Patents
Literature
2407 results about "Choke valve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In an internal combustion engine, a choke valve modifies the air pressure in the intake manifold, thereby altering the ratio of fuel and air quantity entering the engine. Choke valves are generally used in naturally aspirated engines with carburetors to supply a richer fuel mixture when starting the engine. Most choke valves in engines are butterfly valves mounted in the manifold upstream from the carburetor jet to produce a higher partial vacuum, which increases the fuel draw.
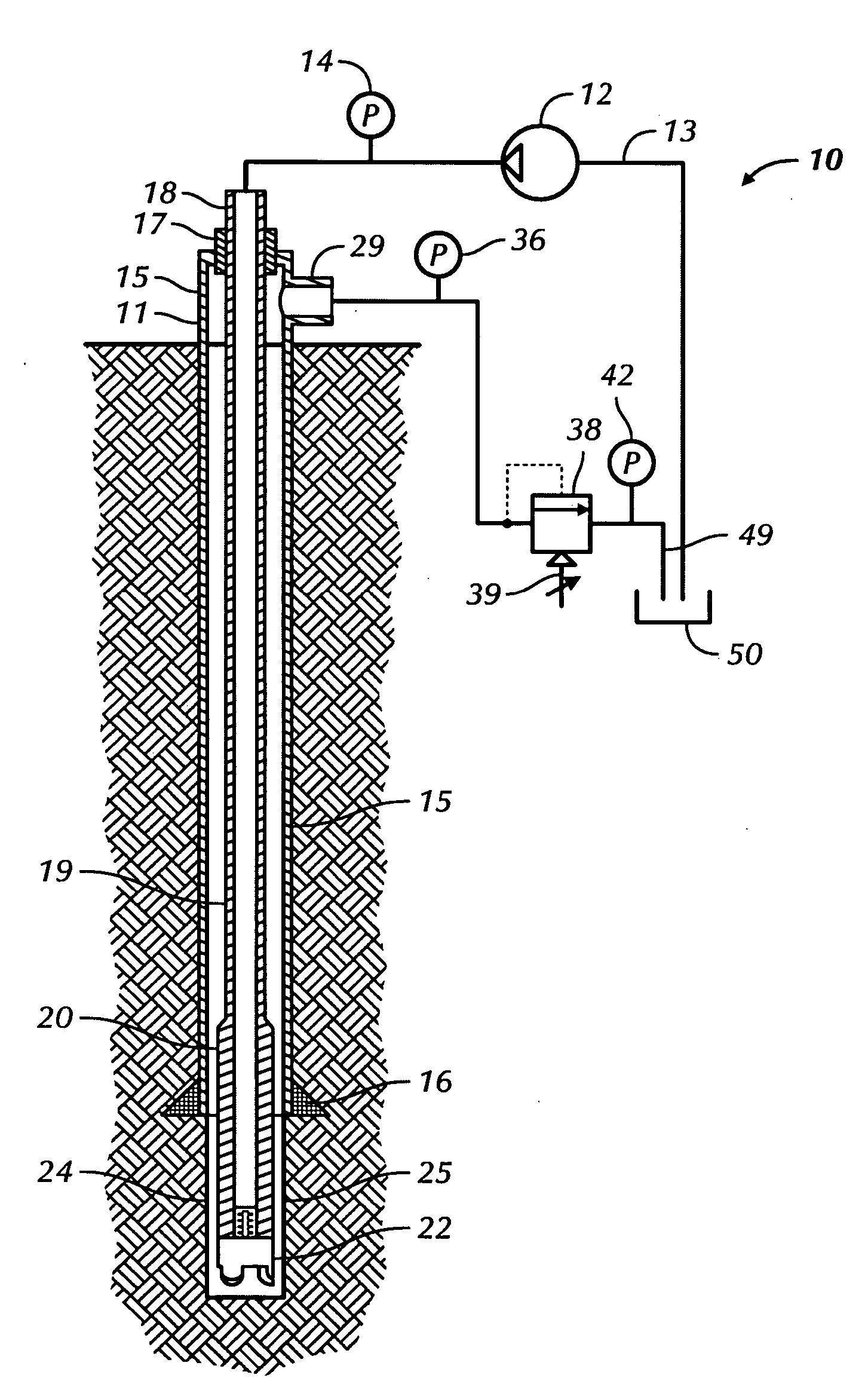
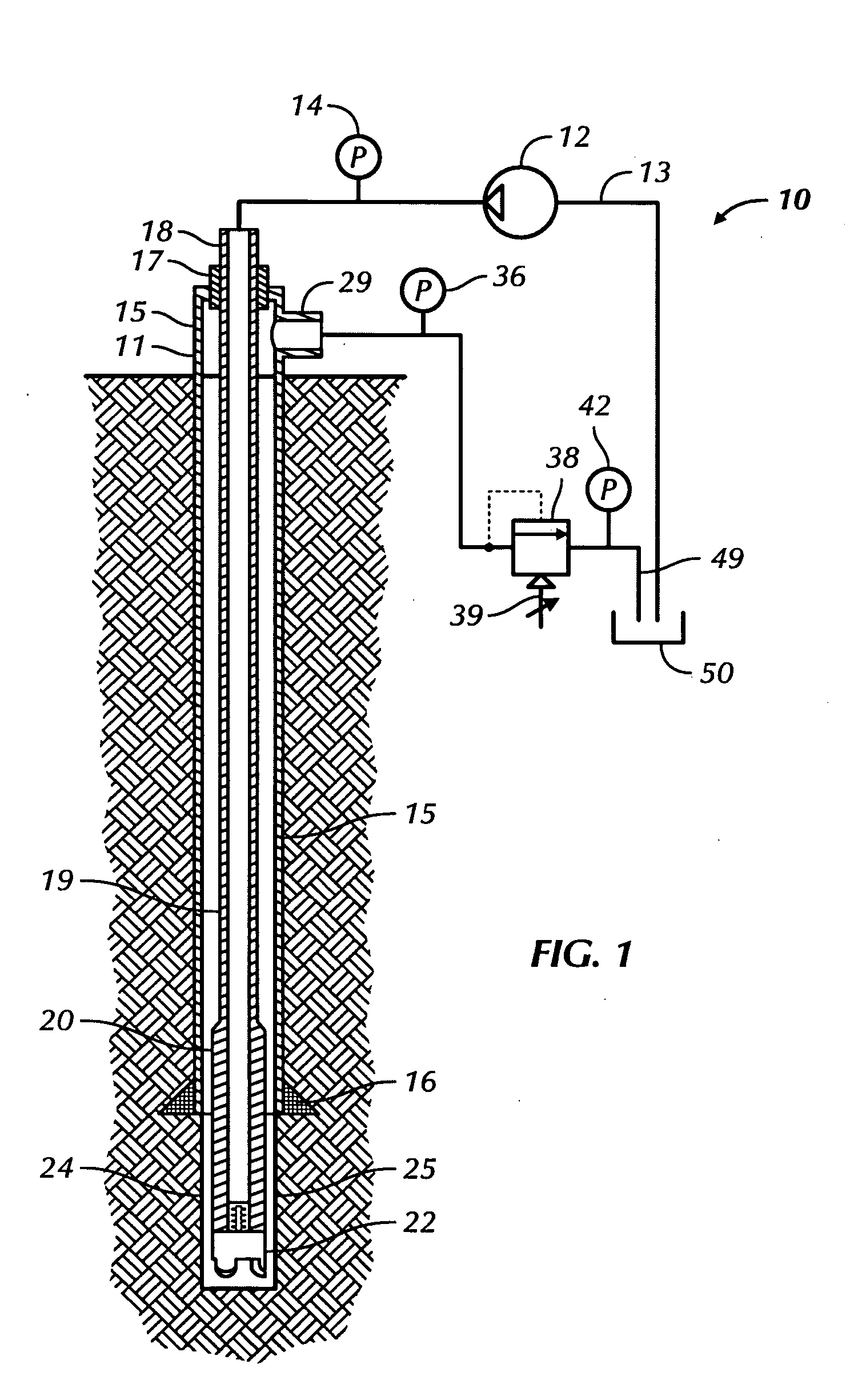
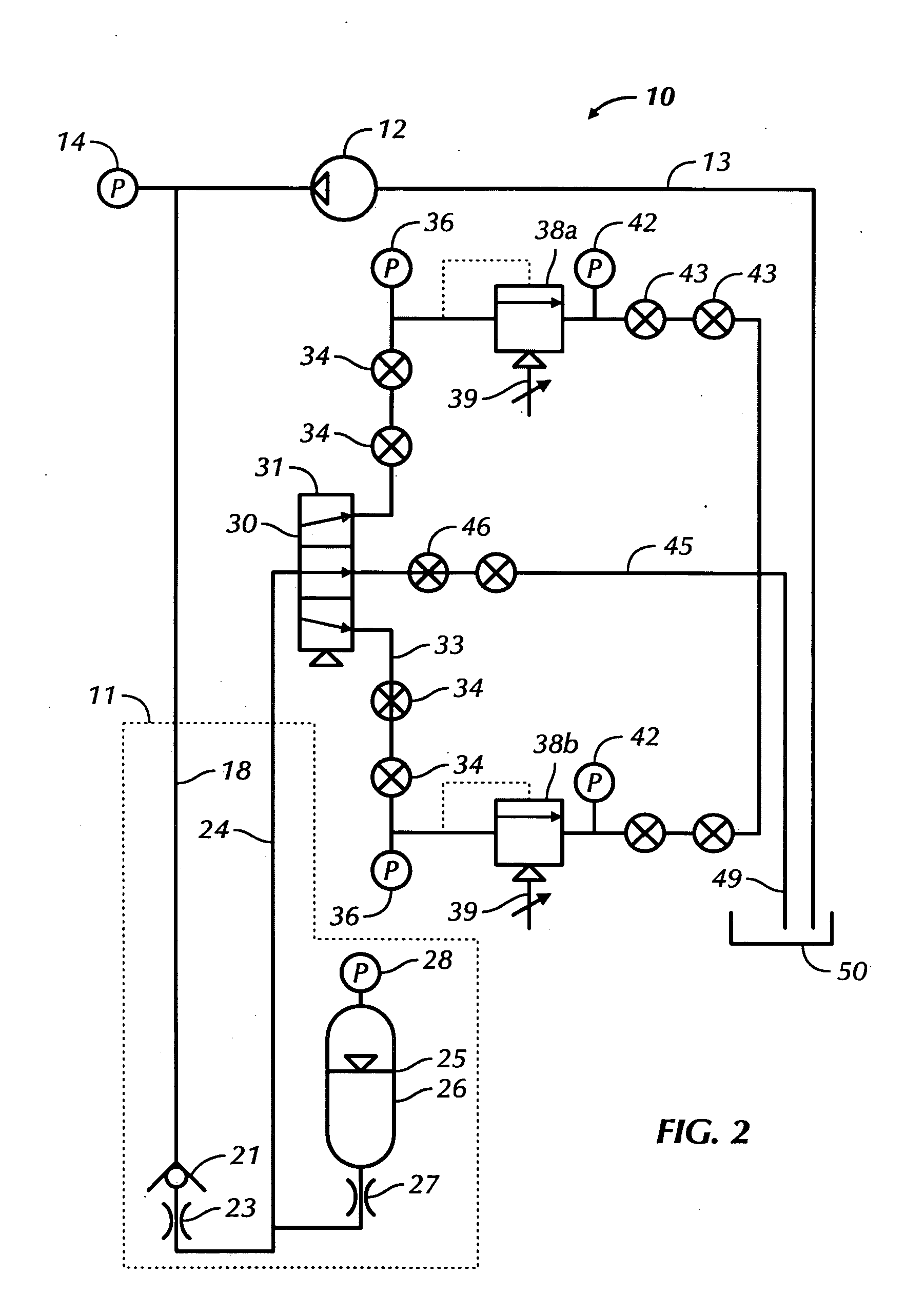
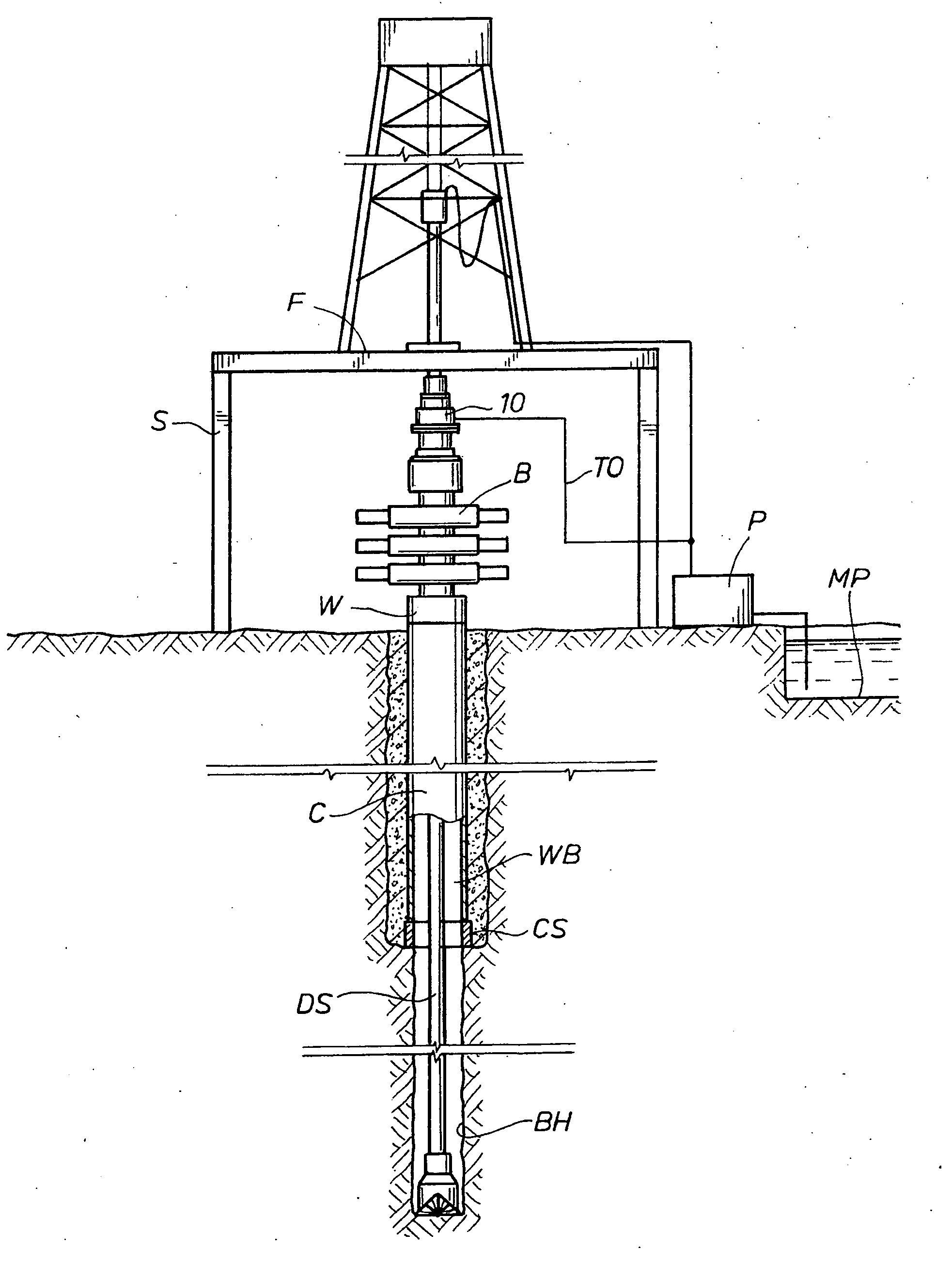
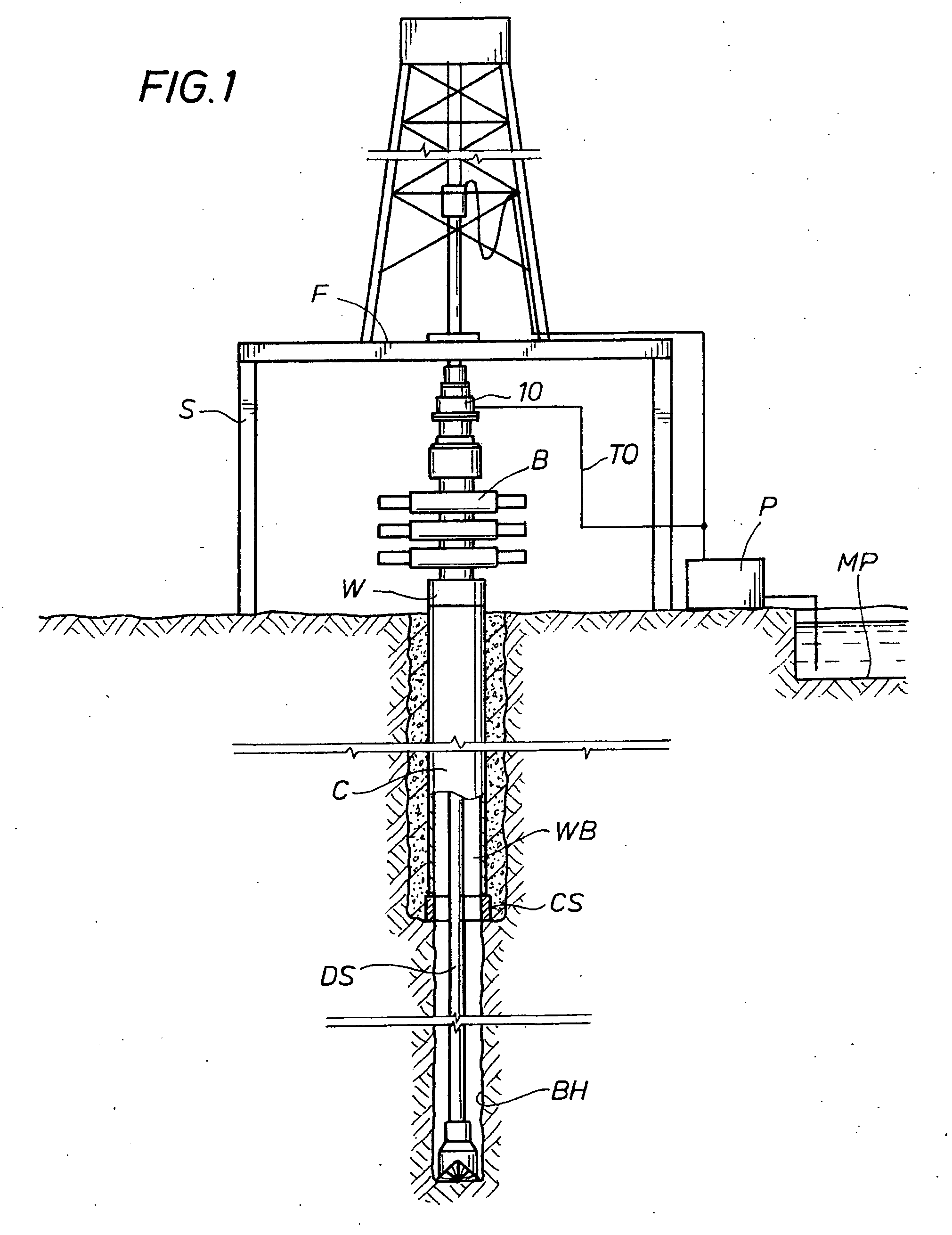
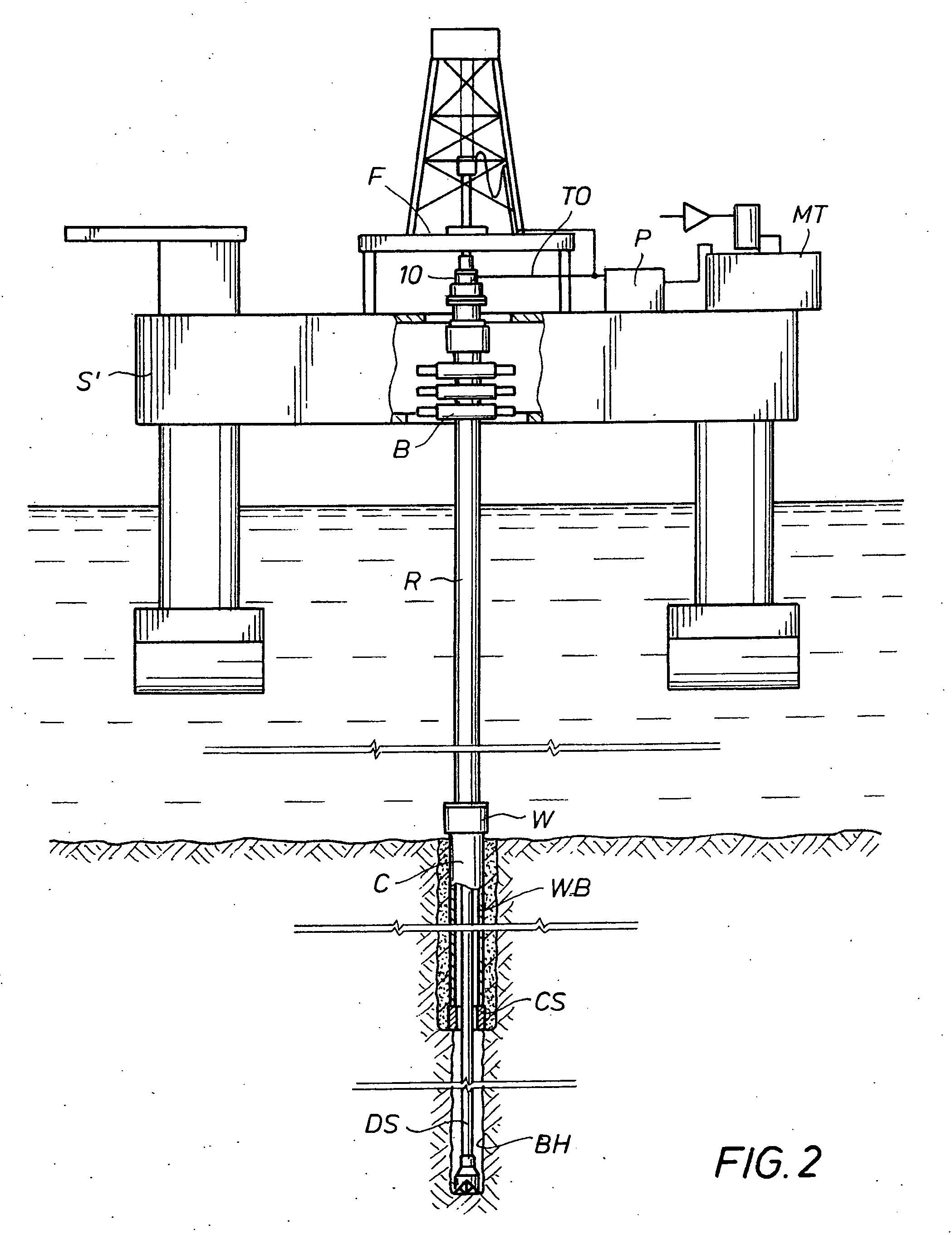
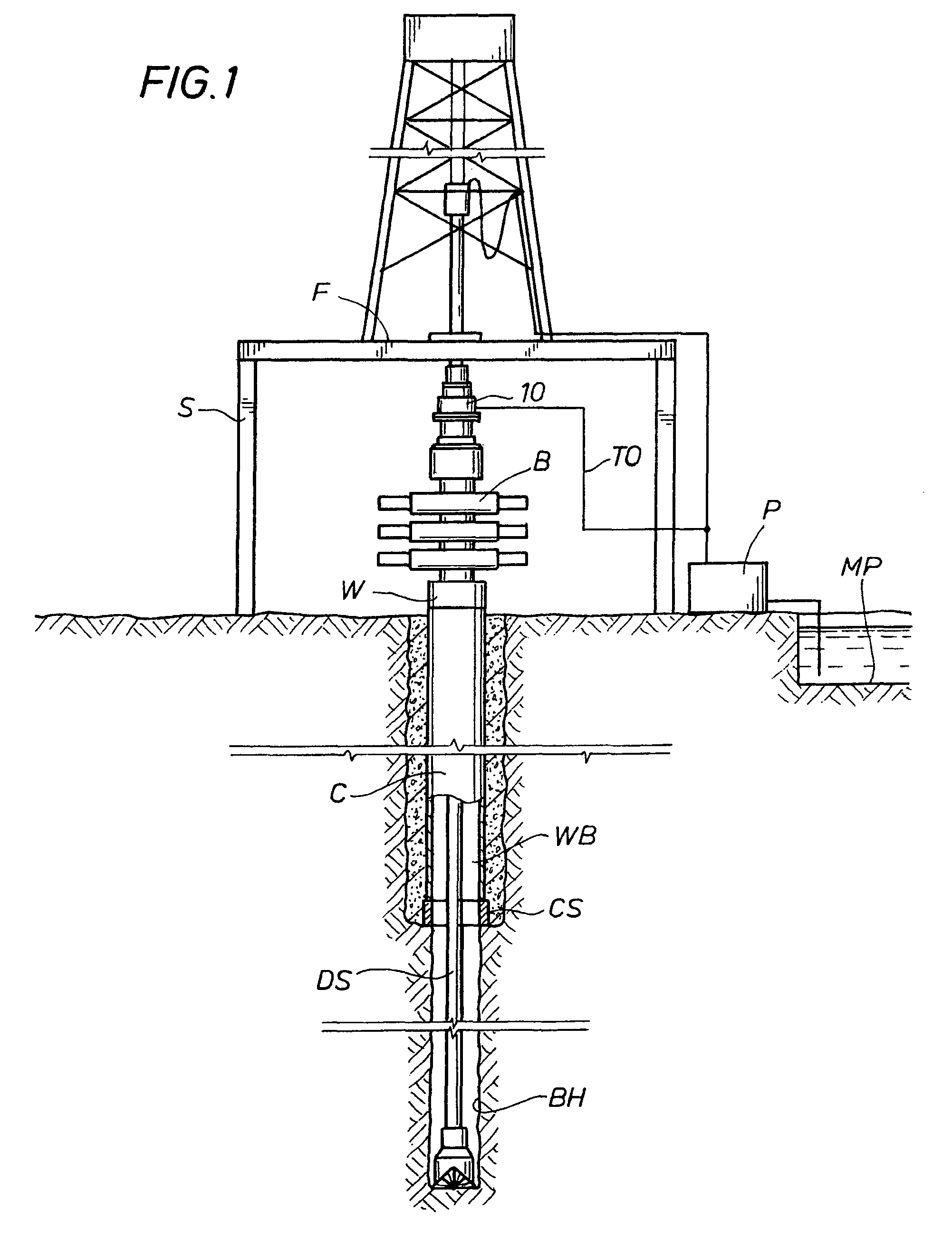
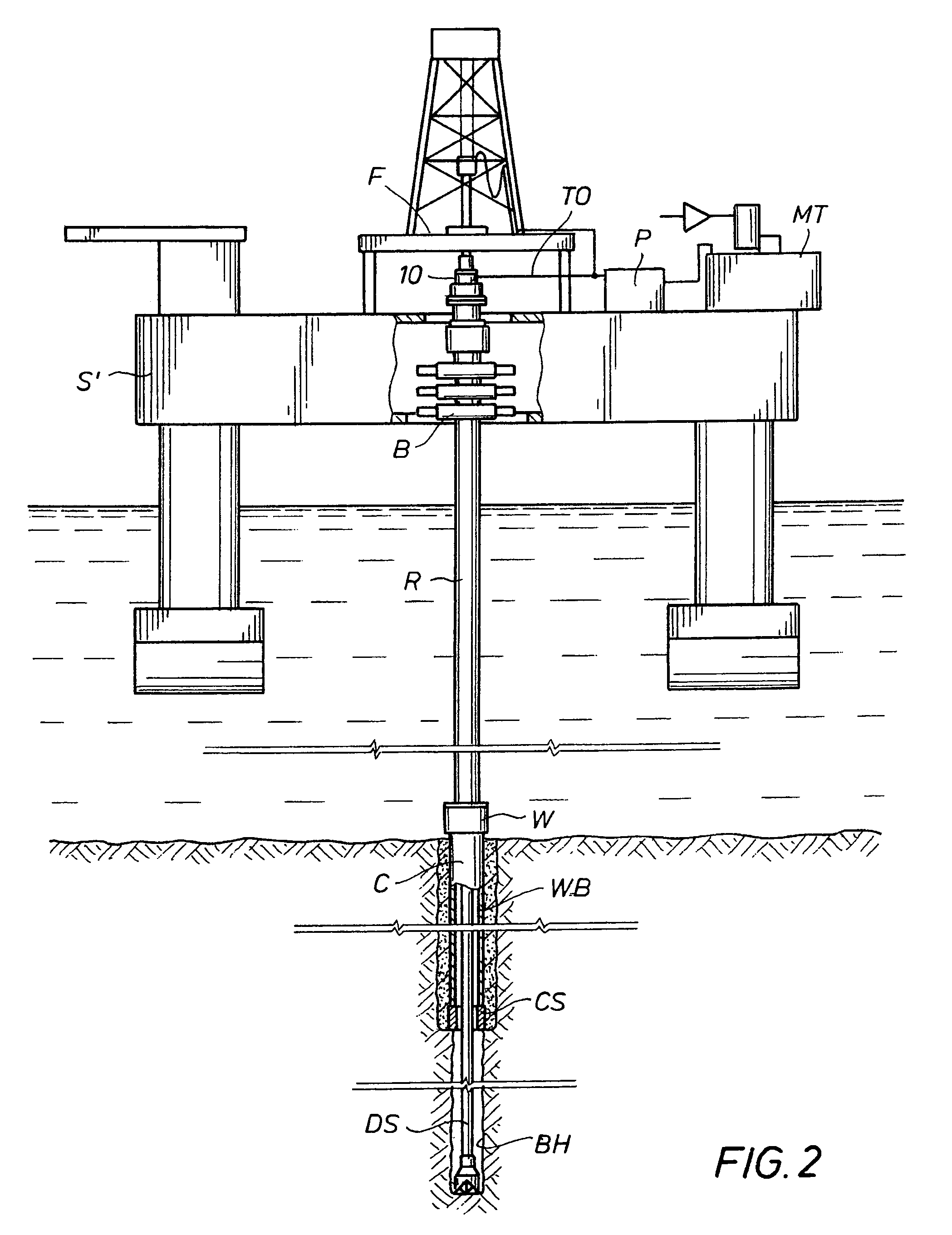
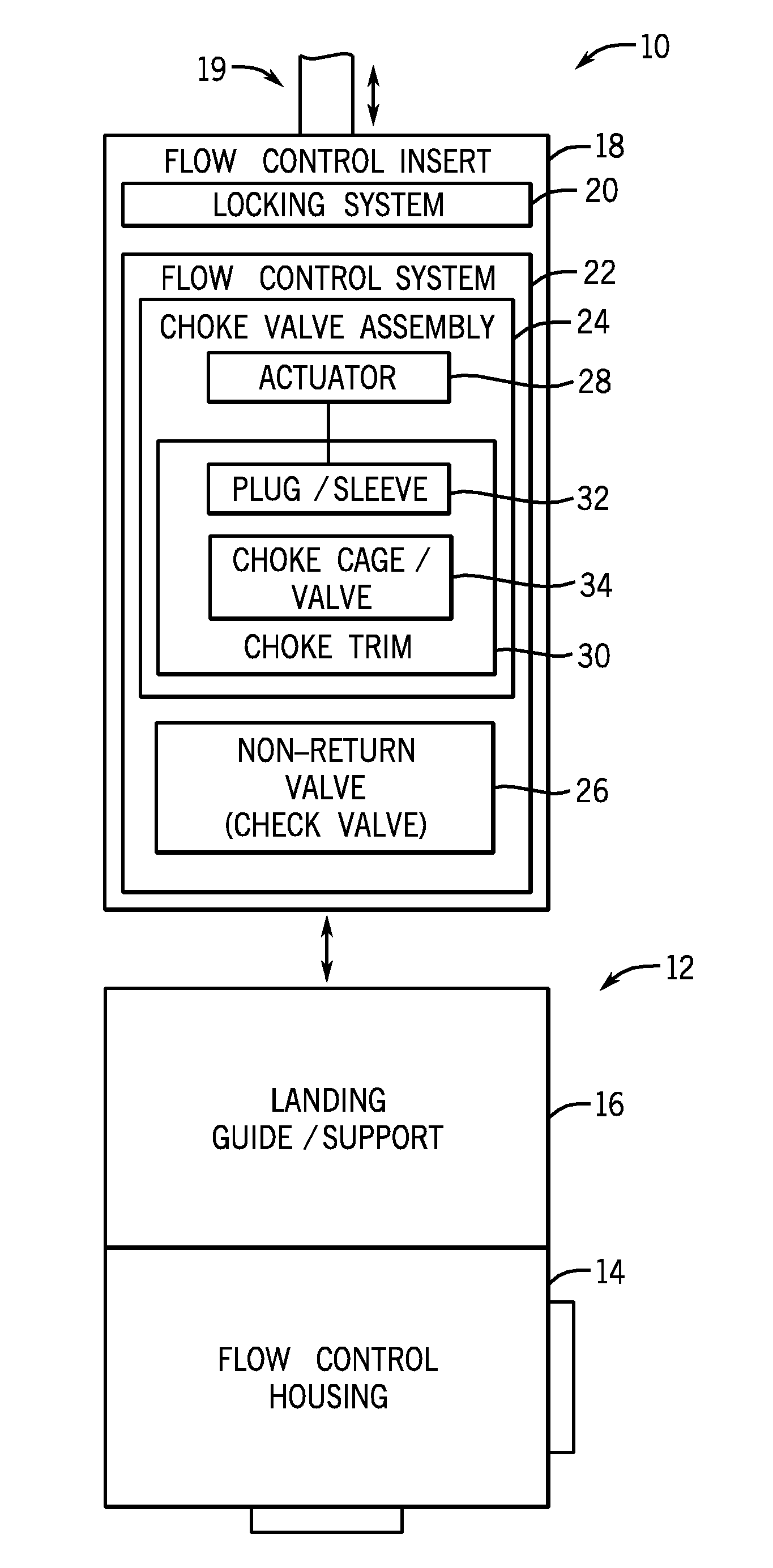
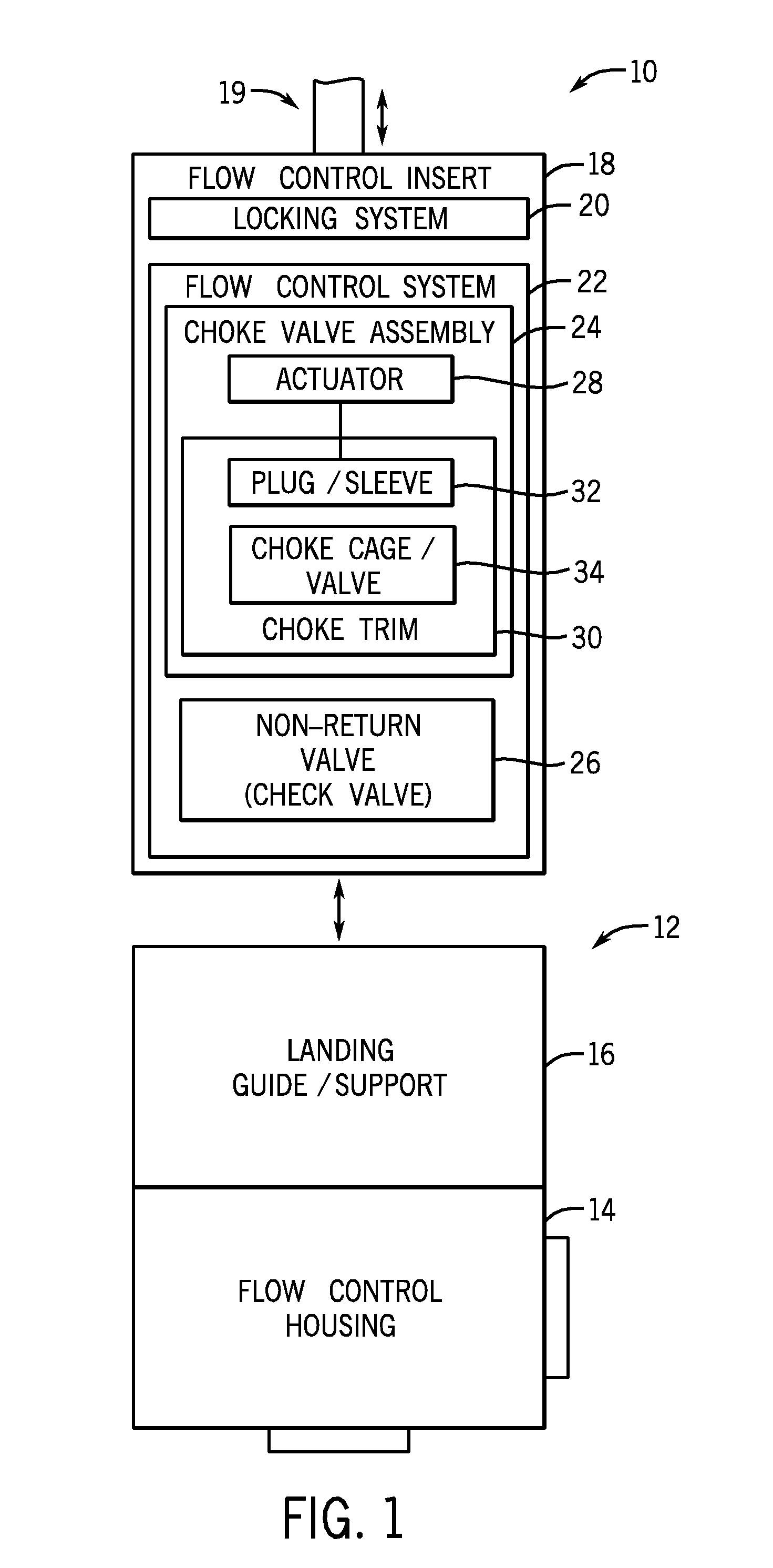
Well pressure control system
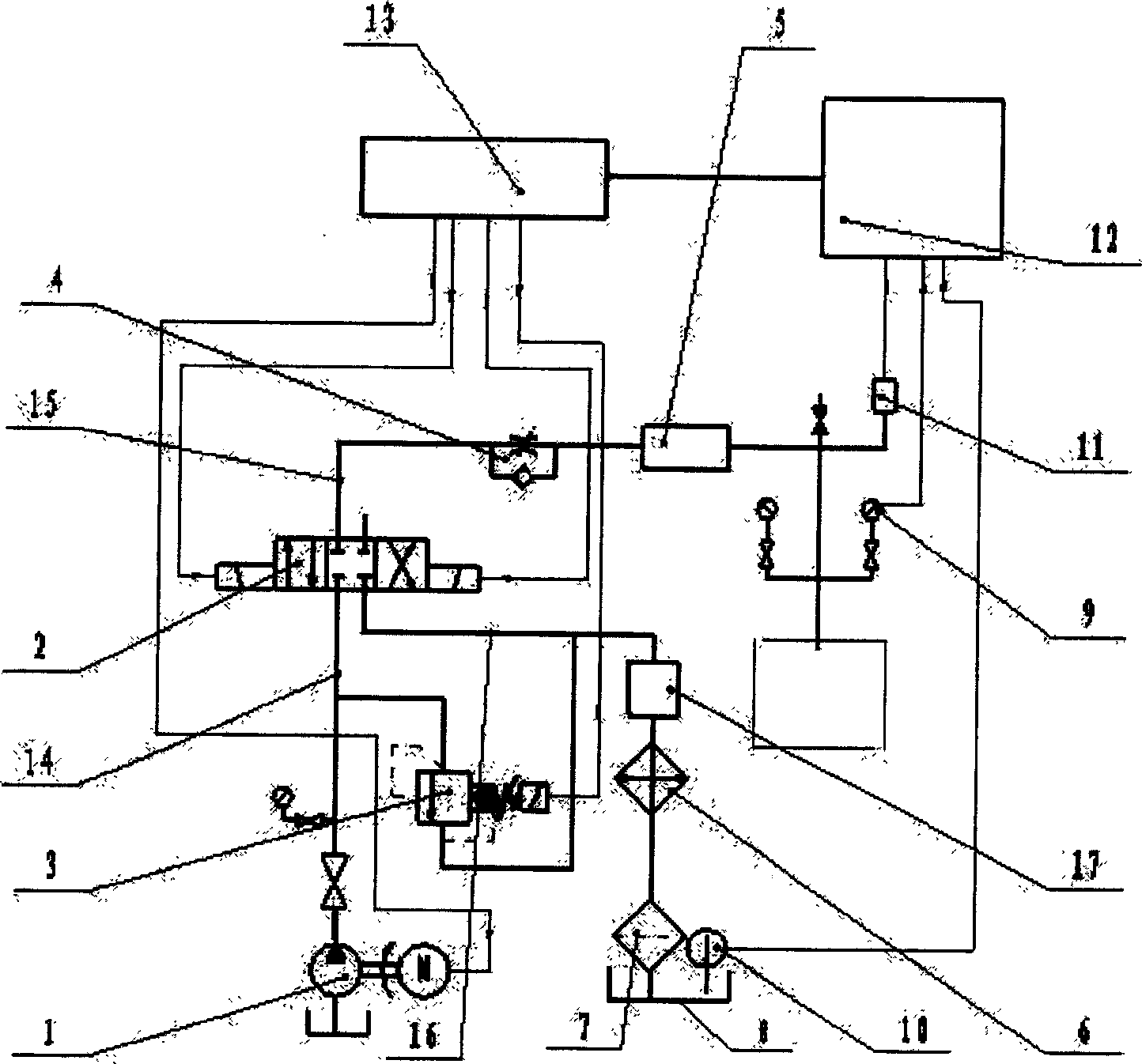
The present invention contemplates a choke control system that provides for local and off-site monitoring and control of the annulus flow pressure of a well. The choke control system includes a choke manifold connected to at least one choke and its associated actuator; a variety of instrumental drilling sensors, pump stroke counter switches, and choke position indicators; a local choke and hydraulic pressure control console; and a programmable controller in communication with the local choke and hydraulic pressure control console. The programmable controller handles the logical operations of the choke control system, including processing instrument measurements and operator input data to produce control signals for operating the choke, the choke actuator and the various valves associated with the choke manifold. The programmable controller is typically either an electronic digital computer and / or a programmable logic controller (PLC). The present invention further contemplates the two-way communication between the choke control system and the Internet via a satellite linkage.
Owner:EXPRO AMERICAS
Drilling with a high pressure rotating control device
ActiveUS20110024195A1Operational securityHigh safety factorSurveyDrilling rodsWell drillingControl system
A Drill-To-The-Limit (DTTL) drilling method variant to Managed Pressure Drilling (MPD) applies constant surface backpressure, whether the mud is circulating (choke valve open) or not (choke valve closed). Because of the constant application of surface backpressure, the DTTL method can use lighter mud weight that still has the cutting carrying ability to keep the borehole clean. The DTTL method identifies the weakest component of the pressure containment system, such as the fracture pressure of the formation or the casing shoe leak off test (LOT). With a higher pressure rated RCD, such as 5,000 psi (34,474 kPa) dynamic or working pressure and 10,000 psi (68,948 kPa) static pressure, the limitation will generally be the fracture pressure of the formation or the LOT. In the DTTL method, since surface backpressure is constantly applied, the pore pressure limitation of the conventional drilling window can be disregarded in developing the fluid and drilling programs. Using the DTTL method a deeper wellbore can be drilled with larger resulting end tubulars, such as casings and production liners, than had been capable with conventional MPD applications.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Hydrogen gas generation system
InactiveUS7105033B2ReducingAvoid heat exchangePhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsChemistryAqueous solution
A system for generating hydrogen gas utilizes a volume exchange housing for the storage of a fuel material that reacts to generate hydrogen gas and a hydrogen separation chamber. The system includes a gas permeable membrane or membranes that allow hydrogen gas to pass through the membrane while preventing aqueous solutions from passing therethrough. The system is orientation independent. A throttle valve is also used to self regulate the reaction generating the hydrogen gas.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
Drilling and producing deep water subsea wells
InactiveUS6968902B2Efficient separationMinimize flow disturbanceWaste water treatment from quariesLiquid separation auxillary apparatusOcean bottomWell drilling
