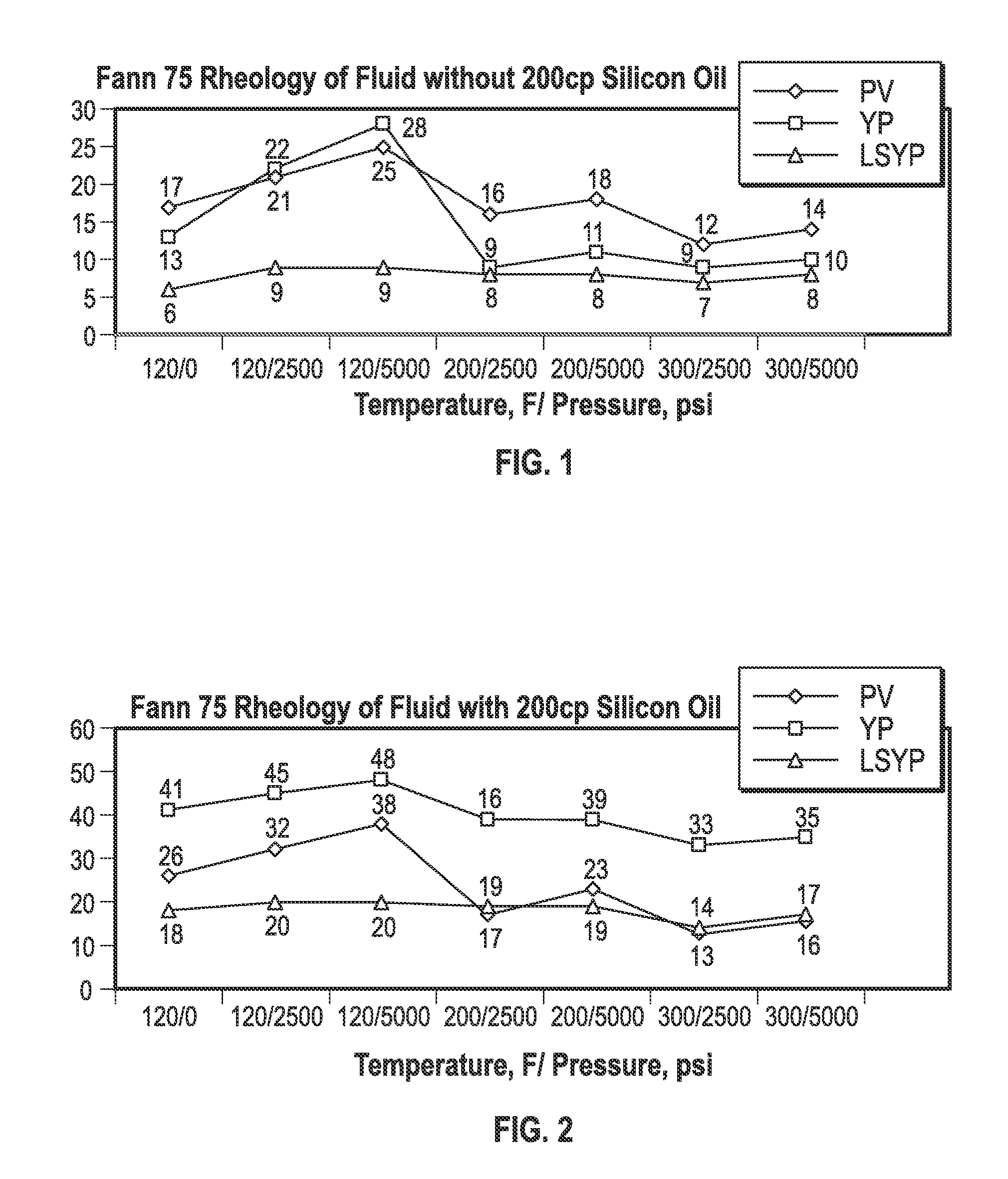
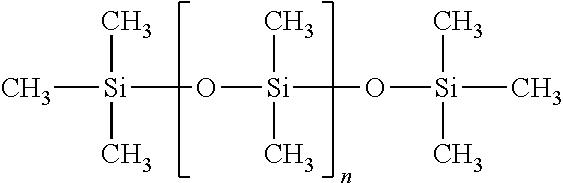
Method for Improving High Temperature Rheology in Drilling Fluids
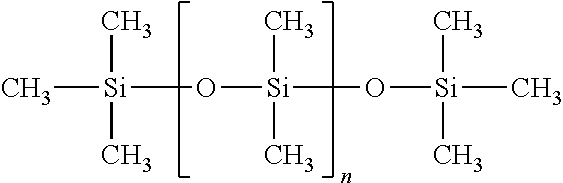
A method for enhancing the rheology of drilling fluids that is effective for any mud weight “clay-free” invert emulsion drilling fluid, even when drilling at high temperatures. The improved rheology is effected with addition of a silicon oil to the drilling fluid. A nonlimiting example of such a rheology additive comprises polydimethylsiloxane.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Production method of sintering brick by using drilling mud
The present invention relates to production of standard sintered brick, and is especially process of producing sintered brick with drilling mud. Drilling mud is first cured via adding curing agent in 10-50 wt% and then used in producing sintered brick through one standard sintered brick producing process. The curing agent consists of high alumina cement 15-20 wt%, Portland cement 15-20 wt% and silt soil 60-70 wt%. The present invention changes waste into useful material and is environment friendly.