Subsea wells are drilled and completed with an offshore floating platform in a manner that allows simultaneous work on more than one well. A first well is drilled and cased. Then a tubing hanger is run through a drilling riser and landed in the wellhead housing. Then, with the same floating platform, the drilling riser is disconnected and moved to a second well. While performing operations on the second well, the operator lowers a production tree from the floating platform on a lift line, and connects it to the first wellhead housing. An ROV assisted subsea plug removal tool is used for plug removal and setting operations. Seabed separation is configured upstream of a production choke valve.
Owner:VETCO GRAY
Carburetor throttle and choke control mechanism
InactiveUS6202989B1Low costEasy to modifyElectrical controlLighting and heating apparatusIdle speedCarburetor
A control mechanism for a carburetor having a throttle valve and a choke valve each having at least a cold-starting position and a full-speed position. The throttle valve is spring biased toward its third, low idle position, and the choke valve is mounted on a choke shaft and is spring biased toward its full-speed open position. When the choke valve is moved by a choke shaft lever from its open position toward its cold start closed position a fast idle lever associated with the choke valve shaft engages, via releasable latch parts, a throttle lever associated with the throttle valve. The interengaging latch parts of these fast idle and throttle levers hold both valves in their respective cold-starting positions in opposition to their respective biasing springs. These latch levers can be released by operator actuation of the throttle valve control, thereby causing the choke valve to be automatically returned to its open position by its biasing spring, or, alternatively, the choke valve can be moved independently to its full-speed position. One of these fast idle and throttle latch levers has a notch, and the other has a pawl selectively engaging the notch when it becomes aligned therewith when the latch levers are operator-actuated to their respective cold start positions. The choke shaft is torsionally resilient so that when the choke shaft lever is forced to override initial-choke-closed position, it thereby twists the choke shaft after the choke valve has been bore-stopped at closed position. Upon release of operator actuating force, this feature prevents most, if not all of the previous retrograde movement of the choke and throttle valves out of their design cold start positions, despite operating slack in the latch system due to manufacturing tolerance stack-up in the various parts of the latch system parts and / or control mechanism in their assembly and operation.
Owner:WALBRO ENGINE MANAGEMENT
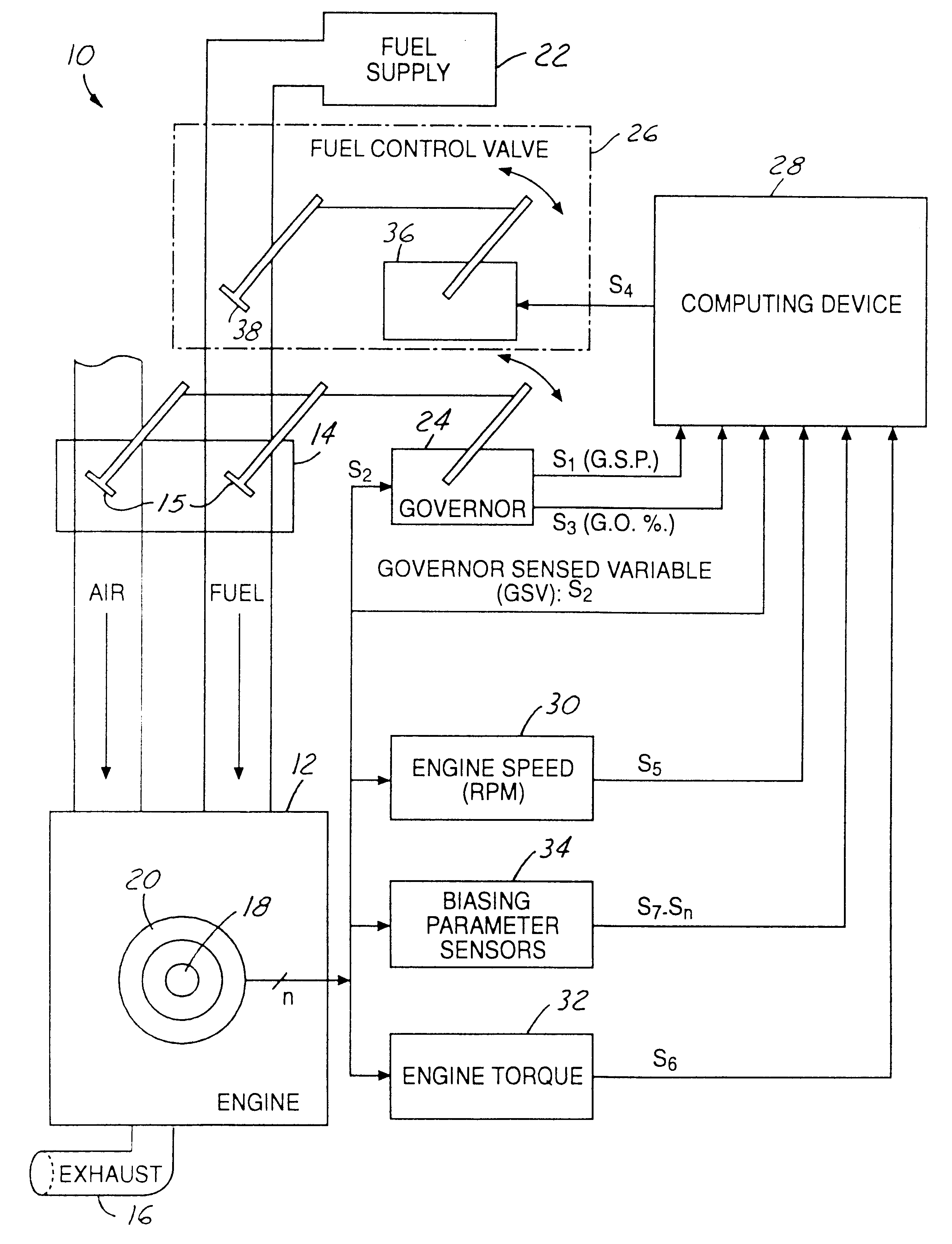
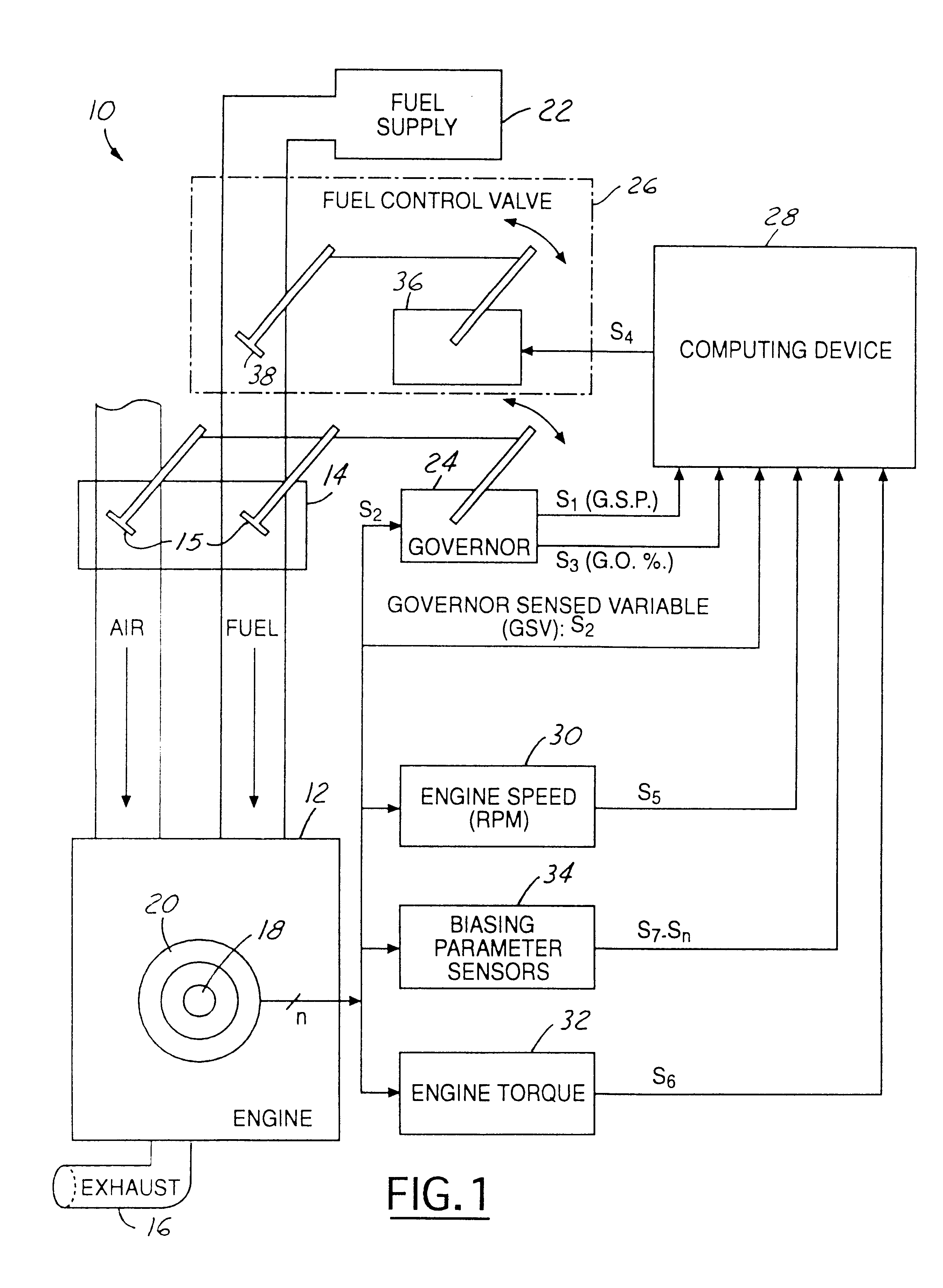
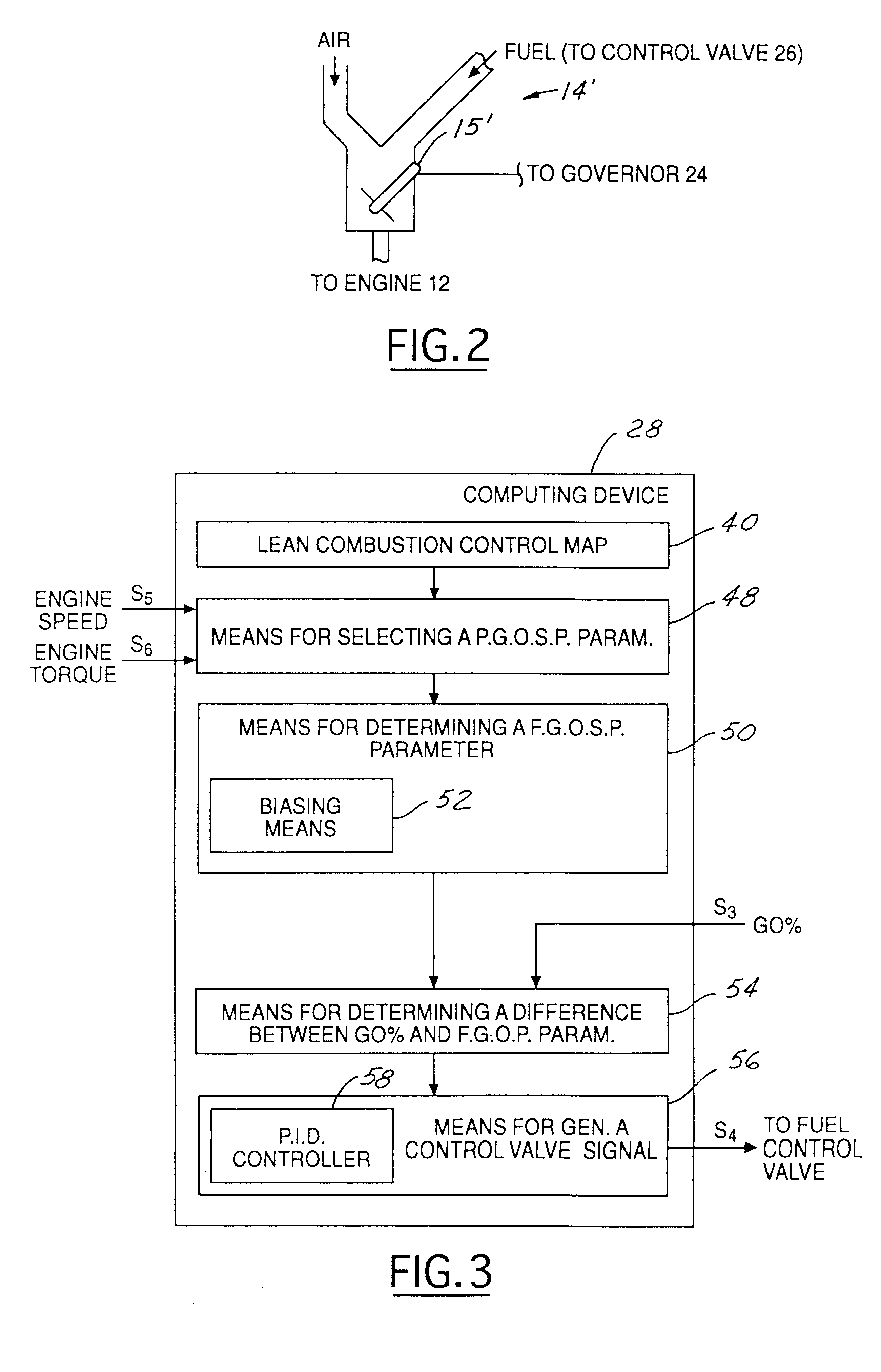
Method and system for controlling an air-to-fuel ratio in a non-stoichiometric power governed gaseous-fueled stationary internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6189523B1Reduces "pumping losses.Less importantAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlControl signalExhaust fumes
A gaseous-fueled reciprocating internal combustion engine includes a carburetor having a throttle valve that is controlled by a speed governor. A proportional fuel control valve is disposed intermediate a fuel supply and the carburetor, and is controlled by an air fuel computing device. The computing device generates a control signal to adjust the fuel control valve based on a governor sensed variable indicative of engine speed, sensed engine torque, a governor output signal from the governor indicative of an opening position of the throttle valve wherein 100% corresponds to a wide open throttle position, and 0% corresponds to a closed position, and a lean combustion control map containing predetermined set point values stored in memory. During operation, the control valve is responsive to the control signal generated by the computing device for adjustment of a fuel flow therethrough so as to obtain a ratio of air to fuel provided to the engine that is substantially at a lean misfire limit of the engine, thereby reducing fuel consumption, NOx emissions, and reducing exhaust gas temperatures. Alternatively, the control signal is generated using engine speed alone.
Owner:ANR PIPELINE
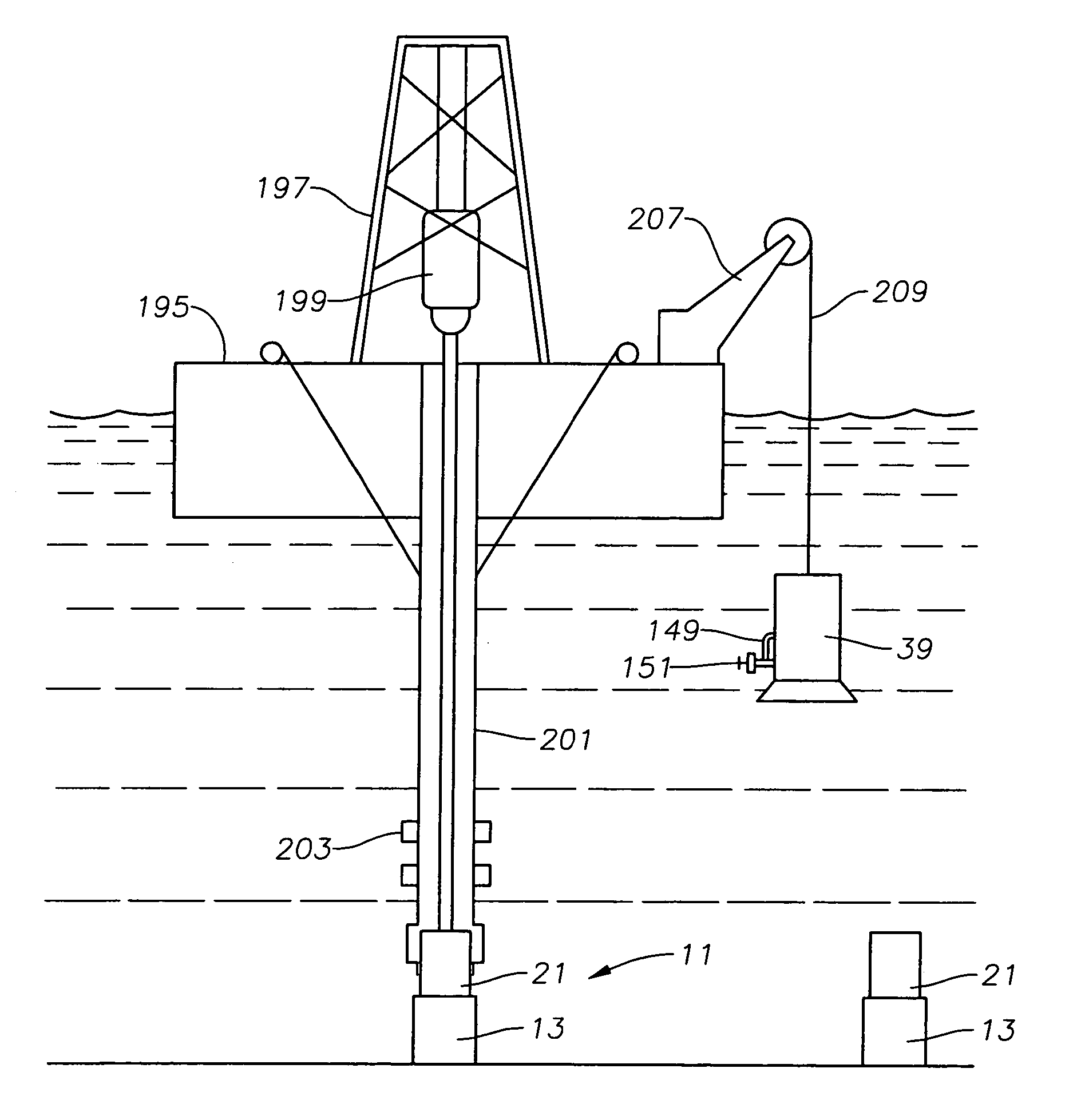
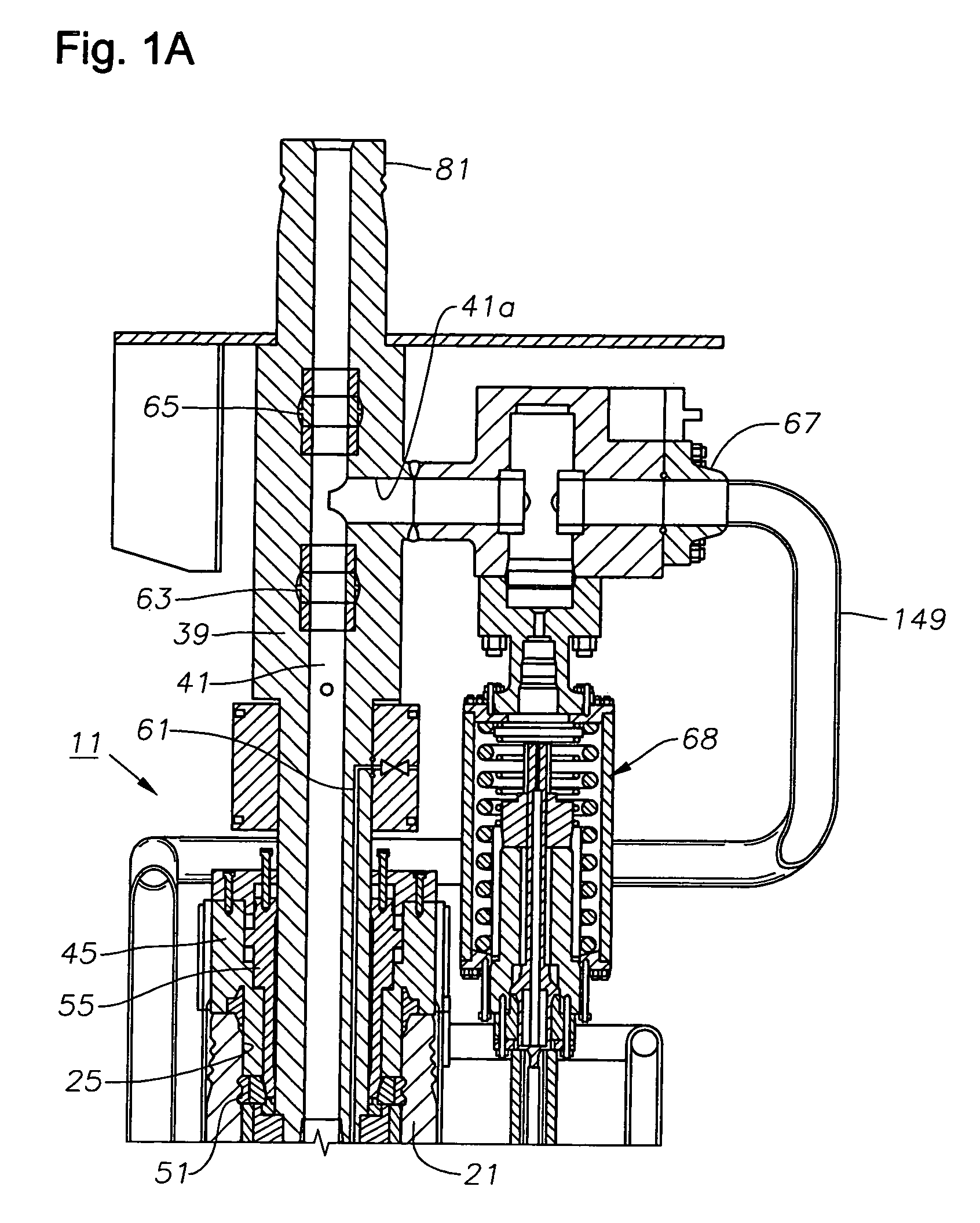
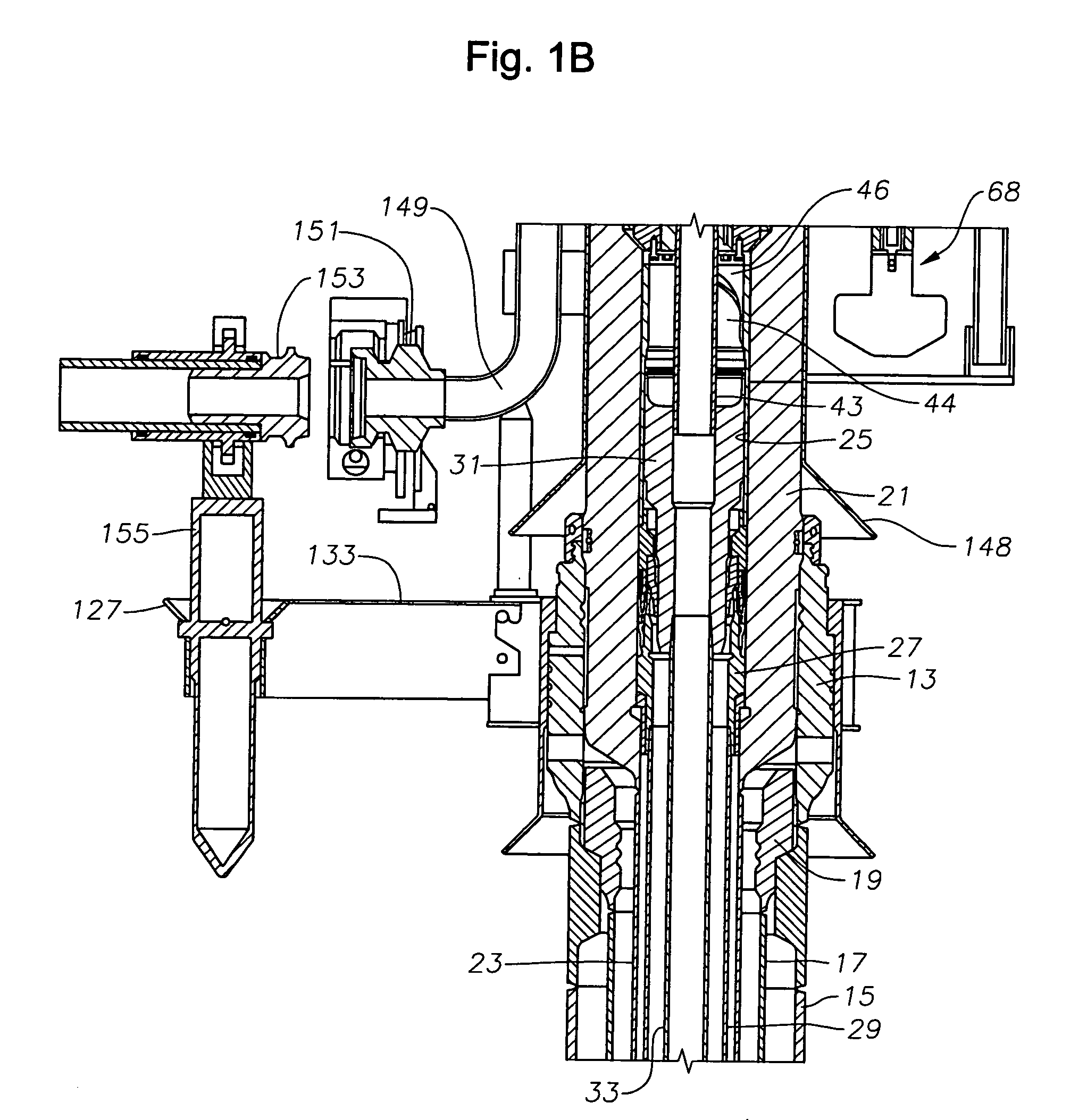
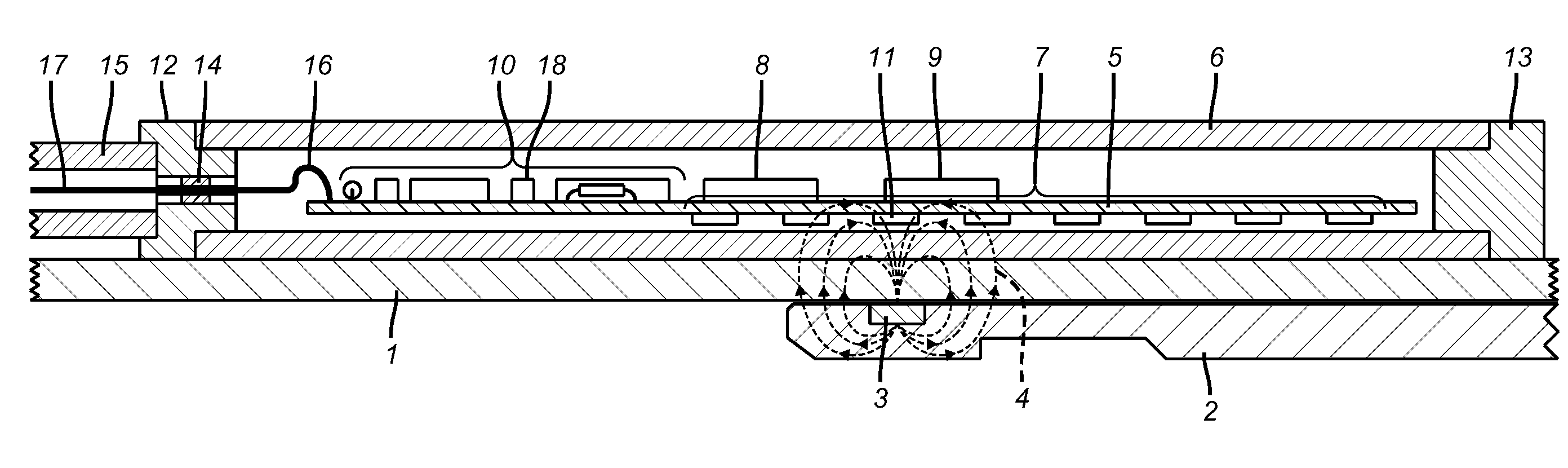
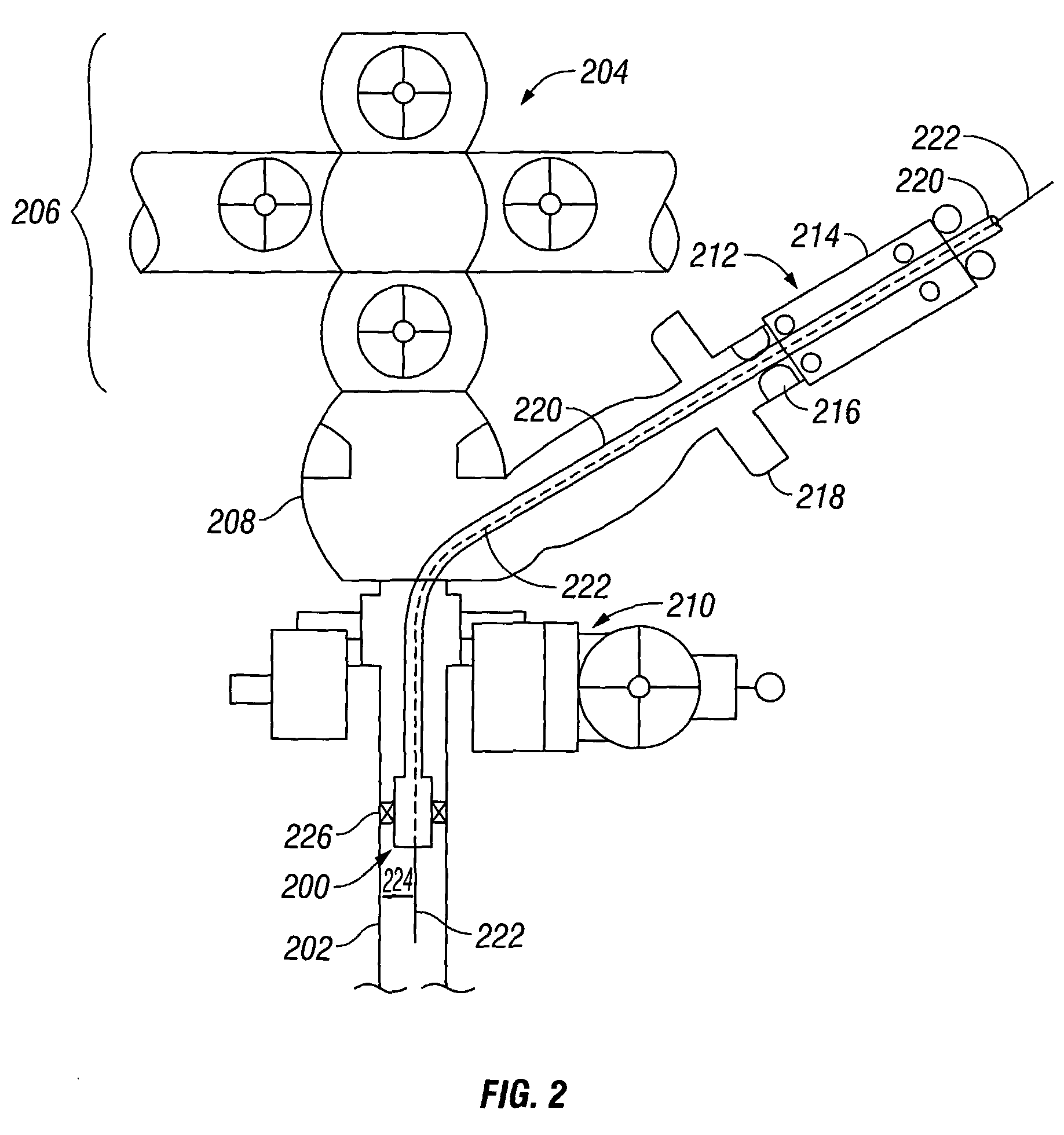
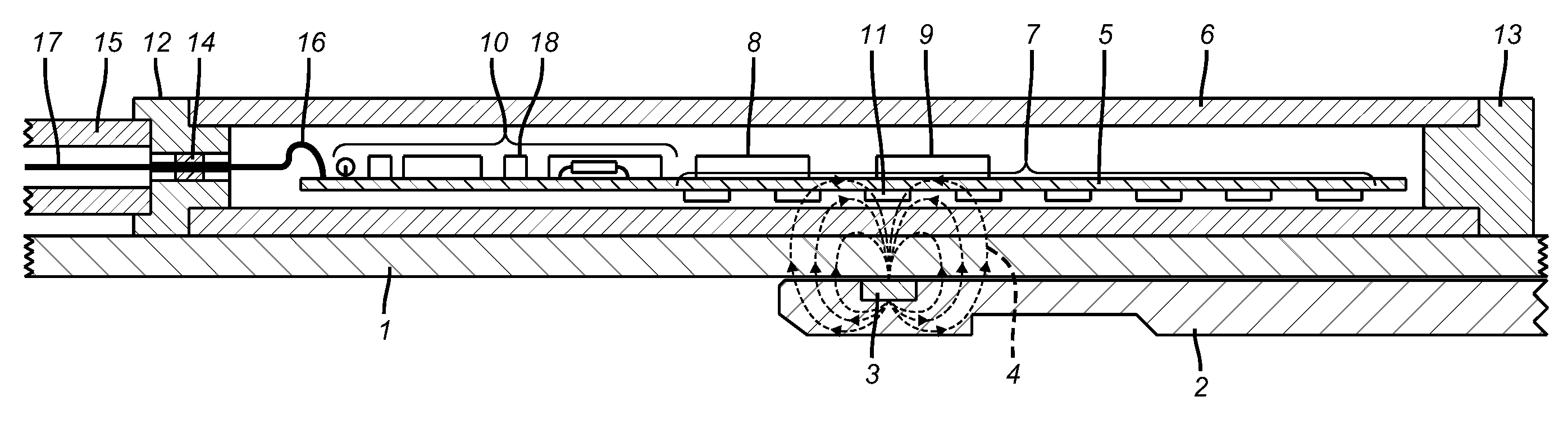
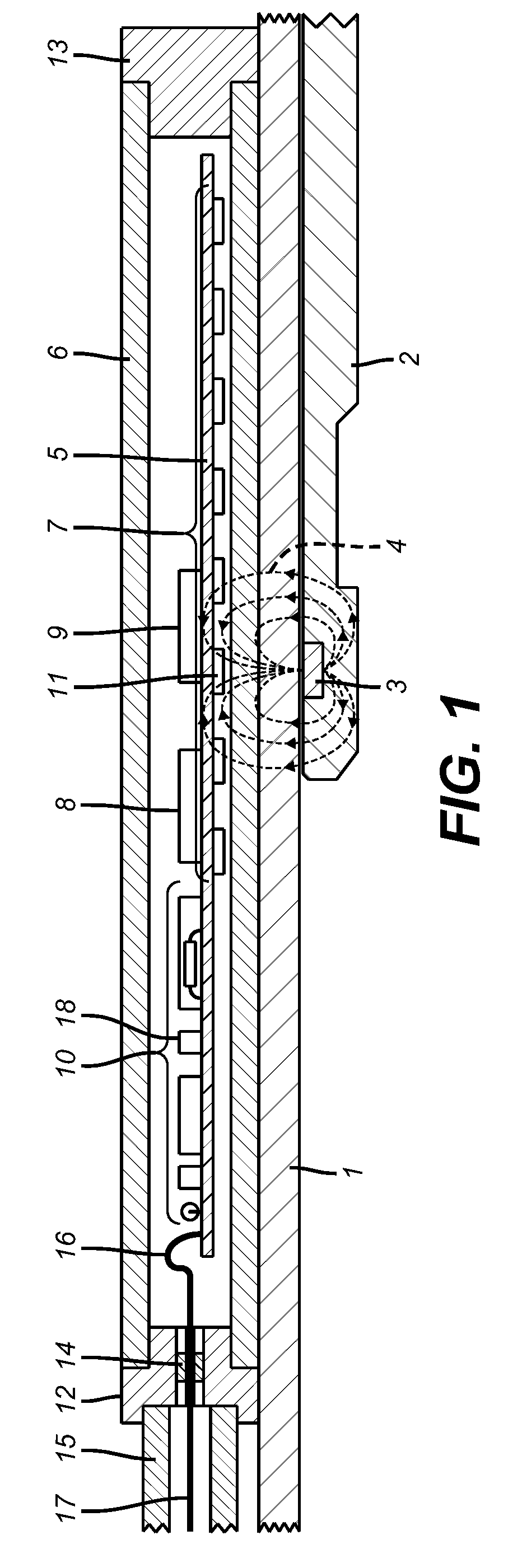
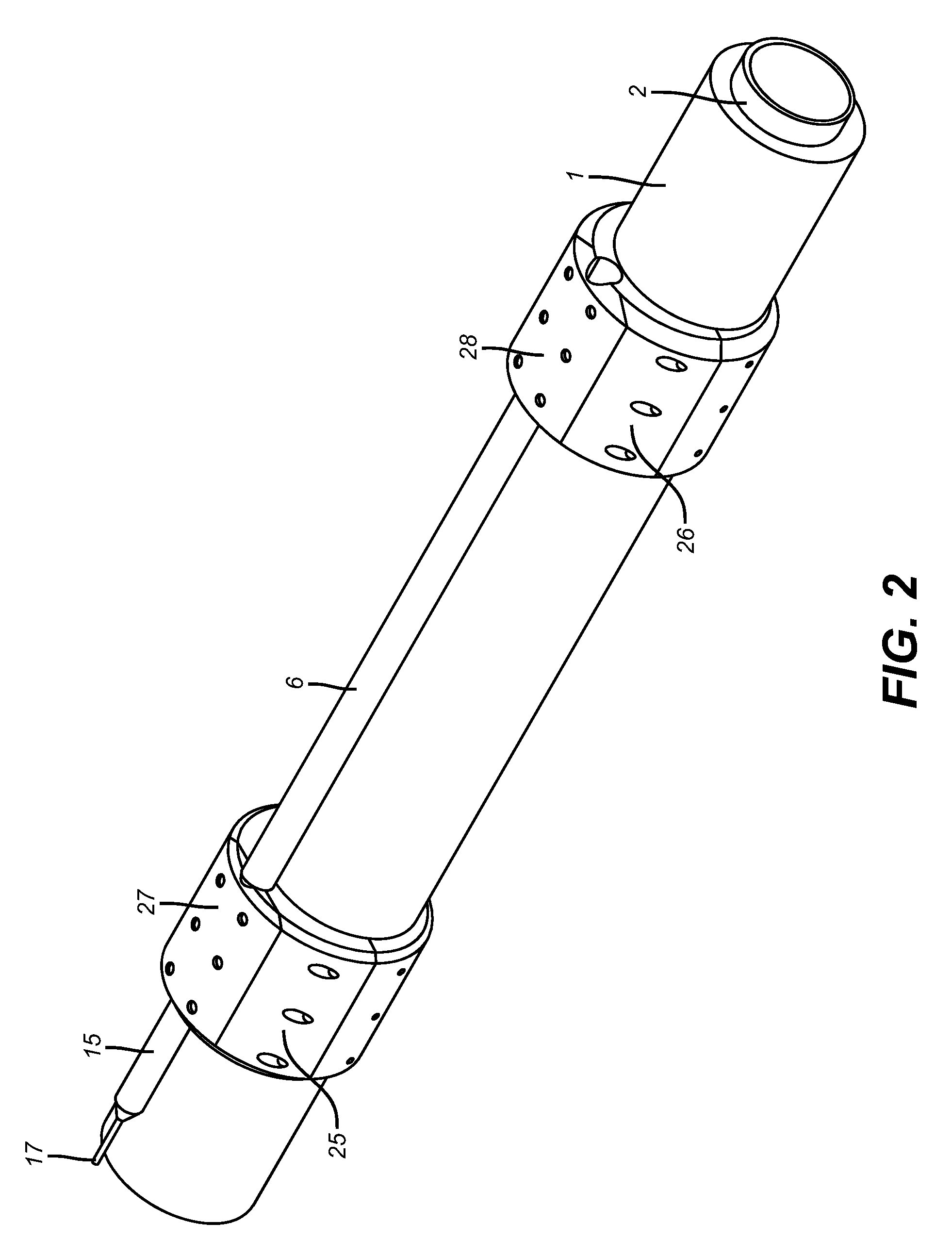
Position Sensor for a Downhole Completion Device
ActiveUS20090128141A1High speedElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsSensor arrayEngineering
The position of a movable downhole component such as a sleeve in a choke valve is monitored and determined using an array of sensors, preferably Hall Effect sensors that measure the strength of a magnetic field from a magnet that travels with the sleeve. The sensors measure the field strength and output a voltage related to the strength of the field that is detected. A plurality of sensors, with readings, transmits signals to a microprocessor to compute the magnet position directly. The sensors are in the tool body and are not mechanically coupled to the sleeve. The longitudinal position of the sleeve is directly computed using less than all available sensors to facilitate the speed of transmission of data and computation of actual position using known mathematical techniques.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Internal combustion engine exhaust gas control system and control method of internal combustion engine exhaust gas control system
ActiveUS20100126142A1Avoid emissionsReciprocating combination enginesElectrical controlExhaust gasThrottle
In a control method of an internal combustion engine exhaust gas control system which is applied to a hybrid vehicle that is powered by an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, an exhaust throttle valve, provided downstream of an exhaust gas control catalyst, is controlled to reduce its opening amount to a target opening amount when it is determined that warm-up control of the internal combustion engine needs to be executed. Next, a target injection quantity of fuel necessary to increase the temperature of exhaust gas flowing into the internal combustion engine to a target exhaust gas temperature is calculated. Then, assist torque from the electric motor is adjusted so that the sum of torque from the internal combustion engine when the fuel injection quantity has been set to the target injection quantity and the assist torque substantially equals a required torque.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
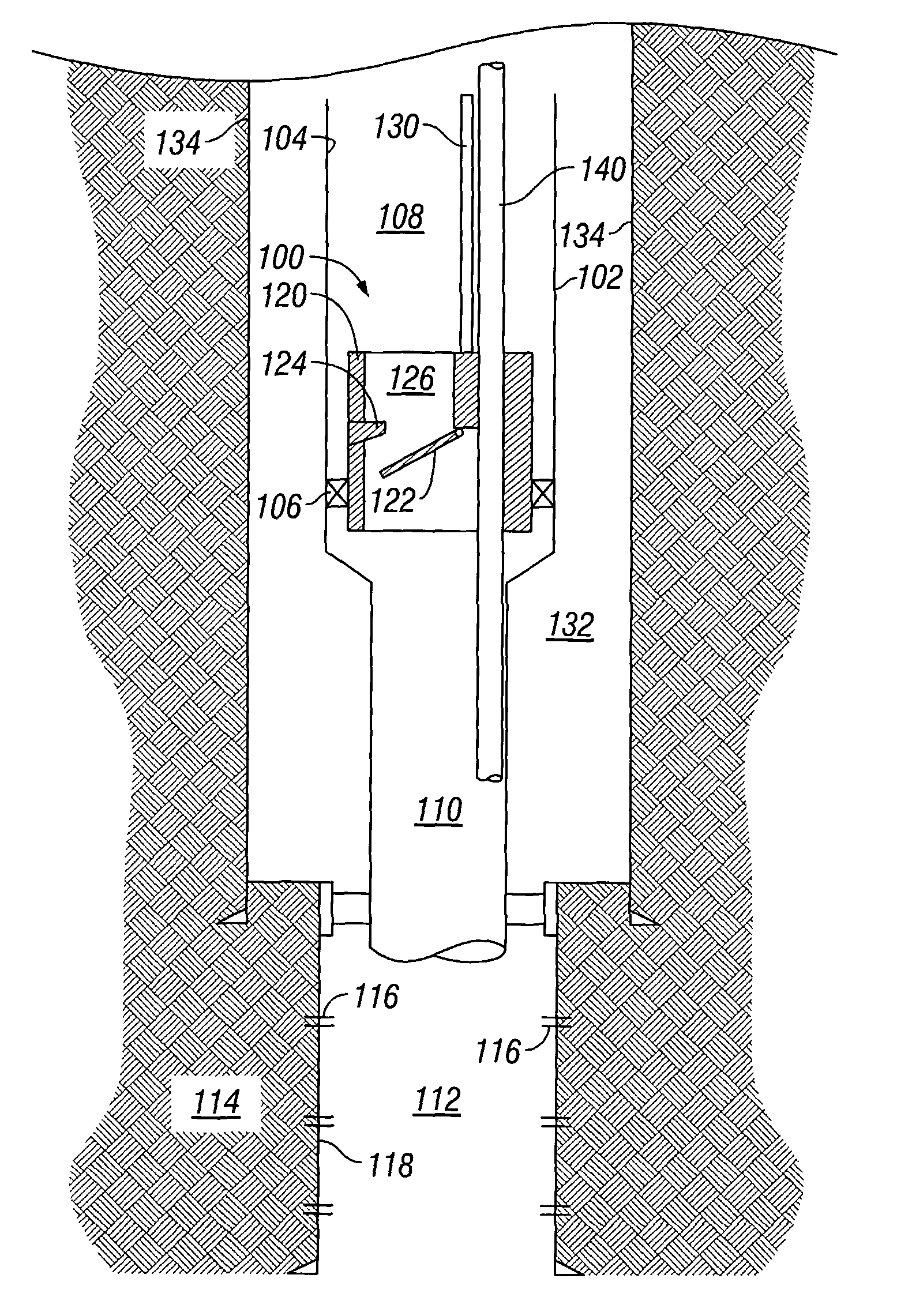
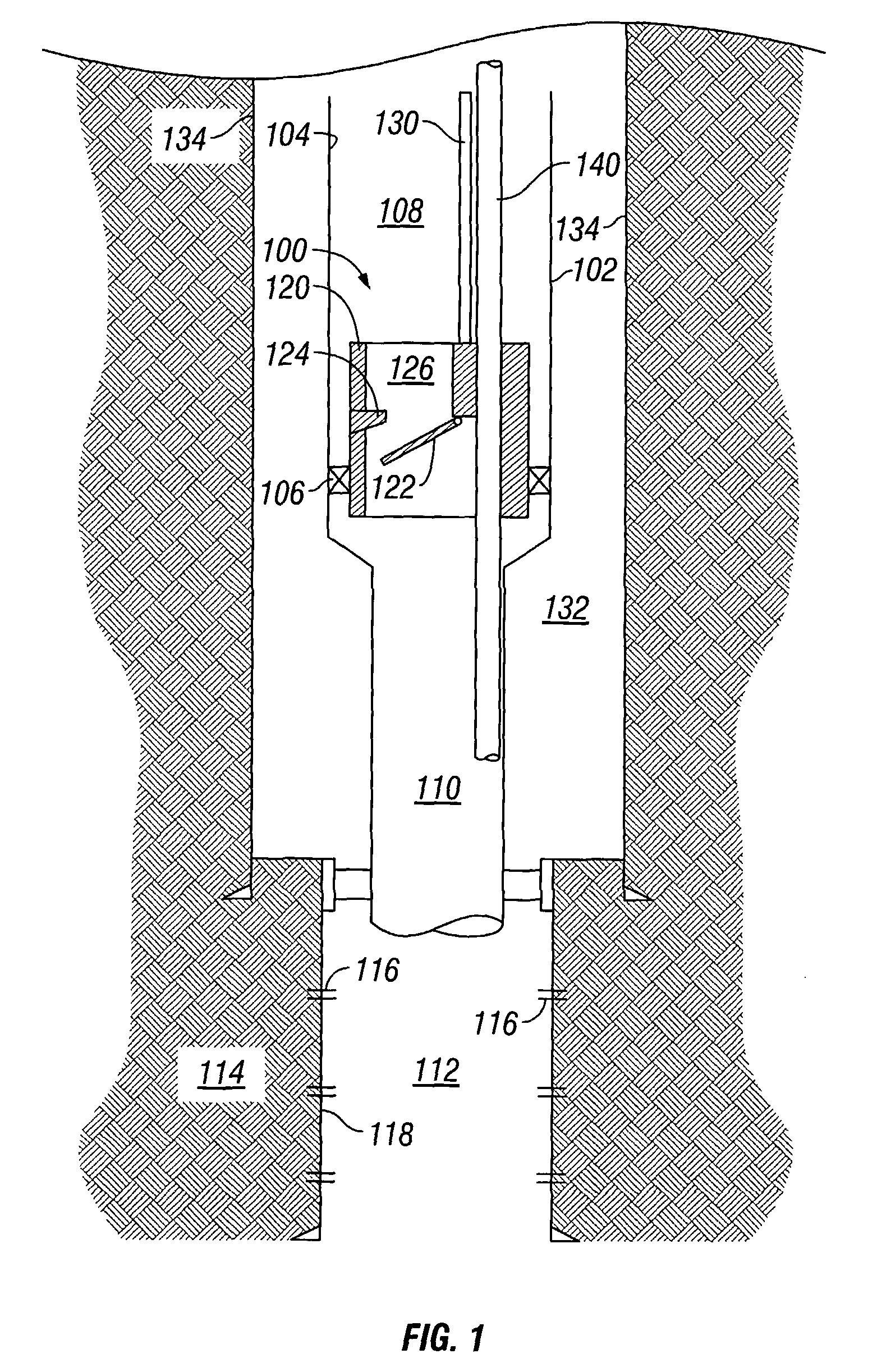
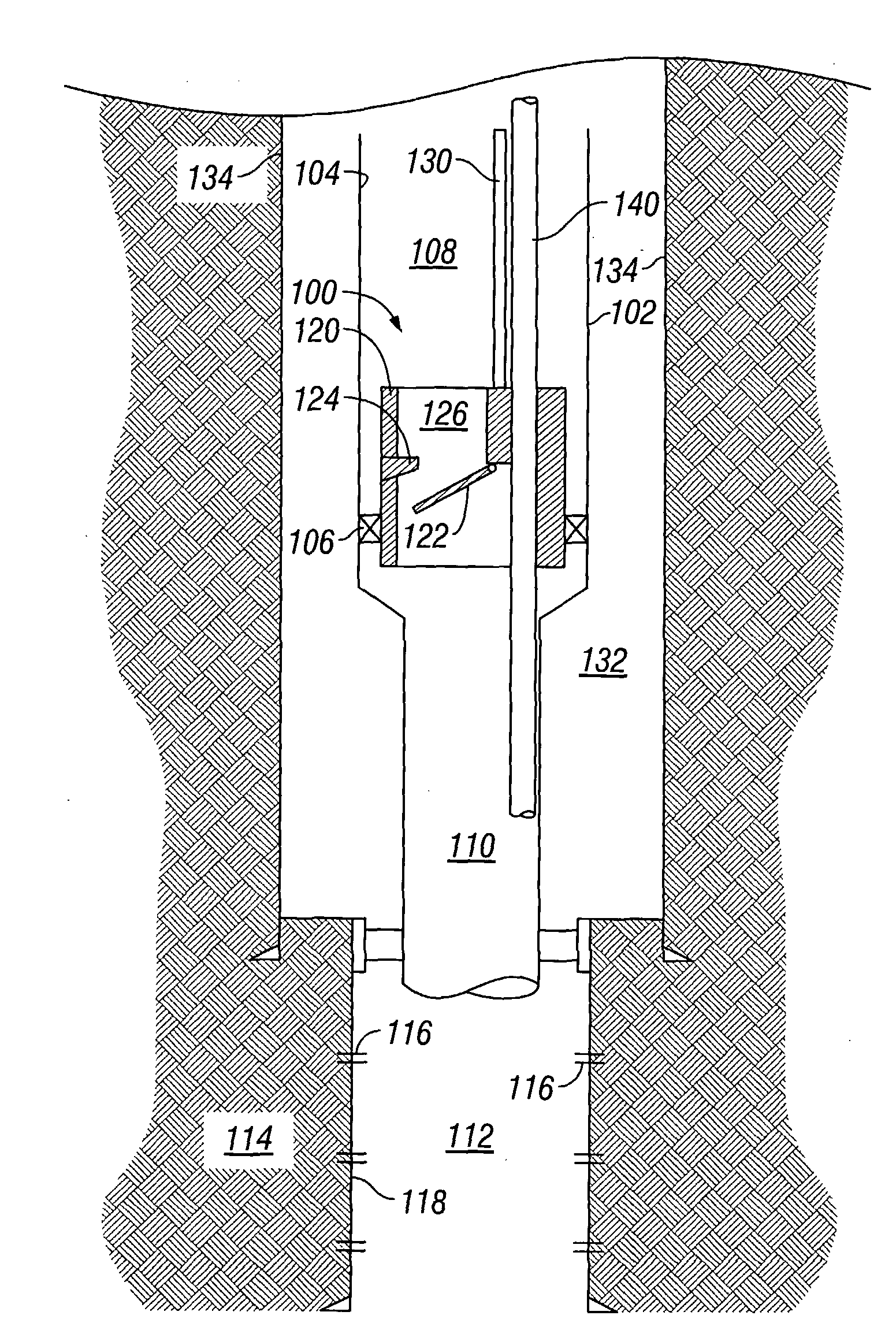
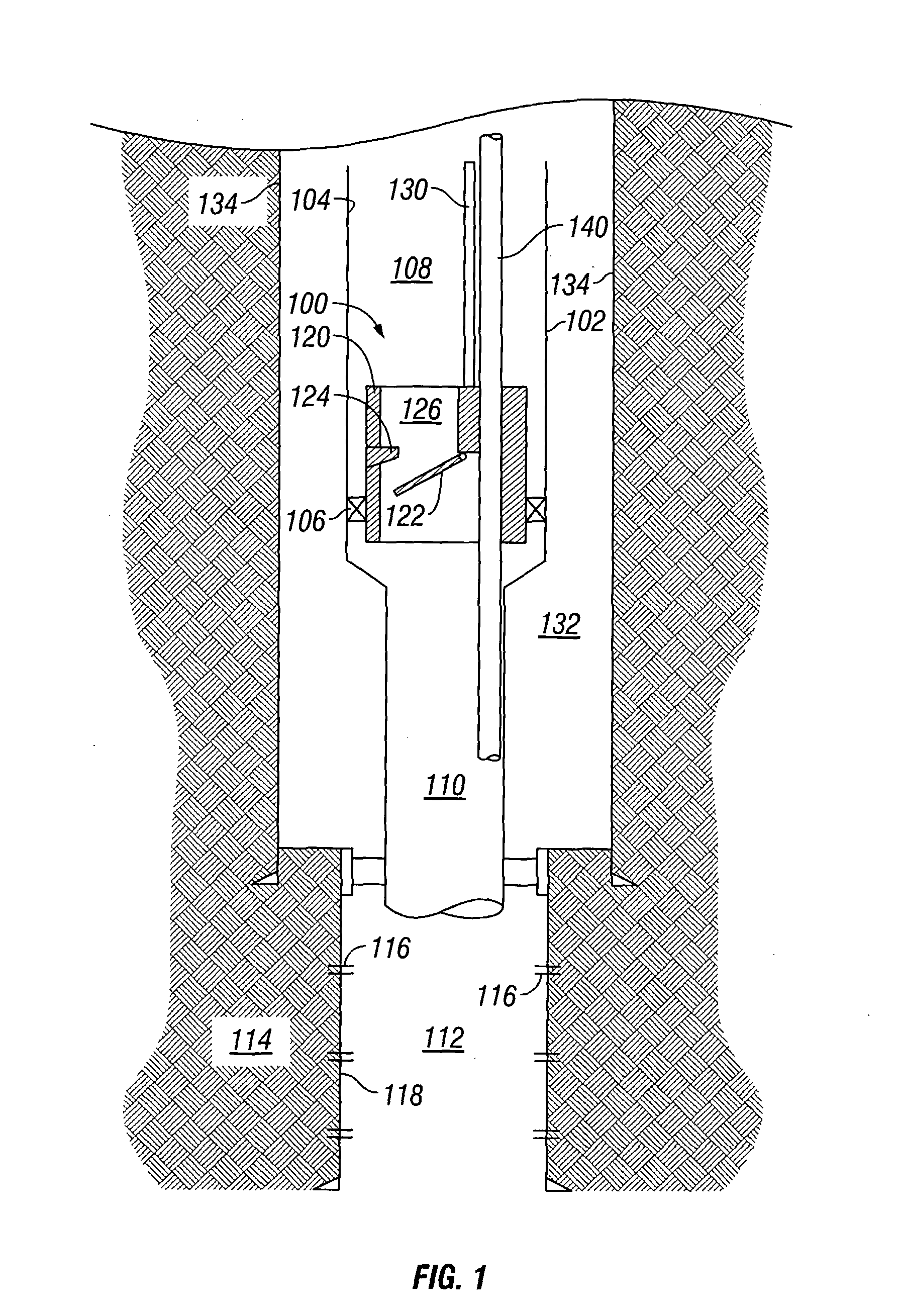
Downhole safety valve apparatus and method
The application discloses a valve, which may include either a safety valve or a storm surge choke valve or the like, to isolate a zone below a valve from a string of production tubing. Preferably, the valve includes a flow interruption surface assembly, such as a flapper valve or a ball valve, displaced by an operating conduit extending from a surface location to the valve through the inside of the production tubing. The application also discloses a bypass-conduit inside the production tubing to allow communication from a surface location to the production zone when the valve is in either an open or a closed location.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Underbalanced drilling method and apparatus