Owner:SICHUAN RENZHI PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Method and system for pore pressure prediction
A method for performing an oilfield operation at a wellsite having a drilling rig configured to advance a drilling tool into a subsurface formation. The method includes generating a borehole temperature model for an area of interest using water depth information and a vertical stress model, generating a formation temperature model using the borehole temperature model, generating a mud-weight pressure model using the formation temperature model and pressure coefficients, generating a formation pore pressure model using the mud-weight pressure model, and adjusting the oilfield operation based on the formation pore pressure model.
Owner:PRAD RES & DEV LTD
Method and apparatus for managing variable density drilling mud
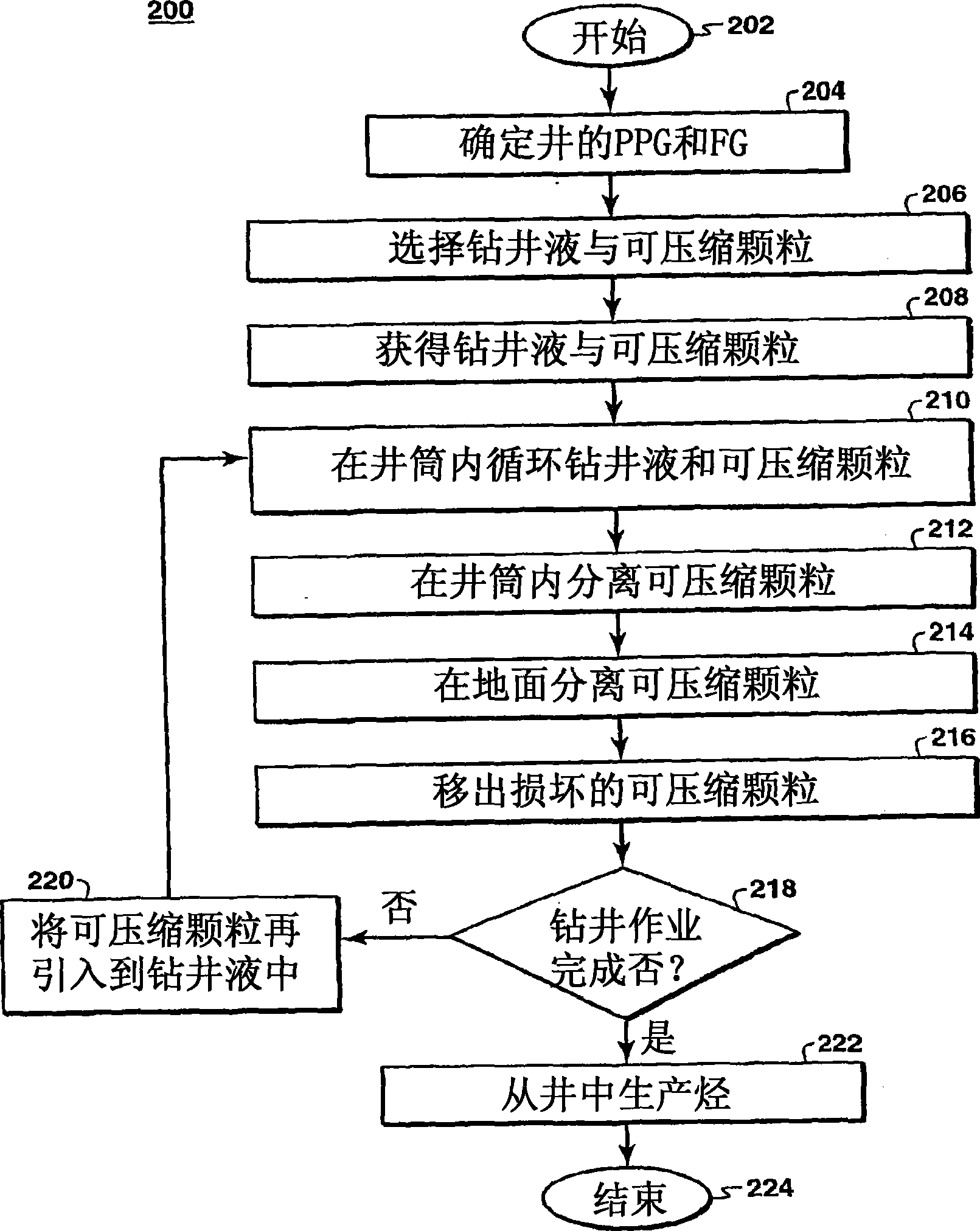
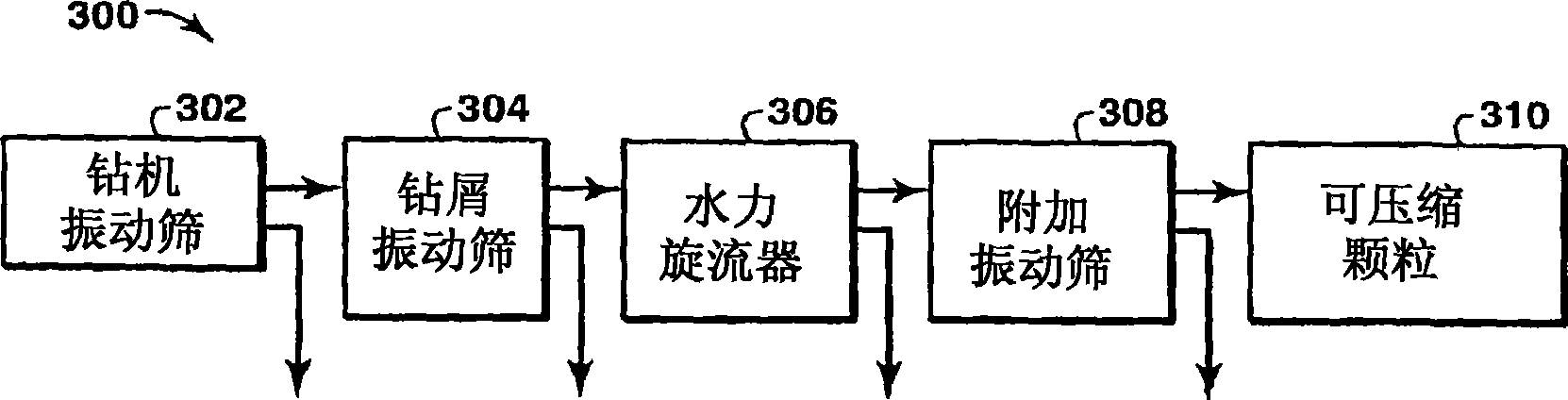
A method and system for drilling a wellbore is described. The syste includes a wellbore with a variable density drilling mud, drilling pipe, a bottom hol assembly disposed in the wellbore and a drilling mud processing unit in flui communication with the wellbore. The variable density drilling mud has compressibl particles and drilling fluid. The bottom hole assembly is coupled to the drilling pipe while the drilling mud processing unit is configured to separate the compressibl particles from the variable density drilling mud. The compressible particles in thi embodiment may include compressible hollow objects filled with pressurized gas an configured to maintain the mud weight between the fracture pressure gradient an the pore pressure gradient. In addition, the system and method may also manag the use of compressible particles having different characteristics, such as size, during the drilling operations.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Formula for viscosity reducer