InactiveUS20050269134A1Loss is particularly problematicCost-effectiveDrilling rodsConstructionsGas liftMechanics
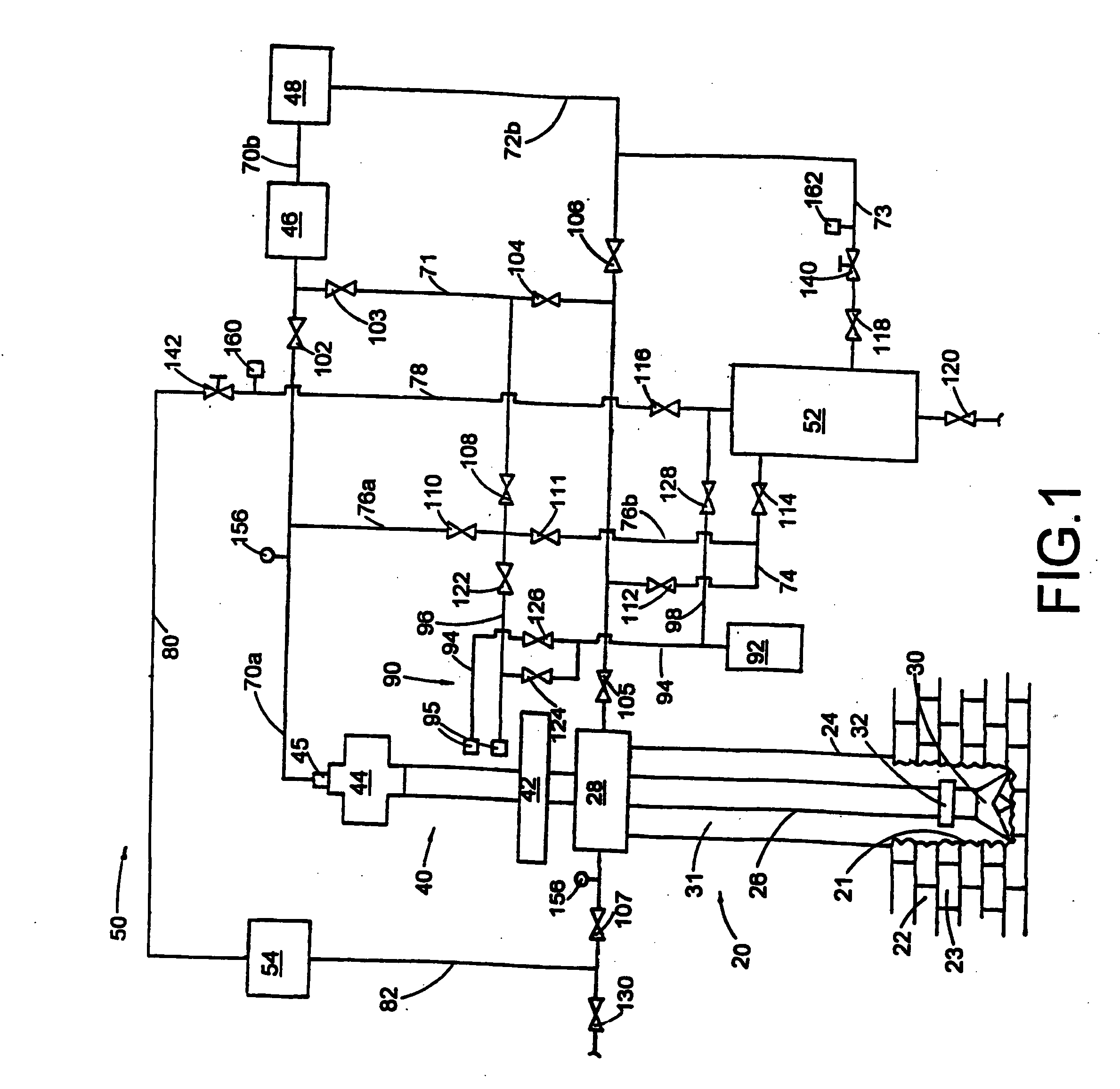
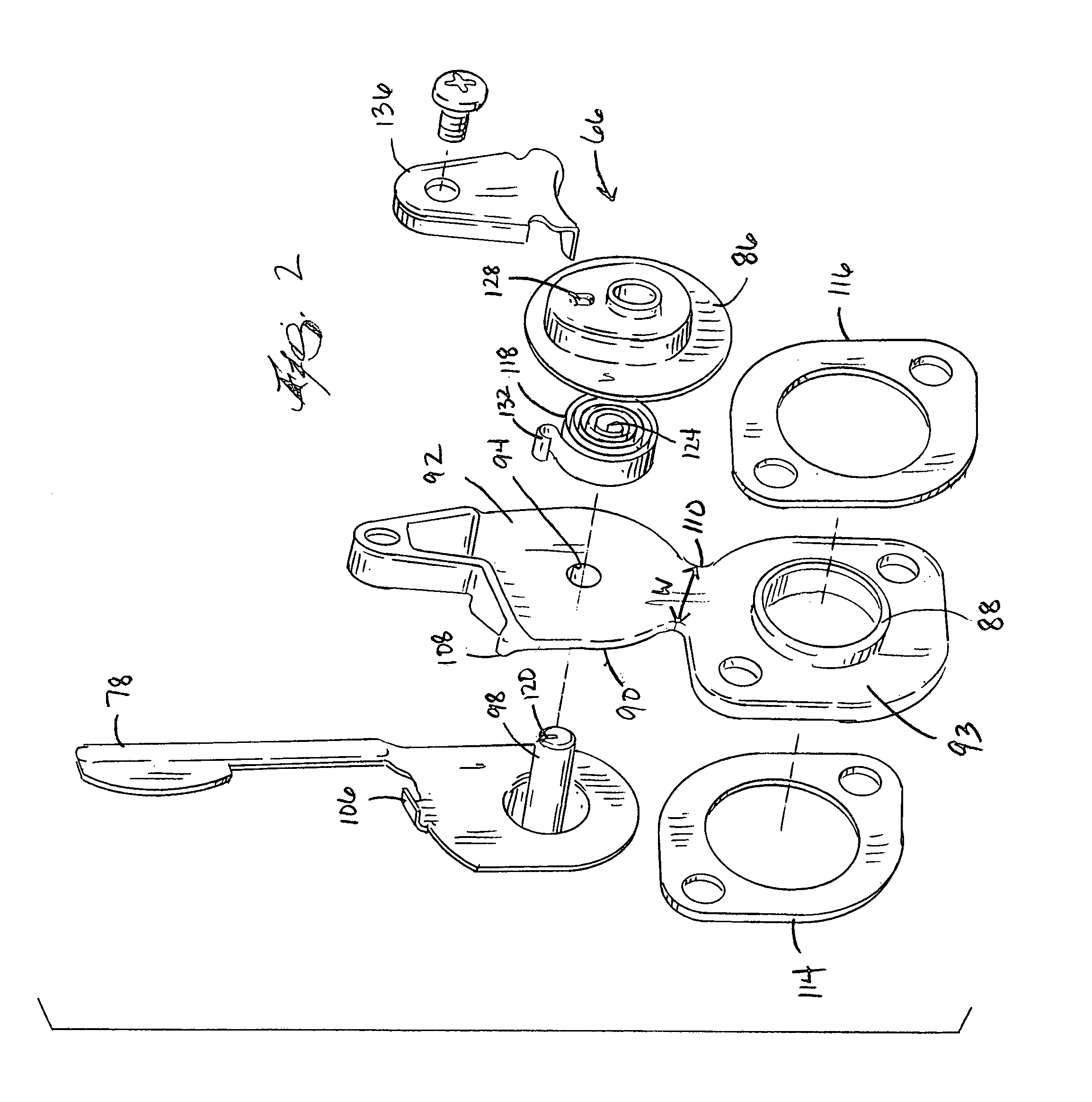
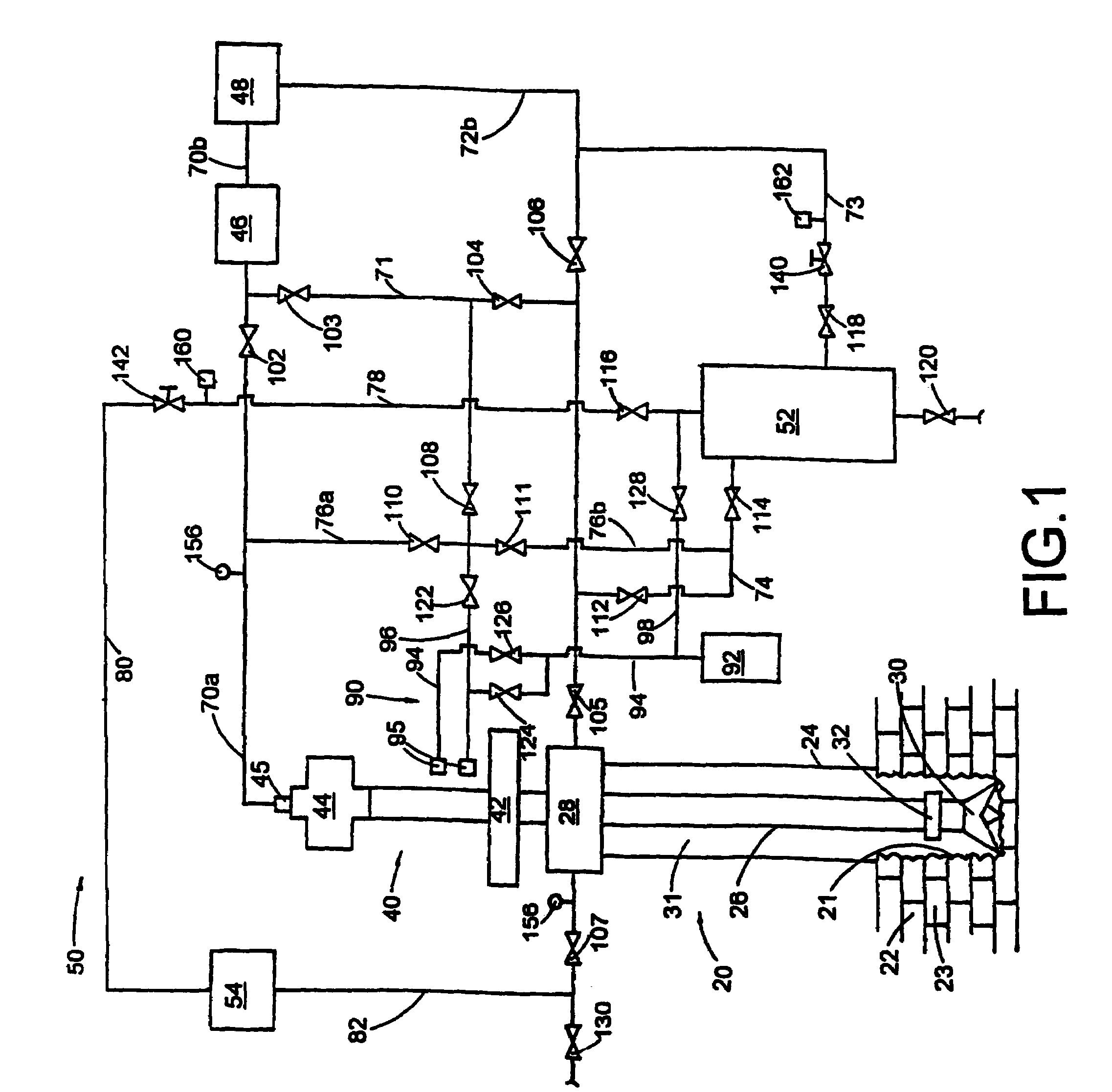
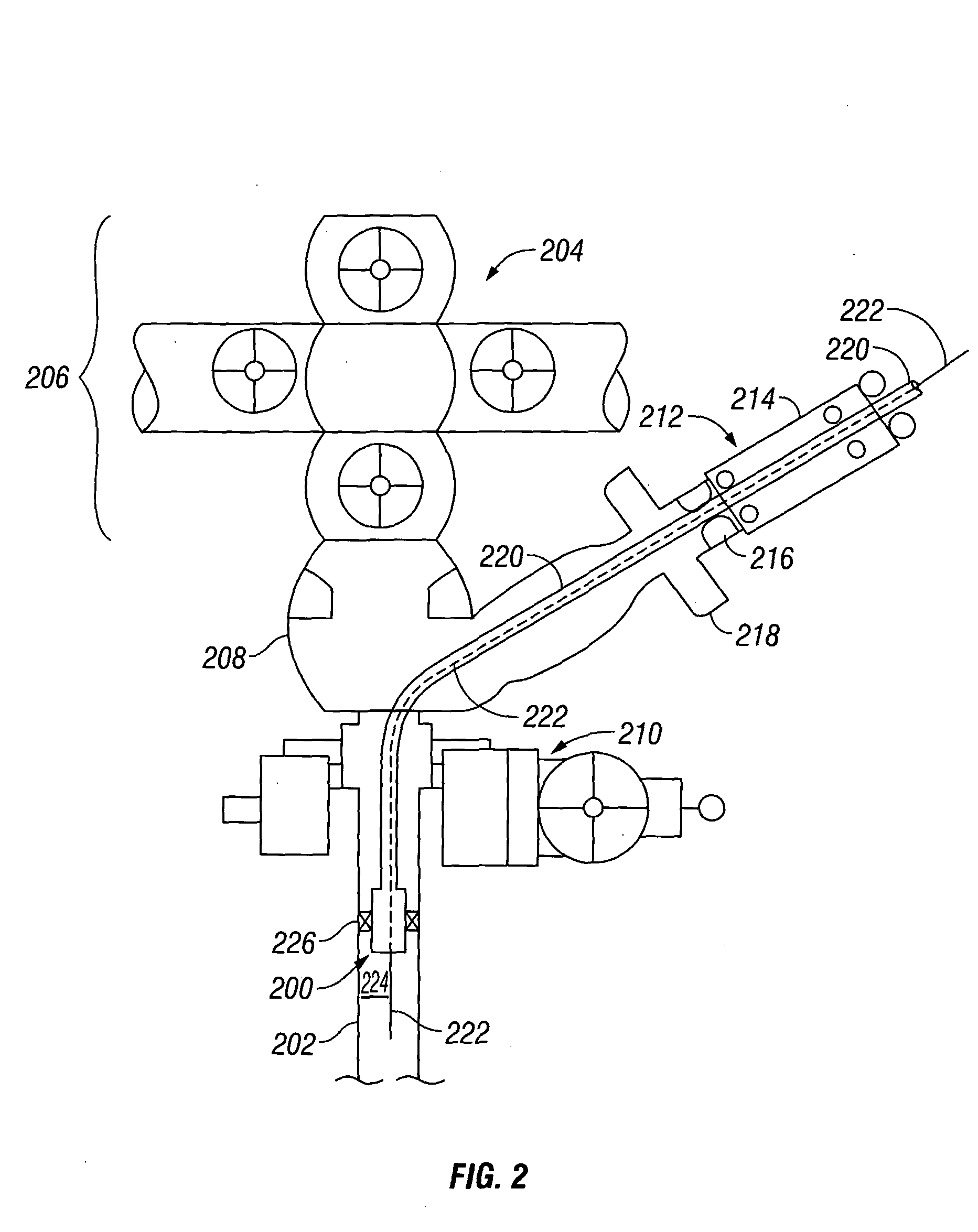
A method of drilling well bore (20) through and below permeable formation (22) bearing such fluids as gas, oil, water wherein drill cuttings may be evacuated by formation fluid (23) being produced through the drill string (26) either by decreasing well head back pressure or by gas lift. Production rate is kept substantially stable by operating choke valves (140) and (142) placed after separator (52). Formation fluid being produced while drilling may be pumped into well bore (20) through annulus (31) or utilized. The unique injector included in the drill string provides for possibility to pump simultaneously into annulus (31) lifting gas and produced liquid and may be operated from the surface. A method and system (90) comprising a plurality of special 3-way valves included in drill string (26), are provided for making connections without interrupting flushing the well bore.
Owner:STRAZHGORODSKIY SEMEN IOSIPHOVICH
Automatic choke for an engine
ActiveUS6990969B2Avoid closingElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngineeringInternal combustion engine
An automatic choke apparatus for use in an internal combustion engine. The choke apparatus includes a choke valve automatically operable in response to the speed of the engine, a thermally conductive assembly that conducts heat from exhaust gases produced by the engine, a thermally responsive member in thermal communication with the thermally conductive assembly, and a mechanism that moves in response to the thermally responsive member to cause the choke valve to remain in at least a partially open position during engine starting when the thermally responsive member senses a temperature above a predetermined temperature. The thermally conductive assembly at least partially surrounds the path of the exhaust gases.
Owner:BRIGGS & STRATTON LLC
Underbalanced drilling method and apparatus
InactiveUS7308952B2Eliminate the problemAvoid excessive volumeConstructionsFluid removalGas liftMechanics
A method of drilling well bore (20) through and below permeable formation (22) bearing such fluids as gas, oil, water wherein drill cuttings may be evacuated by formation fluid (23) being produced through the drill string (26) either by decreasing well head back pressure or by gas lift. Production rate is kept substantially stable by operating choke valves (140) and (142) placed after separator (52). Formation fluid being produced while drilling may be pumped into well bore (20) through annulus (31) or utilized. The unique injector included in the drill string provides for possibility to pump simultaneously into annulus (31) lifting gas and produced liquid and may be operated from the surface. A method and system (90) comprising a plurality of special 3-way valves included in drill string (26), are provided for making connections without interrupting flushing the well bore.
Owner:STRAZHGORODSKIY SEMEN IOSIPHOVICH
Automatic control system and method for bottom hole pressure in the underbalance drilling
ActiveUS7158886B2Accurate calculationRelatively small errorElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsAutomatic controlAutomated control system
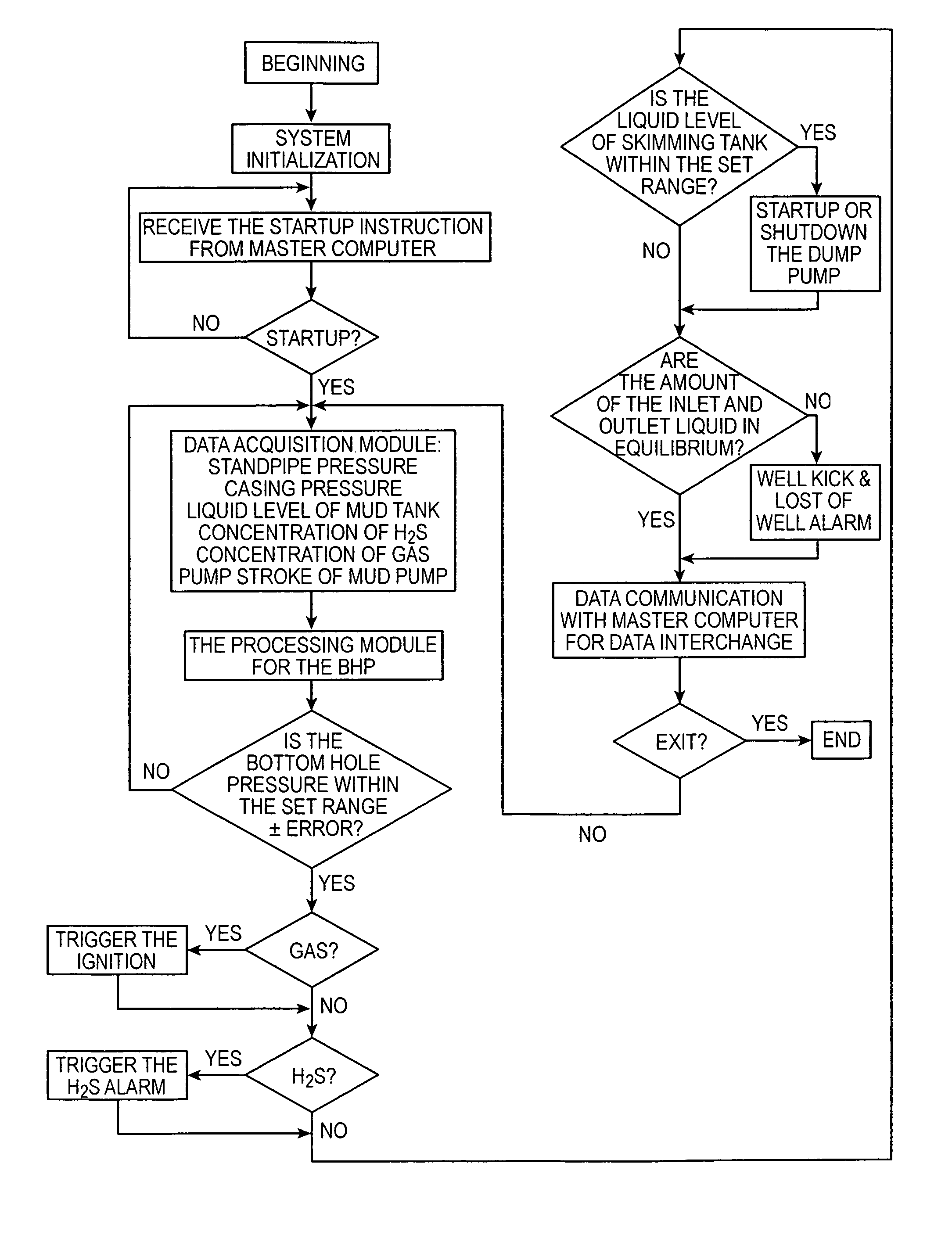
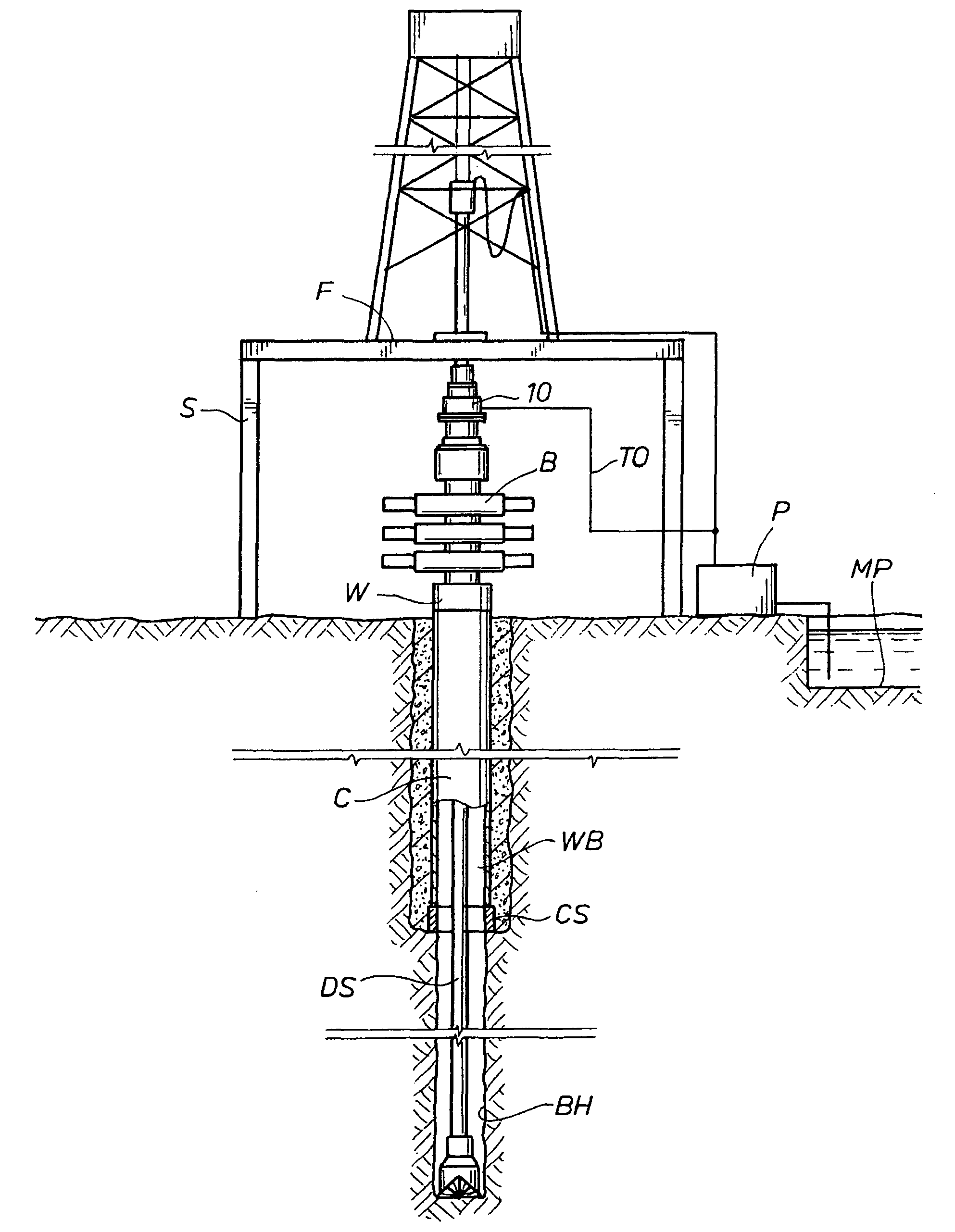
This invention provides an automatic control system and method for bottom hole pressure (BHP) in the underbalanced drilling. It relates to a computer automatic control technology. The automatic control system according to the invention includes a processing module for the BHP based on the mechanisms of hydraulics. The BHP in the underbalanced drilling is calculated from the acquired standpipe pressure (SPP), the calculated circulating pressure loss in the drilling tools, drill bit pressure drop and the fluid colunm pressure in the drill string. The resulting BHP is then compared with the set pressure value of the system. In case that the BHP is higher or lower than the set pressure, an instruction to regulate throttle valve opening will be issued in order to bring the BHP back to the set pressure range and complete BHP monitoring and control.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Drilling with a high pressure rotating control device
A Drill-To-The-Limit (DTTL) drilling method variant to Managed Pressured Drilling (MPD) applies constant surface backpressure, whether the mud is circulating (choke valve open) or not (choke valve closed). Because of the constant application of surface backpressure, the DTTL method can use lighter mud weight that still has the cutting carrying ability to keep the borehole clean. The DTTL method identifies the weakest component of the pressure containment system, such as the fracture pressure of the formation or the casing shoe leak off test (LOT). With a higher pressure rated RCD, such as 5,000 psi (34,474 kPa) dynamic or working pressure and 10,000 psi (68,948 kPa) static pressure, the limitation will generally be the facture pressure of the formation or the LOT. In the DTTL method, since surface backpressure is constantly applied, the pore pressure limitation of the conventional drilling window can be disregarded in developing the fluid and drilling programs.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
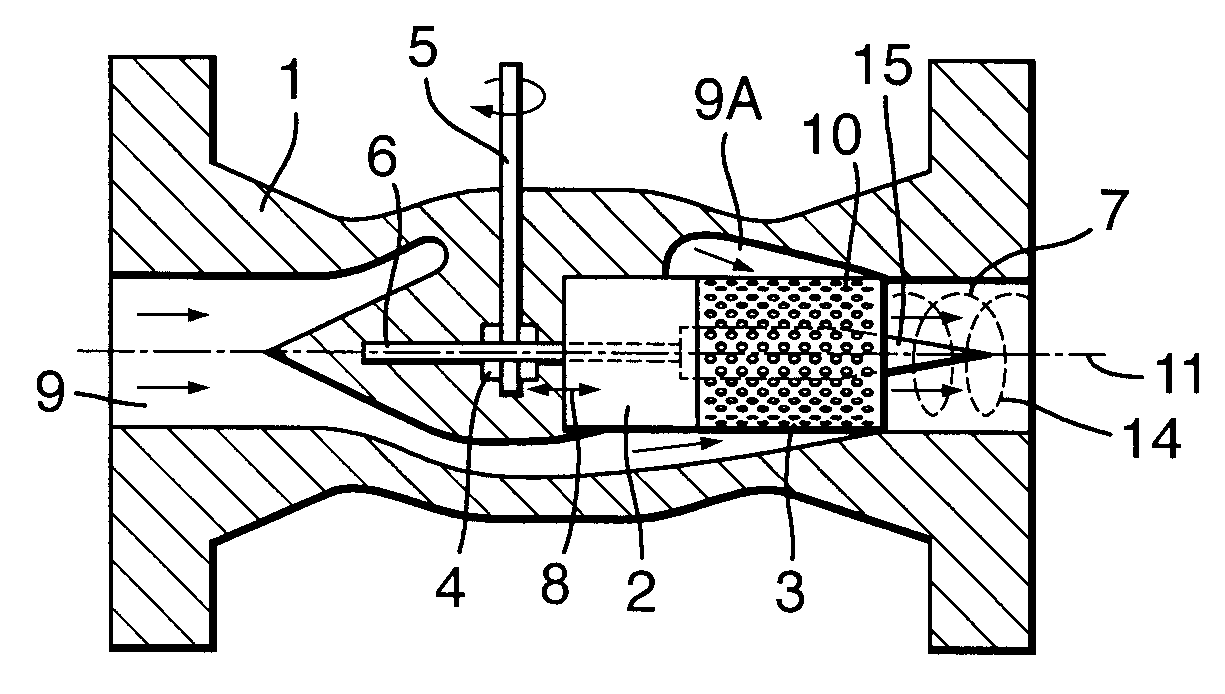
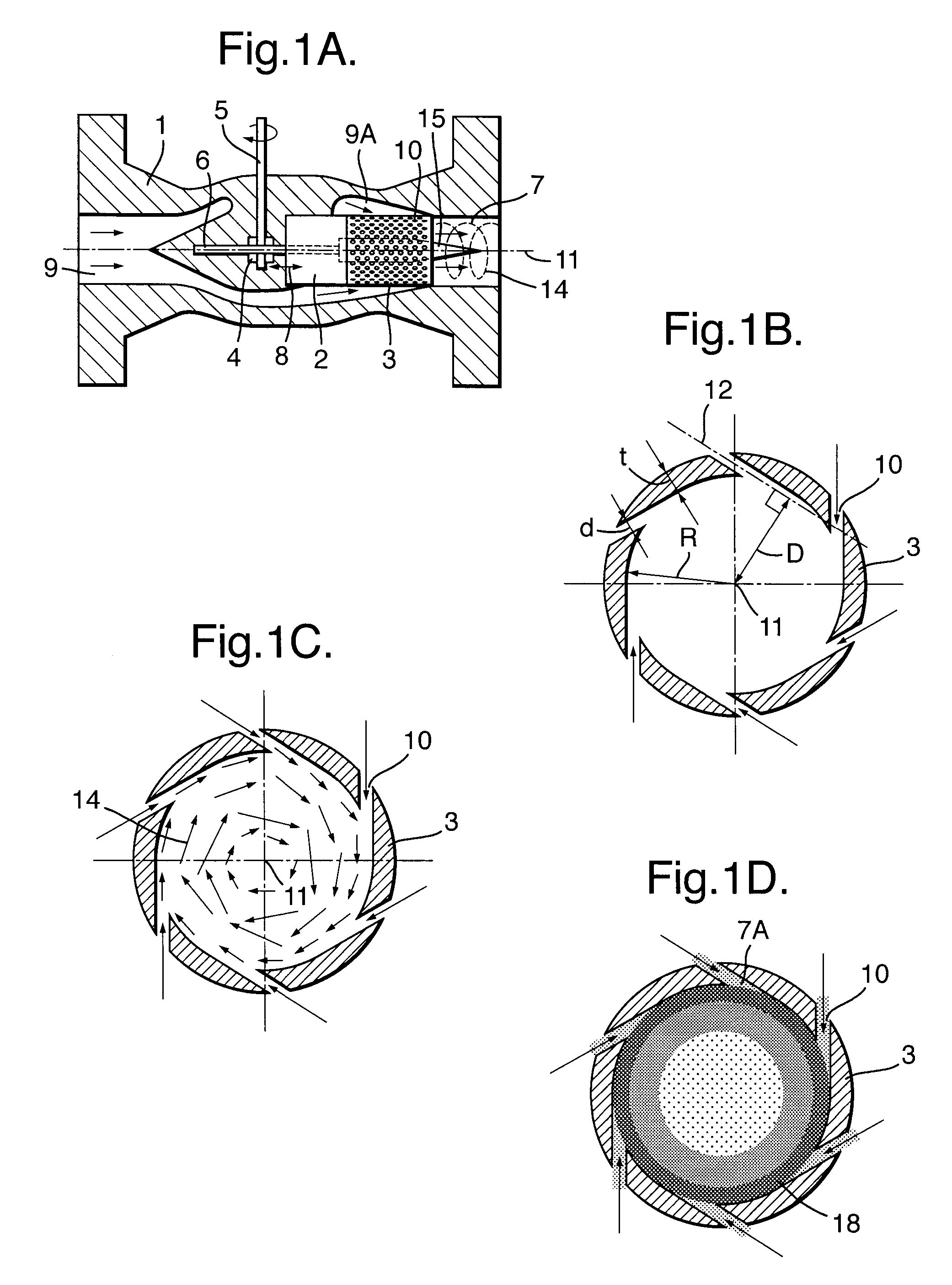
Throttling Valve and Method for Enlarging Liquid Droplet Sizes in the Throttled Fluid Stream
ActiveUS20080173363A1Promote growthIncrease the cross-sectional areaSolidificationDiaphragm valvesCarrier fluidEngineering
A Joule-Thompson or other throttling valve comprises an outlet channel (7) in which swirl imparting means (10) impose a swirling motion to the cooled fluid stream discharged by the valve, thereby inducing liquid droplets to swirl towards the outer periphery (7A) of the fluid outlet channel (7) and to coalesce into enlarged liquid droplets (17) which can be separated easily from a gaseous or other carrier fluid.
Owner:TWISTER BV
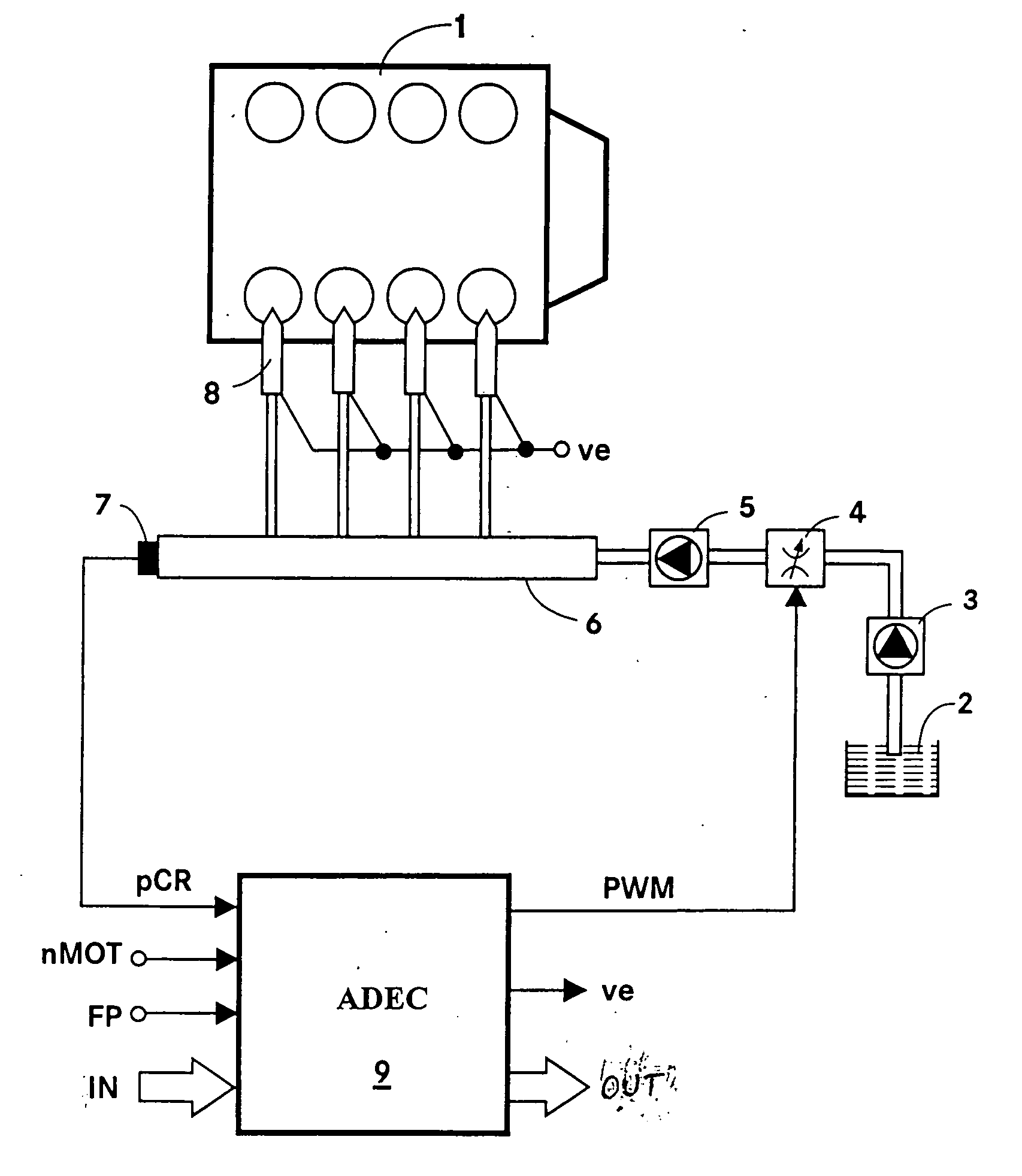
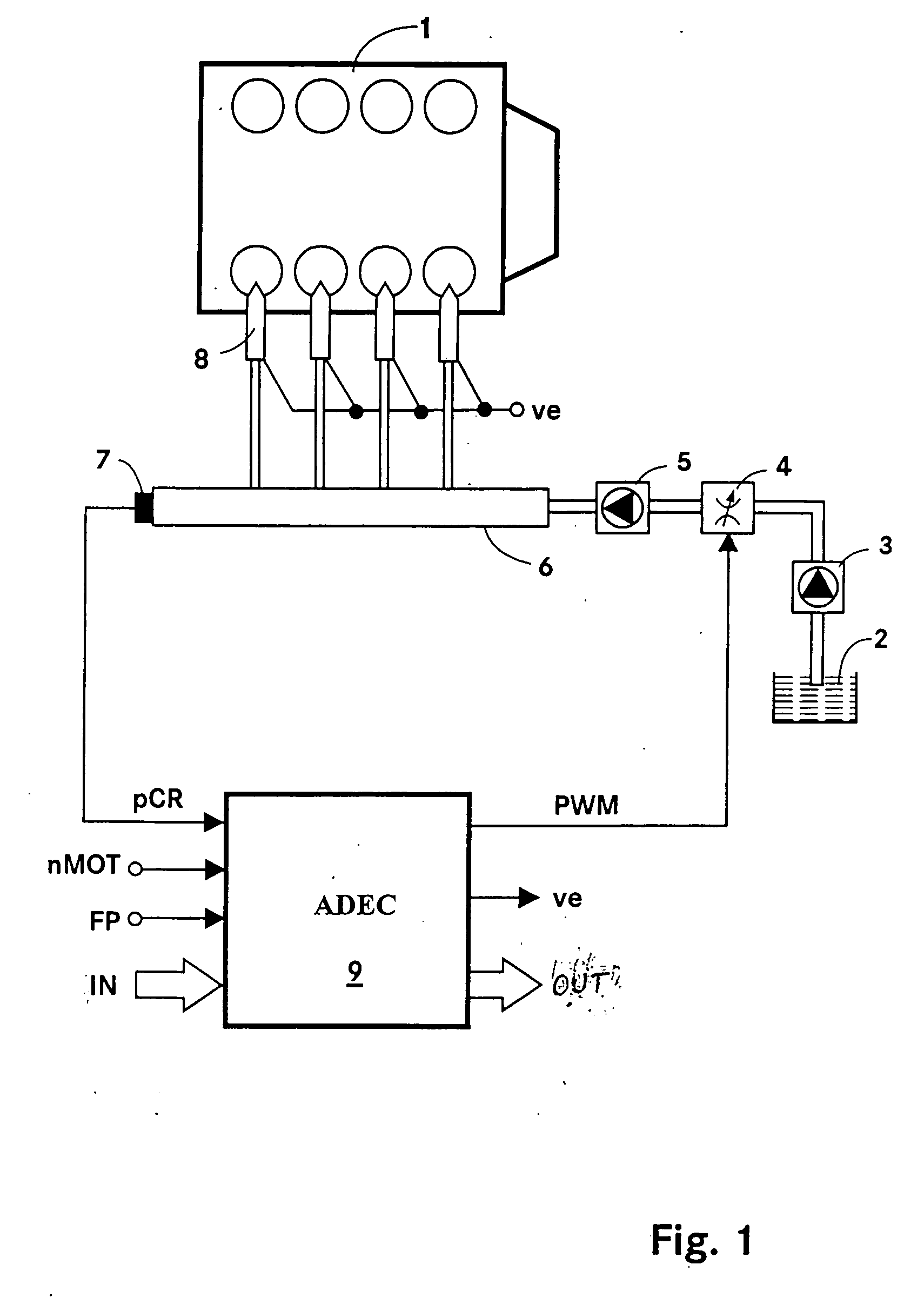
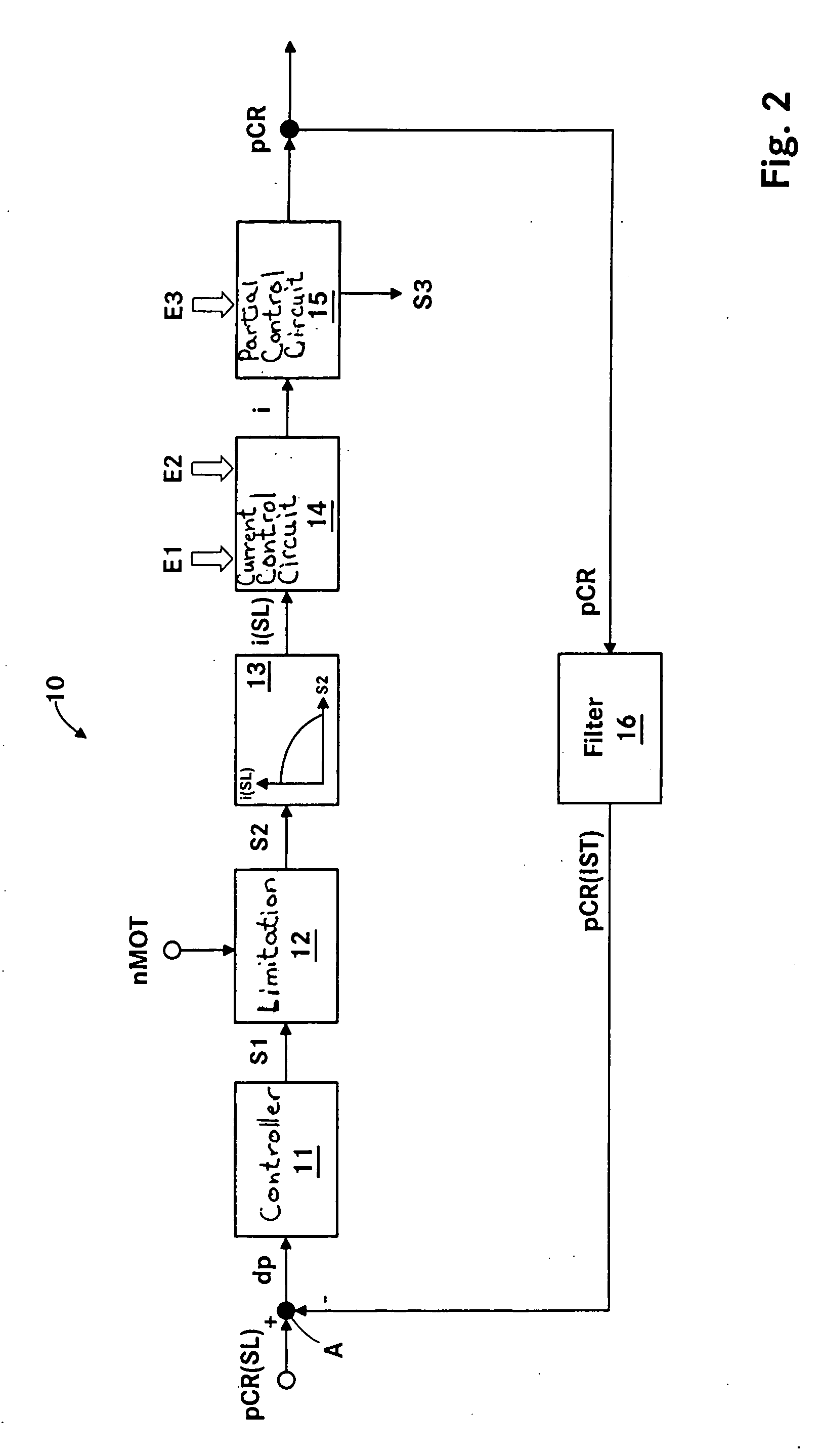
Method and apparatus for controlling the pressure in a common rail system