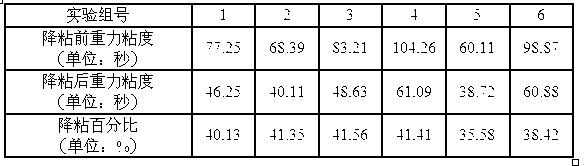
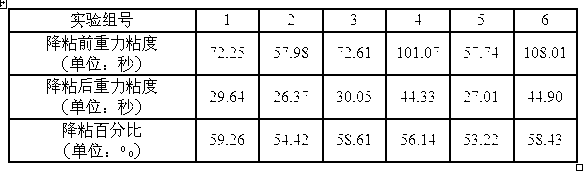
ActiveCN102786245AImprove liquidityLow viscosityDrilling compositionSodium bicarbonateEconomic benefits
The invention provides a formula for a viscosity reducer which is prepared from the following components: aluminum potassium sulfate dodecahydrate, sodium hexametaphosphate, sodium bicarbonate and sodium citrate. The viscosity reducer accounting for 0.13 to 0.3% of the weight of slurry is added into shield and drilling engineering slurry for viscosity adjustment. The above-mentioned aluminum potassium sulfate, sodium hexametaphosphate, sodium bicarbonate and sodium citrate are all industrial products, cost little, have stable physical and chemical properties and are harmless to the environment. The formula for the viscosity reducer provided by the invention can effectively reduce the viscosity of high-viscosity engineering slurry; and the viscosity reducer is convenient to blend, transport, store and use and has obvious economic benefits.
Owner:三川德青工程机械有限公司 +1
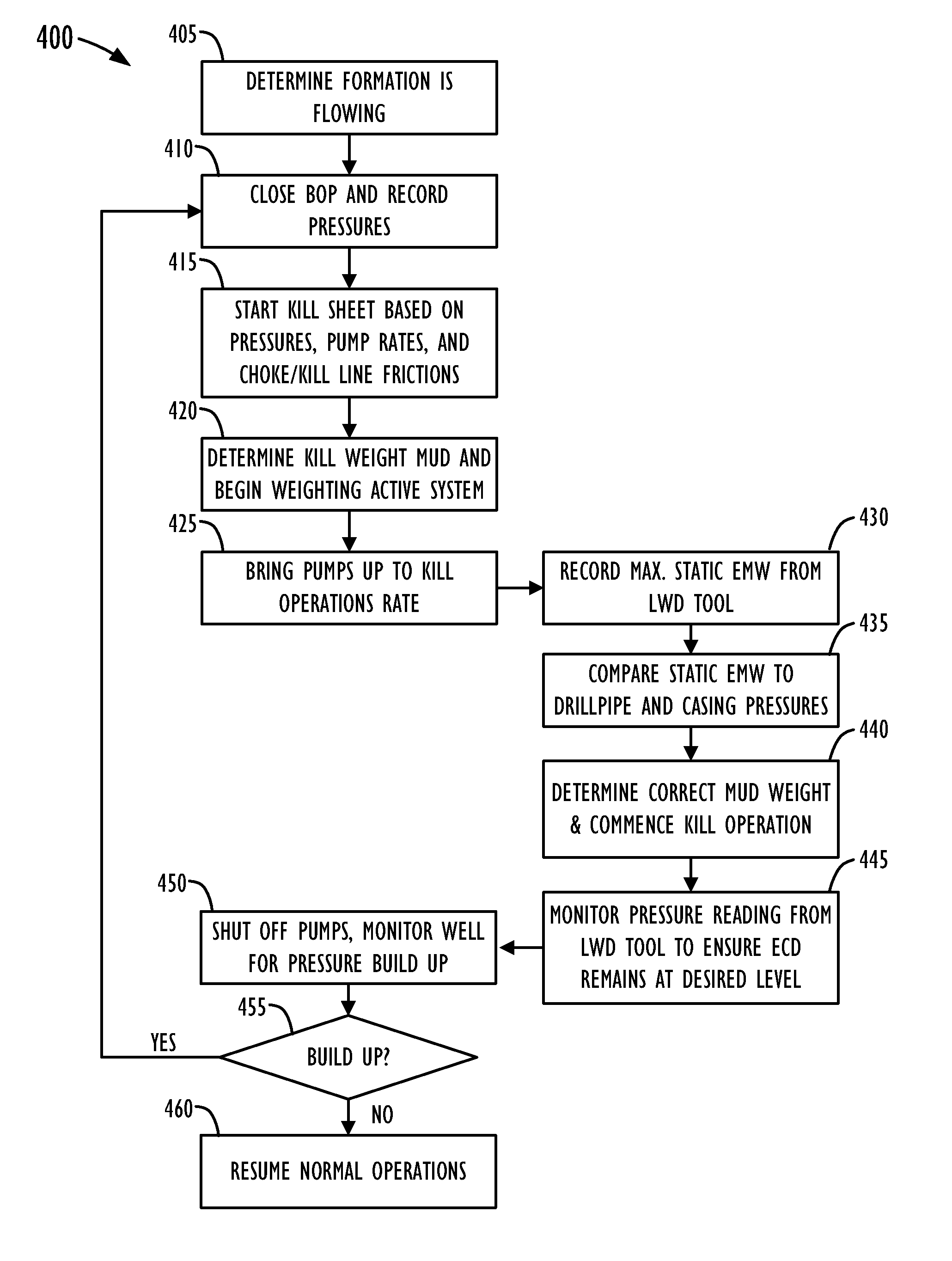
System and method for obtaining and using downhole data during well control operations
InactiveUS8781746B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyAccelerometer dataWell drilling
A tool driver activates a telemetry tool when a predetermined threshold of accelerometer data measured by an accelerometer. The threshold preferably corresponds to an acceleration level expected while drilling mud is pumped at a slow pump rate through the well's drill pipe. When a fluid influx occurs during drilling, the well is shut-in, and the tool driver turns off the telemetry tool. The drill pipe and casing pressures of the shut-in well are obtained. Then, drilling mud having a first weight is pumped at a