ActiveUS20060130813A1Improve stabilityEliminates temperature dependenceElectrical controlLow-pressure fuel injectionRail pressureControl engineering
In a common rail operating method and system, an arrangement for controlling the rail pressure is provided with a rail pressure controller including a current control circuit for controlling a suction throttle valve operating current (i) which valve is arranged in the fuel supply line to a high pressure pump supplying high pressure fuel to the common rail. The suction valve operating current control circuit includes a preliminary control value generator which serves also as an emergency control signal generator for the control of the suction valve if an error occurs in the system at least to permit an orderly engine shutdown procedure.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE SOLUTIONS GMBH
Hydraulic fatigue test system for pressure container
InactiveCN1587972ALow costEasy to implementMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesPress ramSolenoid valveFiltration
A pressure vessel fatigue test system belongs to pressure vessel test technical field, comprising oil circuit pressure device, pressurizer, weight relieving motion, and measuring and control system. The oil circuit pressure device, pressurizer, weight relieving motion consists of pump linked by pipeline and oil pump driven by electric machinery, solenoid valve, overflow valve, water cooled oil cooler, back oil filtration device, oil tank and pipelines linked with them, the measuring and control system is consisted of electric contact pressure gauge, temperature sensor, pressure sensor, computer, controller for measurement and control temperature of pressure vessel, hydraulic oil, one-way throttle valve and high pressure filtration device are fitted with pipeline linked with solenoid valve and the container, stabilization tank is fitted with oil return pipe linked to solenoid valve and oil tank. The invention is suitable for fatigue test of pressure vessel containing impurity within and fairly high pressure needed and reconstruction to present pressure vessel fatigue test device.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
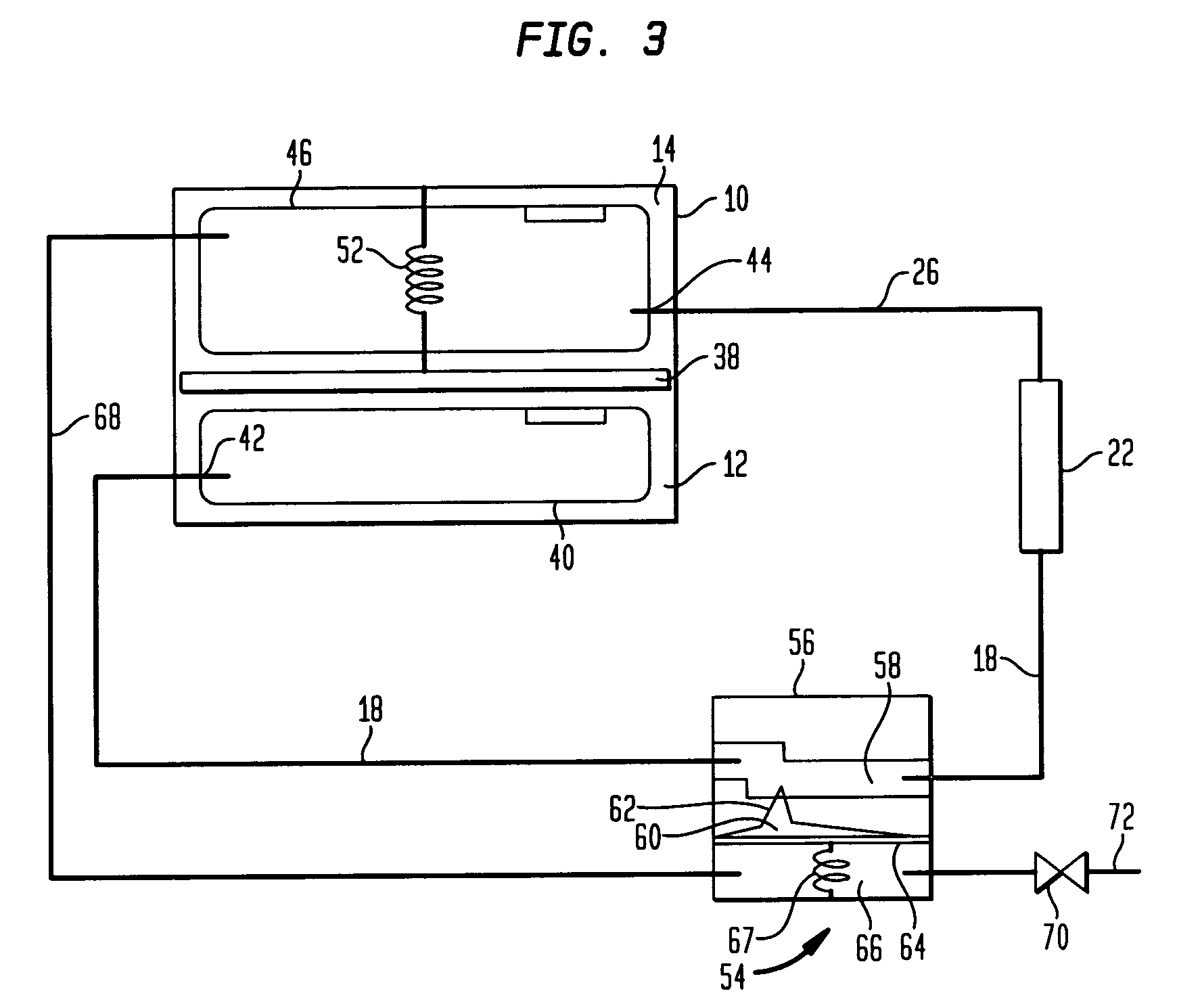
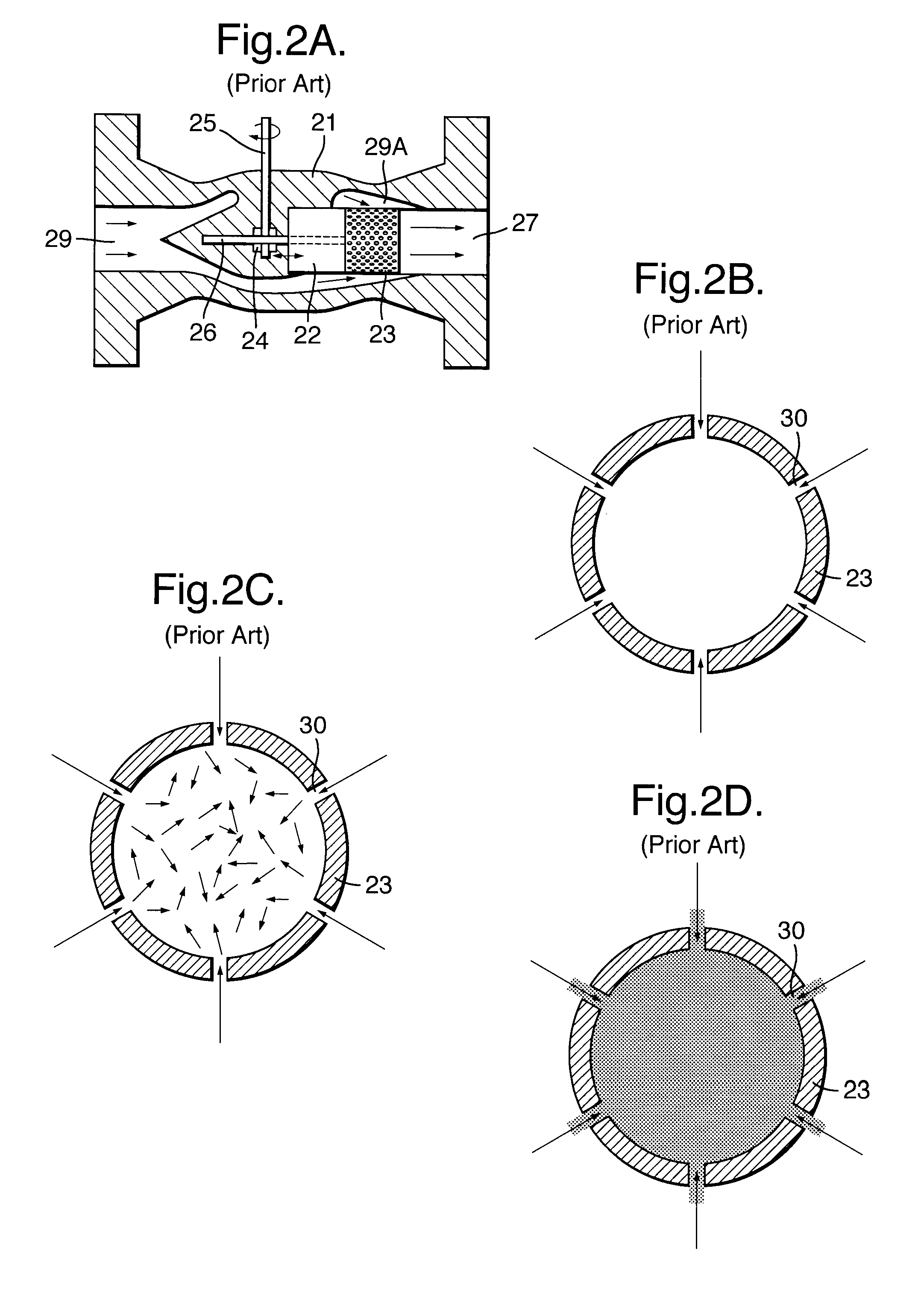
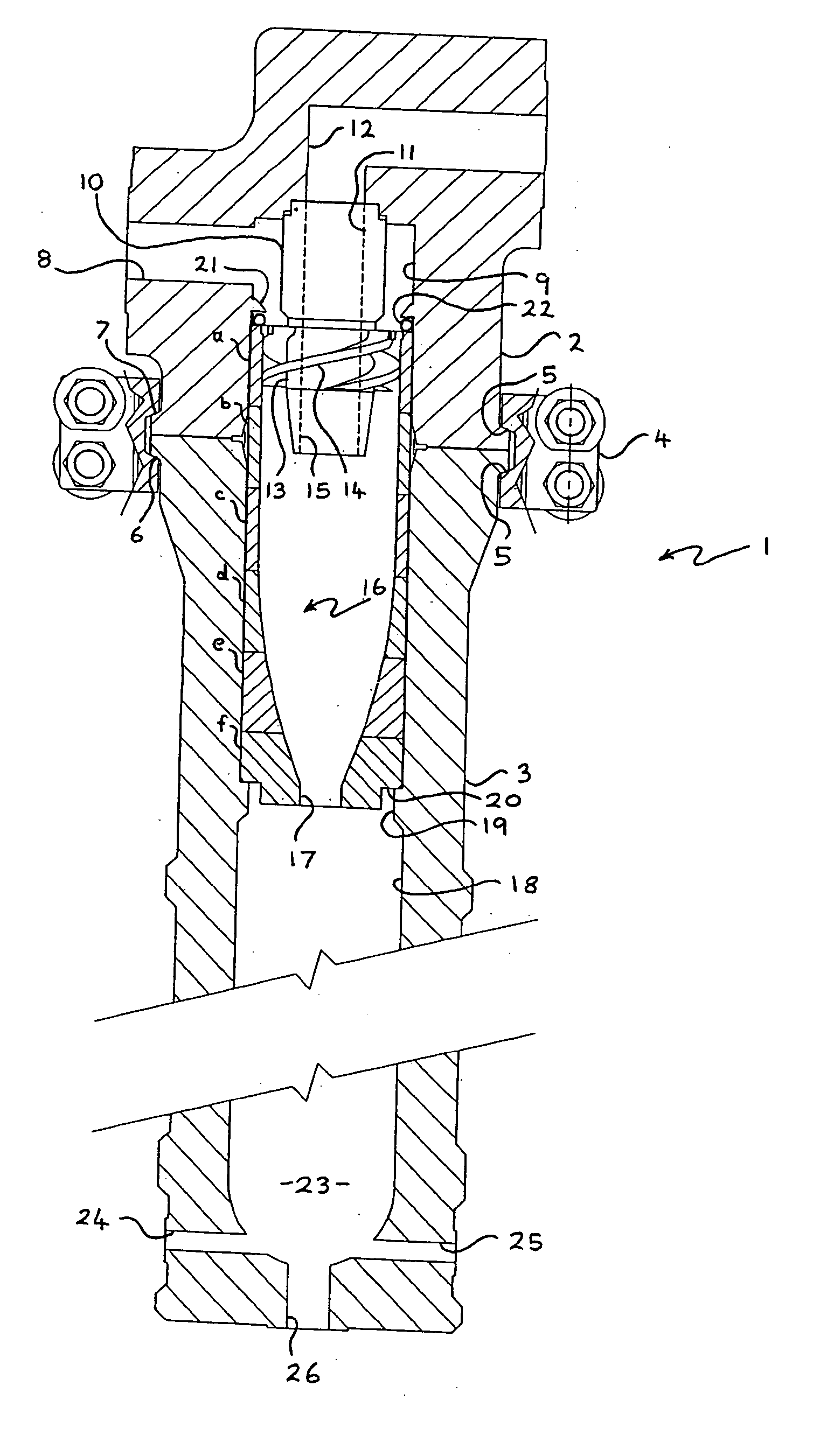
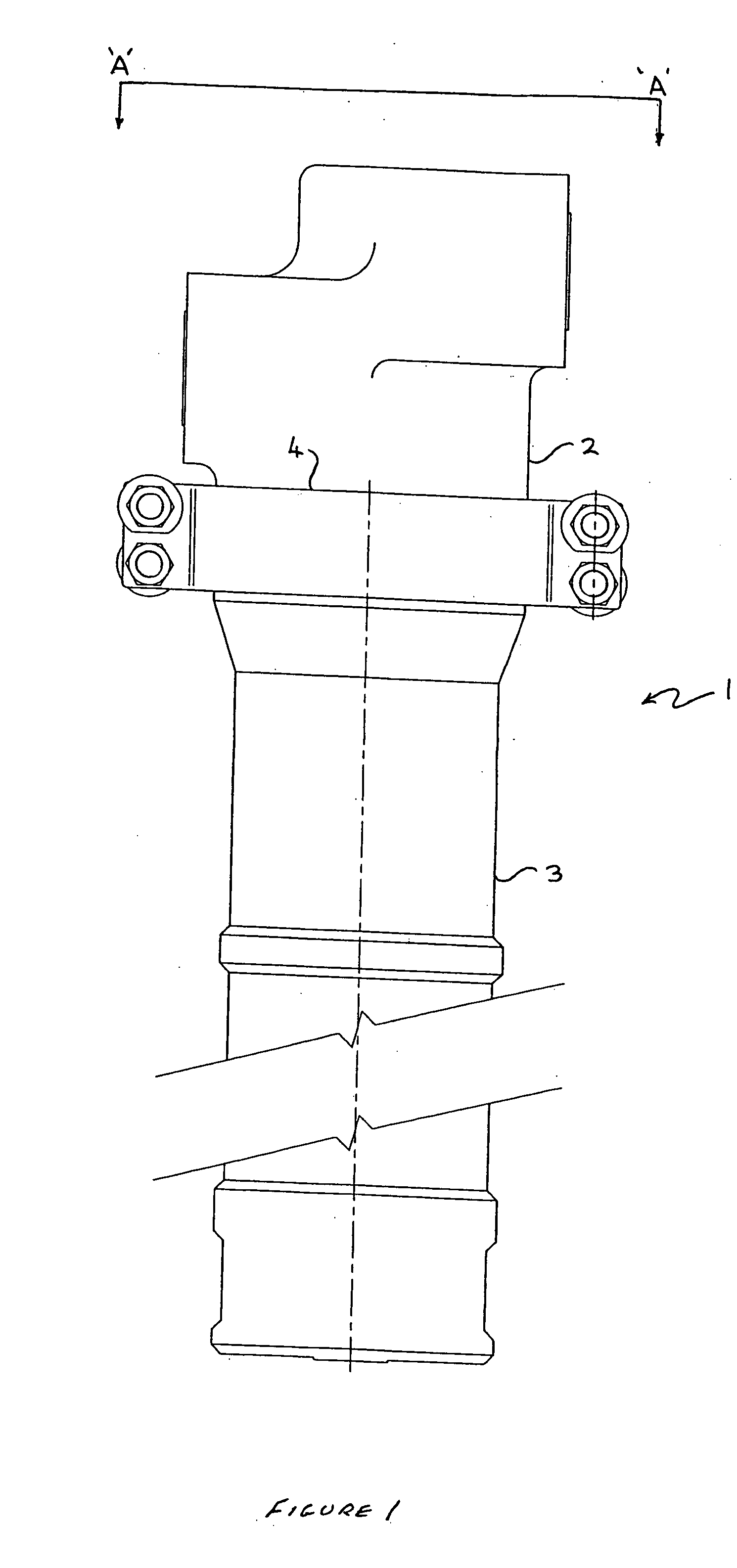
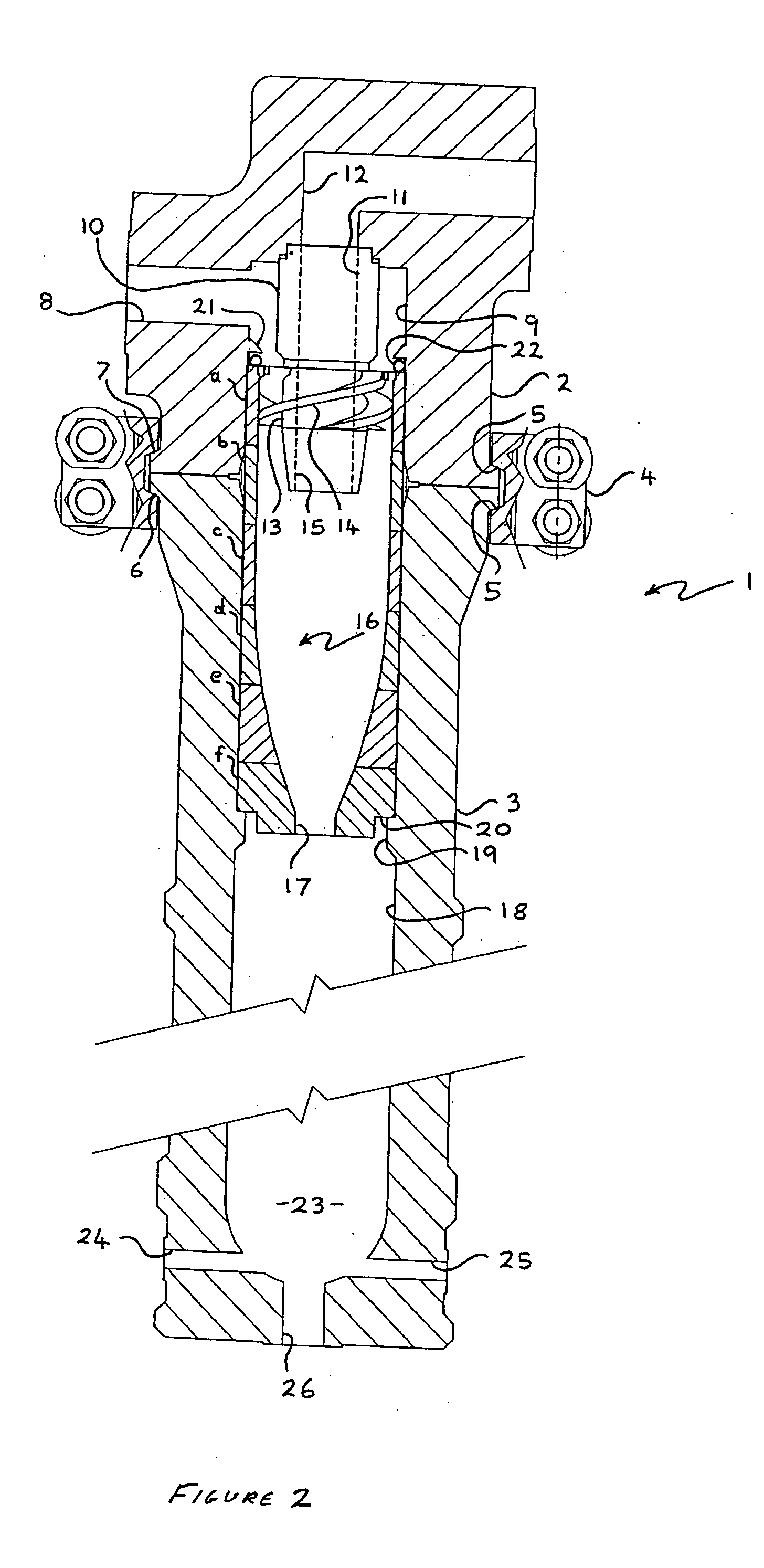
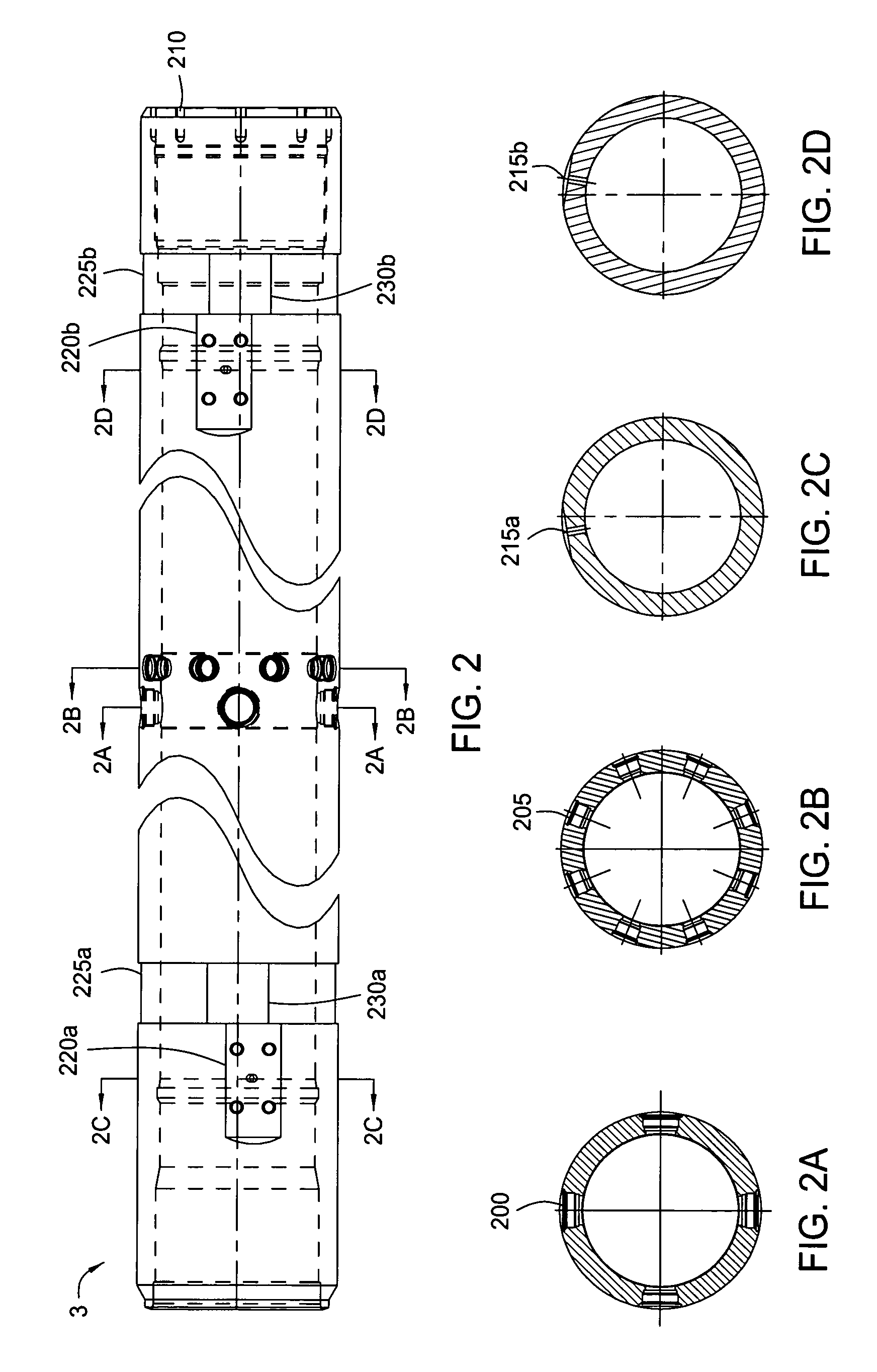
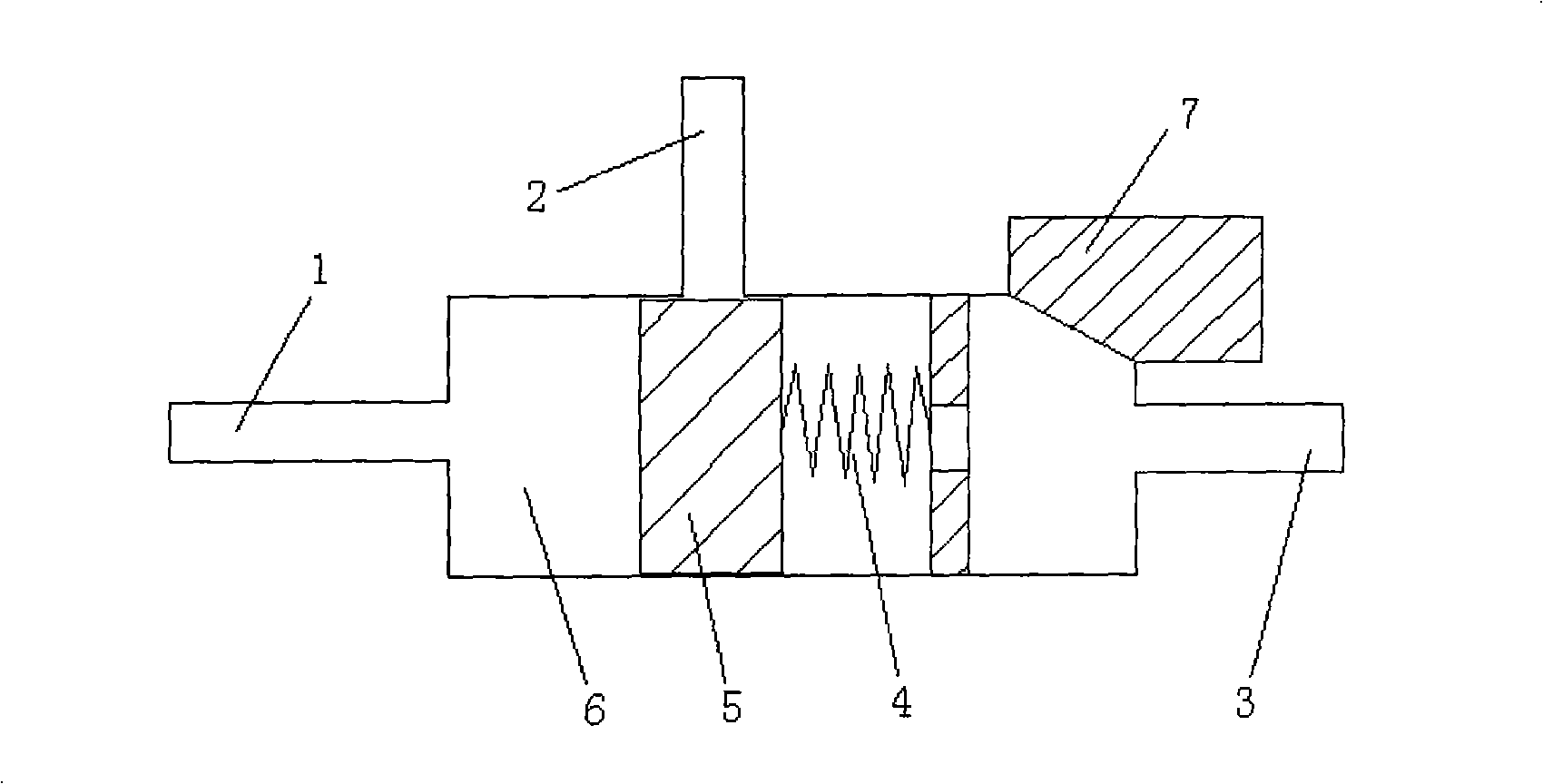
Choke valve
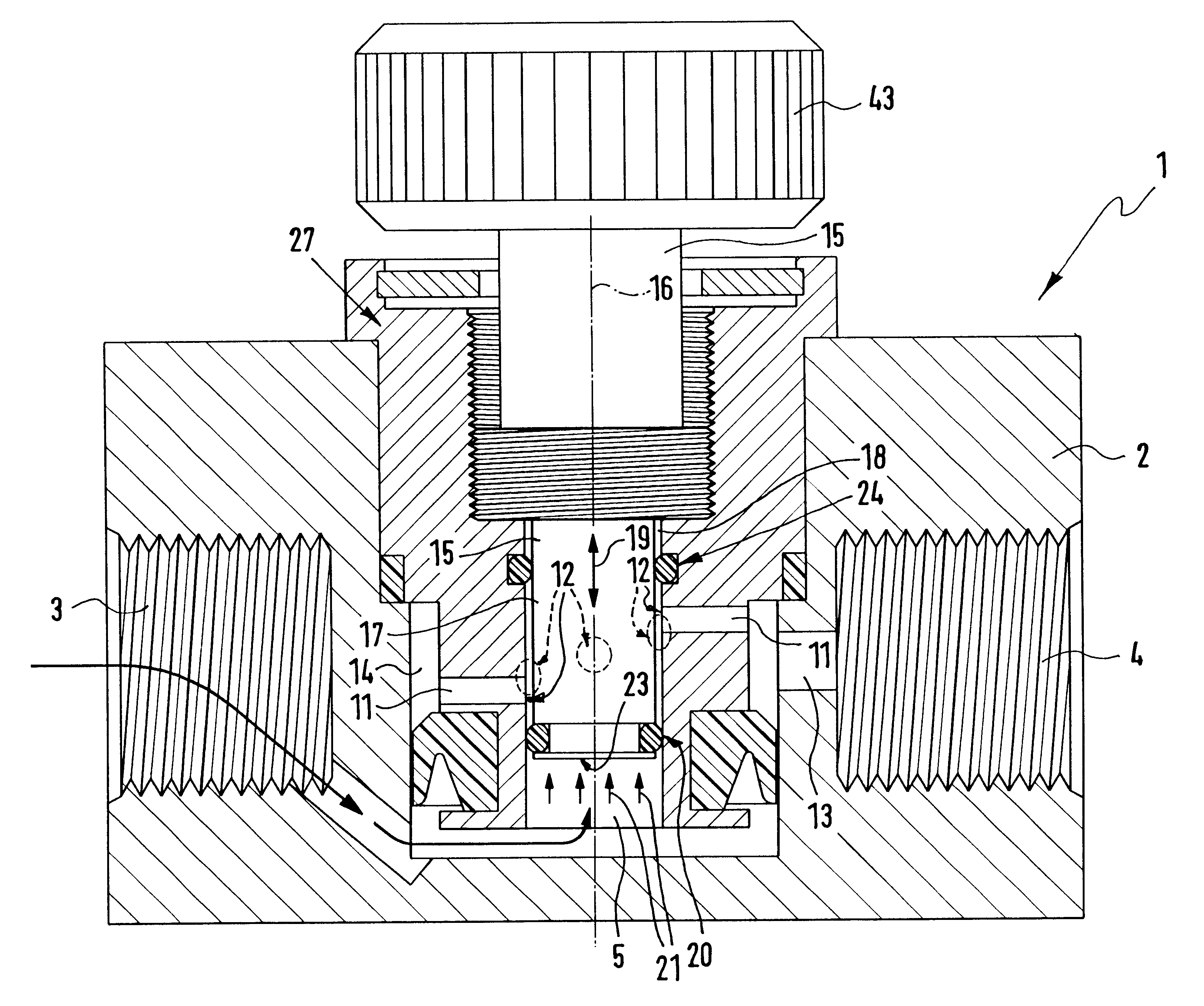
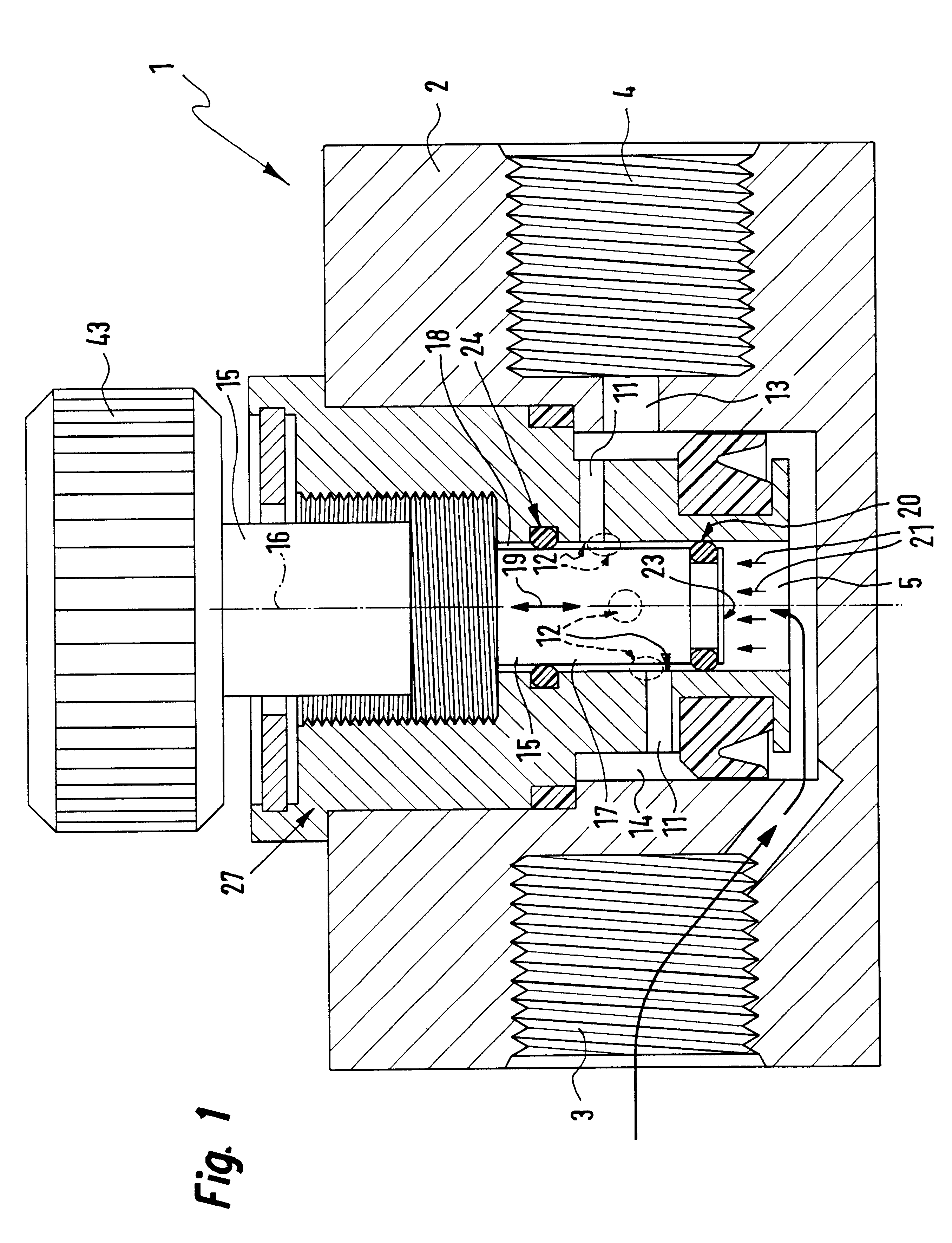
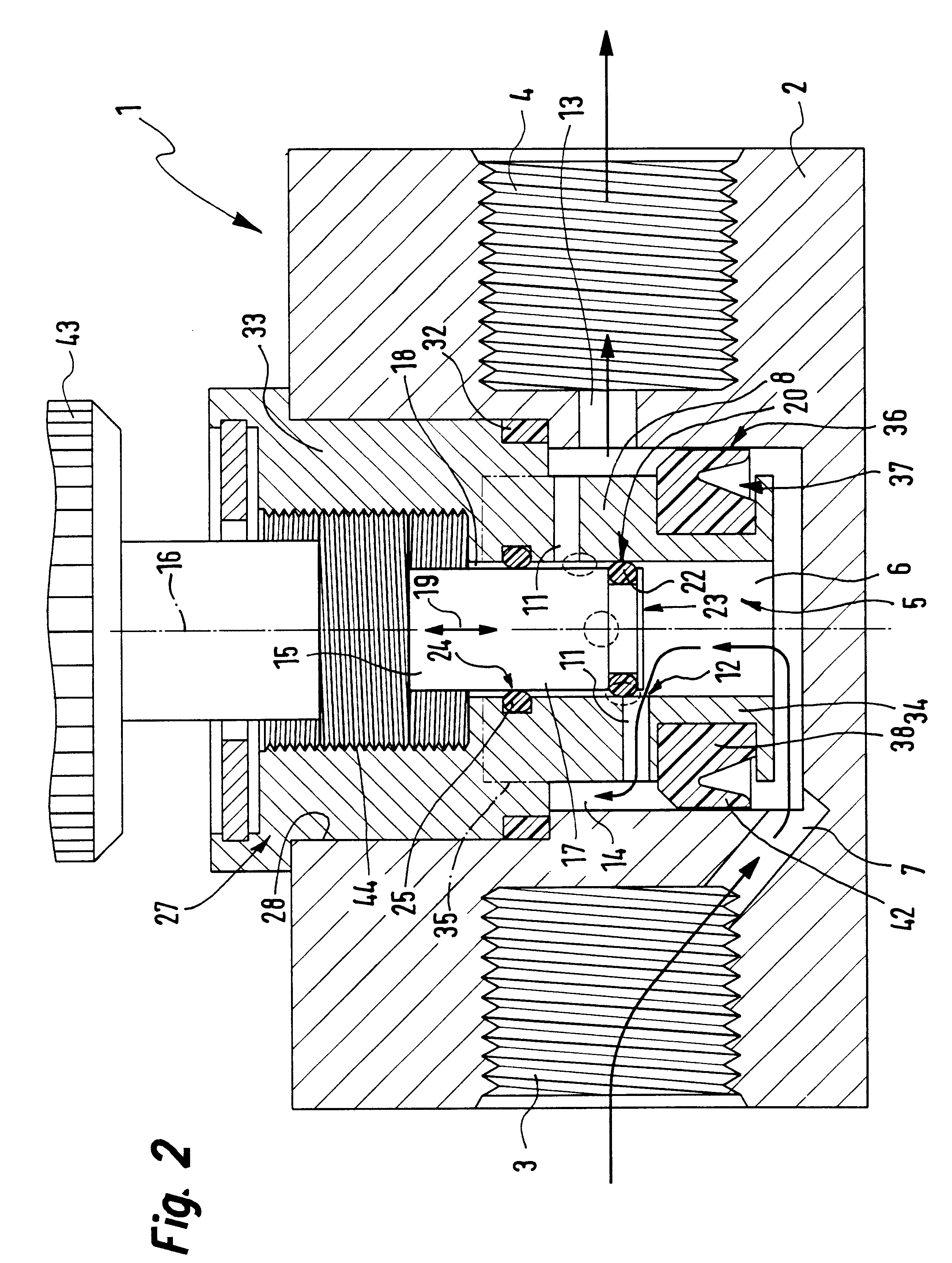
InactiveUS6325101B1Favorable effect on the positional stability of the choke bodySimple wayCheck valvesValve members for absorbing fluid energyEngineeringCheck valve
A choke valve, whose choke body comprises a cylindrical choke position plunging coaxially into an inlet duct. The inlet flow duct is connected on the one hand with an inlet and on the other hand communicates through transfer openings with outlet flow ducts extending through the wall of the flow duct, such outlet flow ducts begin connected with the outlet. Between the choke piston and the inlet flow duct wall a seal area is provided, which on resetting the choke body is shifted axially and, cooperating with the transfer apertures, sets the aperture for the pressure medium.
Owner:FESTO AG & CO KG
Relating to well head separators
ActiveUS20050236324A1Easy to shapeEconomising on manufacturing costWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationReversed direction vortexParticulatesCyclone
Well head hydrocyclone separators are typically used for separating particulates from fluids such as gas, oil and water and mixtures thereof. Well head separators are useful to prevent wear and blocking of choke valves, rupture of piping, damage to instruments and to prevent vessels from filling with particulate materials. In the present invention, the cyclone separator assembly includes an inlet, an overflow outlet and a segmented cyclone separator tube.
Owner:AXSIA SERCK BAKER
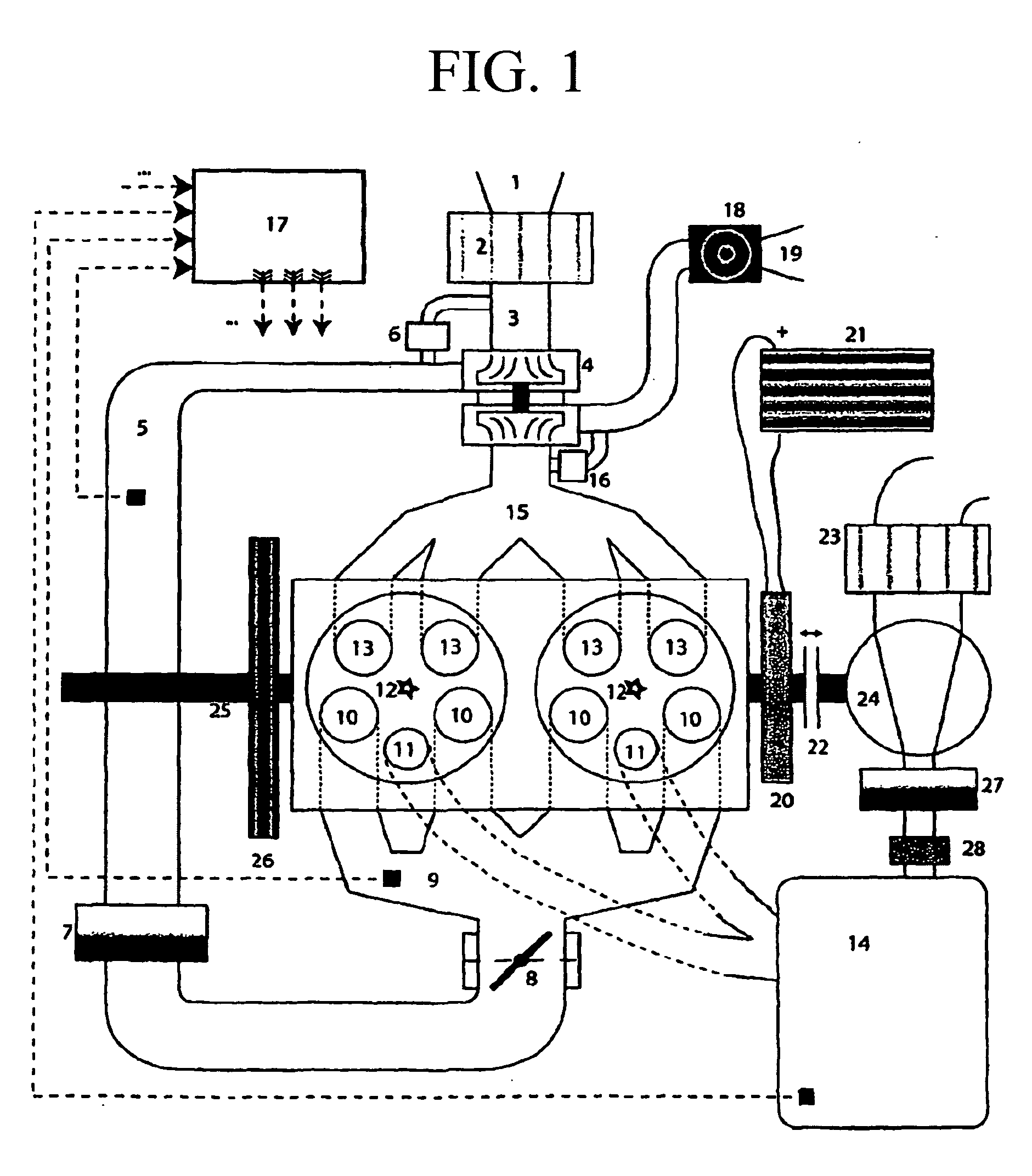
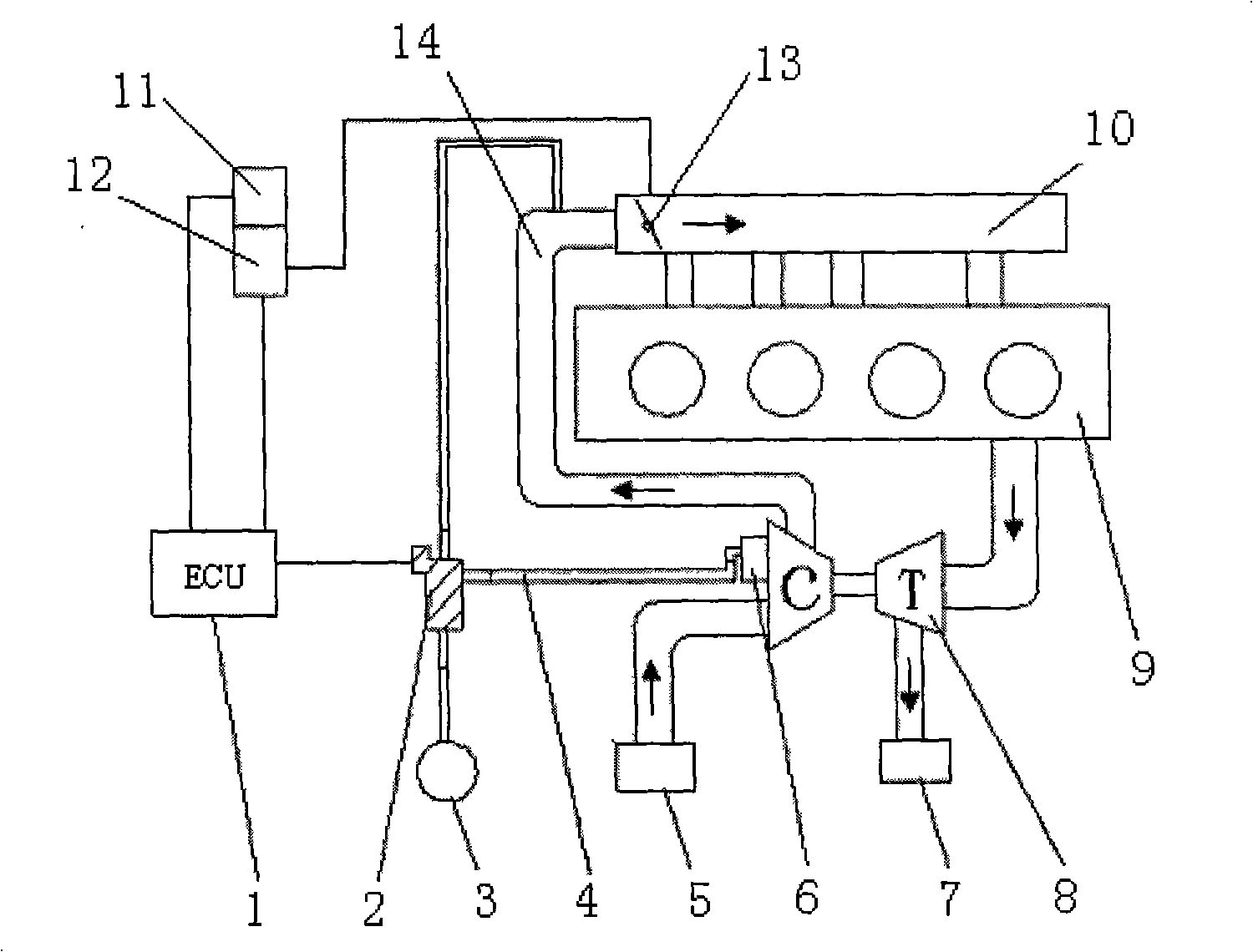
Turbocharged reciprocating piston engine having a connected pressure tank for bridging turbo lag, and method for operating said engine
InactiveUS20120186249A1Decrease in cubic capacityReduce capacityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberTurbocharger
The present invention relates to a turbo-charged reciprocating piston engine having a combustion chamber, and to a method for operating said engine. The combustion chamber has at least one inlet valve (10), one outlet valve (13) and at least one additional charging valve (11), for the additional feed of compressed air to bridge the turbo lag. All the valves (10, 11, 13) are operatively connected to the crankshaft via a camshaft and the operative connection of the charging valves to the crankshaft can be deactivated, with the result that the at least one charging valve (11) remains closed. The correct metering of the air for a stoichiometric or approximately stoichiometric combustion mixture is additionally achieved by a turbocharger (4) and a throttle valve (8). By displacement of the opening instant of the charging valves (11), air can be pumped from the cylindrical combustion chambers into the compressed air tank (14), instead of removing said air from the latter. Furthermore, an additional compressor (24), driven by the crankshaft, can likewise deliver air into the compressed air tank (14) if required.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Variable choke valve
Embodiments of the present invention generally provide a more reliable variable choke flow control valve. In one embodiment, a variable choke valve for use in a wellbore is provided. The valve includes a tubular housing having an axial bore therethrough and a port through a wall thereof. The valve further includes a tubular sleeve having an axial bore therethrough and first and second holes through a wall thereof and disposed within the housing. The first hole is larger than the second hole, and the sleeve is actuatable among three positions: a first position where the first hole is aligned with the port, a second position where the second hole is aligned with the port, and a third position where the sleeve wall is aligned with the port.
Owner:WEATHERFORDLAMB
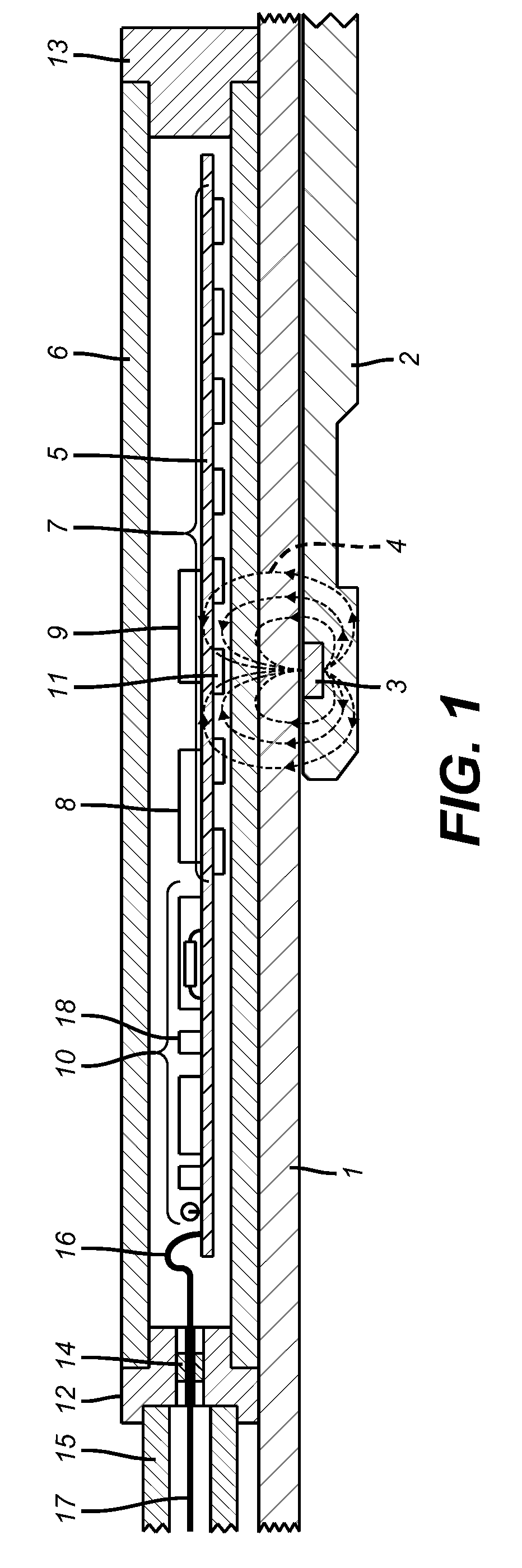
Position sensor for a downhole completion device
ActiveUS8237443B2High speedElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsSensor arrayEngineering
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Air induction system having bypass flow control
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
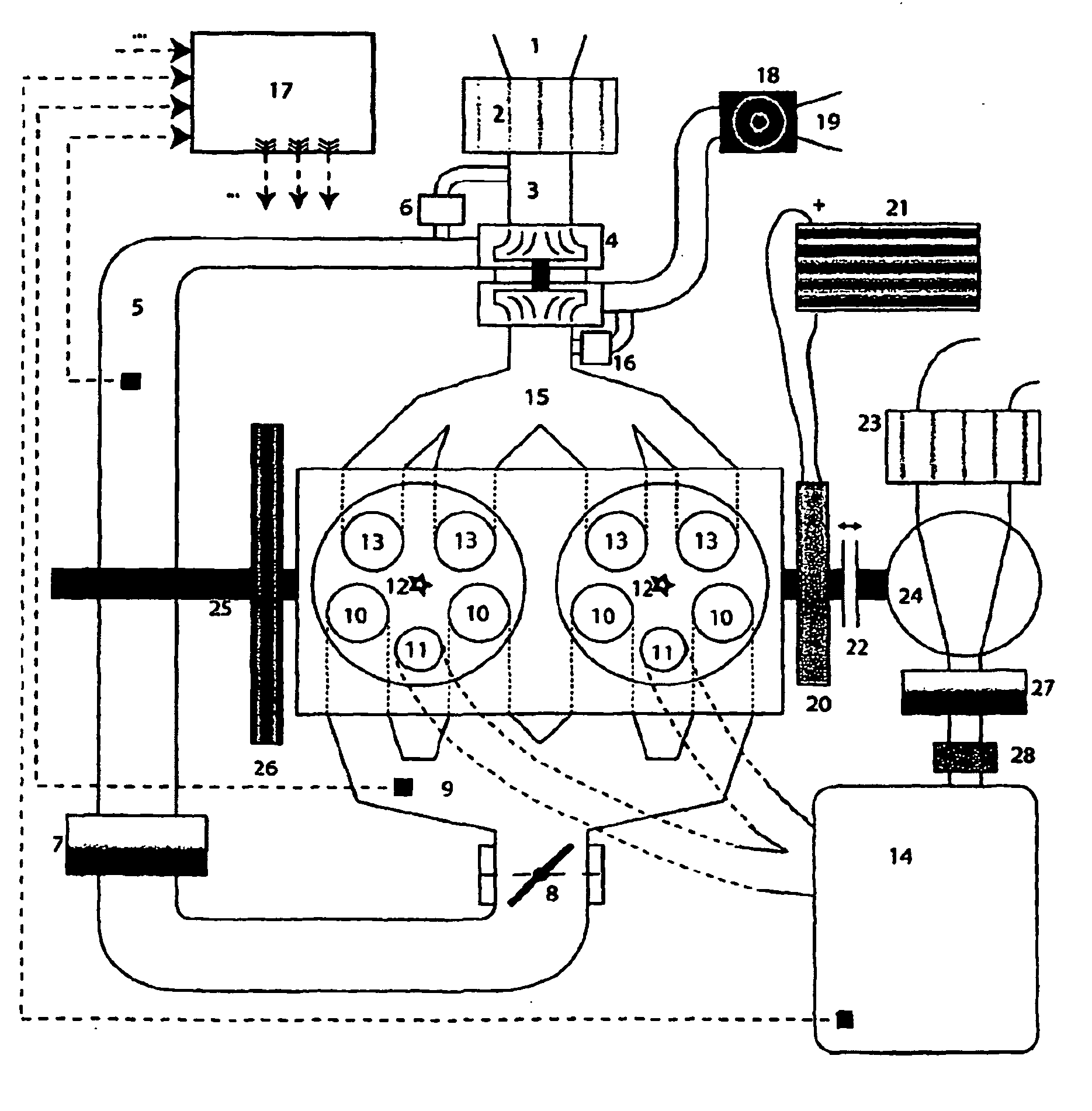
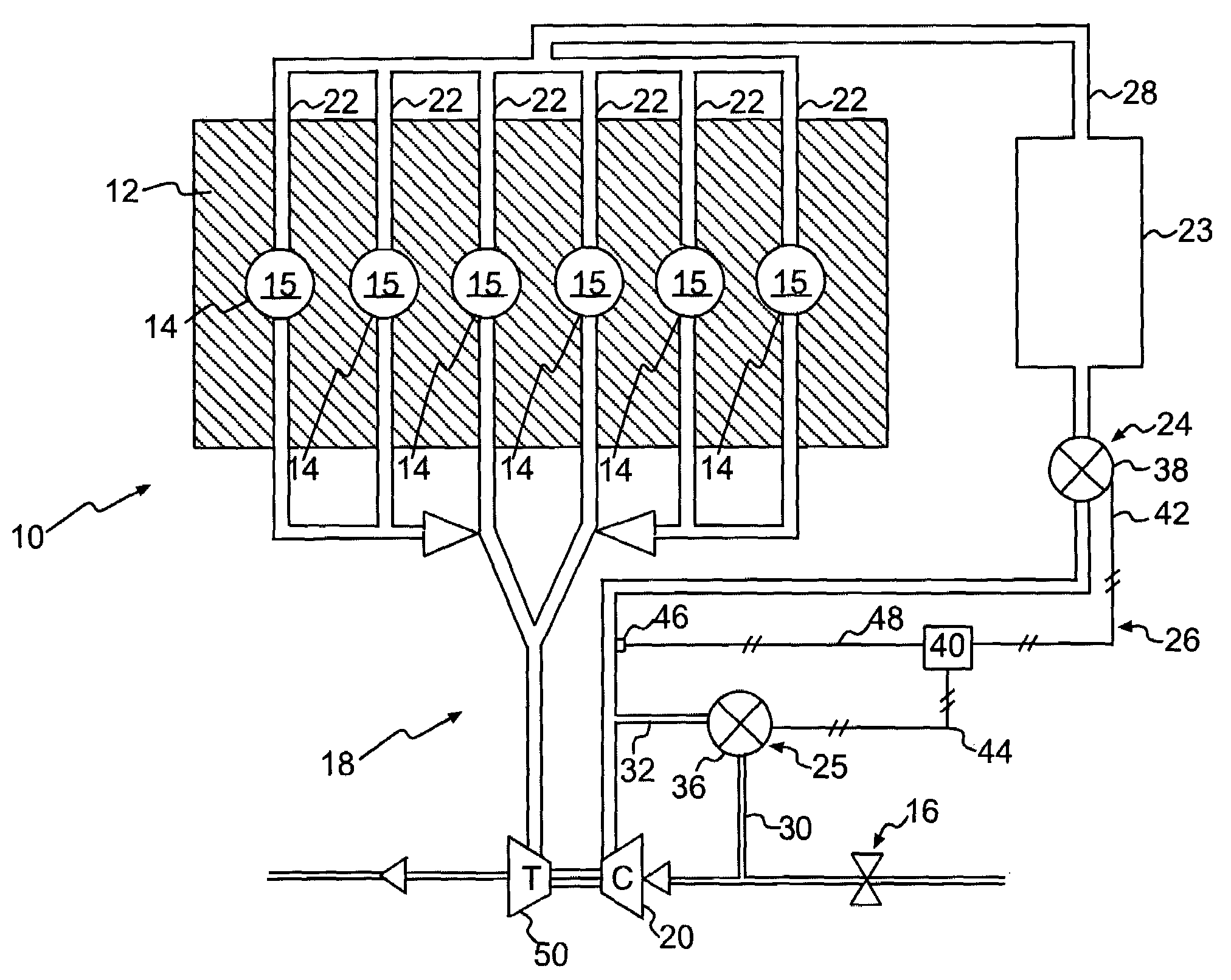
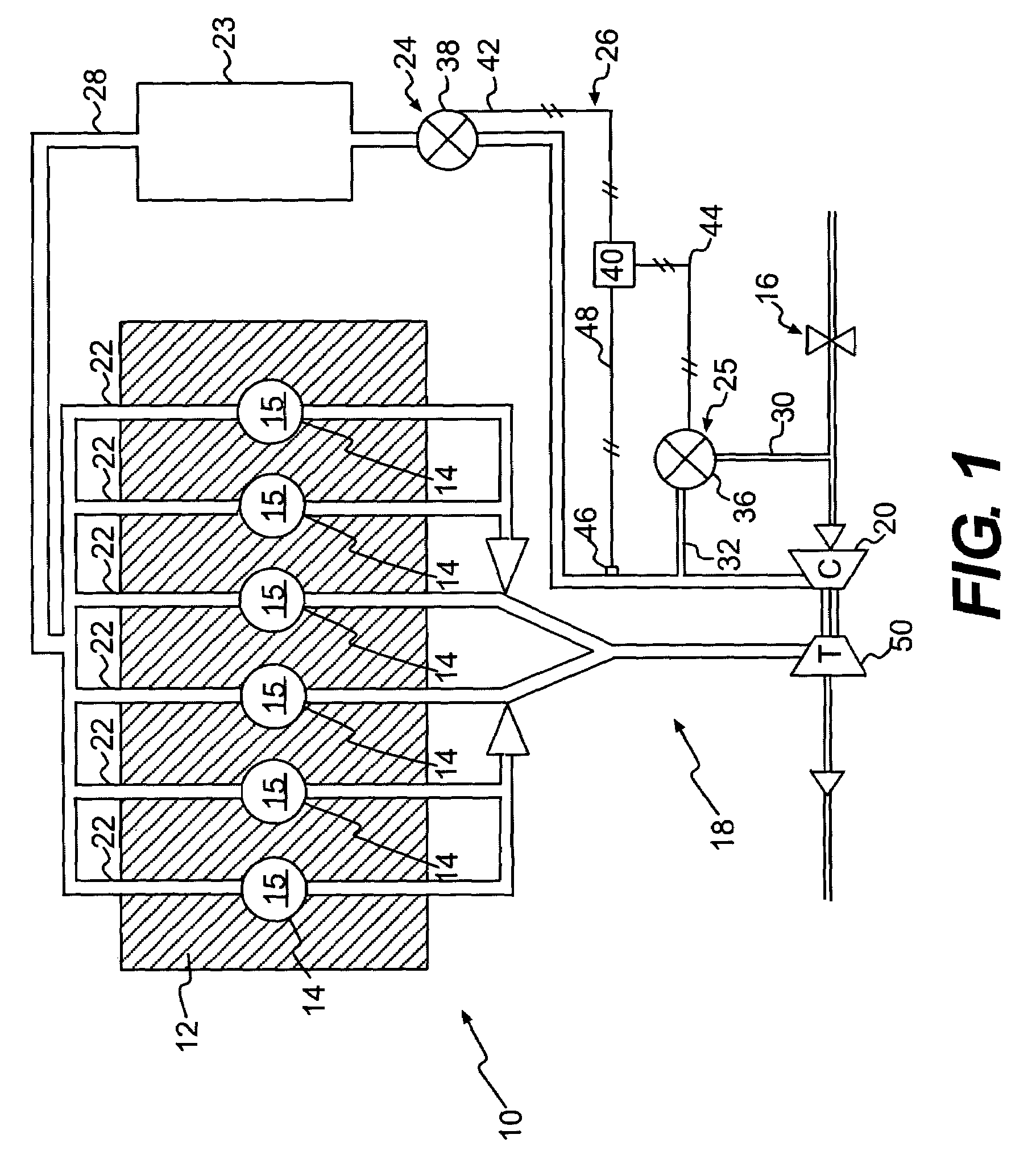
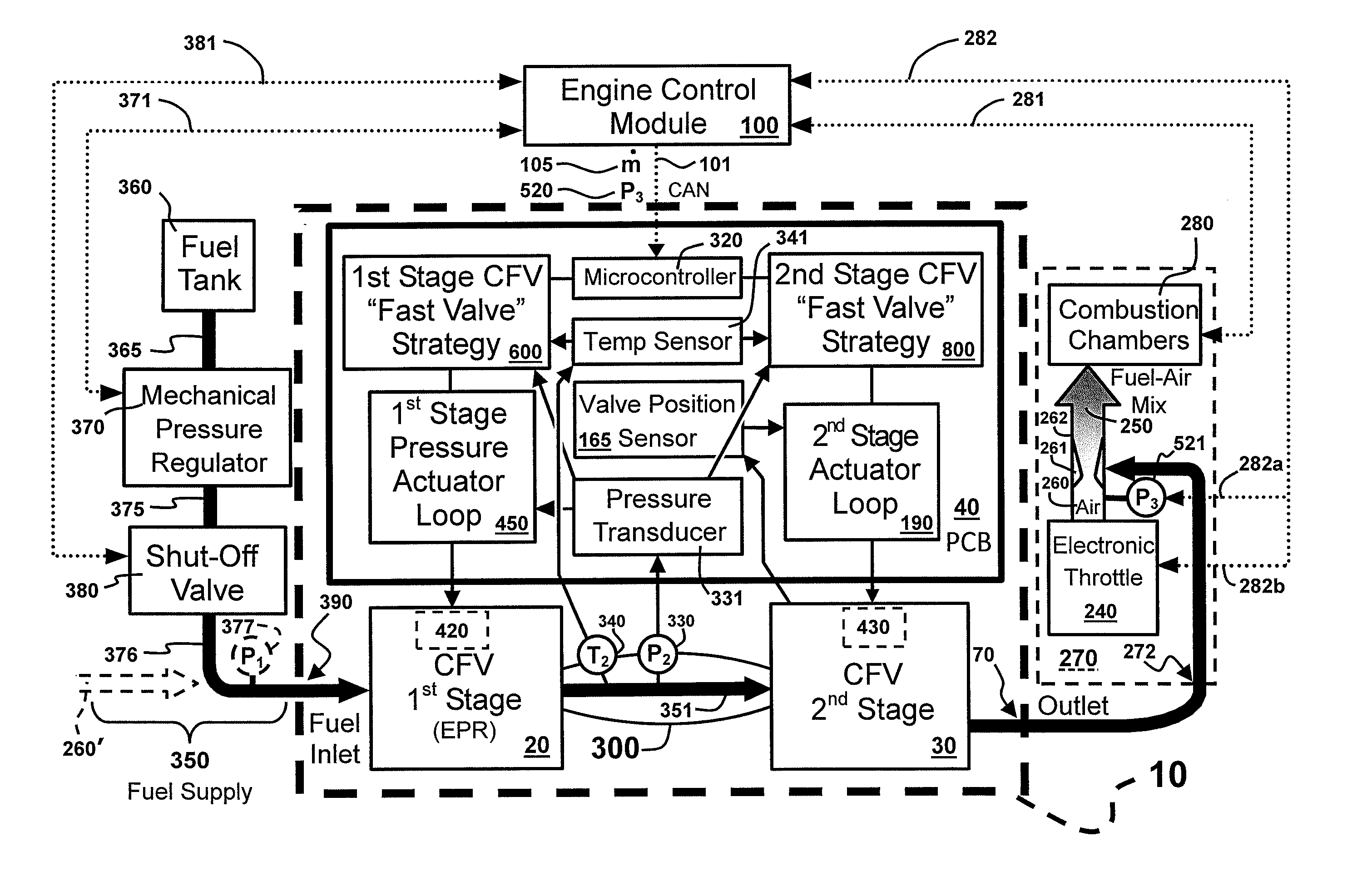
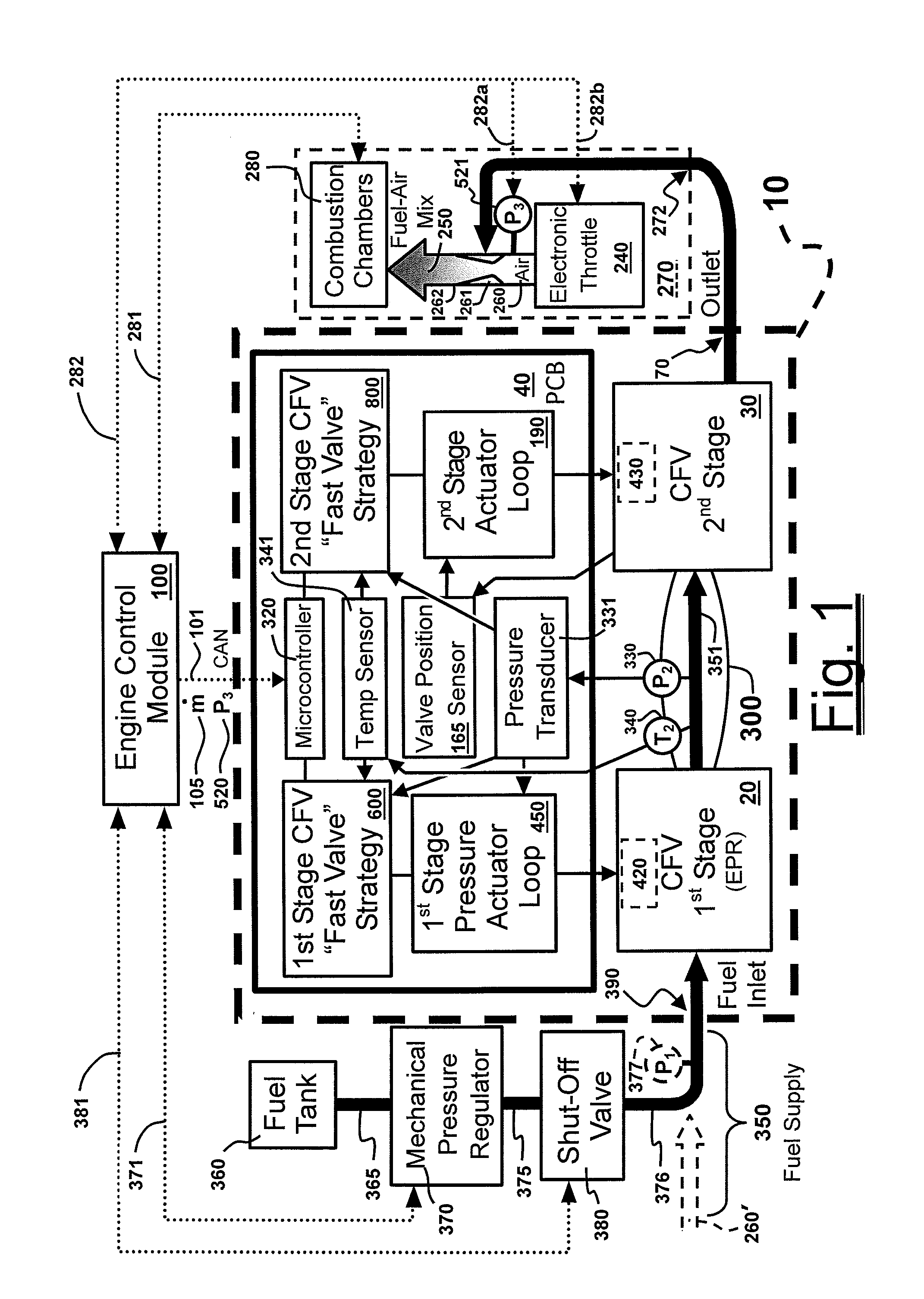
Highly Accurate Continuous-Flow Vaporized Fuel Supply for Large Dynamic Power Ranges
ActiveUS20130333671A1Extreme accuracyHighly-accurate gaseous fuel flowrate controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesDual stageValve actuator
Methods and systems for accurate and precise fuel supply control for continuous-flow of gaseous fuel to an internal combustion engine over a large dynamic power range, including a dual-stage valve that allows optimal control—a first stage in the form of a voice-coil driven electronic pressure regulator, and a second stage in the form of a voice-coil-driven choked-flow valve; monitoring the pressure of the fuel intermediate the two stages and making appropriate adjustments to the first stage via a pressure actuator loop; feeding the gaseous fuel mixture through a unitary block assembly into the second stage; monitoring the pressure of the air / fuel mixture and making appropriate adjustments to the second stage via a valve actuator control loop.