slow mud pump rate. Because the tool driver is set to activate the telemetry tool in response to accelerometer data at the slow pump rate, the telemetry tool begins sending downhole pressure data to the surface. In this way, rig operations can change the mud weight and adjust the choke line during the kill operation based on an analysis of the downhole pressure data obtained.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Methods and materials to enhance high temperature rheology in invert emulsions
ActiveUS9346995B2Quantity minimizationLow pour pointFlushingDrilling compositionOrganic acidEmulsion
An invert emulsion drilling fluid, and a method of drilling with such fluid, having improved rheology at low mud weights and high temperatures. The improved rheology is effected with addition of a rheology additive of the invention comprising fatty dimer diamines or dimer diamines and an organic acid or ester of the acid. A nonlimiting example of such a rheology additive comprises a C36 fatty dimer diamine and adipic acid or dimethyl adipate.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
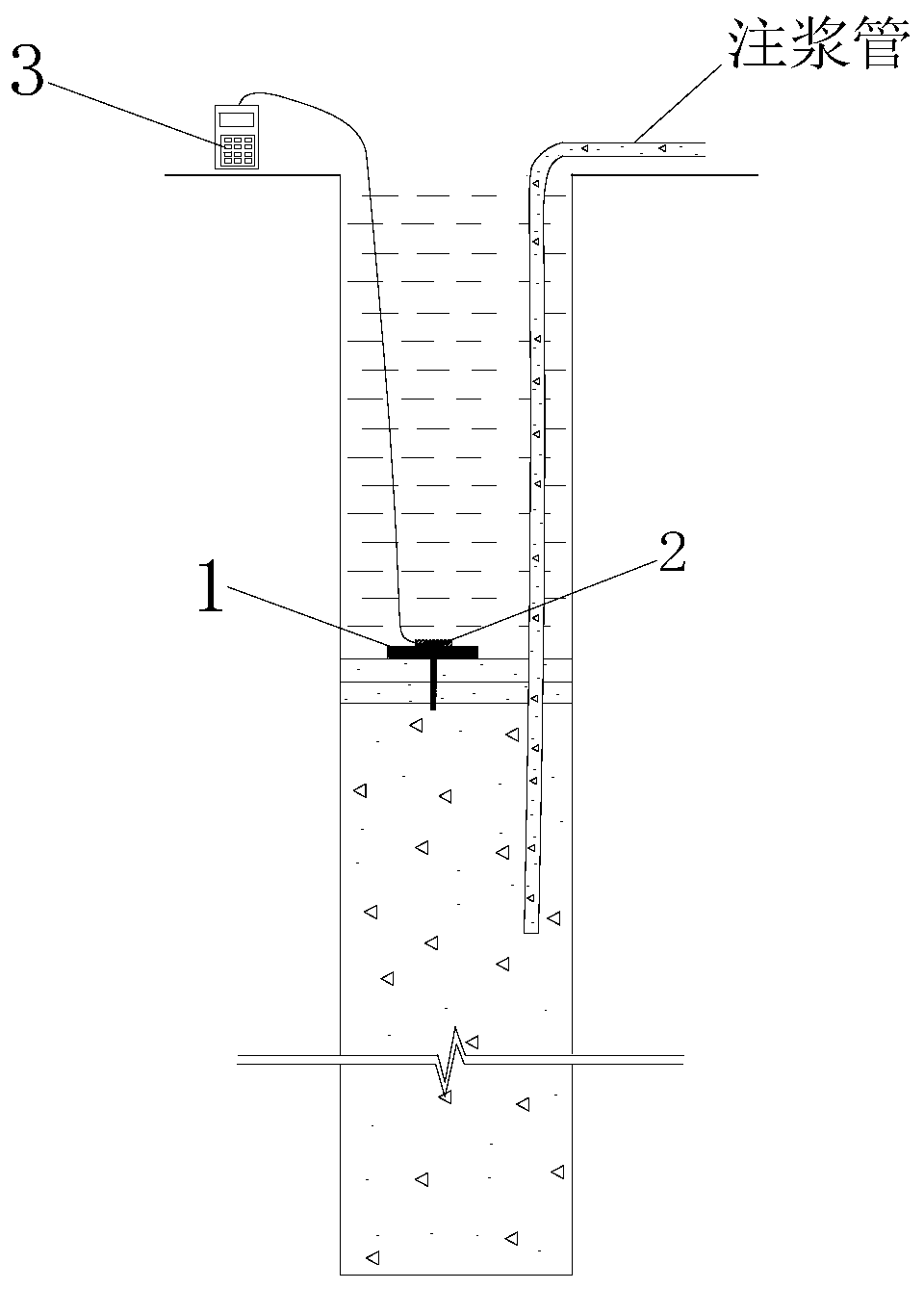
Device for detecting overfilling height of cast-in-situ bored pile in real time and detection method thereof
PendingCN109989433AQuality assuranceAvoid wastingFoundation testingEngineeringCalibration coefficient
The invention discloses a device for detecting the overfilling height of a cast-in-situ bored pile in real time and a detection method thereof. The device comprises a floating tray, a pressure box anda frequency acquisition instrument, the pressure box is mounted on the upper surface of the floating tray, the lower surface of the floating tray is connected with a threaded rod, and the threaded rod is provided with a counterweight. Concrete is poured into a drilled hole for the first time, the floating tray is placed down in the drilled hole and repeatedly lifted up and down to ensure that thefloating tray is in contact with a hybrid layer, after the floating tray is stable, the frequency of the pressure box is acquired, the pressure P of floating mud on the pressure box at different depths in the pouring process is calculated according to the measured frequency and a corresponding pressure box calibration coefficient, then the mud weight gamma is measured, and the distance between the pressure box and the orifice elevation is obtained according to P=gamma h so as to obtain the length of the bored pile.
Owner:TIANJIN PORT ENG INST LTD OF CCCC FIRST HARBOR ENG +2
Large-diameter drilled pile construction method
The invention discloses a large-diameter drilled pile construction method. The large-diameter drilled pile construction method comprises the following steps: (1) a drilling platform is built; (2) a steel protection cylinder is constructed; the top surface of the steel protection cylinder is higher than the top surface of the drilling platform by 50 cm; (3) a down-hole drill is used for construction; 28-30 small holes are drilled in the pile foundation plane range; gaps between the small holes are controlled within 35-40 cm; and the drilling depth is above the pile bottom elevation by 30 cm; (4) finished holes are constructed; (5) the holes are cleaned through reverse circulation, so that the residue thicknesses at the bottoms of the finished holes are lower than 5 cm, the mud weights in the holes are 1.03-1.1, and the sand contents are not higher than 2%; (6) a reinforcement cage is placed; and (7) concrete is poured. The large-diameter drilled pile construction method can overcome theconstruction difficulties of high-strength rock layers, improves the quality of drilled piles, and guarantees the stability of a bridge main tower.