Owner:ECONTROLS LLC
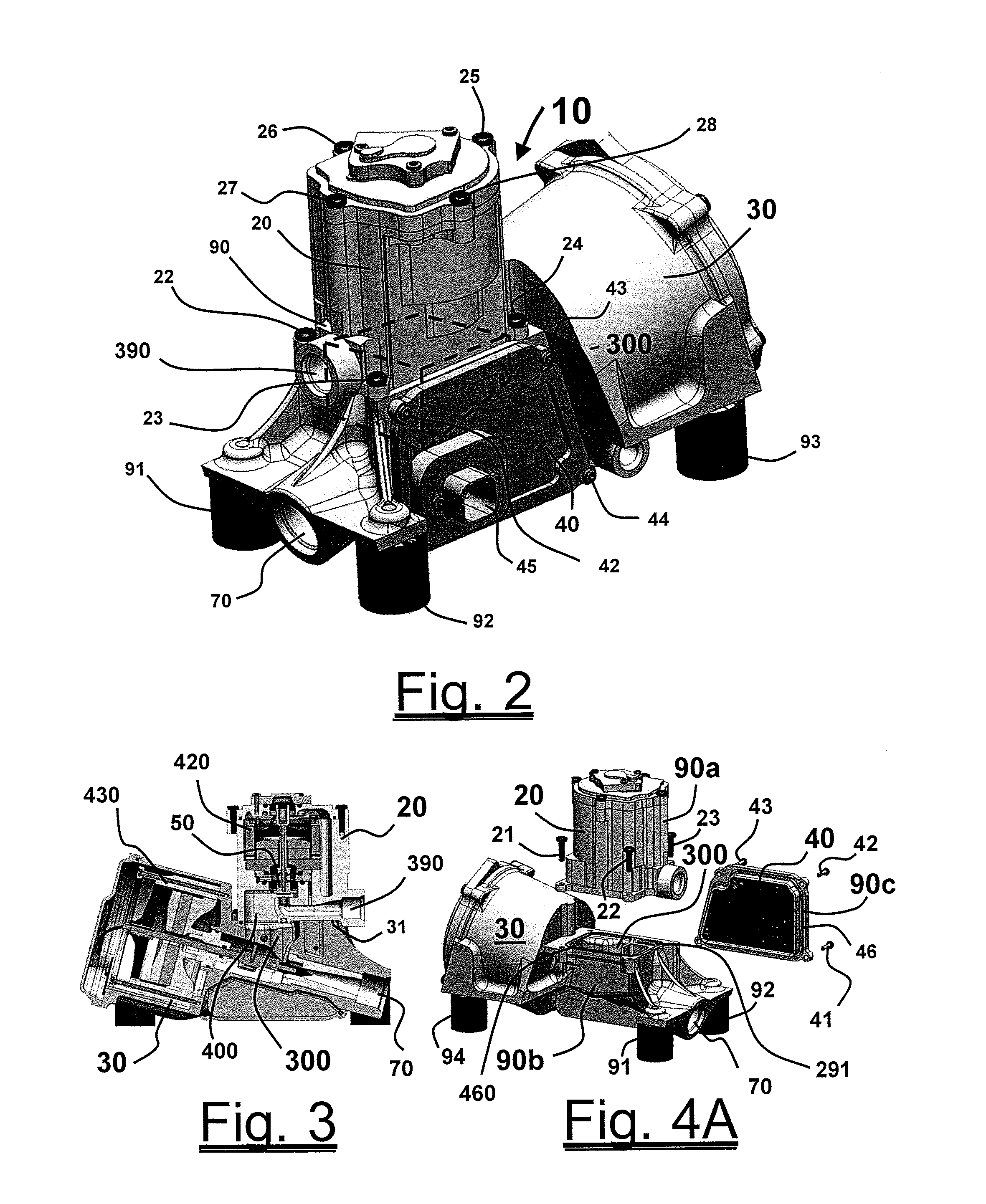
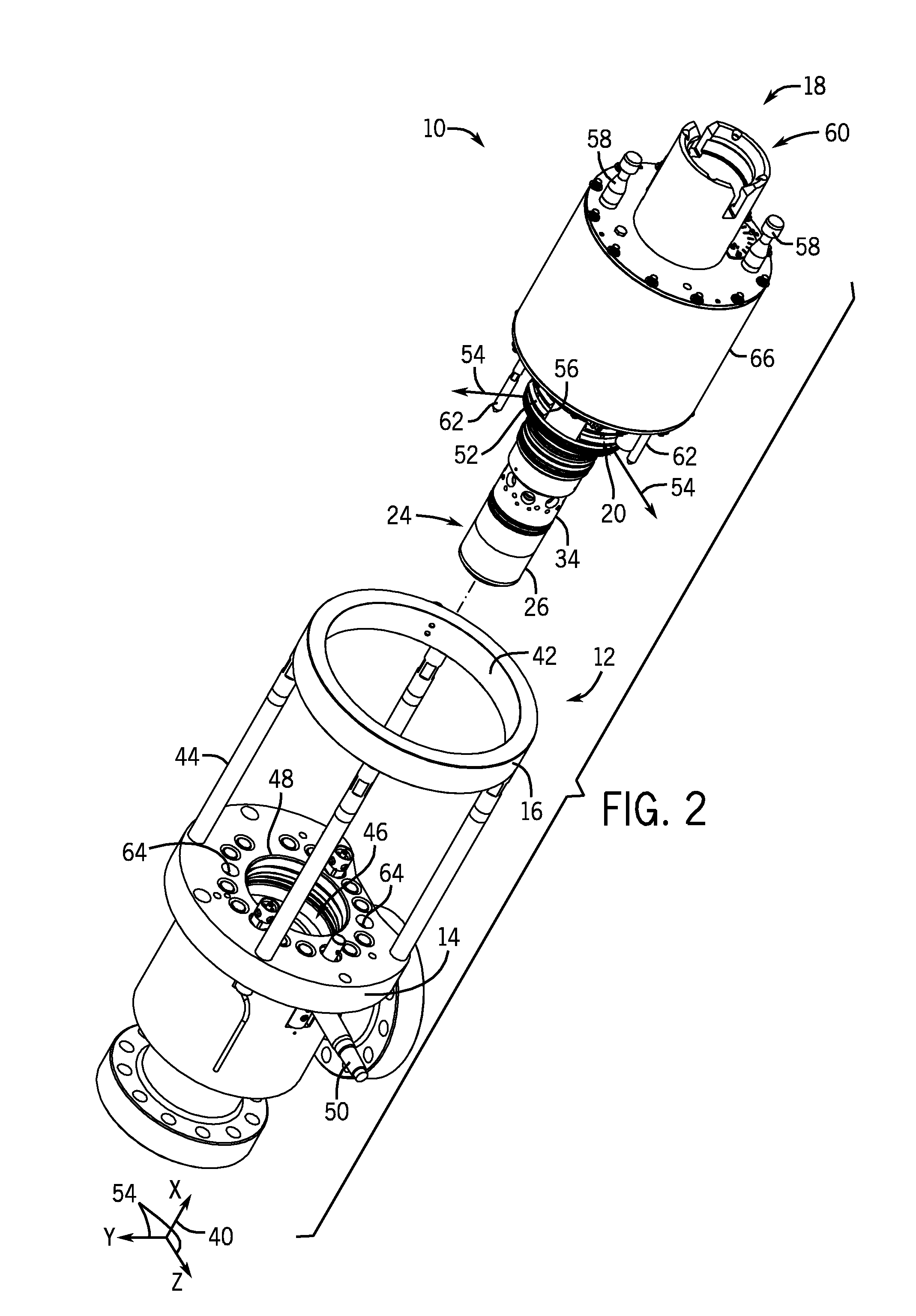
Subsea retrievable insert with choke valve and non return valve
Owner:CAMERSON INT CORP
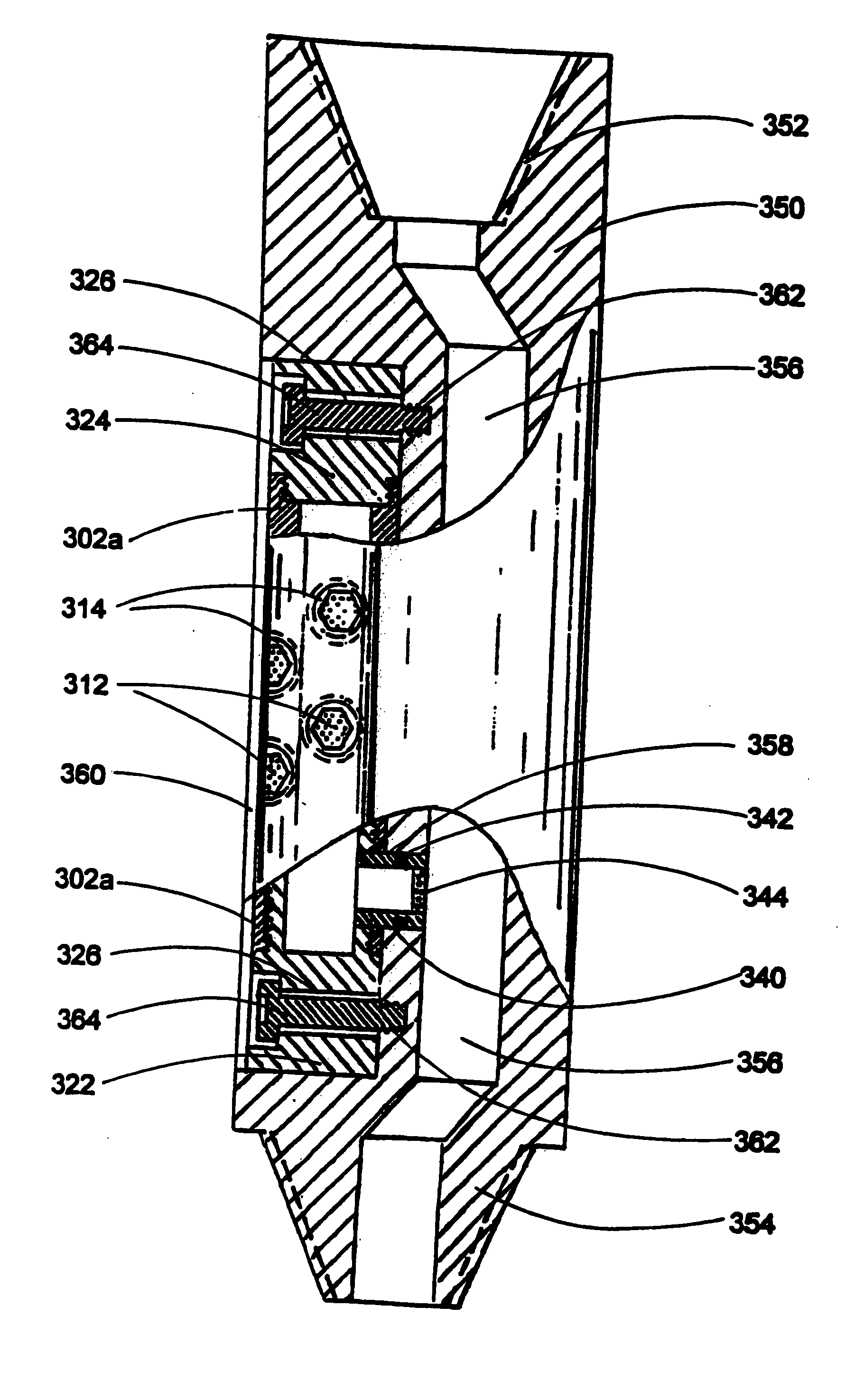
Choke valve flow trim for fracture prevention
ActiveUS7426938B2Large resistanceAvoid direct impactValve members for absorbing fluid energyPipe elementsFracture preventionStreamflow
A choke valve having flow trim components, namely a tubular cage and a flow collar or plug, and related components, designed and arranged for reduced fracturing. The invention includes a protective tubular sleeve, or insert cartridge in which the side ports are located to overlap with the intersection of axes of the inlet and outlet bores, but to avoid direct impingement of fluid along the axis of the inlet bore. In the cage, at least a pair of main flow ports are located to overlap with the intersection of the axes of the inlet and outlet bores, and are aligned with the side ports of the tubular sleeve or cartridge to communicate directly with the side ports. In this manner fluid may enter the choke valve through the inlet bore and pass through the main flow ports at reduced pressure and continue out through the outlet bore, without direct impingement on the side wall of the flow trim components.
Owner:MASTER FLO VALVE
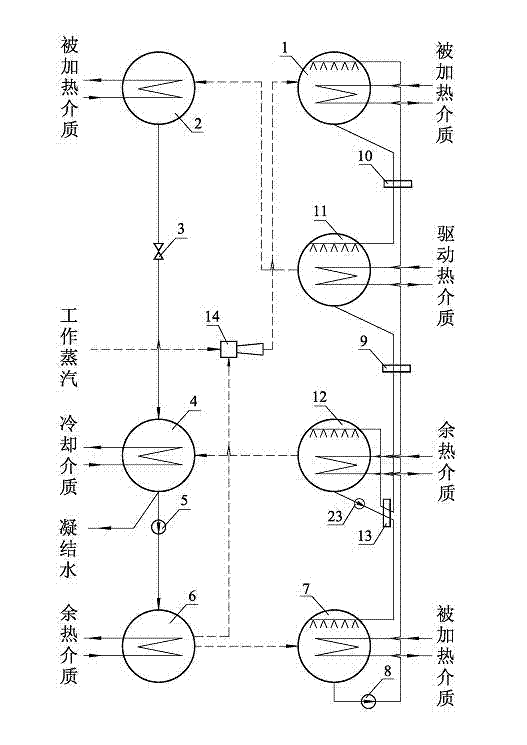
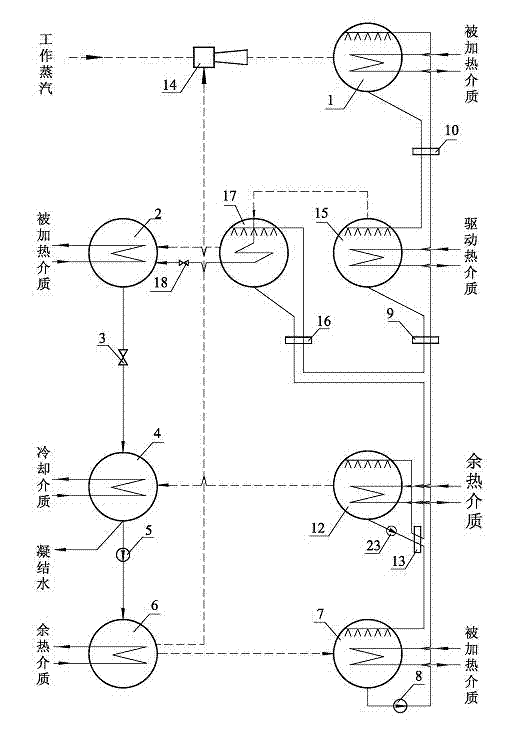
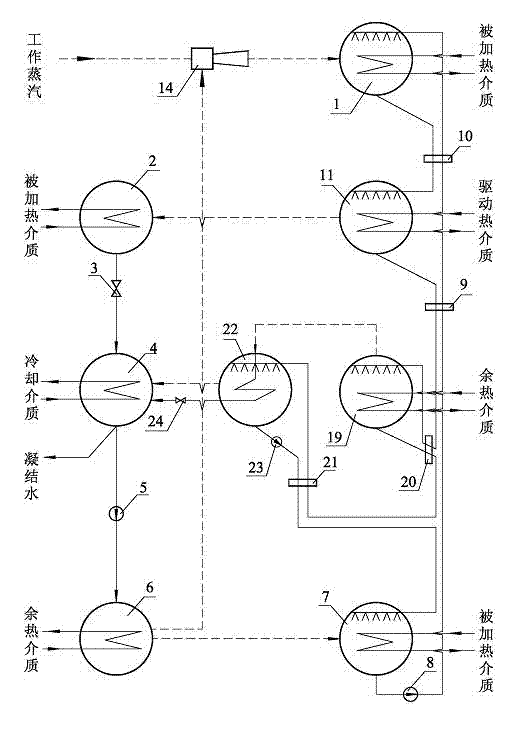
Fourth type heat pump cycle
InactiveCN103574978AEnergy efficient heating/coolingClimate change adaptationEngineeringAbsorption heat pump
The invention relates to fourth type heat pump cycle, which consists of a high-temperature absorber, a first condenser, a first throttling valve, a second condenser, a refrigerant liquid pump, an evaporator, an absorber, a first solution pump, a first solution heat exchanger, a second solution heat exchanger, a third solution heat exchanger, a second solution pump, an ejector and a plurality of generators. Jet type heat pump cycle and two types of absorption heat pump cycle are organically combined, so high-grade driving steam temperature difference and pressure difference are effectively utilized, high heat supply temperature and high-efficiency heat energy utilization ratio are obtained, high-grade driving steam can be efficiently utilized, smaller compression ratio and higher ejection coefficient are achieved, and the fourth type heat pump cycle is excellent in energy-saving efficiency as compared with the traditional heat supply method.
Owner:刘辉
Valve and system used for turbosupercharger recirculation
InactiveCN101403442APrevent intake noiseOperating means/releasing devices for valvesInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerAir filter
The invention discloses a valve and a system used for the recycling of a turbocharger, wherein, the valve is a three-way magnetic valve, and the recycling system of the turbocharger comprises an engine and an ECU which controls the work of the engine; air is mixed with the waste gas of the recycling outlet of the turbocharger by an air filter, and then enters an engine intake manifold by the front hose of a throttle valve and the throttle valve; an engine exhaust manifold is connected with the inlet of the turbocharger; the exhaust outlet of the turbocharger is connected with a three-way catalysis; the recycling outlet of the turbocharger is also connected with a relief valve; the valve controls the work of the relief valve; and the ECU is connected with a pressure sensor, a throttle valve position sensor and the valve by electricity. The valve is the three-way magnetic valve; a first interface of the valve is connected with a vacuum tank; a second interface is connected with the relief valve, and a third interface is connected with the front hose of the throttle valve. The invention is used for solving the problems of turbocharger noise which is caused by the weak opening of the relief valve ahead of time or slow closing of the valve when the supercharged engine is at emergency deceleration status and the acceleration responsiveness.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Downhole Safety Valve Apparatus and Method
The application discloses a valve, which may include either a safety valve or a storm surge choke valve or the like, to isolate a zone below a valve from a string of production tubing. Preferably, the valve includes a flow interruption surface assembly, such as a flapper valve or a ball valve, displaced by an operating conduit extending from a surface location to the valve through the inside of the production tubing. The application also discloses a bypass-conduit inside the production tubing to allow communication from a surface location to the production zone when the valve is in either an open or a closed location.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
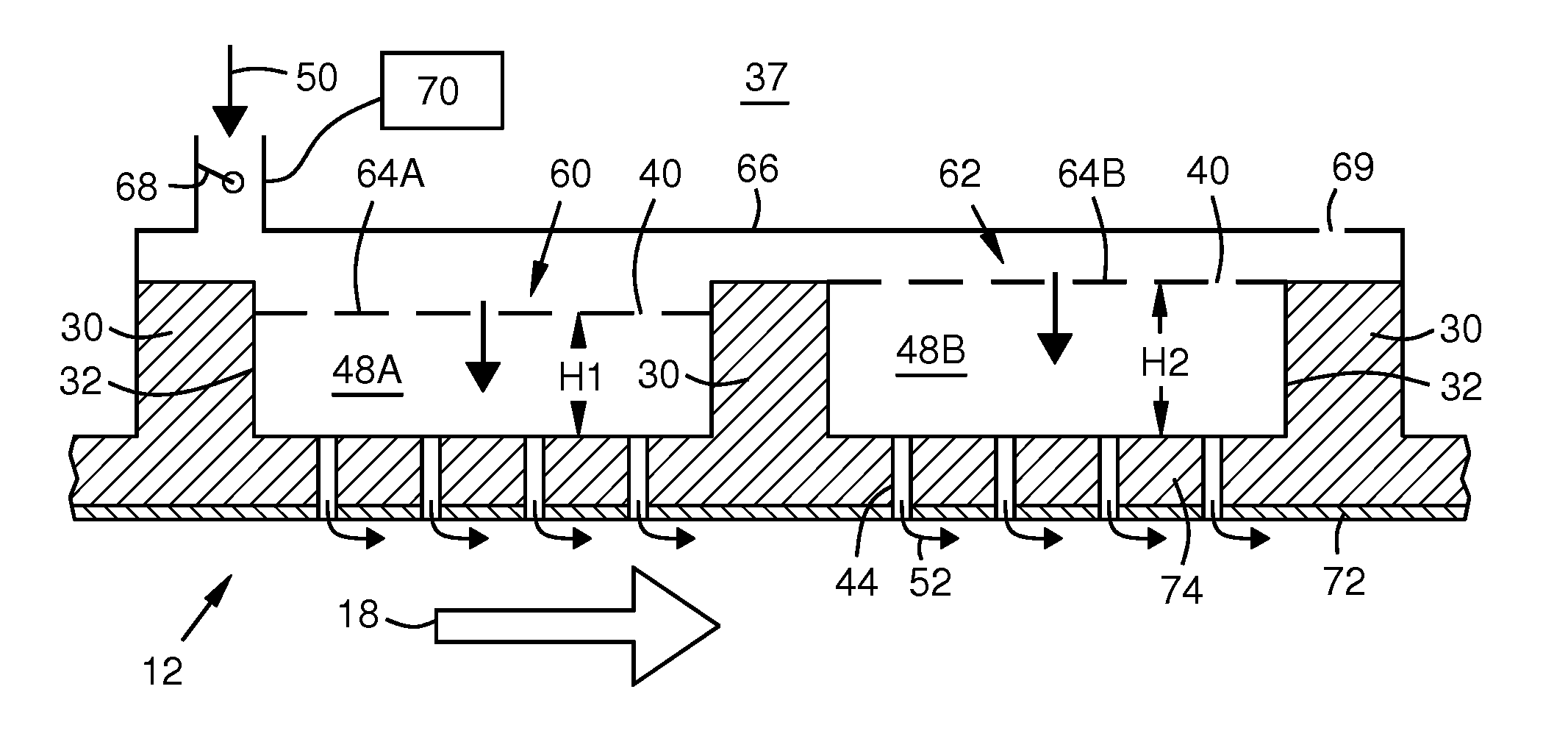
Apparatus for acoustic damping and operational control of damping, cooling, and emissions in a gas turbine engine
Acoustic damping resonators (60, 62, 76, 78) formed in pockets (32) between reinforcing ribs (30) in a grid of ribs on the outer surface of a wall (74) surrounding a combustion gas flow path (18). Each resonator has a perforated cover plate (64A-C) spanning between sides formed by the ribs (30). Film cooling exit holes (44) are provided in the wall (74) under each resonator. Resonating chambers (48A-C) of different volumes may be provided on the wall to damp different unwanted frequencies. Different sets of resonators with different volumes may be separately controlled by respective airflow control manifolds (66) via throttle valves (68, T1-T3). Control logic (70) may control the valves based on frequency / airflow response functions (80, 82) for each size of resonator to optimize damping and cooling and to lower emissions over varying engine operating conditions.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com