Owner:SHANGHAI CIVIL ENG GRP FIFTH
Variable density drilling mud
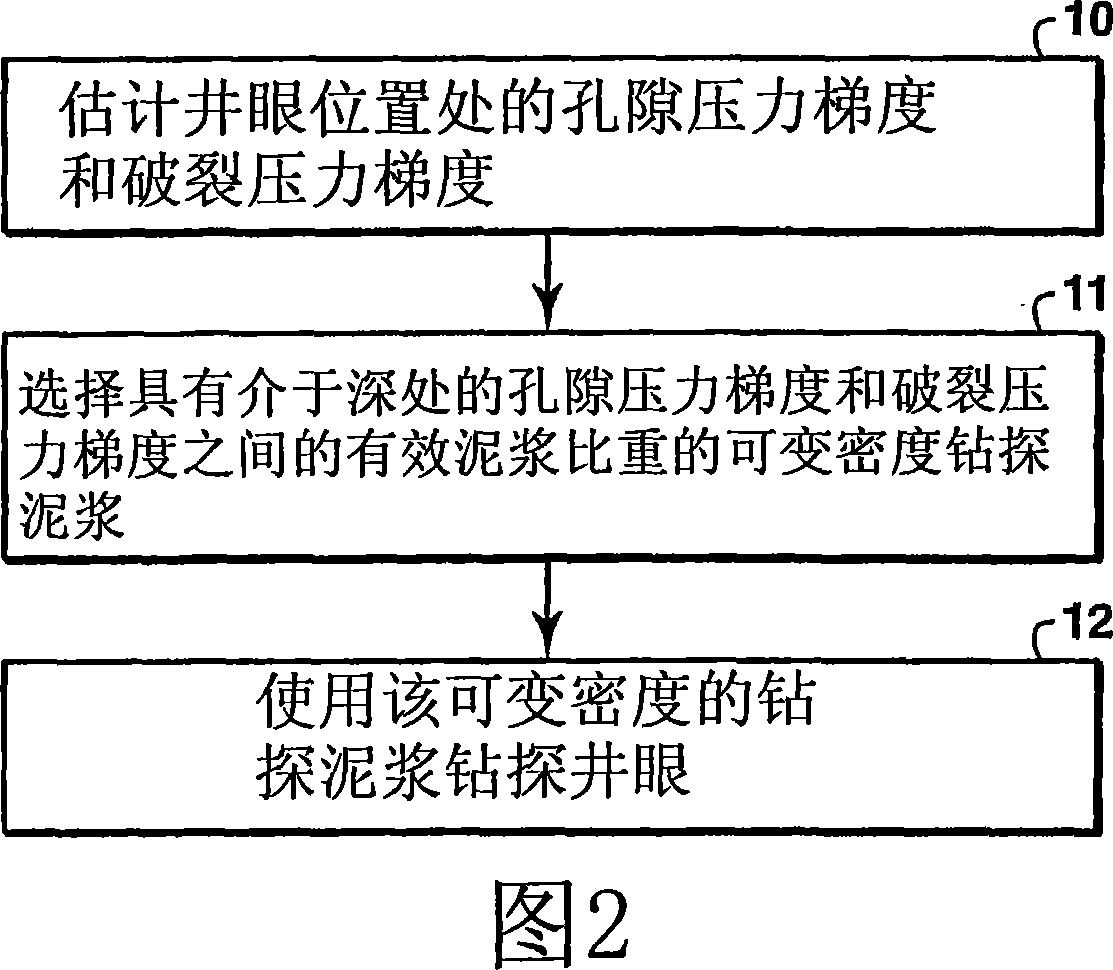
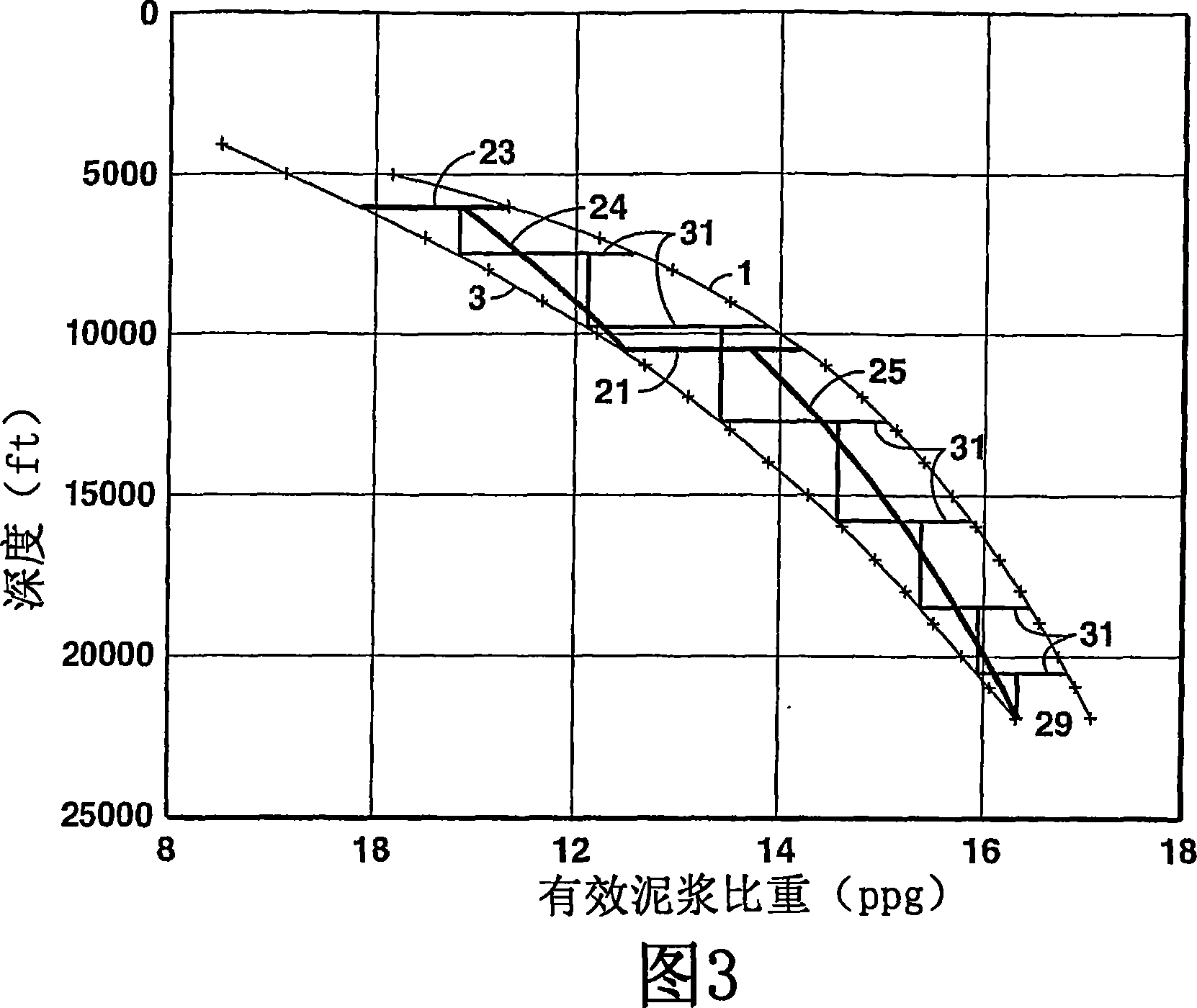
One embodiment of the invention is a variable density drilling mud comprising compressible particulate material in the drilling mud wherein the density of the drilling mud changes in response to pressure changes at depth. A second embodiment is a method for varying drilling mud density. The method comprises estimating the pore pressure and fracture gradient, and choosing a drilling mud with compressible materials wherein the effective mud weight of the drilling mud remains between the pore pressure and the fracture gradient in at least one interval of the well bore. A third embodiment is an apparatus for drilling a wellbore.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Drilling fluid parameter measuring device and control method thereof
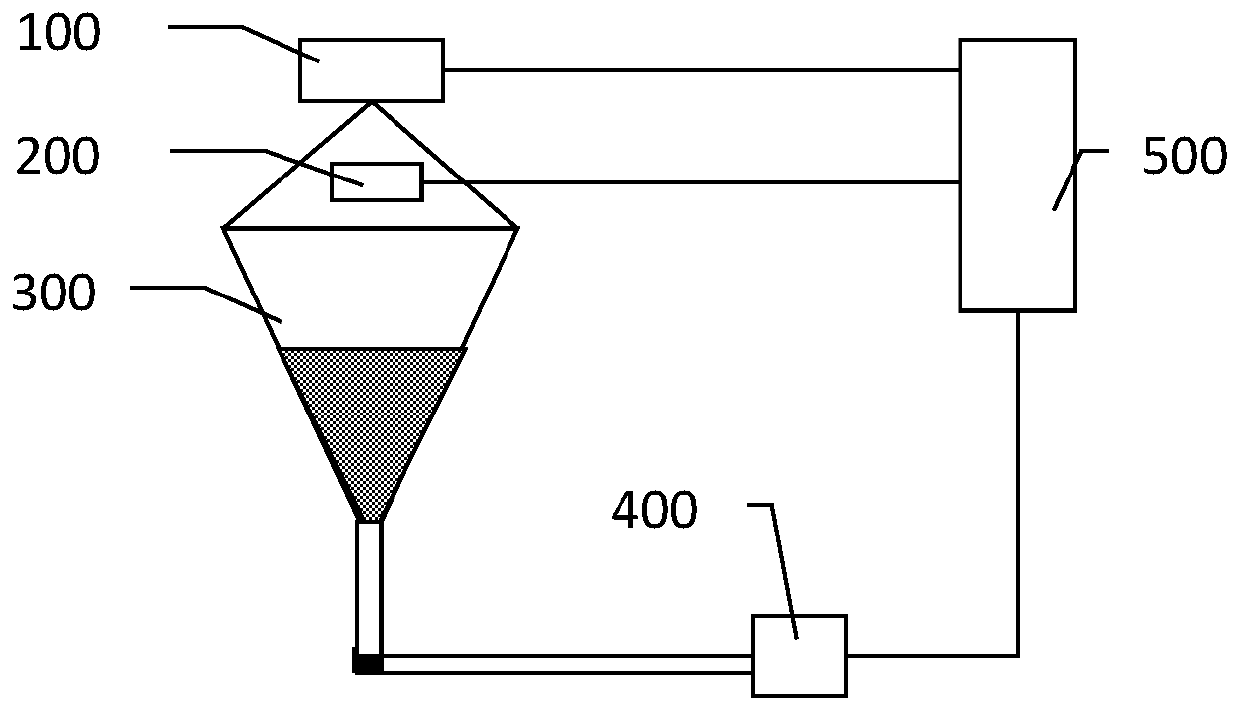
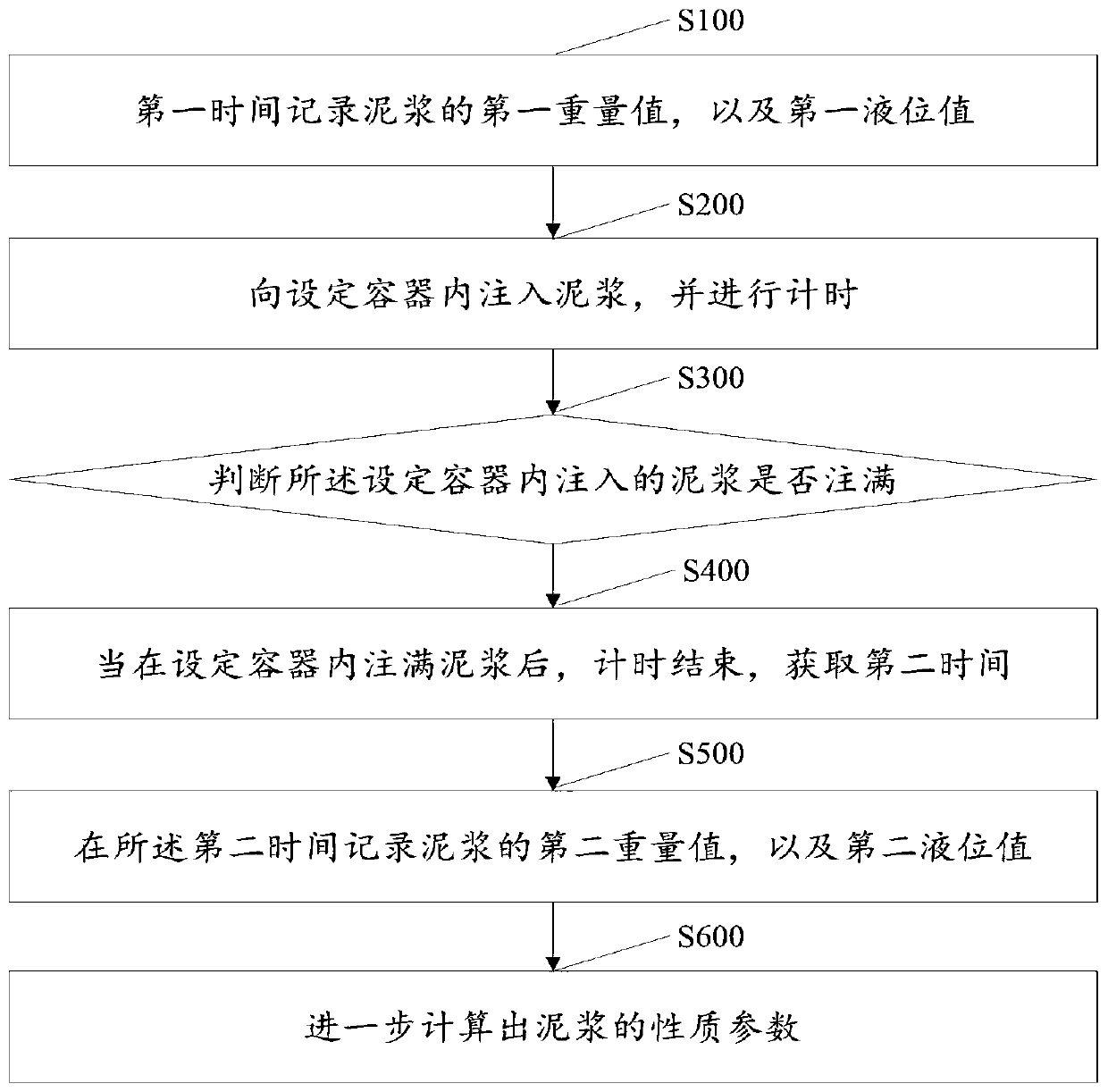
InactiveCN110658105ARealize measurementRealize automatic timingDirect flow property measurementSpecific gravity measurementMeasurement deviceSlurry
The invention discloses a drilling fluid parameter measuring device and a control method thereof. The measuring device is characterized in that a Marsh funnel is suspended on a gravity sensor througha support member, and the gravity sensor measures the Marsh funnel and the weight parameter of slurry injected into the Marsh funnel and sends the weight parameter to a circuit control board; the ultrasonic sensor is arranged in the circumference of the Marsh funnel, measures slurry liquid level parameters in different periods in the Marsh funnel, and sends the measured liquid level parameters tothe circuit control board; the circuit control board controls the electromagnetic switch according to the received weight parameter and liquid level parameter of the slurry, and the electromagnetic switch controls circulation of the slurry in the Marsh funnel according to a command of the circuit control board; and the property parameters of the slurry are further calculated. Automatic timing is realized through the circuit control board, and the slurry parameters are automatically received, so that the error of manual measurement is avoided, and the working efficiency is further improved.
Owner:延安思凡石油设备有限公司 +1
Mud saver valve
A three-part sub-assembly comprising a wire line retrievable spear. The spear having two fluid chambers. A diverter valve having a truncated, inverted cone valve seat is preferably threaded into the interior of the spear. A diverter valve stem, having back-to-back cones is located within the interior of the spear / diverter valve combination, with one of the cones having a linear extension which prevents the first cone from completely seating against the valve seat within the interior of the spear. The spear / diverter valve assembly and a spring-loaded piston is placed within the interior of the cylinder and utilizes an adjustable ring within the interior of the cylinder as an adjustment for varying mud weights.
Owner:MUDSAVER
Mud weighting technology and special device thereof
ActiveCN103537213AClosed and evenly mixedImprove efficiencyFlow mixersTransportation and packagingWell drillingInlet valve
The invention relates to a mud weighting technology and a special device thereof, belonging to the technical field of a petroleum exploration and development drilling mud weighting technology. The special device consists of a mud pit, a sand pump, an air compressor, a limestone powder tank and a limestone powder mixing pump, wherein the limestone powder mixing pump has a tubular body combination structure, and one end of the limestone powder mixing pump is provided with two inlets in a square crossing way; the vertical inlet is connected with the mud pit by a heavy mud valve, a mud supply pipeline and a sand pump, and the horizontal inlet is connected with the limestone powder tank by a powder inlet valve and a limestone powder pipeline; the other end of the limestone powder mixing pump is connected with the mud pit by a mixing pipeline; the limestone powder tank is connected with the air compressor by an air inlet pipeline and an air source valve. The mud weighting technology comprises the steps of (1) basic mud circulation, namely enabling basic mud in the mud pit to carry out self-circulation by the sand pump, the limestone powder mixing pump and the mud pipeline; (2) mud weighting, namely gasifying limestone powder in the limestone powder tank by the air compressor, enabling the gasified limestone powder to flow into the limestone powder mixing pump, mixing the gasified limestone powder and the basic mud for weighting, and then enabling heavy mud to flow into the mud pit.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com